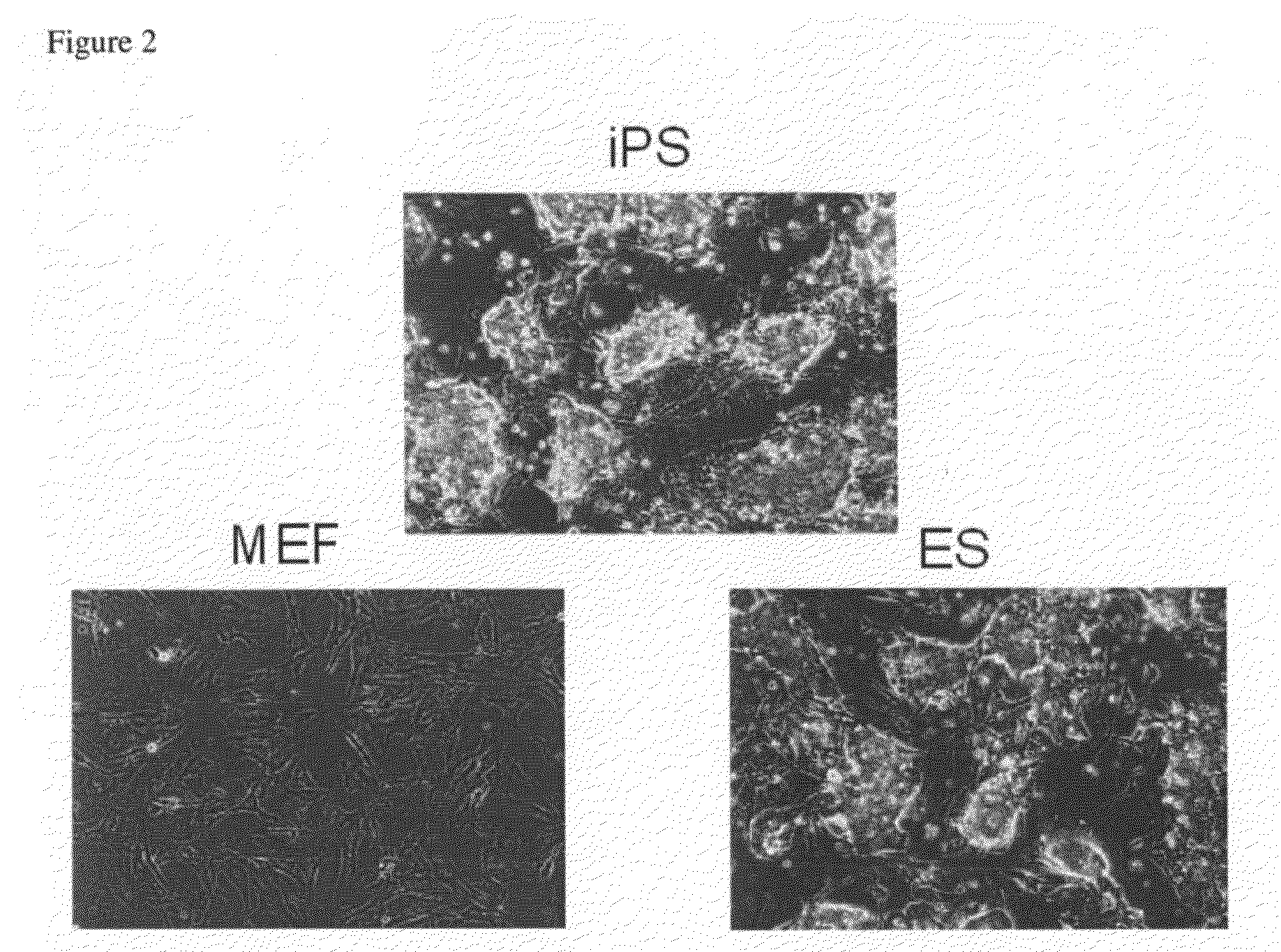Patents
Literature
95735results about How to "Easy to prepare" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
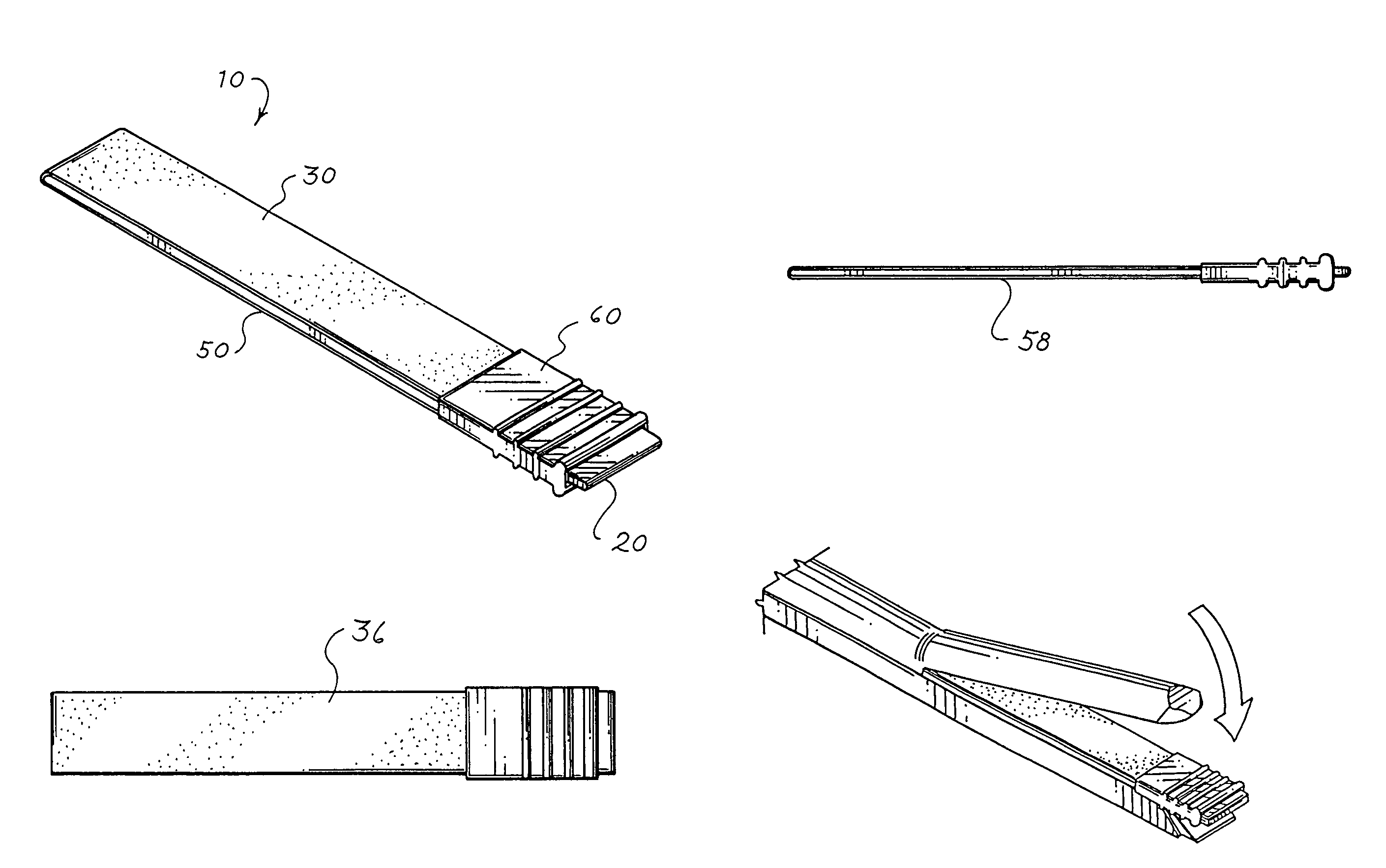
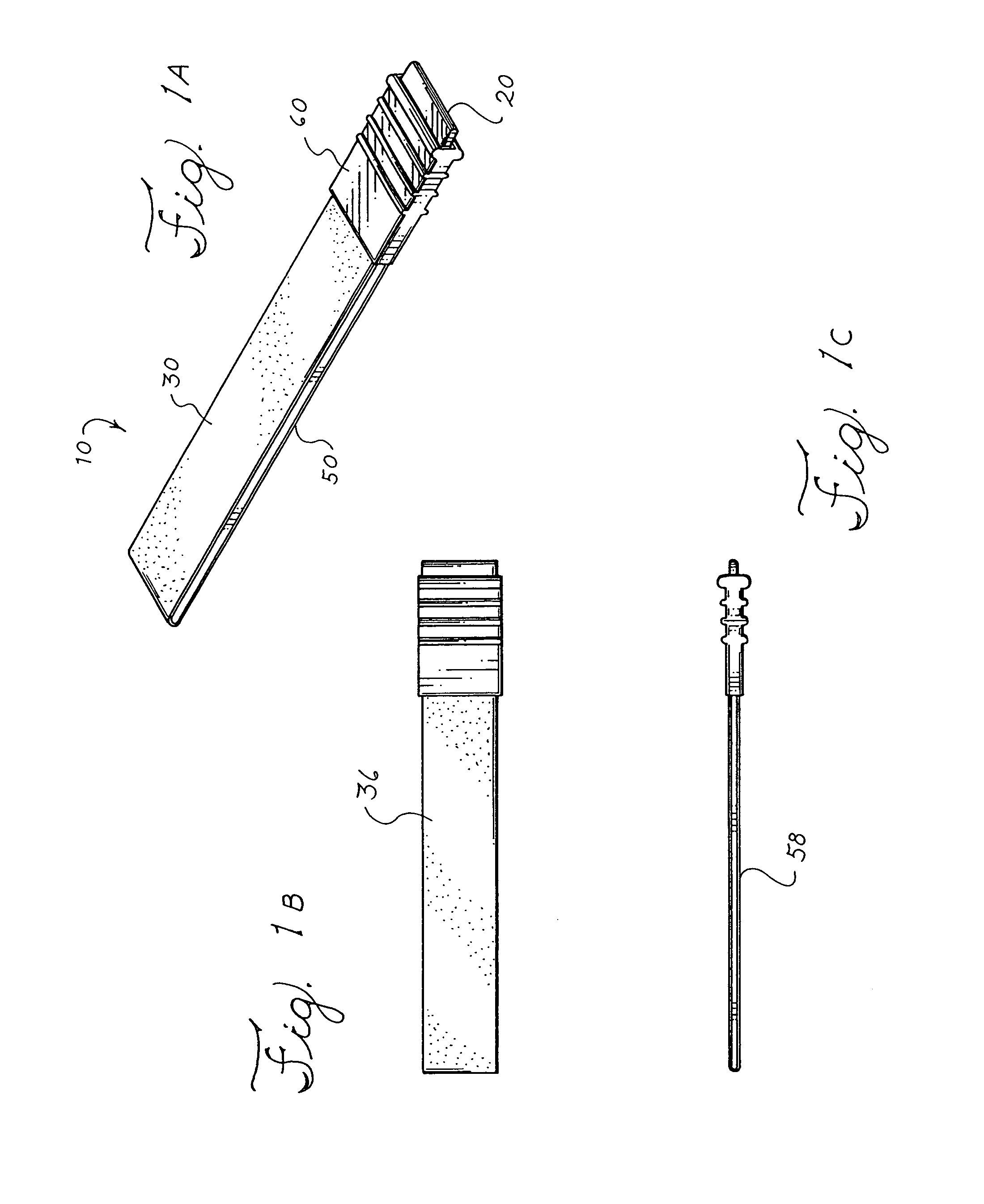
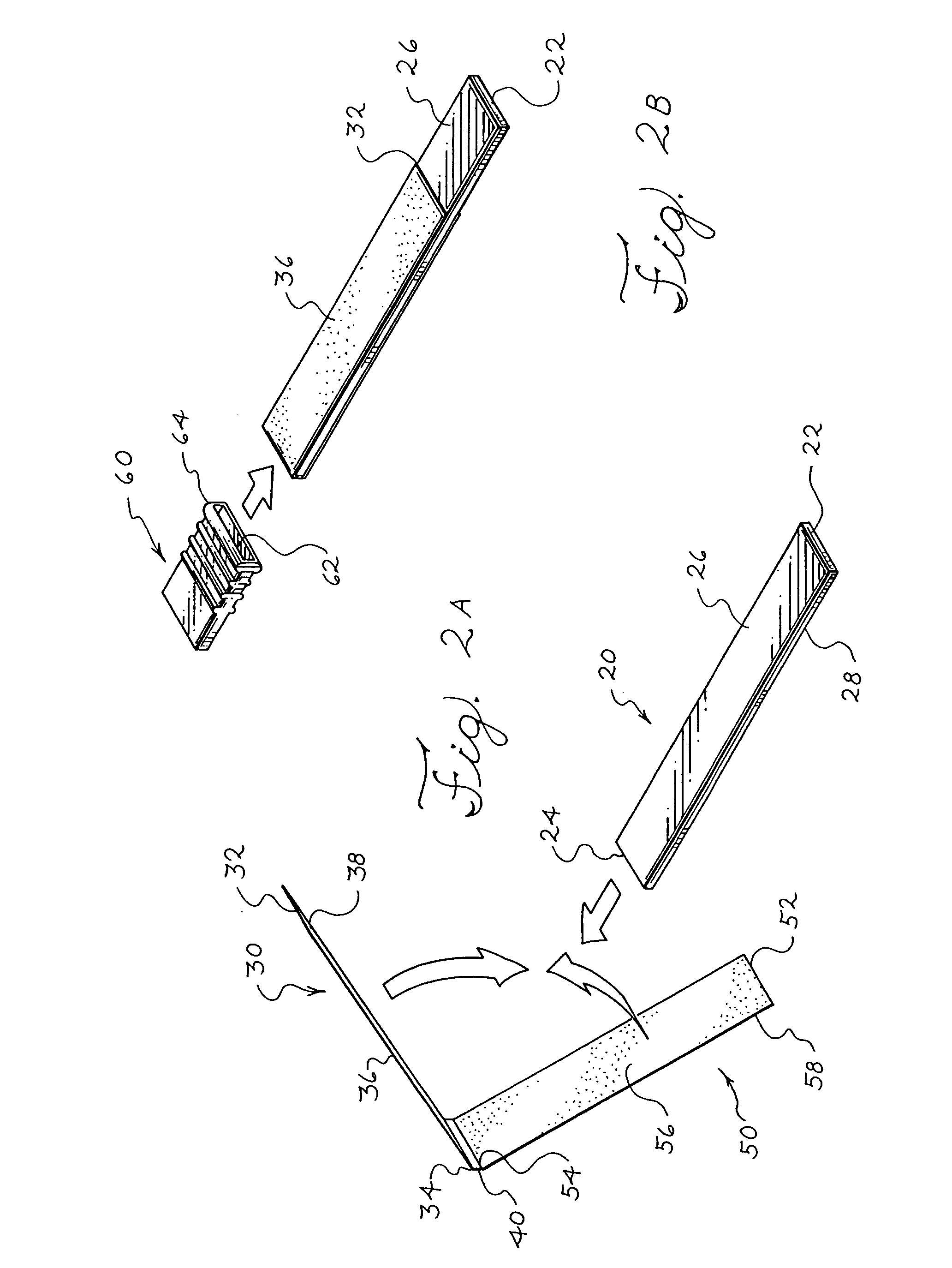
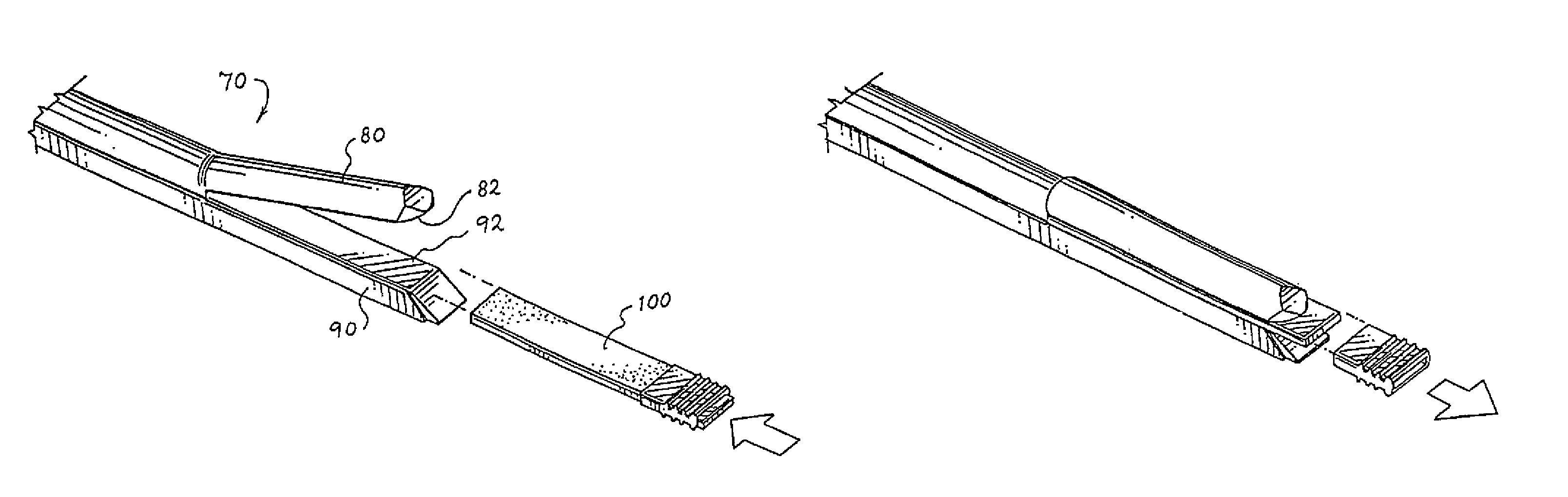
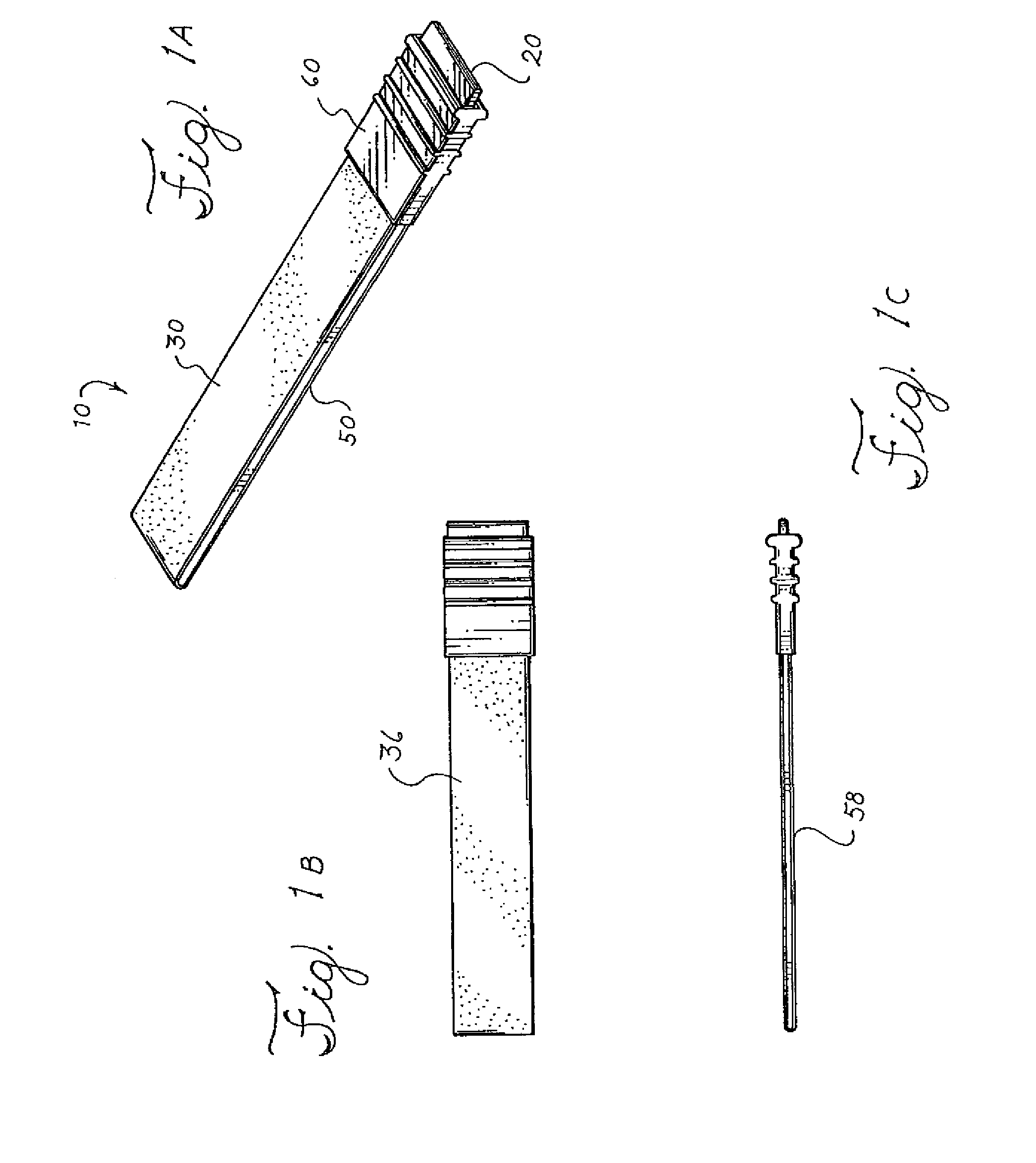
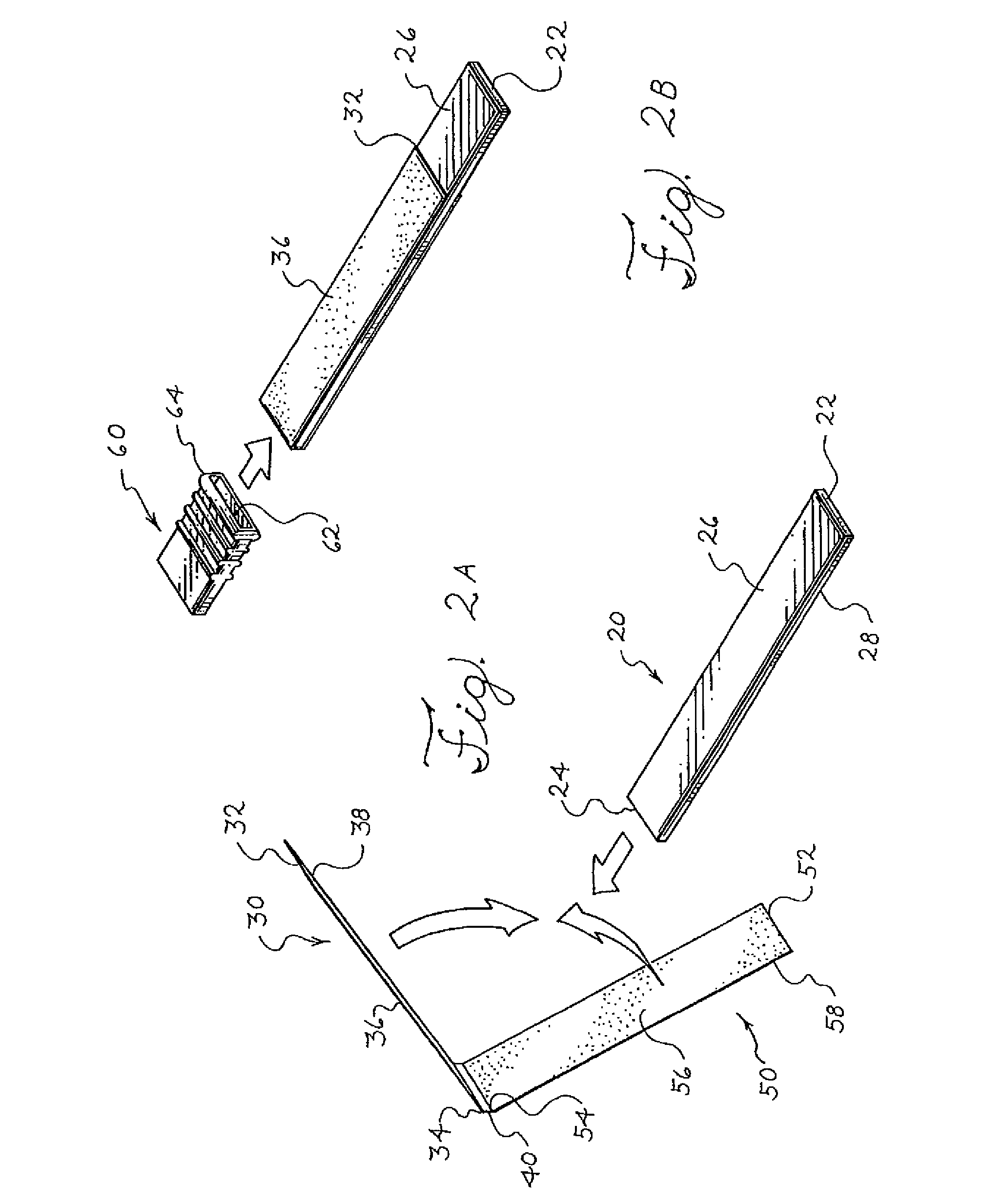
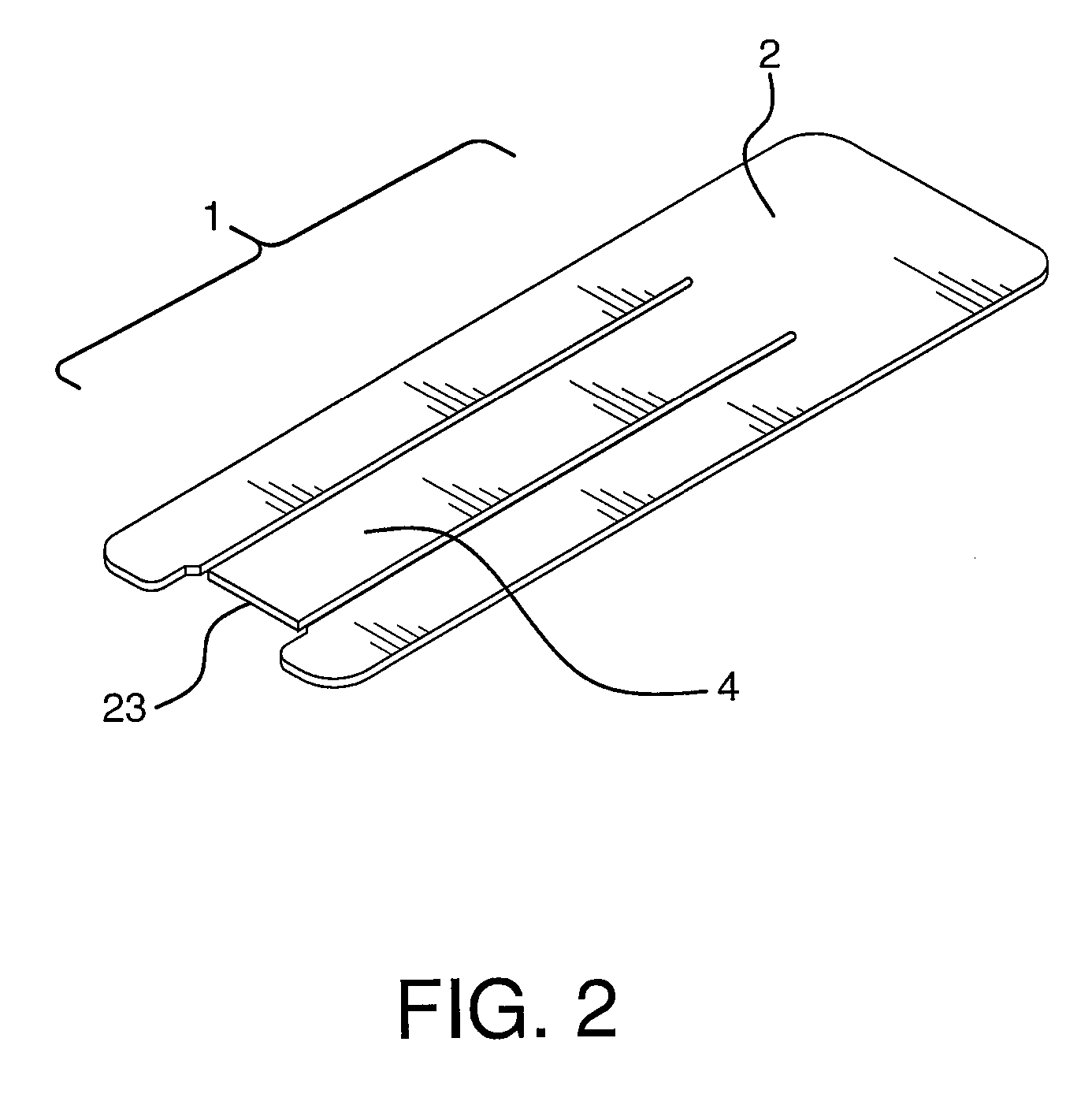
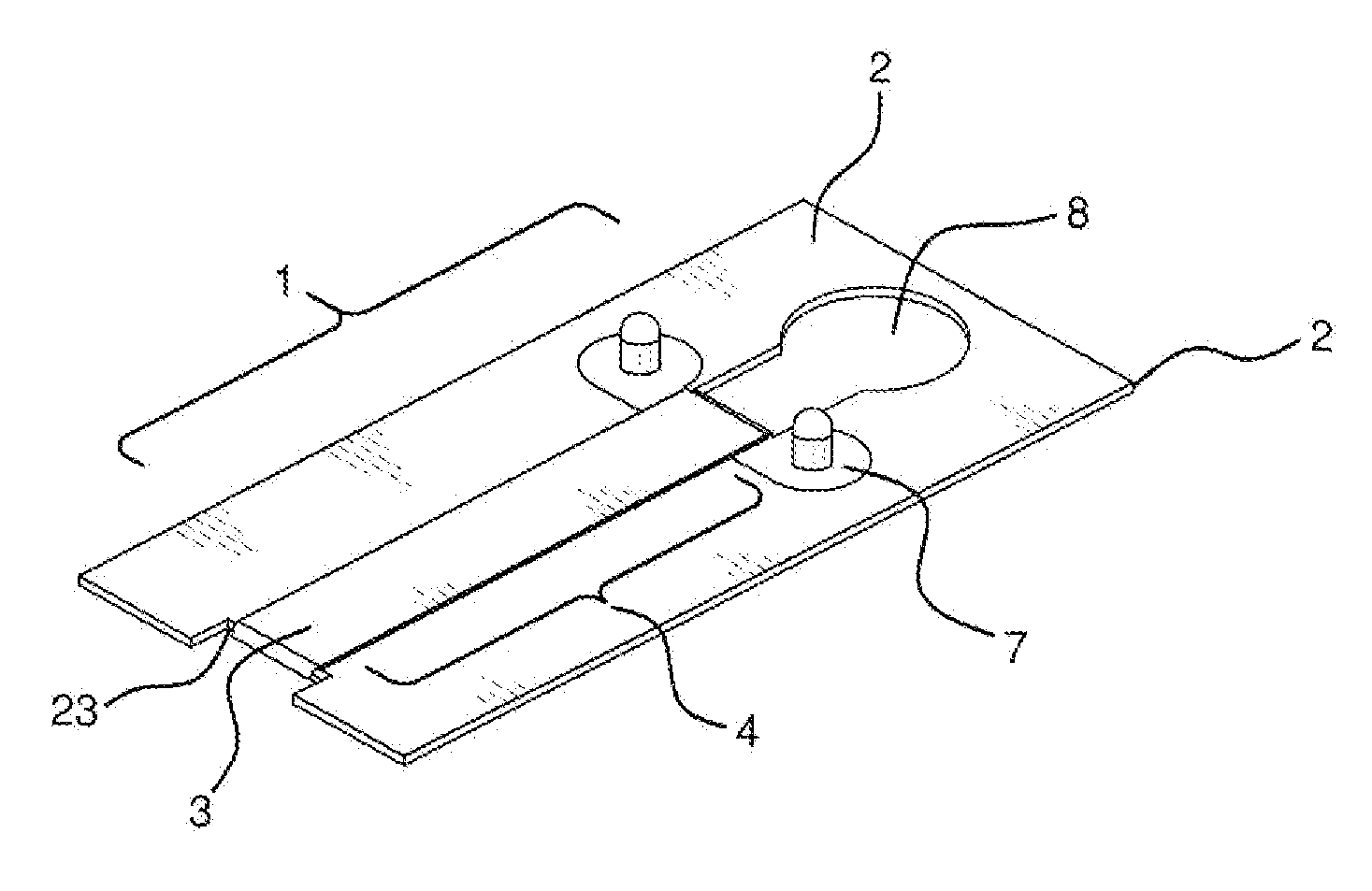
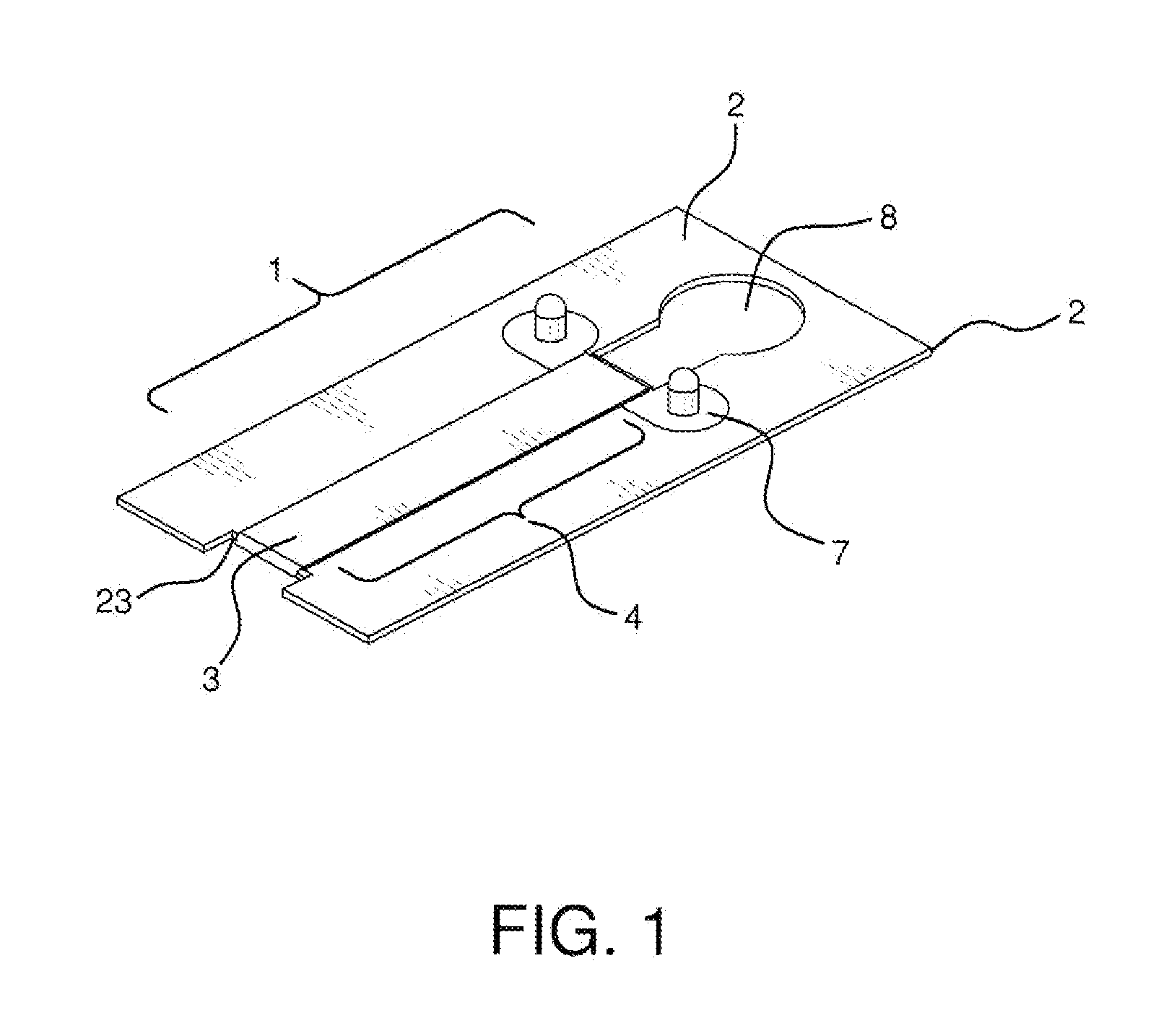
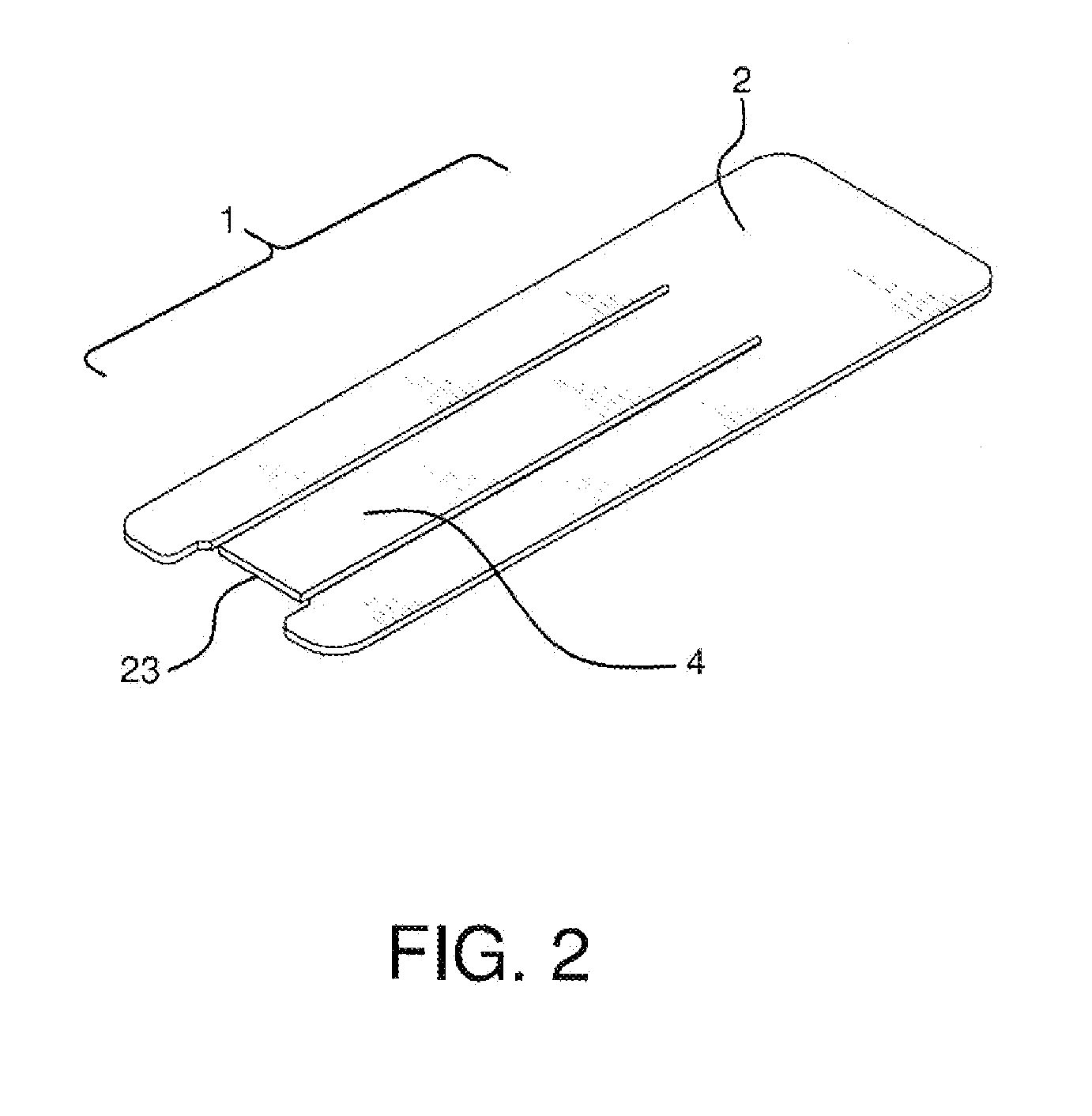
Apparatus and method for producing a reinforced surgical staple line
ActiveUS7377928B2Easy to prepareEasy to useSurgical staplesWound clampsSurgical stapleBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for use with a surgical stapler to provide a reinforced surgical staple line. The apparatus includes an applicator that carries a first and second bioimplantable material connected by a hinge. An applicator clip may be provided to releasably secure the first and second bioimplantable material onto the applicator.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Apparatus and method for producing a reinforced surgical staple line
InactiveUS7789889B2Easy to prepareEasy to useSurgical staplesWound clampsSurgical stapleBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for use with a surgical stapler to provide a reinforced surgical staple line. The apparatus includes an applicator that carries a first and second bioimplantable material connected by a hinge. An applicator clip may be provided to releasably secure the first and second bioimplantable material onto the applicator.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Apparatus for supplying surgical staple line reinforcement
InactiveUS8453904B2Accurately and successfully positionedMaintain strengthSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for supplying surgical buttress material to a surgical stapler is provided. The apparatus has a pivotable area for attaching surgical buttress material. The apparatus may also have an adhesive and a release liner disposed over the buttress material.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Apparatus for Supplying Surgical Staple Line Reinforcement
InactiveUS20120289979A1Accurately and successfully positionedMaintain strengthSurgical staplesWound clampsSurgical stapleMaterial supply
An apparatus for supplying surgical buttress material to a surgical stapler is provided. The apparatus has a pivotable area for attaching surgical buttress material. The apparatus may also have an adhesive and a release liner disposed over the buttress material.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
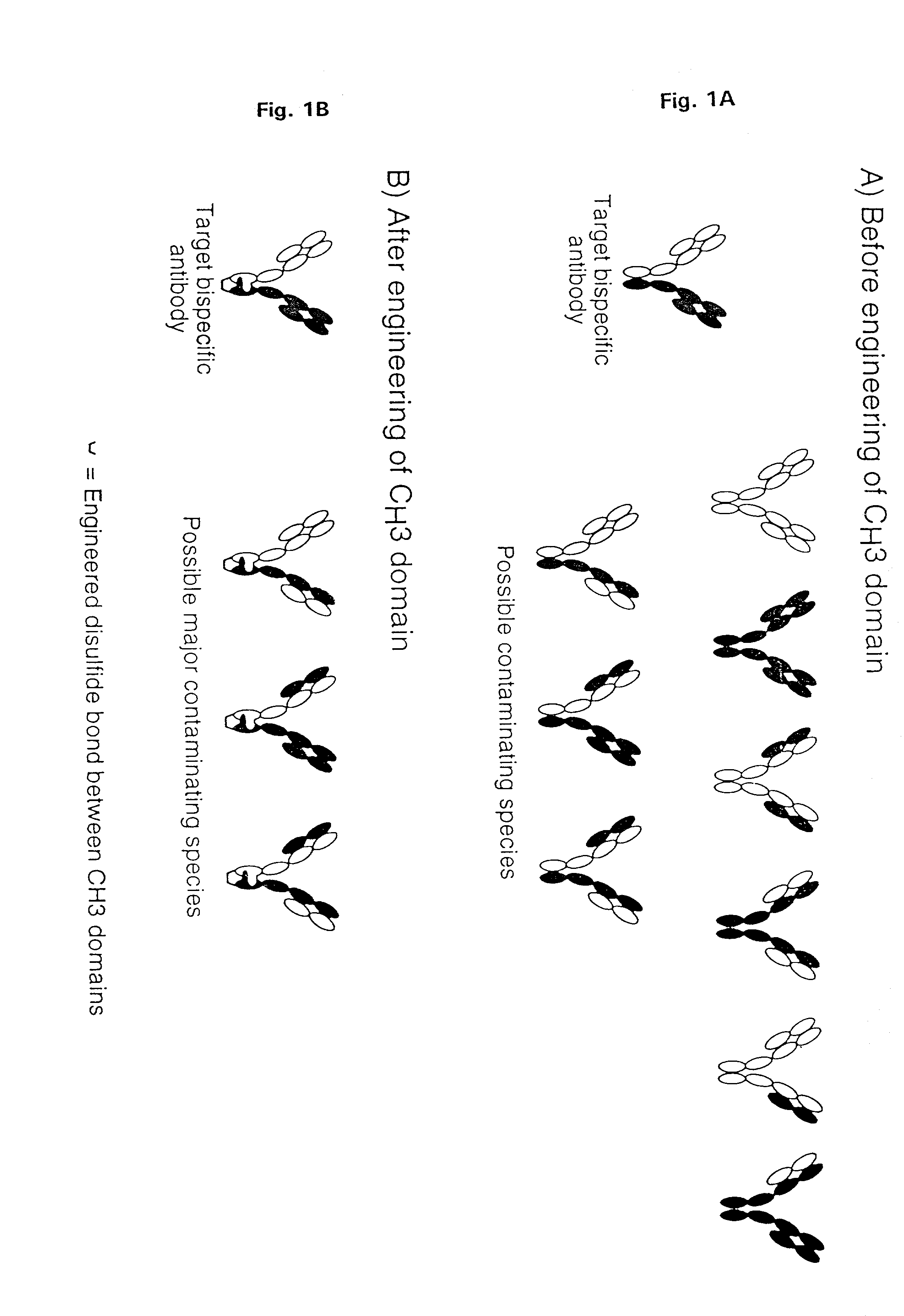
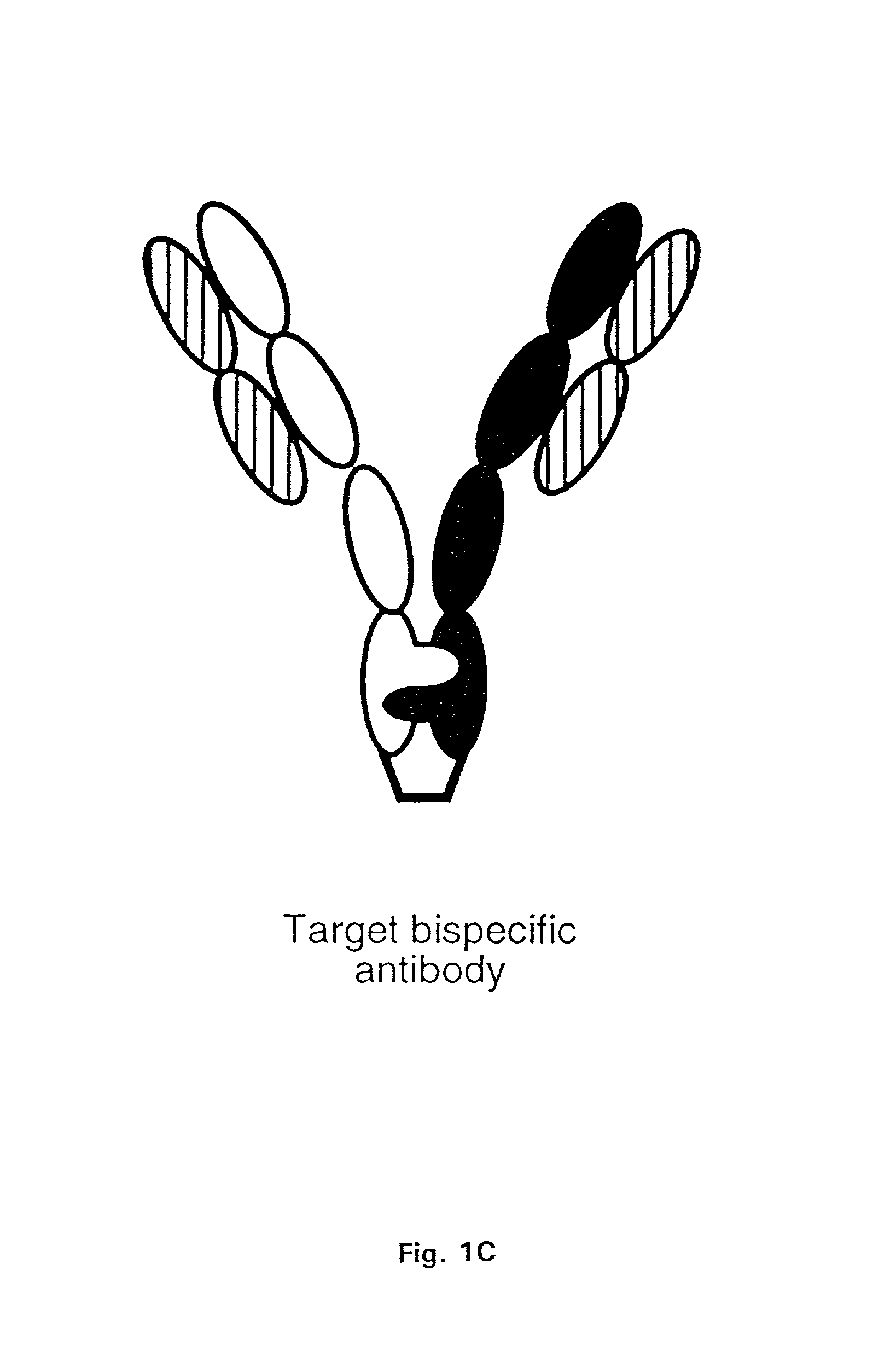
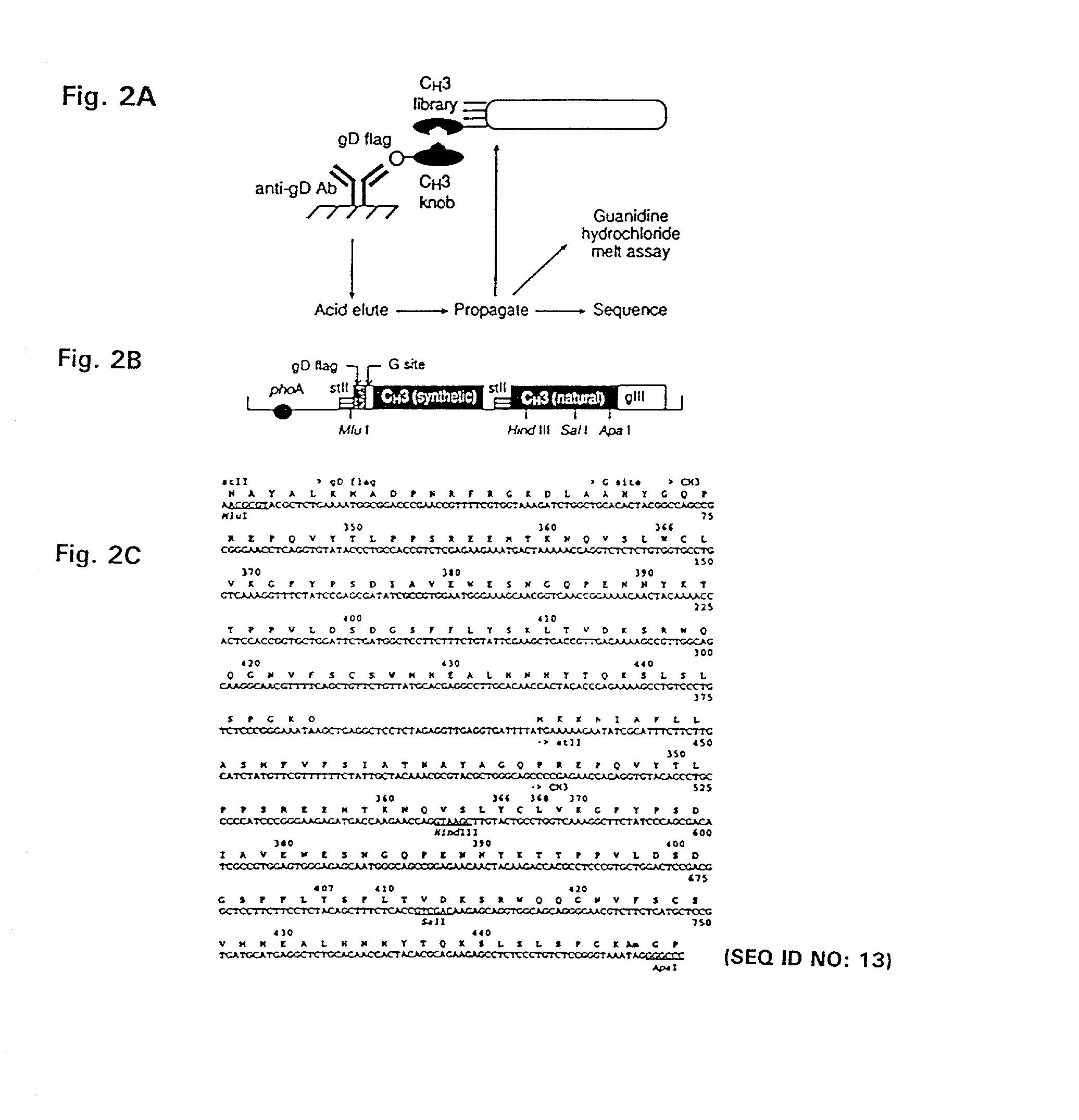
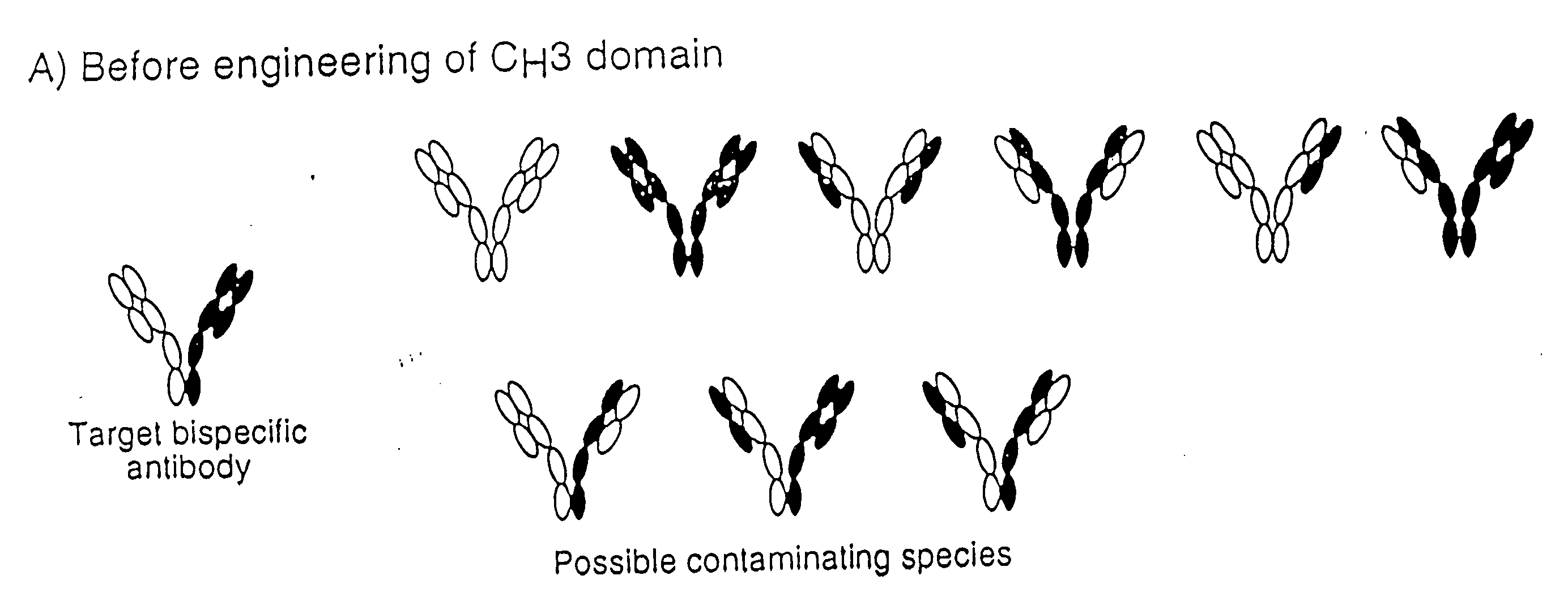
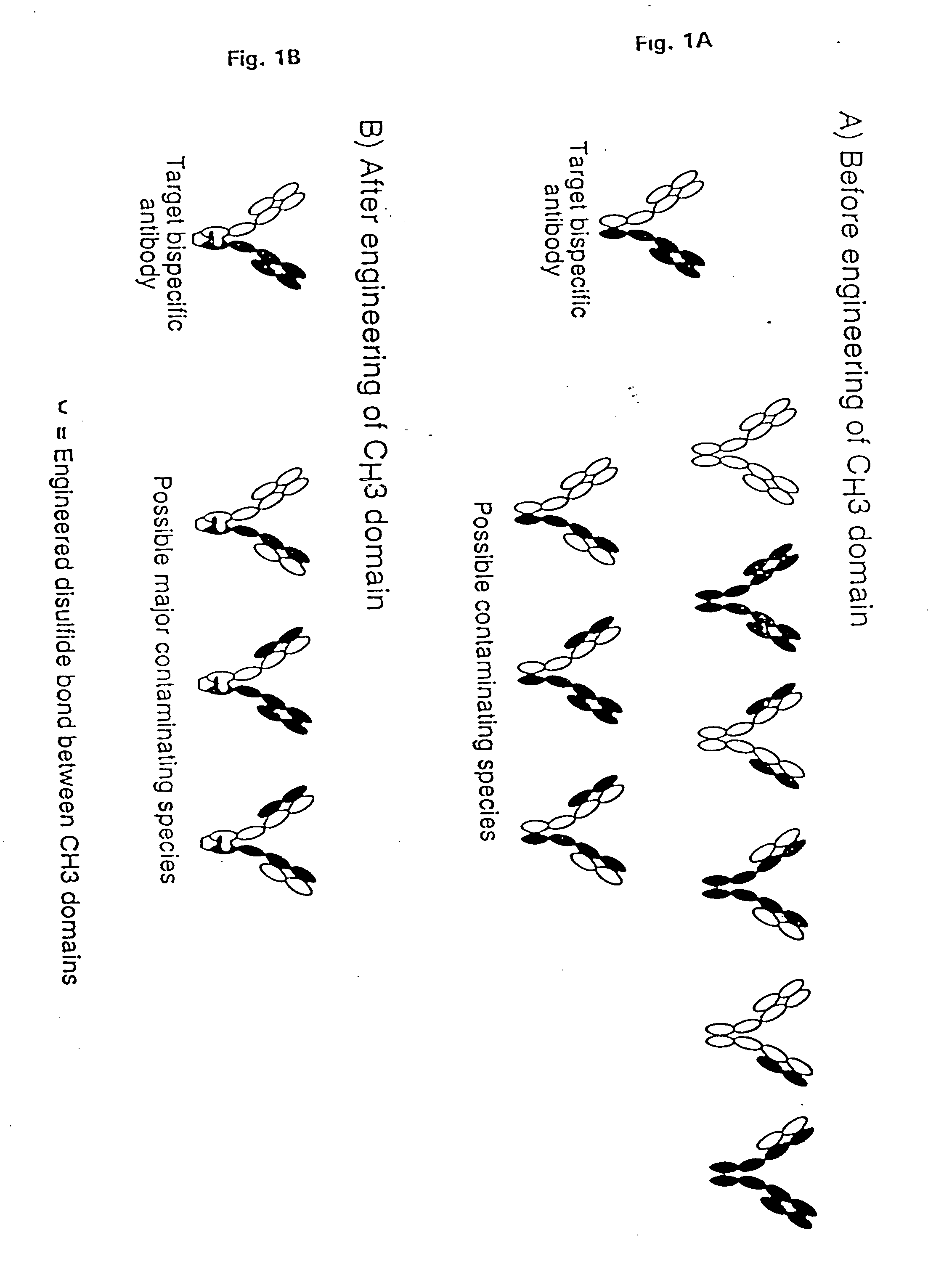
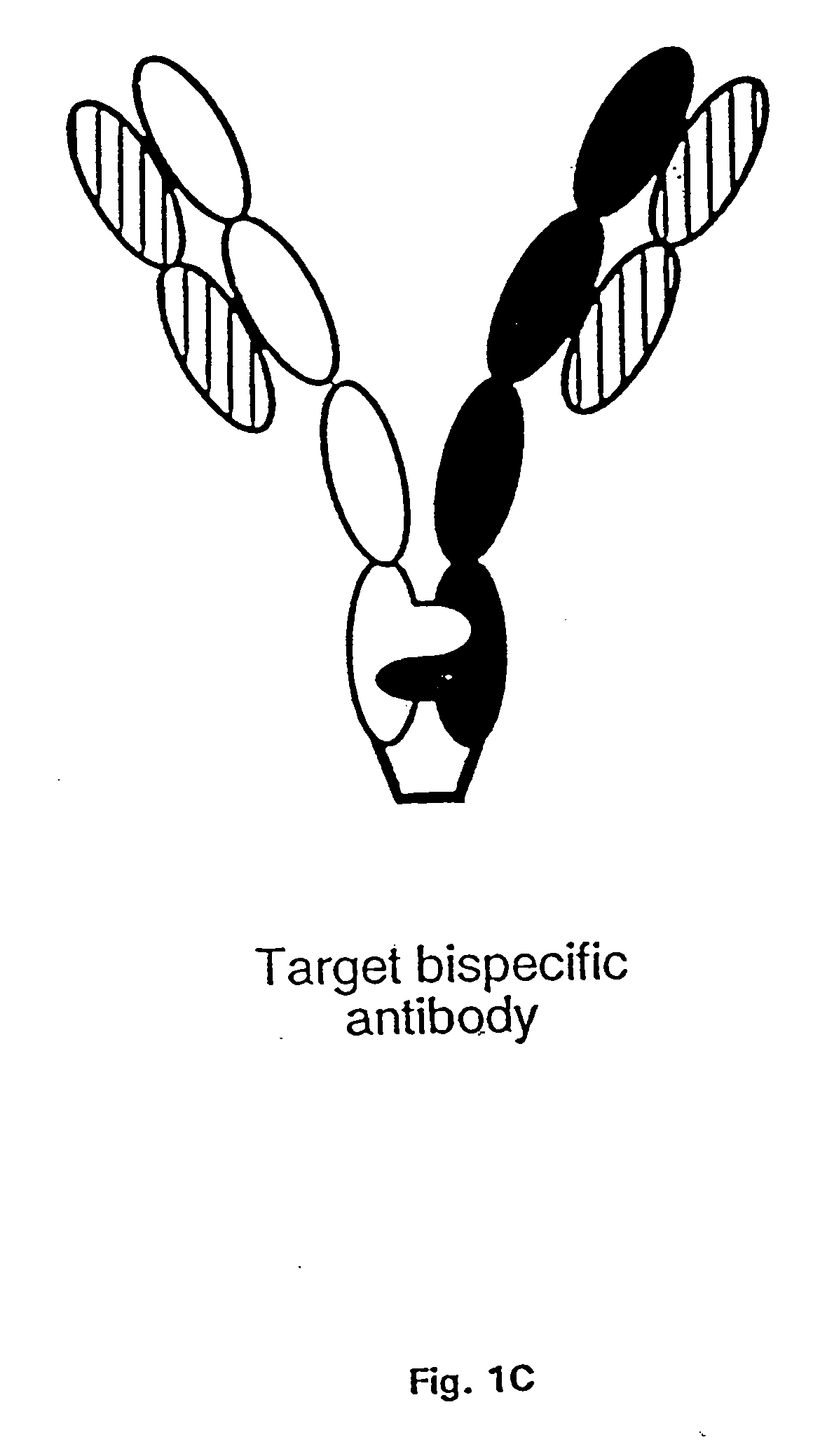
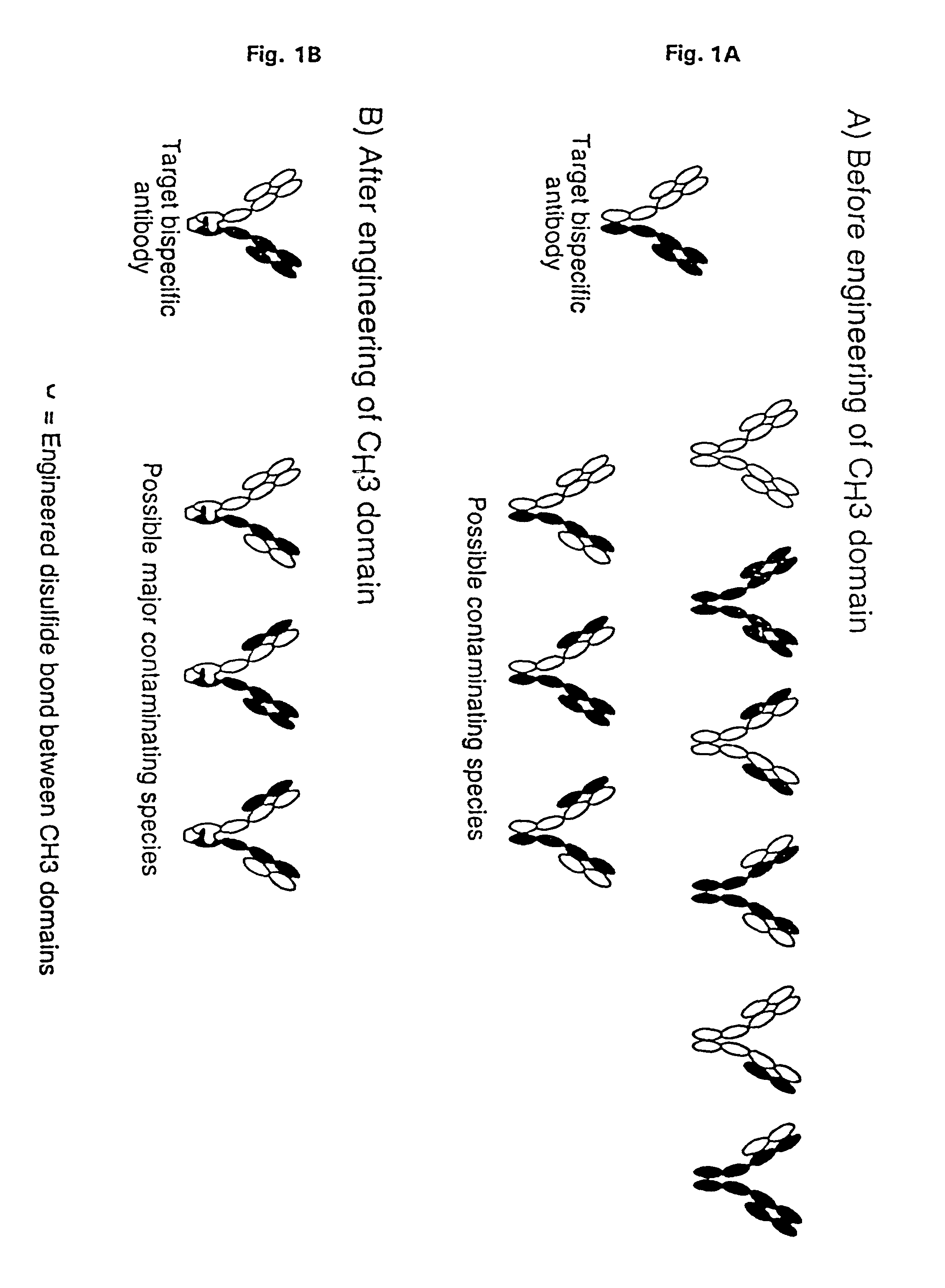
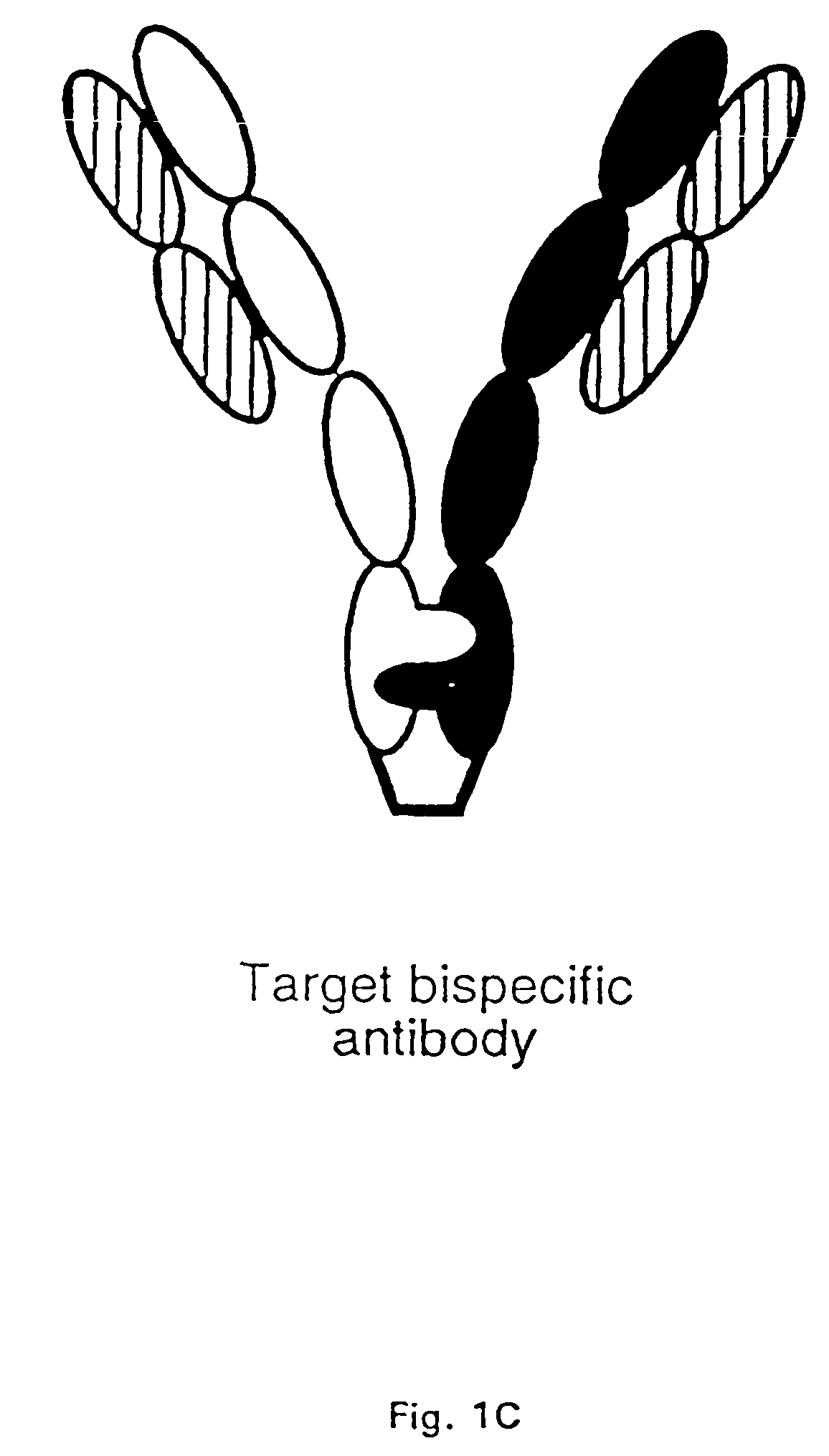
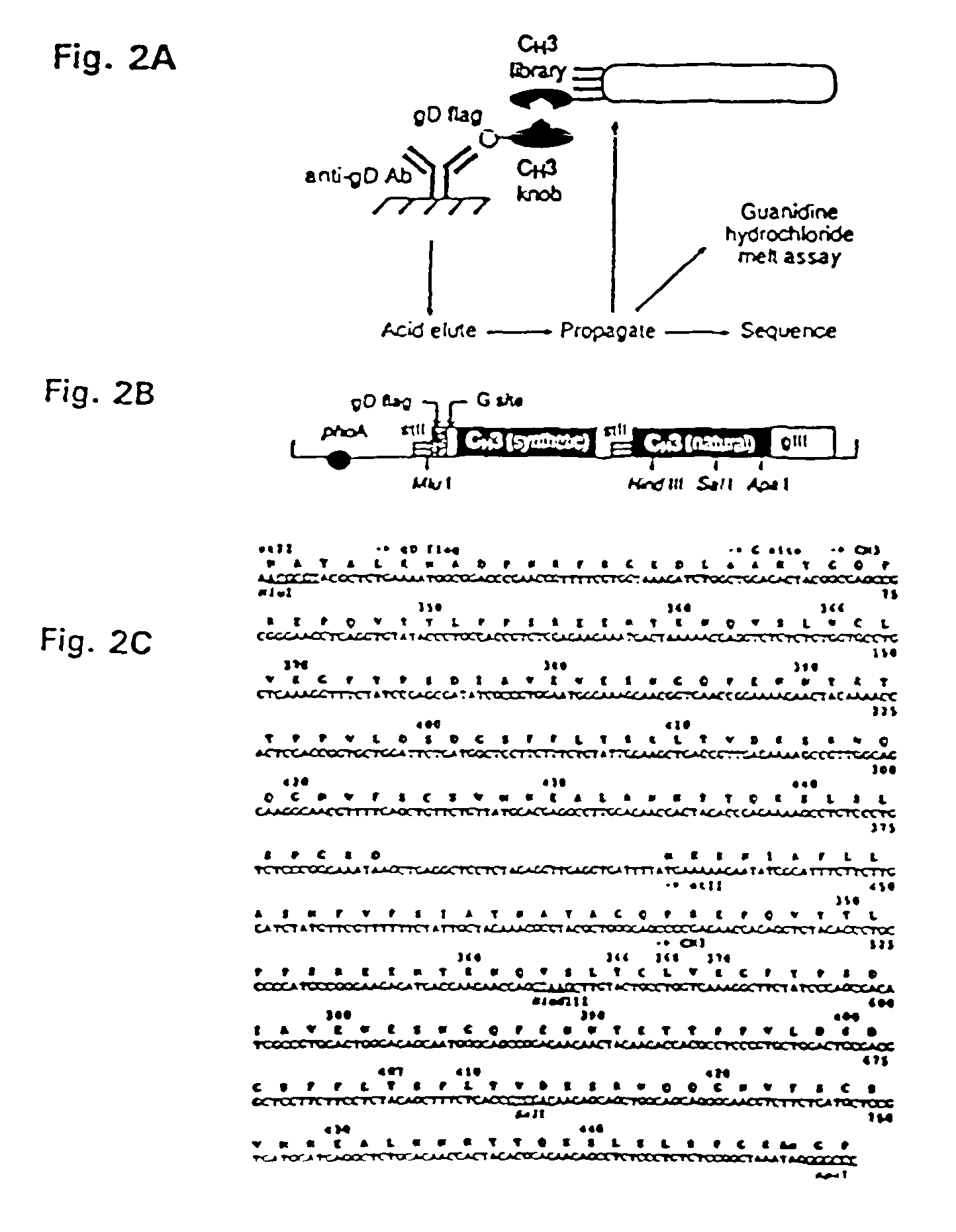
Method for making multispecific antibodies having heteromultimeric and common components
InactiveUS7183076B2Increased formationIncrease productionAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSpecific immunityBispecific antibody
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method futher involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
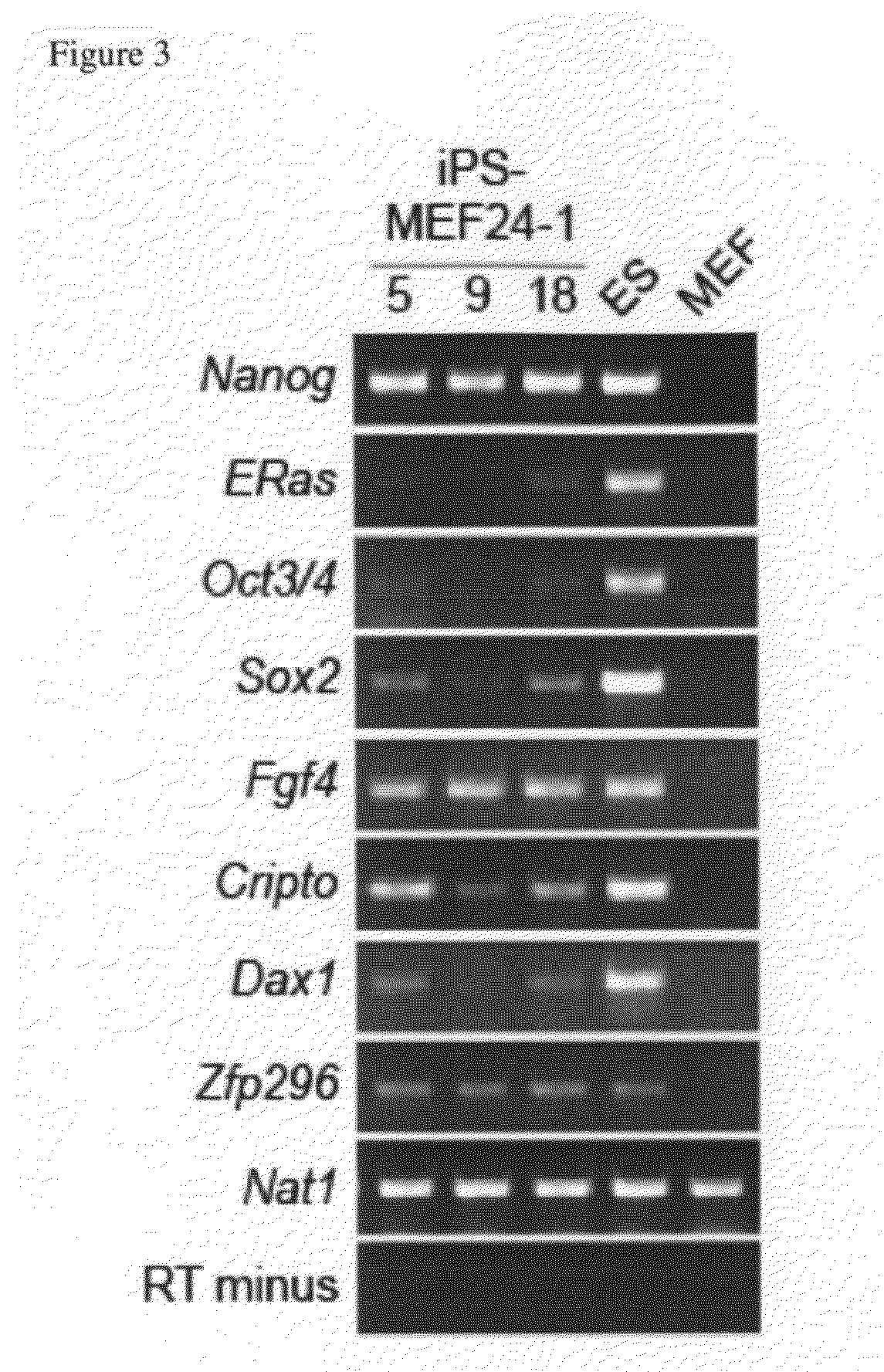
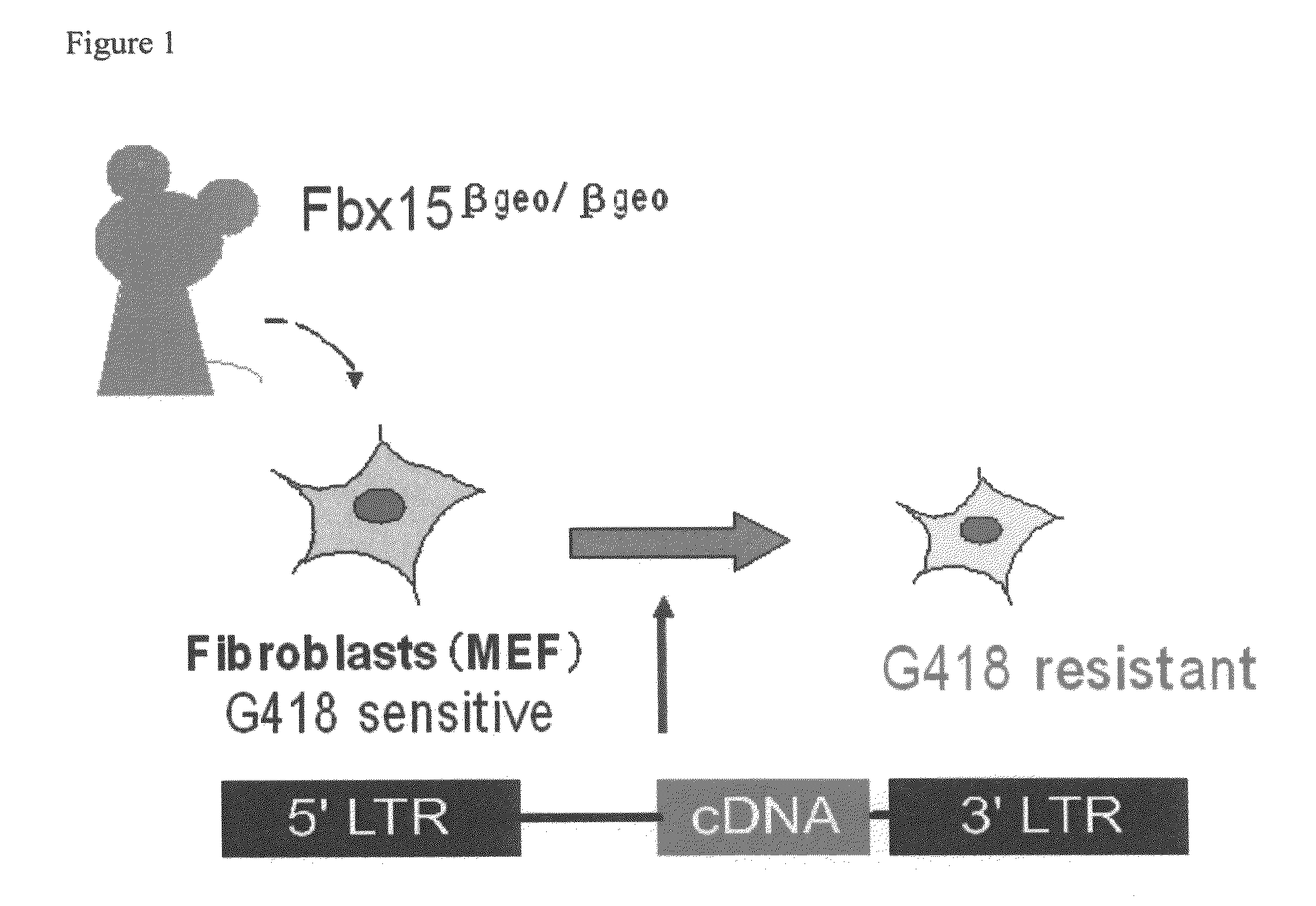
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20090047263A1Type be limitEfficiently isolateBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsStem-cell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
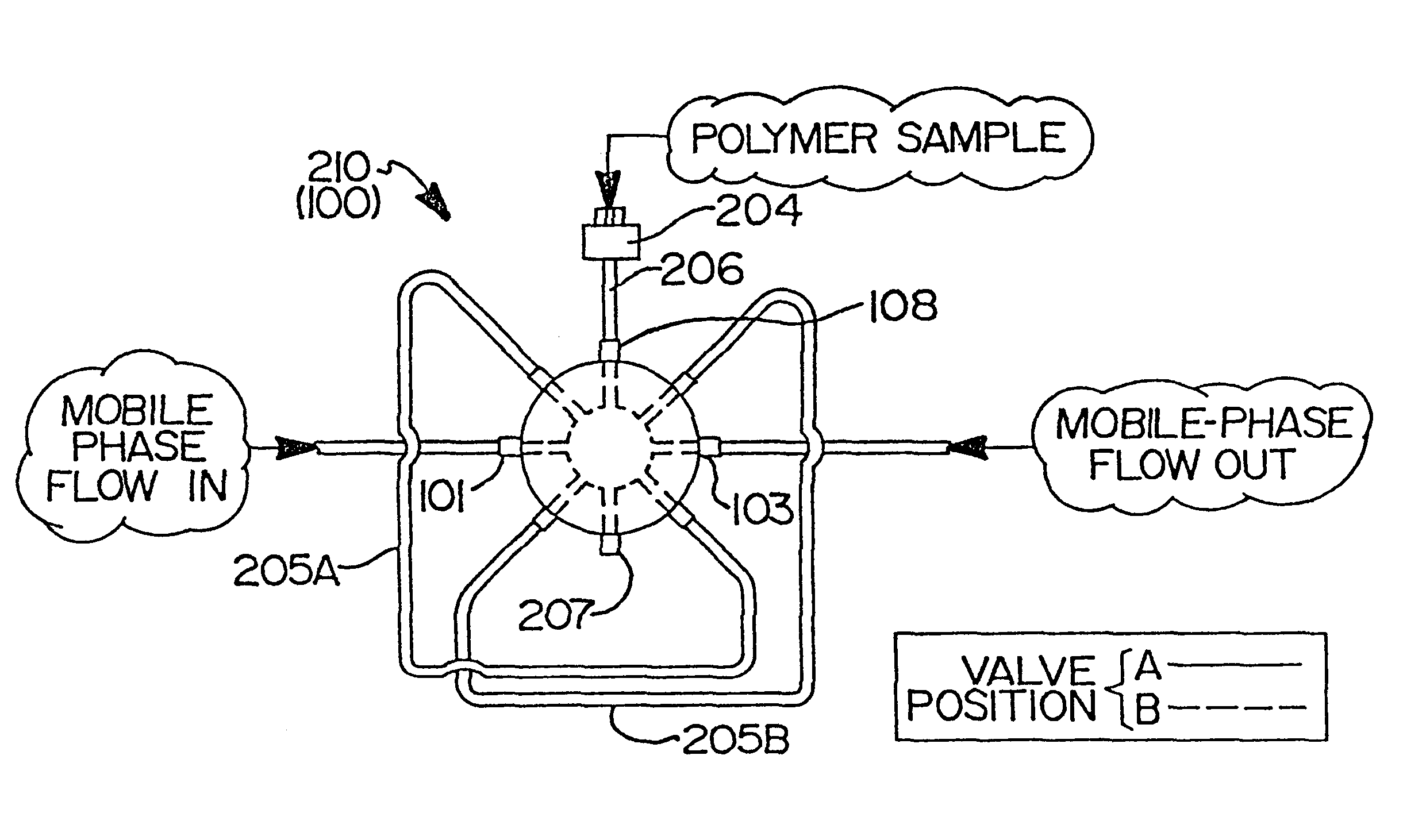
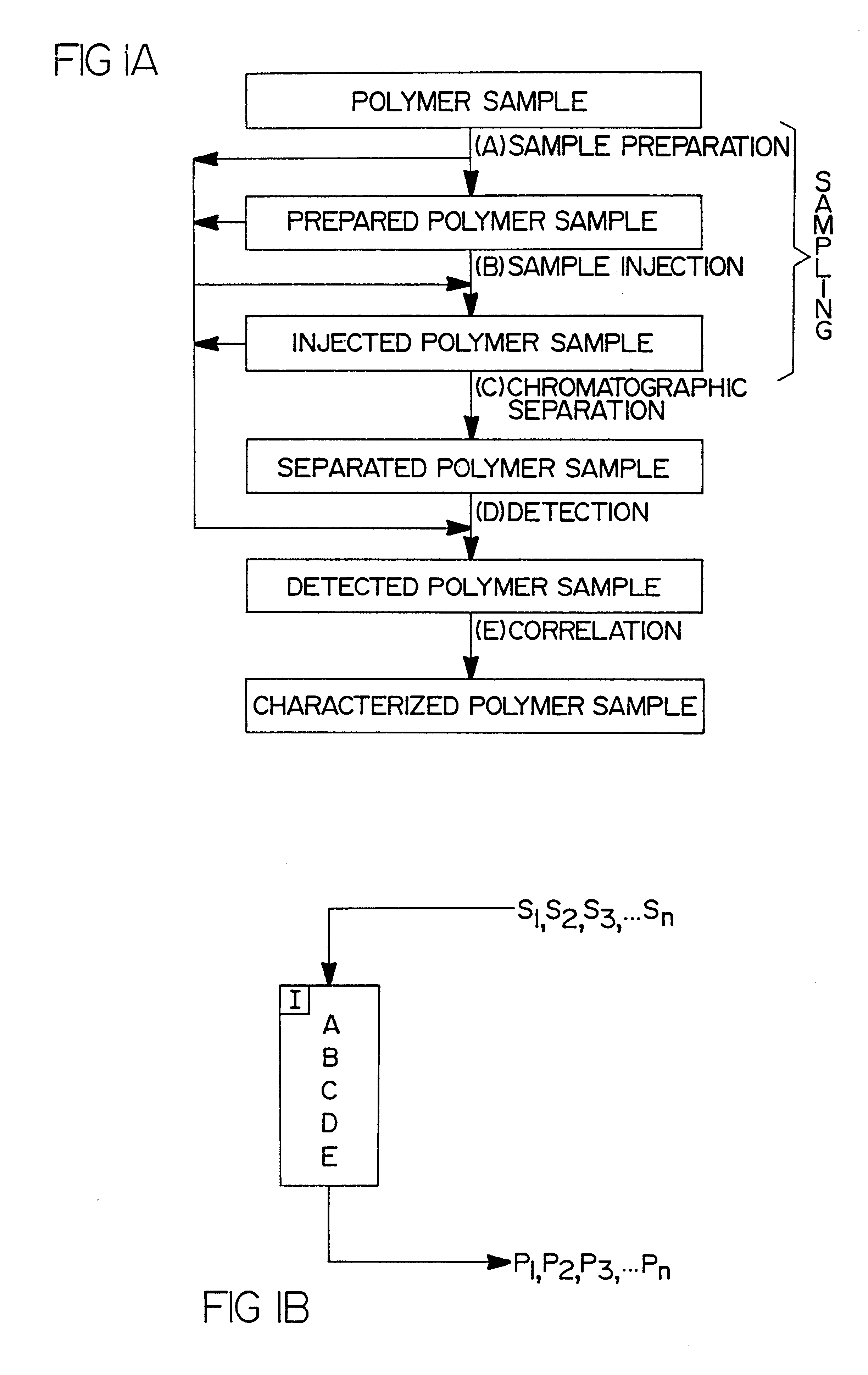
High-temperature characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6260407B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationElutionChromatography column
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. In preferred high-temperature embodiments, the polymer sample is maintained at a temperature of not less than about 75° C. during sample preparation, loading into a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, injection into a mobile phase of a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, and / or elution from chromatographic column. The described methods, systems, and device have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
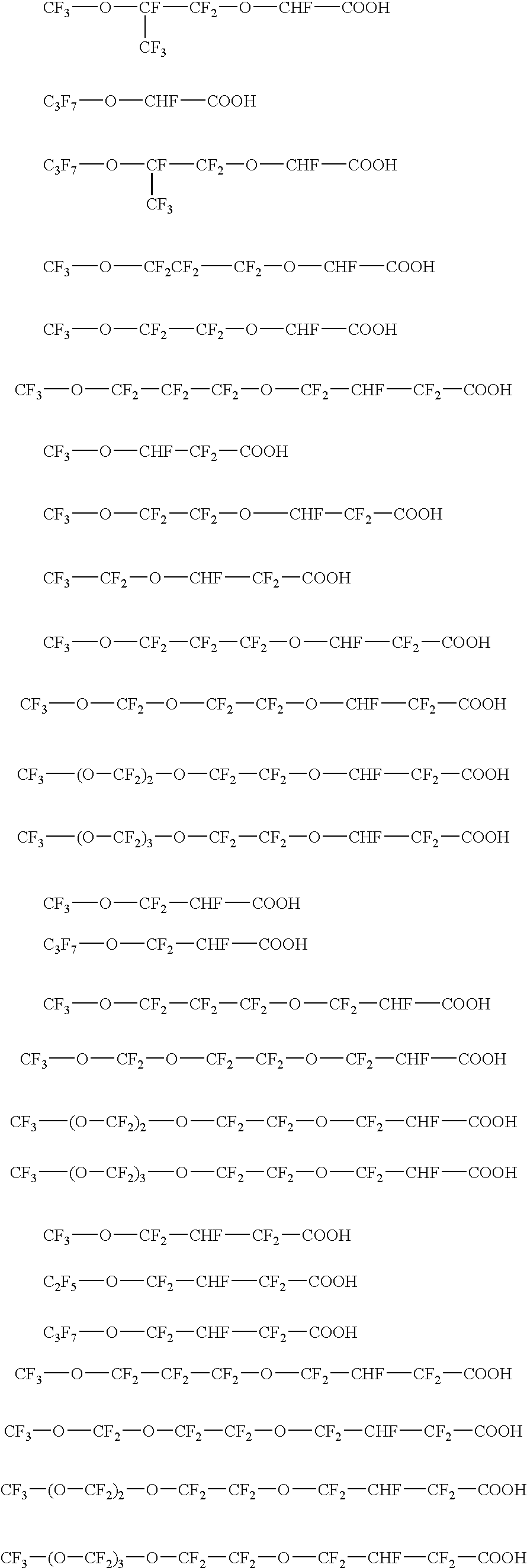
Fluorinated surfactants for making fluoropolymers
ActiveUS20070142541A1Easy to preparePrepared cost-effectivelyLiquid surface applicatorsTransportation and packagingEmulsion polymerizationFluoropolymer
The invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula: [Rf—(O)t—CHF—(CF2)n—COO—]iXi+ (I) wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, t is 0 or 1 and n is 0 or 1, Xi+ represents a cation having a valence i and i is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant can be used in emulsion polymerization of fluoromonomers to prepare fluoropolymers.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Anthranilamide compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an anthranilamide compound as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound has the chemical name as follows: 3-bromine-1-(3-Cl-2-pyridyl)-N-[4-methanethioamido-2-methyl-6-(methylaminoformyl)-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-methanamide, and is obtained through enabling bromine cyanide insect amide and a vulcanizing agent to react in the existence of a polar organic solvent and a catalyst at the temperature of 0-100 DEG C. The compound disclosed by the invention can be used for independently preparing an insecticide or preparing a mixed insecticide together with abamectin insecticides, neonicotinoid insecticides or pyrethroid insecticides, and the independently prepared insecticide is used for preventing and controlling Lepidoptera pests, dipteral pests or hemiptera pests.
Owner:江苏省农用激素工程技术研究中心有限公司 +1
Indirect calibration of polymer characterization systems
InactiveUS6294388B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingPolymer characterizationFlow injection analysis
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
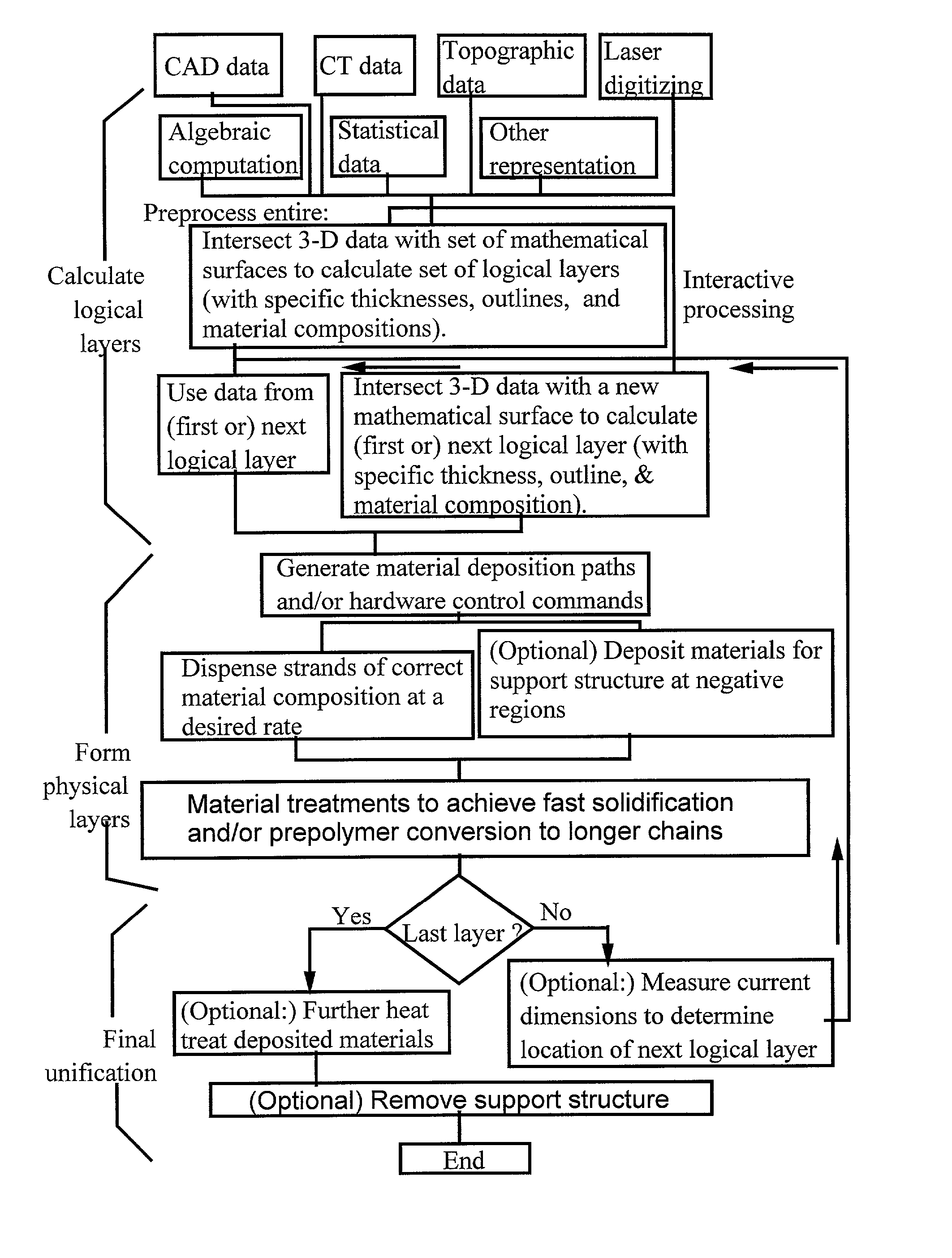
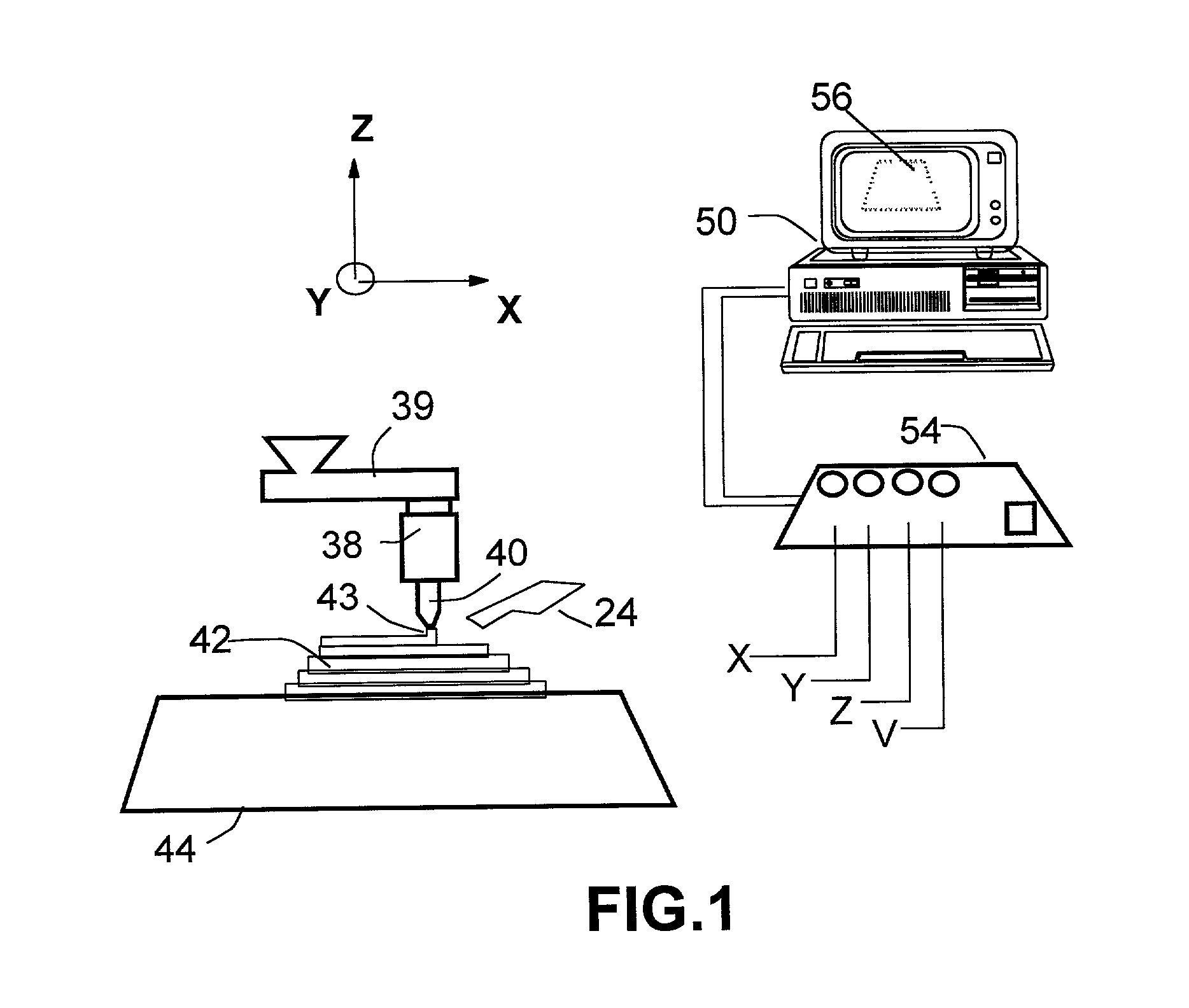
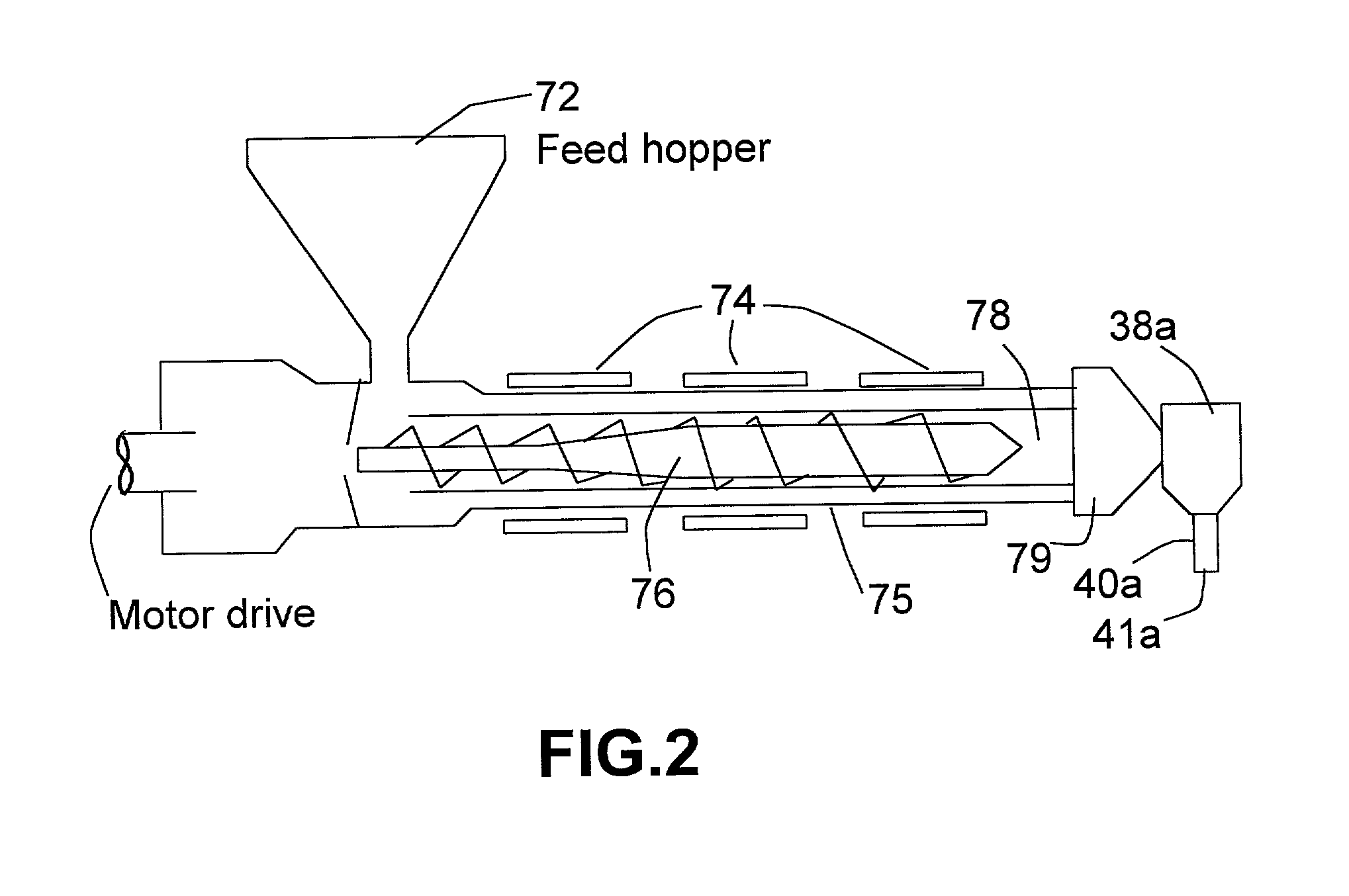
Freeform fabrication method using extrusion of non-cross-linking reactive prepolymers
InactiveUS20020113331A1Fast formingDifficult to prepareProgramme controlComputer controlCross-linkThermoplastic
An extrusion-based freeform fabrication method for making a three-dimensional object from a design created on a computer, including (a) providing a support member; (b) operating a dispensing head having at least one dispensing nozzle with a discharge orifice for dispensing continuous strands of a material composition in a fluent state at a first temperature onto the support member, the material composition including a reactive prepolymer with a melting point above 23° C. and the first temperature being greater than the prepolymer melting point; (c) operating material treatment devices for causing the dispensed strands of material composition to rapidly achieve a rigid state in which the material composition is substantially solidified to build up the 3-D object, the material treatment devices also working to convert the reactive prepolymer to a higher molecular weight thermoplastic resin; and (d) operating control devices for generating control signals in response to coordinates of the object design to control the movement of the dispensing nozzle relative to the support member and for controlling the strand dispensing of the material composition to construct the 3-D object.
Owner:ZHANG TAN +3
Method of growing oxide films
InactiveUS20030188682A1Easy to prepareExcellent dielectric propertiesPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideOxygen
Abstract of Disclosure Process for producing silicon oxide containing thin films on a growth substrate by the ALCVD method. In the process, a vaporisable silicon compound is bonded to the growth substrate, and the bonded silicon compound is converted to silicon dioxide. The invention comprises using a silicon compound which contains at least one organic ligand and the bonded silicon compound is converted to silicon dioxide by contacting it with a vaporised, reactive oxygen source, in particular with ozone. The present invention provides a controlled process for growing controlling thin films containing SiO2, with sufficiently short reaction times.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
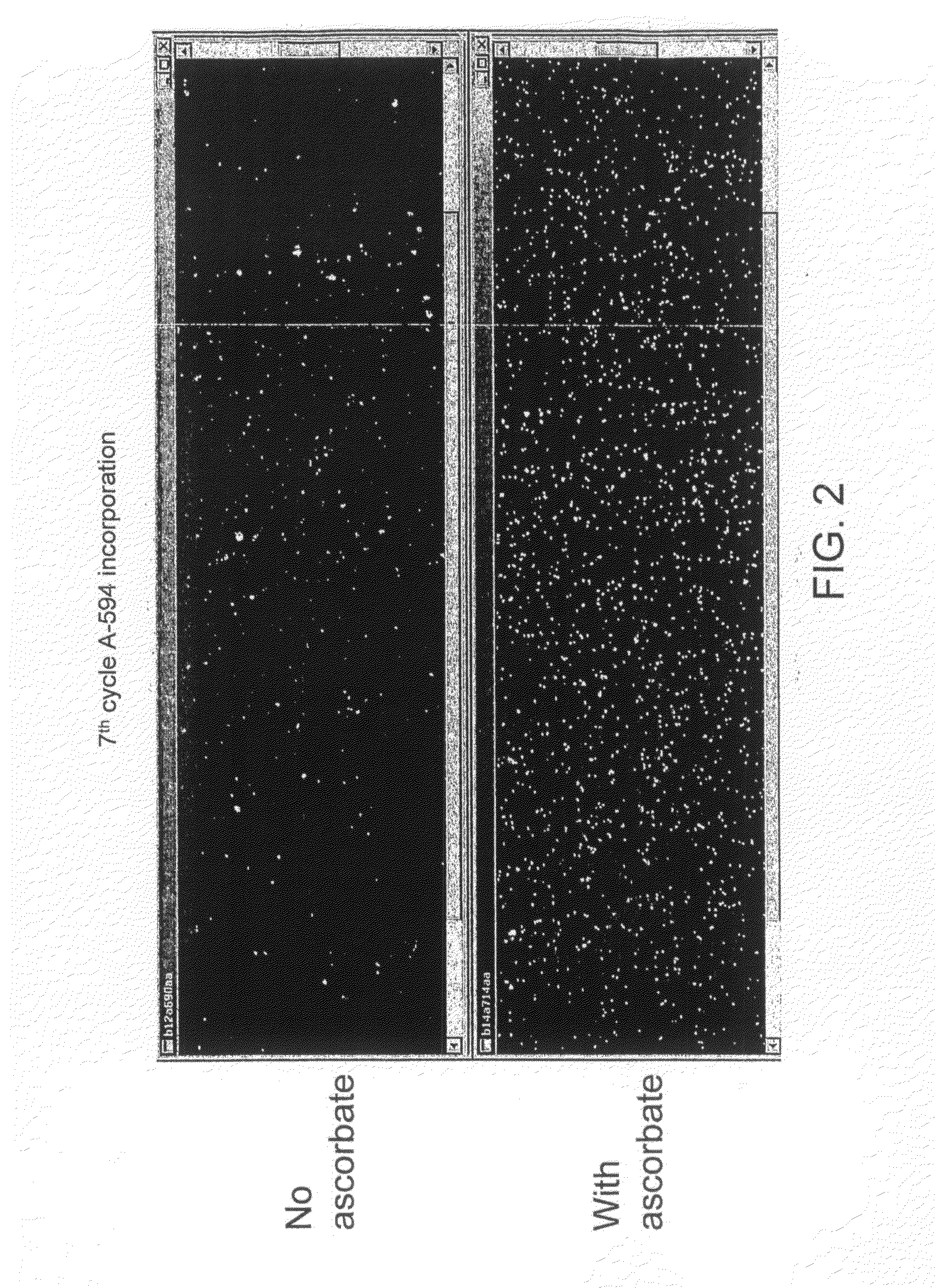
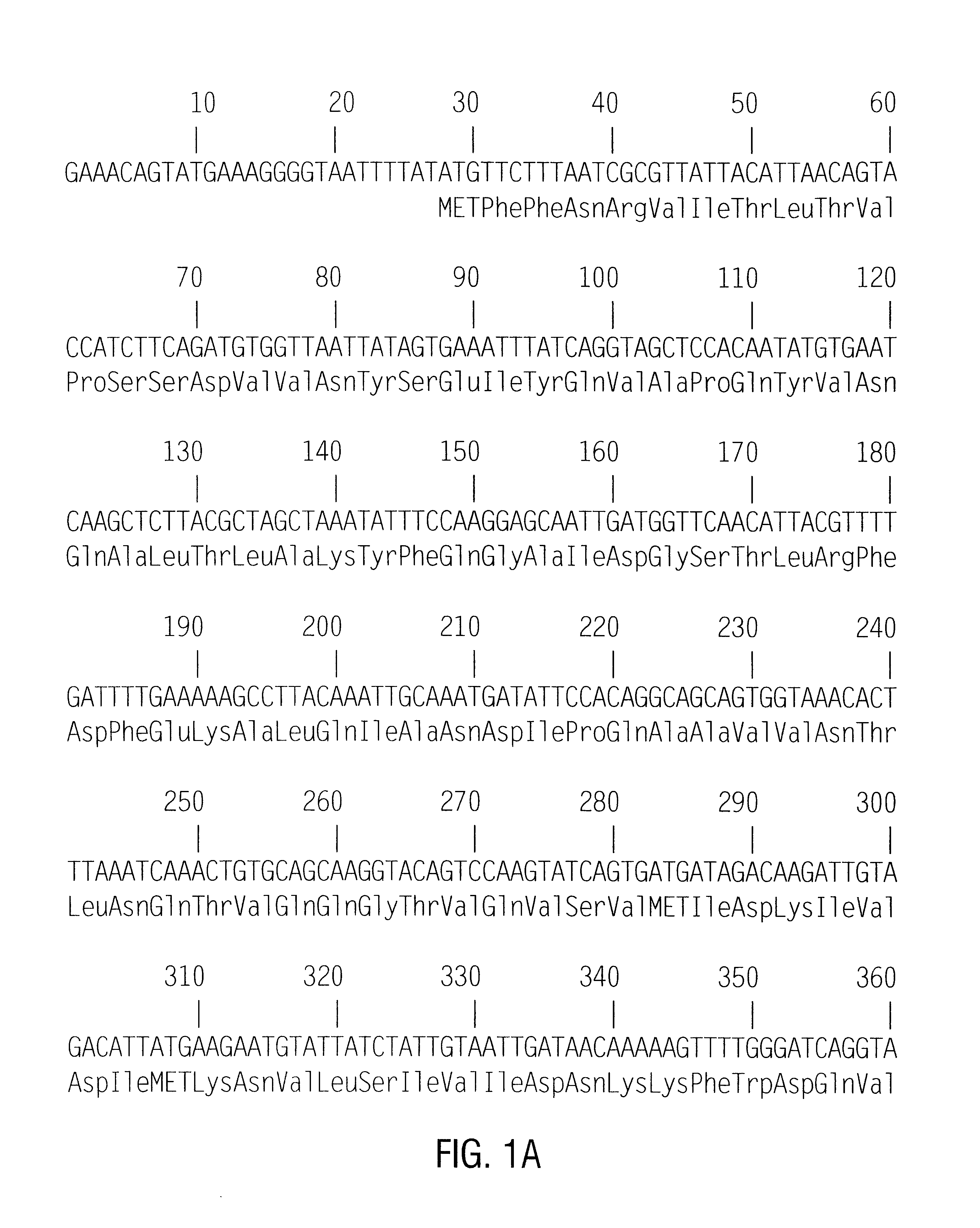
Method of Nucleotide Detection
ActiveUS20080280773A1Improve performanceIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFluorescenceNucleotide
The invention relates to an additive which can be added to buffers used in nucleotide detection processes and improved methods of nucleic acid sequencing using this additive. In particular the invention relates to use of the additive to improve the efficiency of fluorescence-based multiple cycle nucleic acid sequencing reactions.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Apparatus and method for producing a reinforced surgical staple line
InactiveUS20080125812A1Easy to prepareEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for use with a surgical stapler to provide a reinforced surgical staple line. The apparatus includes an applicator that carries a first and second bioimplantable material connected by a hinge. An applicator clip may be provided to releasably secure the first and second bioimplantable material onto the applicator.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH
Apparatus for supplying surgical staple line reinforcement
InactiveUS20090095791A1Thinner materialAccurately and successfully positionedSuture equipmentsStapling toolsBiomedical engineeringMaterial supply
An apparatus for supplying surgical buttress material to a surgical stapler is provided. The apparatus has a pivotable area for attaching surgical buttress material. The apparatus may also have an adhesive and a release liner disposed over the buttress material.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
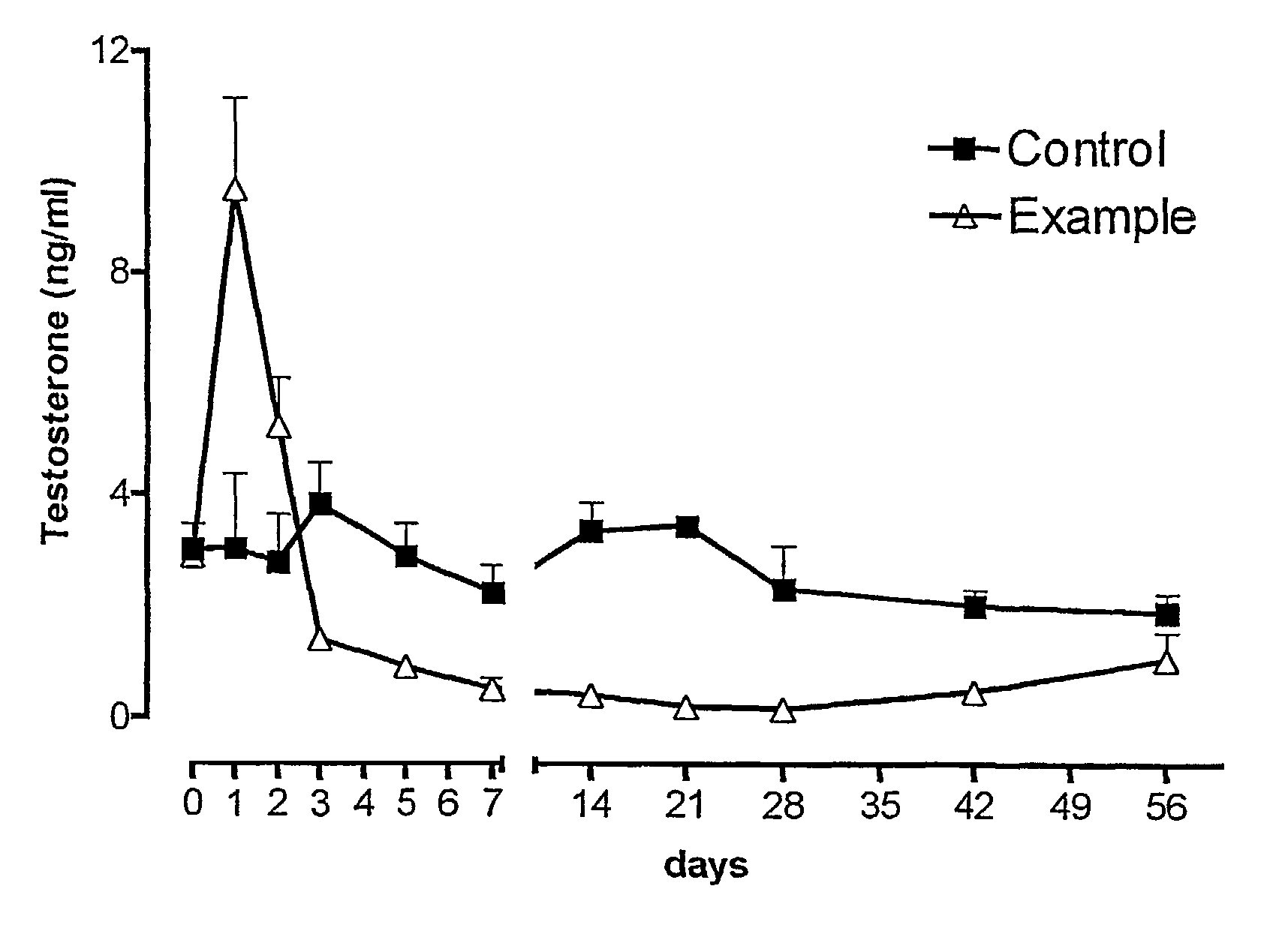
Sustained release pharmaceutical compositions for the parenteral administration of hydrophilic compounds
InactiveUS7157099B2Easy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsParenteral nutritionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:ITALFARMACO SPA
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Antifungal polypeptide and methods for controlling plant pathogenic fungi
InactiveUS6121436AConvenient labelingGood reproducibilitySugar derivativesPlant peptidesDna encodingFungal growth
Antifungal polypeptides, isolated from Medicago plants, are shown to control fungal damage to plants. DNA encoding the polypeptides was cloned into vectors for transformation of plant-colonizing microorganisms or plants, thereby providing a method of inhibiting fungal growth on plants. The polypeptides can be formulated into compositions useful in controlling undesired fungi.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Antifungal polypeptide from alfalfa and methods for controlling plant pathogenic fungi
InactiveUS6316407B1Convenient labelingGood reproducibilityBiocideAntimycoticsPathogenic fungusNigella sativa
Antifungal polypeptides, isolated from Medicago plants, are shown to control fungal damage to plants. The polypeptides can be formulated into compositions useful in controlling undesired fungi.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Fluorinated surfactants for use in making a fluoropolymer
InactiveUS20070117914A1Convenient and easy preparationPrepared cost-effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationEmulsion polymerizationCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula:[Rf—(O)t—CQH—CF2—O]n—R-G (I)wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, Q is CF3 or F, R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon group, G represents a carboxylic or sulphonic acid or salt thereof, t is 0 or 1 and n is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant is particularly useful in polymerizing fluorinated monomers in an aqueous emulsion polymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20090227032A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Lepidopteran-active Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6593293B1Low steady state levelGreat and less stabilityBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinAureobasidium sp.
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis genes and their encoded crystal proteins, as well as methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for transforming monocotyledons
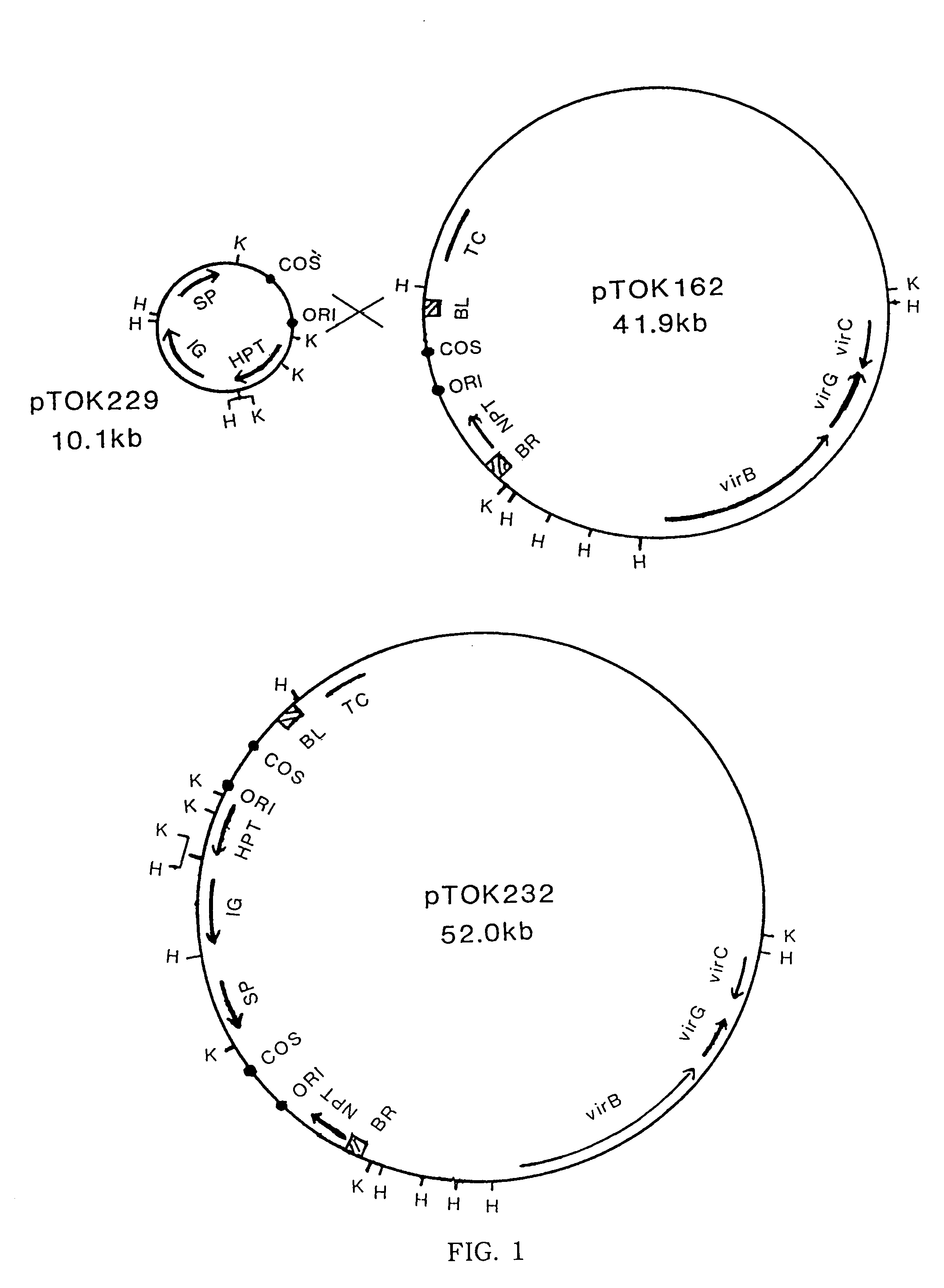
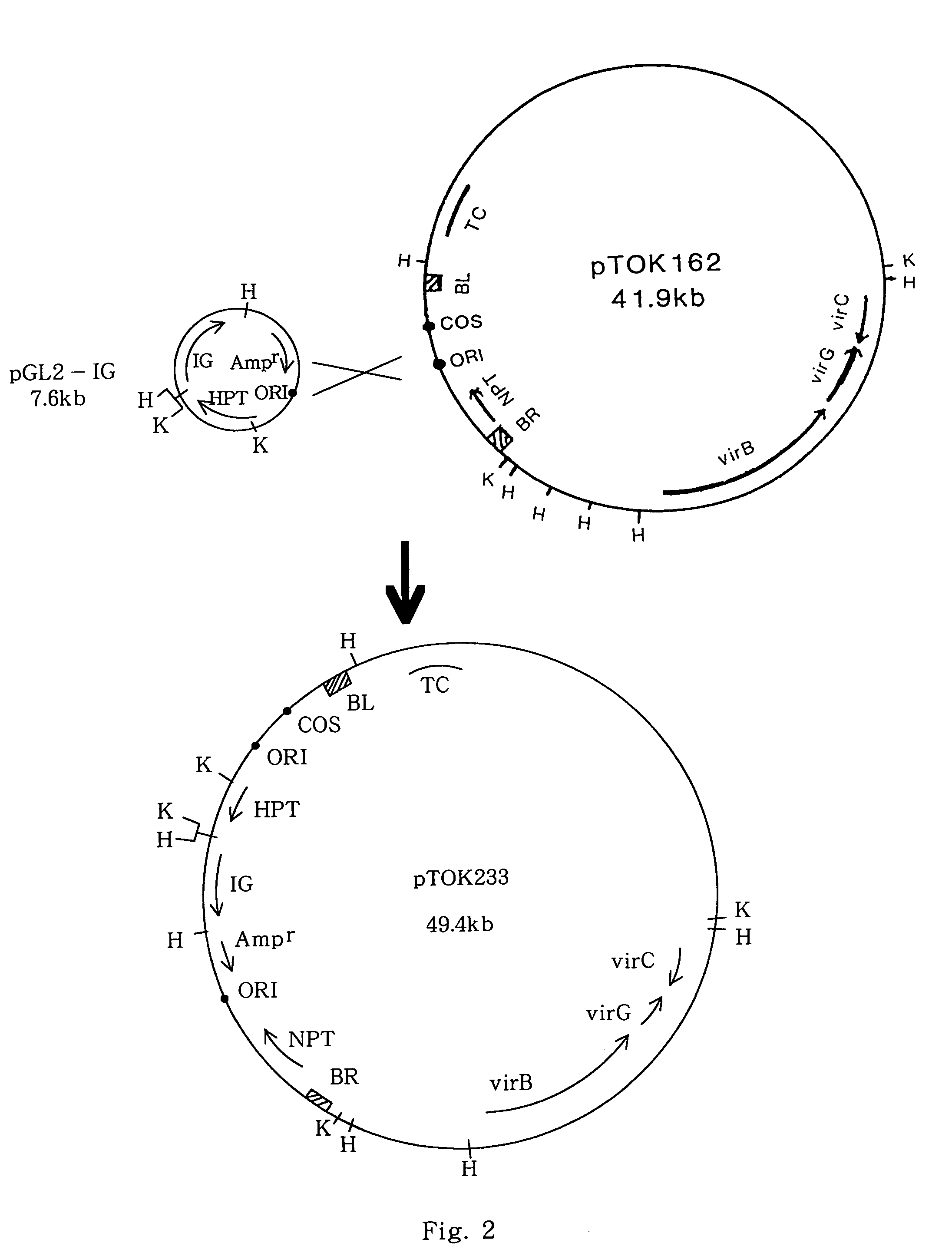
InactiveUS7060876B2Easily obtainDecrease frequencySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBacilliMutant
The invention relates to a method for transforming a monocotyledonous plant. The time required from transformation to regeneration of a plant is shorter using the inventive method so that the frequency of emergence of mutants is smaller than the conventional methods. The inventive method may be generally applied even to the plants for which a regeneration method from a protoplast to a plant has not been established, and with which the preparation of the material to be subjected to the method is easy. That is, the present invention provides a method for transforming a monocotyledonous plant, comprising contacting a cultured tissue of said monocotyledonous plant during dedifferentiation thereof obtained by culturing an explant on a dedifferentiation-inducing medium for less than 7 days with a bacterium belonging to the genus Agrobacterium containing a super binary vector having the virulence region of a Ti plasmid, left and right border sequences of T-DNA of a Ti plasmid or an Ri plasmid of a bacterium belonging to the genus Agrobacterium, and a desired gene located between said left and right border sequences.
Owner:METABOLIX
Fragrance pro-accords and aldehyde and ketone fragrance libraries
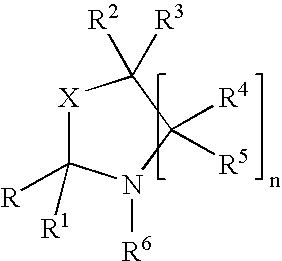
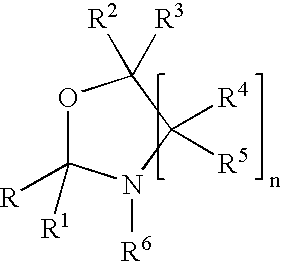
InactiveUS7018978B2Extend your lifeEasy to prepareCosmetic preparationsOrganic chemistryFlavorOxazolidine E
The present invention relates to novel heterocyclic pro-fragrances, preferably oxazolidines, tertahydro-1,3-oxazines, thiazolidines, or tetrahydro-1,3-thiazines, more preferably oxazolidines, or tertahydro-1,3-oxazines, most preferably oxazolidines, which are capable of sustained release of fragrance raw material ketones and aldehydes and to fragrance delivery systems which comprise said pro-fragrances.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Mono-active center Ziegler-Natta catalyst for olefinic polymerization
The invention relates to a new catalyst for single active central Ziegler-Natta alkene polymerization. Said catalyst takes salicylal containing dentate or substituted salicylal derivatives as electrons, and is prepared by adding pretreated carrier, metallic compound and electrons into magnesium compound / tetrahydrofuran solution. The catalyst can produce ethane homopolymer and copolymer with narrow molecular weight distribution (1.6-3.8) and even comonomer distribution, with high activity and under action of adjuvant catalyst of alkyl aluminium and alkyl aluminoxanes. The ethane polymerization, homopolymerization or combined polymerization of ethane and 1- olefin, ring olefin and polar monomer through slurry method or gas phase method by using said catalyst can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for Making Multispecific Antibodies Having Heteromultimeric and Common Components
InactiveUS20070178552A1Increased formationIncrease productionAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsSpecific immunityBiology
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method further involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
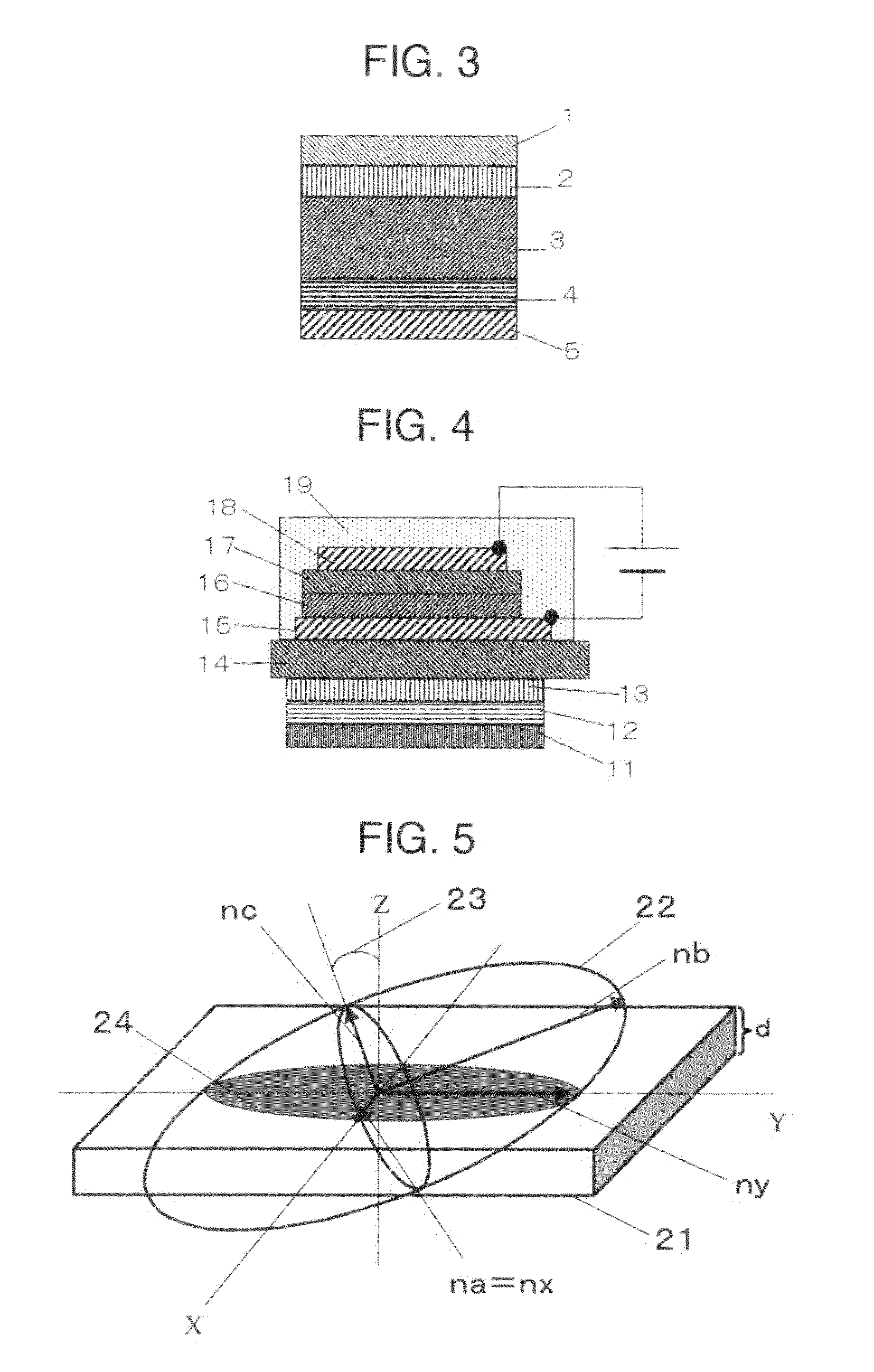
Quarter wave plate comprising two optically anisotropic layers
InactiveUS20020159005A1Improve adhesionReduce yieldPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical propertyLength wave
A circularly polarizing plate comprises a linearly polarizing membrane and a quarter wave plate. The quarter wave plate comprises an optically anisotropic layer A and an optically anisotropic layer B. The quarter wave plate has such an optical characteristic that a retardation value essentially is a quarter of a wavelength when the retardation value is measured at the wavelength of 450 nm, 550 nm and 650 nm. One of the optically anisotropic layers A and B is a layer made from liquid crystal molecules, and the other is a polymer film or a layer made from liquid crystal molecules.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for making multispecific antibodies having heteromultimeric and common components
InactiveUS7951917B1Increased formationIncrease productionHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsSpecific immunityBispecific antibody
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method further involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and Ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6537756B1Remarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta-endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against coleopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Films and Processes for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20090072194A1Easy to produceEasy to prepareLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsHydrogenProton
A birefringent film which comprises a compound having a proton-accepting group and a compound having a proton-donating group; and a birefringent film which comprises a compound having a proton-accepting group and a proton-donating group. The proton-accepting group and proton-donating group are combined with each other through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com