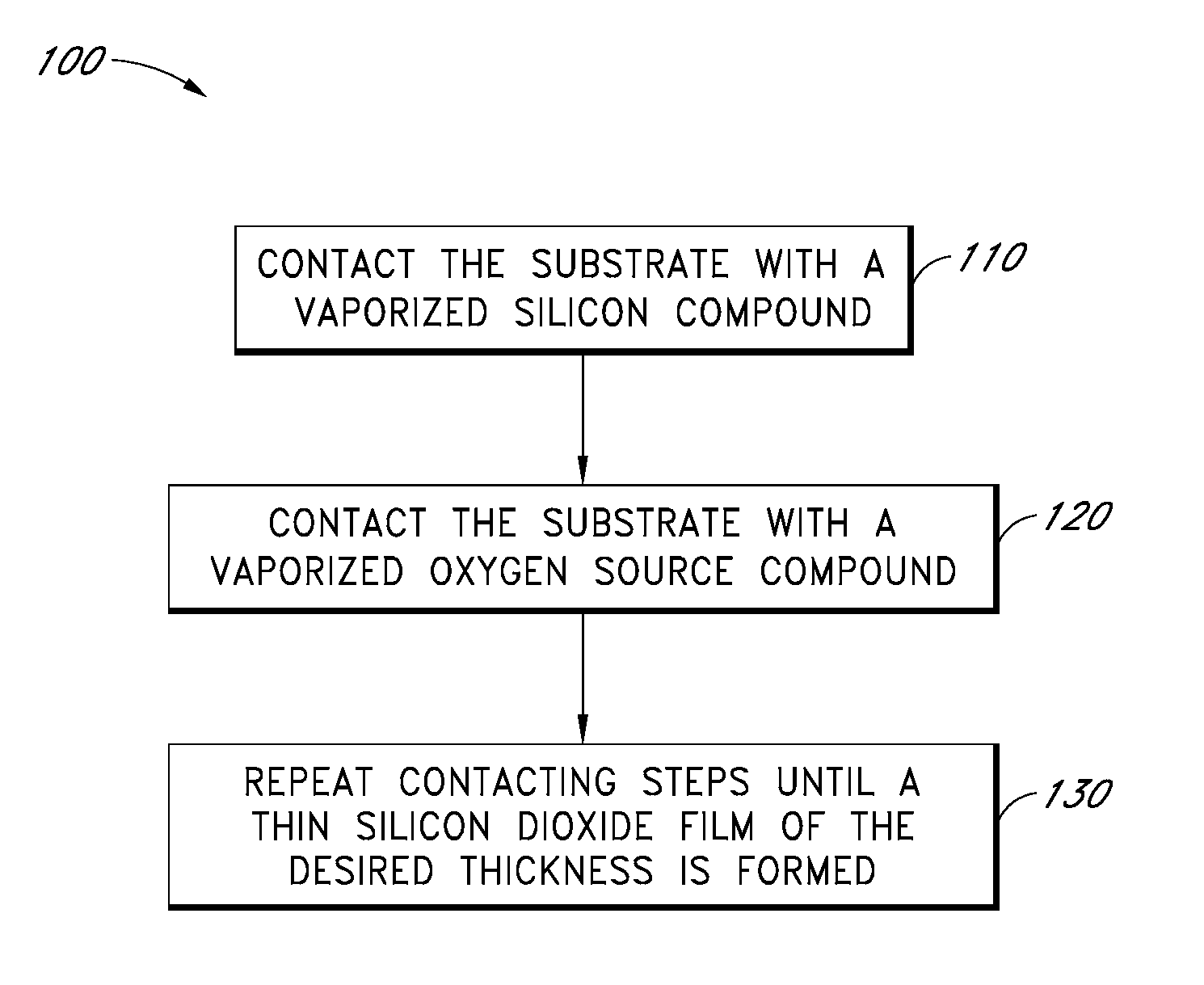
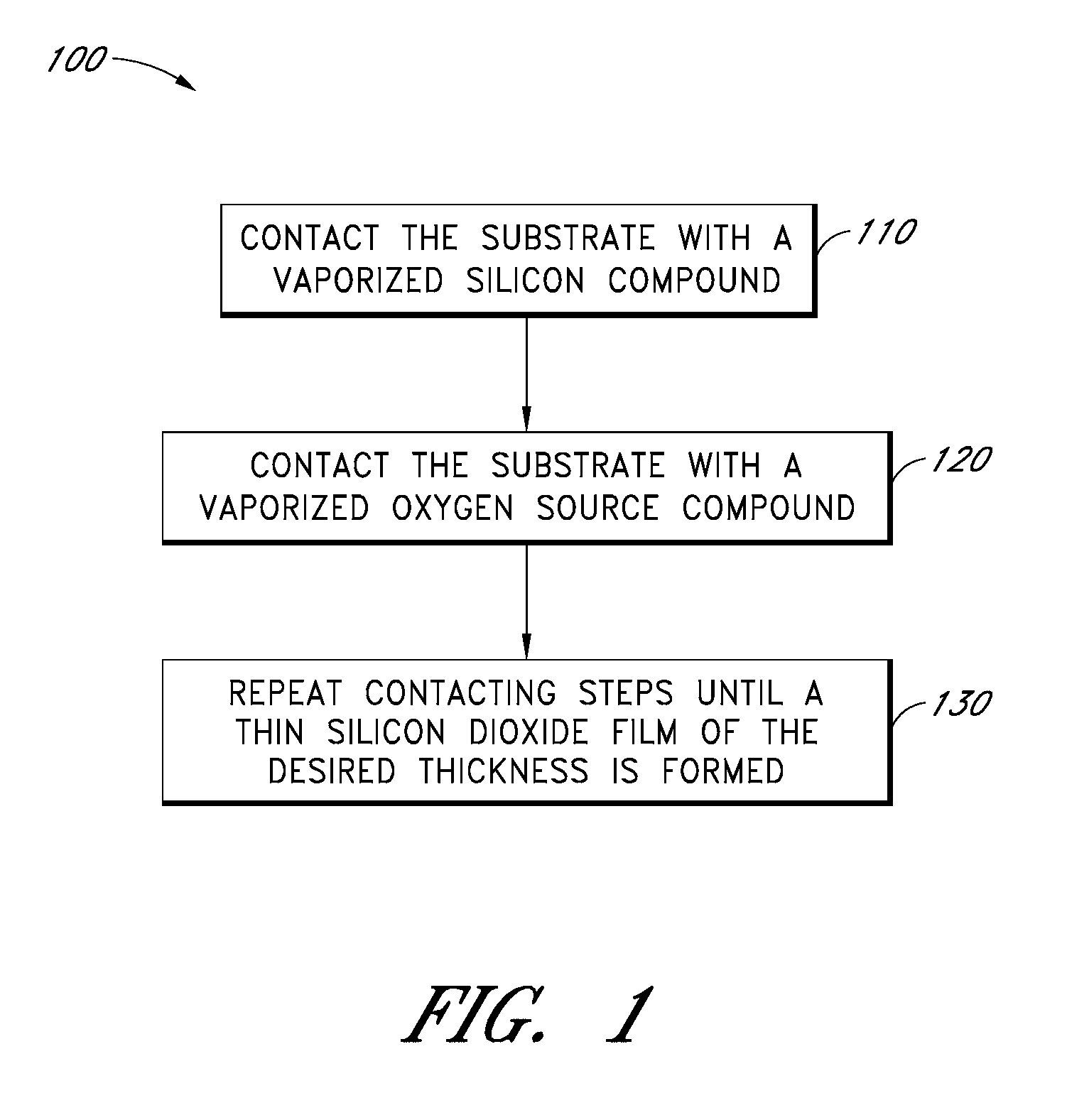
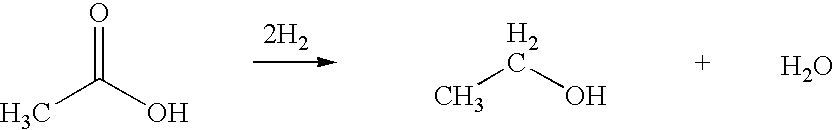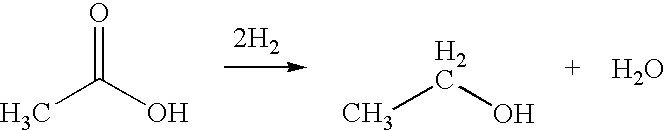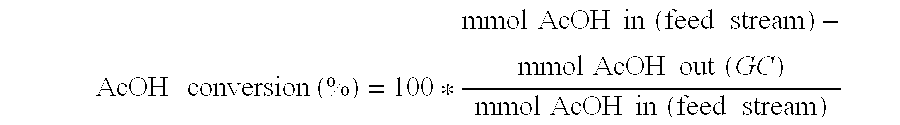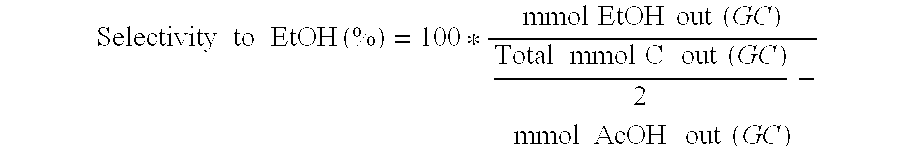Patents
Literature
65566 results about "Silicon dioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula SiO₂, most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
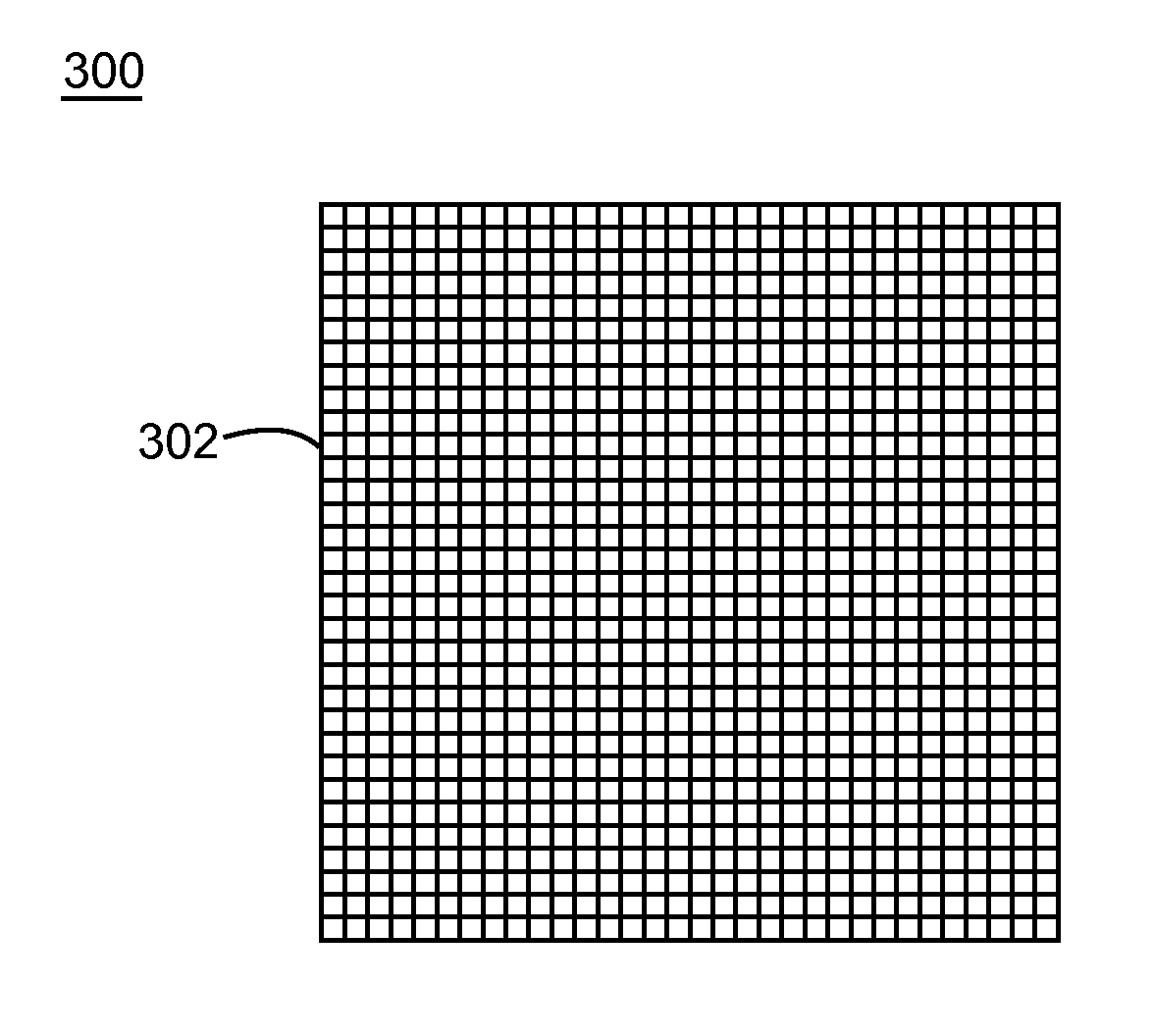
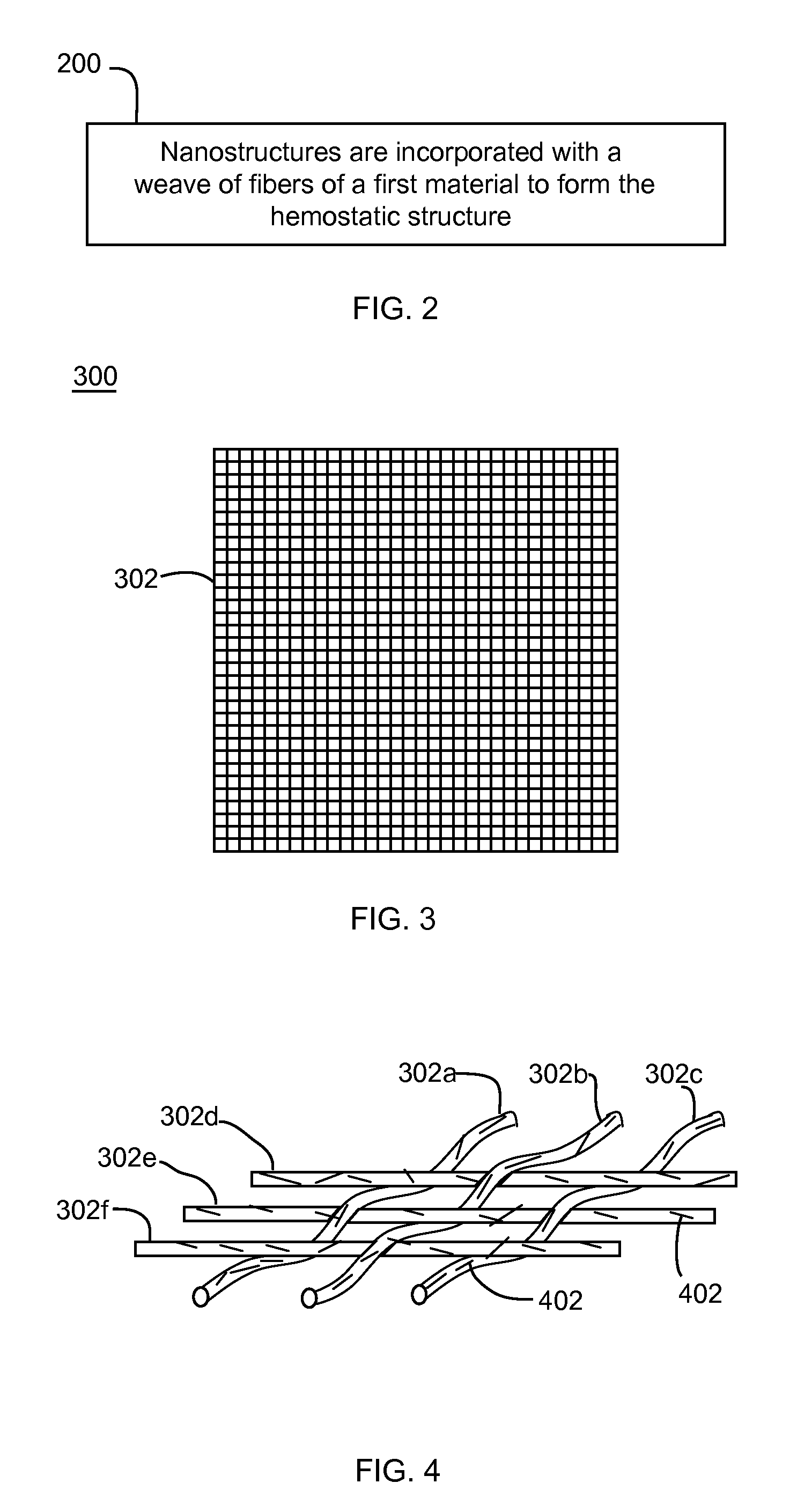
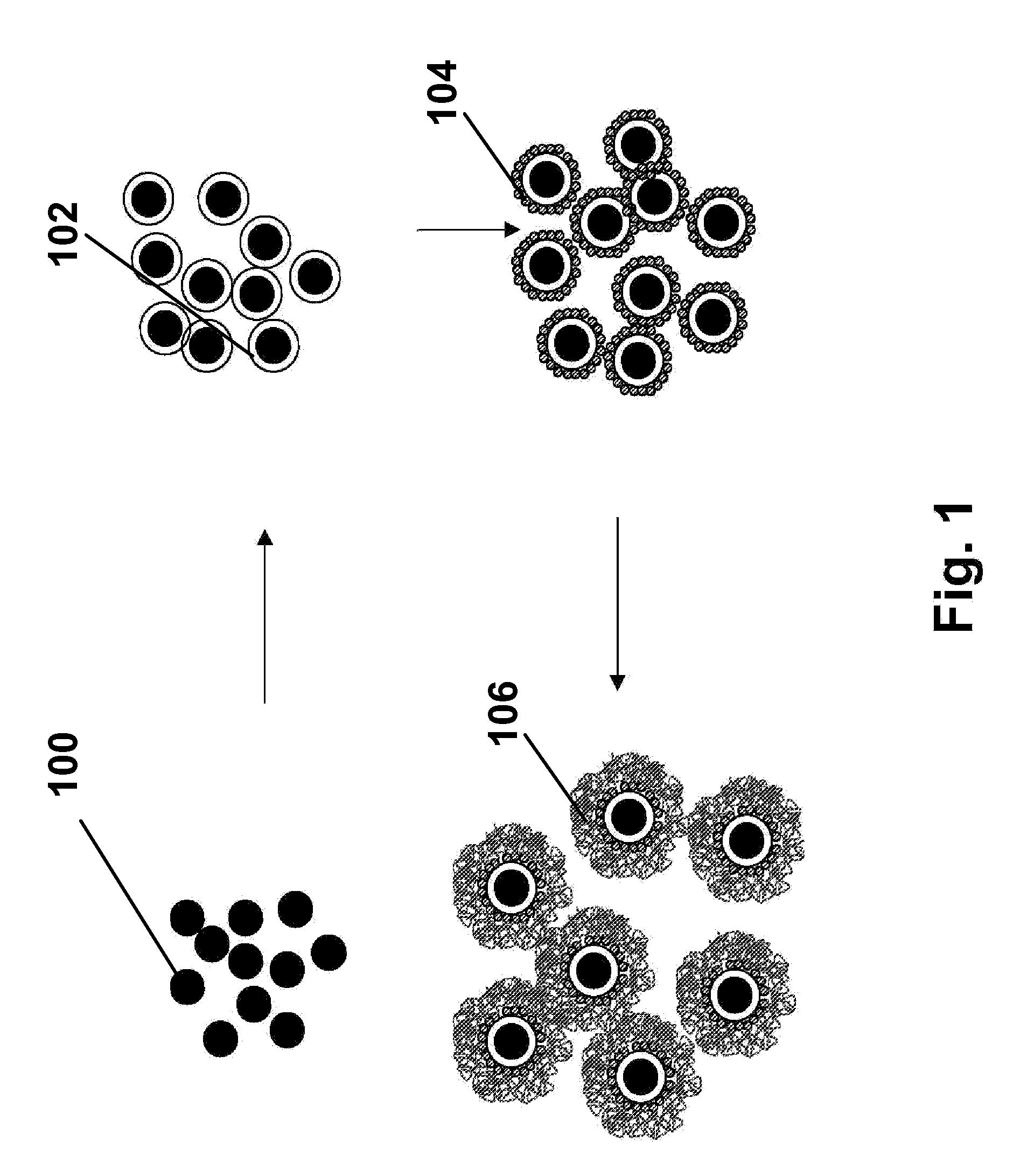
Nanostructure-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic structures
InactiveUS8319002B2Enhancing overall rate and strengthInduce platelet binding and efficient hemostasisBiocideSurgical adhesivesPlateletNanofiber
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for nanomaterial-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic medical devices are provided. Hemostatic materials and structures are provided that induce platelet binding, including platelet binding and the coagulation of blood at a wound / opening caused by trauma, a surgical procedure, ulceration, or other cause. Example embodiments include platelet binding devices, hemostatic bandages, hemostatic plugs, and hemostatic formulations. The hemostatic materials and structures may incorporate nanostructures and / or further hemostatic elements such as polymers, silicon nanofibers, silicon dioxide nanofibers, and / or glass beads into a highly absorbent, gelling scaffold. The hemostatic materials and structures may be resorbable.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
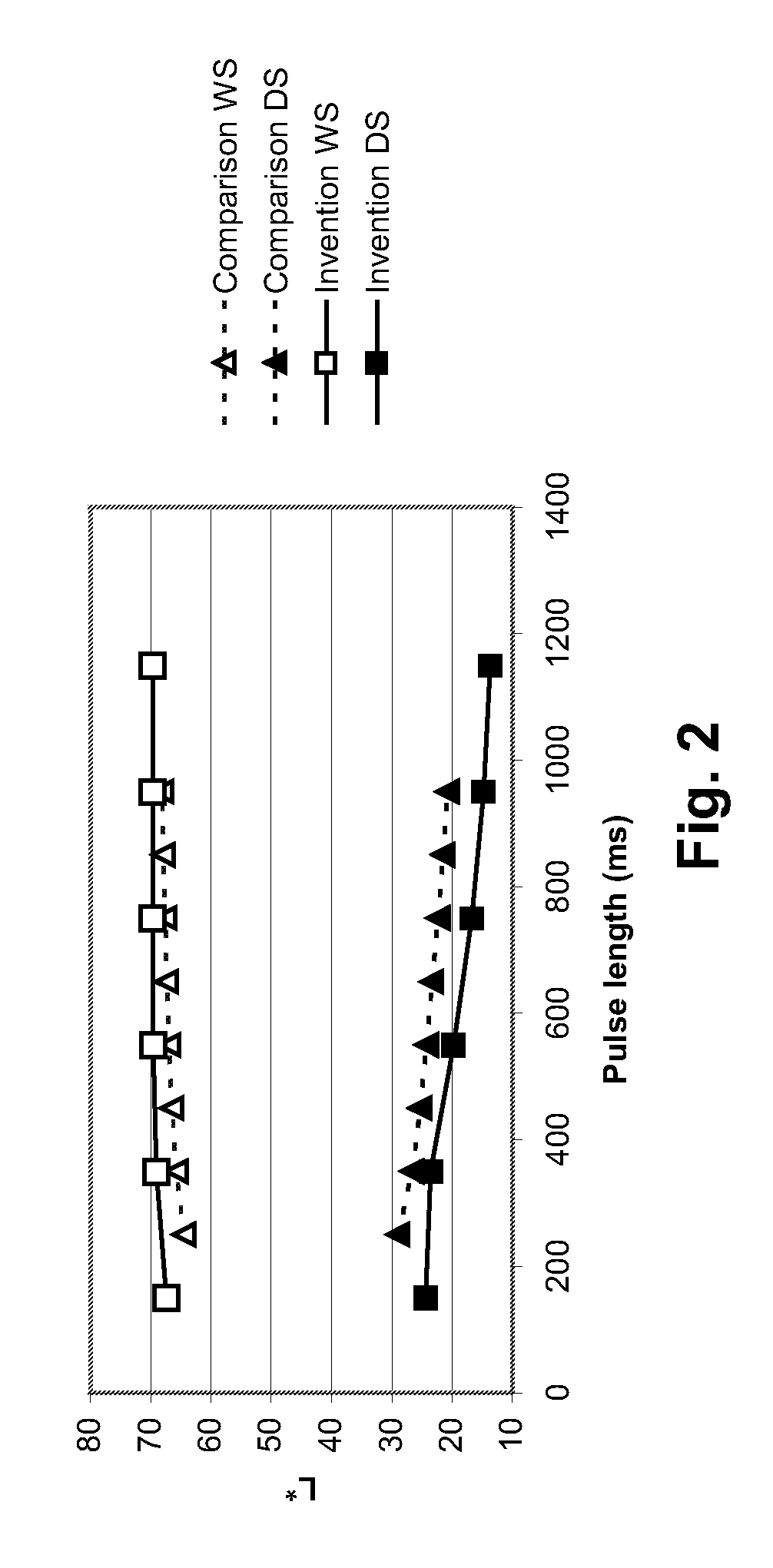
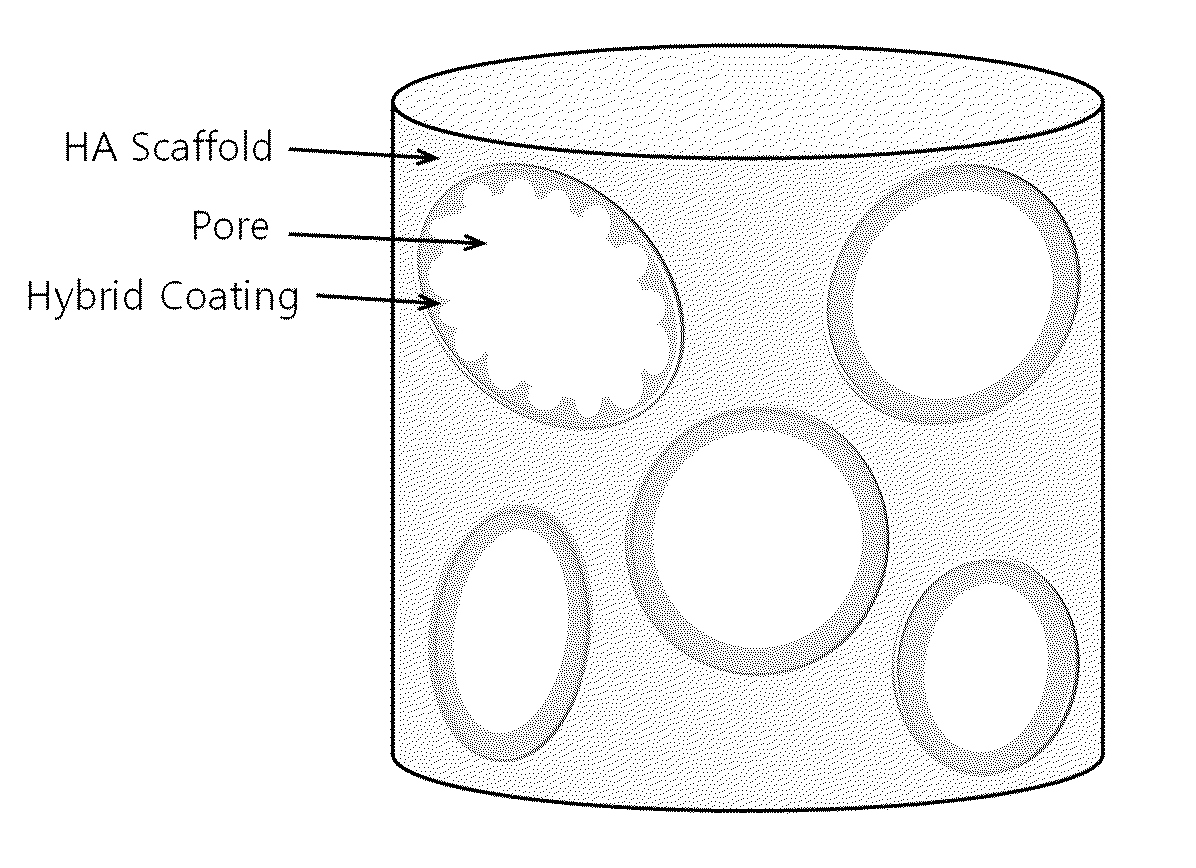
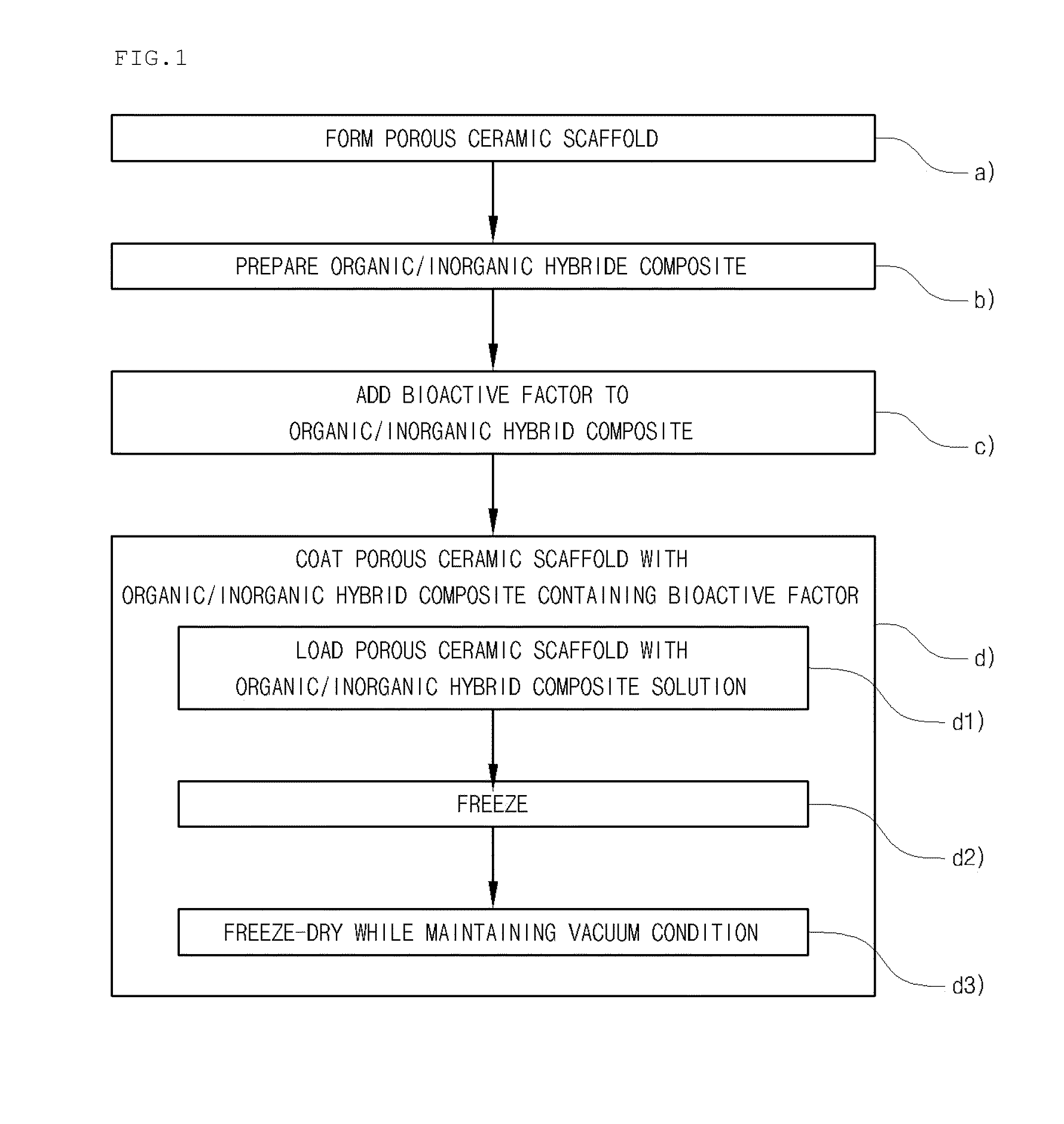
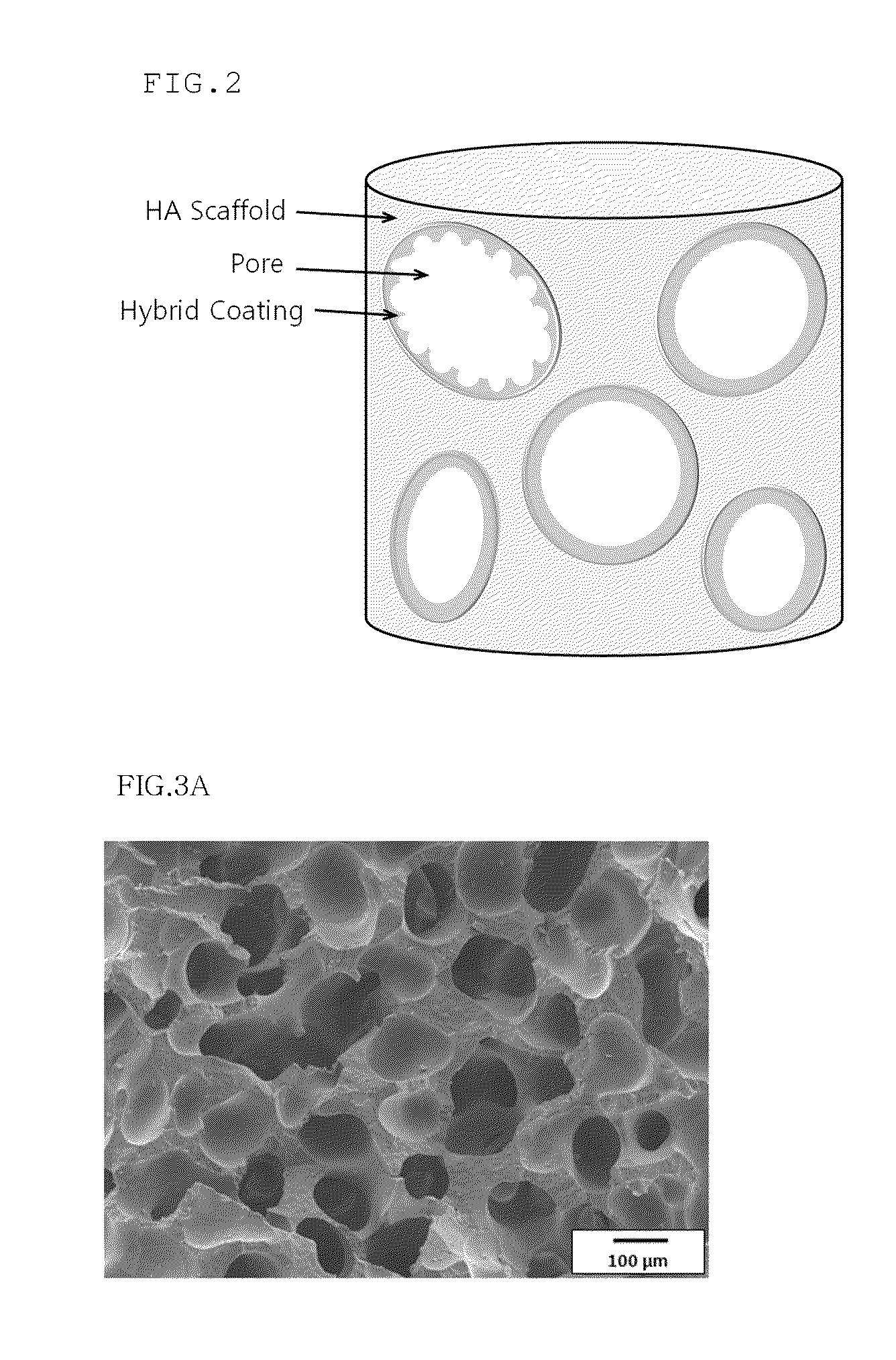
Method for manufacturing a porous ceramic scaffold having an organic/inorganic hybrid coating layer containing a bioactive factor
ActiveUS8734831B2Good biocompatibilityEasy to controlBiocideSurgical adhesivesOrganic matterPorous ceramics
A method for manufacturing a porous ceramic scaffold having an organic / inorganic hybrid coating layer containing a bioactive factor includes (a) forming a porous ceramic scaffold; (b) mixing a silica xerogel and a physiologically active organic substance in a volumetric ratio ranging from 30:70 to 90:10 and treating by a sol gel method to prepare an organic / inorganic hybrid composite solution; (c) adding a bioactive factor to the organic / inorganic hybrid composite solution and agitating until gelation occurs; and (d) coating the porous ceramic scaffold with the organic / inorganic composite containing the bioactive factor added thereto. In accordance with the method, the porous ceramic scaffold may be uniformly coated with the organic / inorganic hybrid composite while maintaining an open pore structure, and stably discharge the bioactive factor over a long period of time.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
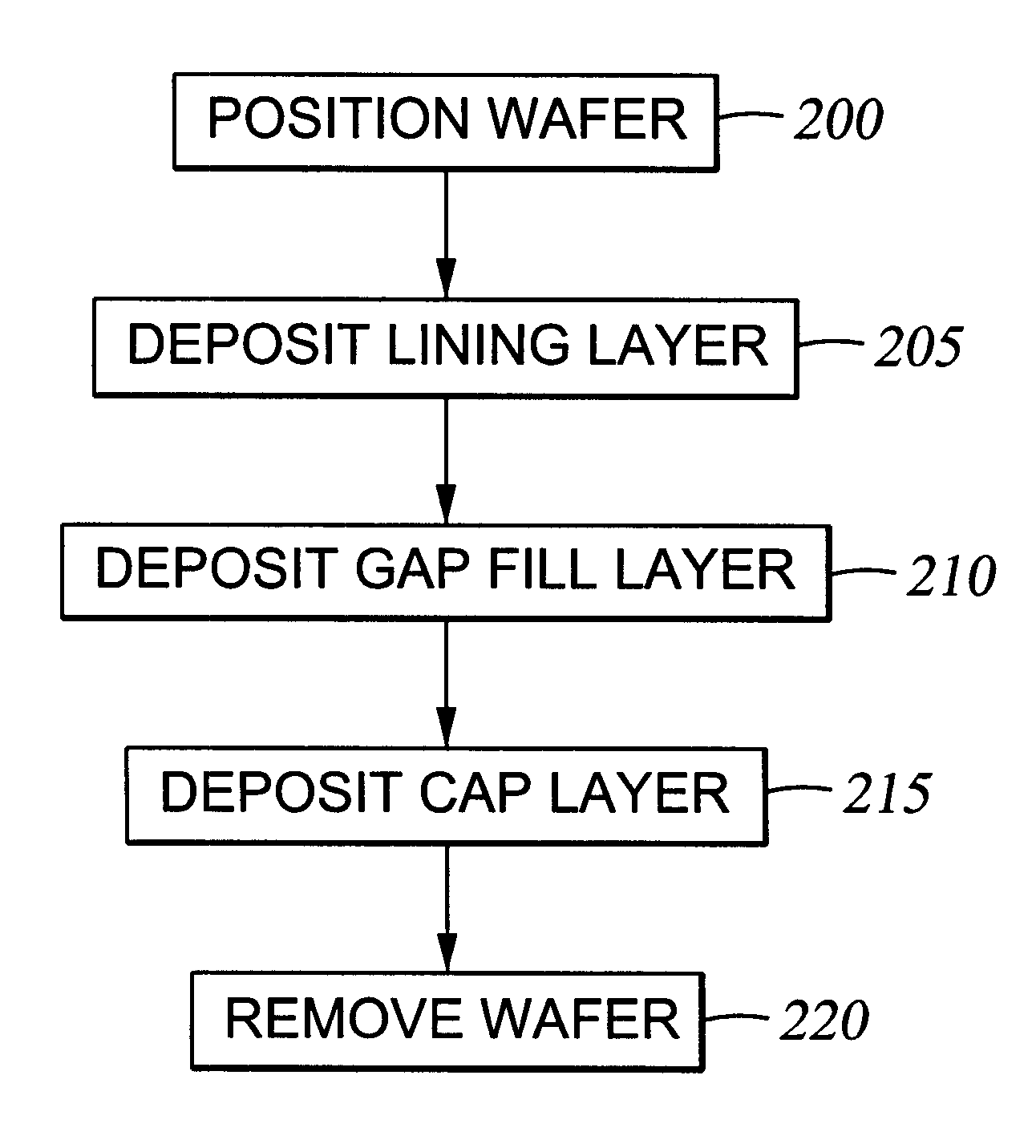
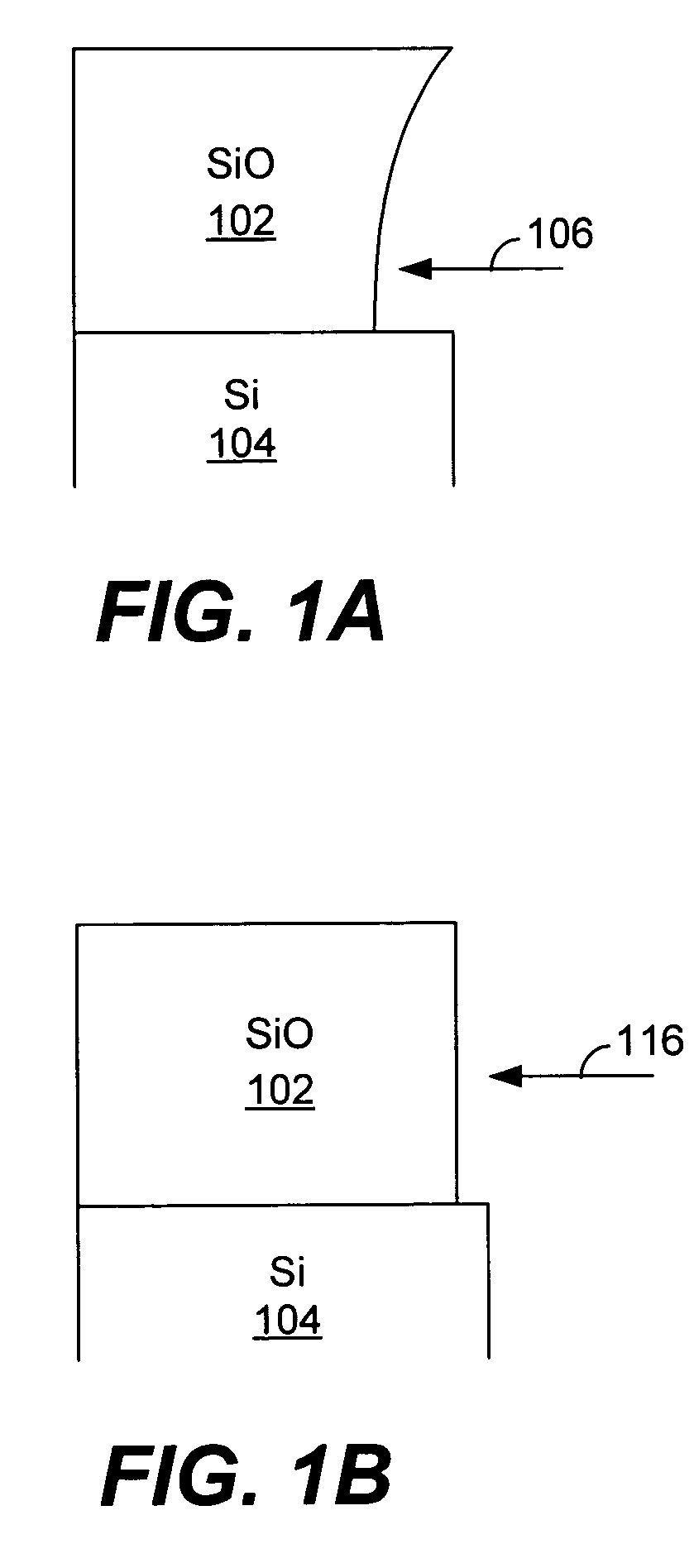
Formation of a liquid-like silica layer by reaction of an organosilicon compound and a hydroxyl forming compound
InactiveUS6413583B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon oxideSilicon dioxide
A method for depositing silicon oxide layers having a low dielectric constant by reaction of an organosilicon compound and a hydroxyl forming compound at a substrate temperature less than about 400° C. The low dielectric constant films contain residual carbon and are useful for gap fill layers, pre-metal dielectric layers, inter-metal dielectric layers, and shallow trench isolation dielectric layers in sub-micron devices. The hydroxyl compound can be prepared prior to deposition from water or an organic compound. The silicon oxide layers are preferably deposited at a substrate temperature less than about 40° C. onto a liner layer produced from the organosilicon compound to provide gap fill layers having a dielectric constant less than about 3.0.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ethanol production from acetic acid utilizing a cobalt catalyst
InactiveUS7608744B1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidPlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either cobalt and palladium supported on graphite or cobalt and platinum supported on silica selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
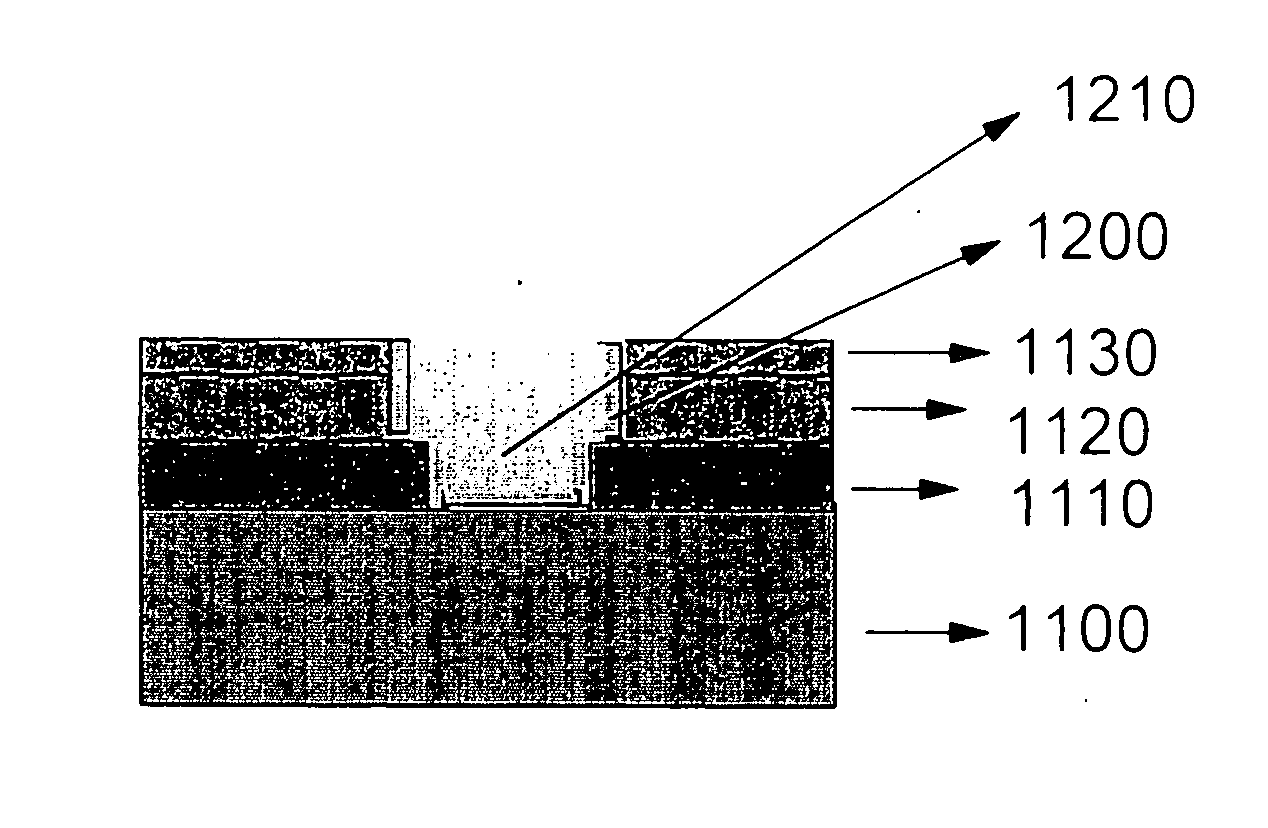
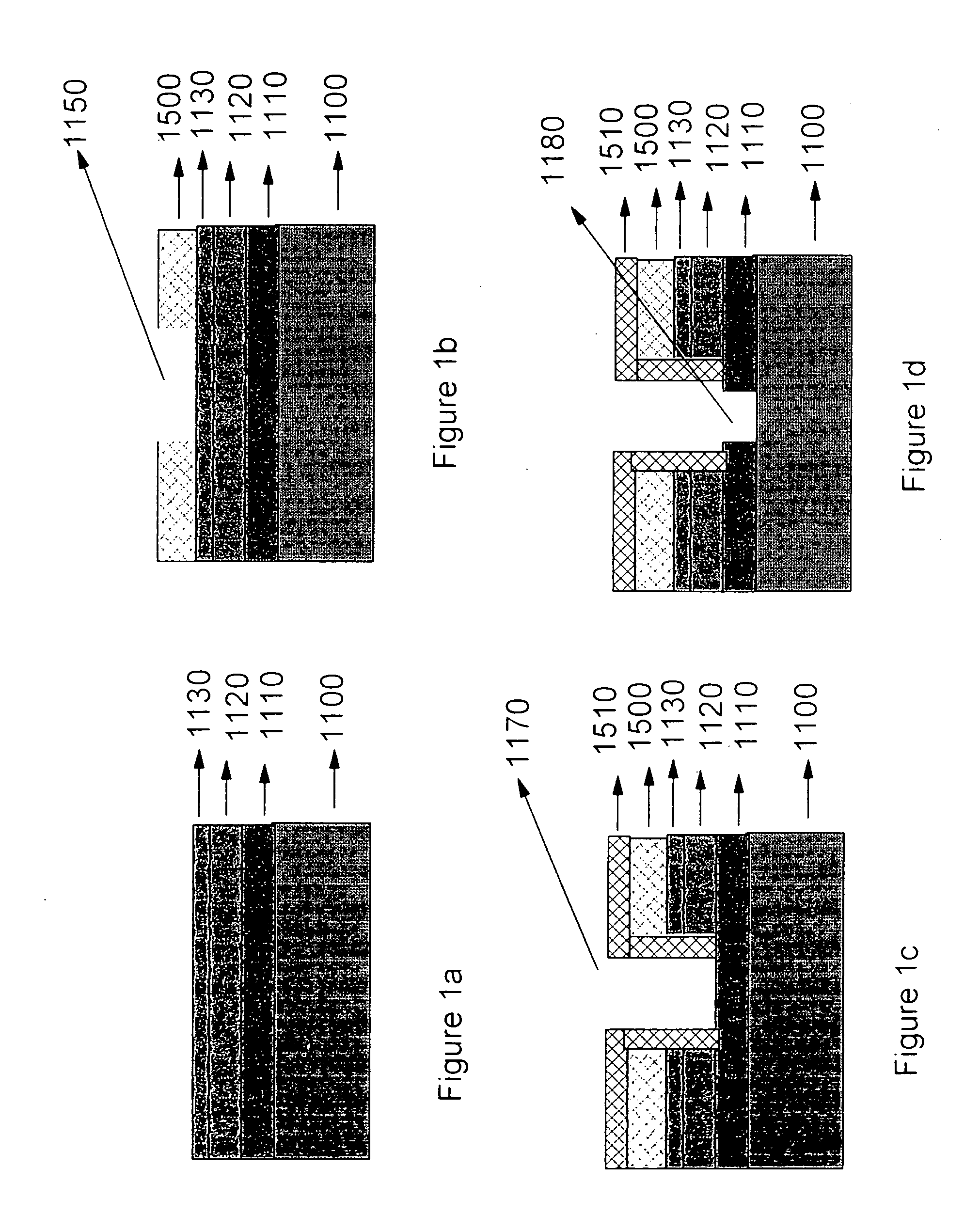
Formation of well-controlled thin SiO, SiN, SiN, SiON layer for multilayer high-K dielectric applications
A process for fabricating a semiconductor device having a high-K dielectric layer over a silicon substrate, including steps of growing on the silicon substrate an interfacial layer of a silicon-containing dielectric material; and depositing on the interfacial layer a layer comprising at least one high-K dielectric material, in which the interfacial layer is grown by laser excitation of the silicon substrate in the presence of oxygen, nitrous oxide, nitric oxide, ammonia or a mixture of two or more thereof. In one embodiment, the silicon-containing material is silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride or a mixture thereof.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
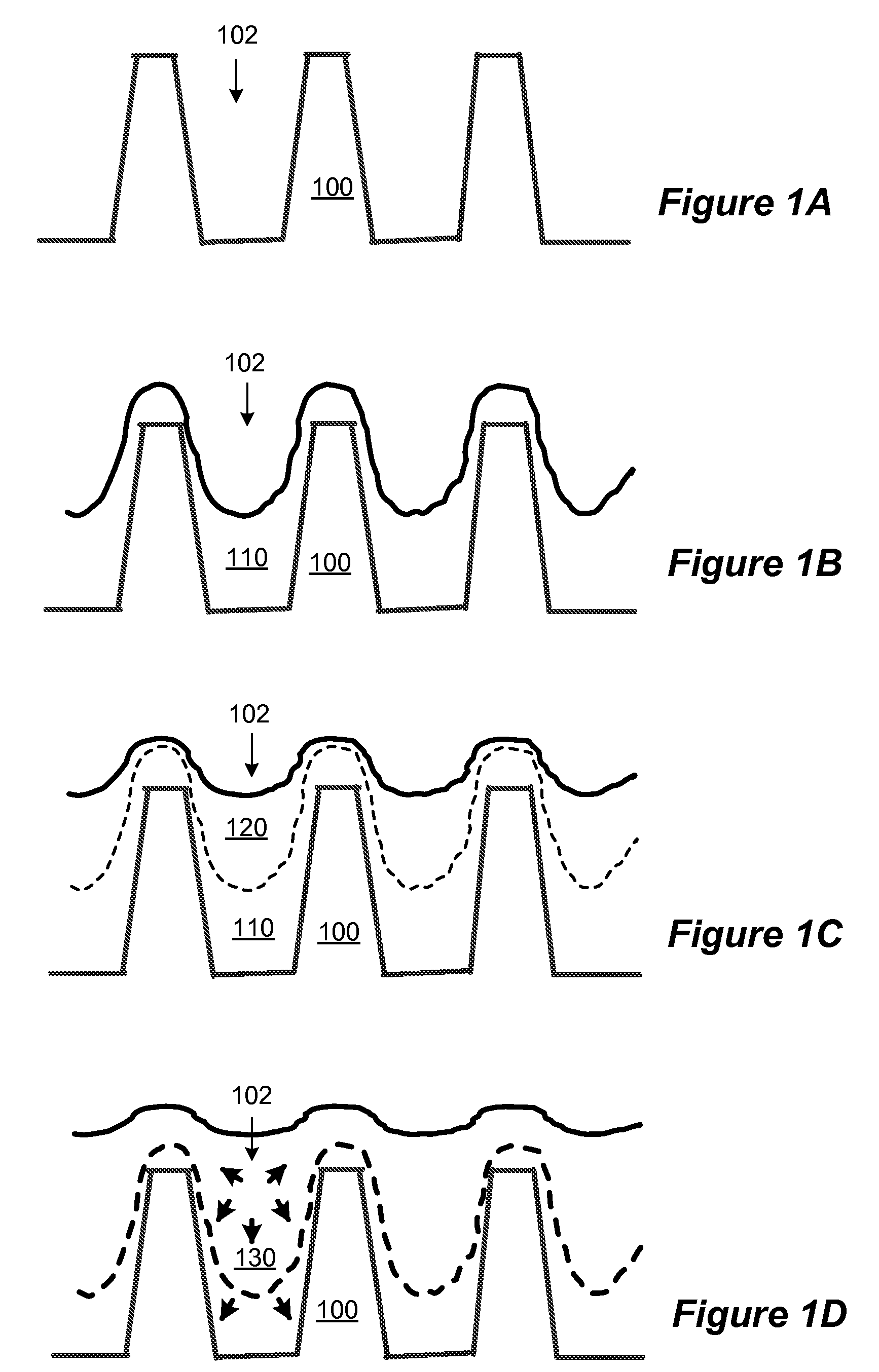
Method and system for improving dielectric film quality for void free gap fill
ActiveUS7541297B2Quality improvementHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAmorphous siliconSilicon oxide
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS7863489B2High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicateAcetic acid
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Acrylic microchannels and their use in electrophoretic applications
Microchannels having at least an acrylic inner surface and methods of their use in electrophoretic applications are provided. The subject microchannels may be in the form of a variety of configurations suitable for holding an electrophoretic medium. The subject microchannels give rise to substantially reduced EOF and / or adsorption as compared to fused silica under conditions of electrophoresis and find use in a variety of electrophoretic applications in which charged entities are moved through a medium under the influence of the an applied electric field.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
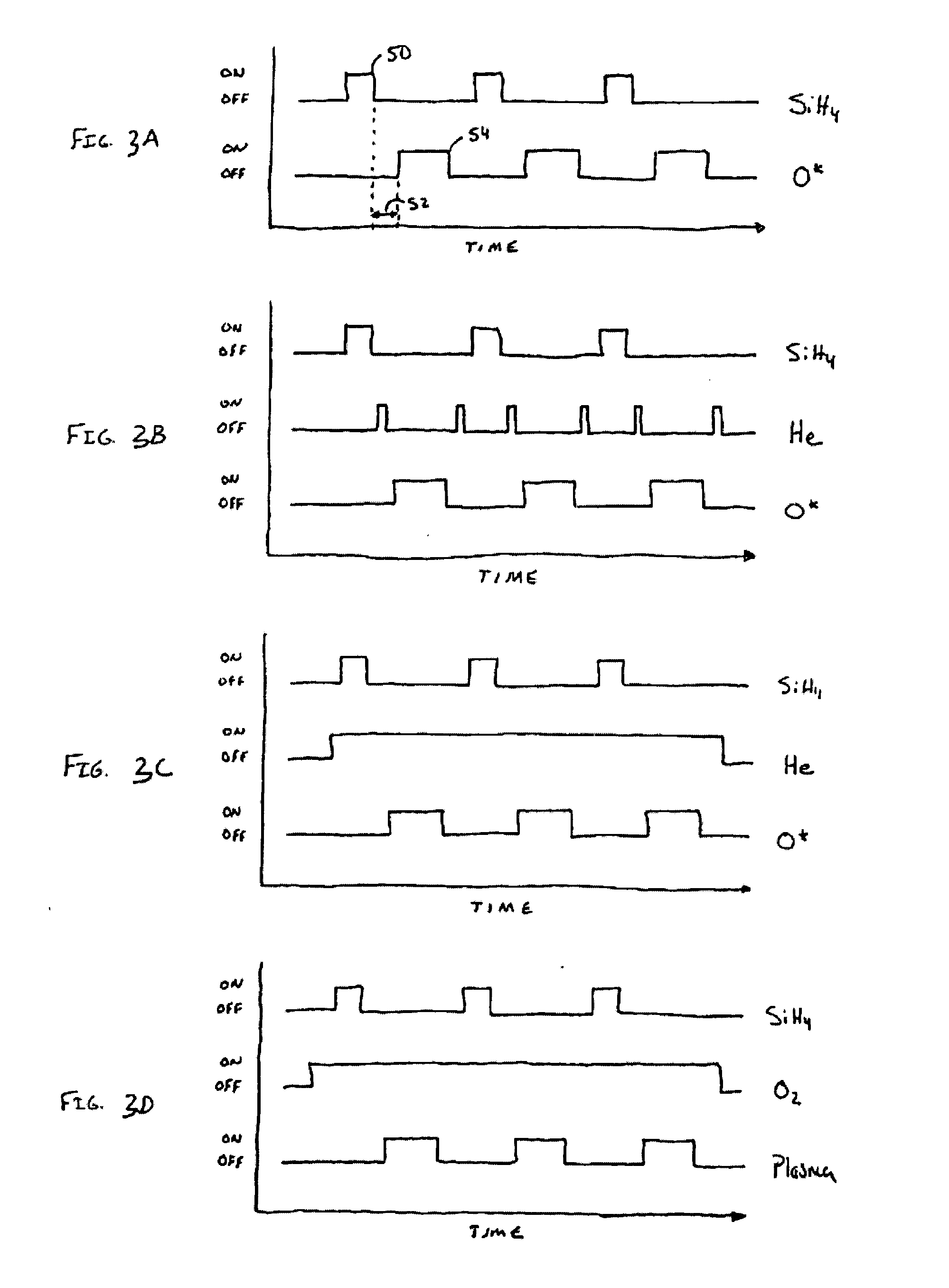
Silicon Dioxide Thin Films by ALD
ActiveUS20090209081A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon dioxideAtomic layer deposition
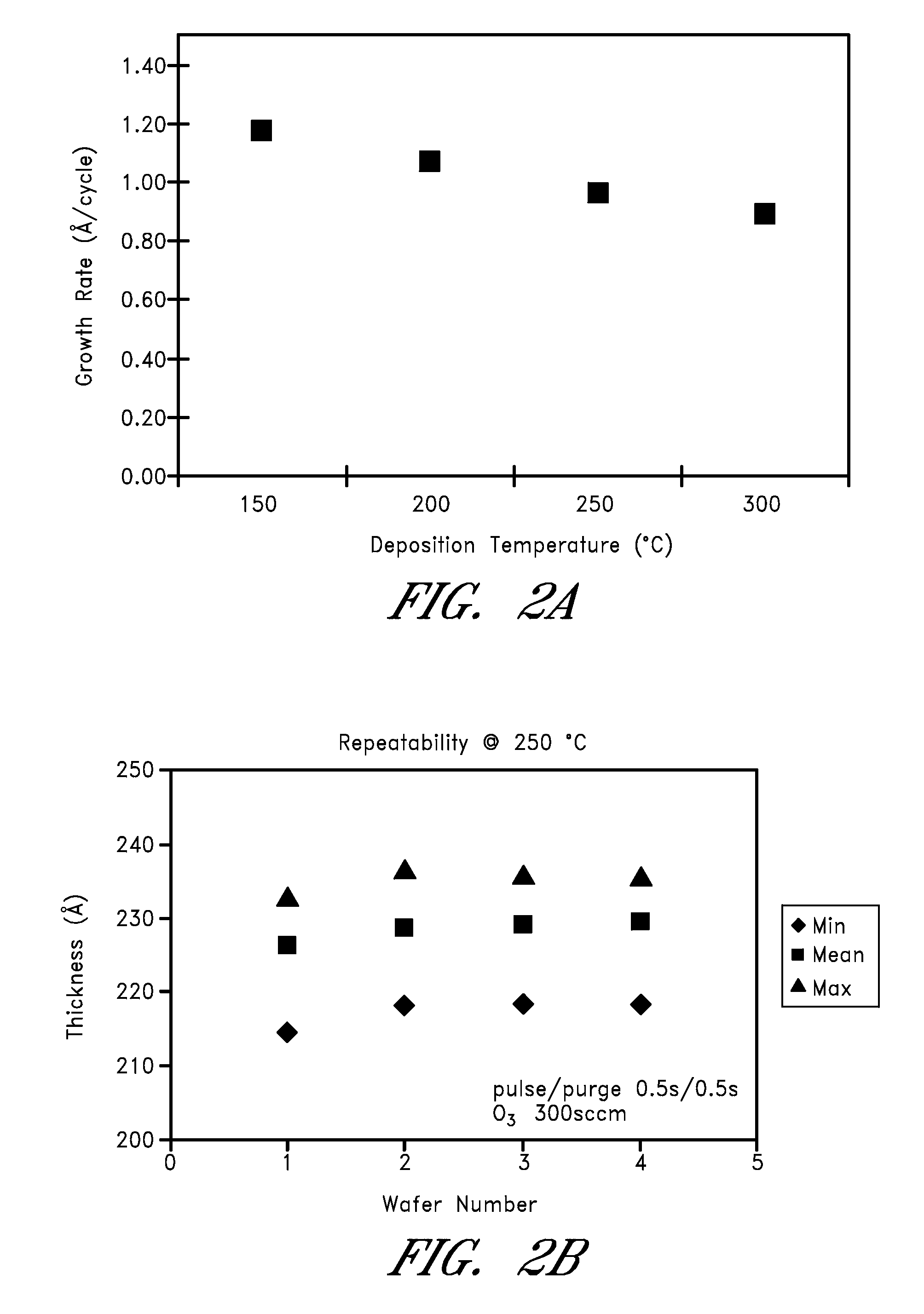
Methods are provided for depositing silicon dioxide containing thin films on a substrate by atomic layer deposition ALD. By using disilane compounds as the silicon source, good deposition rates and uniformity are obtained.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Curing methods for silicon dioxide thin films deposited from alkoxysilane precursor with harp ii process
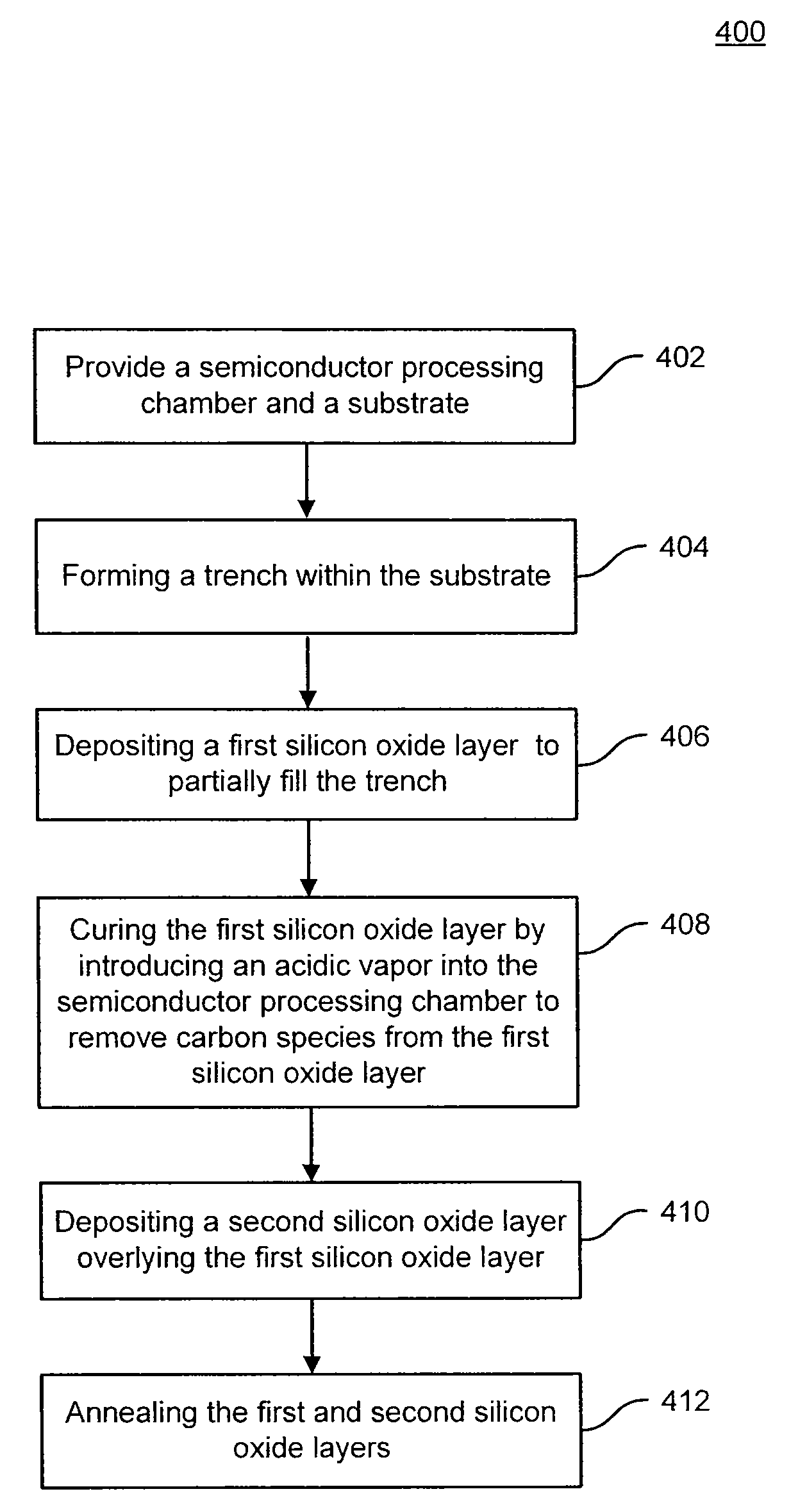
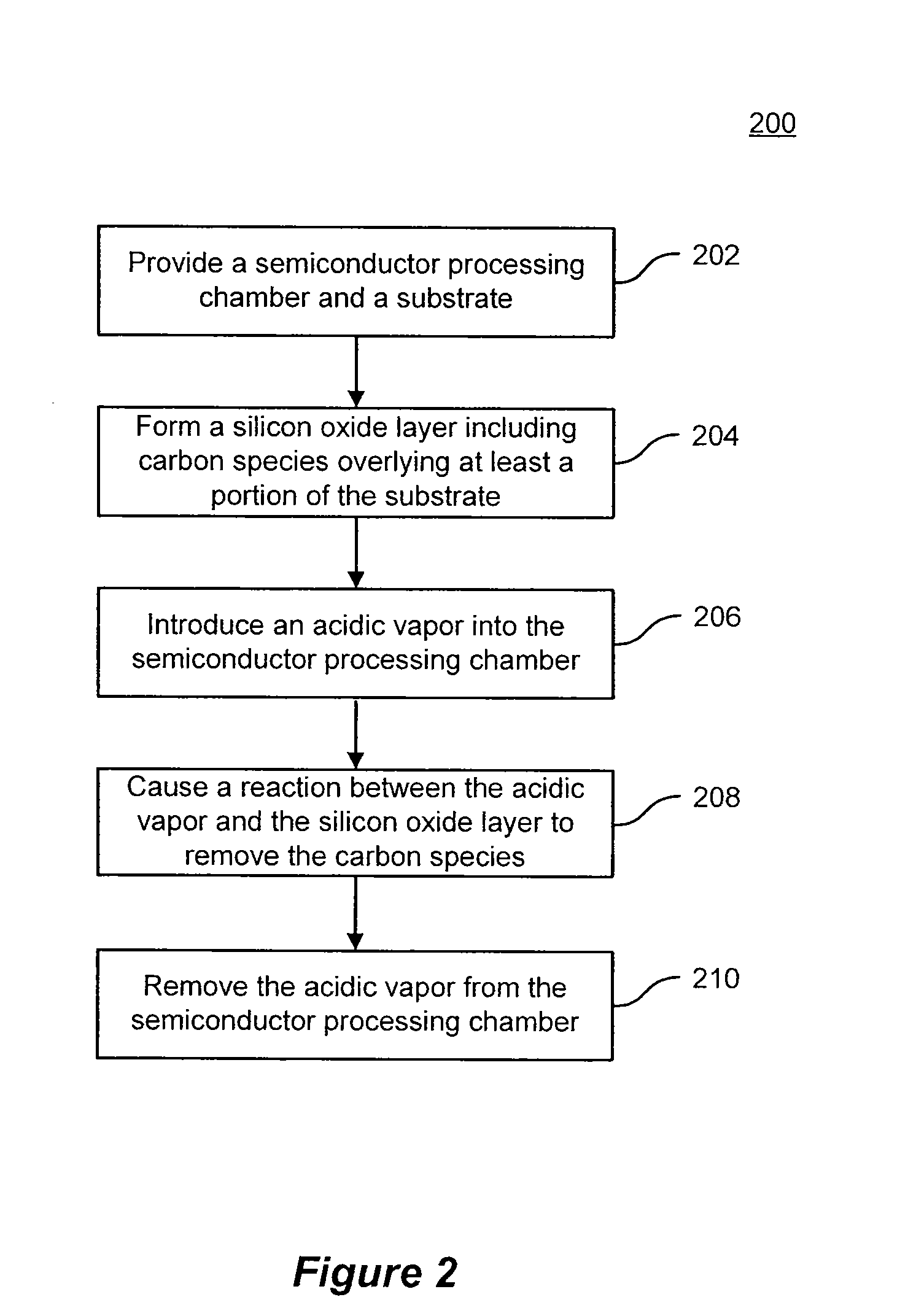
Methods of curing a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are provided. The methods may include the processes of providing a semiconductor processing chamber and a substrate and forming an silicon oxide layer overlying at least a portion of the substrate, the silicon oxide layer including carbon species as a byproduct of formation. The methods may also include introducing an acidic vapor into the semiconductor processing chamber, the acidic vapor reacting with the silicon oxide layer to remove the carbon species from the silicon oxide layer. The methods may also include removing the acidic vapor from the semiconductor processing chamber. Systems to deposit a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are also described.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
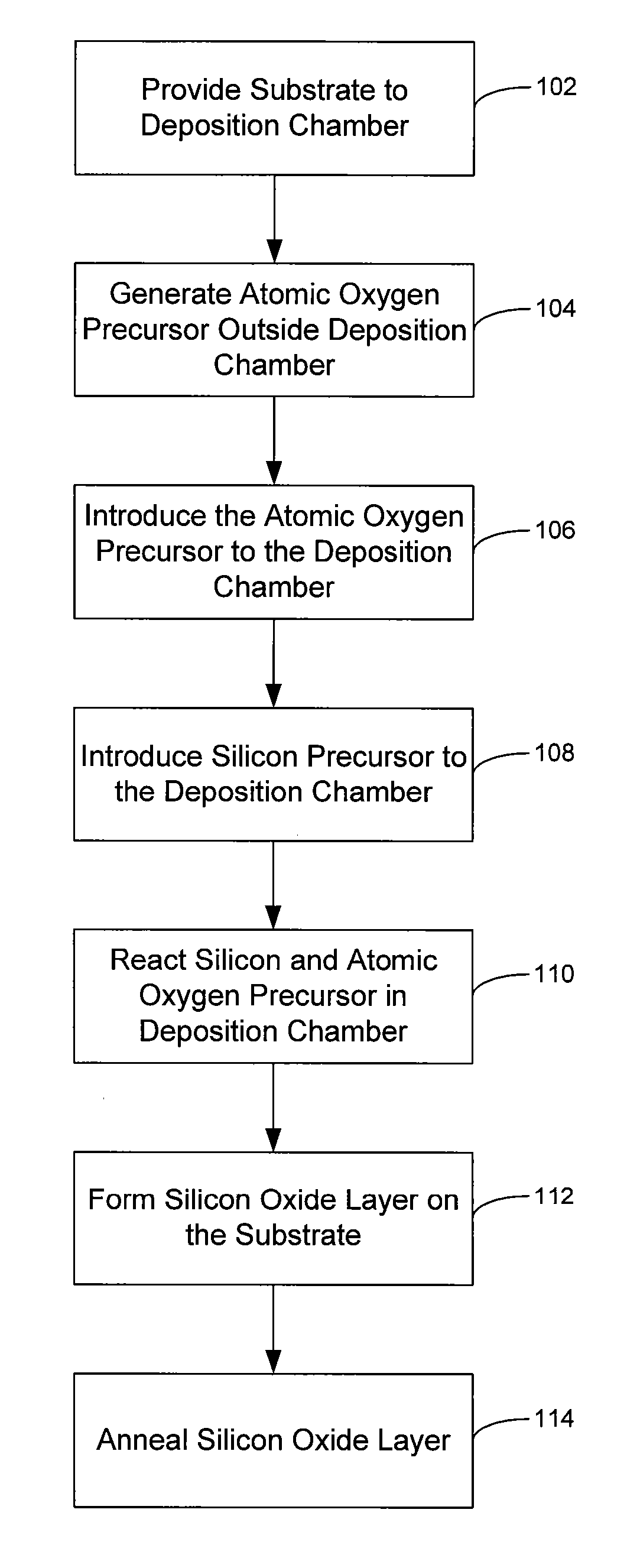
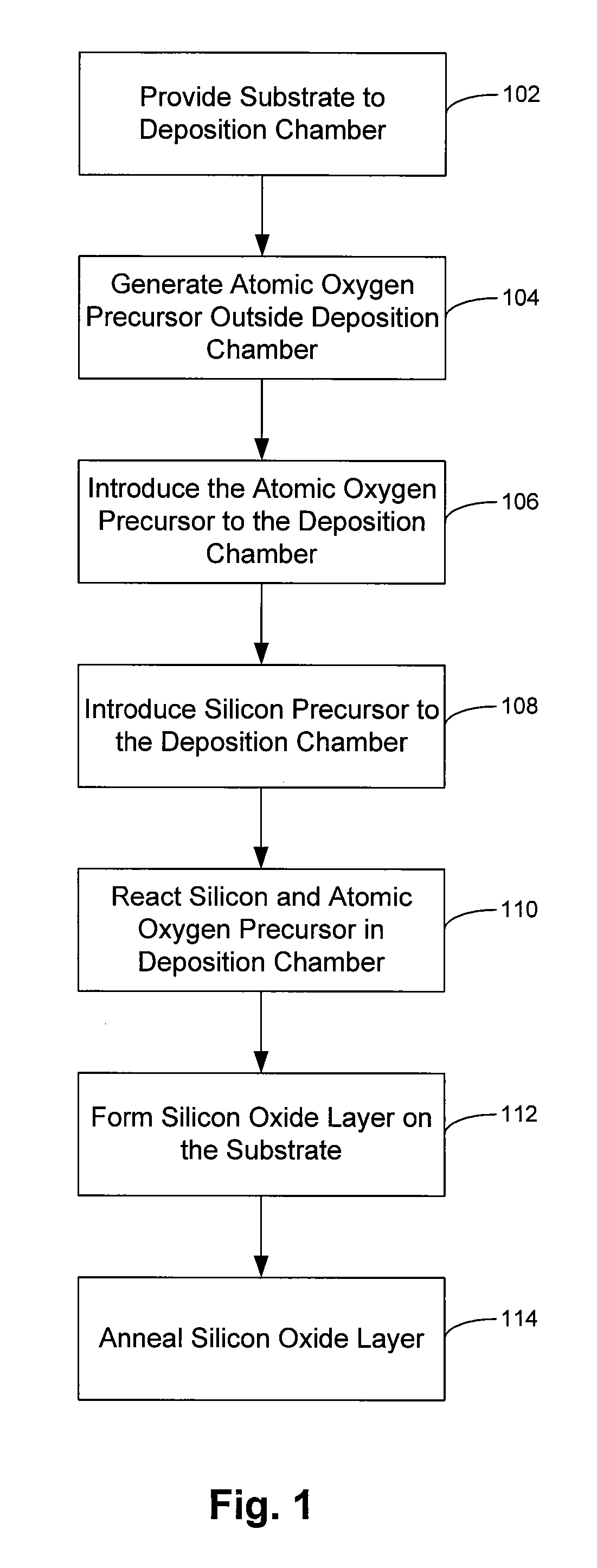
Chemical vapor deposition of high quality flow-like silicon dioxide using a silicon containing precursor and atomic oxygen
ActiveUS20070281496A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilicon oxide
Methods of depositing a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are described. The methods may include the steps of providing a substrate to a deposition chamber, generating an atomic oxygen precursor outside the deposition chamber, and introducing the atomic oxygen precursor into the chamber. The methods may also include introducing a silicon precursor to the deposition chamber, where the silicon precursor and the atomic oxygen precursor are first mixed in the chamber. The silicon precursor and the atomic oxygen precursor react to form the silicon oxide layer on the substrate, and the deposited silicon oxide layer may be annealed. Systems to deposit a silicon oxide layer on a substrate are also described.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
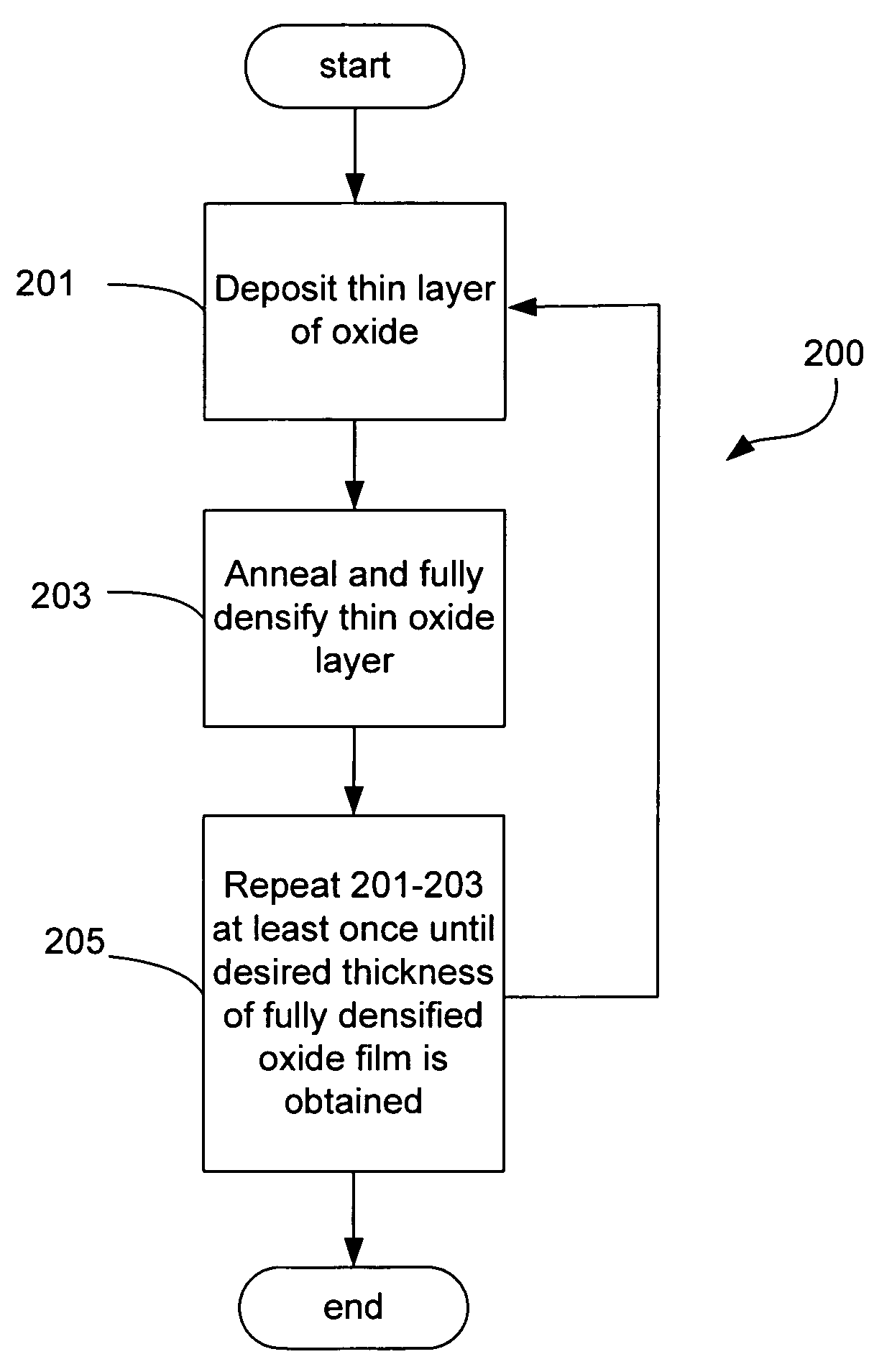
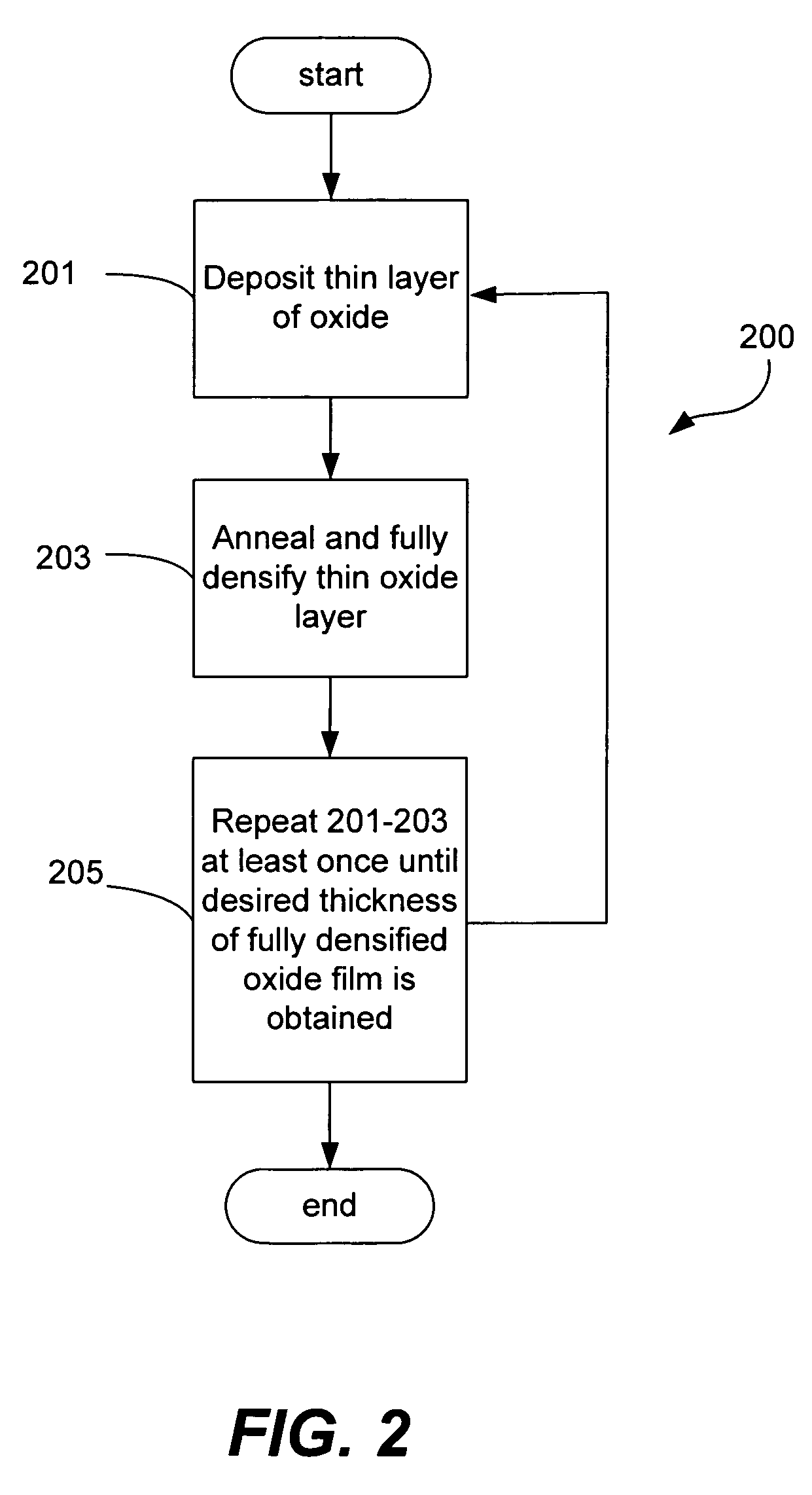
Sequential deposition/anneal film densification method
ActiveUS7790633B1Maintaining film propertyMaintain propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcedure AgentsOptoelectronics
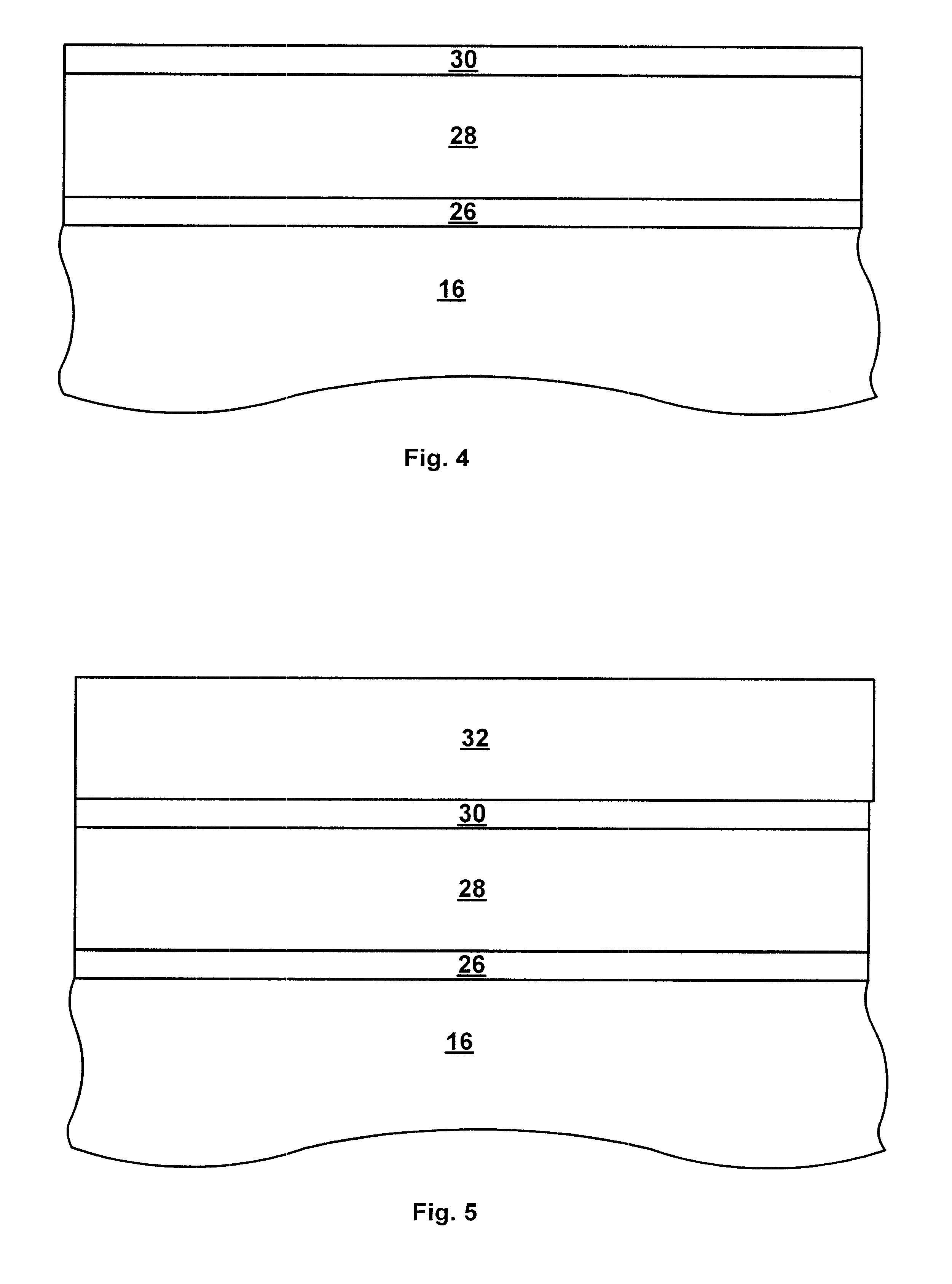
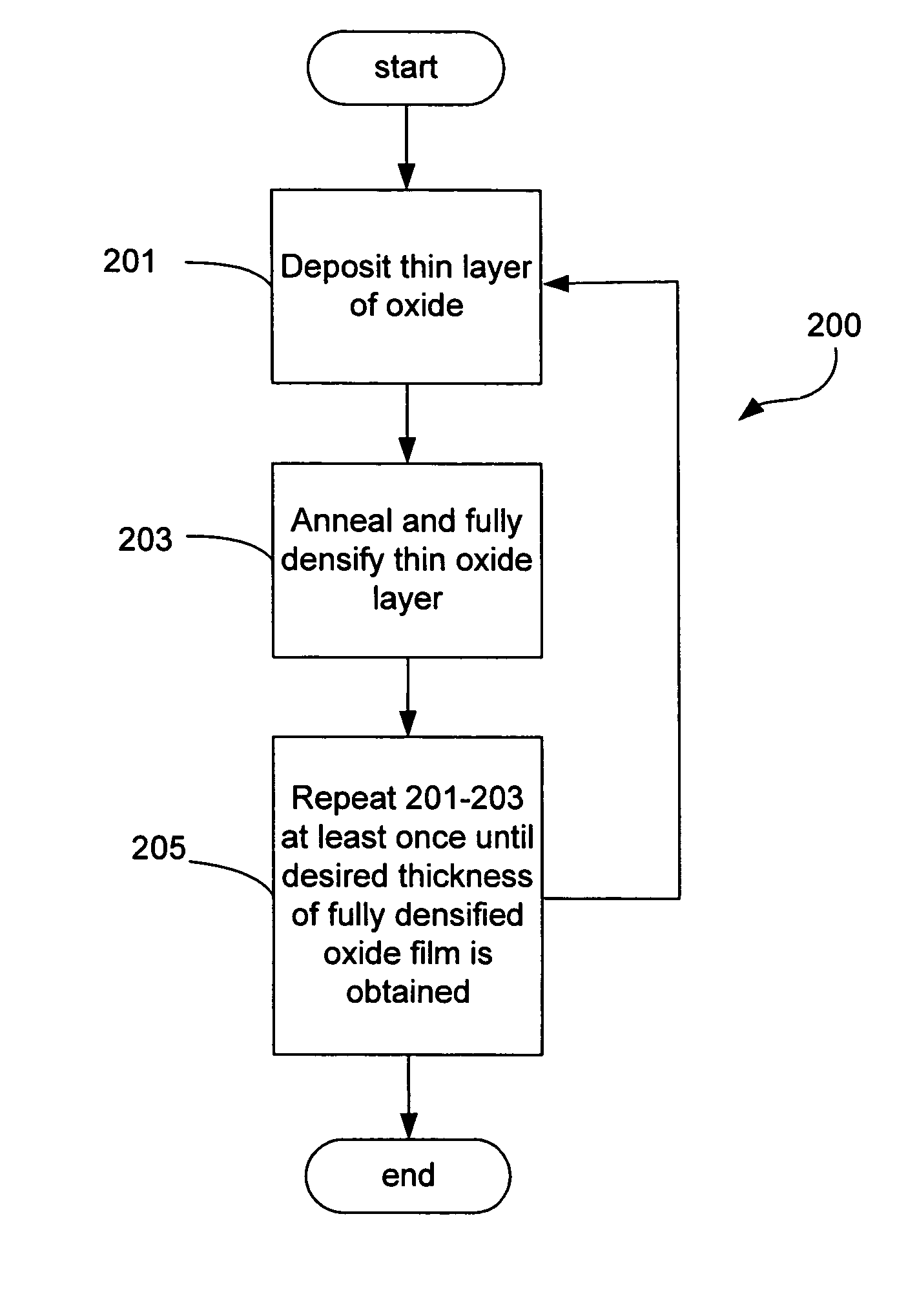
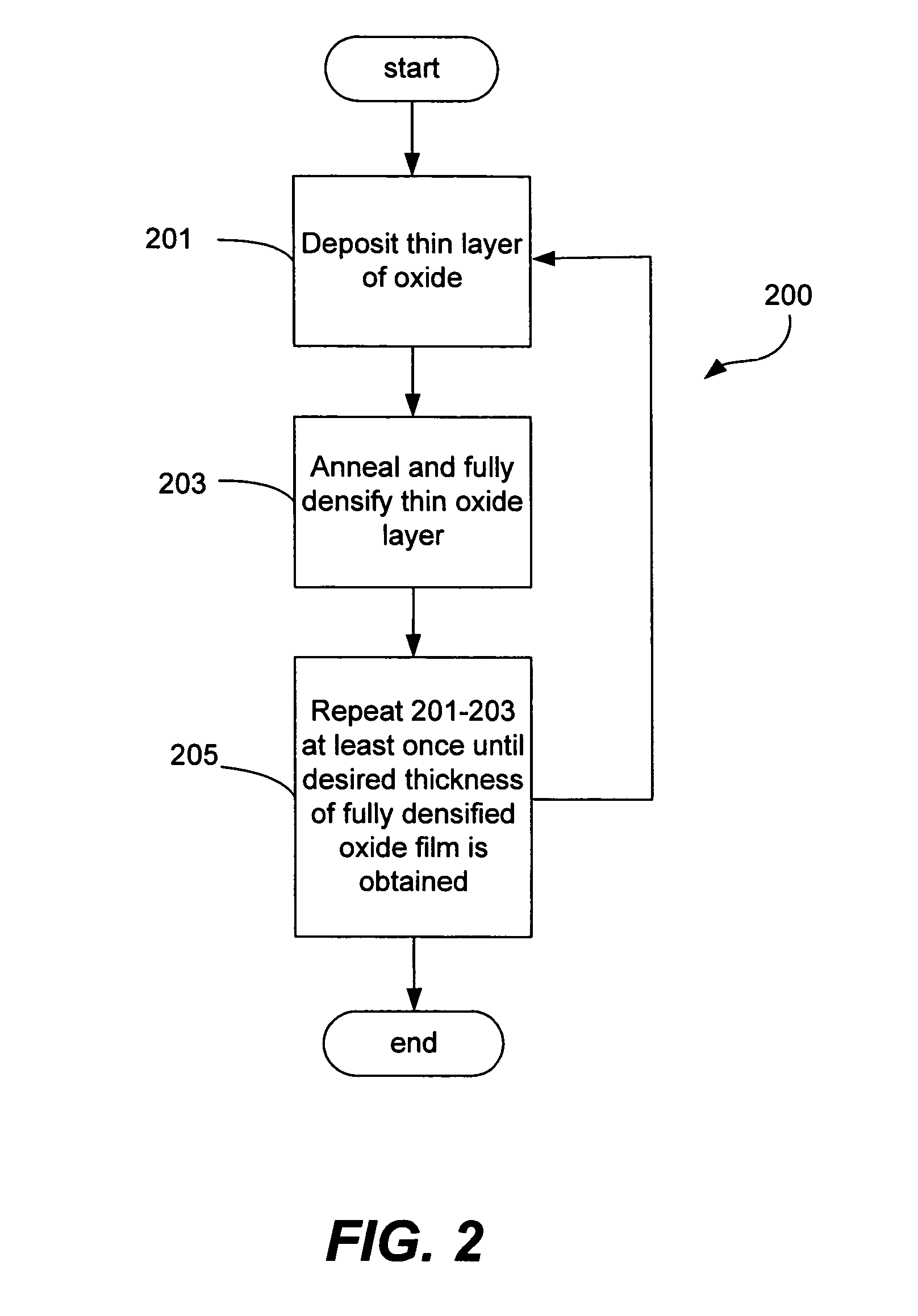
A silicon dioxide-based dielectric layer is formed on a substrate surface by a sequential deposition / anneal technique. The deposited layer thickness is insufficient to prevent substantially complete penetration of annealing process agents into the layer and migration of water out of the layer. The dielectric layer is then annealed, ideally at a moderate temperature, to remove water and thereby fully densify the film. The deposition and anneal processes are then repeated until a desired dielectric film thickness is achieved.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
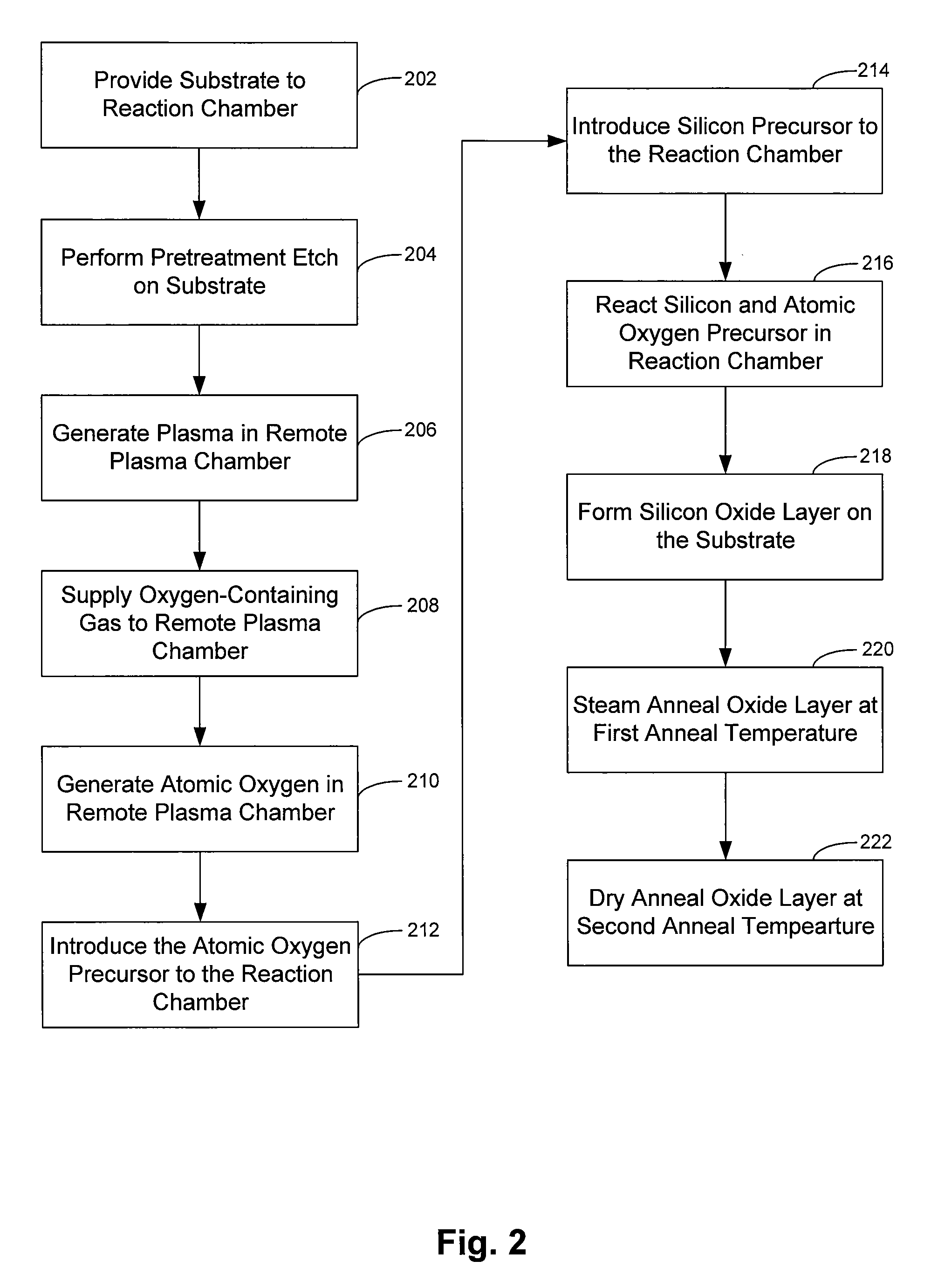
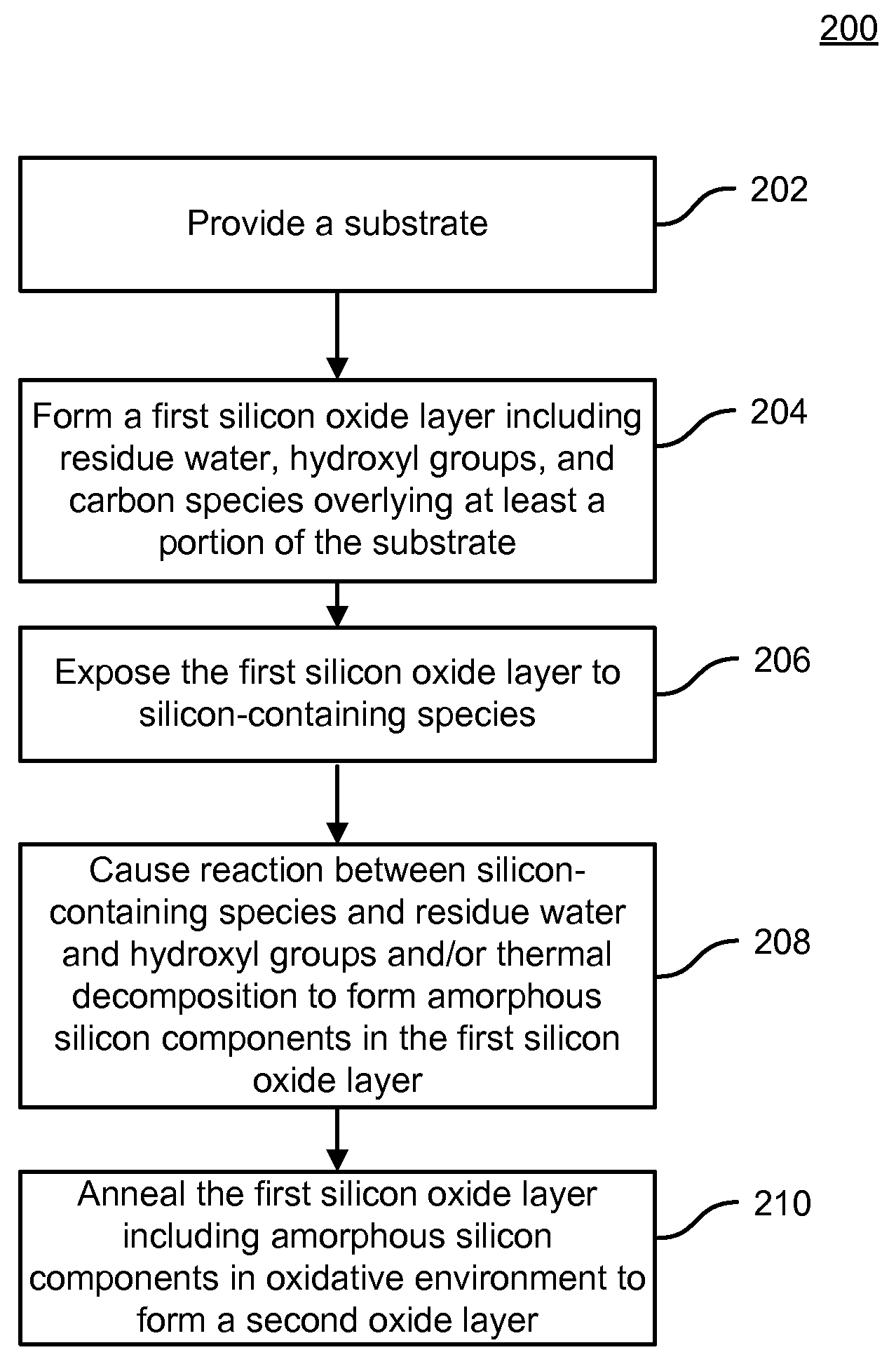
Method and system for improving dielectric film quality for void free gap fill
ActiveUS20090104789A1Quality improvementHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon monoxideAmorphous silicon
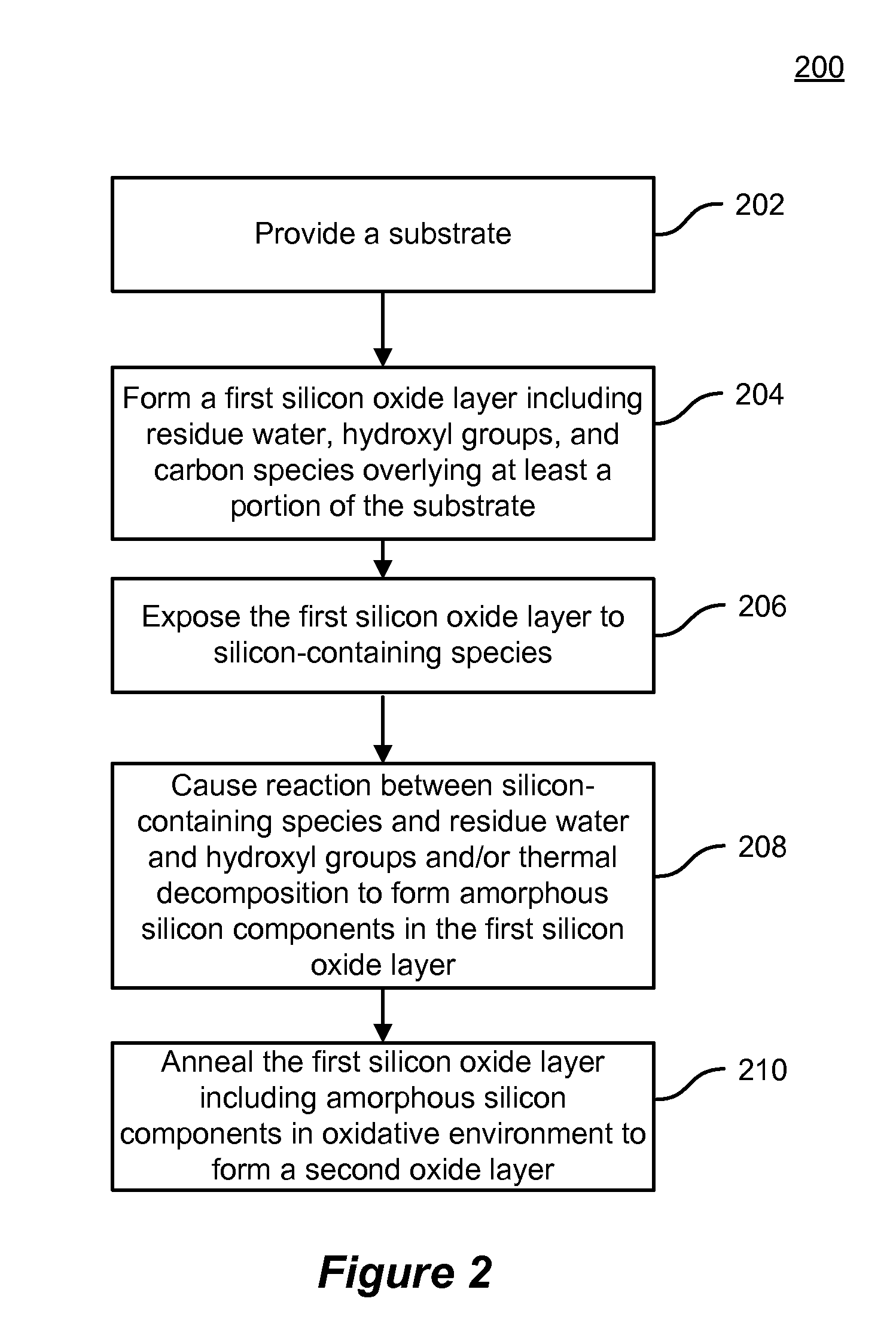
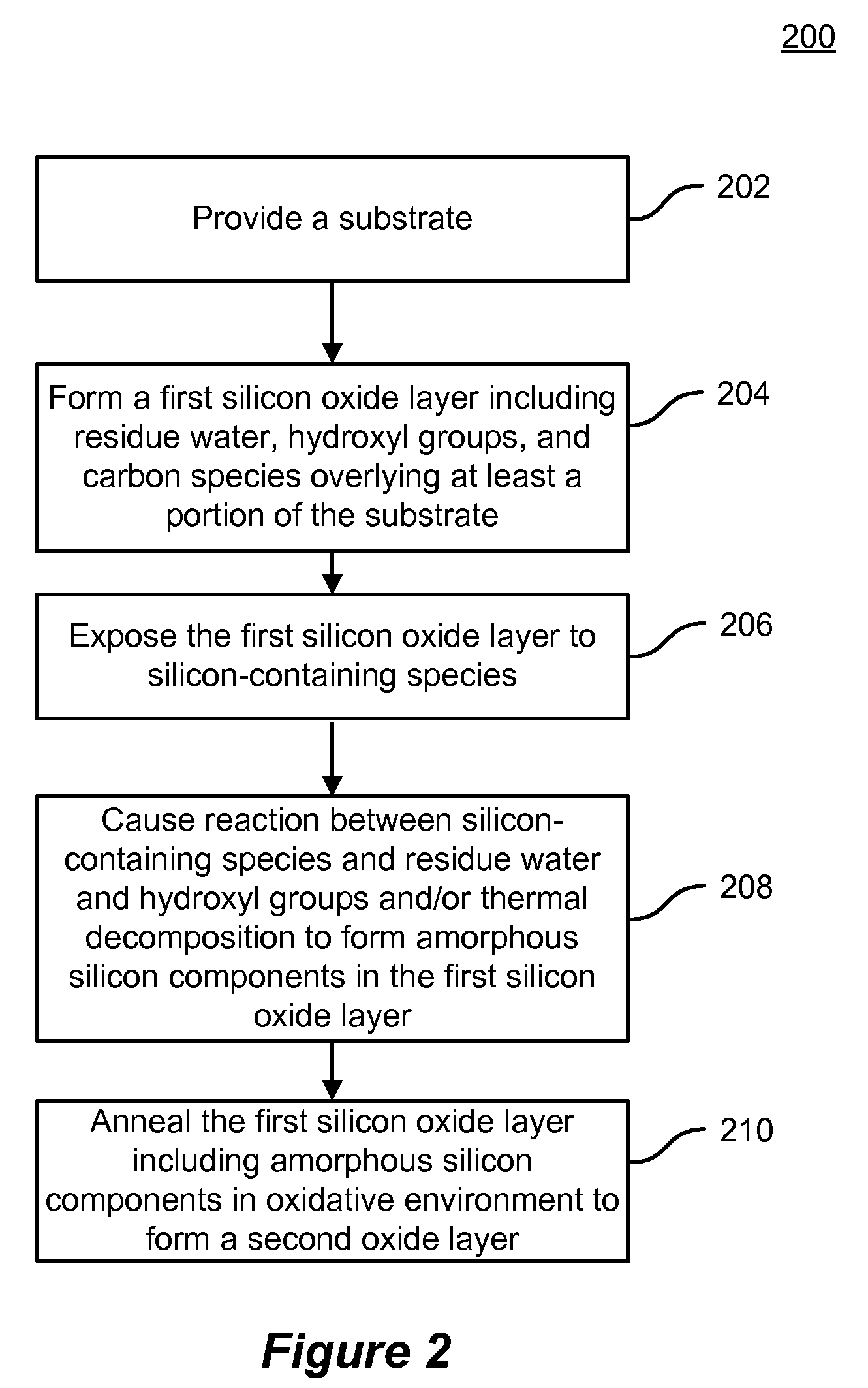
A method of forming a silicon oxide layer on a substrate. The method includes providing a substrate and forming a first silicon oxide layer overlying at least a portion of the substrate, the first silicon oxide layer including residual water, hydroxyl groups, and carbon species. The method further includes exposing the first silicon oxide layer to a plurality of silicon-containing species to form a plurality of amorphous silicon components being partially intermixed with the first silicon oxide layer. Additionally, the method includes annealing the first silicon oxide layer partially intermixed with the plurality of amorphous silicon components in an oxidative environment to form a second silicon oxide layer on the substrate. At least a portion of amorphous silicon components are oxidized to become part of the second silicon oxide layer and unreacted residual hydroxyl groups and carbon species in the second silicon oxide layer are substantially removed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
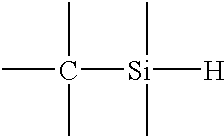
Plasma curing process for porous silica thin film
InactiveUS6558755B2Low dielectric constantHigh elastic modulusSilicaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon dioxideHeat treated
Low dielectric constant films with improved elastic modulus. The method of making such coatings involves providing a porous network coating produced from a resin containing at least 2 Si-H groups and plasma curing the coating to convert the coating into porous silica. Plasma curing of the network coating yields a coating with improved modulus, but with a higher dielectric constant. The costing is plasma cured for between about 15 and about 120 seconds at a temperature less than or about 350° C. The plasma cured coating can optionally be annealed. Rapid thermal processing (RTP) of the plasma cured coating reduces the dielectric constant of the coating while maintaining an improved elastic modulus as compared to the plasma cured porous network coating. The annealing temperature is typically loss than or about 475° C., and the annealing time is typically no more than or about 180 seconds. The annealed, plasma cured coating has a dielectric constant in the range of from about 1.1 to about 2.4 and an improved elastic modulus.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES +1
Process for catalytically producing ethylene directly from acetic acid in a single reaction zone
InactiveUS20100030001A1High selectivityHigh yieldHydrocarbonsBulk chemical productionAcetic acidHydrogen
A process for the selective production of ethylene by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethylene in a single reaction zone is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either a copper supported on iron oxide, copper-aluminum catalyst, cobalt supported on H-ZSM-5, ruthenium-cobalt supported on silica or cobalt supported on carbon selectively produces ethylene in a vapor phase at a temperature in the range of about 250° C. to 350° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Sequential deposition/anneal film densification method
ActiveUS7148155B1Maintaining film propertyMaintain propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric membraneThin membrane
A silicon dioxide-based dielectric layer is formed on a substrate surface by a sequential deposition / anneal technique. The deposited layer thickness is insufficient to prevent substantially complete penetration of annealing process agents into the layer and migration of water out of the layer. The dielectric layer is then annealed, ideally at a moderate temperature, to remove water and thereby fully densify the film. The deposition and anneal processes are then repeated until a desired dielectric film thickness is achieved.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
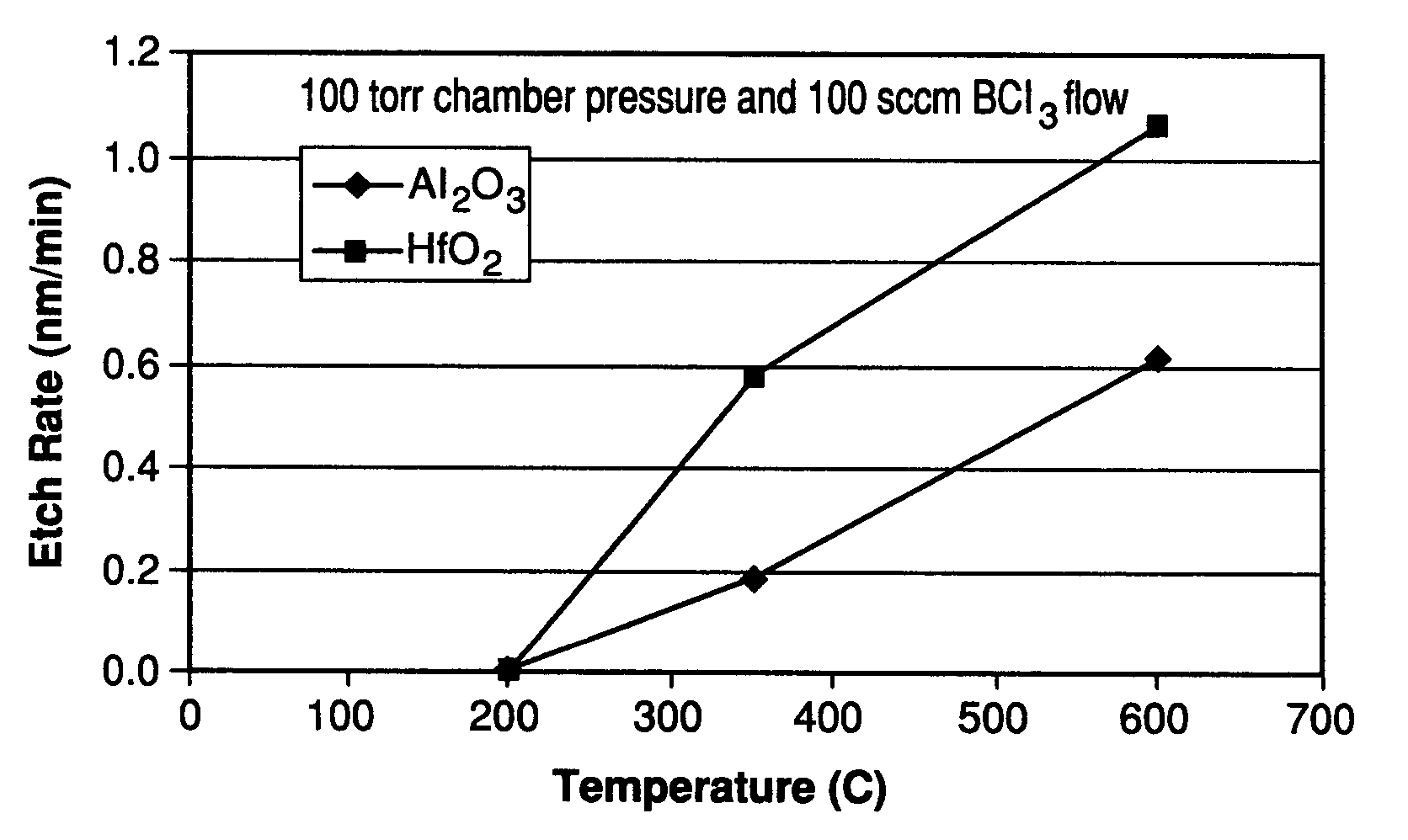
Method for etching high dielectric constant materials and for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A process for the removal of a substance from a substrate for etching and / or cleaning applications is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, there is provided a process for removing a substance having a dielectric constant greater than silicon dioxide from a substrate by reacting the substance with a reactive agent that comprises at least one member from the group consisting a halogen-containing compound, a boron-containing compound, a hydrogen-containing compound, nitrogen-containing compound, a chelating compound, a carbon-containing compound, a chlorosilane, a hydrochlorosilane, or an organochlorosilane to form a volatile product and removing the volatile product from the substrate to thereby remove the substance from the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
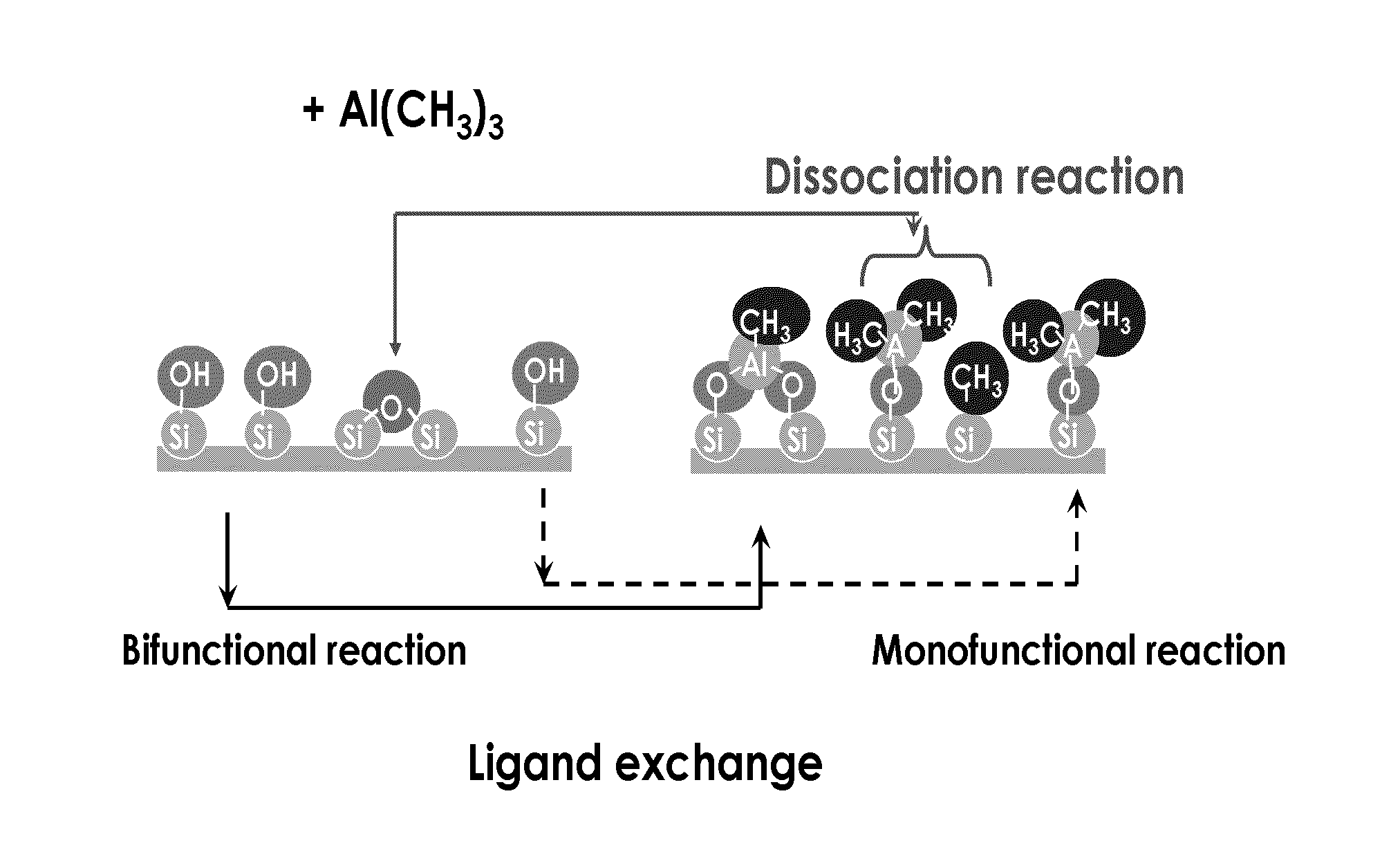
Method of increasing deposition rate of silicon dioxide on a catalyst
ActiveUS20060046518A1Good step coverageIncrease production outputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxideOxygen
Methods for forming dielectric layers, and structures and devices resulting from such methods, and systems that incorporate the devices are provided. The invention provides an aluminum oxide / silicon oxide laminate film formed by sequentially exposing a substrate to an organoaluminum catalyst to form a monolayer over the surface, remote plasmas of oxygen and nitrogen to convert the organoaluminum layer to a porous aluminum oxide layer, and a silanol precursor to form a thick layer of silicon dioxide over the porous oxide layer. The process provides an increased rate of deposition of the silicon dioxide, with each cycle producing a thick layer of silicon dioxide of about 120 Å over the layer of porous aluminum oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Atomic layer deposition of metal oxynitride layers as gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20060051925A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricHafnium
A metal oxynitride layer formed by atomic layer deposition of a plurality of reacted monolayers, the monolayers comprising at least one each of a metal, an oxide and a nitride. The metal oxynitride layer is formed from zirconium oxynitride, hafnium oxynitride, tantalum oxynitride, or mixtures thereof. The metal oxynitride layer is used in gate dielectrics as a replacement material for silicon dioxide. A semiconductor device structure having a gate dielectric formed from a metal oxynitride layer is also disclosed.
Owner:AHN KIE Y +1
LOW TEMPERATURE ALD SiO2
InactiveUS20080113097A1Reduce interactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPyridineSilicon dioxide
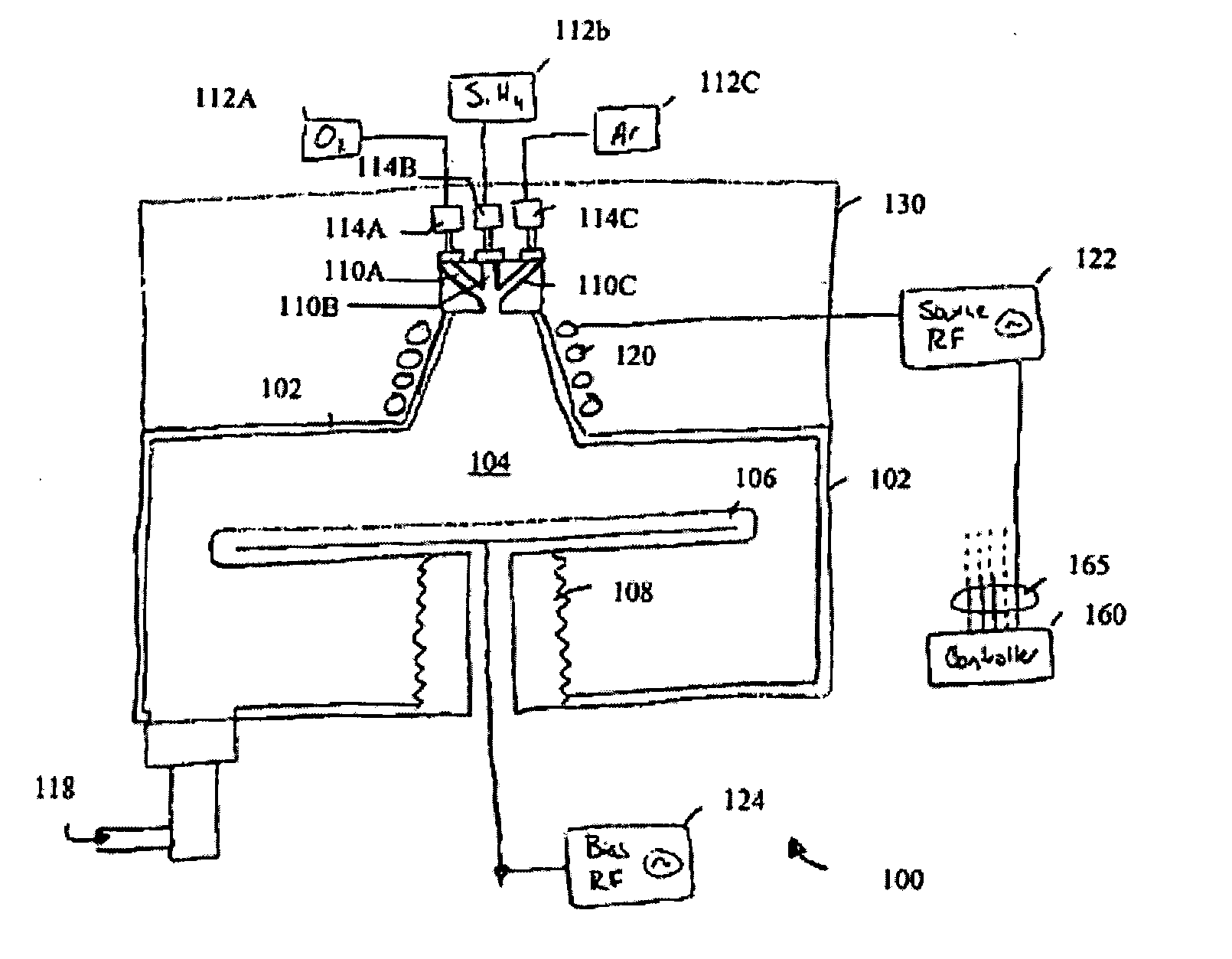
The present invention generally comprises a silicon dioxide atomic layer deposition method. By providing pyridine as a catalyst, water may be utilized as the oxidization source while depositing at a low temperature. Prior to exposing the substrate to the water, the substrate may be exposed to a pyridine soak process. Additionally, the water may be co-flowed to the chamber with the pyridine through separate conduits to reduce interaction prior to entering the chamber. Alternatively, the pyridine may be co-flowed with a silicon precursor that does not react with pyridine.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
InactiveUS20050019494A1High aspect ratioGood effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOxygenSilicon dioxide
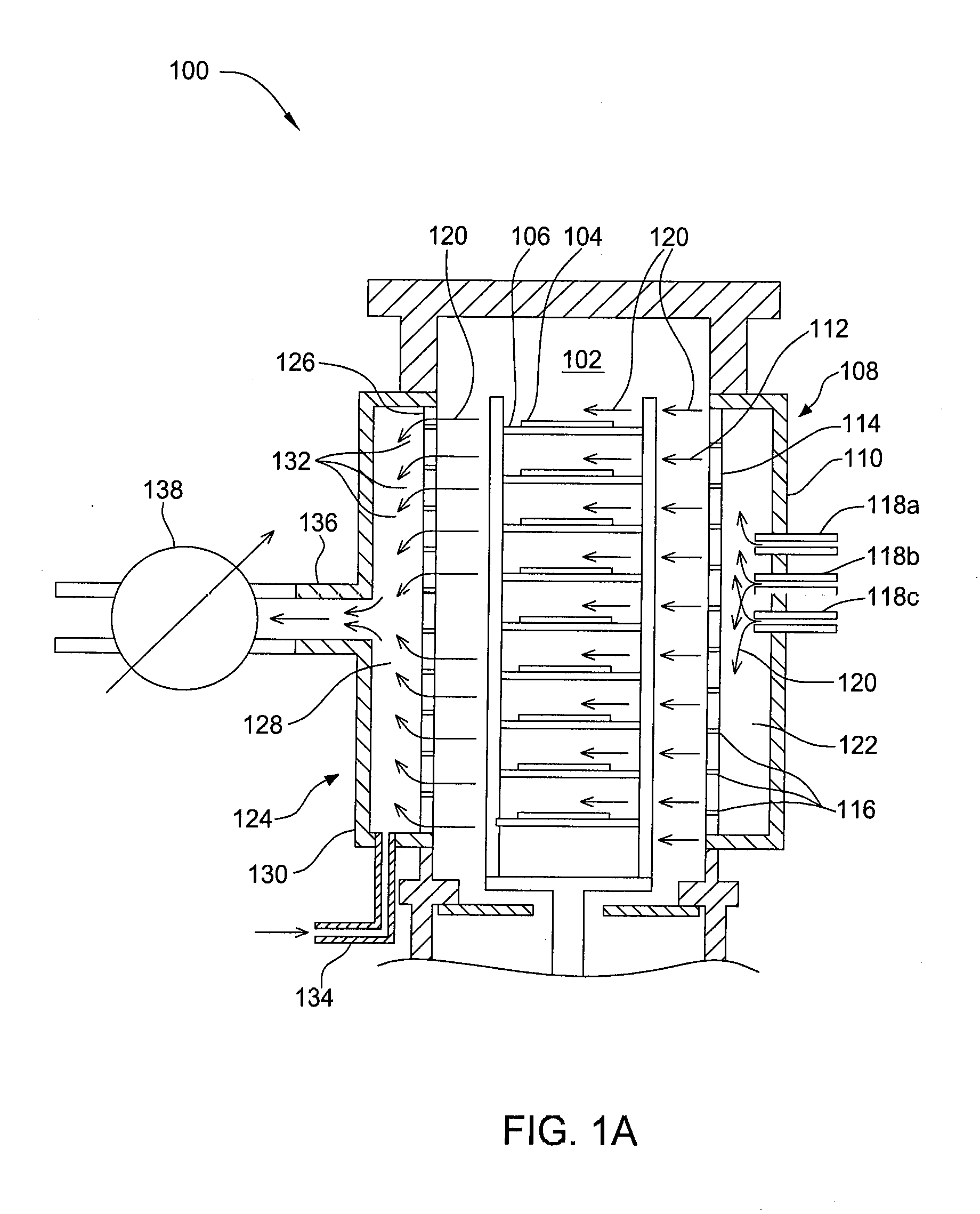
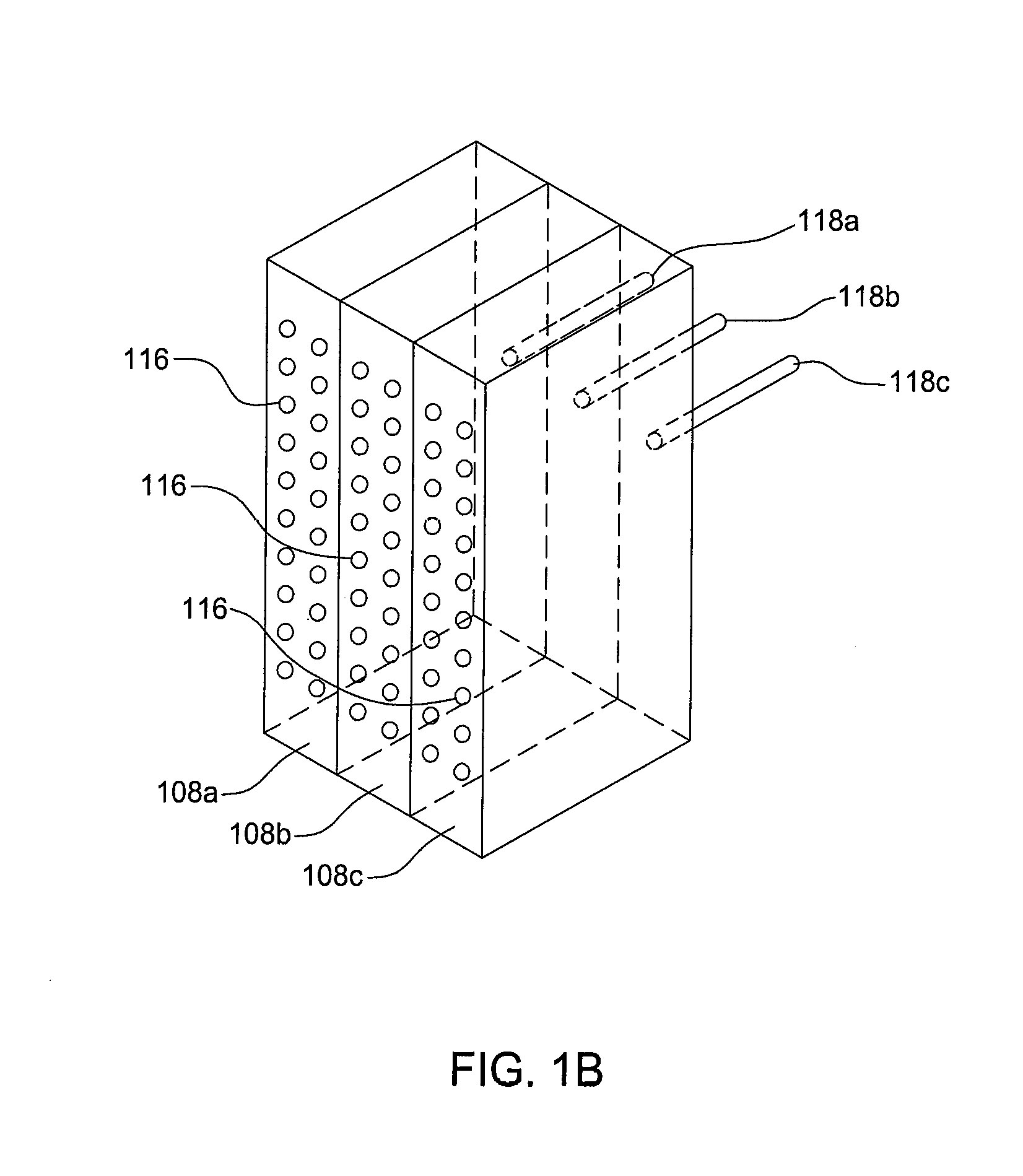
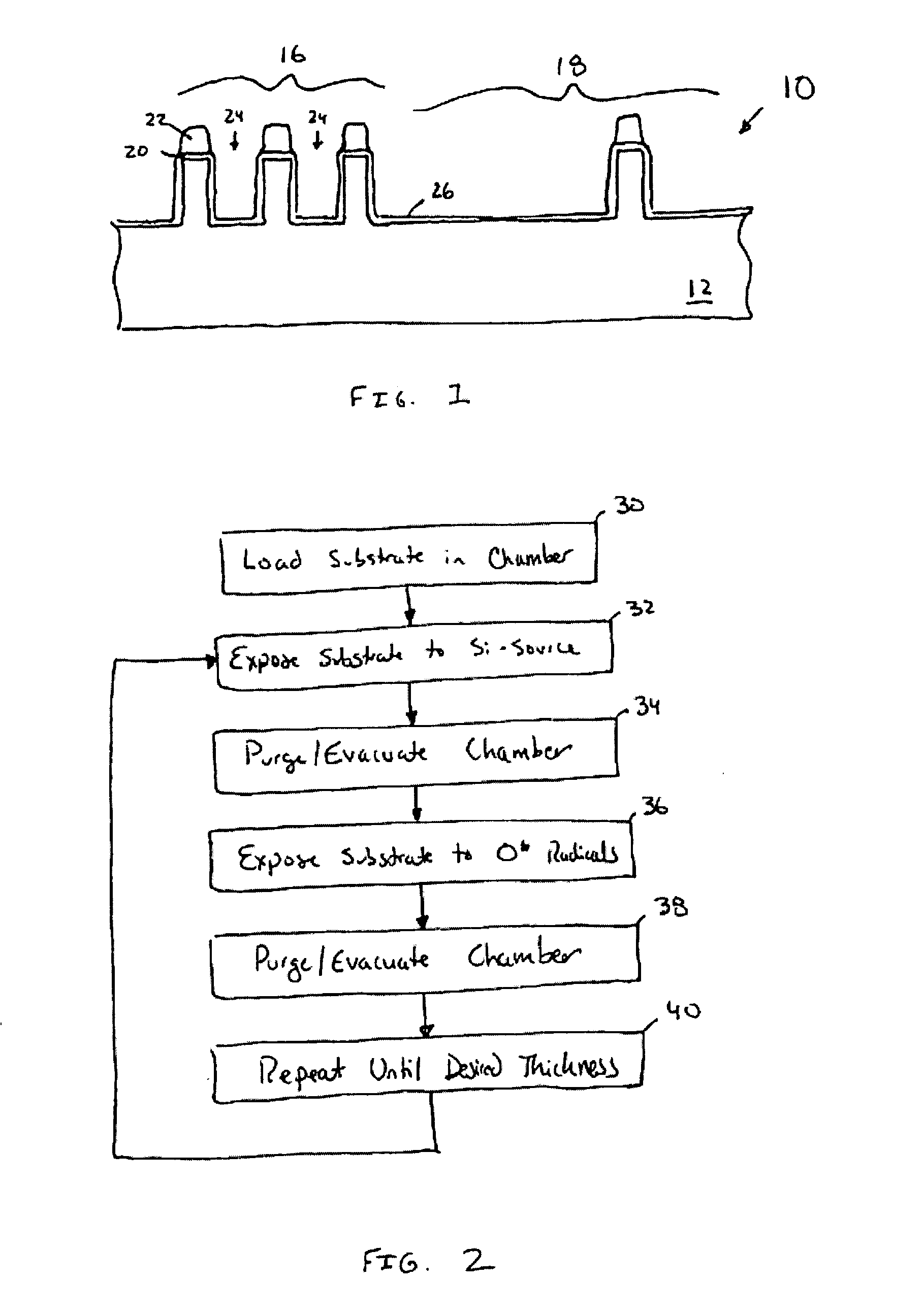
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
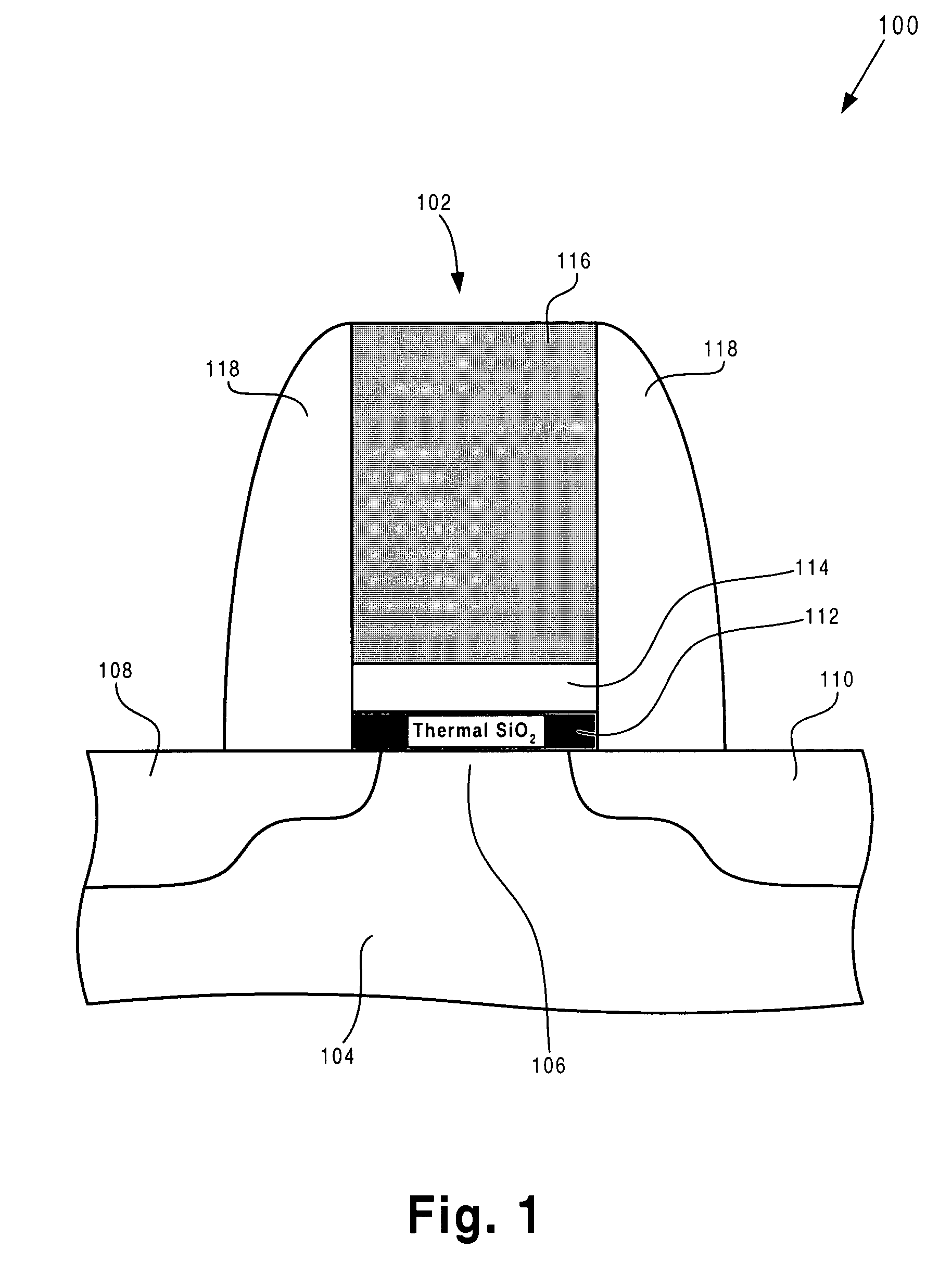
Method for forming a thin, high quality buffer layer in a field effect transistor and related structure
ActiveUS7071051B1Readily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOrganic field-effect transistorOptoelectronics
According to one exemplary embodiment, a method for forming a field-effect transistor on a substrate comprises a step of forming a buffer layer on the substrate, where the buffer layer comprises ALD silicon dioxide. The buffer layer can be formed by utilizing a silicon tetrachloride precursor in an atomic layer deposition process, for example. The buffer layer comprises substantially no pin-hole defects and may have a thickness, for example, that is less than approximately 5.0 Angstroms. The method further comprises forming a high-k dielectric layer over the buffer layer. The high-k dielectric layer may be, for example, hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, or aluminum oxide. According to this exemplary embodiment, the method further comprises forming a gate electrode layer over the high-k dielectric layer. The gate electrode layer may be polycrystalline silicon, for example.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
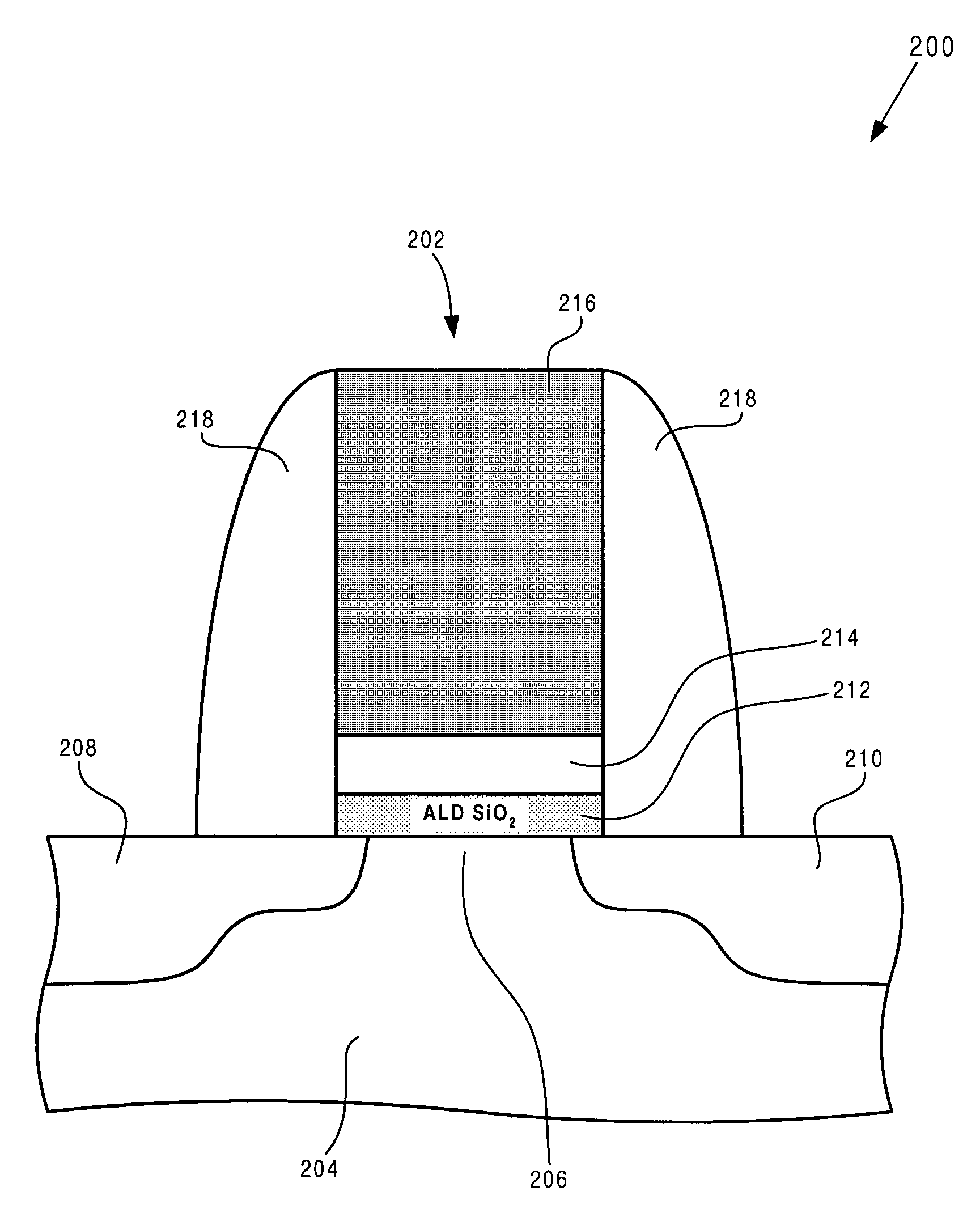
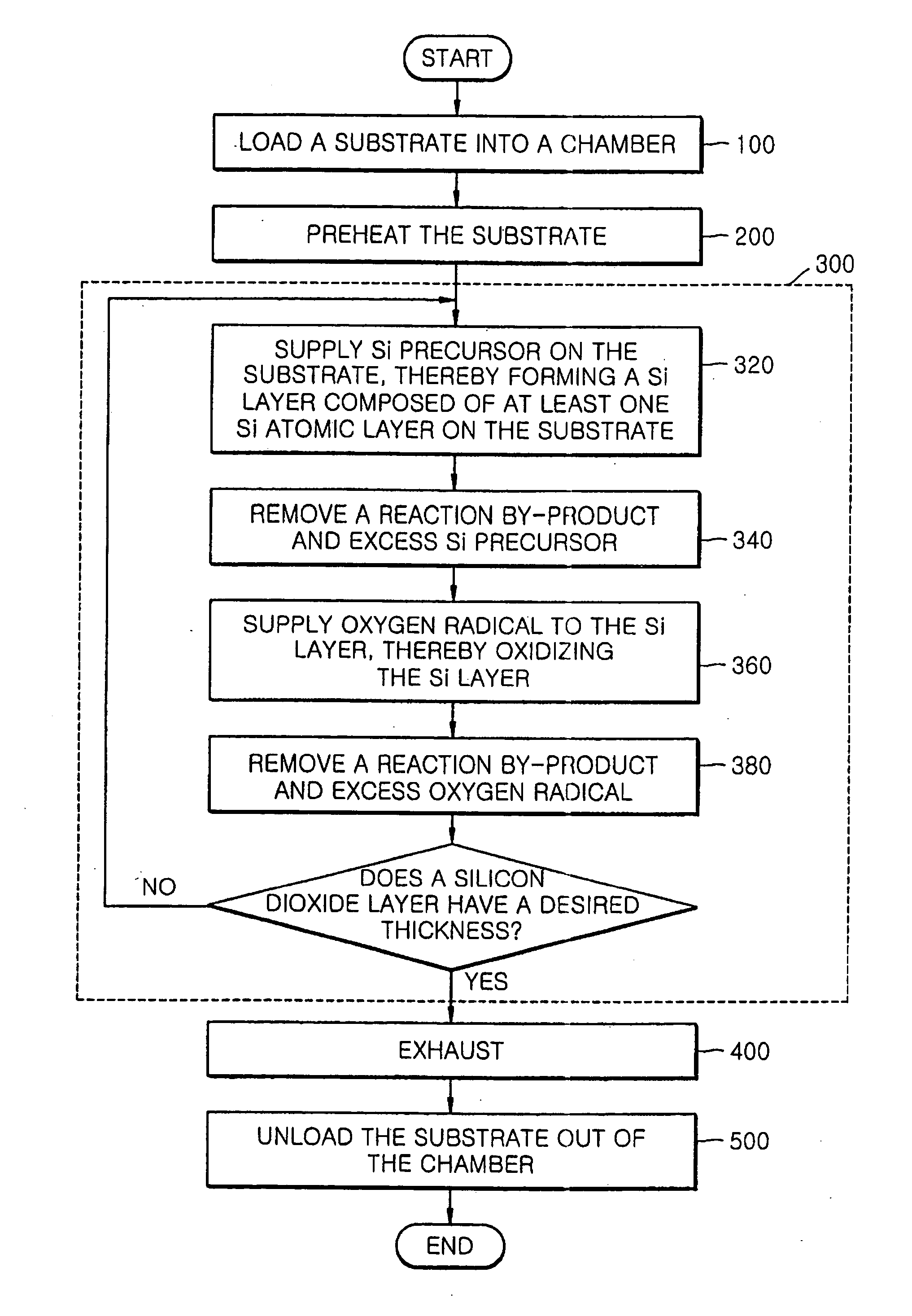
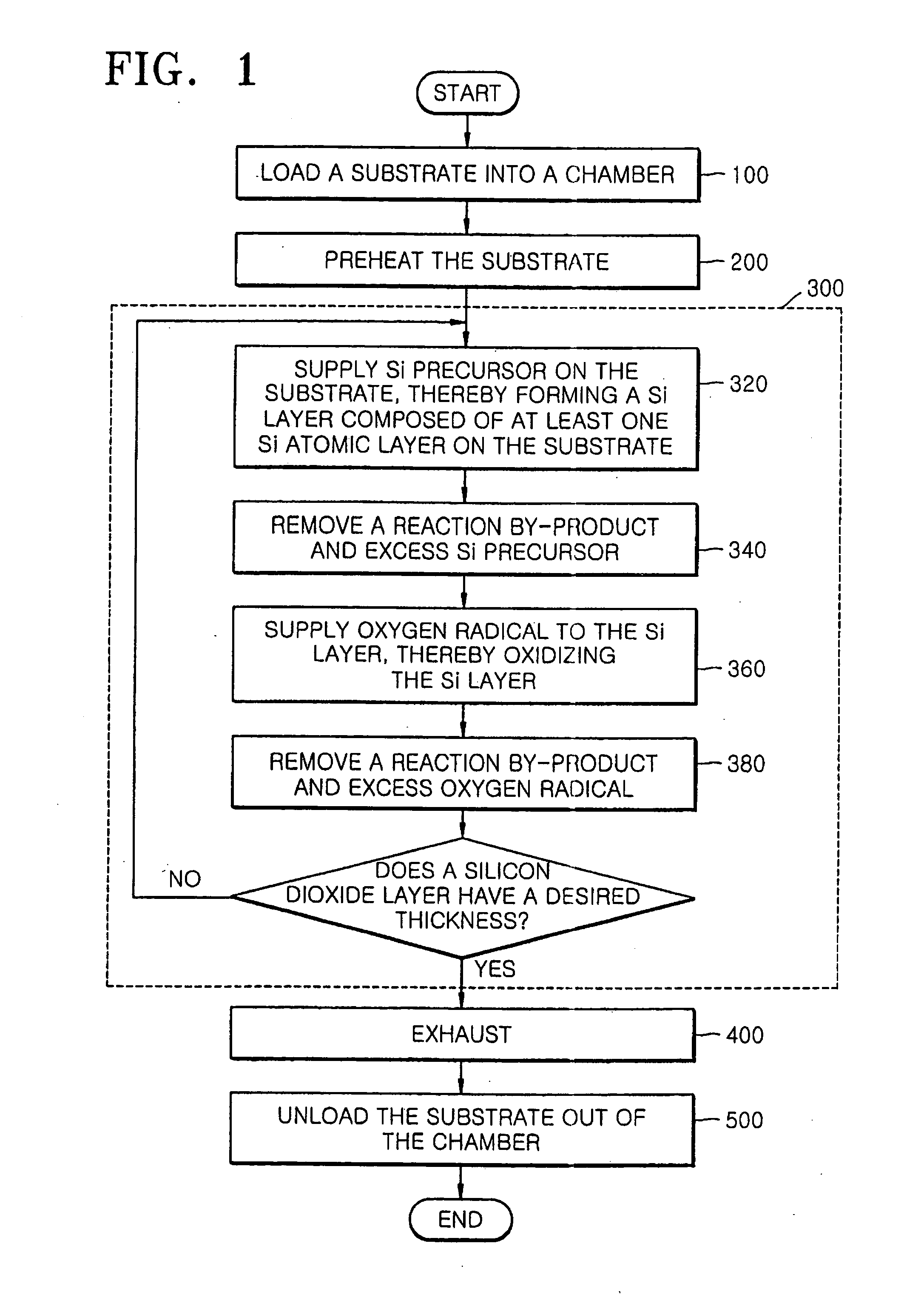
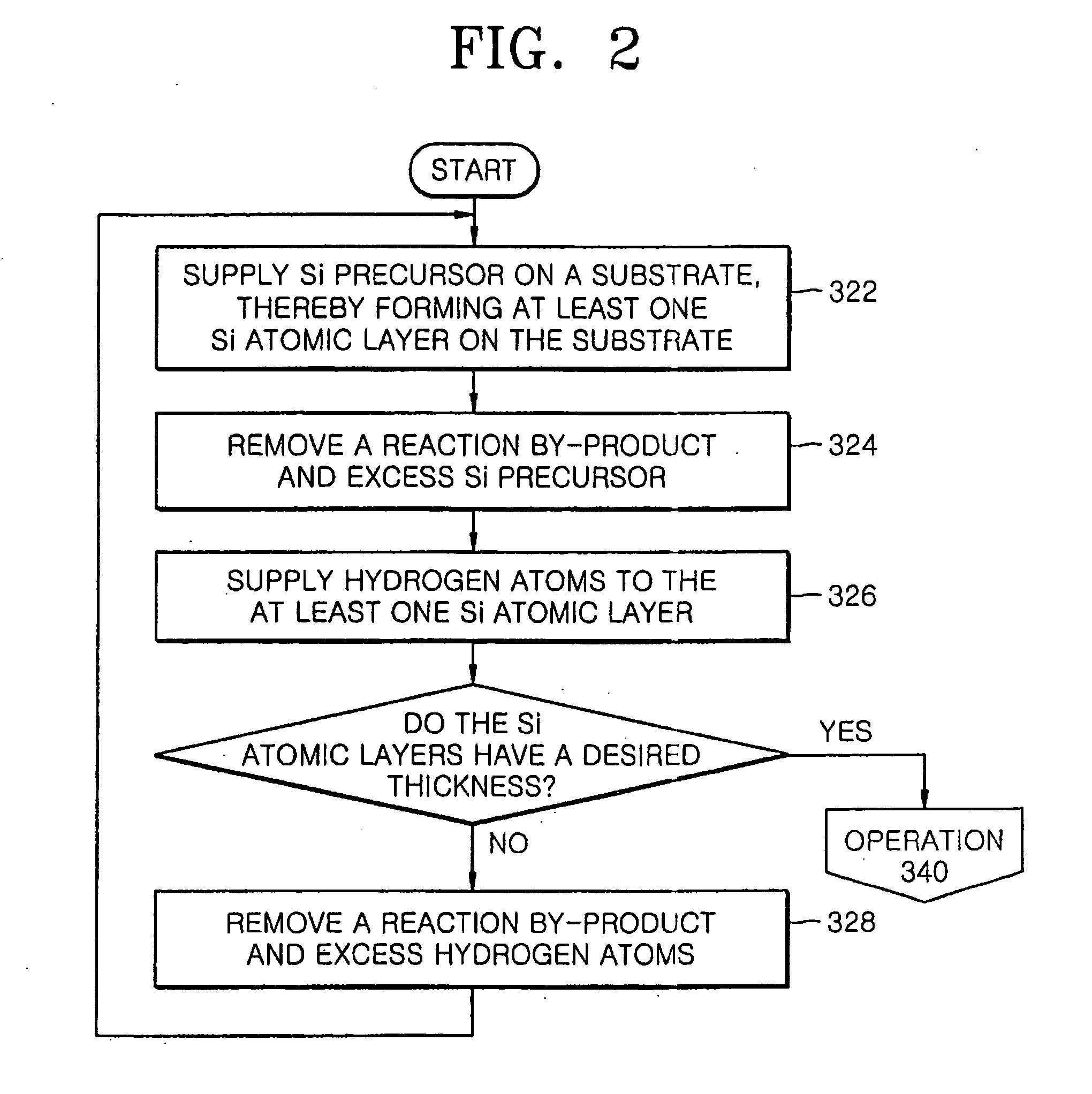
Methods of forming silicon dioxide layers using atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20070111545A1Good step coverageReduce trap densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingOptoelectronicsOxygen
Provided herein are methods of forming a silicon dioxide layer on a substrate using an atomic layer deposition (ALD) method that include supplying a Si precursor to the substrate and forming on the substrate a Si layer including at least one Si atomic layer; and (b) supplying an oxygen radical to the Si layer to replace at least one Si—Si bond within the Si layer with a Si—O bond, thereby oxidizing the Si layer, to form a silicon dioxide layer on the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
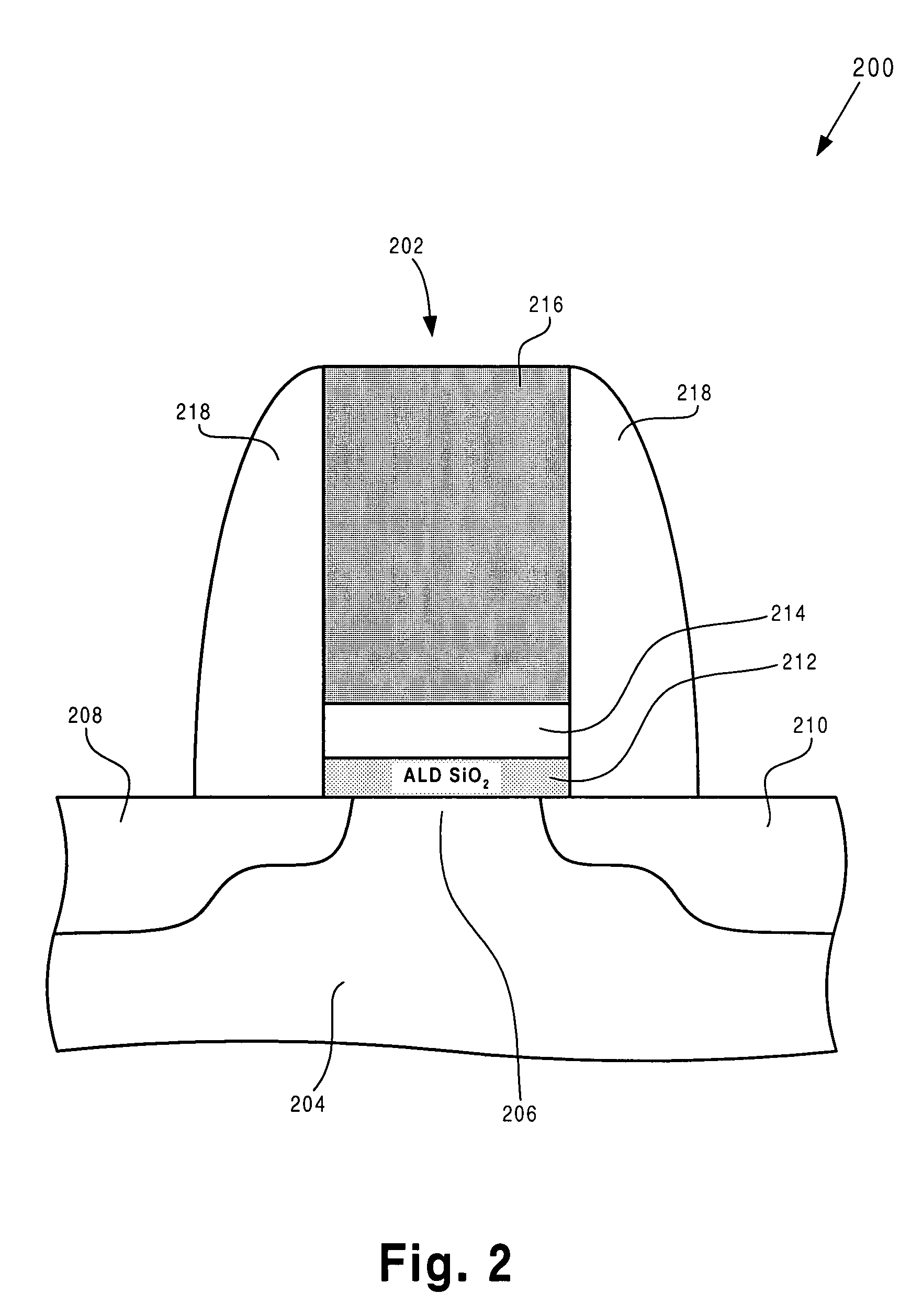
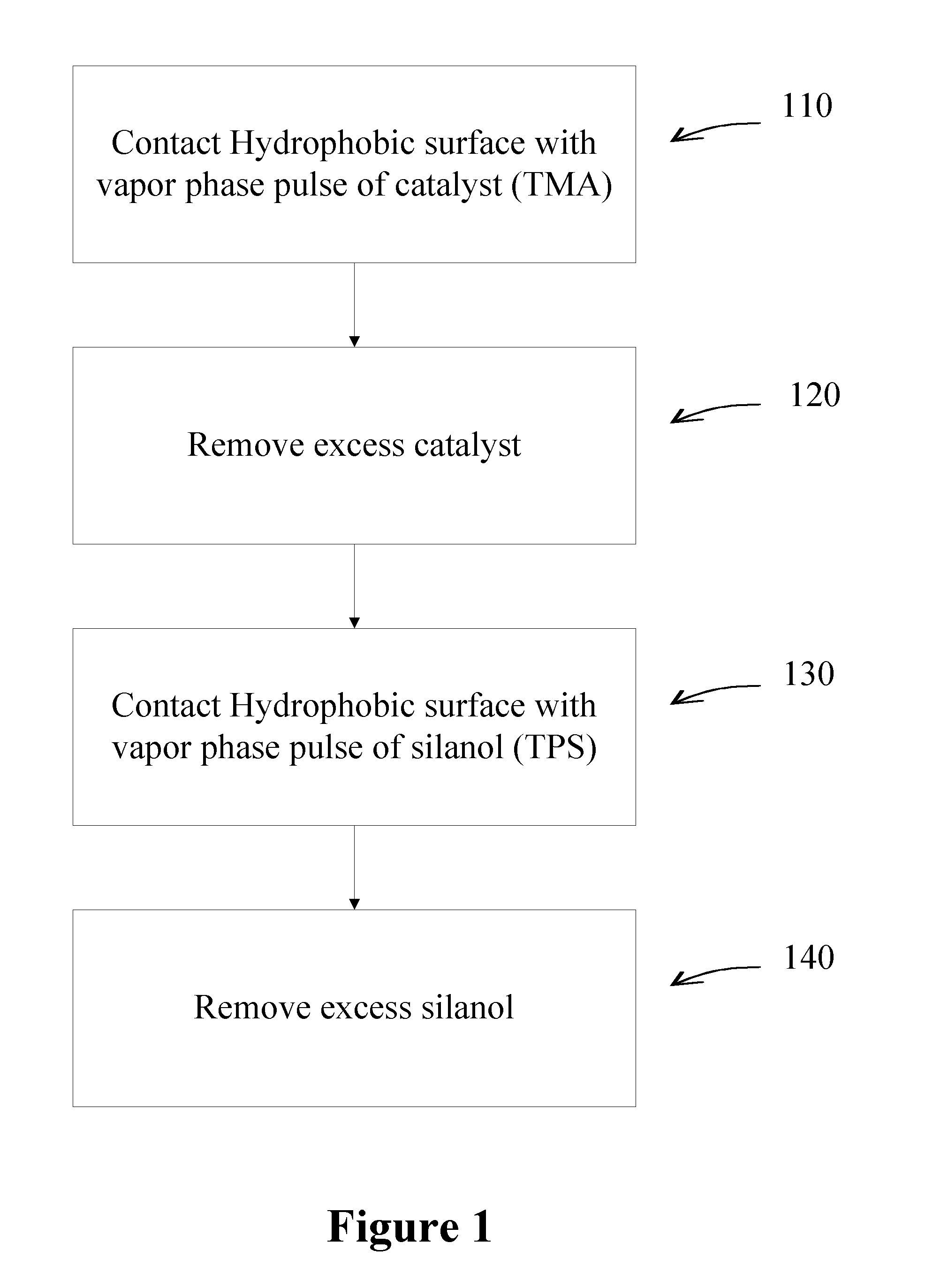
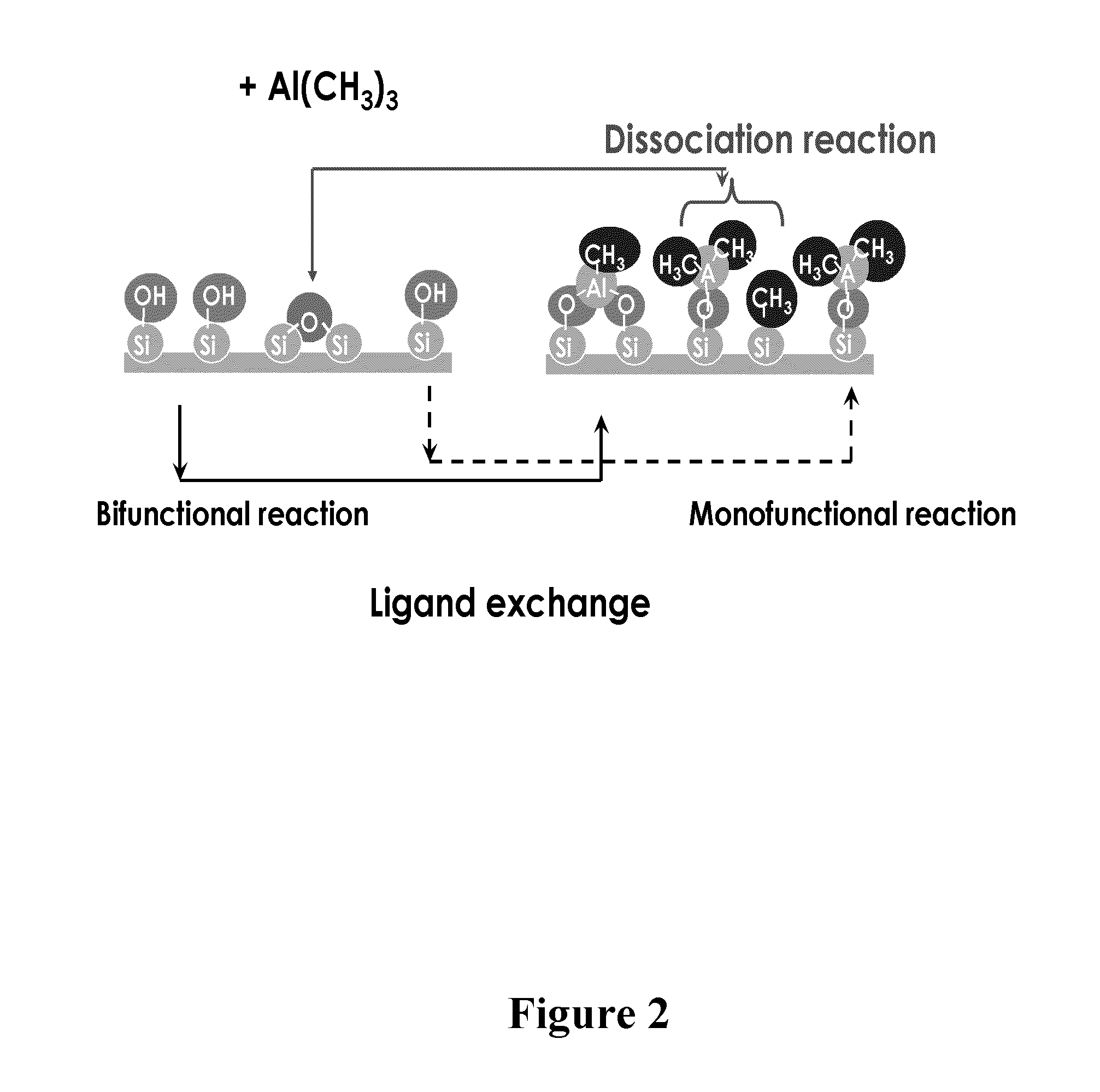
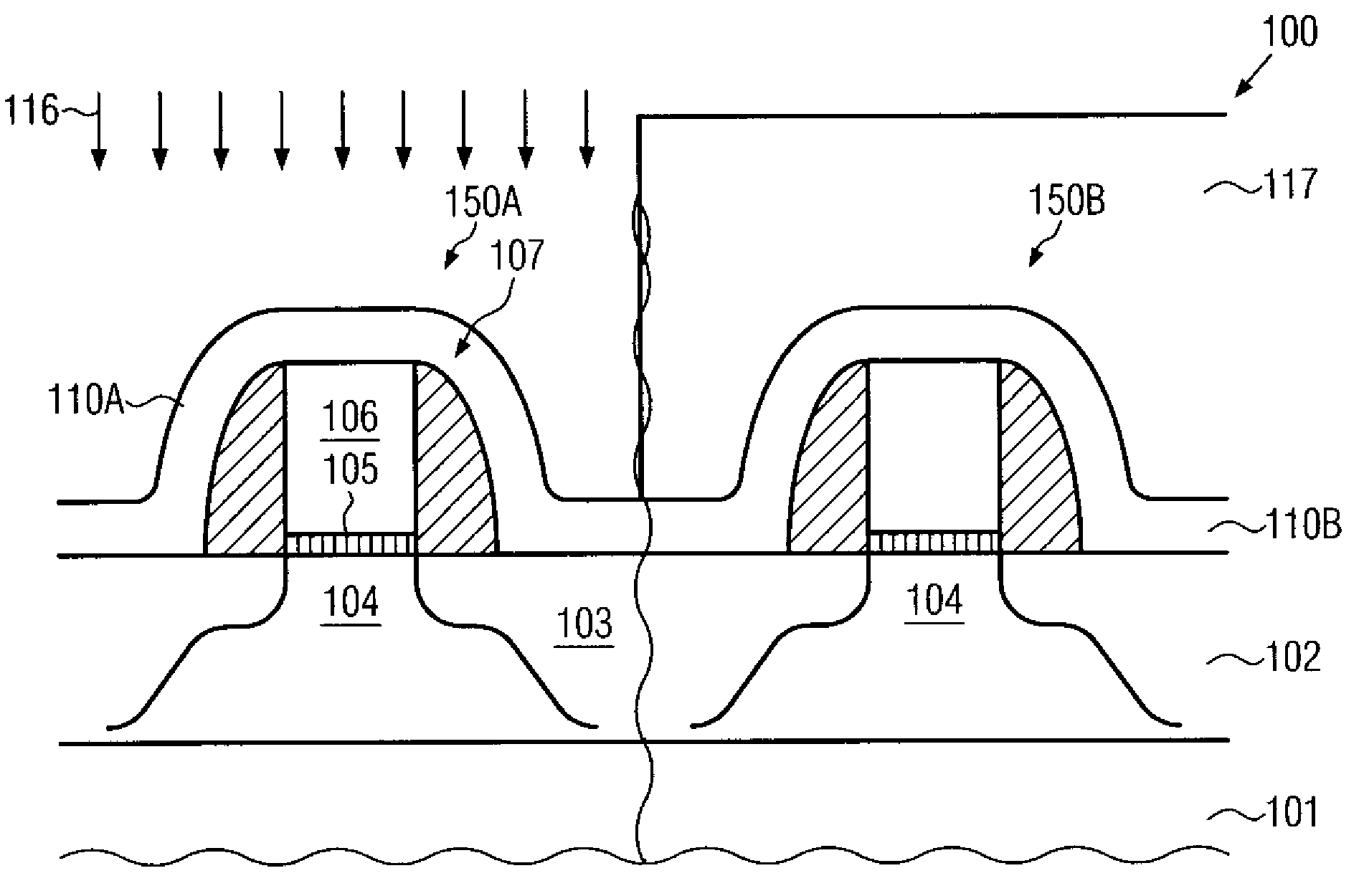
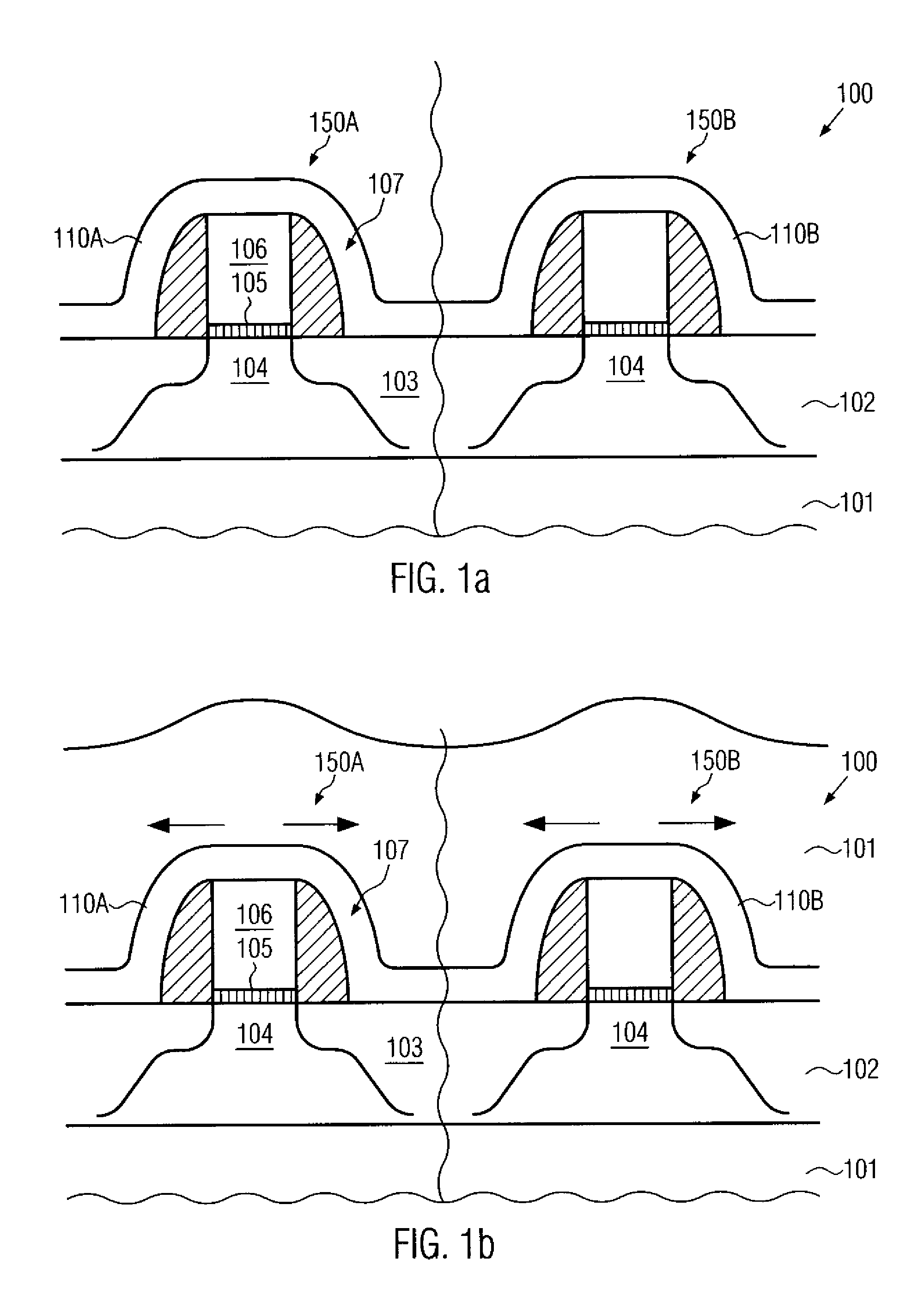
Deposition of silicon dioxide on hydrophobic surfaces
InactiveUS20120263876A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanolSilicon dioxide
Methods for forming silicon dioxide thin films on hydrophobic surfaces are provided. For example, in some embodiments, silicon dioxide films are deposited on porous, low-k materials. The silicon dioxide films can be deposited using a catalyst and a silanol. In some embodiments, an undersaturated dose of one or more of the reactants can be used in forming a pore-sealing layer over a porous material.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Field effect transistor having an interlayer dielectric material having increased intrinsic stress
InactiveUS20080203487A1Optimization mechanismImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentField-effect transistor
By providing a highly stressed interlayer dielectric material, the performance of at least one type of transistor may be increased due to an enhanced strain-inducing mechanism. For instance, by providing a highly compressive silicon dioxide of approximately 400 Mega Pascal and more as an interlayer dielectric material, the drive current of the P-channel transistors may be increased by 2% and more while not unduly affecting the performance of the N-channel transistors.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Vapor deposition of silicon dioxide nanolaminates
ActiveUS20050112282A1Easy to produceUniform thicknessMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPorosityElectrical conductor
This invention relates to materials and processes for thin film deposition on solid substrates. Silica / alumina nanolaminates were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of an aluminum-containing compound with a silanol. The nanolaminates have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in holes with aspect ratios over 40:1. The films are transparent and good electrical insulators. This invention also relates to materials and processes for producing improved porous dielectric materials used in the insulation of electrical conductors in microelectronic devices, particularly through materials and processes for producing semi-porous dielectric materials wherein surface porosity is significantly reduced or removed while internal porosity is preserved to maintain a desired low-k value for the overall dielectric material. The invention can also be used to selectively fill narrow trenches with low-k dielectric material while at the same time avoiding deposition of any dielectric on the surface area outside of the trenches.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS20100029995A1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicatePlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Recovery of hydrophobicity of low-k and ultra low-k organosilicate films used as inter metal dielectrics
InactiveUS20050106762A1Low costHigh mechanical strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentSilylation
Often used to reduce the RC delay in integrated circuits are dielectric films of porous organosilicates which have a silica like backbone with alkyl or aryl groups (to add hydrophobicity to the materials and create free volume) attached directly to the Si atoms in the network. Si—R bonds rarely survive an exposure to plasmas or chemical treatments commonly used in processing; this is especially the case in materials with an open cell pore structure. When Si—R bonds are broken, the materials lose hydrophobicity, due to formation of hydrophilic silanols and low dielectric constant is compromised. A method by which the hydrophobicity of the materials is recovered using a novel class of silylation agents which may have the general formula (R2N)XSiR′Y where X and Y are integers from 1 to 3 and 3 to 1 respectively, and where R and R′ are selected from the group of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, allyl and a vinyl moiety. Mechanical strength of porous organosilicates is also improved as a result of the silylation treatment.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com