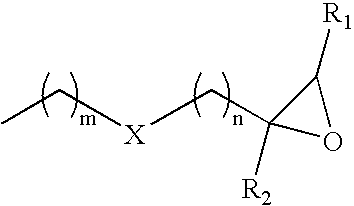
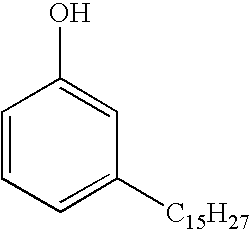
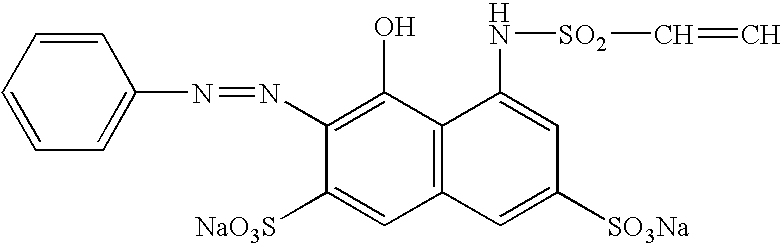
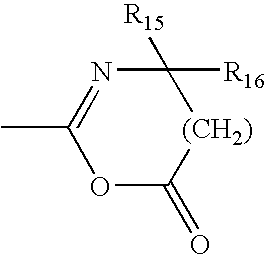
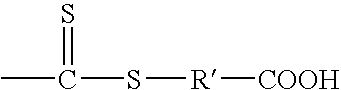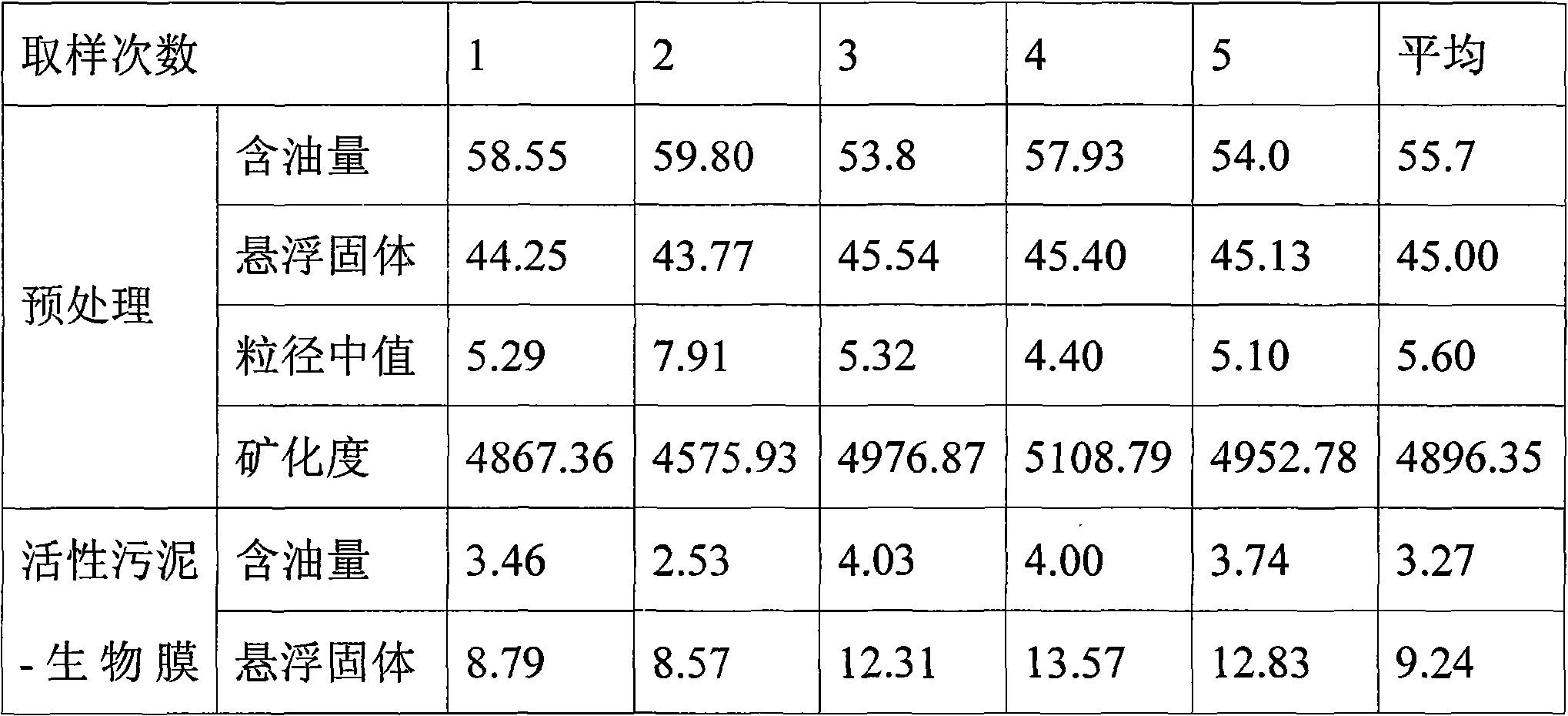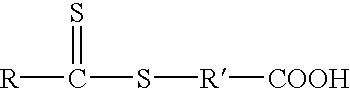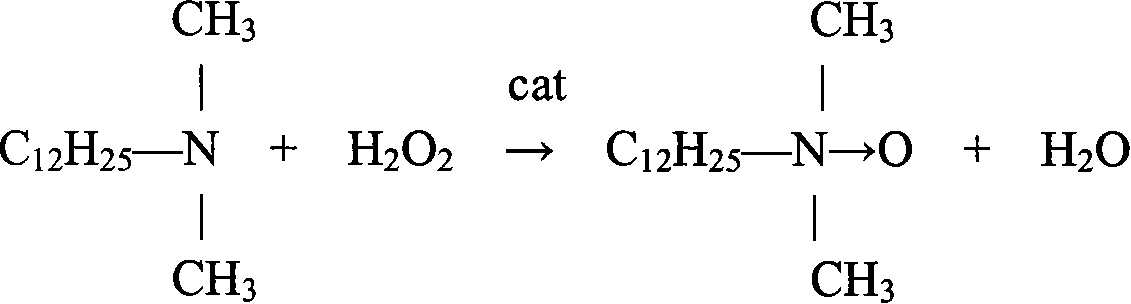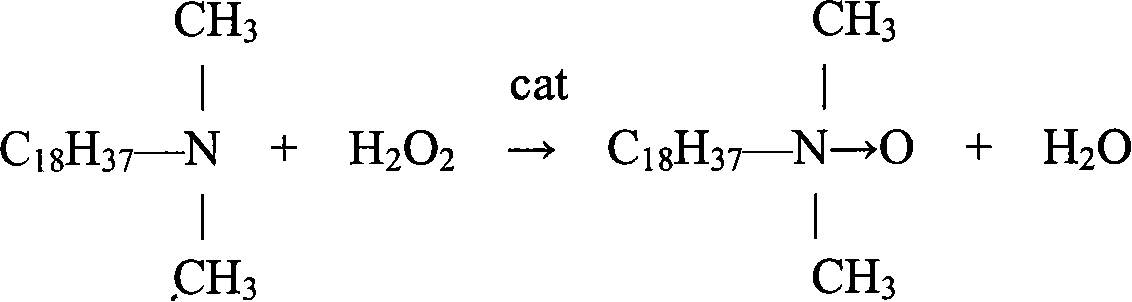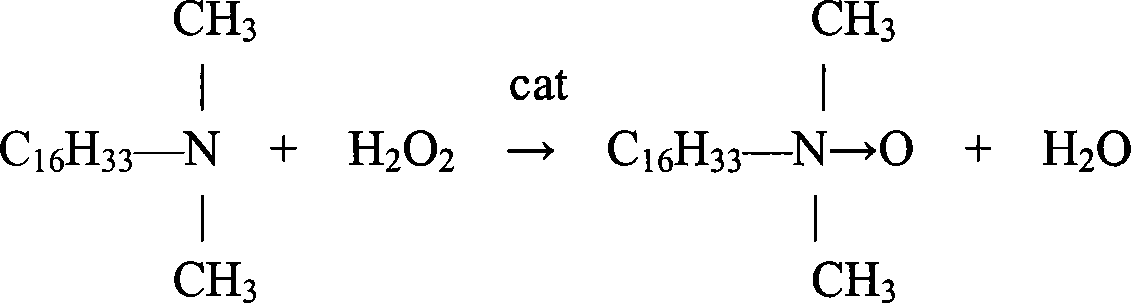Patents
Literature
122 results about "Reactive agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reactive agents are software agents that carry out a simple task of retrieving pre-set behaviors similar to reflexes.
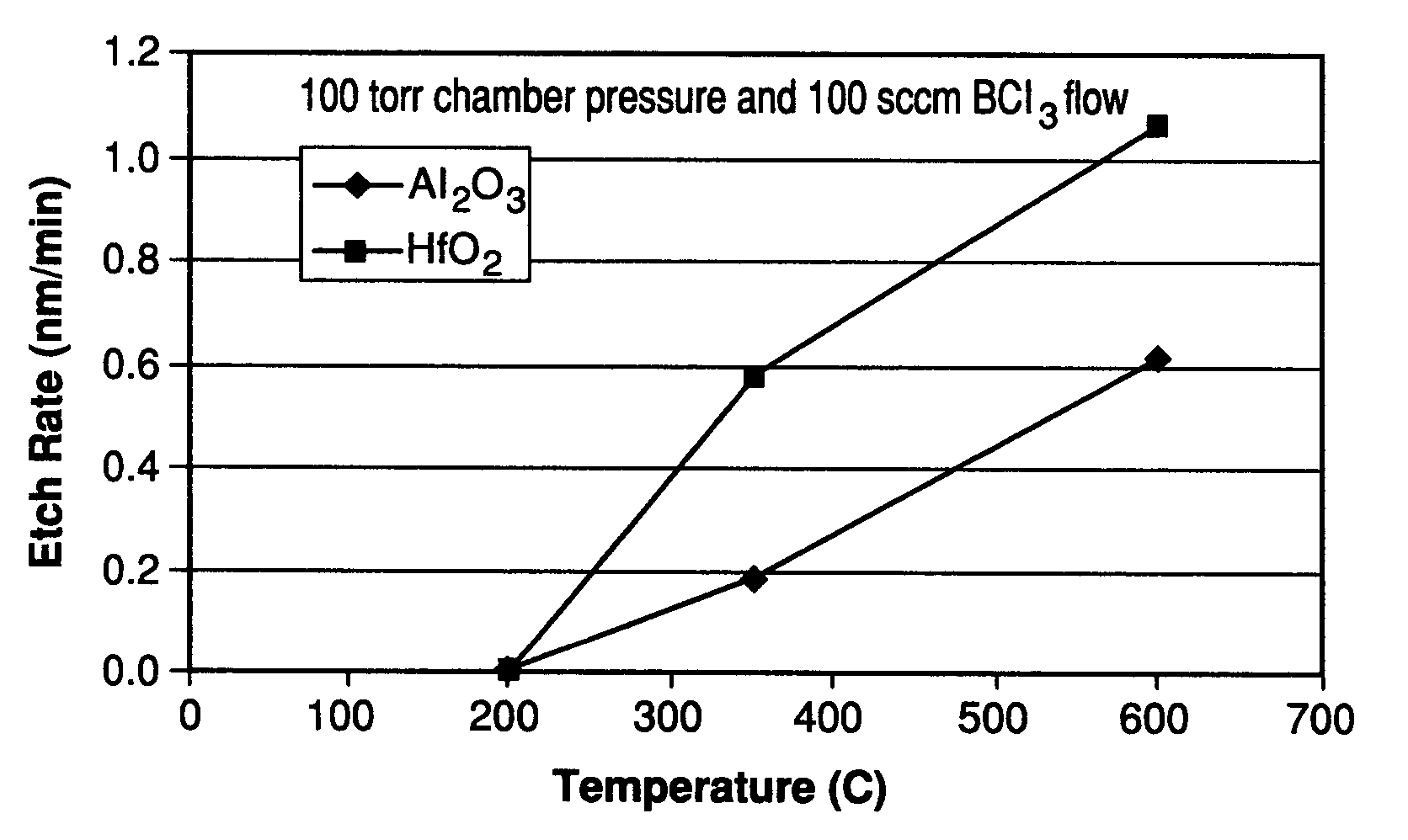
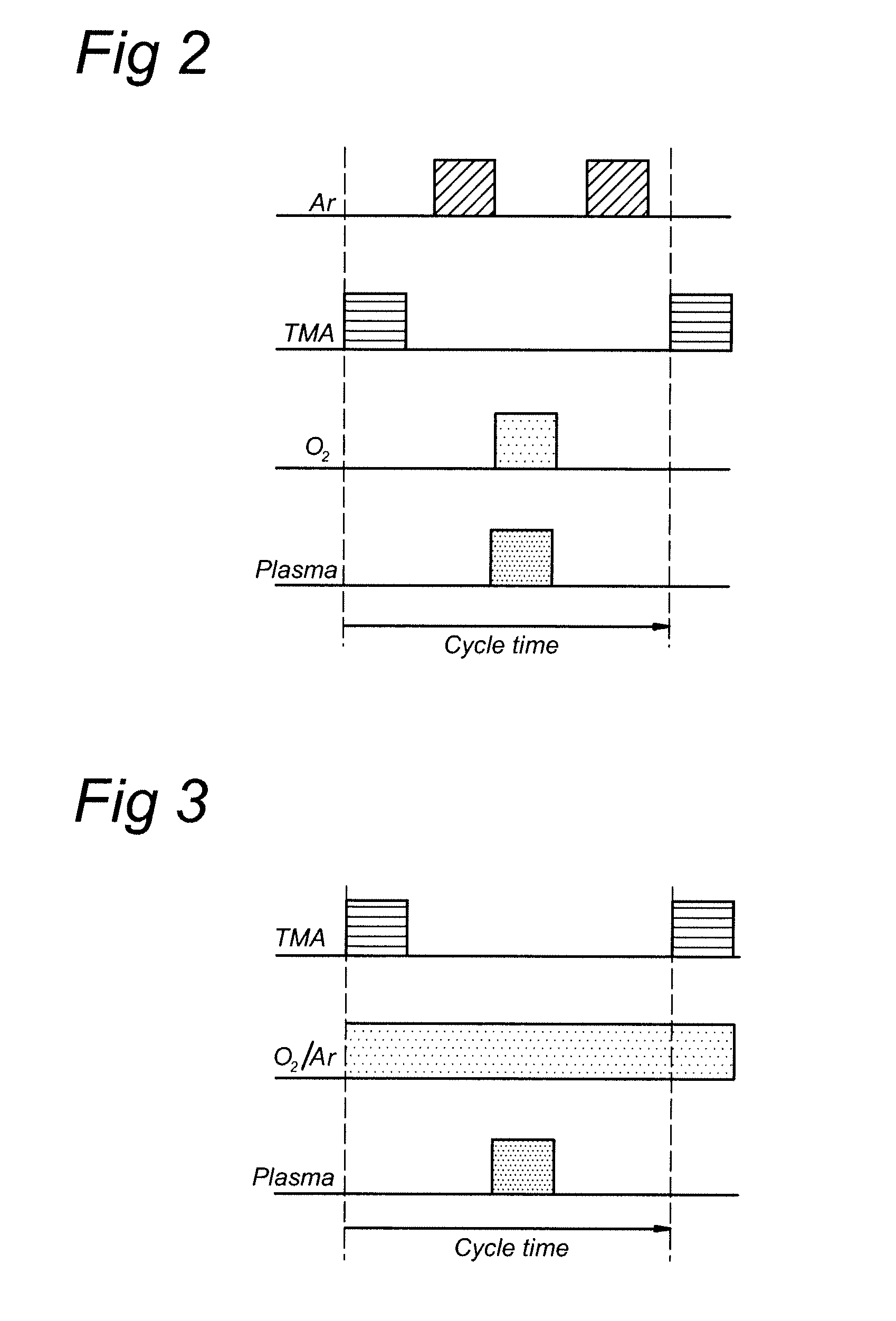
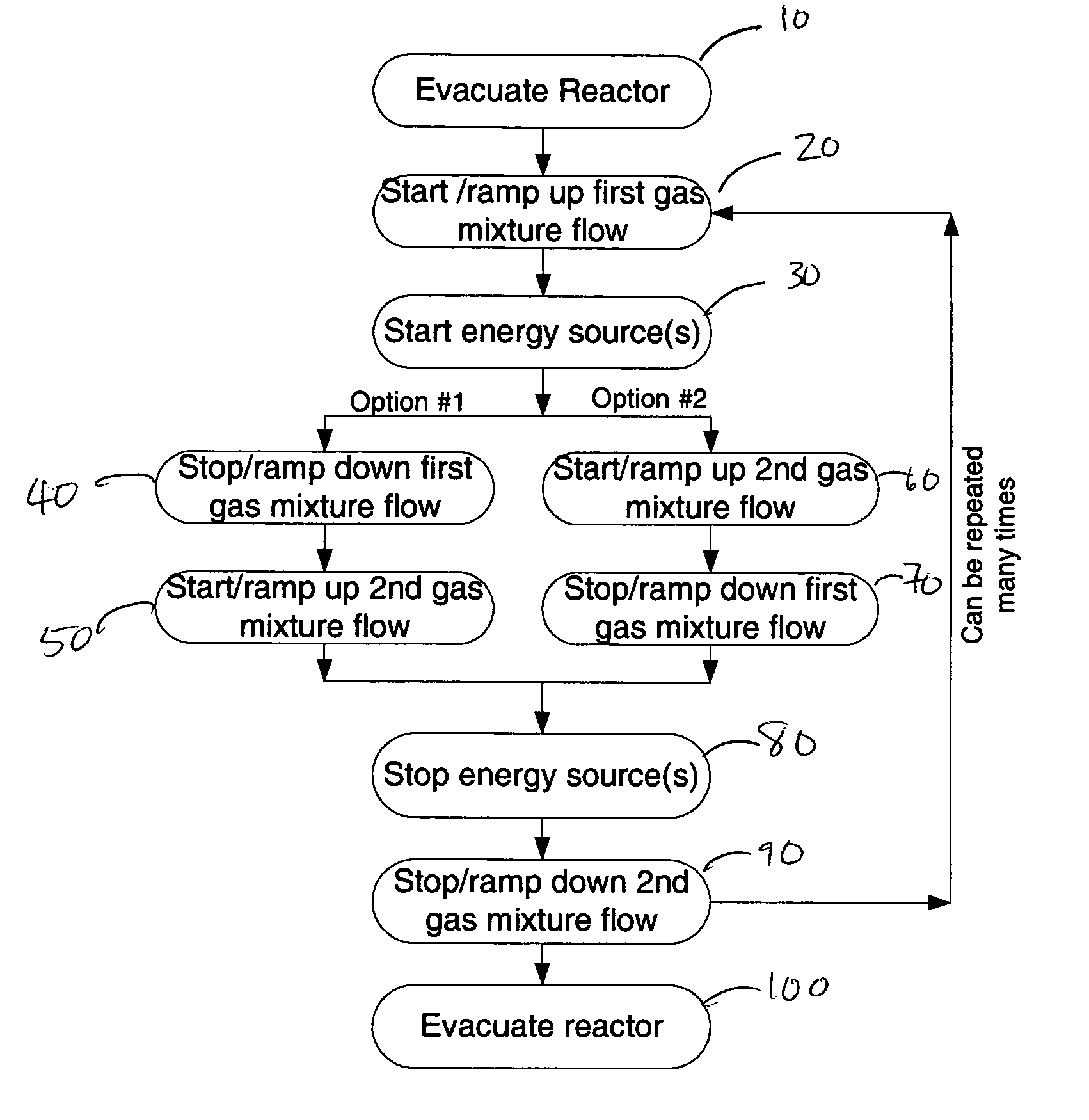
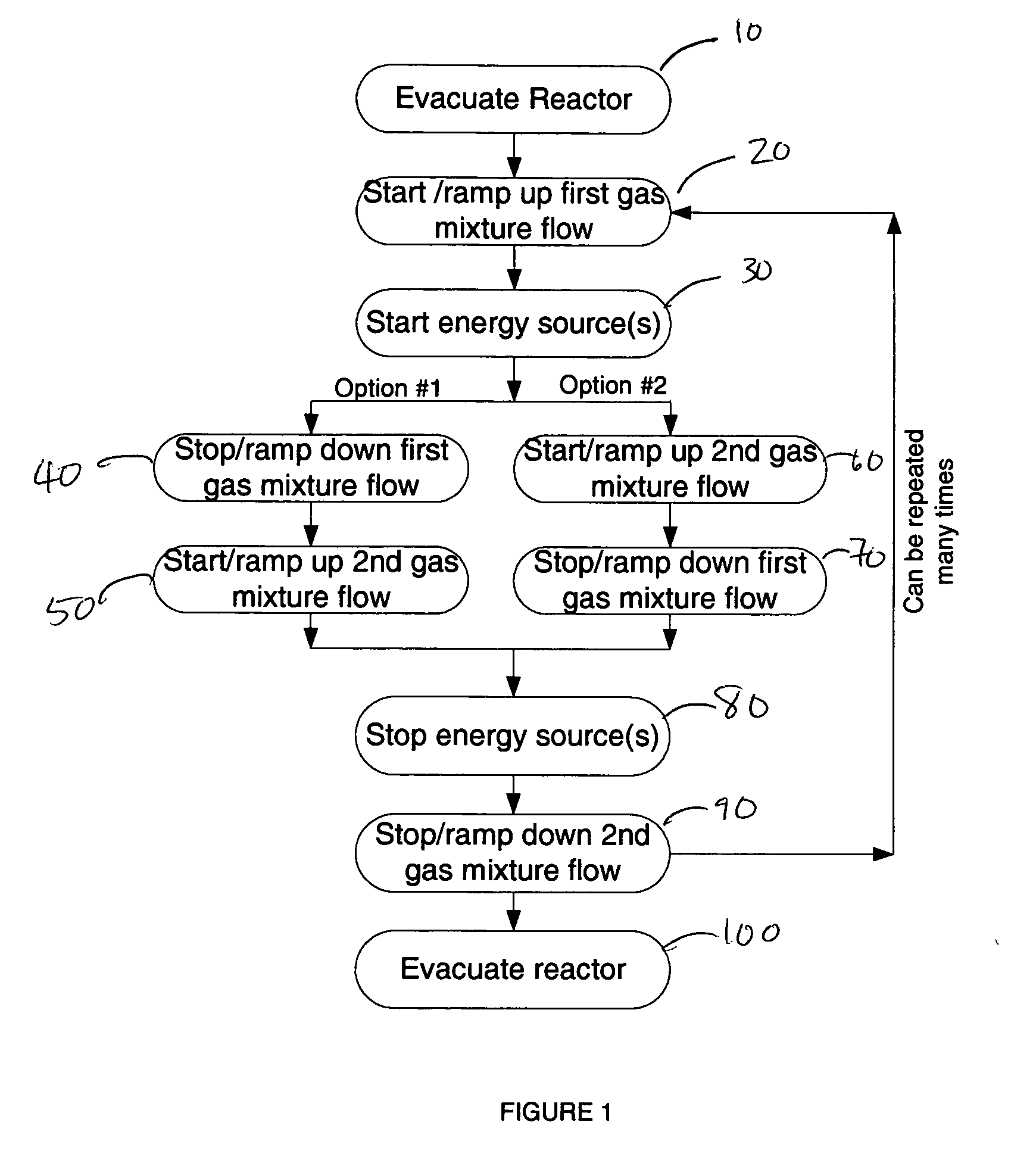
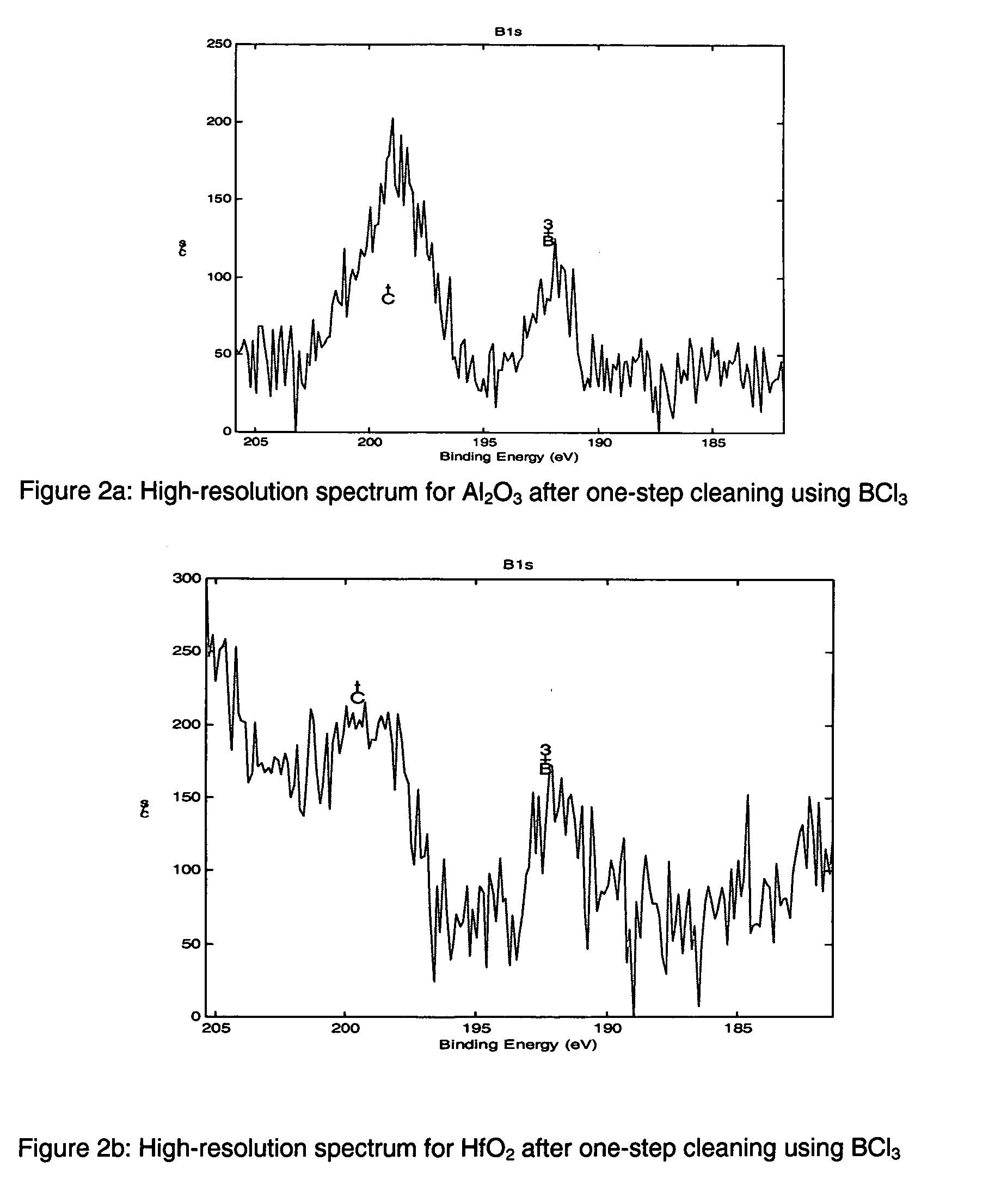
Method for etching high dielectric constant materials and for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A process for the removal of a substance from a substrate for etching and / or cleaning applications is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, there is provided a process for removing a substance having a dielectric constant greater than silicon dioxide from a substrate by reacting the substance with a reactive agent that comprises at least one member from the group consisting a halogen-containing compound, a boron-containing compound, a hydrogen-containing compound, nitrogen-containing compound, a chelating compound, a carbon-containing compound, a chlorosilane, a hydrochlorosilane, or an organochlorosilane to form a volatile product and removing the volatile product from the substrate to thereby remove the substance from the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
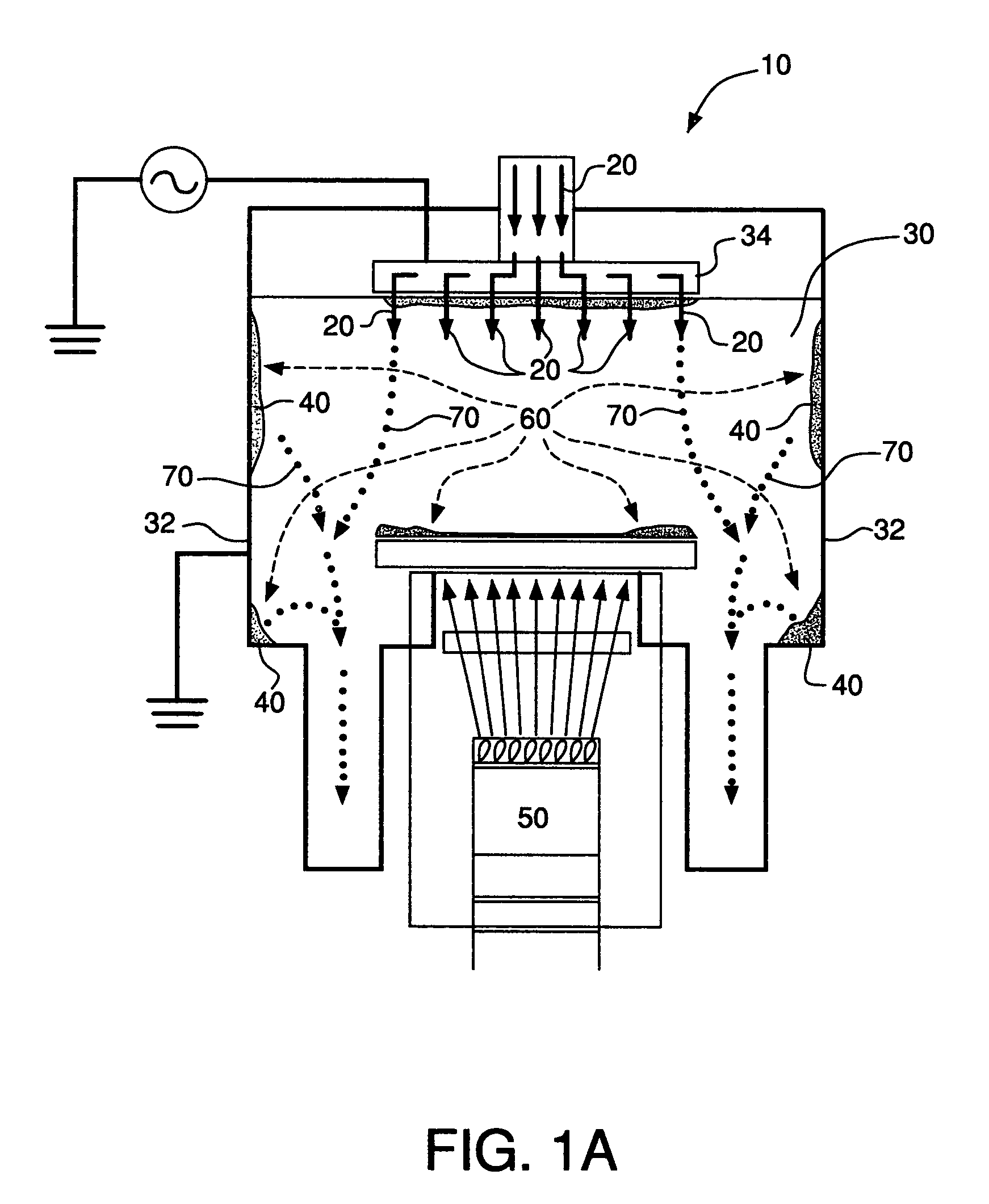
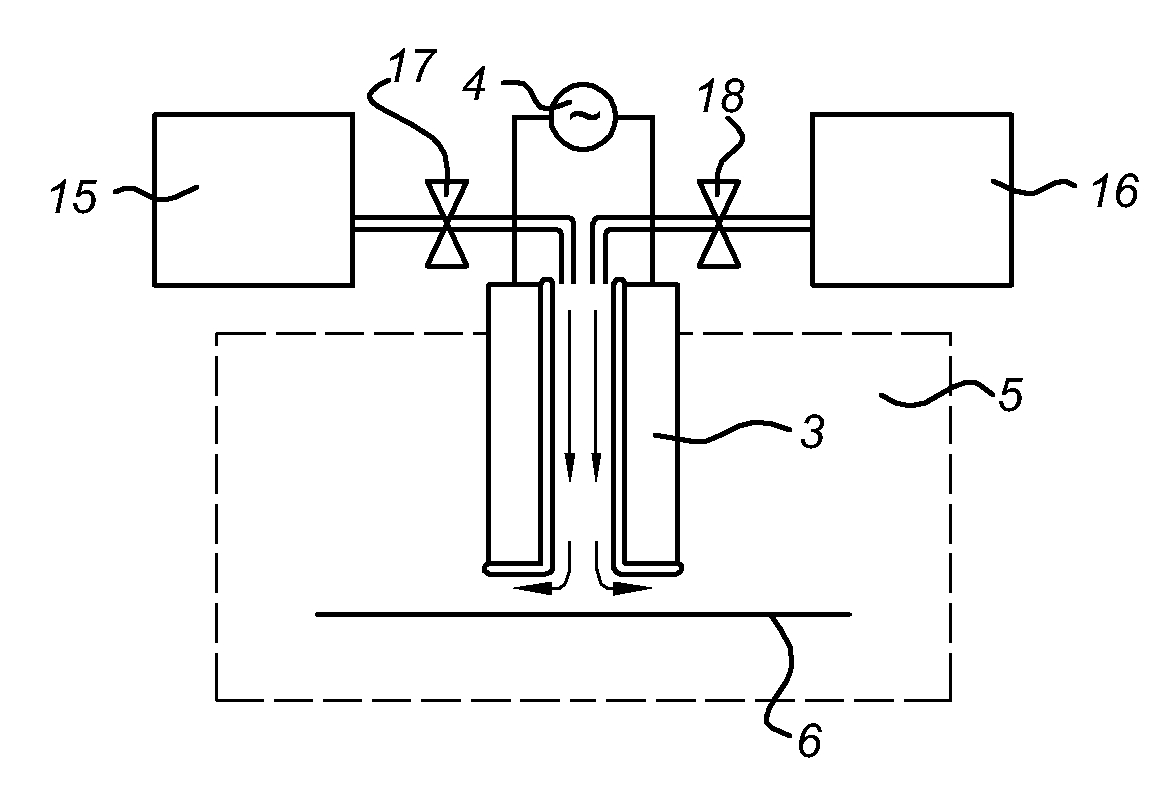
Method and apparatus for atomic layer deposition using an atmospheric pressure glow discharge plasma
InactiveUS20100255625A1Comparable and good performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma generatorProduct gas
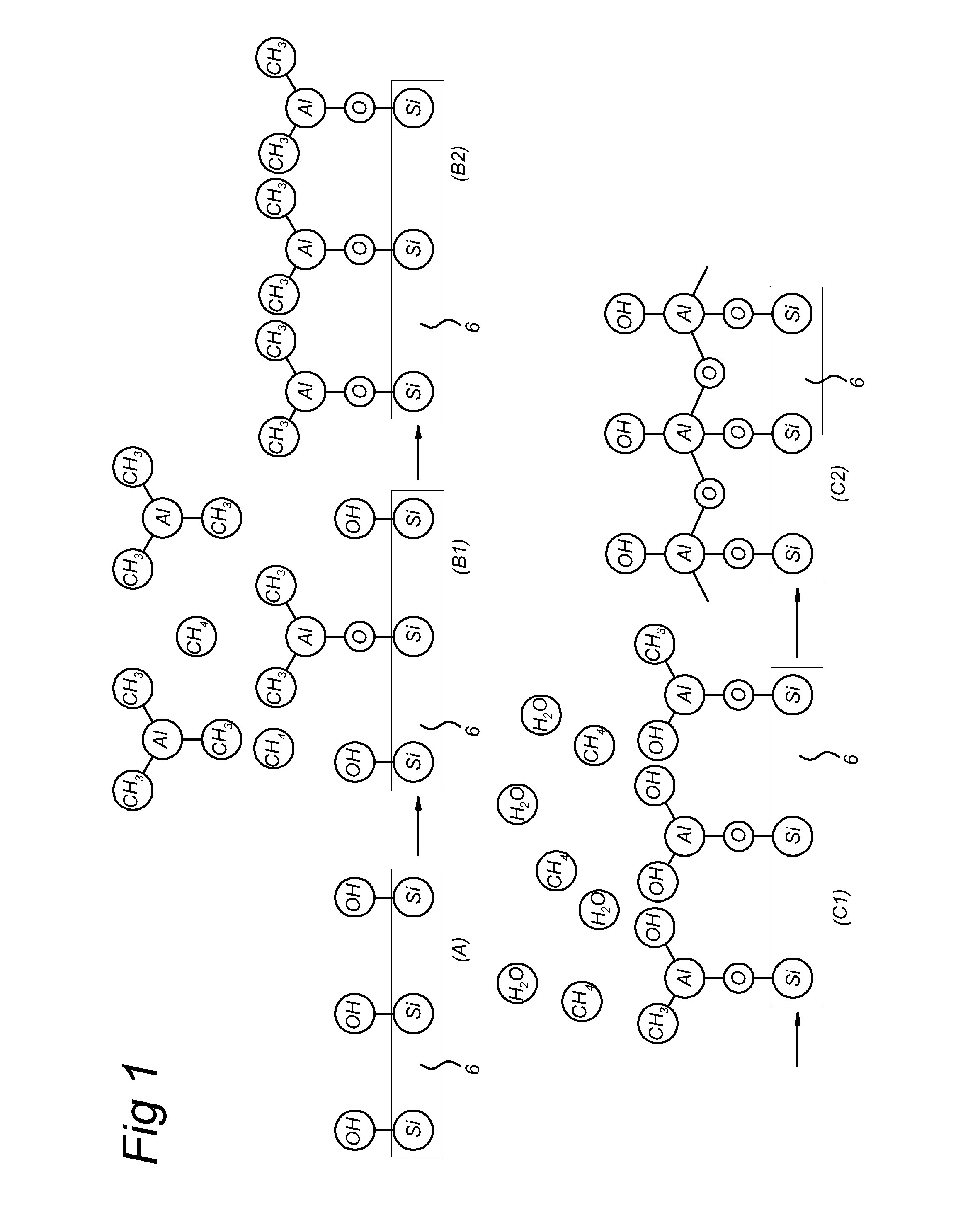
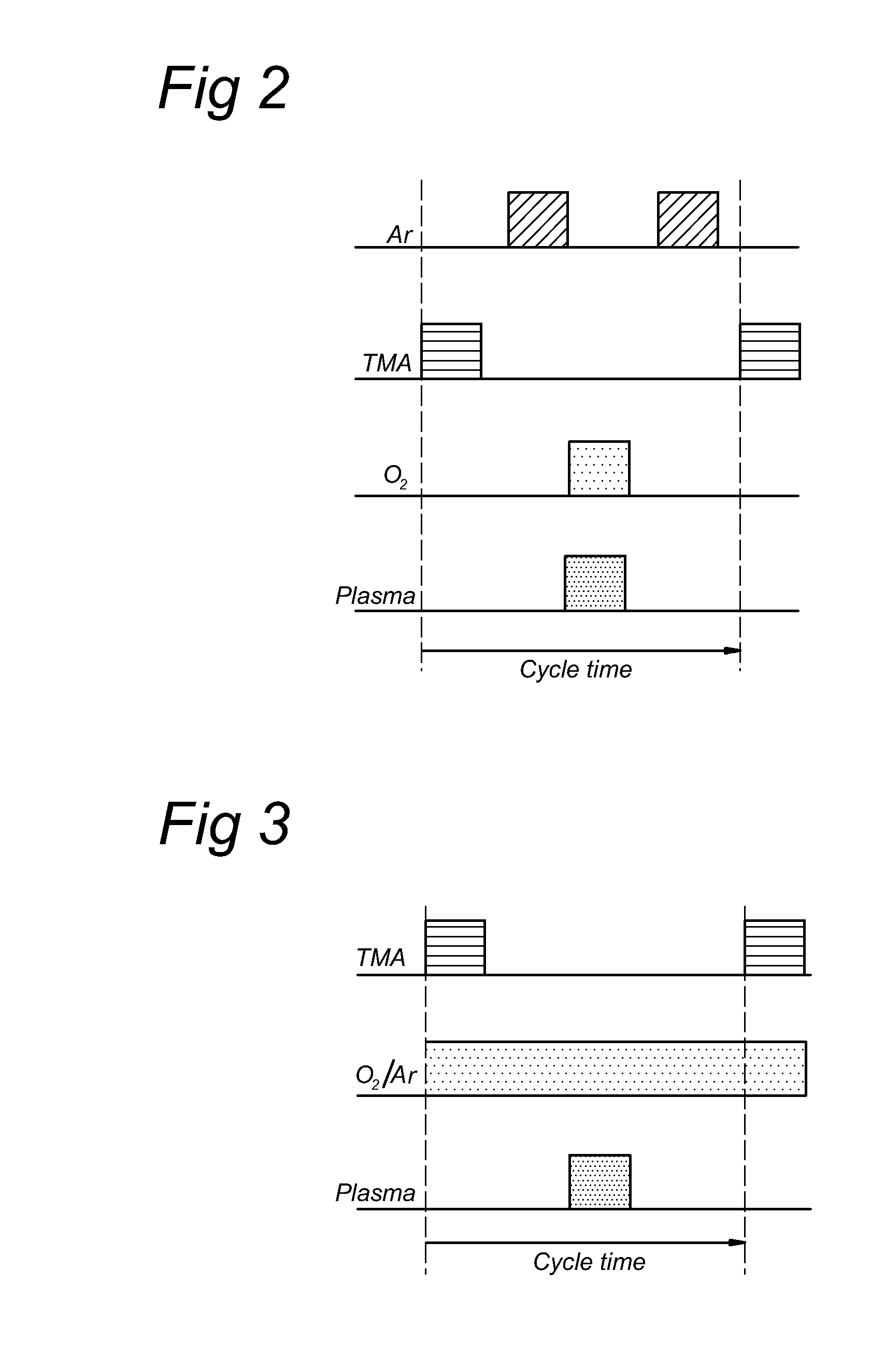
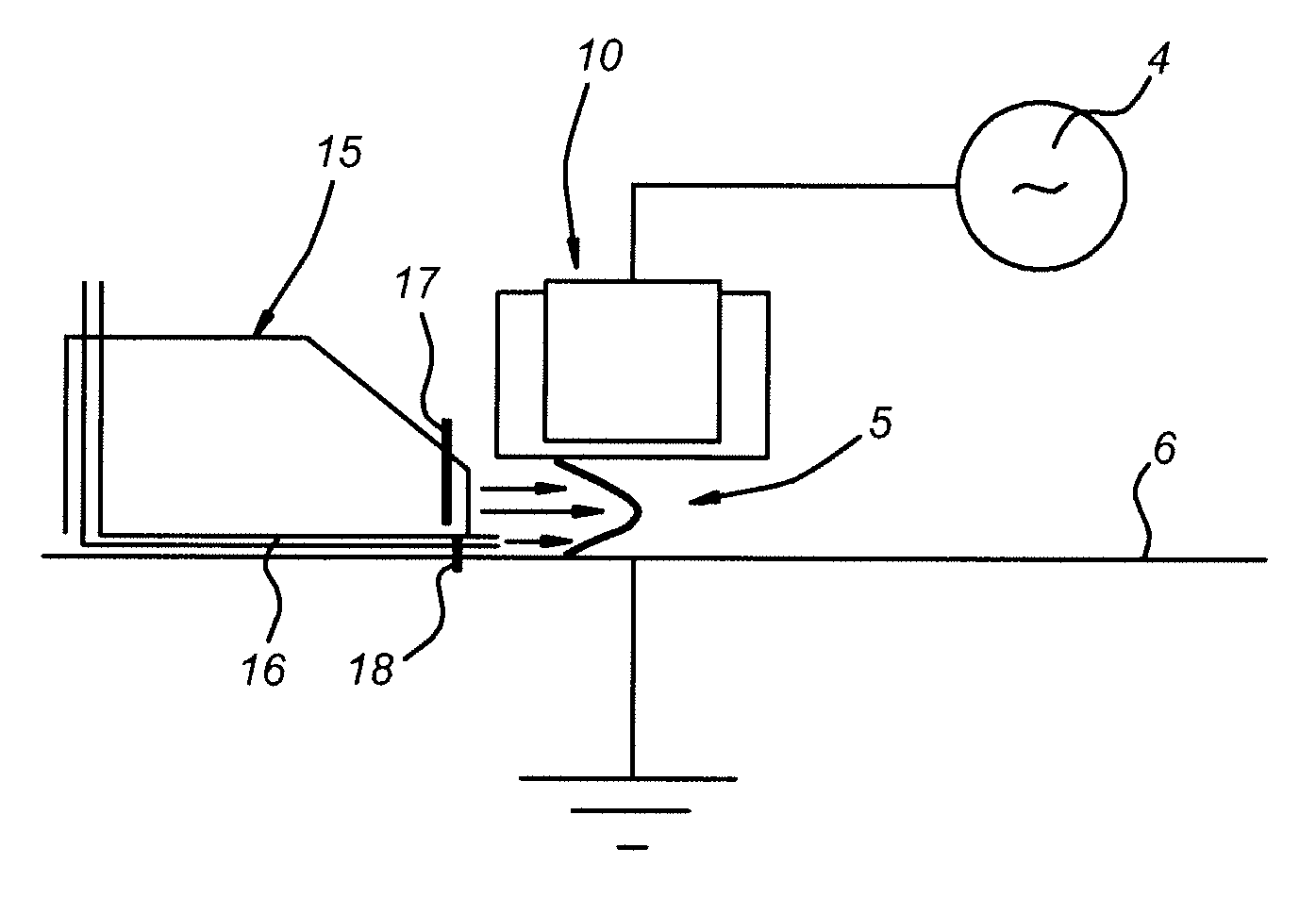
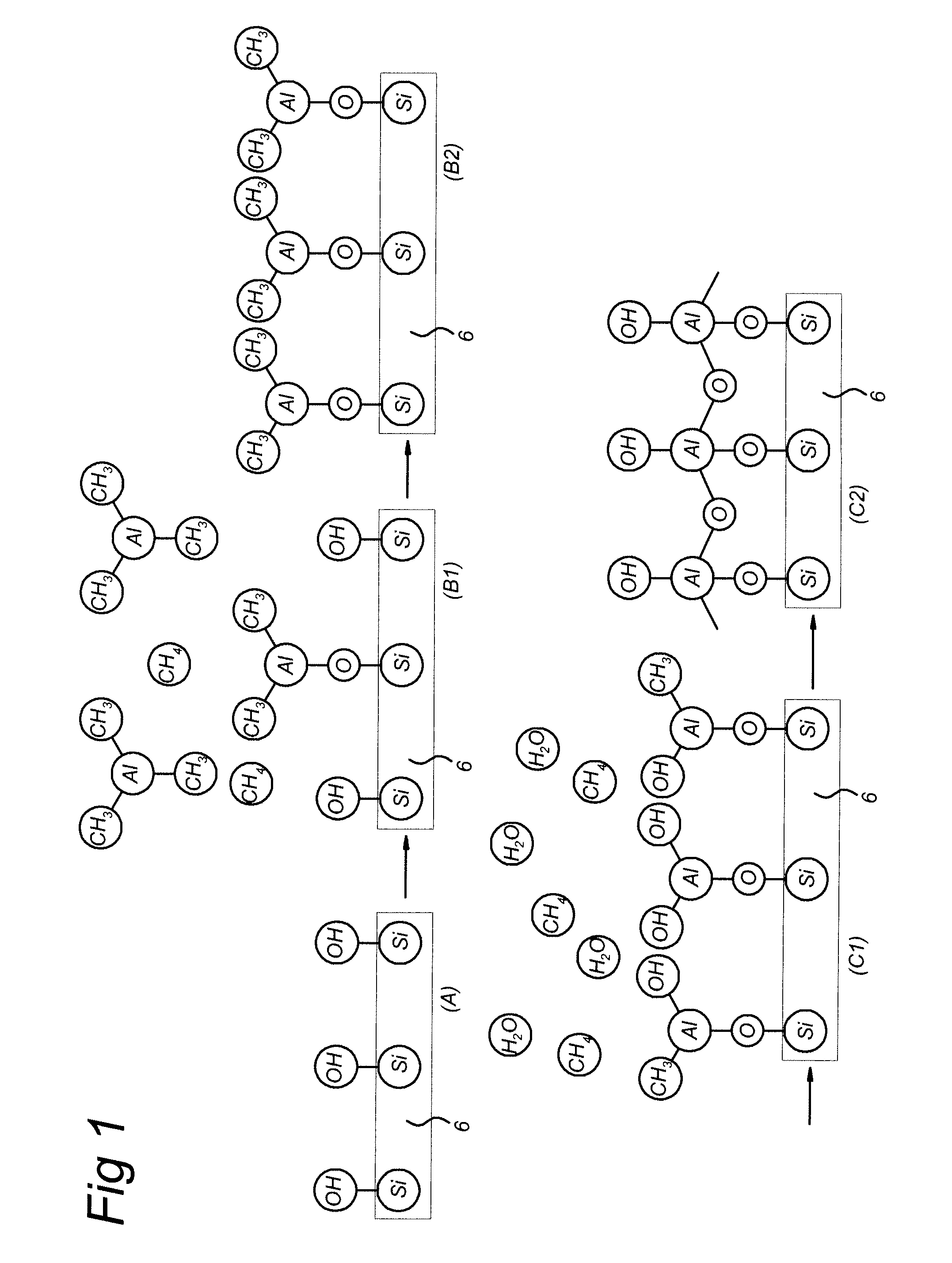
Apparatus and method for atomic layer deposition on a surface of a substrate (6) in a treatment space. A gas supply device (15, 16) is present for providing various gas mixtures to the treatment space (1, 2). The gas supply device (15, 16) is arranged to provide a gas mixture with a precursor material to the treatment space for allowing reactive surface sites to react with precursor material molecules to give a surface covered by a monolayer of precursor molecules attached via the reactive sites to the surface of the substrate. Subsequently, a gas mixture comprising a reactive agent capable to convert the attached precursor molecules to active precursor sites is provided. A plasma generator (10) is present for generating an atmospheric pressure plasma in the gas mixture comprising the reactive agent, the plasma generator being arranged remote from the treatment space (1, 2).
Owner:FUJIFILM MFG EURO
Method and apparatus for atomic layer deposition using an atmospheric pressure glow discharge plasma
InactiveUS20090324971A1Increase response rateImprove productivitySynthetic resin layered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma generatorProduct gas
Apparatus and method for atomic layer deposition on a surface of a substrate (6) in a treatment space. A gas supply device (15, 16) is present for providing various gas mixtures to the treatment space. The gas supply device (15, 16) is arranged to provide a gas mixture with a precursor material to the treatment space for allowing reactive surface sites to react with precursor material molecules to give a surface covered by a monolayer of precursor molecules attached via the reactive sites to the surface of the substrate. Subsequently, a gas mixture comprising a reactive agent capable to convert the attached precursor molecules to active precursor sites is provided. A plasma generator (10) is present for generating an atmospheric pressure plasma in the gas mixture comprising the reactive agent.
Owner:FUJIFILM MFG EURO
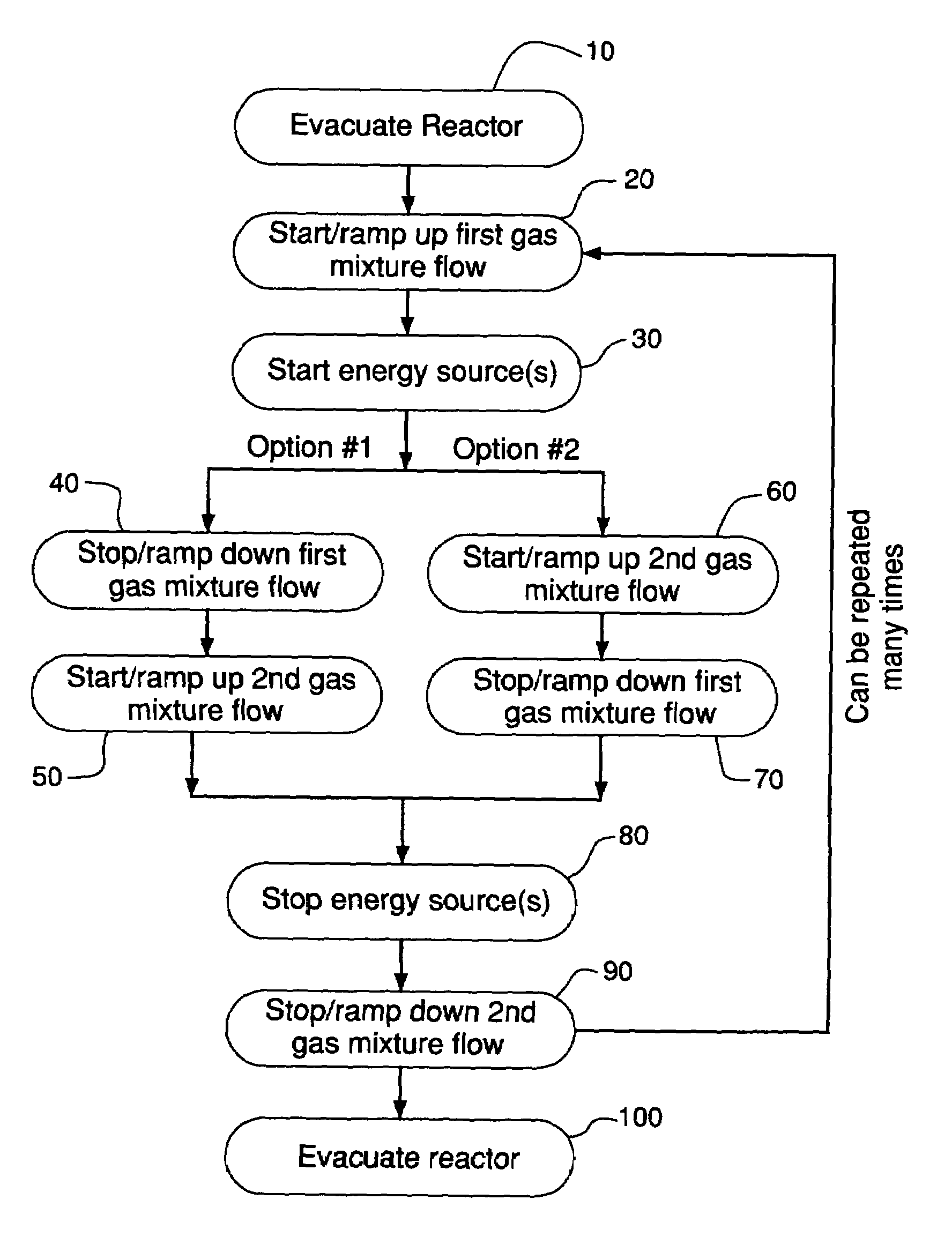
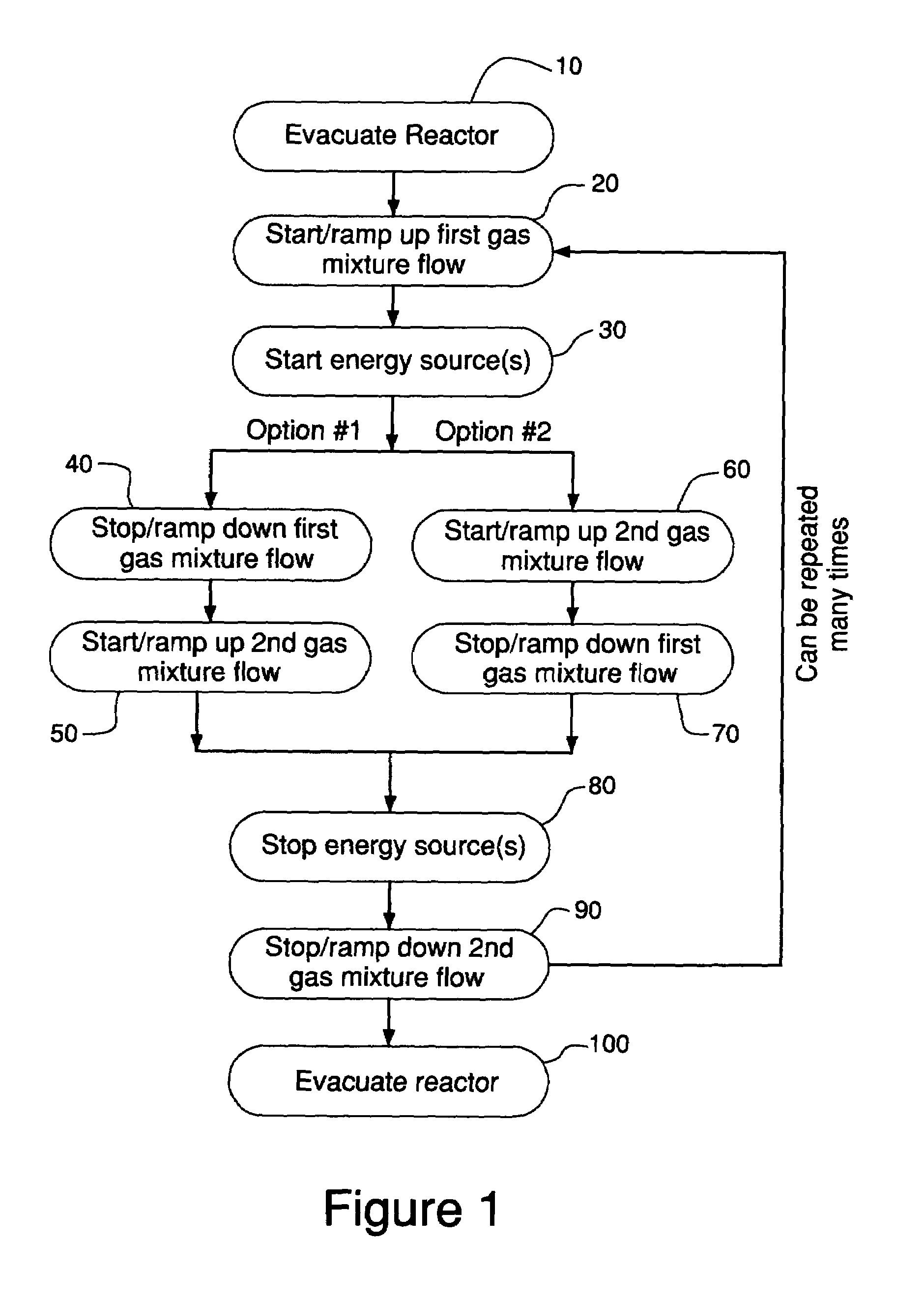
Method for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A method for dry etching and chamber cleaning high dielectric constant materials is disclosed herein. In one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a process for cleaning a substance comprising a dielectric constant greater than the dielectric constant of silicon dioxide from at least a portion of a surface of a reactor comprising: introducing a first gas mixture comprising a boron-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the first gas mixture reacts with the substance contained therein to provide a volatile product and a boron-containing by-product; introducing a second gas mixture comprising a fluorine-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the second gas mixture reacts with the boron-containing by-product contained therein to form the volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reactor.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method and device for pressurizing containers
Owner:INOFLATE
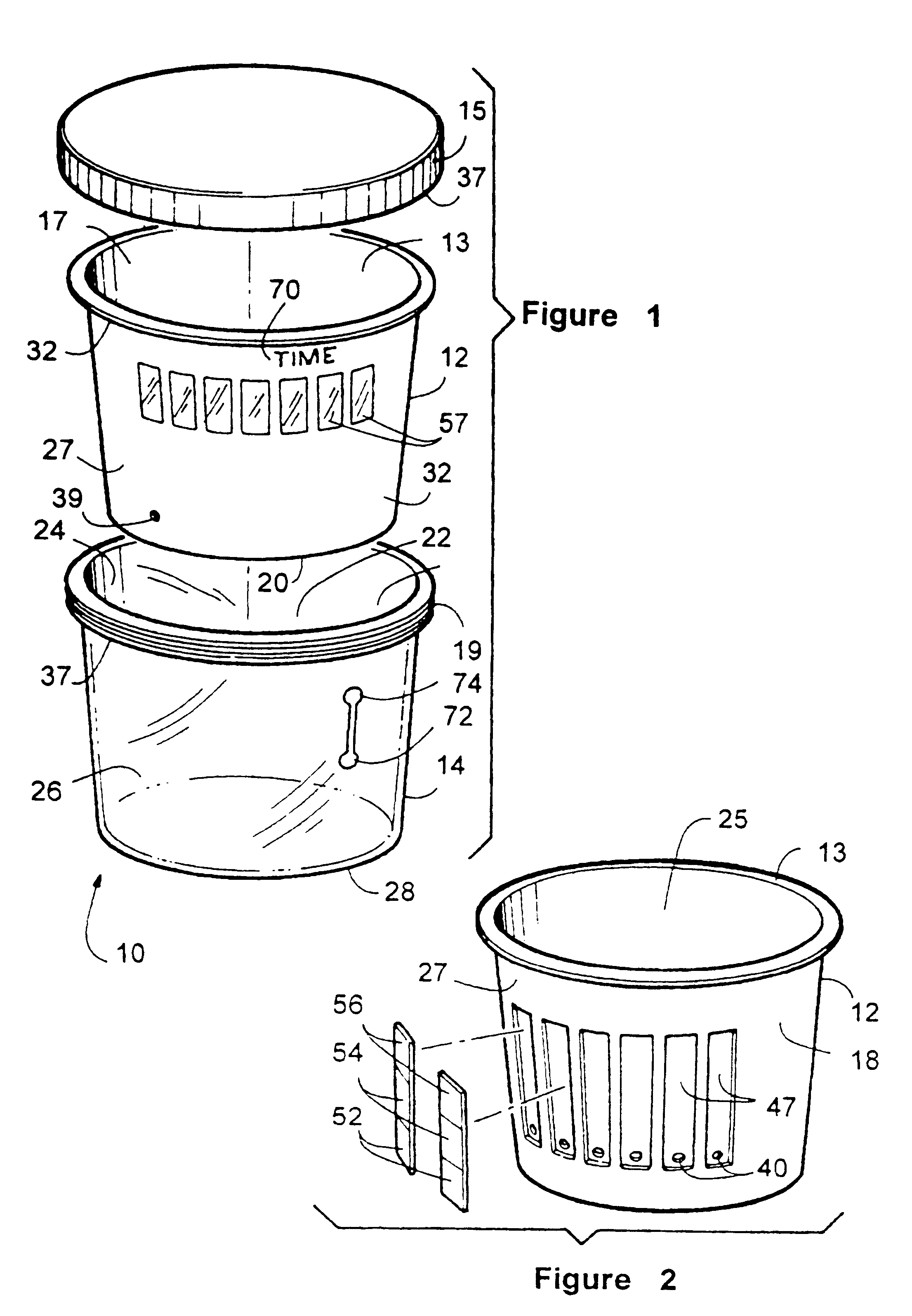
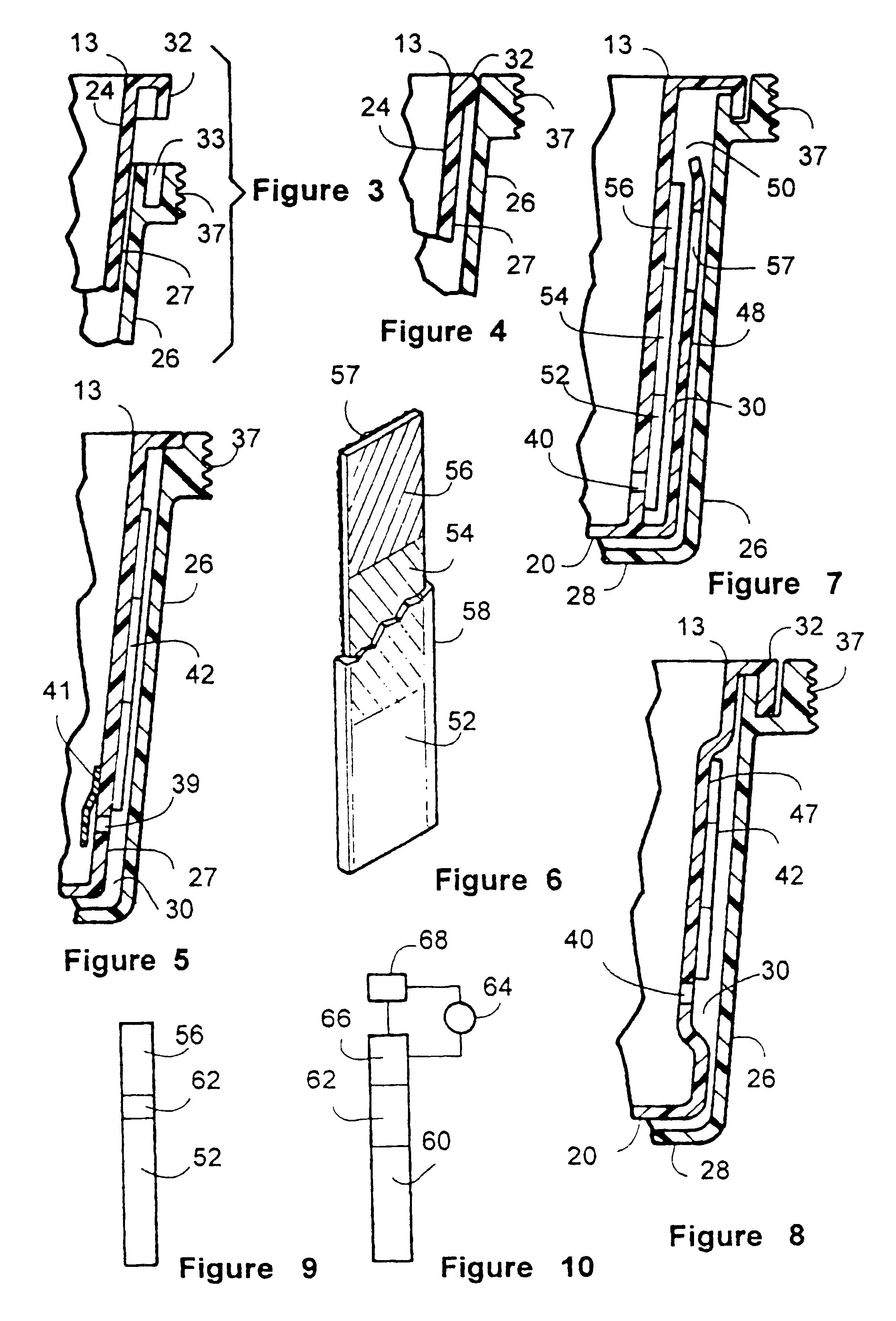
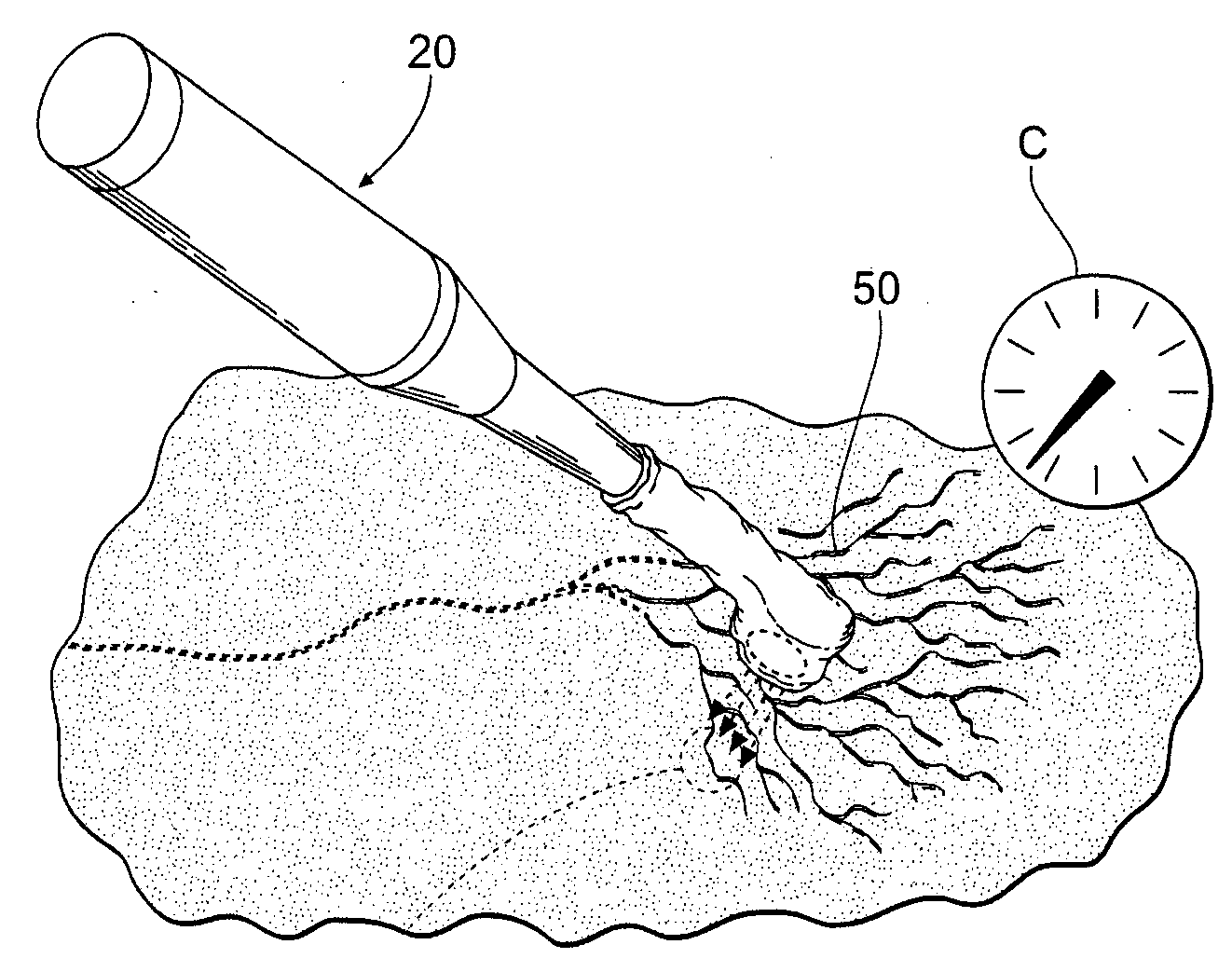
Diagnostic testing kit for collection and testing of fluid samples with user configurable test strips and timer
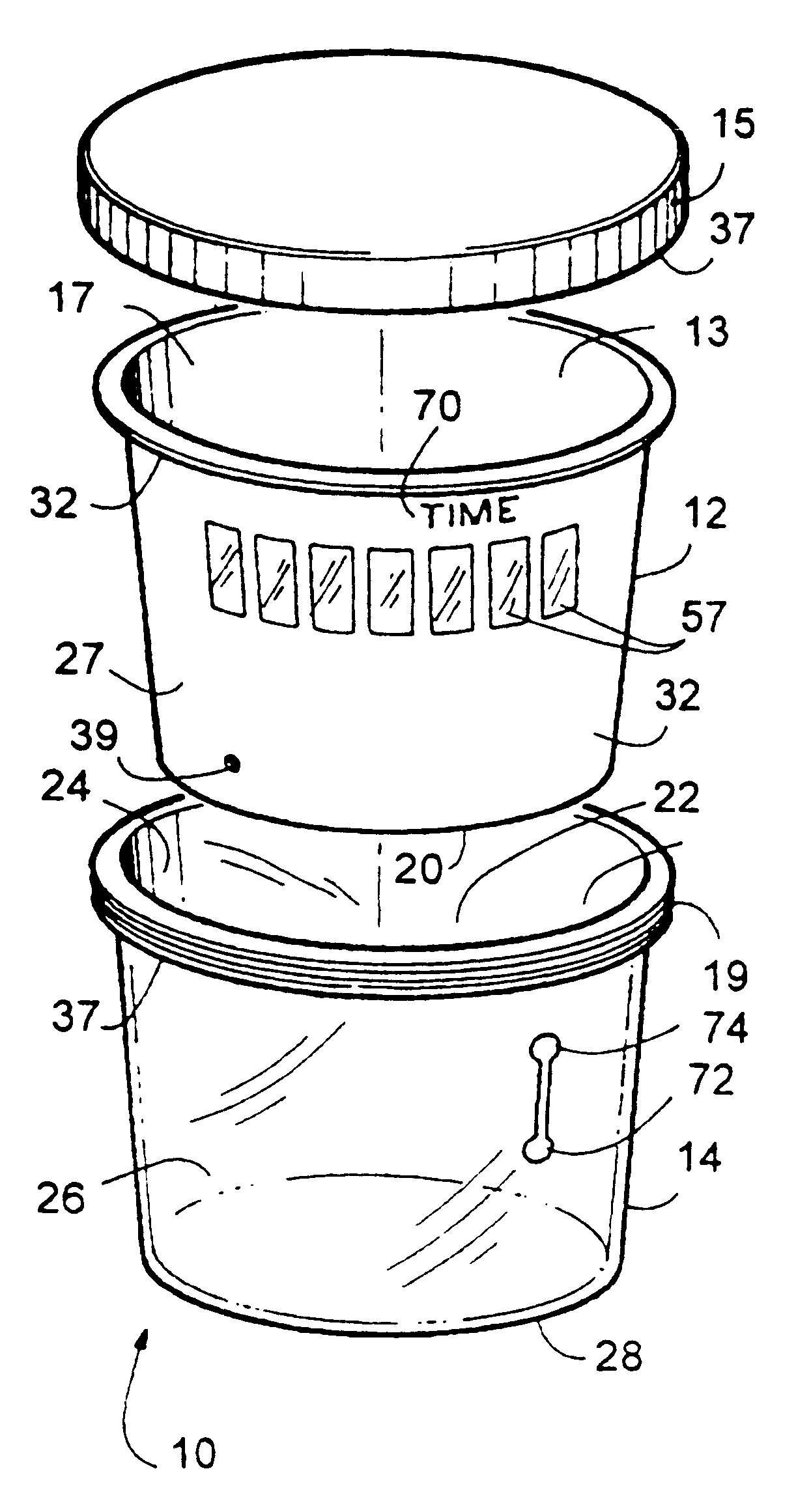
InactiveUS6616893B1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorEngineeringReactive agent
A diagnostic testing kit for collection of fluid samples comprising a reservoir cup insertable into a container vessel. Fluid placed in the cup is communicated to reactive test strips located in a separation cavity between the cup and the container vessel when assembled. The test strips have a reactive agent impregnated in them that reacts to specific substances in the fluid and provide a visual result through the sidewall of the container vessel to the user. An optional alarm is provided to show minimum and maximum test times.
Owner:PHAM TUAN
Dissolvable connector guard
A connector guard is provided to protect one or both downhole connectors during wellbore run in prior to mating downhole. The connector guard may comprise dissolvable or degradable material and include an engagement sections and a removal feature. The connector guard may be dissolved or degraded via a reactive agent or temperature either introduced downhole proximate to the guards or contained within a chamber included in or created by a connector guard. The connector guard may be further coupled by a non-reactive cover in order to control the rate of reaction of the dissolvable material. The cover may be breached prior to mating of the downhole connectors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Multiple extruder assembly and process for continuous reactive extrusion
Methods are disclosed for a novel and useful single pass extrusion process for the reactive extrusion and compounding of polymers. Traditional extruders utilized in reactive processes are of length to diameter ratios ranging from 30 to 1 to as high as 56 to 1. The process disclosed uses a series of sequential, very closely-coupled, independently driven screw extruders having a total effective length to diameter ratio much greater than 70 to 1 and as high as 132 to 1 or greater, and providing greatly extended reaction times, separate and multiple introductions of reactive and non-reactive agents and mechanical connections allowing for convenient screw changes and differential thermal expansion. The assembly is employed to economically produce grafted polyolefins, produce ionomers without employing the use of strong caustic agents, remove large volumes of unwanted polymer processing solvents and produce other reacted polymer species in one continuous pass.
Owner:ORREX PLASTICS CO LLC
Preparation of functional gel particles with a dual crosslink network
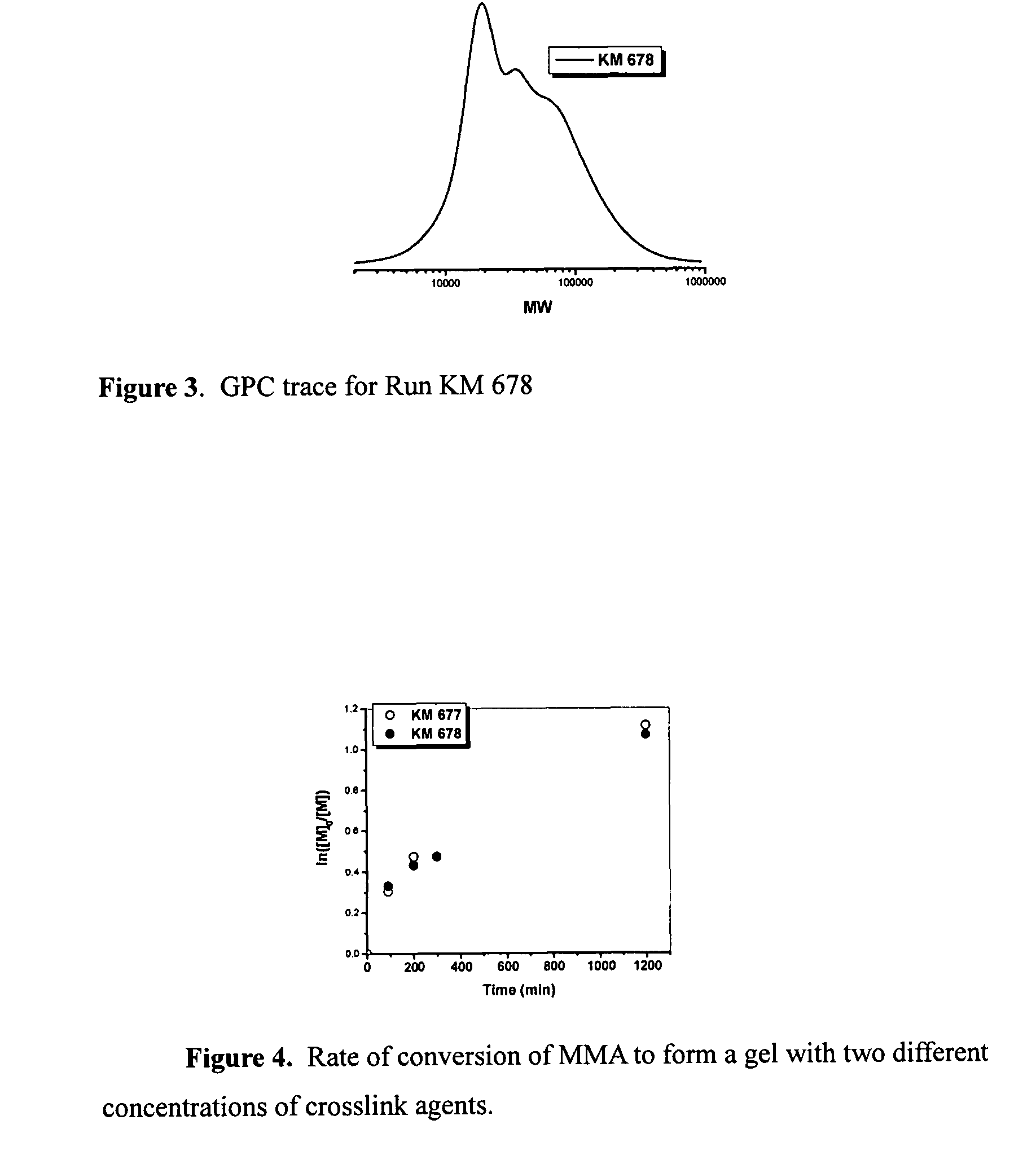
ActiveUS8367051B2Improve surface propertiesAvoid rapid degradationPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsCrosslinked polymersReactive agent
Functional gel particle formed from a crosslinked polymeric network including a fraction of stable crosslinks and a second fraction of cleavable crosslinks are disclosed. Functional compounds may be chemically or physically encapsulated within and / or released from the gel particle by selective cleavage of the cleavable crosslinks. The functional compounds may be delivered and released to a pre-selected target site. Peripheral or other accessible functionality on the surface of the gel particle allows attachment of a surface reactive agent, thereby modifying one or more surface properties of the gel particle. Processes of preparing the gel particles and processes of delivering the functional compounds to a target site are also disclosed.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
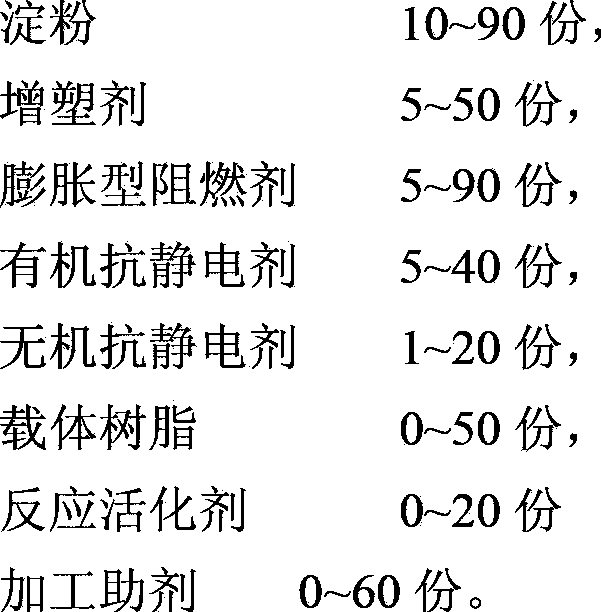
Novel flame retardant and anti-static biodegradable material and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of biodegradable materials and relates to a flame retardant and anti-static biodegradable material, and a preparation method thereof. The biodegradable material is prepared by the following components by weight: 5-90 parts of a biodegradable resin, 0-10 parts of a reactive agent and 5-90 parts of flame retardant and anti-static starch master batch. By compounding an organic anti-static agent and an inorganic anti-static agent, a durable anti-static property is endowed to the biodegradable material; and dependency of the anti-static property to environment humidity is reduced. Meanwhile, by adding an intumescent flame retardant with the starch as a carbon source, inflammability of the biodegradable material is effectively overcome. The anti-static agent and the intumescent flame retardant are environment-friendly; and excellent mechanical properties and processing properties of the biodegradable material are retained.
Owner:肖同剑
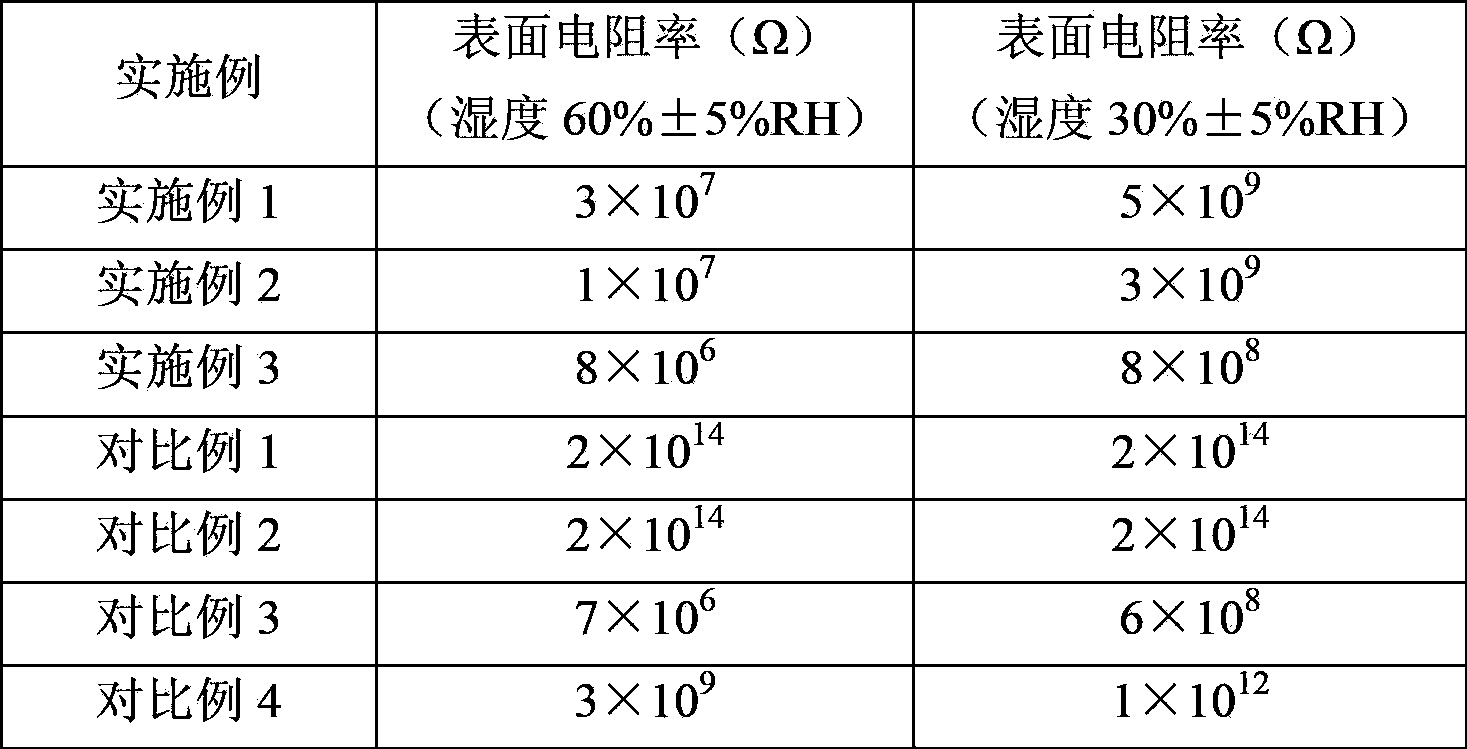
Systems and methods for treating superficial venous malformations like spider veins
InactiveUS20070299431A1Quality improvementLow costSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyLight energyMedicine
Systems and methods treat superficial venous malformations, such as spider veins. The systems and methods distribute a reactive agent, e.g., a light-reactive agent such as talaporfin sodium or verteporfin, at or near an inner wall of a vein. The systems and methods activate the reactive agent by applying energy, e.g. non-thermal light energy at a wavelength that activates the reactive agent to cause localized injury to the inner wall of the vein.
Owner:GREEN MEDICAL
Method for characterizing polypeptides
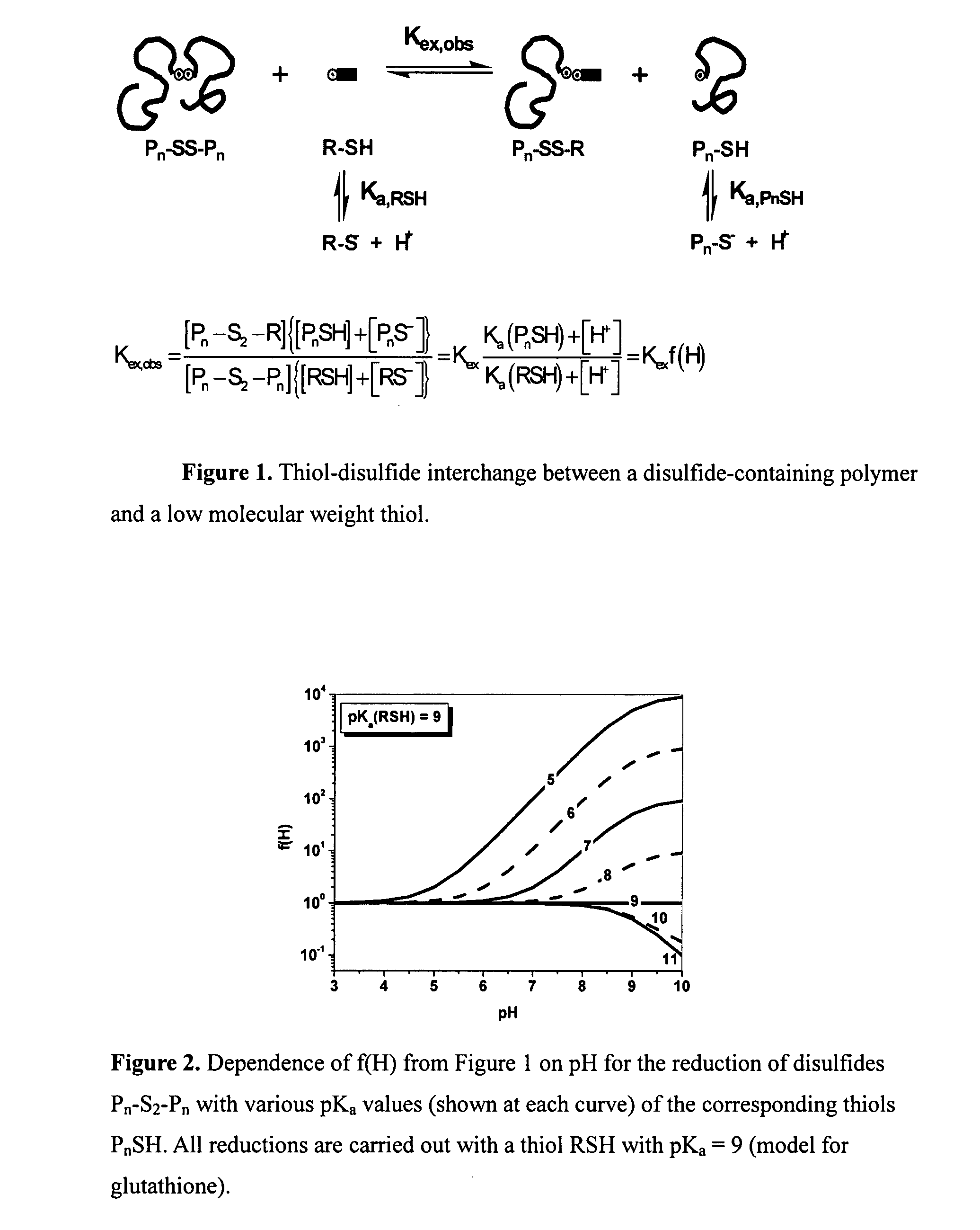
InactiveUS7163803B2Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementCysteine thiolateMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
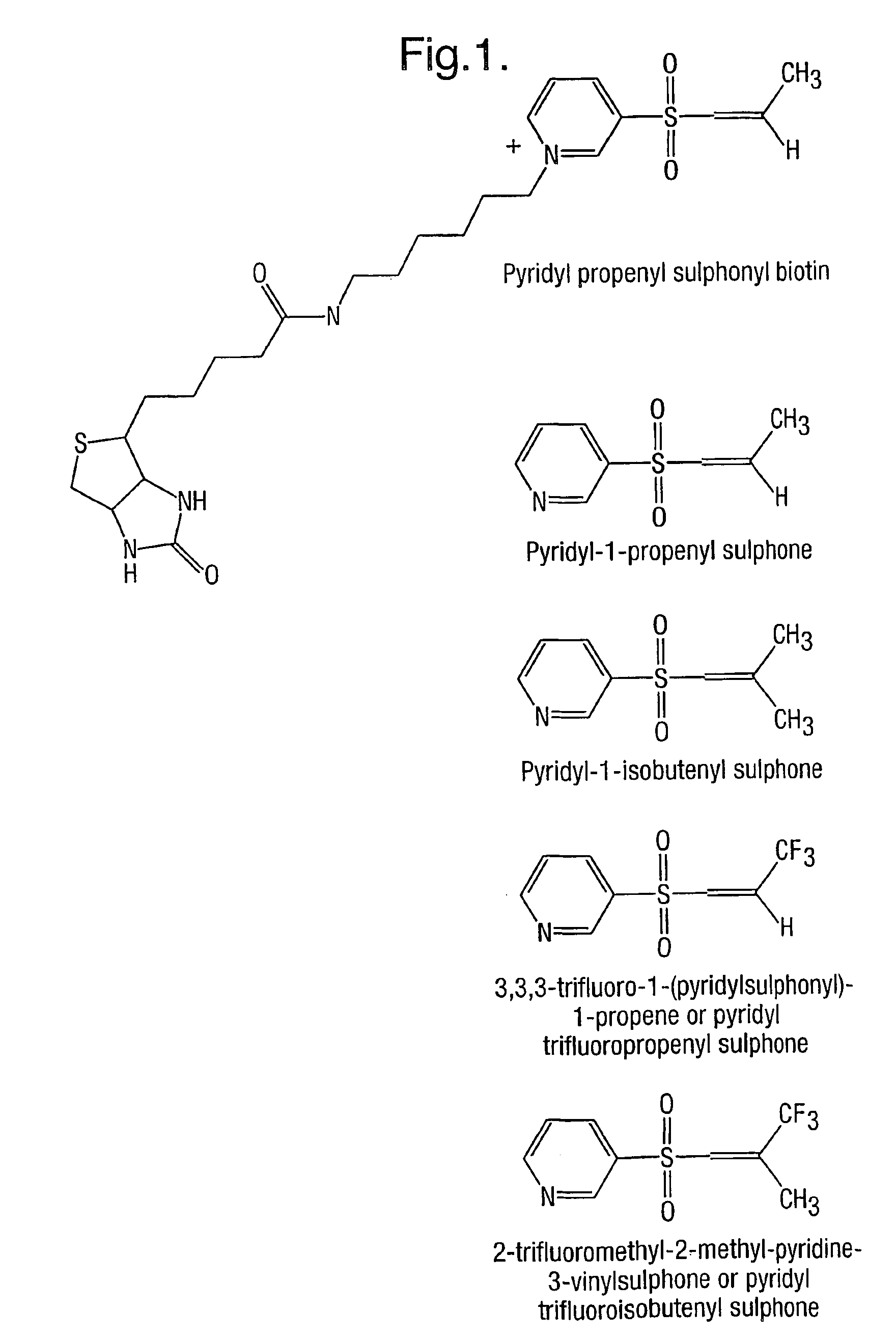
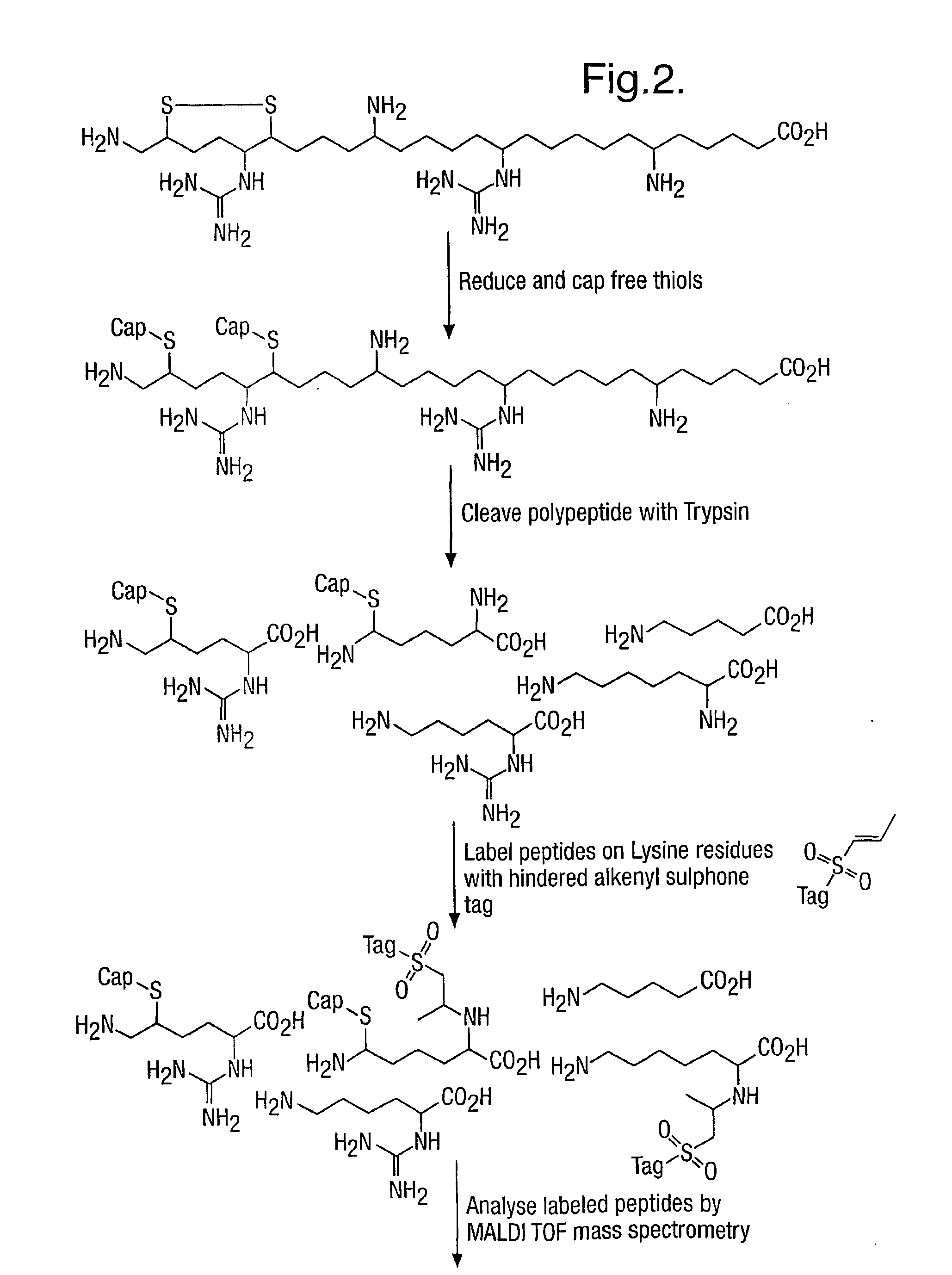
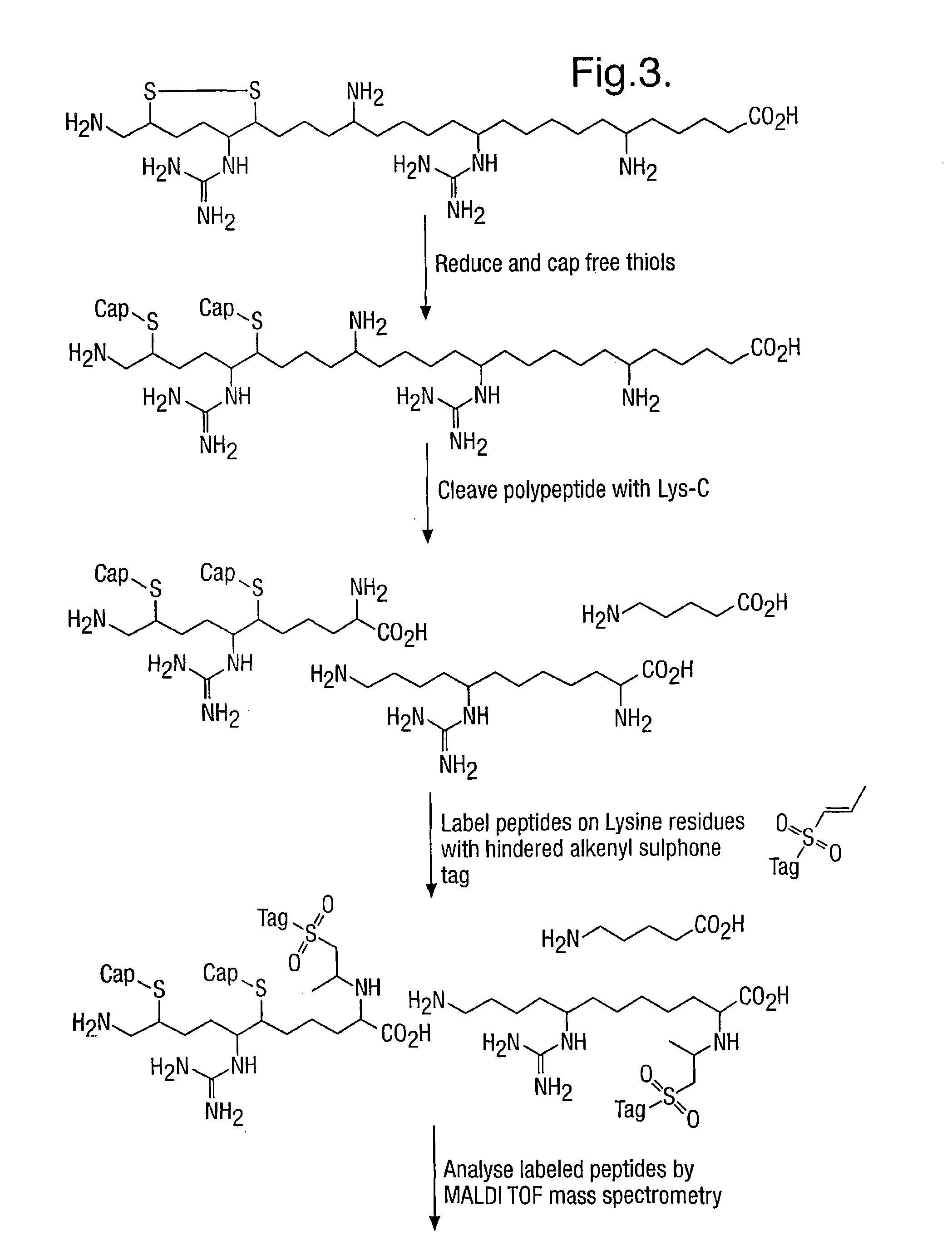
Provided is a method for characterizing a polypeptide, which method comprises the steps of: (a) optionally reducing cysteine disulphide bridges in the polypeptide to form free thiols, and capping the free thiols; (b) cleaving the polypeptide with a sequence specific cleavage reagent to form peptide fragments; (c) optionally deactivating the cleavage reagent; (d) capping one or more ε-amino groups that are present with a lysine reactive agent; (e) analyzing peptide fragments by mass spectrometry to form a mass fingerprint for the polypeptide; and (f) determining the identity of the polypeptide from the mass fingerprint.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
Biomolecule diagnostic devices and method for producing biomolecule diagnostic devices
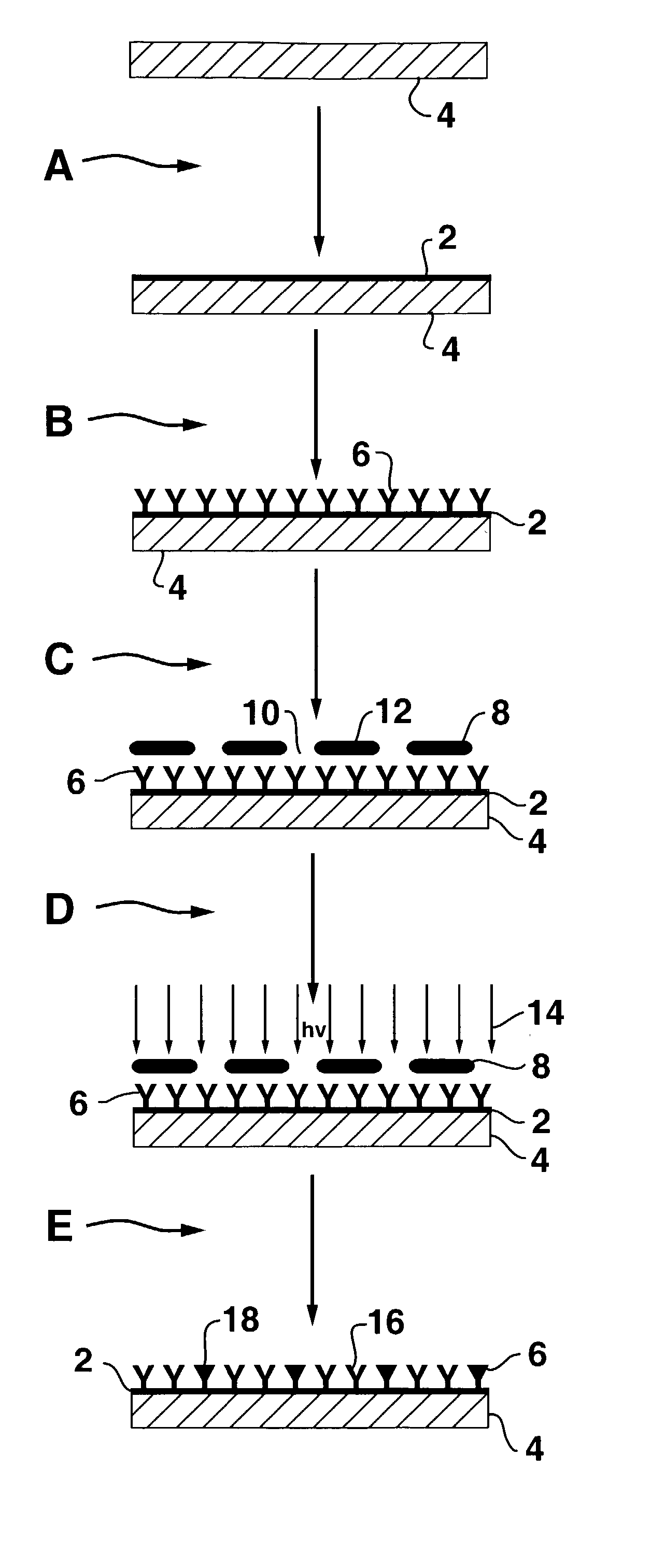
InactiveUS7214530B2Avoid pollutionUniform applicationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteReactive agent
A biosensor includes a substrate with a layer of receptive material disposed thereon overlying a layer containing a photo-reactive agent. The receptive material is specific for an analyte of interest. A pattern of active and inactive areas of the receptive material are defined in the receptive material layer by a masking process wherein the photo-reactive agent is activated in the exposed regions of the mask.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
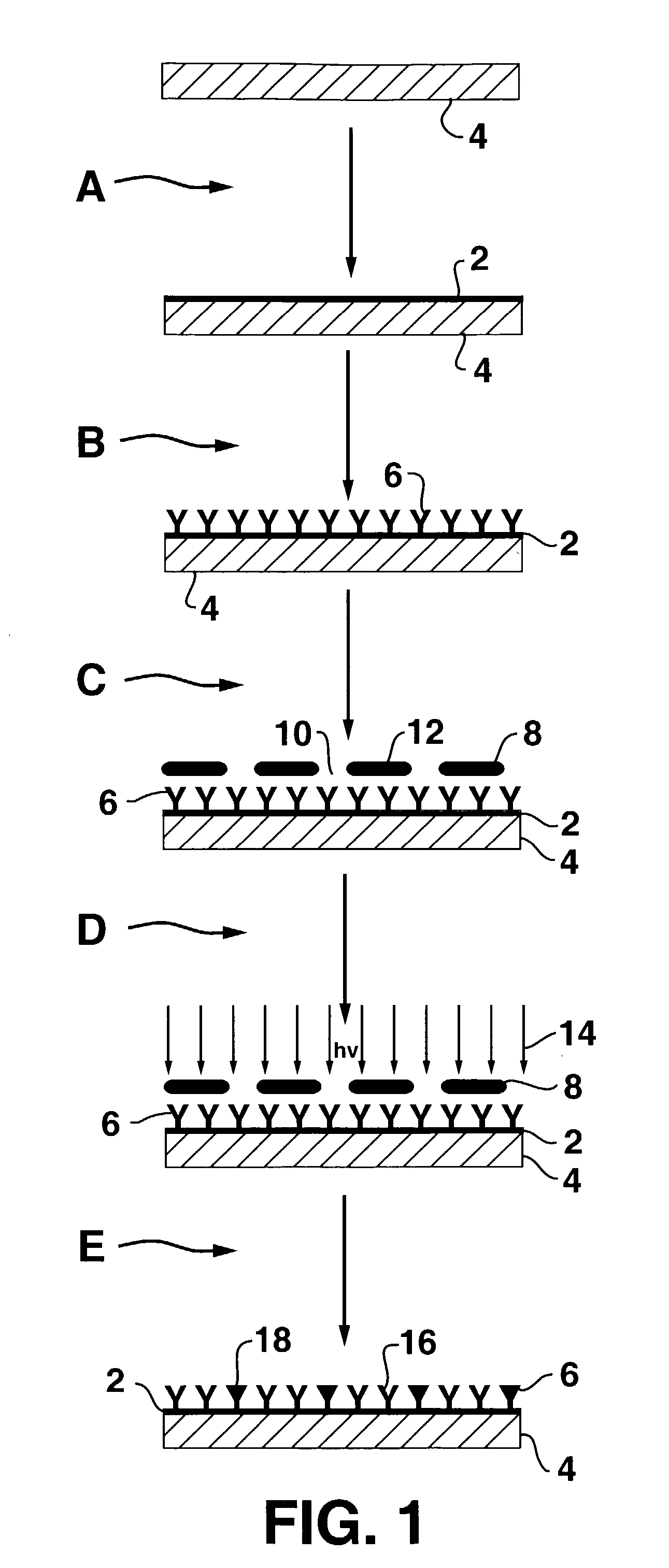
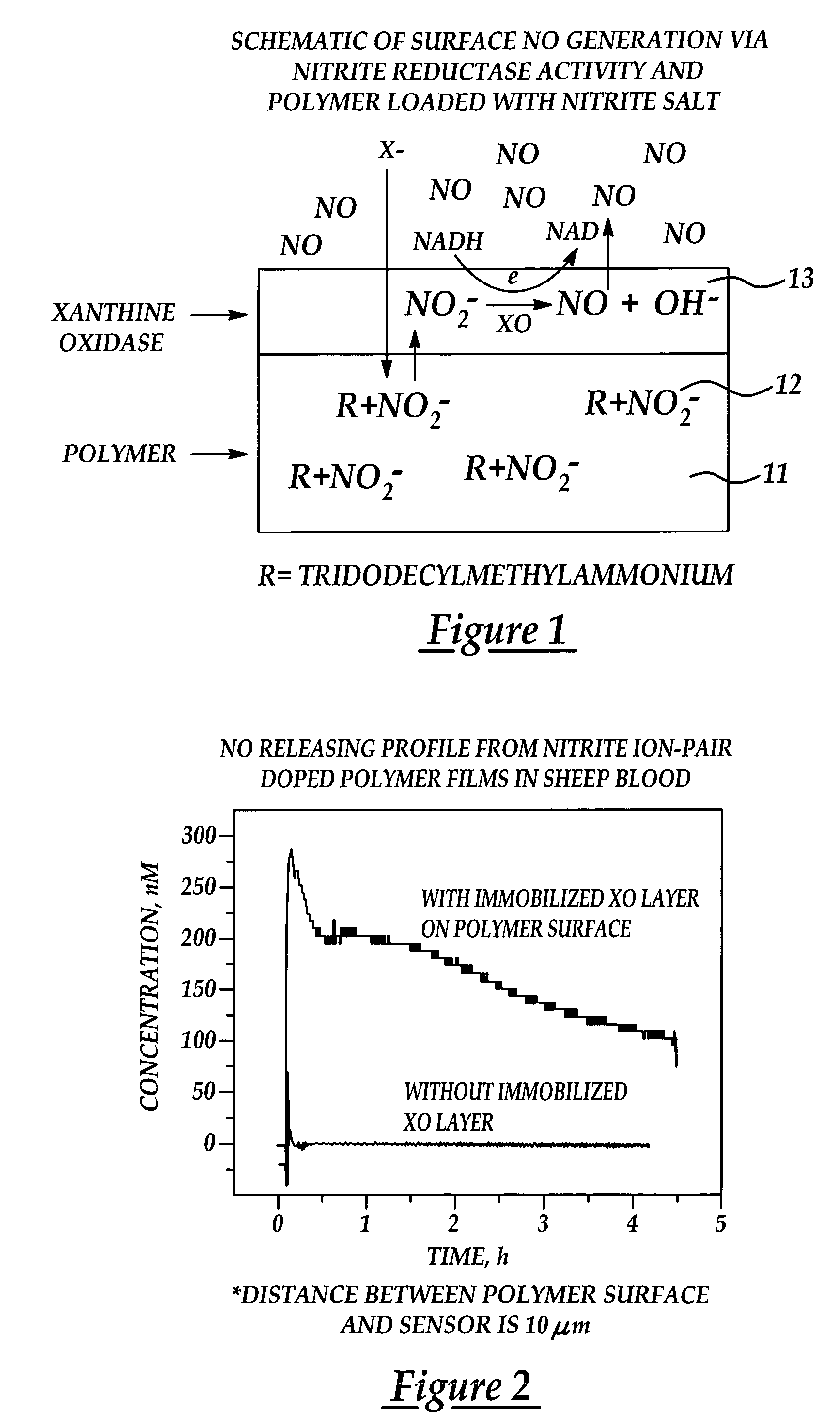
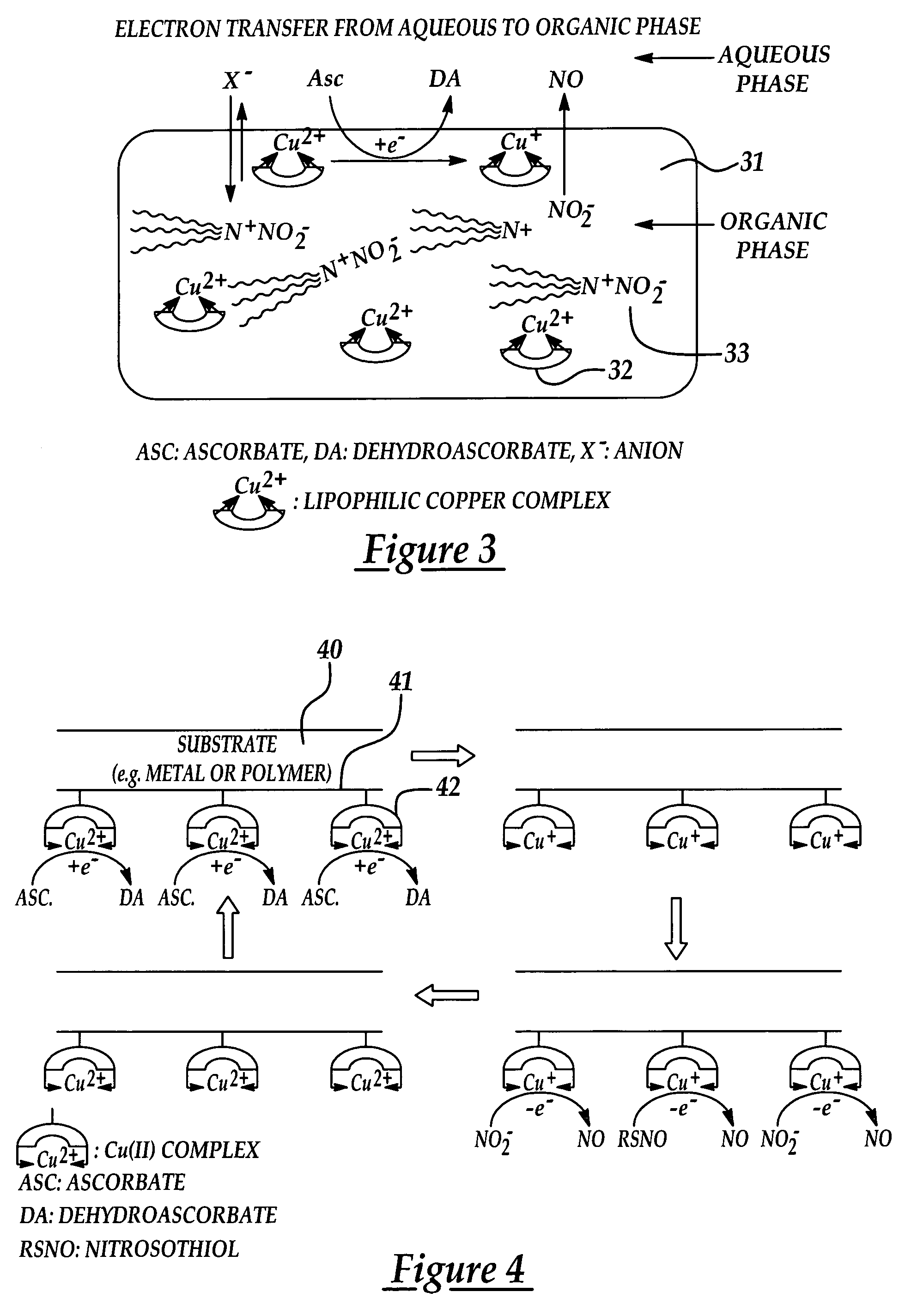
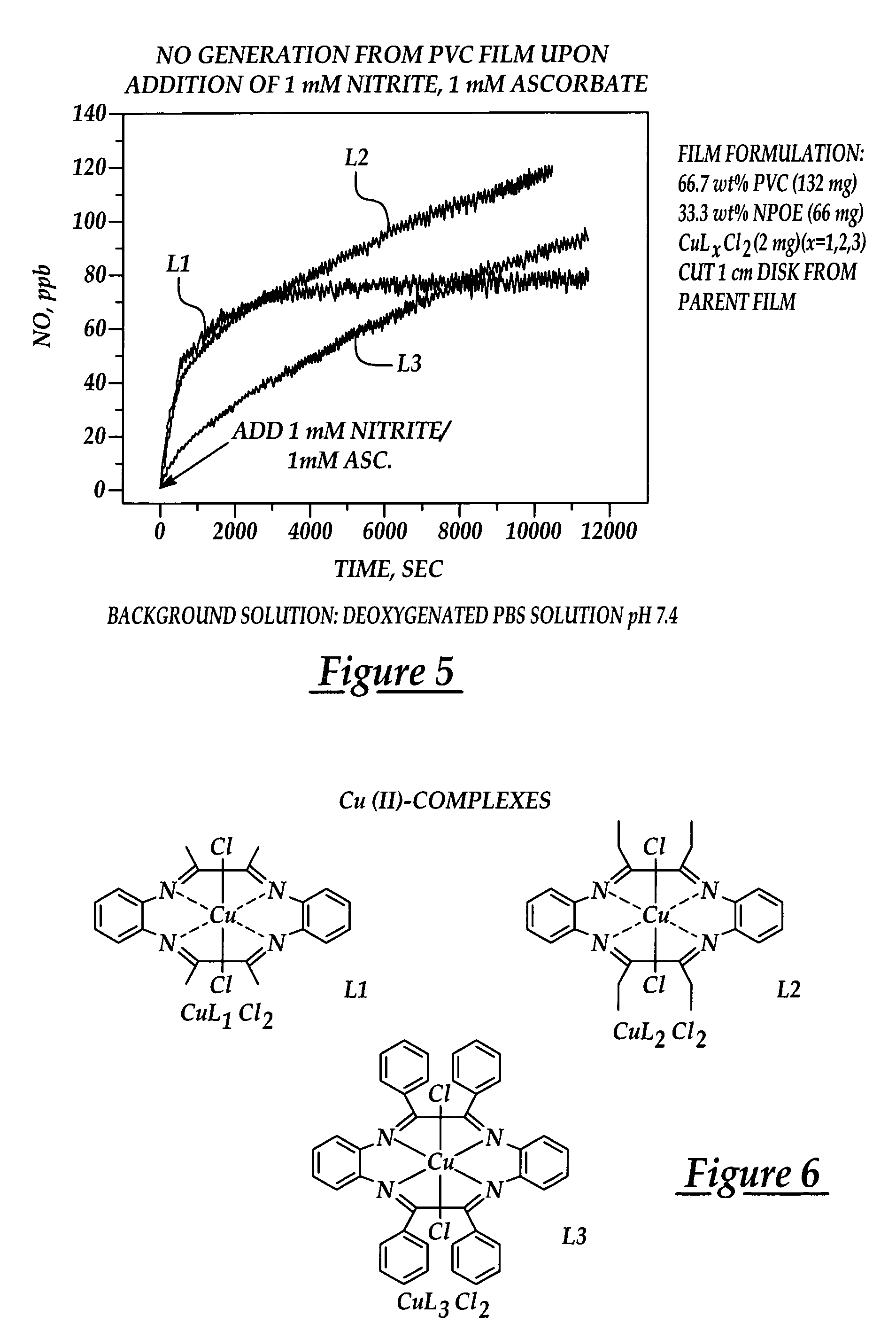
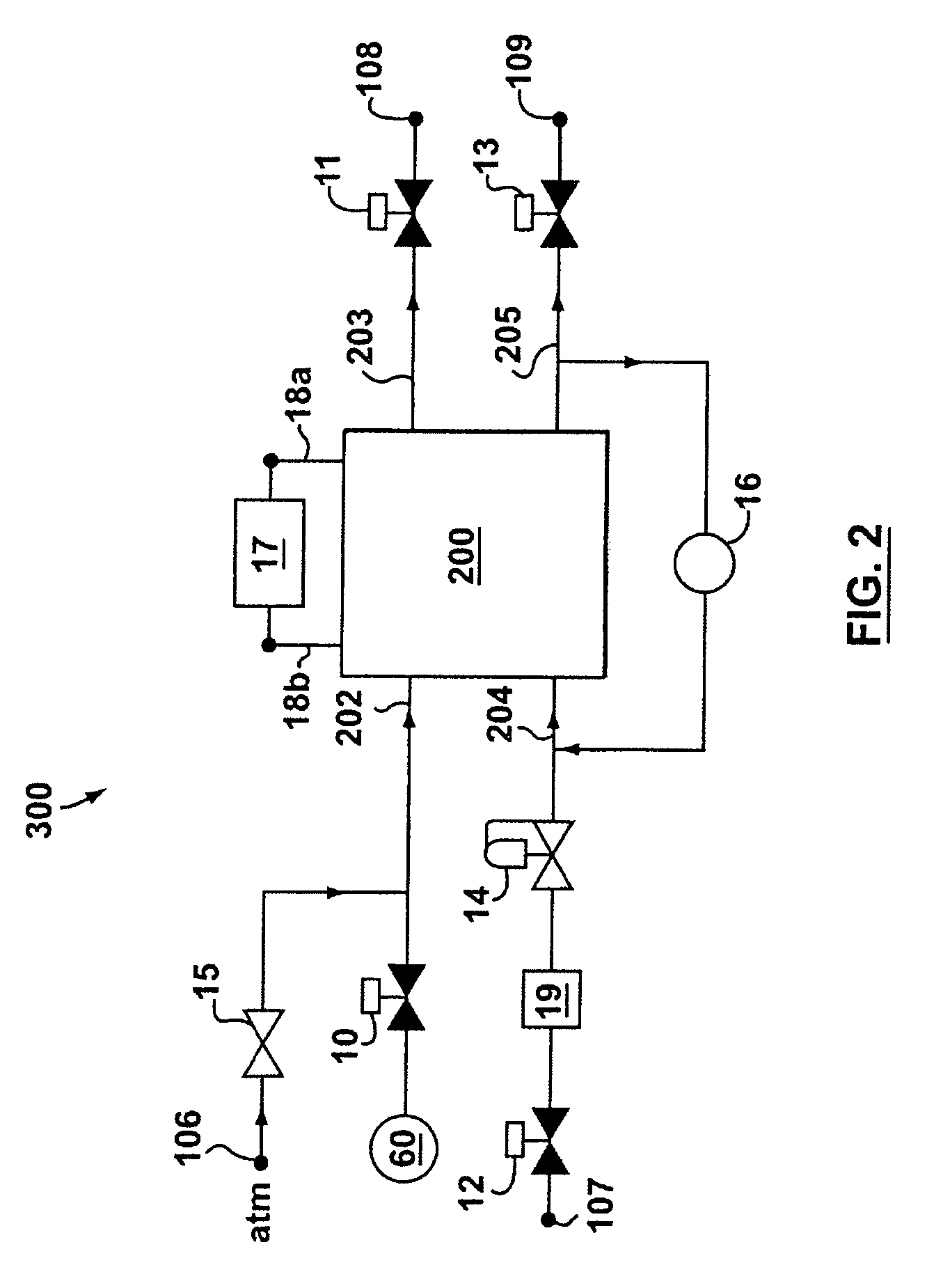
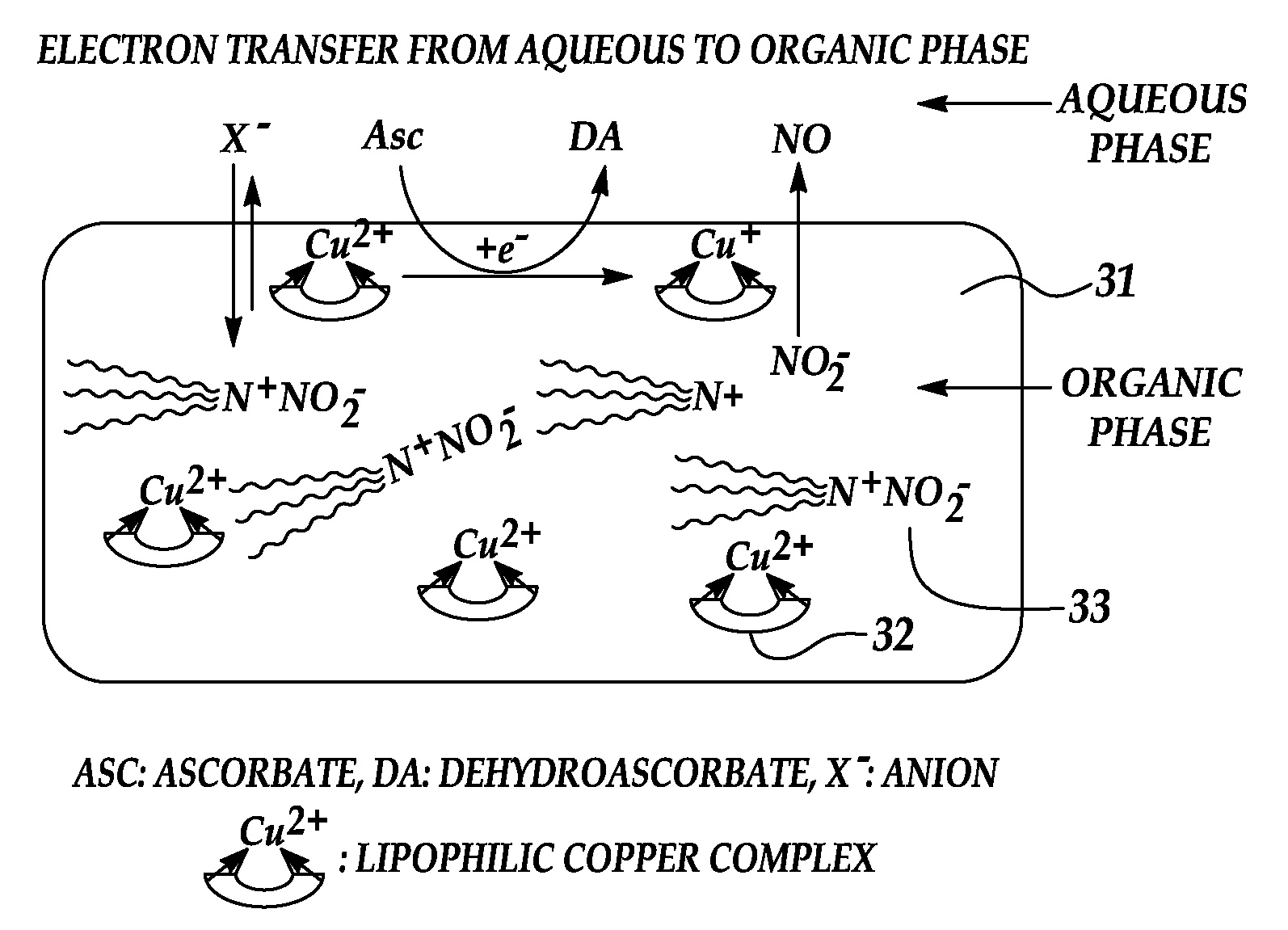
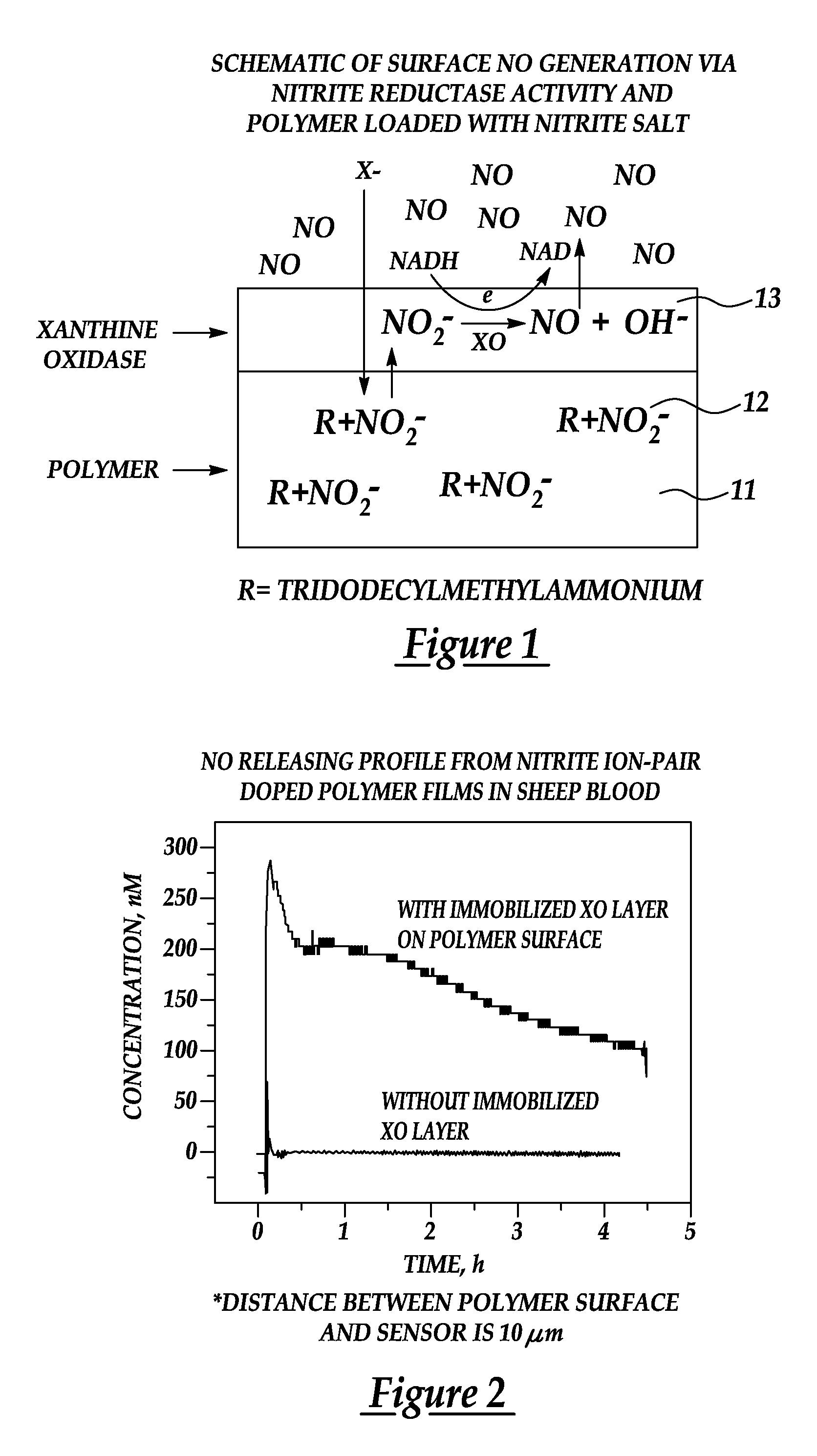
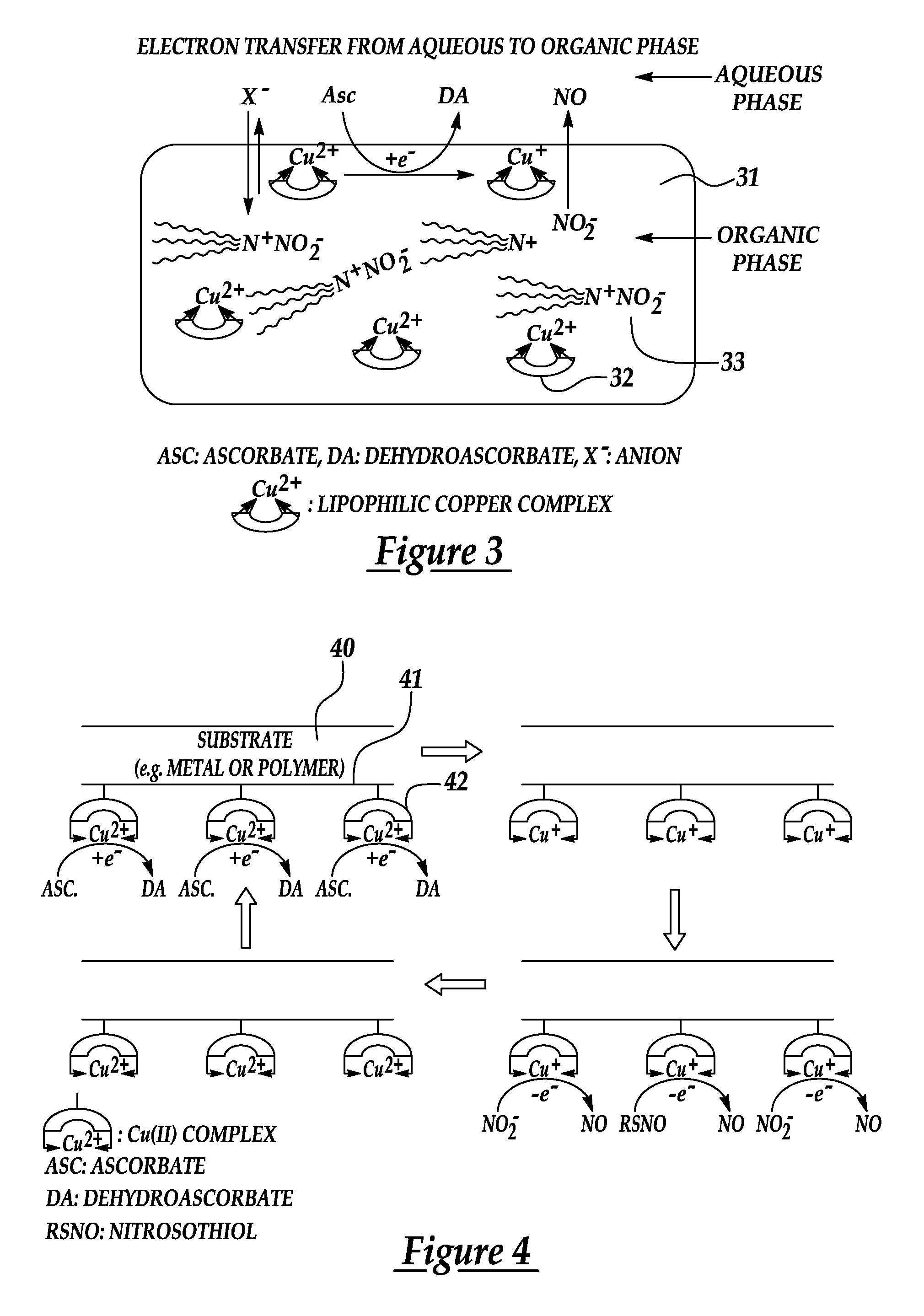
Generation of nitric oxide in vivo from nitrite, nitrate or nitrosothiols endogenous in blood
A material includes a surface and a reactive agent that is located at the surface of the material, covalently attached to a backbone of the material, and / or located within the material. The reactive agent has nitrite reductase activity, nitrate reductase activity, and / or nitrosothiol reductase activity. The reactive agent also converts at least one of nitrites, nitrates and nitrosothiols to nitric oxide when in contact with blood. A reproducible nitrosothiol sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:MICHIGAN CRITICAL CARE CONSULTANTS +1
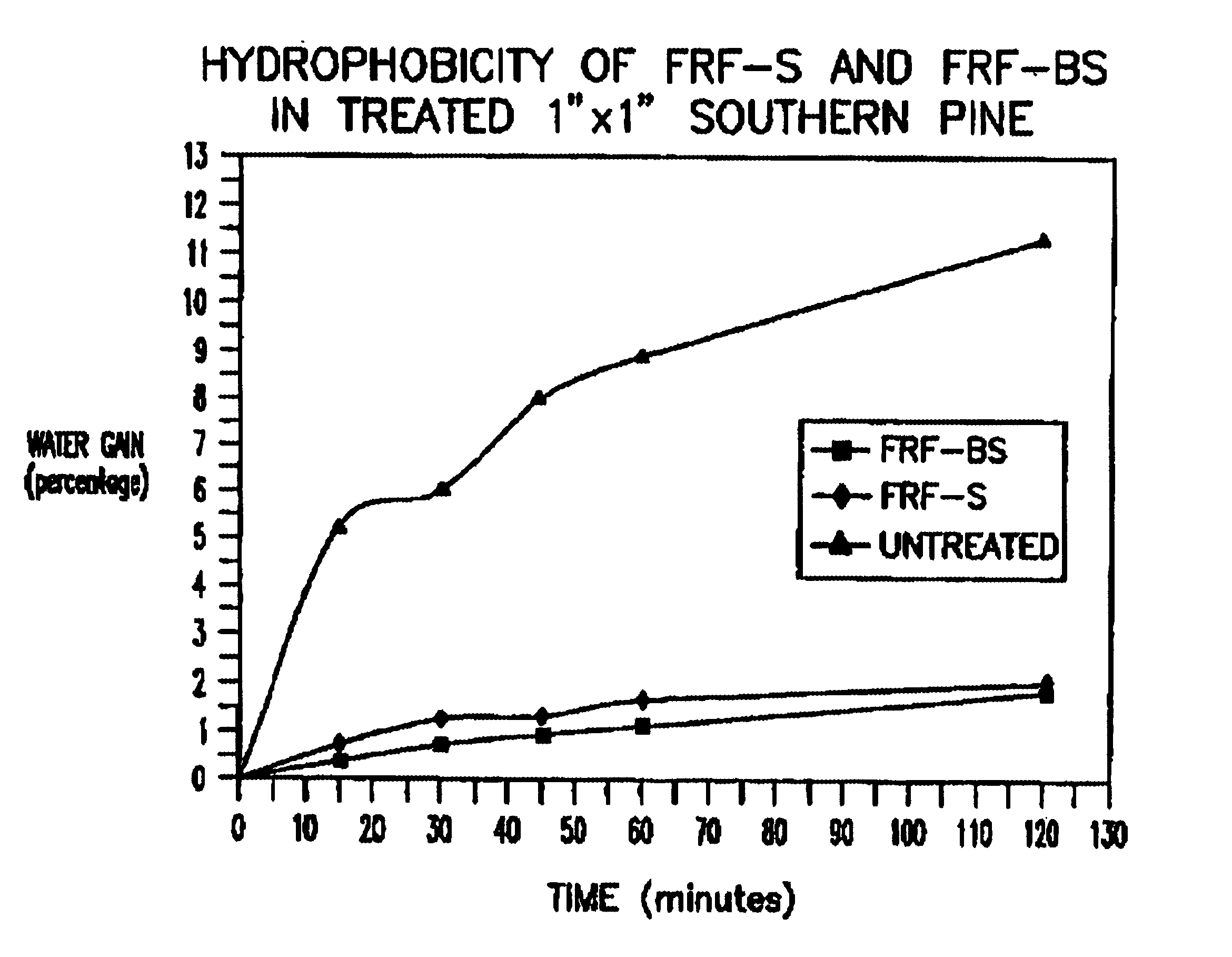
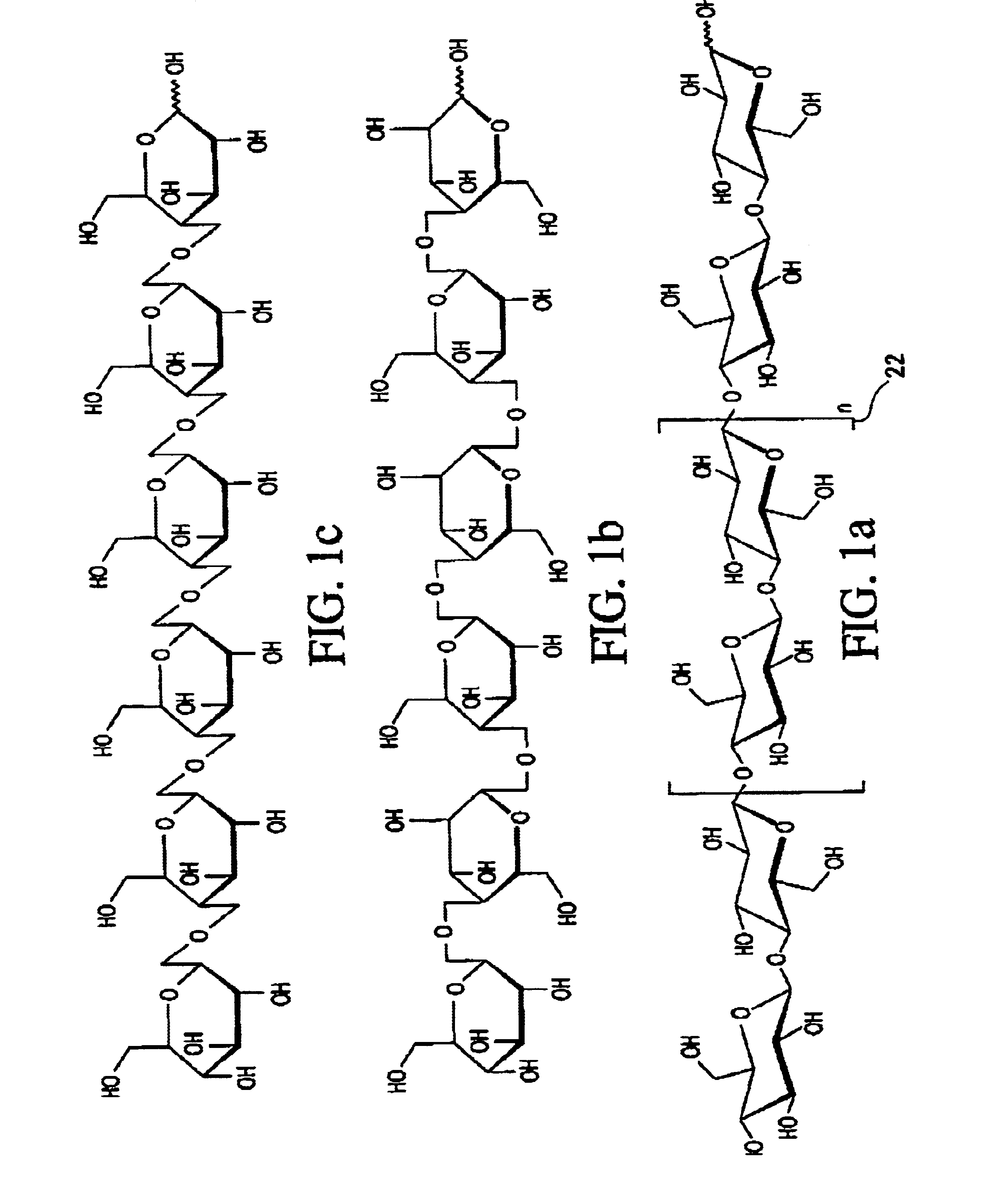
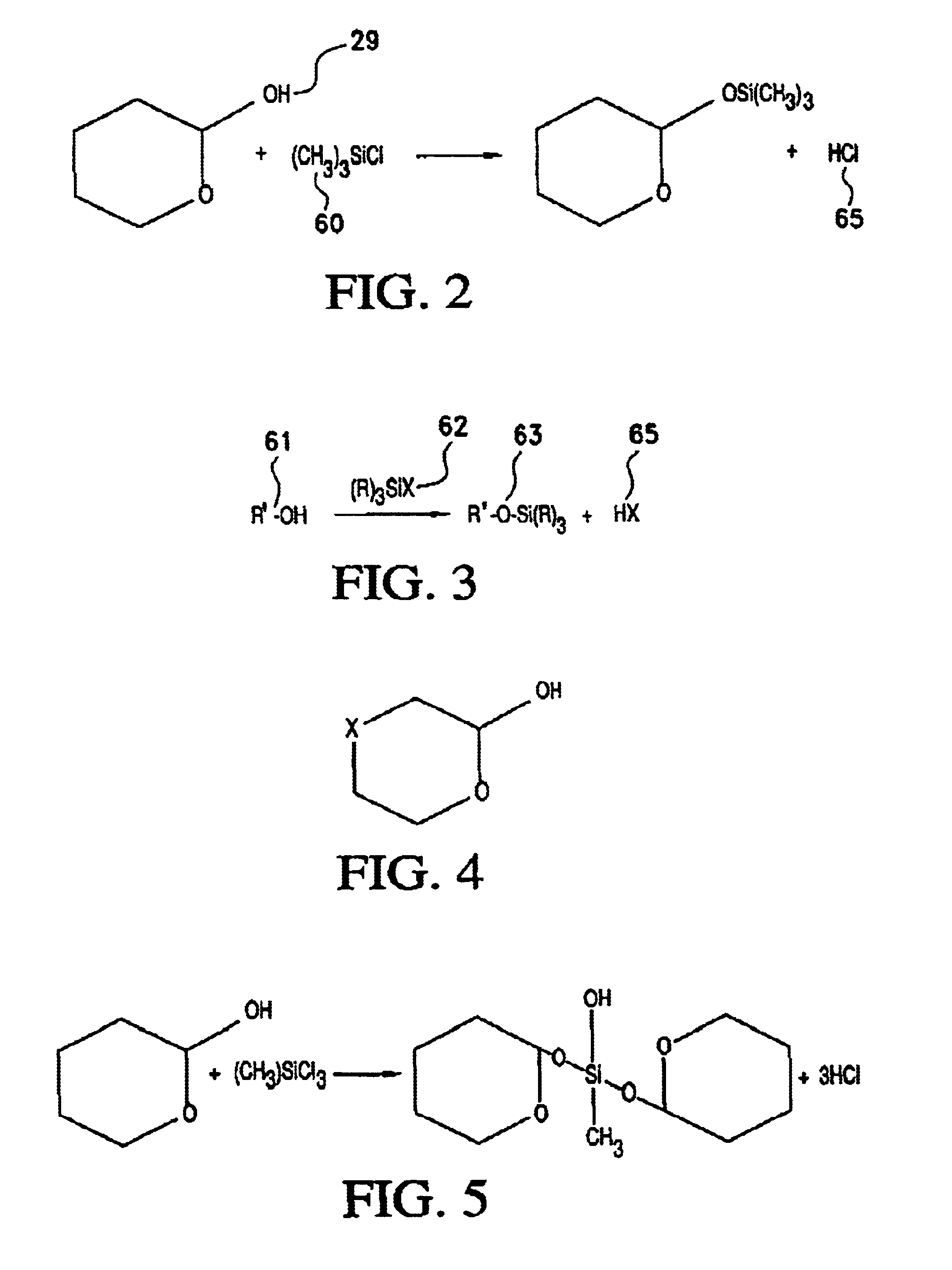
Process for treating wood and products from treated wood
InactiveUS6902767B2Increased durabilityHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyPretreated surfacesCelluloseAnti-degradant
Wood cellulose is treated with a reactive silicate. The reaction is done to cellulose within the wood and may be catalyzed with acid or base catalysts or a carbon silicon halogen combination which produces in situ acid catalysts or a different combination to produce an in situ base catalyst which replaces some of the molecules or atoms within the cellulose structure with silicon, boron or other hydrophobic or anti-degrading agents. Preferably an organic solvent, such as alcohol is used to accelerate the reaction with the water in the wood. Here, the hydroxyl (OH) group on some or all of the cellulose molecules is partially replaced with silicon or an alternative atom or molecule to changes the character of the wood. The process may be modified to insert a preliminary step of adding a reactive agent to be locked into the wood. Manufacturing techniques to enhance the process using ultrasound or other wave generating techniques are also taught.
Owner:D & L +1
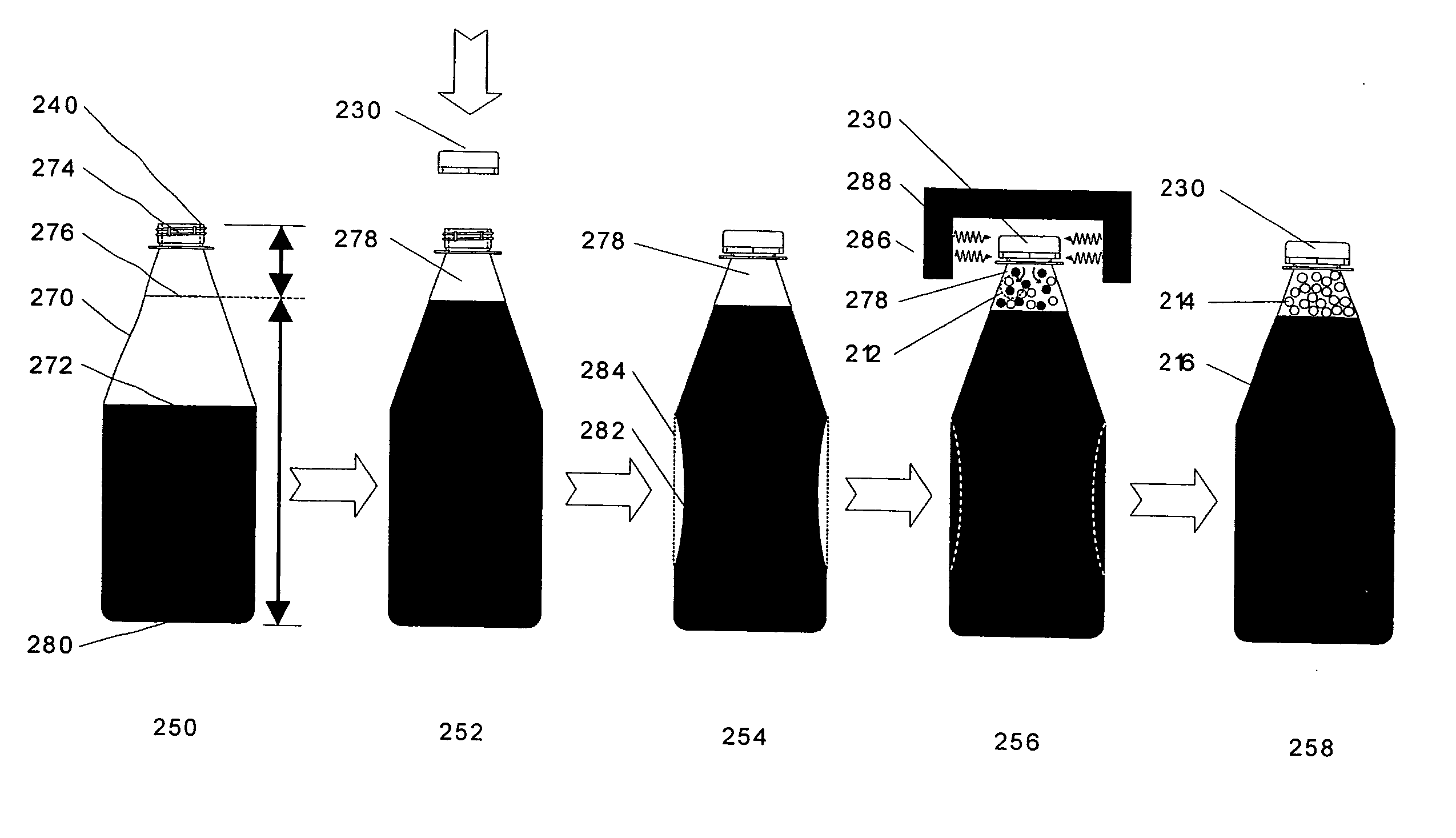
Method and device for pressurizing containers
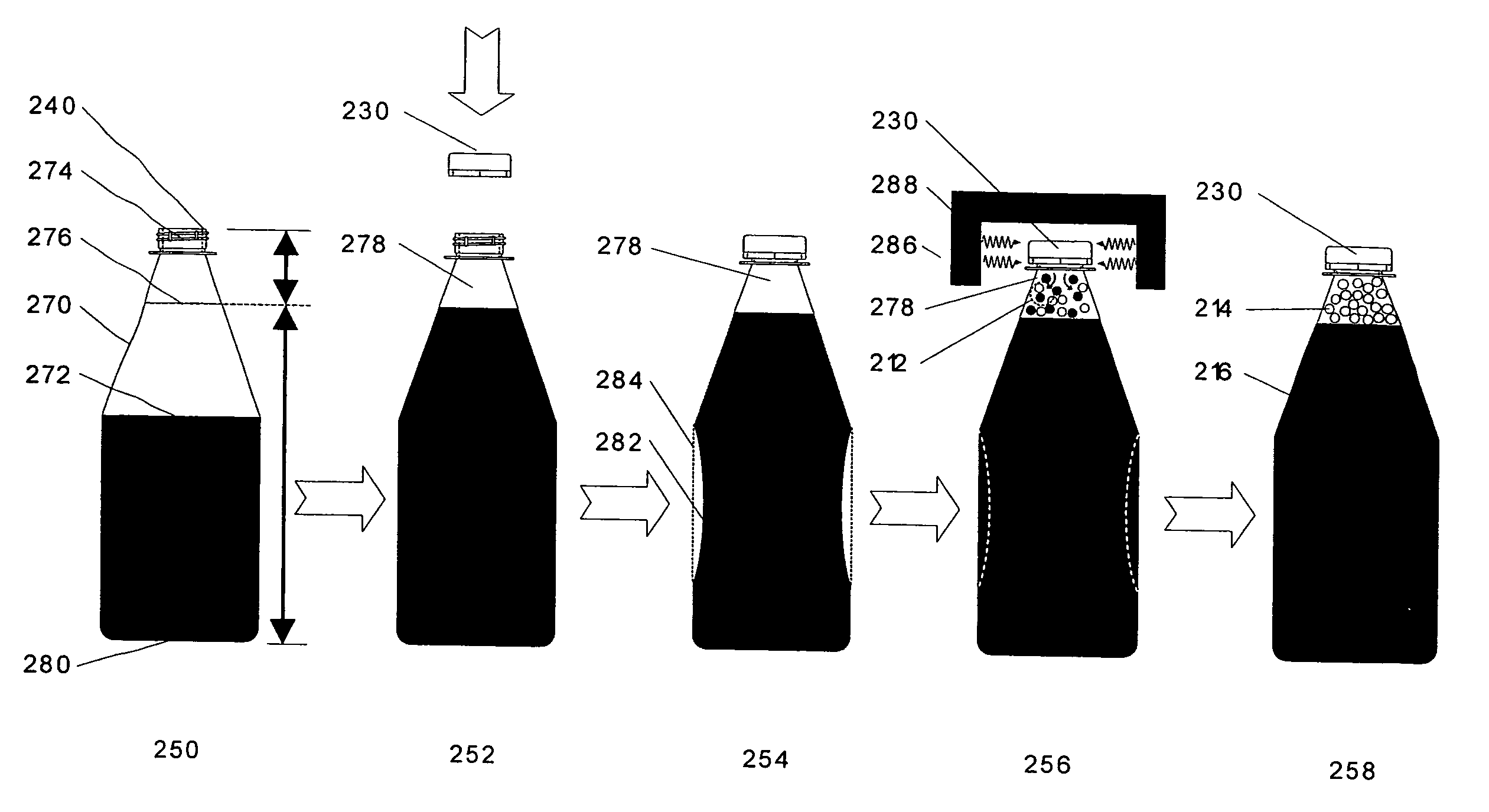
Devices and a method for releasing gas in a container after closing and sealing to pressurize and / or prevent or counteract buckling thereof, and or provide structural rigidity and strength thereto and or release components. The method introduces a reactive agent into the container after filling and before sealing. The reactive agent is controlled to react to provide a gas and optionally components, which a) provides a positive pressure to prevent or counteract buckling and provide structural rigidity to the container and b) and or changes the state or characteristics of the headspace and or contents of the closed container. The devices include a closure, a cap and a container. The reactive agent is brought to chemical reaction by moistening, heating, catalyst and the like. The closure includes the reactive agent and is disposed in the container. The external trigger is a device that emits energy that provides heat to the reactive agent to stimulate the chemical reaction.
Owner:INOFLATE
Passive electrode blanketing in a fuel cell
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Generation of nitric oxide in situ at substrate/blood interfaces and reproducible nitric oxide sensor for detecting nitrosothiols
A material includes a surface and a reactive agent that is located at the surface of the material, covalently attached to a backbone of the material, and / or located within the material. The reactive agent has nitrite reductase activity, nitrate reductase activity, and / or nitrosothiol reductase activity. The reactive agent also converts at least one of nitrites, nitrates and nitrosothiols to nitric oxide when in contact with blood. A reproducible nitrosothiol sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
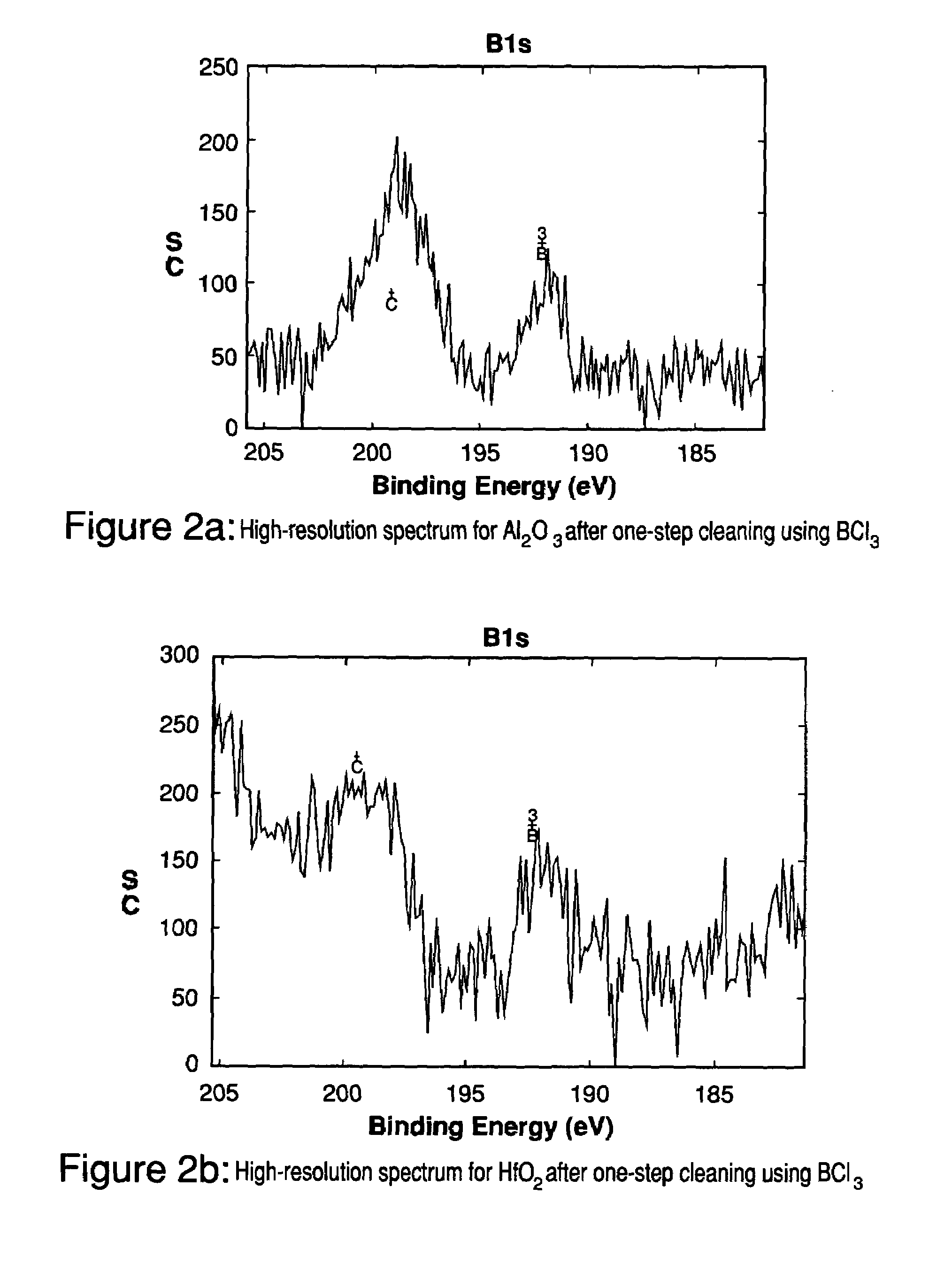
Method for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
InactiveUS20050108892A1High resolutionDrying solid materials with heatElectrostatic cleaningDielectricBoron containing
A method for dry etching and chamber cleaning high dielectric constant materials is disclosed herein. In one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a process for cleaning a substance comprising a dielectric constant greater than the dielectric constant of silicon dioxide from at least a portion of a surface of a reactor comprising: introducing a first gas mixture comprising a boron-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the first gas mixture reacts with the substance contained therein to provide a volatile product and a boron-containing by-product; introducing a second gas mixture comprising a fluorine-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the second gas mixture reacts with the boron-containing by-product contained therein to form the volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reactor.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Hydrophobically modified fluid loss additives and viscosifier products
A wellbore fluid that includes an oleagninous continuous phase; a non-oleaginous phase; and a polymeric additive formed by reaction of at least one lipophilic epoxy modifier and at least one epoxide-reactive agent, wherein the at least one epoxide-reactive agent comprises at least one selected from lignins, tannins, biopolymers, starches, carboxy methyl cellulose, polyacrylates, polyacrylamides, and synthetic polymers is disclosed.
Owner:MI
Delivery of reactive agents via self emulsification for use in shelf-stable products
Disclosed are treatment compositions comprising a liquid emulsifiable concentrate which comprises a chemically unstable reactive agent wherein the reactive agent is comprised of one or more reactive groups of the electrophilic, nucleophilic or protected thiol type, a water immiscible solvent, one or more surfactants, which is usable upon dilution within a separate aqueous composition to form a micro- or macro-emulsion in-situ immediately prior or simultaneous to application to the substrate and wherein the reactive agent is chemically shelf stable. Also disclosed are methods for treating amino acid based substrates, and methods for bleaching, coloring and conditioning hair with these treatment compositions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Thiol reactive agents as a therapeutic modality
InactiveUS20080145449A1Useful in treatmentImprove heart functionBiocideNervous disorderSkeletal muscle atrophyDisease
A patient with a disease associated with a receptor having a cysteine residue is treated with a thiol reactive agent. The diseases include neurodegenerative diseases. Diseases characterized by skeletal muscle atrophy are also treated.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Antigenic protein conjugates and process for preparing same
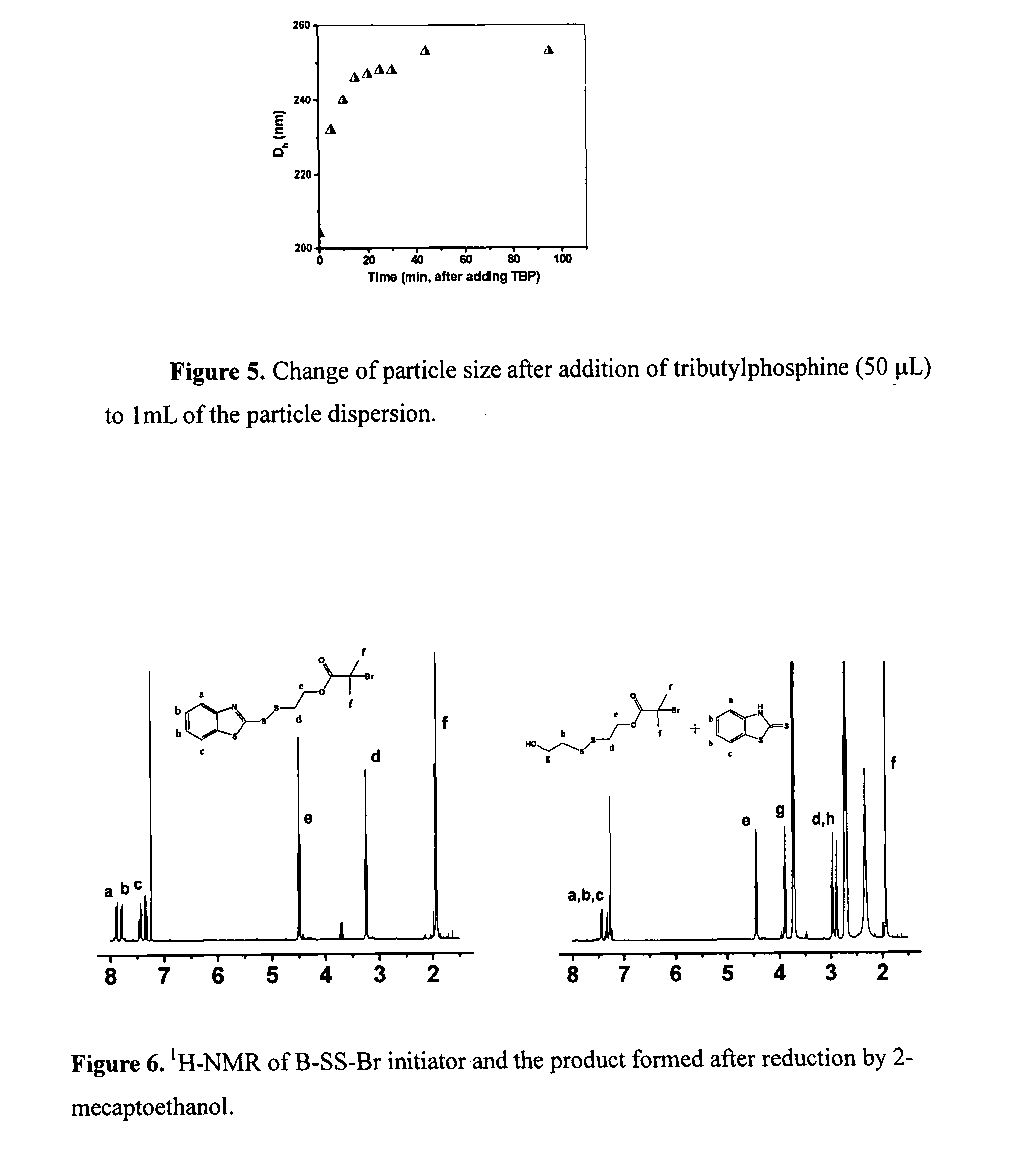
InactiveUS20080220448A1ImmunoglobulinsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImproved methodReactive agent
An improved process for the preparation of antigenic protein conjugates is provided. The conjugates preferably are formed through reaction with one or more free sulfhydryl groups in the antigenic protein. The process of the present invention preferably employs a trialkylphosphine as the reducing agent and allows for reduction of disulfide bonds in the antigenic protein and conjugation with a conjugate moiety, preferably in a single reaction vessel (i.e. “in situ”) because the process optimally does not require the removal of the reducing agent before subsequent addition of the sulfhydryl reactive agent. Antigenic protein conjugates prepared by the in situ process and their use in diagnostic immunoassays are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Hardenable materials which contain uretdione groups, method for the production and processing thereof, and their utilization
InactiveUS7019088B1Improve responseReduce the temperatureSynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsLacquerLewis acid catalysis
The invention is used in the fields of chemistry and relates to hardenable materials which can be used for producing lacquers. The aim of the invention is to provide materials which harden at low temperatures in the same amount of time as the others. This is achieved by using hardenable materials containing uretdione groups and containing (A) a binding agent constituent, whereby this component either (A1) does not contain carboxyl groups, or (A2) the concentration of carboxyl groups is less than that of the catalyst (C) or (A3) in the case of a high level of concentration, a quantity of a reactive agent is added. The hardenable materials also contain (B) a polyaddition compound which comprises uretdione groups, and (C) at least one Lewis acid catalyst. The aim of the invention is also achieved using a method for producing materials of this type in which the starting materials are homogenized in a solution and / or in a melt, the solution and / or melt is then rapidly cooled, and the subsequent processing is carried out afterwards to effect a complete cross-linking.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Low density polylactic acid polymeric foam and articles made thereof
This invention presents a process whereby thermoplastic polylactic acid polymers foams having the desirable properties for manufacture of thermoformed articles may be made. It has been found that introduction of a dual functional reactive agent into the melt will improve the relevant properties of the melt and thus, the resultant foam. An example of such an agent is pyromellitic di-anhydride, but it is envisioned that a wide number of dual functional reactive agents can be utilized. It has been found that such dual functional reactive agents do not shift crystalline melt point of the material by any appreciable amount. It has been found that, by carefully controlling such a reaction, melt strength can be increased sufficiently to produce stable foam at temperatures above the melt point of the polymer, to permit the production of foamed polylactic acid polymer and product formed therefrom on conventional process equipment.
Owner:AJOVER
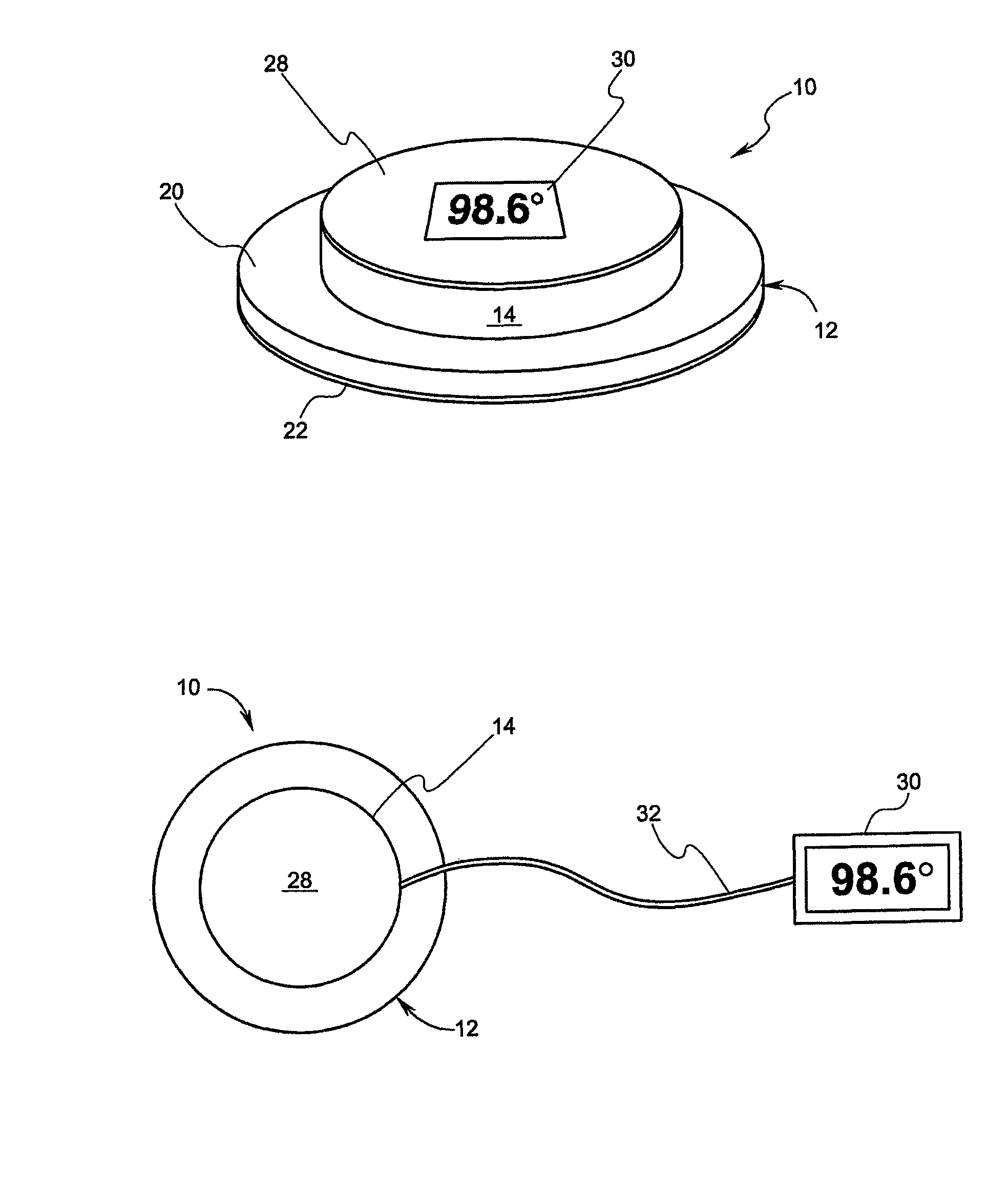
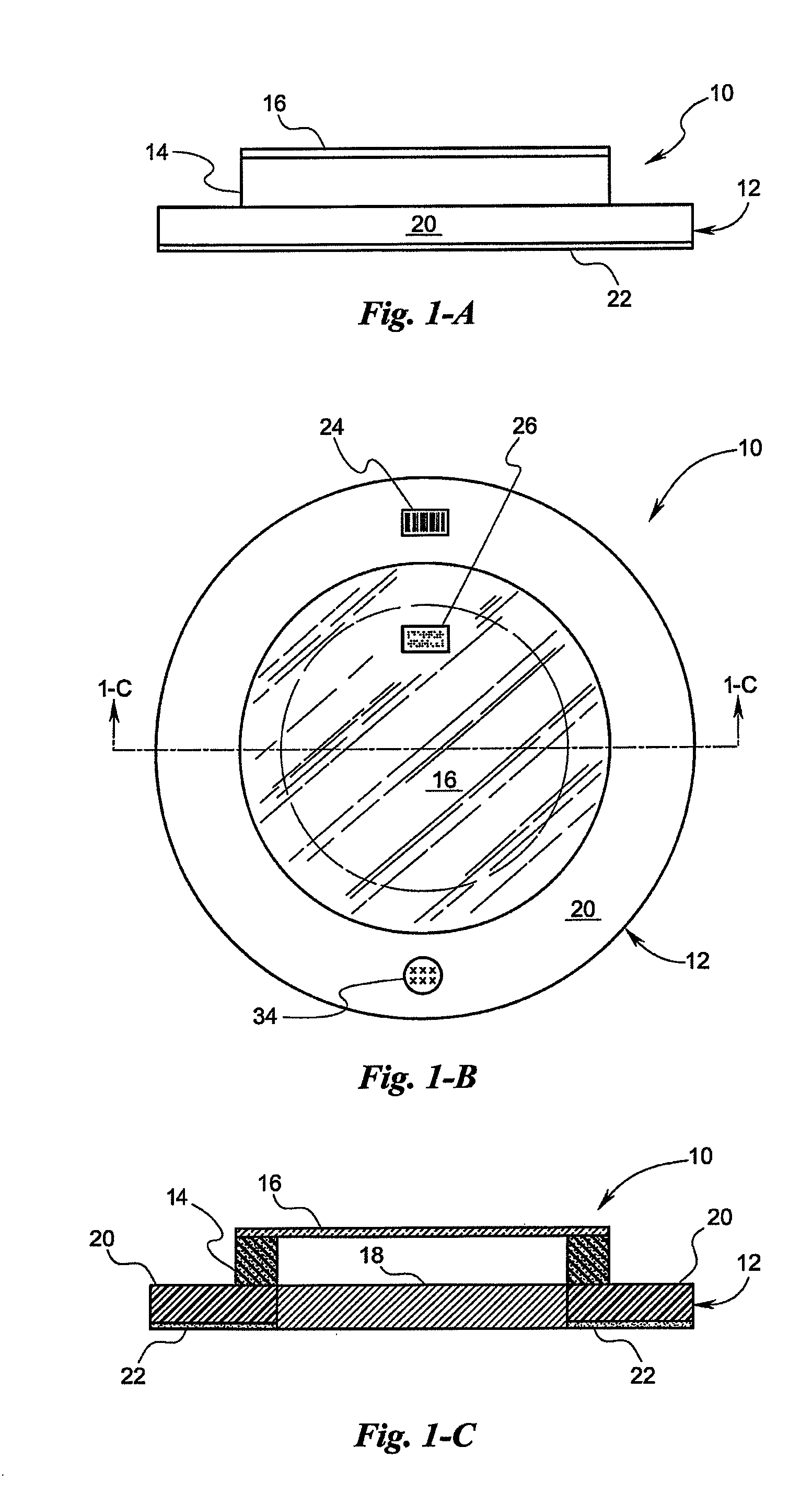
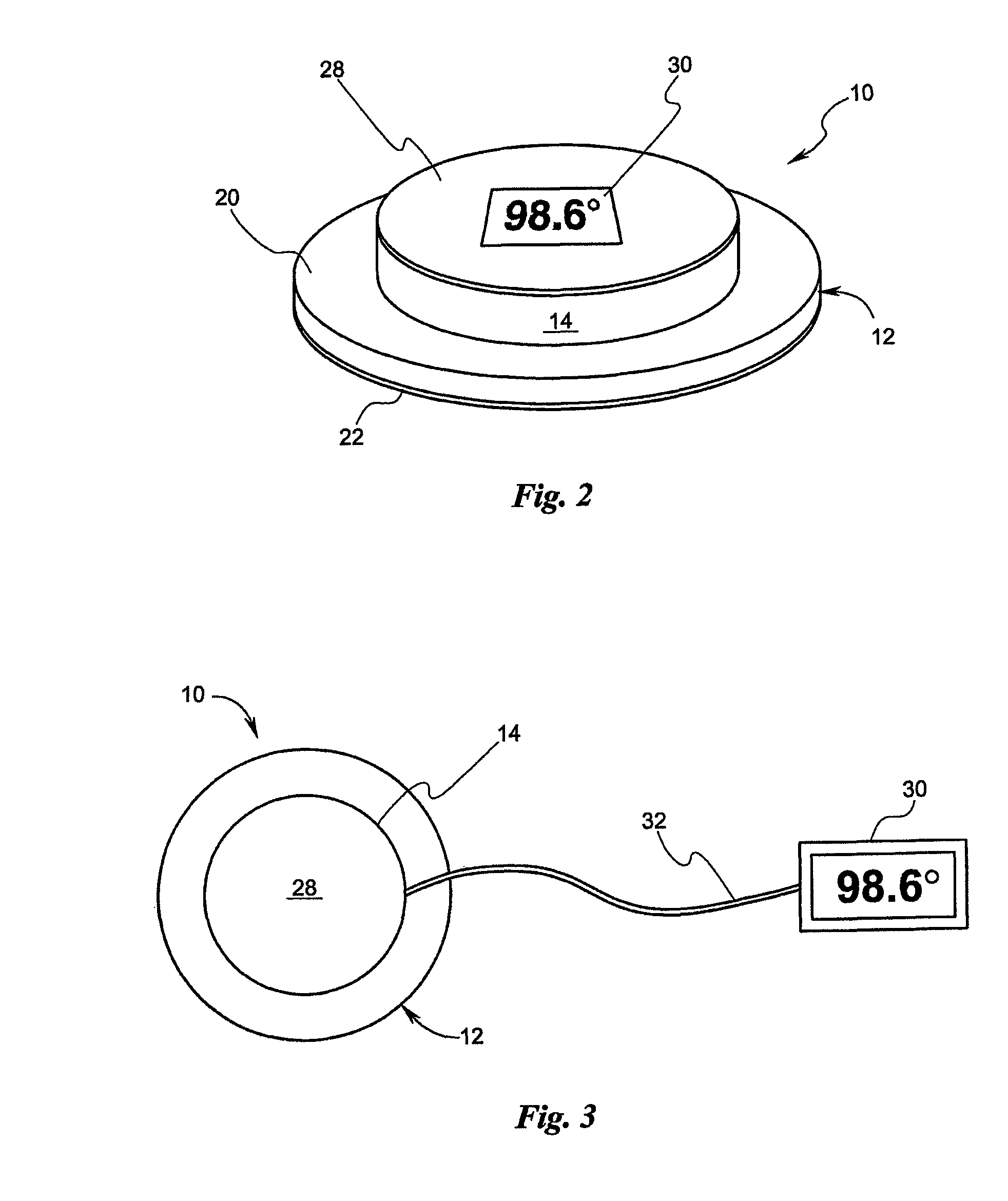
Temperature patch and method of using the same
A patch having an infrared (IR) target is placed proximate to the surface of a mammal. The patch may include an insulator for protecting the target from exterior, ambient IR and may include bar codes or other indicia uniquely associated with either the patch or the mammal. The patch may also include a bio-reactive agent for indicating characteristics such as the pH of the mammal's skin. The patch may also include a thermometer for sensing the level of IR radiation from the IR target and may include a display of the temperature associated with such a level. The patch may also include a transmitter for wirelessly communicating information about such level to a remote location. A method of using the patch is also disclosed.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Method for removing fluorine from a fluorine-containing wastewater
A method for removing fluorine from wastewater includes the steps of: adding a fluorine-reactive agent, that comprises a water-soluble sodium compound and a water-soluble aluminum compound, into the wastewater so as to form sodium ions and aluminum ions in the wastewater and so as to precipitate sodium aluminum fluoride by reaction of the sodium ions and the aluminum ions with fluorine ions in the wastewater; and removing the precipitate of sodium aluminum fluoride from the wastewater.
Owner:LIAO MING HUI
Processing method for produced water for ultra-low permeable oil field reinjection
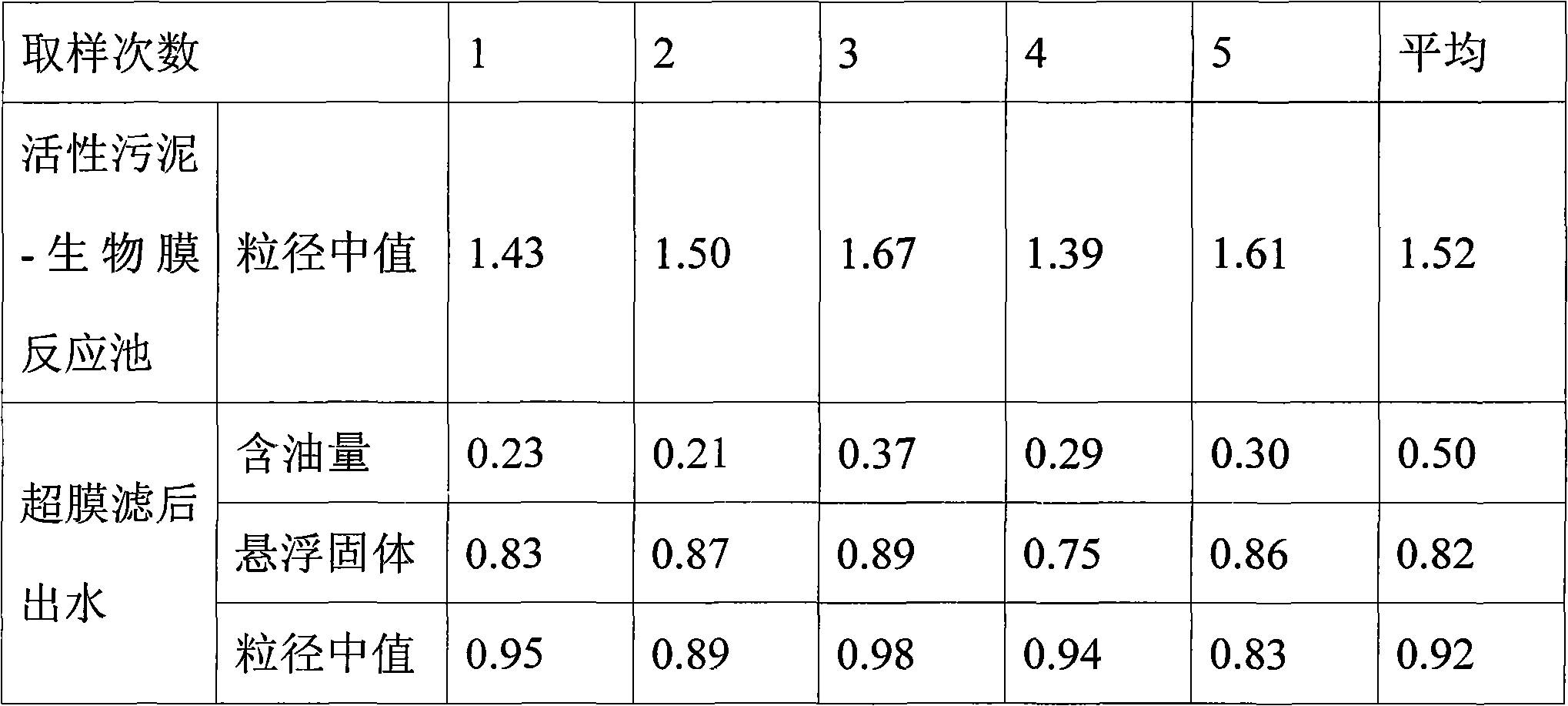
InactiveCN101671091AImprove the efficiency of biochemical reactionsExtended service lifeTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeWater quality
A processing method for produced water for ultra-low permeable oil field reinjection relates to a waste water processing method which solves the problems of complex operation, high cost, solid content suspended in effluent quality and incapability of medium particle size for achieving the 5, 1, 1 standard of produced water of the ultra-low permeable oil field existing in the existing method for processing oil field produced water. The processing method comprises the following steps: 1. preparing a supernatant; 2. carrying out acclimatization treatment in an activated sludge-biomembrane reaction tank, and then introducing the supernatant; and 3. after precipitation, carrying out hyperfiltration. The processing method adopts an activated sludge-biomembrane compound technology as a reactive agent, can give consideration to long-and-short sludge age, aerobic / anaerobic / anoxic environments, simultaneously removes nutritive materials and hard-degradable organic material in water and has highbiochemical reaction efficiency; the processing method has simple operation and low cost; after the processing method of the invention is adopted, effluence can stably achieve the water quality standard-the 5, 1, 1 standard of produced water of the ultra-low permeable oil field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Delivery of reactive agents via multiple emulsions for use in shelf stable products
Emulsion treatment compositions comprise an aqueous continuous phase and a discontinuous phase in the form of an oil-in-oil emulsion. The oil-in-oil emulsion comprises a reactive component including a reactive agent and an internal oil, wherein the internal oil solubilizes the reactive agent, and a middle oil in which the reactive component is dispersed. The middle oil is immiscible with the internal oil, does not solubilize the reactive agent, is immiscible in the aqueous continuous phase, and includes a hydrophobic particulate thickener. Methods for treating hair comprise applying the emulsion treatment compositions to hair.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of synthesizing axungia alkyl dimethyl group amine oxide
InactiveCN101108814ALow reaction temperatureDelayed reaction timeOrganic chemistryReaction temperatureSodium bisulfite
A synthetic method of the fatty alkyl dimethyl amine oxide is provided, which belongs to the synthesis technology field of the amphoteric surface reactive agent in the organic chemical. The fatty alkyl dimethyl amine and the hydrogen peroxide are utilized as raw materials and perform oxidation reaction in the polar dielectric under the condition that the hydrogen peroxide stabilizer and the phase transfer catalyst exist; the sodium bisulfite is added to remove the residual hydrogen peroxide after reaction to produce the fatty alkyl dimethyl amine oxide; the phase transfer catalyst is the tetrabutylammonium bromide or the hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and the addition of the phase transfer catalyst is 1 per cent to 10 per cent of the weight of the fatty alkyl dimethyl amine; the mol ratio between the fatty alkyl dimethyl amine and the hydrogen peroxide is 1 : 1.0 to 1.5. The invention reasonably utilizes the phase transfer catalyst and greatly shortens the reaction time and increases the product yield through reasonably adjusting the addition and mixture ratio of the fatty alkyl dimethyl amine and the hydrogen peroxide and optimally selecting the reaction temperature and time.
Owner:王伟松
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com