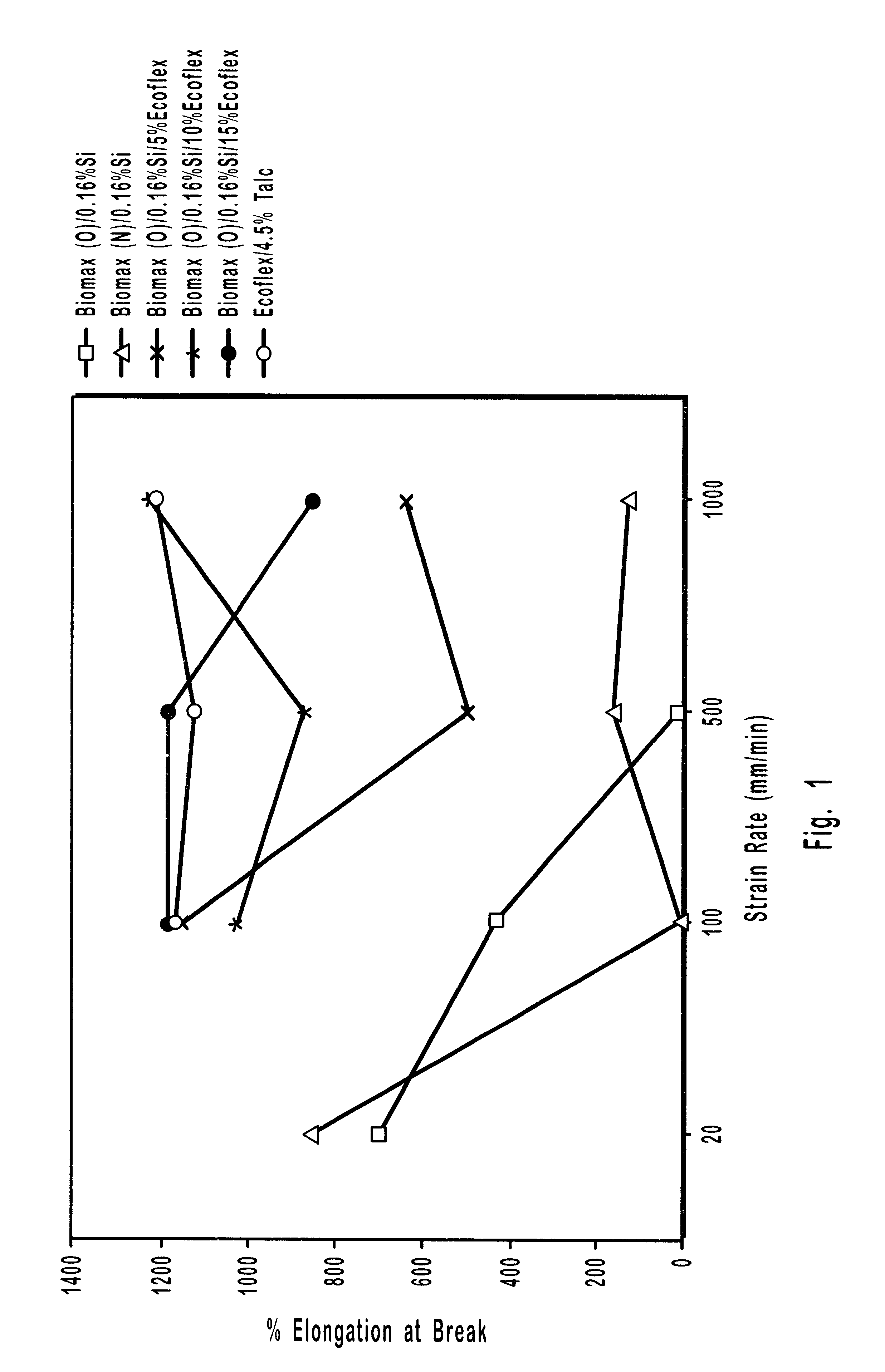
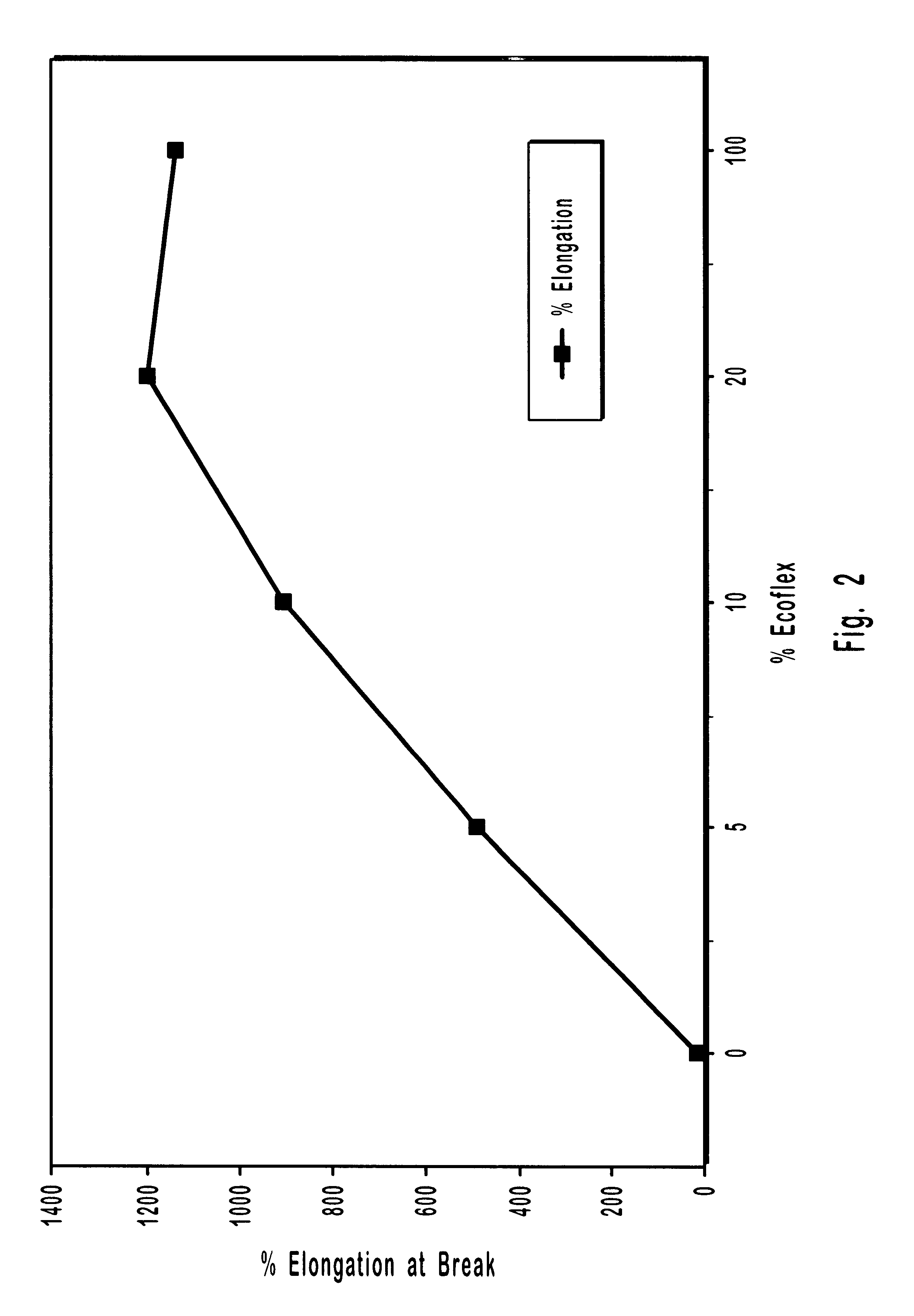
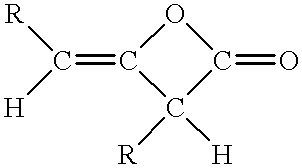
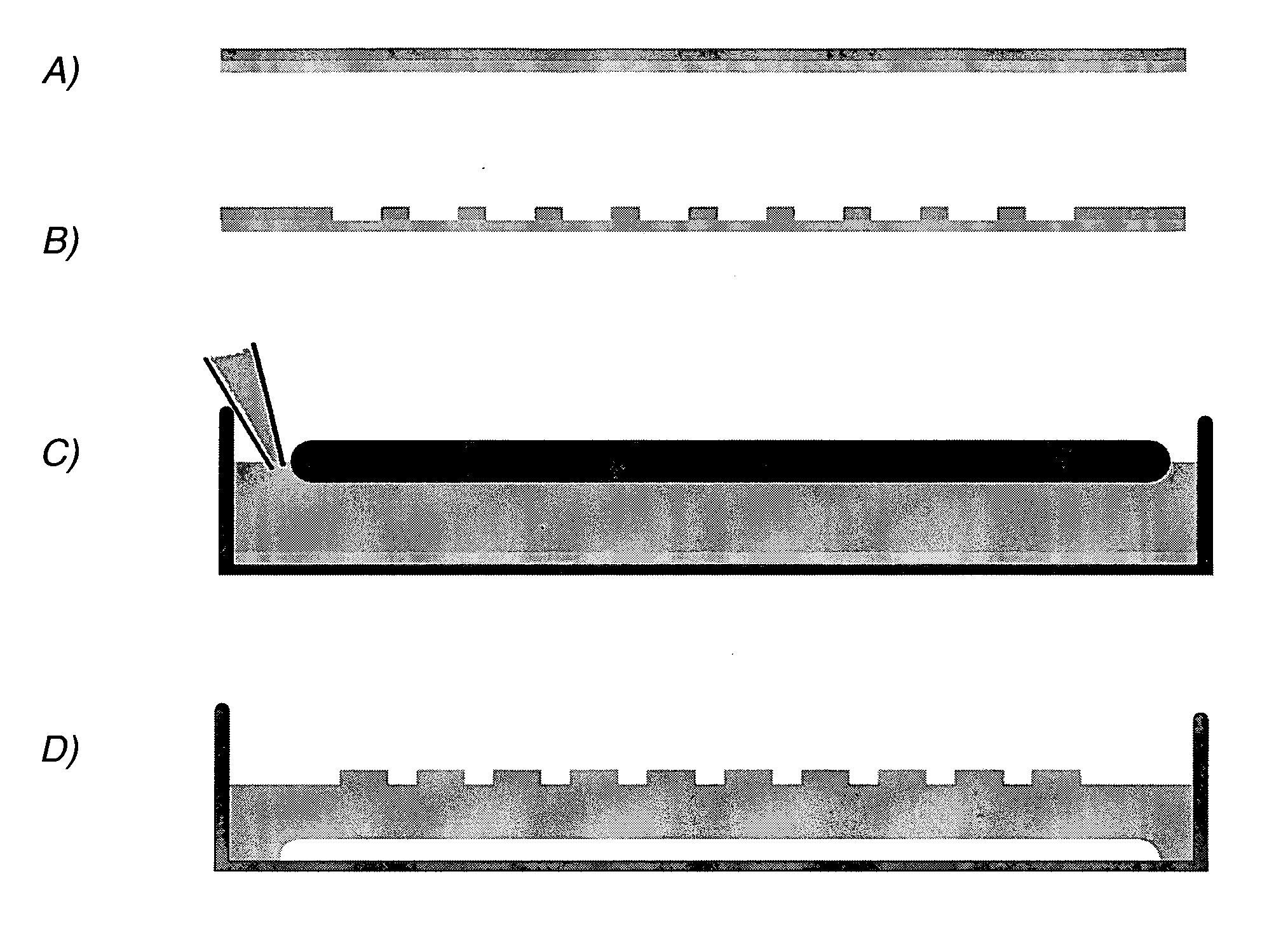
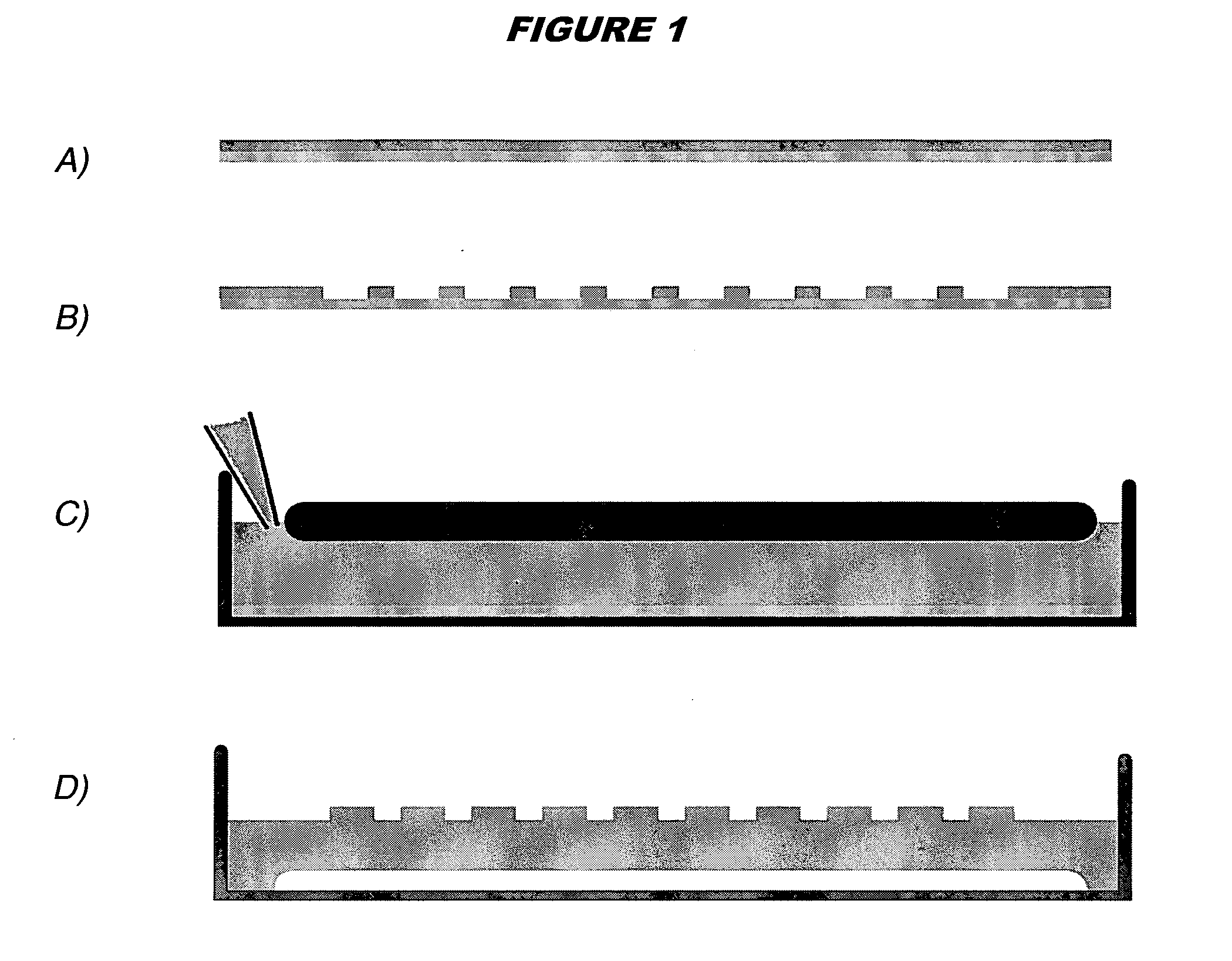
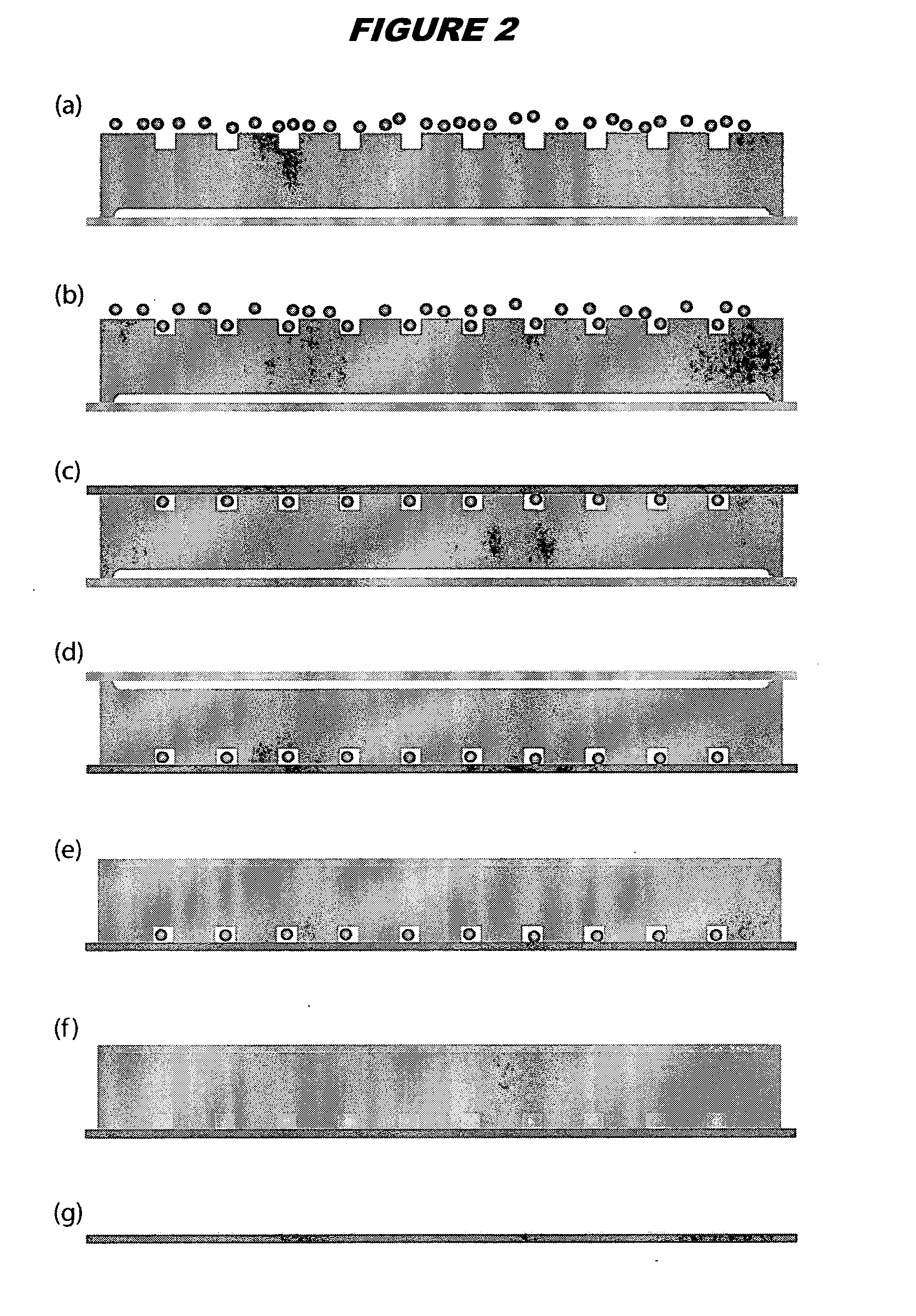
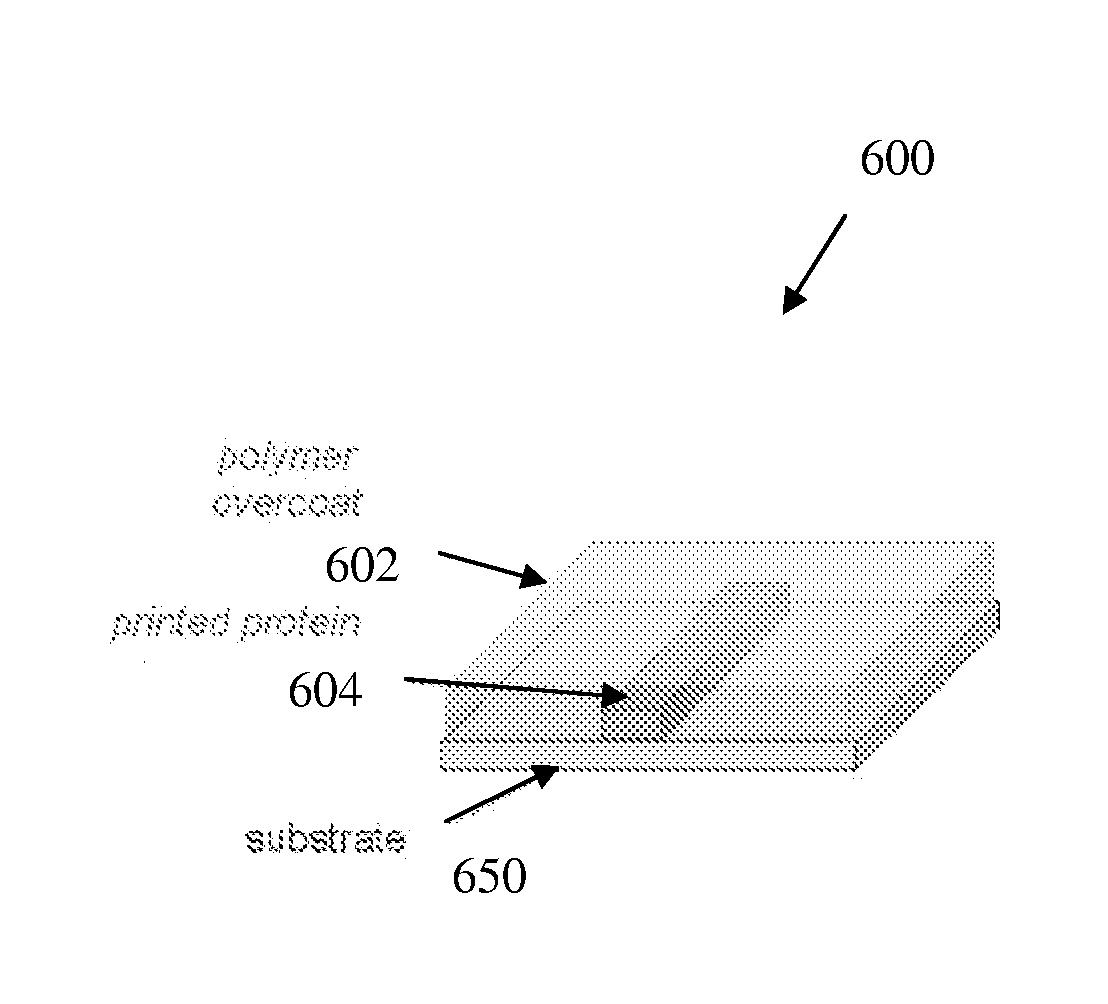
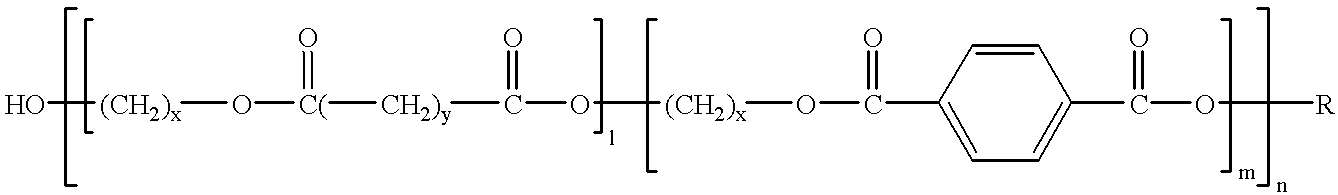Patents
Literature
2073 results about "Biopolymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biopolymers are polymers produced by living organisms; in other words, they are polymeric biomolecules. Biopolymers contain monomeric units that are covalently bonded to form larger structures. There are three main classes of biopolymers, classified according to the monomeric units used and the structure of the biopolymer formed: polynucleotides (RNA and DNA), which are long polymers composed of 13 or more nucleotide monomers; polypeptides, which are short polymers of amino acids; and polysaccharides, which are often linear bonded polymeric carbohydrate structures. Other examples of biopolymers include rubber, suberin, melanin and lignin.
Drug administration method
InactiveUS7427607B2Reduce weightPrevention of the adhesion of an organBiocidePowder deliveryBiopolymerDrug administration
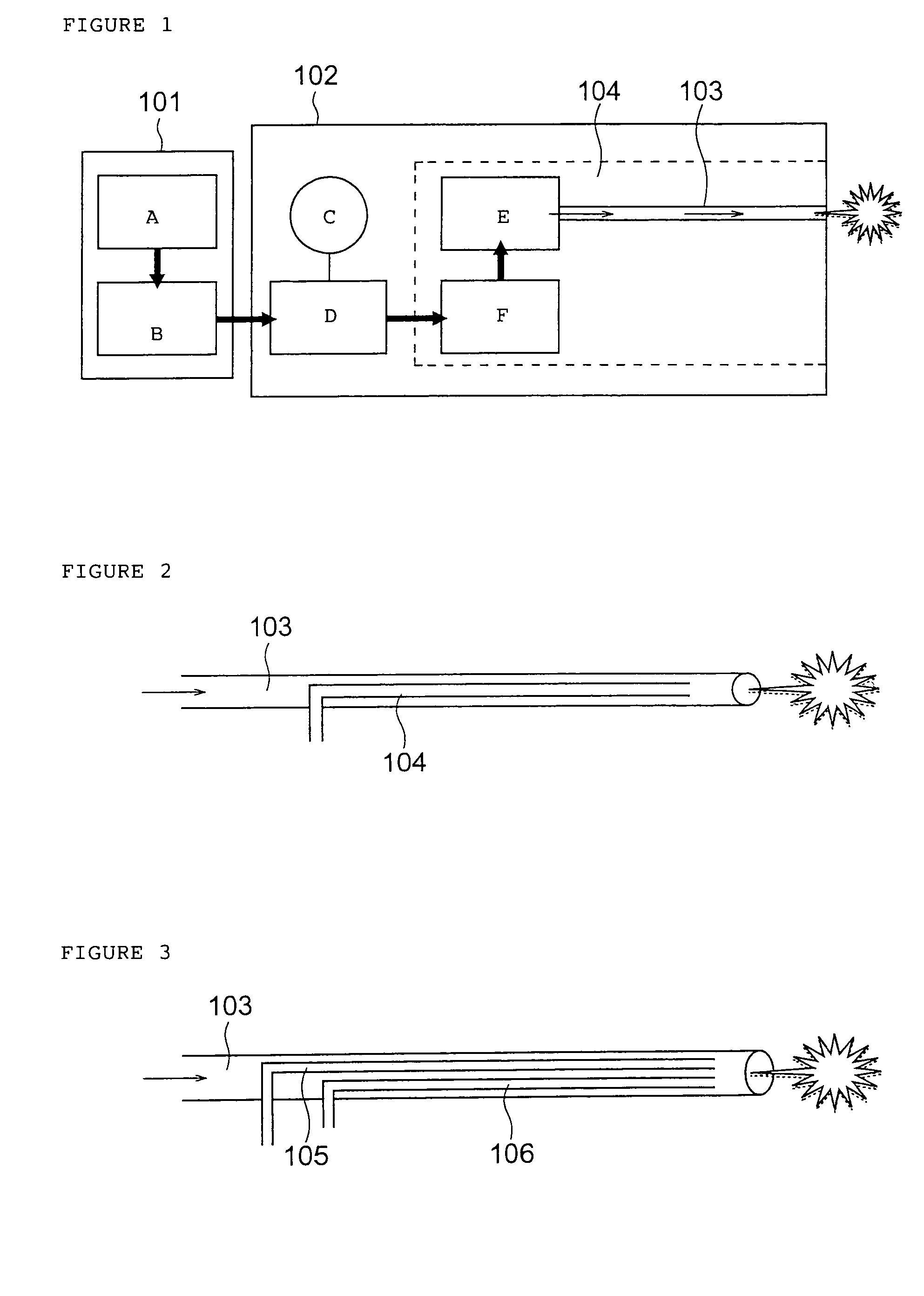
A method of administering a drug whereby a fine drug powder can be accurately administered to a target site (in particular, a target site in the body cavity) via fluidization and spraying with a gas by using a micro tube. Concerning the administration mode, in particular, the drug alone or a biopolymer is administered or the biopolymer is employed as a carrier in the above method. More specifically speaking, a method of administering a fine drug powder which comprises finely milling one or more types fine particles of the drug and / or the biopolymer, blending them each other, fluidizing the blend with a gas, then transporting the fluidized matter in a micro tube by the gas stream and spraying the fine drug powder from the tip of the micro tube toward the target site. Further, an administration method which comprises concentrically providing a capillary tube in the micro tube, supplying an aqueous solution of the drug and / or the biopolymer from the capillary tube into the gas stream and then mixing it with other fine particles of the drug and / or the biopolymer under transportation by the gas.
Owner:NEXT21 KK
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional biopolymeric materials and methods
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional cross-linked proteinaceous biopolymeric materials that may be implanted in vivo, and methods of making such materials are disclosed. The biopolymeric materials most preferably include reinforcing media, such as biocompatible fibrous or particulate materials. In use, the preformed, shaped biopolymeric materials may be applied to tissue in need of repair and then sealed around its edges with a liquid bioadhesive. In such a manner, repaired tissue which is capable of withstanding physiological pressures may be provided.
Owner:CRYOLIFE
Nanoparticles for manipulation of biopolymers and methods of thereof
InactiveUS20060177855A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementCrystallographyNanoparticle
Matrices for manipulation of biopolymers, including the separation, purification, bilization and archival storage of biopolymers is disclosed.
Owner:ARGYLLA TECH
Fragmented polymeric compositions and methods for their use
InactiveUS6063061AImprove liquidityEasy to controlSurgical adhesivesSurgical drugsCross-linkBreast implant
Molecular cross-linked gels comprise a variety of biologic and non-biologic polymers, such as proteins, polysaccharides, and synthetic polymers. Such molecular gels may be applied to target sites in a patient's body by extruding the gel through an orifice at the target site. Alternatively, the gels may be mechanically disrupted and used in implantable articles, such as breast implants. When used in vivo, the compositions are useful for inhibiting post-surgical spinal and other tissue adhesions, for filling tissue divots, tissue tracts, body cavities, surgical defects, and the like.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
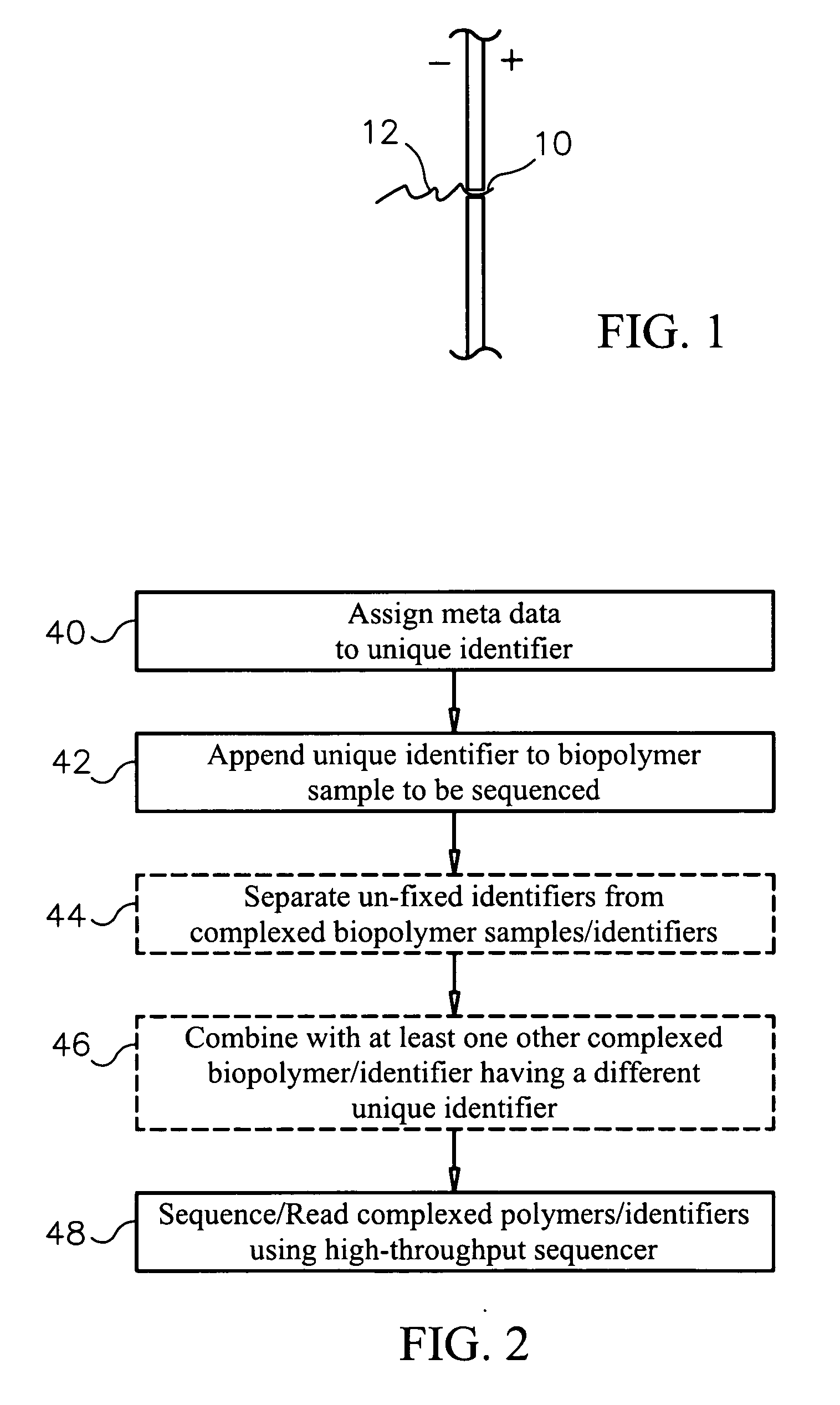
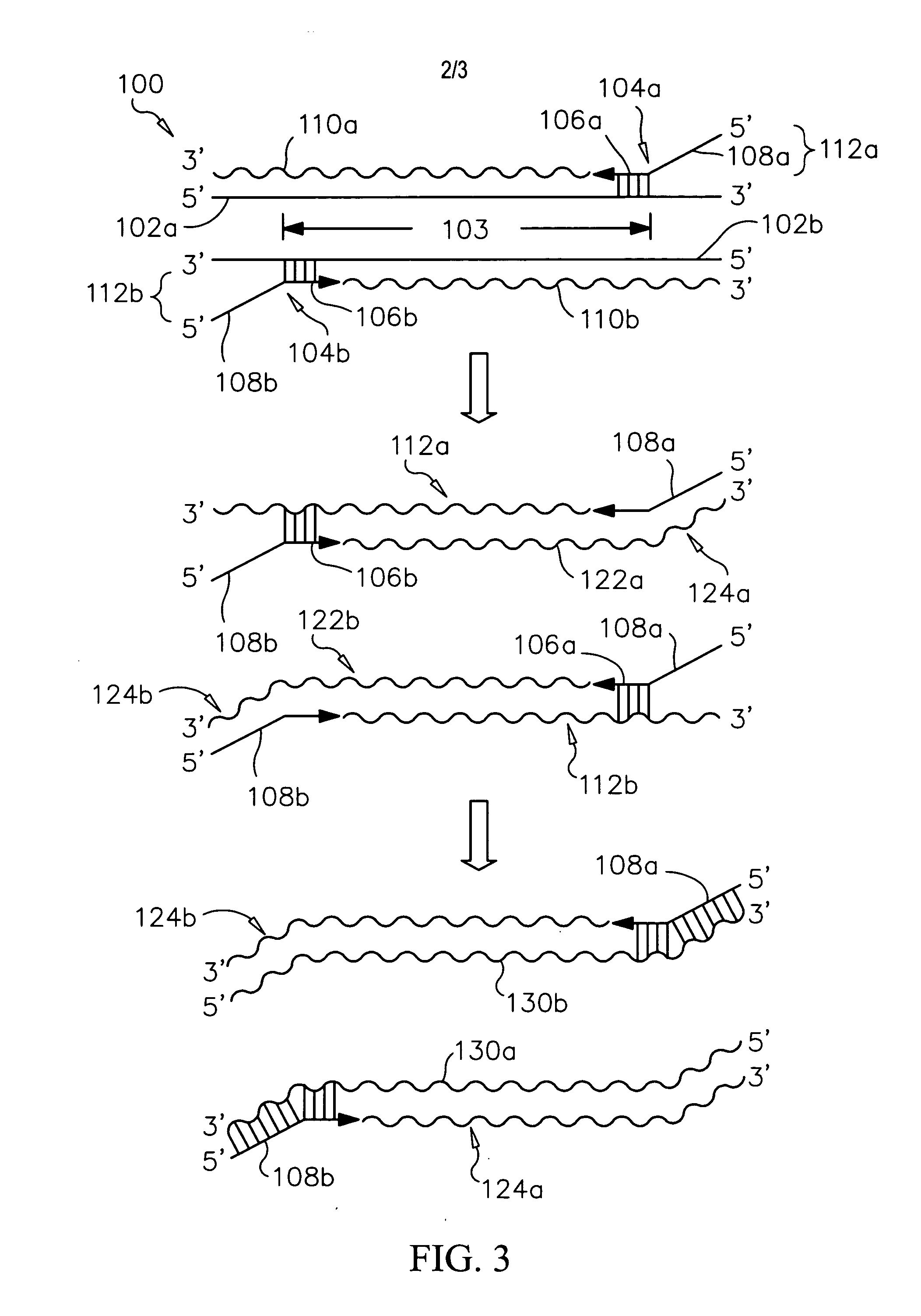
Unique identifiers for indicating properties associated with entities to which they are attached, and methods for using
InactiveUS20060263789A1Efficiently sequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiopolymerUnique identifier
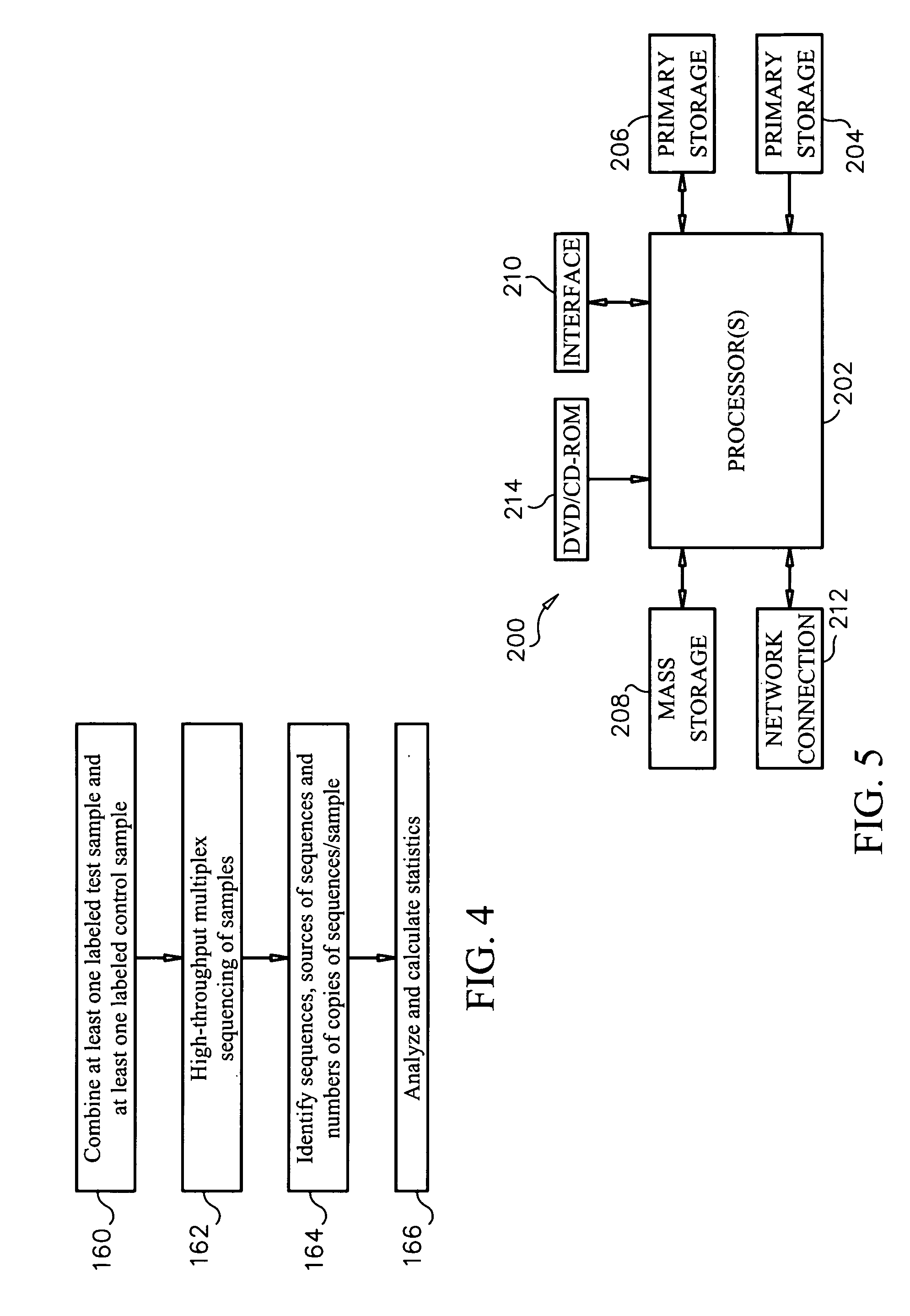
Methods, systems and computer readable media for sequencing a biopolymer specimen and tracking a source from which the specimen was derived. Methods, systems and computer readable media for multiplex sequencing biopolymer samples. Methods, systems and computer readable media for efficiently sequencing biopolymeric specimens through a high-throughput sequencer. Methods, systems and computer readable media for performing ratio-based analysis with a high throughput sequencer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Controlled delivery of therapeutic agents by insertable medical devices
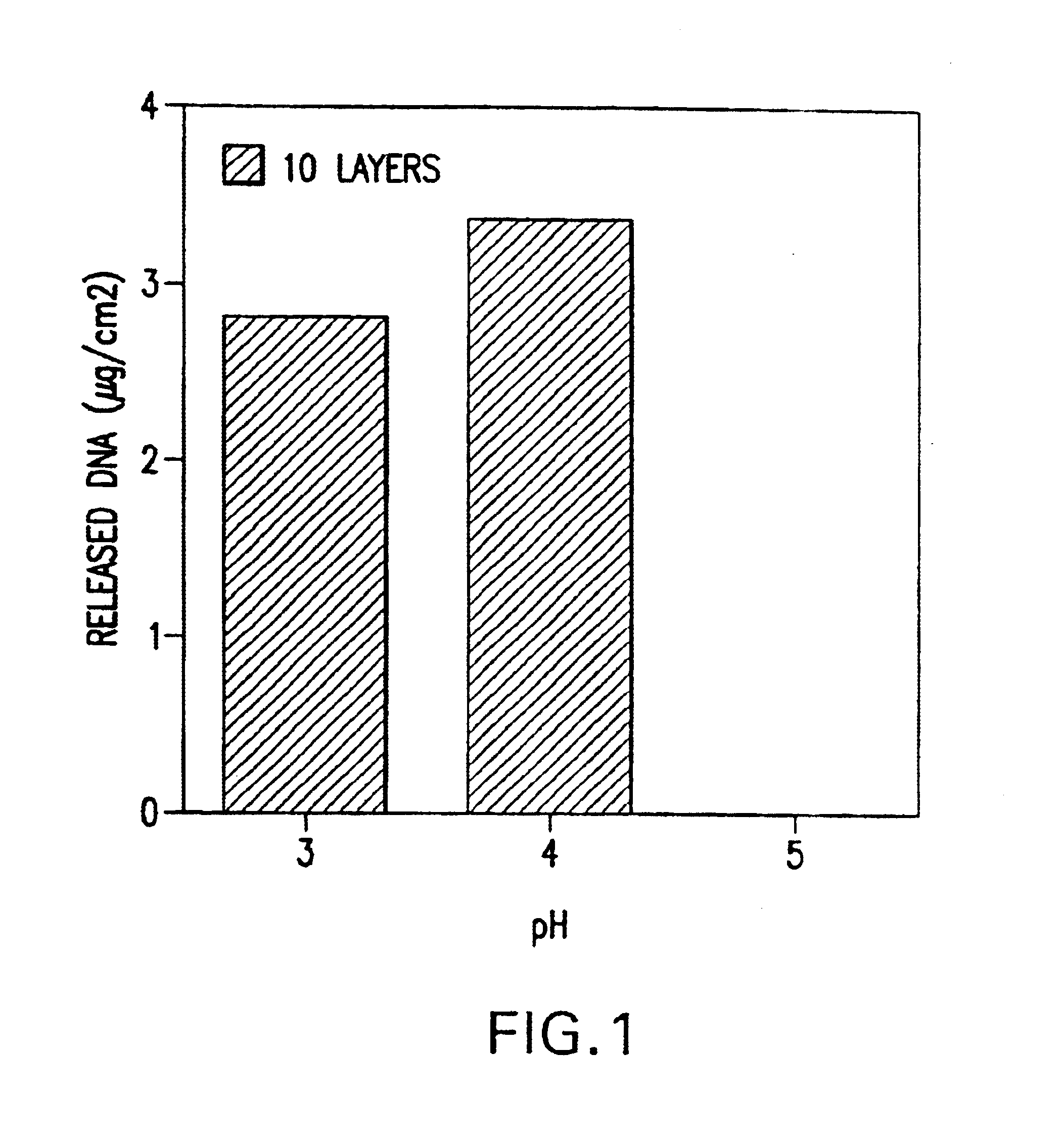
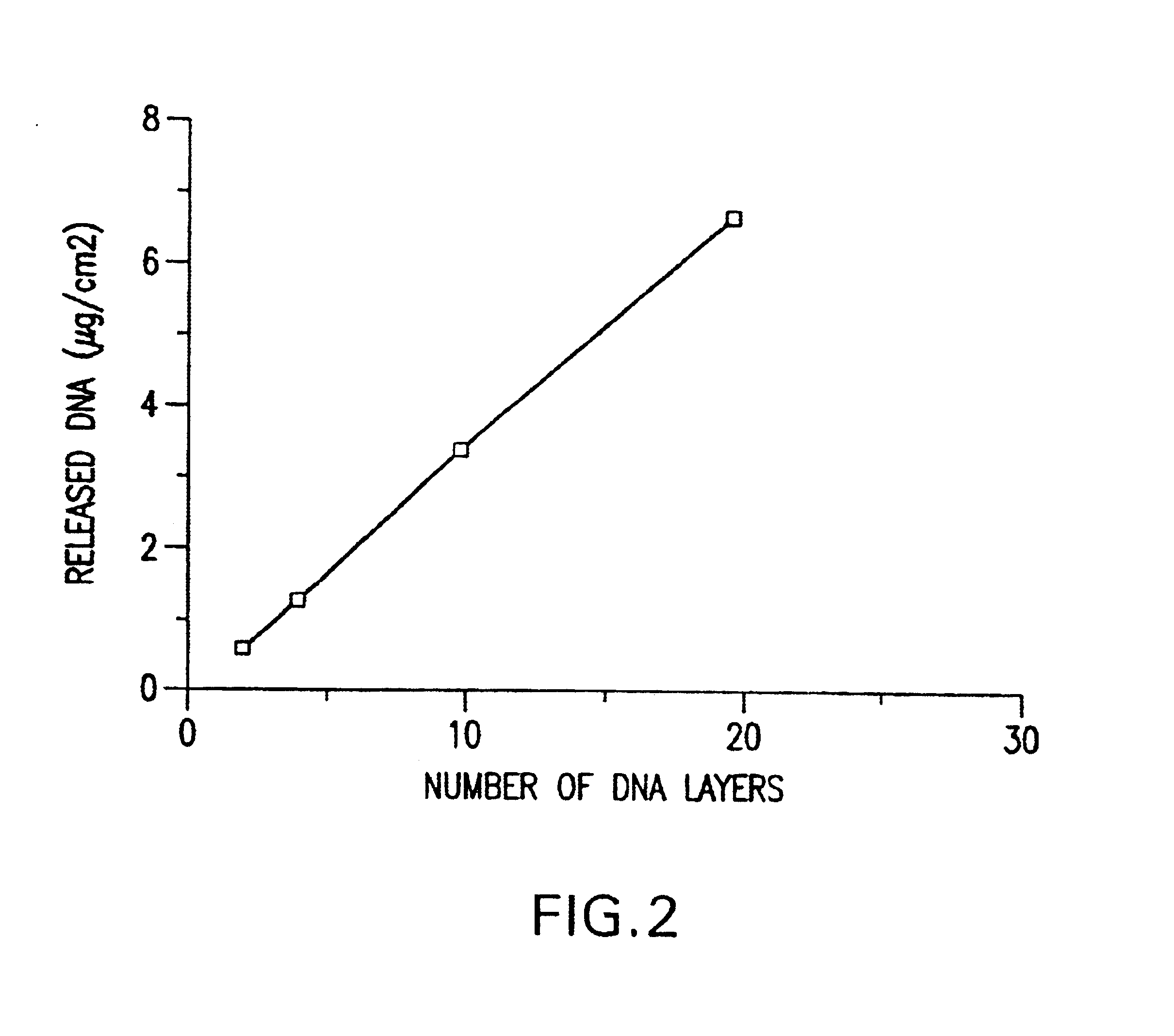
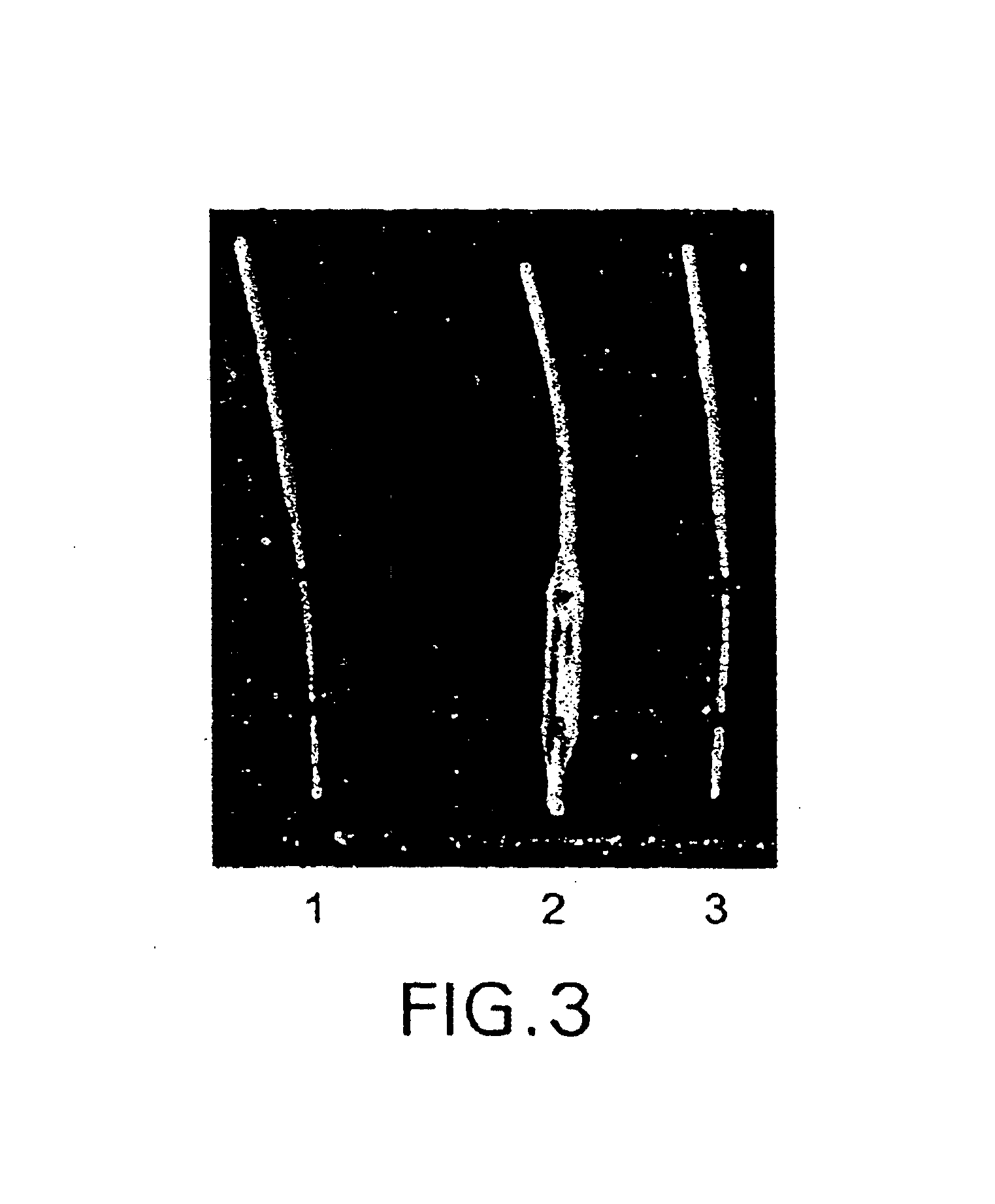
A medical device and method for transportation and release of a therapeutic agent into a mammalian body are disclosed. The medical device is coated with alternating layers of a negatively charged therapeutic agent and a cationic polyelectrolyte, following a controlled adsorption technique. The method is simple, with minimal perturbation to the therapeutic agent and uses clinically acceptable biopolymers such as human serum albumin. The amount of the therapeutic agent that can be delivered by this technique is optimized by the number of the layers of the therapeutic agent adsorbed on the surface of medical device. There is a washing step between alternate layers of the therapeutic agent and cationic polyelectrolyte carrier, so that the amount of the therapeutic agent on the insertable medical device represents the portion that is stably entrapped and adsorbed on to the medical device. The insertable medical device and method according to this invention are capable of reproducibly delivering therapeutic agent to a site in a mammalian body, and allow for a highly reproducible and controllable release kinetics of the therapeutic agent.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Sol-gel matrices for direct colorimetric detection of analytes
InactiveUS6022748AEasily associated with transducing deviceRobust and stableMaterial nanotechnologyBiological testingAnalyteBiopolymer
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the direct detection of analytes using color changes that occur in immobilized biopolymeric material in response to selective binding of analytes to their surface. In particular, the present invention provides methods and compositions related to the encapsulation of biopolymeric material into metal oxide glass using the sol-gel method.
Owner:SANDIA +1
Biodegradable polymer films and sheets suitable for use as laminate coatings as well as wraps and other packaging materials
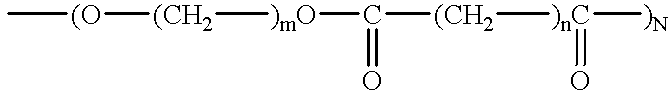
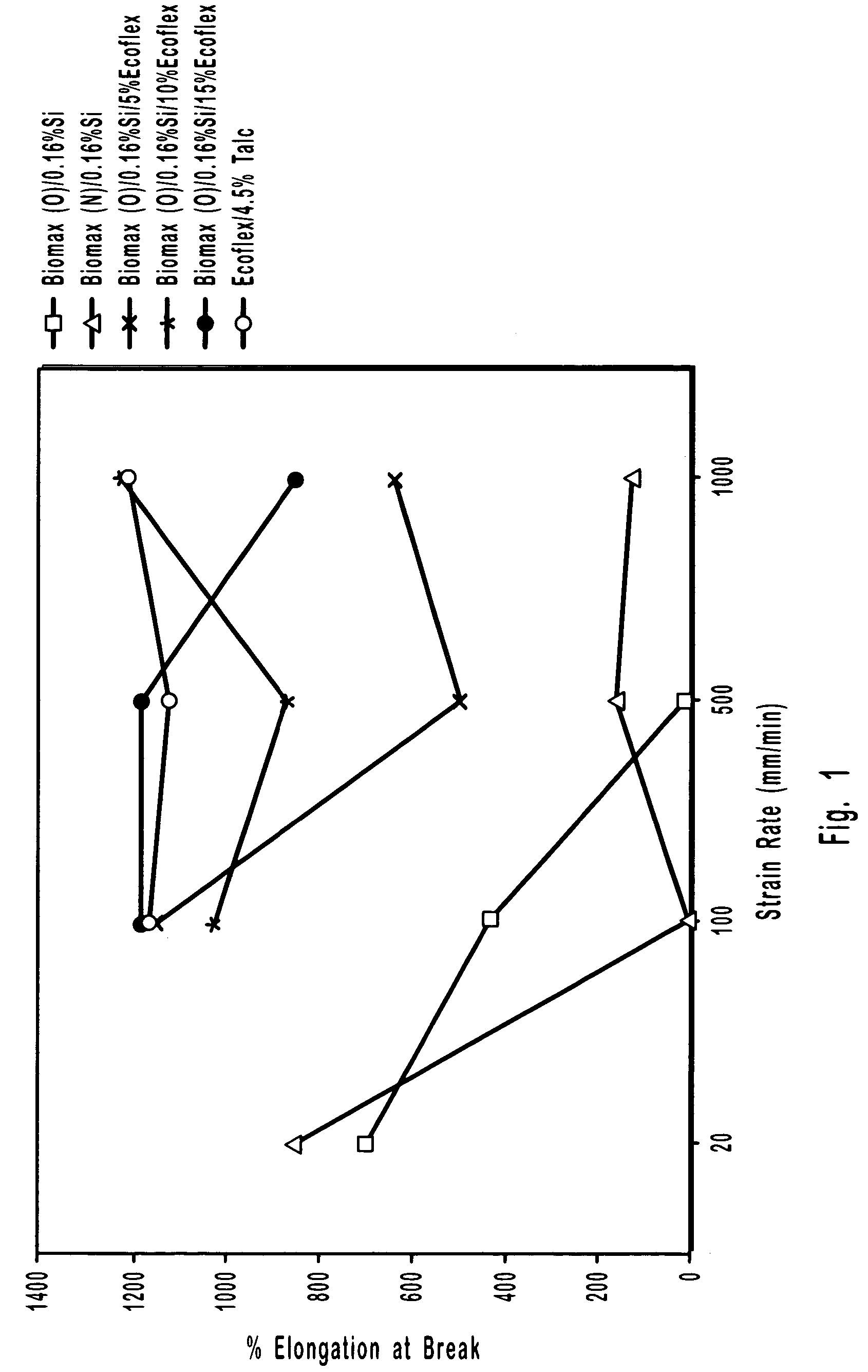
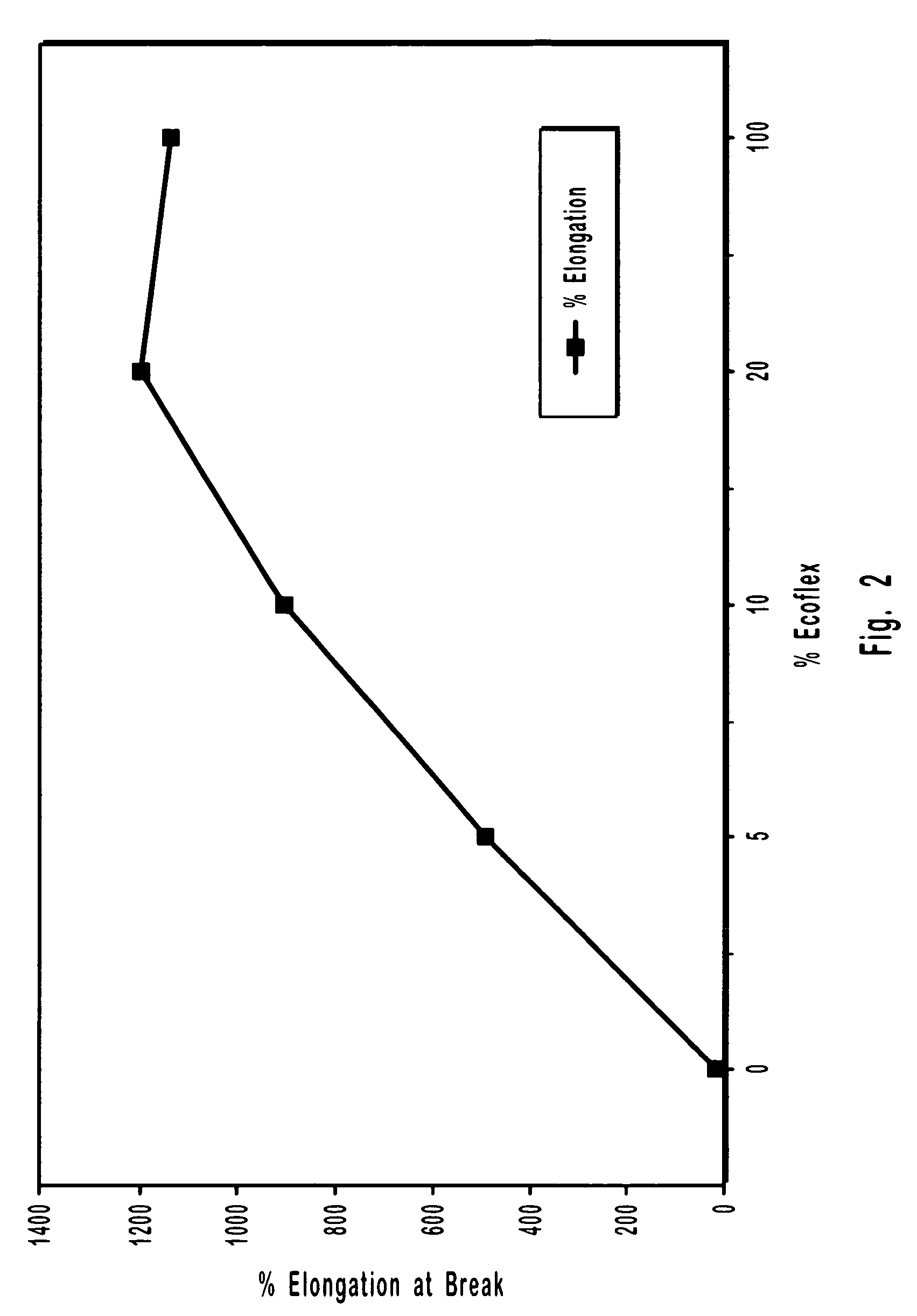
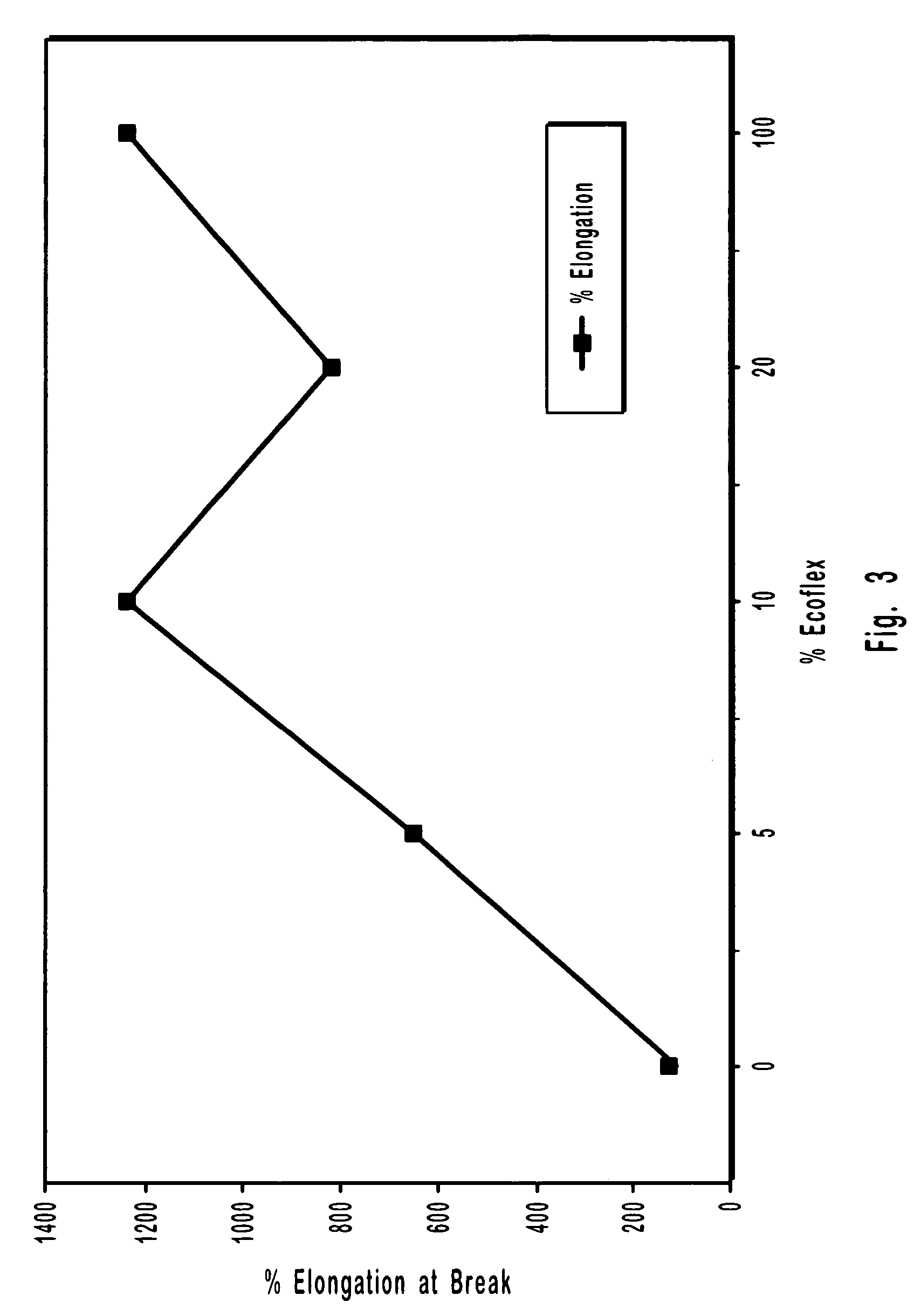
Biodegradable polymer blends suitable for laminate coatings, wraps and other packaging materials manufactured from at least one "hard" biopolymer and at least one "soft" biopolymer. "Hard" biopolymers tend to be more brittle and rigid and typically have a glass transition temperature greater than about 10° C. "Soft" biopolymers tend to be more flexible and pliable and typically have a glass transition temperature less than about 0° C. While hard and soft polymers each possess certain intrinsic benefits, certain blends of hard and soft polymers have been discovered which possess synergistic properties superior to those of either hard or soft polymers by themselves. Biodegradable polymers include polyesters, polyesteramides and thermoplastically processable starch. The polymer blends may optionally include an inorganic filler. Films and sheets made from the polymer blends may be textured so as to increase the bulk hand feel. Wraps will typically be manufactured so as to have good "dead-fold" properties so as to remain in a wrapped position and not spring back to an "unwrapped" and planar form. Laminate films will typically have good water vapor barrier properties as measured by the their Water Vapor Permeability Coefficient (WVPC).
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Compositions and methods for manufacturing thermoplastic starch blends
InactiveUS6235816B1Improved chemical and physical propertyPromote degradationFireproof paintsPaper coatingPolyesterPolymer science
A biologically degradable polymer mixture containing at least one biopolymer made from renewable raw materials and a polymer selected from the following materials: an aromatic polyester; a polyester-copolymer with both aliphatic and aromatic blocks; a polyesteramide; a polyglycol; a polyester urethane; and / or mixtures of these components. The preferred renewable raw material is starch, more preferably native starch, most preferably native starch that has been predried.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Crystallization control method for organic compound and crystallization control solid-state component employed therefor
InactiveUS6123769APolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsValence electronBiopolymer
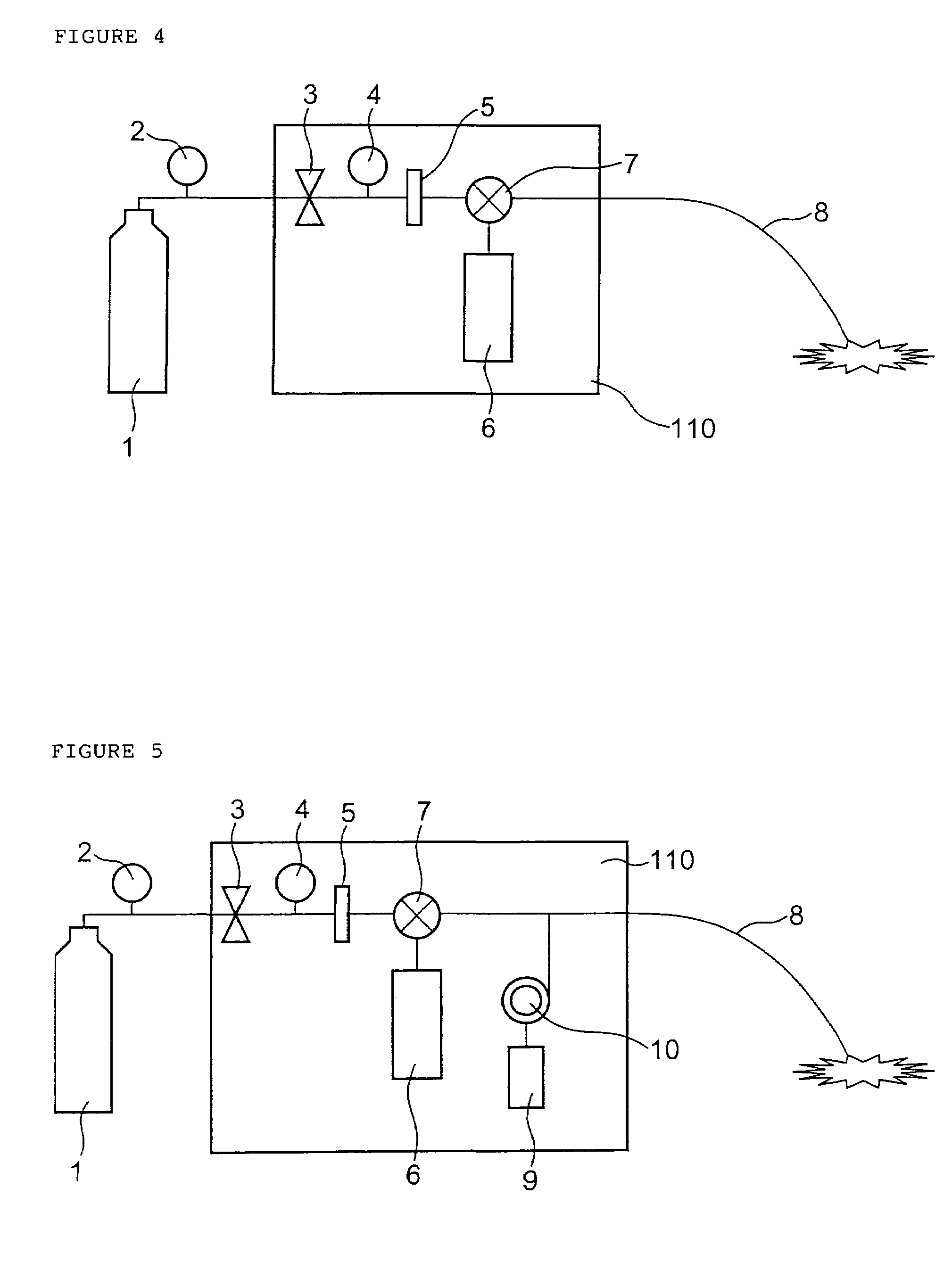
A method which can control crystallization of a biopolymer such as protein is provided. A silicon crystal (15) whose valence electrons are controlled to be capable of controlling the concentration of holes or electrons of the surface part in response to the environment of a buffer solution (14) containing the biopolymer such as protein is brought into contact with the solution (14), for getting a crystal of the biopolymer deposited on the surface of the silicon crystal (15). Crystallization is controlled by an electrical state which is generated by the controlled valence electrons on the surface of the silicon crystal (15).
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL IND LTD
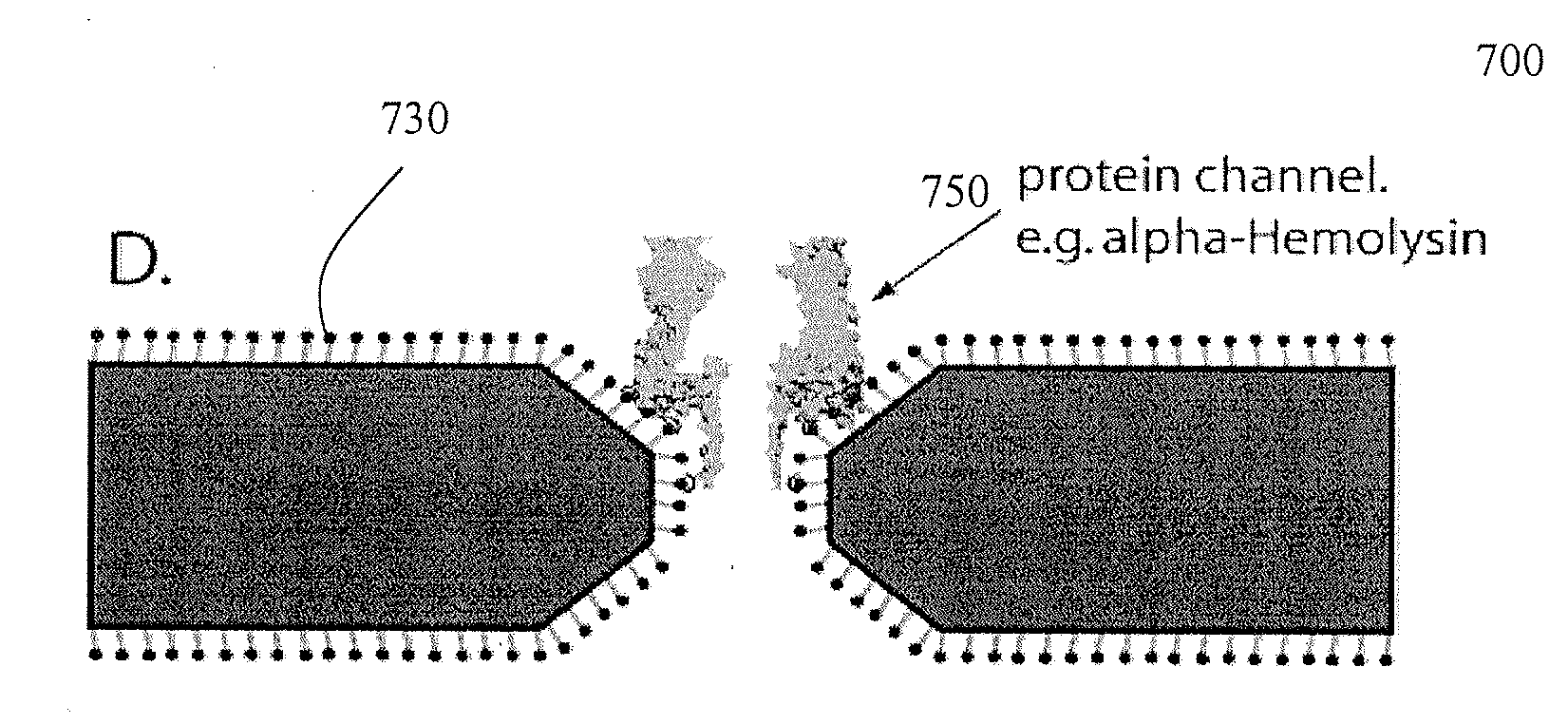
Nanopore with resonant tunneling electrodes
InactiveUS20070138132A1Paper/cardboard articlesDecorative surface effectsPotential differenceBiopolymer
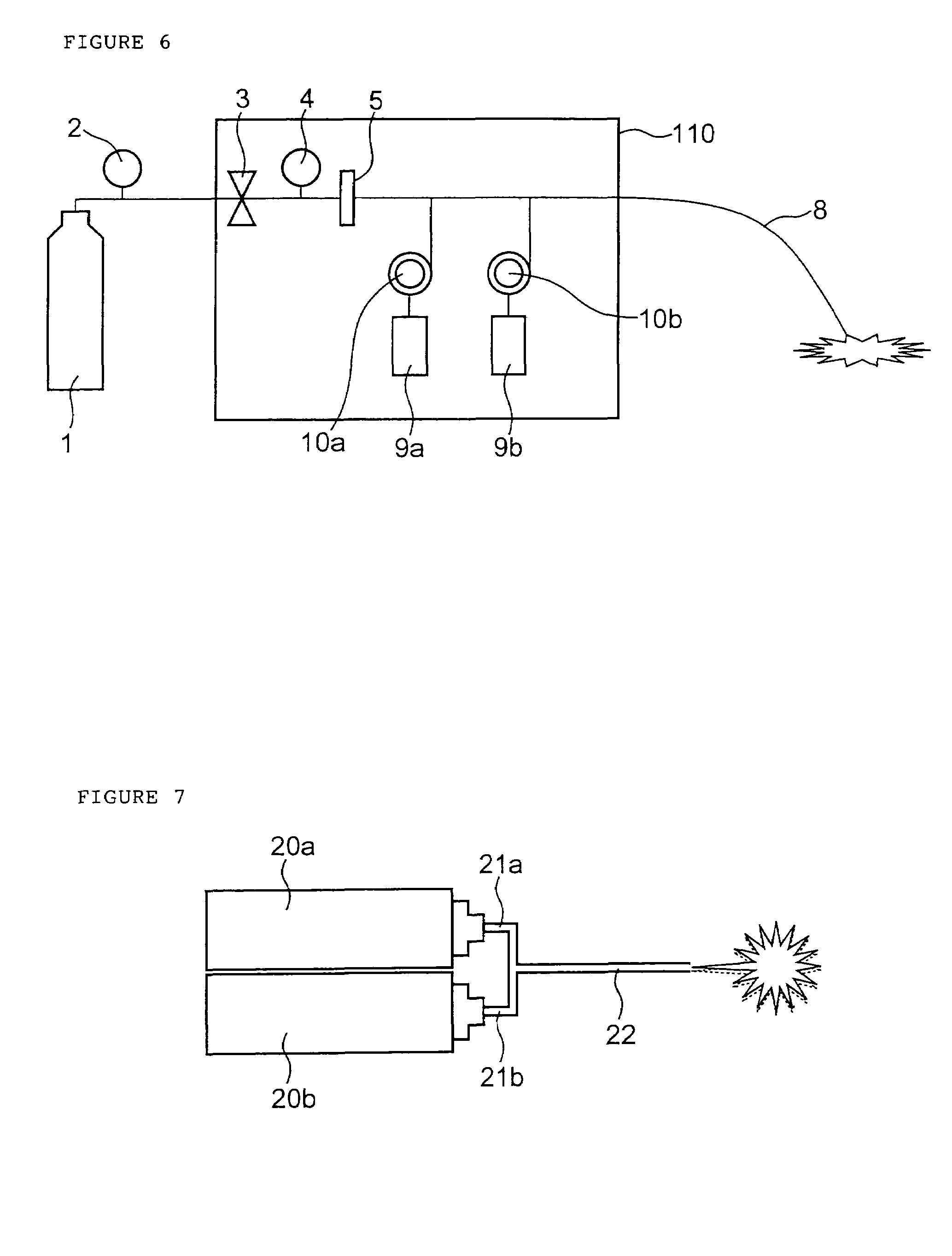
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for making an apparatus for sensing and / or characterizing a biopolymer translocating a nanopore. The apparatus of the present invention provides a first electrode, a first insulator, a second electrode, a optional insulator, a voltage source for applying a time varying potential difference between the electrodes, and a means of measuring the resulting current between the two electrodes. A method for making the apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Masks Based on Ion-Pair Delivery System
InactiveUS20040219124A1Easy to disassembleMaximum absorption and bioavailabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCross-linkBiopolymer
The present invention discloses a novel ion-pair delivery system based mask compositions for face, hair, skin, and body applications. These compositions come off from the site of their application essentially in one piece with the appearance, for example, of a piece of sea-weed or a continuous film. These mask compositions are suitable for a variety of delivery system methods, such as peel-off mask, moisturizing mask, exfoliating mask, prosthetic mask, soaking mask, depilatory mask, rub-off mask, two-phase mask, two-compartment mask, heat-releasing mask, and such. These mask compositions are made from the biopolymer based films that are cross-linked with divalent or trivalent metal cations. During the cross-linking process, such divalent and trivalent metal cations may also act as release agents for other face, hair, skin, and body beneficial compositions in their enhanced bioavailable forms by an ion-pair activation mechanism.
Owner:GUPTA SHYAM K
Gelled biopolymer based foam
InactiveUS20050137272A1Improve water absorptionWet strengthCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPersonal careCross-link
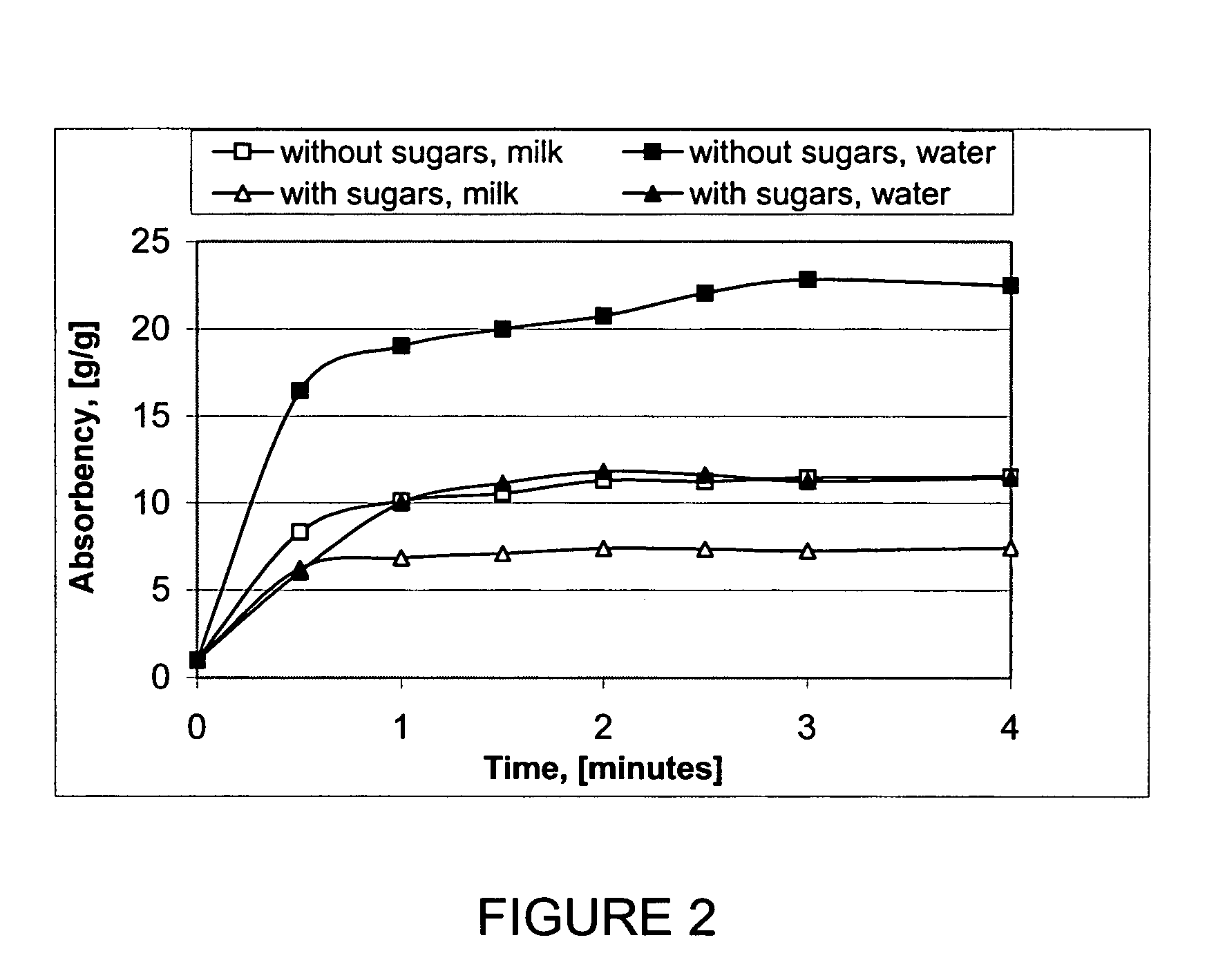
Gelled biopolymer based foams are disclosed. The gelled foams comprise a cross-linked biopolymer, preferably alginate; optionally, a foaming agent such as hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose; and a plasticizer, preferably glycerin sorbitol, or a mixture thereof, that forms the predominant portion of the gelled foam. The foams are soft and pliable and have high absorbency. They are used as wound dressing materials, controlled release delivery systems, cell culture, barrier media for preventing tissue adherence, and bioabsorbable implants. They also have various personal care applications, especially in oral hygiene, and can be used in food applications.
Owner:FMC BIOPOLYMER AS
Interpenetrating Networks, and Related Methods and Compositions
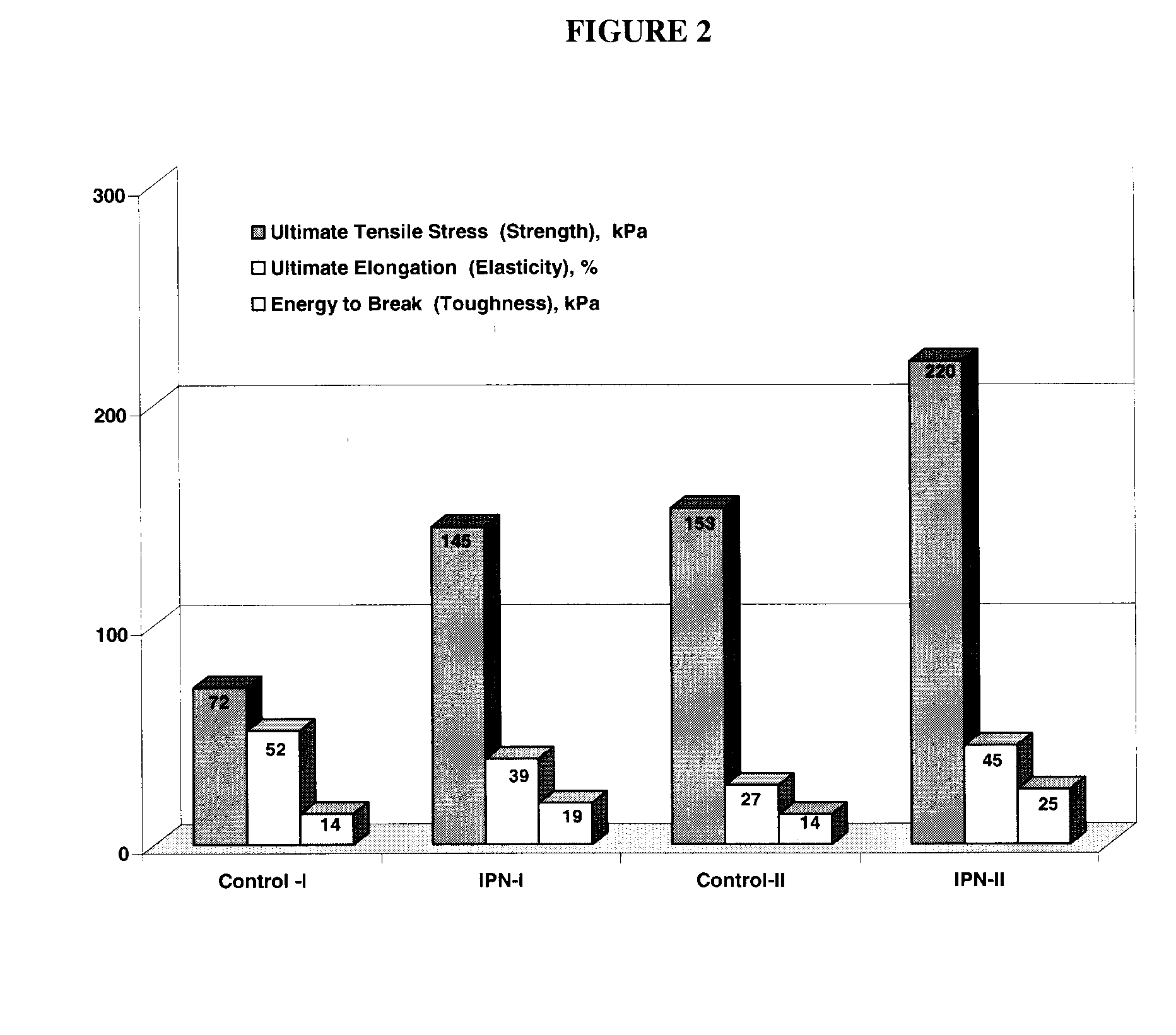
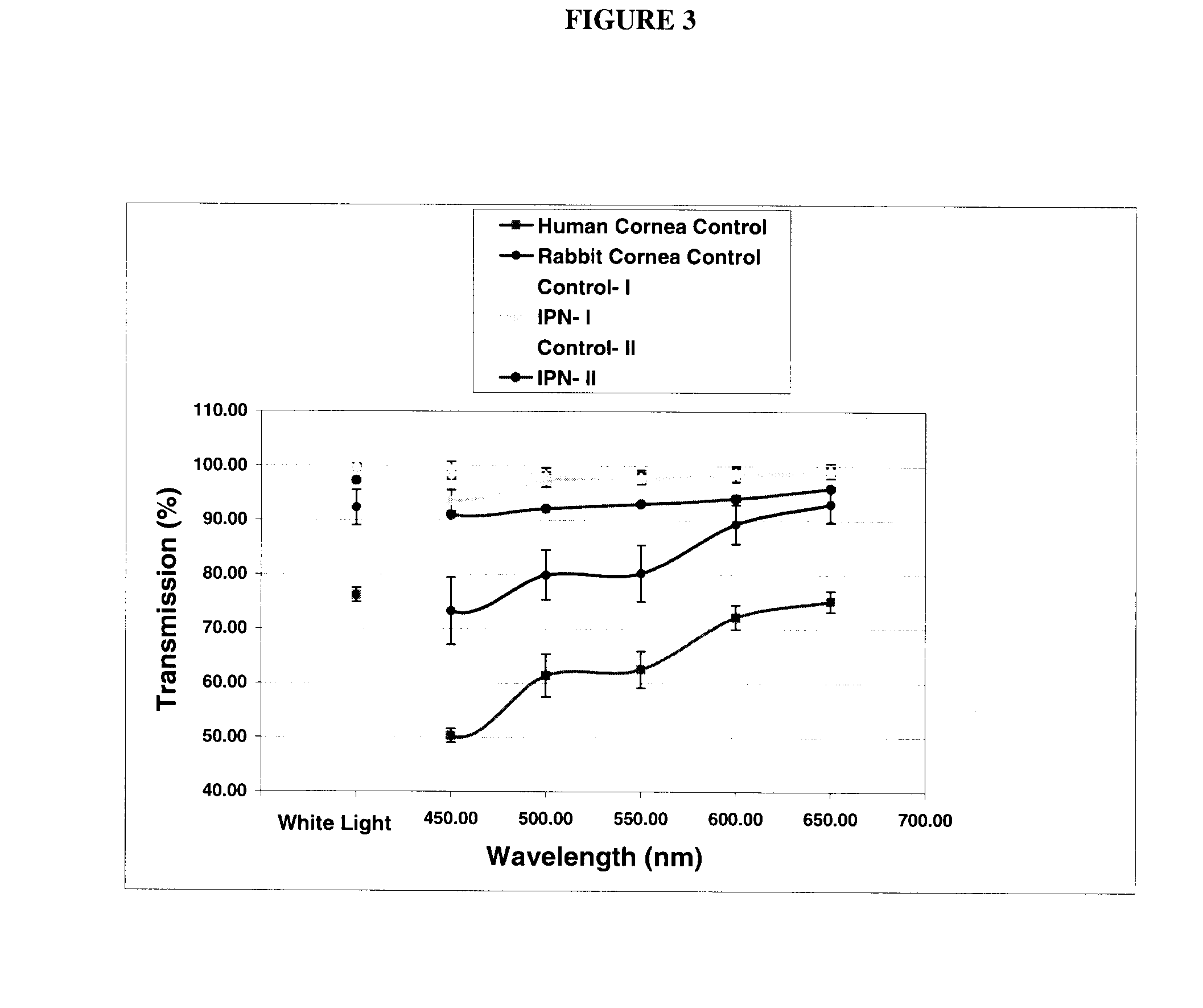
The present invention provides interpenetrating polymeric networks (IPNs), and related methods and compositions. The hydrogel material of this invention comprises an interpenetrating network of two or more polymer networks, wherein at least one of the polymer networks is based on a biopolymer. Also provided is a method of producing the hydrogel material comprising, combining a first polymeric network with a second polymeric network, wherein the first polymeric network or the second polymeric network is based on a biopolymer. The present application also discloses devices manufactured from the IPN hydrogel material and uses thereof.
Owner:OTTAWA HOSPITAL RES INST +1
Seamless capsule for synthesizing biopolymer and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6251661B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsViscous liquidBiopolymer
This invention provides a seamless capsule for synthesizing biopolymer, comprising:(a) an aqueous mixture for synthesizing biopolymer,(b) a seamless capsule layer encapsulating said aqueous mixture, formed from polysaccharide or protein, and,(c) a viscous liquid intermediate layer, present between said aqueous mixture and said seamless capsule layer, which is immiscible with water,wherein said seamless capsule has a diameter of 0.01 to 10.0 mm.This invention can also provide a method for producing the seamless capsule.
Owner:MORISHITA JINTAN CO LTD
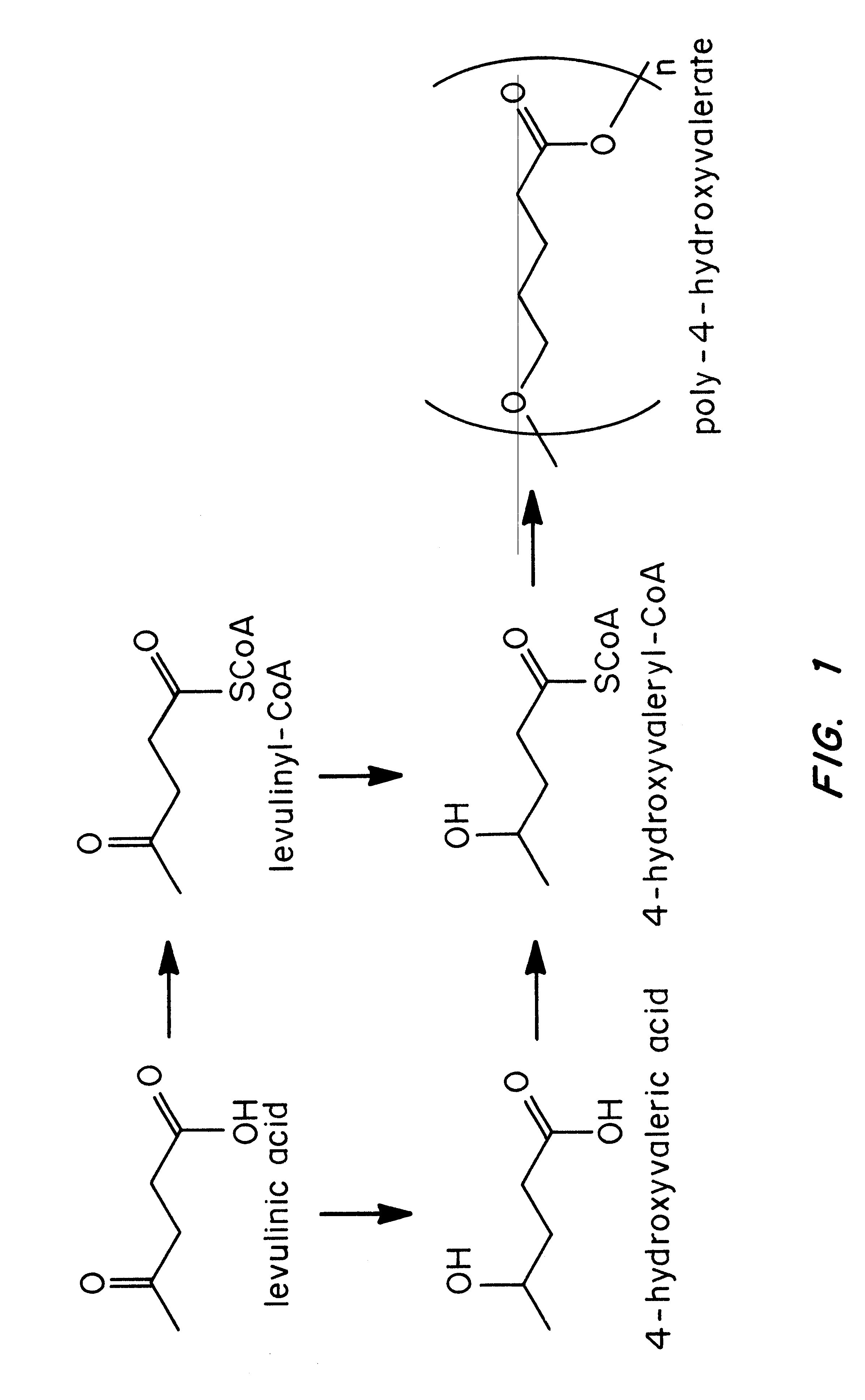
Polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer compositions
Several novel PHA polymer compositions produced using biological systems include monomers such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxypropionate, 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, 4-hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate. These PHA compositions can readily be extended to incorporate additional monomers including, for example, 3-hydroxyhexanoate, 4-hydroxyhexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate or other longer chain 3-hydroxyacids containing seven or more carbons. This can be accomplished by taking natural PHA producers and mutating through chemical or transposon mutagenesis to delete or inactivate genes encoding undesirable activities. Alternatively, the strains can be genetically engineered to express only those enzymes required for the production of the desired polymer composition. Methods for genetically engineering PHA producing microbes are widely known in the art (Huisman and Madison, 1998, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63: 21-53). These polymers have a variety of uses in medical, industrial and other commercial areas.
Owner:METABOLIX
Picowell capture devices for analysing single cells or other particles
InactiveUS20120156675A1Easy to adaptCompared rapidly and convenientlyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIndividual analysisBiopolymer
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH IP
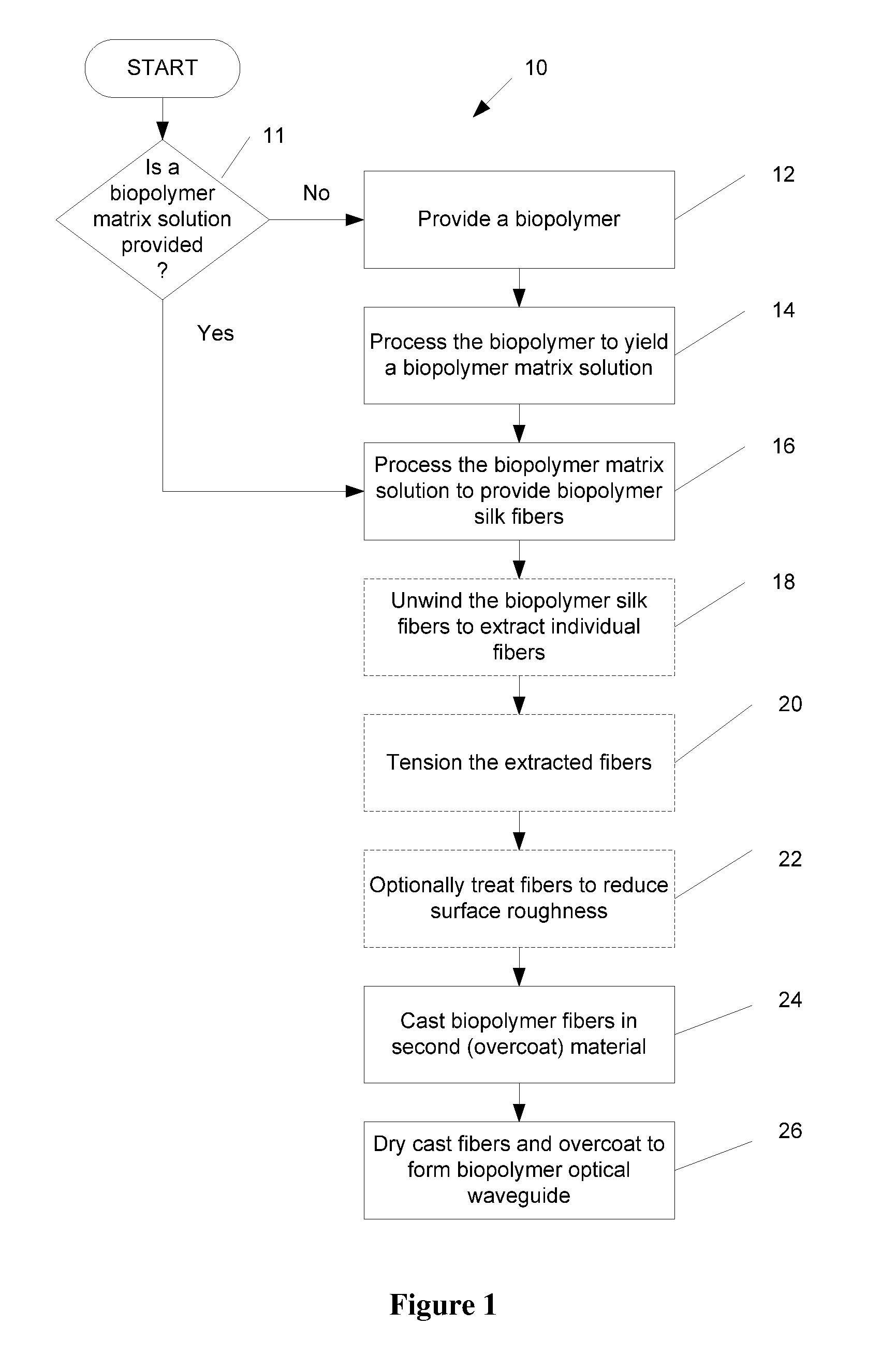
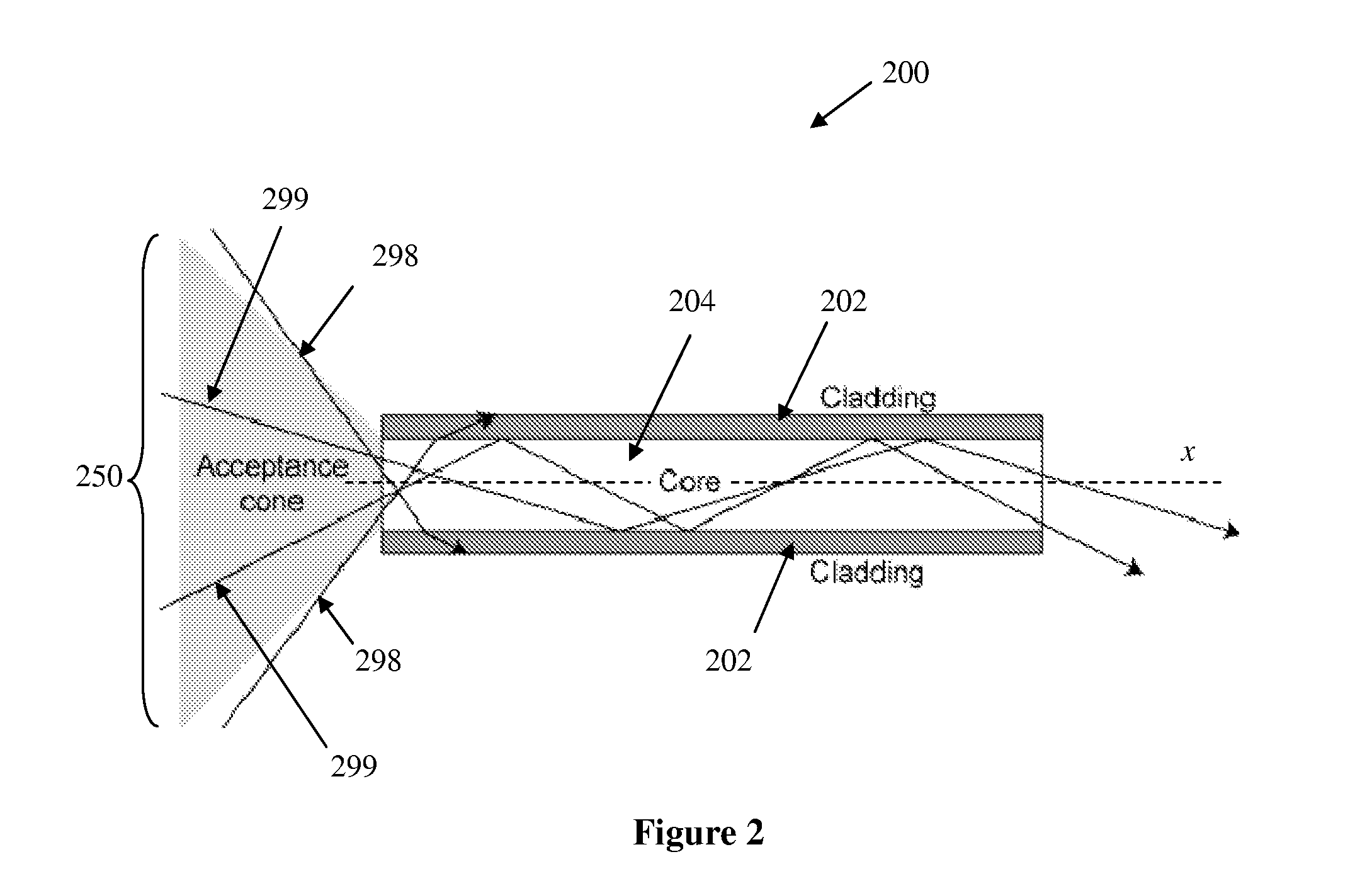
Biopolymer optical waveguide and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100063404A1Minimize negative impactImprove functional propertiesBiological material analysisMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentFiberBiopolymer
A method of manufacturing a biopolymer optical waveguide includes providing a biopolymer, unwinding the biopolymer progressively to extract individual biopolymer fibers, and putting the unwound fibers under tension. The tensioned fibers are then cast in a different polymer to form a biopolymer optical waveguide that guides light due to the difference in indices of refraction between the biopolymer and the different polymer. The optical fibers may be used in biomedical applications and can be inserted in the body as transmissive media. Printing techniques may be used to manufacture the biopolymer optical waveguides.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
Tissue scaffold having aligned fibrils, apparatus and method for producing the same, and artificial tissue and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050009178A1Improve structural strengthMinimal immunological responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHollow filament manufactureFiberRadial position
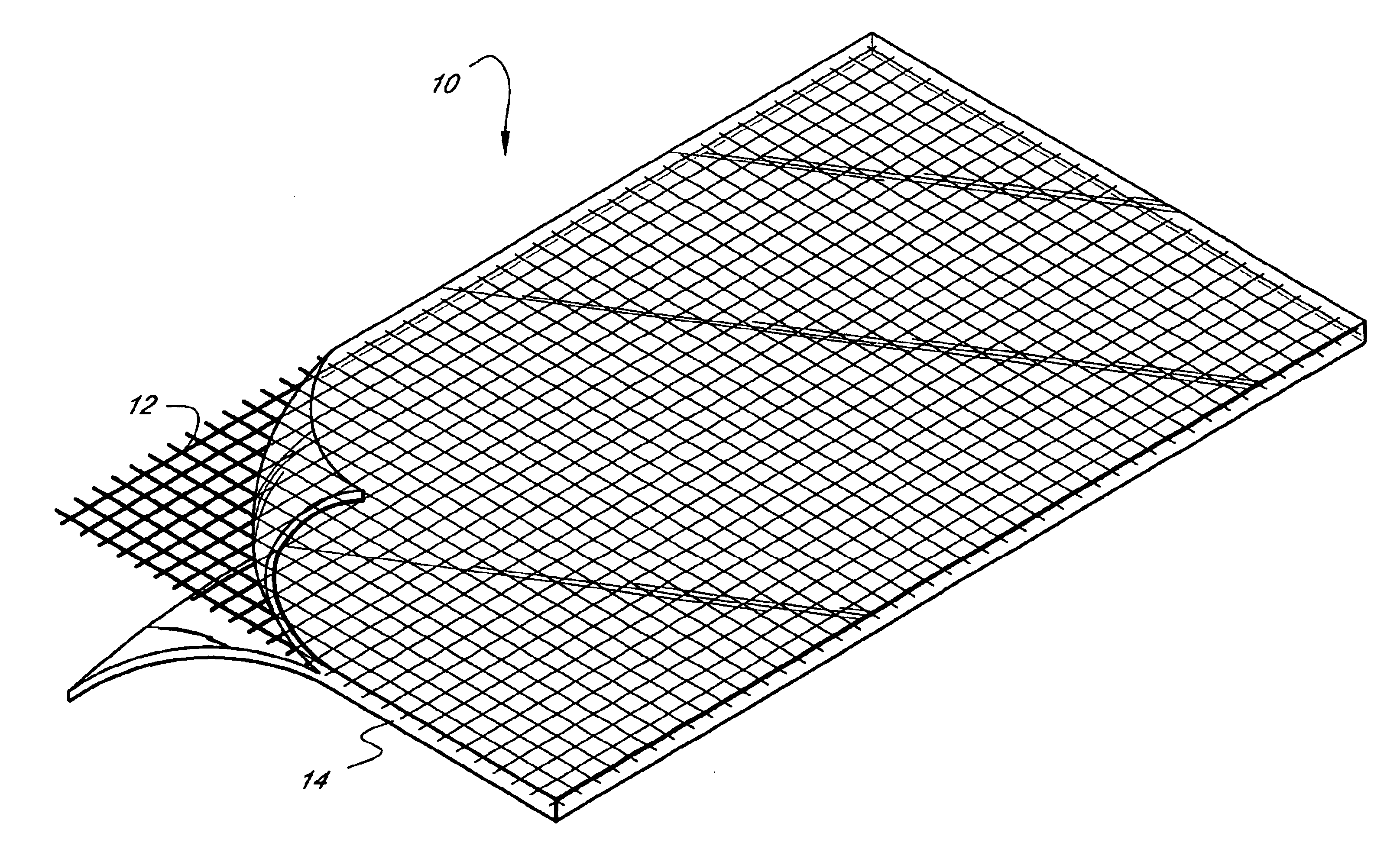
A tubular tissue scaffold is described which comprises a tube having a wall, wherein the wall includes biopolymer fibrils that are aligned in a helical pattern around the longitudinal axis of the tube where the pitch of the helical pattern changes with the radial position in the tube wall. The scaffold is capable of directing the morphological pattern of attached and growing cells to form a helical pattern around the tube walls. Additionally, an apparatus for producing such a tubular tissue scaffold is disclosed, the apparatus comprising a biopolymer gel dispersion feed pump that is operably connected to a tube-forming device having an exit port, where the tube-forming device is capable of producing a tube from the gel dispersion while providing an angular shear force across the wall of the tube, and a liquid bath located to receive the tubular tissue scaffold from the tube-forming device. A method for producing the tubular tissue scaffolds is also disclosed. Also, artificial tissue comprising living cells attached to a tubular tissue scaffold as described herein is disclosed. Methods for using the artificial tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
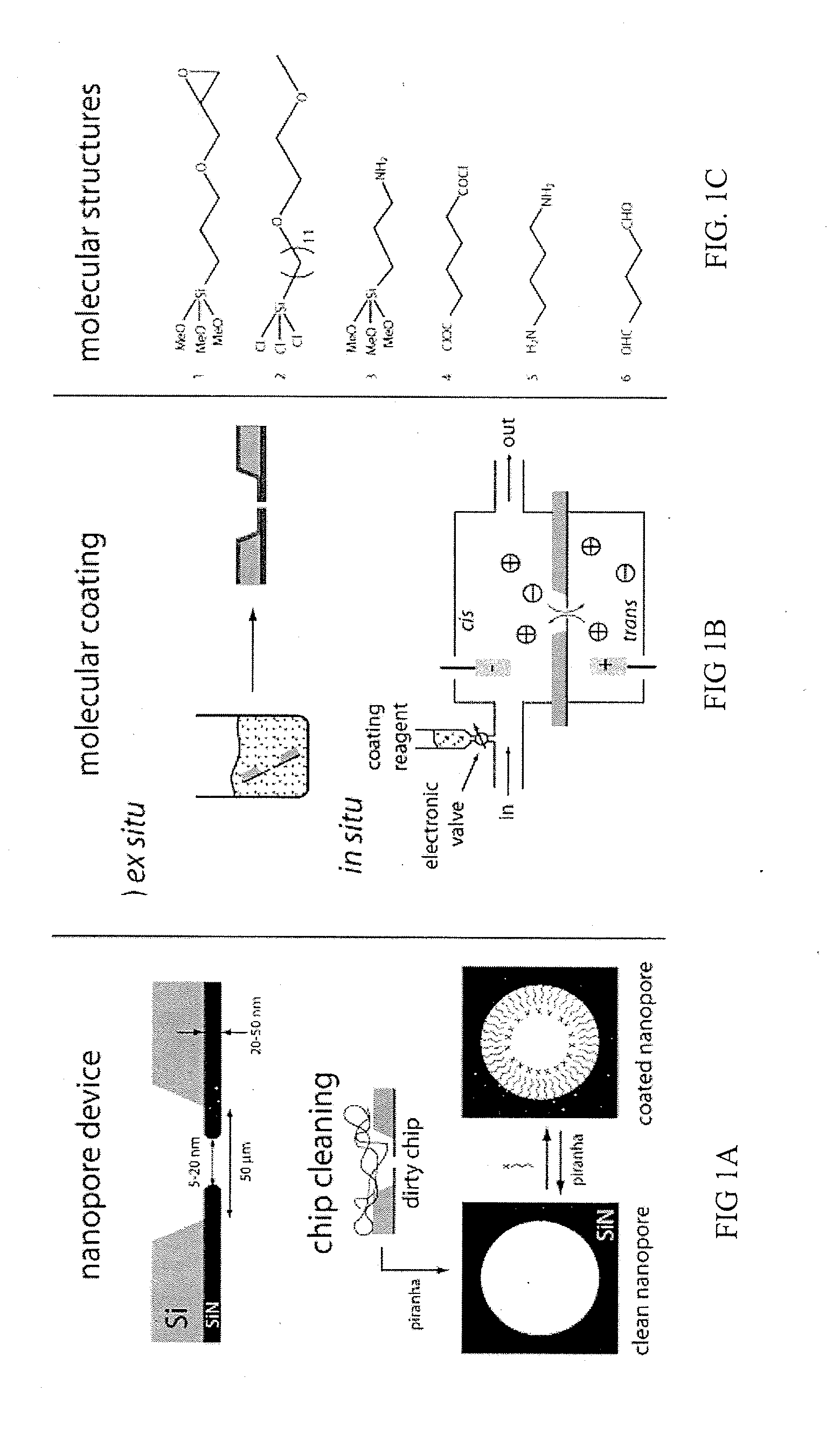
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof
ActiveUS20110053284A1Avoid stickingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiopolymerElectron
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof. Nanopores are extremely sensitive single-molecule sensors. Recently, electron beams have been used to fabricate synthetic nanopores in thin solid-state membranes with sub-nanometer resolution. A new class of chemically modified nanopore sensors are provided with two approaches for monolayer coating of nanopores by: (1) self-assembly from solution, in which nanopores −10 nm diameter can be reproducibly coated, and (2) self-assembly under voltage-driven electrolyte flow, in which 5 nm nanopores may be coated. Applications of chemically modified nanopore are provided including: the detection of biopolymers such as DNA and RNA; immobilizing enzymes or other proteins for detection or for generating chemical gradients; and localized pH sensing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Electronic systems and component devices for macroscopic and microscopic molecular biological reactions, analyses and diagnostics
InactiveUS6780584B1Favorable zoneImprove responseMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsAntigenElectronic systems
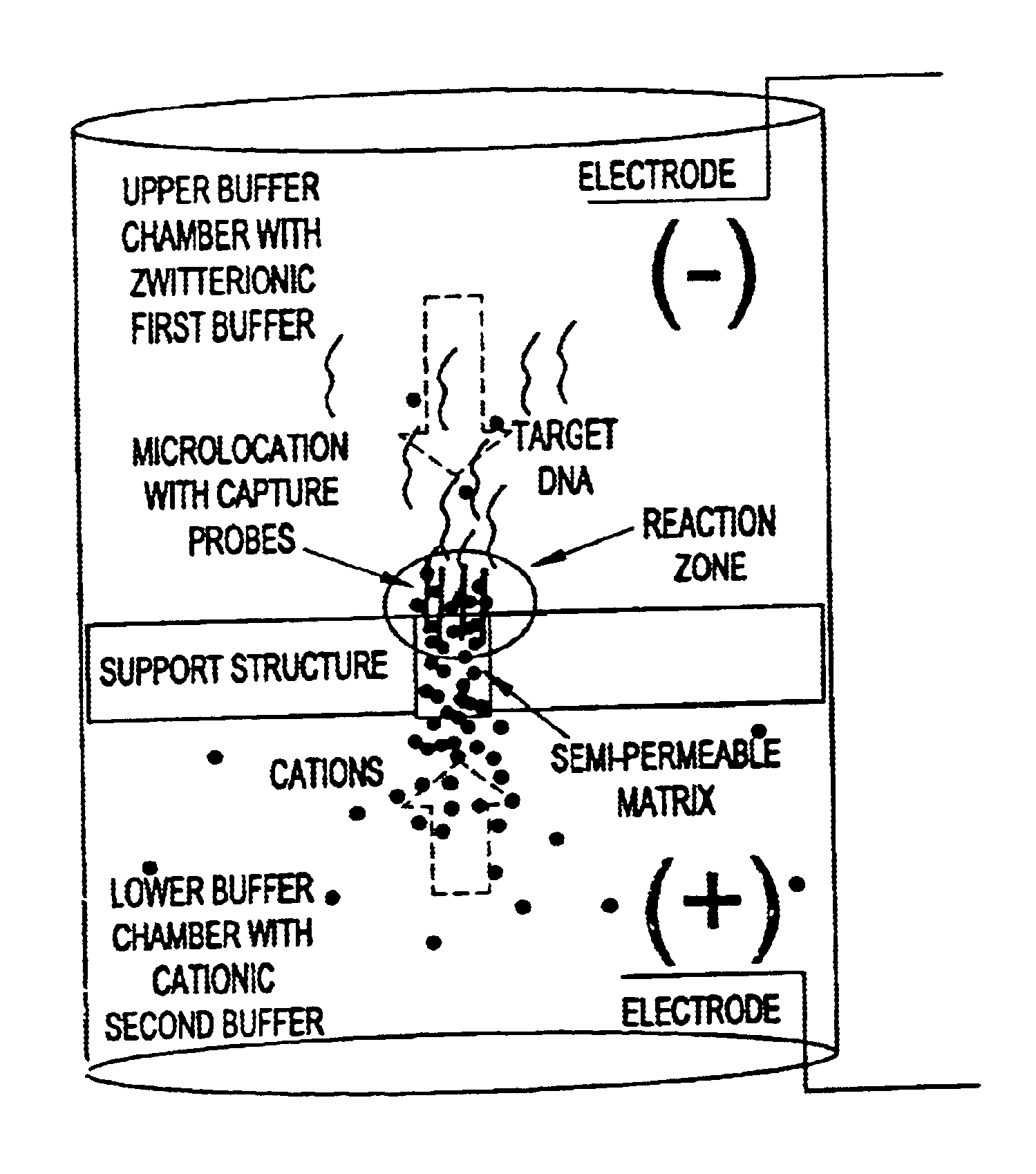
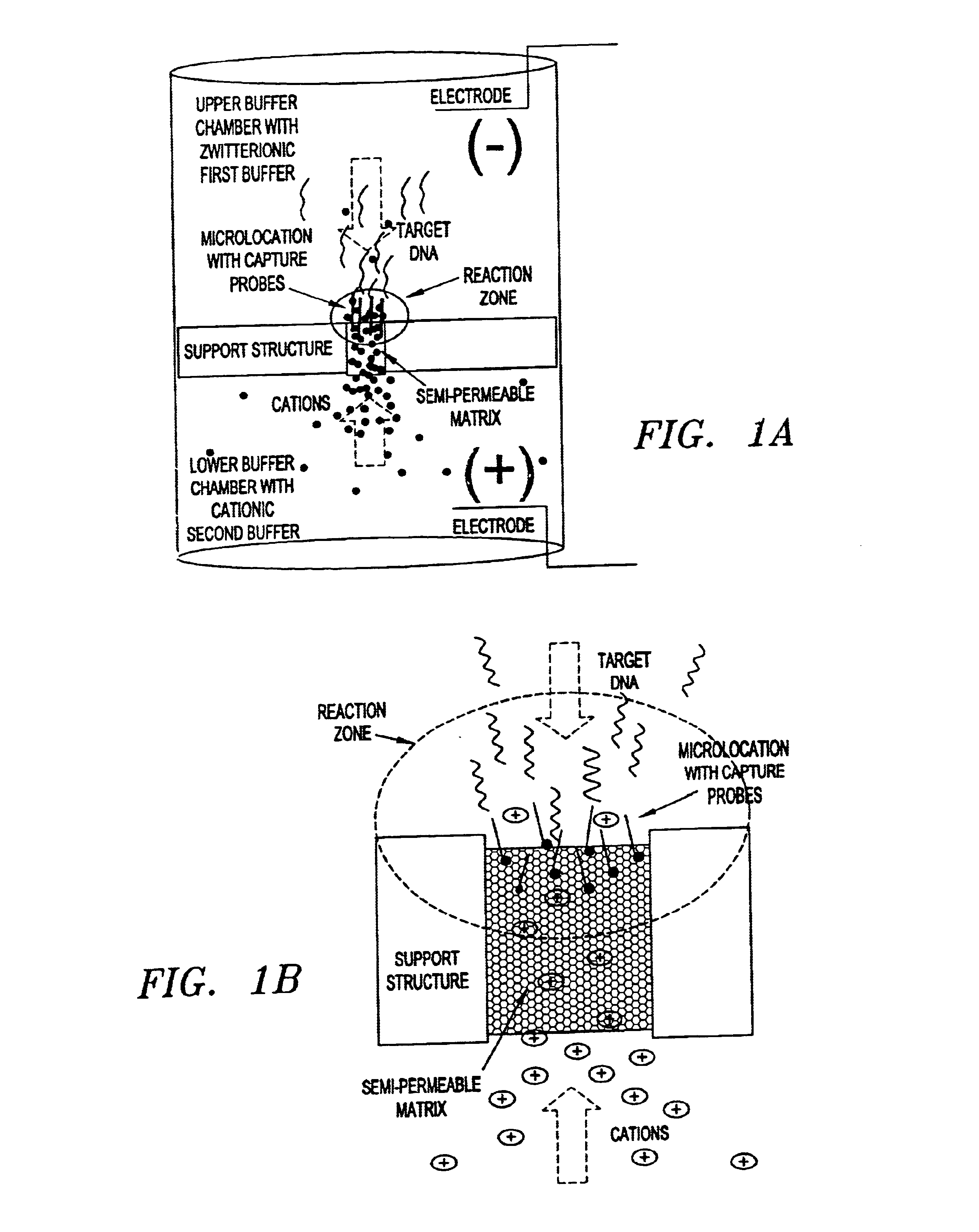
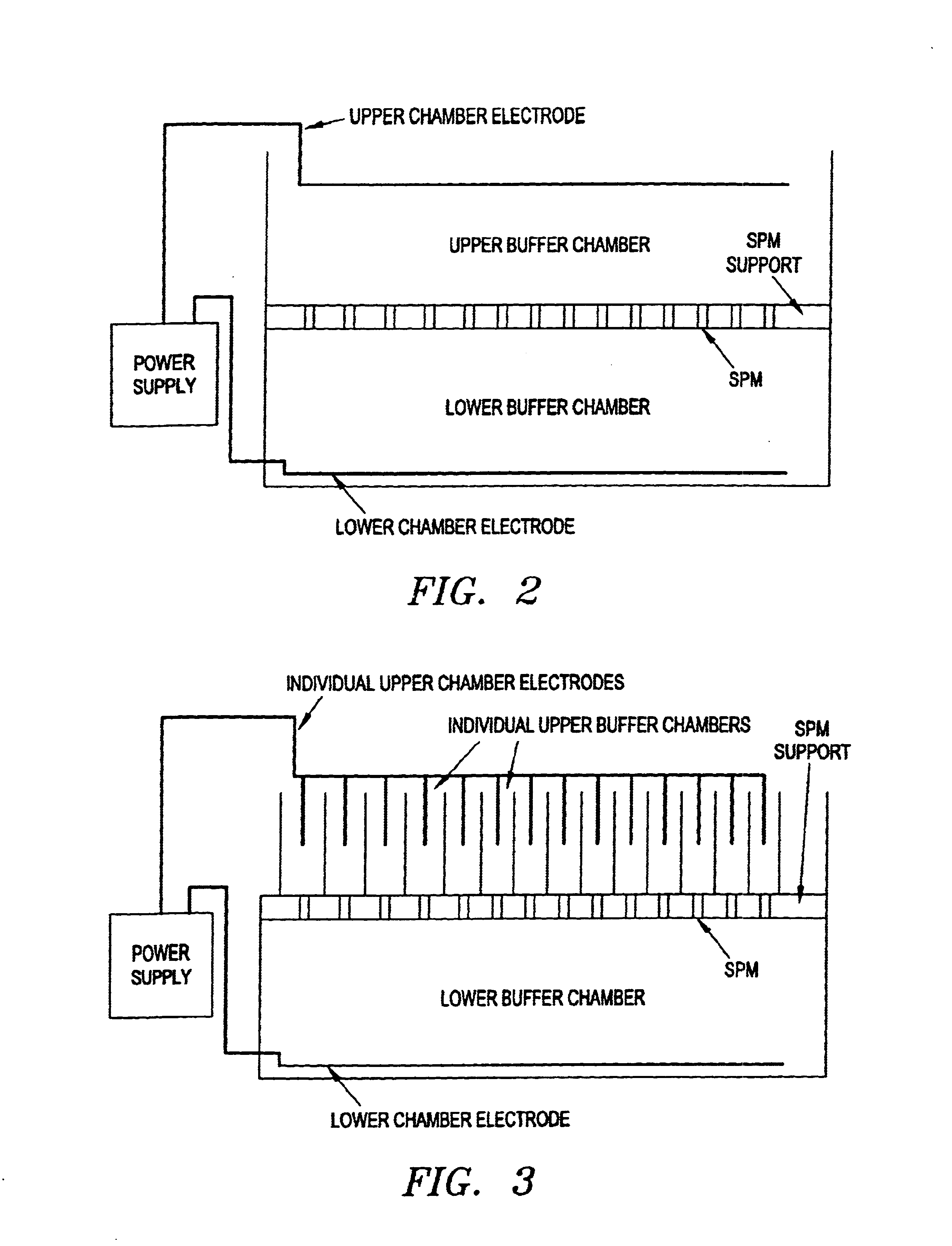
This invention pertains to the design, fabrication, and uses of an electronic system which can actively carry out and control multi-step and multiplex reactions in macroscopic or microscopic formats. In particular, these reactions include molecular biological reactions, such as nucleic acid hybridizations, nucleic acid amplification, sample preparation, antibody / antigen reactions, clinical diagnostics, combinatorial chemistry and selection, drug screening, oligonucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis, peptide synthesis, biopolymer synthesis and catalytic reactions. A key feature of the present invention is the ability to control the localized concentration of two or more reaction-dependant molecules and their reaction environment in order to greatly enhance the rate and specificity of the molecular biological reaction.
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL +1
Regeneration and augmentation of bone using mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS6863900B2Reduce functionReduce the numberBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMedicineBiopolymer
Disclosed are compositions and methods for augmenting bone formation by administering isolated human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) with a ceramic material or matrix or by administering hMSCs; fresh, whole marrow; or combinations thereof in a resorbable biopolymer which supports their differentiation into the osteogenic lineage. Contemplated is the delivery of (i) isolated, culture-expanded, human mesenchymal stem cells; (ii) freshly aspirated bone marrow; or (iii) their combination in a carrier material or matrix.
Owner:MESOBLAST INT
Biopolymer nano tunica fibrosa material capable of being biological degraded and absorbed, preparing method and uses of the same
InactiveCN101172164AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationSurgeryFilament/thread formingFiberCellulose
The invention relates to compound millimicron fibrous membrane material of cellulose and cellulose matrix which can perform the biological degradation and the biological absorption and a preparation method thereof and an industry and medical purpose, and belongs to the biological macro-molecule non woven fabric material field which can perform the biological degradation and the biological absorption. Electrostatic spinning equipment is used to obtain the fibrous membrane material which can perform the biological degradation and the biological absorption, the weight of the cellulose is taken as basic reference, the component of the material comprises cellulose more than 0 and less than or equal to 100 weight parts, other biomacromolecule more than and equal to 0 and less than 100 weight parts, 0 to 10 weight parts of curative drug or 0 to 50 weight parts of inorganic catalyzer and / or 0 to 50 weight parts of inorganic strengthening agent. The material of the invention has good biological compatibility, biological degradation property and degradation absorptivity, and can be used for haemostasia material, wound cladding material, organization engineering supporting rack material, the transportation and release of medicine, artificial skin and blood vessel, and postoperation anti blocking material, beauty material and catalyzer carrier, filtering membrane and radiation protection material and so on.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multifunctional and biologically active matrices from multicomponent polymeric solutions
The present invention relates to a biologically active functionalized electrospun matrix to permit immobilization and long-term delivery of biologically active agents. In particular the invention relates to a functionalized polymer matrix comprising a matrix polymer, a compatibilizing polymer and a biomolecule or other small functioning molecule. In certain aspects the electrospun polymer fibers comprise at least one biologically active molecule functionalized with low molecular weight heparin. Examples of active molecules that may be used with the multicomponent polymer of the invention include, for example, a drug, a biopolymer, for example a growth factor, a protein, a peptide, a nucleotide, a polysaccharide, a biological macromolecule or the like. The invention is further directed to the formation of functionalized crosslinked matrices, such as hydrogels, that include at least one functionalized compatibilizing polymer capable of assembly.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
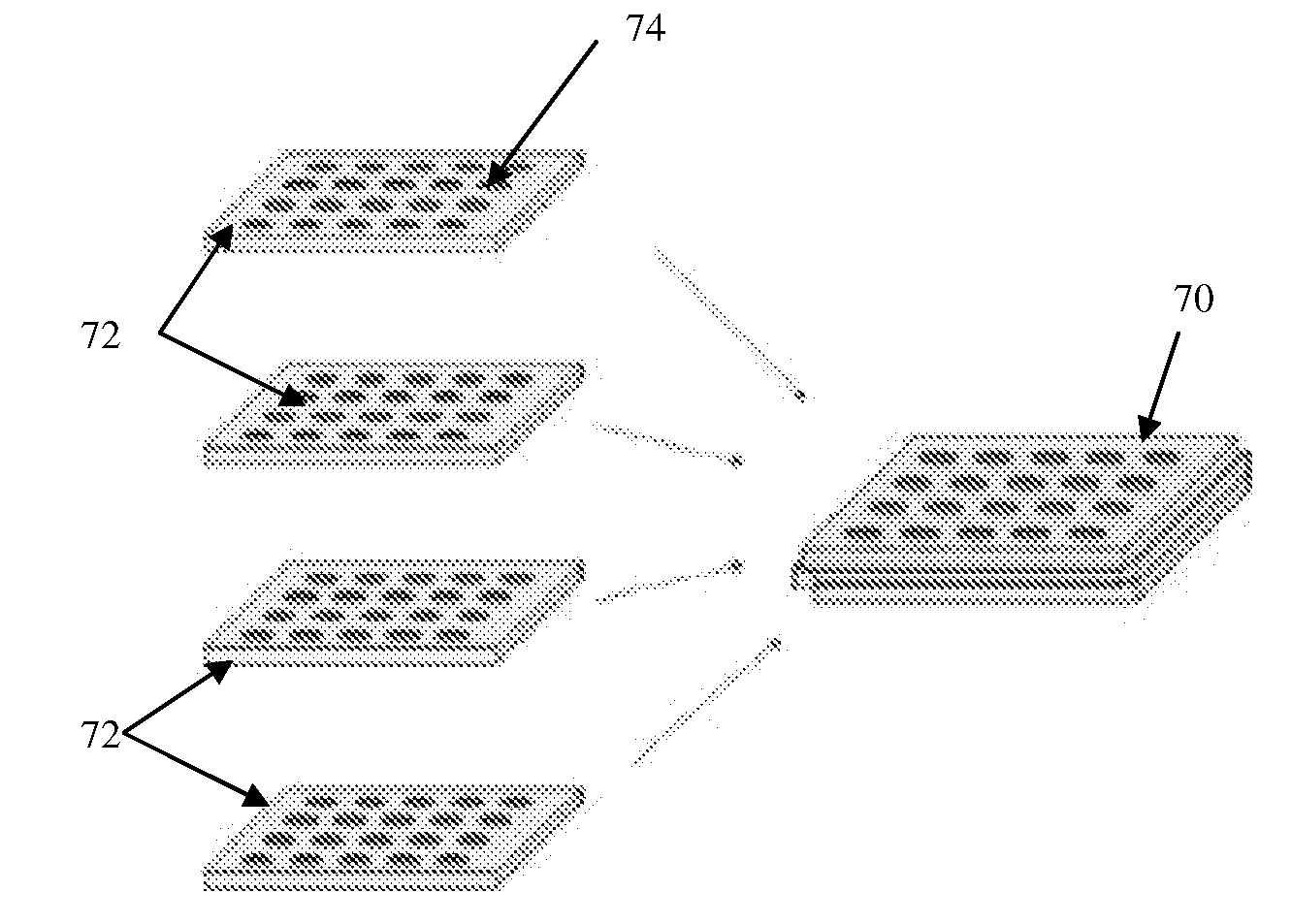
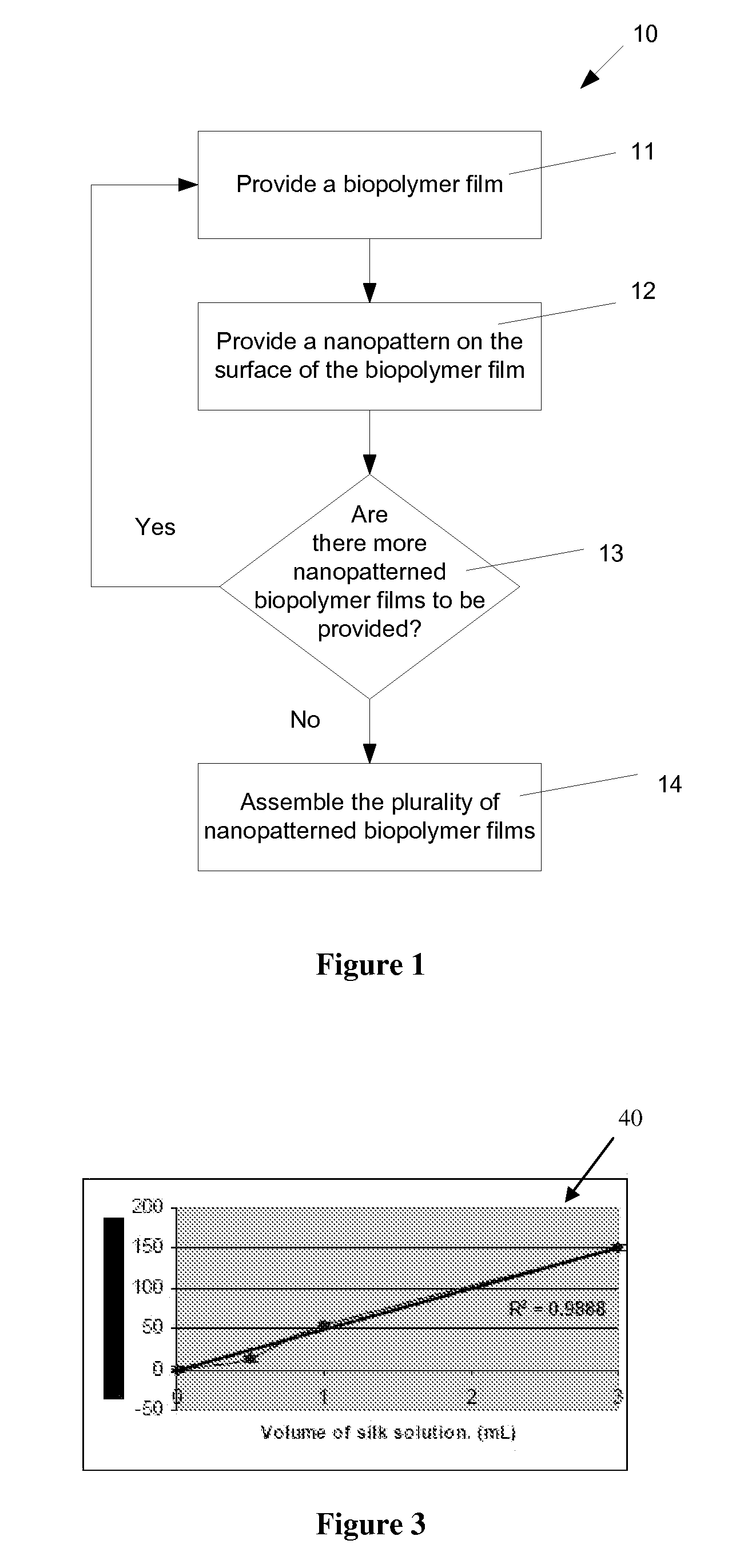
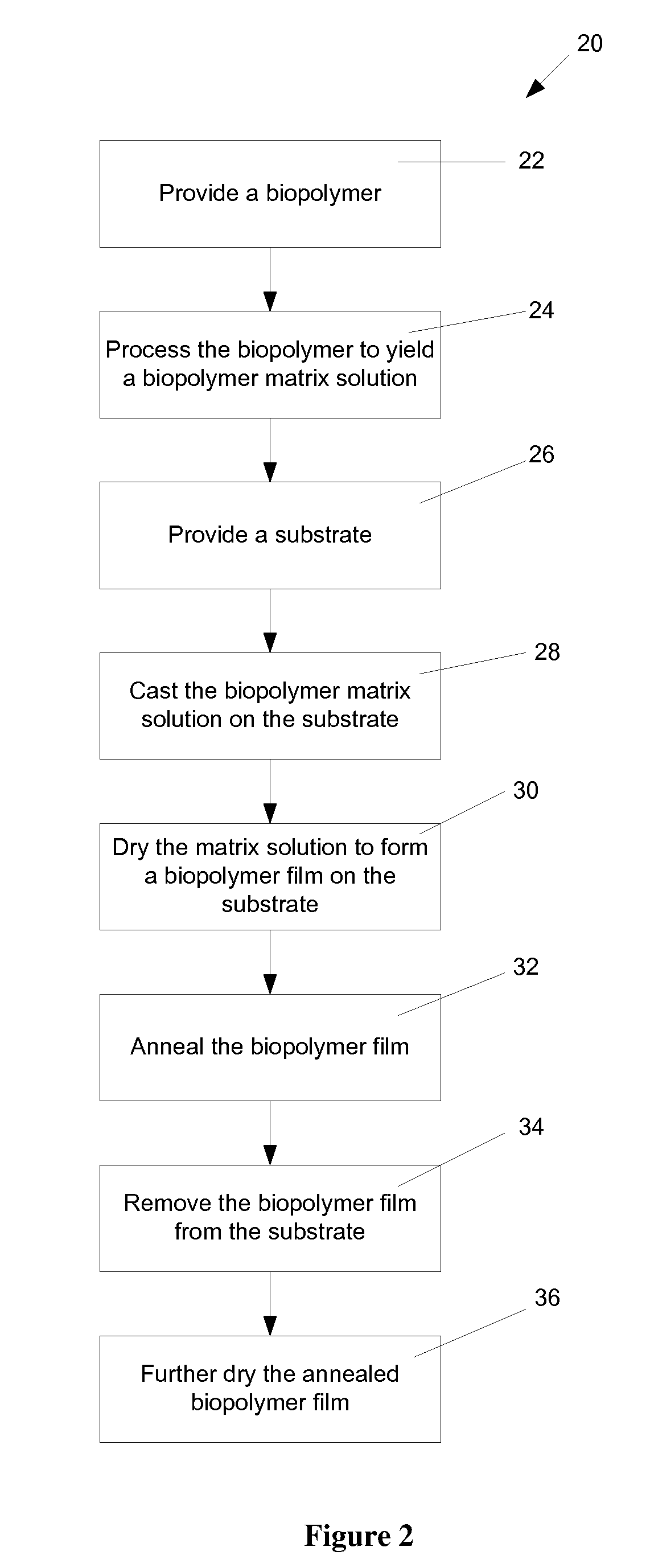
Nanopatterned biopolymer optical device and method of manufacturing the same
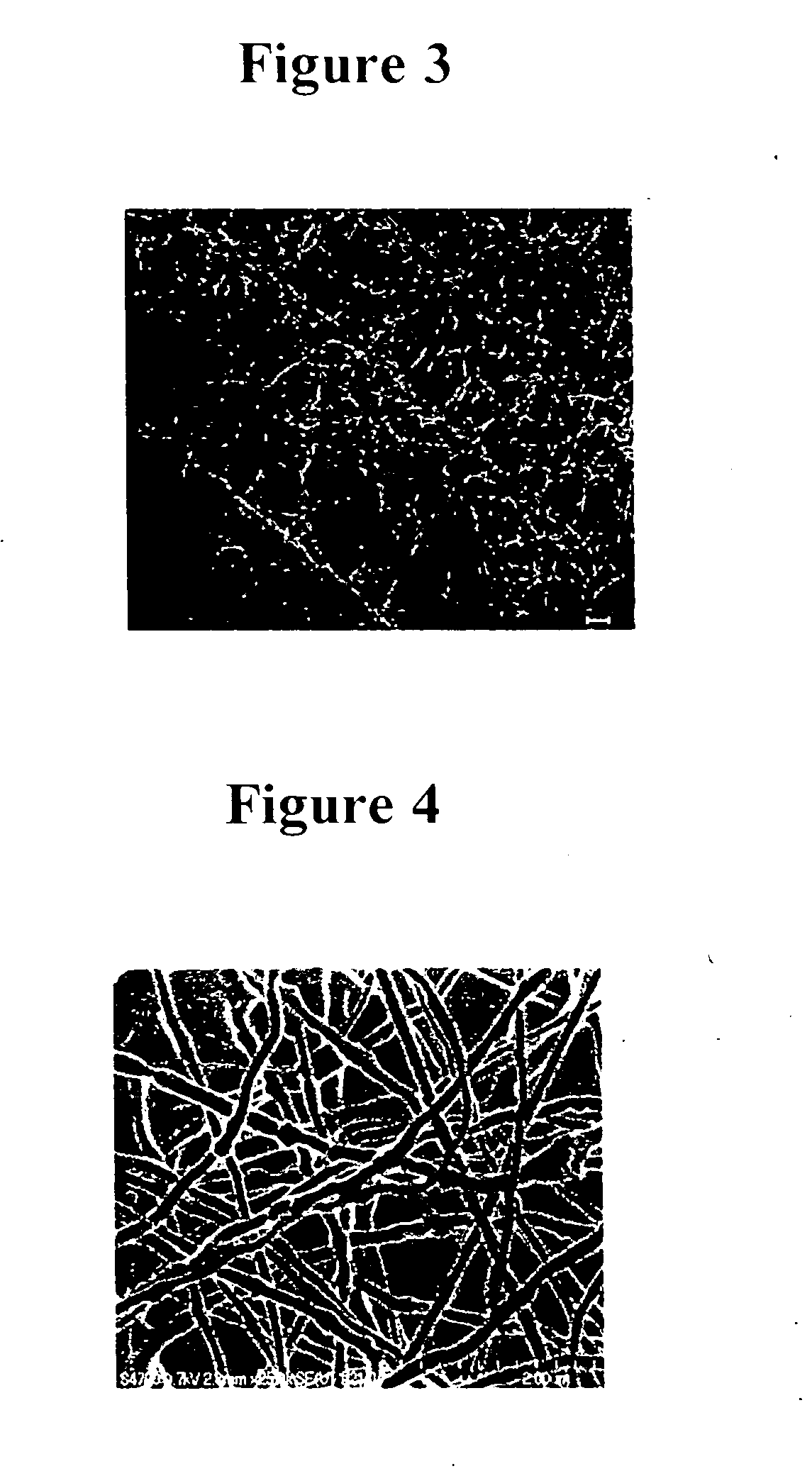
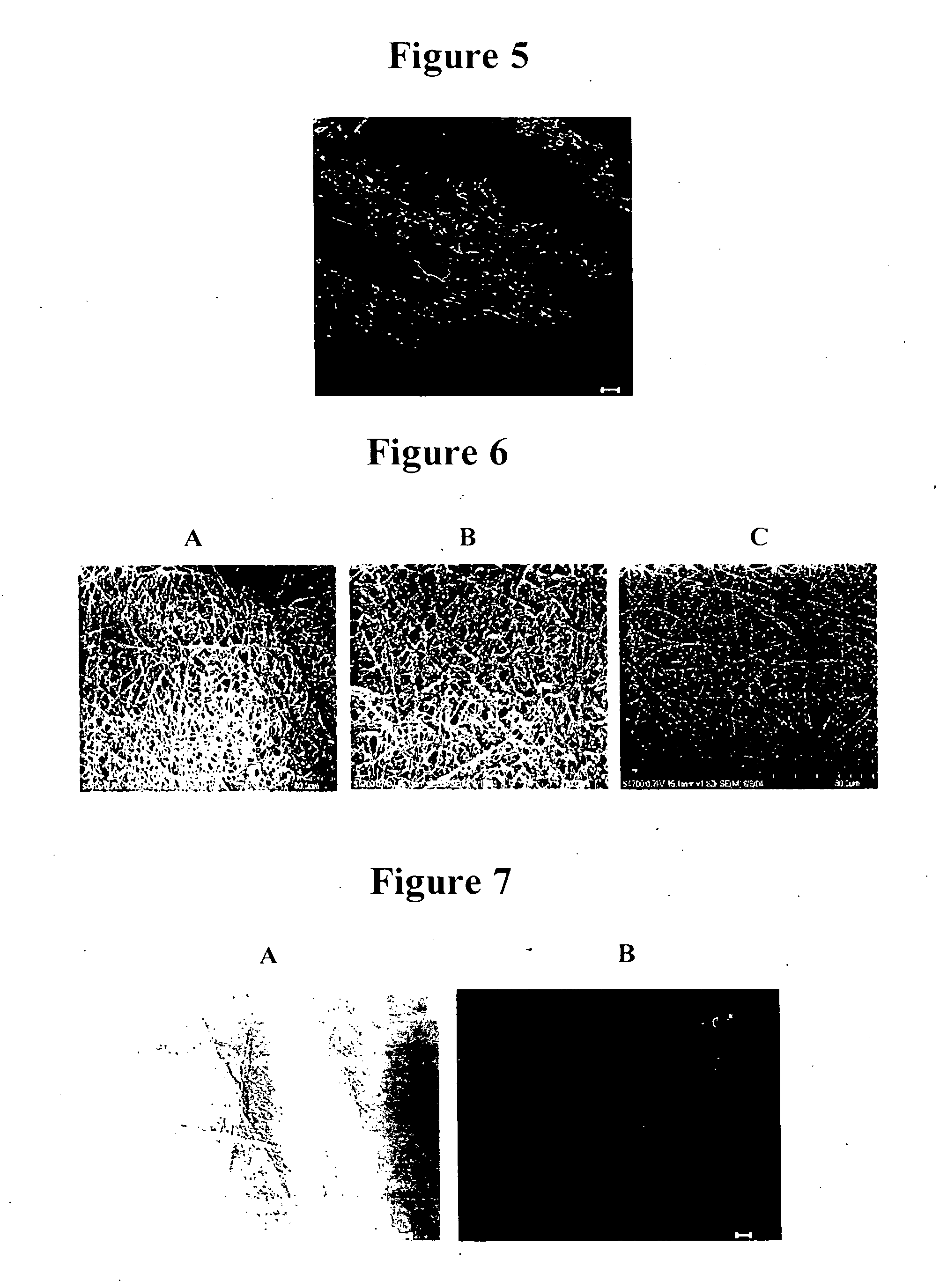
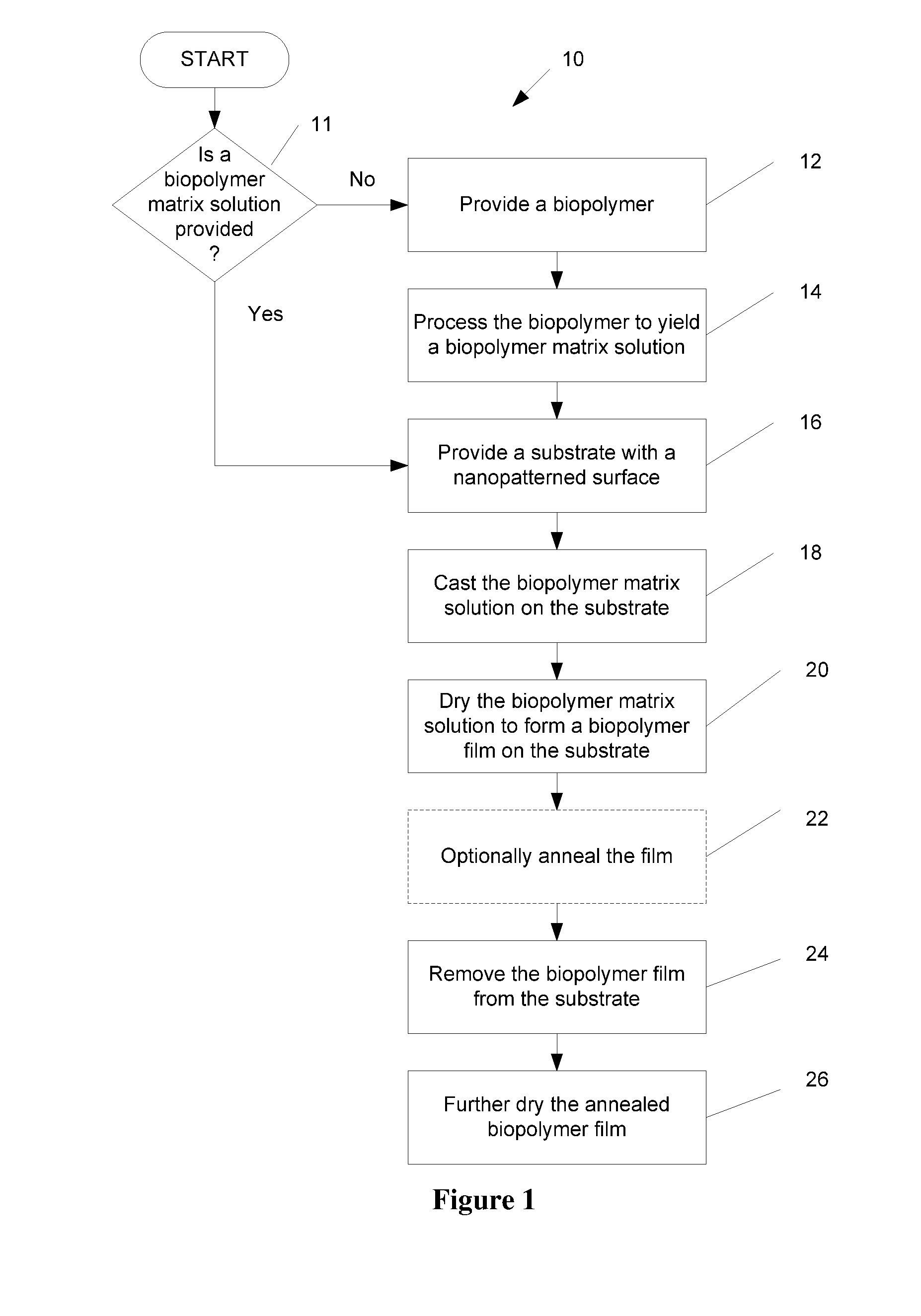
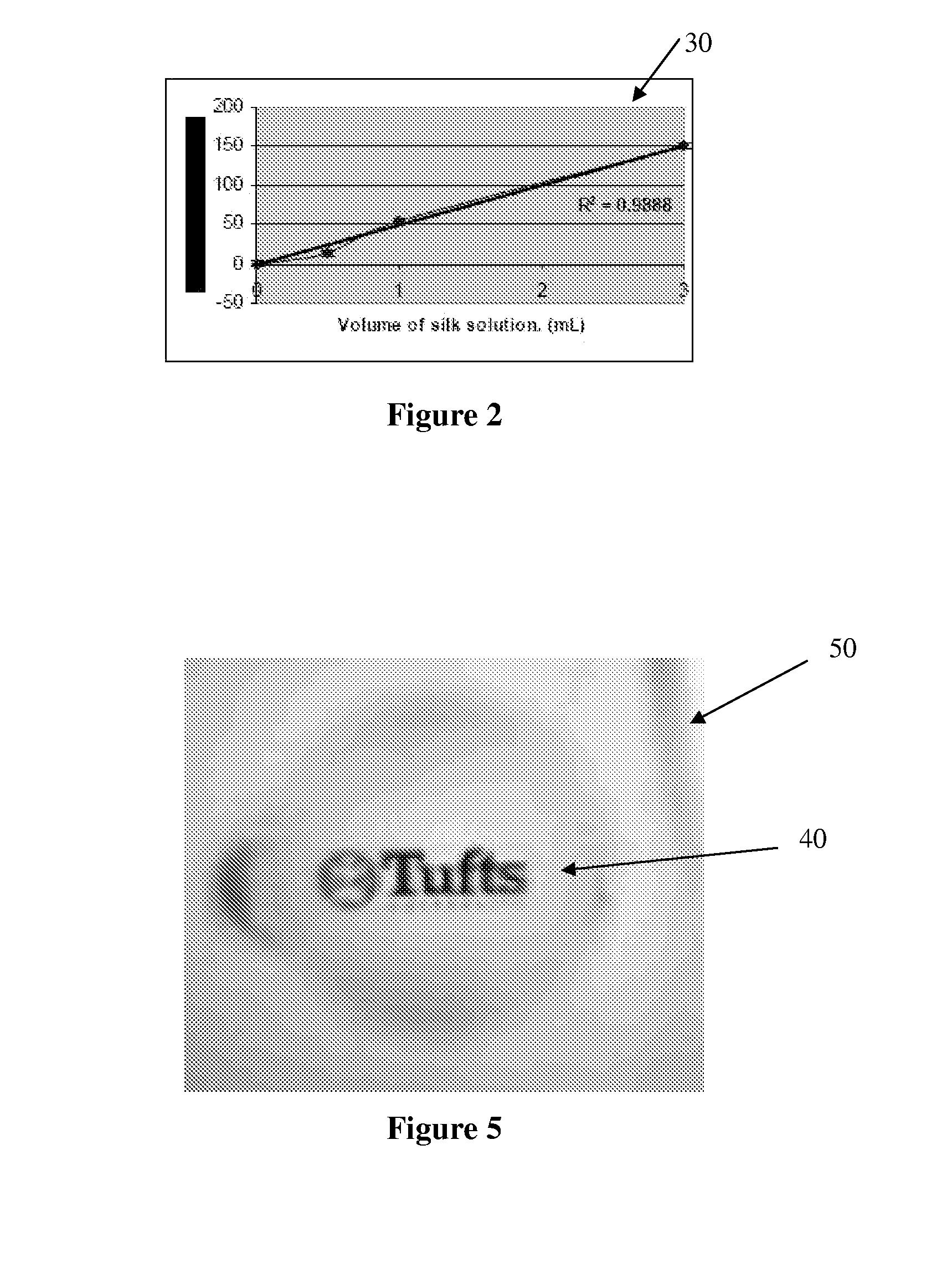
ActiveUS20100120116A1Minimize negative impactImprove functional propertiesLayered productsOptical articlesMatrix solutionBiopolymer
A method of manufacturing a nanopatterned biopolymer optical device includes providing a biopolymer, processing the biopolymer to yield a biopolymer matrix solution, providing a substrate with a nanopatterned surface, casting the biopolymer matrix solution on the nanopatterned surface of the substrate, and drying the biopolymer matrix solution to form a solidified biopolymer film on the substrate, where the solidified biopolymer film is formed with a surface having a nanopattern thereon. In another embodiment, the method also includes annealing the solidified biopolymer film. A nanopatterned biopolymer optical device includes a solidified biopolymer film with a surface having a nanopattern is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Biopolymer photonic crystals and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100046902A1Minimize negative impactImprove functional propertiesOptical articlesNanoopticsPhotonic crystalMatrix solution
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
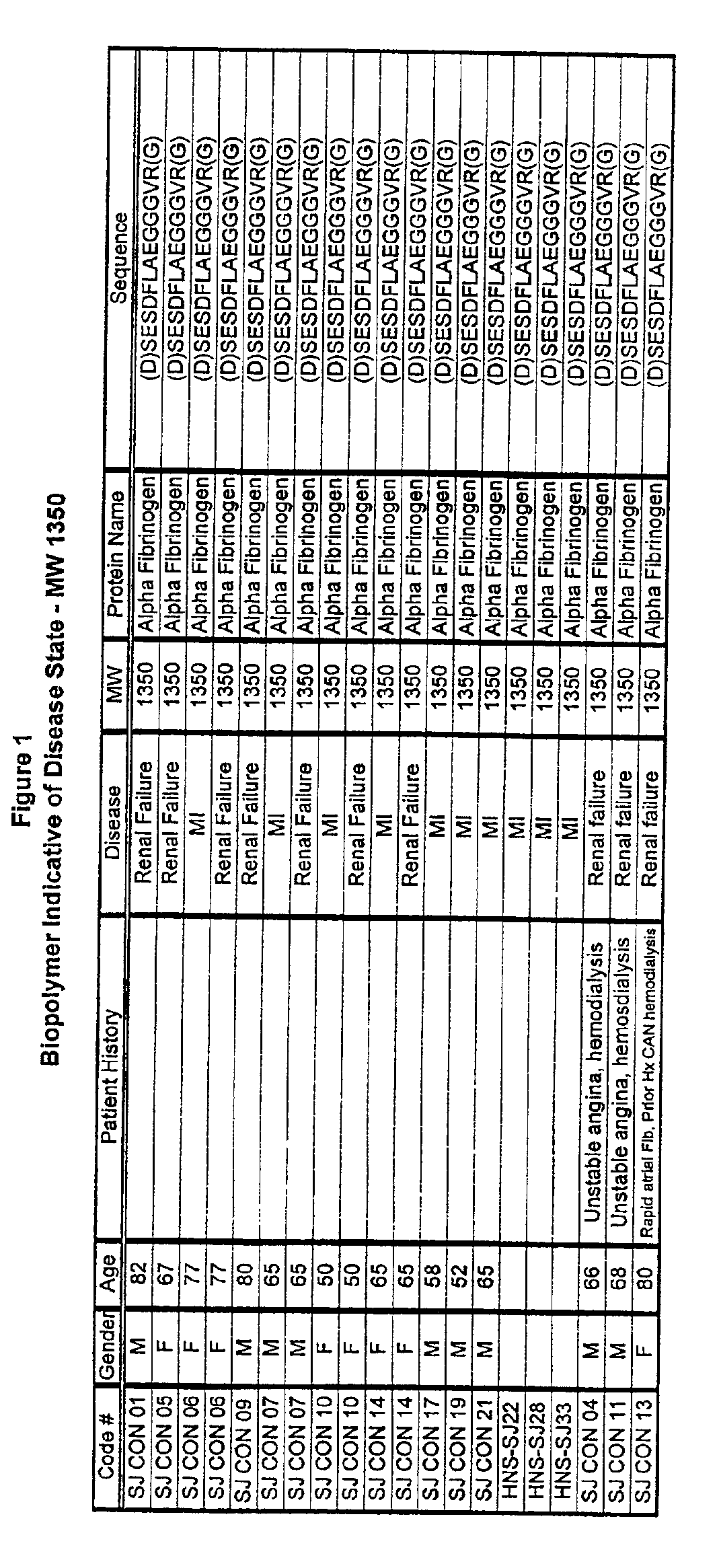
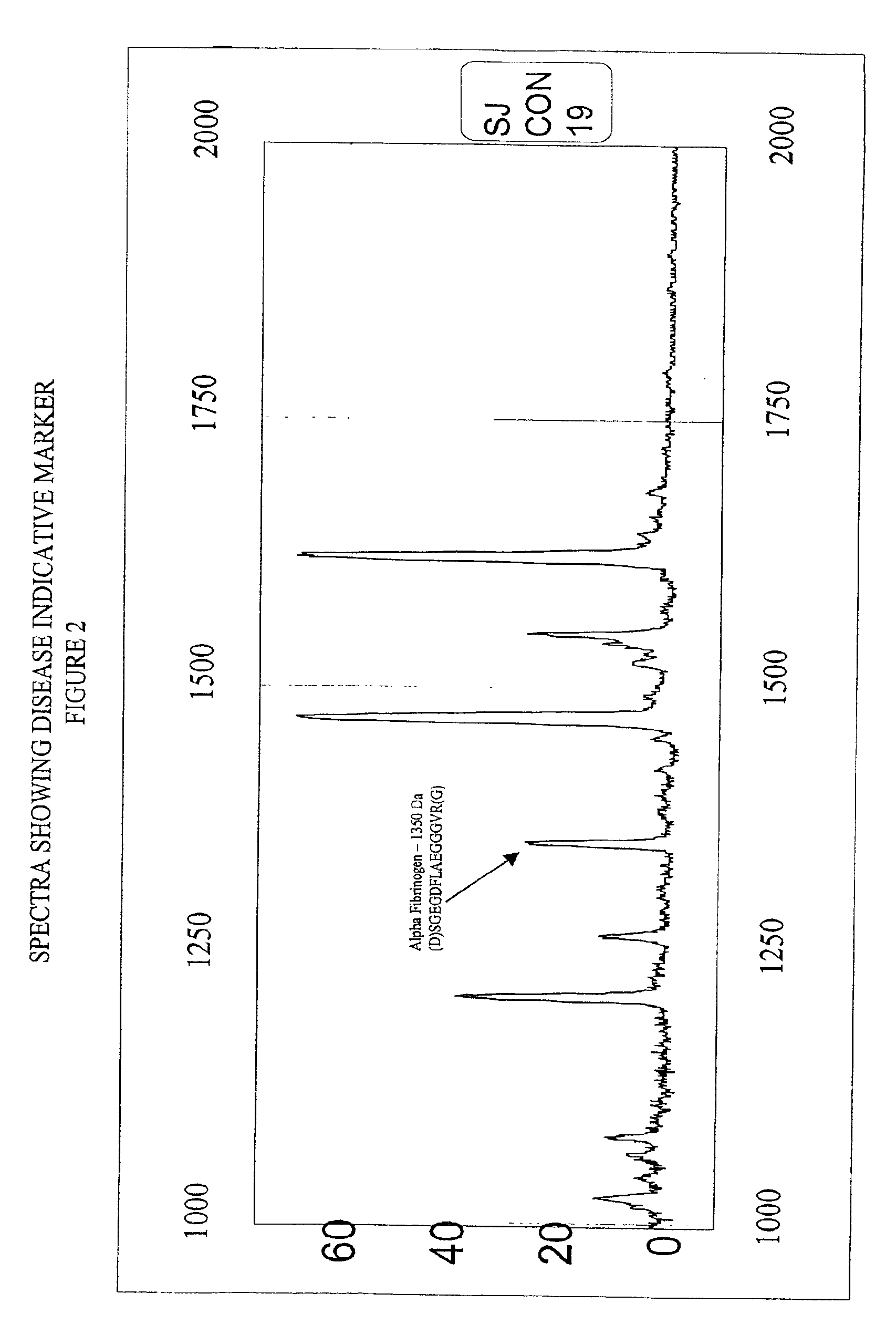
Biopolymer marker indicative of disease state having a molecular weight of 1350 daltons
InactiveUS6890763B2Maximize diversityThwart these maladiesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBiopolymer
The instant invention involves the use of a combination of preparatory steps in conjunction with mass spectroscopy and time-of-flight detection procedures to maximize the diversity of biopolymers which are verifiable within a particular sample. The cohort of biopolymers verified within such a sample is then viewed with reference to their ability to evidence at least particular disease state; thereby enabling a diagnostician to gain the ability to characterize either the presence or absence of at least one disease state relative to recognition of the presence and / or the absence of the biopolymer.
Owner:NANOGEN INC
Biodegradable polymer blends for use in making films, sheets and other articles of manufacture
InactiveUS7214414B2Increase stiffnessIncrease flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsEmulsion paintsPolyesterThermoplastic
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Systems and methods for antibody engineering
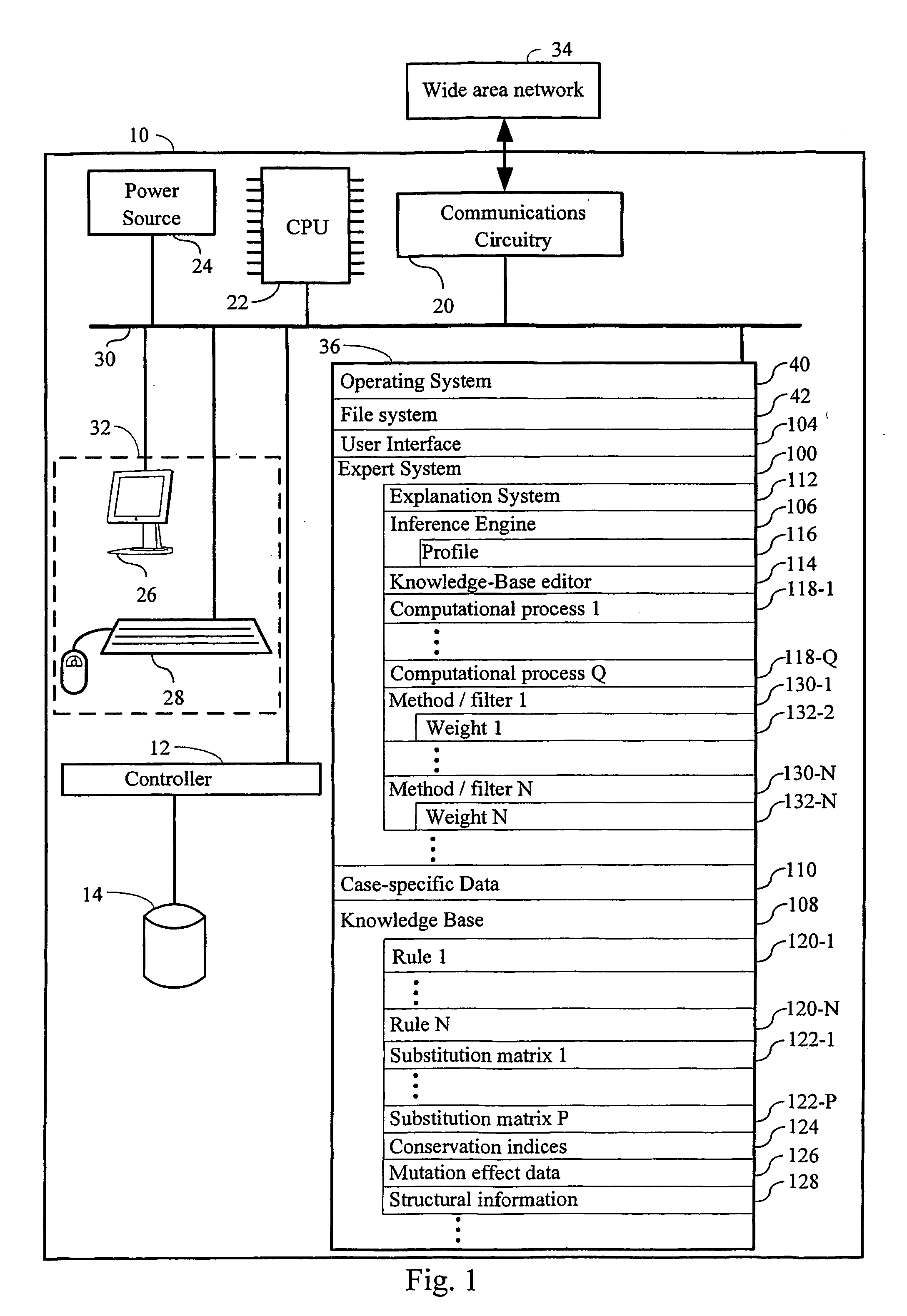
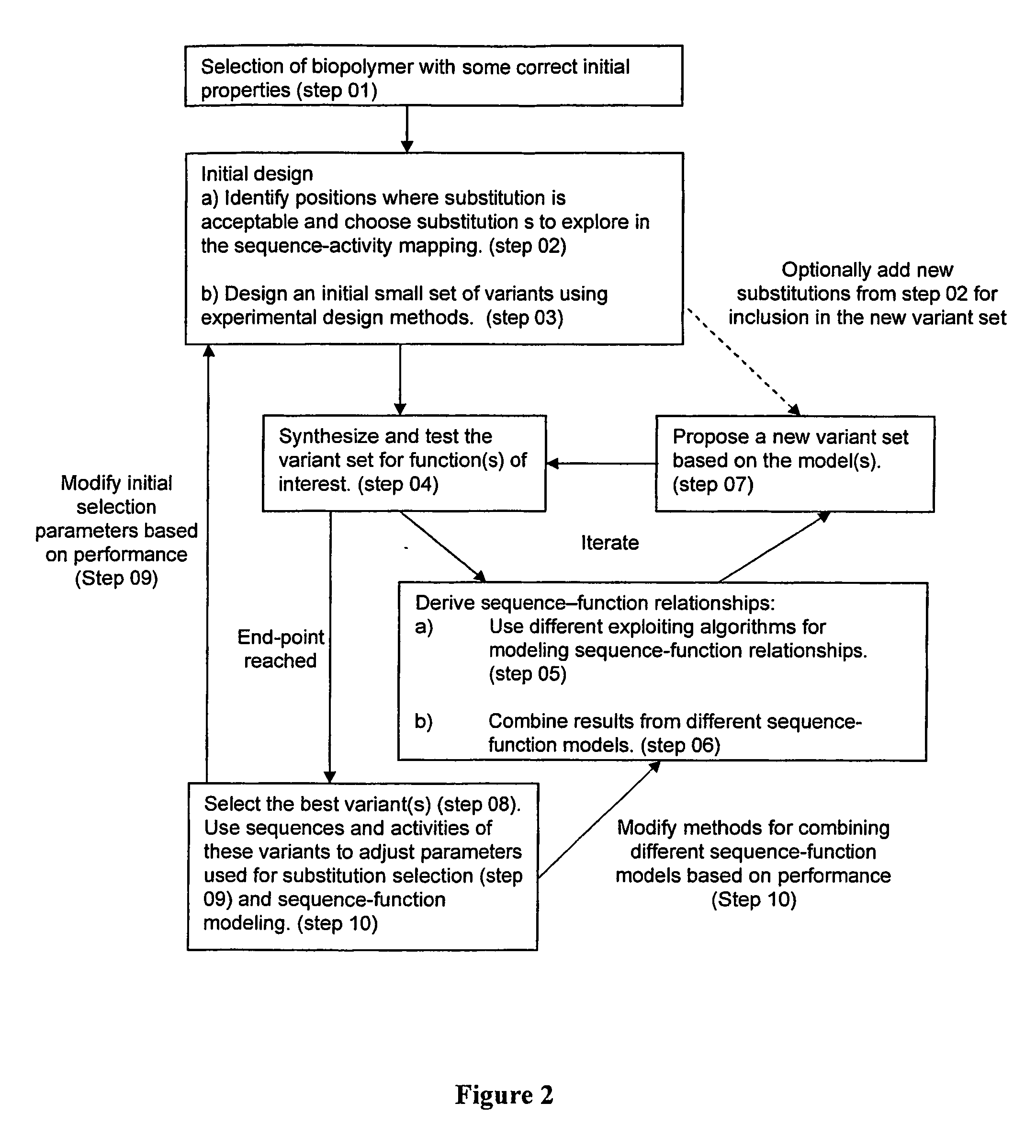
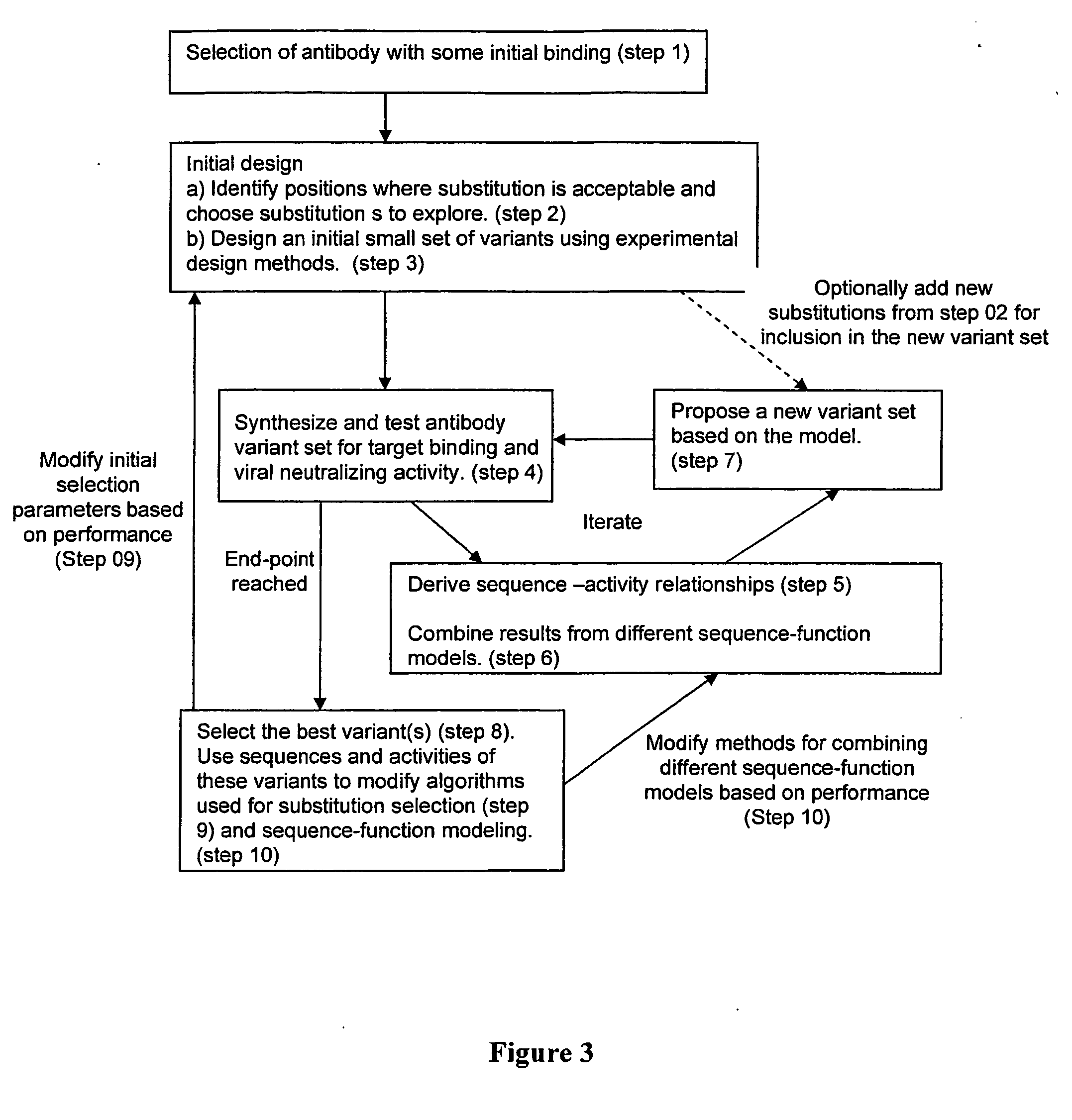
ActiveUS20060136184A1Reduce in quantityMaximizing numberAnalogue computers for chemical processesProteomicsBiopolymerComputer science
Methods, computer systems, and computer program products for biopolymer engineering. A variant set for a biopolymer of interest is constructed by identifying, using a plurality of rules, a plurality of positions in the biopolymer of interest and, for each respective position in the plurality of positions, substitutions for the respective position. The plurality of positions and the substitutions for each respective position in the plurality of positions collectively define a biopolymer sequence space. A variant set comprising a plurality of variants of the biopolymer of interest is selected. A property of all or a position of the variants in the variant set is measured. A sequence-activity relationship is modeled between (i) one or more substitutions at one or more positions of the biopolymer of interest represented by the variant set and (ii) the property measured for all or the portion of the variants in the variant set. The variant set is redefined to comprise variants that include substitutions in the plurality of positions that are selected based on a function of the sequence-activity relationship.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
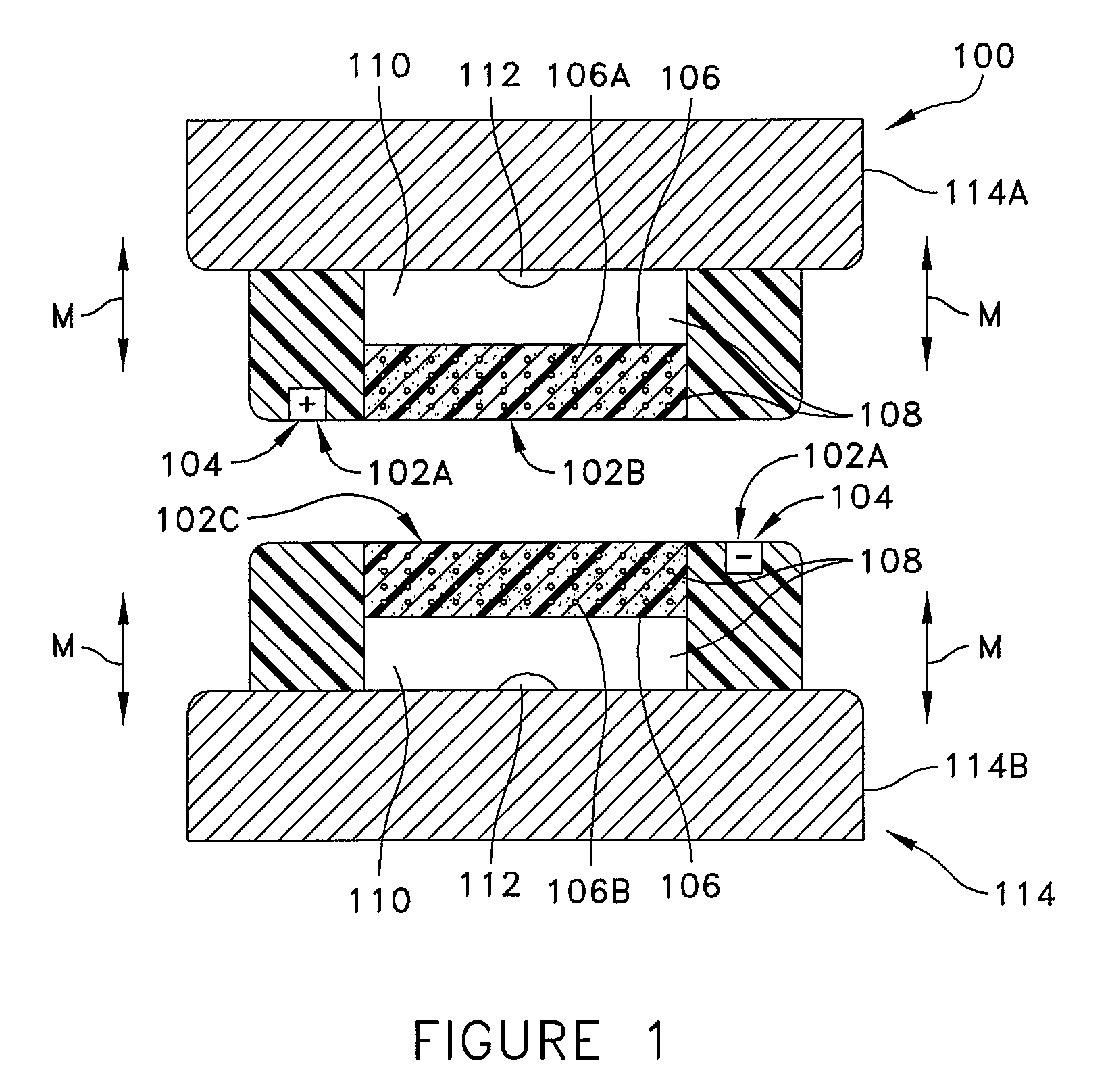
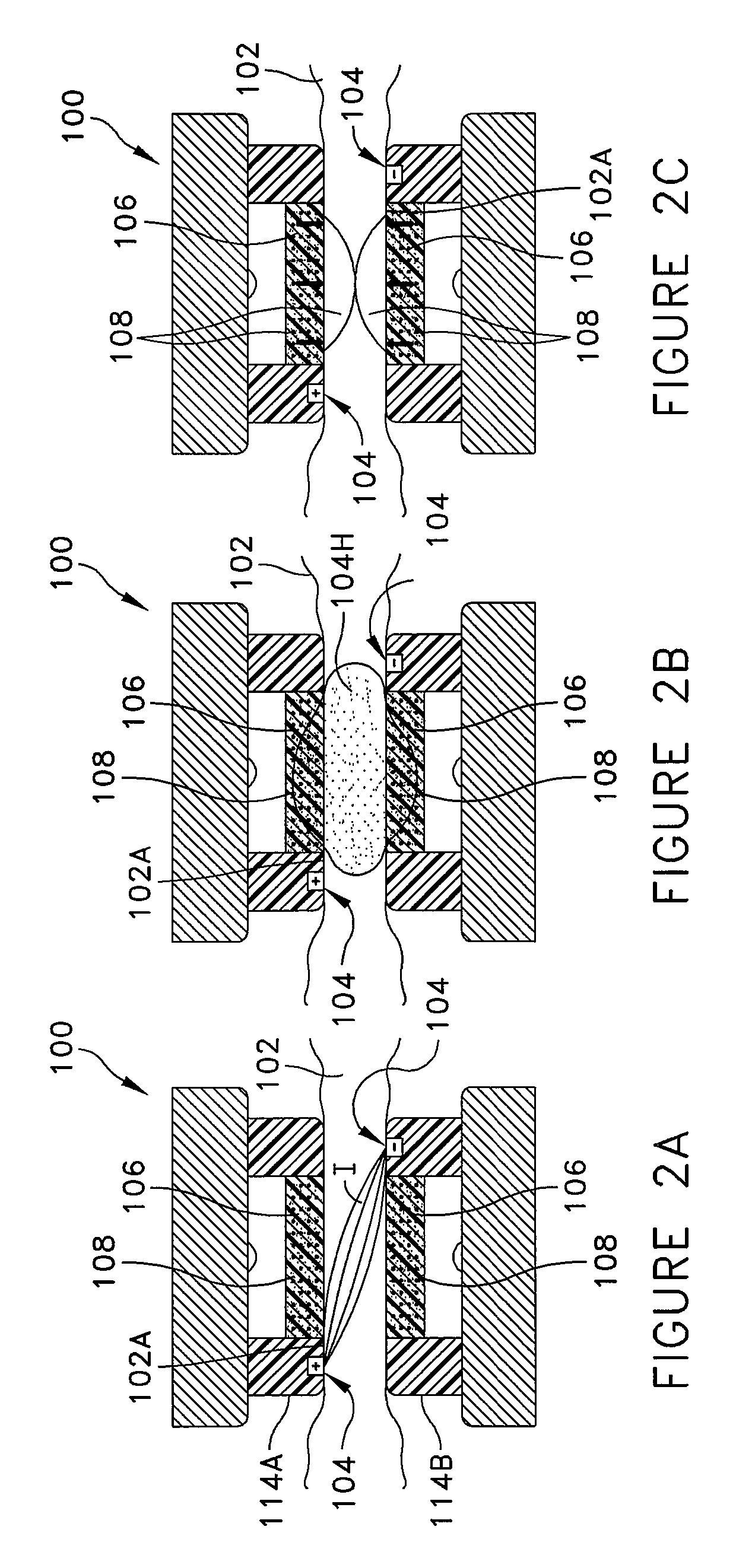
Apparatus for attachment and reinforcement of tissue, apparatus for reinforcement of tissue, methods of attaching and reinforcing tissue, and methods of reinforcing tissue
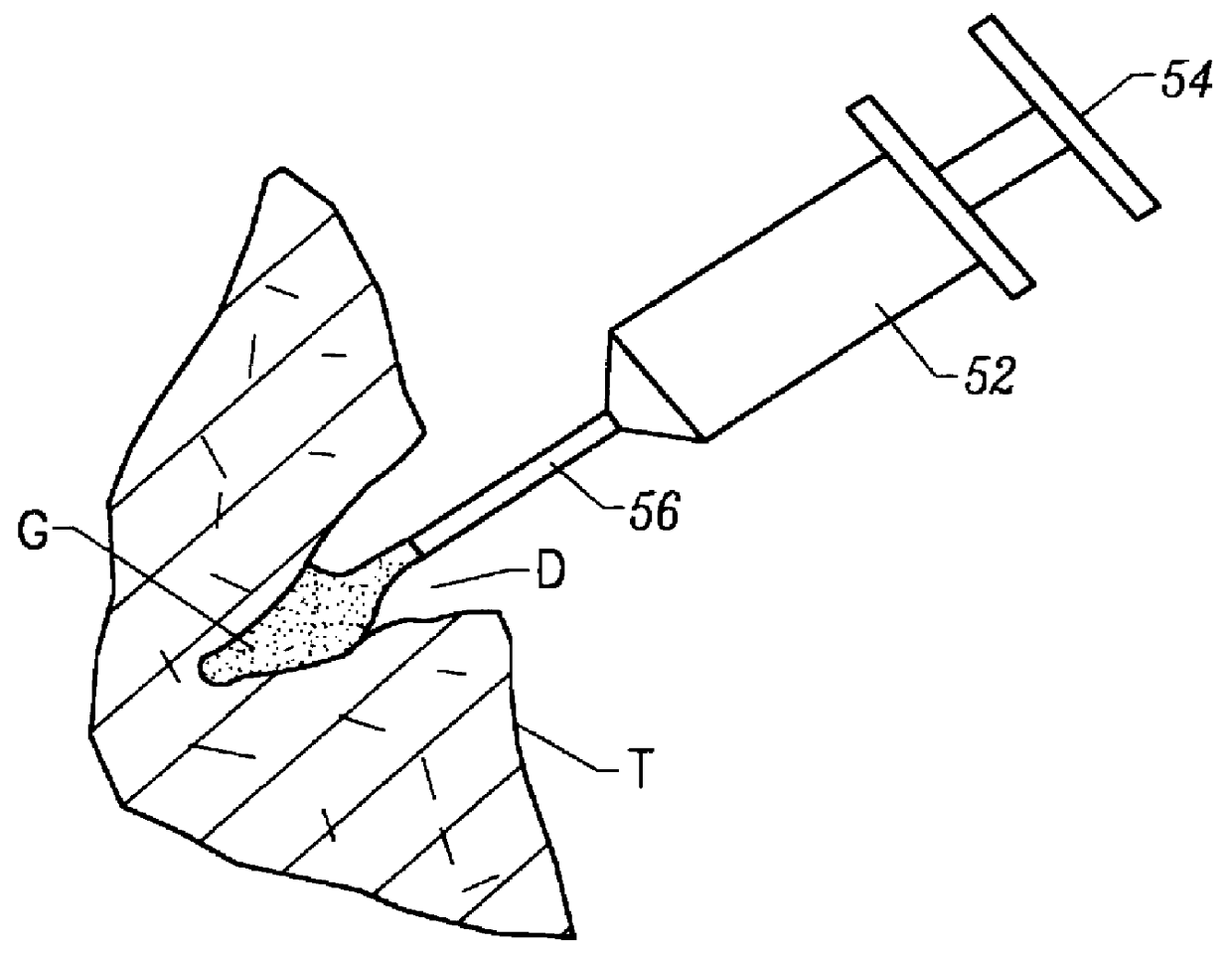
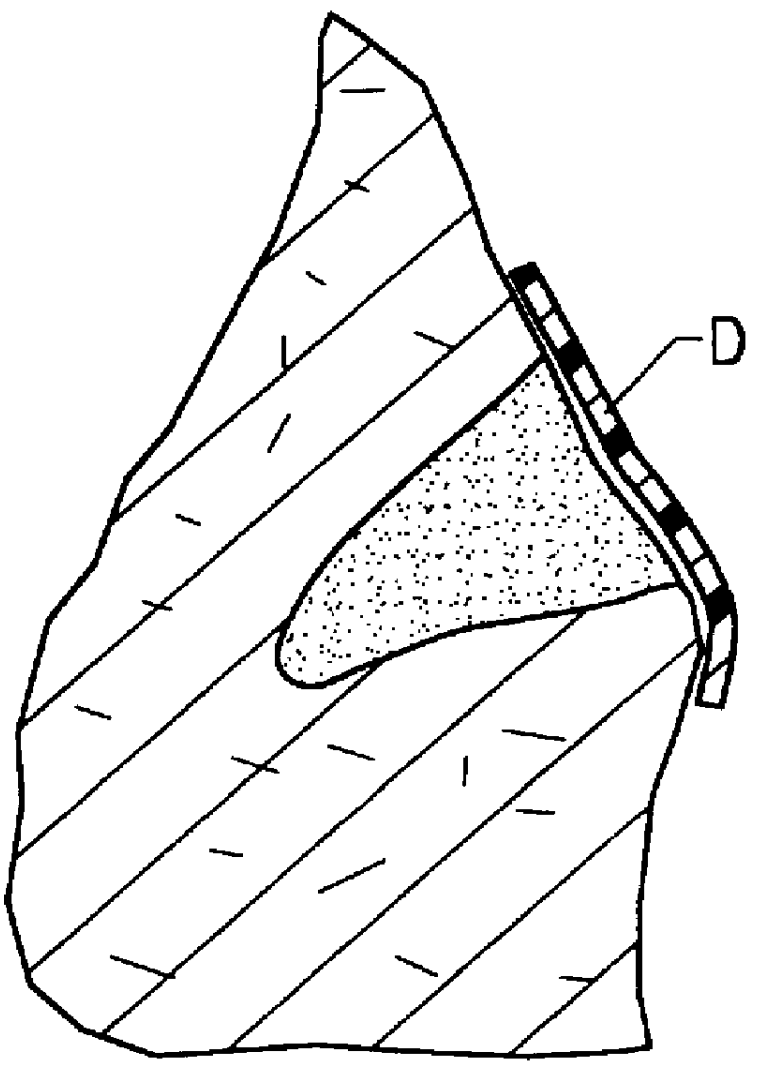
There are disclosed methods and apparatus for attachment and reinforcement of tissue, and methods and apparatus for reinforcement of tissue. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an energy applicator configured to apply energy to generate heat within a target tissue to evaporate water to create dried tissue, and denature at least one of collagen and elastin to attach portions together, and a biopolymer applicator configured for to receive the heat generated to allow biopolymer material to change from solid to molten, and to allow the biopolymer to fill dried tissue to reinforce portions of the target tissue and provide a hermetic seal.In another embodiment, the method includes applying energy to tissue surfaces with an energy applicator, and applying a biopolymer material into the tissue surfaces with a biopolymer applicator disposed on a housing in connection with the energy applicator. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:SCHECHTER DAVID A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com