Patents
Literature
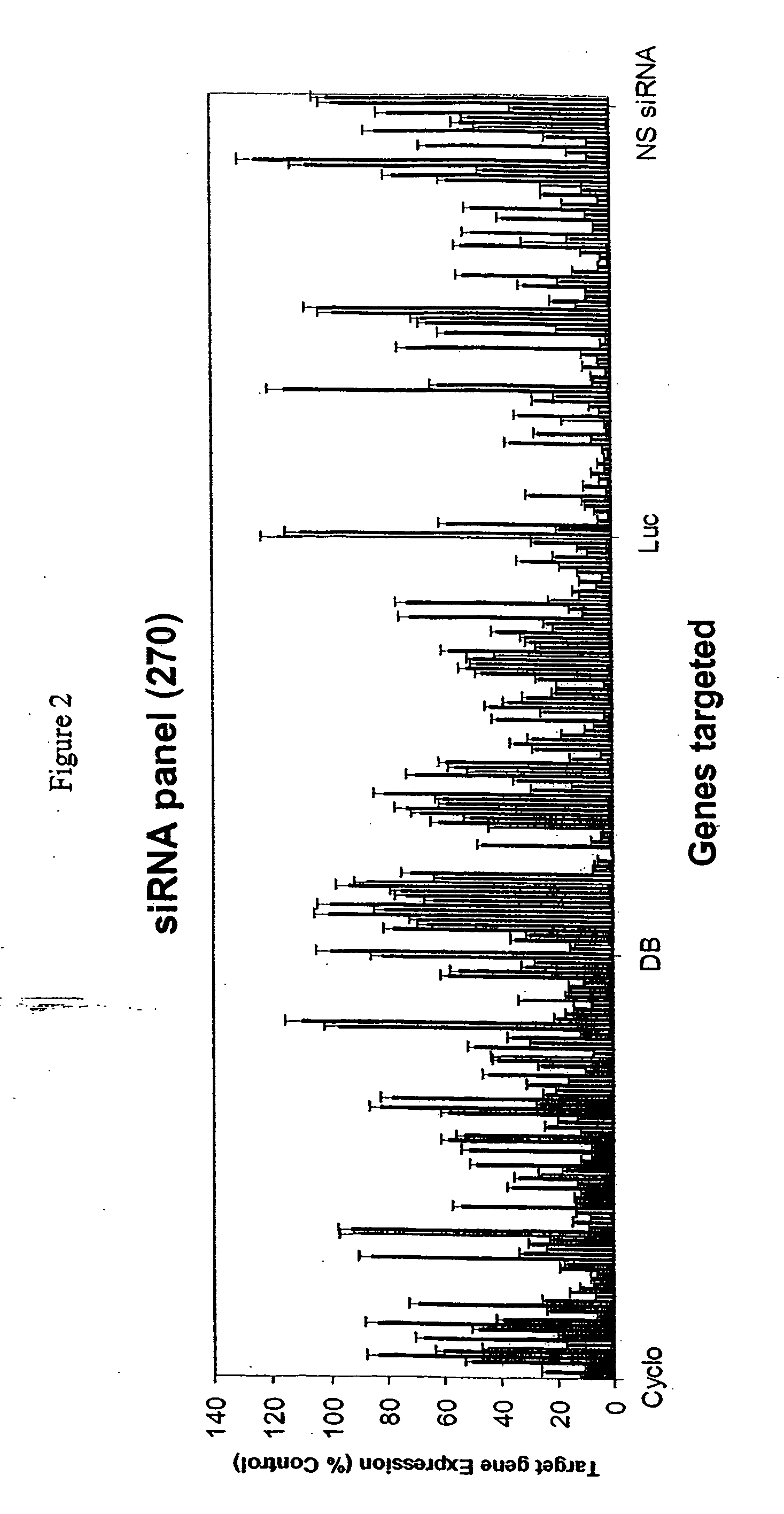
6614results about "Proteomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
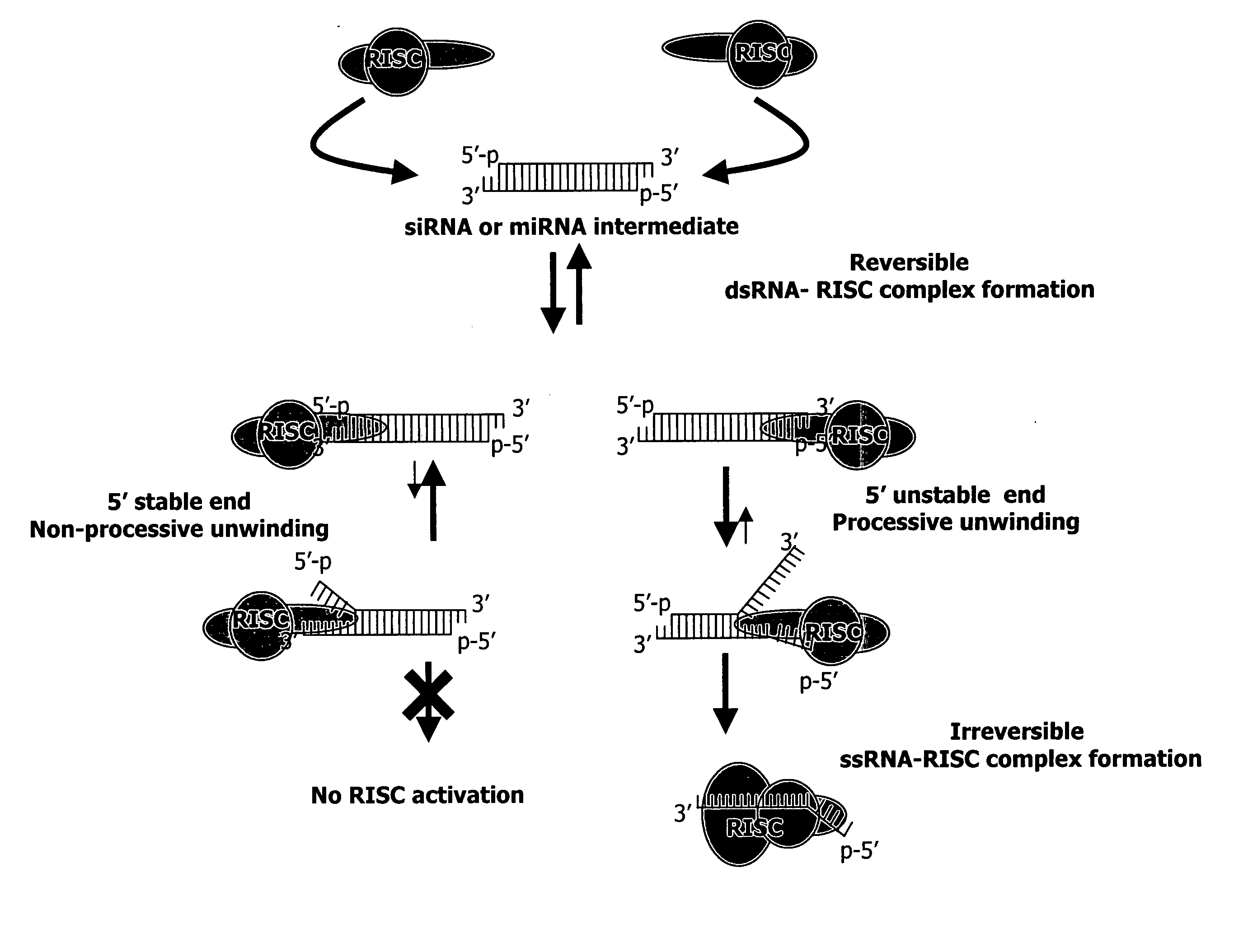
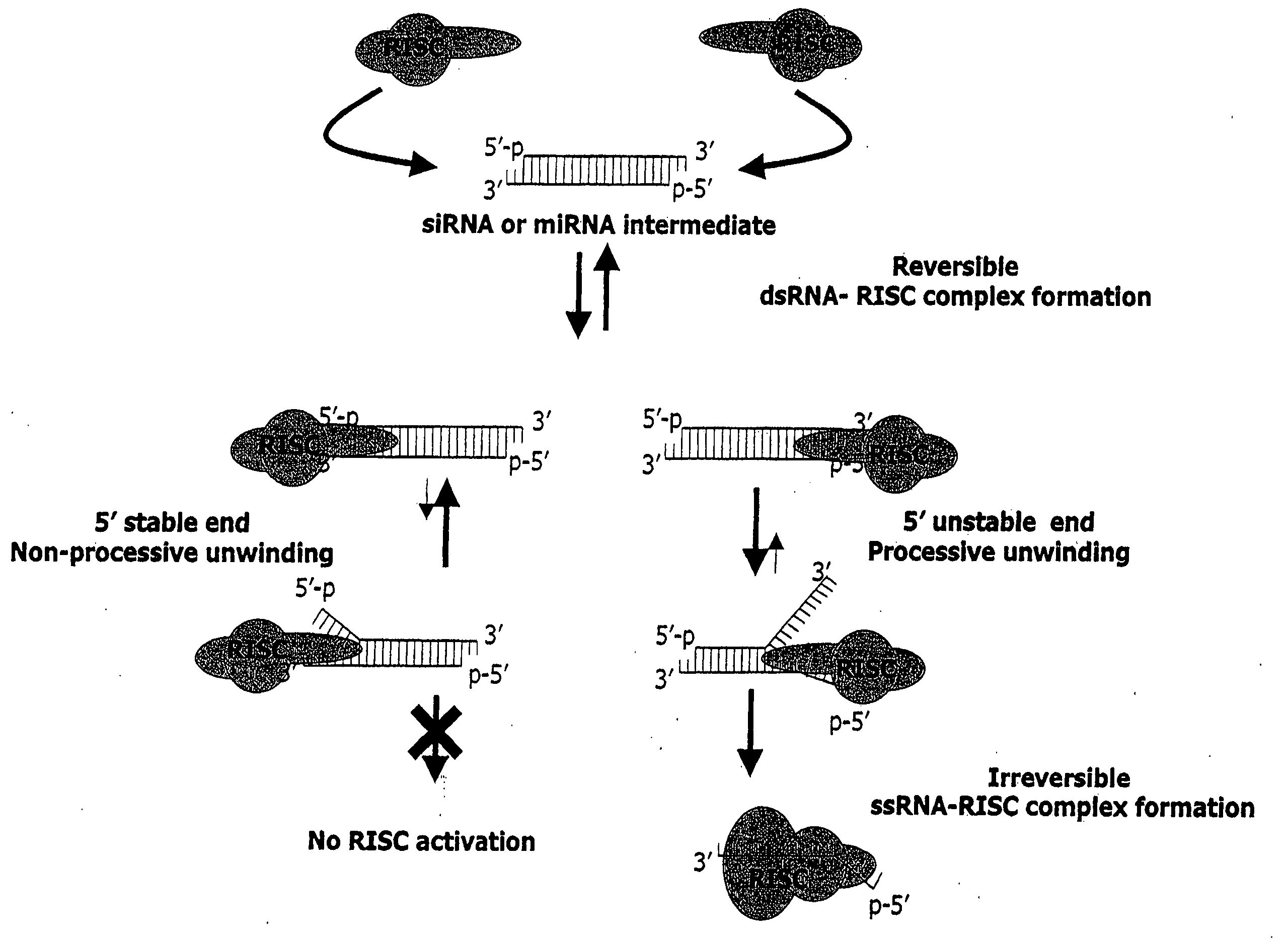
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
InactiveUS20050255487A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene silencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
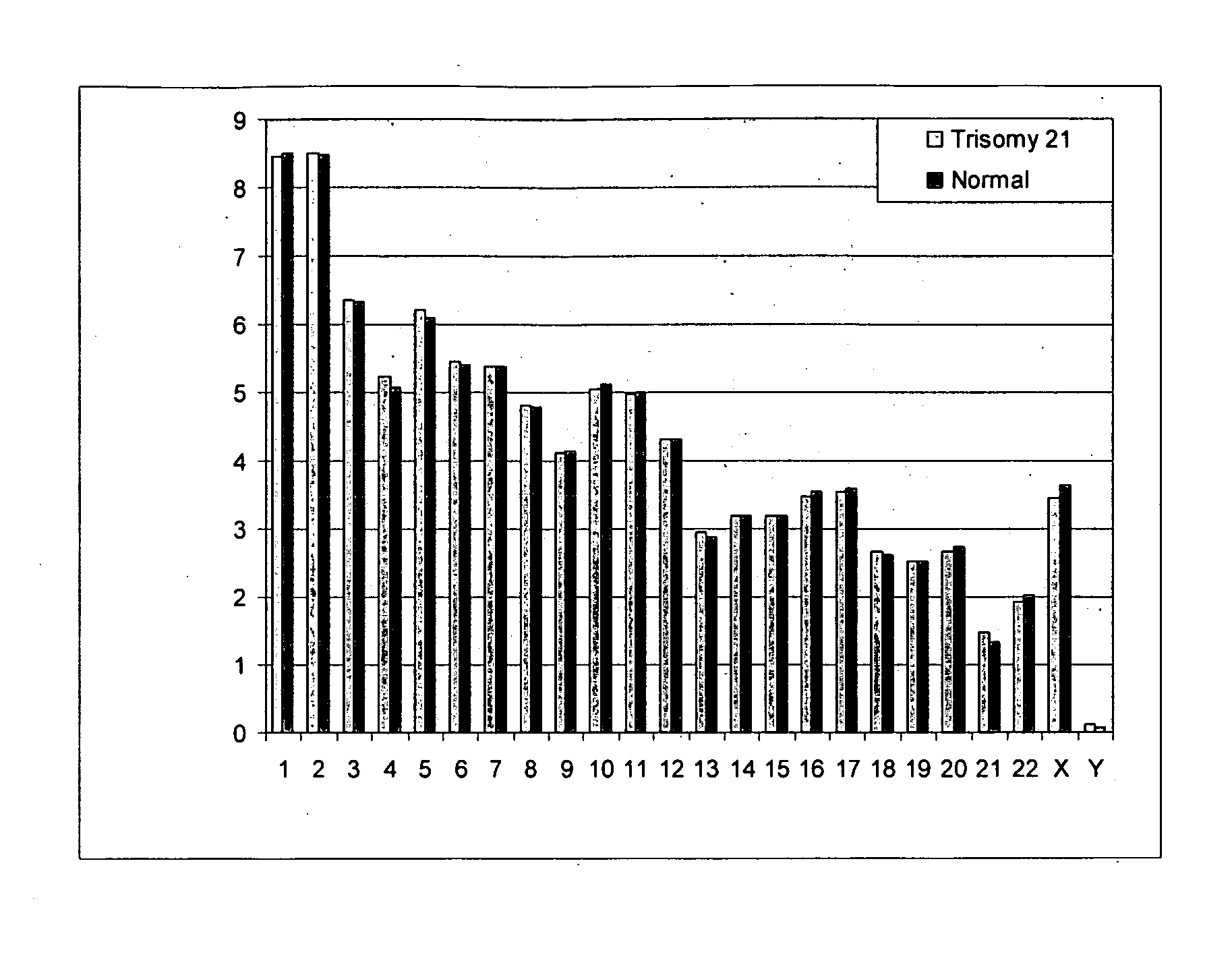
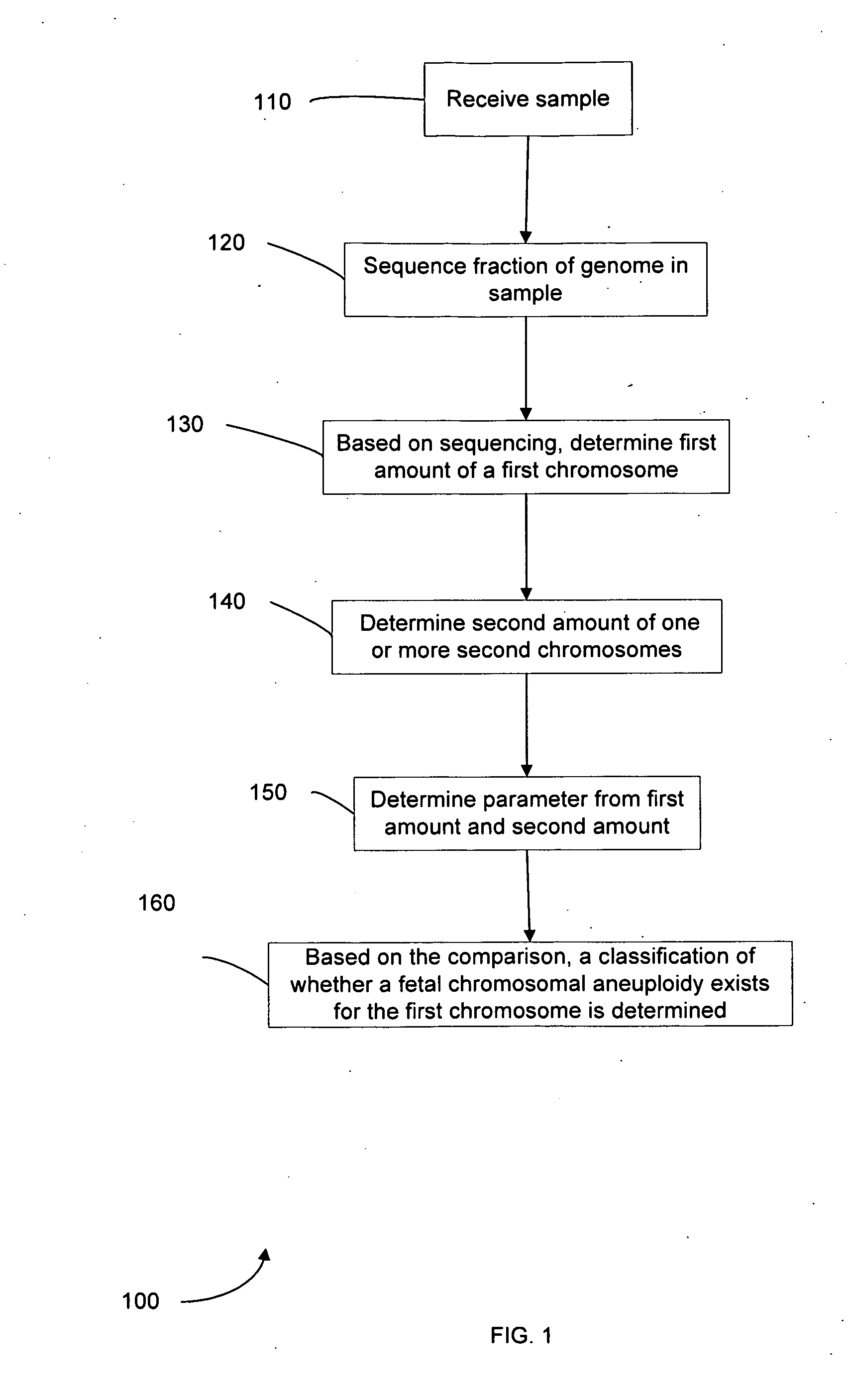
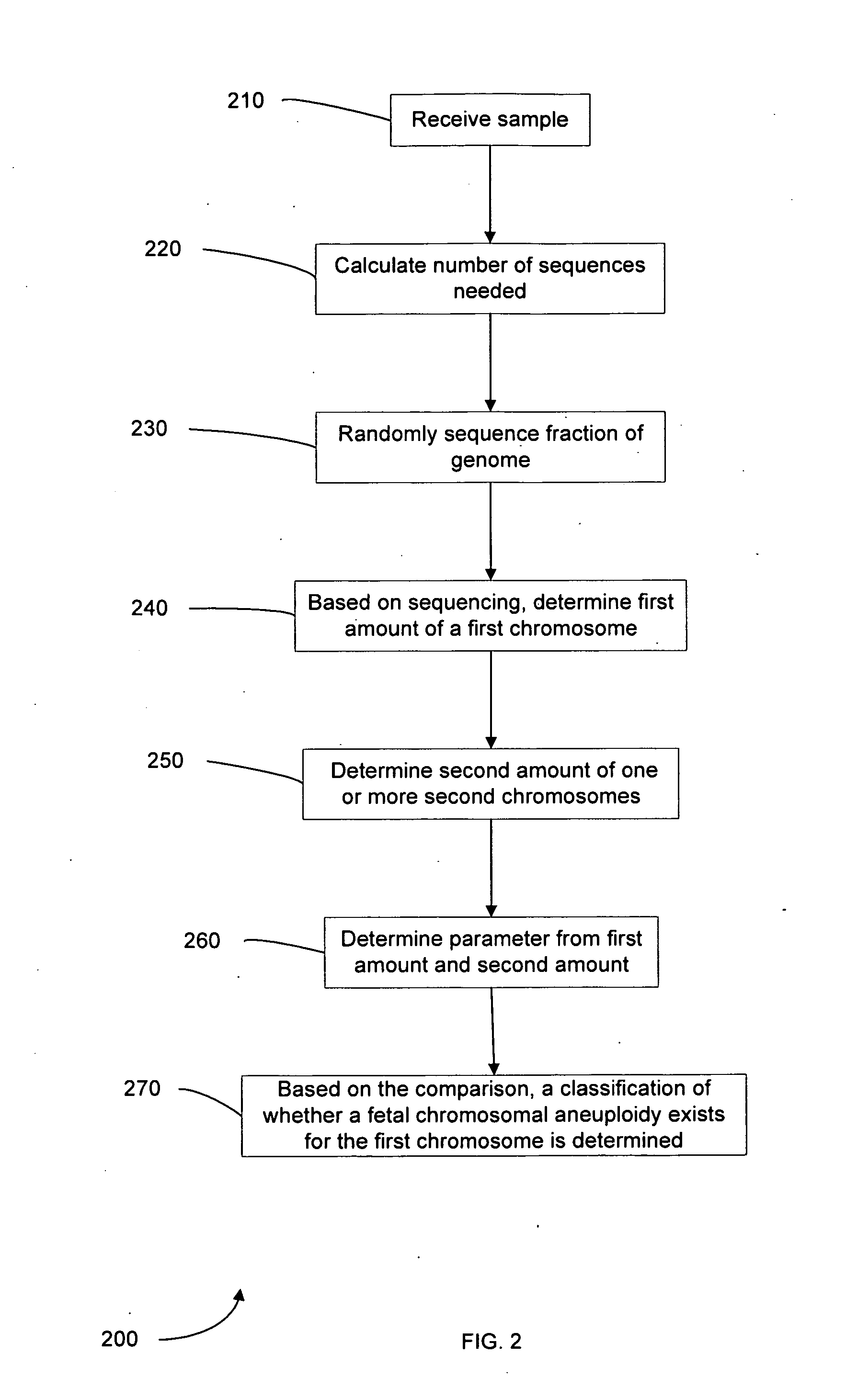
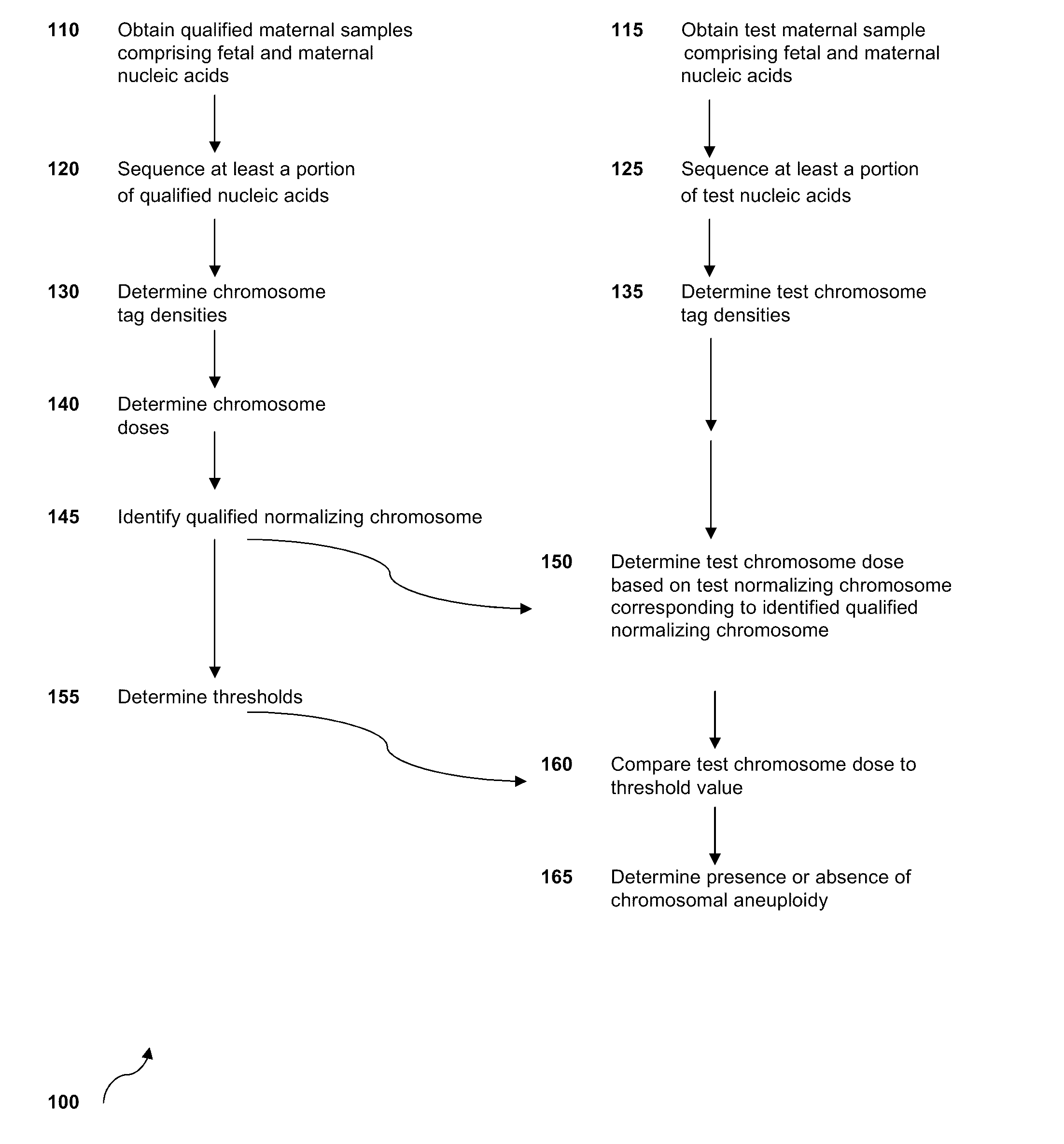
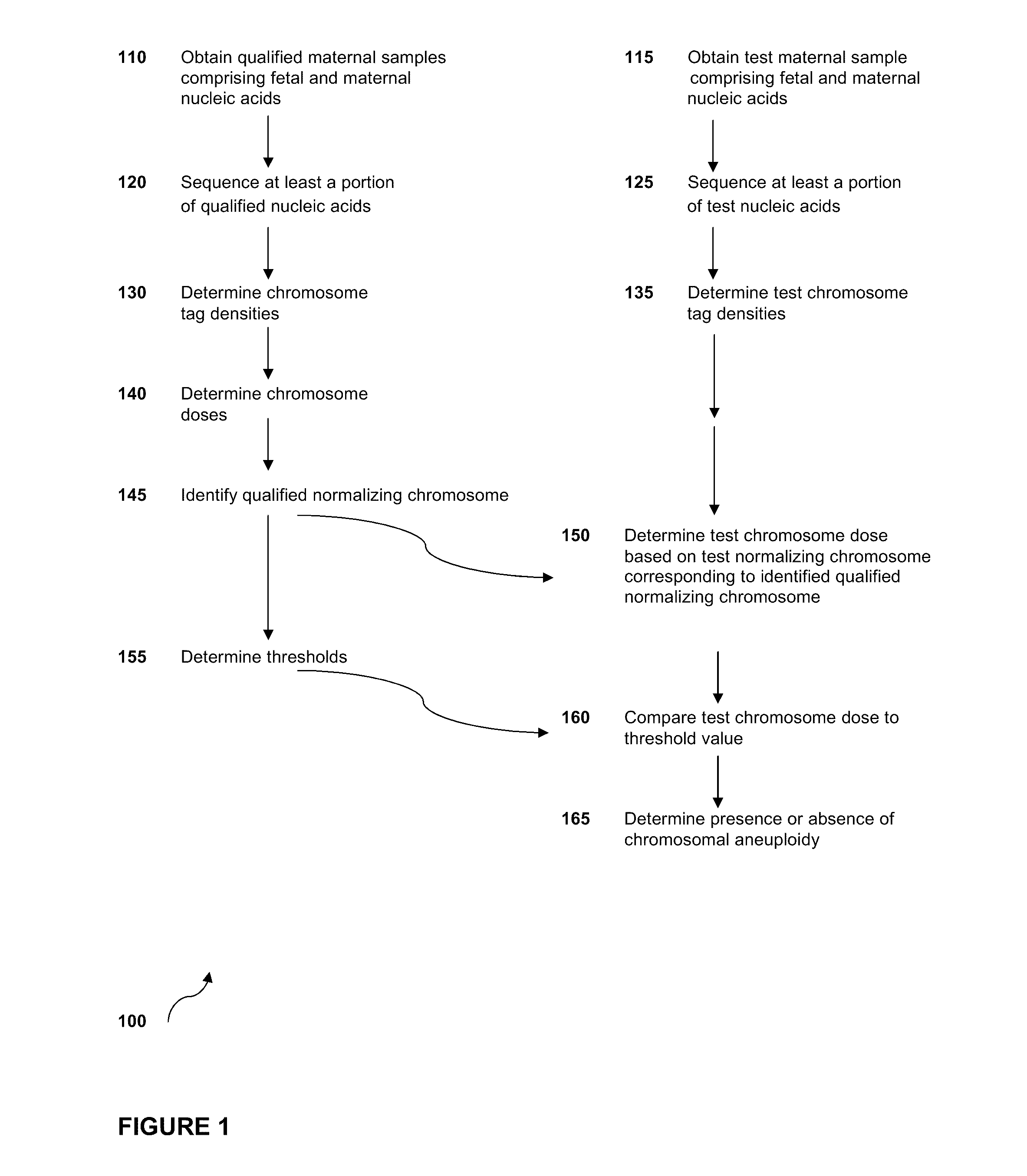
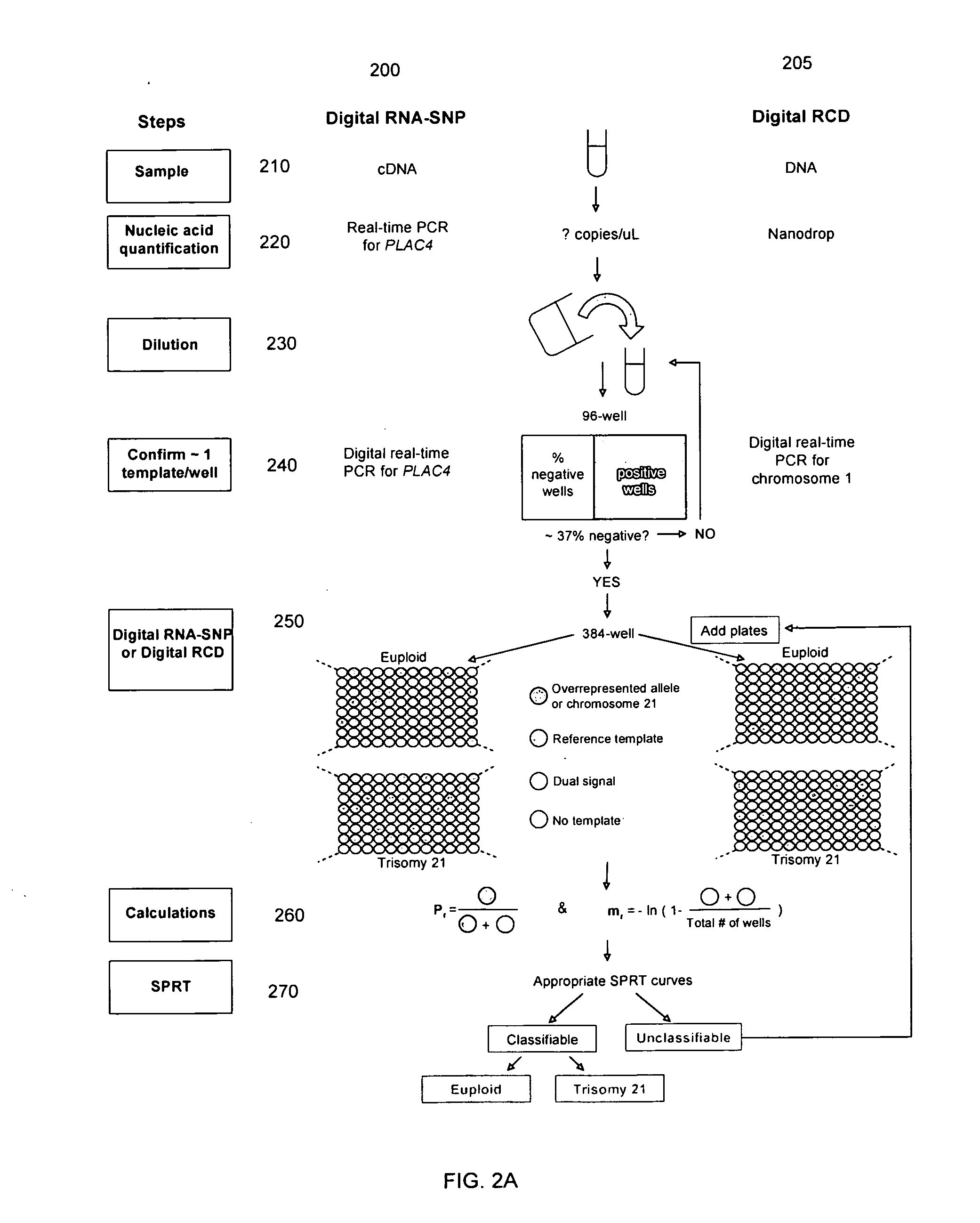
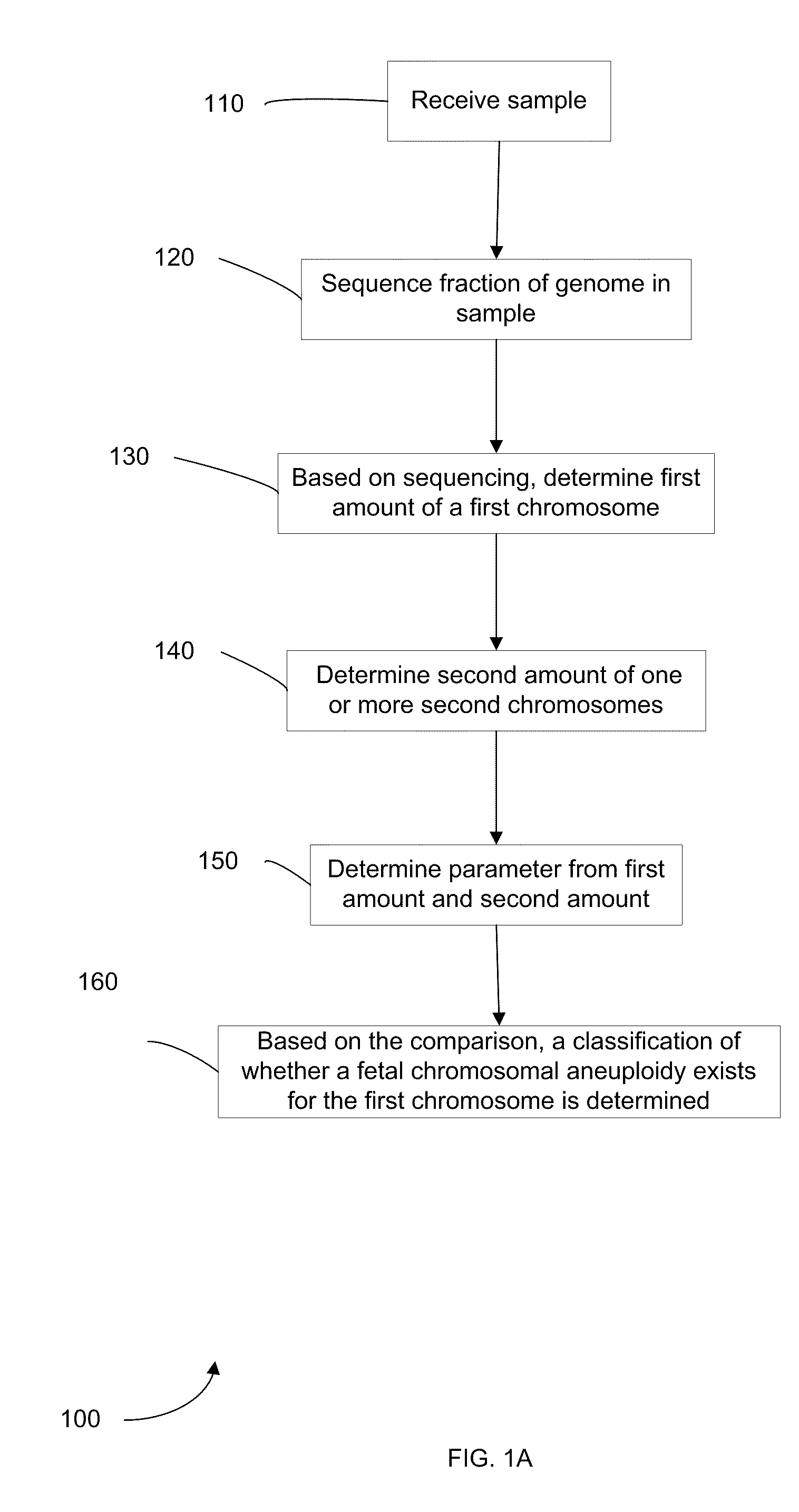
Diagnosing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy using massively parallel genomic sequencing
PendingUS20090029377A1Quantity maximizationSufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGenomic sequencingGenome
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods and systems for annotating biomolecular sequences
A method of annotating biomolecular sequences. The method comprises (a) computationally clustering the biomolecular sequences according to a progressive homology range, to thereby generate a plurality of clusters each being of a predetermined homology of the homology range; and (b) assigning at least one ontology to each cluster of the plurality of clusters, the at least one ontology being: (i) derived from an annotation preassociated with at least one biomolecular sequence of each cluster; and / or (ii) generated from analysis of the at least one biomolecular sequence of each cluster thereby annotating biomolecular sequences.
Owner:COMPUGEN
Functional and hyperfunctional siRNA
ActiveUS20050246794A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSilent geneGene silencing
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Sequencing methods and compositions for prenatal diagnoses
ActiveUS20110201507A1Quality improvementEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPrenatal diagnosisGenetics
The invention provides methods for determining aneuploidy and / or fetal fraction in maternal samples comprising fetal and maternal cfDNA by massively parallel sequencing. The method comprises a novel protocol for preparing sequencing libraries that unexpectedly improves the quality of library DNA while expediting the process of analysis of samples for prenatal diagnoses.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Pharmaceutical composition containing a stabilised mRNA optimised for translation in its coding regions
ActiveUS20050032730A1Overcome disadvantagesImprove efficiencyAntibacterial agentsVirusesTranslational efficiencyCoding region
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a modified mRNA that is stabilised by sequence modifications and optimised for translation. The pharmaceutical composition according to the invention is particularly well suited for use as an inoculating agent, as well as a therapeutic agent for tissue regeneration. In addition, a process is described for determining sequence modifications that promote stabilisation and translational efficiency of modified mRNA of the invention.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
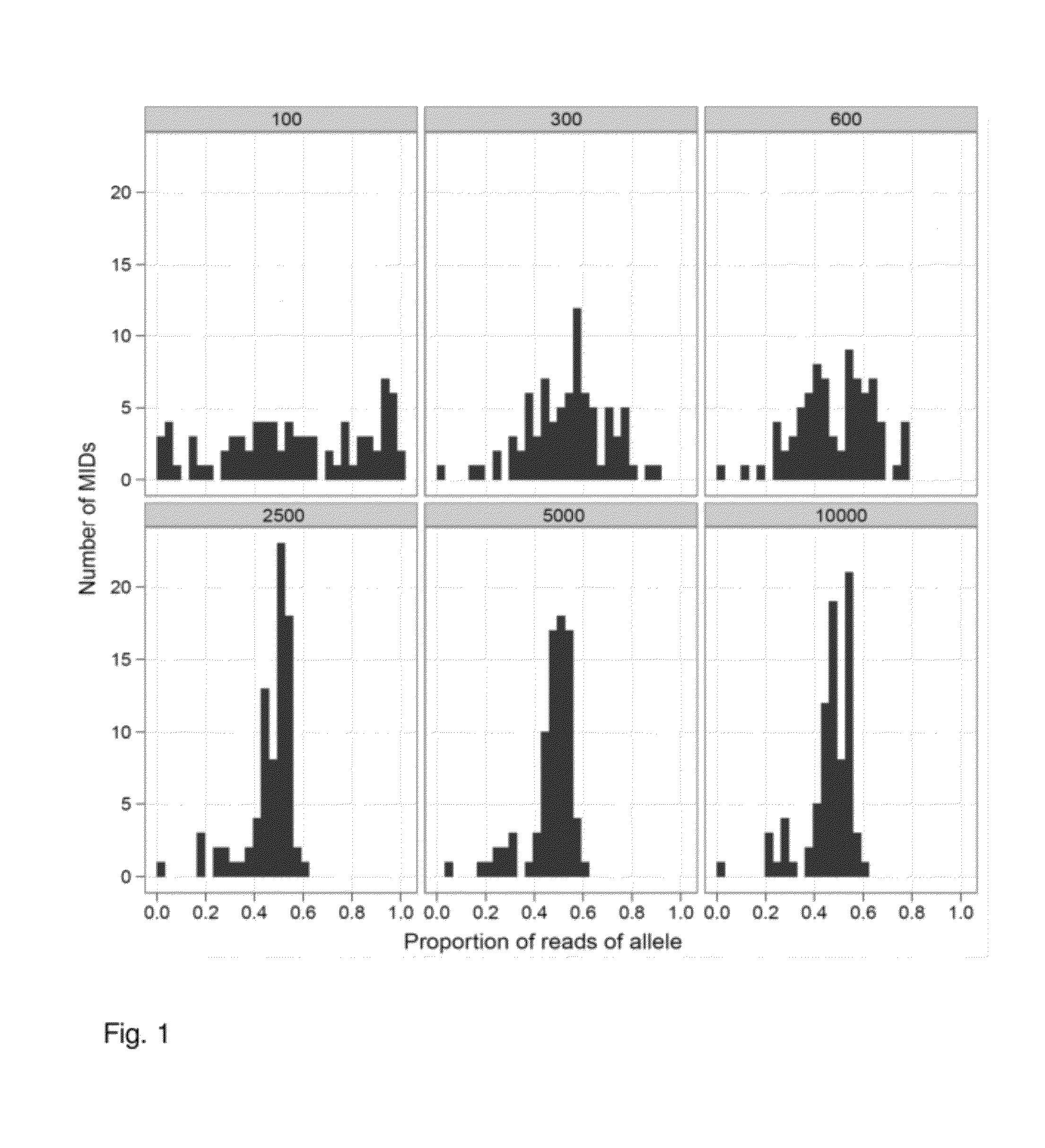
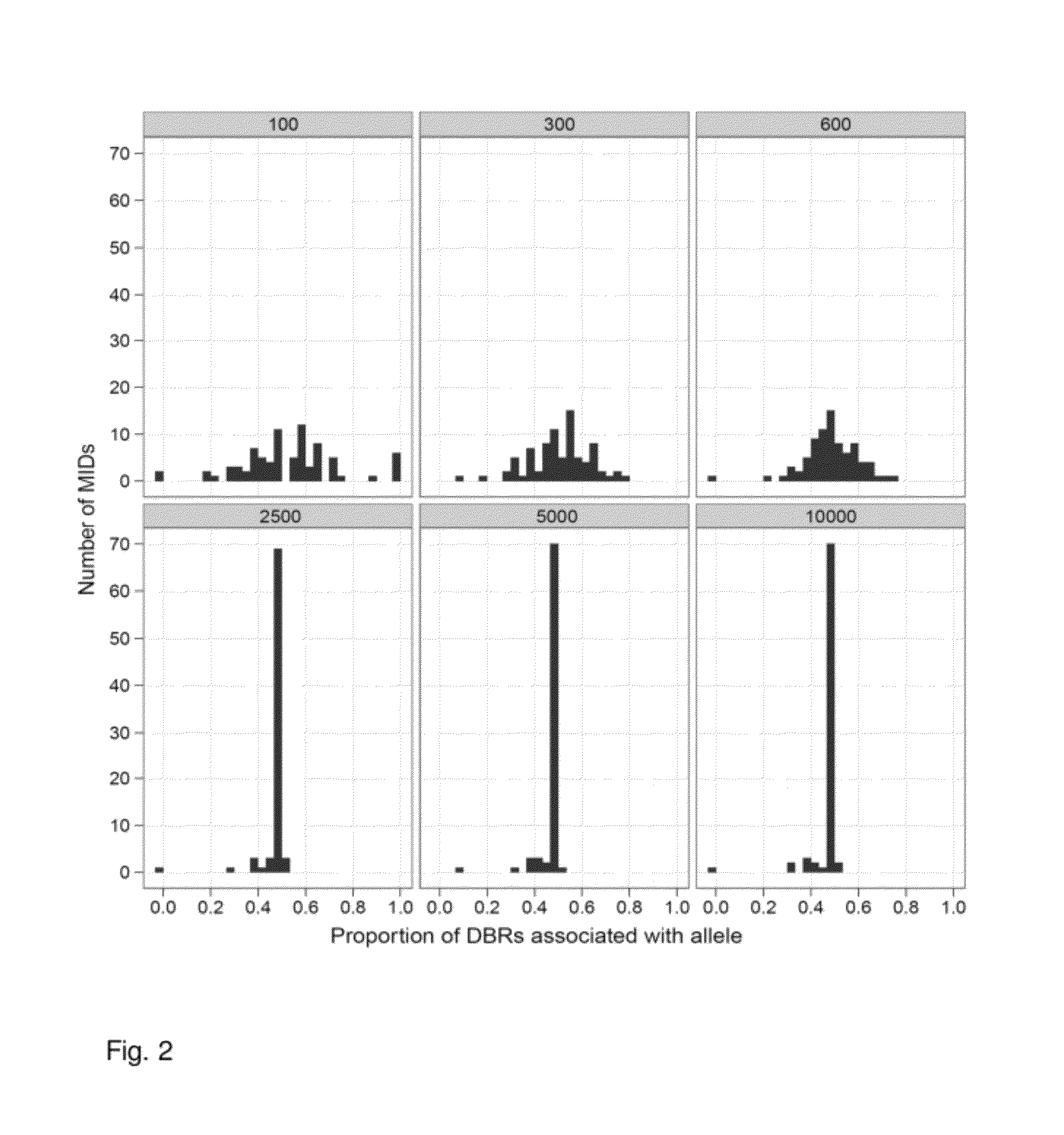
Increasing confidence of allele calls with molecular counting
ActiveUS8481292B2Easy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotide
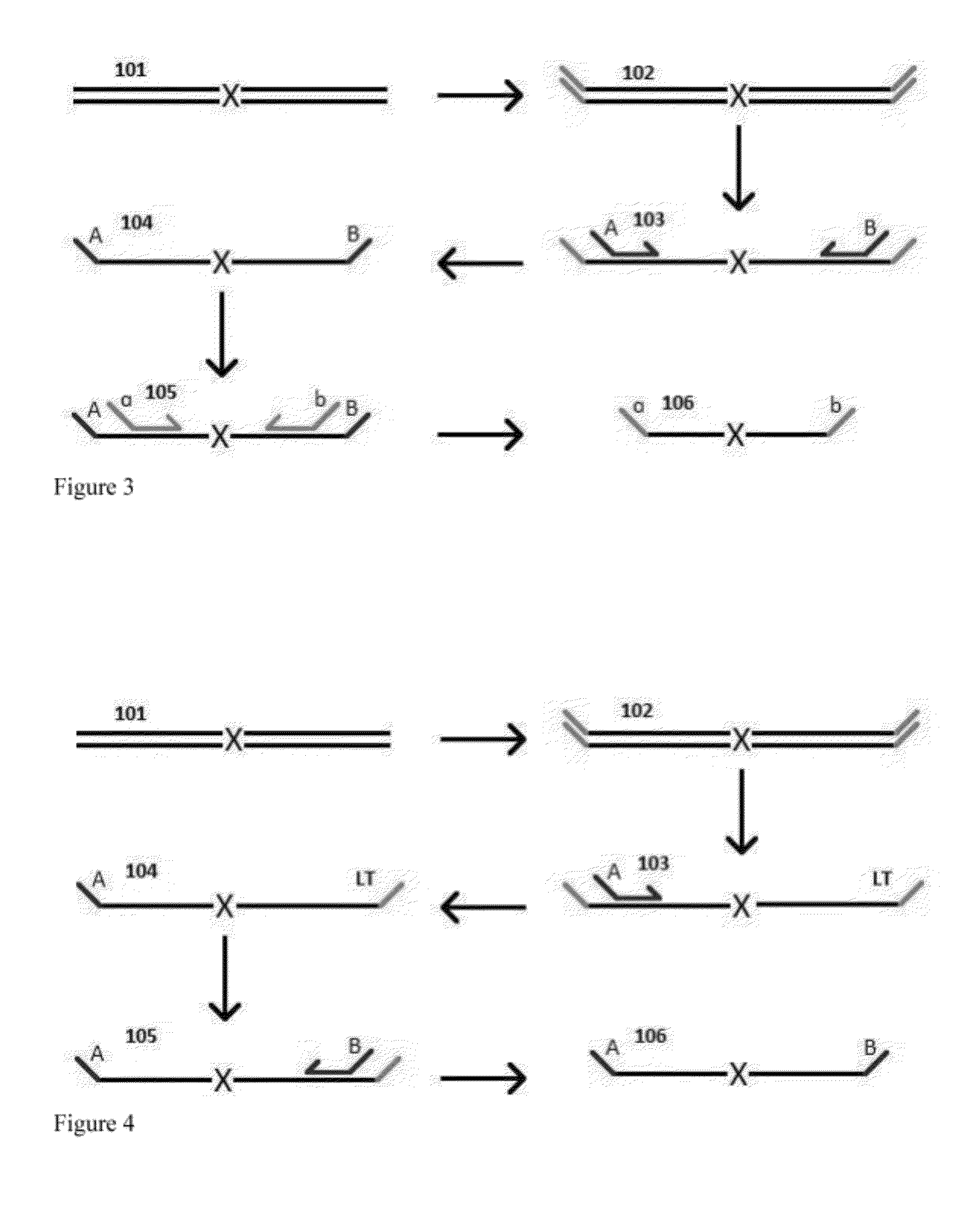
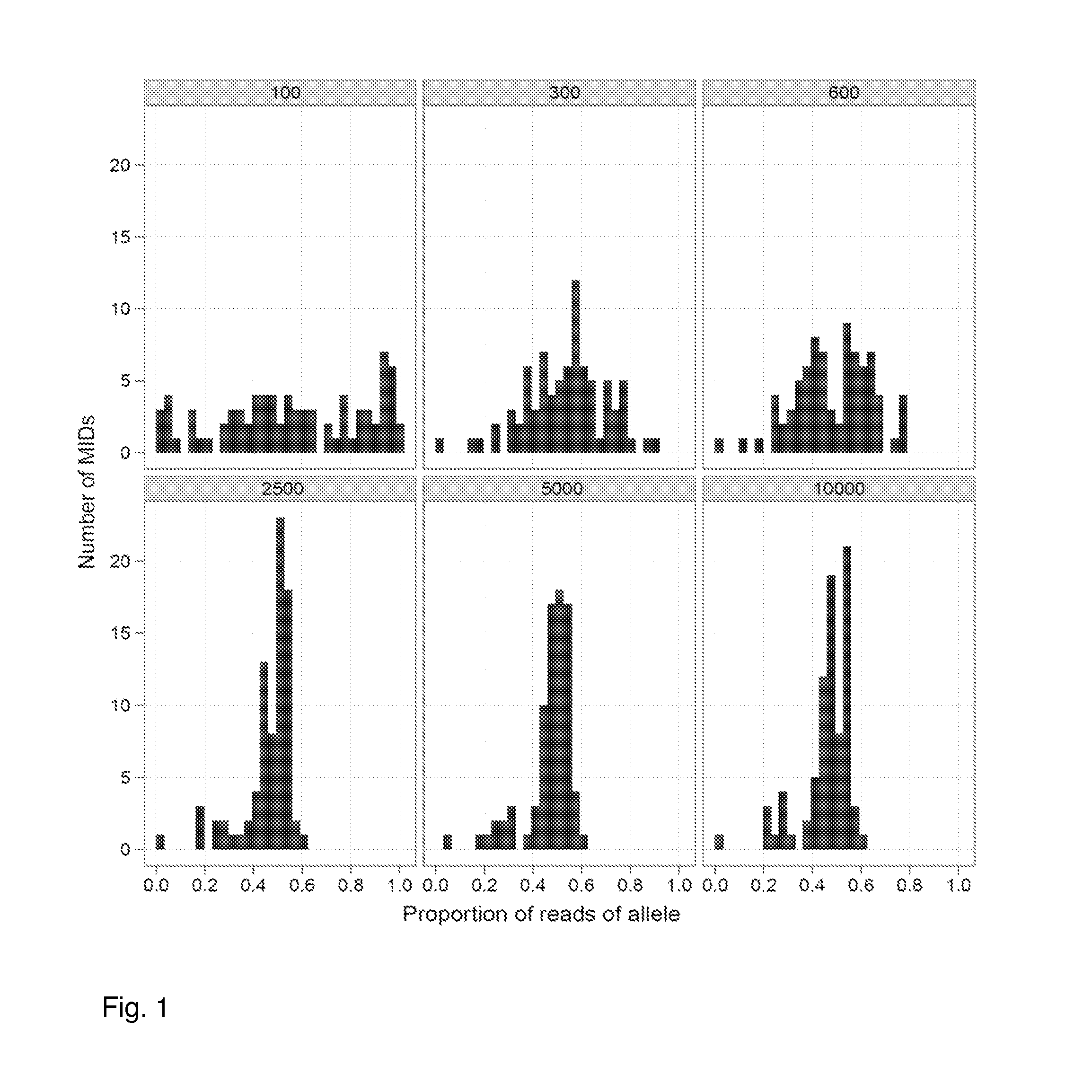
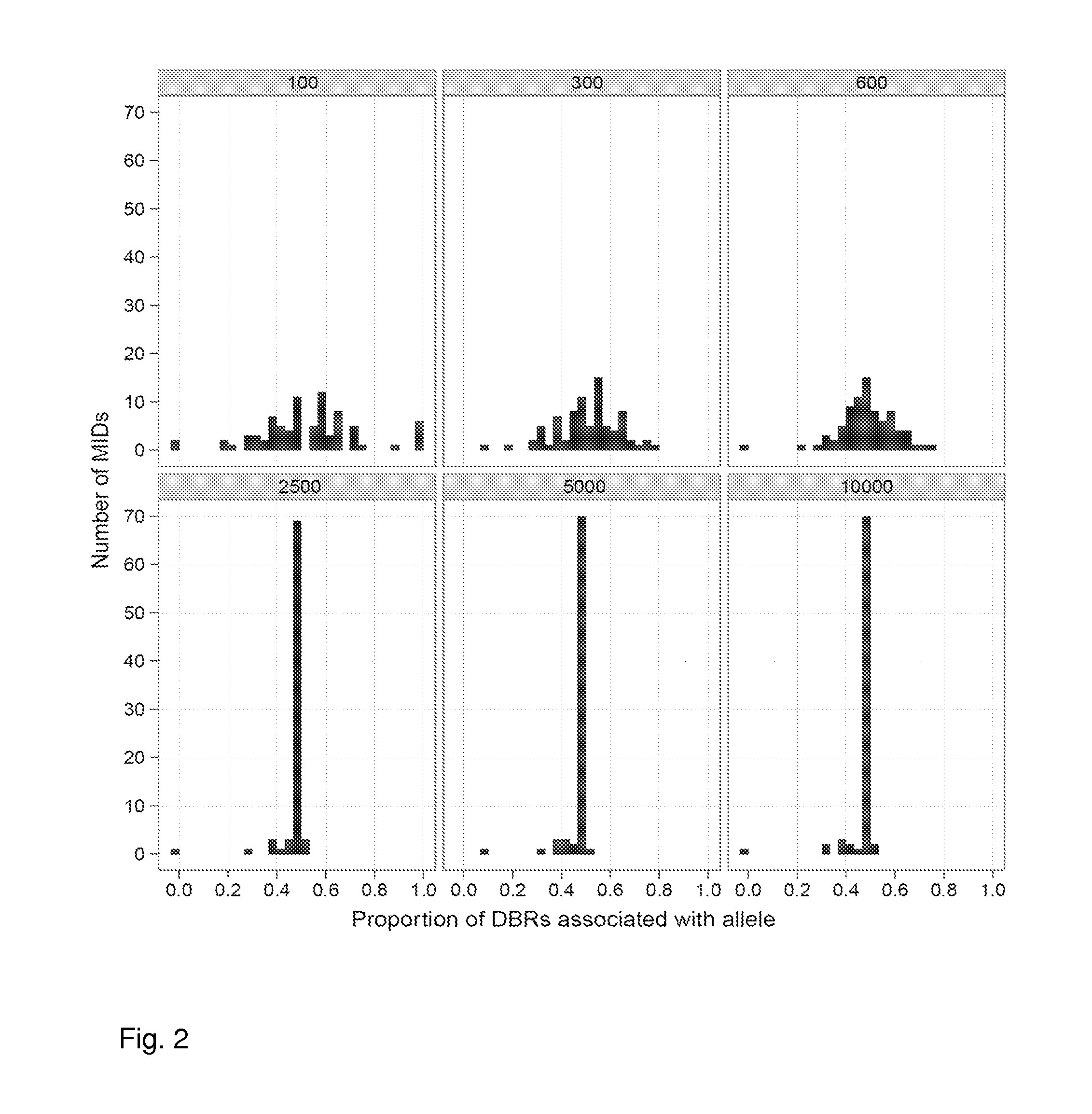
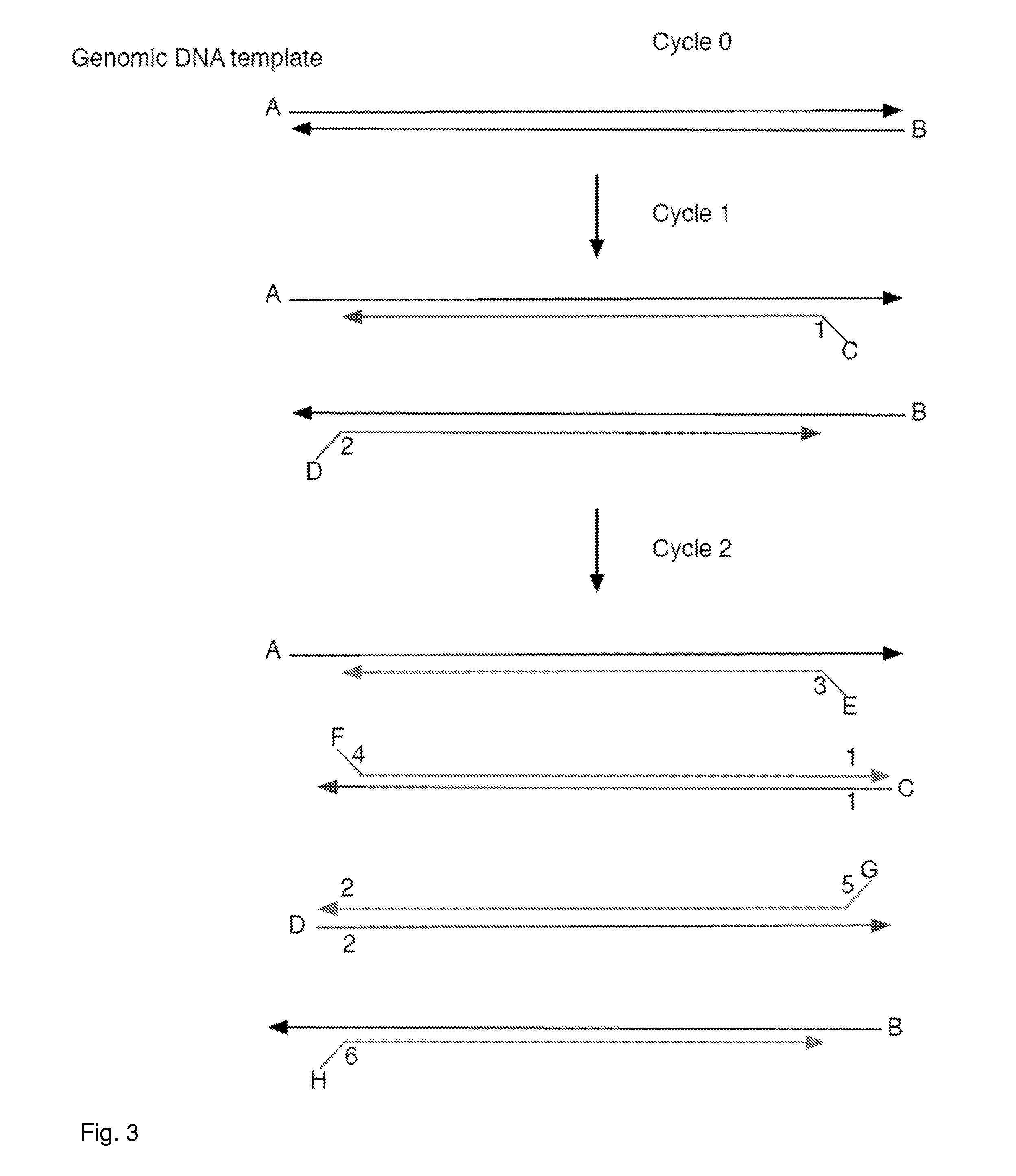
Aspects of the present invention include methods and compositions for determining the number of individual polynucleotide molecules originating from the same genomic region of the same original sample that have been sequenced in a particular sequence analysis configuration or process. In these aspects of the invention, a degenerate base region (DBR) is attached to the starting polynucleotide molecules that are subsequently sequenced (e.g., after certain process steps are performed, e.g., amplification and / or enrichment). The number of different DBR sequences present in a sequencing run can be used to determine / estimate the number of different starting polynucleotides that have been sequenced. DBRs can be used to enhance numerous different nucleic acid sequence analysis applications, including allowing higher confidence allele call determinations in genotyping applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
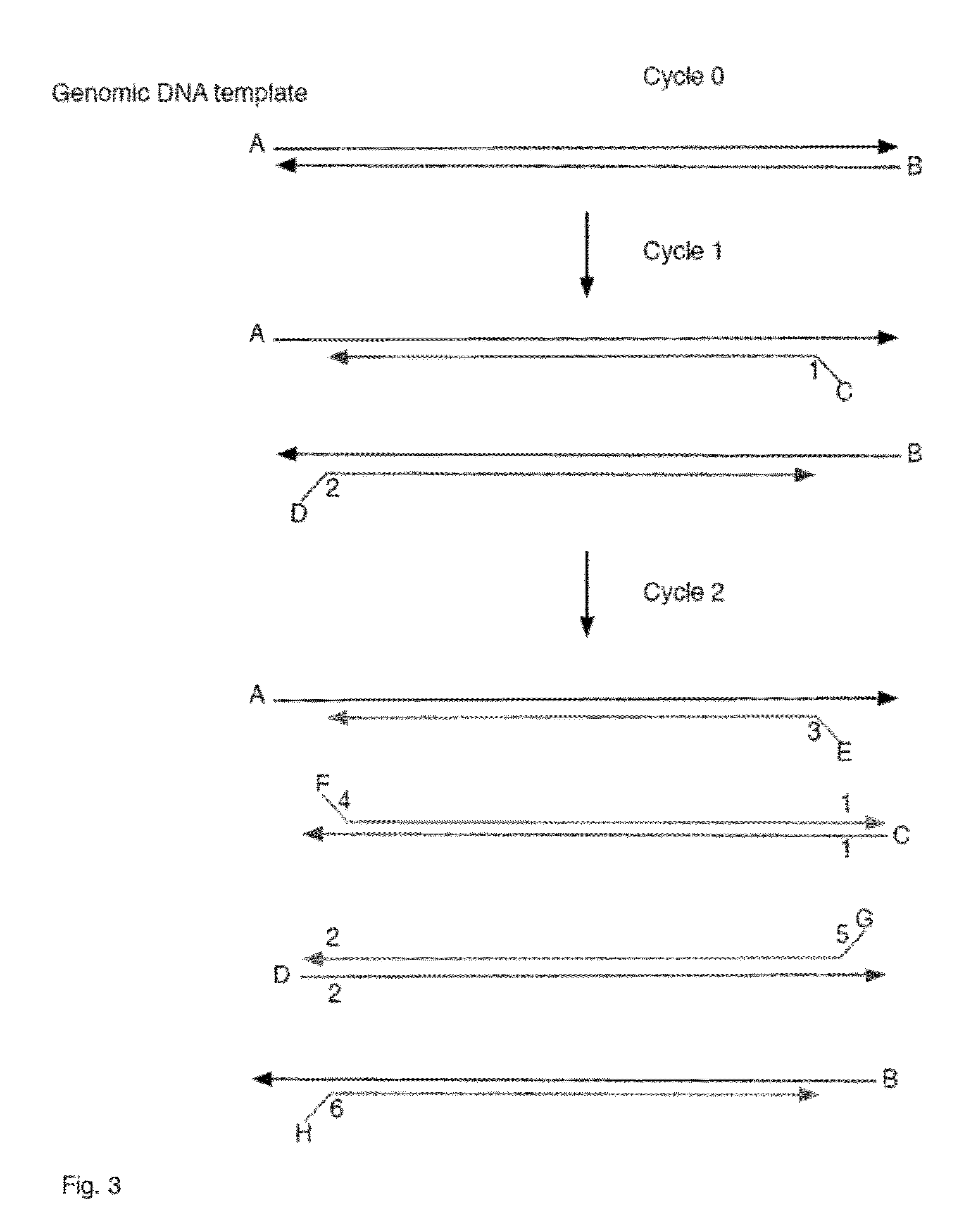
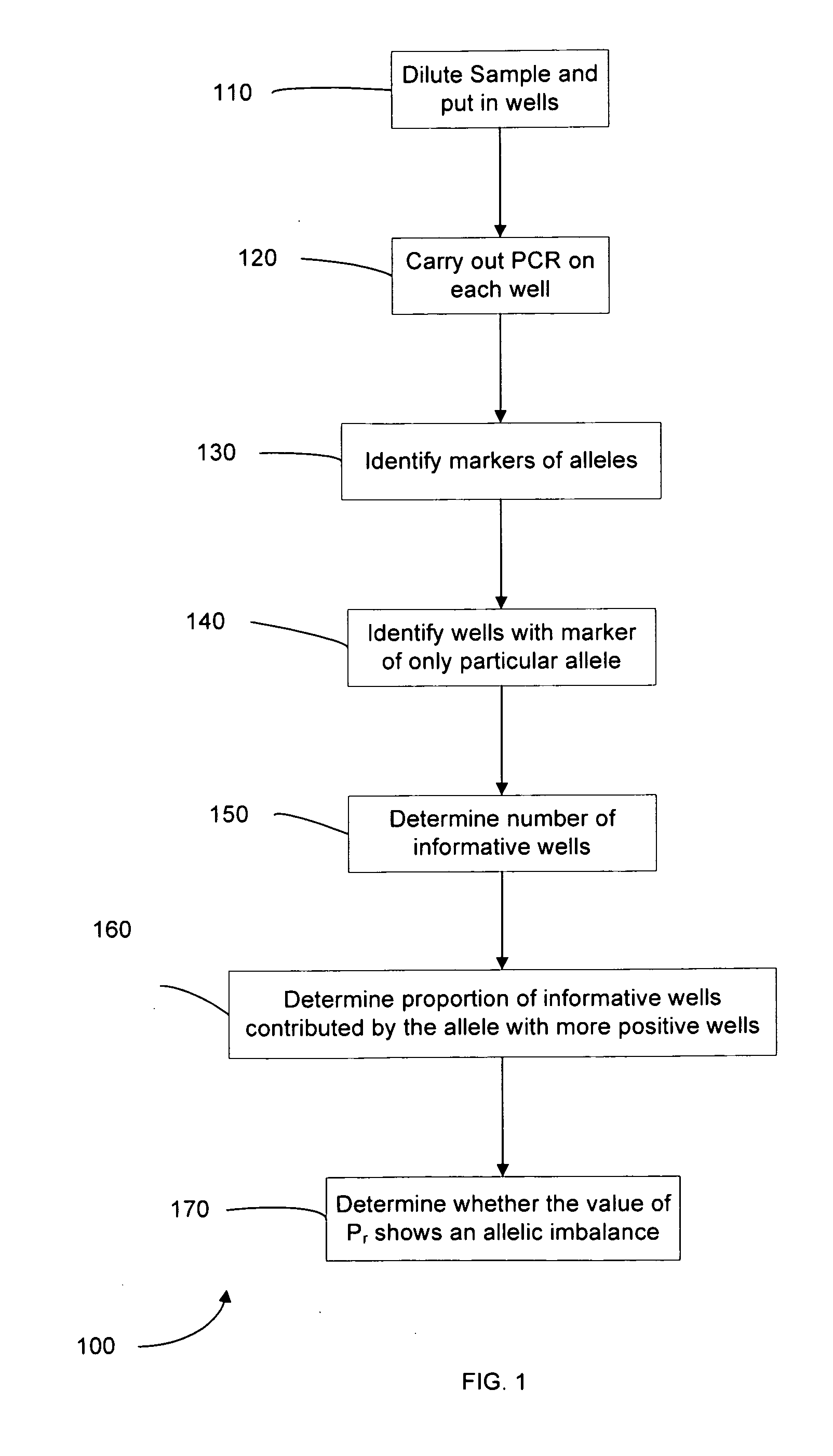
Determining a nucleic acid sequence imbalance
ActiveUS20090087847A1Quantity minimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Methods, systems, and apparatus are provided for determining whether a nucleic acid sequence imbalance exists within a biological sample. One or more cutoff values for determining an imbalance of, for example, the ratio of the two sequences (or sets of sequences) are chosen. The cutoff value may be determined based at least in part on the percentage of fetal DNA in a sample, such as maternal plasma, containing a background of maternal nucleic acid sequences. The cutoff value may also be determined based on an average concentration of a sequence per reaction. In one aspect, the cutoff value is determined from a proportion of informative wells that are estimated to contain a particular nucleic acid sequence, where the proportion is determined based on the above-mentioned percentage and / or average concentration. The cutoff value may be determined using many different types of methods, such as sequential probability ratio testing (SPRT).
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
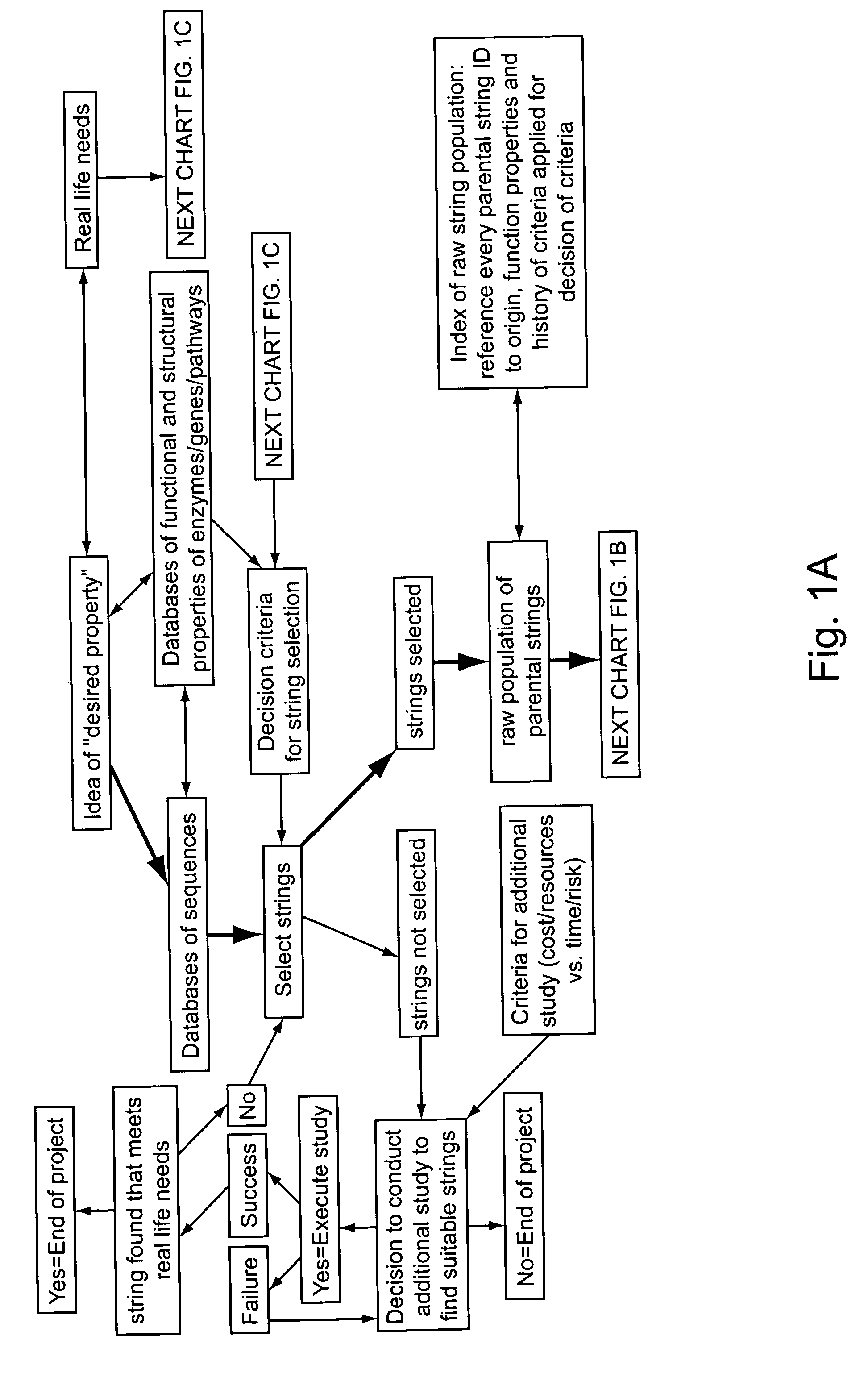
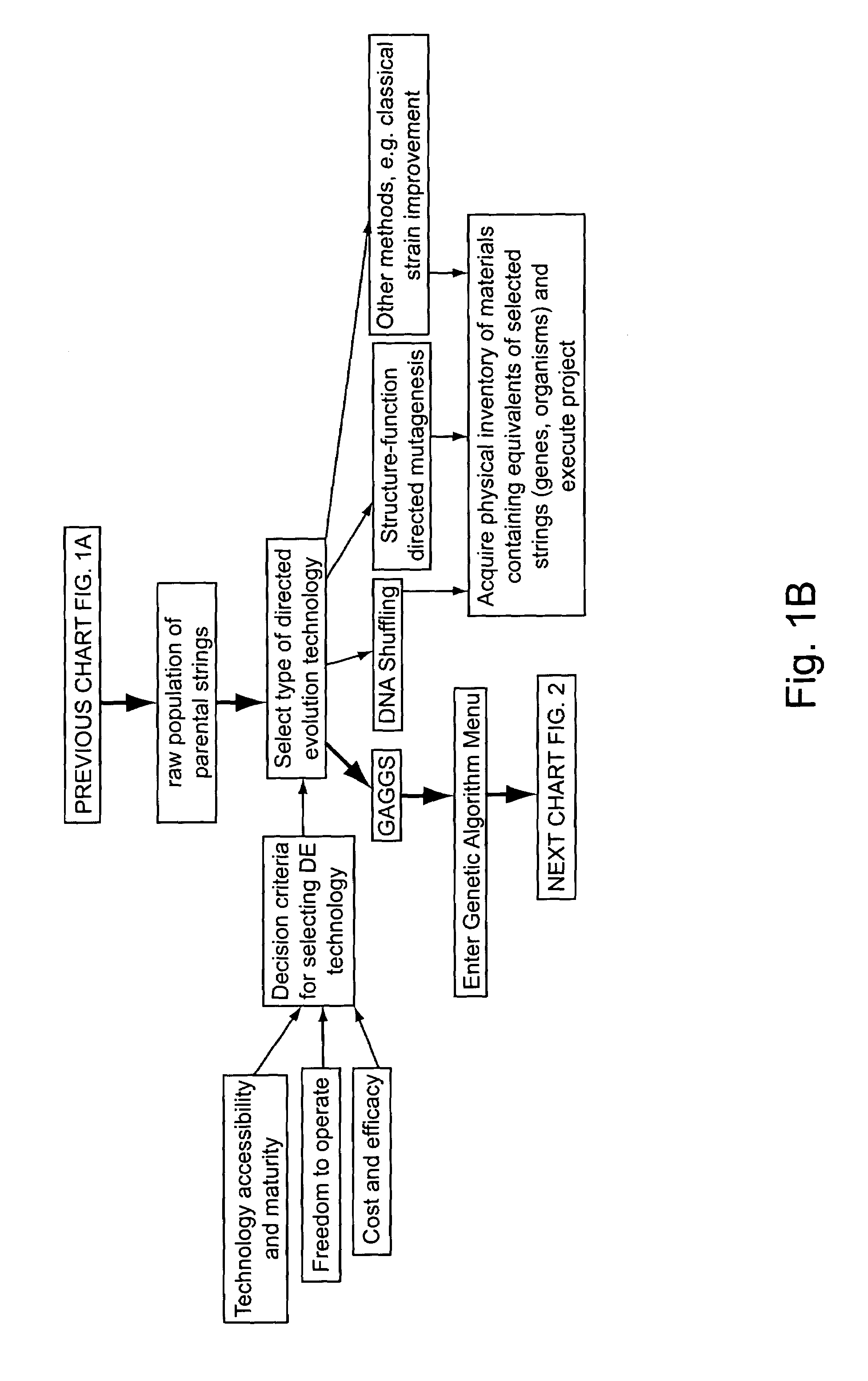
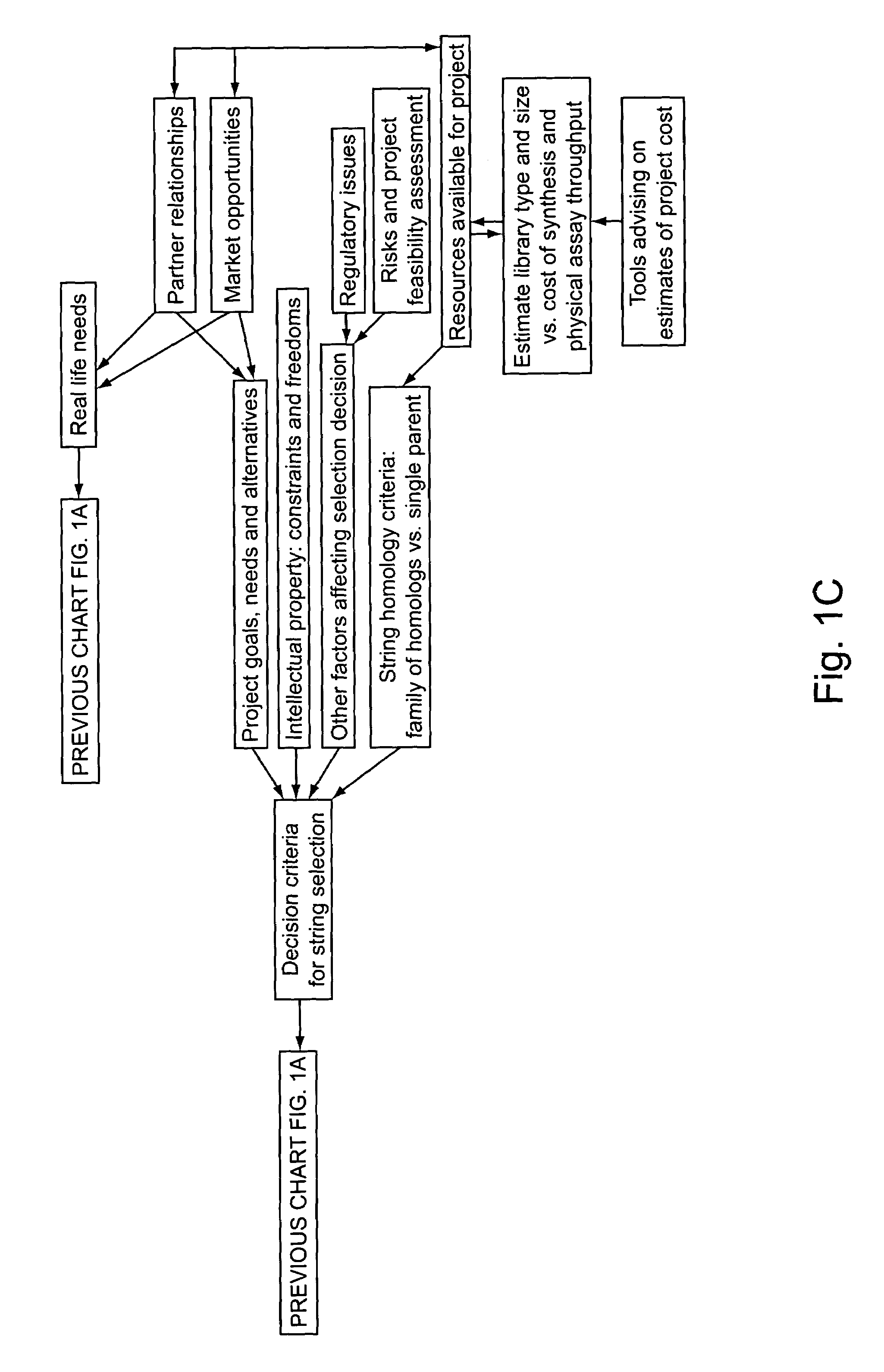
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
InactiveUS7024312B1Simplifies overall synthesis strategyLow levelPeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsPolynucleotideIn silico
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
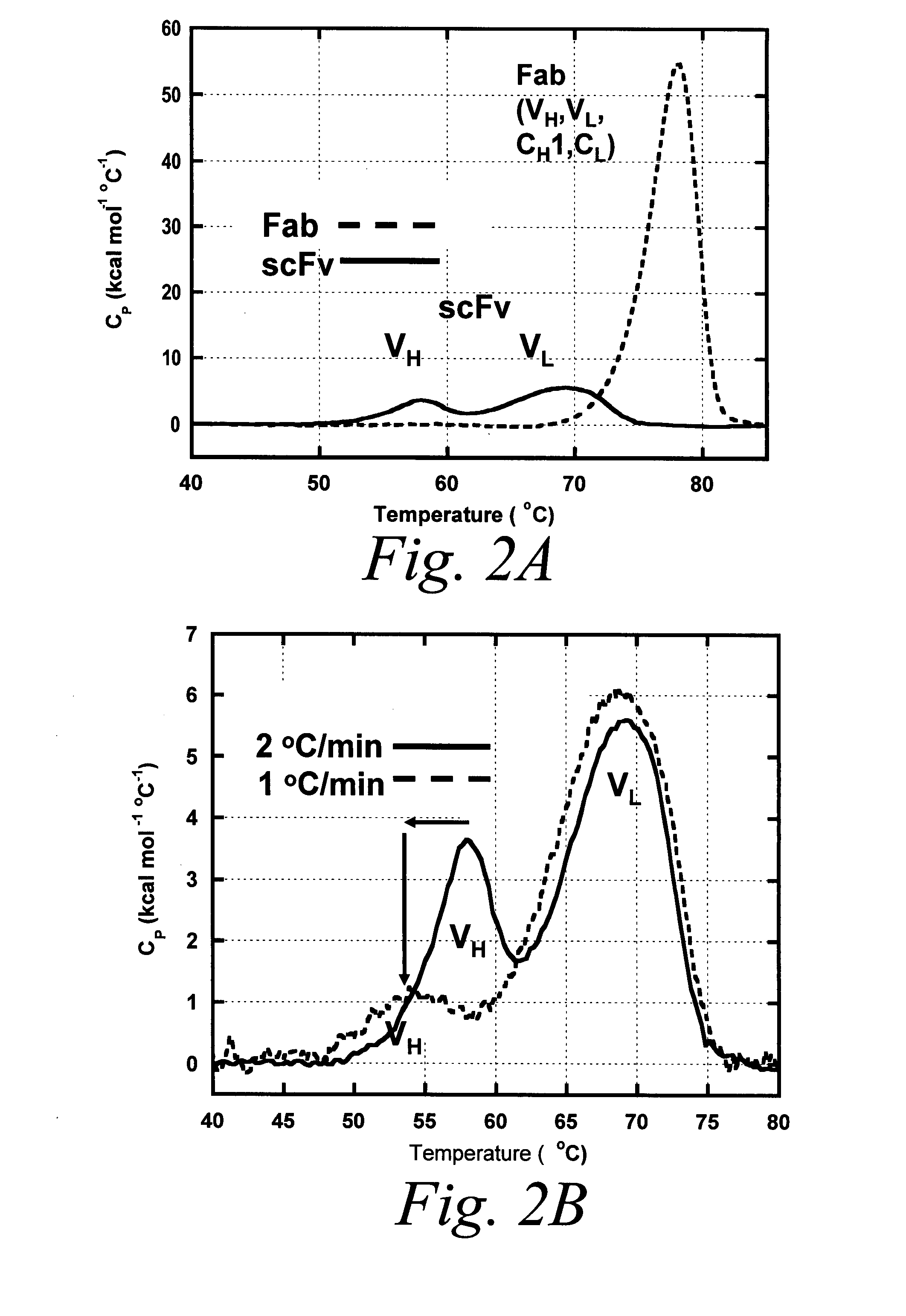
Stabilized polypeptide compositions
ActiveUS20080050370A1Improved polypeptide compositionImprove methodPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCrystallographyPolypeptide composition
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
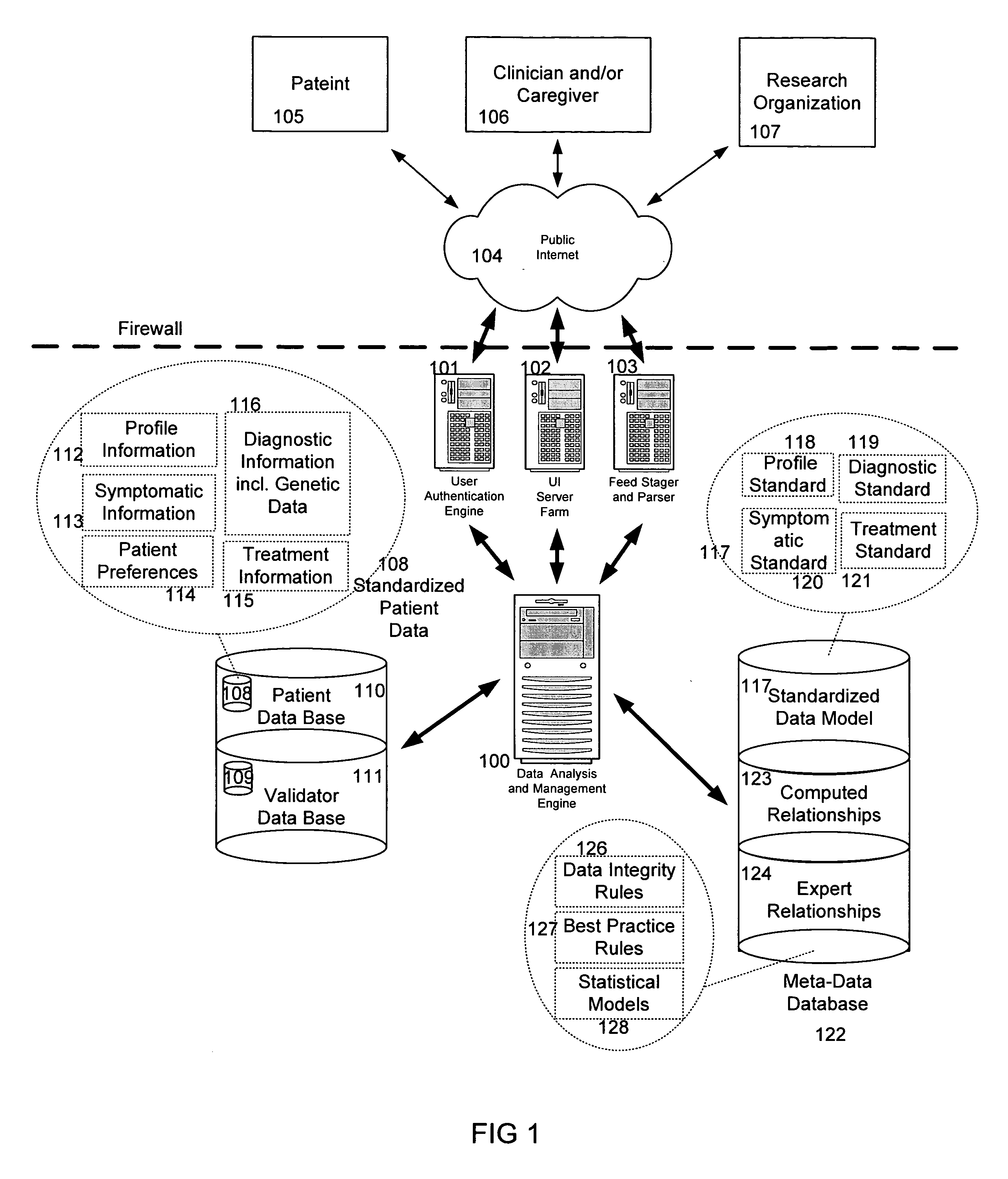
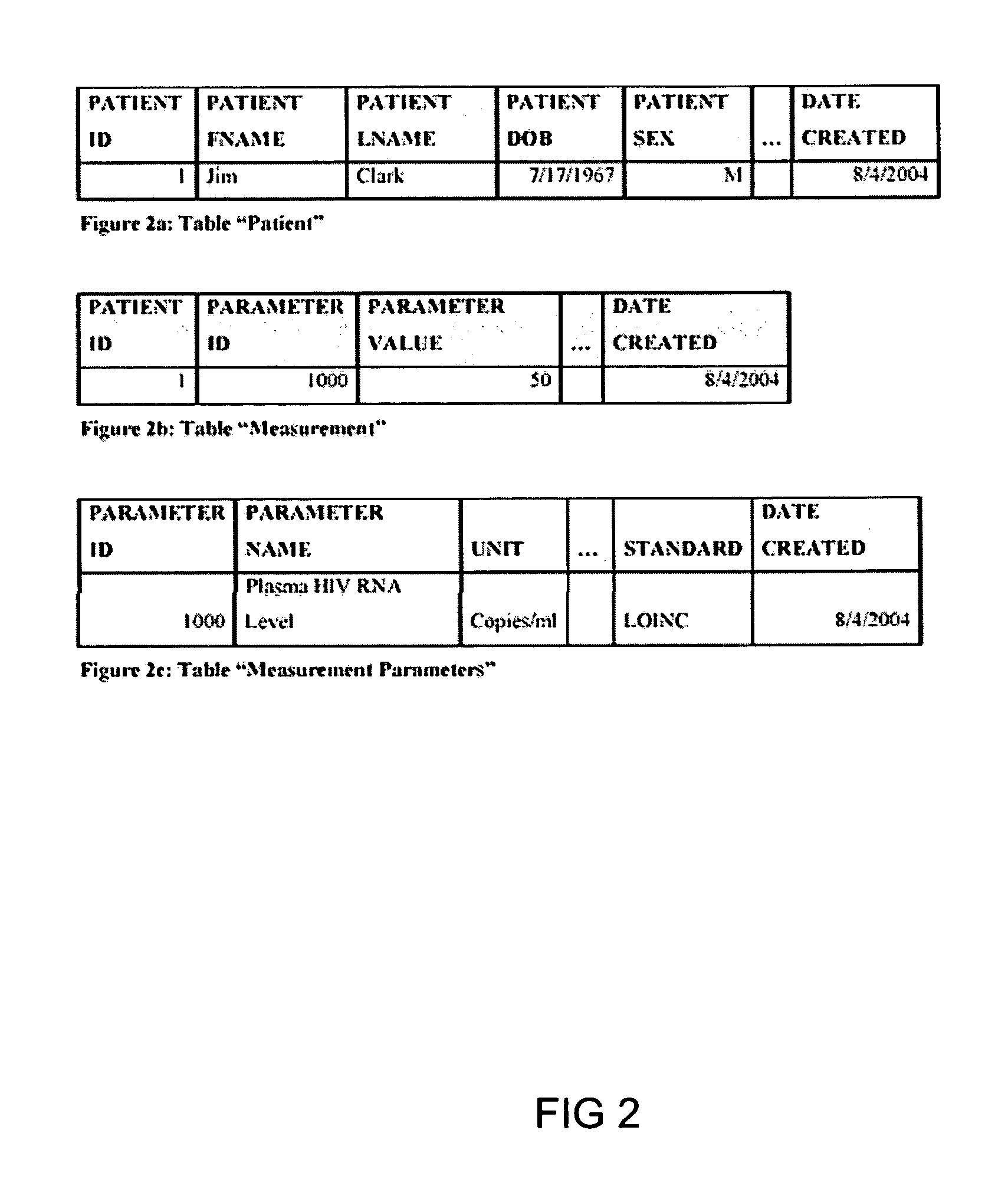
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions, faster, using aggregated genetic and phenotypic data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects who may be at distributed facilities. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes that encompass patient profile information, patient symptomatic information, patient treatment information, and patient diagnostic information including genetic information. Data from other systems is converted into the format of the standardized data classes using a data parser, or cartridge, specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes that are based on expert rules and statistical models. The relationships are used both to validate new data, and to predict phenotypic outcomes based on available data. The prediction may relate to a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention by a caregiver. The statistical models may be inhaled into the system from electronic publications that define statistical models and methods for training those models, according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic and clinical data, in particular for underdetermined data sets that are typical of genetic information. The disclosure also describes how security of the data is maintained by means of a robust security architecture, and robust user authentication such as biometric authentication, combined with application-level and data-level access privileges.
Owner:NATERA
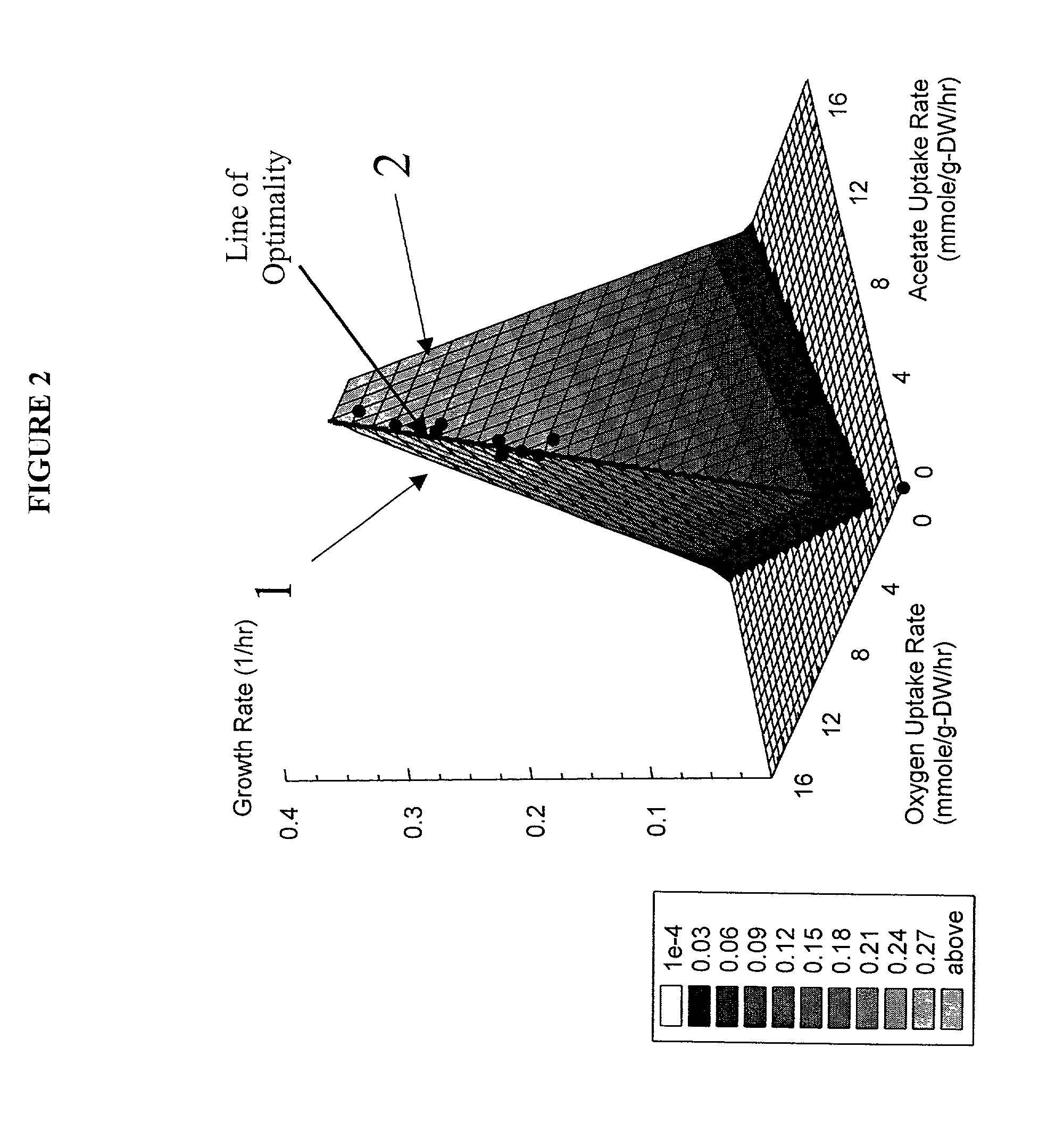
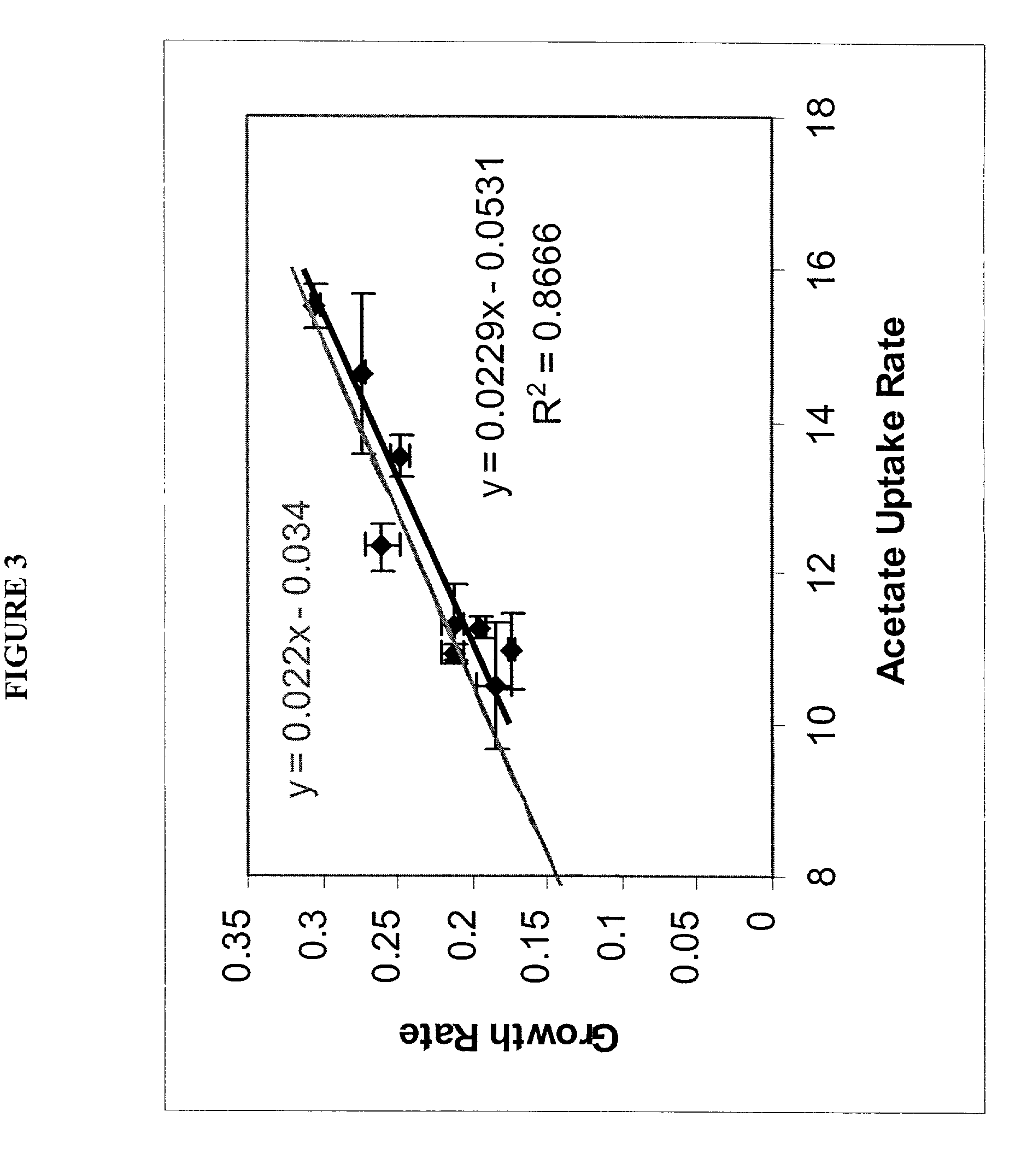
Method for the evolutionary design of biochemical reaction networks
The present invention relates to methods for achieving an optimal function of a biochemical reaction network. The methods can be performed in silico using a reconstruction of a biochemical reaction network of a cell and iterative optimization procedures. The methods can further include laboratory culturing steps to confirm and possibly expand the determinations made using the in silico methods, and to produce a cultured cell, or population of cells, with optimal functions. The current invention includes computer systems and computer products including computer-readable program code for performing the in silico steps of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of generating variant proteins with increased host string content and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20060008883A1Low immunogenicityMaximizes contentImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProteomicsMolecular biology
Owner:XENCOR INC
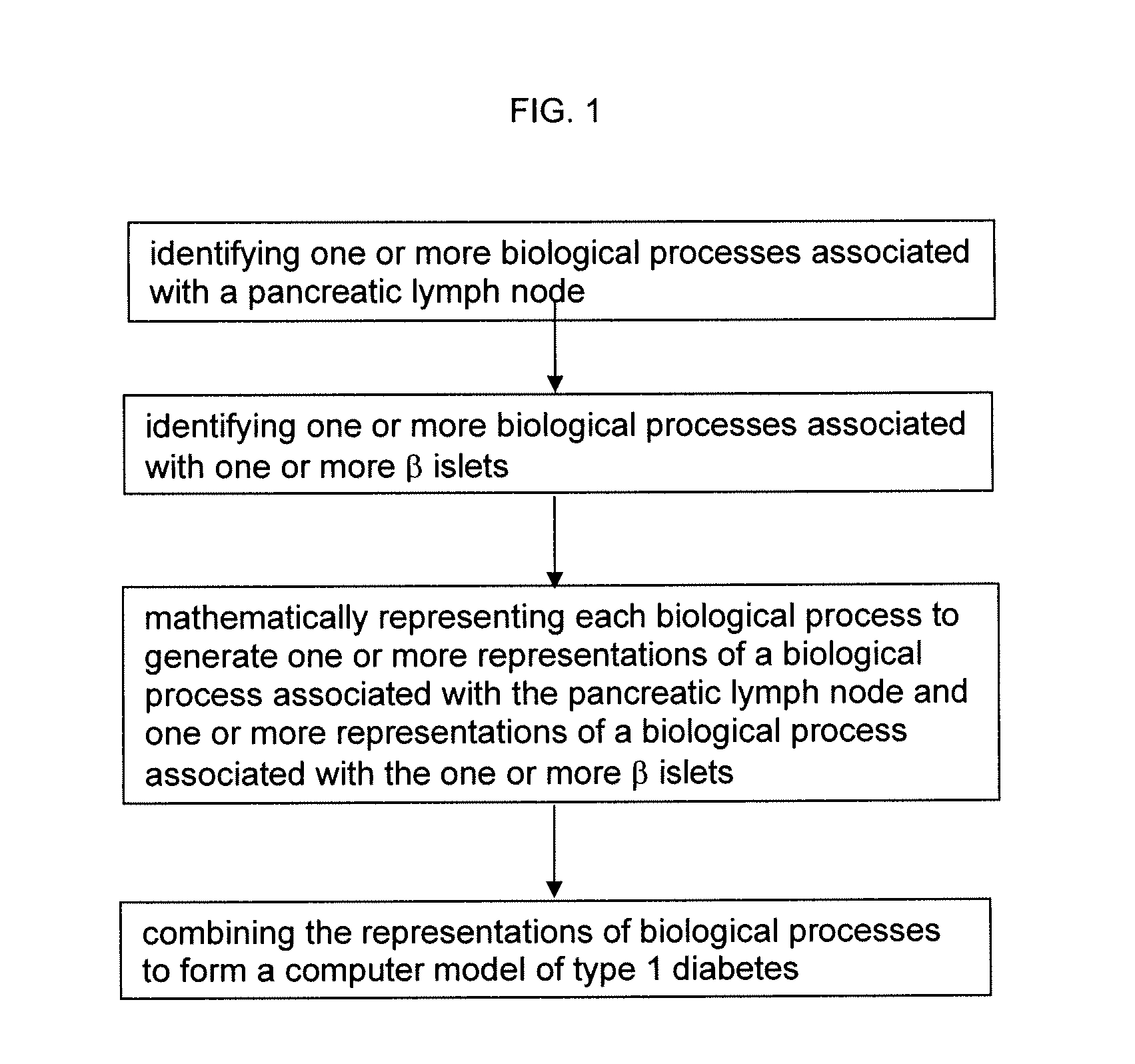
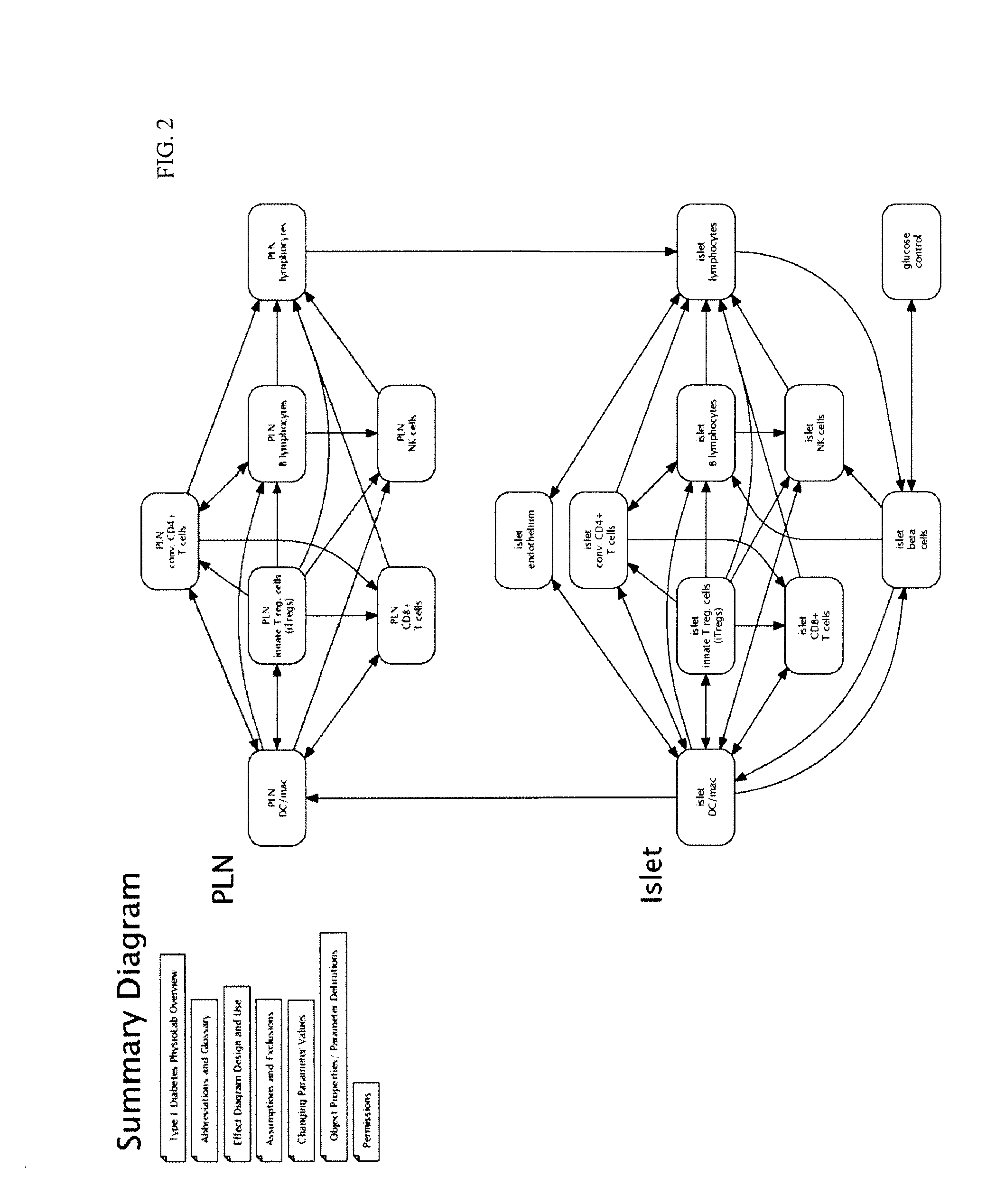
Apparatus and method for computer modeling type 1 diabetes
The invention encompasses novel methods for developing a computer model of type 1 diabetes in a mammal. In particular, the models can include representations of biological processes associated with a pancreatic lymph node and one or more pancreatic islets. Alternatively, the models can include representations of biological processes associated with at least two conditions selected from the group consisting of autoreactive T cell production, autoreactive T cell priming, insulitis and hyperglycemia. The invention also provides methods for developing a computer model of a non-insulin replacement treatment of type 1 diabetes. The invention also encompasses computer models of type 1 diabetes, methods of simulating type 1 diabetes and computer systems for simulating type 1 diabetes and the uses thereof.
Owner:ENTELOS INC
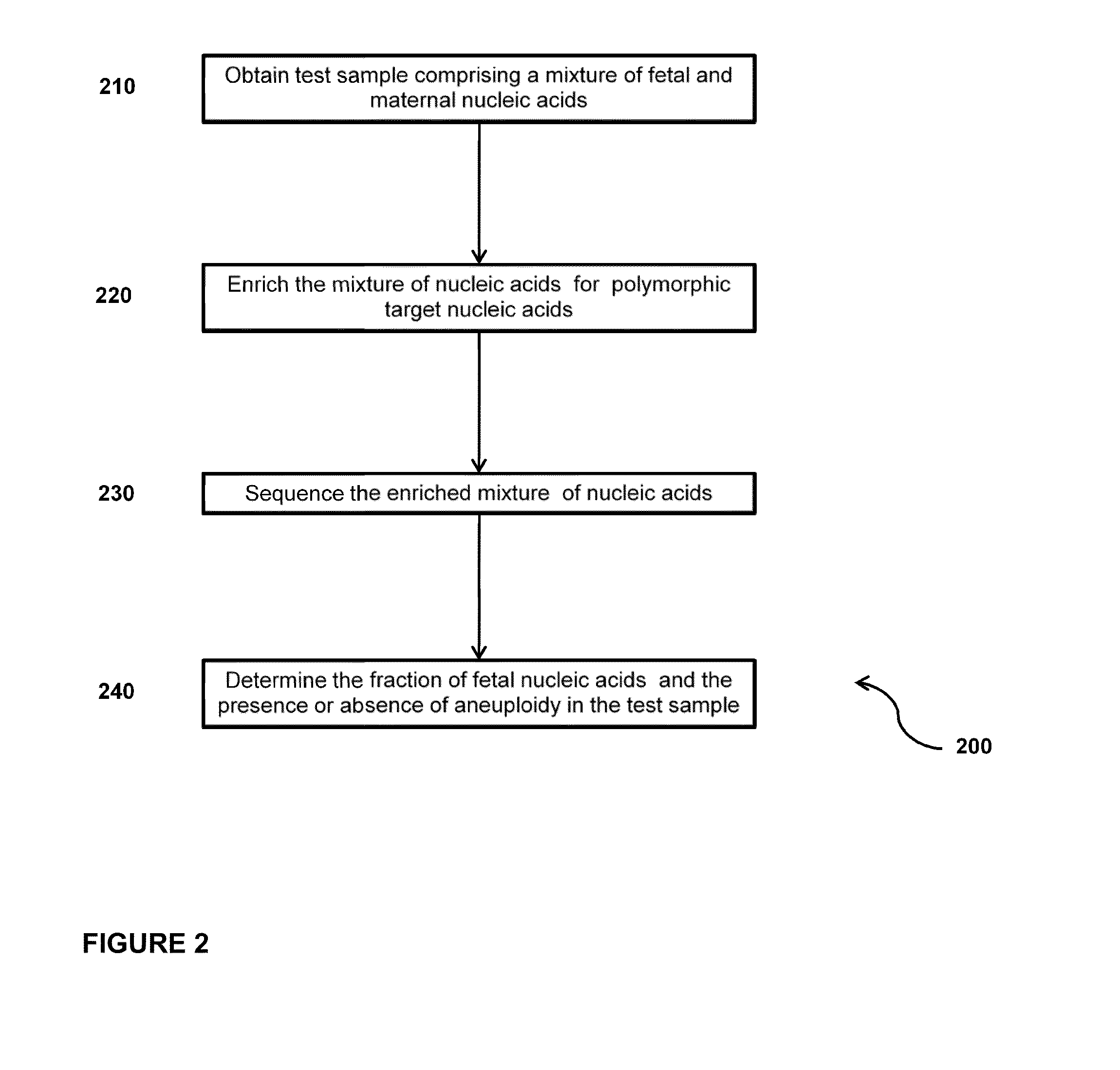
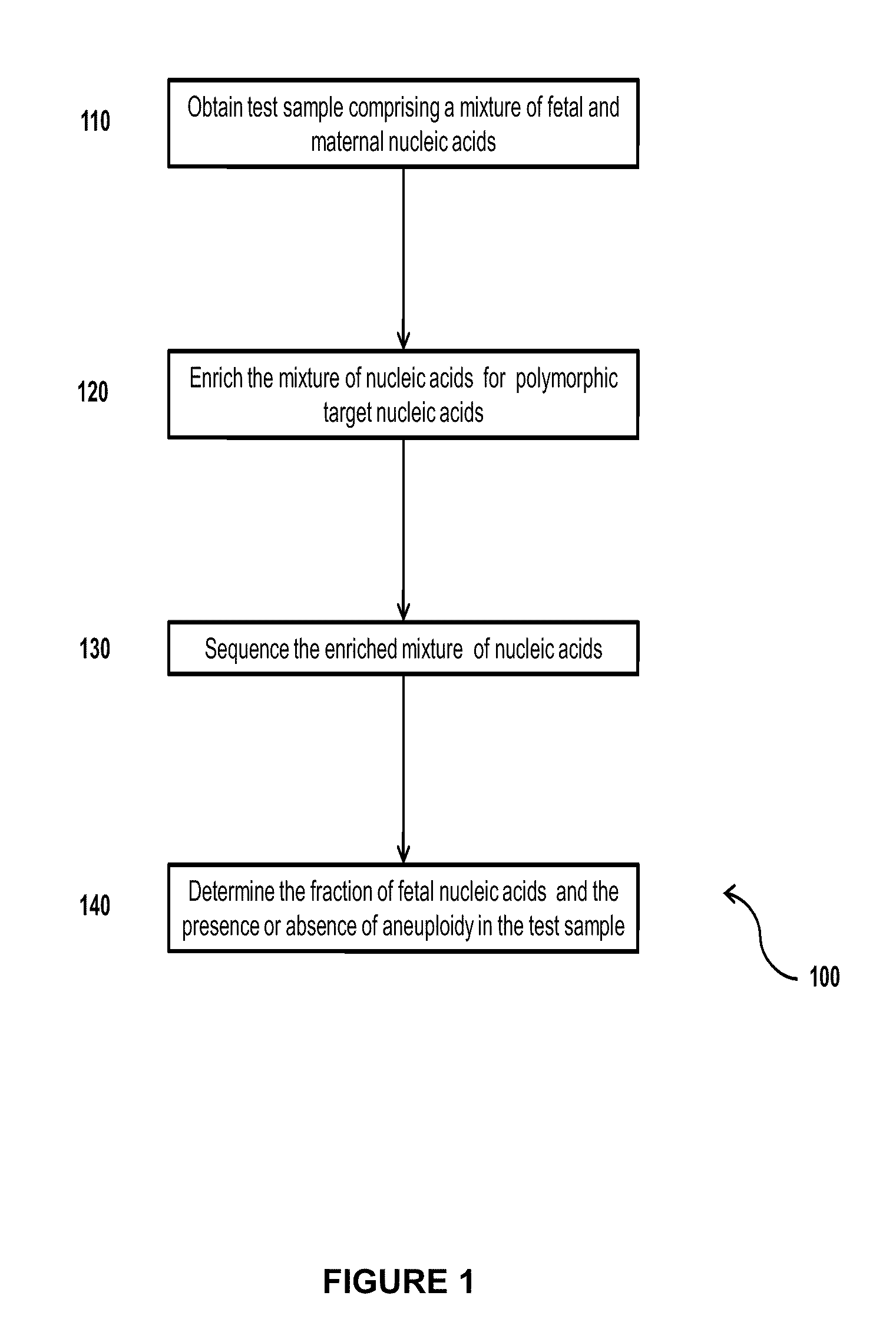
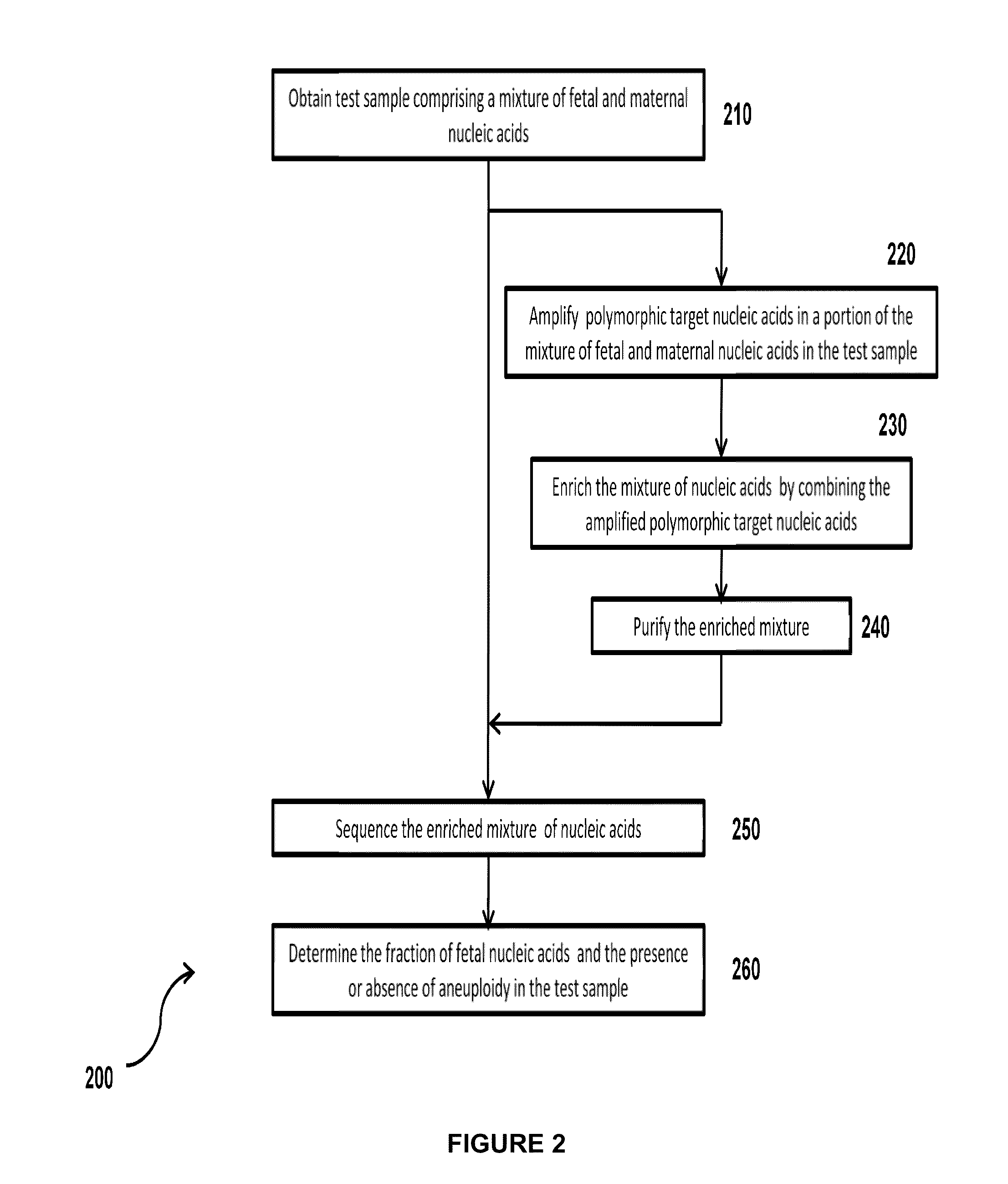
Simultaneous determination of aneuploidy and fetal fraction
InactiveUS20110224087A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal aneuploidyBiology
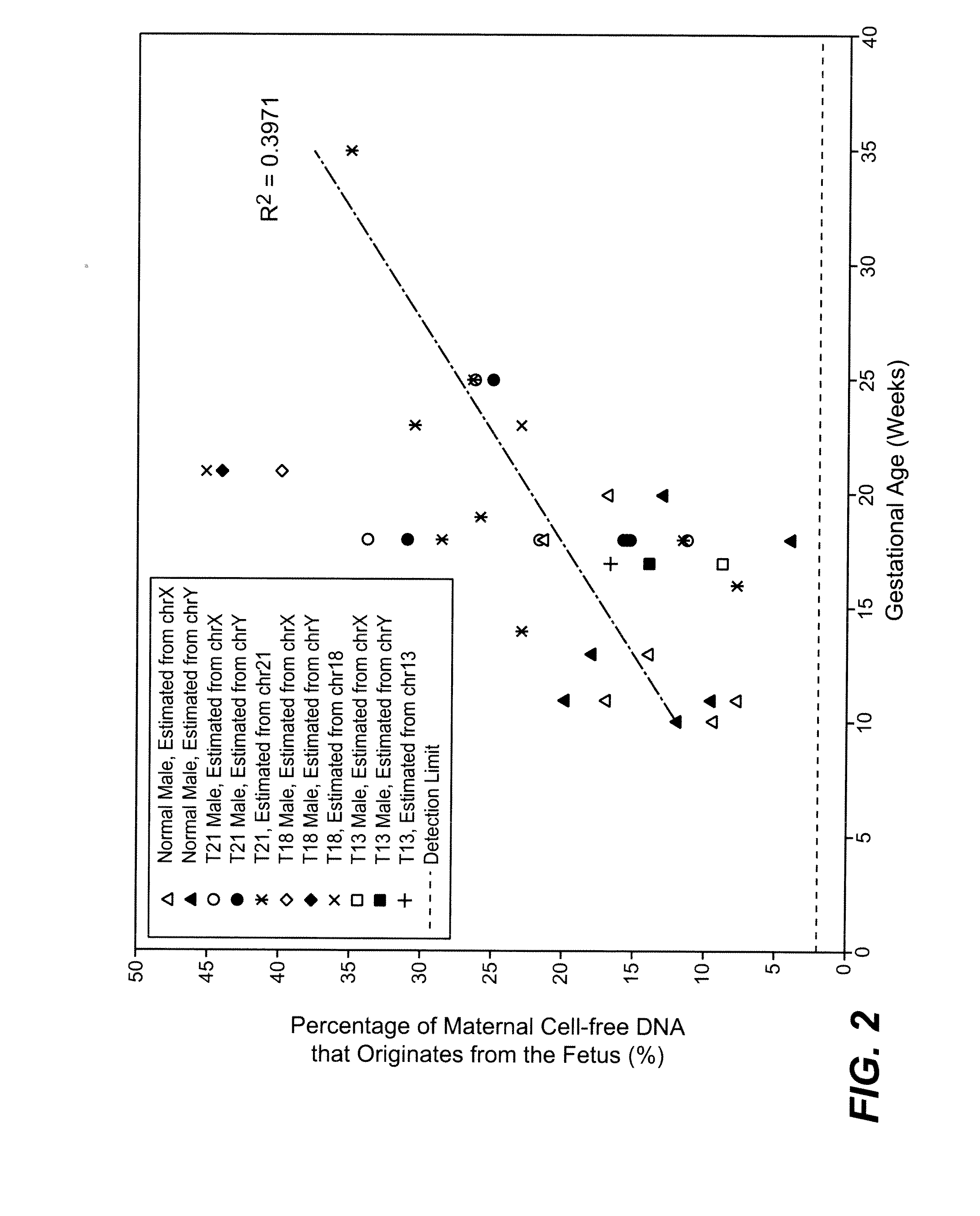
The invention provides compositions and methods for simultaneously determining the presence or absence of fetal aneuploidy and the relative amount of fetal nucleic acids in a sample obtained form a pregnant female. The method encompasses the use of sequencing technologies and exploits the occurrence of polymorphisms to provide a streamlined noninvasive process applicable to the practice of prenatal diagnostics.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Noninvasive Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy by Sequencing
InactiveUS20100112575A1Maximum resultMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMassive parallel sequencingFetal aneuploidy
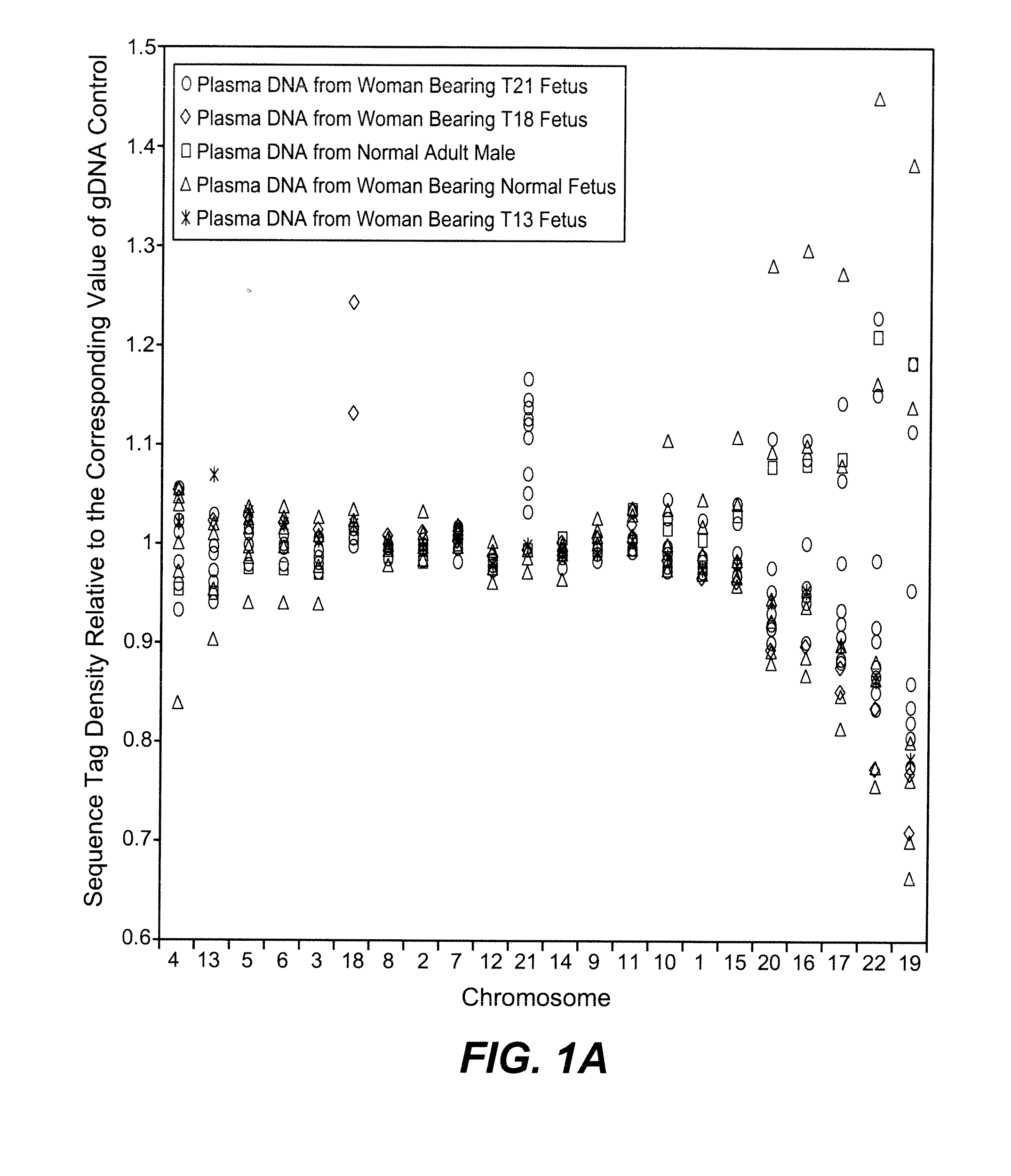
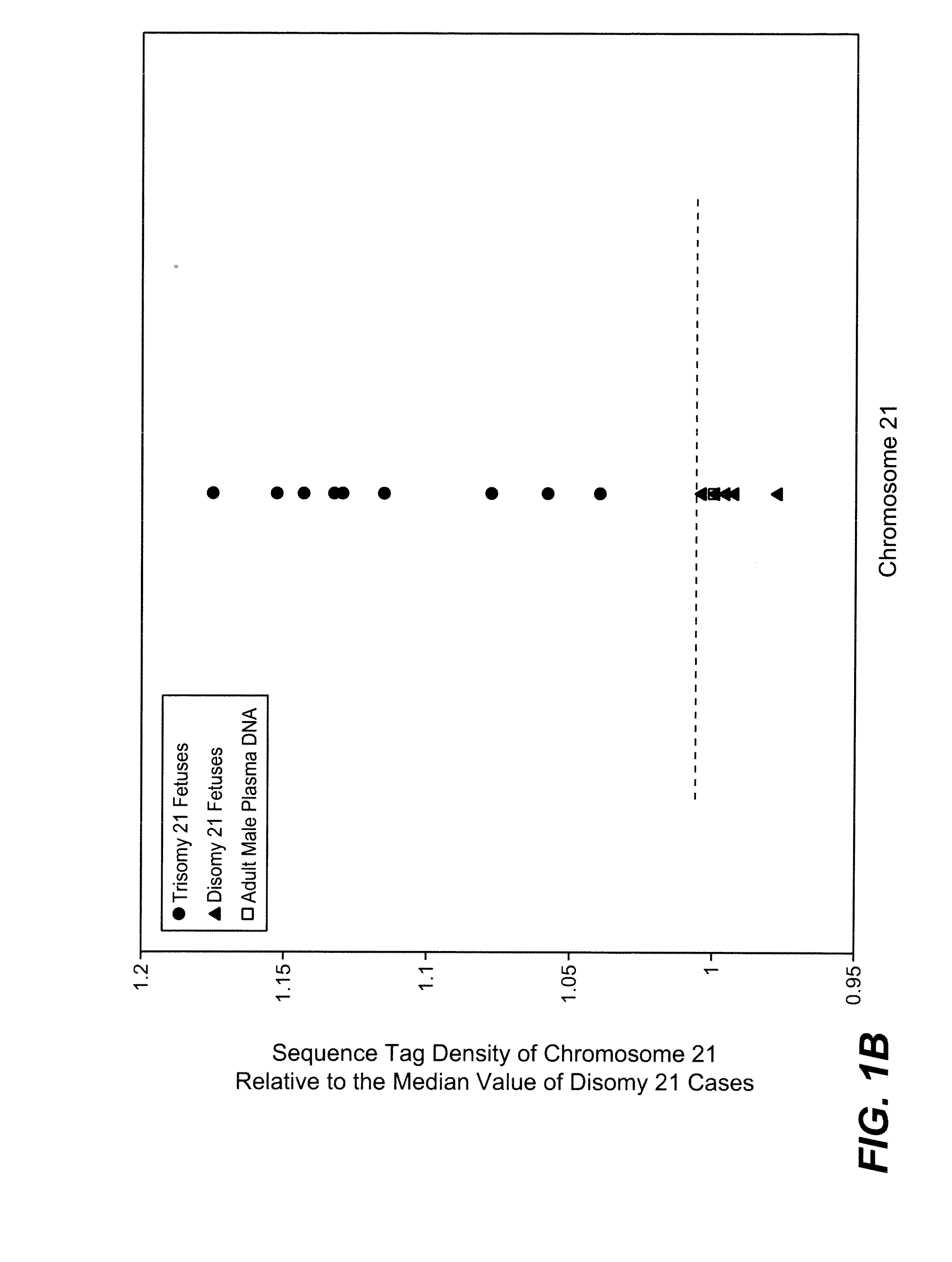
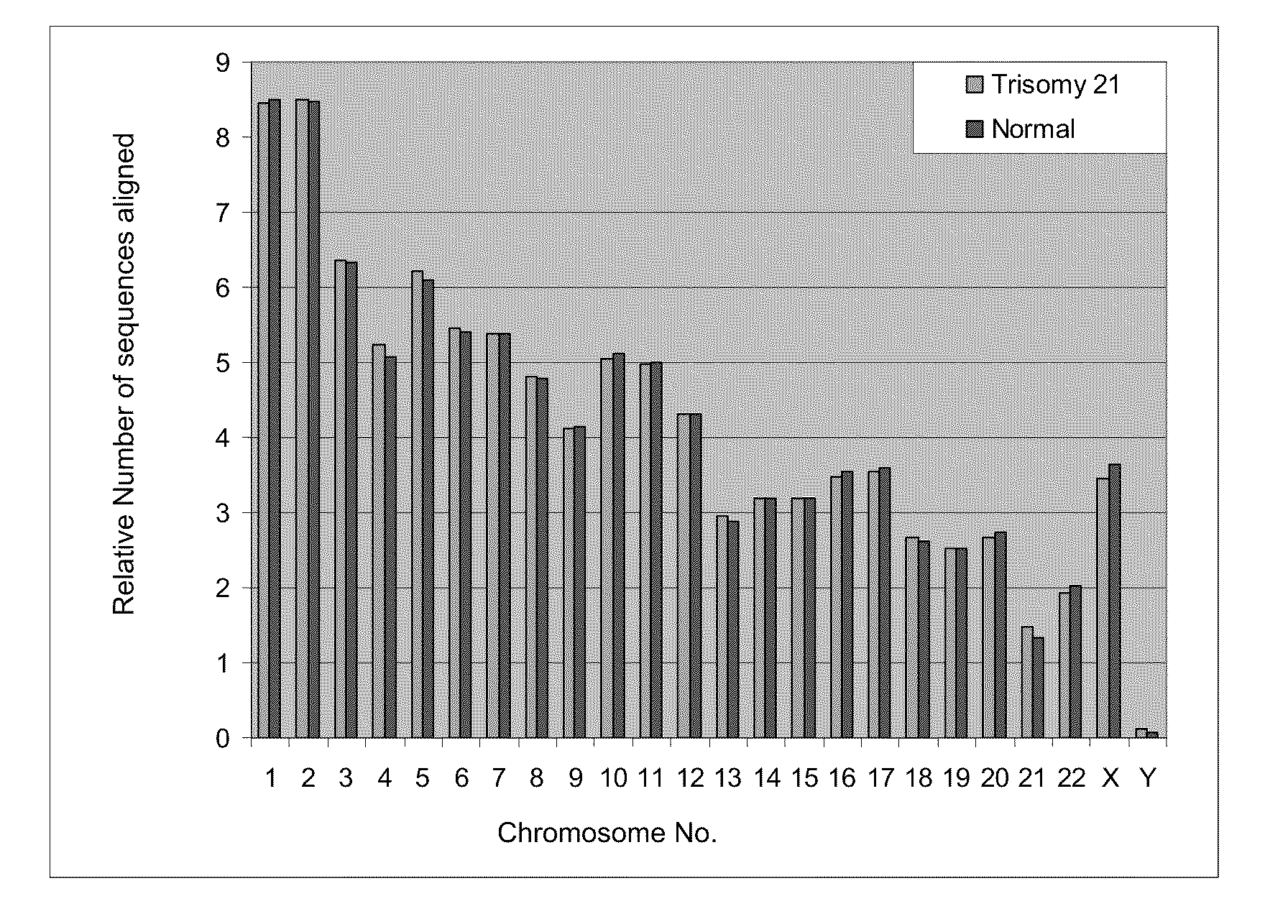
Disclosed is a method to achieve digital quantification of DNA (i.e., counting differences between identical sequences) using direct shotgun sequencing followed by mapping to the chromosome of origin and enumeration of fragments per chromosome. The preferred method uses massively parallel sequencing, which can produce tens of millions of short sequence tags in a single run and enabling a sampling that can be statistically evaluated. By counting the number of sequence tags mapped to a predefined window in each chromosome, the over- or under-representation of any chromosome in maternal plasma DNA contributed by an aneuploid fetus can be detected. This method does not require the differentiation of fetal versus maternal DNA. The median count of autosomal values is used as a normalization constant to account for differences in total number of sequence tags is used for comparison between samples and between chromosomes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Categorization and filtering of scientific data
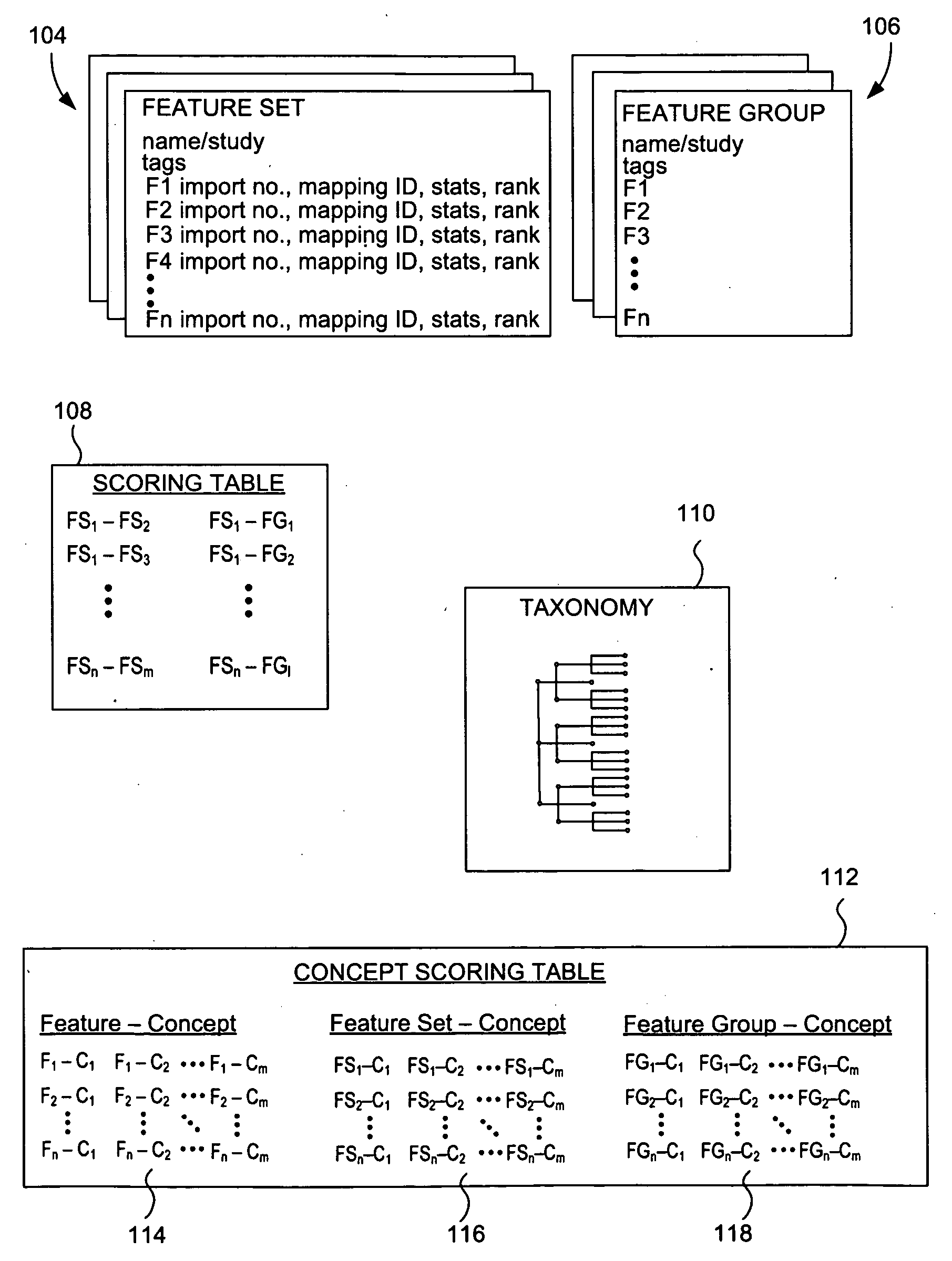
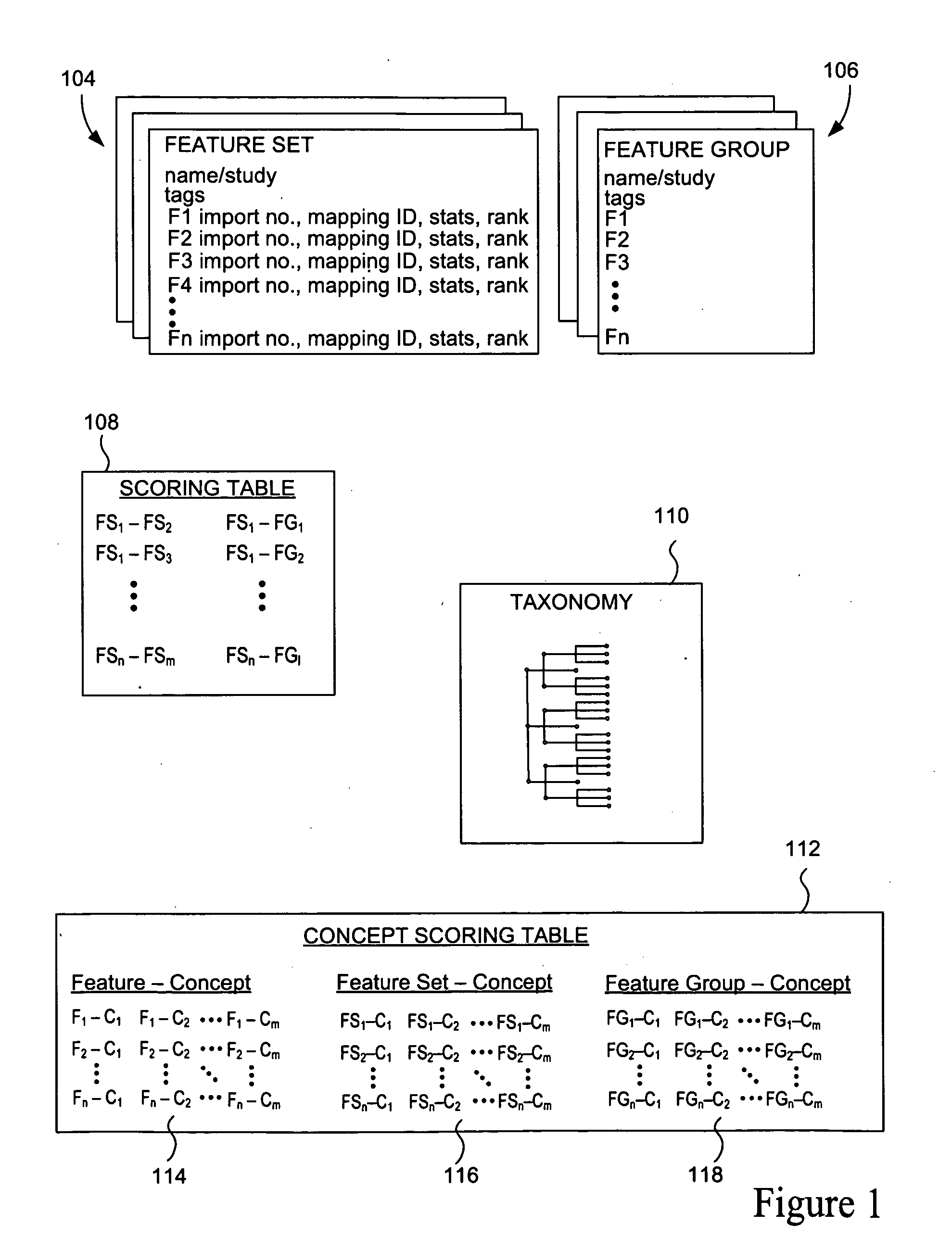
ActiveUS20090222400A1Improve efficiencyChaos modelsNon-linear system modelsBiological bodyMeta-analysis
The present invention relates to methods, systems and apparatus for capturing, integrating, organizing, navigating and querying large-scale data from high-throughput biological and chemical assay platforms. It provides a highly efficient meta-analysis infrastructure for performing research queries across a large number of studies and experiments from different biological and chemical assays, data types and organisms, as well as systems to build and add to such an infrastructure. According to various embodiments, methods, systems and interfaces for associating experimental data, features and groups of data related by structure and / or function with chemical, medical and / or biological terms in an ontology or taxonomy are provided. According to various embodiments, methods, systems and interfaces for filtering data by data source information are provided, allowing dynamic navigation through large amounts of data to find the most relevant results for a particular query.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
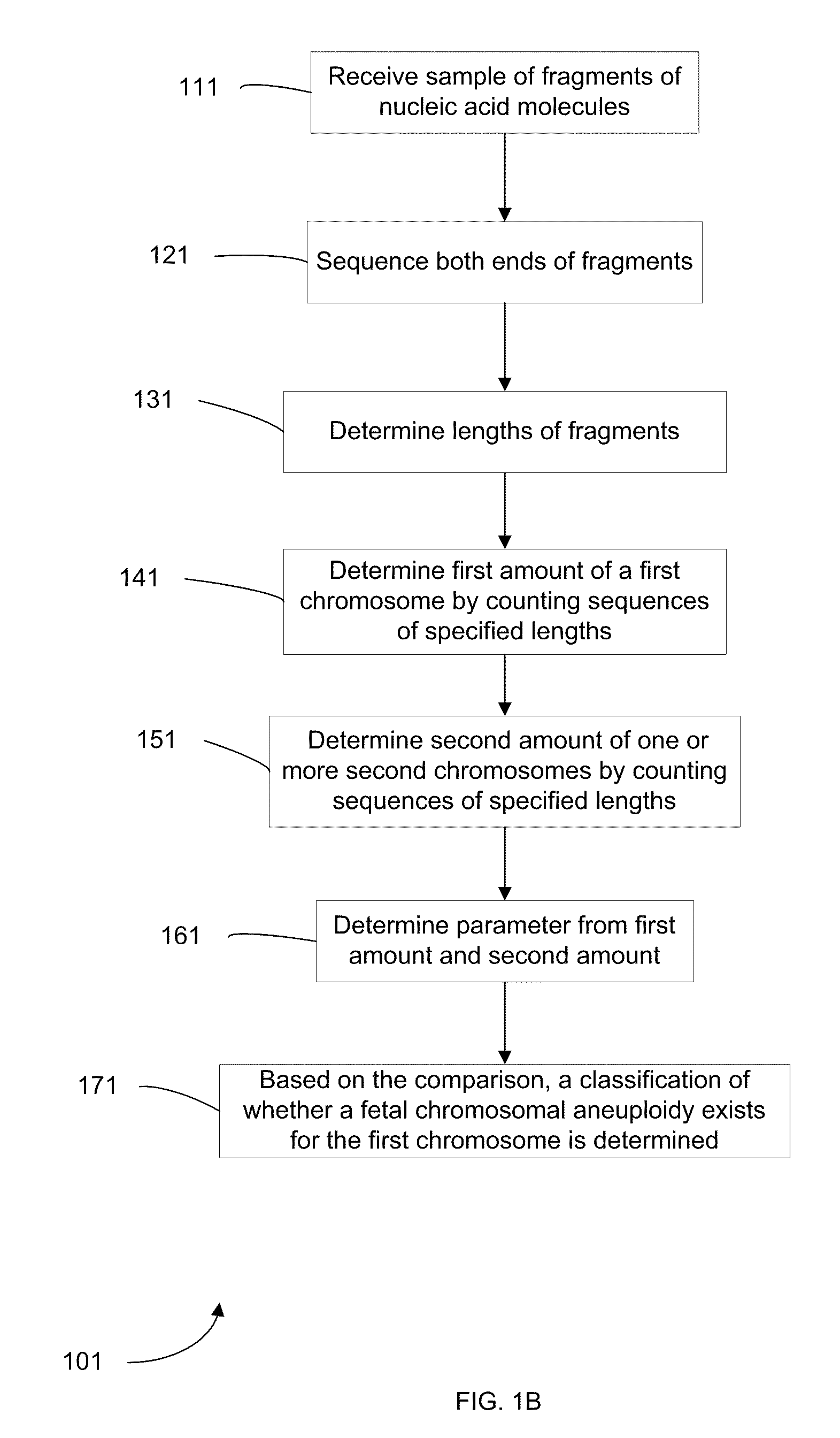
Diagnosing Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidy Using Genomic Sequencing With Enrichment
PendingUS20100112590A1High sensitivityMore accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic sequencingDNA fragmentation
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. The determination of the relative amounts may count sequences of only certain length. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists. Prior to sequencing, the biological sample may be enriched for DNA fragments of a particular sizes.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods for Non-Invasive Prenatal Ploidy Calling
ActiveUS20120270212A1Fill in the blanksMathematical modelsMicrobiological testing/measurementDistribution patternGenotype
The present disclosure provides methods for determining the ploidy status of a chromosome in a gestating fetus from genotypic data measured from a mixed sample of DNA comprising DNA from both the mother of the fetus and from the fetus, and optionally from genotypic data from the mother and father. The ploidy state is determined by using a joint distribution model to create a plurality of expected allele distributions for different possible fetal ploidy states given the parental genotypic data, and comparing the expected allelic distributions to the pattern of measured allelic distributions measured in the mixed sample, and choosing the ploidy state whose expected allelic distribution pattern most closely matches the observed allelic distribution pattern. The mixed sample of DNA may be preferentially enriched at a plurality of polymorphic loci in a way that minimizes the allelic bias, for example using massively multiplexed targeted PCR.
Owner:NATERA
Increasing confidence of allele calls with molecular counting
ActiveUS20120071331A1Easy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSequence analysisAllele
Aspects of the present invention include methods and compositions for determining the number of individual polynucleotide molecules originating from the same genomic region of the same original sample that have been sequenced in a particular sequence analysis configuration or process. In these aspects of the invention, a degenerate base region (DBR) is attached to the starting polynucleotide molecules that are subsequently sequenced (e.g., after certain process steps are performed, e.g., amplification and / or enrichment). The number of different DBR sequences present in a sequencing run can be used to determine / estimate the number of different starting polynucleotides that have been sequenced. DBRs can be used to enhance numerous different nucleic acid sequence analysis applications, including allowing higher confidence allele call determinations in genotyping applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
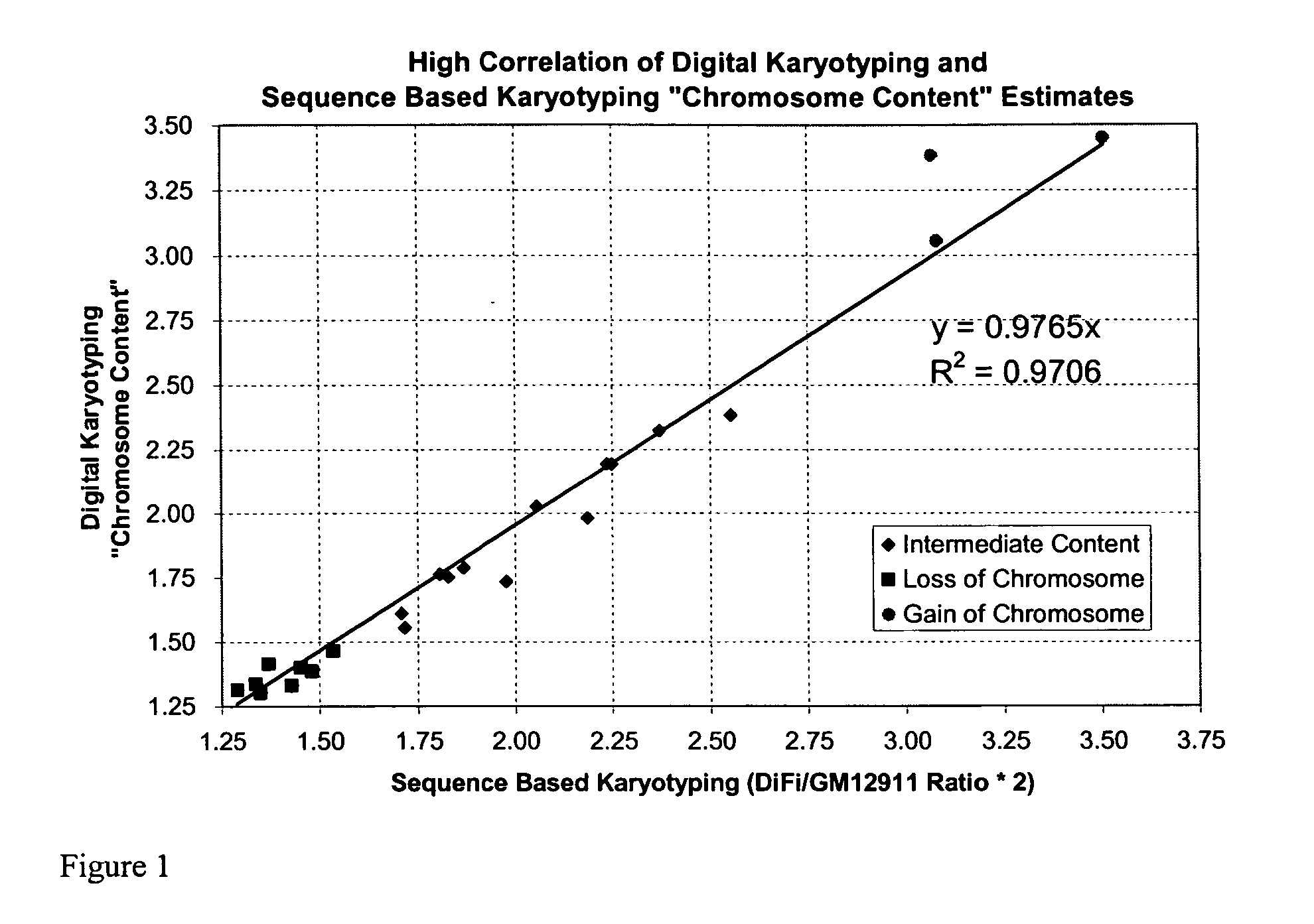
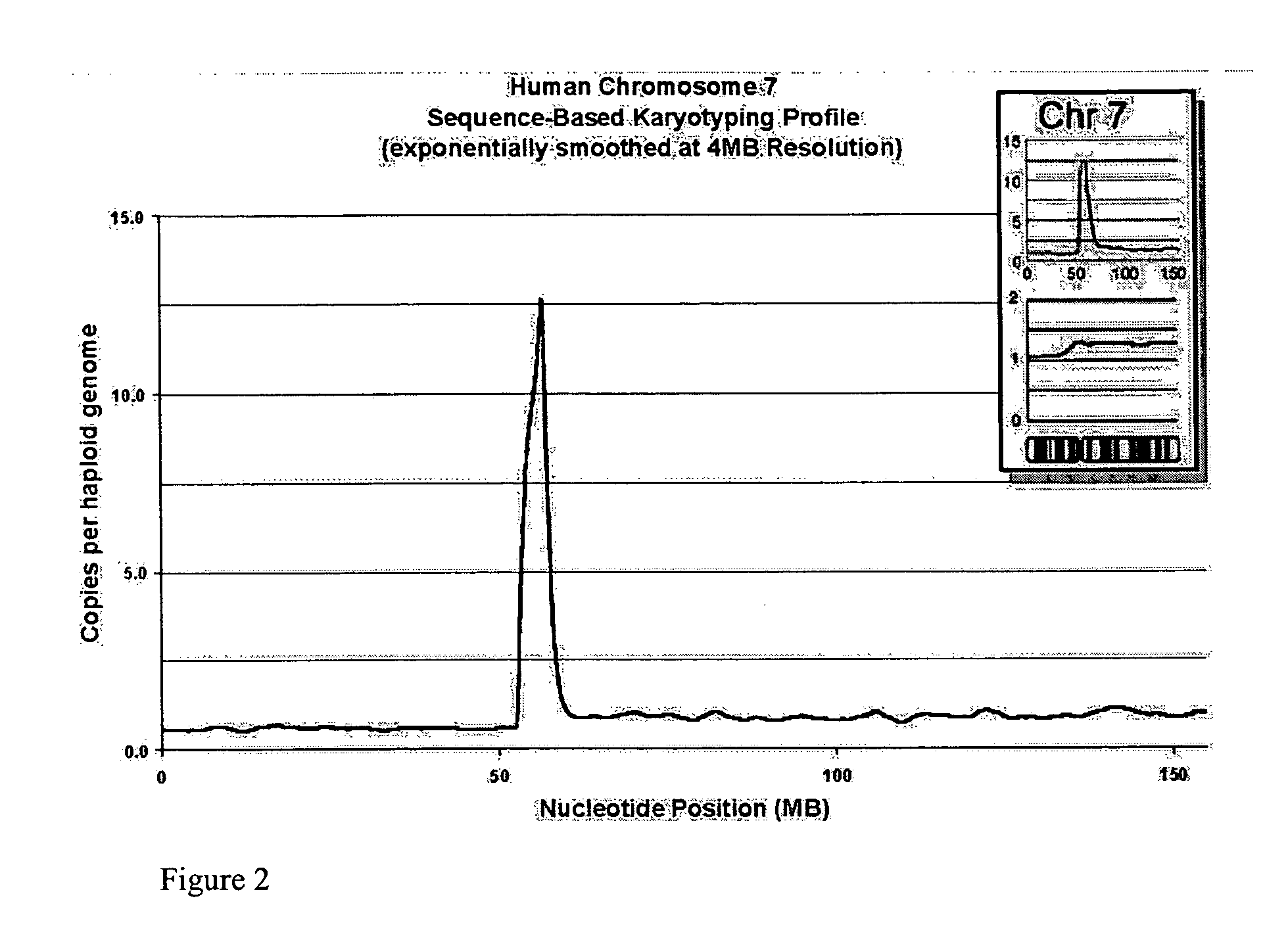
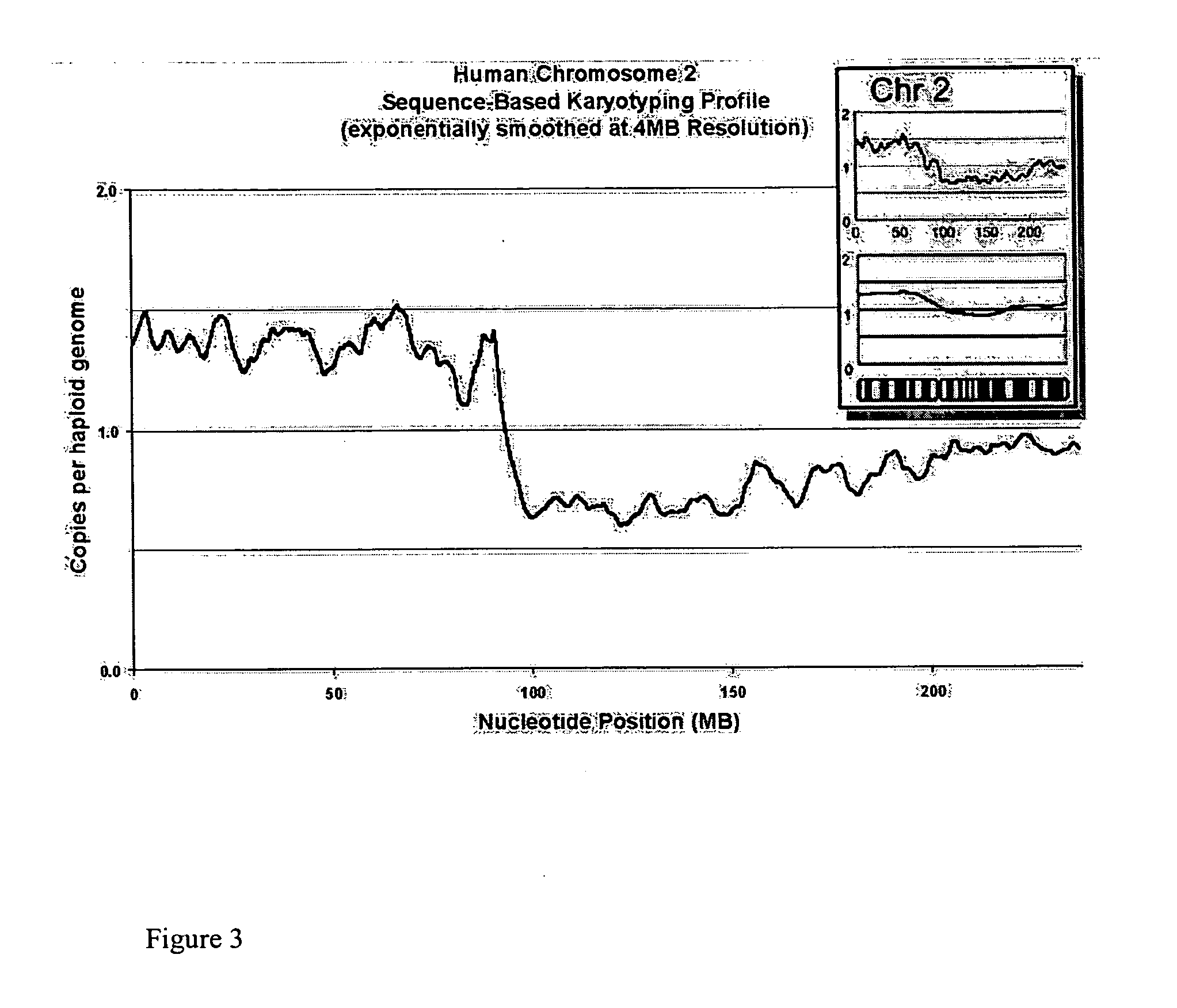
Sequence-based karyotyping
InactiveUS20050221341A1Great alterationUseful in detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic mutationKaryotype
A new method for genomic analysis, termed “Sequence-Based Karyotyping,” is described. Sequence-Based Karyotyping methods for the detection of genomic abnormalities, for diagnosis of hereditary disease, or for diagnosis of spontaneous genomic mutations are also described.
Owner:454 CORP
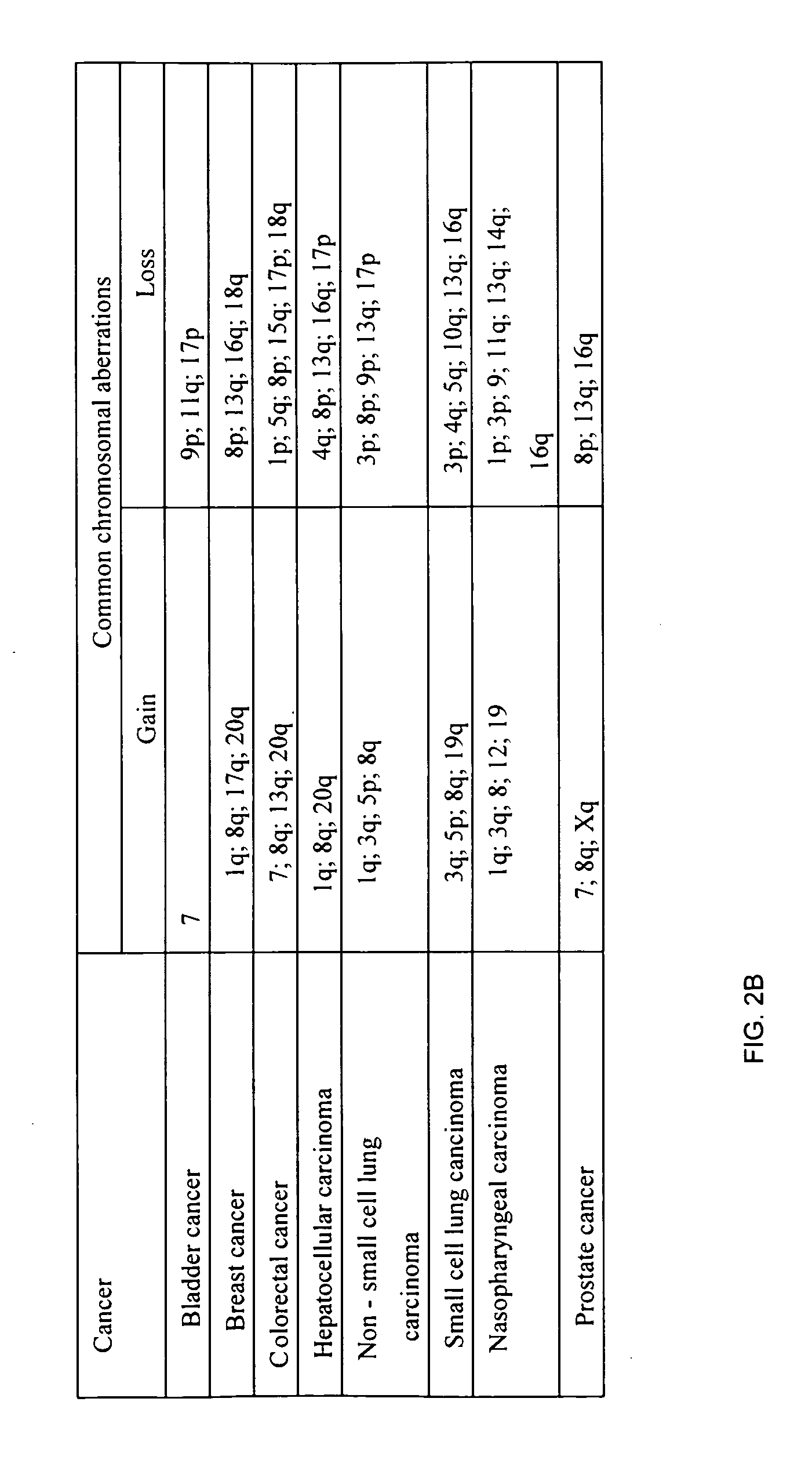
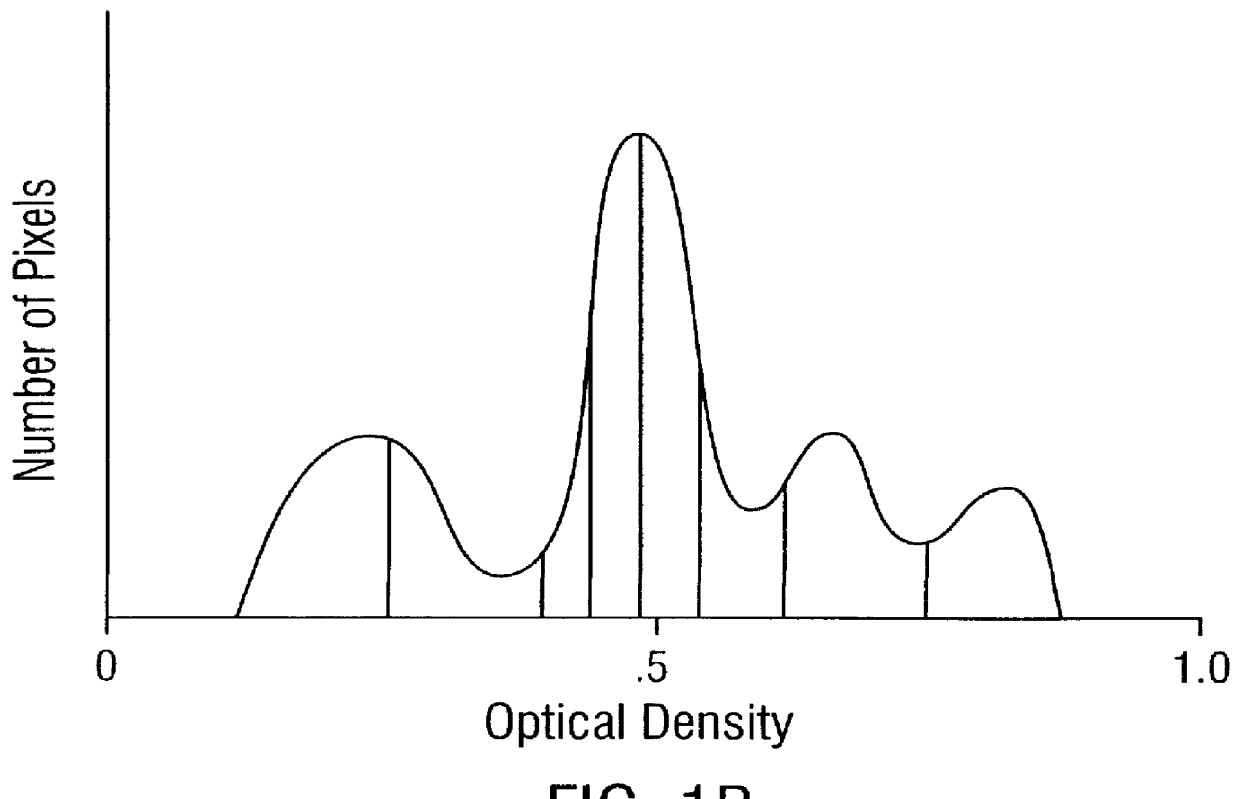
Prediction of prostate cancer progression by analysis of selected predictive parameters
InactiveUS6025128AImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingStatistical analysisFactor ii
A method for screening individuals at risk for prostate cancer progression is disclosed. The method is useful for evaluating cells from patients at risk for recurrence of prostate cancer following surgery for prostate cancer. Specifically, the method uses specific Markovian nuclear texture factors, alone or in combination with other biomarkers, to determine whether the cancer will progress or lose organ confinement. In addition, methods of predicting the development of fatal metastatic disease by statistical analysis of selected biomarkers is also disclosed. The invention also contemplates a method that uses a neural network to analyze and interpret cell morphology data. Utilizing Markovian factors and other biomarkers as parameters, the network is first trained with a sets of cell data from known progressors and known non-progressors. The trained network is then used to predict prostate cancer progression in patient samples.
Owner:CYTODIAGNOSTICS +3
Evaluating Genetic Disorders
ActiveUS20070259351A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsGeneticsArray-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization
The present invention relates to genetic analysis and evaluation utilizing copy-number variants or polymorphisms. The methods utilize array comparative genomic hybridization and PCR assays to identify the significance of copy number variations in a subject or subject group.
Owner:POPULATION BIO INC
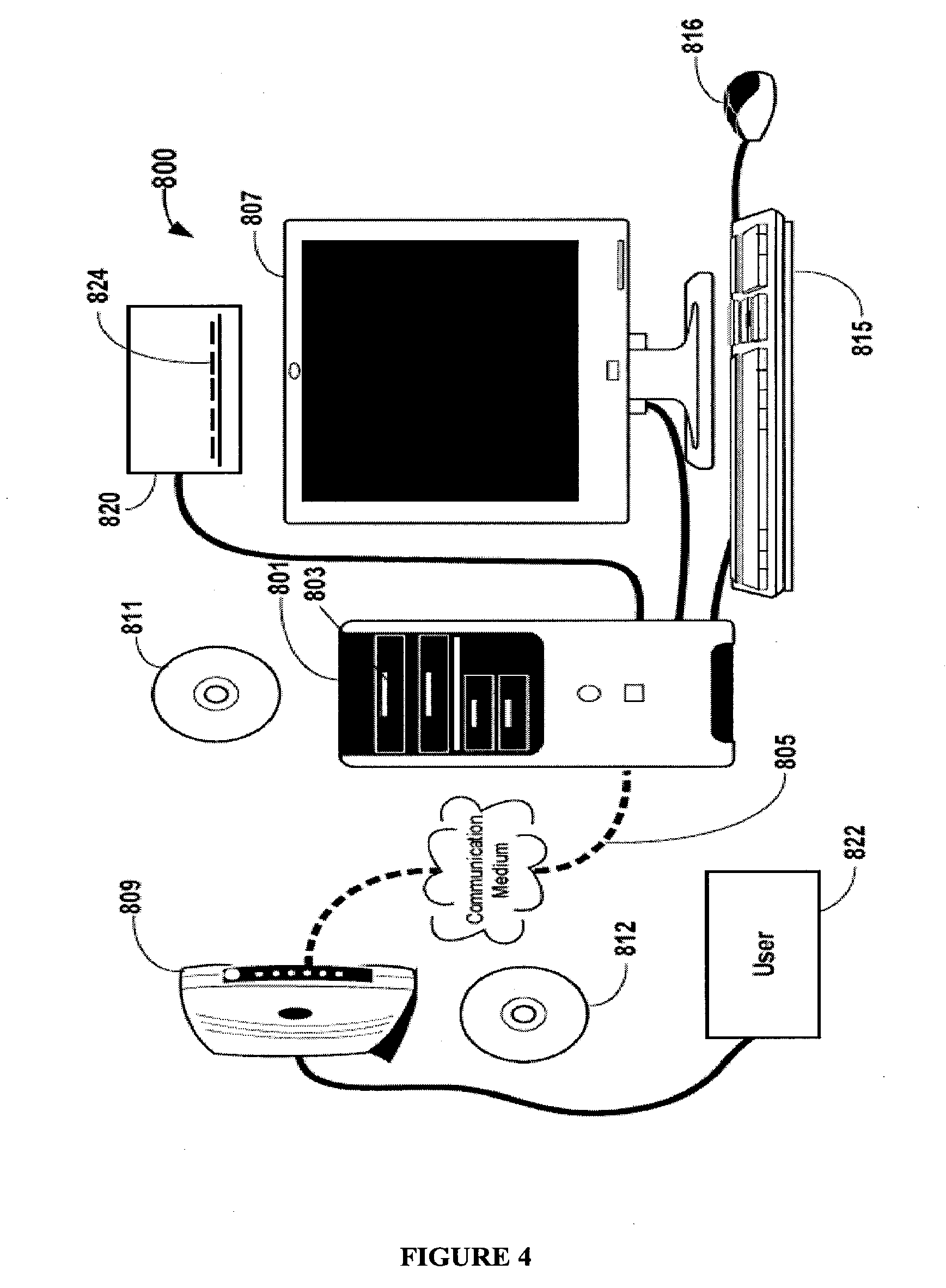
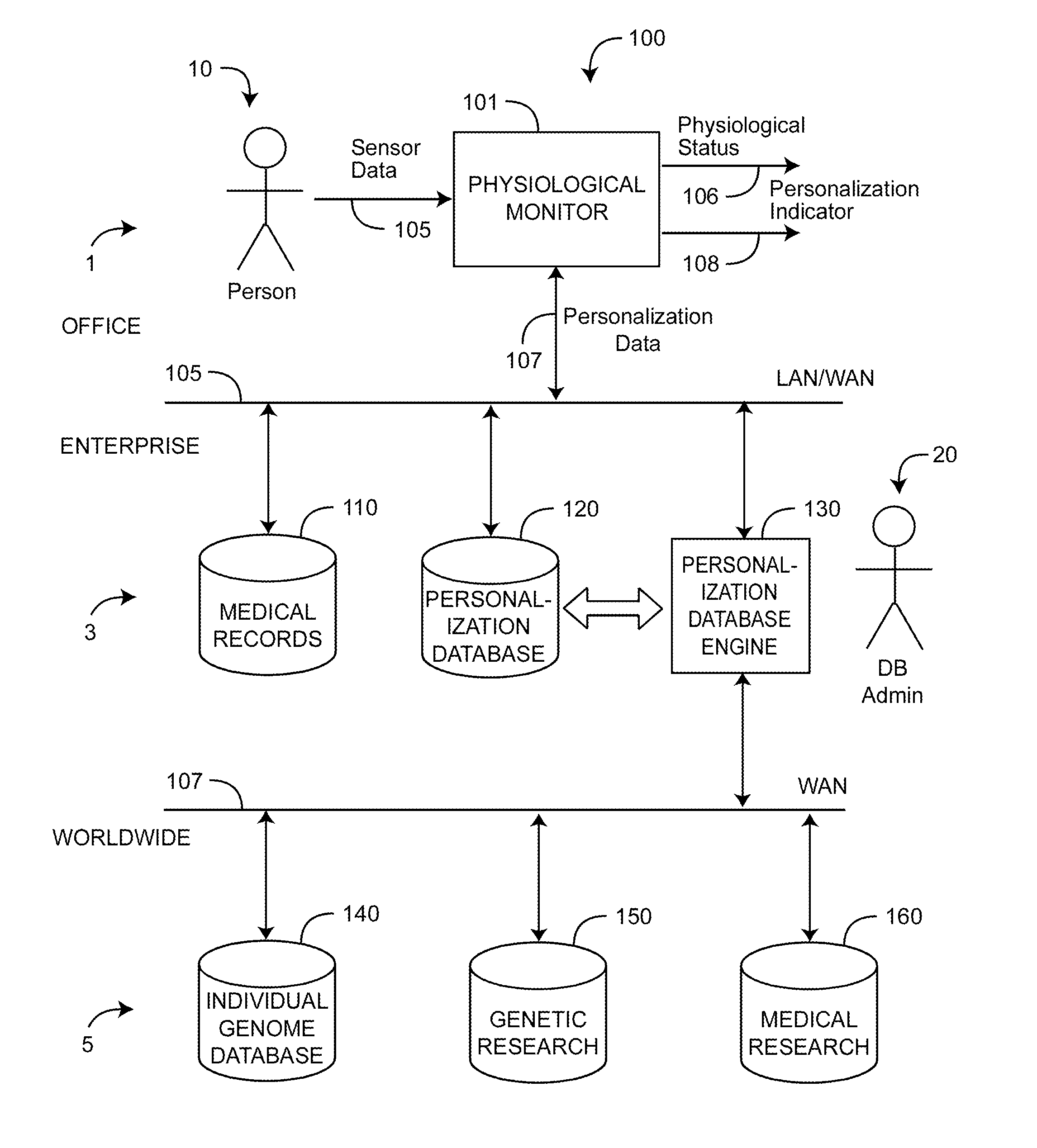
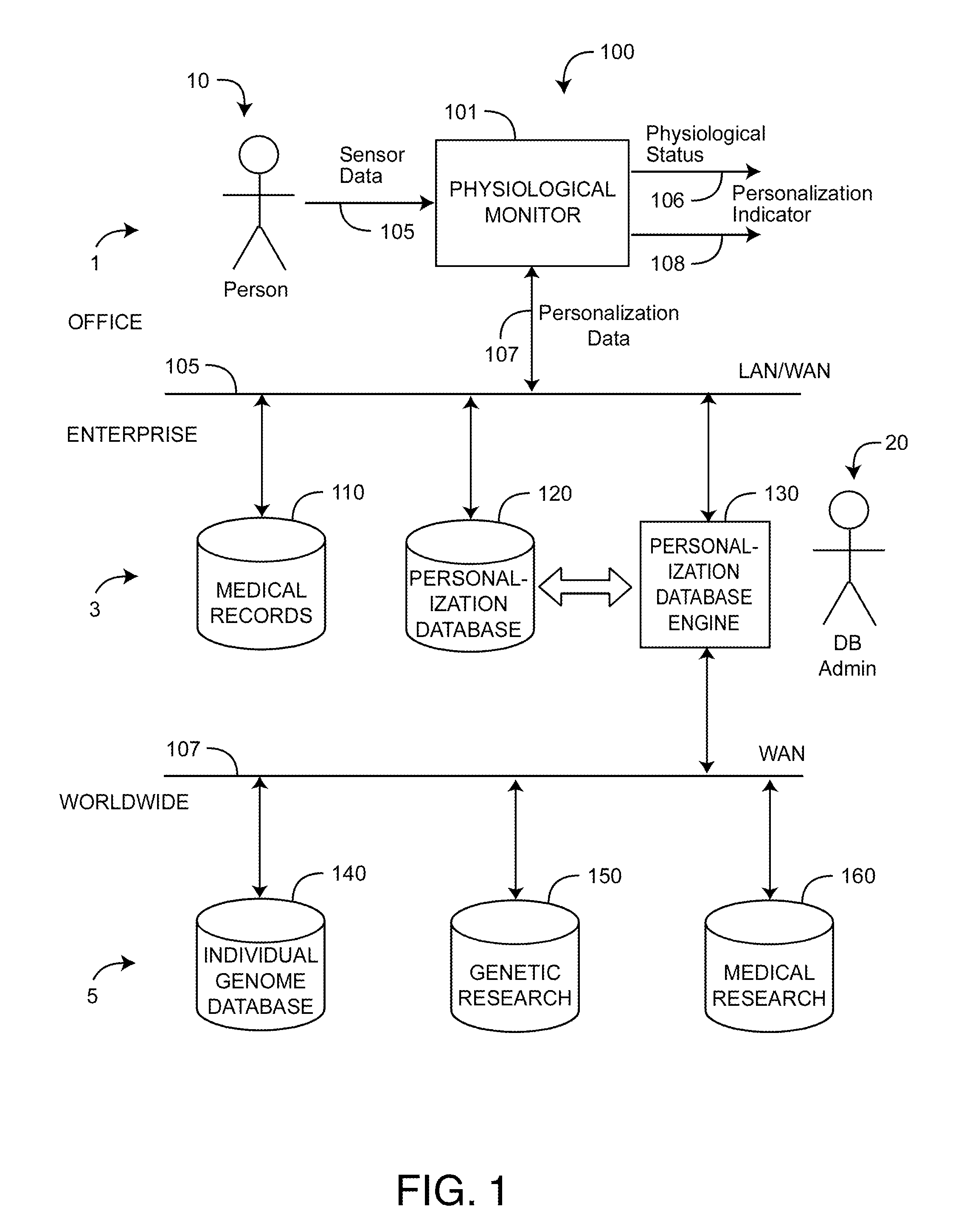
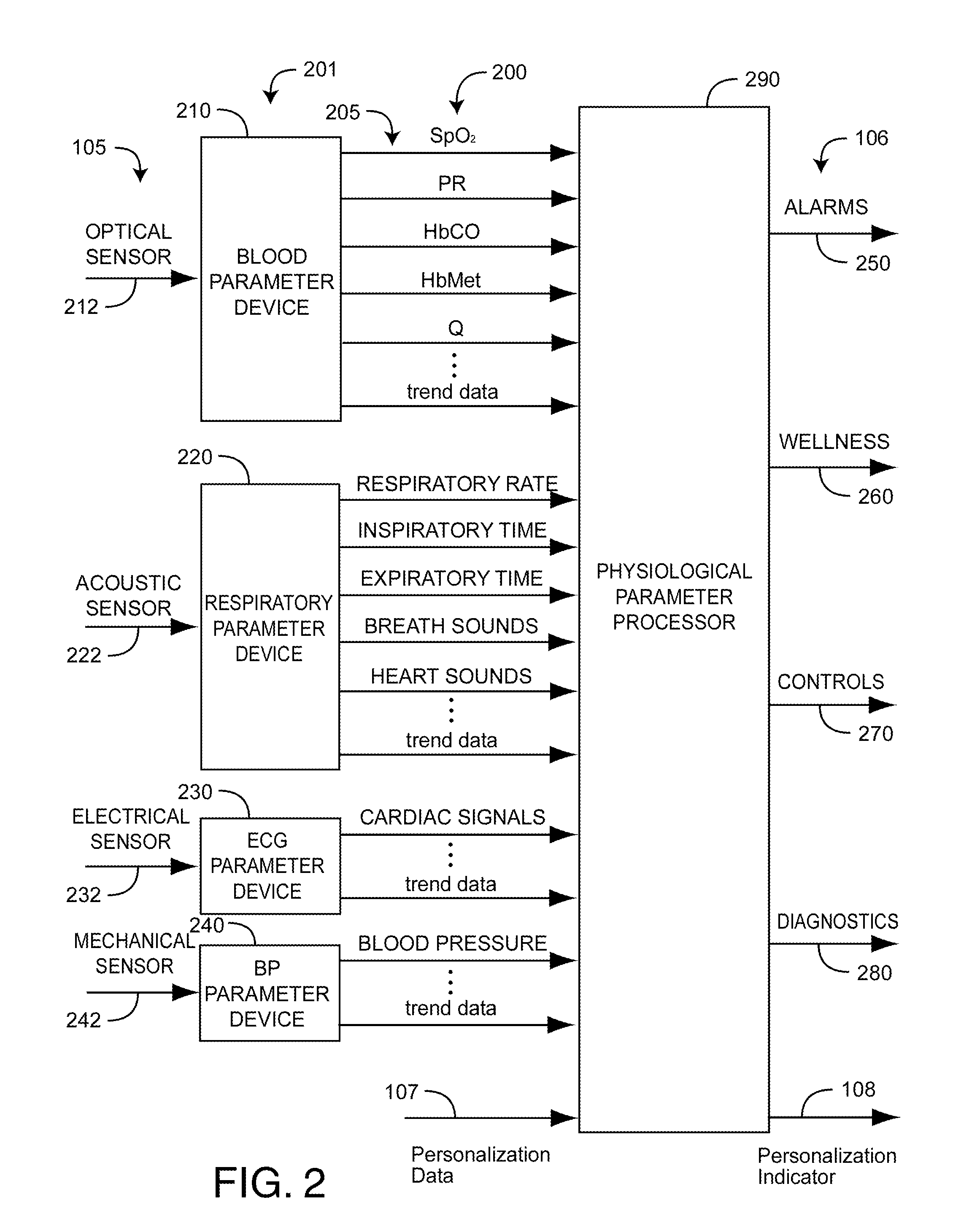
Personalized physiological monitor
InactiveUS20110087081A1Improve accuracyImprove monitoring effectMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateAngiographyPersonalizationDrug reaction
A personalized physiological monitor utilizes an individual genome sequence along with genetic and medical research databases so as to define a person's genetic predisposition to disease, drug reactions and environmental sensitivities so as to enhance the ability of the monitor to determine the physiological status of the person.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
System of components for preparing oligonucleotides
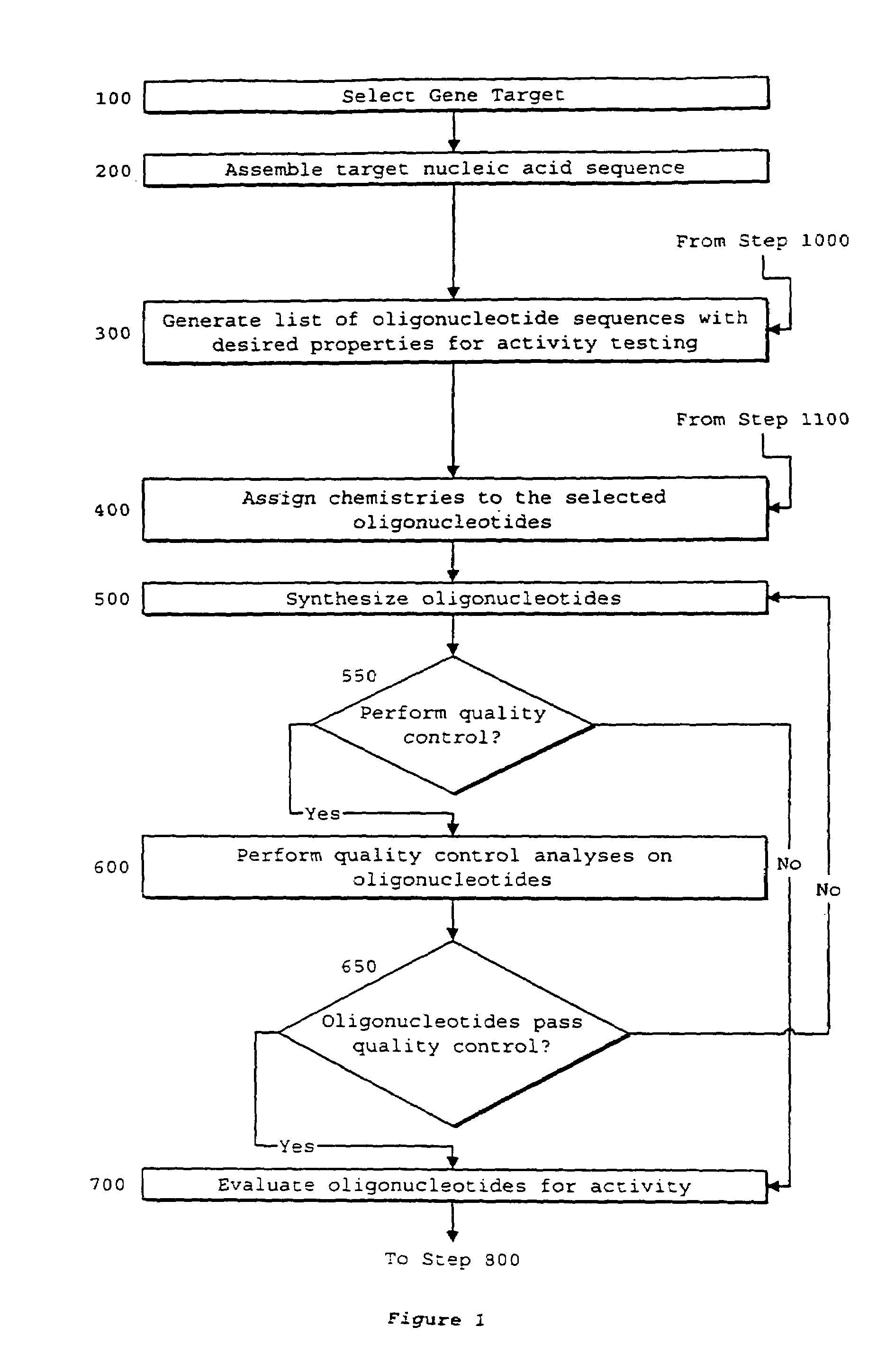
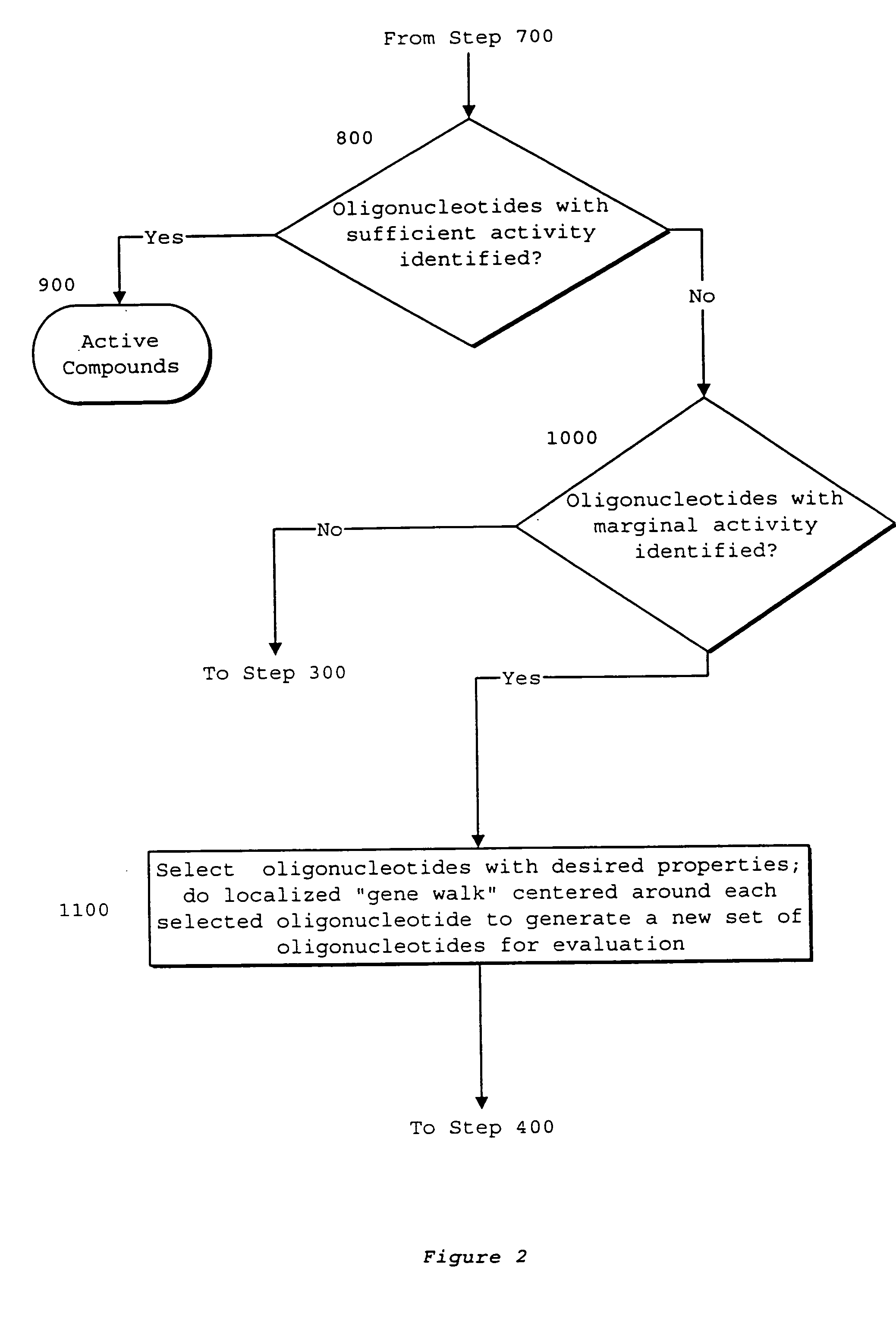
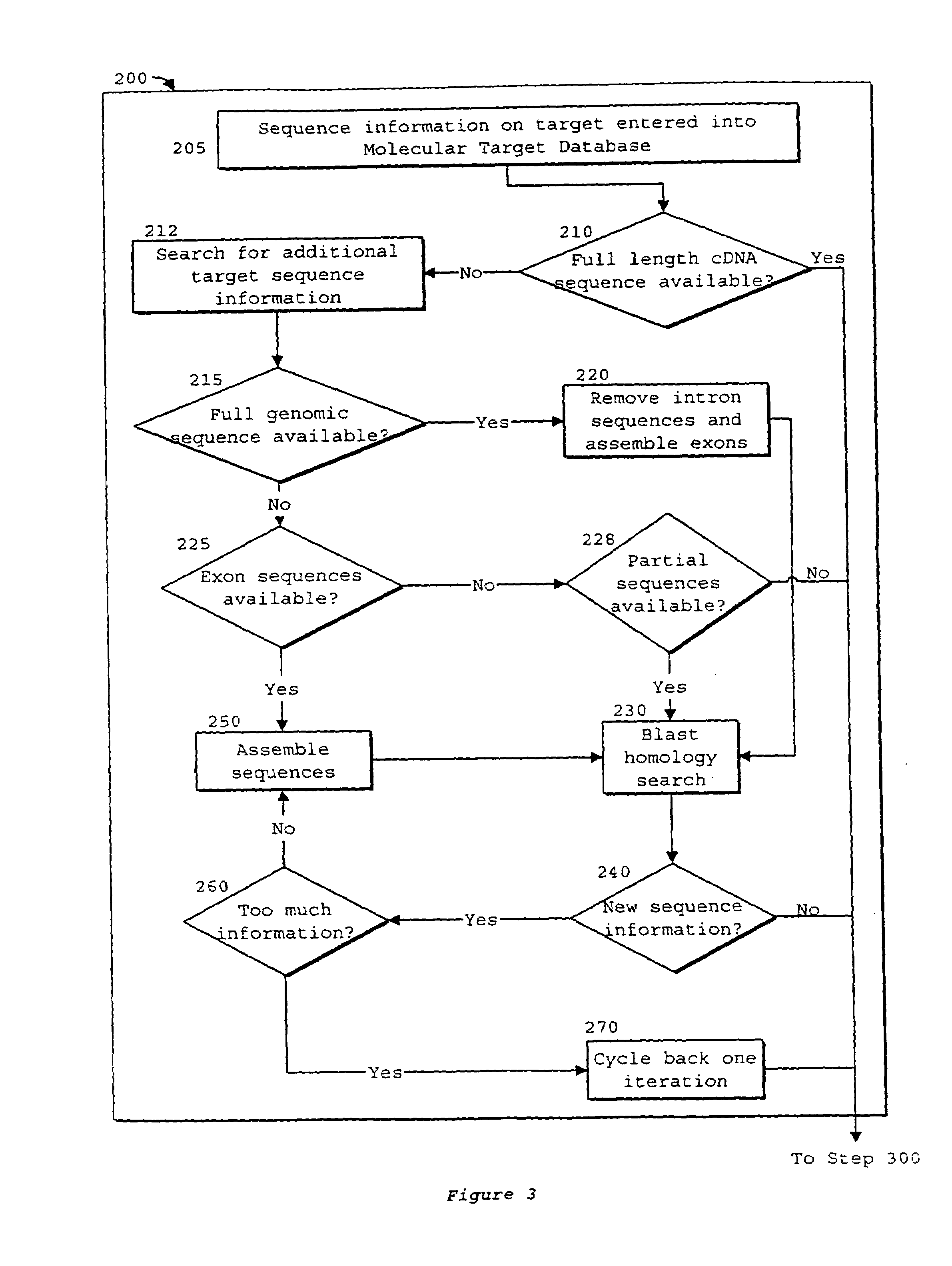
Interative, preferably computer based iterative processes for generating synthetic compounds with desired physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties, i.e., active compounds, are provided. During iterations of the processes, a target nucleic acid sequence is provided or selected, and a library of candidate nucleobase sequences is generated in silico according to defined criteria. A “virtual” oligonucleotide chemistry is chosen and a library of virtual oligonucleotide compounds having the selected nucleobase sequences is generated. These virtual compounds are reviewed and compounds predicted to have particular properties are selected. The selected compounds are robotically synthesized and are preferably robotically assayed for a desired physical, chemical or biological activity. Active compounds are thus generated and, at the same time, preferred sequences and regions of the target nucleic acid that are amenable to oligonucleotide or sequence-based modulation are identified.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
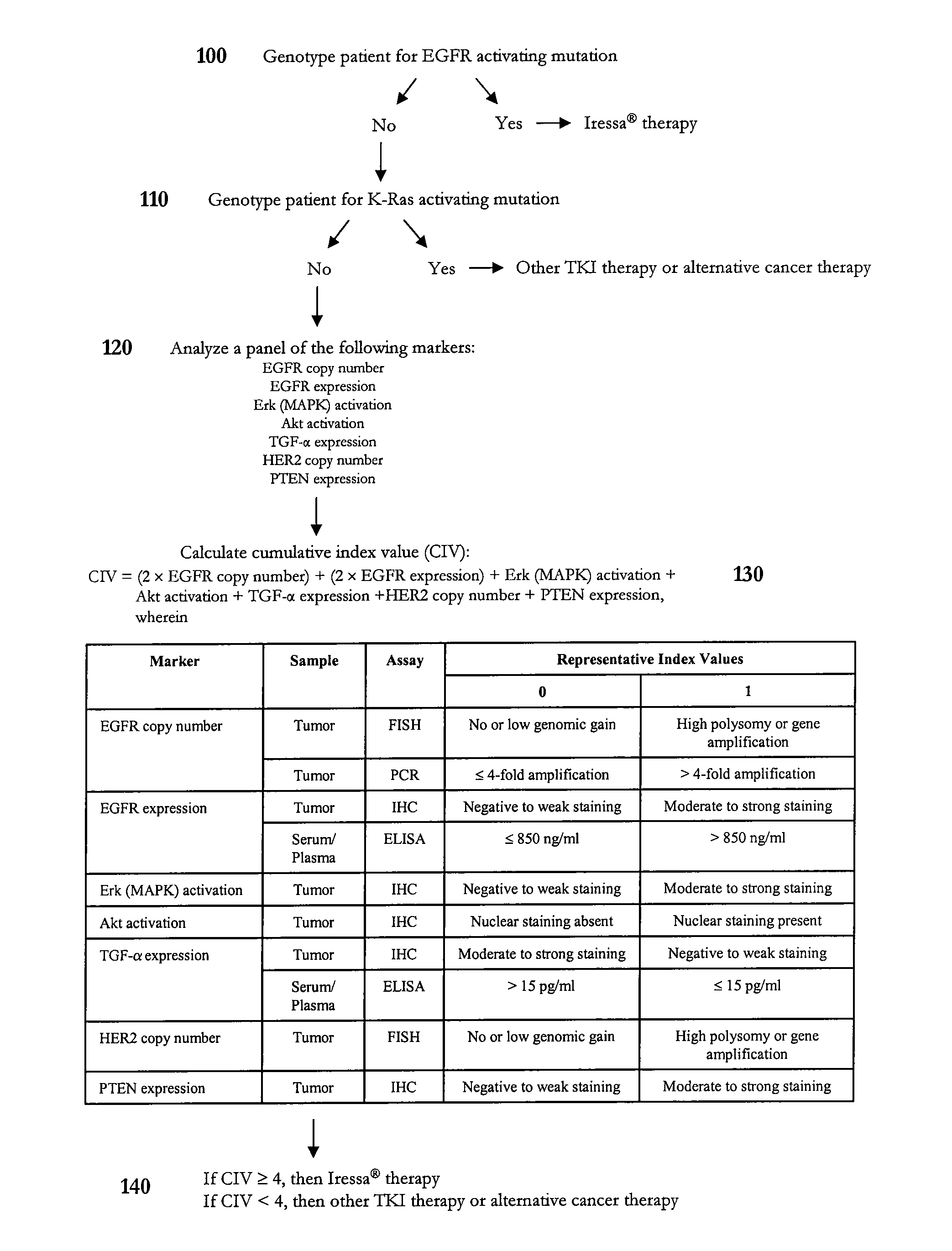
Methods of predicting and monitoring tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy
InactiveUS20070254295A1Eliminate side effectsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAbnormal tissue growthSide effect
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
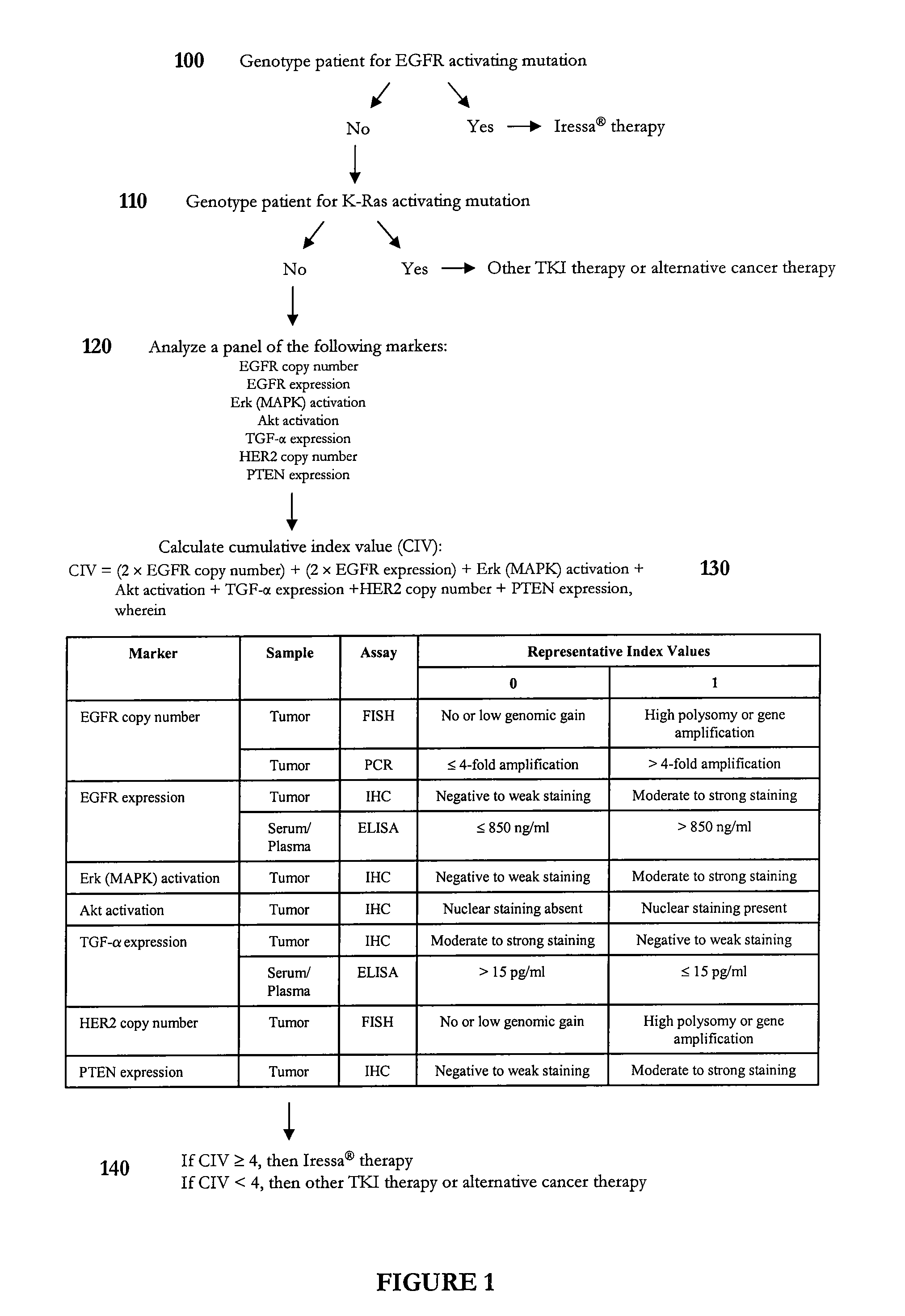
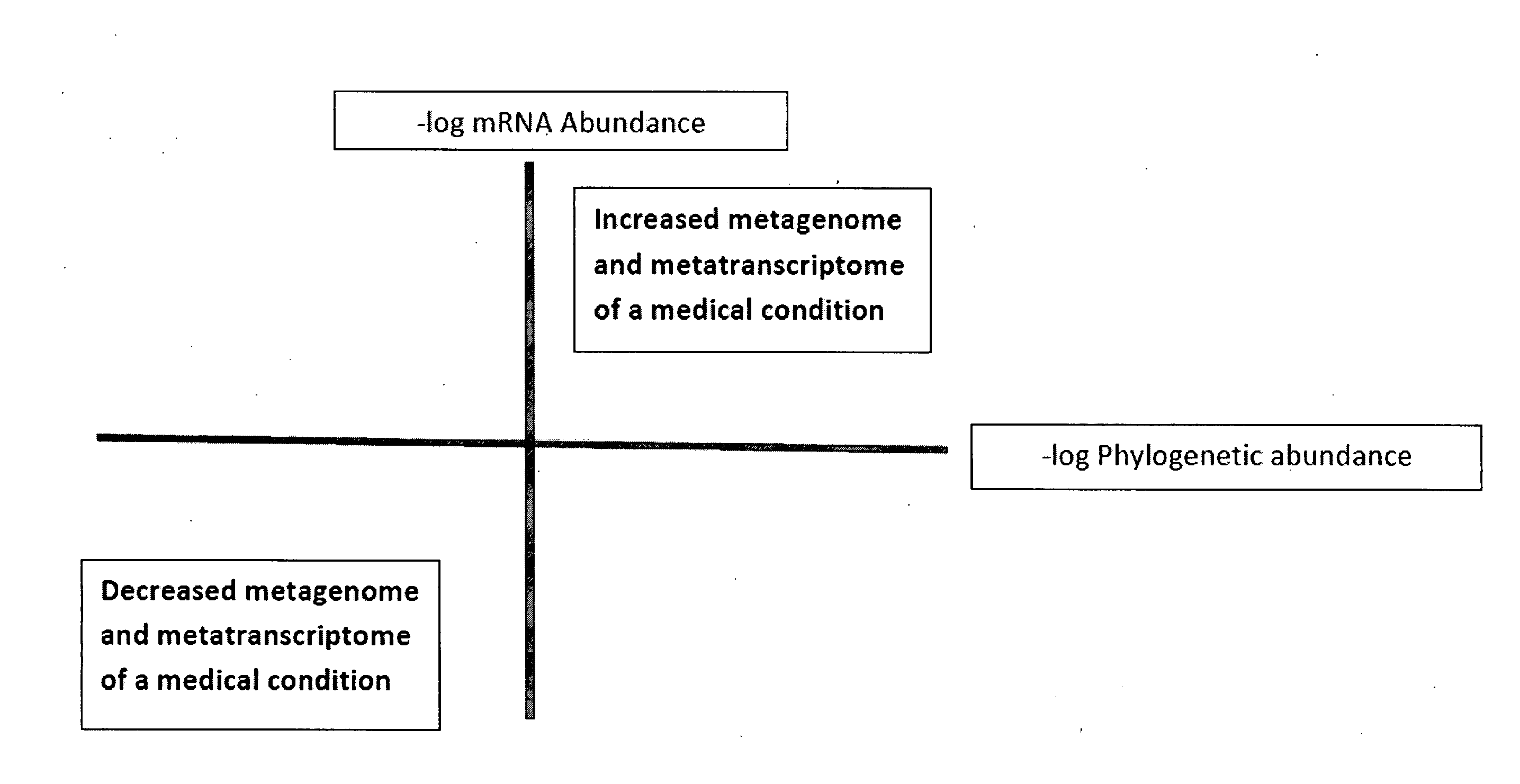
Methods of combining metagenome and the metatranscriptome in multiplex profiles
The present invention describes changes in bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated various mammalian medical conditions. Described are diagnostic tests that arise from combining phylogenetic information about the families, genus, and species of the microbiome and their relative abundance with the metabolic information contained in the metatranscriptome to determine the presence and absence of a disease or medical condition. Provided are compositions of bacteria, co-cultures of bacteria and a carrier for use in treating the disclosed medical conditions. The described compositions restore or correct disease- or medical condition-related imbalances in the microbiome profile with culture-conditioned formulations in which the transcriptome activity of the administered organisms is optimized. Alternatively, formulations of metabolites that drive changes in the metatranscriptome native to the mammal that treat disease or a medical condition or restore health are taught.
Owner:ENSISHEIM PARTNERS
Systems and methods for monitoring behavior informatics
InactiveUS20030100998A2Improve statistics performanceExpand selectionDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsMulti dimensionalOrganism
Abstract of Disclosure A system and method used to assess animal behavior includes a module having sensors that collects a variety of physical and biological data from a test subject. Interpretation of the data is provided to assess the test subject's behavior, neurology, biochemistry and physiology. The module is useful in observing the effects of a drug on the test animal and providing information on the drug's signature. Another advantage is module's portability that allows it to be used in standard laboratory cages. This portability allows the animal to be tested in its own habitat, that can reduce any erroneous data due to stressing the animal when removed to a test cage. Additionally, the module's design allows for parallel data collection and interpretation from several laboratory animals undergoing different experiments. Multi-dimensional modeling of the test subject based the system's interpretation of the data allows pattern recognition of the drug signature, and predictive drug analysis.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
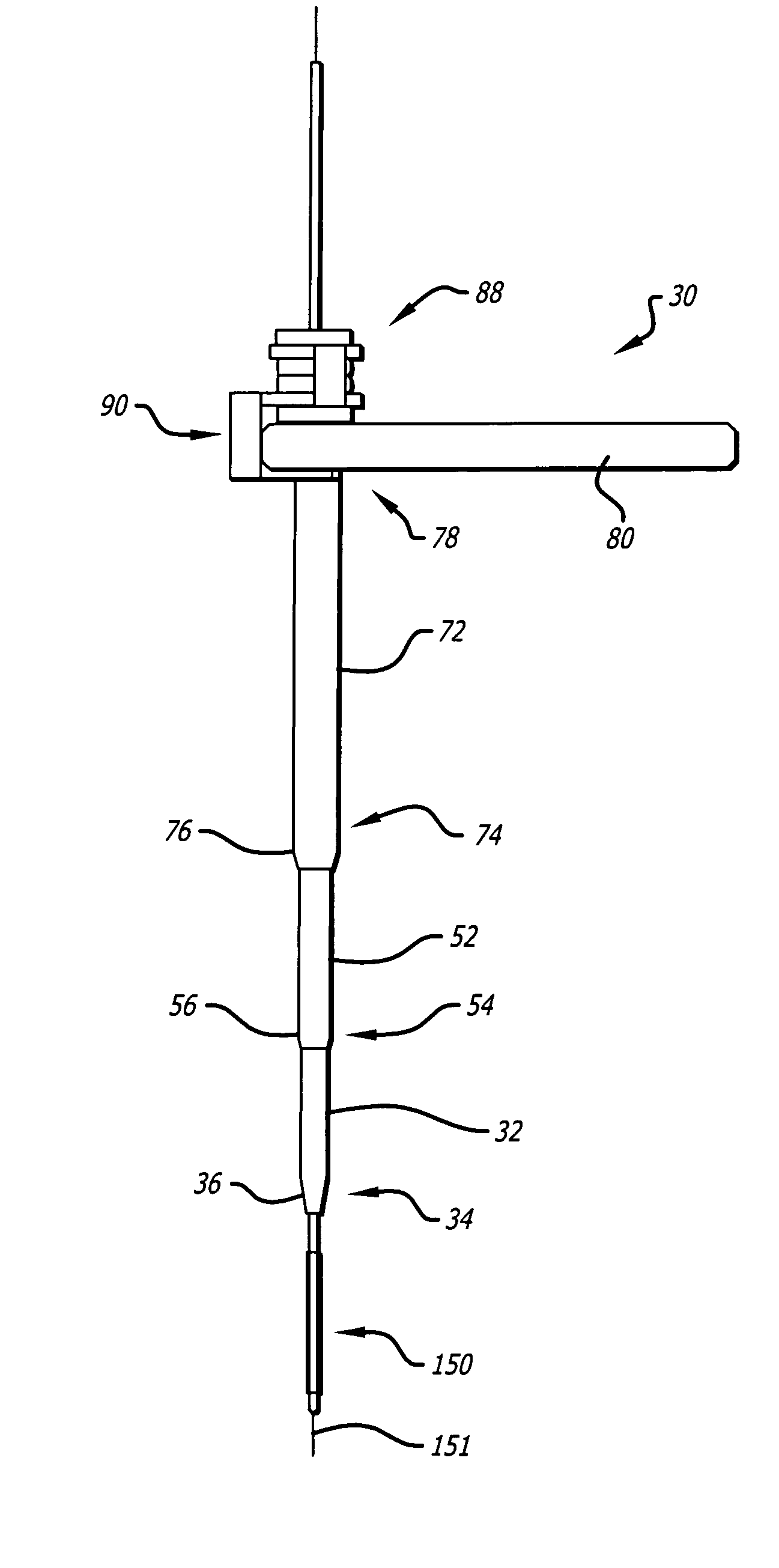
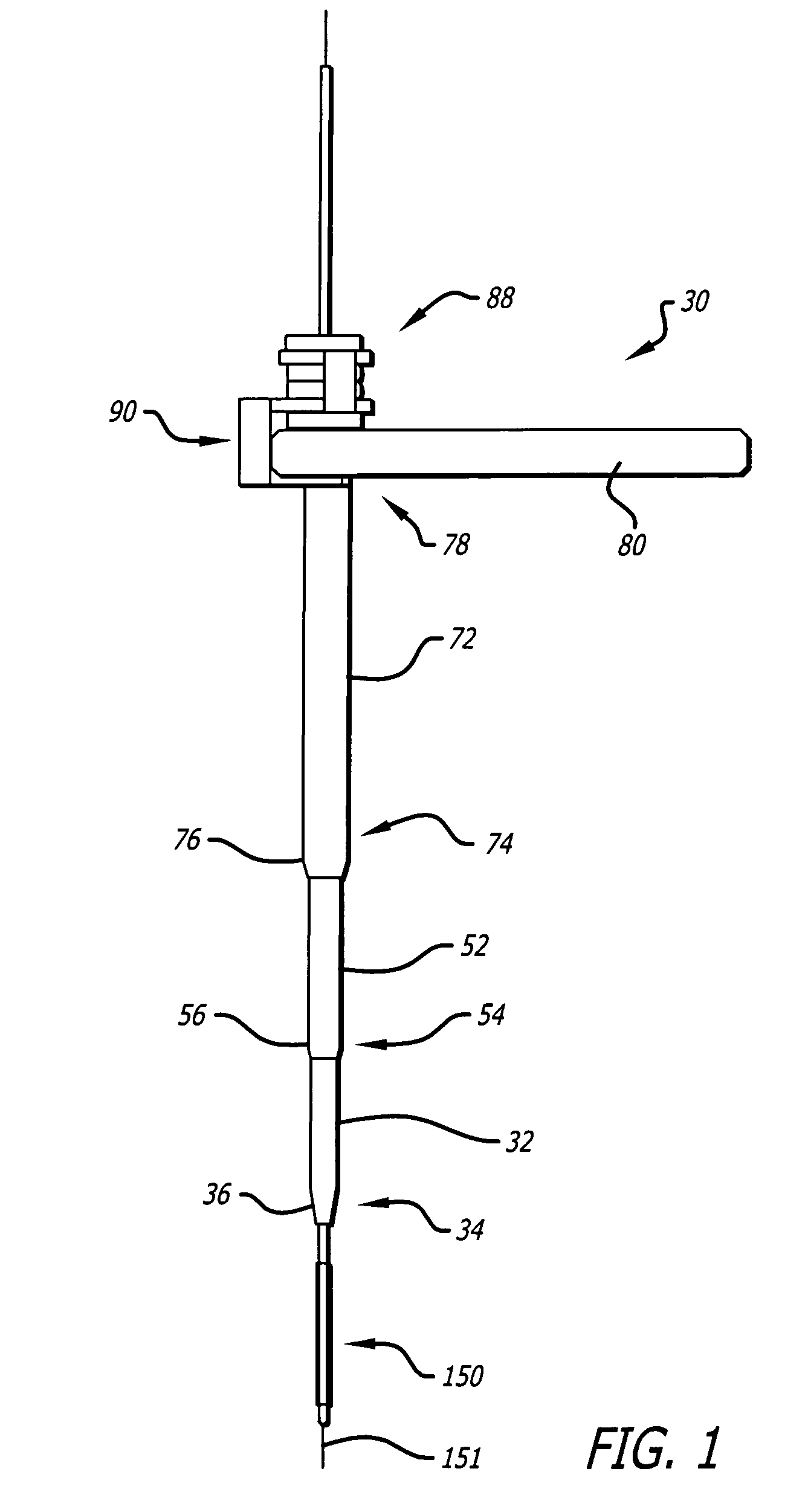
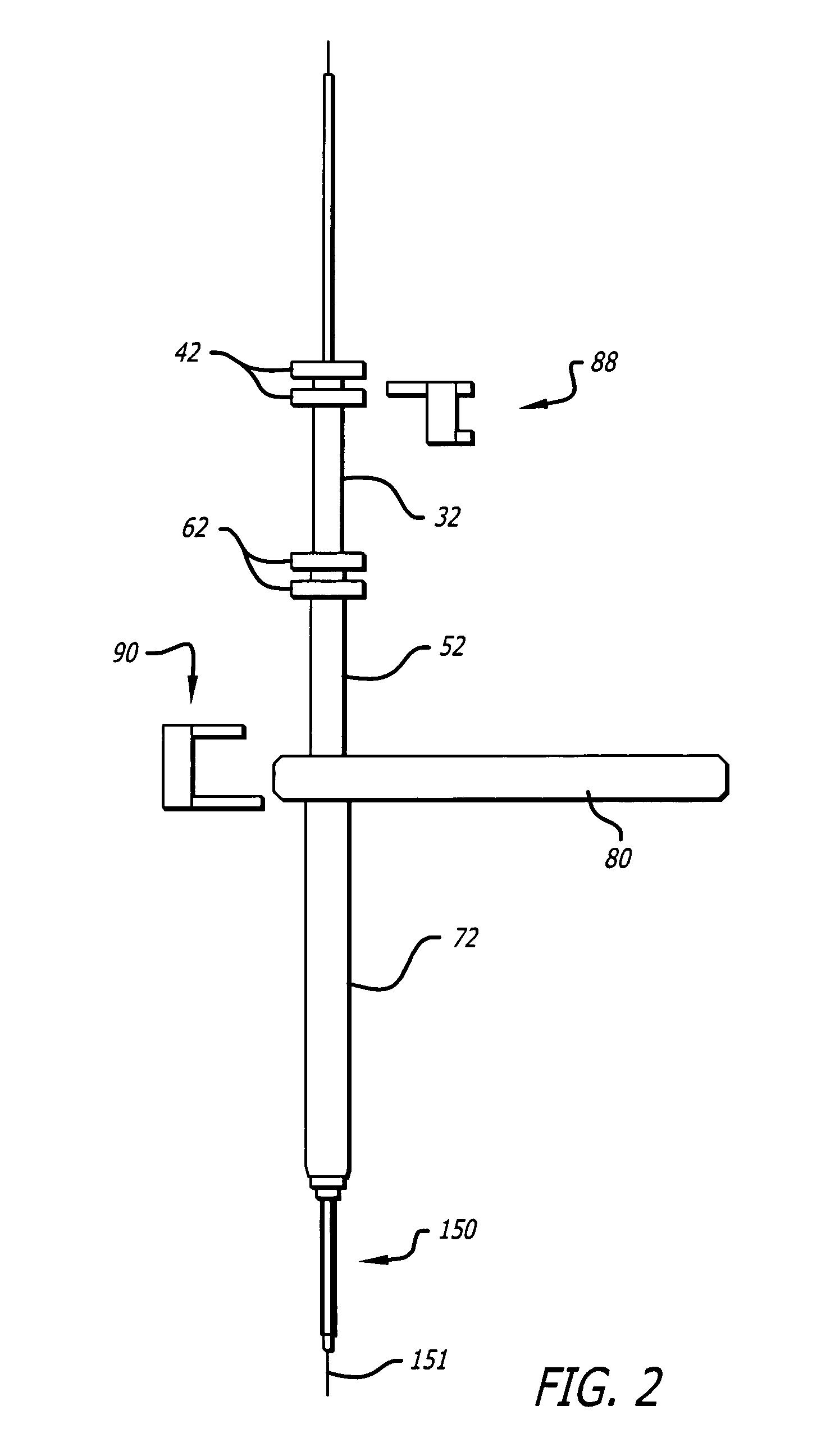
Dilation introducer for orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS20050256525A1Lowering chance damageInvasive surgical procedureOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDilatorBone tissue
The dilation introducer has a locked assembled configuration for placement of the dilation introducer against a patient's tissue to be treated, and an unlocked, collapsed configuration for dilating the patient's soft tissue down to tissue to be treated. Dilator tubes are successively released and advanced to progressively expand the patient's soft tissue down to the bone tissue to be treated. The dilator tubes and a guide insert may include spikes for engaging bone tissue. The dilation introducer may include a light emitter disposed in a dilator tube. A telescoping expander sleeve is also provided.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL SPINE
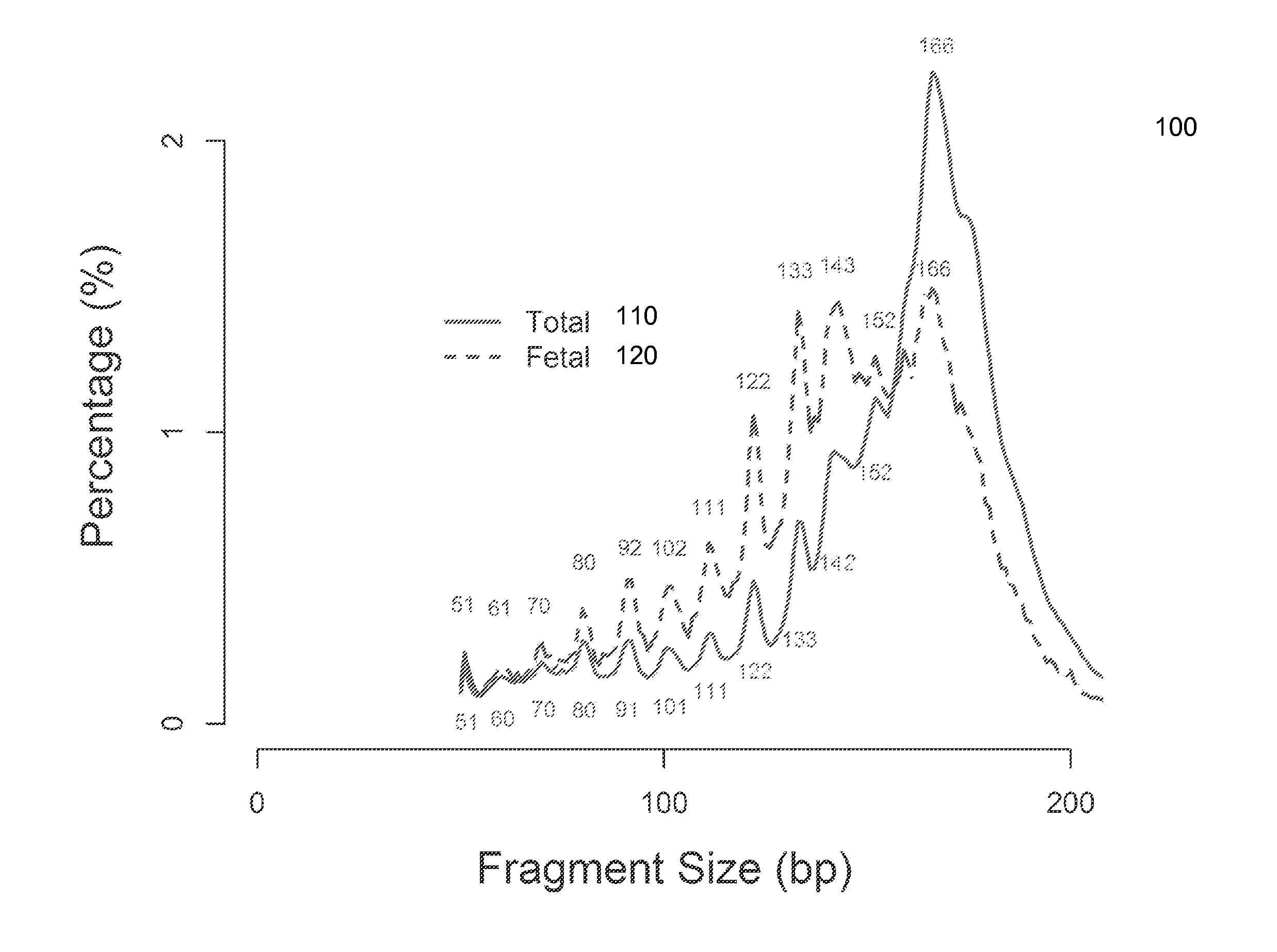
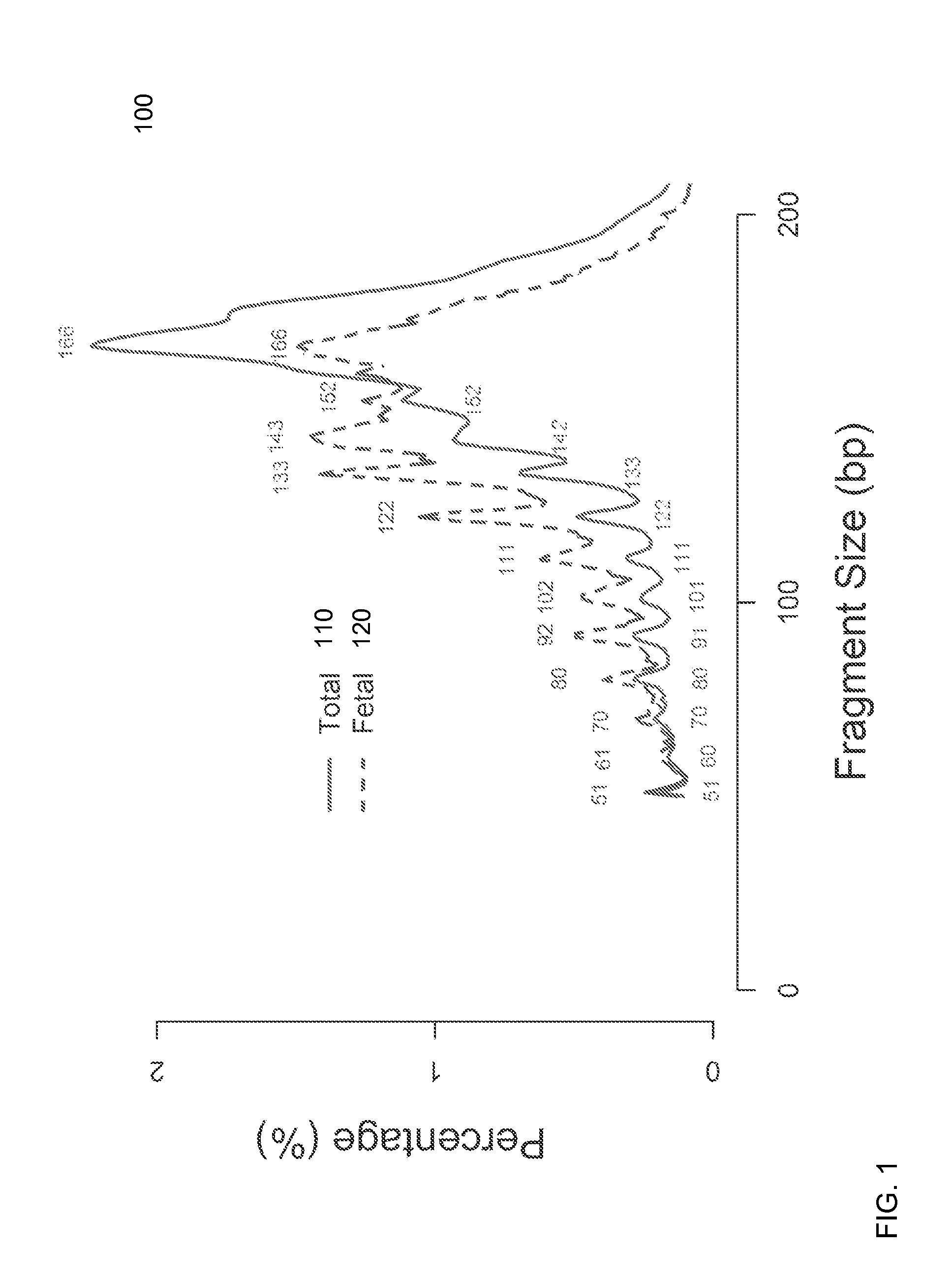
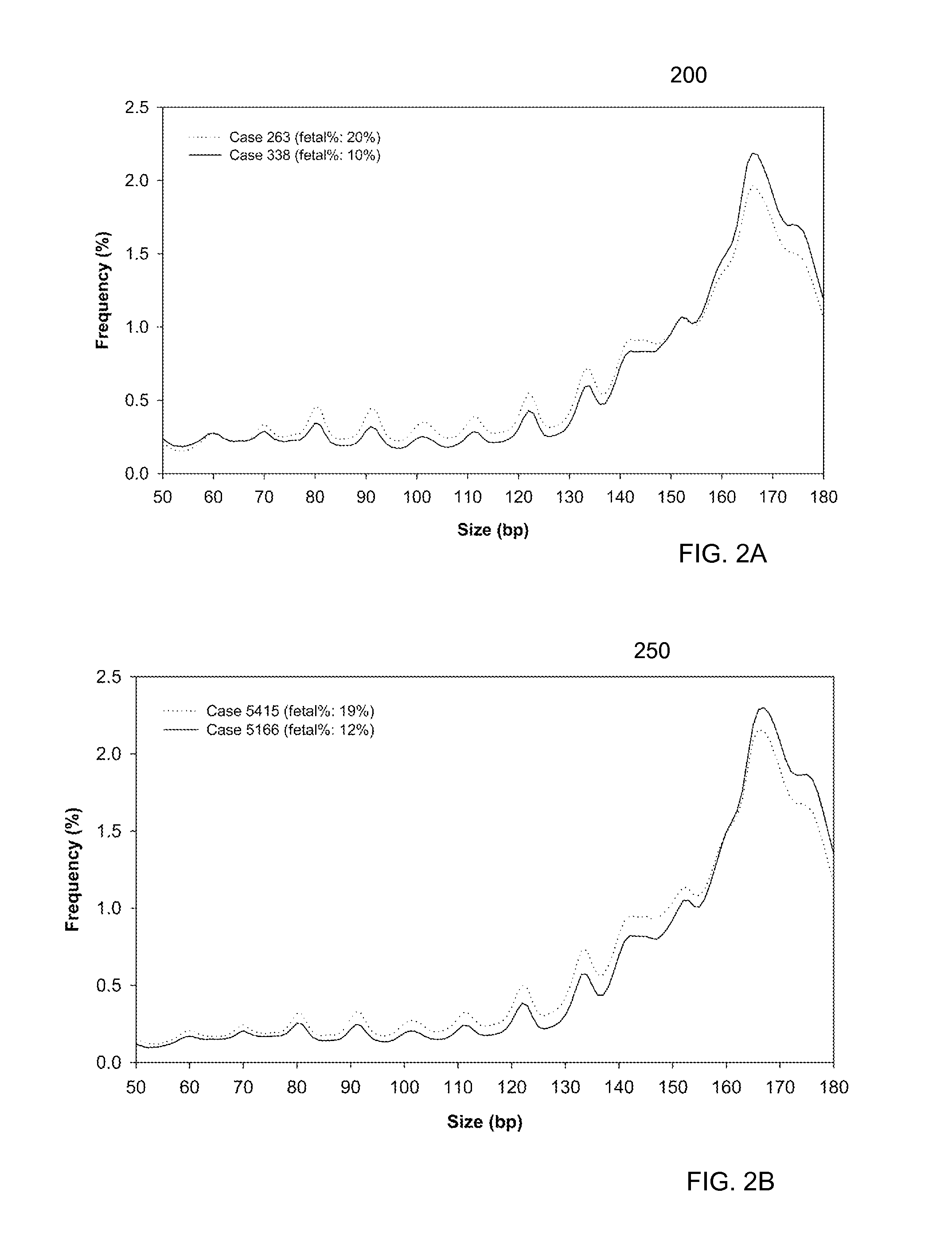
Size-based analysis of fetal DNA fraction in maternal plasma
ActiveUS20130237431A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthBlood plasma
A fractional concentration of clinically-relevant DNA in a mixture of DNA from a biological sample is determined based on amounts of DNA fragments at multiple sizes. For example, the fractional concentration of fetal DNA in maternal plasma or tumor DNA in a patient's plasma can be determined. The size of DNA fragments in a sample is shown to be correlated with a proportion of fetal DNA and a proportion of tumor DNA, respectively. Calibration data points (e.g., as a calibration function) indicate a correspondence between values of a size parameter and the fractional concentration of the clinically-relevant DNA. For a given sample, a first value of a size parameter can be determined from the sizes of DNA fragments in a sample. A comparison of the first value to the calibration data points can provide the estimate of the fractional concentration of the clinically-relevant DNA.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com