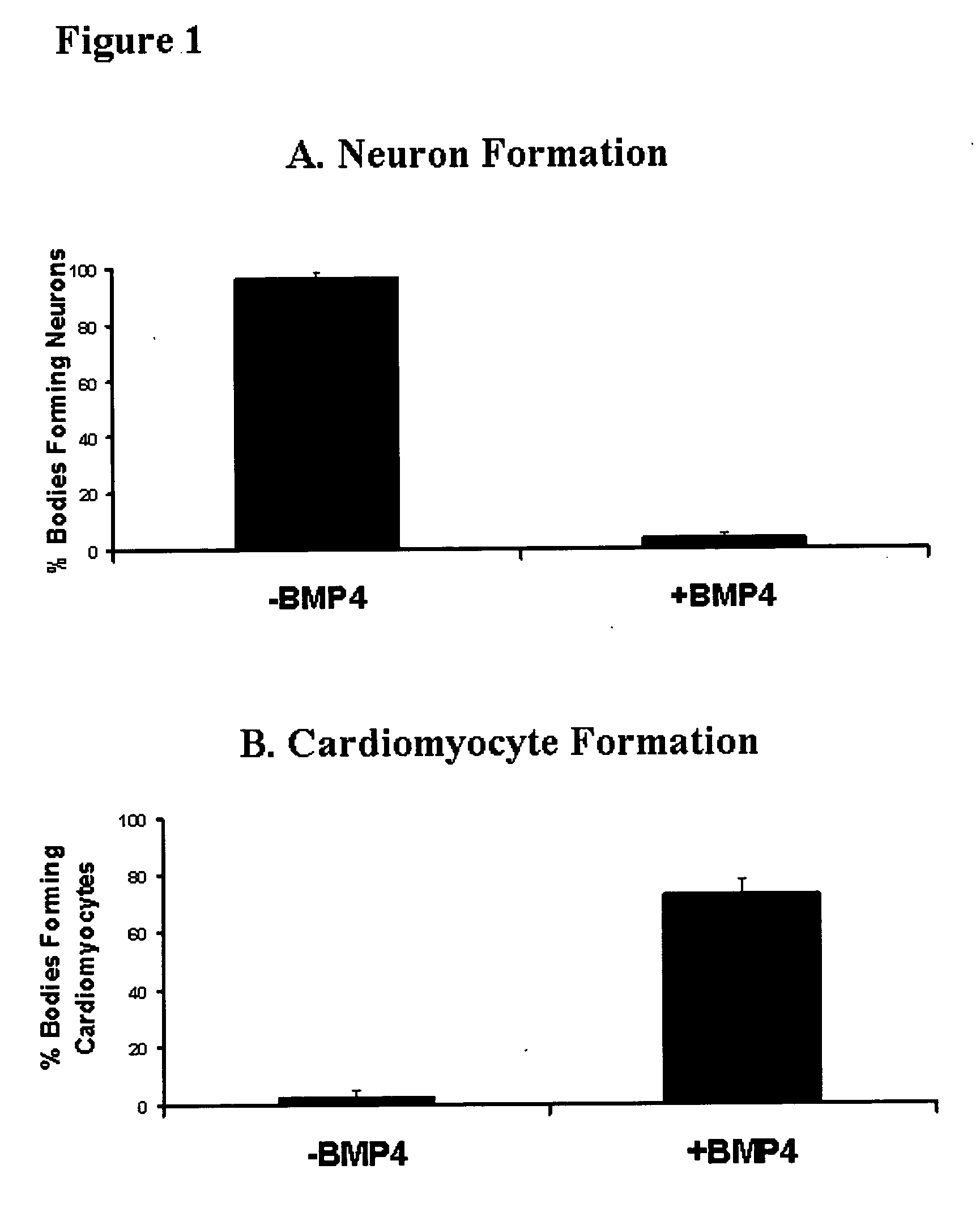
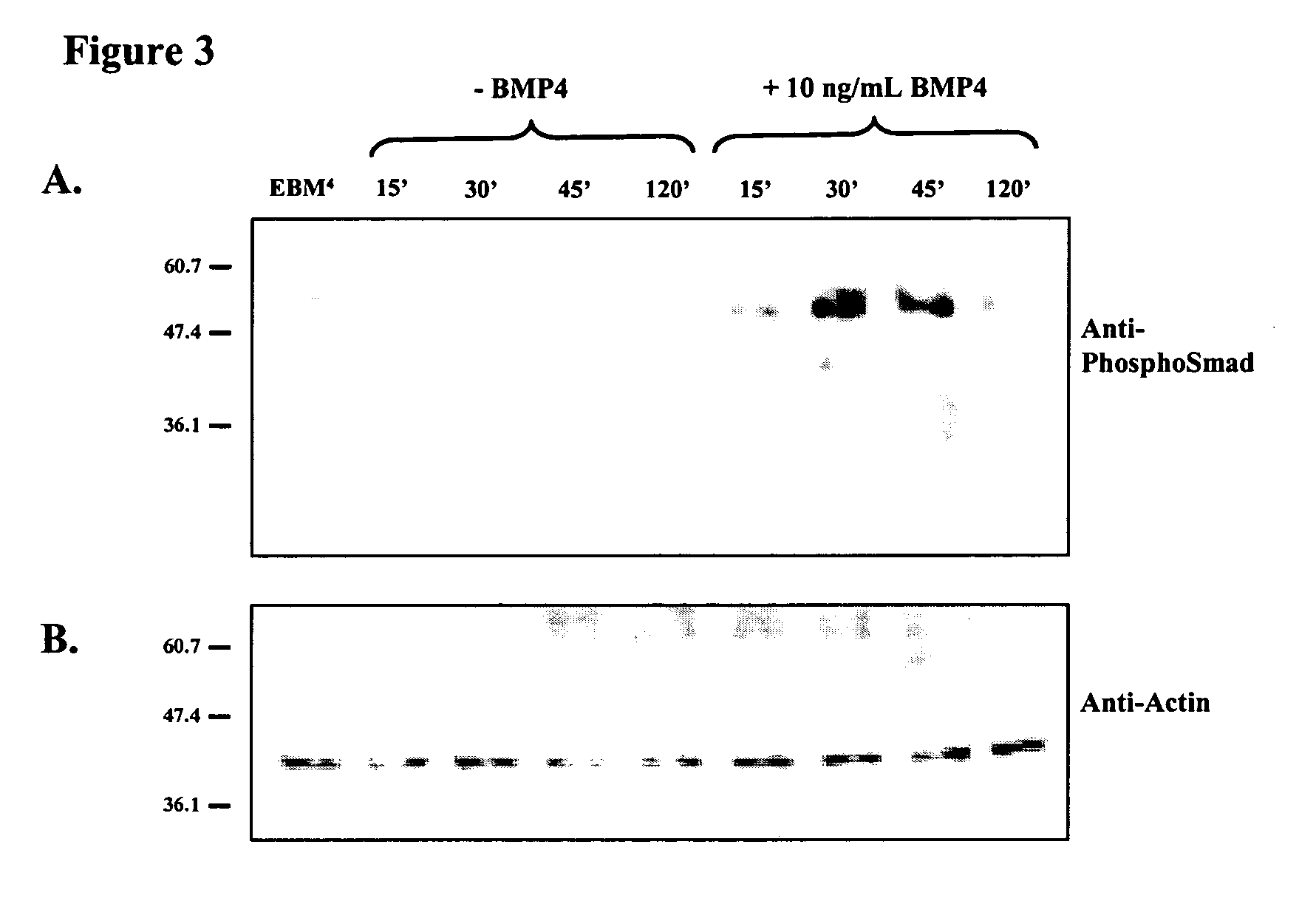
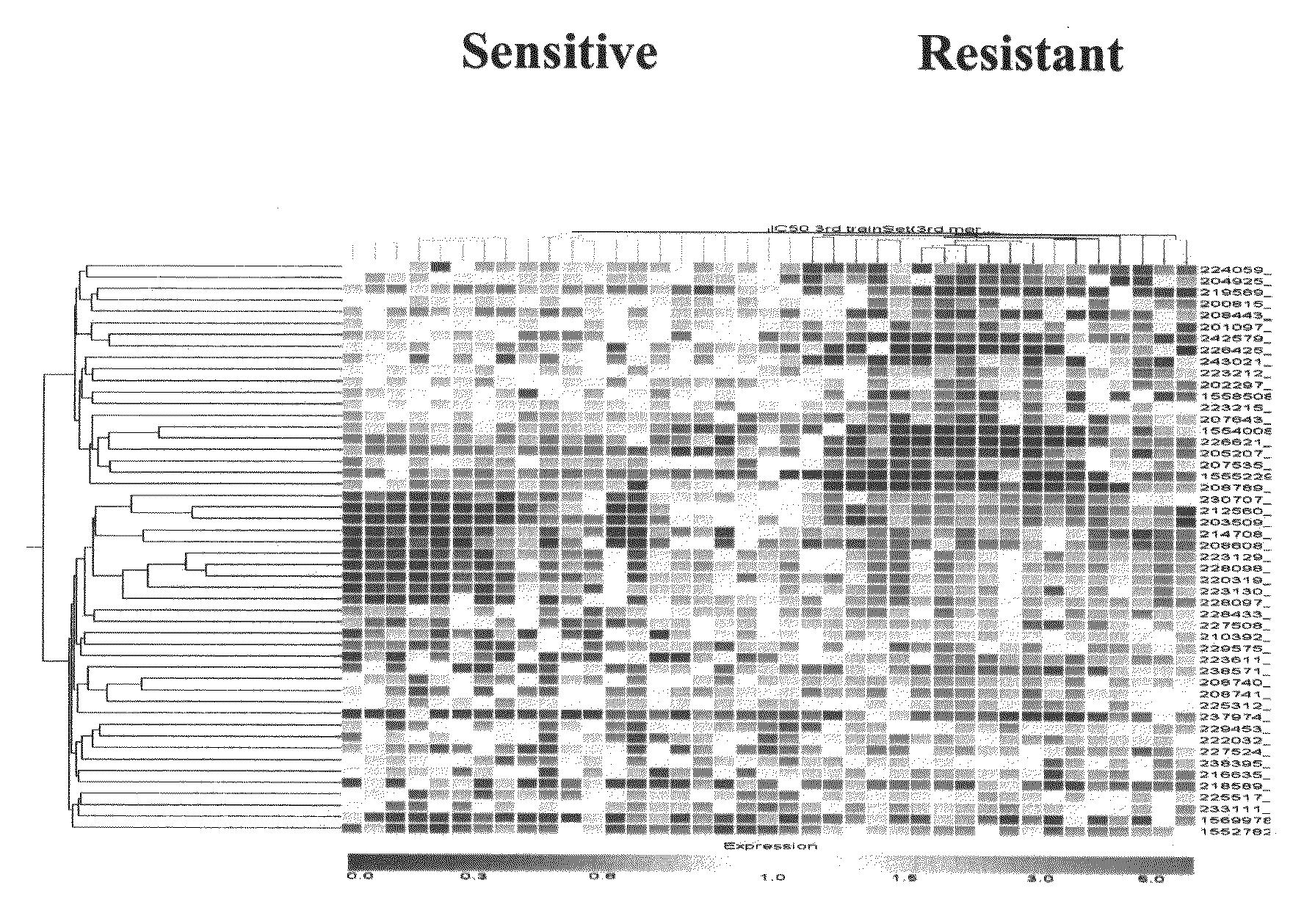
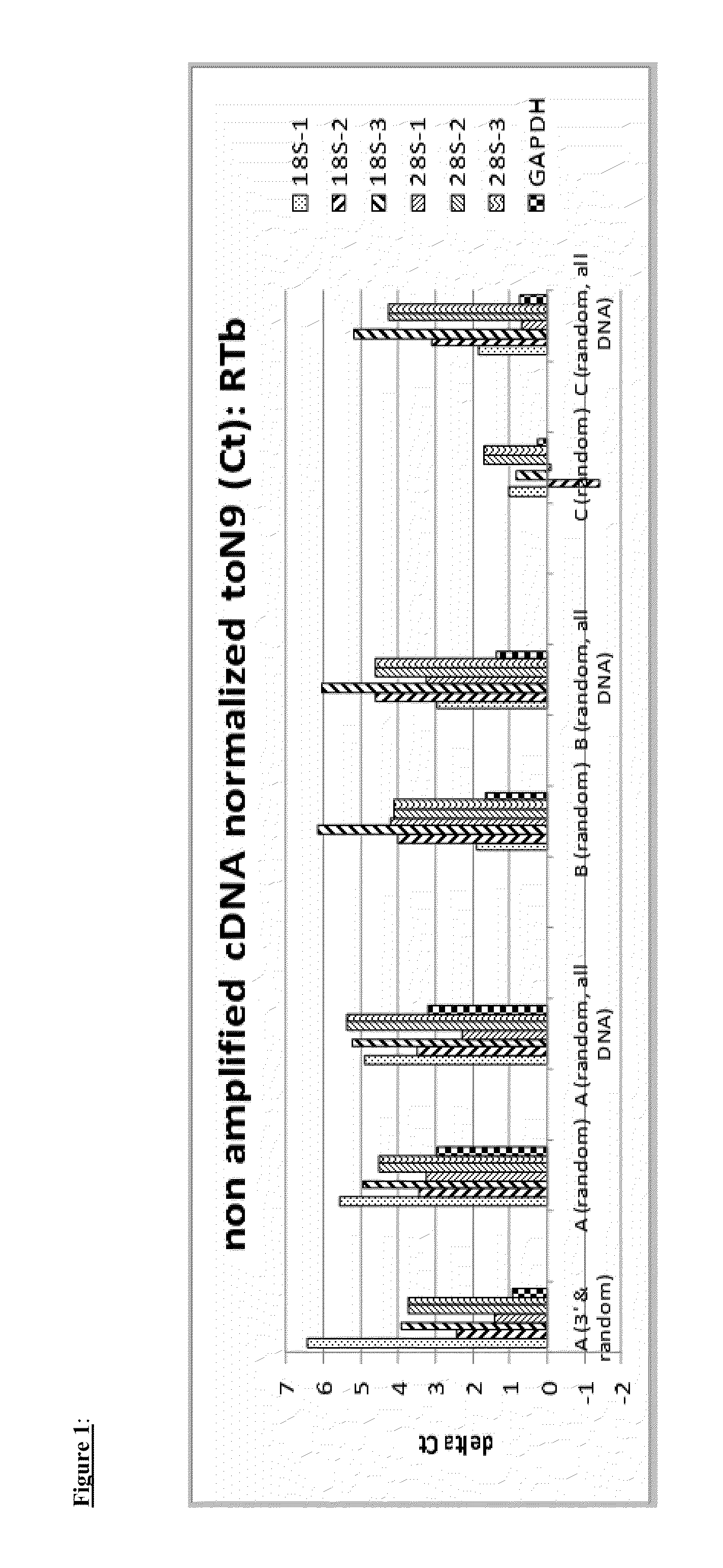
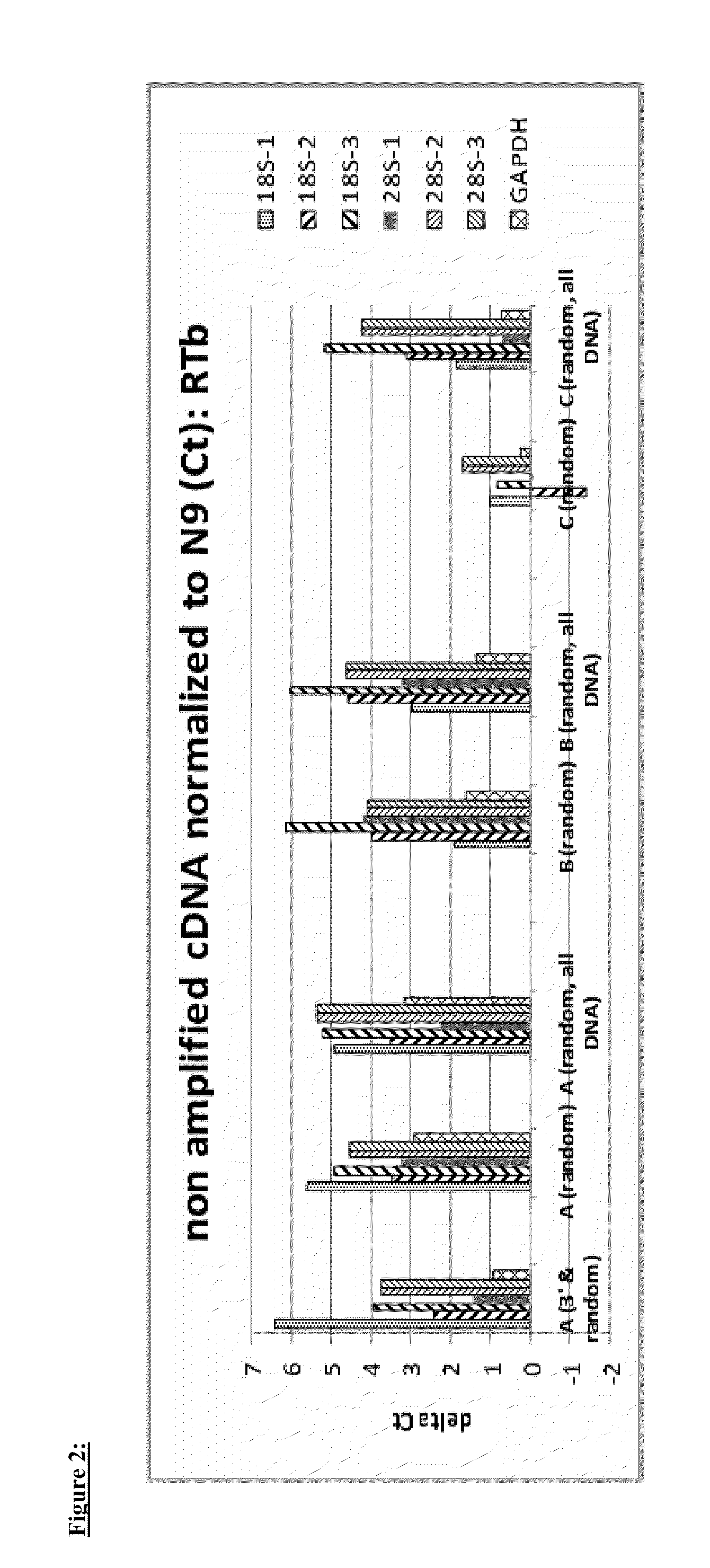
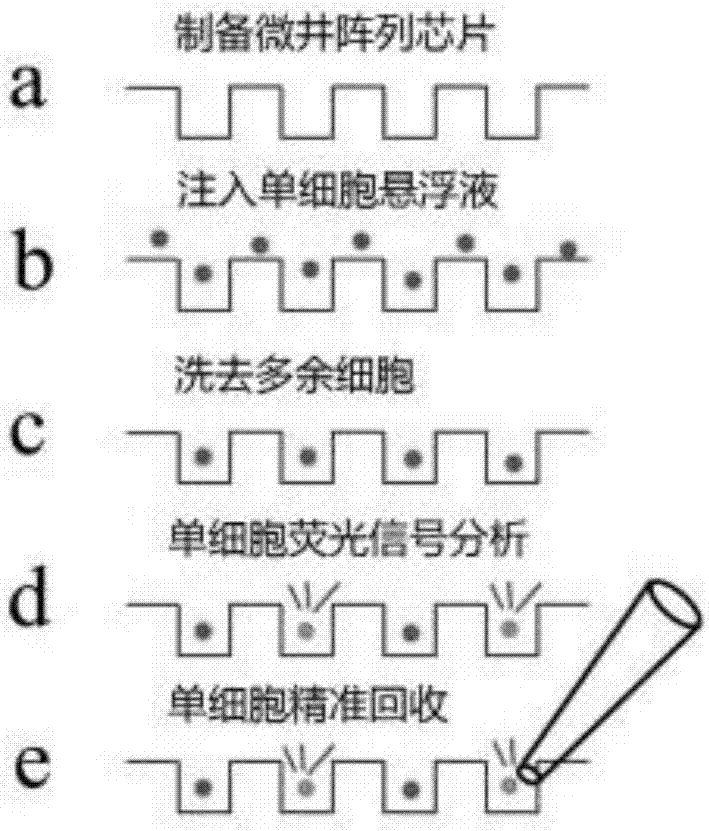
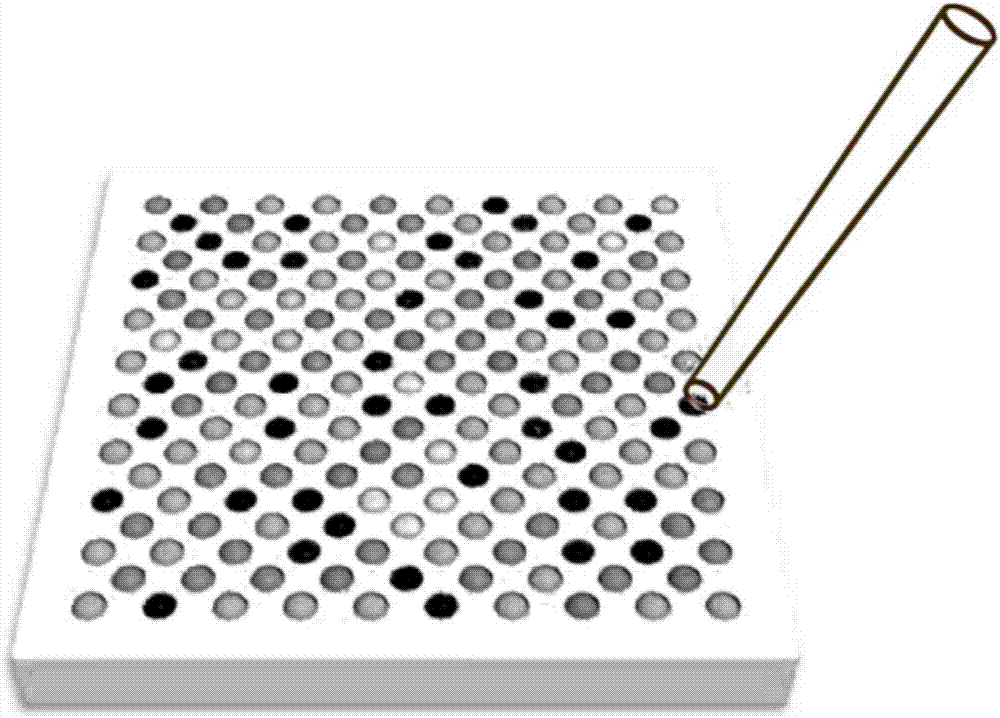
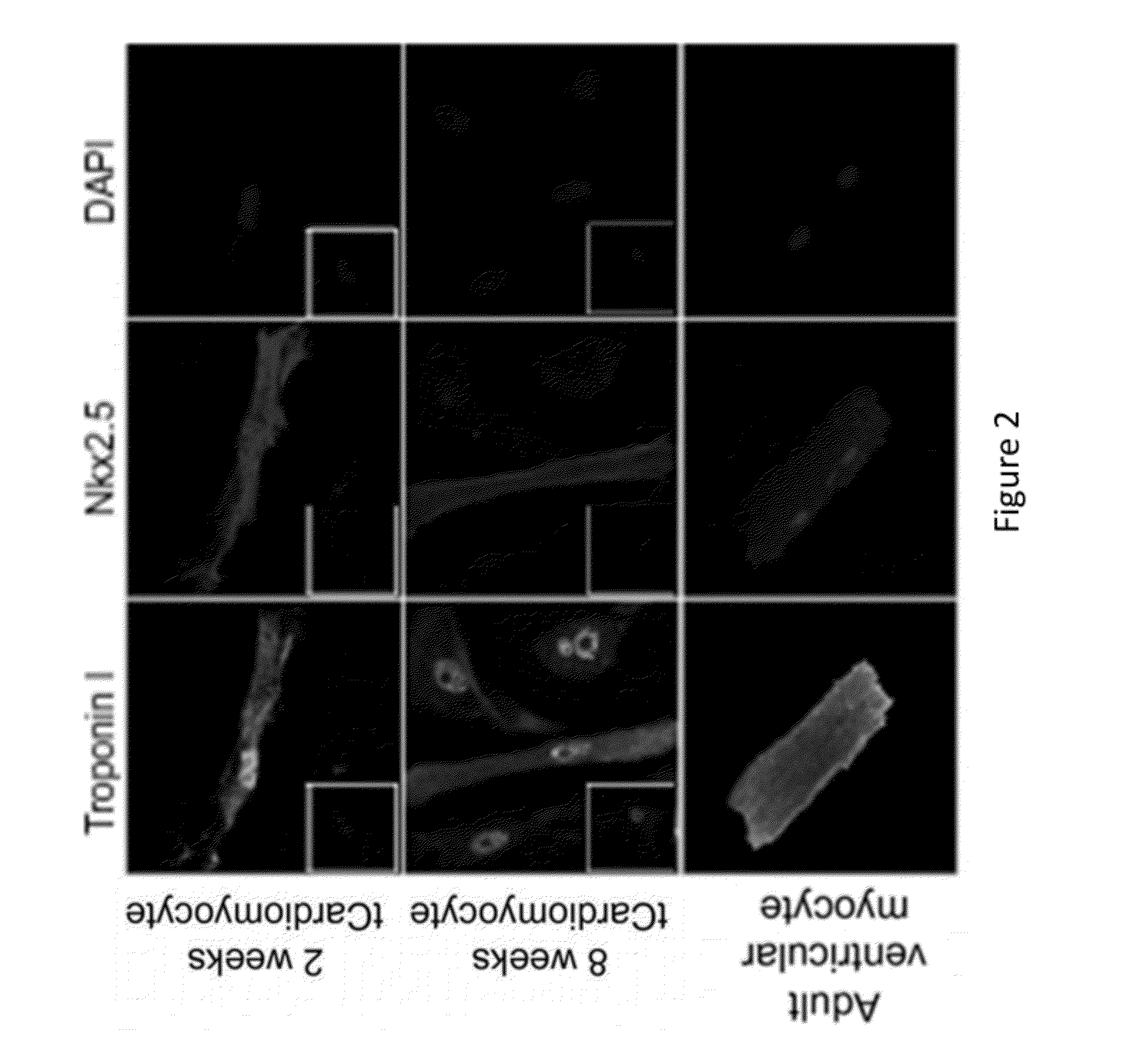
Patents
Literature
686 results about "Transcriptome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA molecules in one cell or a population of cells. It is sometimes used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. It differs from the exome in that it includes only those RNA molecules found in a specified cell population, and usually includes the amount or concentration of each RNA molecule in addition to the molecular identities.
Transcriptome microarray technology and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060134663A1Stable designFacilitates cross-validation studiesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sampleDiagnoses diseases
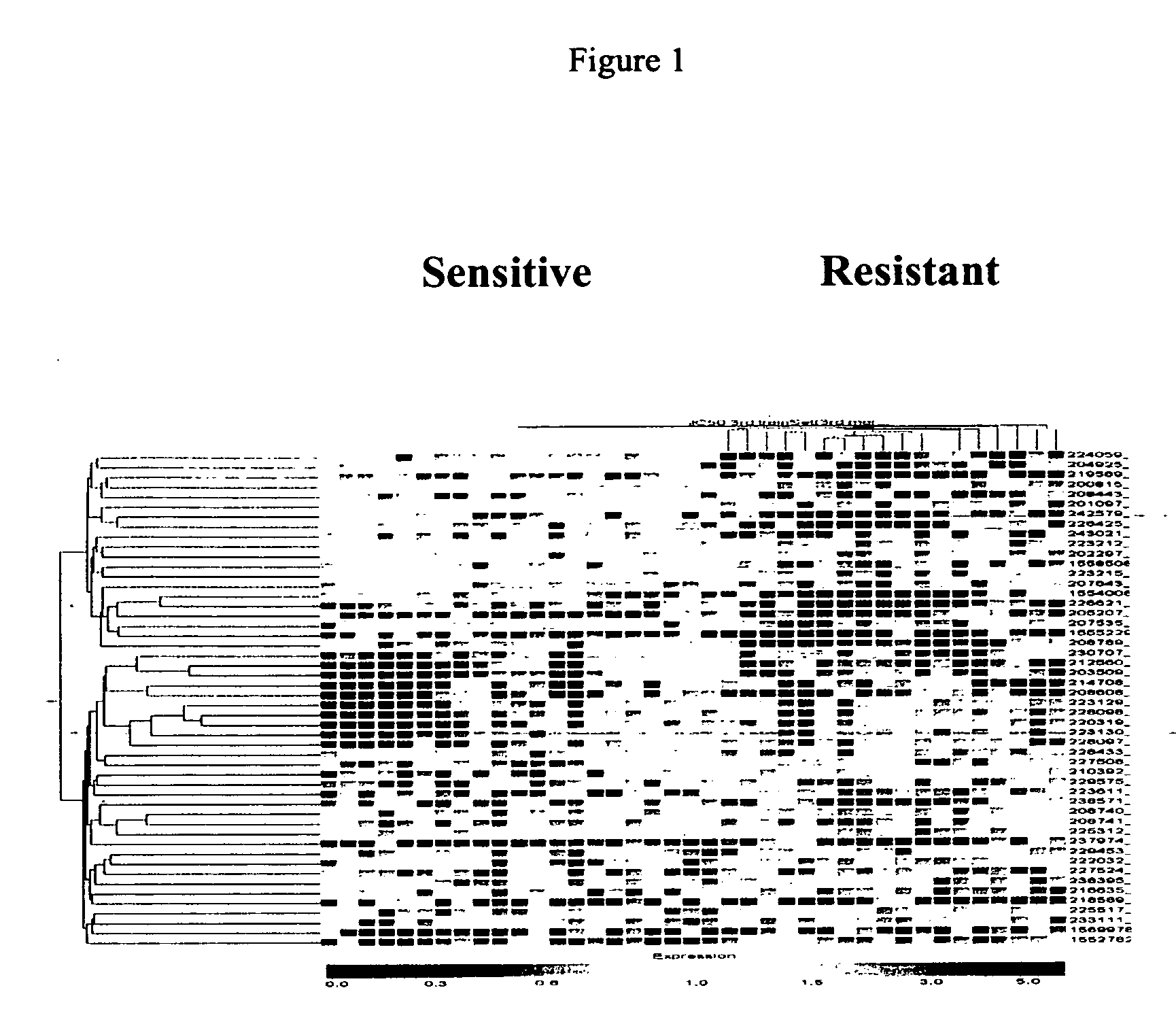
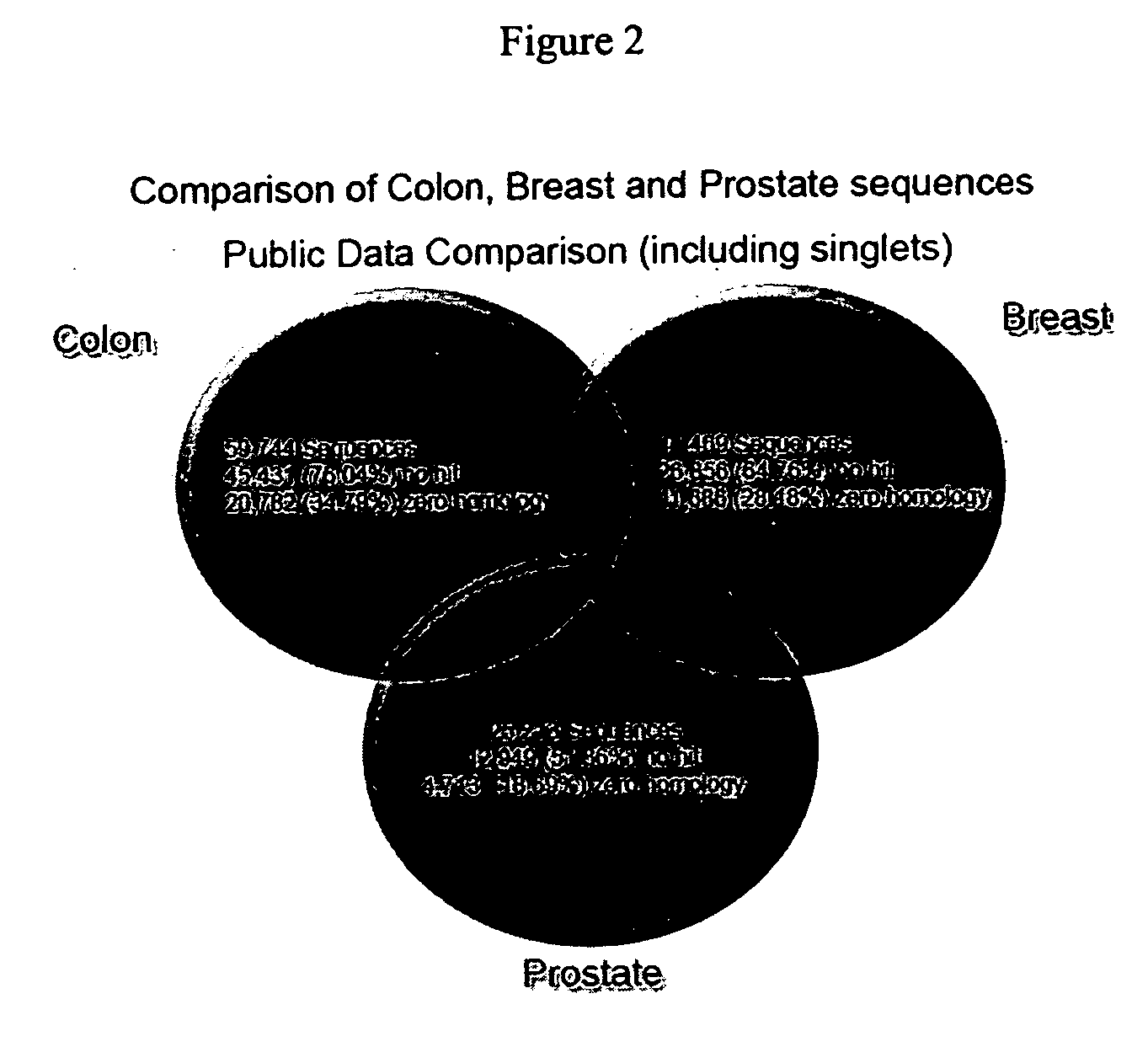
Arrays containing a transcriptome of a diseased tissue and methods of using the arrays for diagnosis, prognosis, screening, and identification of disease are provided herein. The transcriptome arrays from diseased tissue are useful for diagnosis of a disease by analysis of the genetic profile of a tissue sample specific to a disease state. The genetic profiles are then correlated with data on the effectiveness of specific therapeutic agents. Correlating expression profiles to the effectiveness of therapeutic agents provides a way to screen and select further patients predicted to respond to those therapeutic agents, thereby minimizing needless exposure to ineffective therapy.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS LIMITED
Method and device for detecting mutated proteins
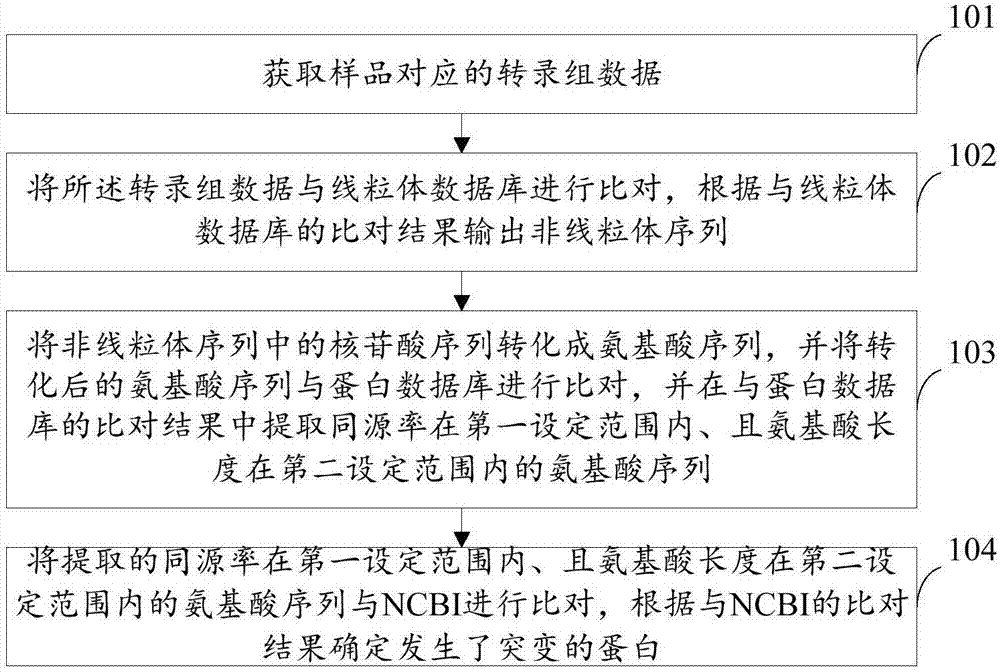
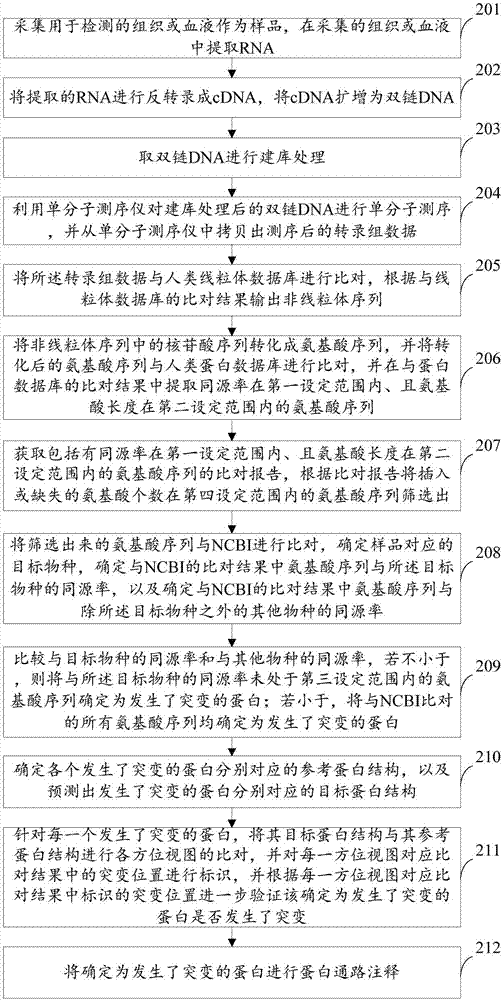
The invention provides a method and a device for detecting mutated proteins. The method includes acquiring transcriptome data corresponding to samples; comparing the transcriptome data to mitochondrion databases and outputting non-mitochondrion sequences according to comparison results of the transcriptome data and the mitochondrion databases; transforming nucleotide sequences in the non-mitochondrion sequences into amino acid sequences, comparing the transformed amino acid sequences to protein databases and extracting amino acid sequences with homogenous rates in first set ranges and amino acid lengths in second set ranges from comparison results of the transformed amino acid sequences and the protein databases; comparing the extracted amino acid sequences with the homogenous rates in the first set ranges and the amino acid lengths in the second set ranges to NCBI (national center of biotechnology information) and determining the mutated proteins according to comparison results of the extracted amino acid sequences and the NCBI. According to the scheme, the method and the device have the advantage that the mutated proteins in the samples can be detected by the aid of the method and the device.
Owner:天津市湖滨盘古基因科学发展有限公司
Methods and genotyping panels for detecting alleles, genomes, and transcriptomes
Disclosed are methods and genotyping panels for detecting alleles, genomes, and transcriptomes in admixtures of two individuals.
Owner:PROGENITY INC
Amplification and analysis of whole genome and whole transcriptome libraries generated by a DNA polymerization process
ActiveUS8206913B1Increase success rateEnhance single-copy sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LA-DNA
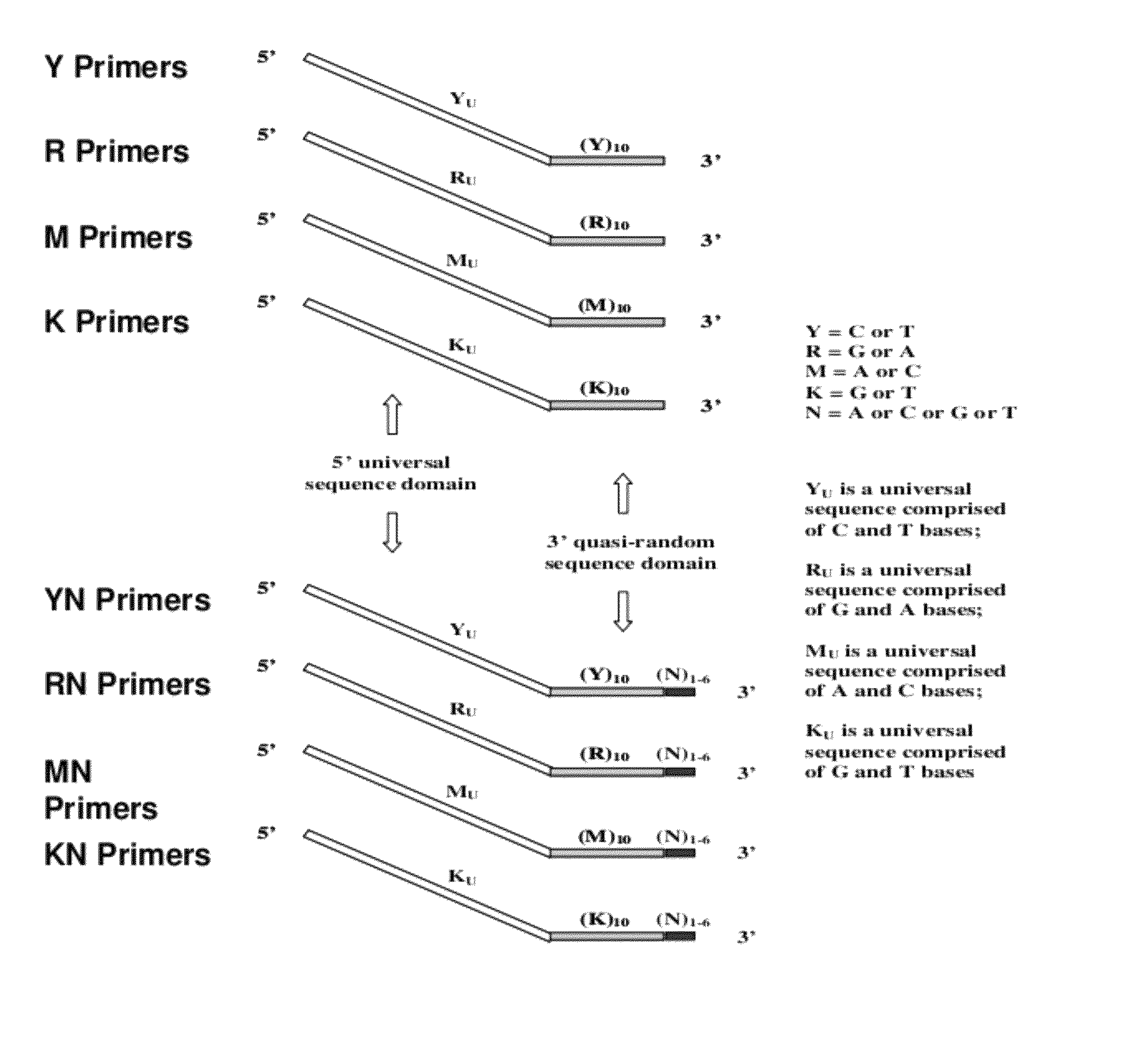
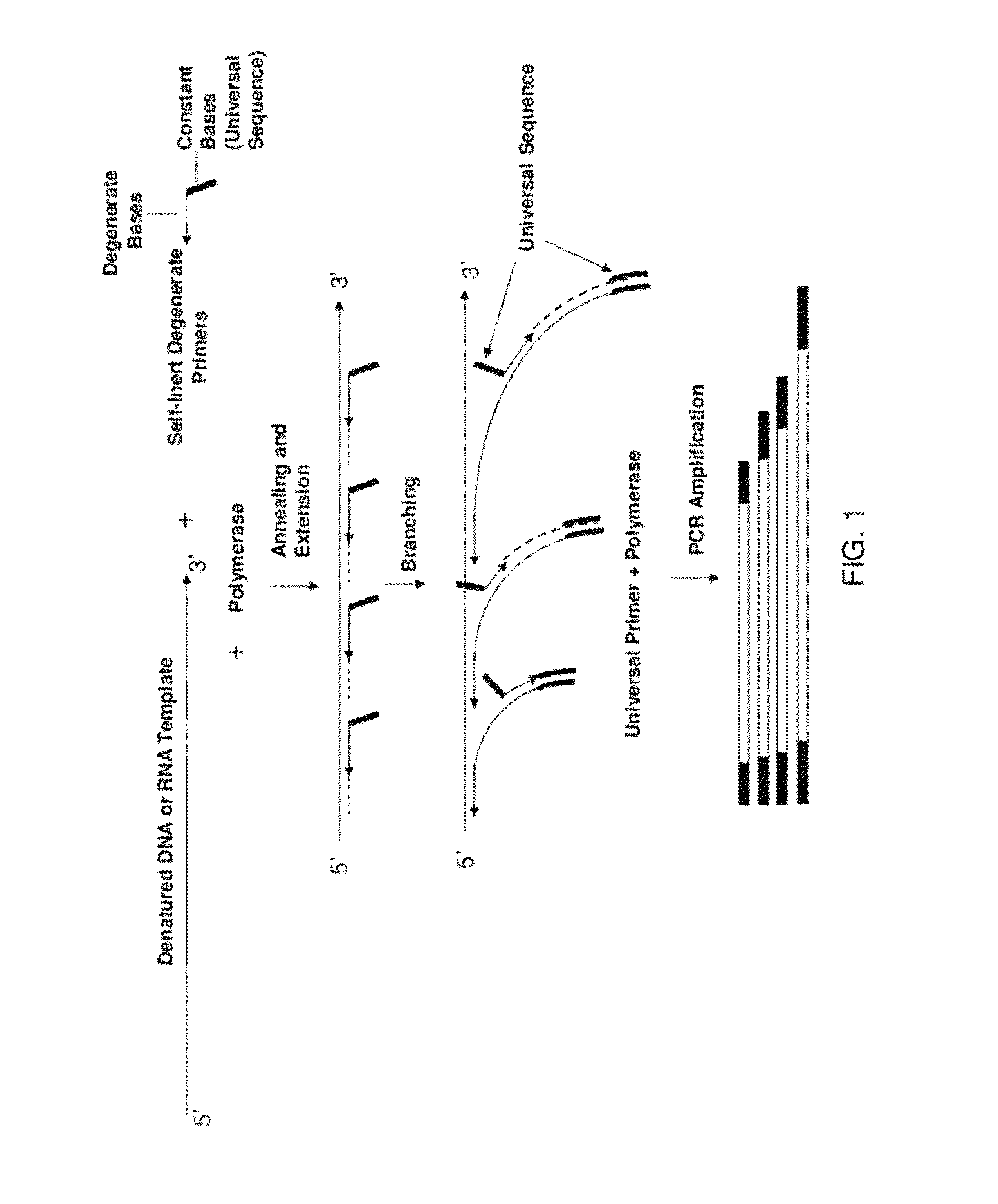
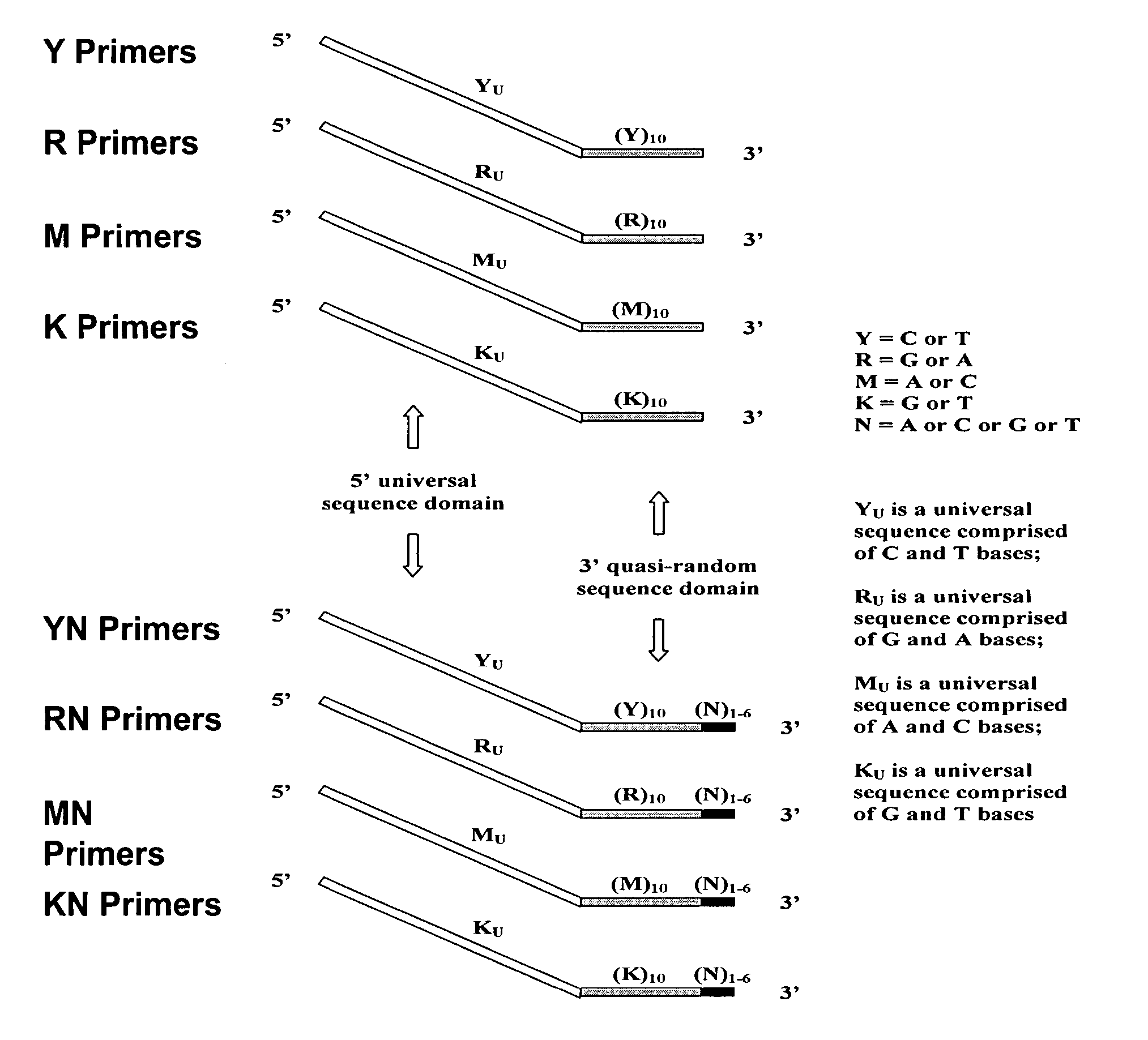
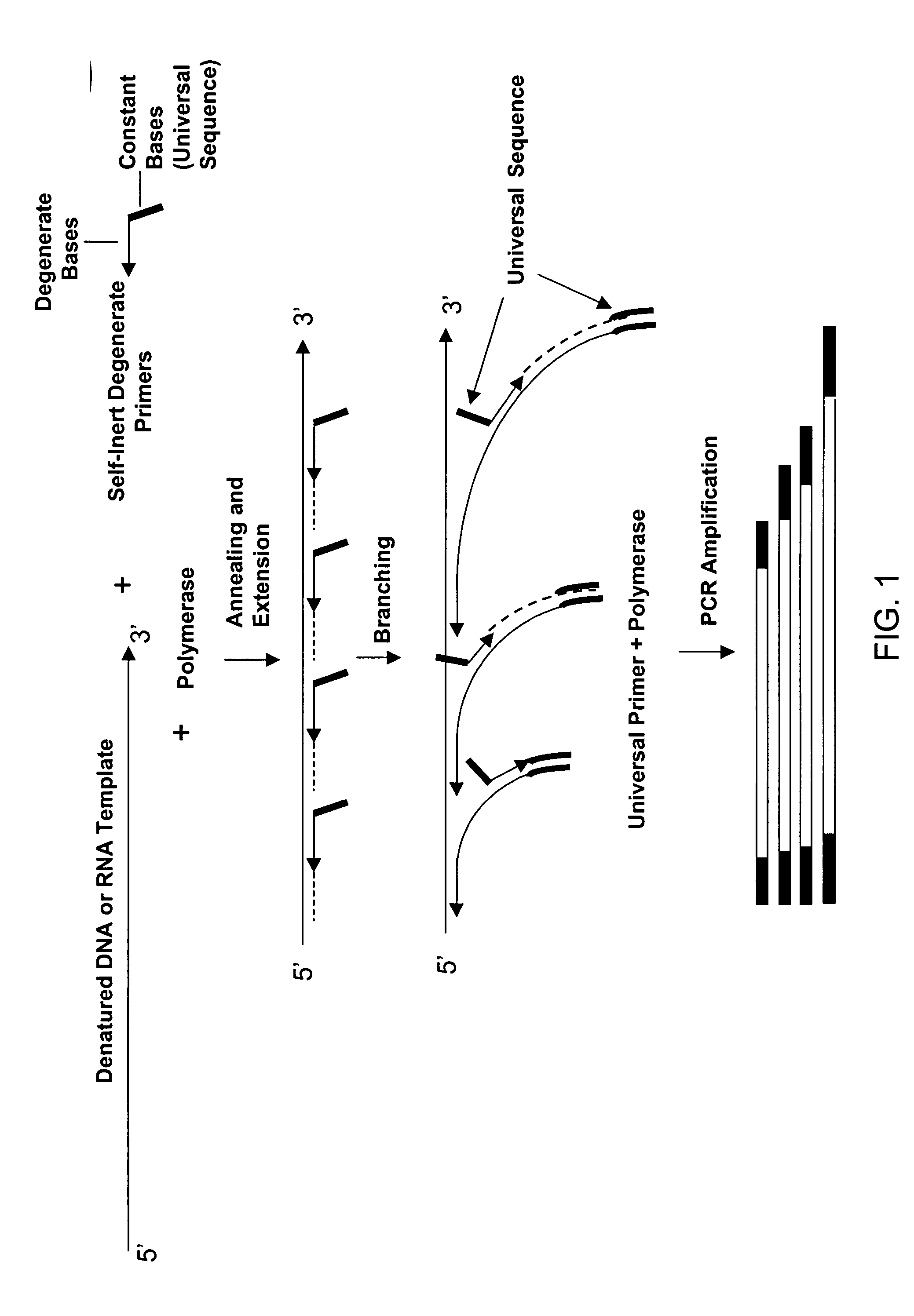
The present invention regards a variety of methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and whole transcriptome amplification. In a particular aspect of the present invention, there is a method of amplifying a genome comprising a library generation step followed by a library amplification step. In specific embodiments, the library generating step utilizes specific primer mixtures and a DNA polymerase, wherein the specific primer mixtures are designed to eliminate ability to self-hybridize and / or hybridize to other primers within a mixture but efficiently and frequently prime nucleic acid templates.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Methods and compositions for identifying or quantifying targets in a biological sample
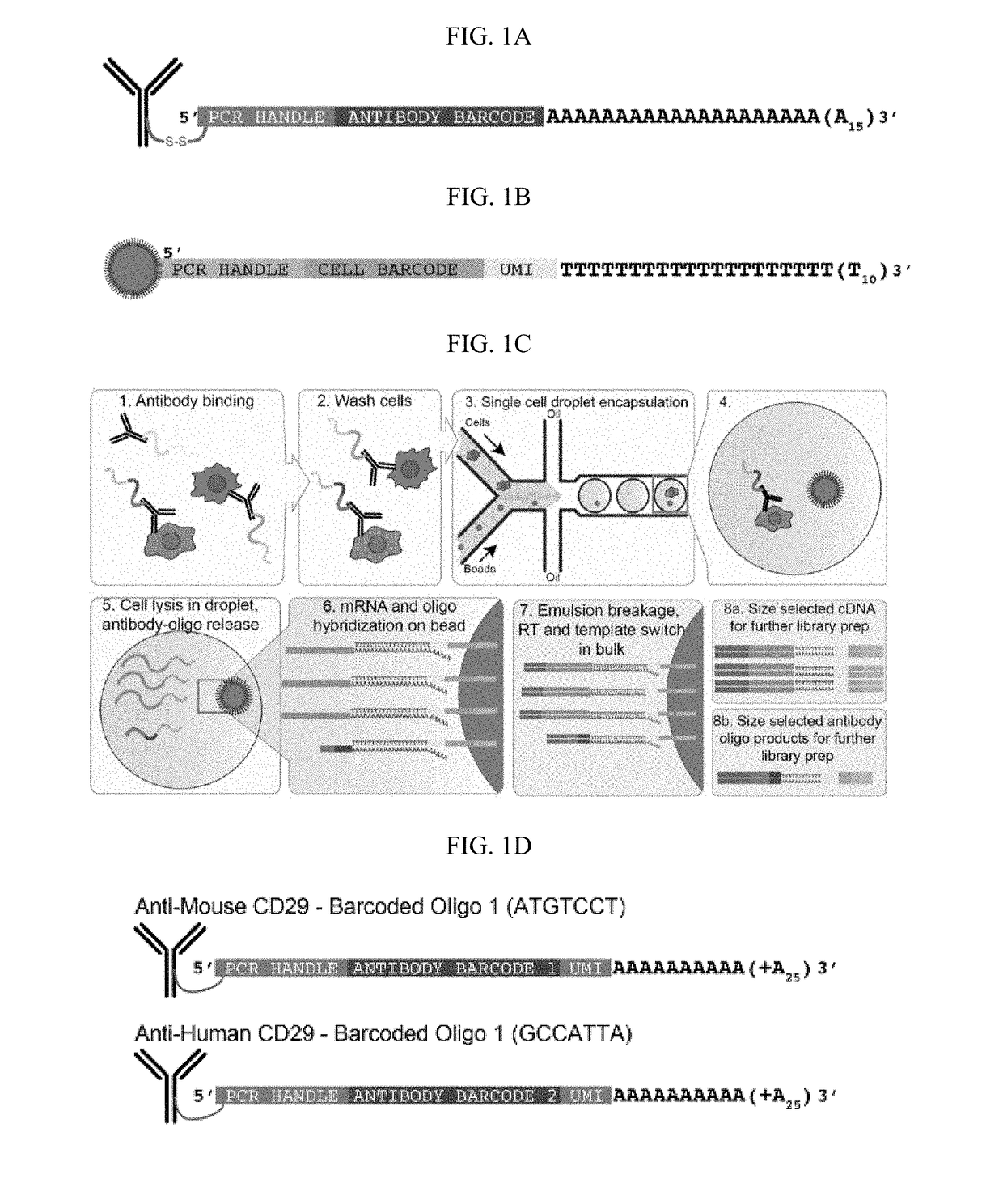
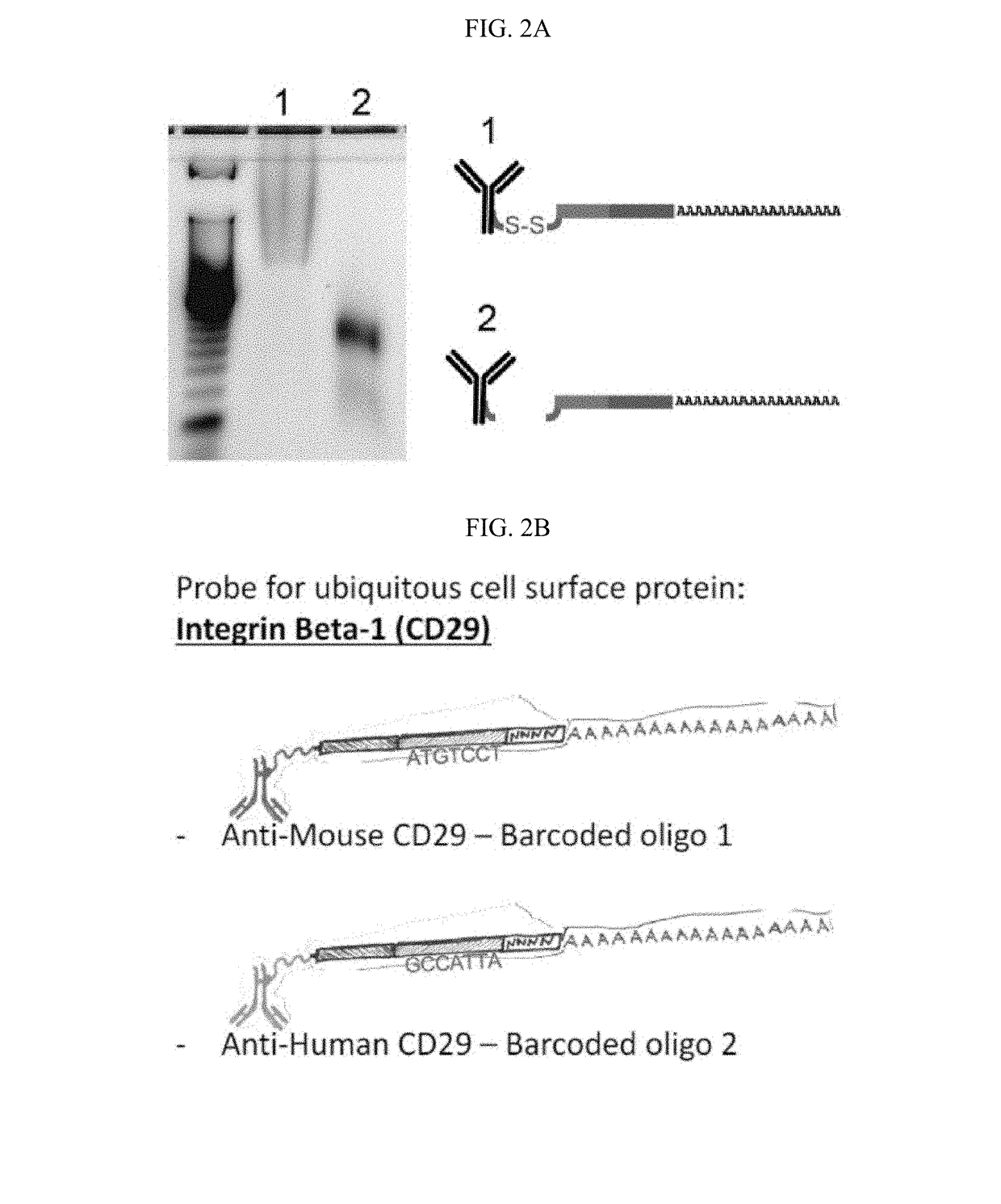
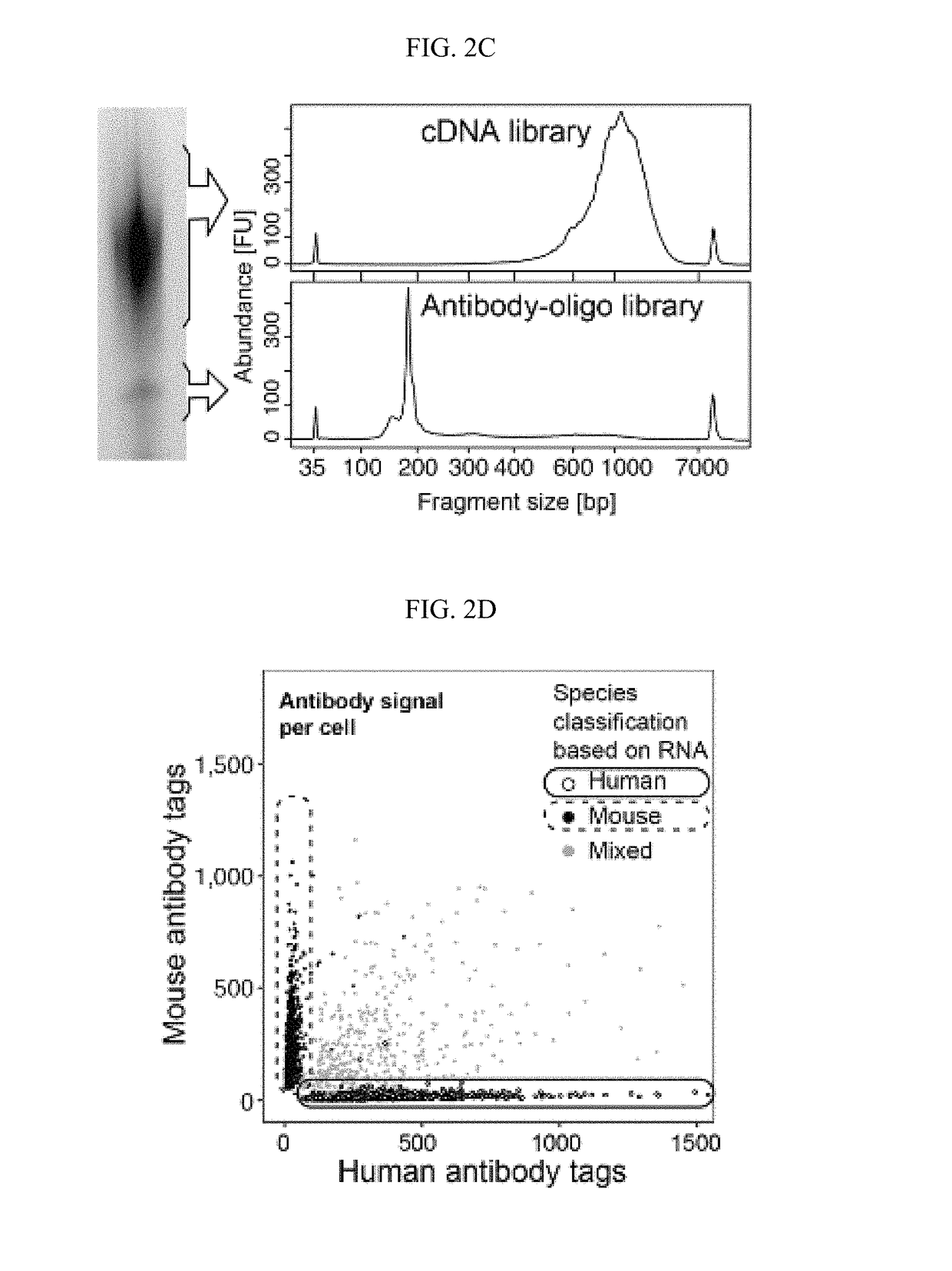
Compositions, kits and methods are described that comprise one or more constructs, each construct comprising a ligand attached or conjugated to a polymer construct, e.g., an oligonucleotide sequence, by a linker, each ligand binding specifically to a single target located in or on the surface of a cell. The polymer construct comprises a) an Amplification Handle; b) a Barcode that specifically identifies a single ligand; c) an optional Unique Molecular Identifier that is positioned adjacent to the Barcode on its 5′ or 3′ end; and d) an Anchor for hybridizing to a complementary sequence, e.g., for generation of a double-stranded oligonucleotide. These compositions are used in methods, including high throughput methods, for detecting one or more targets or epitopes in a biological sample. These compositions are also used in a high throughput method for characterizing a cell by simultaneous detection of one or more epitopes located in or on the cell and its transcriptome.
Owner:NEW YORK GENOME CENT
Amplification and analysis of whole genome and whole transcriptome libraries generated by a DNA polymerization process
The present invention regards a variety of methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and whole transcriptome amplification. In a particular aspect of the present invention, there is a method of amplifying a genome comprising a library generation step followed by a library amplification step. In specific embodiments, the library generating step utilizes specific primer mixtures and a DNA polymerase, wherein the specific primer mixtures are designed to eliminate ability to self-hybridize and / or hybridize to other primers within a mixture but efficiently and frequently prime nucleic acid templates.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
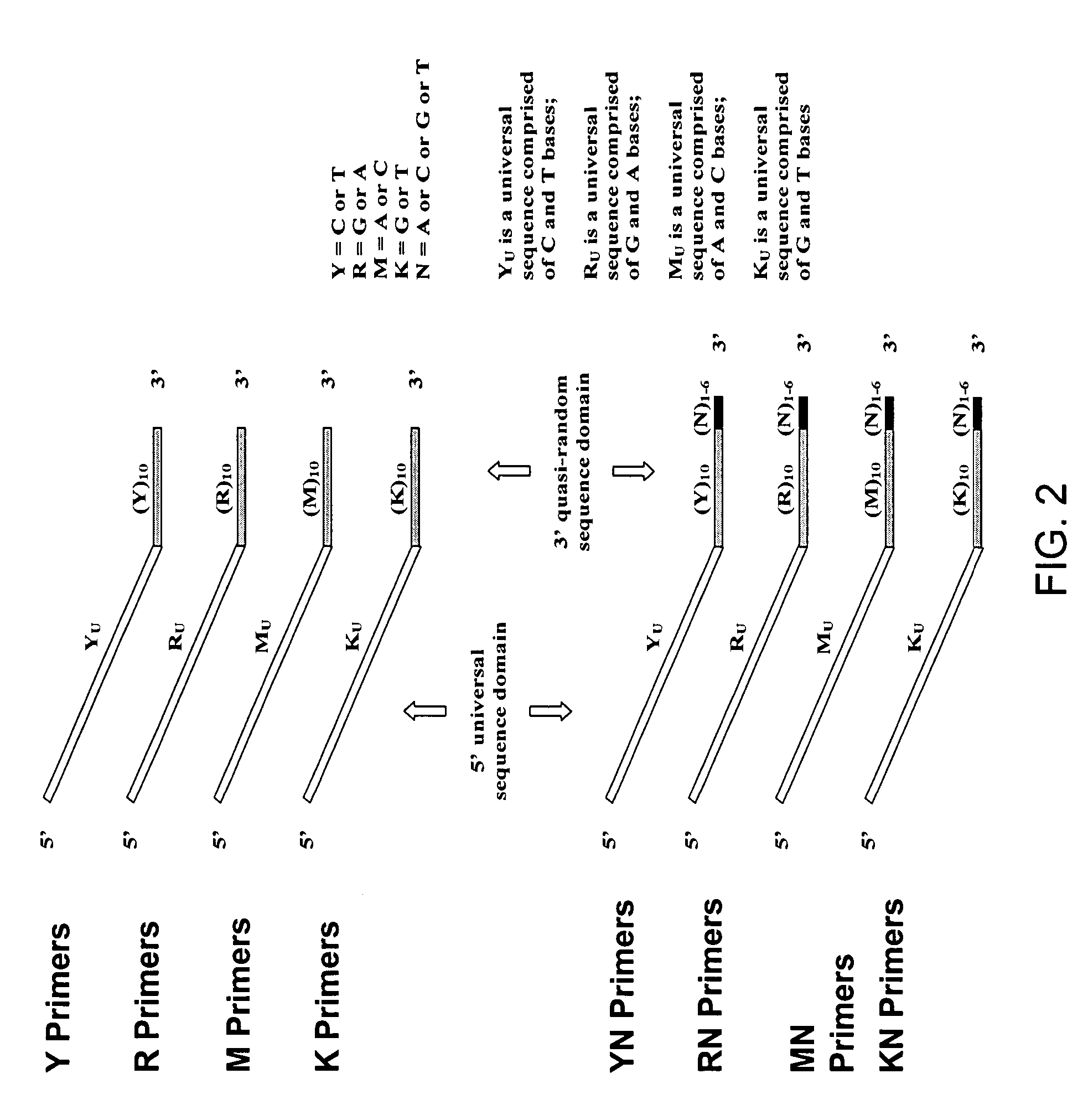
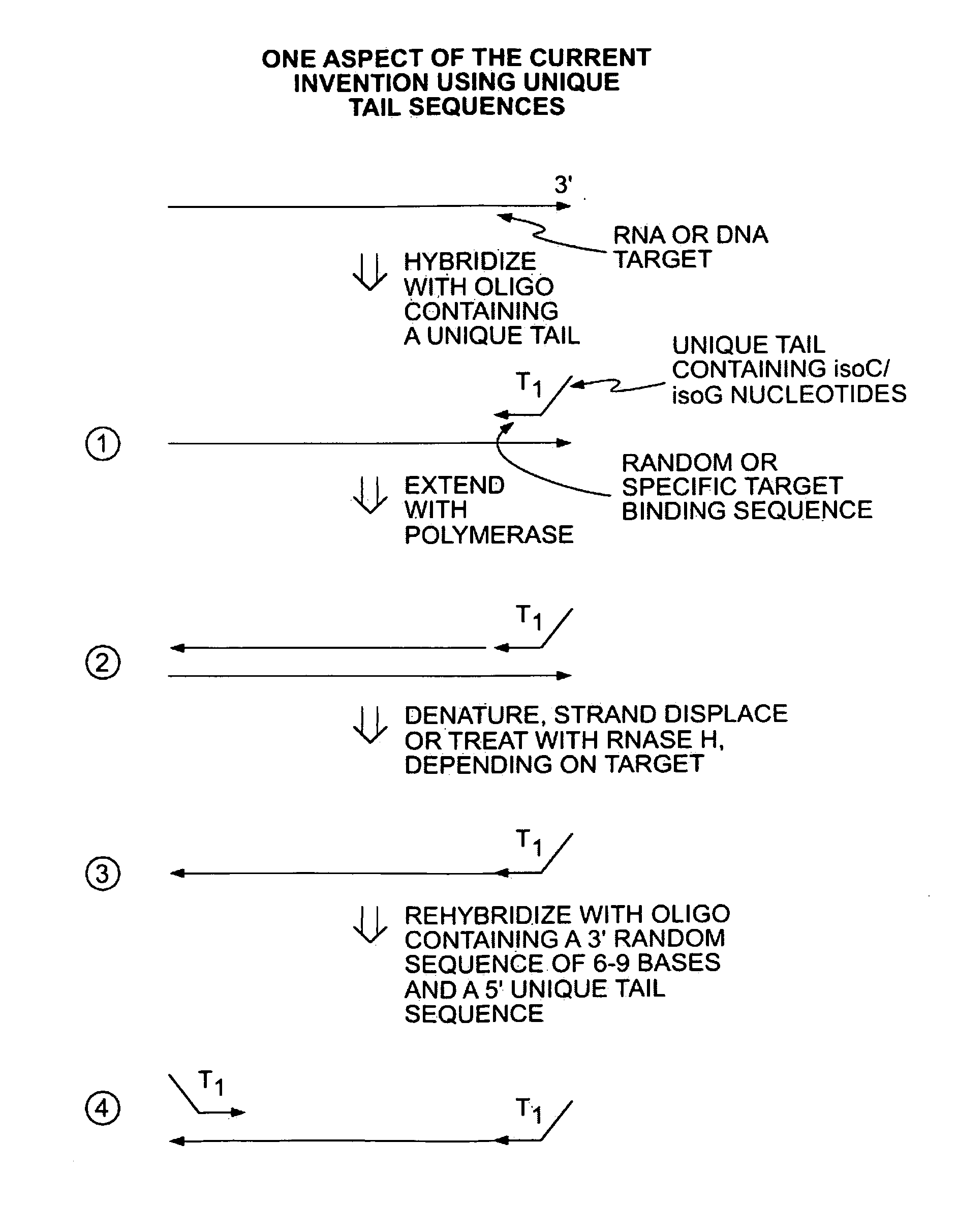
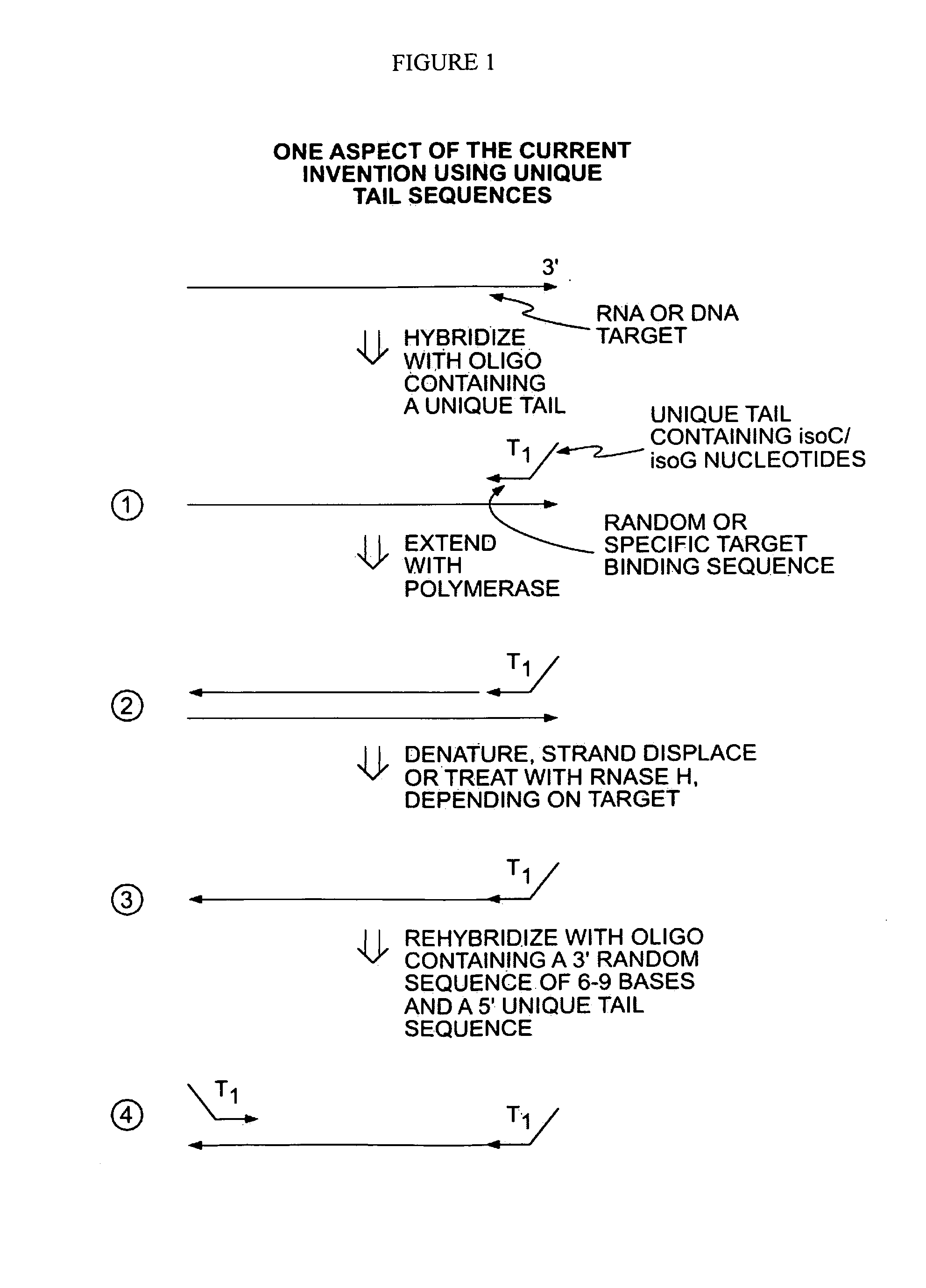
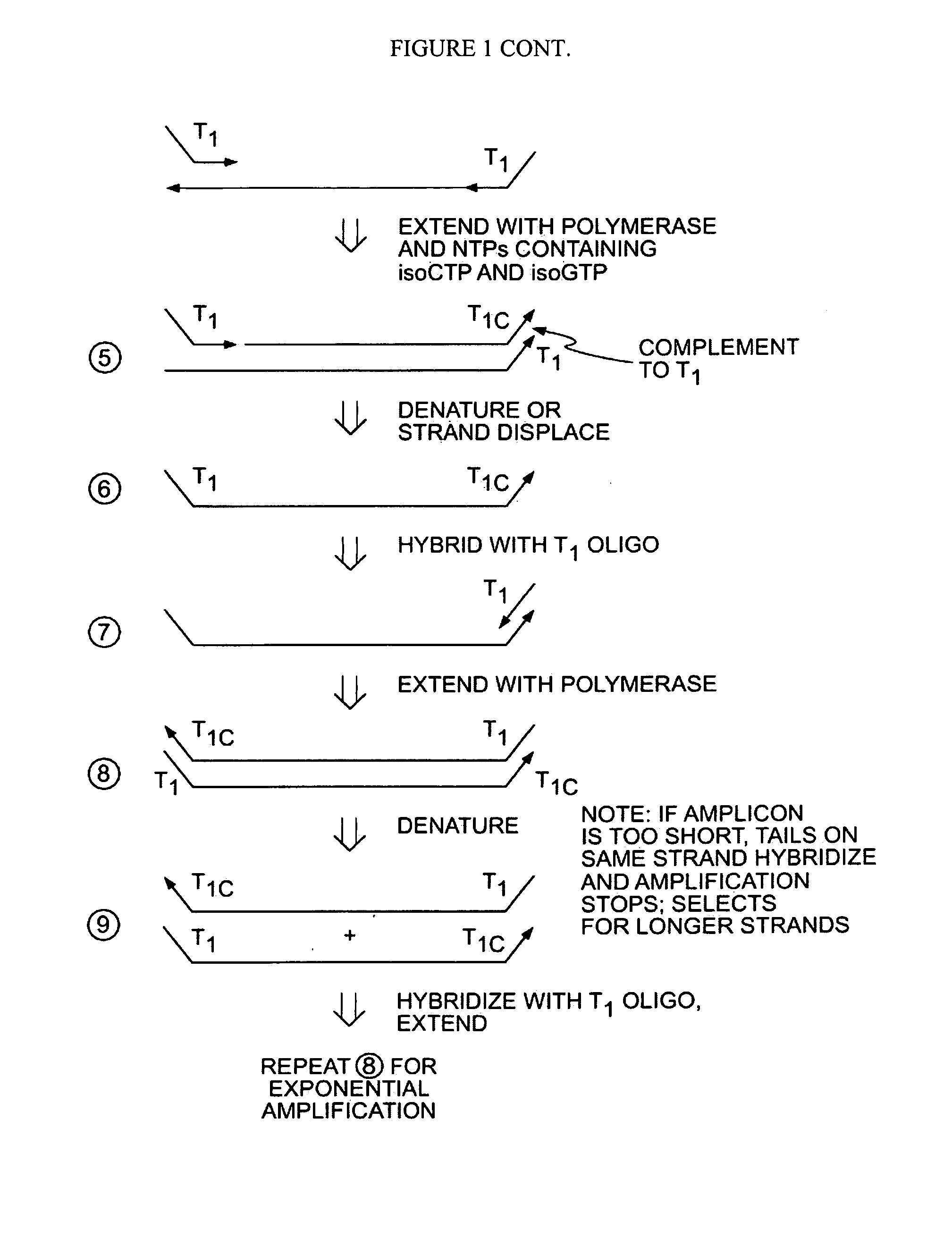
Methods for Amplifying a Complete Genome or Transcriptome
InactiveUS20140274811A1Eliminates misprimingReduces misprimingLibrary creationDNA preparationNucleotidePolymerase L
The present invention provides methods for amplifying a complete genome or transcriptome. The genome or transcriptome is prepared as a set of target nucleic acids and mixed with a first primer. The first primer comprises a target-binding region having a first random sequence of about 6 to about 9 nucleotides and a tag sequence that contains one or more non-natural nucleotides. The first primer is annealed to the target nucleic acids and extended by polymerase to produce a first duplex nucleic acid. The target nucleic acid is removed from the first nucleic acid. A second primer is annealed to the first nucleic acid having a second random sequence of about 6 to about 9 nucleotides and a tag sequence that contains one or more non-natural nucleotides. The second primer is extended by polymerase to produce a second duplex nucleic acid. The second nucleic acid contains a tag sequence on one terminus and a complement of the tag sequence on the other. The first nucleic acid is removed from the second nucleic acid. A third primer is annealed to the second nucleic acid having the same sequence as the tag sequence or a portion thereof and at least one of the non-natural nucleotides of the tag sequence. The third primer is extended by polymerase to produce a third duplex nucleic acid. The second nucleic acid is removed from the third nucleic acid. The third primer is annealed to the second nucleic acid and the third nucleic acid. The third primer is extended by polymerase. Repeating these last three steps thereby results in amplification of the genome or transcriptome.
Owner:AEGEA BIOTECH
Method for the preparation of cells of mesodermal lineage
The present invention relates generally to the generation of cells of mesodermal lineage. More particularly, the present invention contemplates a method for the preparation of differentiated or partially differentiated mesodermal cells and their use in tissue repair, regeneration and / or augmentation therapy. The identification and generation of the mesodermal cells further provides a source of transcriptome or proteome data to assess the expression profile of genes associated with the maintenance of mesodermal cells as well as their differentiation, proliferation, expansion and / or renewal potential.
Owner:ADELAIDE RES & INNOVATION PTY LTD
Transcriptome microarray technology and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20090221437A1Stable designFacilitates cross-validation studiesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTissue sampleDisease status
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS LIMITED
Profiling expression at transcriptome scale
ActiveUS9938566B2Exclude false positive resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsTranscriptome
Owner:BIOSPYDER TECH
Detection methods for disorders of the lung
InactiveUS20060154278A1Induces xenobiotic and redox regulating genesReduce expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease riskLung cancer
The present invention is directed to prognostic and diagnostic methods to assess lung disease risk caused by airway pollutants by analyzing expression of one or more genes belonging to the airway transcriptome provided herein. Based on the finding of a so called “field defect” affecting the airways, the invention further provides a minimally invasive sample procurement method in combination with the gene expression-based tools for the diagnosis and prognosis of diseases of the lung, particularly diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Compositions and methods for whole transcriptome analysis
InactiveUS20110189679A1Reduction and substantial eliminationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRibosomal RNABioinformatics
The present invention provides methods and compositions, including kits, for the generation of cDNA from mRNA with reduced ribosomal RNA representation.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Efficient capturing, high-content imaging and whole transcriptome analyzing device and method for single cell
InactiveCN107389642AEfficient captureReduce consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh fluxHigh throughput imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of single-cell capturing and analysis and in particular relates to an efficient capturing, high-content imaging and whole transcriptome analyzing device and method for a single cell. The device is used for capturing the single cell; the device comprises a polydimethylsiloxane micro-well array chip and a cell culture plate substrate or a cell culture dish substrate; the micro-well array chip is fitted to the cell culture plate substrate or the cell culture dish substrate. The invention provides the device and method, which can be used for simultaneously carrying out single-cell high-throughput imaging analysis, whole transcriptome analysis of the target single cell and deep exploration of heterogeneity between the single cells from a whole transcriptome level of the single cells.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
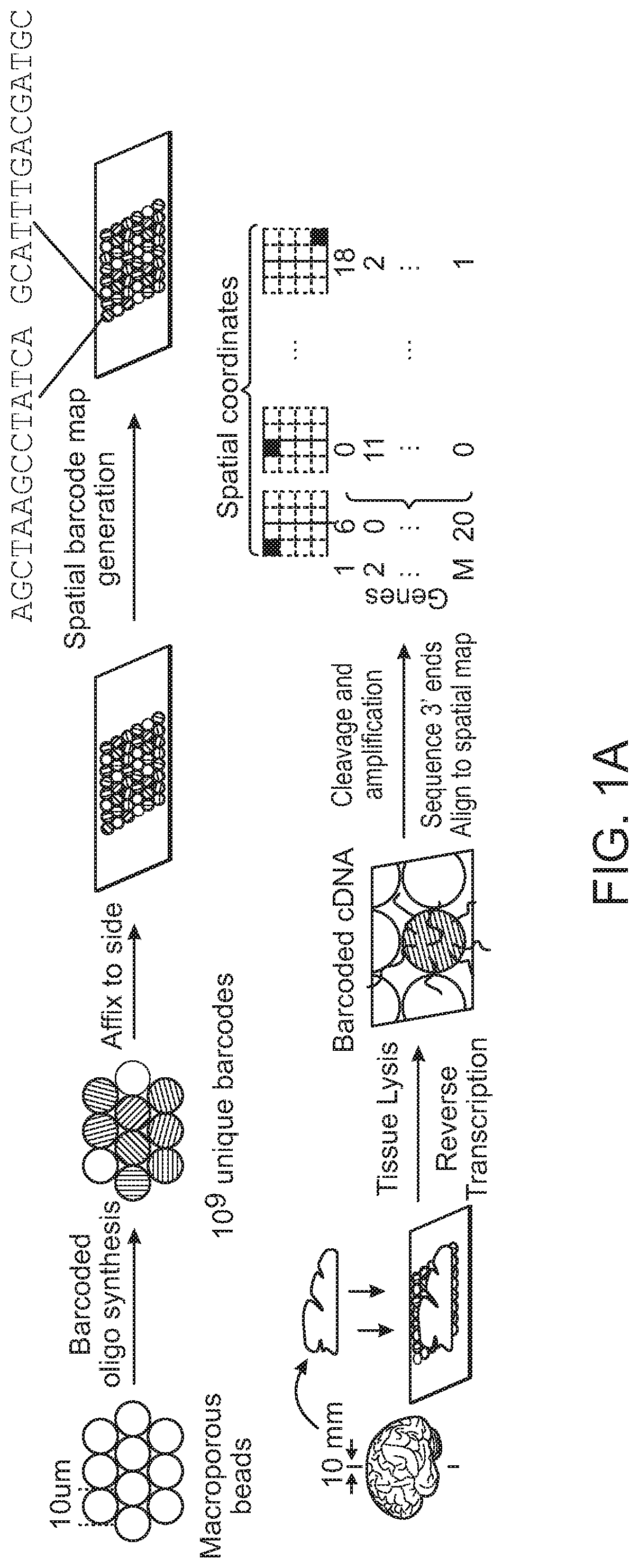
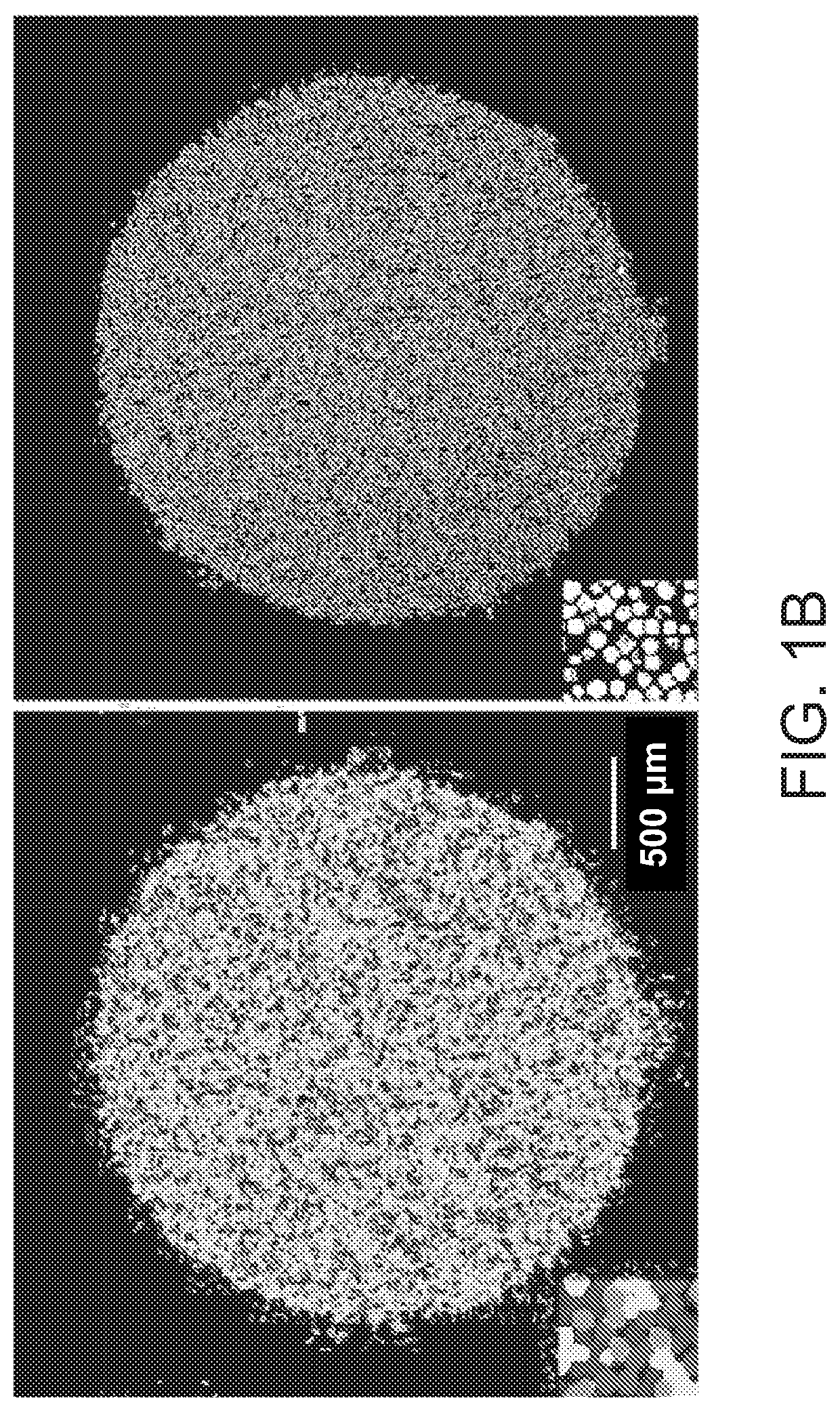
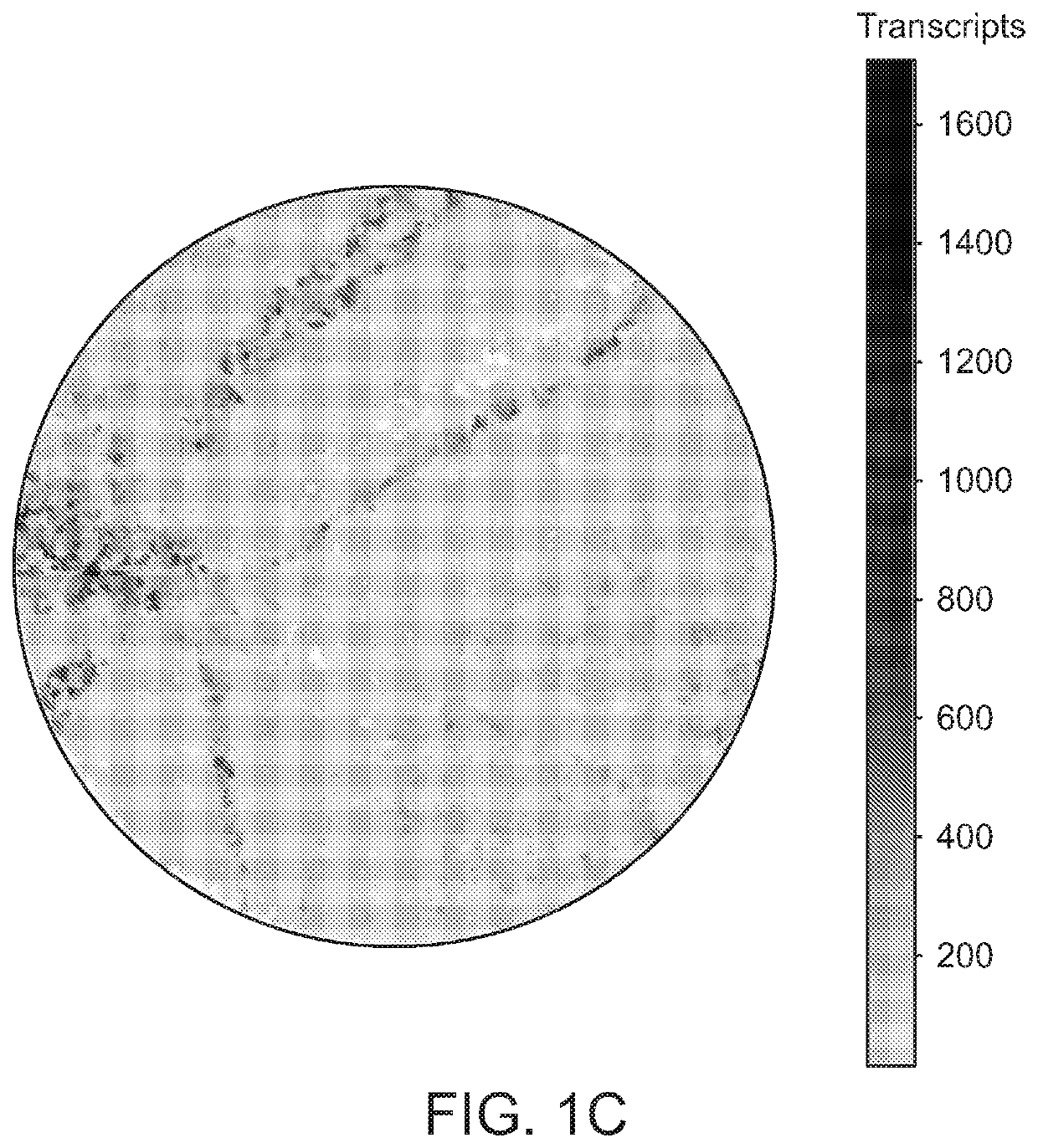
High-resolution spatial macromolecule abundance assessment
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods for assessing relative macromolecule abundance (e.g., RNA expression levels) in a spatially-defined manner across a tissue sample, specifically providing deep transcriptomic coverage at high-resolution across multiple locations assessed across the tissue sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Transcriptome-based tumor neoantigen identification method
ActiveCN108491689AImprove accuracyComprehensive identificationSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSample sequenceTumor-specific antigen
The invention discloses a transcriptome-based tumor antigen identification method. The method comprises four steps of: obtaining an RNA sample of a patient tumor tissue, and carrying out library construction and amplification on the RNA sample to obtain an RNA sample sequencing result of the tumor tissue; aligning short read segments of the RNA sample sequencing result to a human reference genometo obtain an RNA alignment result; calculating gene expression quantity according to the RNA alignment result, and carrying out mutation detection and prediction of fusion gene events according to theRNA alignment result; and predicting transcriptome HLA typing according to the alignment result, wherein calculation of the gene expression quantity, mutation detection and prediction of the fusion gene events are carried out according to a specified order or simultaneously carried out; and using the gene expression quantity of a transcriptome sample, depth of transcriptome mutation sites in a whole-exon sequencing sample and binding force of neonatal short peptides and the patient HLA typing as an analysis result to submit the same to a downstream analyst. The invention provides the method capable of identifying a tumor-specific antigen of an individual sample from tumor patient transcriptome NGS data.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEOANTIGEN THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
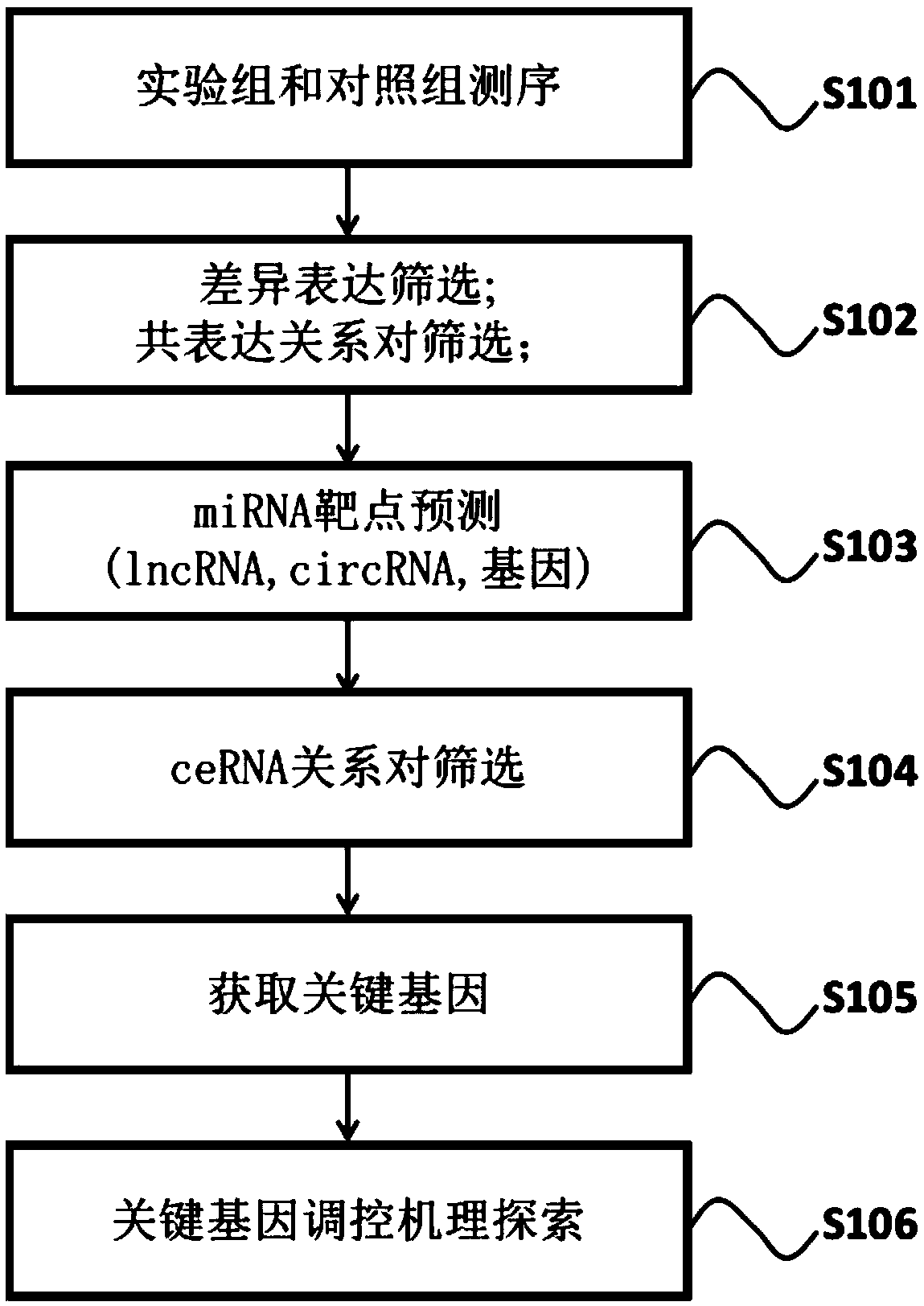
Method for constructing genetic regulation network based on total-transcriptome high-throughput sequencing
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to a method for constructing a genetic regulation network based on total-transcriptome high-throughput sequencing.The method comprises the steps that a disease related competitive endogenous RNA regulation network is constructed on the basis of total-transcriptome high-throughput sequencing data through the screening of differently expressed genes, lncRNA, circRNA and miRNA, the co-expression analysis of the genes, the lnc RNA and the circRNA and the miRNA combining target prediction, key genes in the regulation network are screened according to a random walking algorithm, the pathway in which the key genes are significantly enriched is determined through pathway enrichment analysis, and the biological mechanism of the key genes in the disease regulation process is analyzed combining with the genetic regulation relationship of the pathway. The invention provides methods for the verification of the disease related key genes and the construction of the regulation network of the key genes, and a novel approach is provided for the study of generating developing mechanisms of complicated diseases.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
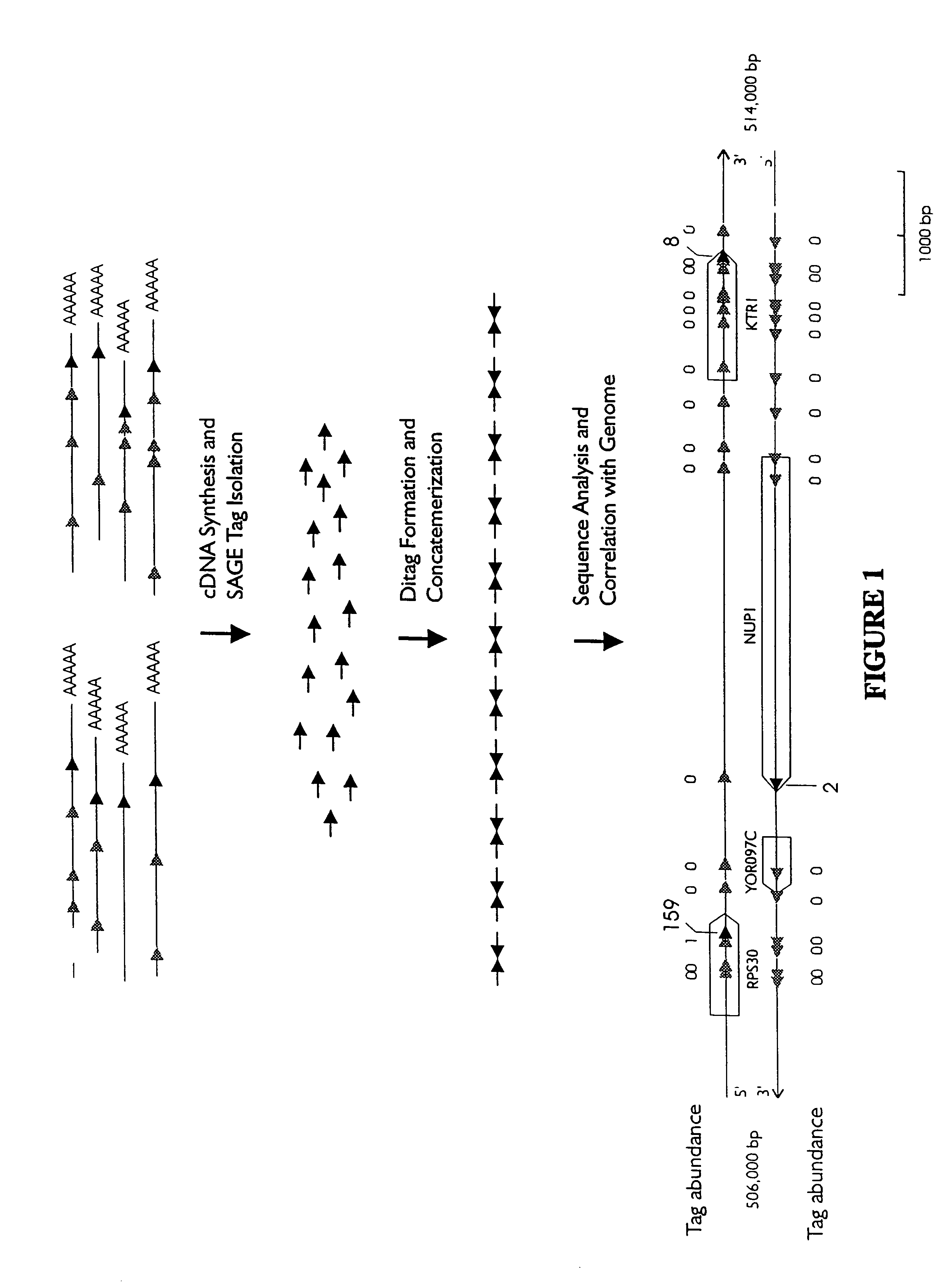
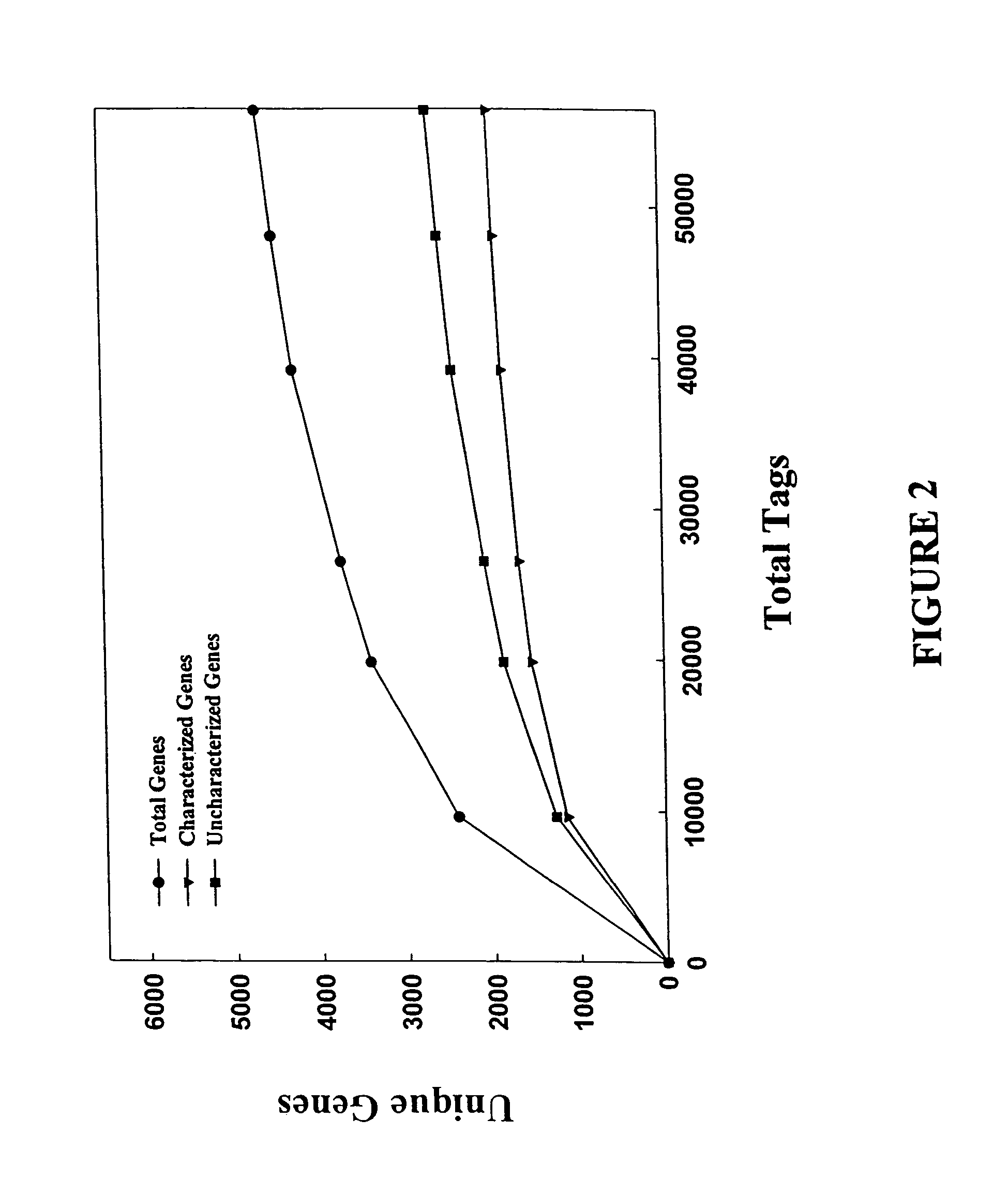
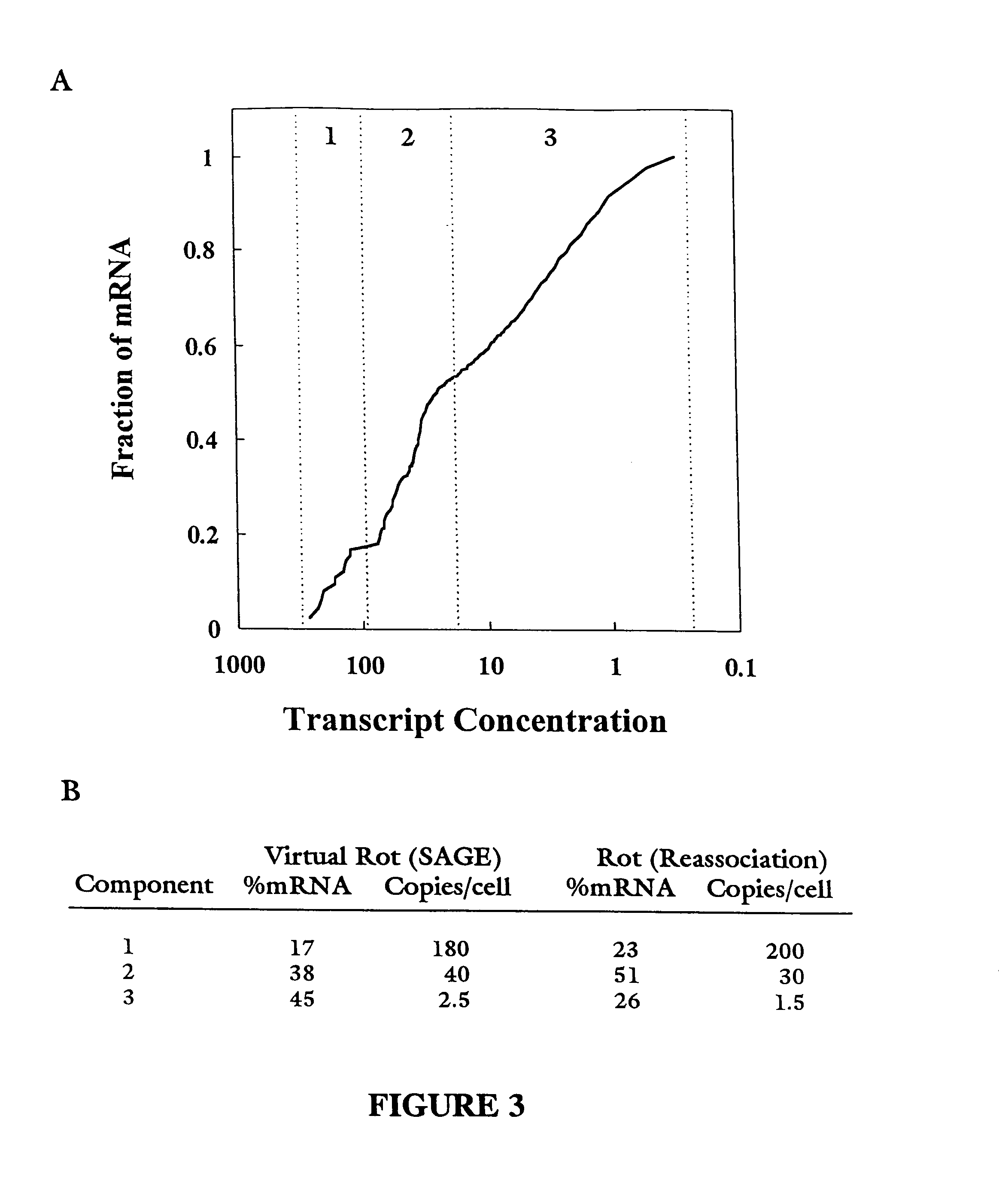
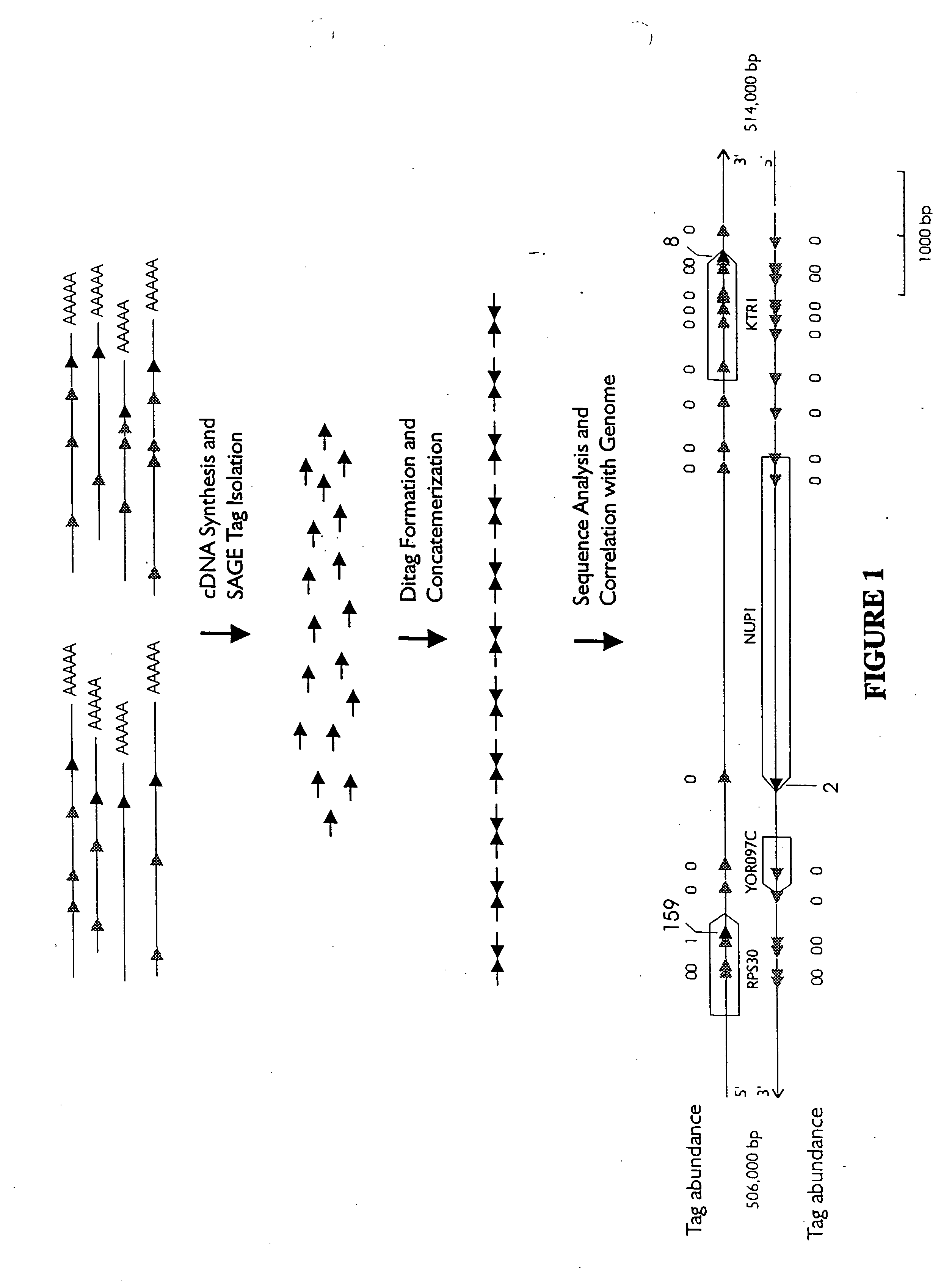
Characterization of the yeast transcriptome
Yeast genes which are differentially expressed during the cell cycle are described. They can be used to study, affect, and monitor the cell cycle of a eukaryotic cell. They can be used to obtain human homologs involved in cell cycle regulation. They can be used to identify antifungal agents and other classes of drugs. They can be formed into arrays on solid supports for interrogation of a cell's transcriptome under various conditions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Characterization of the yeast transcriptome
InactiveUS20070031851A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesYeast geneYeast form
Yeast genes which are differentially expressed during the cell cycle are described. They can be used to study, affect, and monitor the cell cycle of a eukaryotic cell. They can be used to obtain human homologs involved in cell cycle regulation. They can be used to identify antifungal agents and other classes of drugs. They can be formed into arrays on solid supports for interrogation of a cell's transcriptome under various conditions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2 and application thereof
InactiveCN104059982AGood correlationConvenient for clinical operationMicrobiological testing/measurementTumour tissuePcr method
The invention relates to an oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2 and application of the oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2. RNA is extracted from oral squarmous tissue, tissue adjacent to the oral squarmous cell carcinomas and normal tissue, deep sequencing and analyzing are performed on a transcriptome, the oral squarmous cell carcinomas relevant gene BPIFB2 is obtained through screening, an RT-PCR method is adopted for analyzing the expression conditions, on the carcinomas tissue and the tissue adjacent to the carcinomas of a patient with the oral squarmous cell carcinomas, of the screened BPIFB2, and the result shows that the obtained BPIFB2 through screening has good relevance to the oral squarmous cell carcinomas and can be used for preparing an oral squarmous cell carcinomas auxiliary diagnosis preparation or a pregnosis preparation. The invention further discloses a fluorogenic quantitative PCR kit and a using method of the fluorogenic quantitative PCR kit. The kit can detect the expression level of the BPIFB2 in oral squarmous cell carcinomas tissue sensitively, rapidly, quantitatively, accurately and stably and has good application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
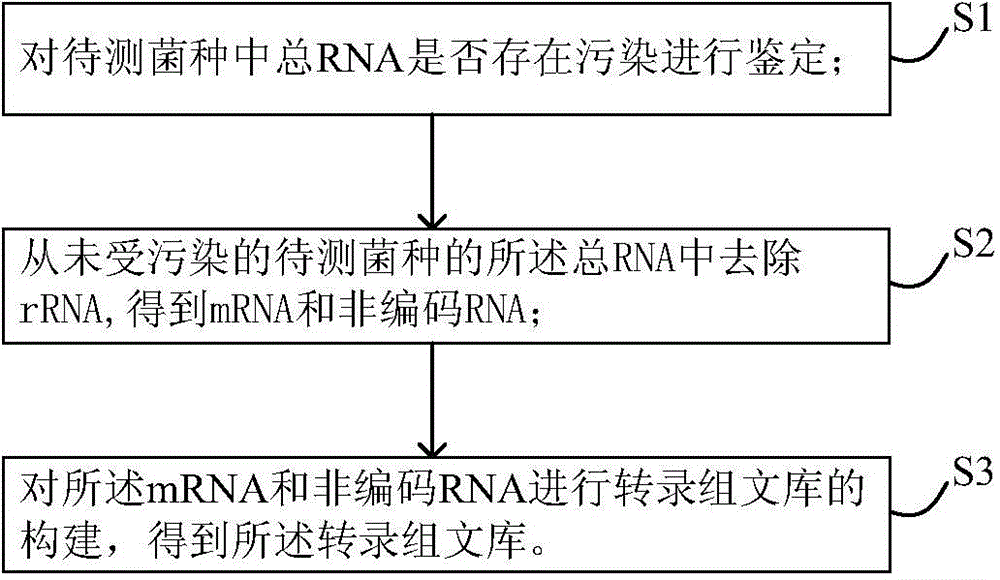
Method for constructing transcriptome library
InactiveCN104630206AAvoid wasting human and financial resourcesReduce adverse effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationTotal rnaNon-coding RNA
The invention discloses a method for constructing a transcriptome library. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1, verifying whether total RNA in a strain to be measured is polluted; S2, removing rRNA from the total RNA of the unpolluted strain to be measured to obtain mRNA and non-coding RNA; and S3, using the mRNA and the non-coding RNA to construct the transcriptome library to obtain the transcriptome library. In the method, a step of controlling the quality of the total RNA is added to ensure that the RNA sample is not polluted, and a subsequent transcriptome library construction step is carried out to avoid the waste of manpower and financial resources caused by the polluted RNA and perfect the problem of low comparison rate of subsequent sequencing data. Few samples are needed in the verification step, the operation is simple, a result is obtained quickly and accurately, and the verification step has high throughput capacity, so that the verification step can be widely used in the transcriptome library construction step to verify the total RNA to the strain to be measured.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Methods, Compositions, and Kits for Making Targeted Nucleic Acid Libraries
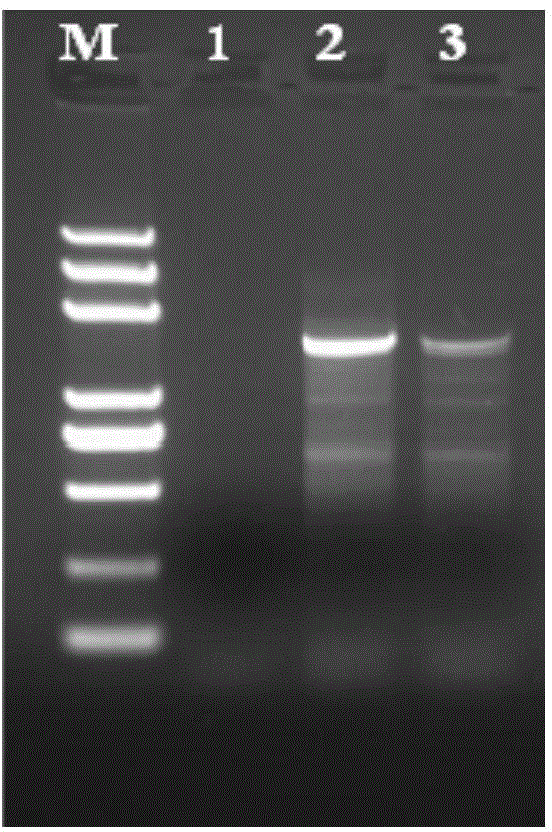
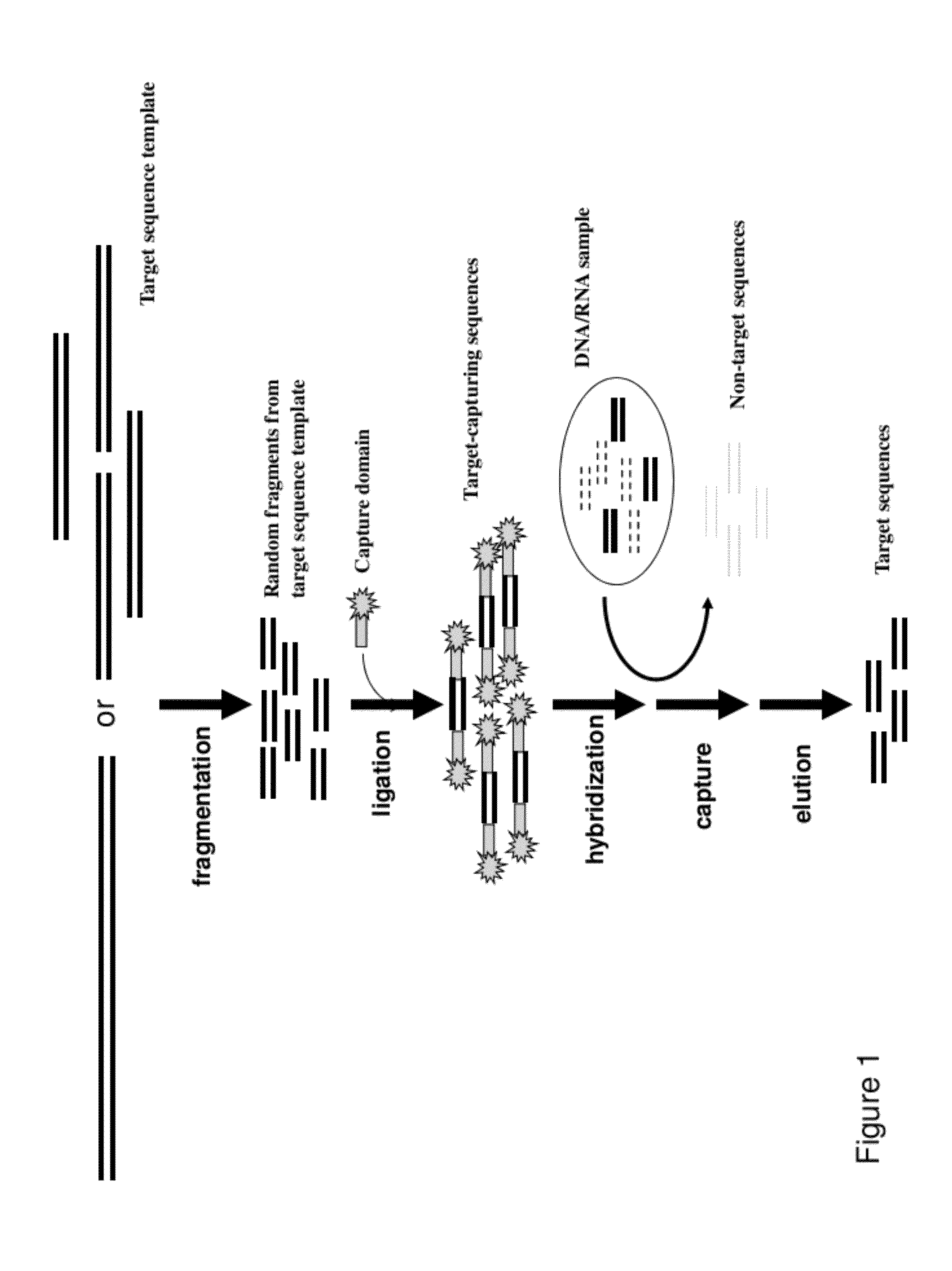
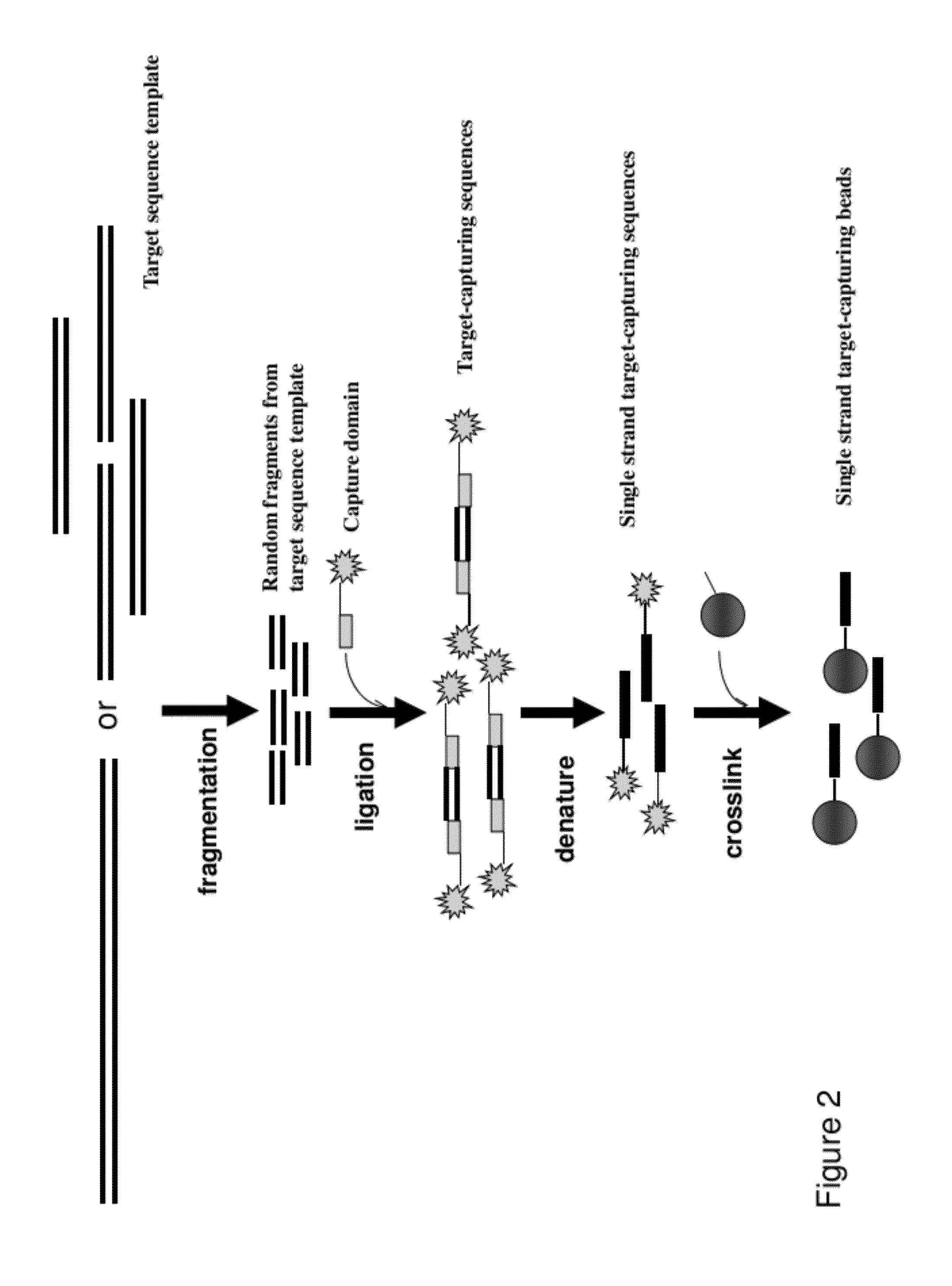
InactiveUS20120258892A1Low costReduce designTransferasesLibrary creationTarget captureGenome resequencing
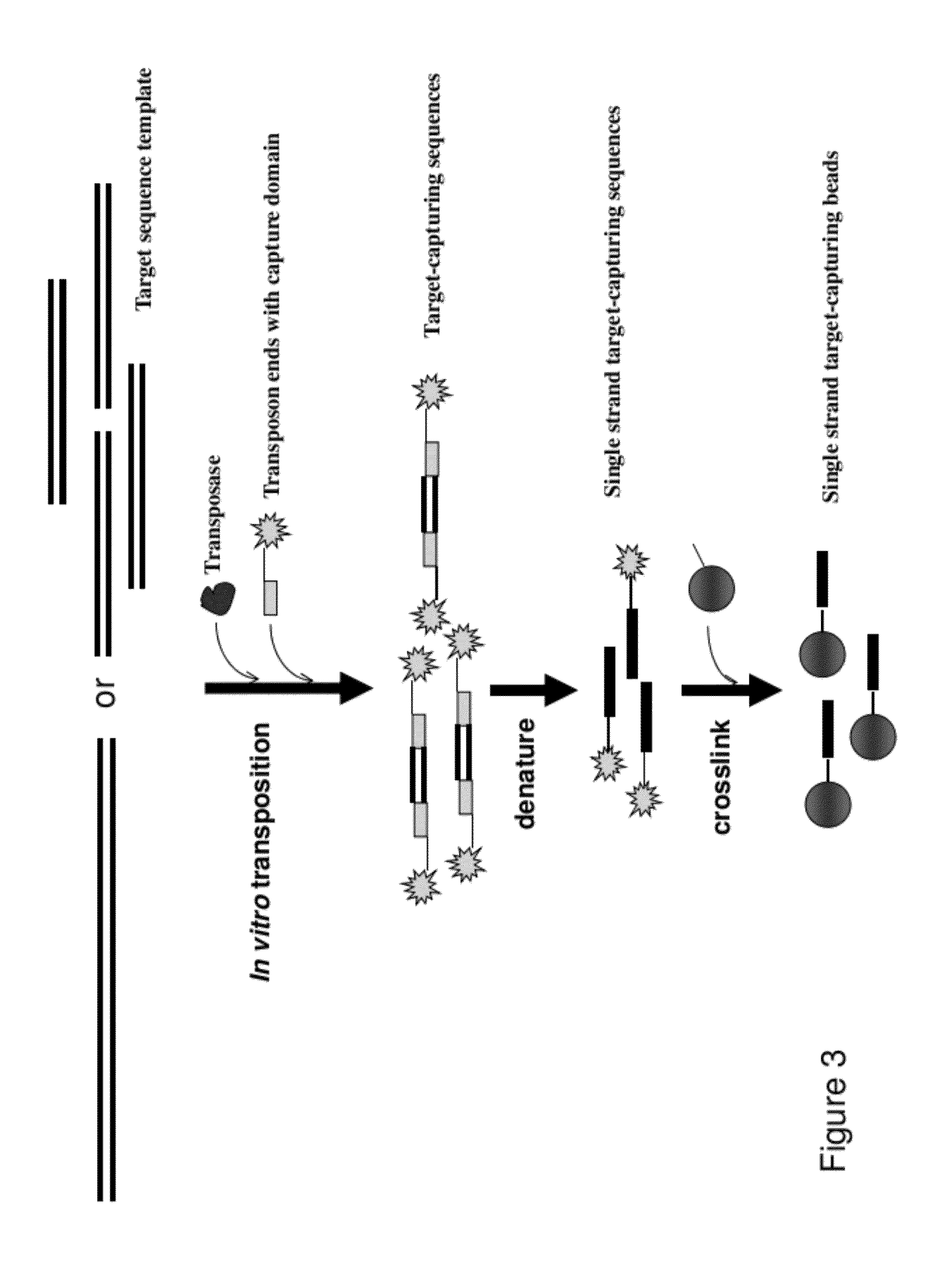
The present invention provides a method and a kit for selecting and enriching target sequences specific for a genomic region of interest or a subset of a transcriptome using a target-capturing sequence library. The target-capturing sequence library comprises random DNA fragments generated from a target sequence template encompassing all the target sequences. The present invention provides an efficient and cost-effective method of target selection for targeted genome resequencing.
Owner:WANG YAN
Method for high-throughput analysis of single cell inclusions by using paired micro-fluidic chip
ActiveCN107012220AWon't interfereEasy to shareMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMetaboliteMicrosphere
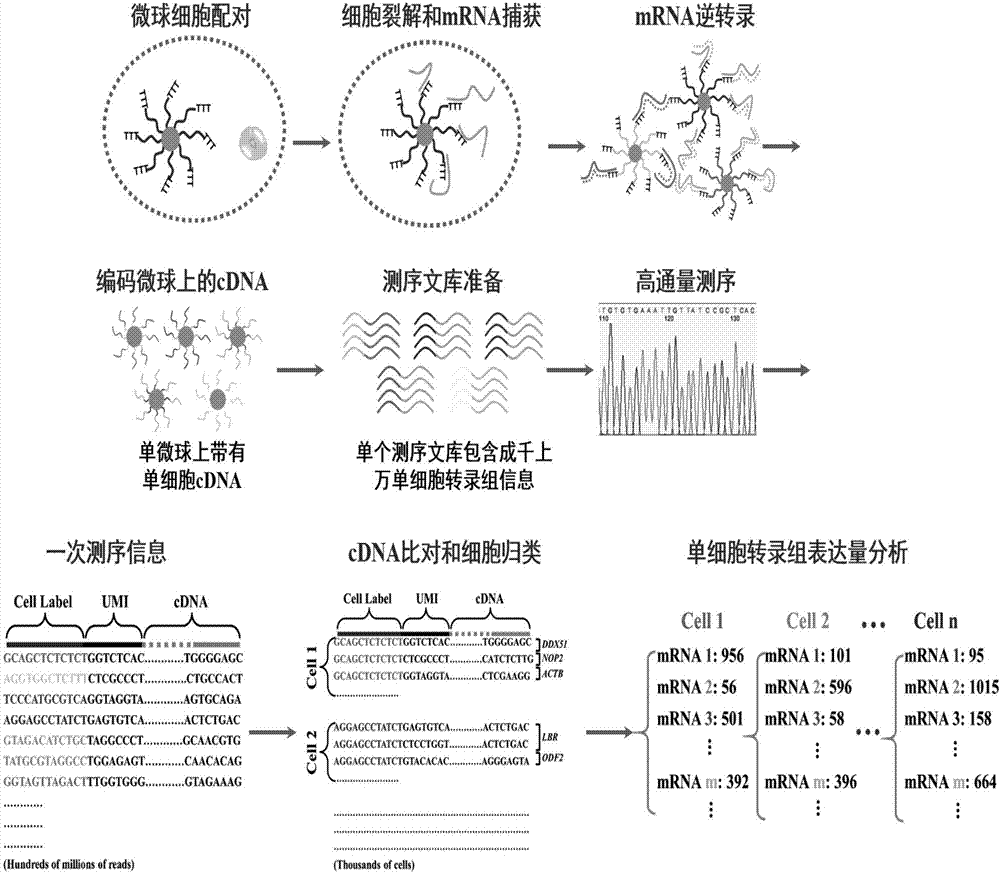
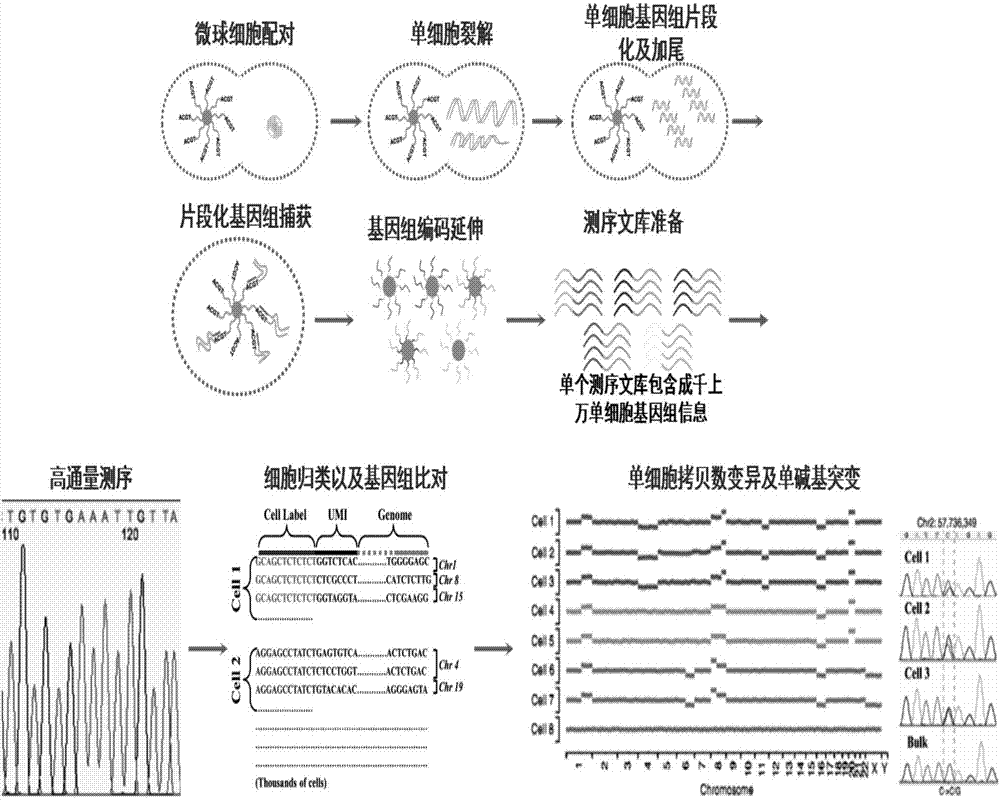
The invention relates to a method for high-throughput analysis of single cell inclusions by using a paired micro-fluidic chip. The paired micro-fluidic chip is the micro-fluidic chip for high-throughput capturing single microspheres / single cells. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out high-throughput pairing capturing on single microspheres / single cells; (b) carrying out parallel control on a pairing unit, for example, isolation, cultivation and pyrolysis of a lot of single cells, and capturing of various inclusions in the single cells; and (c) converting information of the single cell inclusions into DNA sequence information through encoding the microspheres, analyzing a lot of single cell inclusions, such as a transcriptome, a genome, an miRNA, a proteome, a methylated DNA, a metabolite, a lipidosome and phospholipid by adopting a high-throughput sequencing technology and a bioinformatics method. According to the method, the single cell inclusion information can be comprehensively and completely analyzed, and the method has the advantages of high throughput, high accuracy, low cost and wide analyzable target.
Owner:HANGZHOU WEIZHU BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method and computer software product for genomic alignment and assessment of the transcriptome
InactiveUS20050244883A1Reduce quality problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenome alignmentNucleic Acid Probes
In one embodiment of the invention, computerized methods are provided for analyzing transcript sequence clusters by aligning the transcripts with genomic sequences to determine whether a cluster needs to be sub-clustered and whether clusters should be merged. In addition, in some embodiments, transcript sequences are trimmed according to their alignment with their corresponding genomic sequences. The modified clusters and trimmed sequences may be used for nucleic acid probe array design.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
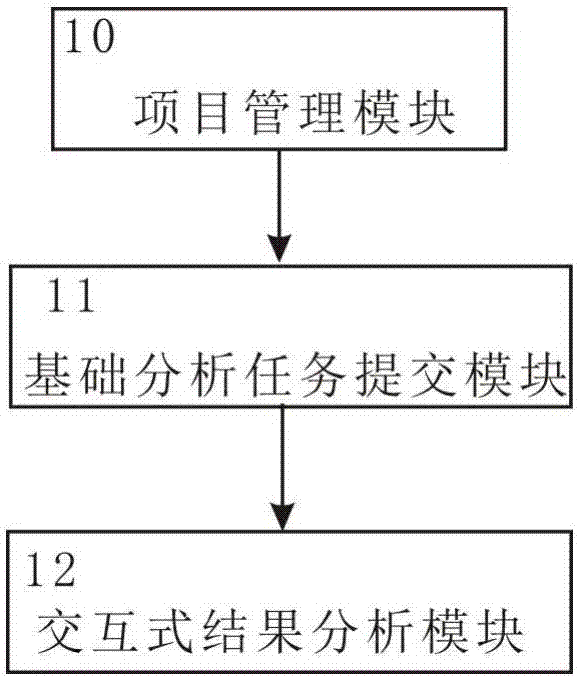
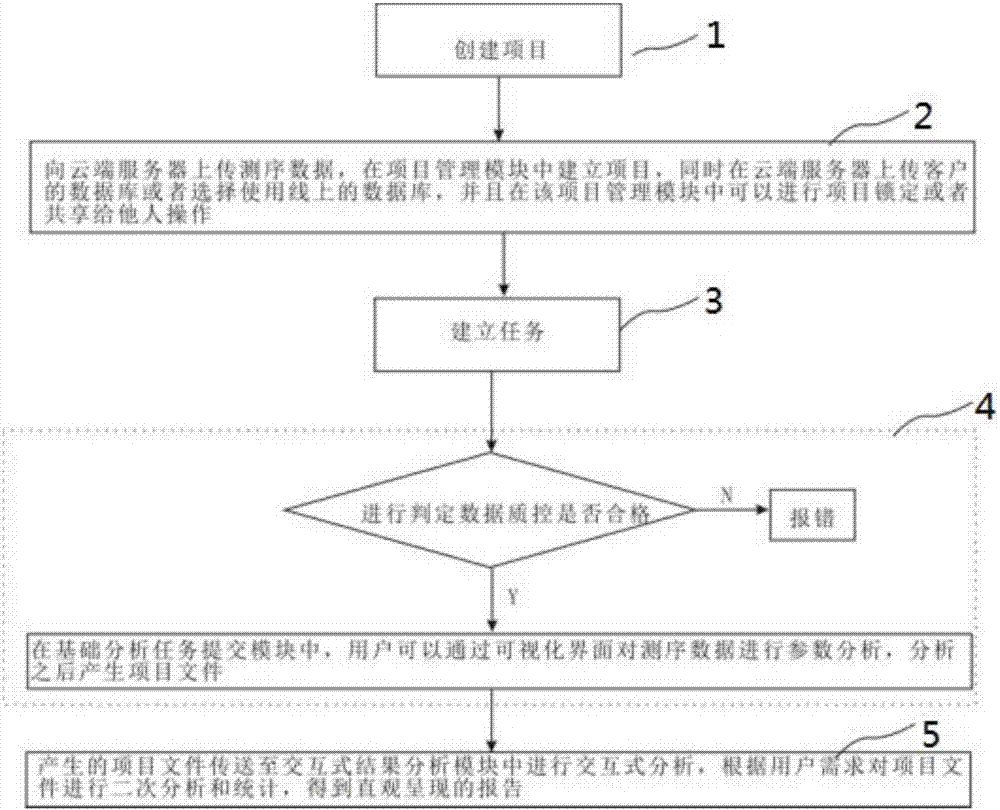
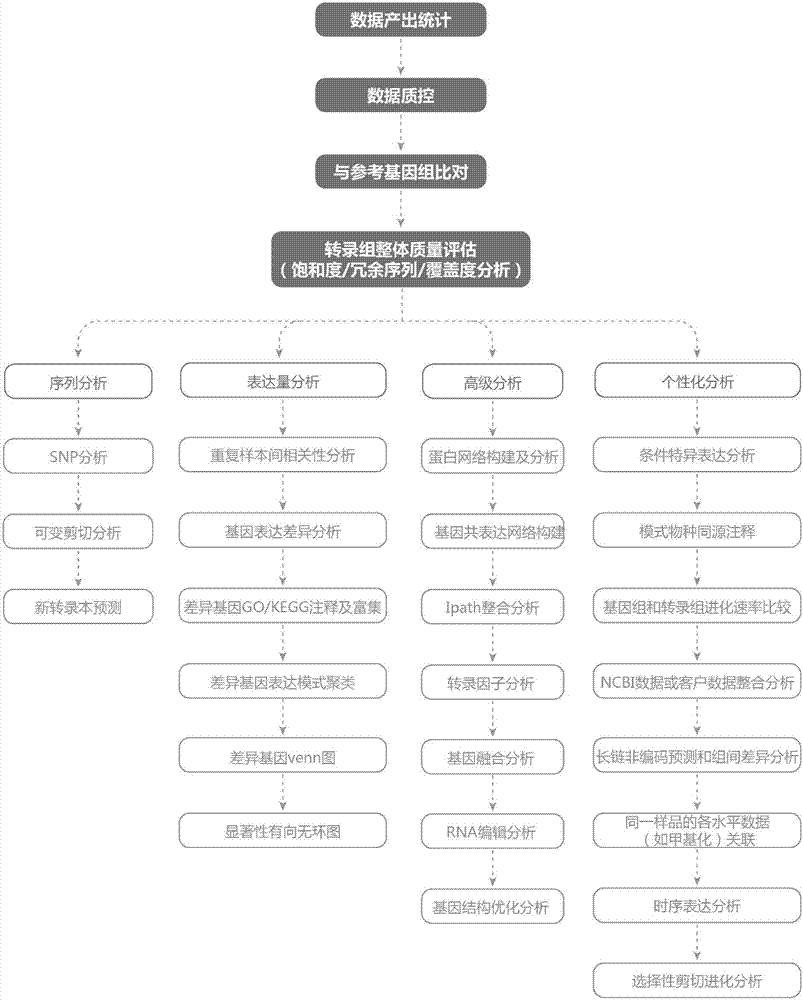
Eukaryotic parameter-free transcriptome interactive analysis system and method based on cloud computing platform
InactiveCN107391963AMeet huge demandMeet needsData visualisationHybridisationProject managementData quality
The invention discloses a eukaryotic parameter-free transcriptome interactive analysis system and method based on a cloud computing platform. The system comprises a project management module, a basic analysis task submission module and an interactive result analysis module. The method comprises the steps that firstly, sequencing data is uploaded to a local cluster server, a project is built in the project management module, meanwhile, a database of a client is uploaded to the local cluster server or an online database is selected, and project locking operation or the operation of sharing with others can be conducted in the project management module; then, in the basic analysis task submission module, a user can conduct parameter analysis on the sequencing data through a visual interface, and a project file is generated after analysis; before the analysis, whether the data quality control is qualified or not is judged first, and if yes, the parameter analysis is conducted; if not, the sequencing data is directly returned, and an error is reported; the generated project file is transferred to the interactive result analysis module for interactive analysis, and a visually presented report is obtained.
Owner:上海桑格信息技术有限公司
Transcriptome Transfer Produces Cellular Phenotype Conversion
The present invention includes methods for effecting phenotype conversion in a cell by transfecting the cell with phenotype-converting nucleic acid. Expression of the nucleic acids results in a phenotype conversion in the transfected cell. Preferably the phenotype-converting nucleic acid is a transcriptome, and more preferably an mRNA transcriptome.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
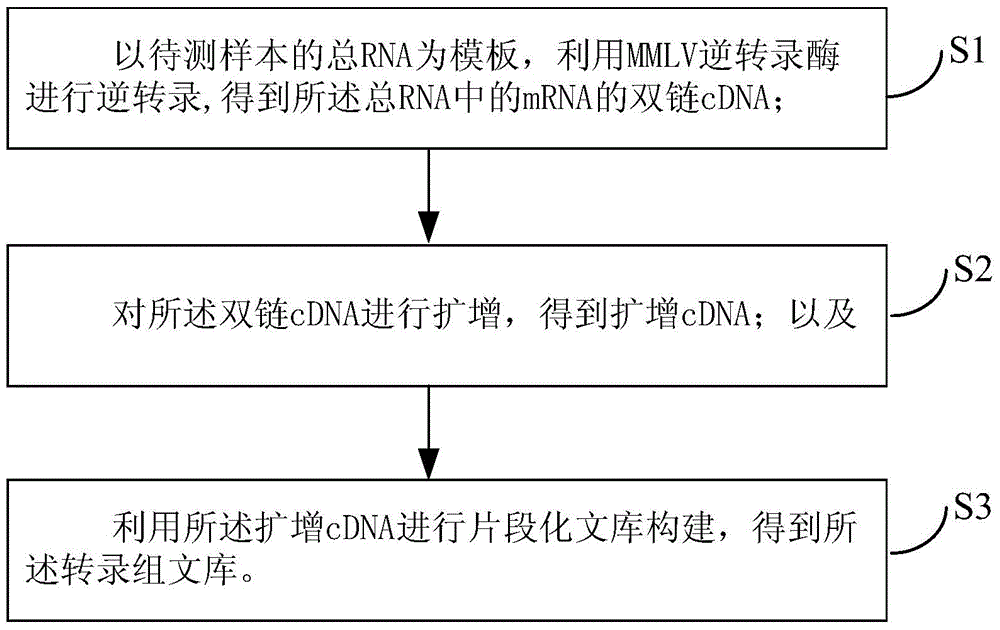
Transcriptome library and construction method thereof
InactiveCN105002569AThe build was successfully implementedImplement the buildNucleotide librariesLibrary creationTotal rnaReverse transcriptase
The invention provides a transcriptome library and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: total RNA of a sample to be detected is adopted as a template; reverse transcription is carried out with MMLV reverse transcriptase, such that double-stranded cDNA of the mRNA in the total RNA is obtained; the double-stranded cDNA is amplified, such that amplified cDNA is obtained; and the amplified cDNA is used in fragmented library construction, such that the transcriptome library is obtained. According to the invention, mRNA in the total RNA is reverse-transcribed into full-length fragment double-stranded cDNA with the MMLV reverse transcriptase, and the double-stranded cDNA is amplified, such that a DNA amount needed by library construction is reached, and subsequent segmented library construction can be realized smoothly. With the method, a complete full-length transcript can be enriched; cDNA can be amplified with high sensitivity and no preference; and the fullness of the transcripts of original mRNA can be maintained, such that the construction of trace sample transcriptome library can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
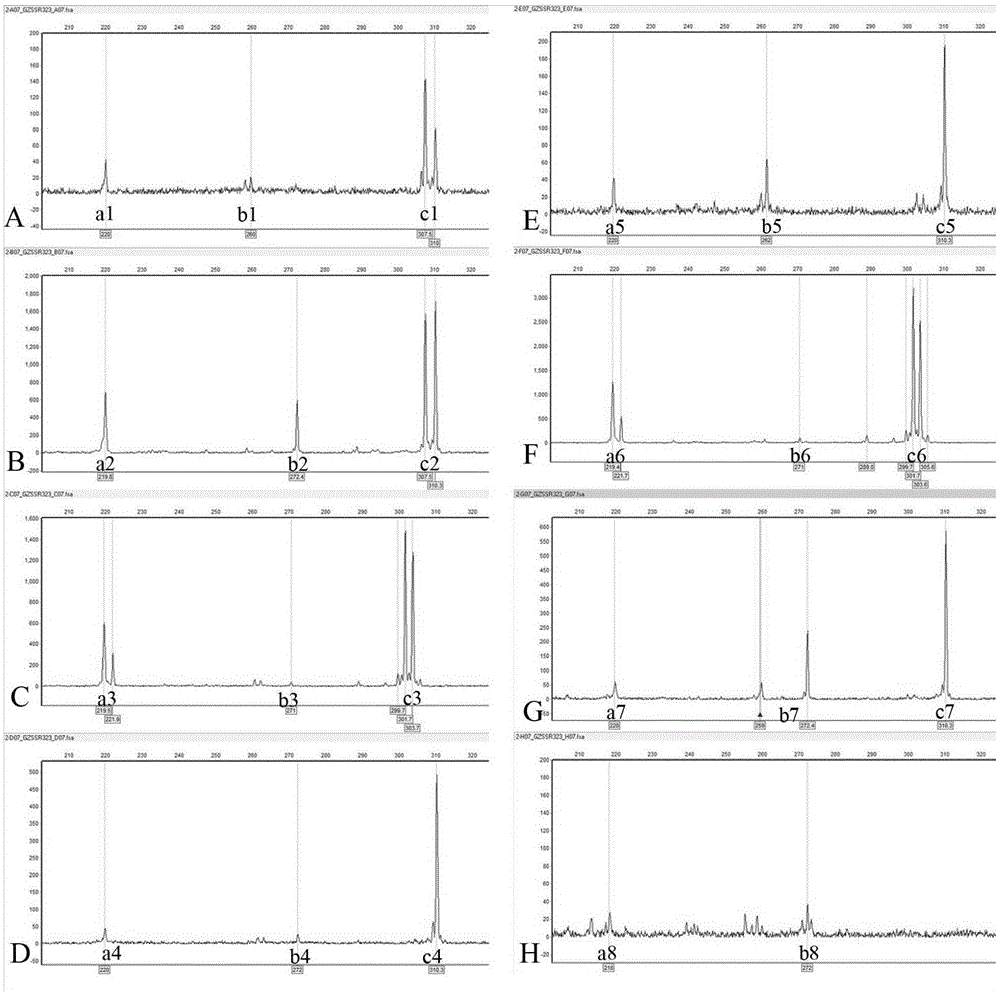
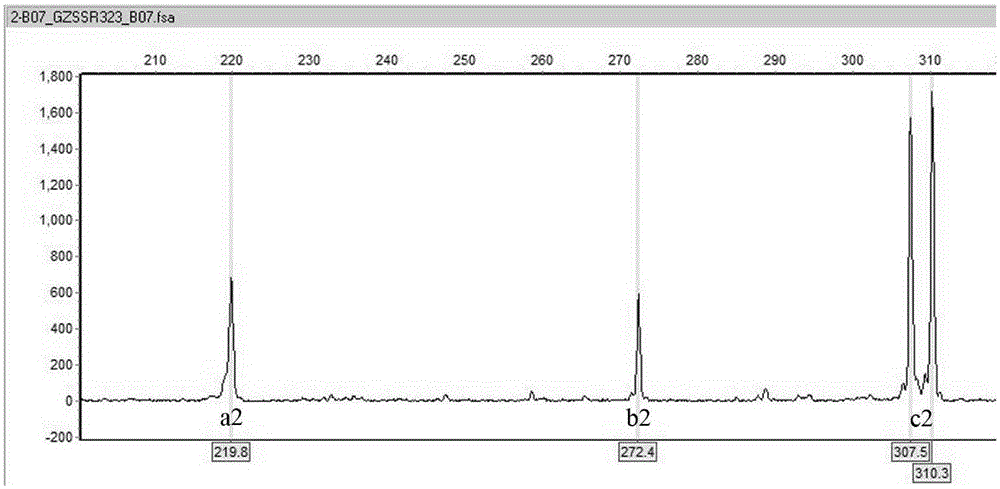
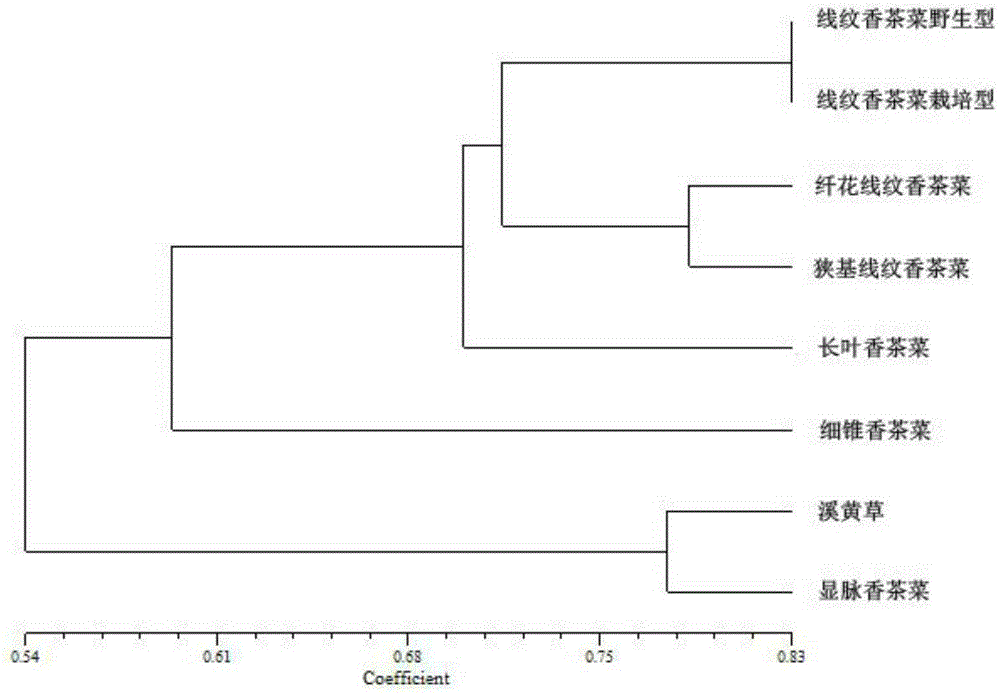
Method utilizing EST-SSR marker for identification of traditional Chinese medicine serrate rabdosia herb varieties and primers
InactiveCN105349651AReliable resultsGood for dry sample analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMedicinal herbsHerb medicine
The present invention relates to a method utilizing an EST-SSR marker for identification of traditional Chinese medicine serrate rabdosia herb varieties , the method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomic DNA of a sample to be tested; (2) using the DNA extracted by the step (1) as a template, and using a serrate rabdosia herb transcriptome sequence-based EST-SSR core primer group for PCR amplification; and (3) typing amplified products on the basis of sequencing; the EST-SSR core primer group comprises at least 10 pairs of primers of the 24 pairs of primers, each pair of the primers comprise an upstream primer and a downstream primer, and the nucleotide sequences are SEQ ID NO. 1-SEQ ID NO.48. The method can achieve effective and rapid identification of common serrate rabdosia herb medicine-based source varieties and adulterants, and is accurate and reliable in results, simple, easy, high in timeliness, and suitable for the serrate rabdosia herb medicinal material variety identification and variety protection in the market and the production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
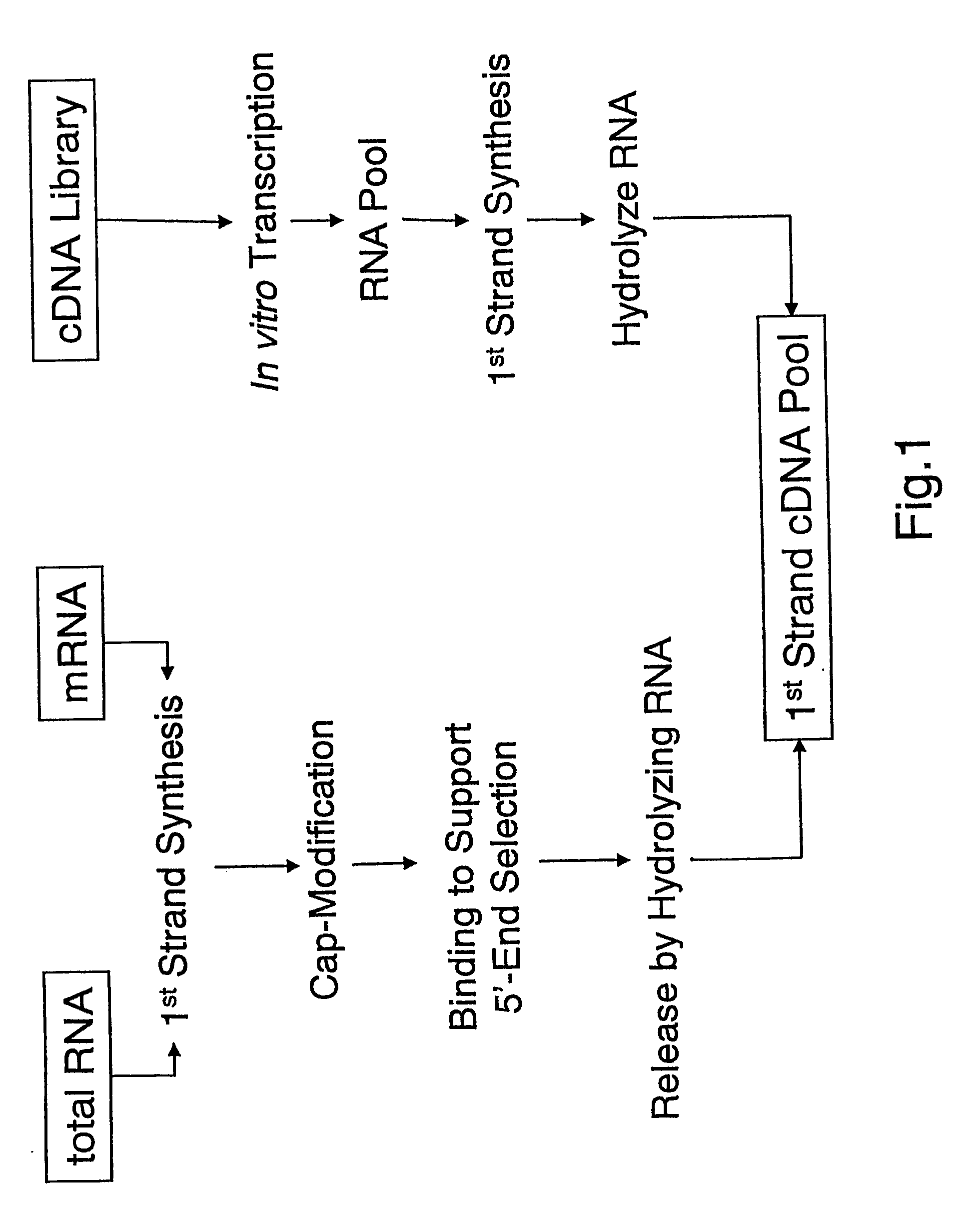
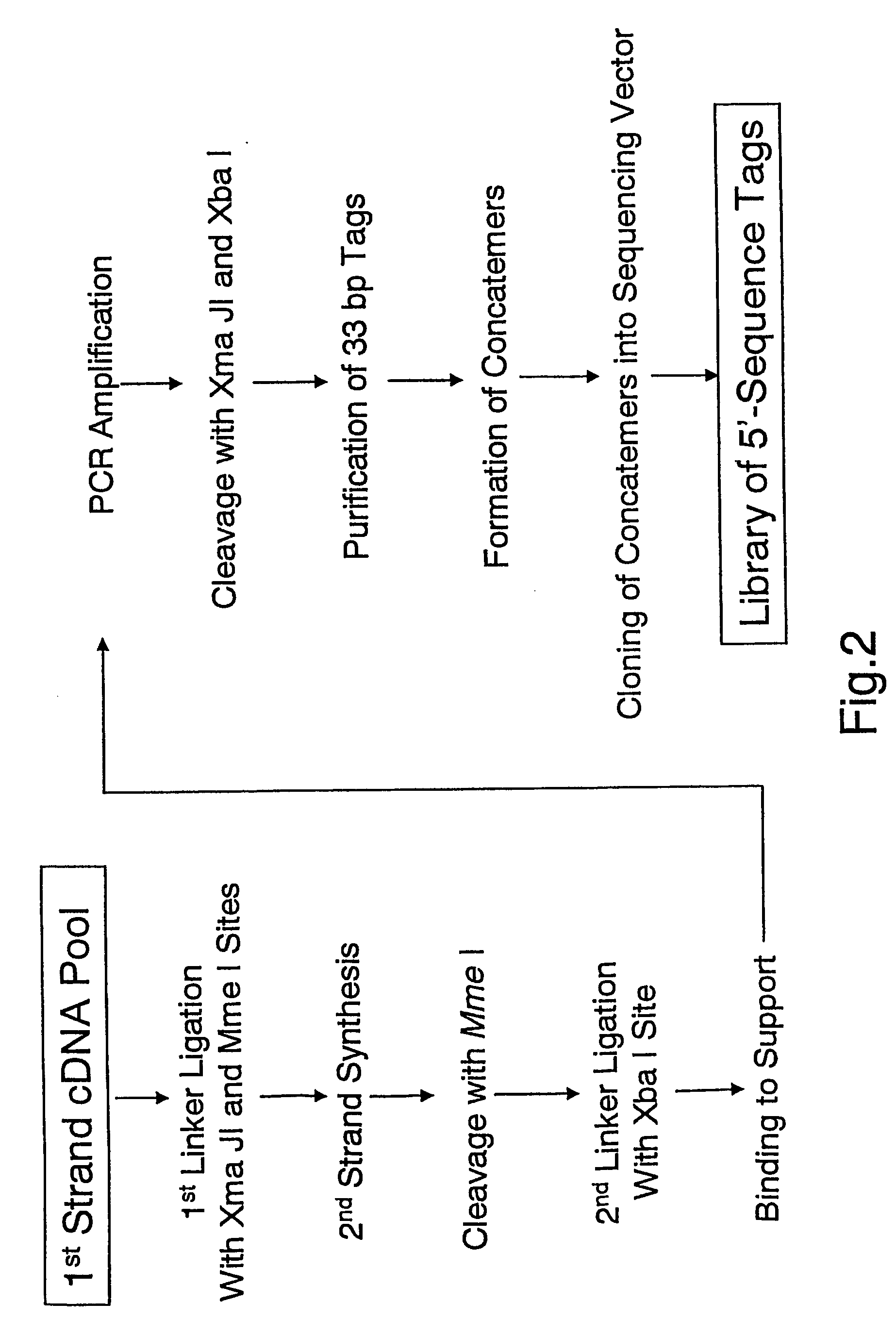
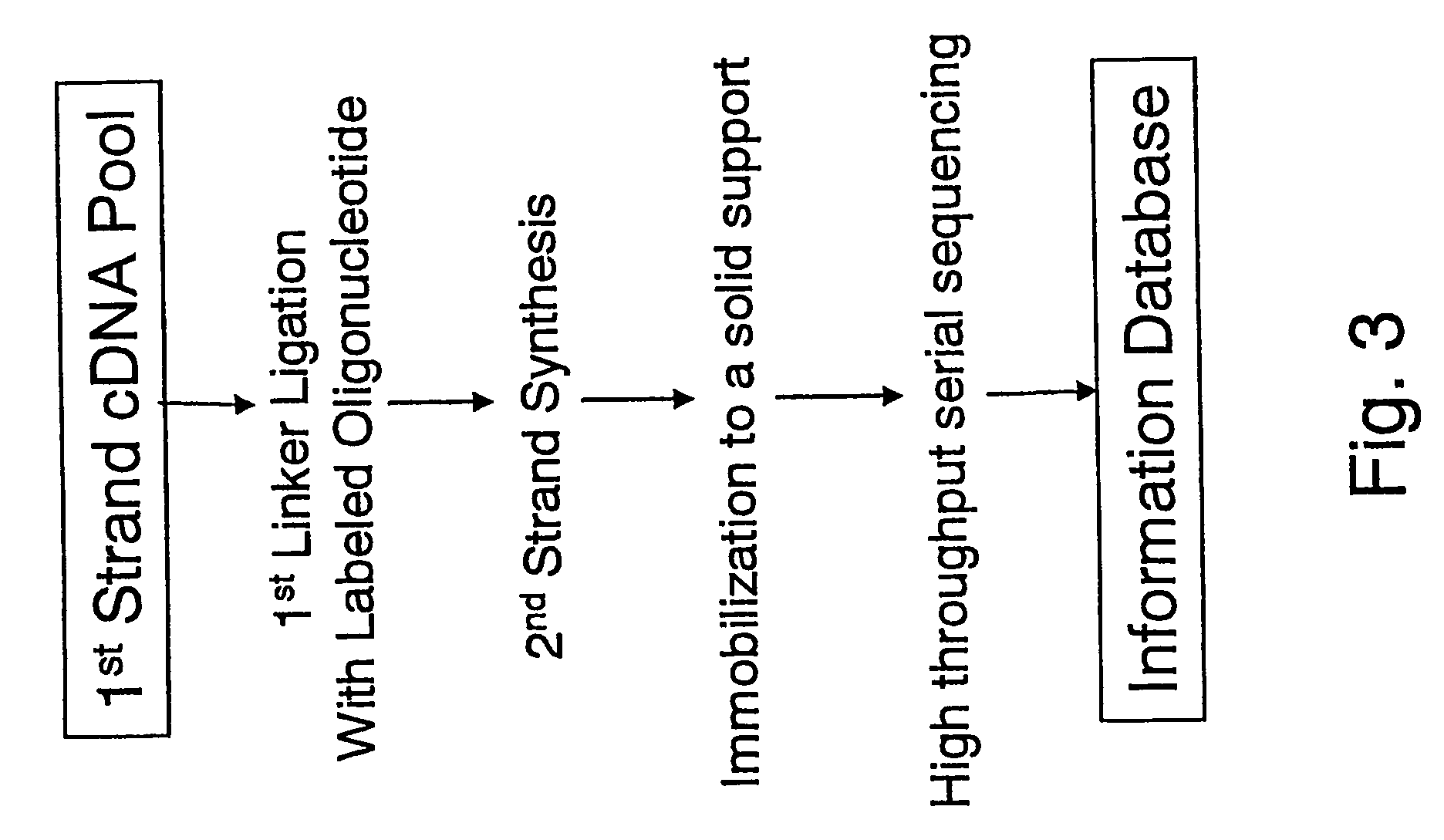
Method of utilizing the 5'end of transcribed nucleic acid regions for cloning and analysis
InactiveUS20050250100A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationIndividual analysisBiological materials
A method is disclosed for obtaining the 5′ends of transcribed regions from a plurality of nucleic acid fragments obtained from biological materials or synthetic pools. DNA fragments encoding the 5′ends are enriched for their individual analysis or for the analysis of concatemers thereof. The sequence information derived from 5′ ends can be used for characterization and cloning of the transcriptome.
Owner:RIKEN +1
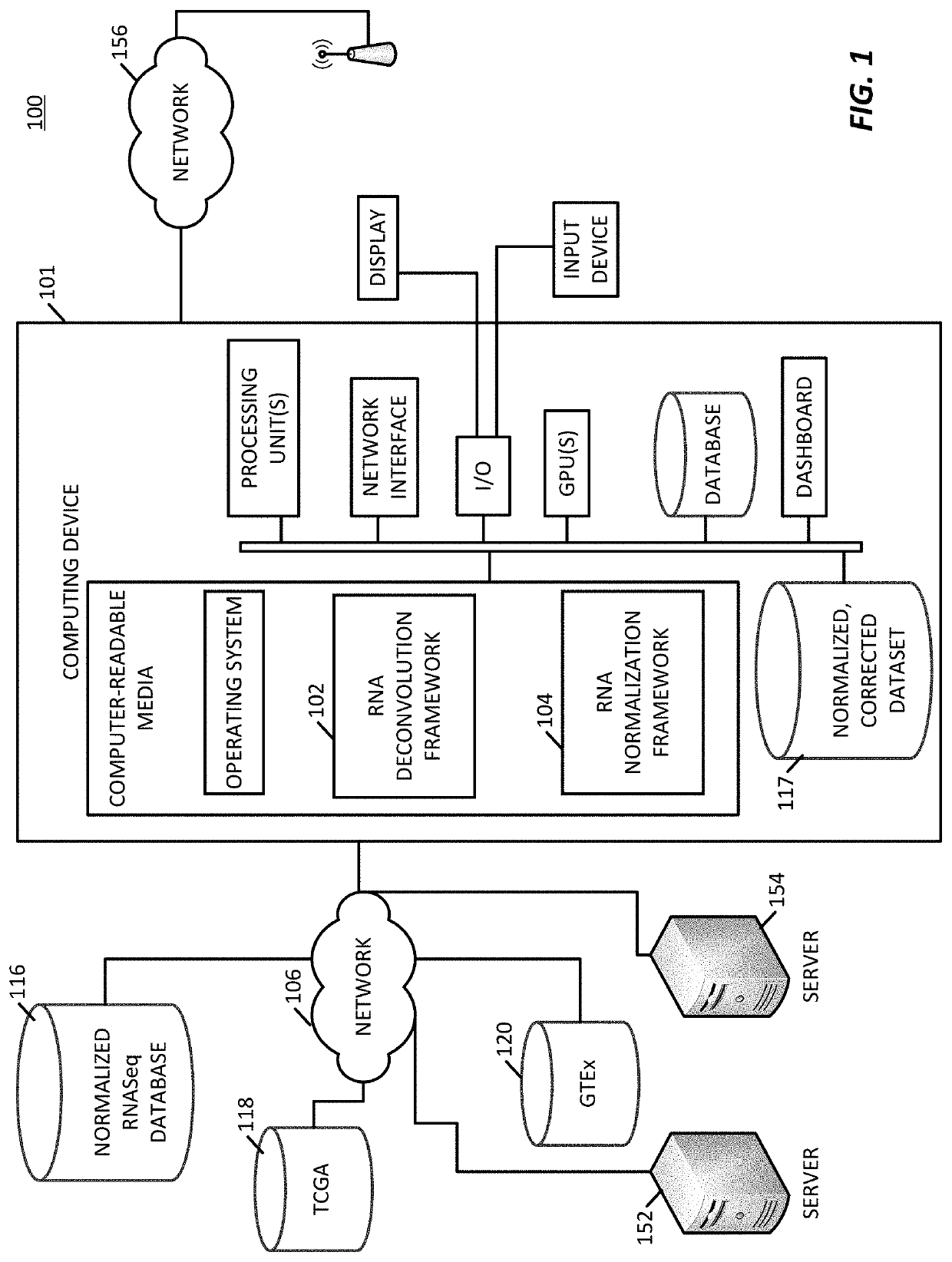
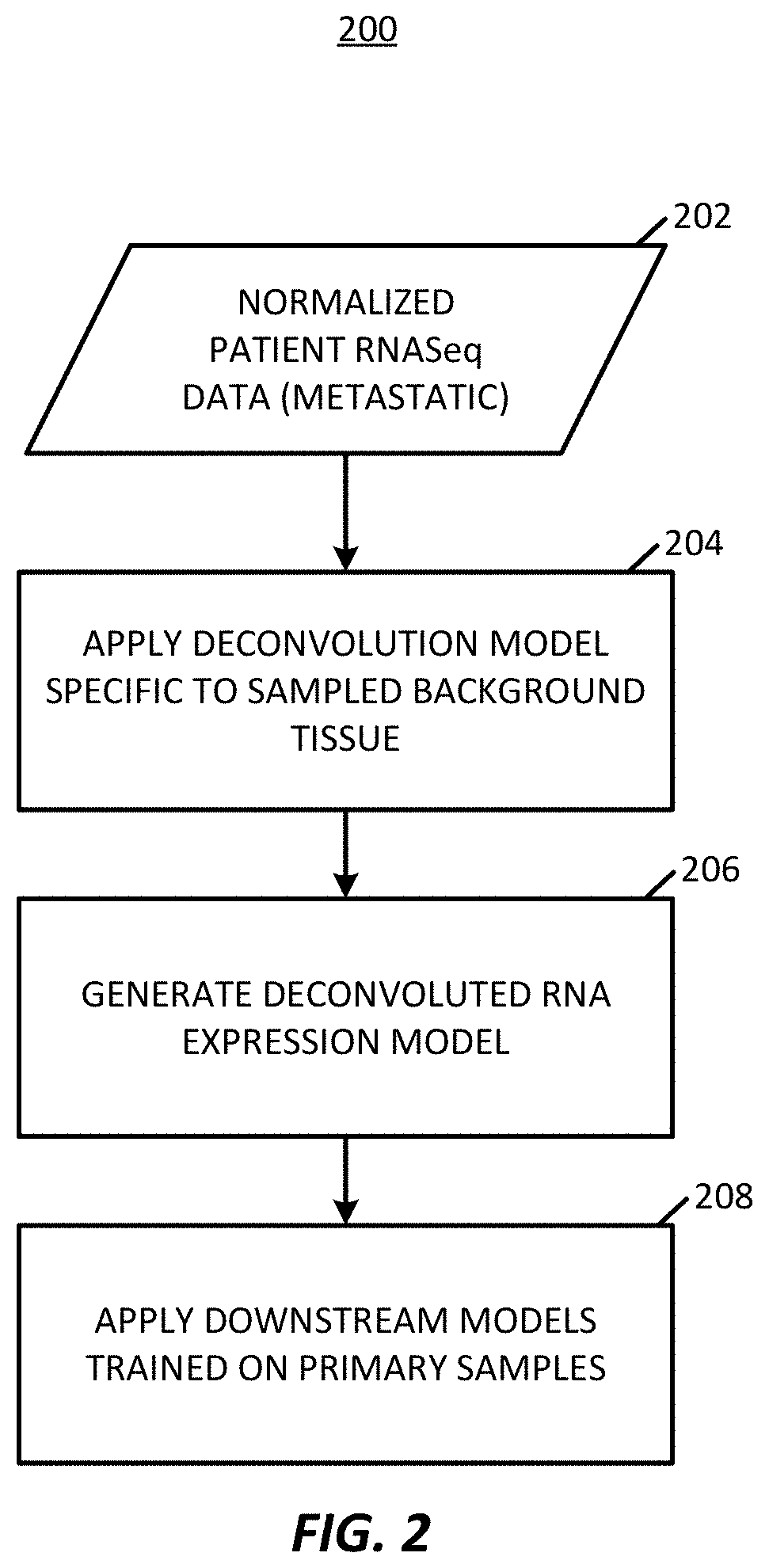
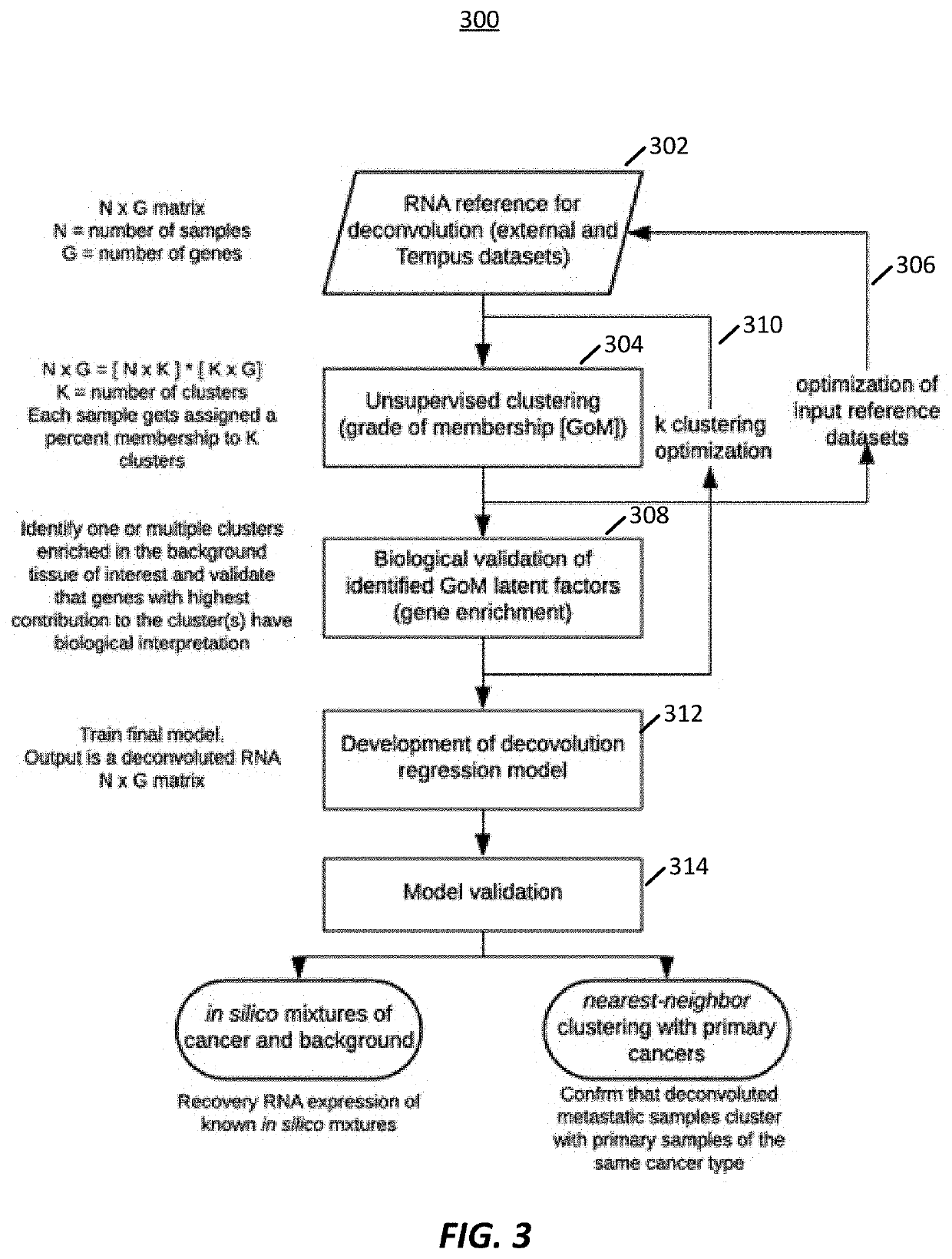
Transcriptome deconvolution of metastatic tissue samples
PendingUS20200210852A1Improve responseIncrease resistanceMathematical modelsKernel methodsTissue sampleExpression gene
A platform for transcriptome deconvolution of gene expression data is provided and may be used in assessing metastatic cancer samples. The deconvolution is performed using an unsupervised clustering technique, such as grade of membership, that allows for samples to be assigned to multiple clusters during a training process. A deconvolution gene expression model is generated as a result and is used for accurate assess of metastases in subsequent samples.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com