Patents
Literature
40 results about "Cellular phenotype" patented technology
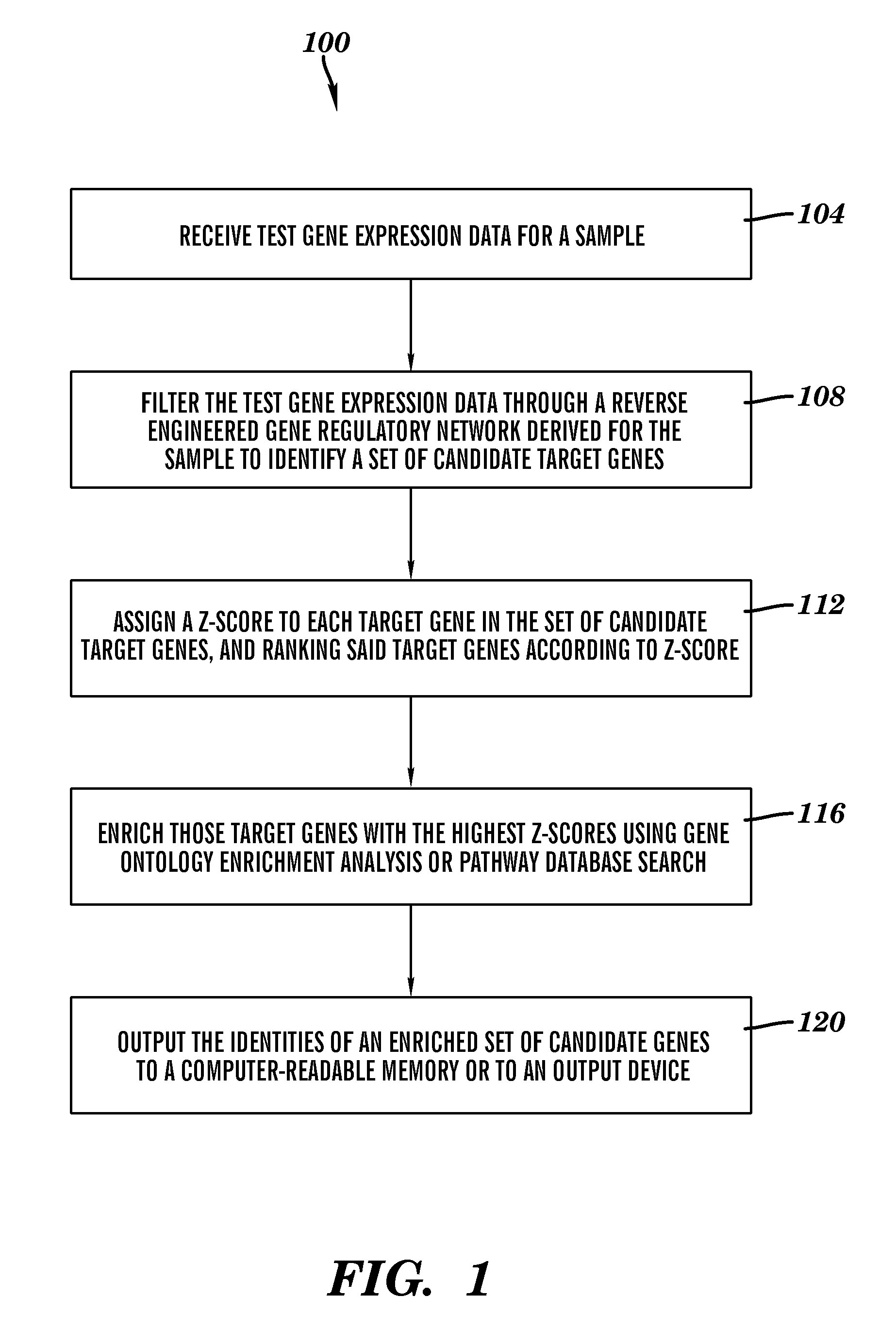
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular phenotype. Cellular phenotype is the conglomerate of multiple cellular processes involving gene and protein expression that result in the elaboration of a cell's particular morphology and function.
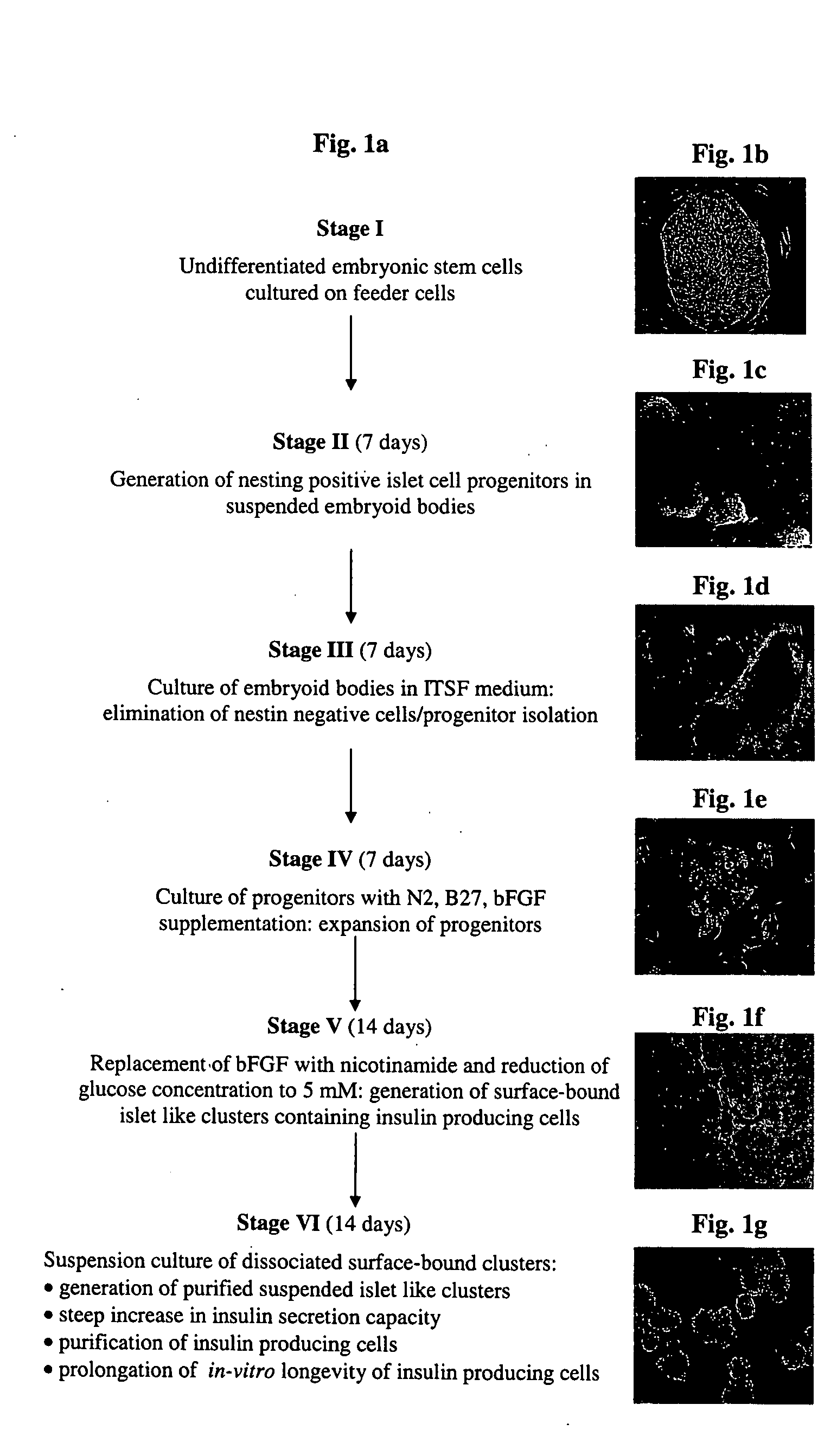
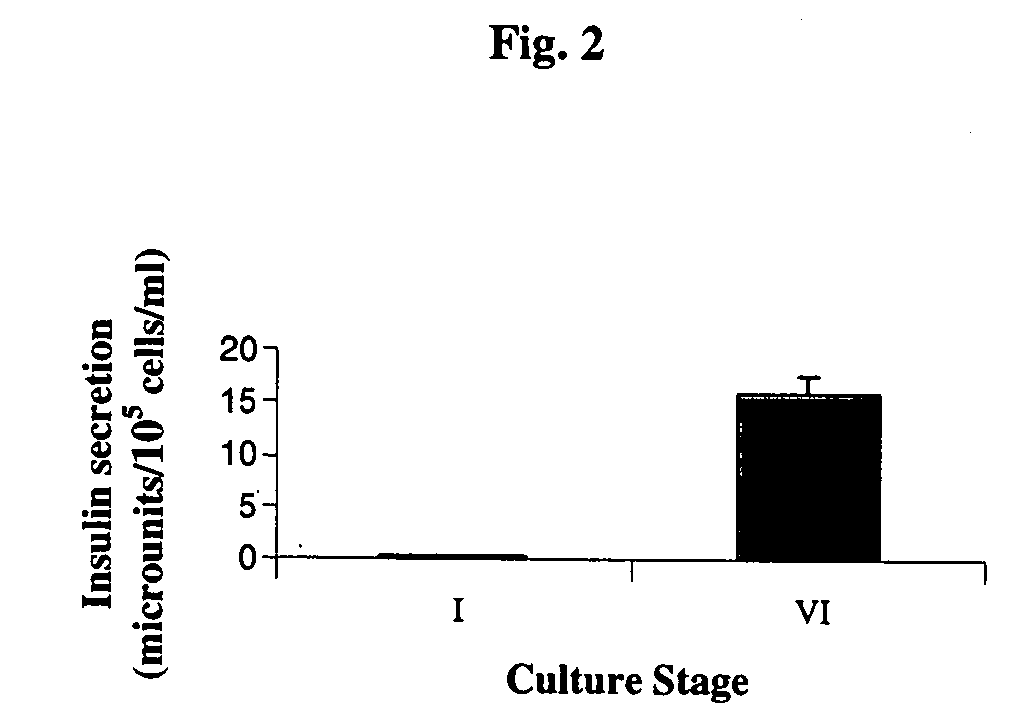
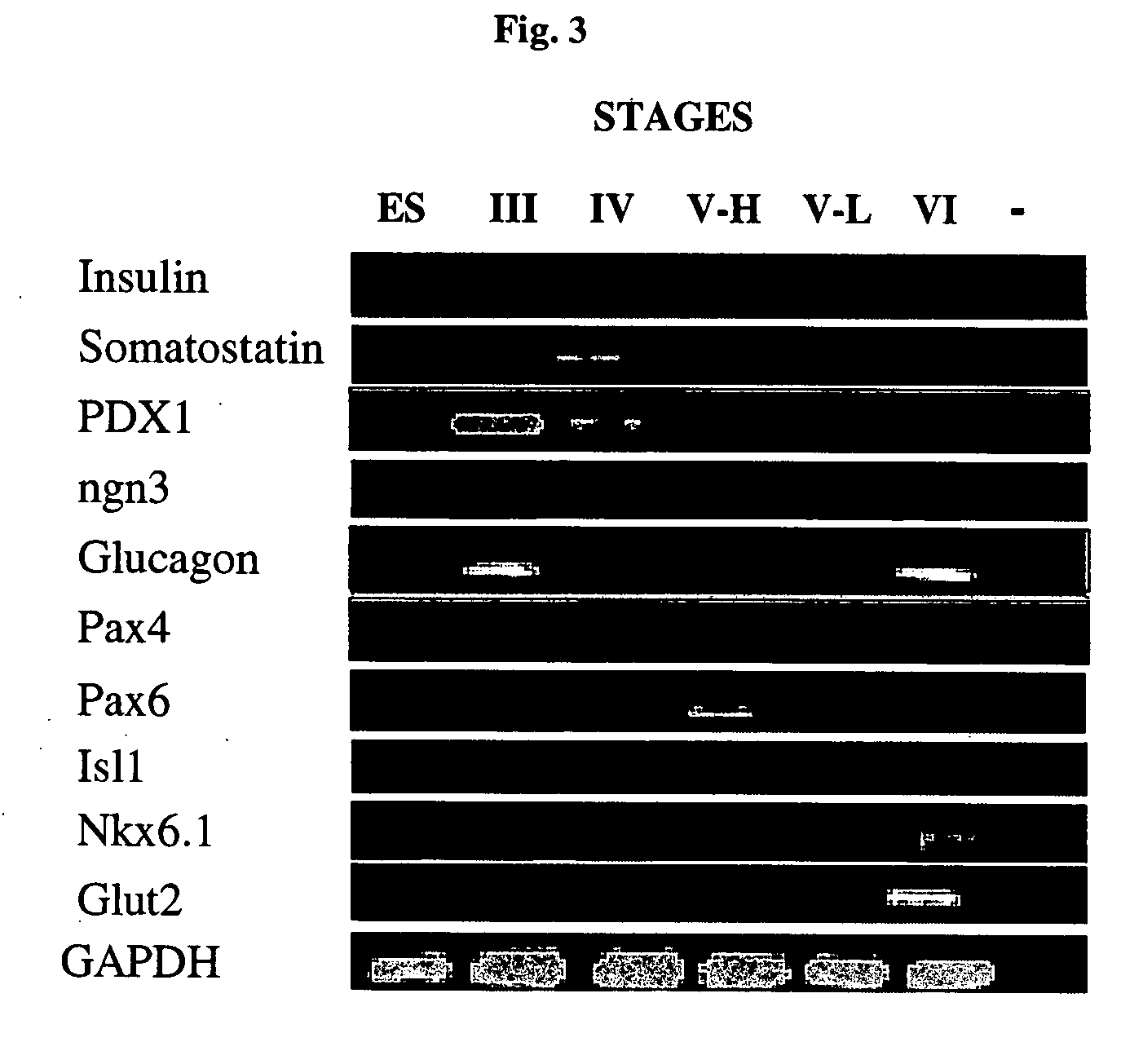
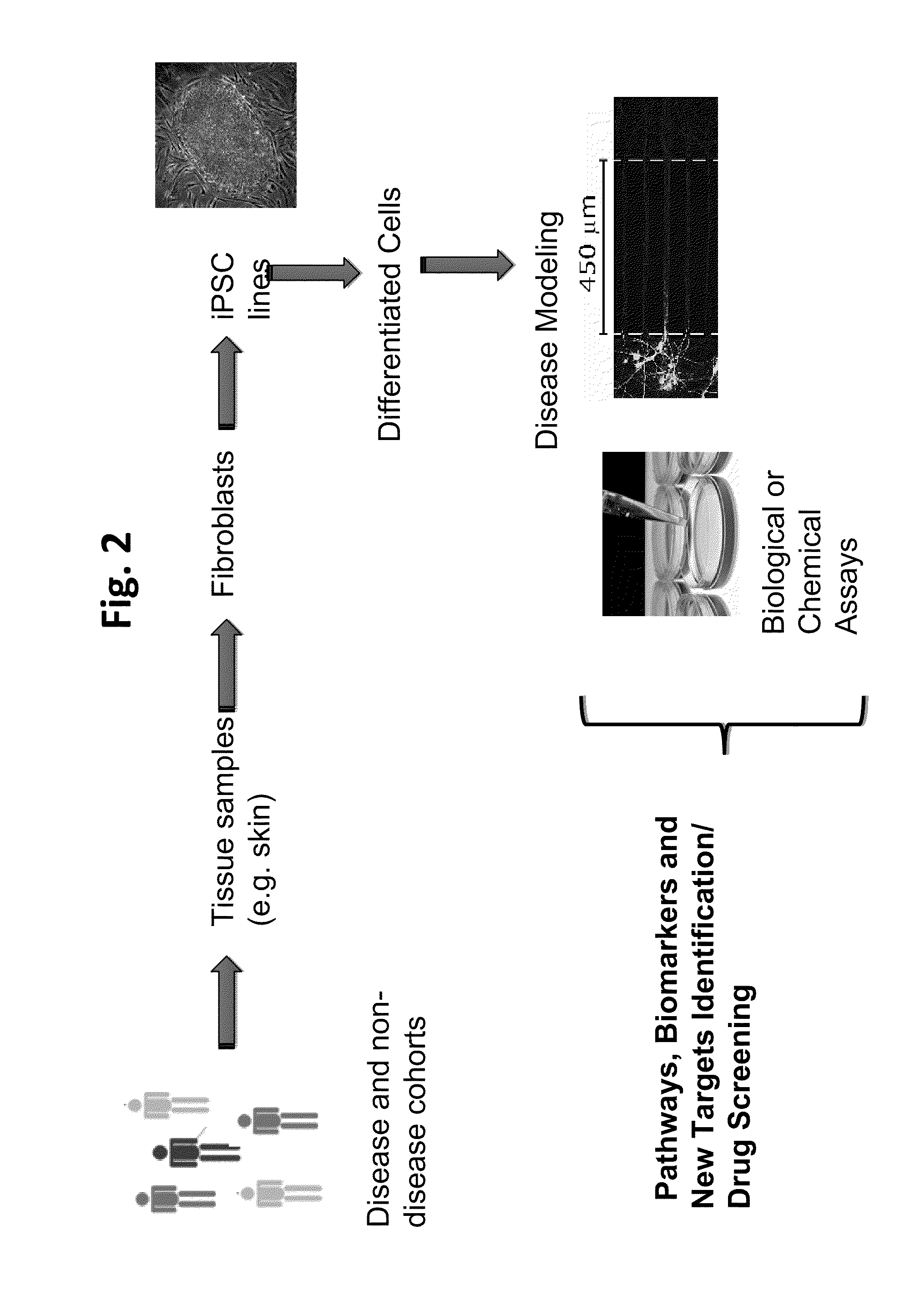
Cultured human pancreatic islets, and uses thereof
A method of generating cells capable of secreting insulin is disclosed. The method comprises subjecting mammalian embryonic stem cells to set of culturing conditions suitable for differentiation of at least a portion thereof into cells displaying at least one characteristic associated with a pancreatic islet cell progenitor phenotype, and subjecting such differentiated cells to a set of culturing conditions suitable for formation of surface bound cell clusters including insulin producing cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
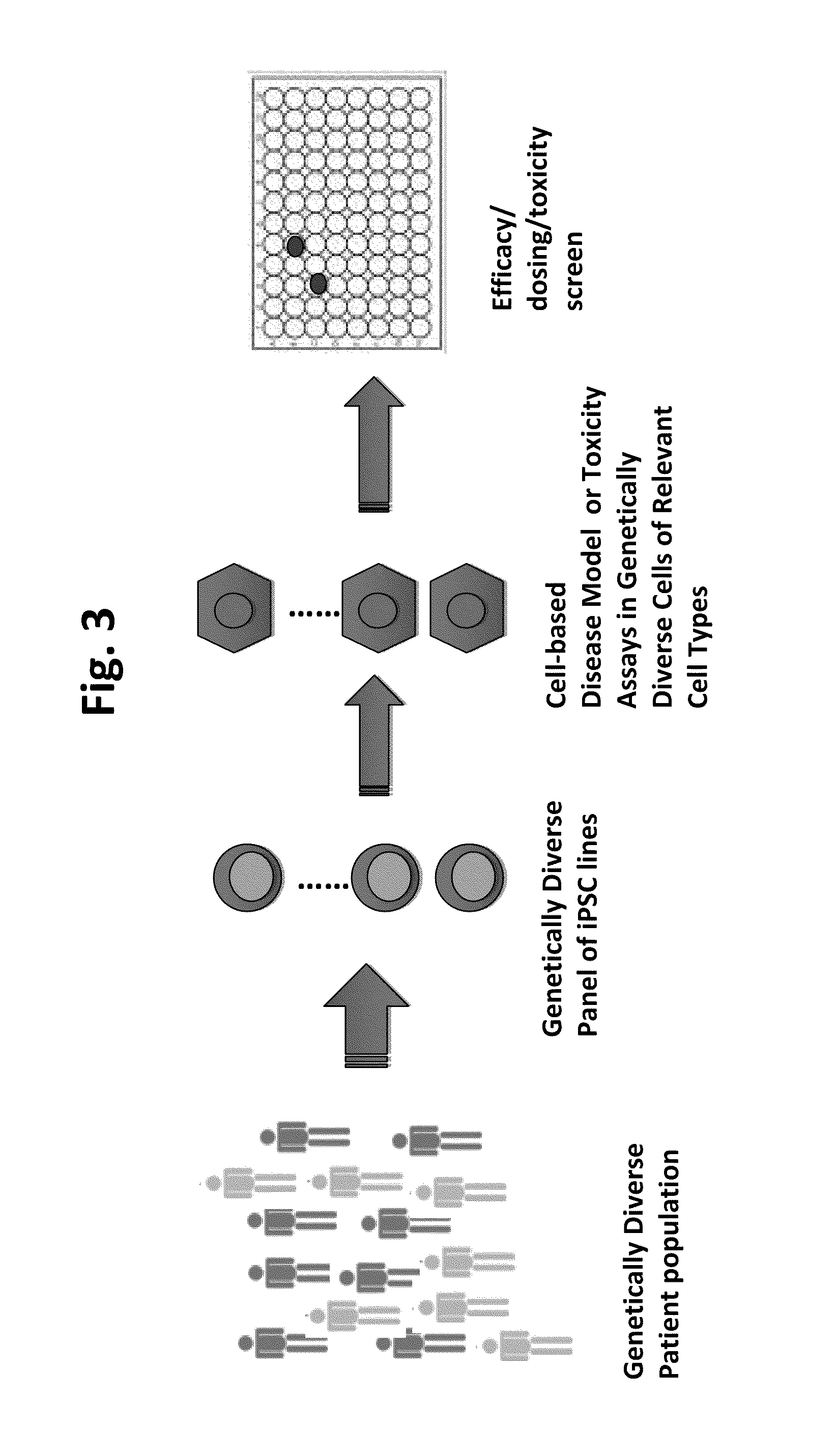
Methods and platforms for drug discovery
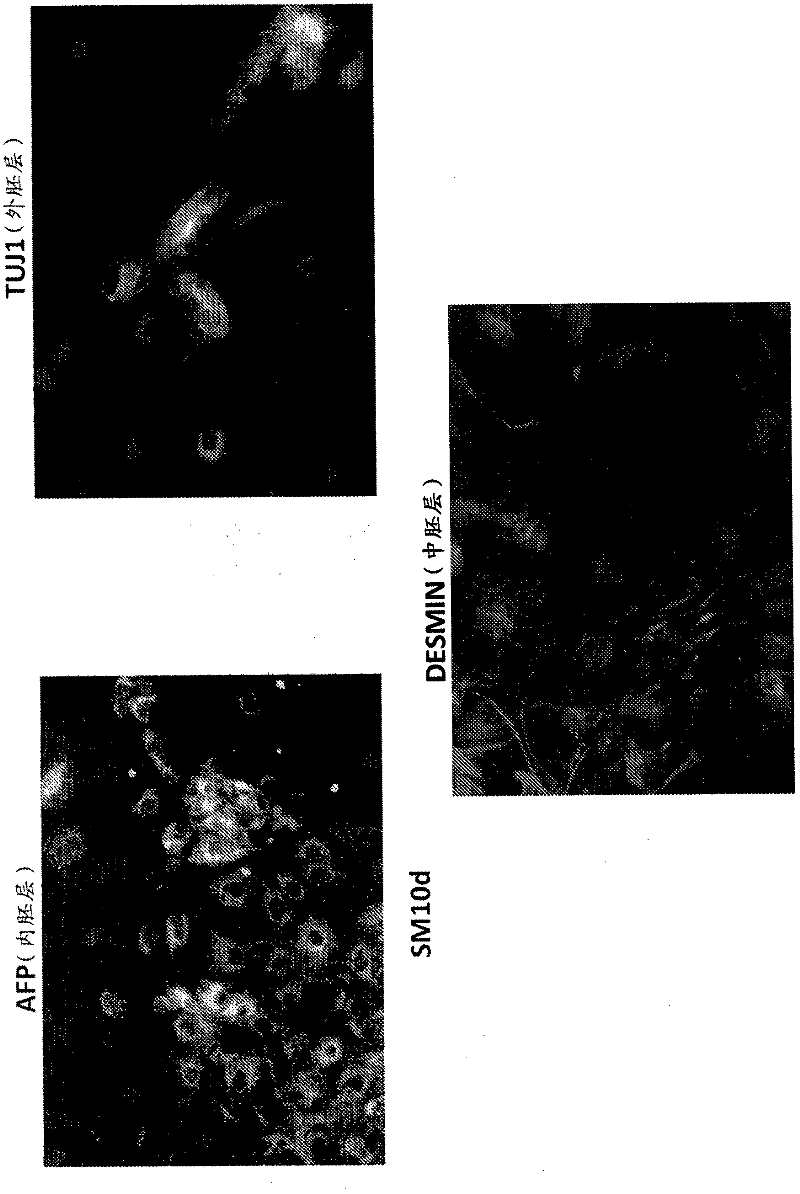
The present invention involves methods for identifying an agent that corrects a phenotype associated with a health condition or a predisposition for a health condition. The invention also involves methods for identifying a diagnostic cellular phenotype, determining the risk of a health condition in a subject, methods for reducing the risk of drug toxicity in a human subject, and methods for identifying a candidate gene that contributes to a human disease. The invention also discloses human induced pluripotent stem cell lines.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
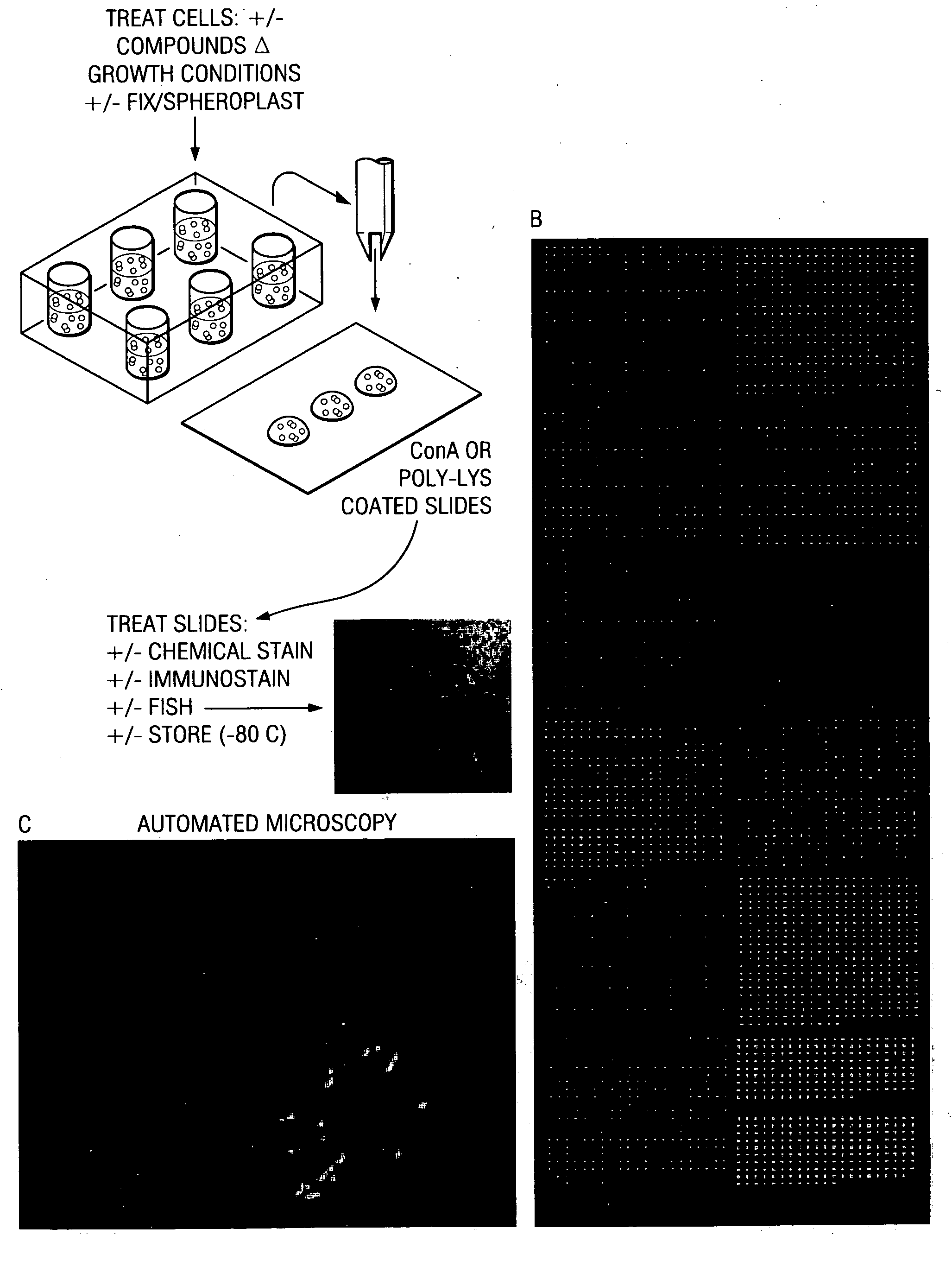
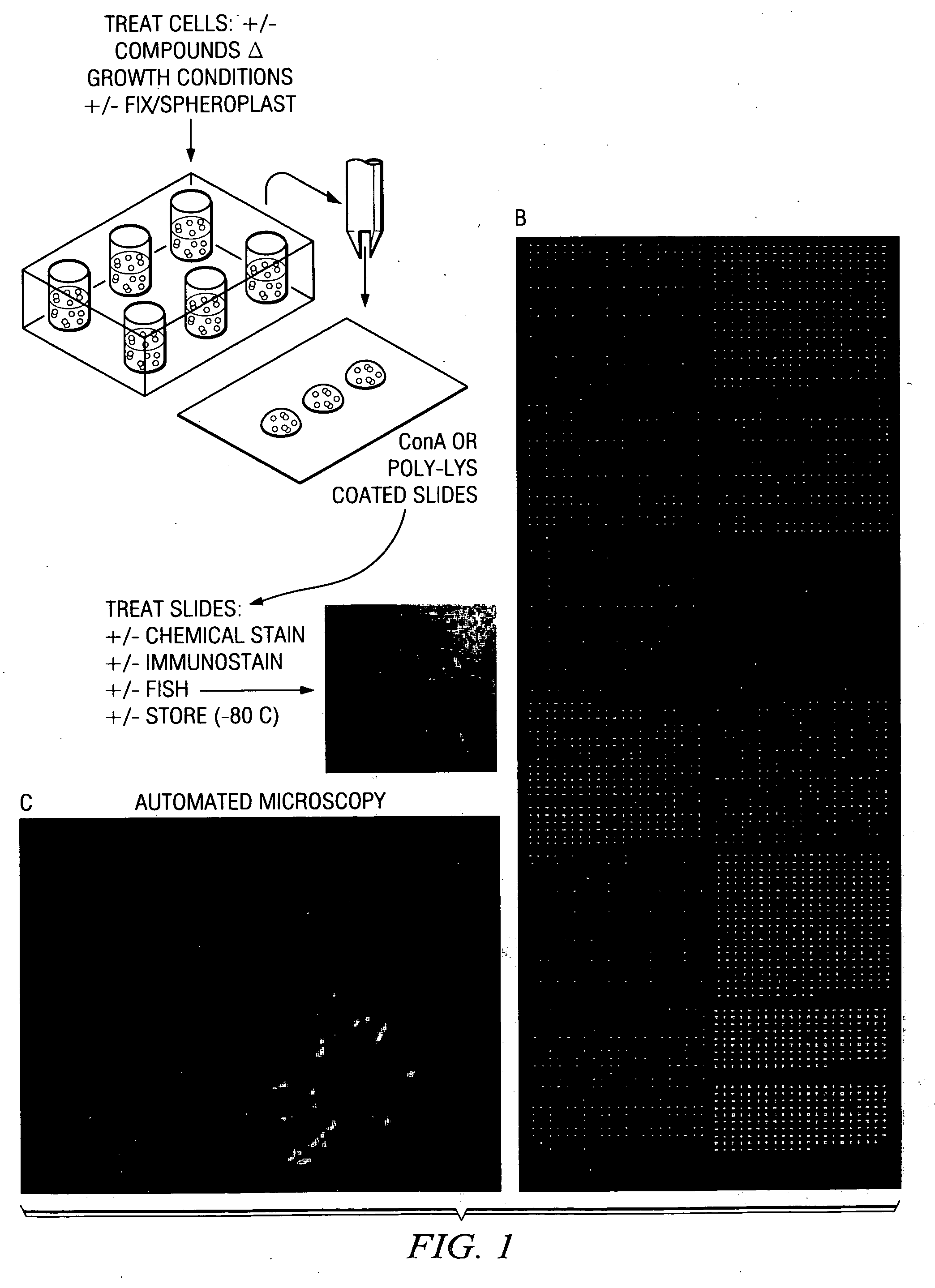
Cell microarray for profiling of cellular phenotypes and gene function
InactiveUS20060160169A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell featureCellular phenotype
The present invention includes compositions, methods and systems for analyzing one or more cell characteristics including the steps of depositing one or more spots on a substrate that include one or more cells from a strain collection, contacting the one or more cells with one or more agents and evaluating optically effect of the agent on the one or more cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Co-culture compositions and methods
Co-culture compositions and methods are described for identifying agents that modulate a cellular phenotype, particularly of neurons or pancreatic beta cells are provided herein, where the methods include co-culturing differentiated cells, wherein at least one of the cell-types are derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells from a subject having or predisposed to a neurodegenerative or metabolic disorder. Co-culture compositions of differentiated cells from two different human subjects are also described.
Owner:IPIERIAN
Transcriptome Transfer Produces Cellular Phenotype Conversion
The present invention includes methods for effecting phenotype conversion in a cell by transfecting the cell with phenotype-converting nucleic acid. Expression of the nucleic acids results in a phenotype conversion in the transfected cell. Preferably the phenotype-converting nucleic acid is a transcriptome, and more preferably an mRNA transcriptome.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
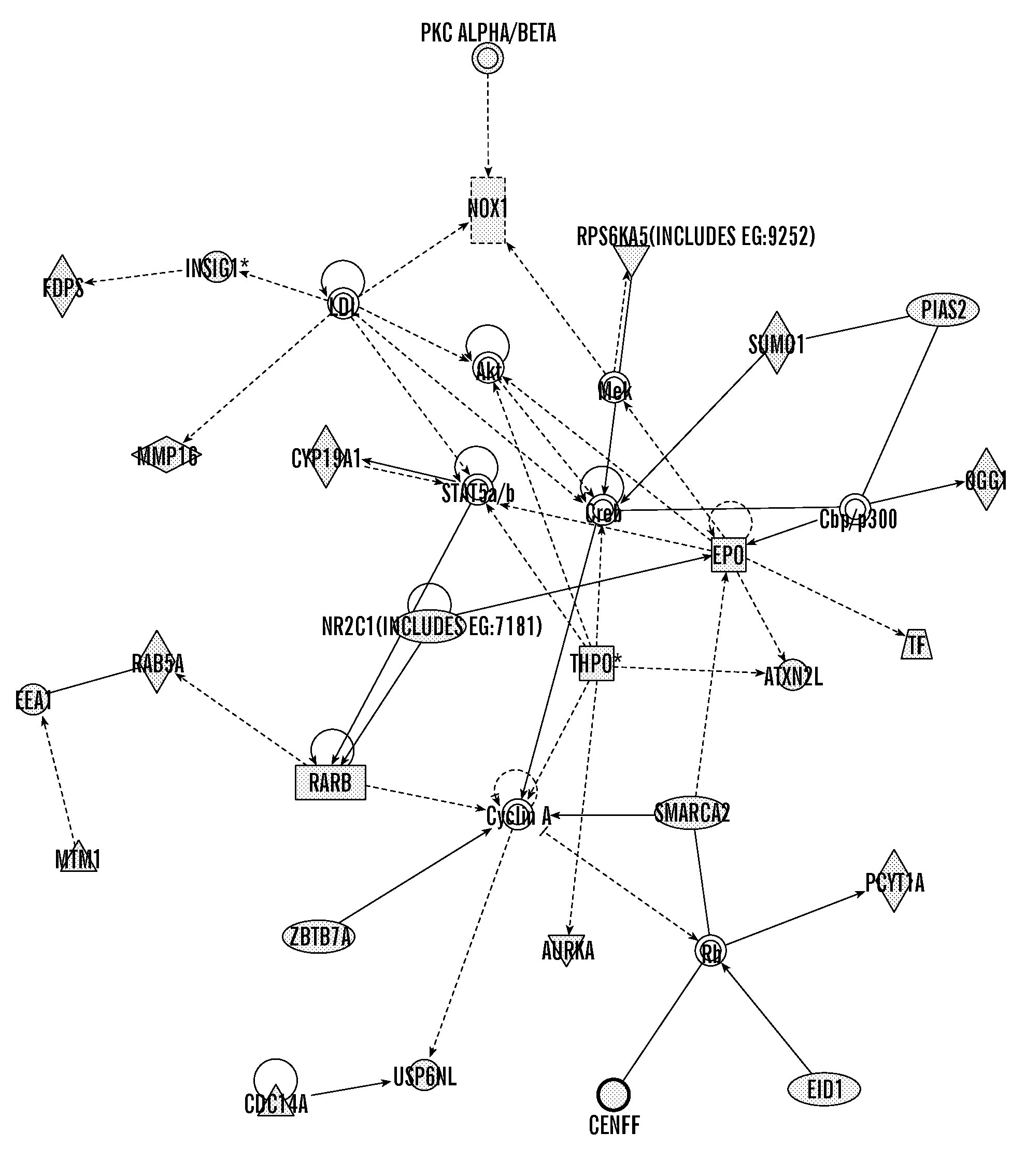
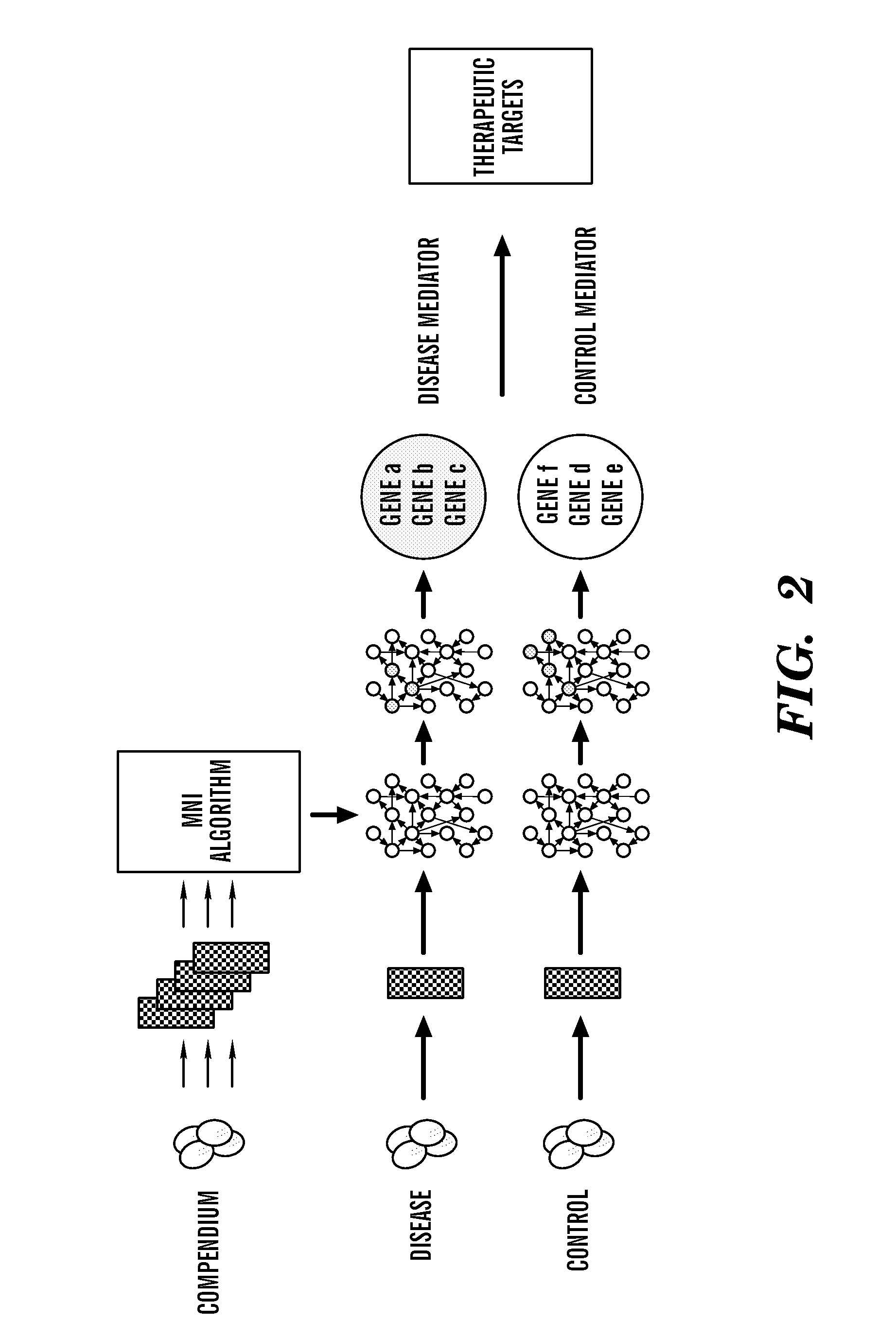
Network biology approach for identifying targets for combination therapies
InactiveUS20110119259A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsDigital data processing detailsSystems biologySide effectDrug compound
Described herein is a network biology approach useful for the identification of multiple therapeutic targets, which can be targeted simultaneously using an agent (or a plurality of agents) to modulate cellular phenotypes, or in combination with pharmaceutical compounds to improve drug sensitivity and / or reduce drug doses to maintain efficacy while minimizing side effects. The preferred approach disclosed herein relies on first identifying the mediators of a condition of interest, and second, selecting gene combinations that are in competing / parallel pathways as targets for combination therapy.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
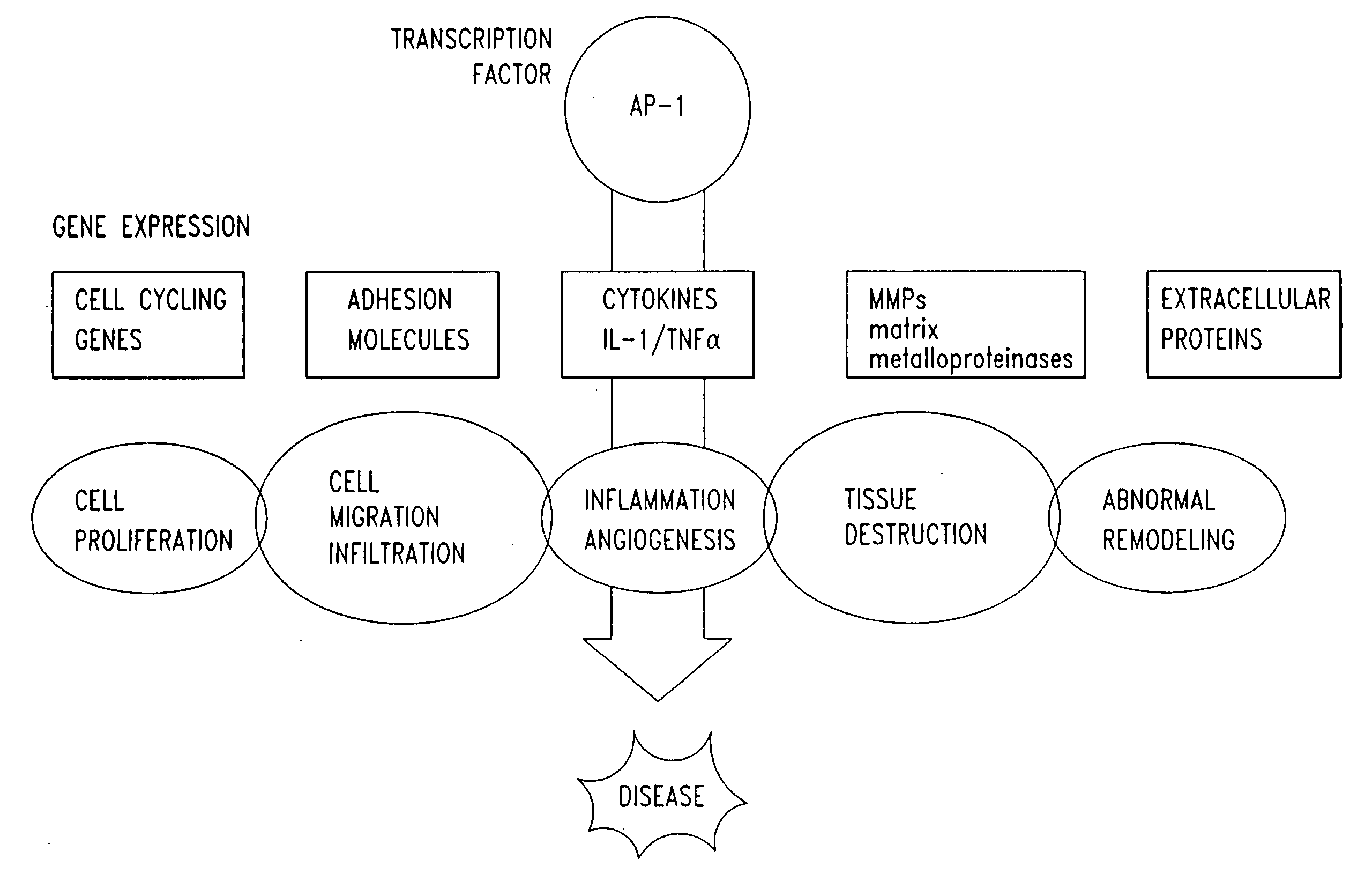
Compositions and methods for treating cellular response to injury and other proliferating cell disorders regulated by hyaladherin and hyalurons
InactiveUS20050058646A1Inhibit cell proliferationPrevent proliferationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCancer cell
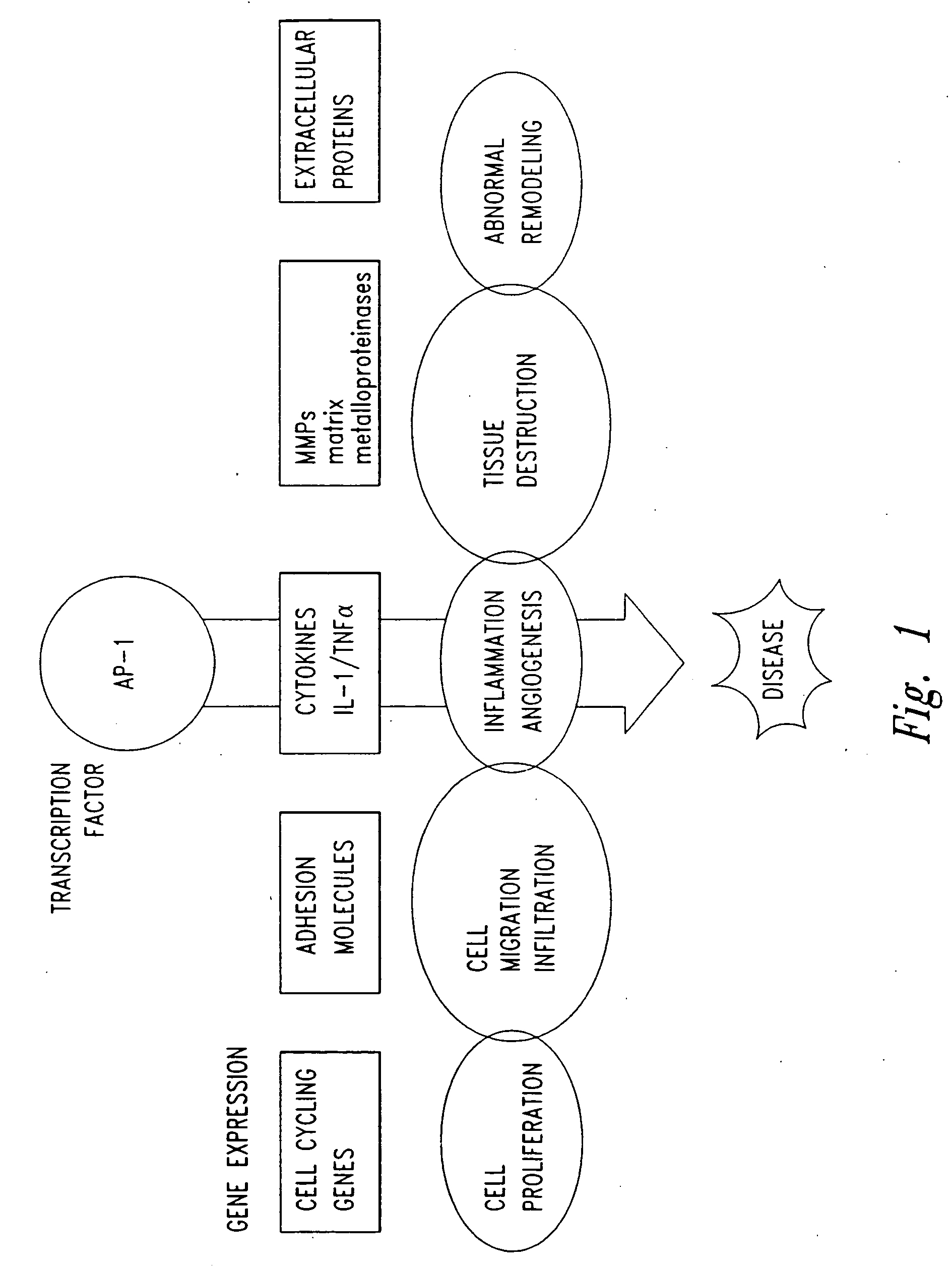
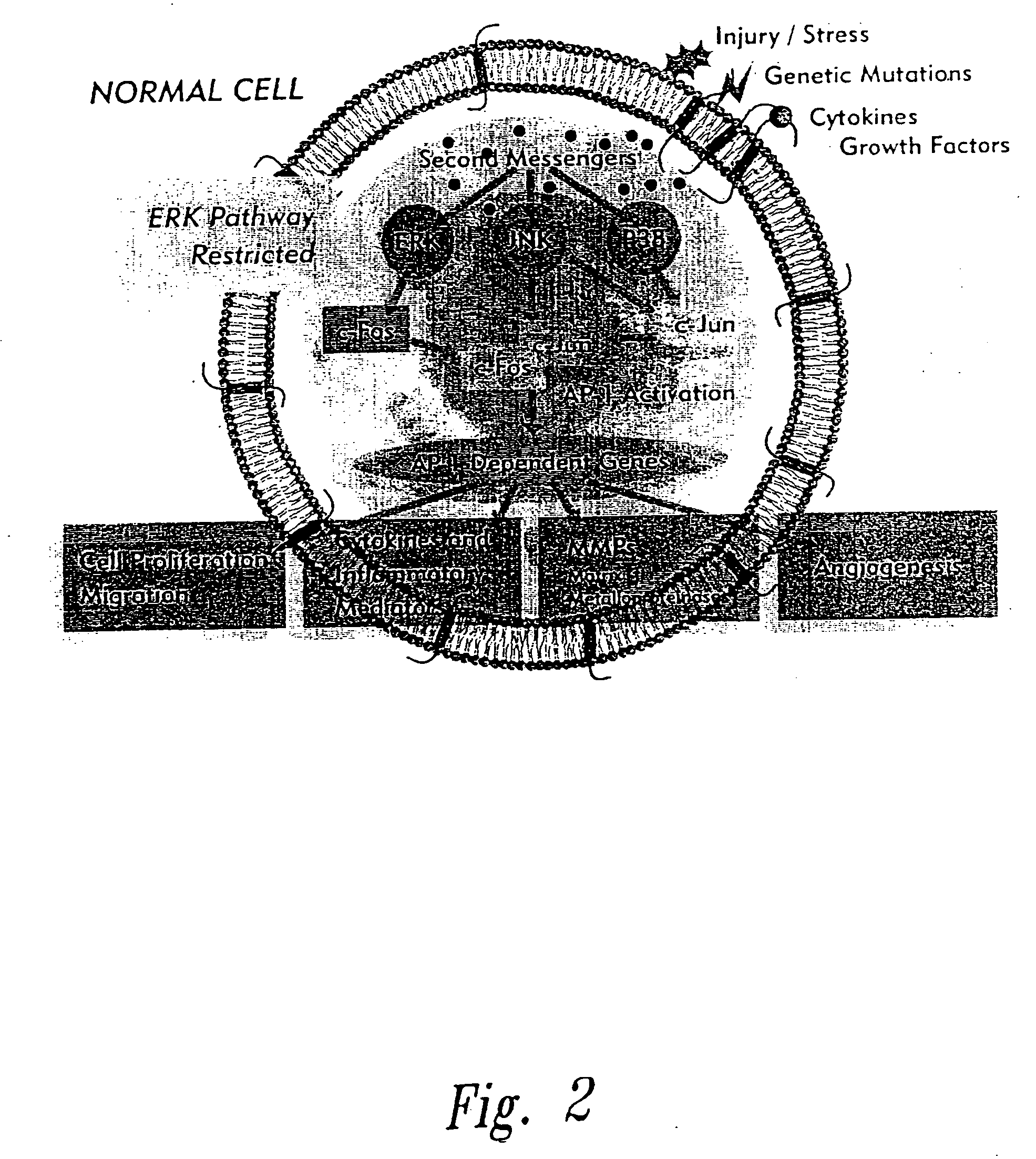
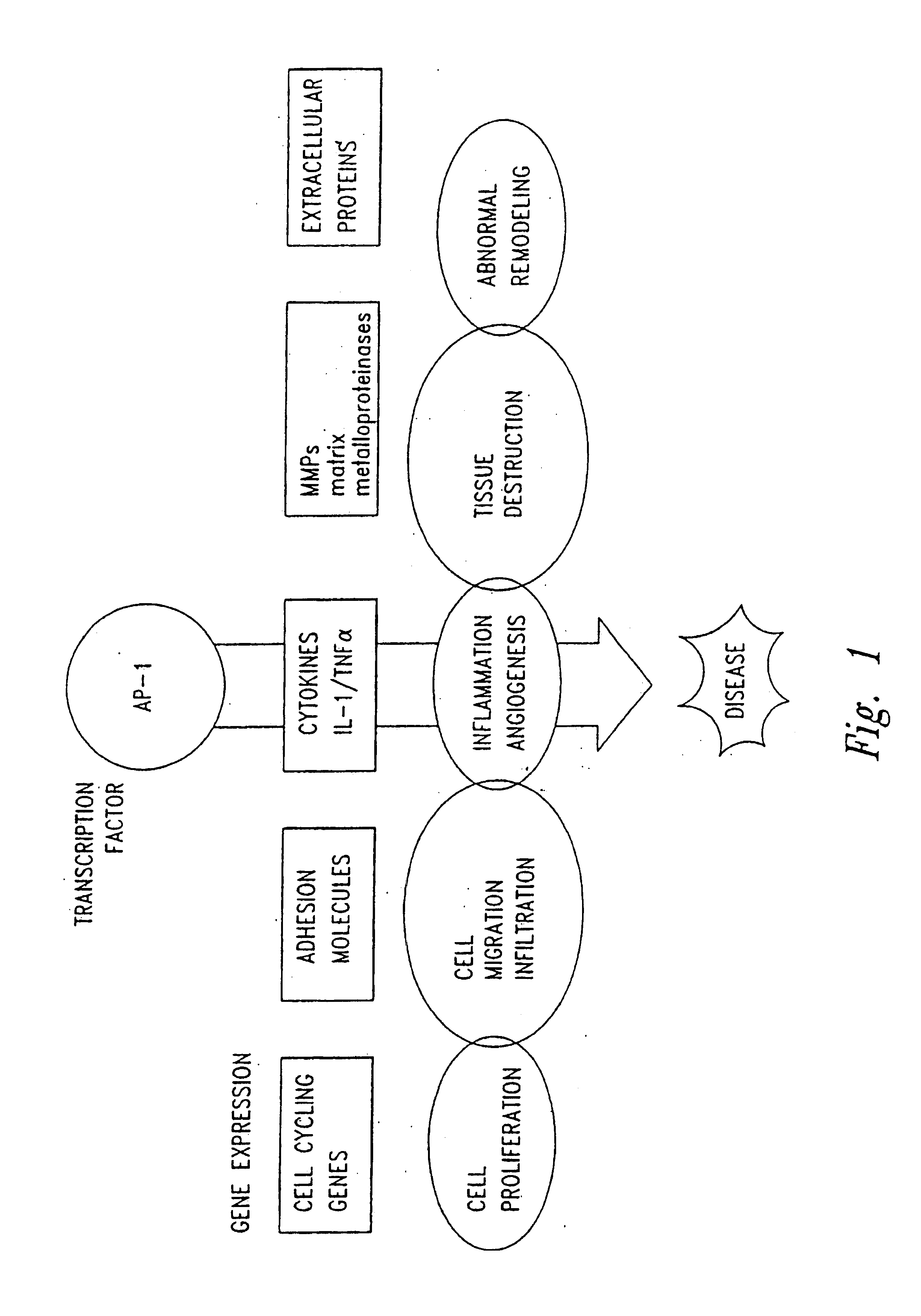
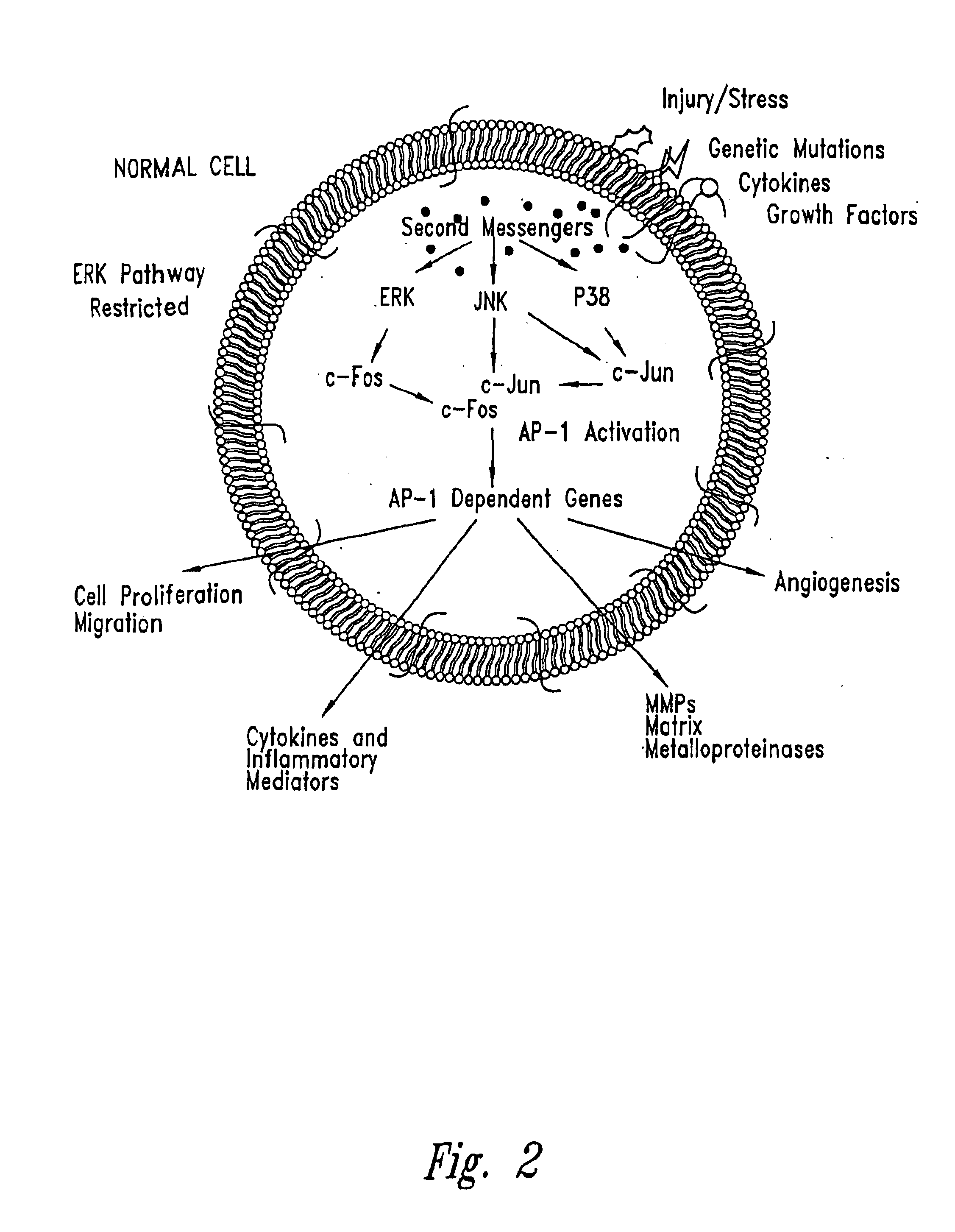
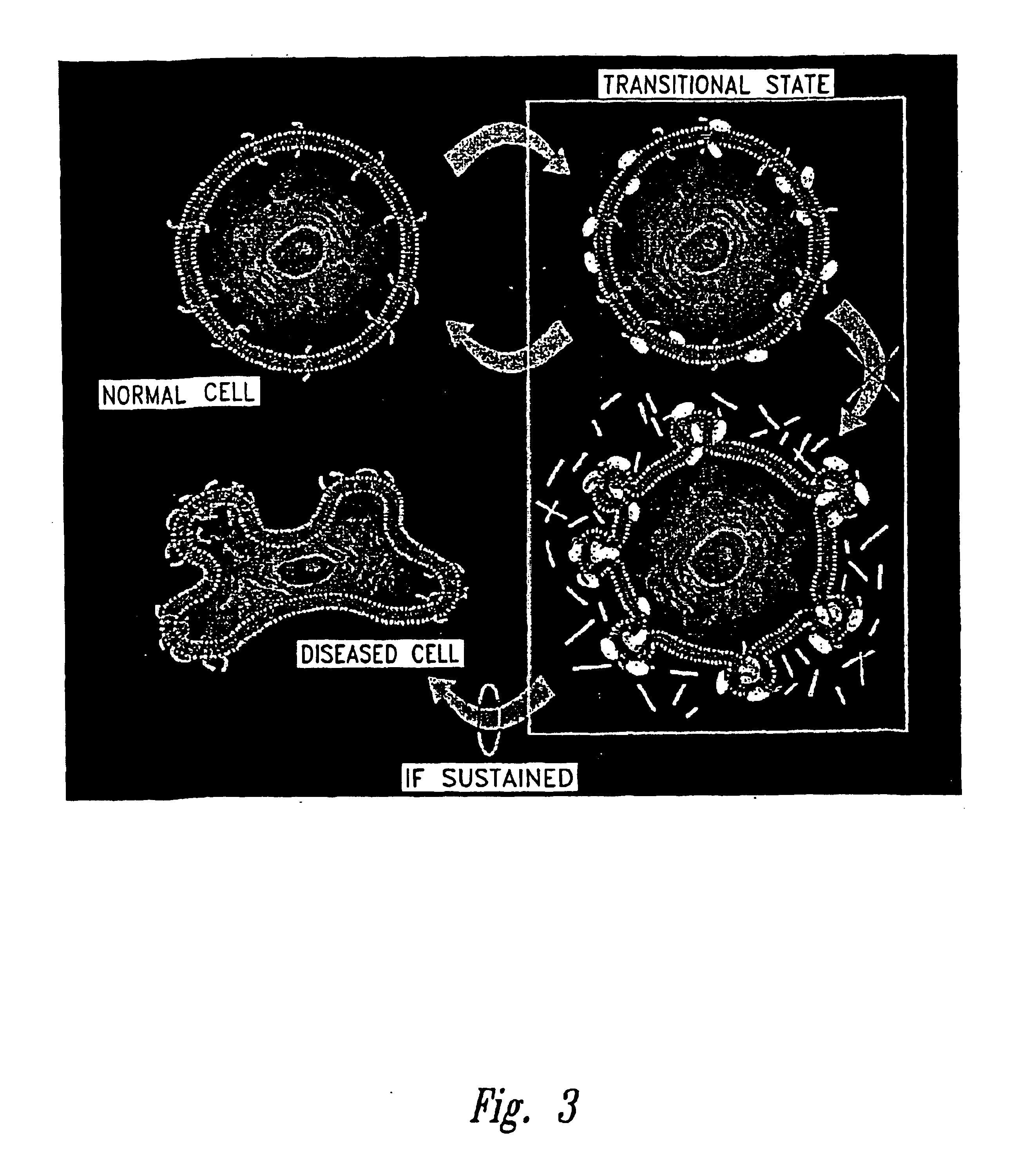
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating a tissue disorder associated with a response-to-injury process or proliferating cells in a mammal. These tissue disorders are associated with a novel cellular phenotype designated as “transition cells” which are described herein. This cellular phenotype is characterized in having an activated erk kinase signaling activity, a stimulated AP-1 binding activity, and at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of: (a) increased podosome formation, (b) increased flux of intracellular or extracellular hyaluronans or hyaladherins, (c) increased expression of a hyaladherin, (d) an inability to form focal adhesions, (e) increased metalloproteinase activity, and (f) increased expression of a hyaladherin. Example tissue disorders include fibrosis, inflammation, degeneration and invasive disorders such as occur in cancerous cells. The methods provided herein include administering to the mammal, an effective amount of a composition that alters the activity of transition molecules within a cell Transition molecules are shown to be comprised of hyaladherins, hyaluronans and associated molecules that regulate the transitional phenotype. A novel cell culture comprising transition cells is also provided, as well as compositions comprising particular peptides, polypeptides, and antibodies that affect the transitional phenotype.
Owner:TURLEY EVA +1
Methods and Compositions for Expanding, Identifying, Characterizing and Enhancing Potency of Mammalian-Derived Glial Restricted Progenitor Cells
Methods for producing a population of human-derived glial restricted progenitor cells (GRPs) with decreased potentially unintended or undesired cellular phenotypes and / or decreased standard deviation in the cells of the population are provided. Also provided are antibody panels and gene expression profiles to characterize GRPs and a method for its use in characterizing GRP cells. In addition methods for use of these GRP cells to generate astrocytes and / or oligodendrocytes, to re-myelinate neurons and to treat glial cell related and other neurodegenerative diseases or disorders or injuries or damage to the nervous system are provided. A method to manufacture neural cells depleted of A2B5 positive cells is also provided.
Owner:Q THERAPEUTICS
Determination of cell viability and phenotype
InactiveUS7018804B1Accurate and straightforward quantificationFurther processing may be delayedMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFluorescenceBiology
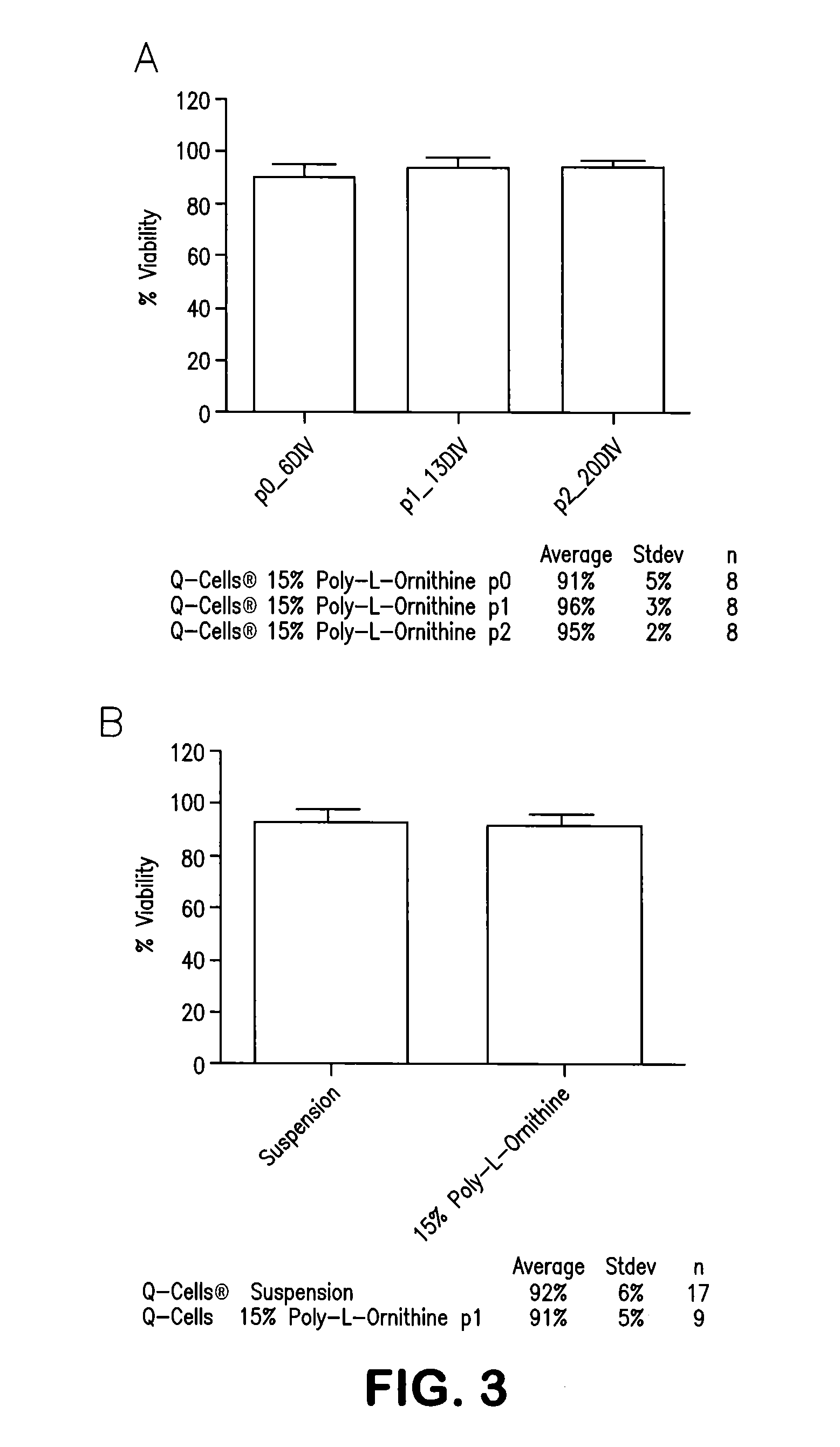
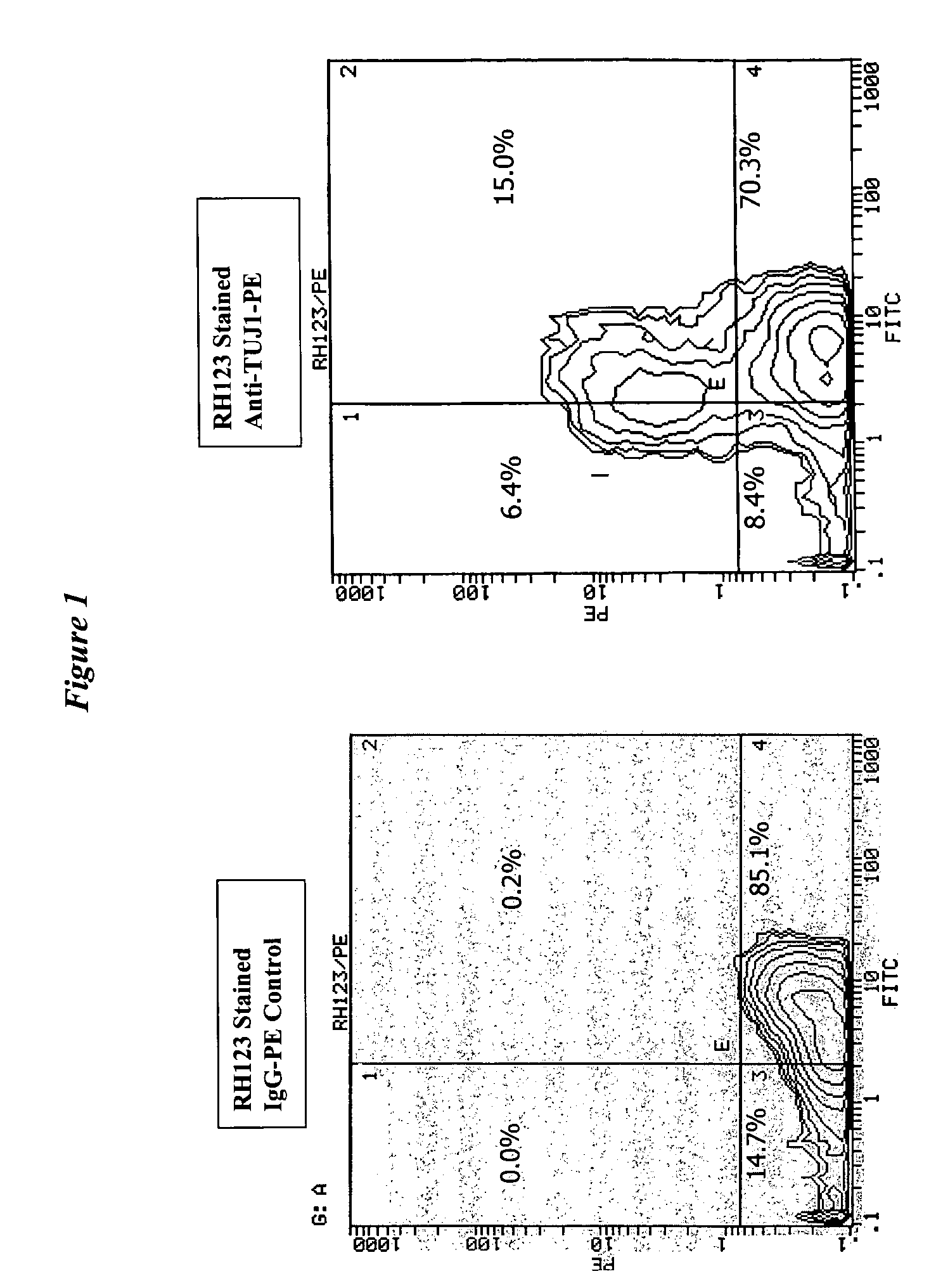
This invention provides methods to the determination of the viability of the cell by a first reagent and the phenotype of a cell by use of one or more second reagent. The first reagent is one that is detectable in viable, or living, cells even after they have been fixed such that they are no longer viable. The one or more second reagent is compatible for use in fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) including intracellular FACS. The invention thus provides methods of simultaneously identifying a cell as both viable and having a phenotype of interest. The invention also provides compositions for use in the disclosed methods.
Owner:ORION BIOSOLUTIONS
Methods for identifying and modulating co-occurant cellular phenotypes
PendingUS20200115753A1Improvement effortsOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCell phenotypeBioinformatics
The present invention provides tools and methods for the systematic analysis of genetic interactions between cells. The present invention provides tools and methods for modulating cell phenotypes and compositions, combinatorial probing of cellular circuits, for dissecting cellular circuitry, for delineating molecular pathways, and / or for identifying relevant targets for therapeutics development.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods of switching the phenotype of t cells by transgenic lineage factor foxp3
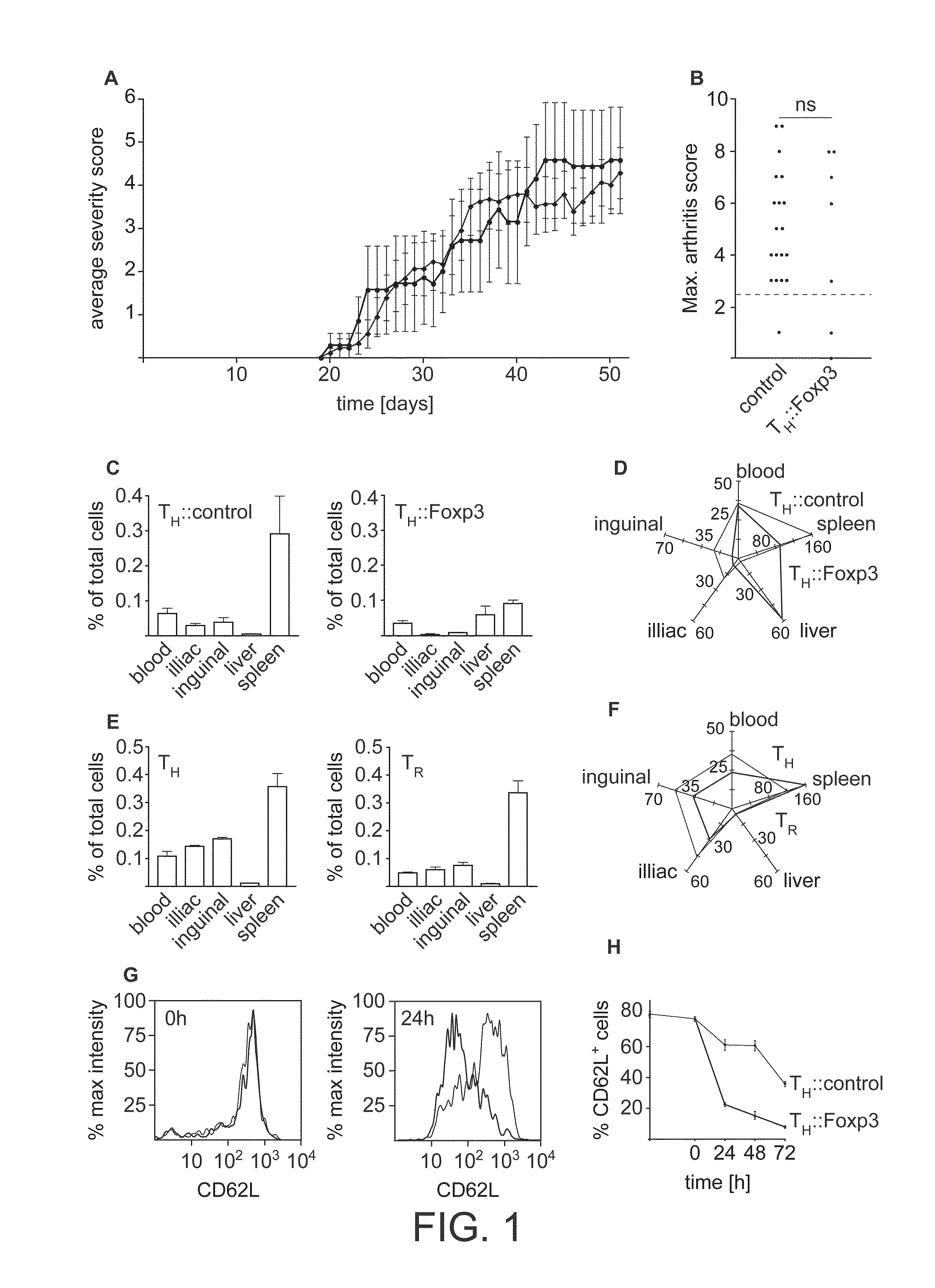
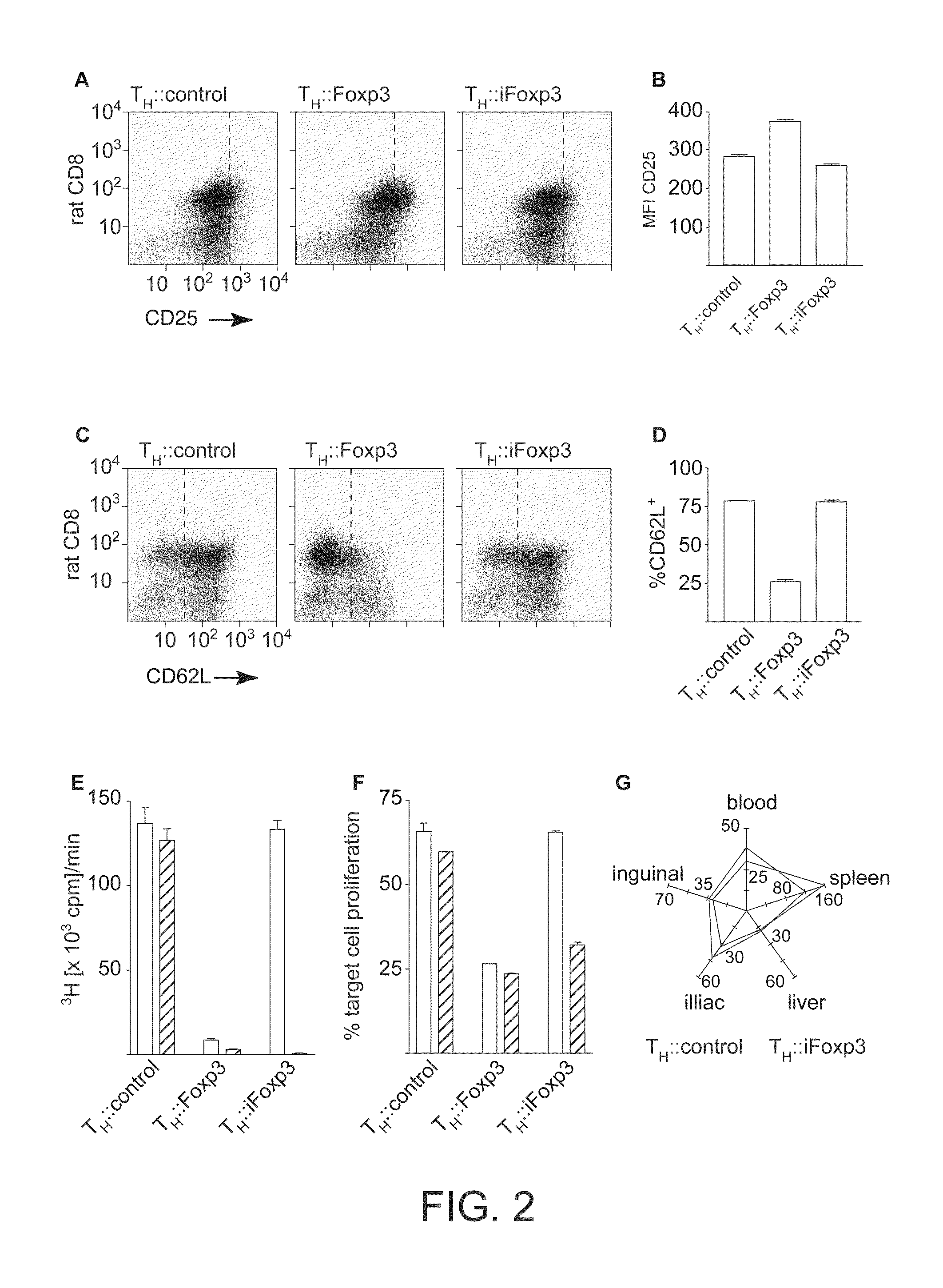
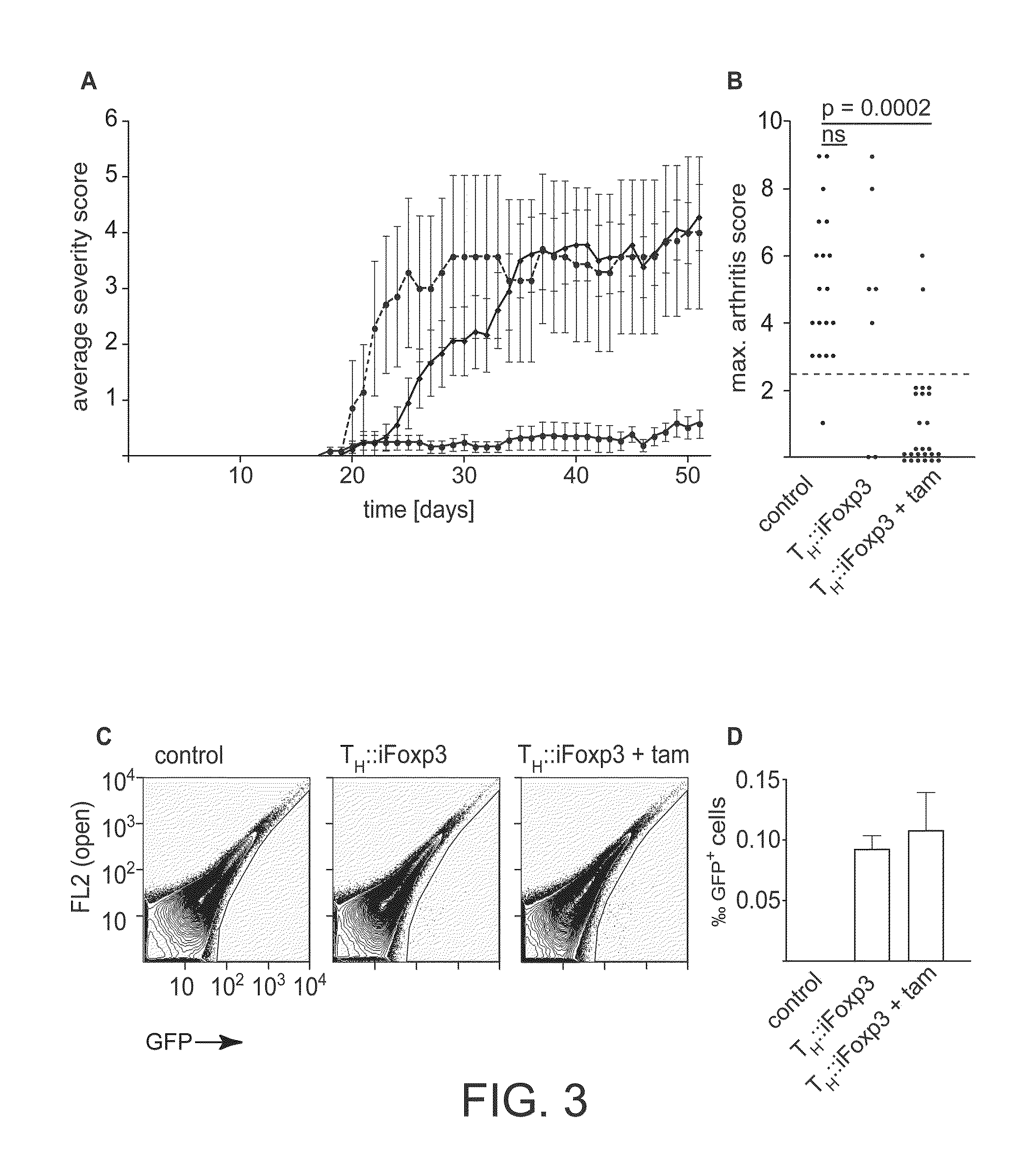
InactiveUS20100203068A1Conveniently removedReduce needGenetically modified cellsSnake antigen ingredientsGenetic elementT cell
In one aspect the invention relates to a method of switching the phenotype of a target cell, said method comprising inducing lineage factor activity in said cell via a transgene. In another aspect, the invention relates to a method of switching the phenotype of a target cell, said method comprising introducing to said cell a genetic element capable of inducibly generating lineage factor activity, and inducing lineage factor activity in said cell. The invention also relates to methods of suppressing immune responses and methods of treating subjects.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
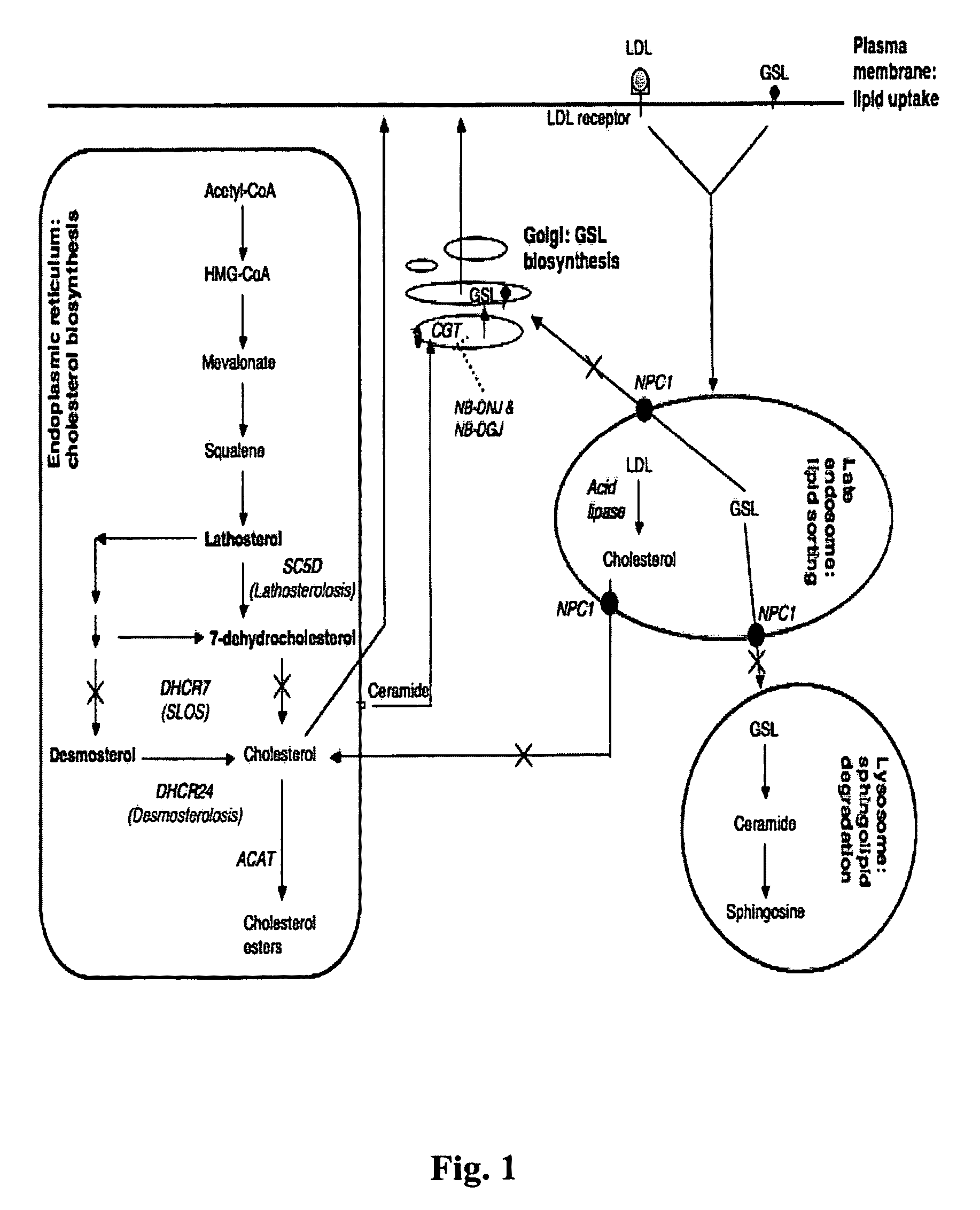
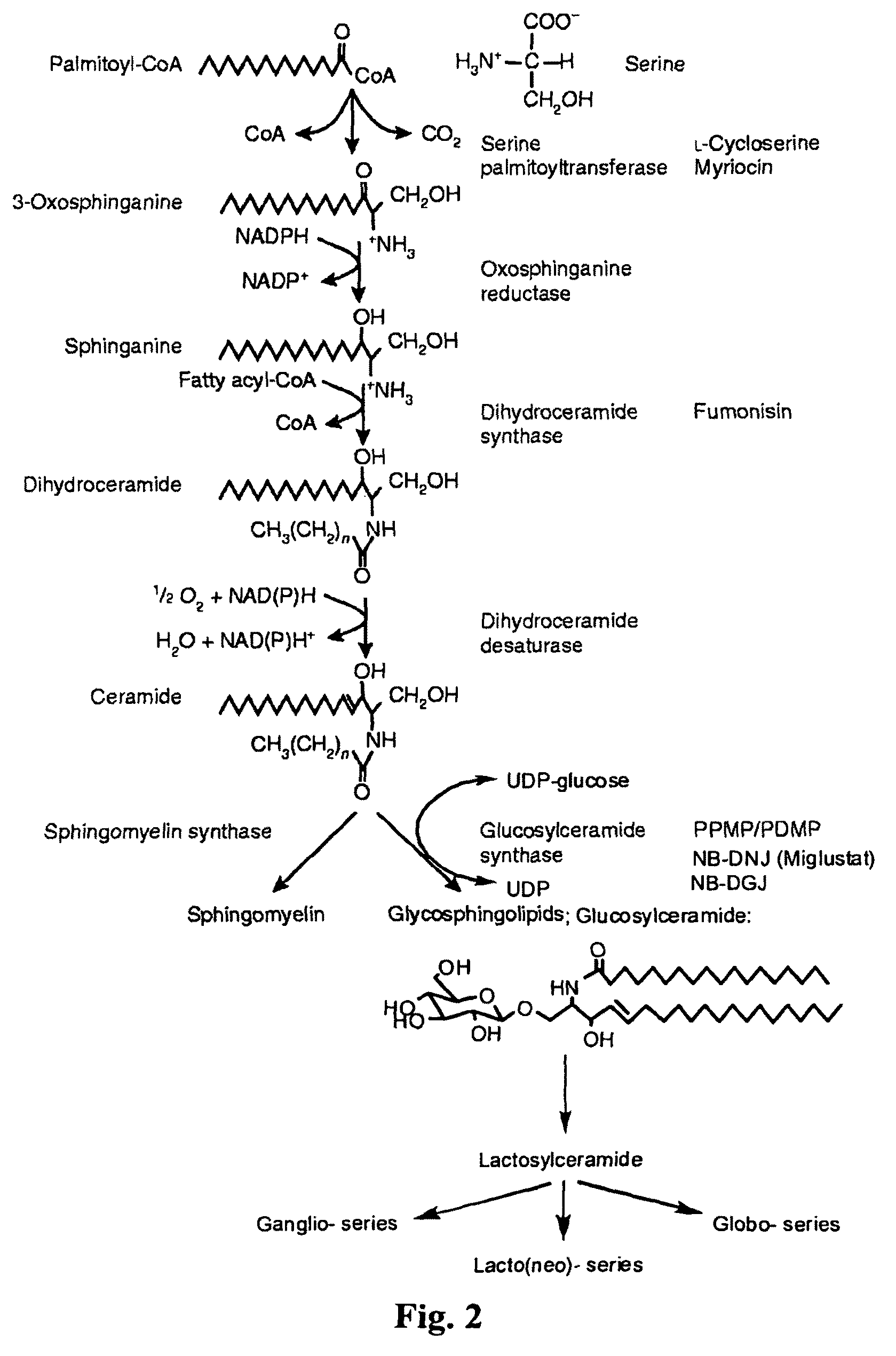
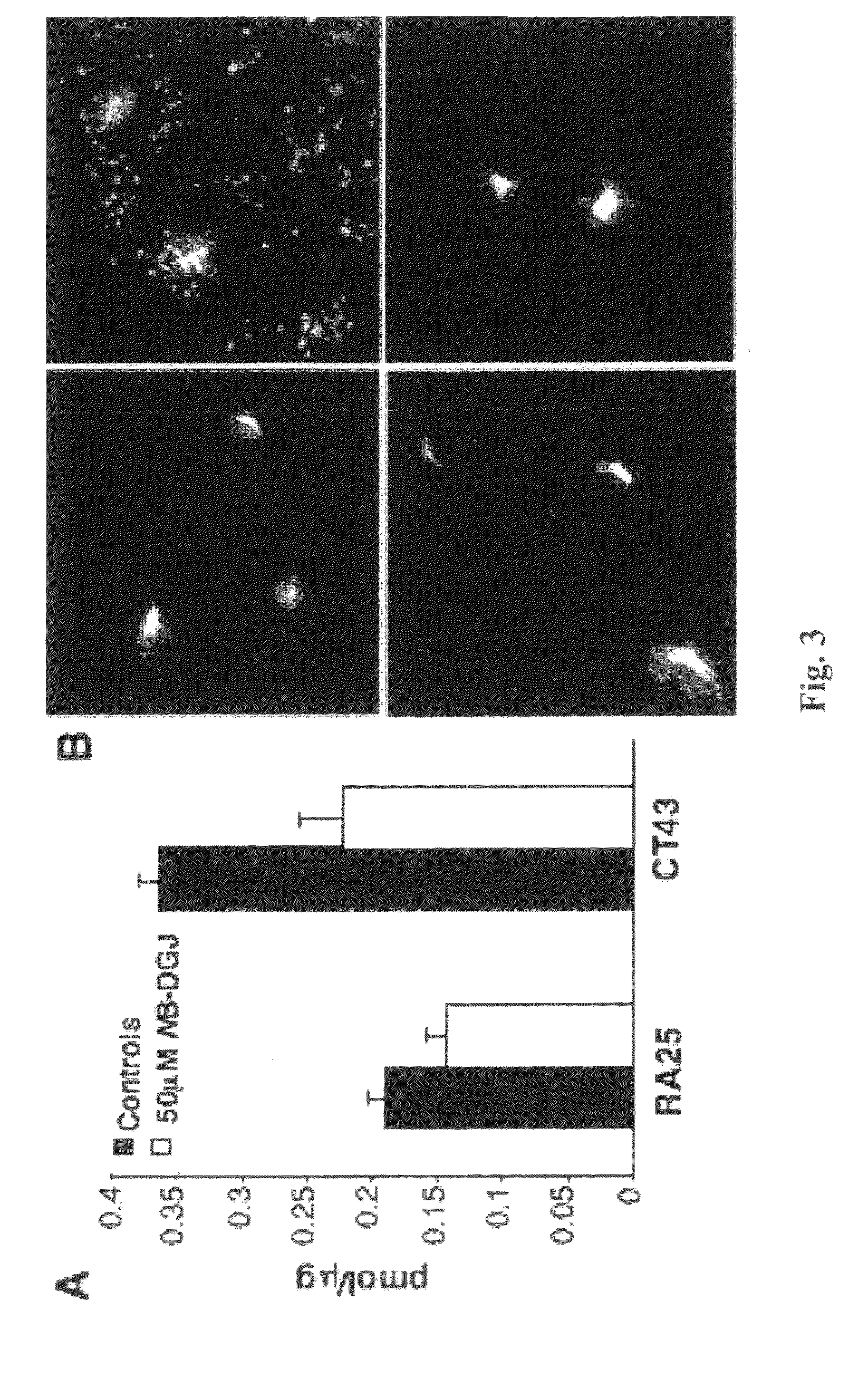
Substrate reduction therapy
ActiveUS8557844B2Transportation defectPotential therapeutic benefitBiocideNervous disorderSphingolipid biosynthesisNiemann-pick type c disease
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
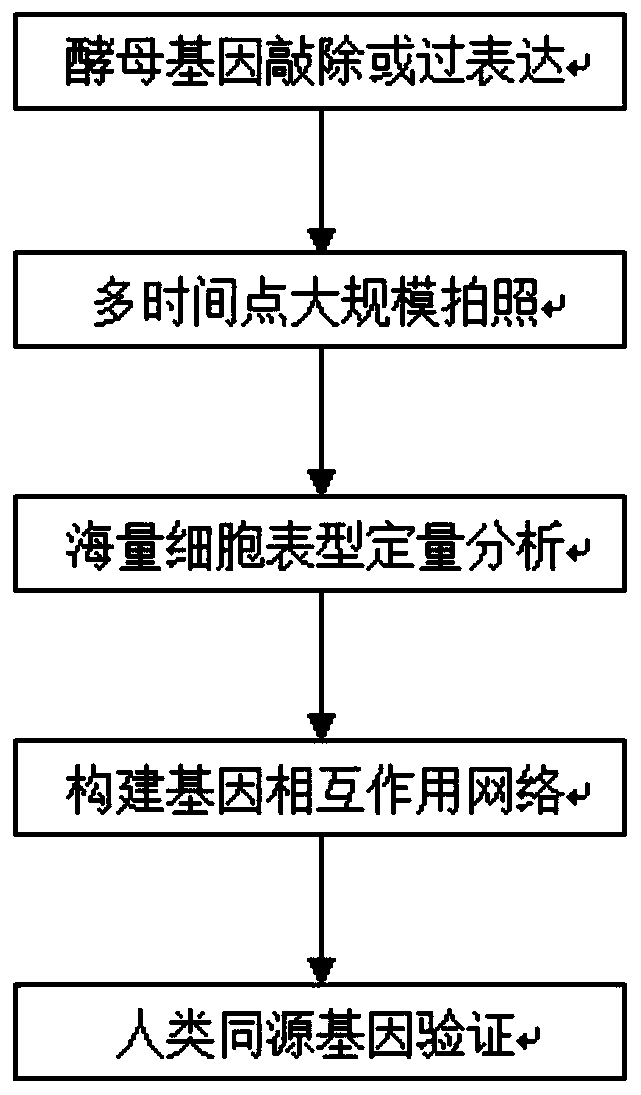
A high-throughput functional gene screening method and system for cell phenotypic image quantitative analysis
ActiveCN109815870AImprove accuracyImprove screening efficiencyImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansScreening methodFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a high-throughput functional gene screening method and system for cell phenotypic image quantitative analysis, and belongs to the technical field of gene screening. The methodcomprises the steps of using a full-automatic fluorescence microscope to shoot a cell image of the phenotype to be screened and a cell image without the phenotype to be screened; respectively converting the images into a to-be-screened phenotype and a black-white binary image without the to-be-screened phenotype; then segmenting into an image containing a single phenotypic cell to be screened andan image containing a single phenotypic cell without being screened; taking the corresponding part of the image containing the single to-be-screened phenotypic cell in the cell image of the to-be-screened phenotypic cell as a positive training set, and taking the corresponding part of the image containing the single to-be-screened phenotypic cell in the cell image of the to-be-screened phenotypiccell as a negative training set to obtain a final model capable of identifying the cell phenotypic; and carrying out final model identification on the image of the knockout or overexpression cell of the to-be-screened gene to obtain the relevance between the to-be-screened gene and the phenotype. The method improves the screening efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compositions and methods for treating cellular response to injury and other proliferating cell disorders regulated by hyaladherin and hyaluronans
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating a tissue disorder associated with a response-to-injury process or proliferating cells in a mammal. These tissue disorders are associated with a novel cellular phenotype designated as “transition cells” which are described herein. This cellular phenotype is characterized in having an activated erk kinase signaling activity, a stimulated AP-1 binding activity, and at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of: (a) increased podosome formation, (b) increased flux of intracellular or extracellular hyaluronans or hyaladherins, (c) increased expression of a hyaladherin, (d) an inability to form focal adhesions, (e) increased metalloproteinase activity, and (f) increased expression of a hyaladherin. Example tissue disorders include fibrosis, inflammation, degeneration and invasive disorders such as occur in cancerous cells. The methods provided herein include administering to the mammal, an effective amount of a composition that alters the activity of transition molecules within a cell Transition molecules are shown to be comprised of hyaladherins, hyaluronans and associated molecules that regulate the transitional phenotype. A novel cell culture comprising transition cells is also provided, as well as compositions comprising particular peptides, polypeptides, and antibodies that affect the transitional phenotype.
Owner:TRANSITION THERAPEUTICS INC
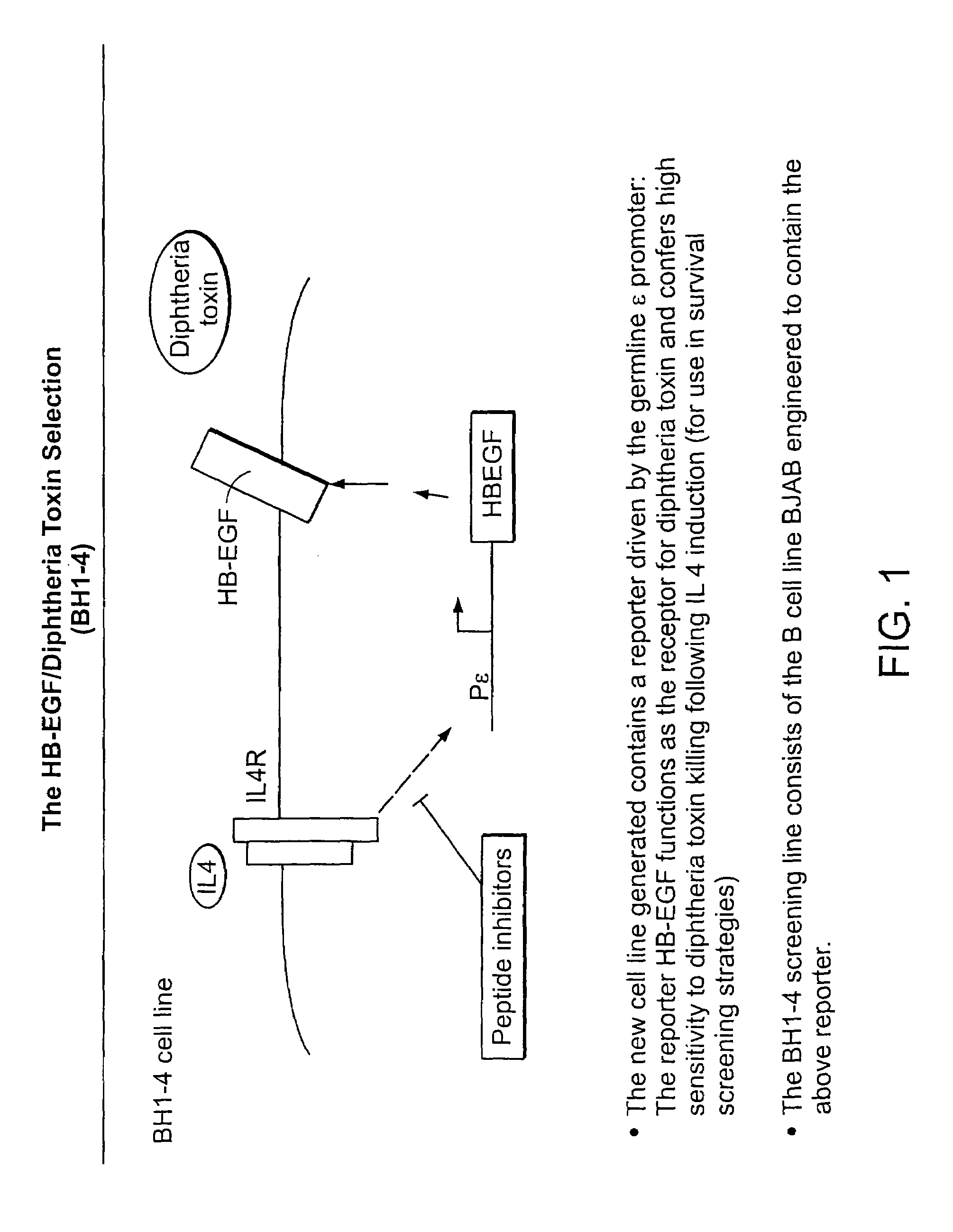
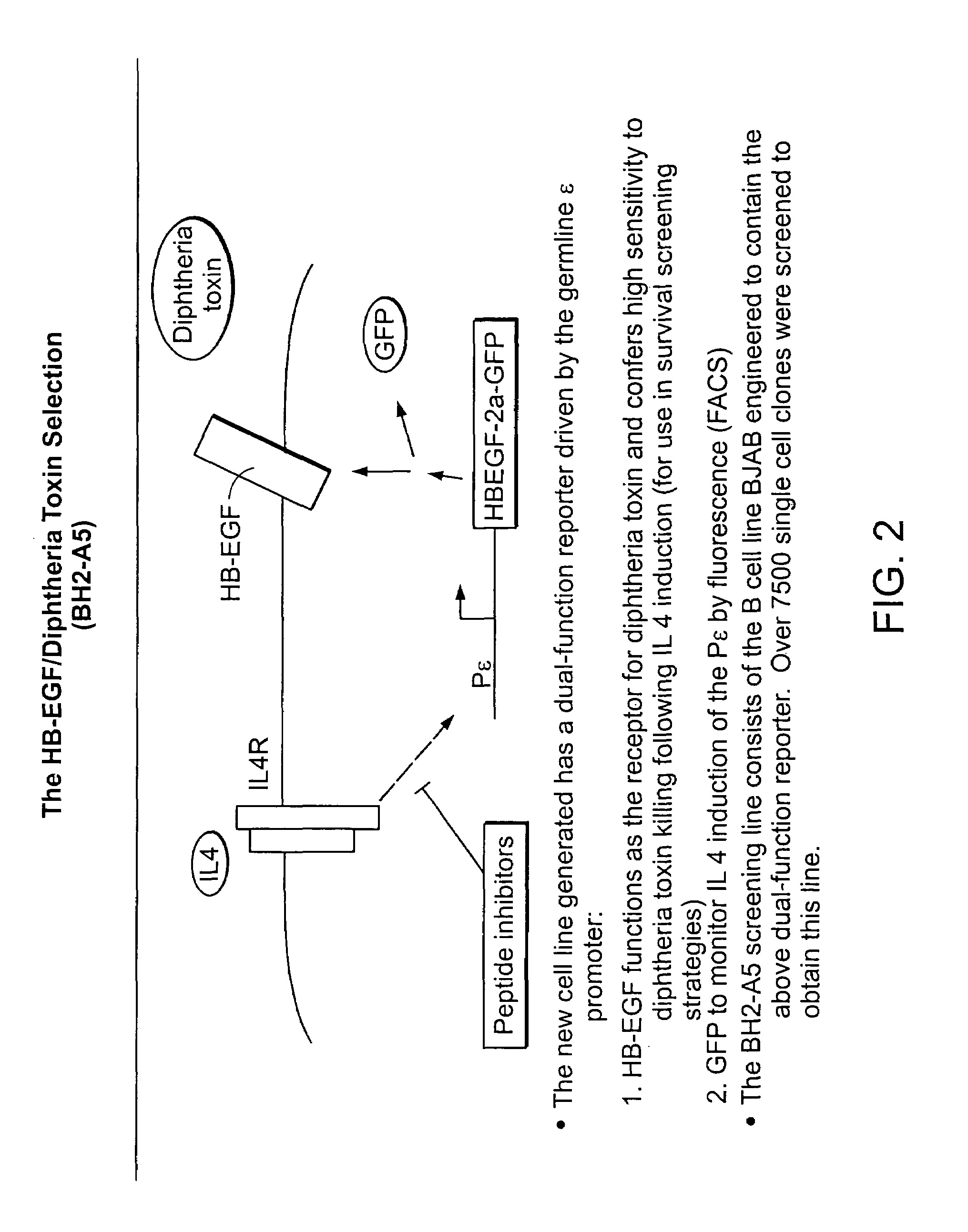
Methods and compositions for screening for altered cellular phenotypes
The invention relates to methods and compositions useful for screening for altered cellular phenotypes using an inducible expression system to enrich for and detect the altered phenotypes and, more particularly, relates to screening libraries of candidate bioactive agents, for example, nucleic acids and peptides, in cells using an regulatable expression system to enrich for a subpopulation of cells having an altered phenotype due to the presence of a candidate bioactive agent.
Owner:RIGEL
Methods and platforms for drug discovery
InactiveCN102203275AMicrobiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsCandidate Gene Association StudyCvd risk
The present invention involves methods for identifying an agent that corrects a phenotype associated with a health condition or a predisposition for a health condition. The invention also involves methods for identifying a diagnostic cellular phenotype, determining the risk of a health condition in a subject, methods for reducing the risk of drug toxicity in a human subject, and methods for identifying a candidate gene that contributes to a human disease. The invention also discloses human induced pluripotent stem cell lines.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Methods and compositions for screening for altered cellular phenotypes
InactiveUS7056687B2Reduced CD6 levelCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDrug biological activityCell biology
The invention relates to methods and compositions useful for screening for altered cellular phenotypes using an inducible expression system to enrich for and detect the altered phenotypes and, more particularly, relates to screening libraries of candidate bioactive agents, for example, nucleic acids and peptides, in cells using an regulatable expression system to enrich for a subpopulation of cells having an altered phenotype due to the presence of a candidate bioactive agent.
Owner:RIGEL PHARMA
Diagnostic and drug screening for molecular signatures of early onset sporadic parkinson's disease
PendingUS20210033628A1Compound screeningNervous disorderCell phenotypeHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
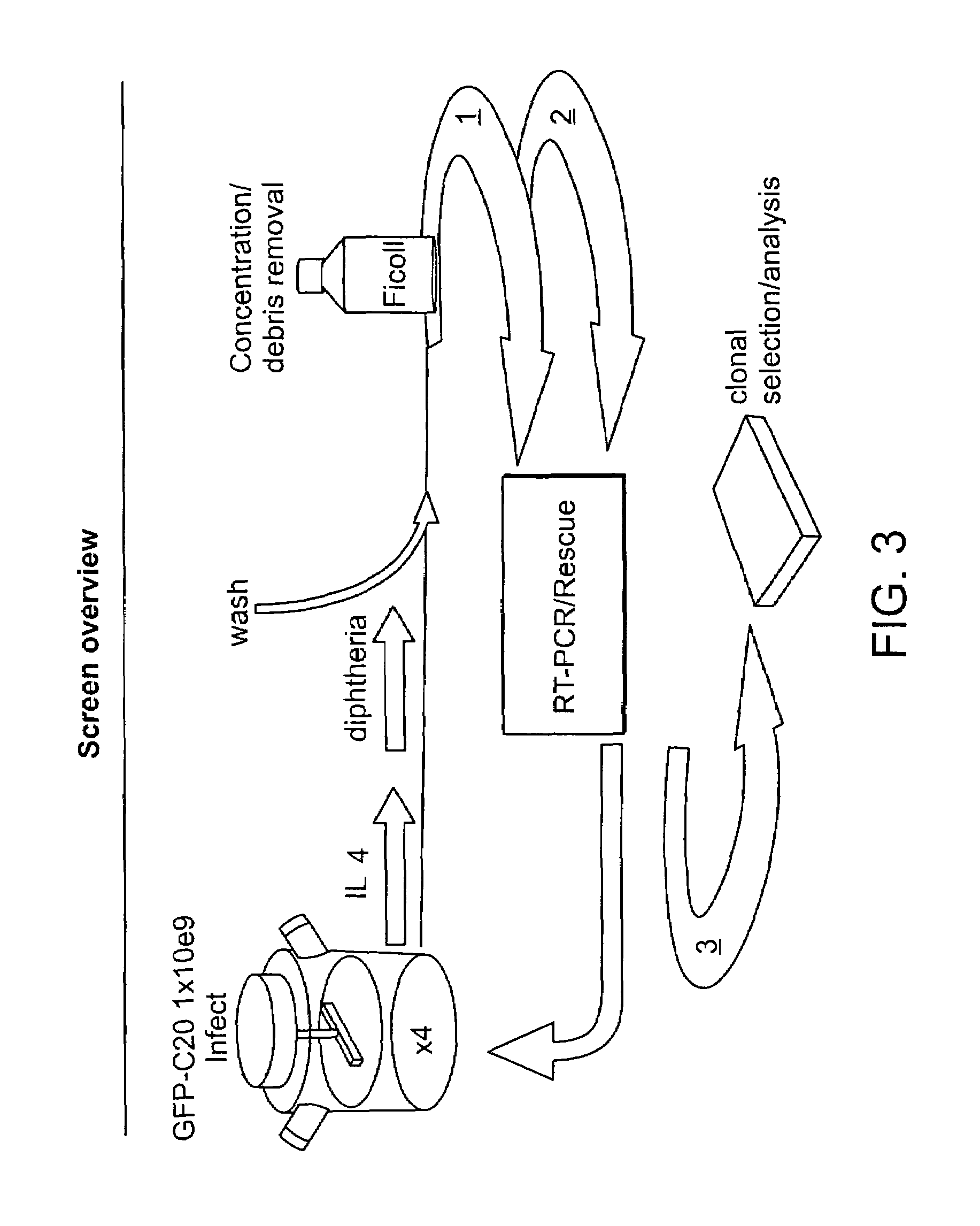
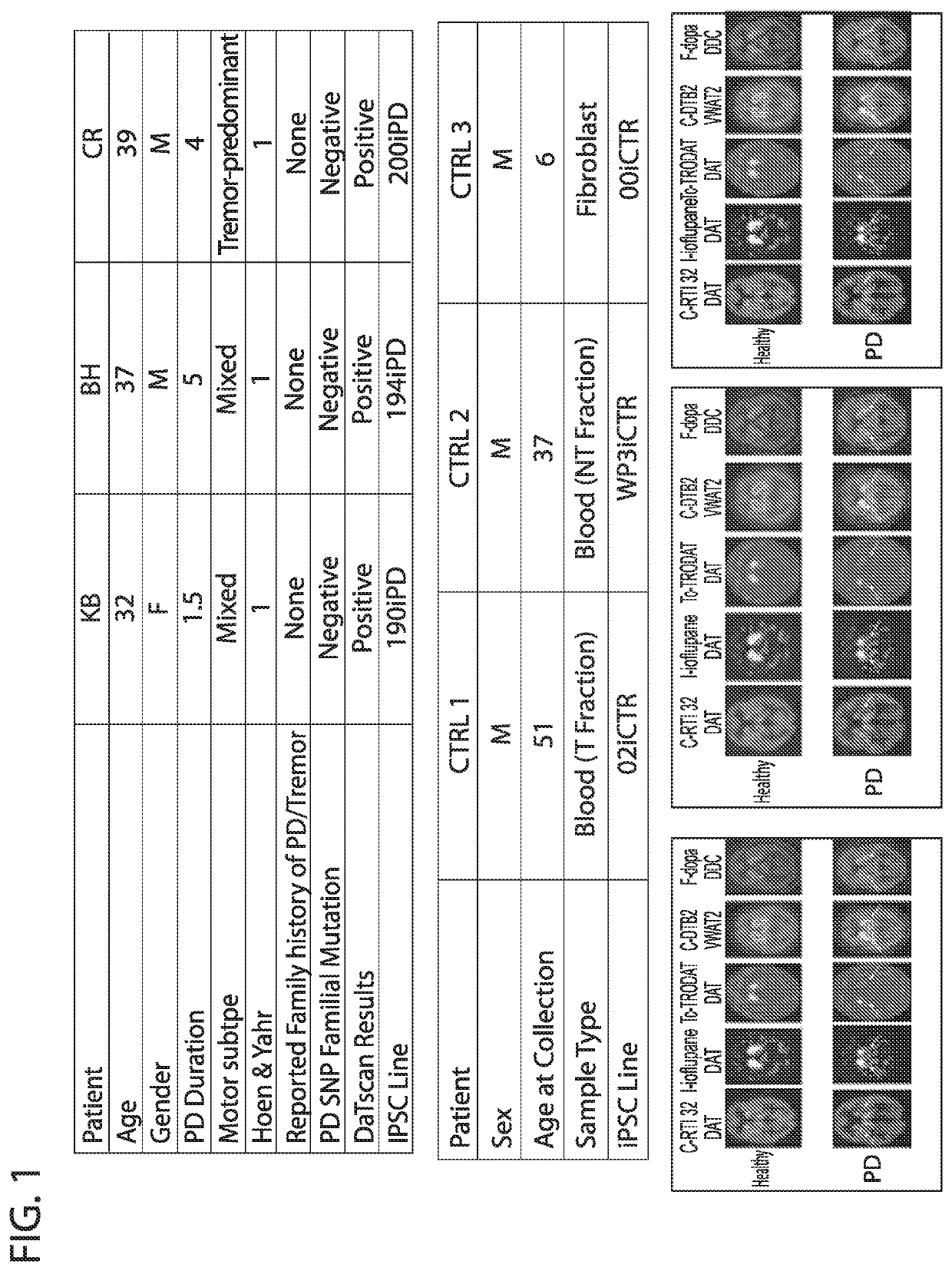
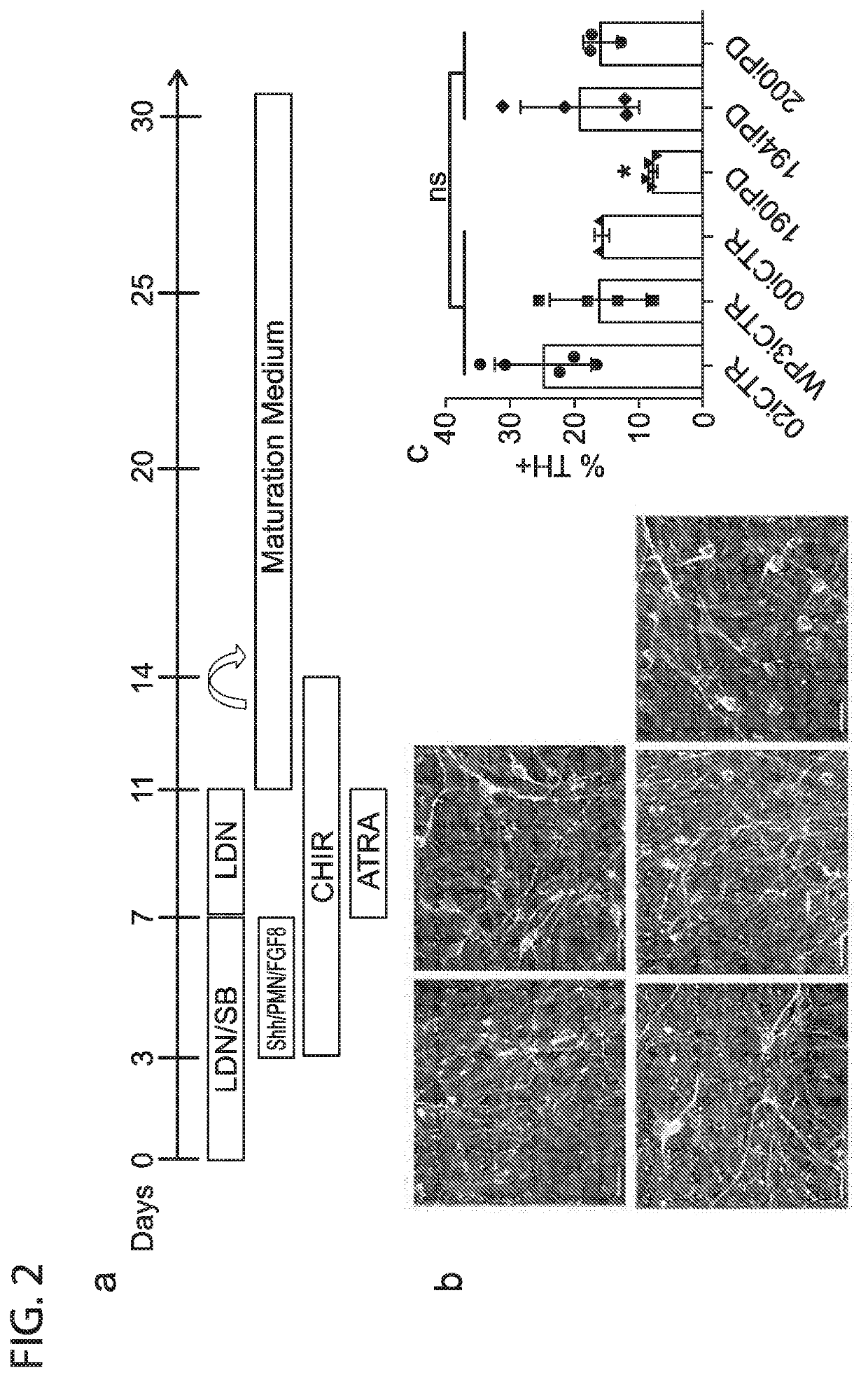
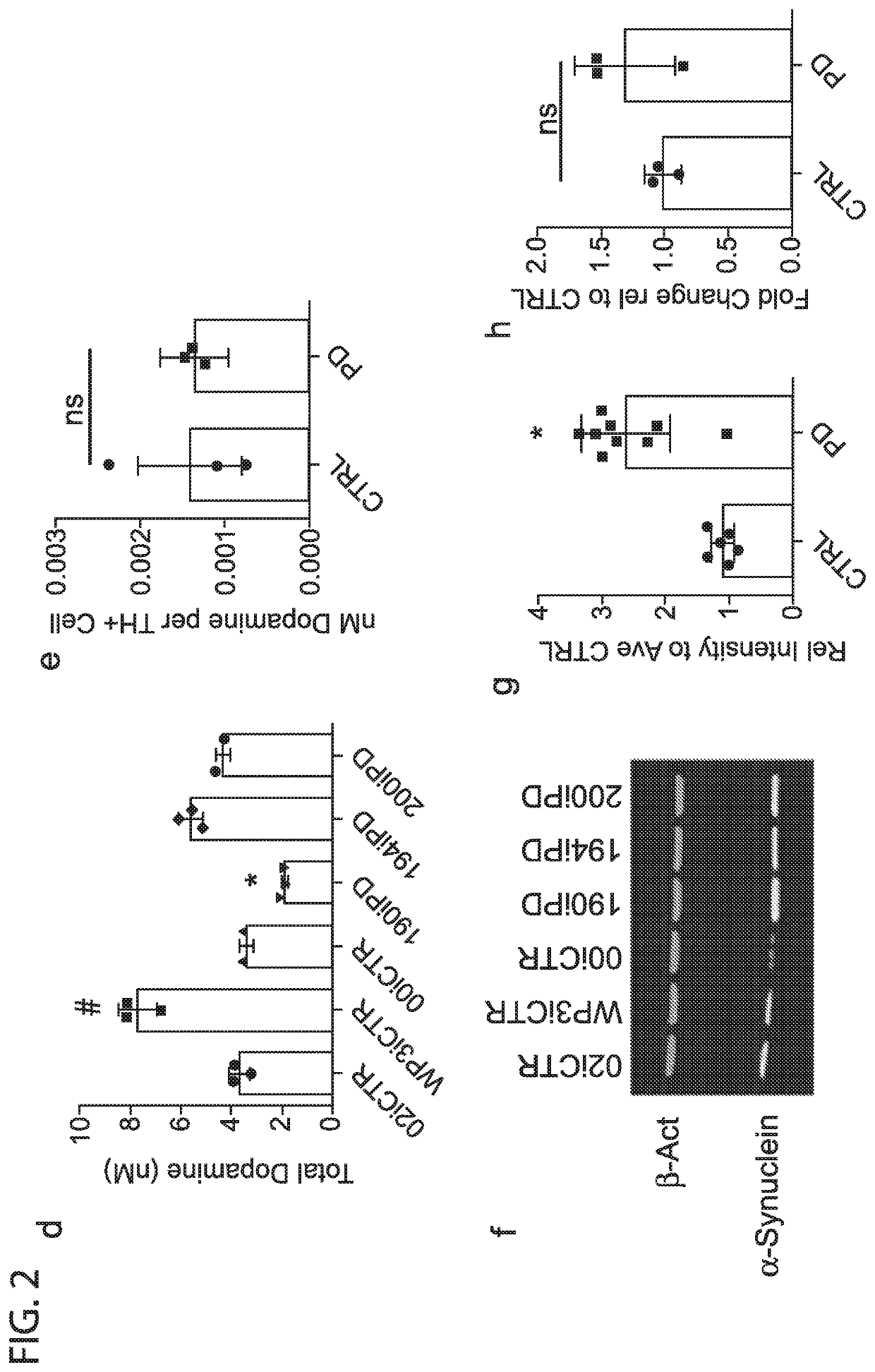
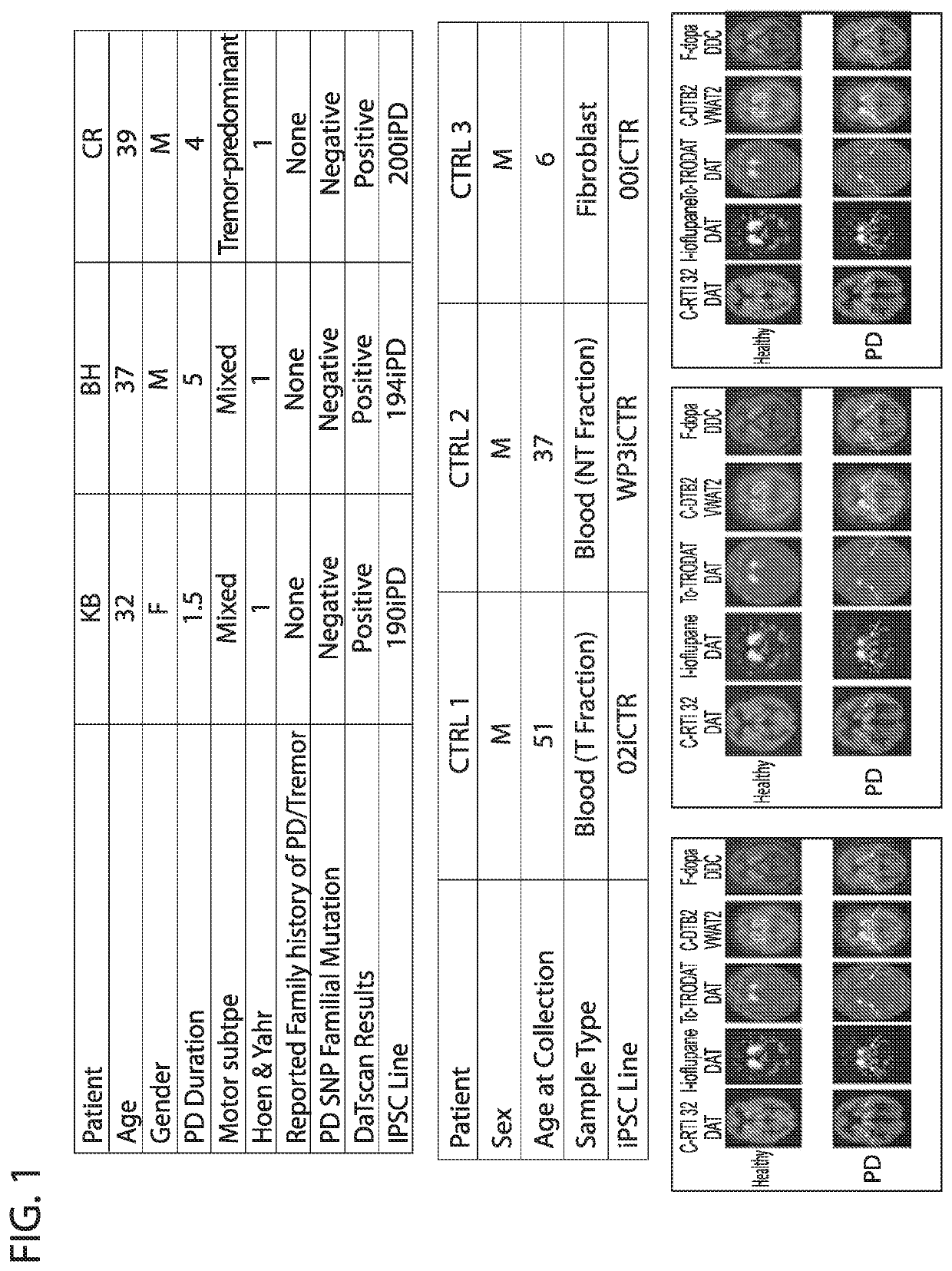
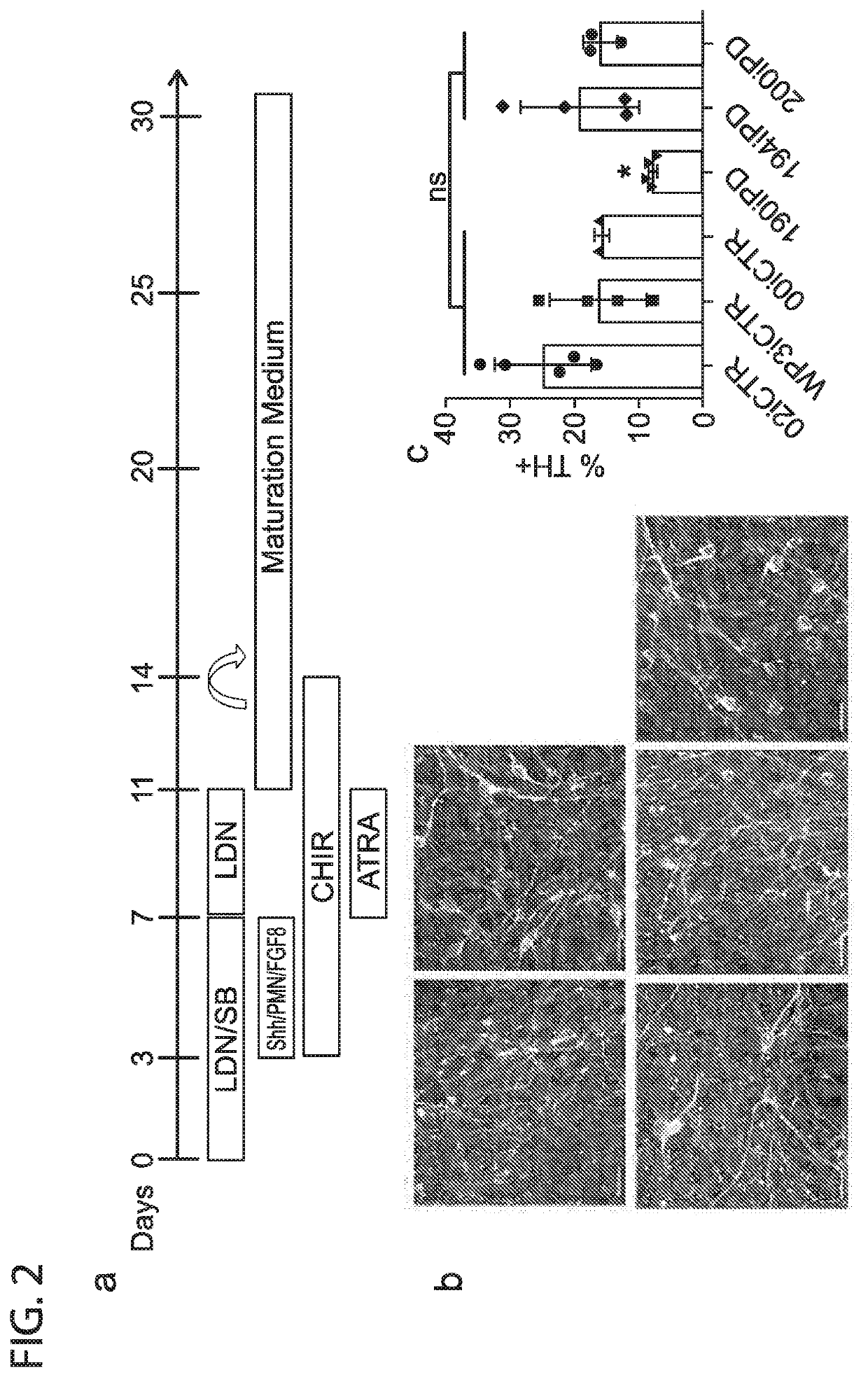
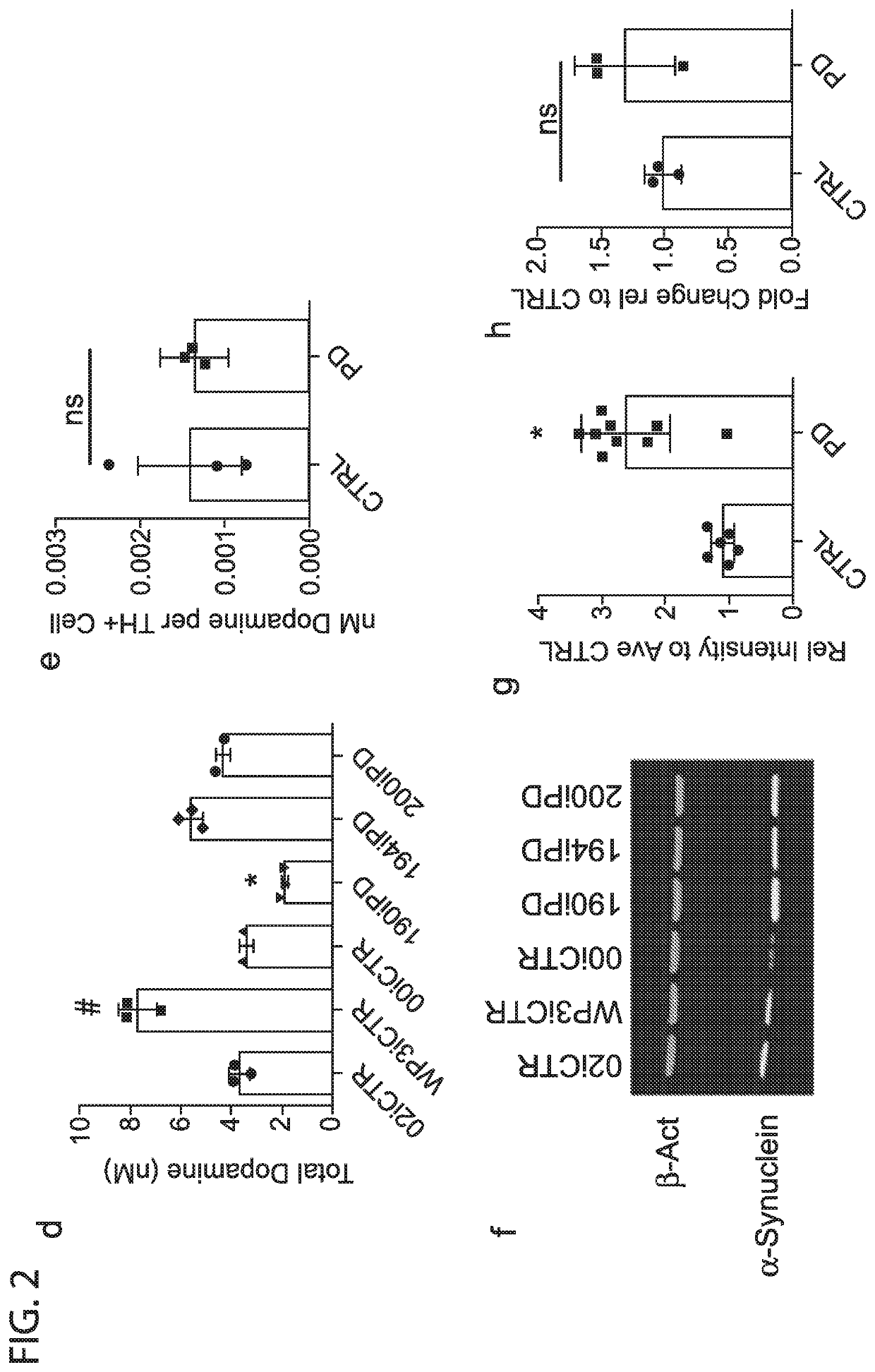
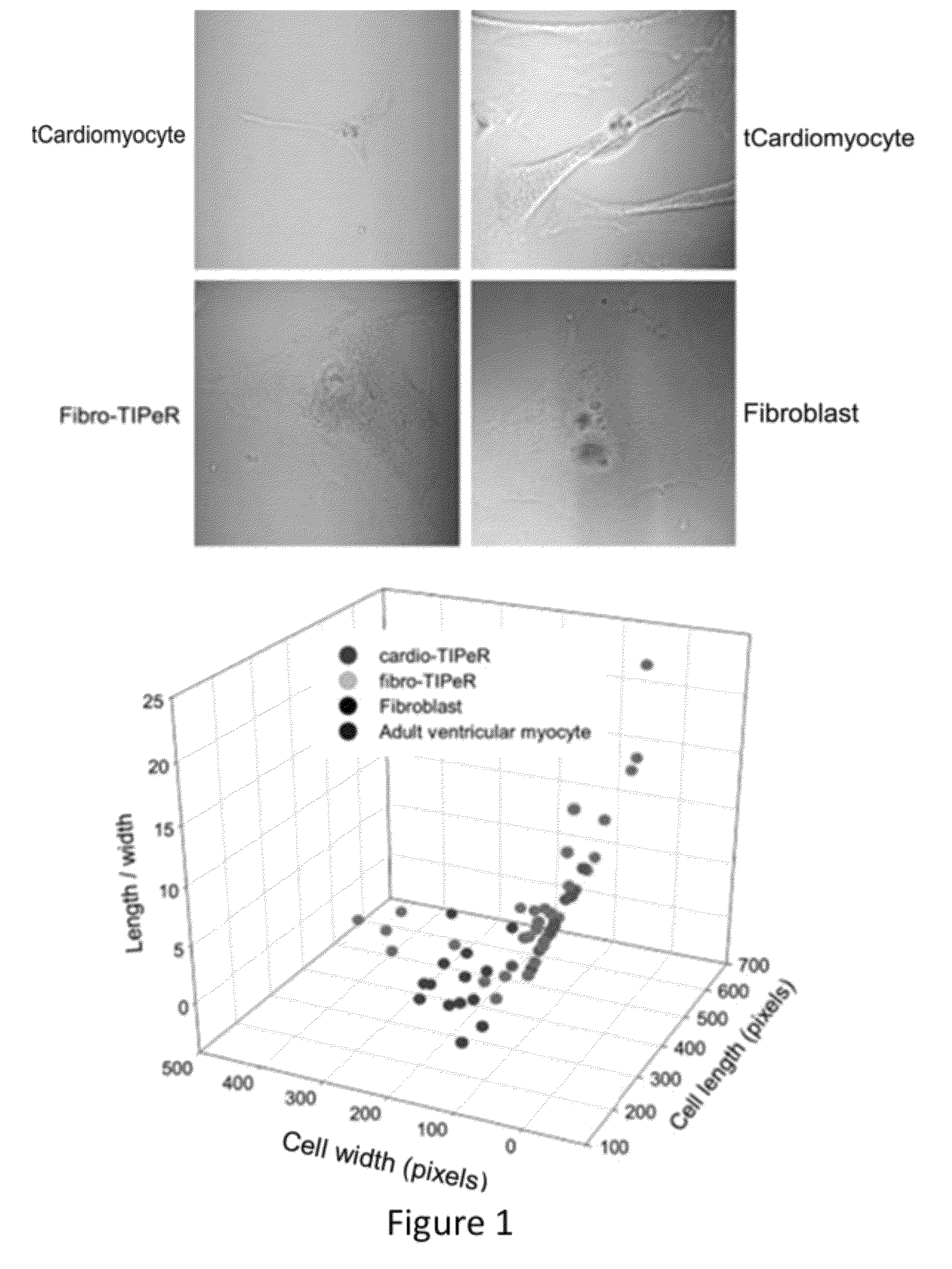
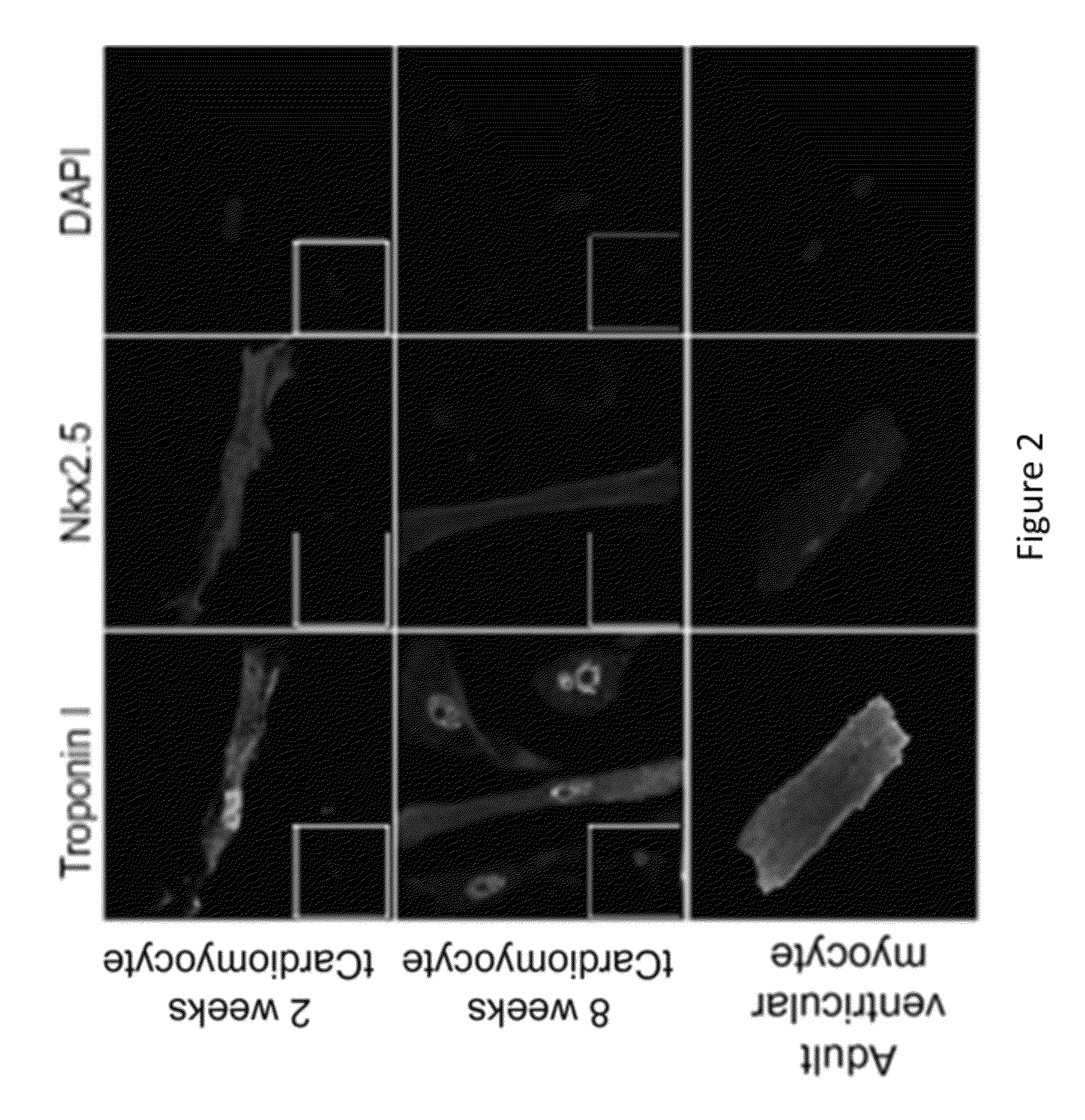
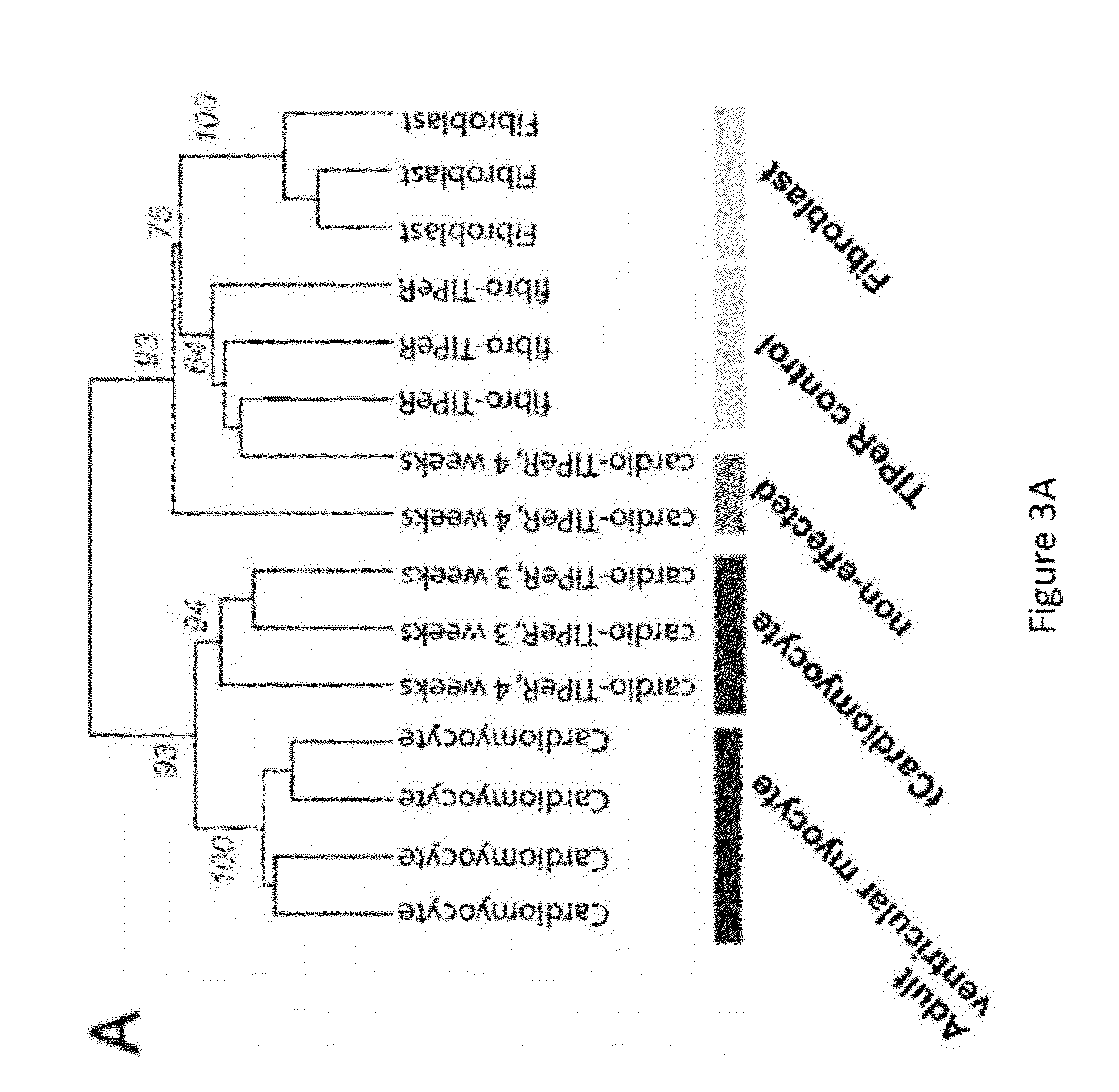
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (Ipsc) technology enables the generation and study of living brain tissue relevant to Parkinson's disease (PD) ex vivo. Utilizing cell lines from PD patients presents a powerful discovery system that links cellular phenotypes observed in vitro with real clinical data. Differentiating patient-derived iPSCs towards a dopaminergic (DA) neural fate revealed that these cells exhibit molecular and functional properties of DA neurons in vitro that are observed to significantly degenerate in the substantia nigra of PD patients. Clinical symptoms that drive the generation of other relevant cell types may also yield novel PD-specific phenotypes in vitro that have the potential to lead to new therapeutic avenues for patients with PD. Due to their early onset and non-familial origin, differentiated nervous tissue from these patients offer a key opportunity to discover neuron subtype-specific pathological mechanisms and importantly interrogate the contribution of their genetic background in susceptibility to PD.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
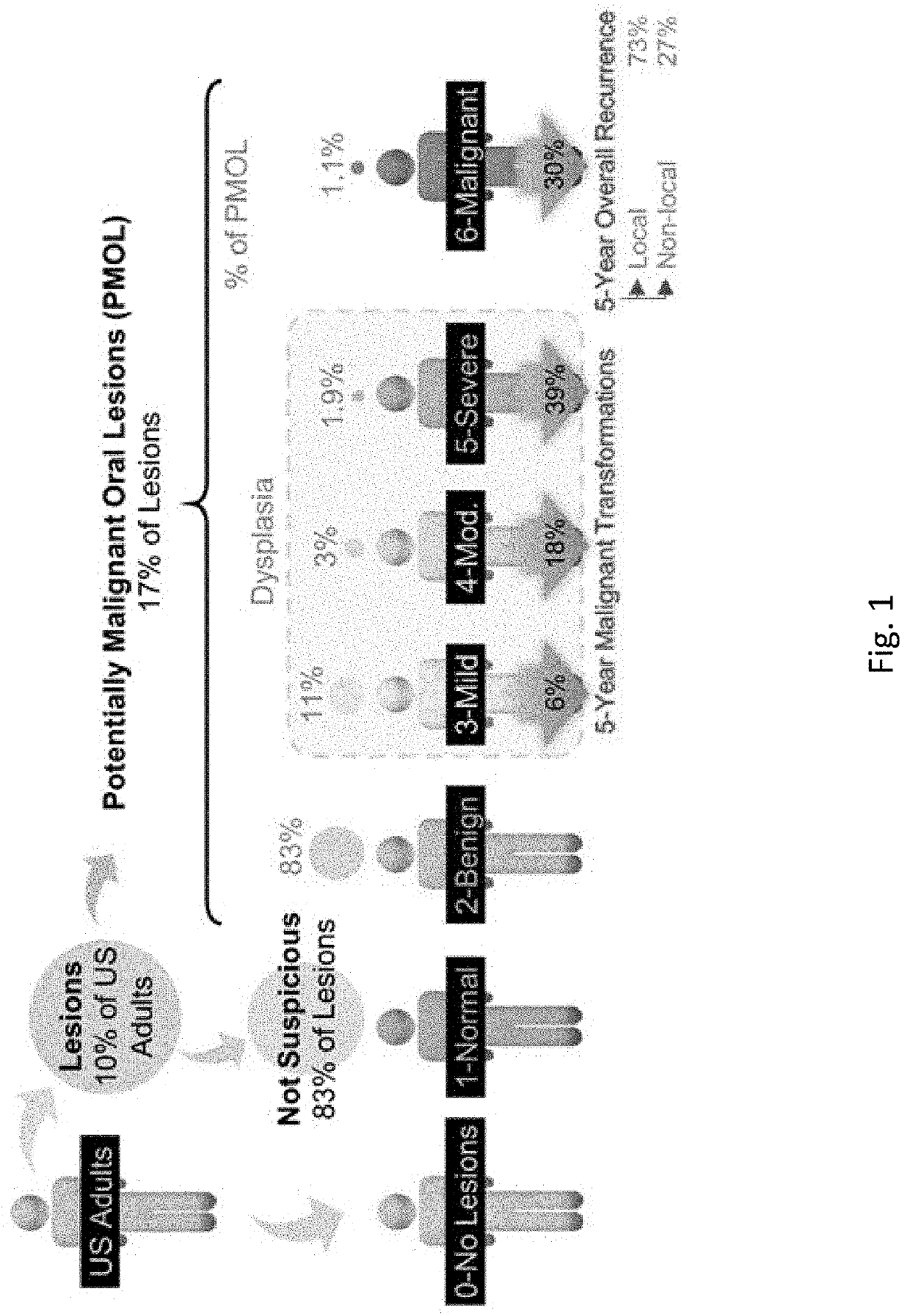
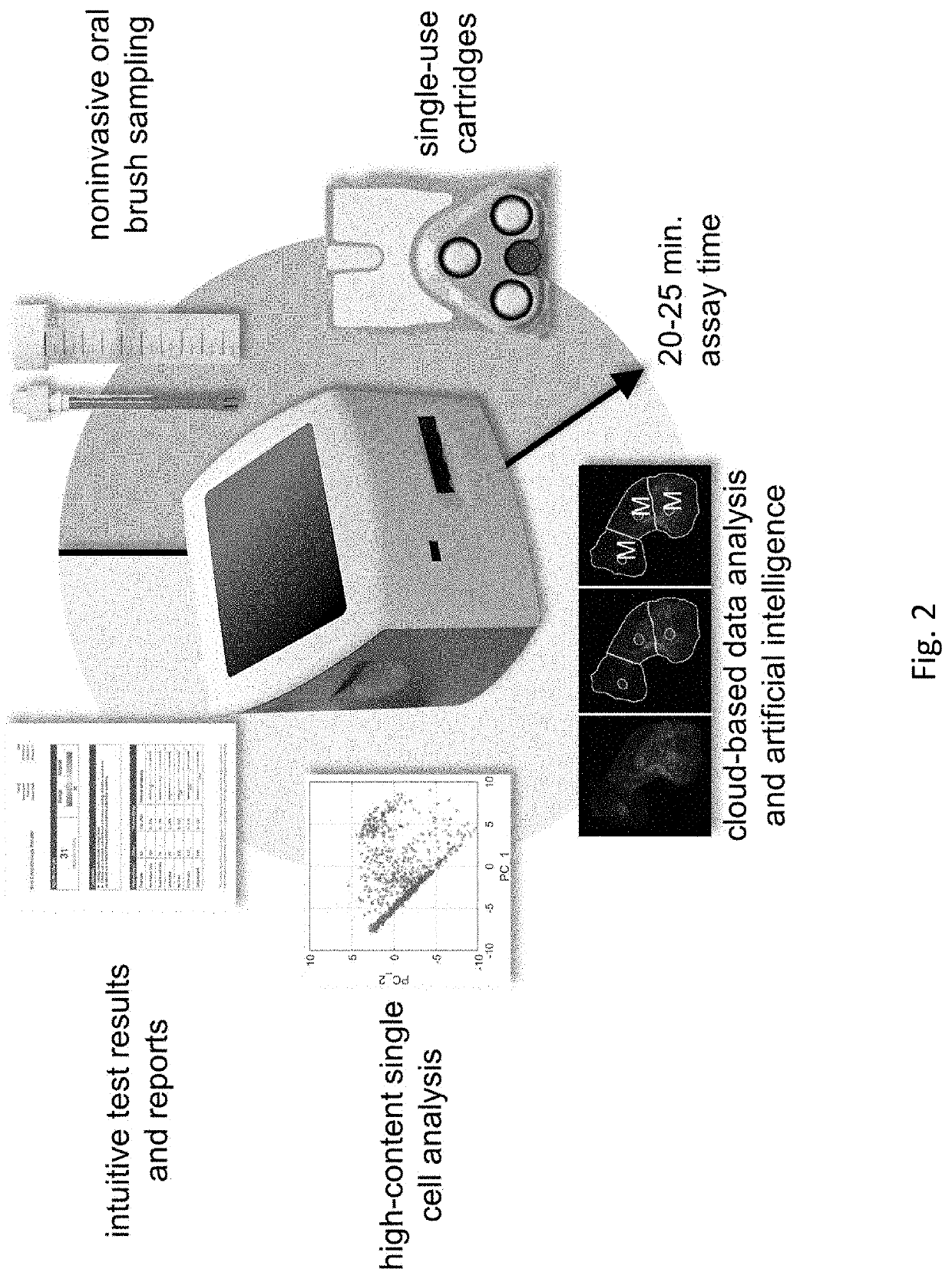
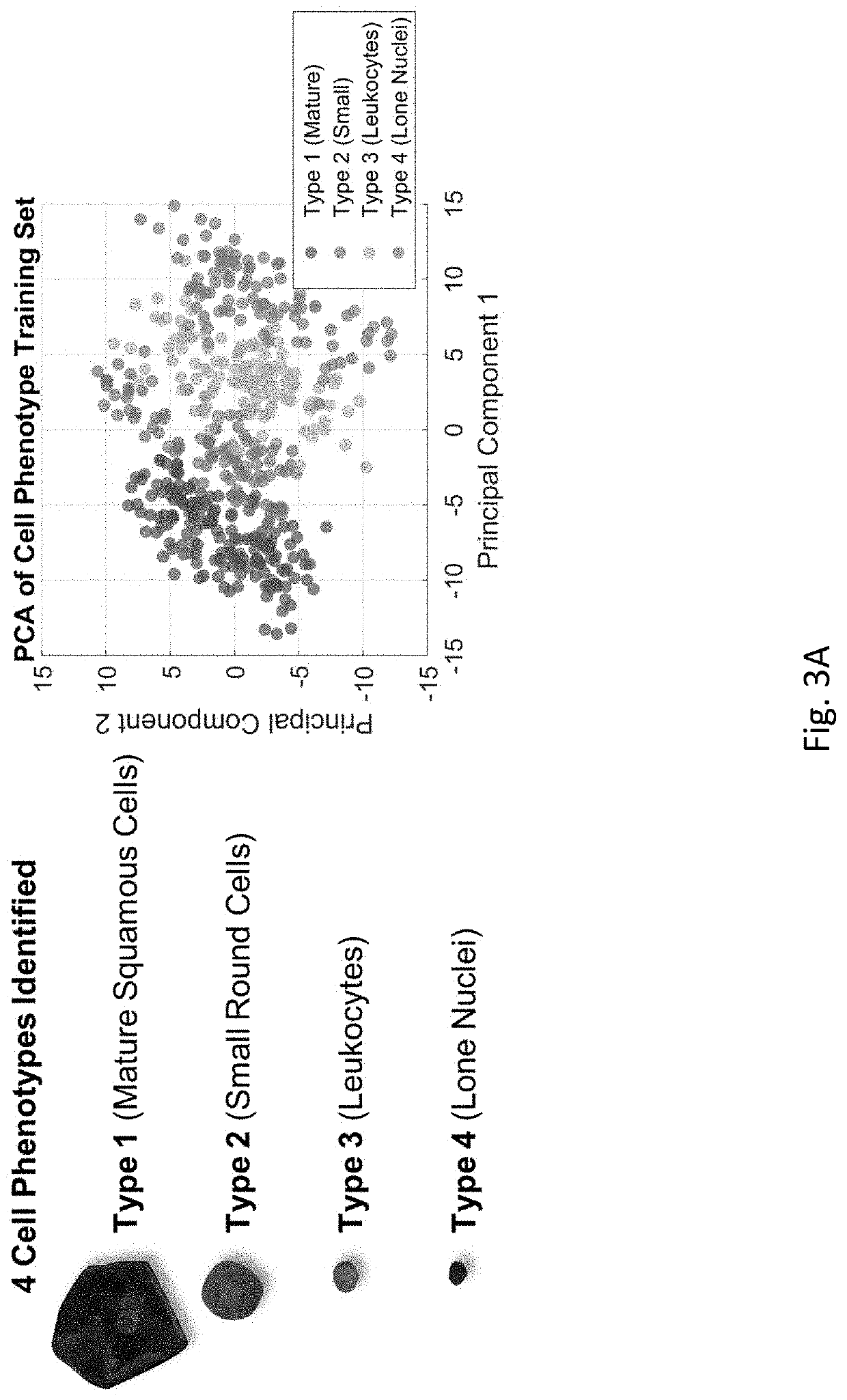
Systems and Methods of Oral Cancer Assessment Using Cellular Phenotype Data
The present disclosure is related to systems and methods to be used as aids in the diagnosis of risk for oral cancer by identifying cellular phenotype characteristics of a noninvasive brush biopsy sample.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Phenotype maintaining and in-vitro high-activity three-dimensional amplification method of hepatic stem cells
ActiveCN106754659AThe ingredients are not complicatedEasy to prepareCulture processCell culture supports/coatingSodium acetateHigh activity
The invention provides a phenotype maintaining and in-vitro high-activity three-dimensional amplification method of hepatic stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a medium, wherein the medium comprises 1L of DMEM / F12, 15-20 mg / L of a fibroblast growth factor, 10-15 mg / L of insulin, 0.1-0.2 mg / L of glutamic acid, 0.5-0.8 mg / L of nicotinamide, 0.1-0.2 mg / L of seleninic acid, 0.05-0.1 mg / L of beta-mercaptoethanol, 0.1-0.6 mg / L of alpha-actin, 0.2-0.3 mg / L of sodium acetate, 0.001-0.003 mg / L of sodium pyruvate and 2-3 wt% of fetal calf serum; and 2, immersing sterilized porous gel in the medium, inoculating the porous gel with hepatic stem cells, and culturing the hepatic stem cells. Stem cells with stable phenotype and high activity are obtained in the invention, and the good characteristics of the stem cells are kept.
Owner:绍兴橡树企业管理咨询合伙企业(有限合伙)
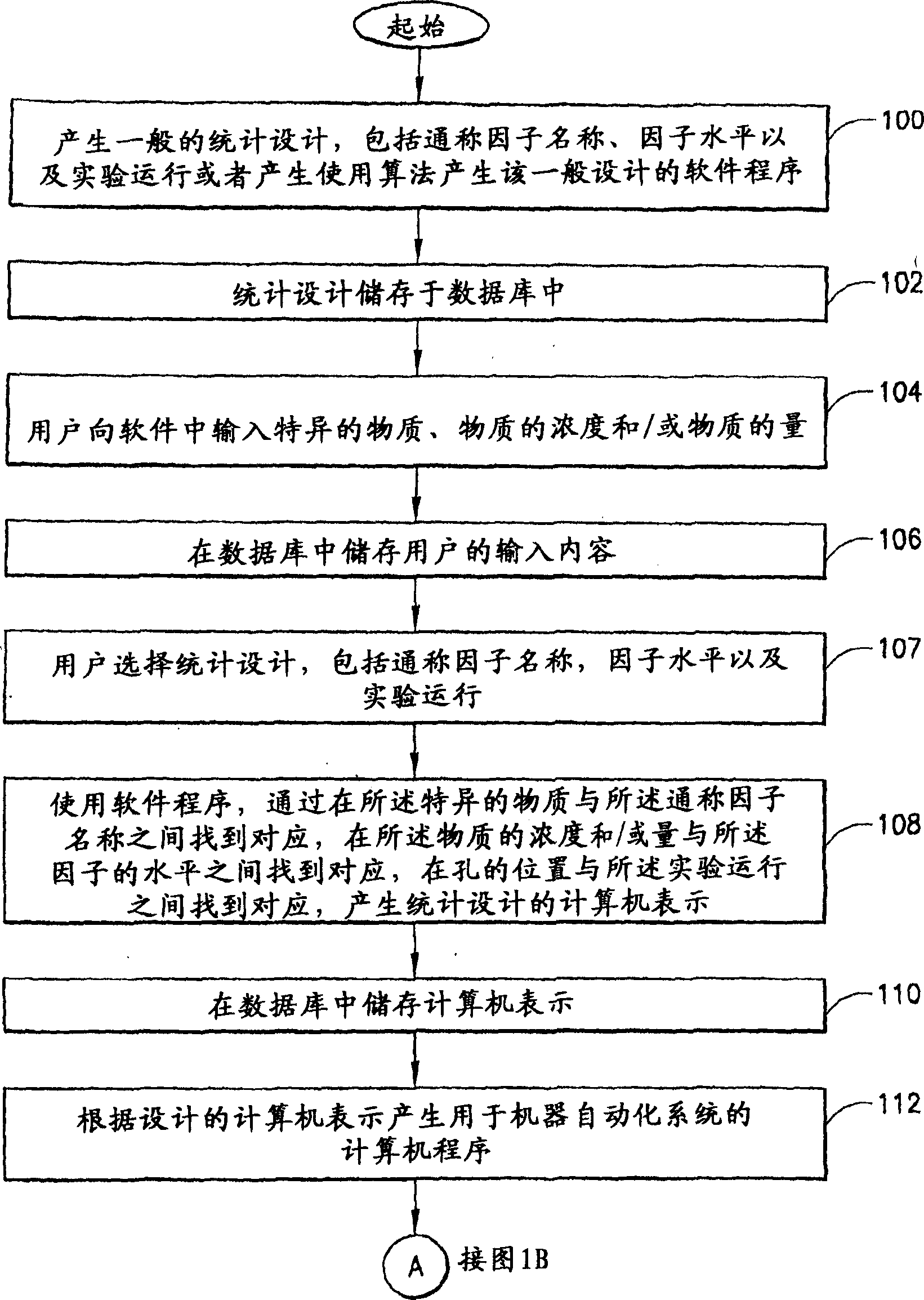
Computer software and algorithms for systems biologically linked to cellular phenotype
InactiveCN1890676ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle substanceCell type
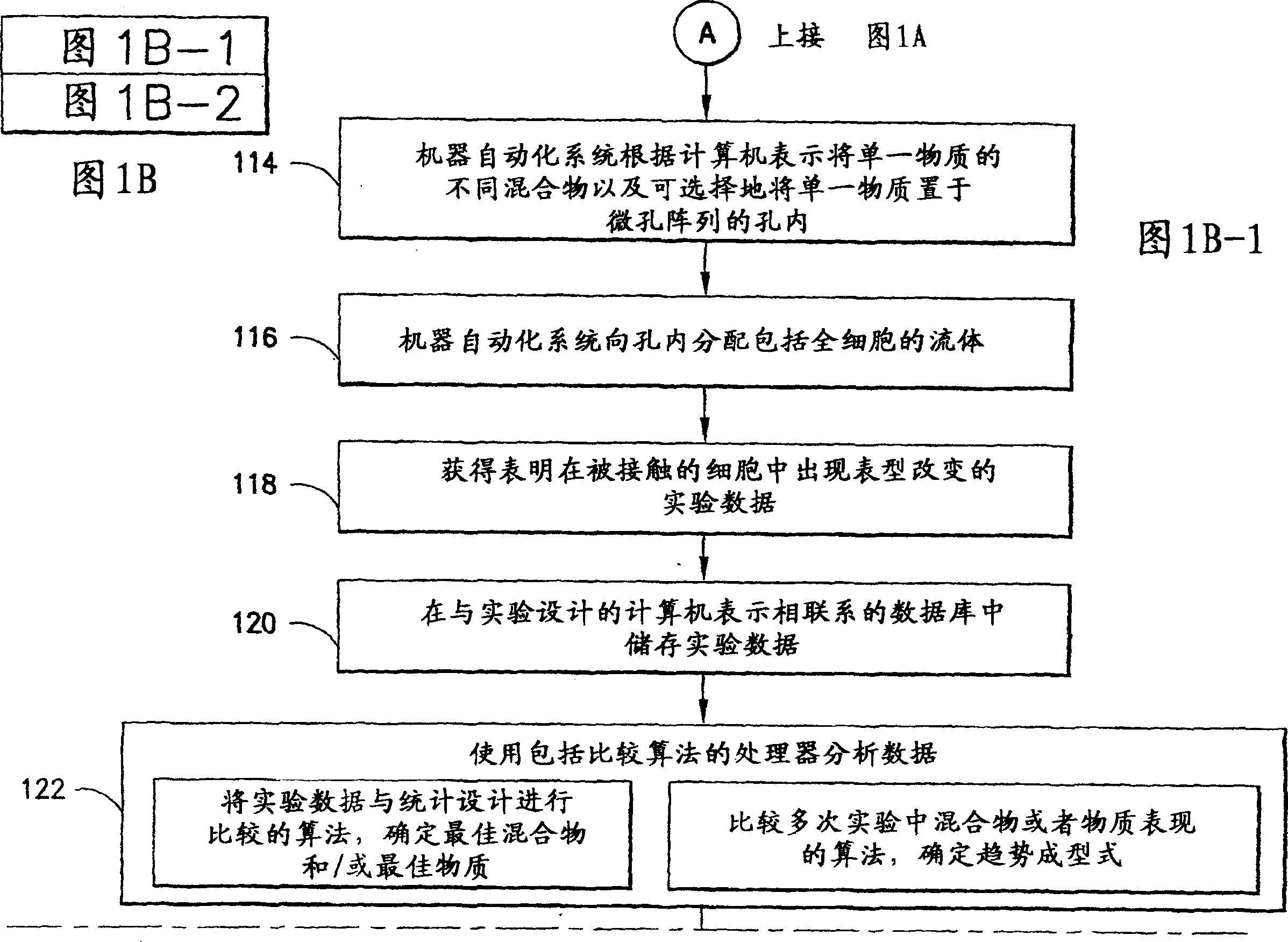
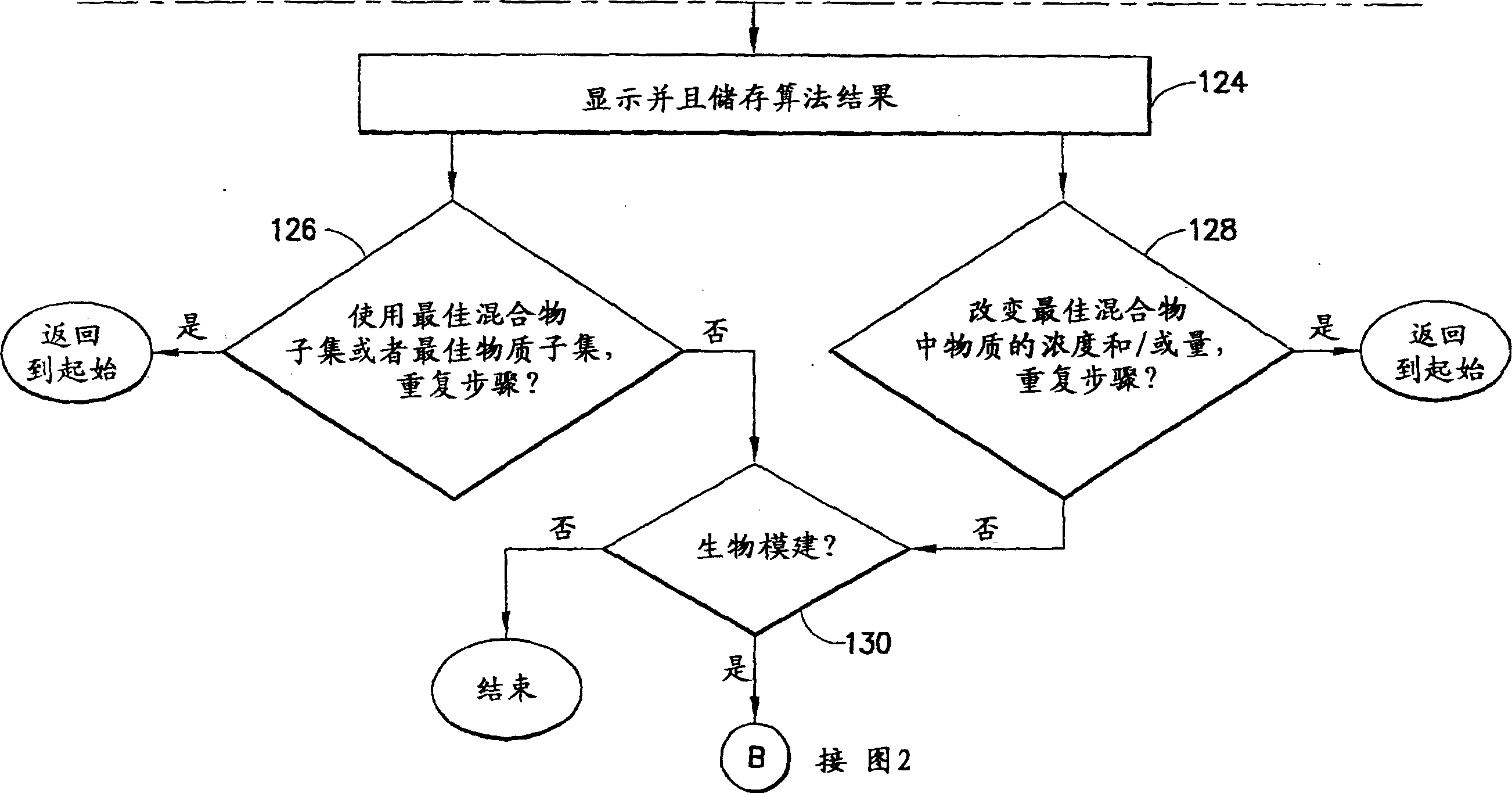
An automated method and system for identifying agents capable of eliciting a phenotypic change in a cell-type is provided. The method includes the steps of: providing receptacles in an array; and providing a statistical design including generic factor names, factor levels and experimental runs. The method further includes the steps of utilizing a software program to generate a computer representation of the statistical design by automatically mapping the identities of the agents to the generic factor names, by mapping the concentration or amounts of the agents to the factor levels and by mapping the locations of the receptacles within the array to the experimental runs. The method also includes placing different mixtures of single agents into receptacles in the array based on the computer representation of the statistical design; contacting the placed mixtures with cells; acquiring experimental data from the contacted cells; and utilizing a processor including an algorithm for comparing the acquired data with the statistical design to identify particular agent mixtures or single agents that cause a phenotypic change in the contacted cells.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Novel differentiation technique to generate dopaminergic neurons from induced pluripotent stem cells
PendingUS20210024886A1Reliable generationNervous disorderNervous system cellsCell phenotypeCell type
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (Ipsc) technology enables the generation and study of living brain tissue relevant to Parkinson's disease (PD) ex vivo. Utilizing cell lines from PD patients presents a powerful discovery system that links cellular phenotypes observed in vitro with real clinical data. Differentiating patient-derived iPSCs towards a dopaminergic (DA) neural fate revealed that these cells exhibit molecular and functional properties of DA neurons in vitro that are observed to significantly degenerate in the substantia nigra of PD patients. Clinical symptoms that drive the generation of other relevant cell types may also yield novel PD-specific phenotypes in vitro that have the potential to lead to new therapeutic avenues for patients with PD. Due to their early onset and non-familial origin, differentiated nervous tissue from these patients offer a key opportunity to discover neuron subtype-specific pathological mechanisms and importantly interrogate the contribution of their genetic background in susceptibility to PD.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Transcriptome transfer produces cellular phenotype conversion
The present invention includes methods for effecting phenotype conversion in a cell by transfecting the cell with phenotype-converting nucleic acid. Expression of the nucleic acids results in a phenotype conversion in the transfected cell. Preferably the phenotype-converting nucleic acid is a transcriptome, and more preferably an mRNA transcriptome.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods of determining cellular phenotypes
ActiveUS10281463B2Spectrum investigationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsRefractive indexCell based
Methods of determining a phenotype of cells in a biological sample are provided. The methods are based measuring a refractive index of said cells based on a diffraction pattern received from a diffraction grating having a plurality of compartments having lateral dimensions such that said cells can fit therein.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Identifying compounds modifying a cellular phenotype
InactiveUS20190353641A1Easy to testOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMedicineDrug target
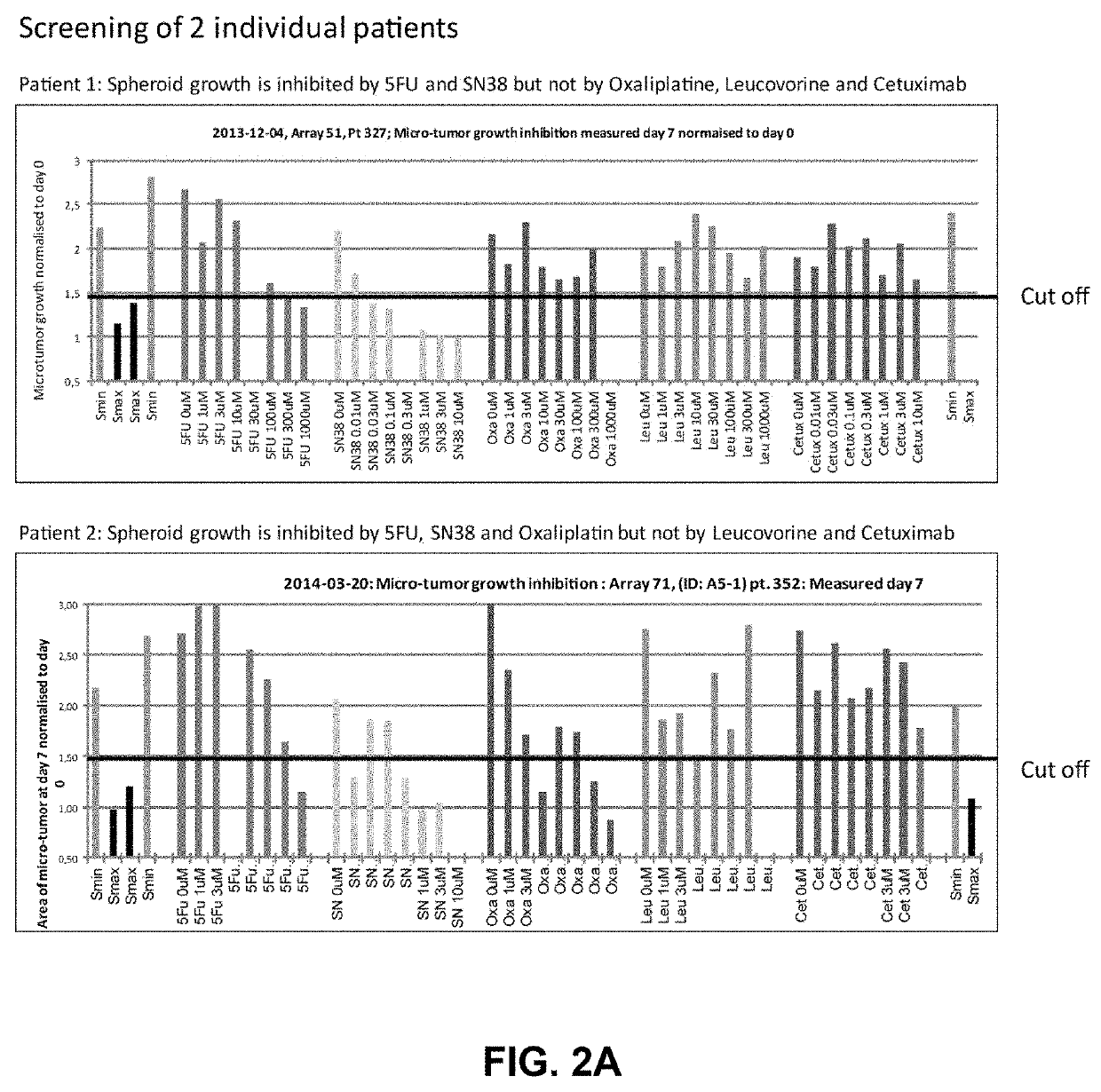
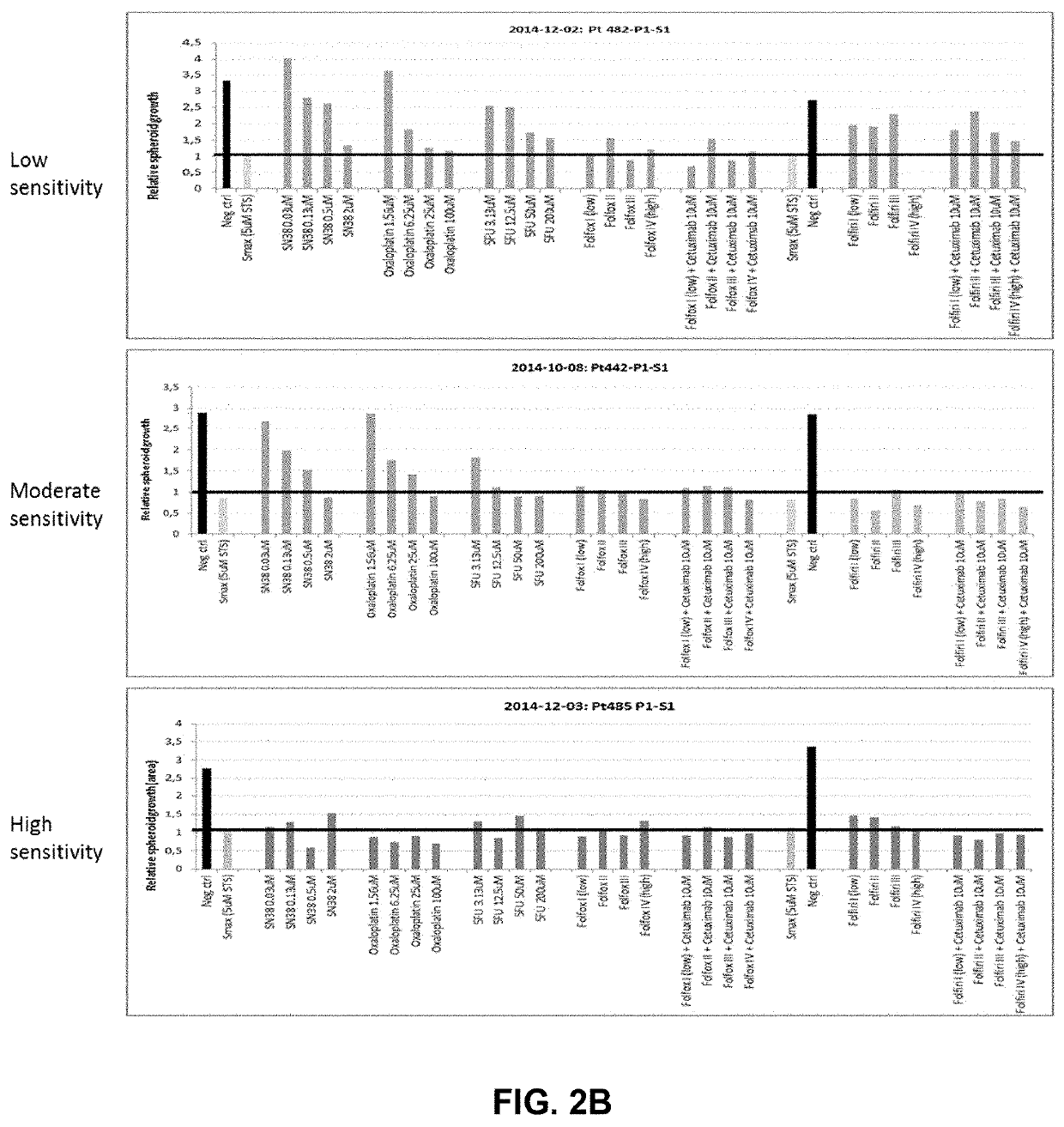
The present invention relates to a method and tools for extracting information on a compounds influence on a cellular phenotype. The method of the invention may be used as a very efficient procedure for testing the efficacy or resistance of single drugs or combinations of drugs on cells from individual patients. Thus, the methods may be useful for predicting efficacy of a drug on a given patient. The methods are also useful for testing of compounds for toxicity, identifying drug targets for known or novel compounds.
Owner:2CUREX APS
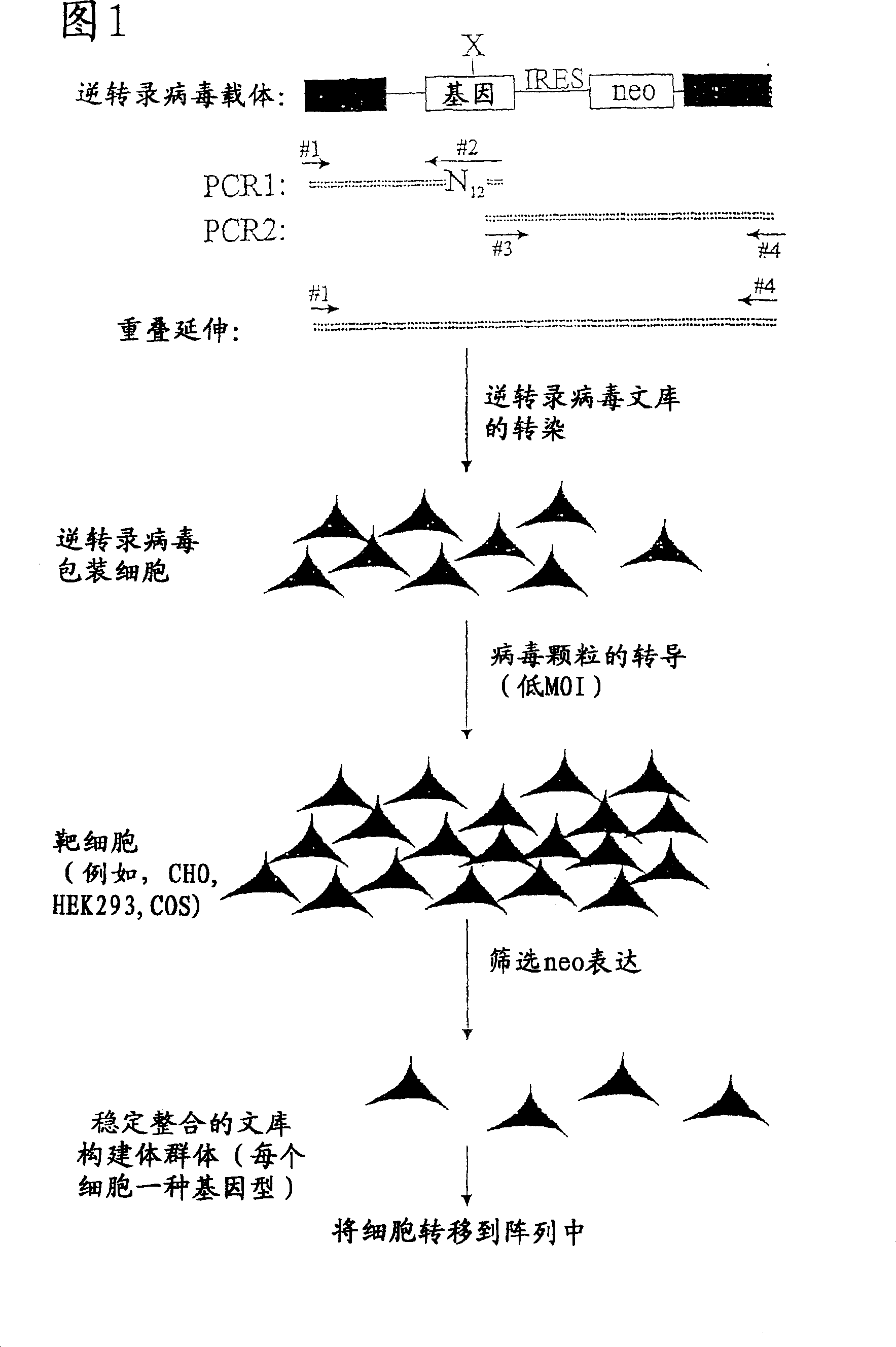
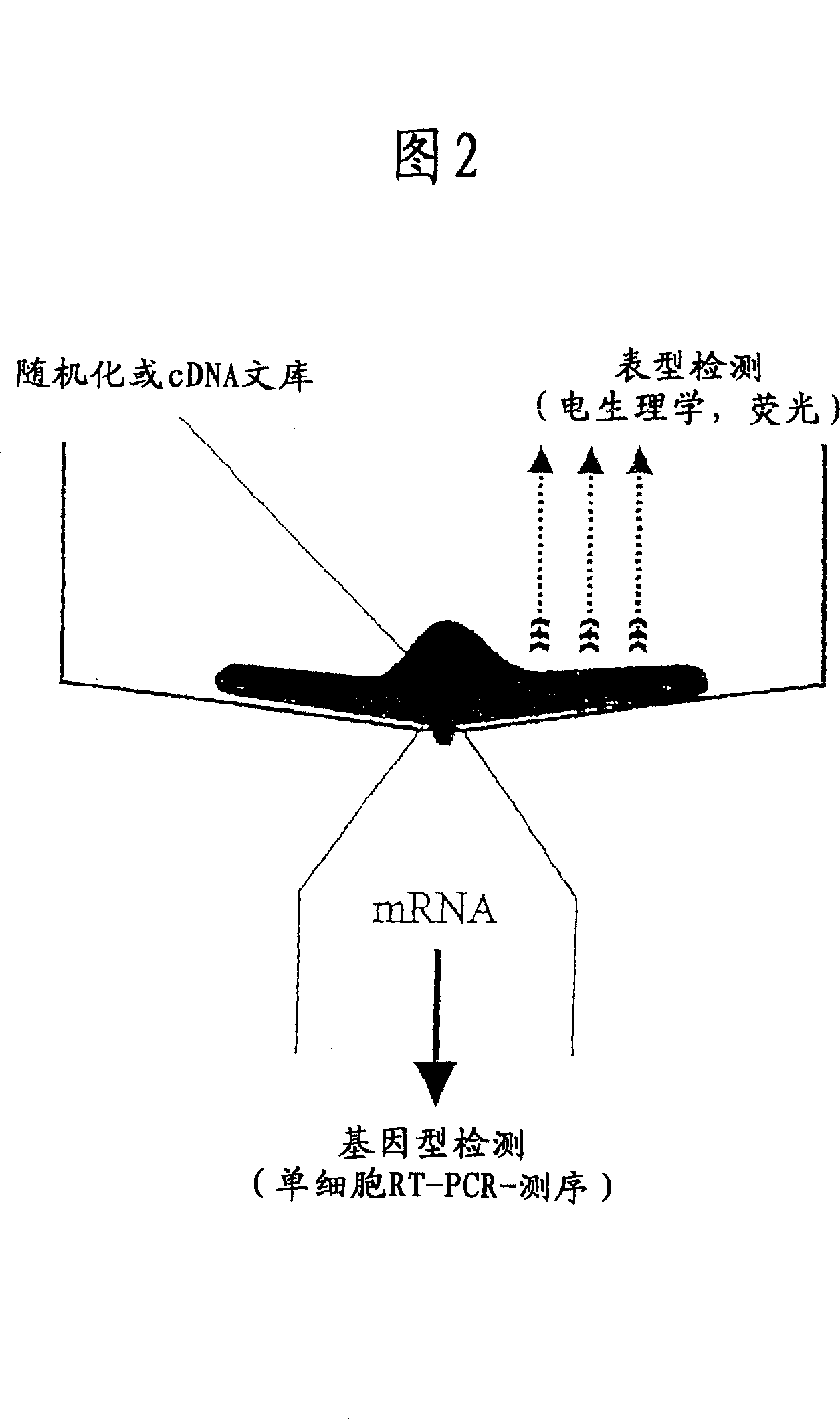
Screening methods
InactiveCN100335630CBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCDNA libraryScreening method
The present invention relates to screening methods, and in particular, to methods of screening DNA libraries to identify DNA molecules which when expressed in a host cell, give rise to at least one change in the phenotype of the host cell and such phenotype changes being detected using a patch clamp chip construct. Furthermore, the invention concerns the isolation of mRNA, corresponding to the DNA molecule, giving rise to said cellular phenotypic change.
Owner:SOPHION BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for expanding, identifying, characterizing and enhancing potency of mammalian-derived glial restricted progenitor cells
Methods for producing a population of human-derived glial restricted progenitor cells (GRPs) with decreased potentially unintended or undesired cellular phenotypes and / or decreased standard deviation in the cells of the population are provided. Also provided are antibody panels and gene expression profiles to characterize GRPs and a method for its use in characterizing GRP cells. In addition methods for use of these GRP cells to generate astrocytes and / or oligodendrocytes, to re-myelinate neurons and to treat glial cell related and other neurodegenerative diseases or disorders or injuries or damage to the nervous system are provided. A method to manufacture neural cells depleted of A2B5 positive cells is also provided.
Owner:Q THERAPEUTICS
Screening and Assessment of Potentially Malignant Oral Lesions
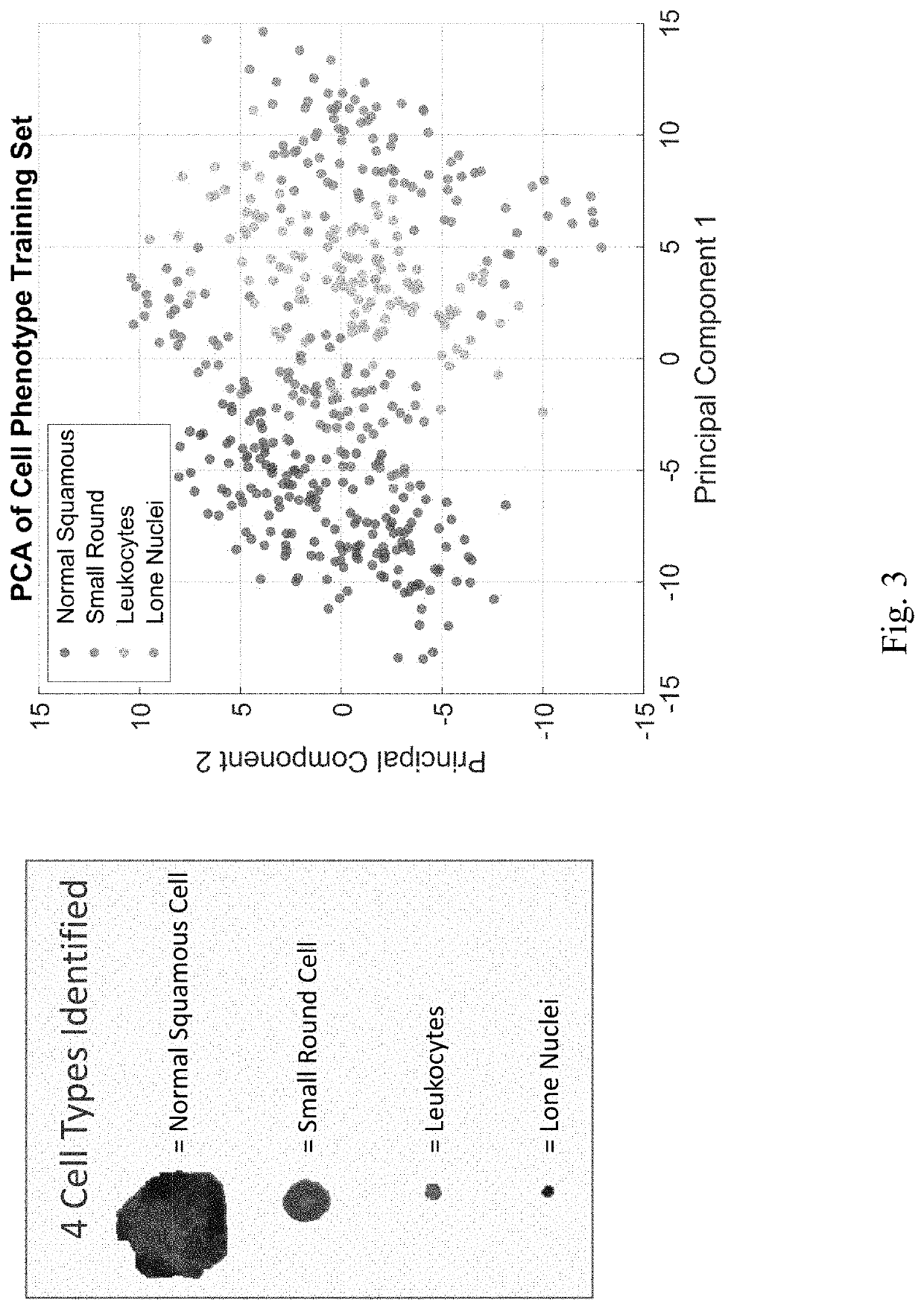
The present disclosure is related to systems and methods to be used as aids in the diagnosis of risk for oral cancer, potentially malignant oral lesion (PMOL), and / or oral epithelial dysplasia (OED) by identifying cellular phenotype characteristics of cell samples, including percentage of mature squamous cells, presence or absence of nuclear actin in mature squamous cells, percentage of non-mature squamous cells, percentage of small round cells, percentage of white blood cells, and percentage of lone nuclei.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Cost-optimized design analysis for rapid microbial prototyping
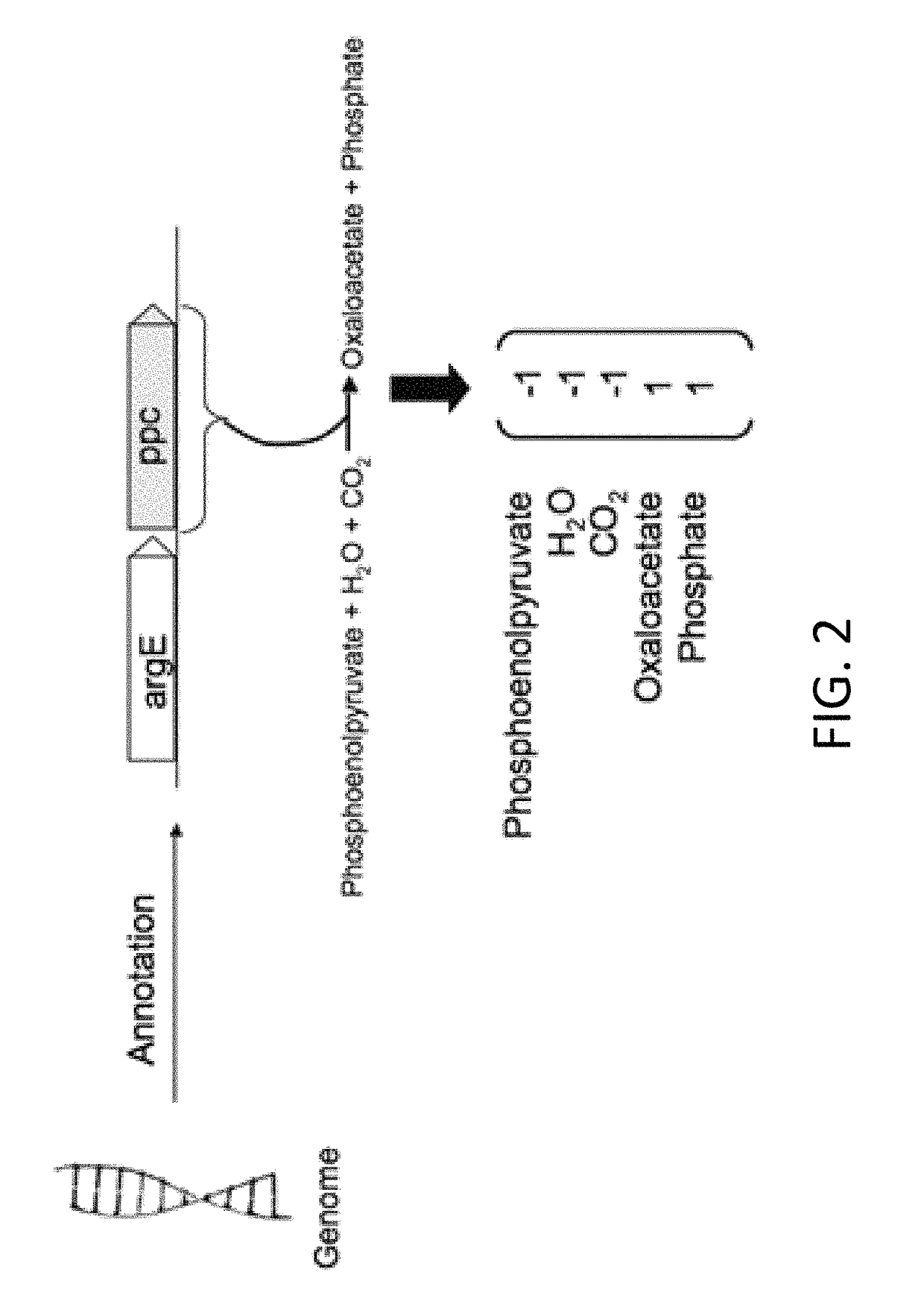
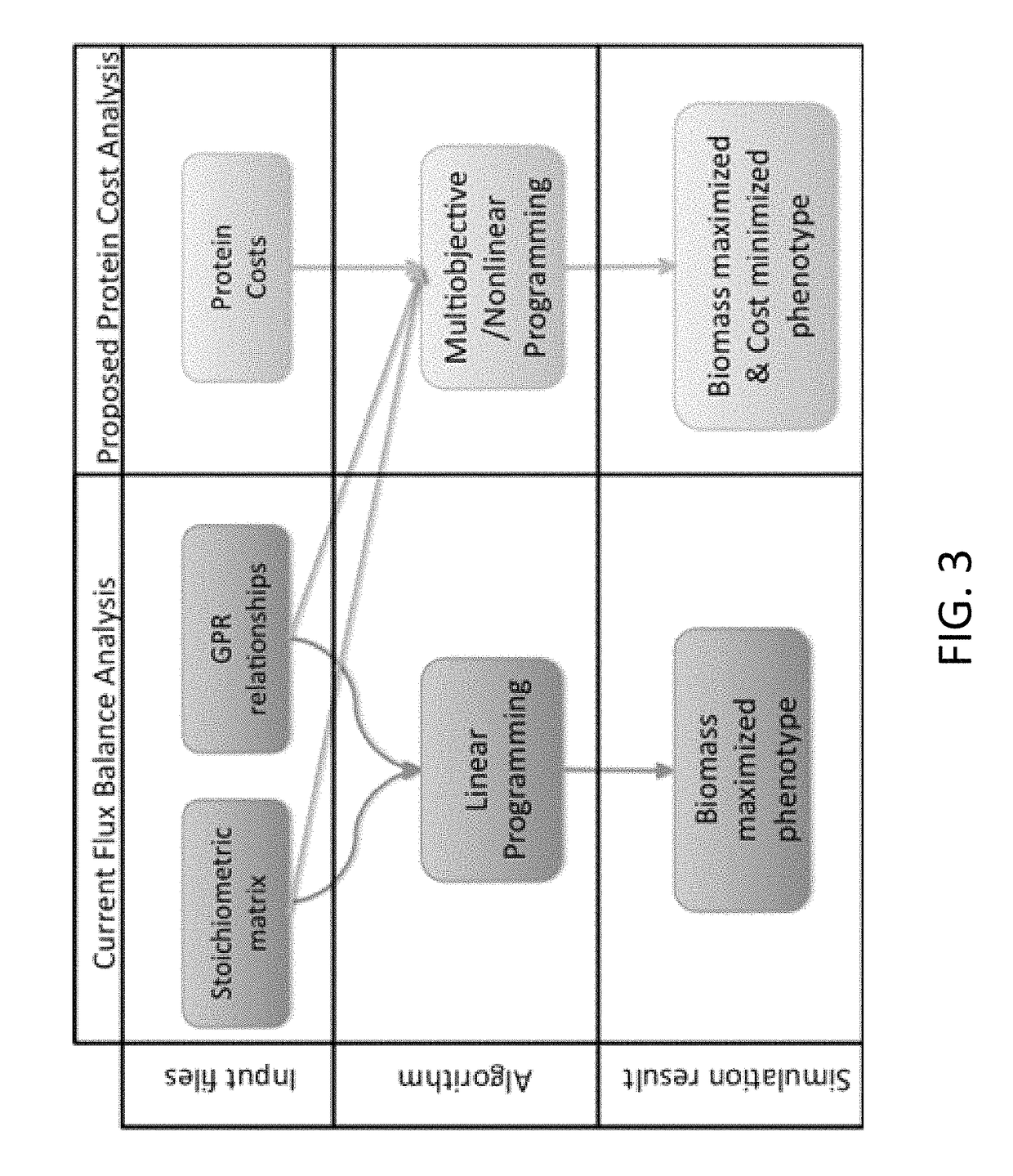
ActiveUS10102335B2Maximizes a cellular phenotype of a modeled organismLow costProteomicsGenomicsProtein compositionDesign analysis
Computer-implemented methods for providing improvements in genome-scale metabolic models are described. The methods identify and optimize metabolic flux states that minimize the cost of enzyme production while maximizing a desired cellular phenotype. The computer-implemented methods may maximize cellular phenotypes such as growth (biomass) or production of a metabolite, such as a commercially valuable chemical compound, through the selection of metabolic pathways that maximize these phenotypes while minimizing metabolic costs associated with production of the proteomic constituents of individual metabolic pathways. The computer implemented methods may be useful for computationally designing microbial strains for the production of chemicals.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
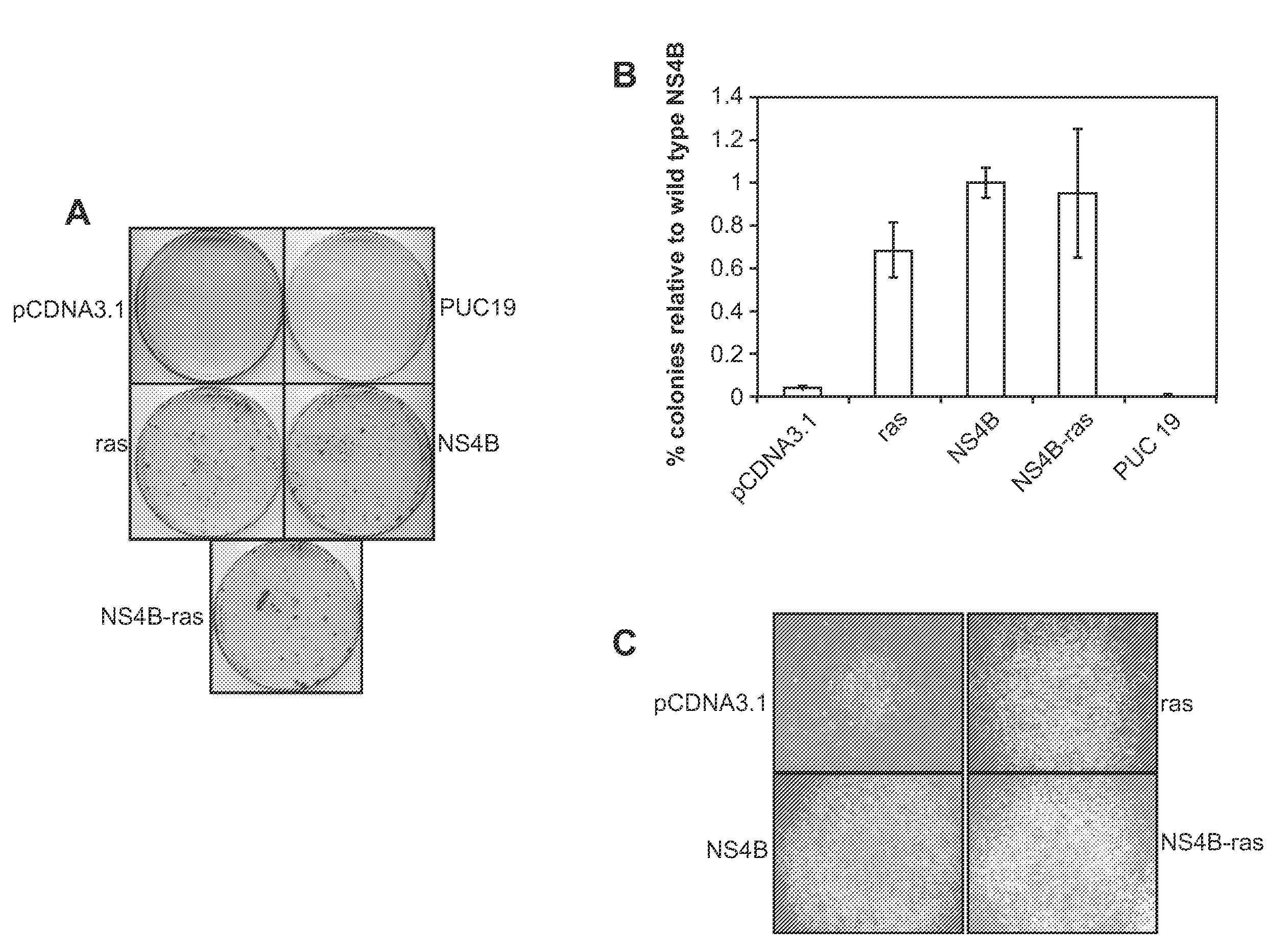
Methods and compositions for identifying agents that inhibit an ns4b-mediated neoplastic cellular phenotype of hcv infected cells
InactiveUS20090083869A1Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalWilms' tumor
The disclosure provides methods and compositions for identifying agents that inhibit a neoplastic cellular phenotype mediated by the NS4B protein nucleotide binding motif (NBM) of hepatitis C virus (HCV). In general, the methods involve contacting a candidate agent with a mammalian cell expressing an NS4B NBM polypeptide of an HCV virus, wherein expression of the NS4B NBM polypeptide in the absence of candidate agent promotes a neoplastic cellular phenotype, and detecting the presence or absence of an effect of said candidate agent on NS4B-mediated promotion of a neoplastic cellular phenotype. The disclosed methods and compositions find use in a variety of therapeutic and screening applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com