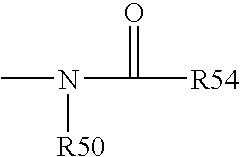
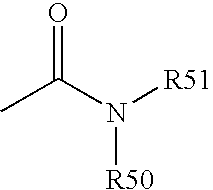
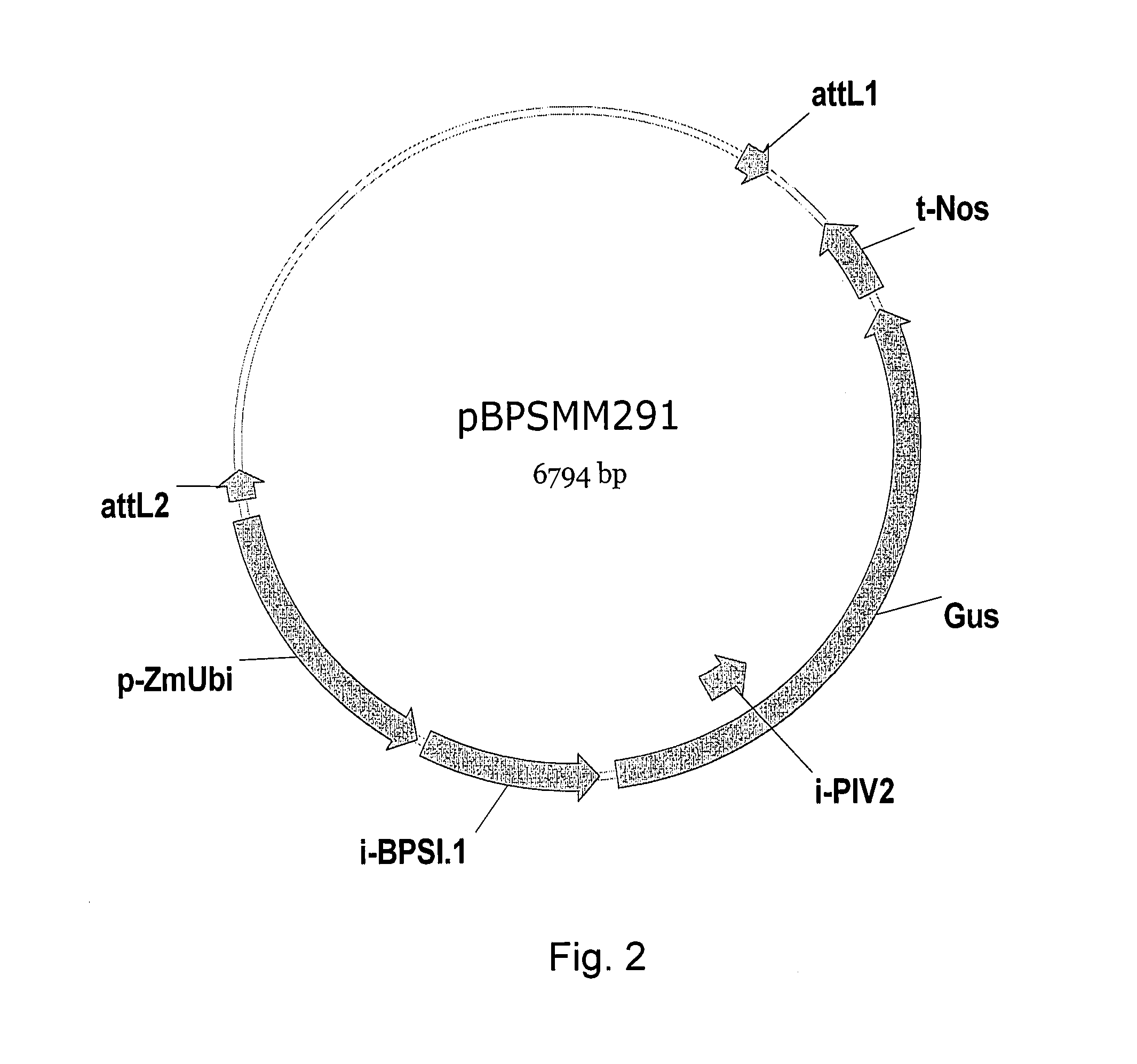
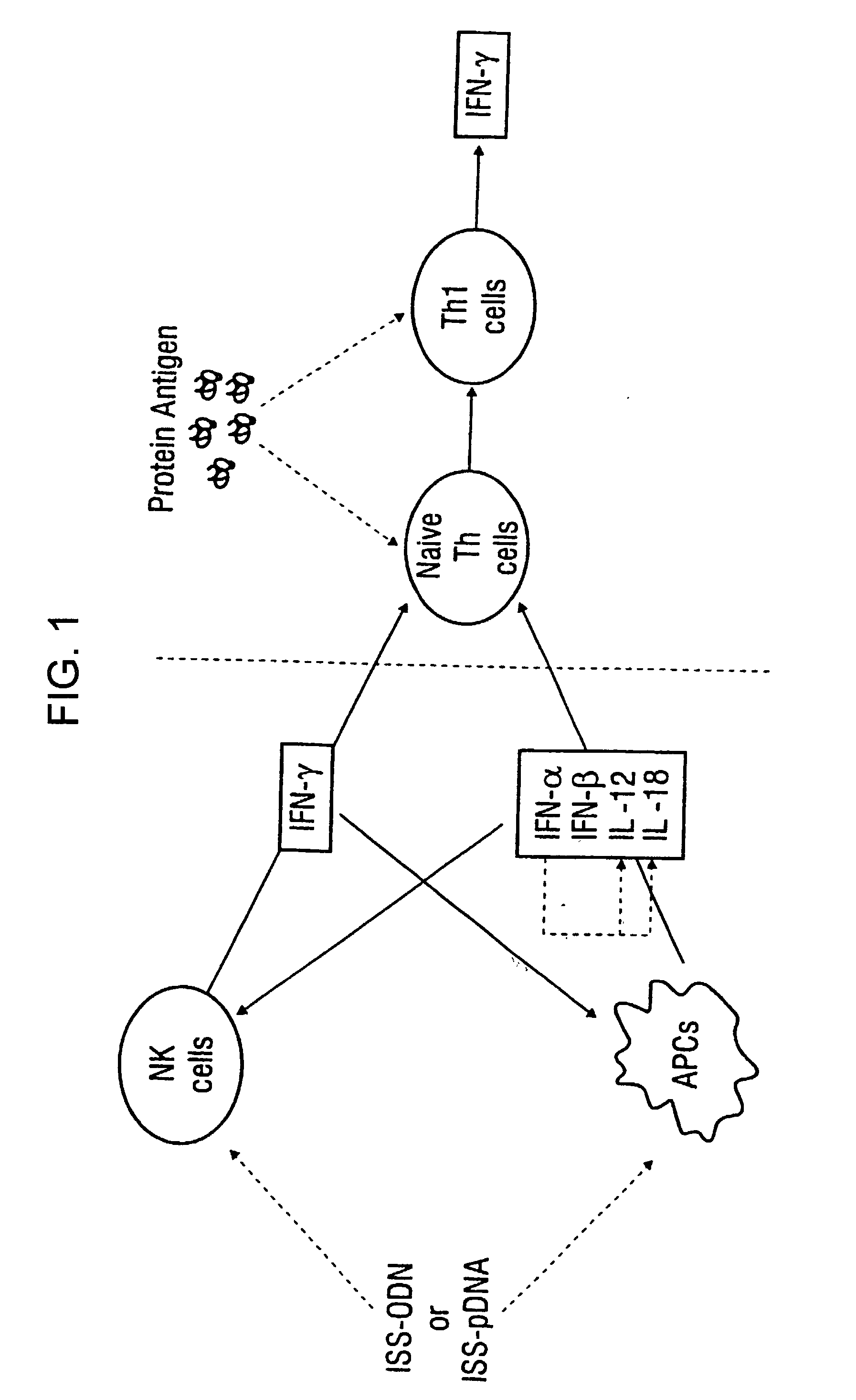
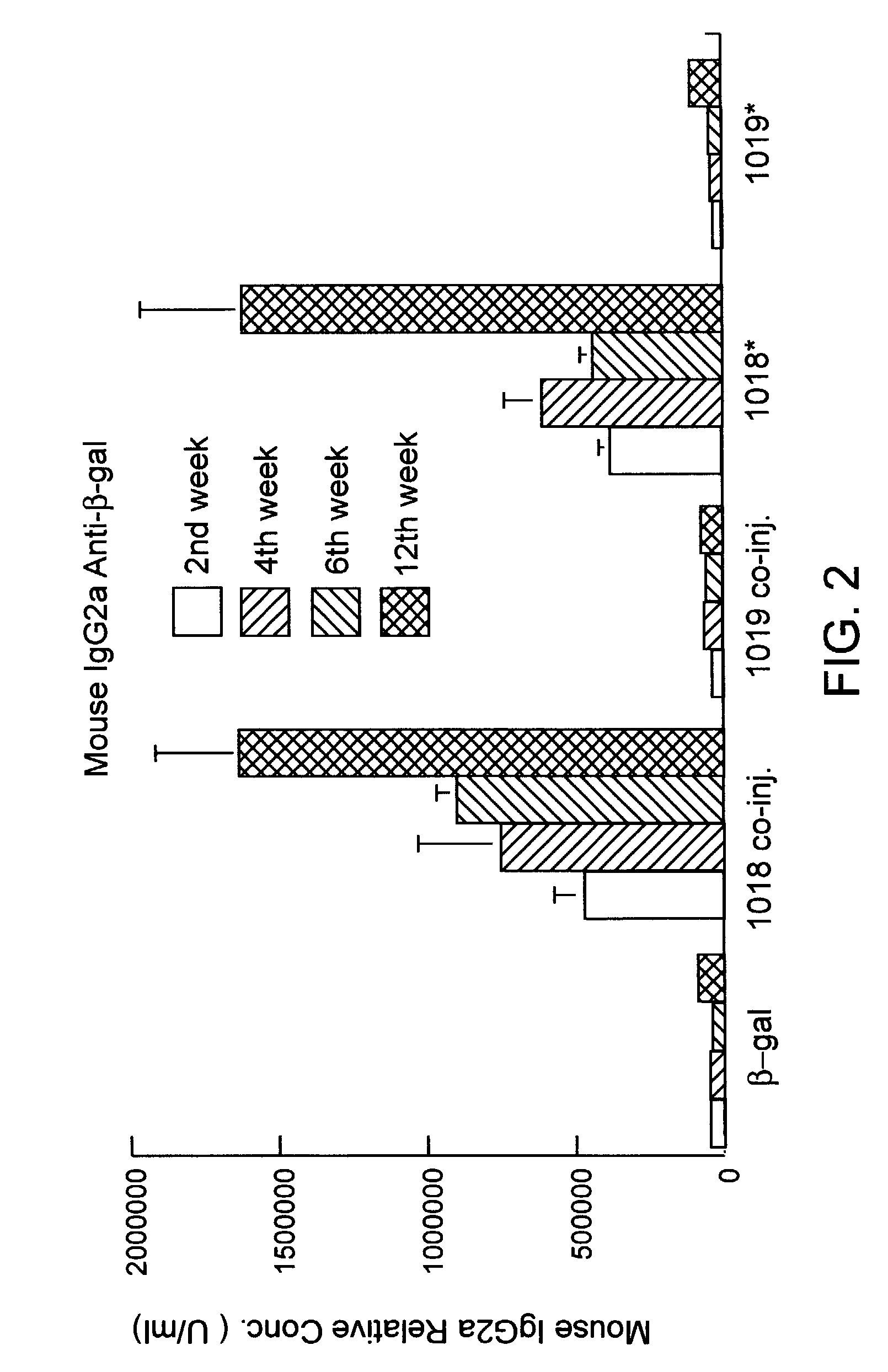
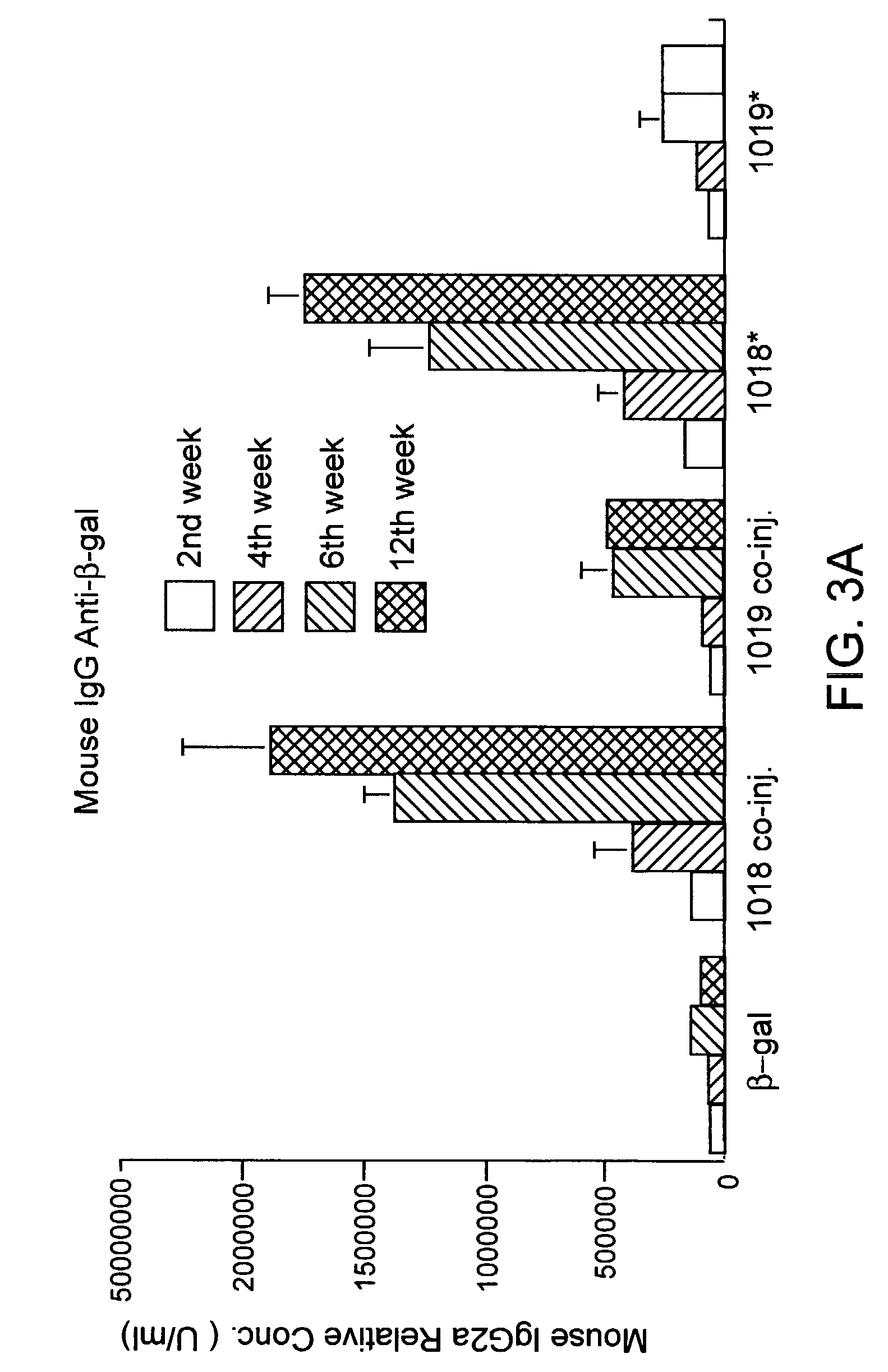
Patents
Literature
3236 results about "Phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, the phenotype (from Greek phainein, meaning 'to show', and typos, meaning 'type') of an organism is the composite of the organism's observable characteristics or traits. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book The Extended Phenotype suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddis-fly larvae cases and beaver dams as "extended phenotypes".
Phage antibodies
Peripheral blood leucocytes incubated with a semi-synthetic phage antibody library and fluorochrome-labeled CD3 and CD20 antibodies were used to isolate human single chain Fv antibodies specific for subsets of blood leucocytes by flow cytometry. Isolated phage antibodies showed exclusive binding to the subpopulation used for selection or displayed additional binding to a restricted population of other cells in the mixture. At least two phage antibodies appeared to display hithereto unknown staining patterns of B lineage cells. This approach provides a subtractive procedure to rapidly obtain human antibodies against known and novel surface antigens in their native configuration, expressed on phenotypically defined subpopulations of cells. Importantly, this approach does not depend on immunization procedures or the necessity to repeatedly construct phage antibody libraries.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
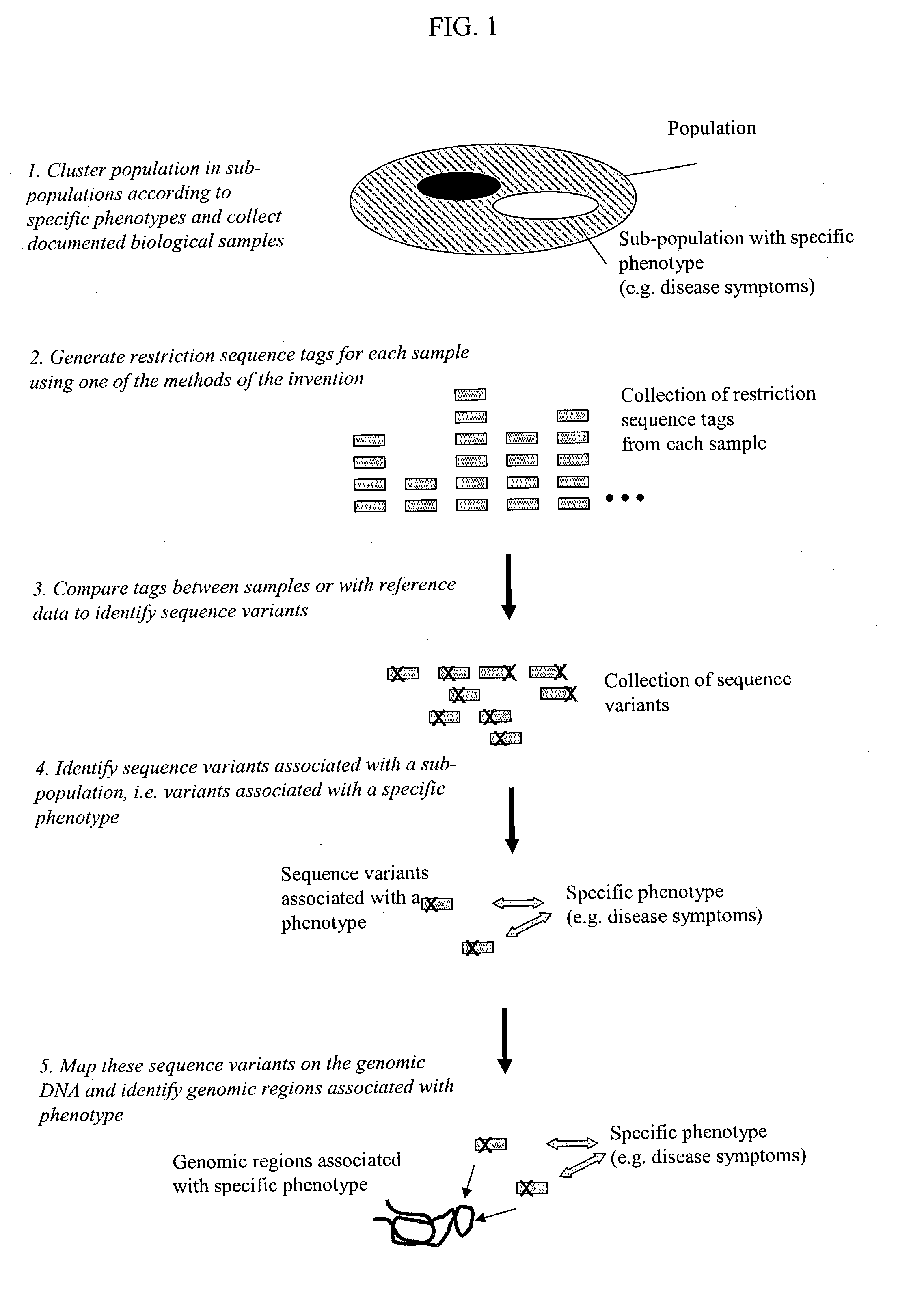
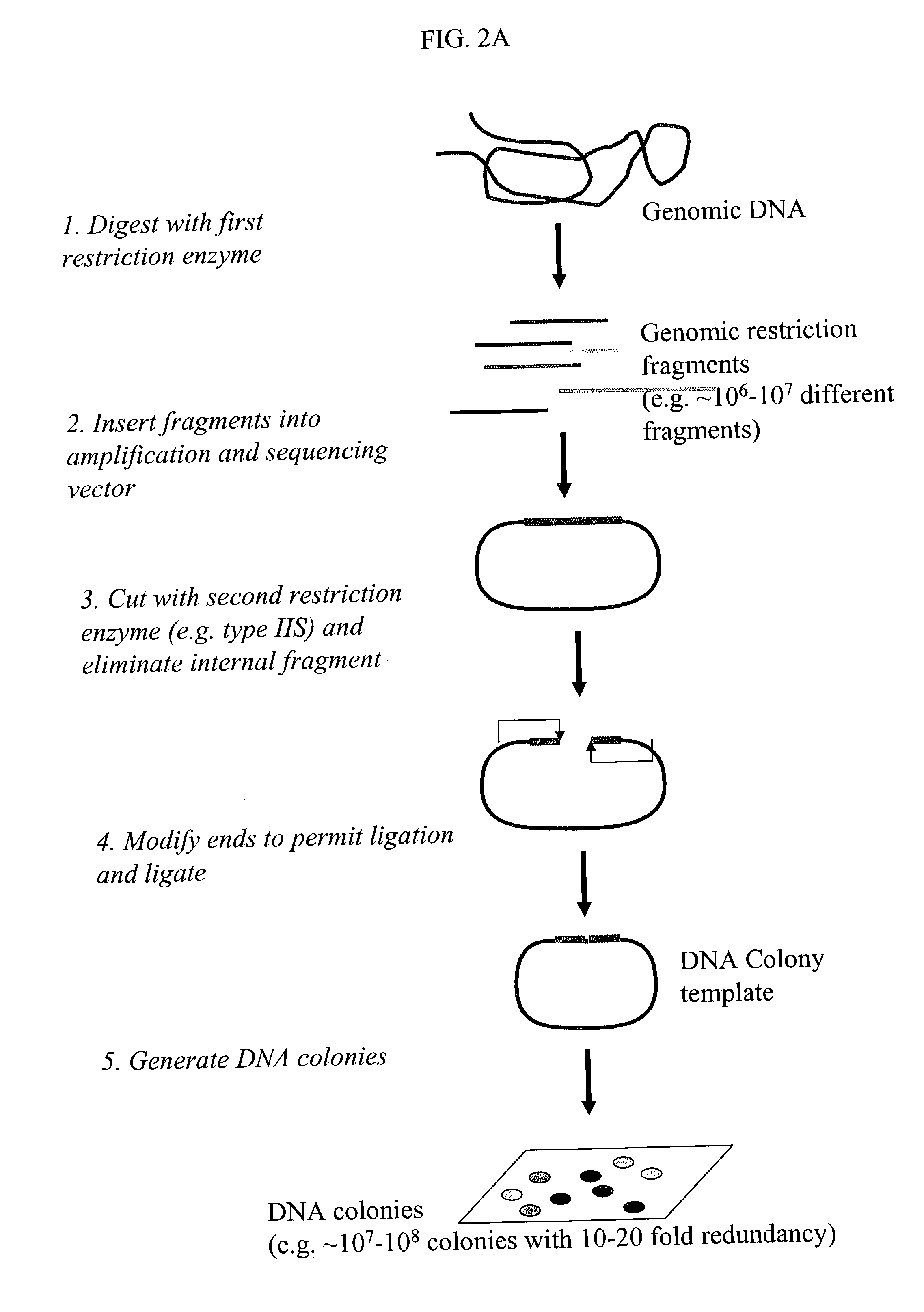
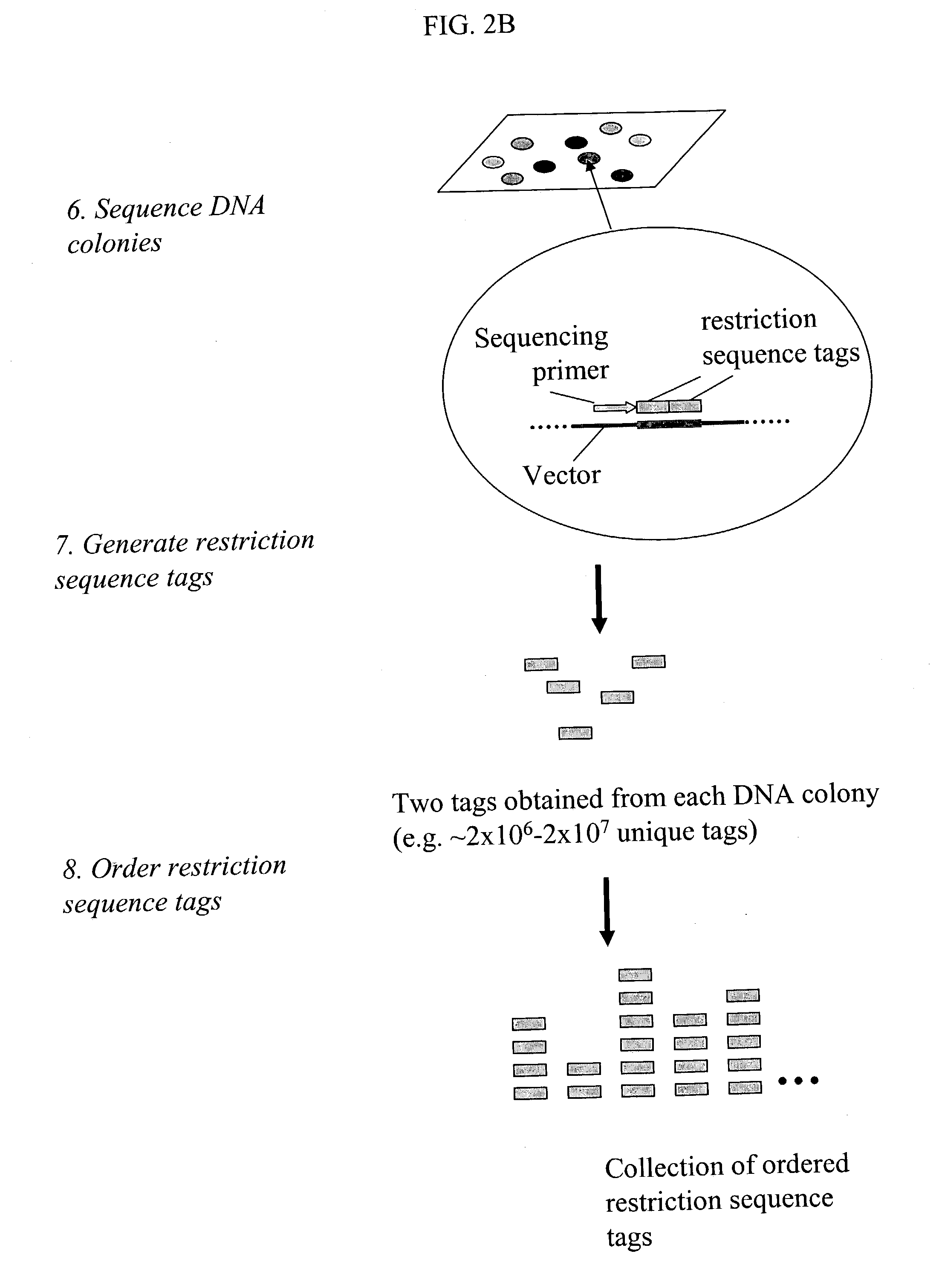
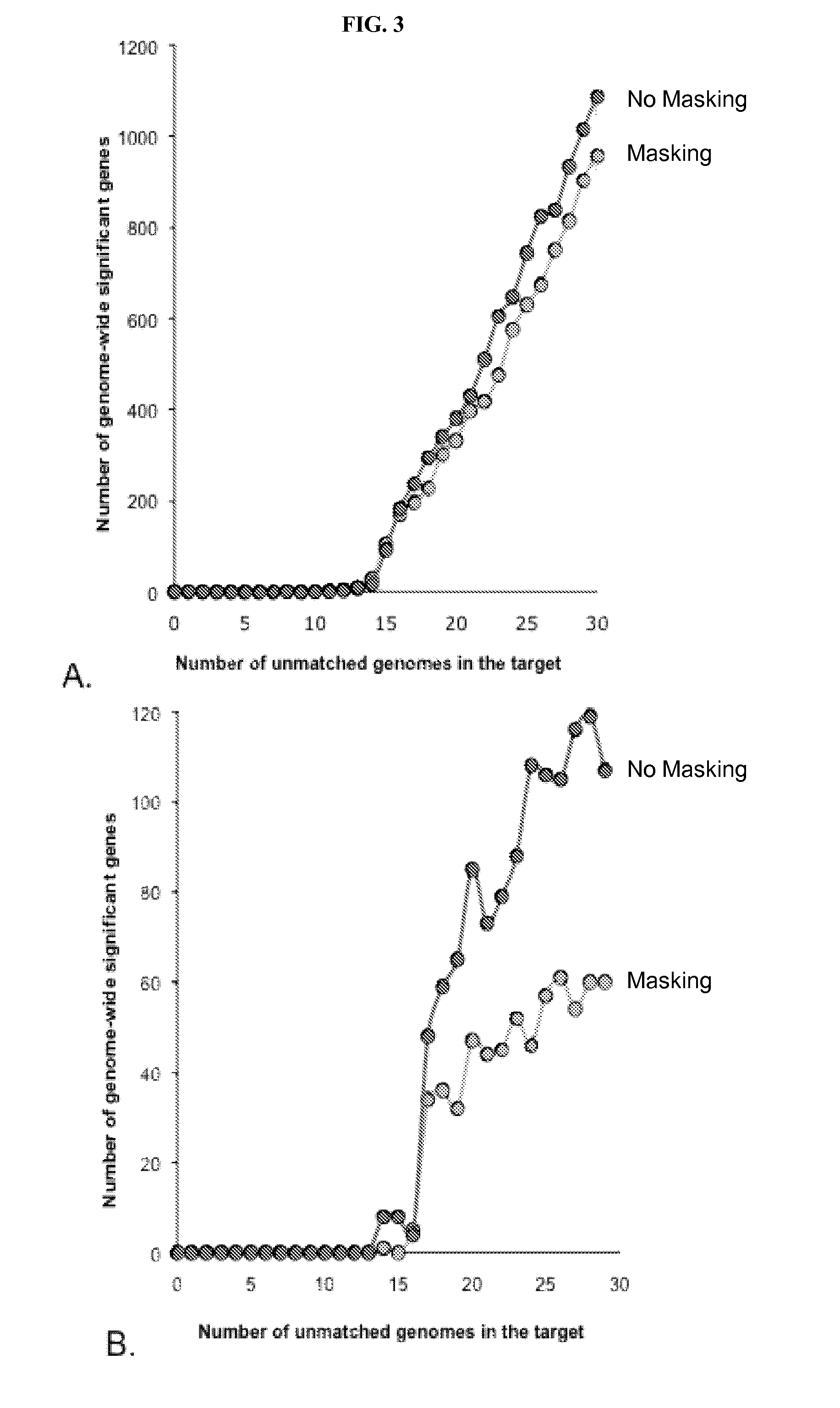
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
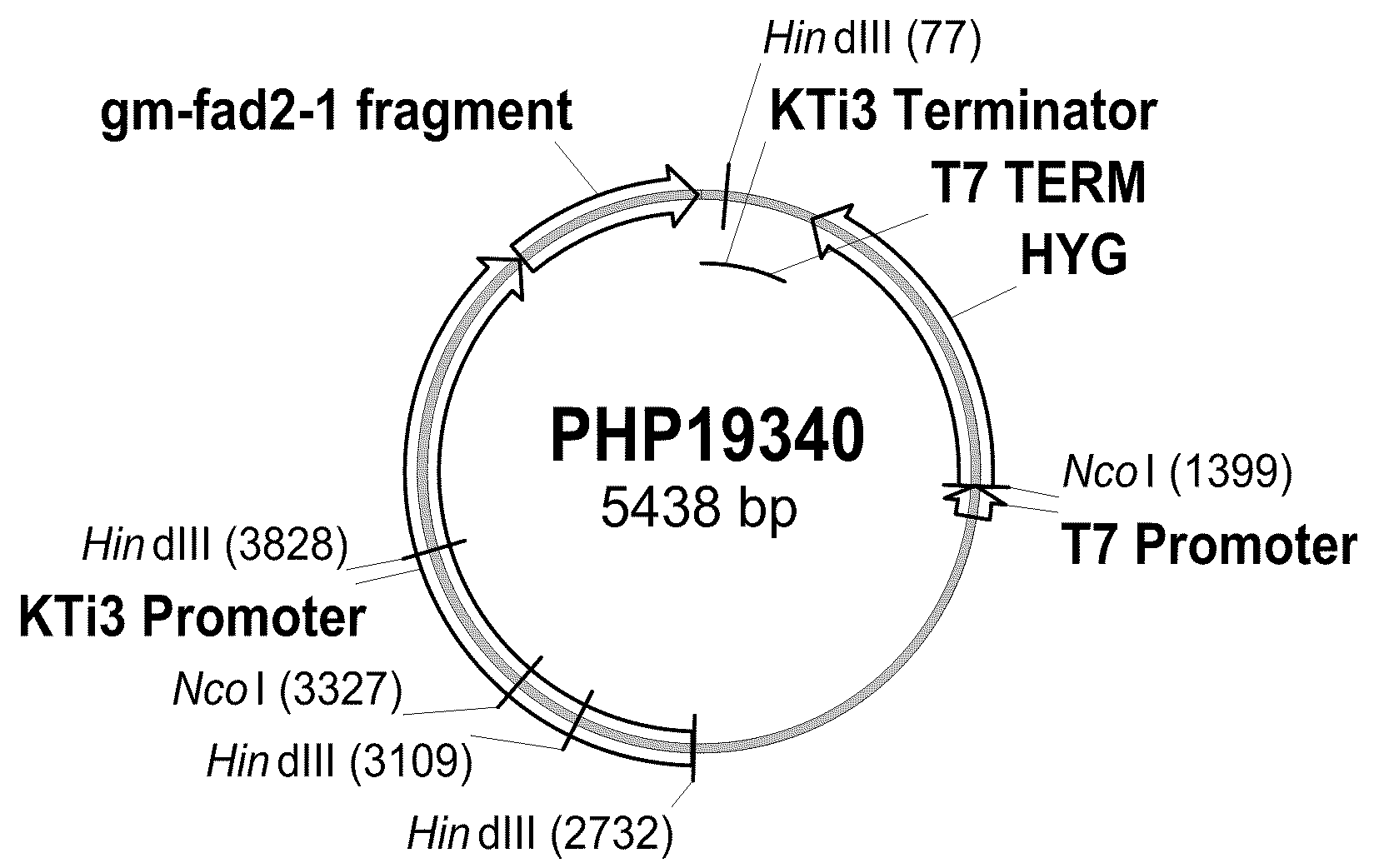
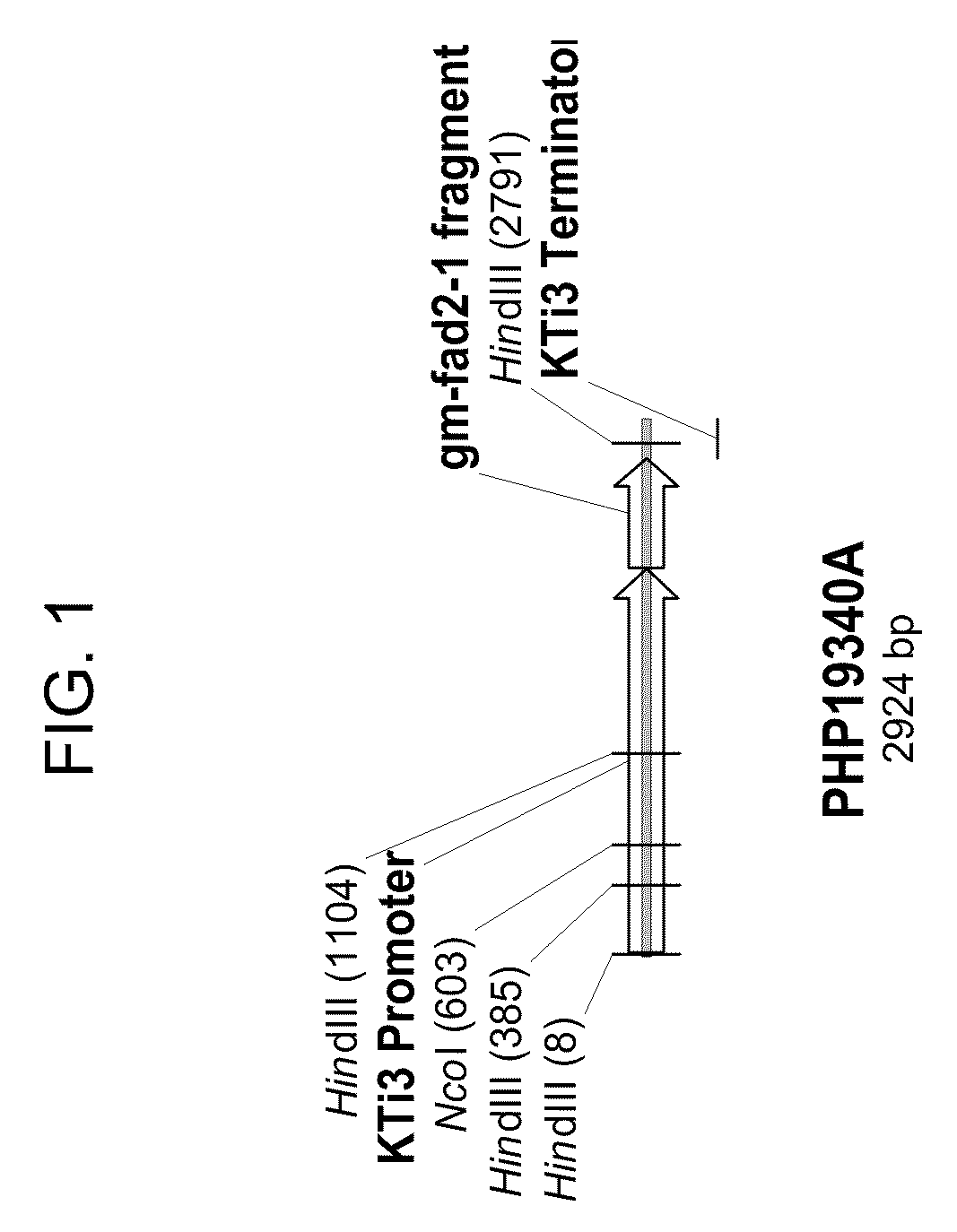
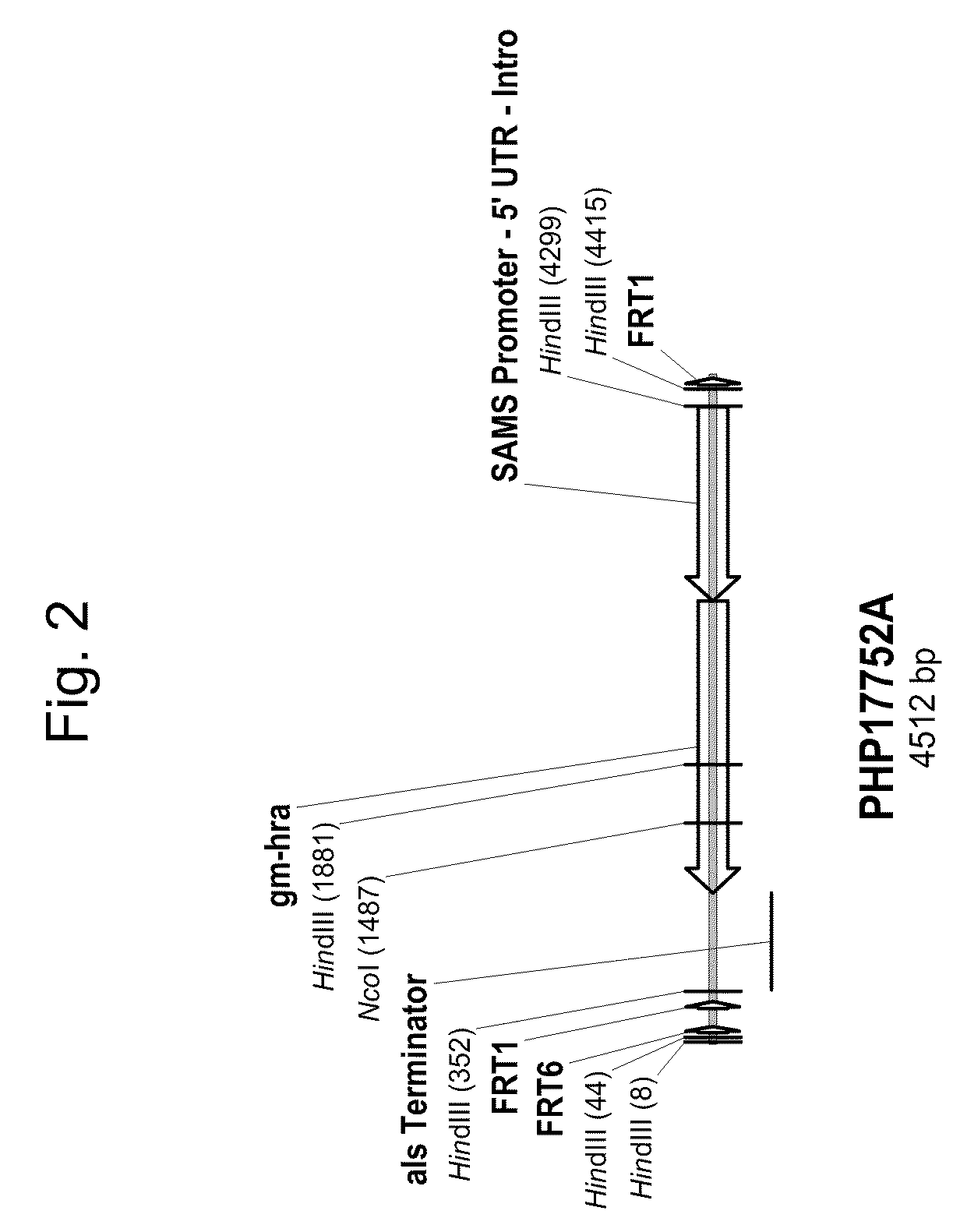
Soybean event dp-305423-1 and compositions and methods for the identification and/or detection thereof
ActiveUS20080312082A1Improve farming efficiencyImprove toleranceBiocideSugar derivativesHigh oleic acidInsertion site
Compositions and methods related to transgenic high oleic acid / ALS inhibitor-tolerant soybean plants are provided. Specifically, the present invention provides soybean plants having a DP-305423-1 event which imparts a high oleic acid phenotype and tolerance to at least one ALS-inhibiting herbicide. The soybean plant harboring the DP-305423-1 event comprises genomic / transgene junctions having at least the polynucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:8, 9, 14, 15, 20, 21, 83 or 84. The characterization of the genomic insertion site of the DP-305423-1 event provides for an enhanced breeding efficiency and enables the use of molecular markers to track the transgene insert in the breeding populations and progeny thereof. Various methods and compositions for the identification, detection, and use of the soybean DP-305423-1 events are provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
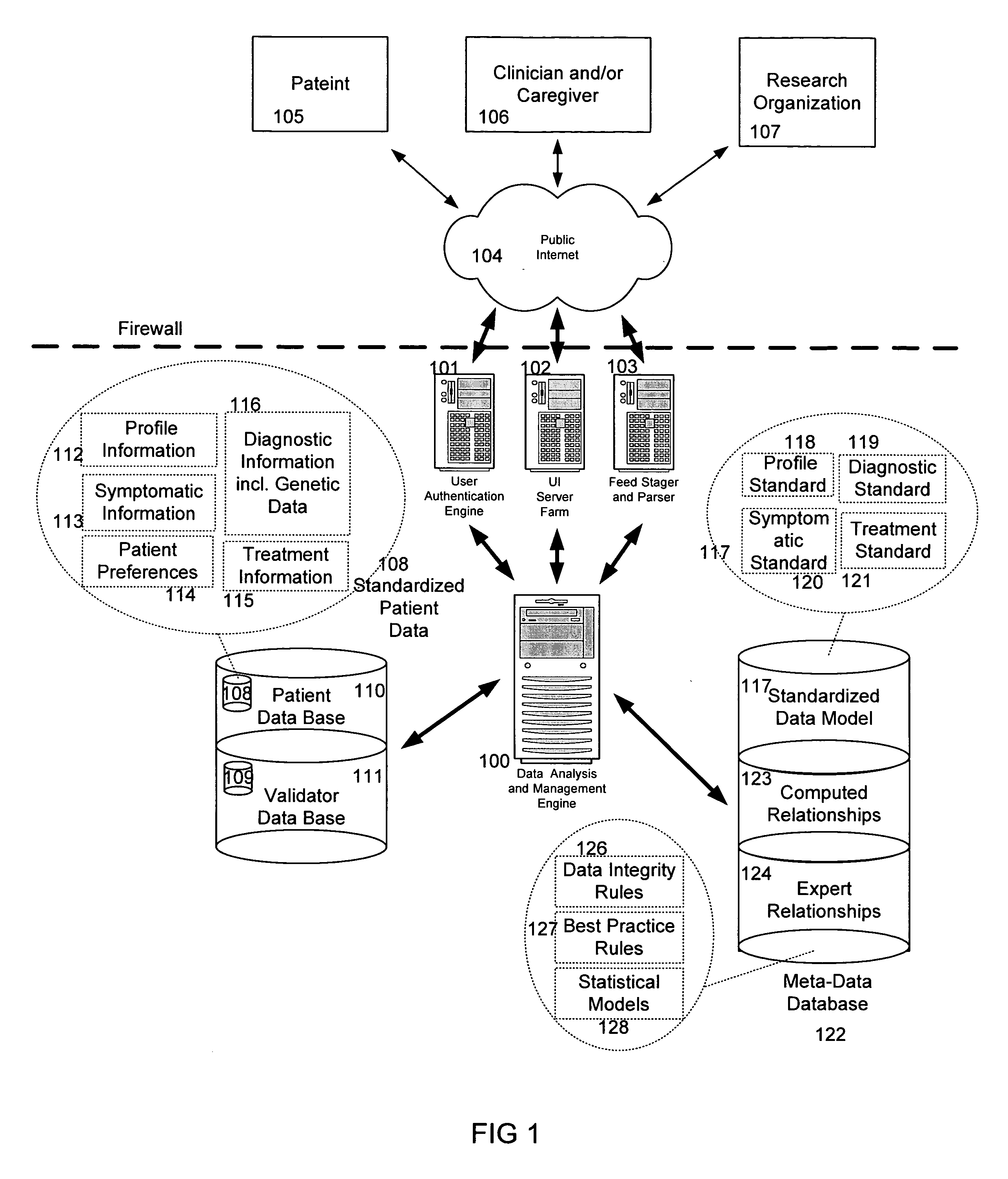
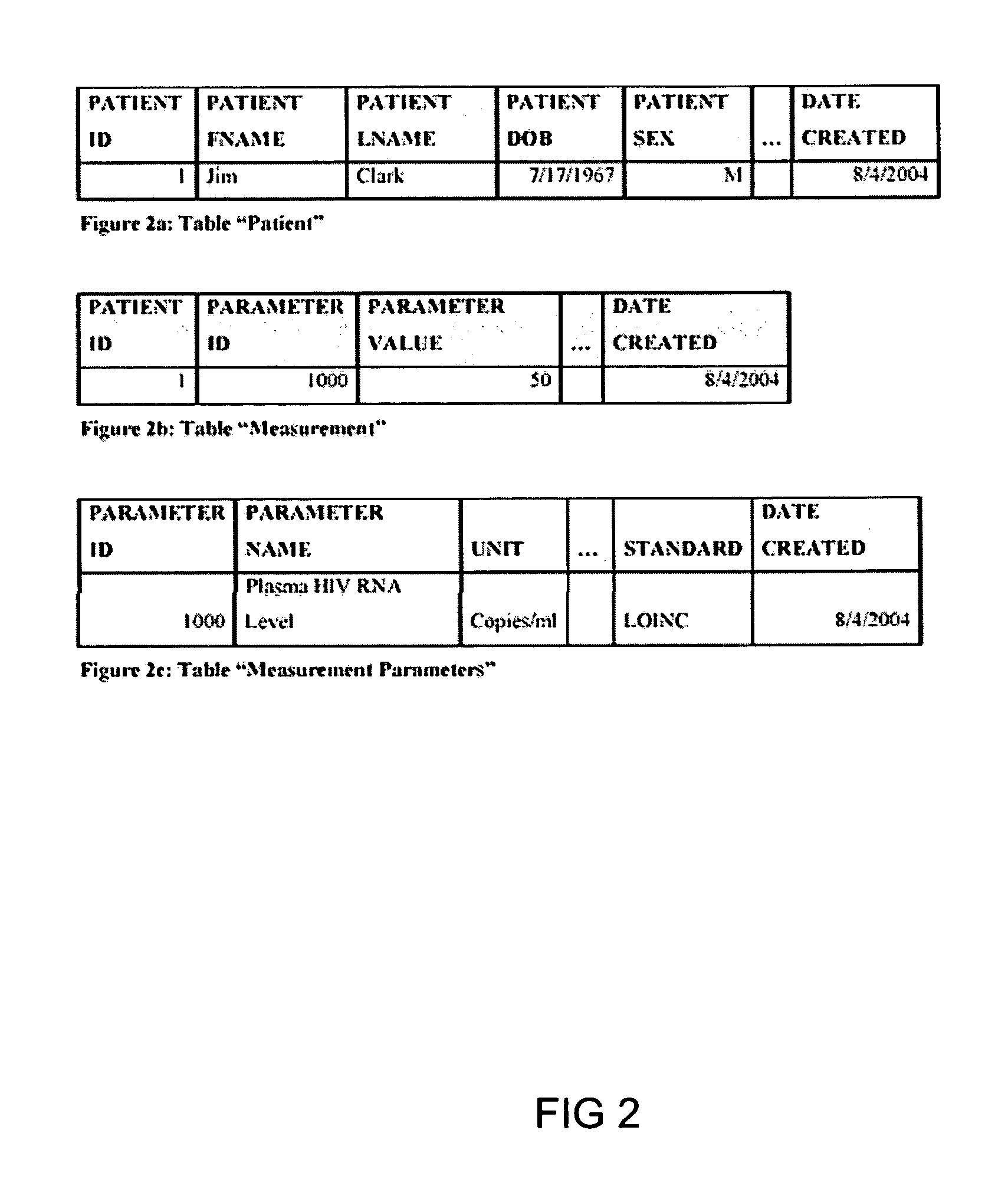
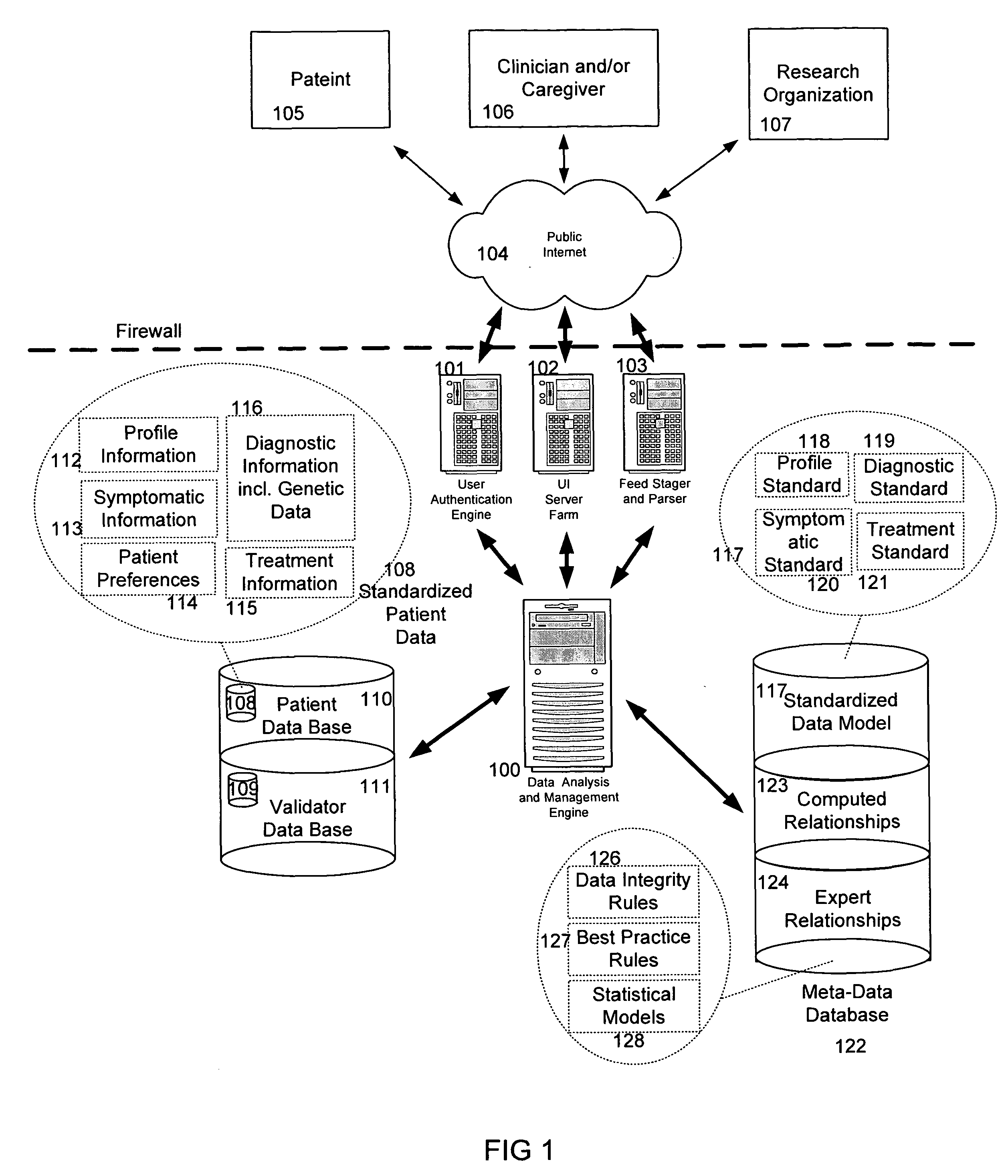
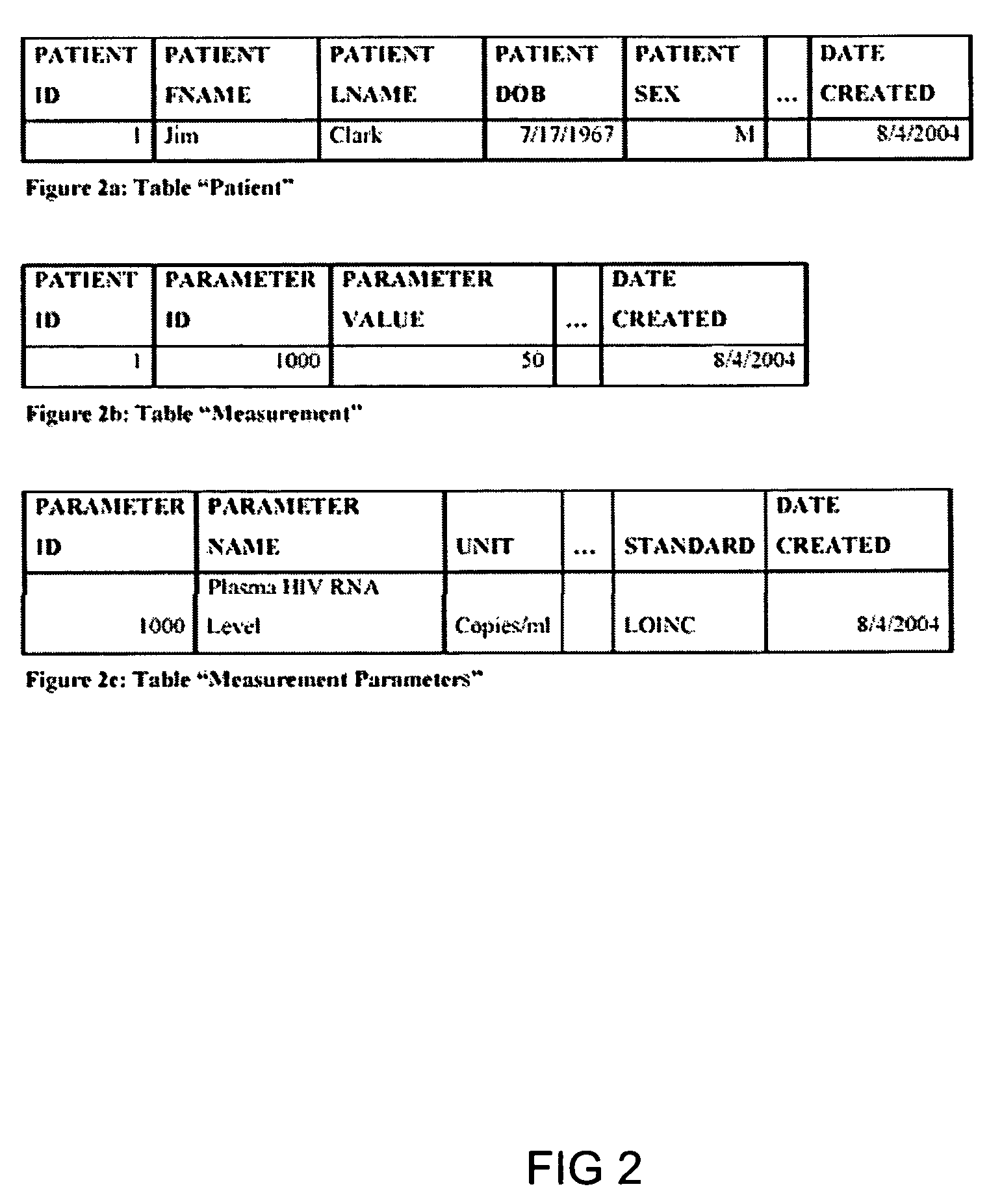
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions, faster, using aggregated genetic and phenotypic data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects who may be at distributed facilities. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes that encompass patient profile information, patient symptomatic information, patient treatment information, and patient diagnostic information including genetic information. Data from other systems is converted into the format of the standardized data classes using a data parser, or cartridge, specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes that are based on expert rules and statistical models. The relationships are used both to validate new data, and to predict phenotypic outcomes based on available data. The prediction may relate to a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention by a caregiver. The statistical models may be inhaled into the system from electronic publications that define statistical models and methods for training those models, according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic and clinical data, in particular for underdetermined data sets that are typical of genetic information. The disclosure also describes how security of the data is maintained by means of a robust security architecture, and robust user authentication such as biometric authentication, combined with application-level and data-level access privileges.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for integrating and validating genotypic, phenotypic and medical information into a database according to a standardized ontology
InactiveUS20070178501A1Safest and most effective treatmentGood decisionData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementData validationMedical record
The system described herein enables clinicians and researchers to use aggregated genetic and phenotypic data from clinical trials and medical records to make the safest, most effective treatment decisions for each patient. This involves (i) the creation of a standardized ontology for genetic, phenotypic, clinical, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and other data sets, (ii) the creation of a translation engine to integrate heterogeneous data sets into a database using the standardized ontology, and (iii) the development of statistical methods to perform data validation and outcome prediction with the integrated data. The system is designed to interface with patient electronic medical records (EMRs) in hospitals and laboratories to extract a particular patient's relevant data. The system may also be used in the context of generating phenotypic predictions and enhanced medical laboratory reports for treating clinicians. The system may also be used in the context of leveraging the huge amount of data created in medical and pharmaceutical clinical trials. The ontology and validation rules are designed to be flexible so as to accommodate a disparate set of clients. The system is also designed to be flexible so that it can change to accommodate scientific progress and remain optimally configured.
Owner:NATERA
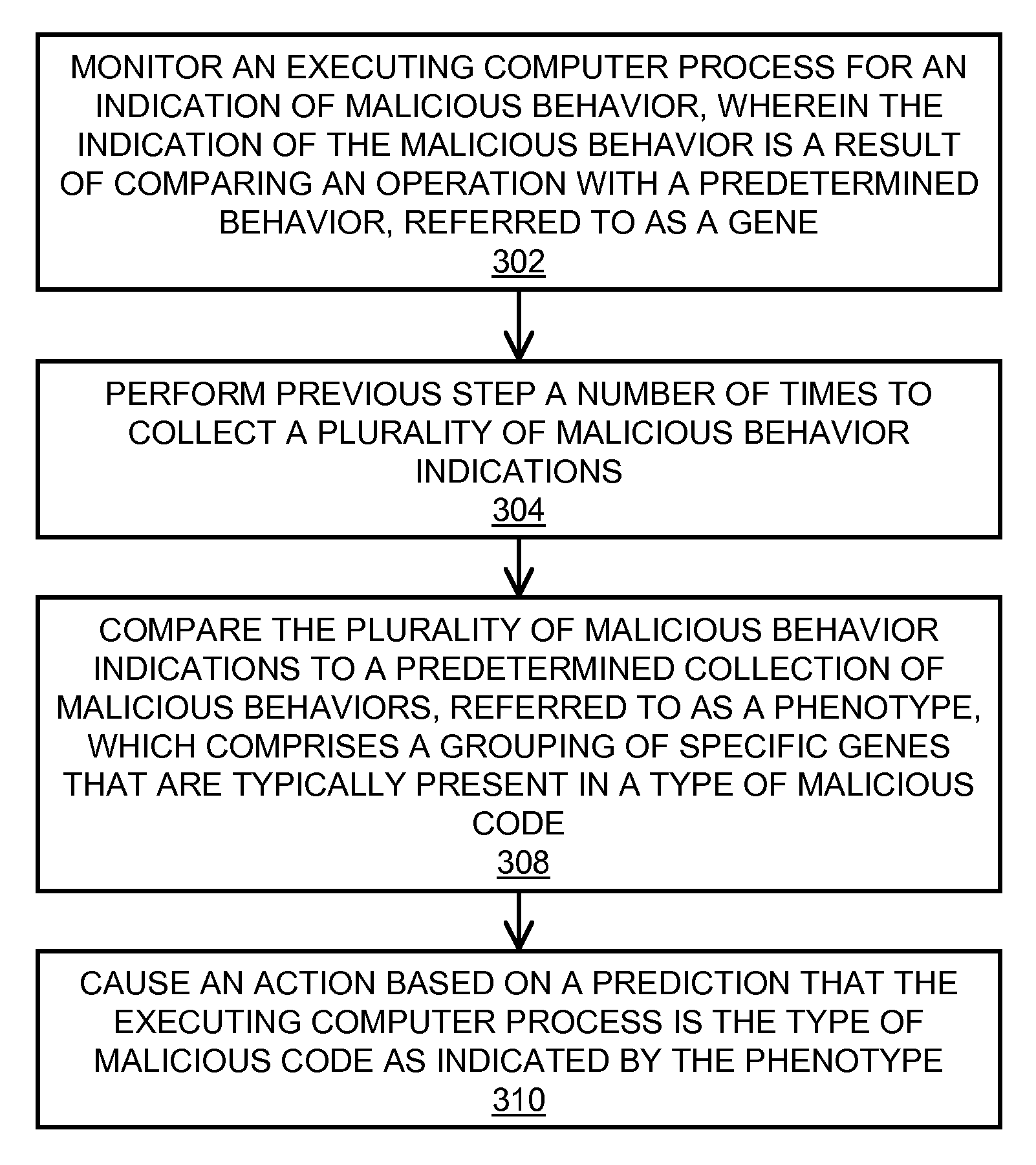
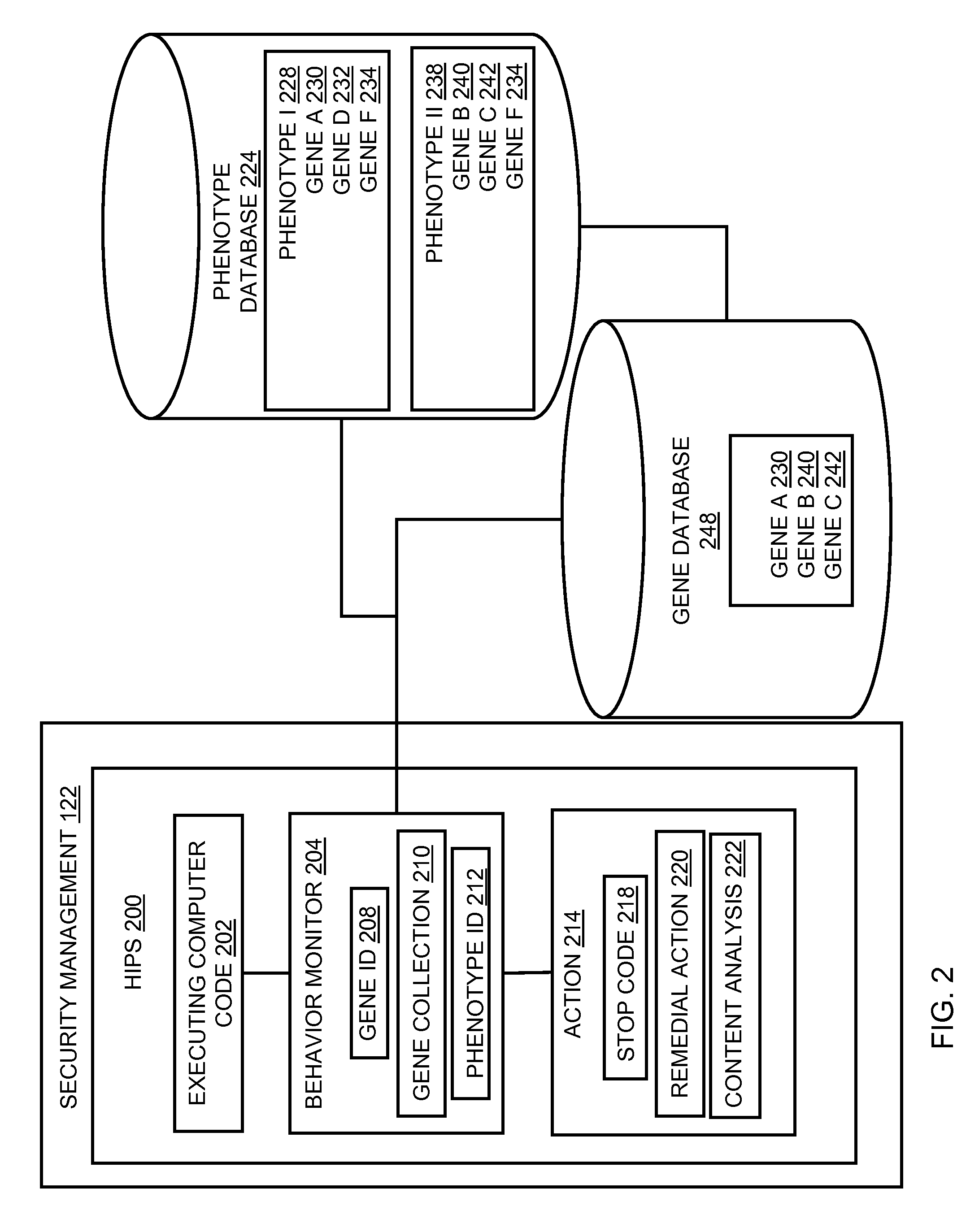
Behavioral-based host intrusion prevention system
ActiveUS20110023118A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionApplication softwareIntrusion prevention system
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for behavioral-based threat detection. An executing computer process is monitored for an indication of malicious behavior, wherein the indication of the malicious behavior is a result of comparing an operation with a predetermined behavior, referred to as a gene. A plurality of malicious behavior indications observed for the executing process are compared to a predetermined collection of malicious behaviors, referred to as a phenotype, which comprises a grouping of specific genes that are typically present in a type of malicious code. Upon matching the malicious behavior indications with a phenotype, an action may be caused, where the action is based on a prediction that the executing computer process is the type of malicious code as indicated by the phenotype. Related user interfaces, applications, and computer program products are disclosed.
Owner:SOPHOS
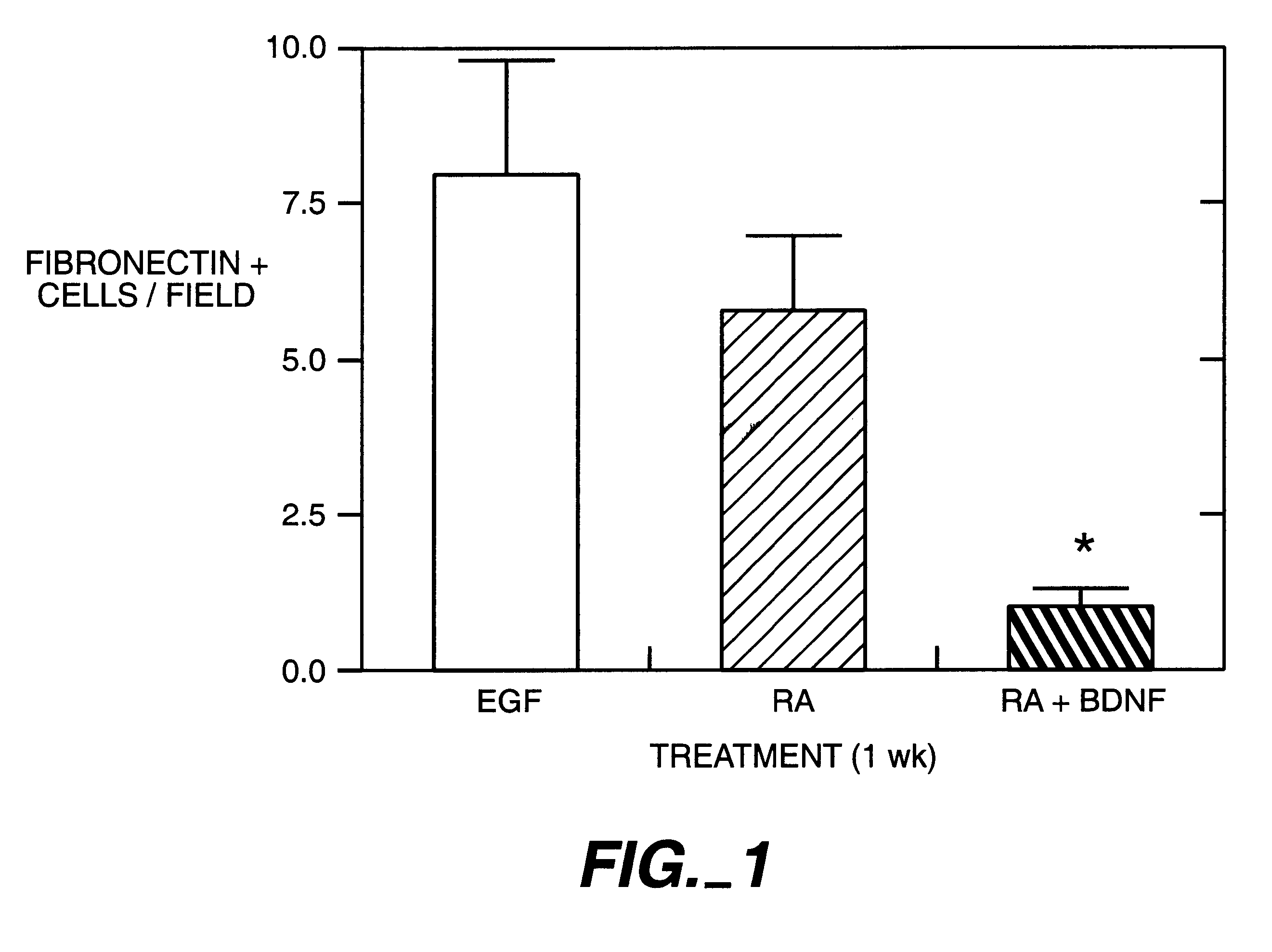
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions by using aggregated data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes comprising patient profile, genetic, symptomatic, treatment and diagnostic information. Data is converted into standardized data classes using a data parser specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes, based on expert rules and statistical models, and are used to validate new data and predict phenotypic outcomes. The prediction may comprise a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention. The statistical models and methods for training those models may be input according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic, clinical and undetermined data sets.
Owner:NATERA
Innate immune suppression enables repeated delivery of long RNA molecules
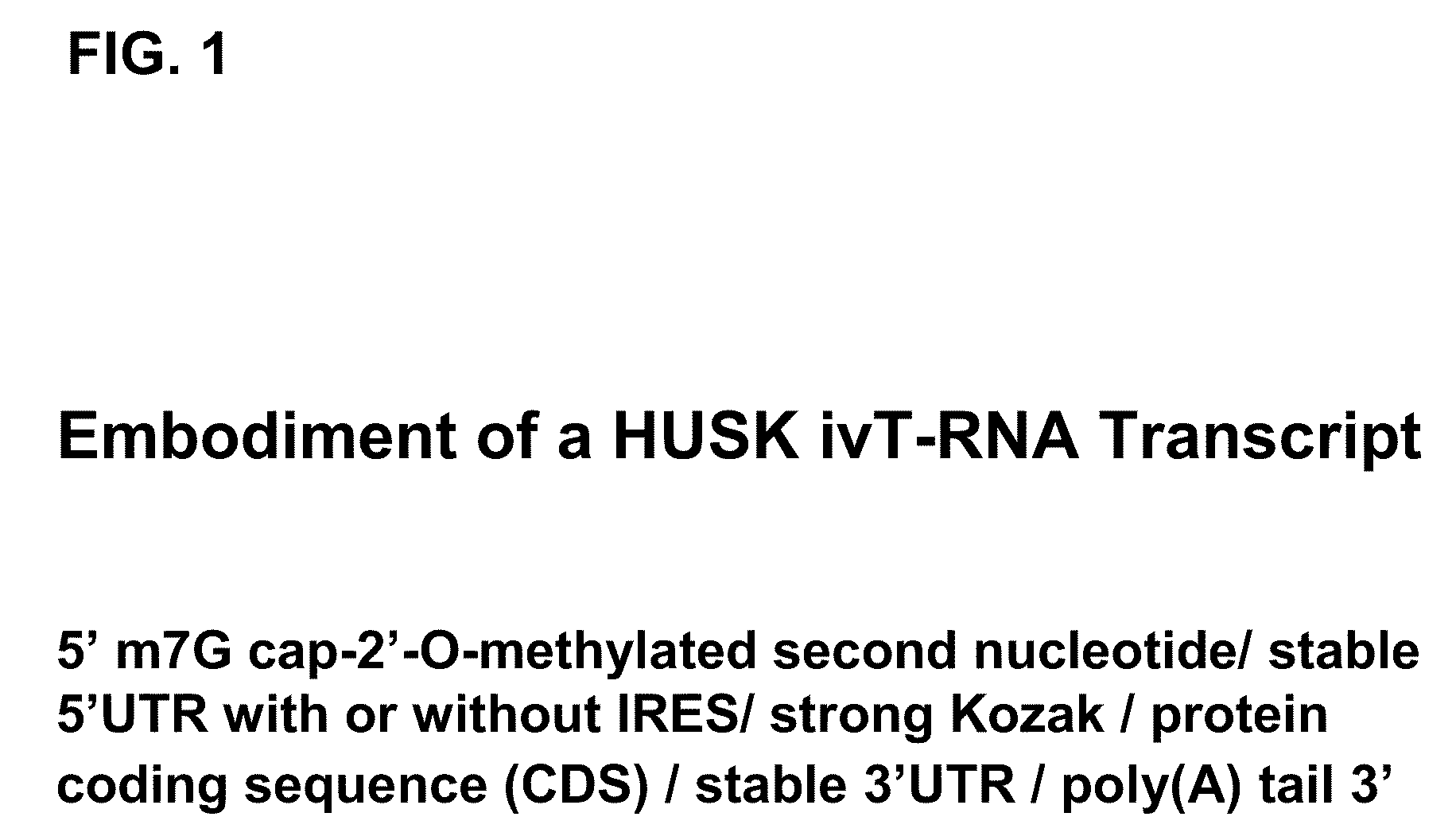
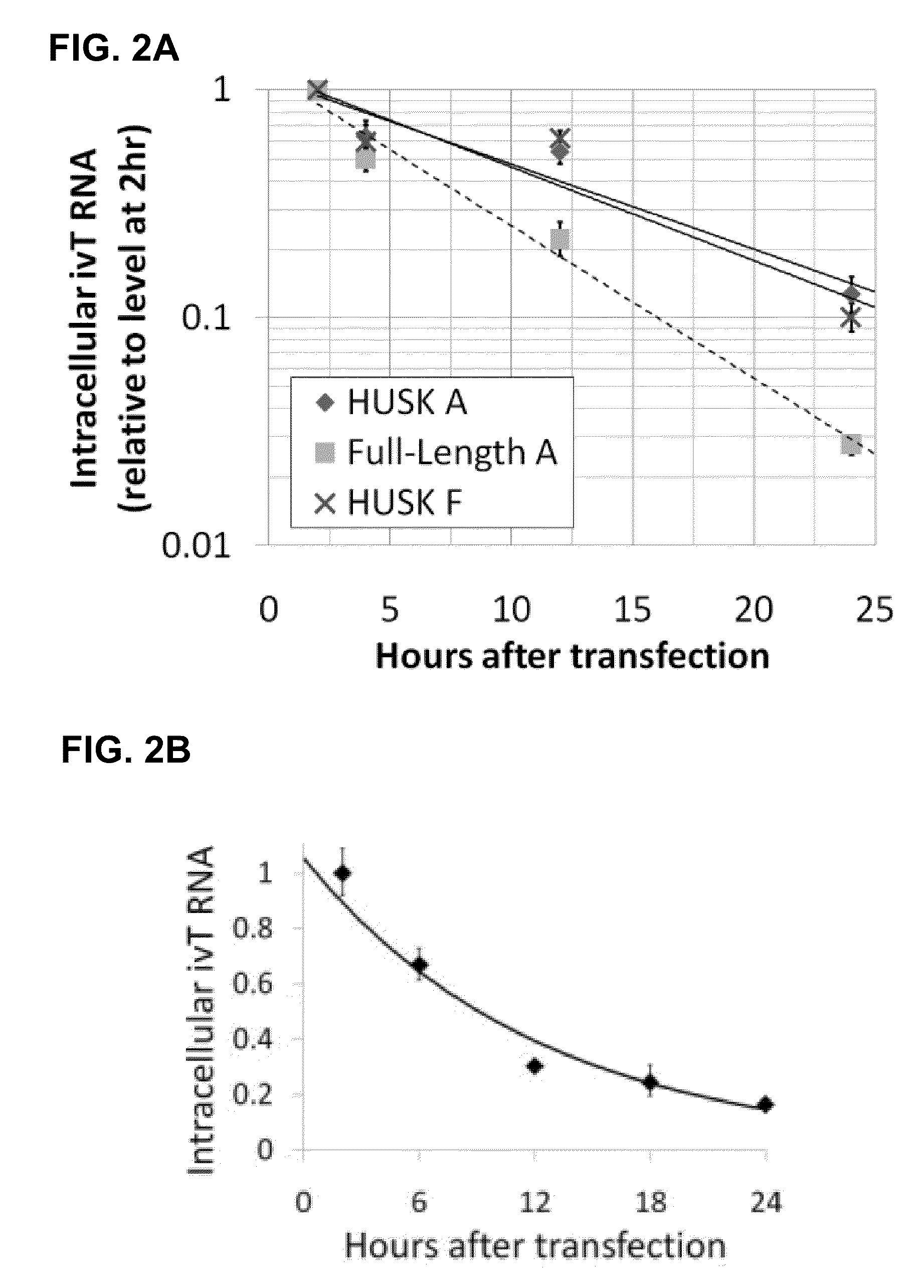
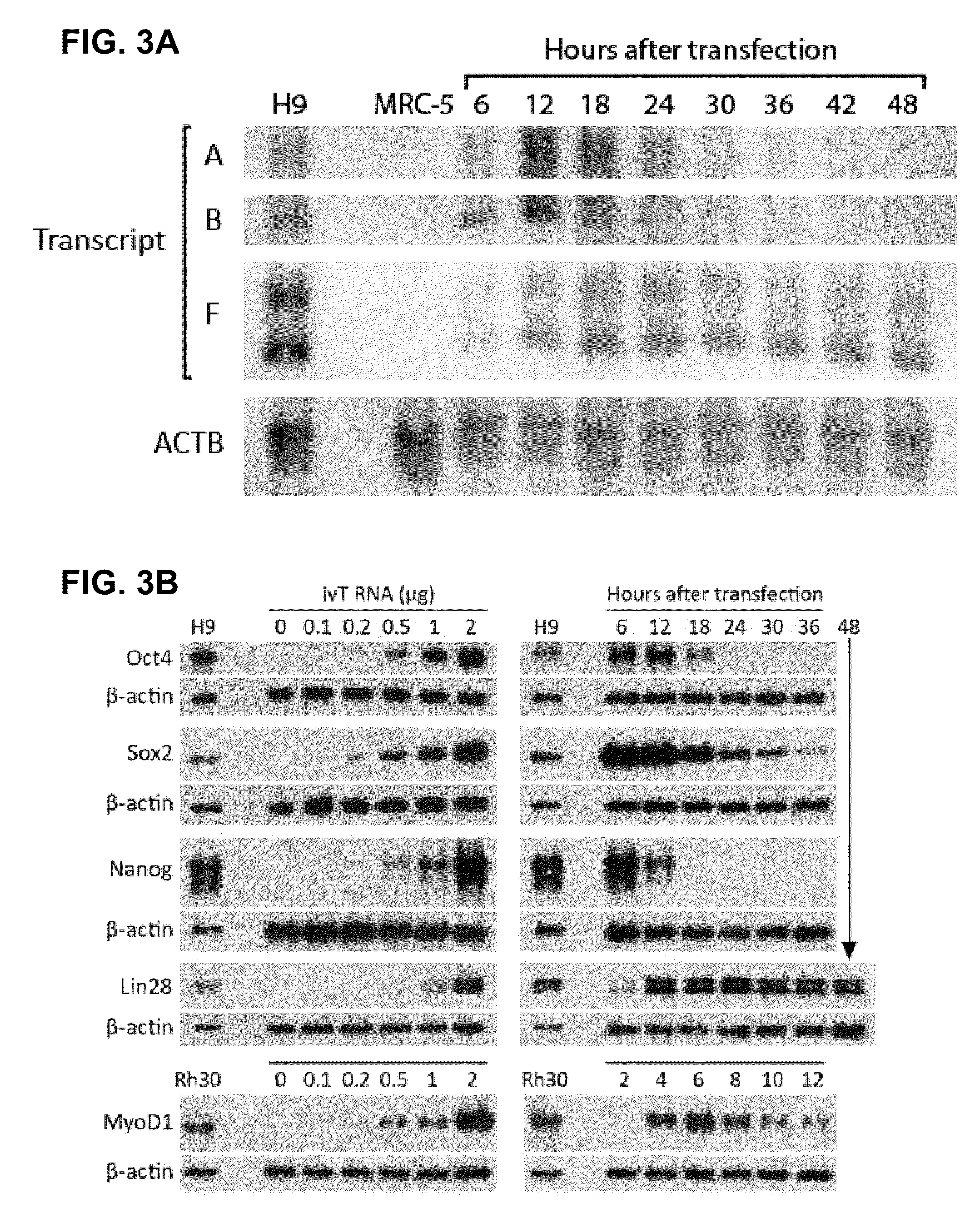
InactiveUS20100273220A1Suppressing innate immune responseReduce expressionSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsENCODETransient transfection
The present invention relates in part to methods for suppressing the innate immune response of a cell to transfection with an exogenous nucleic acid, to methods for increasing expression of a protein encoded by an exogenous nucleic acid by repeated delivery of the exogenous nucleic acid to a cell, and to methods of changing the phenotype of a cell by differentiating, transdifferentiating or dedifferentiating cells by repeatedly delivering one or more nucleic acids that encode defined proteins. A method is provided for extended transient transfection by repeated delivery of an in vitro-transcribed RNA (“ivT-RNA”) to a cell to achieve a high and sustained level of expression of a protein encoded by an ivT-RNA transcripts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
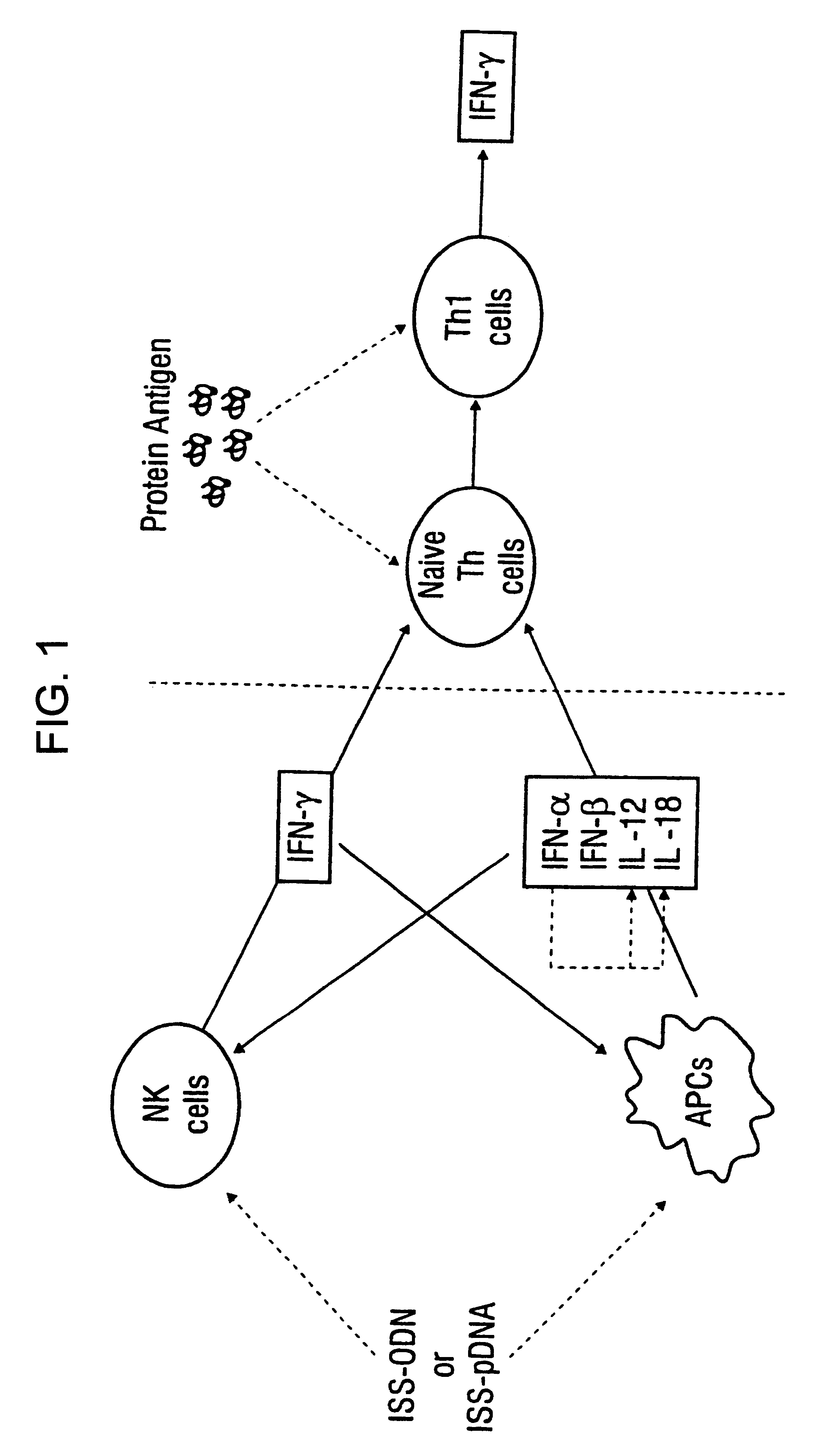
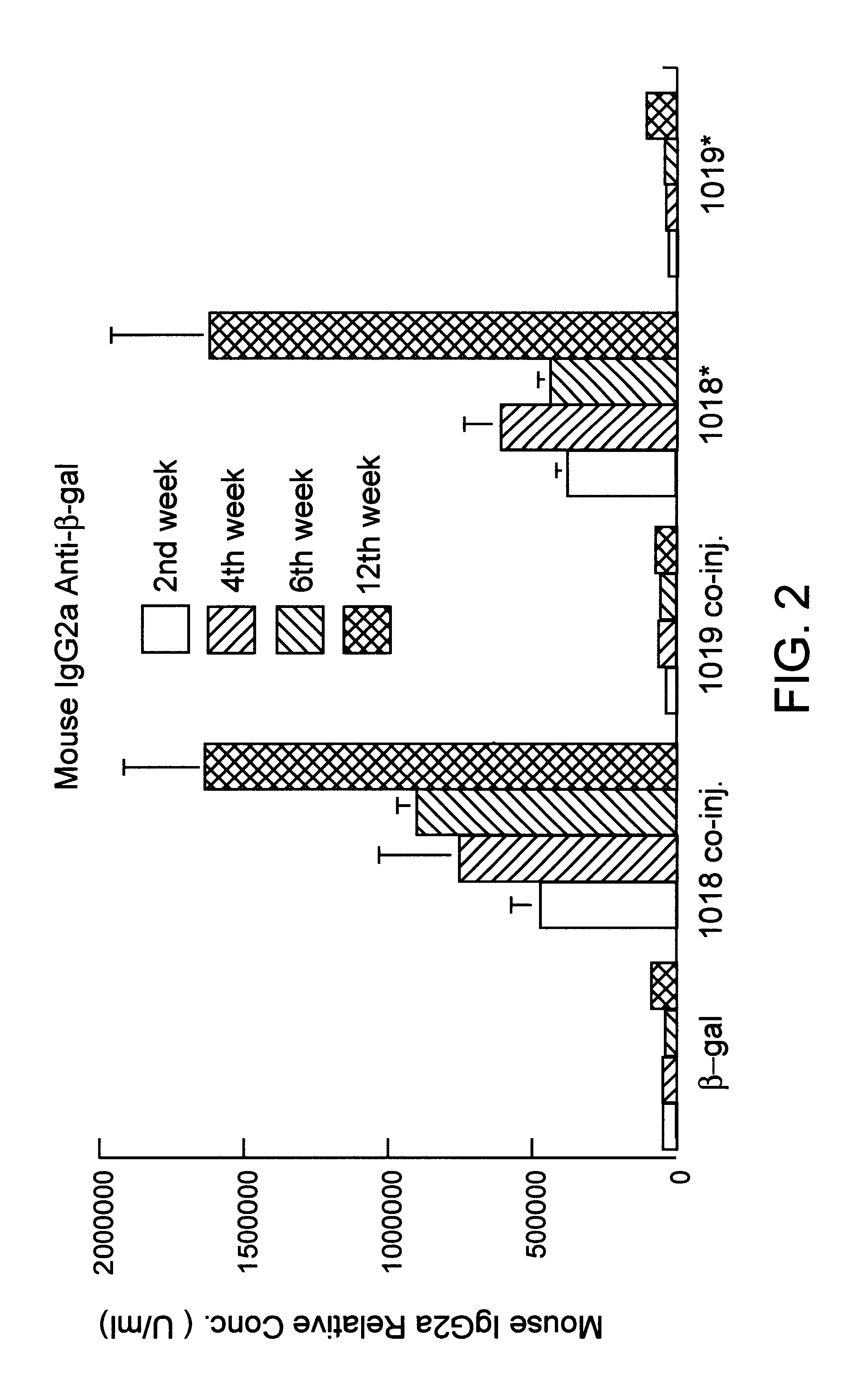
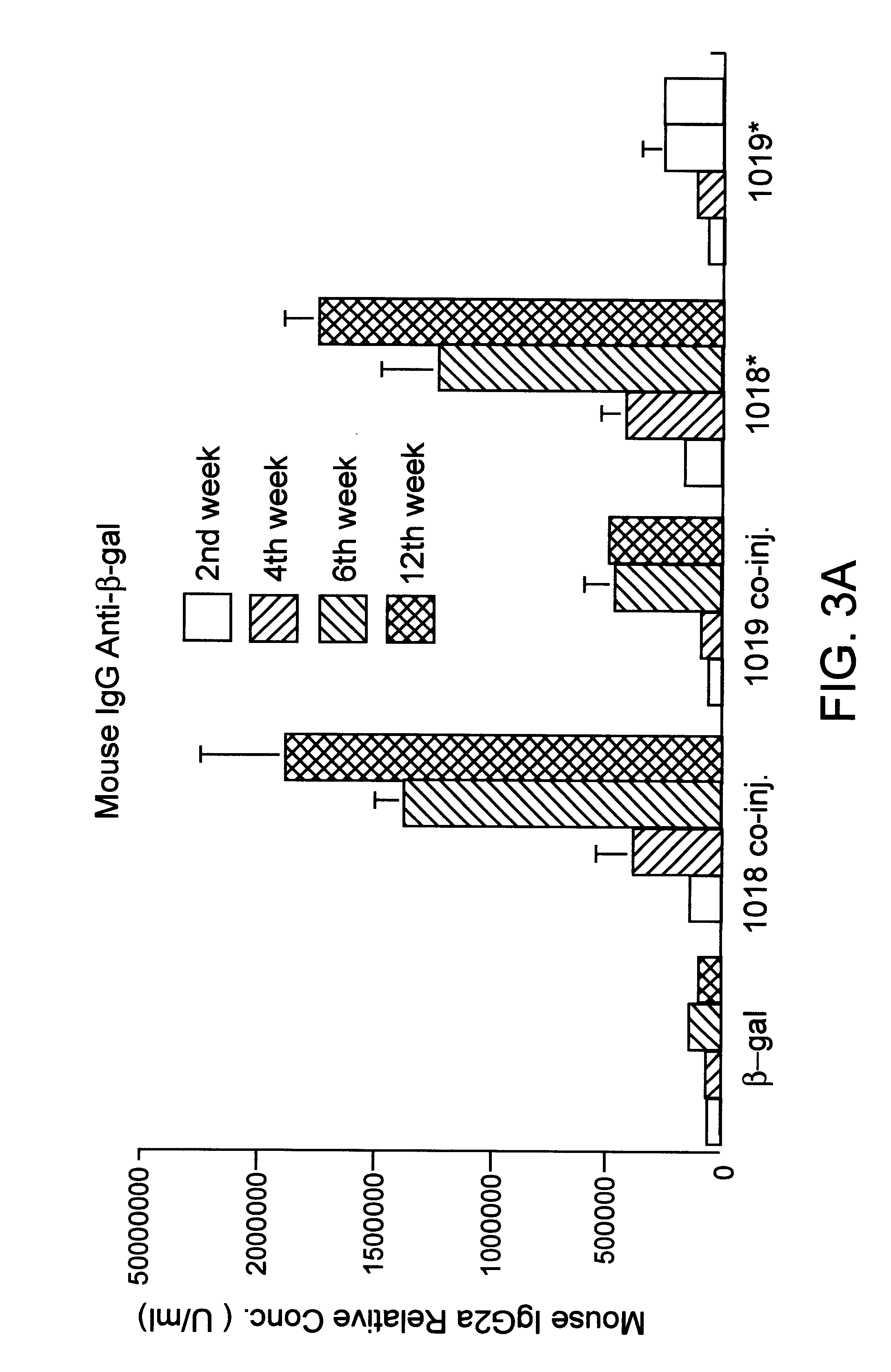
Immunization-free methods for treating antigen-stimulated inflammation in a mammalian host and shifting the host's antigen immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype
InactiveUS6498148B1Treatment and prevention of inflammationSuppresses antigen-stimulated granulocyte infiltrationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAntigen stimulationTherapeutic intent
The invention relates to methods for preventing or reducing antigen-stimulated, granulocyte-mediated inflammation in tissue of an antigen-sensitized mammal host by delivering an immunostimulatory oligonucleotide to the host. In addition, methods for using the immunostimulatory oligonucleotides to boost a mammal host's immune responsiveness to a sensitizing antigen (without immunization of the host by the antigen) and shifting the host's immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype to achieve various therapeutic ends are provided. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nucleotide sequences and corresponding polypeptides conferring modulated plant characteristics
InactiveUS20110167514A1Increase the number ofIncrease biomassLibrary screeningFruits/vegetable preservation using acidsNucleotidePlant cell
The present invention relates to isolated nucleic acid molecules and their corresponding encoded polypeptides. The present invention further relates to the uses of these nucleic acid molecules and polypeptides. For example, the nucleic acid molecules and polypeptides could be used in making enzymes or used to make plants, plant cells, plant materials or seeds of a plant having such modulated growth or phenotype characteristics that are altered with respect to wild type plants grown under similar conditions.
Owner:CERES INC
Cyclopamine analogues and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7230004B2Antagonize Smo-dependent pathway activationStop and slow cell proliferationBiocideNervous disorderGain of function mutationBiological activation
The present invention provides compositions and methods for modulating smoothened-dependent pathway activation. The present invention provides analogs of cyclopamine that can be used to counteract the phenotypic effects of unwanted activation of a hedgehog pathway, such as resulting from hedgehog gain-of-function, Ptc loss-of-function or smoothened gain-of-function mutations. The compounds of the present invention are particularly useful in treating cancers.
Owner:ROYALTY SECURITY LLC
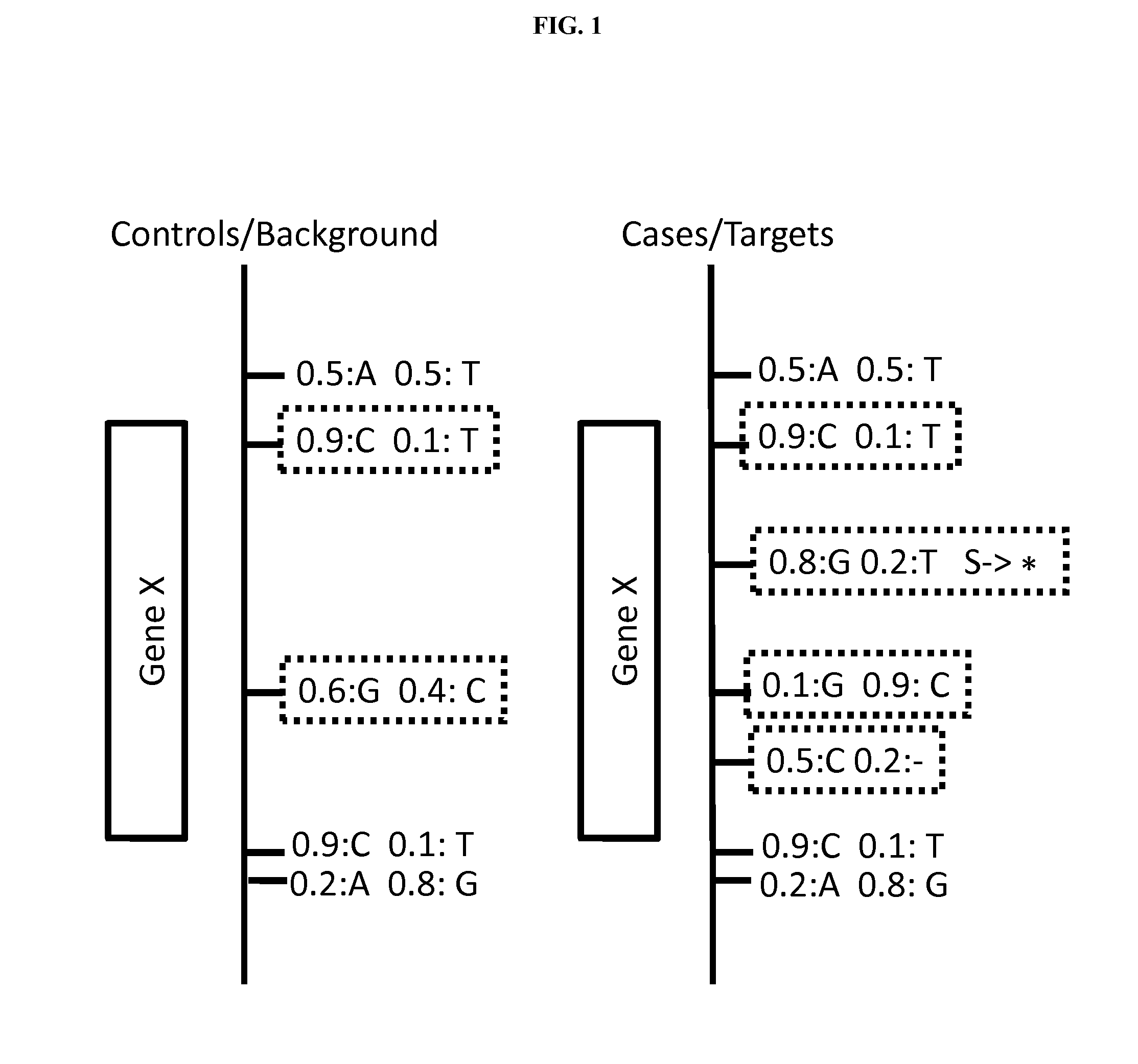
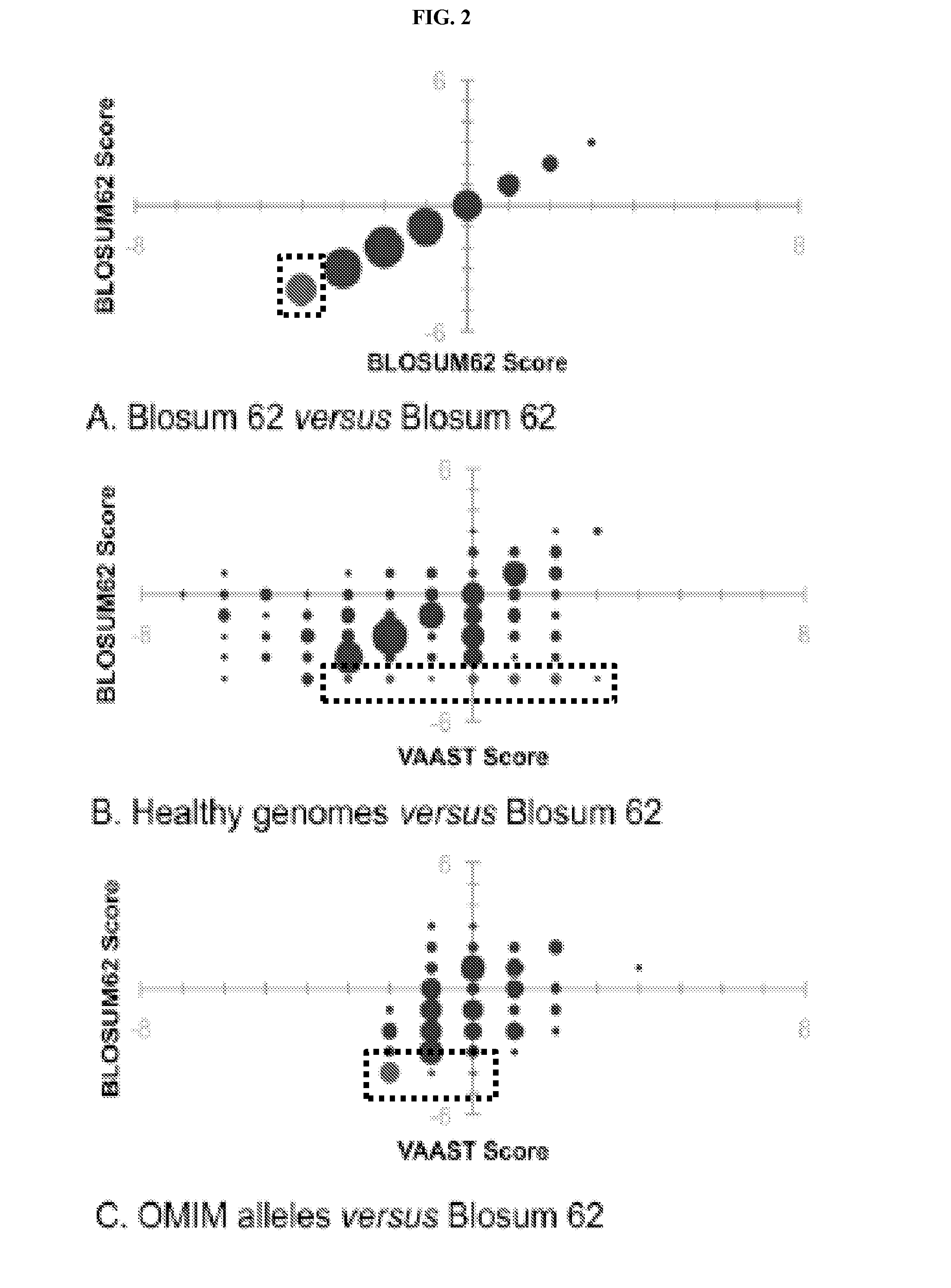
Variant annotation, analysis and selection tool
Disclosed are methods for detecting and / or prioritizing phenotype-causing genomic variants and related software tools. The methods include genomic feature based analysis and can combine variant frequency information with sequence characteristics such as amino acid substation. The methods disclosed are useful in any genomics study; for example, rare and common disease gene discovery, tumor growth mutation detection, personalized medicine, agricultural analysis, and centennial analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Chimeric infectious DNA clones, chimeric porcine circoviruses and uses thereof
InactiveUS7279166B2Facilitate cell culture growthEnsure vaccine safetyFungiBacteriaSpecific immunityADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to infectious DNA clones, infectious chimeric DNA clones of porcine circovirus (PCV), vaccines and means of protecting pigs against viral infection or postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) caused by PCV2. The new chimeric infectious DNA clone and its derived, avirulent chimeric virus are constructed from the nonpathogenic PCV1 in which the immunogenic ORF gene of the pathogenic PCV2 replaces a gene of the nonpathogenic PCV1, preferably in the same position. The chimeric virus advantageously retains the nonpathogenic phenotype of PCV1 but elicits specific immune responses against the pathogenic PCV2. The invention further embraces the immunogenic polypeptide expression products. In addition, the invention encompasses two mutations in the PCV2 immunogenic capsid gene and protein, and the introduction of the ORF2 mutations in the chimeric clones.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Enzymes resistant to photodamage
ActiveUS20100093555A1Reduce oxidationImprove the immunitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising modified DNA polymerases that exhibit improved photostability compared to the parental polymerases from which they were derived. Provided are methods for generating enzymes, such as DNA polymerases, with the aforementioned phenotype. Provided are methods of using polymerases with increased resistance to photodamage to make a DNA or to sequence a DNA template.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
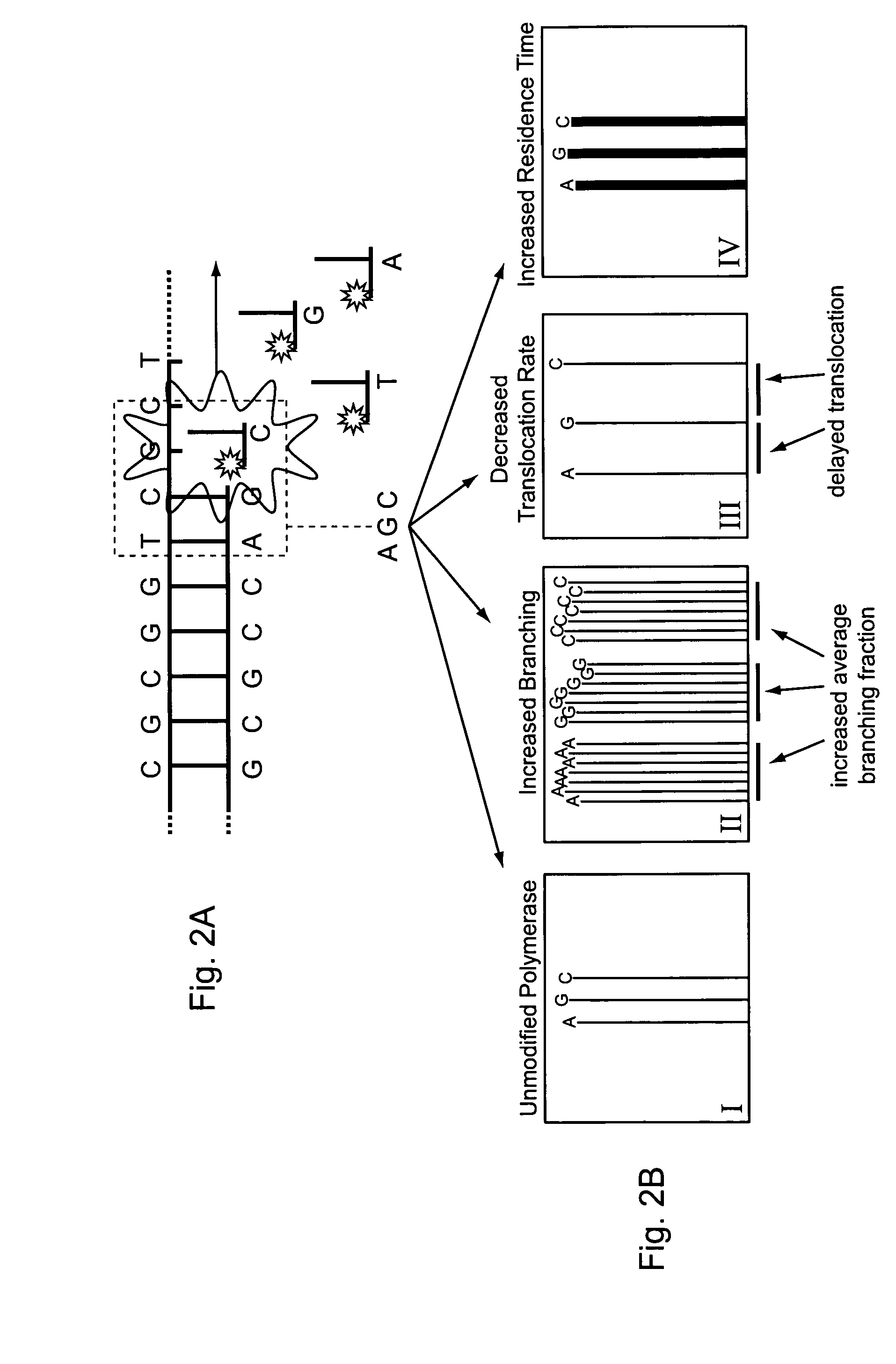
Engineering polymerases and reaction conditions for modified incorporation properties
ActiveUS20100075332A1Easy to identifyDelayed translocationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LA-DNA
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods for classifying plants for evaluation and breeding programs by use of remote sensing and image analysis technology
InactiveUS6212824B1Improve performanceLow costSeed and root treatmentPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryImaging analysisBreeding program
Methods for classifying plants by remote sensing and image analysis technology are presented. These methods are useful for evaluating plants and for selecting plants for a plant breeding program which has as its goal to selectively alter phenotype. The methods combine the newer techniques of remote sensing technology to obtain indirect correlates of the traits of interest, with classical pedigree breeding strategies. Thermal and infrared reflectance measures of plant canopies are examples of energy values measured by remote sensing, used to indirectly predict the selected traits.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
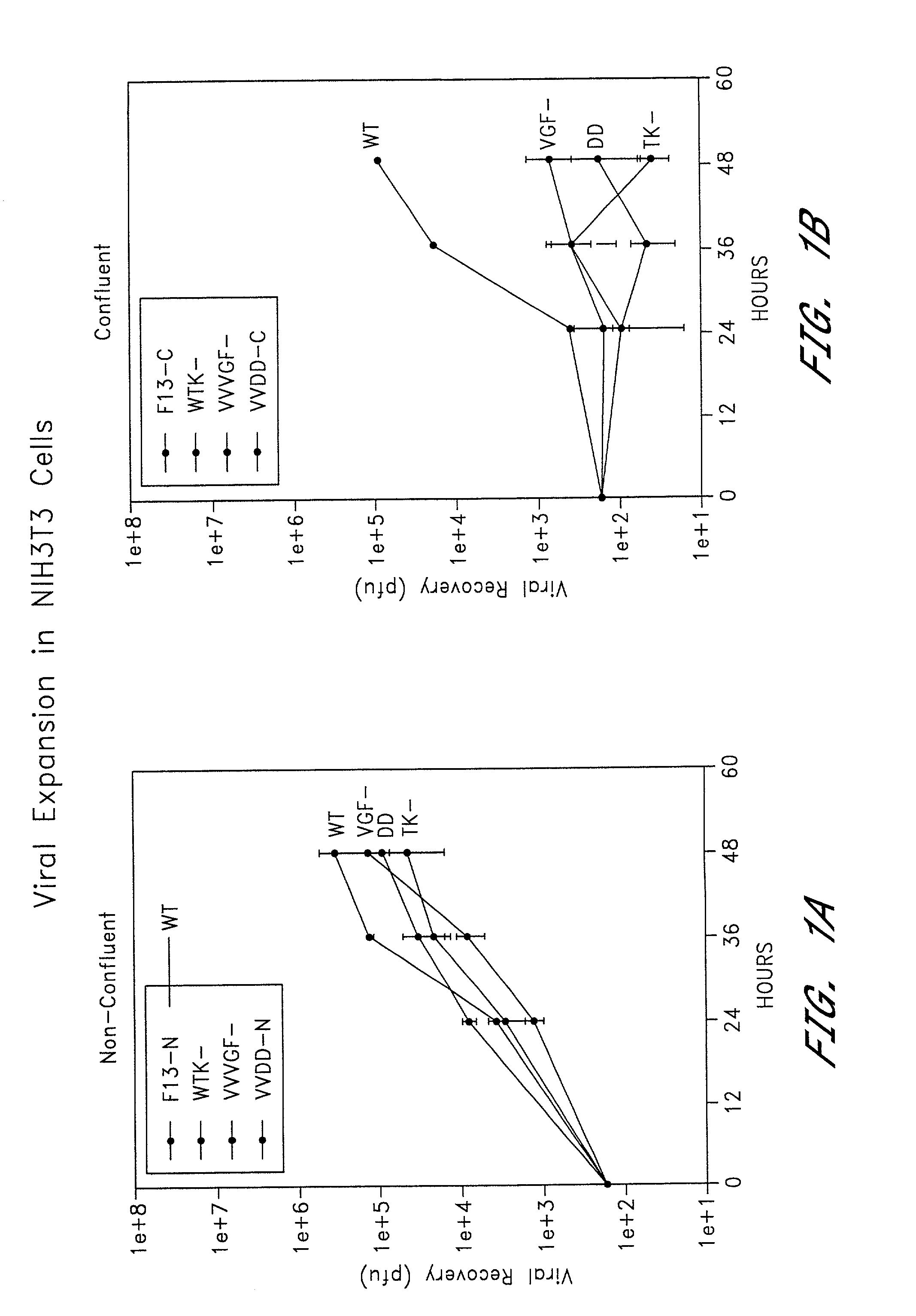
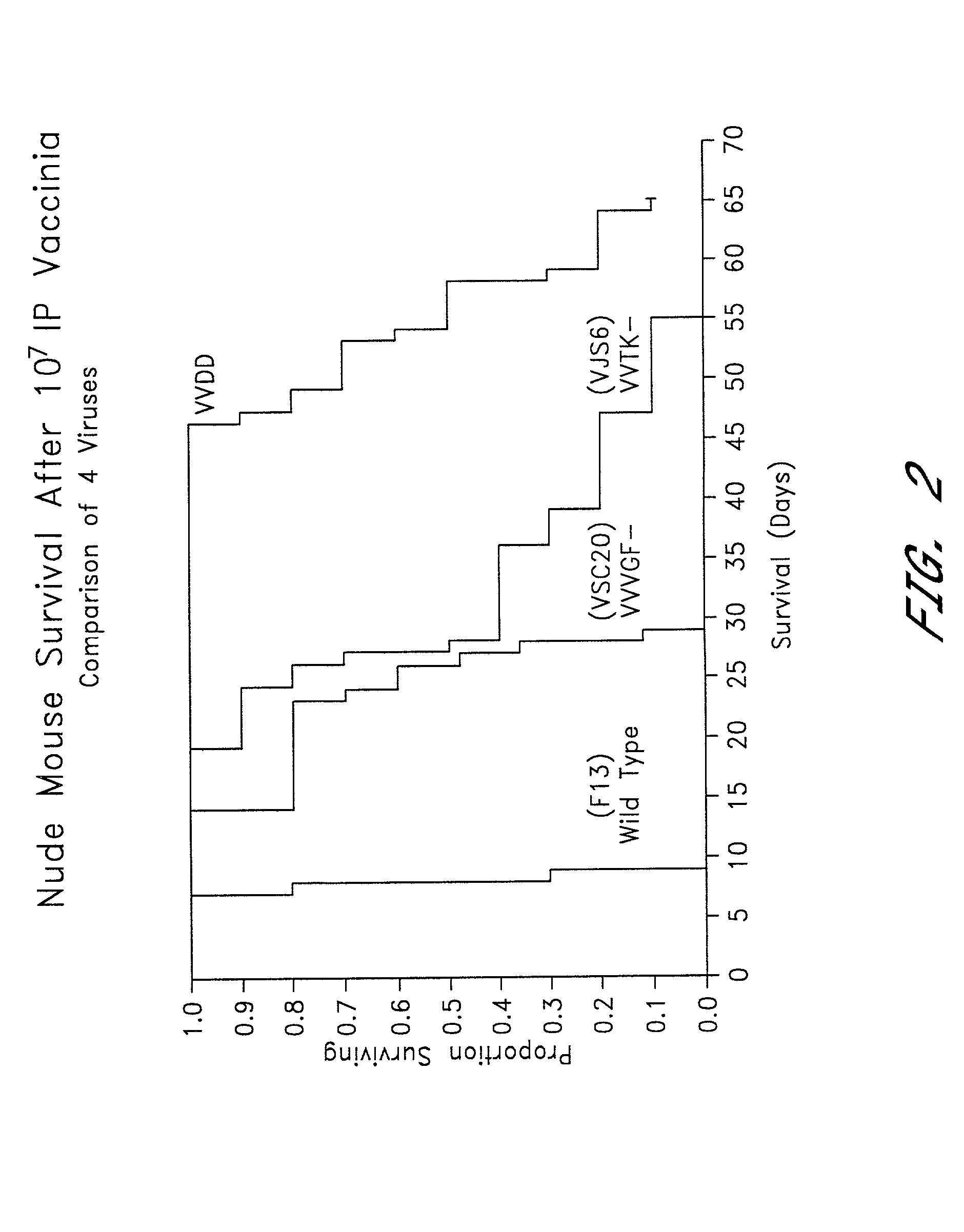
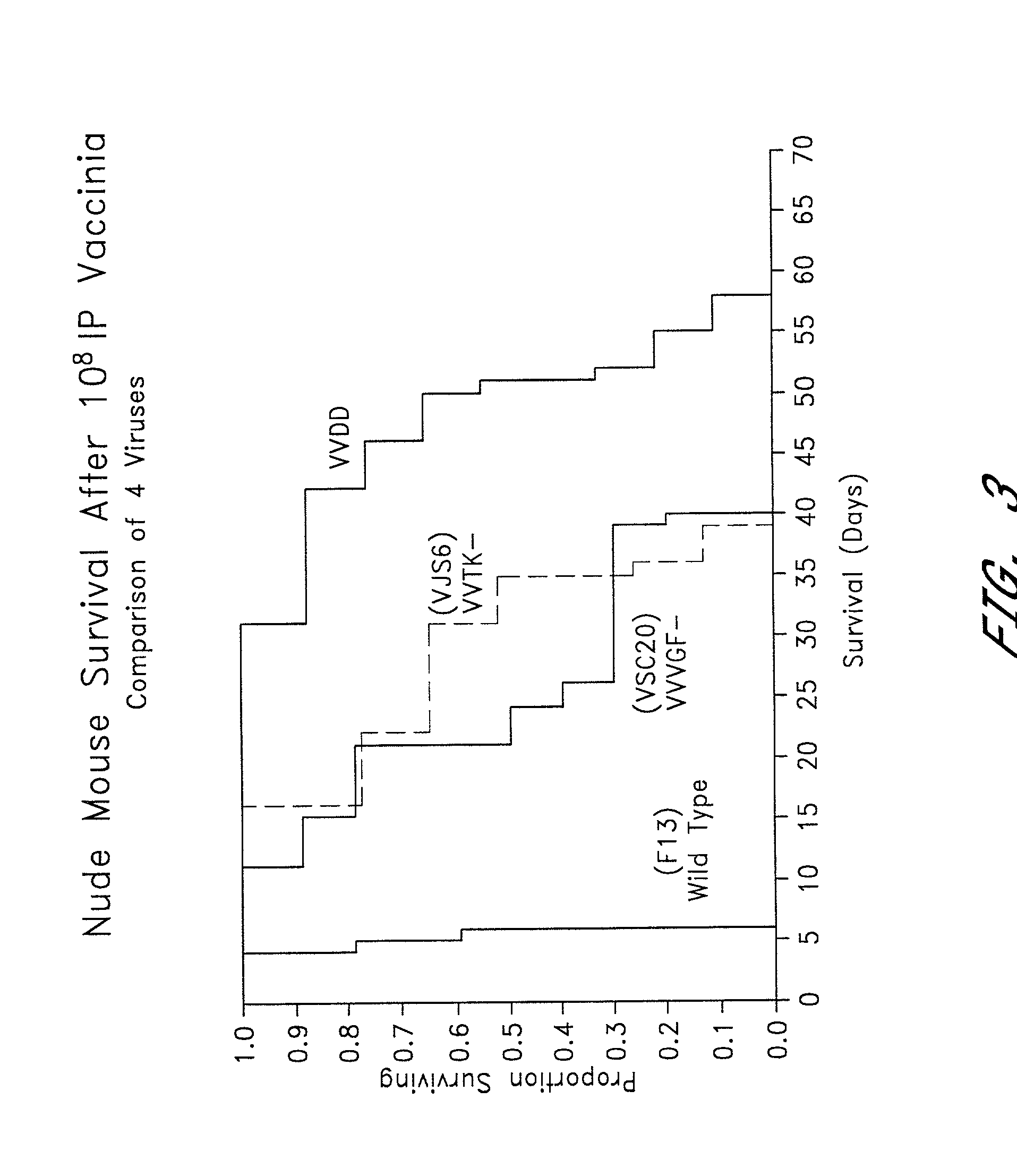
Combined growth factor-deleted and thymidine kinase-deleted vaccinia virus vector
A composition of matter comprising a vaccinia virus expression vector with a negative thymidine kinase phenotype and a negative vaccinia virus growth factor phenotype.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE
Alternative compositions and methods for the culture of stem cells
InactiveUS20050037488A1Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Expression Enhancing Intron Sequences
The invention relates to methods for the identification and use of introns with gene expression enhancing properties. The teaching of this invention enables the identification of introns causing intron-mediated enhancement (IME) of gene expression. The invention furthermore relates to recombinant expression construct and vectors comprising said IME-introns operably linked with a promoter sequence and a nucleic acid sequence. The present invention also relates to transgenic plants and plant cells transformed with these recombinant expression constructs or vectors, to cultures, parts or propagation material derived there from, and to the use of same for the preparation of foodstuffs, animal feeds, seed, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals, to improve plant biomass, yield, or provide desirable phenotypes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Immunization-free methods for treating antigen-stimulated inflammation in a mammalian host and shifting the host's antigen immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype
InactiveUS20030092663A1Useful in treatment and prevention of inflammationSuppresses antigen-stimulated granulocyte infiltrationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAntigen stimulationTherapeutic intent
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
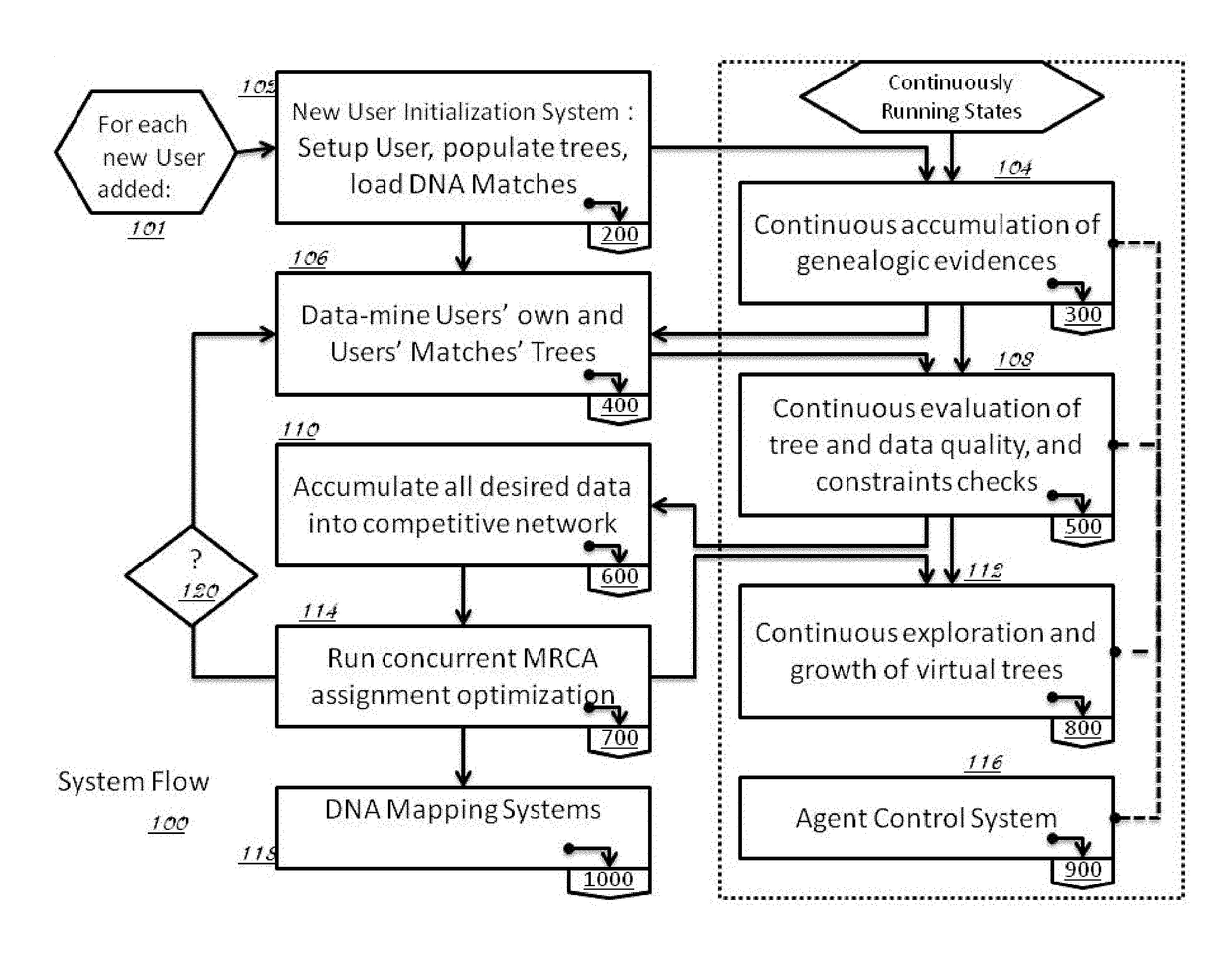
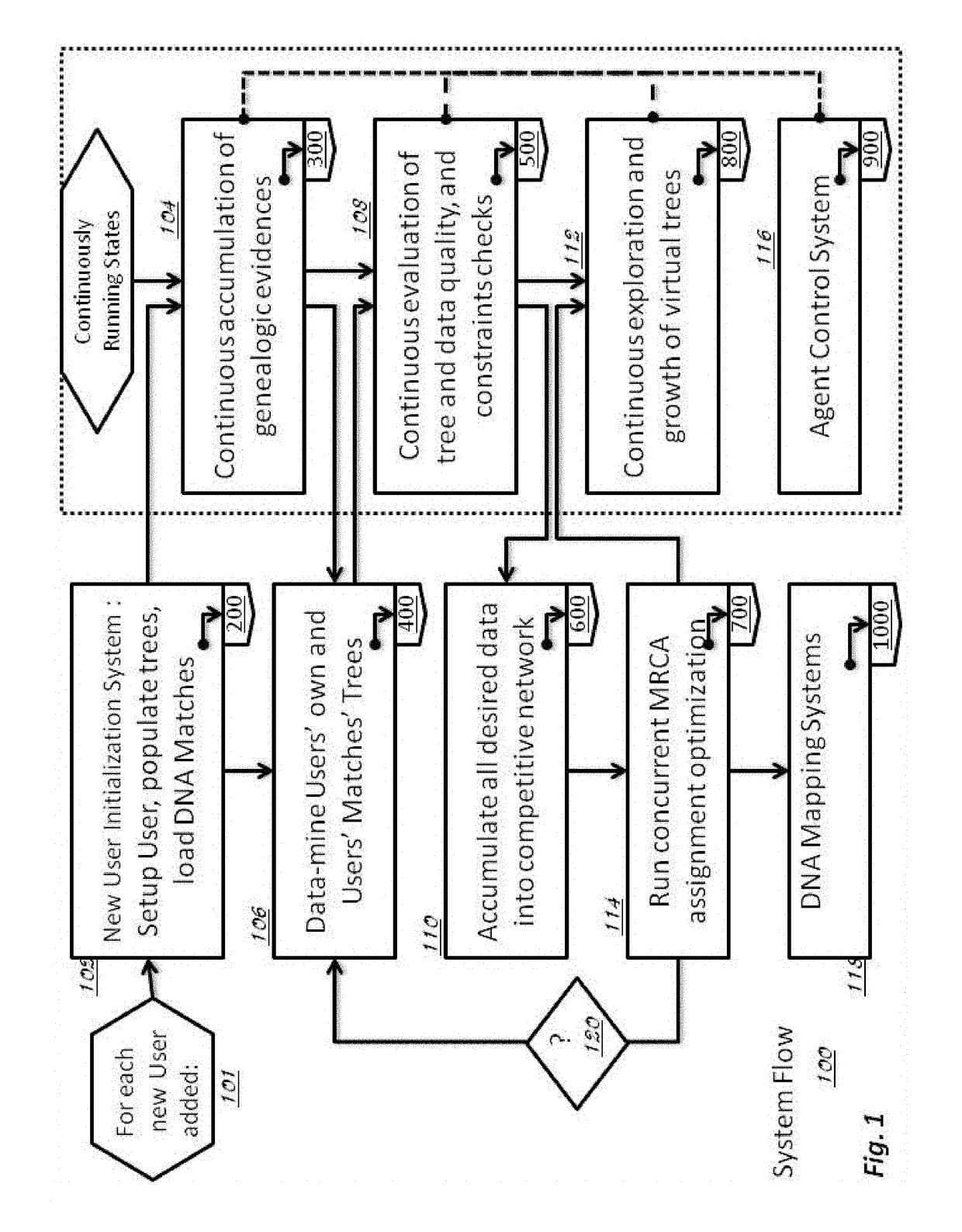
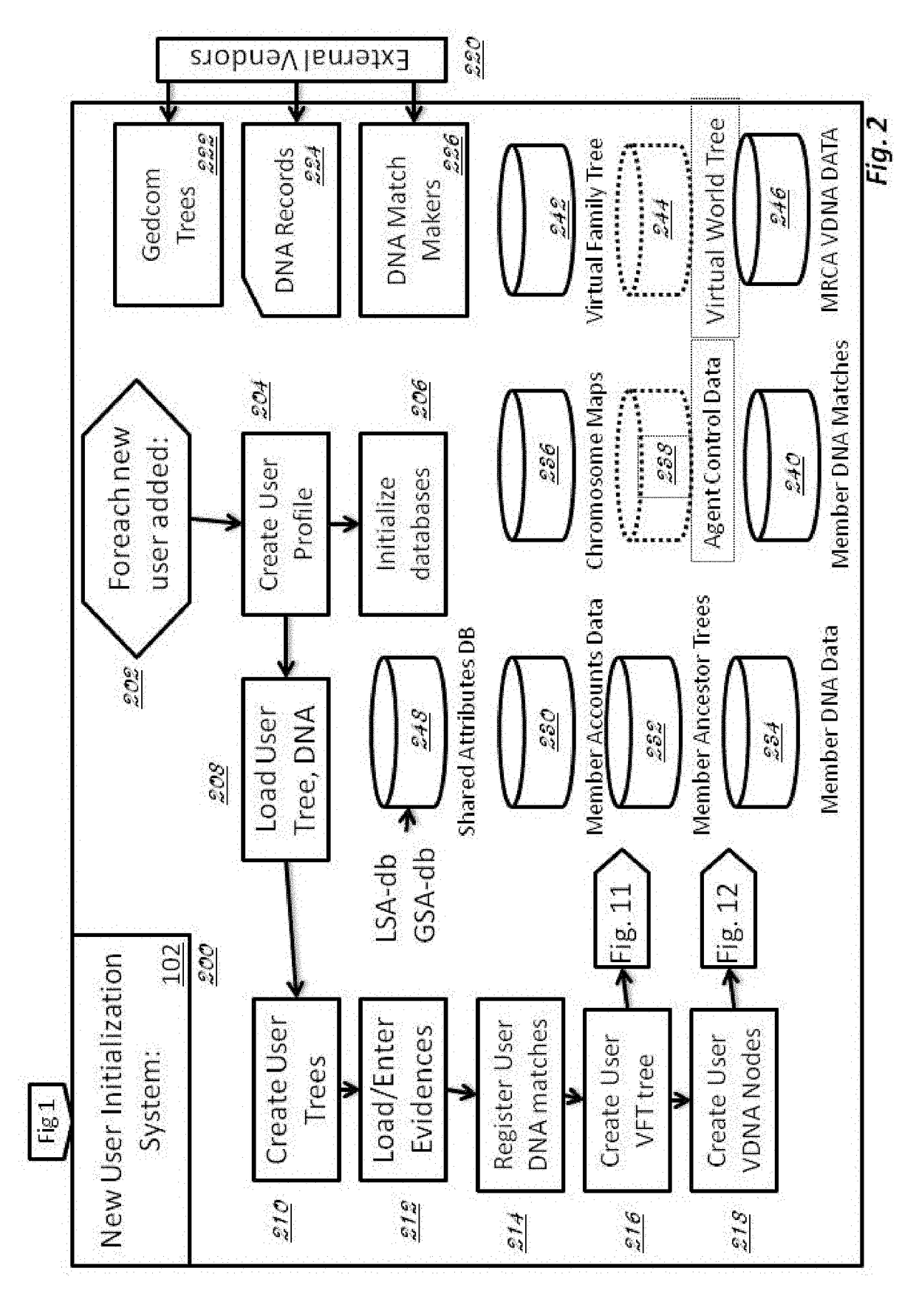
Method and System for Discovering Ancestors using Genomic and Genealogic Data
InactiveUS20170213127A1Reduced travel tendencyReduce in quantityData visualisationBiostatisticsCommon ancestryGenotype
Described invention and its embodiments, in part, facilitate discovery of ‘Most Recent Common Ancestors’ in the family trees between a massive plurality of individuals who have been predicted to be related according to amount of deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) shared as determined from a plurality of 3rd party genome sequencing and matching systems. This facilitation is enabled through a holistic set of distributed software Agents running, in part, a plurality of cooperating Machine Learning systems, such as smart evolutionary algorithms, custom classification algorithms, cluster analysis and geo-temporal proximity analysis, which in part, enable and rely on a system of Knowledge Management applied to manually input and data-mined evidences and hierarchical clusters, quality metrics, fuzzy logic constraints and Bayesian network inspired inference sharing spanning across and between all data available on personal family trees or system created virtual trees, and employing all available data regarding the genome-matching results of Users associated to those trees, and all available historical data influencing the subjects in the trees, which are represented in a form of Competitive Learning network. Derivative results of this system include, in part, automated clustering and association of phenotypes to genotypes, automated recreation of ancestor partial genomes from accumulated DNA from triangulations and the traits correlated to that DNA, and a system of cognitive computing based on distributed neural networks with mobile Agents mediating activation according to connection weights.
Owner:DUNCAN MATTHEW CHARLES
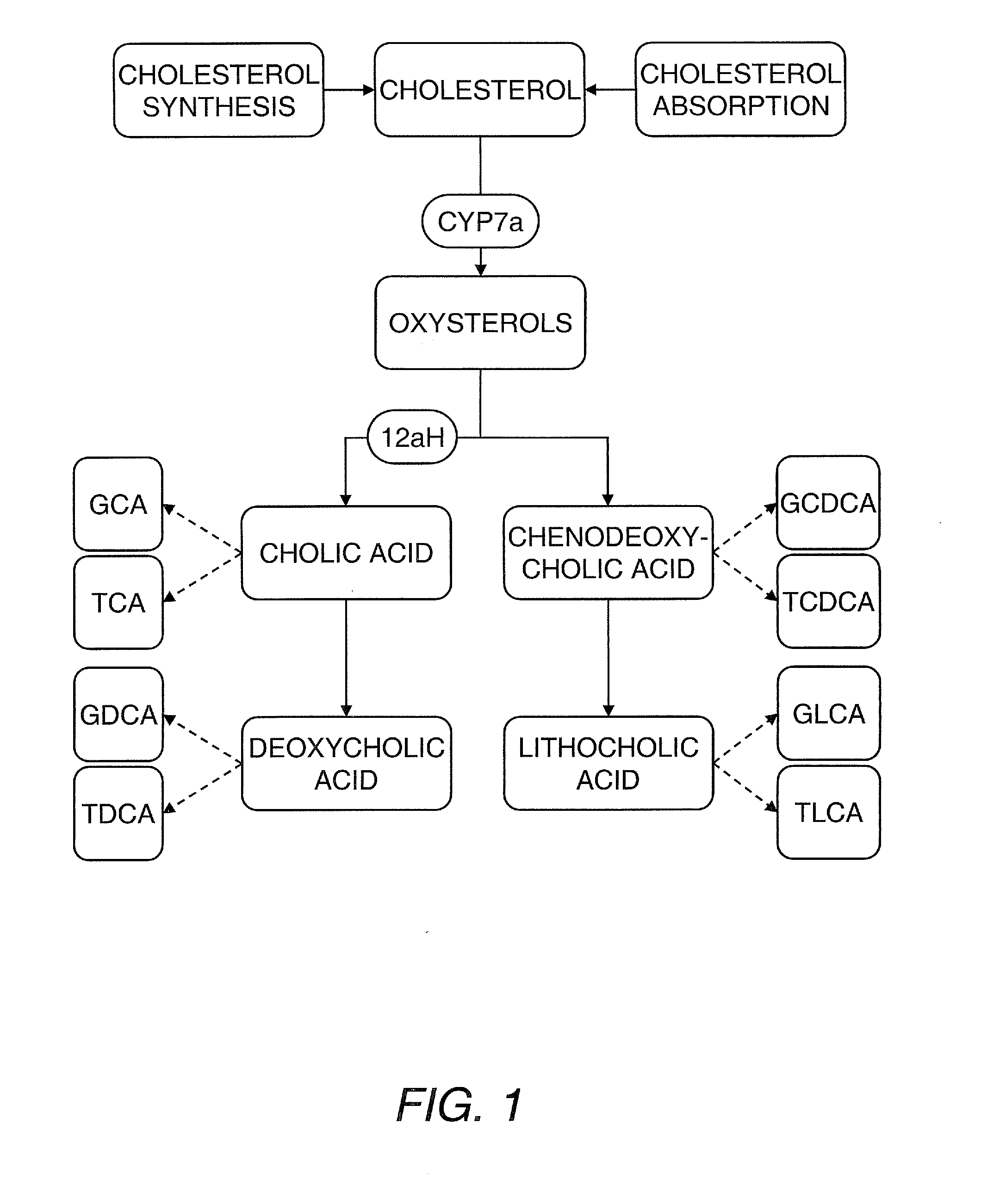
Lipidomic Approaches to Determining Drug Response Phenotypes in Cardiovascular Disease
The present invention concerns the application of lipidomics to statin treatment for disorders such as cardiovascular disorders. Hence, the invention provides, among other things, a method of correlating a lipid profile with a positive or negative response to a statin treatment regimen by obtaining a lipid profile of a sample from a mammalian subject following commencement of the treatment regimen; and correlating the lipid profile in the sample with a positive or negative response to the treatment regimen. The invention further provides a method of correlating a lipid profile with a positive or negative response to a statin treatment regimen by obtaining a lipid profile of a sample from a mammalian subject before commencement of the treatment regimen; and correlating the lipid profile in the sample with a positive or negative response to the treatment regimen.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN +4
Deterministic High-Density Single-Cell Trap Array
ActiveUS20130078163A1Meet needsReduce shearBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityShear stress
A microfluidic platform for single-cell capture, stimulation, and imaging. It passively traps 4,000 single cells on a 4.5 mm2 footprint in 30 seconds, with a single-cell loading efficiency of 95%. The array format and optimized geometry allows for easy, robust and efficient single-cell loading, while maintaining captured cells in a low shear stress environment for long-term studies. Because cells are captured sequentially, the system is adequate for rare cell samples. Trapped cells can be exposed to various environmental conditions and chemical stimulus and their dynamic response can be monitored over time. The information gained from high-throughput, single-cell time lapsed imaging presents new opportunities in quantifying cellular responses, as averaged information by other measurement methods eliminates sub-population phenotypes.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Multiple virus resistance in plants
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) differentiate into neuron-like phenotypes in vitro and in vivo, engrafted into normal or denervated rat striatum. The BMSC did not remain localized to the site of the graft, but migrated throughout the brain and integrated into specific brain regions in various architectonic patterns. The most orderly integration of BMSC was in the laminar distribution of cerebellar Purkinje cells, where the BMSC-derived cells took on the Purkinje phenotype. The BMSC exhibited site-dependent differentiation and expressed several neuronal markers including neuron-specific nuclear protein, tyrosine hydroxylase and calbindin. BMSC can be used to target specific brain nuclei in strategies of neural repair and gene therapy.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Method for identifying polymorphic markers in a population
InactiveUS6799122B2Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionGenomic DNAGenotype
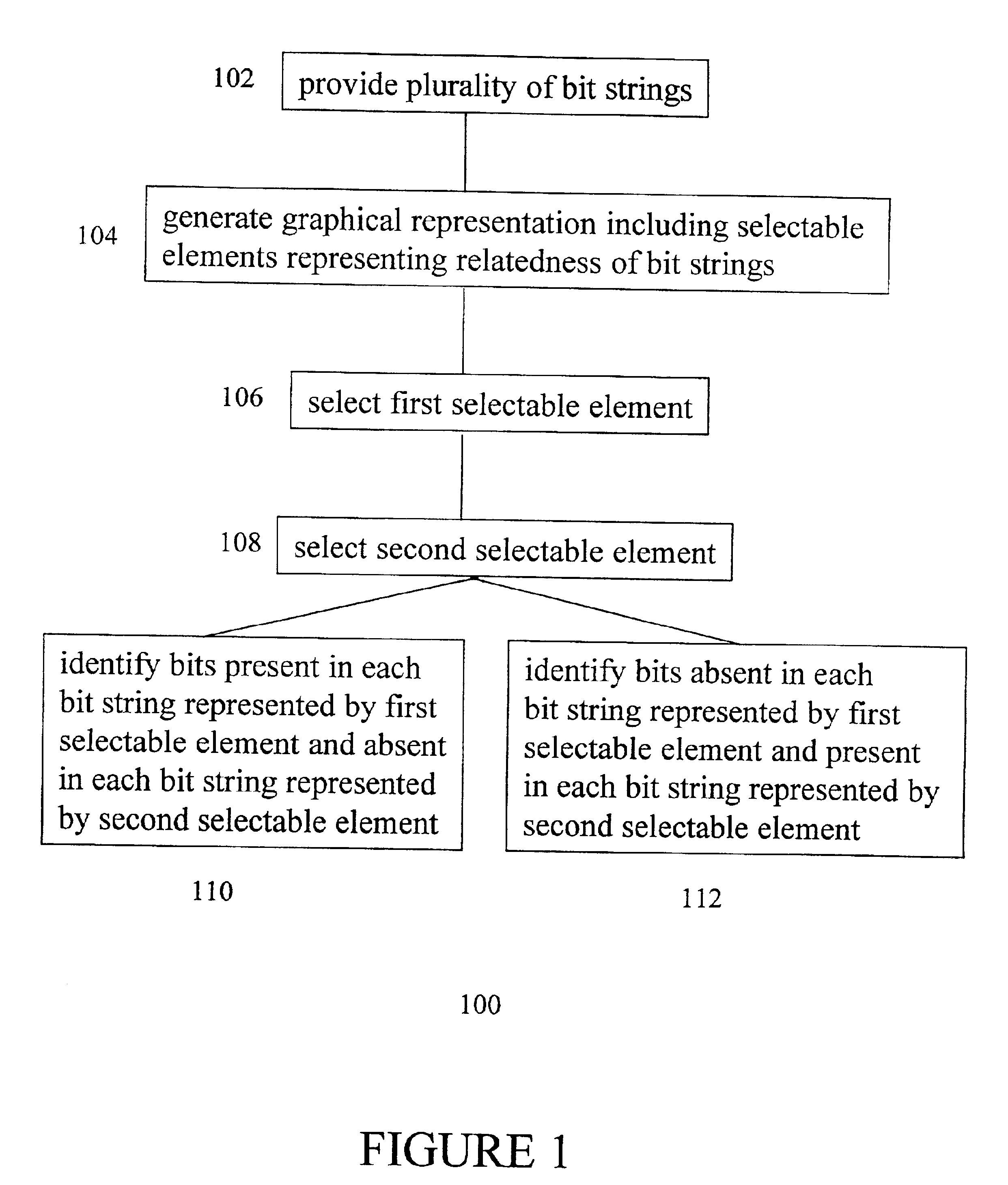
A method is provided for the identification of polymorphic markers in a population. The method includes genotypically characterizing a first sample of a population, selecting one or more individuals of the first sample based upon the genotypic characterization, fabricating a microarray with genomic DNA from each individual selected, and genotyping a second sample of the population using each fabricated microarray as a reference, thereby identifying the polymorphic markers in the population. Also provided is a method for the identification of polymorphic markers in a bacterial population. The method includes phenotypically characterizing a first sample of a population, selecting one or more individuals of the first sample based upon the phenotypic characterization, fabricating a microarray with genomic DNA from each individual selected, and genotyping a second sample of the population using each fabricated microarray as a reference, thereby identifying the polymorphic markers in the population. Also provided is a method for identifying unique bits among a plurality of bit strings including providing a plurality of bit strings, wherein each string has the same number and position of bits, and each bit has a value of 0 or 1, generating a graphical representation-including selectable elements-representing the relatedness of the bit strings, making a selection of a first selectable element, making a selection of a second selectable element, and identifying bits that are present in each bit string represented by the first selectable element and absent in each bit string represented by the second selectable element, or vice-versa.
Owner:BEACON VENTURE MANAGEMENT +1
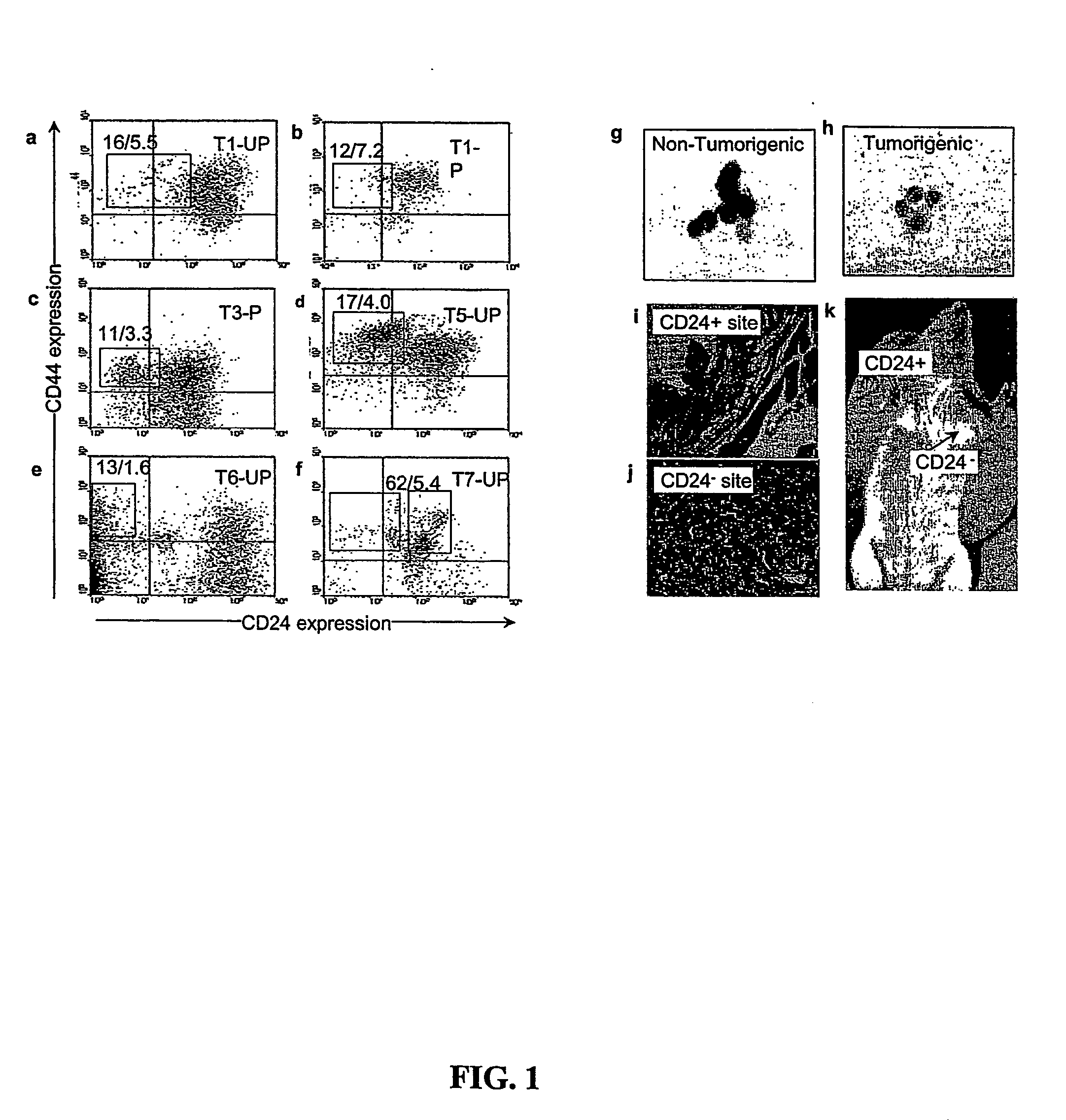
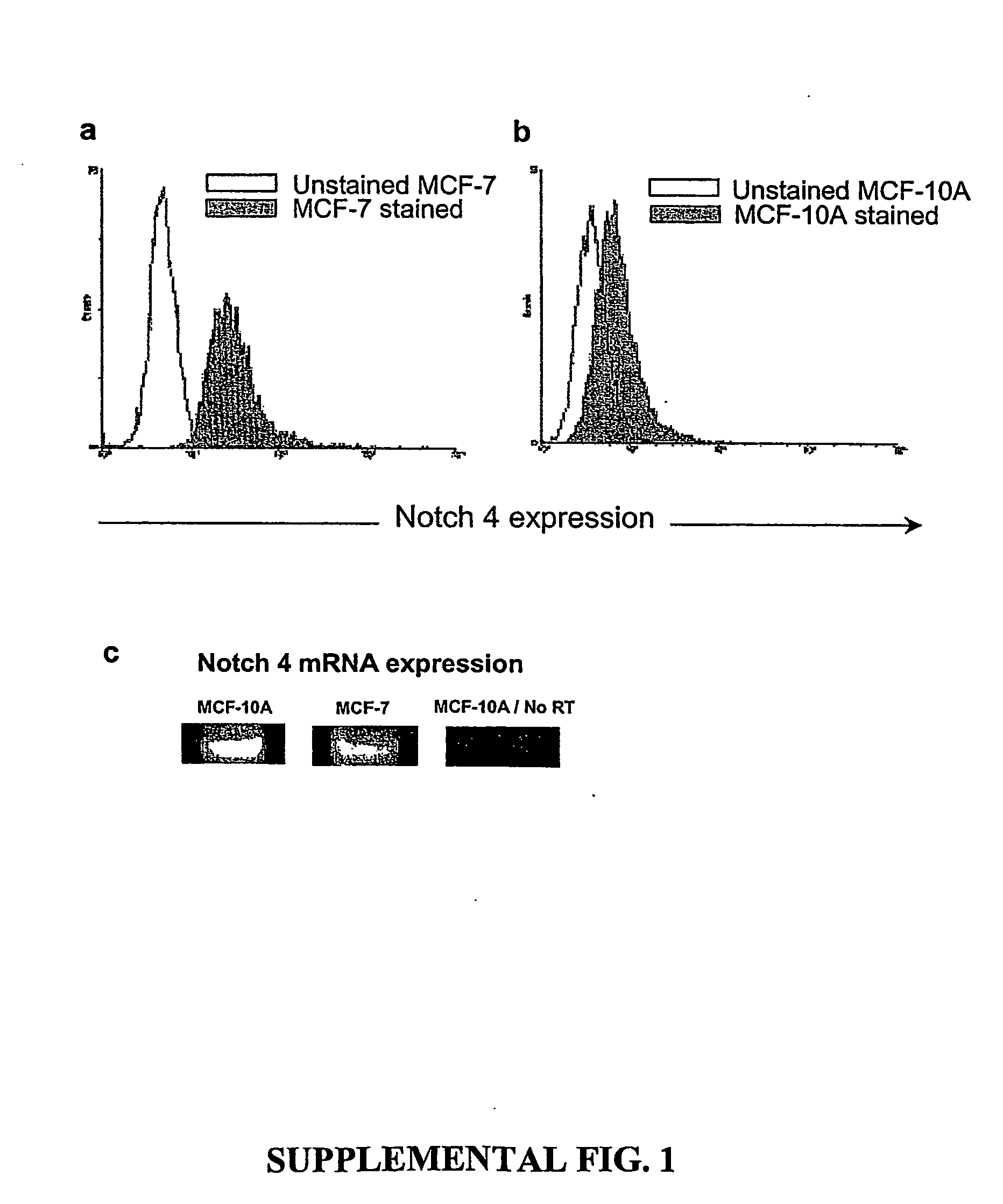
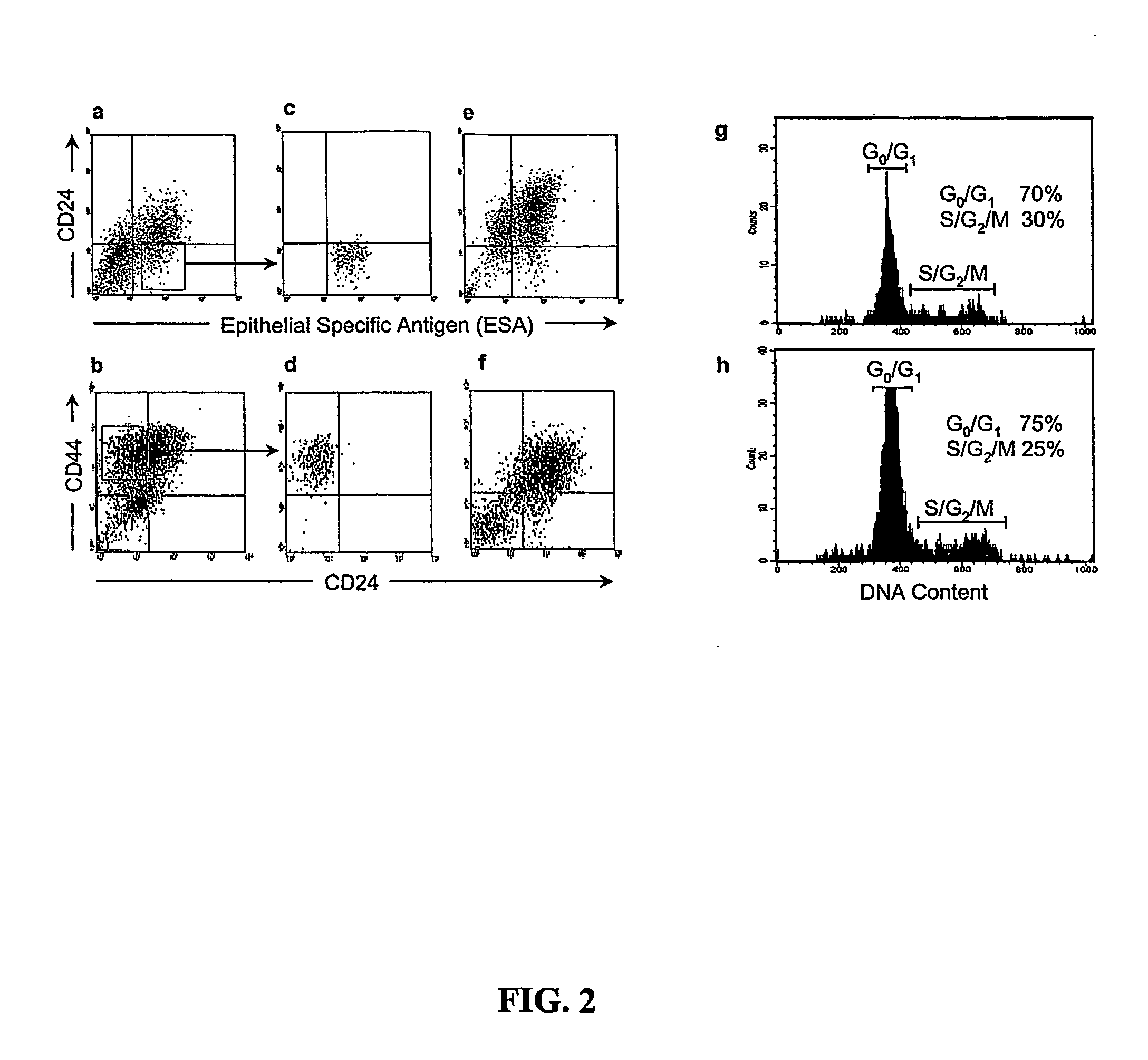
Prospective identification and characterization of breast cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20050089518A1Capacity loseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSurface marker
Human breast tumors contain hetrogeneous cancer cells. using an animal xenograft model in which human breast cancer cells were grown in immunocompromised mice we found that only a small minority of breast cancer cells had capacity to form new tumors. The ability to form new tumors was not a slochastic property, rather certain populations of cancer cells were depleted for the ability to form new tumors, while other populations were enriched for the ability to form new tumors. Tumorigenic cells could be distinguished from non-tumorigenic cancer cells based on surface marker expression. We prospectively identified and isolated the tumorigenic cells as CD4430CD24− / lowLINEAGE A few as 100 cells from this population were able to form tumors the animal xenograft model, while tens of thousands of cells from non-tumorigenic populations failed to form tumors. The tumorigenic cells could be serially passaged, each time generating new tumors containing and expanded numbers of CD44+CD24 Lineage tumorigenic cells as well as phenotypically mixed populations of non-tumorigenic cancer cells. This is reminiscent of the ability of normal stem cells to self-renew and differentiate. The expression of potential therapeutic targets also differed between the tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic populations. Notch activation promoted the survival of the tumorigenic cells, and a blocking antibody against Notch 4 induced tumorigenic breast cancer cells to undergo apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
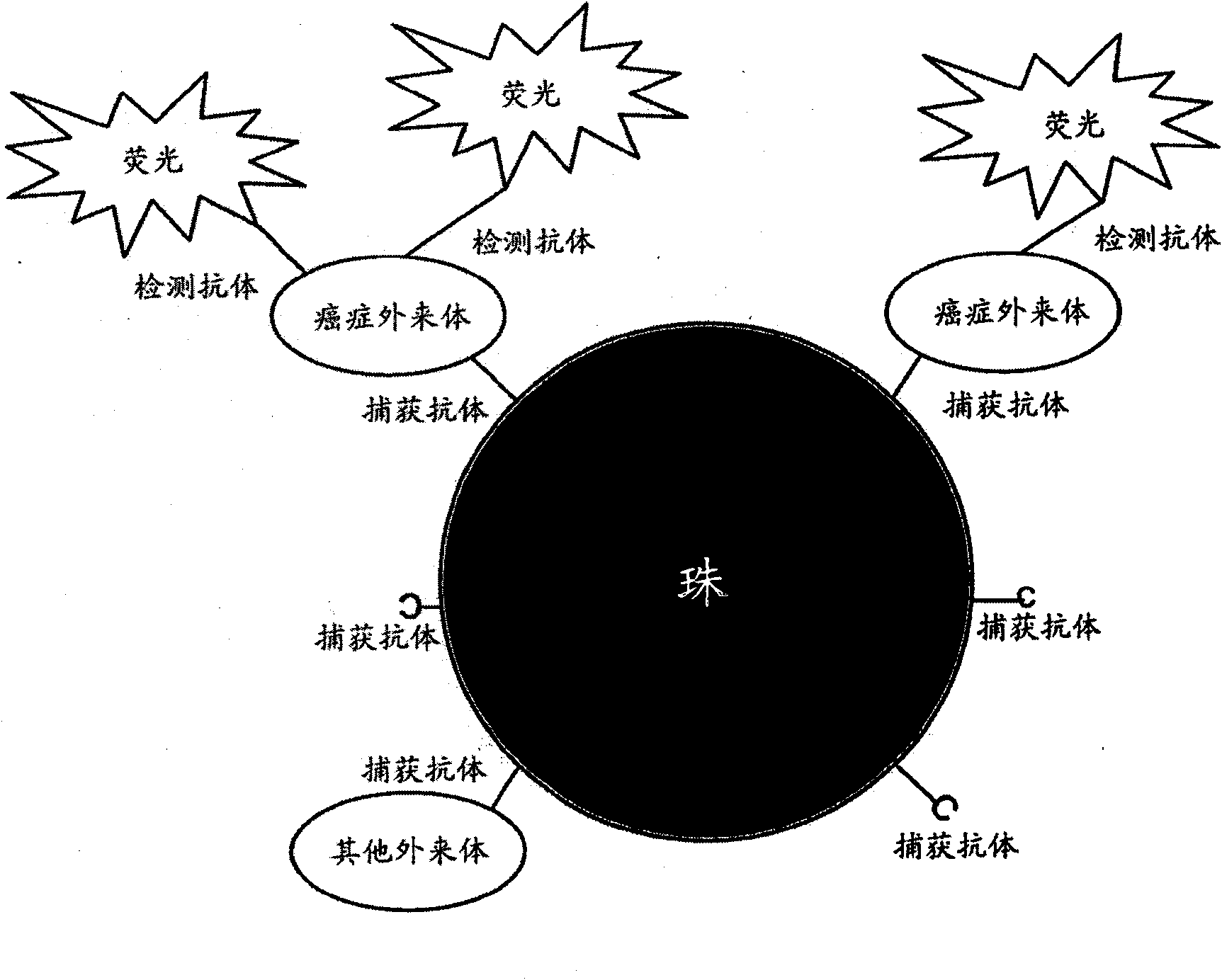
Methods and systems for determining phenotypes using exosomes
InactiveCN102301002AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTherapy relatedBiomarker (petroleum)
Exosomes can be used for detecting biomarkers for diagnostic, therapy-related or prognostic methods to identify phenotypes, such as a condition or disease, for example, the stage or progression of a disease. Cell-of-origin exosomes can be used in profiling of physiological states or determining phenotypes. Biomarkers or markers from cell-of-origin specific exosomes can be used to determine treatment regimens for diseases, conditions, disease stages, and stages of a condition, and can also be used to determine treatment efficacy. Markers from cell-of-origin specific exosomes can also be used to identify conditions of diseases of unknown origin.
Owner:CARIS LIFE SCI LUXEMBOURG HLDG
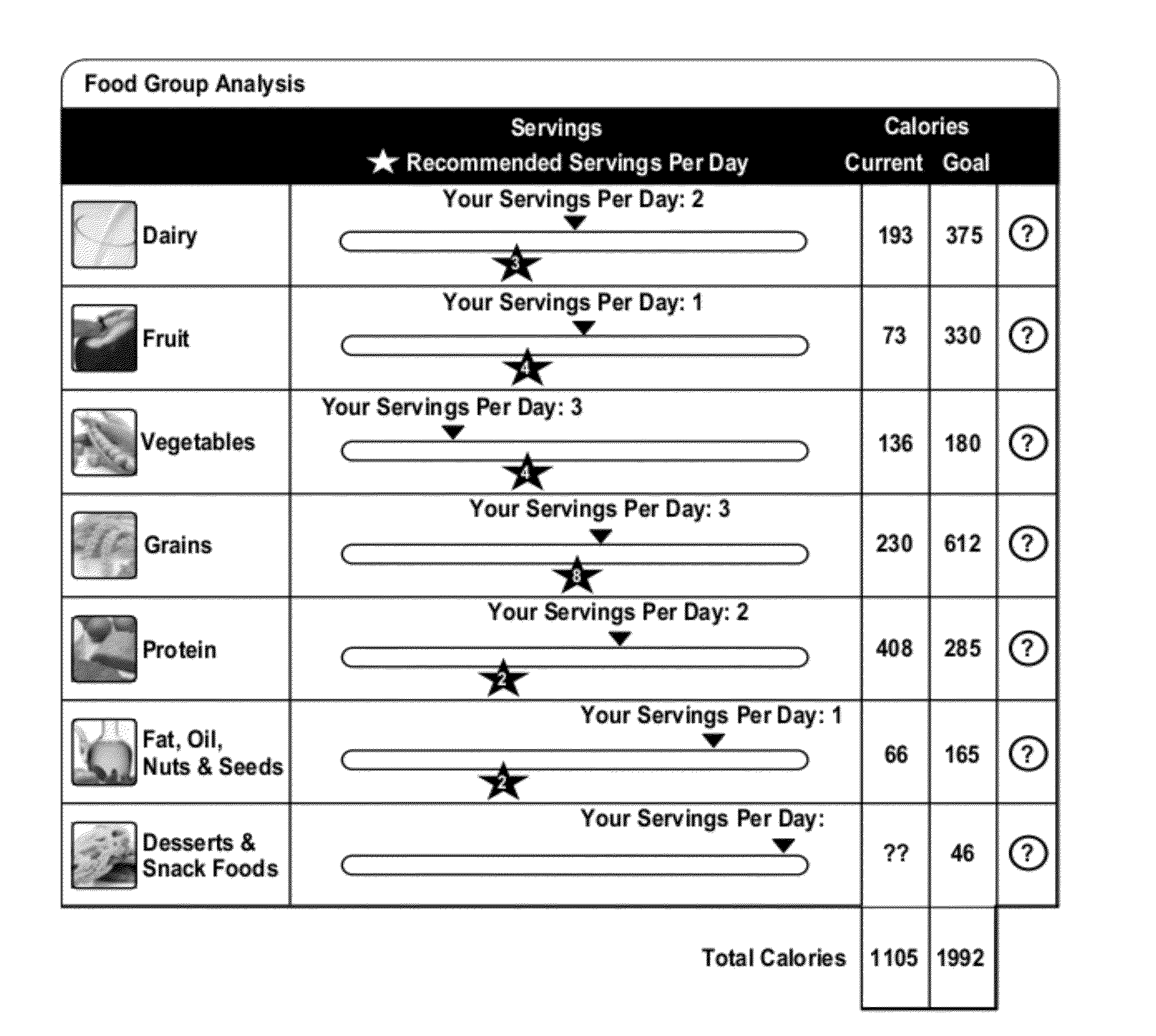
Medical health information system for health assessment, weight management and meal planning
A system and method provide nutrition assessments and tools for enabling users to achieve health-related goals based on specific health needs. The tools can include a nutrition assessment tool, a weight solution tool, a meal planning tool, and a meal tracking tool. The method includes receiving patient phenotype data. The phenotype data can include, but is not limited to, biometric data specific to the patient, medical claims data specific to the patient, organizational data specific to an organization to which the patient belongs, and behavioral data including dietary habits and nutritional history. One or more algorithms are executed on at least one processor of a computing apparatus to provide analyses of patient data in order. The results are output to a user in various web pages customized to provide features to the user.
Owner:PHENOTYPEIT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com