Patents
Literature
10430results about How to "Improve tolerance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
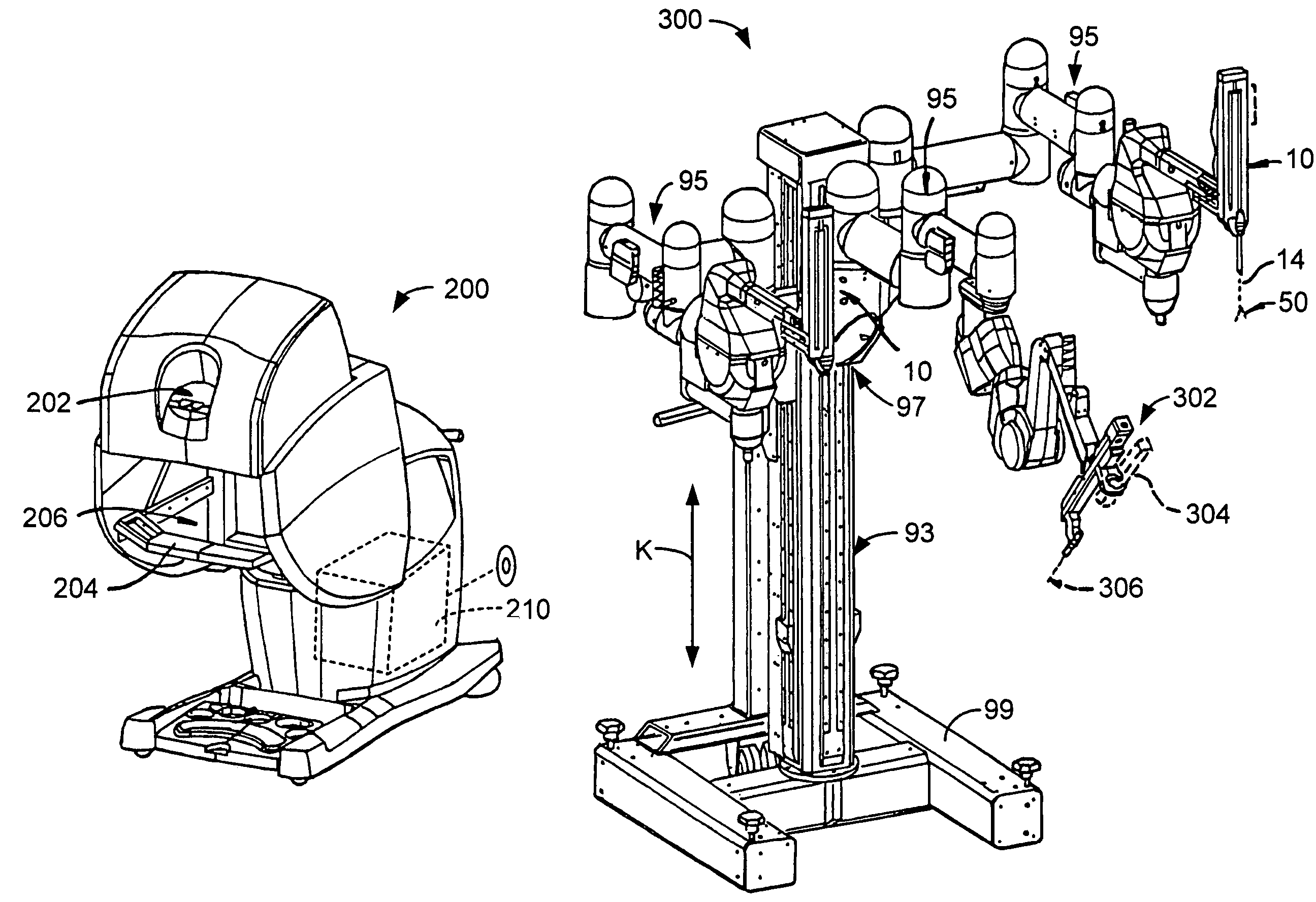
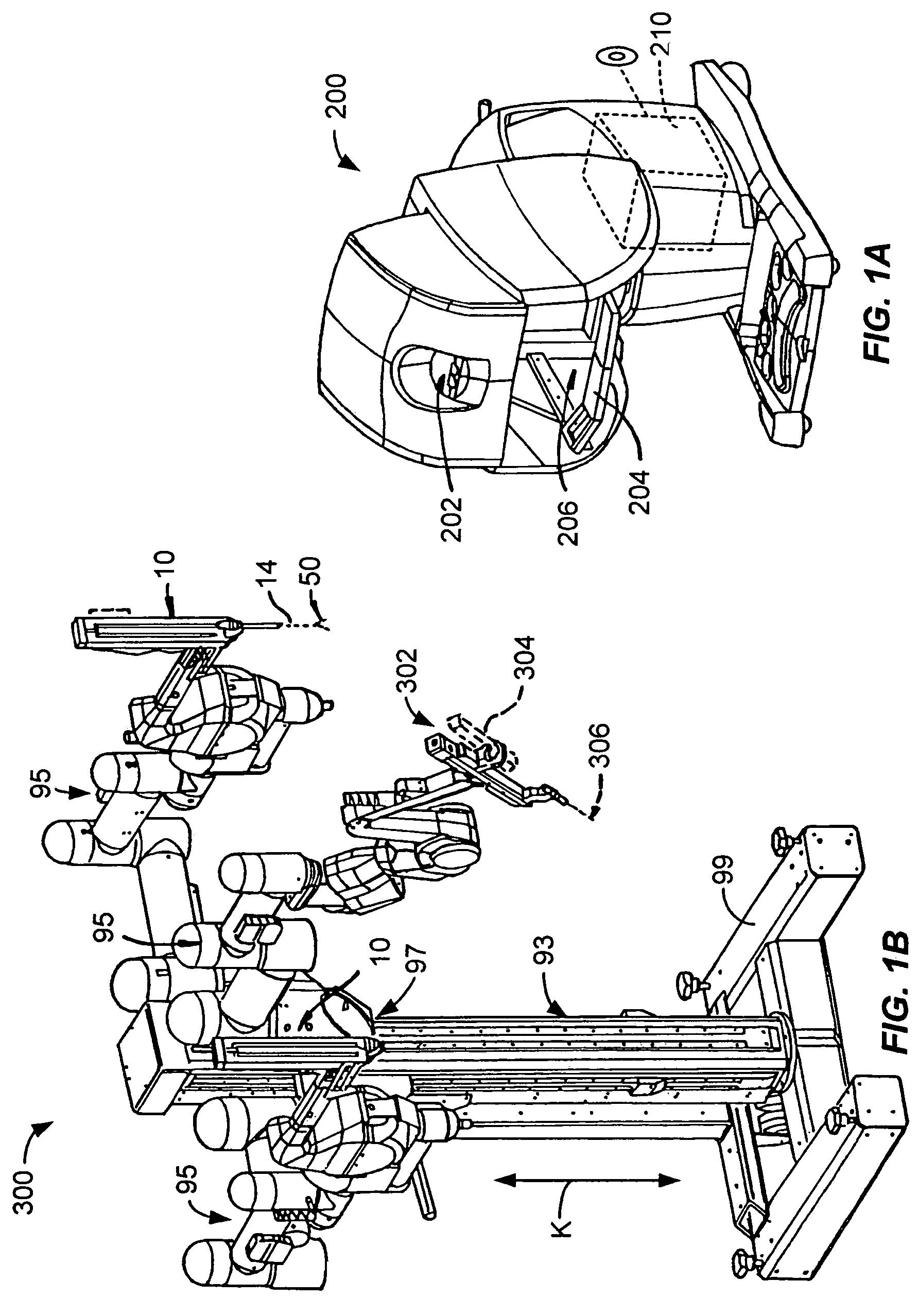
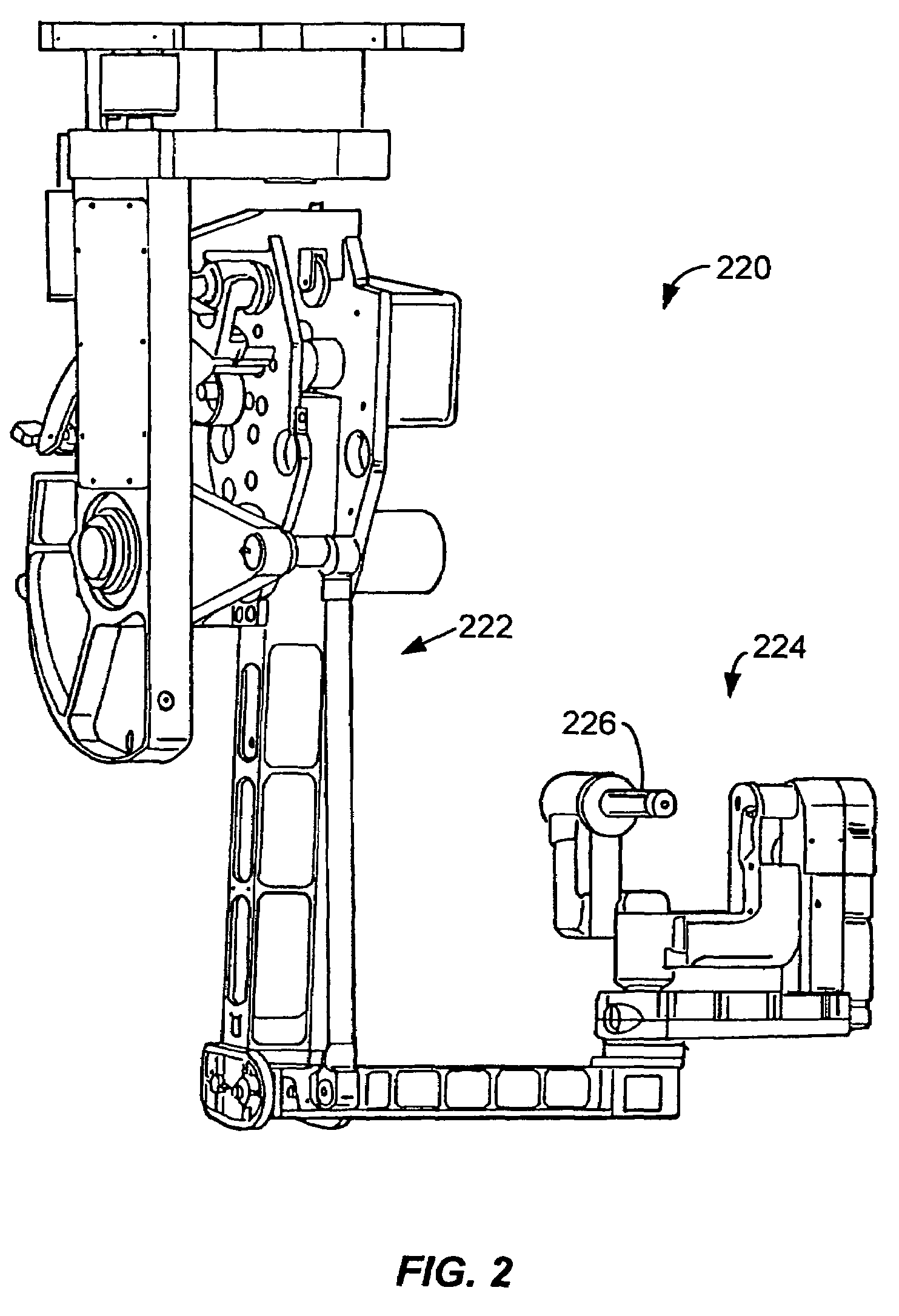
Tool grip calibration for robotic surgery
ActiveUS7386365B2Limited tool lifeStringent manufacturing toleranceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringActuator
Telerobotic, telesurgical, and surgical robotic devices, systems, and methods selectively calibrate end effector jaws by bringing the jaw elements into engagement with each other. Commanded torque signals may bring the end effector elements into engagement while monitoring the resulting position of a drive system, optionally using a second derivative of the torque / position relationship so as to identify an end effector engagement position. Calibration can allow the end effector engagement position to correspond to a nominal closed position of an input handle by compensating for wear on the end effector, the end effector drive system, then manipulator, the manipulator drive system, the manipulator / end effector interfacing, and manufacturing tolerances.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
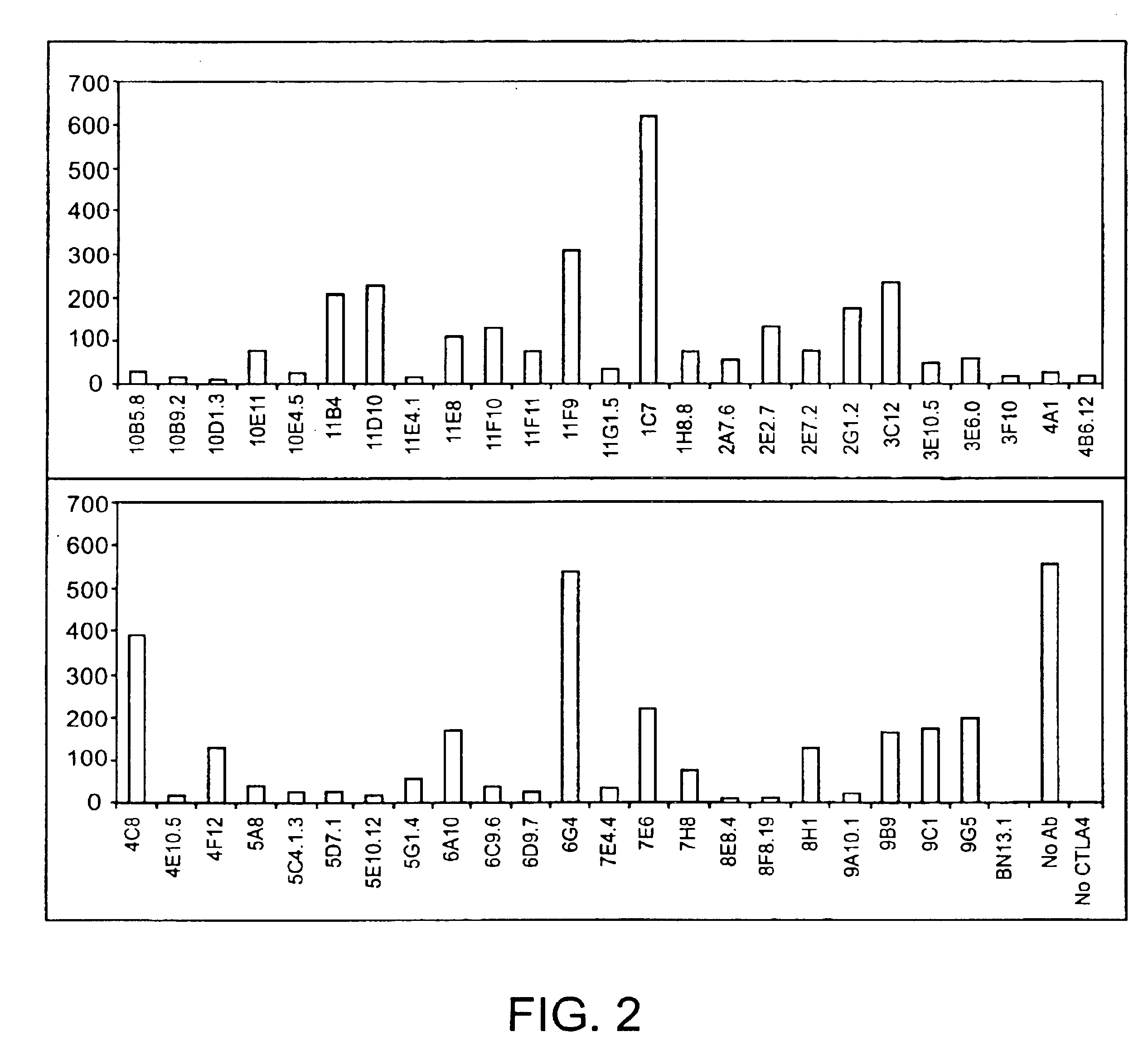
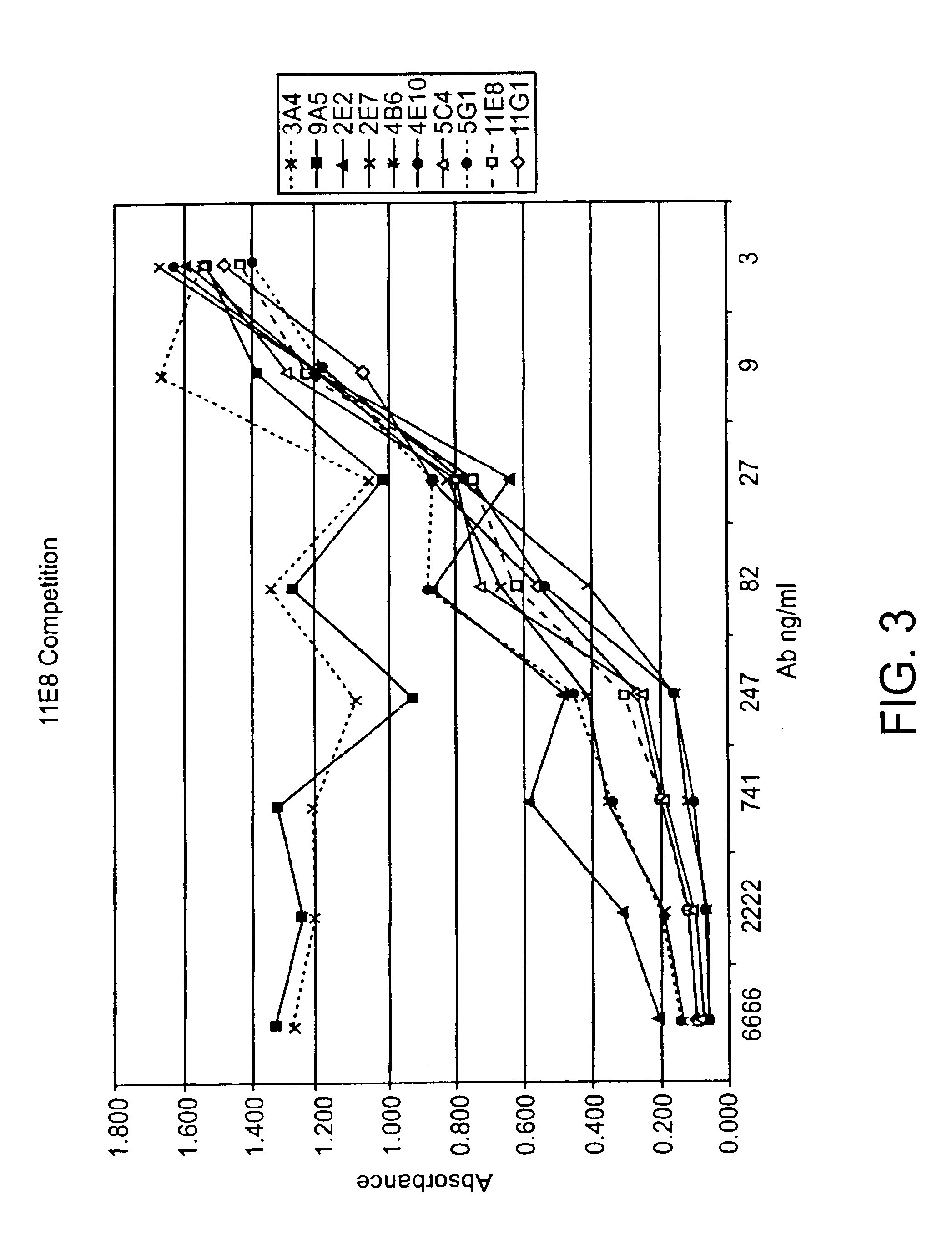
Human CTLA-4 antibodies
The present invention provides human sequence antibodies against CTLA-4 and methods of treating human diseases, infections and other conditions using these antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
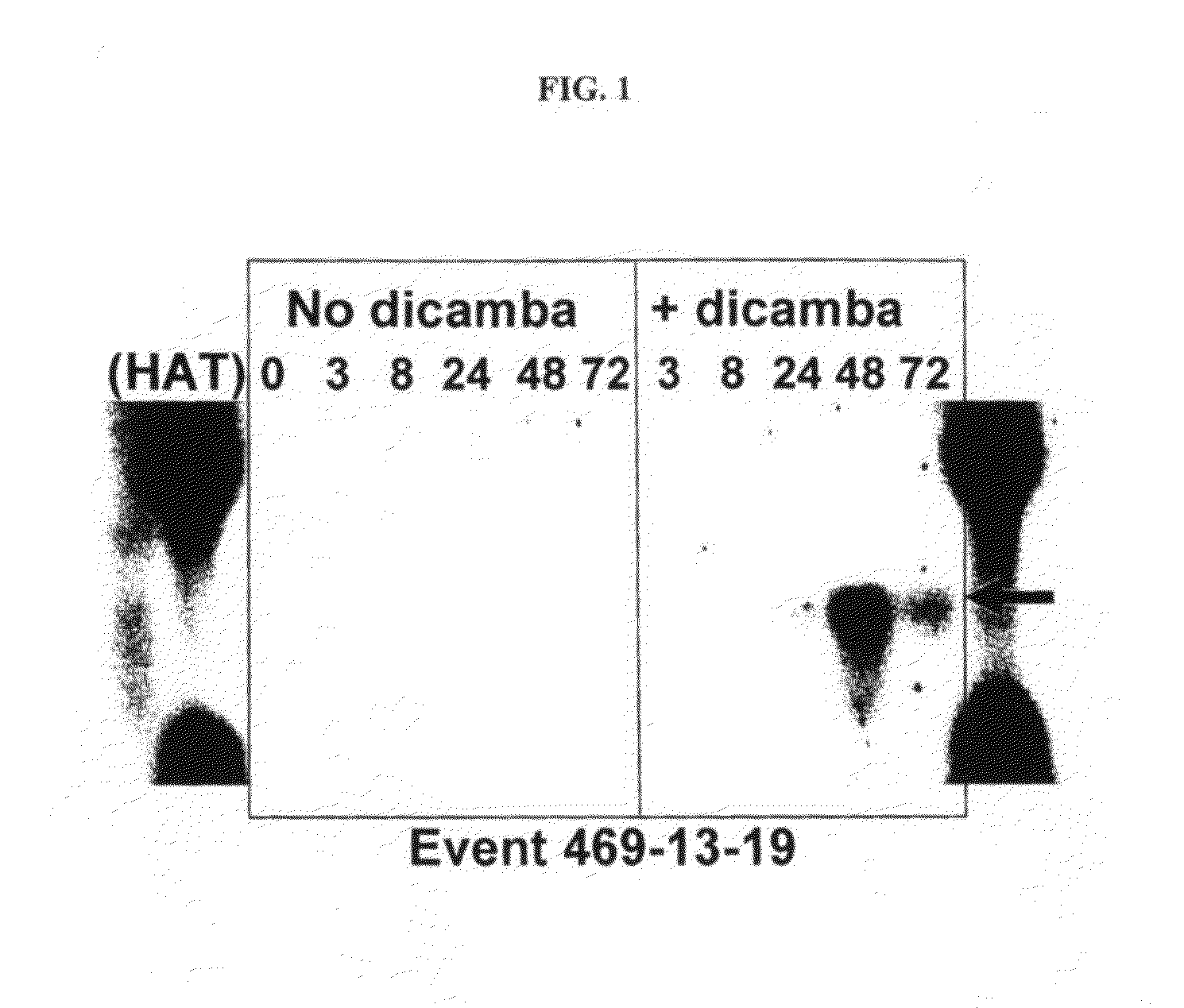
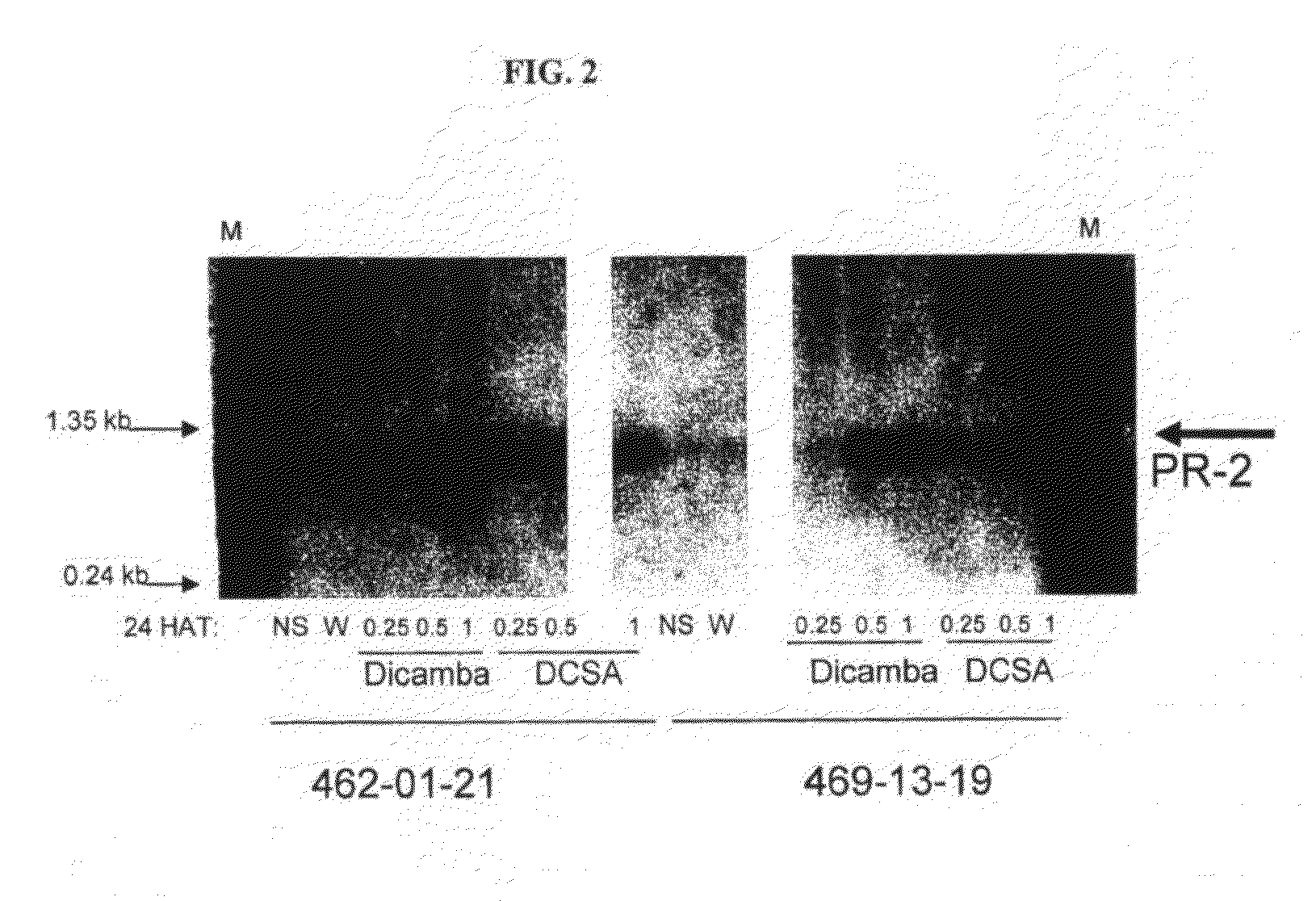
Methods and compositions for improving plant health
ActiveUS8754011B2Good for healthTolerance to oxidative stressBiocideOrganic chemistryMetaboliteGlyphosate
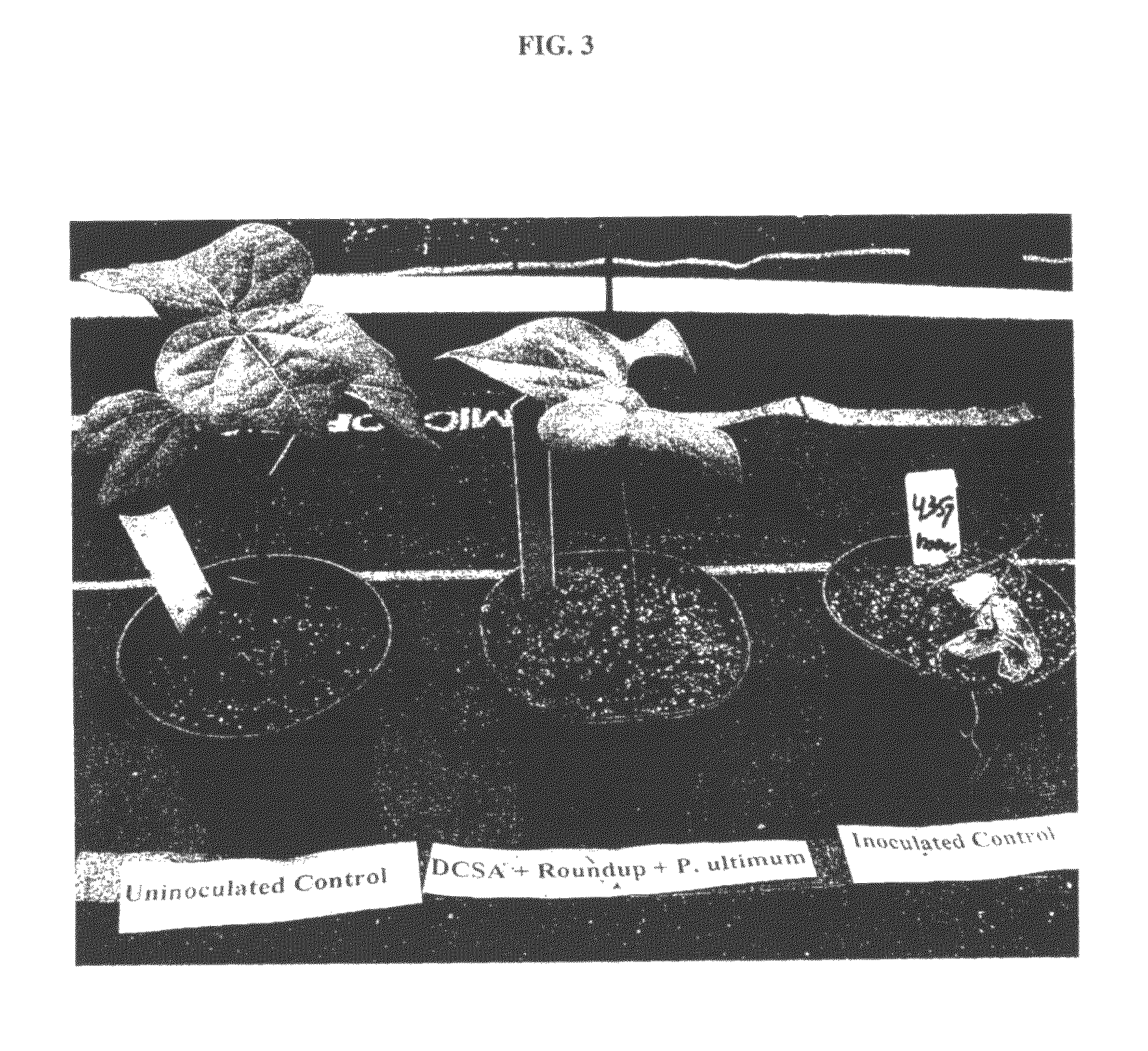
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving plant health. In particular, application of dicamba or another substrate of DMO, or metabolites thereof including DCSA, to a plant confers tolerance to, or defense against, abiotic or biotic stresses such as oxidative stress including herbicide application, and plant disease, and enhances crop yield. Such application may be in combination with the application of another herbicide such as glyphosate.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Soybean event dp-305423-1 and compositions and methods for the identification and/or detection thereof
ActiveUS20080312082A1Improve farming efficiencyImprove toleranceBiocideSugar derivativesHigh oleic acidInsertion site
Compositions and methods related to transgenic high oleic acid / ALS inhibitor-tolerant soybean plants are provided. Specifically, the present invention provides soybean plants having a DP-305423-1 event which imparts a high oleic acid phenotype and tolerance to at least one ALS-inhibiting herbicide. The soybean plant harboring the DP-305423-1 event comprises genomic / transgene junctions having at least the polynucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO:8, 9, 14, 15, 20, 21, 83 or 84. The characterization of the genomic insertion site of the DP-305423-1 event provides for an enhanced breeding efficiency and enables the use of molecular markers to track the transgene insert in the breeding populations and progeny thereof. Various methods and compositions for the identification, detection, and use of the soybean DP-305423-1 events are provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
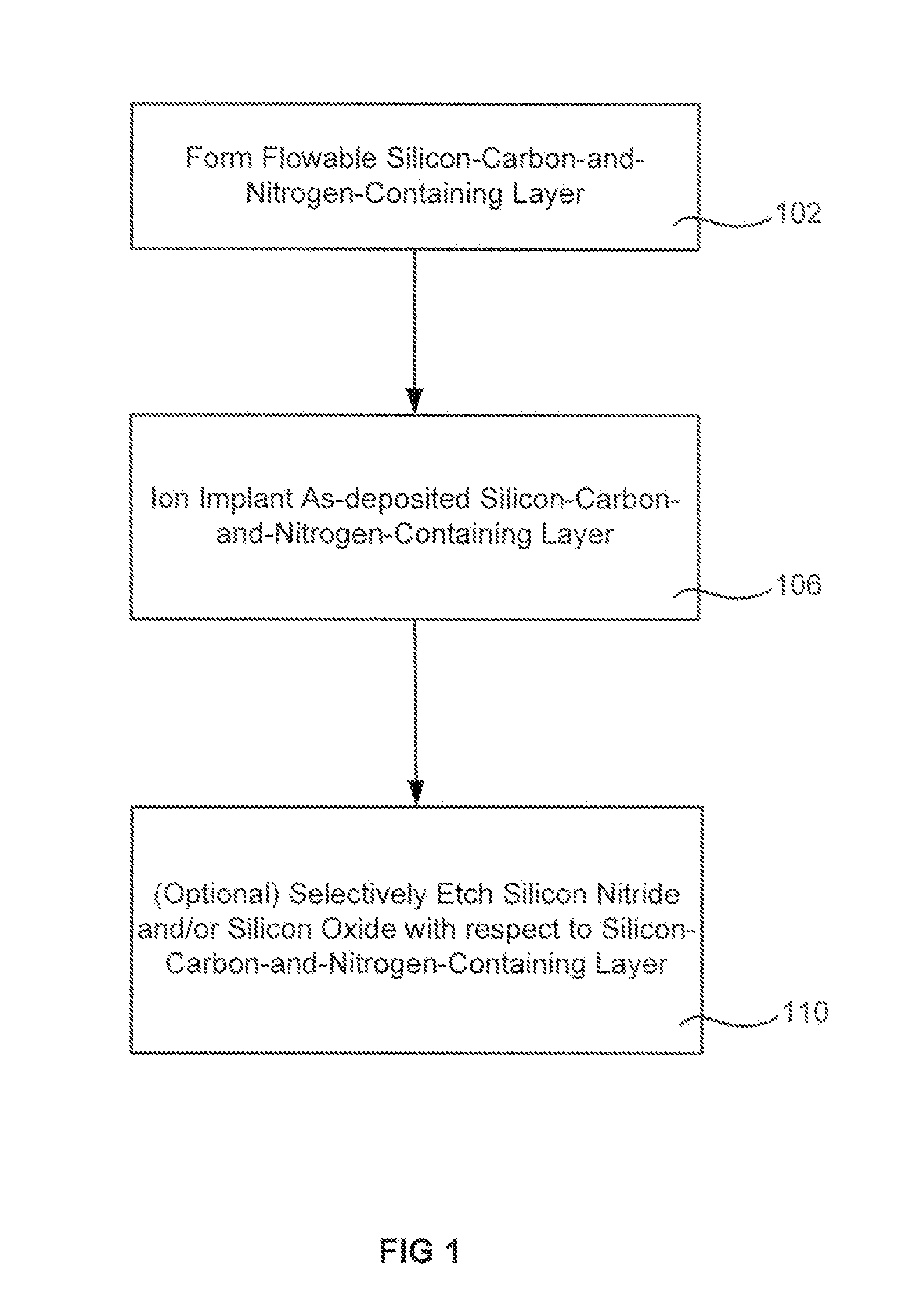
Doping of dielectric layers
InactiveUS20130217243A1Increase etch tolerancePrevent shrinkageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperaturePhysical chemistry
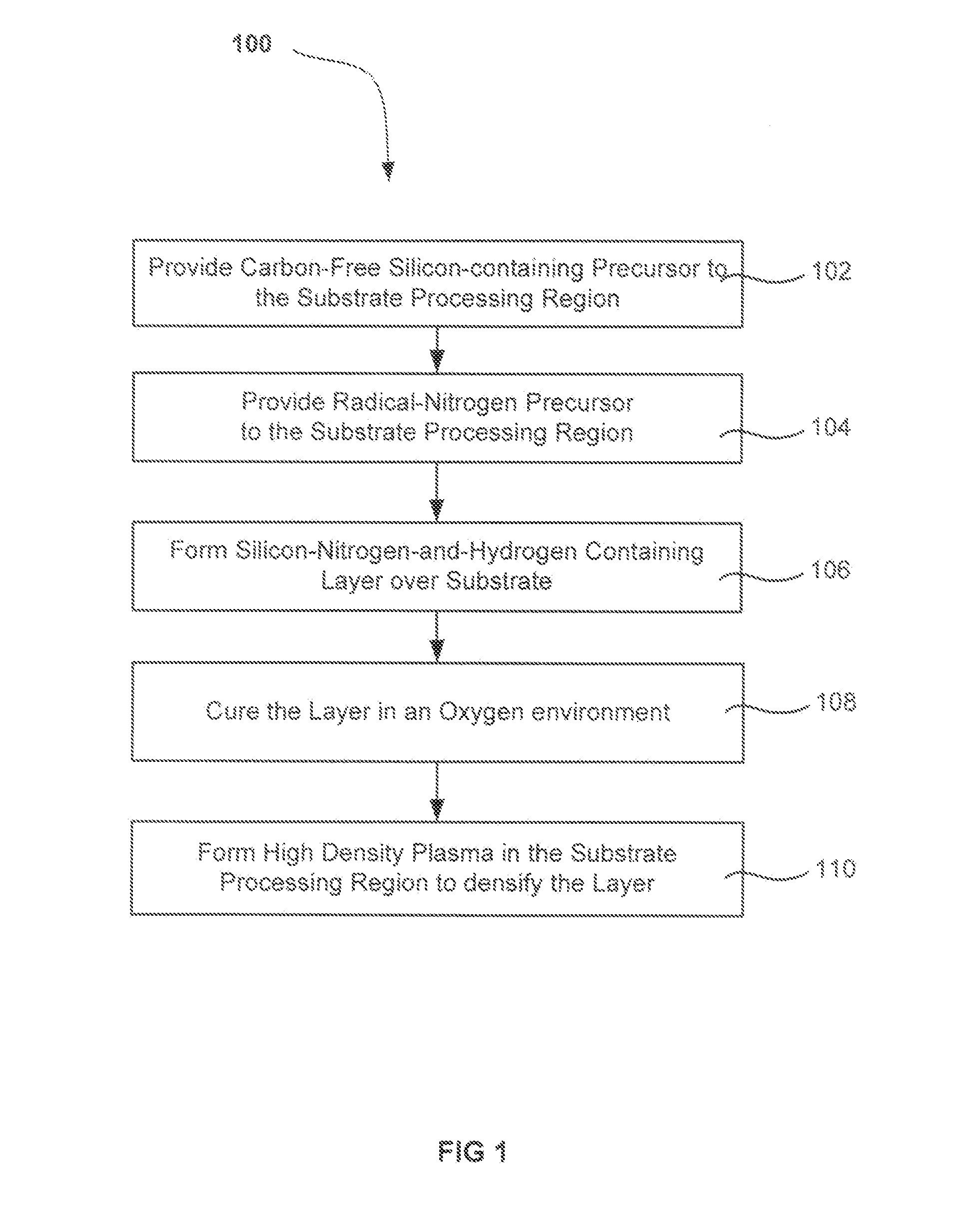
Methods are described for forming and treating a flowable silicon-carbon-and-nitrogen-containing layer on a semiconductor substrate. The silicon and carbon constituents may come from a silicon-and-carbon-containing precursor while the nitrogen may come from a nitrogen-containing precursor that has been activated to speed the reaction of the nitrogen with the silicon-and-carbon-containing precursor at lower deposition temperatures. The initially-flowable silicon-carbon-and-nitrogen-containing layer is ion implanted to increase etch tolerance, prevent shrinkage, adjust film tension and / or adjust electrical characteristics. Ion implantation may also remove components which enabled the flowability, but are no longer needed after deposition. Some treatments using ion implantation have been found to decrease the evolution of properties of the film upon exposure to atmosphere.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
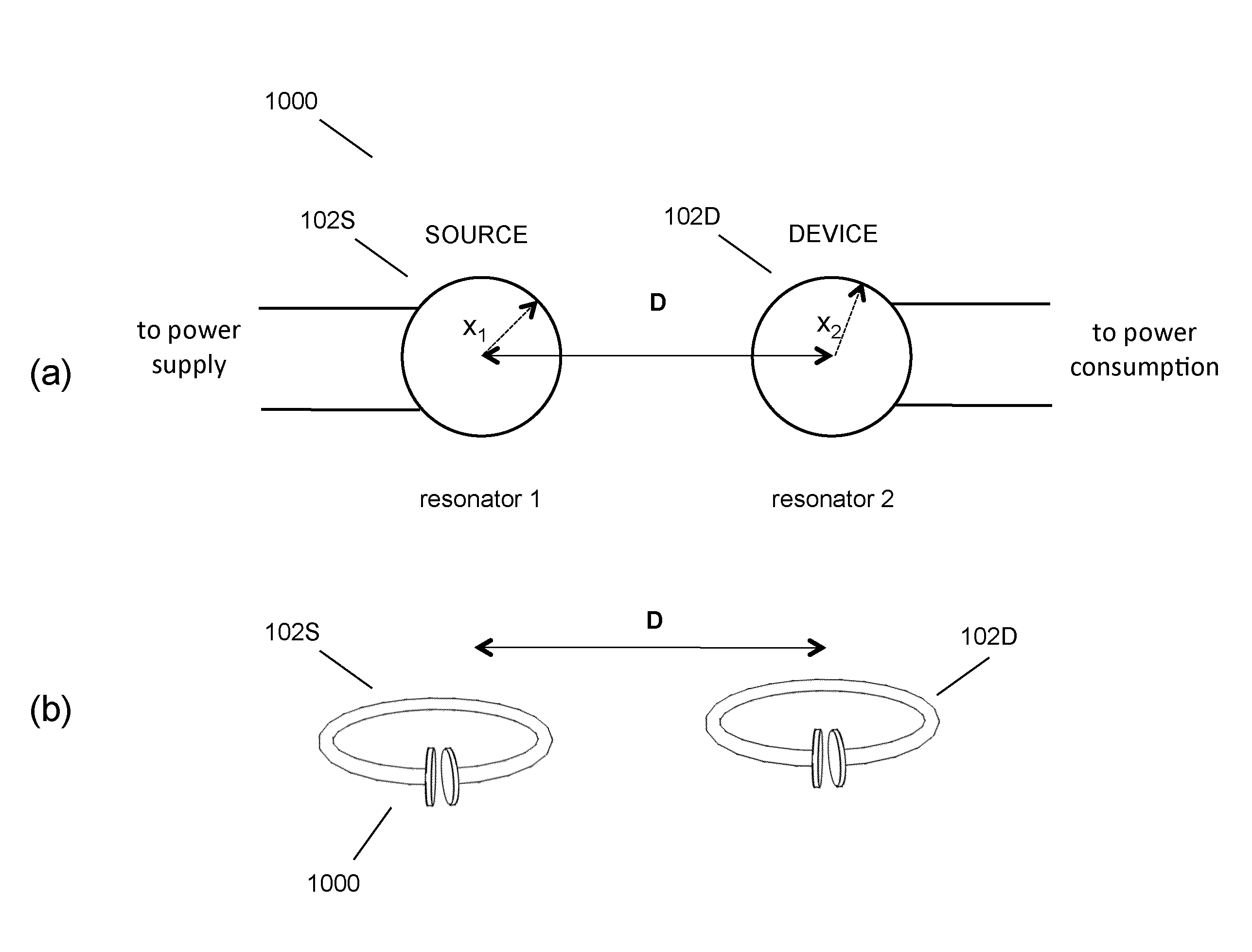
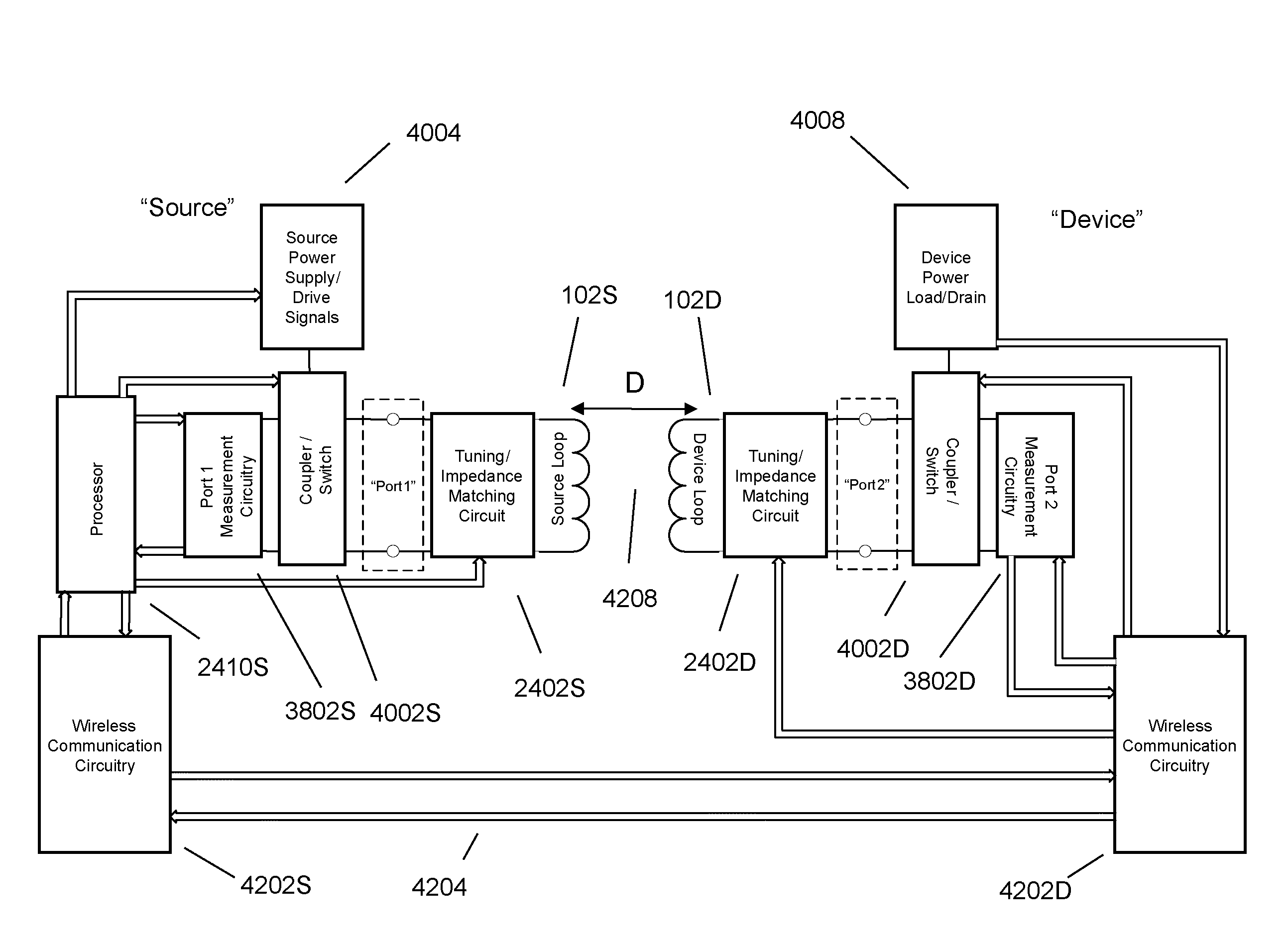
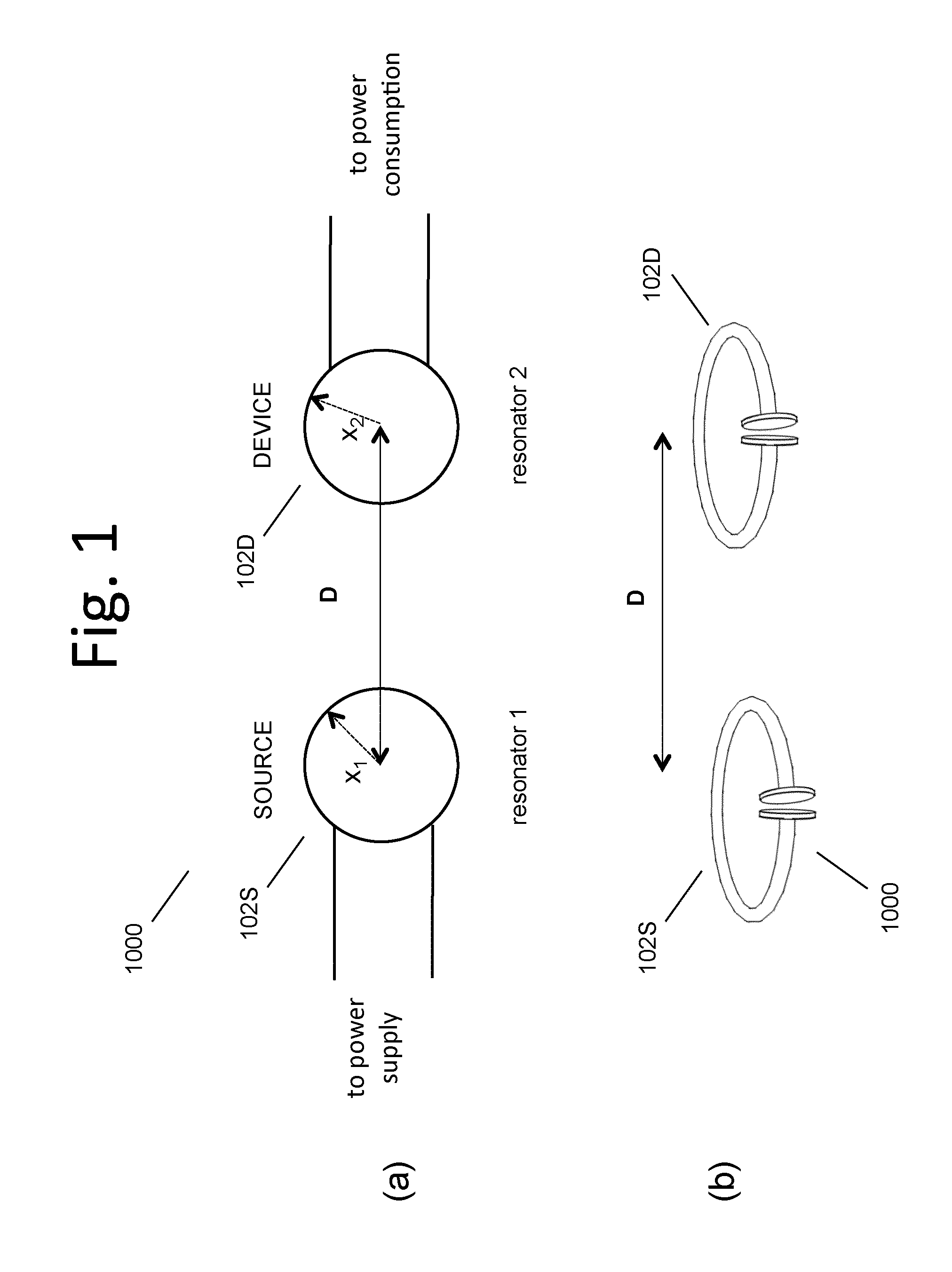
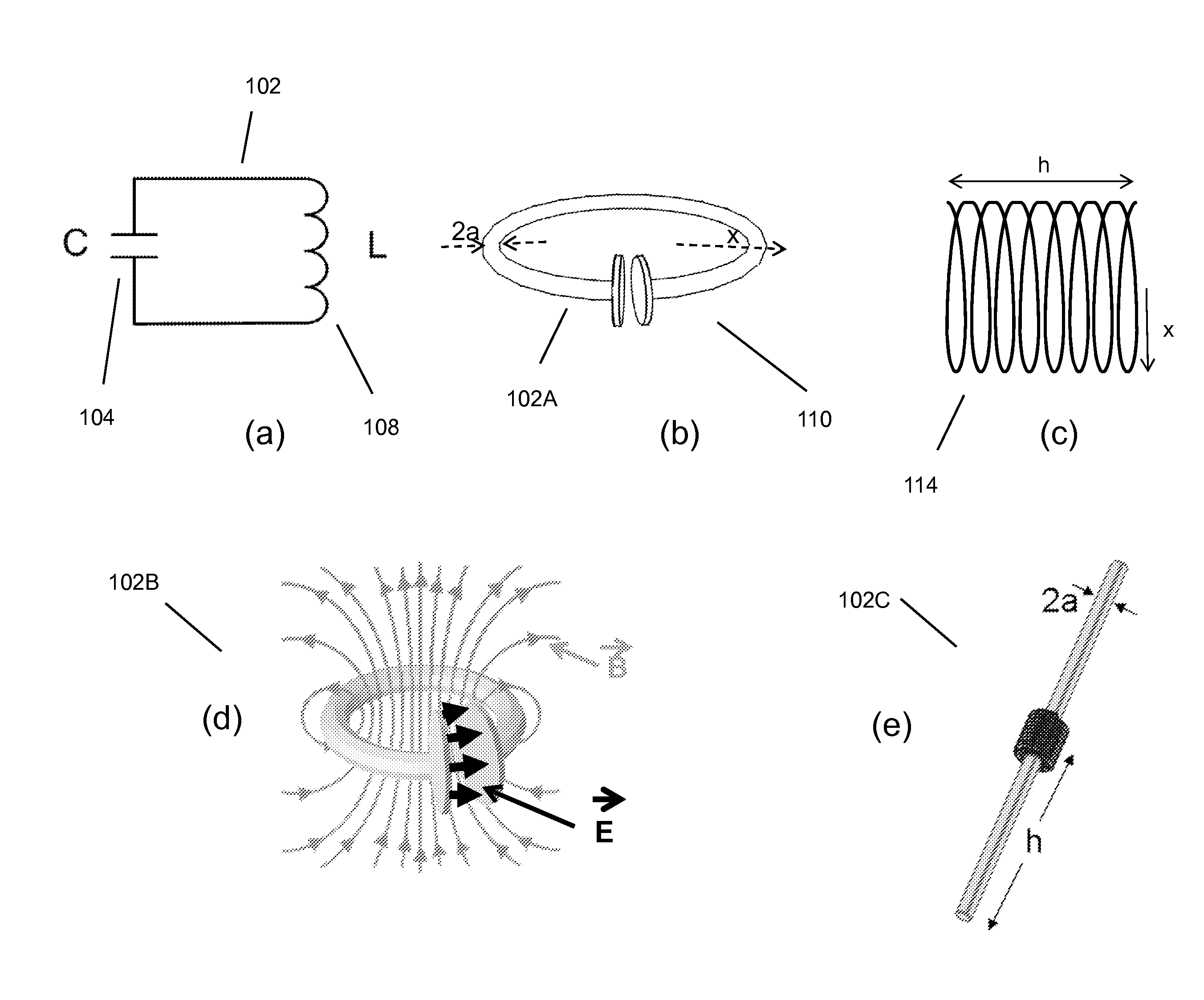
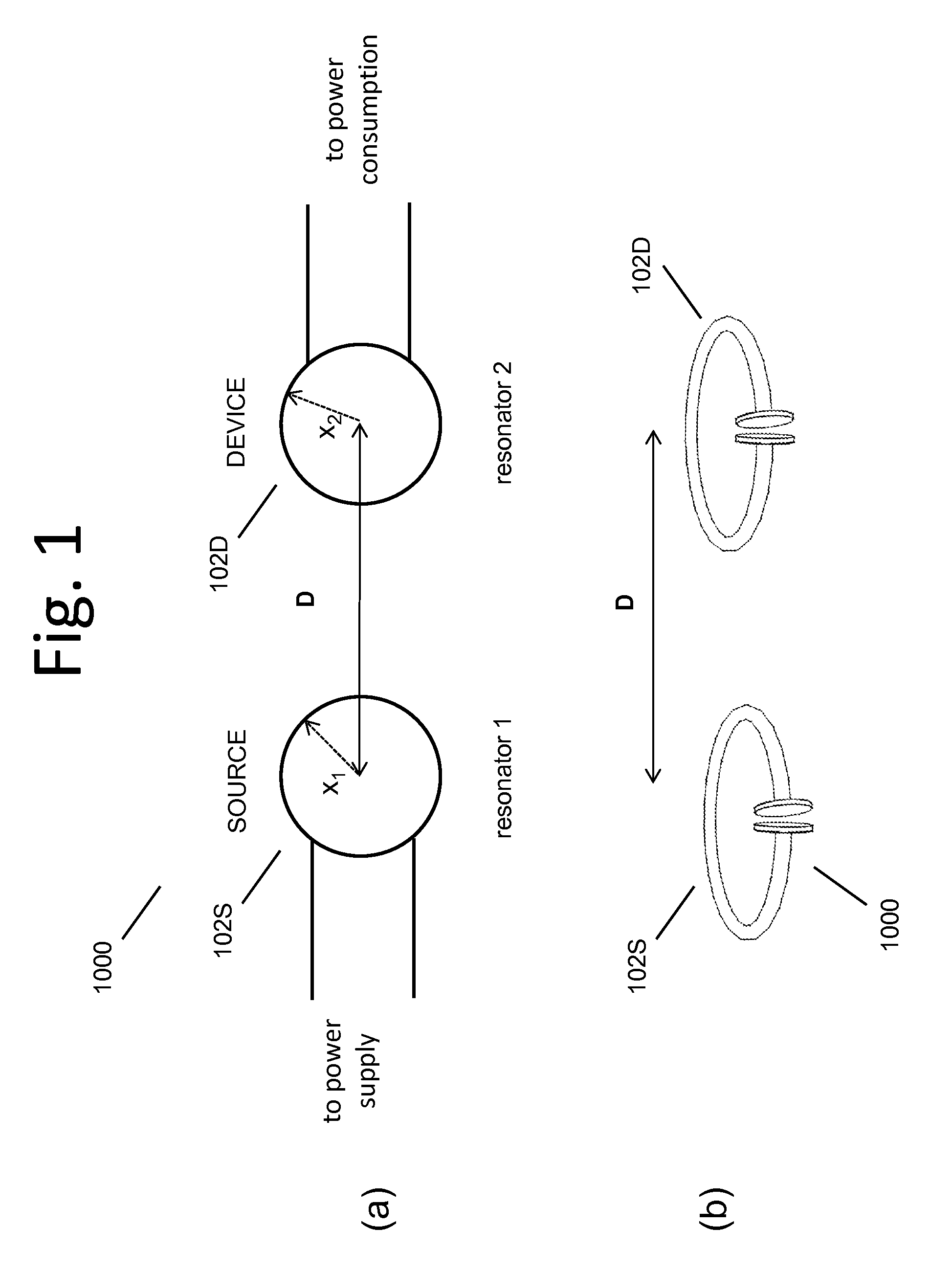
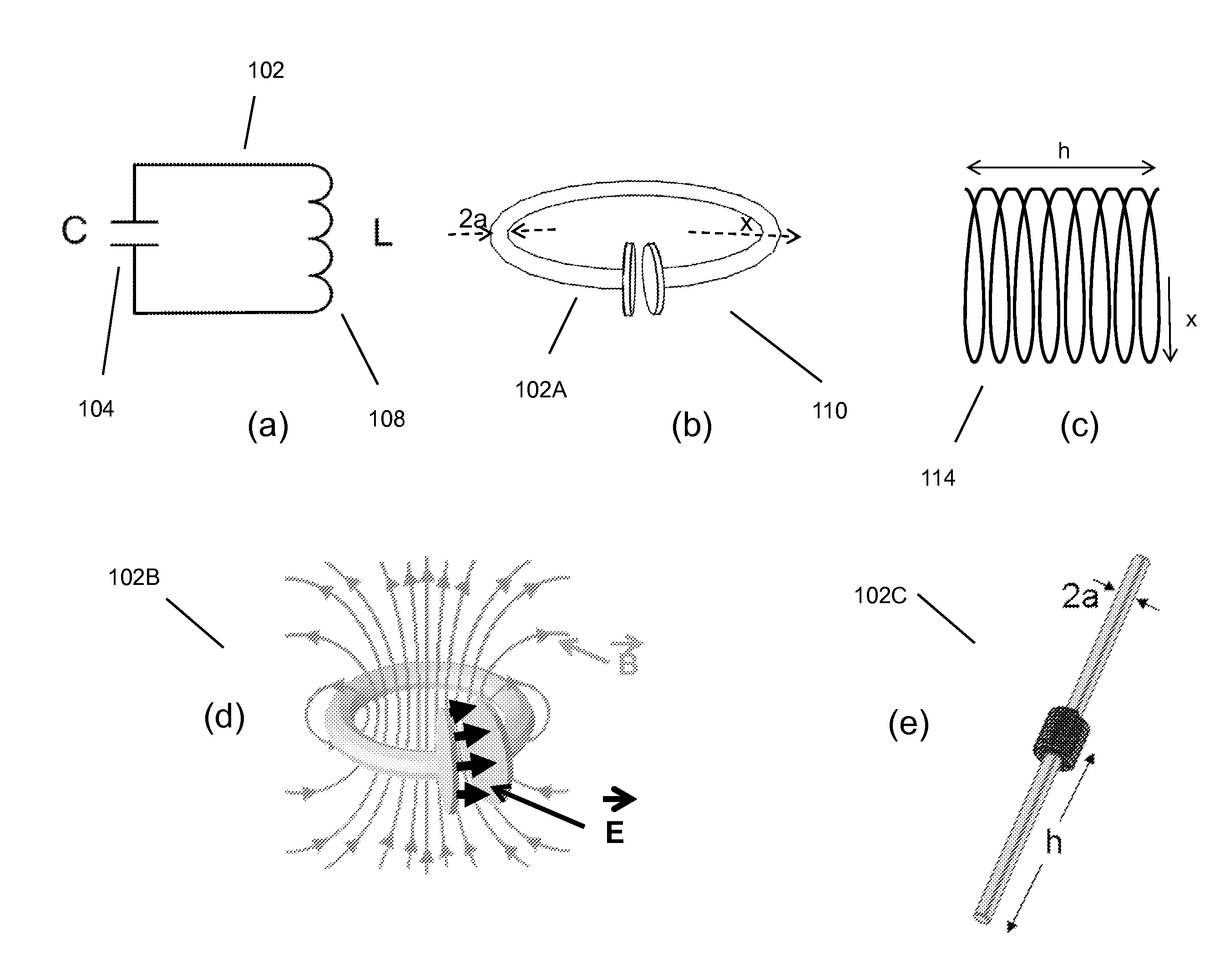
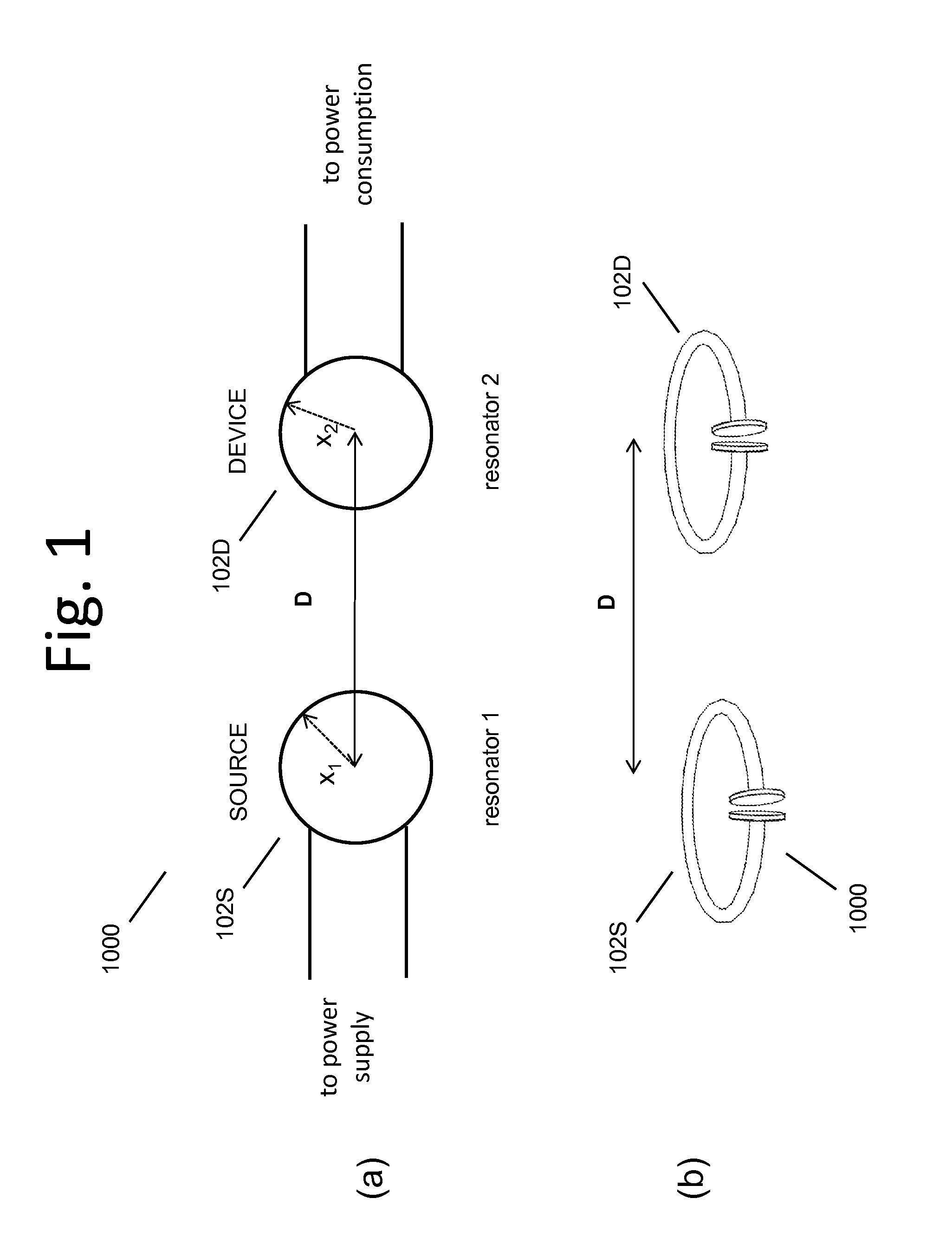
Wireless energy transfer systems
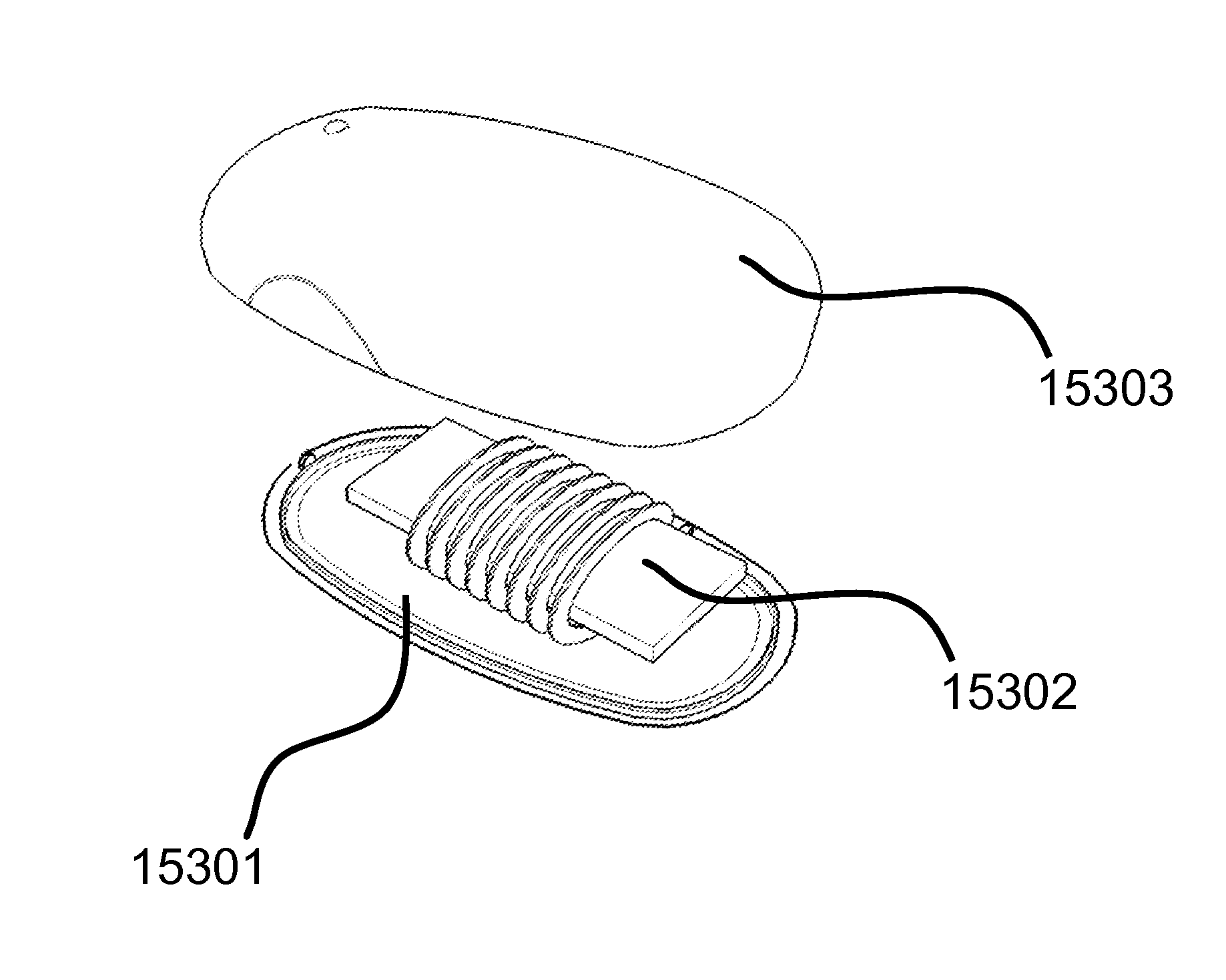
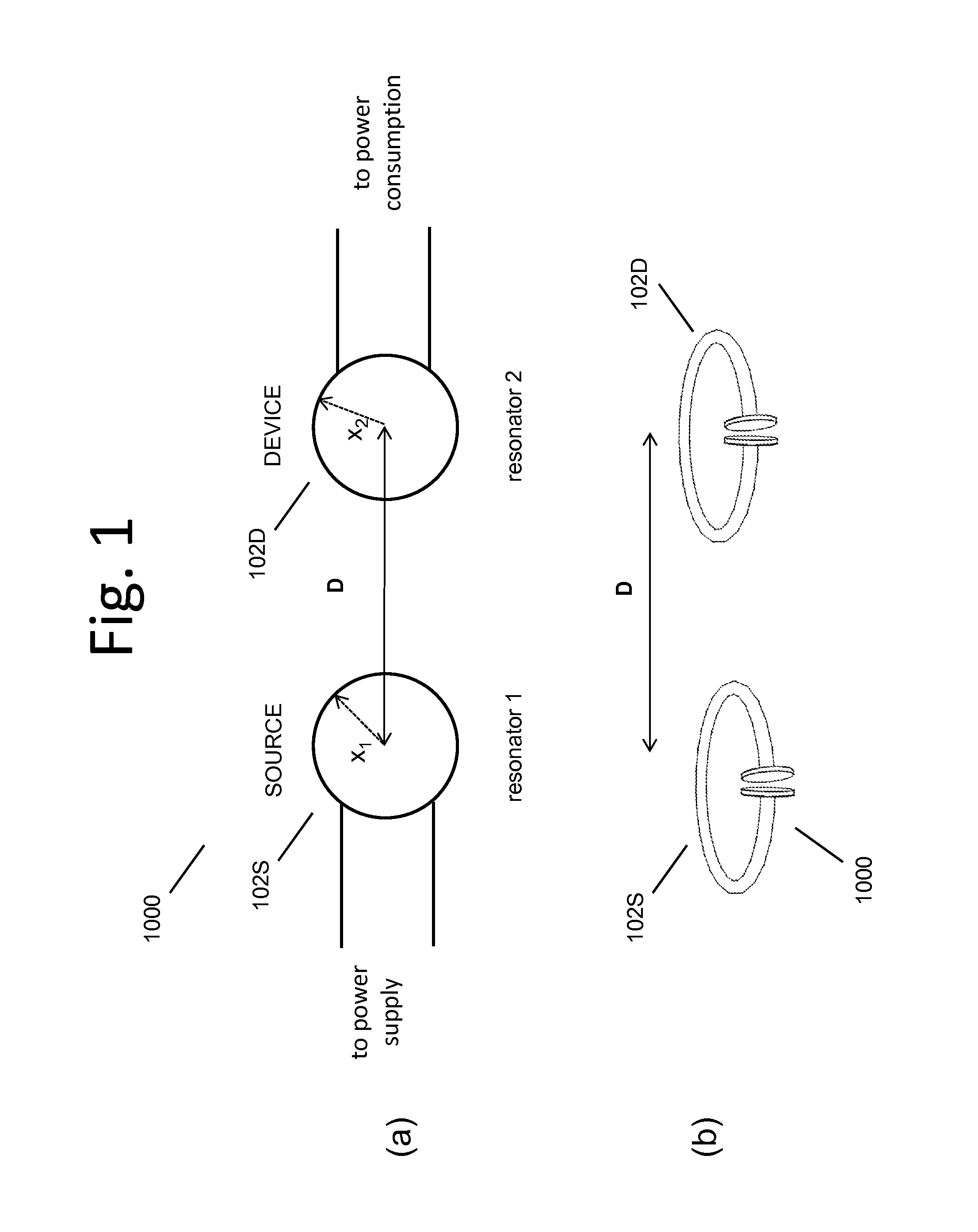
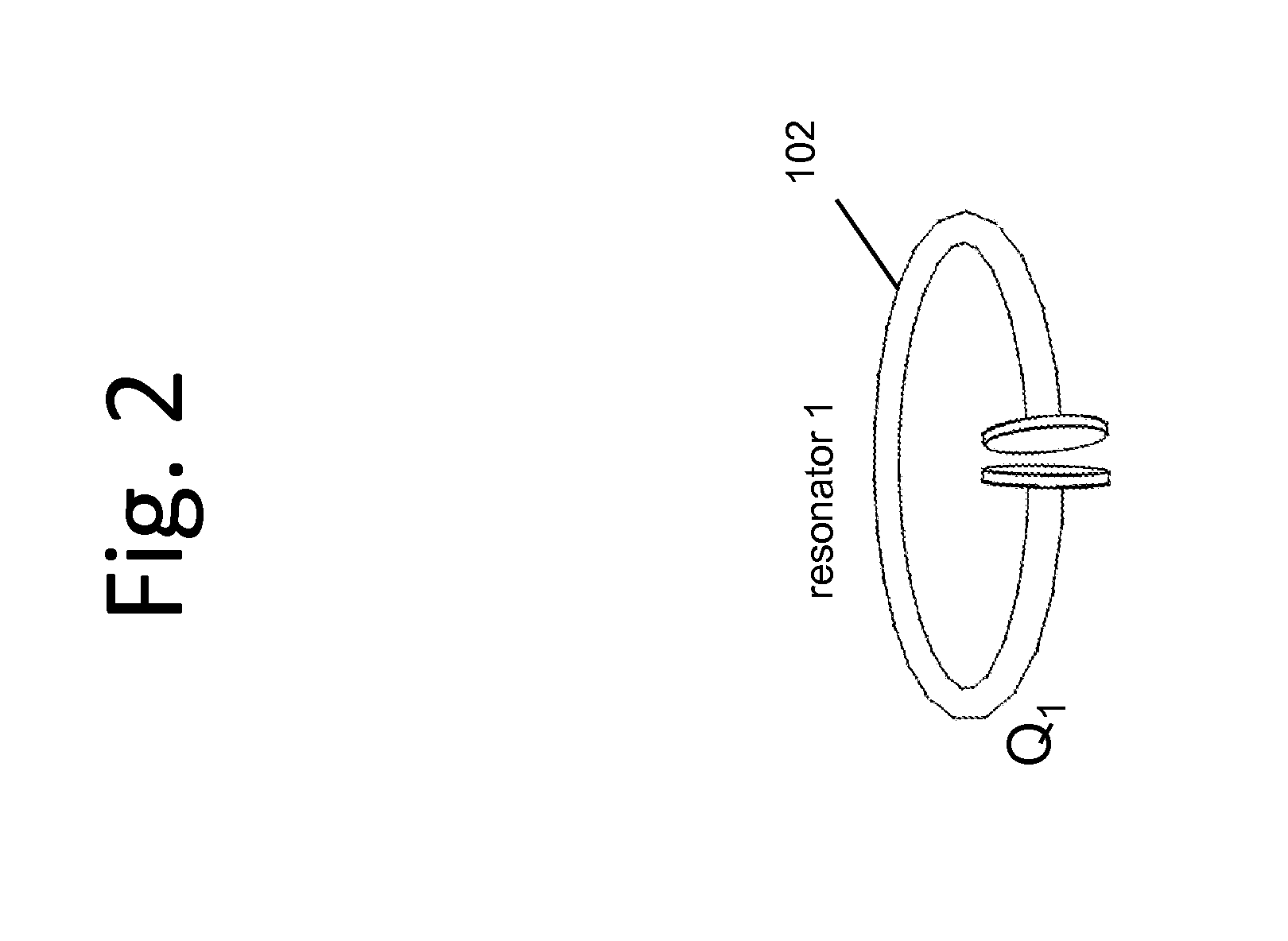
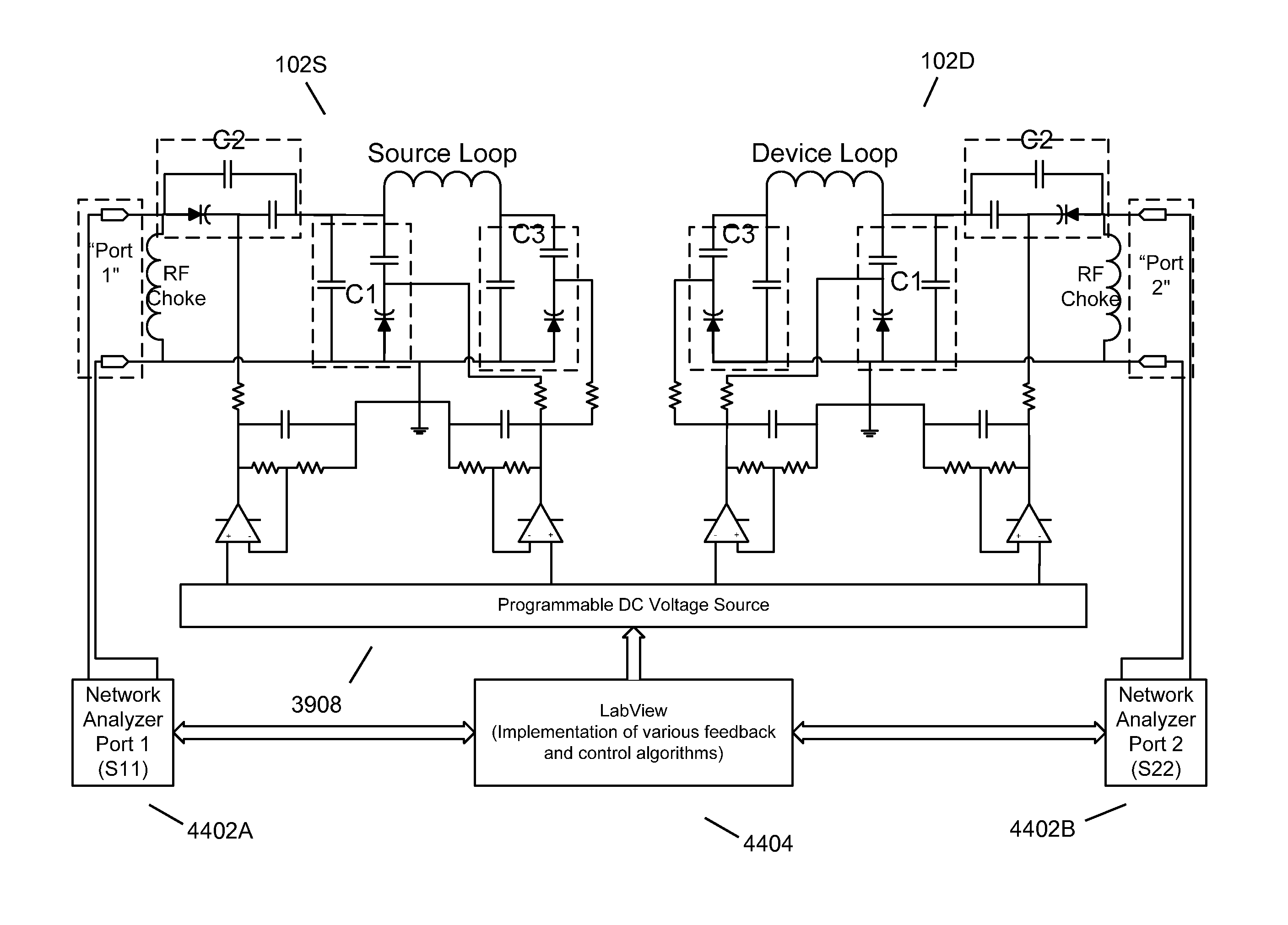
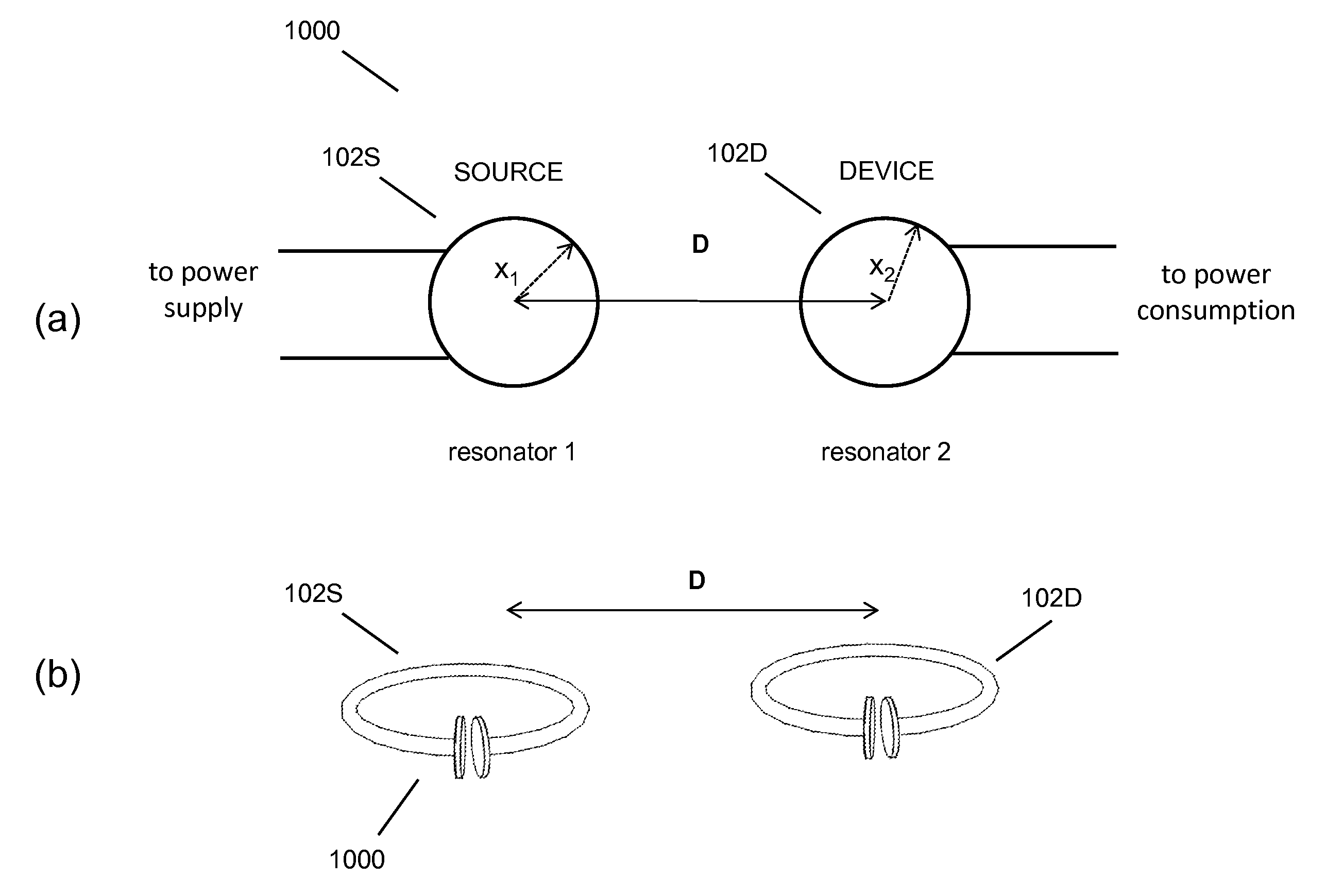
ActiveUS20100141042A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
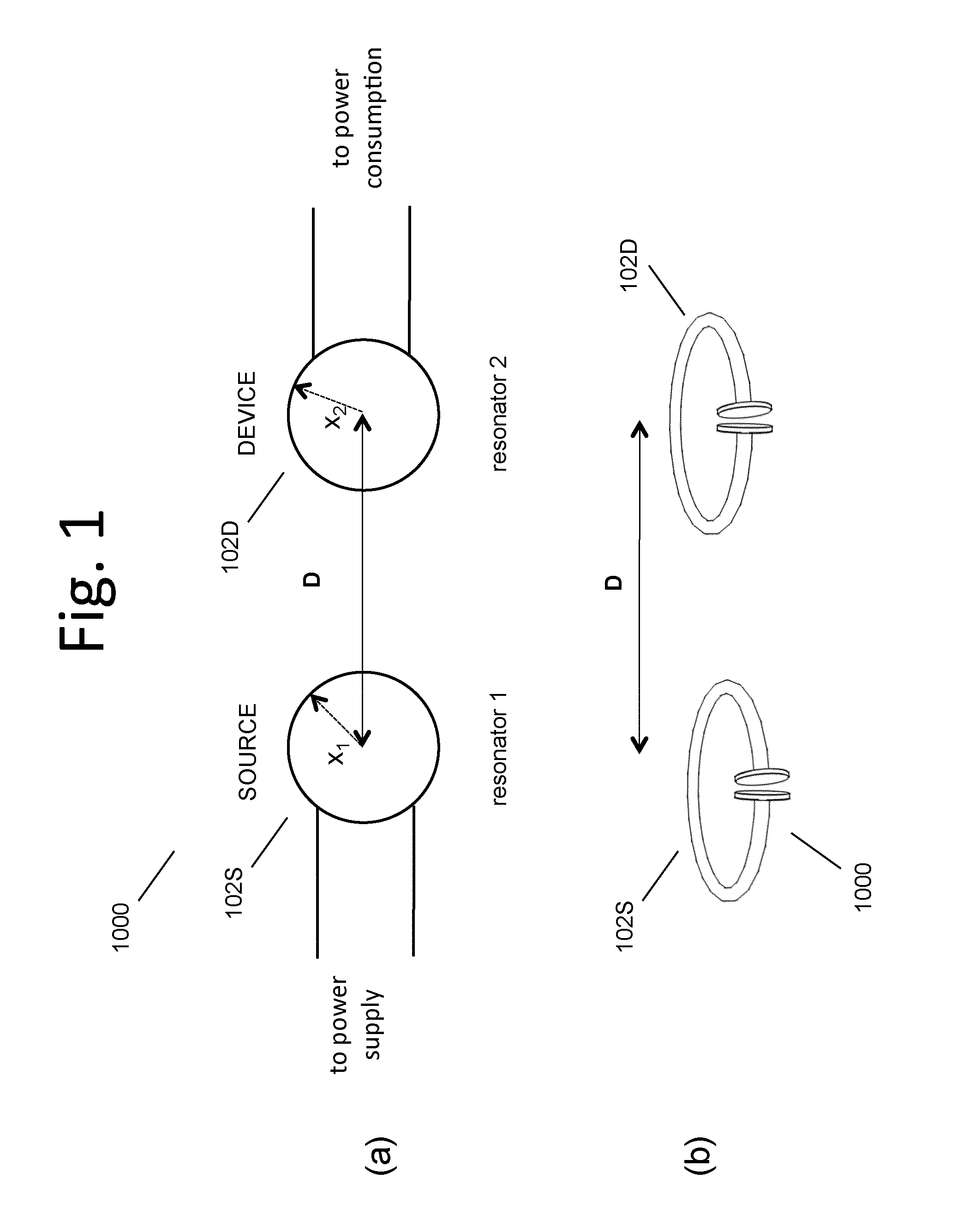
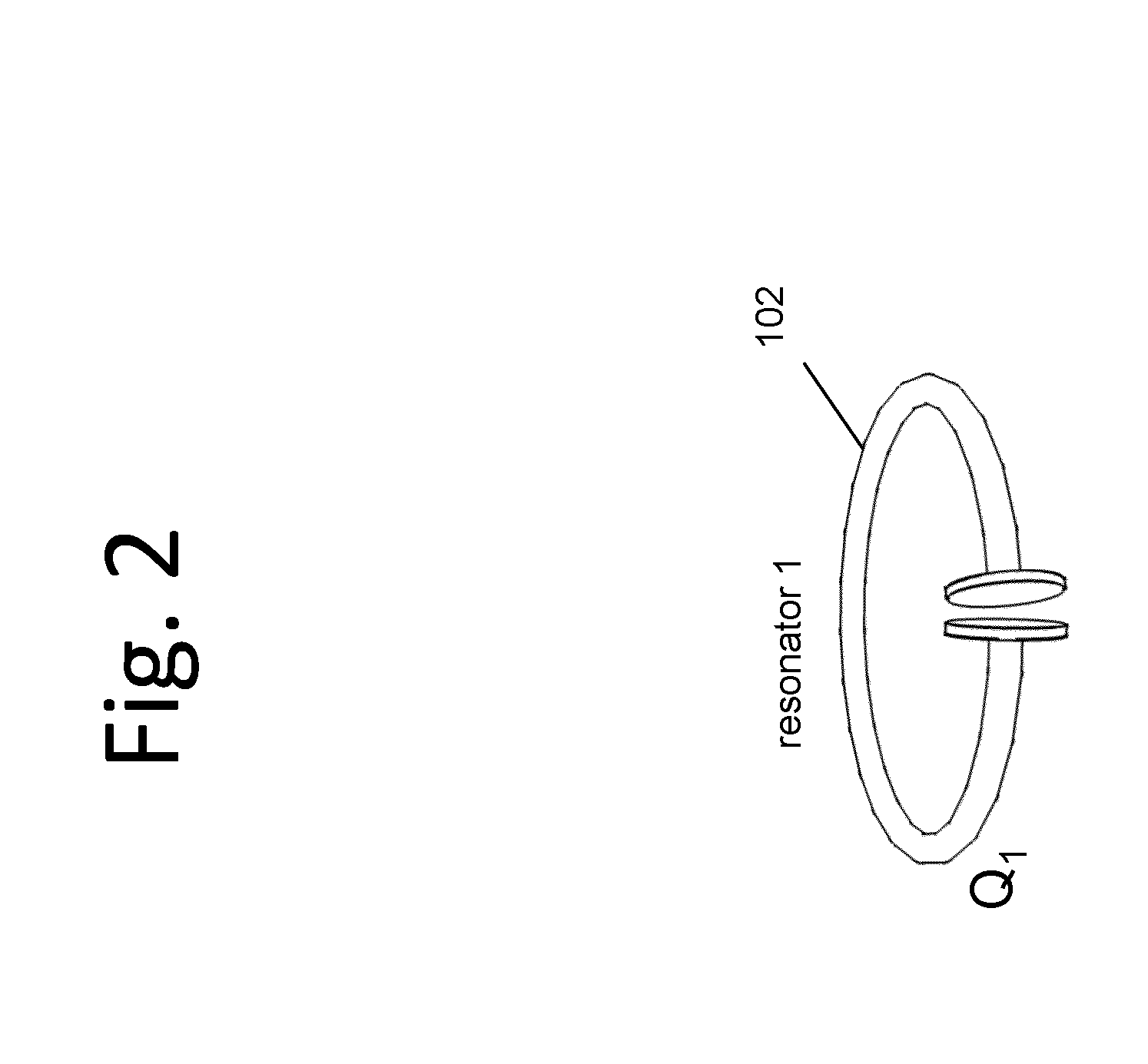
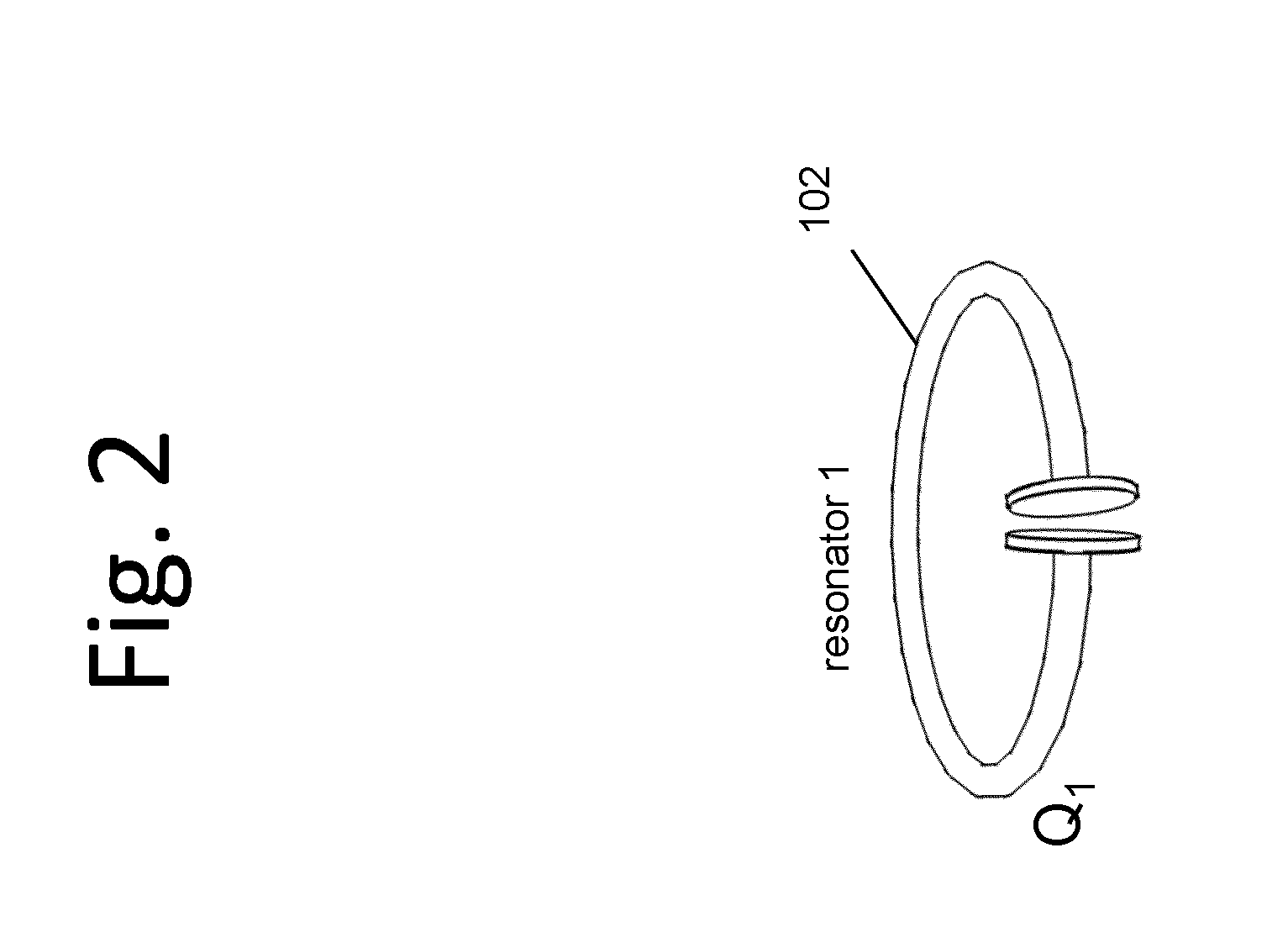
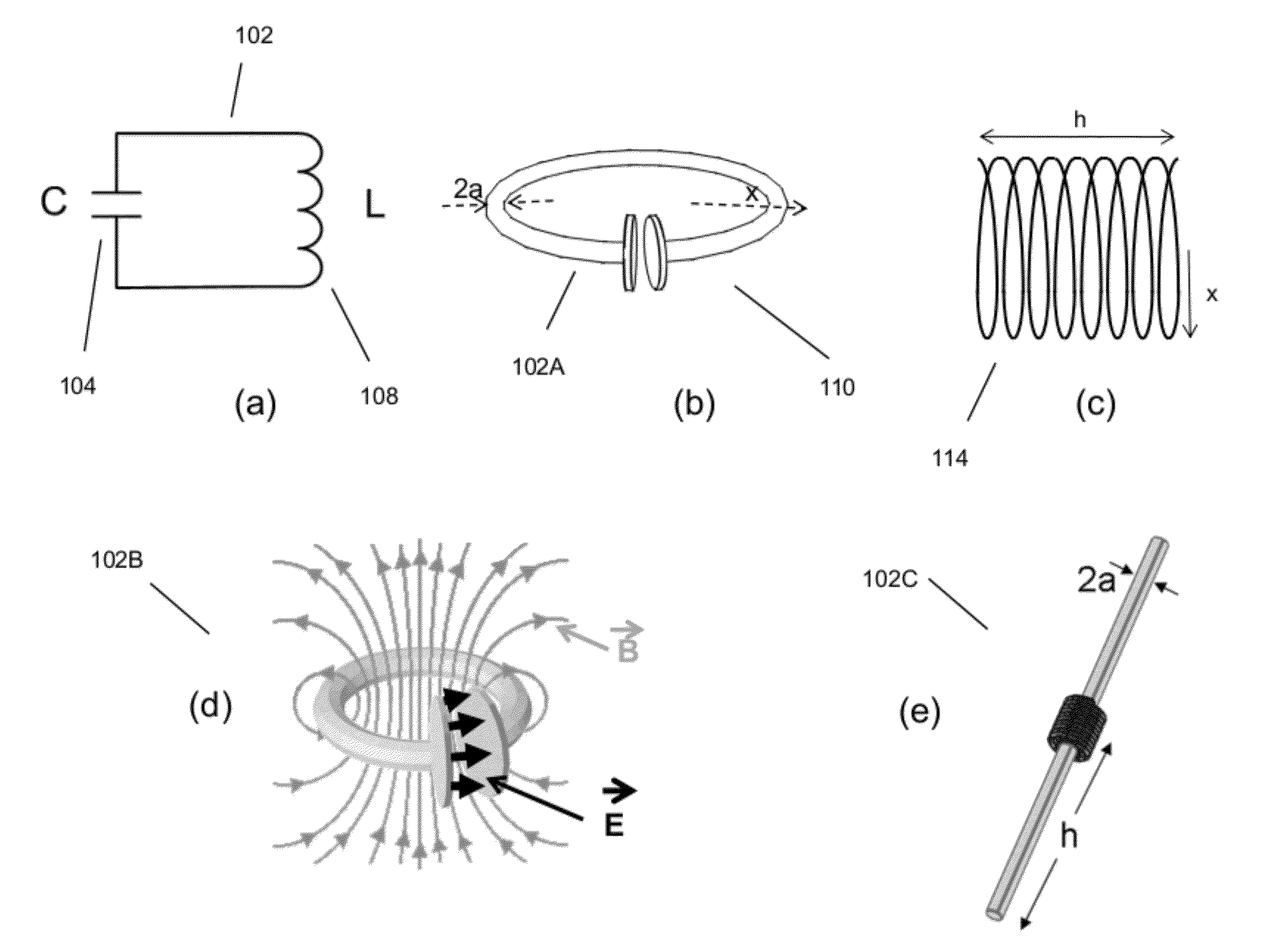
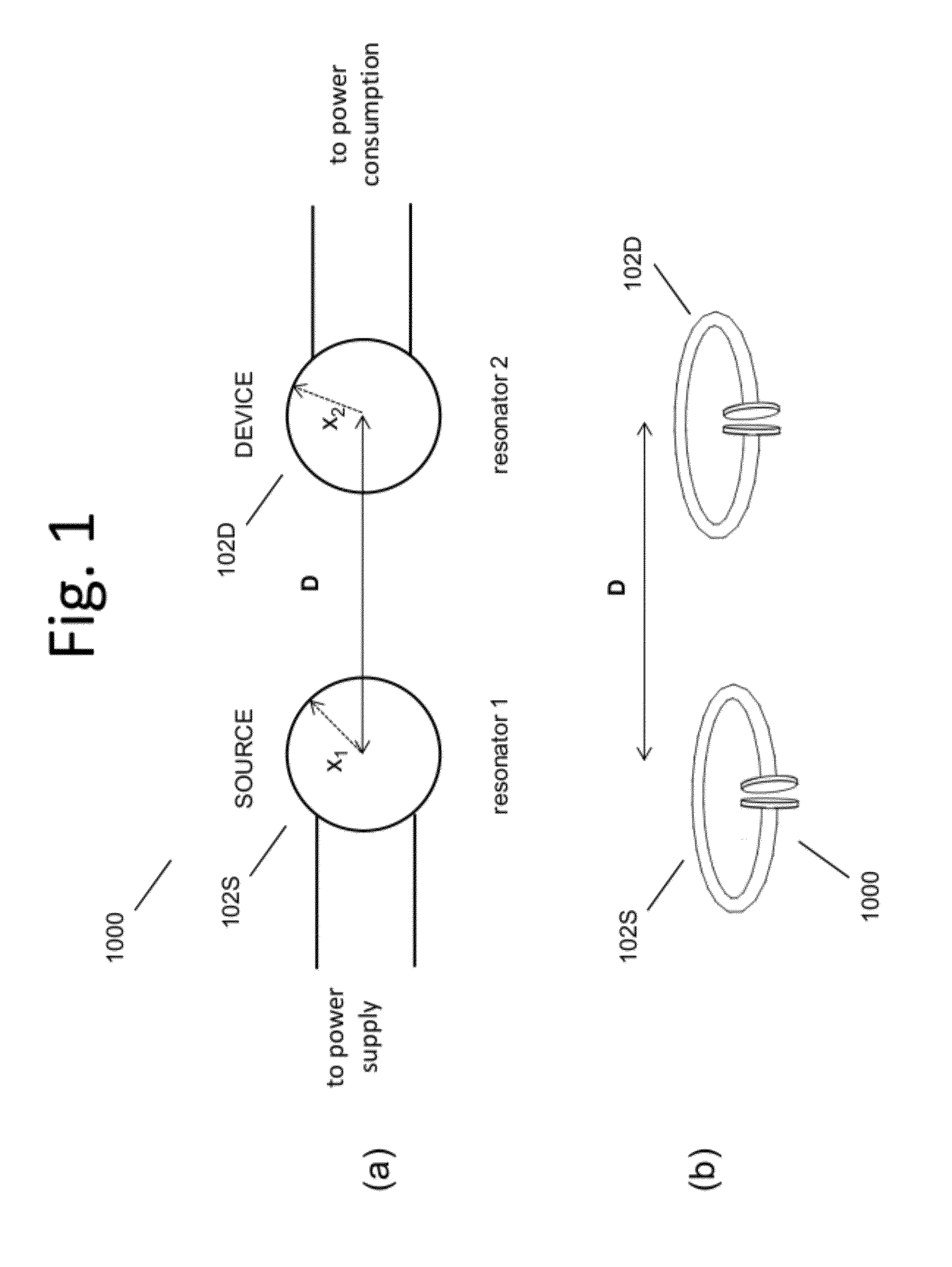
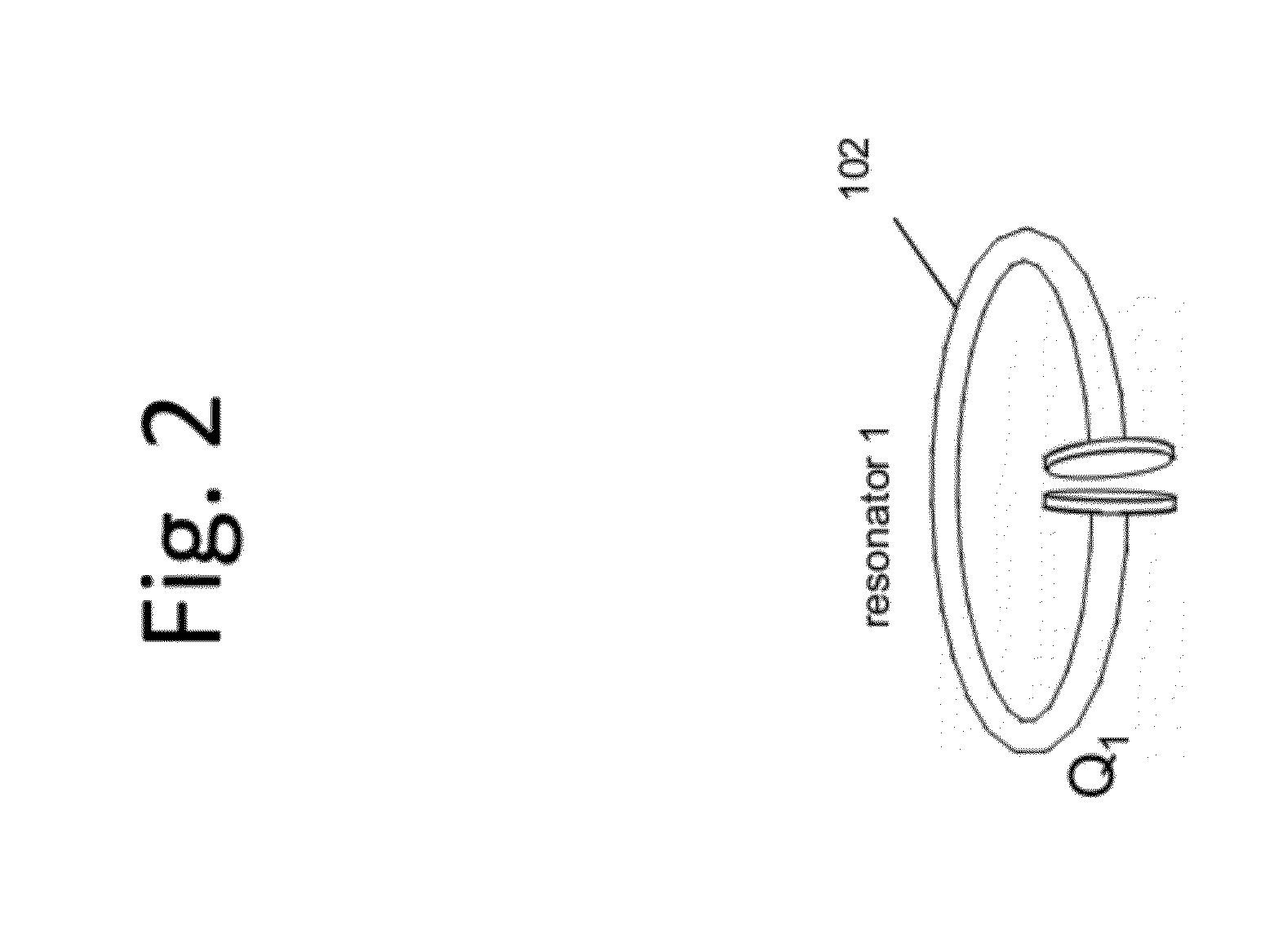
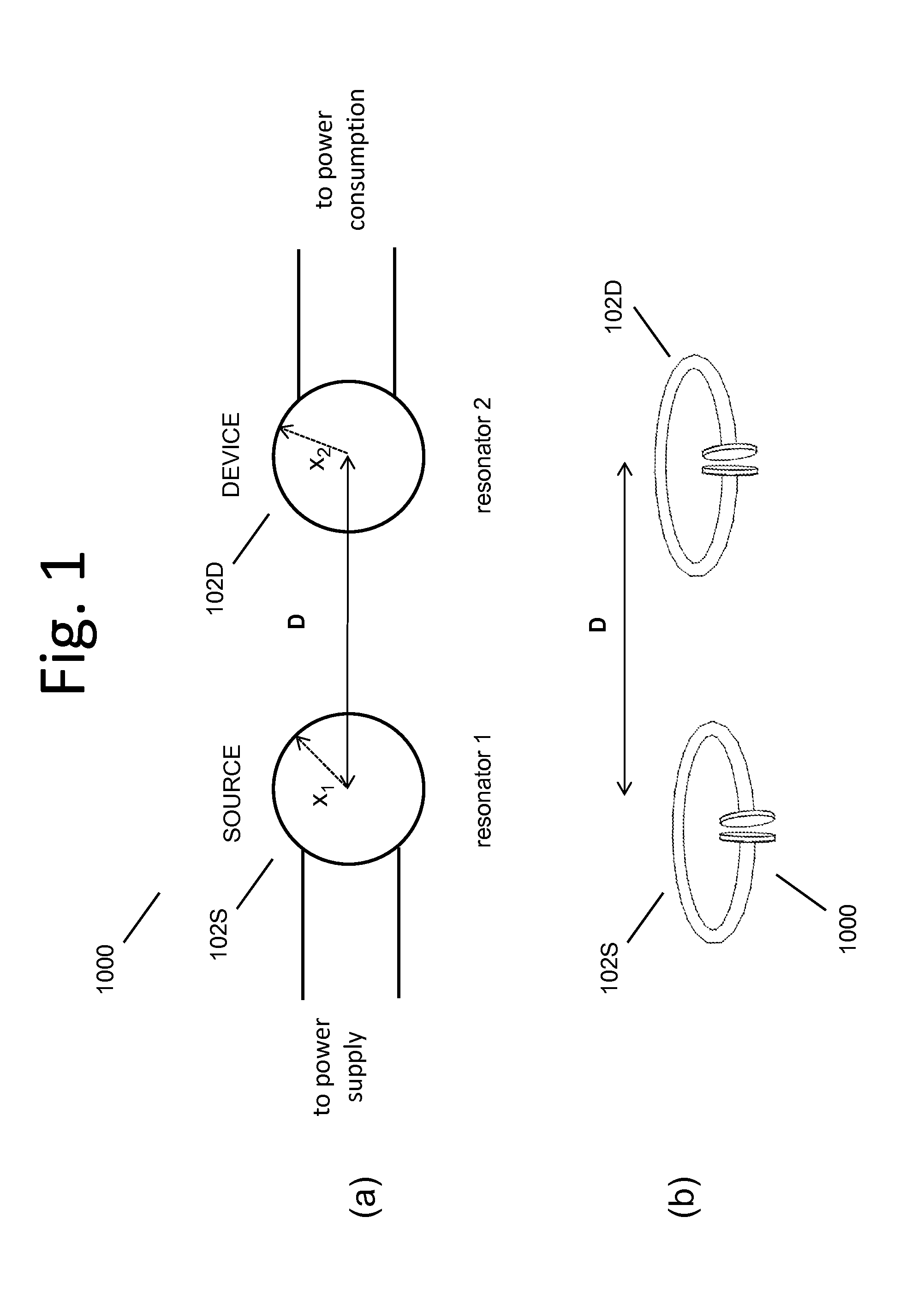
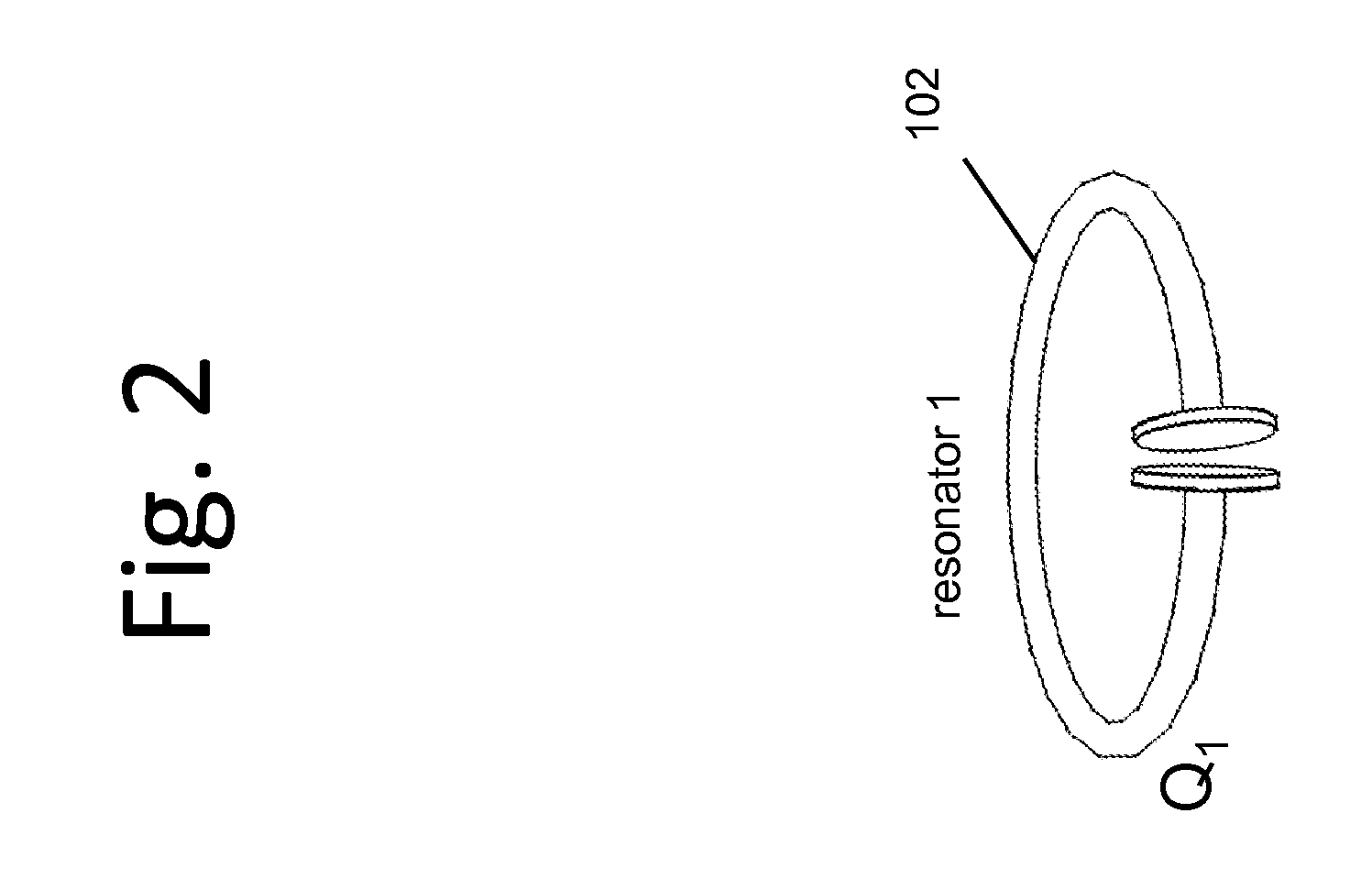
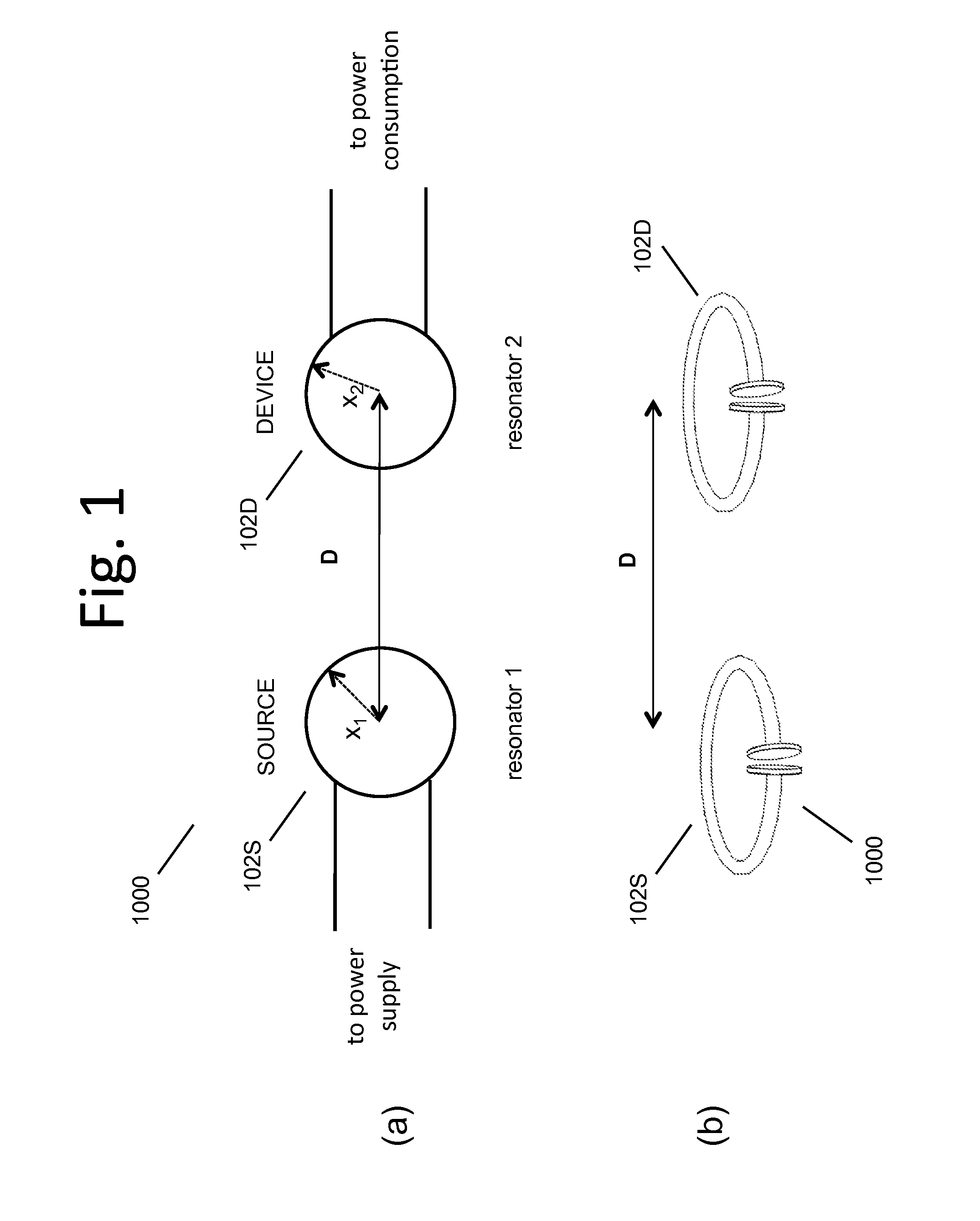
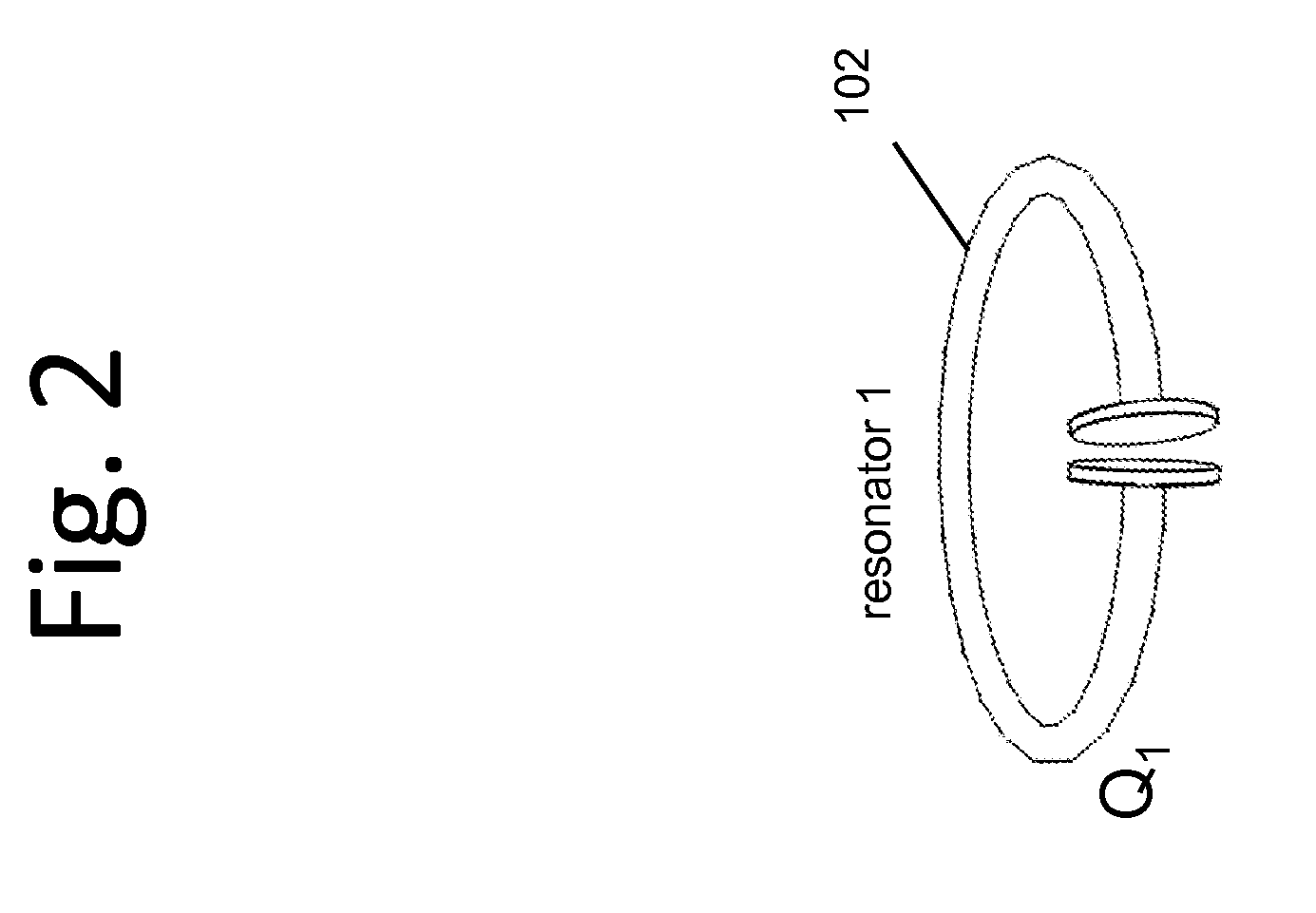
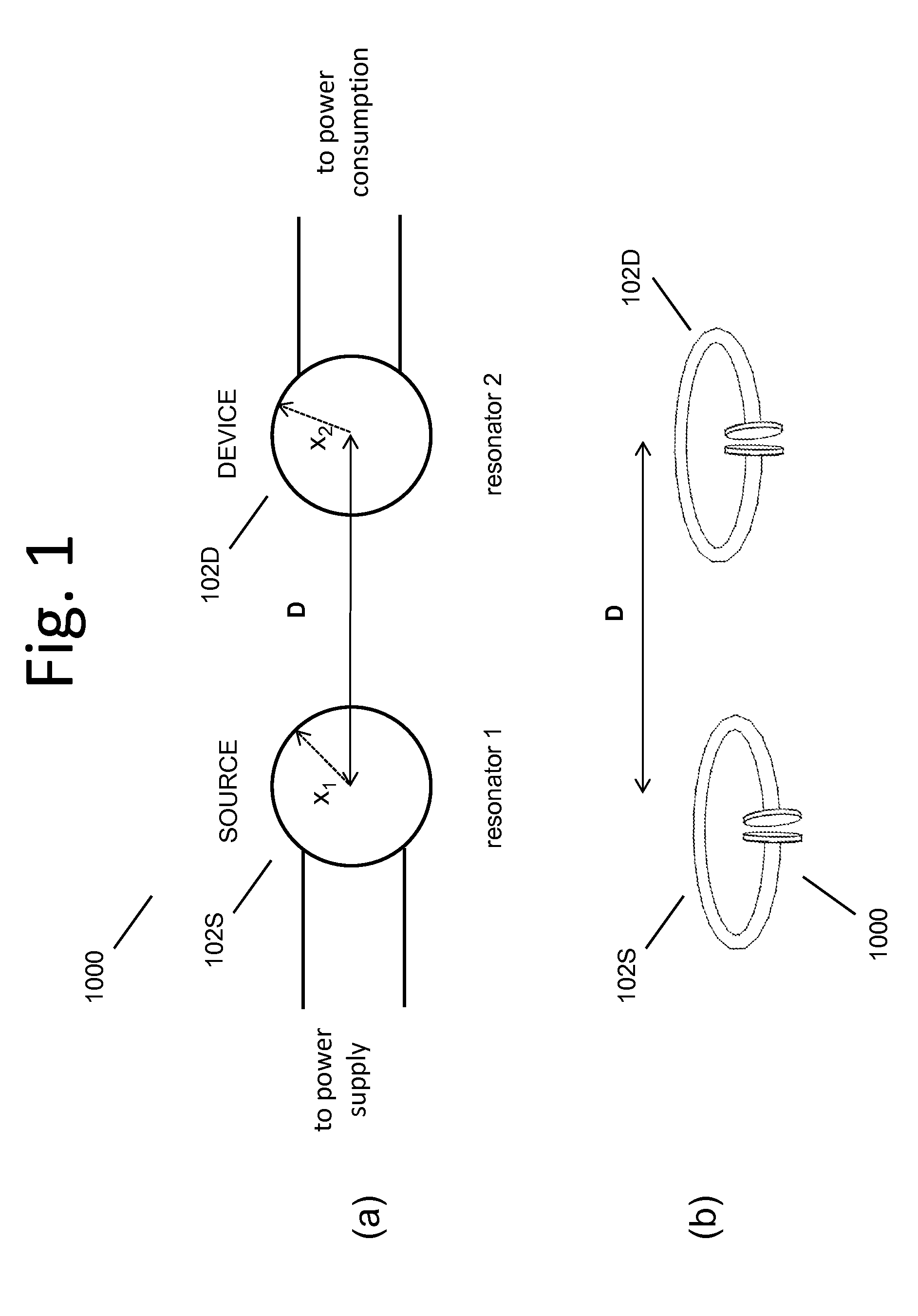
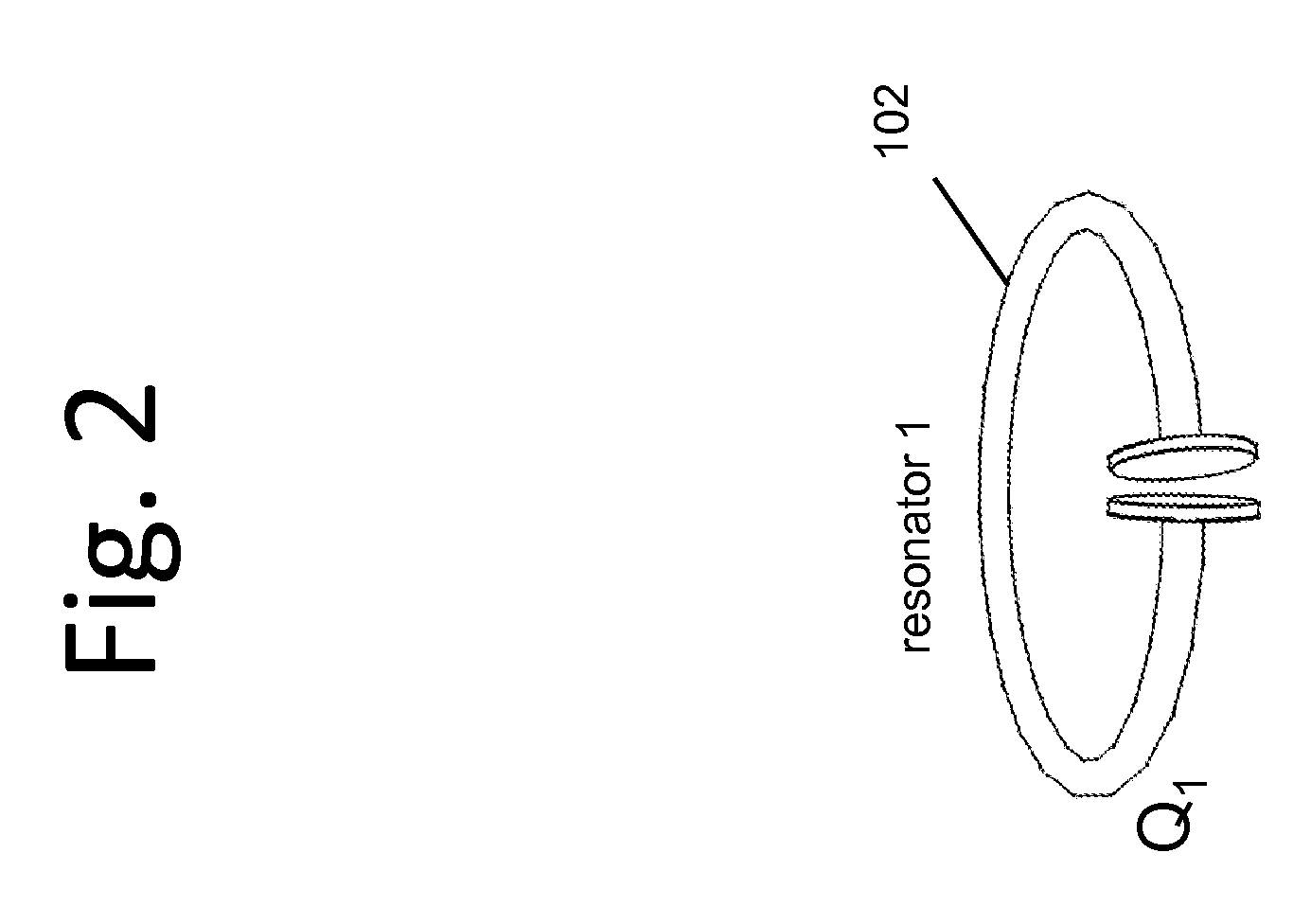
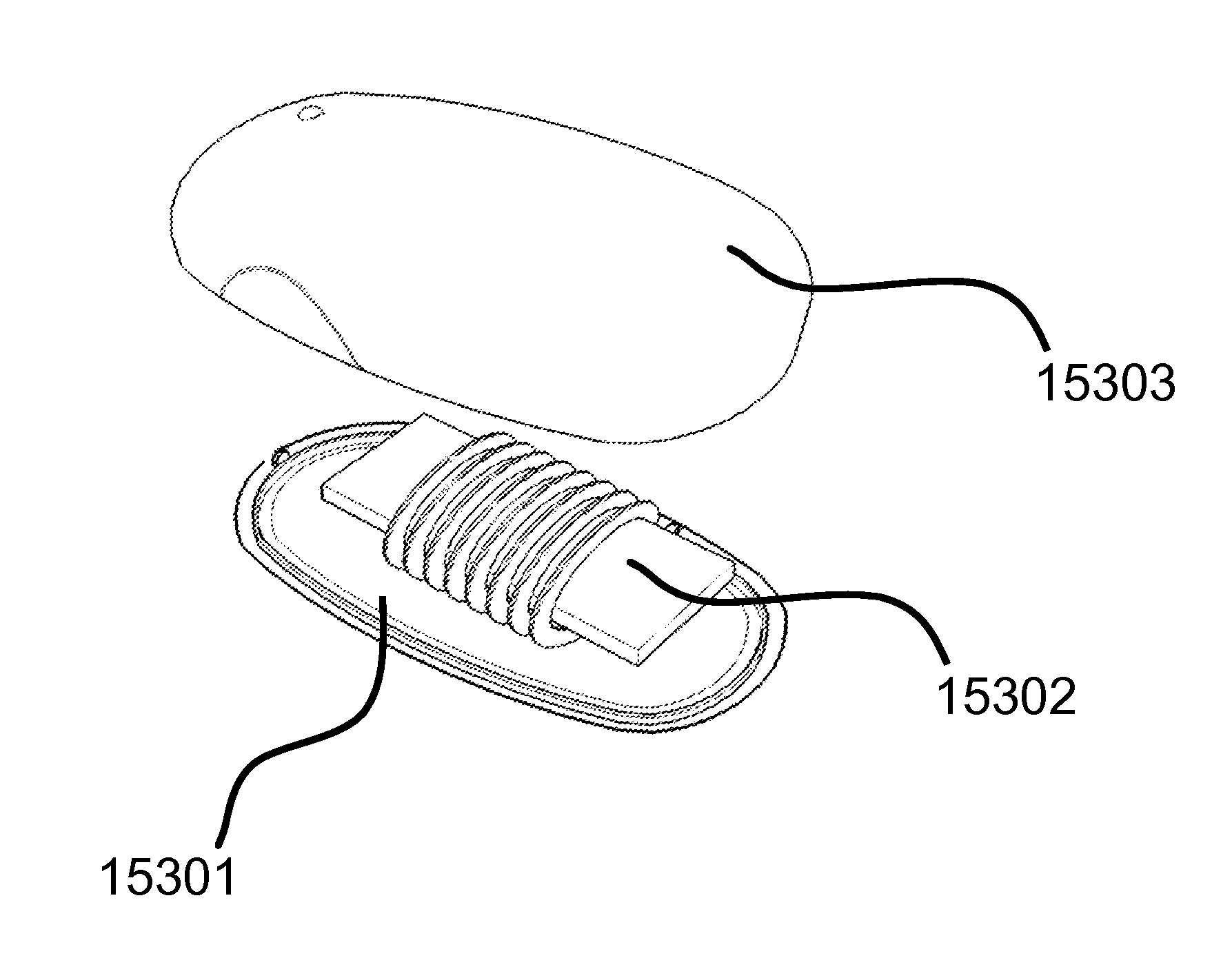
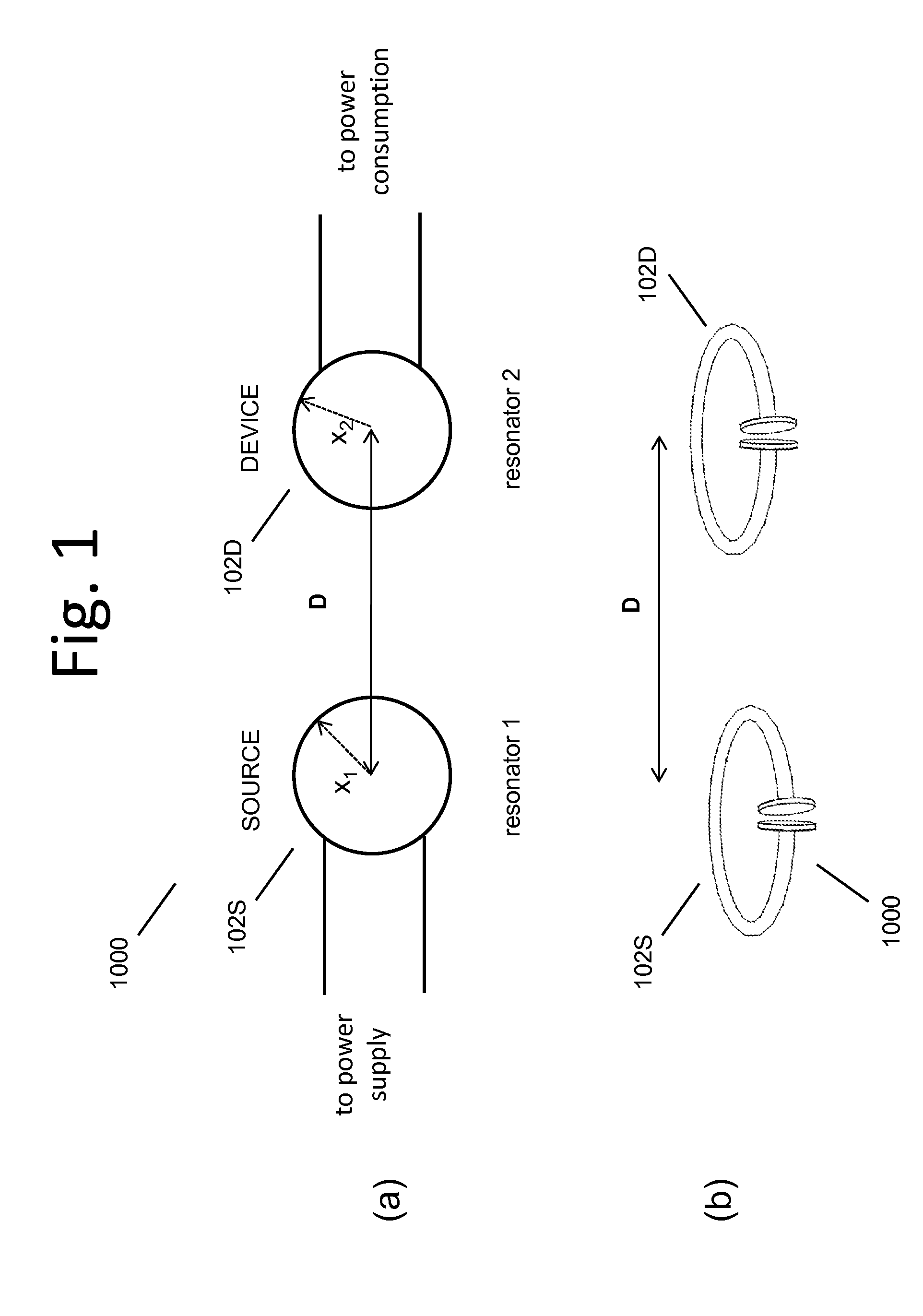
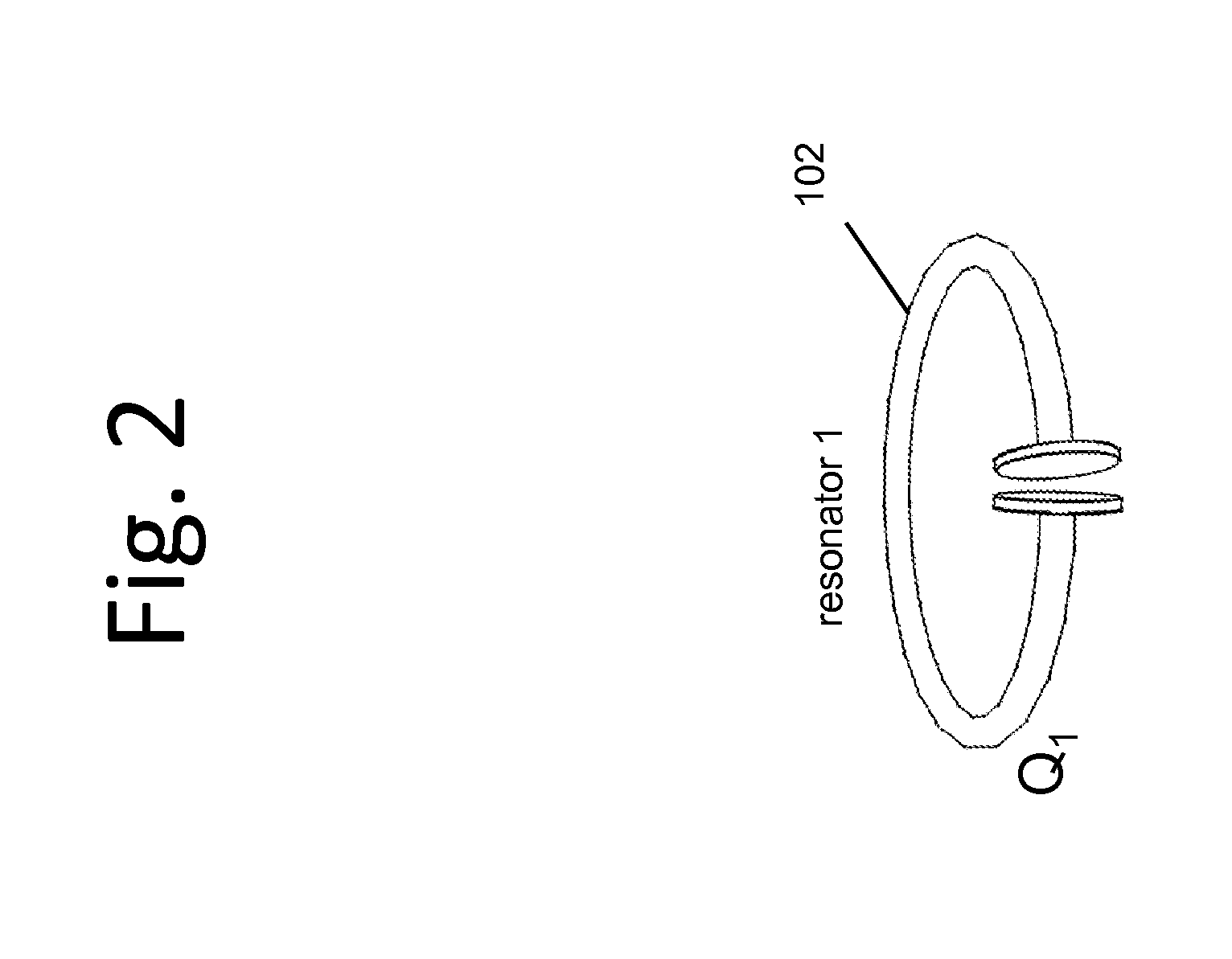
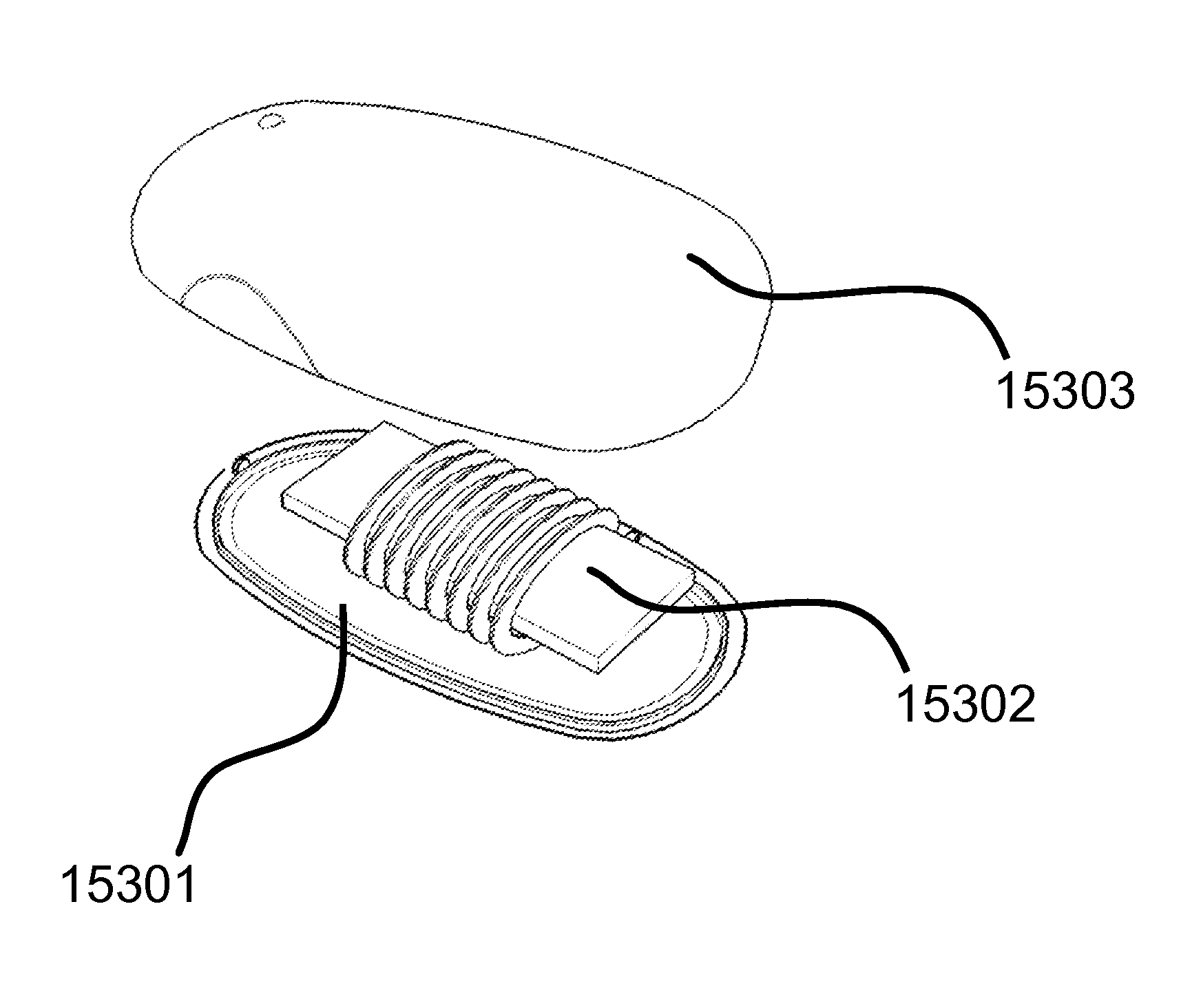
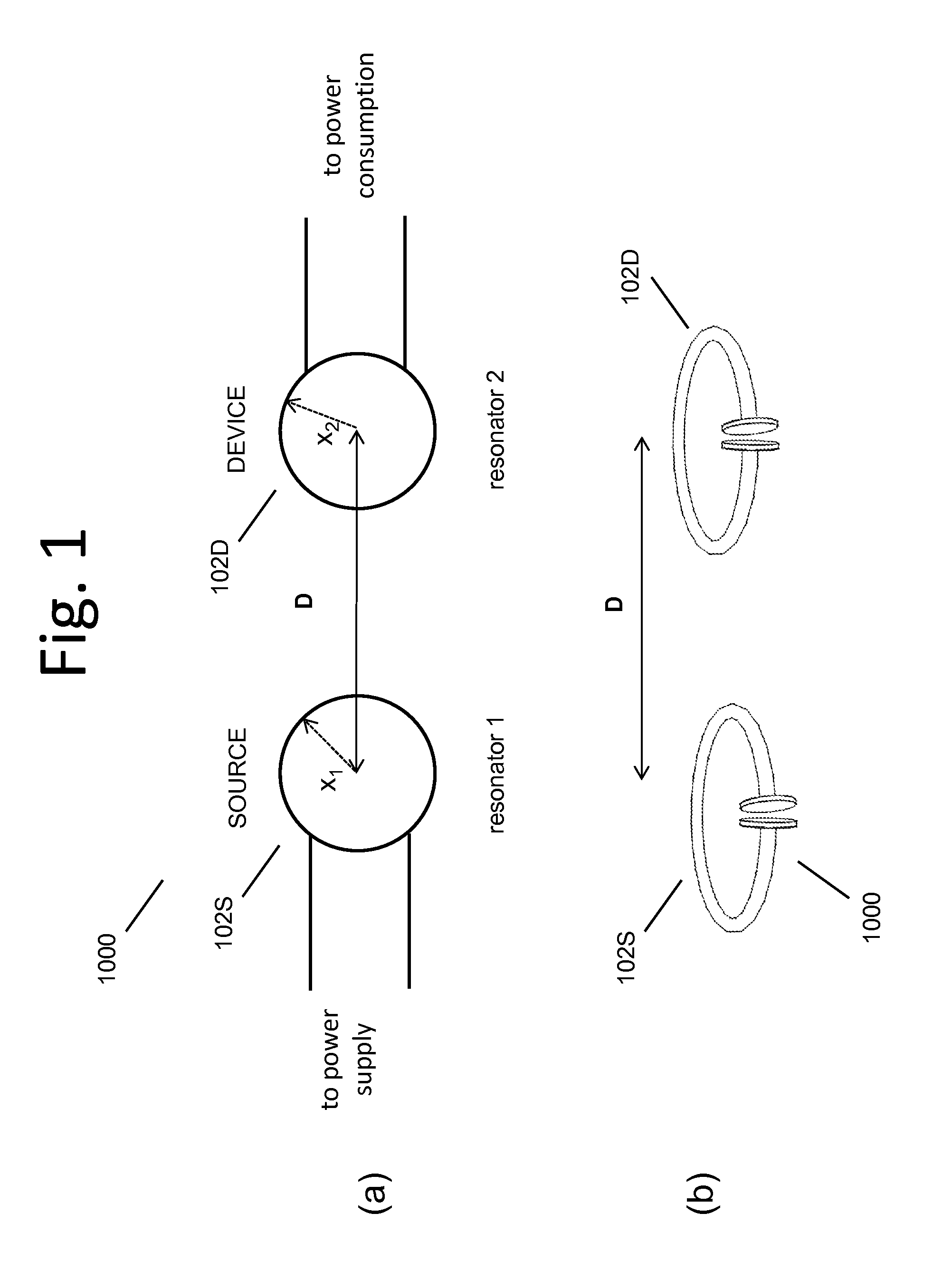
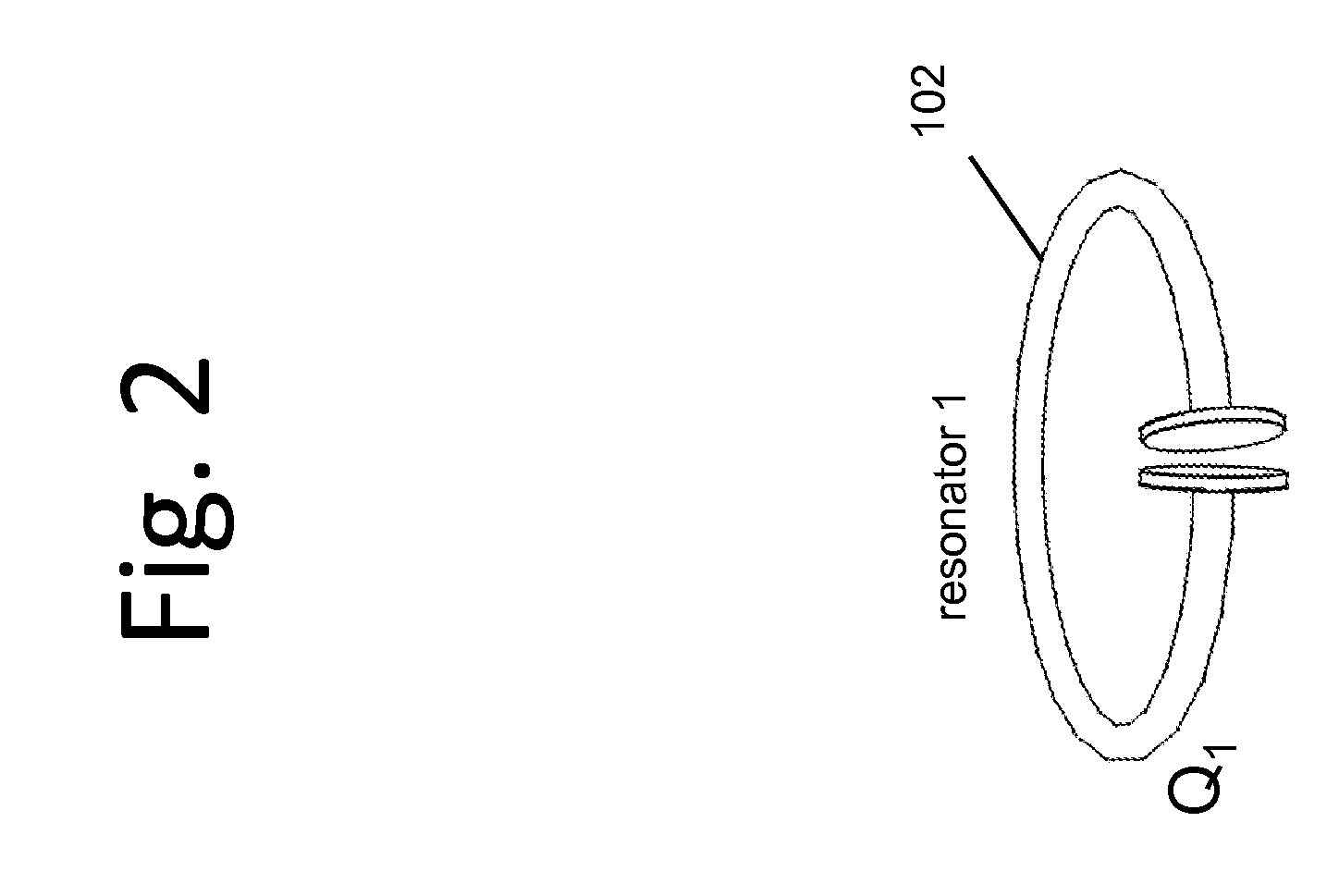
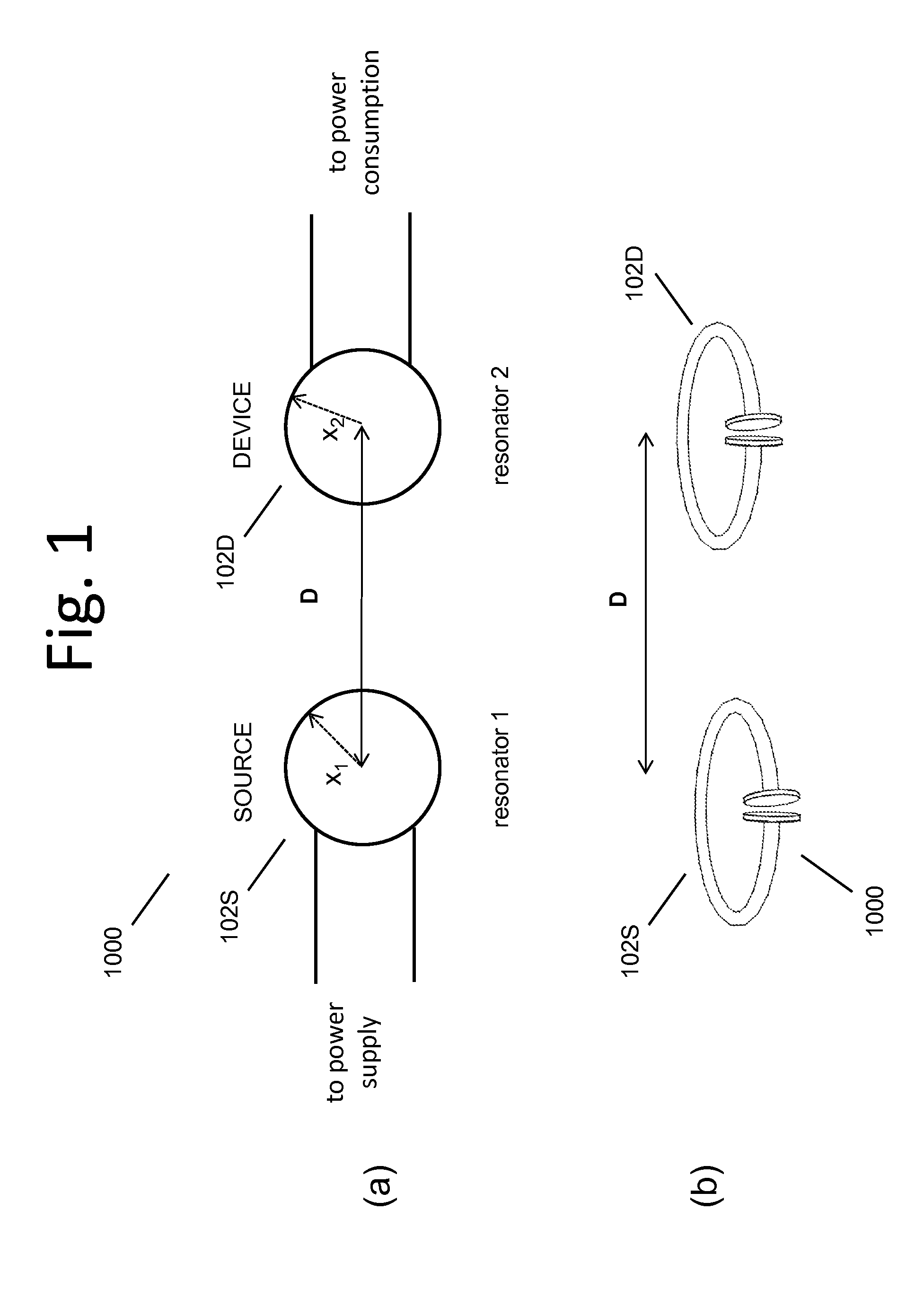
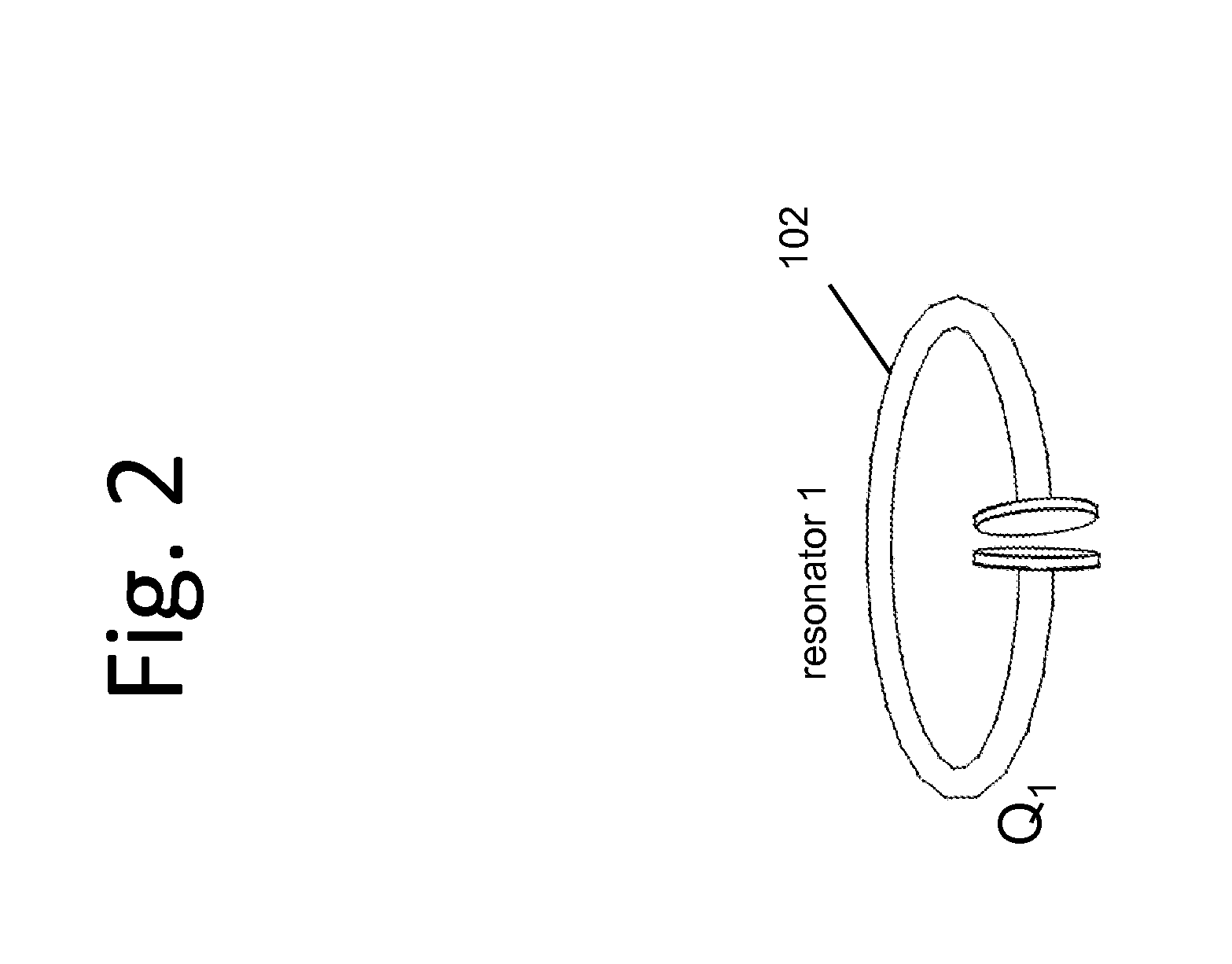
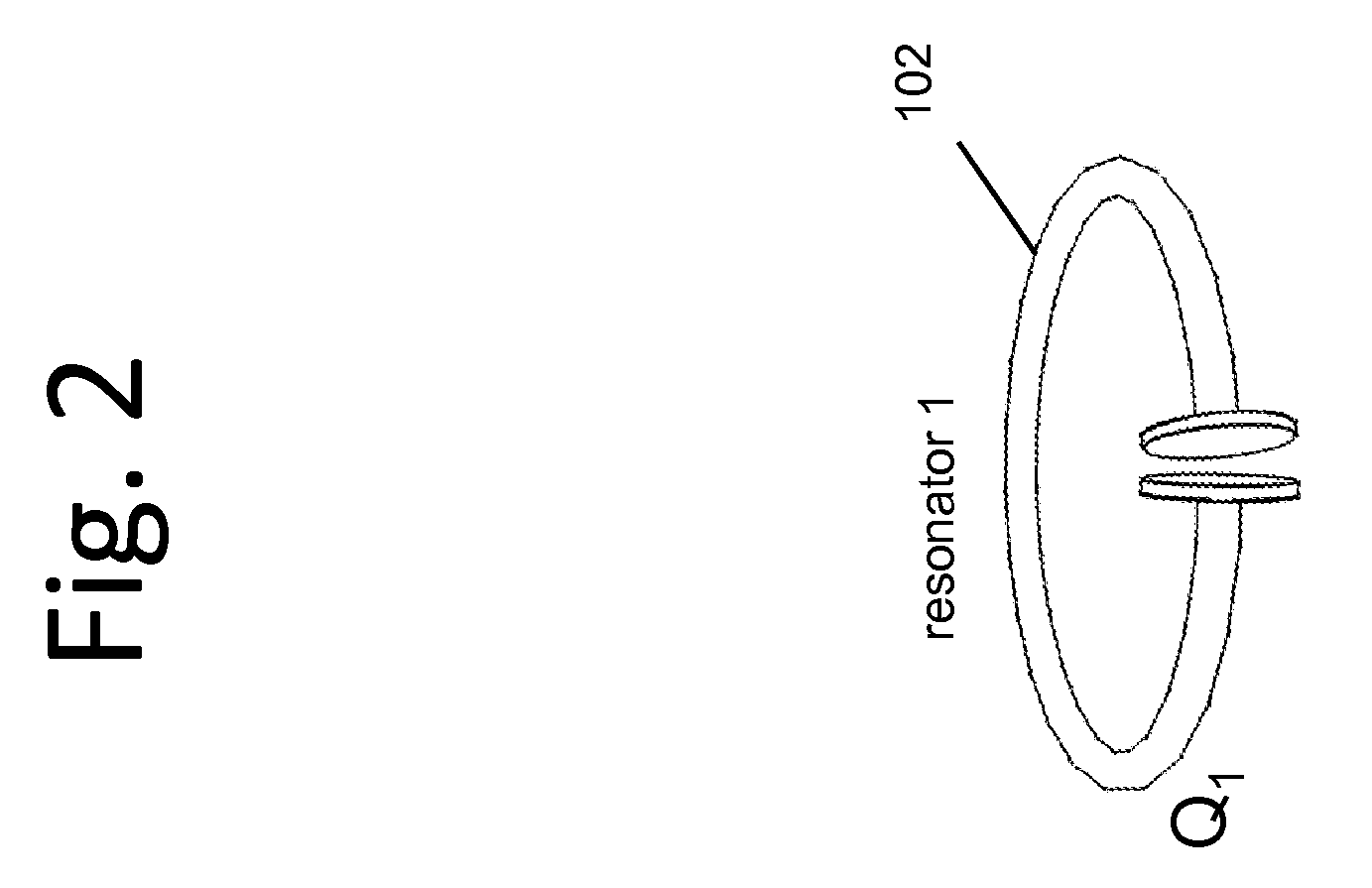
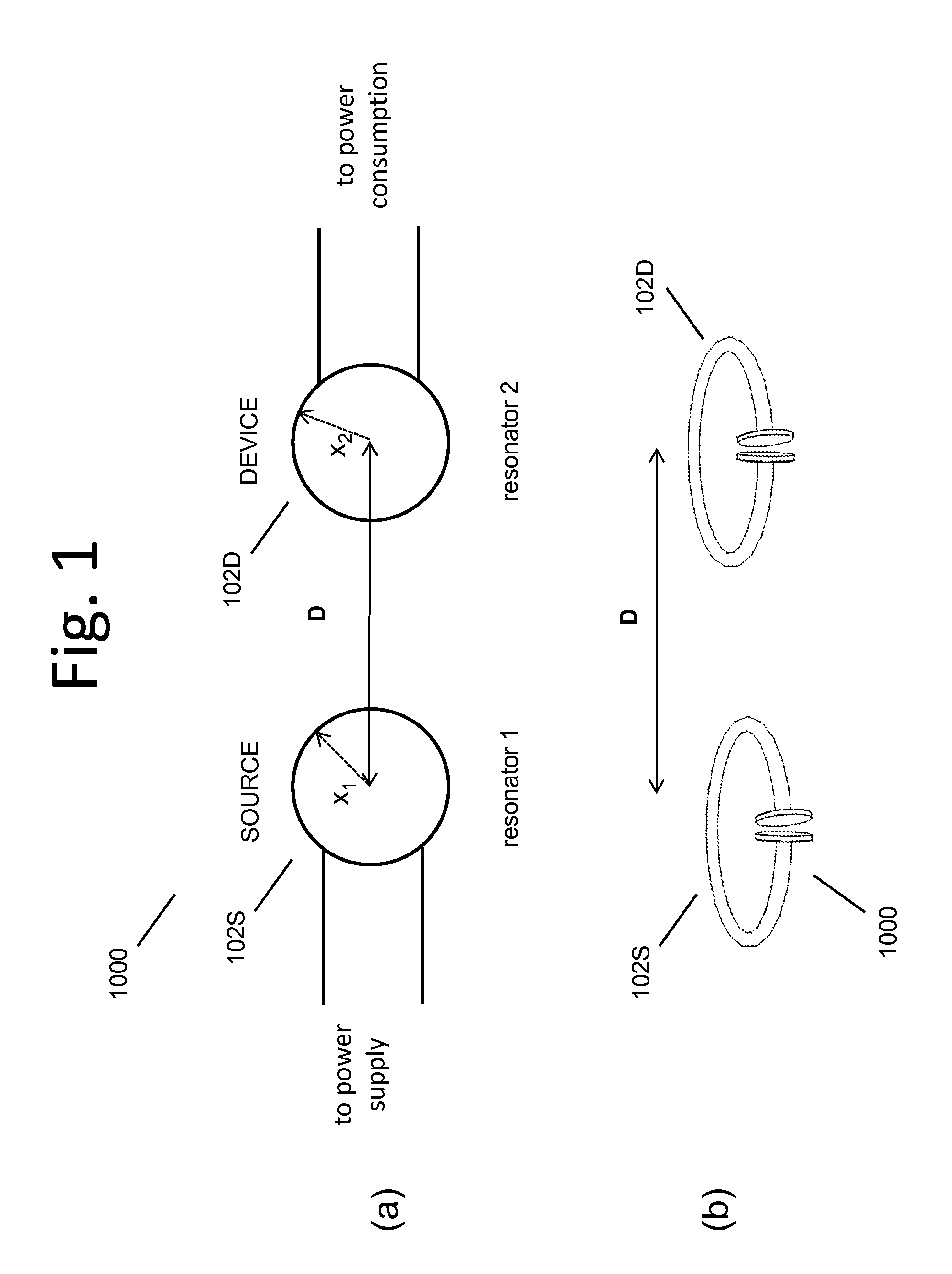
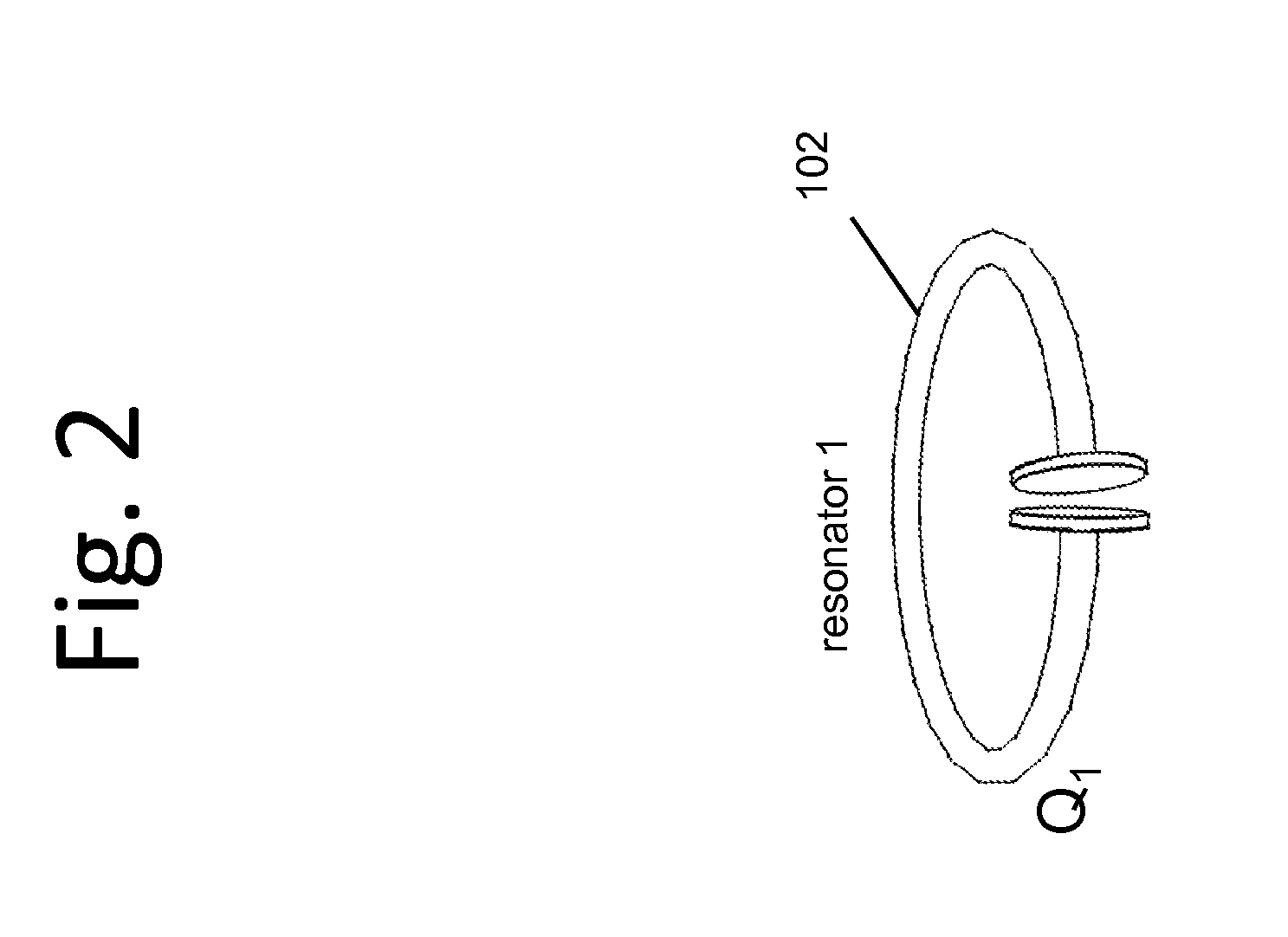
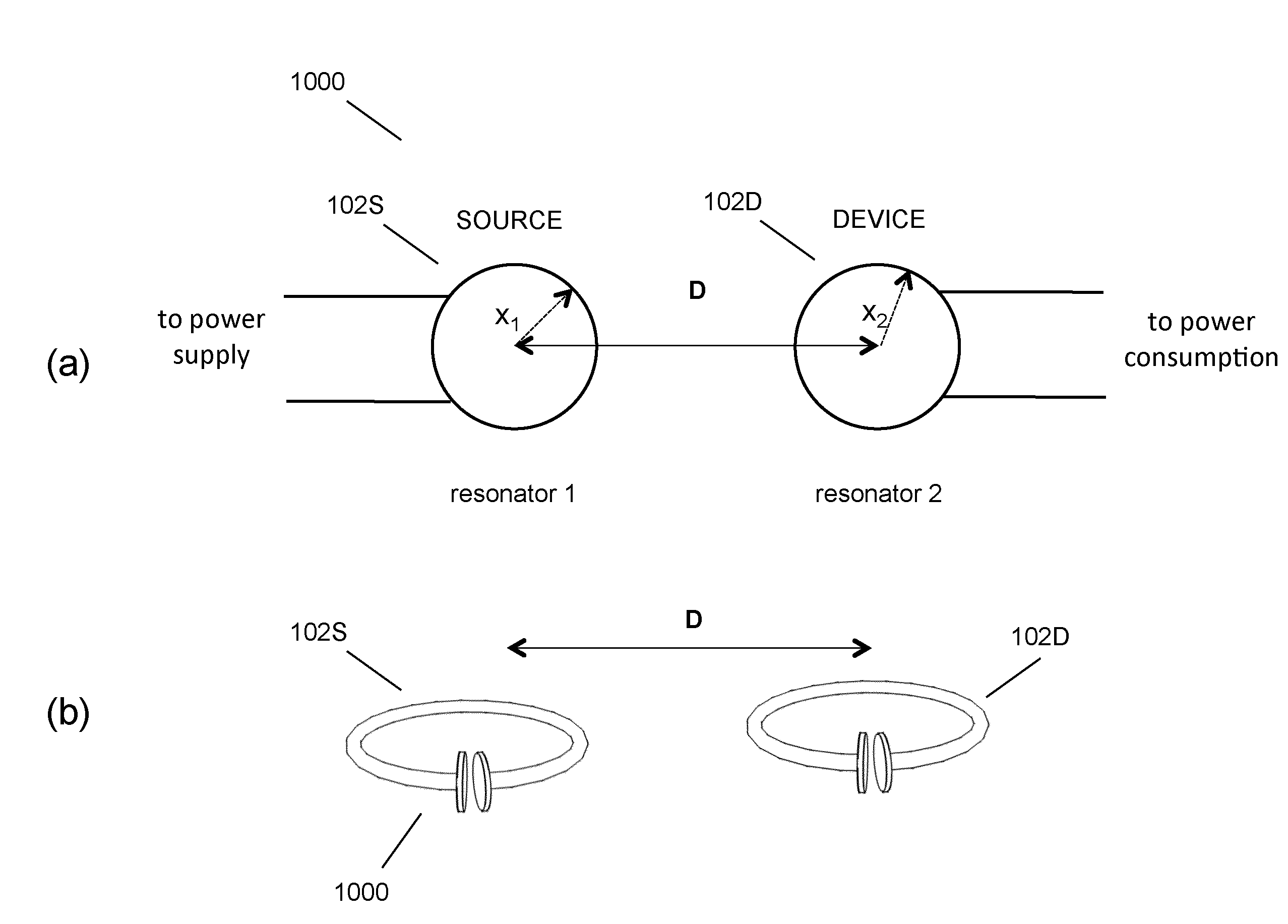
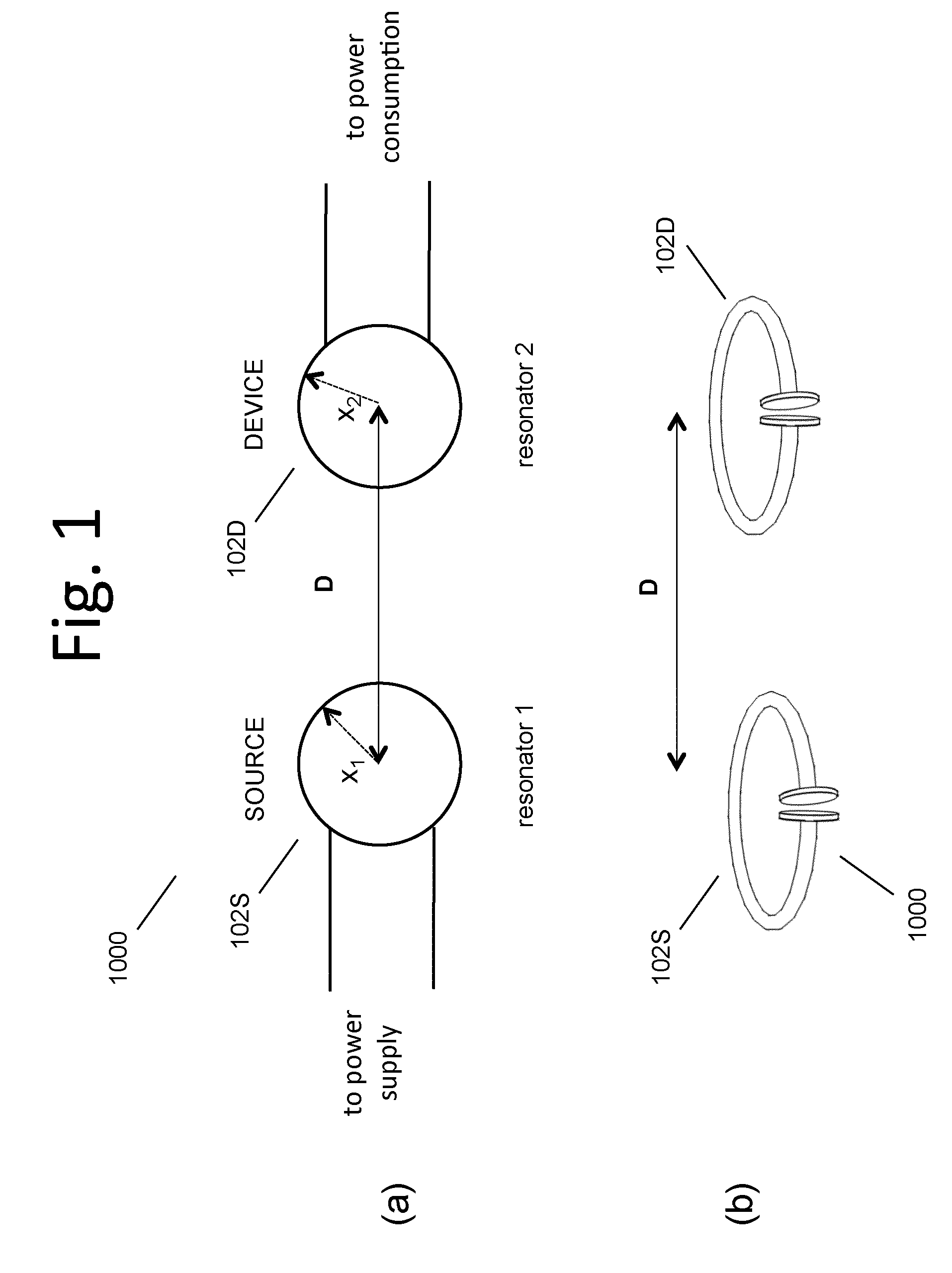
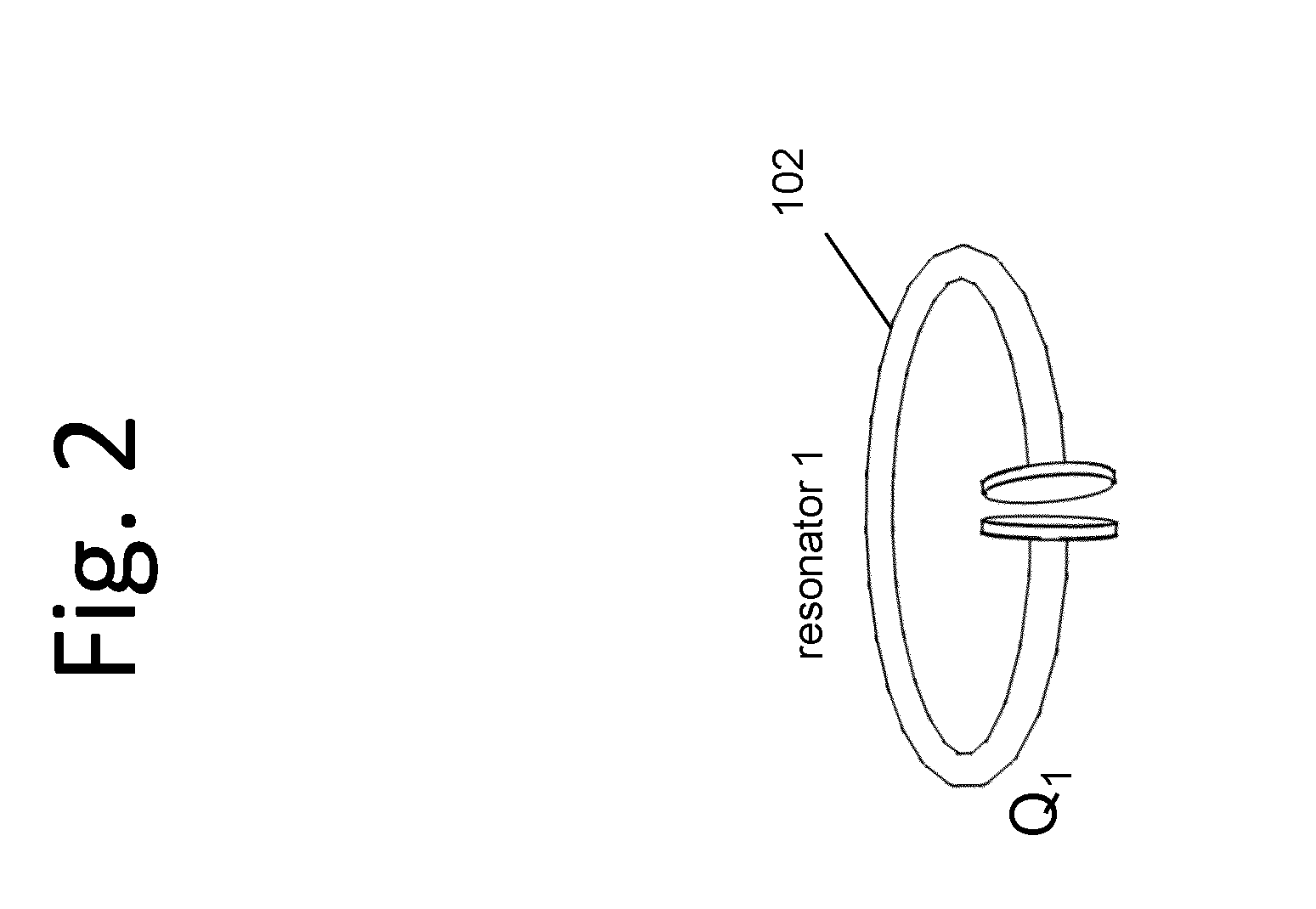
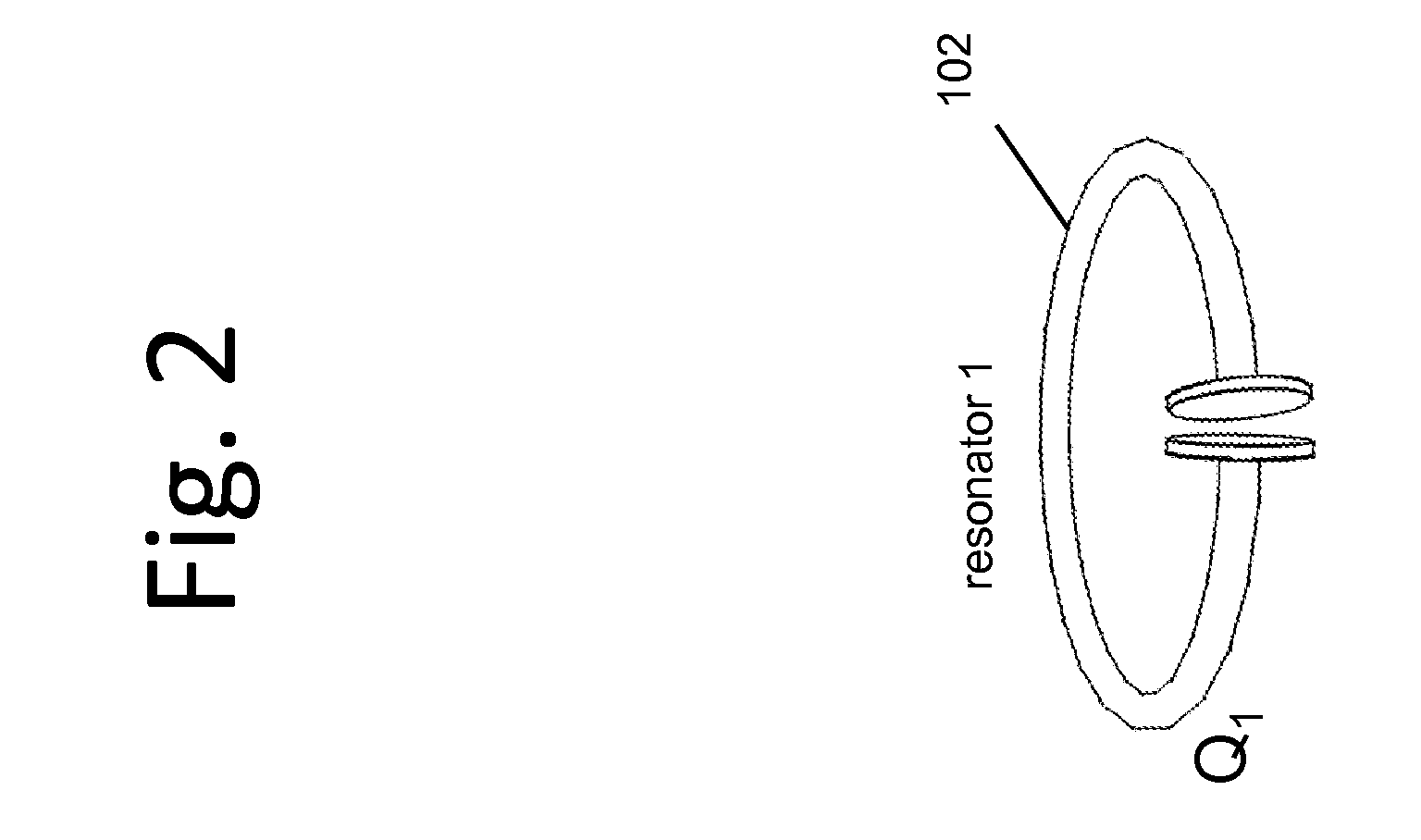
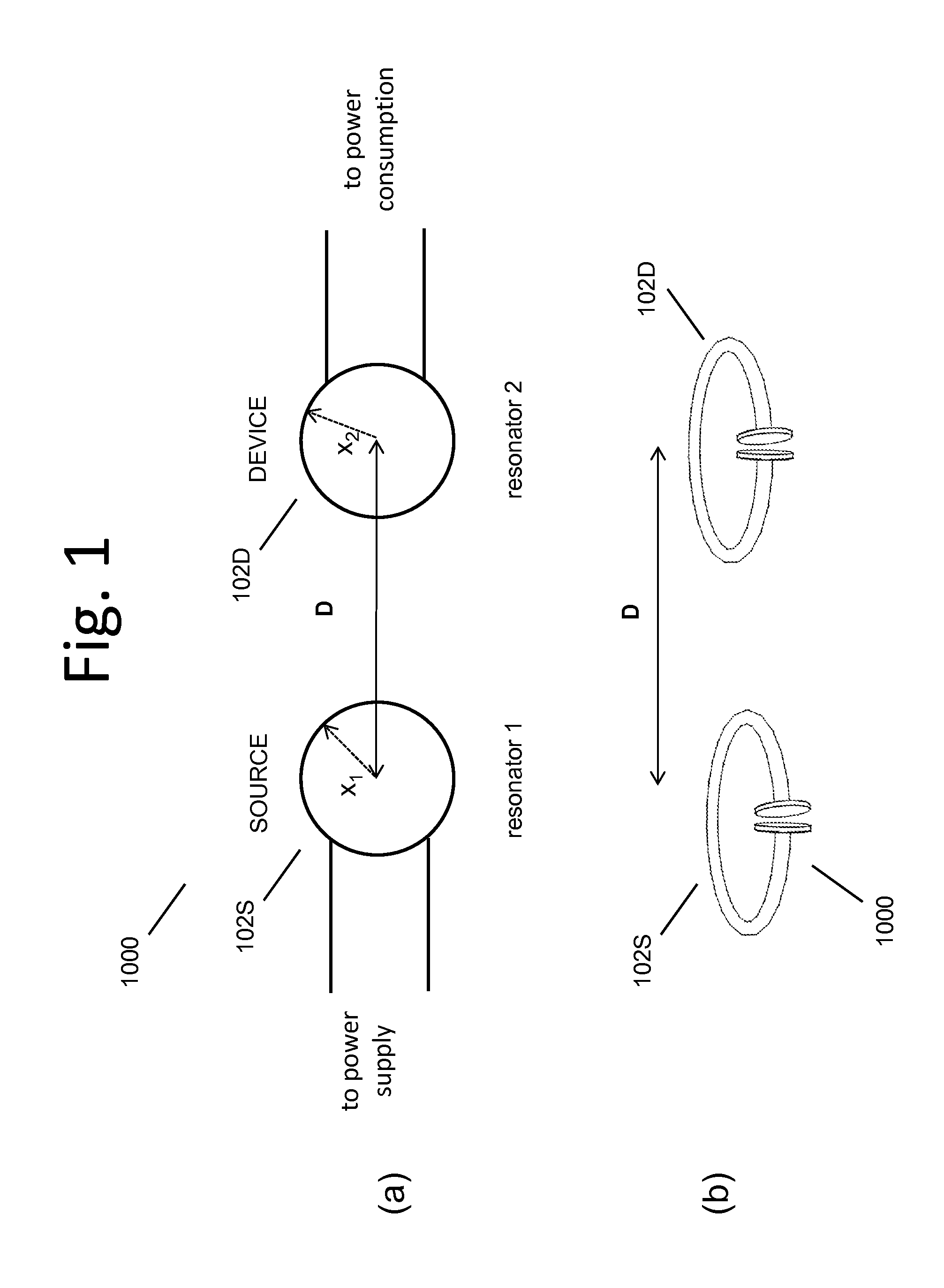
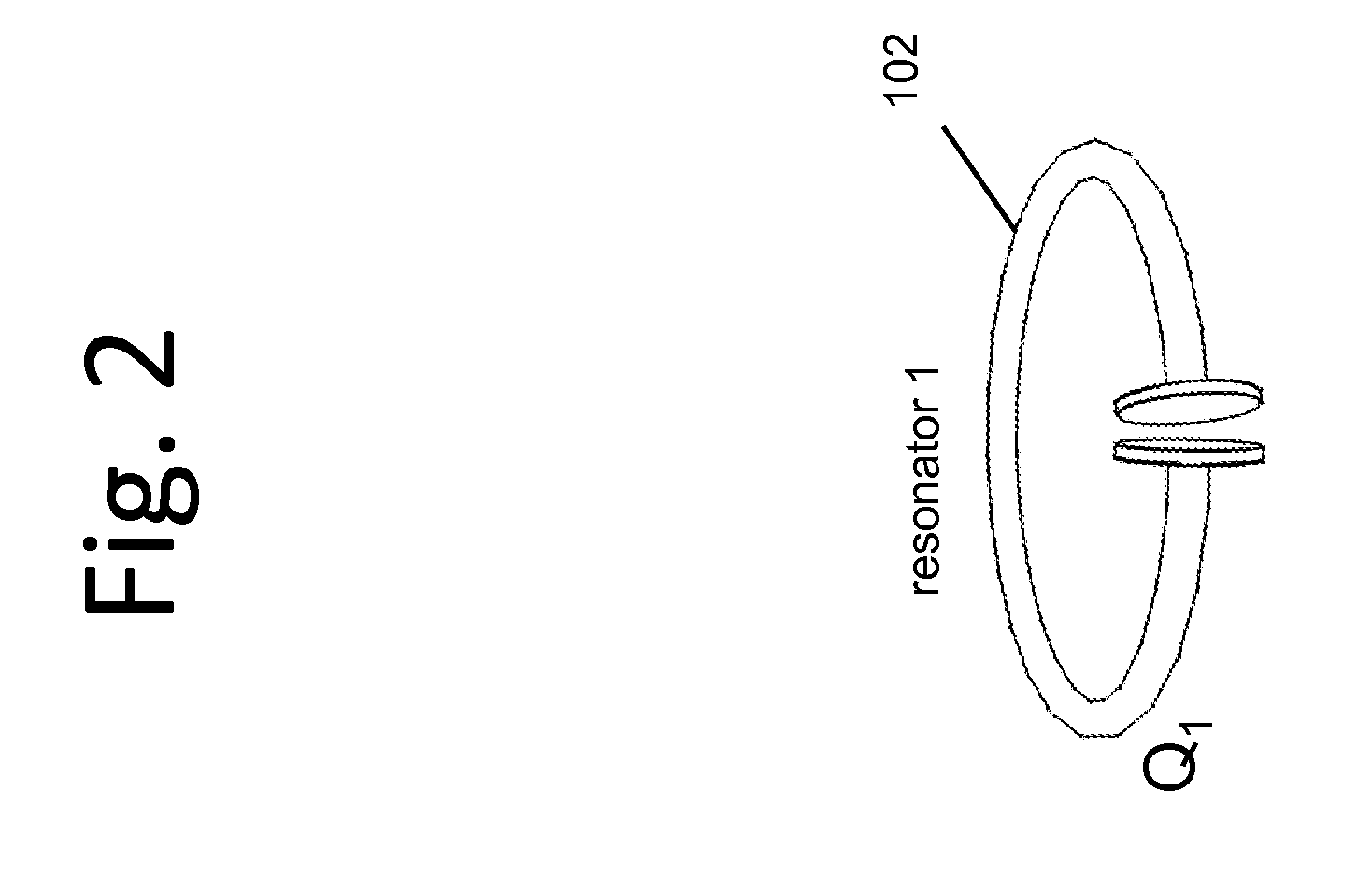
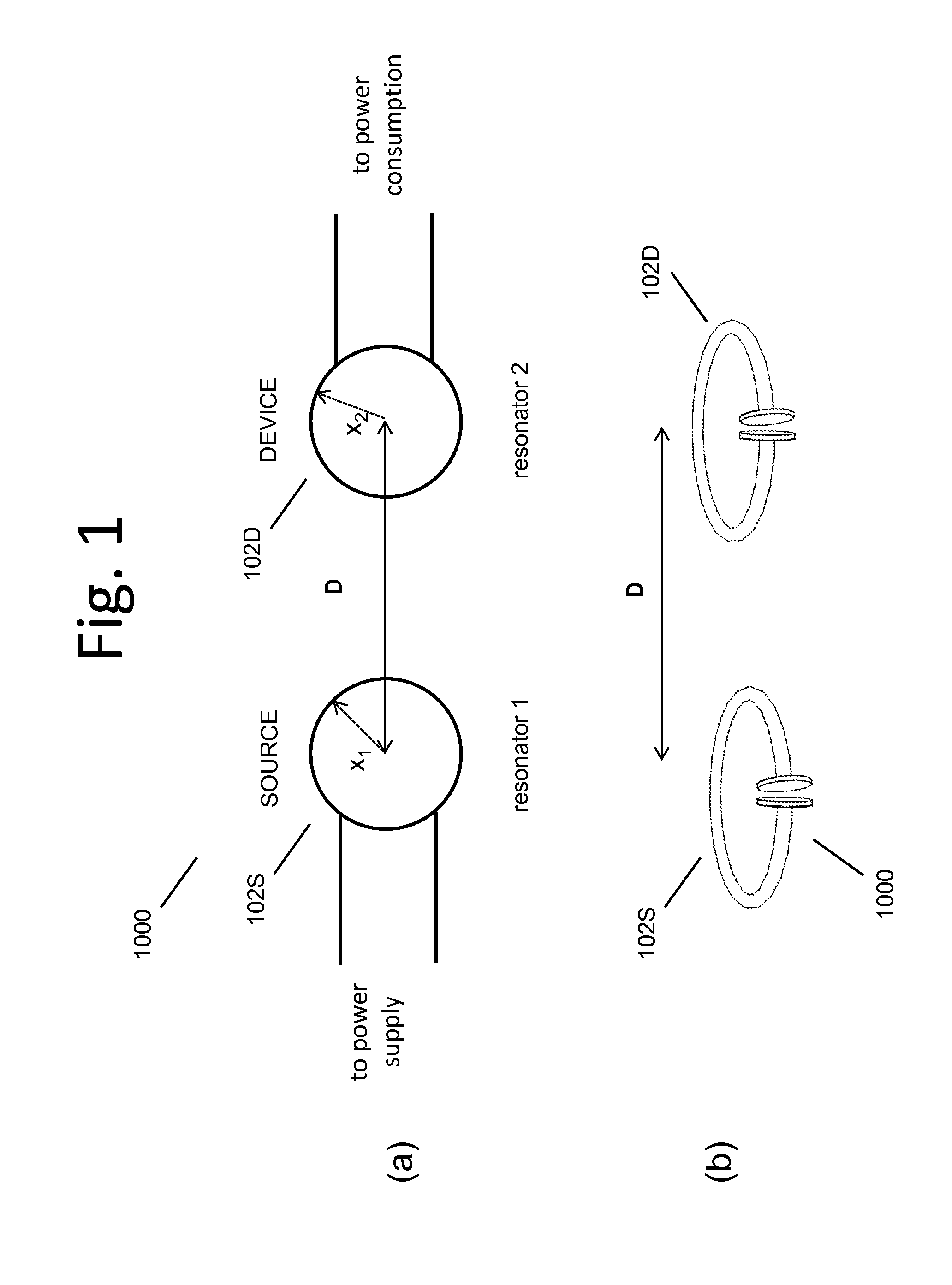
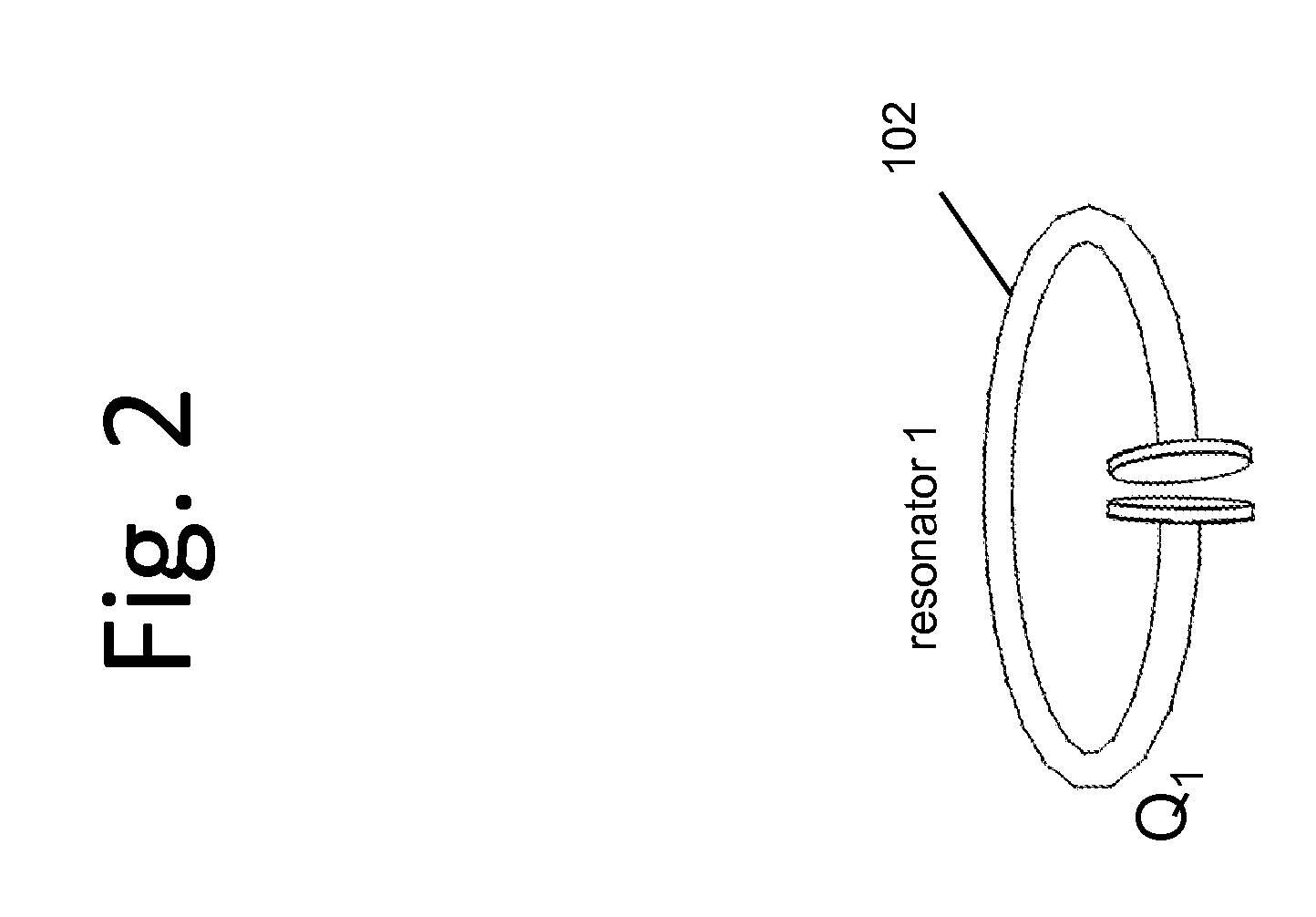
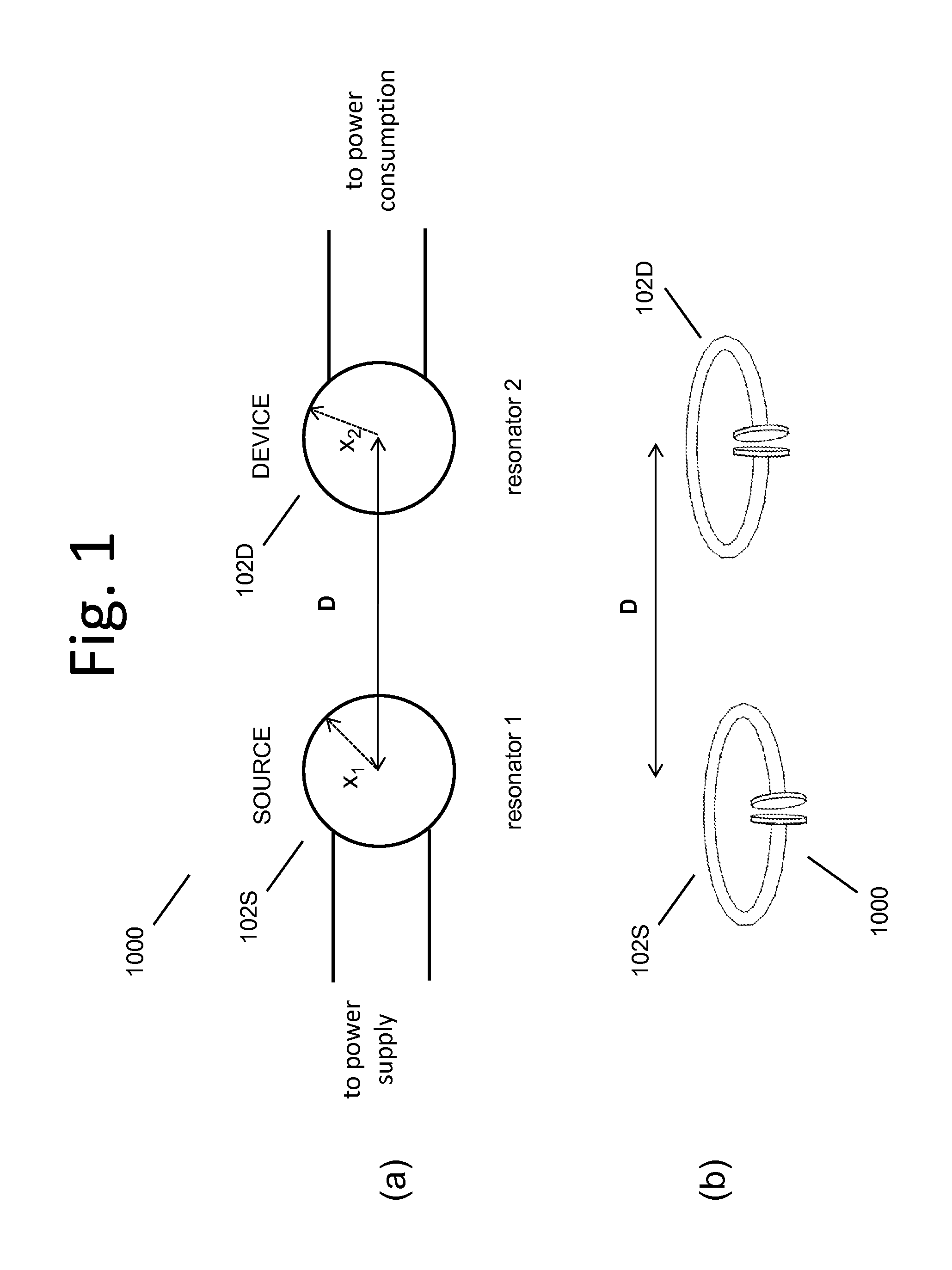
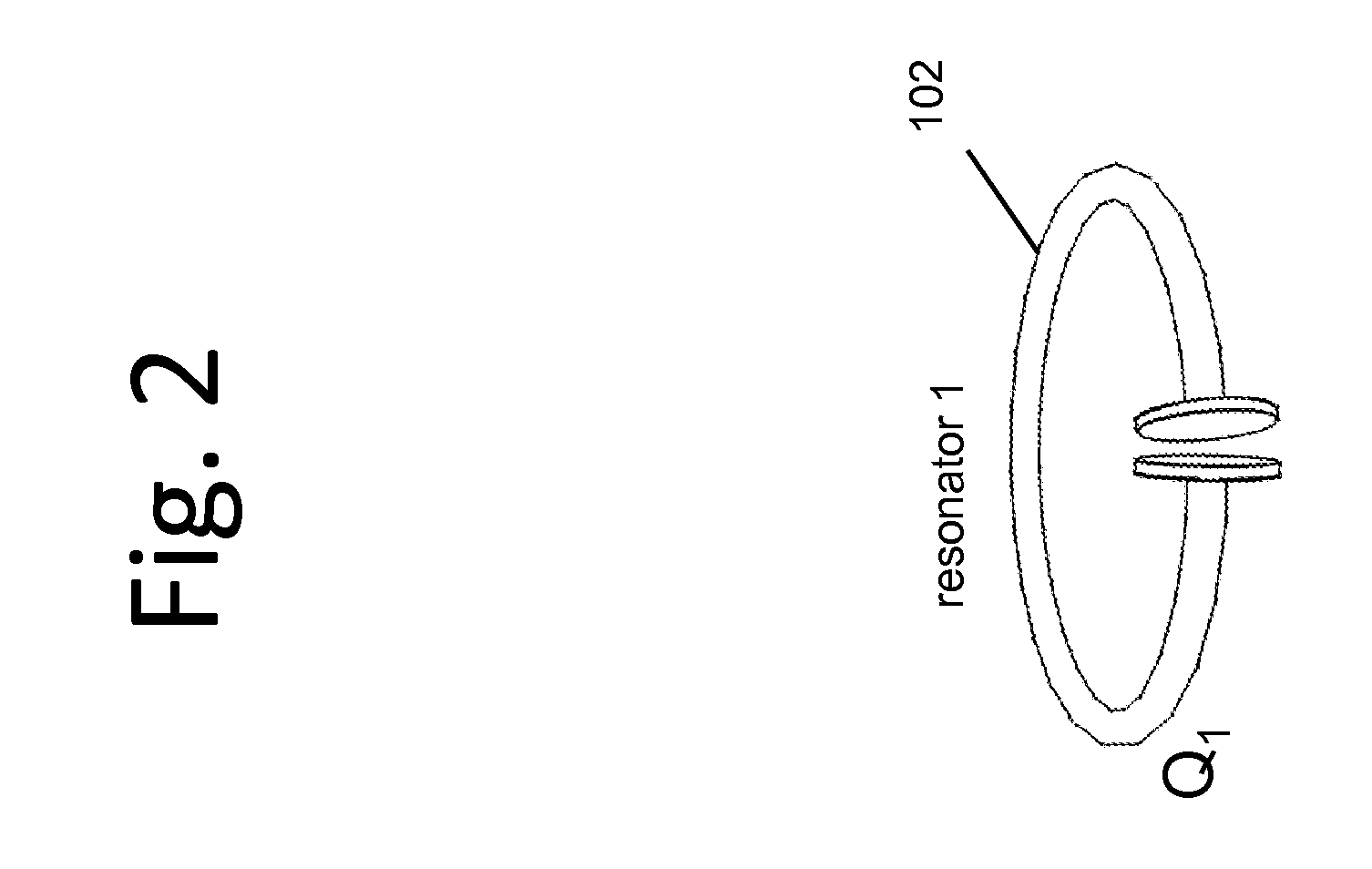
Described herein are improved capabilities for a source resonator having a Q-factor Q1>100 and a characteristic size x1 coupled to an energy source, and a second resonator having a Q-factor Q2>100 and a characteristic size x2 coupled to an energy drain located a distance D from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to exchange energy wirelessly among the source resonator and the second resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
System and method for contact free transfer of power
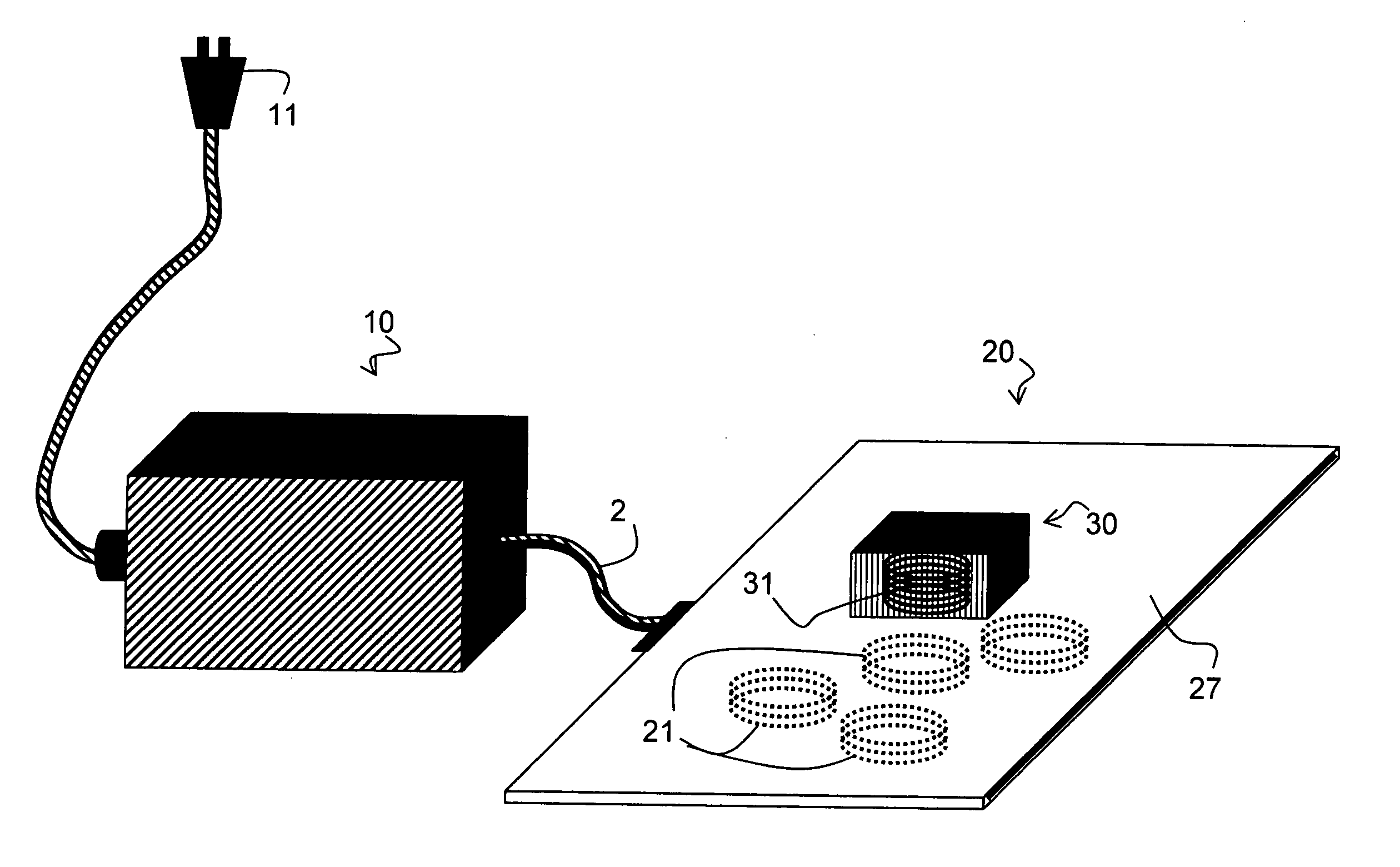
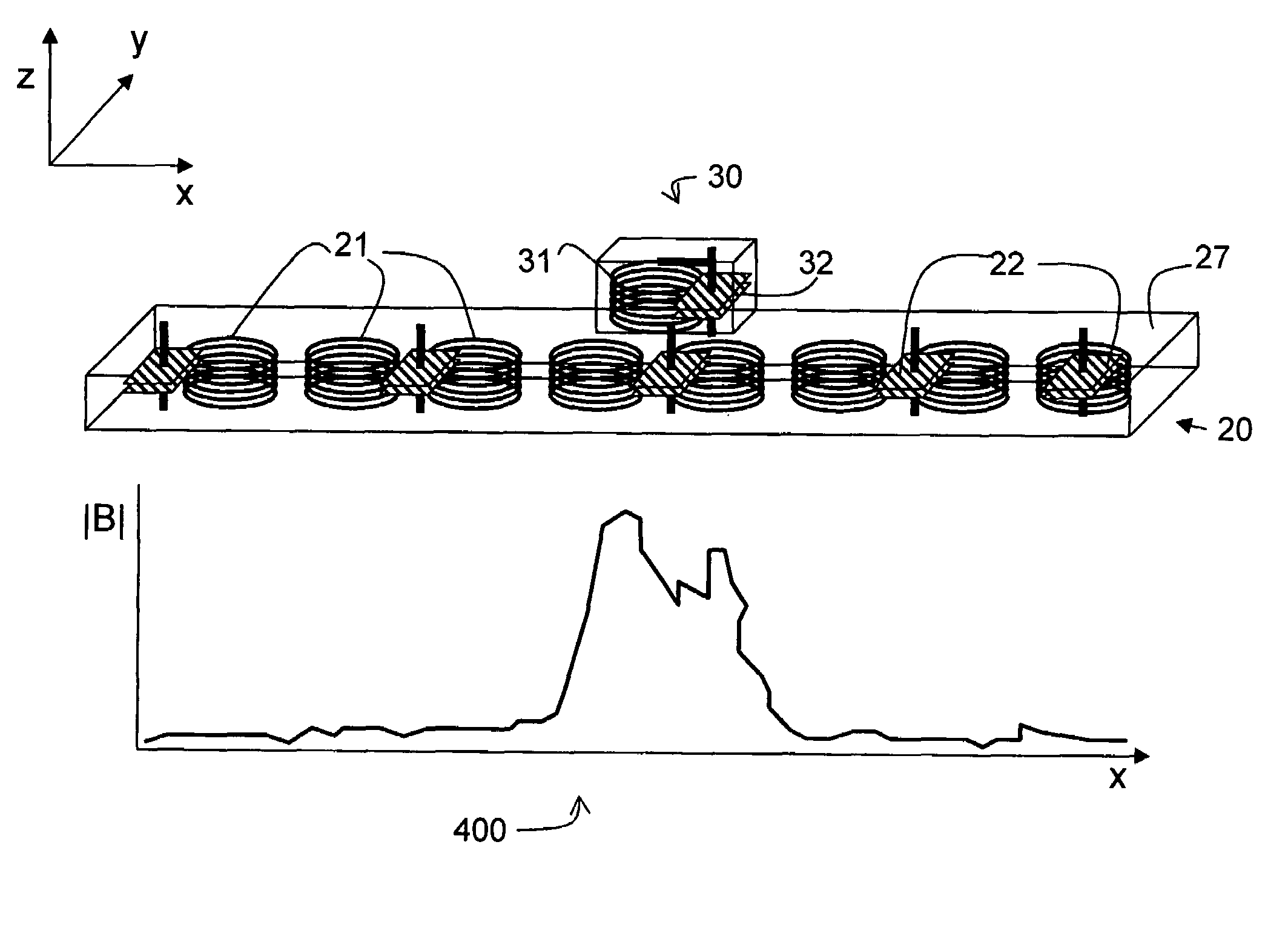
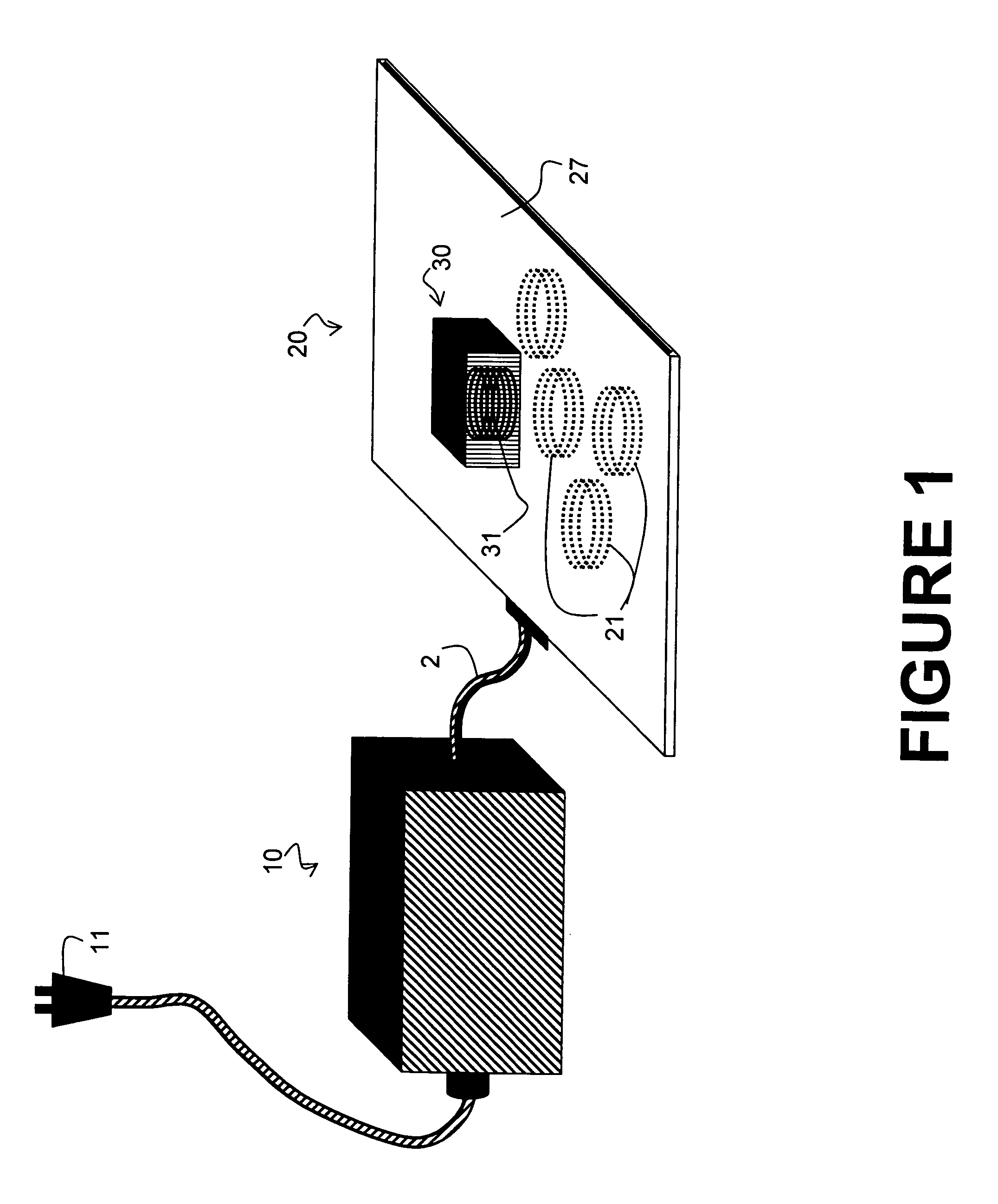
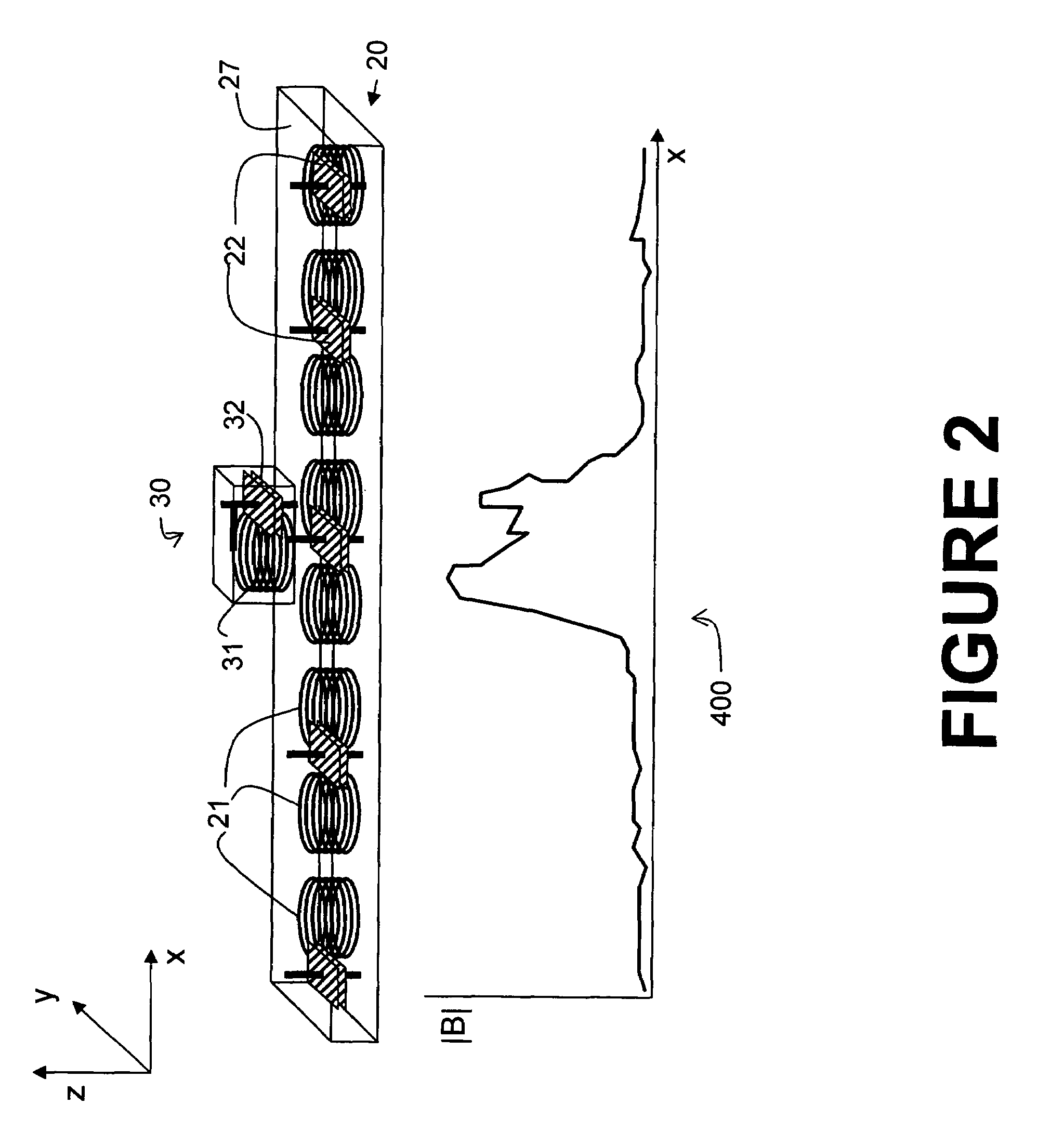
InactiveUS20070145830A1Improve toleranceSufficient powerElectric switchesElectric powerPower gridEngineering
A system and method is provided for the inductive transfer of electric power between a substantially flat primary surface and a multitude of secondary devices in such a way that the power transfer is localized to the vicinities of individual device coils. The contact free power transfer does not require precise physical alignment between the primary surface and the secondary device and can allow the secondary device or devices to be placed anywhere and in arbitrary orientation with respect to the primary surface. Such power transfer is realized without the need of complex high frequency power switching network to turn the individual primary coils on or off and is completely scalable to almost arbitrary size. The local anti-resonance architecture of the primary device will block primary current from flowing when no secondary device or devices are in proximity to the local RF power network. The presence of a tuned secondary device detunes the local anti-resonance on the primary surface; thereby enable the RF power to be transferred from the local primary coils to the secondary device. The uniformity of the inductive coupling between the active primary surface and the secondary devices is improved with a novel multi-pole driving technique which produces an apparent traveling wave pattern across the primary surface.
Owner:MOBILEWISE
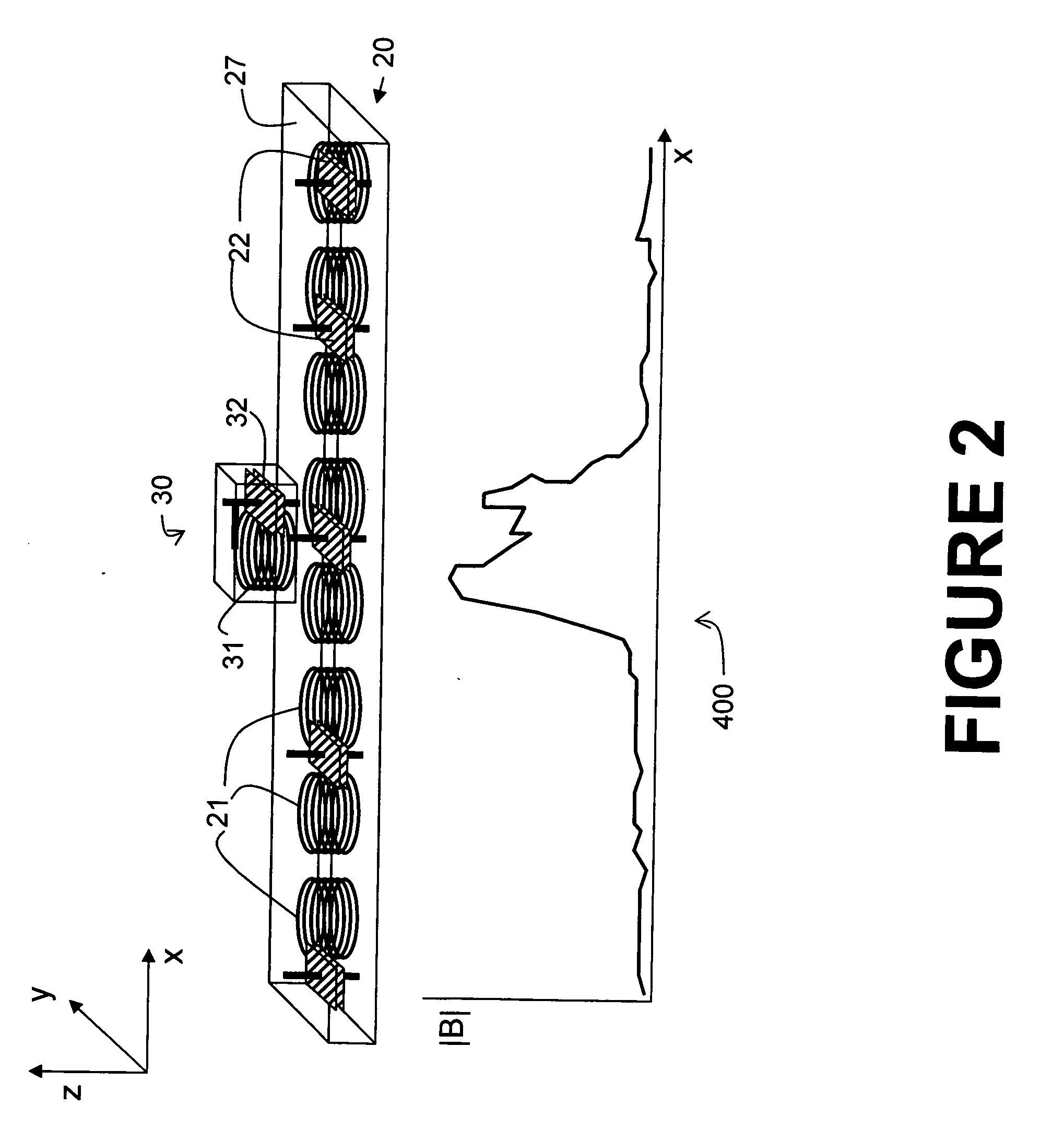
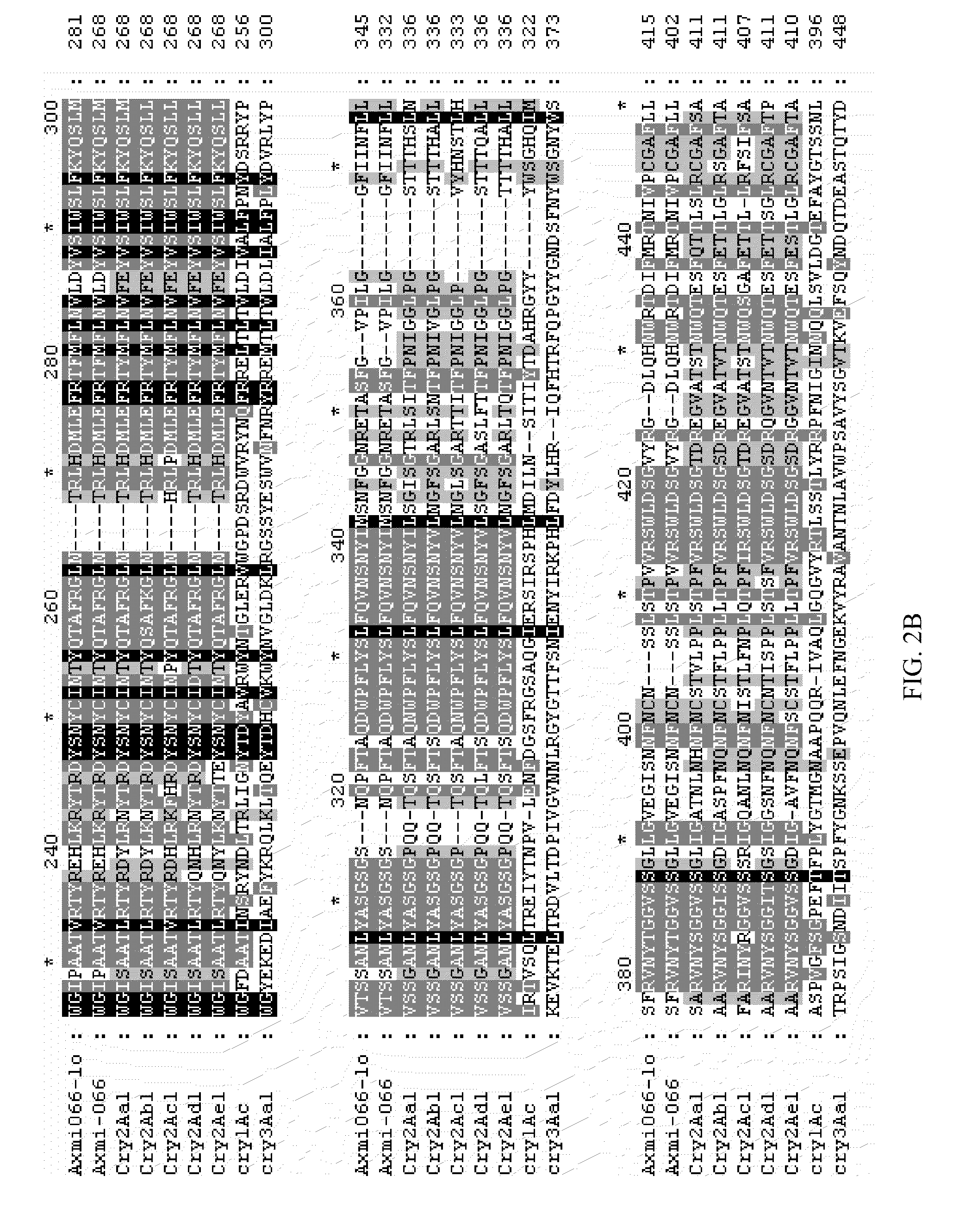
Axmi-066 and axmi-076: delta-endotoxin proteins and methods for their use
InactiveUS20090144852A1Increase productionIncrease resistanceBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:5, 2, or 10, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:4, 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, or 11, or the nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession No. B-50045, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Wireless energy transfer systems
ActiveUS20100109445A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
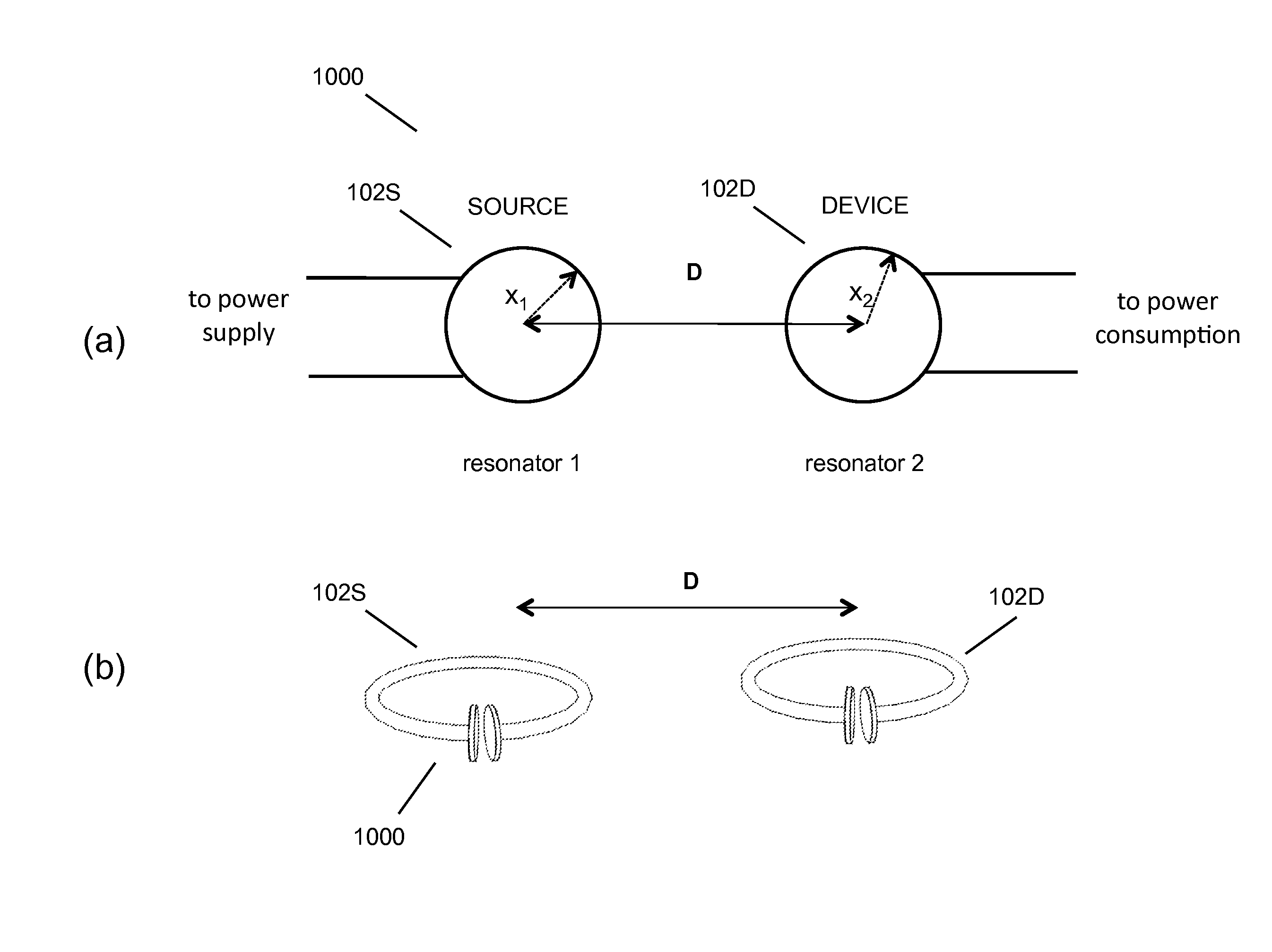
Described herein are improved capabilities for a source resonator having a Q-factor Q1>100 and a characteristic size x1 coupled to an energy source, and a second resonator having a Q-factor Q2>100 and a characteristic size x2 coupled to an energy drain located a distance D from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to exchange energy wirelessly among the source resonator and the second resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Tunable wireless energy transfer for in-vehicle applications
ActiveUS20120112532A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCharging stationsEnergy transferIn vehicle
A mobile wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes a load associated with an electrically powered system that is disposed interior to a vehicle, and a second electromagnetic resonator configured to be coupled to the load and moveable relative to the first electromagnetic resonator, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator; and wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be tunable during system operation so as to at least one of tune the power provided to the second electromagnetic resonator and tune the power delivered to the load.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Multi-resonator wireless energy transfer to mobile devices
InactiveUS20120248886A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferEngineering
A mobile wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply and a second electromagnetic resonator coupled to at least one of a power supply and the first electromagnetic resonator. The mobile wireless receiver includes a load associated with a mobile device such that the load delivers electrical energy to the mobile device, and a third electromagnetic resonator configured to be coupled to the load and movable relative to at least one of the first electromagnetic resonator and the second electromagnetic resonator, wherein the third resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to at least one of the first electromagnetic resonator and the second electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the third electromagnetic resonator from at least one of the first electromagnetic resonator and the second electromagnetic resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless power transfer within a circuit breaker
InactiveUS20120091820A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCharging stationsElectric forceTransmitted power
A wireless power service panel source includes power and control circuitry that receives power from a wired power connection at a position in a service panel, and generates an electronic drive signal at a frequency, f, and a source magnetic resonator configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field in response to the electronic drive signal, wherein the source magnetic resonator is configured to wirelessly transmit power to sensors in other positions within the service panel.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer using field shaping to reduce loss
ActiveUS20110043047A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a method and system comprising a source resonator optionally coupled to an energy source and a second resonator located a distance from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to provide near-field wireless energy transfer among the source resonator and the second resonator and where the field of at least one of the source resonator and the second resonator is shaped to avoid a loss-inducing object.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer with variable size resonators for medical applications
ActiveUS20120235634A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferInductor
A medical device-powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply. The wireless receiver includes a load configured to power an implantable medical device using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed within the medical device and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator, the area circumscribed by the inductive element of at least one of the electromagnetic resonators can be varied to improve performance.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer with resonator arrays for medical applications
InactiveUS20120248888A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferEngineering
A medical device-powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes, a load configured to power an implantable medical device using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed within the medical device and configured to be coupled to the load, at least one other electromagnetic resonator configured with the first electromagnetic resonator and the second electromagnetic resonator in an array of electromagnetic resonators to distribute power over an area, and wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Tunable wireless energy transfer for medical applications
InactiveUS20120256494A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemEnergy transferMedical device
A mobile wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes a load associated with powering an electrically powered medical device, and a second electromagnetic resonator configured to be coupled to the load and moveable relative to the first electromagnetic resonator, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator, and wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be tunable during system operation so as to at least one of tune the power provided to the second electromagnetic resonator and tune the power delivered to the load.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer for vehicles
InactiveUS20120119698A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferCircuit authenticationMultiple-port networksEnergy transferEngineering
A vehicle powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply. The wireless receiver includes a load configured to power the drive system of a vehicle using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed upon the vehicle and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein at least one of the first electromagnetic resonator and the second electromagnetic resonator is variable in size, and wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Densification for flowable films
InactiveUS20130288485A1Increase etch toleranceImprove toleranceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityDielectric layer
A method of forming a dielectric layer is described. The method first deposits an initially-flowable layer on a substrate. The initially-flowable layer is then densified by exposing the substrate to a high-density plasma (HDP). Essentially no additional material is deposited on the initially-flowable layer, in embodiments, but the impact of the accelerated ionic species serves to condense the layer and increase the etch tolerance of the processed layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
System and method for selective transfer of radio frequency power
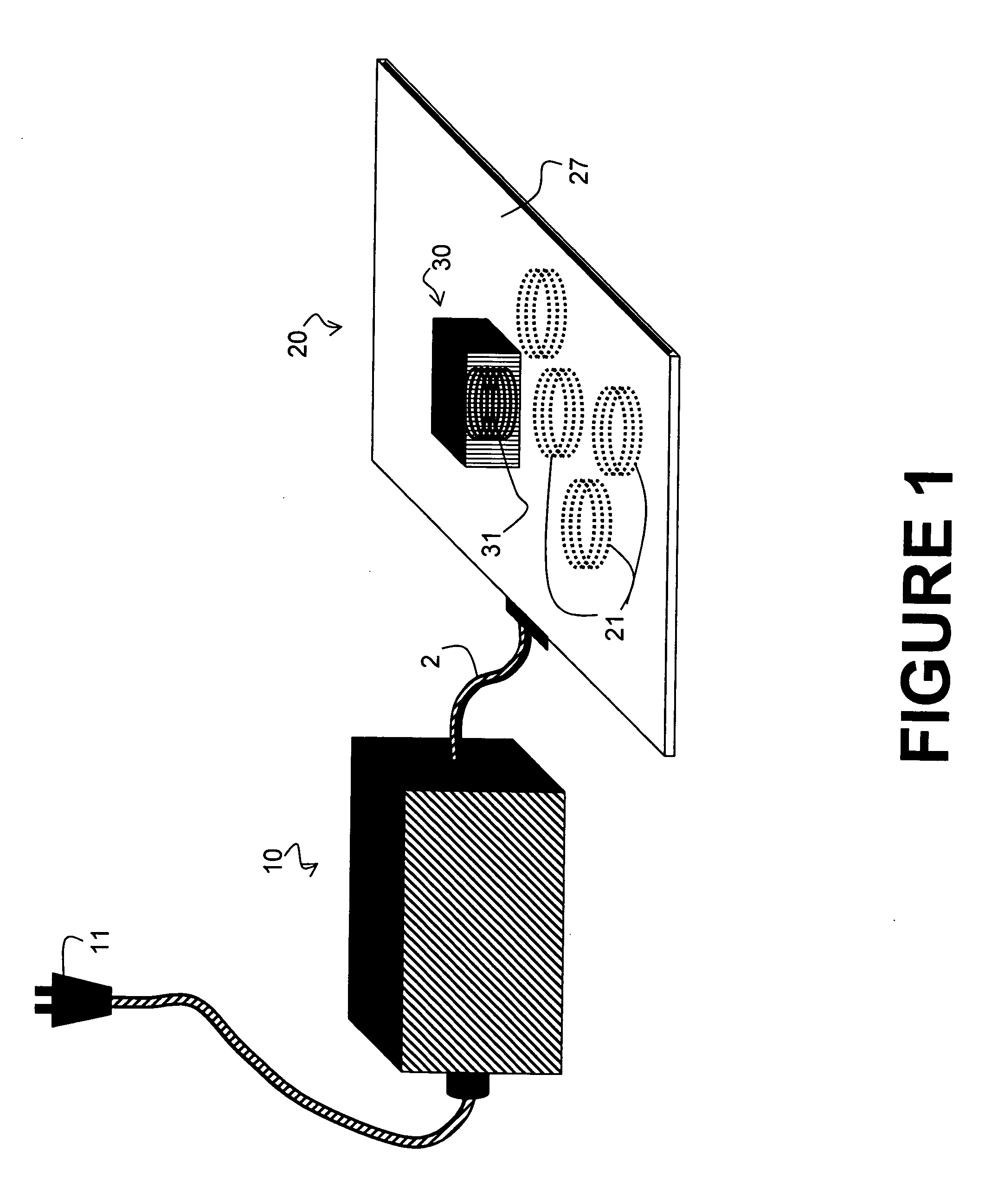
InactiveUS7521890B2Improve toleranceSufficient powerSecondary cellsElectric switchesHigh frequency powerRadio frequency
A system and method is provided for the inductive transfer of electric power between a substantially flat primary surface and a multitude of secondary devices in such a way that the power transfer is localized to the vicinities of individual device coils. The contact free power transfer does not require precise physical alignment between the primary surface and the secondary device and can allow the secondary device or devices to be placed anywhere and in arbitrary orientation with respect to the primary surface. Such power transfer is realized without the need of complex high frequency power switching network to turn the individual primary coils on or off and is completely scalable to almost arbitrary size. The local anti-resonance architecture of the primary device will block primary current from flowing when no secondary device or devices are in proximity to the local RF power network. The presence of a tuned secondary device detunes the local anti-resonance on the primary surface; thereby enable the RF power to be transferred from the local primary coils to the secondary device. The uniformity of the inductive coupling between the active primary surface and the secondary devices is improved with a novel multi-pole driving technique which produces an apparent traveling wave pattern across the primary surface.
Owner:MOBILEWISE
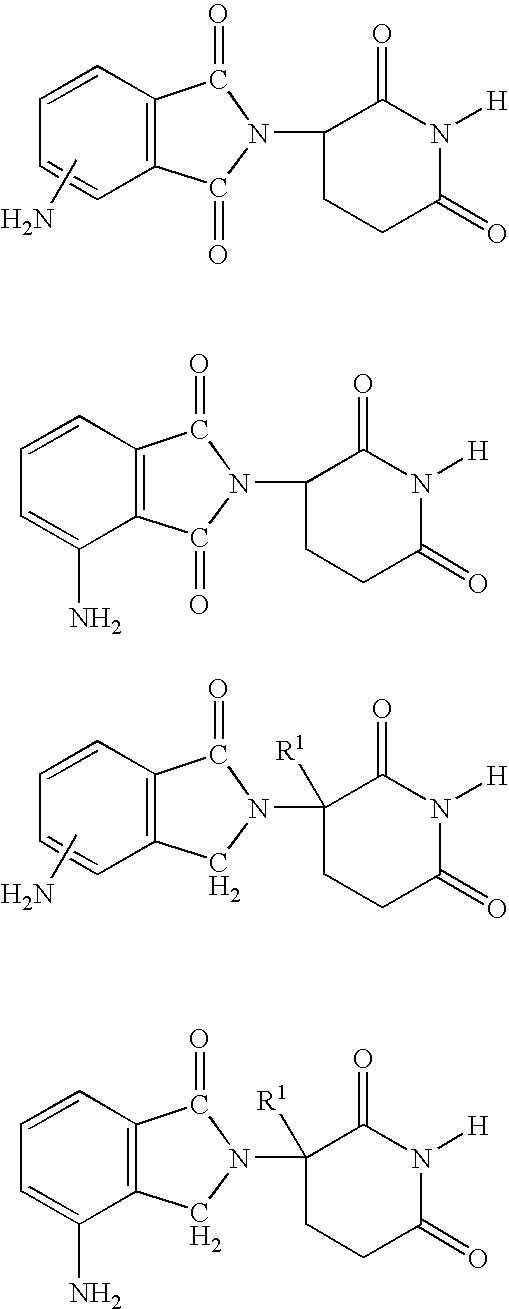
Methods of using and compositions comprising immunomodulatory compounds for the treatment and management of myeloproliferative diseases
InactiveUS20040087546A1Reduce adverse effectsImprove toleranceBiocideNervous disorderActive agentMyeloproliferative disease
Methods of treating, preventing and / or managing a myeloproliferative disease are disclosed. Specific methods encompass the administration of an immunomodulatory compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, hydrate, stereoisomer, clathrate, or prodrug thereof, alone or in combination with a second active agent, and / or the transplantation of blood or cells. Particular second active agents are capable of suppressing the overproduction of hematopoietic stem cells or ameliorating one or more of the symptoms of a myeloproliferative disease. Pharmaceutical compositions, single unit dosage forms, and kits suitable for use in methods of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
Wireless energy transfer for vehicles
ActiveUS20120119575A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemResonatorEnergy transfer
A vehicle powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply. The wireless receiver includes a load configured to power the drive system of a vehicle using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed upon the vehicle and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator; and wherein the field of at least one of the first electromagnetic resonator and the second electromagnetic resonator is shaped using a conducting surface to avoid a loss-inducing object.
Owner:WITRICITY
Wireless energy transfer using repeater resonators
ActiveUS8729737B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferCircuit authenticationMultiple-port networksEnergy transferElectrical battery
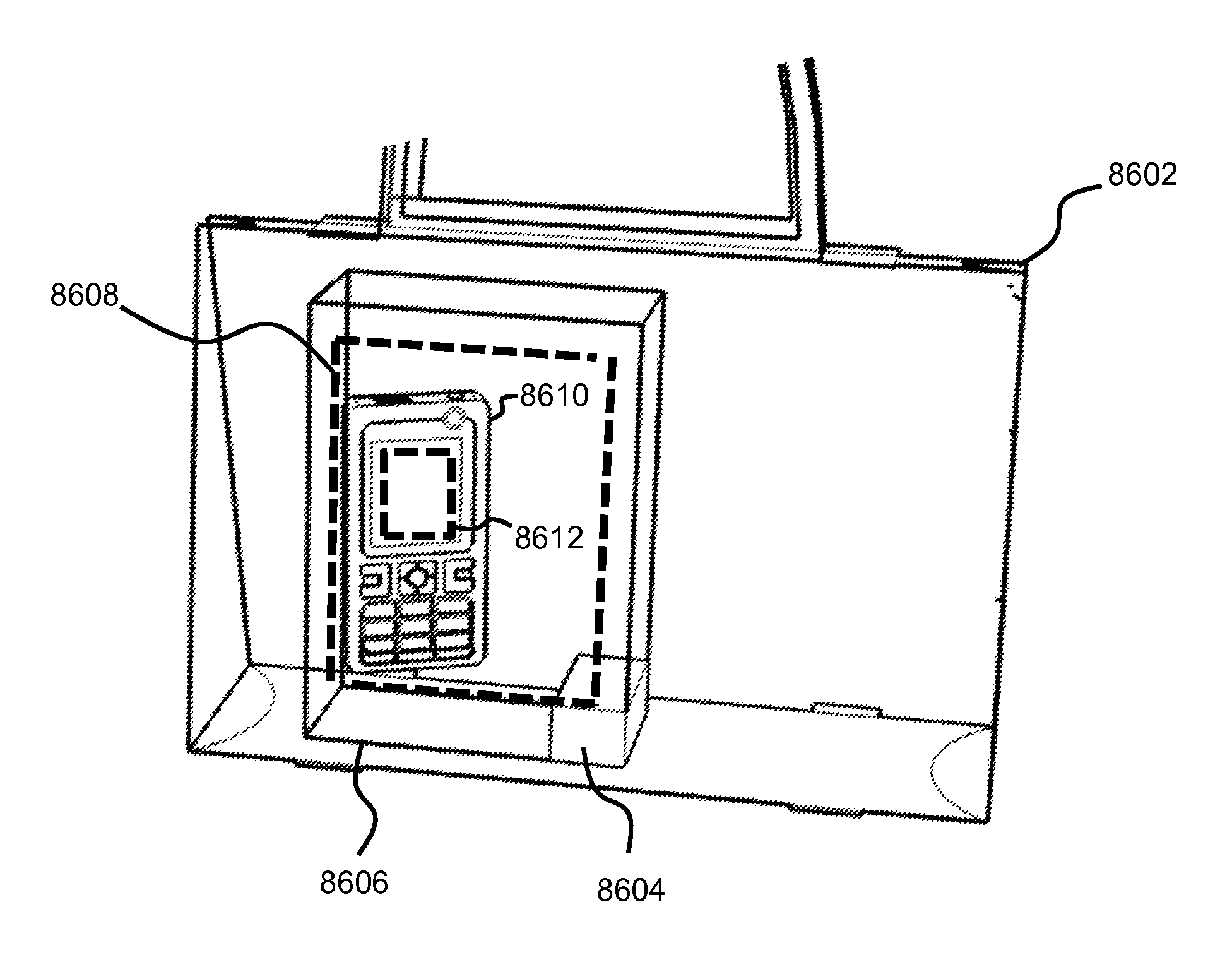
A bag for wireless energy transfer comprising a compartment for storing an electronic device enabled for wireless energy transfer, and at least one magnetic resonator positioned for wireless energy transfer to the electronic device, wherein a the at least one magnetic resonator optionally operates in one of three modes: (1) as a repeater resonator to extend the energy transfer to the electronic device from an external wireless energy source, (2) as a source resonator transferring energy from a battery in the bag to the electronic device, and (3) as an energy capture resonator receiving wireless energy from an external source to recharge a battery in the bag.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer using repeater resonators
ActiveUS20110095618A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferCircuit authenticationMultiple-port networksEnergy transferElectricity
Described herein are improved configurations for a device for wireless power transfer that includes a conductor forming at least one loop of a high-Q resonator, a capacitive part electrically coupled to the conductor, and a power and control circuit electrically coupled to the conductor, the power and control circuit providing two or more modes of operation and the power and control circuit selecting how the high-Q resonator receives and generates an oscillating magnetic field.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
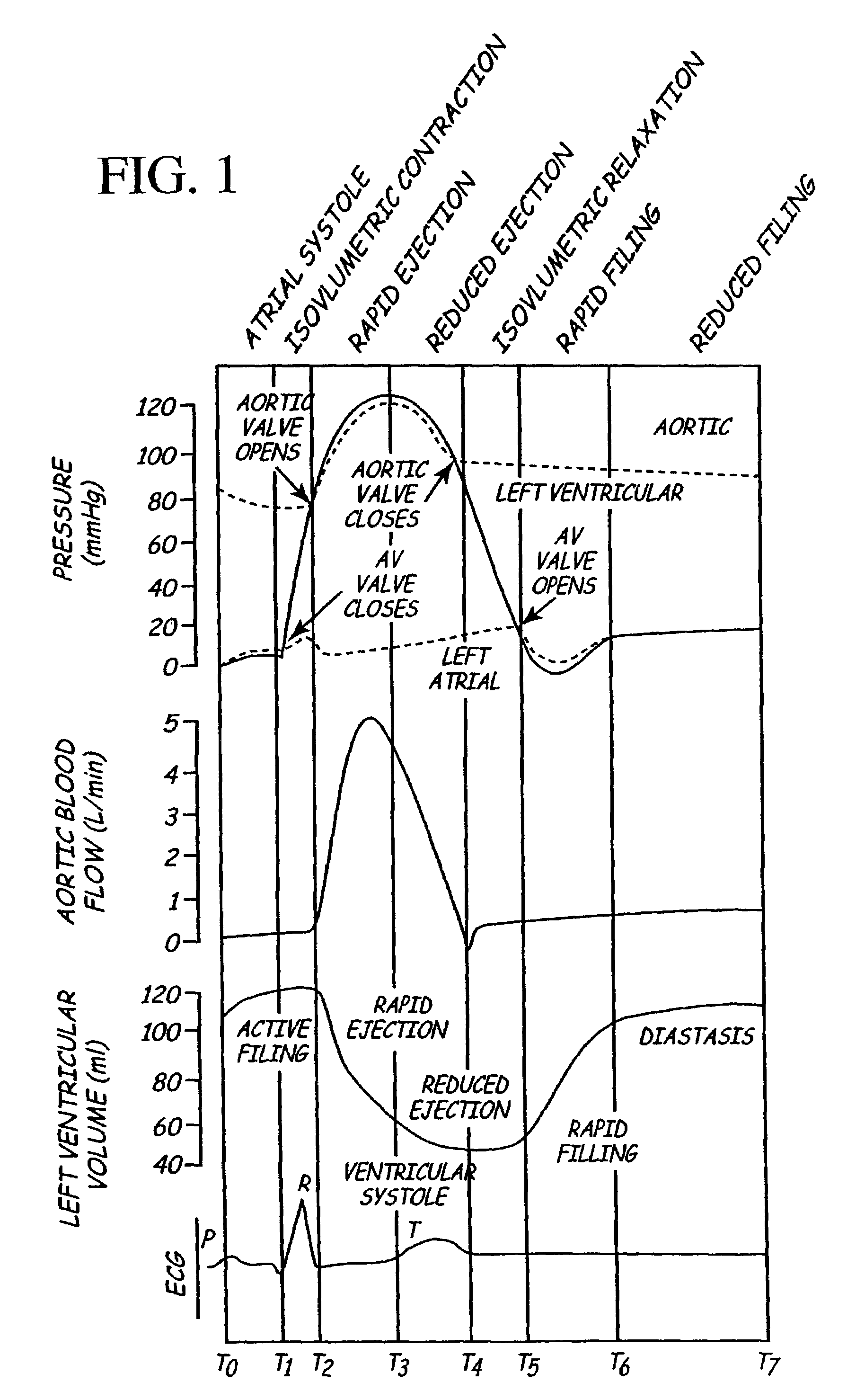
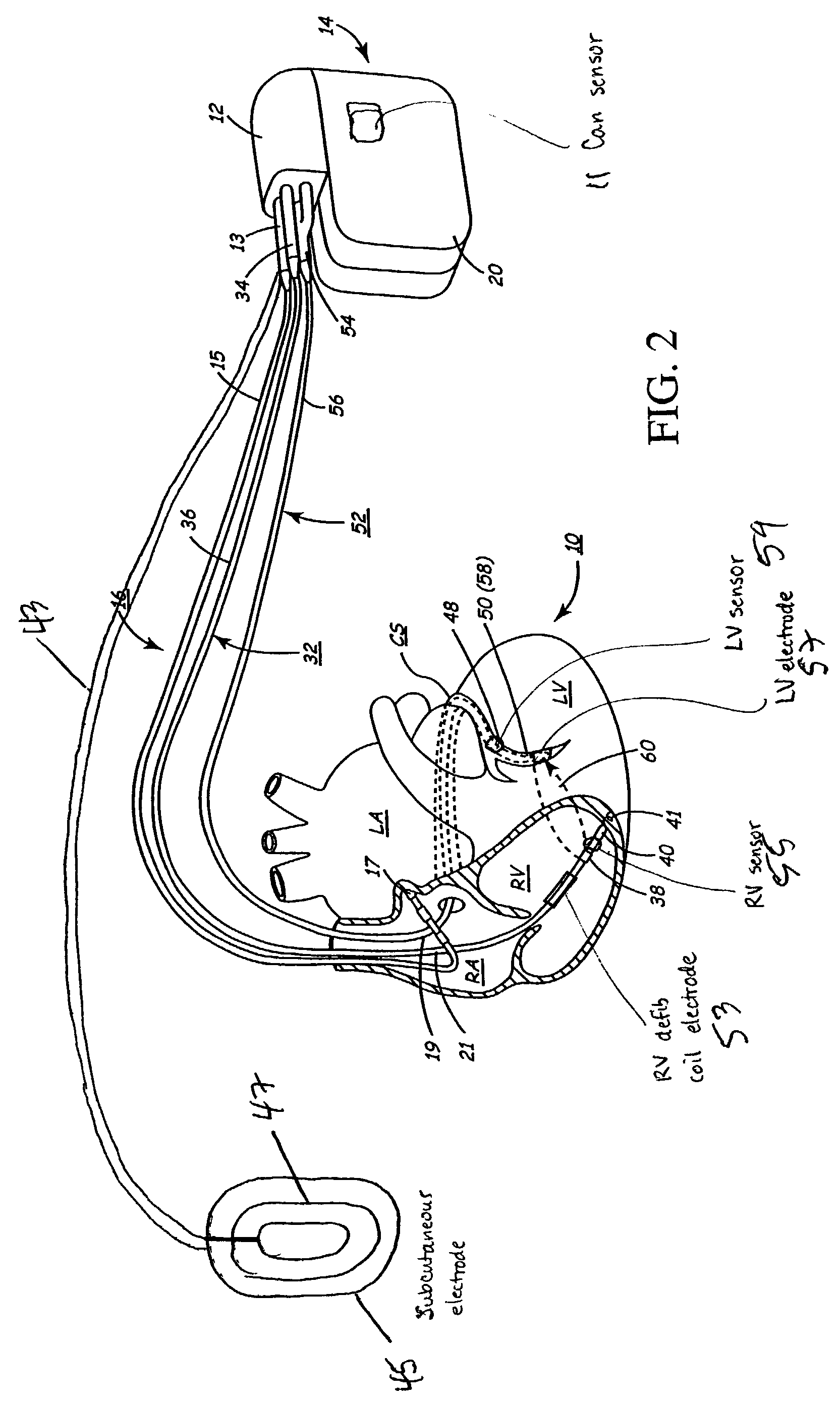
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
InactiveUS7096064B2Improve toleranceExtension of timeHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionElectrical stimulations
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of particular benefit for patients suffering heart failure including cardiac dysfunction, chronic HF, and the like and all variants thereof. According to the disclosure monitoring and therapy delivery for a wide variety of acute and chronic cardiac dysfunctions are described and depicted. Various forms of paired or coupled pacing therapy delivery provided alone or in combination with neurostimulation therapy delivered by both implantable and external apparatus, including defibrillation therapy are also provided herein.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Wireless energy transfer for vehicles
InactiveUS20120112691A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferCircuit authenticationMultiple-port networksElectric power transmissionEnergy transfer
A vehicle powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply. The wireless receiver includes a load configured to power the drive system of a vehicle using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed upon the vehicle and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator, and wherein the frequency of at least one electromagnetic resonator is selected to prevent transfer of power to unauthorized devices.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer with variable size resonators for implanted medical devices
ActiveUS20120235633A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferInductor
A medical device-powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply. The wireless receiver including a load is configured to power the medical device using electrical power, and a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed within the medical device and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator, the area circumscribed by the inductive element of at least one of the electromagnetic resonators can be varied to improve performance.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Lipid formulations for nucleic acid delivery
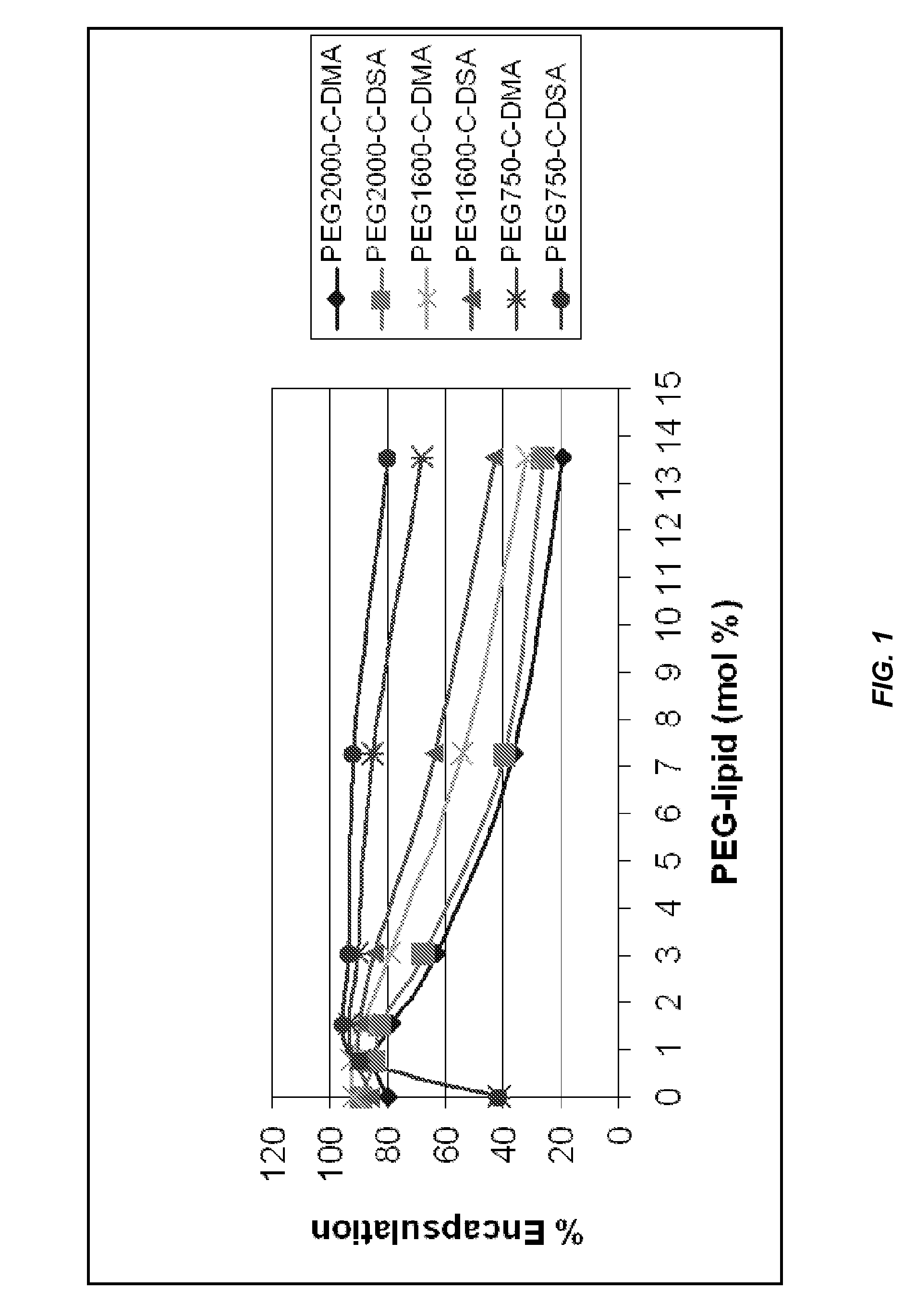
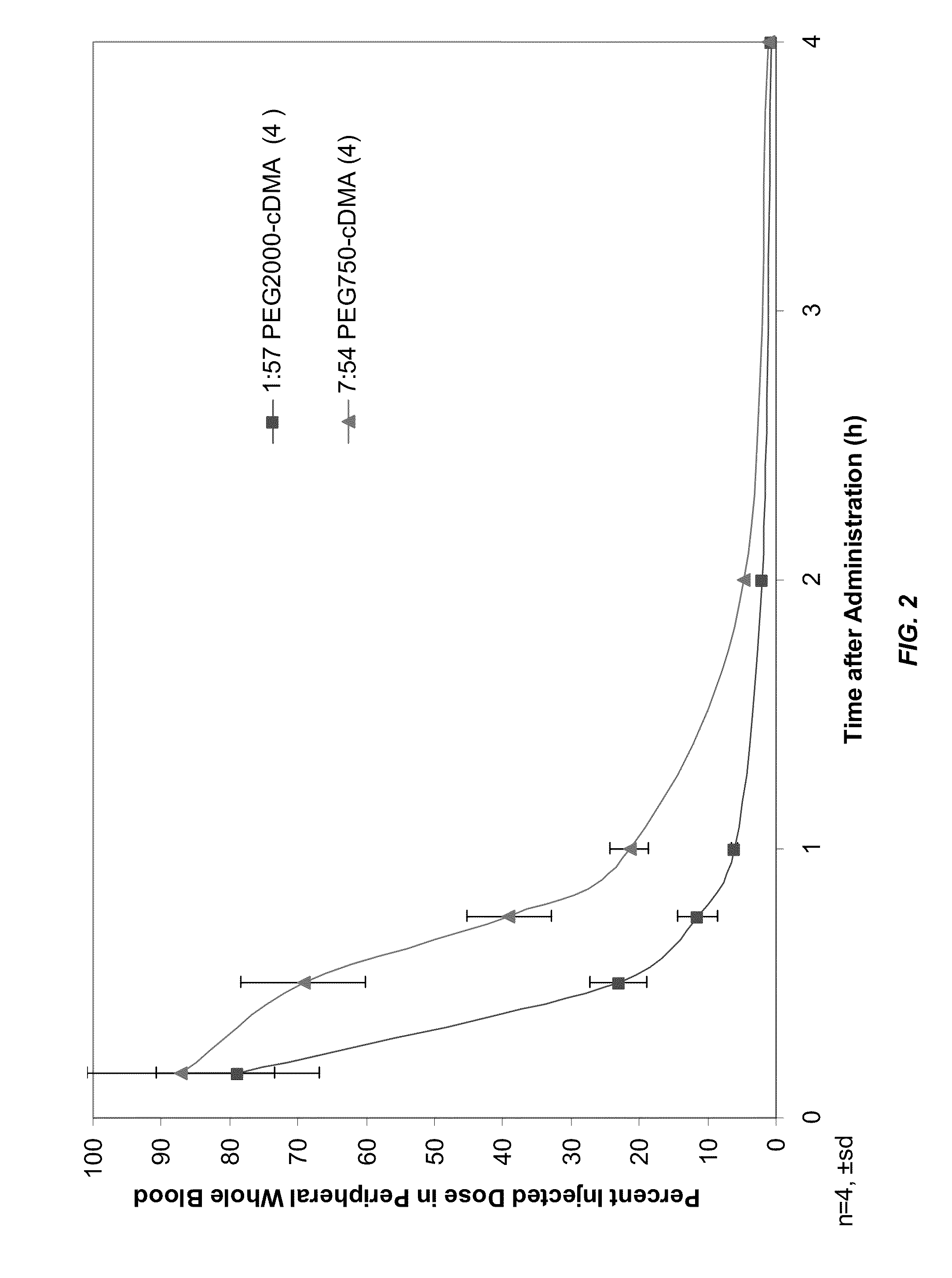
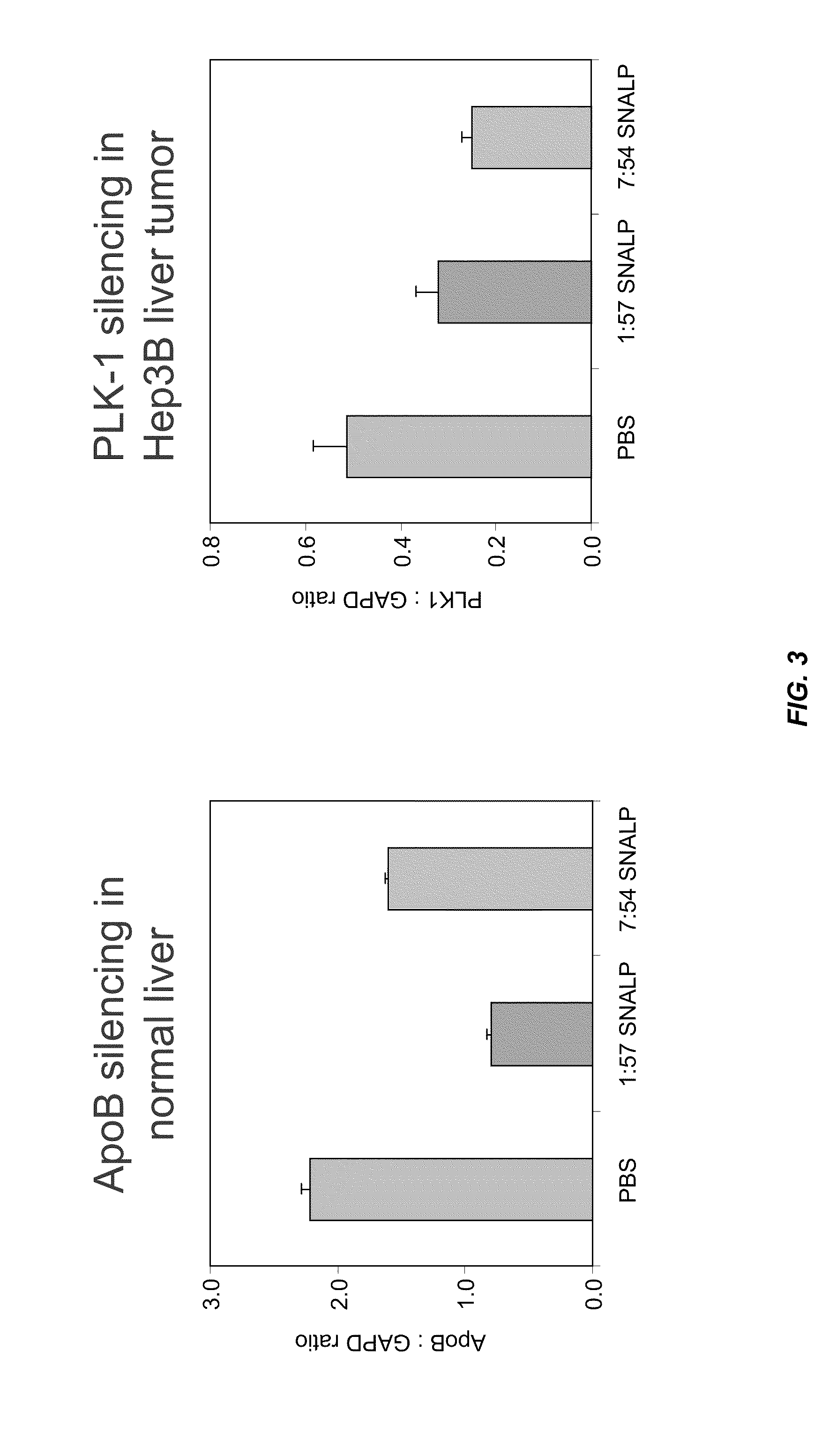
ActiveUS8283333B2Improve effectivenessHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesLipid particleActive agent
The present invention provides novel, serum-stable lipid particles comprising one or more active agents or therapeutic agents, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles. More particularly, the present invention provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles (SNALP) comprising a nucleic acid (e.g., one or more interfering RNA molecules), methods of making the SNALP, and methods of delivering and / or administering the SNALP (e.g., for the treatment of cancer). In particular embodiments, the present invention provides tumor-directed lipid particles that preferentially target solid tumors. The tumor-directed formulations of the present invention are capable of preferentially delivering a payload such as a nucleic acid to cells of solid tumors compared to non-cancerous cells.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Secure wireless energy transfer for vehicle applications
ActiveUS20120112531A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferAuthorization
A vehicle powering wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes a load configured to power the drive system of a vehicle using electrical power, a second electromagnetic resonator adapted to be housed upon the vehicle and configured to be coupled to the load, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator; and an authorization facility to confirm compatibility of the resonators and provide authorization for initiation of transfer of power.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Constitutive expression of costimulatory ligands on adoptively transferred T lymphocytes
ActiveUS8252592B2Increase self-toleranceIncrease and reduces immune responseFused cellsFermentationRegulatory T cellLymphocyte
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Tunable wireless energy transfer for sensors
InactiveUS20120235504A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemEnergy transferEngineering
A mobile wireless receiver for use with a first electromagnetic resonator coupled to a power supply includes, a load associated with a sensor and configured to power a sensor, and a second electromagnetic resonator configured to be coupled to the load and moveable relative to the first electromagnetic resonator, wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be wirelessly coupled to the first electromagnetic resonator to provide resonant, non-radiative wireless power to the second electromagnetic resonator from the first electromagnetic resonator, and wherein the second electromagnetic resonator is configured to be tunable during system operation so as to at least one of tune the power provided to the second electromagnetic resonator and tune the power delivered to the load.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com