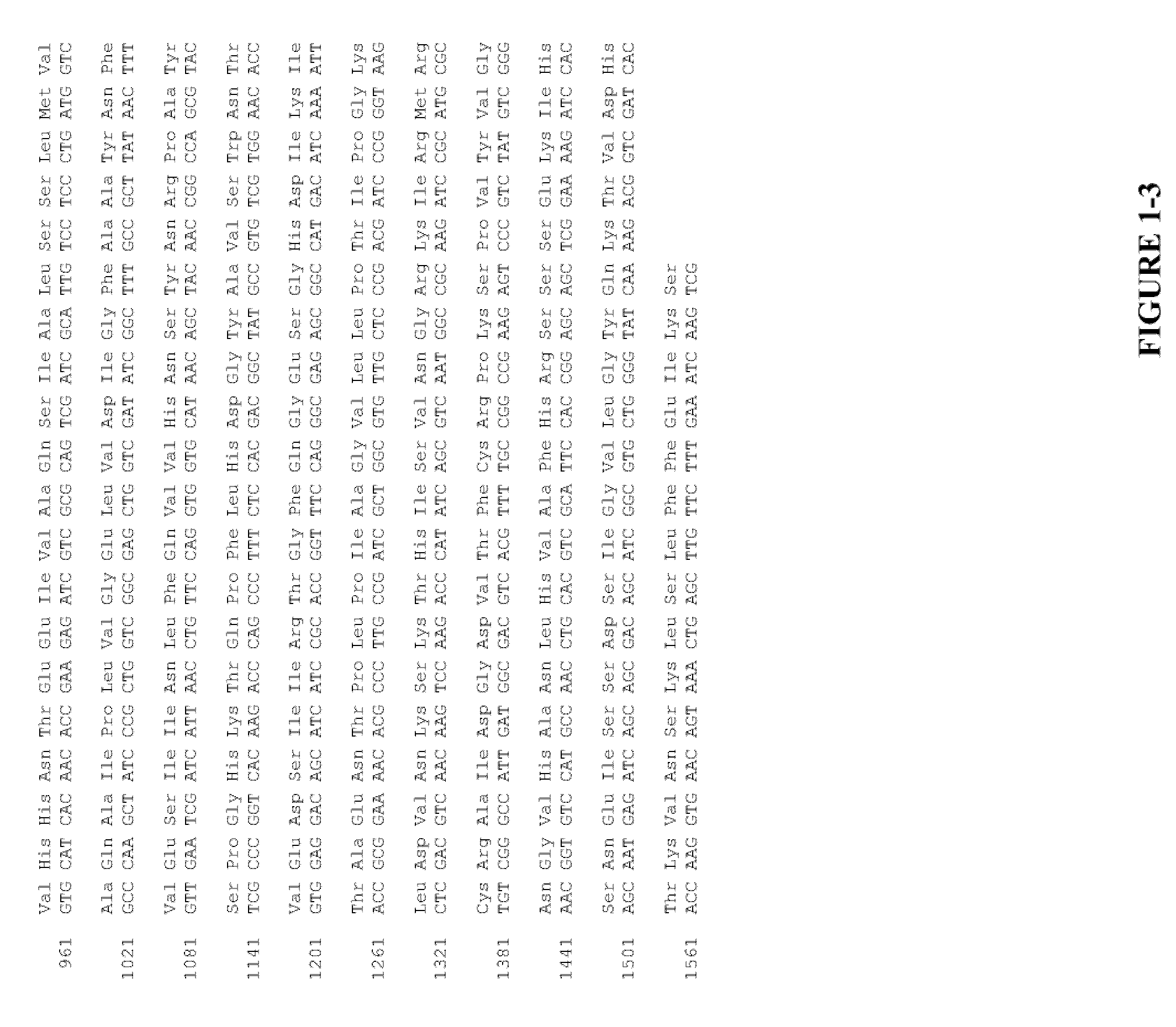Patents
Literature
158 results about "Bacterial host" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacteria and Host is a specialty section within Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, publishing rigorously peer-reviewed research that advances our knowledge on the interactions between bacterial pathogens and their host at the cellular and organism levels.
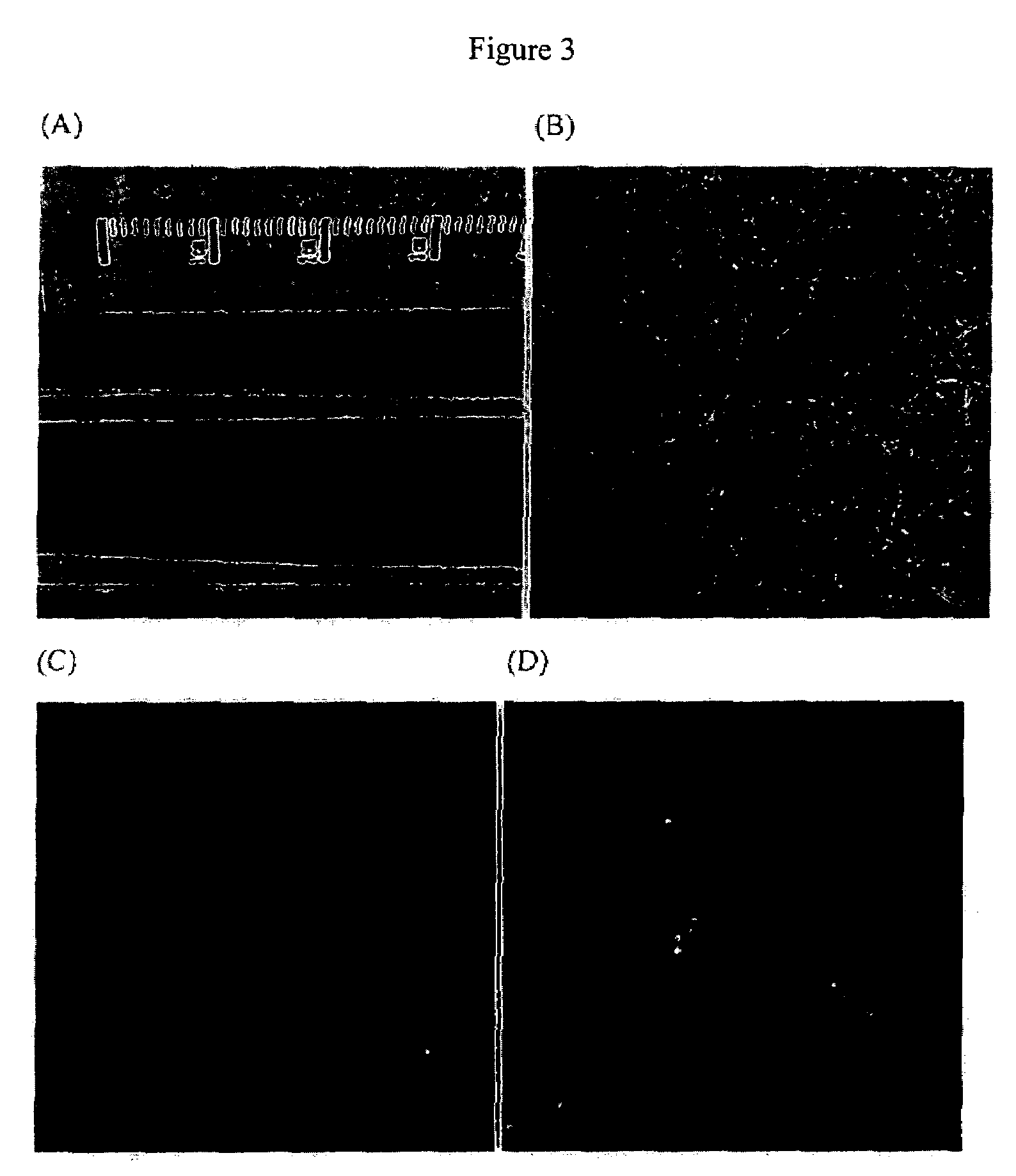
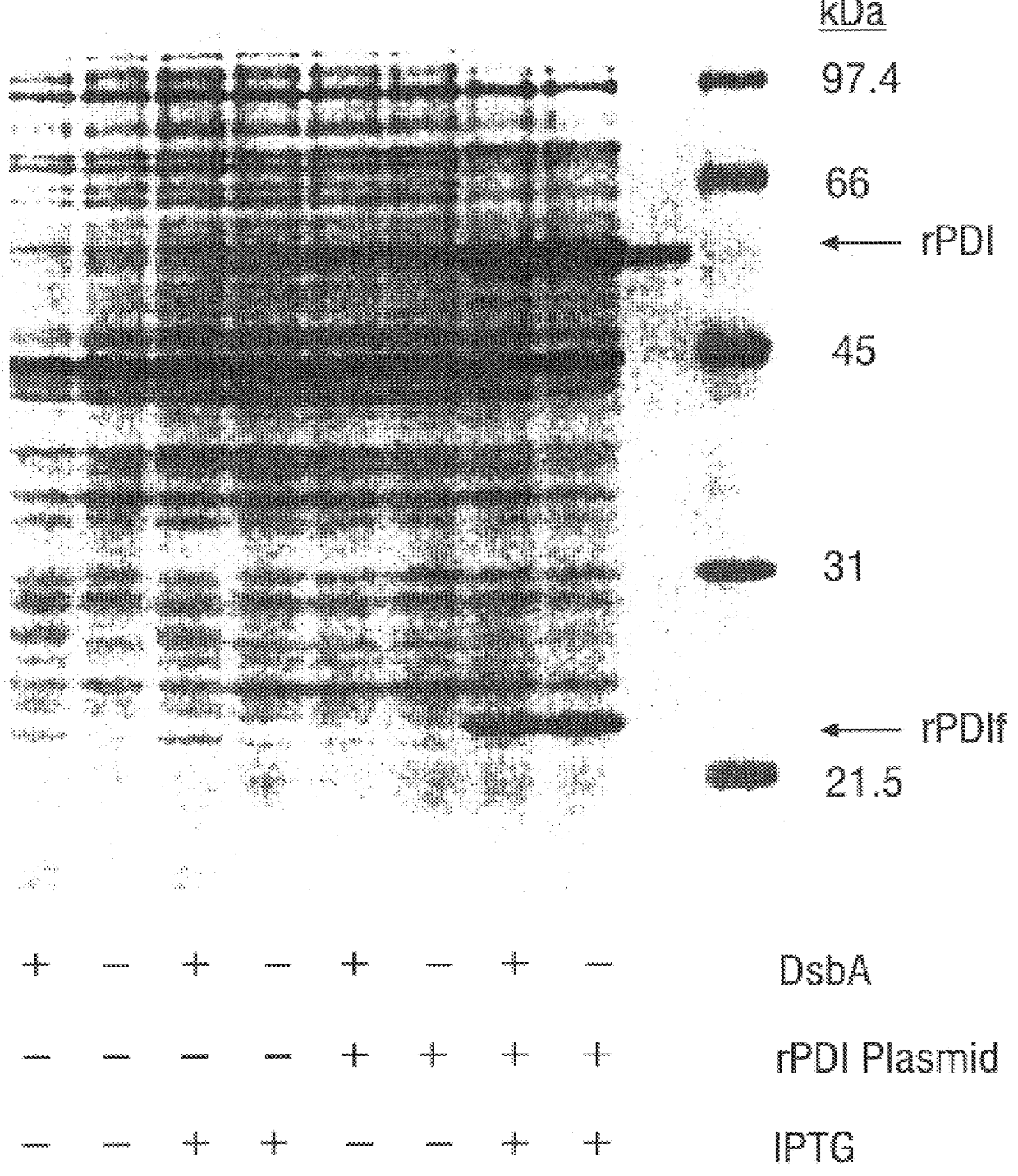
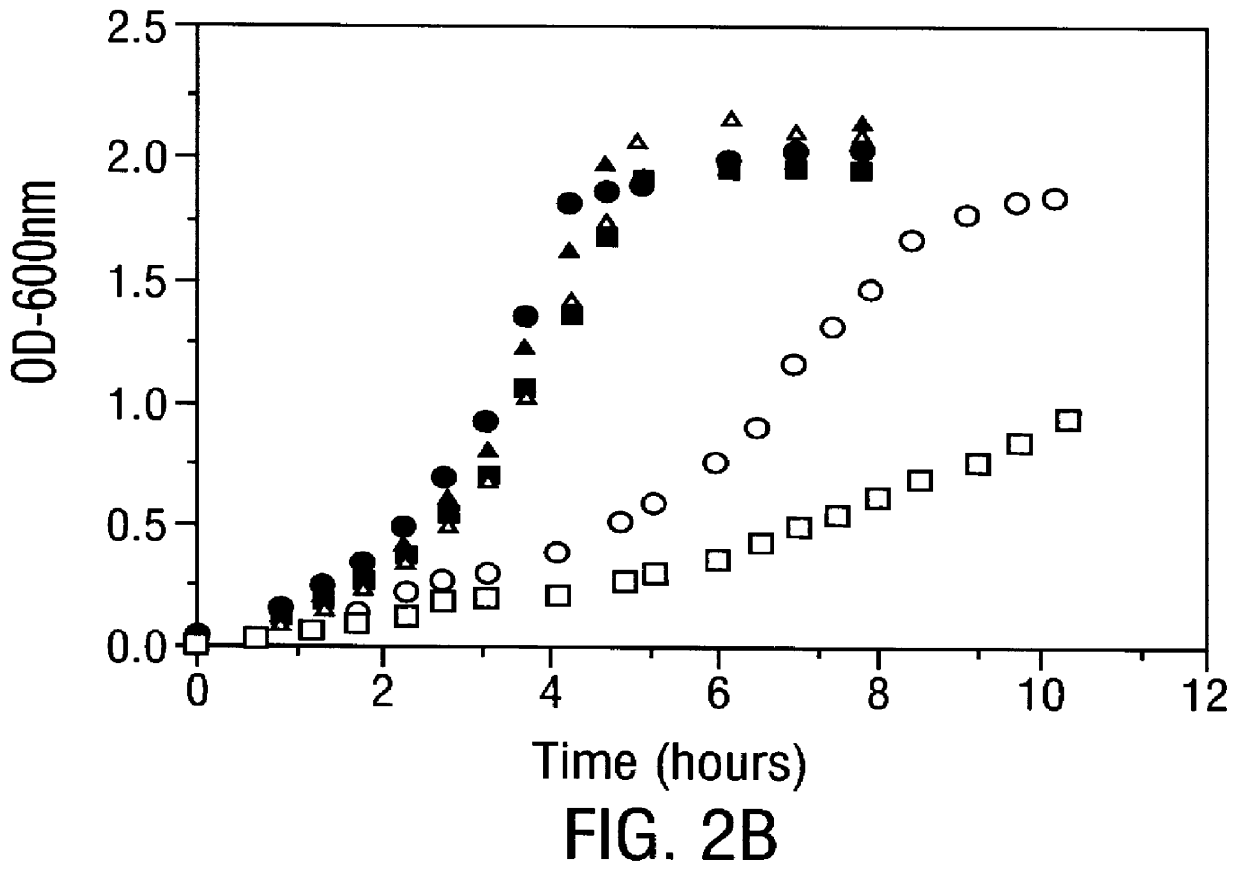
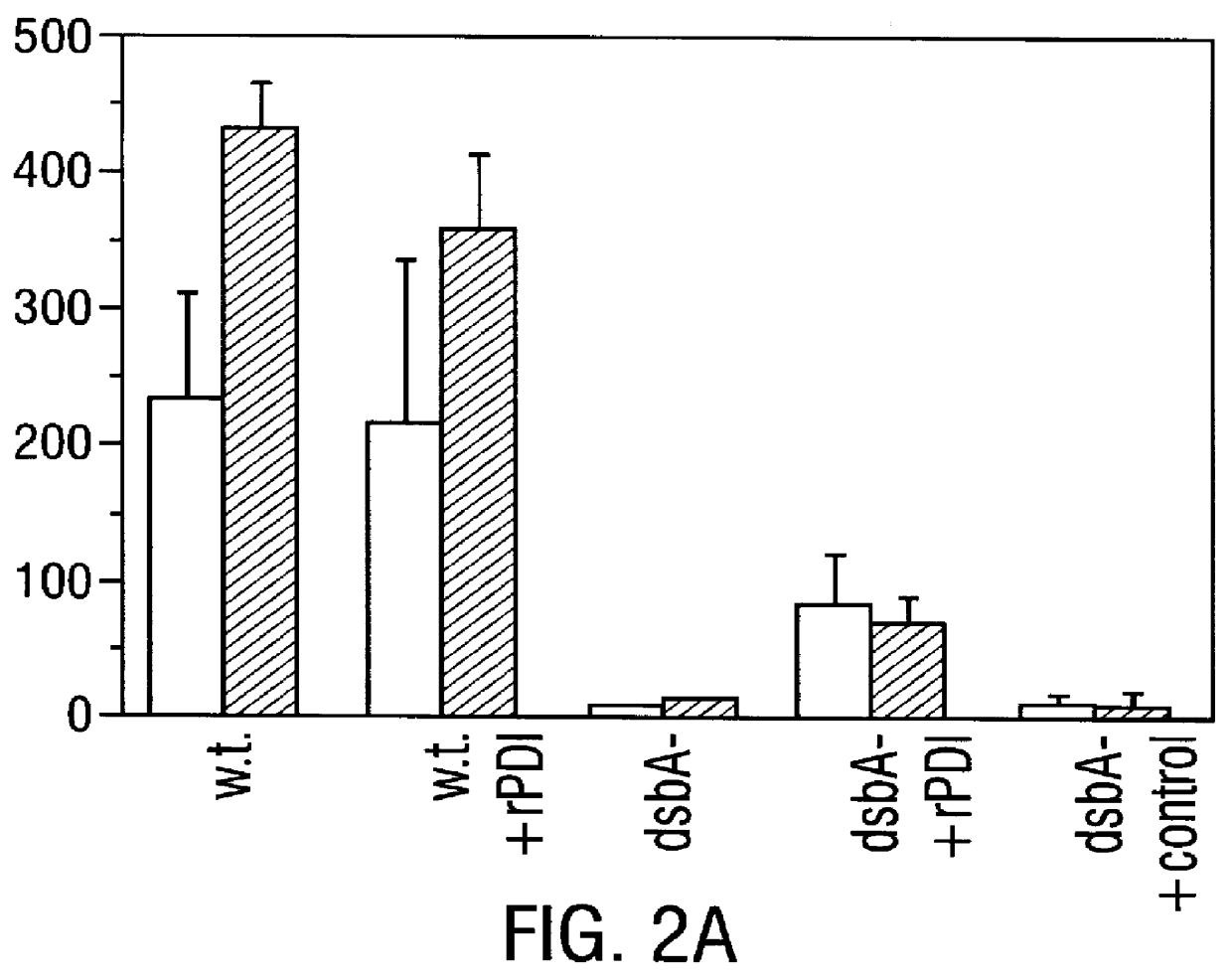
Methods for producing soluble, biologically-active disulfide-bond containing eukaryotic proteins in bacterial cells
InactiveUS6027888AEfficient productionFold preciselyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsDisulfide bondingZymogen
Disclosed are methods of producing eukaryotic disulfide bond-containing polypeptides in bacterial hosts, and compositions resulting therefrom. Co-expression of a eukaryotic foldase and a disulfide bond-containing polypeptide in a bacterial host cell is demonstrated. In particular embodiments, the methods have been used to produce mammalian pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) in soluble, biologically-active forms, which are isolatable from the bacterial periplasm. Also disclosed are expression systems, recombinant vectors, and transformed host cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
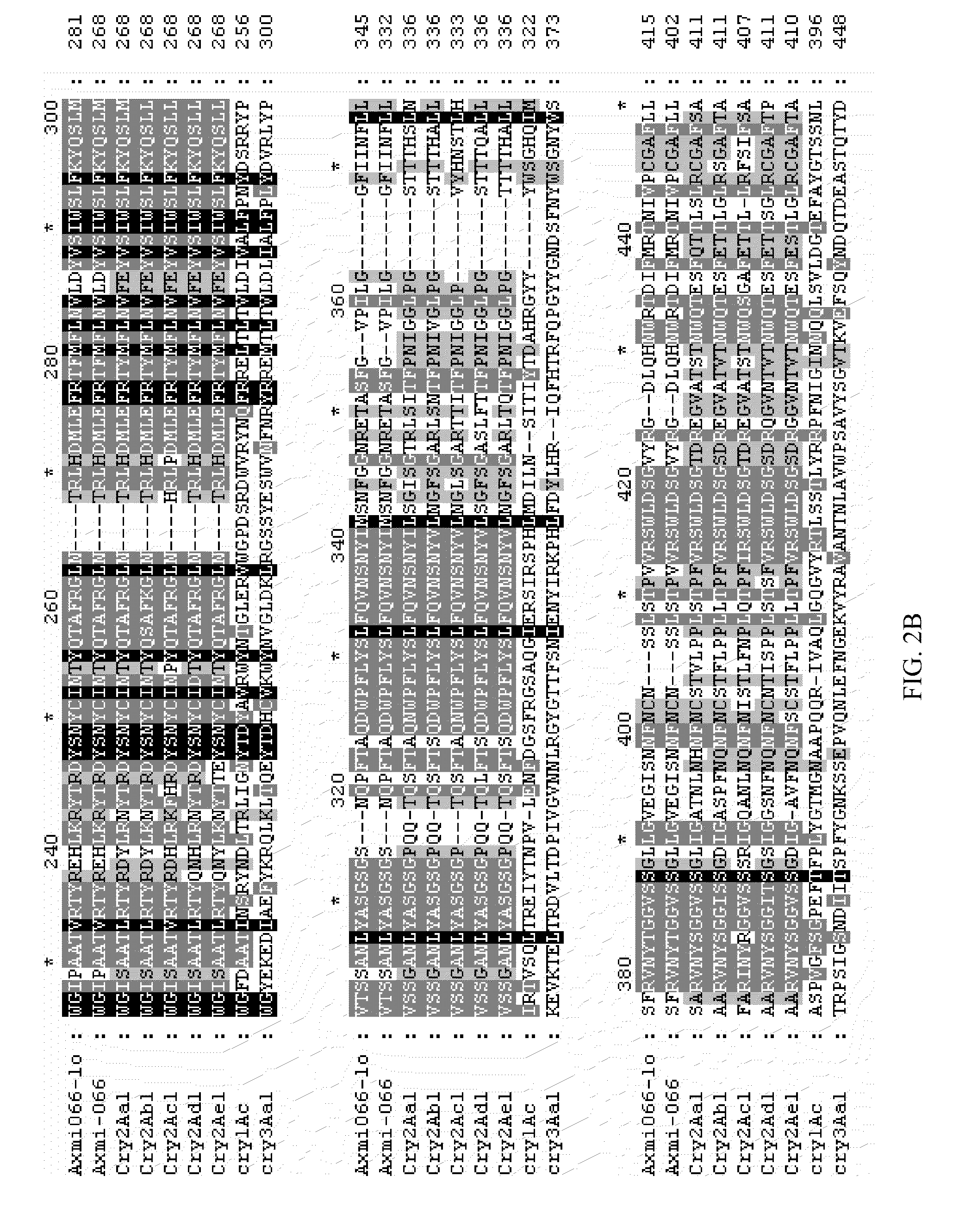
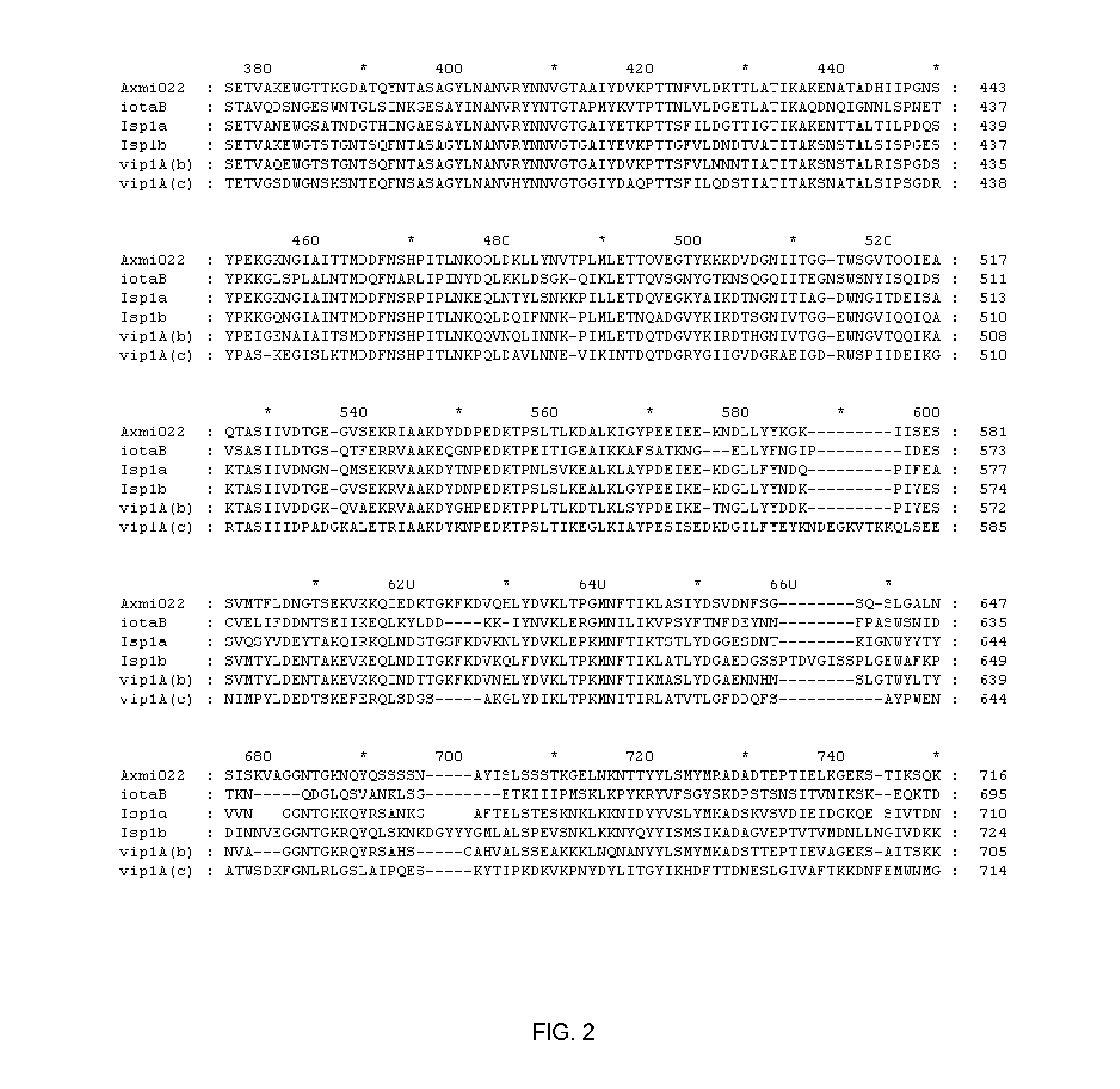
Axmi-066 and axmi-076: delta-endotoxin proteins and methods for their use
InactiveUS20090144852A1Increase productionIncrease resistanceBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:5, 2, or 10, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:4, 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, or 11, or the nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession No. B-50045, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Family of pesticidal proteins and methods for their use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37 or 61, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, or 60, or the nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession No. NRRL B-30961, B-30955, B-30956, B-30957, B-30958, B-30942, B-30939, B-30941, B-50047, B-50047, B-30959, B-30960, B-30943, B-50048, or B-50048, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
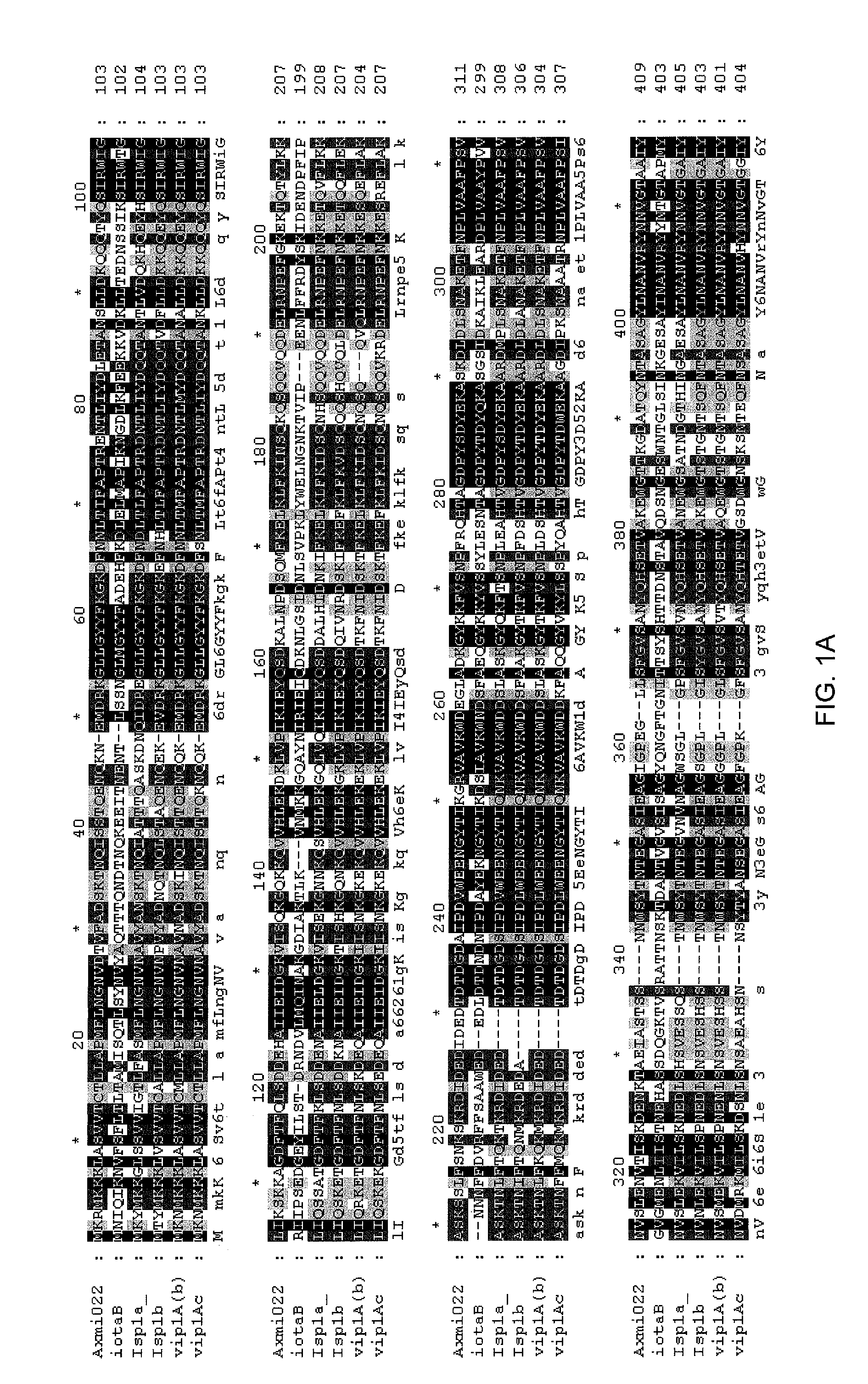
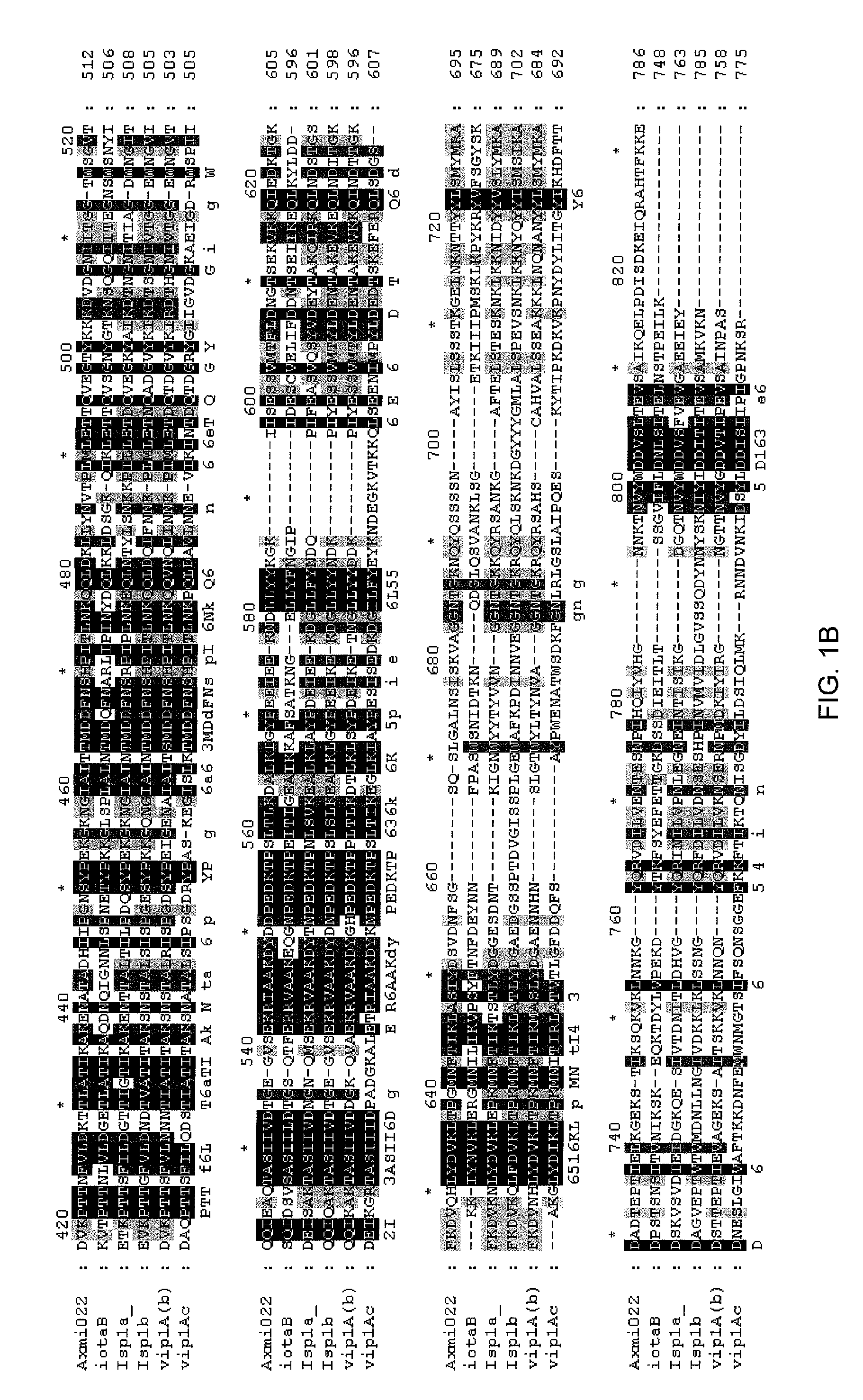
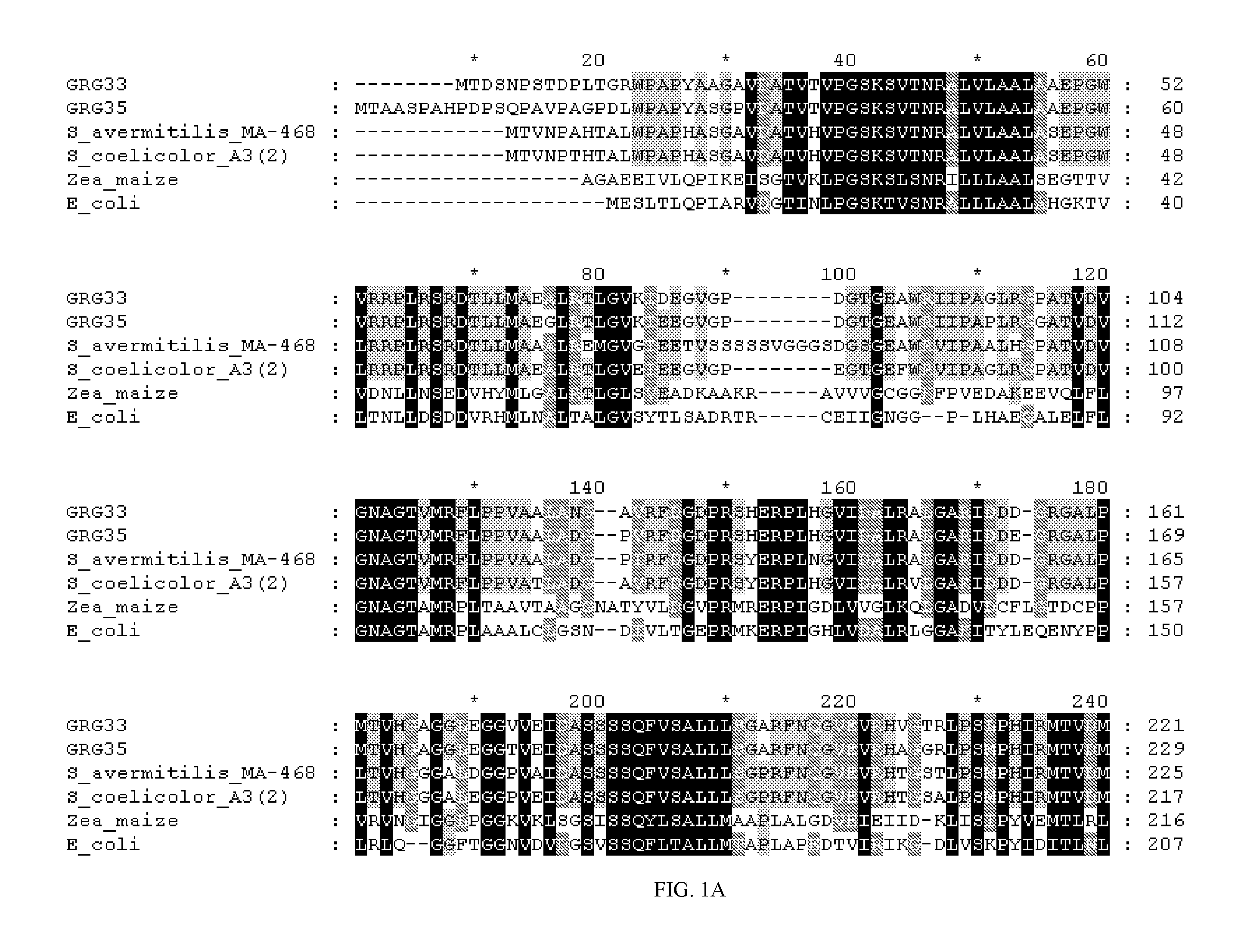
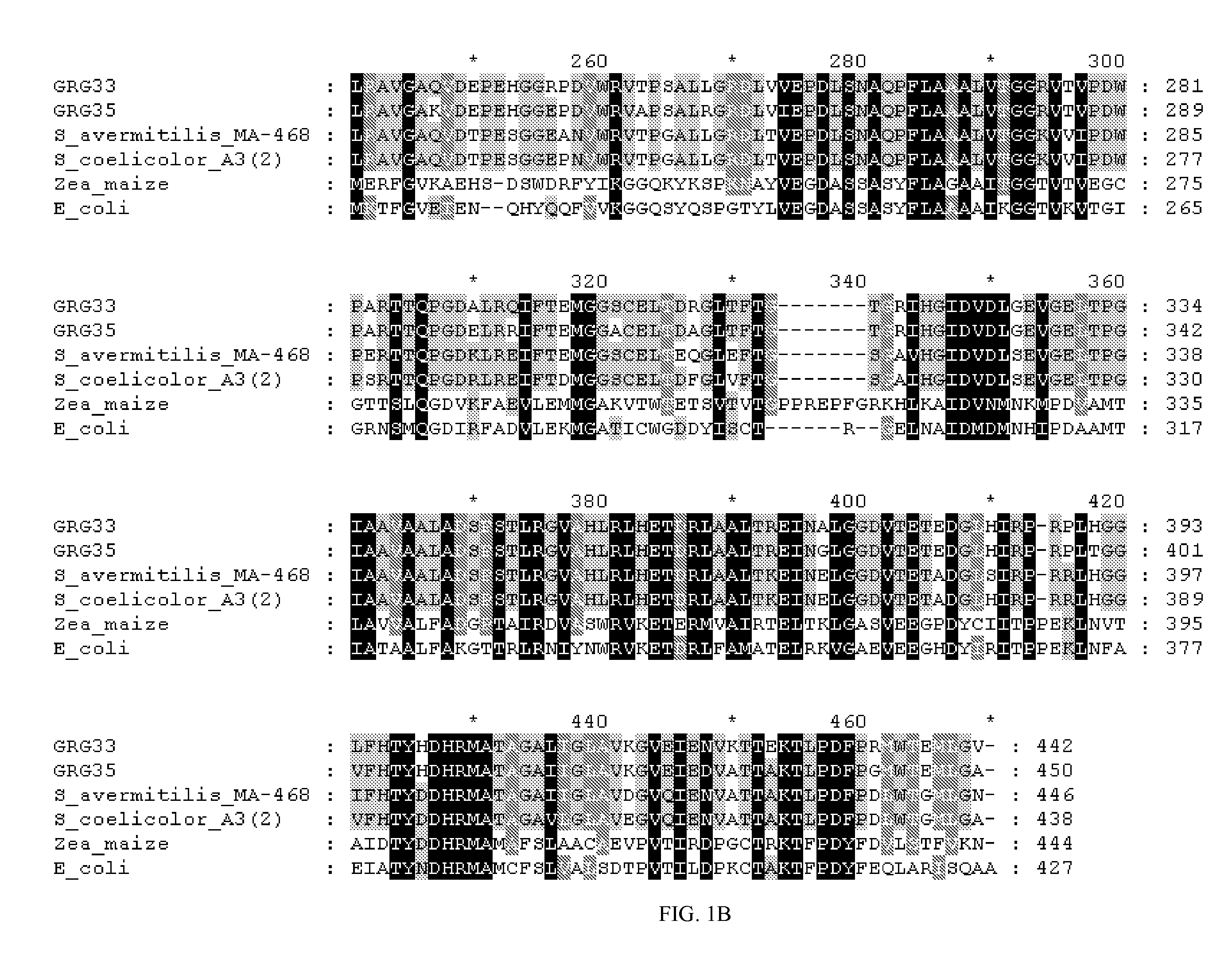
Grg33, grg35, grg36, grg37, grg38, grg39 and grg50: novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, or 23, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 16, 19, or 22, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30932, B-30933, B-30934, B-30945, B-30946, B-30947, or B-30948, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
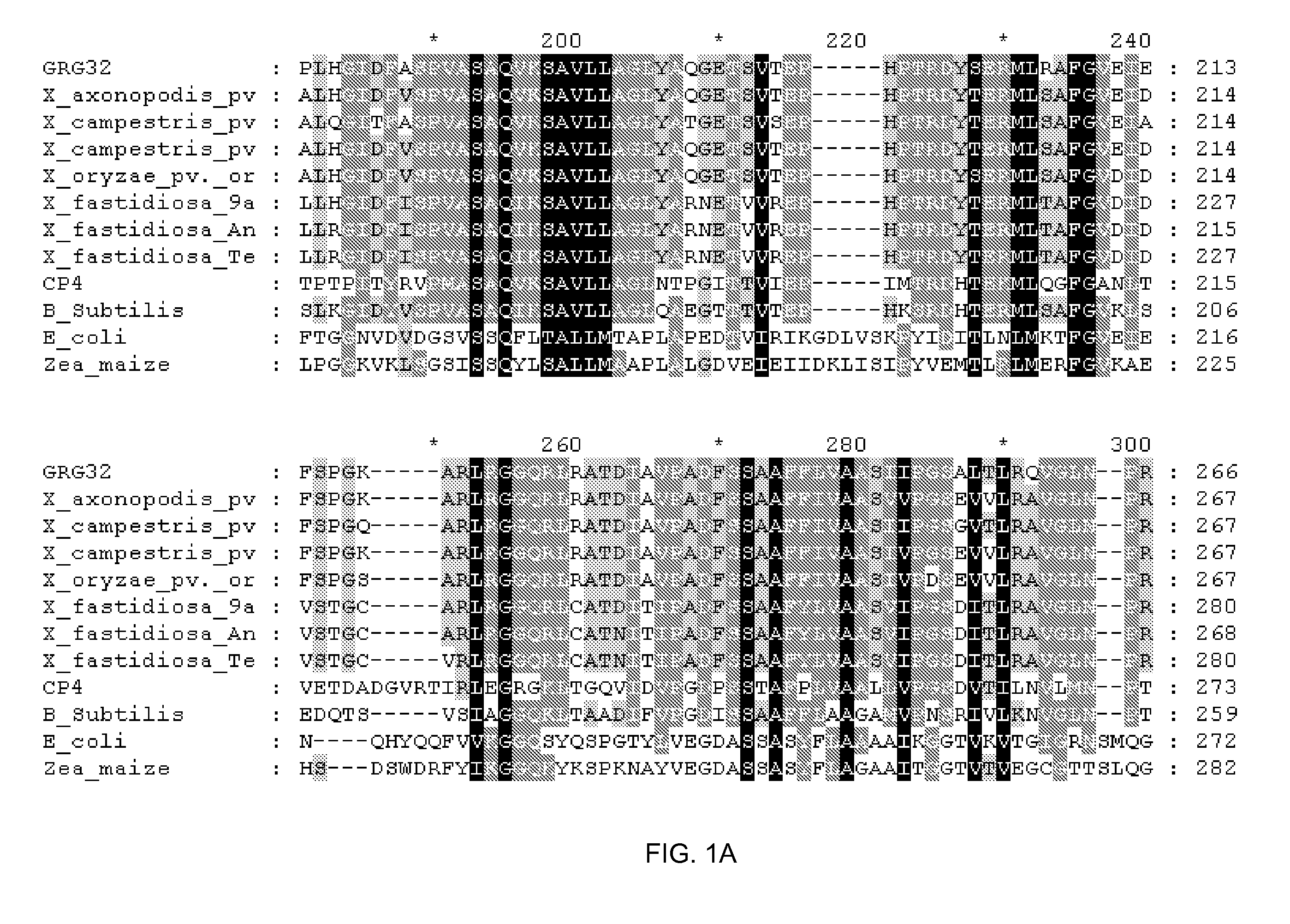
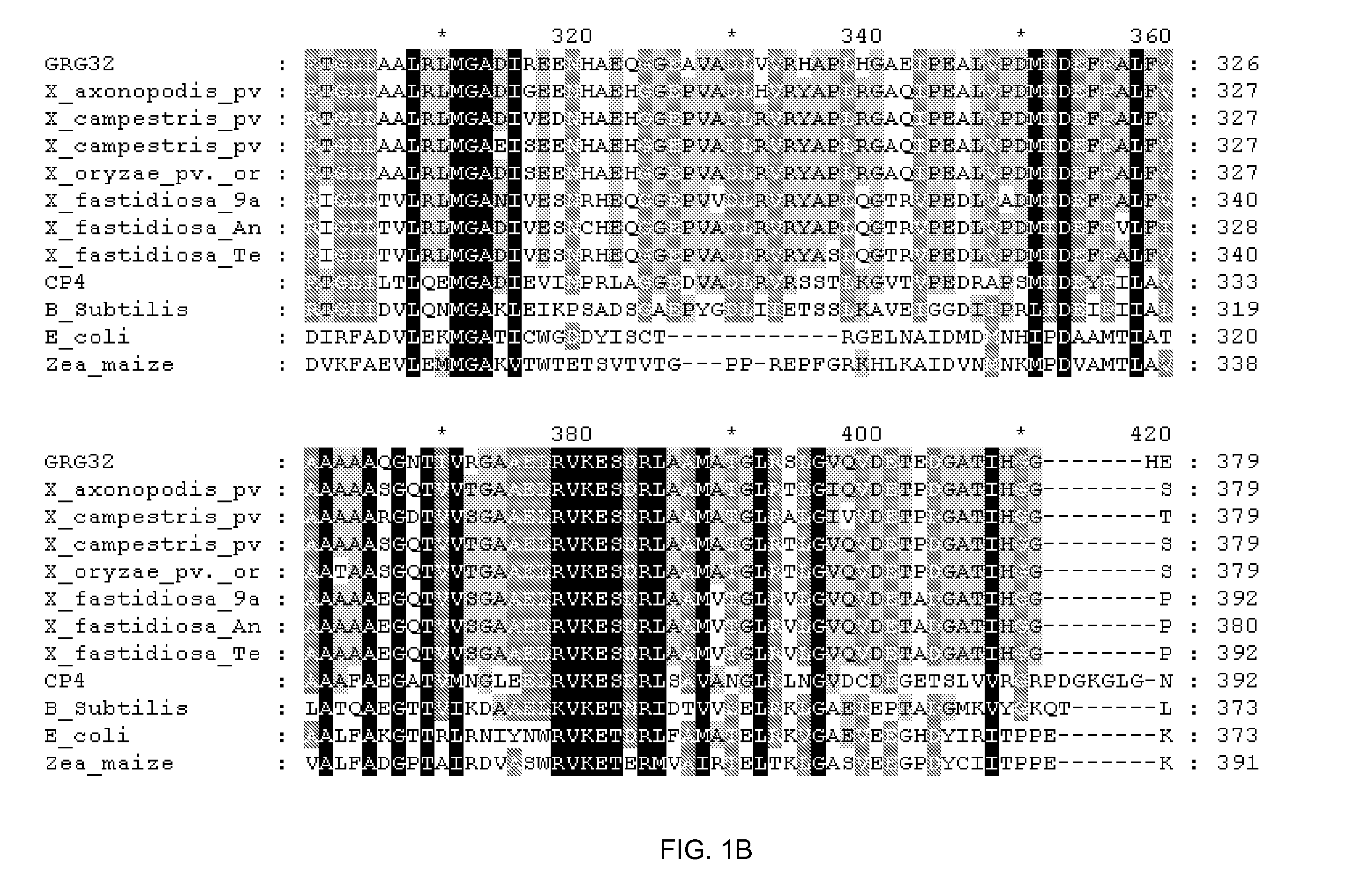
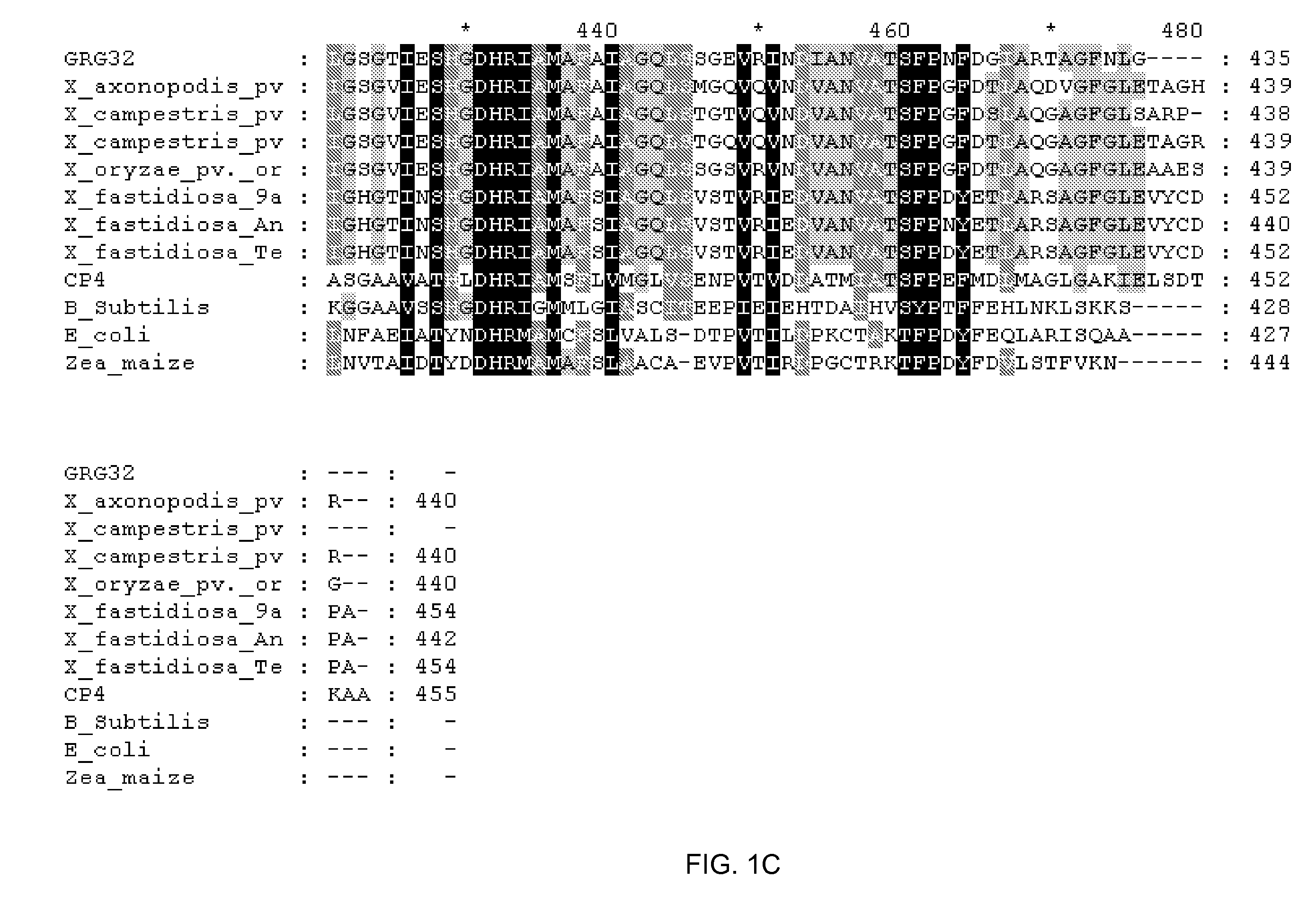
Grg32: a novel epsp synthase gene conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 or 14, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30931, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Family of pesticidal proteins and methods for their use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37 or 61, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, or 60, or the nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession No. NRRL B-30961, B-30955, B-30956, B-30957, B-30958, B-30942, B-30939, B-30941, B-50047, B-30959, B-30960, B-30943, or B-50048, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Methods for expression and purification of recombinant human growth hormone
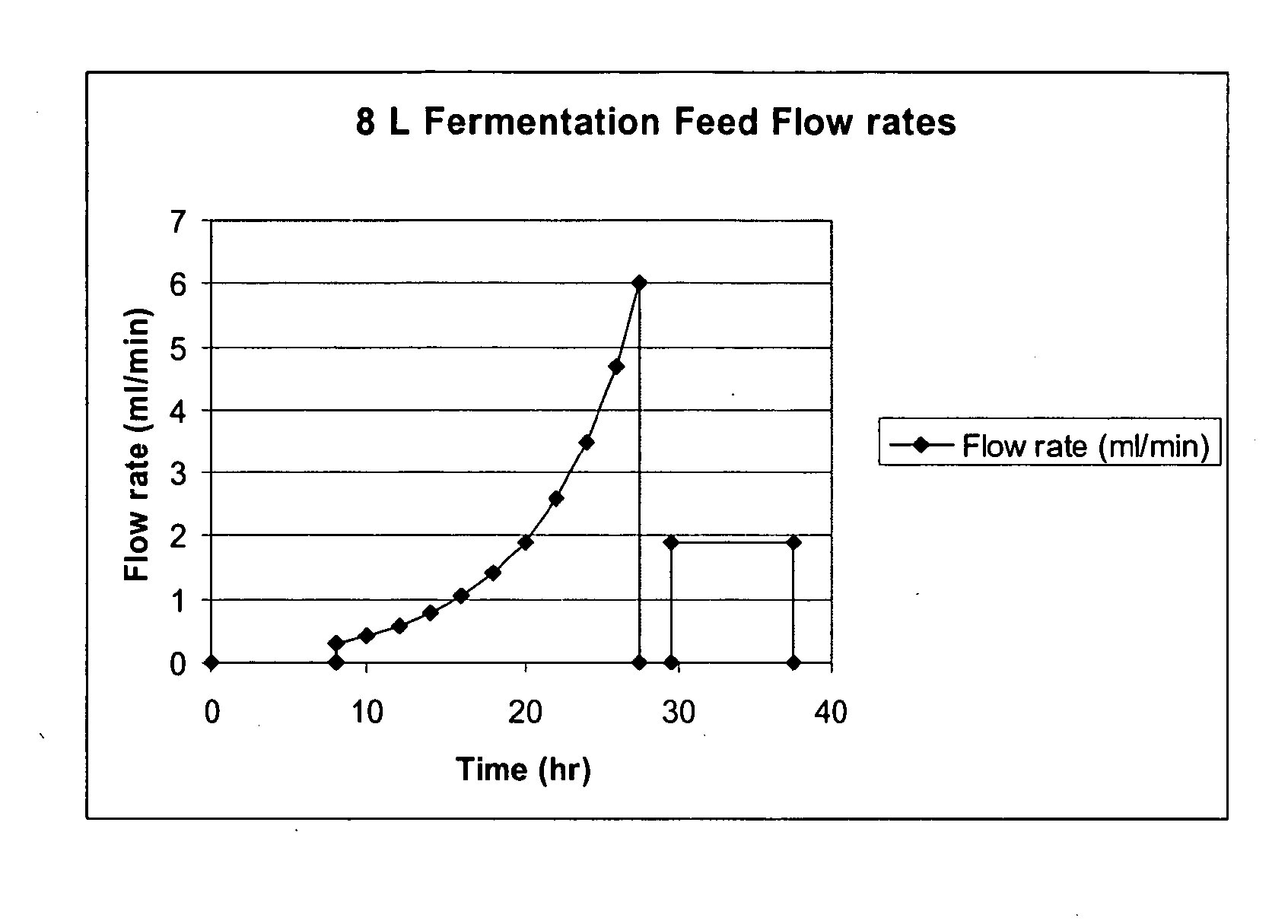
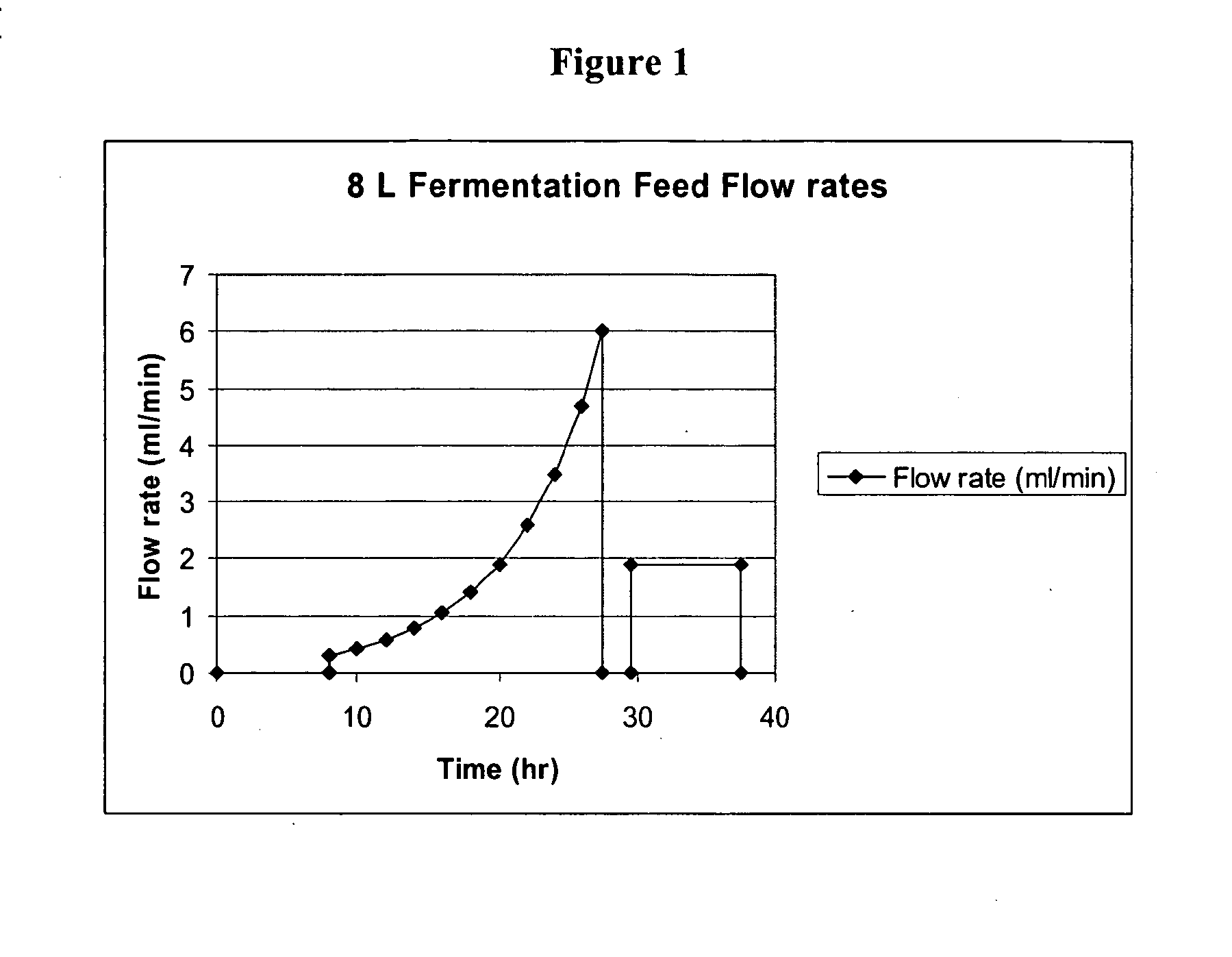
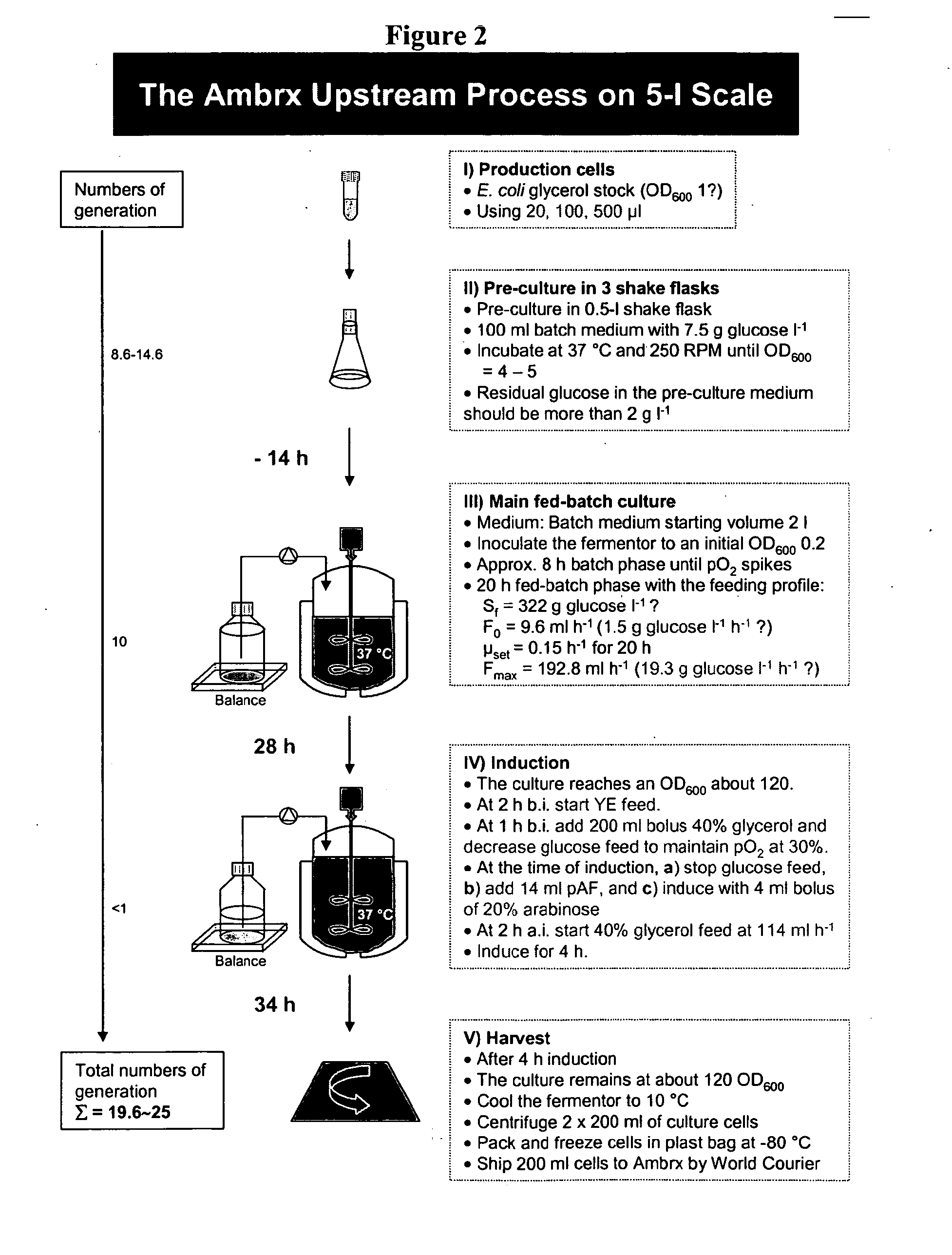
The present invention relates generally to the production, purification, and isolation of human growth hormone (hGH). More particularly, the invention relates to the production, purification, and isolation of substantially purified hGH from recombinant host cells or culture medium including, for example, yeast, insect, mammalian and bacterial host cells. The process of the present invention is also useful for purification of hGH linked to polymers or other molecules.
Owner:AMBRX
Viral fibers
InactiveUS20050180992A1Improve the level ofHigh surface energyMicroorganismsNanomedicineFiberLiquid crystalline
Long rod shaped M13 viruses were used to fabricate one dimensional (1D) micro- and nanosized diameter fibers by mimic the spinning process of the silk spider. Liquid crystalline virus suspensions were extruded through the micrometer diameter capillary tubes in cross-linking solution (glutaraldehyde). Resulting fibers were tens of micrometers in diameter depending on the inner diameter of the capillary tip. AFM image verified that molecular long axis of the virus fibers were parallel to the fiber long axis. Although aqueous M13 virus suspension could not be spun by electrospinning, M13 viruses suspended in 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol were spun into fibers. After blending with highly water soluble polymer, polyvinyl 2-pyrolidone (PVP), M13 viruses was spun into continuous uniform virus blended PVP (virus-PVP) fibers. Resulting virus-PVP electrospun fibers showed intact infecting ability to bacterial hosts after suspending in the buffer solution.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
High level expression of recombinant toxin proteins
ActiveUS20110287443A1High yieldQuality improvementAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesBacteroidesHigh level expression
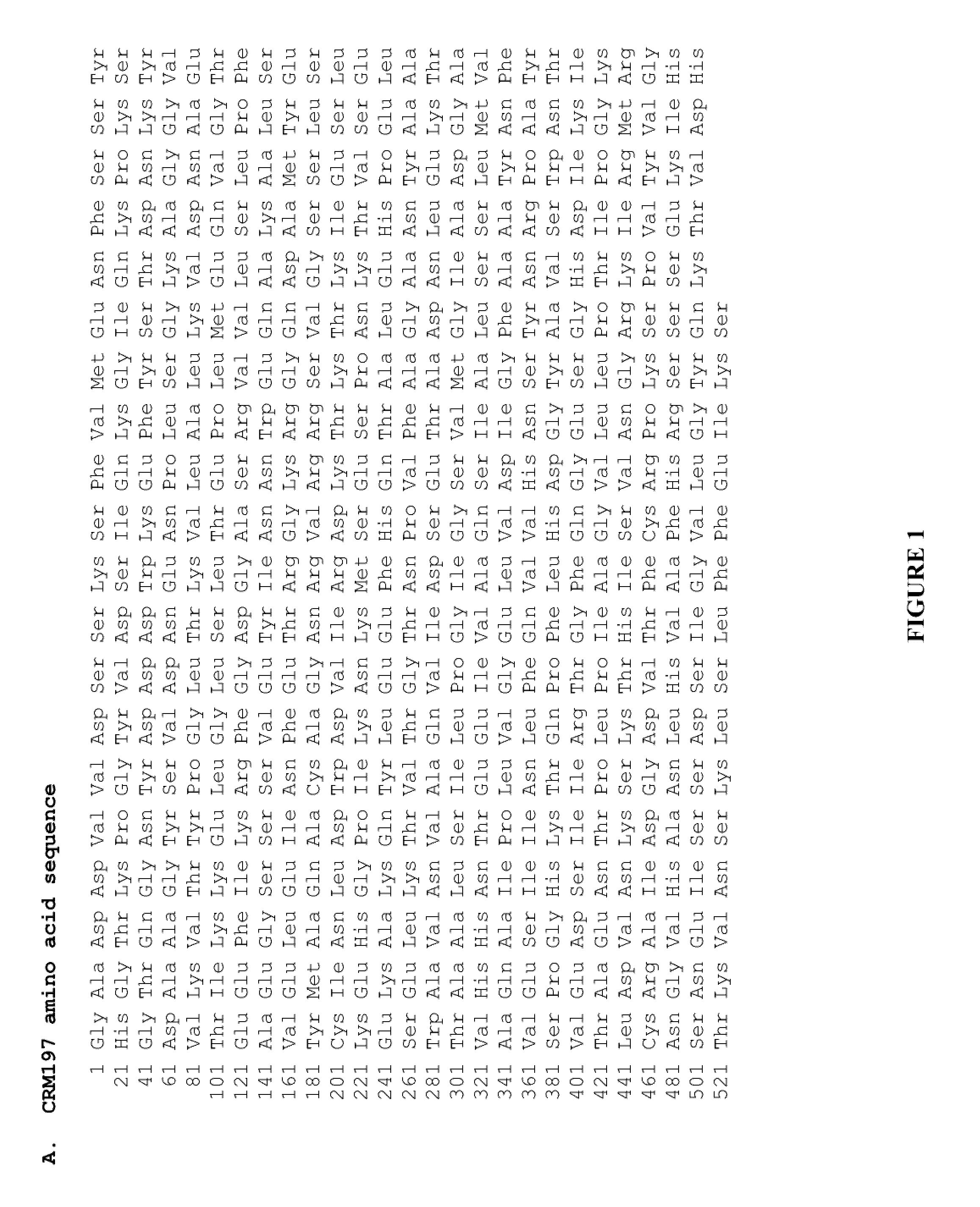
The present invention relates to the field of recombinant toxin protein production in bacterial hosts. In particular, the present invention relates to production processes for obtaining high levels of a recombinant CRM197, Diphtheria Toxin, Pertussis Toxin, Tetanus Toxoid Fragment C, Cholera Toxin B, Cholera holotoxin, and Pseudomonas Exotoxin A, from a bacterial host.
Owner:PFENEX
Folded recombinant catalytic fragments of multidomain serine proteases, preparation and uses thereof
Owner:TARGETEX
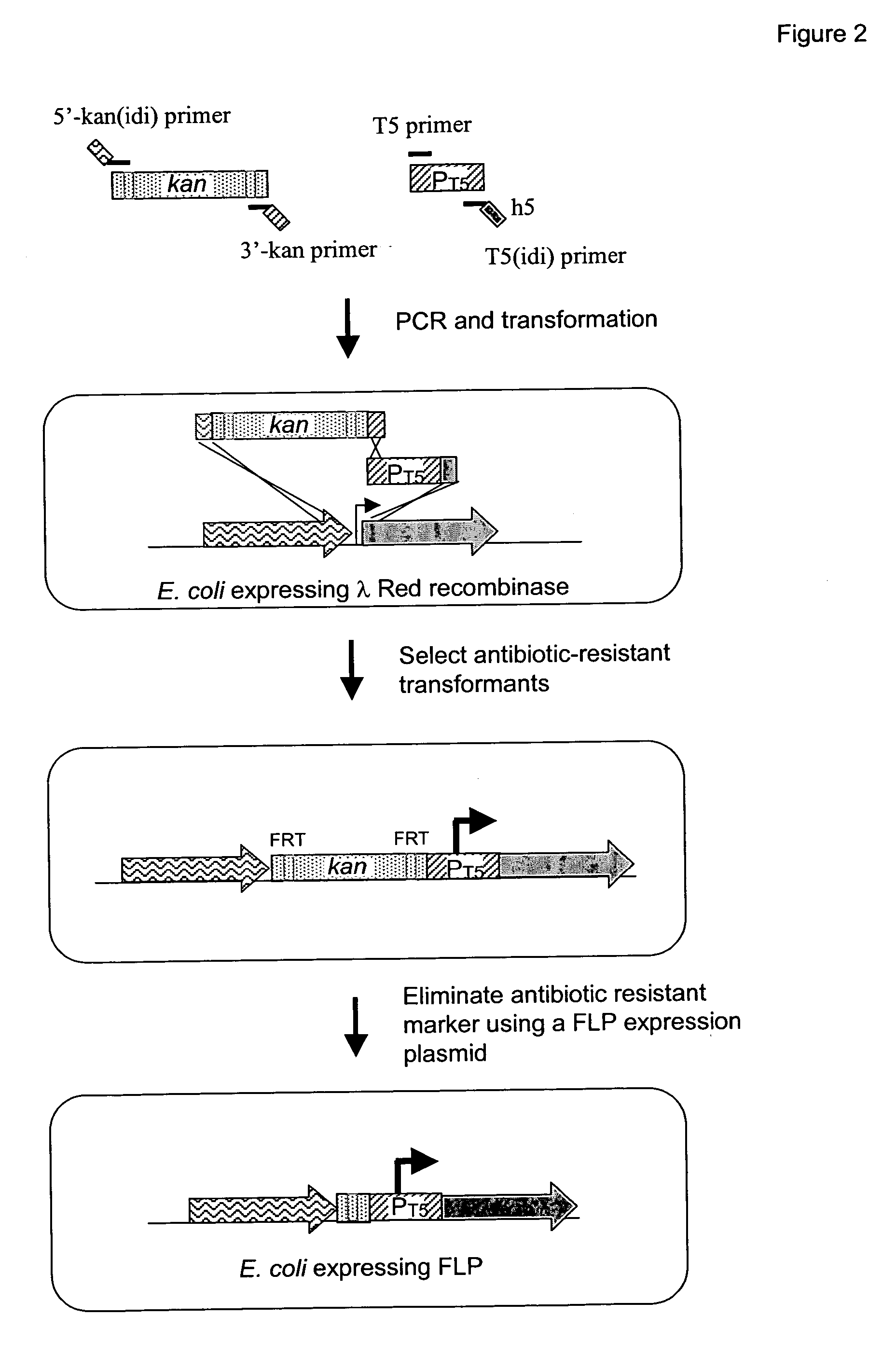
Method of creating a library of bacterial clones with varying levels of gene expression
InactiveUS20060014146A1Reduced expression levelHigh expressionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteRibosomal binding site
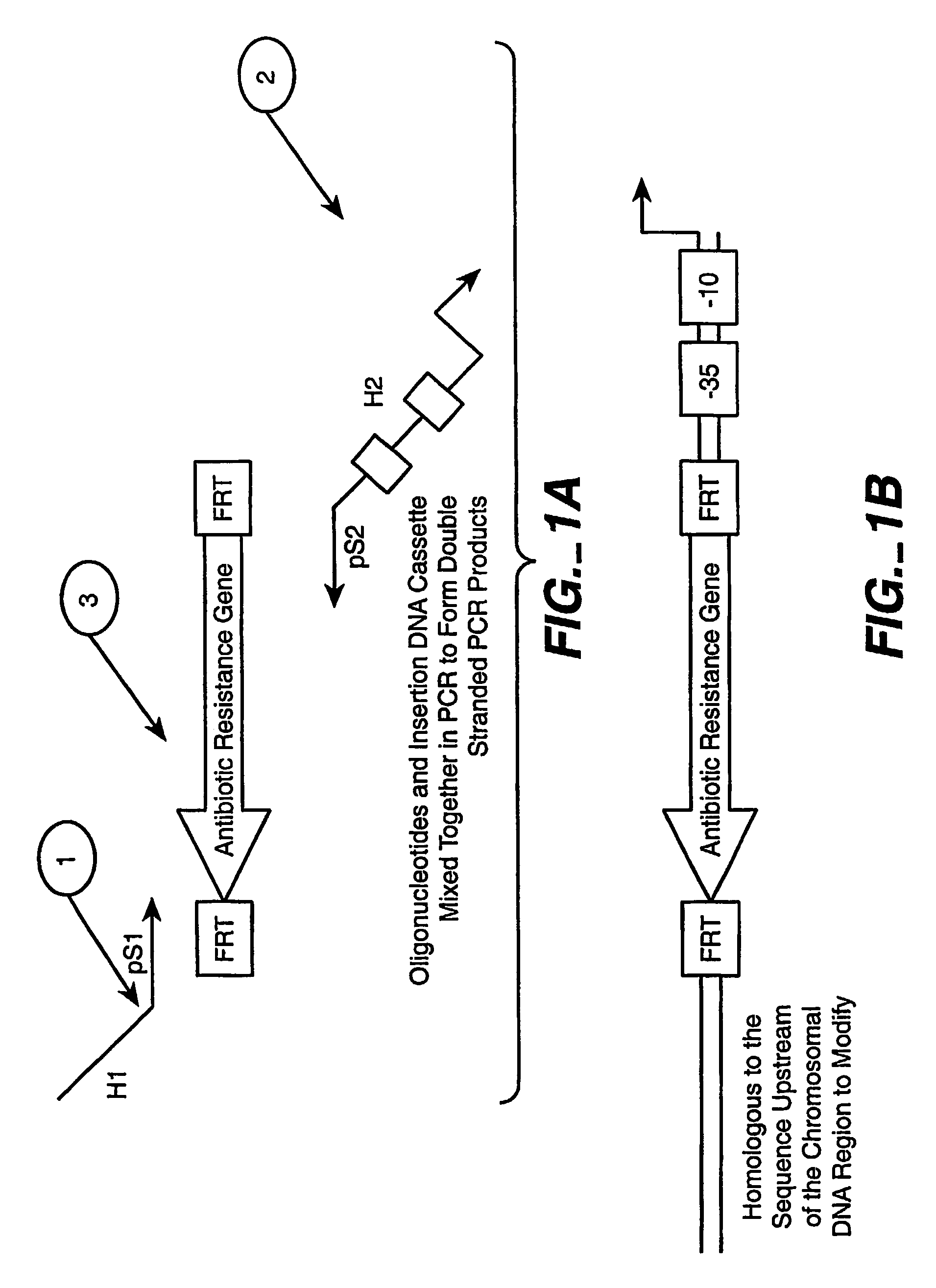
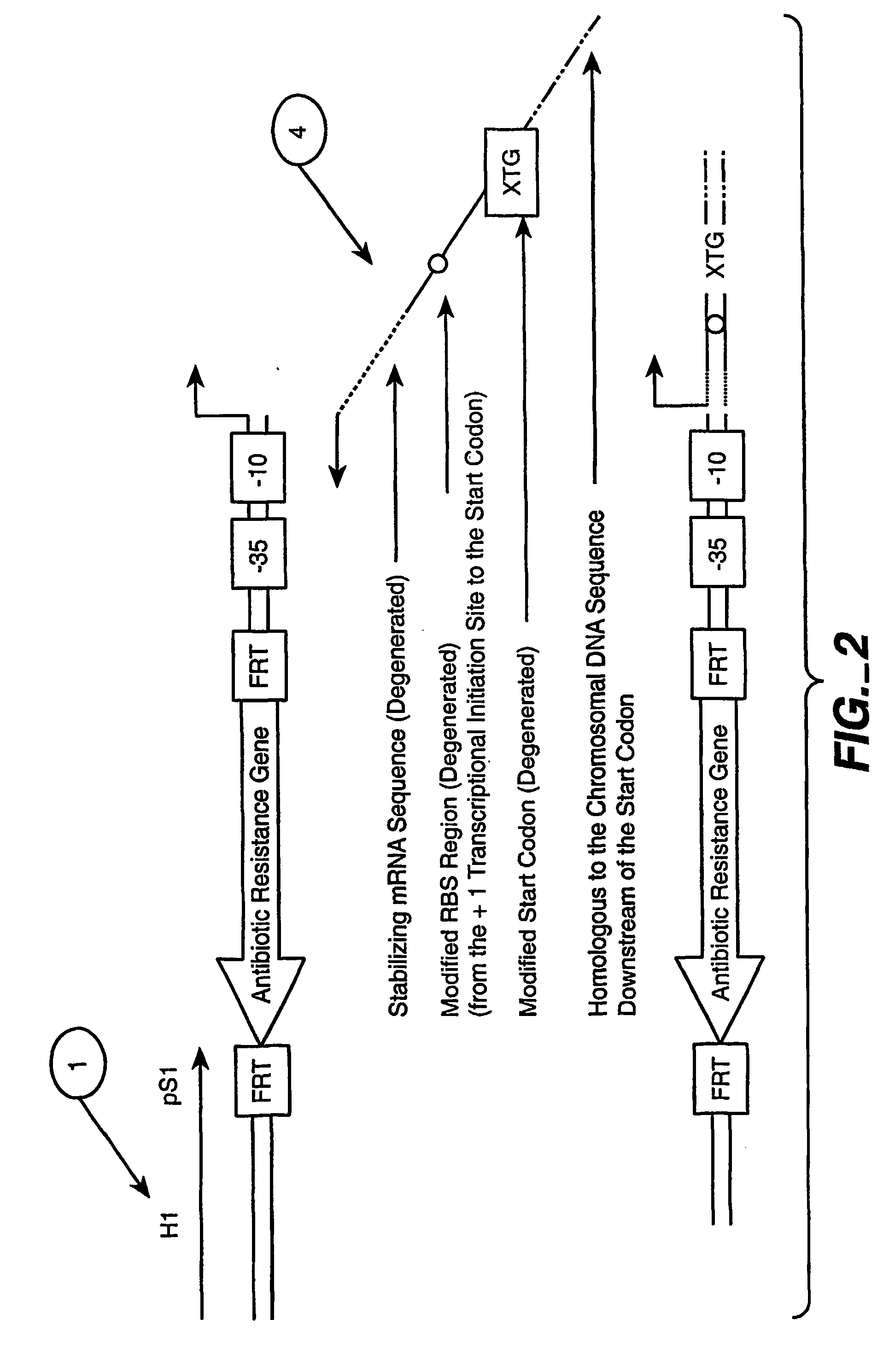
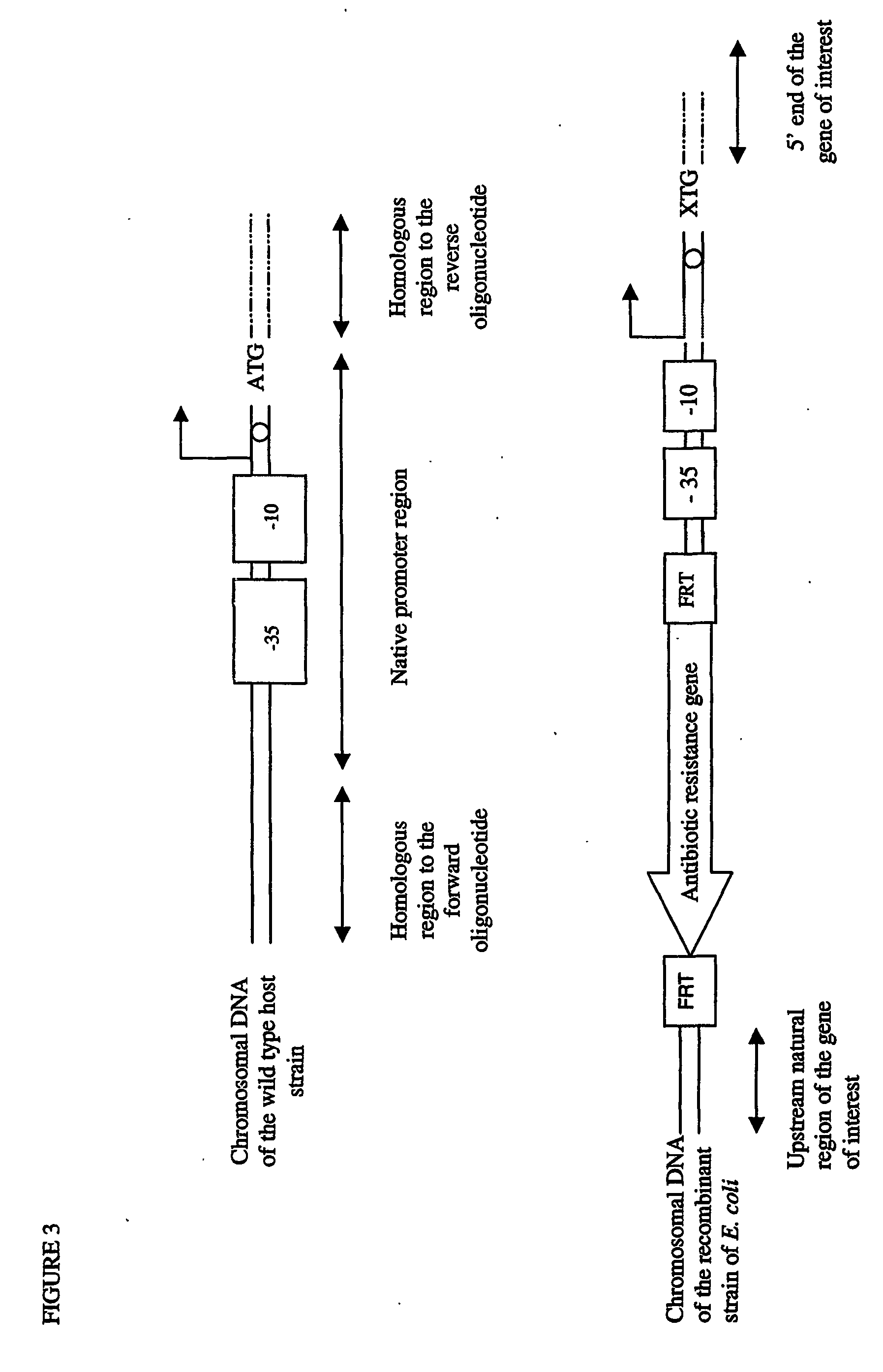
The present invention relates to a method of creating DNA libraries that include an artificial promoter library and / or a modified ribosome binding site library and transforming bacterial host cells with the library to obtain a population of bacterial clones having a range of expression levels for a chromosomal gene of interest.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Methods for Expression and Purification of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone
InactiveUS20080050777A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatotropic hormoneHuman growth hormone
The present invention relates generally to the production, purification, and isolation of human growth hormone (hGH). More particularly, the invention relates to the production, purification, and isolation of substantially purified hGH from recombinant host cells or culture medium including, for example, yeast, insect, mammalian and bacterial host cells. The process of the present invention is also useful for purification of hGH linked to polymers or other molecules.
Owner:AMBRX
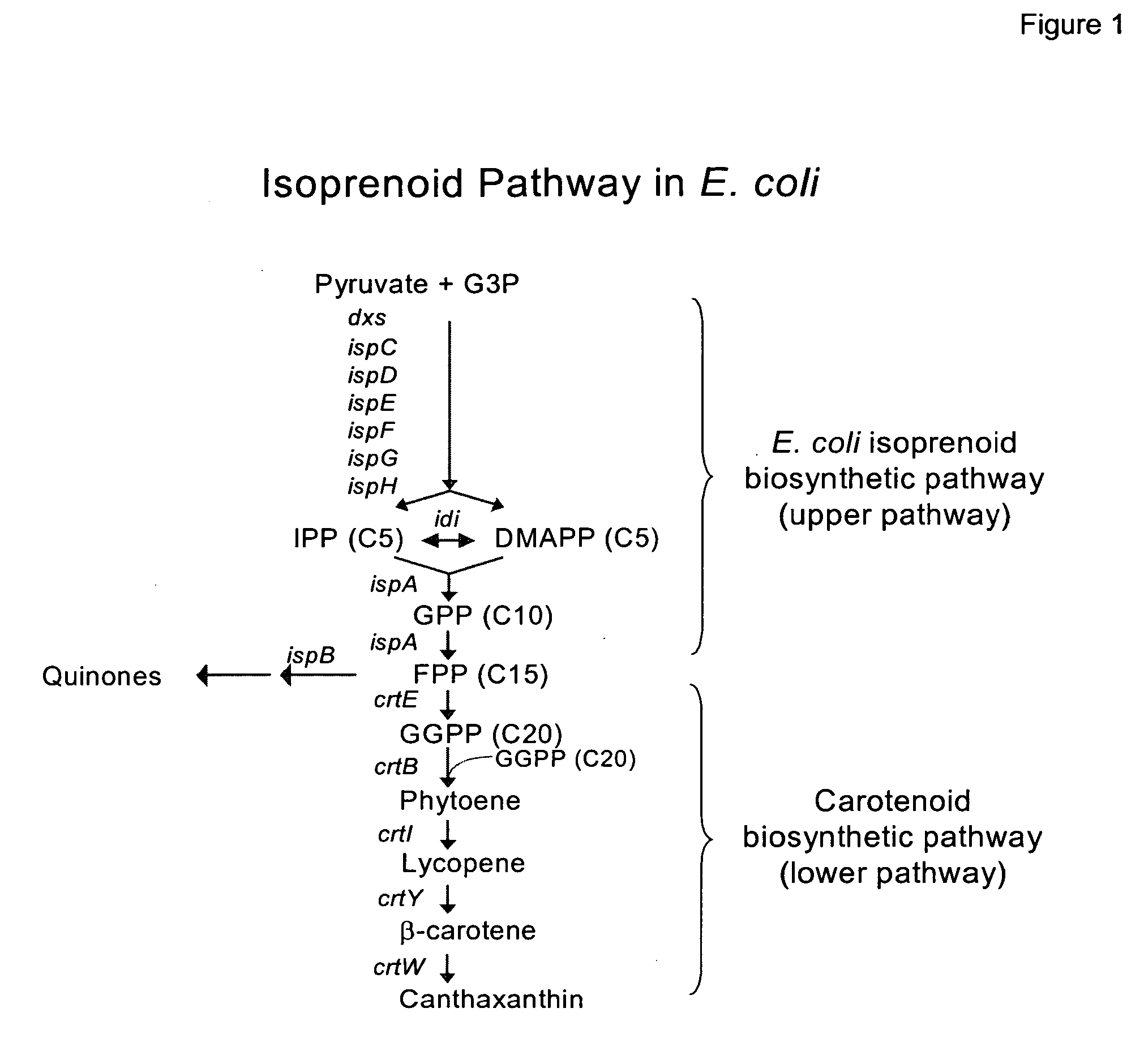
Method to increase hydrophobic compound titer in a recombinant microorganism
InactiveUS20070026484A1Improve compoundImprove the level ofBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismBiotechnology
Expression of at least one plant oleosin gene in a microbial cell engineered to produce hydrophobic / lipophilic compounds significantly increases the overall titer of the compound. The hydrophobic nature of the oleosin core is believed to increase the microbial host cell's internal storage capacity for any hydrophobic / lipophilic compound. The method is exemplified using a bacterial host cell engineered to produce significant amount of various carotenoids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Viral fibers
Long rod shaped M13 viruses were used to fabricate one dimensional (1D) micro- and nanosized diameter fibers by mimic the spinning process of the silk spider. Liquid crystalline virus suspensions were extruded through the micrometer diameter capillary tubes in cross-linking solution (glutaraldehyde). Resulting fibers were tens of micrometers in diameter depending on the inner diameter of the capillary tip. AFM image verified that molecular long axis of the virus fibers were parallel to the fiber long axis. Although aqueous M13 virus suspension could not be spun by electrospinning, M13 viruses suspended in 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol were spun into fibers. After blending with highly water soluble polymer, polyvinyl 2-pyrolidone (PVP), M13 viruses was spun into continuous uniform virus blended PVP (virus-PVP) fibers. Resulting virus-PVP electrospun fibers showed intact infecting ability to bacterial hosts after suspending in the buffer solution.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
High level expression of recombinant toxin proteins
The present invention relates to the field of recombinant toxin protein production in bacterial hosts. In particular, the present invention relates to production processes for obtaining high levels of a recombinant CRM197, Diphtheria Toxin, Pertussis Toxin, Tetanus Toxoid Fragment C, Cholera Toxin B, Cholera holotoxin, and Pseudomonas Exotoxin A, from a bacterial host.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Optimized bacterial host strains of methylomonas sp. 16a
InactiveUS20050124033A1Easy to useIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMethylomonas albusMethanotrophic bacterium
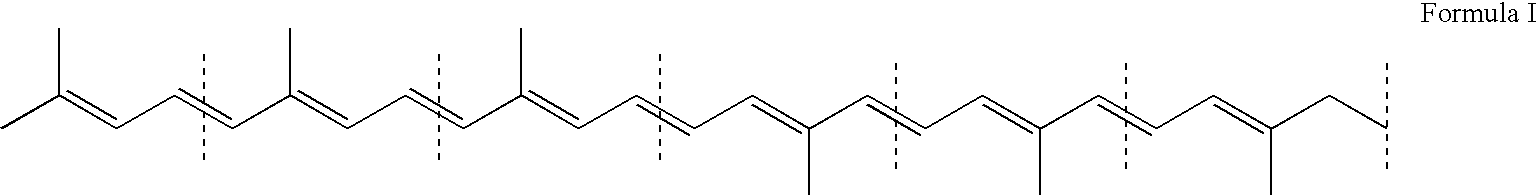
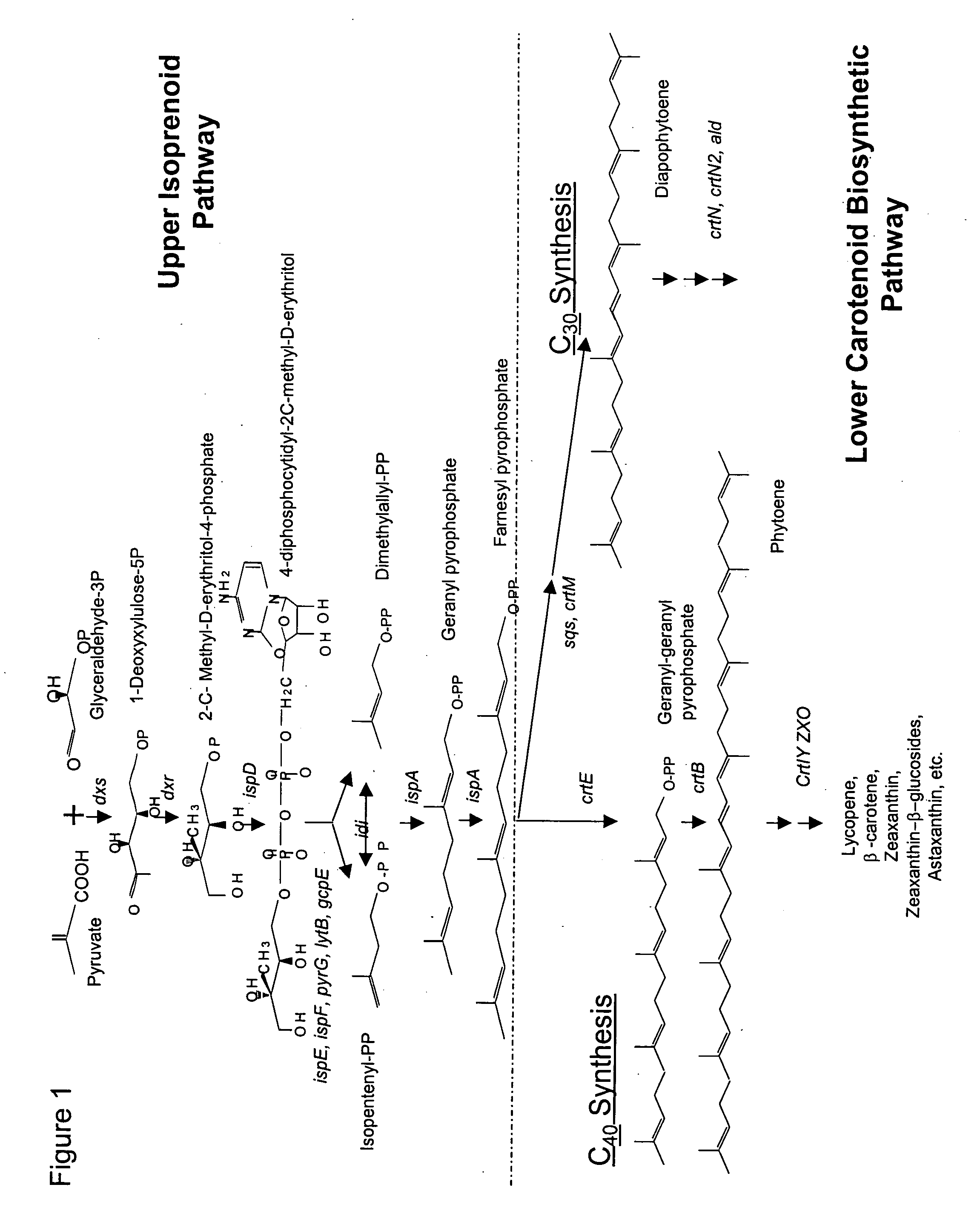
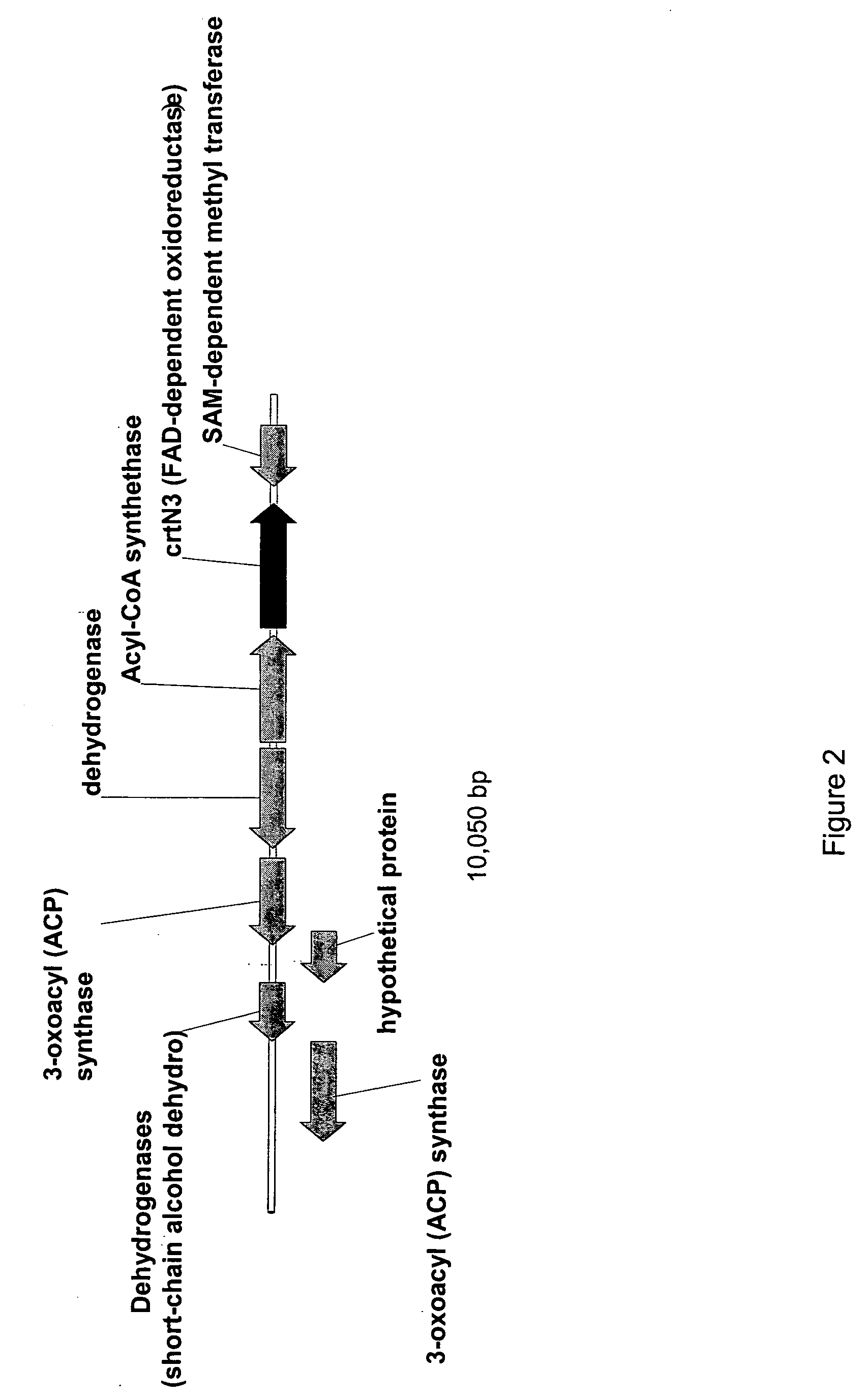
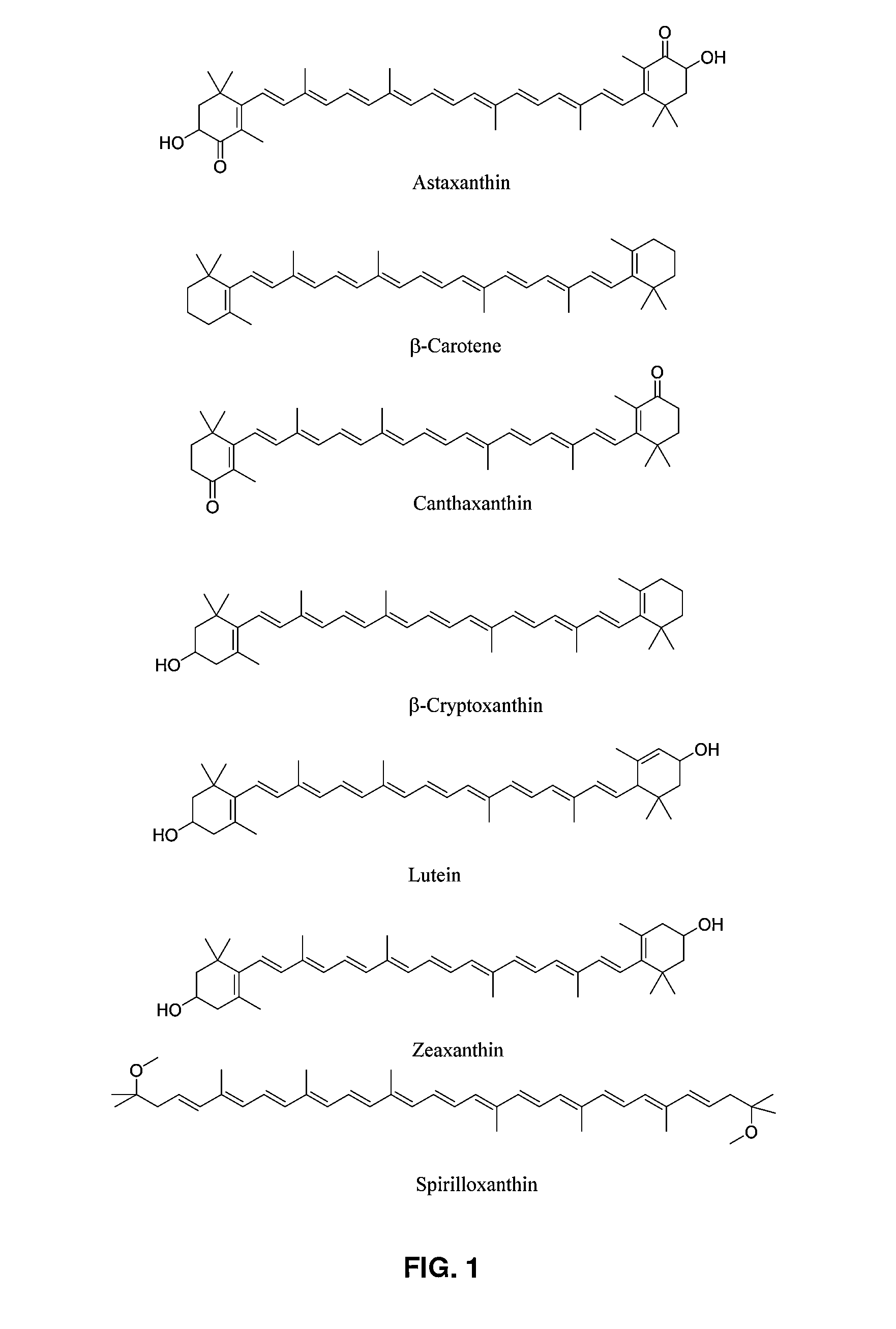
Methanotrophic bacterial strains are provided that have been optimized for the production of carotenoid compounds through the down-regulation of one or more of the crtN1, aid, crtN2 and crtN3 genes of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway. The resulting strains lack pigmented C30 carotenoid compounds, and show an increase in the production of C40 carotenoids. The use of the optimized host strains for the production of the C40 carotenoids canthaxanthin and astaxanthin is also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Novel phage and composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106282127AIncreased toxicityStable survivalAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganismHealth risk
The invention relates to the field of microbes and provides a novel salmonella phage and a composition, a preparation method and application thereof. The novelsalmonella phage is Myoviridaesp. BP-66 with the preservation numberCCTCC NO: M2015146,Myoviridaesp. BP-63 with preservation number CCTCC NO: M2015145, or Chilikevirussp. BP-12 with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2015141. The novel phage is a strict virulent phage, has high toxicity to host bacteria, has a wider host range and still has high toxicity to the host bacteria at low concentration. The DNA of the phage cannot encode protein possibly causing potential health risks. The novel phage stably survives in a culture solution at room temperature and survive for more than 6 months at the temperature below 4 DEG C. In addition, the phage can be proliferated on pathogenic bacterial hosts, and large-scale industrial production can be achieved. The salmonella phage can provide excellent strain resources for application of phage therapy.
Owner:PHAGELUX (NANJING) BIO-TECH CO LTD
Microbial cell sensor for detecting toluene organic pollutants
The invention discloses a microbial cell sensor for detecting toluene organic pollutants and a detection method thereof, and relates to a microbial cell sensor for detecting toluene organic pollutants, which is constructed by using a regulatory sequence of pseudomonas putida degradation genes and a plasmid sequence of regulatory protein genes and commercial report genes, and a detection method thereof. The bacterial host is Escherichia coli, and is used for detecting toluene organic matters. The lowest detection concentration on the toluene is 40 micromoles per liter, and the highest detection concentration on the toluene is 1,000 micromoles per liter.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
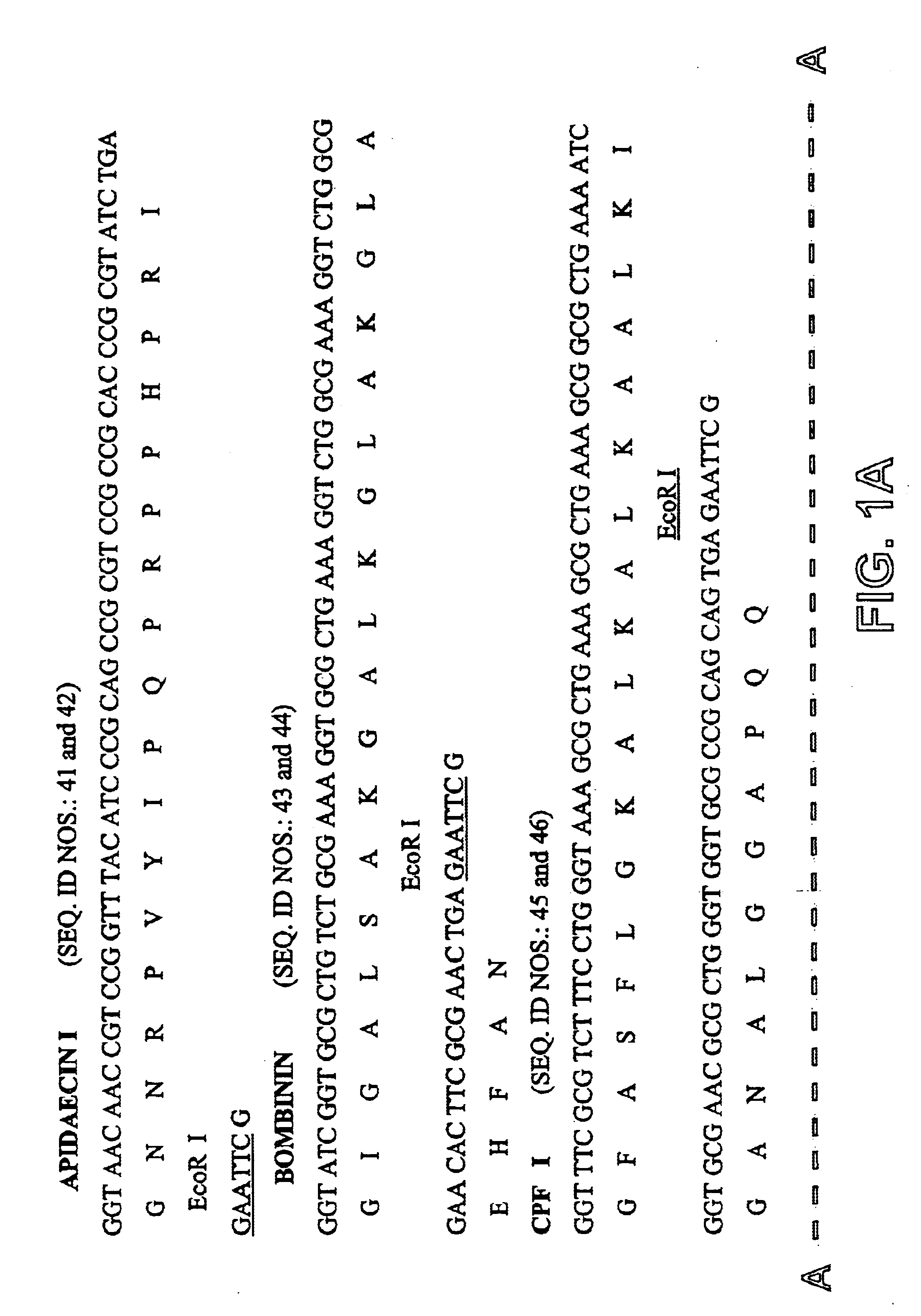
Mass production method of antimicrobial peptide and DNA construct and expression system thereof
InactiveUS6699689B1Improve expression efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesAntimikrobielle peptideAnti microbial peptide
The present invention relates to DNA constructs that can produce antimicrobial materials efficiently from microorganisms and the preparation method thereof. The present invention also relates to the useful vector for the DNA construct. The DNA construct according to the present invention comprises a first gene coding for entire, a part of or a derivative of purF gene and a second gene coding for antimicrobial peptide. According to the present invention, antimicrobial peptides can be mass-produced by the following steps: preparing an expression vector containing a DNA construct comprising a first gene coding for an entire, a part of or a derivative of purF gene and a second gene coding for antimicrobial peptide; transforming the bacterial host cells with the above-mentioned vector, culturing the transformed cell to express the above-mentioned DNA construct; and recovering the above antimicrobial peptide.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
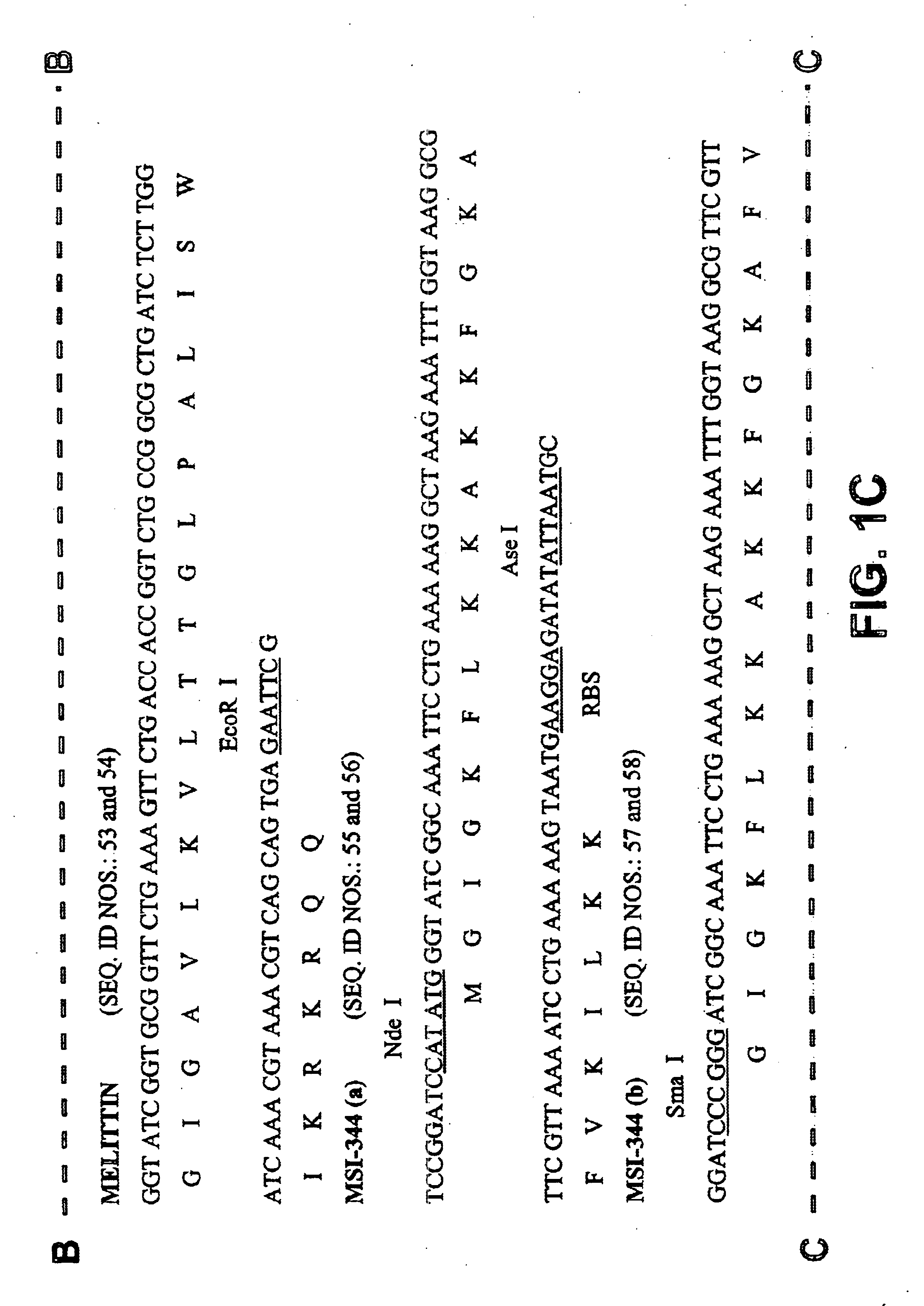
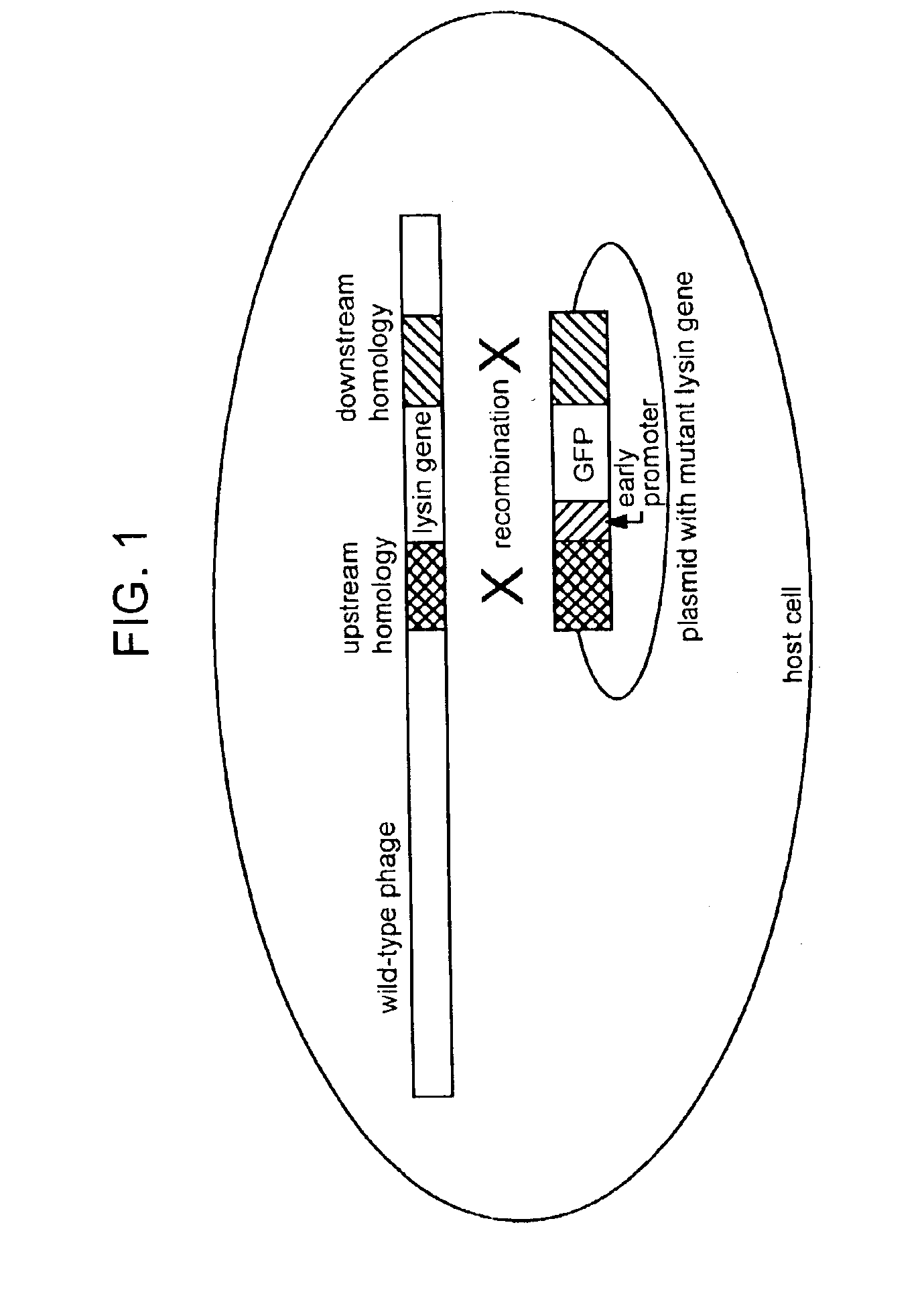
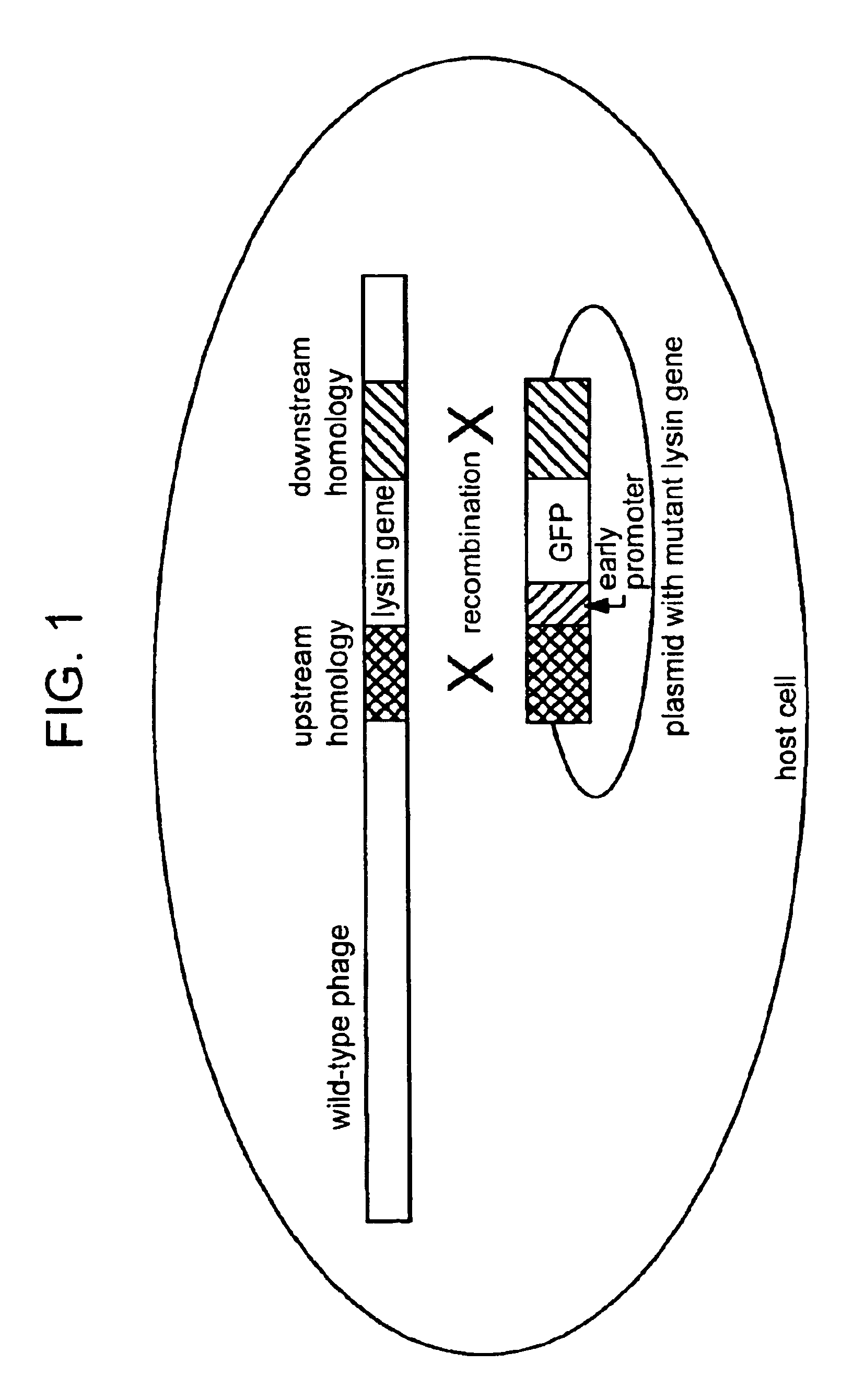
Lysin-deficient bacteriophages having reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS6896882B2Reduce gapBlocking can be undesirableAntibacterial agentsBiocidePhagocyteBacteroides
The present invention features therapeutic bacteriophage deficient in the lysin protein (“Lys minus” phage). Lys minus bacteriophage are incapable of facilitating efficient lysis of the bacterial host since the enzymatic activity of the lysin of the phage is needed for breaking down the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall. Lys minus bacteriophage retain activity in invasion of its appropriate bacterial host, destruction of the bacterial genome, and replication, which are sufficient to inhibit bacterial growth and replication. Therefore, the therapeutic Lys minus phage stops the spread of infection by the bacterial pathogen without lysis of the bacterium. This approach is attractive as it also prevents the release of the phage progeny, thus reducing or eliminating the potential for generation of immune responses against the phage. The incapacitated bacterial pathogen is then removed by the normal defense systems such as phagocytes and macrophages.
Owner:BACTOCLEAR HLDG PTE LTD
Incapacitated whole-cell immunogenic bacterial compositions
The invention features incapacitated whole cell bacterial immunogenic compositions produced by infecting a bacterium with Lys minus bacteriophage, which are deficient in the lysin protein. Lys minus bacteriophage retain activity in infection of its appropriate bacterial host, destruction of the bacterial genome, and replication, which are sufficient to inhibit bacterial growth and replication. The resulting, Lys minus-infected bacterium is provided in a state of bacteriostasis, and is not capable of replicating further (e.g., is “incapacitated”). The incapacitated bacterium can then be used as to elicit an immune response for prophylactic and / or therapeutic purposes. The invention thus also features incapacitated bacteria formulated appropriately for use in immunogenic compositions for eliciting an immune response, e.g., for production of antibodies in a non-human host or in a whole cell bacterial vaccine.
Owner:BACTOCLEAR HLDG PTE LTD
Methylotrophs for aquaculture and animal feed
Disclosed are methods of producing carotenoid compounds in a methylotrophic bacterial host cell. Such a host cell may be an unmodified Methylobacterium, spontaneous mutant, or transformed cell, any of which exhibit favorable properties, such as overproduction of carotenoid compounds, increased carbon flux, improved growth, or the production of additional nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, antioxidants, or fatty acids. Also disclosed are feed compositions for use in aquaculture, or as animal feed, or as human nutritional supplements containing processed or unprocessed biomass from such cells, as are methods of preparation of the feed compositions.
Owner:KNIPBIO INC
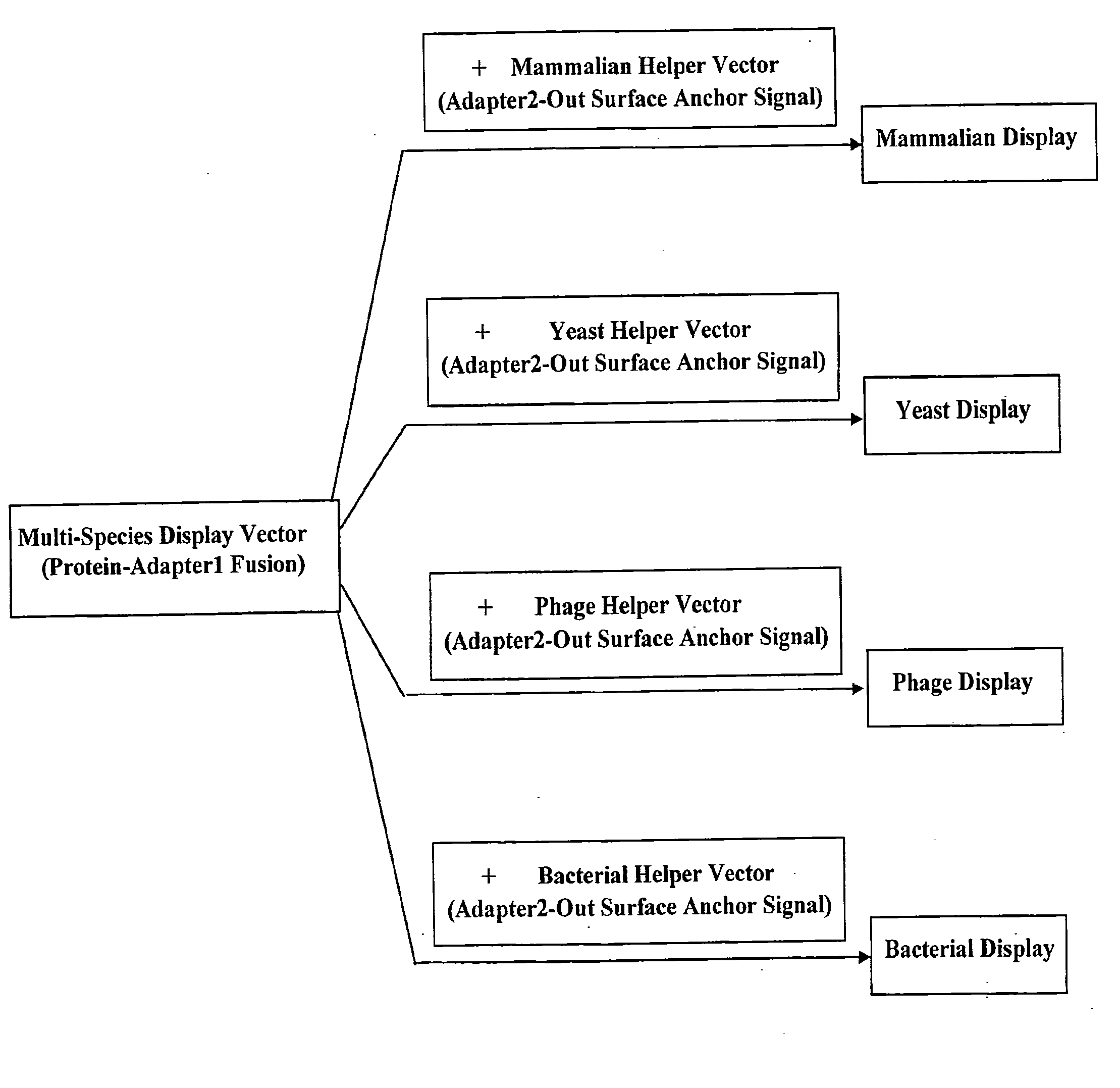
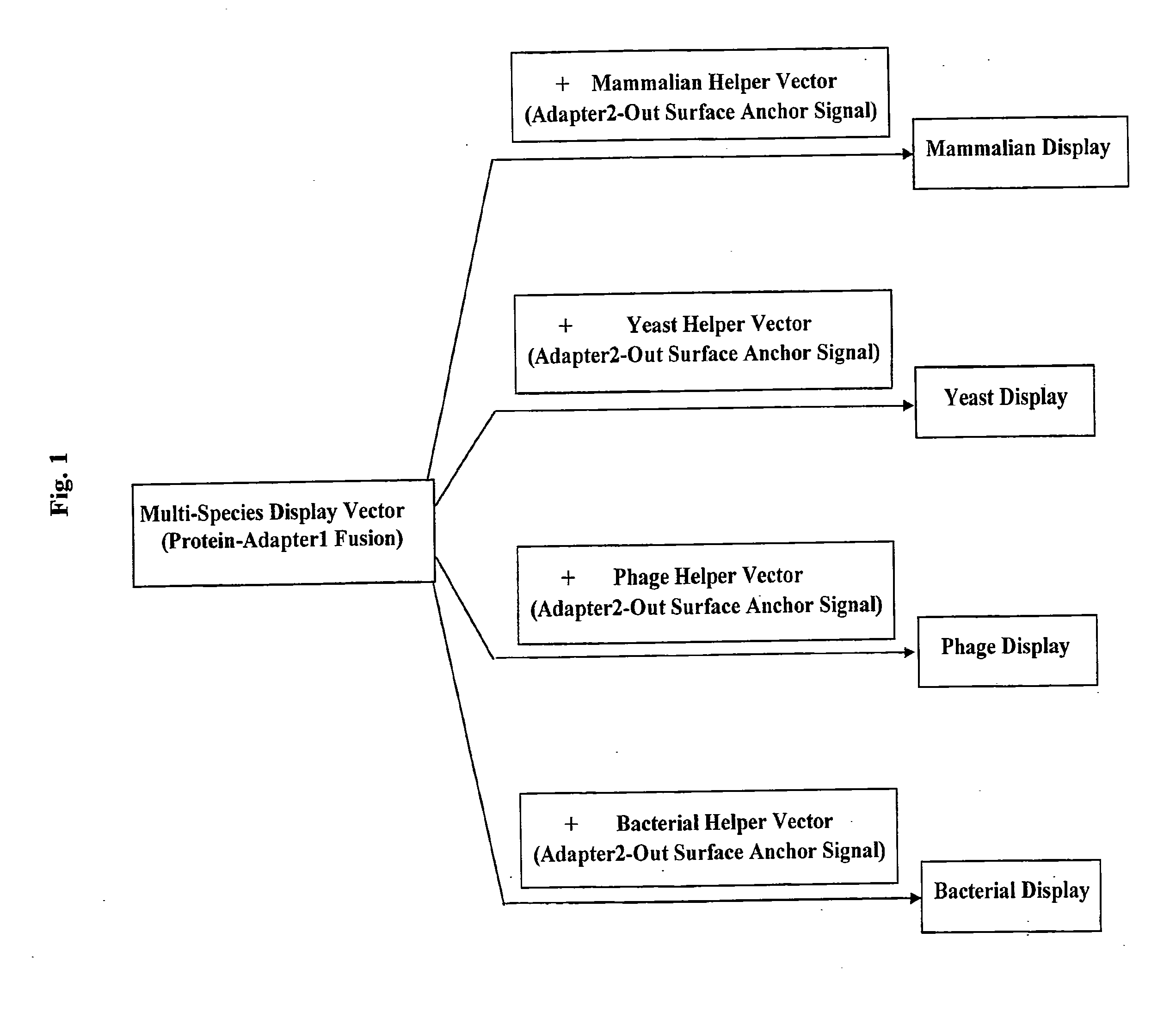
Cross-Species and Multi-Species Display Systems
The present invention provides expression vectors and helper display vectors which can be used in various combinations as vector sets for multi-species and cross-species display of polypeptides on the outer surface of prokaryotic genetic packages and / or eukaryotic host cells. The multi-species and cross-species display systems can be practiced using the vector sets of the invention without having to change or reengineer the display vectors. The display systems of the invention are particularly useful for displaying a genetically diverse repertoire or library of polypeptides on the surface of phage, bacterial host cells, yeast cells, and mammalian cells.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Production of human milk oligosaccharides in microbial hosts with engineered import / export
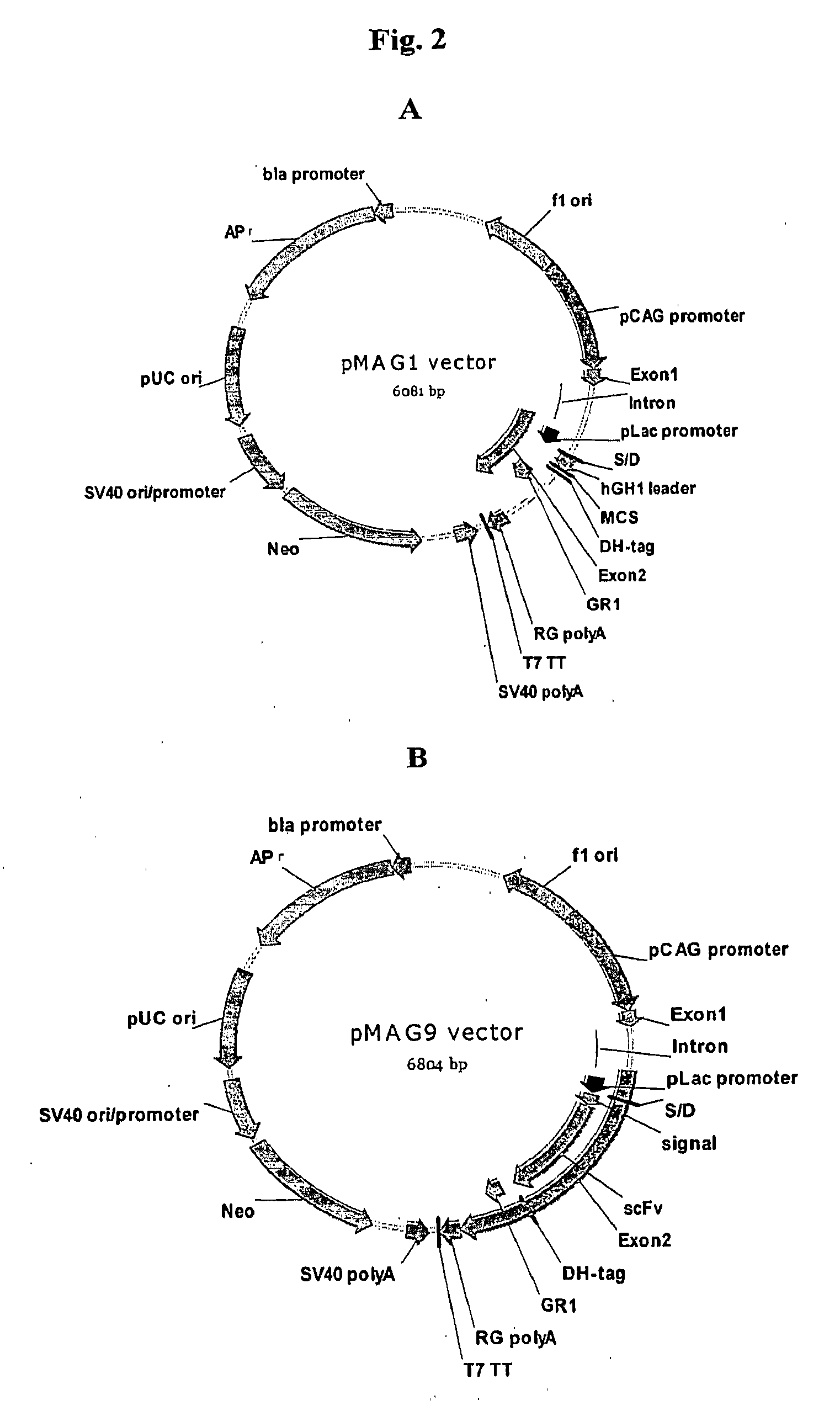
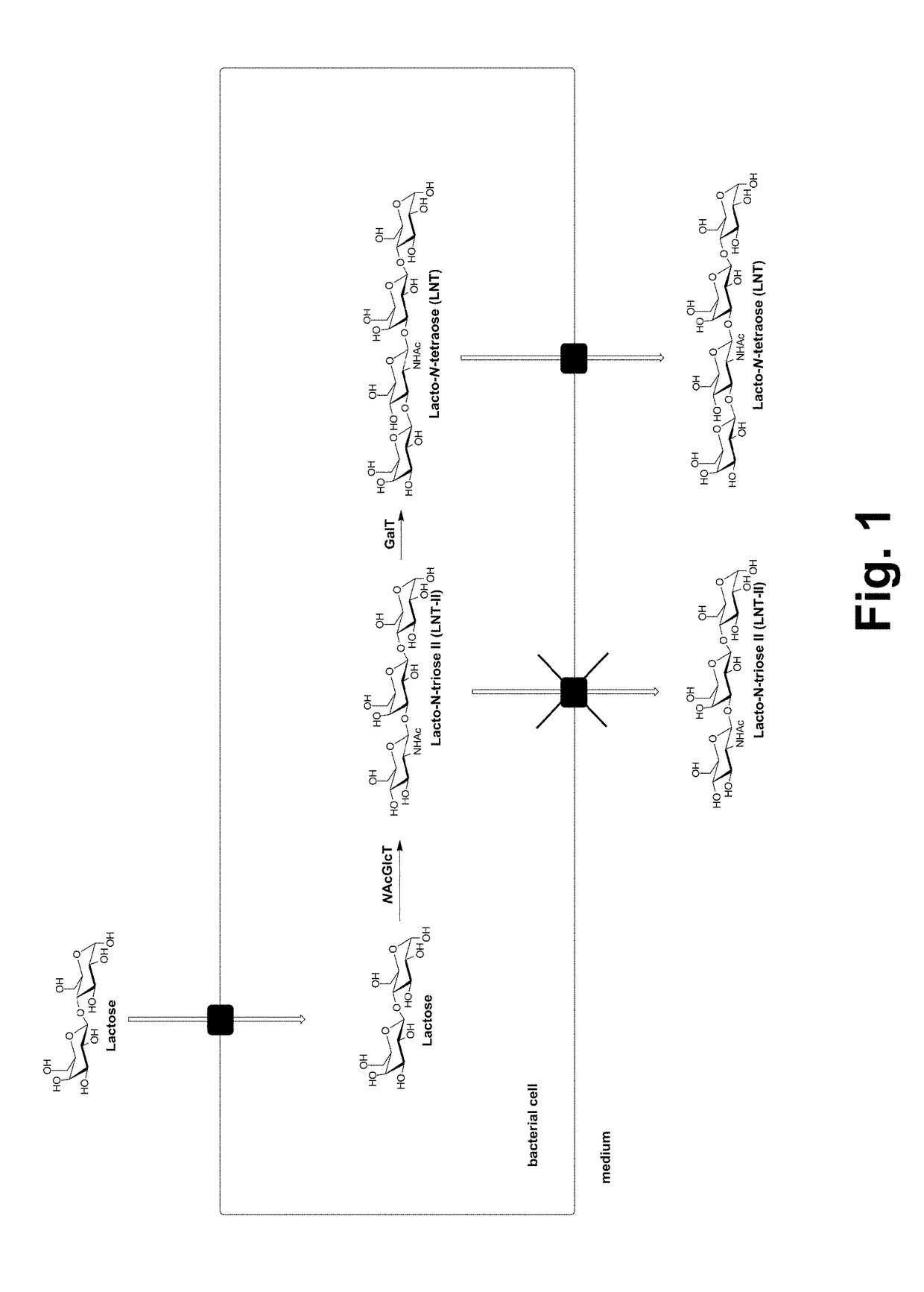
The present invention relates to methods for the production of oligosaccharides in genetically modified bacterial host cells, as well as to the genetically modified host cells used in the methods. The genetically modified host cell comprises at least one recombinant glycosyltransferase, and at least one nucleic acid sequence coding for a protein enabling the export of the oligosaccharide.
Owner:CHR HANSEN HMO GMBH
Folded recombinant catalytic fragments of multidomain serine proteases, preparation and uses thereof
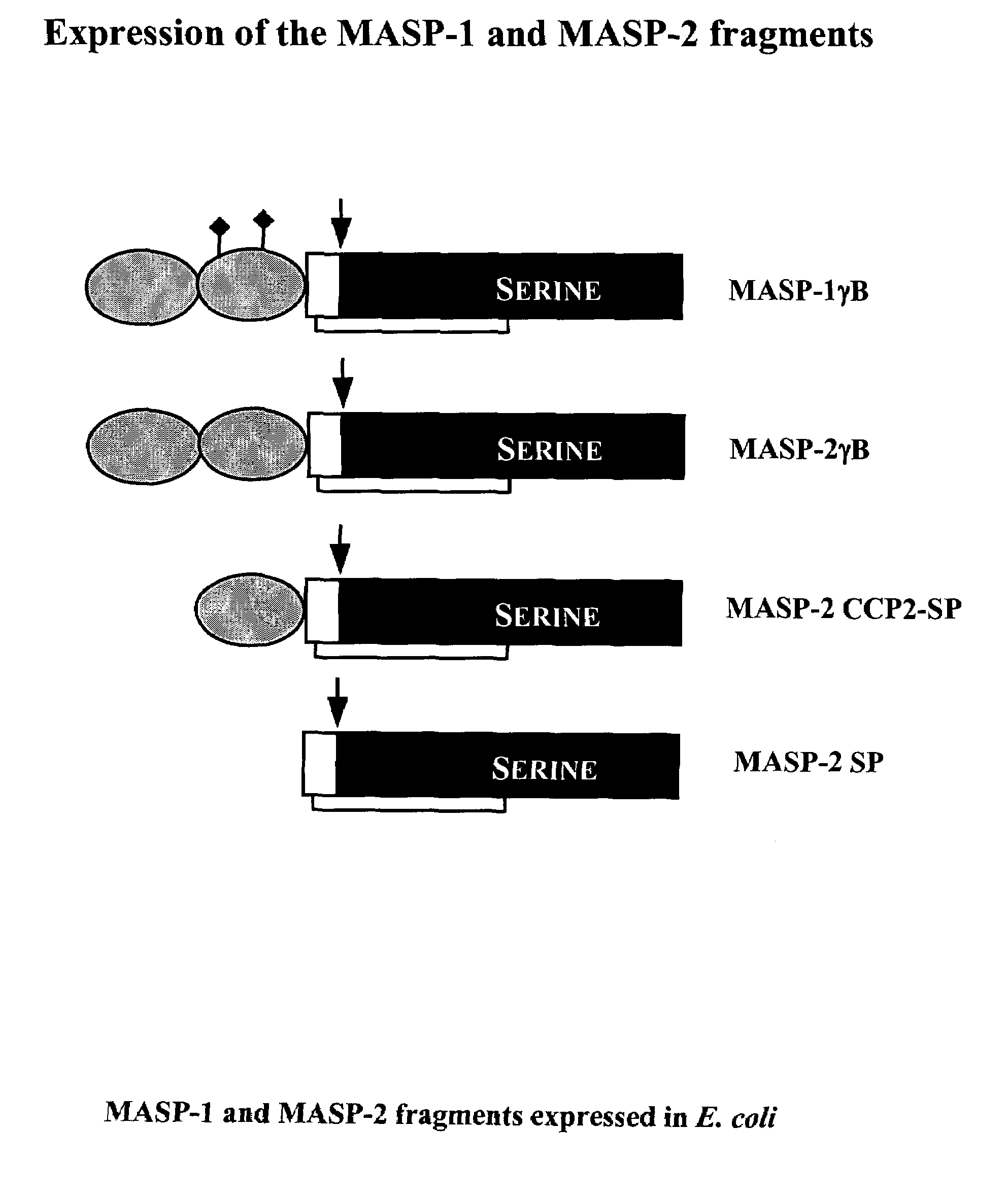
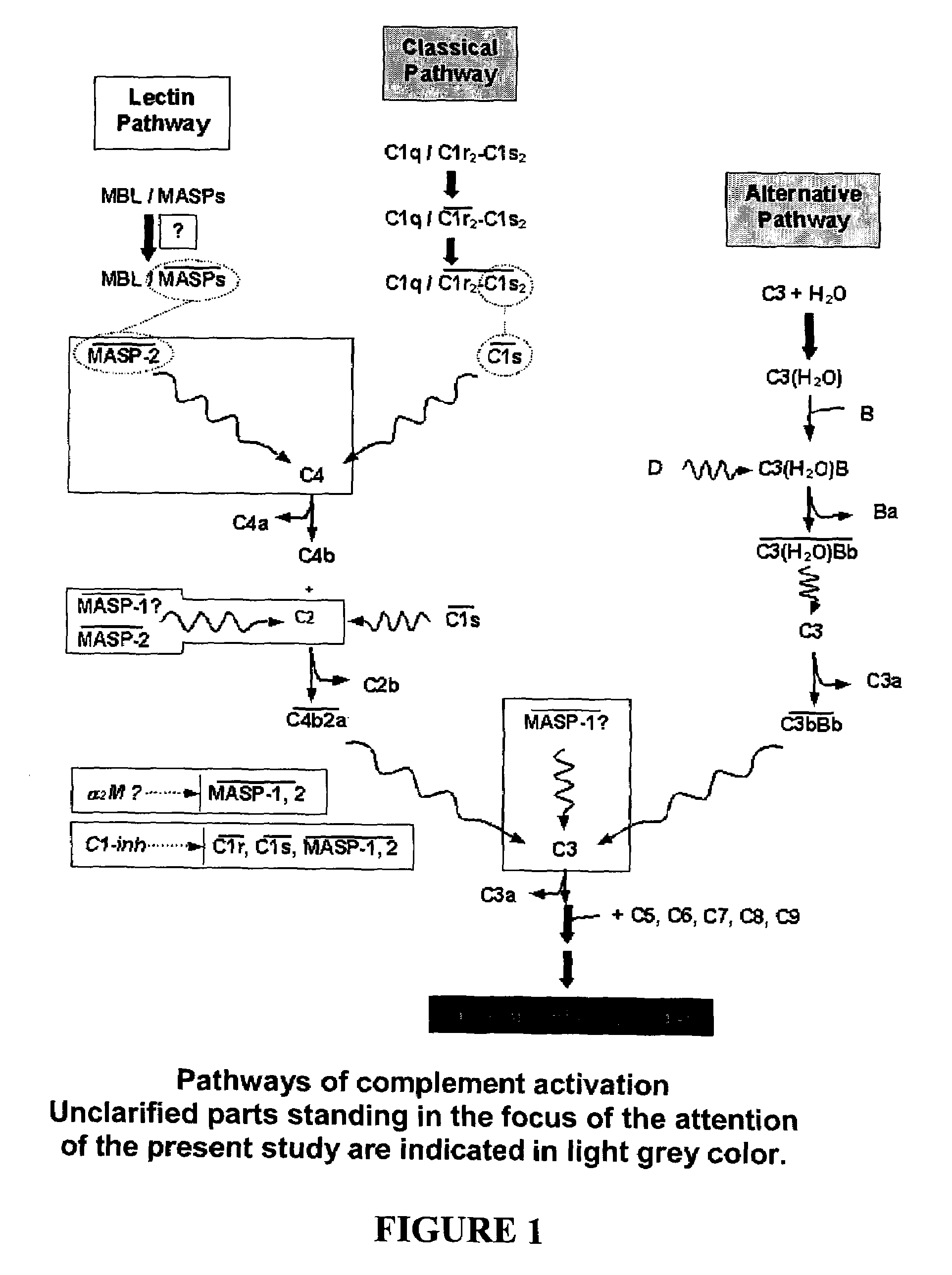
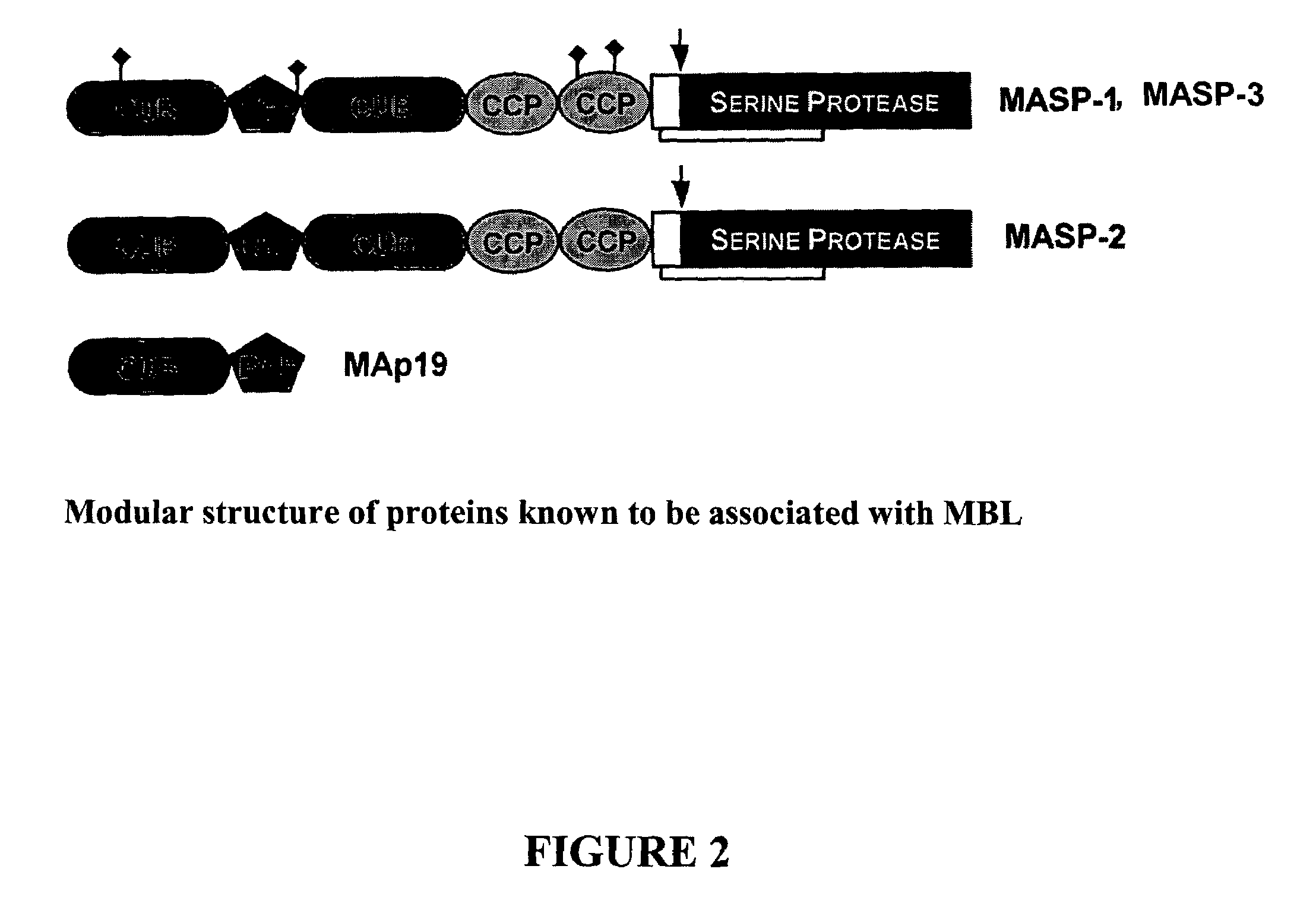
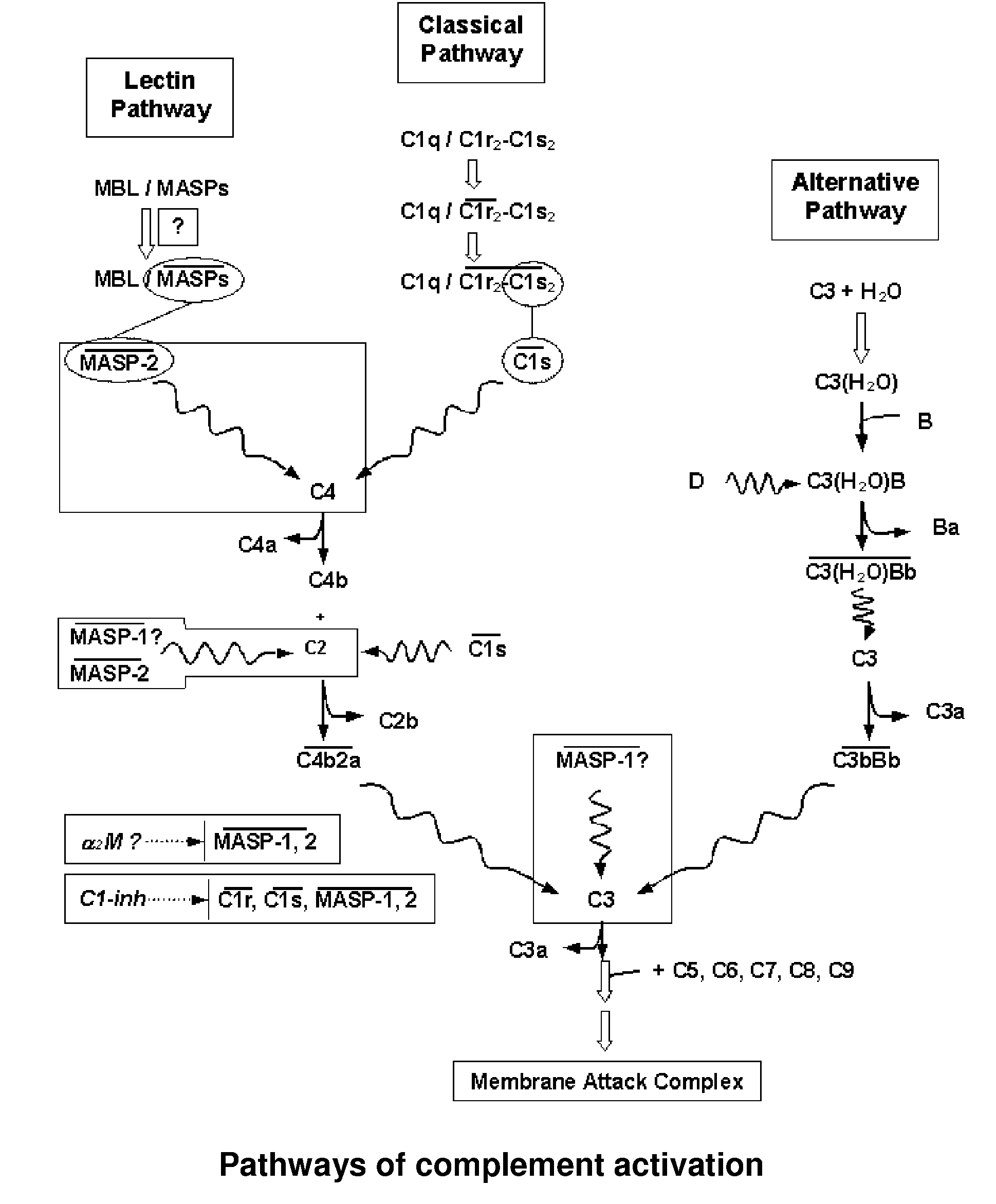
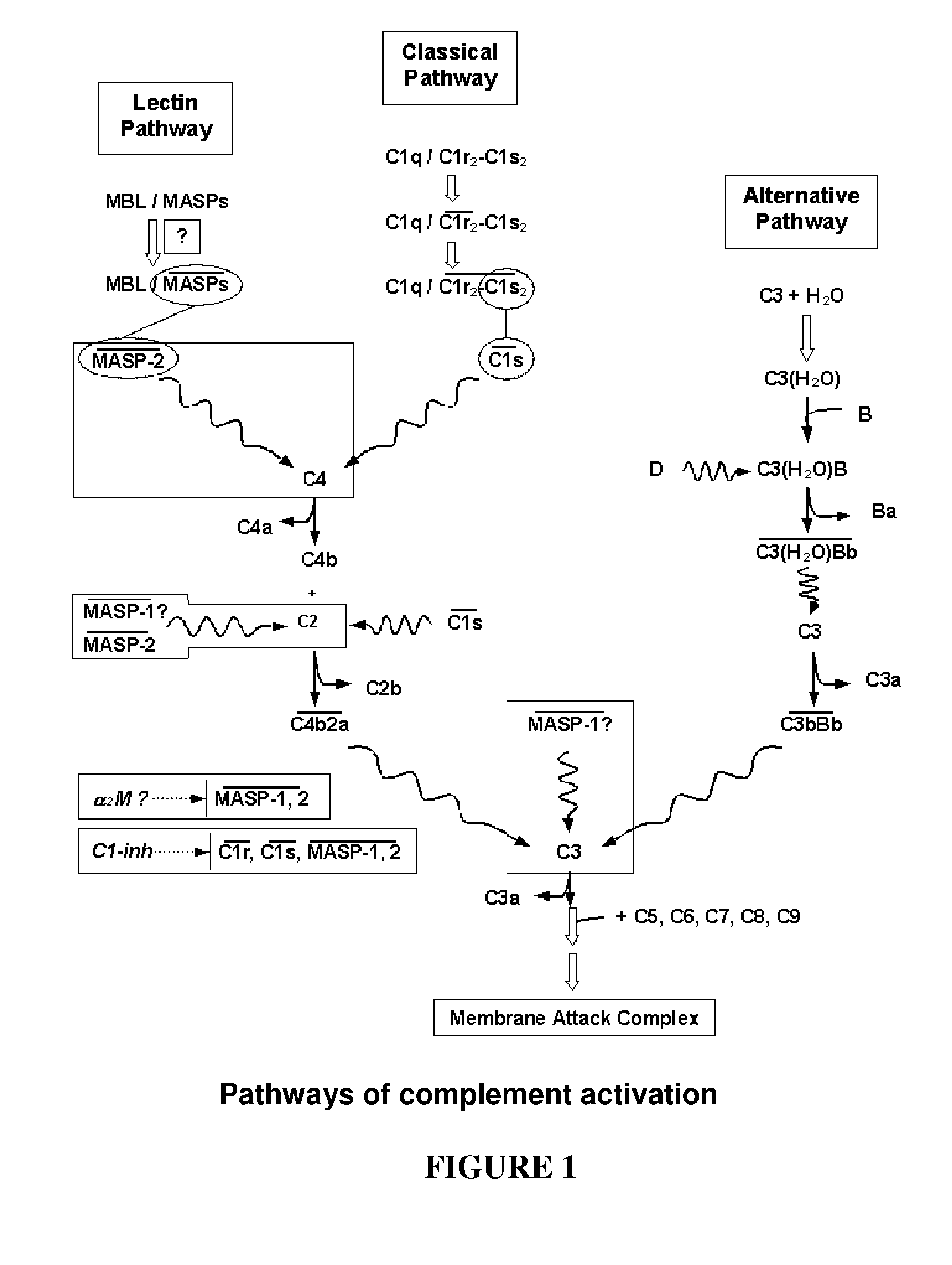
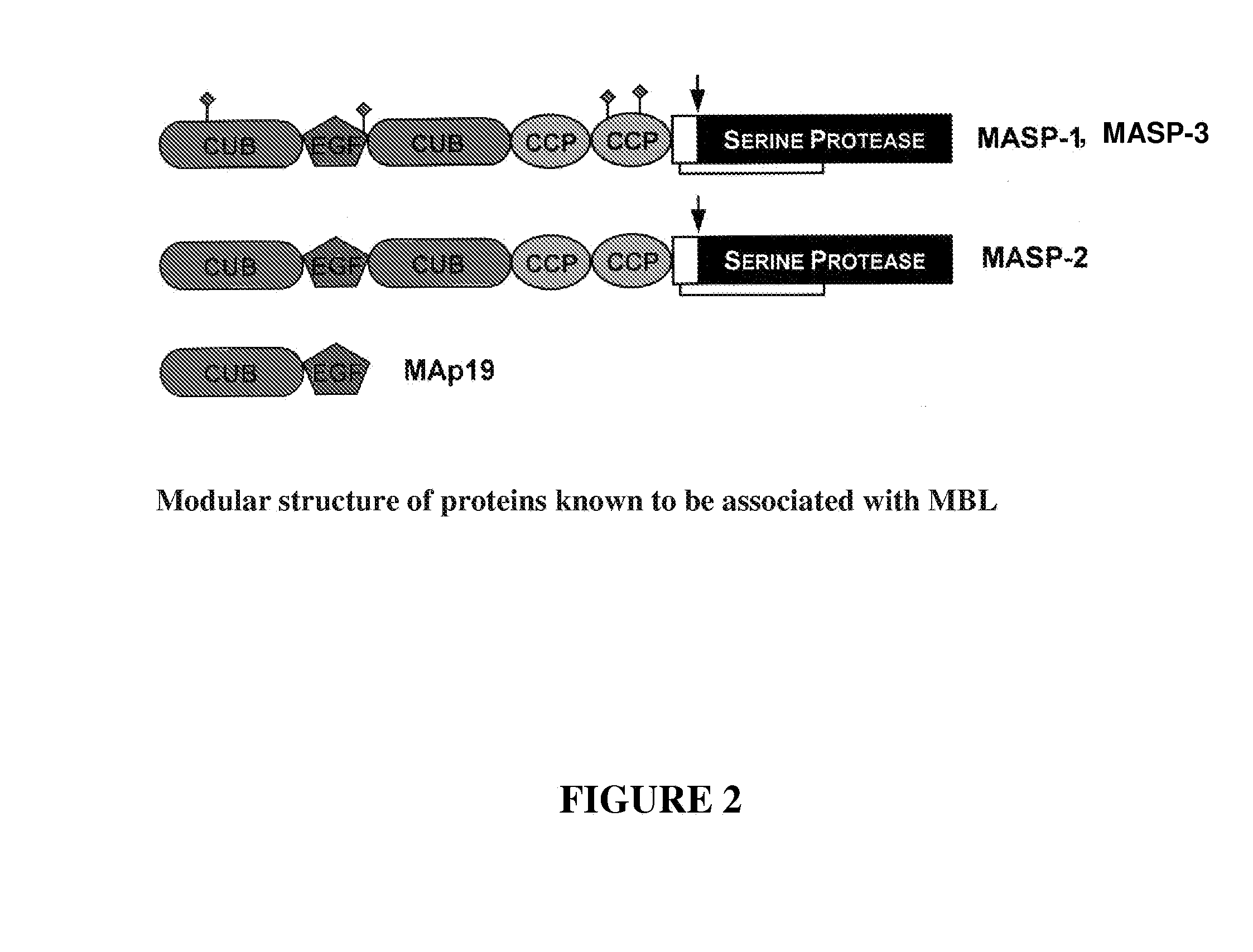
The invention relates to unglycosylated folded C-terminal fragments of a multidomain serine protease of the complement cascade obtainable by expression in a bacterial host, wherein said serine protease is capable of binding a recognition molecule of the complement cascade, e.g. C1 or MBL. The invention also relates to methods and bacterial expression vectors for the preparation of said fragments, uses of said fragments for raising antibodies and screening substrates or inhibitors of said serine proteases and uses of the fragments in research and treatment of complement related disorders. The invention also relates to assay methods for assessing MASP-1 and MASP-2 levels in a sample of biological origin.The invention provides for research tools, assays and diagnostic kits useful in complement research and research and diagnosis of complement related disorders.
Owner:TARGETEX
Family of pesticidal proteins and methods for their use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37 or 61, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, or 60, or the nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession No. NRRL B-30961, B-30955, B-30956, B-30957, B-30958, B-30942, B-30939, B-30941, B-50047, B-30959, B-30960, B-30943, or B-50048, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Novel vibrio parahaemolyticus phage as well as composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107686832AAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganismHealth risk
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and provides a novel vibrio parahaemolyticus phage as well as a composition, a preparation method and application thereof. The novel vibrio parahaemolyticus phage specifically refers to a vibrio parahaemolyticus phage VP46 of which the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2016290, a vibrio parahaemolyticus phage VP48 of which the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2016291 or a vibrio parahaemolyticus phage VP7 of which the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2016289. The phage is a strictly virulent phage, is highly toxic to host bacteria, has a widerhost range, and is highly toxic to the host bacteria at a low concentration; DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of the phage cannot encode proteins which may cause a potential health risk; the phage survives stably in a culture solution at room temperature, and survives for more than 12 months at a temperature of below 4 DEG C; the phage can be well proliferated on a non-pathogenic bacterial host; and large-scale industrial production can be realized.
Owner:PHAGELUX (NANJING) BIO-TECH CO LTD
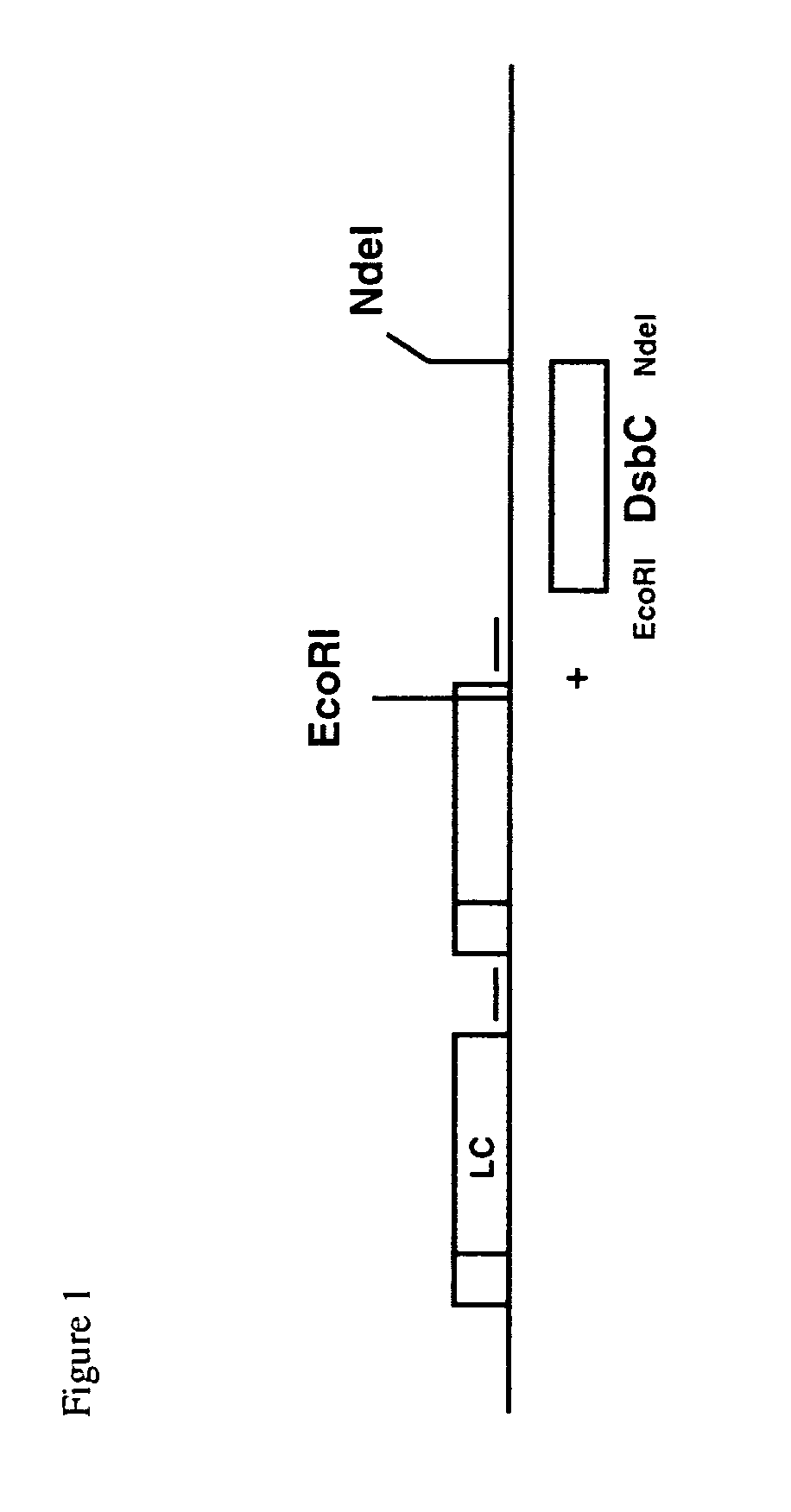
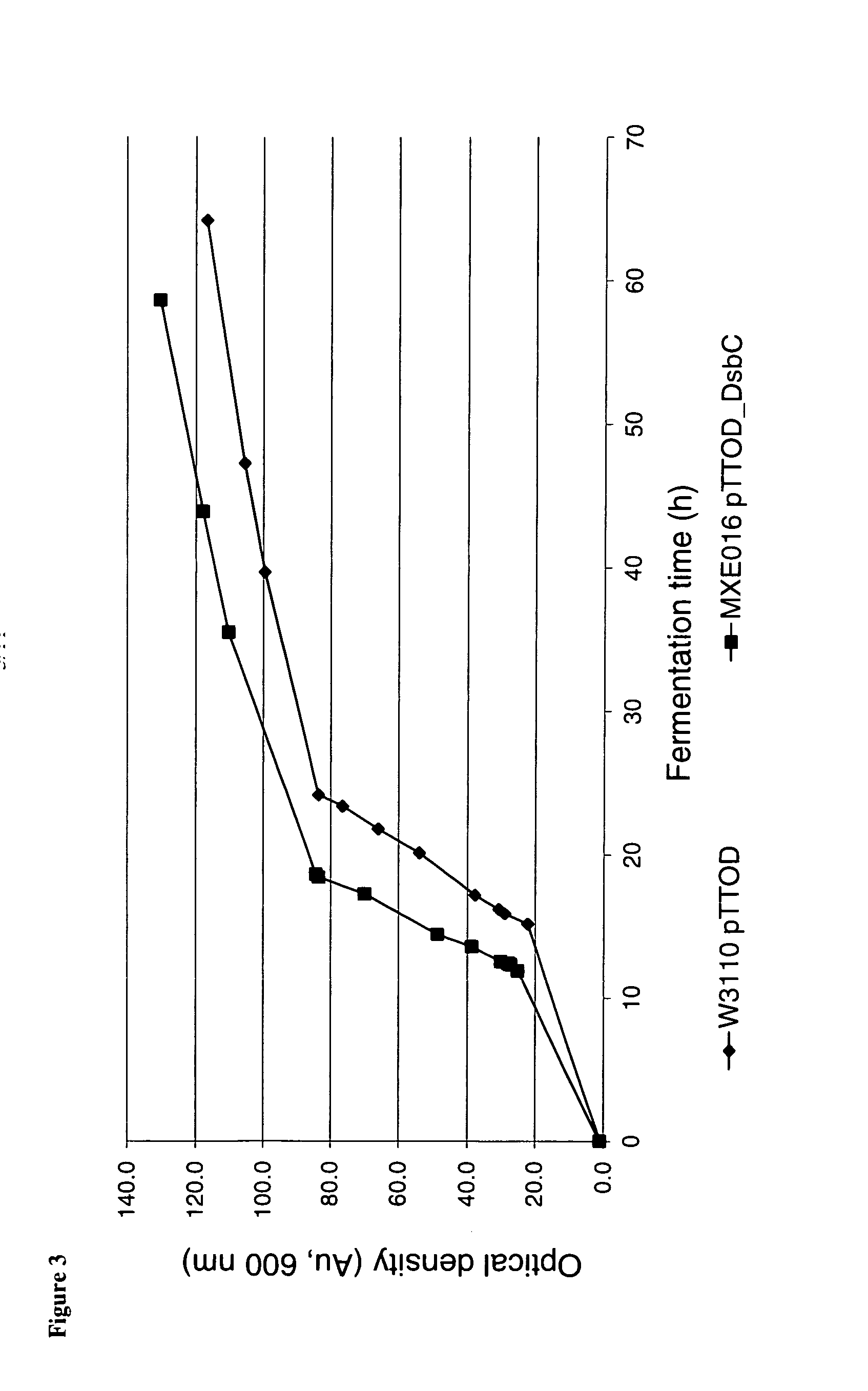
Bacterial host strain expressing recombinant dsbc
ActiveUS20140141468A1Reduced activityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenBacteroides
The present invention provides a recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising an expression vector, comprising a recombinant polynucleotide encoding DsbC and one or more polynucleotides encoding an antibody or an antigen binding fragment thereof specifically binding to CD154.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
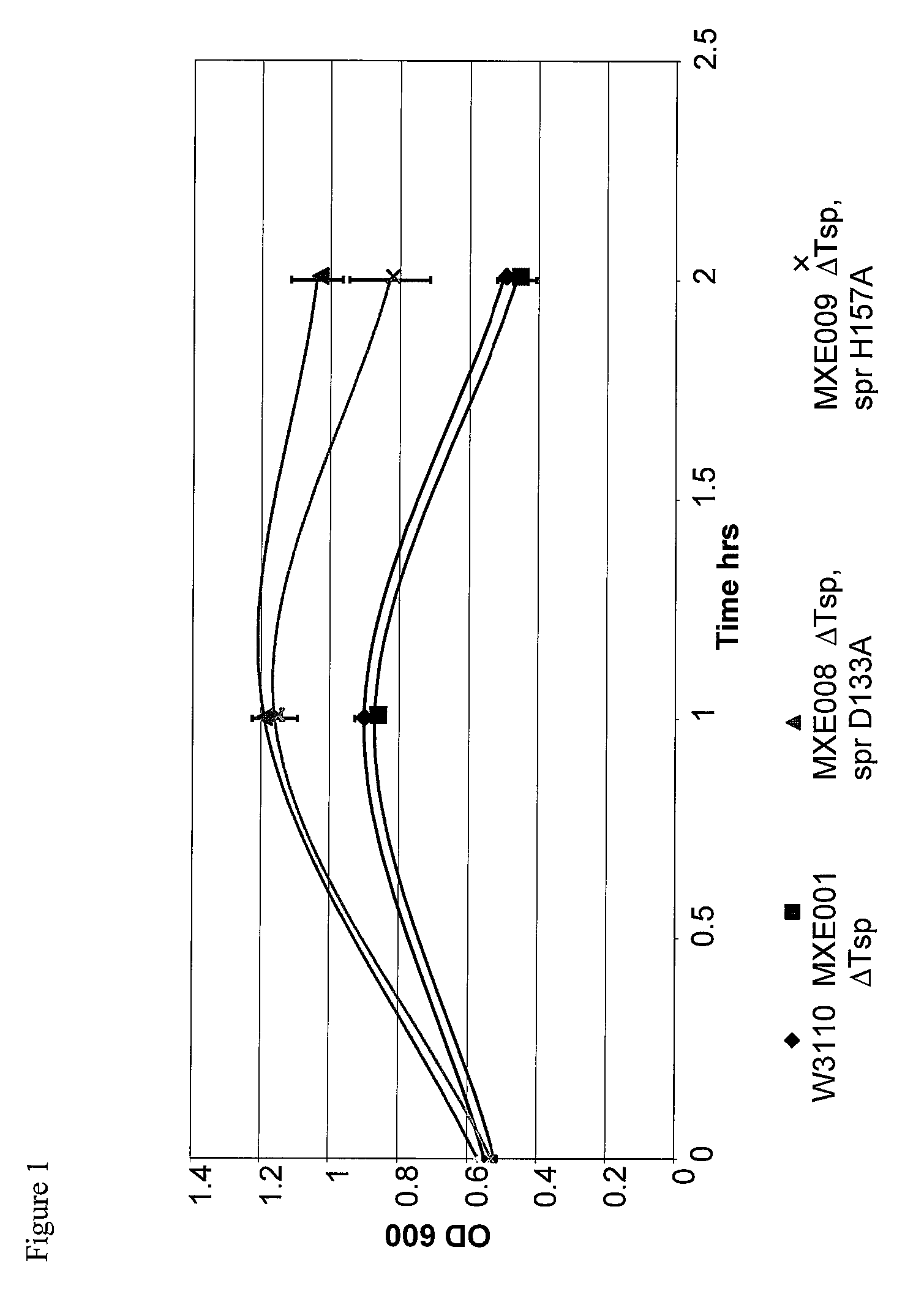
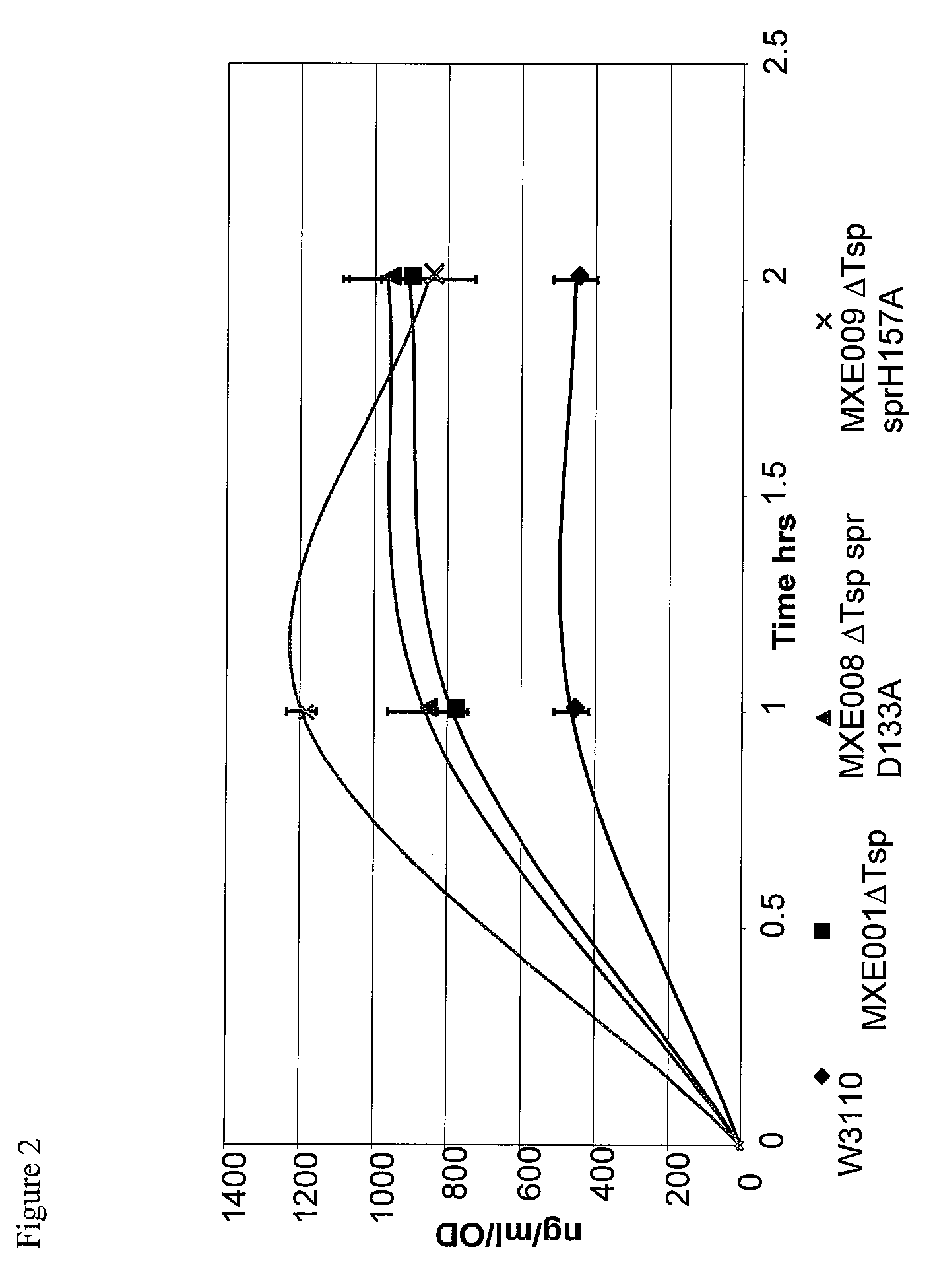
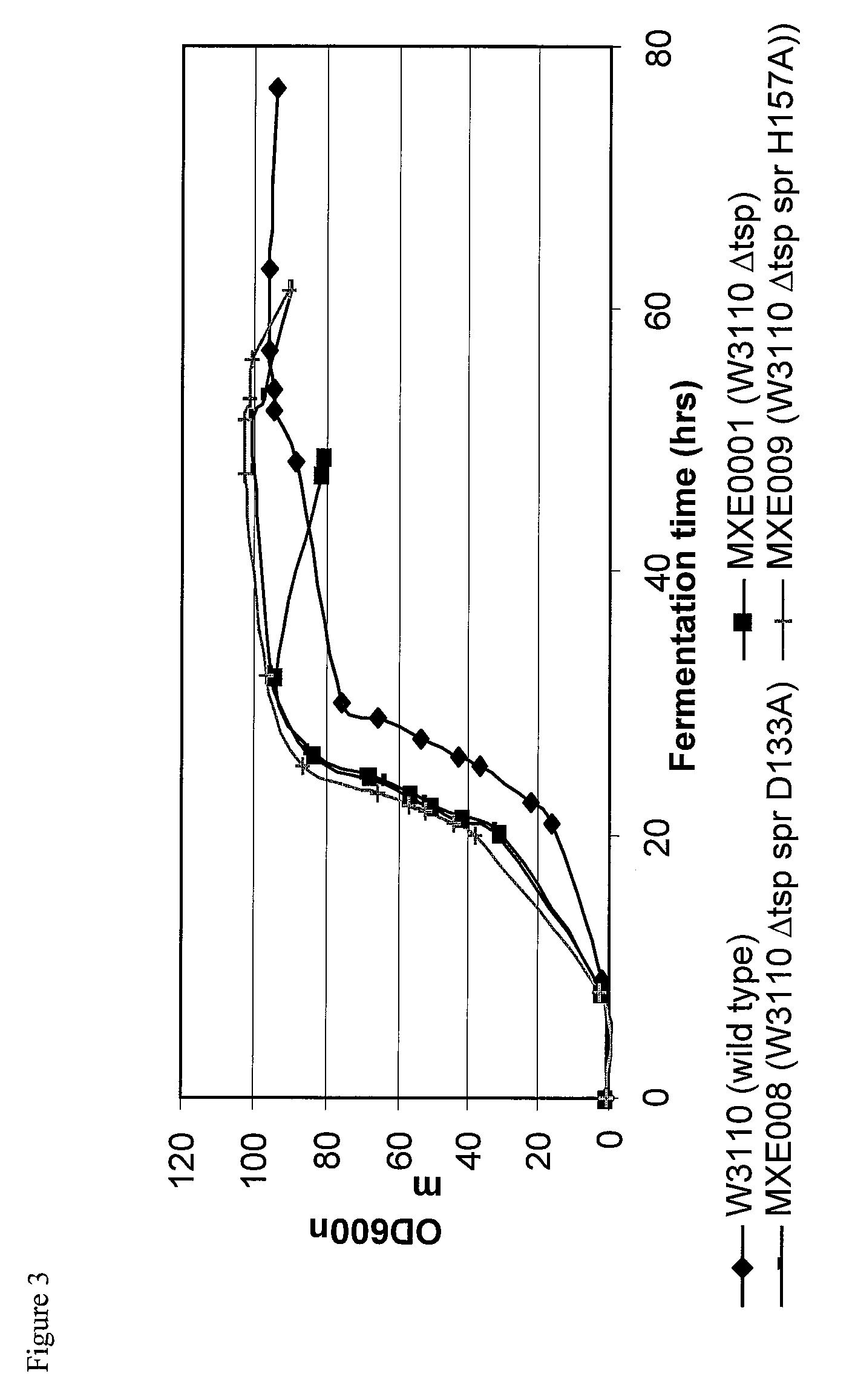
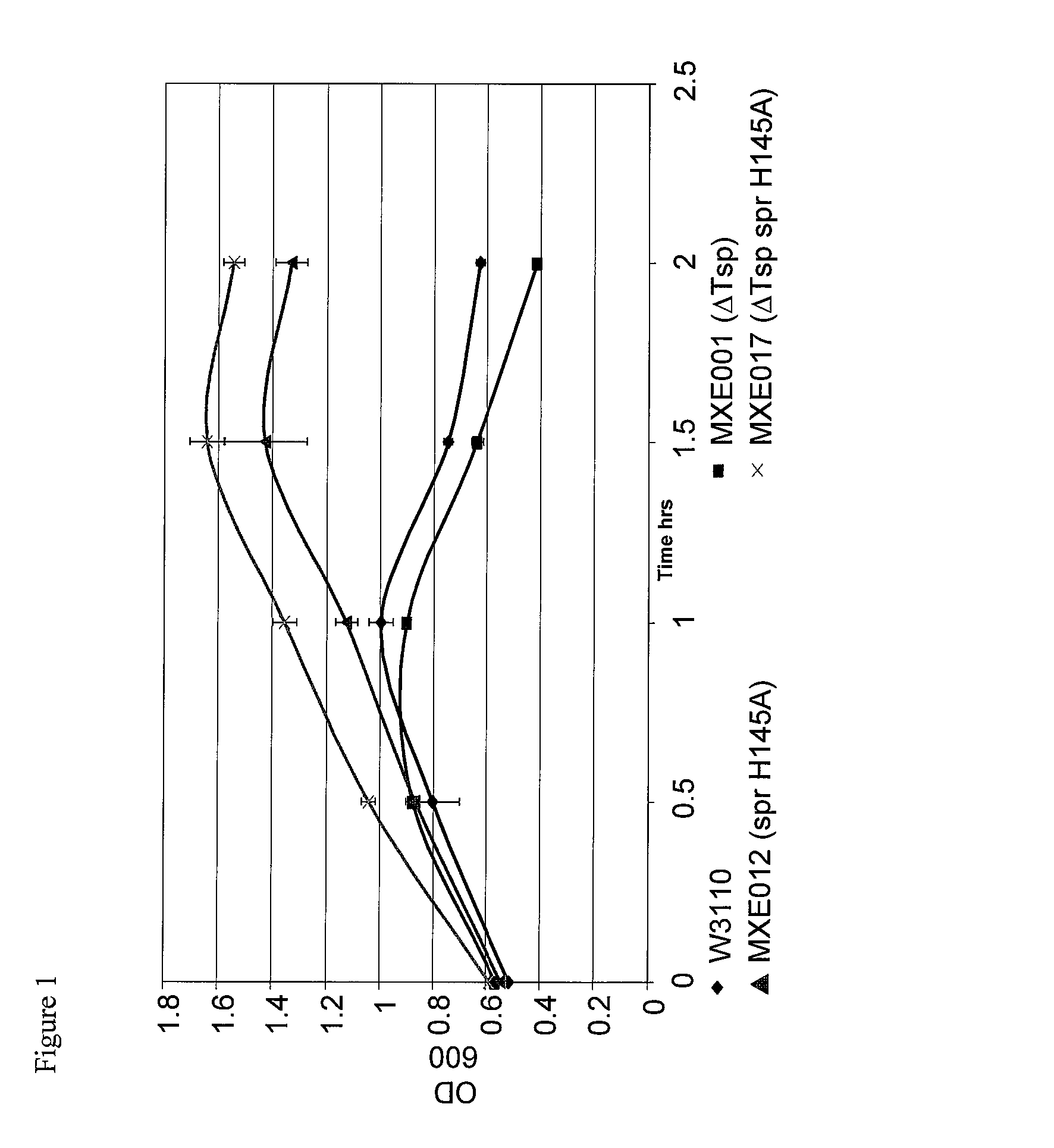
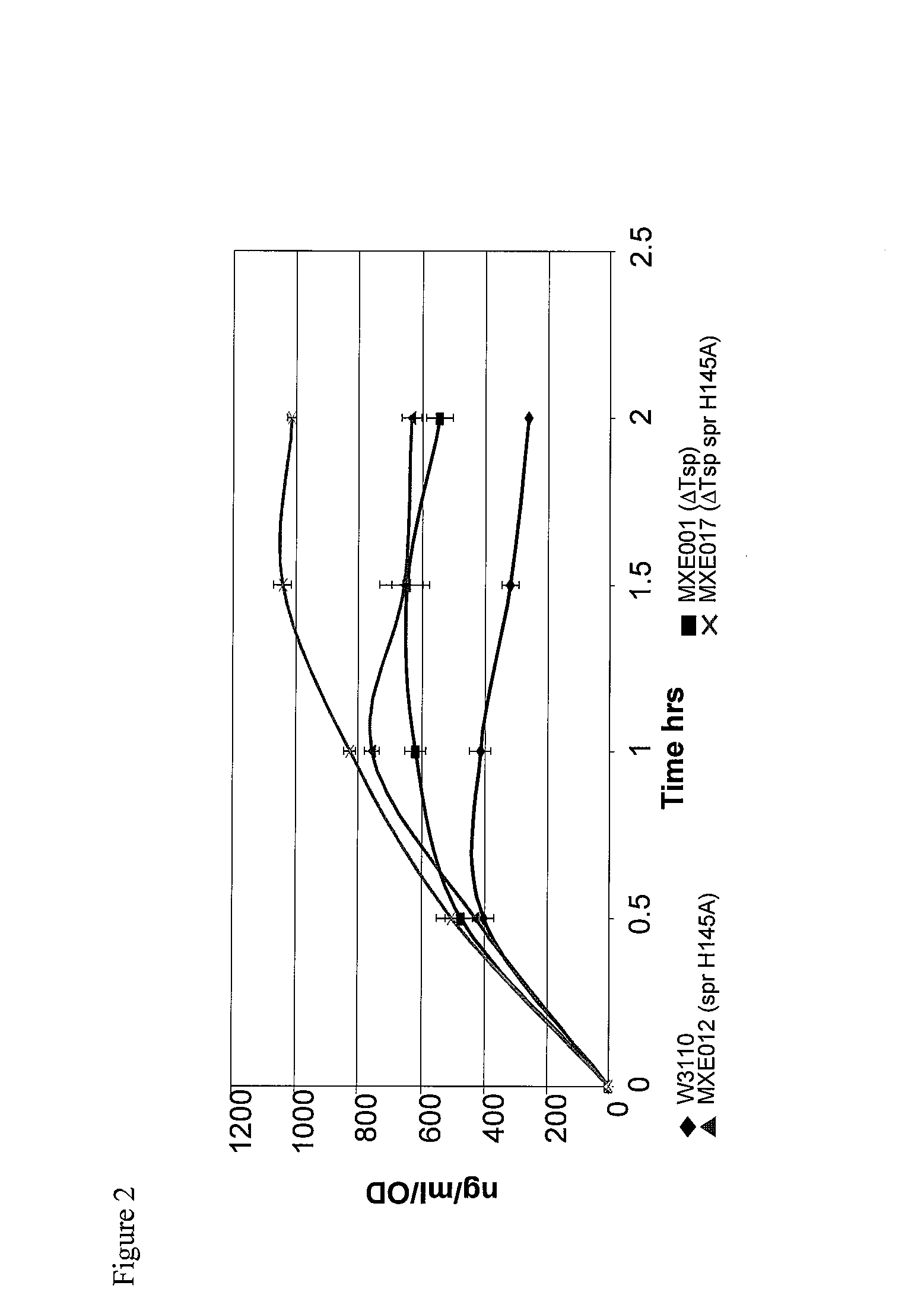
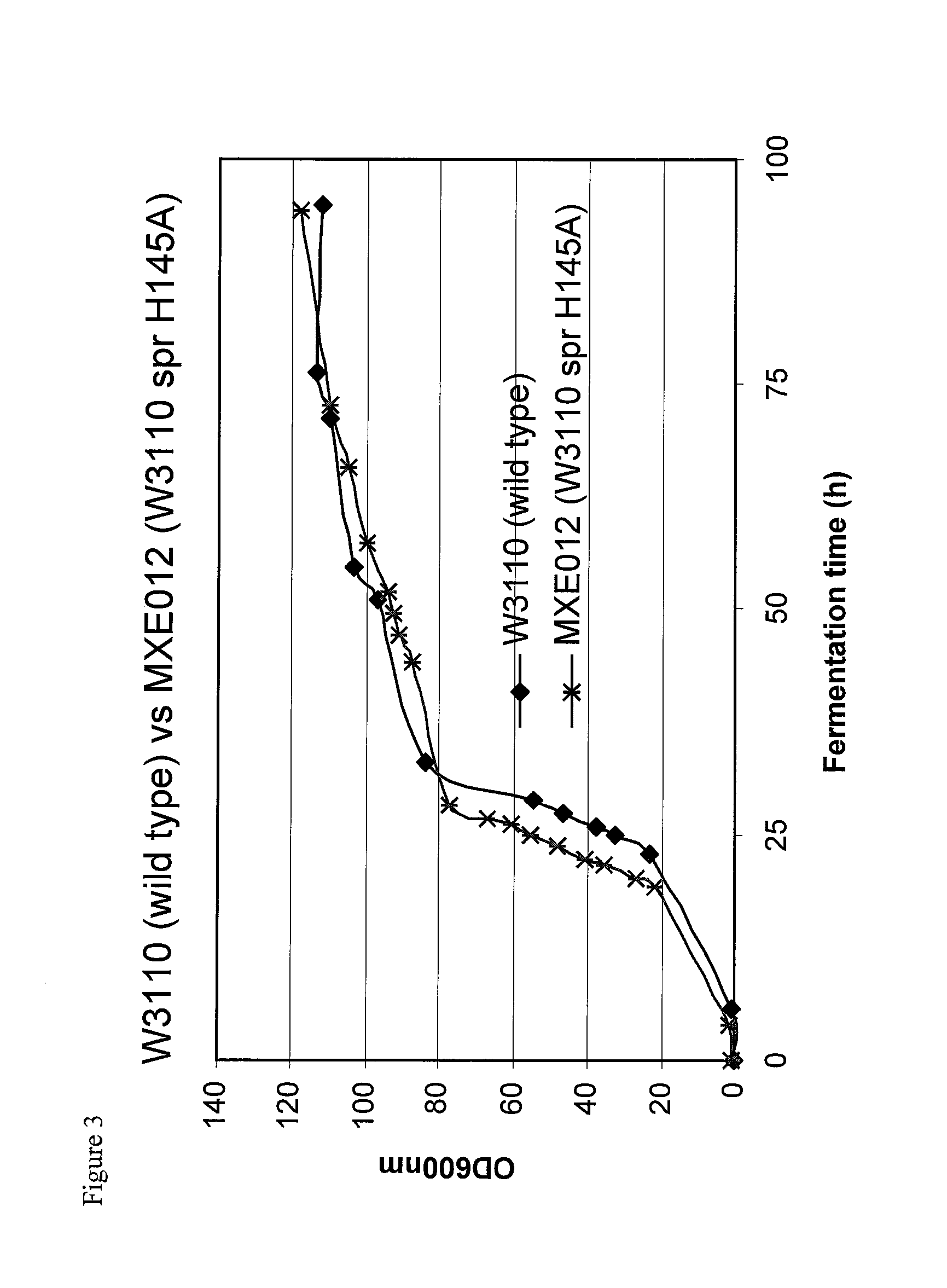
Bacterial host strain comprising a mutant SPR gene and having reduced TSP activity
ActiveUS8969039B2Advantageous growth and protein production phenotypeBacteriaHydrolasesProtein activityAmino acid
The present invention provides a recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising a mutant spr gene encoding a spr protein having a mutation at one or more amino acids selected from D133, H145, H157, N31, R62, I70, Q73, C94, S95, V98, Q99, R100, L108, Y115, V135, L136, G140, R144 and G147 and wherein the cell has reduced Tsp protein activity compared to a wild-type cell.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Bacterial host strain comprising a mutant spr gene and a wild-type tsp gene
ActiveUS20120301920A1Promote growthAdvantageous protein production phenotypeBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesGram
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com