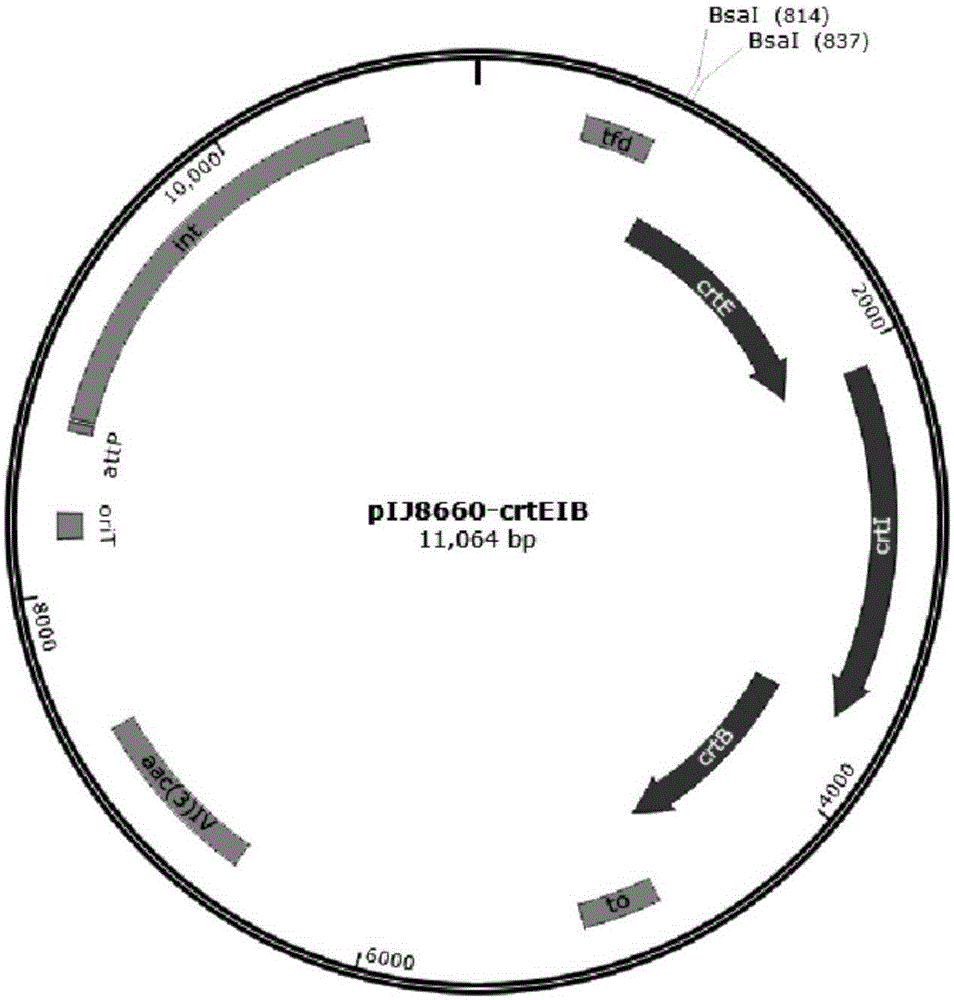
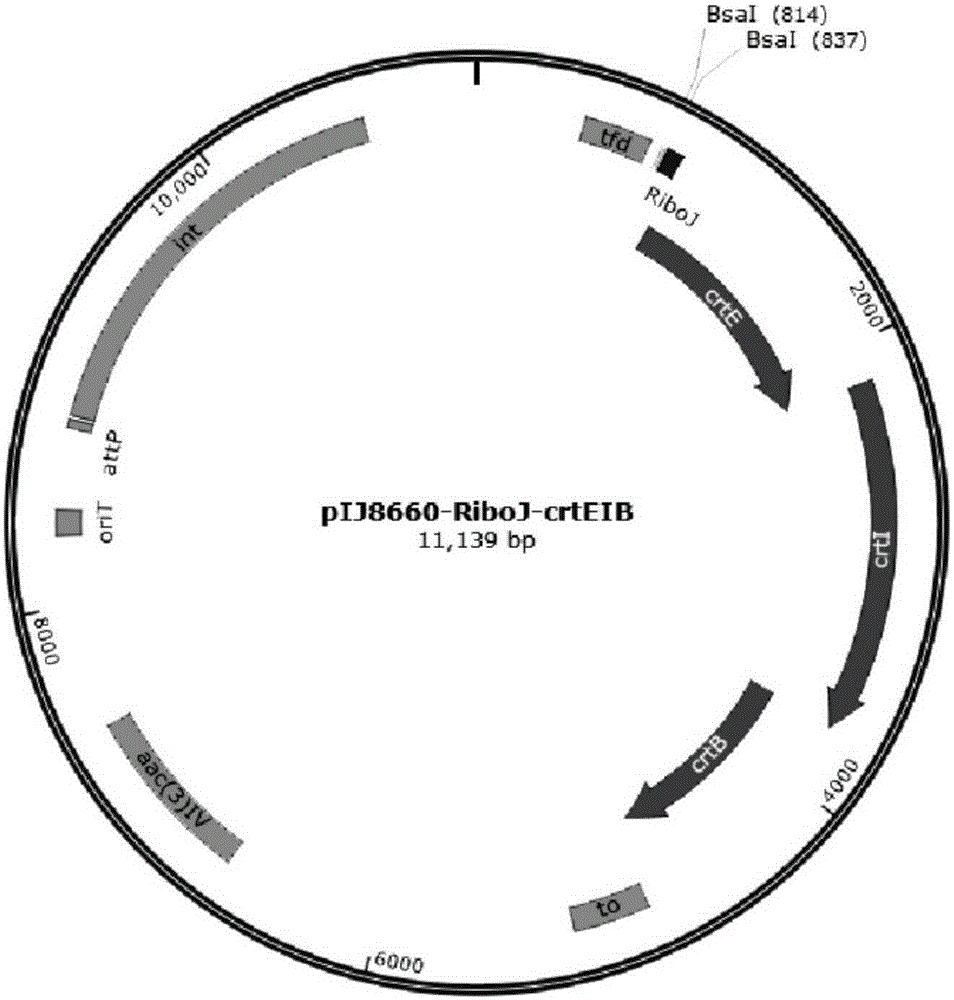
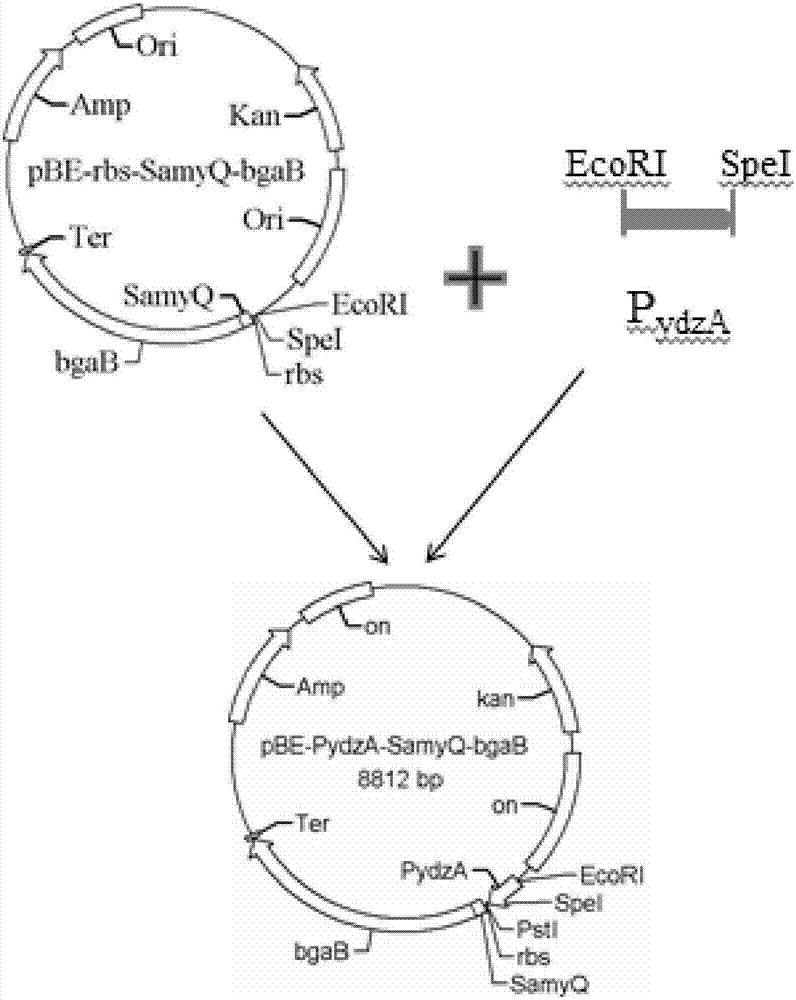
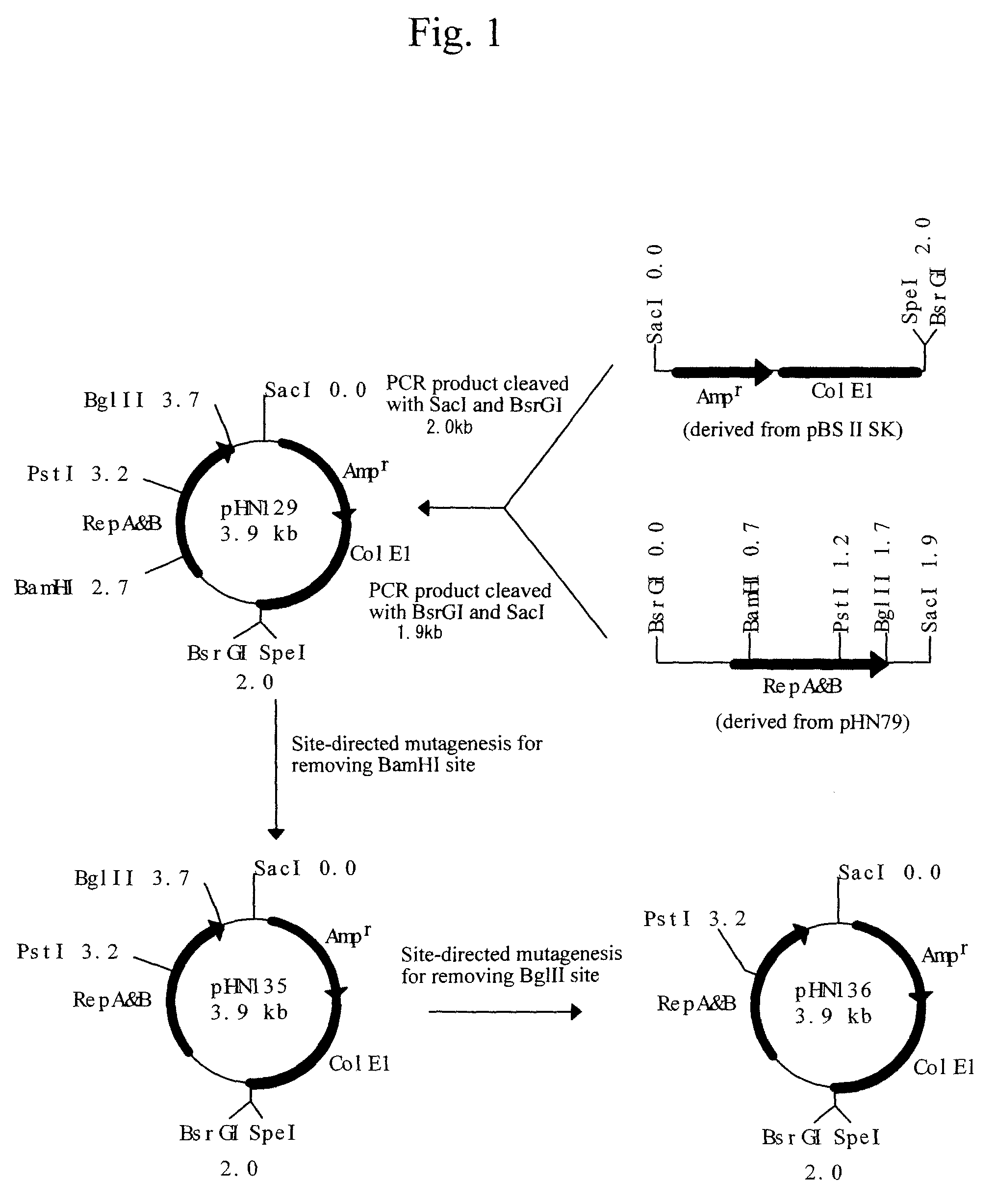
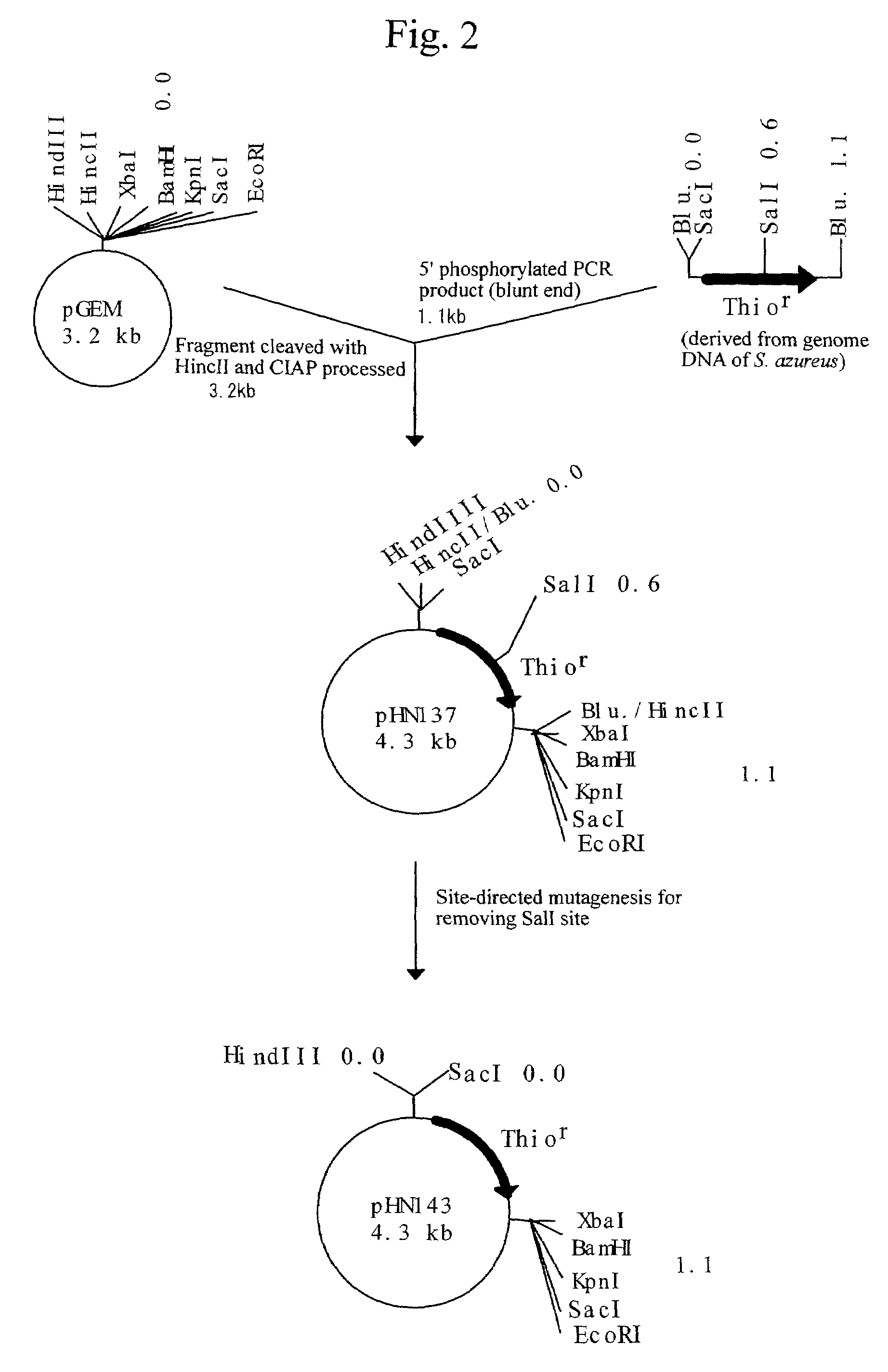
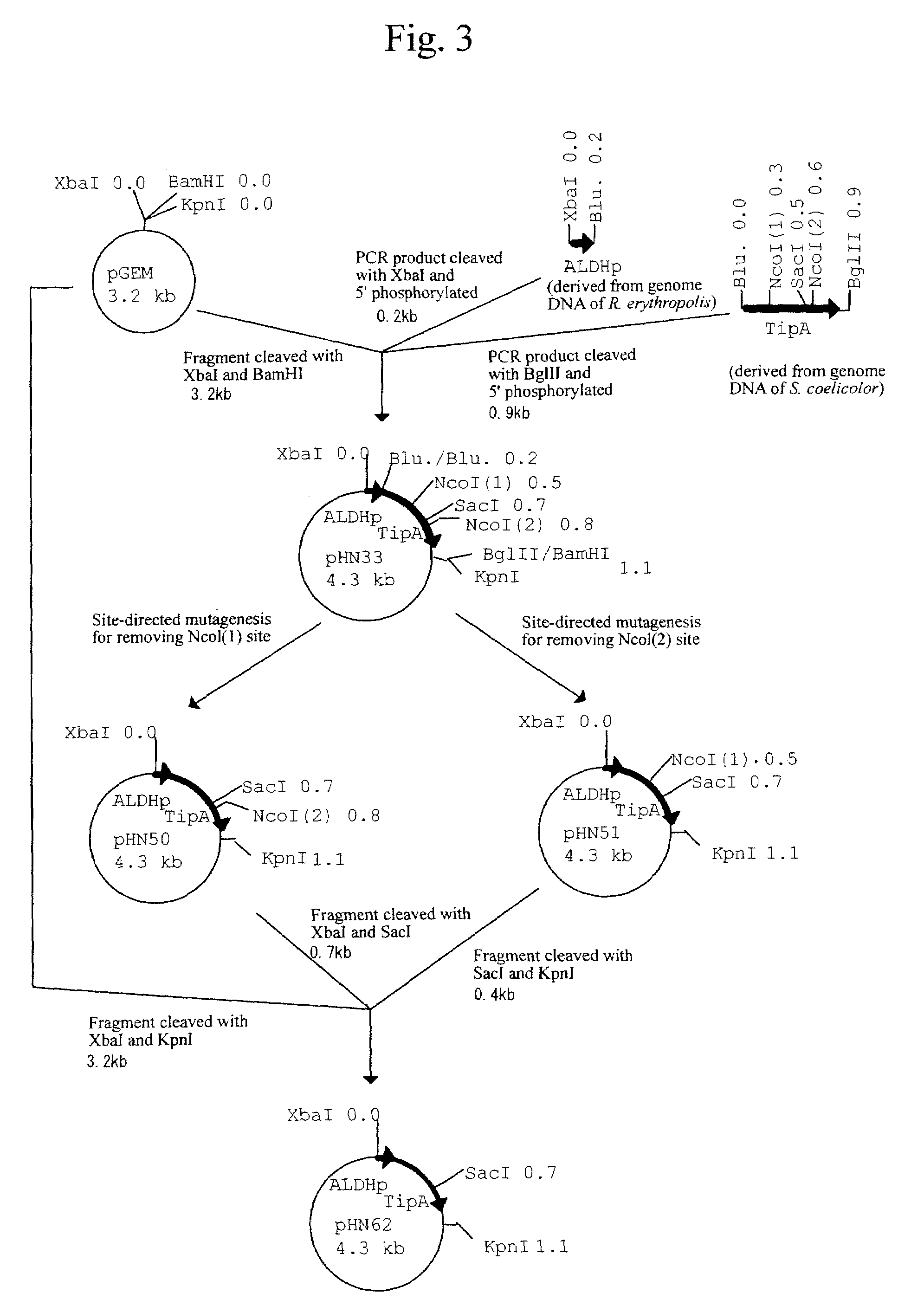
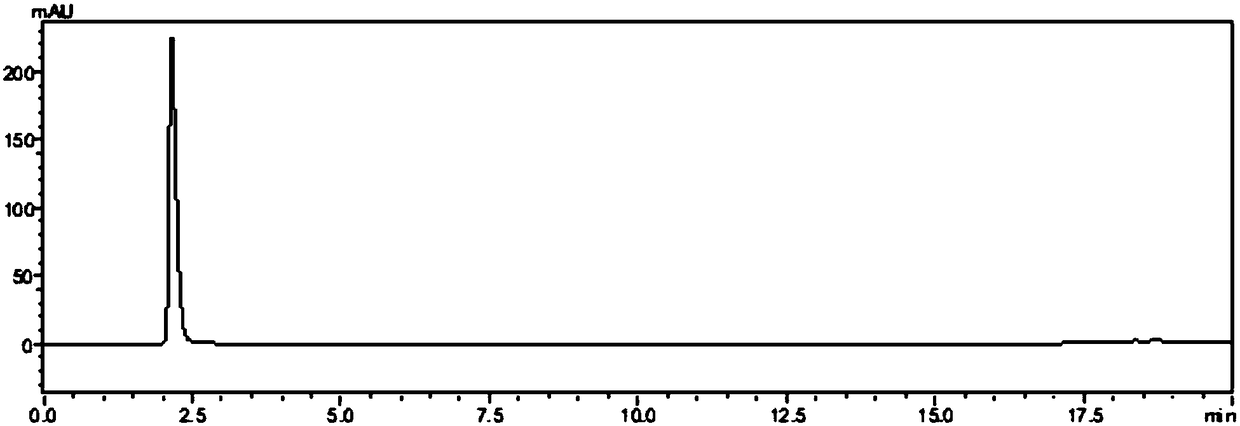
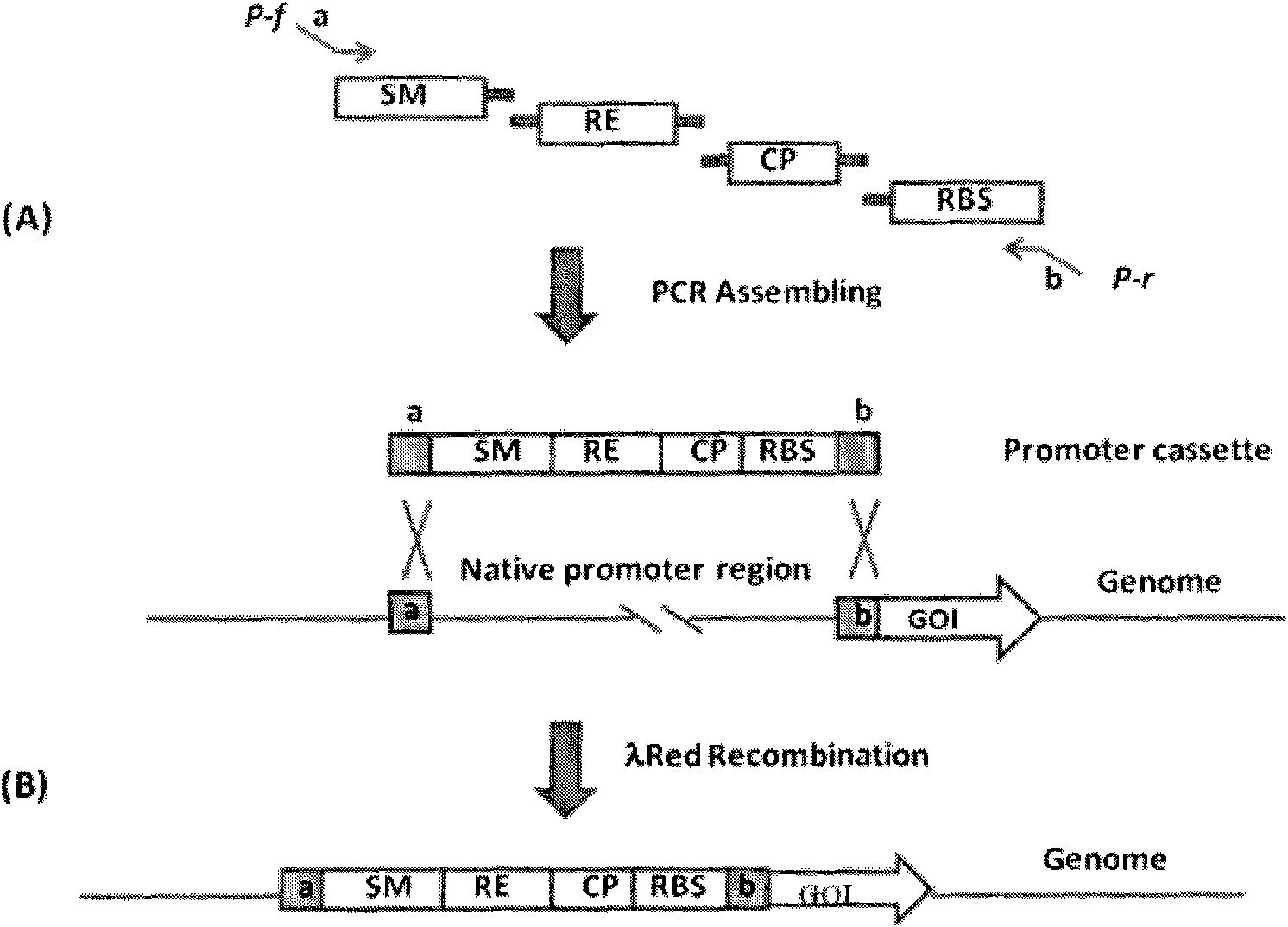
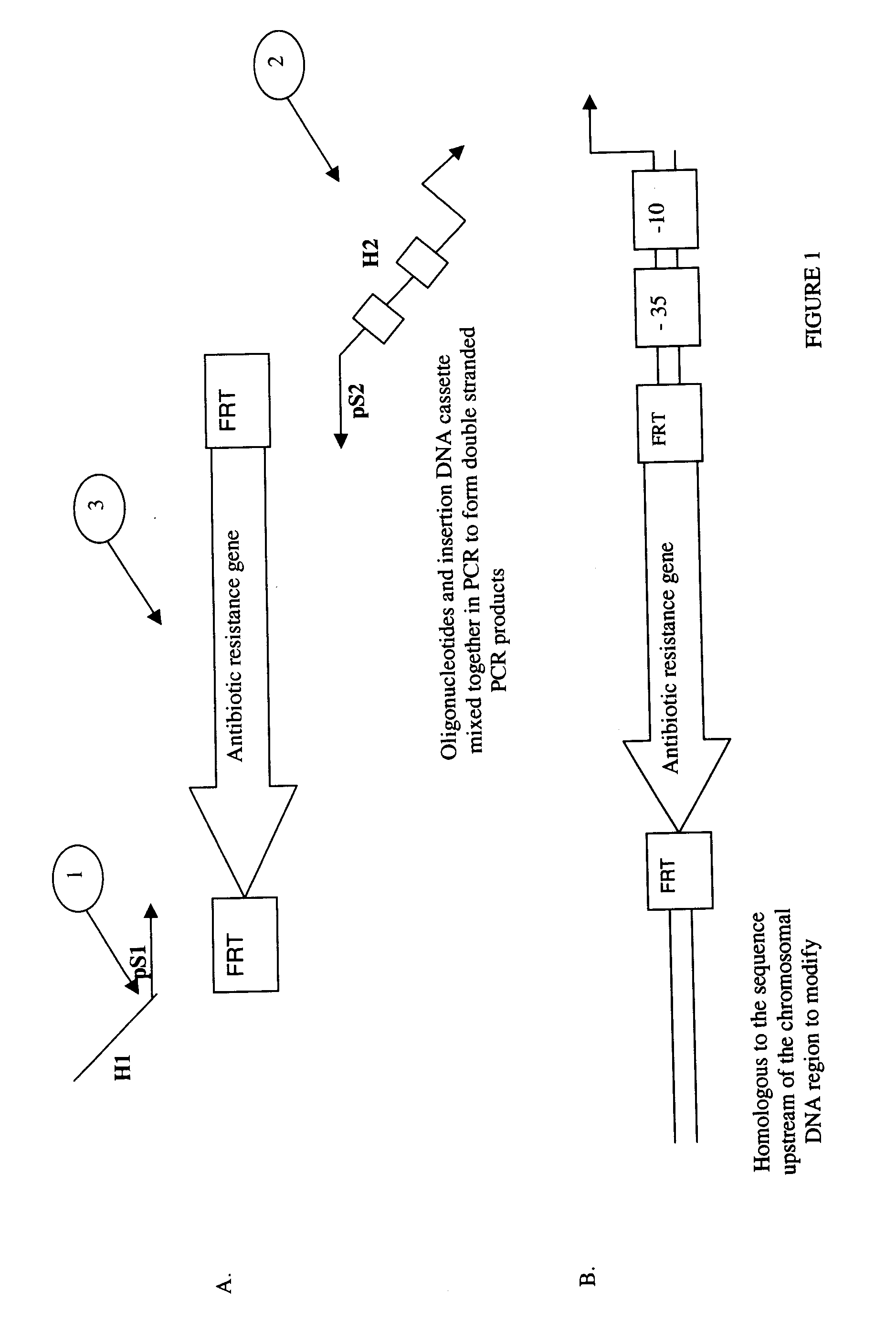
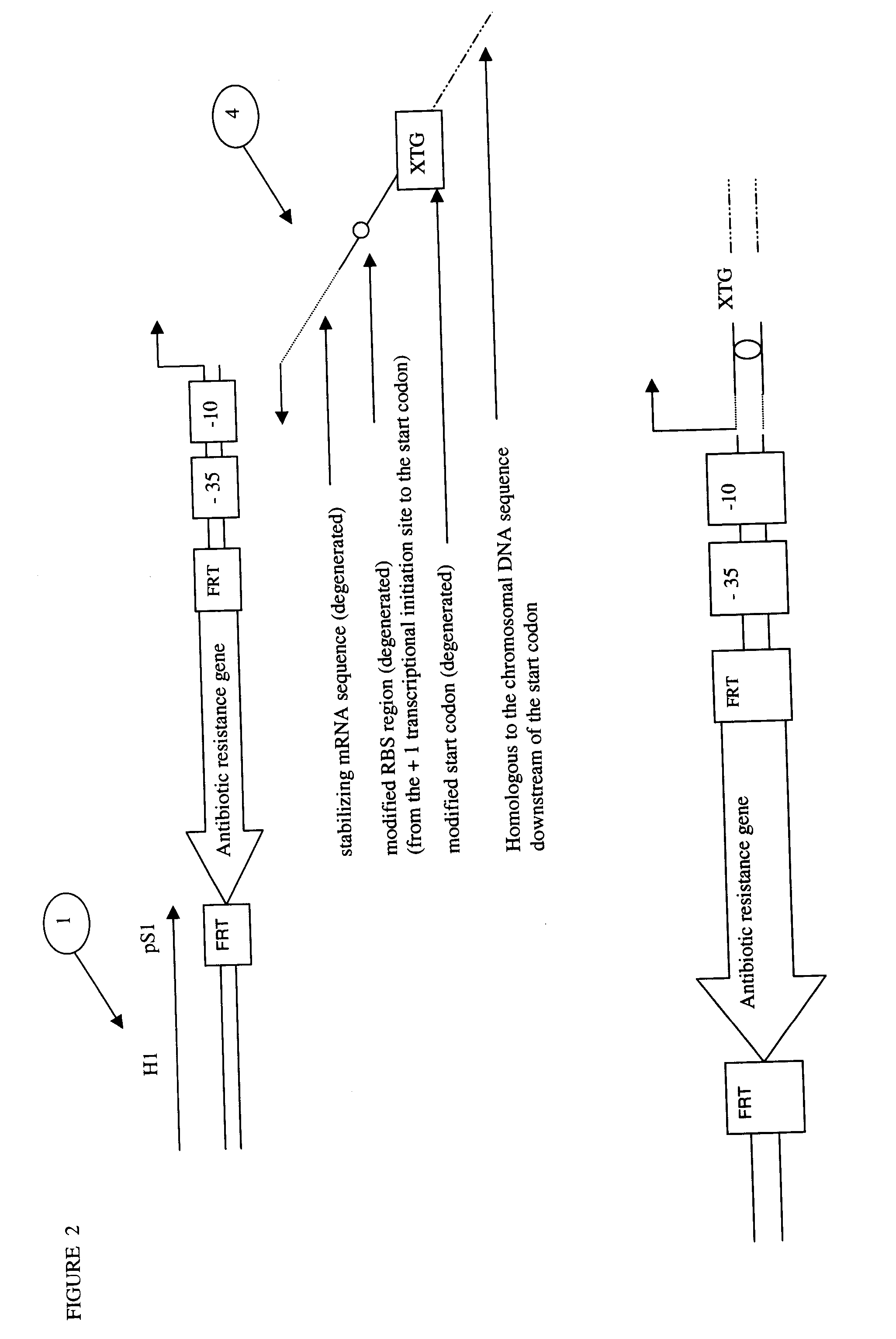
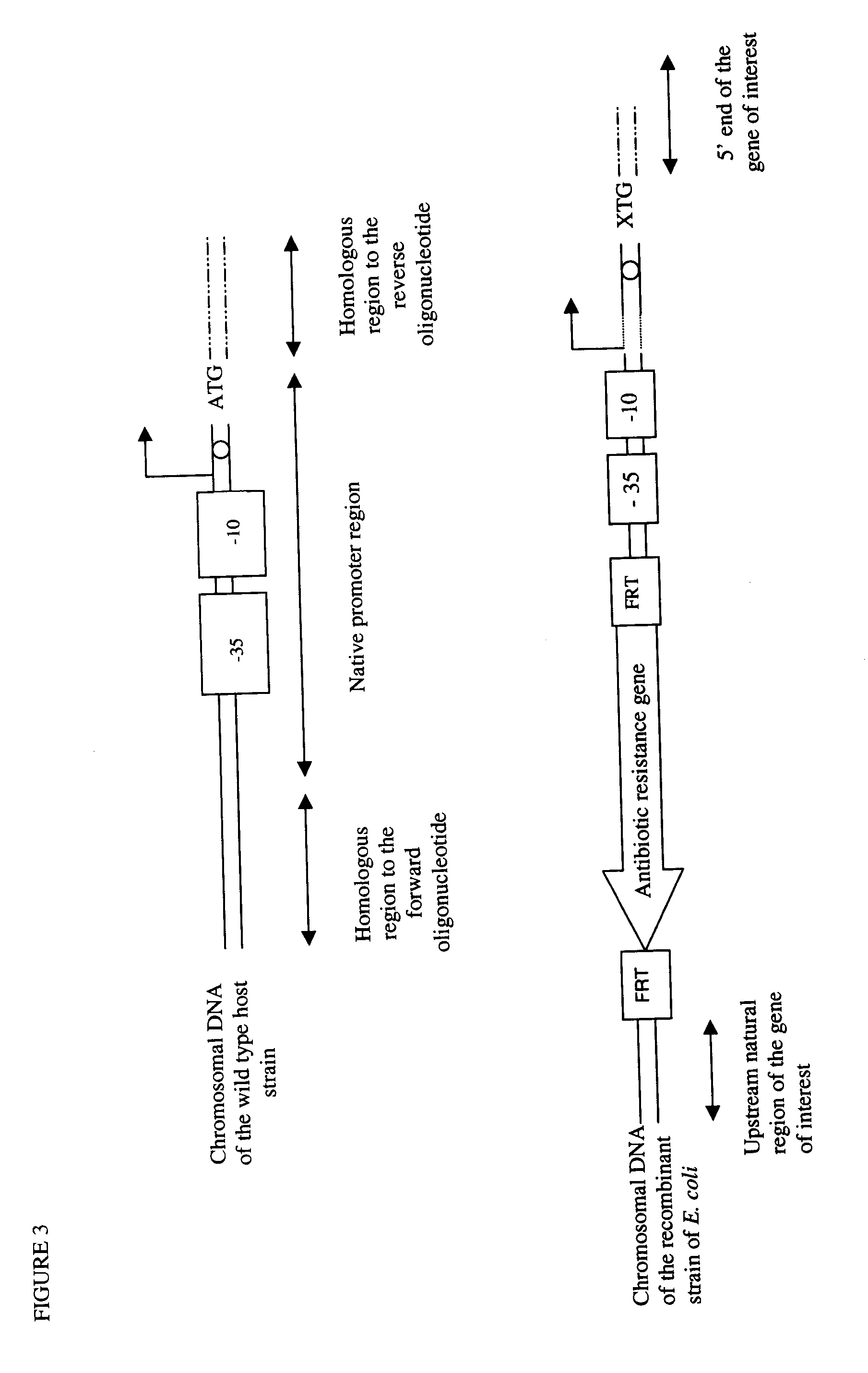
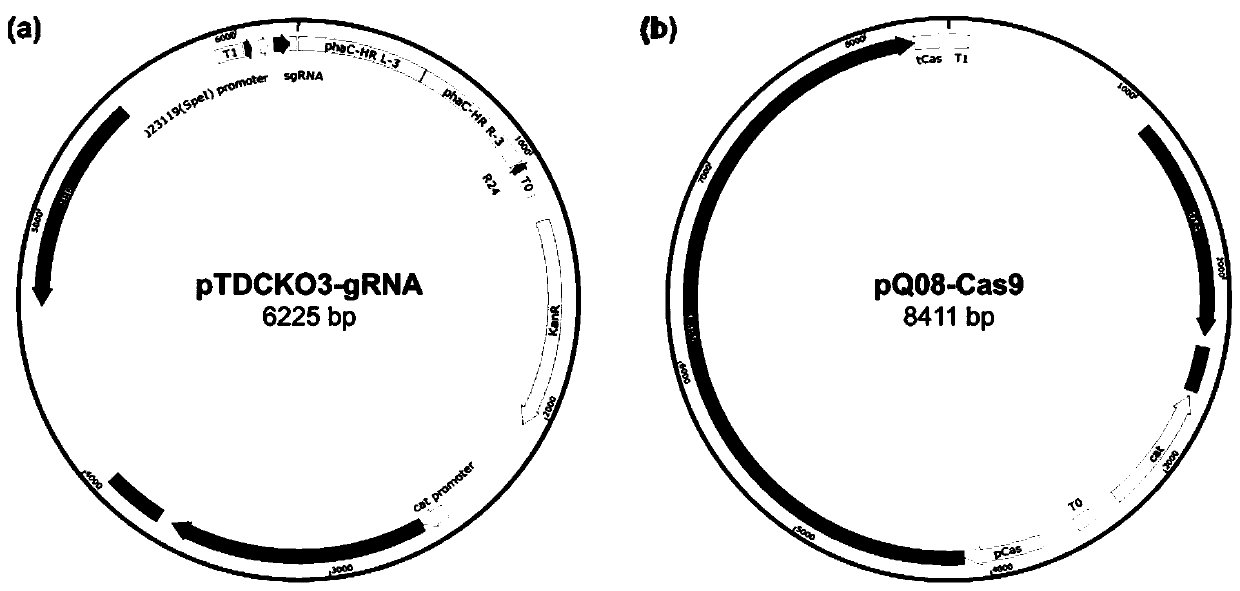
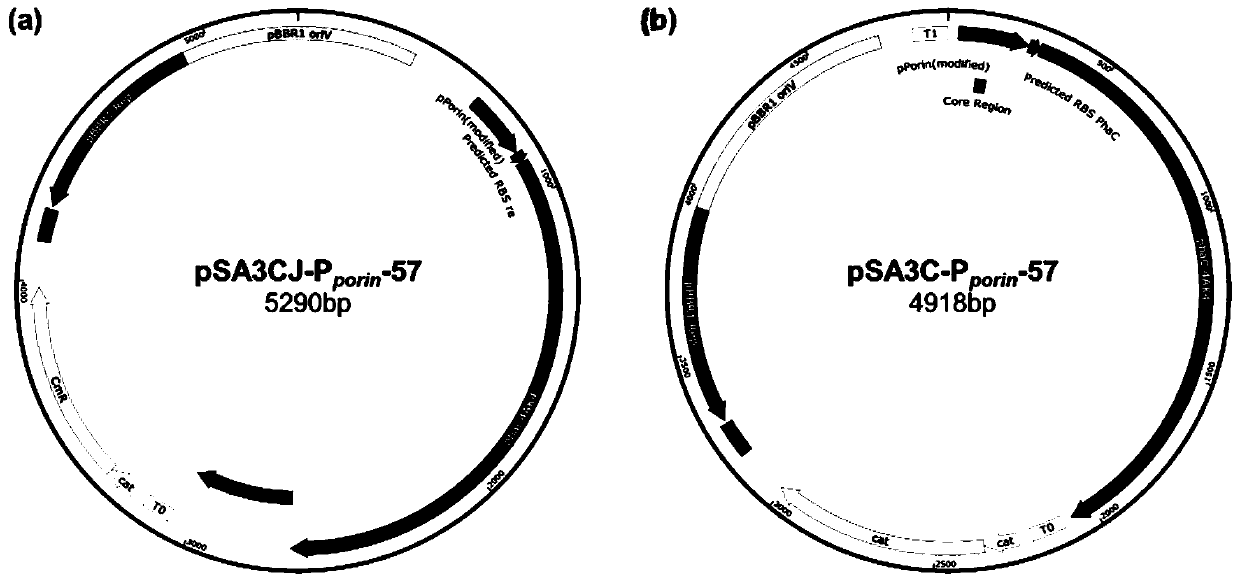
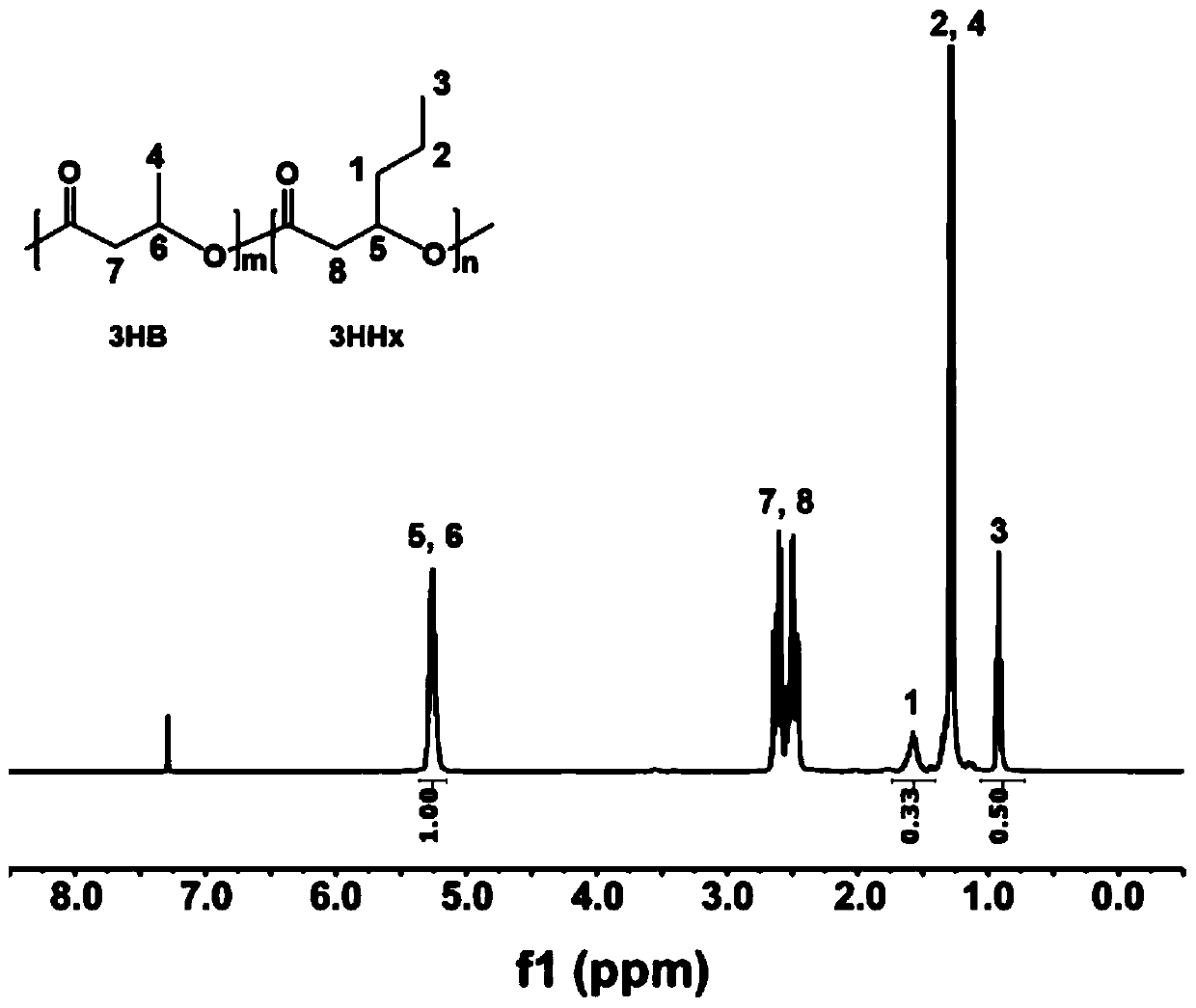
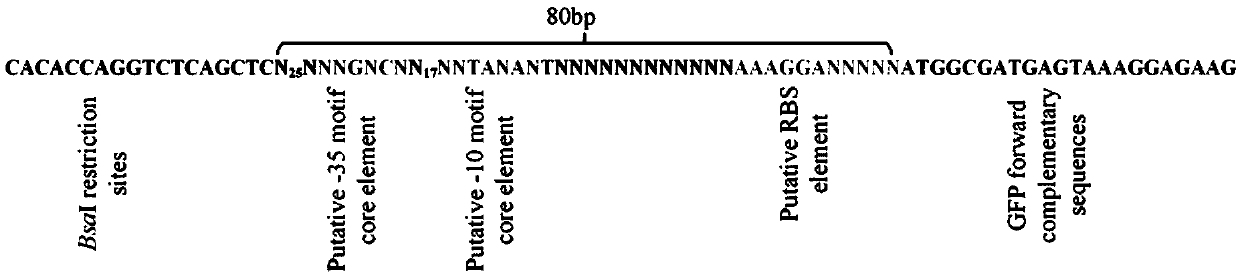
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Ribosomal binding site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A ribosome binding site, or ribosomal binding site (RBS), is a sequence of nucleotides upstream of the start codon of an mRNA transcript that is responsible for the recruitment of a ribosome during the initiation of protein translation. Mostly, RBS refers to bacterial sequences, although internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) have been described in mRNAs of eukaryotic cells or viruses that infect eukaryotes. Ribosome recruitment in eukaryotes is generally mediated by the 5' cap present on eukaryotic mRNAs.
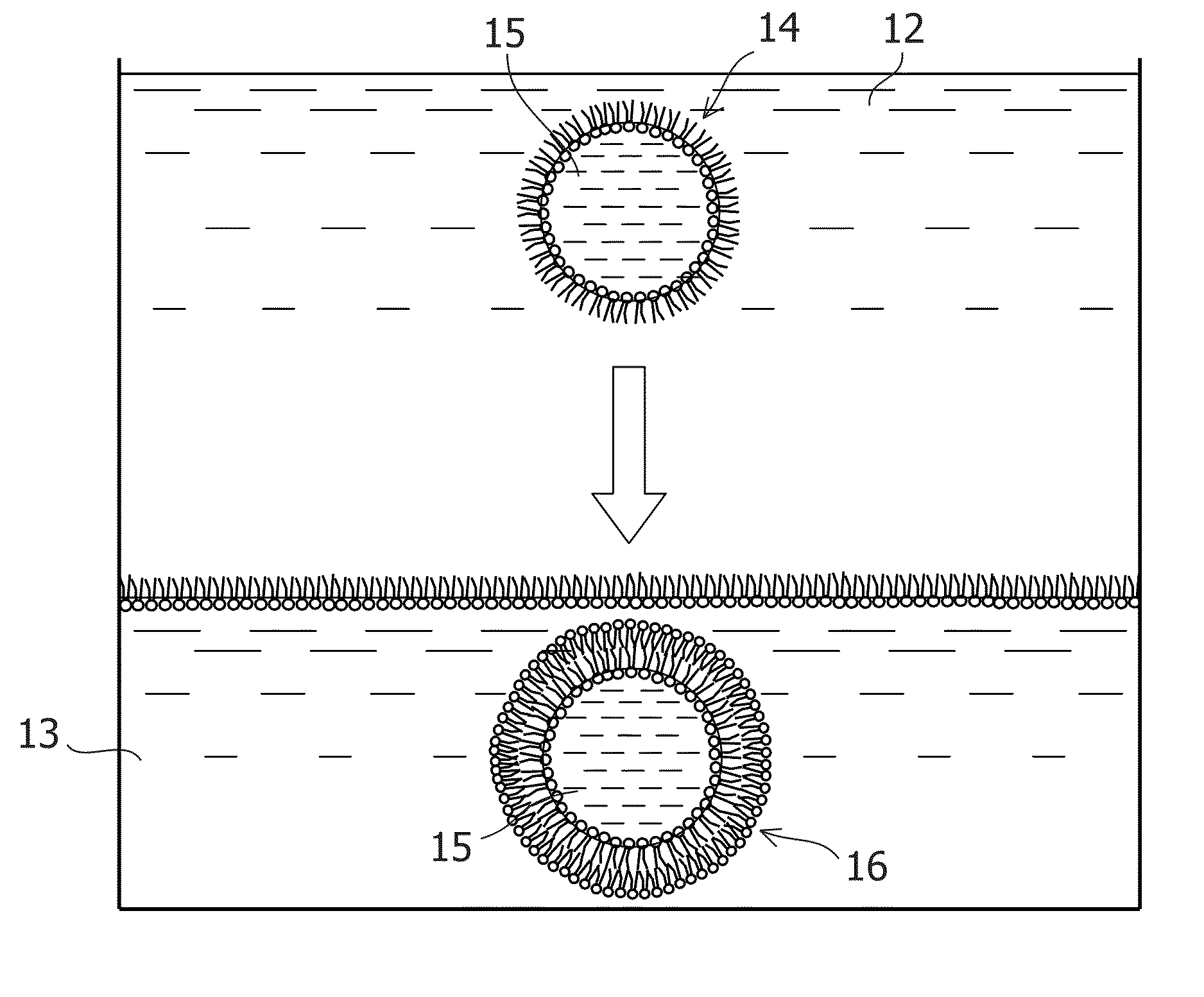
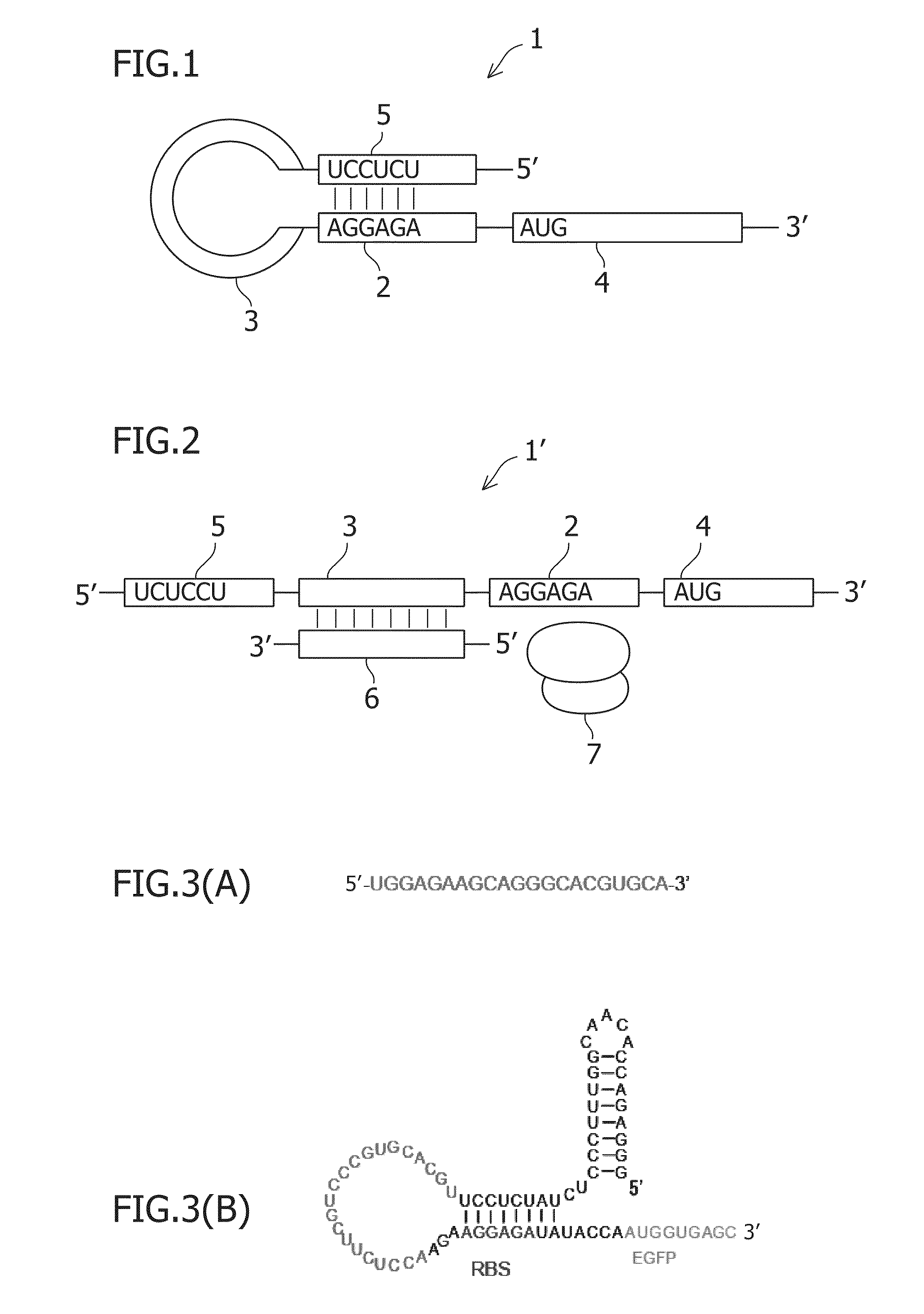
Small rna-dependent translational regulatory system in cell or artificial cell model
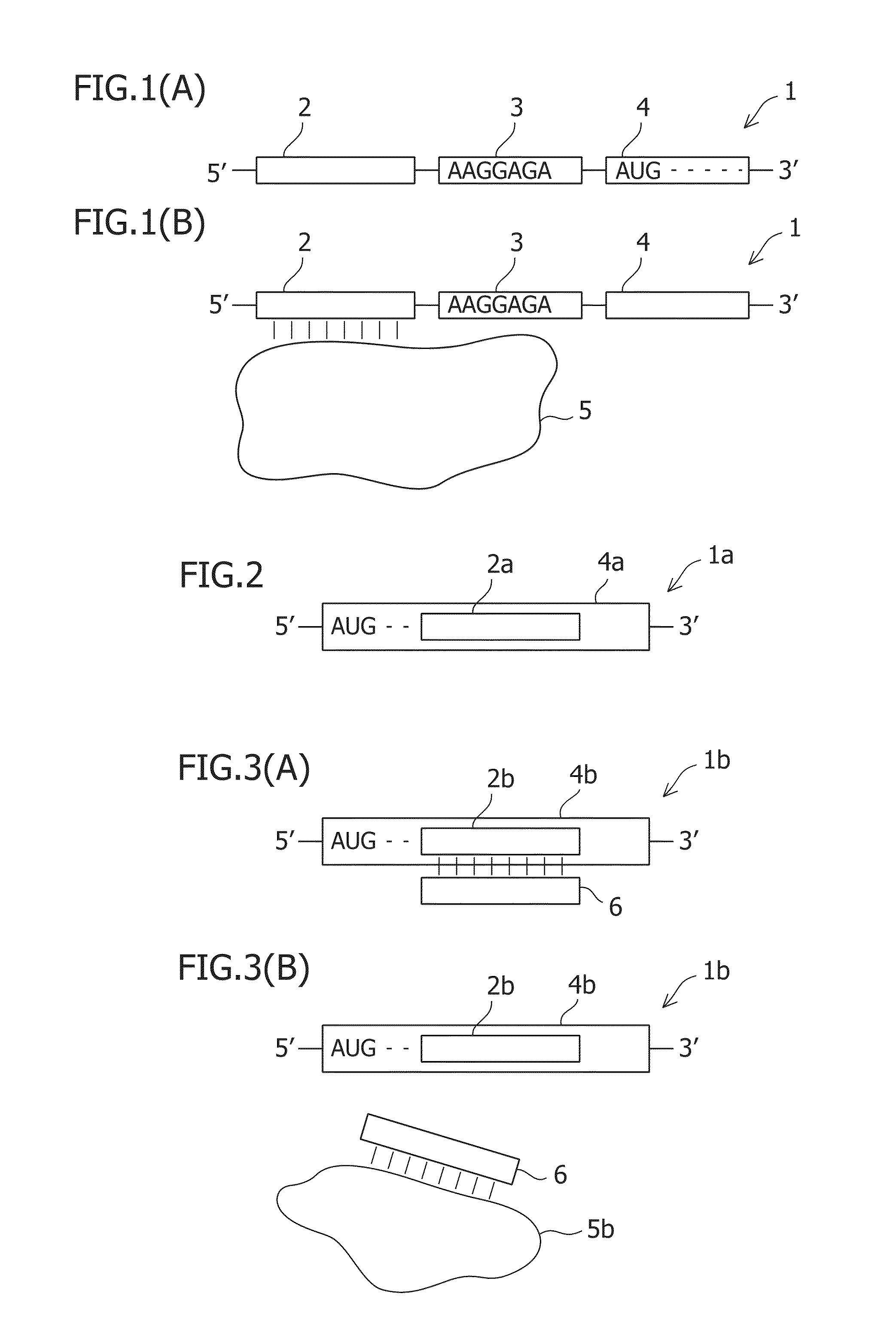
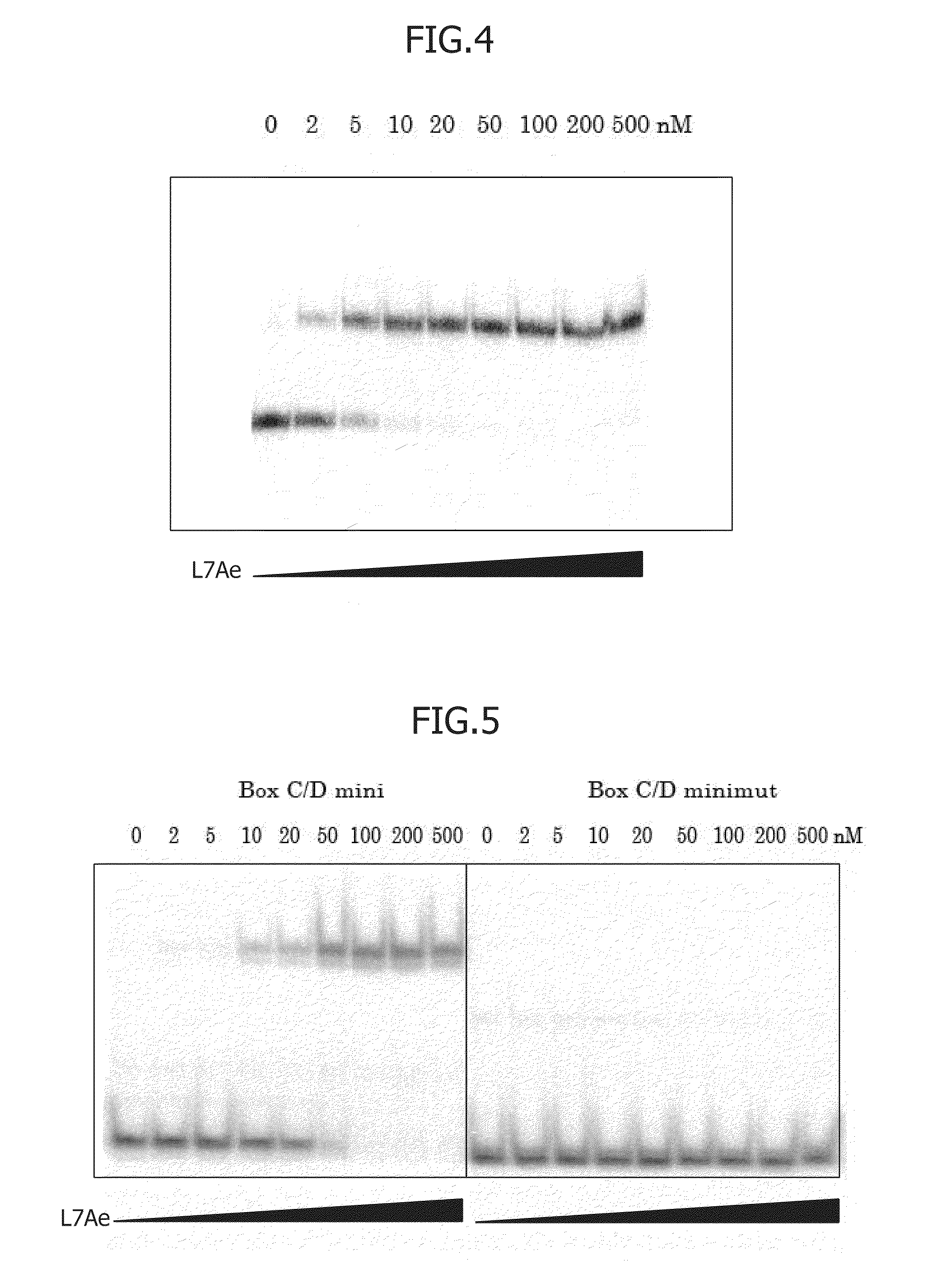
An object of the present invention is to construct an mRNA which specifically responds to a short RNA sequence and can activate, repress, and regulate the translation of the desired gene, and to construct an artificial cell model system using a liposome comprising the mRNA and a cell-free translational system encapsulated therein. The present invention provides: an mRNA comprising a target RNA-binding site located immediately 5′ to the ribosome-binding site, and a nucleotide sequence located 5′ to the target RNA-binding site, the nucleotide sequence being complementary to the ribosome-binding site; an mRNA comprising a small RNA-binding site located 3′ to the start codon, and a nucleotide sequence located 3′ to the small RNA-binding site, the nucleotide sequence encoding a protein; and a liposome comprising any of these mRNAs encapsulated therein.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
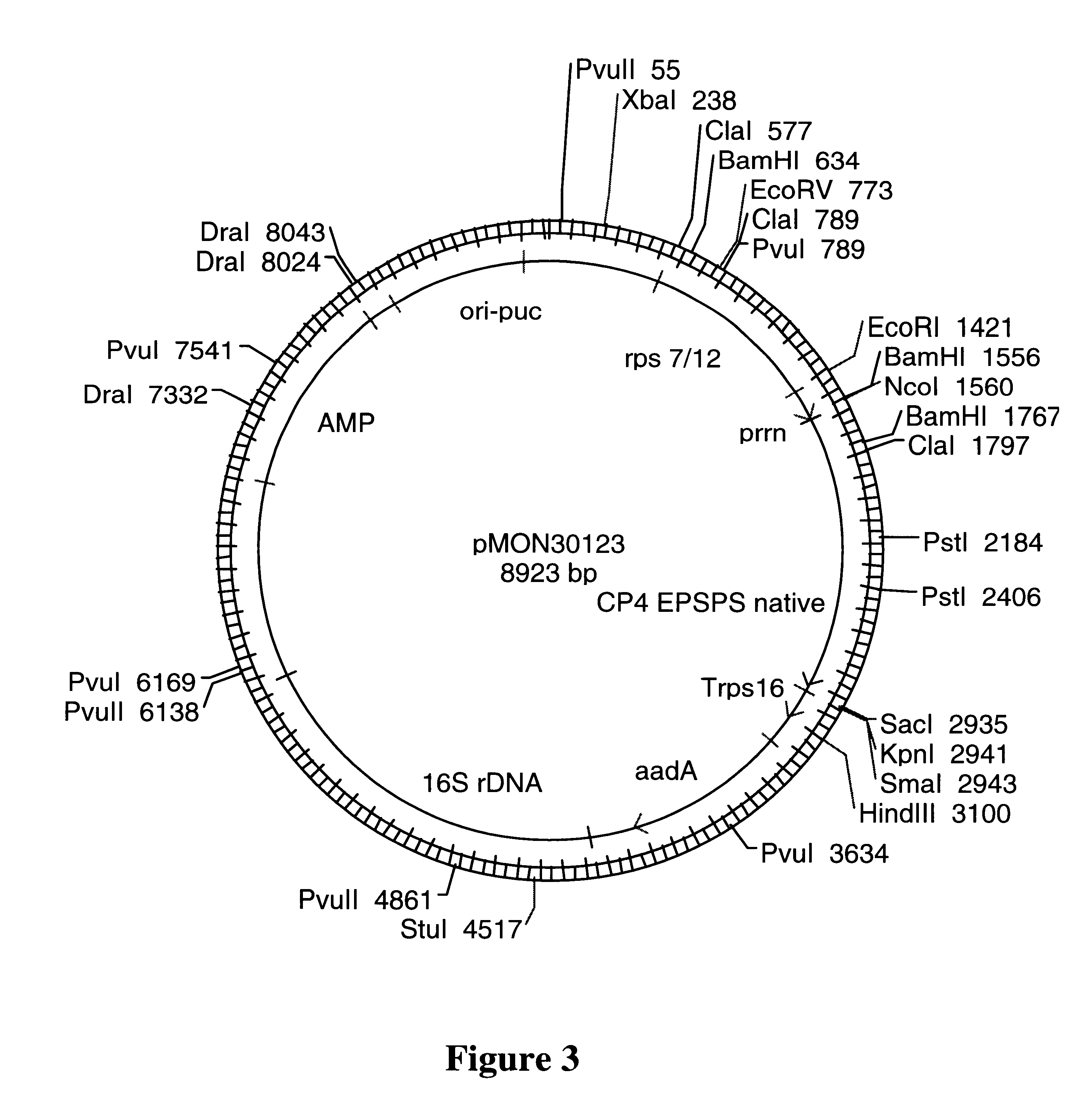
Enhancer elements for increased translation in plant plastids
InactiveUS6271444B1Improve translationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHigh level expressionBinding site
Provided are methods for increasing the production of protein in a plant cell by transforming plastids of plant cells with a construct comprising a promoter functional in a plant plastid, a ribosome binding site, DNA sequence of interest and a transcription termination region, and growing plant cells comprising the transformed plastids under conditions wherein the DNA encoding sequence is transcribed in the plastid. Also provided are methods for increasing protein production by fusing a coding sequence to a gene of interest to a secondary protein for cleavage or targetting of the protein of interest within the plastid, whereby high levels of expression of protein is achieved.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
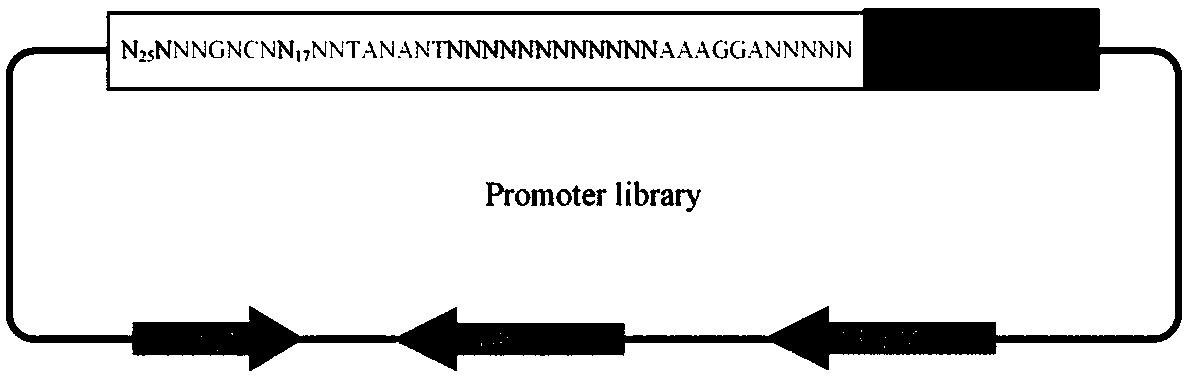
Method of creating a library of bacterial clones with varying levels of gene expression
InactiveUS20060014146A1Reduced expression levelHigh expressionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteRibosomal binding site
The present invention relates to a method of creating DNA libraries that include an artificial promoter library and / or a modified ribosome binding site library and transforming bacterial host cells with the library to obtain a population of bacterial clones having a range of expression levels for a chromosomal gene of interest.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
DNA fragment with promoter function and application
ActiveCN104630229AStrong specific expression activityHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBinding siteNucleotide
The invention discloses a DNA fragment with a promoter function and an application. The DNA fragment is any one of the following sequences: (a) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary sequence of the nucleotide sequence; (b) a nucleotide sequence having a promoter function identical to SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary sequence of the nucleotide sequence obtained by substituting, deleting or adding one or more nucleotides on the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO: 1; and (c) sequences of one or more ribosome bind sites added in the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO: 1. The DNA has a promoter function and is high in expression activity, and high expression of exogenous genes can be realized under a condition that inducers are not needed, and the DNA fragment is applied to expression of heatproof beta-galactosidase and transglutaminase. An effective tool is particularly provided for expression of bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Actinobacillus succinogenes shuttle vector and methods of use
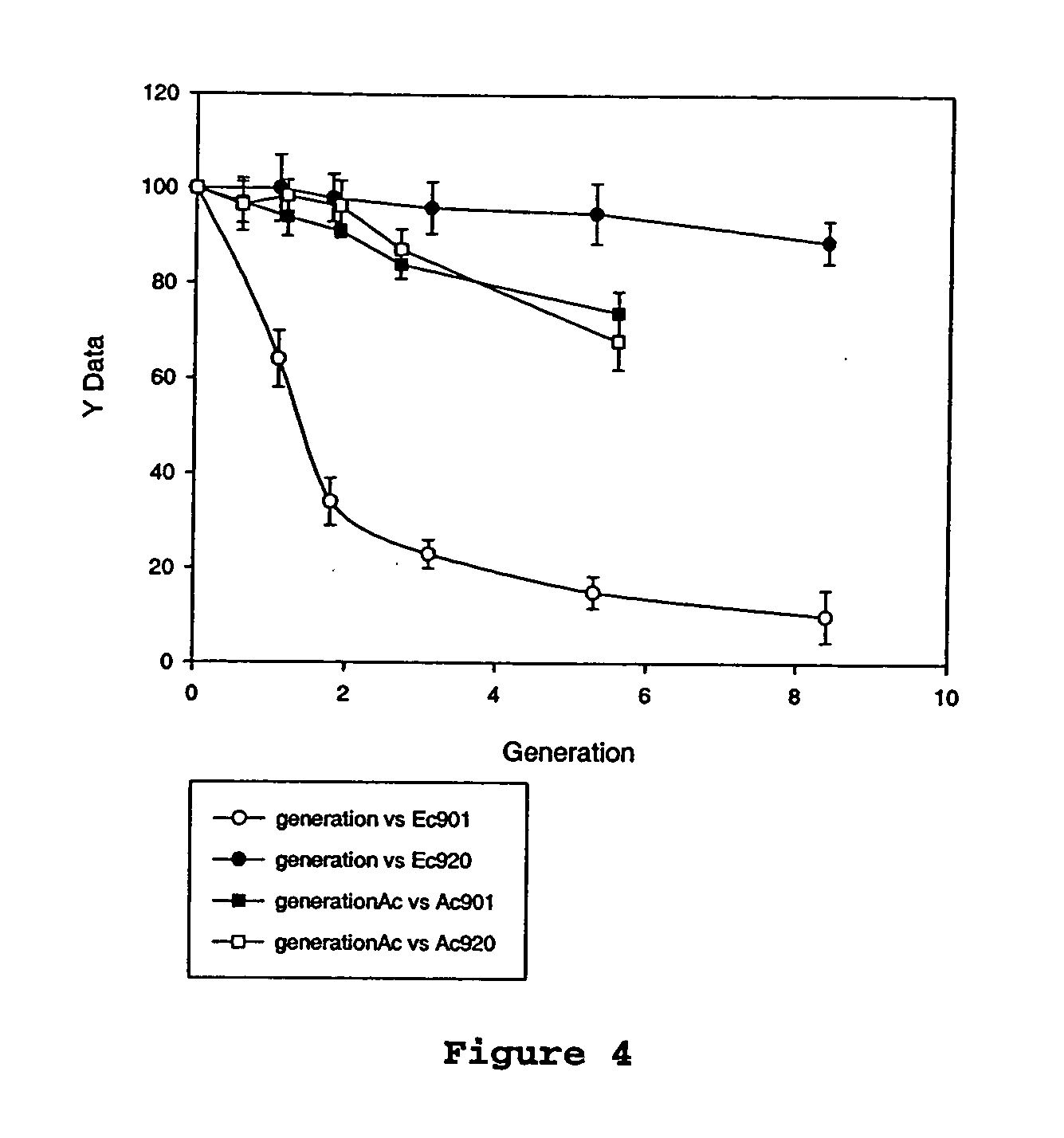
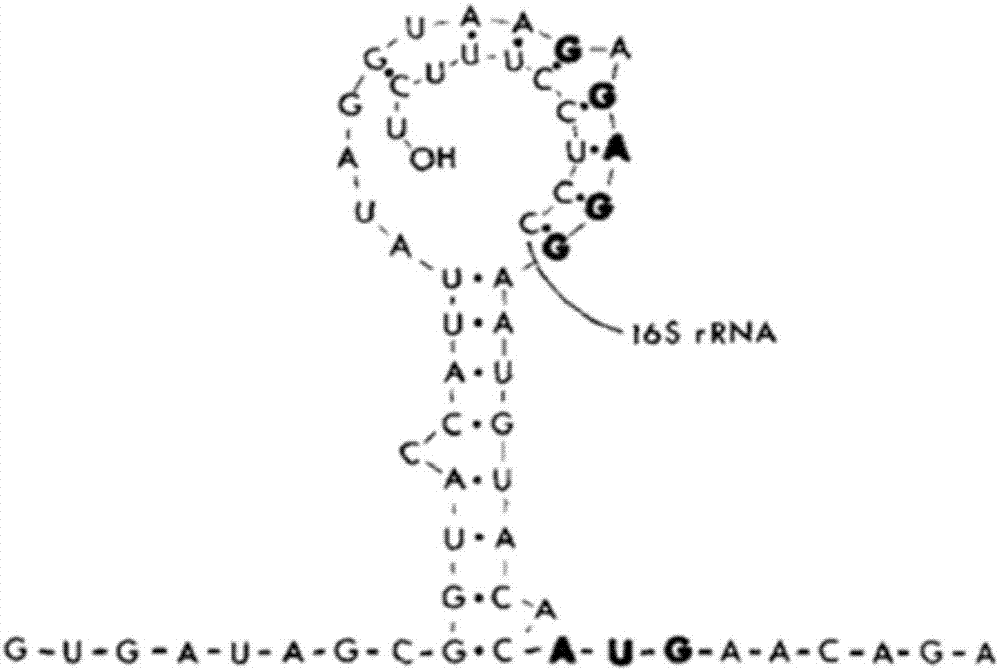
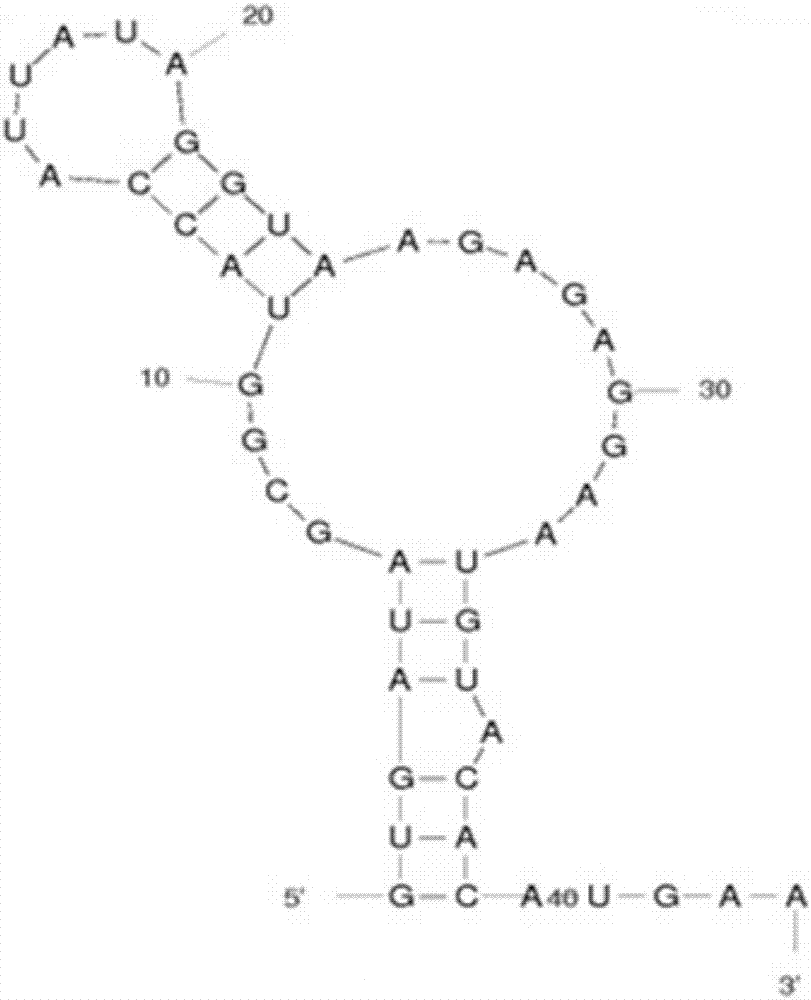
An Actinobacillus succinogenes plasmid vector which provides a means to overexpress proteins in A. succinogenes. The plasmid can be transformed efficiently by electroporation, and replicates in a stable manner in A. succinogenes. The plasmid comprises at least one marker gene, operably linked to a first promoter functional in Actinobacillus succinogenes, an origin of replication functional in Actinobacillus succinogenes, a second promoter isolated from Actinobacillus succinogenes, and a cloning site downstream from the second promoter. Plasmids pLGZ901, pLGZ920, pLGZ921, and pLGZ922 are disclosed. The pckA gene polypeptide sequence and nucleic acid sequence of Actinobacillus succinogenes, including the promoter and ribosome binding site, is disclosed. Furthermore, a method for producing a recombinant Actinobacillus succinogenes is described, including a method of transformation. Additionally, a recombinant Actinobacillus succinogenes is disclosed and a method for producing succinate utilizing this recombinant Actinobacillus succinogenes is described.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Ribosome binding site reconstruction-based promoter optimization method
ActiveCN106939310AIncreased binding levelsImprove expression levelPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionTranscription initiation siteBinding site
A ribosome binding site reconstruction-based promoter optimization method comprises the following steps: 1, amplifying the sequence of a ribosome binding site behind the transcription initiation site of a P43 promoter in Bacillus subtillis; and 2, amplifying a P43 promoter with the ribosome binding site sequence through primer design to obtain a sequence with at least one structure function. The ribosome binding site in the P43 promoter is optimized through the method to make the binding level of the optimized promoter and mRNA improved in order to improve the expression level of target gene.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
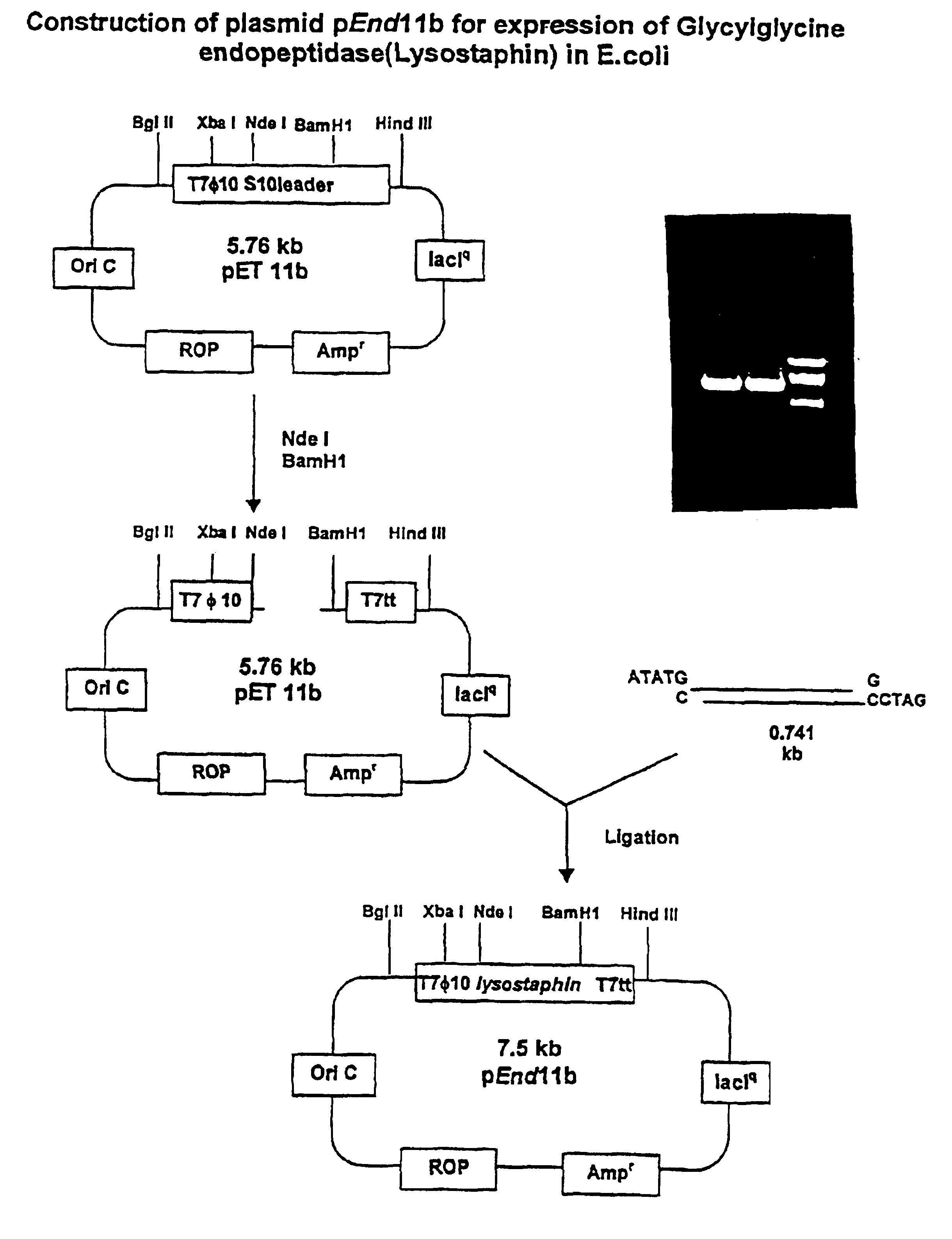
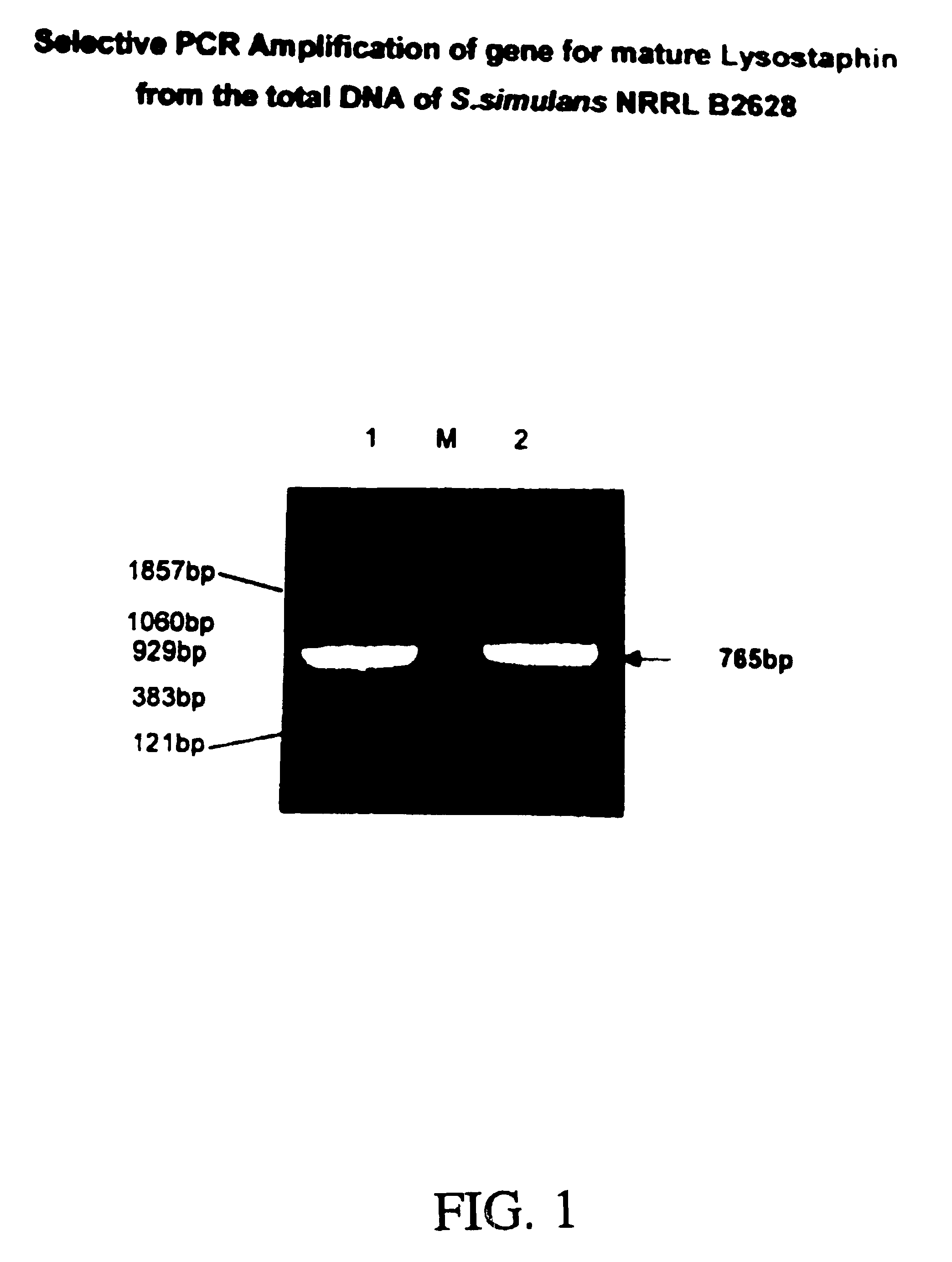
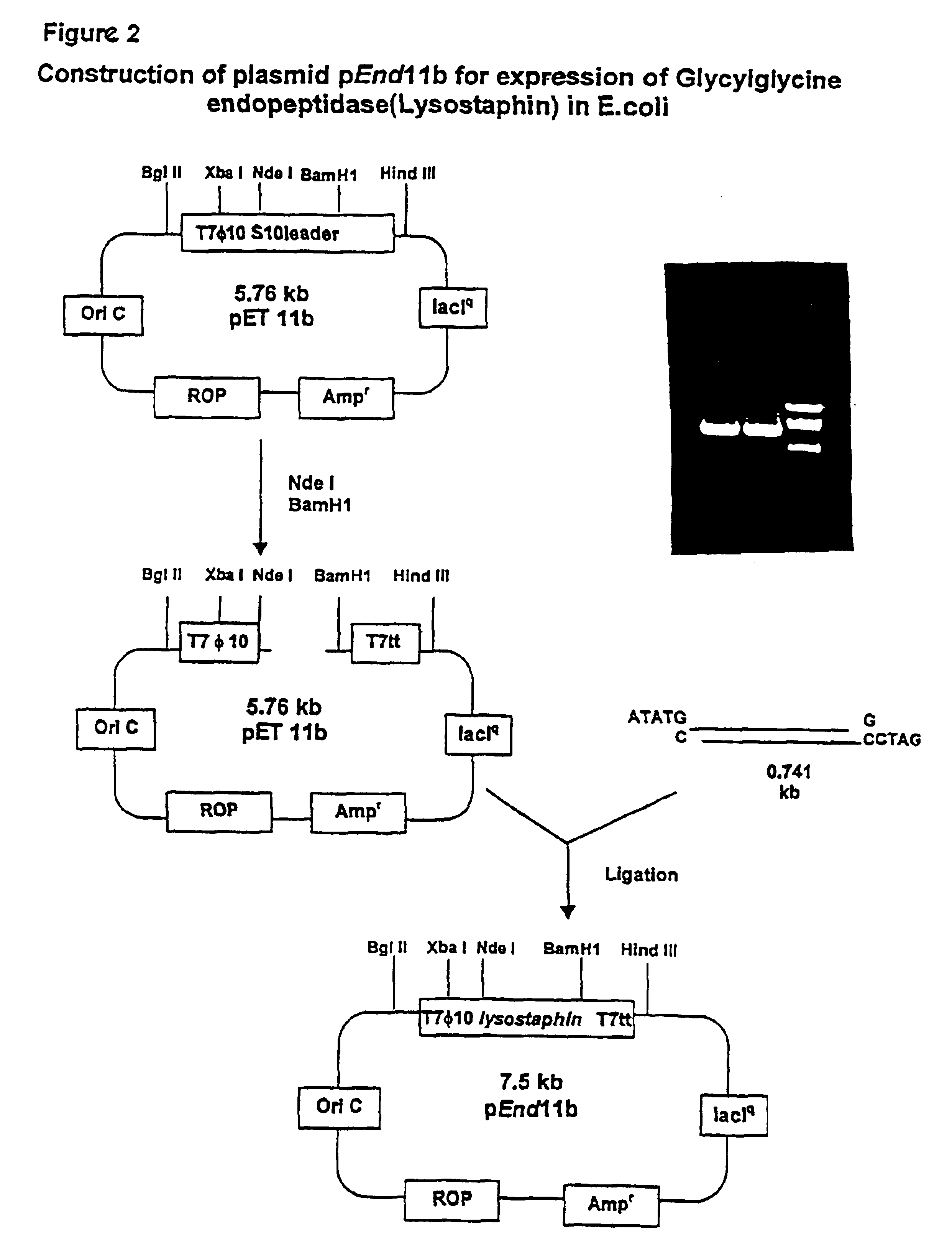
Expression of recombinant mature lysostaphin
A portion of the lysostaphin gene of Staphylococcus simulans has been cloned and overexpressed in the cytoplasm of E. coli to yield lysostaphin, in the absence of preprolysostaphin and prolysostaphin, under the transcriptional control of an IPTG-inducible promoter and a ribosome binding site. IPTG induction of the transformed host cells produces intracellular, soluble, mature lysostaphin (27 kDa), in the complete absence of preprolysostaphin and prolysostaphin. The mature lysostaphin so formed dose not require post-translational modification. The mature lysostaphin so formed can be used treat and prevent staphylococcal infections.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
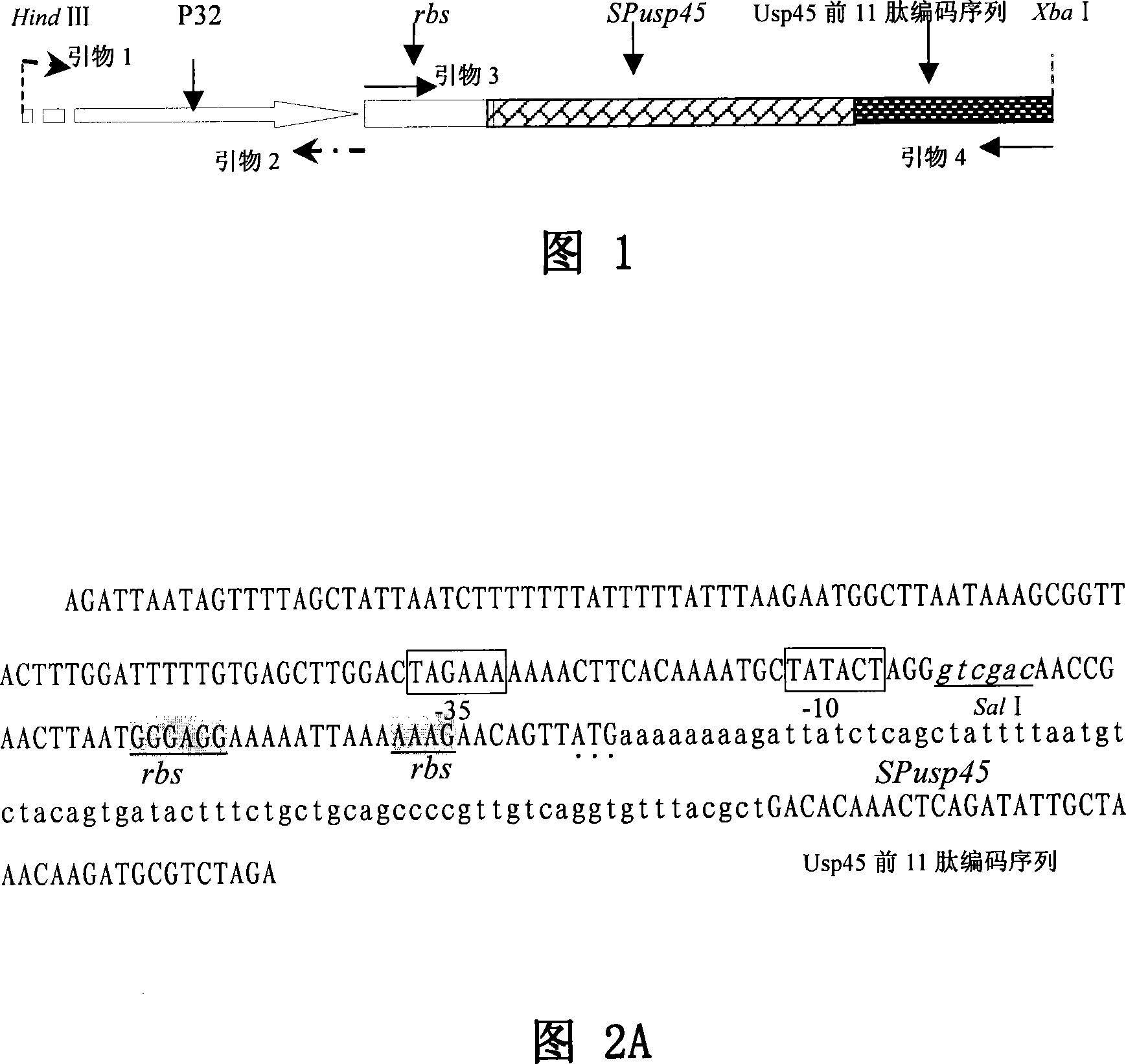
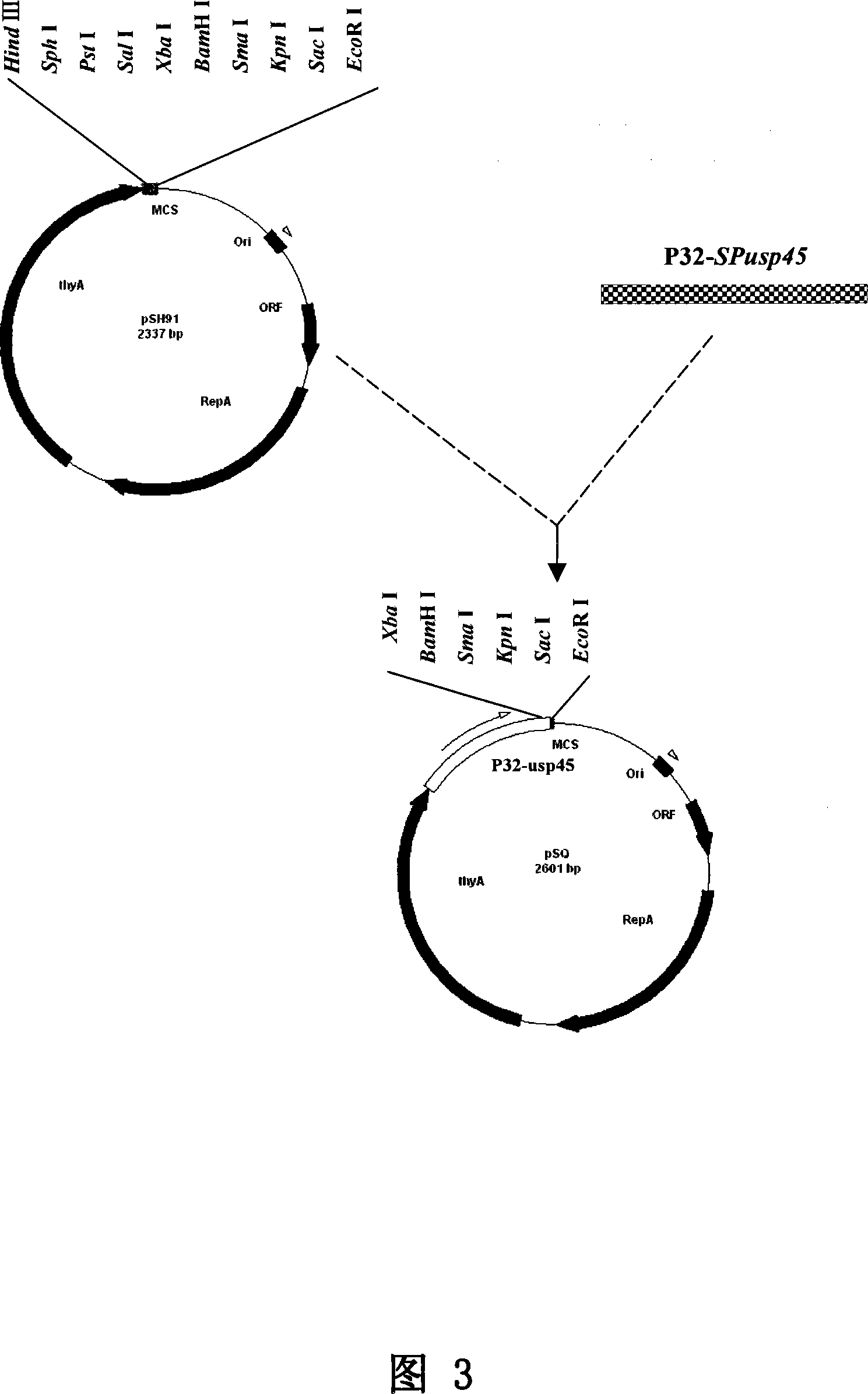
Lactococcus lactis food-sate secretion expression carrier and its preparing method and application
ActiveCN101168741ABacterial antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBinding siteGene selection
The invention relates to lactic acid galactococcus food-grade secretion expression vector, and the preparation method and the application thereof, in particular to the lactic acid galactococcus food-grade secretion expression vector which comprises the following components: a thyA gene selection marker, replicons of plasmid pWV01, multiple cloning sites, promoter used for secretion expression, a ribosome bind site of Usp45, a signal peptide sequence of Usp45 and a partial Usp45 mature peptides coded sequence.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
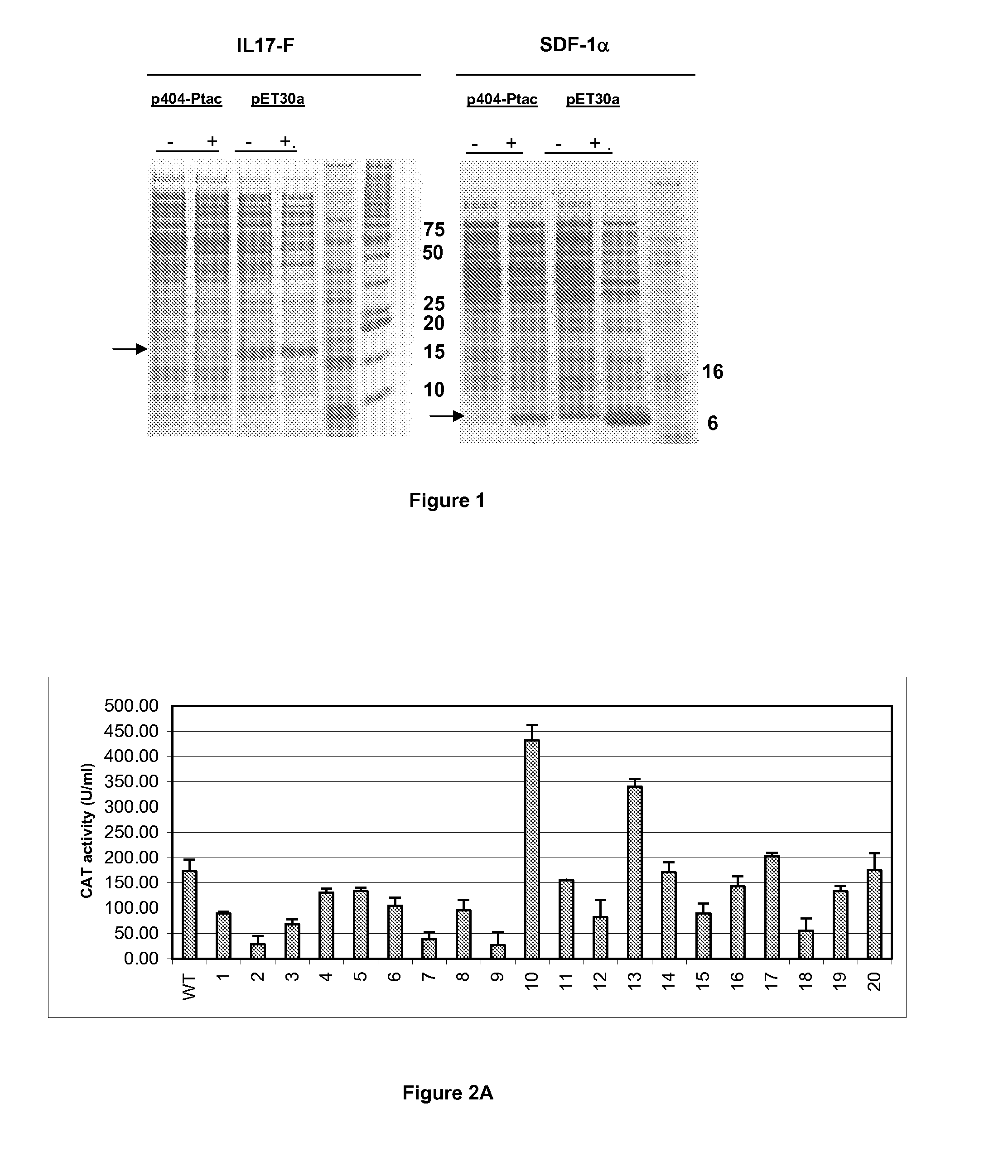
Variation of Recombinant Expression Titres By Optimising Bacterial Ribosome Binding Sites
The present invention provides a method for optimising the ribosome binding site of a promoter for the expression of a gene encoding a polypeptide of interest, placed under the control of said promoter. The invention also relates to a vector containing such optimised promoters, a prokaryotic host cell transformed by said vector, as well as a method for producing a recombinant protein of interest.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Escherichia coli for producing riboflavin and constructing method and use of Escherichia coli
ActiveCN103865944AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRiboflavin Metabolism
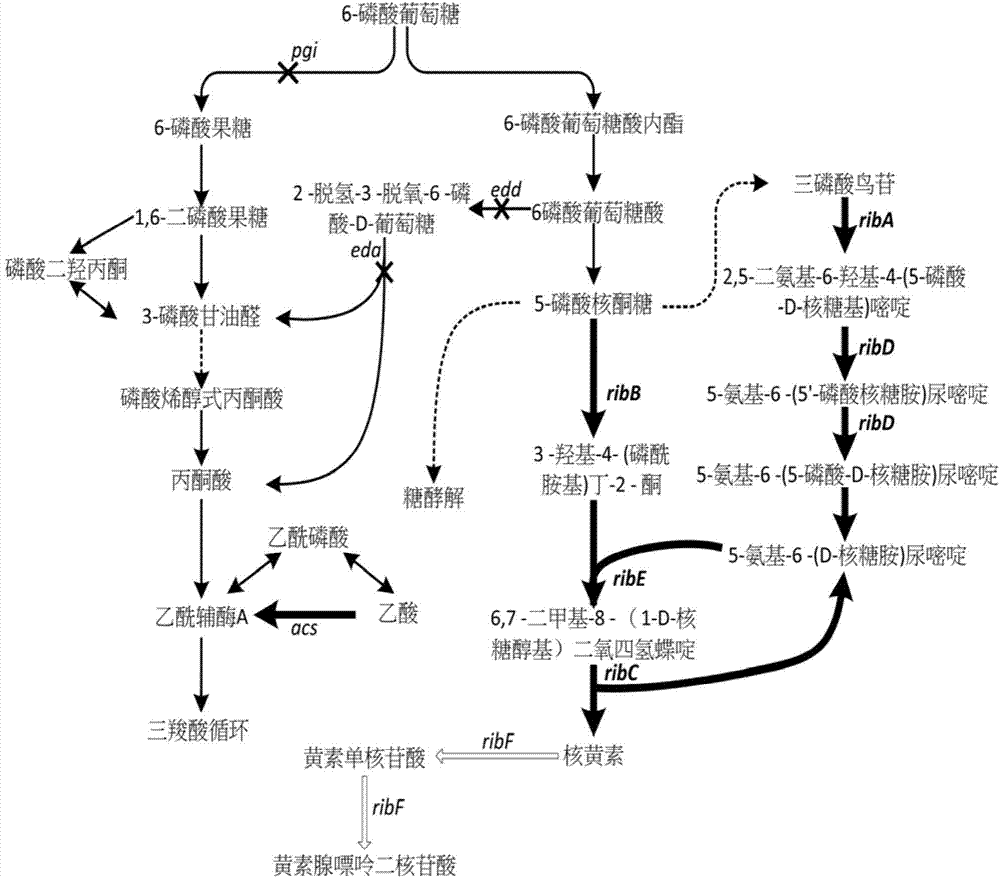
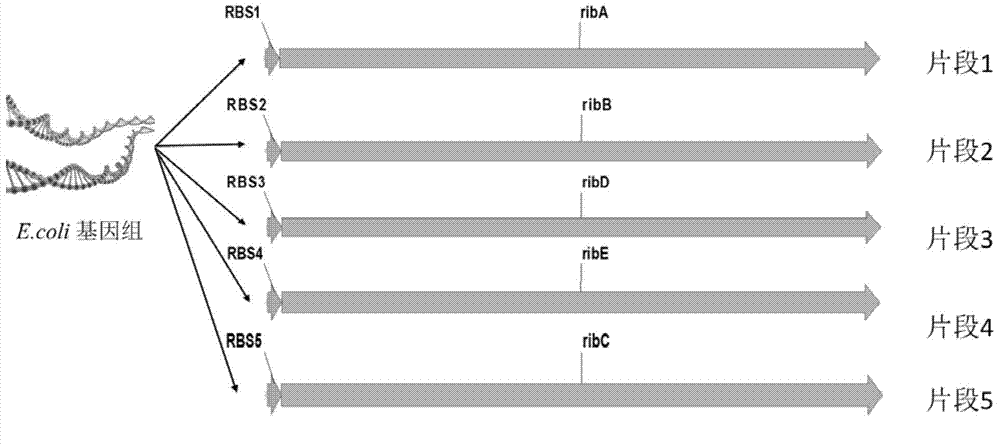
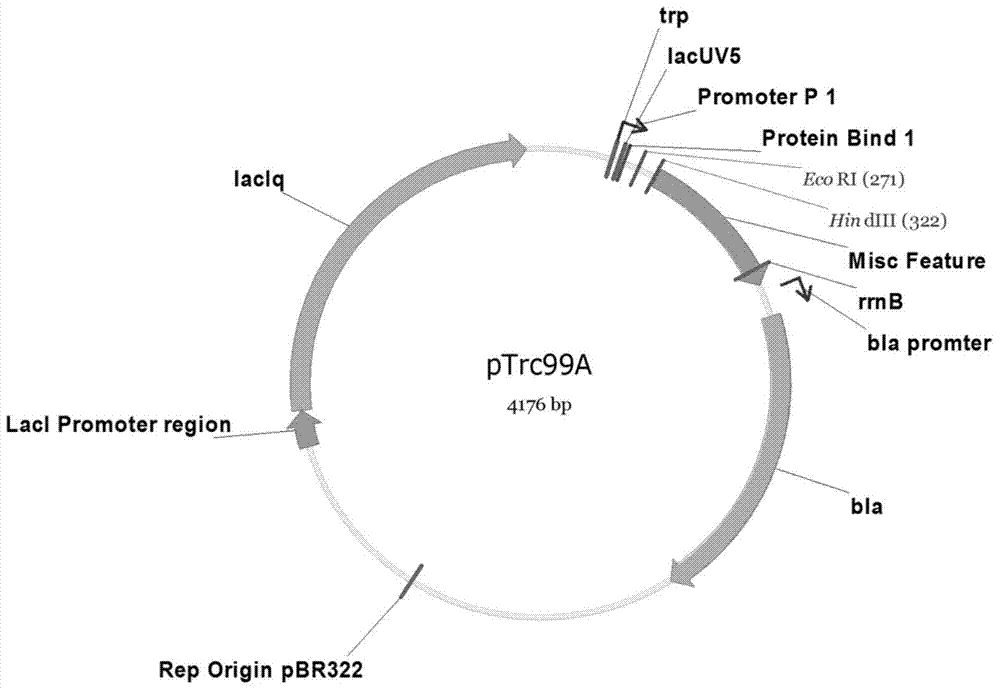
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli for producing riboflavin and constructing method and use of Escherichia coli. The preparation method comprises the following steps: designing ribosome bind sites RBS1, RBS2, RBS3, RBS4 and RBS5, respectively connecting the ribosome bind sites with genes ribA, ribB, ribD, ribE and ribC into fragments, splicing the fragments in order and enzyme-cutting and linking to a plasmid pTrc99a to obtain plasmid p20C-EC10, transferring into the Escherichia coli to obtain RF01S strain, transforming related gene of glycolytic pathway and ED pathway of the RF01S strain so as to improve the output of the riboflavin, and transforming the consumption pathway of the riboflavin to decrease the metabolism velocity of the riboflavin so as to further improve the riboflavin accumulation, inserting a Ptrc strong promoter into genome of the strain to obtain the Escherichia coli for producing the riboflavin. The constructed Escherichia coli strain has clear genetic background, and the glucose can be used as substrate to produce the riboflavin, and the shake-flask fermenting result is more than 1g / L, and a foundation is provided for improving the riboflavin output and yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for constructing recombinant strain capable of producing target gene product at high yield, and recombinant strain and application thereof
InactiveCN105176899AReduce distractionsImprove interferenceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousBinding site
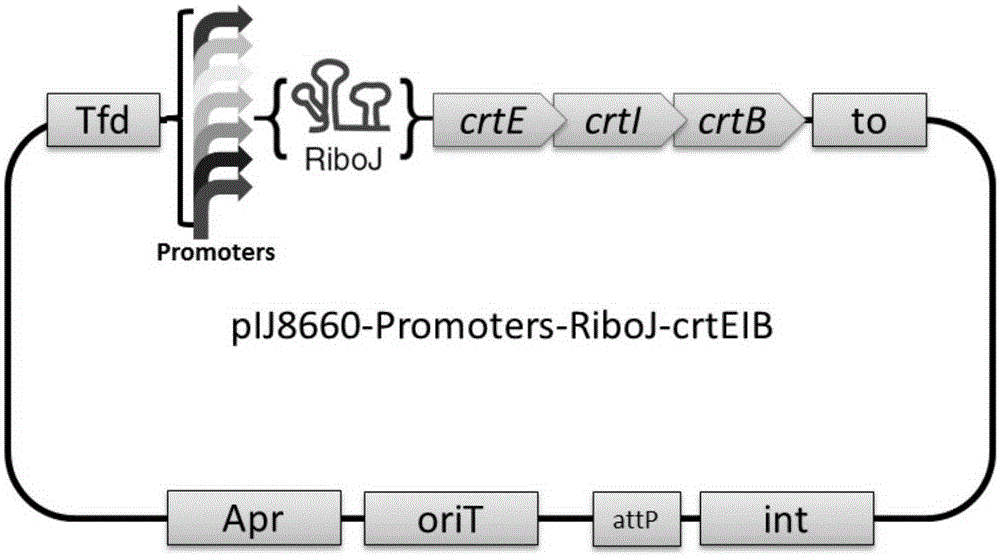
The invention relates to a method for constructing a recombinant strain capable of producing a target gene product at high yield, which comprises the following steps: (1) selecting an initial strain and a target gene; (2) constructing an expression vector comprising the target gene; (3) inserting a sequence with insulator function before a ribosome binding site of the target gene in the step (2), and inserting a heterogenous or artificial promoter sequence before the sequence with insulator function; and (4) transforming the expression vector constructed in the step (3) into the initial strain. The invention also relates to a recombinant strain constructed according to the method and a method for producing lycopene by fermentation by using the recombinant bacterium.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
DNA fragment of bacillus subtilis with promoter function and application thereof
ActiveCN106947766AHigh activityIncrease transcriptional activityVectorsBacteriaNucleotideBinding site
The invention discloses a DNA fragment of bacillus subtilis with a promoter function and application thereof. The DNA fragment is any one of a, the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or a complementary sequence thereof; b, a nucleotide sequence obtained by substituting, deleting or adding one or more nucleotides of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and having the promoter function the same as that of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or a complementary sequence thereof; and c, a sequence obtained by adding one or more ribosome bind sites to the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The DNA fragment has the promoter function, and also has high expression activity. High expression of exogenous genes can be achieved without adding an inductor. The DNA fragment can be applied to expression of thermostable beta-galactosidase and transglutaminase, and particularly, an effective element is provided for a bacillus subtilis expression-secretion system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing recombinant protein in bacterium belonging to the genus Rhodococcus
Provided is an expression vector capable of constitutive expression of a foreign gene in a bacterium belonging to the genus Rhodococcus. The vector is a constitutive expression vector for a bacterium belonging to the genus Rhodococcus comprising: DNA comprising a nucleotide sequence of a mutated TipA gene promoter where a mutation is incorporated into a −10 region sequence of a TipA gene promoter, the mutated TipA gene promoter being capable of thiostrepton-independent and constitutive expression of a gene located downstream thereof; a promoter sequence for the constitutive expression of a foreign gene; a ribosome-binding site sequence located downstream of the promoter sequence; and a multiple-cloning site sequence capable of incorporating a foreign gene therein, located downstream of the ribosome-binding site sequence.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
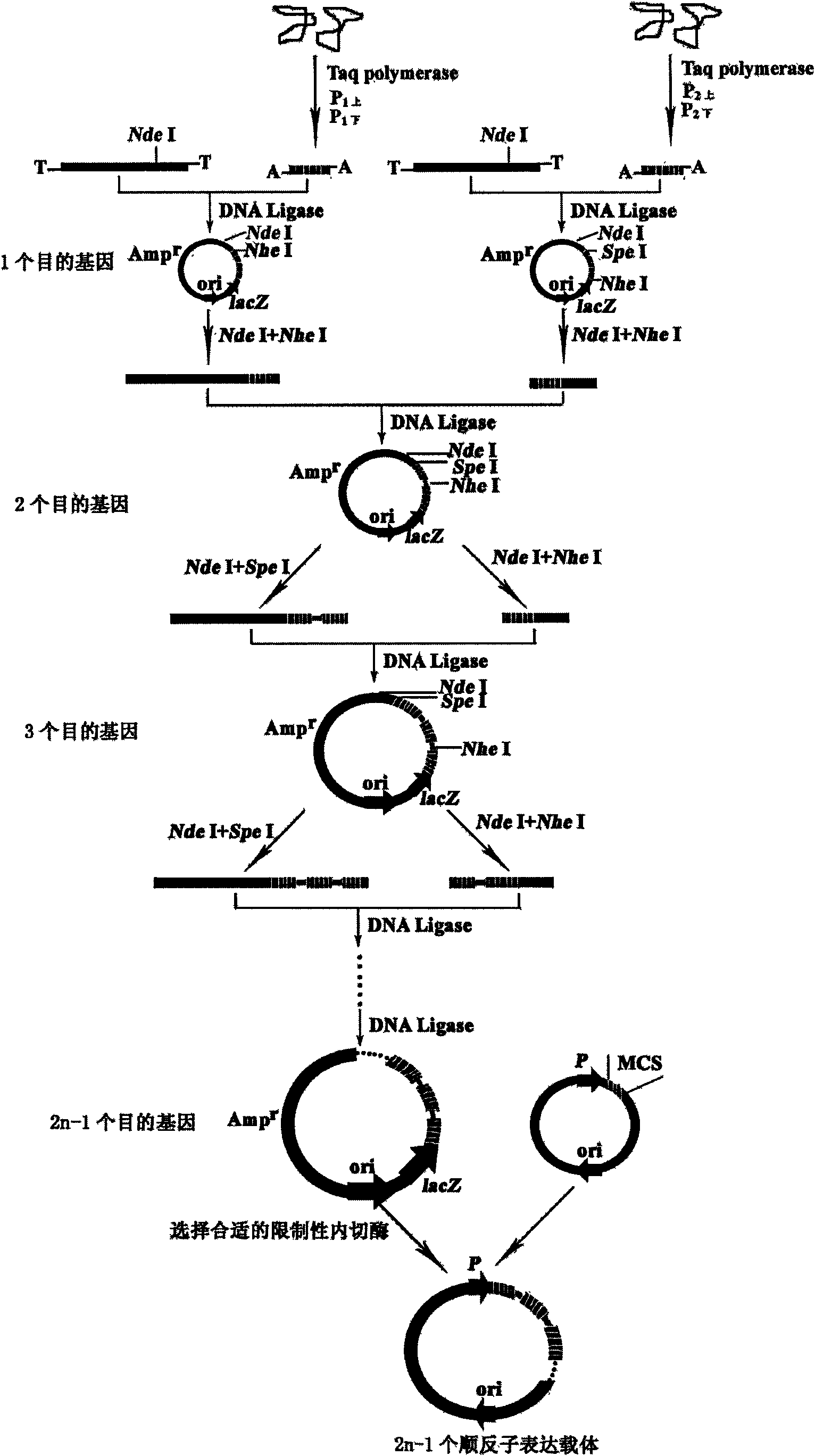
Construction method of polycistron expression vector
InactiveCN101608187AWide range of applicable genesReduce typesMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionDNA ligaseRibosomal binding site
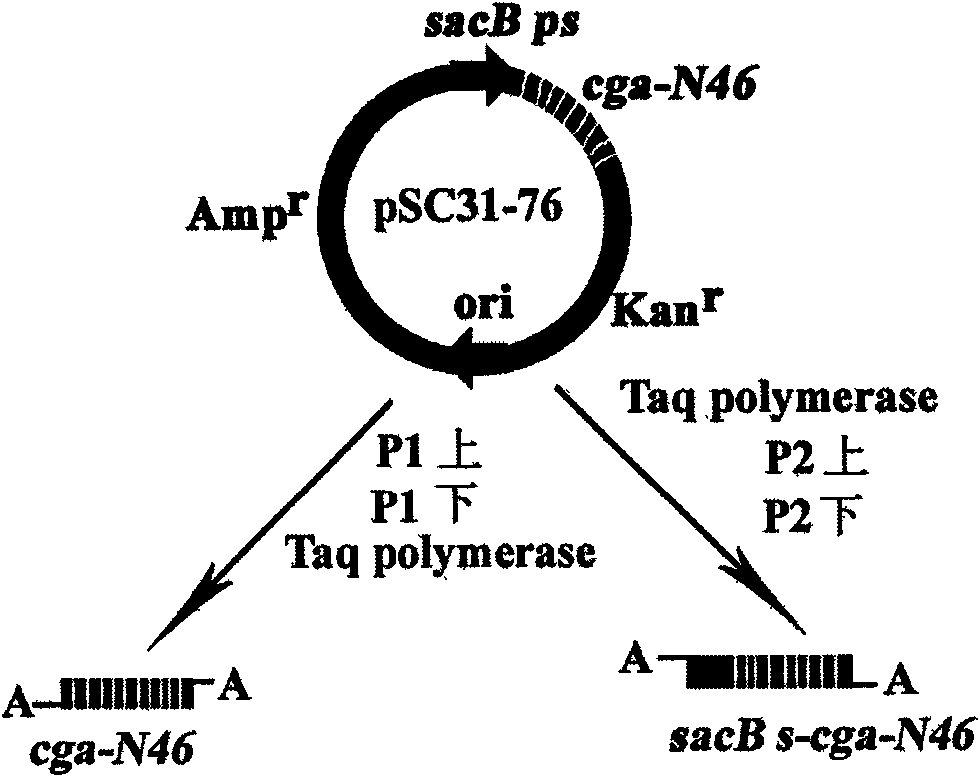
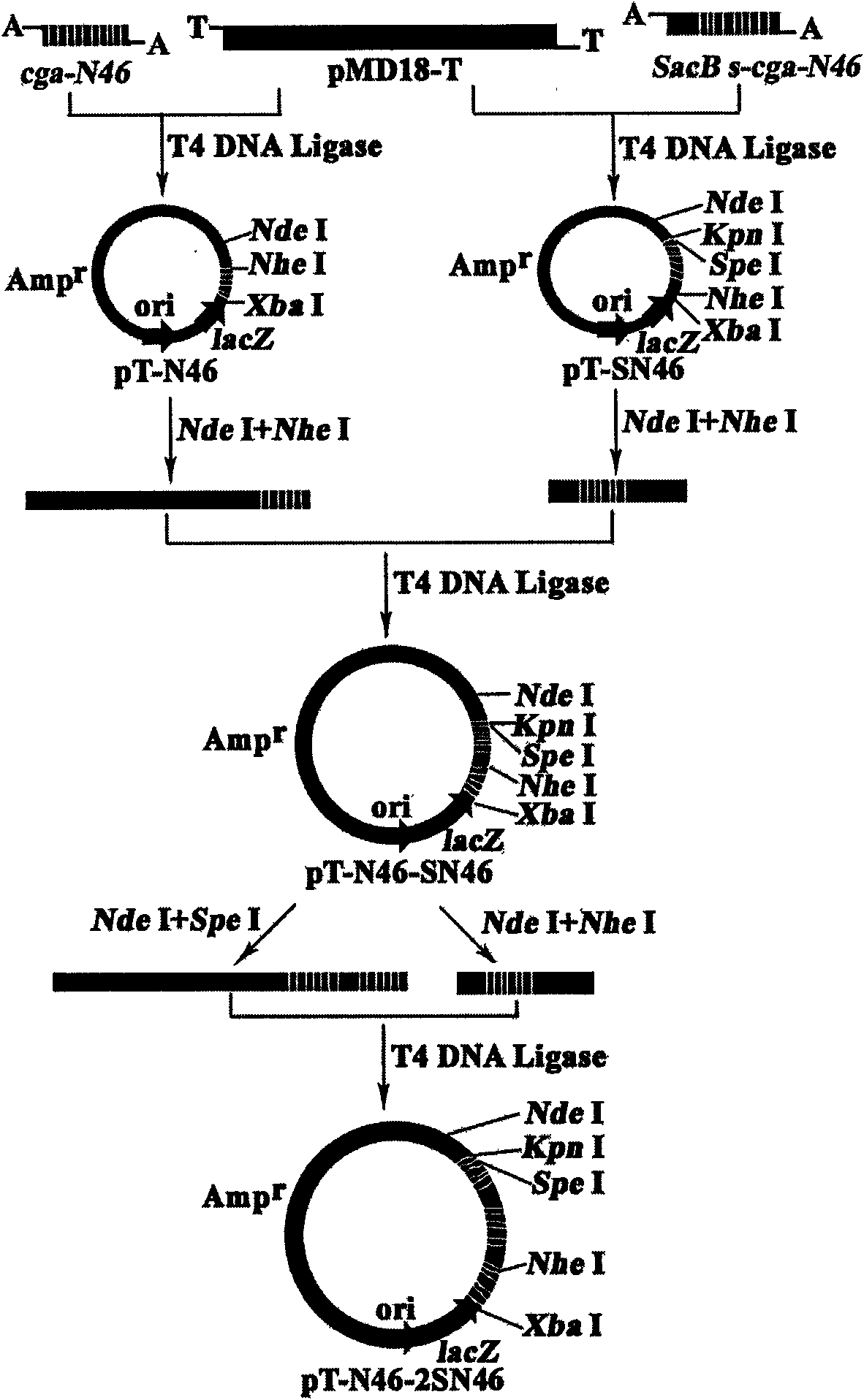
The invention relates to a construction method of a polycistron expression vector, which comprises the following steps: designing two pairs of primers by utilizing a commercial T-vector as an intermediate vector, introducing Nhel and Spel enzyme cutting sites and a ribosome bind site (RBS) in each primer, connecting an amplified product with the T-vector, cutting the obtained recombinant T-vector by using Nhel and Spel enzymes, and connecting an obtained DNA segment by using a DNA joining enzyme to enable an individual heterologous gene to increase progressively in the manner of 2n-1 (n is Gene number of the back recombinant T-vector), finally cutting the DNA segment containing a plurality of heterologous genes through a restriction enzyme corresponding to the enzyme cutting sites at two ends of the DNA segment, subcloning to the downstream of an expression vector promoter, and then obtaining the polycistron expression vector. The invention has the advantages of simple operation and wide application scope, and is applicable to all proteins, in particular to the expression of small peptides. The constructed expression vector can be directly converted into a procaryotic host cell and provide a technical platform for solving the bottleneck problem of low expression in the prokaryotic protein gene engineering expression.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A method for producing extracellular ferulic acid esterase from Escherichia coli
InactiveCN109182297ASimple purification processEase of industrial productionHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a method for producing extracellular ferulic acid esterase from Escherichia coli. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a recombinant Escherichia coli containing a ferulic acid esterase gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the ferulic acid esterase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; (2) subjecting the recombinant Escherichia coli obtained in the step (1)to IPTG or lactose induced fermentation, removing the bacterial cell, wherein the ferulic acid esterase is purified to obtain the ferulic acid esterase. The invention firstly adopts the restriction enzyme Nde I to digest the ferulic acid esterase gene, and the first enzyme digestion site after the ribosome binding site is changed into the Nde I enzyme digestion site, so that the obtained ferulic acid esterase has a natural N-terminal sequence; this special structure enables ferulic acid esterase to be secreted to extracellular after Escherichia coli synthesis, which greatly simplifies the purification and utilization of ferulic acid esterase, and has a significant role in promoting the industrial production of ferulic acid.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
DNA fragment with promoter function and use thereof
ActiveCN106086025AHigh activityIncrease transcriptional activityVectorsBacteriaBinding siteNucleotide
The invention discloses a DNA fragment with a promoter function and a use thereof. The DNA fragment has a sequence selected from (a), a nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 or its complementary sequence, (b), a nucleotide sequence which is derived from the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 through replacement, deletion or addition of one or multiple nucleotides and has a promoter function the same to that of the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1, or its complementary sequence, and (c), a sequence derived from the nucleotide sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 through addition of one or more ribosome binding sites. The DNA fragment has a promoter function and strong specific expression activity, realizes high exogenous gene expression without an inducer and provides an effective element for bacillus subtilis expression of an exogenous gene.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method of carrying out rapid and efficient DNA combination and evolution based on synthesis of single-chain DNA library
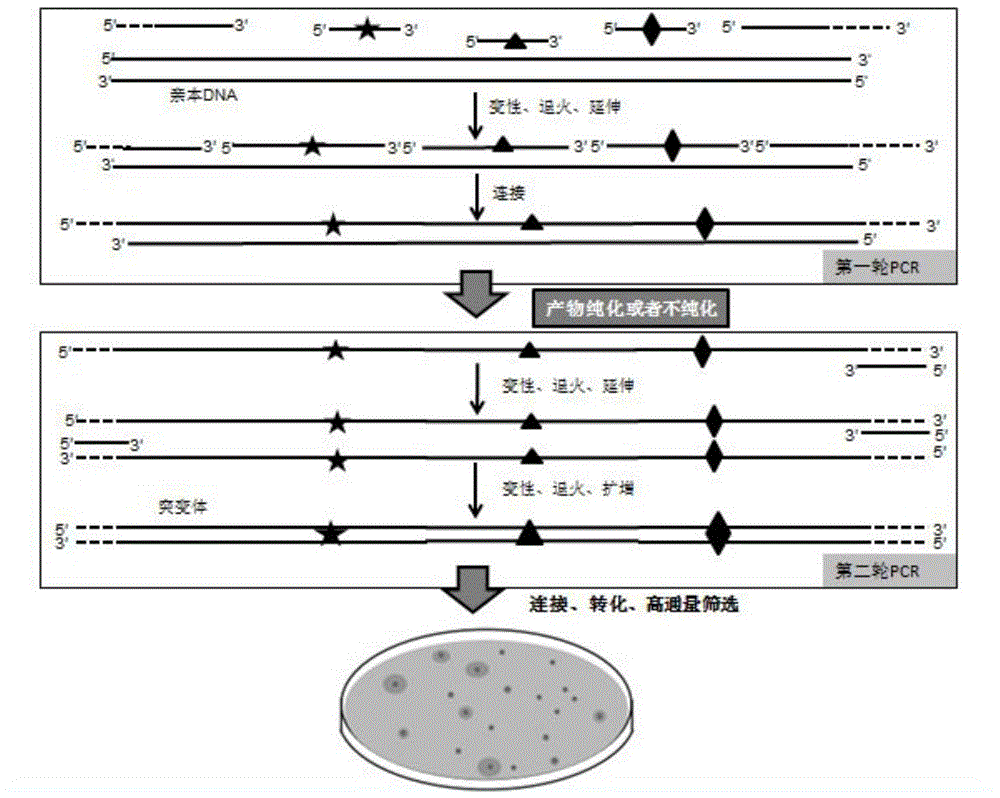
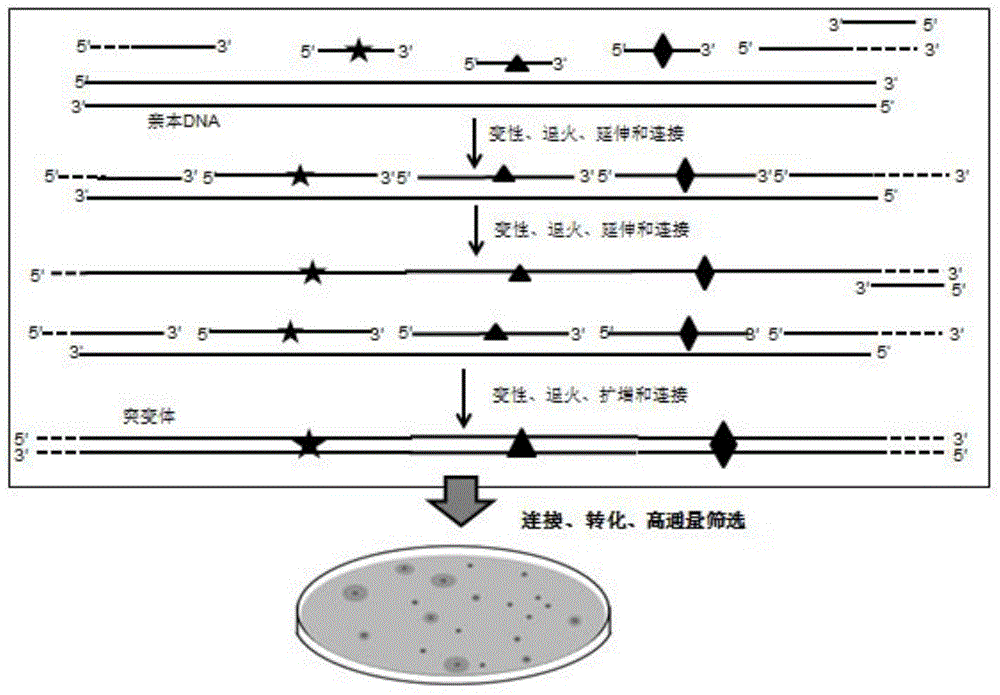
InactiveCN104789556AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCDNA libraryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a method of carrying out rapid and efficient DNA combination and evolution based on synthesis of single-chain DNA library and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: constructing DNA single-chain mutant library and double-chain mutant library sequentially or simultaneously; and after an expression vector of the mutation library is recombined, transforming a host, and high throughput screening evolved mutant strains. According to the method disclosed by the invention, with the adoption of the technology, transformation in vitro is successfully carried out on a promoter, enzyme and metabolic pathway, and the mutant strain with very excellent property is obtained; rapid evolution in vitro of the gene is realized, and the method is simple to operate and is particularly suitable for carrying out rapid oriented evolution for introducing rich mutation diversity in the gene.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Single cell factory capable of efficiently synthesizing L-phenylglycine as well as construction and application of single cell factory
ActiveCN108103038AOptimize regeneration rateReduce the cost of trainingMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliCell factory
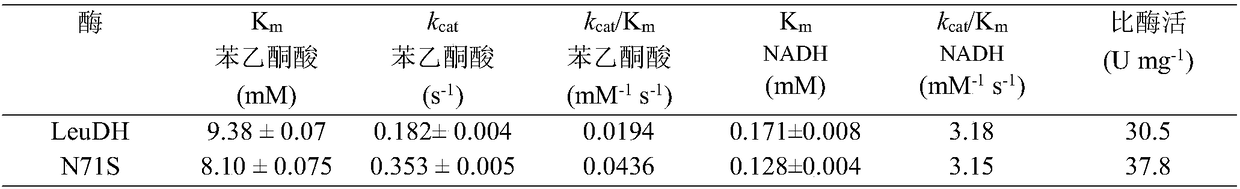
The invention discloses a single cell factory capable of efficiently synthesizing L-phenylglycine as well as construction and application of the single cell factory and belongs to the technical fieldof microorganisms. Firstly, efficient expression of leucine dehydrogenase obtained from Bacillus cereus in escherichia coli is realized, and site-directed mutation is carried out to obtain a mutant N71S with a remarkably improved reduction property; a mutant enzyme and a formate dehydrogenase mutant are co-expressed in the escherichia coli to form an intracellular in-situ co-factor NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) circulating system; the expression amount of the formate dehydrogenase mutant is optimized and controlled through a promoter and an RBS (Ribosomal Binding Site) sequence to successfully construct a recombinant escherichia coli single cell factory; the single cell factory is subjected to whole-cell conversion to prepare the L-phenylglycine. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple and rapid conversion process, low cost, no byproduct and easiness for separation and purification; when conversion is carried out in a 5L fermentation tank for 4h, the yield of the L-phenylglycine can reach 105.7g / l, the conversion rate is 93.3 percent and the space-time yield of the L-phenylglycine is 26.3g / L; an actually practical and effective strategy is provided for industrial production of the L-phenylglycine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Vector for expression of heterologous protein and methods for extracting recombinant protein and for purifying isolated recombinant insulin
InactiveUS6068993AFast degenerationOvercome problemsBacteriaInsulinsBacteroidesOrigin of replication
The present invention relates to a vector for expression of a heterologous protein by a Gram negative bacteria, wherein the vector includes a nucleic acid such as DNA encoding the following: an origin of replication region; optionally and preferably a selection marker; a promoter; an initiation region such as translation initiation region and / or a ribosome binding site, at least one restriction site for insertion of heterologous nucleic acid, e.g. DNA, encoding the heterologous protein, and a transcription terminator. The inventive vector may contain DNA encoding the heterologous protein, e.g., pro-insulin such as pro-insulin with a His tag. Additionally, the invention provides a method for extracting a recombinant protein from within a recombinant Gram negative bacteria having a cell membrane, without lysing the bacteria, as well as a method for purifying an isolated recombinant human insulin, wherein the isolated recombinant human pro-insulin is subjected to sulfitolysis, Ni-chelation chromatography, renaturation, limited proteolysis and chromatography separation to provide purified, isolated, recombinant human insulin.
Owner:BIOMM +1
Method for regulating chromosome genome functions by using combined promoter
InactiveCN101892258AChanging binding efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationBinding siteBacterial strain
The invention provides a method for regulating chromosome genome functions by using a combined promoter, comprising the following step of: regulating and optimizing the expression of a plurality of genes in a related metabolic pathway by constructing an artificially combined type promoter sublibrary to replace a self promoter on chromosome, and therefore, the selected microorganisms can effectively generate needed products. The combined promoter comprises four artificially combined double-stranded DNA units with homologous ends, wherein the four units are assembled by a selectively marked and reformed regulating and controlling sublibrary, a reformed core promoter sublibrary and a reformed ribosome bind site library and are transformed into one or a plurality of target cells to replace the self promoters of a plurality of target chromosome genes in a specific cell pathway to cause high-expression target genes of a large amount of target cells. The method can be used for constructing a plurality of integrated bacterial strains in multiple-chromosome sites. The artificially combined type promoter can accurately, simultaneously or singly regulate and control several kinds of gene activity in cells and is suitable for metabolism optimization and metabolism control analysis in eukaryotic cells and procaryotic cells.
Owner:苏州神洲基因有限公司
Method of Creating a Library of Bacterial Clones with Varying Levels of Gene Expression
InactiveUS20120015849A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBinding siteRibosomal binding site
The present invention relates to a method of creating DNA libraries that include an artificial promoter library and / or a modified ribosome binding site library and transforming bacterial host cells with the library to obtain a population of bacterial clones having a range of expression levels for a chromosomal gene of interest.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for producing short-and-medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) and functional derivatives thereof
ActiveCN111235173AControllable ratioReduce energy consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLong chain fatty acidBinding site
The invention discloses a construction method of a recombinant bacterium for producing short-and-medium-chain-length PHA and functional derivatives thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a coding gene of specific PHA polymerase, a coding gene of a key protein of a PHA synthesis pathway, a promoter or a mutated promoter, related genes capable of enhancing carbon source utilization capacity of medium-chain and long-chain fatty acids, the ribosome binding site RCJ and the ribosome binding site RD into a starting strain from which an endogenous PHA polymerase gene is knocked out; and adjusting the proportions of all monomers in the short-and-medium-chain-length PHA and the functional derivatives thereof in the recombinant bacteria so as to realize controllable production of the short-and-medium-chain-length PHA and the functional derivatives thereof.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
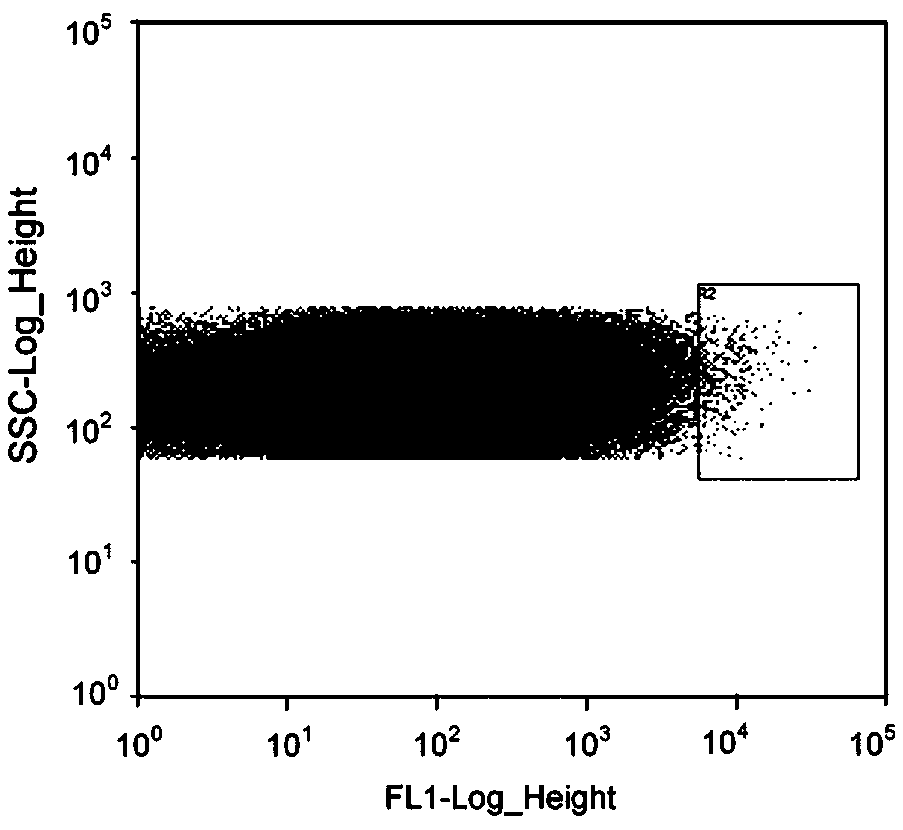
Corynebacterium glutamicum artificial promoter library
The invention discloses a library of artificial promoter regulatory elements with different expression intensities in corynebacterium glutamicum. Firstly, according to the core region of promoters ofcorynebacterium glutamicum housekeeping genes and the conserved sequences of the -10 region and the -35 region, the corynebacterium glutamicum artificial promoter regulatory element library is designed and built. Each regulatory element comprises a promoter region and a ribosome binding site region, and a promoter upstream region exists. Subsequently, the artificial promoter regulatory element library is subjected to a three-step screening method of flow cytometry screening, plate screening and 96-well plate screening, and the artificial promoter regulatory element library with with differentexpression intensities and wide control range is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
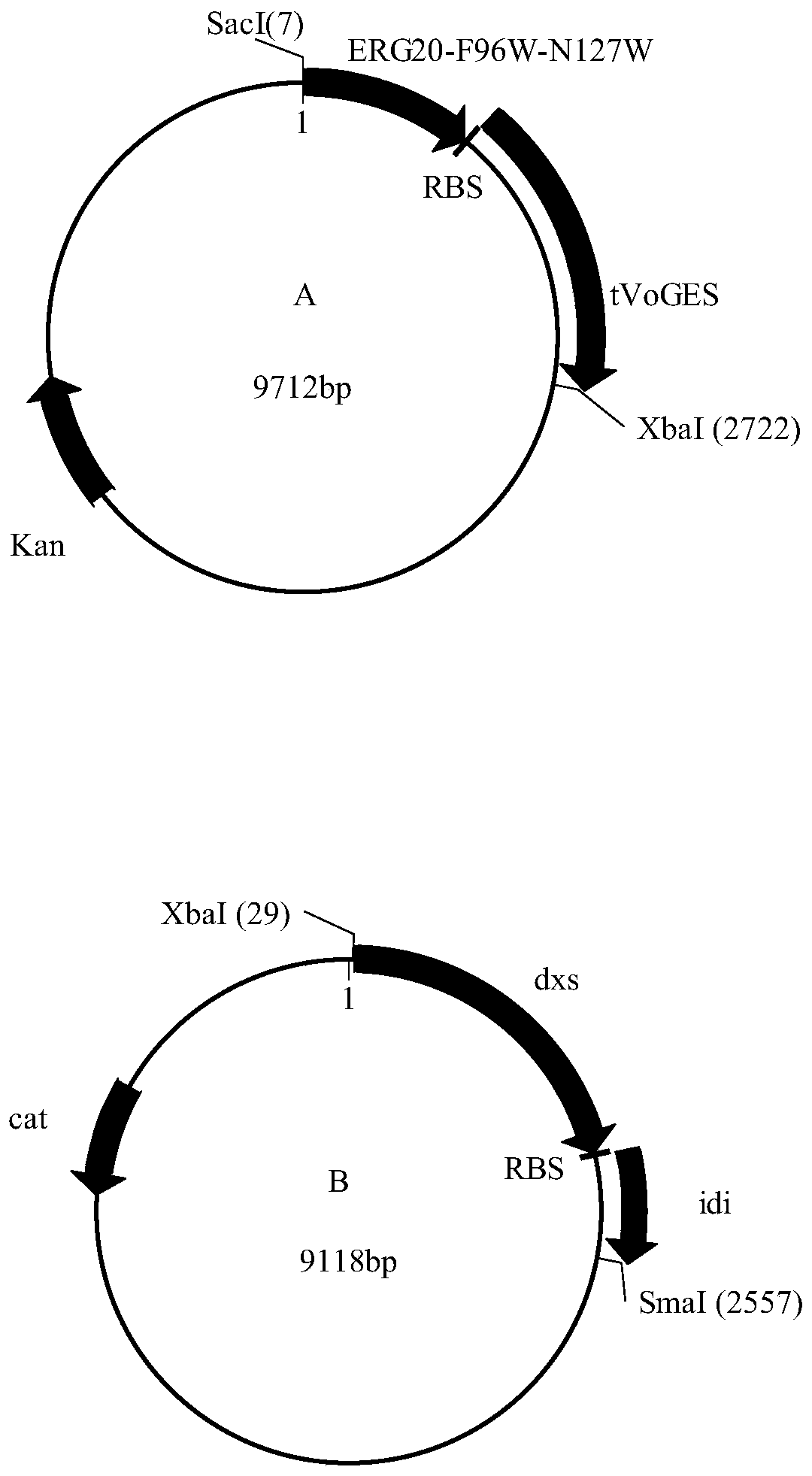
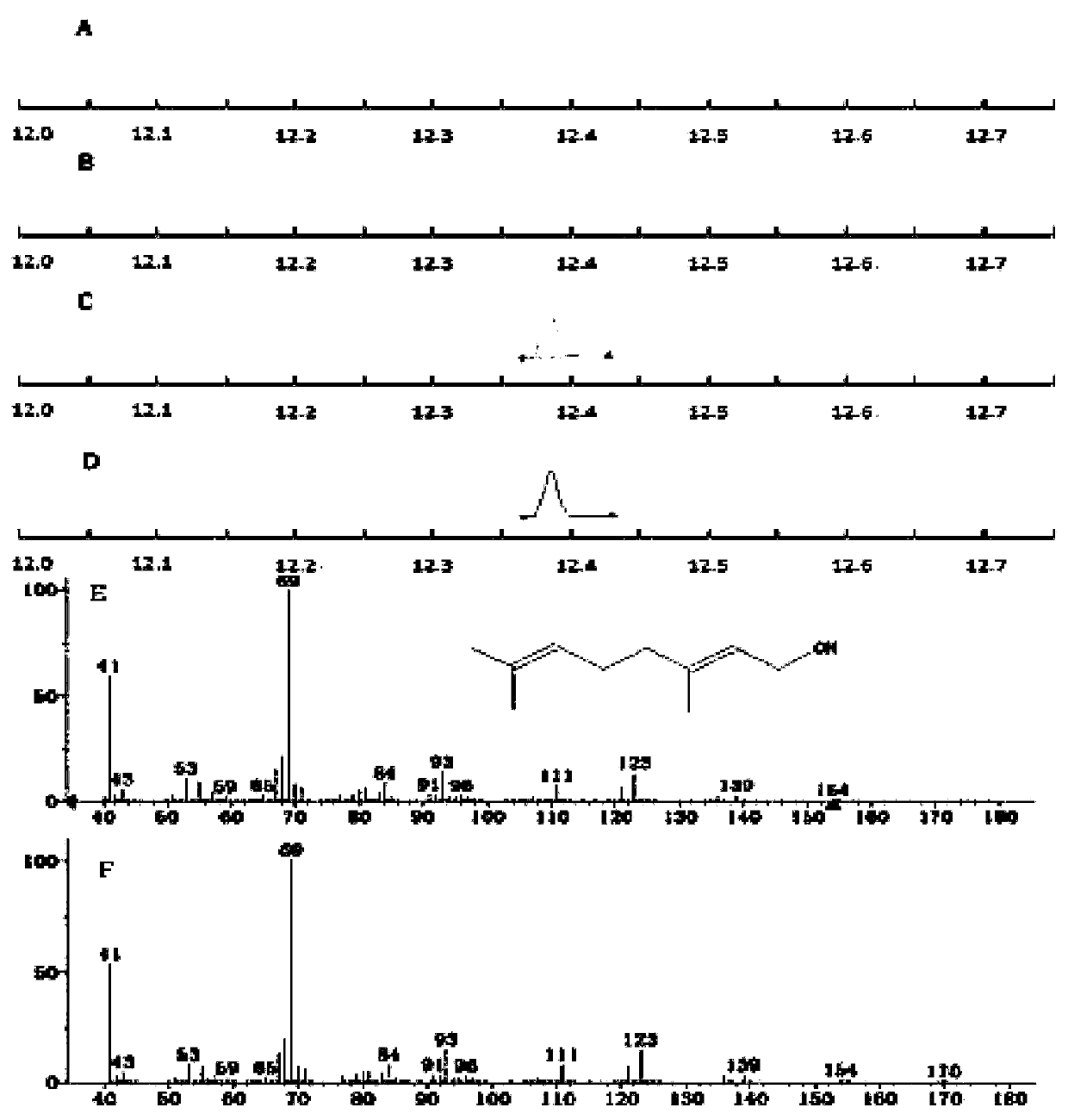
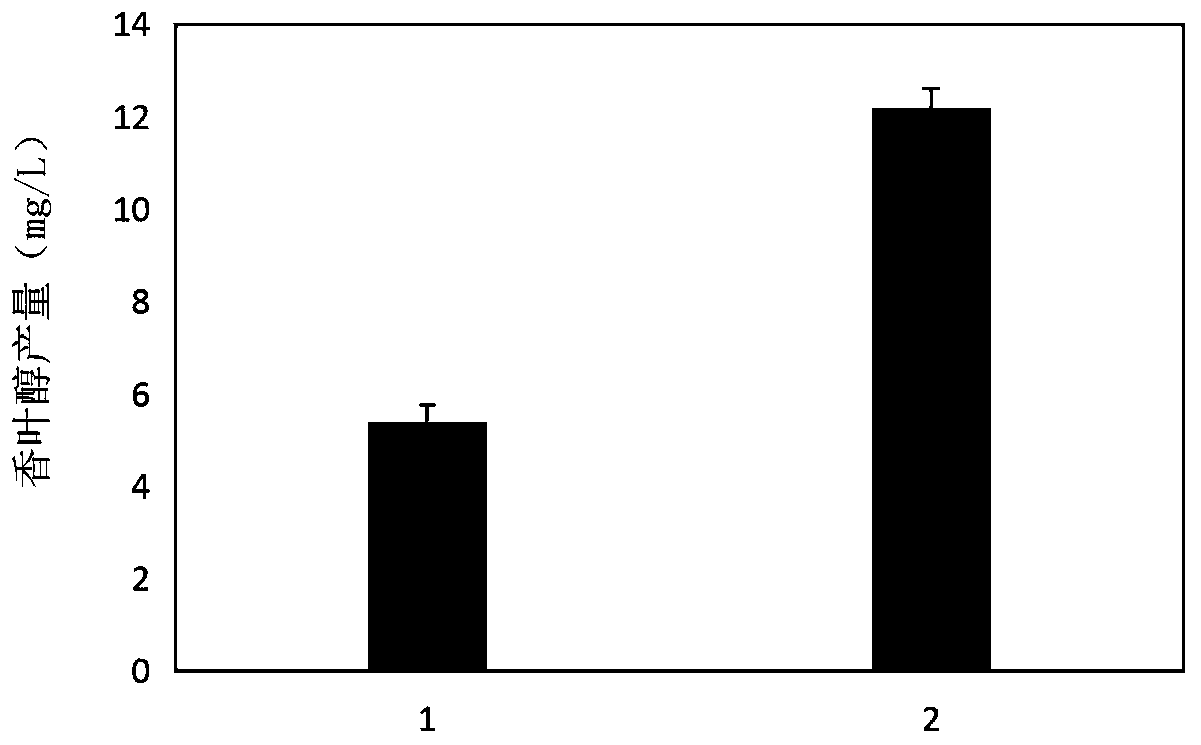
Corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate
InactiveCN110438145AShort fermentation timeBacteriaTransferasesCorynebacterium efficiensBinding site
The present invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and a construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate. The construction method of corynebacteriumglutamate comprises the following steps: connecting a saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived mutant geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene ERG20<F96W-N127W> and a valerian-derived geranol synthase gene tVoGEStruncated through cutting off of C-terminal 53 amino acid residues by fusion PCR, adding a ribosome binding site sequence to a homologous region, inserting SacI and XbaI enzyme cutting sites of a corynebacterium glutamate expression plasmid pEC-XK99E to obtain a plasmid 1; converting the plasmid 1 into corynebacterium glutamate to obtain corynebacterium glutamate 1 for synthesizing geraniol. Theconstruction method provides more precursors and short fermentation time (42 to 48 hours) for the synthesis of geraniol, and corresponding by-products are not detected out by GC-MS detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Vector for non-background directed cloning of PCR products, preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102628057AAchieve no backgroundTo achieve the effect of directional cloningVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
The invention discloses a vector for non-background directed cloning of PCR products, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The vector is characterized in that an XcmI box is introduced before the vector screens and labels gene, and the XcmI box is characterized in that a protruded dT end is formed after XcmI enzyme digestion, an inactive ribosome binding site is formed before gene screening and labeling and after sequence splicing, and the screened and labeled gene cannot express during self-joining of the vector. The protruded dT end formed after the XcmI enzyme digestionof the vector prepared in the invention can be applied to TA cloning, and can be filled in by a T4DNA polymerase to form blunt ends, so as to be applied to blunt end joining; the method of the invention has the advantages of easy implementation, and low cost; and effects of no background and directed cloning are reached in the application of two cloning methods.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Protein-Responsive Translational Regulatory System Using RNA-Protein Interacting Motif
ActiveUS20110040077A1Regulate the translation reaction of the desired geneSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesOpen reading frameNucleotide
An object of the present invention is to provide a translationally regulatable mRNA which has wider application and can perform specific ON-OFF regulation, an RNA-protein complex specifically bound to the mRNA, and a translational regulatory system. The present invention provides an mRNA having an RNA-protein complex interacting motif-derived nucleotide sequence 5′ to the ribosome-binding site or within the 5′ region of the open reading frame, and an mRNA having a nucleotide sequence complementary to an RNA-protein complex interacting motif-derived nucleotide sequence 5′ to the ribosome-binding site or within the 5′ region of the open reading frame.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Modified bacillus source and Alpha-amylase gene recombination lactobacillus as well as product and application thereof
InactiveCN102363762AStable expressionFast growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFeed conversion ratioBinding site
The invention discloses a modified bacillus source and Alpha-amylase gene recombination lactobacillus as well as a product and the application thereof. An Alpha-amylase gene and a signal peptide gene are connected, are then inserted into a multiple cloning site of a lactobacillus expression vector pIlac, and are further integrated into a ribosome bind site of lactobacillus casei L.CECT5276, wherein the Alpha-amylase gene is a starch liquefaction bacillus with an accession number of GU591658, and a sequence used for amplification is a 1-1545bp basic group; and the signal peptide gene is a short lactobacillus L.brevis1.2028 with an accession number of Z14250, and a sequence used for amplification is a 260-349bp basic group. The recombination lactobacillus can be applied to the production of animals, of which the feed is rich in starch, particularly newborn piglets and chicken, and has great significance in improving the growth speed, reducing the feed conversion ratio, increasing the economic benefits and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Construction method of seamless multi-segment cloning vector
ActiveCN108103089ATo achieve the purpose of seamless connectionClone worksVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a construction method of a seamless multi-segment cloning vector. The vector sequentially comprises a promoter sequence, a ribosome-binding site, a Golden Gate reaction site, asuicide gene, a Golden Gate reaction site, a terminator, a screening gene, an escherichia coli replicon and a coding suppressor. The scheme has the following advantages: plasmid of the vector is unnecessary to undergo such treatment as linear treatment and the like in advance, and the vector is low in plasmid dosage and is capable of reducing plasmid extraction cost; a restriction enzyme digestion reaction and a ligation reaction can be implemented in a same system; each reaction just needs one restriction enzyme, and such problems as reaction condition conflicts and the like cannot be takeninto consideration; in the reactions, restriction enzyme cutting sites can be excised, and it is unnecessary to consider whether the introduction of residual segments can cause bad influence to the generation of a target gene or not; through artificial control over a sticky end, a background caused on self-ligation of the cloning vector can be avoided; and seamless connection of nine segments to the greatest extent can be achieved.
Owner:CYAGEN BIOSCI GUANGZHOU
Phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene
InactiveCN104278015AImprove conversion efficiencyIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBinding site
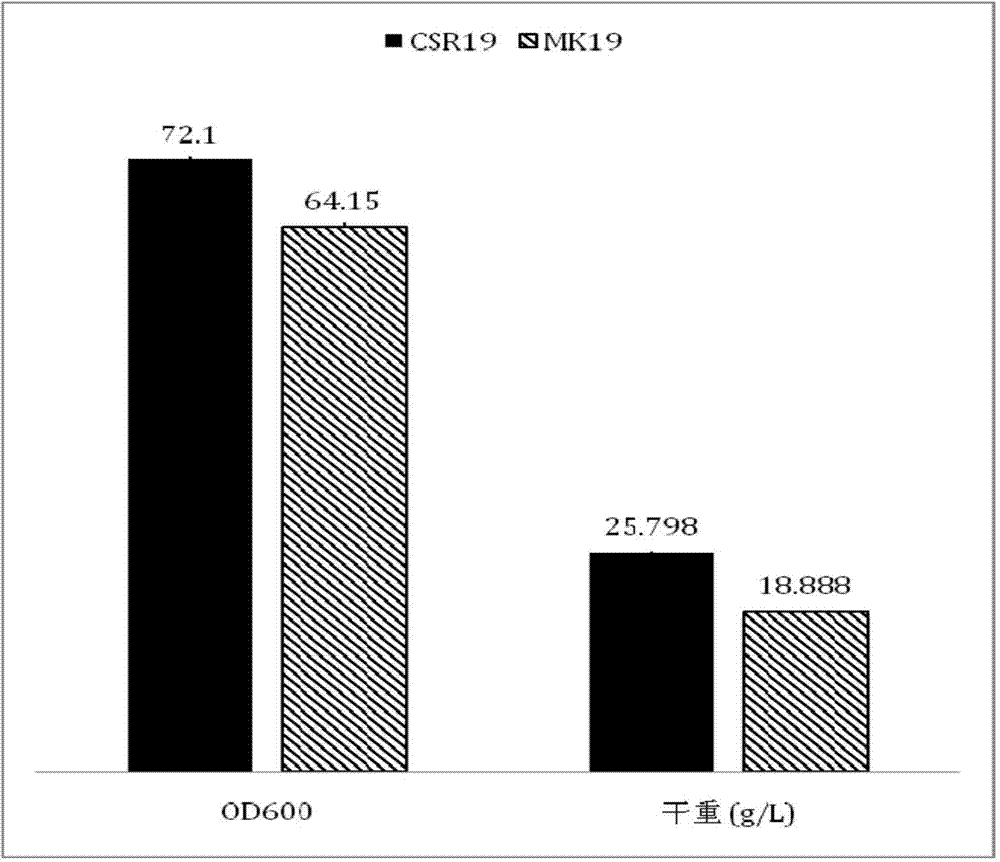
The invention discloses a phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently an over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. The invention provides a phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield, obtained by over-expressing an endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. A phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain (MK19-pGBKT7crtS) capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield is obtained by over-expressing the astaxanthin synthetase gene crtS by virtue of free plasmids and the strain is named CSR19. An endogenous ribosome bind site sequence (Rbs. sequence for short) exists in front of the crtS gene expressed by the strain. By virtue of fermentation cultivation and in comparison with a receptor strain MK19, the astaxanthin yield of the engineering strain is increased by 33.5%, and the engineering strain is good in stability, and thus, the phaffia rhodozyma strain has a good application prospect in the feed industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Plasmid, phage-assisted continuous directed evolution system and directed evolution method
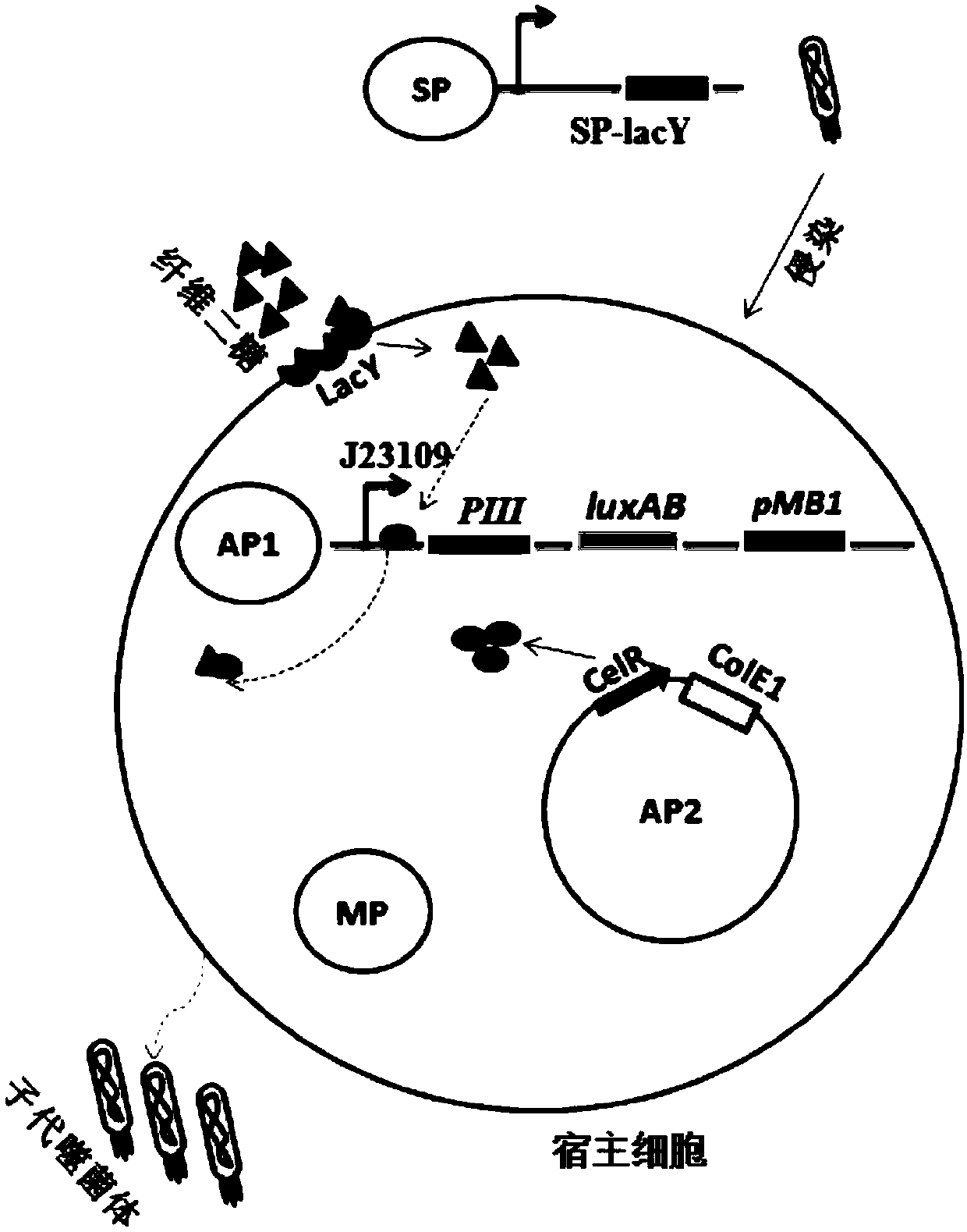
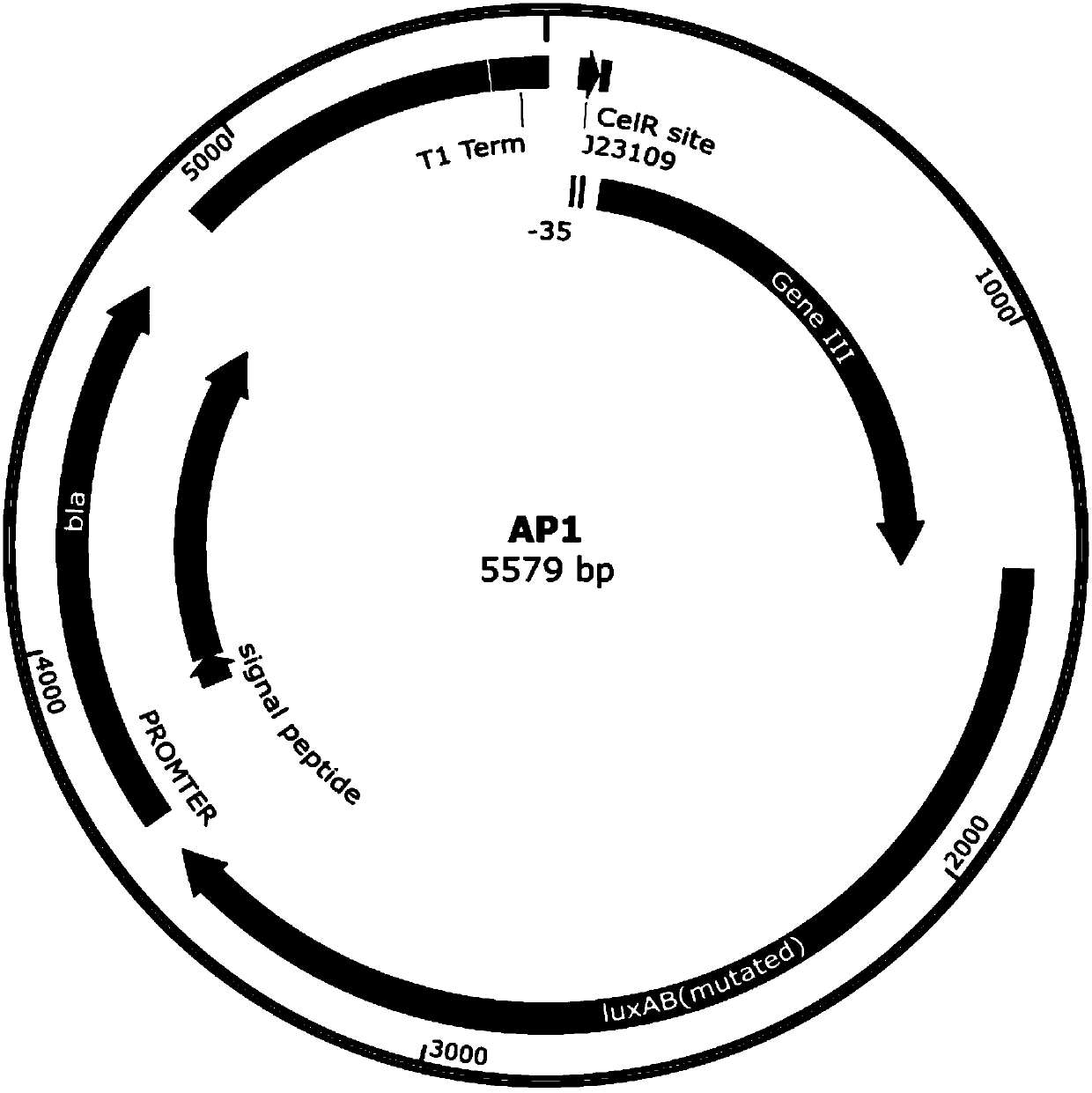
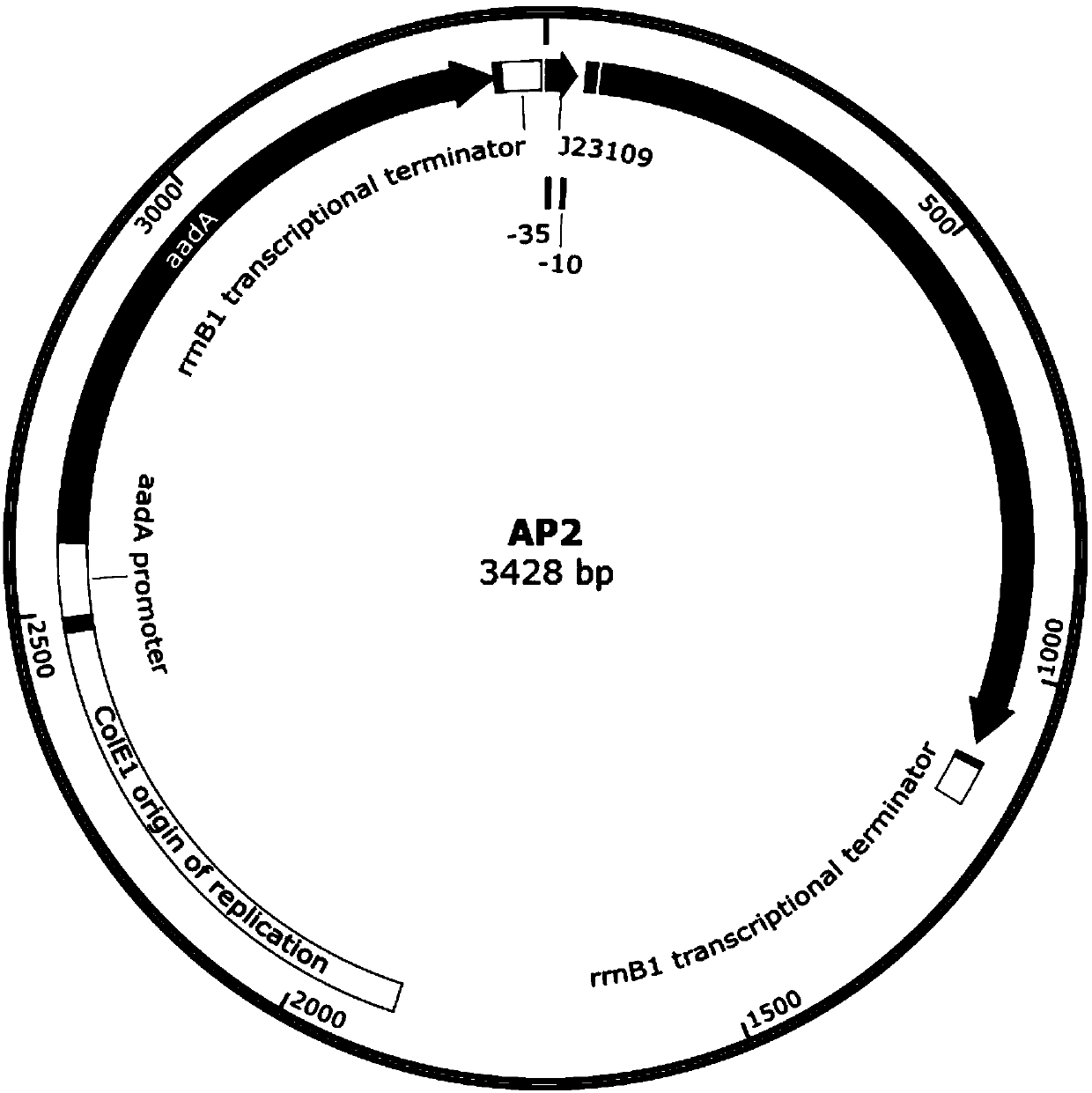
ActiveCN109943581ADisinhibition effectAchieve directed evolutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetBinding site
The invention relates to the field of directed evolution of membrane proteins, in particular to a plasmid, a phage-assisted continuous directed evolution system and a directed evolution method. The plasmid comprises one or two of a plasmid AP1and a plasmid AP2; the plasmid AP1 carries a gIII gene, and a functional protein recognition site is arranged between a promoter of the plasmid and a ribosome binding site; the plasmid AP2 carries a functional protein gene. According to the plasmid, the phage-assisted continuous directed evolution system and the directed evolution method, the new assisting plasmids AP1 and AP2 are designed, the transport activity of the target protein to intracellular and extracellular substrate molecules and the gIII expression on the AP1 are coupled, the reproductive capability of SP and the activity of the target protein are coupled in the indirect mode, and the effect of continuous directed evolution of the target protein is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com