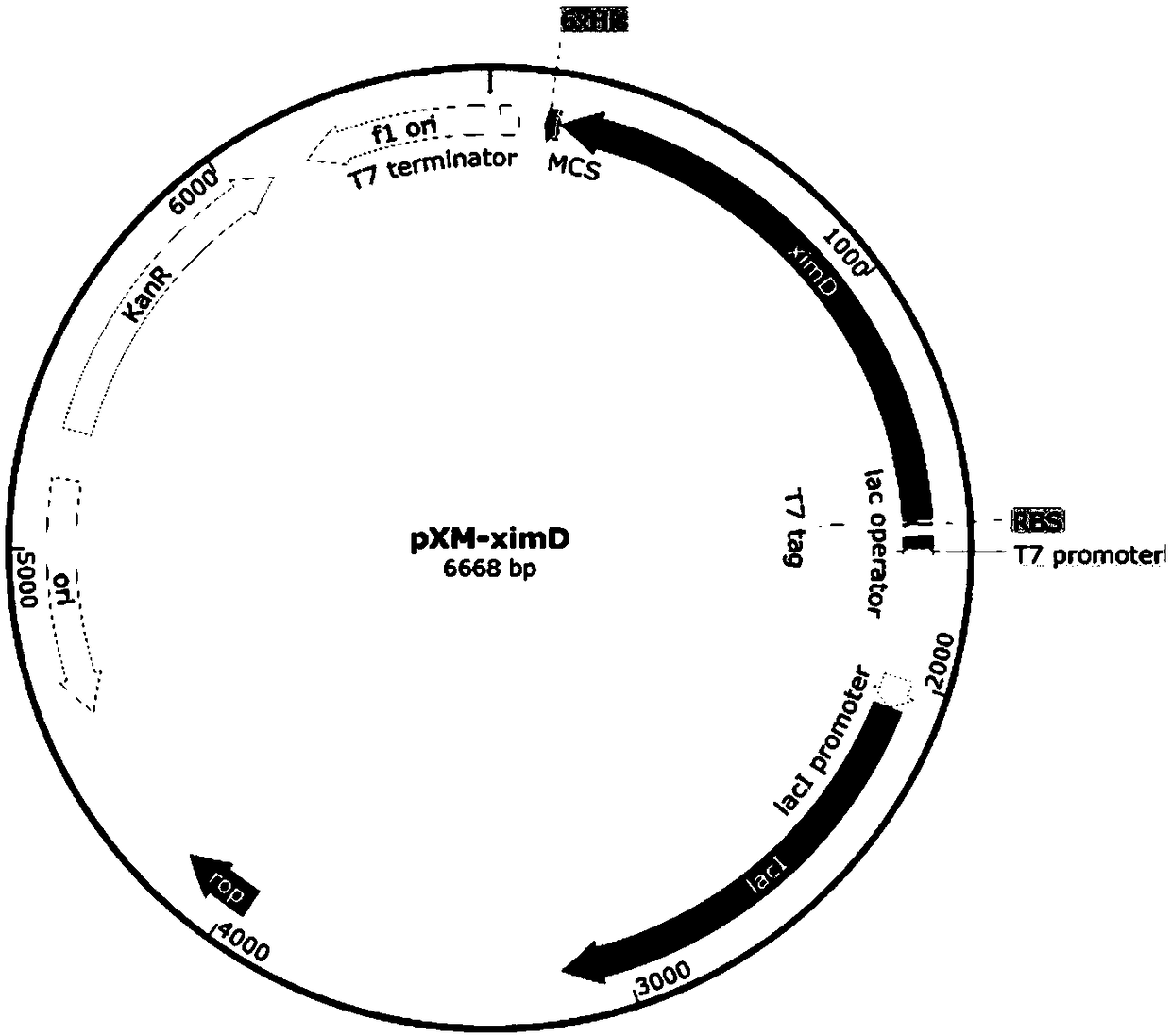
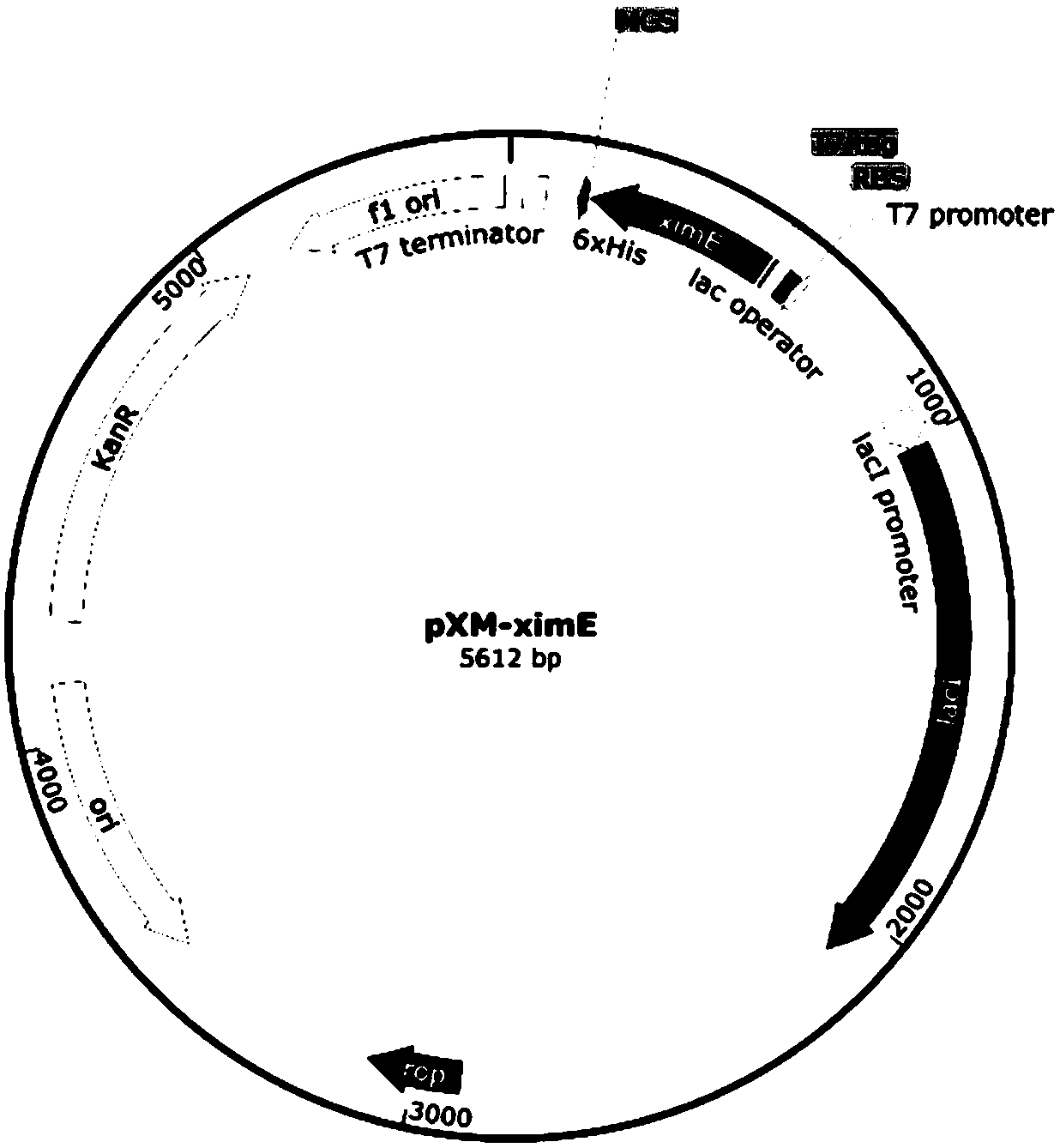
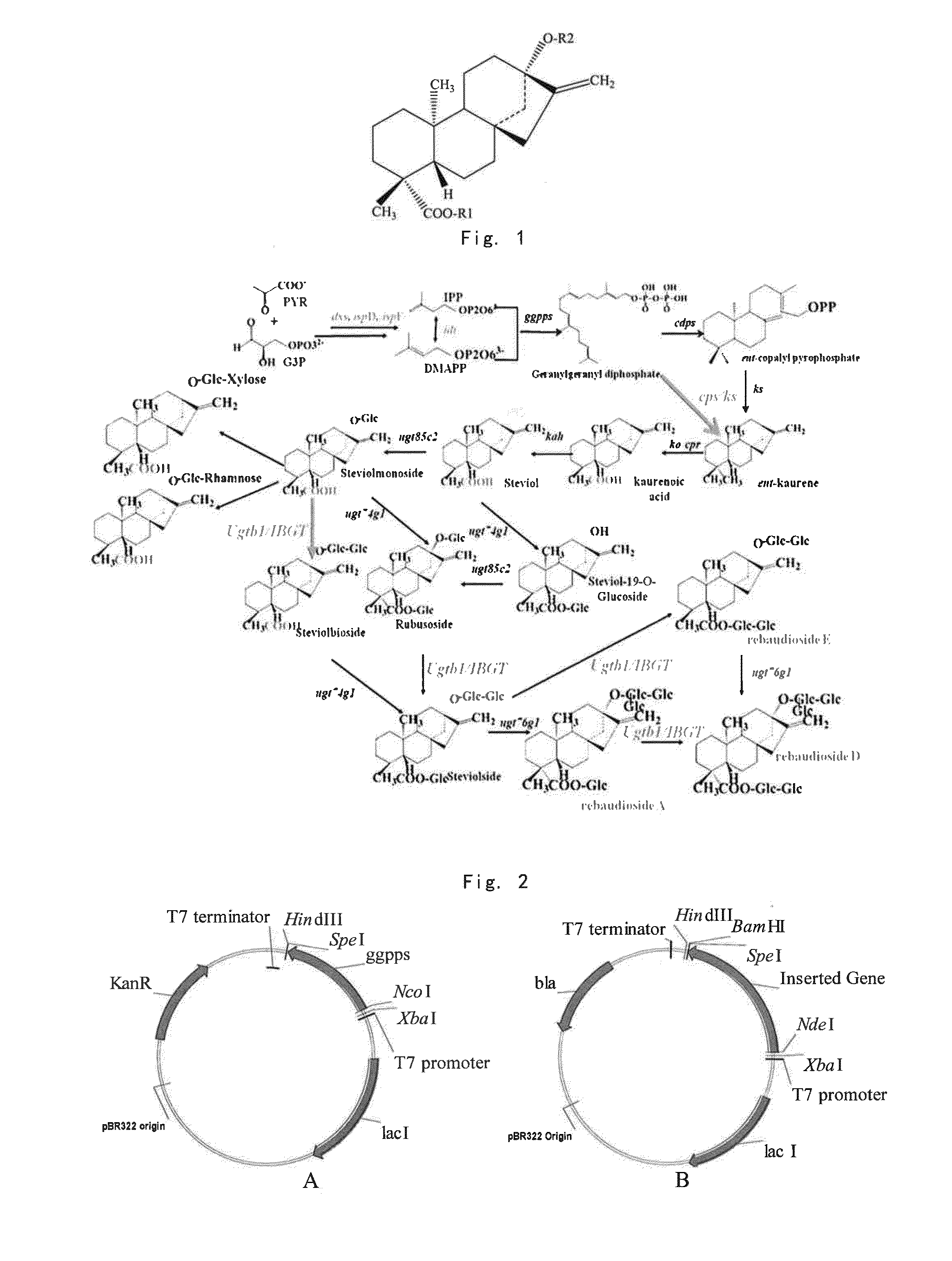
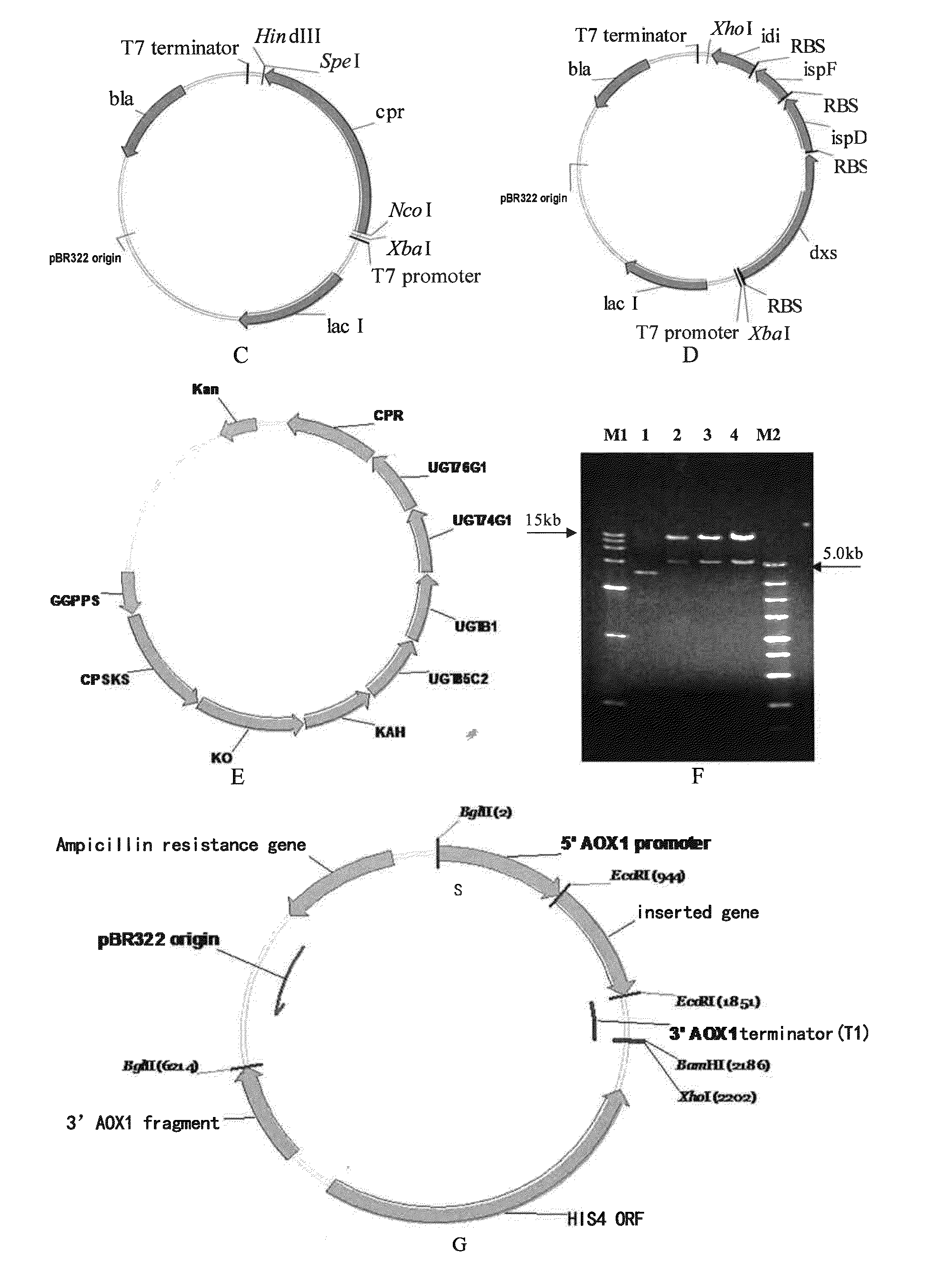
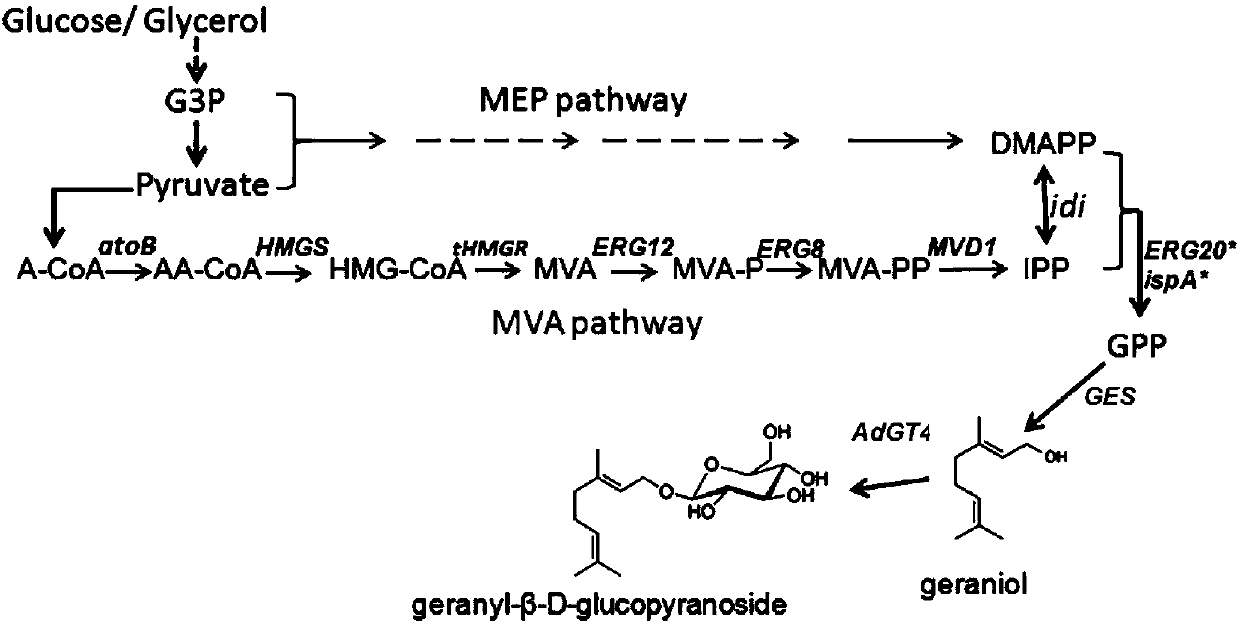
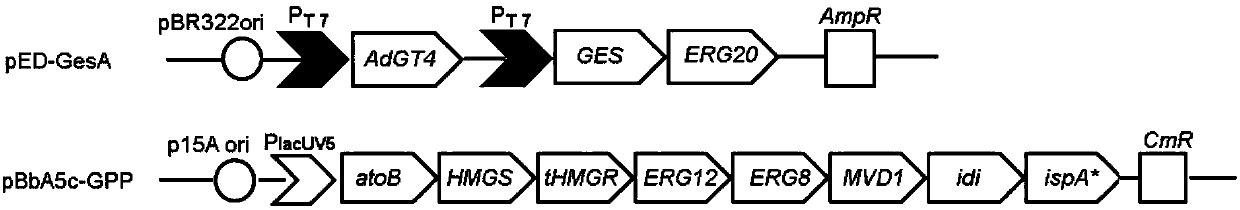
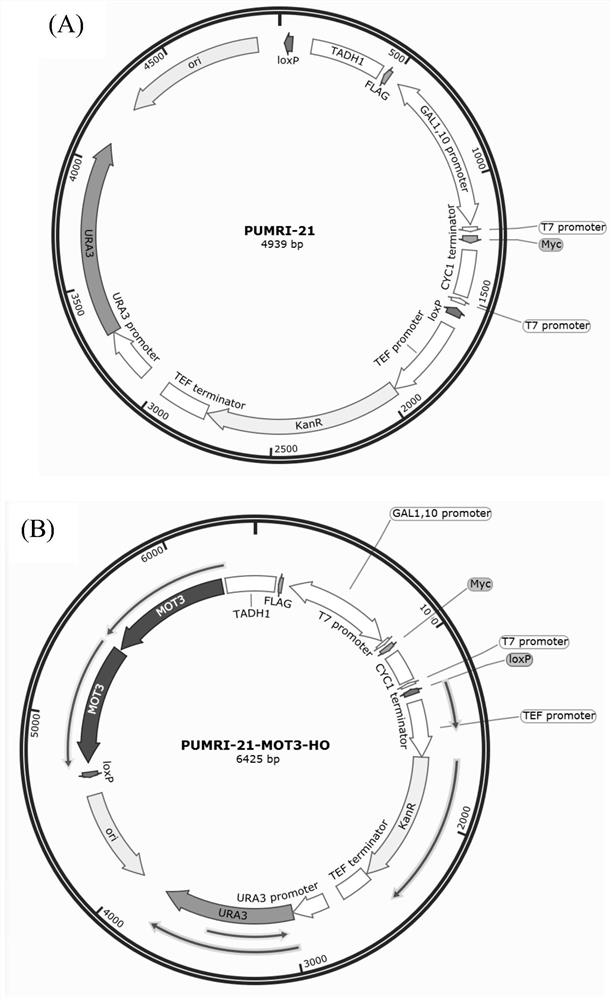
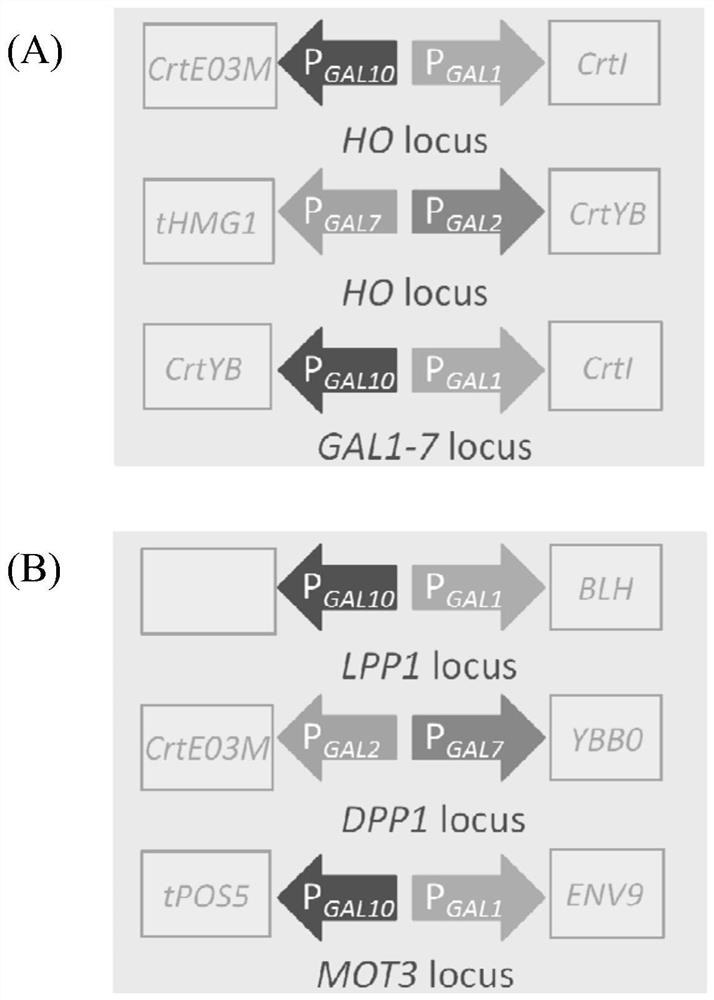
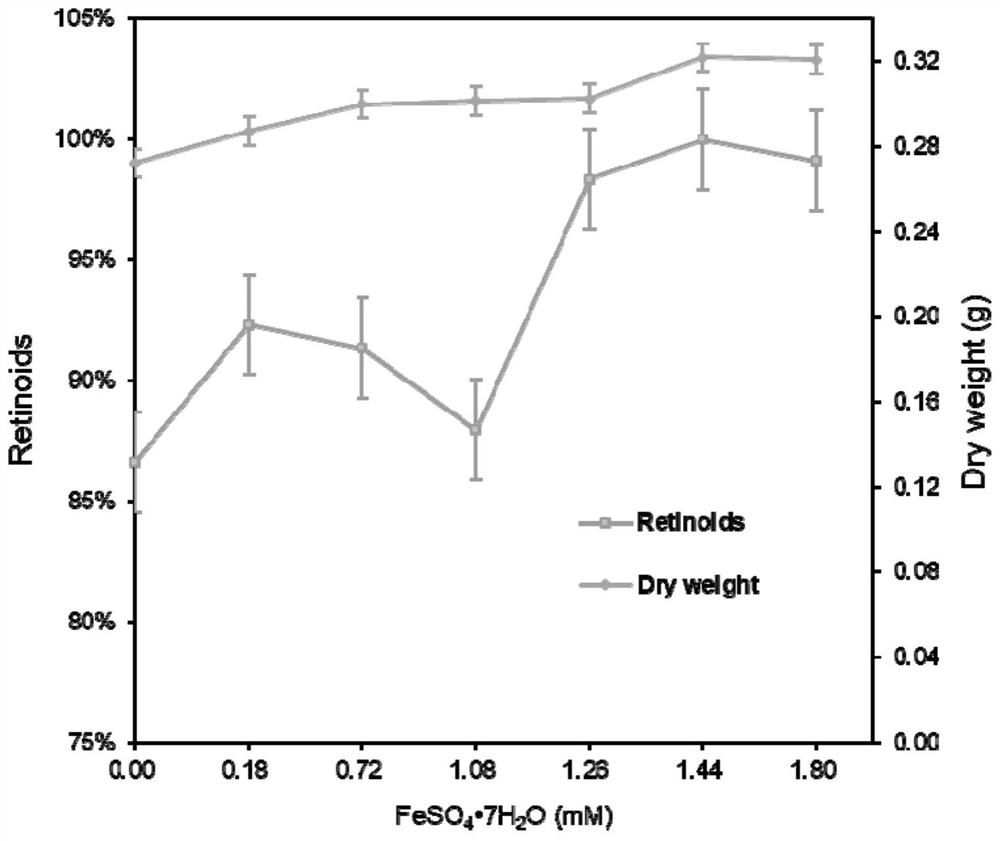
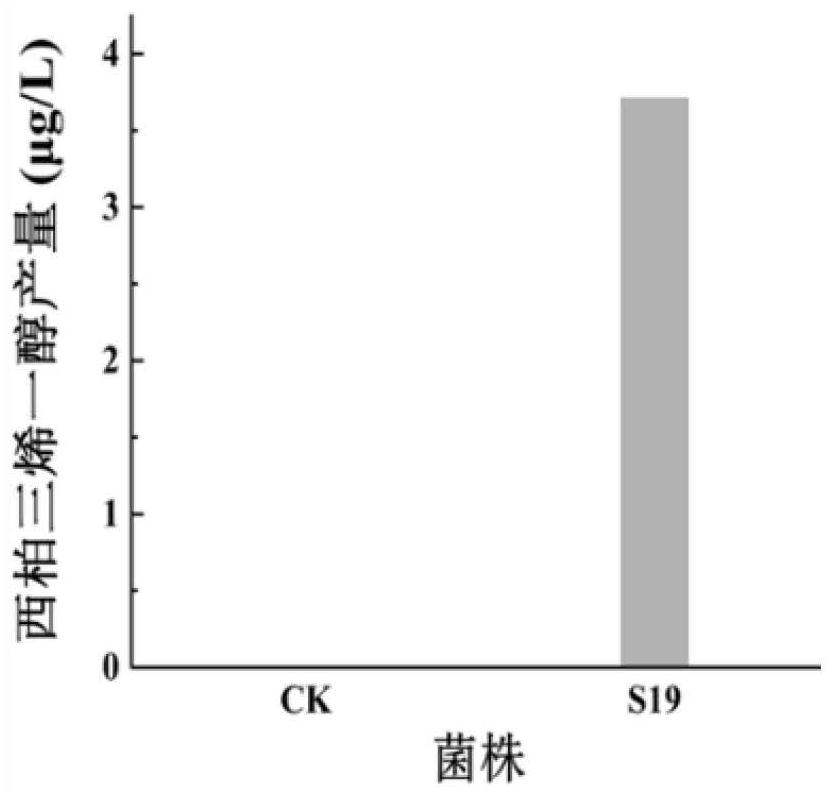
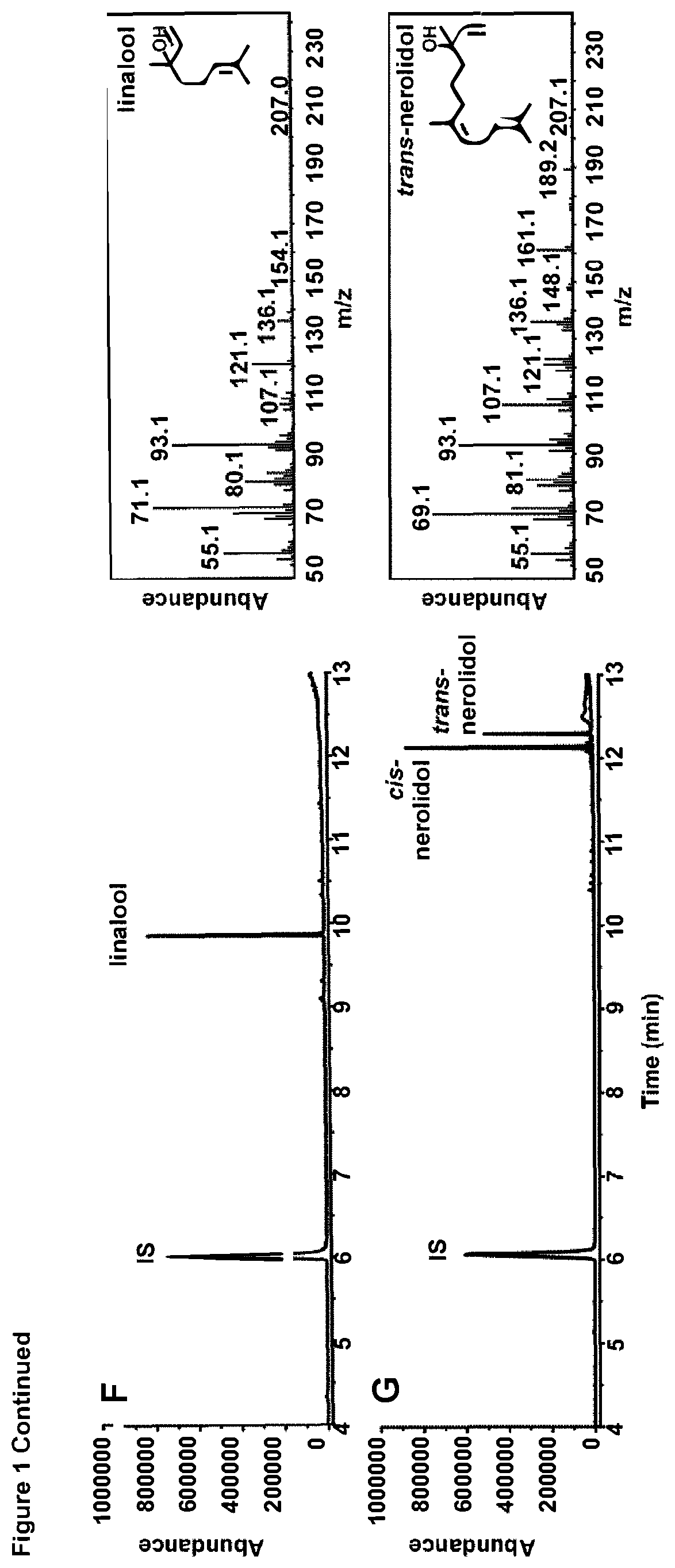
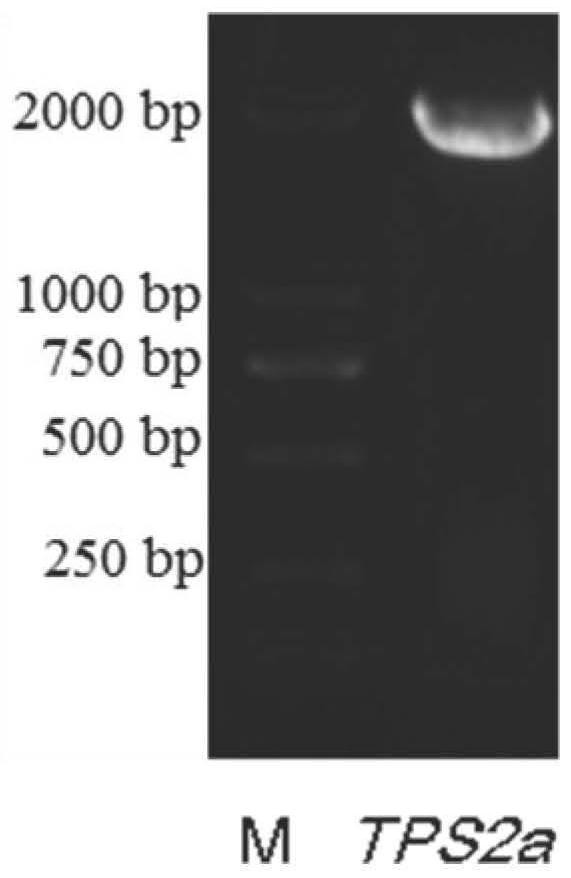
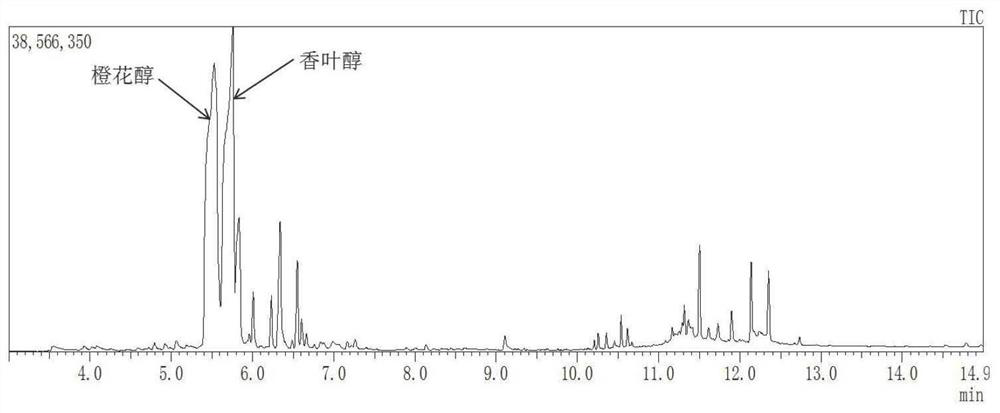
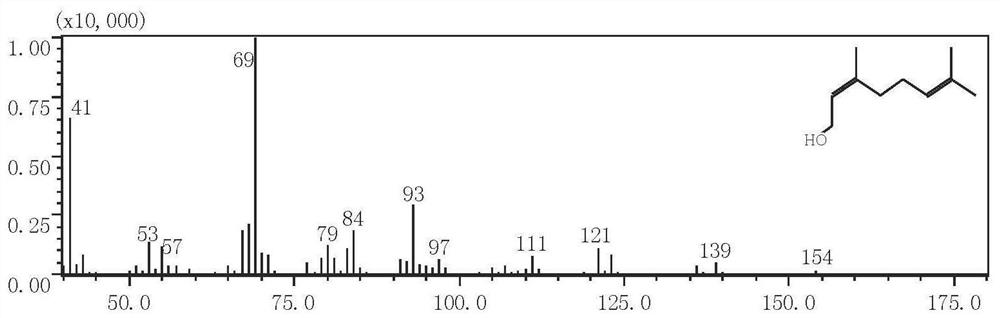
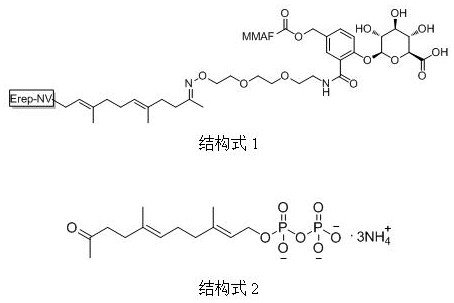
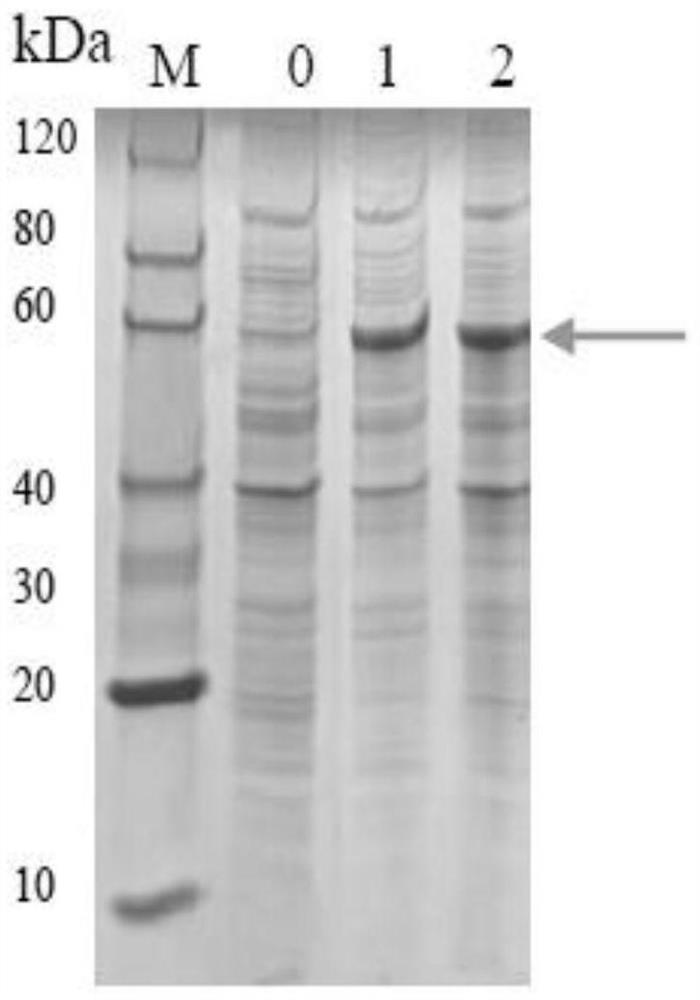
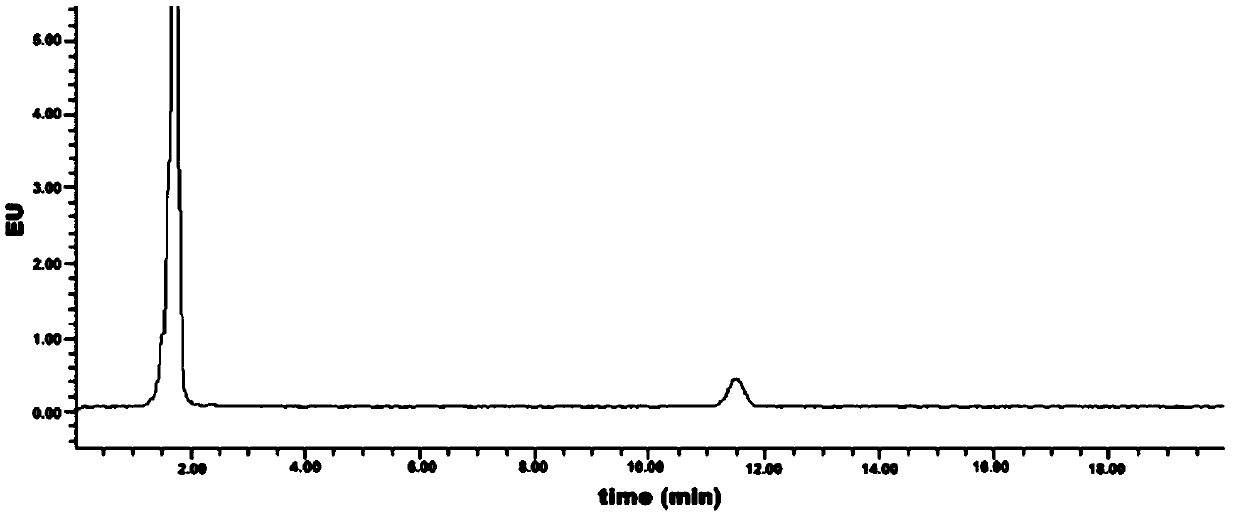
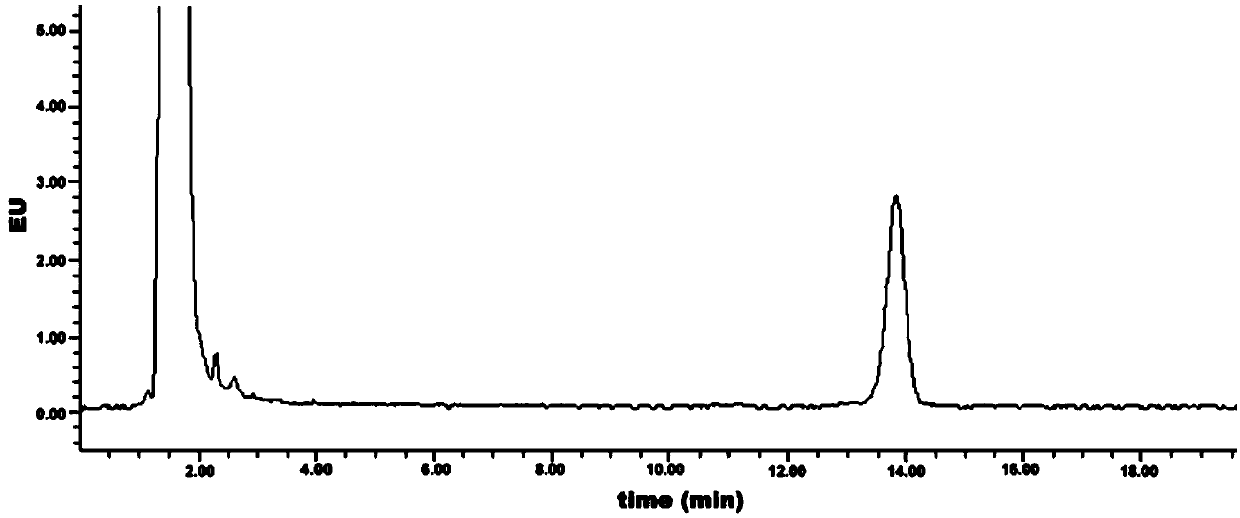
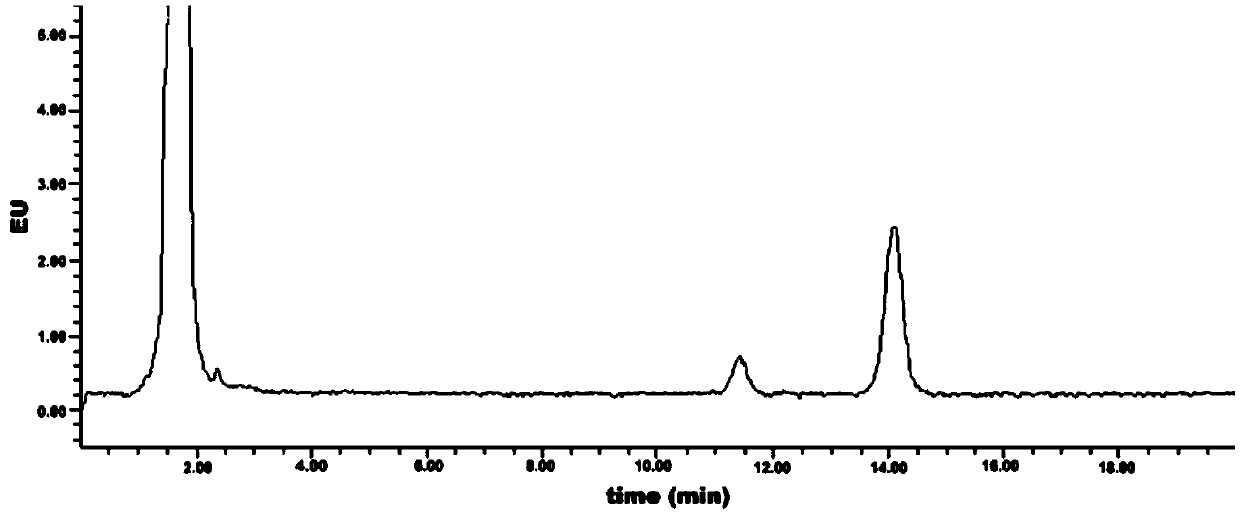
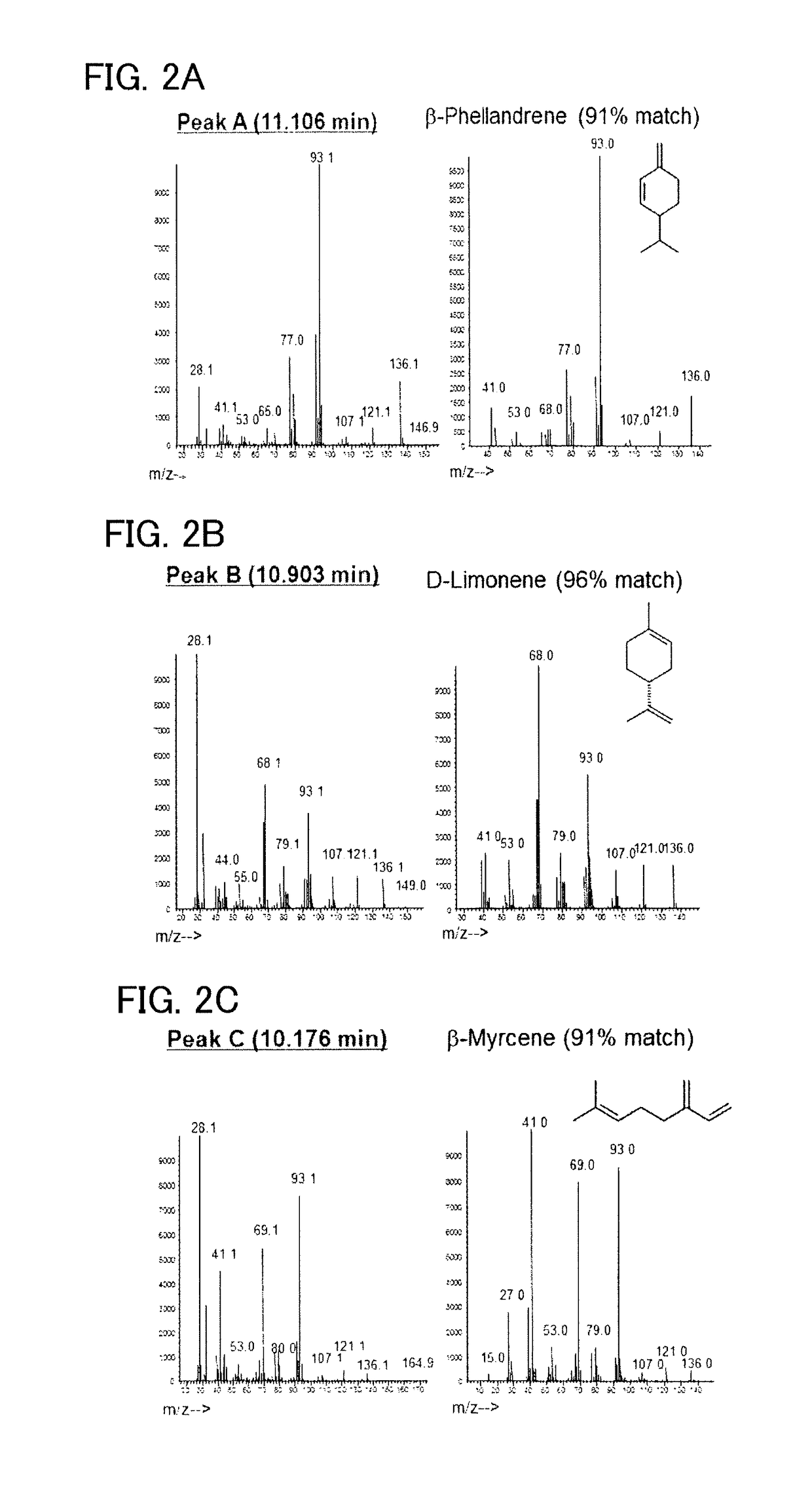
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Geranyl pyrophosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
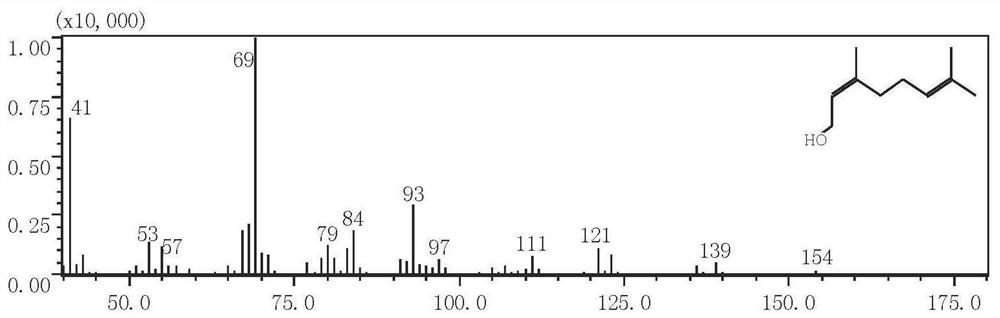
Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), also known as geranyl diphosphate (GDP), is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. These species are respectively precursors to sesquiterpenes and diterpenes.
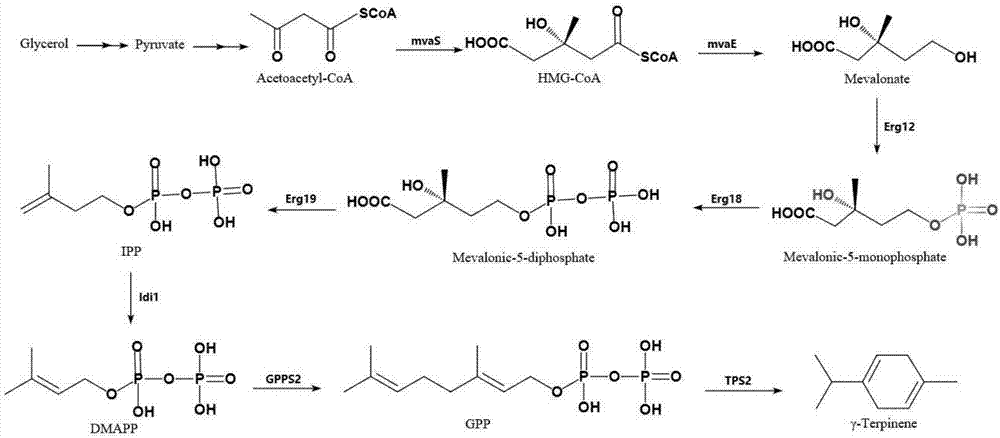
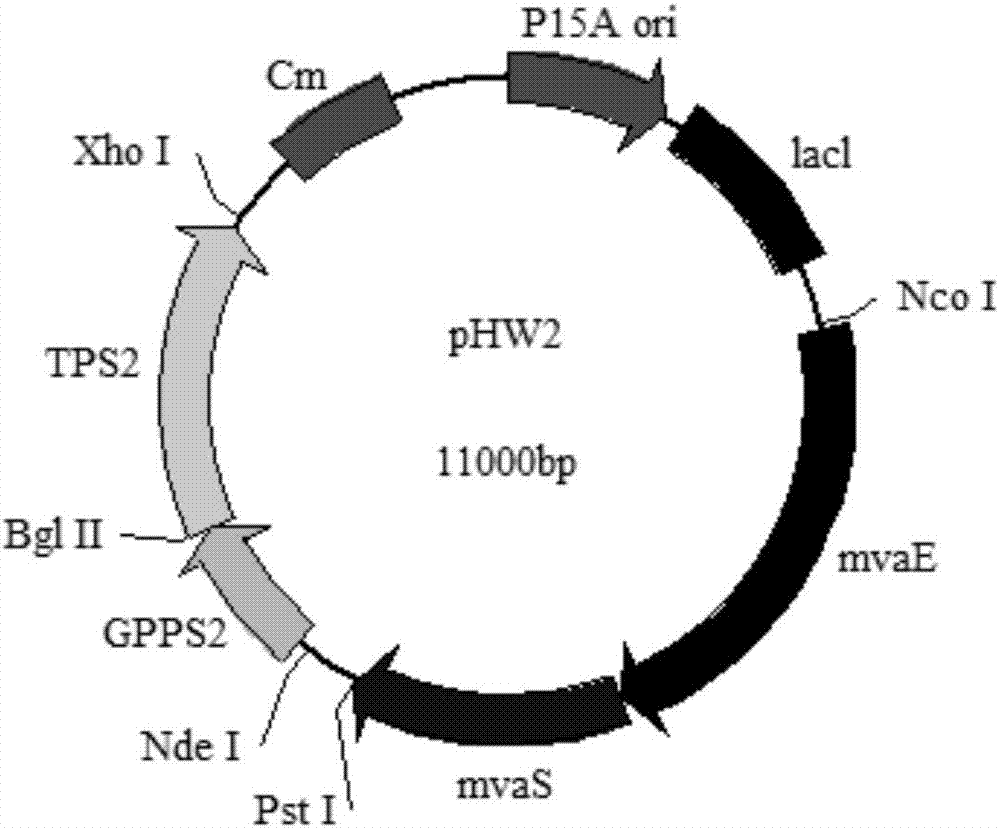
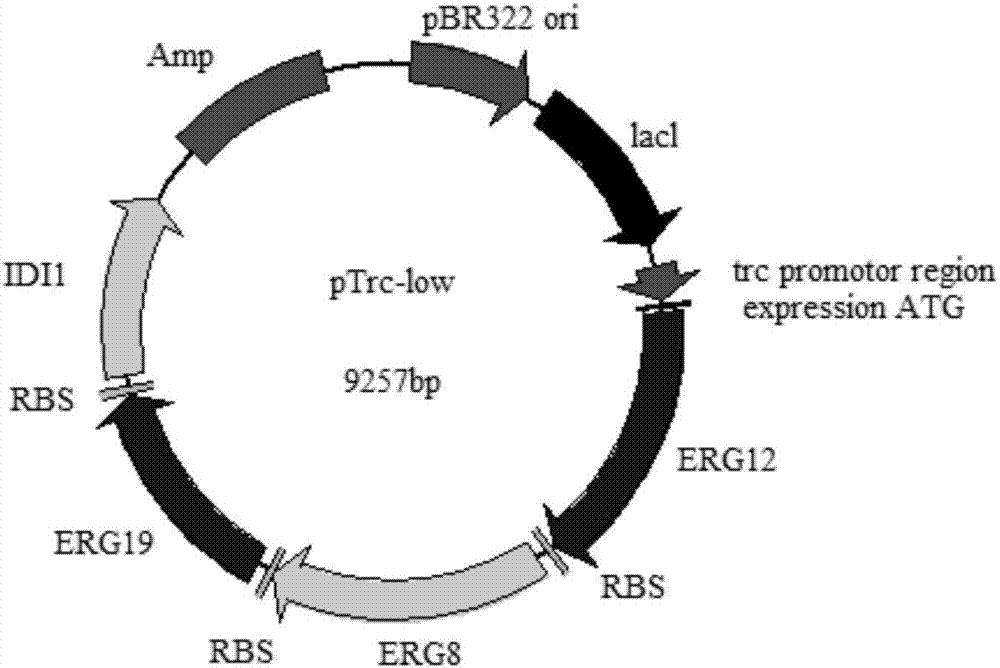
Genetically engineered bacterium with gamma-terpinene synthesis capacity and constructing method and application thereof
ActiveCN107354118AEfficient fermentation productionIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium with gamma-terpinene synthesis capacity and a constructing method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to engineered escherichia coli, a path for synthesizing MVA from mevalonic acid is reconstructed by heterogeneous expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A synthetase mvaS, hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase mvaE, mevalonate kinase Erg12, phosphomevalonate kinase Erg8, mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase Erg19 and Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase Idi1, meanwhile, geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase GPPS2 and gamma-terpinene TPS2 are led into a bacterium body, and by utilizing the biotransformation capacity of the genetically engineered bacterium, gamma-terpinene can be efficiently produced in an environment-friendly mode. Through fermentation with the genetically engineered bacterium, the output of gamma-terpinene can reach 80 mg / L. The genetically engineered bacterium and the gamma-terpinene synthesis method are suitable for practical industrial production.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
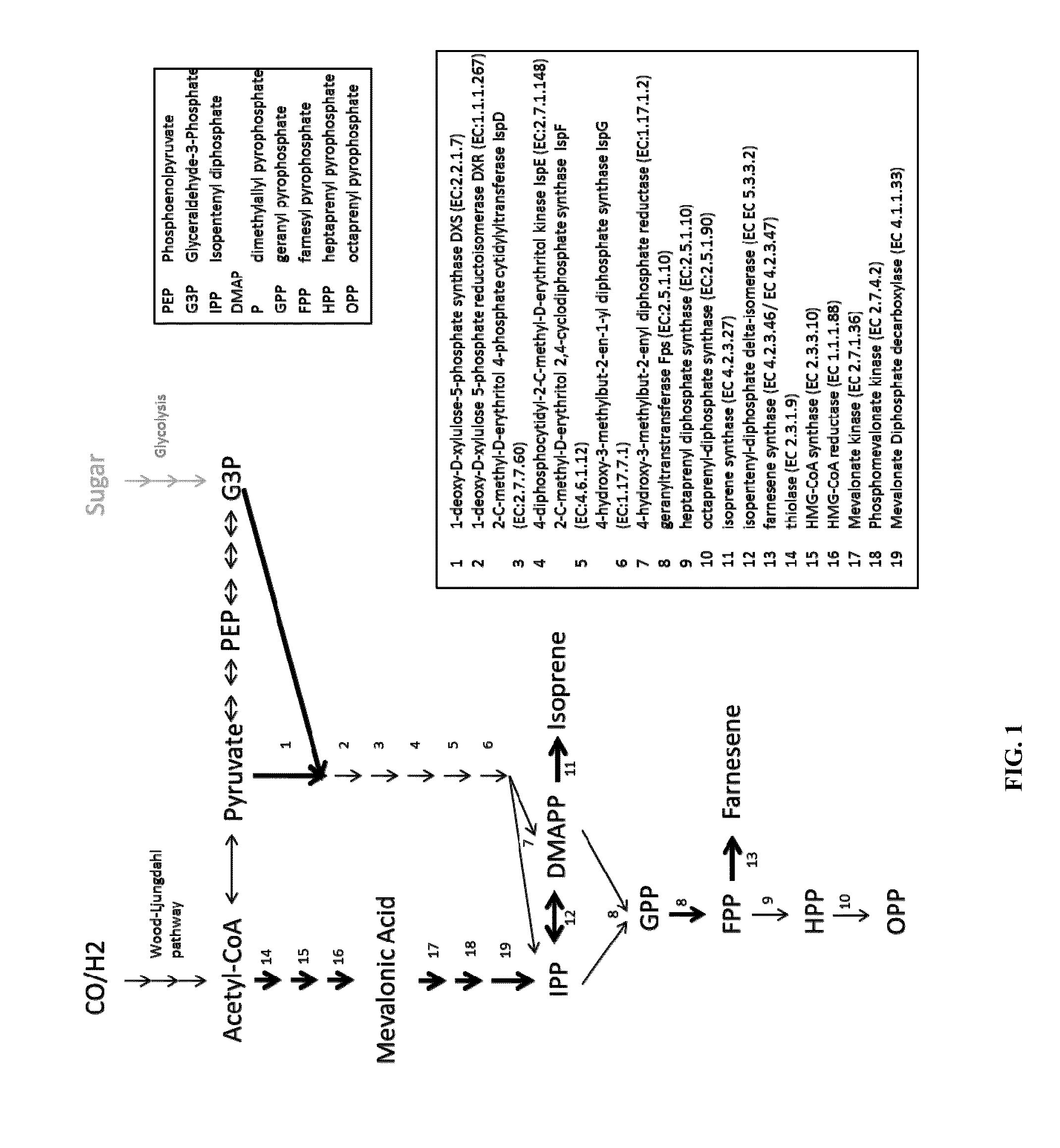
Microbial fermentation for the production of terpenes
The invention provides a method for producing a terpene or a precursor thereof by microbial fermentation. Typically, the method involves culturing a recombinant bacterium in the presence of a gaseous substrate whereby the bacterium produces a terpene or a precursor thereof, such as mevalonic acid, isopentenyl pyrophosphate, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, isoprene, geranyl pyrophosphate, farnesyl pyrophosphate, and / or farnesene. The bacterium may comprise one or more exogenous enzymes, such as enzymes in mevalonate, DXS, or terpene biosynthesis pathways.
Owner:LANZATECH NZ INC
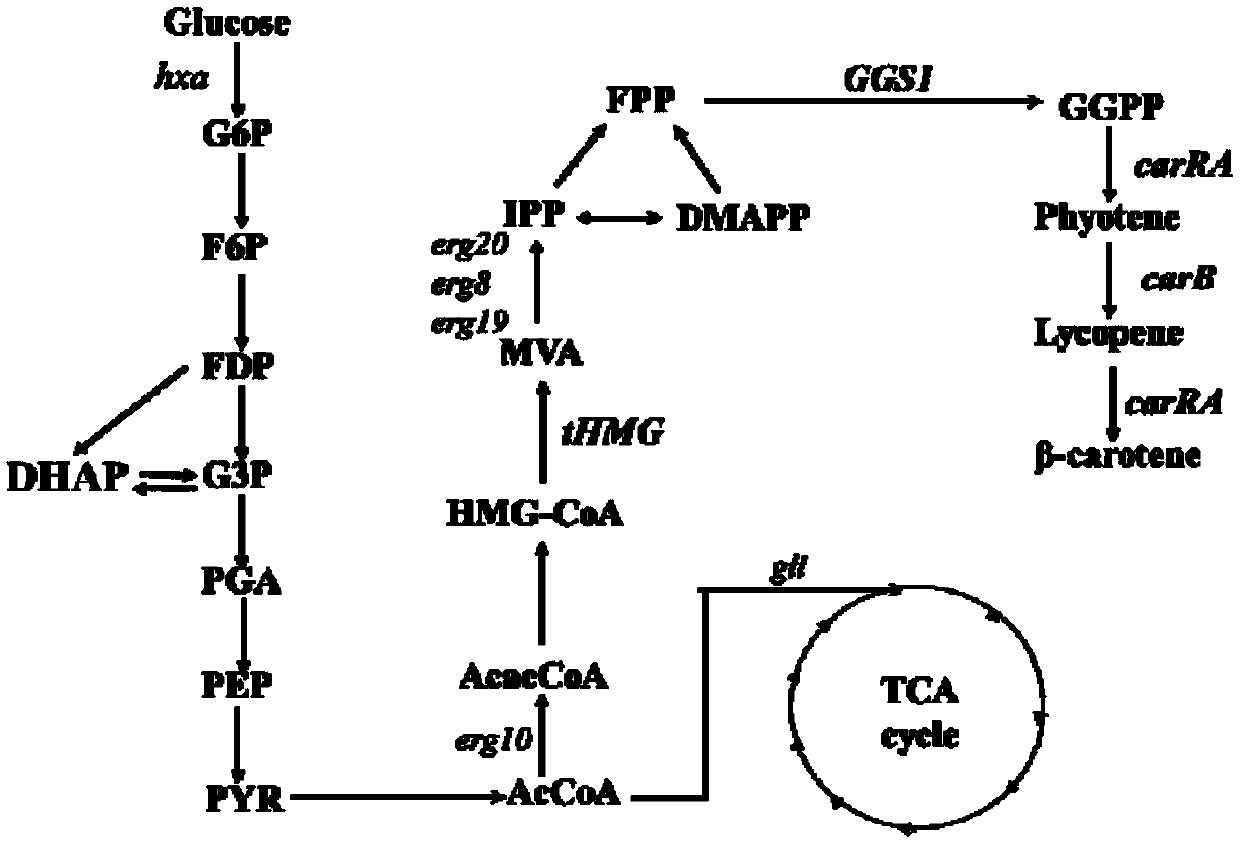
Recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and construction method utilizing Crispr-Cas9 technology
PendingCN109666596AIncrease the efficiency of homologous recombinationImprove stabilityFungiStable introduction of DNABeta-CaroteneKu70
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and a construction method utilizing a Crispr-Cas9 technology. A Ku70 gene is subjected to knockout from yarrowia lipolytica, and then phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA), phytoene desaturase (carB), geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene take snfas a target point and are integrated in a yarrowia lipolytica gene set after knockout of the ku70 gene, wherein the phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA) and phytoene desaturase (carB) are from blakeslea trispora, and the geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and the 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene are from the yarrowia lipolytica; the Crispr-Cas9 technology isutilized for regulating the copy number of the carRA, the carRA, the GGS1 and the tHMG, and the recombinant bacteria capable of producing the high-yield beta-carotene is constructed. After the recombinant bacteria is fermented, cultured, extracted and separated, the content of the beta-carotene can reach the dry cell weight of 35 mg / g, and the bacterial strain stability is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
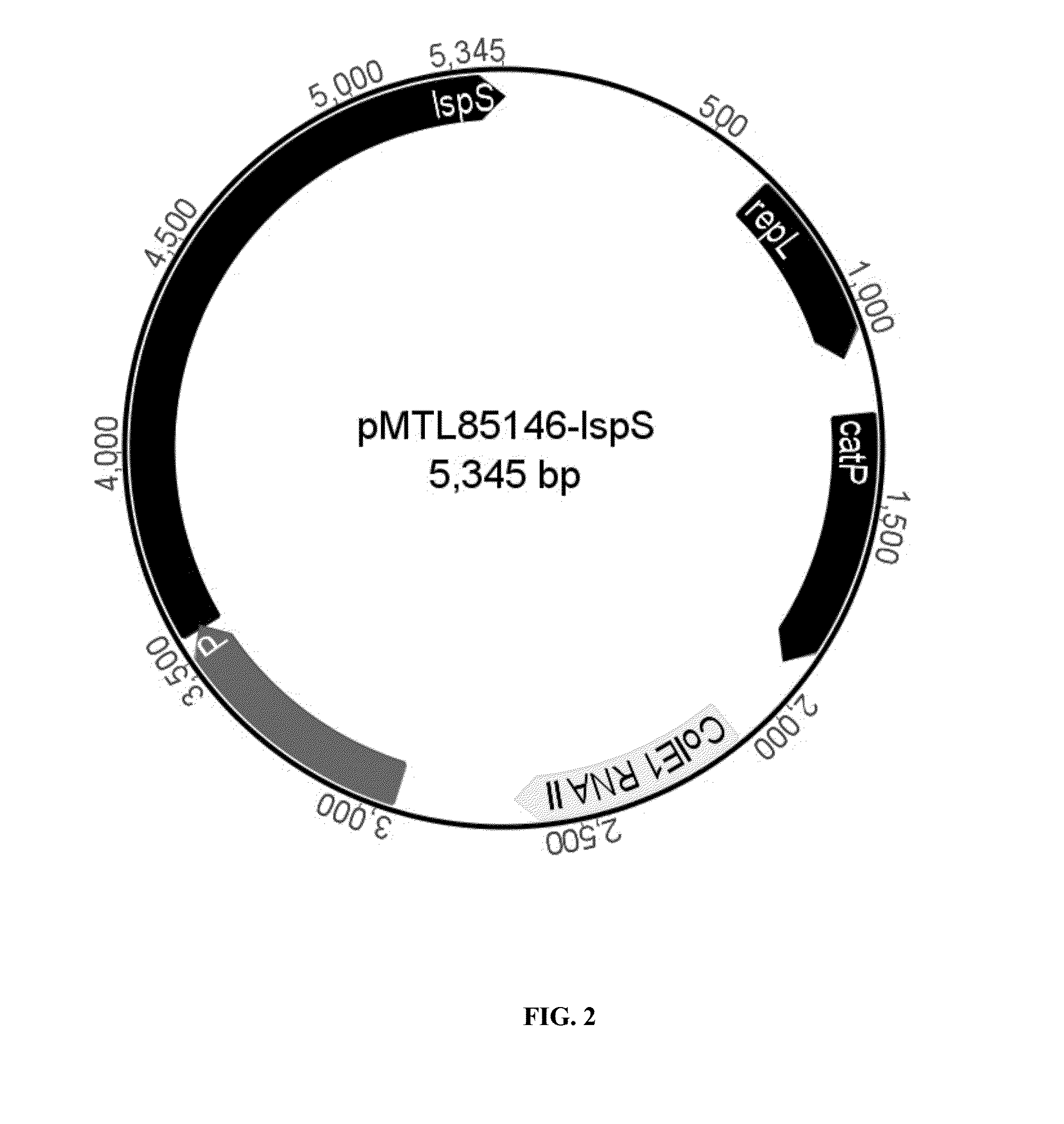
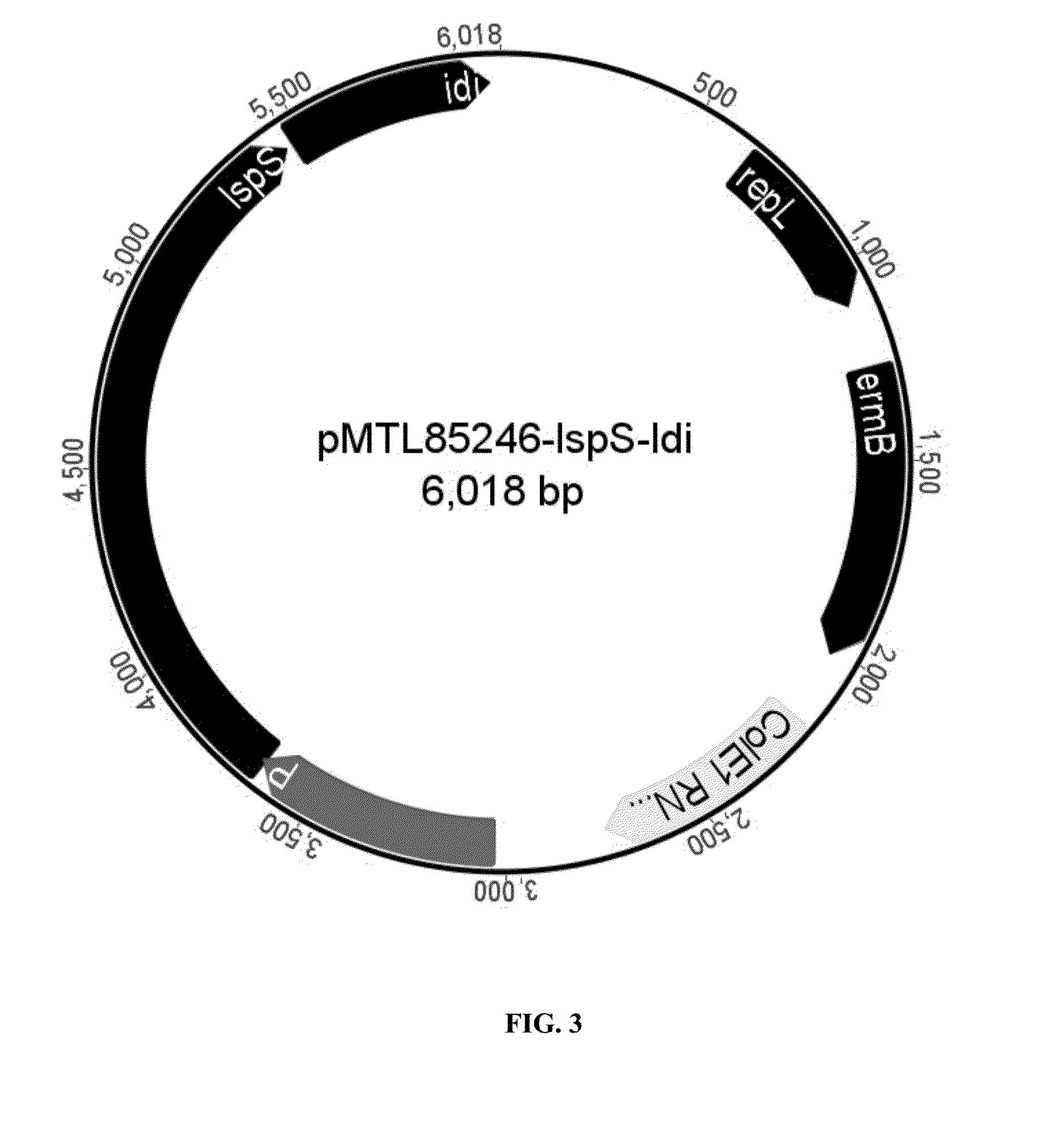
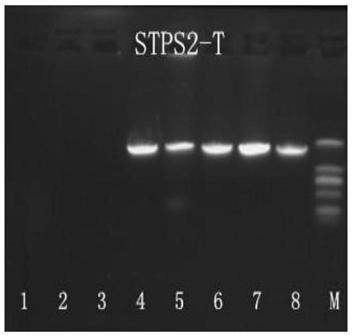
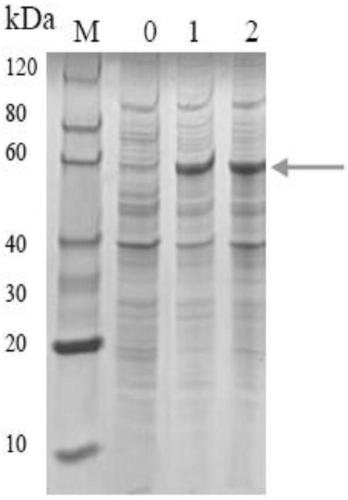
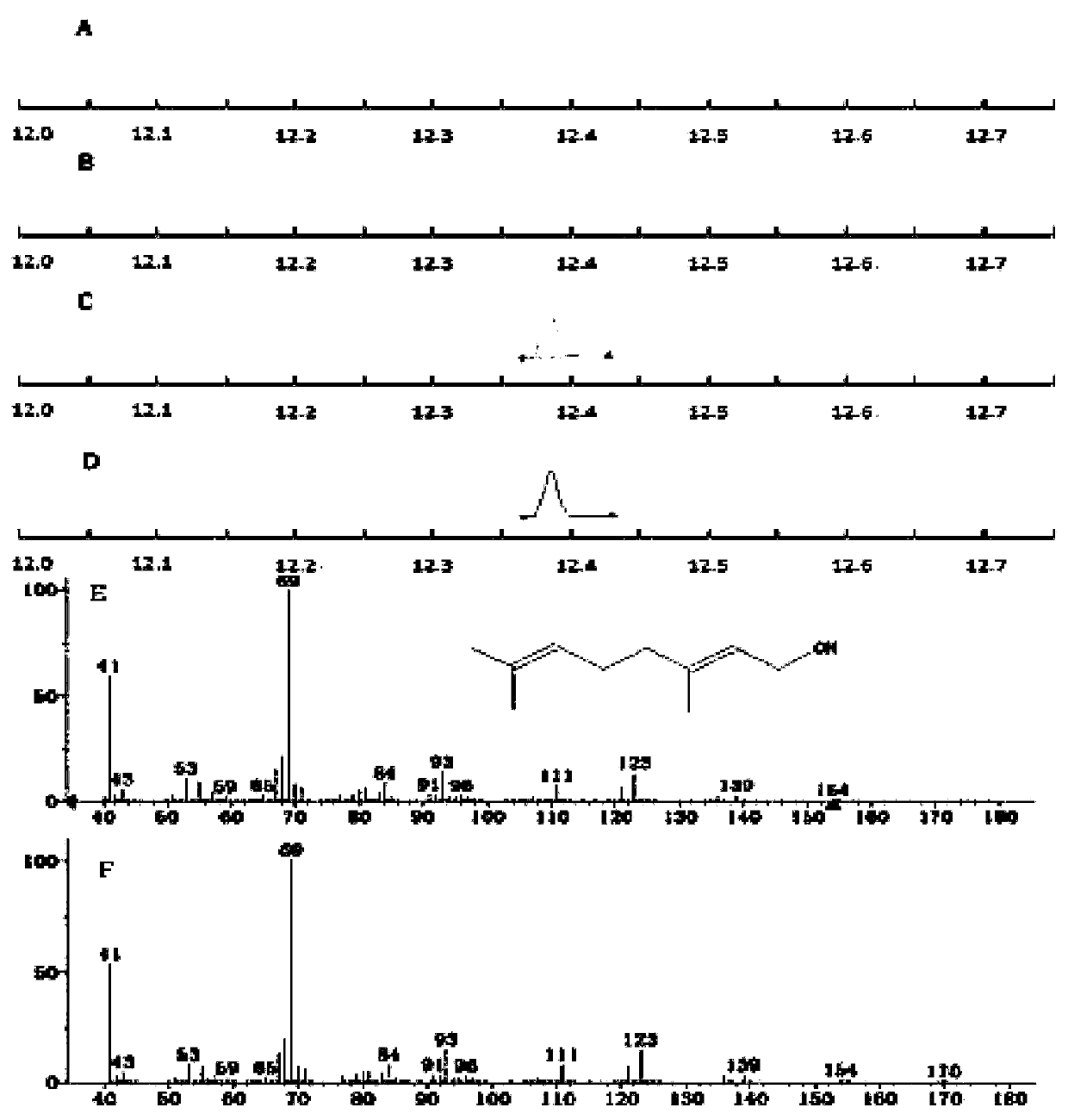
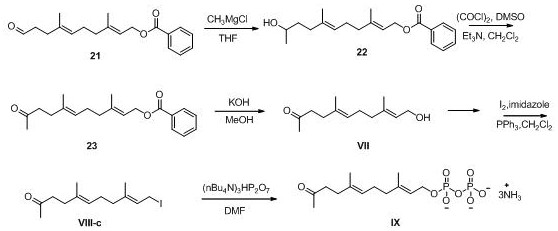
Sindora glabra sesquiterpenoid synthase SgSTPS2 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses sindora glabra sesquiterpenoid synthase SgSTPS2 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The novel sesquiterpenoid synthase, namely, sindora glabra sesquiterpenoid synthase SgSTPS2 as well as the encoding gene thereof are provided. The protein can generate active sesquiterpenoid synthase after prokaryotic expression, catalyzes FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) orGPP (geranyl pyrophosphate) to generate multiple sesquiterpene or monoterpene compounds and can be used for mass production.
Owner:RES INST OF TROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
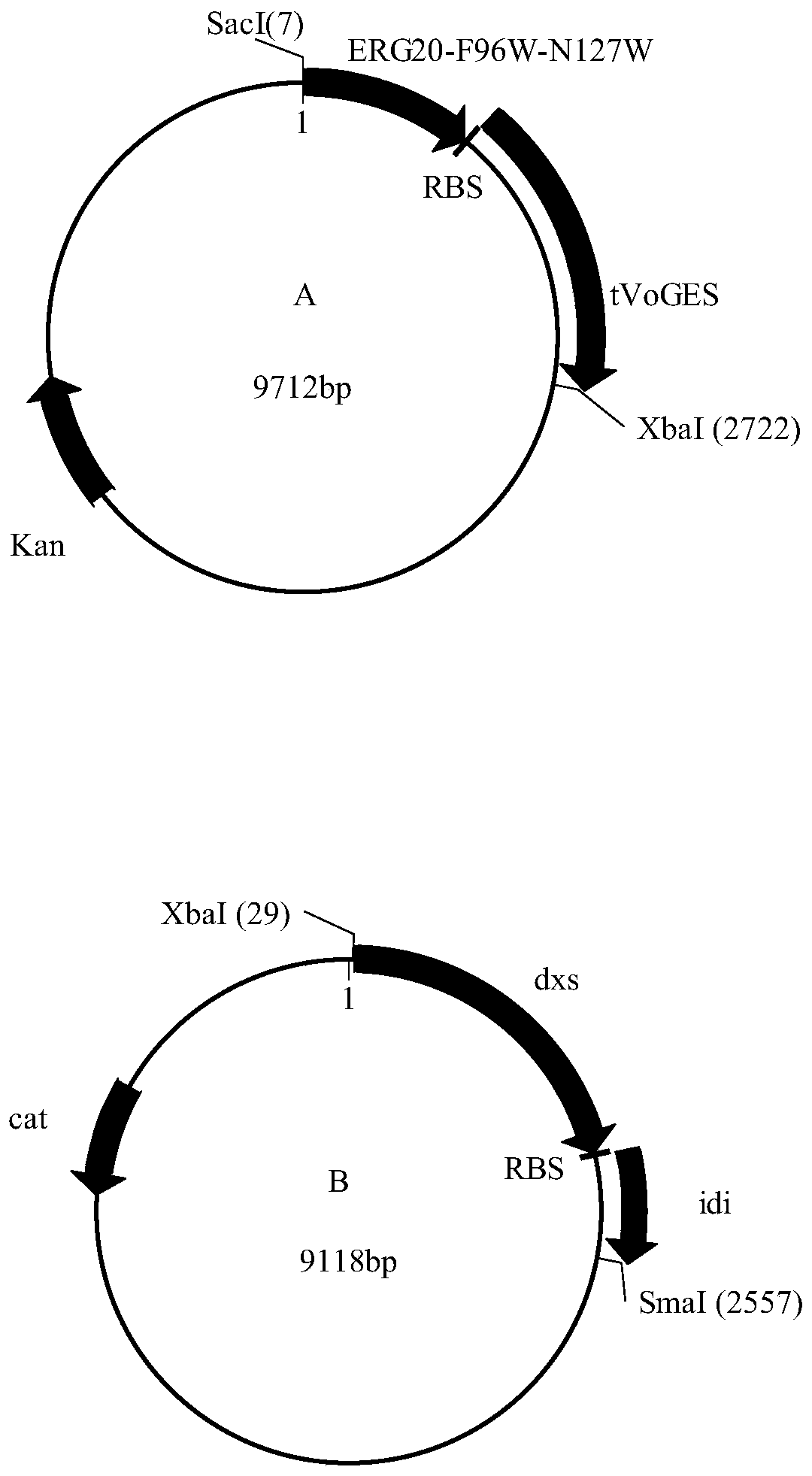
Corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate
InactiveCN110438145AShort fermentation timeBacteriaTransferasesCorynebacterium efficiensBinding site
The present invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamate for synthesizing geraniol and a construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamate. The construction method of corynebacteriumglutamate comprises the following steps: connecting a saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived mutant geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene ERG20<F96W-N127W> and a valerian-derived geranol synthase gene tVoGEStruncated through cutting off of C-terminal 53 amino acid residues by fusion PCR, adding a ribosome binding site sequence to a homologous region, inserting SacI and XbaI enzyme cutting sites of a corynebacterium glutamate expression plasmid pEC-XK99E to obtain a plasmid 1; converting the plasmid 1 into corynebacterium glutamate to obtain corynebacterium glutamate 1 for synthesizing geraniol. Theconstruction method provides more precursors and short fermentation time (42 to 48 hours) for the synthesis of geraniol, and corresponding by-products are not detected out by GC-MS detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant cell, and method for producing beta-phellandrene
ActiveUS20150218589A1High purityAvoid small quantitiesBacteriaTransferasesPhellandreneNeryl pyrophosphate
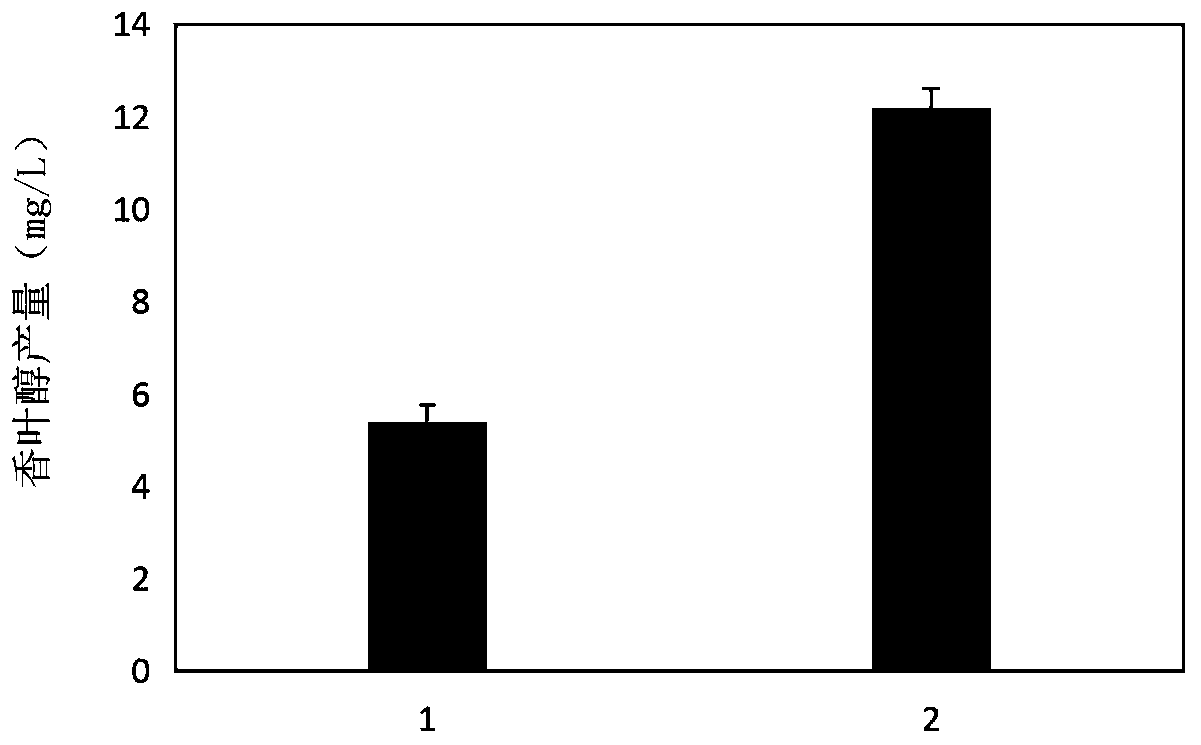
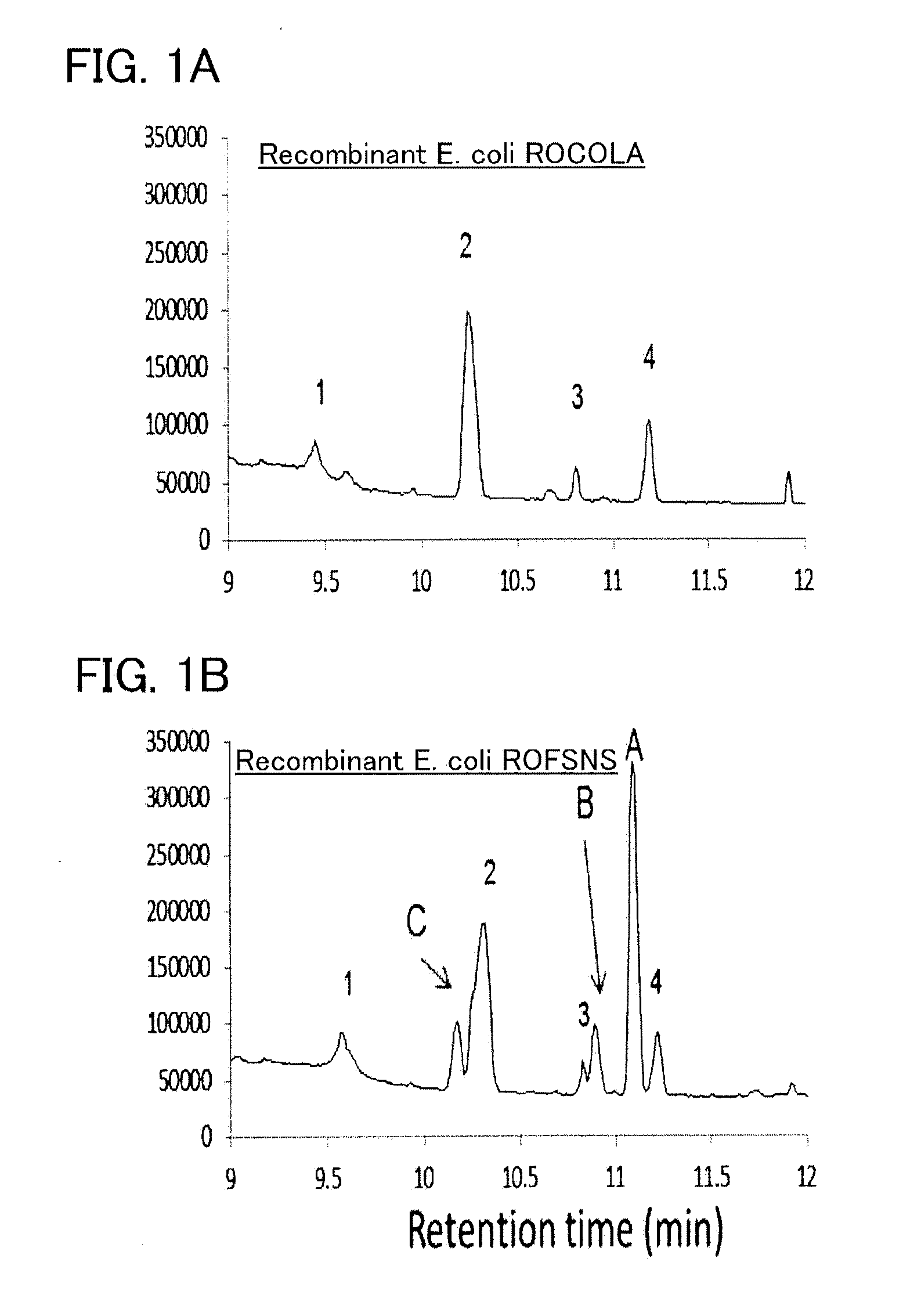
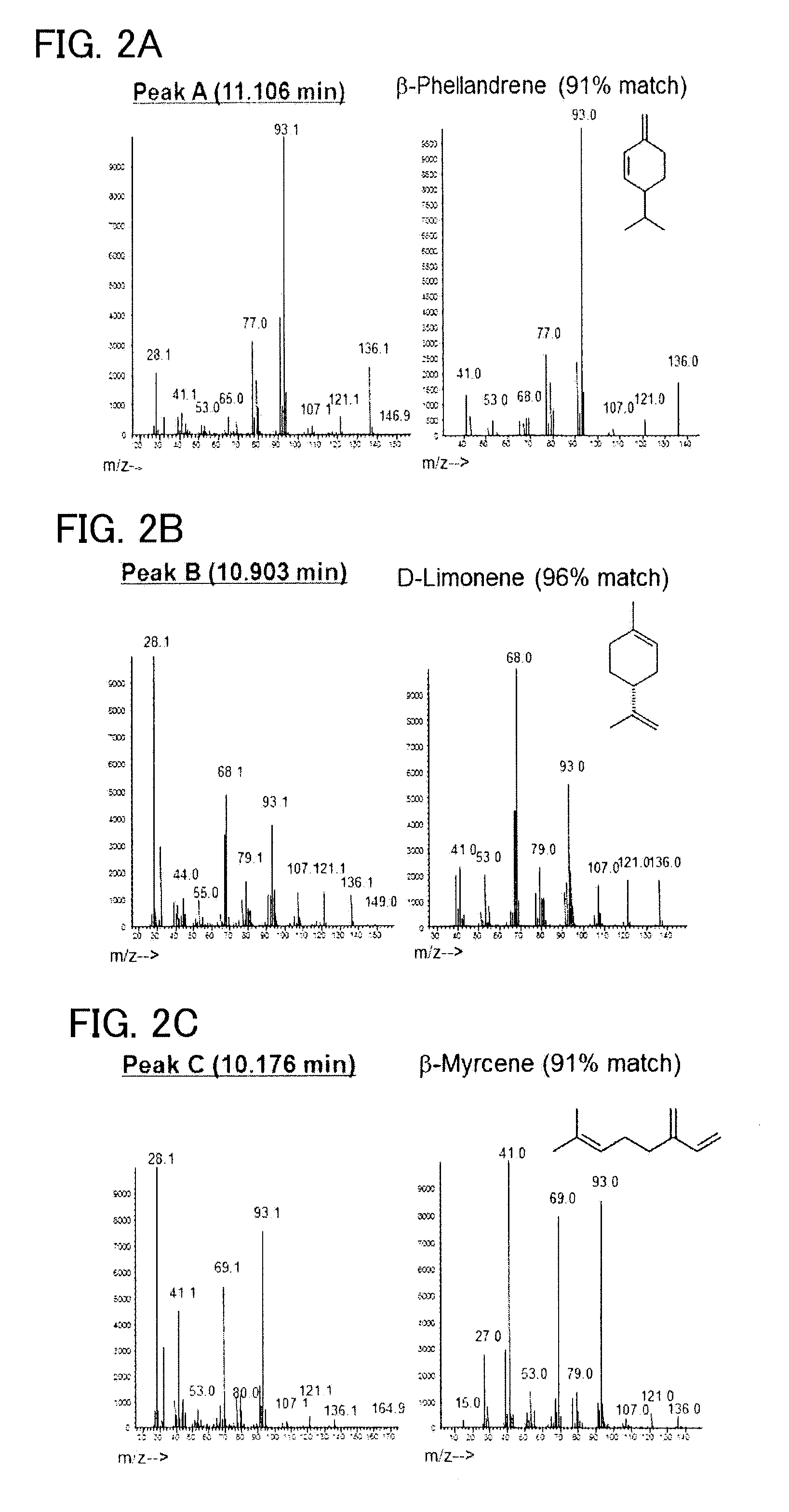
To provide a series of techniques for obtaining β-phellandrene with high purity and in a large quantity.Provided is a recombinant cell capable of producing β-phellandrene, prepared by introducing at least one nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid encoding geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) synthase and a nucleic acid encoding neryl pyrophosphate (NPP) synthase, and a nucleic acid encoding β-phellandrene synthase into a host cell in such a manner that these nucleic acids are expressed in the host cell. Also provided is a method for producing β-phellandrene by culturing the recombinant cell to produce β-phellandrene in the recombinant cell.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD +1
Method for synthesizing 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and xiamenmycin by utilizing escherichia coli
ActiveCN108865961AIncrease productionAchieve biosynthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGeranyl pyrophosphate
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and xiamenmycin by utilizing escherichia coli. According to the method, an adopted escherichia coli strain contains xiamenmycin synthesis related genes and mevalonic acid pathway related genes which are partially or entirely subjected to codon optimization; three genes required by synthesis of the xiamenmycin are imported into the escherichia coli; the three genes are subjected to inducible expression, and GBA and the xiamenmycin are synthesized in the escherichia coli; the feed of intracellular geranyl pyrophosphate of the escherichia coli is further improved by introducing a mevalonic acid synthesis pathway, and the yield of the GBA is further increased by adding 4-hydroxybenzoic acid into a fermentation medium; the yield of the synthesized 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid reaches 94 mg / L, and the yield of the xiamenmycin reaches 11 mg / L; and the biosynthesis of the 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and the xiamenmycin in the escherichia coli is realized for the first time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for producing stevioside compounds by microorganism
ActiveUS20150252401A1Increase productivityEfficient synthesisSugar derivativesTransferasesMicroorganismCopalyl pyrophosphate
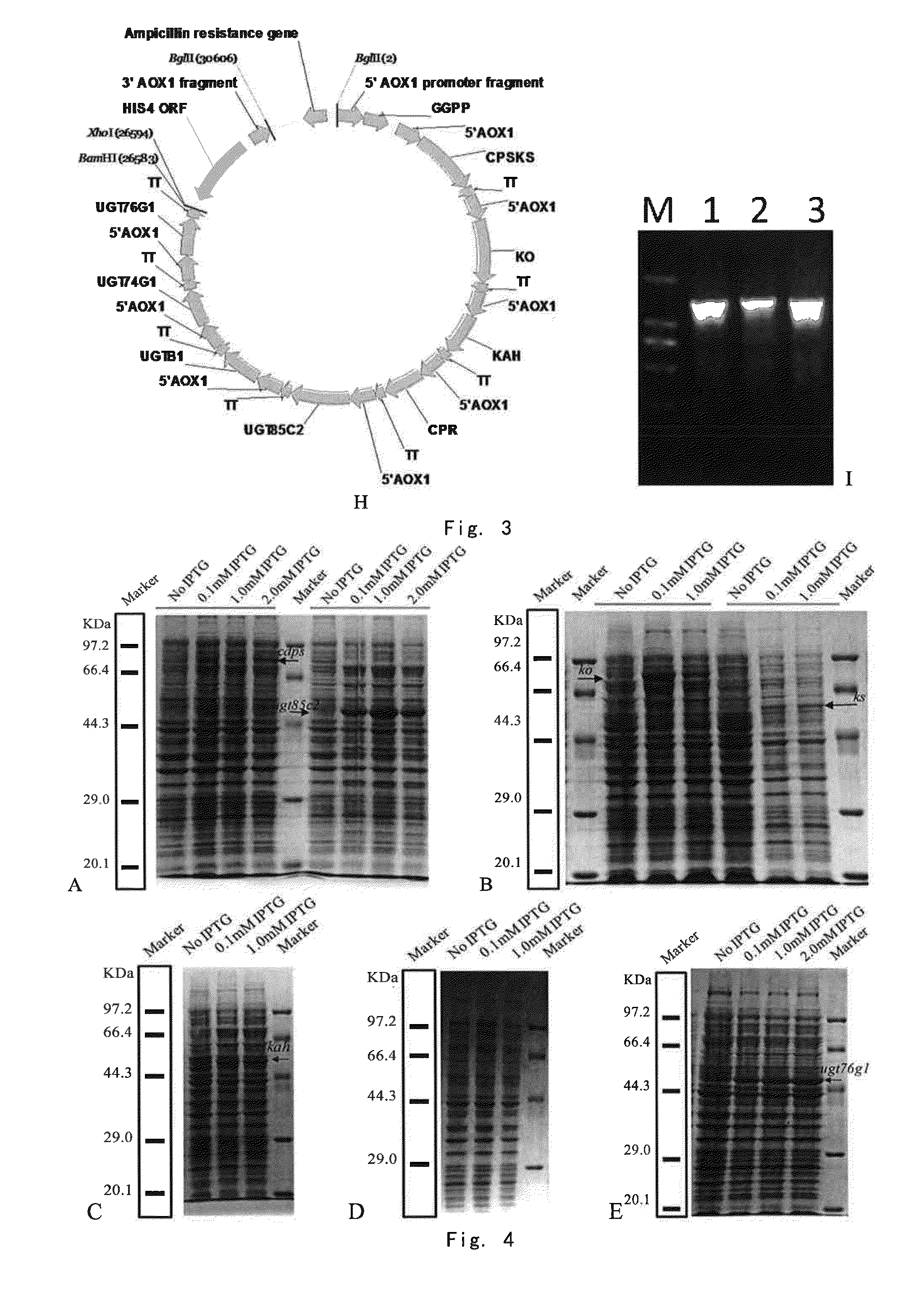
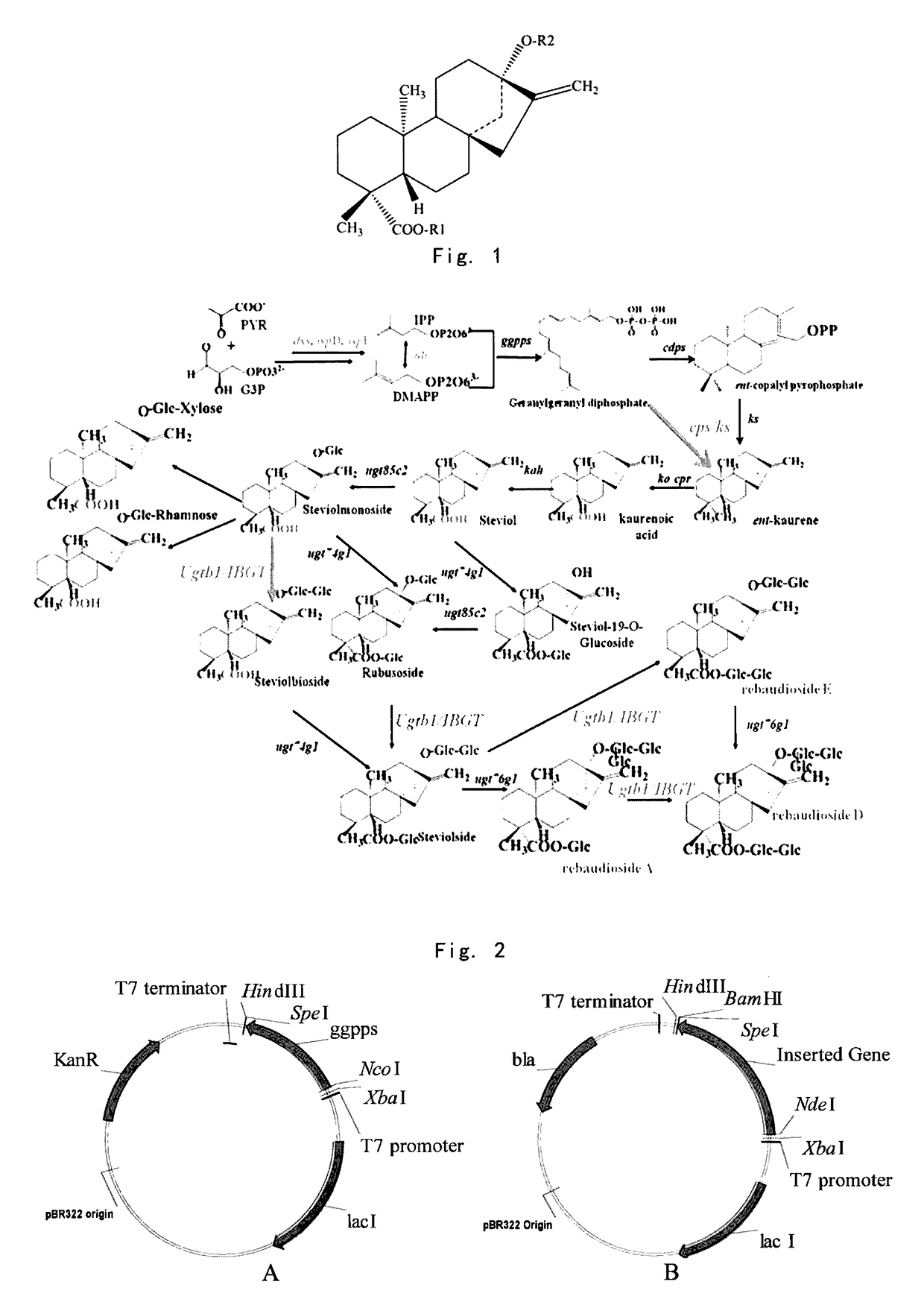
The present invention provides a method for producing stevioside compounds by microorganism, comprising carrying out heterologous biosynthesis of stevioside compounds from geranyl geranyl pyrophosphate synthase (GGPPS), Copalyl pyrophosphate synthase (CDPS), Kaurene synthase (KS), dual-function kaurene synthase (CPS / KS), kaurene oxidase (KO), a cytochrome P450 redox protein (CPR), kaurenoic acid-13[alpha]-hydroxylase, UGT85C2 glycosyltransferase and UGTB1 / IBGT glycosyltransferase (optionally comprising UGT74G1 glycosyltransferase and / or UGT76G1 glycosyltransferase).
Owner:SICHUAN INGIA BIOSYNTHETIC CO LTD
Method for improving linalool synthesizing capacity of saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN107937431AImprove the ability to synthesize linaloolIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesPeptidesEnzyme digestionReaction rate
The invention discloses a method for improving a linalool synthesizing capacity of saccharomyces cerevisiae, and belongs to the technical field of metabolic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, conducting codon optimization on a CoLIS gene sequence SEQ ID NO:1 from cinnamomum pedumculatum nees and an ERG20 gene sequence SEQ ID NO:2 from the saccharomyces cerevisiae; on the basis of enzyme digestion and connection, cloning the SEQ ID NO:1 and the SEQ ID NO:2 to a plasmid pESC-URA; and conducting regulating and controlling by virtue of double promoters, namely Gal10 and Gal1, on a pESC-URA vector, so that activities of CoLIS and ERG 20 enzyme protein are reserved; through high-expression of the ERG20 protein, a substrate, namely geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), which is required by the synthesis of linalool, can be effectively supplied by virtue of recombinant bacteria; therefore, an enzymatic reaction rate for synthesizing linalool can be obviously improved and fermentation conditions can be further optimized, so that the effective synthesis of the linalool is achieved.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
Cannabinoid Production by Synthetic In Vivo Means
In some aspects of the design, novel forms of geranylpyrophosphate:olivetolate geranyltransferase; of olivetol synthase or of geranyl pyrophosphate synthase; of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase; of olivetolic acid cyclase; and / or of olivetolic acid synthase for making large scale amounts of cannabinoids in cells, in vitro are presented.
Owner:BIOTIC SCI INC
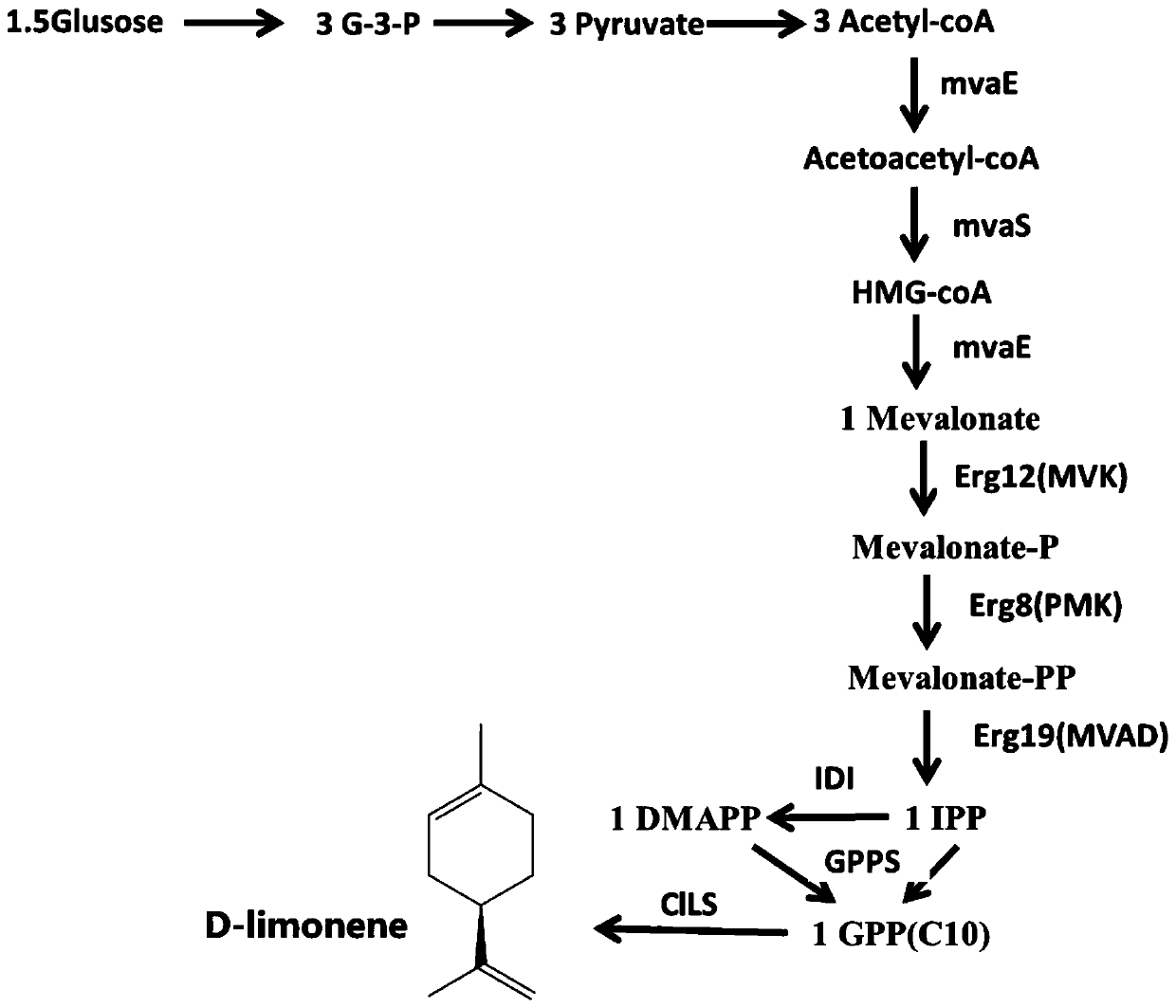
Genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing D-limonene, and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
PendingCN110669713AExtensive living environmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing D-limonene, and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and relates to the field of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. In the genetically engineered bacterium, an HMG-CoA synthetase gene, an acetyl CoA acetylase mvaE, a GPPS (geranyl pyrophosphate synthase) gene, a D-limonene synthetase gene C1L2, an MVA kinase ERG12 gene, an MVAP kinase ERG8 gene, a mevalonic acid decarboxylase ERG19 gene and an isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase IDI gene are subjected to overexpression. In an LB culture medium, after flask shaking fermentation is carried out, the D-limonene can be subjected to heterologous synthesis, and the yield of the D-limonene is 27.3mg / L of fermentationliquor. The genetically engineered bacterium can be used for the industrial production of the D-limonene.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
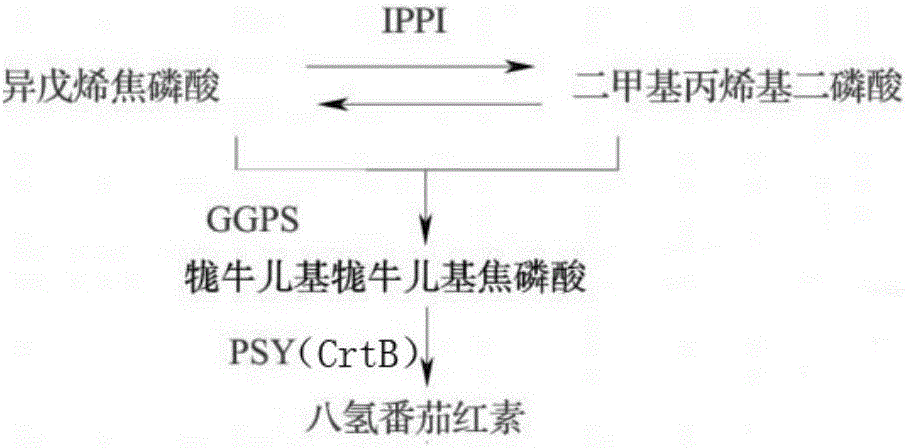
Phytoene synthase of endophytic fungi of saffron, encoding gene of phytoene synthase and application of encoding gene
The invention relates to phytoene synthase of endophytic fungi of saffron, an encoding gene of the phytoene synthase and application of the encoding gene, belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and further discloses an open reading frame sequence of the gene of the phytoene synthase of the endophytic fungi of the saffron and an amino acid sequence encoded by the gene of the phytoene synthase of the endophytic fungi. The phytoene synthase, the encoding gene and the application have the advantages that typical phytoene synthesis functions of proteins encoded by the gene of the phytoene synthase of the endophytic fungi of the saffron are verified by means of color genetic complementation reaction, accordingly, 2-molecule geranyl geranyl pyrophosphate can be catalyzed to synthesize phytoene, or the phytoene synthase can be used for catalyzing synthesis of terpenoid such as carotenoids.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Escherichia coli expression strain for high yield of geraniol glucoside and application thereof
ActiveCN110317765AEasy to synthesizeEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGeranyl pyrophosphate
The invention provides an Escherichia coli expression strain for high yield of geraniol glucoside, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The Escherichia coli expression strain jointly expresses an acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase gene, a methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthetase gene, a HMG-CoA reductase gene, a mevalonate kinase gene, phosphomevalonate kinase gene, a pyrophosphate mevalonate decarboxylase gene, an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase gene, a geranyl pyrophosphate GPP synthetase ispA*, a geraniol synthetase gene, a geranyl pyrophosphate GPP synthetase ERG20* and a glycosyltransferase gene. The yield of geraniol glucoside produced from the Escherichia coli expression strain is high, reliable in mass and good in application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium for selectively producing retinol as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN113265344ASynthetic participationIncrease productionFungiTransferasesCell factoryRetinol dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for selectively producing retinol as well as a construction method and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the genetically engineered bacterium, an engineering strain for producing beta-carotene is taken as a starting bacterium, beta-carotene 15, 15'-dioxygenase coding genes and aldehyde reductase coding genes or / and retinol dehydrogenase coding genes are introduced, and selective production of retinol in a cell factory is realized. In order to further improve the yield of retinol, a geranyl-geranyl pyrophosphate synthase mutant encoding gene is further introduced into the genetically engineered bacterium, an NADH kinase encoding gene of an N-terminal mitochondrial positioning peptide is cut off, and meanwhile, a mevalonic acid pathway transcription inhibition factor gene is knocked out, so that the supply of precursors and coenzymes is increased. The invention also provides a method for producing retinol by using the genetically engineered bacterium, ferrous ions and an antioxidant are added in the fermentation process, so that the yield of retinol is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing cembratrienol
PendingCN113388536AEfficient productionAchieving de novo productionFungiTransferasesHeterologousEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a construction method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing cembratrienol, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering and microbial engineering. According to the method, two key enzymes, namely geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene gpps and cembratrienol synthase gene cbts, synthesized by cembratrienol are heterologously expressed in the saccharomyces cerevisiae W303-1A, so that the production of the cembratrienol in the saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized from the source; furthermore, through tandem overexpression of a key enzyme farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase (ERG20) with the cembratrienol synthase gene cbts, the yield of cembratrienol of the obtained recombinant strain is remarkably improved. The way is constructed into the saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741, and the yield of cembratrienol is increased to 3 times of that of a control strain. A promoter is added in front of the key enzyme farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene, so that the yield of cembratrienol of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae is further improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering bacterium used for co-production of geraniol and nerol, and construction method and application of engineering bacterium
ActiveCN112391327AIncrease productionWith scale developmentBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium used for co-production of geraniol and nerol, and a construction method and application of the engineering bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The construction method of the engineering bacterium includes the following steps: introducing a tobacco geraniol and nerol synthetase gene into a receptor strain capable of generating geranyl pyrophosphate to obtain a recombinant bacterium; and obtaining the engineering bacterium used for producing the geraniol and the nerol from the recombinant bacterium. According to the engineering bacterium, a bioengineering technology is successfully applied to realize the heterologous reconstruction of a geraniol and nerol biosynthetic pathway and the co-production of products, andthe yield of the geraniol and the yield of the nerol reach 137.3 mg / L and 62.8 mg / L respectively by a shake-flask fermentation method; and meanwhile, the yield of geraniol and the yield of nerol are increased by about 10 times through a high-density fermentation technology of recombinant strains.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Microbial fermentation for the production of terpenes
ActiveUS20180142265A1Phosphorus-oxygen lyasesWaste based fuelGeranyl pyrophosphateDimethylallyl pyrophosphate
The invention provides a method for producing a terpene or a precursor thereof by microbial fermentation. Typically, the method involves culturing a recombinant bacterium in the presence of a gaseous substrate whereby the bacterium produces a terpene or a precursor thereof, such as mevalonic acid, isopentenyl pyrophosphate, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, isoprene, geranyl pyrophosphate, farnesyl pyrophosphate, and / or farnesene. The bacterium may comprise one or more exogenous enzymes, such as enzymes in mevalonate, DXS, or terpene biosynthesis pathways.
Owner:LANZATECH NZ INC
Synthesis of isoprenoids and derivatives
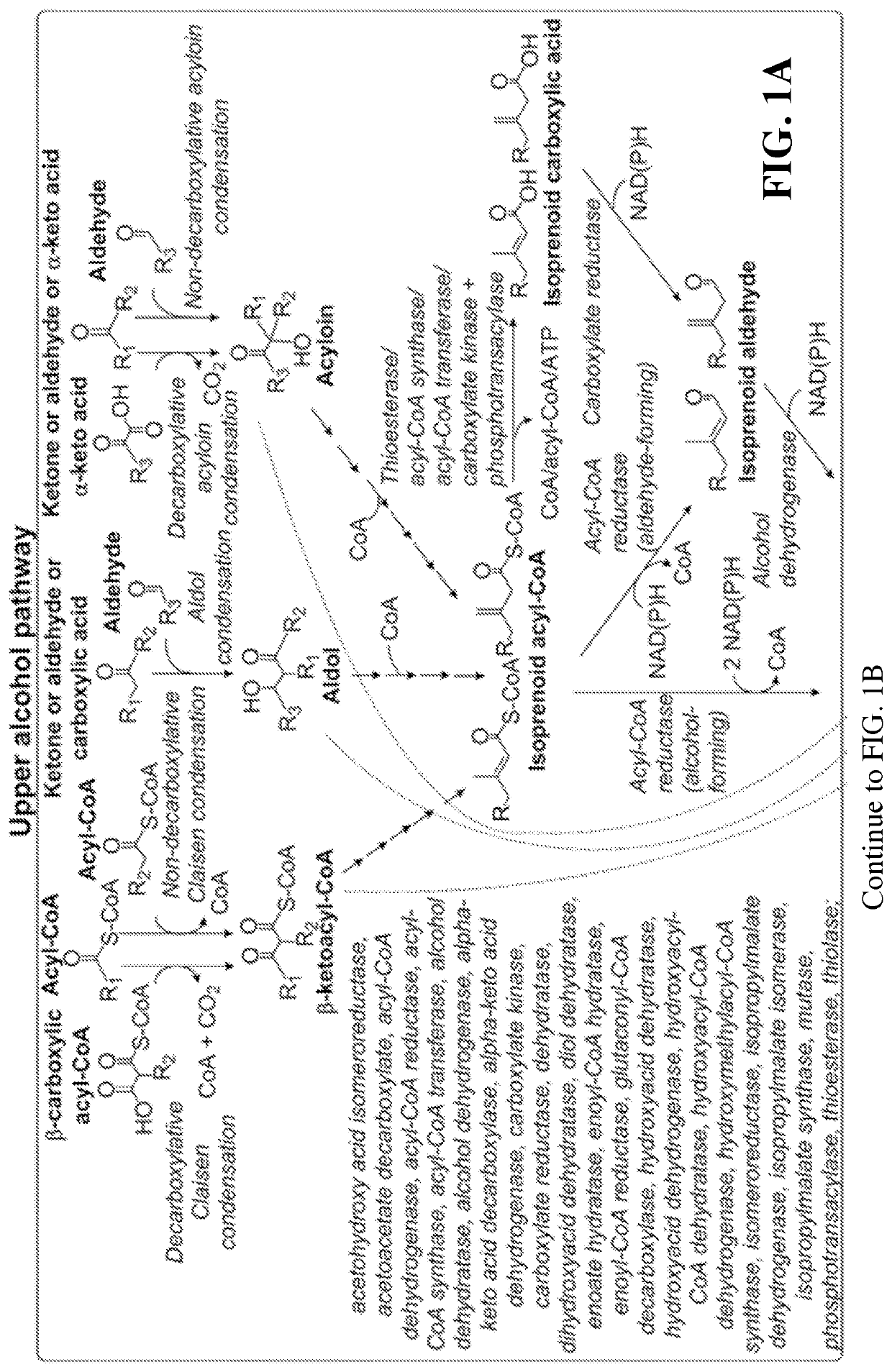
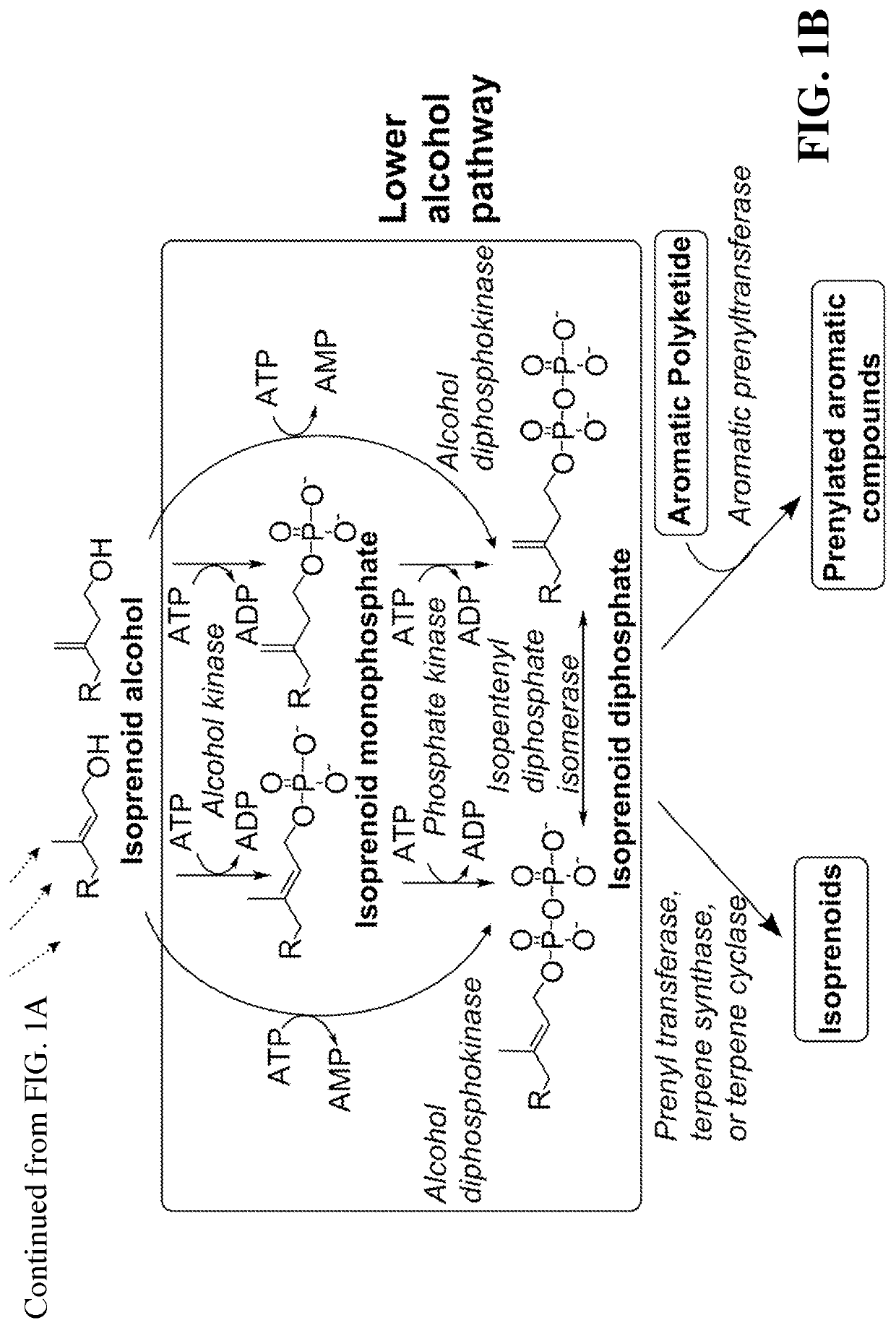
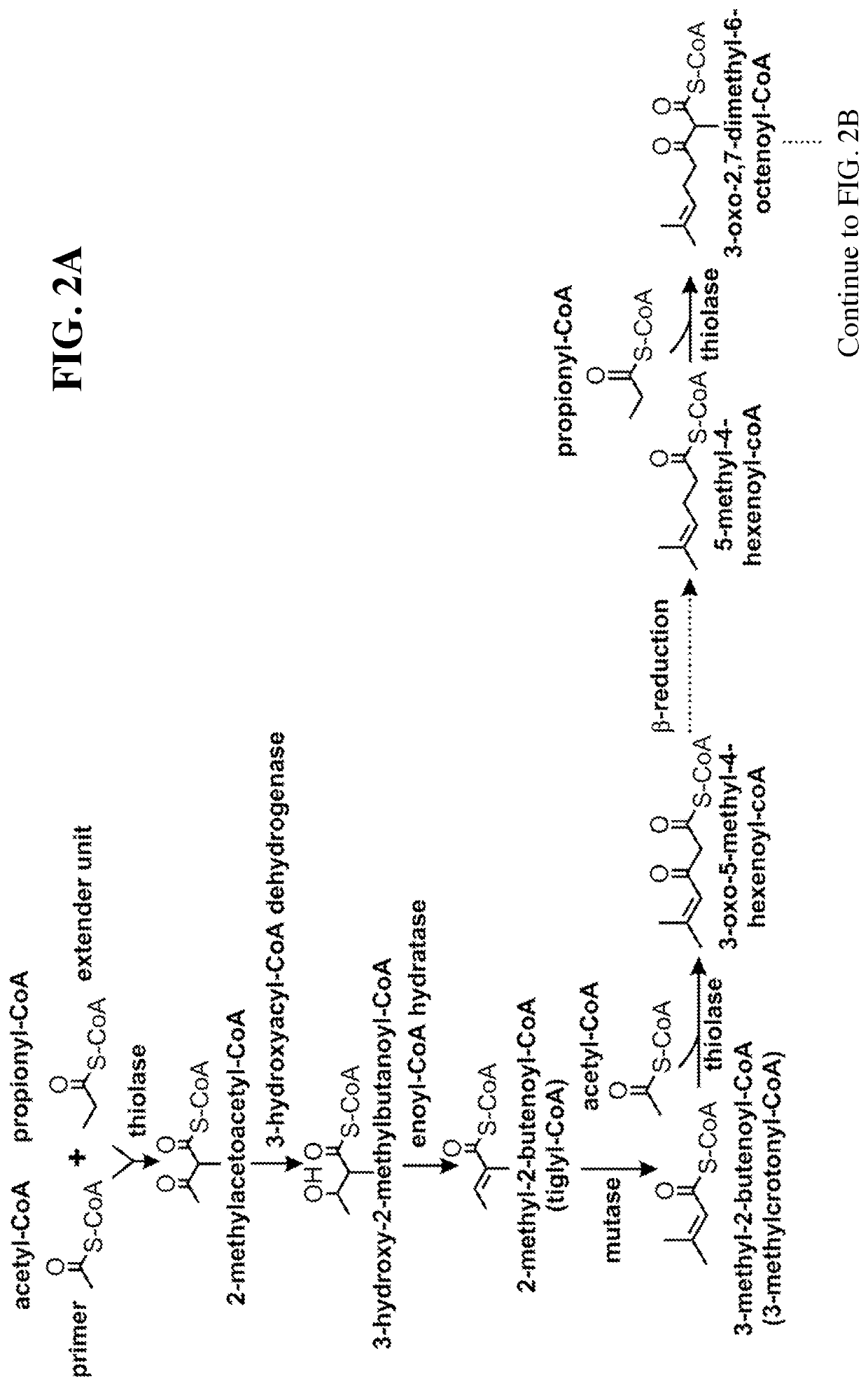
This disclosure generally relates to the use of enzyme combinations or recombinant microbes comprising same to make isoprenoid precursors, isoprenoids and derivatives thereof including prenylated aromatic compounds. Novel metabolic pathways exploiting Claisen, aldol, and acyioin condensations are used instead of the natural mevalonate (MVA) pathway or 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) pathways for generating isoprenoid precursors such as isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), and geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP). These pathways have the potential for better carbon and or energy efficiency than native pathways. Both decarboxylative and non-carboxylative condensations are utilized, enabling product synthesis from a number of different starting compounds. These condensation reactions serve as a platform for the synthesis of isoprenoid precursors when utilized in combination with a variety of metabolic pathways and enzymes for carbon rearrangement and the addition / removal of functional groups. Isoprenoid alcohols are key intermediary products for the production of isoprenoid precursors in these novel synthetic metabolic pathways.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene from anoectochilus roxburghii and application of geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene from anoectochilus roxburghii
ActiveCN110894503AAdd depthEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention provides a geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene from anoectochilus roxburghii and an application of the geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene from anoectochilus roxburghii, and relates to the technical field of genetic engineering. The geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQID NO.1, and an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQID NO.2. An important basis is provided for variety breeding of the anoectochilus roxburghii, and a base is provided for researching terpenoid enriched transgenic plant strains.
Owner:SANMING UNIV
Method for producing stevioside compounds by microorganism
ActiveUS9611498B2Increase productivityEfficient synthesisTransferasesFermentationMicroorganismCopalyl pyrophosphate
The present invention provides a method for producing stevioside compounds by microorganism, comprising carrying out heterologous biosynthesis of stevioside compounds from geranyl geranyl pyrophosphate synthase (GGPPS), Copalyl pyrophosphate synthase (CDPS), Kaurene synthase (KS), dual-function kaurene synthase (CPS / KS), kaurene oxidase (KO), a cytochrome P450 redox protein (CPR), kaurenoic acid-13[alpha]-hydroxylase, UGT85C2 glycosyltransferase and UGTB1 / IBGT glycosyltransferase (optionally comprising UGT74G1 glycosyltransferase and / or UGT76G1 glycosyltransferase).
Owner:SICHUAN INGIA BIOSYNTHETIC CO LTD
Fusion proteins useful for producing pinene
The present invention provides for a modified host cell comprising a heterologous pinene synthase (PS), or enzymatically active fragment or variant thereof, and optionally a geranyl pyrophosphate synthase (GPPS), or enzymatically active fragment or variant thereof, or a fusion protein comprising: (a) a PS and (b) a GPPS linked by a linker.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process of producing monoterpenes
PendingUS20210238640A1High yieldHigh purityFermentationCarbon-oxygen lyasesMicroorganismGeranyl pyrophosphate
The present invention relates to a process of producing a monoterpene and / or derivatives thereof. The process comprises the steps of: a) providing a host microorganism genetically engineered to express a bacterial monoterpene synthase (mTS); and b) contacting geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) with said bacterial mTS to produce said monoterpene and / or derivatives thereof. The present invention also relates to a microorganism for use in producing a monoterpene and / or derivatives thereof and a recombinant microor-ganism adapted to conduct the step of converting geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) into a monoterpene and / or derivatives thereof by ex-pression of a bacterial mTS. It was shown to produce 1,8 cineole using 1,8 cineole synthase and to produce linalool using linalool synthase, both from Streptomyces clavuligerus.
Owner:C3 BIOTECHNOLOGIES LTD
Primer for amplifying geranyl pyrophosphate synthase from mango
The present invention discloses primers for amplifying geranyl pyrophosphate synthases, having sequence selected from the group consisting of Seq. Id. Nos. 2-13, from mango. Also disclosed herein is a novel nucleotide sequence of Seq. Id nos. 14 and 15 encoding said amplified geranyl pyrophosphate synthases (GPPS) for enzyme production in an artificial system thus generating the desired flavor in food products.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Isopentenyl transferase mutant and method for producing cannabinoid phenol
PendingCN114350635AHigh catalytic activityHigh purityBacteriaTransferasesGeranyl pyrophosphateSite-directed mutagenesis
According to the isopentenyl transferase mutant and the method for producing cannabinoid phenol, existing isopentenyl transferase is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis, so that olive alcohol and geranyl pyrophosphate can be helped to catalyze to generate cannabinoid phenol with relatively high catalytic activity and purity, and the isopentenyl transferase mutant has relatively high production and application prospects.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
A kind of engineering bacteria for co-producing geraniol and nerol and its construction method and application
ActiveCN112391327BIncrease productionWith scale developmentBacteriaTransferasesHeterologousEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for co-producing geraniol and nerol, a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The construction method of the engineering bacteria comprises the following steps: introducing tobacco geraniol and nerol synthase genes into a recipient strain capable of producing geranyl pyrophosphate to obtain recombinant bacteria; obtaining the recombinant bacteria from the recombinant bacteria Engineered bacteria for the production of geraniol and nerol. The present invention successfully utilizes the bioengineering technology to realize the heterologous reconstruction of the biosynthetic pathway of geraniol and nerol and the co-production of the products, and the yields of geraniol and nerol by the shake flask fermentation method reach 137.3 mg / L and 62.8 mg / L respectively. ; At the same time and through the high-density fermentation technology of recombinant strains, the yields of geraniol and nerol were increased by about 10 times.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
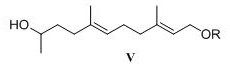
A kind of preparation method of acetonyl geranyl pyrophosphate intermediate
ActiveCN108250055BAvoid generatingSimple post-processingGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationEpoxyGrignard reagent
The invention provides a method for preparing an intermediate of acetonyl geranyl pyrophosphate. Farnesol is used as a raw material, hydroxyl group is protected, and then an epoxy intermediate is prepared, which is cut by epoxy to form an aldehyde, and then mixed with methyl Grignard reagent. Reaction, re-oxidation of hydroxyl group, deprotection to obtain (5E, 9E)-11-hydroxyl-5,9-dimethylundec-5,9-dien-2-ketone 7, then hydroxy halogenation, then with pyrophosphoric acid A salt reaction is performed to finally obtain acetonyl geranyl pyrophosphate. The method is cheap to synthesize, has mild reaction conditions, and has less isomer impurities, and is suitable for scale-up production.
Owner:CHONGQING PHARMA RES INST +1
A kind of Phoebe sesquiterpene synthase sgstps2 and its coding gene and application
Owner:RES INST OF TROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for detecting content of geranyl pyrophosphate based on prenylation reaction
The invention discloses a method for detecting the content of geranyl pyrophosphate. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, purifying and enriching a to-be-detected sample, designing and synthesizing two fluorescent peptides that generate a prenylation reaction with geranyl pyrophosphate according to the principle of the prenylation reaction, respectively adding the two peptides into a to-be-detected sample solution and a solution containing a fixed amount of geranyl pyrophosphate pure product to generate the prenylation reaction to respectively obtain a target compound and an internal standard substance for indirectly detecting the geranyl pyrophosphate, detecting the target compound and the internal standard substance by using a high performance liquid chromatograph-fluorescence detector to obtain an initial detection value of the geranyl pyrophosphate, designing a recovery experiment to calculate the mass of the geranyl pyrophosphate that is lost when the to-be-detected sampleis purified, and establishing a recovery calibration curve to correct an initial measured value to finally obtain the content of the geranyl pyrophosphate. The method provided by the invention is stable and reliable, and has high reproducibility, and the applicable scope covers the detection of geranyl pyrophosphate in different organisms.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene and its application from Fujian Aureus aureus
ActiveCN110894503BAdd depthEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention provides a geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene derived from Fujian Aureus aureus and its application, and relates to the technical field of genetic engineering. The geranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention provides an important basis for the selection and breeding of clematis varieties, and also provides a basis for the research on transgenic plant strains enriched in terpenoids.
Owner:SANMING UNIV
Recombinant cell, and method for producing β-phellandrene
ActiveUS9617563B2High purityAvoid small quantitiesFungiSugar derivativesNeryl pyrophosphatePhellandrene
To provide a series of techniques for obtaining β-phellandrene with high purity and in a large quantity.Provided is a recombinant cell capable of producing β-phellandrene, prepared by introducing at least one nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid encoding geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) synthase and a nucleic acid encoding neryl pyrophosphate (NPP) synthase, and a nucleic acid encoding β-phellandrene synthase into a host cell in such a manner that these nucleic acids are expressed in the host cell. Also provided is a method for producing β-phellandrene by culturing the recombinant cell to produce β-phellandrene in the recombinant cell.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com