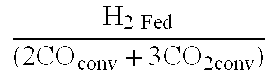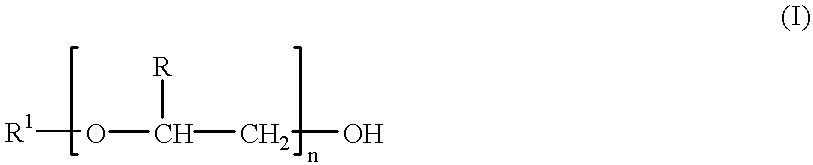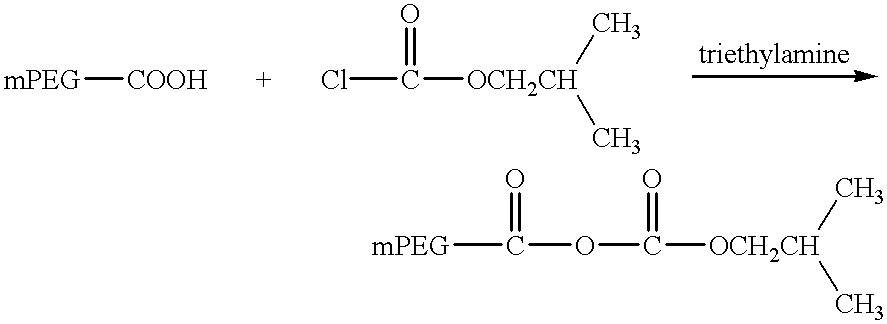Patents
Literature
100978results about "Microorganism based processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chimeric receptor genes and cells transformed therewith
ActiveUS7741465B1Limit acquisitionMicroorganismsGenetic material ingredientsAntibody typesLymphocyte
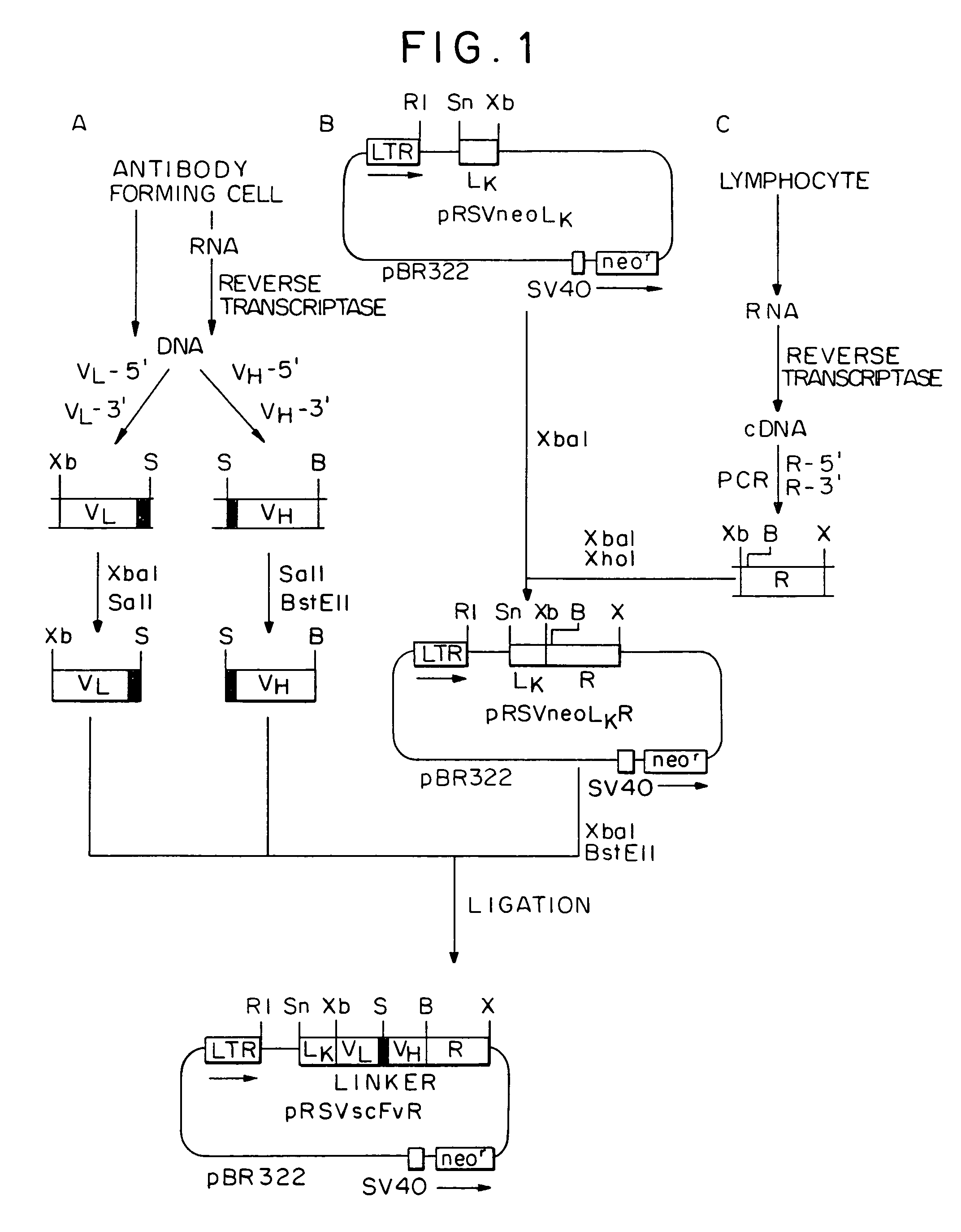
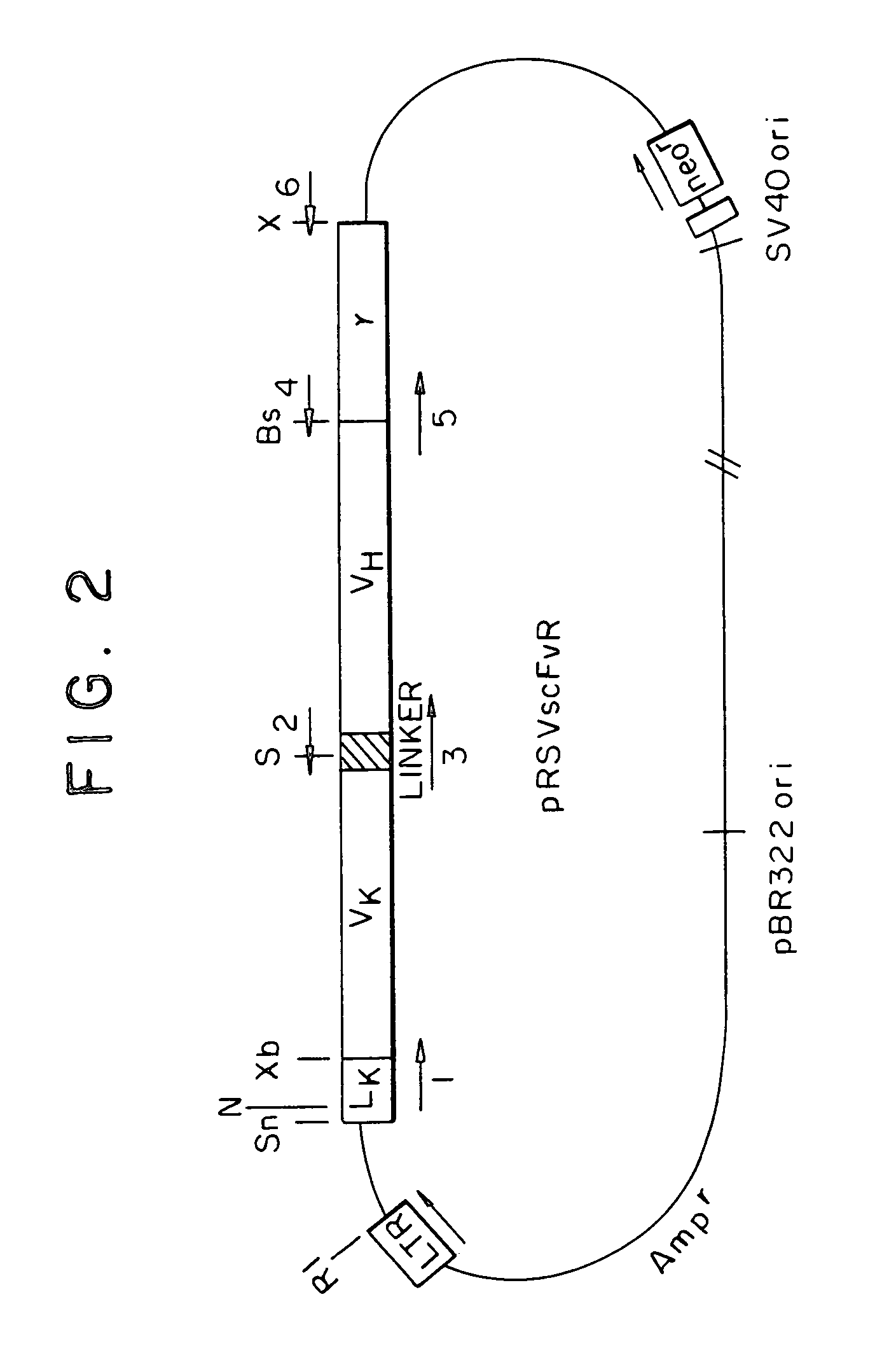
Chimeric receptor genes suitable for endowing lymphocytes with antibody-type specificity include a first gene segment encoding a single-chain Fv domain of a specific antibody and a second gene segment encoding all or part of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains, and optionally the extracellular domain, of an immune cell-triggering molecule. The chimeric receptor gene, when transfected to immune cells, expresses the antibody-recognition site and the immune cell-triggering moiety into one continuous chain. The transformed lymphocytes are useful in therapeutic treatment methods.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF +1
Method for making heteromultimeric polypeptides
InactiveUS7642228B2Increase productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAmino acid side chain
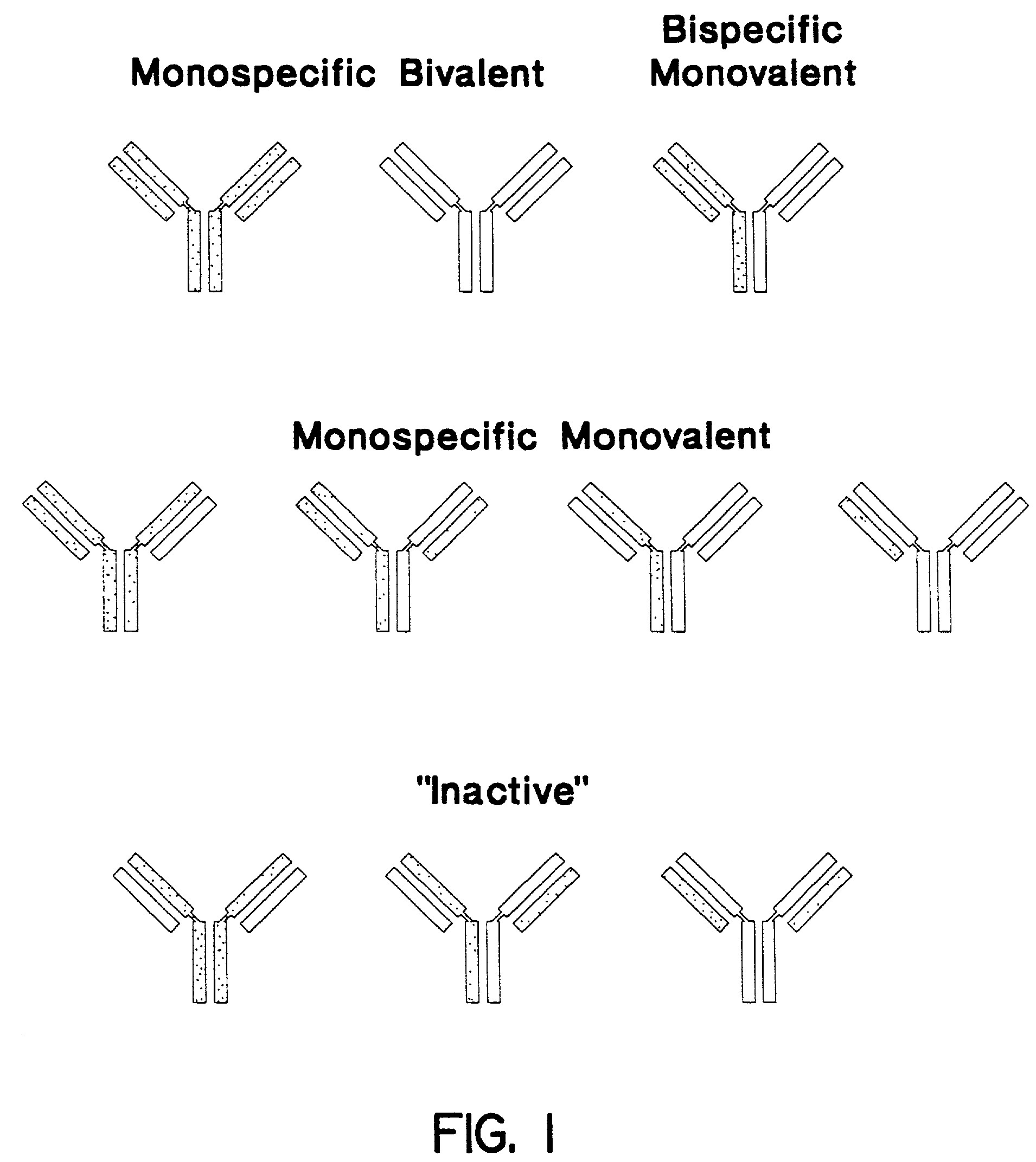
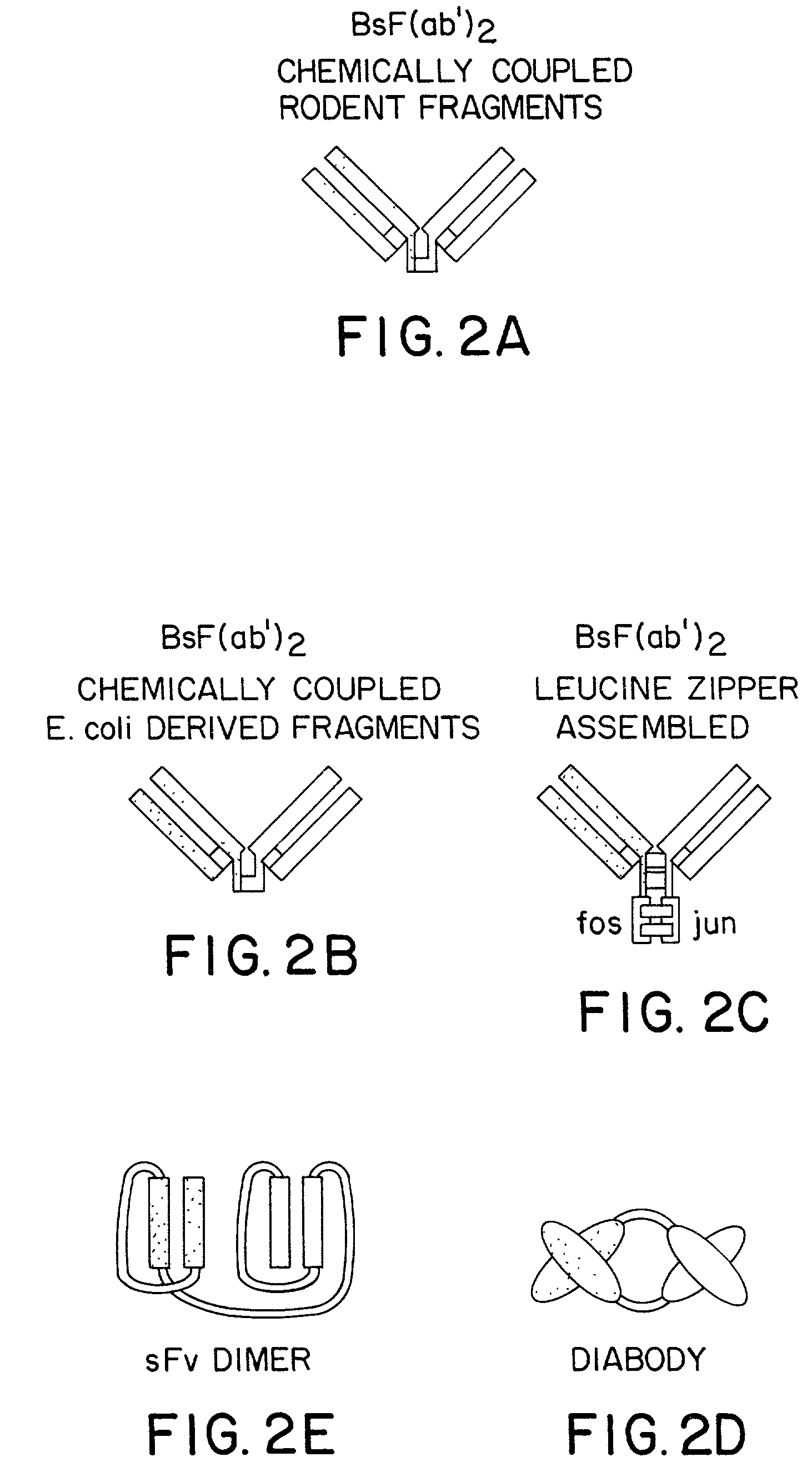
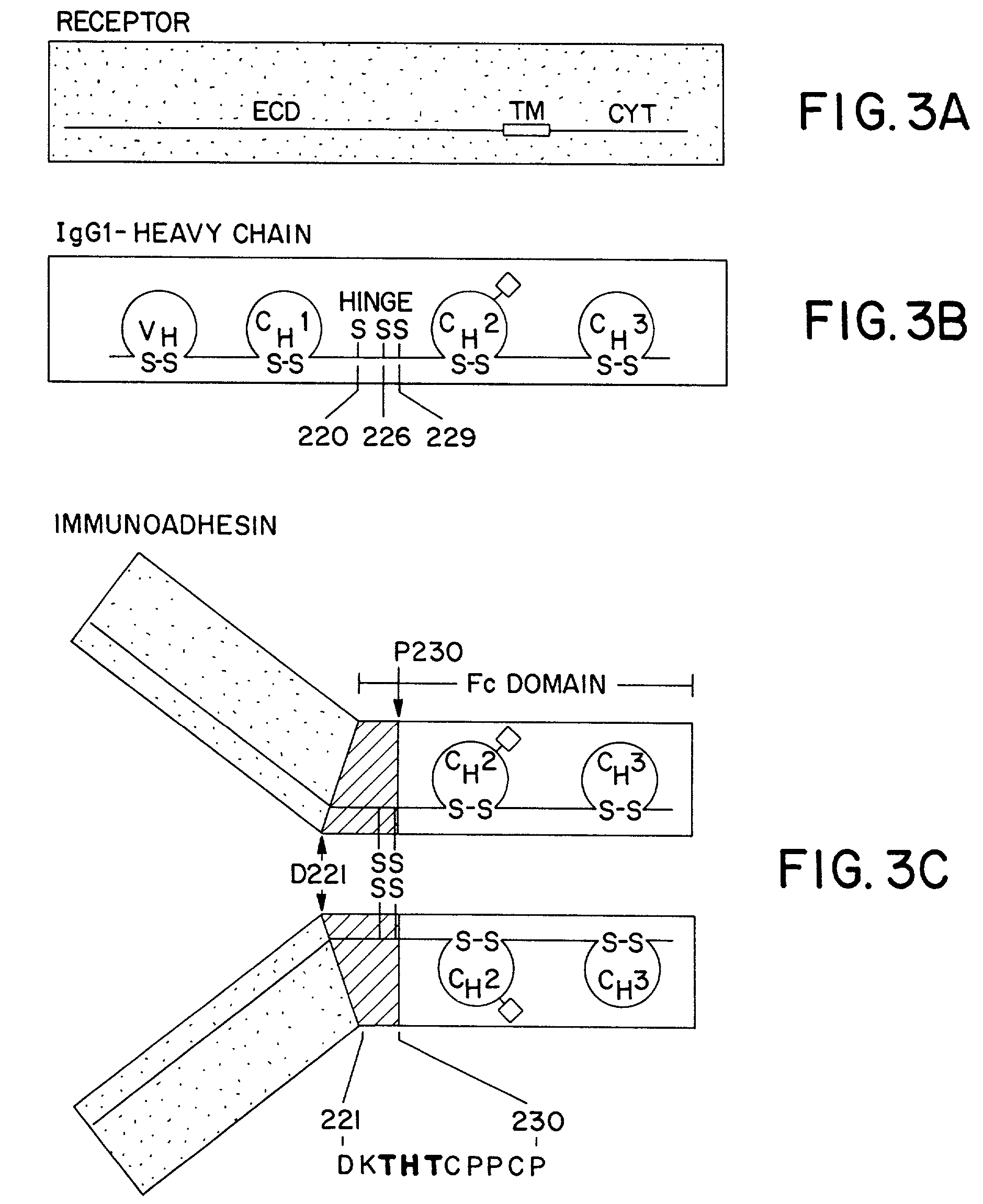
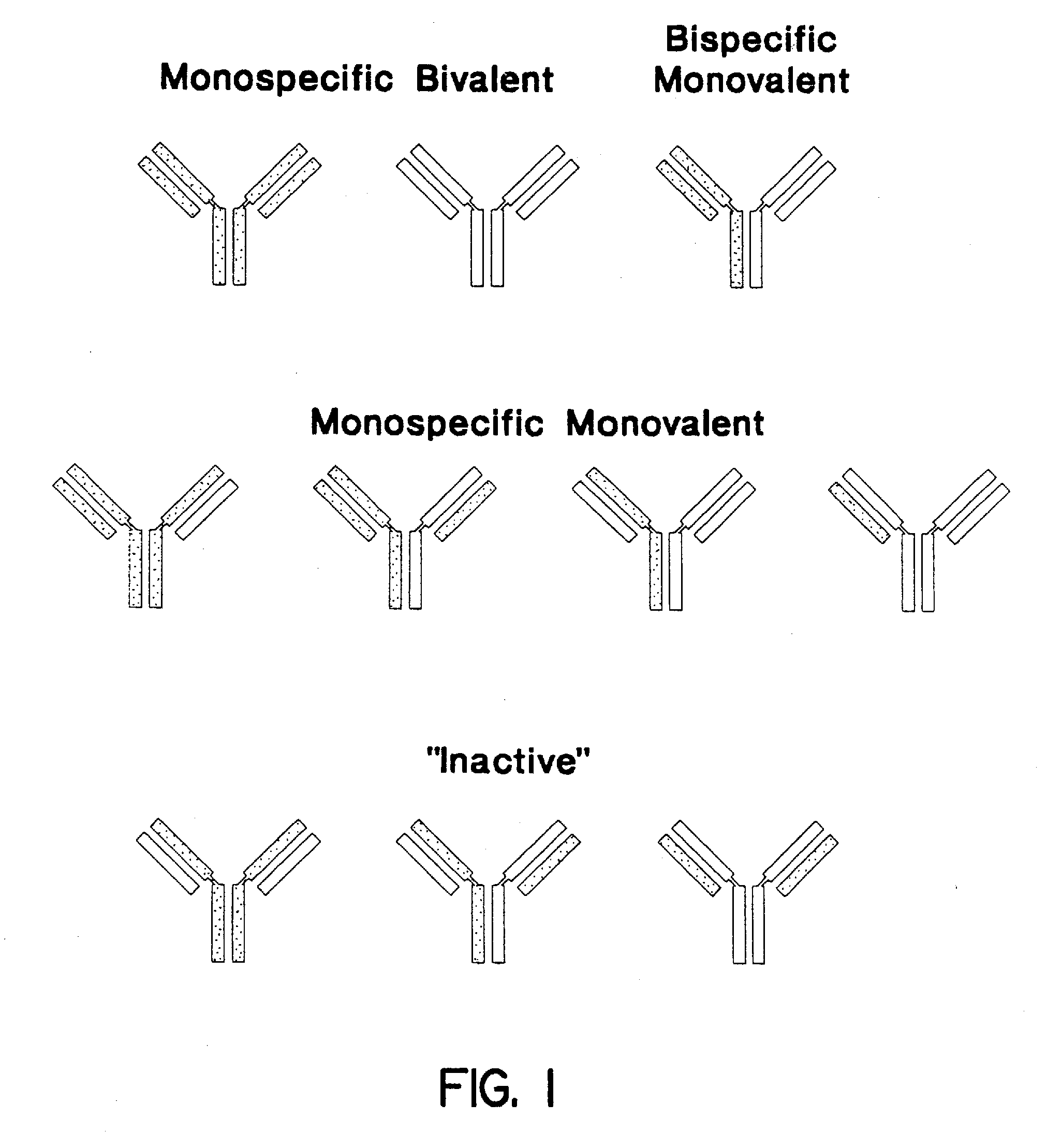
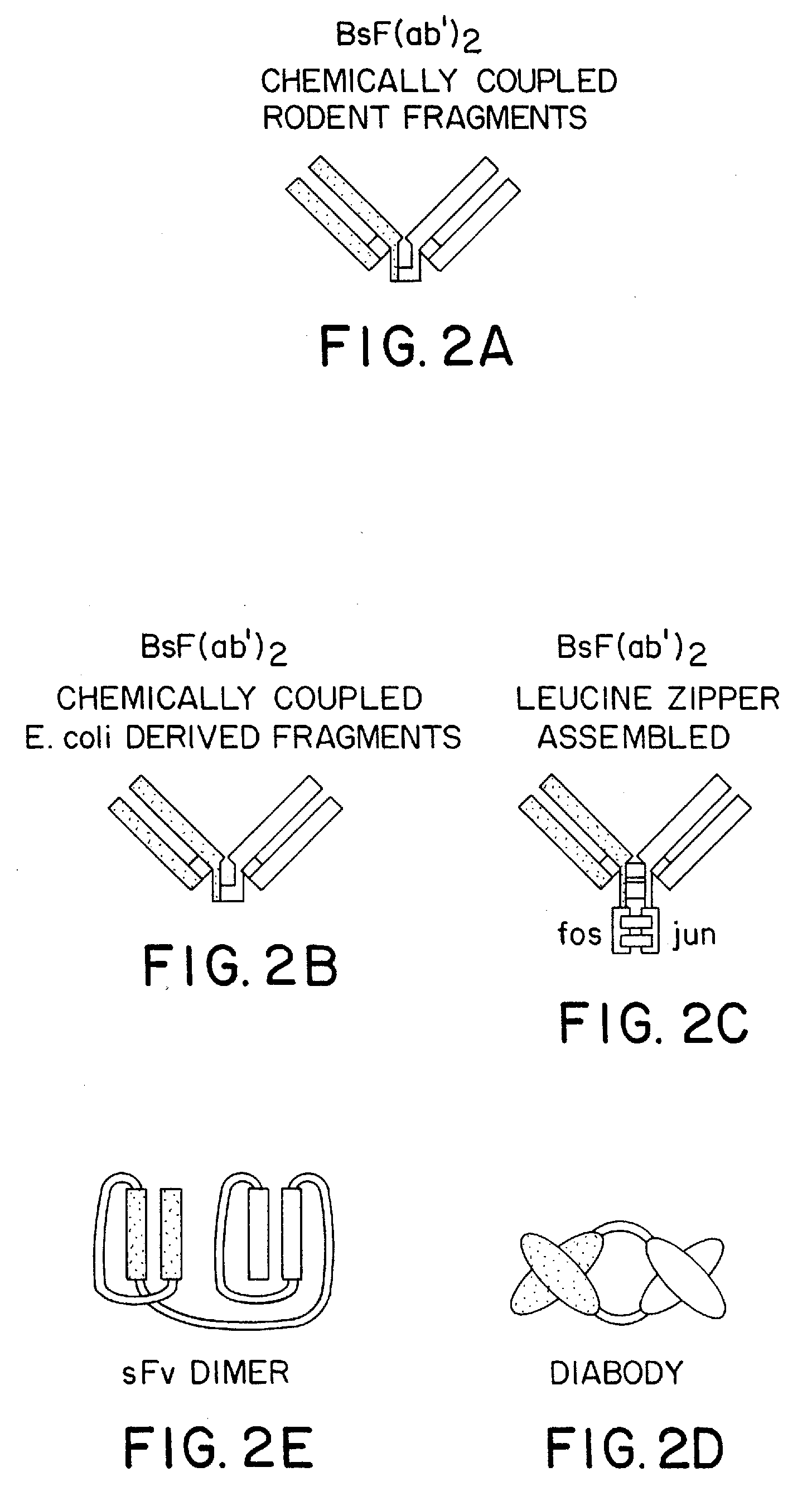
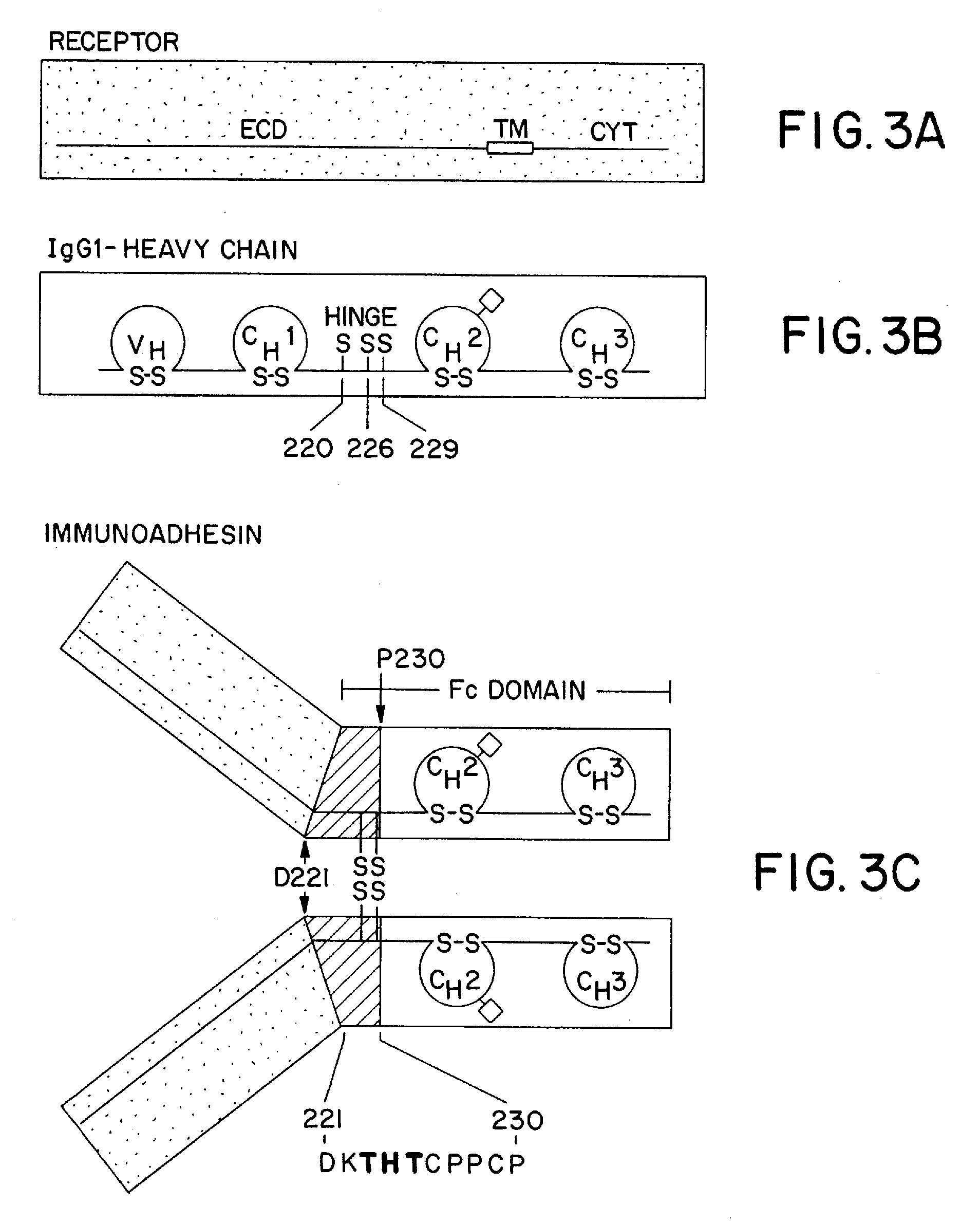
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method involves introducing a protuberance at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding cavity in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that the protuberance can be positioned in the cavity so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation. “Protuberances” are constructed by replacing small amino acid side chains from the interface of the first polypeptide with larger side chains (e.g. tyrosine or tryptophan). Compensatory “cavities” of identical or similar size to the protuberances are created in the interface of the second polypeptide by replacing large amino acid side chains with smaller ones (e.g. alanine or threonine). The protuberance and cavity can be made by synthetic means such as altering the nucleic acid encoding the polypeptides or by peptide synthesis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Anthranilate synthase gene and method of use thereof for conferring tryptophan overproduction
InactiveUS6118047AGrowth inhibitionNot susceptibleSugar derivativesBacteriaDNA fragmentationGMO Plants
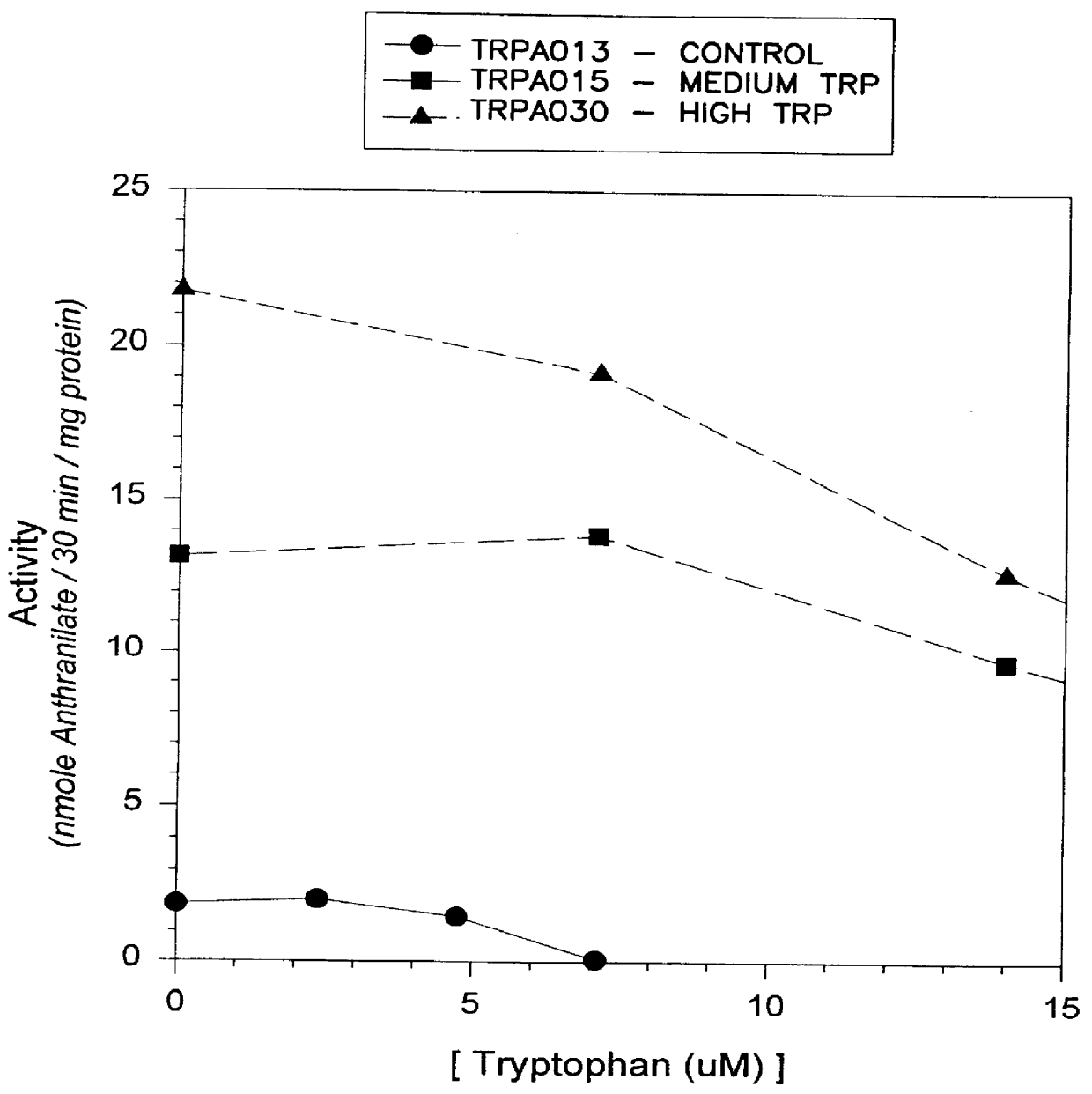
The present invention provides a method for conferring tolerance to an amino acid analog of tryptophan to a plant and / or altering the tryptophan content of a plant by introducing and expressing an isolated DNA segment encoding an anthranilate synthase in the cells of the plant. Transgenic plants transformed with an isolated DNA segment encoding an anthranilate synthase, as well as seeds and progeny derived from these plants, are also provided. The present invention also provides a cDNA sequence of an alpha and a beta subunit of a maize anthranilate synthase.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for making heteromultimeric polypeptides
InactiveUS20070014794A1Increase productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAmino acid side chain
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method involves introducing a protuberance at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding cavity in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that the protuberance can be positioned in the cavity so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation. “Protuberances” are constructed by replacing small amino acid side chains from the interface of the first polypeptide with larger side chains (e.g. tyrosine or tryptophan). Compensatory “cavities” of identical or similar size to the protuberances are created in the interface of the second polypeptide by replacing large amino acid side chains with smaller ones (e.g. alanine or threonine). The protuberance and cavity can be made by synthetic means such as altering the nucleic acid encoding the polypeptides or by peptide synthesis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
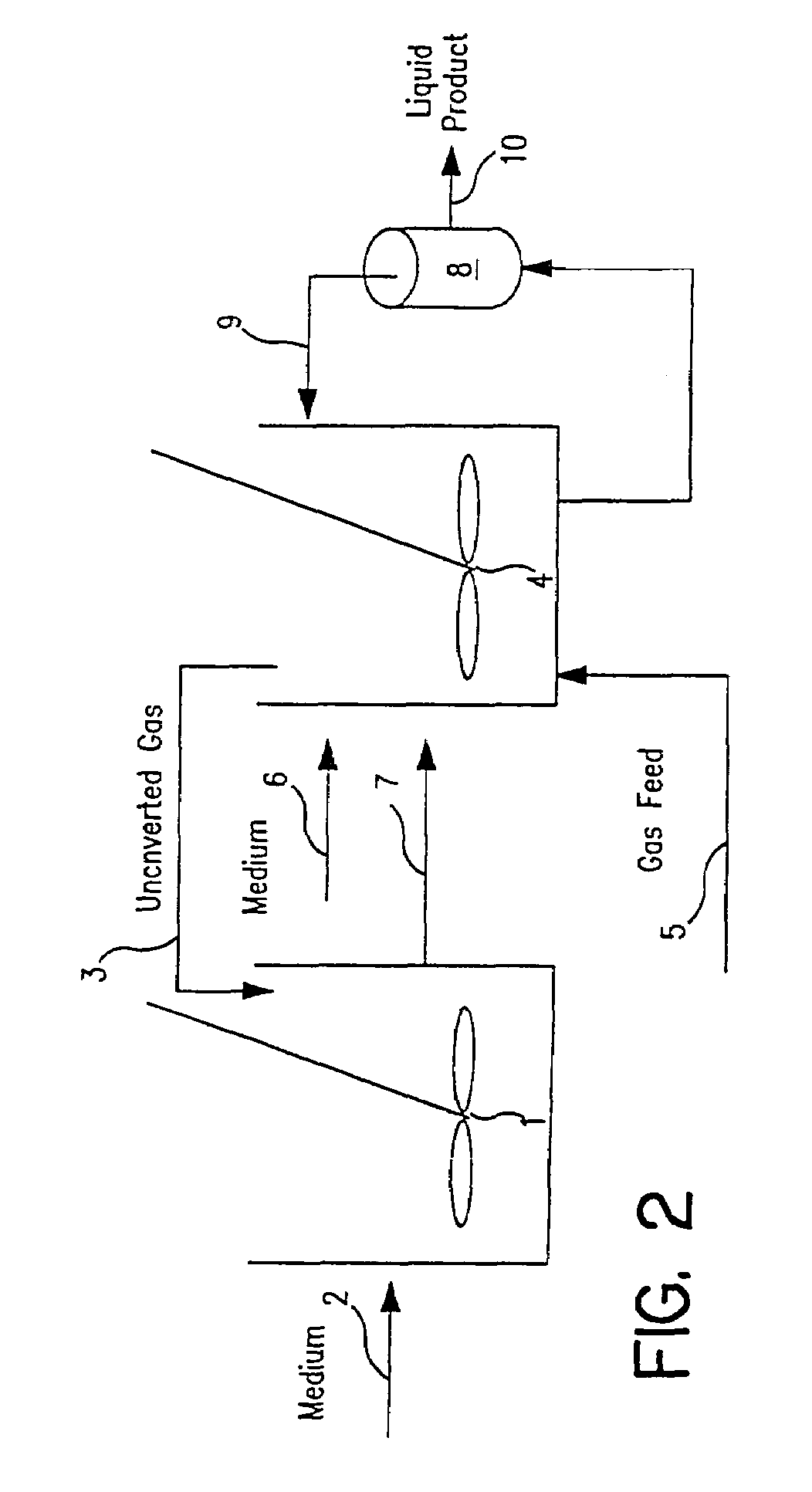
Methods for increasing the production of ethanol from microbial fermentation
InactiveUS7285402B2Good culture stabilityPermit growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSolid waste disposalBioreactorNutrient
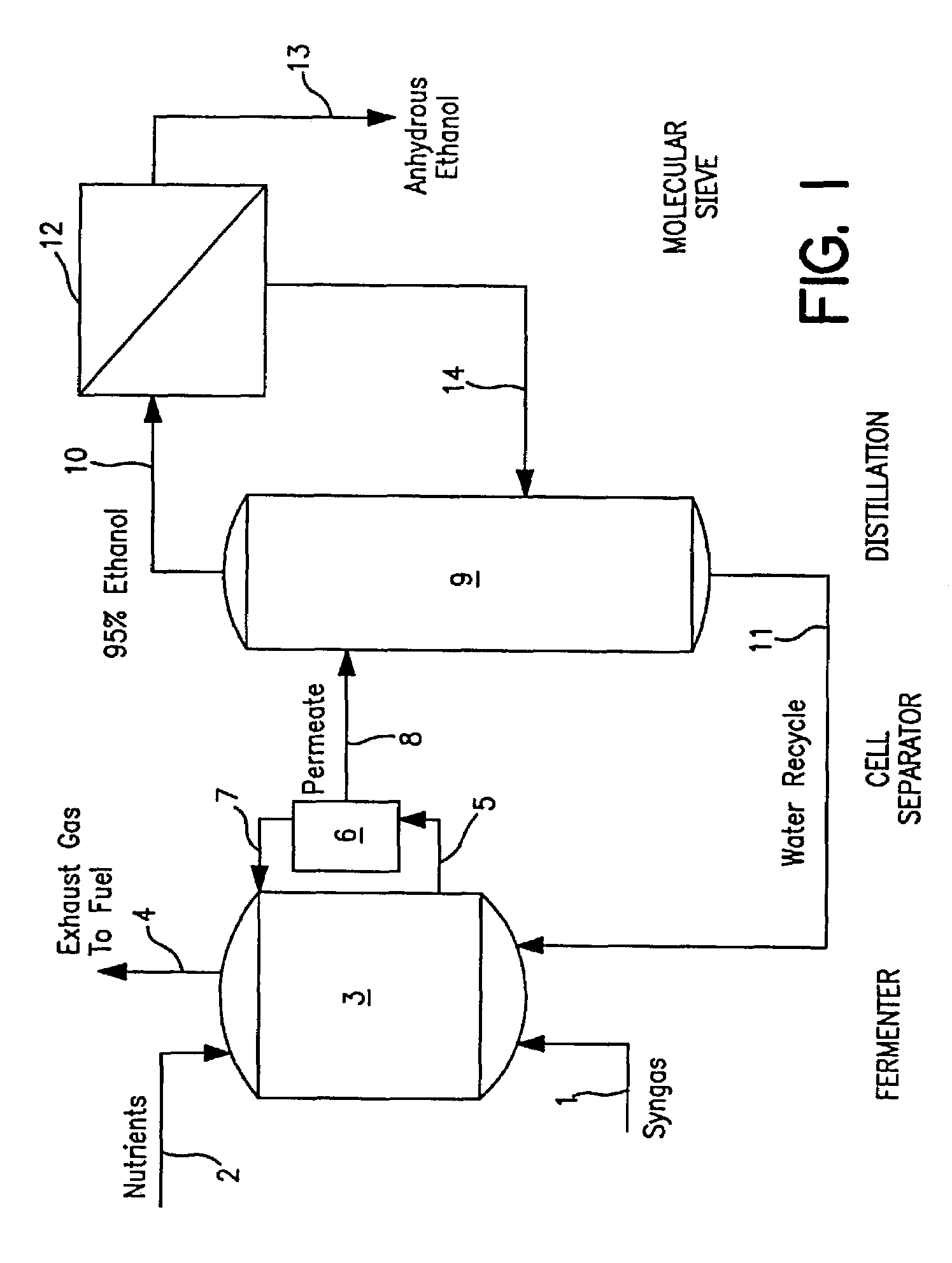
A stable continuous method for producing ethanol from the anaerobic bacterial fermentation of a gaseous substrate containing at least one reducing gas involves culturing a fermentation bioreactor anaerobic, acetogenic bacteria in a liquid nutrient medium; supplying the gaseous substrate to the bioreactor; and manipulating the bacteria in the bioreactor by reducing the redox potential, or increasing the NAD(P)H TO NAD(P) ratio, in the fermentation broth after the bacteria achieves a steady state and stable cell concentration in the bioreactor. The free acetic acid concentration in the bioreactor is maintained at less than 5 g / L free acid. This method allows ethanol to be produced in the fermentation broth in the bioreactor at a productivity greater than 10 g / L per day. Both ethanol and acetate are produced in a ratio of ethanol to acetate ranging from 1:1 to 20:1.
Owner:JUPENG BIO HK LTD
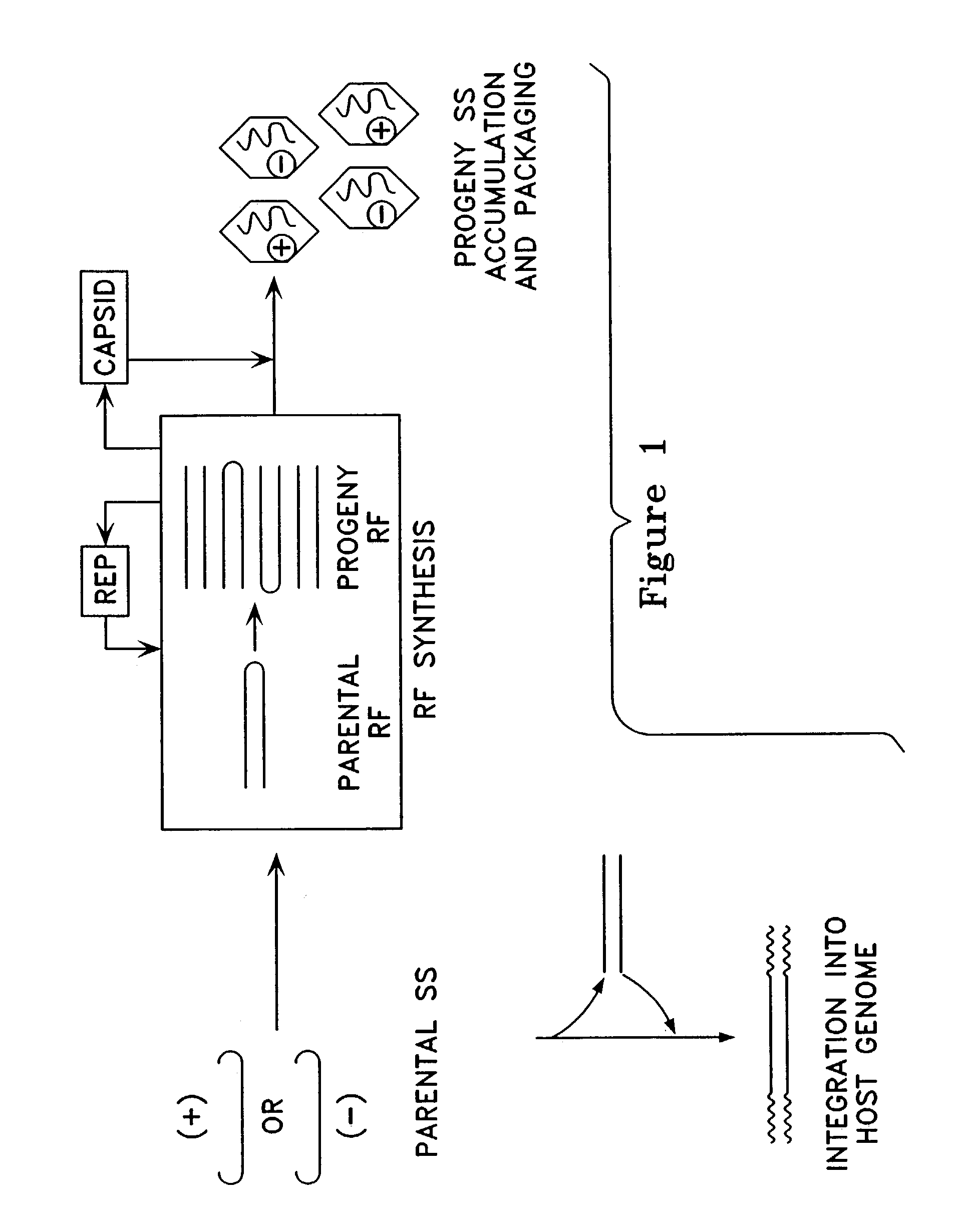
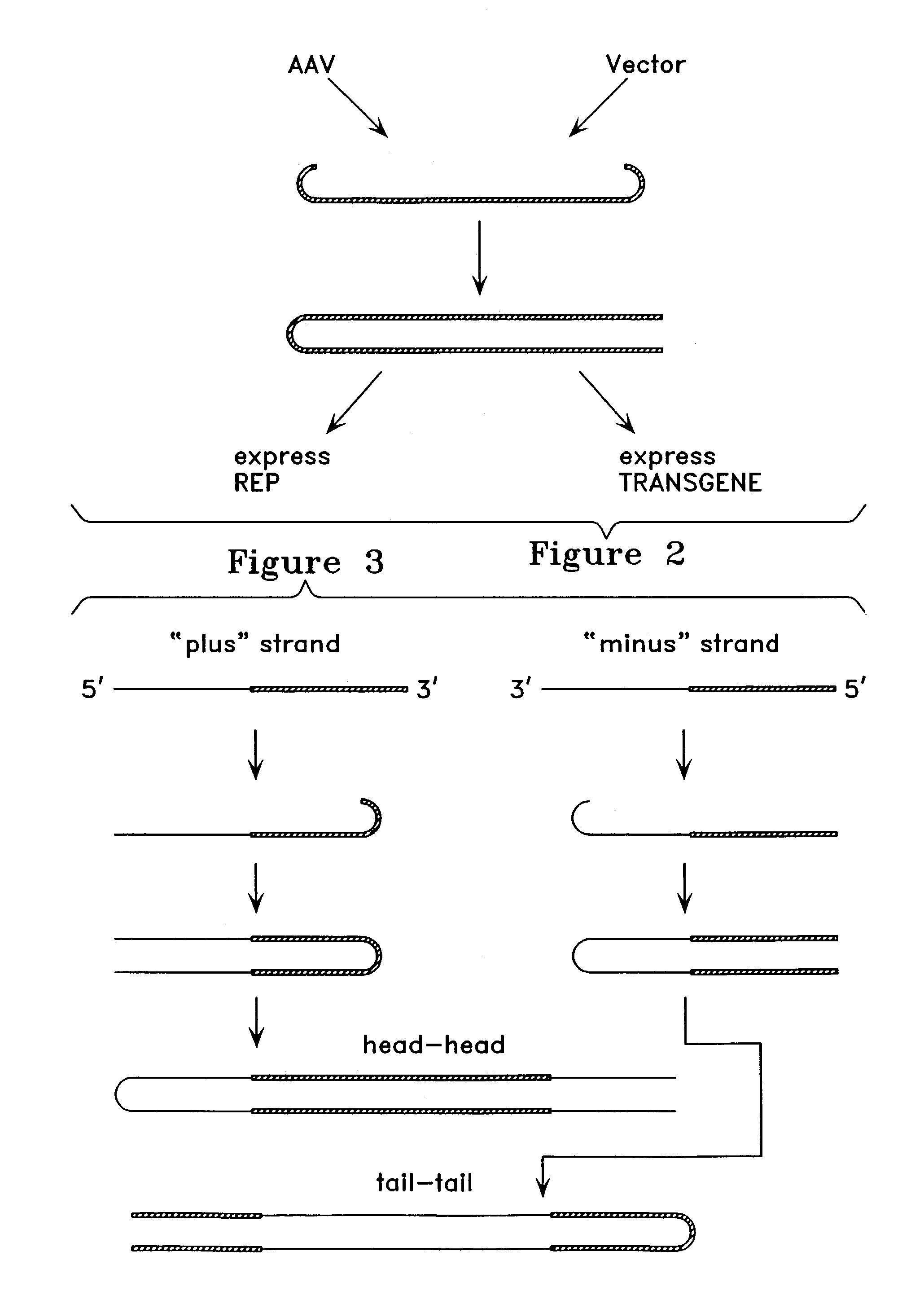
Metabolically activated recombinant viral vectors and methods for their preparation and use
Recombinant viral vectors, especially parvovirus vectors such as adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, capable of enhanced expression of heterologous sequences, and methods for their construction and use, are provided. The vectors have a structure, or are capable of rapidly adopting a structure, which involves intrastrand base pairing of at least one region in a heterologous sequence.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET33 and CryET34 compositions and uses therefor
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against coleopteran insects including red flour beetle larvae (Tribolium castaneum) and Japanese beetle larvae (Popillia japonica). Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis crystal toxin genes, designated cryET33 and cryET34, which encode respectively the coleopteran-toxic proteins, CryET33 (29-kDa) crystal protein, and CryET34 (14-kDa) crystal protein. Also disclosed are methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bacillus thuringiensis cryET33 and cryET34 compositions and uses therefor
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against coleopteran insects including red flour beetle larvae (Tribolium castaneum) and Japanese beetle larvae (Popillia japonica). Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis crystal toxin genes, designated cryET33 and cryET34, which encode the colepteran-toxic crystal proteins, CryET33 (29-kDa) crystal protein, and the cryET34 gene encodes the 14-kDa CryET34 crystal protein. The CryET33 and CryET34 crystal proteins are toxic to red flour beetle larvae and Japanese beetle larvae. Also disclosed are methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
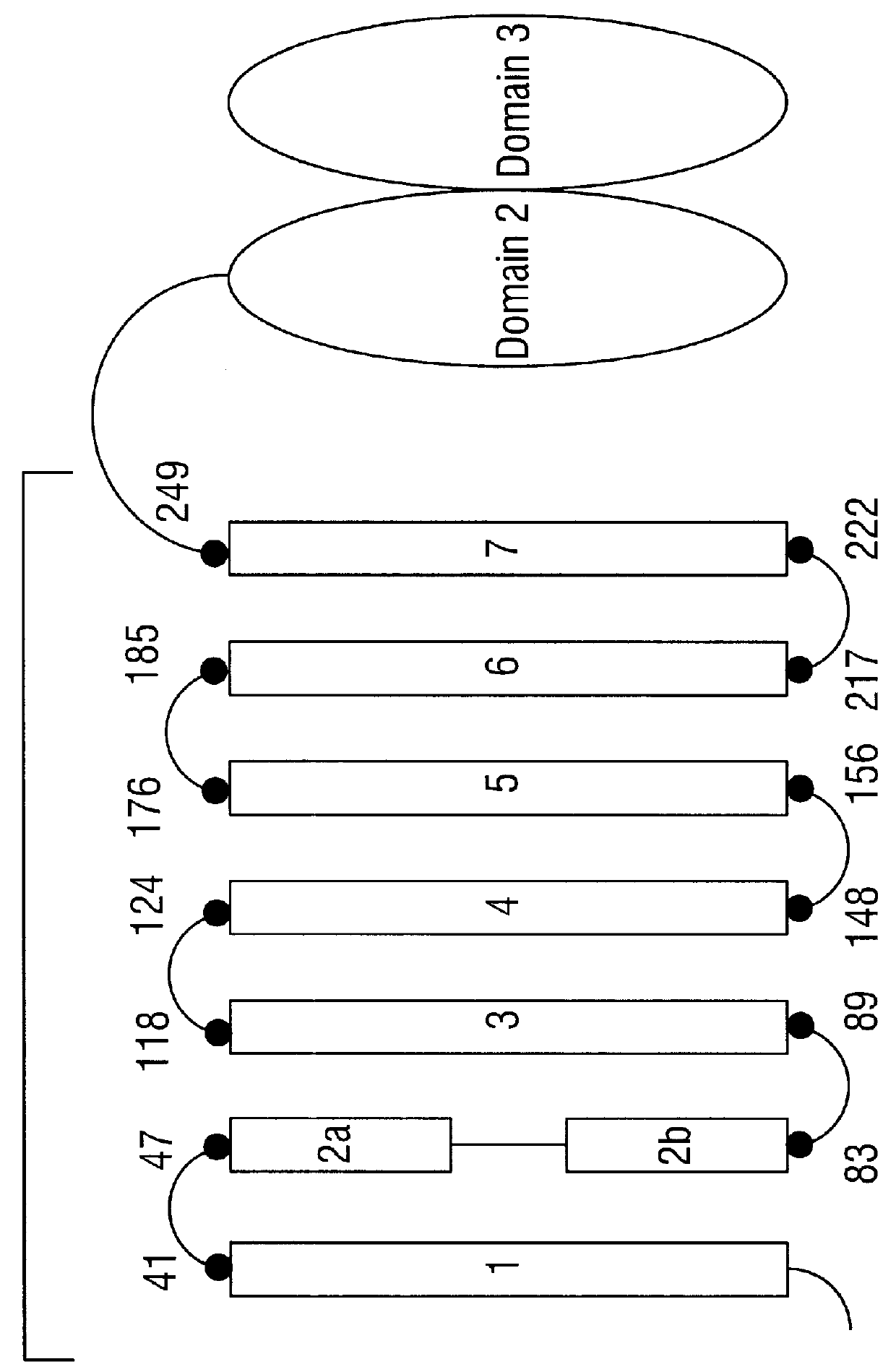
CRY1C polypeptides having improved toxicity to lepidopteran insects
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis nucleic acid segments encoding delta -endotoxins having insecticidal activity against lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are synthetic crystal proteins encoded by these novel nucleic acid sequences. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention. Also disclosed are methods for modifying, altering, and mutagenizing specific loop regions between the alpha helices in domain 1 of these crystal proteins, including Cry1C, to produce genetically-engineered recombinant cry* genes, and the proteins they encode which have improved insecticidal activity. In preferred embodiments, novel Cry1C* amino acid segments and the modified cry1C* nucleic acid sequences which encode them are disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Broad-spectrum insect resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6281016B1Improve insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityBiocideNanotechAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and tansgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Monoclonal antibodies specific for the extracellular domain of prostate-specific membrane antigen
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies that bind to the extracellular domain of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), hybridoma cell lines producing the antibodies, and methods of using such antibodies for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. In particular, thirty-five monoclonal antibodies reactive with PSMA expressed on the cell surface are exemplified. Additionally, the present invention relates to a novel protein variant (PSM') of PSMA detected by a number of the antibodies of the invention. The hydrolase activity of PSMA and PSM' allows the use of an immunoenzymatic assay for their detection.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Reshaped human antibody to human interleukin-6 receptor
InactiveUS7479543B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComplementarity determining regionV region
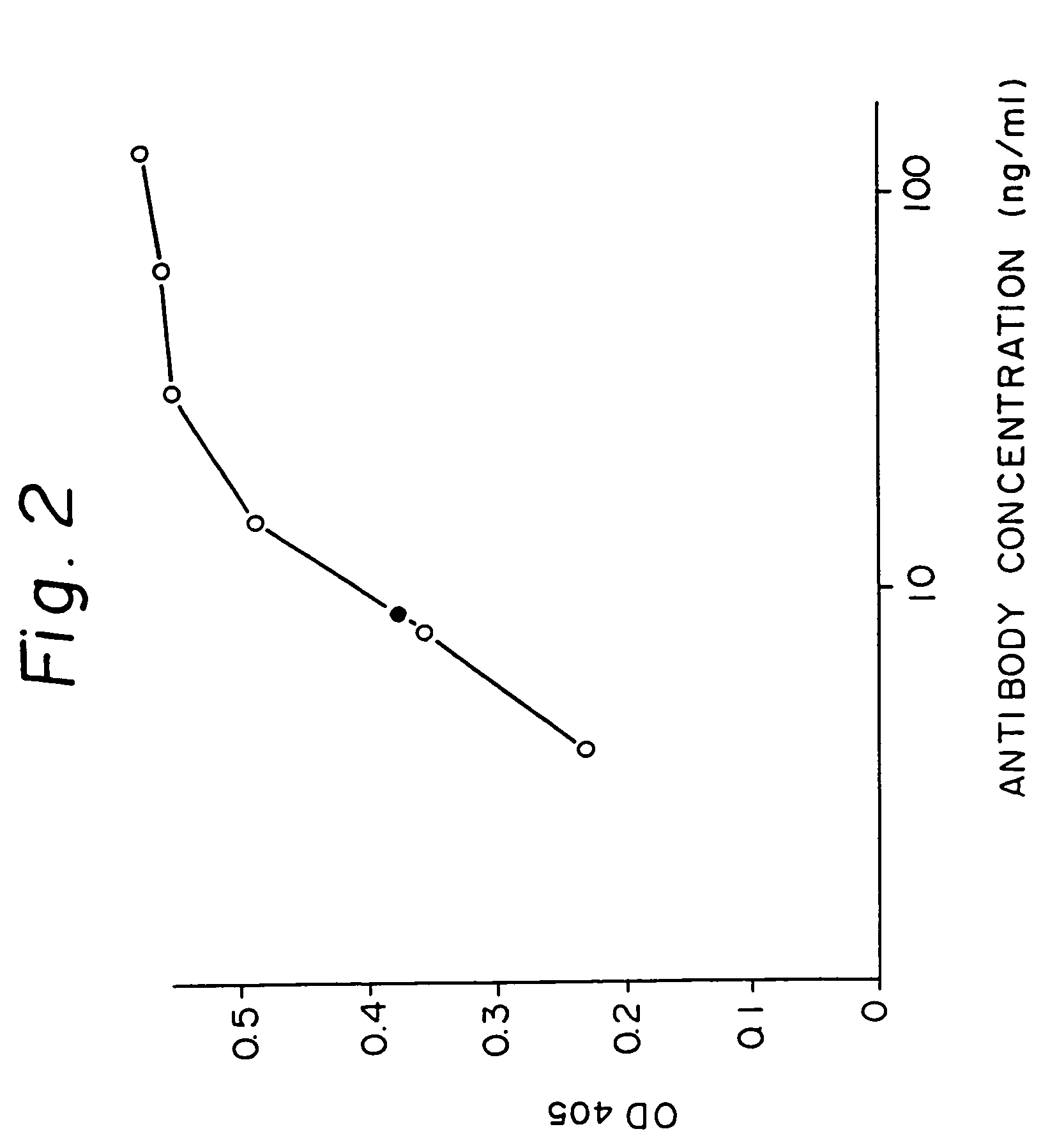
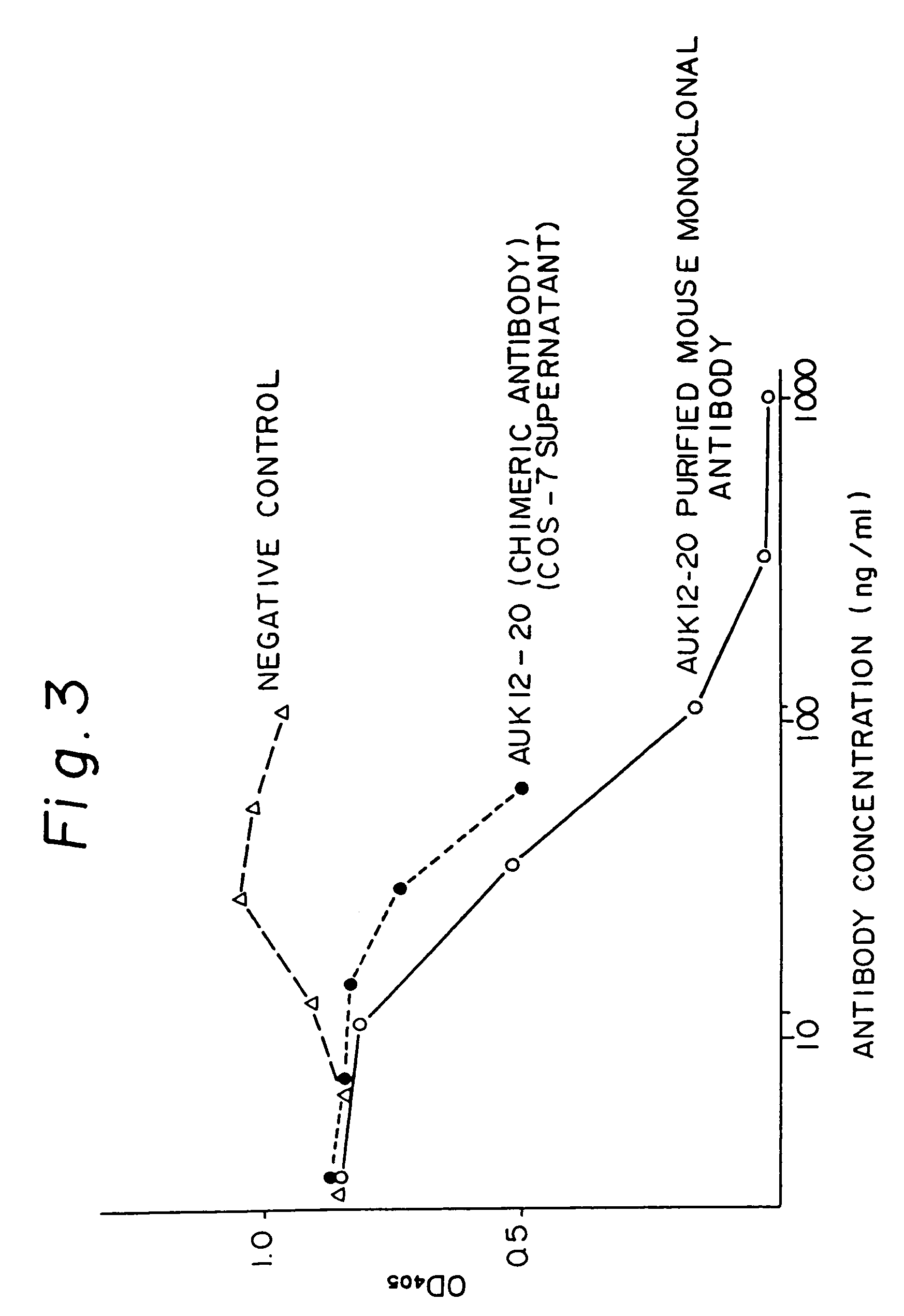
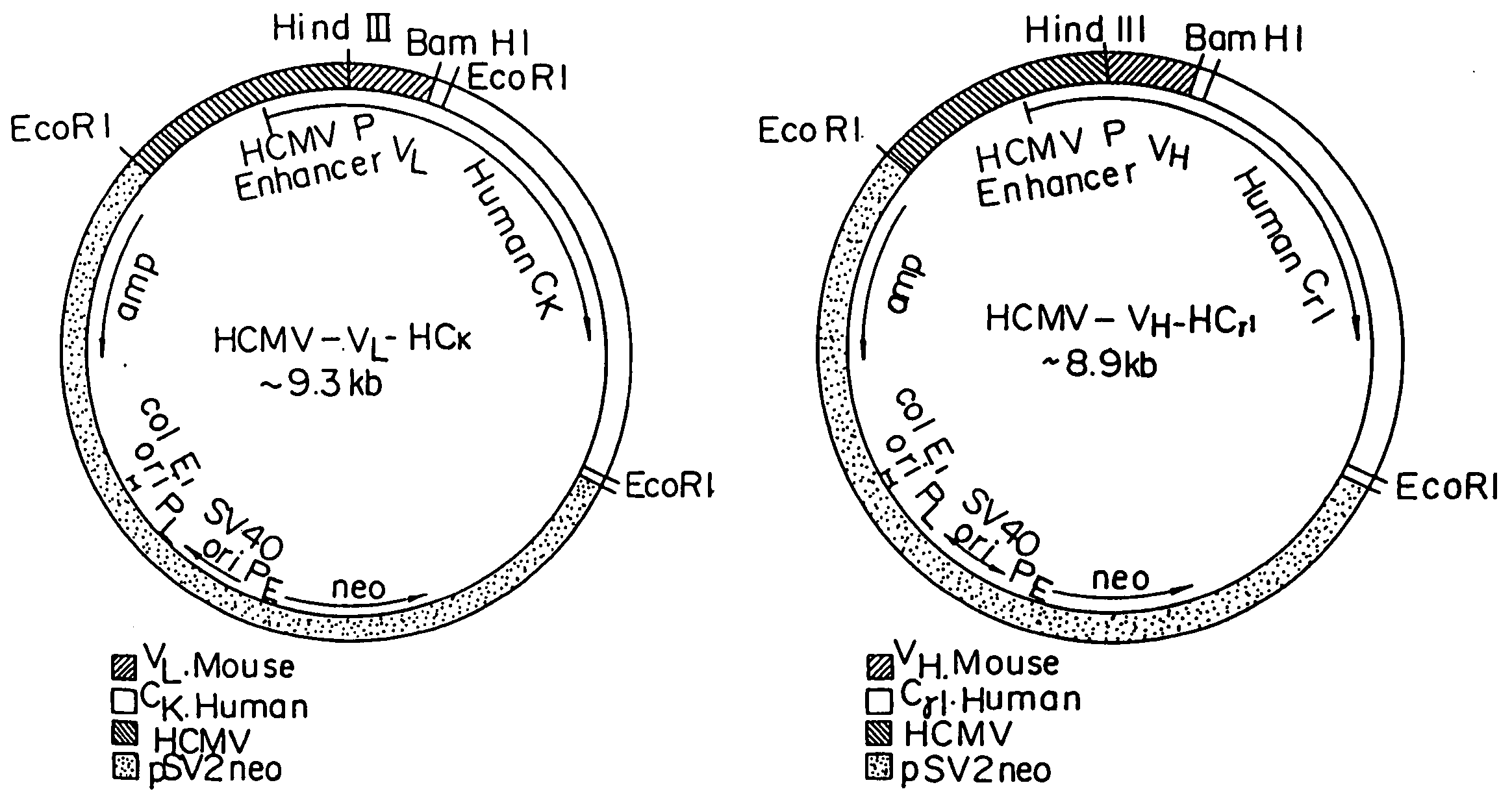
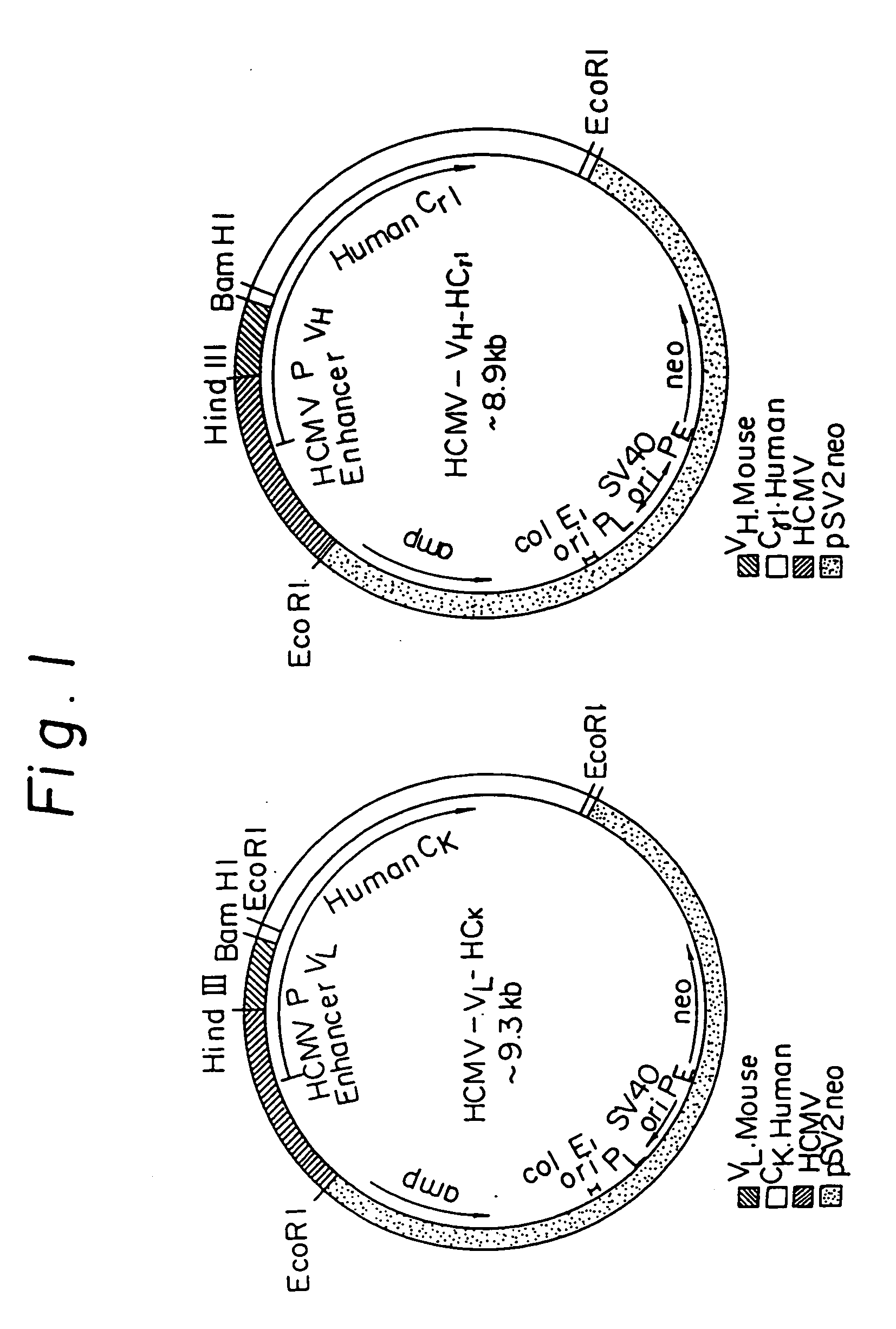
A reshaped human antibody to the human IL-6R, comprising:(A) an L chain comprising,(1) a human L chain C region, and(2) an L chain V region comprising human L chain framework regions (FRs), and mouse L chain complementary determination regions (CDRs) of a momoclonal antibody to the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R); and(B) an H chain comprising,(1) a human H chain C region, and(2) an H chain V region comprising human H chain FRS, and mouse H chain CDRs of a monoclonal antibody to the IL-6R.Since major portion of the reshaped human antibody is derived from a human antibody and the mouse CDRs which are less immunogenic, the present reshaped human antibody is less immunogenic to human, and therefor is promised for therapeutic uses.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Cultivation of primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050148070A1Improve cloning efficiencyAvoid variabilityOrganic active ingredientsCulture processMammalFeeder Layer
The invention relates to methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells by culturing the stem cells in an environment essentially free of mammalian fetal serum and in a stem cell culture medium including amino acids, vitamins, salts, minerals, transferring, insulin, albumin, and a fibroblast growth factor that is supplied from a source other than just a feeder layer the medium. Also disclosed are compositions capable of supporting the culture and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells without the need for feeder cells or for exposure of the medium to feeder cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
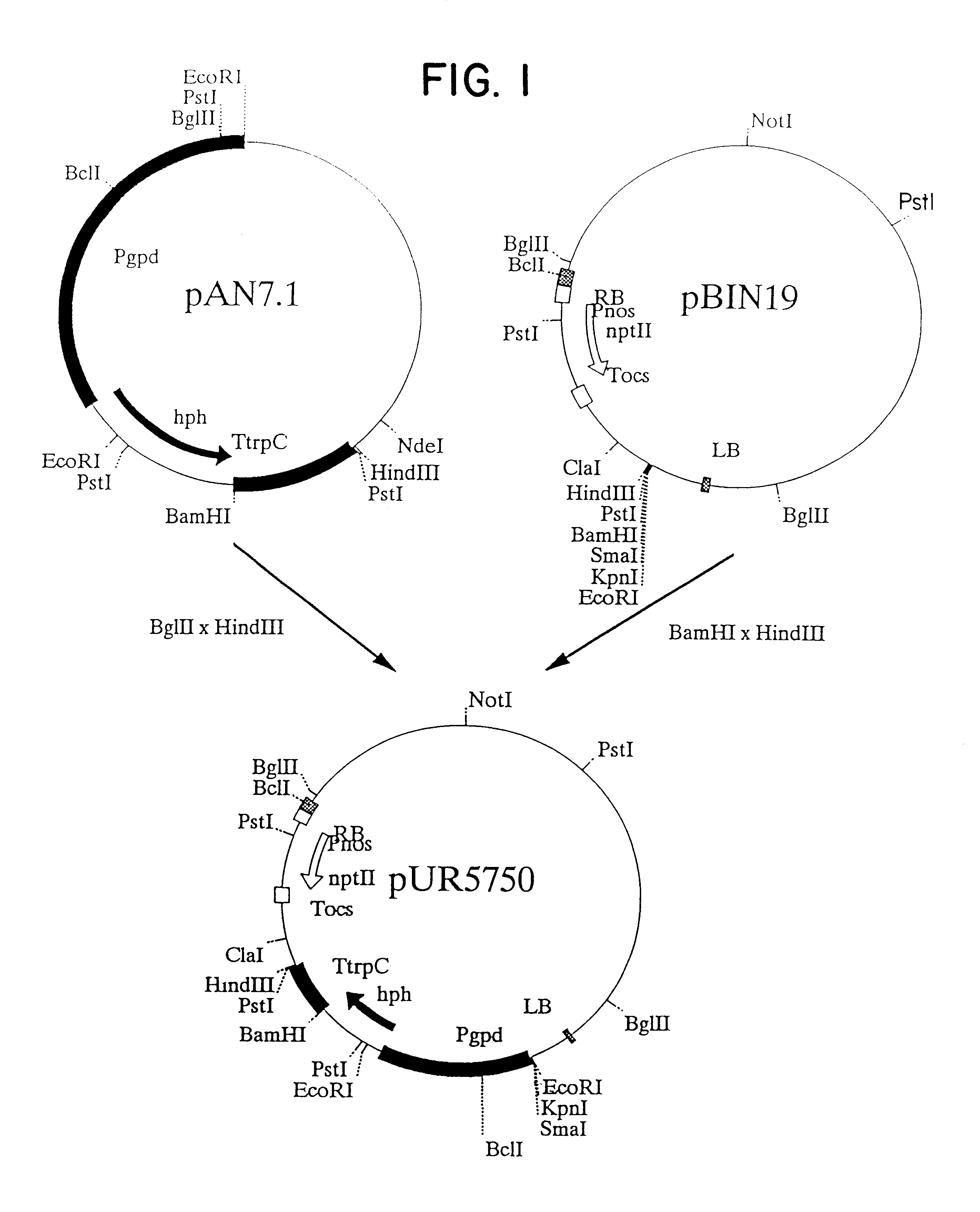
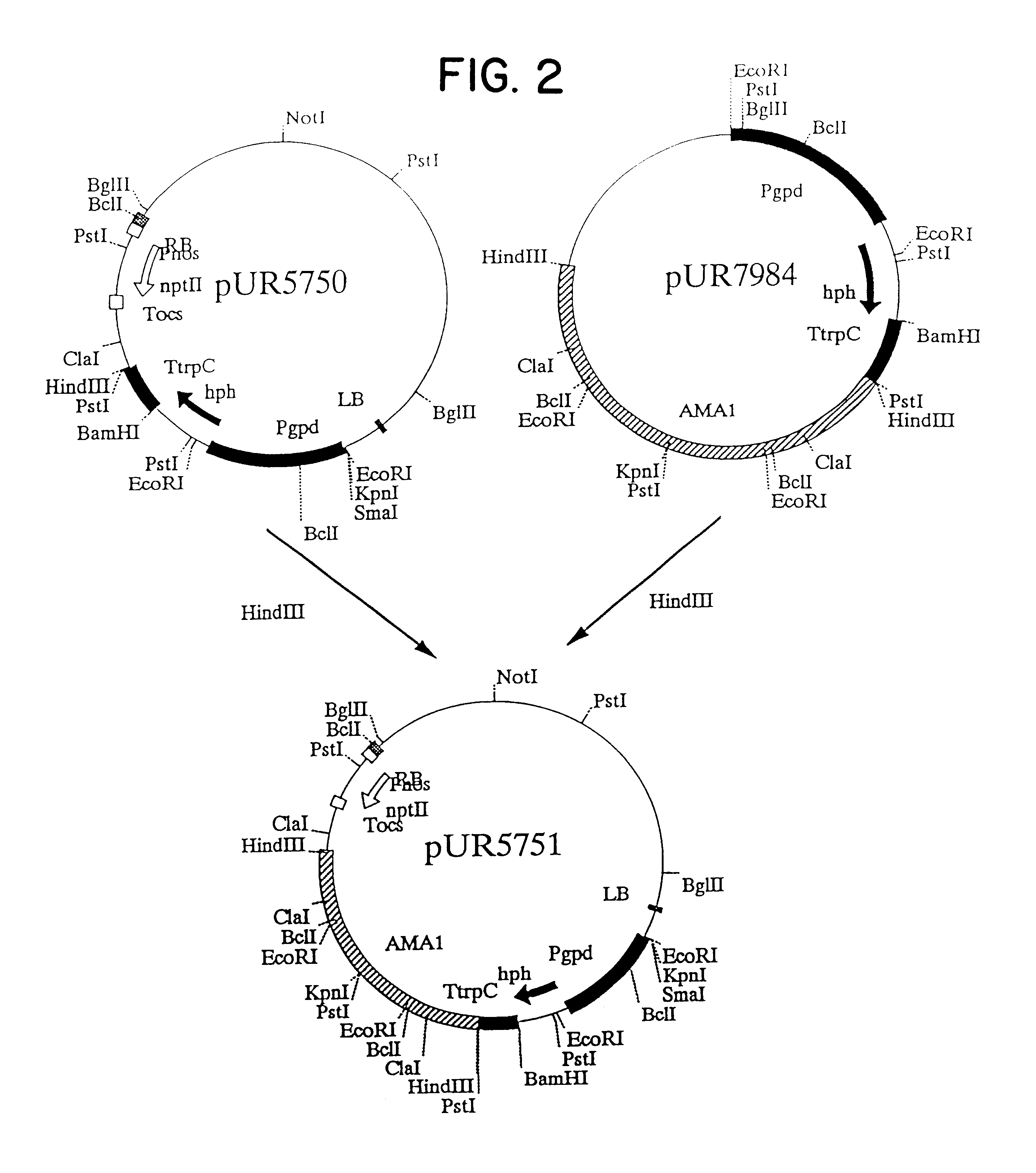
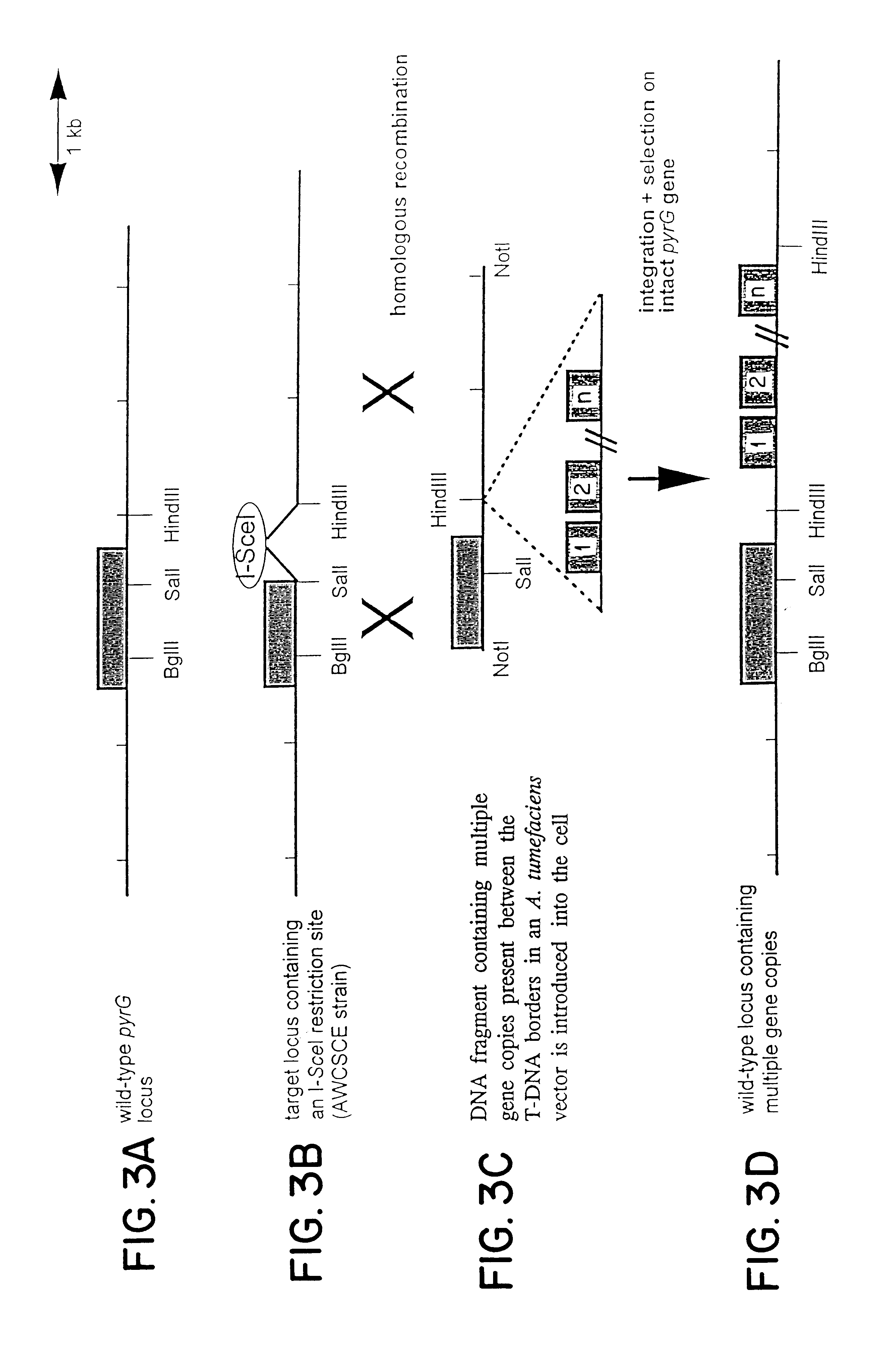
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Single-chain antigen-binding proteins capable of glycosylation, production and uses thereof
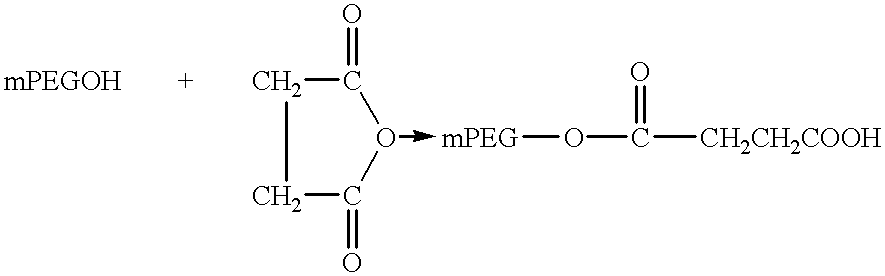
The present invention relates to single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of glycosylation. Compositions of, genetic constructions coding for, and methods for producing monovalent and multivalent single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of glycosylation are described and claimed. Composition of, genetic constructions coding for, and methods for producing glycosylated monovalent and multivalent single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of polyalkylene oxide conjugation are described and claimed. The invention also relates to methods for producing a polypeptide having increased glycosylation and the polypeptide produced by the described method. Uses resulting from the multifunctionality of a glycosylated / polyalkylene oxide conjugated antigen-binding protein are also described and claimed.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
Human cord blood as a source of neural tissue for repair of the brain and spinal cord
InactiveUS20020028510A1Easy to distinguishImprove neurological dysfunctionNervous disorderCell differentiationDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The present invention relates to the use of umbilical cord blood cells from a donor or patient to provide neural cells which may be used in transplantation. The isolated cells according to the present invention may be used to effect autologous and allogeneic transplantation and repair of neural tissue, in particular, tissue of the brain and spinal cord and to treat neurodegenerative diseases of the brain and spinal cord.
Owner:SANERON CCEL THERAPEUTICS +1
Recombinant binding proteins and peptides
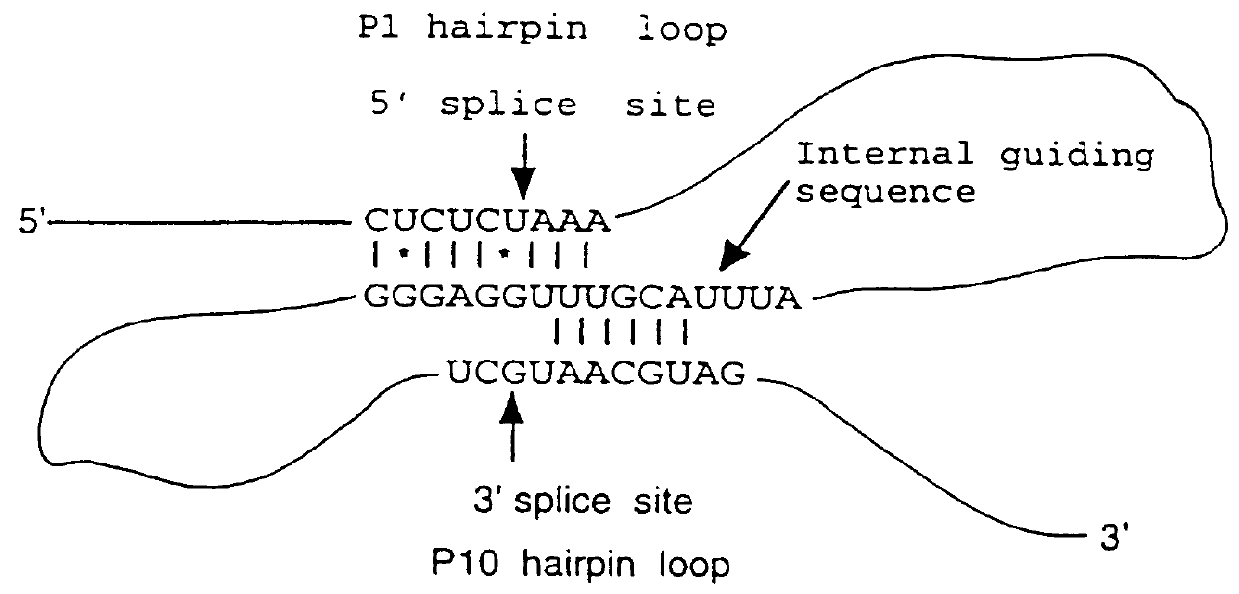
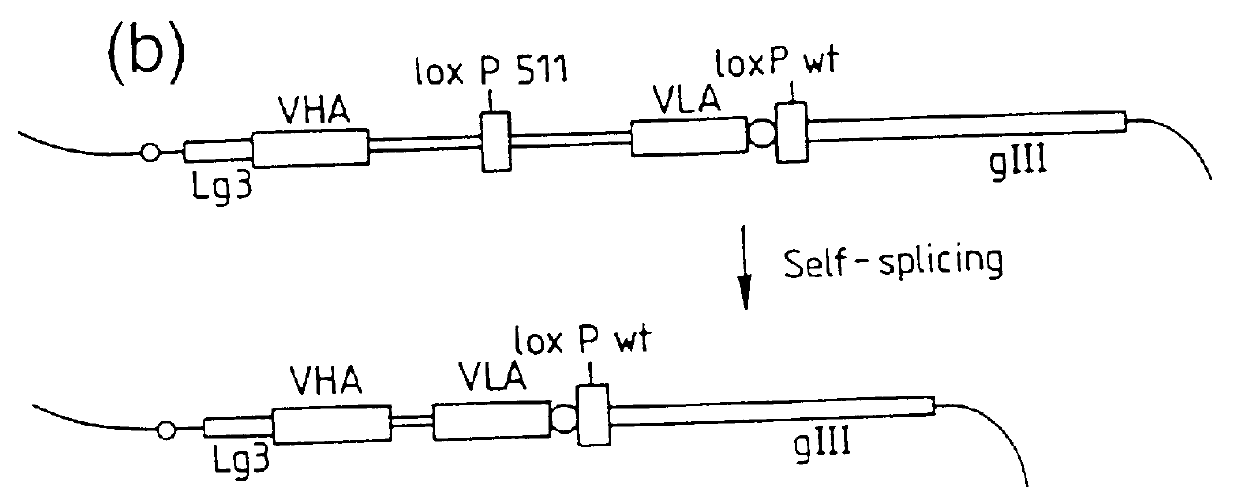
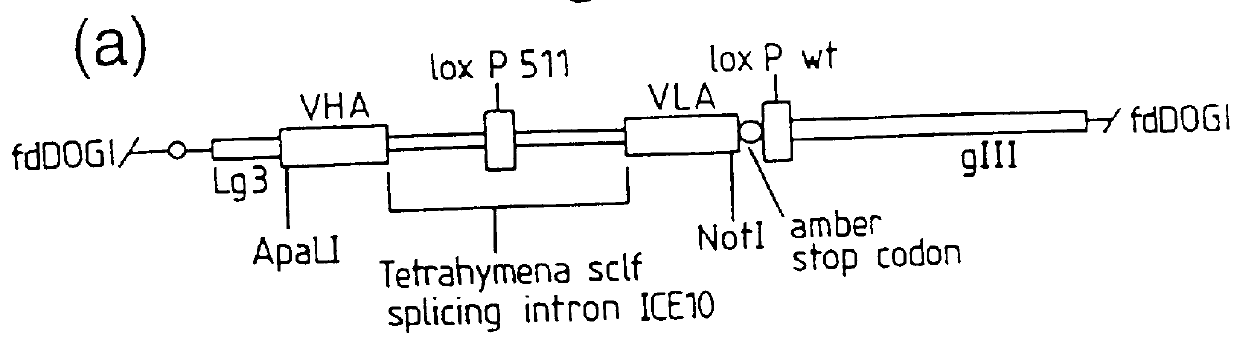
DNA constructs comprise a first exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a first peptide or polypeptide, a second exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a second peptide or polypeptide and a third sequence of nucleotides between the first and second sequences encoding a heterologous intron, for example that of Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear pre-rRNA, between RNA splice sites and a site-specific recombination sequence, such as loxP, within the intron, the exons together encoding a product peptide or polypeptide. Such constructs are of use in methods of production of peptides or polypeptides, transcription leading to splicing out of the intron enabling translation of a single chain product peptide or polypeptide. Isolated nucleic acid constructs consisting essentially of a sequence of nucleotides encoding a self-splicing intron with a site-specific recombination sequence within the intron, for use in creation of constructs for expression of peptides or polypeptides, are also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Therapeutic application of chimeric and radiolabelled antibodies to human B lymphocyte restricted differentiation antigen for treatment of B cell lymphoma
Disclosed herein are therapeutic treatment protocols designed for the treatment of B cell lymphoma. These protocols are based upon therapeutic strategies which include the use of administration of immunologically active mouse / human chimeric anti-CD20 antibodies, radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies, and cooperative strategies comprising the use of chimeric anti-CD20 antibodies and radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies.
Owner:IDEC PHARM CORP
Humanized antibodies that sequester abeta peptide
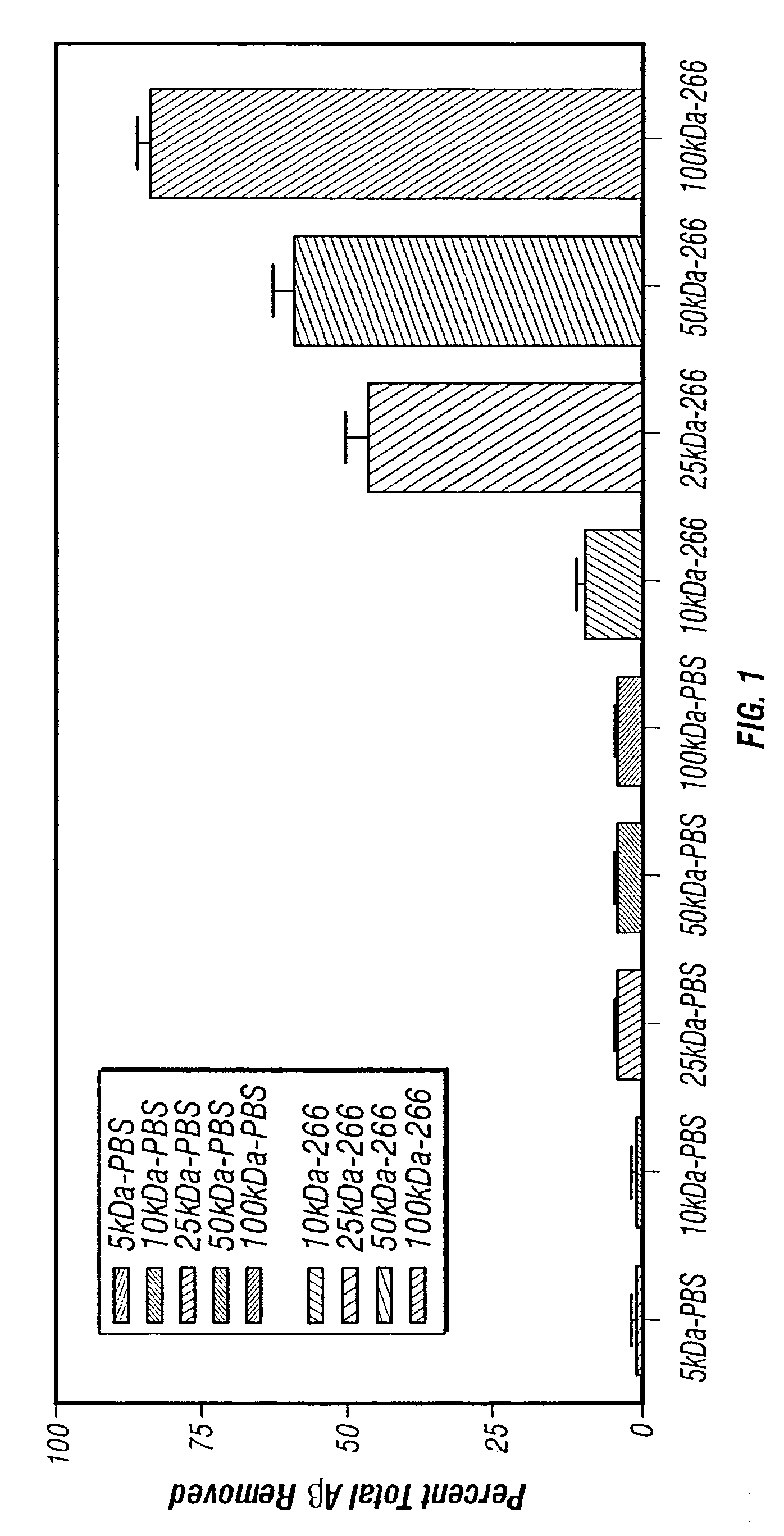
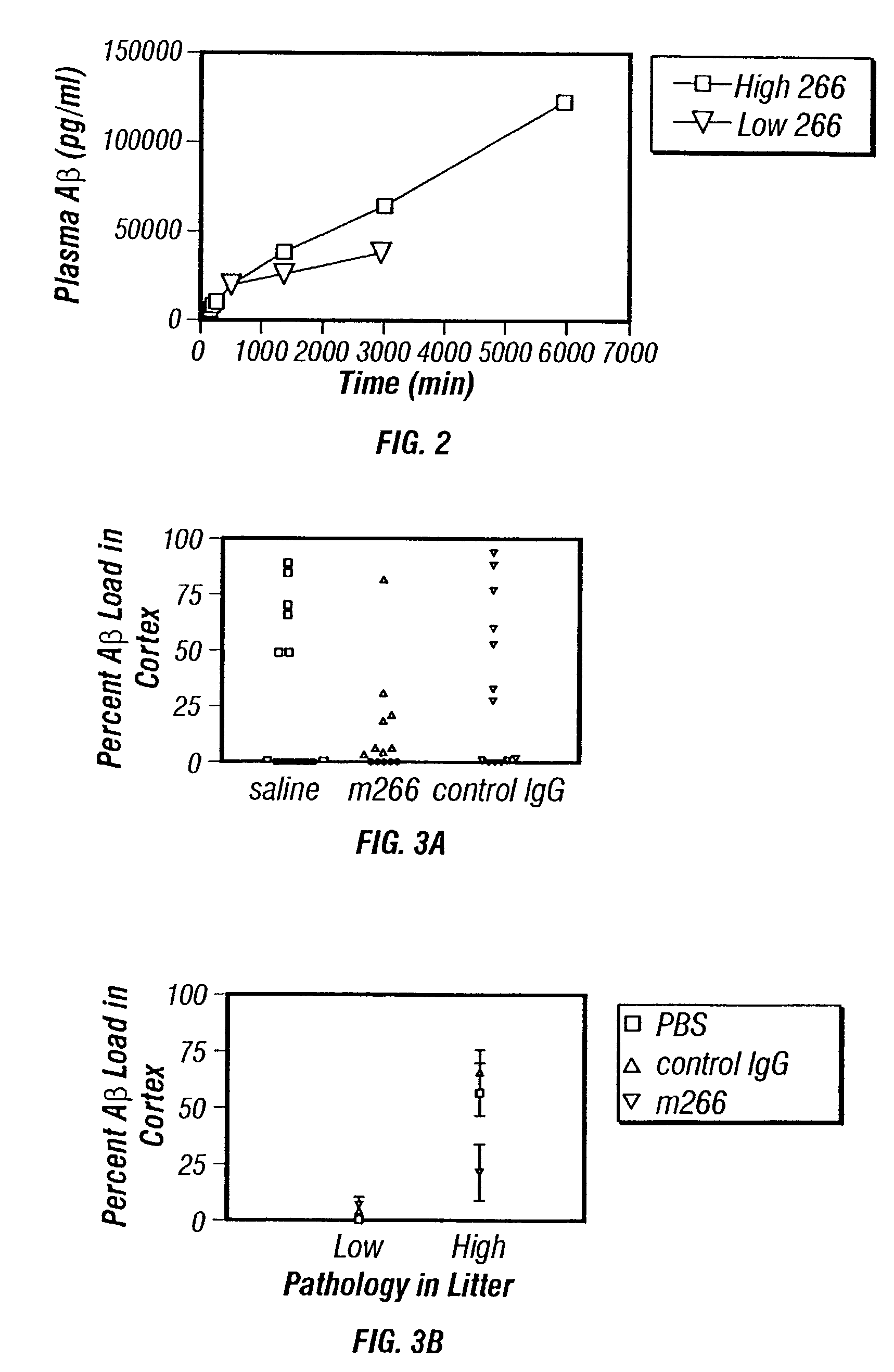
A method to treat conditions characterized by formation of amyloid plaques both prophylactically and therapeutically is described. The method employs humanized antibodies which sequester soluble Aβ peptide from human biological fluids or which preferably specifically bind an epitope contained within position 13–28 of the amyloid beta peptide Aβ.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO +1
Chimeric gene for the transformation of plants
InactiveUSRE37287E1Most efficientPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationIncreased tolerance
Chimeric gene for conferring to plants an increased tolerance to a herbicide having as its target EPSPS comprises, in the direction of transcription, a promoter region, a transit peptide region, a coding sequence for glyphosate tolerance and a polyandenylation signal region, wherein the transit peptide region comprises, in the direction of translation, at least one transit peptide of a plant gene encoding a plastid-localized enzyme and then a second transit peptide of a plant gene encoding, a plastid-localized enzyme. Production of glyphosate-tolerant plants is disclosed.
Owner:BAYER SAS
Reshaped human antibody to human interleukin-6 receptor
InactiveUS20050142635A1Less immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesComplementarity determining regionV region
A reshaped human antibody to the human IL-6R, comprising: (A) an L chain comprising, (1) a human L chain C region, and (2) an L chain V region comprising human L chain framework regions (FRs), and mouse L chain complementary determination regions (CDRs) of a momoclonal antibody to the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R); and (B) an H chain comprising, (1) a human H chain C region, and (2) an H chain V region comprising human H chain FRS, and mouse H chain CDRs of a monoclonal antibody to the IL-6R. Since major portion of the reshaped human antibody is derived from a human antibody and the mouse CDRs which are less immunogenic, the present reshaped human antibody is less immunogenic to human, and therefor is promised for therapeutic uses.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
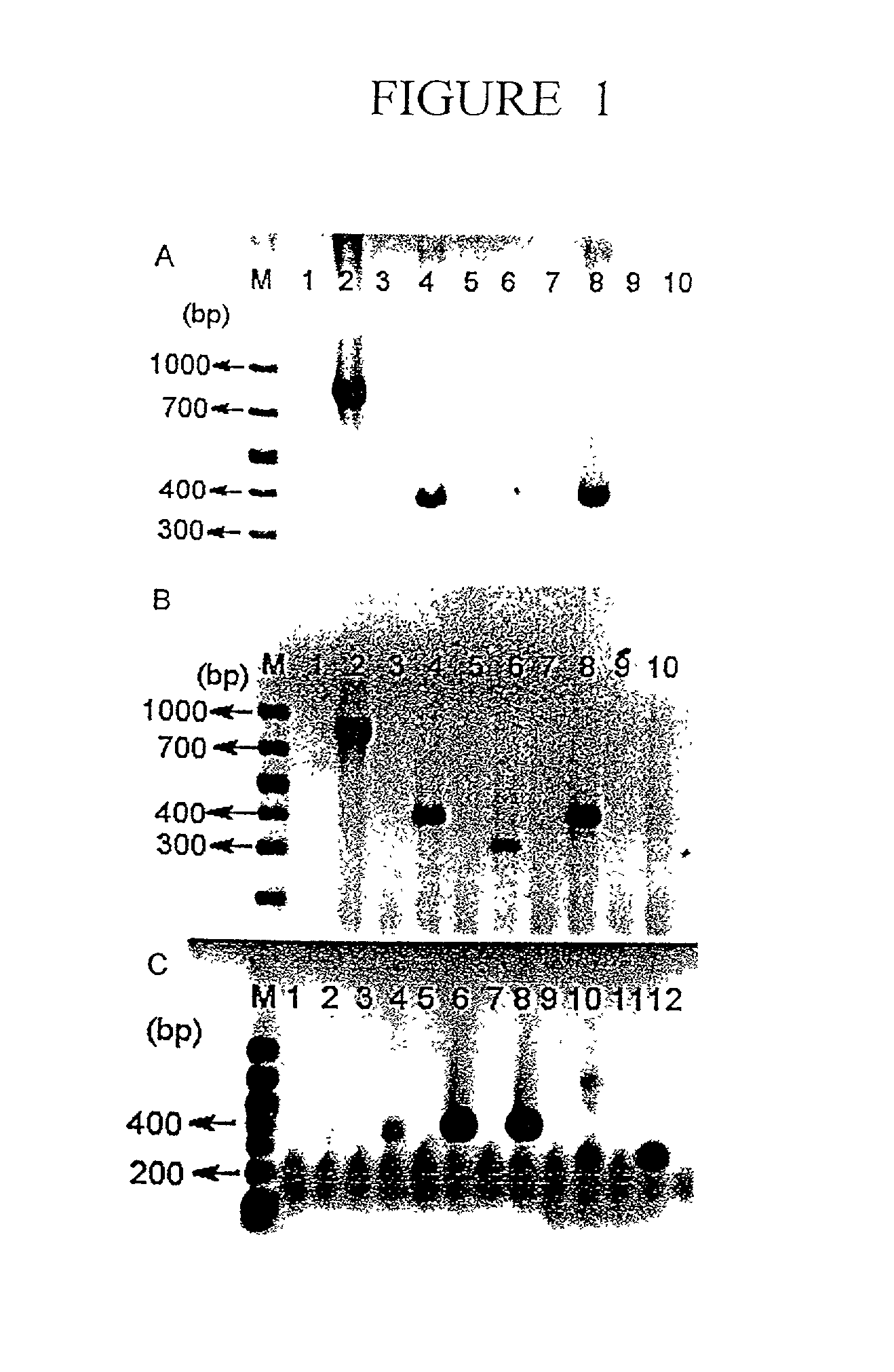
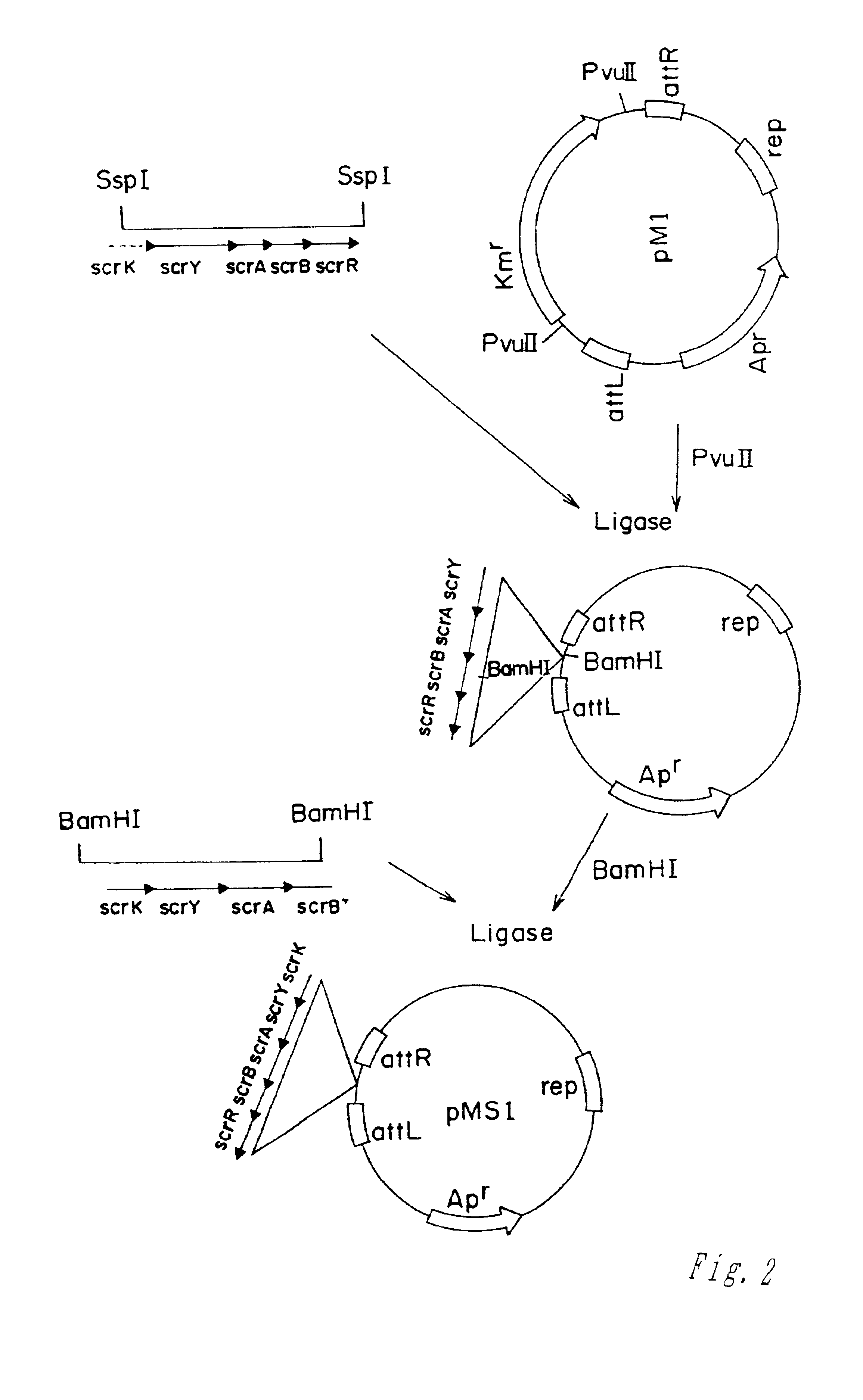
Methods of making amino acids using E. coli transformed with csc genes
An amino acid such as threonine, homoserine, isoleucine, lysine, valine and tryptophan is produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has been constructed from sucorse non-assimilative strain belonging to the genus Escherichia and which harbors sucrose non-PTS (phosphoenol pyruvate-dependent sucrose-6-phosphotransferase system) genes and has an ability to produce the amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for the preparation of purified HCV RNA by exosome separation
InactiveUS7198923B1Simple preparation processPromote progressSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementExosomeBlood plasma
Owner:GRIFOLS WORLDWIDE OPERATIONS +1
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and Ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6537756B1Remarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta-endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against coleopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
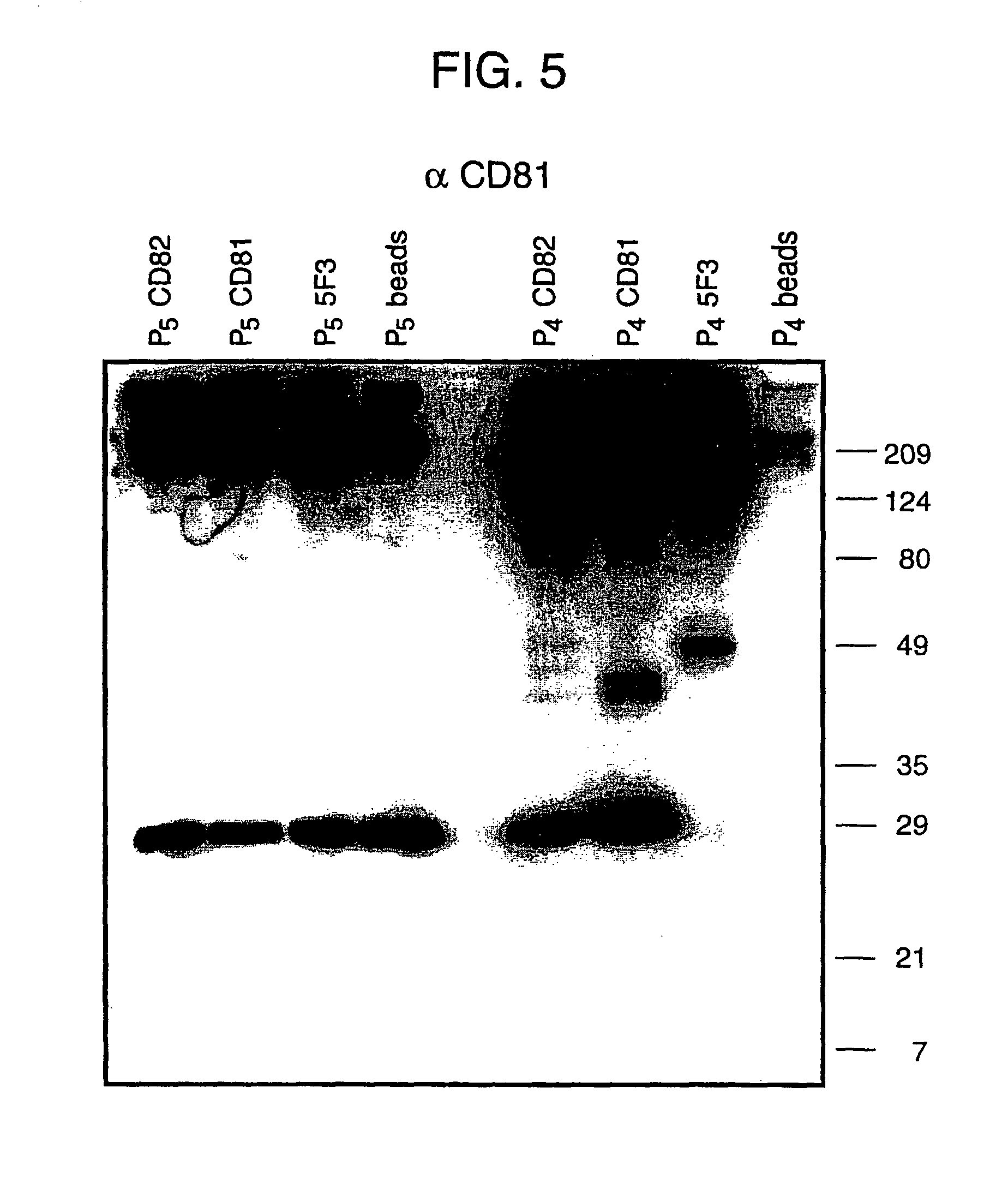
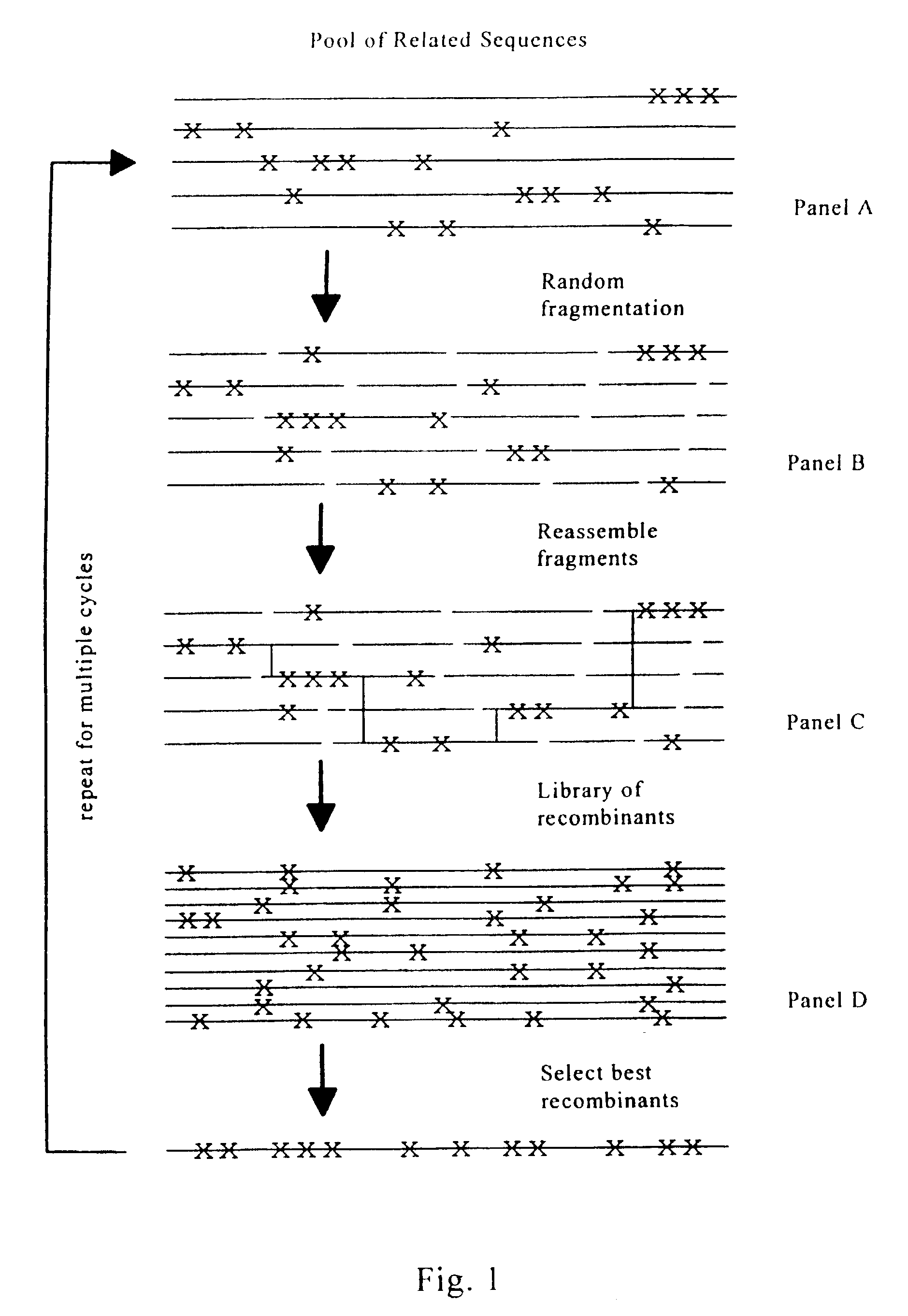
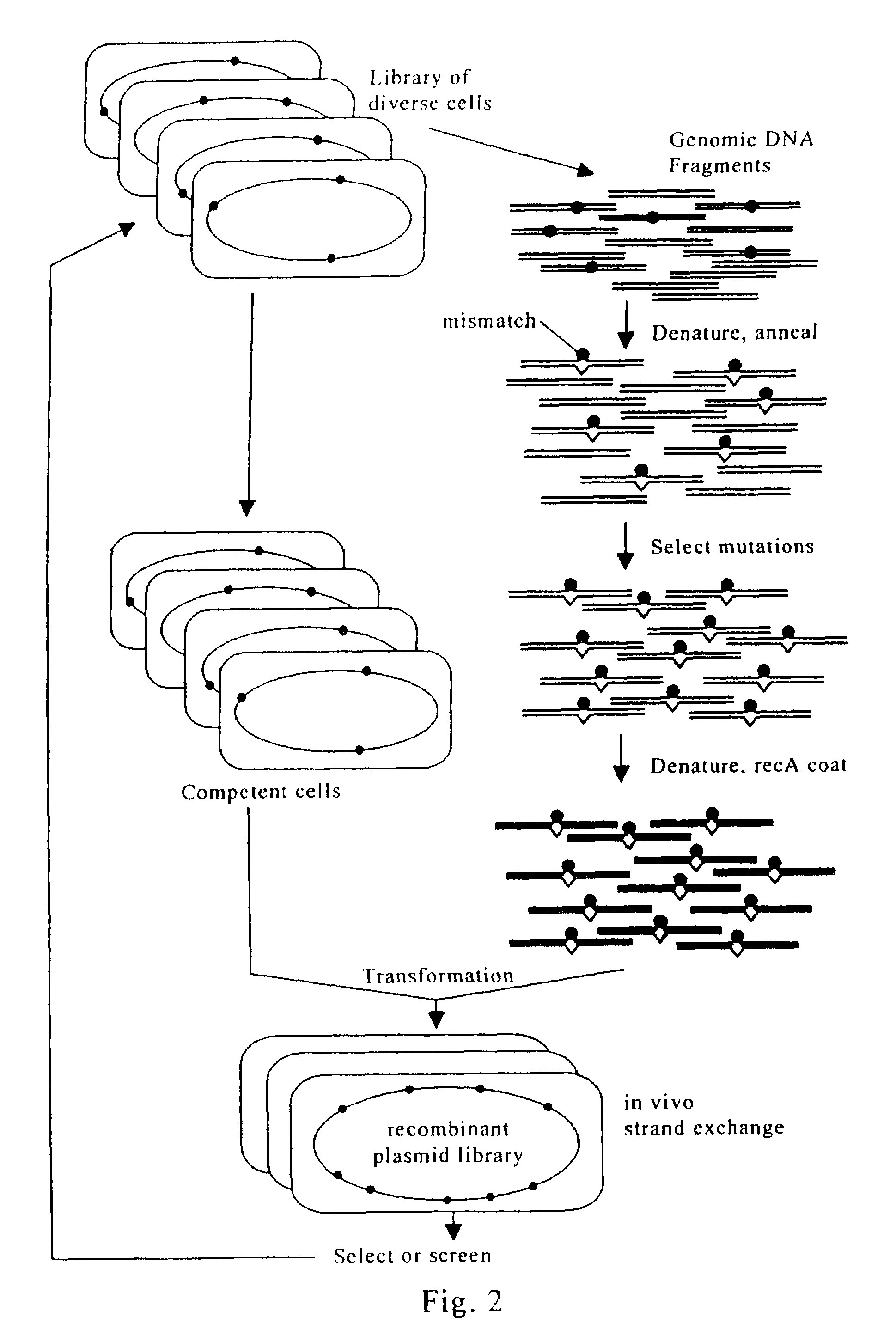
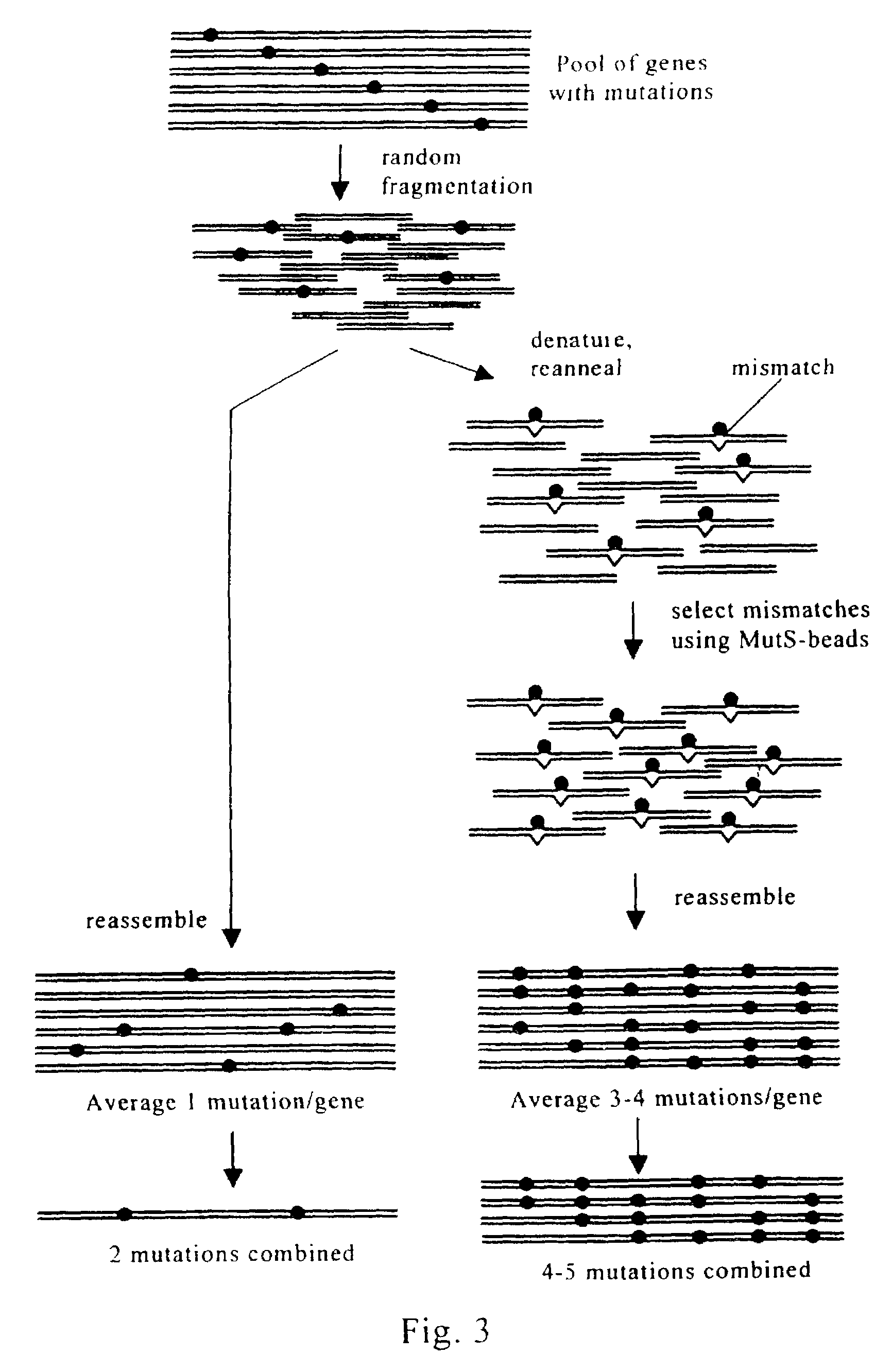
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS7148054B2Increase diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Therapeutic application of chimeric and radiolabelled antibodies to human B lymphocyte restricted differentiation antigen for treatment of B cell lymphoma
Disclosed herein are therapeutic treatment protocols designed for the treatment of B cell lymphoma. These protocols are based upon therapeutic strategies which include the use of administration of immunologically active mouse / human chimeric anti-CD20 antibodies, radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies, and cooperative strategies comprising the use of chimeric anti-CD20 antibodies and radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
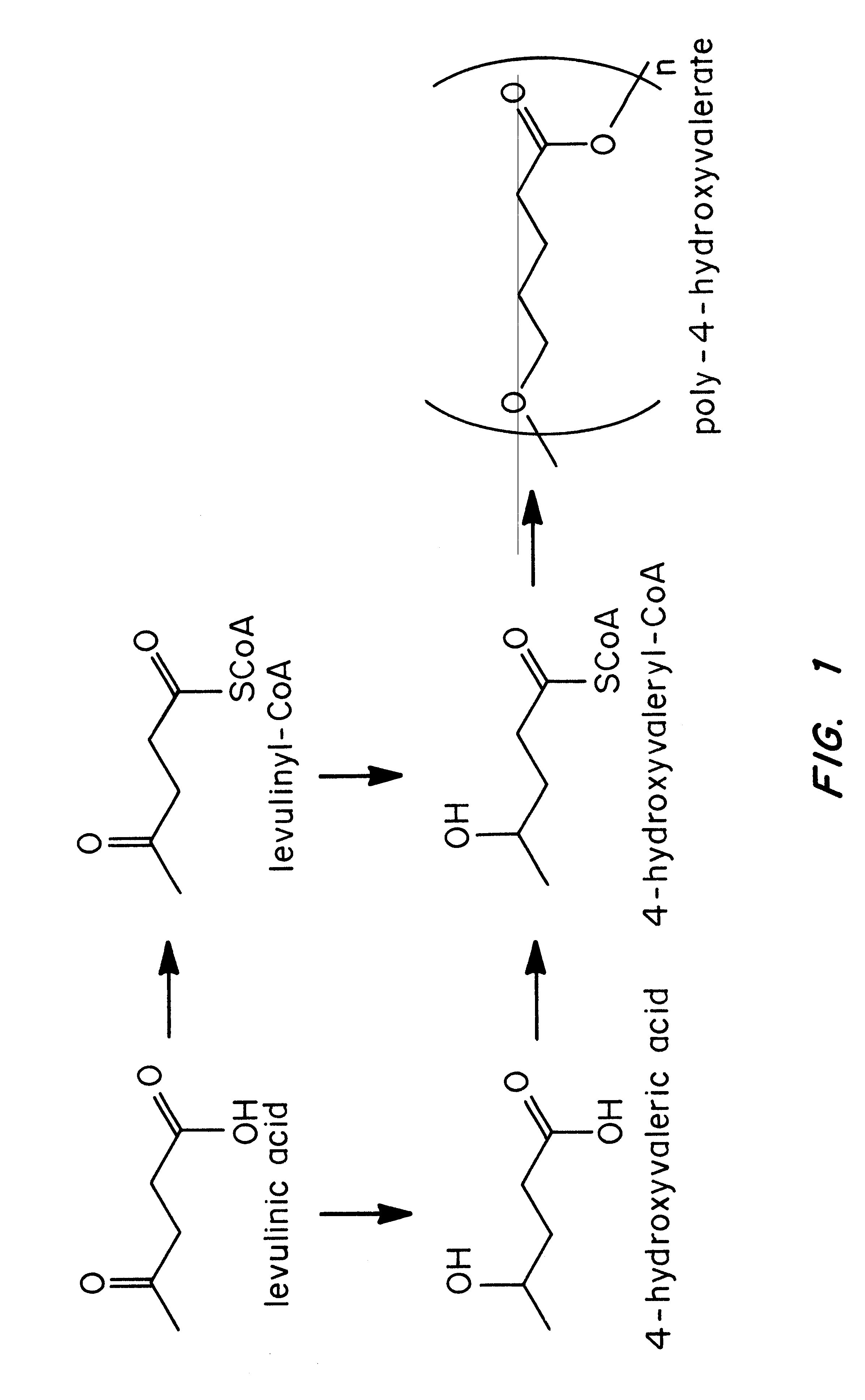
Polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer compositions
Several novel PHA polymer compositions produced using biological systems include monomers such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxypropionate, 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, 4-hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate. These PHA compositions can readily be extended to incorporate additional monomers including, for example, 3-hydroxyhexanoate, 4-hydroxyhexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate or other longer chain 3-hydroxyacids containing seven or more carbons. This can be accomplished by taking natural PHA producers and mutating through chemical or transposon mutagenesis to delete or inactivate genes encoding undesirable activities. Alternatively, the strains can be genetically engineered to express only those enzymes required for the production of the desired polymer composition. Methods for genetically engineering PHA producing microbes are widely known in the art (Huisman and Madison, 1998, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63: 21-53). These polymers have a variety of uses in medical, industrial and other commercial areas.
Owner:METABOLIX
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS7704723B2High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSyngasAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com