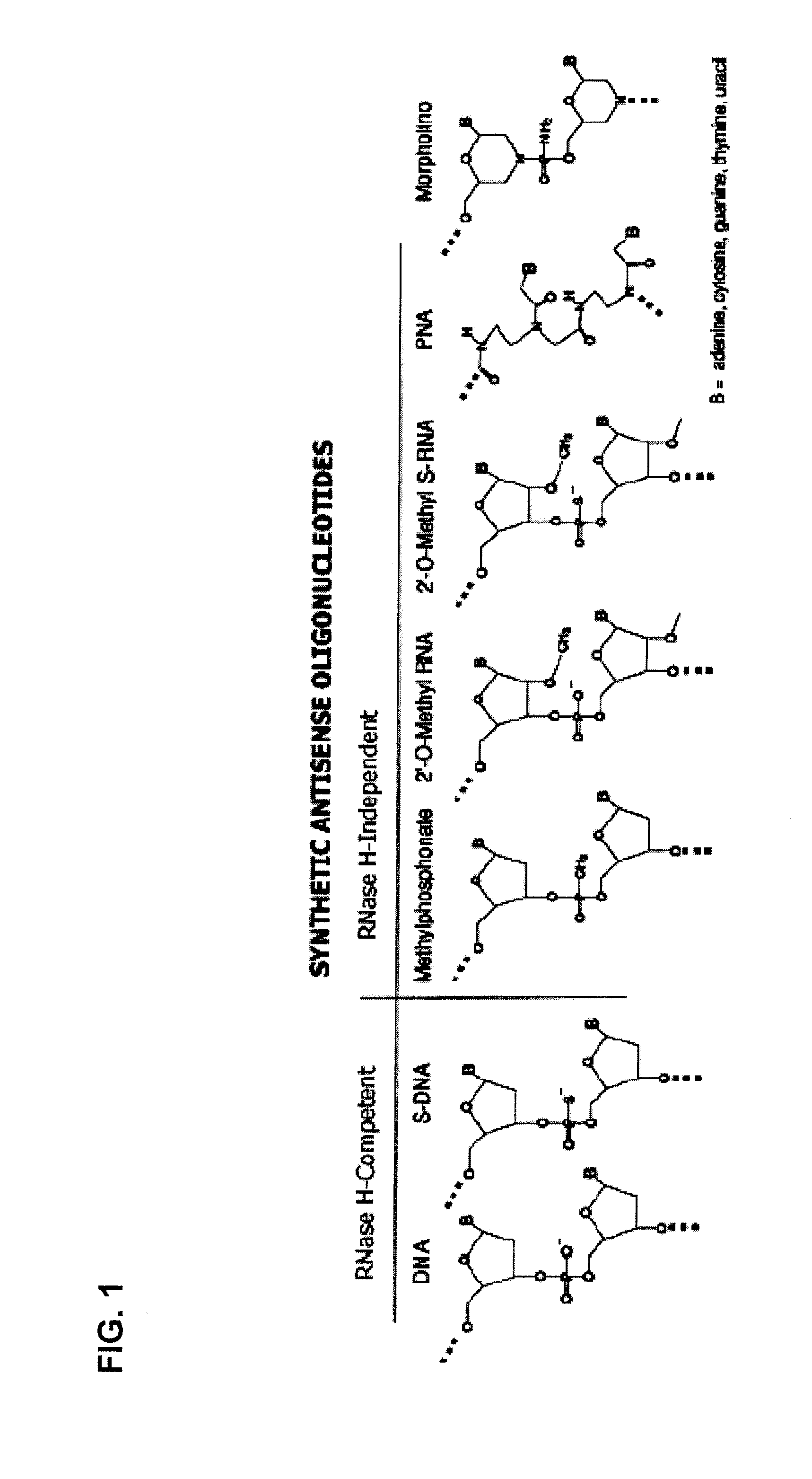
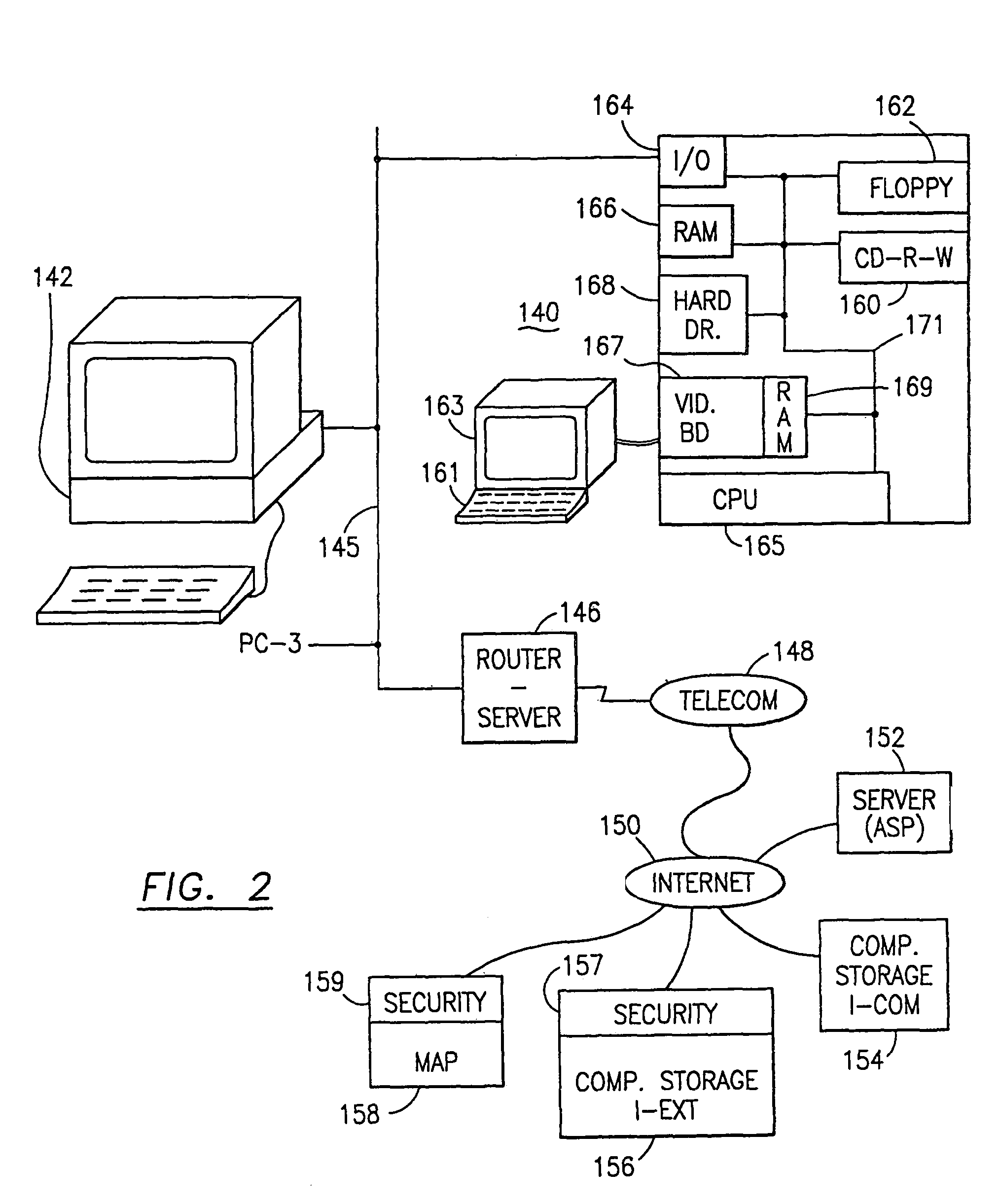
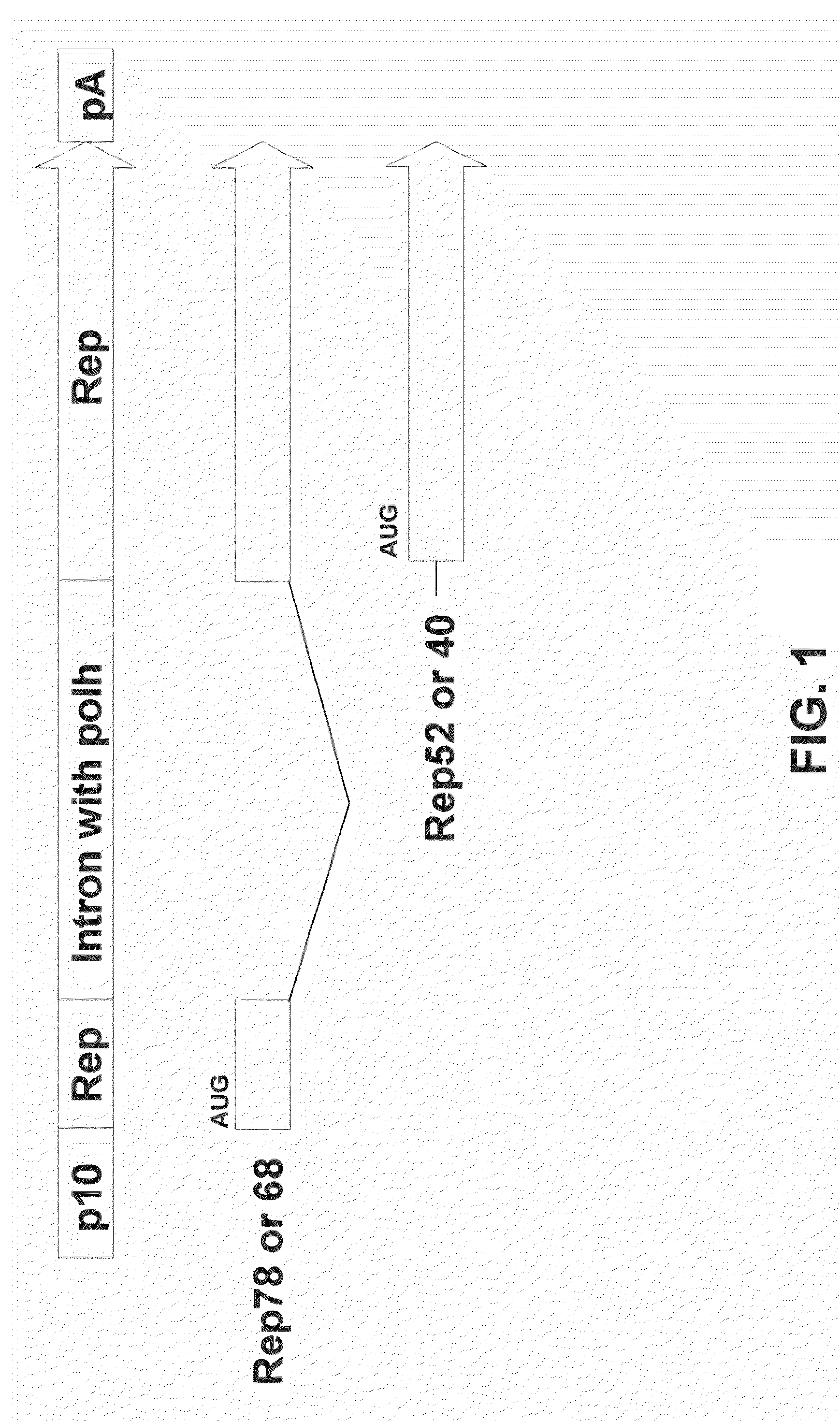
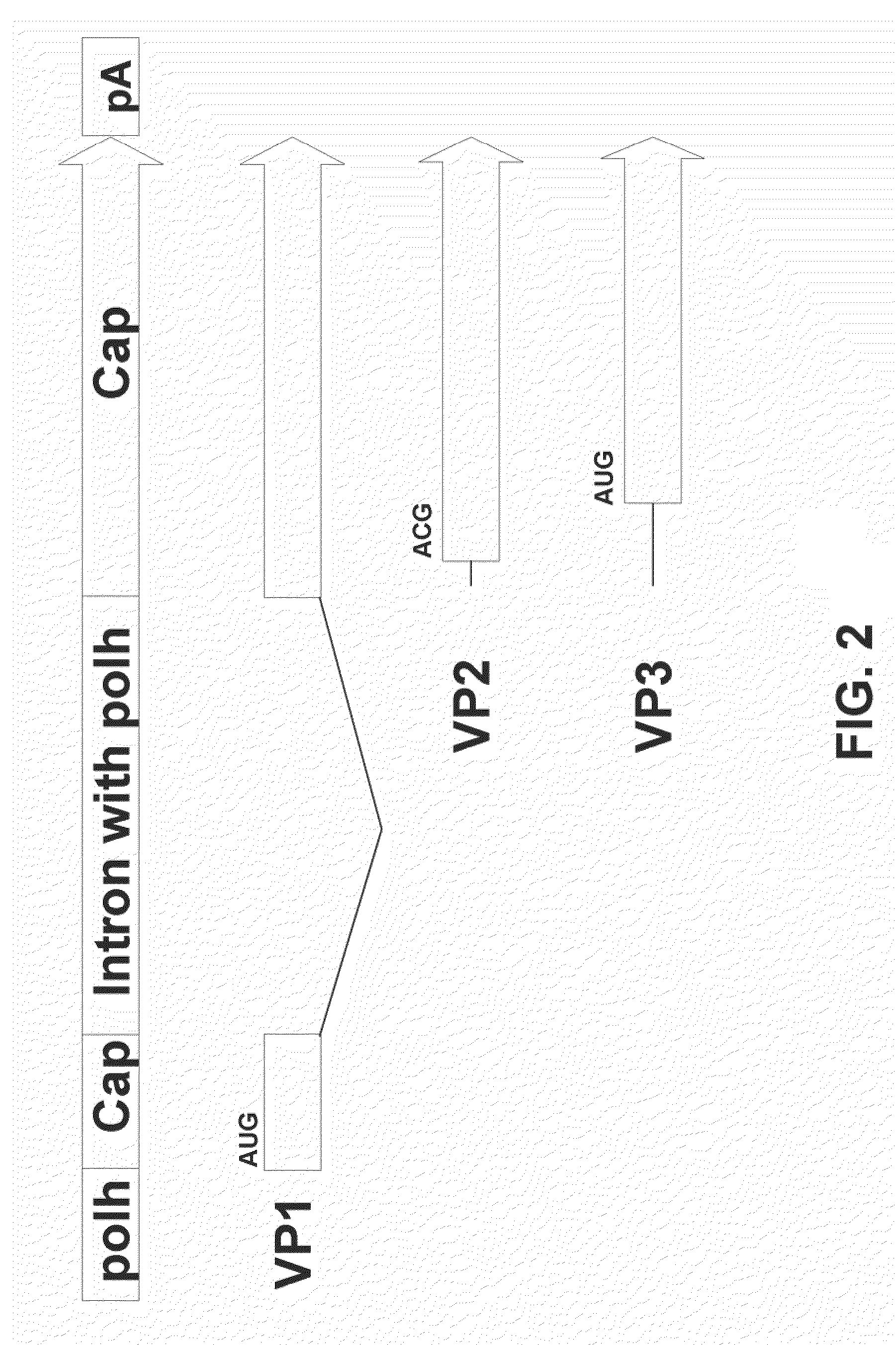
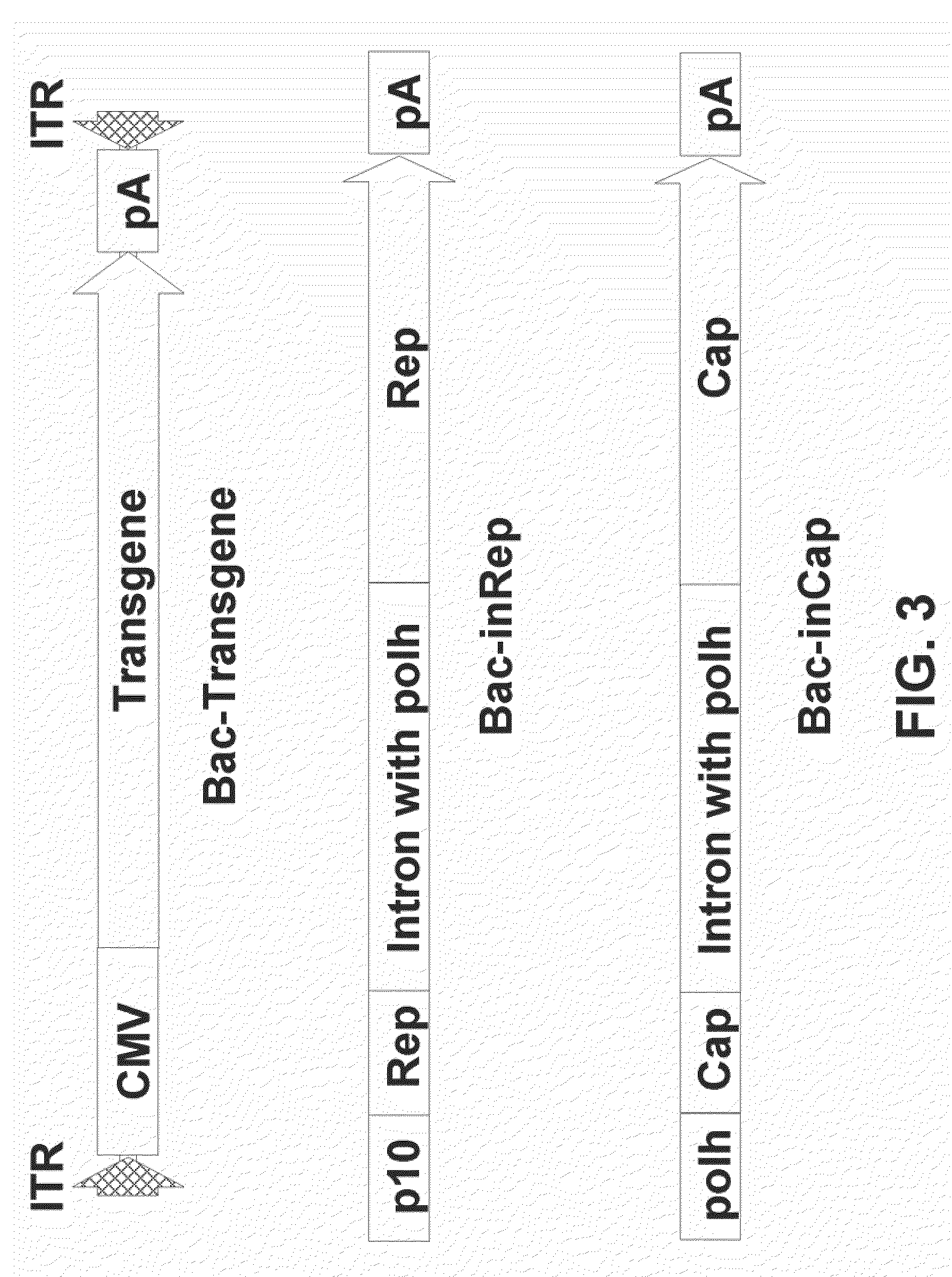
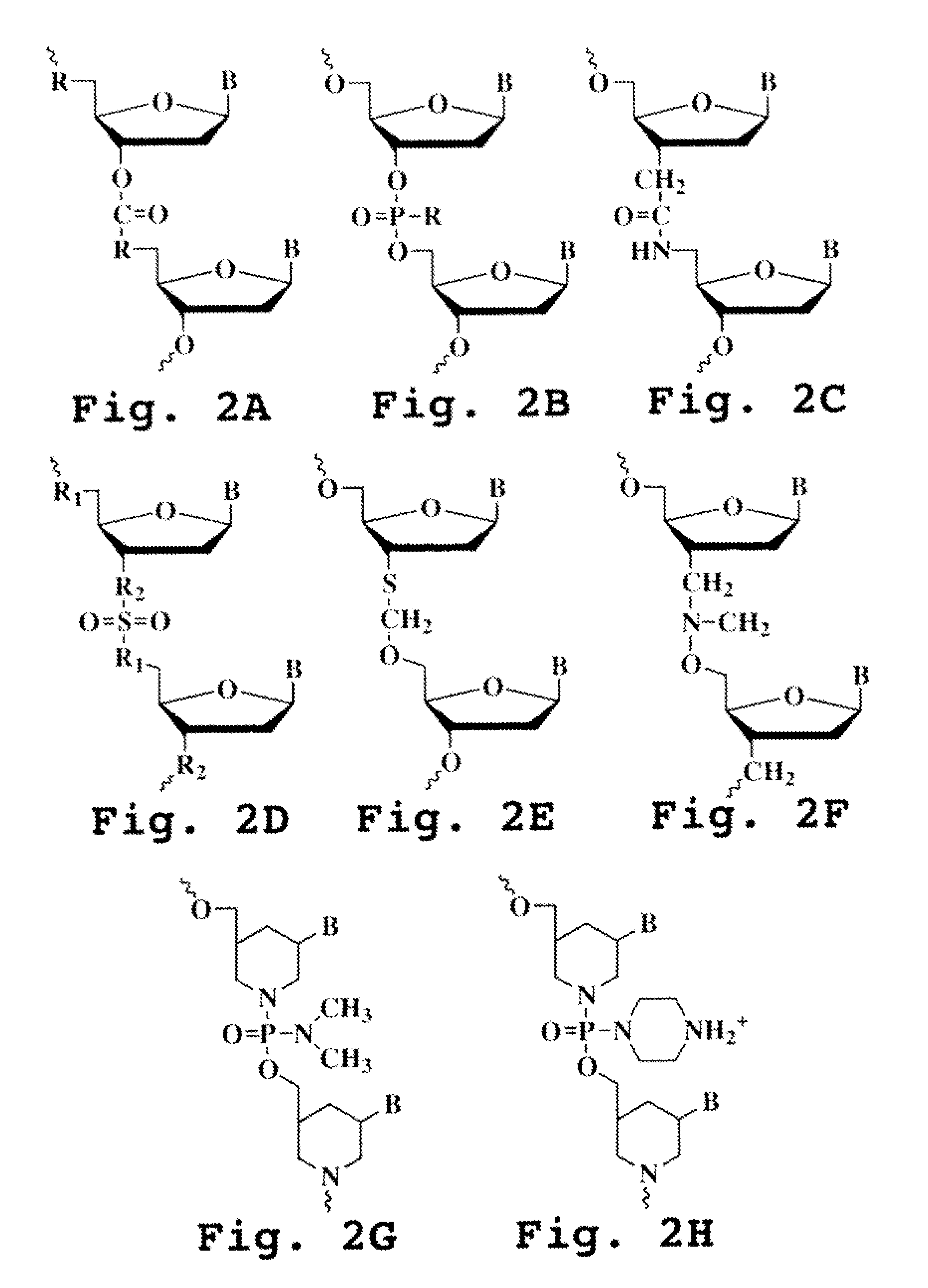
Patents
Literature
1267 results about "Intron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
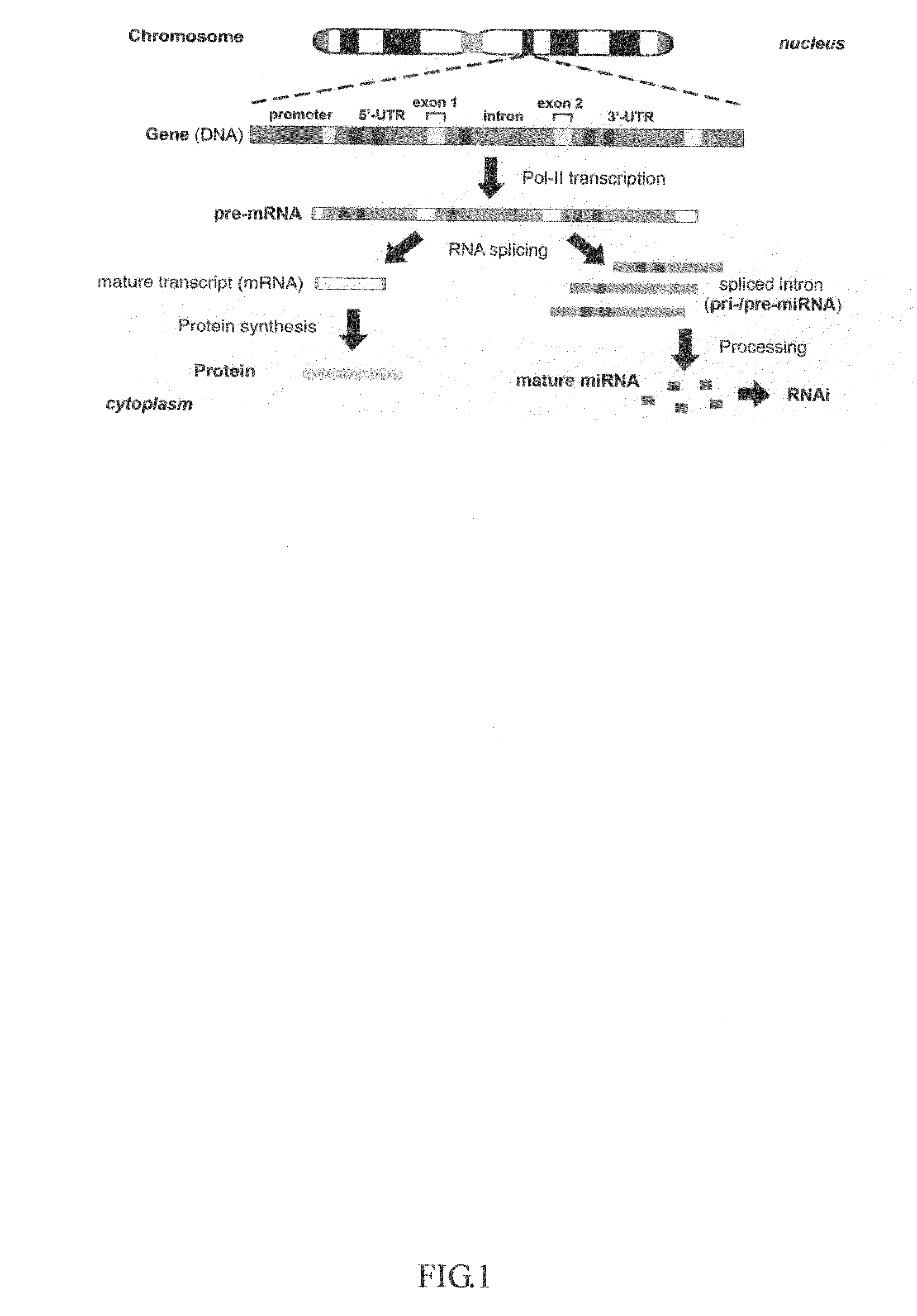
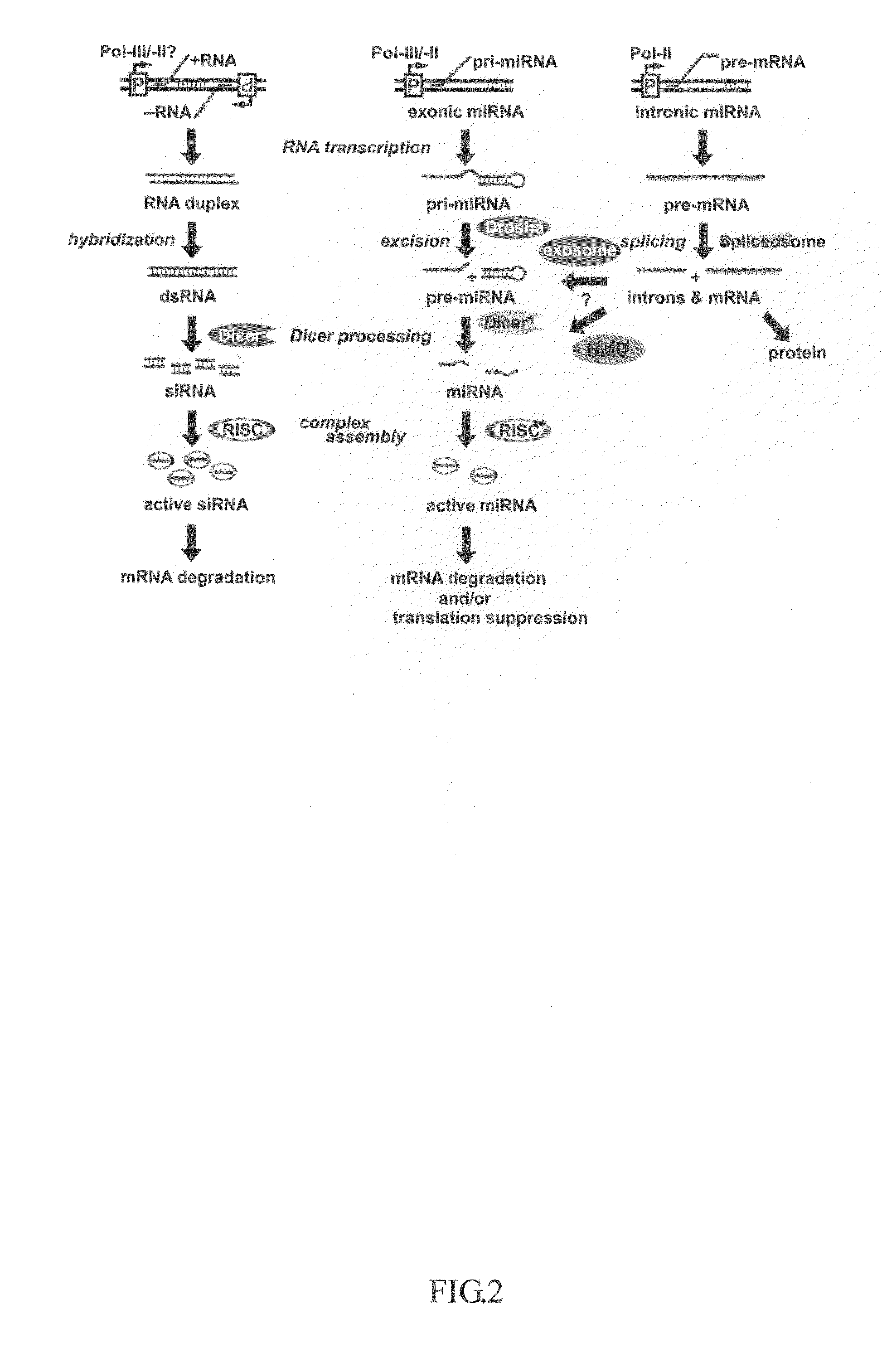
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing during maturation of the final RNA product. The word intron is derived from the term intragenic region, i.e. a region inside a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. Sequences that are joined together in the final mature RNA after RNA splicing are exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses, and can be located in a wide range of genes, including those that generate proteins, ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA). When proteins are generated from intron-containing genes, RNA splicing takes place as part of the RNA processing pathway that follows transcription and precedes translation.
Full-length plant cDNA and uses thereof
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Recombinant DNA constructs and methods for controlling gene expression
InactiveUS20060200878A1Reduce accumulationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention provides molecular constructs and methods for use thereof, including constructs including heterologous miRNA recognition sites, constructs for gene suppression including a gene suppression element embedded within an intron flanked on one or on both sides by non-protein-coding sequence, constructs containing engineered miRNA or miRNA precursors, and constructs for suppression of production of mature microRNA in a cell. Also provided are transgenic plant cells, plants, and seeds containing such constructs, and methods for their use. The invention further provides transgenic plant cells, plants, and seeds containing recombinant DNA for the ligand-controlled expression of a target sequence, which may be endogenous or exogenous. Also disclosed are novel miRNAs and miRNA precursors from crop plants including maize and soy.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
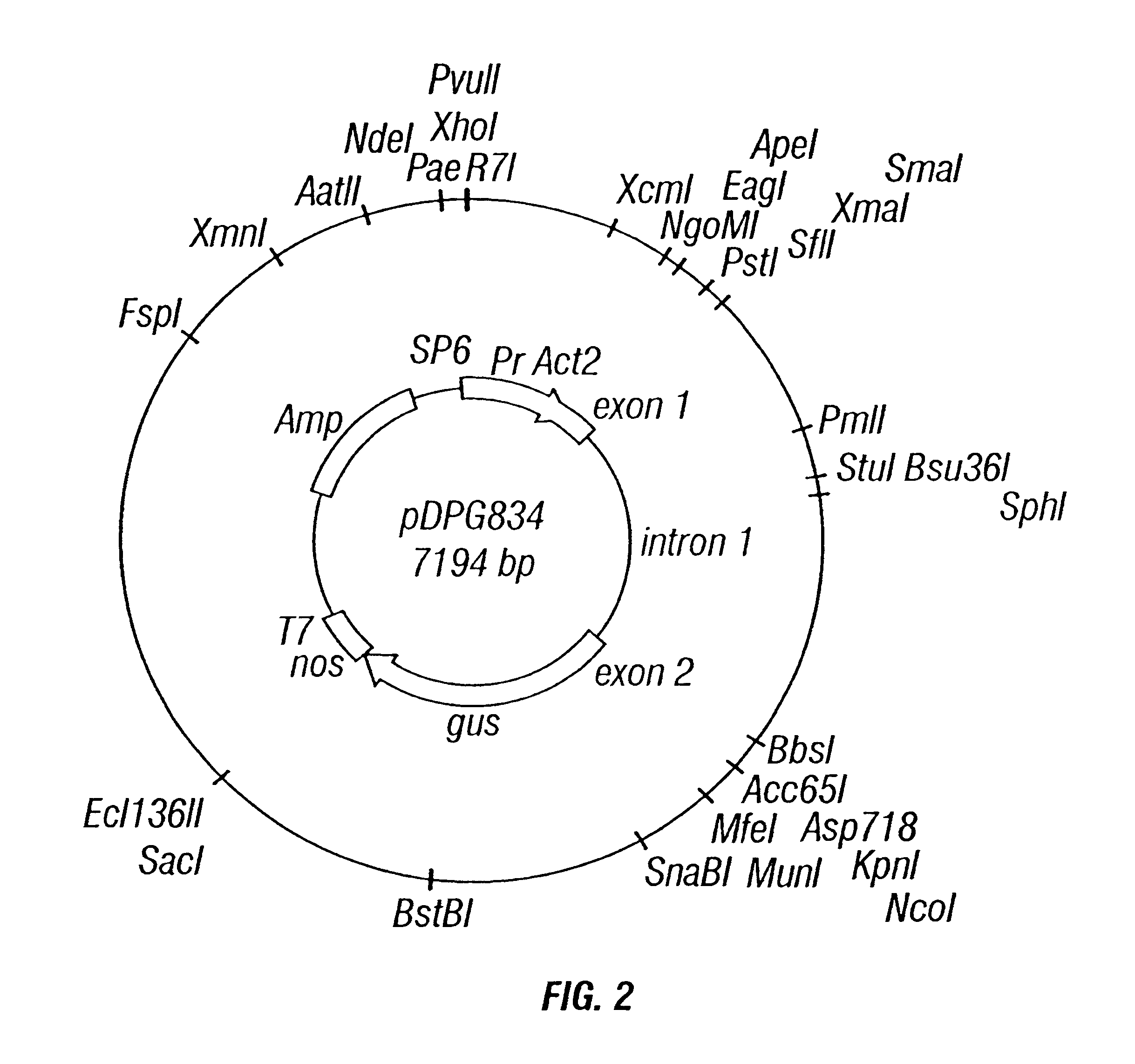
Rice actin 2 promoter and intron and methods for use thereof
The current invention provides regulatory regions from the rice actin 2 gene. In particular, the current invention provides the rice actin 2 promoter and actin 2 intron. Compositions comprising these sequences are described, as well as transformation constructs derived therefrom. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the rice actin 2 intron and / or promoter directly by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The actin 2 sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
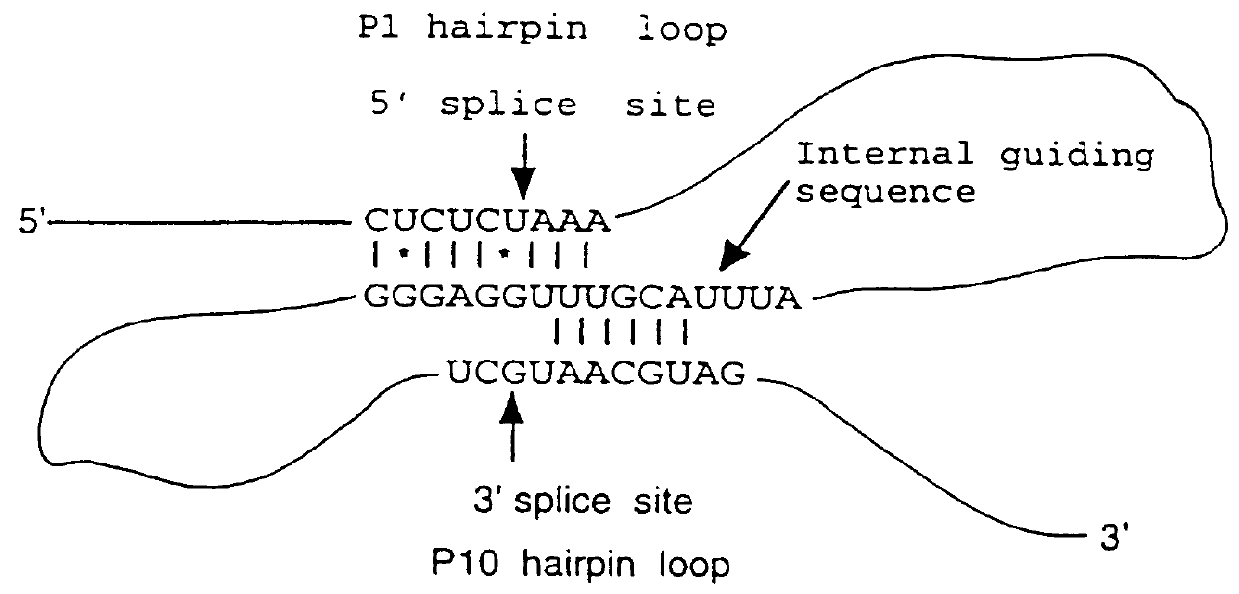
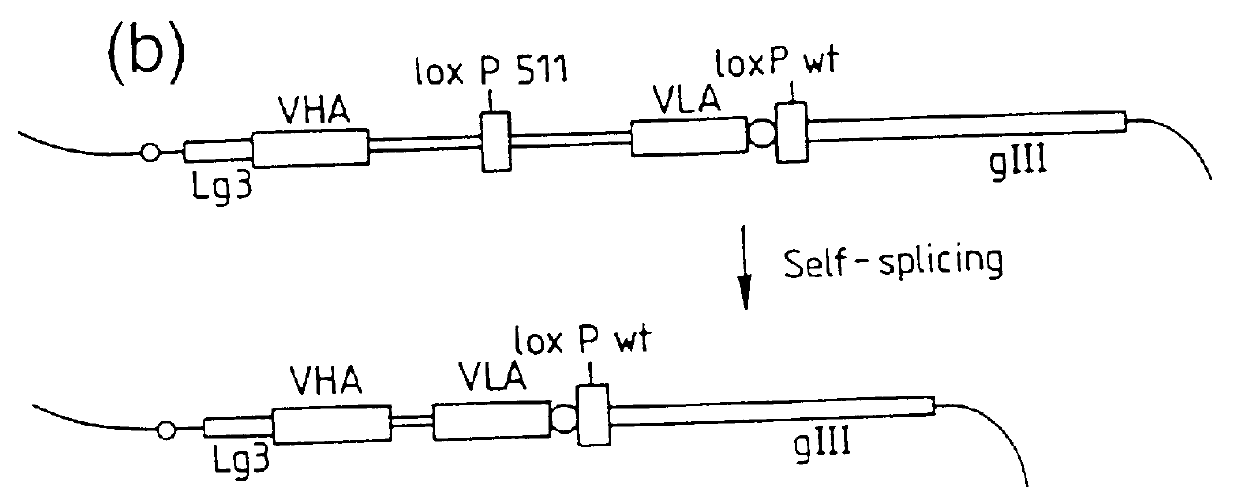
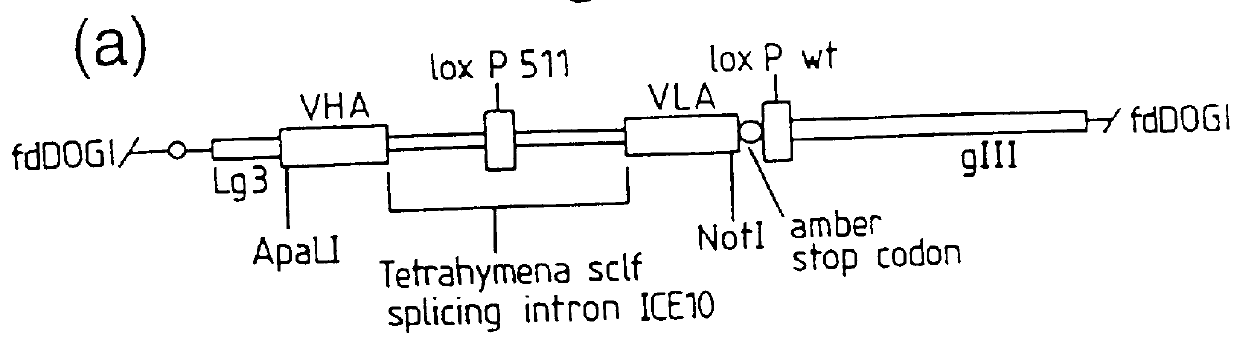
Recombinant binding proteins and peptides
DNA constructs comprise a first exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a first peptide or polypeptide, a second exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a second peptide or polypeptide and a third sequence of nucleotides between the first and second sequences encoding a heterologous intron, for example that of Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear pre-rRNA, between RNA splice sites and a site-specific recombination sequence, such as loxP, within the intron, the exons together encoding a product peptide or polypeptide. Such constructs are of use in methods of production of peptides or polypeptides, transcription leading to splicing out of the intron enabling translation of a single chain product peptide or polypeptide. Isolated nucleic acid constructs consisting essentially of a sequence of nucleotides encoding a self-splicing intron with a site-specific recombination sequence within the intron, for use in creation of constructs for expression of peptides or polypeptides, are also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
ActiveUS20100293625A1Increase transgene expressionImprove stabilityVectorsSugar derivativesReticulum cellIntein
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20160122817A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationInteinNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and systems for capturing and analyzing sequence information contained in targeted regions of a genome. Such targeted regions may include exomes, partial exomes, introns, combinations of exonic and intronic regions, genes, panels of genes, and any other subsets of a whole genome that may be of interest.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Transgenic organism
InactiveUS20090007284A1Efficient productionEfficiency advantageAnimal cellsVectorsNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
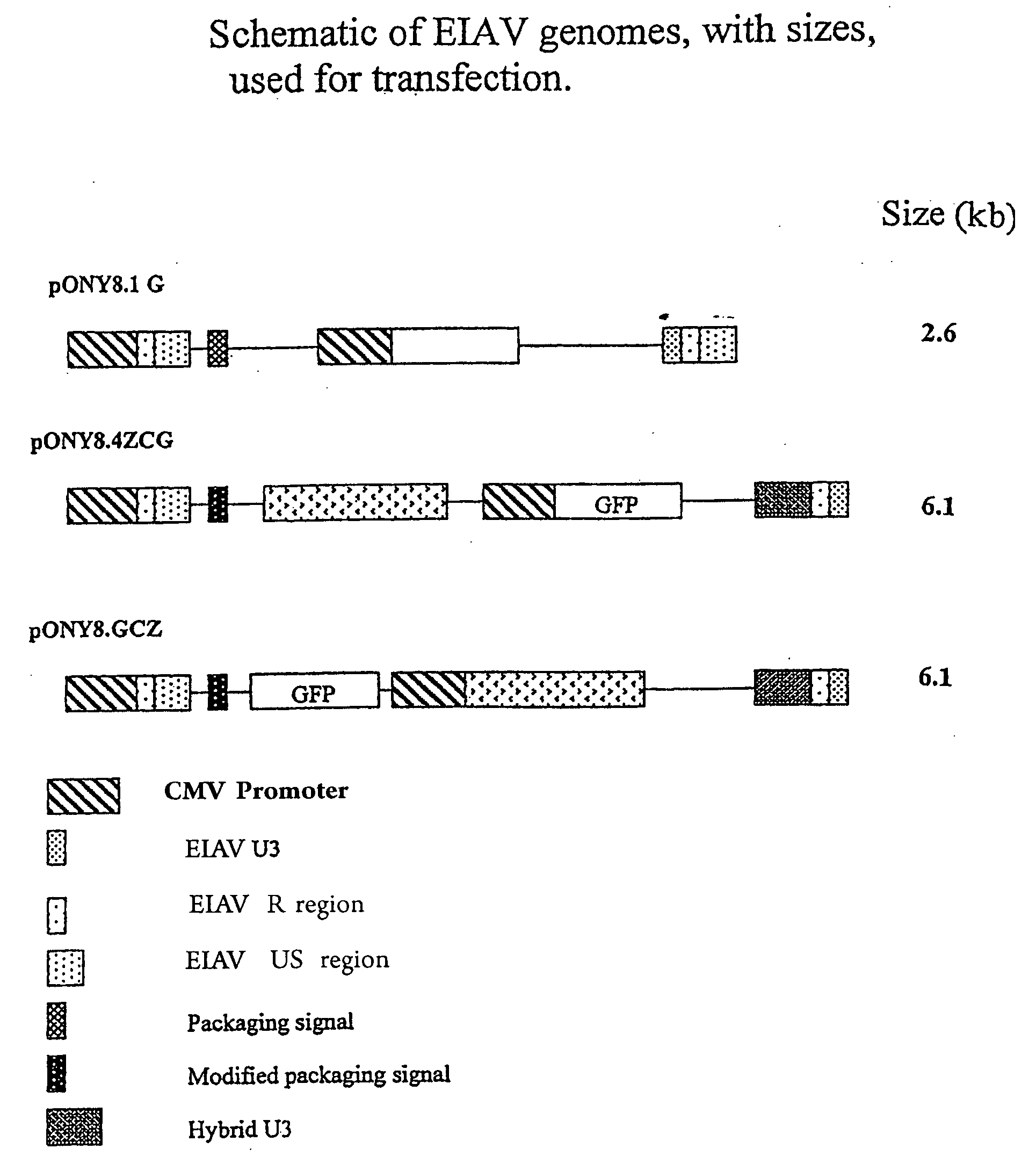
A method of producing a transgenic cell comprising introducing into a cell a non-primate lentiviral expression vector comprising a nucleotide of interest (NOI). Also described is a method of producing a transgenic cell comprising introducing into a cell a lentiviral expression vector comprising a NOI capable of generating an antisense oligonucleotide, a ribozyme, an siRNA, a short hairpin RNA, a micro-RNA or a group 1 intron. Also described is a viral vector comprising a first nucleotide sequence, wherein said first nucleotide sequence comprises: (a) a second nucleotide sequence comprising an aptazyme; and (b) a third nucleotide sequence capable of generating a polynucleotide; wherein (a) and (b) are operably linked and wherein the aptazyme is activatable to cleave a transcript of the first nucleotide sequence such that said polynucleotide is generated.
Owner:RADCLIFFE PHILIPPA +2
Generation of human embryonc stem-like cells using intronic RNA
ActiveUS20080293143A1Stable and relatively long-term effectDelivery stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentReprogrammingMammal
This invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting human embryonic stem (hES)-like pluripotent cells using transgenic expression of intronic microRNA-like RNA agents. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its intronic components capable of being processed into mir-302-like RNA molecules in mammalian cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on differentiation-related and fate-determinant genes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into a pluripotent embryonic stem (ES)-cell-like state. The ES-like cells so obtained are strongly express hES cell markers, such as Oct3 / 4, SSEA-3 and SSEA-4, and can be guided into various tissue cell types by treating certain hormones and / or growth factors under a feeder-free cell culture condition in vitro, which may be used for transplantation and gene therapies. Therefore, the present invention offers a simple, effective and safe gene manipulation approach for not only reprogramming somatic cells into ES-like pluripotent cells but also facilitating the maintenance of pluripotent and renewal properties of ES cells under a feeder-free cell culture condition, preventing the tedious retroviral insertion of four large transcription factor genes into one single cell as used in the previous iPS methods.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH +1
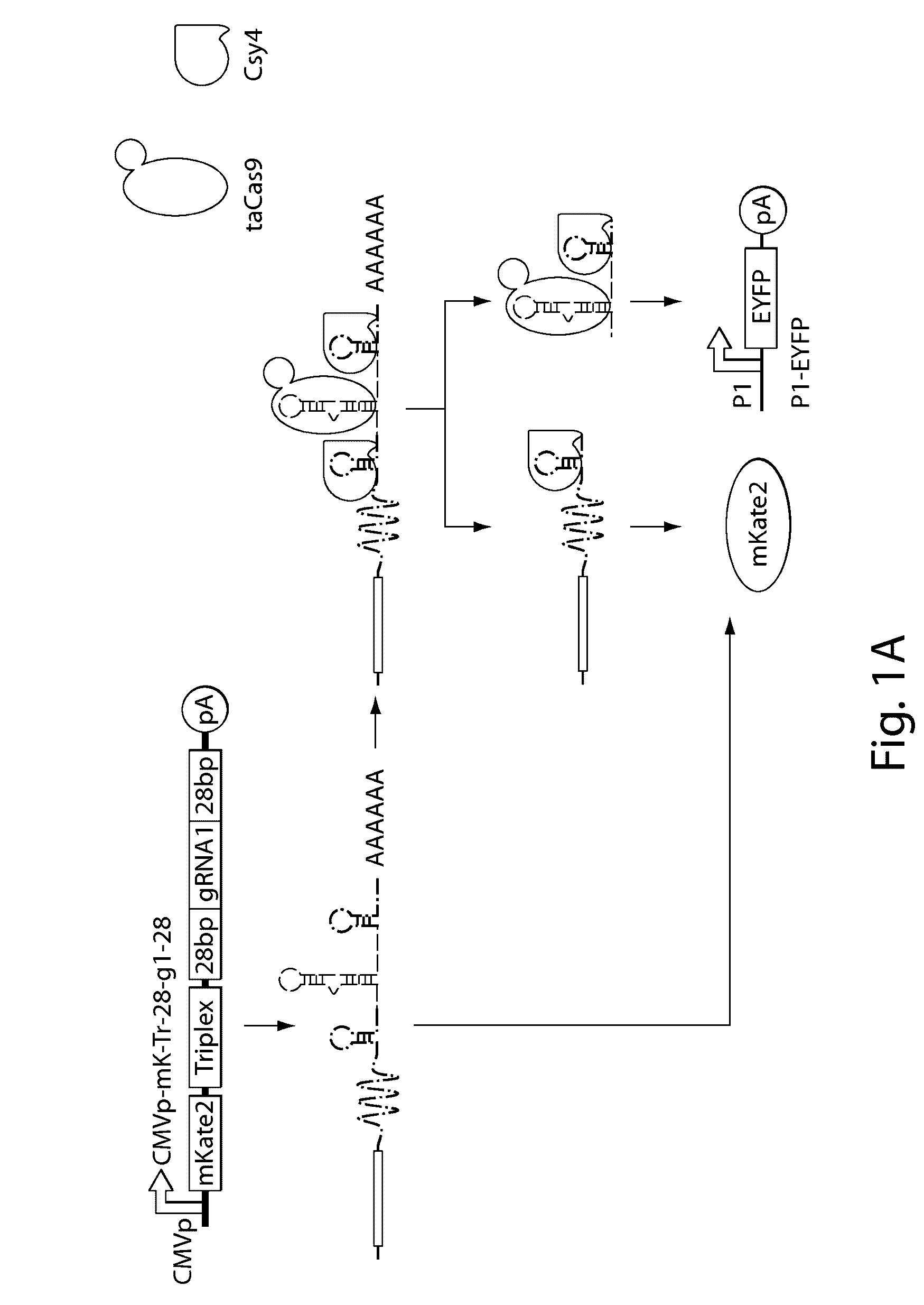
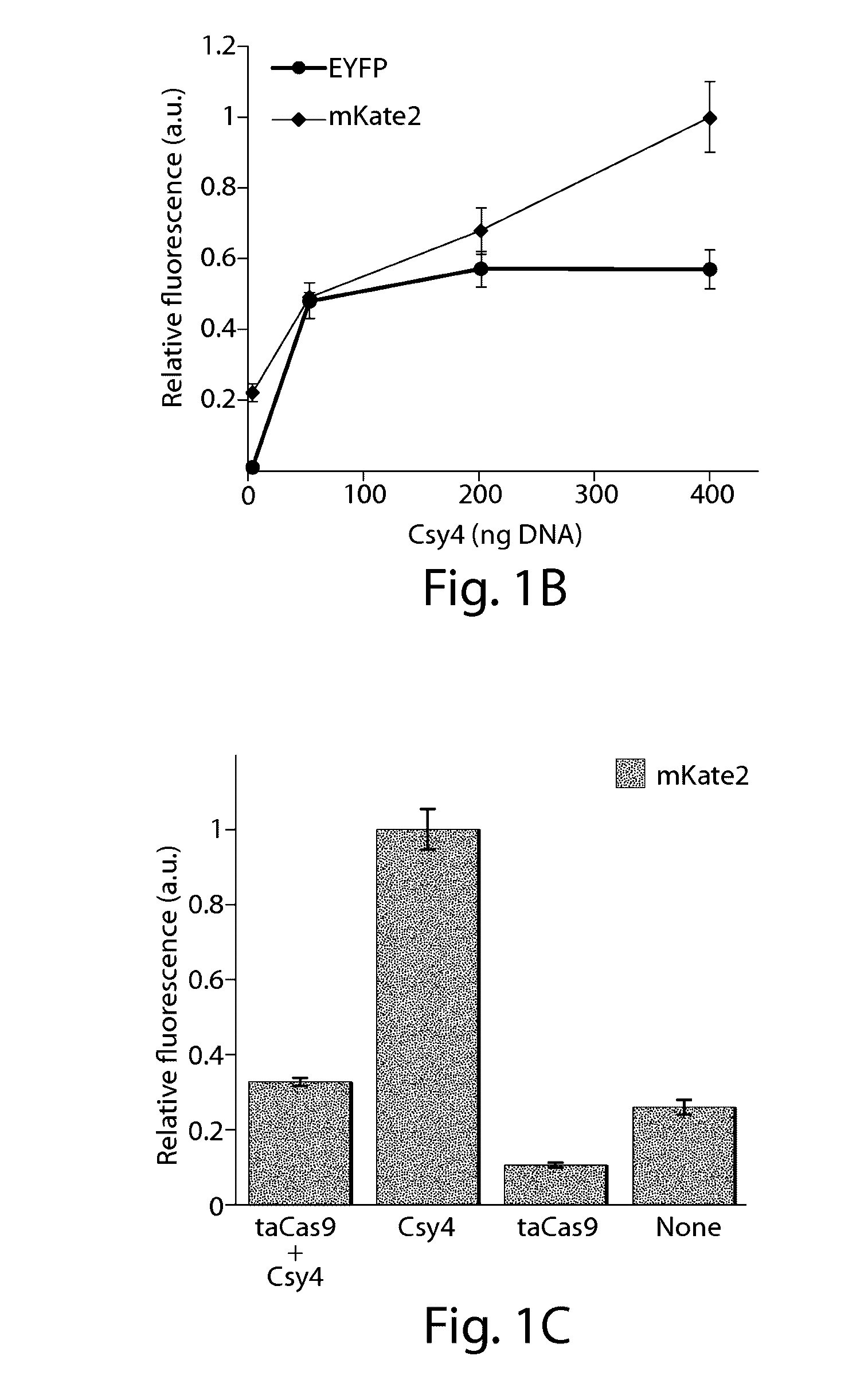
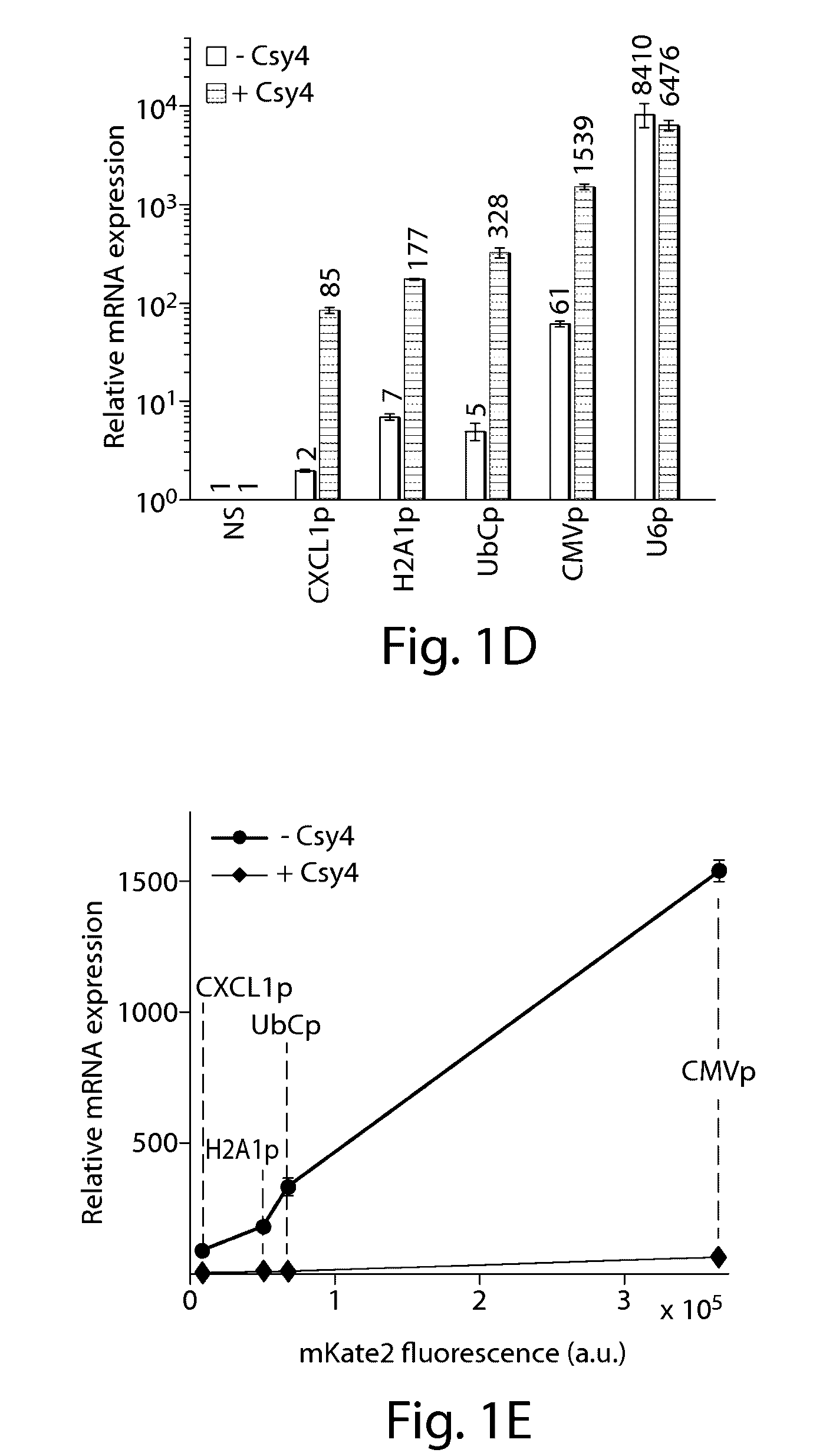
Methods and compositions for the production of guide RNA
Various aspects and embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods and compositions that combine multiple mammalian RNA regulatory strategies, including RNA triple helix structures, introns, microRNAs, and ribozymes with Cas-based CRISPR transcription factors and ribonuclease-based RNA processing in human cells. The methods and compositions of the present disclosure, in some embodiments, enable multiplexed production of proteins and multiple guide RNAs from a single compact RNA-polymerase-II-expressed transcript for efficient modulation of synthetic constructs and endogenous human promoters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
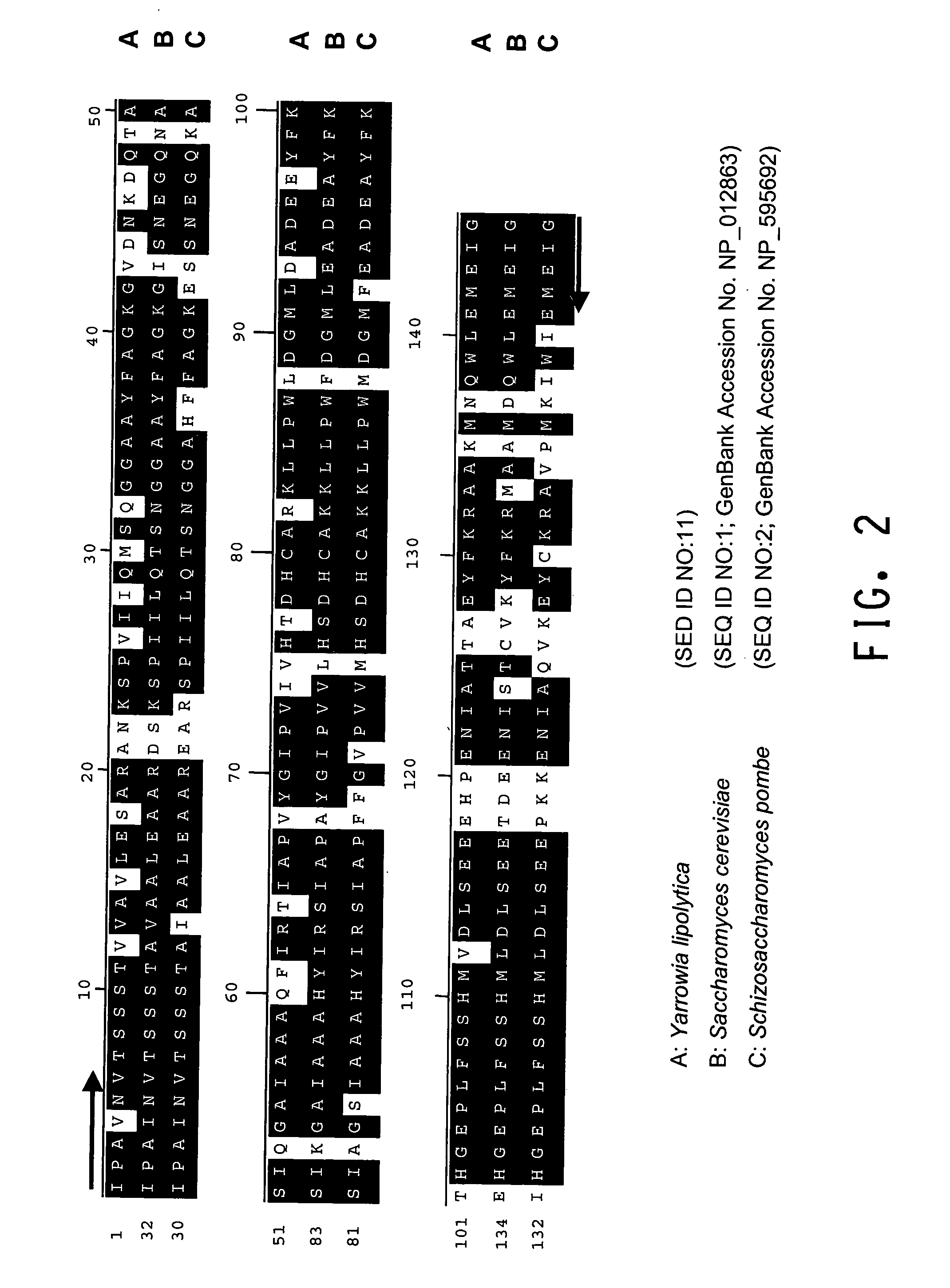
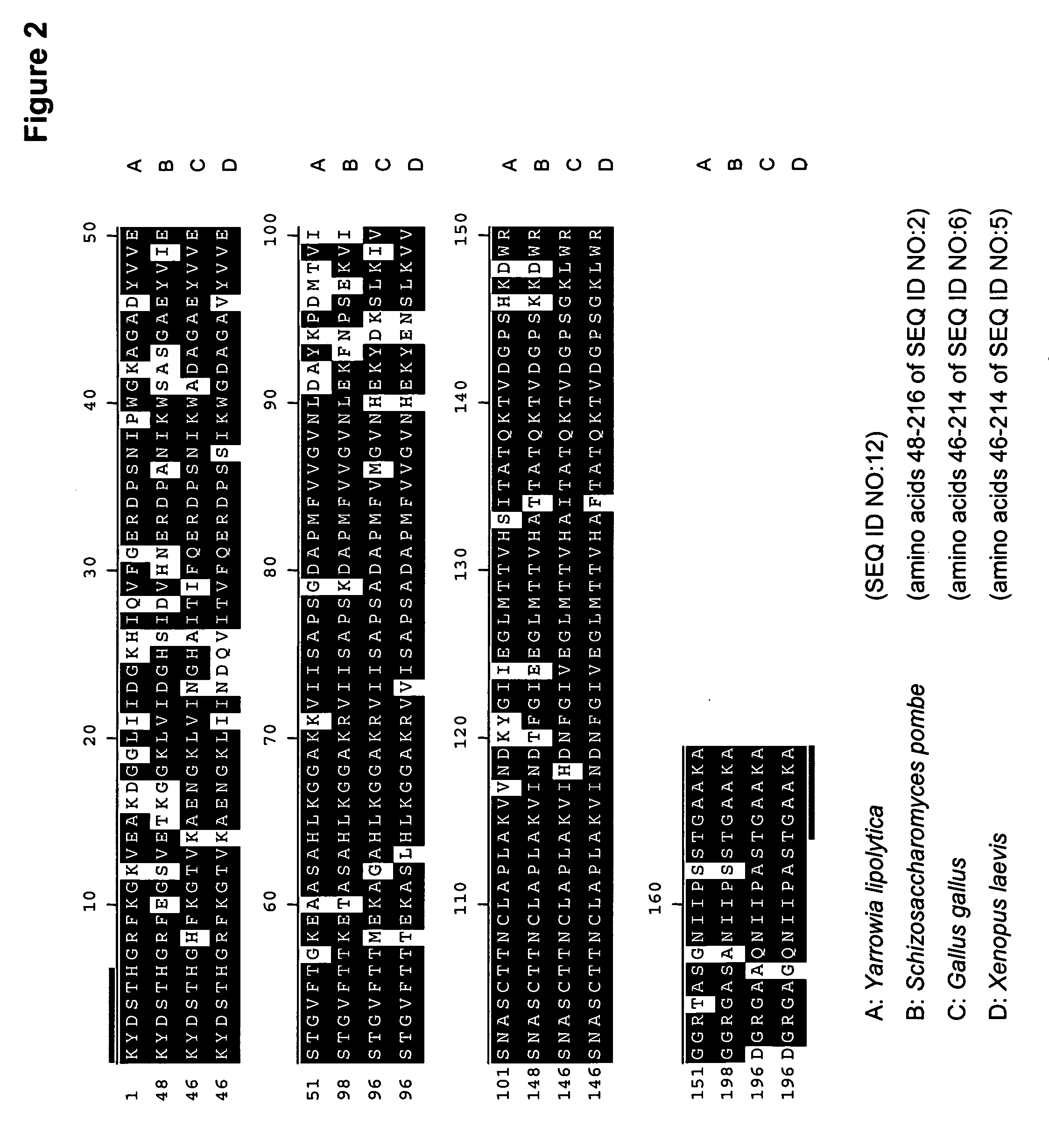
The regulatory sequences (i.e., promoter regions, introns and enhancers) associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica gene encoding fructose bis-phospate aldolase (FBA1) have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologus genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Expression Enhancing Intron Sequences
The invention relates to methods for the identification and use of introns with gene expression enhancing properties. The teaching of this invention enables the identification of introns causing intron-mediated enhancement (IME) of gene expression. The invention furthermore relates to recombinant expression construct and vectors comprising said IME-introns operably linked with a promoter sequence and a nucleic acid sequence. The present invention also relates to transgenic plants and plant cells transformed with these recombinant expression constructs or vectors, to cultures, parts or propagation material derived there from, and to the use of same for the preparation of foodstuffs, animal feeds, seed, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals, to improve plant biomass, yield, or provide desirable phenotypes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
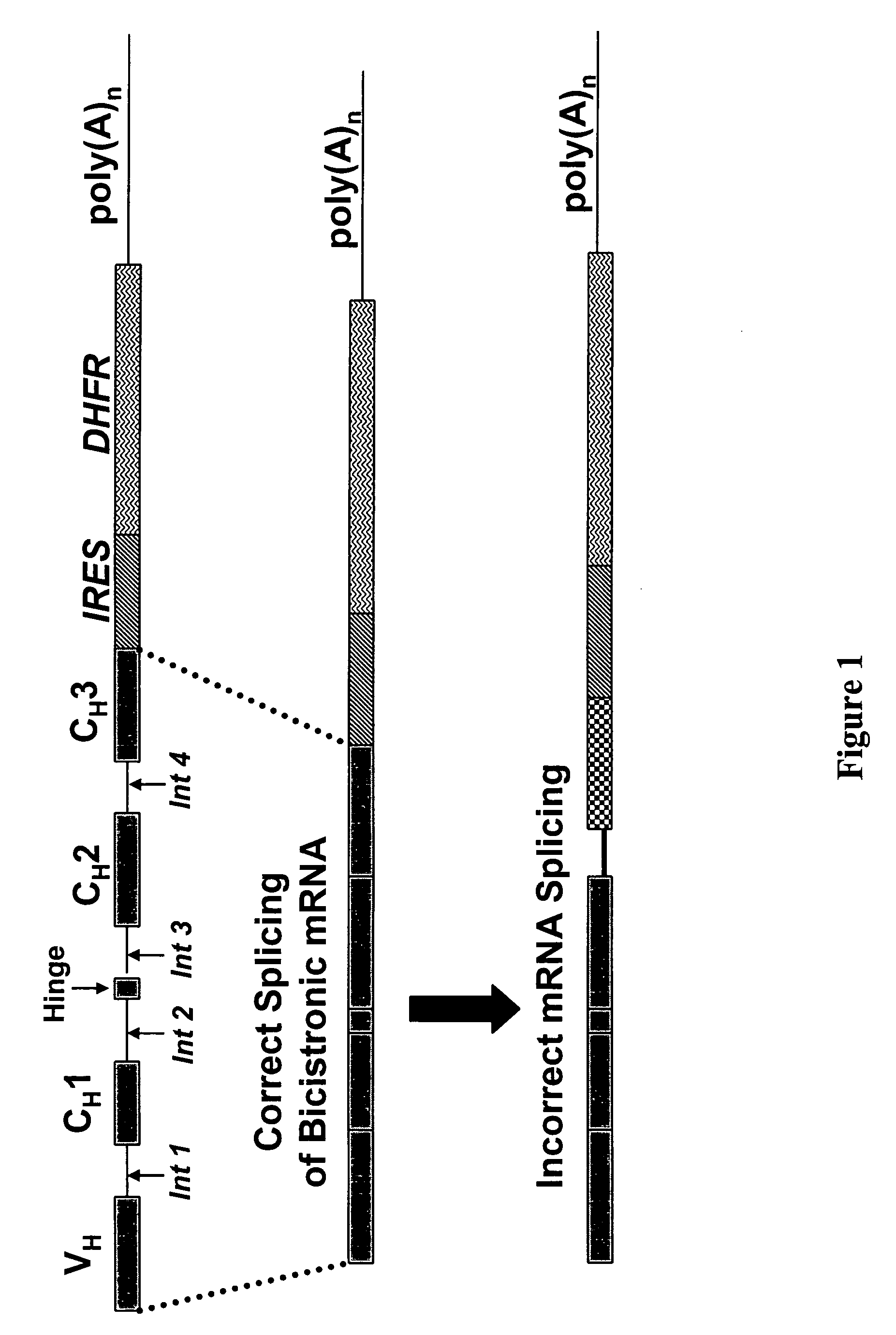
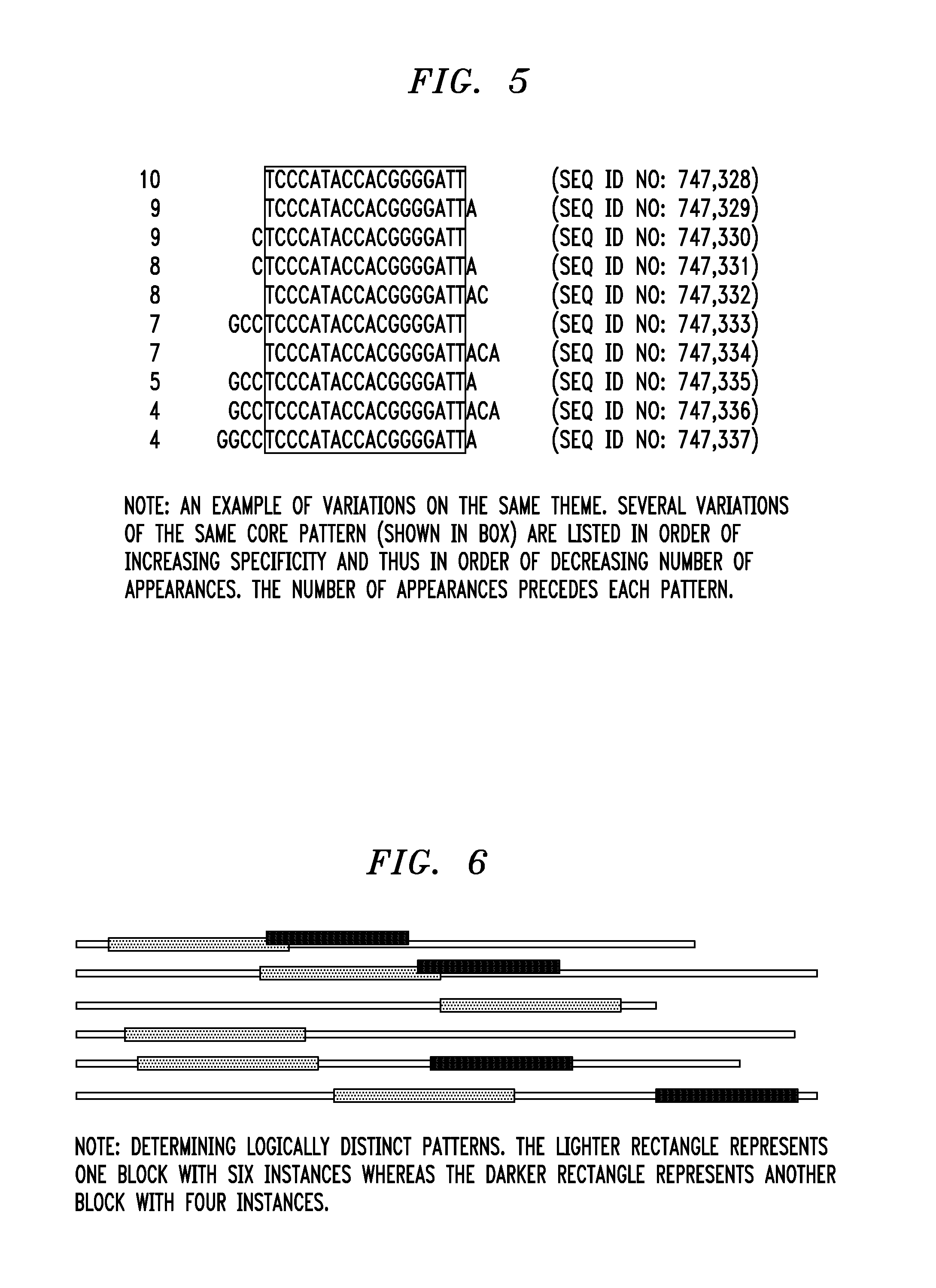
Dual expression vector system for antibody expression in bacterial and mammalian cells
ActiveUS7112439B2Maintaining their functionalityEasy to identifyAnimal cellsBacteriaAntigenBacteroides
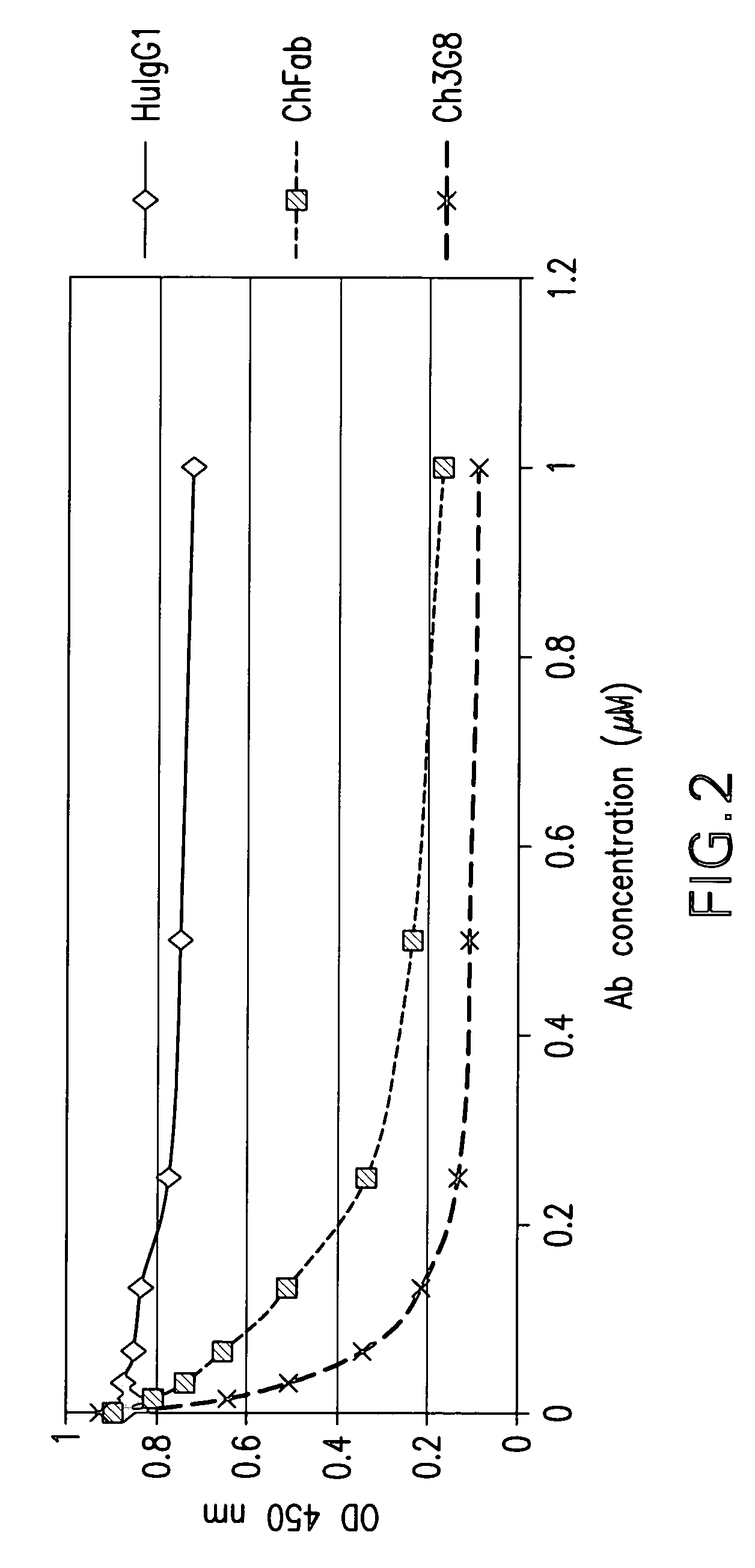
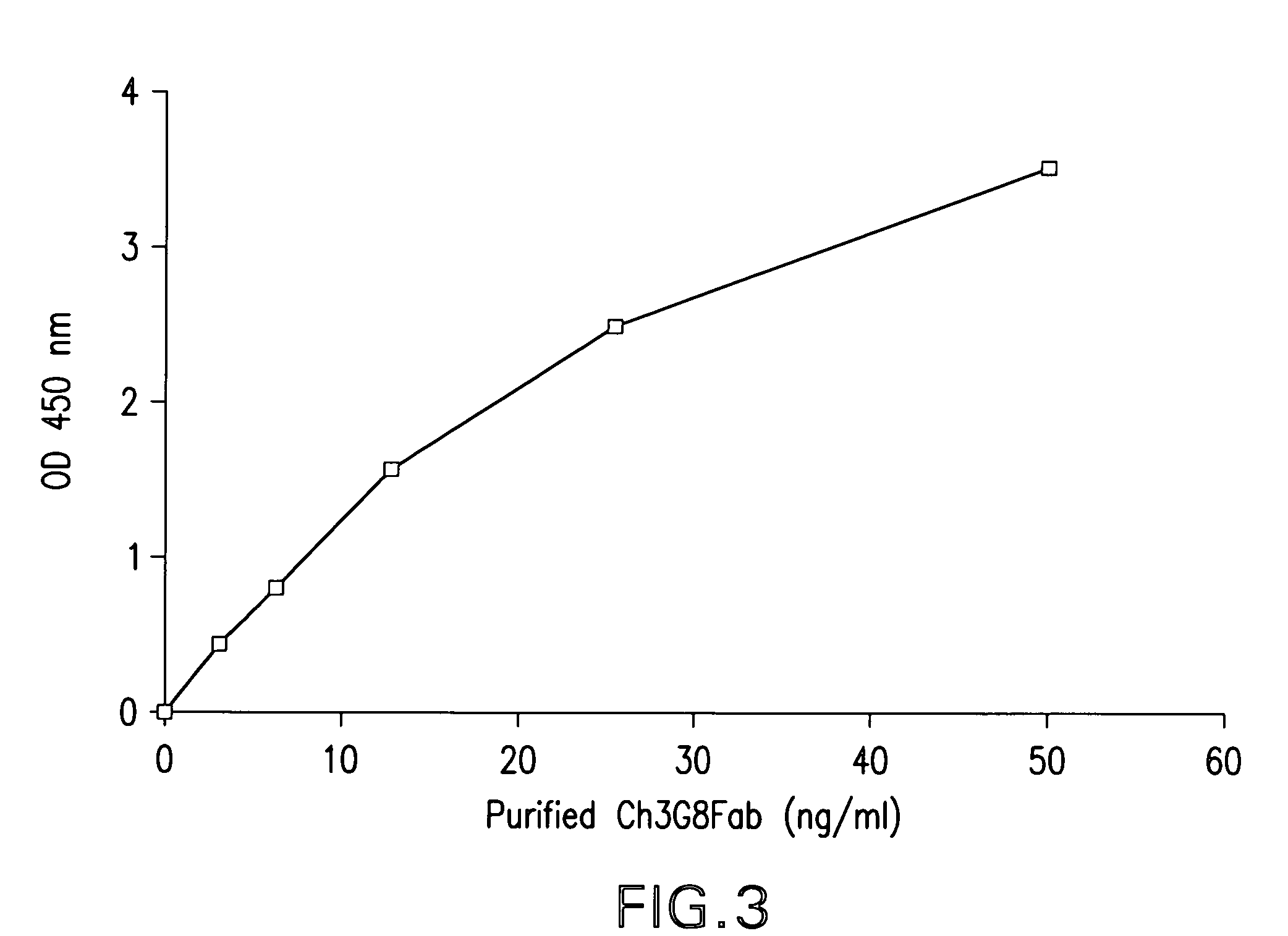
The present invention provides a dual expression vector, and methods for its use, for the expression and secretion of a full-length polypeptide of interest in eukaryotic cells, and a soluble domain or fragment of the polypeptide in bacteria. When expressed in bacteria, transcription from a bacterial promoter within a first intron and termination at the stop codon in a second intron results in expression of a fragment of the polypeptide, e.g., a Fab fragment, whereas in mammalian cells, splicing removes the bacterial regulatory sequences located in the two introns and generates the mammalian signal sequence, allowing expression of the full-length polypeptide, e.g., IgG heavy or light chain polypeptide. The dual expression vector system of the invention can be used to select and screen for new monoclonal antibodies, as well as to optimize monoclonal antibodies for binding to antigenic molecules of interest.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Computer implemented machine learning method and system including specifically defined introns
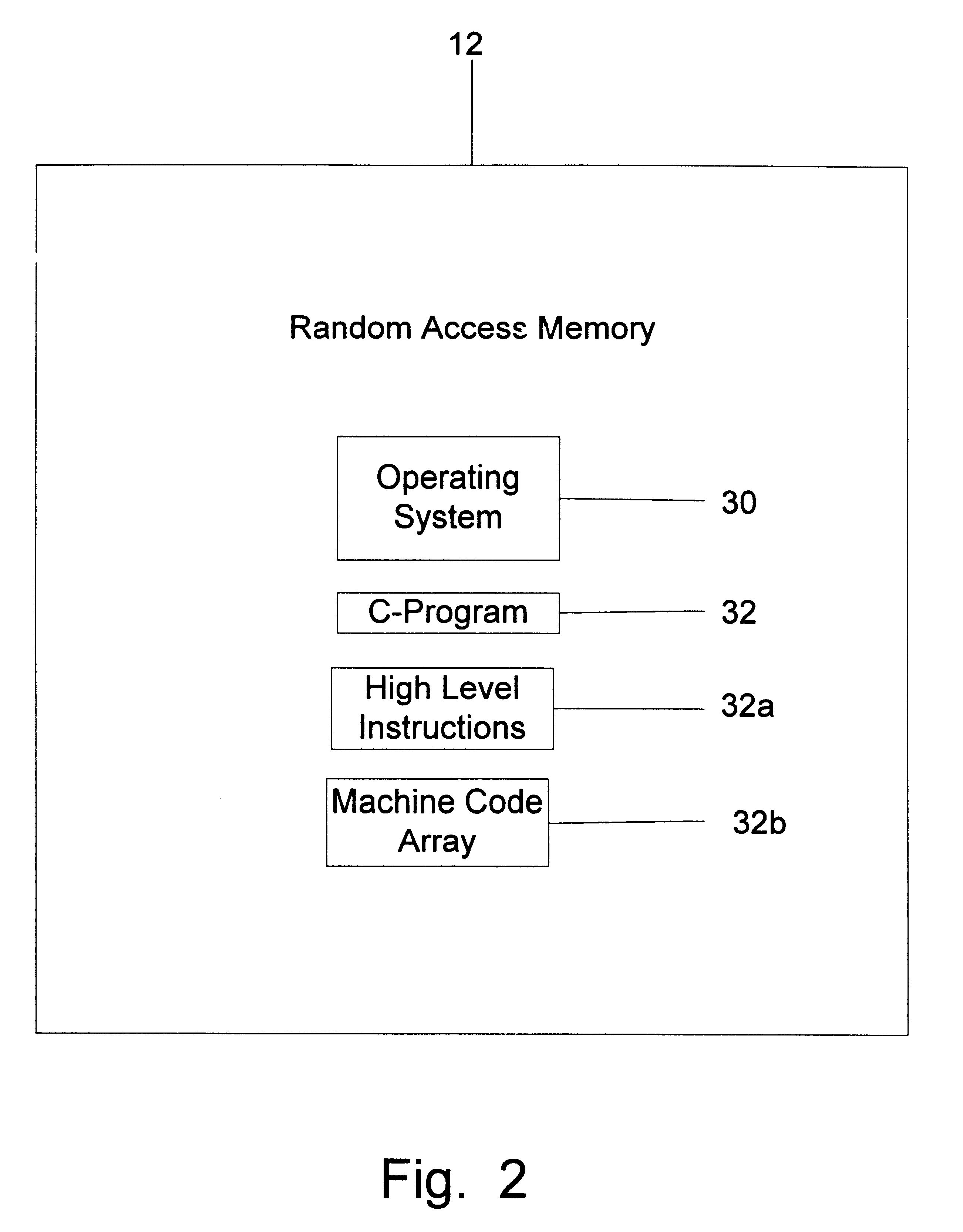
InactiveUS6493686B1Loss in flexibilityImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital computer detailsArray data structureAlgorithm
In a computer implemented learning and / or process control system, a computer model is constituted by the most currently fit entity in a population of computer program entities. The computer model defines fitness as a function of inputs and outputs. A computing unit accesses the model with a set of inputs, and determines a set of outputs for which the fitness is highest. This associates a sensory-motor (input-output) state with a fitness in a manner that might be termed "feeling".The learning and / or control system preferably utilizes a Compiling Genetic Programming System (CGPS) in which one or more machine code entities such as functions are created which represent solutions to a problem and are directly executable by a computer. The programs are created and altered by a program in a higher level language such as "C" which is not directly executable, but requires translation into executable machine code through compilation, interpretation, translation, etc. The entities are initially created as an integer array that can be altered by the program as data, and are executed by the program by recasting a pointer to the array as a function type. The entities are evaluated by executing them with training data as inputs, and calculating fitnesses based on a predetermined criterion. The entities are then altered based on their fitnesses using a genetic machine learning algorithm by recasting the pointer to the array as a data (e.g. integer) type. This process is iteratively repeated until an end criterion is reached.
Owner:FRANCONE FR D +2
Direct molecular diagnosis of Friedreich ataxia
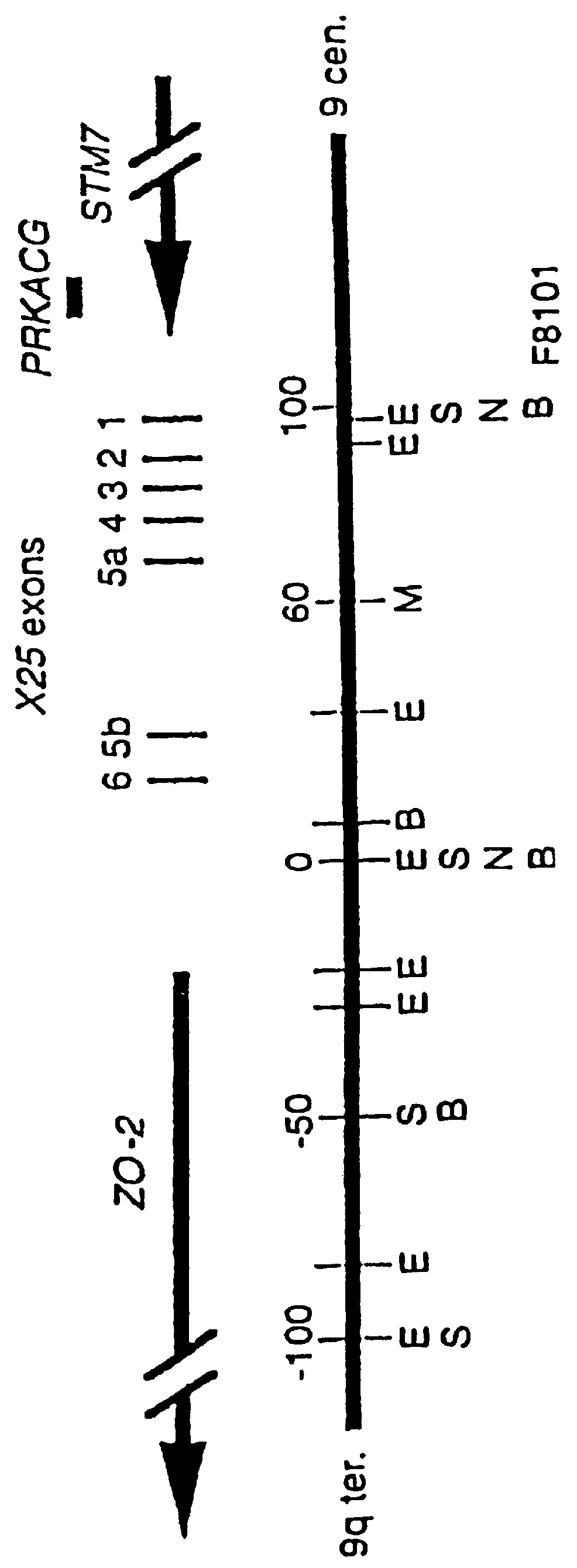
This invention relates generally to methods for the diagnosis and therapeutic treatment of Friedreich Ataxia. Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal recessive, degenerative disease that involves the central and peripheral nervous system and the heart. A gene, X25, was identified in the critical region for the FRDA locus on chromosome 9q13. The gene encodes a 210 amino acid protein, frataxin, that has homologues in distant species such as C. elegans and yeast. A few FRDA patients have been found to have point mutations in X25, but the vast majority are homozygous for a variable, unstable GAA trinucleotide expansion in the first X25 intron. Mature X25 mRNA was severely reduced in abundance in individuals with FRDA. Carriers and individuals at risk for developing FRDA can be ascertained by the methods of the present invention. Further, the methods of the present invention provide treatment to those individuals having FRDA.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
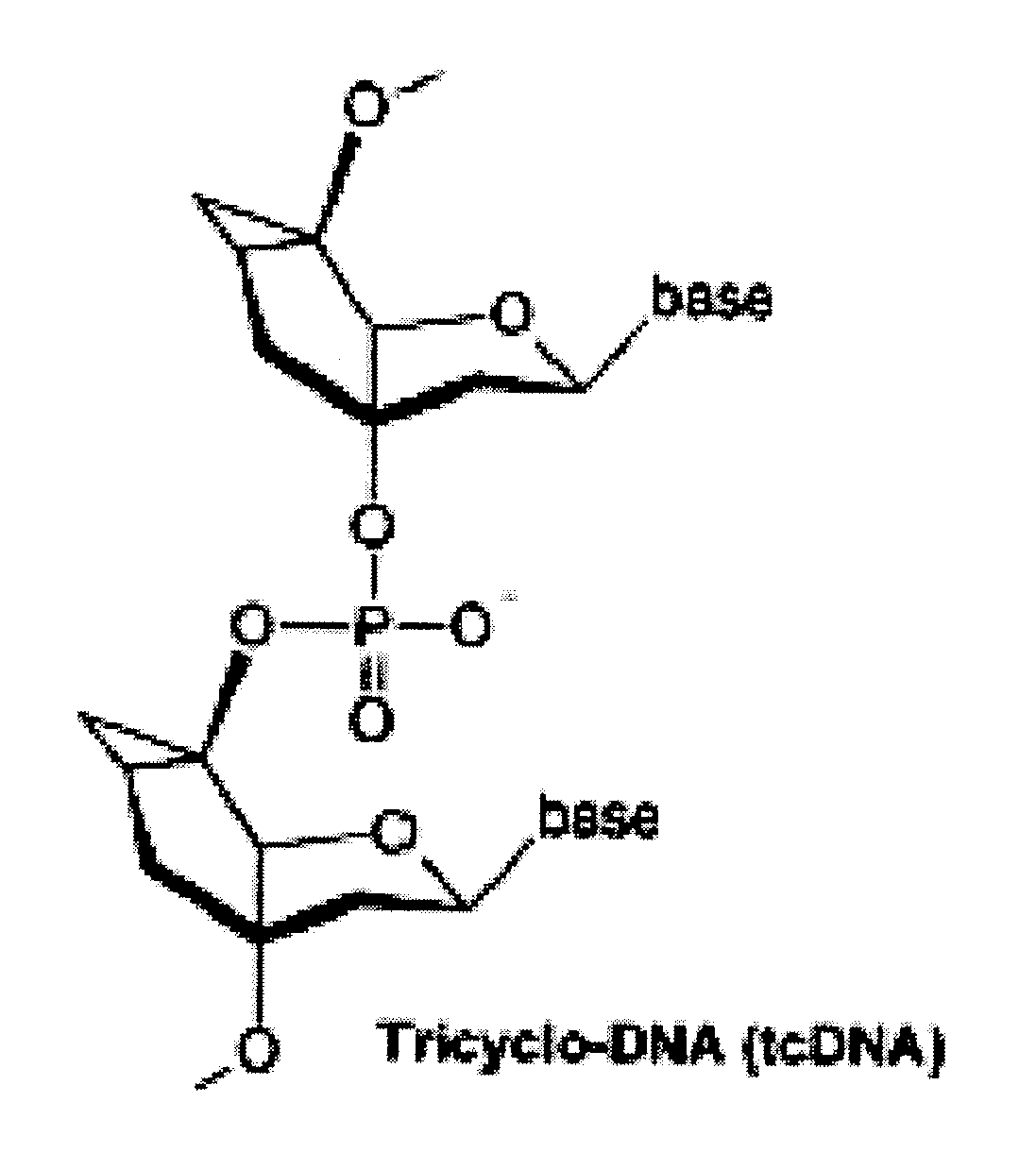
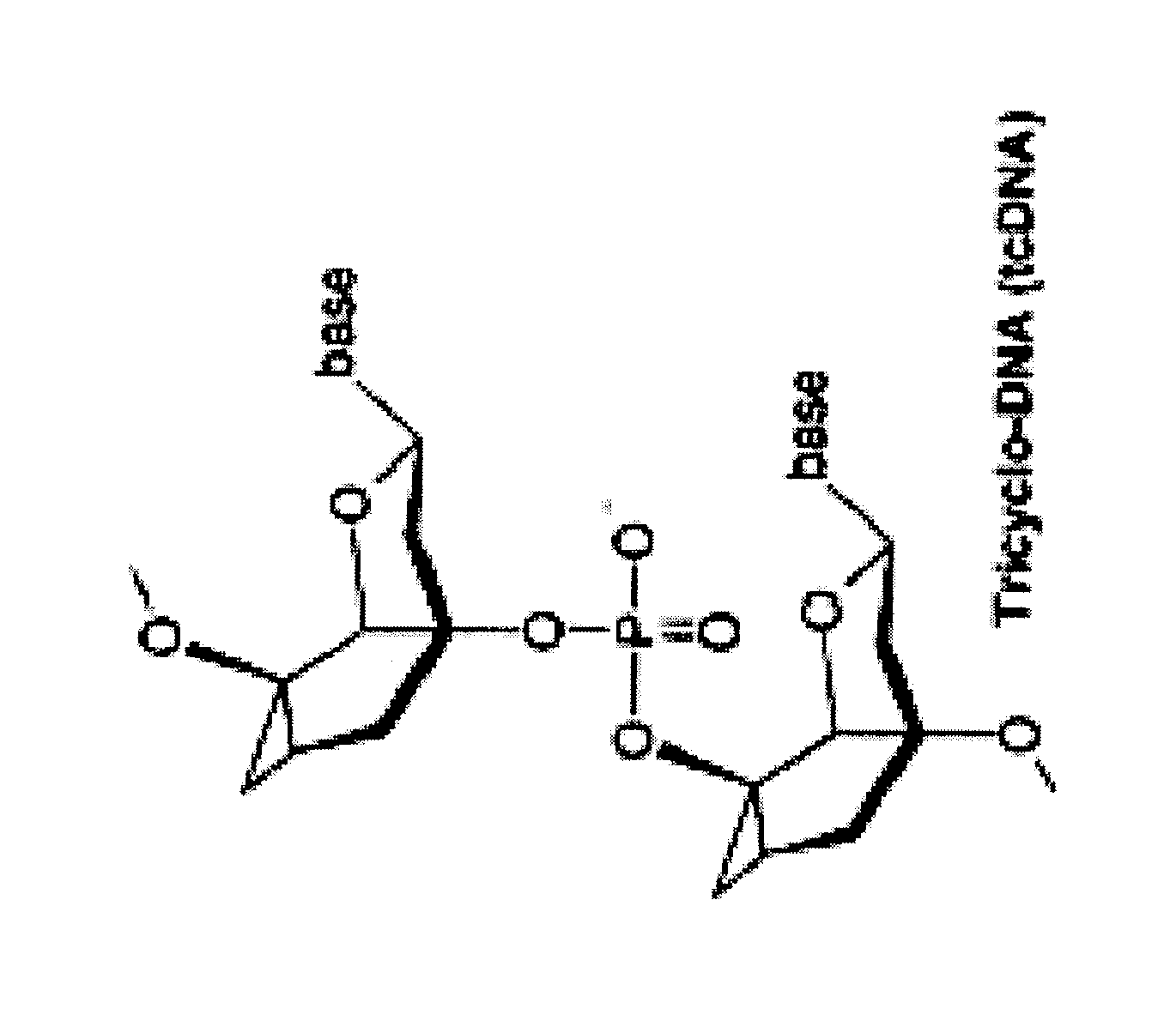
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20120149756A1Find utilityFacilitates inclusionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stem-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
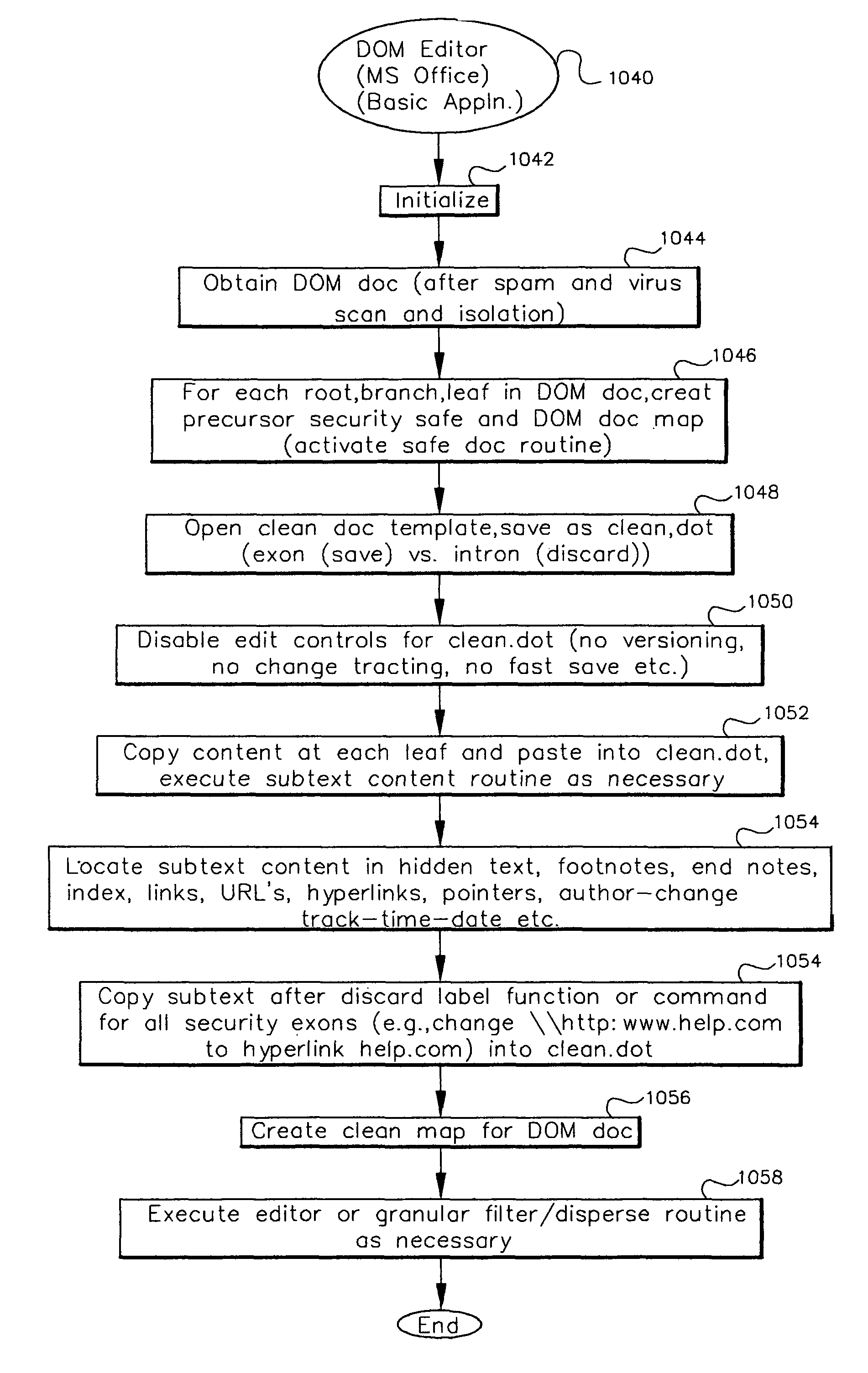
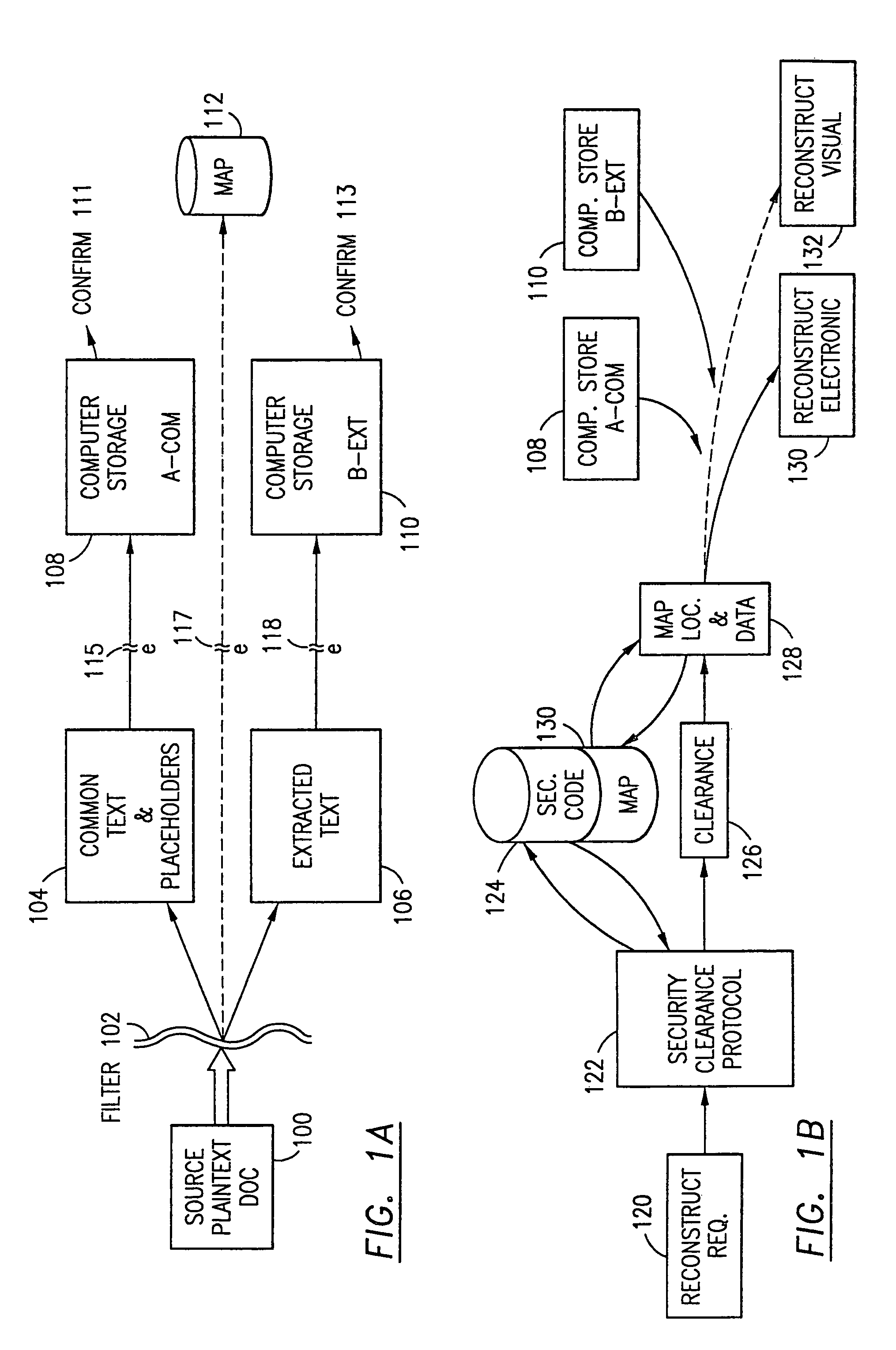
Data security system and method with editor
ActiveUS8176563B2Digital data processing detailsTelephonic communicationDocument preparationDocument Object Model
The method, program and system secures sensitive data / objects found in a data source document with an editor. The simple editor identifies and displays, in situ, the sensitive words / objects per each security level. Level tags are inserted and adjunctive words / objects are marked / displayed per the level's protocol. The precursor document is processed to extract sensitive and adjunctive words / objects. The stripped data is either separately stored or partial versions of the secured document are stored per protocol. A comprehensive editor secures content data and meta data contained in a data document object model (DOM). The editor maps the source document root, branch and leaf components as binary files populated with content data and meta data. Security introns, earlier identified based upon the level's informational attributes, are excluded. Security exons are copied from the source content and meta data binary files into a security safe document (template). Filtration, extraction, dispersal and storage follow.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
Expression in insect cells of genes with overlapping open reading frames, methods and compositions therefor
ActiveUS20090203071A1Reduce riskEfficient infectionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesOpen reading framePromoter
The present teachings disclose nucleic acid cassettes for expressing in an insect cell a plurality of polypeptides encoded by a gene comprising overlapping open reading frames (ORFs). A cassette comprises, in 5′ to 3′ order, a) a first insect cell-operable promoter, b) a 5′ portion of a gene comprising a first ORF of the gene, c) an intron comprising a second insect cell-operable promoter, and d) a 3′ portion of the gene comprising at least one additional ORF. Vectors and insect cells comprising the cassettes are also disclosed, as well as methods for production of recombinant adeno-associated virus in insect cells using the cassettes.
Owner:VIROVEK
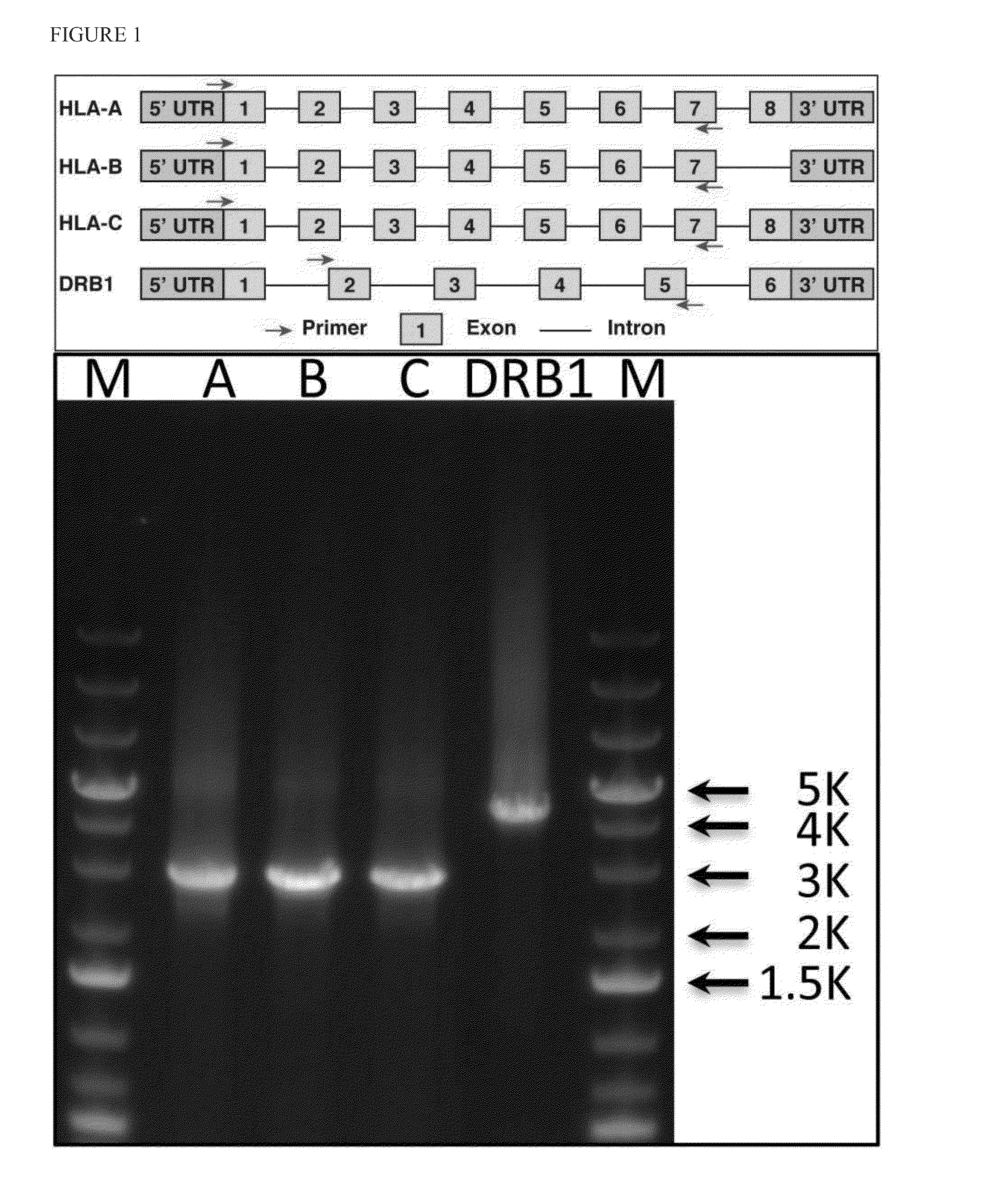
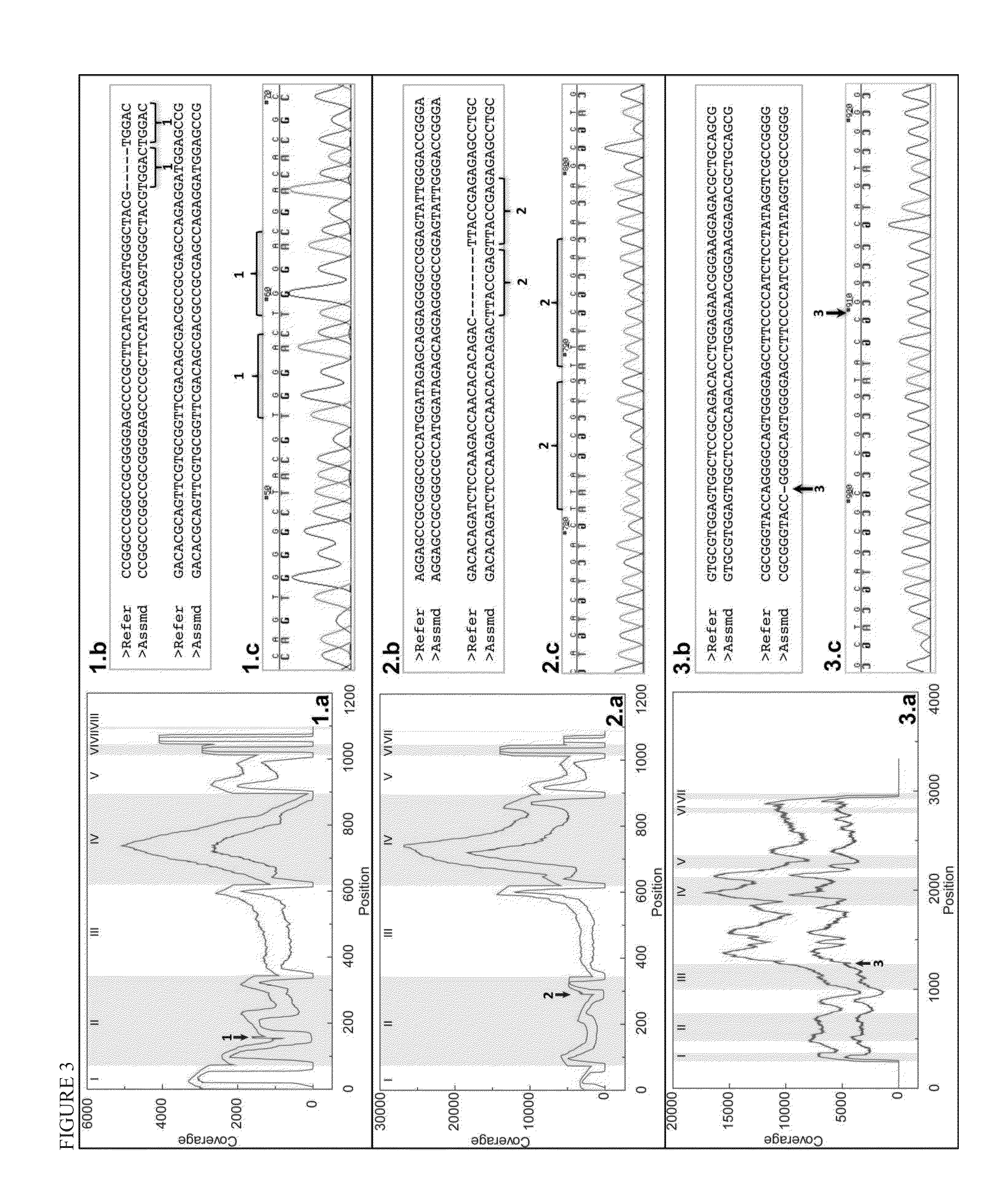
Haplotying of HLA loci with ultra-deep shotgun sequencing
ActiveUS20140206547A1Minimize biasEfficient reconstructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHaploidisationHaplotype
Methods are provided to determine the entire genomic region of a particular HLA locus including both intron and exons. The resultant consensus sequences provides linkage information between different exons, and produces the unique sequence from each of the two genes from the individual sample being typed. The sequence information in intron regions along with the exon sequences provides an accurate HLA haplotype.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
InactiveUS20110247090A1High expressionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideReticulum cell
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate mutase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
The regulatory sequences associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) and phosphoglycerate mutase (gpm) genes have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologous genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention, intron and enhancer have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
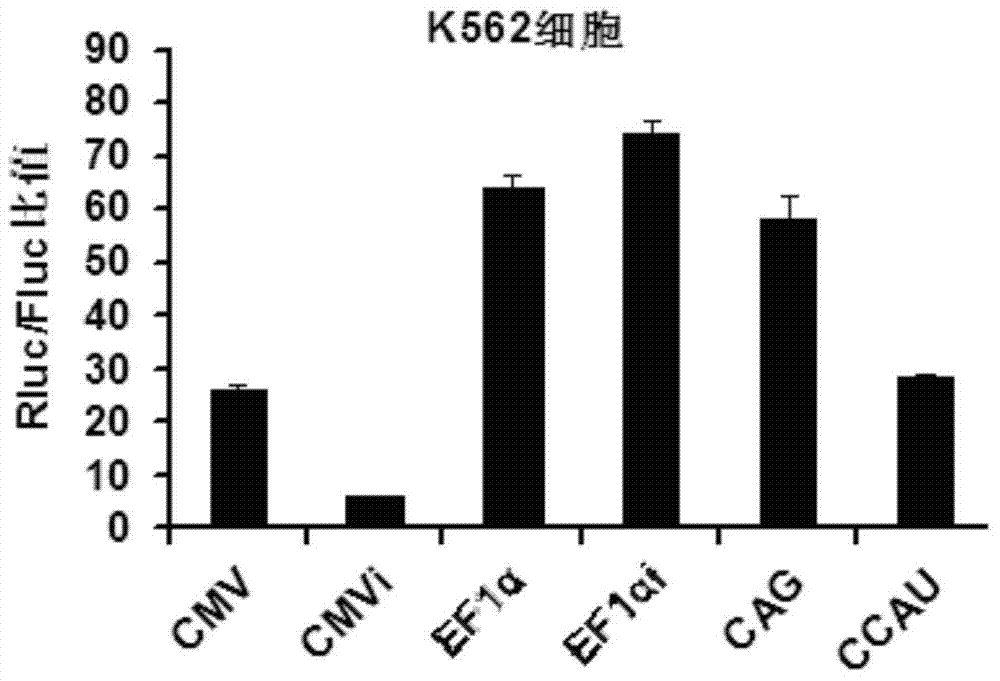
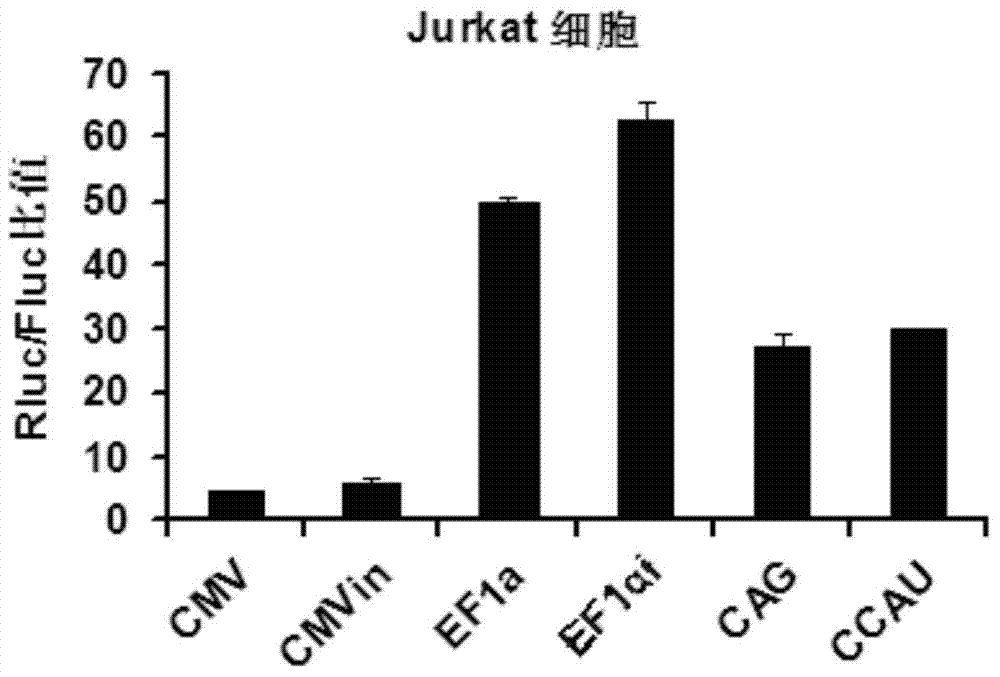
High-activity T-cell promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104745581AEfficient expressionSequence stabilityGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAdoptive cellular immunotherapyT cell
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a high-activity T-cell promoter and an application thereof. Particularly, the high-activity T-cell promoter comprises an element 1 and an element 2, wherein the element 1 is an EF1 alpha promoter and / or an EF1 alpha promoter containing an intron; and the element 2 is any one or more of an mCMV promoter, an hCMV promoter and a CD3e promoter. The high-activity T-cell promoter provided by the invention can be used for efficiently expressing a foreign gene in a T cell, has a stable sequence and is free from sequence loss during the transfer process of a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. The high-activity T-cell promoter is applicable to driving the high-efficiency expression of the foreign gene, especially a full-length antibody gene, in the T cell during the process of adoptive cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +2
Overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105087620AHigh copy numberLower activation thresholdVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryInteinEmbryo
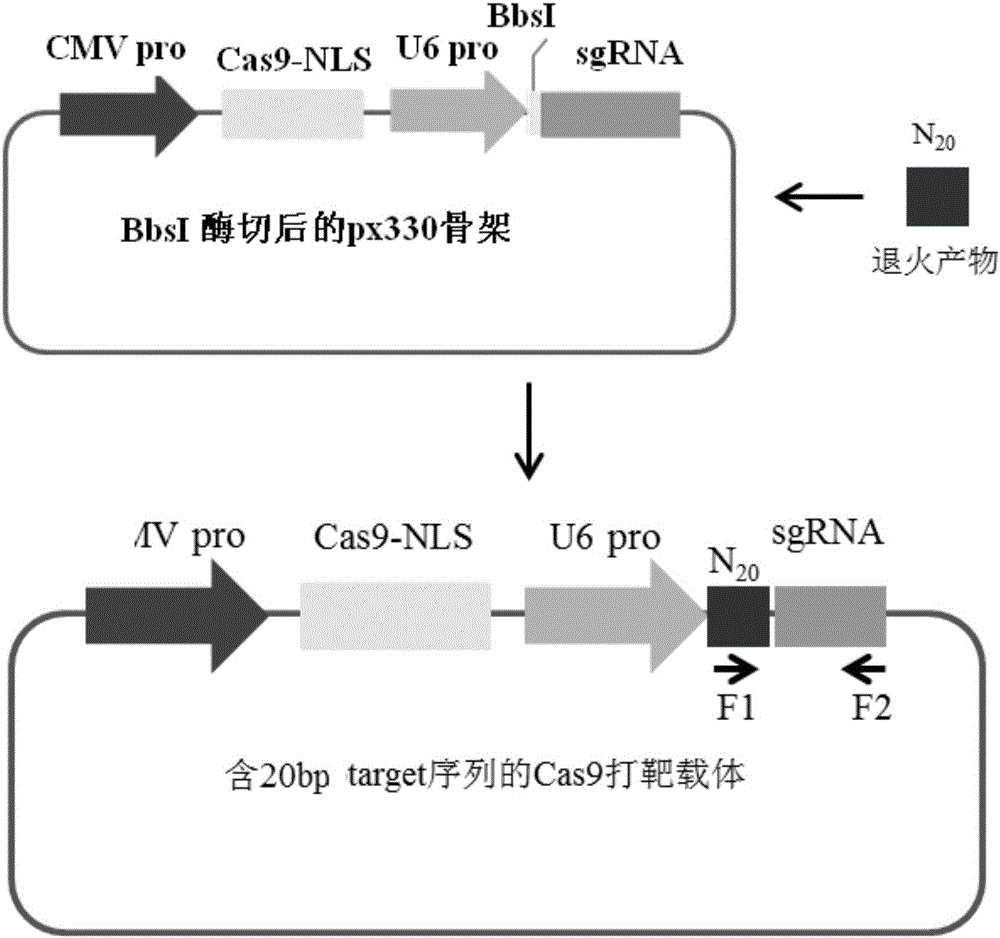
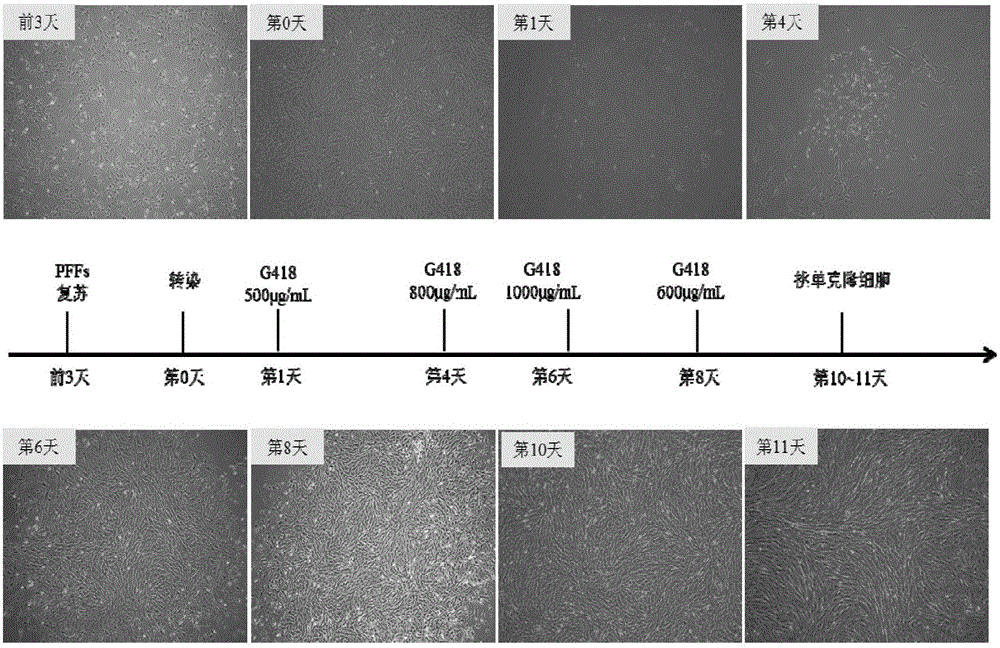
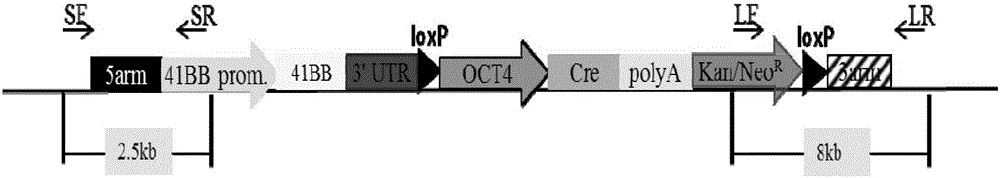
The invention provides an overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on a left homologous arm and a right homologous arm of an intron 1 of a rosa26 gene, a 4-1BB regulatory sequence and an OCT4 specific promoter; the left homologous arm, a 4-1BB expression cassette, LoxP locus-contained Cre and Neo expression cassettes, the right homologous arm and negative selection DTA diphtheria toxin are connected in sequence to obtain a 4-1BB homologous recombinant vector p4BOCNDR; the vector and a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated) targeting vector of sgRNA (small guide ribonucleic acid) containing the intron 1 of the specific targeting porcine rosa26 gene are transferred together into a porcine fetus fibroblast; by taking a positive cell as a donor cell and an oocyte as a recipient cell, a cloned embryo is obtained through a somatic cell nuclear transfer technique; the cloned embryo is transplanted into a porcine uterus for fetation to obtain a transgenic pig integrating a 4-1BB gene at the fixed point of a first intron of the rosa26 gene and automatically deleting a marker gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for acquiring aromatic rice strain by targeting Badh2 gene via CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology
InactiveCN105505979AScalableEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAromatic riceGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for acquiring an aromatic rice strain by targeting a Badh2 gene via CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology. The method comprises the following steps: separately targeting sequences, recognizable by Cas9, of every exon and intron of an aromatic gene by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology and then cutting a genomic DNA sequence to initiate DNA restoration so as to obtain an afunctional Badh2 gene; with the callus of Indica rice, japonica rice or glutinous rice as a receptor material of genetic transformation and an mature embryo, young ear, ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a diploid callus, introducing a targeting vector into cells of the callus by using an Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening and identifying positive plants and separating the plants from a T1 colony so as to obtain an aromatic rice strain; and with anther, pollen, unfertilized ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a haploid callus, introducing the targeting vector into cells of the callus by using the Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening a positive callus, reduplicating the positive callus by using colchicine, carrying out differentiation to form seedlings and identifying genetic transformation positive plants so as to eventually obtain the aromatic rice strain.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Methods and compositions for improving recombinant protein production
InactiveUS20060099206A1Enhance protein expressionReduction and elimination of mis-splicedAnimal cellsNervous disorderAntibody expressionRead through
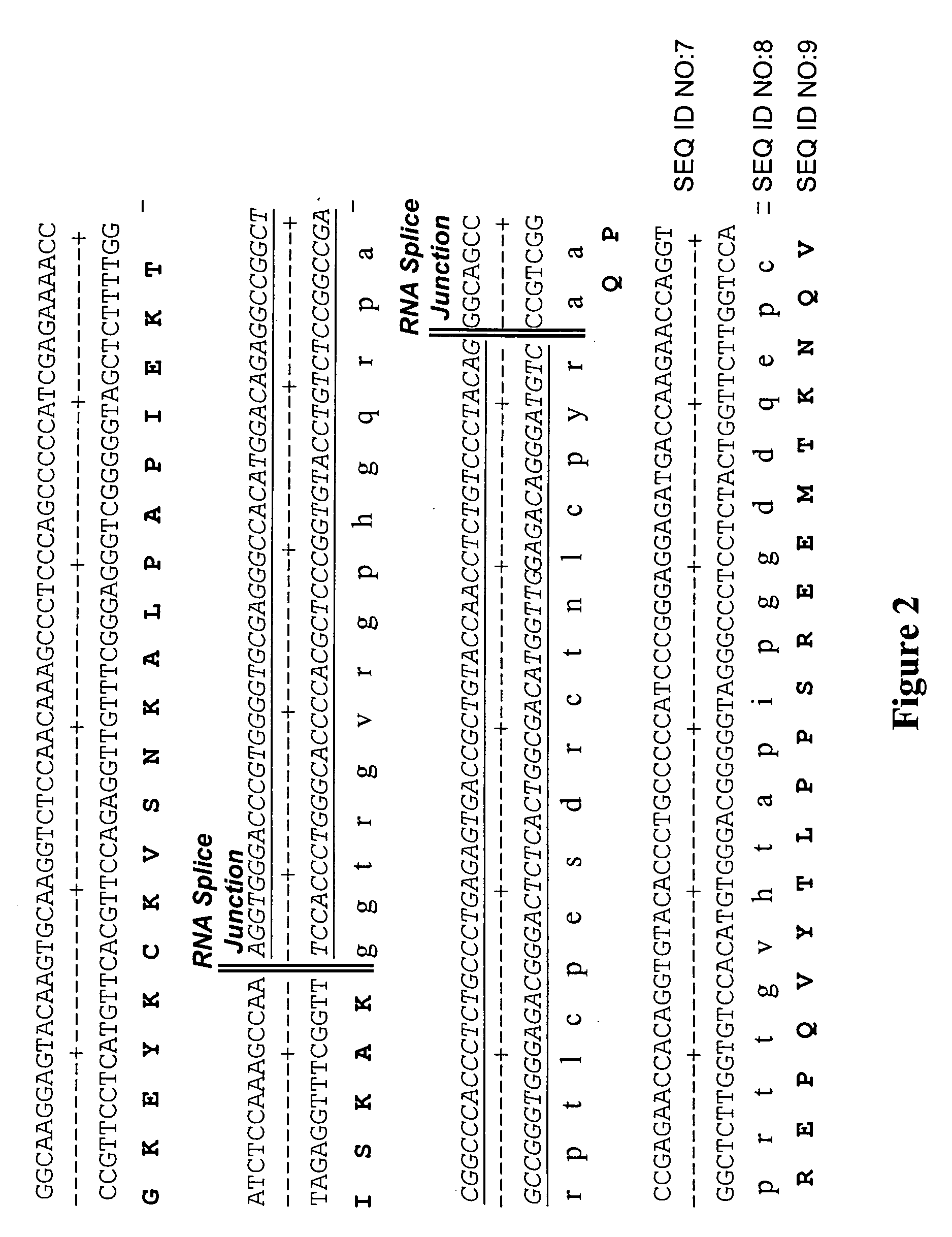
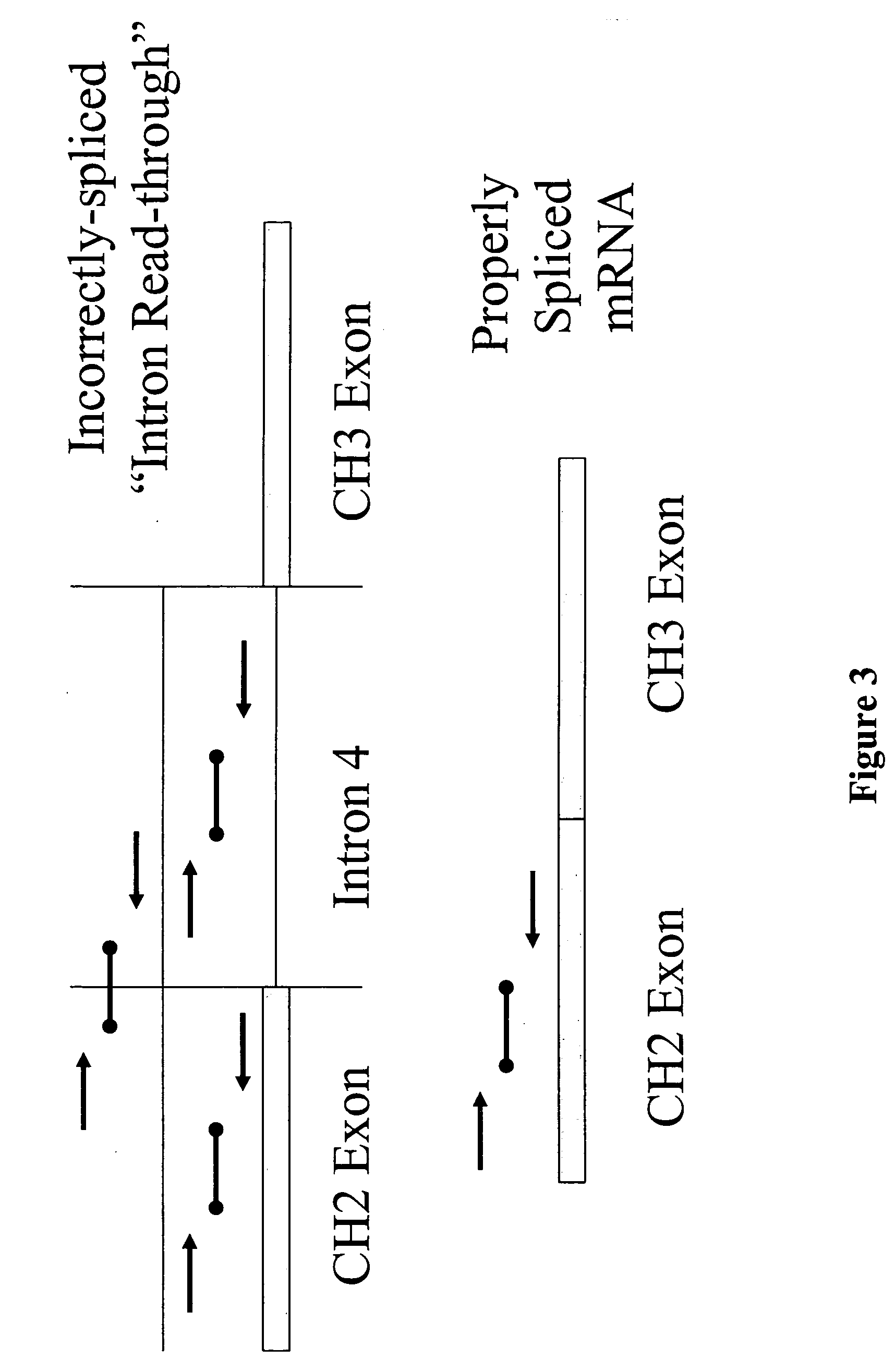
Nucleic acid molecules modified to enhance recombinant protein, e.g., antibody, expression and / or reduce or eliminate mis-spliced and / or intron read-through (IRT) by-products are disclosed. The invention also provides methods for producing proteins devoid of mis-spliced and / or intron read-through by-products by the use of such vectors in host cells under cell culture conditions suitable for recombinant protein expression.
Owner:WYETH
Ribonucleic acid interference molecules and binding sites derived by analyzing intergenic and intronic regions of genomes
In one aspect of the invention, a method for regulating the expression of a transcript comprises using at least one interfering RNA molecule that binds to an area of transcript containing a region that corresponds to at least one sequence having SEQ ID NO: 1, the interfering RNA molecule regulating the expression of the transcript through post-transcriptional silencing. In another aspect, a method for regulating the expression of a transcript comprises at least one of the provided sequences having SEQ ID NO: 1 being used to design an interfering RNA molecule that contains a region that corresponds to the reverse complement of one or more sequences having SEQ ID NO: 1, the interfering molecule regulating, through post-transcriptional silencing, transcripts that contain the sequence having SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dual expression vector system for antibody expression in bacterial and mammalian cells
The present invention provides a dual expression vector, and methods for its use, for the expression and secretion of a full-length polypeptide of interest in eukaryotic cells, and a soluble domain or fragment of the polypeptide in bacteria. When expressed in bacteria, transcription from a bacterial promoter within a first intron and termination at the stop codon in a second intron results in expression of a fragment of the polypeptide, e.g., a Fab fragment, whereas in mammalian cells, splicing removes the bacterial regulatory sequences located in the two introns and generates the mammalian signal sequence, allowing expression of the full-length polypeptide, e.g., IgG heavy or light chain polypeptide. The dual expression vector system of the invention can be used to select and screen for new monoclonal antibodies, as well as to optimize monoclonal antibodies for binding to antigenic molecules of interest.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
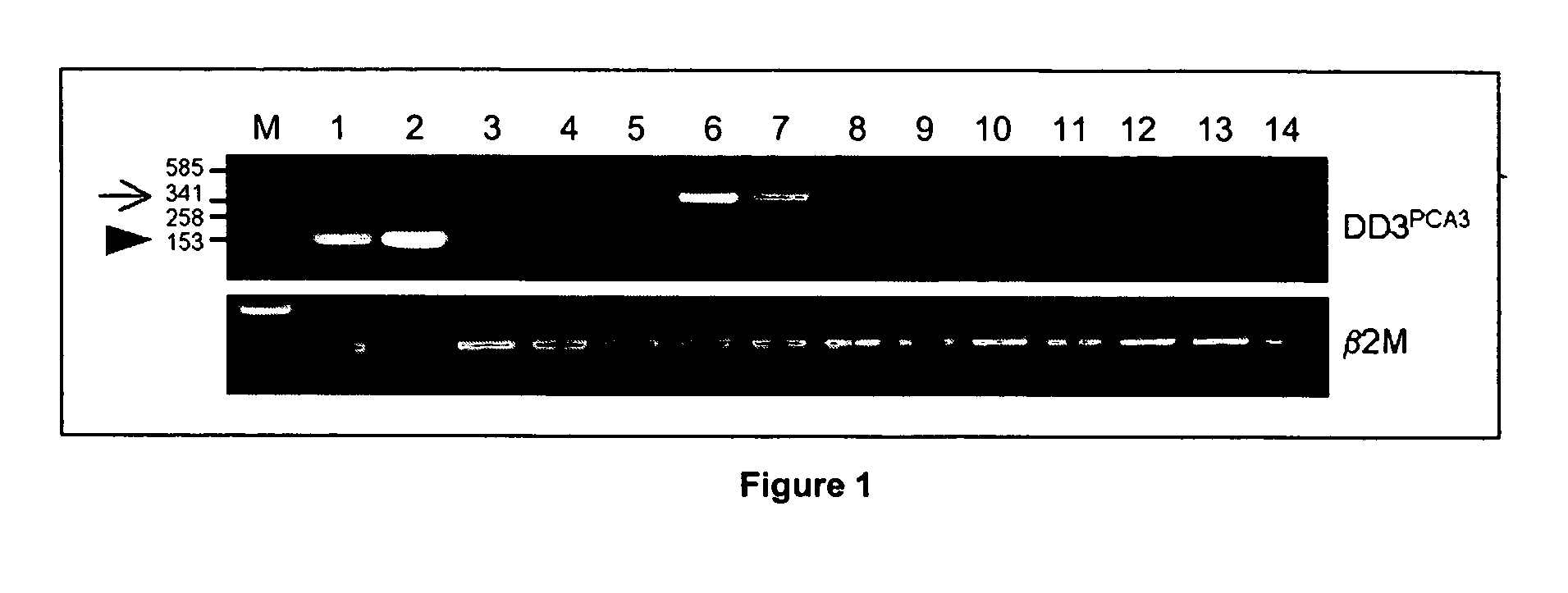
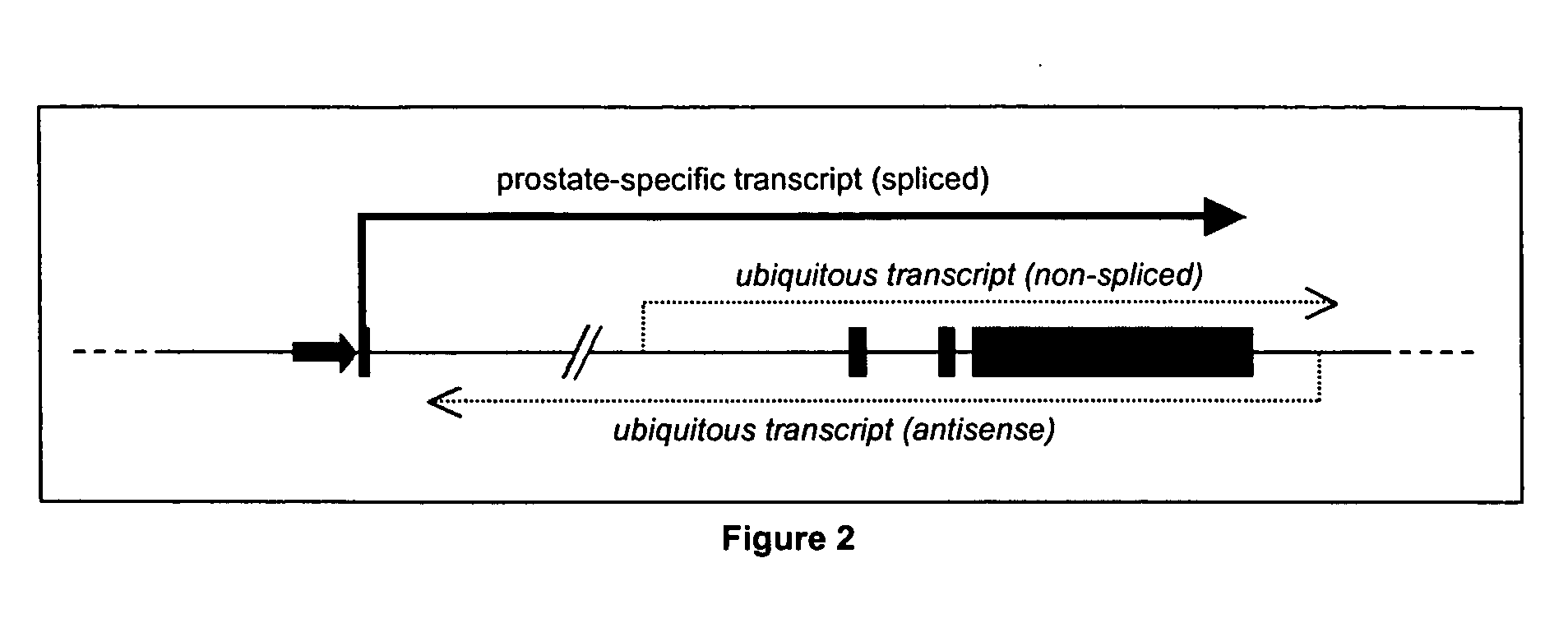
Specific method of prostate cancer detection based on PCA3 gene and kits therefor
InactiveUS20050164223A1Strong specificityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesExon
The present invention relates, in general, to prostate cancer. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method to diagnose prostate cancer in a patient by detecting a PCA3 sequence, and more particularly a PCA3 RNA, the PCA3 sequence detected in a sample from the patient being specifically associated with prostate cancer. In a particular embodiment the method and kit enables an amplification of a PCA3 RNA through an exon-exon junction of a spliced PCA3 mRNA. The invention also related to methods and kits to detect such an amplified PCA3 RNA, using a probe which spans the amplified exon-exon junction. The invention also relates to kits containing nucleic acid primers and kits containing nucleic acid primers and nucleic acid probes to diagnose, assess, or prognose a human afflicted with prostate cancer. In particular the methods and kits are designed to detect a PCA3 RNA which lacks one intron or more, and in particular case is intron-less.
Owner:STICHTING KATHOLIEKE UNIV
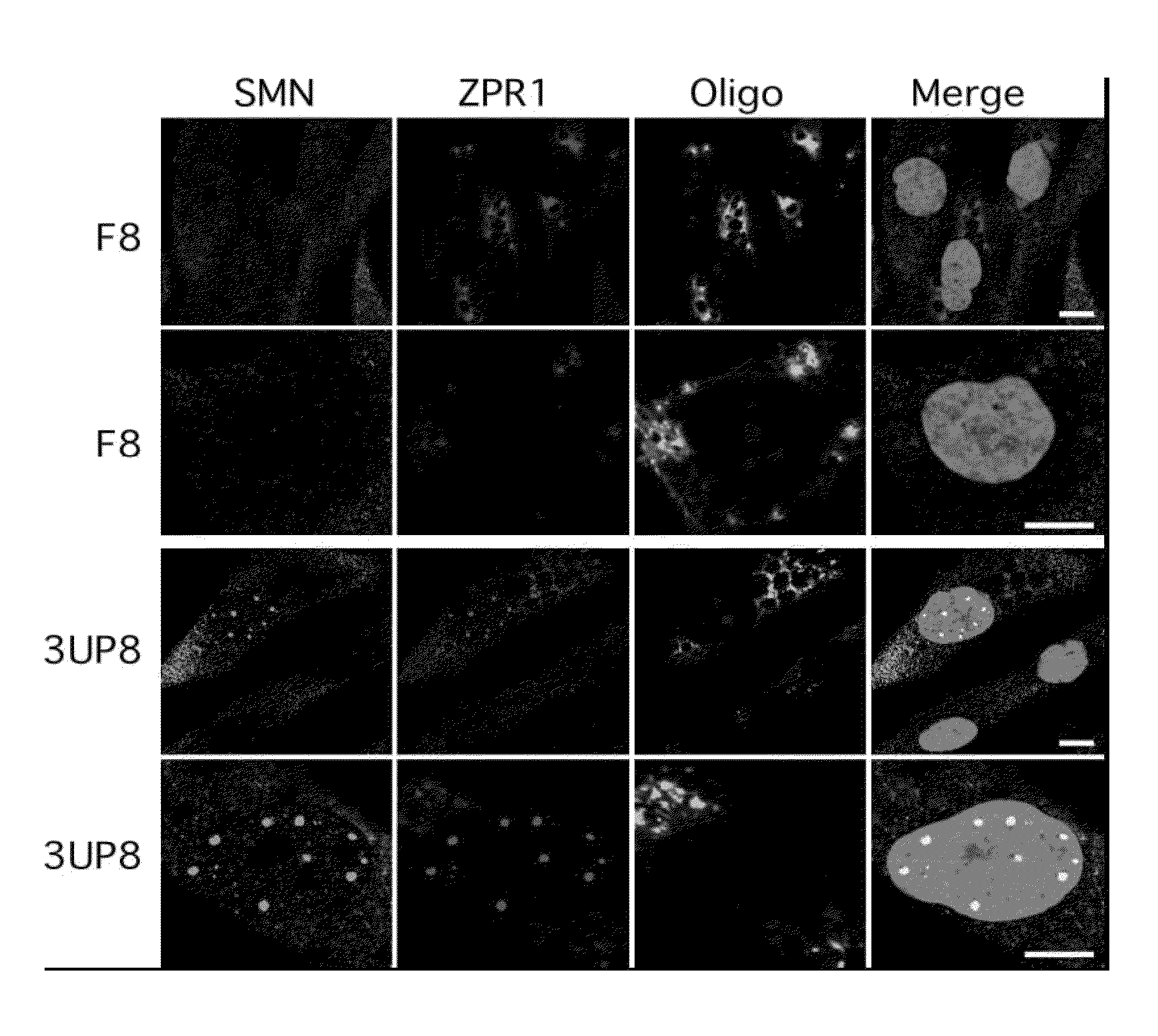
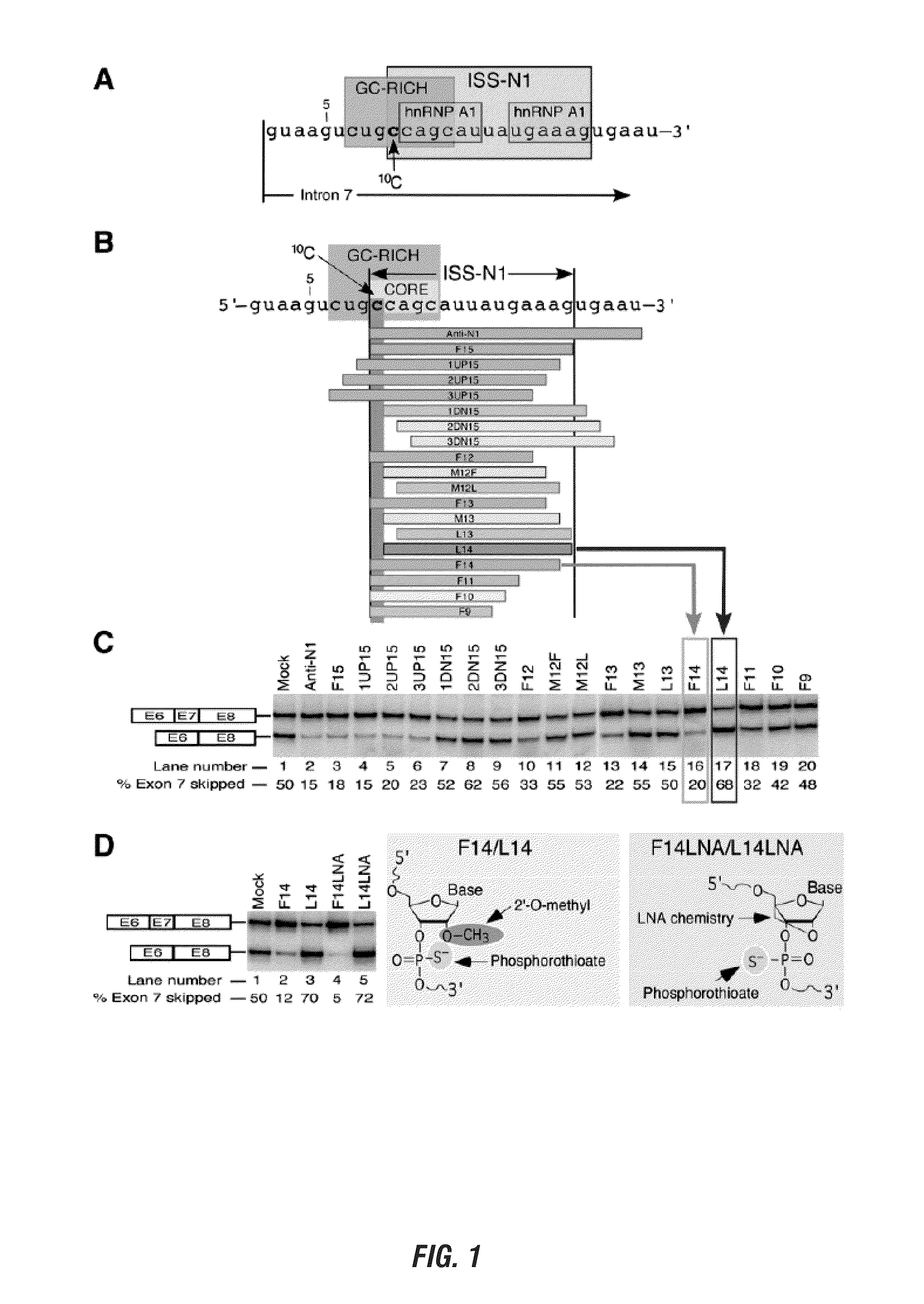
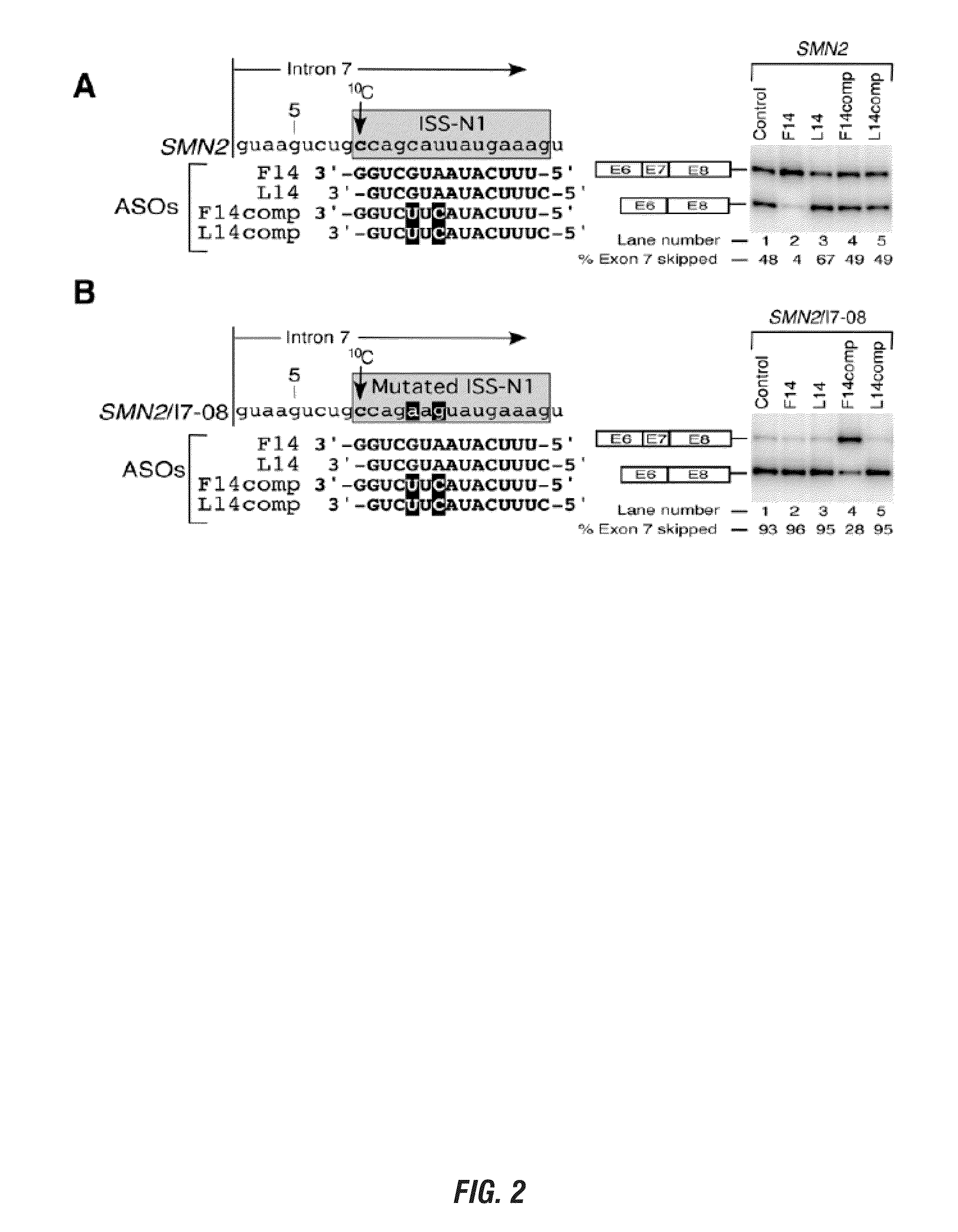
Spinal muscular atrophy treatment via targeting smn2 catalytic core
ActiveUS20110269820A1Increase productionEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationOligoribonucleotidesPrecursor mRNA
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for blocking the effect of the intronic inhibitory splicing region of intron 7 of the SMN2 gene. The compositions and methods of the instant invention include short oligonucleotide reagents (e.g., oligoribonucleotides) that effectively target sites in the SMN2 pre-mRNA, thereby modulating the splicing of SMN2 pre-mRNA to include exon 7 in the processed transcript. The short target regions are 8-mers and 5-mers and also include the identification of a single nucleotide base that is essential for initiating a long distance stearic inhibitory interactions as well as novel targets distant from intron 7 which block the intronic inhibitory splicing of the same. These short target regions and concomitant inhibitory blocking oligonucleotides are less expensive and easier to manufacture and are small enough to cross the blood brain barrier.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for obtaining bmp2a gene knocked-out zebra fish through CRISPR/Cas9
The invention discloses a method for obtaining bmp2a gene knocked-out zebra fish through CRISPR / Cas9. A novel gRNA sequence is designed between a first exon and an intron of BMP2a, the gRNA sequence is GGAGCCCATCACTAGACTCTTGG, and enzyme digestion is HinfI. Compared with a traditional gene knockout technology, the CRISPR / Cas9 technology has the advantages of low toxicity, high accuracy, high efficiency, short success cycle and the like. Therefore, the BMP2a gene can be theoretically knocked out faster.
Owner:WUXI NO 2 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
ActiveUS20090110689A1Suppress immune responseSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderHeteroduplexAutoimmune condition
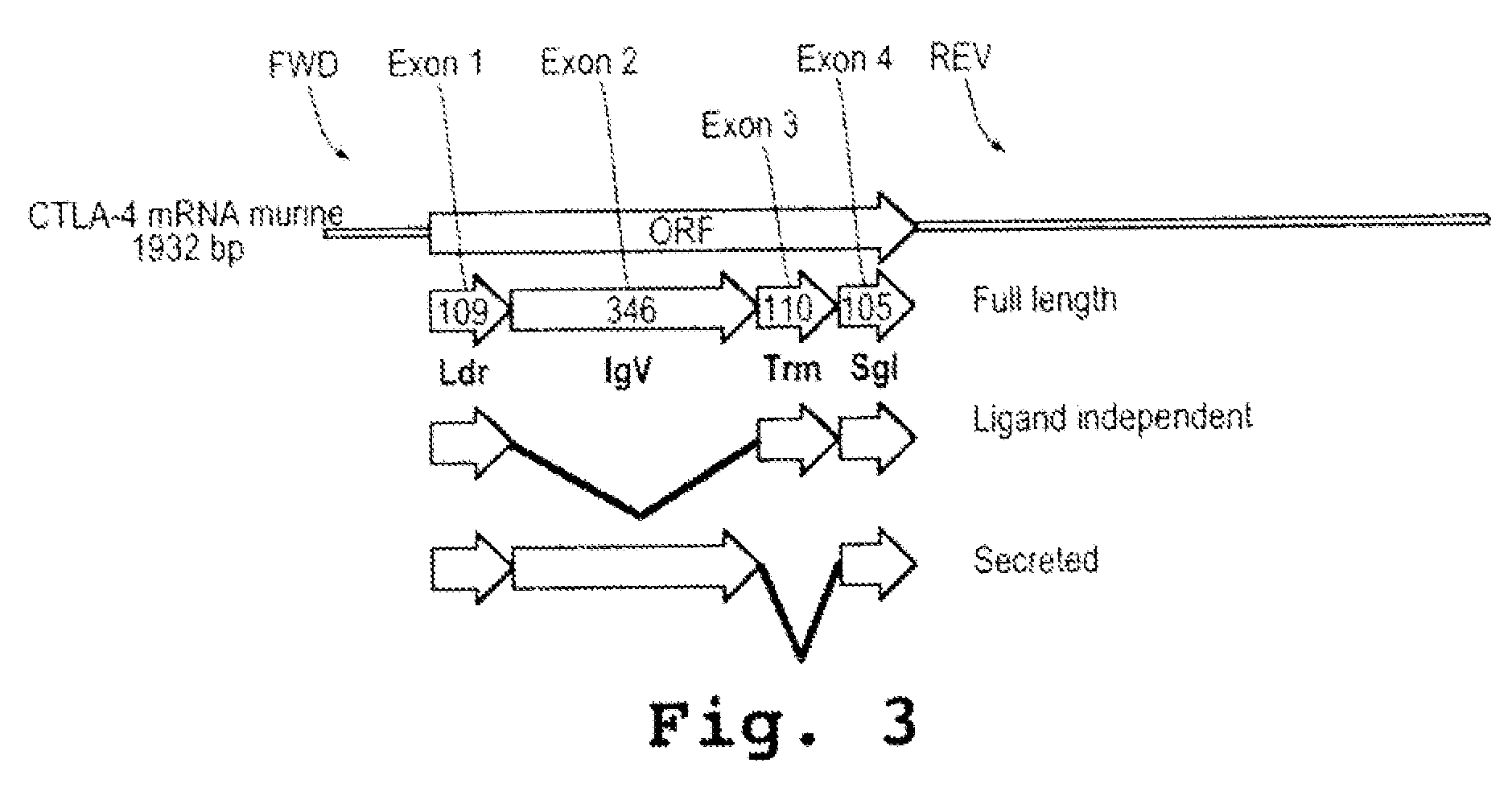
A method and compound for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection are disclosed. The compound is an antisense oligonucleotide analog compound having a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region identified by SEQ ID NO: 22 in SEQ ID NO: 1, spanning the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed mRNA of the subject. The compound is effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com