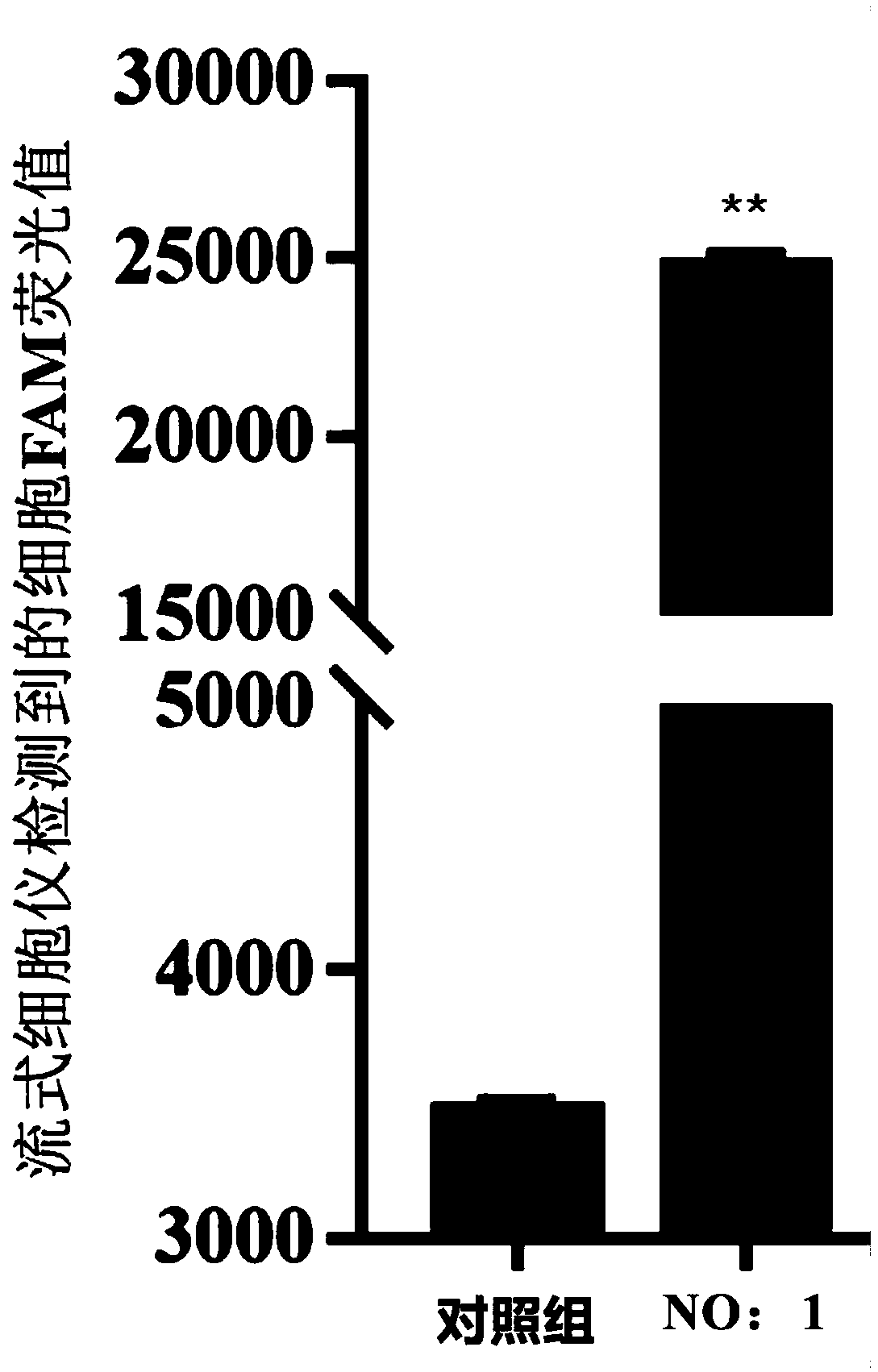
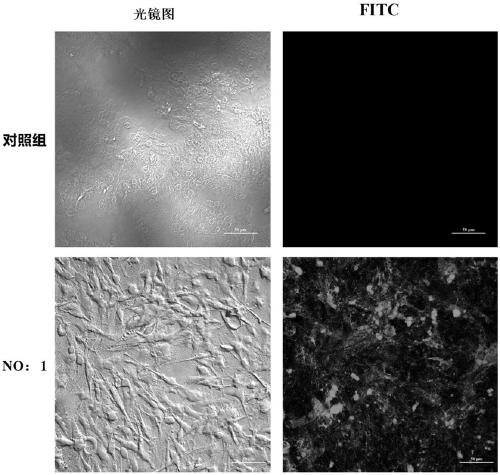
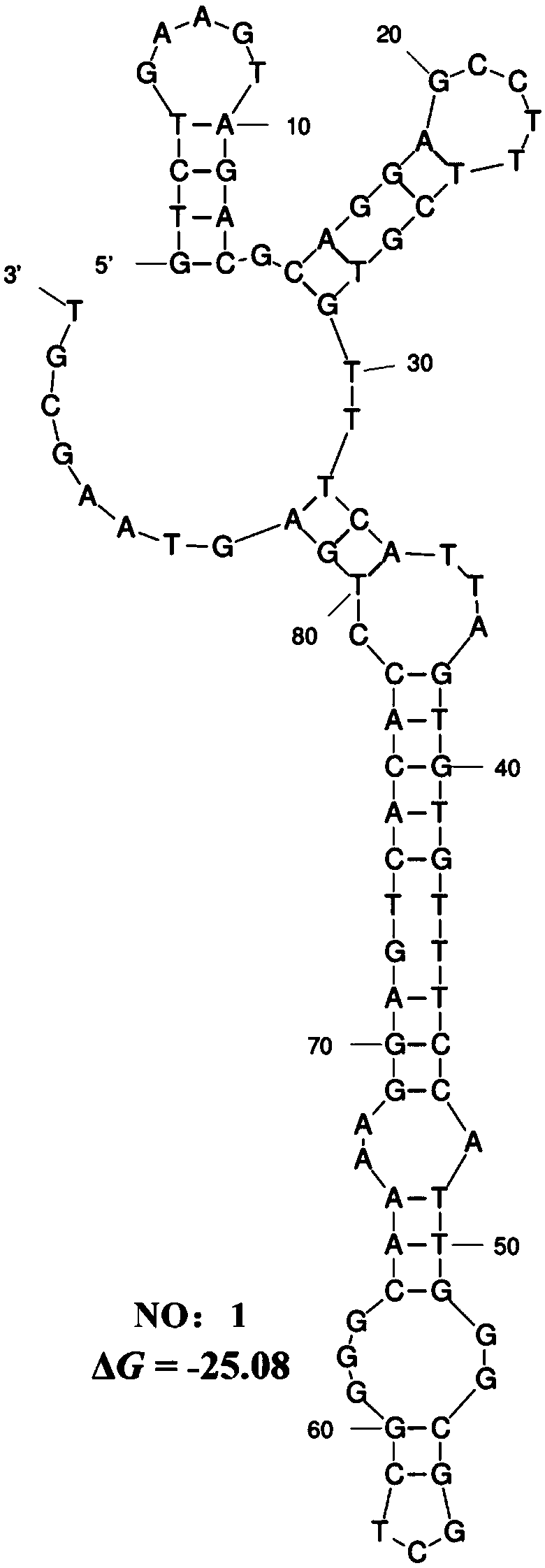
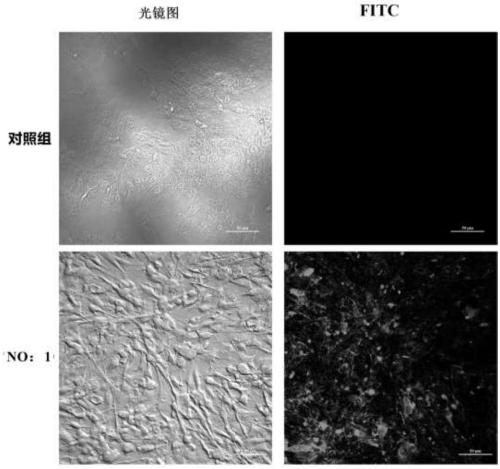
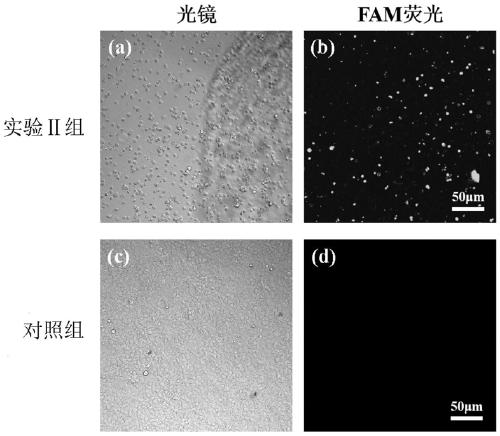
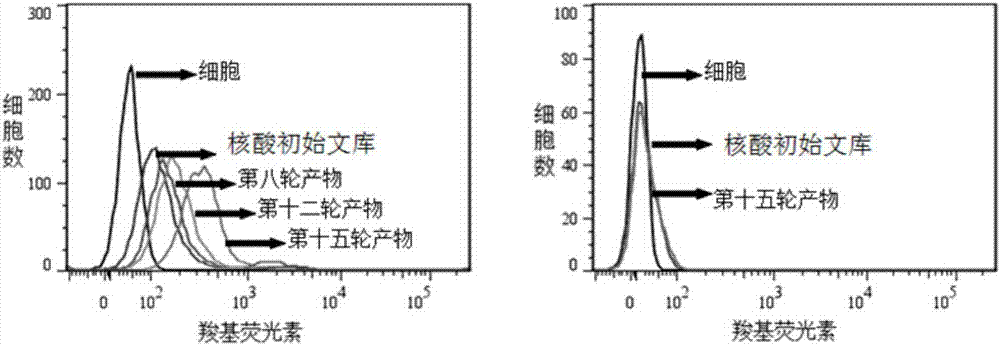
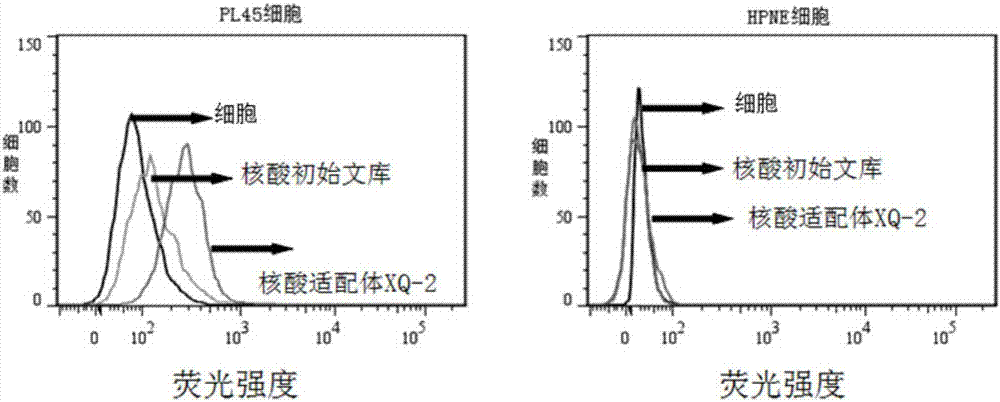
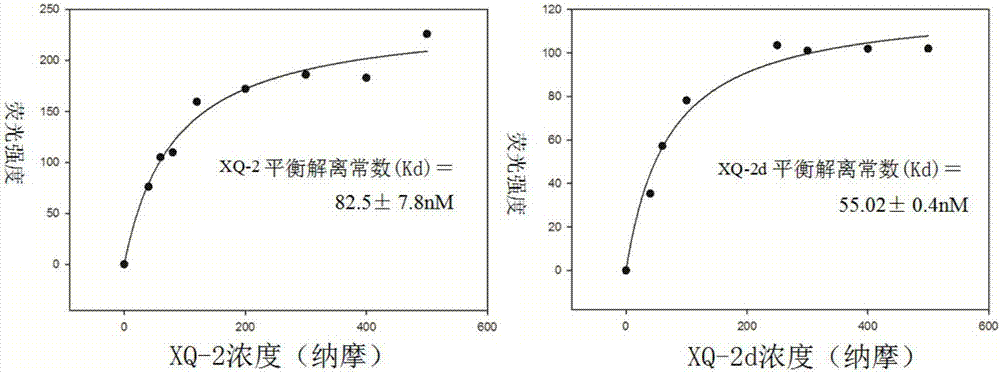
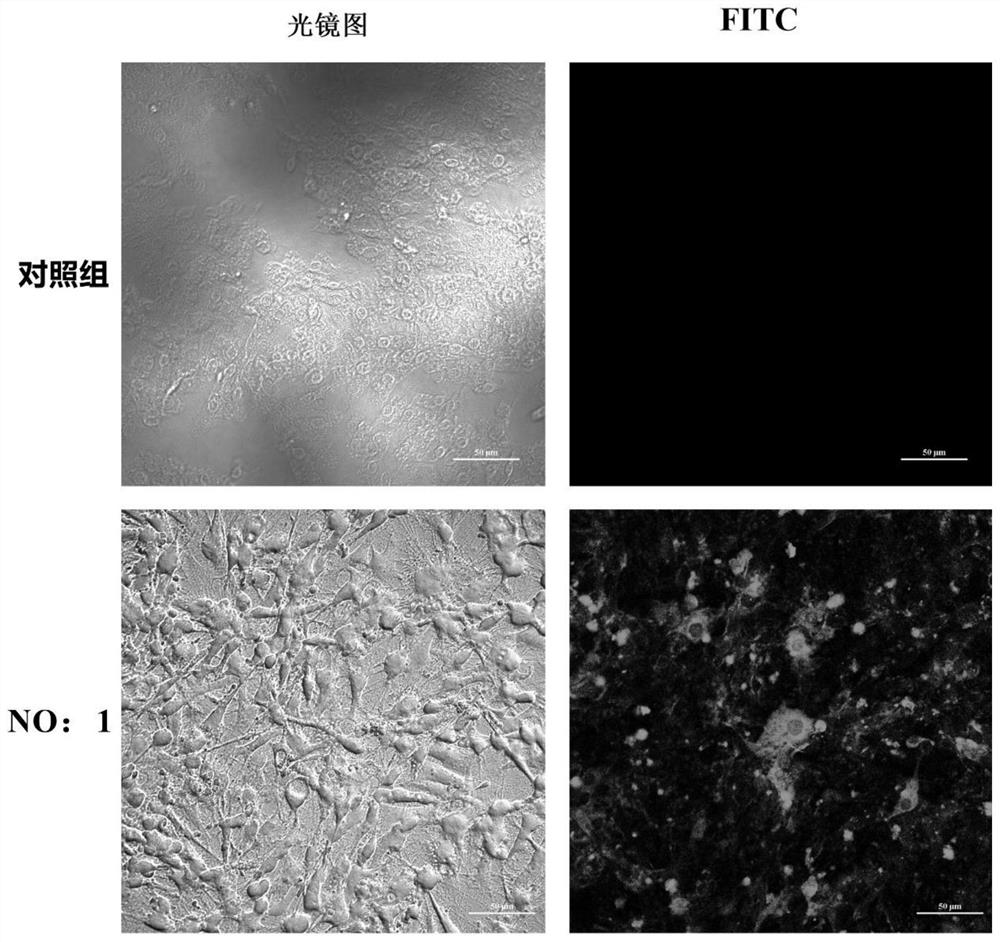
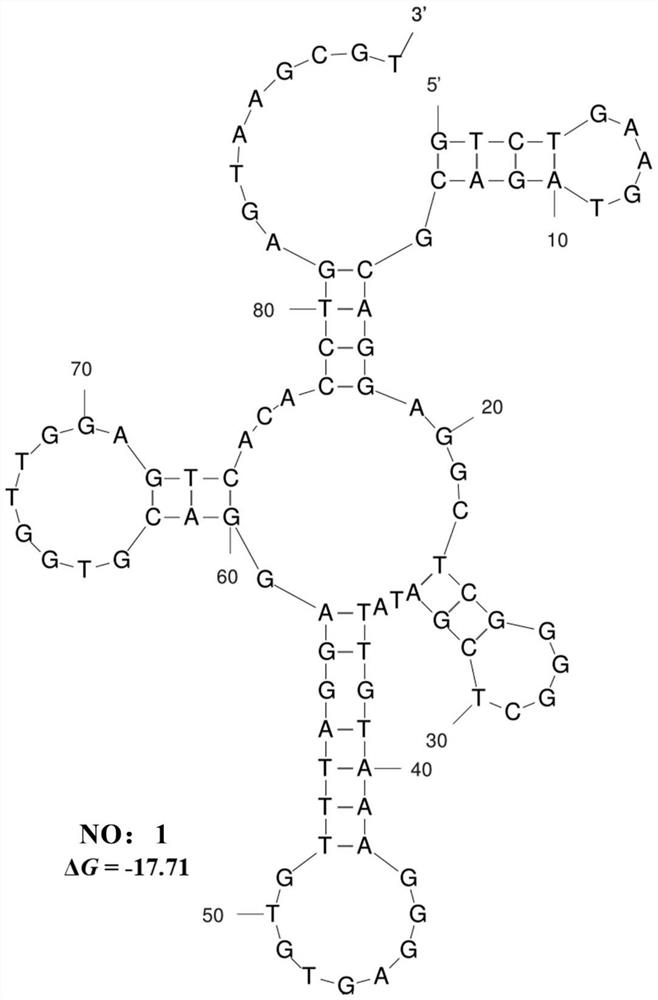
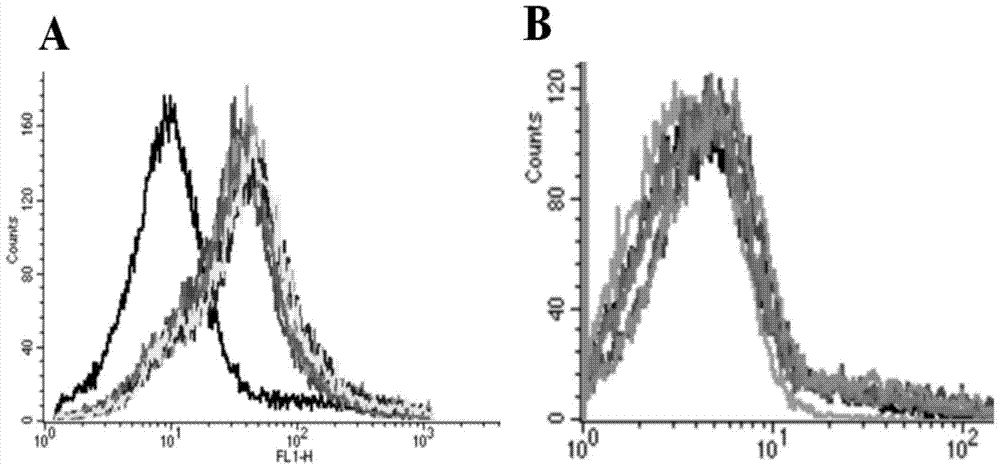
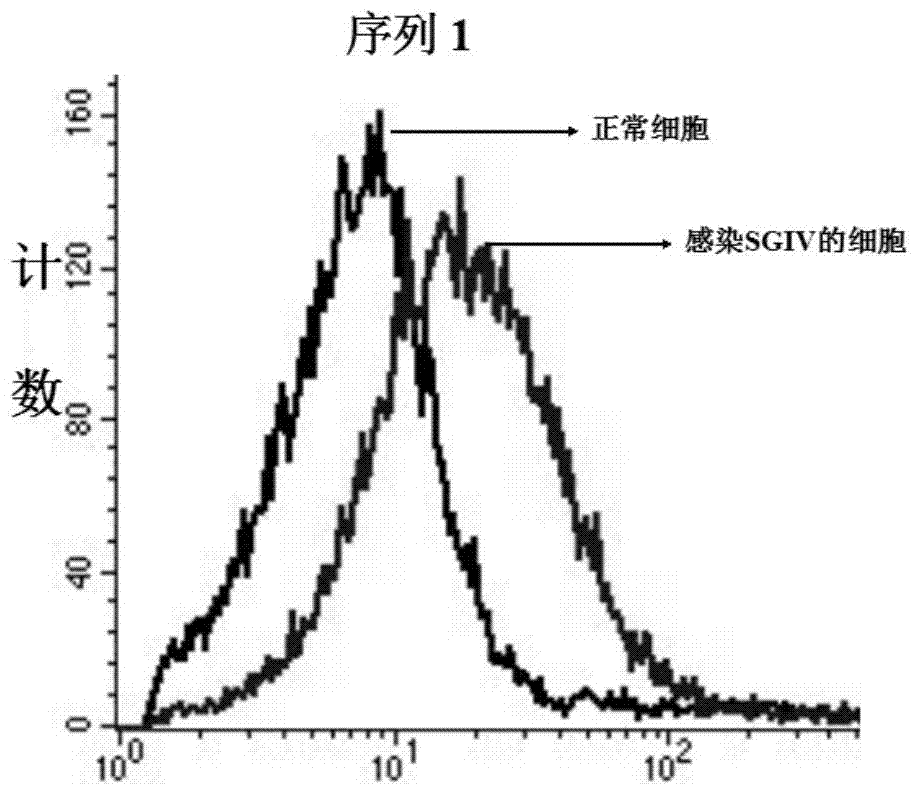
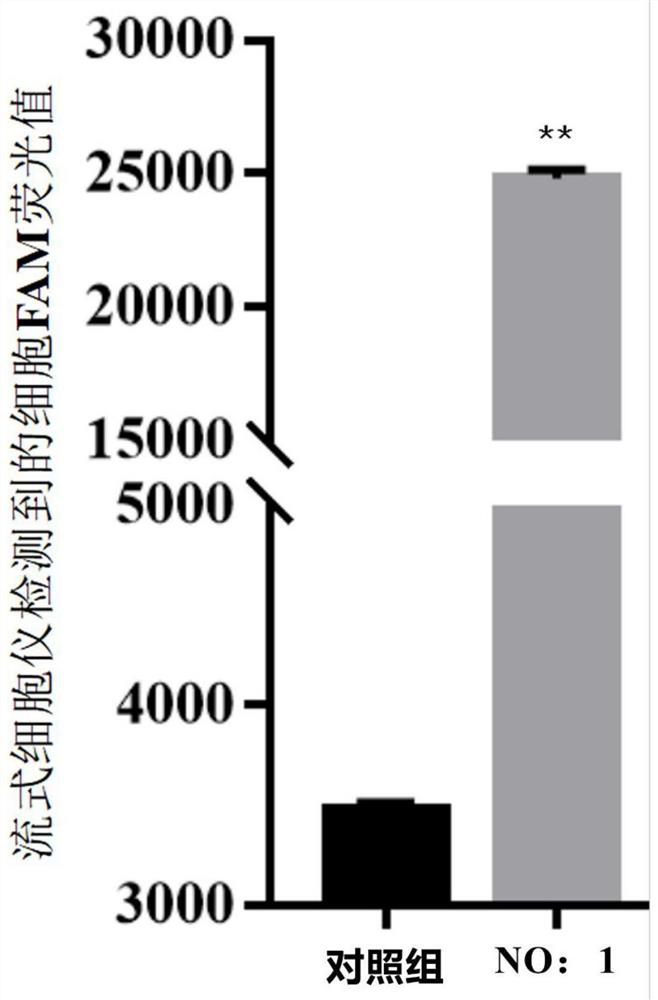
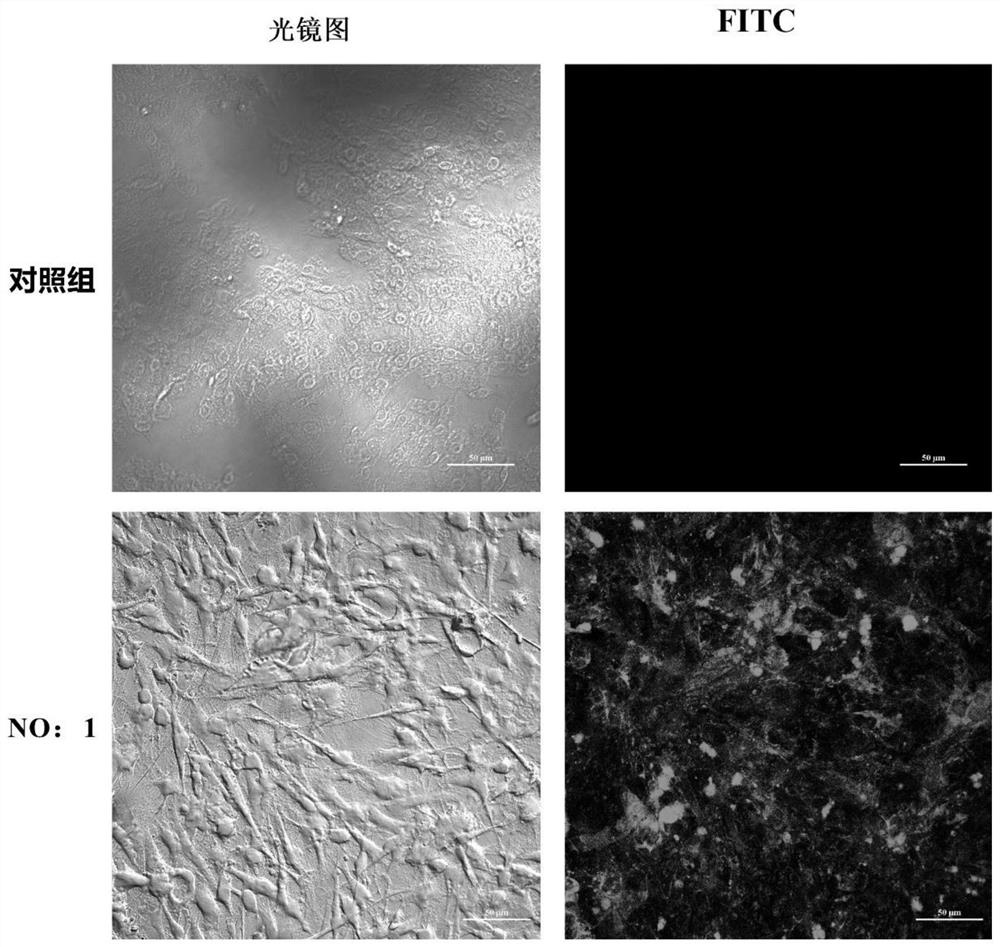
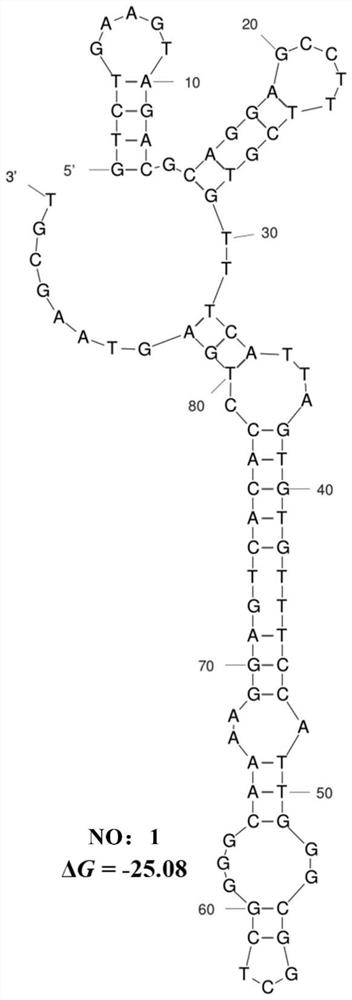
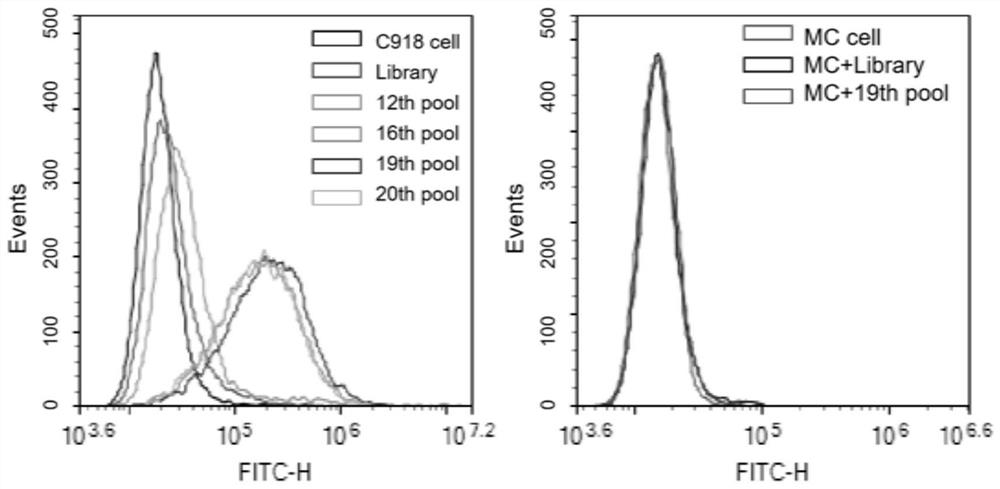
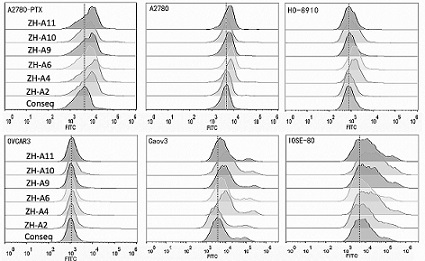
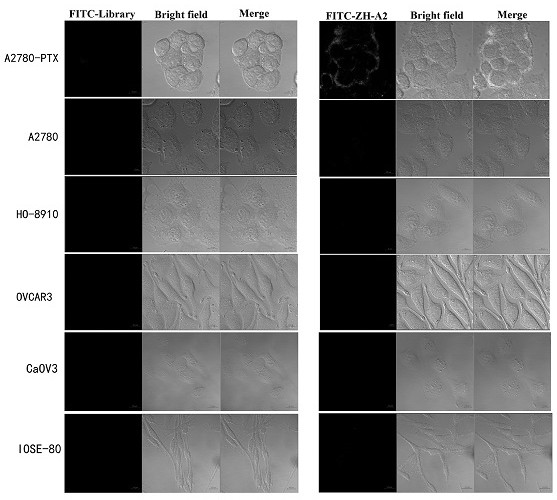
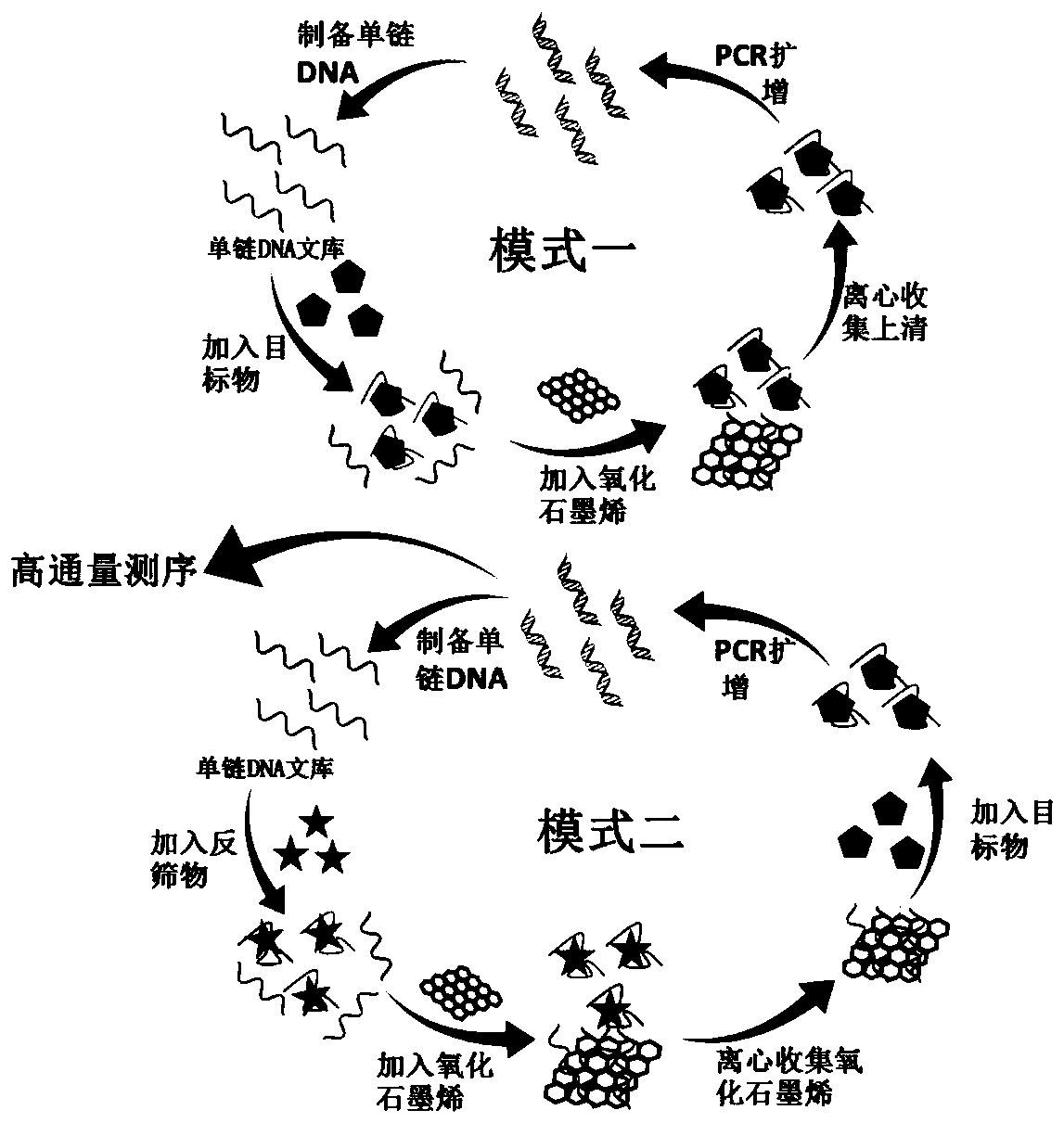
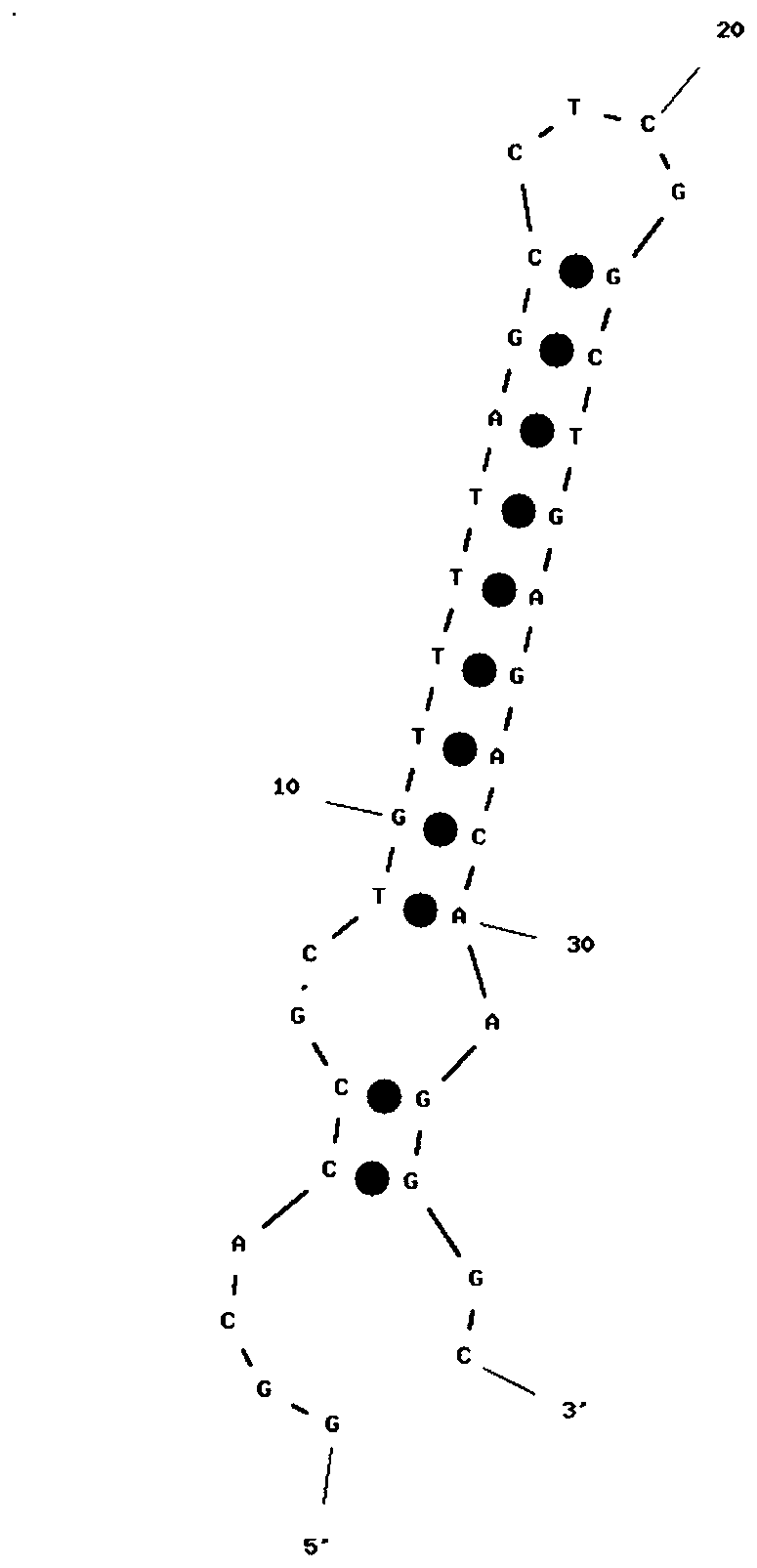
Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Sequence stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-activity T-cell promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104745581AEfficient expressionSequence stabilityGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAdoptive cellular immunotherapyT cell
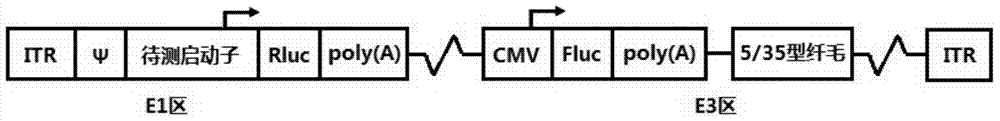
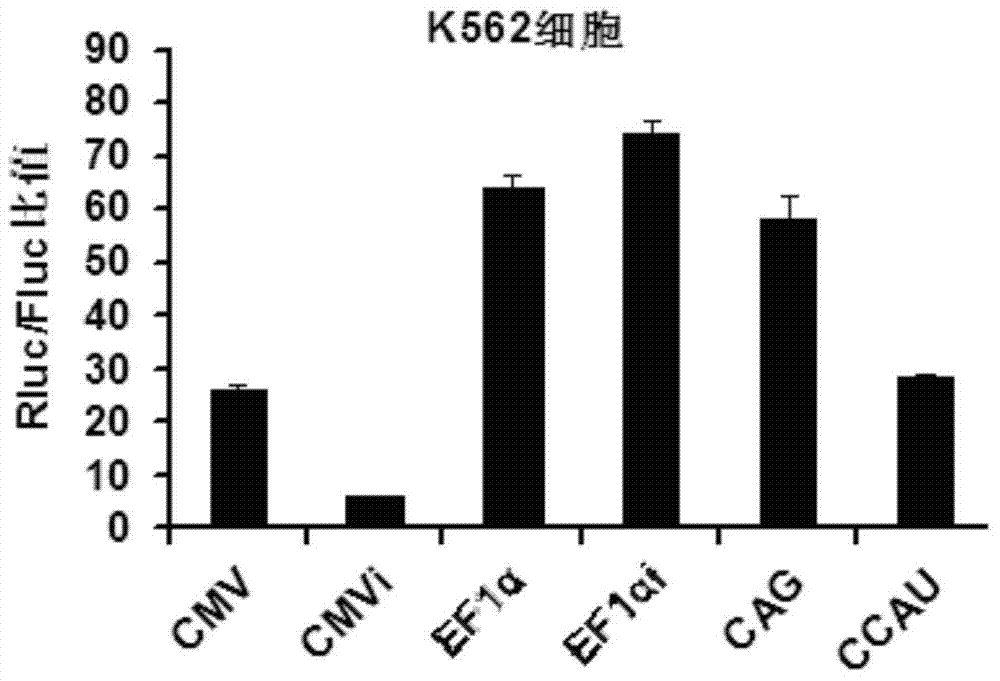
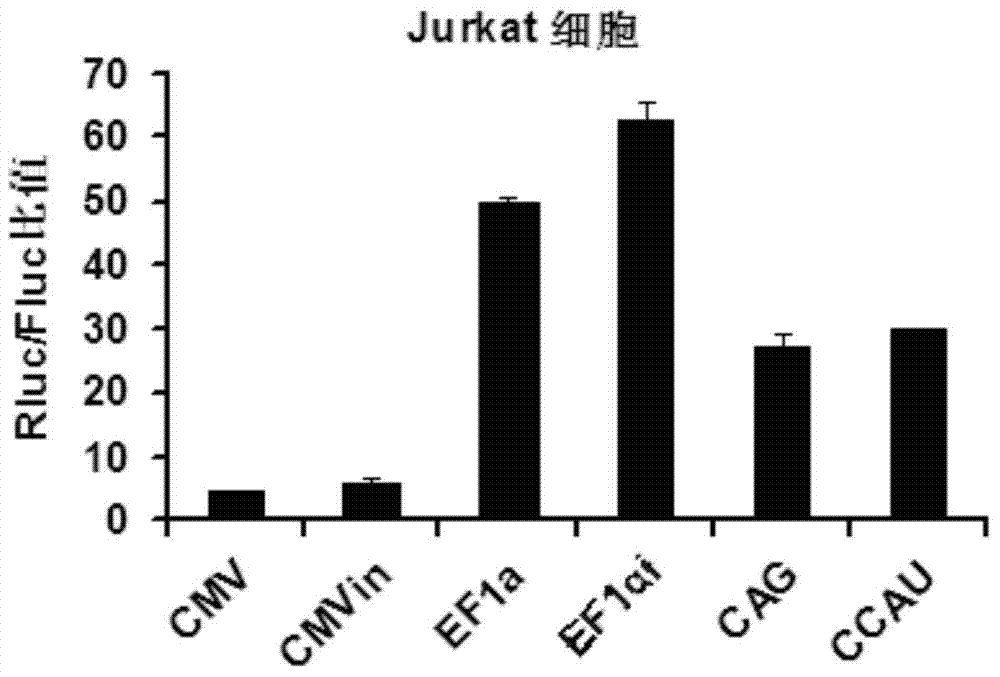
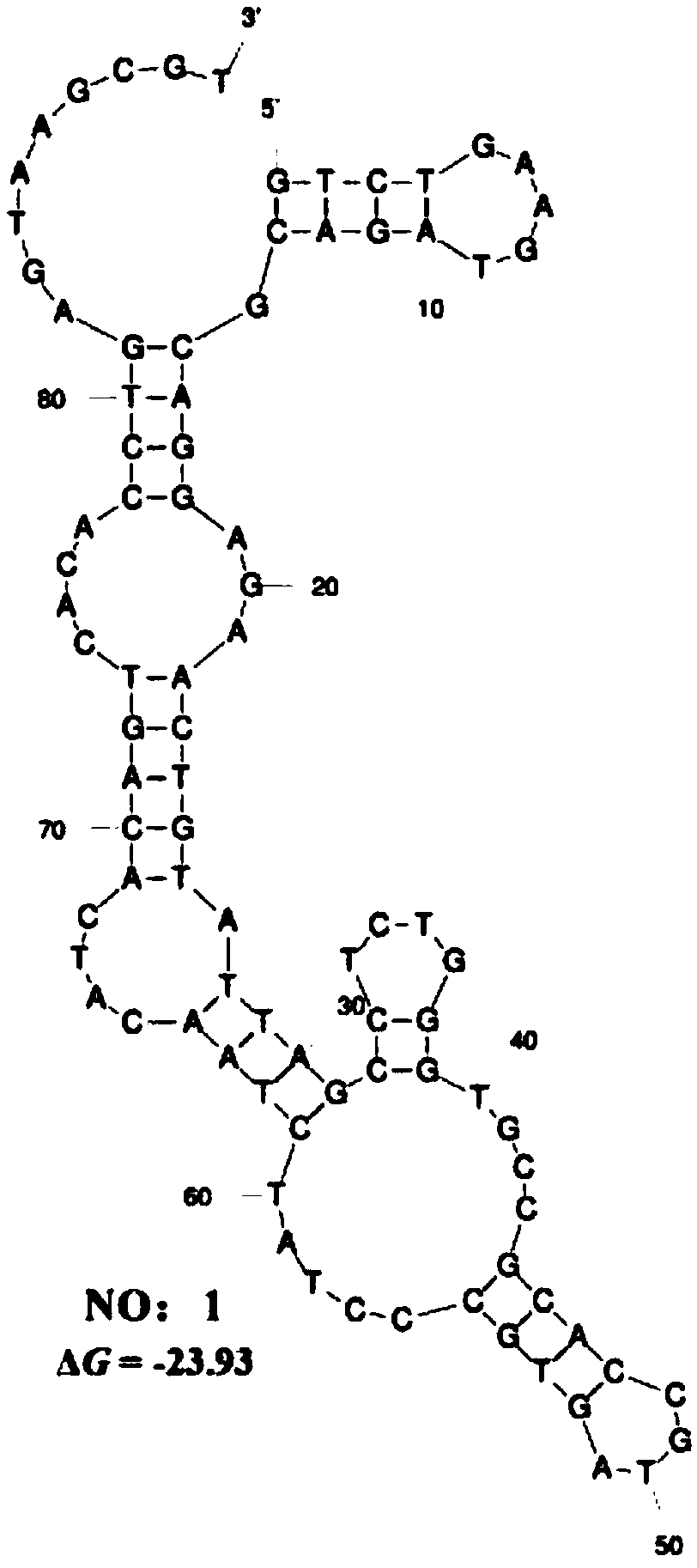
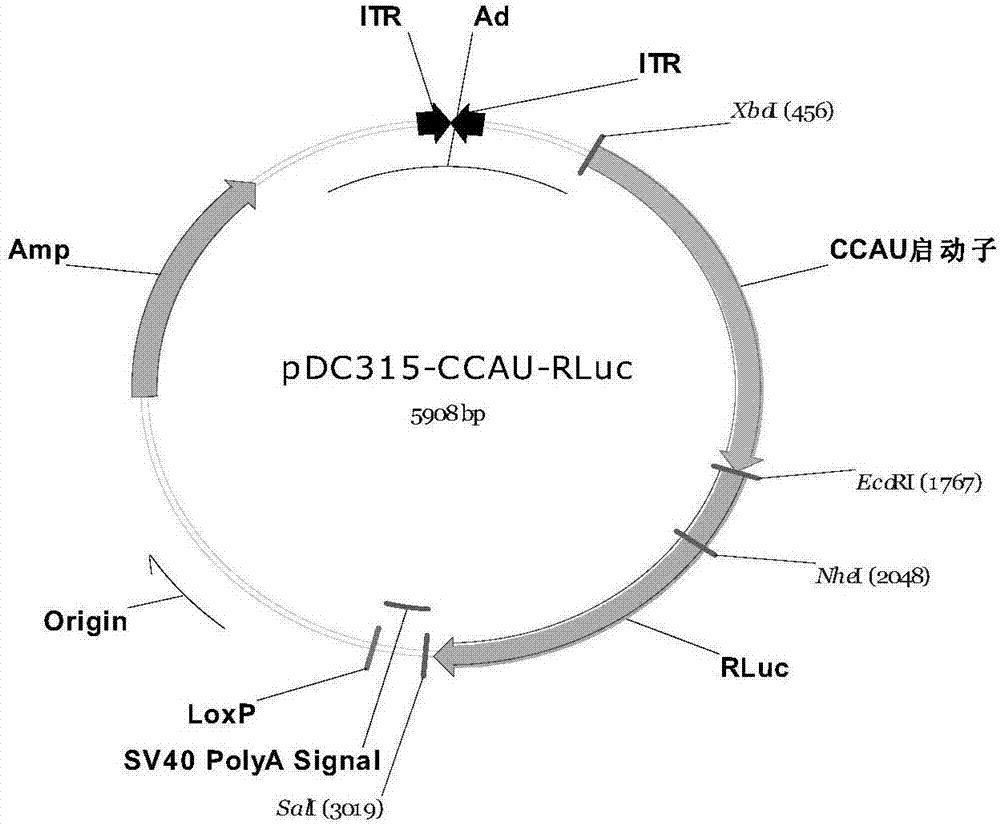
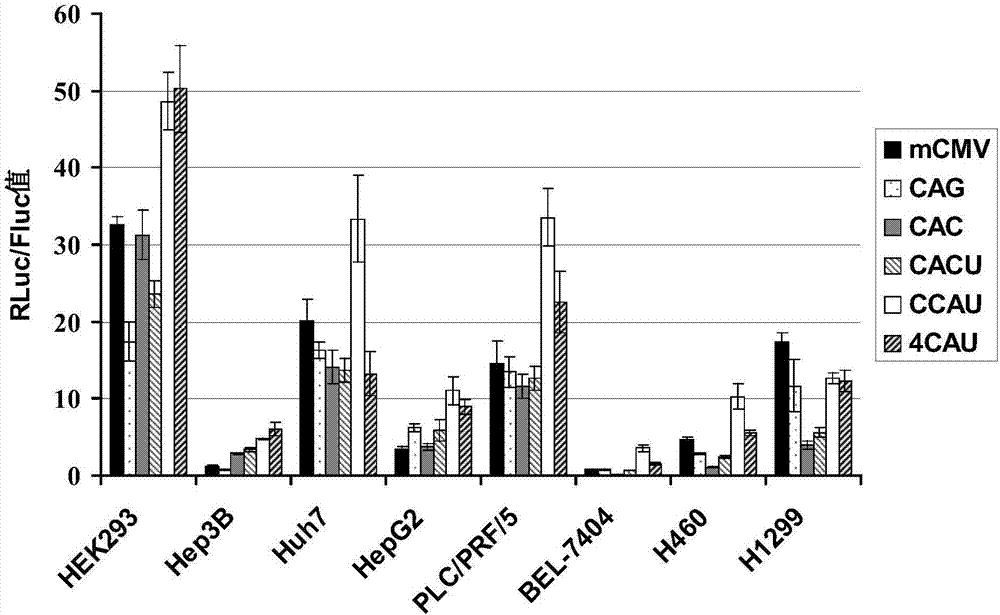
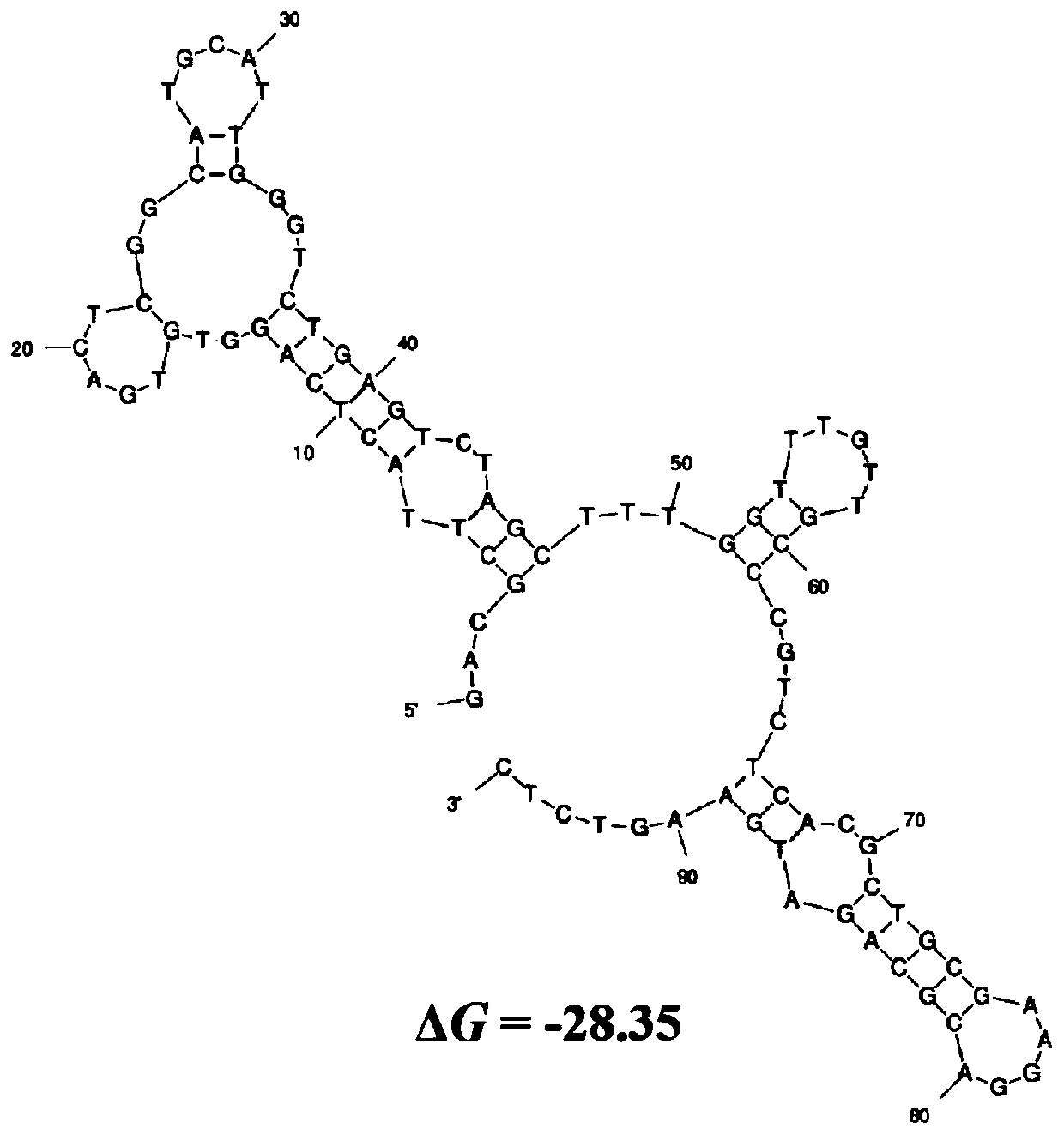
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a high-activity T-cell promoter and an application thereof. Particularly, the high-activity T-cell promoter comprises an element 1 and an element 2, wherein the element 1 is an EF1 alpha promoter and / or an EF1 alpha promoter containing an intron; and the element 2 is any one or more of an mCMV promoter, an hCMV promoter and a CD3e promoter. The high-activity T-cell promoter provided by the invention can be used for efficiently expressing a foreign gene in a T cell, has a stable sequence and is free from sequence loss during the transfer process of a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. The high-activity T-cell promoter is applicable to driving the high-efficiency expression of the foreign gene, especially a full-length antibody gene, in the T cell during the process of adoptive cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +2
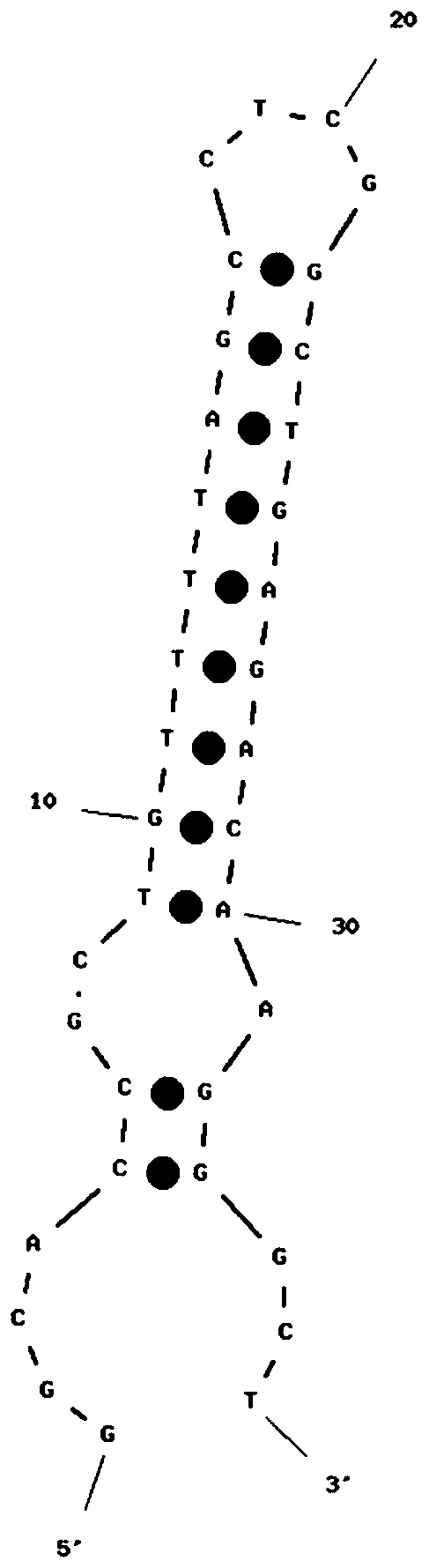
Nucleic acid aptamer and screening method thereof, and application of nucleic acid aptamer in prostate cancer cell strain detection
ActiveCN103642810AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisProstate cancer cellChemical synthesis
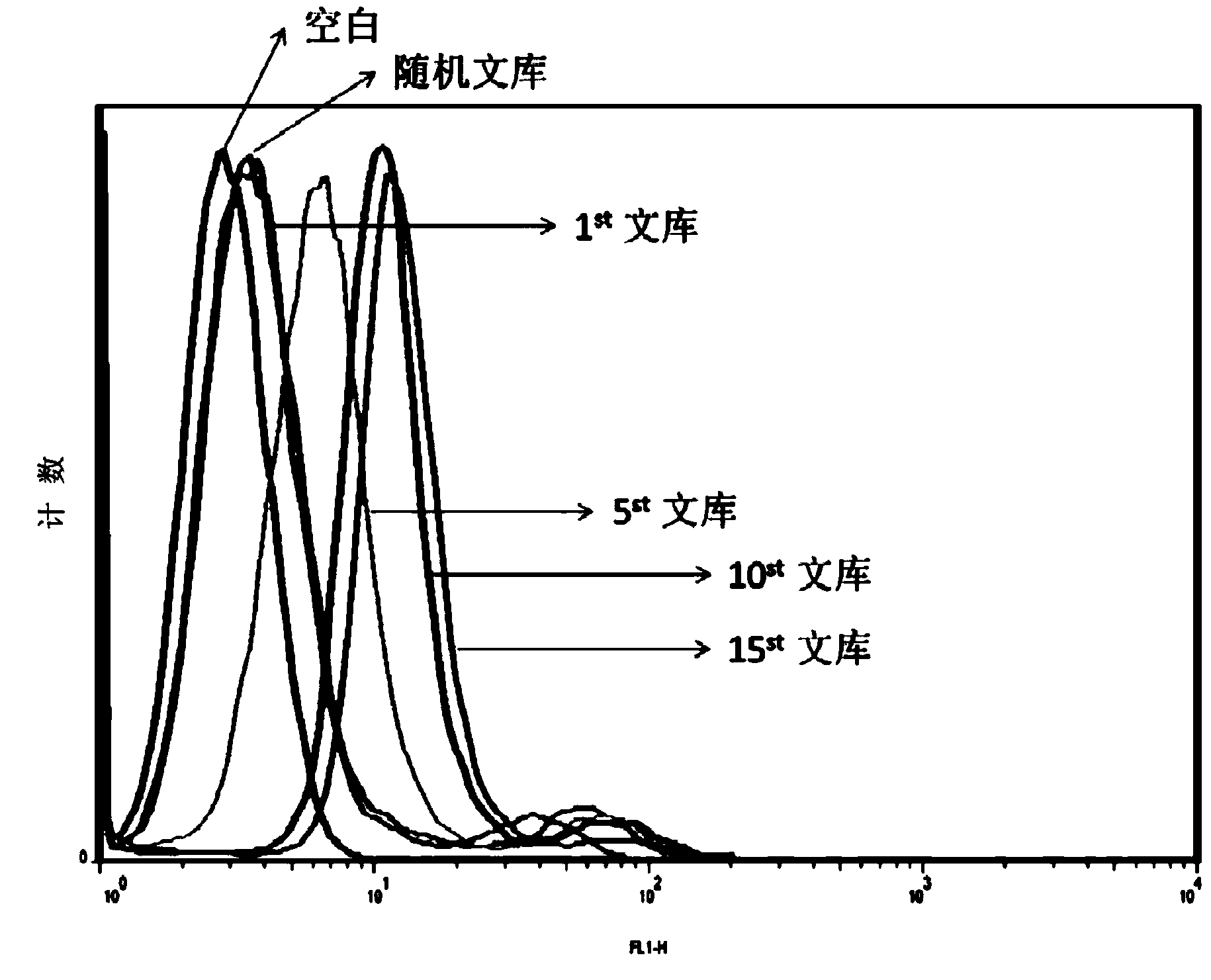
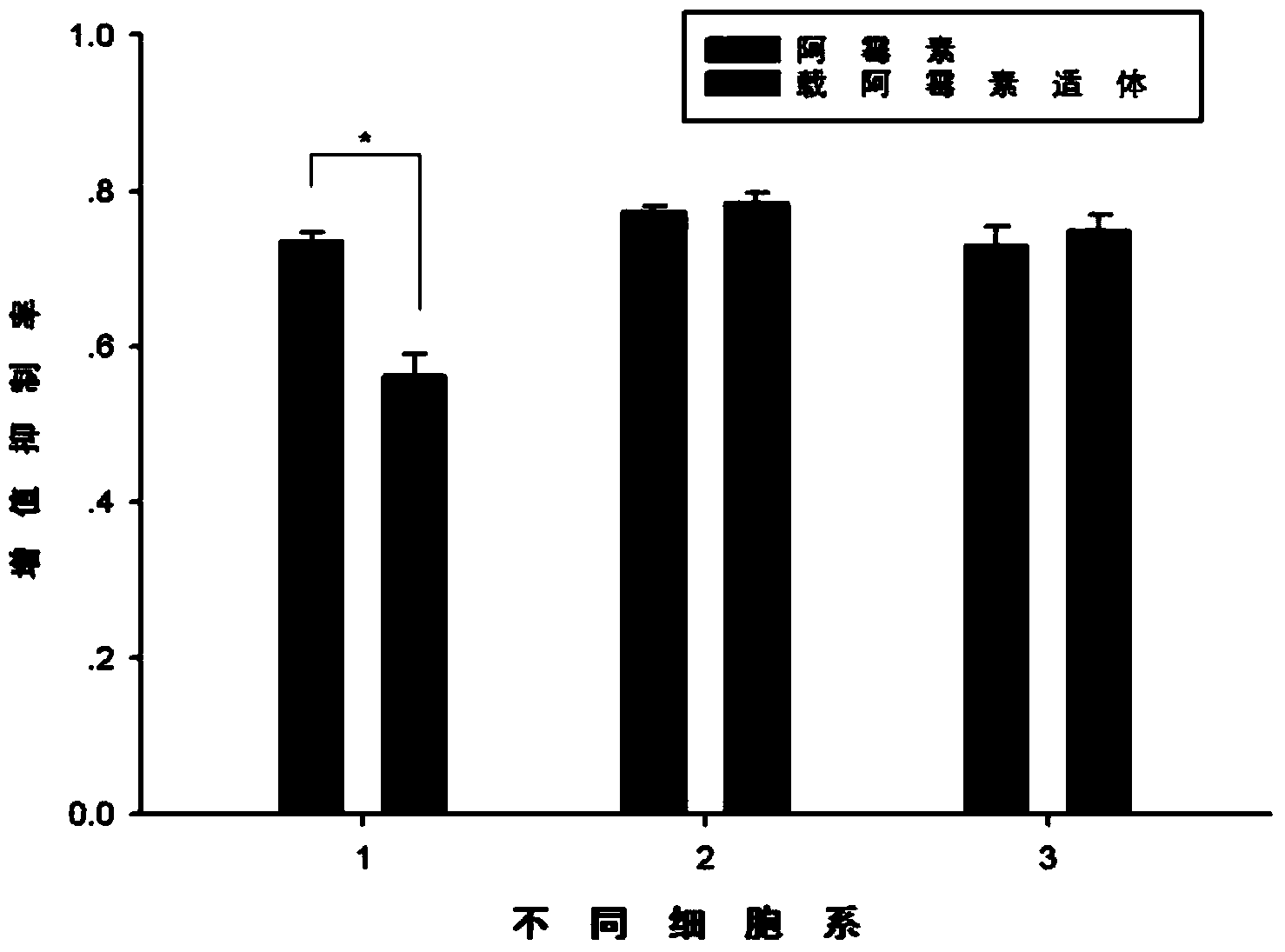
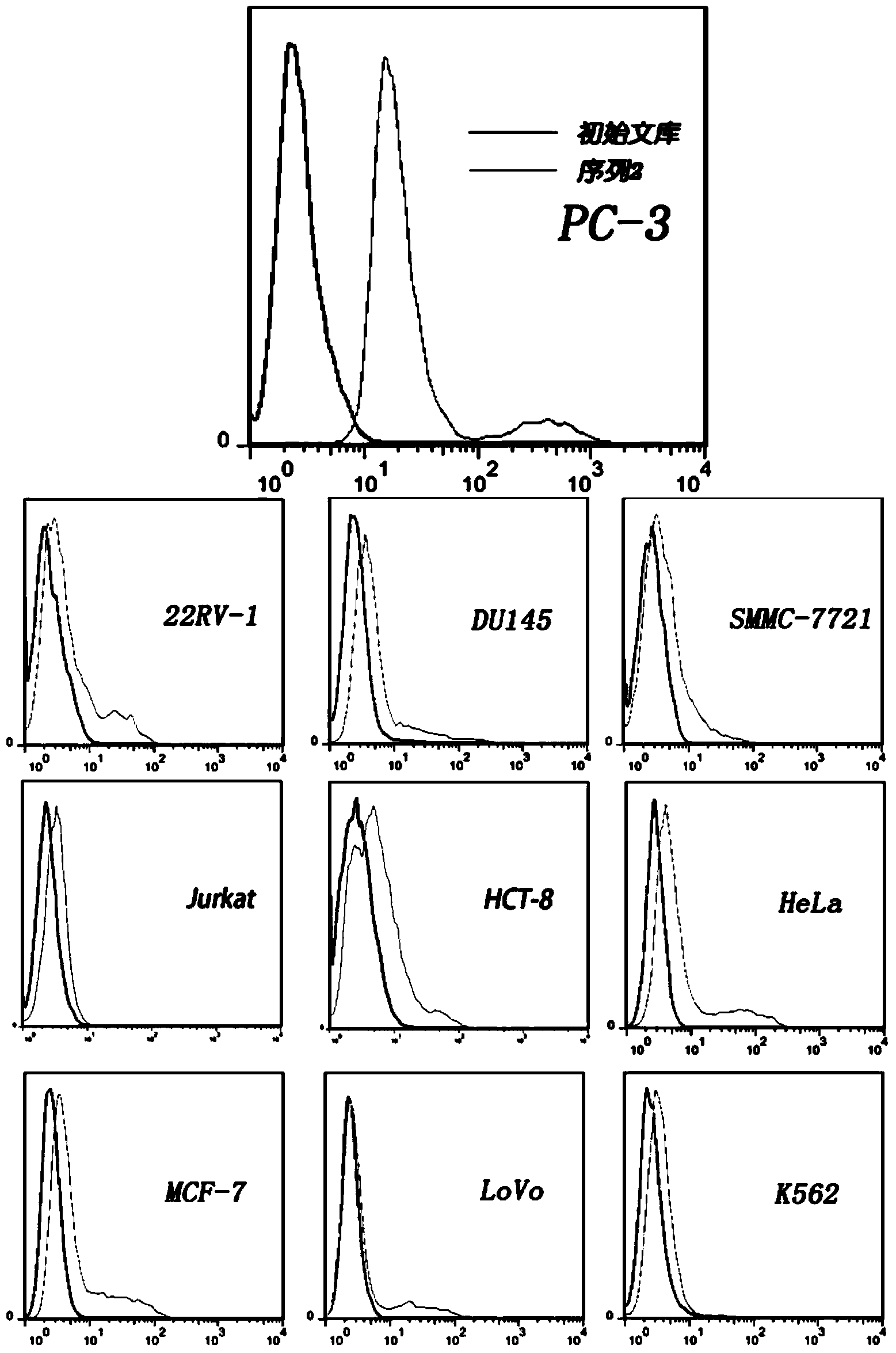
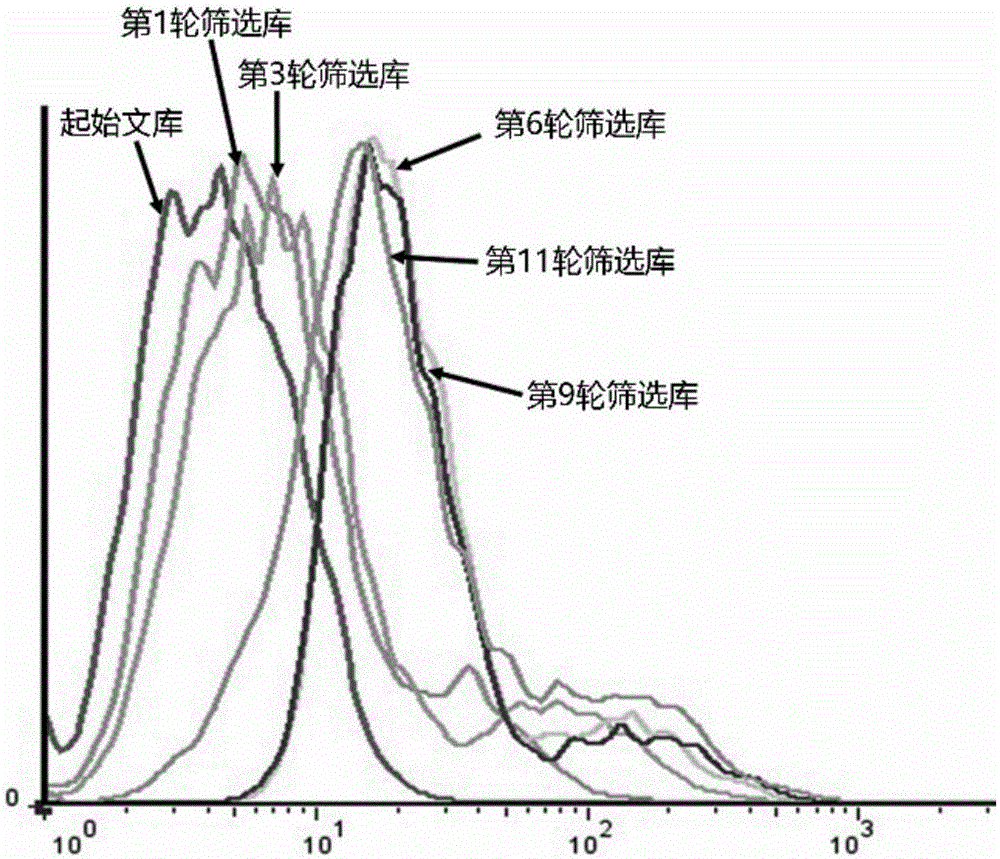
The present invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer, wherein the sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer comprises a DNA segment represented by any one sequence selected from a sequence 1, a sequence 2 and a sequence 3. The nucleic acid aptamer can further be various similar sequences with high homology or a derivative obtained from the sequence of the present invention. The invention further discloses a nucleic acid aptamer screening method, which comprises: synthesizing a random single-stranded DNA library and primers, carrying out SELEX screening, carrying out PCR amplification of library, preparing a DNA single strand library, and finally carrying out repeated screening, negative screening and multi-round screening to obtain the nucleic acid aptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer and the derivative thereof can be used in recognition of the prostate cancer cell strain PC-3 or preparation of kits, molecular probes and targeted mediums for prostate cancer detection, and can further be used in design and preparation of prostate cancer treatment drugs. Compared with the protein antibody, the nucleic acid aptamer of the present invention has advantages of high affinity, high specificity, no immunogenicity, capability of being chemically synthesized, small molecular weight, stability, easy storage, easy labeling and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIWEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Nucleic acid aptamer and derivatives thereof, screening method of nucleic acid aptamer, application of nucleic acid aptamer and derivatives in detecting human biliary duct carcinoma cell line
ActiveCN103205431AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAptamerChemical synthesis
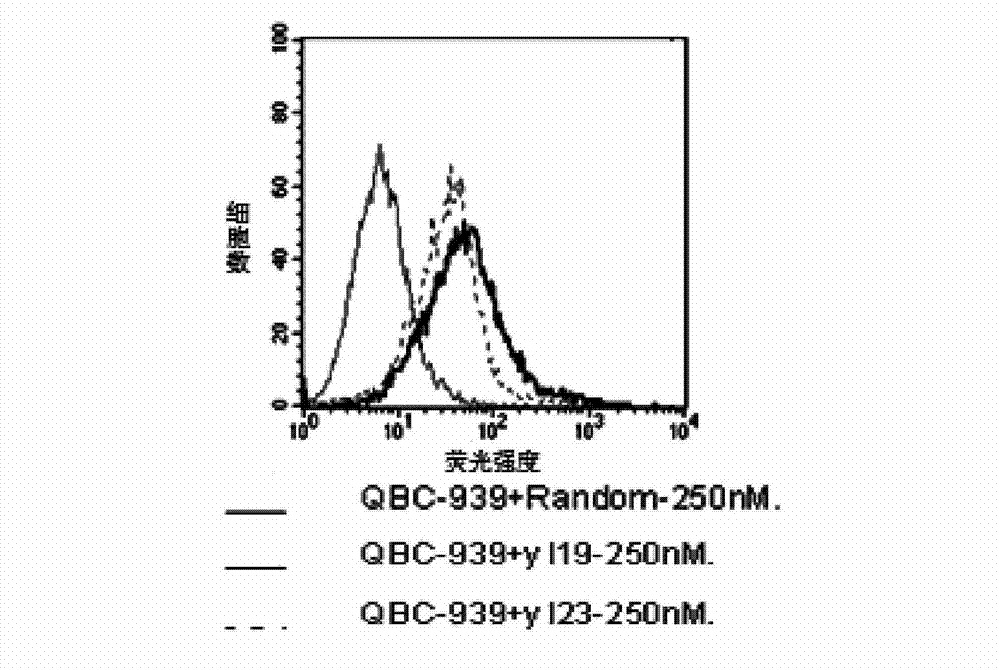
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer with a sequence containing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segments shown by any of a sequence 1 and a sequence 2. The nucleic acid aptamer can also be derivatives obtained by various similar sequences high in homology or the sequence. The invention further discloses a screening method of the nucleic acid aptamer. The method includes: synthesizing a random single-strand DNA library and a primer, performing Cell-SELEX screening and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) library amplification, preparing a DNA single-strand library, and obtaining the nucleic acid aptamer through repeated screening, negative screening and several rounds of screening. The nucleic acid aptamer and derivatives thereof can be applied to recognizing human biliary duct carcinoma cell line QBC-939 or preparing a reagent box for detecting the human biliary duct carcinoma cell line QBC-939, has affinity and specificity higher than anti-keratin antibodies, and is free of immunogenicity, capable of being chemically synthesized, small in molecular weight, stable, easy to store and mark, and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
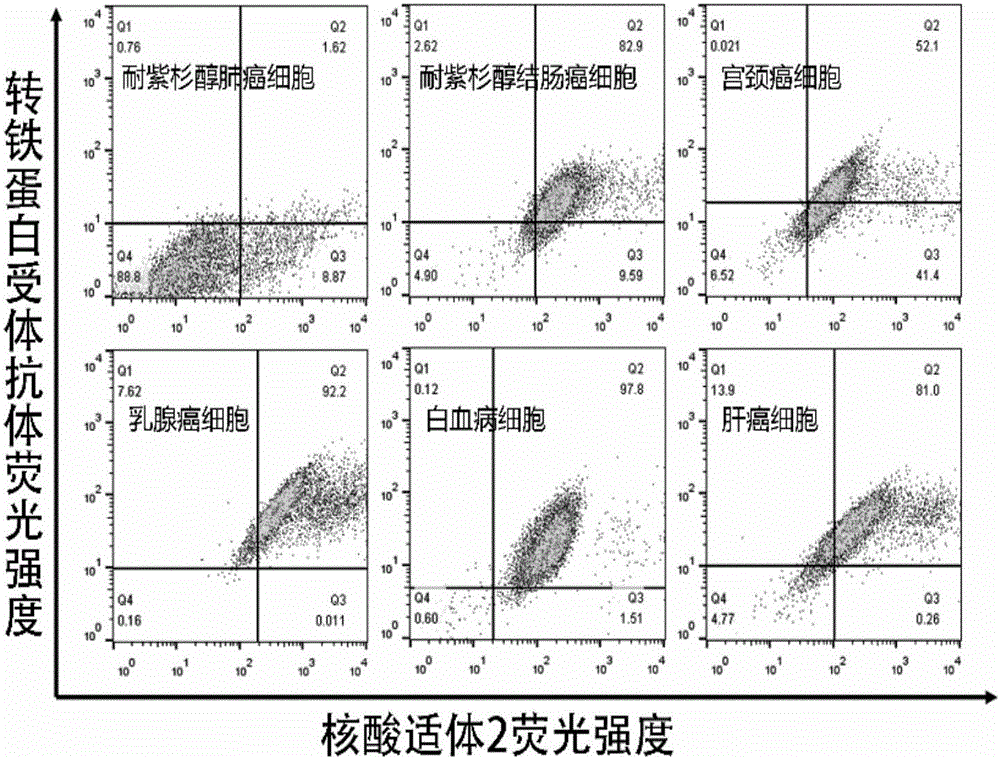
Nucleic acid aptamer sequence for recognizing and being combined with human transferrin receptor and application of nucleic acid aptamer sequence
ActiveCN106191069AHigh affinityNon-immunogenicBiological material analysisBiological testingAptamerChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer sequence for recognizing and being combined with a human transferrin receptor and application of the nucleic acid aptamer sequence. A nucleic acid aptamer and derivatives thereof can be applied in kits, molecular probes and targeted media for recognizing or preparing and detecting transferrin receptor high-expression tumors and applied in nucleic acid probes for designing, preparing and detecting transferrin receptors. The nucleic acid aptamer has the advantages that the affinity and specificity are higher than those of the prior art, the aptamer is free of immunogenicity, chemical synthesis can be achieved, and the nucleic acid aptamer is small in molecular weight, stable, easy to store and mark and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid aptamer for recognizing liver cancer cells, and screening method and purpose thereof
InactiveCN108866061AStrong specificityImprove performanceOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAptamerFluorescence
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer for recognizing liver cancer cells, and a screening method and a purpose thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer comprises the feature sequence part shown as Seq ID No.1. The purpose comprises the purpose of the nucleic acid aptamer to the design and preparation of anti-liver-cancer medicine or detection reagents. The detection reagents comprise enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunoradiometric assay or fluorescence method. The invention also comprises a target preparation and a medicine composition. The target preparationcomprises the nucleic acid aptamer and a medically acceptable carrier or a shaping agent. The medicine composition comprises the nucleic acid aptamer, at least one antitumor medicine and a medically acceptable carrier. Compared with the prior art, the nucleic acid aptamer can be used for specifically recognizing the liver cancer cells; good application prospects are realized.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A nucleic acid aptamer for detecting human uveal melanoma cells
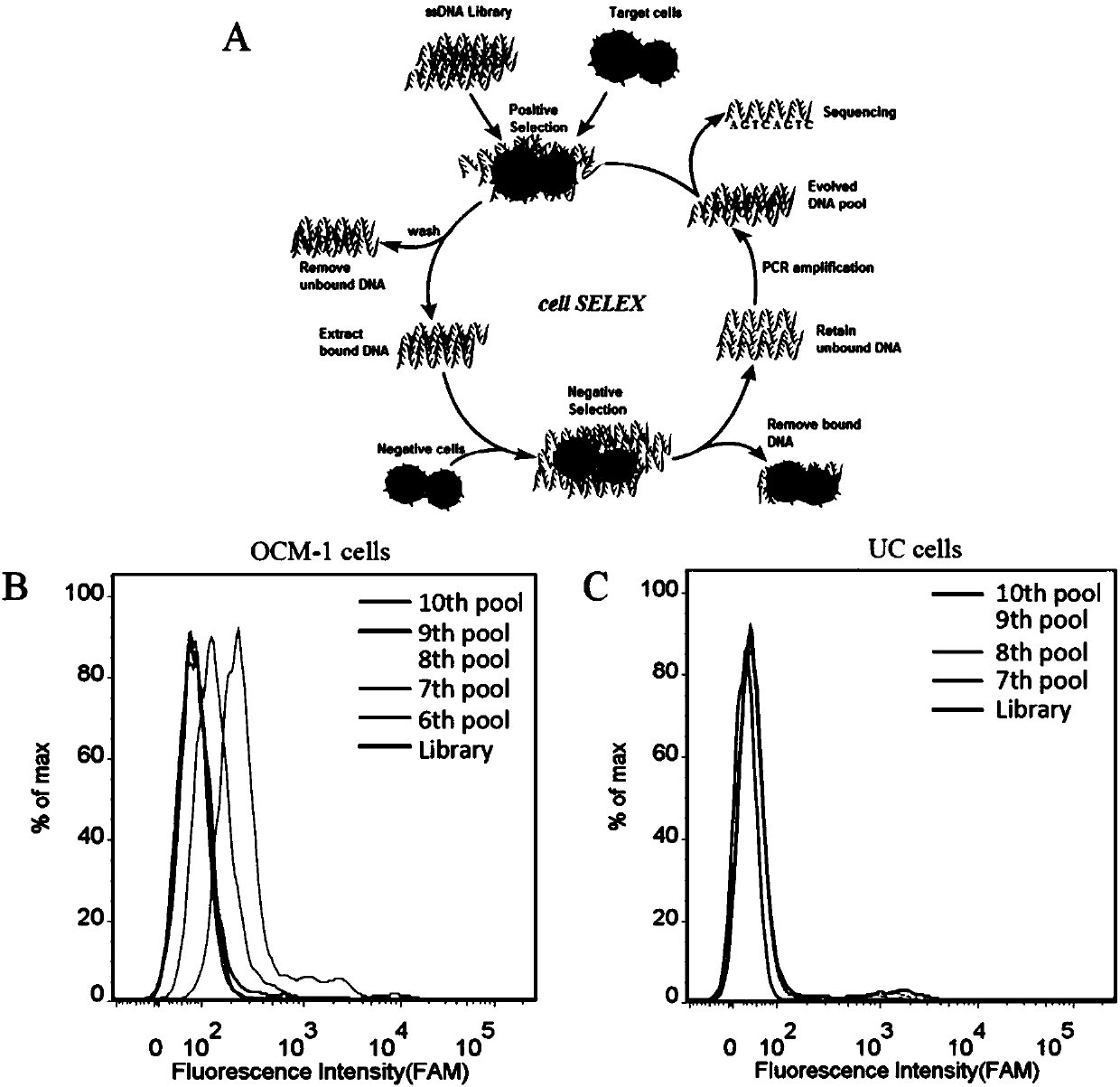
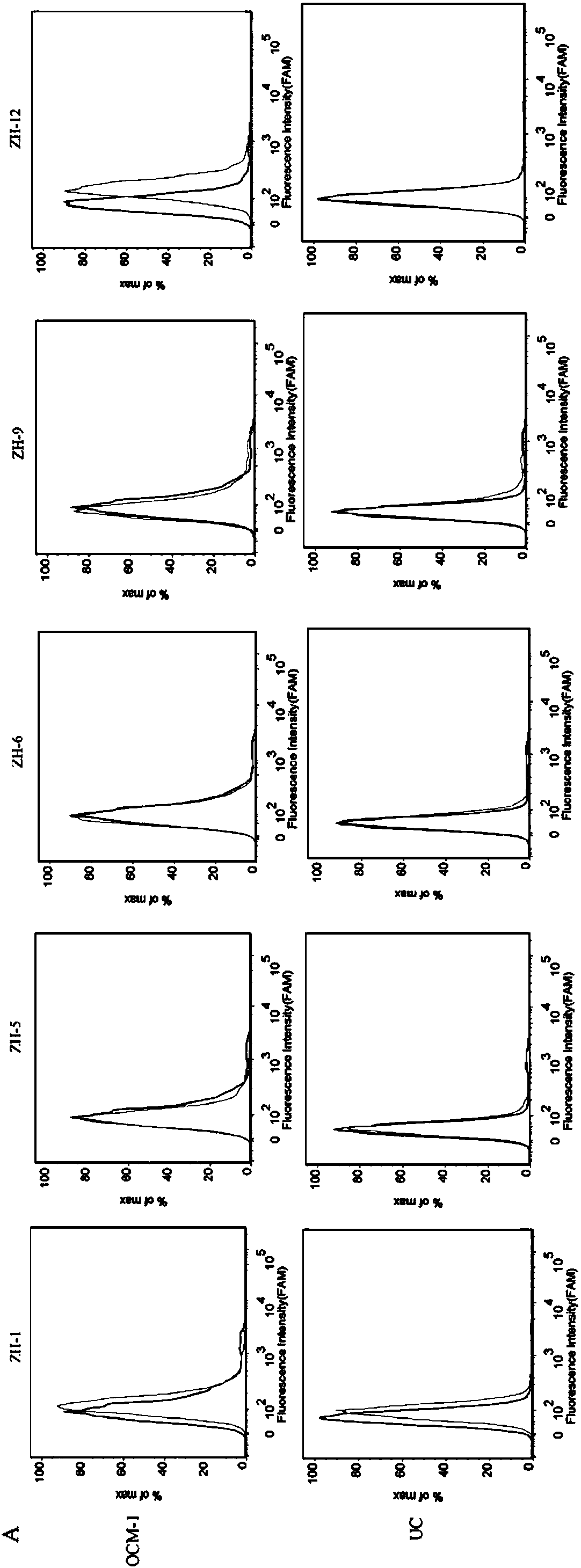
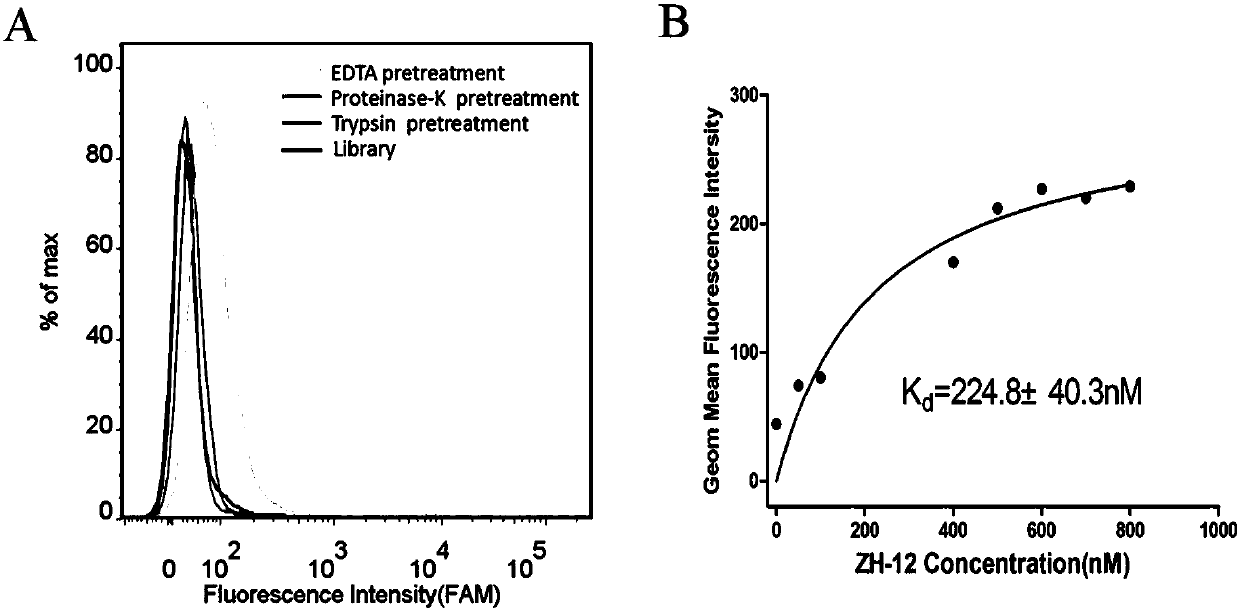
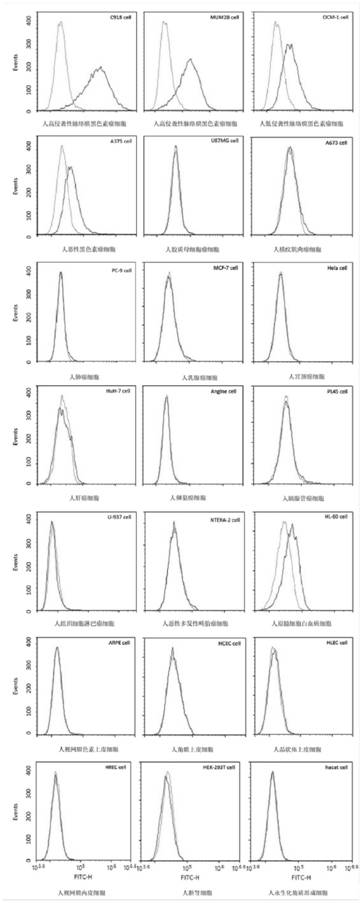
PendingCN108034658ASmall molecular weightSequence stabilityMaterial analysisDNA/RNA fragmentationImmunogenicityIn vitro
A nucleic acid aptamer used for detecting human uveal melanoma cells (OCM-1) and applications thereof in preparation of detection preparations are disclosed. Compared with the prior art, the nucleic acid aptamer and the applications are advantageous in that the prepared nucleic acid aptamer can specifically recognize the uveal melanoma cells, has good affinity, no immunogenicity, and a small molecular weight, and can be chemically synthesized in vitro; and different positions of the nucleic acid aptamer can be modified and substituted. In addition, the nucleic acid aptamer has advantages of astable sequence, capability of being convenient to store and mark, and the like. When the nucleic acid aptamer is adopted for detecting the human uveal melanoma cells, operation is simpler and rapider. The nucleic acid aptamer has a synthesis cost lower than antibody preparing costs, a short period and good reproducibility.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
Cancer cell broad spectrum high-activity promoter and usage thereof
ActiveCN104212802ASequence stabilityGenetic material ingredientsMicroinjection basedCancer cellHigh activity
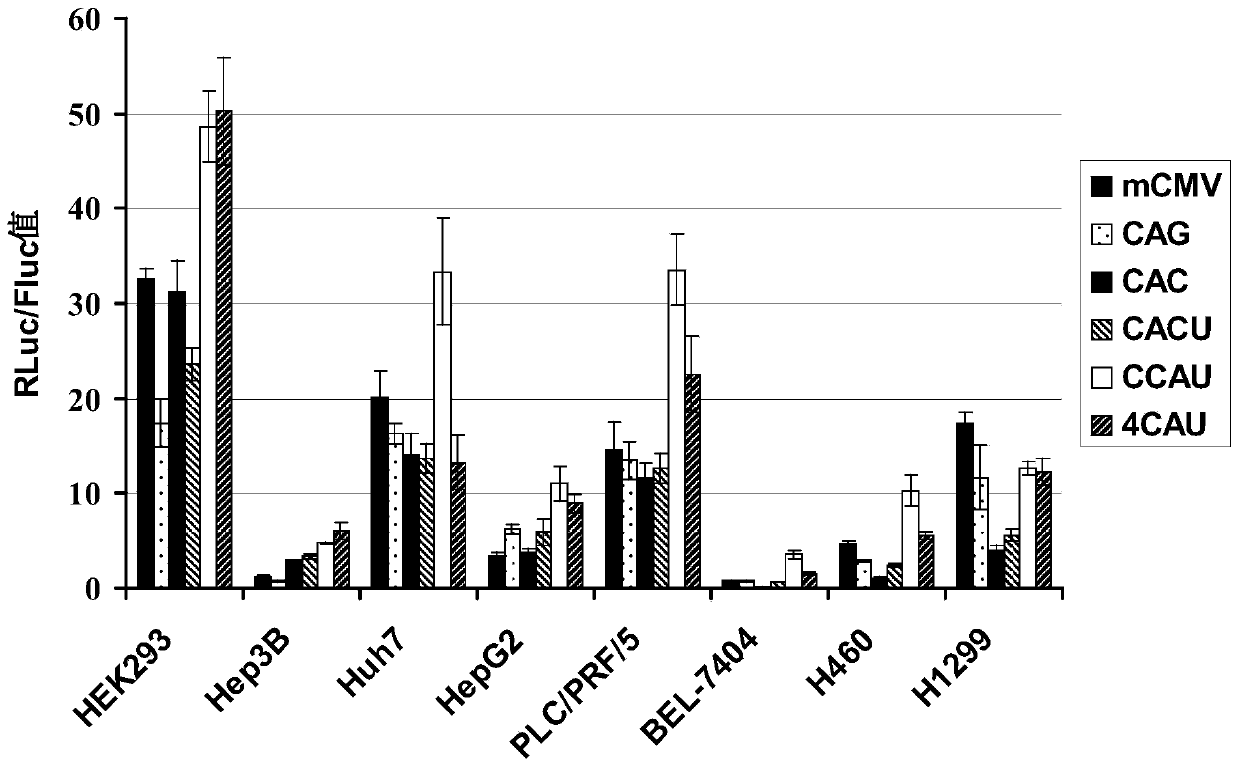
The invention belongs to the field of the molecular biology and relates to a cancer cell broad spectrum high-activity promoter and the usage thereof. The cancer cell broad spectrum high-activity promoter can express exogenous genes in cancer cells with broad spectrums efficiently. The expressive activity of the promoter in a series of cancer cells is higher than the existing CAG promoters and is stable in the sequence (it does not have sequence loss in the transfer process of the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell). The cancer cell broad spectrum high-activity promoter can be applied to the oncogene therapeutic process to drive the exogenous genes to be expressed efficiently in the cancer cells.
Owner:HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV +1
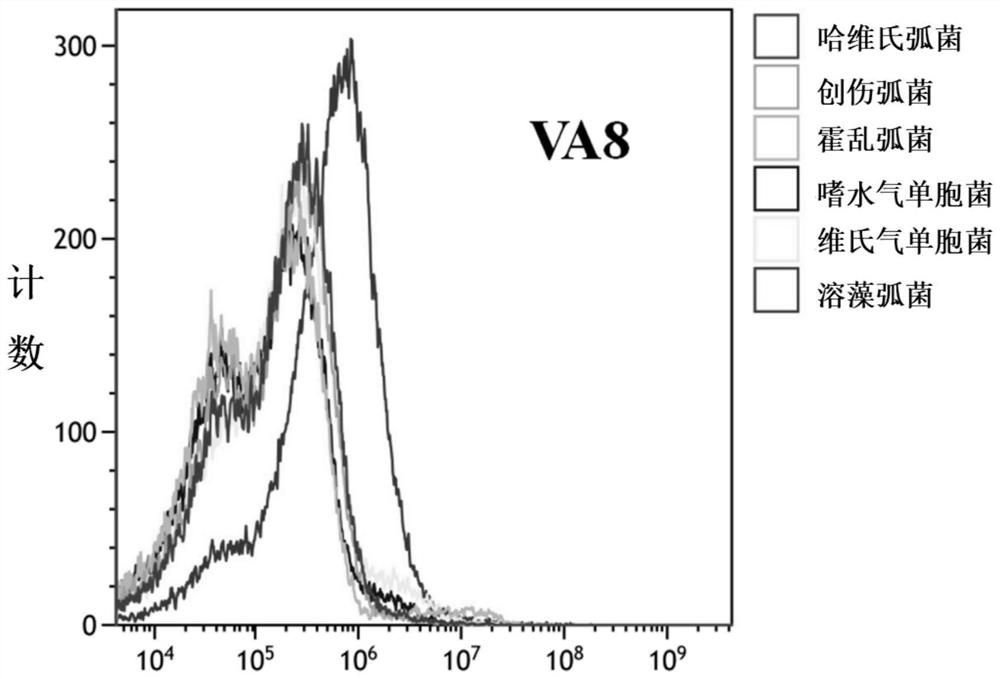
Nucleic acid aptamer and application thereof to detect pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus
ActiveCN109161547AHigh affinityImprove featuresDNA preparationMaterial analysisAptamerNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses an ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer and application thereof to detect pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus. The nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is 5'-GACGCTTACTCAGGTGTGACTCGCGTTTTATTGGTGTGGGGCTGGGGCGGTGGGTGGCTCTACTGGTTCCGTTCGAAGGACGCAGATGAAGTCTC-3'(SEQ ID NO:1). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is specific for and highly sensitive to the trachinotus ovatus source pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus, and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is stable in structure and easy to modify, facilitates synthesis and preservation, and can rapidly and accurately detect and diagnose the trachinotus ovatus source pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Aptamer for specifically recognizing GTONNV (Guangxi trachinotus ovatus nervous necrosis virus) and application of aptamer
ActiveCN109136229AHigh affinity and specificityShort preparation cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationImmunogenicityNucleotide
The invention discloses an ssDNA aptamer capable of specifically recognizing a GTONNV (Guangxi trachinotus ovatus nervous necrosis virus) and an application of the aptamer. The nucleotide sequence ofthe ssDNA aptamer is 5'-GTCTGAAGTAGACGCAGGAGCCTTTCGTGTTTCATTAGTGTGTTTCCATTGGGCGGCTCGGGGCAAAAGGAGTCACACCTGAGTAAGCGT-3'(SEQ ID NO: 1) or 5'-CCTTTCGTGTTTCATTAGTGTGTTTCCATTGGGCGGCTCGGGGCAAAAGG-3'(SEQ ID NO: 2). The ssDNA aptamer has specificity and high sensitivity to GTONNV infected cells and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA aptamer has high specificity and high affinity, and is free of cytotoxicity,stable, easy to modify and convenient to synthesize and preserve, and the GTONNV infected cells can be detected and diagnosed rapidly and accurately.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid aptamer specifically targeting Trachinotus ovatus nerve necrosis virus and application thereof
ActiveCN109207480AHigh affinityImprove featuresDNA preparationMaterial analysisAptamerTrachinotus ovatus
The invention discloses an ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer specifically targeting Trachinotus ovatus nerve necrosis virus and application thereof, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acidaptamer is 5'-GTCTGAAGTAGACGCAGGAGAACTGTATTAGCCTCTGGGTGCCGCACCGTAGTGCCCTATCTAACATCACAGTCACACCTGAGTAAGCGT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1) or 5'-AACTGTATTAGCCTCTGGGTGCCGCACCGTAGTGCCCTATCTAACATCAC-3' (SEQ ID NO:2). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer of the invention has specificity and high sensitivity to nerve necrosis virus infected cells of Trachinotus ovatus , and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer has high specificity, high affinity, no cytotoxicity, stable and easy to modify, easy to synthesize and preserve, and can be used for rapid and accurate detection and diagnosis of nerve necrosis virus infected cells of Trachinotus ovatus.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Chimeric strong promoter, and applications thereof
ActiveCN107043774ASequence stabilityGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid vectorEucaryotic cellAbnormal tissue growth
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and relates to a chimeric strong promoter, and applications thereof. The chimeric strong promoter is capable of realizing wide spectrum high efficiency expression of exogenous genes in tumor cells, the expression activity of the chimeric strong promoter in a series of tumor cells is higher than traditional CAG promoter, and the sequence is stable (sequence missing is not caused in prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell migration process). The chimeric strong promoter is suitable to be used in tumor gene therapy process to drive high efficiency expression of exogenous genes in tumor cells.
Owner:HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV +1
Nucleic acid aptamer and construction method thereof and application thereof in detecting soft-shelled turtle iridovirus
ActiveCN111363748AEasy to retouchEasy to transportDNA preparationMaterial analysisBiotechnologyAptamer
The invention provides a nucleic acid aptamer and a construction method thereof and an application thereof in detecting soft-shelled turtle iridovirus. The nucleic acid aptamer comprises a DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or a derivative thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer provided by the invention has higher affinity and specificity for the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus, and in addition has the advantages such as non-immunogenicity, short preparation cycle, good reproducibility, small molecular weight, being convenient for in vitro chemical synthesis, being convenient for labeling, being easyto modify and replace different parts of the nucleic acid aptamer, stable sequence, and being easy to transport and store. When a rapid detection method based on the nucleic acid aptamer of the invention is used to detect the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus, the operation is simple and rapid, and relatively high accuracy and sensitivity can be achieved. The nucleic acid aptamer can be used to construct molecular probes or detection kits, and is combined with detection equipment such as microplate reader, flow cytometer and fluorescence microscope to realize accurate detection of the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Esophageal carcinoma prognosis marker and application thereof
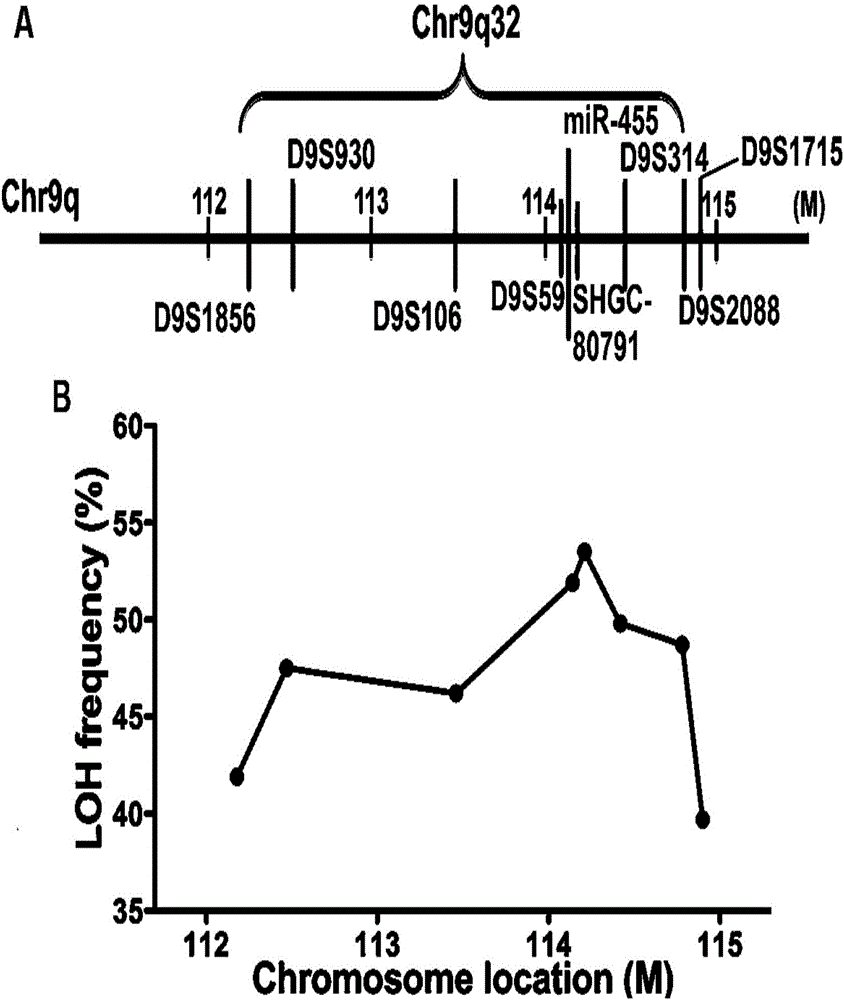
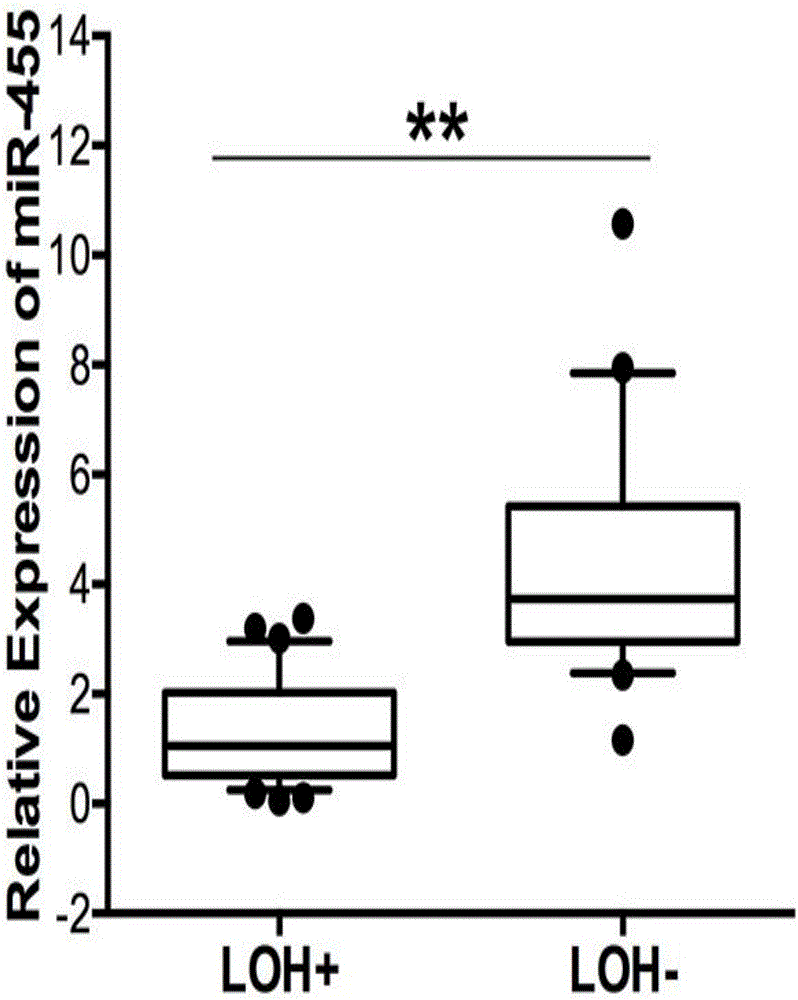
ActiveCN106701992AImprove accuracySequence conservationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringHeterozygosity Loss
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and phymatology, relates to an esophageal carcinoma prognosis marker and application thereof, and in particular relates to a miRNA marker related to esophageal carcinoma chromosome 9q32 heterozygosity loss and application of the miRNA marker. The primer is a primer of the miRNA marker related to esophageal carcinoma chromosome 9q32 heterozygosity loss.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Nucleic acid aptamer ZQ-2 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application of nucleic acid aptamer ZQ-2
InactiveCN113373153ALower synthesis costShort cycleOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAptamerChemical synthesis
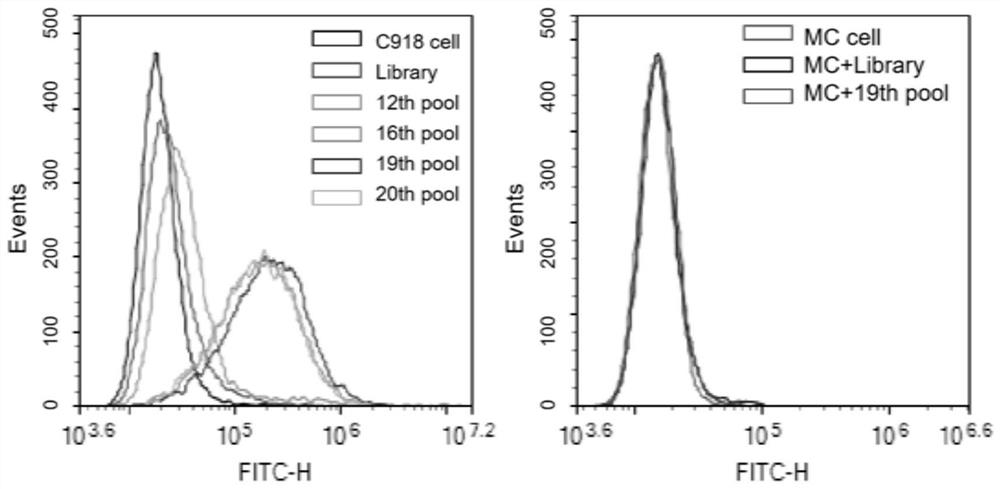
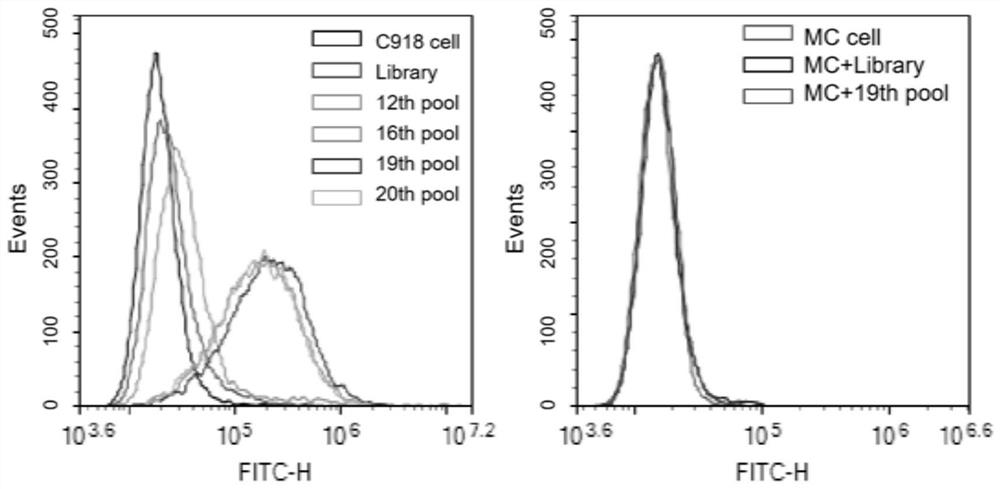
According to the nucleic acid aptamer ZQ-2 for targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and the application thereof, through property characterization of the nucleic acid aptamer ZQ-2 and identification of target molecules, tumor markers of choroidal melanoma can be found, and the nucleic acid aptamer ZQ-2 is used for diagnosis and treatment and targeted therapy of choroidal melanoma and has a wide application prospect. The prepared nucleic acid aptamer can specifically recognize human highly invasive choroidal melanoma cells and choroidal melanoma tissues and has very high affinity; there is no immunogenicity; the molecular weight is small, and in-vitro chemical synthesis can be realized; different parts of the aptamer are easy to modify and replace. Meanwhile, the gene has the advantages of stable sequence, convenience in storage, convenience in marking and the like. When the nucleic acid aptamer is used for detecting human choroidal melanoma cells, the operation is simpler and quicker, the synthesis cost of the nucleic acid aptamer is lower than that of antibody preparation, the period is short, and the reproducibility is good.
Owner:THE EYE HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
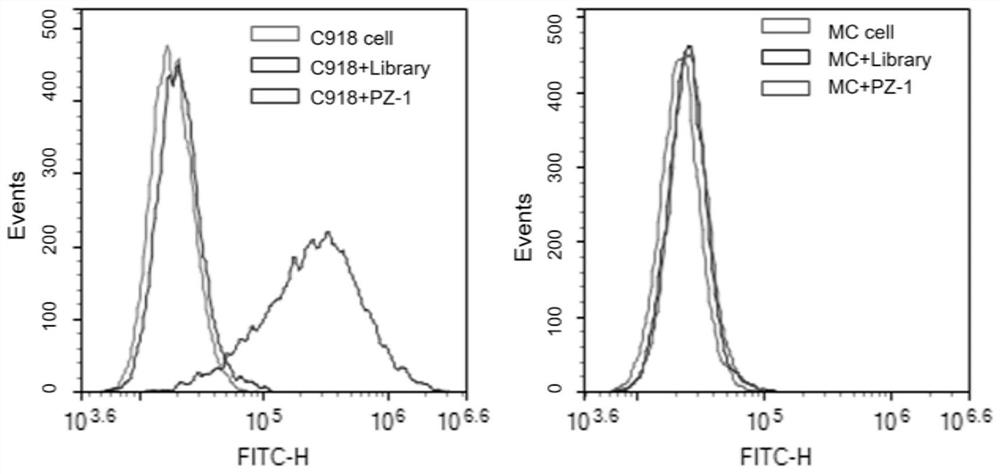
Aptamer PZ-1 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application
PendingCN113373154ALower synthesis costShort cyclePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsAptamerChemical synthesis
The invention relates to an aptamer PZ-1 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application. Through property characterization of the nucleic acid aptamer PZ-1 and identification of target molecules, tumor markers of choroidal melanoma can be found, and the nucleic acid aptamer PZ-1 is used for diagnosis and treatment and targeted therapy of choroidal melanoma. The prepared nucleic acid aptamer can specifically recognize human highly invasive choroidal melanoma cells and choroidal melanoma tissues and has very high affinity; there is no immunogenicity;the molecular weight is small, and in-vitro chemical synthesis can be realized; different parts of the aptamer are easy to modify and replace. Meanwhile, the invention has the advantages of stable sequence, convenience in storage, convenience in marking and the like. When the nucleic acid aptamer is used for detecting human choroidal melanoma cells, the operation is simpler and quicker, the synthesis cost of the nucleic acid aptamer is lower than that of antibody preparation, the period is short, and the reproducibility is good.
Owner:THE EYE HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
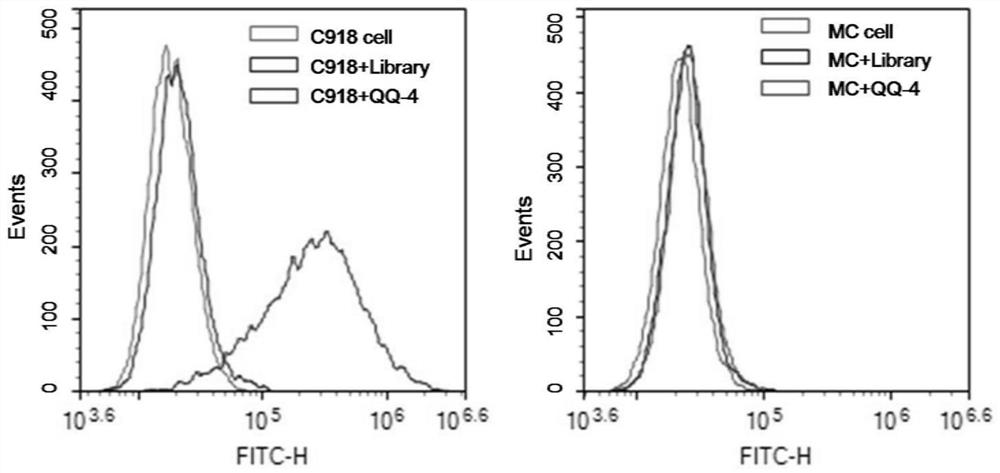
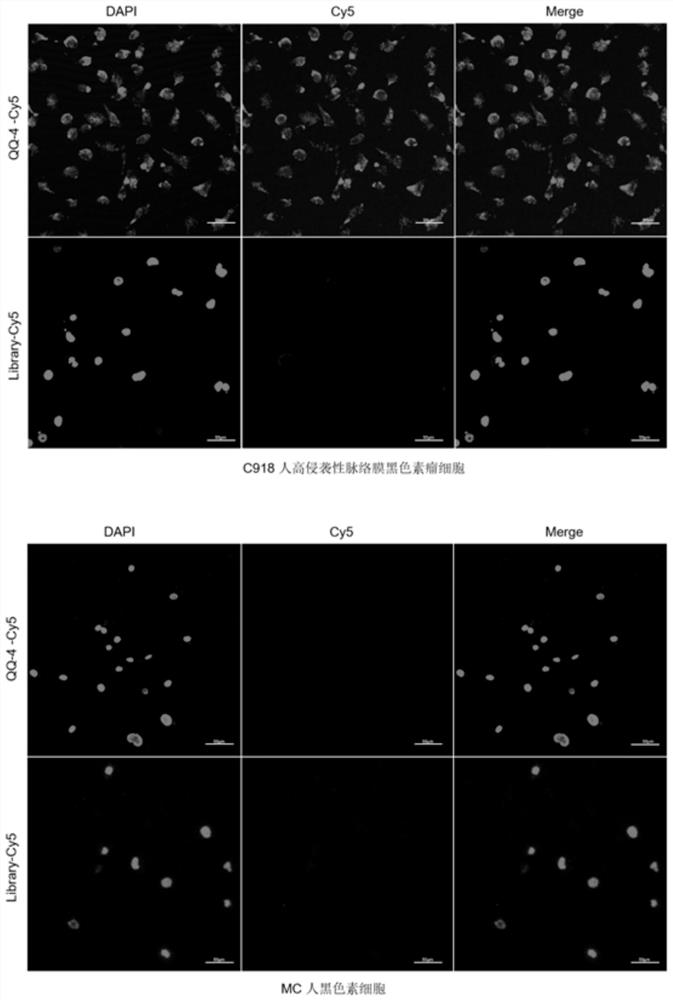
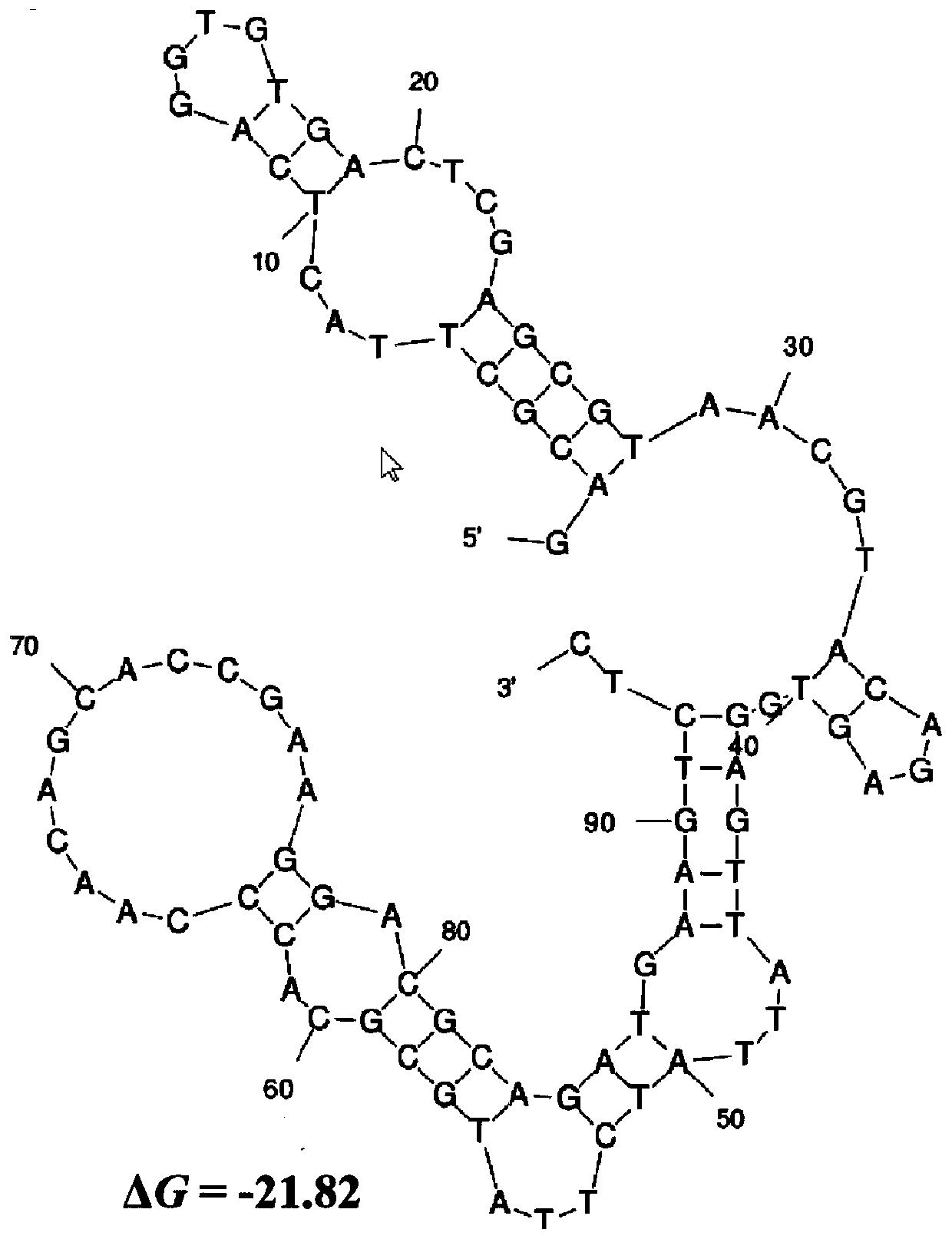
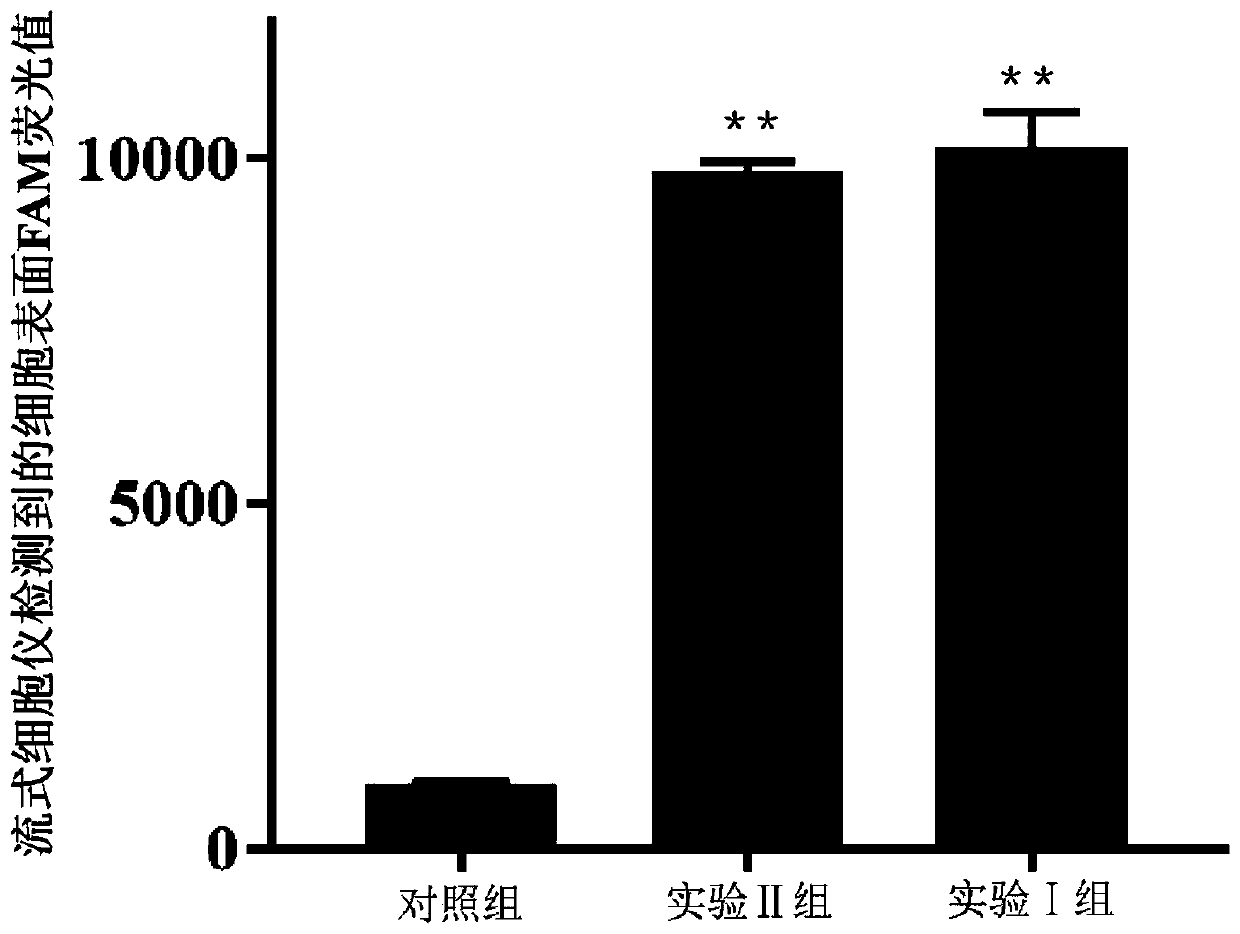
Nucleic acid aptamer QQ-4 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application
PendingCN113337511ALower synthesis costShort cyclePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsAptamerChemical synthesis
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer QQ-4 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application. By identifying the property characterization and target molecules of the nucleic acid aptamer QQ-4, a tumor marker of the choroidal melanoma can be found, and the nucleic acid aptamer QQ-4 is used for diagnosis and treatment and targeted treatment of the choroidal melanoma. The prepared nucleic acid aptamer can specifically recognize human highly invasive choroidal melanoma cells and choroidal melanoma tissues and has high affinity; the nucleic acid aptamer has no immunogenicity; the molecular weight is small, and in-vitro chemical synthesis can be achieved; and different parts of the nucleic acid aptamer are easy to modify and replace. Meanwhile, the nucleic acid aptamer has the advantages of being stable in sequence, convenient to store, convenient to mark and the like. When the nucleic acid aptamer is adopted for detecting the human choroidal melanoma cells, operation is easier and faster, the synthesis cost of the nucleic acid aptamer is lower than the cost of antibody preparation, the period is short, and reproducibility is good.
Owner:THE EYE HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Nucleic acid ligand for soft-shelled turtle iridovirus, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111454956AEasy to retouchEasy to transportDNA preparationMaterial analysisBiotechnologyChemical synthesis
The invention provides a nucleic acid ligand for soft-shelled turtle iridovirus, and a construction method and application thereof. The nucleic acid ligand for the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus comprises a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and a derivative thereof. The nucleic acid ligand provided by the invention has relatively high affinity and specificity for the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus; and furthermore, the nucleic acid ligand also has the advantages of being free form immunogenicity, short in preparation period, good in reproducibility, small in molecular weight, convenient inin-vitro chemical synthesis, convenient to mark, easy to modify and substitute different parts of the nucleic acid ligand, steady in sequence, easy to transport and store, etc. When a rapid detectionmethod of the nucleic acid ligand in the invention is adopted for detecting the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus, operation is simple and rapid; the relatively high accuracy rate and sensitivity can beachieved; the nucleic acid ligand can be utilized for constructing a molecular probe or a detection kit; and furthermore, in combination with detection equipment, such as a microplate reader, a flow cytometry and a luorescence microscope, precise detection of the soft-shelled turtle iridovirus can be realized.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
A nucleic acid aptamer, kit and method for detecting pancreatic ductal carcinoma
ActiveCN104593372BHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAptamerWilms' tumor
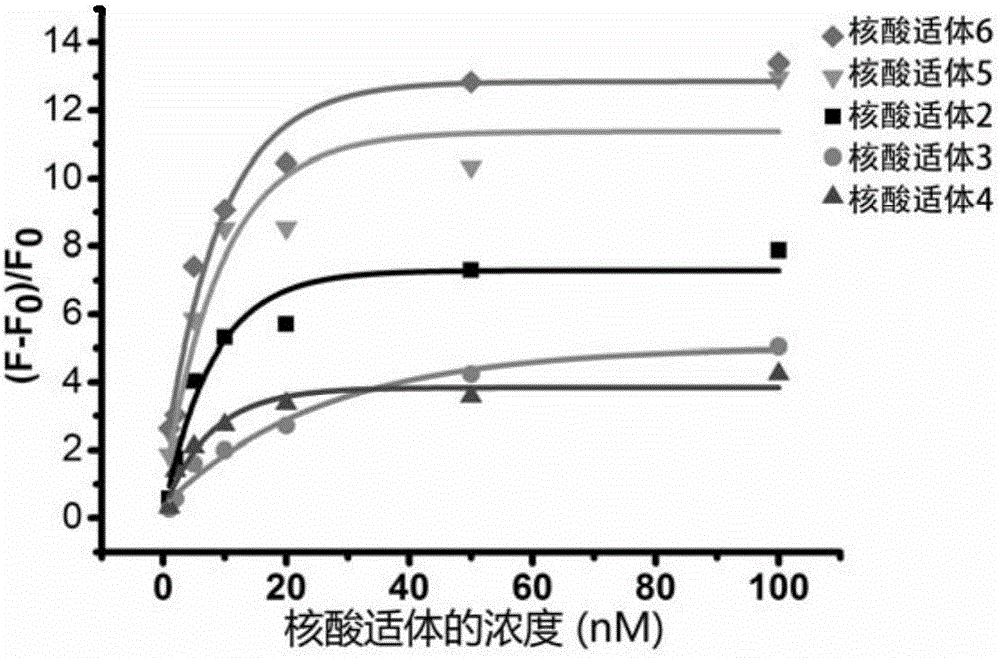
The invention provides an aptamer, a kit and a method for detecting pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma. The sequences of the aptamer are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The aptamer capable of identifying the pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma cell line PL45 is capable of identifying the pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma cell line PL45 specifically and with high affinity, and is highly in binding capacity. The danger of tumors can be layered molecularly by use of the aptamer; the aptamer is capable of specifically recognizing and binding tumor metastatic foci and identifying targets, and then a good method can be provided for diagnosing and treating the metastatic foci, and the method plays an important role in early detection of the pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
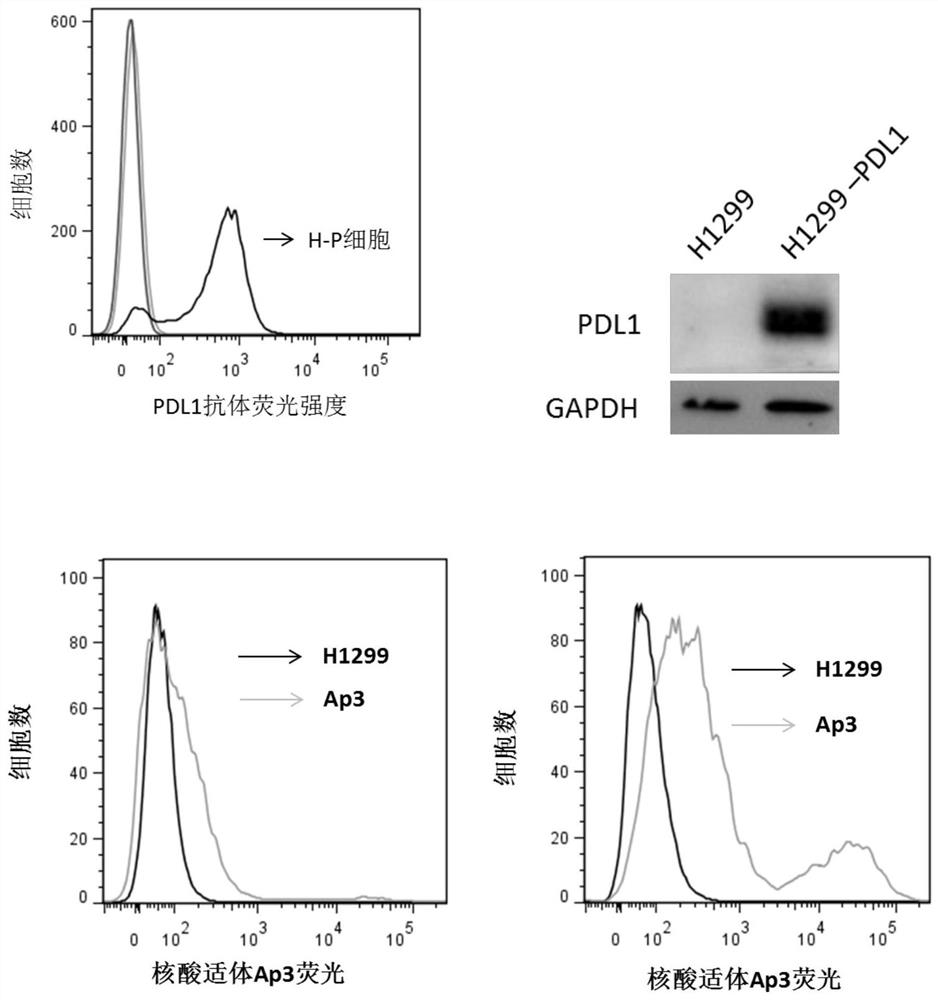
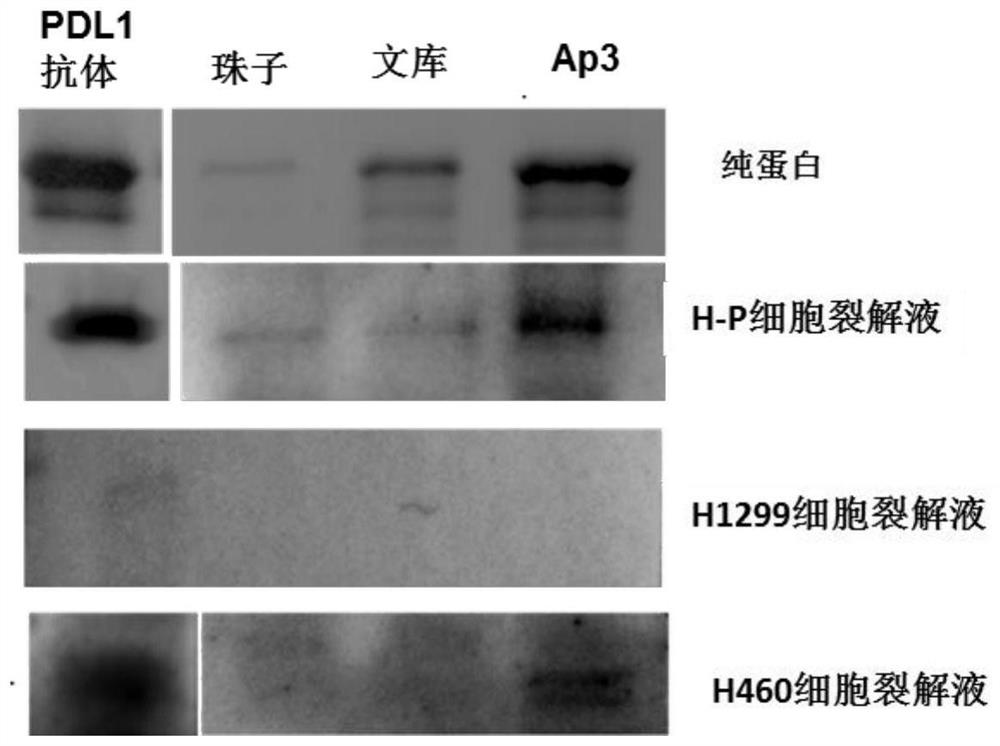
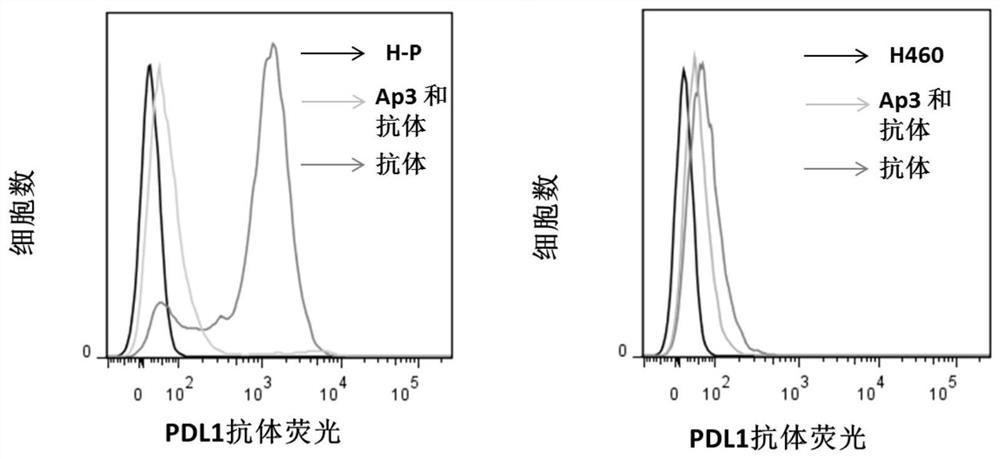
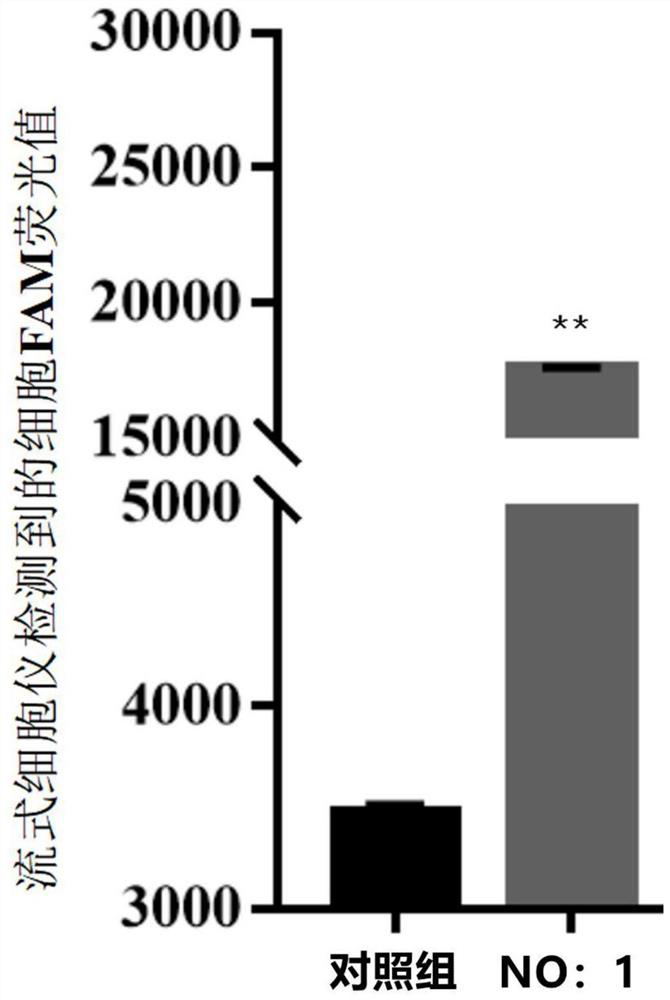
Nucleic acid aptamer for detecting human pdl1 protein and its application in preparation of detection preparation
ActiveCN107794268BSmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicBiological testingDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerProtein level
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer for detecting a human PDL1 protein. The sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer contains a sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1. Compared with theexisting nucleic acid aptamer, the nucleic acid aptamer provided by the invention has affinity and specificity similar to those of a protein, a small molecular weight and low immunogenicity, can be easily synthesized in vitro and modified, has good stability and is easy to store. The nucleic acid aptamer can fast and simply detect a PDL1 protein level, has good repeatability and greatly reduces acost.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Nucleic acid aptamer and its application in the detection of neuronecrosis virus derived from pompano ovata
The invention discloses a ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer and its application in detecting cells infected with neuronecrosis virus derived from pompano pomfret. The nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is 5'-GTCTGAAGTAGACGCAGGAGGCTCGGGGCTCGATATTGTAAAGGGAGTGTGTTTAGGAGGACGTGGTTGGAGTCACACCTGAGTAAGCGT‑3'( SEQ ID NO: 1) or 5'-GCTCGGGGCTCGATATTGTAAAGGGAGTGTGTTTAGGAGGACGTGGTTGG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer of the present invention has specificity and high sensitivity to cells infected with neuronecrosis virus derived from pompano pomfret and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer has high specificity, high affinity, no cytotoxicity, is stable and easy to modify, and is convenient for synthesis and storage, and can quickly and accurately detect and diagnose cells infected with neuronecrosis virus from pomfret ovata.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
A dna nucleic acid aptamer for detecting grouper iridescent virus infection and its screening method and application
ActiveCN104789568BImprove screening efficiencyHigh affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesScreening methodNormal cell
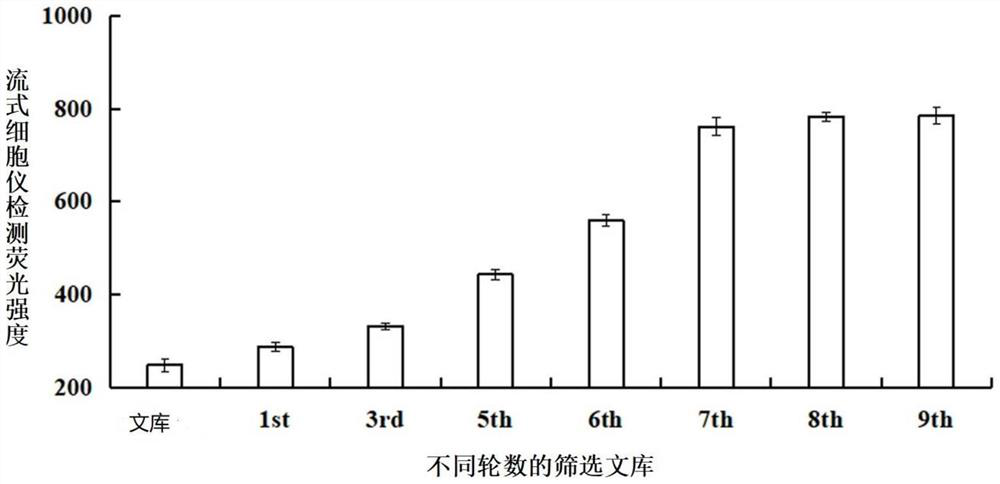
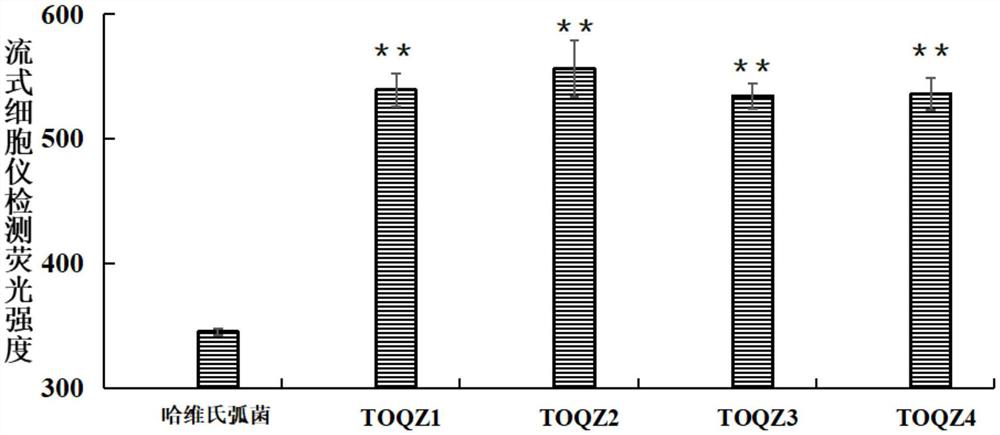
The invention discloses a DNA nucleic acid aptamer for detecting grouper iridescent virus infection, a screening method and application thereof. In each round of screening, two steps of reverse screening were introduced. First, the single-stranded DNA library of the previous round was combined with normal cells to remove non-specific ssDNA combined with normal grouper cells, and then the supernatant was combined with the normal cells. The grouper iridovirus-infected cells were combined for screening, and the ssDNA isolated from the grouper iridovirus-infected cells was then combined with normal cells to obtain the supernatant. PCR amplifies the library to prepare a single-stranded DNA library. Repeat the above screening process, compared with the number of normal cells in the first round of screening, increase the number of normal cells in the screening process by 2-6 times, compared with the binding time of the library and cells in the first round of screening, in the subsequent During the screening process, the binding time between the library and normal cells was increased from 0.5h to 1h, and the binding time between the library and virus-infected cells was shortened from 1h to 0.5h to improve the screening efficiency of each round.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid aptamer and application thereof to detect trachinotus ovatus source pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus
ActiveCN109161546AHigh affinityImprove featuresDNA preparationMaterial analysisTrachinotus ovatusNucleotide
The invention discloses an ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer and application thereof to detect trachinotus ovatus source pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus. The nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is 5'-GACGCTTACTCAGGTGTGACTCGTCGGTCGGGTGGTTGGGGTGGGTGGTCGGTTTTTAAGCTGTGTCATTGTCCGAAGGACGCAGATGAAGTCTC-3'(SEQ ID NO:1). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is specific for and highly sensitive to the trachinotus ovatus source pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus, and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is stable in structure and easy to modify, facilitates synthesis and preservation, and can rapidly and accurately detect and diagnose the trachinotus ovatus source pathogenic vibrio alginolyticus.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid aptamer specifically recognizing neuronecrosis virus derived from pompano ovata and its application
ActiveCN109136229BHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationNecrovirusNucleotide
The present invention discloses a ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically recognizing cells infected with neuronecrosis virus of pompano pomfret origin and its application. The nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is 5'-GTCTGAAGTAGACGCAGGAGCCTTTCGTGTTTCATTAGTGTGTTTCCATTGGGCGGCTCGGGGCAAAAGGAGTCACACCTGAGTAAGCGT‑3 ' (SEQ ID NO: 1) or 5'-CCTTTCGTGTTTCATTAGTGTGTTTCCATTGGGCGGCTCGGGGCAAAAGG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer of the present invention has specificity and high sensitivity to cells infected with neuronecrosis virus derived from pompano pomfret and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer has high specificity, high affinity, no cytotoxicity, is stable and easy to modify, and is convenient for synthesis and storage, and can quickly and accurately detect and diagnose cells infected with neuronecrosis virus from pomfret ovata.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
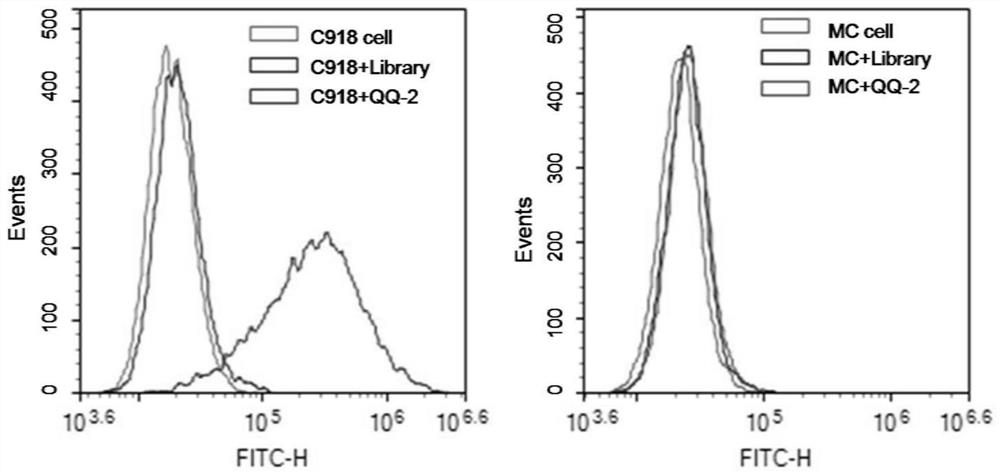
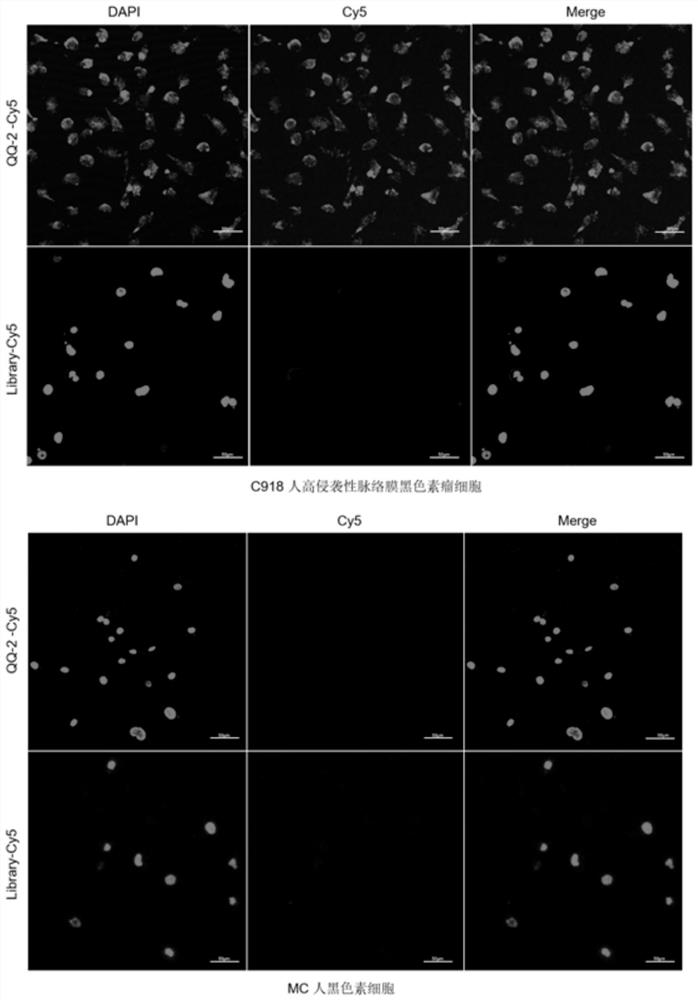
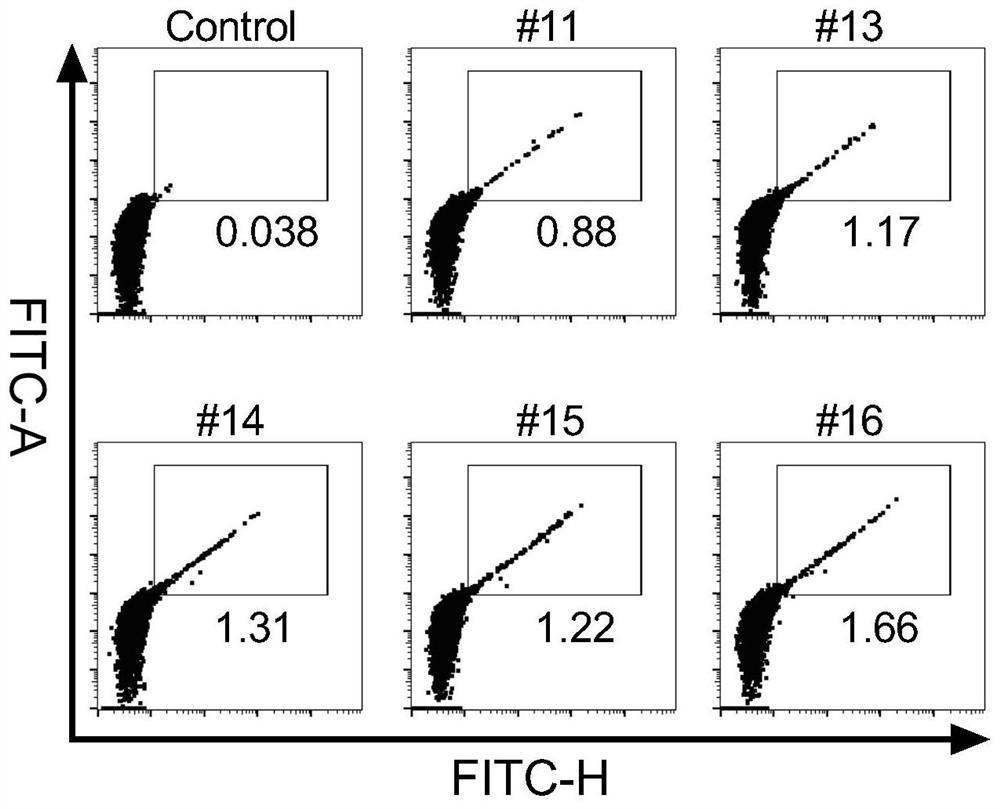
Nucleic acid aptamer QQ-2 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application
InactiveCN113337512ALower synthesis costShort cycleOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTargeted therapyChoroidal melanoma
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer QQ-2 targeting human highly invasive choroidal melanoma and application. By identifying the property characterization and target molecules of the nucleic acid aptamer QQ-2, a tumor marker of the choroidal melanoma can be found, and the nucleic acid aptamer QQ-2 is used for diagnosis and treatment and targeted treatment of the choroidal melanoma. The prepared nucleic acid aptamer can specifically recognize human highly invasive choroidal melanoma cells and choroidal melanoma tissues and has high affinity; the nucleic acid aptamer has no immunogenicity; the molecular weight is small, and in-vitro chemical synthesis can be achieved; and different parts of the nucleic acid aptamer are easy to modify and replace. Meanwhile, the nucleic acid aptamer has the advantages of being stable in sequence, convenient to store, convenient to mark and the like. When the nucleic acid aptamer is adopted for detecting the human choroidal melanoma cells, operation is easier and faster, the synthesis cost of the nucleic acid aptamer is lower than the cost of antibody preparation, the period is short, and reproducibility is good.
Owner:THE EYE HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Nucleic acid aptamer specifically bound with human FXYD2 gamma a and derivative, screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN113481203AHigh affinityImprove featuresLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisAptamerAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention provides a nucleic acid aptamer specifically bound with human FXYD2 gamma a and a derivative, a screening method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer obtained through the screening method is 5'-AACGAAGGTATACAAAAATATAATATAAATATCTACTACG-3', and compared with an FXYD2 gamma a specific antibody, the nucleic acid aptamer has the advantages of being short in screening period, low in cost, stable, easy to store, capable of being transported at normal temperature, wide in application and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
A nucleic acid aptamer and its application in the detection of pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus from pompano ovata
The present invention discloses a ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer and its application in pathogenic alginolyticus vibrio origin from oval pomfret. The nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is 5'-GACGCTTACTCAGGTGTGACTCGTCGGTCGGGTGGTTGGGGTGGGTGGTCGGTTTTTAAGCTGTGTCATTGTCCGAAGGACGCAGATGAAGTCTC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer of the present invention has specificity and high sensitivity to pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus derived from oval pomfret, and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer has a stable structure, is easy to modify, is convenient for synthesis and storage, and can rapidly and accurately detect and diagnose pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus derived from oval pomfret.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Crowd behavior simulation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114155271AEliminate deformationSequence stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisSimulationArtificial intelligence
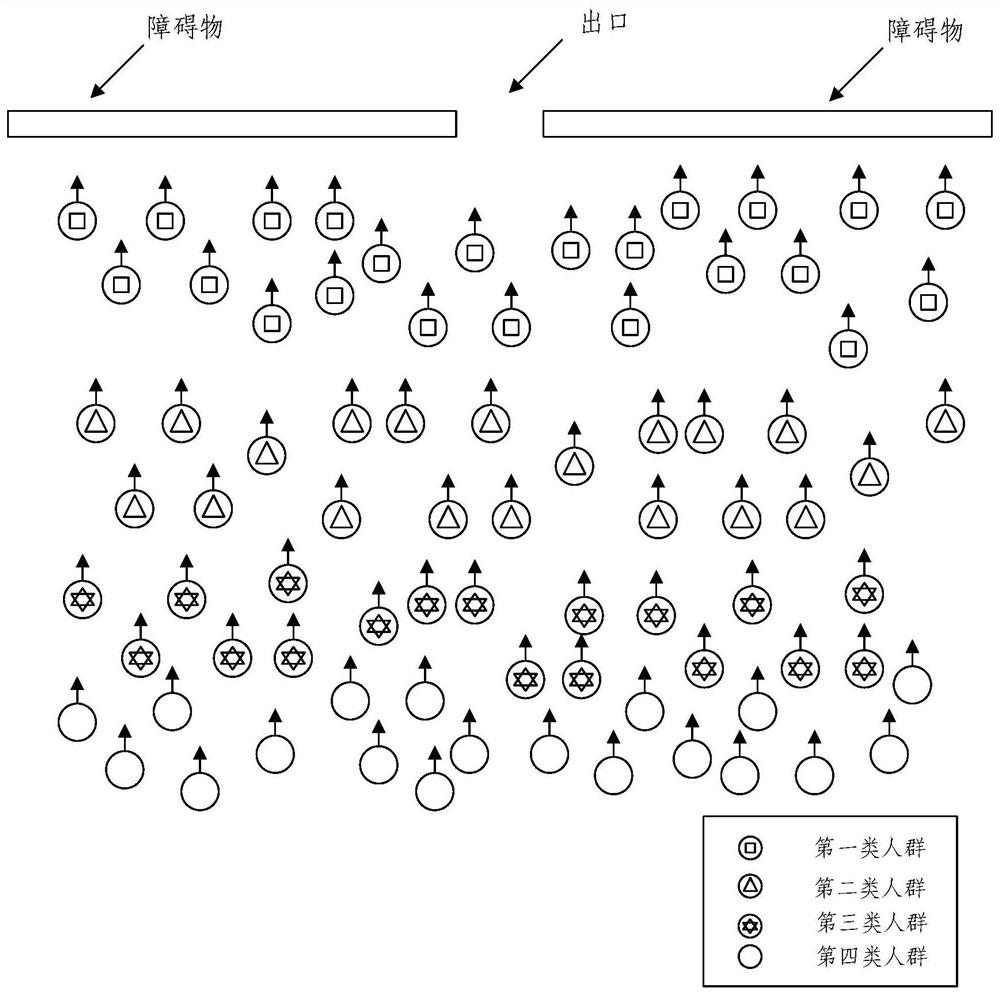
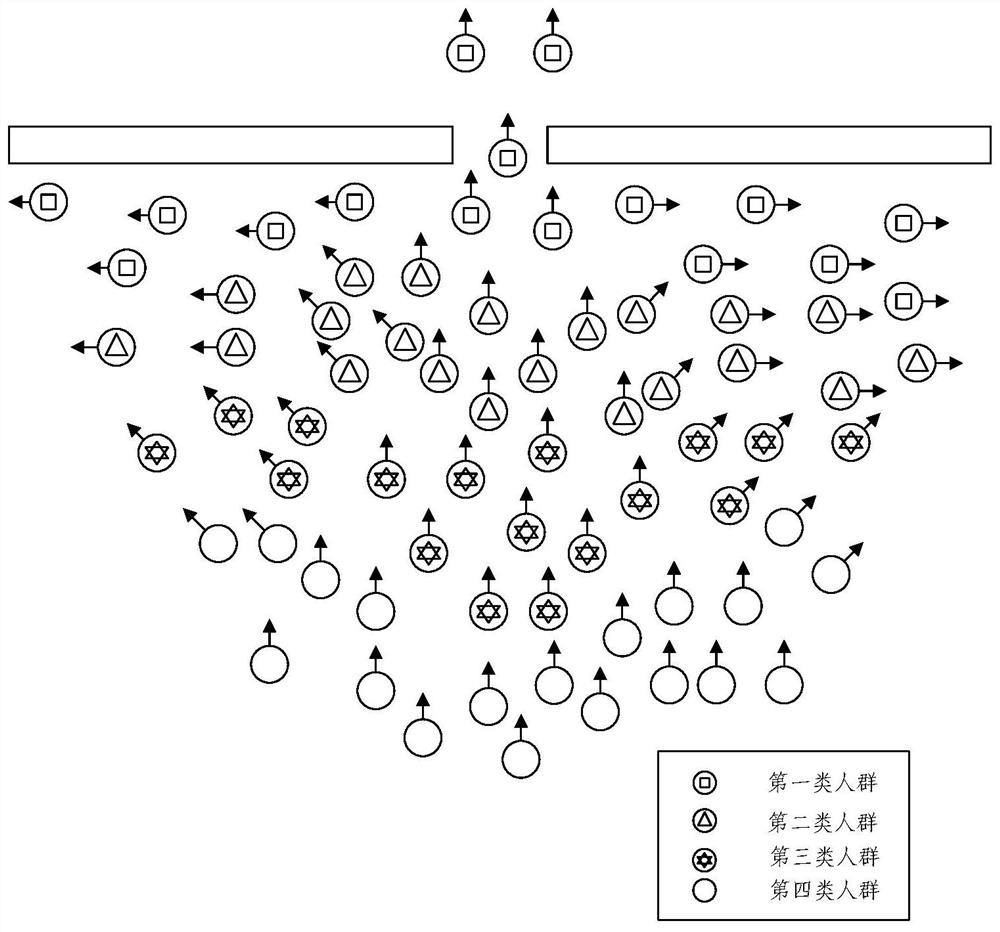
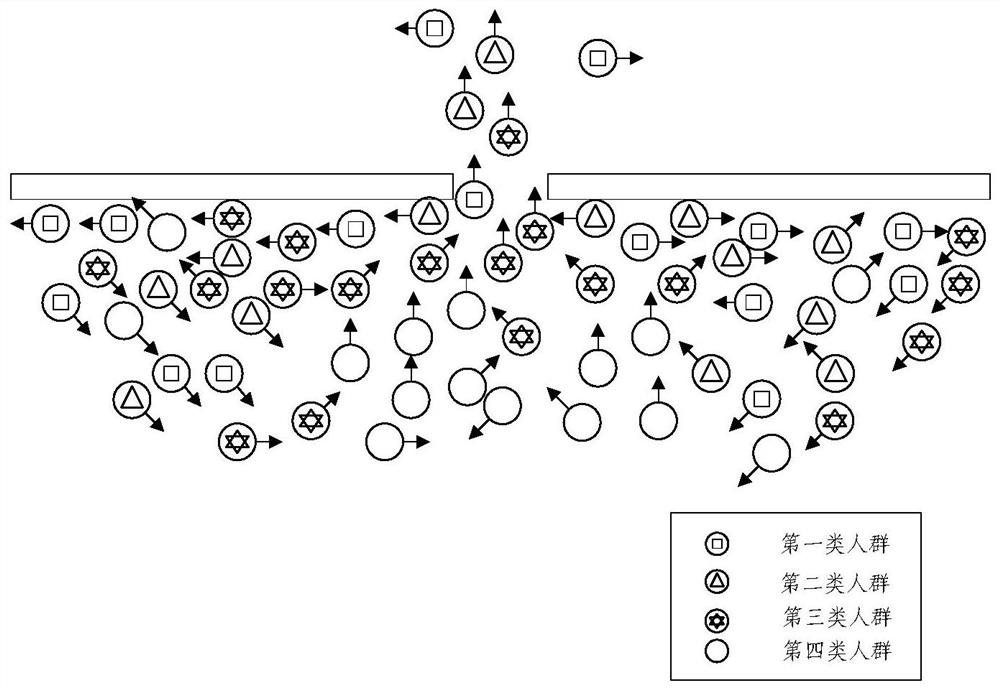
The invention provides a crowd behavior simulation method and apparatus, an electronic device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of determining a target perception domain and a target relative orientation of a target pedestrian; based on the target perception domain and the target relative orientation, determining the sharing proportion of the target pedestrian to the avoidance speed; based on the expected speed of the target pedestrian, determining a retreat avoiding half-plane line, the retreat avoiding half-plane line being used for limiting the feasible speed of the target pedestrian in a feasible solution region of the retreat avoiding half-plane line; and performing crowd behavior simulation through an ORCA model based on the sharing proportion and the back-off avoidance semi-plane line. According to the method, the basic ORCA model is improved by introducing the perception domain and the back-off avoidance configuration, the arch-shaped crowding phenomenon can be stably reproduced, and the sequence stability is achieved.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
Nucleic acid aptamer for recognizing extracellular vesicles of ovarian cancer drug-resistant patient and application of nucleic acid aptamer
ActiveCN114574497AHigh affinityStrong characteristicOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAptamerChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer for recognizing extracellular vesicles of an ovarian cancer drug-resistant patient and application of the nucleic acid aptamer, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The nucleic acid aptamer obtained through cell screening has high affinity and specificity and low immunogenicity, can be chemically synthesized in vitro, is low in cost and small in molecular weight, can modify and replace different parts of the nucleic acid aptamer, and is stable in sequence and easy to store. The nucleic acid aptamer can be used for preparing anti-tumor drugs, ovarian cancer drug-resistant cell strains or ovarian cancer drug-resistant patient serum exosome detection kits or ovarian cancer drug-resistant patient serum exosome detection probes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CANCER HOSPITAL
Human pancreatic polypeptide nucleic acid aptamer and its screening method and application
ActiveCN106282193BHigh affinityImprove featuresBiological testingDNA preparationChemical synthesisScreening method
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
A nucleic acid aptamer and its application in detection of pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus
The invention discloses a ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer and its application in pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus. The nucleotide sequence of the ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer is 5'-GACGCTTACTCAGGTGTGACTCGCGTTTTATTGGTGTGGGGCTGGGGCGGTGGGTGGCTCTACTGGTTCCGTTCGAAGGACGCAGATGAAGTCTC-3' (SEQ ID No: 1). The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer of the invention has specificity and high sensitivity to the pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus derived from pomfret ovata, and has no immunogenicity. The ssDNA nucleic acid aptamer has a stable structure, is easy to modify, and is convenient for synthesis and storage, and can quickly and accurately detect and diagnose pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus derived from pomfret ovata.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com