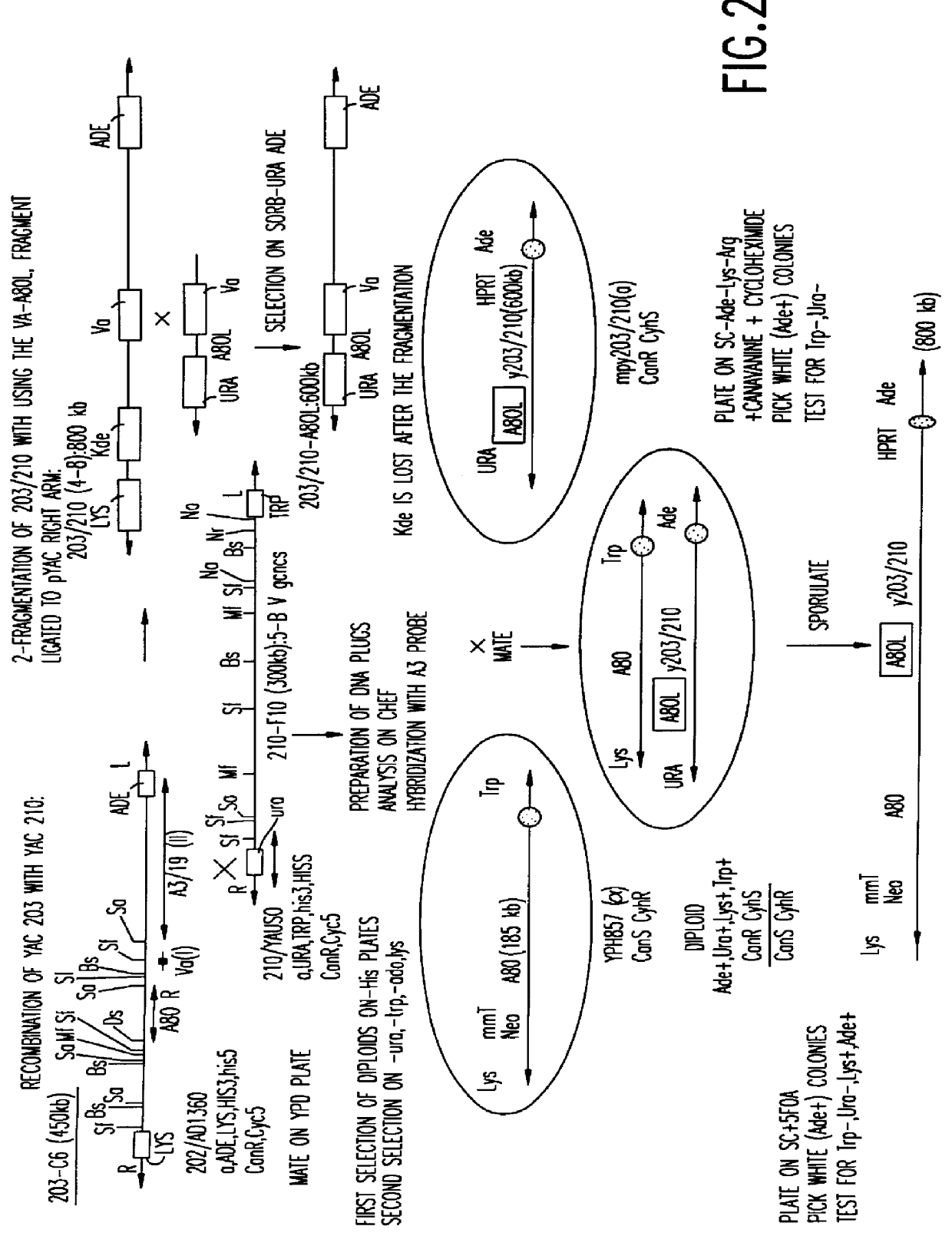
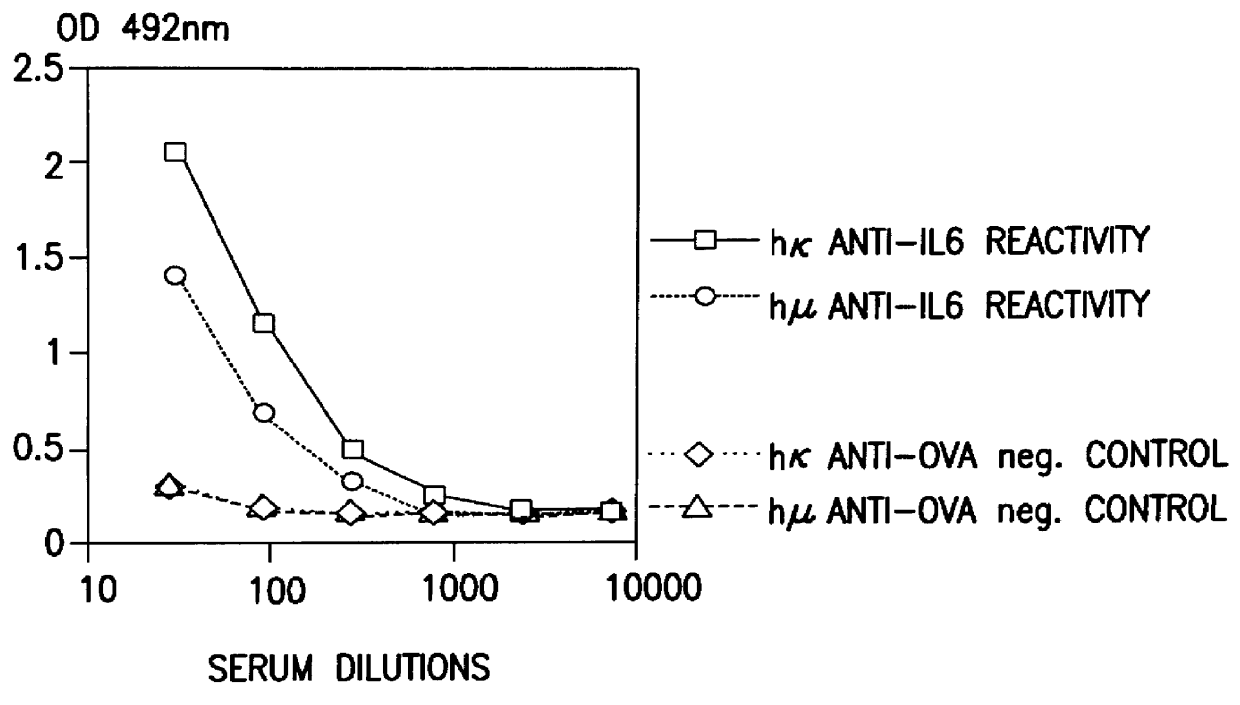
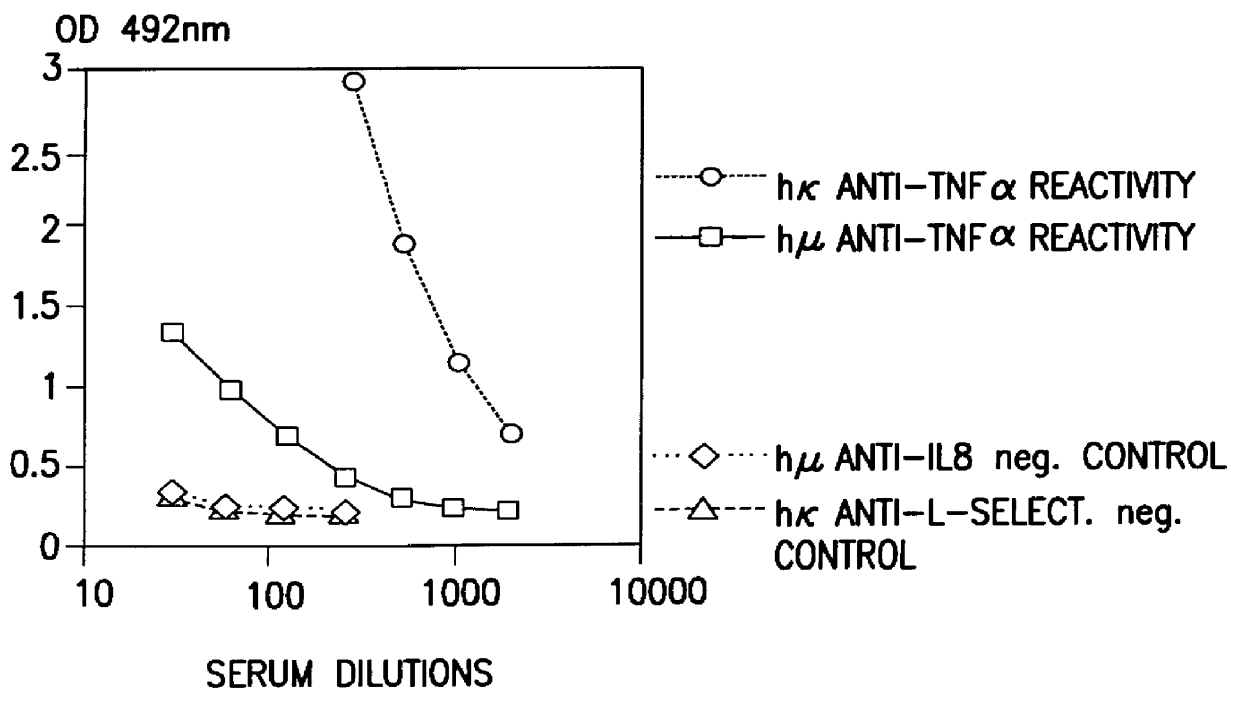
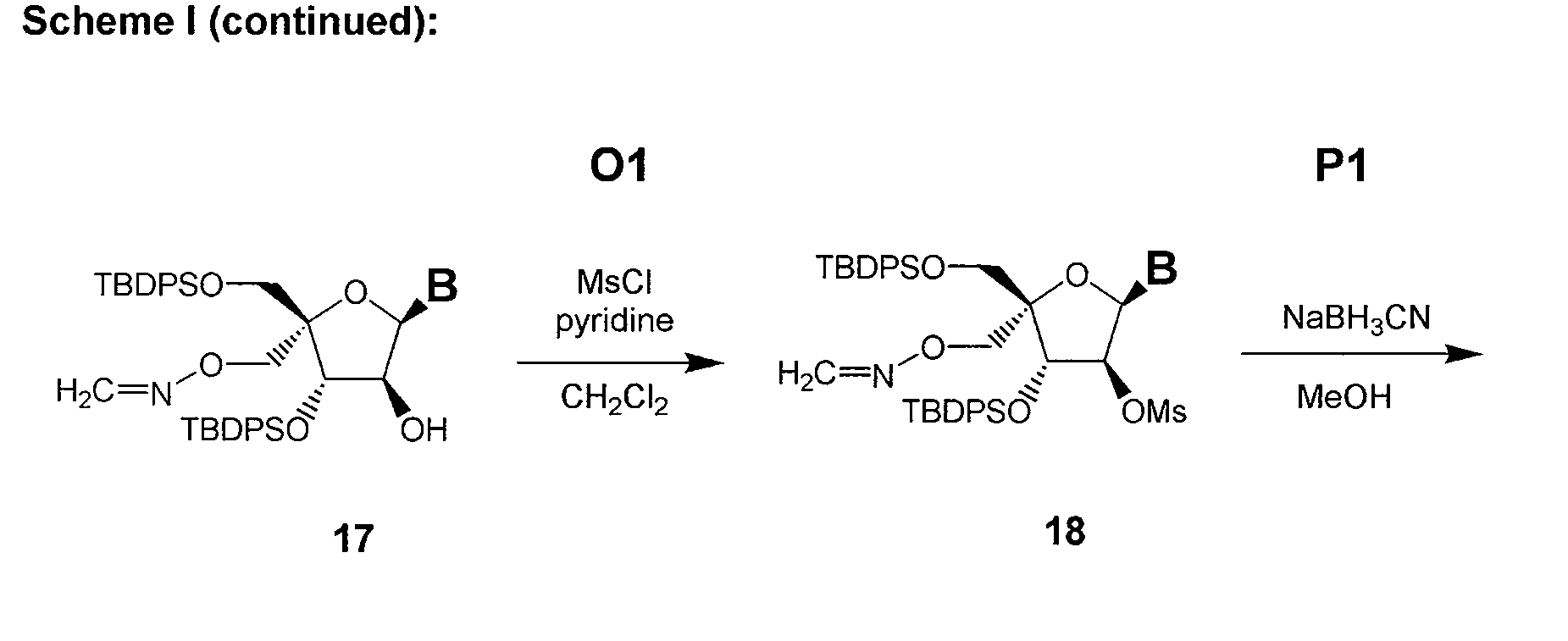
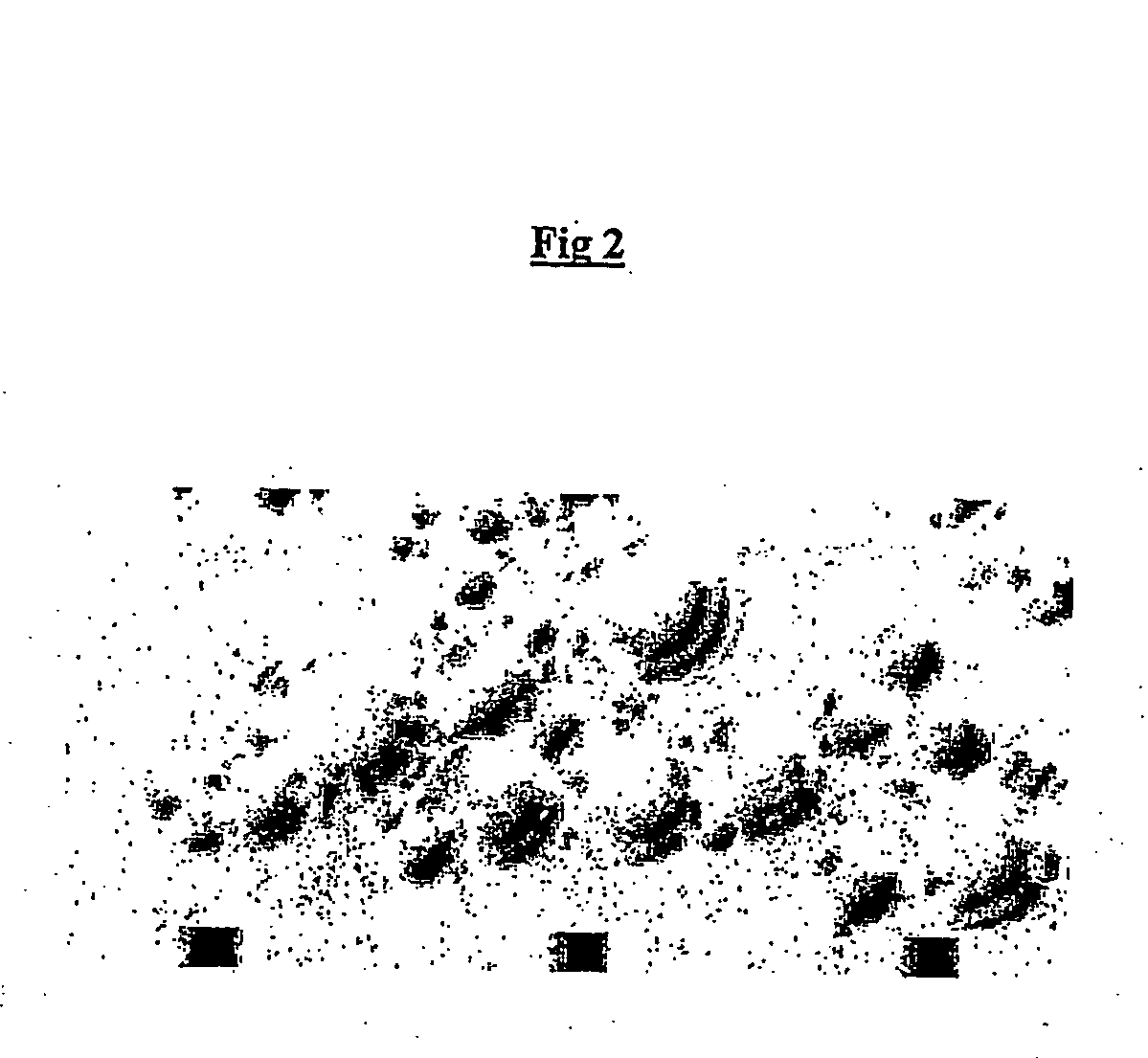
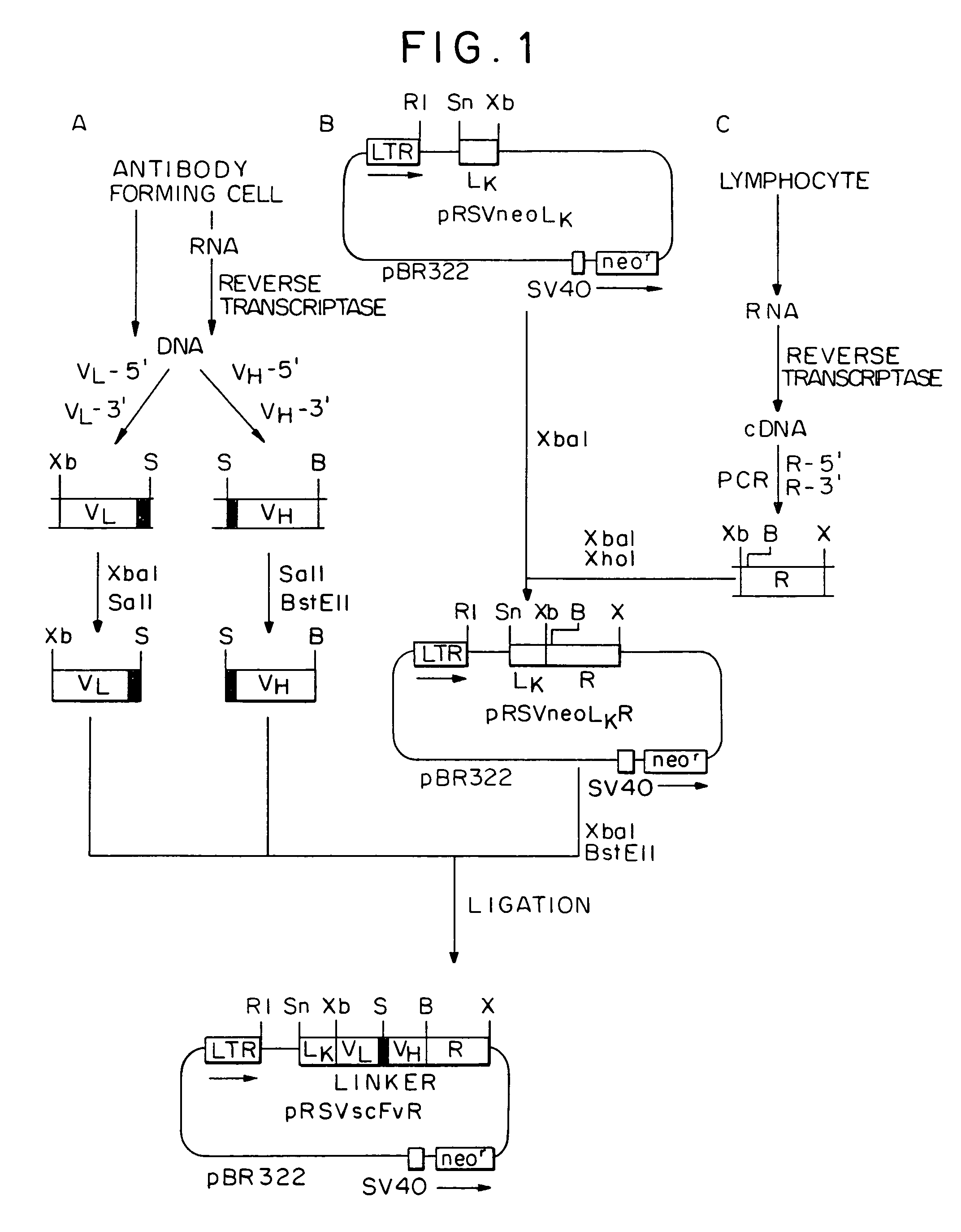
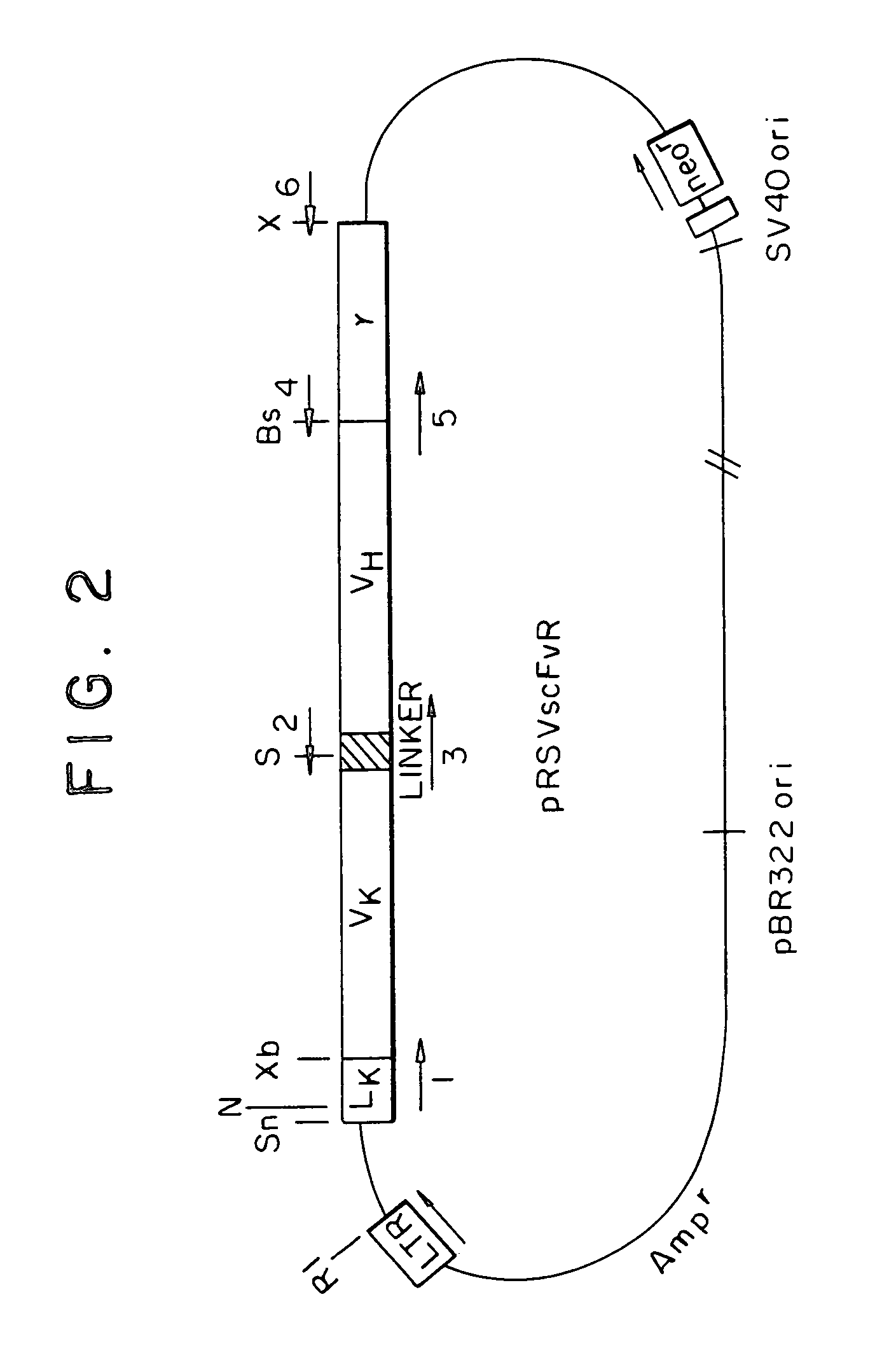
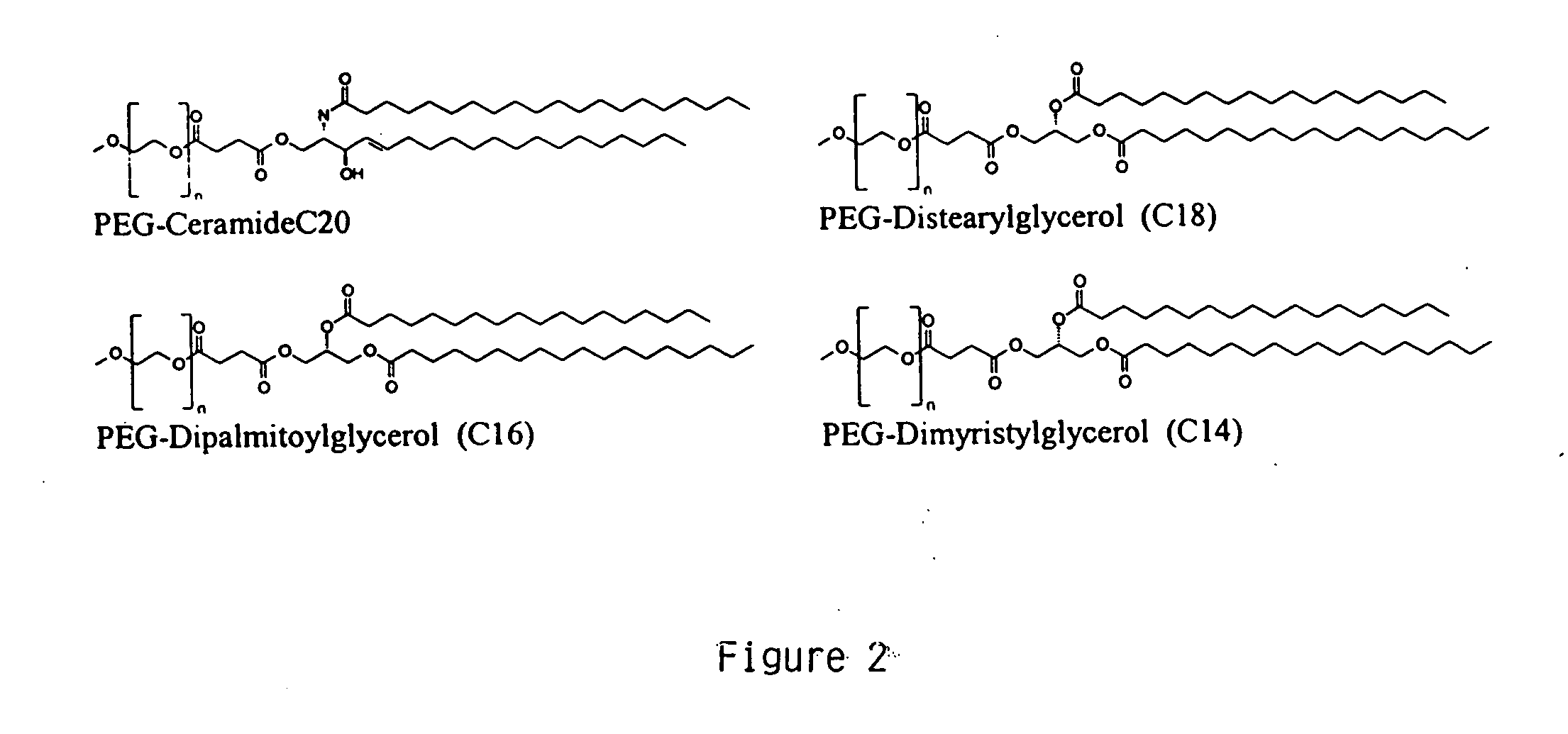
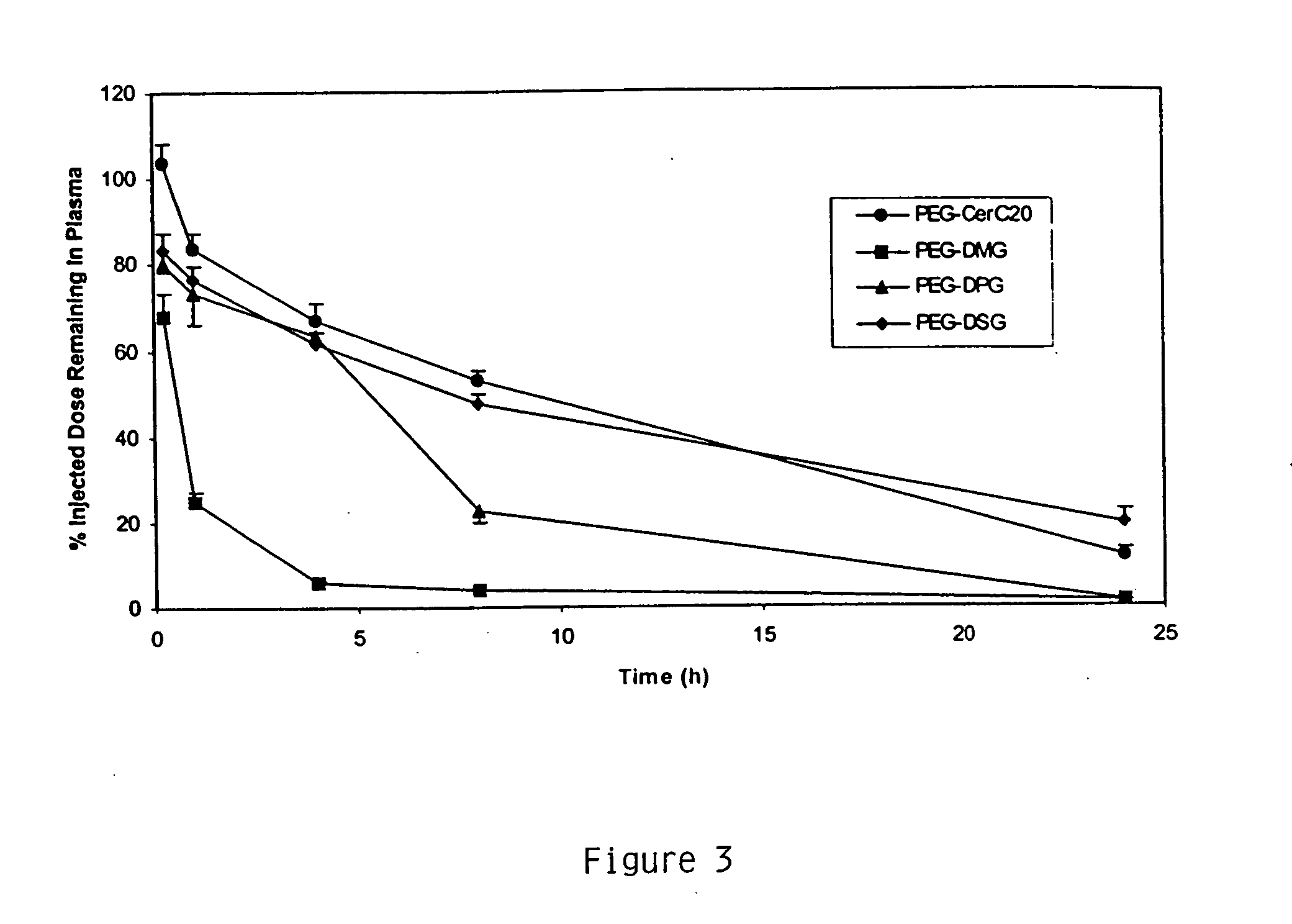
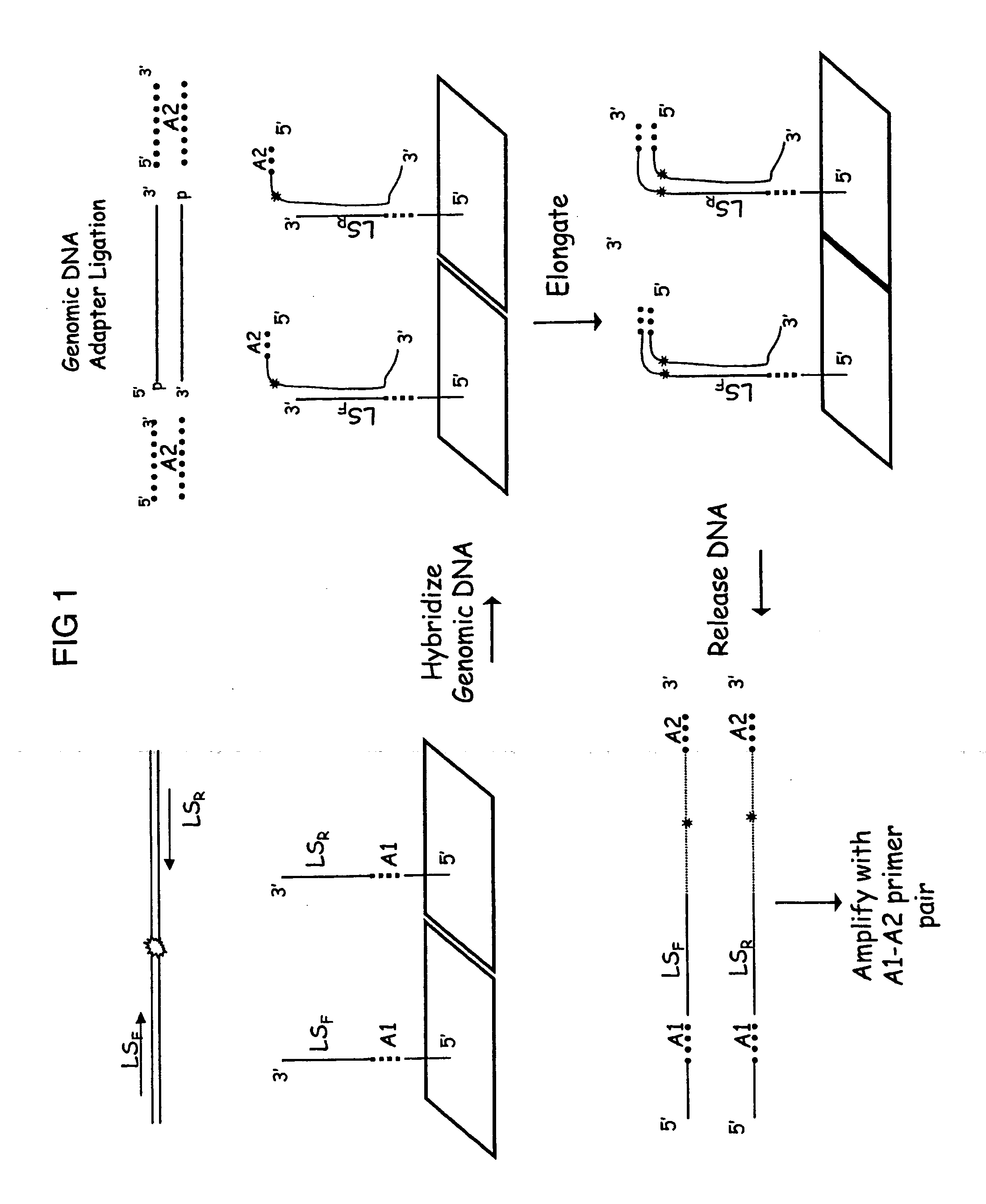
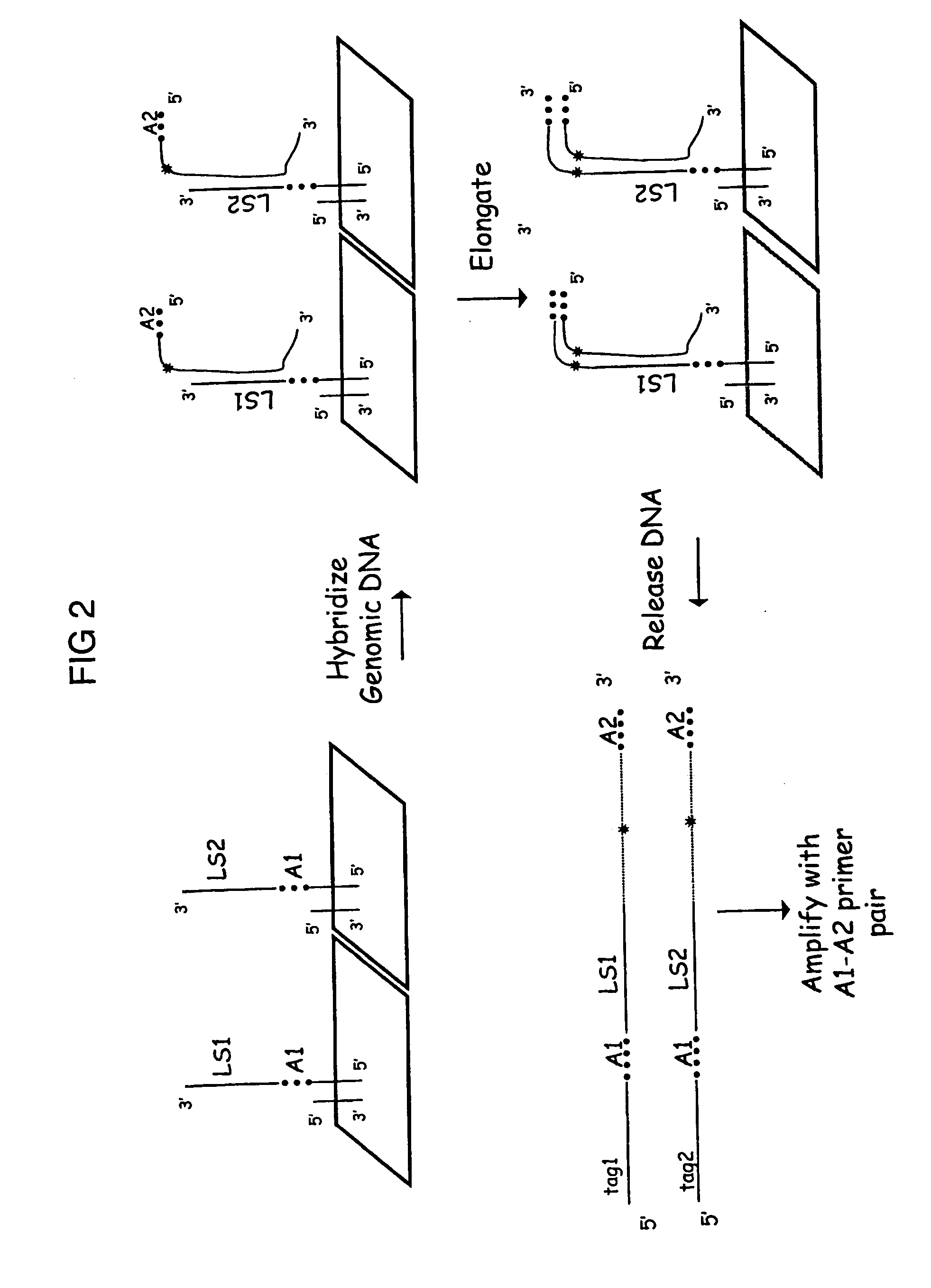
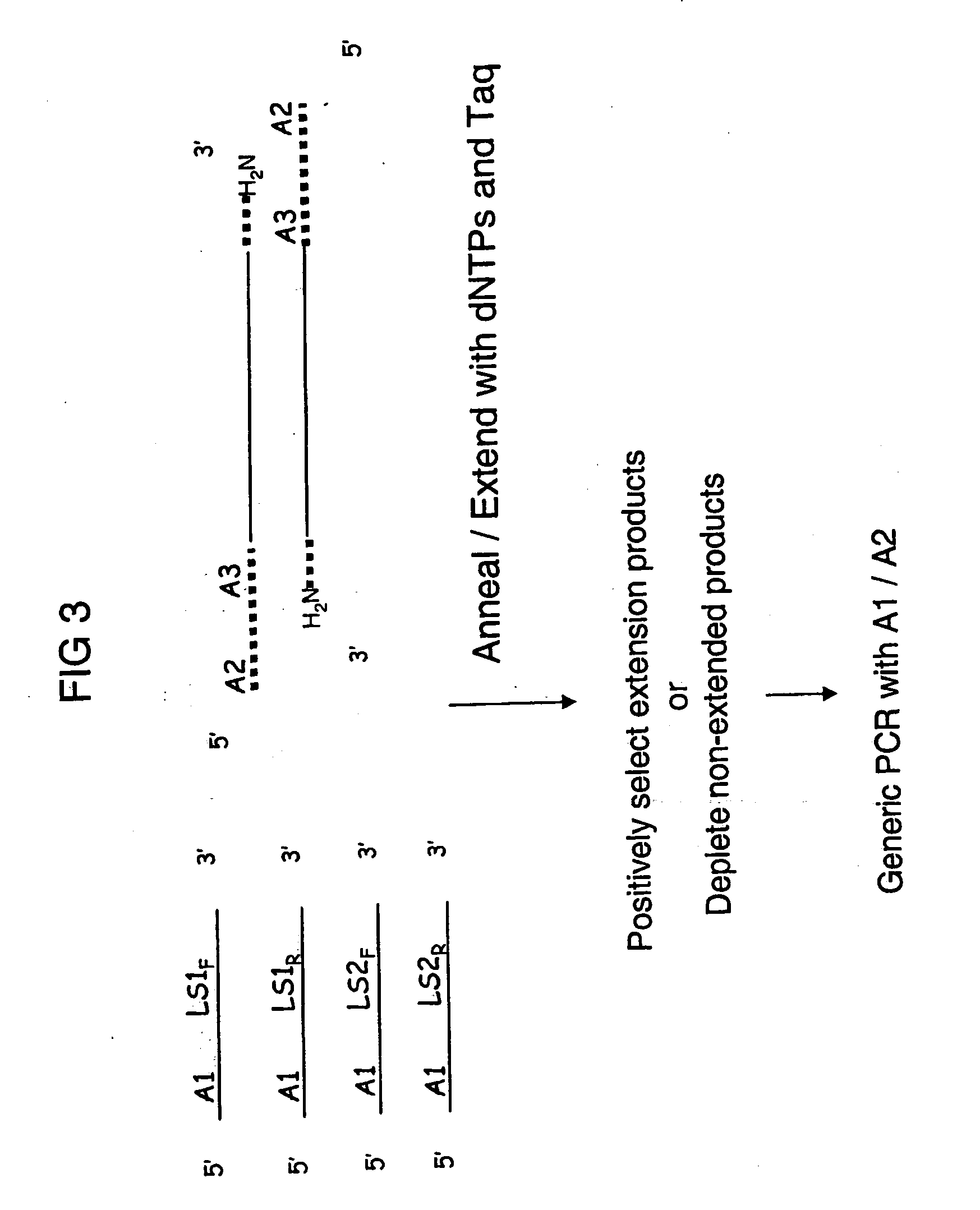
Patents
Literature
28803 results about "Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biology, a gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that encodes the synthesis of a gene product, either RNA or protein. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic trait. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye color or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that constitute life.
Human antibodies derived from immunized xenomice
Fully human antibodies against a specific antigen can be prepared by administering the antigen to a transgenic animal which has been modified to produce such antibodies in response to antigenic challenge, but whose endogenous loci have been disabled. Various subsequent manipulations can be performed to obtain either antibodies per se or analogs thereof.
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC
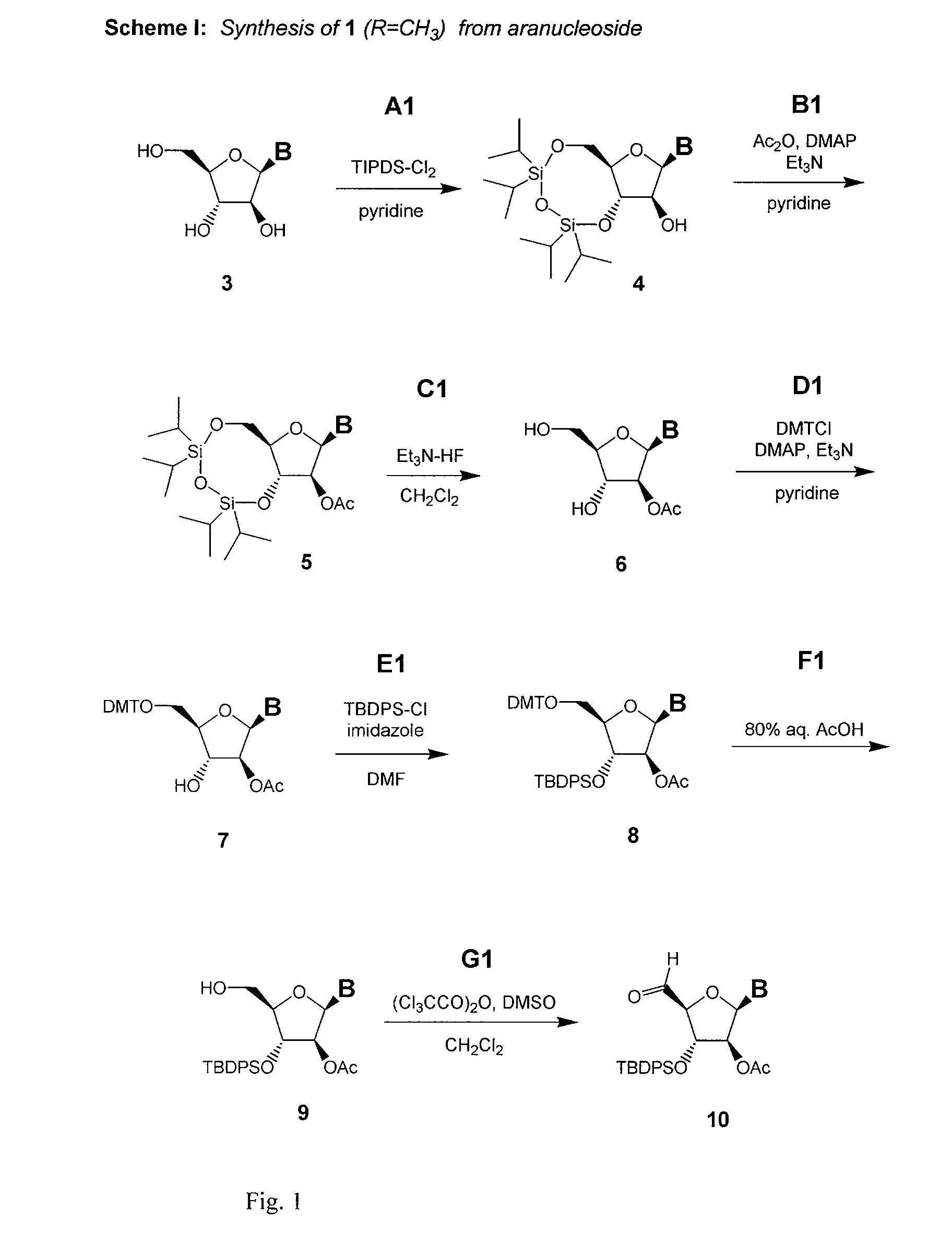
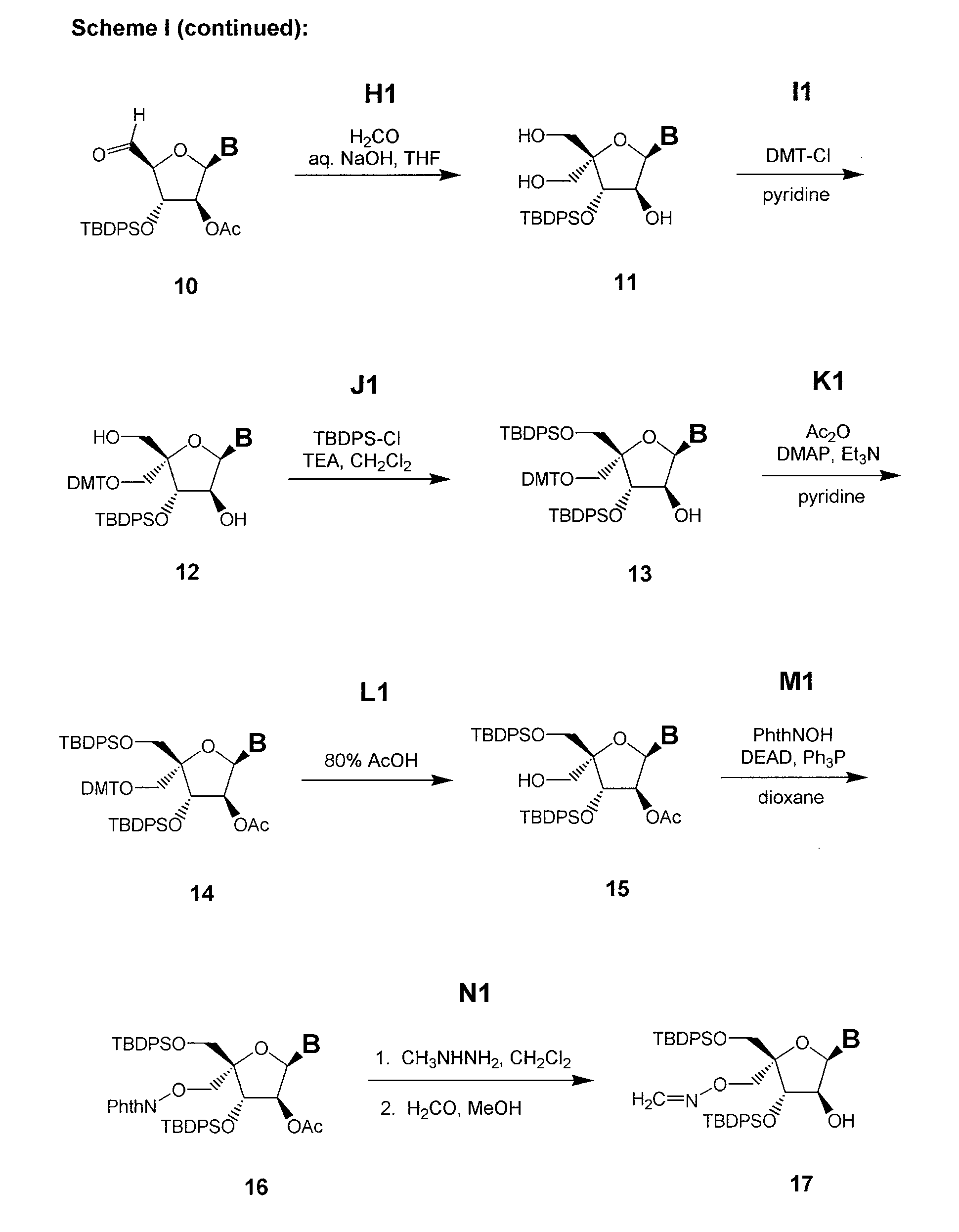
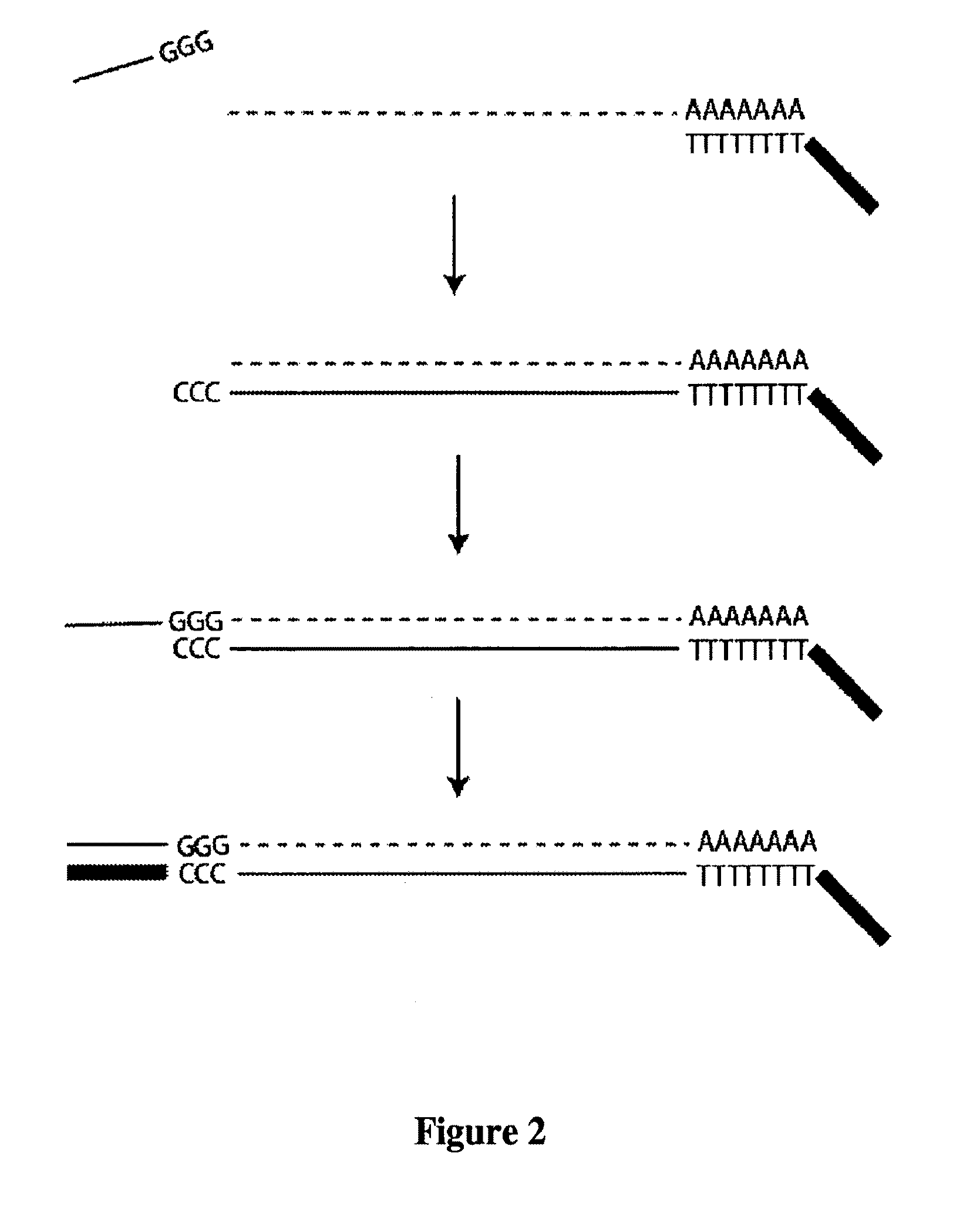
Polycyclic sugar surrogate-containing oligomeric compounds and compositions for use in gene modulation
Compositions comprising first and second oligomers are provided wherein at least a portion of the first oligomer is capable of hybridizing with at least a portion of the second oligomer, at least a portion of the first oligomer is complementary to and capable of hybridizing to a selected target nucleic acid, and at least one of the first or second oligomers includes a modification comprising a polycyclic sugar surrogate. Oligomer / protein compositions are also provided comprising an oligomer complementary to and capable of hybridizing to a selected target nucleic acid and at least one protein comprising at least a portion of an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), wherein at least one nucleoside of the oligomer has a polycyclic sugar surrogate modification.
Owner:ALLERSON CHARLES +6
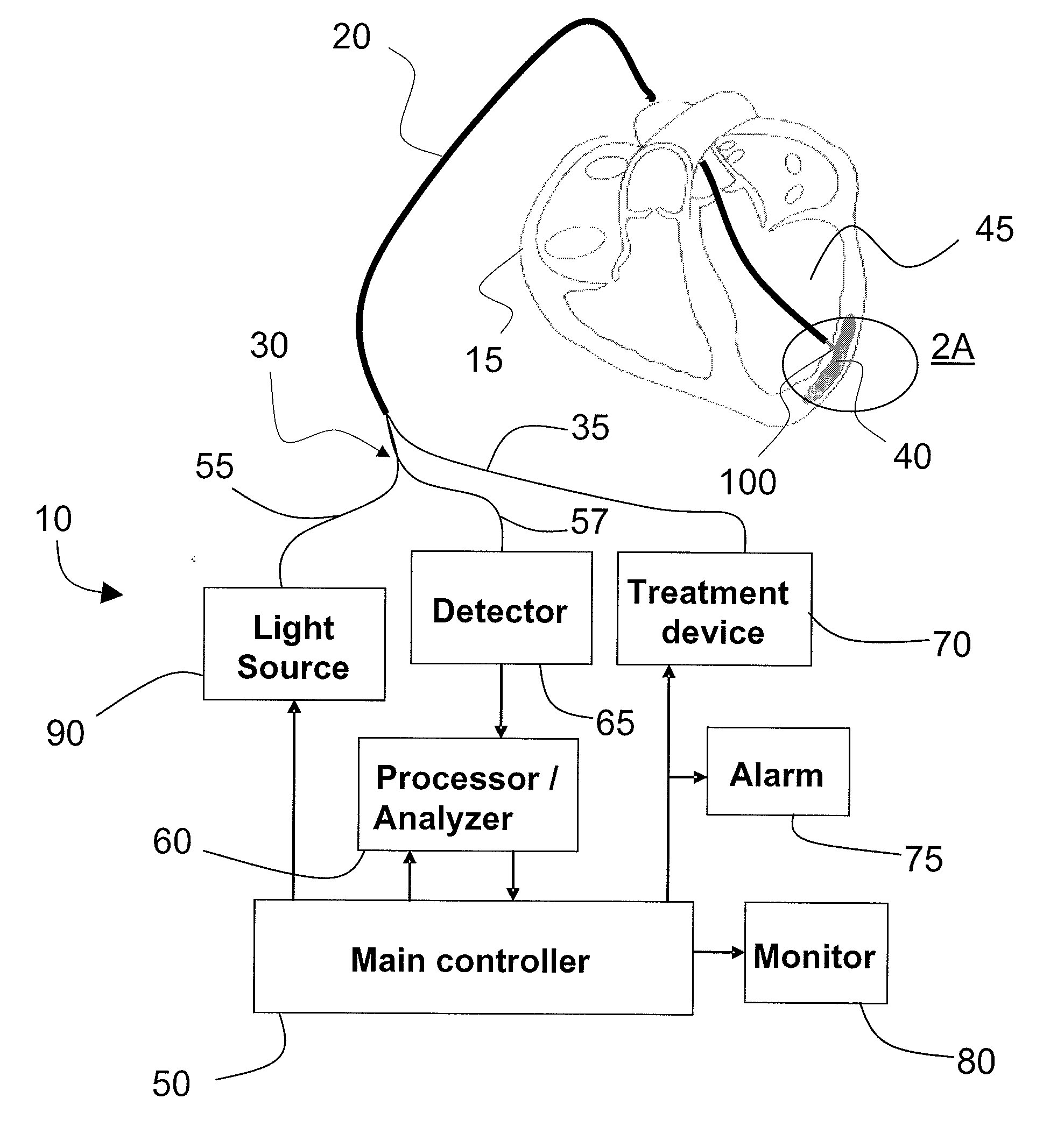
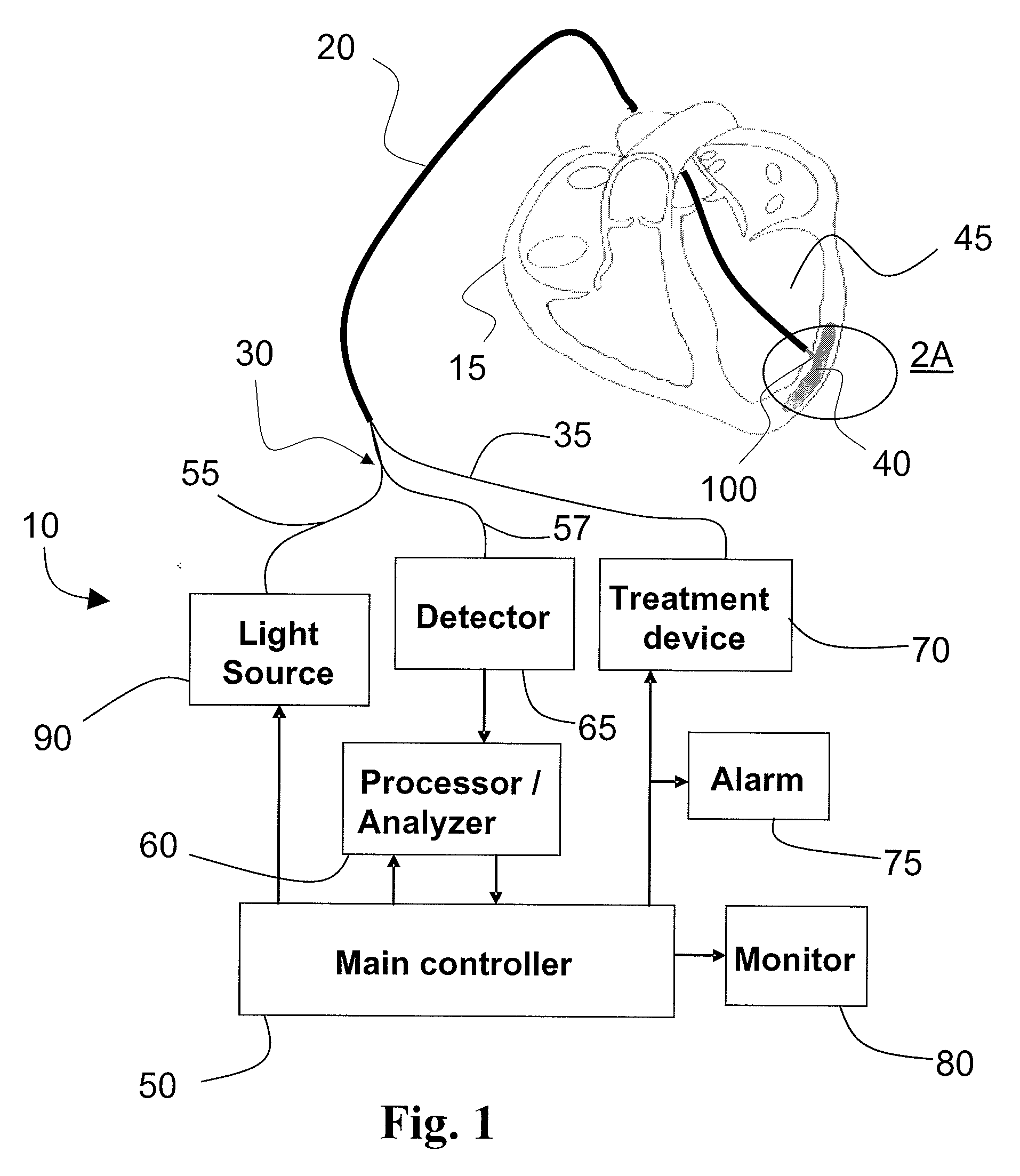
Method and apparatus for identifying and treating myocardial infarction
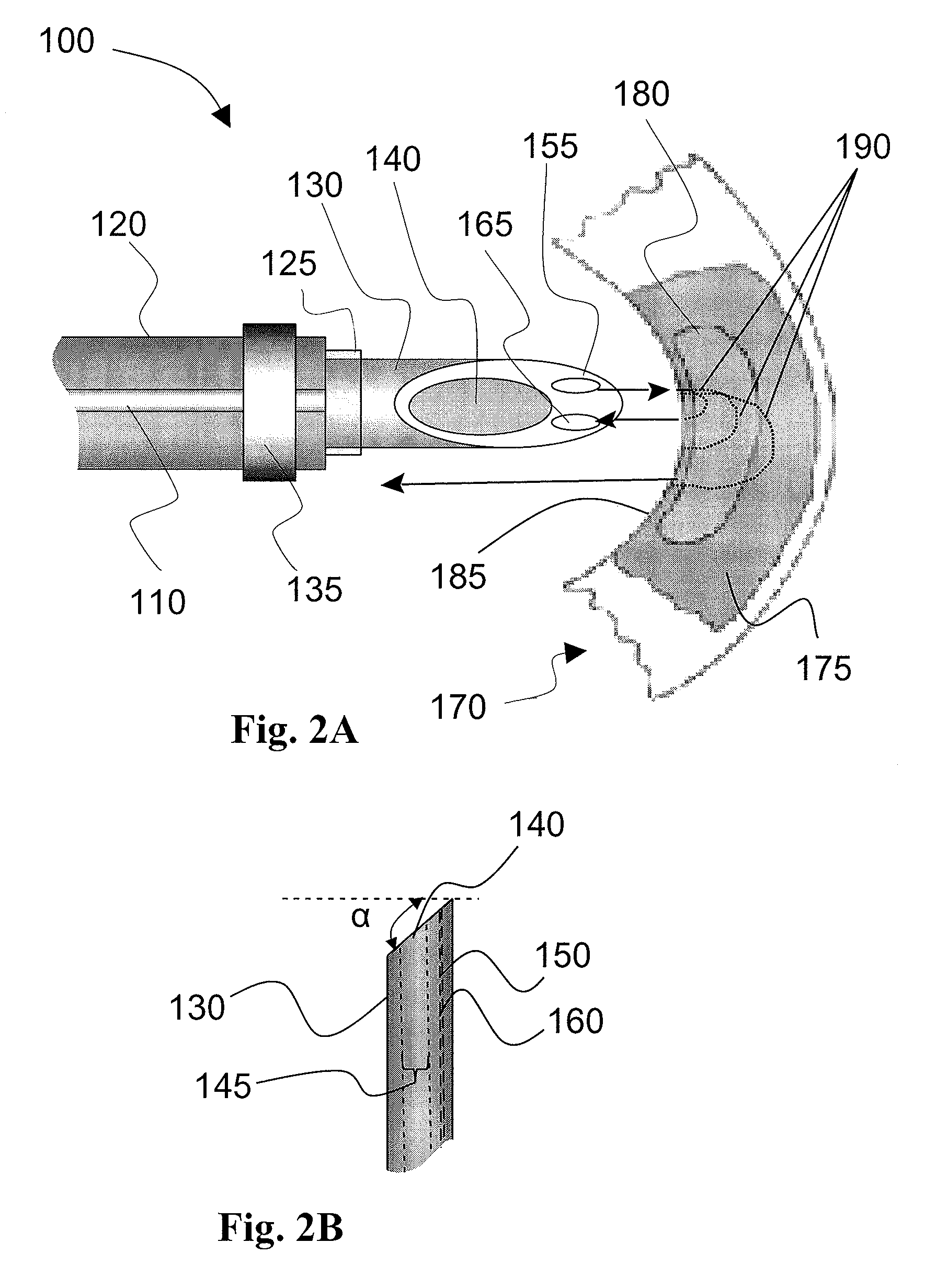
InactiveUS20080125634A1Safe and effectiveAccurate locationGuide needlesSurgical needlesVisual perceptionVisual feedback
A method and apparatus for analyzing and treating internal tissues and, in particular, tissues affected by myocardial infarct. The apparatus includes a catheterized device integrating an optical probe and treatment delivery system. The probe component includes fiber optic lines that can be used in conjunction with infrared spectroscopy to analyze various characteristics of tissues, including chemical, blood, and oxygen content, in order to locate those tissues associated with myocardial infarct, to determine the best location for applying treatment, and to monitor treatment and its effects. Physically integrated with the probe component is a treatment component for delivering treatments including stem cell and gene therapy, known for having beneficial effects on tissues associated with myocardial infarct. A control system coordinates operation of the catheter, including performing chemometric analysis with the use of model data, and for providing control and visual feedback to an operator.
Owner:CORNOVA
Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis
InactiveUS6258540B1% accurate detection rateIncrease the amount of foetal nucleic acid materialMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPrenatal diagnosisBlood typing
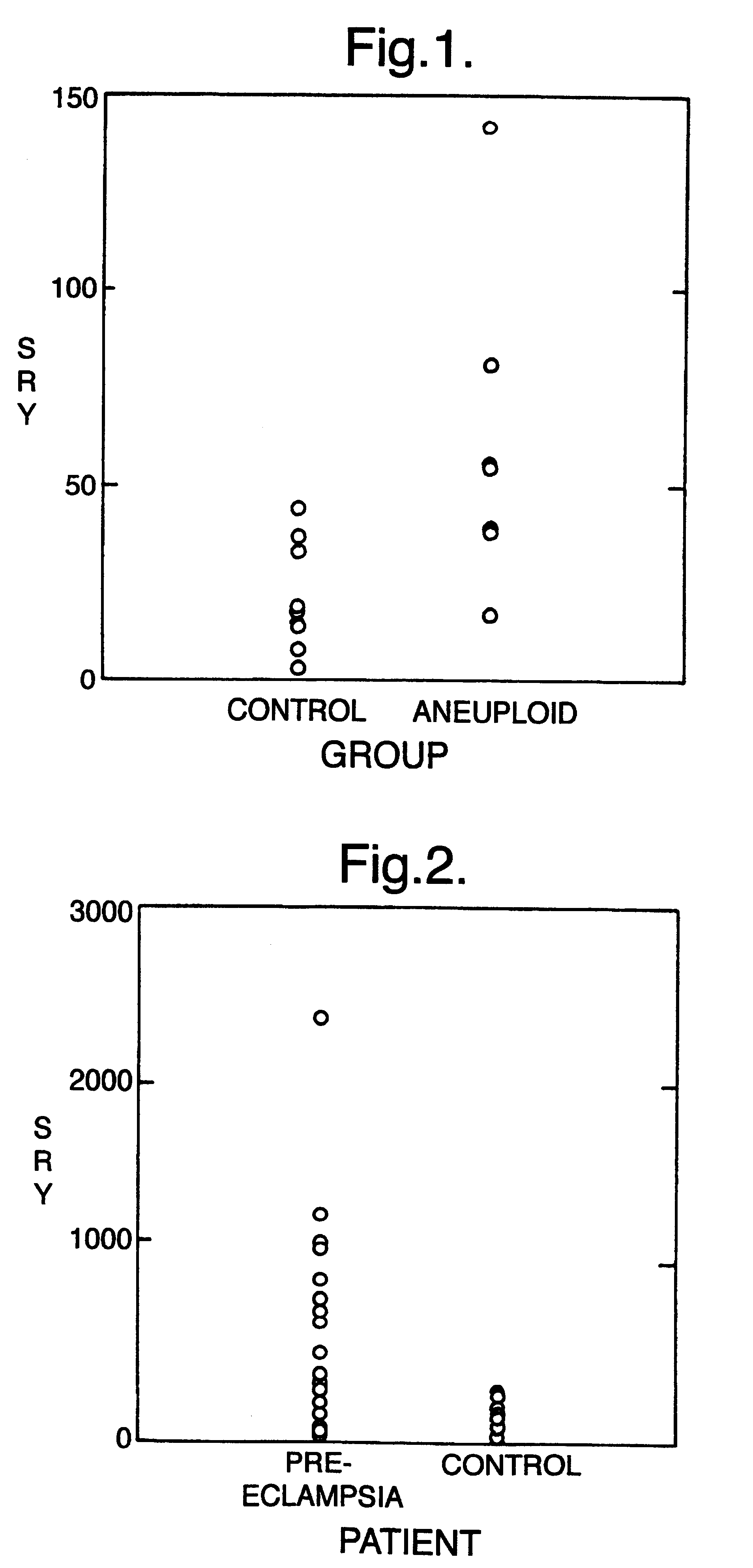
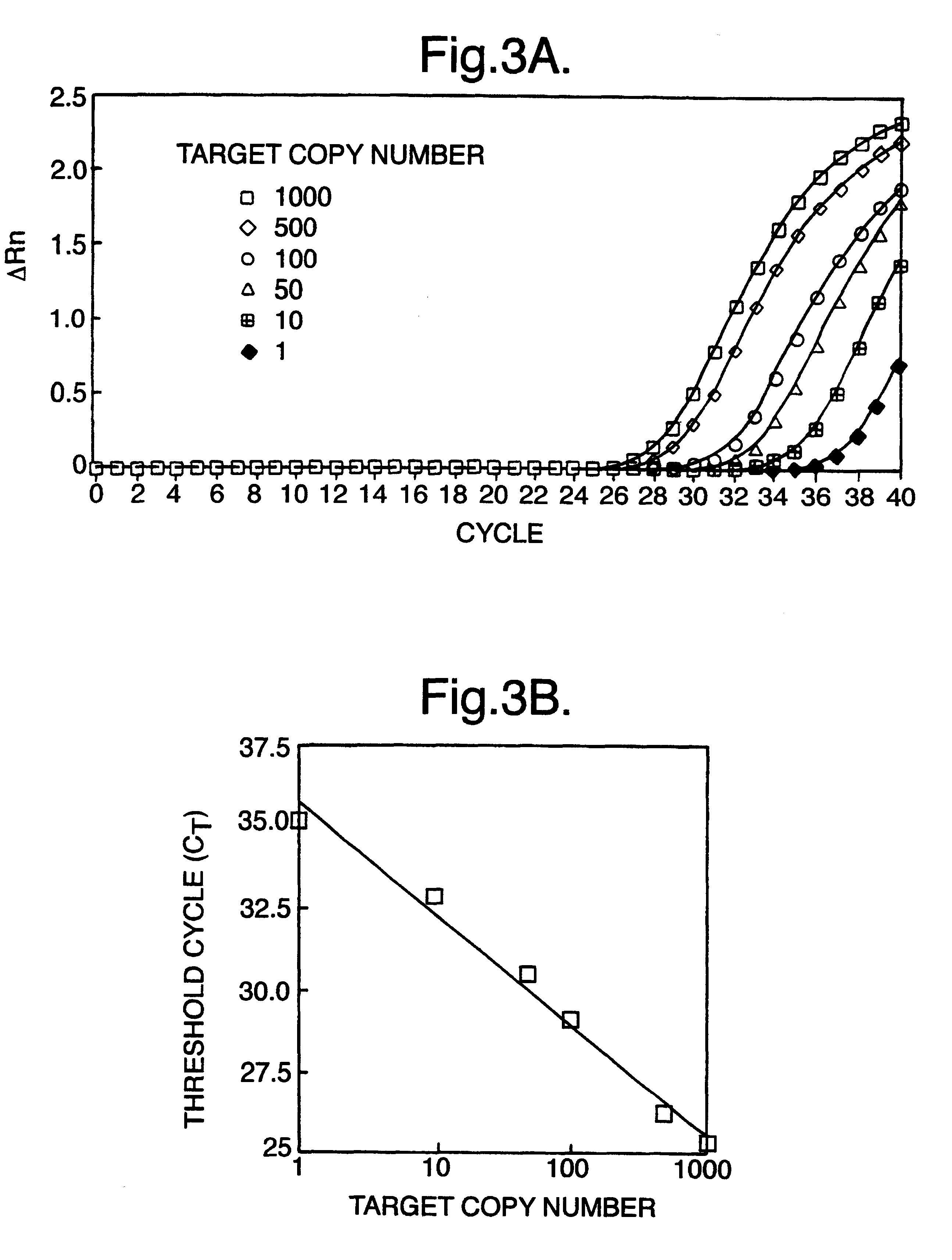
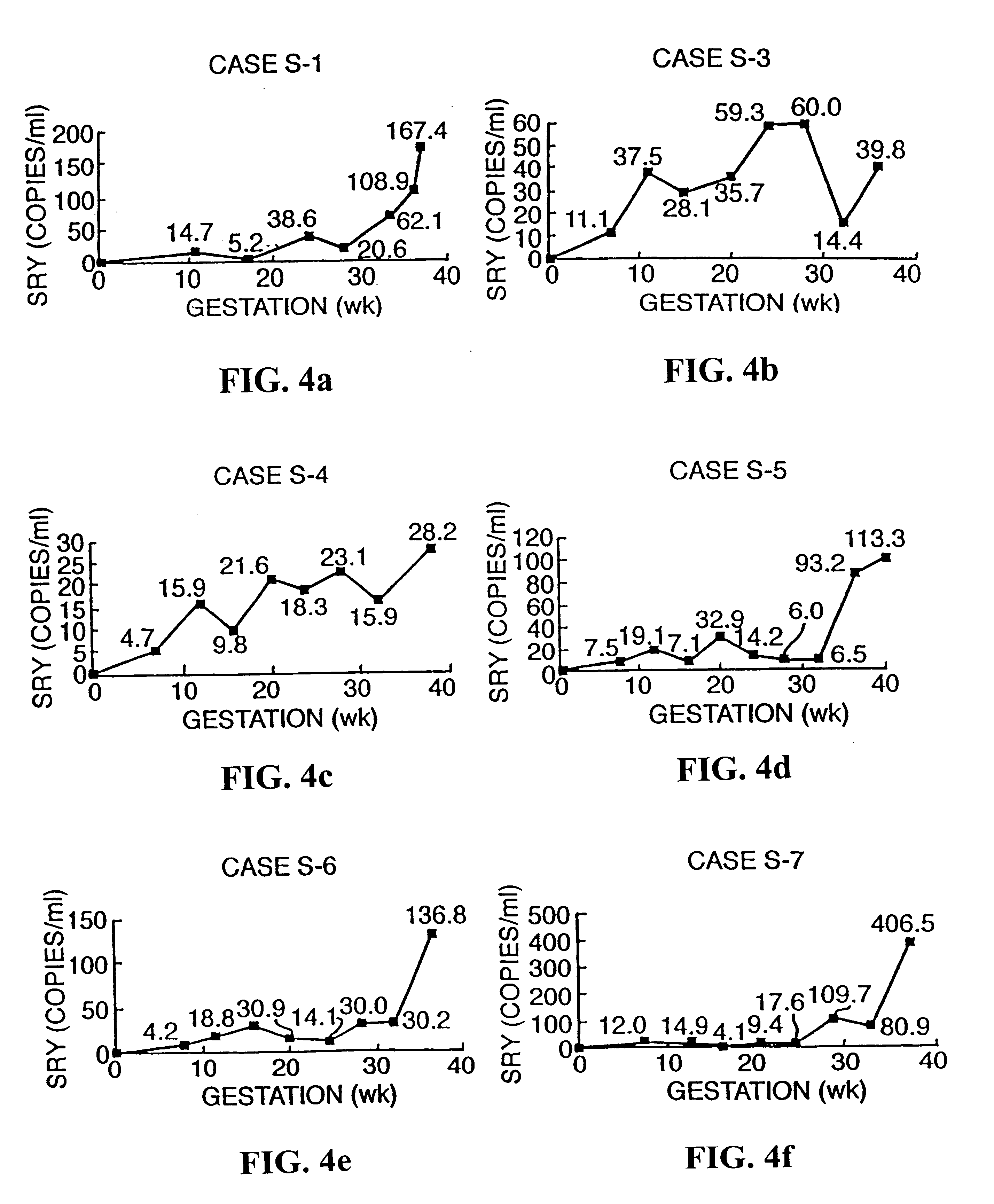
The invention relates to a detection method performed on a maternal serum or plasma sample from a pregnant female, which method comprises detecting the presence of a nucleic acid of foetal origin in the sample. The invention enables non-invasive prenatal diagnosis including for example sex determination, blood typing and other genotyping, and detection of pre-eclampsia in the mother.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
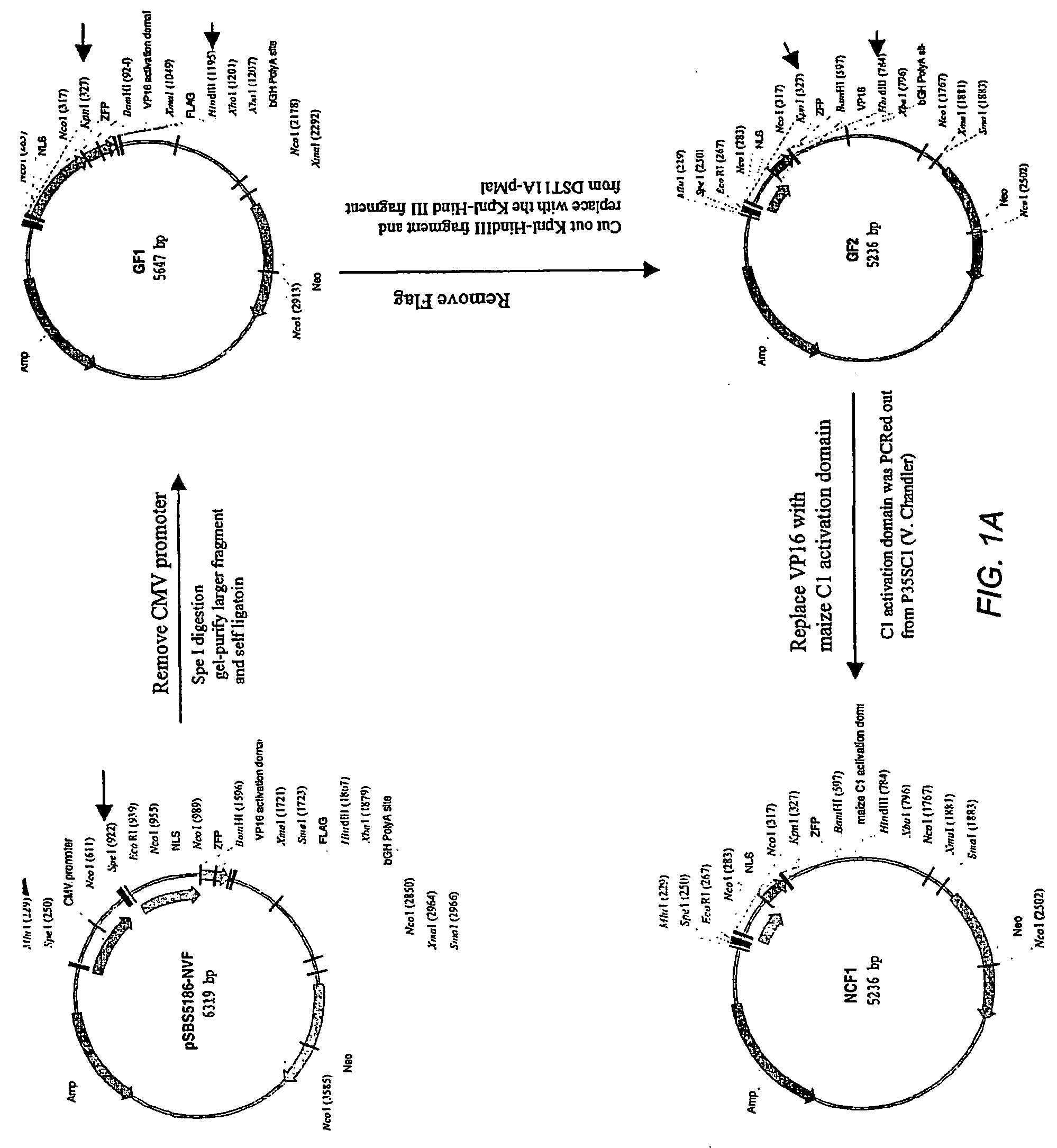
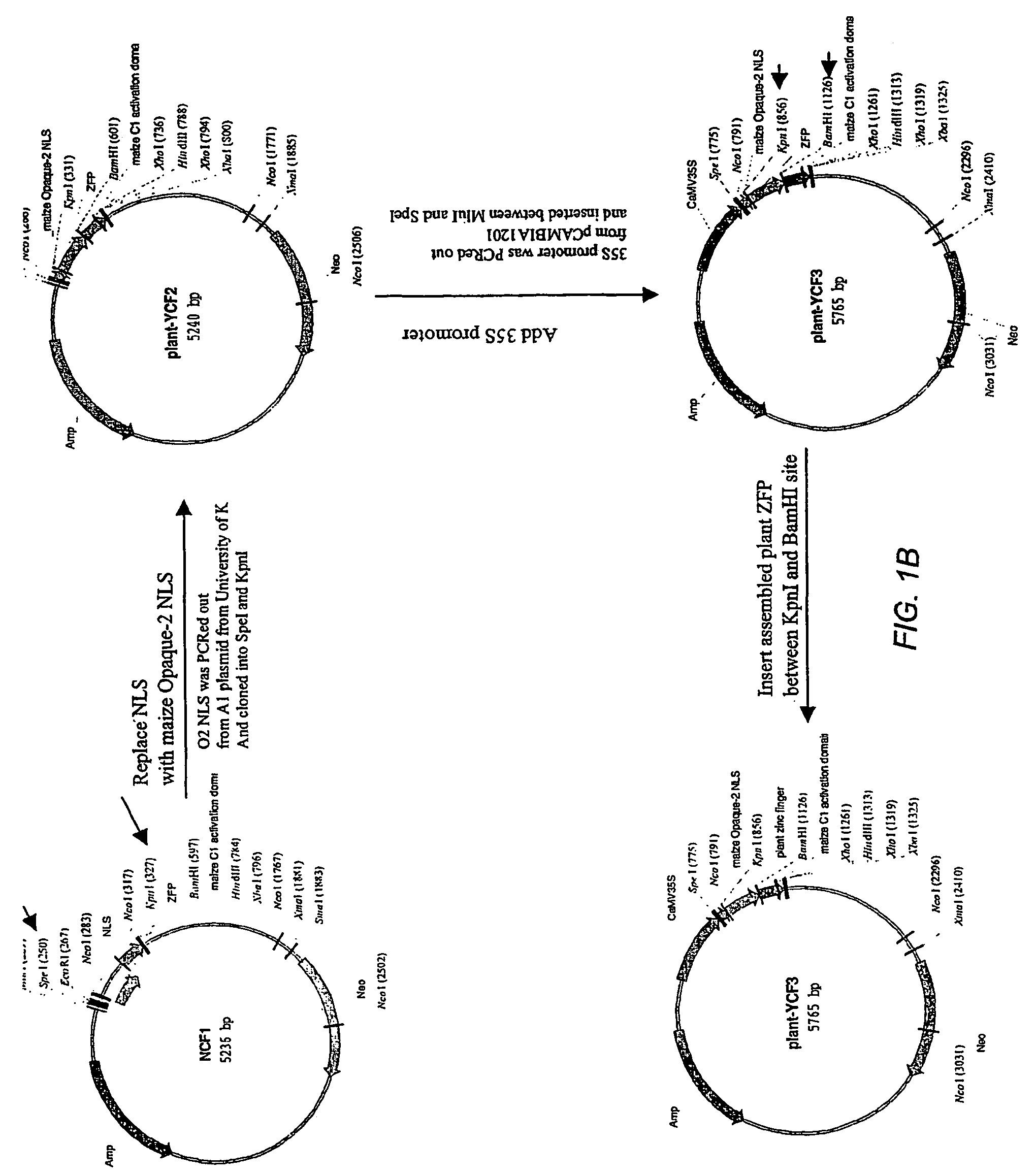
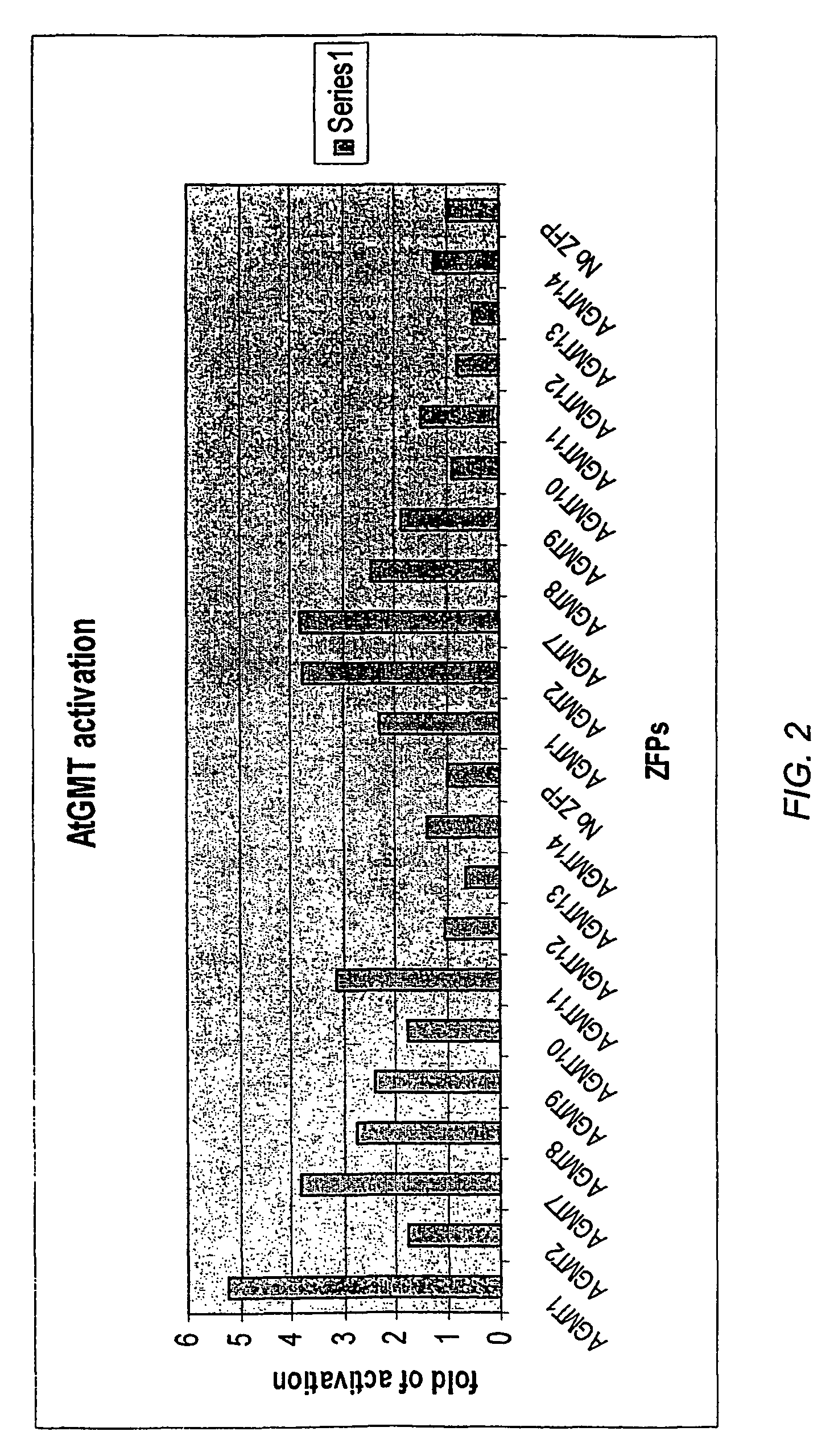
Zinc finger proteins for DNA binding and gene regulation in plants
InactiveUS7262054B2Alters compositionEasy to produceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyZinc finger
Disclosed herein are modified plant zinc finger proteins; compositions comprising modified plant zinc finger proteins and methods of making and using modified plant zinc finger proteins. The modified plant zinc finger proteins, in contrast to naturally-occurring plant zinc finger proteins, have a binding specificity that is determined by tandem arrays of modular zinc finger binding units.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
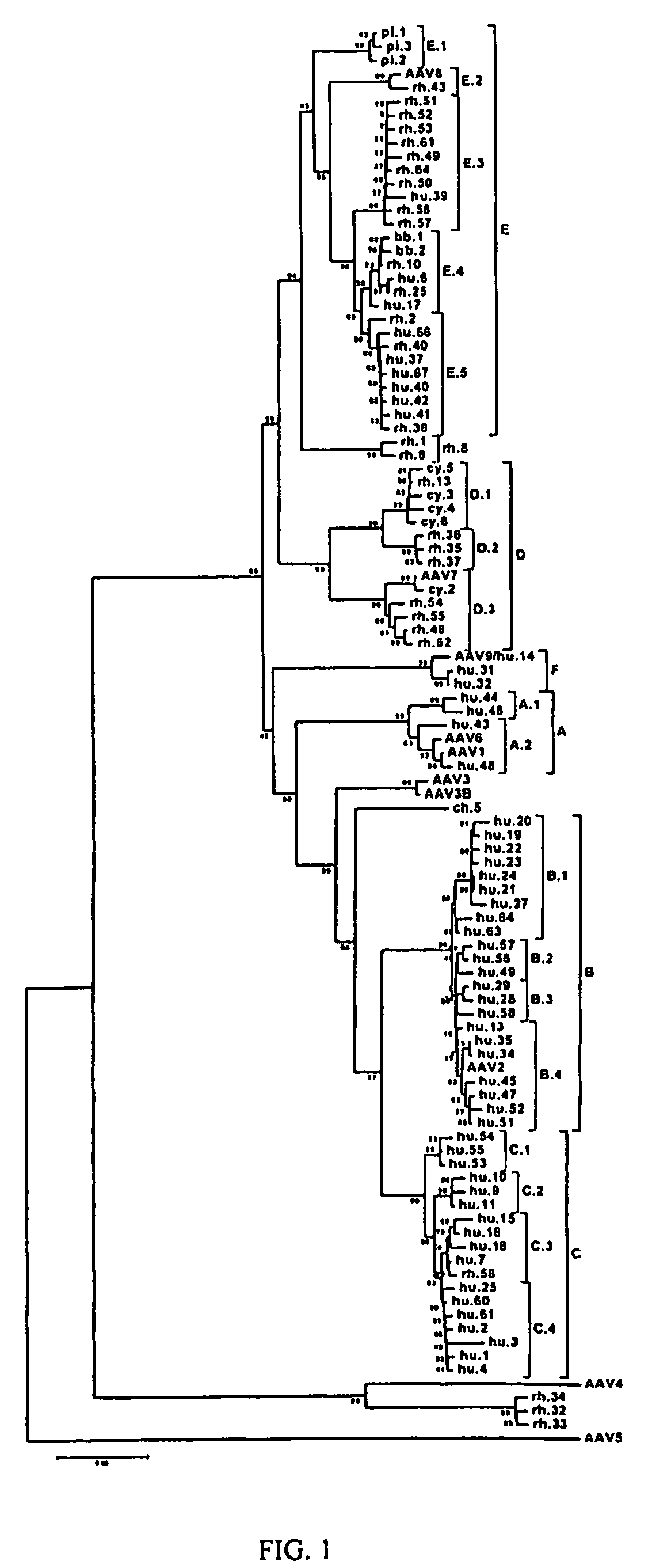
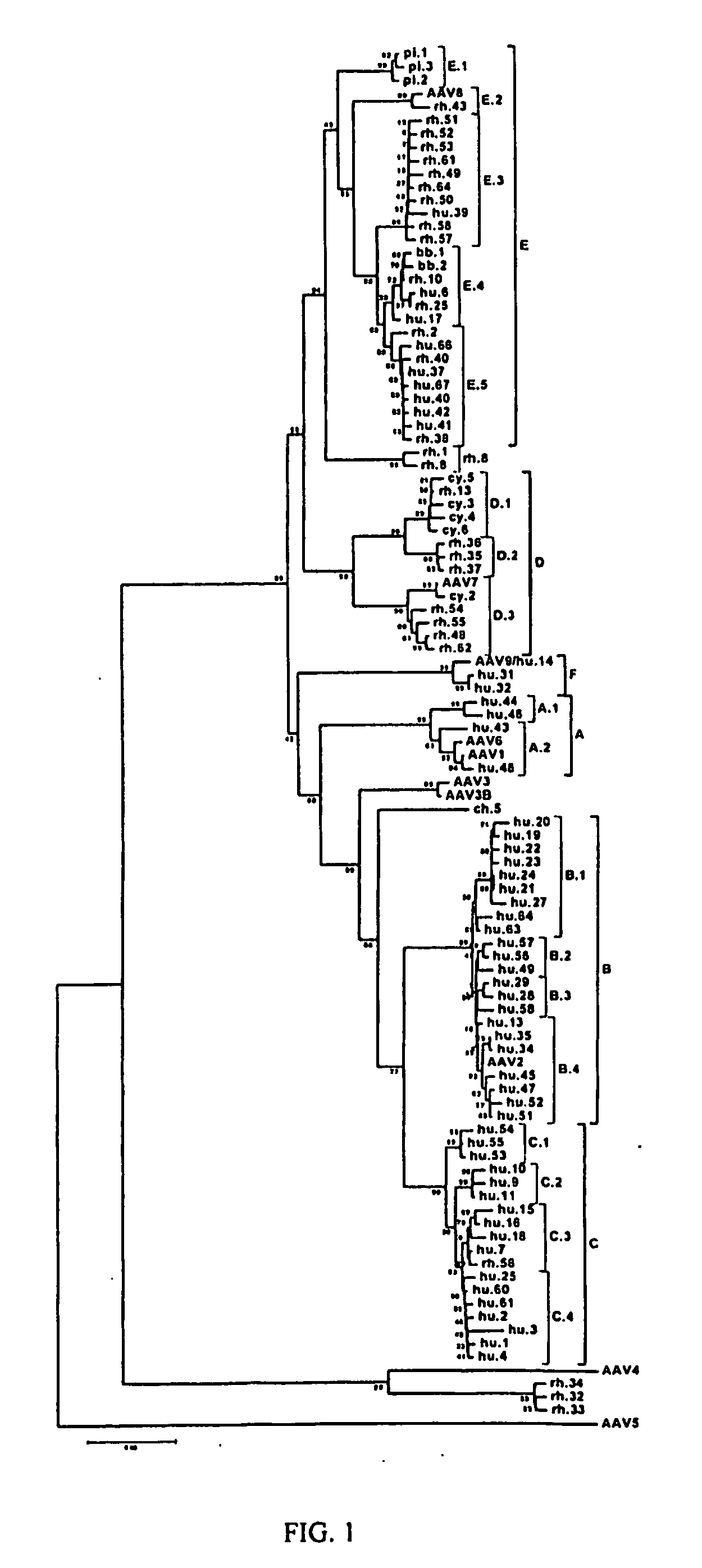
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Emulsion compositions
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
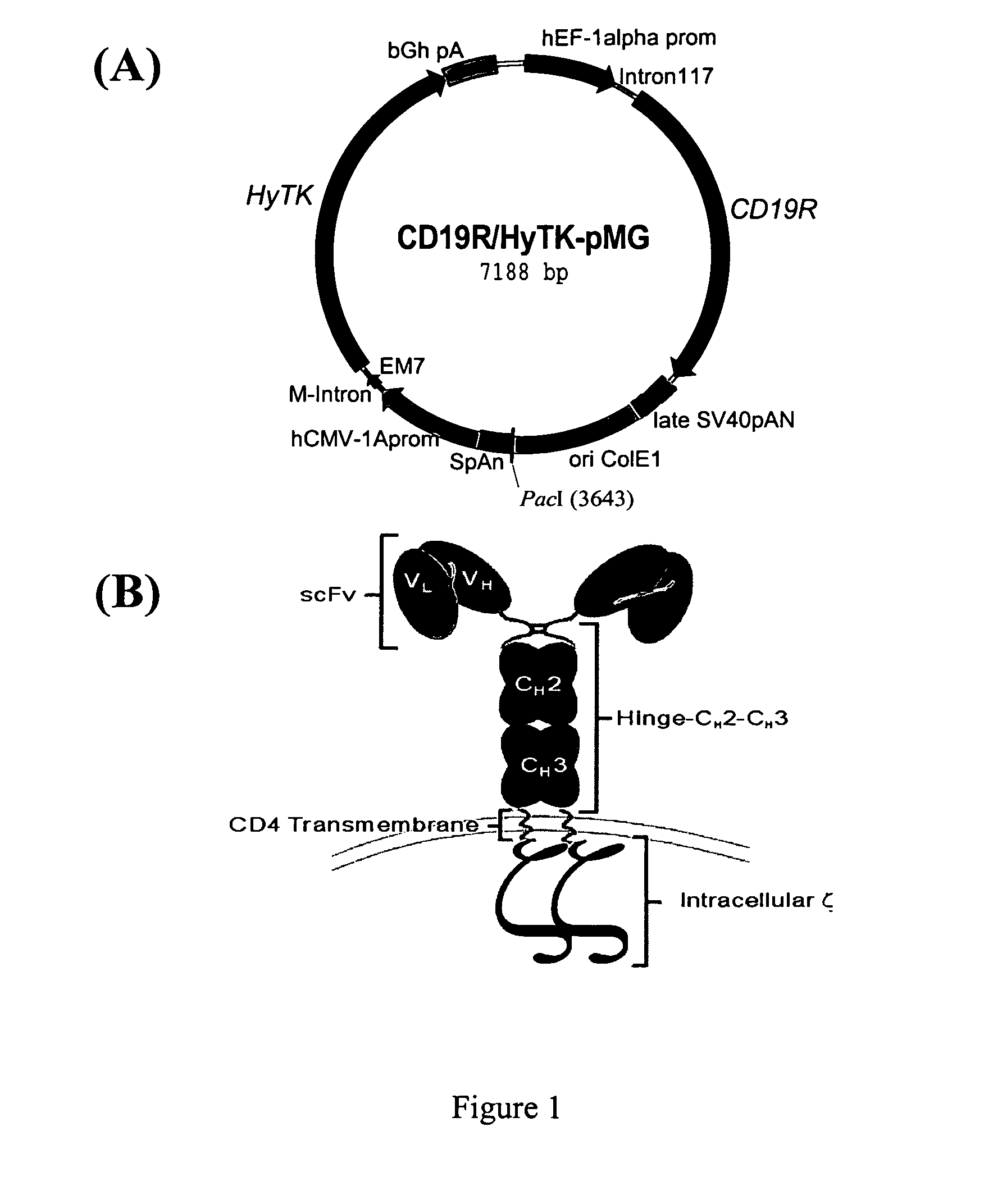
Chimeric receptor genes and cells transformed therewith
ActiveUS7741465B1Limit acquisitionMicroorganismsGenetic material ingredientsAntibody typesLymphocyte
Chimeric receptor genes suitable for endowing lymphocytes with antibody-type specificity include a first gene segment encoding a single-chain Fv domain of a specific antibody and a second gene segment encoding all or part of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains, and optionally the extracellular domain, of an immune cell-triggering molecule. The chimeric receptor gene, when transfected to immune cells, expresses the antibody-recognition site and the immune cell-triggering moiety into one continuous chain. The transformed lymphocytes are useful in therapeutic treatment methods.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF +1
Methods of monitoring disease states and therapies using gene expression profiles
The present invention provides methods for monitoring disease states in a subject, as well as methods for monitoring the levels of effect of therapies upon a subject having one or more disease states. The methods involve: (i) measuring abundances of cellular constituents in a cell from a subject so that a diagnostic profile is obtained, (ii) measuring abundances of cellular constituents in a cell of one or more analogous subjects so that perturbation response profiles are obtained which correlate to a particular disease or therapy, and (iii) determining the interpolated perturbation response profile or profiles which best fit the diagnostic profile according to some objective measure. In other aspects, the invention also provides a computer system capable of performing the methods of the invention, data bases comprising perturbation response profiles for one or more diseases and / or therapies, and kits for determining levels of disease states and / or therapeutic effects according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Mammalian cell surface antigens; related reagents
InactiveUS7025962B1Abnormal immune responseFacilitated DiffusionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammalT cell
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
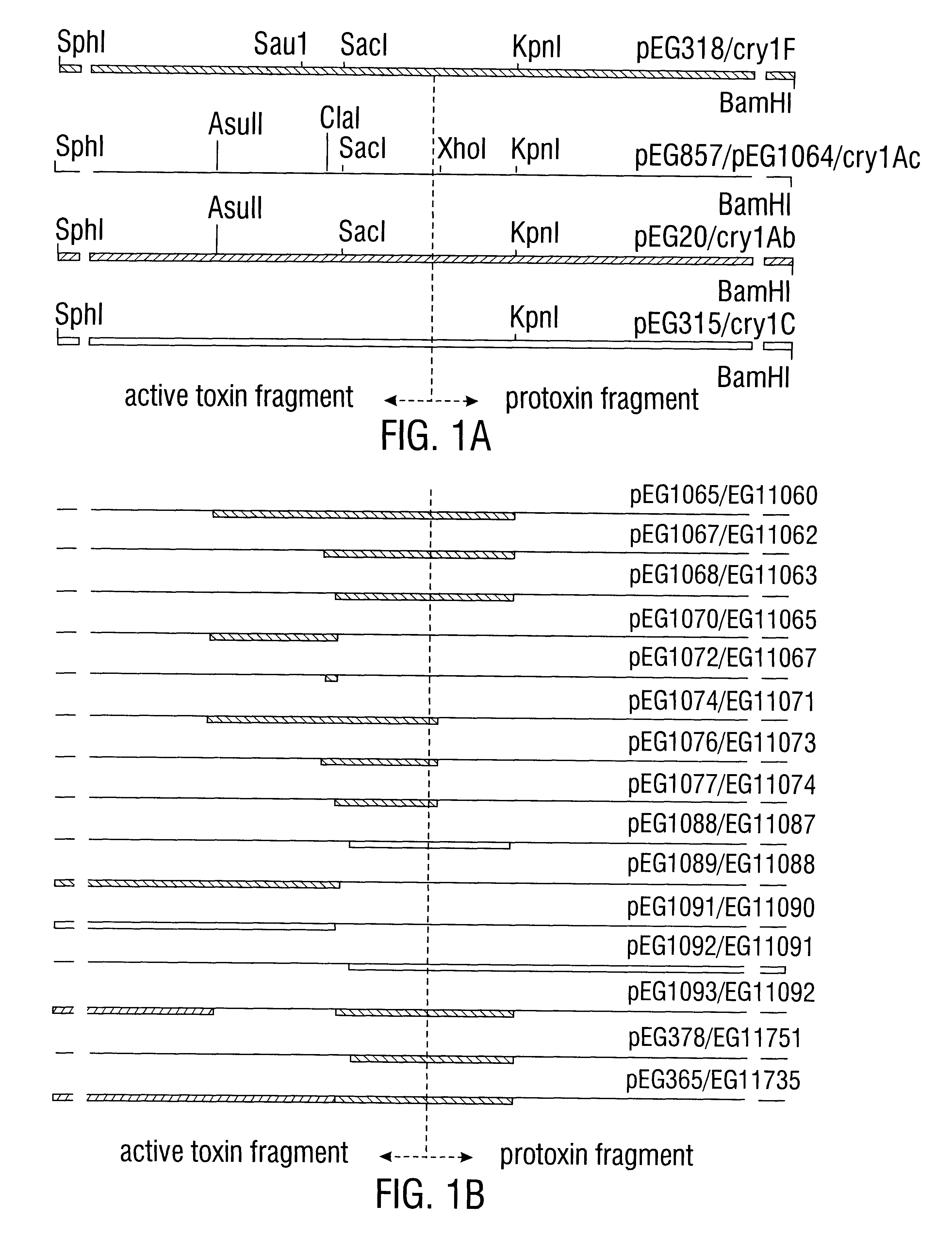
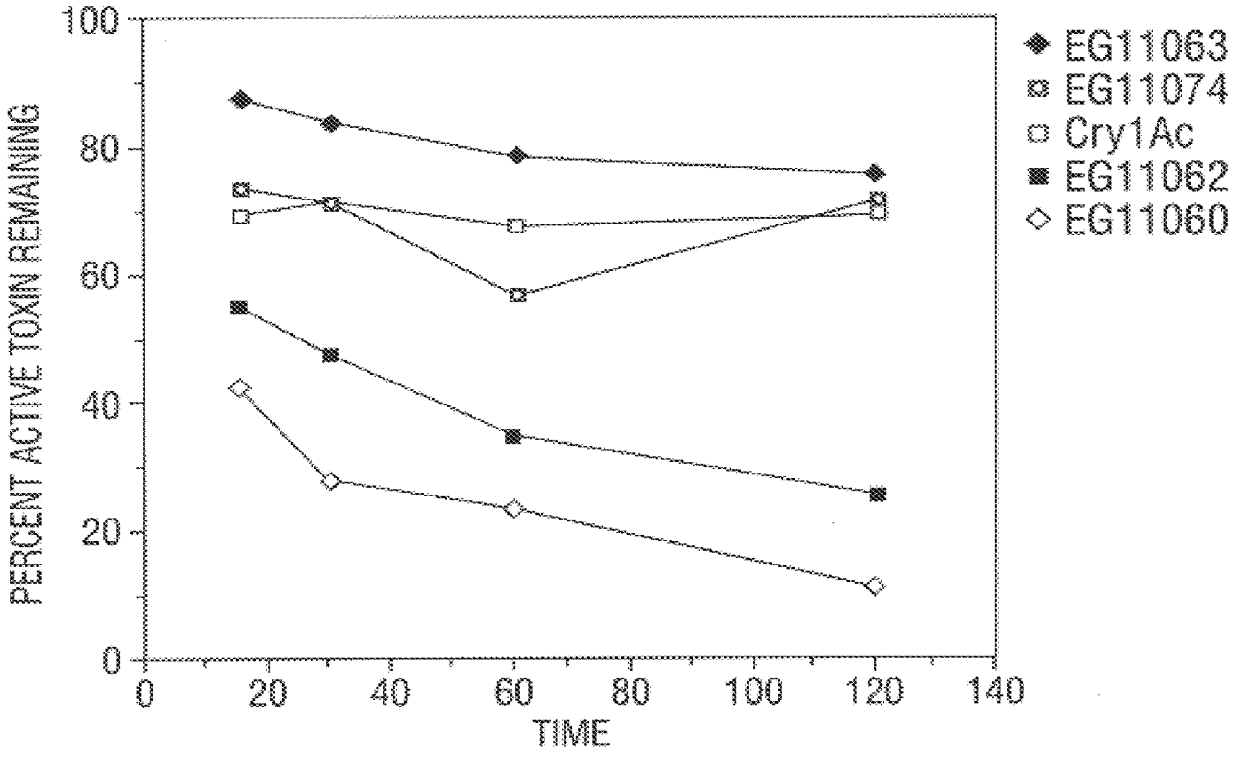
Broad-spectrum delta-endotoxins
InactiveUS6713063B1Improved insecticidal activity and broader host-range activityImproving immunogenicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAureobasidium sp.Toxin
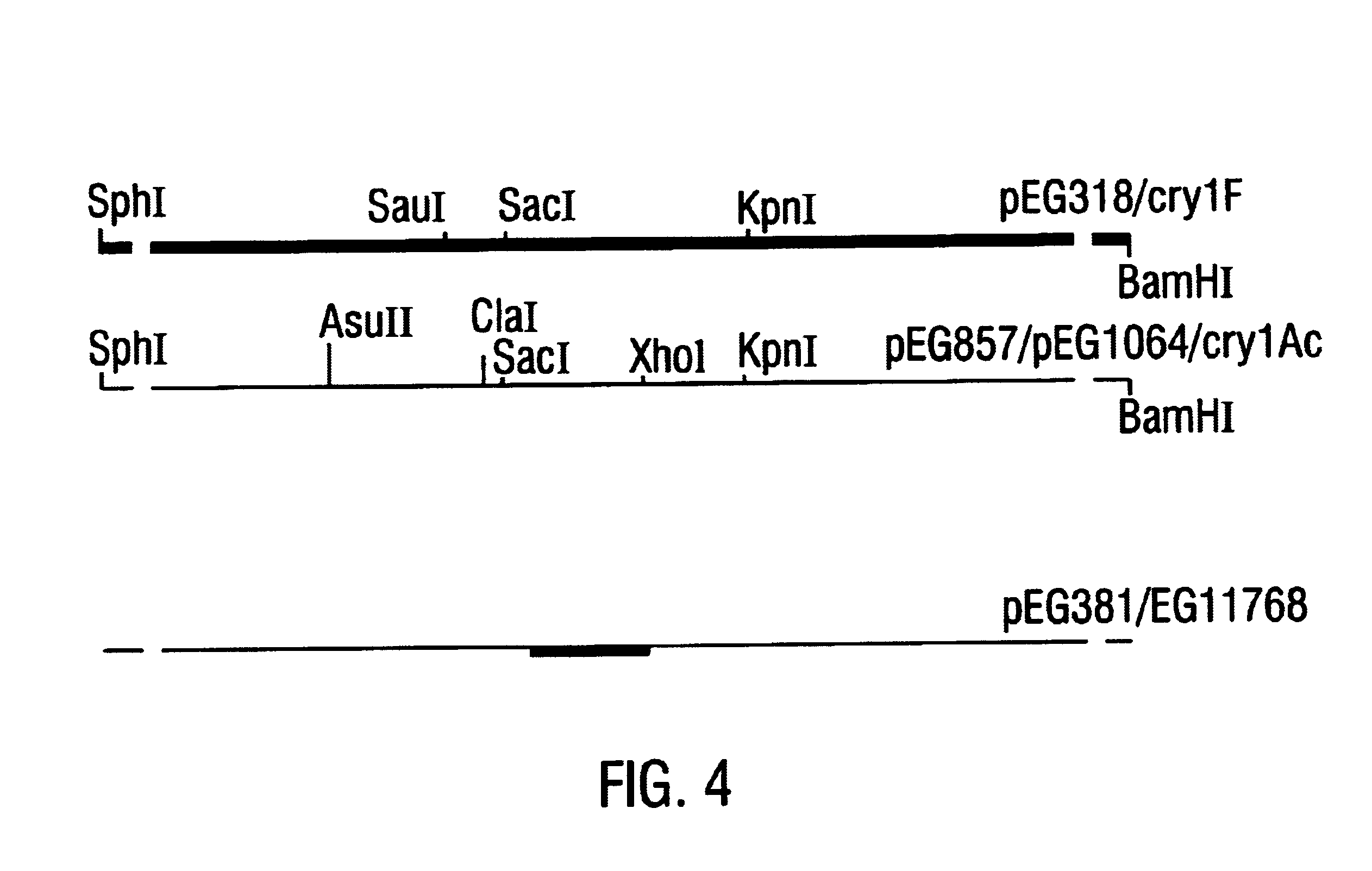
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity and broader insect host range against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
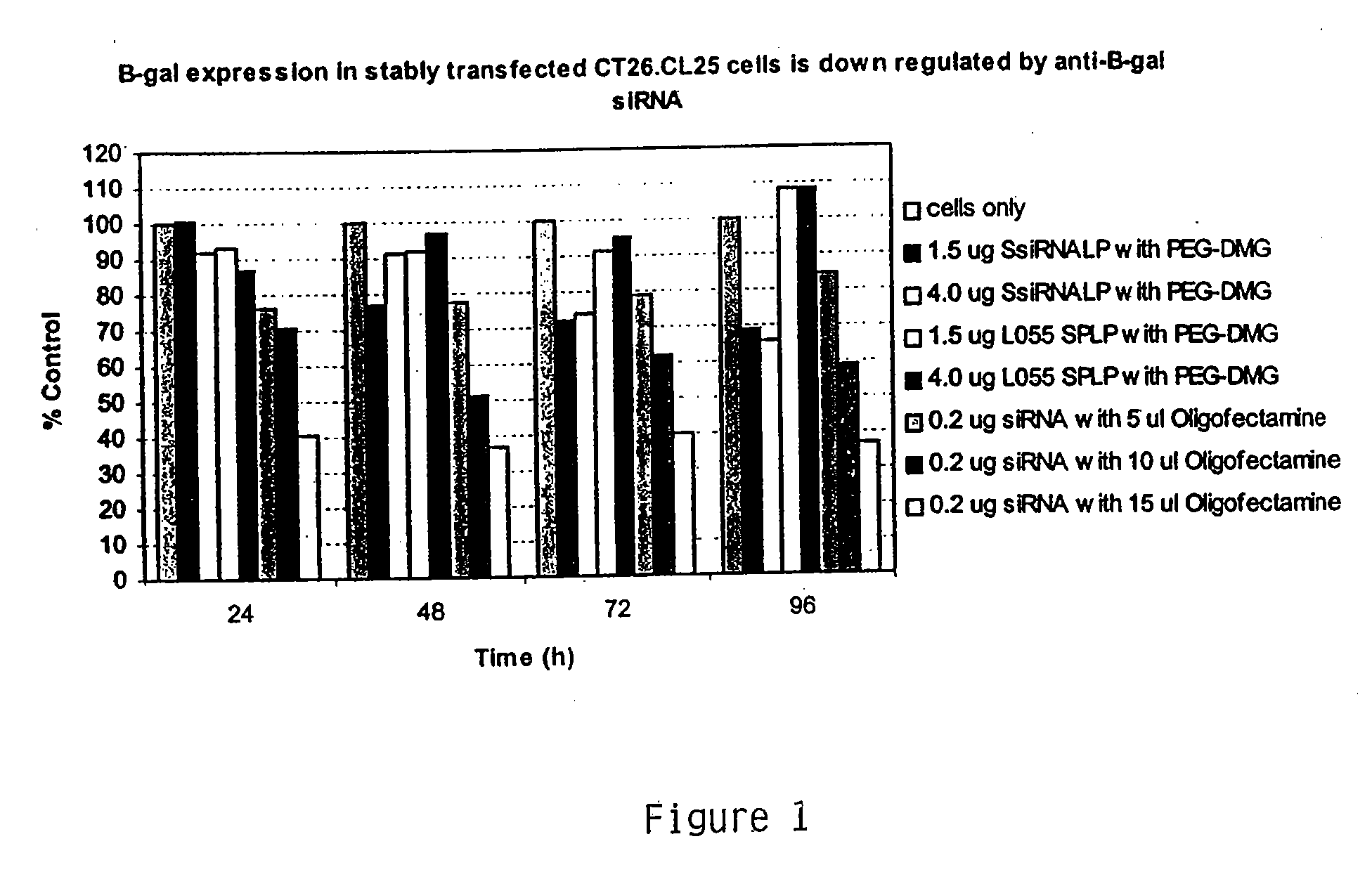
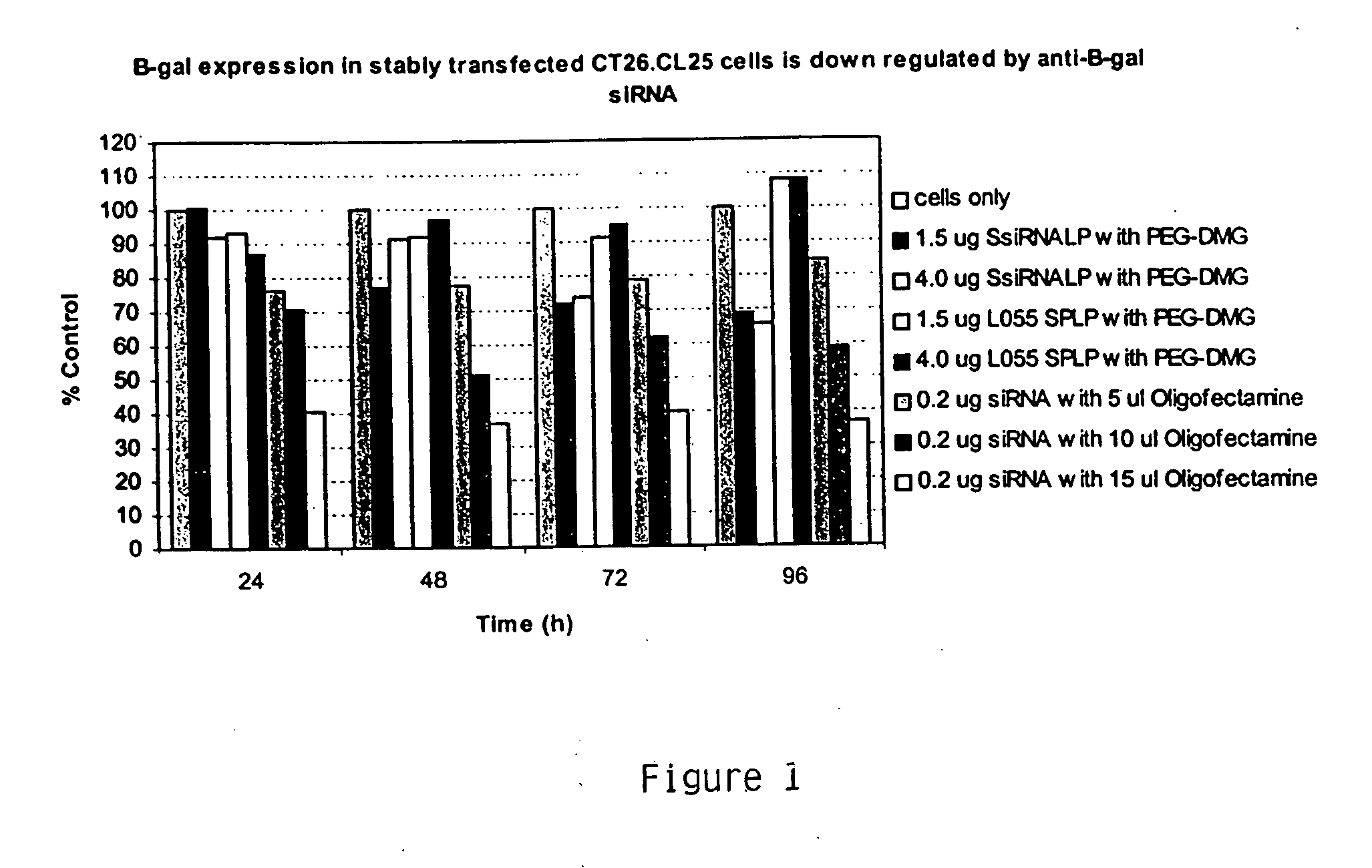
Lipid encapsulated interfering RNA
ActiveUS20060240093A1Inhibit aggregationMetabolism disorderMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention provides compositions and methods for silencing gene expression by delivering nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising a siRNA molecule to a cell.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Insect-resistant transgenic plants
The invention provides transgenic plants and transformed host cells which express modified cry 3B genes with enhanced toxicity to Coleopteran insects. Also disclosed are methods of making and using these transgenic plants, methods of making recombinant host cells expressing these delta -endotoxins, and methods of killing insects such as Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi Barber) and western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Lipid encapsulated interfering RNA
InactiveUS20050064595A1Inhibit aggregationMetabolism disorderMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention provides compositions and methods for silencing gene expression by delivering nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising a siRNA molecule to a cell.
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
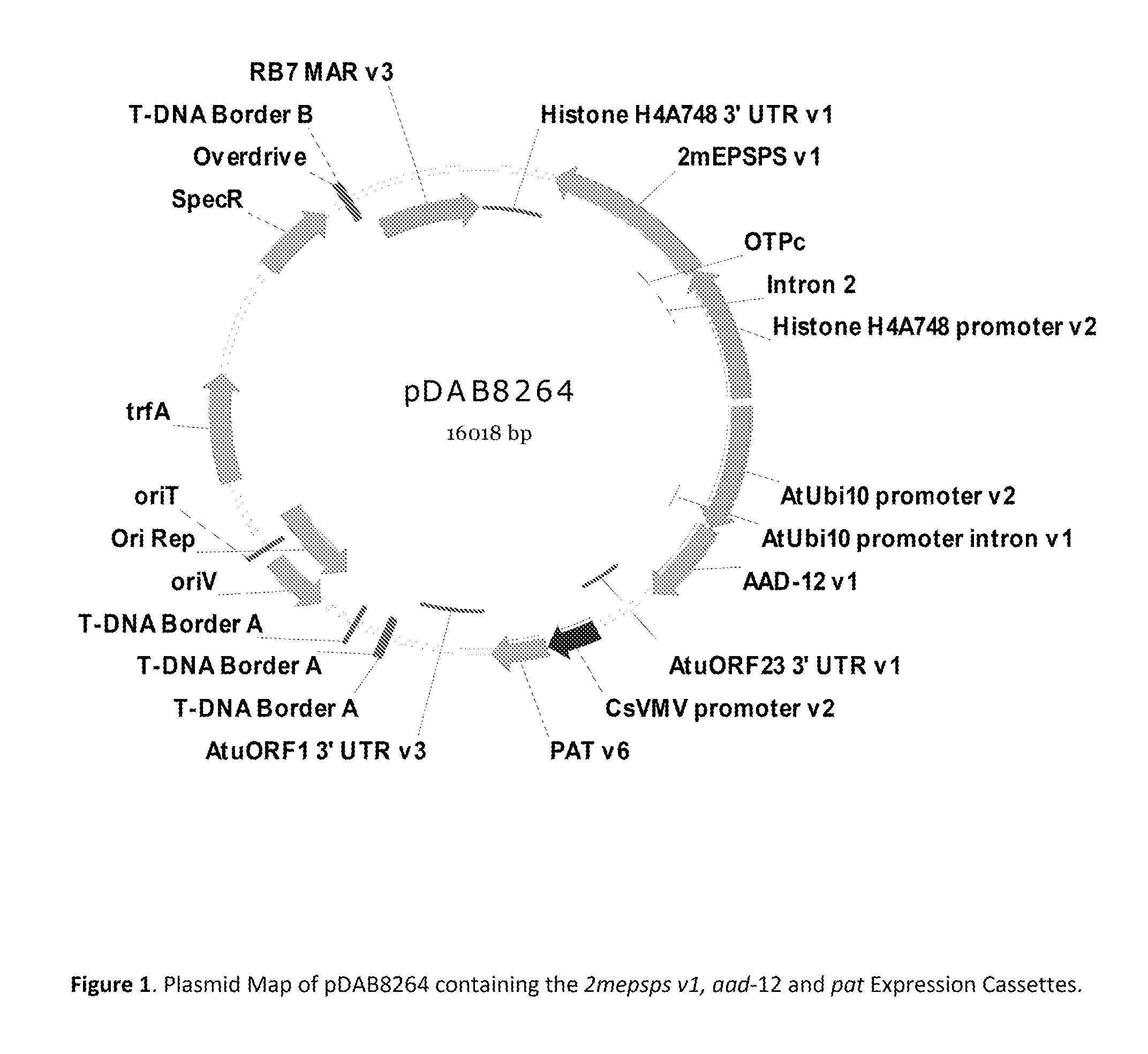
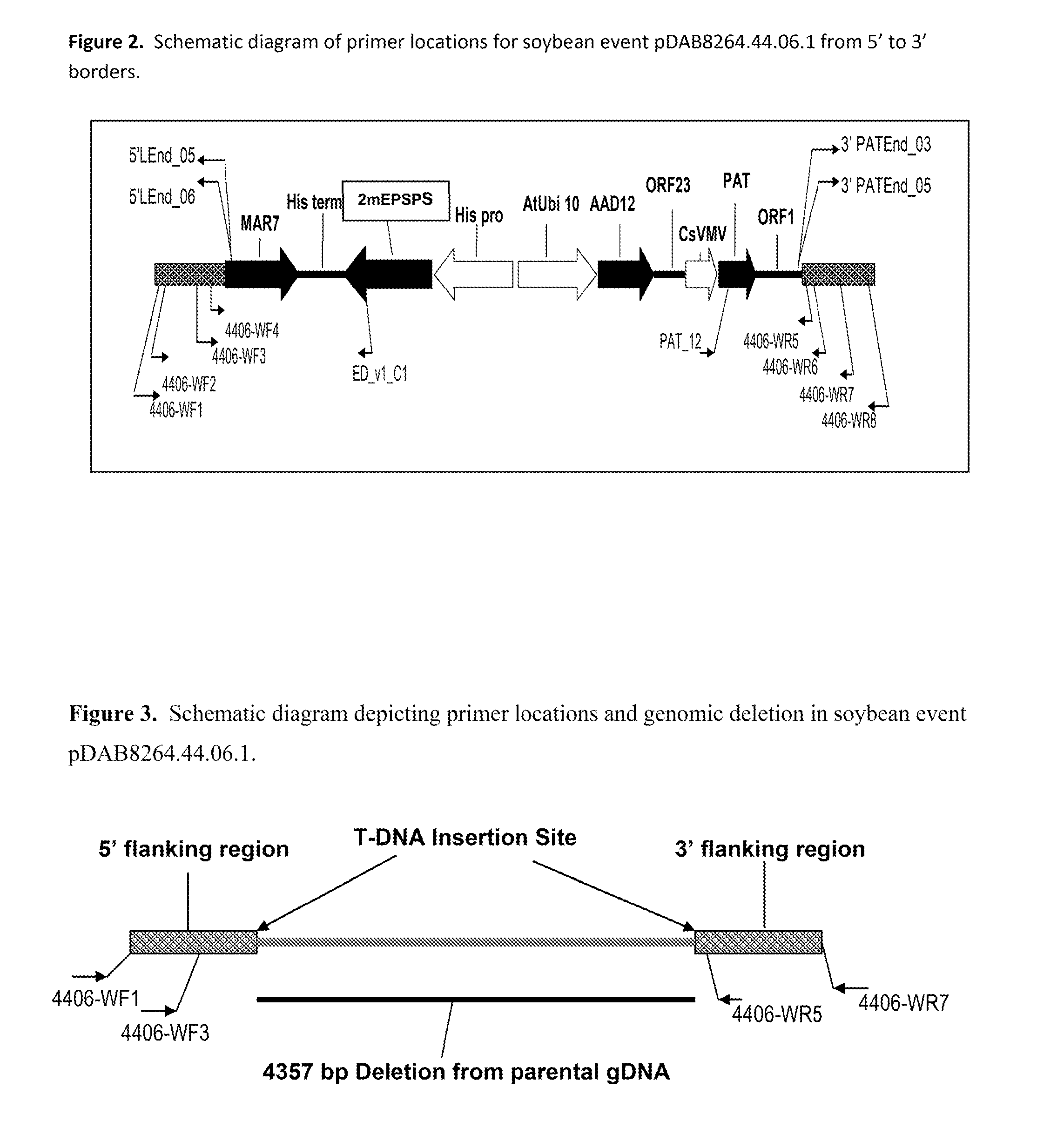
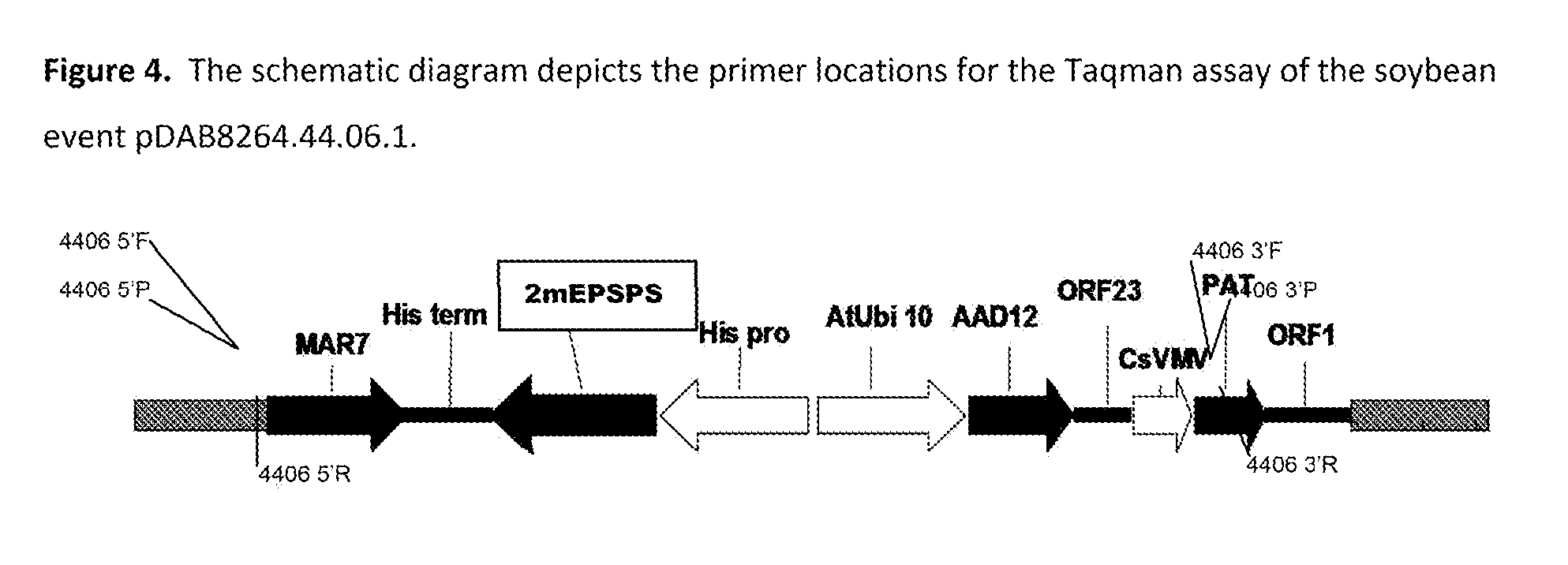
Stacked herbicide tolerance event 8264.44.06.1, related transgenic soybean lines, and detection thereof
ActiveUS9540655B2Preserve usefulnessIncrease flexibilityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayMultiple traits
Owner:M S TECH +1
Adeno-associated virus (aav) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
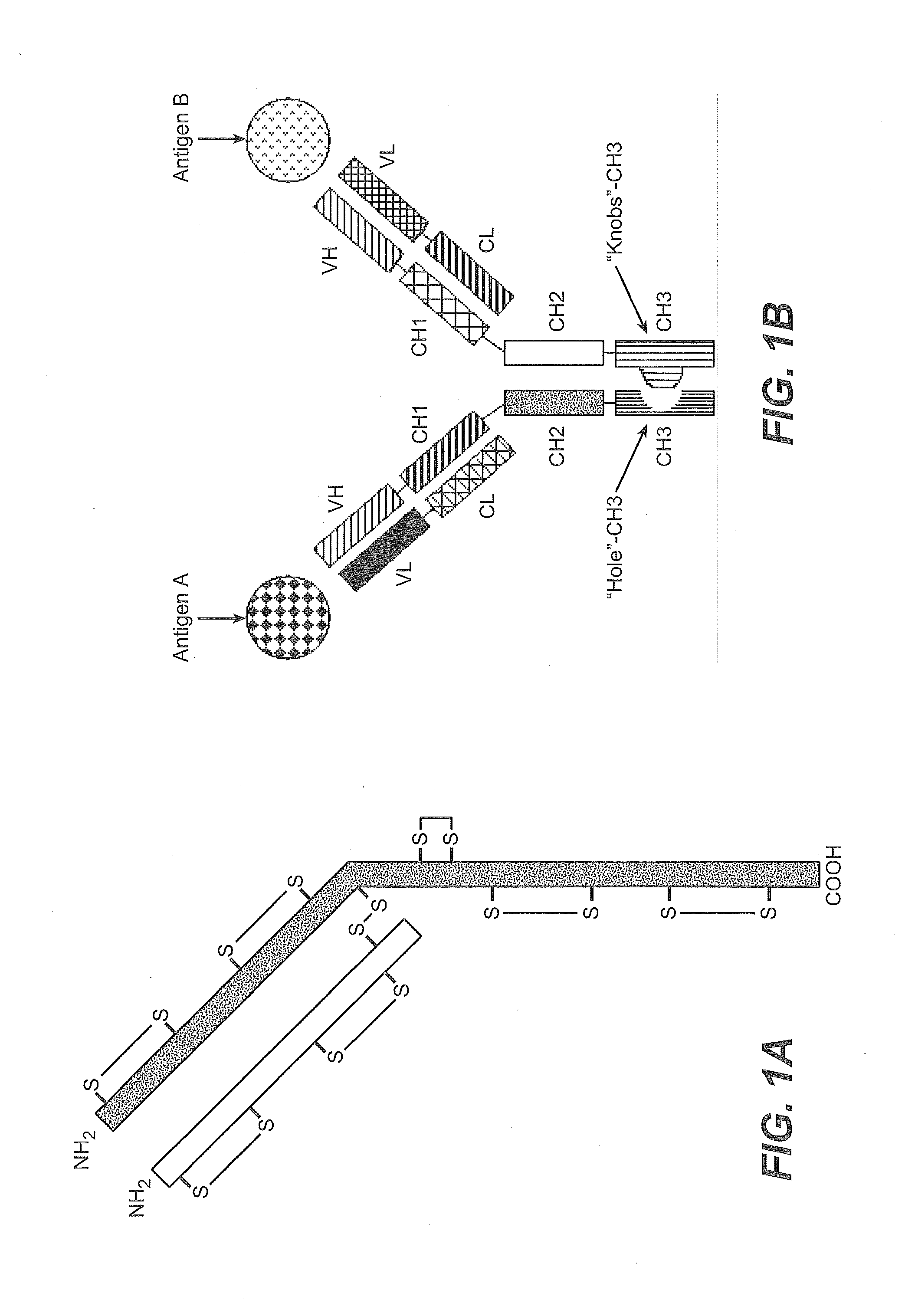
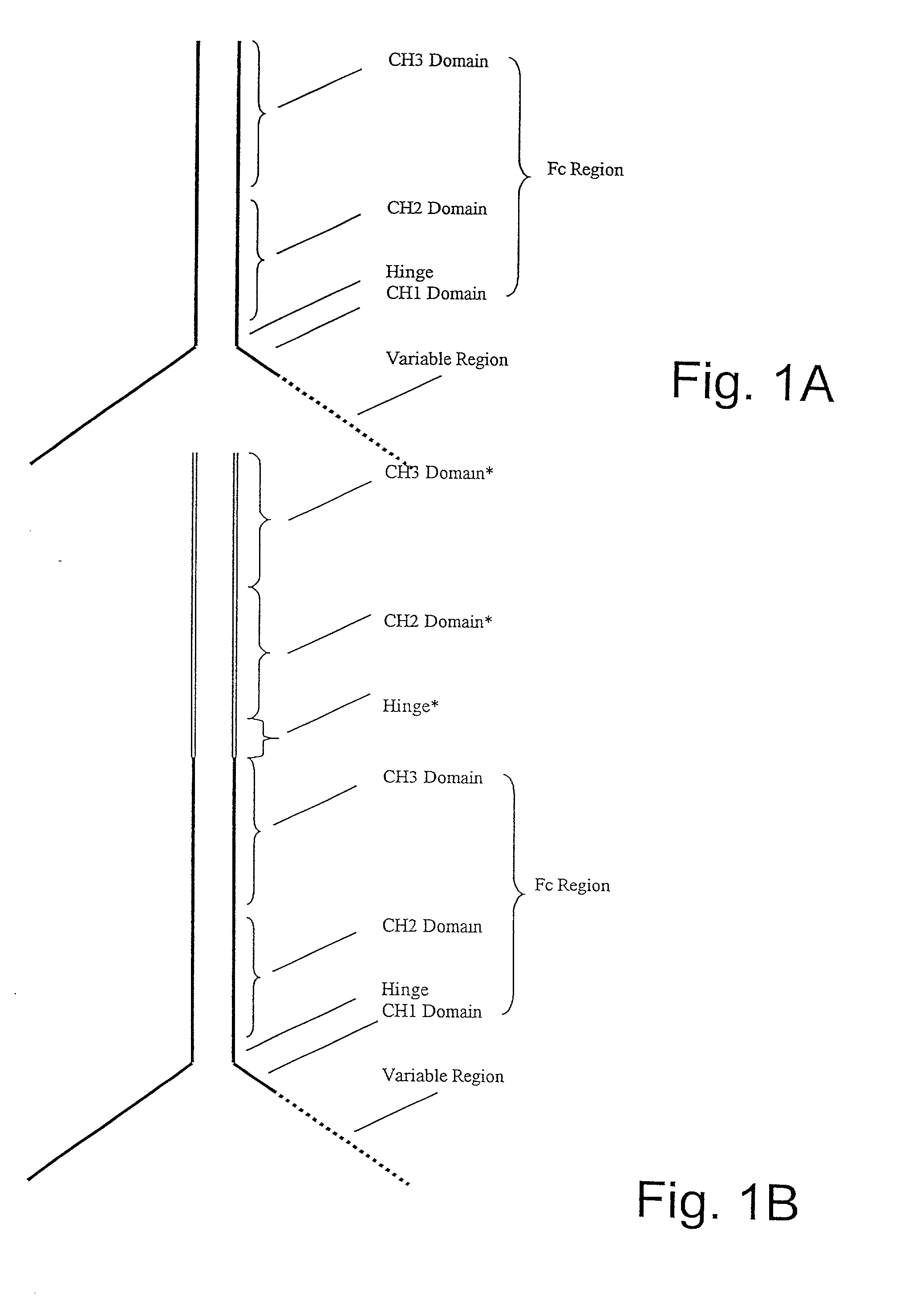
Production of Heteromultimeric Proteins
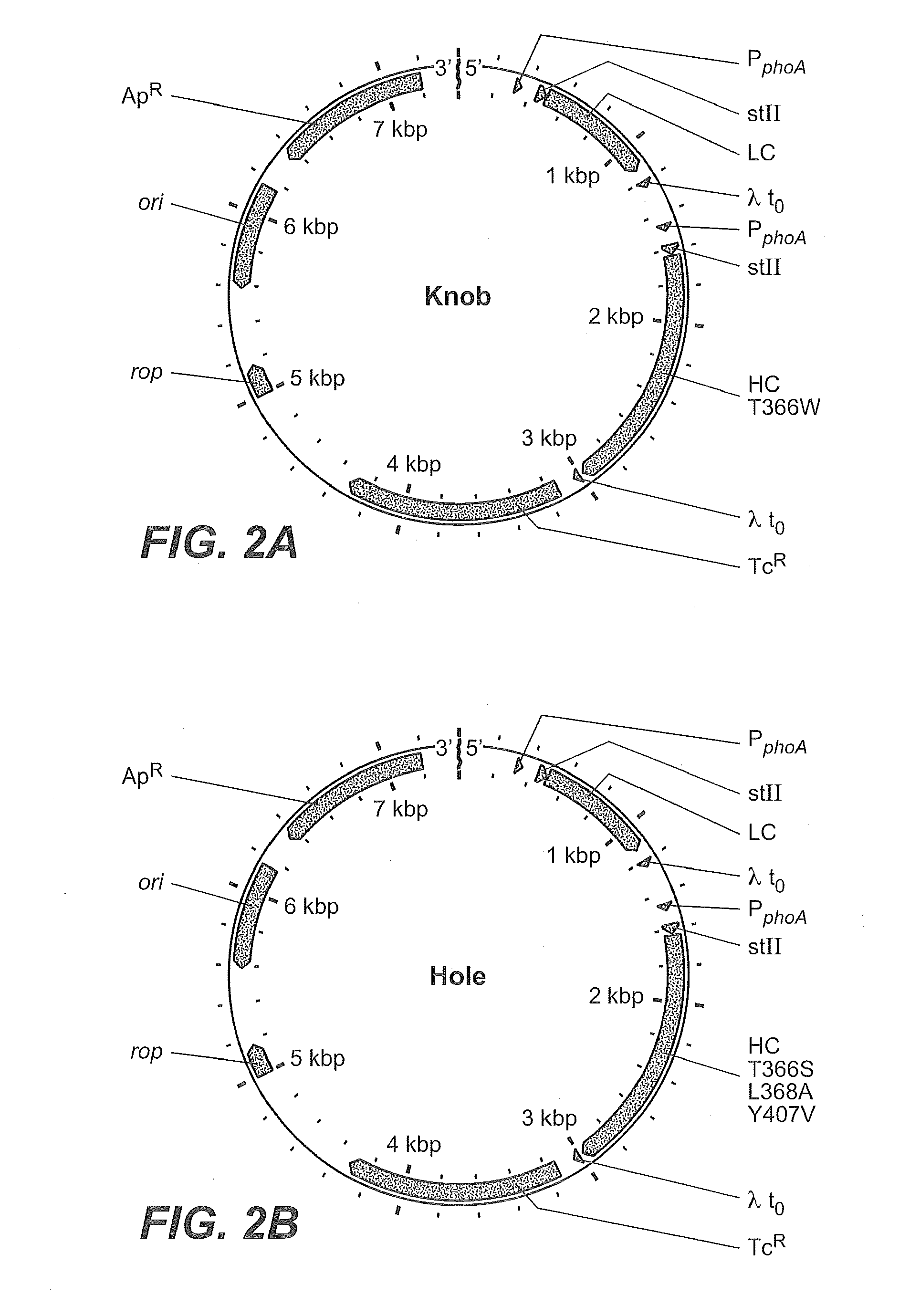
ActiveUS20110287009A1Reduction in yieldDecreased/elimination of effector functionAntipyreticAnalgesicsEpitopeBiochemistry
Described herein are methods for the efficient production of antibodies and other multimeric protein complexes (collectively referred to herein as heteromultimeric proteins) capable of specifically binding to more than one target. The targets may be, for example, different epitopes on a single molecule or located on different molecules. The methods combine efficient, high gene expression level, appropriate assembly, and ease of purification for the heteromultimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods of using these heteromultimeric proteins, and compositions, kits and articles of manufacture comprising these antibodies.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Use
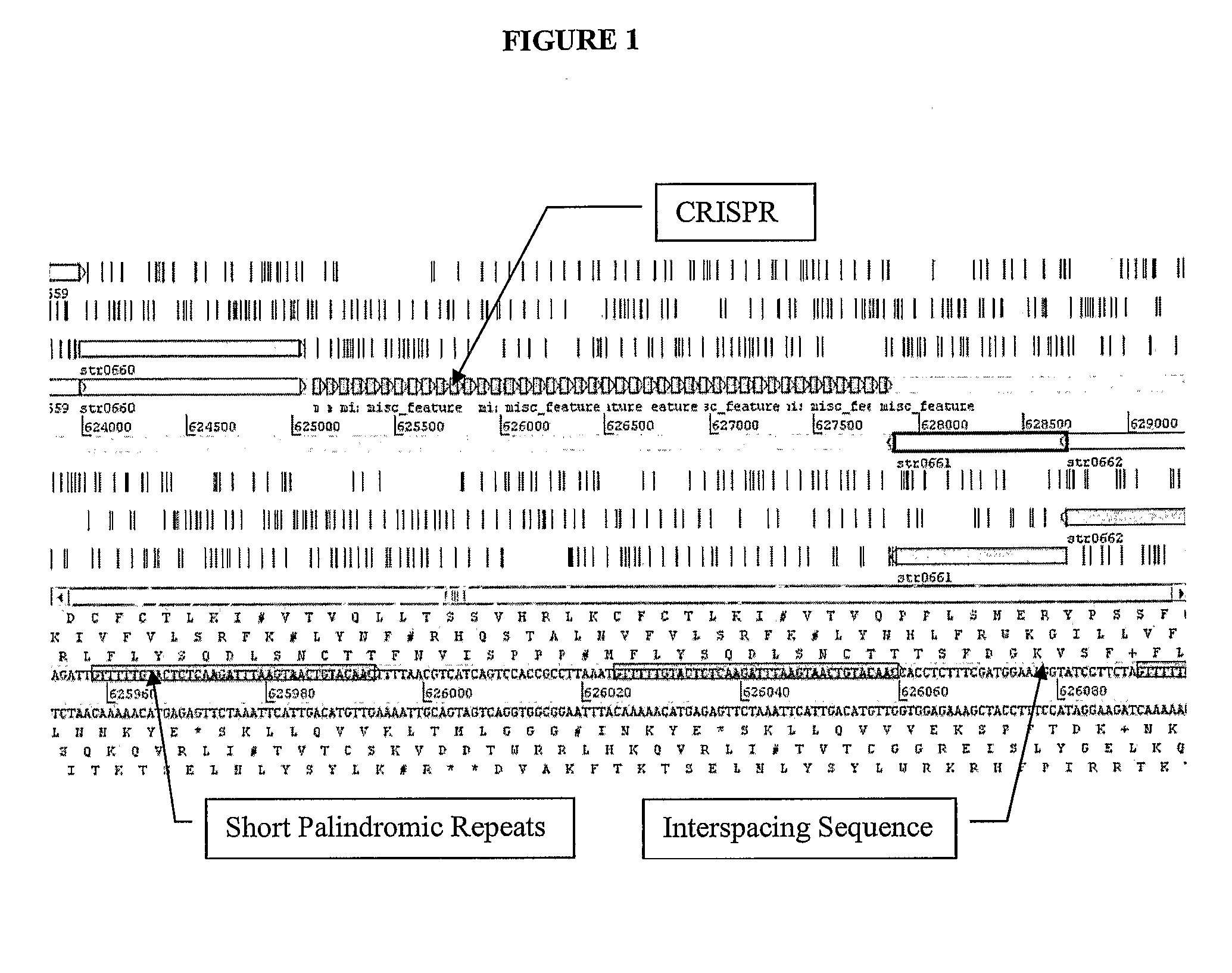
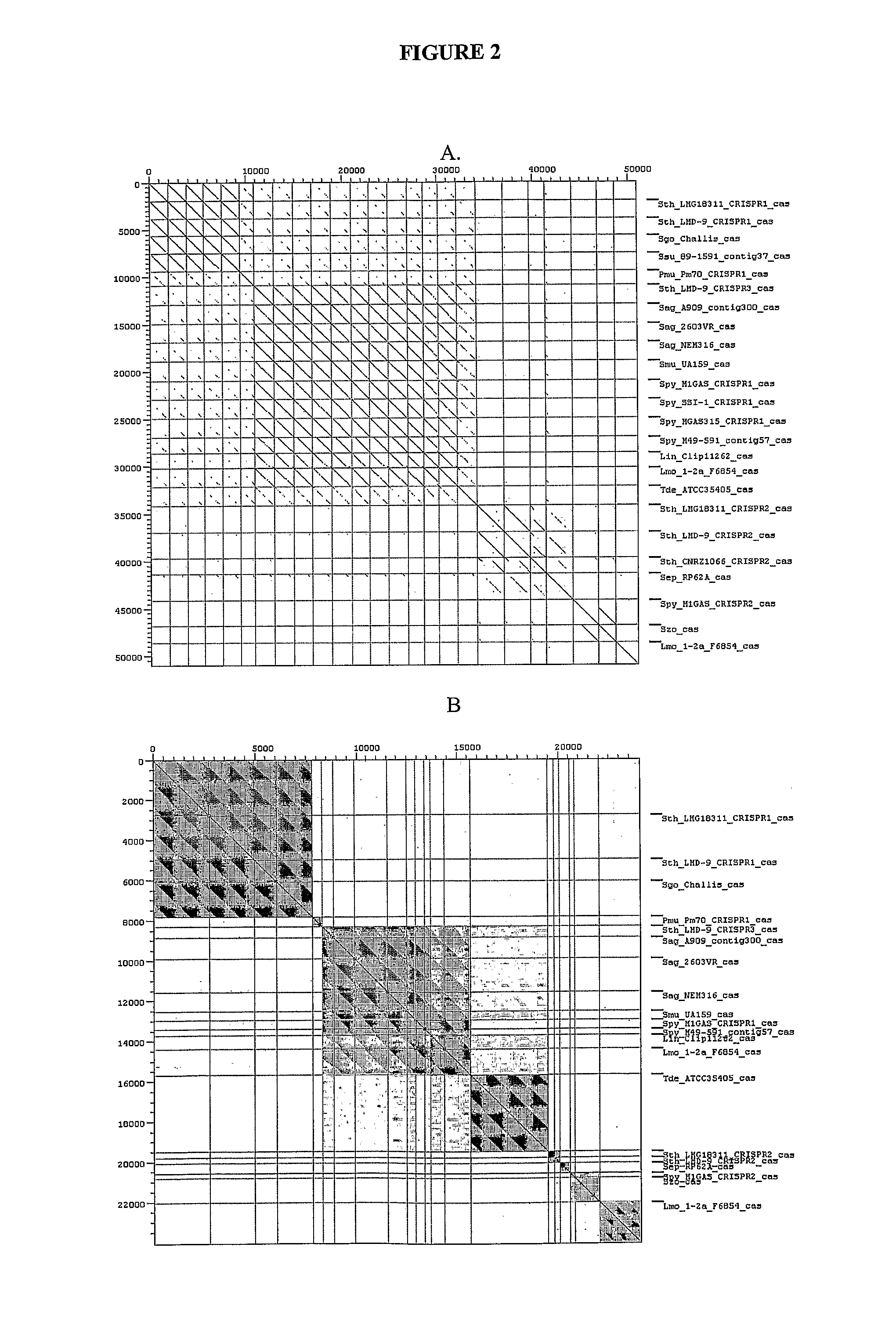
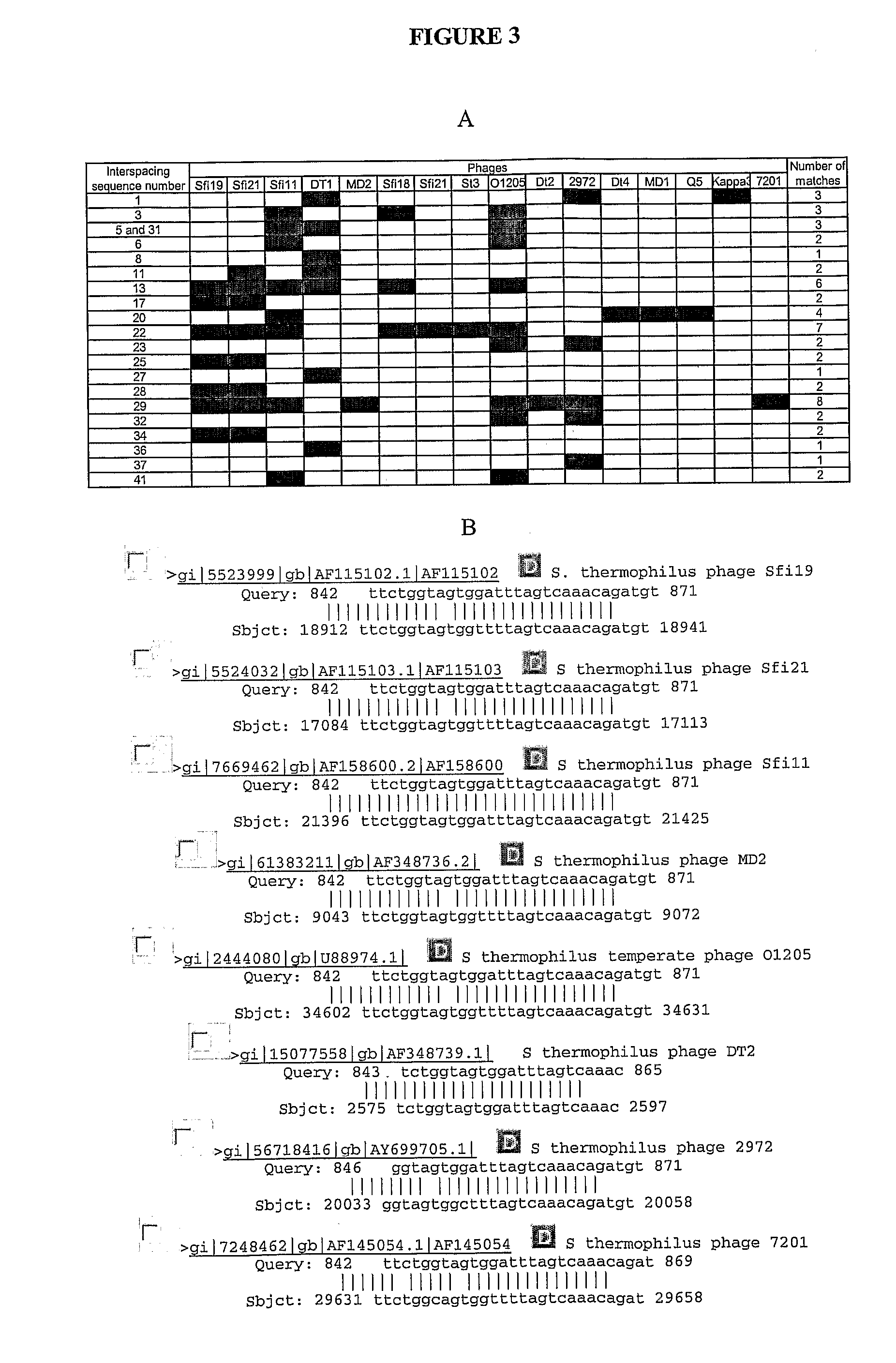
ActiveUS20100093617A1Reduced degree of homologyModulate the resistance of a cellOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaGeneBioinformatics
The present invention relates to the use of one or more cas genes for modulating resistance in a cell against a target nucleic acid or a transcription product thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Methods for genotyping selected polymorphism
InactiveUS20050142577A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDegenerate oligonucleotideGene
Methods for genotyping polymorphisms using a locus specific primer that is complementary to a region near a selected polymorphism are described. Methods for synthesizing pools of locus specific primers that incorporate some degenerate positions are also disclosed. A plurality of different sequence capture probes are synthesized simultaneously using degenerate oligonucleotide synthesis. The sequence of the locus specific regions of the capture probes are related in that they have some bases that are identical in each sequence in the plurality of sequences and positions that vary from one locus specific region to another. The sequences are selected based on proximity to a polymorphism of interest and because they conform to a similar sequence pattern.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
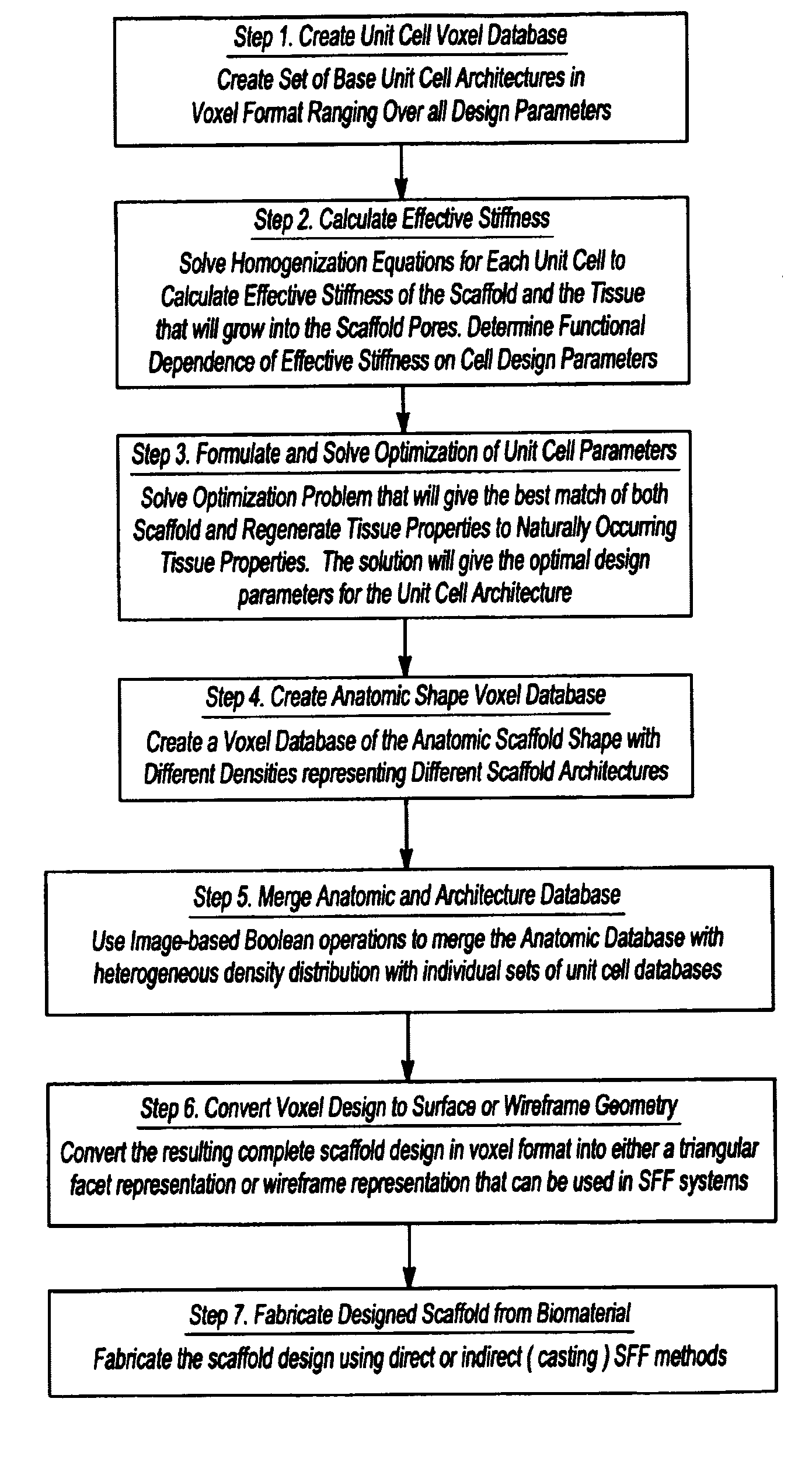
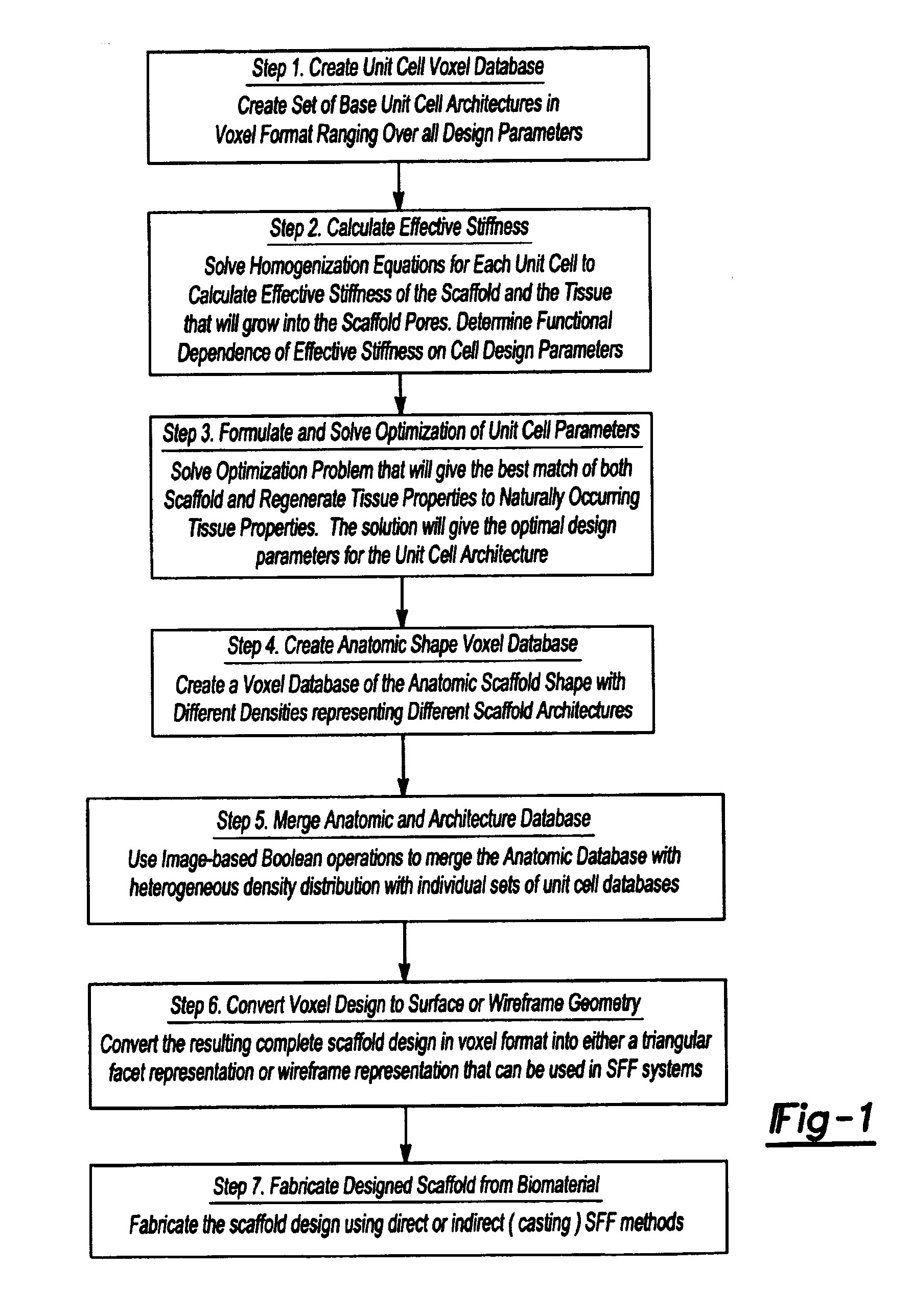
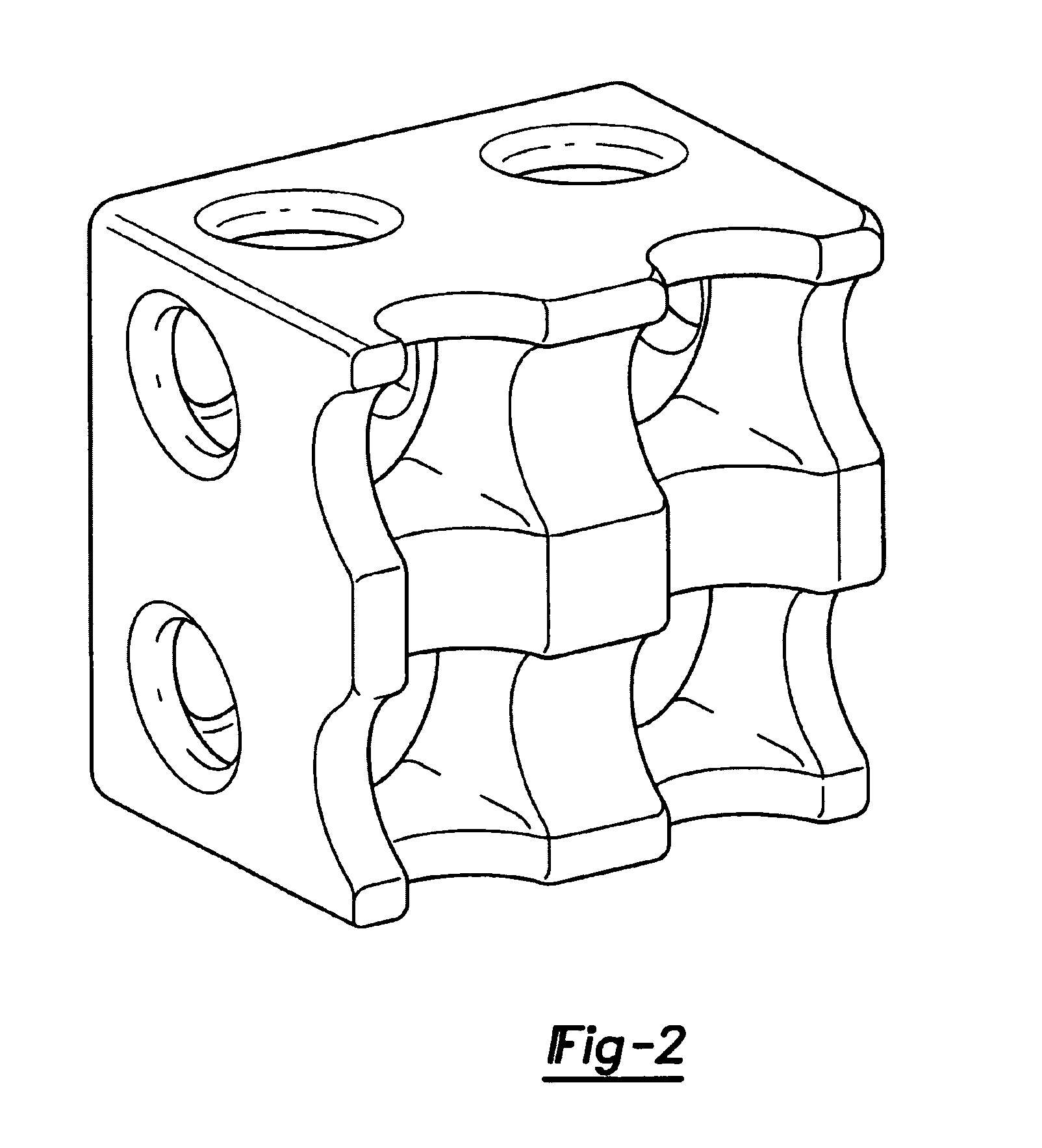
Design methodology for tissue engineering scaffolds and biomaterial implants
A design methodology is provided for creating biomaterial scaffolds optimized for in vivo function with any 3D anatomic shape. The method creates all designs using voxel based design techniques. It also provides for optimization of implant and scaffold microstructure to best match functional and biofactor delivery (including cells, genes and proteins) requirements. The voxel based design techniques readily allow combination of any scaffold or implant microstructure database with any complex 3D anatomic shape created by CT or MRI scanners. These designs can be readily converted to formats for layered manufacturing or casting.
Owner:HOLLISTER SCOTT J +2
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Gene expression analysis in single cells
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the analysis of gene expression in single cells or in a plurality of single cells. The invention provides methods for preparing a cDNA library from individual cells by releasing mRNA from each single cell to provide a plurality of individual mRNA samples, synthesizing cDNA from the individual mRNA samples, tagging the individual cDNA, pooling the tagged cDNA samples and amplifying the pooled cDNA samples to generate a cDNA library. The invention also provides a cDNA library produced by the methods described herein. The invention farther provides methods for analyzing gene expression in a plurality of cells by preparing a cDNA library as described herein and sequencing the library.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Broad-spectrum insect resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6281016B1Improve insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityBiocideNanotechAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and tansgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Broad-spectrum delta -endotoxins
InactiveUS6110464AImprove insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityNanotechBacteriaAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
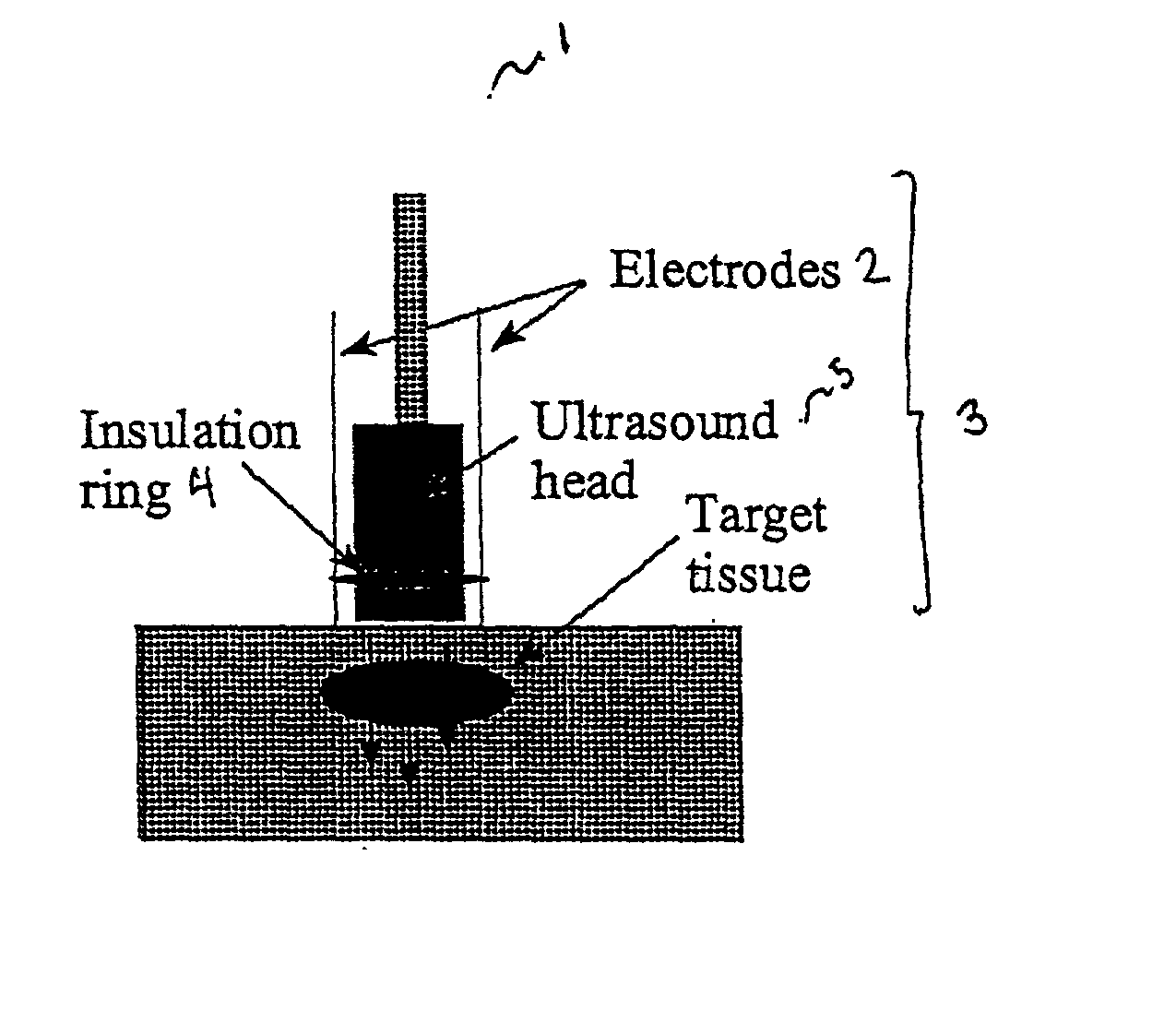
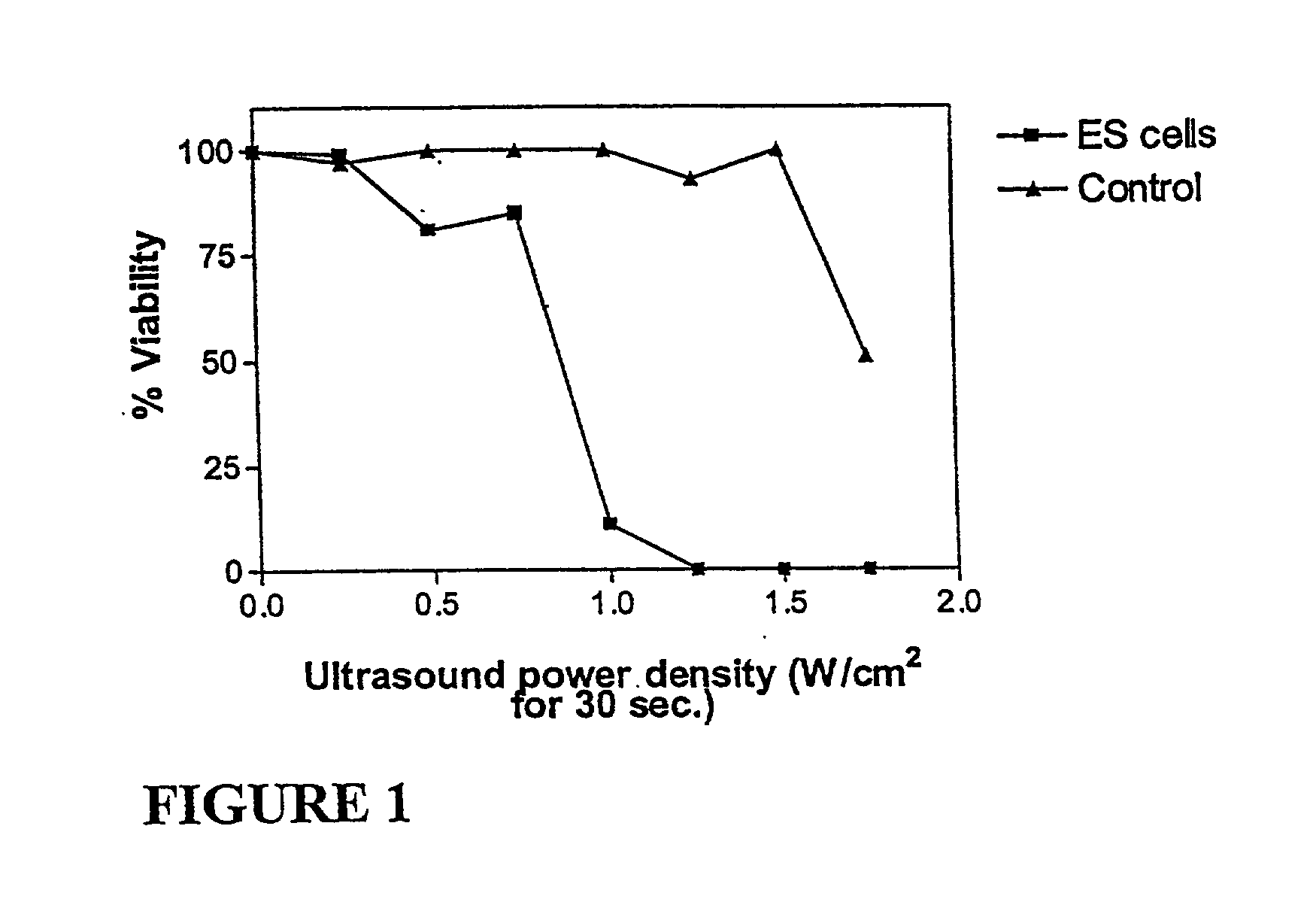
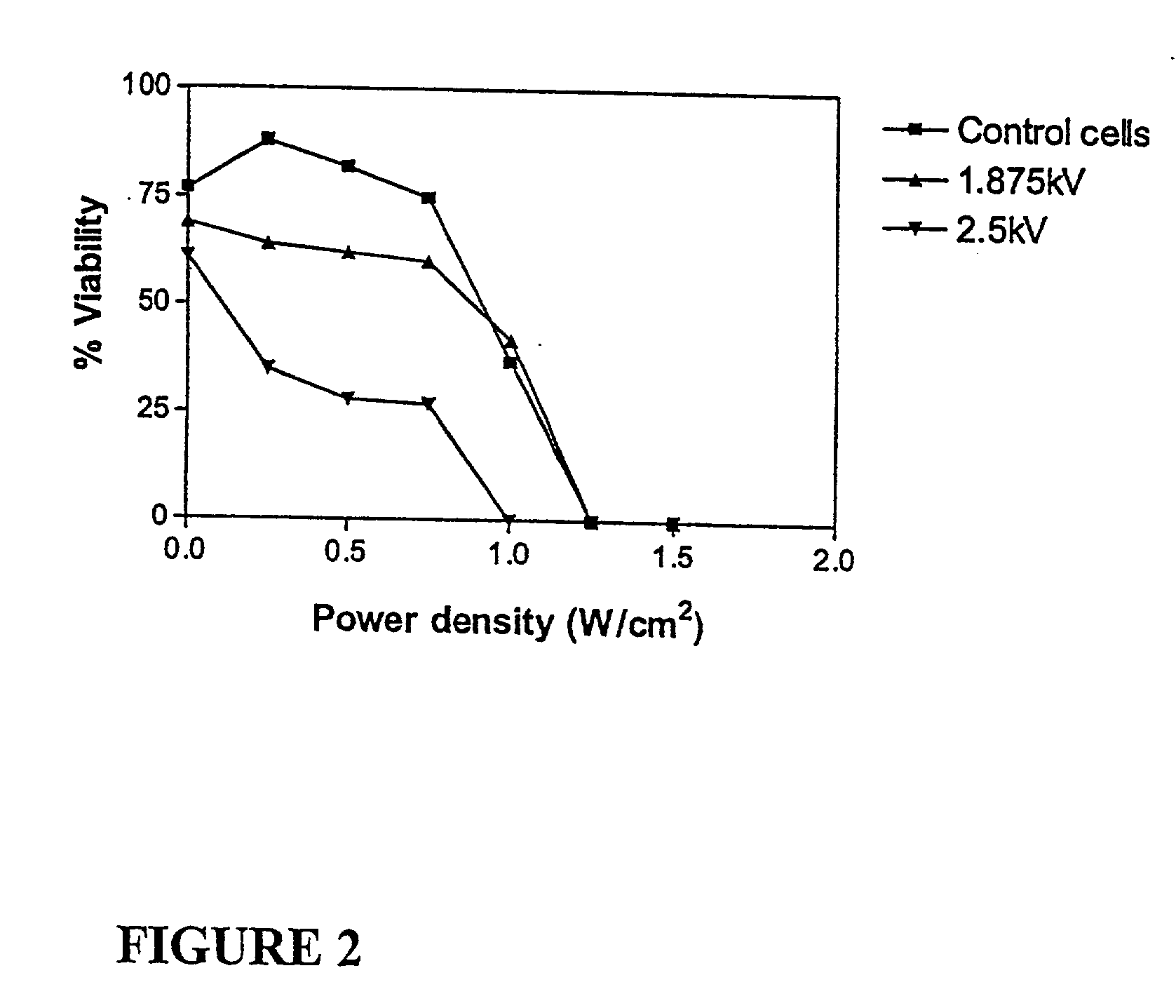
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS20020193784A1Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentApoptosisGene product
The invention provides a method of sensitising target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitised (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimising harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitise cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
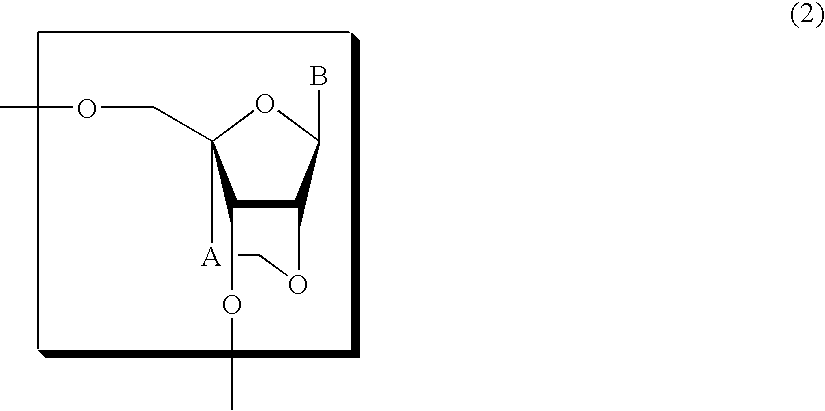
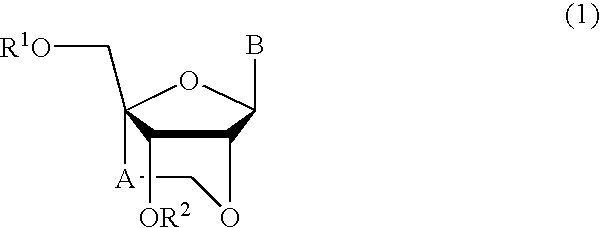
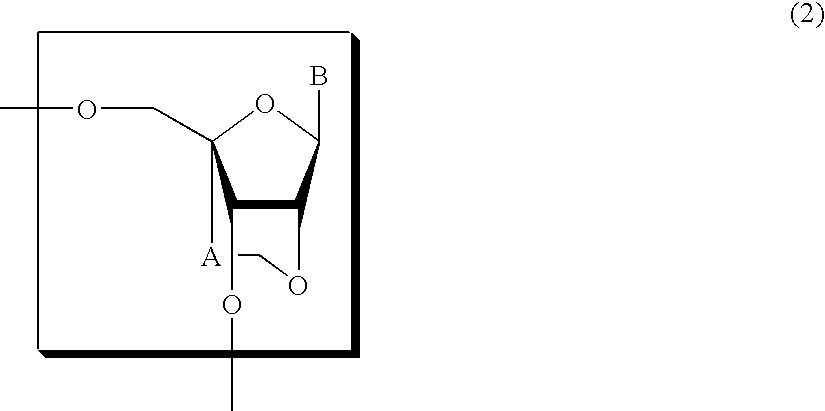
Nucleoside and oligonucleotide analogues
A probe for a gene or a primer for starting amplification comprising an oligonucleotide analogue comprising two or more nucleoside units, wherein at least one of the nucleoside units is a structure of the formula (2):wherein A represents a C1-C4 alkylene group, and B is an unsubstituted purin-9-yl group, an unsubstituted 2-oxo-pyrimidin-1-yl-group, a substituted purin-9-yl-group or a substituted 2-oxo-pyrimidin-1-yl group. Also a method for preventing or treating a disease preventable or treatable by the antisense or antigene activity of an oligonucleotide by administering the oligonucleotide analogue.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Generation and application of universal T cells for B-ALL
InactiveUS20070036773A1Hinder recognitionEnhanced siRNA effectBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigenNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The present invention is directed to universal T cells and their use in treating diseases and other physiological conditions. More specifically, the present invention is directed to universal T cells and their use in treating treating B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) in particular and malignancy in general. The universal T cells contain (i) nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to redirect their antigen specificity and effector function and (ii) nucleic acids encoding shRNA and / or siRNA molecules to down-regulate cell-surface expression of T cell classical HLA class I and / or II genes to avoid recognition by recipient T cells. The universal T cells may also contain a nucleic acid encoding a non-classical HLA gene, such as an HLA E gene to enforce expression of HLA E genes and / or an HLA G gene to enforce expression of HLA G genes, to avoid recognition by recipient NK cells. The universal T cells may further contain a nucleic acid encoding a selection-suicide gene.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Generation of modified molecules with increased serum half-lives
InactiveUS20020142374A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsSerum igeHalf-life
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided methods for the extension of serum half-lives of proteinaceous molecules, particularly antibody molecules, and compositions of molecules modified in accordance with the methods of the invention. In accordance with a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of modifying the half-life of an antibody through providing an antibody containing an FcRn binding domain or the genes encoding such antibody and physically linking the antibody or the antibody as encoded to a second FcRn binding domain. In accordance with a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a molecule that contains at least two distinct FcRn binding moieties.
Owner:ABQENIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com