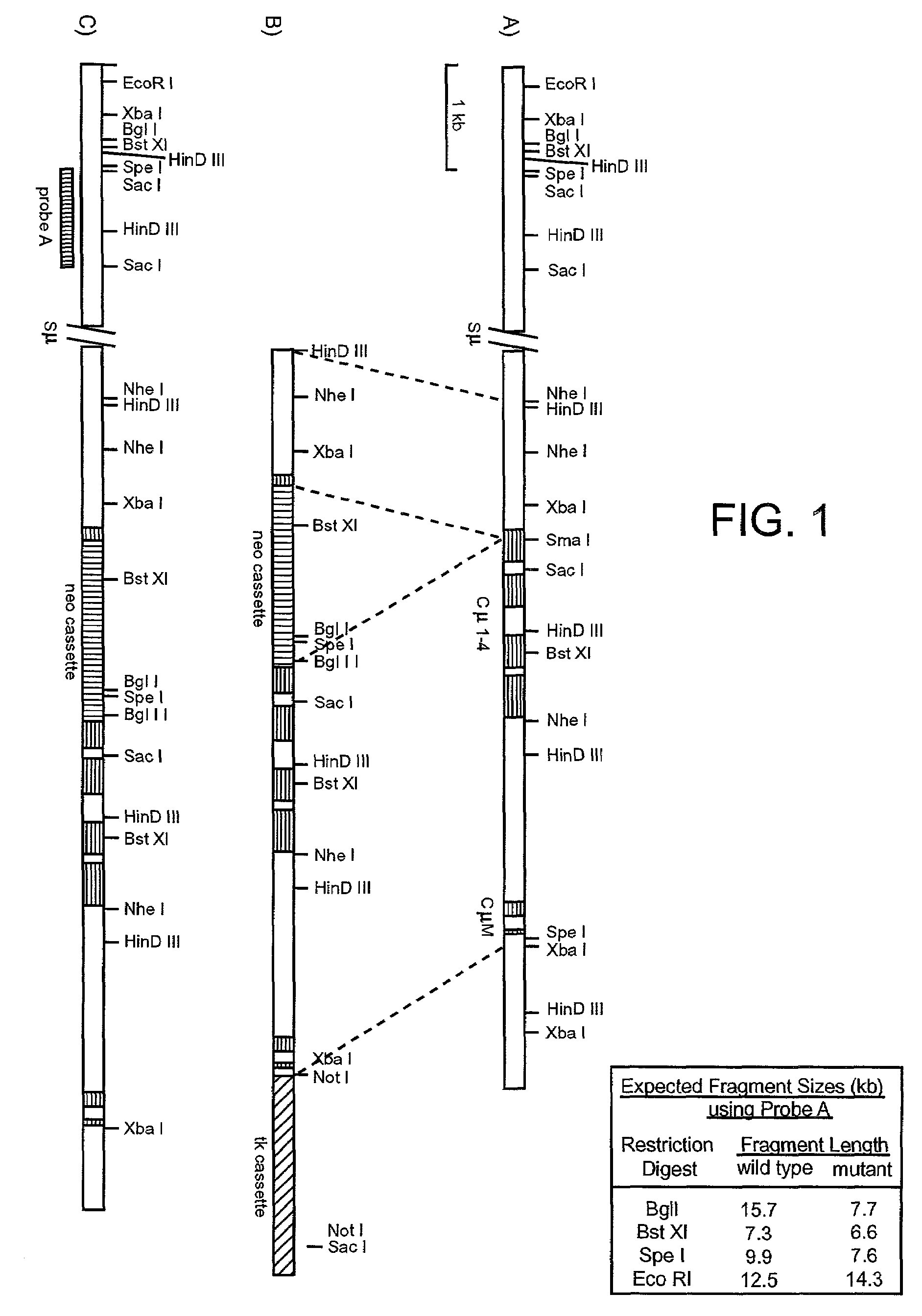
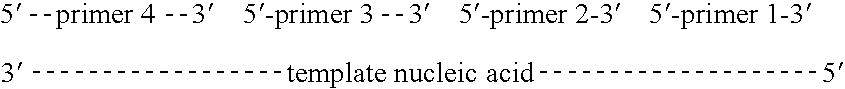Patents
Literature
52657 results about "Bioinformatics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioinformatics /ˌbaɪ.oʊˌɪnfərˈmætɪks/ is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for in silico analyses of biological queries using mathematical and statistical techniques.
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Apparatus for detecting human physiological and contextual information
InactiveUS7020508B2Promote generationWidth dimensionElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using lightThermal energyHeat flux
A detecting apparatus includes a housing support section(s), a housing removably attached thereto, one or more sensors and a processor. An alternate apparatus measures heat flux and includes a known resistivity base member, a processing unit and two temperature measuring devices, one in thermal communication with the body through a thermal energy communicator and the other in thermal communication with the ambient environment. A further alternate apparatus includes a housing or flexible section having an adhesive material on a surface thereof for removably attaching the apparatus to the body. A further alternate apparatus includes a housing having an inner surface having a concave shape in a first direction and convex shape in a second direction substantially perpendicular thereto. Also, an apparatus for detecting heart related parameters includes one or more filtering sensors for generating filtering signals related to the non-heart related motion of the body.
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
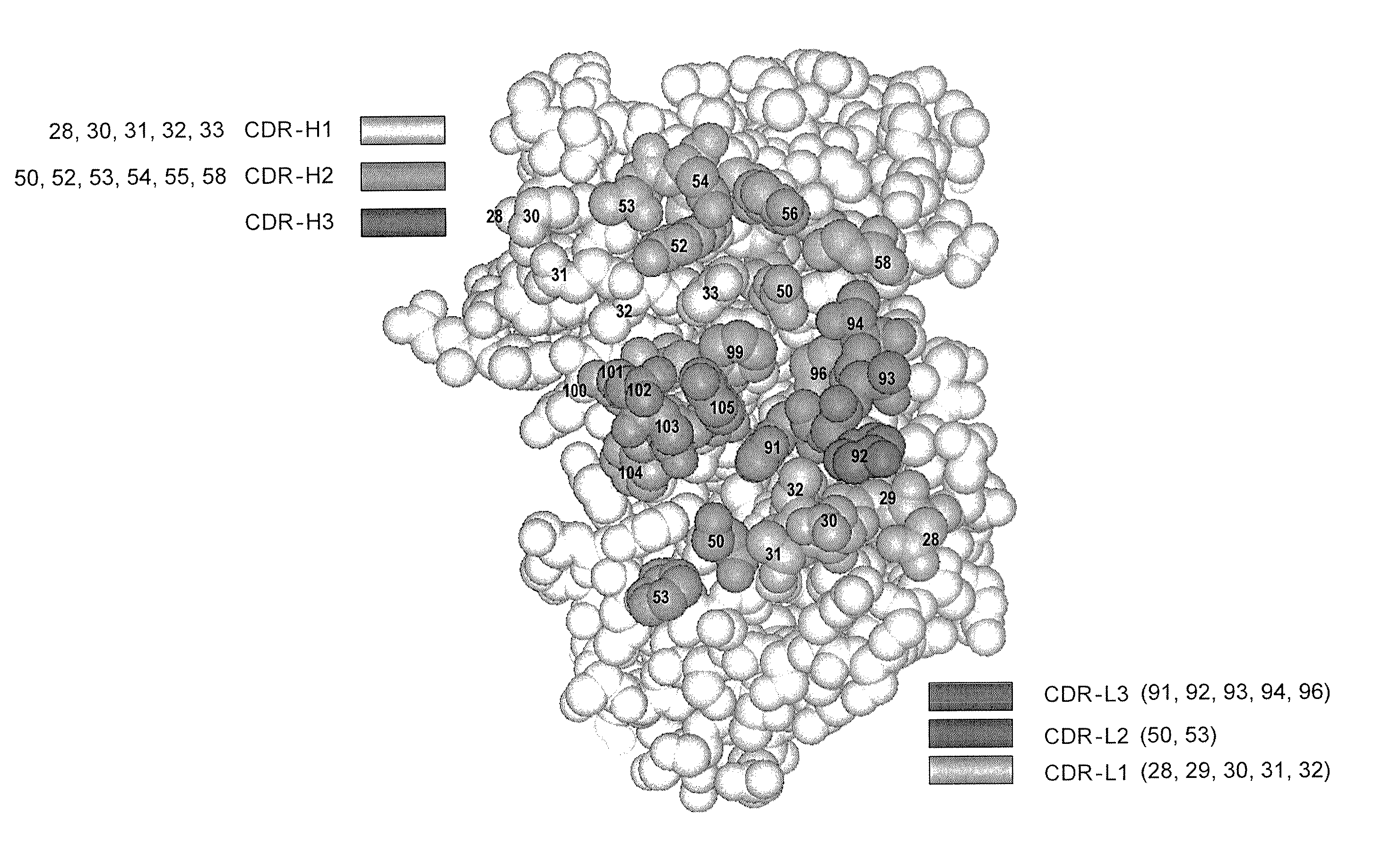
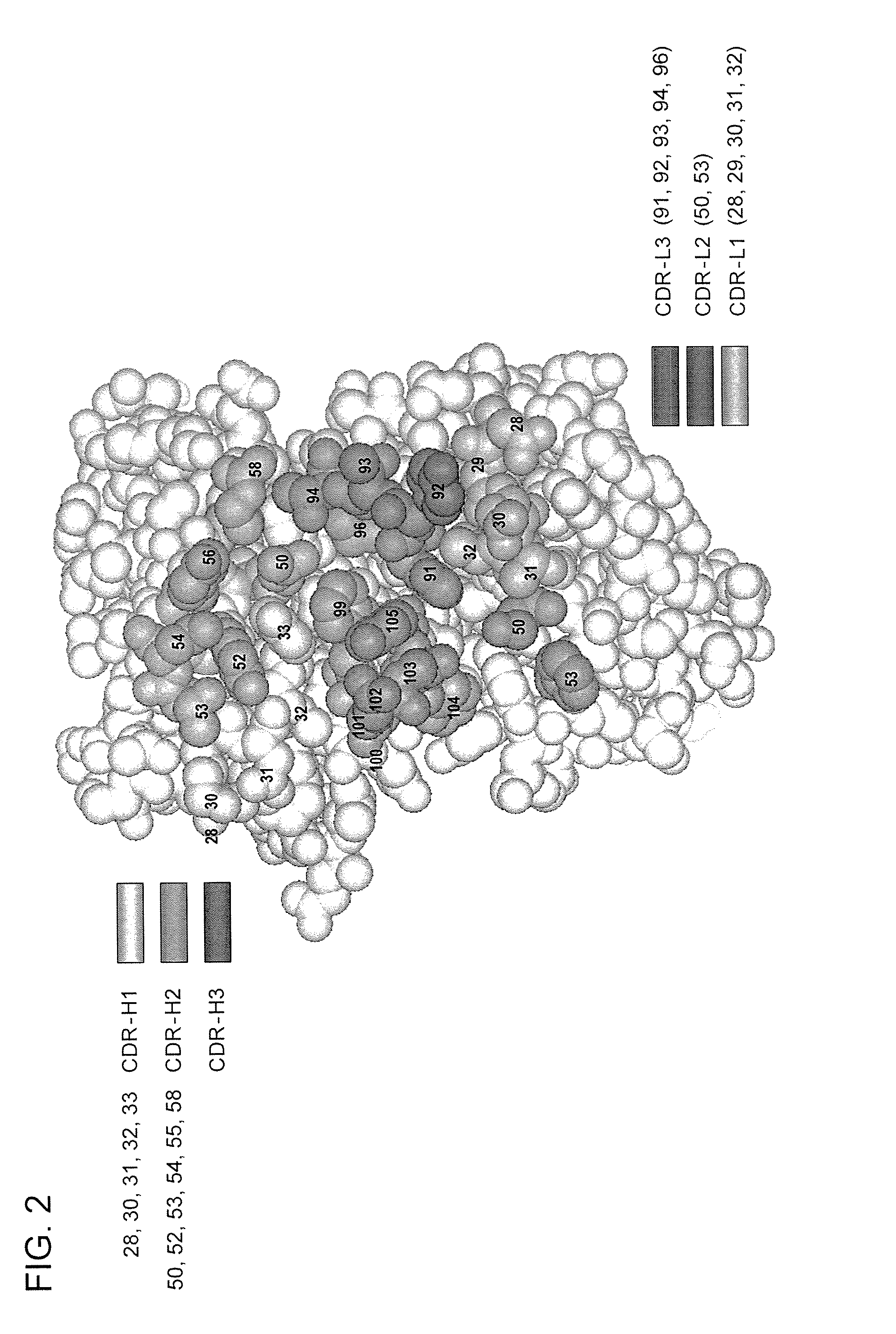
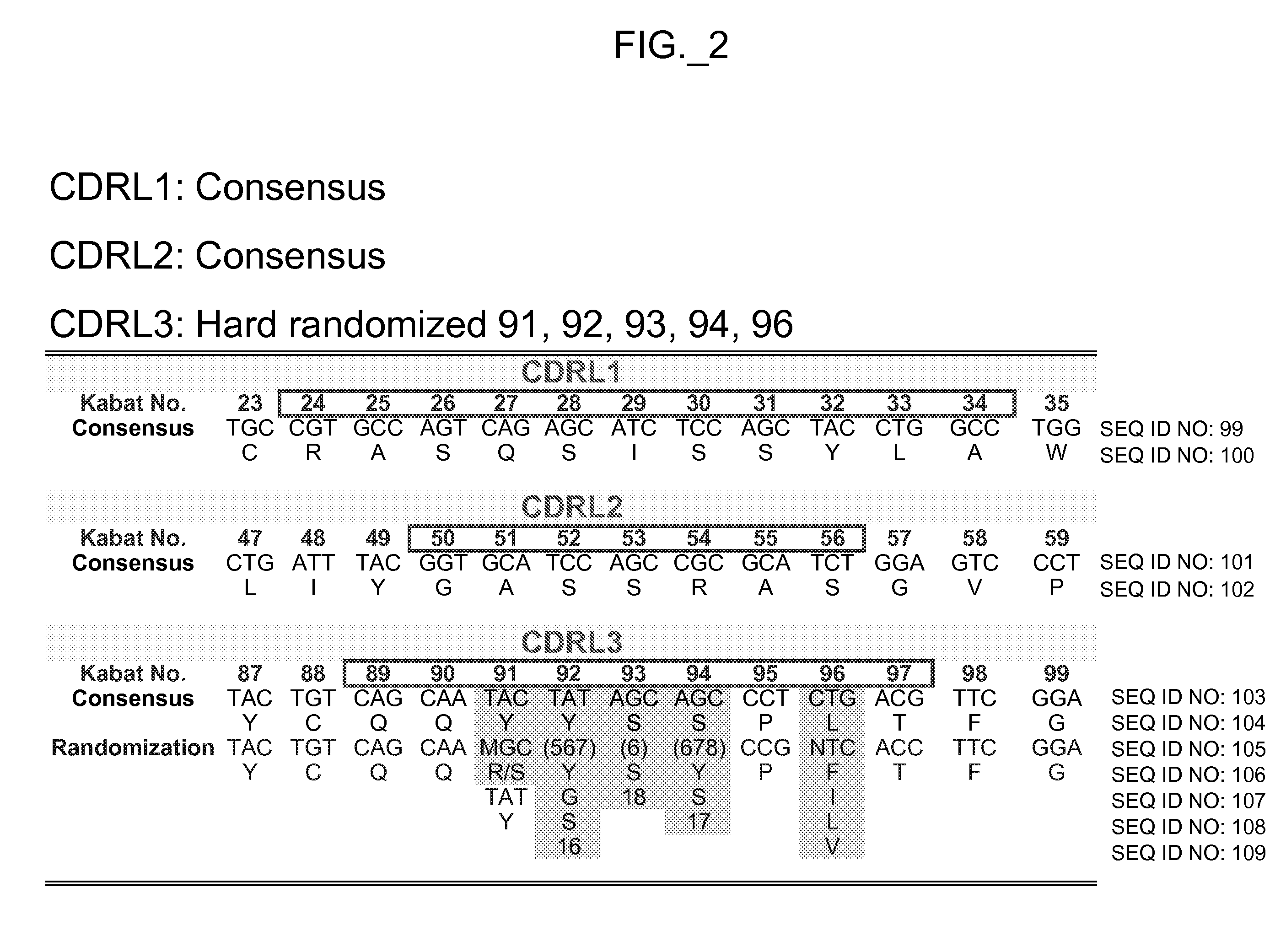
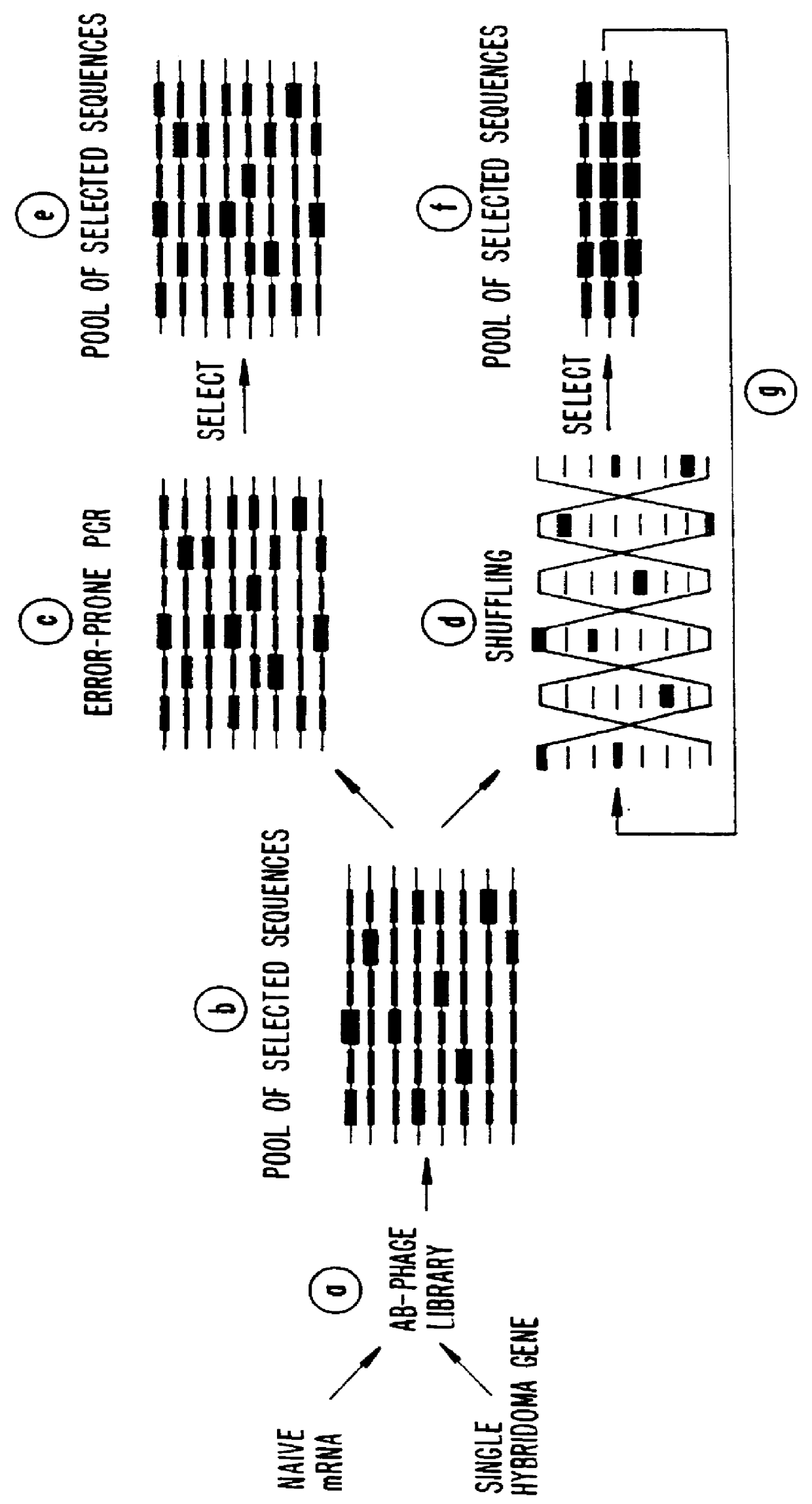
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
InactiveUS20050079574A1High-quality target binding characteristicGenerate efficientlyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousIntravenous gammaglobulin
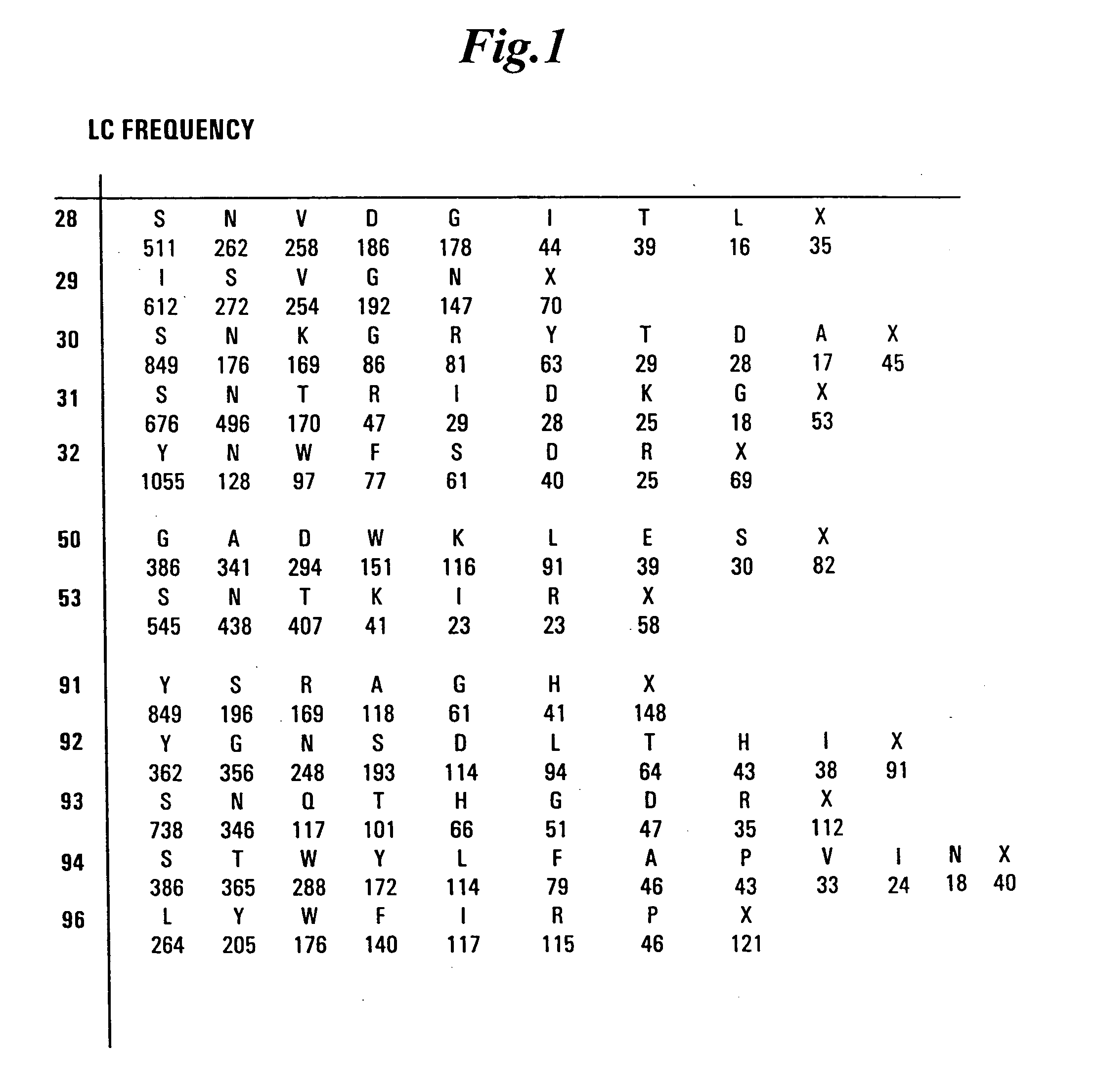
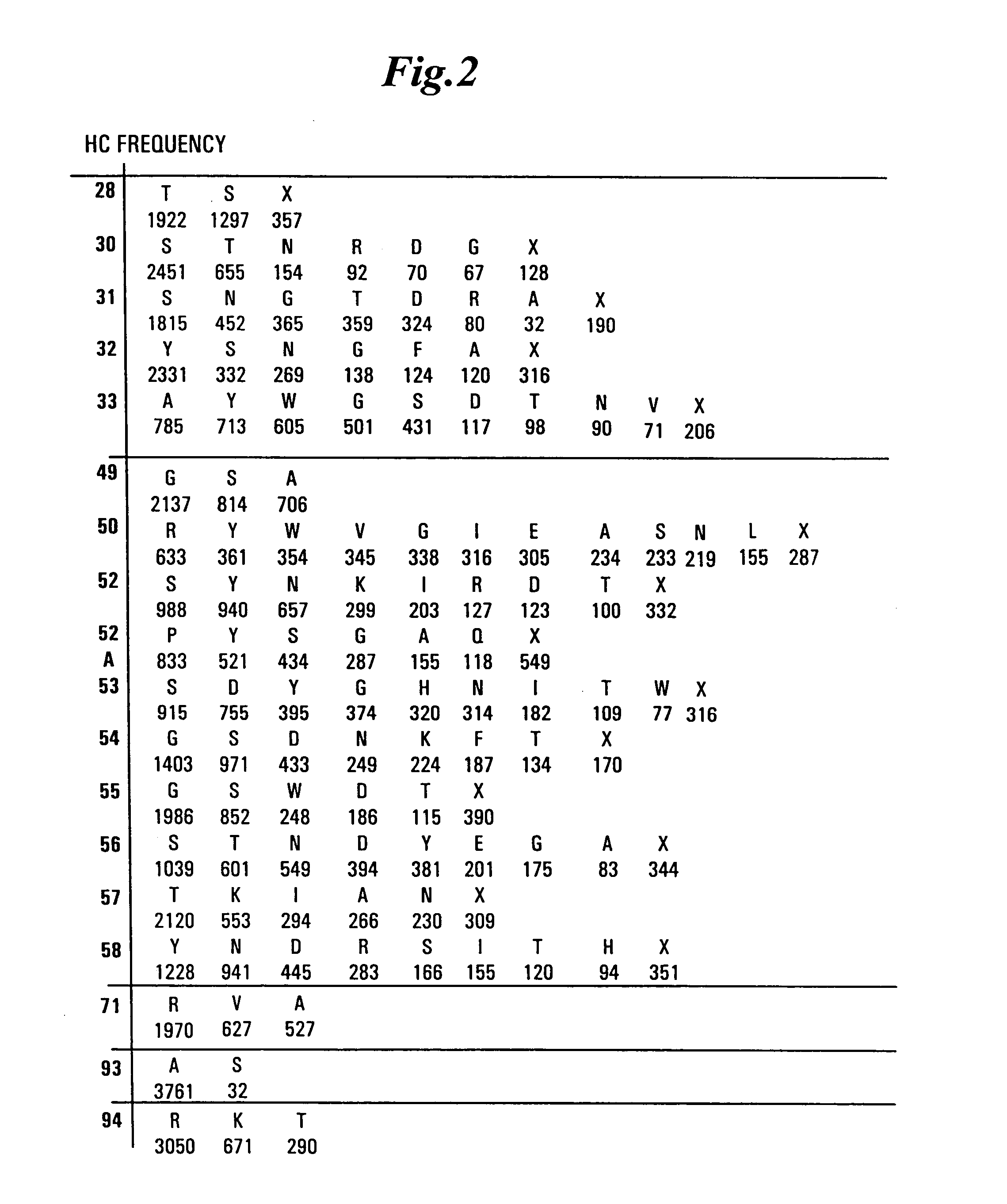
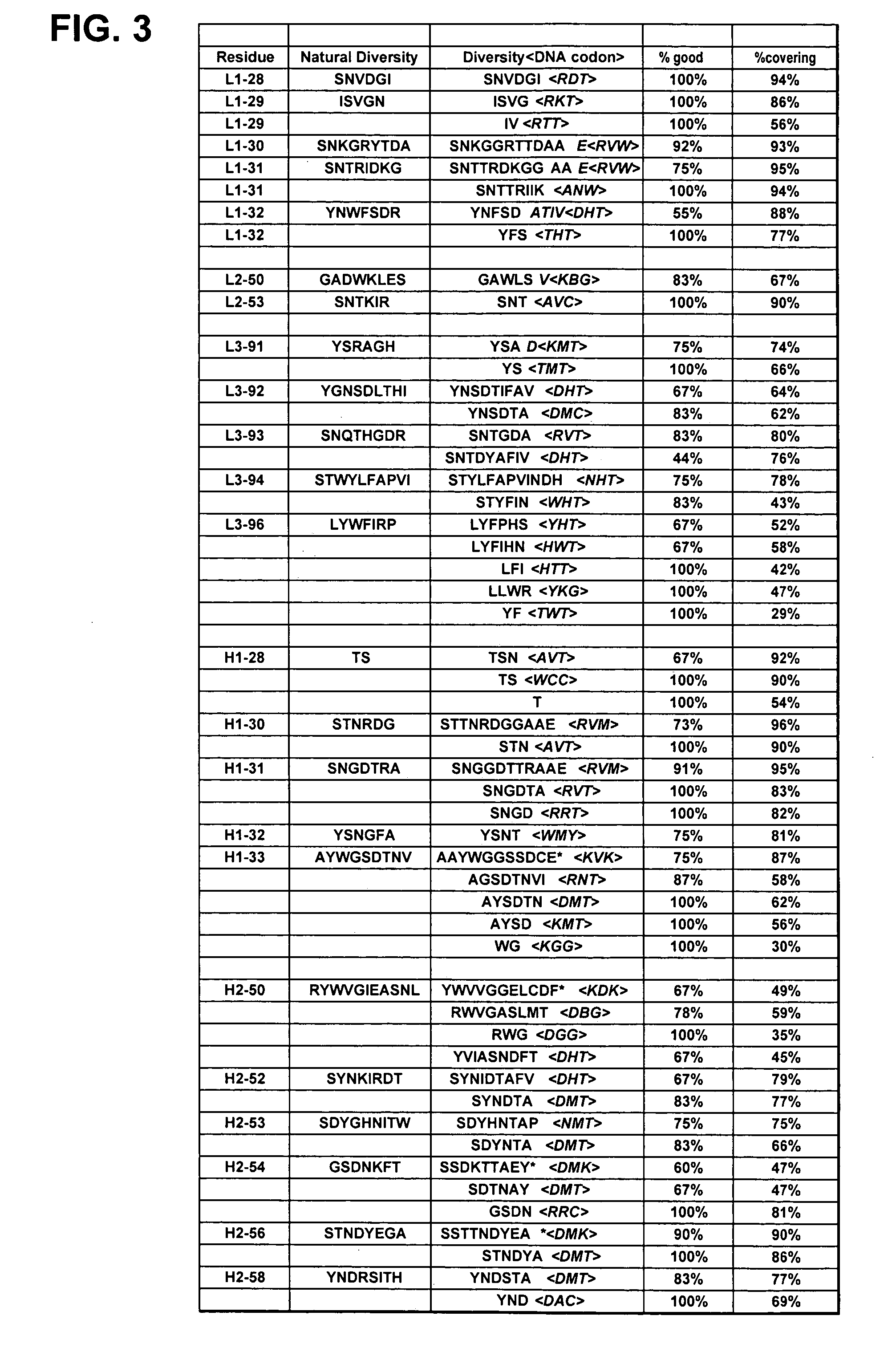
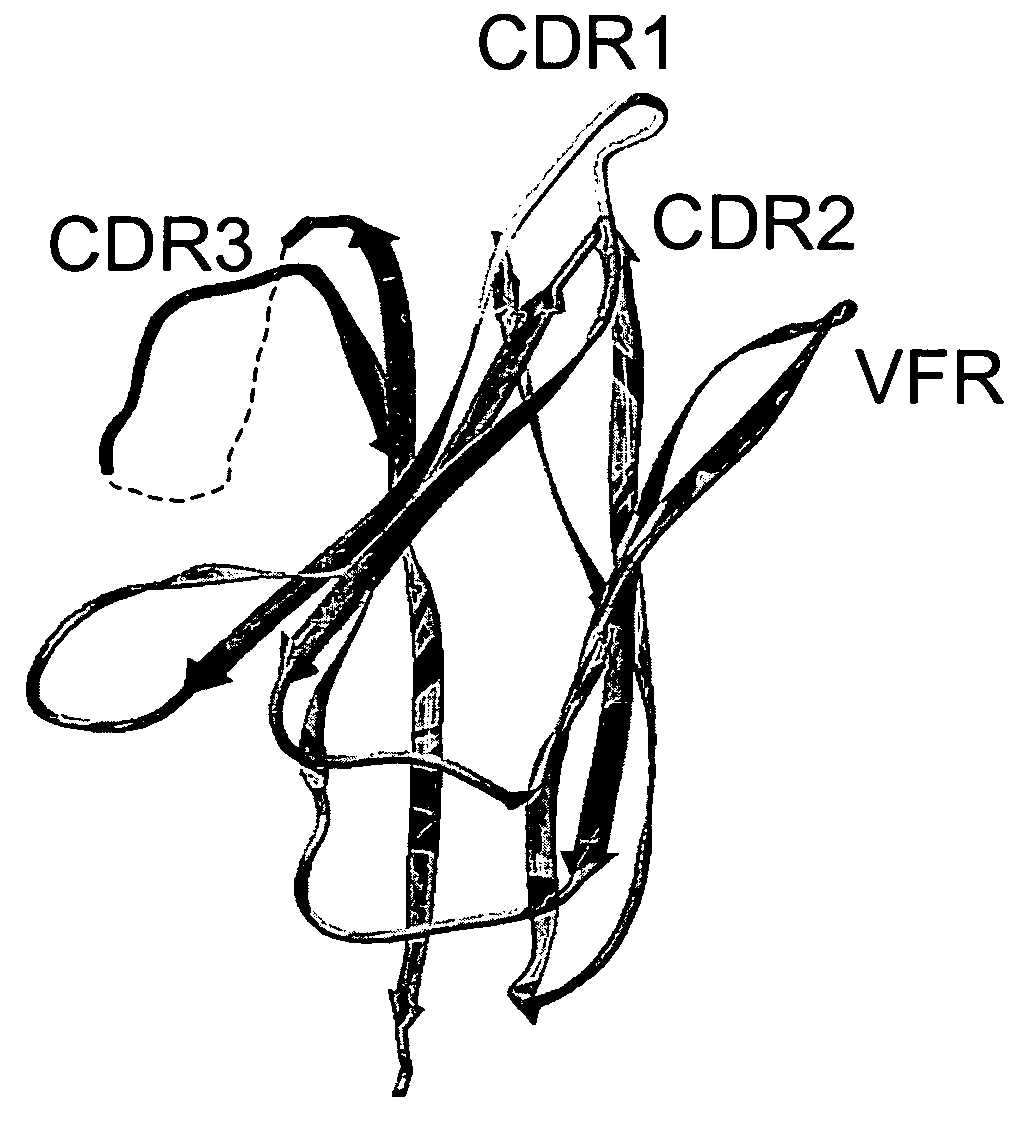
The invention provides immunoglobulin polypeptides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. In one embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant CDRH3 region. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
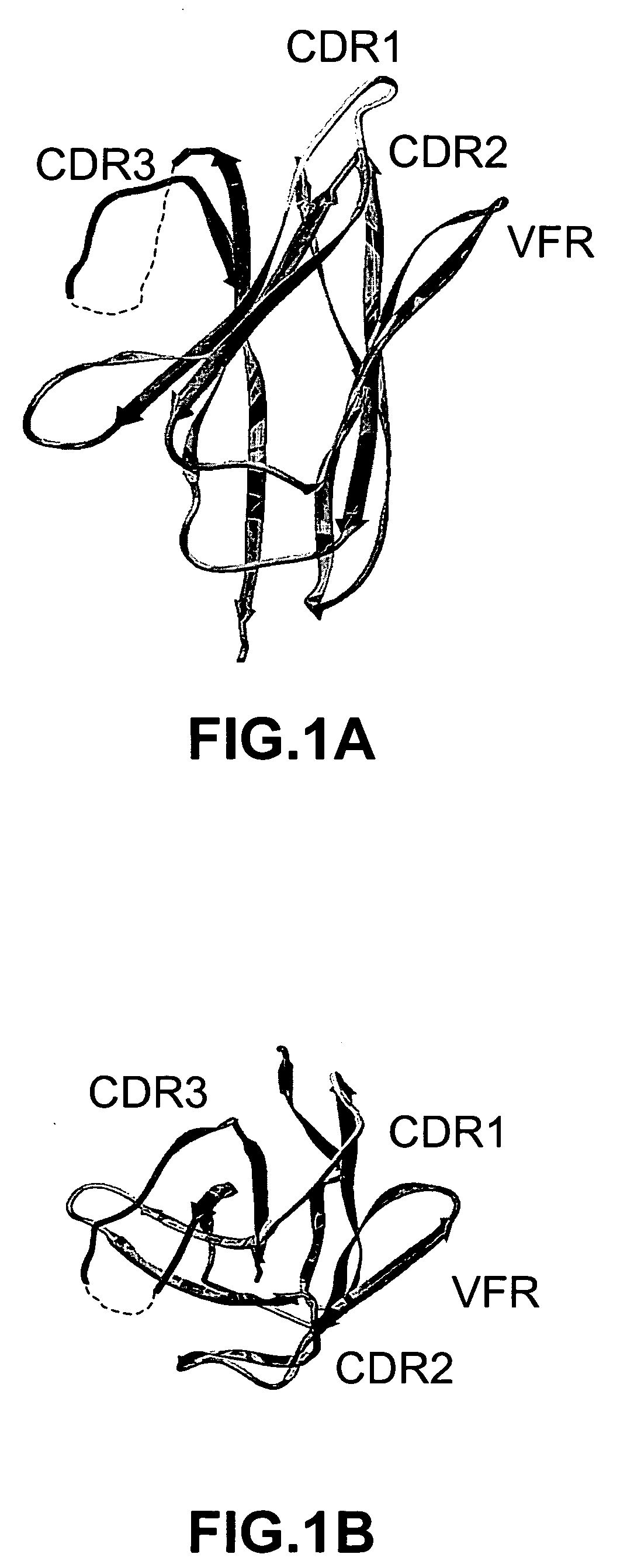
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS20050266000A1Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
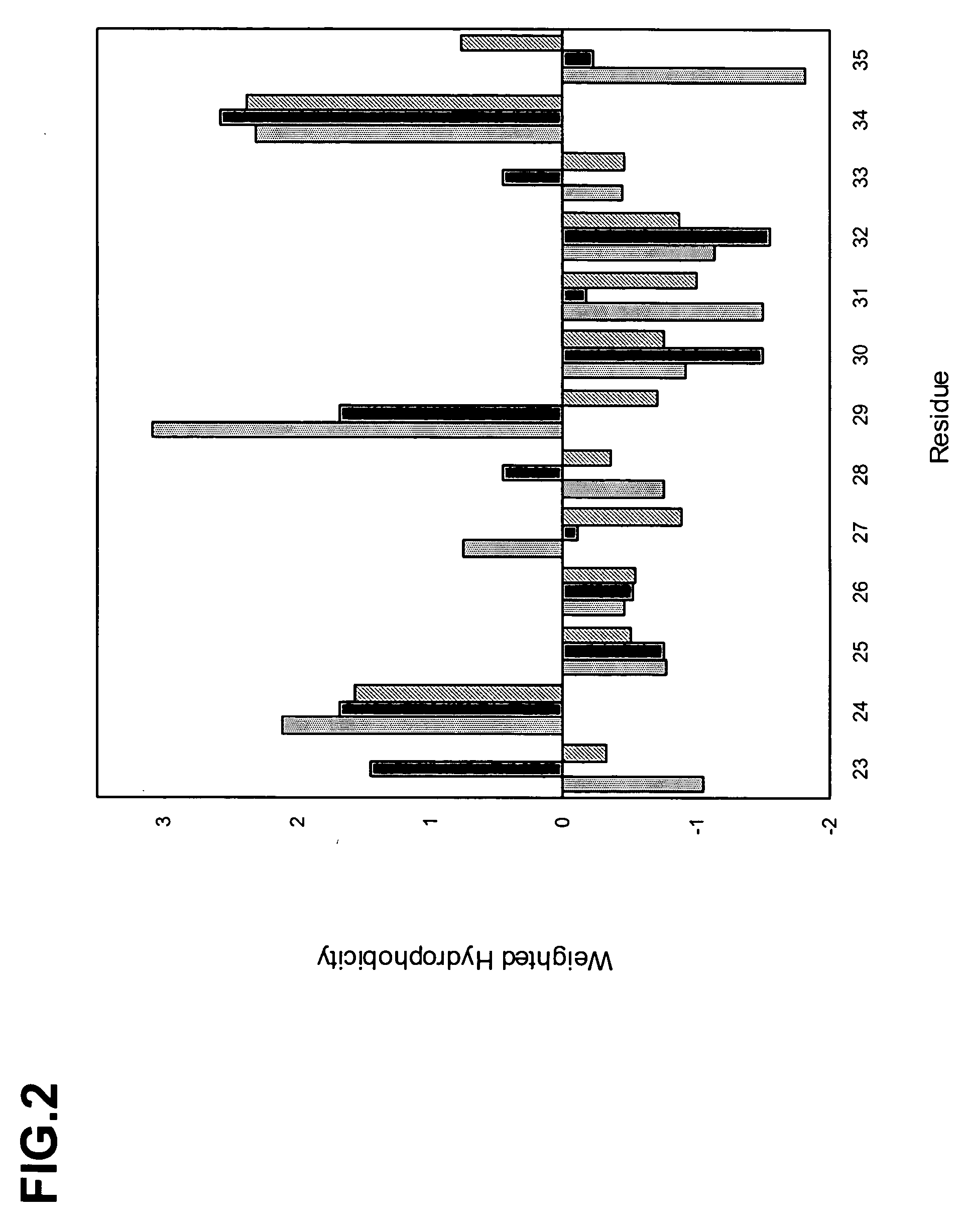
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
InactiveUS20070237764A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousAntigen binding
The invention provides variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. These polypeptides provide a flexible and simple source of sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
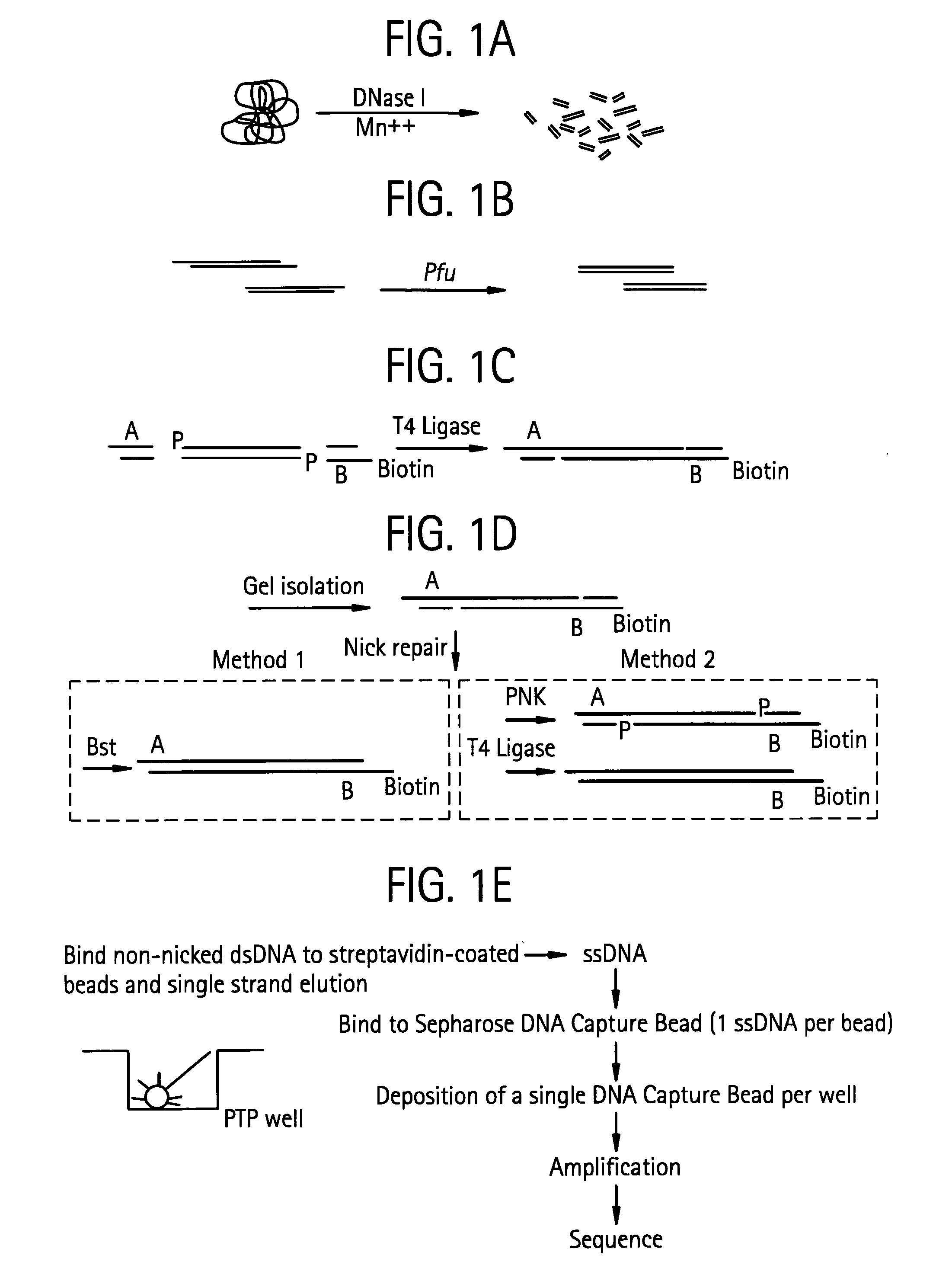
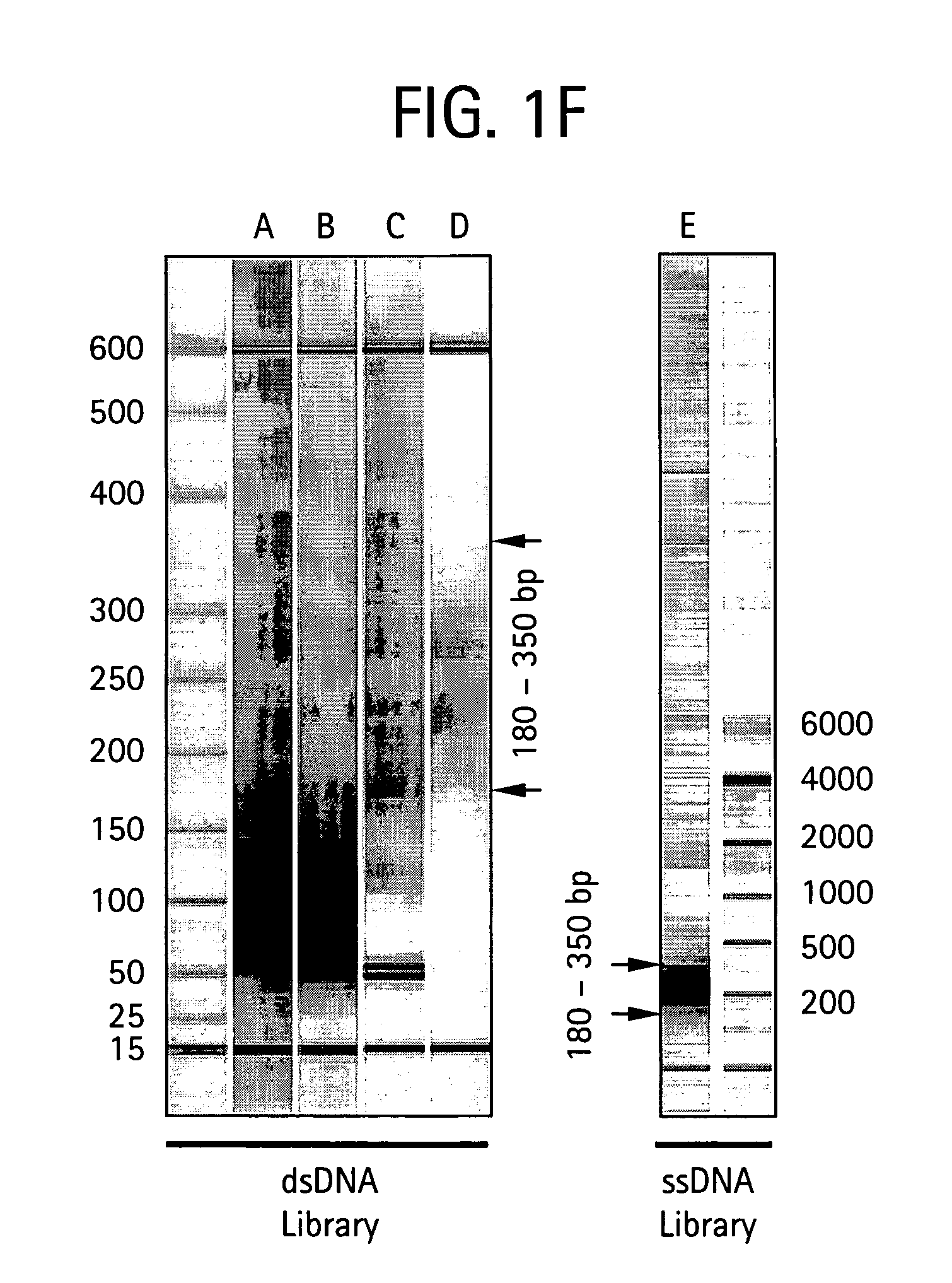
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Binding polypeptides with diversified and consensus vh/vl hypervariable sequences
ActiveUS20070160598A1Raise the possibilitySmall sizeAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntibody hypervariable regionBioinformatics
The invention provides variant hypervariable regions comprising selected amino acid sequence diversity. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7112201B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleElastomer
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a conductive-resistive matrix of a conductively-doped non-conductive elastomer. The engagement surface portions thus can be described as a positive temperature coefficient material that has a unique selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The conductive-resistive matrix can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application—across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a conductive-resistive matrix can induce a “wave” of Rf energy density to sweep across the tissue to thereby weld tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
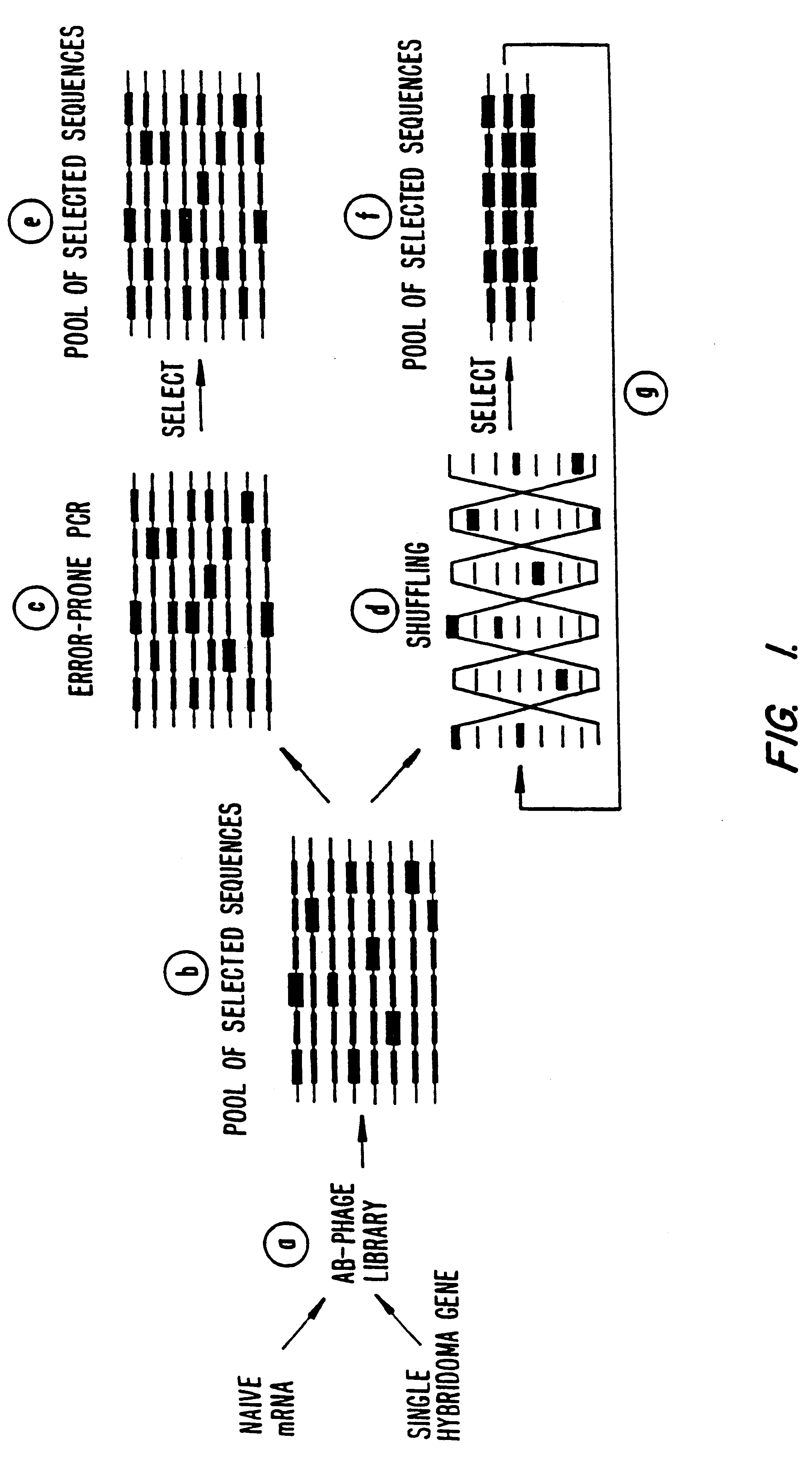
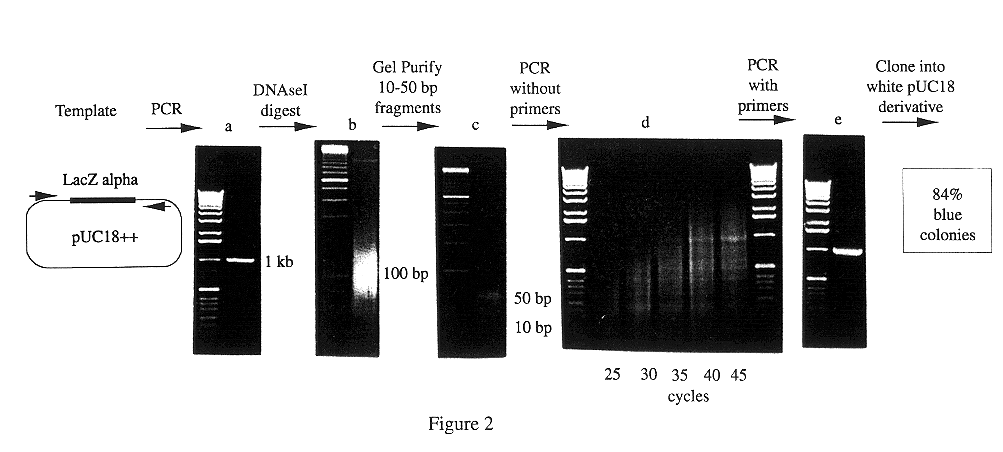
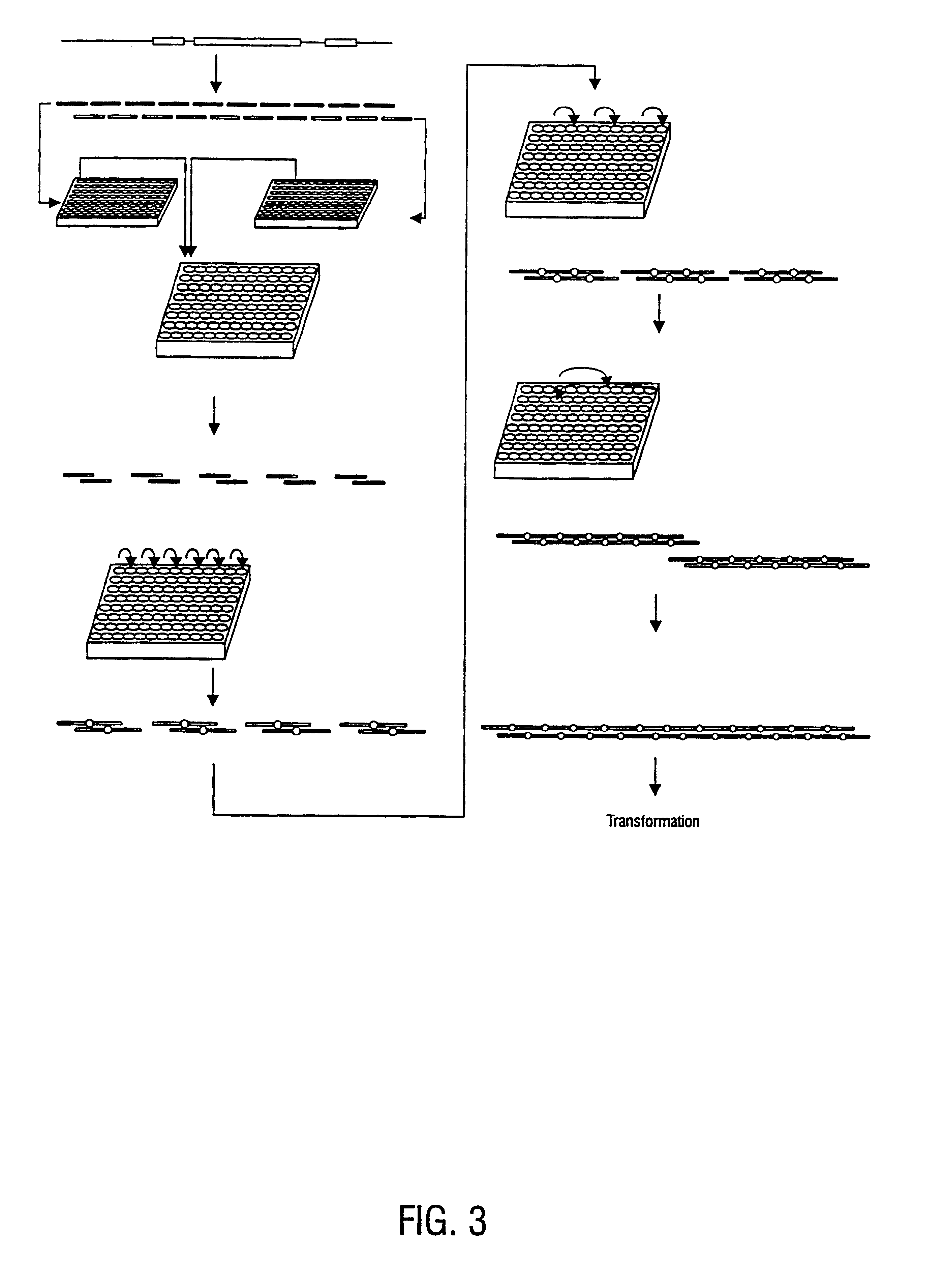
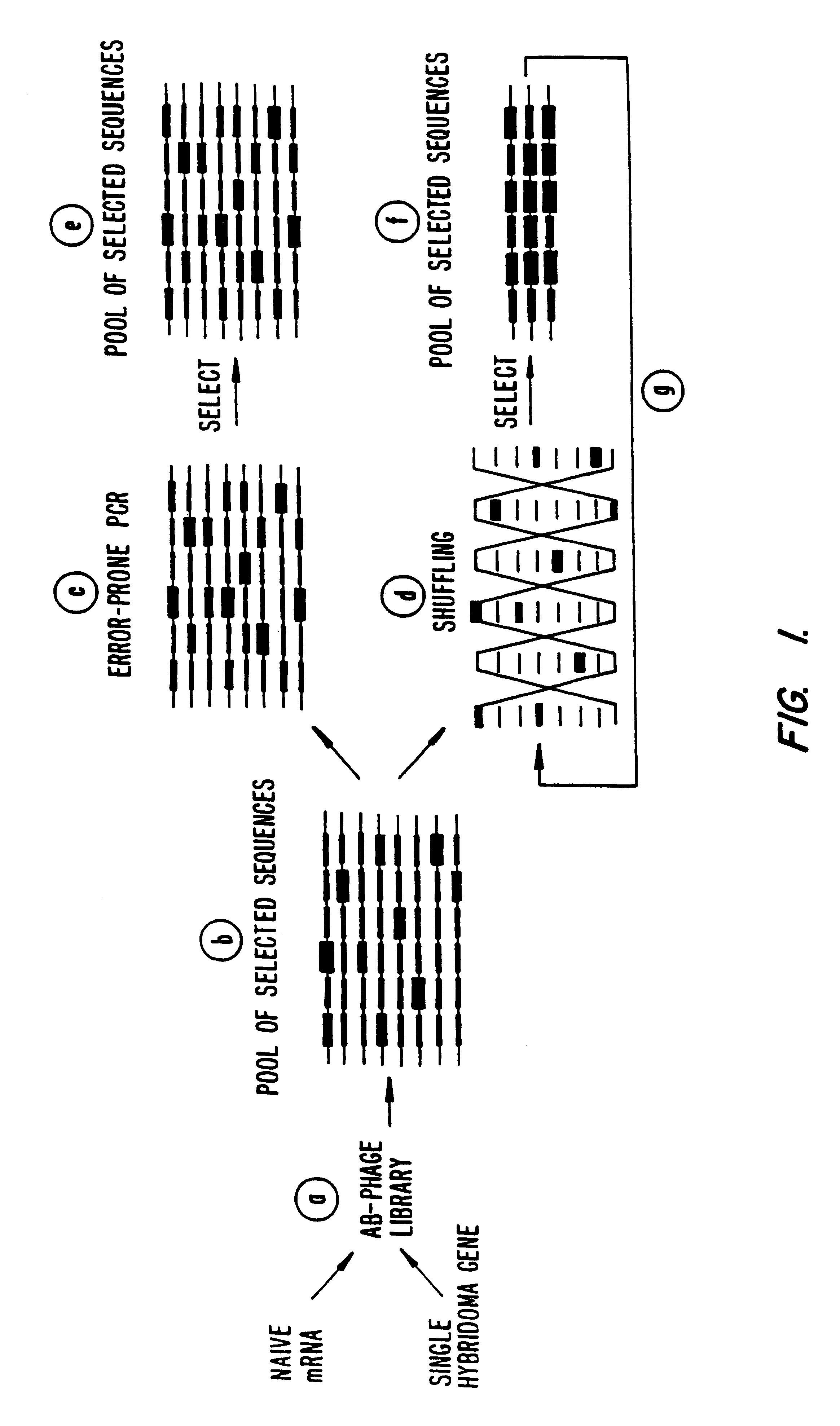
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Method and system for determining an individual's state of attention
Owner:FICO MIRRORS SA
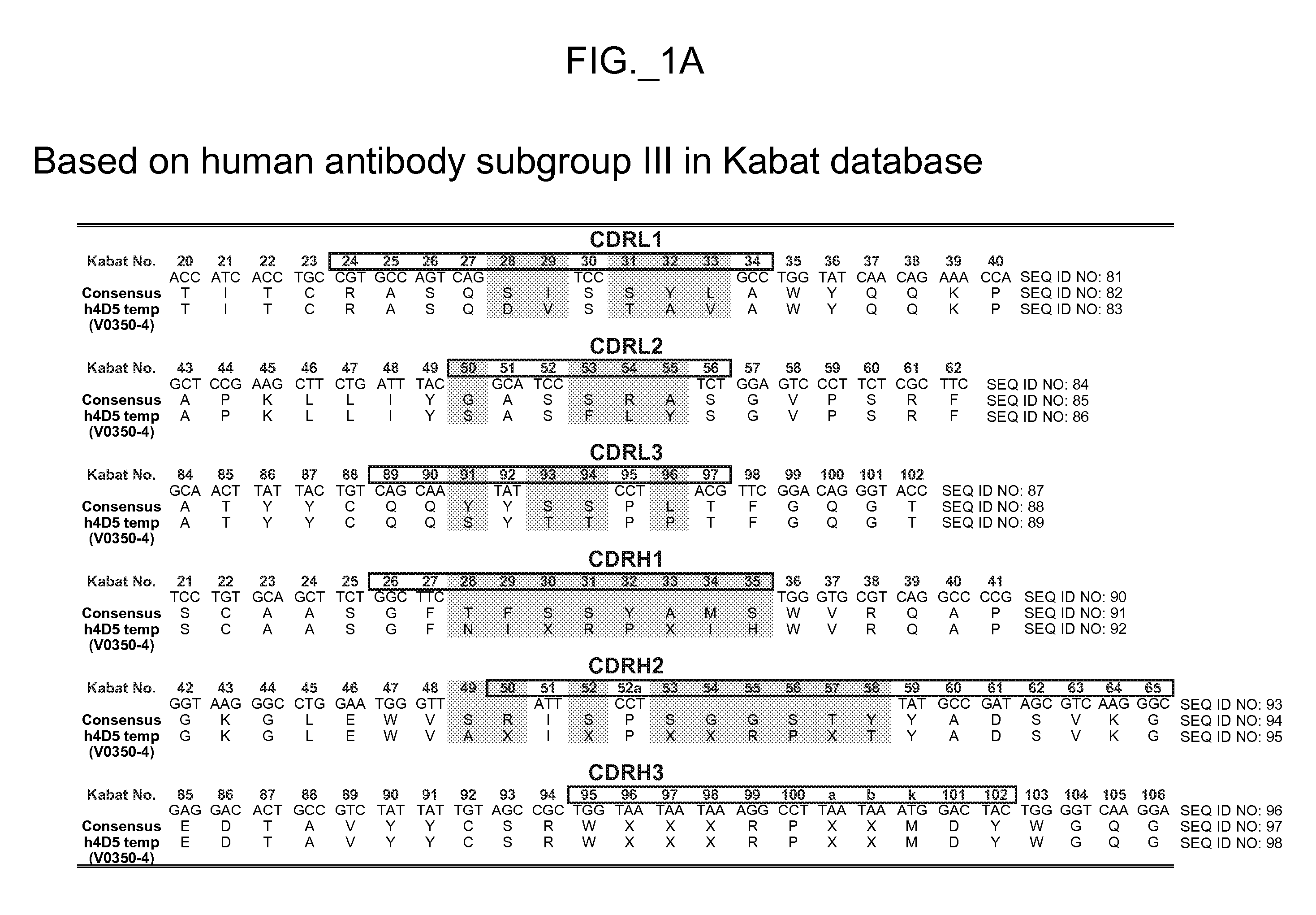
Humanization of antibodies
InactiveUS20050042664A1Limited diversityFast and less labor intensive productionHybrid immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingHumanized antibody
The present invention provides methods of re-engineering or re-shaping an antibody from a first species, wherein the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody does not elicit undesired immune response in a second species, and the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody retains substantially the same antigen binding-ability of the antibody from the first species. In accordance with the present invention, a combinatorial library comprising the CDRs of the antibody from the first species fused in frame with framework regions derived from a second species can be constructed and screened for the desired modified antibody. In particular, the present invention provides methods utilizing low homology acceptor antibody frameworks for efficiently humanizing an antibody or a fragment thereof. The present invention also provides antibodies produced by the methods of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
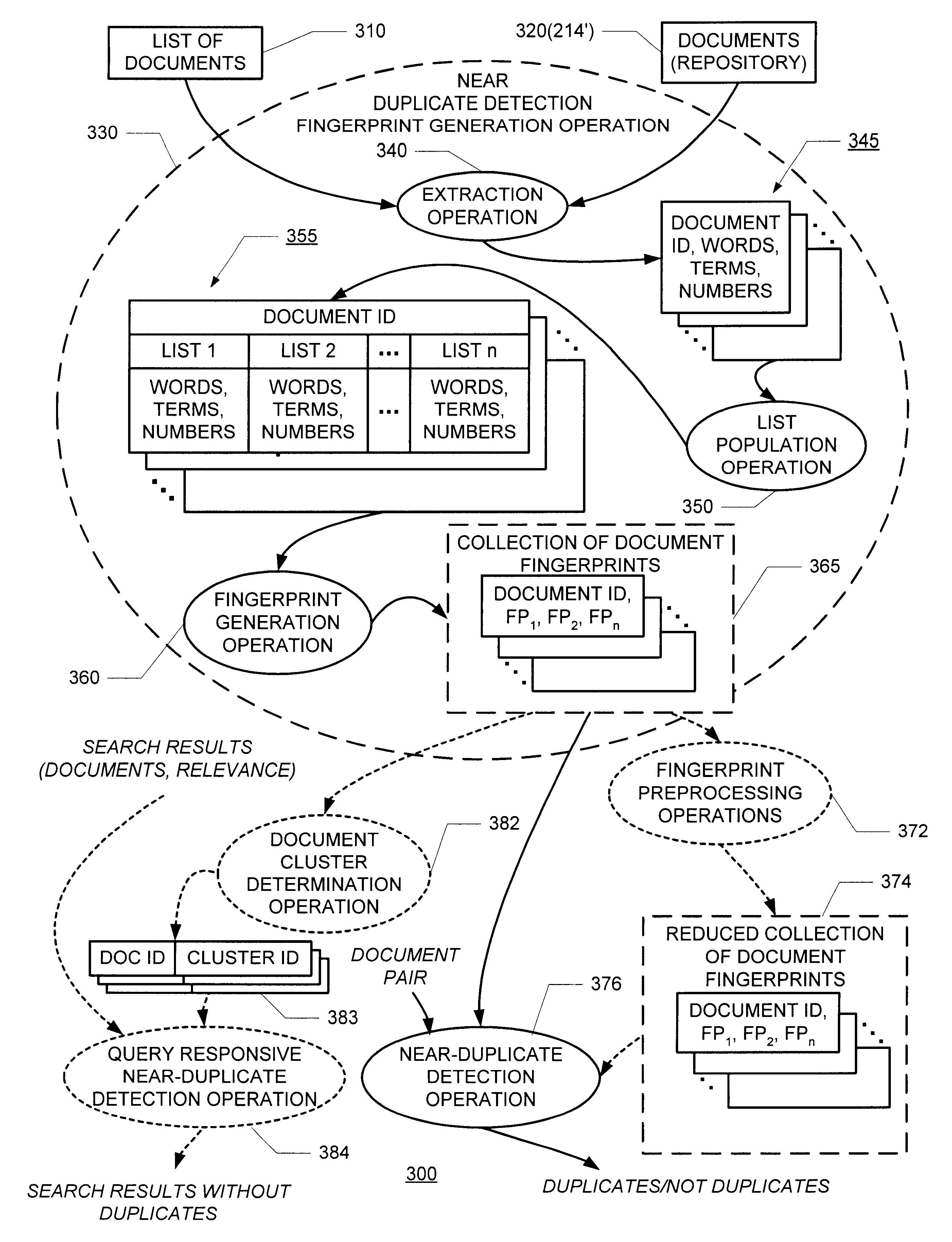
Detecting duplicate and near-duplicate files
InactiveUS6658423B1Save bandwidthStorage requirement be greatly reduceData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDocument preparationFingerprint
Improved duplicate and near-duplicate detection techniques may assign a number of fingerprints to a given document by (i) extracting parts from the document, (ii) assigning the extracted parts to one or more of a predetermined number of lists, and (iii) generating a fingerprint from each of the populated lists. Two documents may be considered to be near-duplicates if any one of their fingerprints match.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
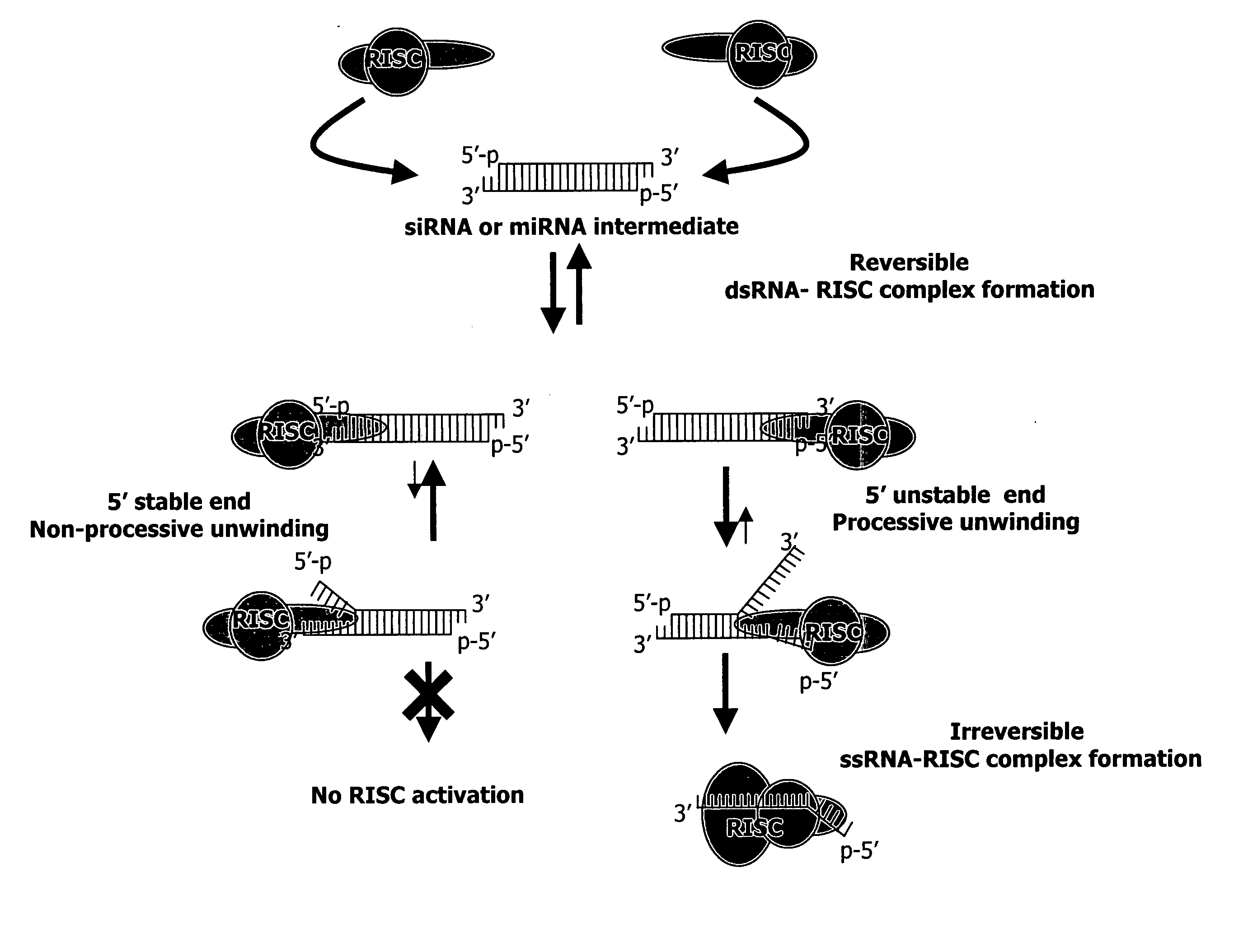
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
InactiveUS20050255487A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene silencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
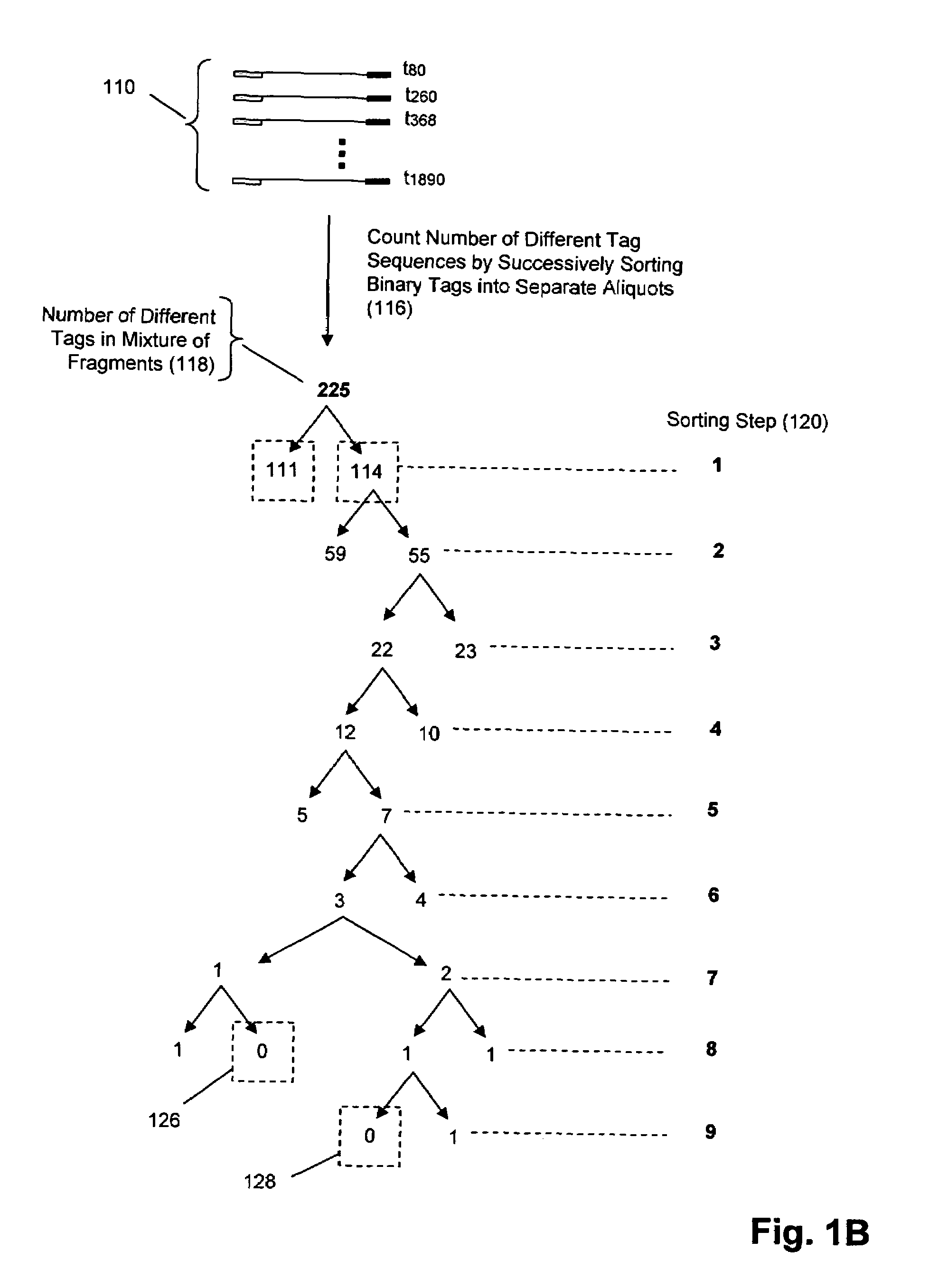
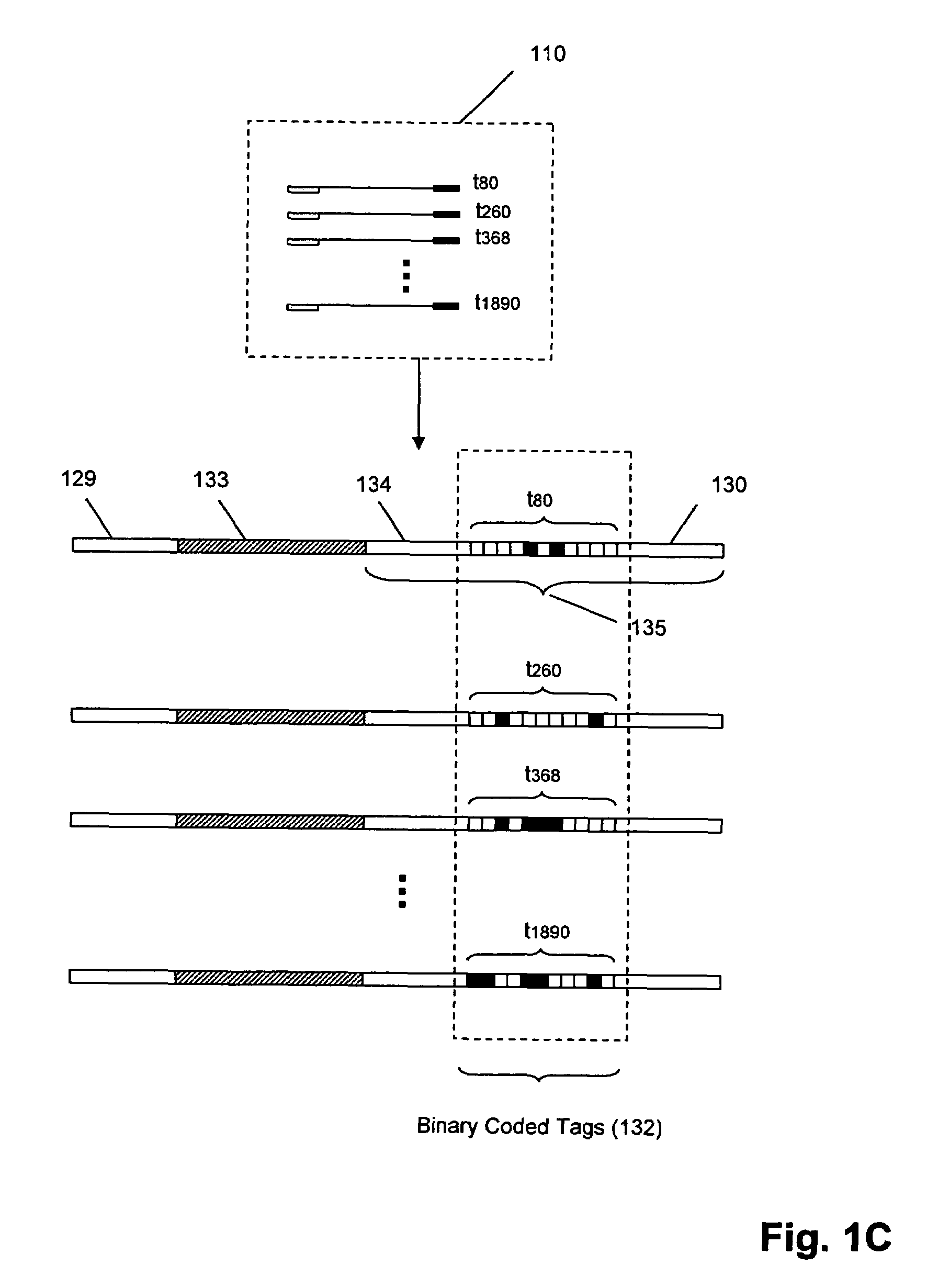
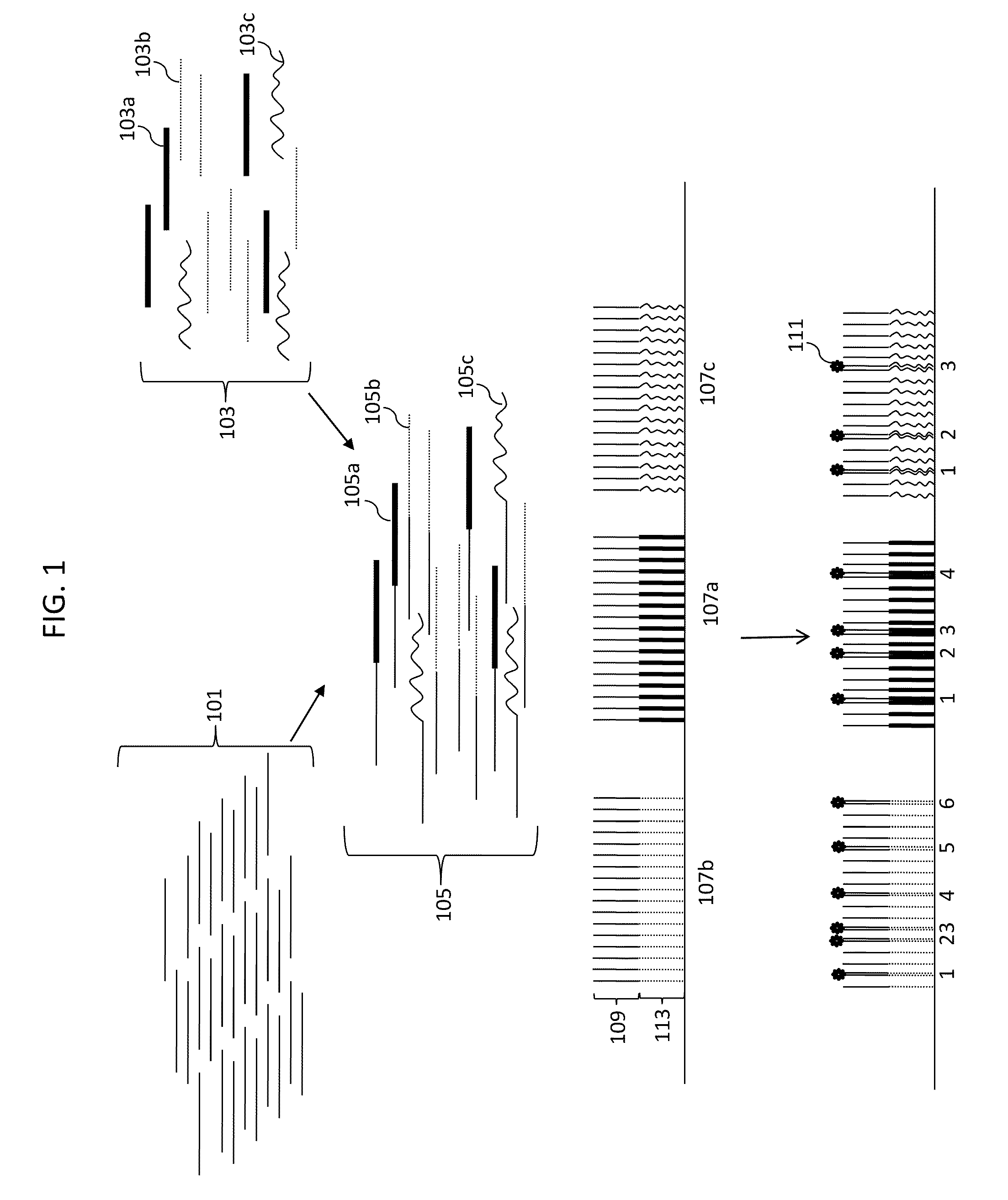
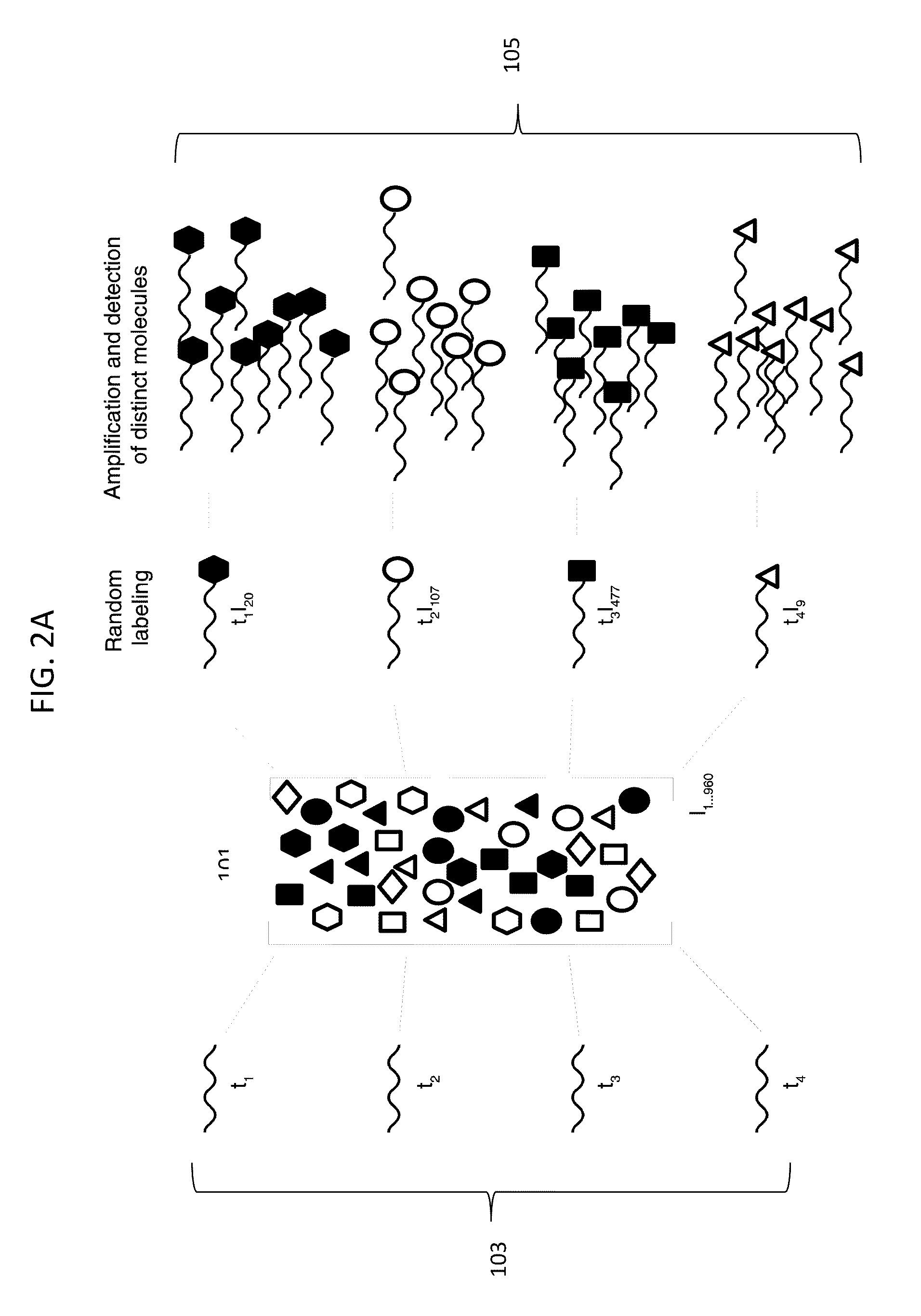
Molecular counting
The invention provides methods and compositions for counting molecules in a sample, wherein each molecule is labeled with a unique oligonucleotide tag. Such tags are amplified and identified rather than the molecules themselves; that is, the problem of counting molecules is converted into the problem of counting tags. In one aspect of the invention, molecules to be counted are labeled by sampling. That is, conjugates are formed between the molecules to be counted and oligonucleotide tags of a very large set, or repertoire.After conjugation, a sample of conjugates is taken that is sufficiently small so that substantially every molecule has a unique oligonucleotide tag. Counting of different tags may be accomplished in a variety of ways. In one aspect, different tags may be counted by carrying out a series of sorting steps to generate successively less complex mixtures in which tags are enumerated using length-encoded “metric” tags. In another aspect, different tags may be counted by directly sequencing a sample of tags using any one of several different sequencing methodologies.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
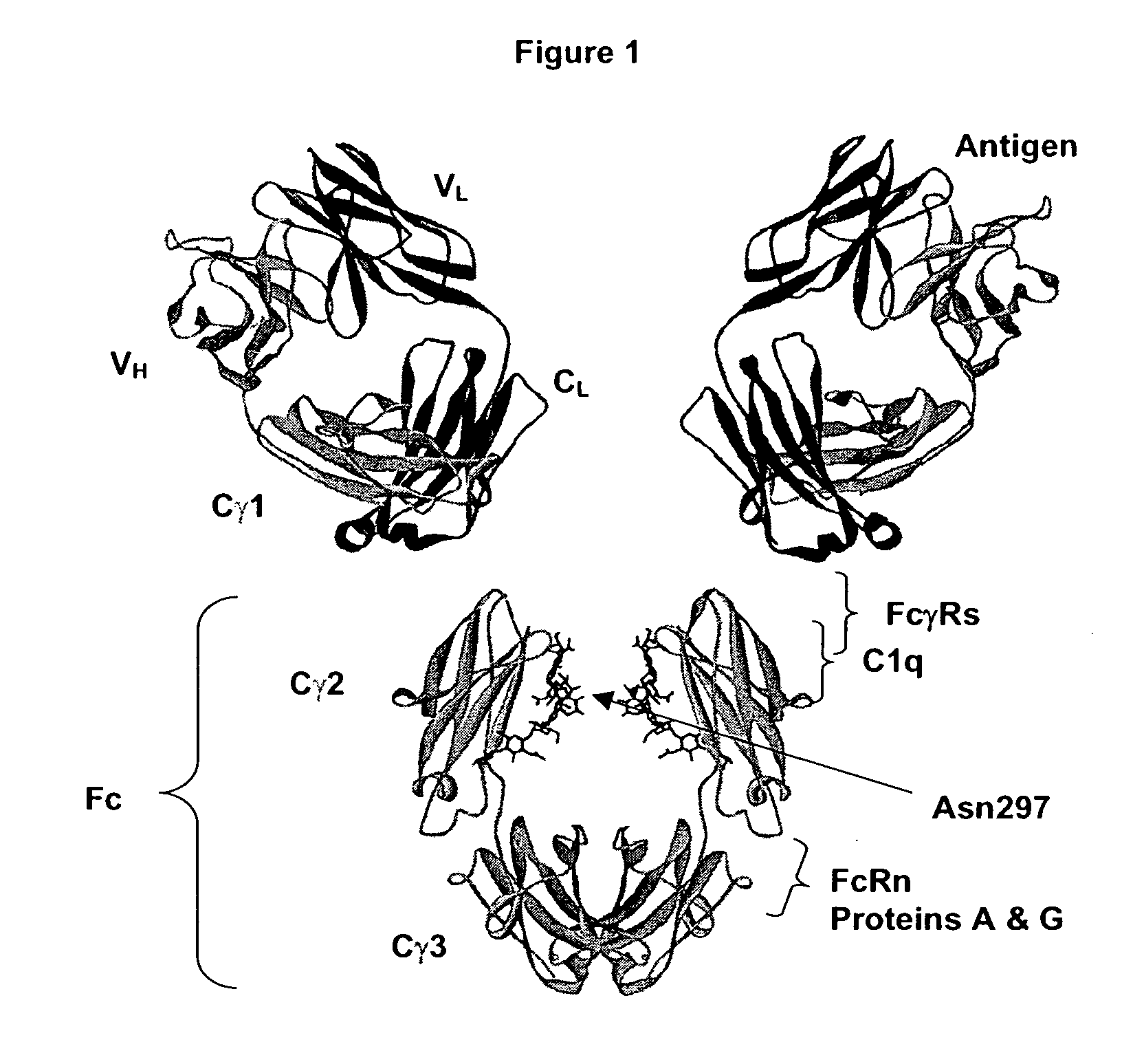
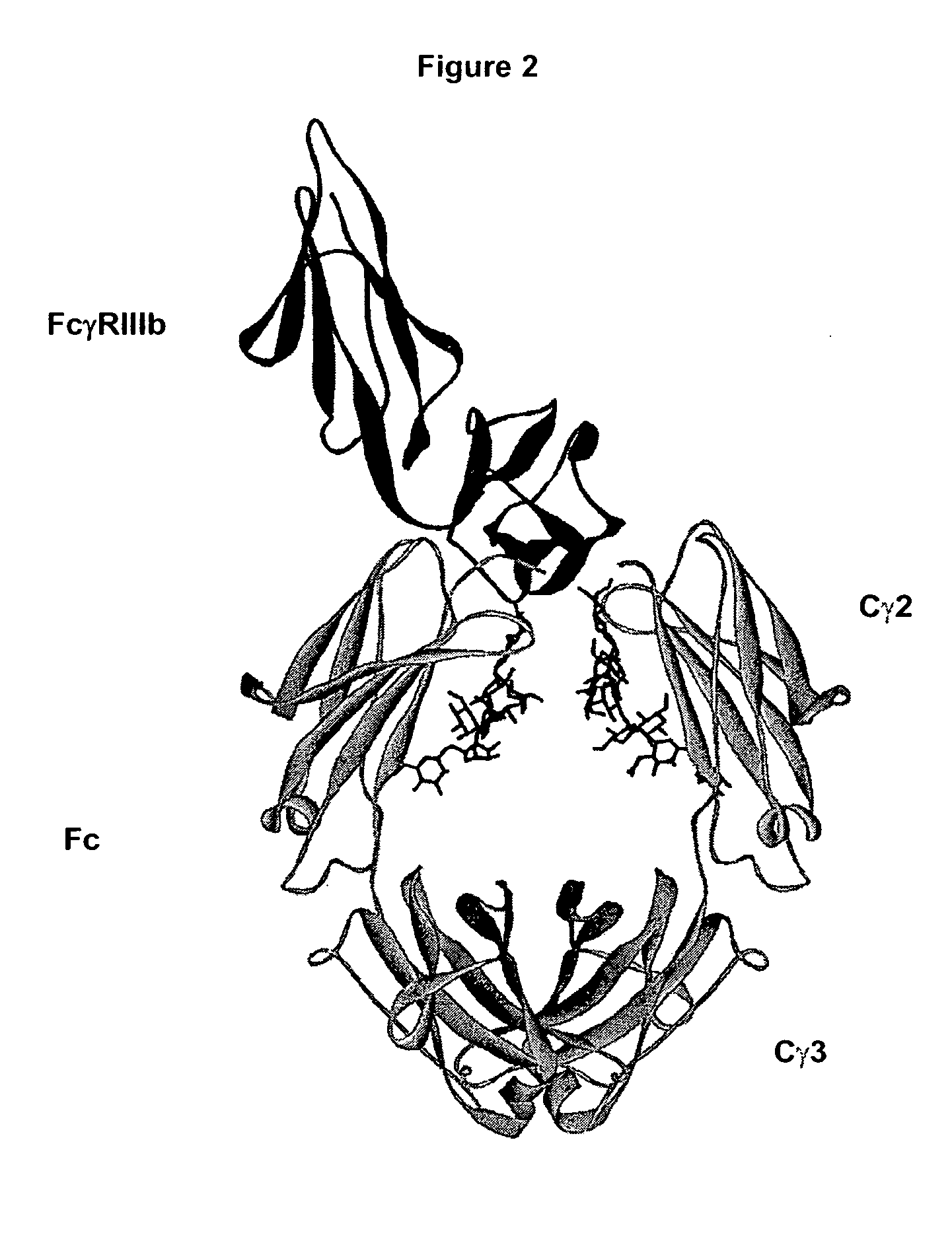
Optimized Fc variants
ActiveUS20060024298A1Weak affinityFunction increaseAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsChemistryBiochemistry
Owner:XENCOR
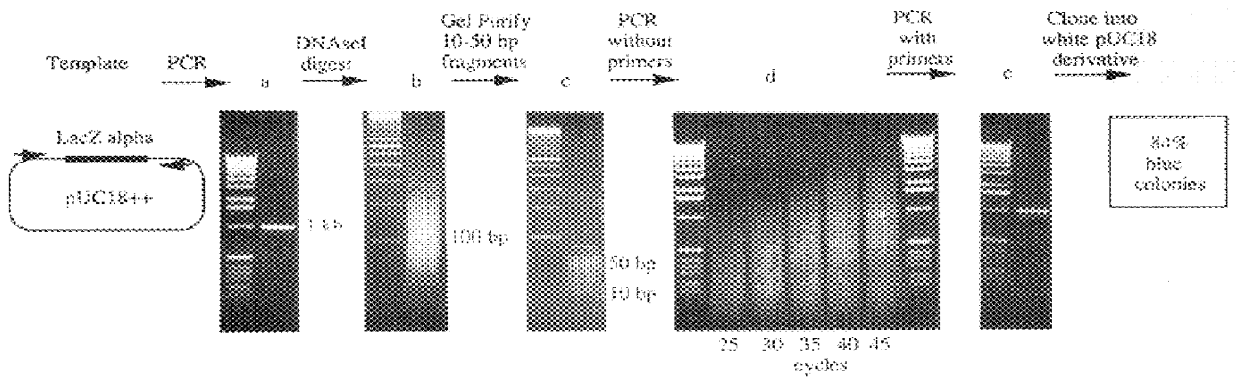
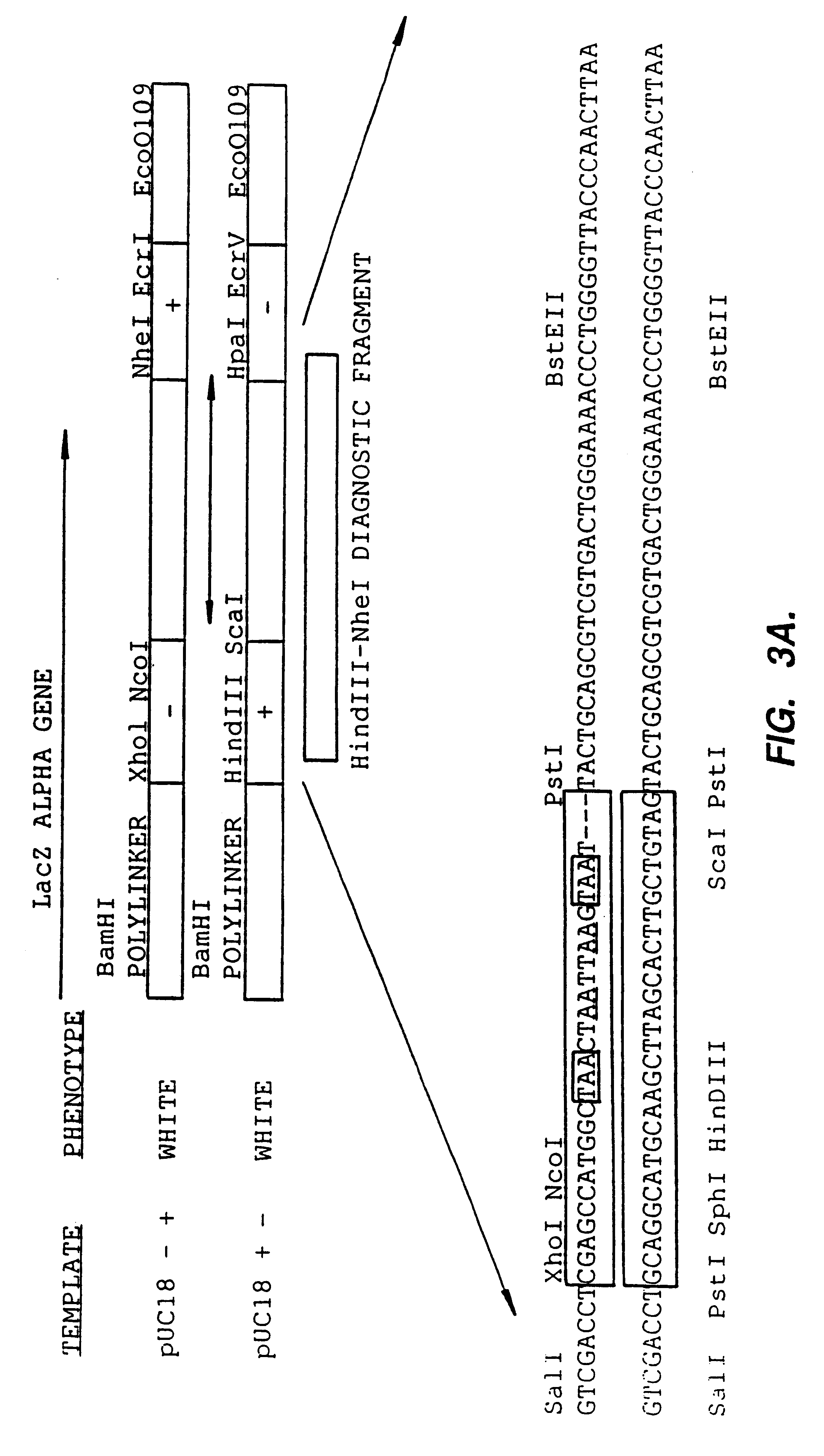
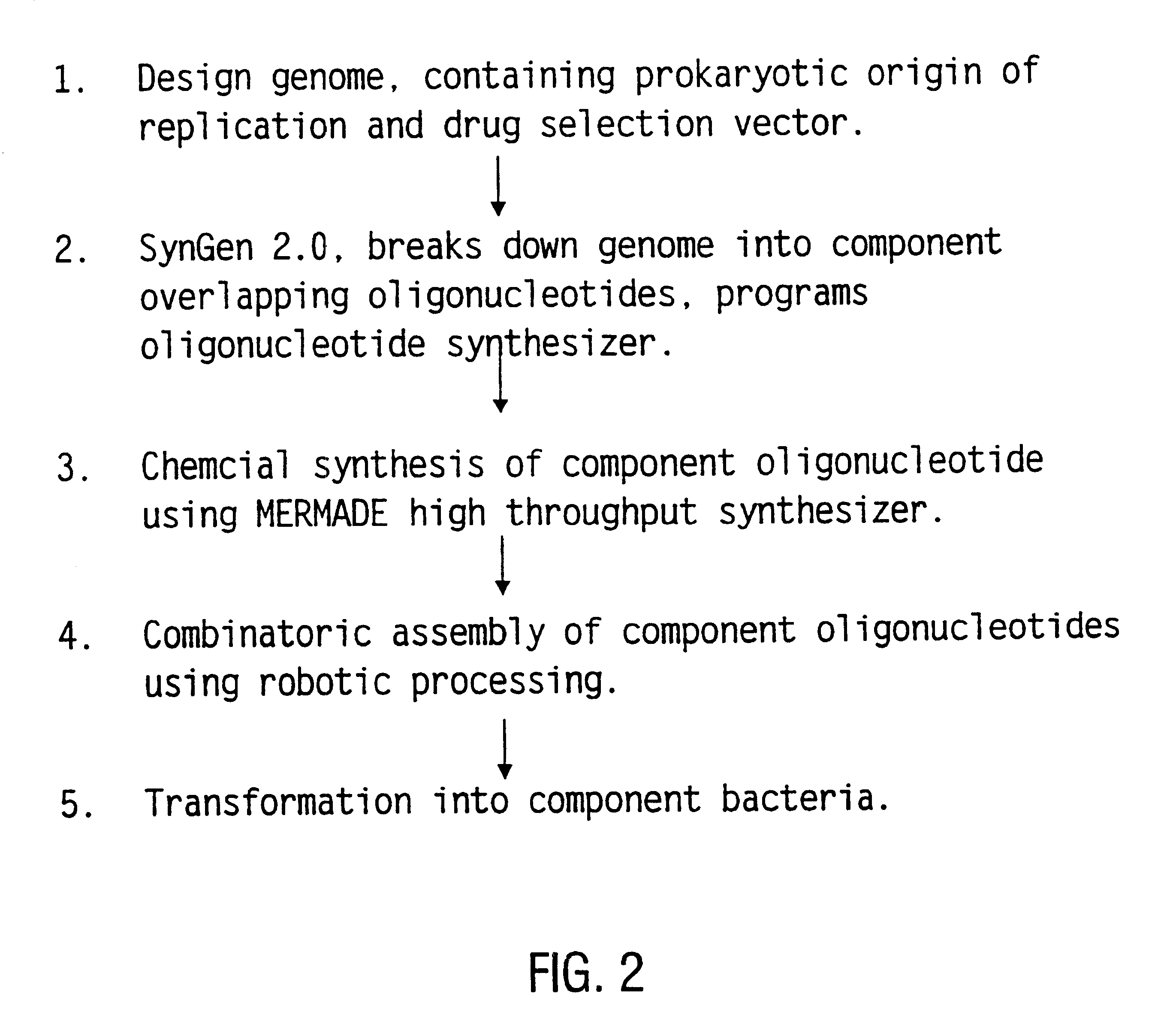
Method for the complete chemical synthesis and assembly of genes and genomes
InactiveUS6521427B1BiocideSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisHuman genome database
The present invention relates generally to the fields of oligonucleotide synthesis. More particularly, it concerns the assembly of genes and genomes of completely synthetic artificial organisms. Thus, the present invention outlines a novel approach to utilizing the results of genomic sequence information by computer directed gene synthesis based on computing on the human genome database. Specifically, the present invention contemplates and describes the chemical synthesis and resynthesis of genes defined by the genome sequence in a host vector and transfer and expression of these sequences into suitable hosts.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US) +3
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
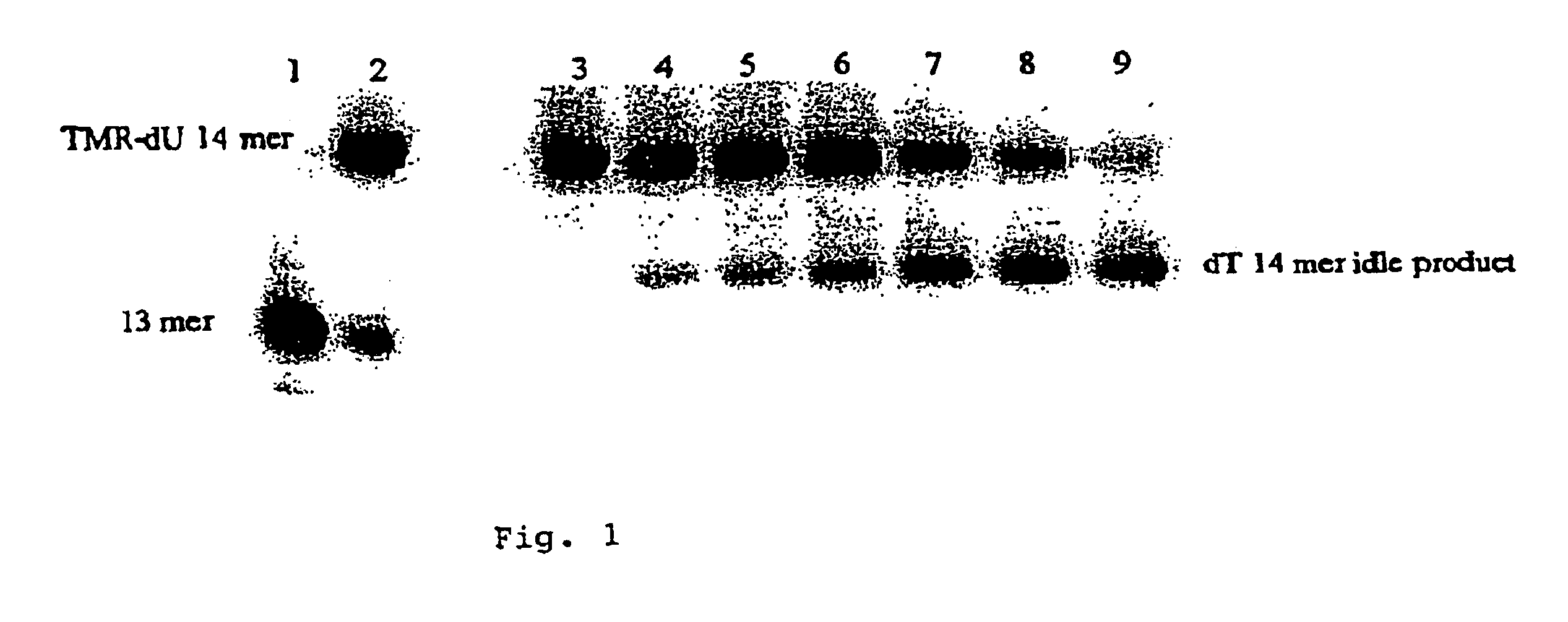
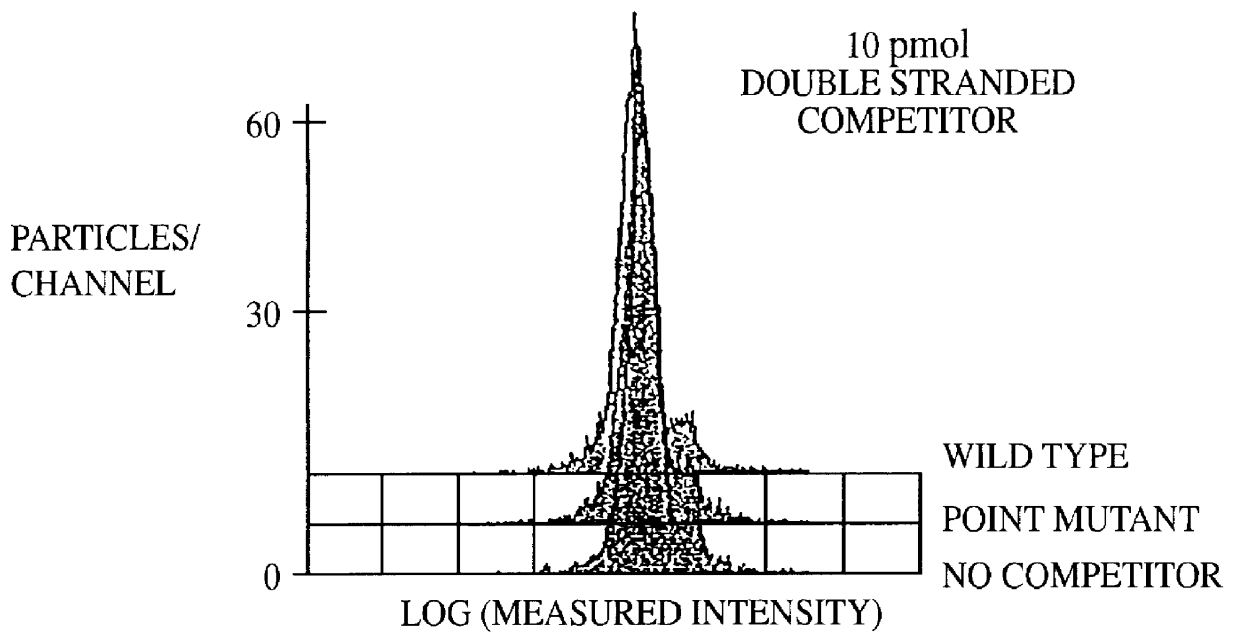
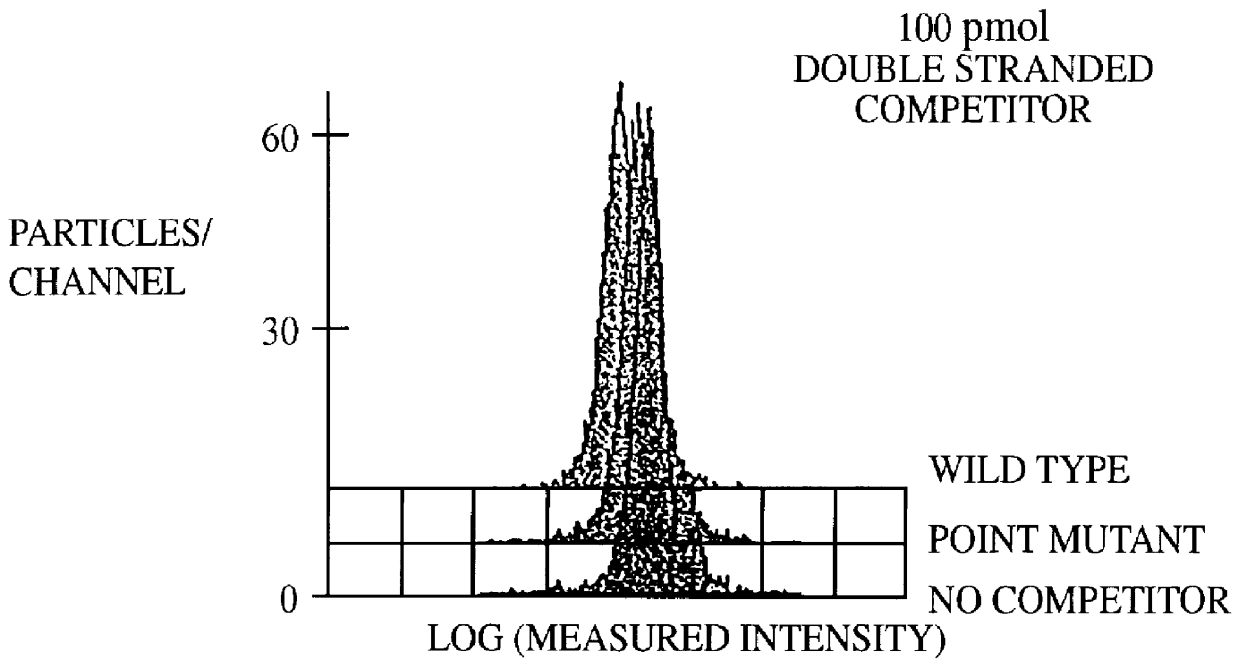
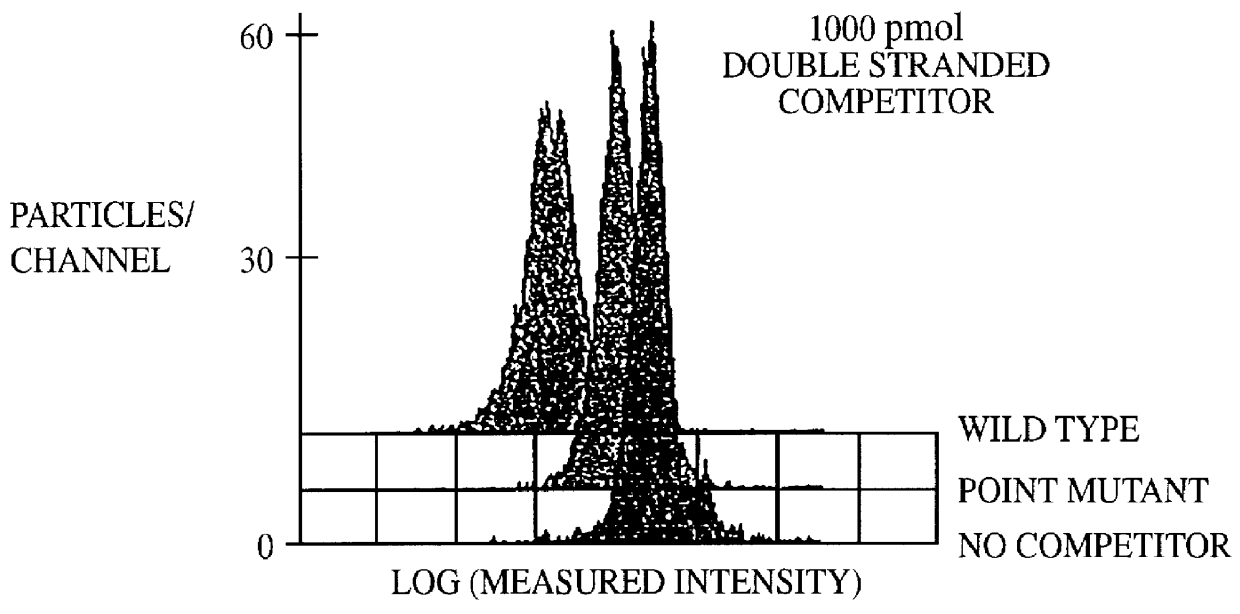
Methods and compositions for flow cytometric determination of DNA sequences
InactiveUS6057107AReduce fluorescenceReduce intensityMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisAnalysis dnaTest sample
A method for the analysis of DNA sequences and PCR products comprises the steps of constructing an oligonucleotide-labeled beadset, and labeled complementary probe, and exposing the beadset and probe to a DNA fragment or PCR product under hybridizing conditions and analyzing the combined sample / beadset by flow cytometry. Flow cytometric measurements are used to classify beads within an exposed beadset to determine the presence of identical or nonidentical sequences within the test sample. The inventive technology enables the rapid analysis of DNA sequences and detection of point mutations, deletions and / or inversions while also reducing the cost and time for performing genetic assays.
Owner:LUMINEX
Multiplexed analysis of clinical specimens apparatus and method
InactiveUS6524793B1Simple methodSure easyMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyReal time analysisDNA fragmentation
A method for the multiplexed diagnostic and genetic analysis of enzymes, DNA fragments, antibodies, and other biomolecules comprises the steps of constructing an appropriately labeled beadset, exposing the beadset to a clinical sample, and analyzing the combined sample / beadset by flow cytometry. Flow cytometric measurements are used to classify, in real-time, beads within an exposed beadset and textual explanations, based on the accumulated data obtained during real-time analysis, are generated for the user. The inventive technology enables the simultaneous, and automated, detection and interpretation of multiple biomolecules or DNA sequences in real-time while also reducing the cost of performing diagnostic and genetic assays.
Owner:LUMINEX
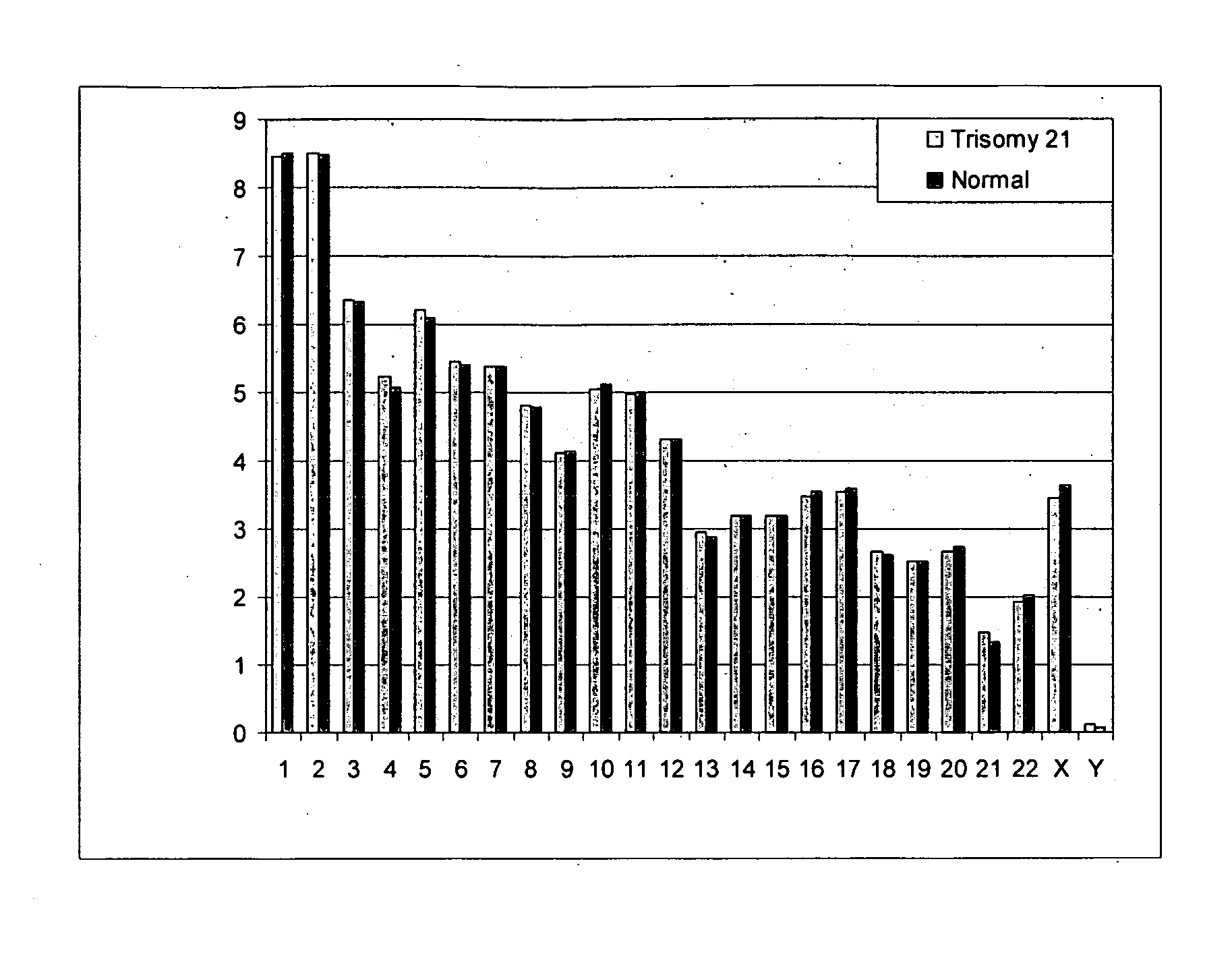
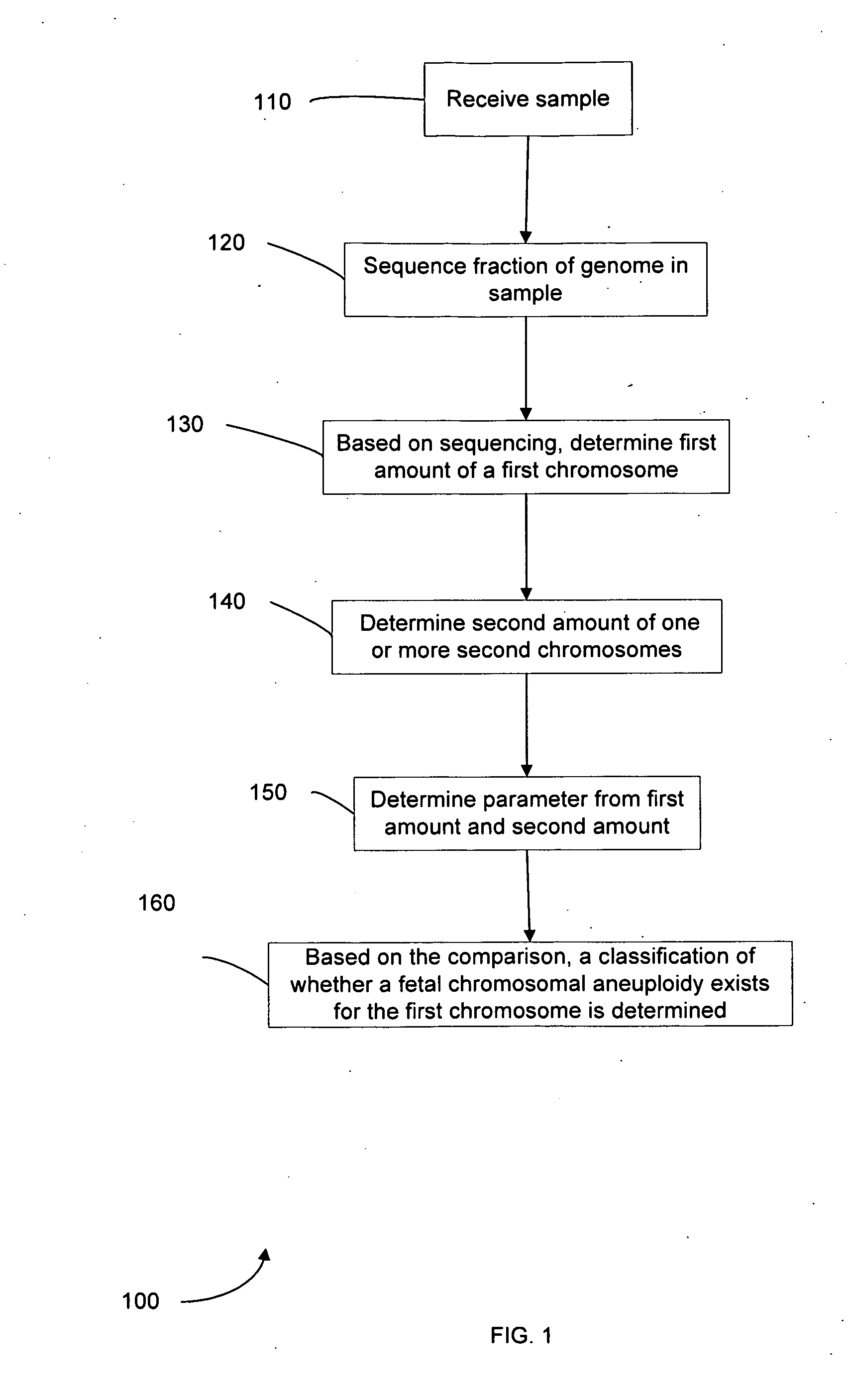
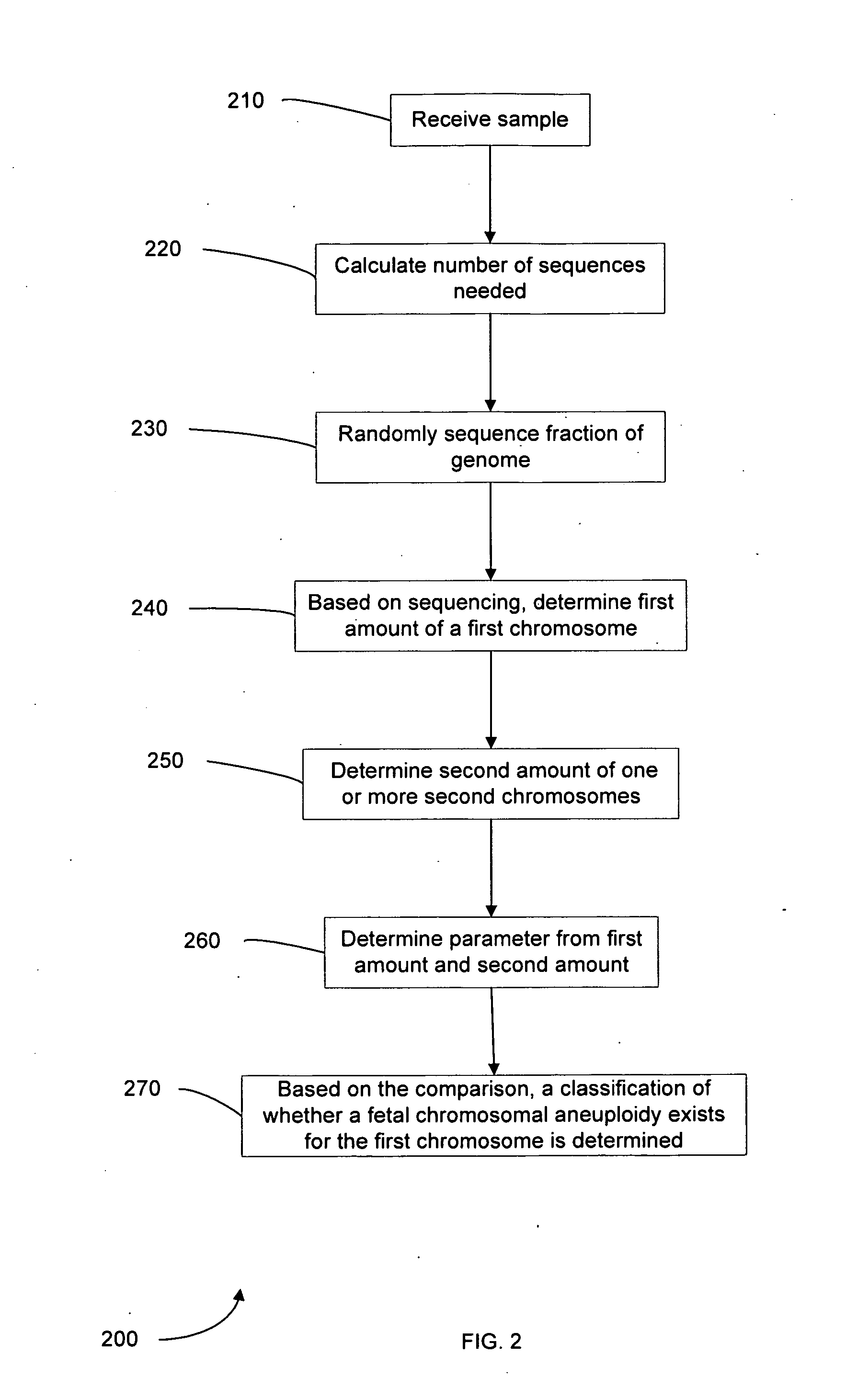
Diagnosing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy using massively parallel genomic sequencing
PendingUS20090029377A1Quantity maximizationSufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGenomic sequencingGenome
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
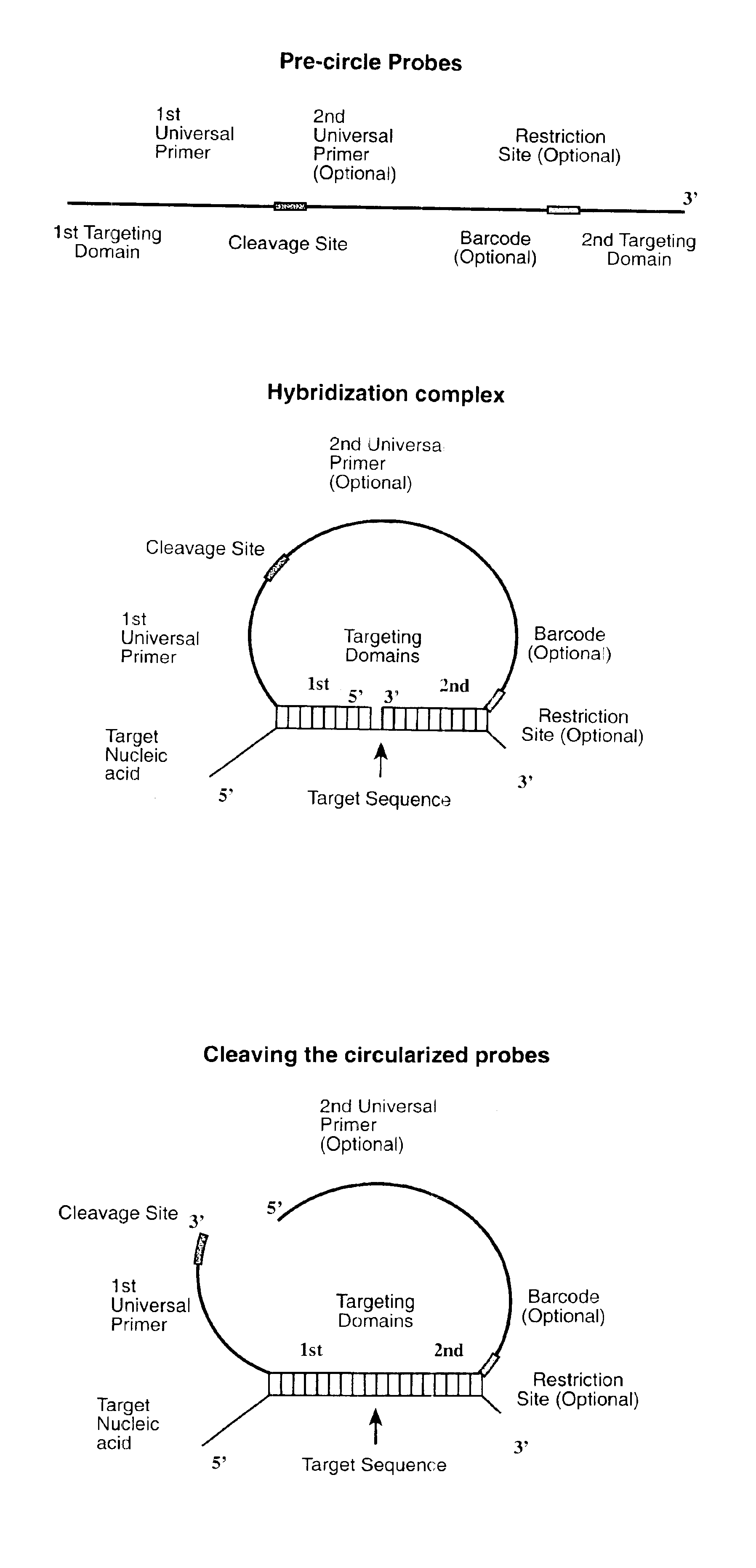
Direct multiplex characterization of genomic DNA
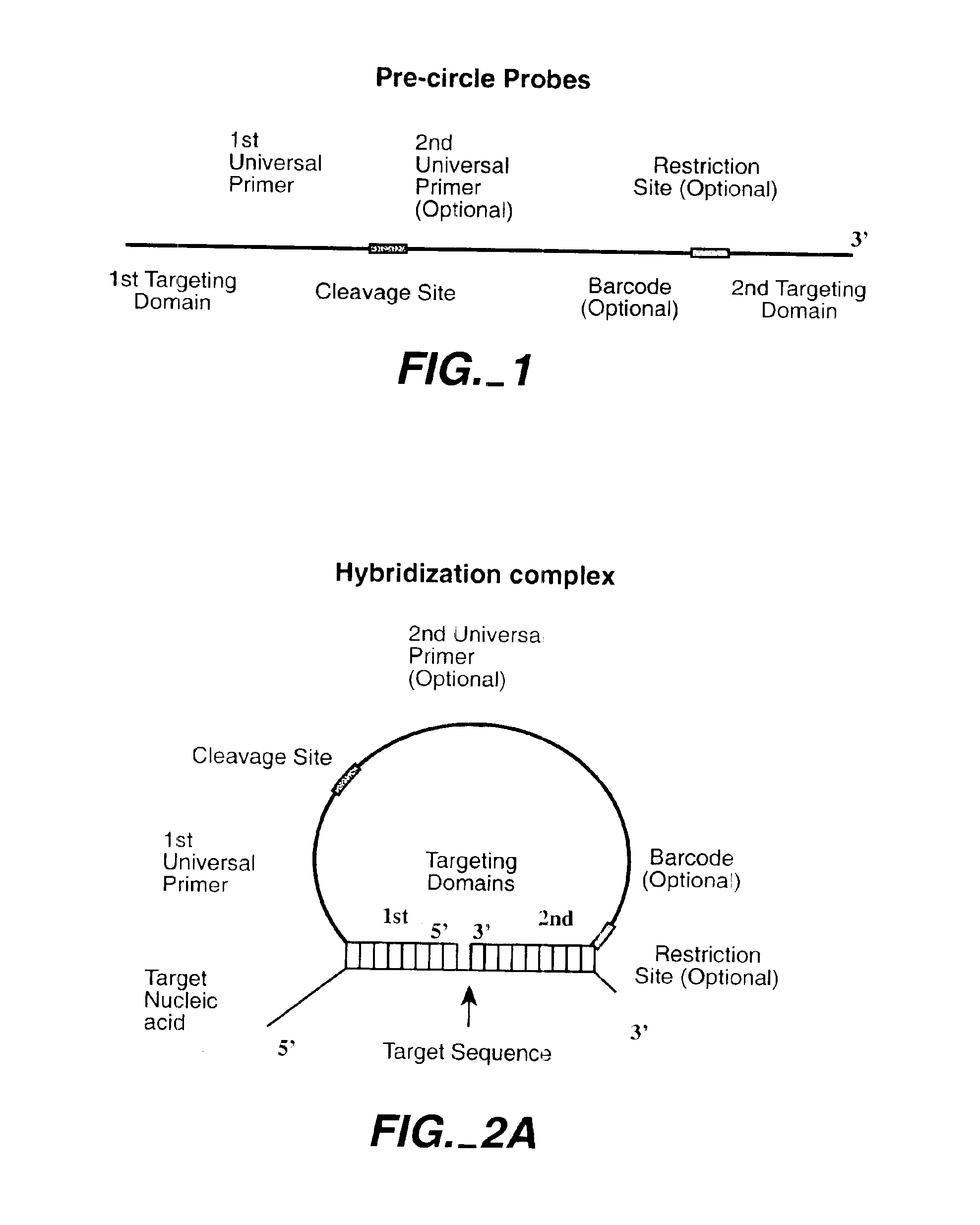
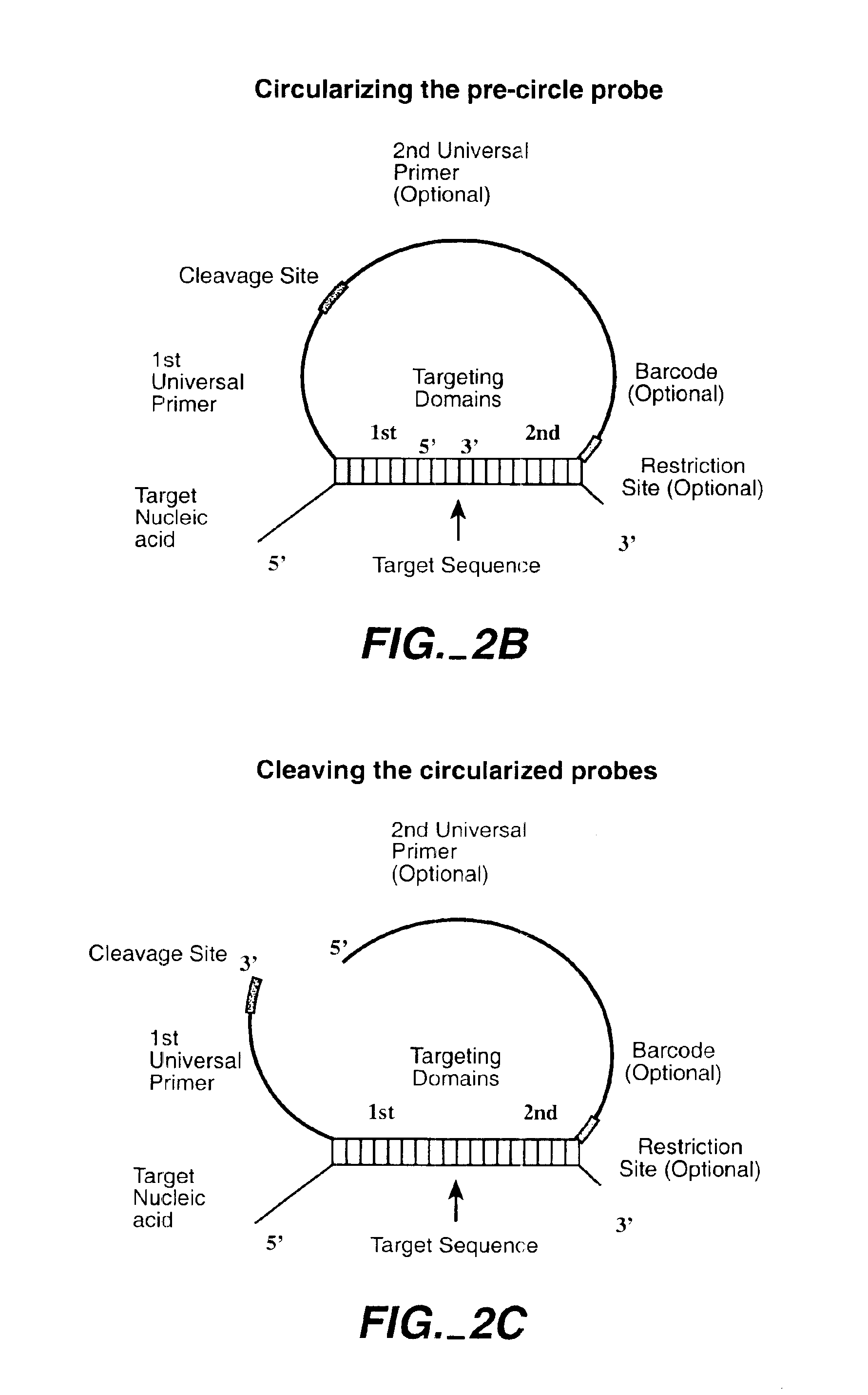
The invention is directed to novel methods of multiplexing nucleic acid reactions, including amplification, detection and genotyping. The invention relies on the use of precircle probes that are circularized in the presence of the corresponding target nucleic acids, cleaved, and then amplified.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
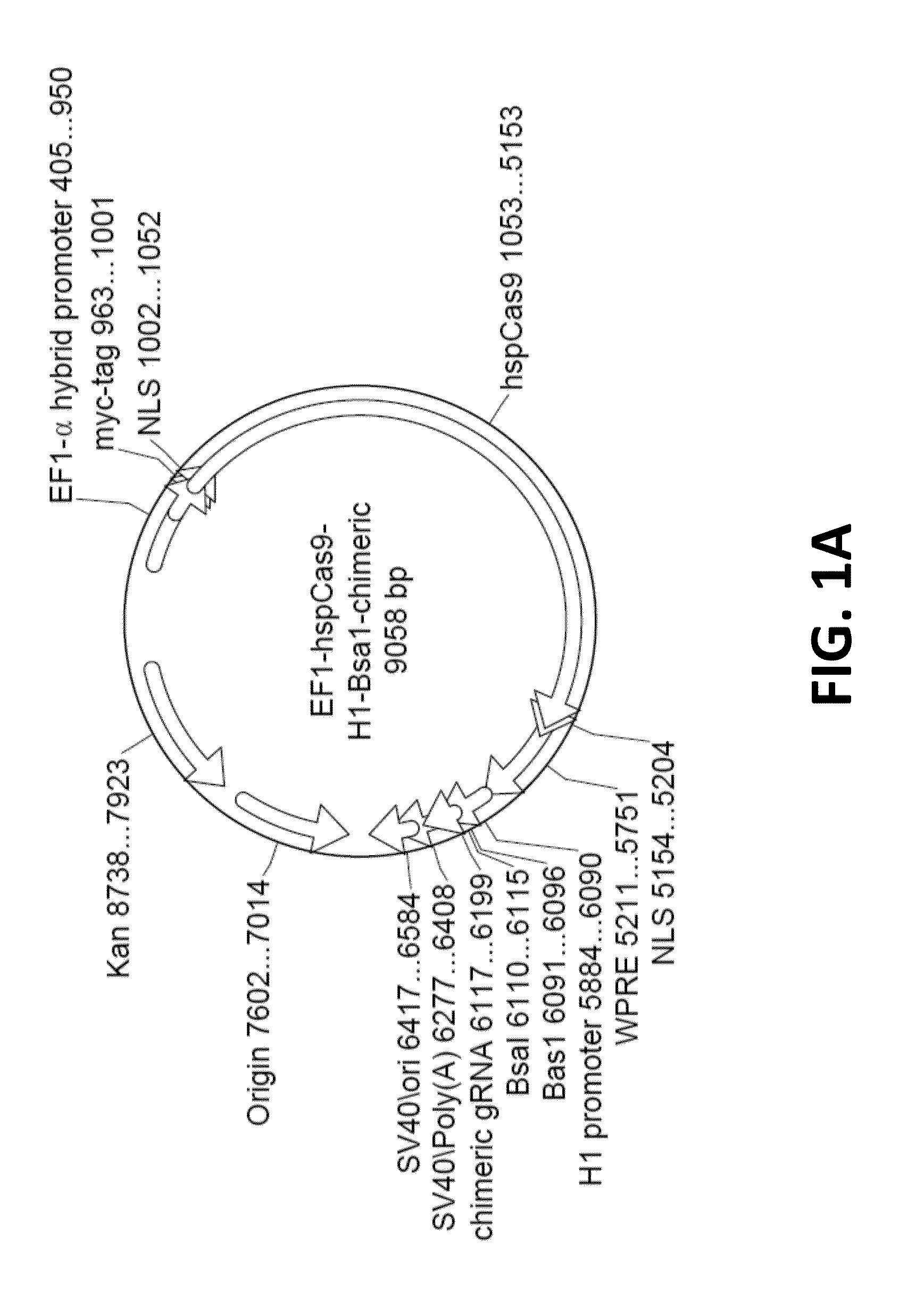
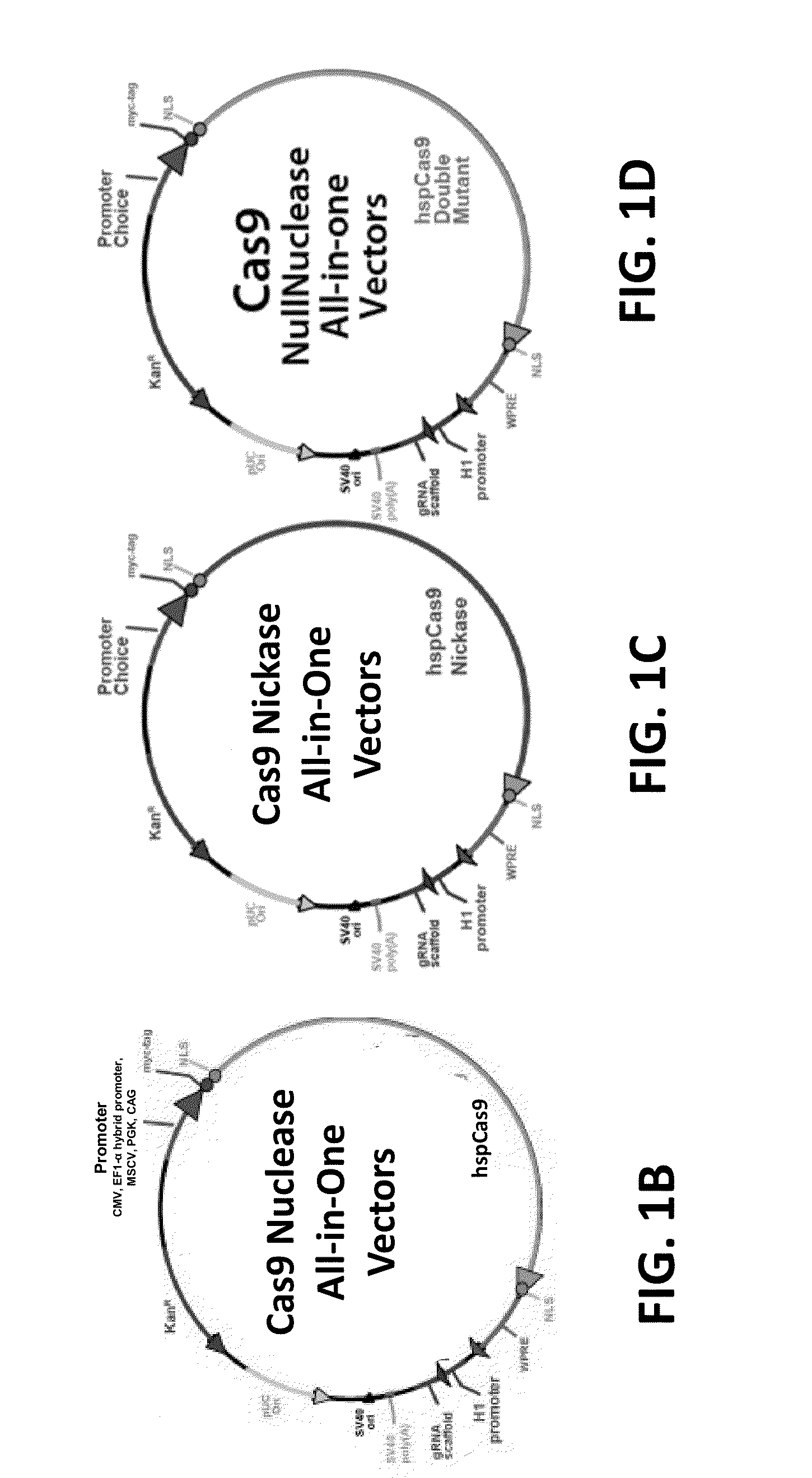
Crispr/cas systems for genomic modification and gene modulation
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification and regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells. The specification describes the design and validation of polynucleotides encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 gene and protein and variants of that protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells, and also modified by fused sequences that enhance various aspects of the CRISPR / Cas system. The specification also describes systems for RNA-guided genome engineering and gene regulation in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
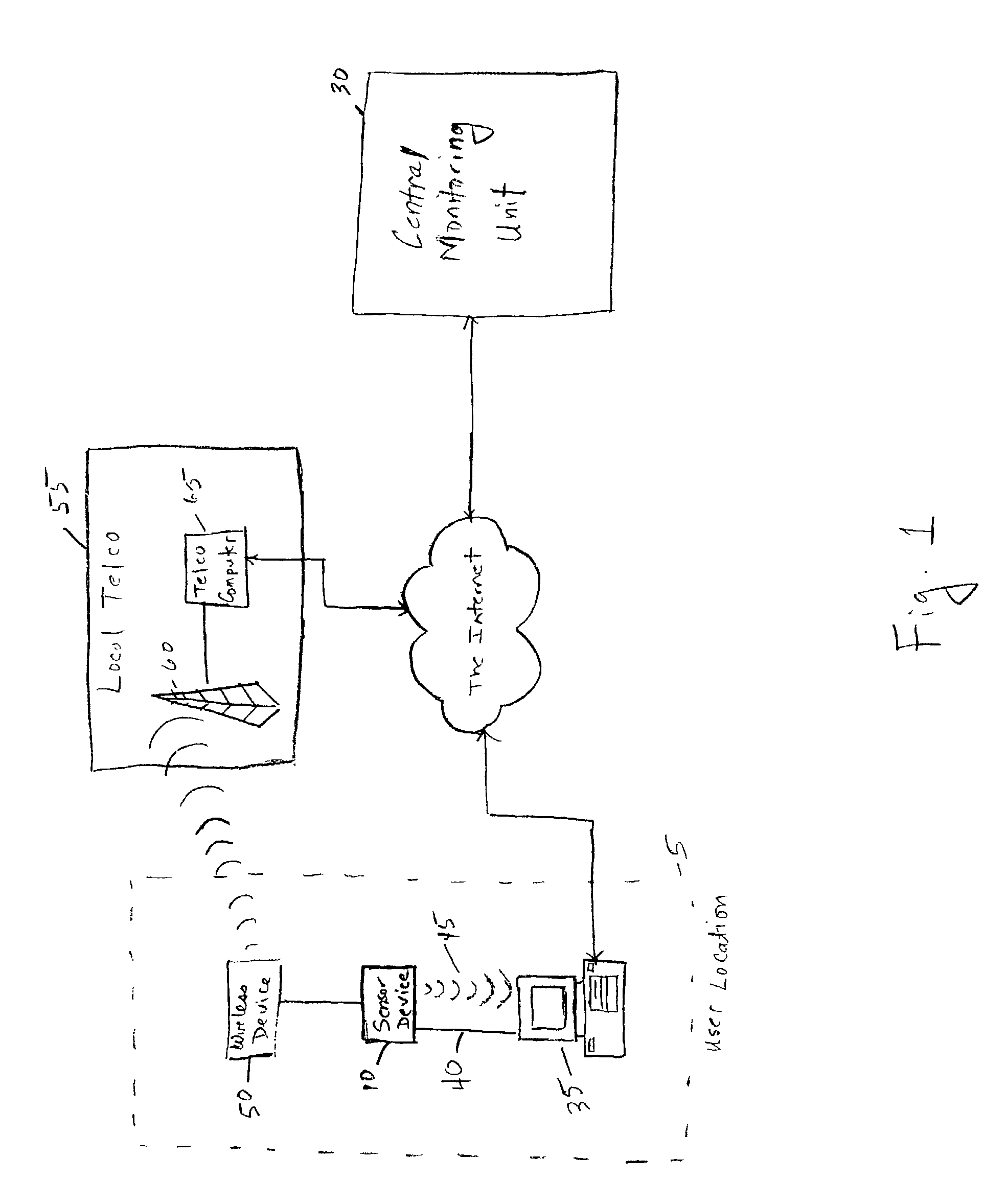
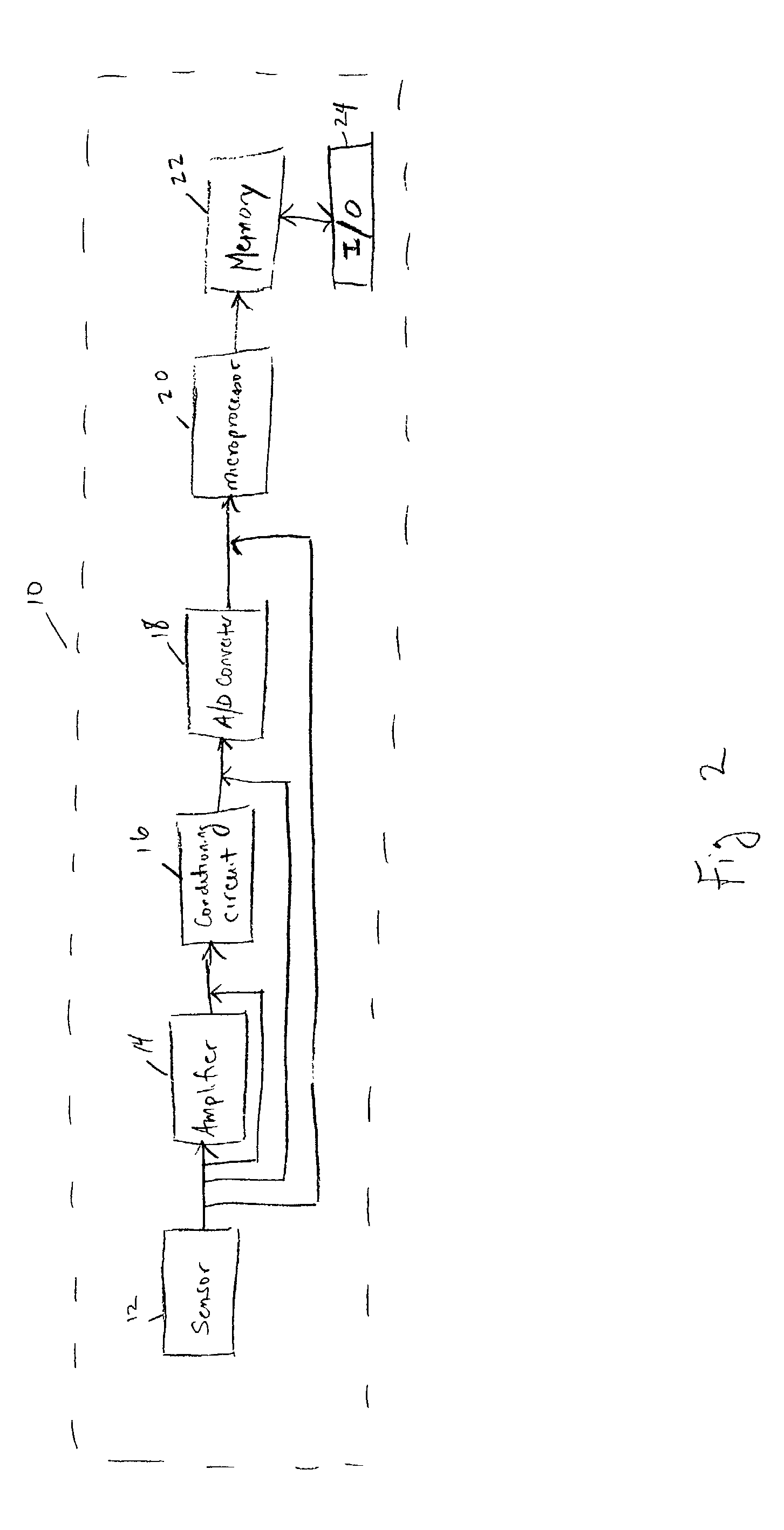
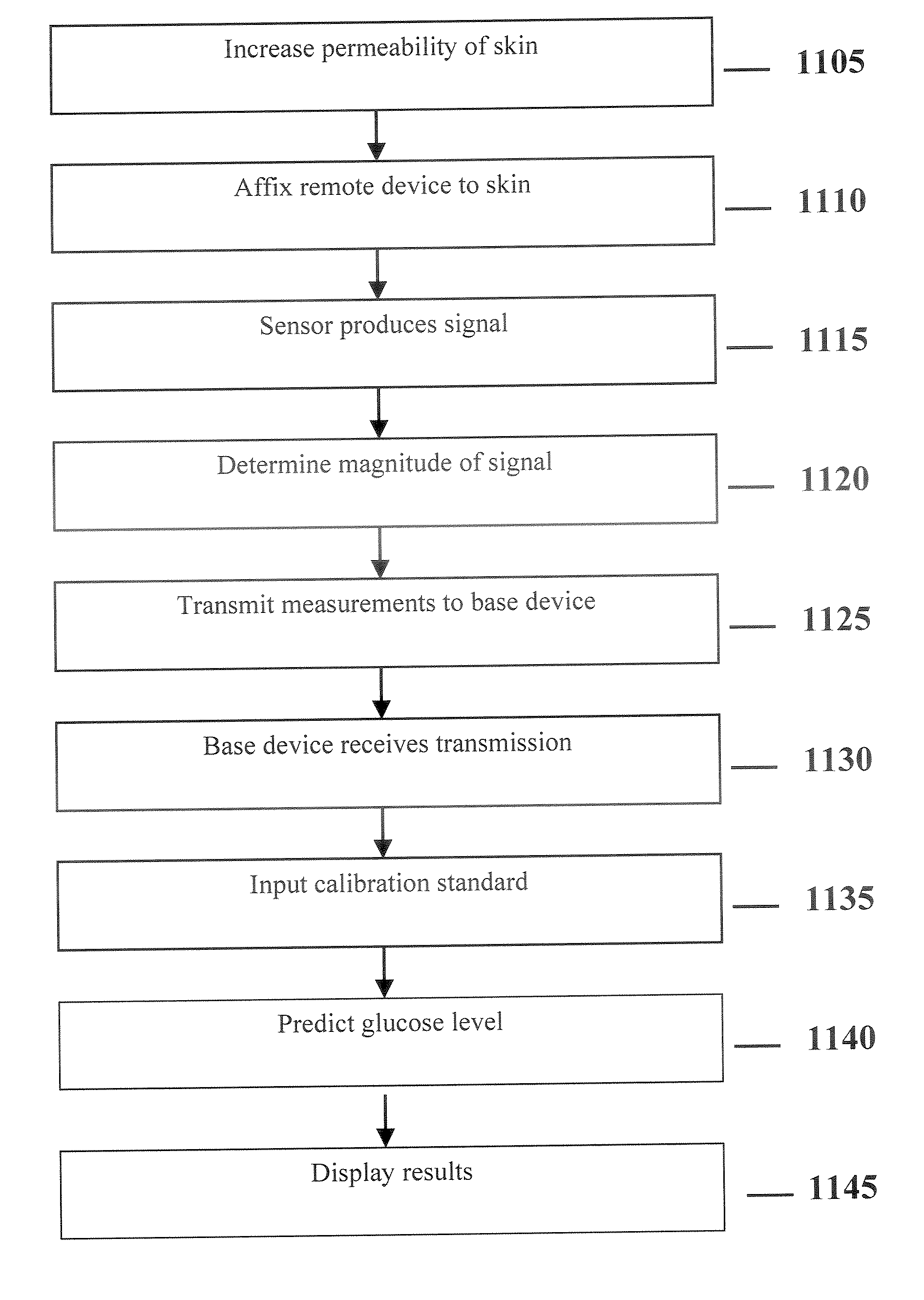
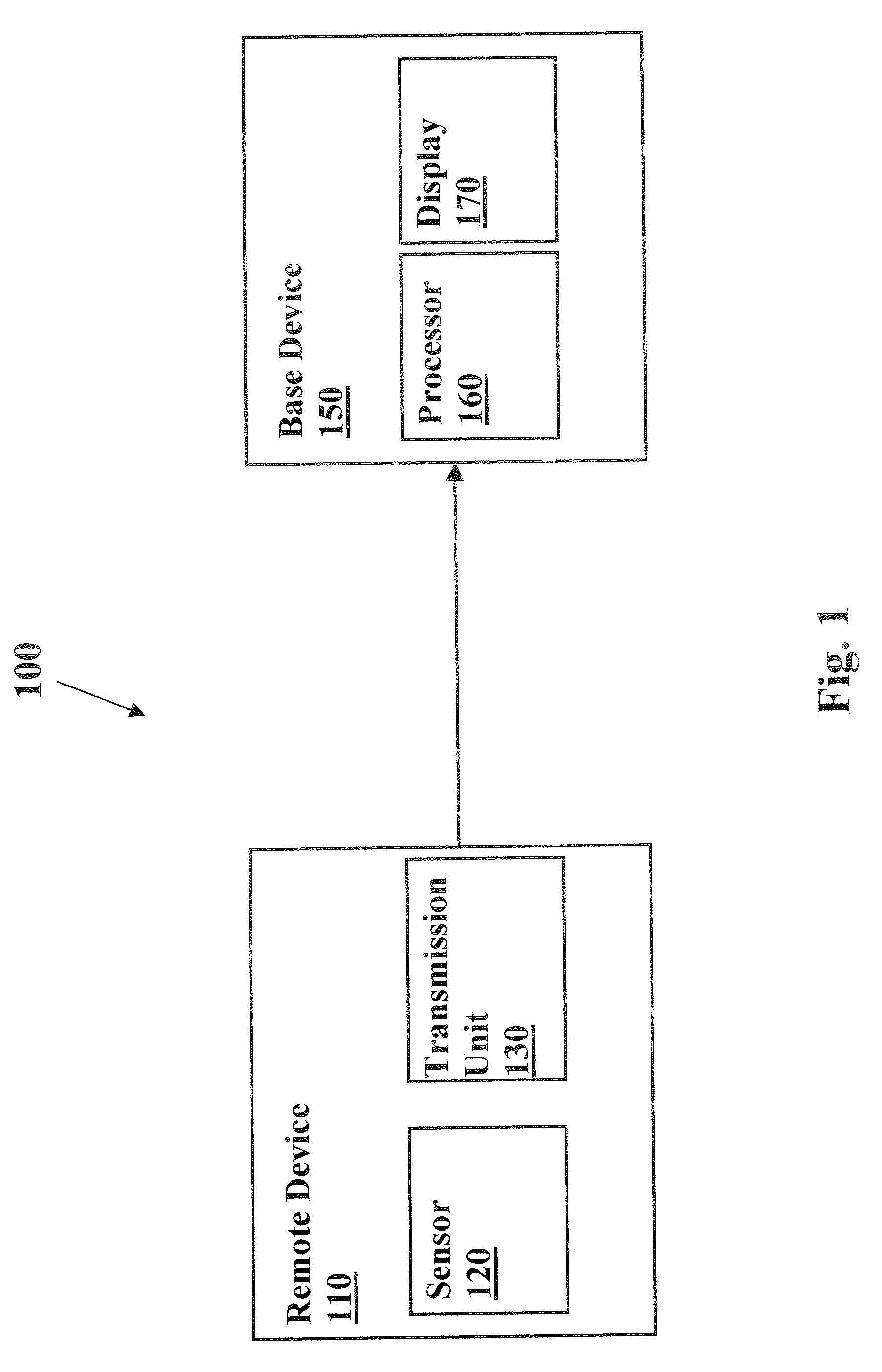
System and method for continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring
A system and method for continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the method includes the steps of (1) contacting a remote device to an area of biological membrane having a permeability level, the remote device comprising a sensor and a transmitter; (2) extracting the at least one analyte through and out of the area of biological membrane and into the sensor; (3) generating an electrical signal representative of a level of the at least one analyte; (4) transmitting the electrical signal to a base device; (5) processing the electrical signal to determine the level of the at least one analyte; and (6) displaying the level of the at least one analyte in real time. The system includes a remote device that includes a sensor that generates an electrical signal representative of the concentration of the at least one analyte; and a transmitter that transmits the electrical signal. The system further includes a base device that includes a receiver that receives the electrical signal; a processor that processes the electrical signal; and a display that displays the processed signal in real time.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
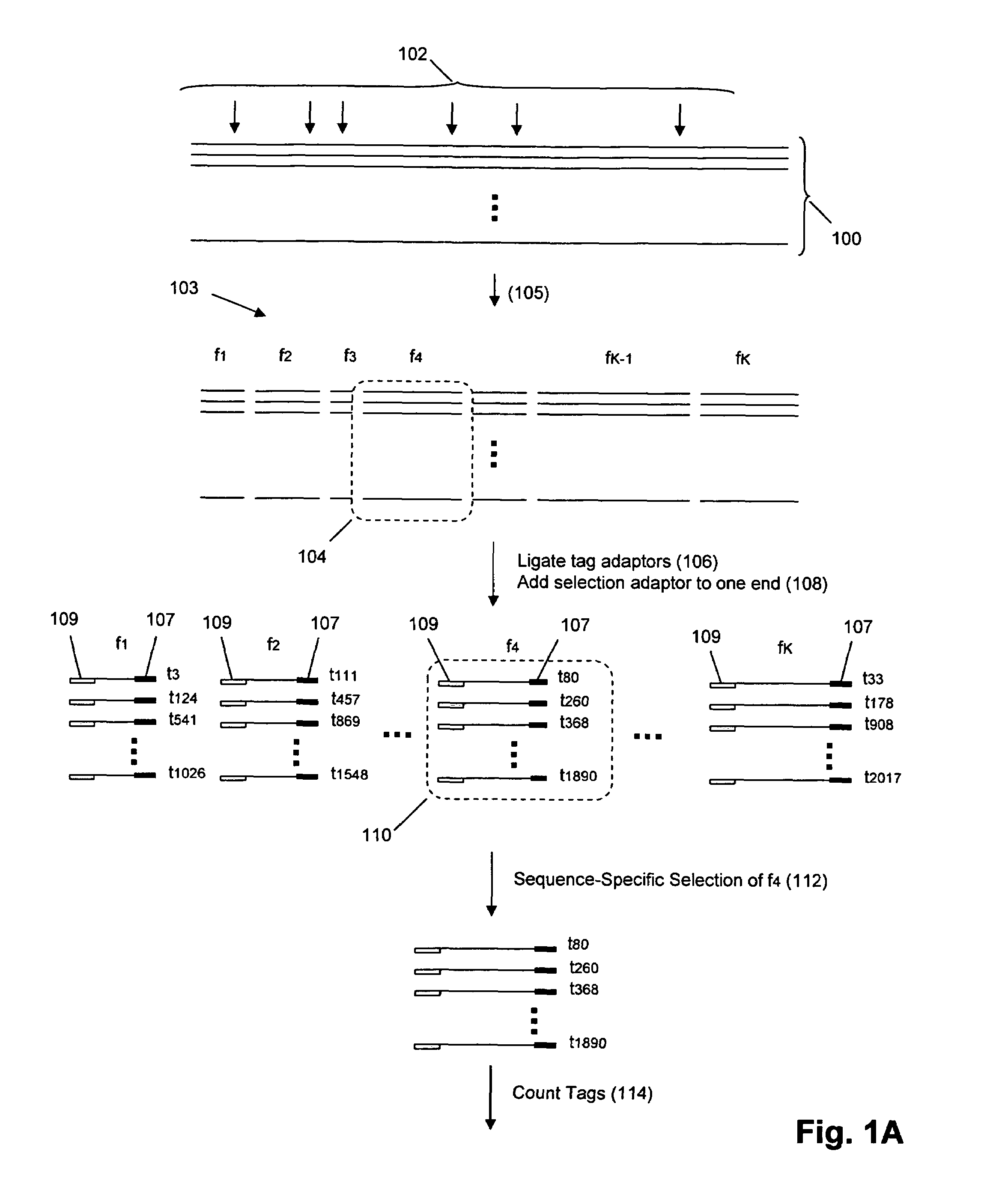
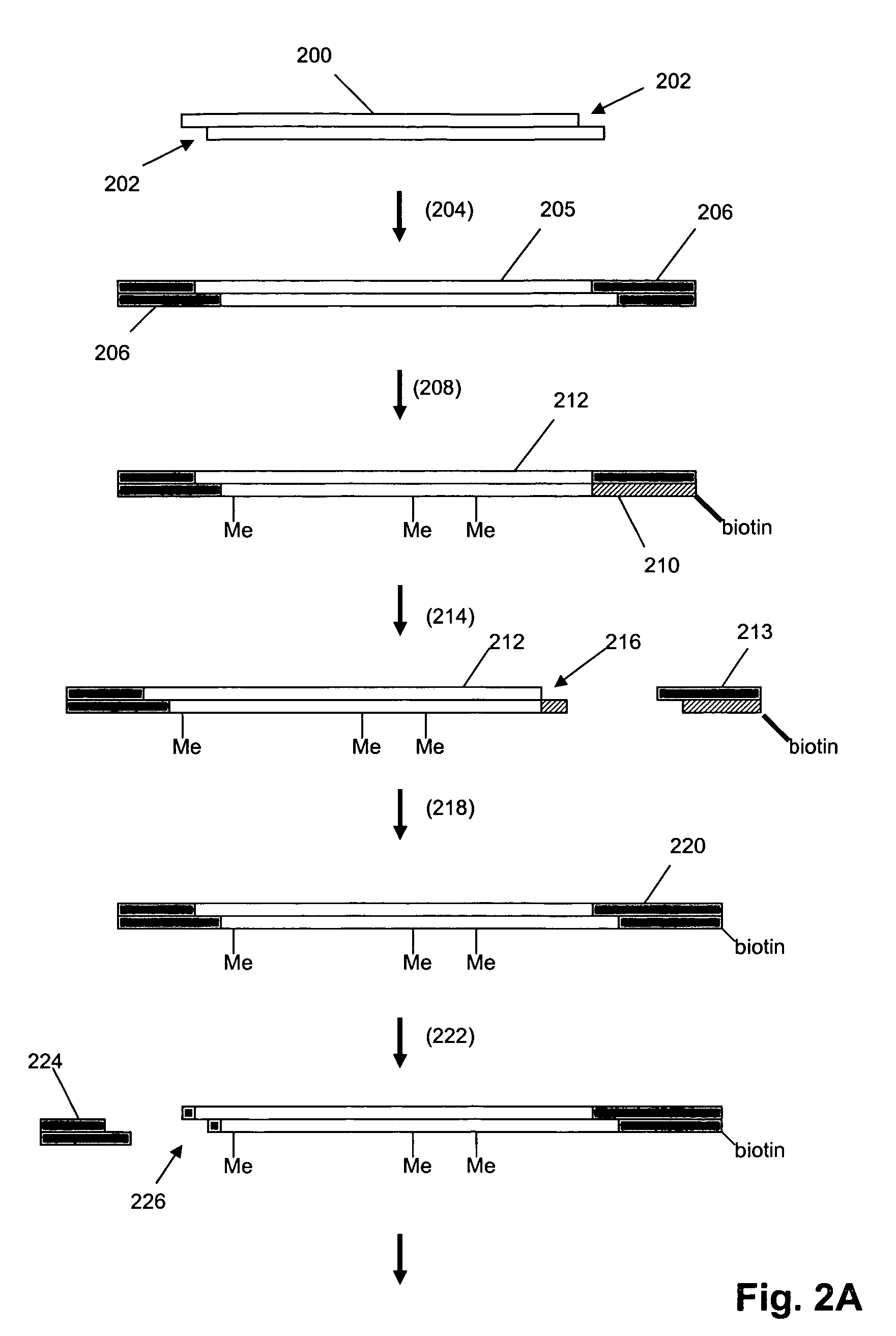
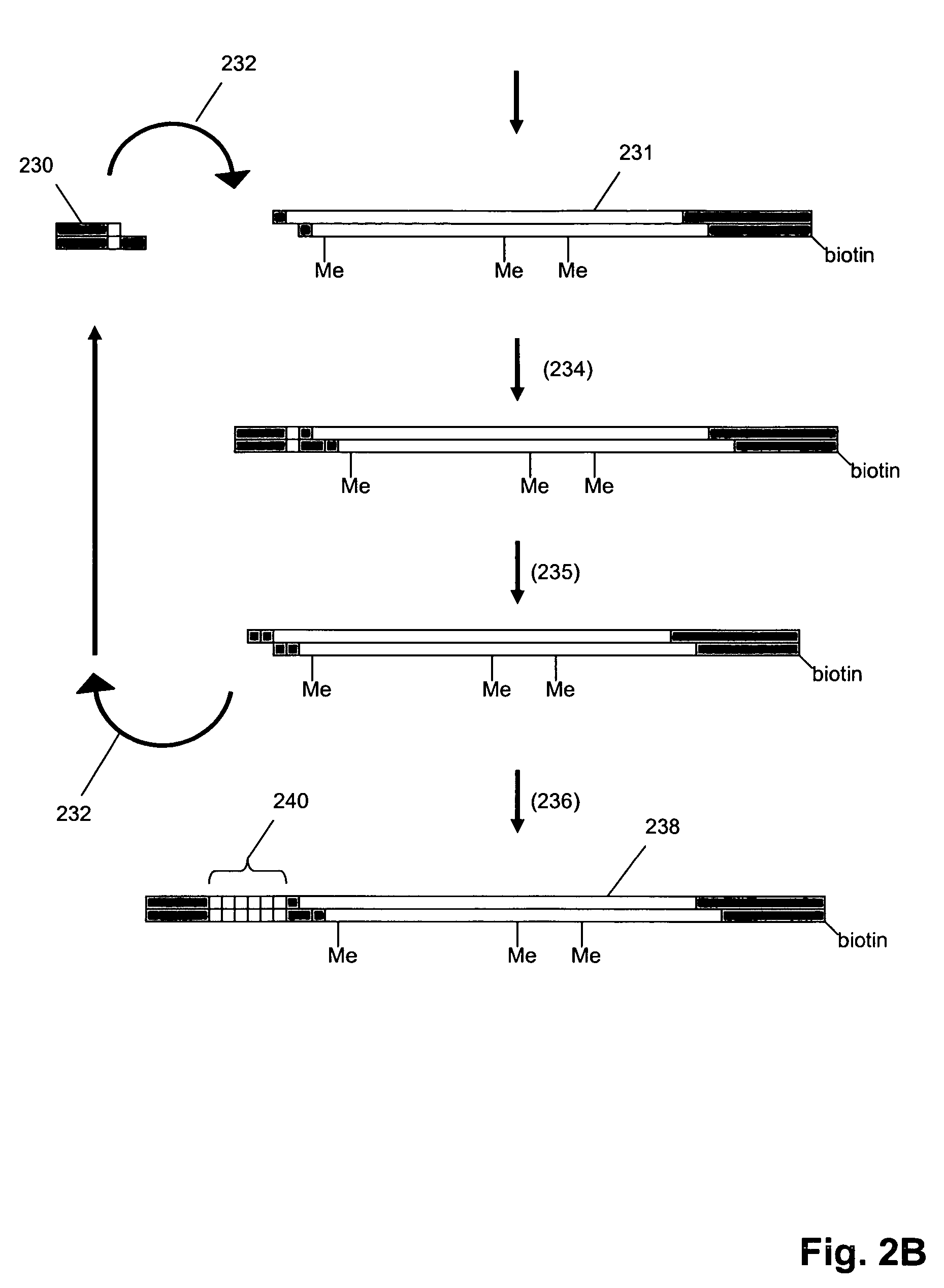
Methods and compositions for tagging and identifying polynucleotides
The invention provides methods and compositions for attaching oligonucleotide tags to polynucleotides for the purpose of carrying out analytical assays in parallel and for decoding the oligonucleotide tags of polynucleotides selected in such assays. Words, or subunits, of oligonucleotide tags index submixtures in successively more complex sets of submixtures (referred to herein as “tiers” of submixtures) that a polynucleotide goes through while successive words are added to a growing tag. By identifying each word of an oligonucleotide tag, a series of submixtures is identified including the first submixture that contains only a single polynucleotide, thereby providing the identity of the selected polynucleotide. The analysis of the words of an oligonucleotide tag can be carried out in parallel, e.g. by specific hybridization of the oligonucleotide tag to its tag complement on an addressable array; or such analysis can be carried out serially by successive specific hybridizations of labeled word complements, or the like.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Digital counting of individual molecules by stochastic attachment of diverse labels
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Methods of monitoring disease states and therapies using gene expression profiles
The present invention provides methods for monitoring disease states in a subject, as well as methods for monitoring the levels of effect of therapies upon a subject having one or more disease states. The methods involve: (i) measuring abundances of cellular constituents in a cell from a subject so that a diagnostic profile is obtained, (ii) measuring abundances of cellular constituents in a cell of one or more analogous subjects so that perturbation response profiles are obtained which correlate to a particular disease or therapy, and (iii) determining the interpolated perturbation response profile or profiles which best fit the diagnostic profile according to some objective measure. In other aspects, the invention also provides a computer system capable of performing the methods of the invention, data bases comprising perturbation response profiles for one or more diseases and / or therapies, and kits for determining levels of disease states and / or therapeutic effects according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
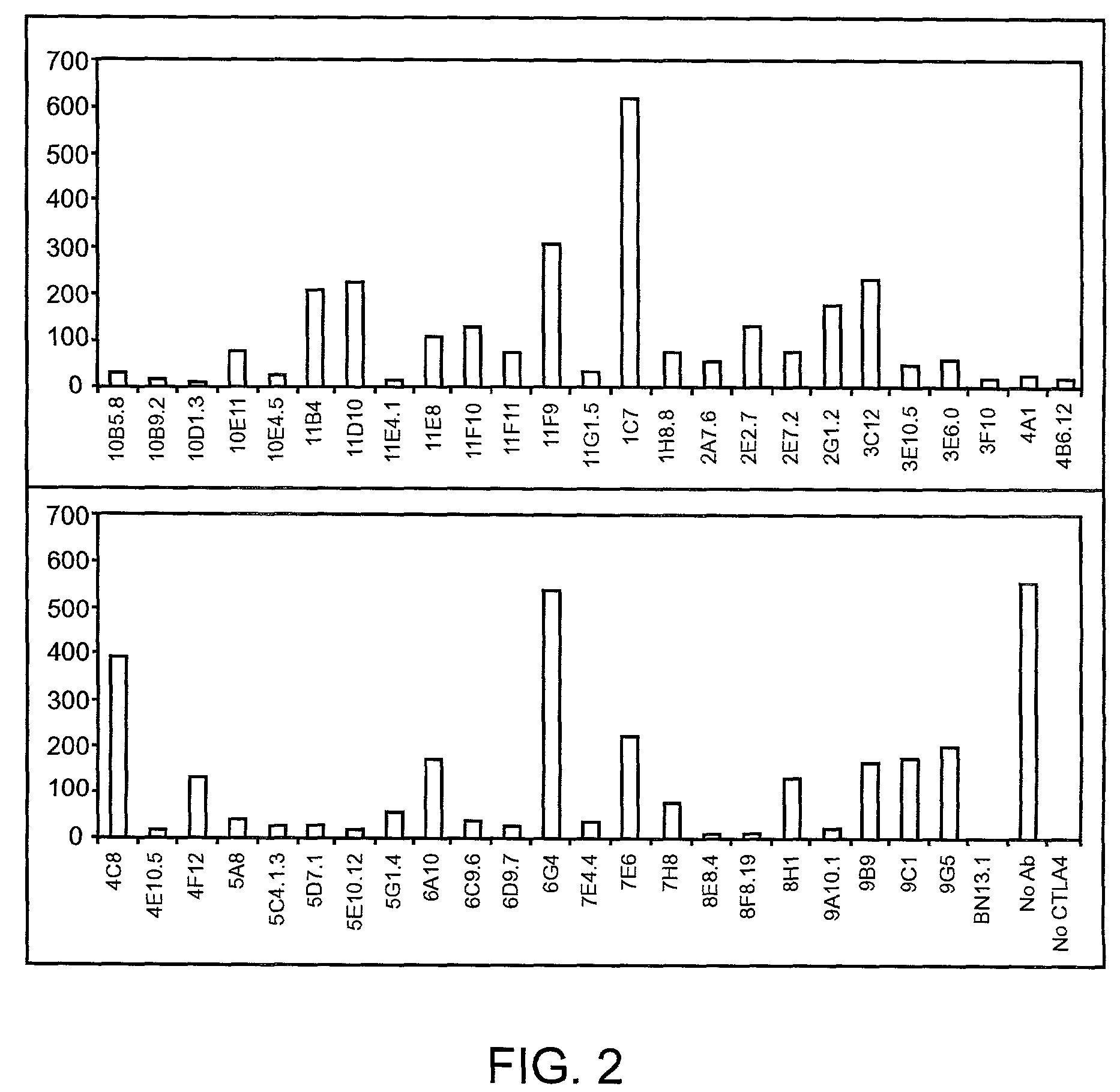
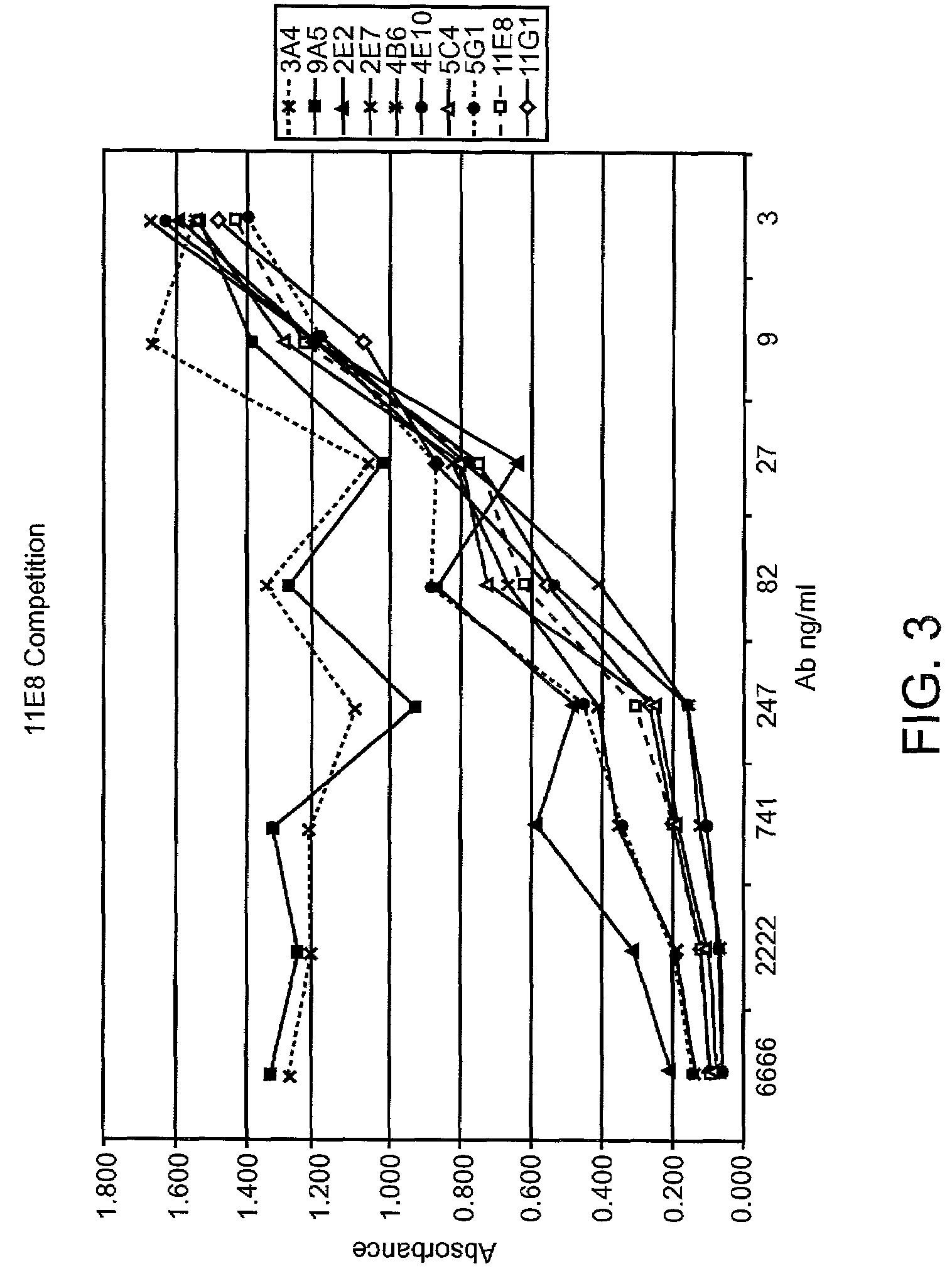
Human CTLA-4 antibodies and their uses
InactiveUS7605238B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesVirology
The present invention provides human sequence antibodies against human CTLA-4 and methods of treating human diseases, infections and other conditions using these antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
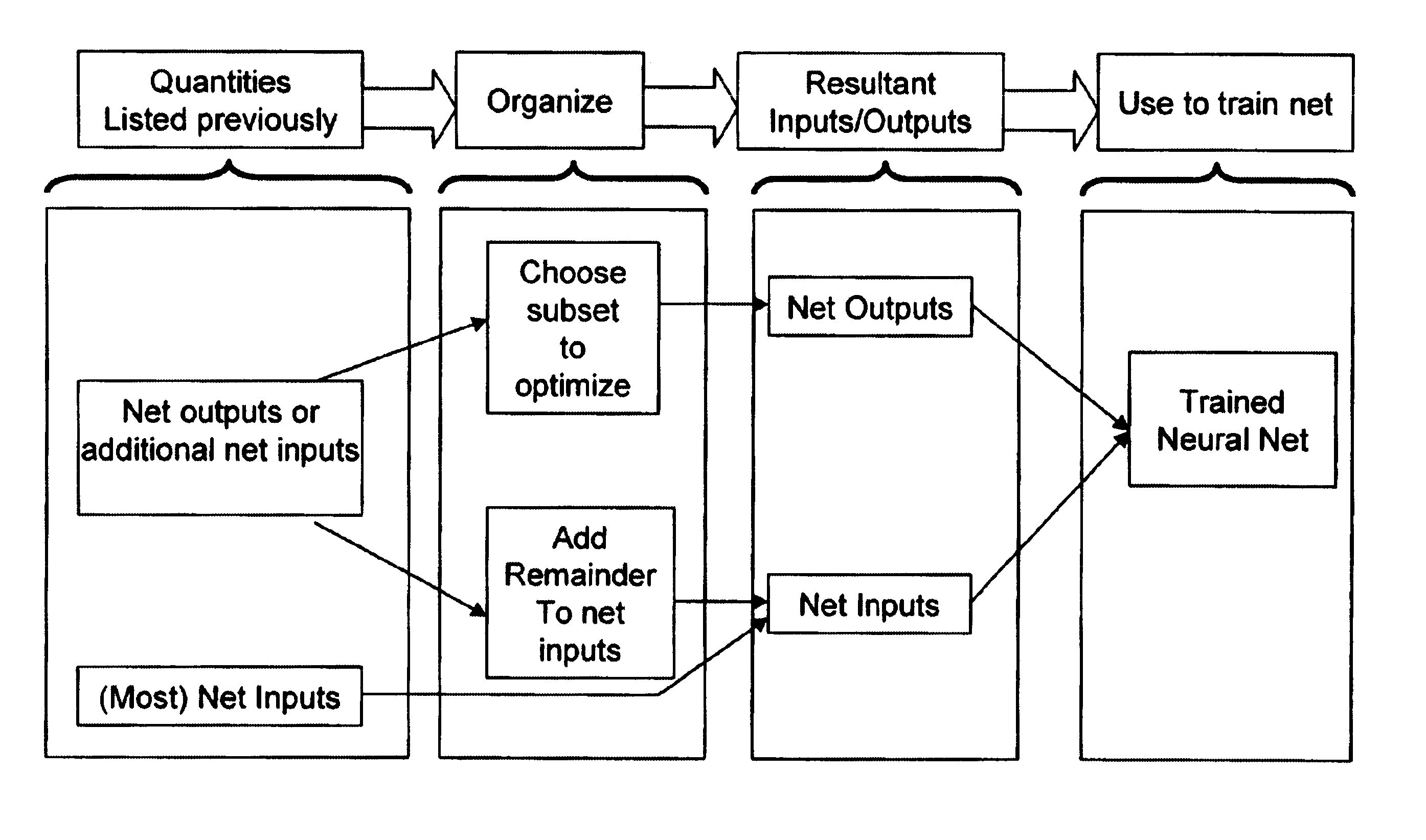
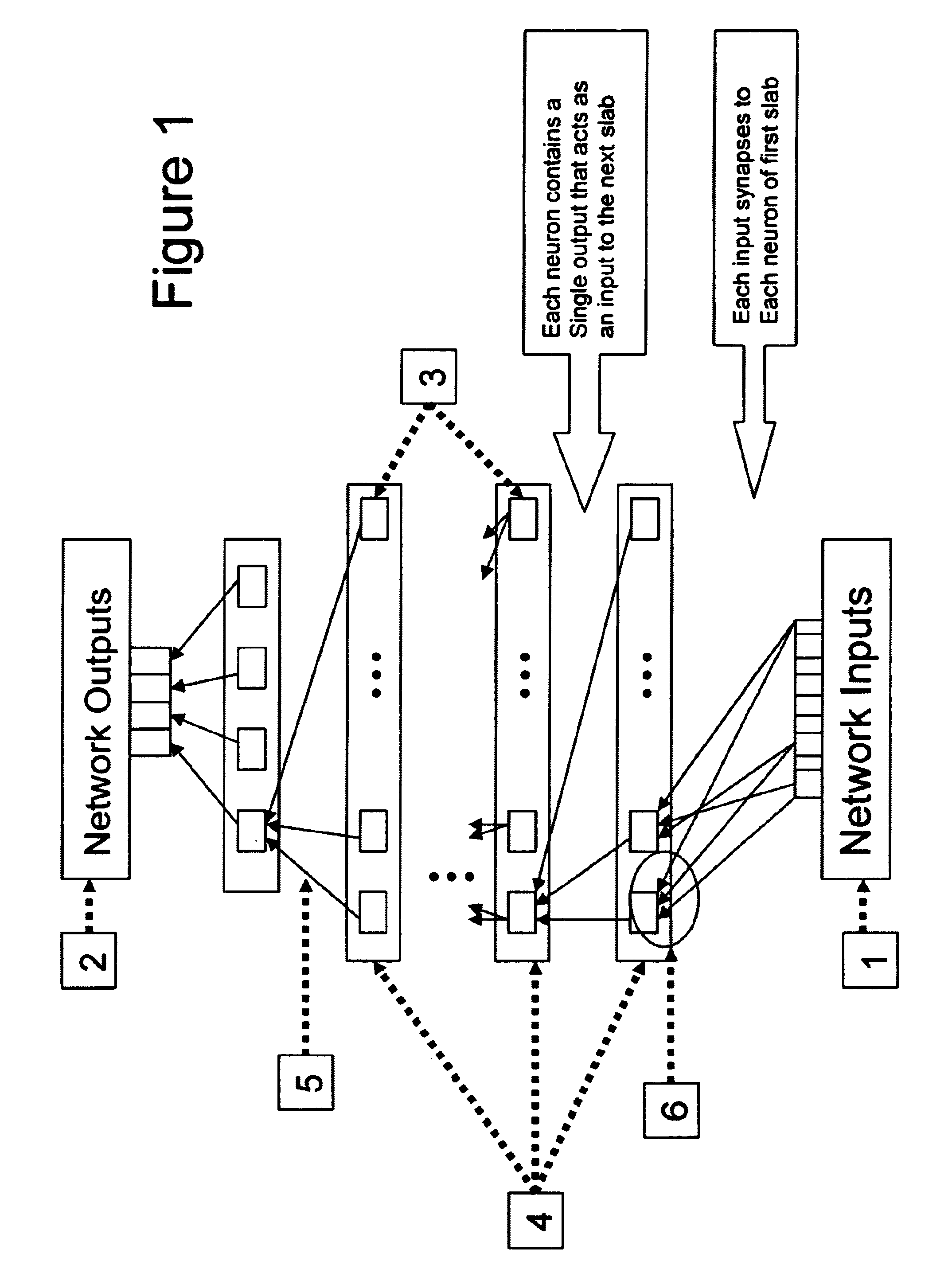
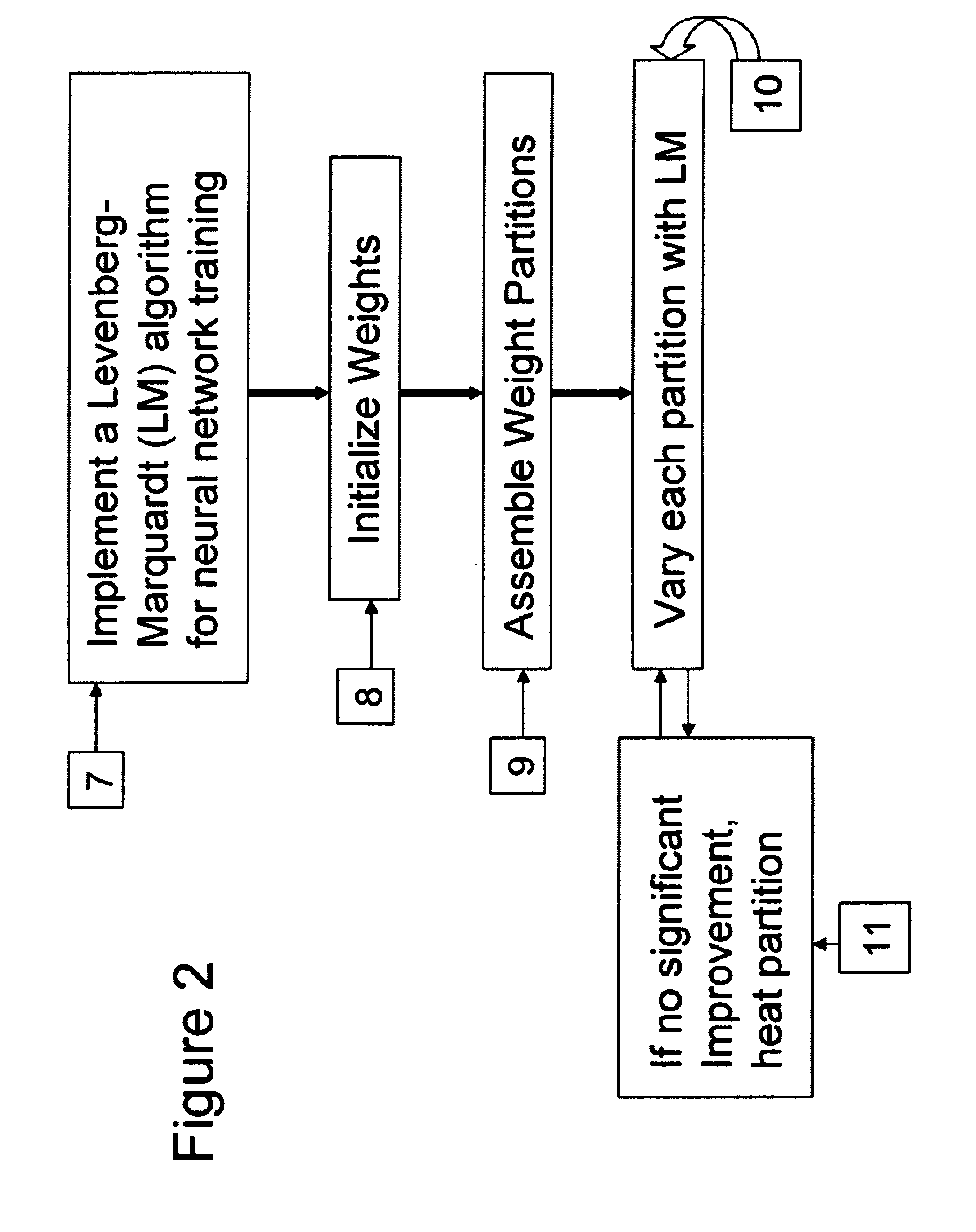
Neural network drug dosage estimation
InactiveUS6658396B1Improve accuracyGood precisionDrug and medicationsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkPatient characteristics
Neural networks are constructed (programmed), trained on historical data, and used to predict any of (1) optimal patient dosage of a single drug, (2) optimal patient dosage of one drug in respect of the patient's concurrent usage of another drug, (3a) optimal patient drug dosage in respect of diverse patient characteristics, (3b) sensitivity of recommended patient drug dosage to the patient characteristics, (4a) expected outcome versus patient drug dosage, (4b) sensitivity of the expected outcome to variant drug dosage(s), (5) expected outcome(s) from drug dosage(s) other than the projected optimal dosage. Both human and economic costs of both optimal and sub-optimal drug therapies may be extrapolated from the exercise of various optimized and trained neural networks. Heretofore little recognized sensitivities-such as, for example, patient race in the administration of psychotropic drugs-are made manifest. Individual prescribing physicians employing deviant patterns of drug therapy may be recognized. Although not intended to prescribe drugs, nor even to set prescription drug dosage, the neural networks are very sophisticated and authoritative "helps" to physicians, and to physician reviewers, in answering "what if" questions.
Owner:PREDICTION SCI
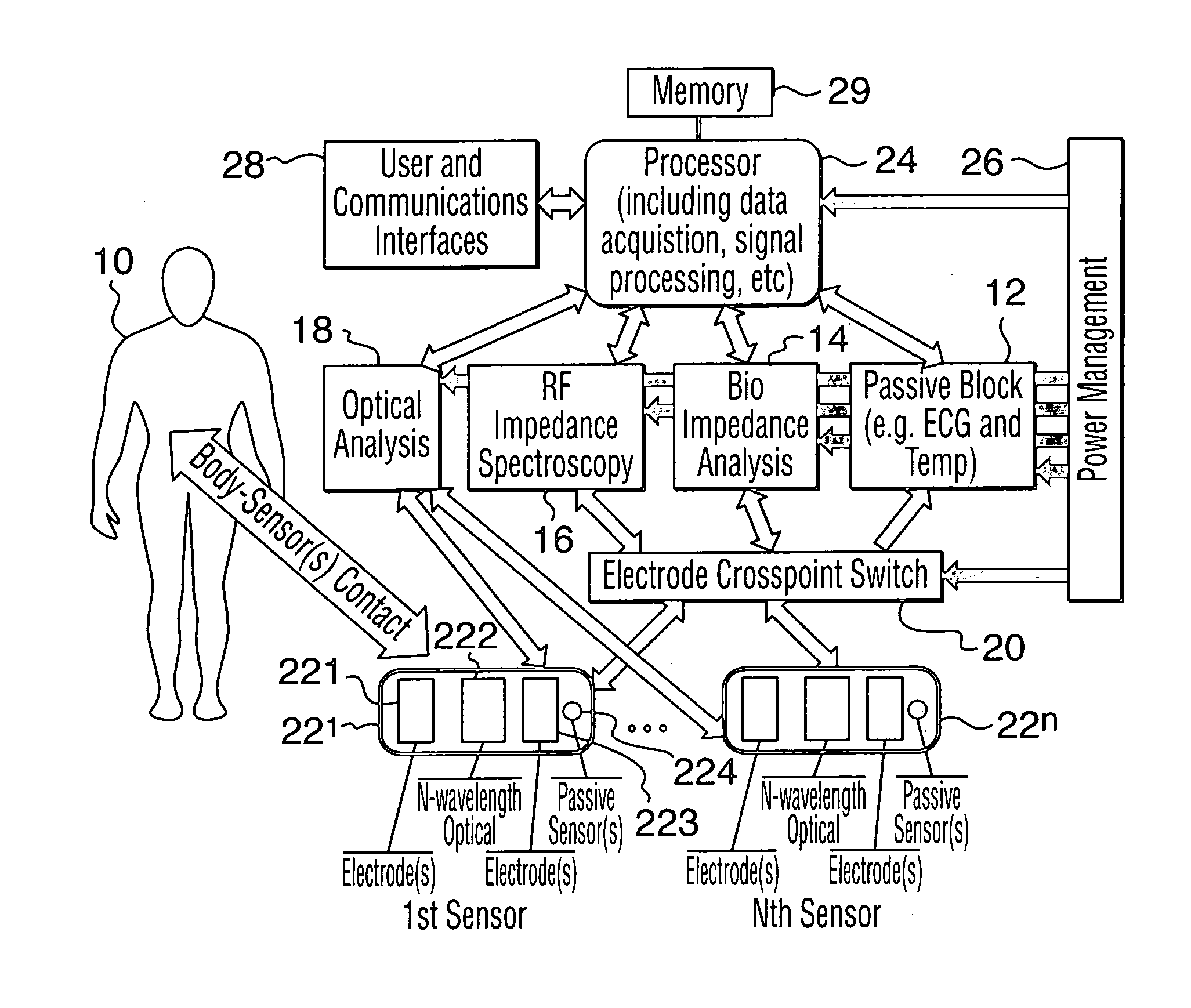
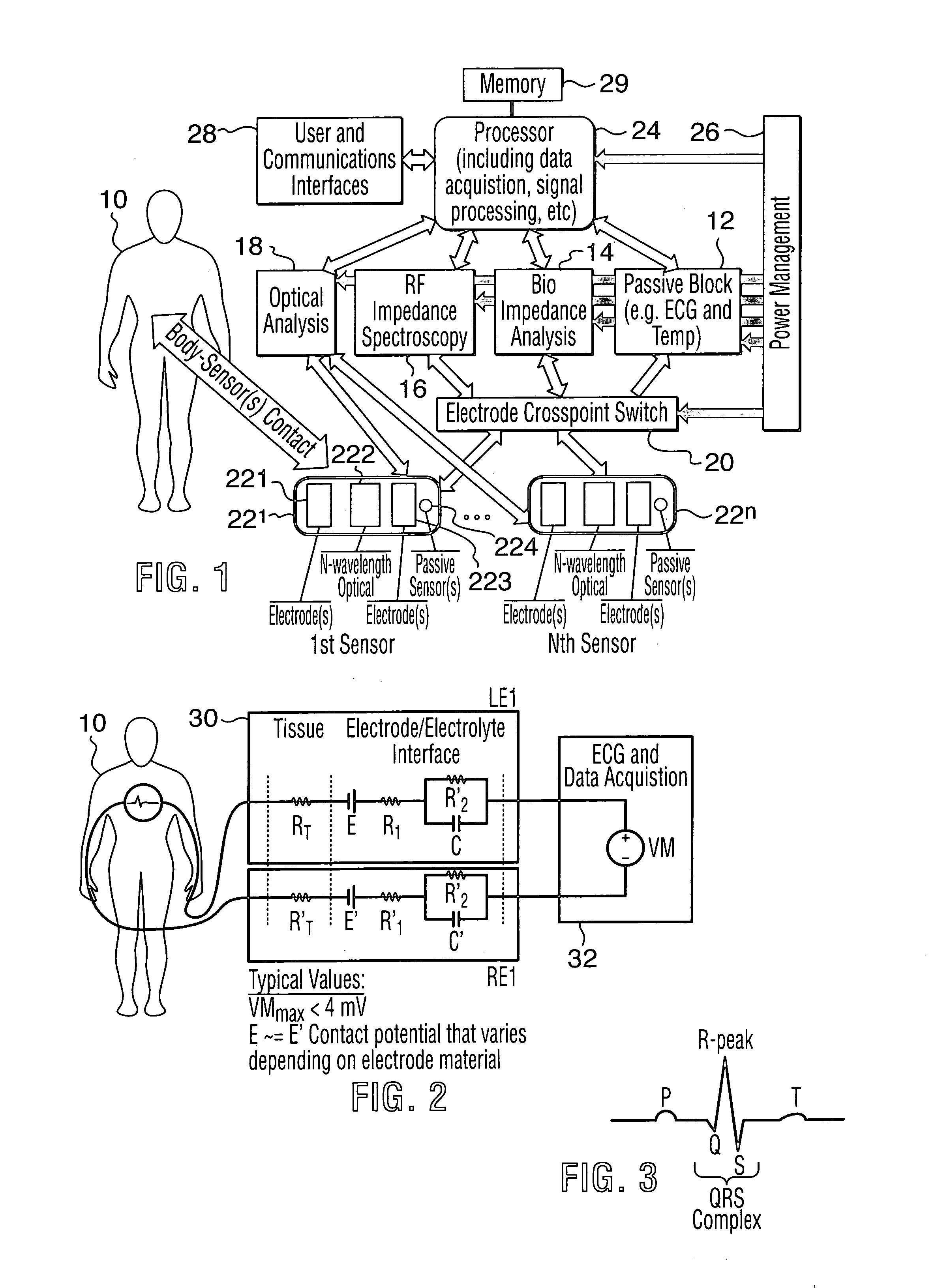
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining a physiological parameter
InactiveUS20050192488A1Accurate resultAccurately measureElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyLinear algorithmNon invasive
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the non-invasive analysis of physiological attributes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, cardiac output, respiratory response, body composition, and blood chemistry analytes including glucose, lactate, hemoglobin, and oxygen saturation. Using a combination of multi-functioning disparate sensors, such as optical and electrical, improvements are made over existing physiological measurement devices and techniques. The special configuration of one or more multi-functional sensors is used to non-invasively measure multi-wavelength optical plus one or more of ECG, Bio-impedance, and RF-impedance spectroscopic data. This information is used to develop self-consistent, non-linear algorithm in order to derive the physiological attributes while compensating for various forms of interfering effects including motion artifacts, sensor attachment variability, device component variability, subject physical and physiology variability, and various interfering physiological attributes.
Owner:BIOPEAK CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com