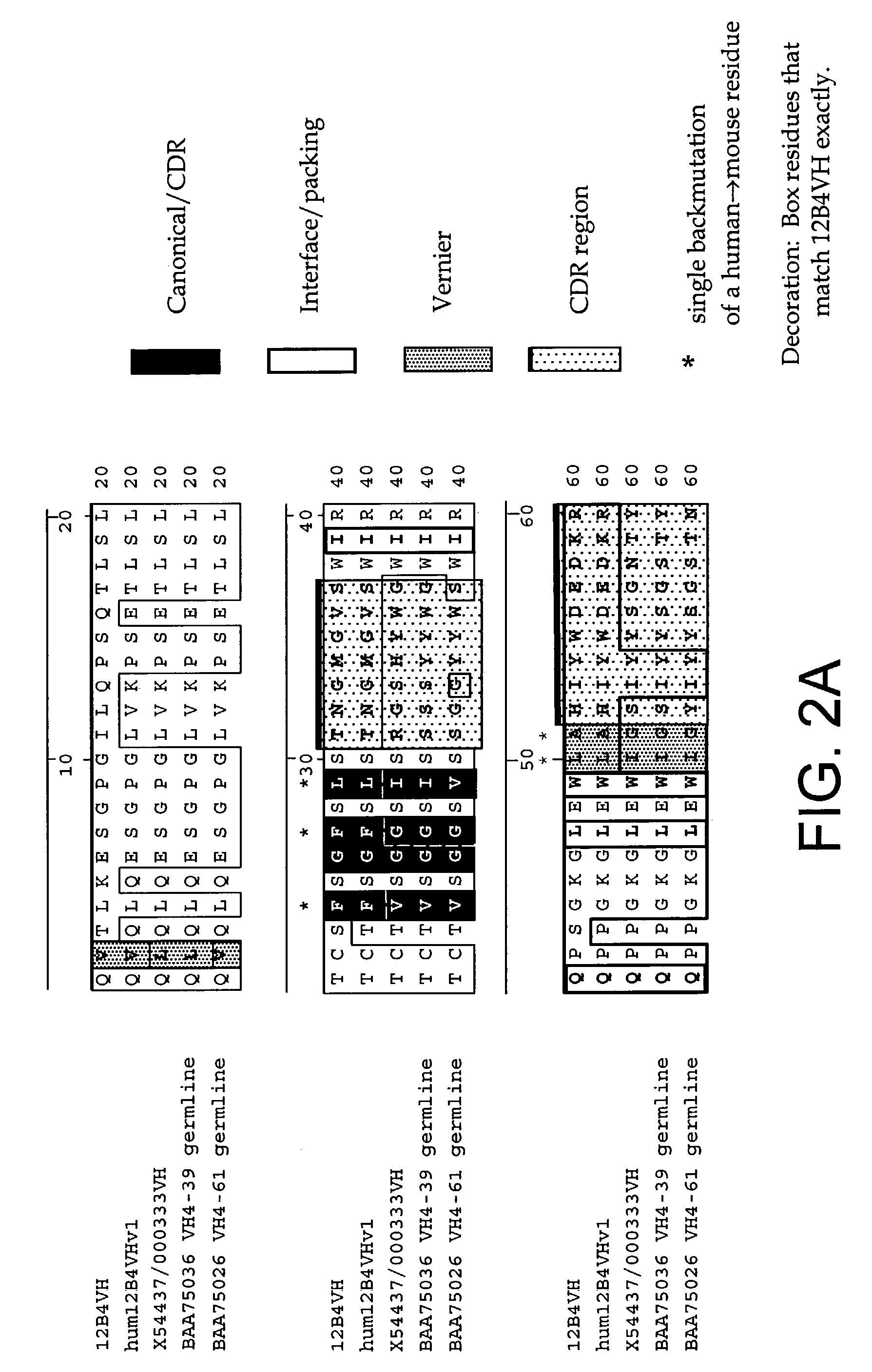
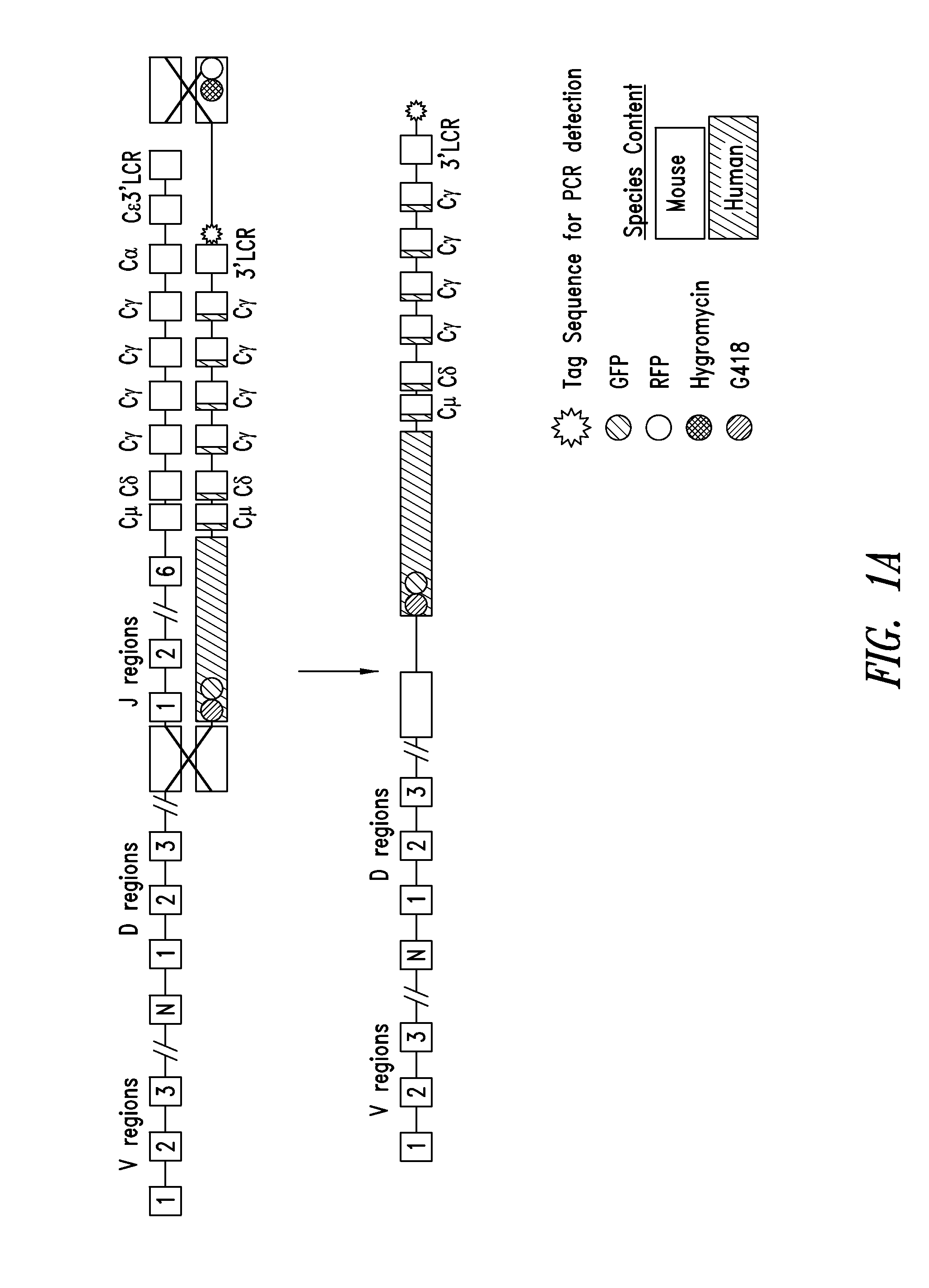
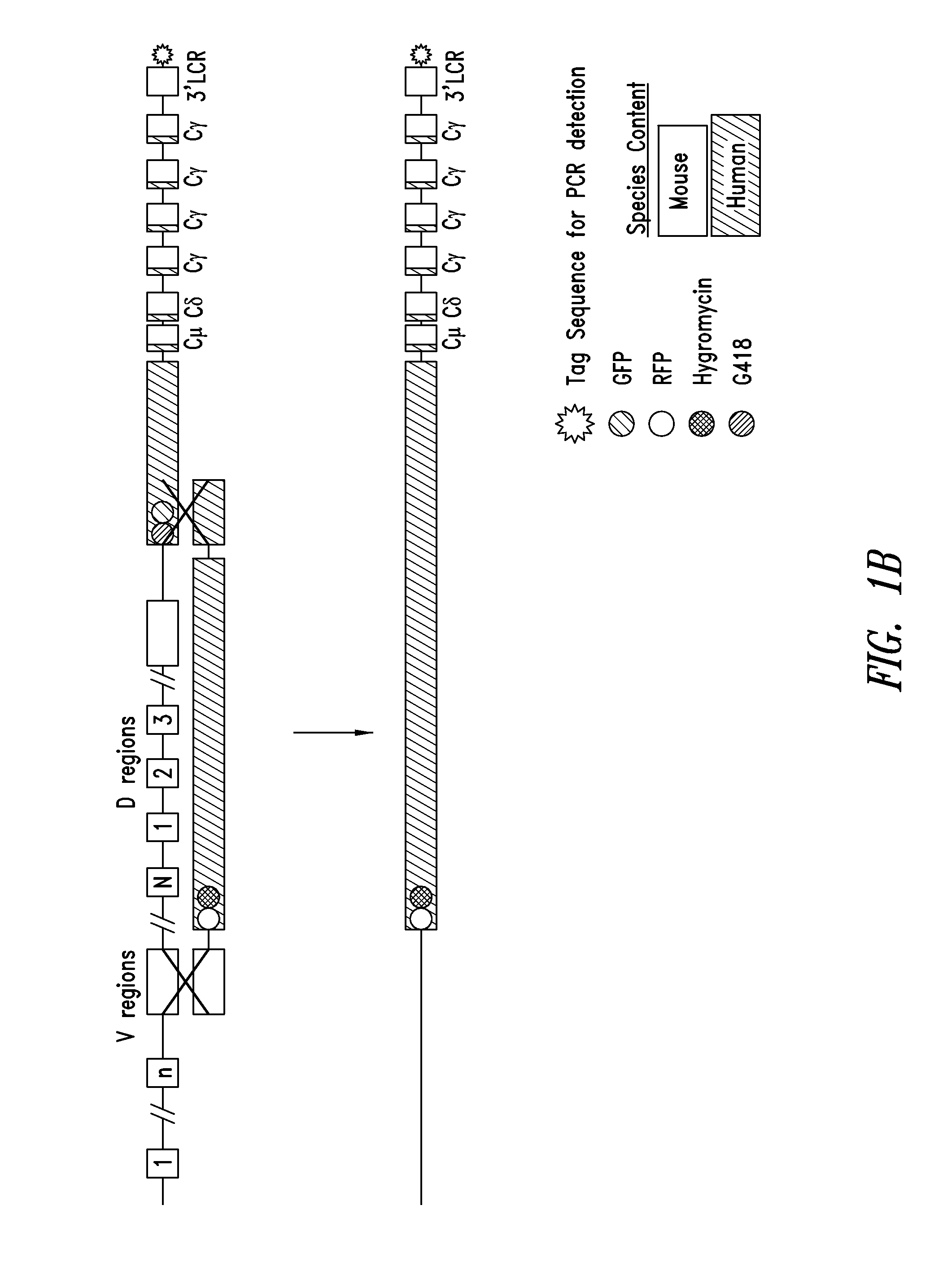
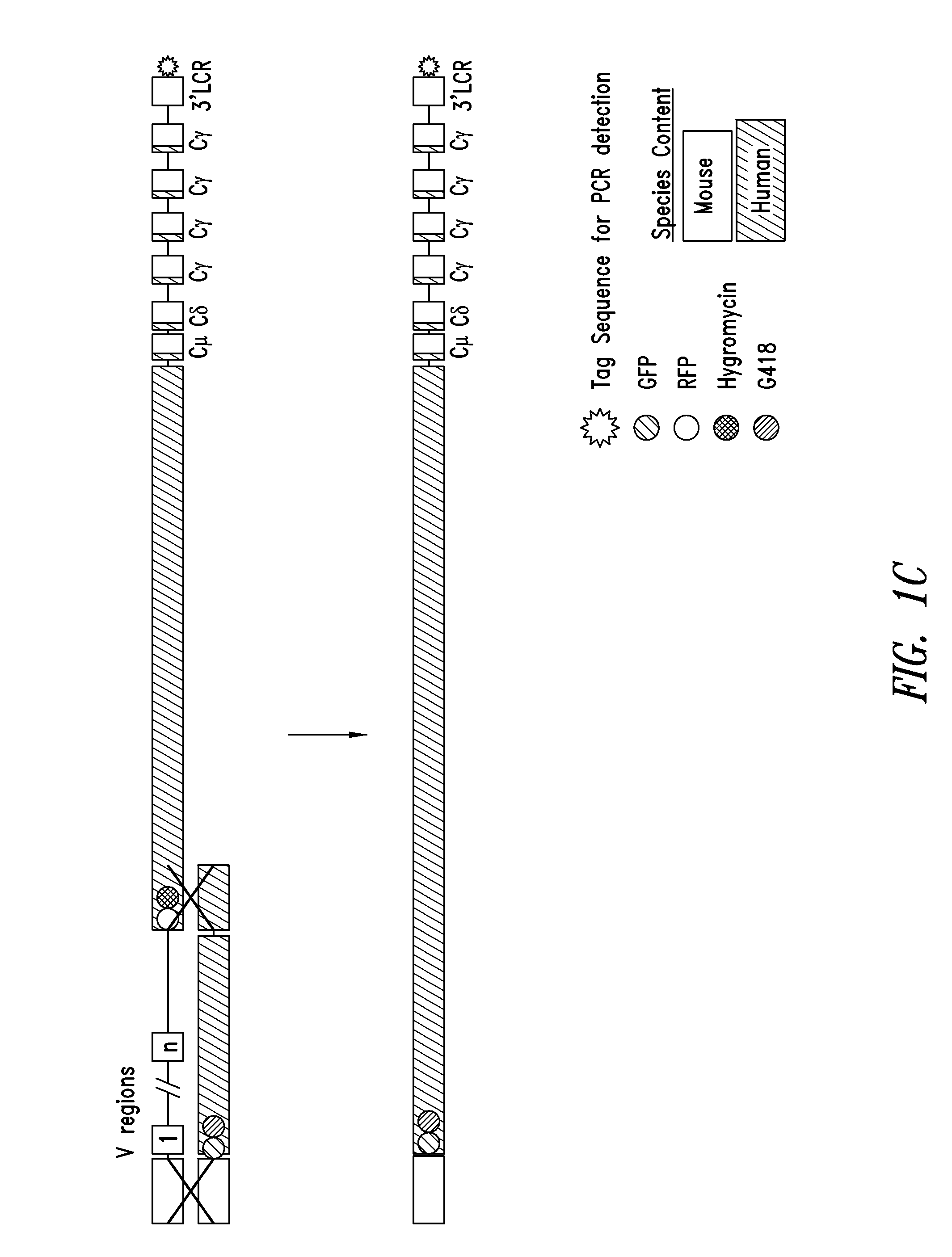
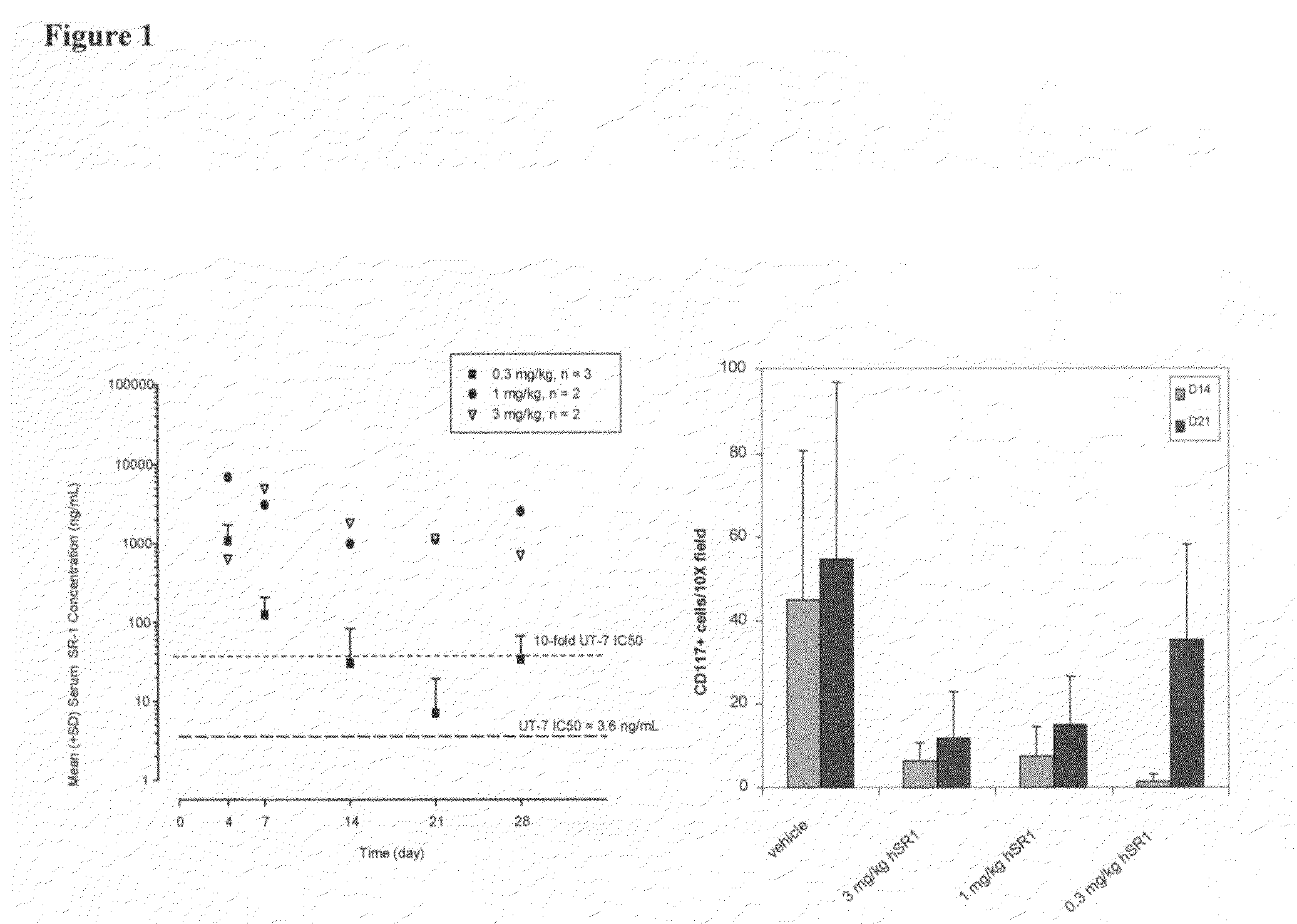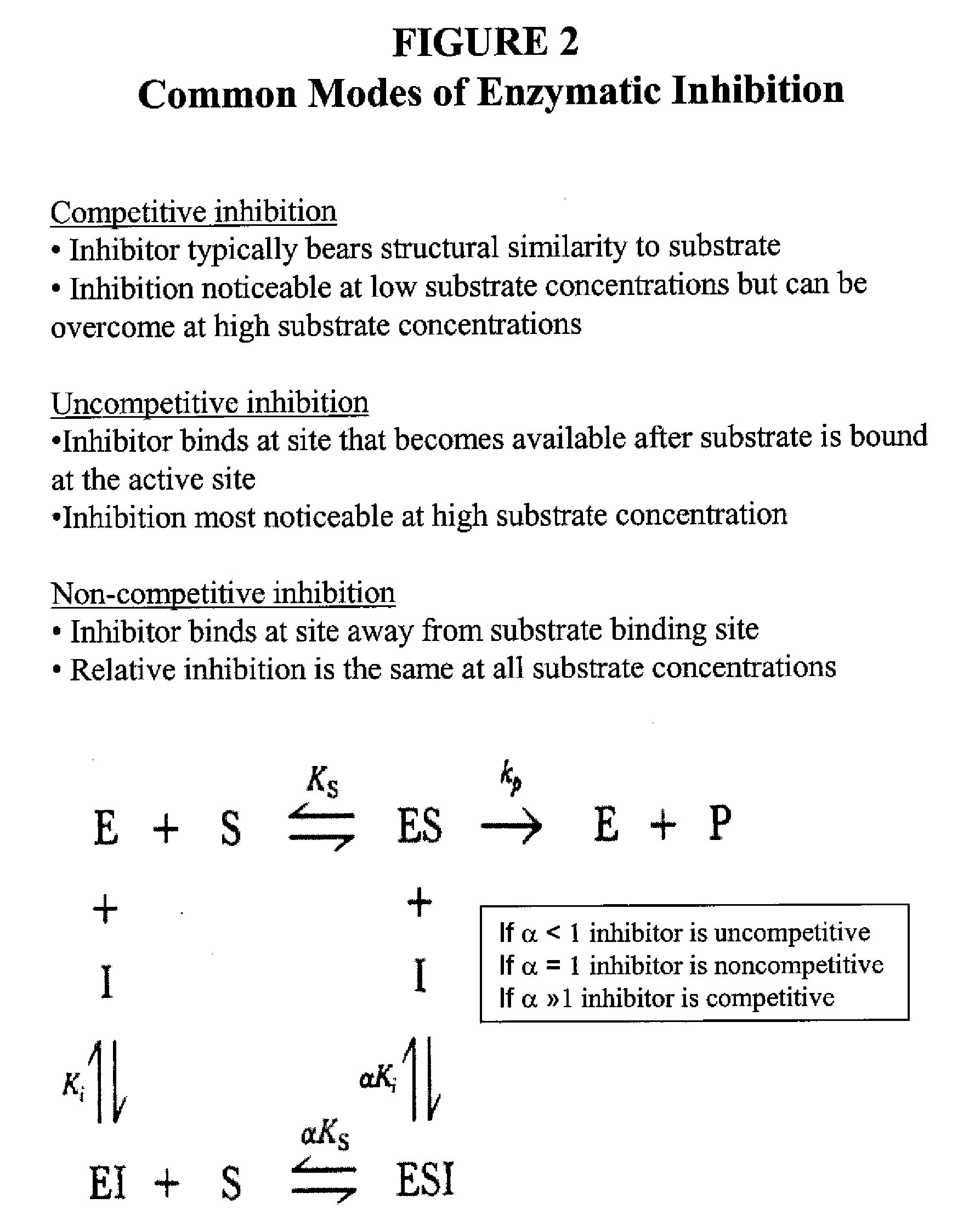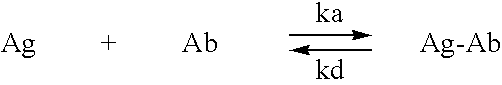Patents
Literature
958 results about "Humanized antibody" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Humanized antibodies are antibodies from non-human species whose protein sequences have been modified to increase their similarity to antibody variants produced naturally in humans. The process of "humanization" is usually applied to monoclonal antibodies developed for administration to humans (for example, antibodies developed as anti-cancer drugs). Humanization can be necessary when the process of developing a specific antibody involves generation in a non-human immune system (such as that in mice). The protein sequences of antibodies produced in this way are partially distinct from homologous antibodies occurring naturally in humans, and are therefore potentially immunogenic when administered to human patients (see also Human anti-mouse antibody). There are other types of antibodies developed. The International Nonproprietary Names of humanized antibodies end in -zumab, as in omalizumab (see Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies).
Antigen binding molecules with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human CD20. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
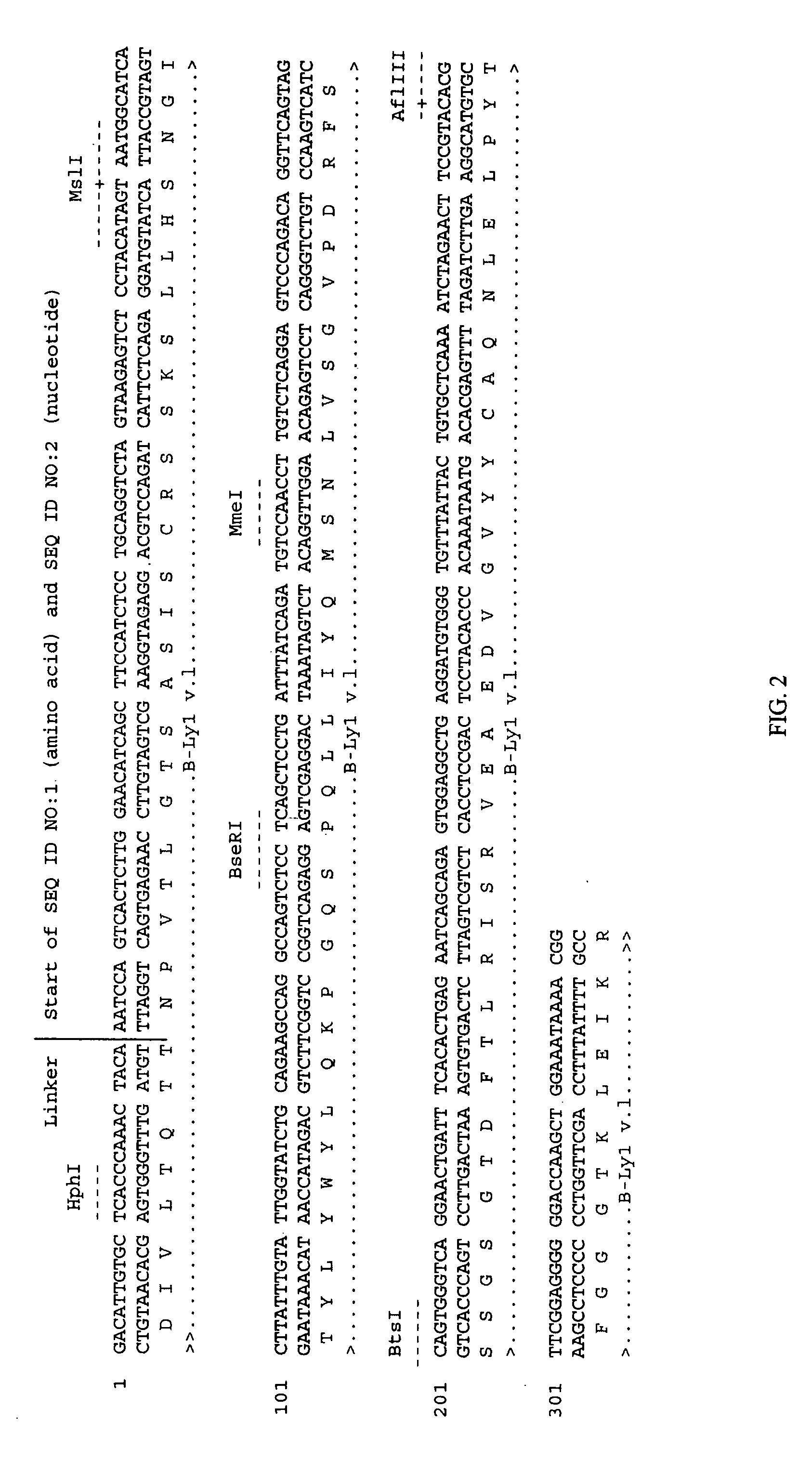
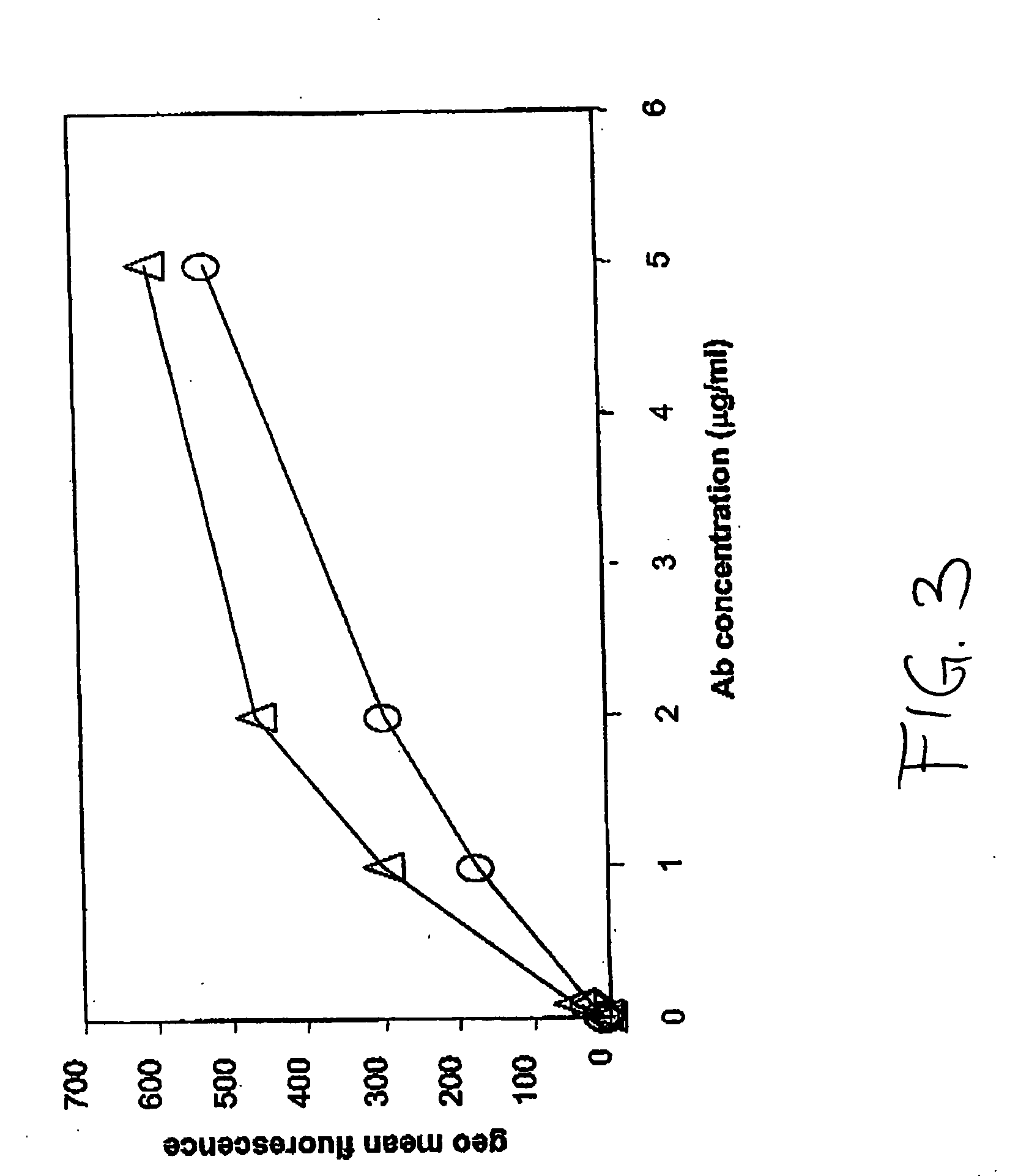
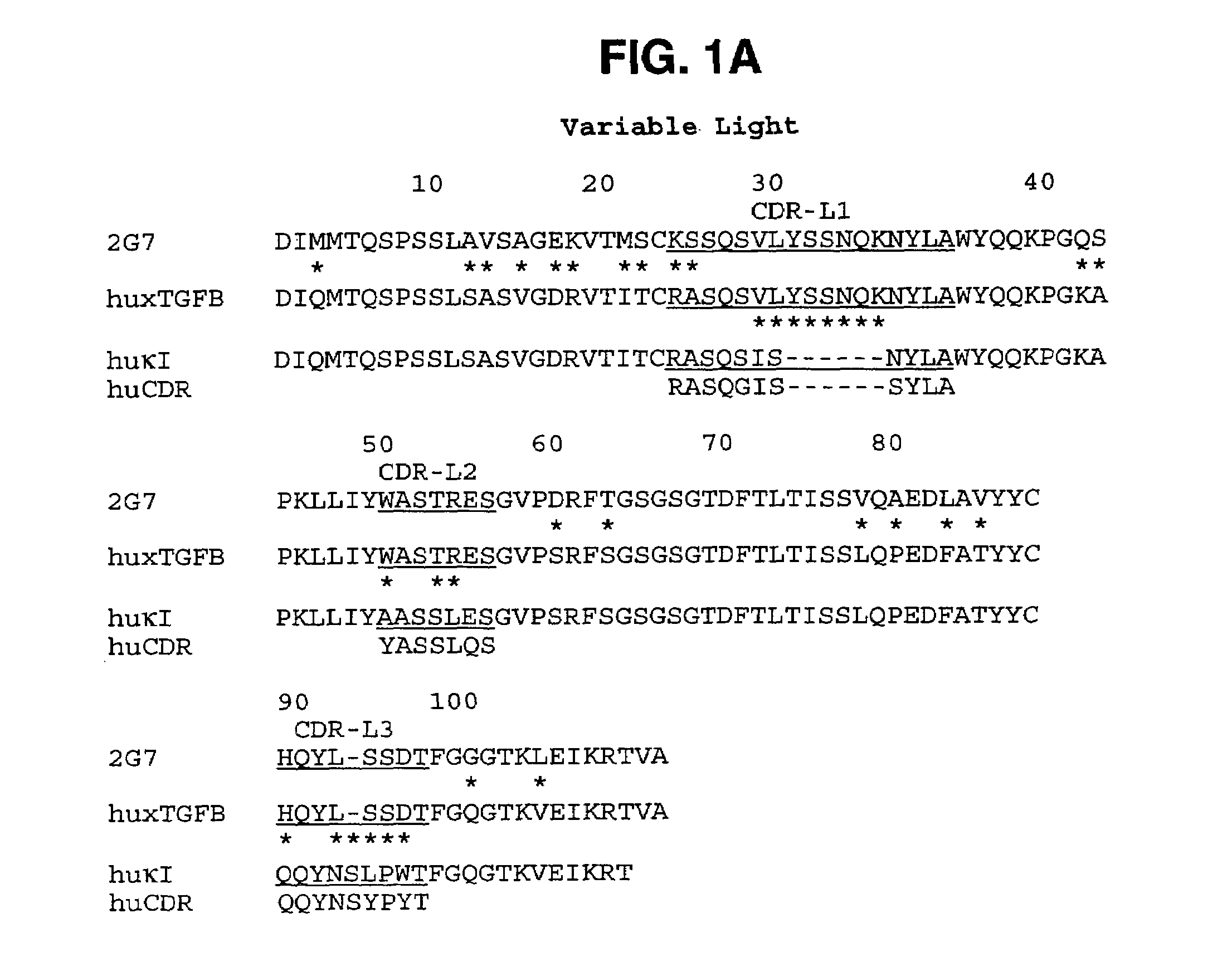
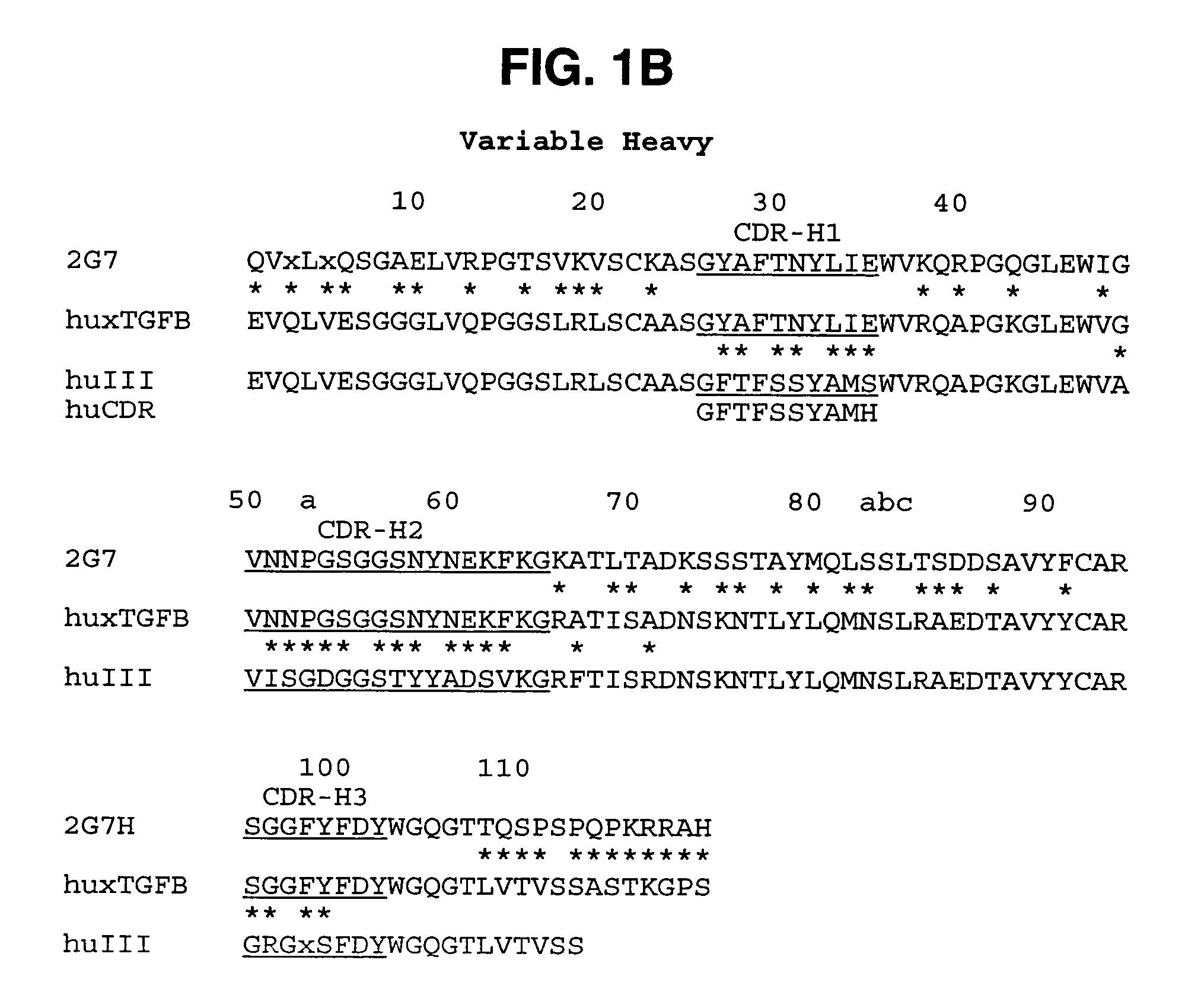
Humanized anti-TGF-beta antibodies
Humanized anti-TGF-beta antibodies are provided, as well as methods for their preparation and use, including methods for treating TGF-beta disorders, for example, cancer. Also provided are articles of manufacture designed for various uses that contain the humanized antibodies.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
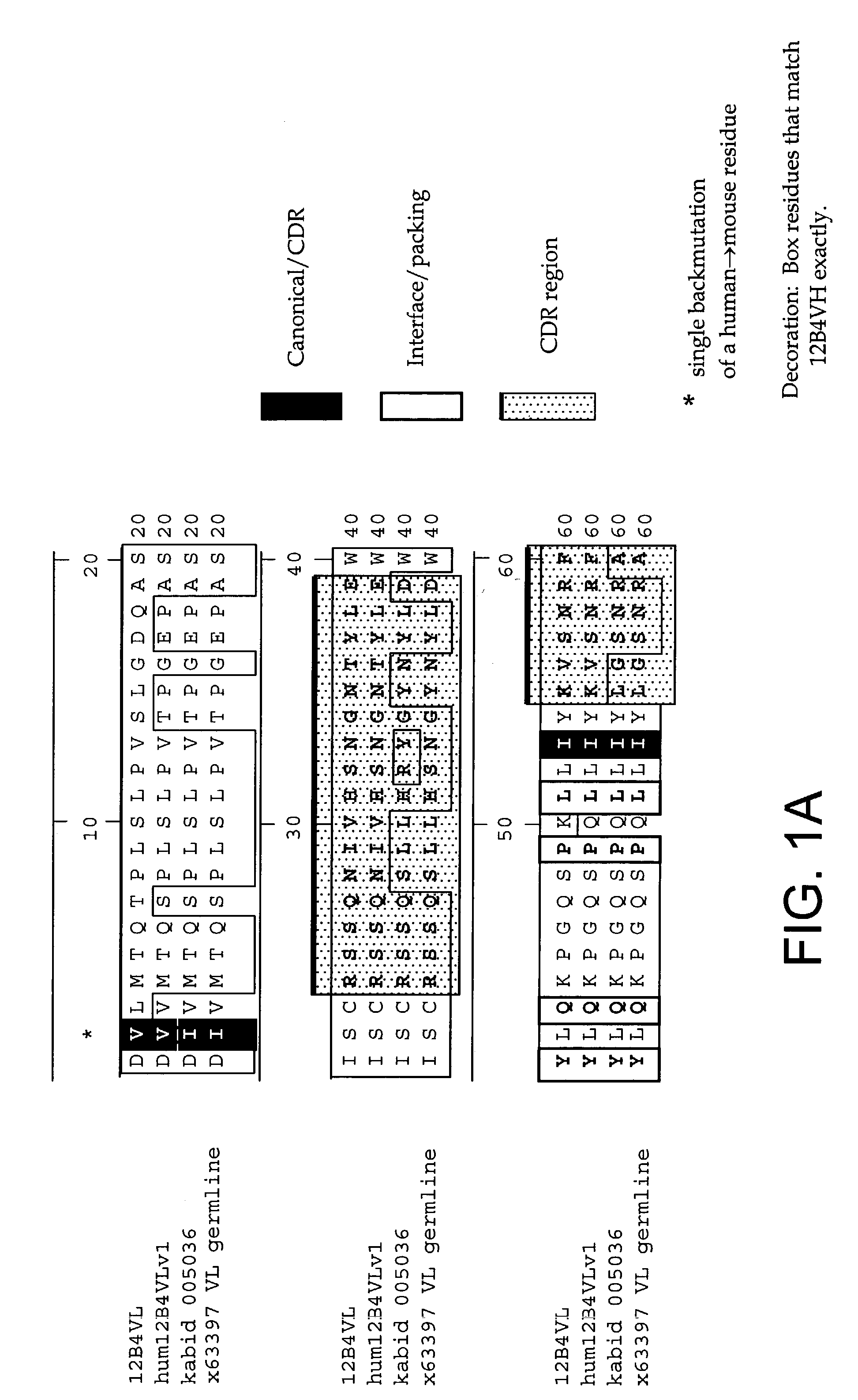
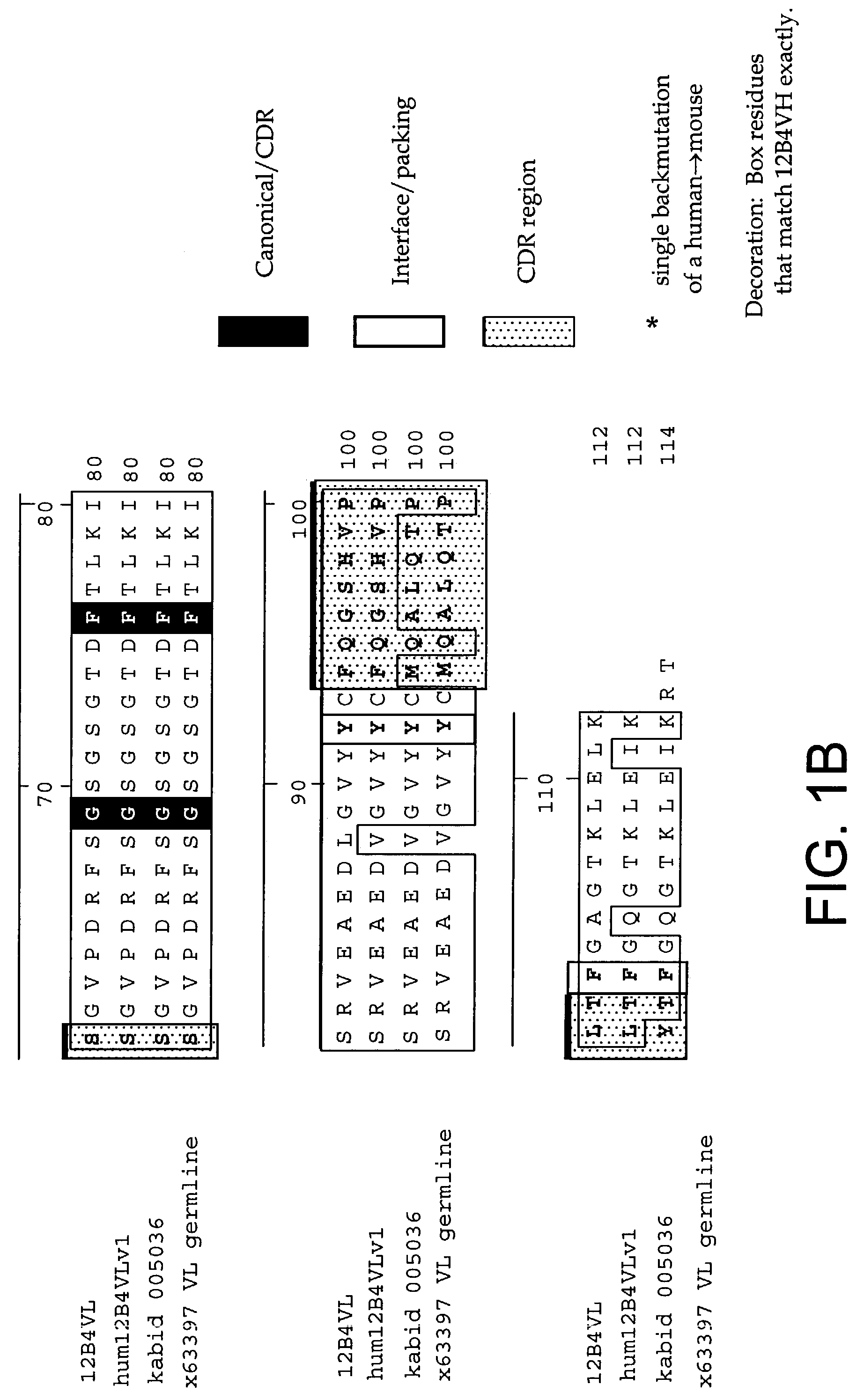
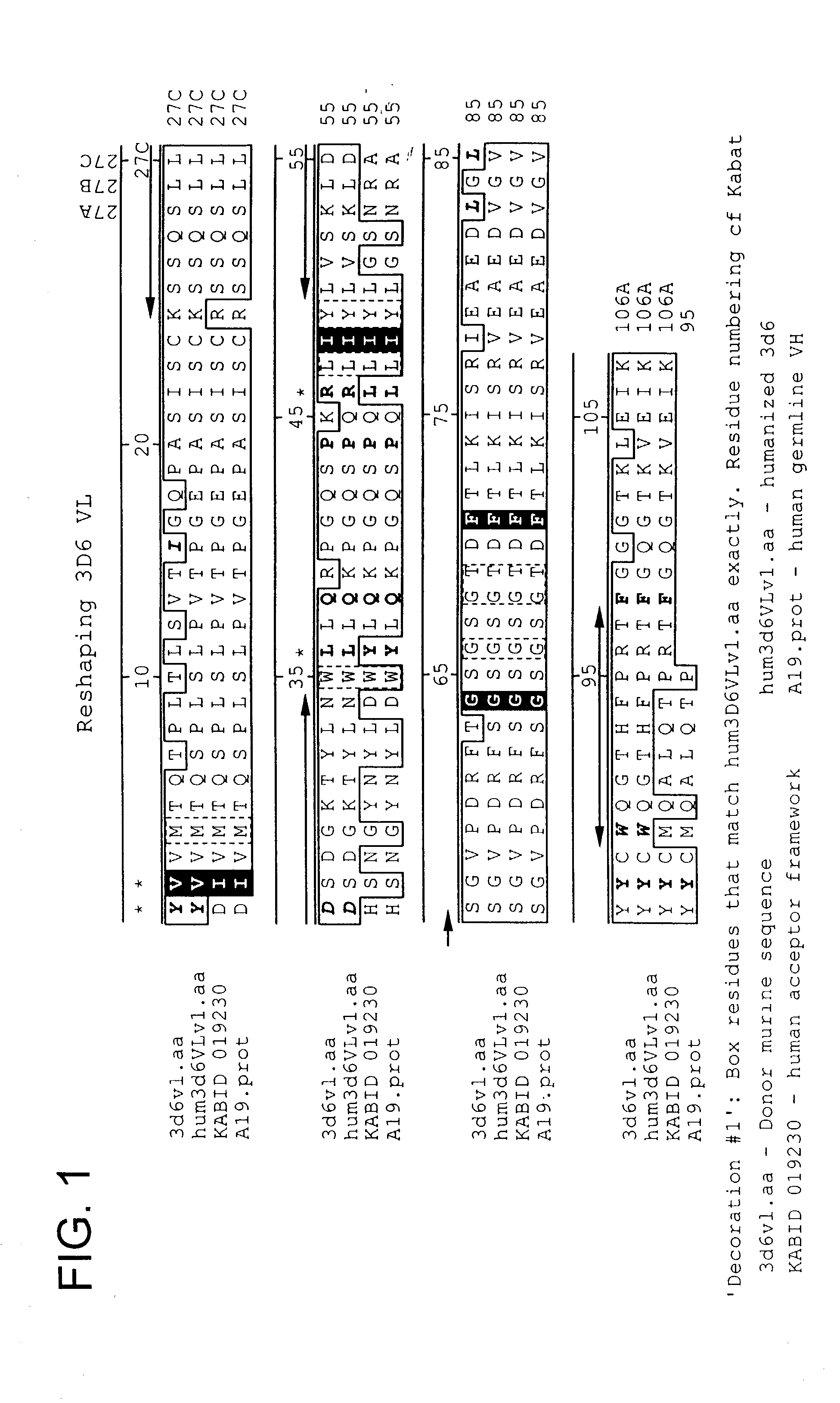
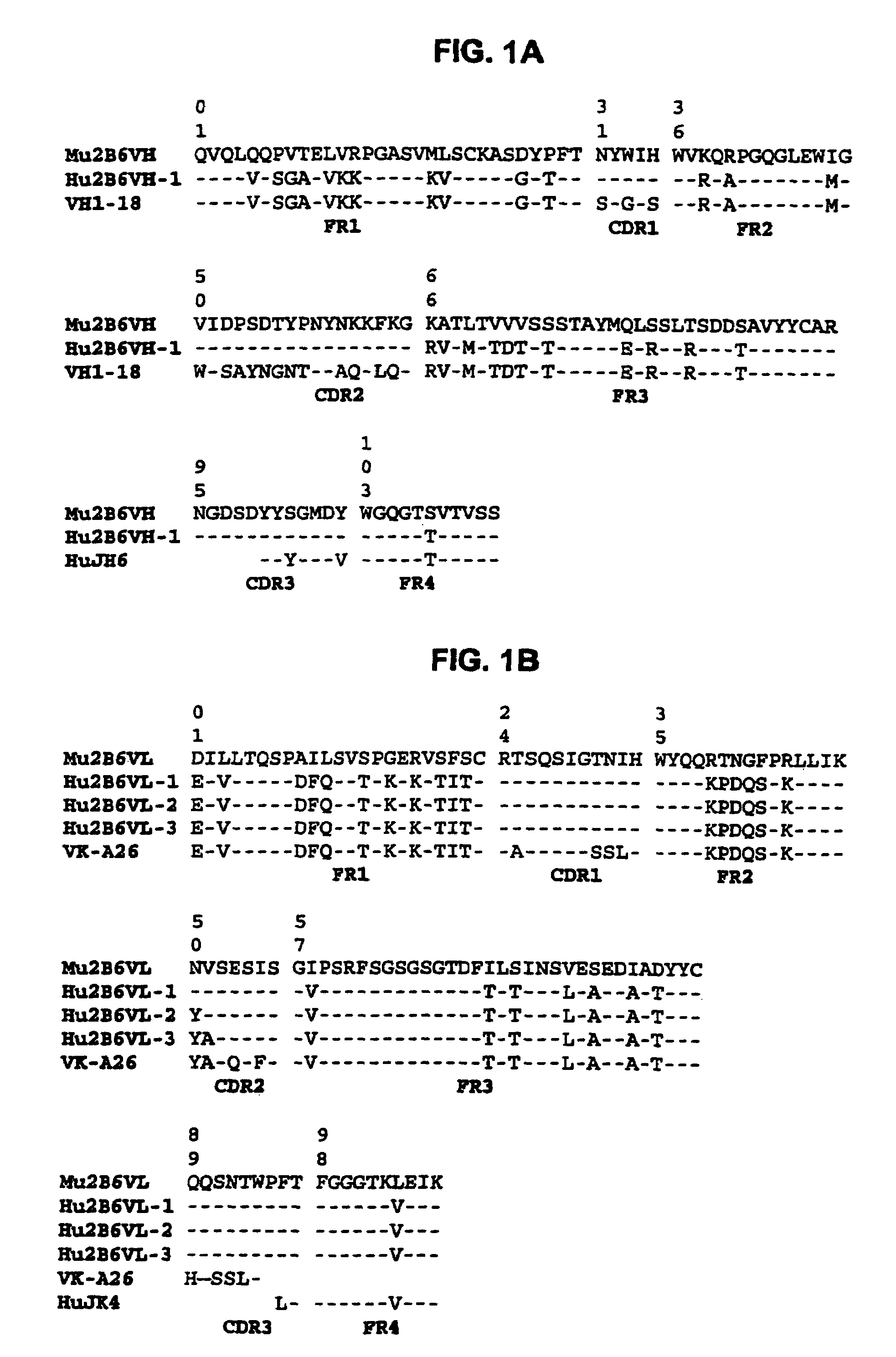
Humanization of antibodies
InactiveUS20050042664A1Limited diversityFast and less labor intensive productionHybrid immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingHumanized antibody
The present invention provides methods of re-engineering or re-shaping an antibody from a first species, wherein the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody does not elicit undesired immune response in a second species, and the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody retains substantially the same antigen binding-ability of the antibody from the first species. In accordance with the present invention, a combinatorial library comprising the CDRs of the antibody from the first species fused in frame with framework regions derived from a second species can be constructed and screened for the desired modified antibody. In particular, the present invention provides methods utilizing low homology acceptor antibody frameworks for efficiently humanizing an antibody or a fragment thereof. The present invention also provides antibodies produced by the methods of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Super humanized antibodies
InactiveUS6881557B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsAnalogue computers for chemical processesHuman sequenceHumanized antibody
Disclosed herein are methods for humanizing antibodies based on selecting variable region framework sequences from human antibody genes by comparing canonical CDR structure types for CDR sequences of the variable region of a non-human antibody to canonical CDR structure types for corresponding CDRs from a library of human antibody sequences, preferably germline antibody gene segments. Human antibody variable regions having similar canonical CDR structure types to the non-human CDRs form a subset of member human antibody sequences from which to select human framework sequences. The subset members may be further ranked by amino acid similarity between the human and the non-human CDR sequences. Top ranking human sequences are selected to provide the framework sequences for constructing a chimeric antibody that functionally replaces human CDR sequences with the non-human CDR counterparts using the selected subset member human frameworks, thereby providing a humanized antibody of high affinity and low immunogenicity without need for comparing framework sequences between the non-human and human antibodies. Chimeric antibodies made according to the method are also disclosed.
Owner:ARROWSMITH TECH
Humanized antibodies to gamma-interferon
The invention provides humanized immunoglobulins that bind to and neutralize gamma-interferon. The antibodies are useful for treatment of diseases of the immune system, particularly autoimmune diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
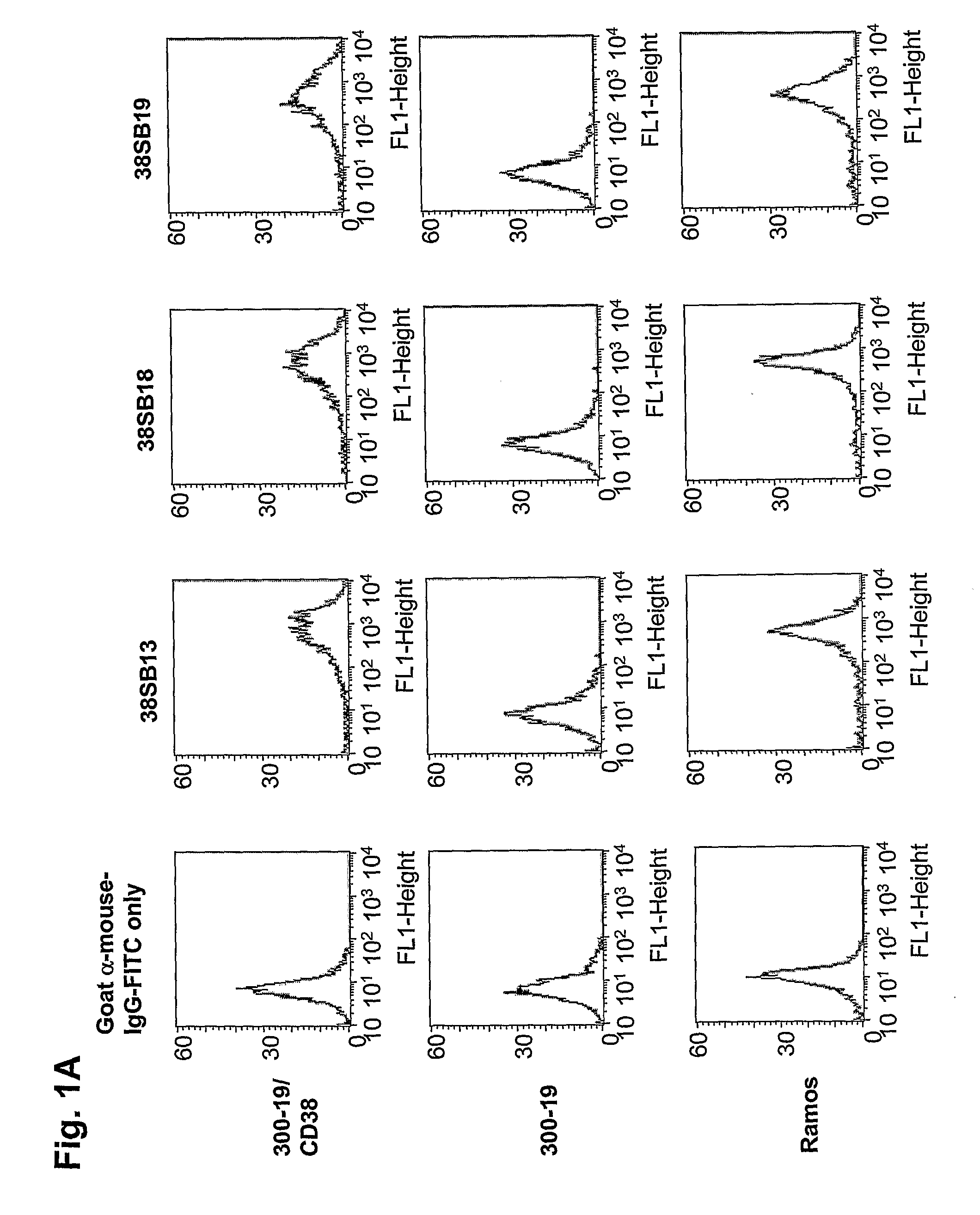
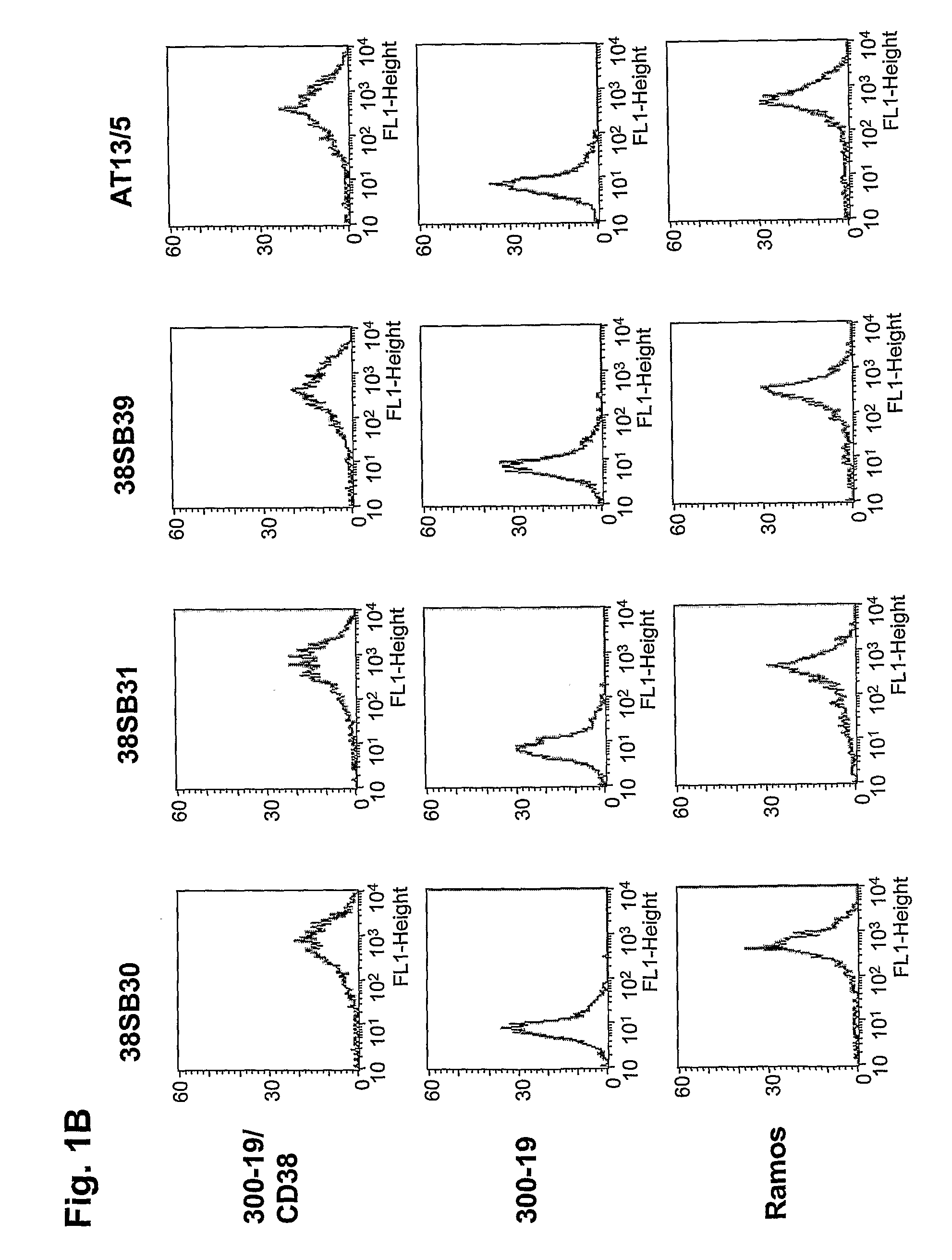
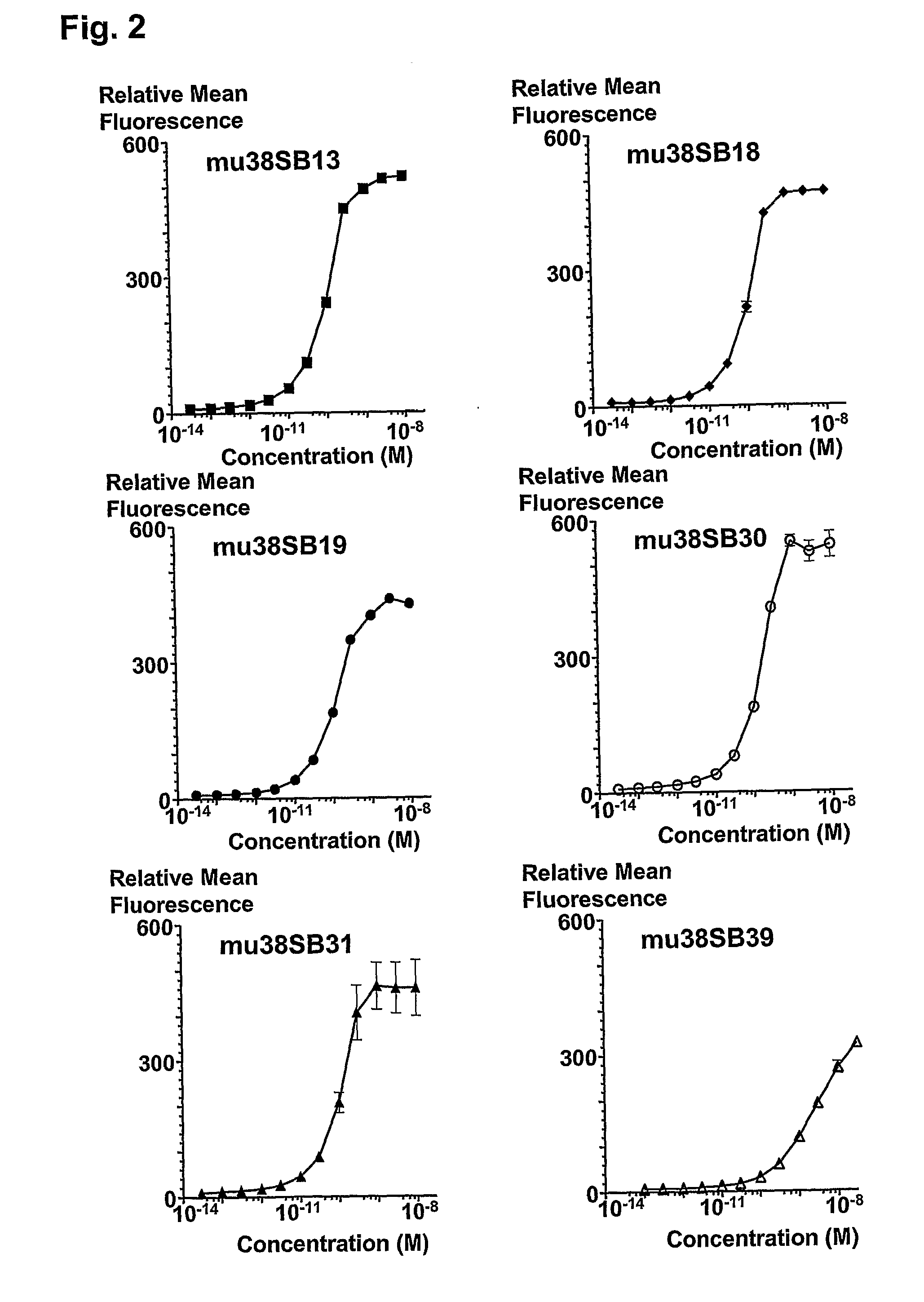
Novel Anti-cd38 antibodies for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20090304710A1Improve propertiesLess immunogenicSenses disorderAntipyreticComplement-dependent cytotoxicityAntibody fragments
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to CD38, are capable of killing CD38+ cells by apoptosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and / or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express CD38 protein, such as multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, or acute lymphocytic leukemia, or the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, erythematosus, and asthma. Said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of CD38. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the CD38 protein.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS US LLC
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20030017534A1Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Antagonist antibody for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20100047257A1High degreeStrong cytotoxicitySugar derivativesBiological material analysisSynovial sarcomaAntibody fragments
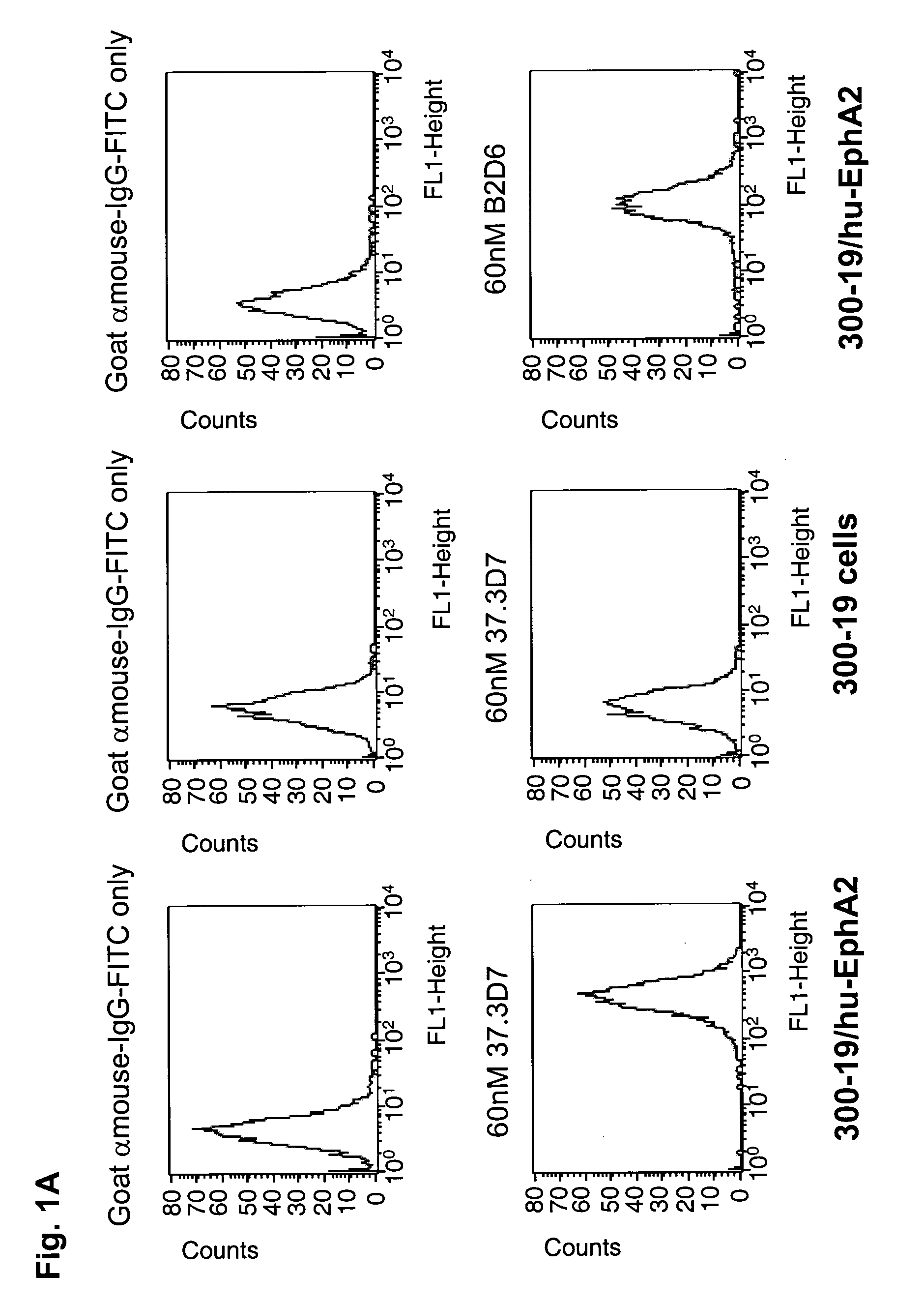
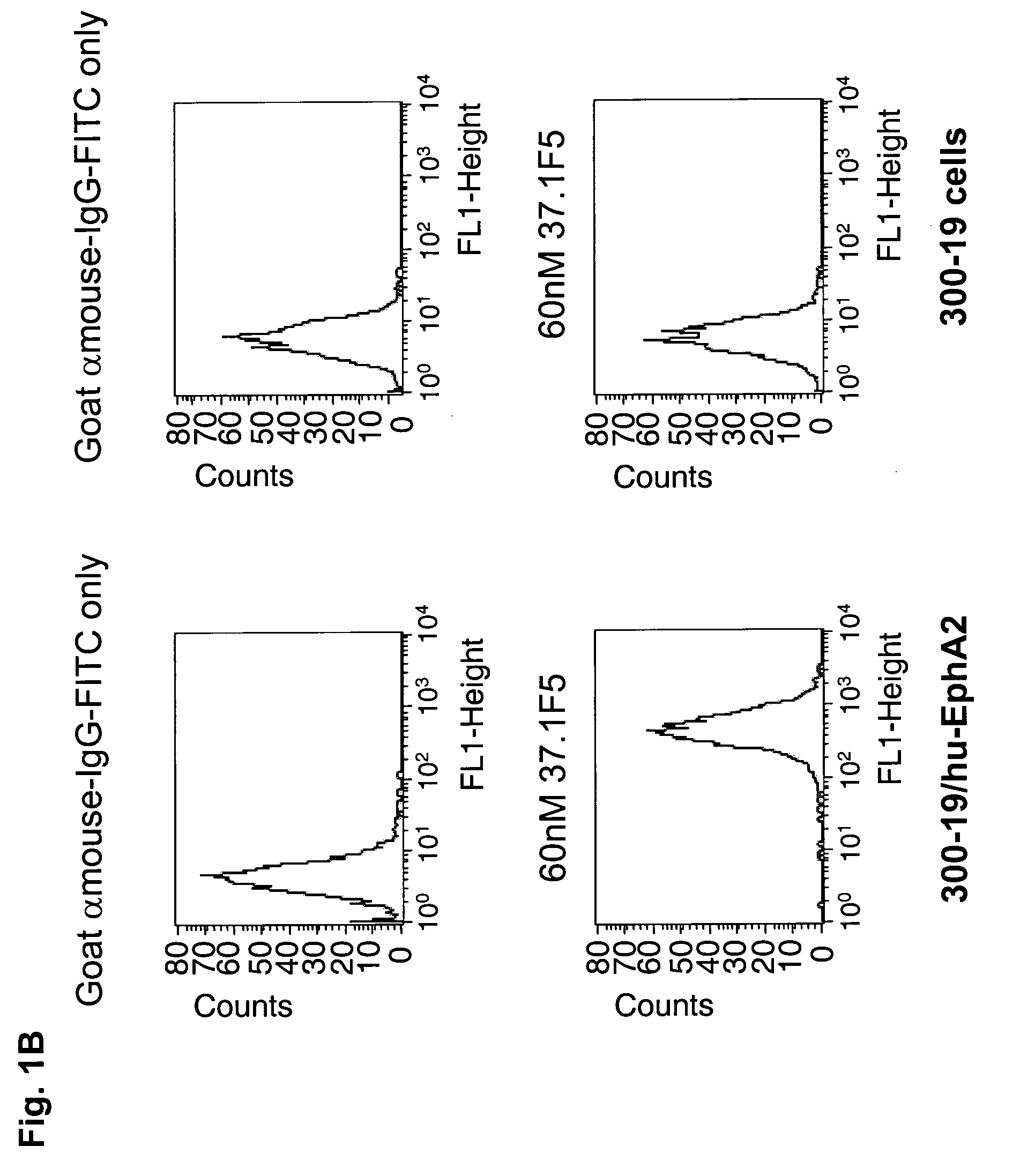
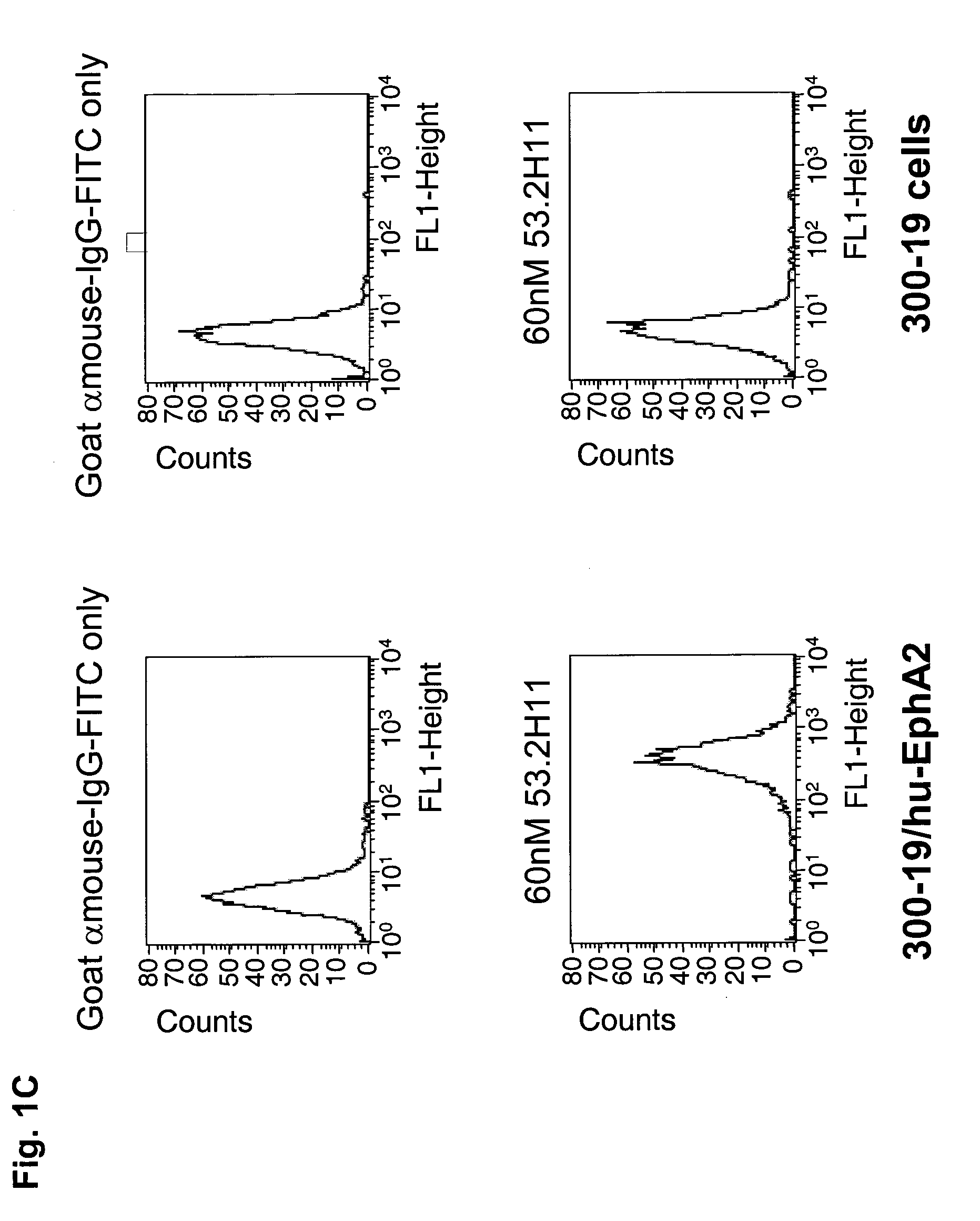
Antibodies, humanized antibodies, resurfaced antibodies, antibody fragments, derivatized antibodies, and conjugates of same with cytotoxic agents, which specifically bind to, and inhibit A class of Eph receptors, antagonize the effects of growth factors on the growth and survival of tumor cells, and which have minimal agonistic activity or are preferentially devoid of agonist activity. Said antibodies and fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of tumors that express elevated levels of A class of Eph receptors, such as breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, ovarian carcinoma, synovial sarcoma and pancreatic cancer, and said derivatized antibodies may be used in the diagnosis and imaging of tumors that express elevated levels of A class of Eph receptors. Also provided are cytotoxic conjugates comprising a cell binding agent and a cytotoxic agent, therapeutic compositions comprising the conjugate, methods for using the conjugates in the inhibition of cell growth and the treatment of disease, and a kit comprising the cytotoxic conjugate are disclosed are all embodiments of the invention. In particular, the cell binding agent is a monoclonal antibody, and epitope-binding fragments thereof, that recognizes and binds the A class of Eph receptors.
Owner:SANOFI SA
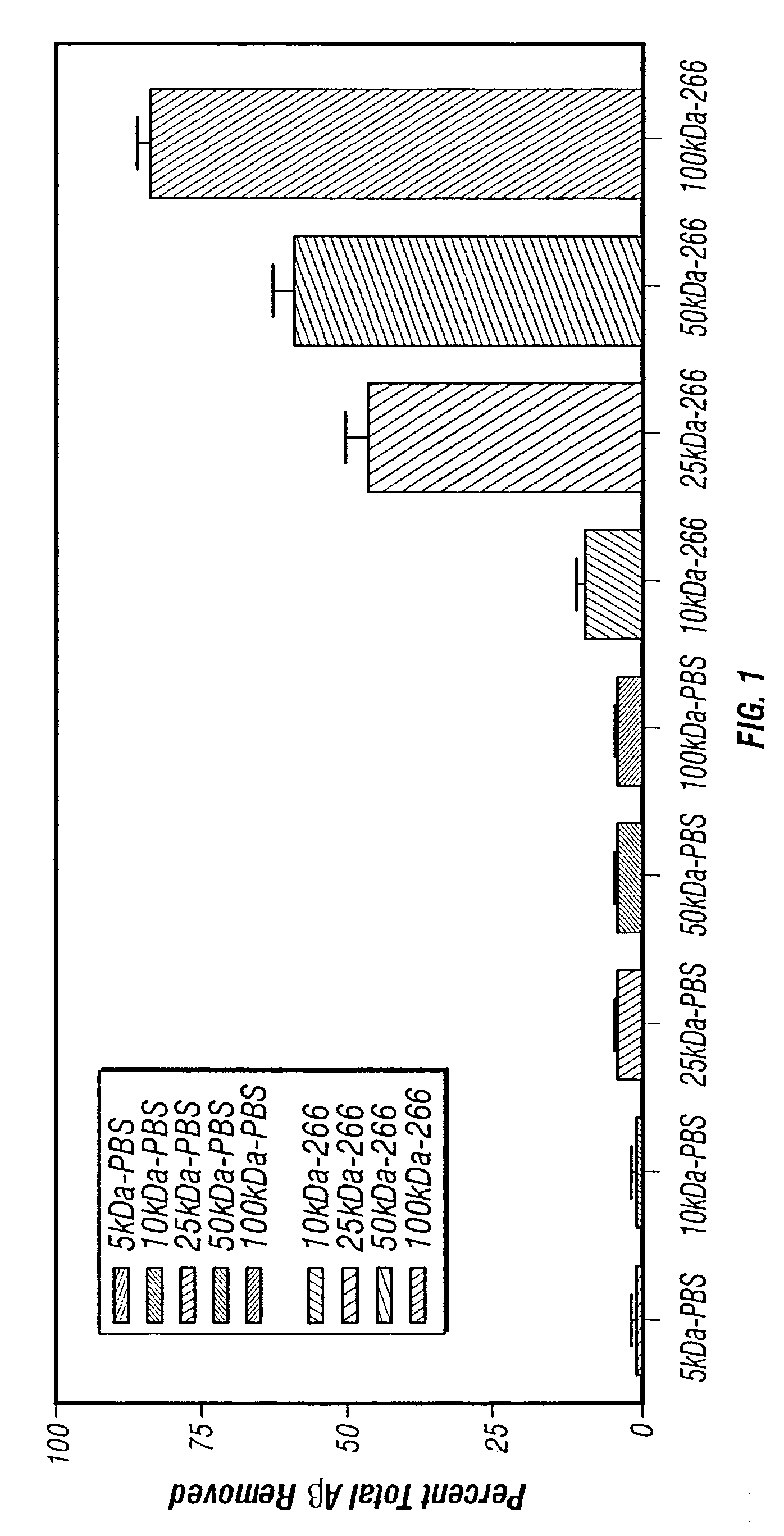
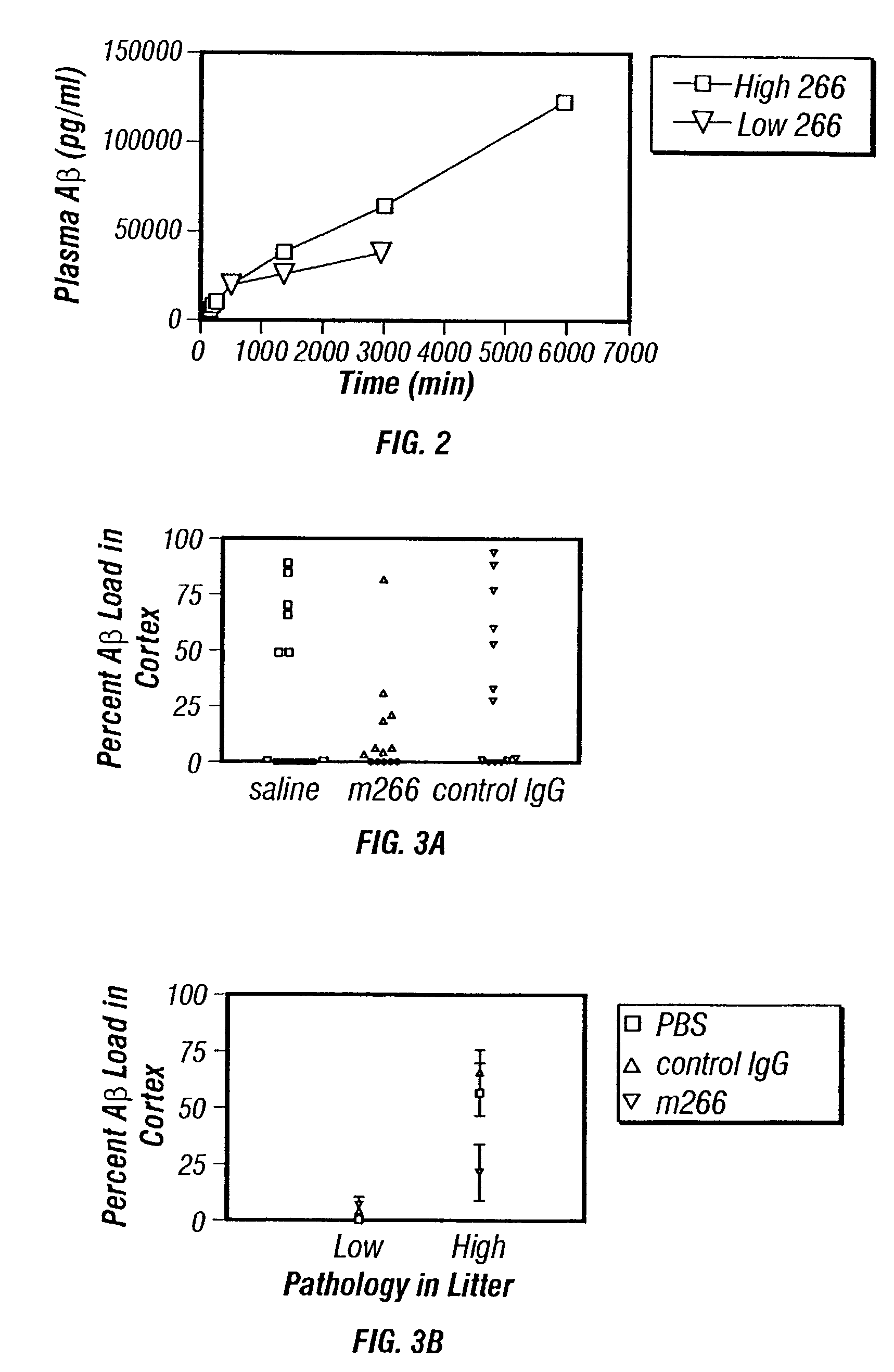
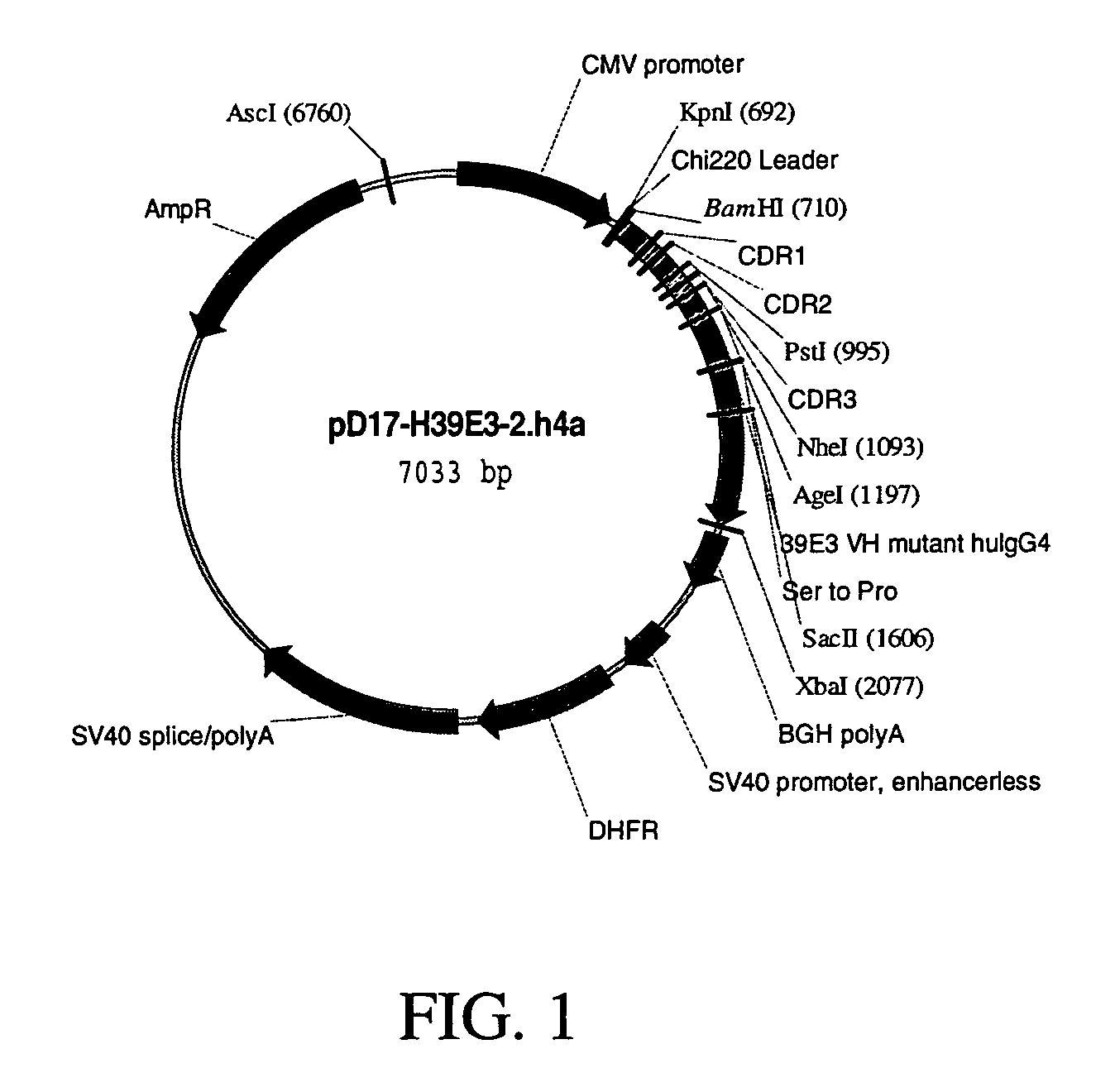
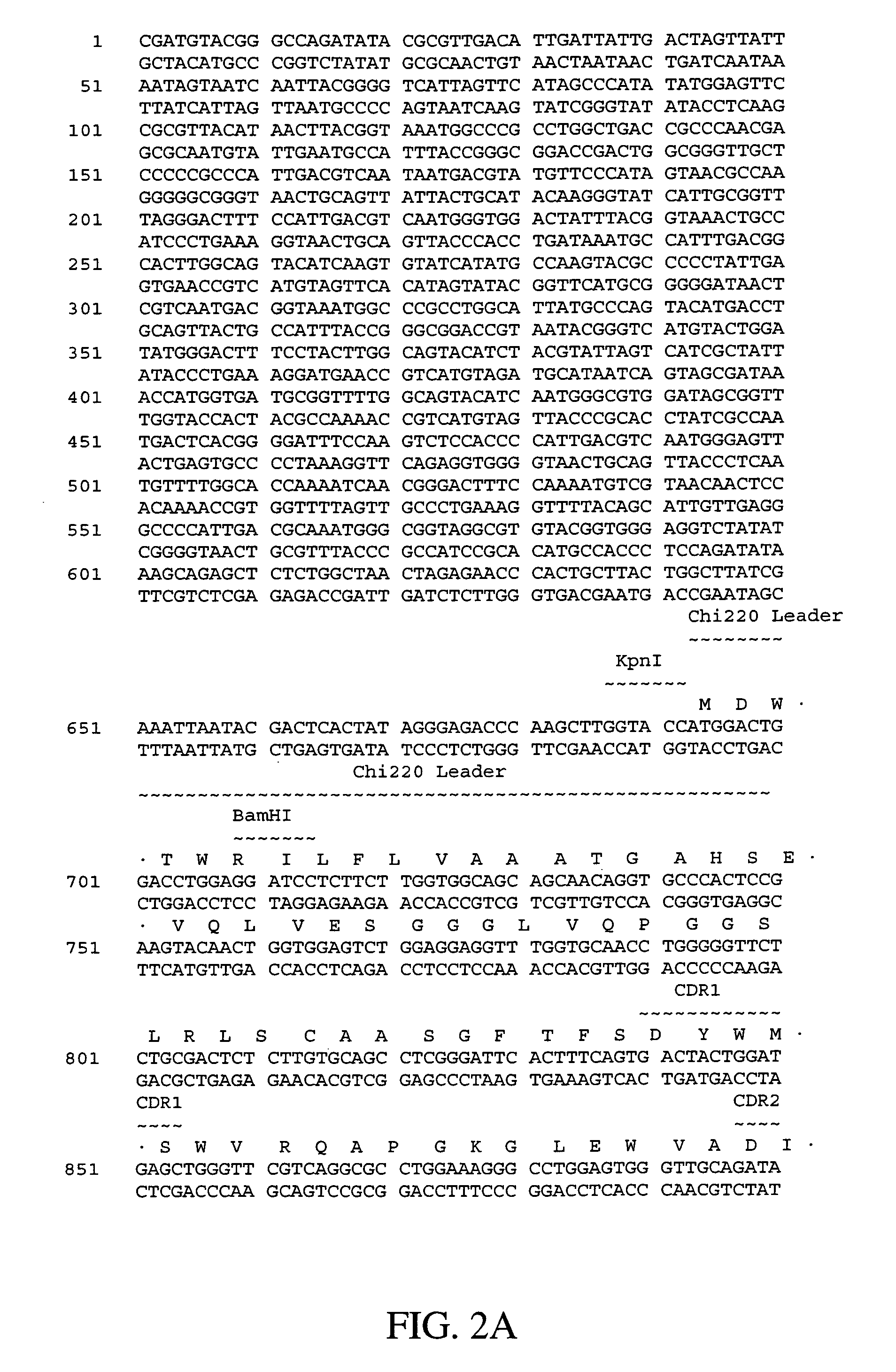
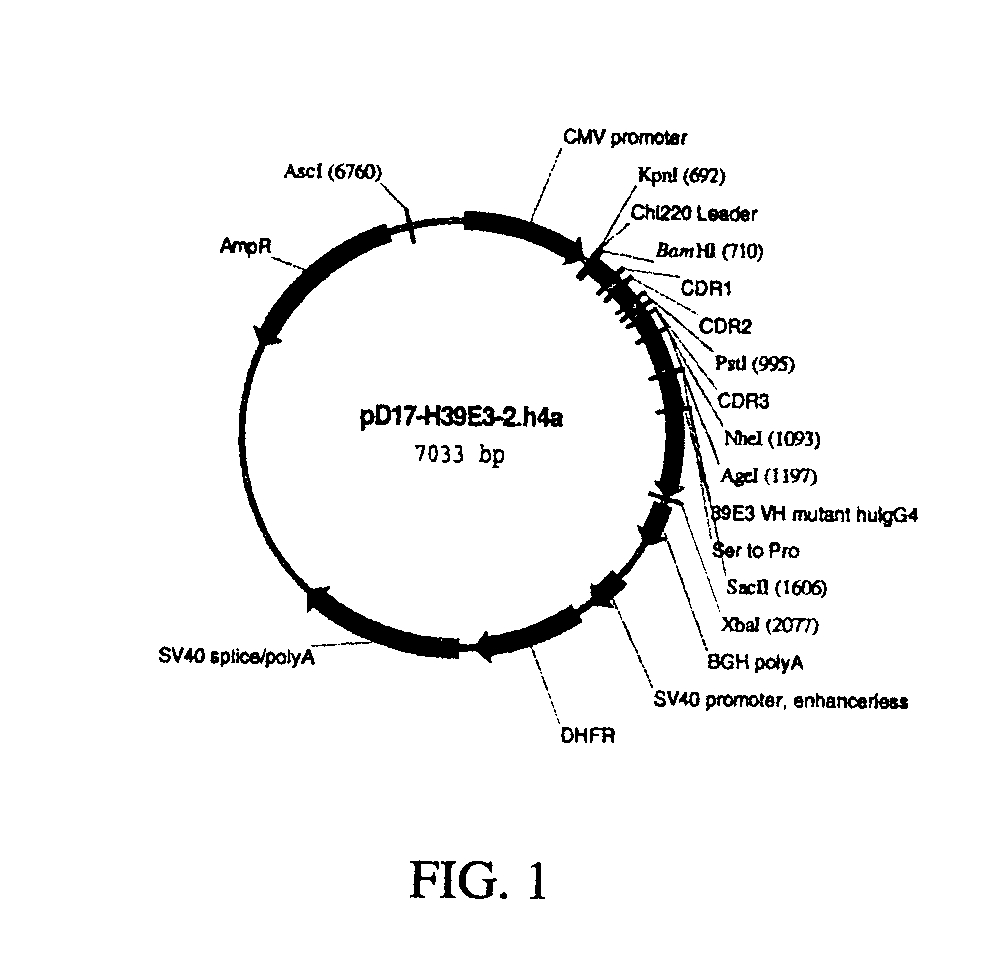
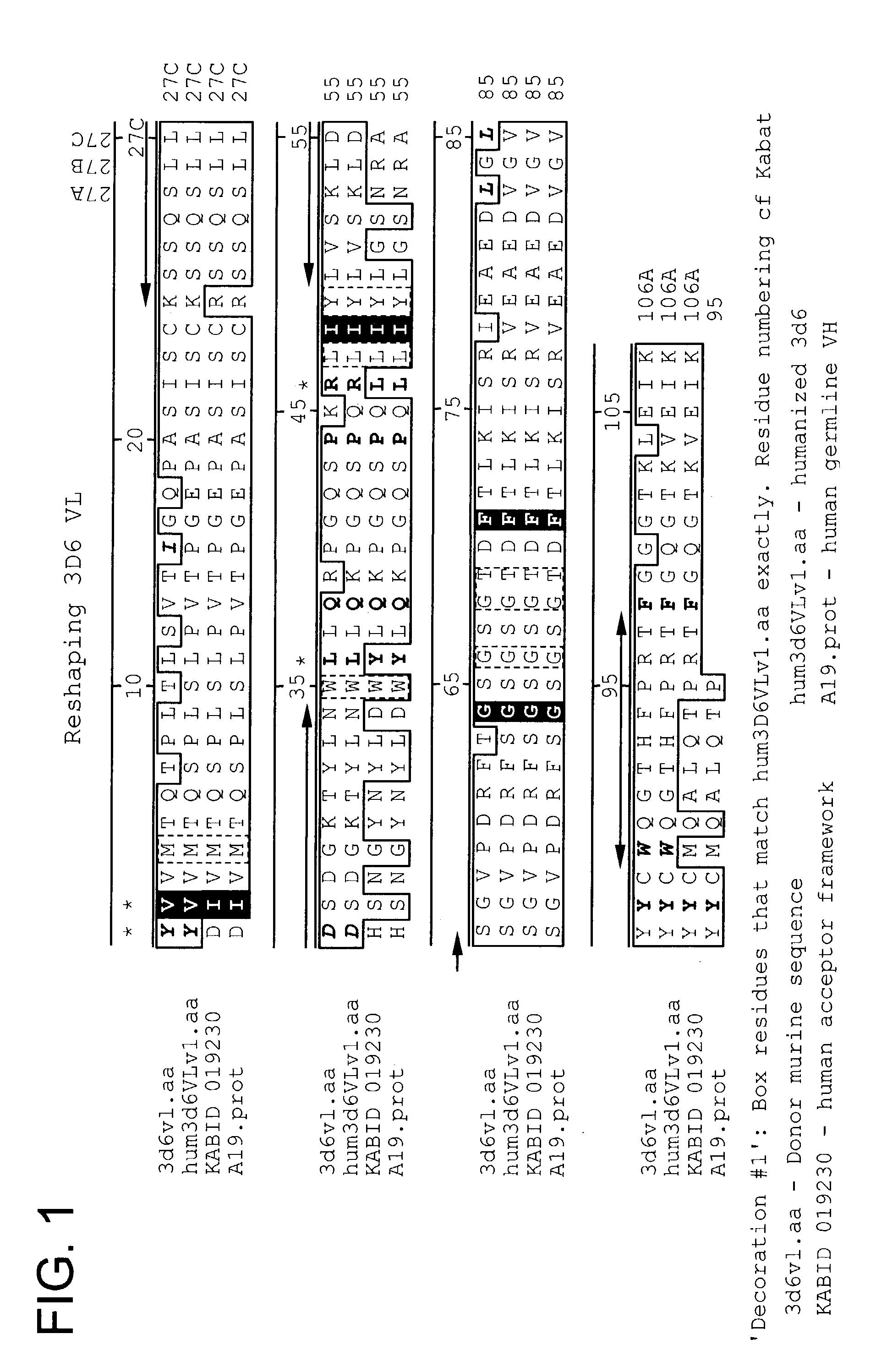
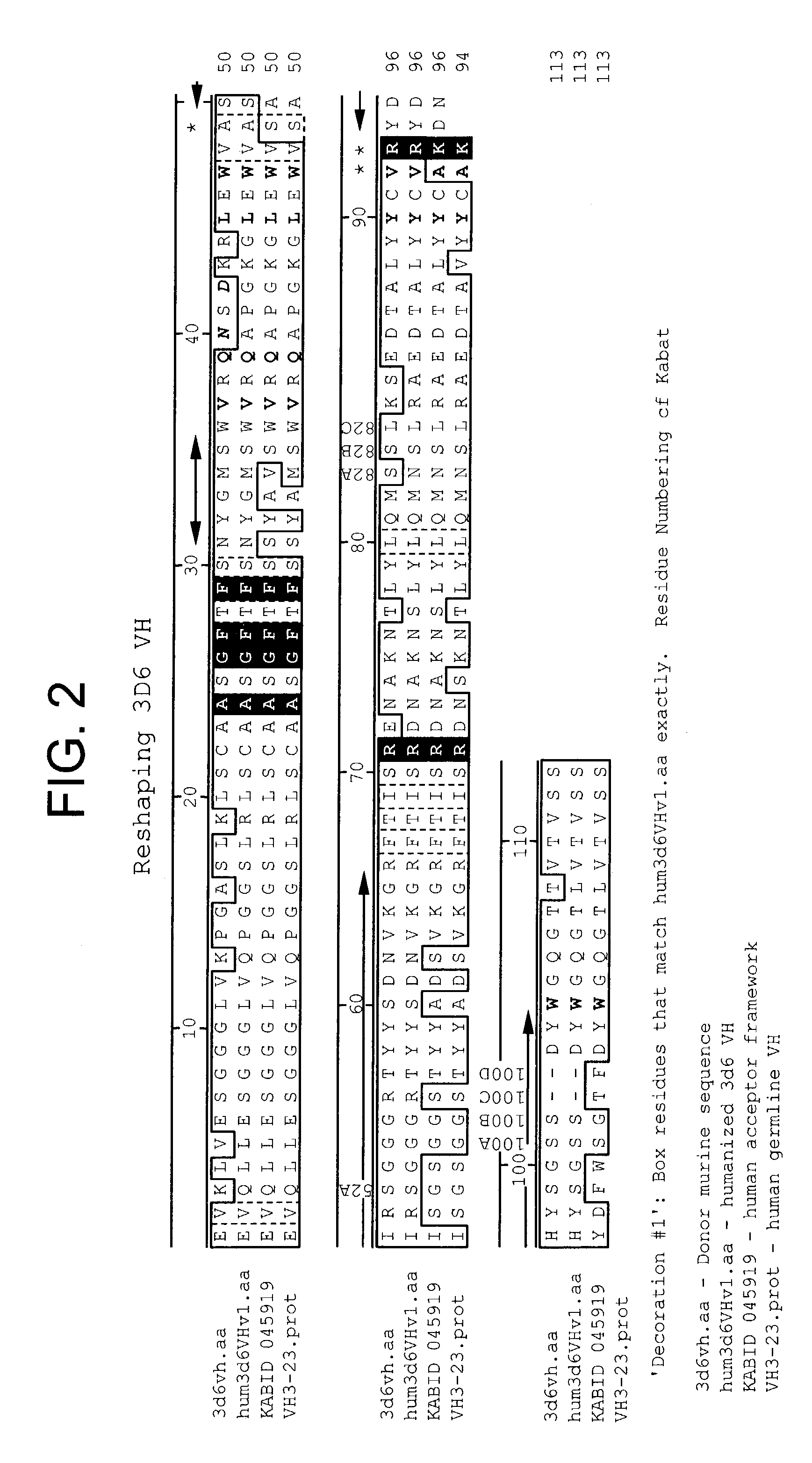
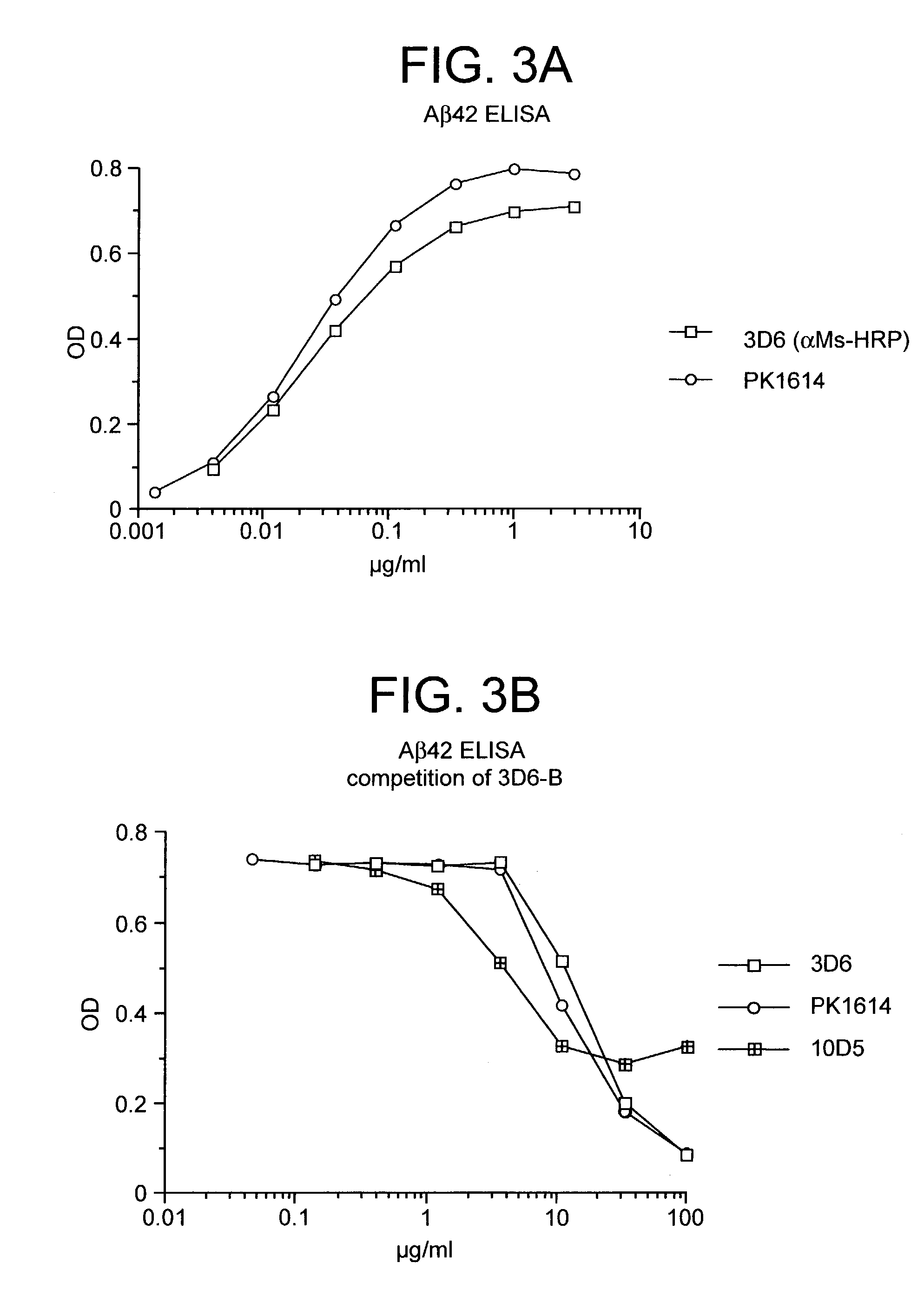
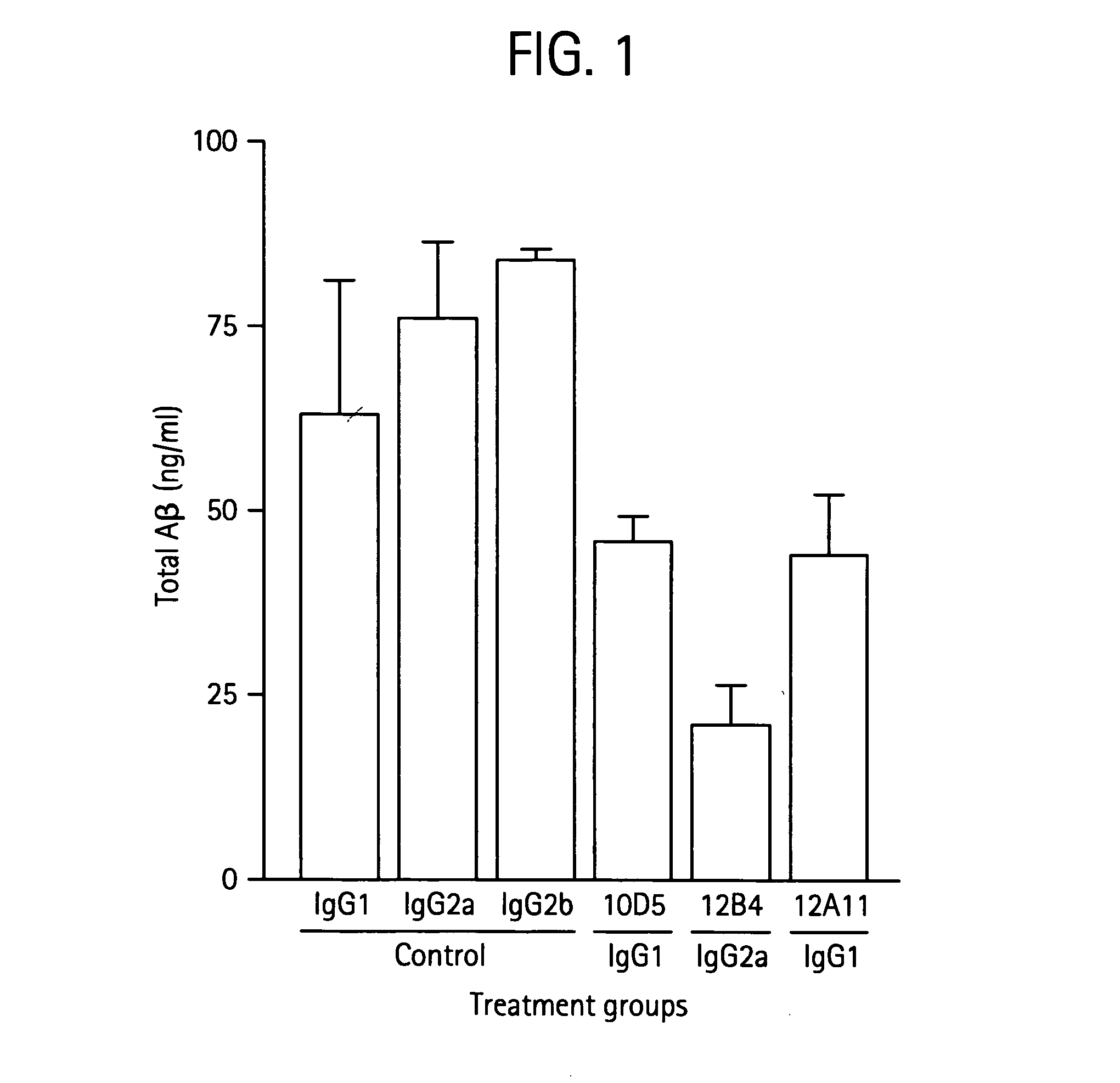
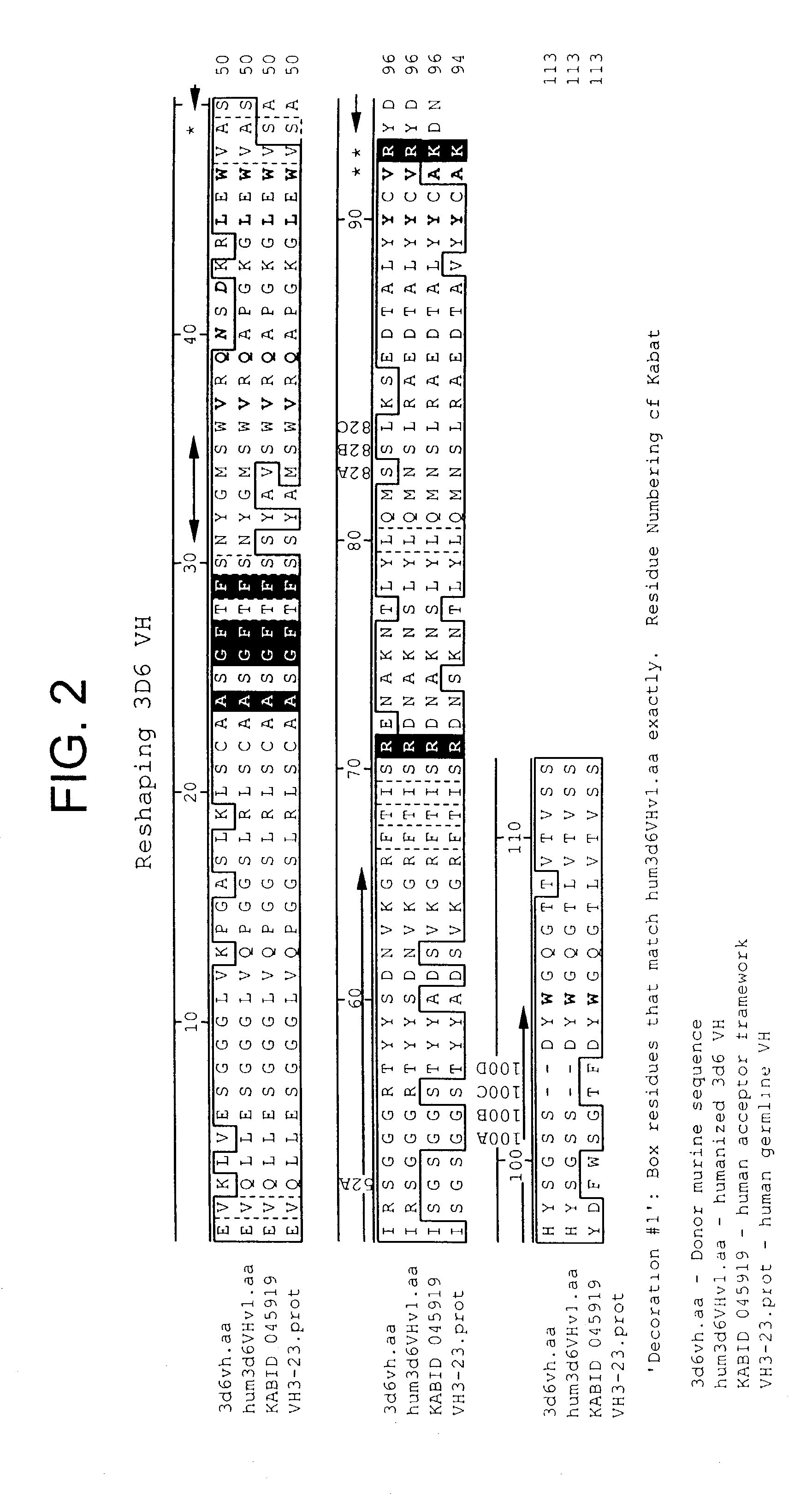
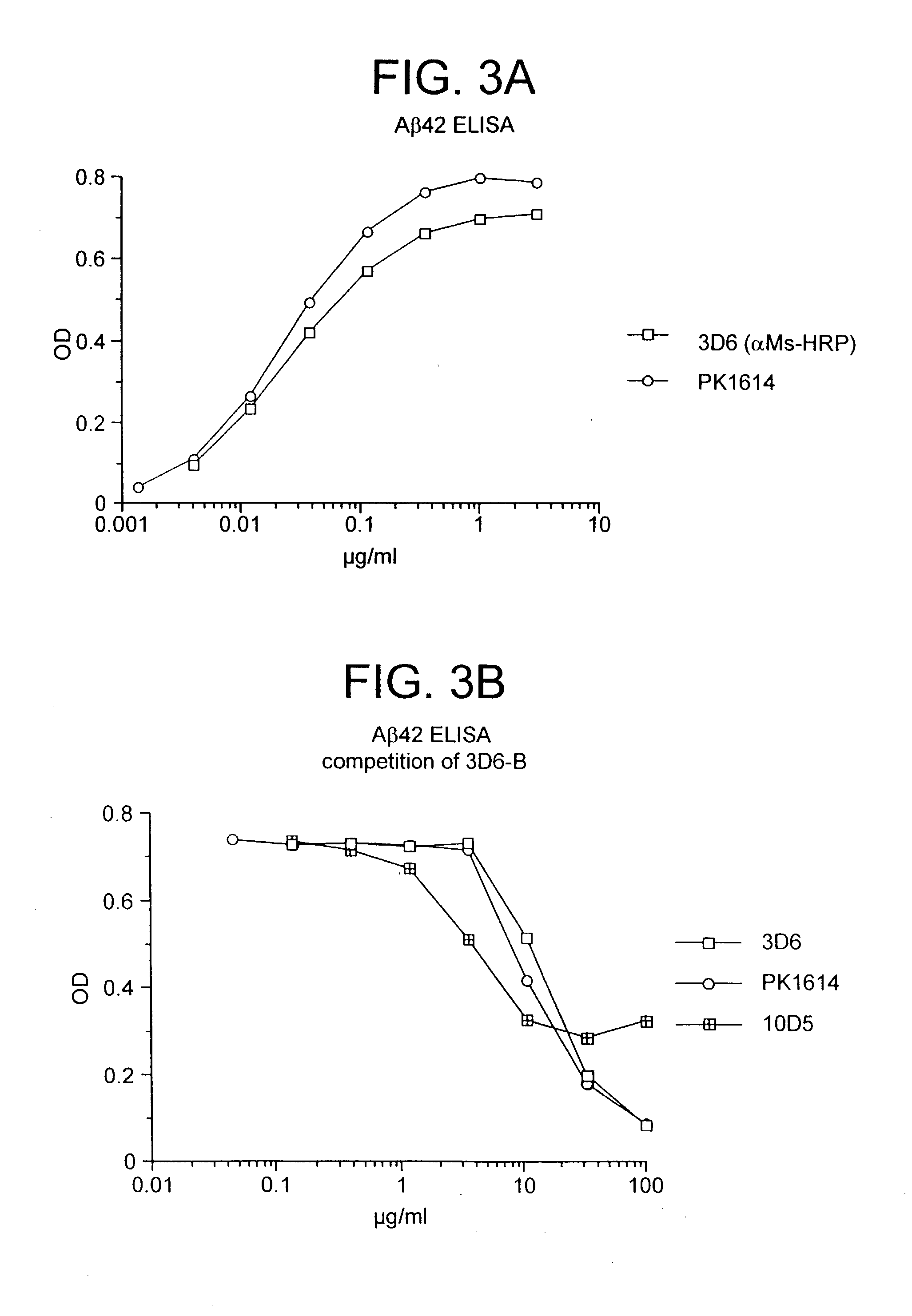
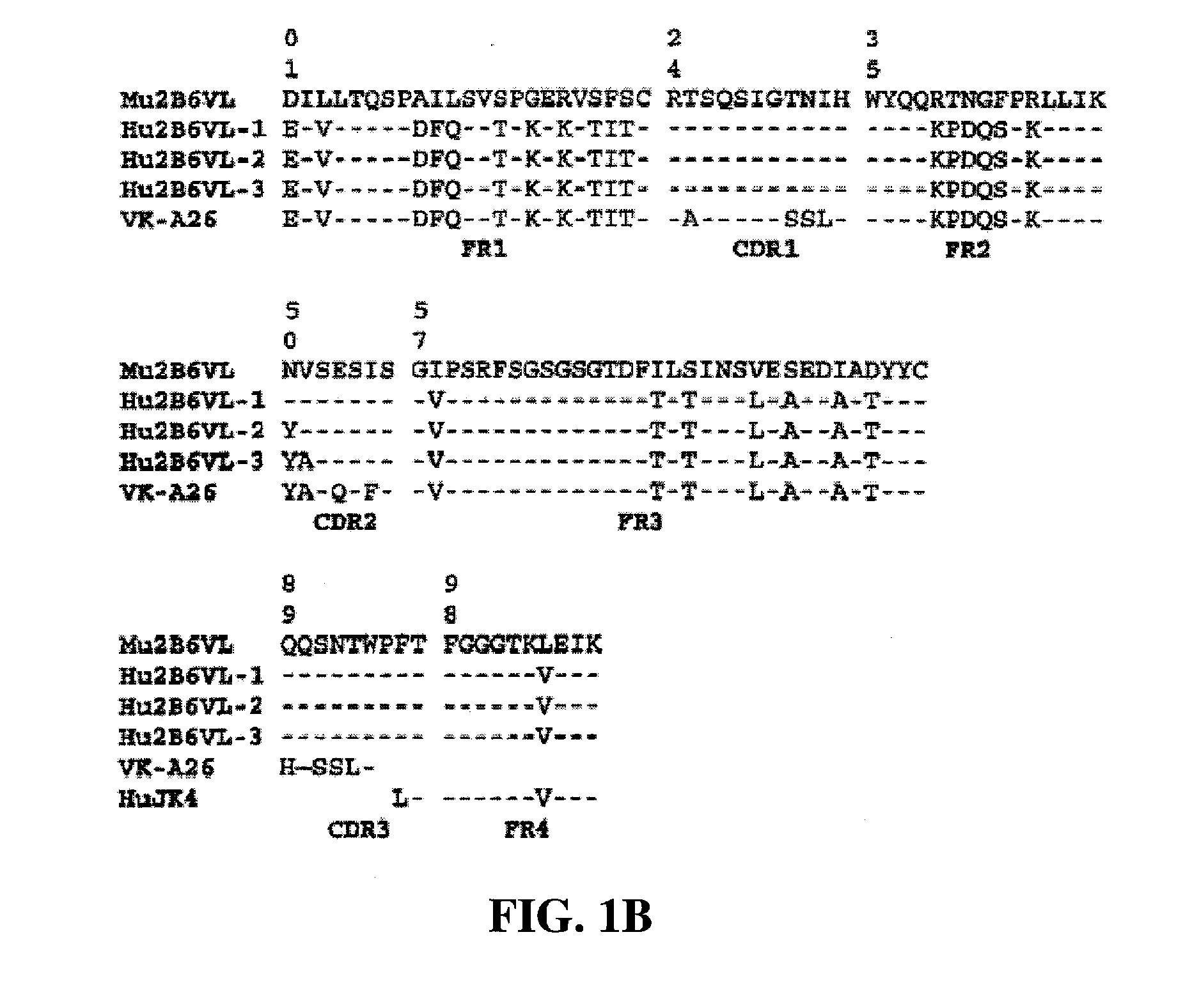
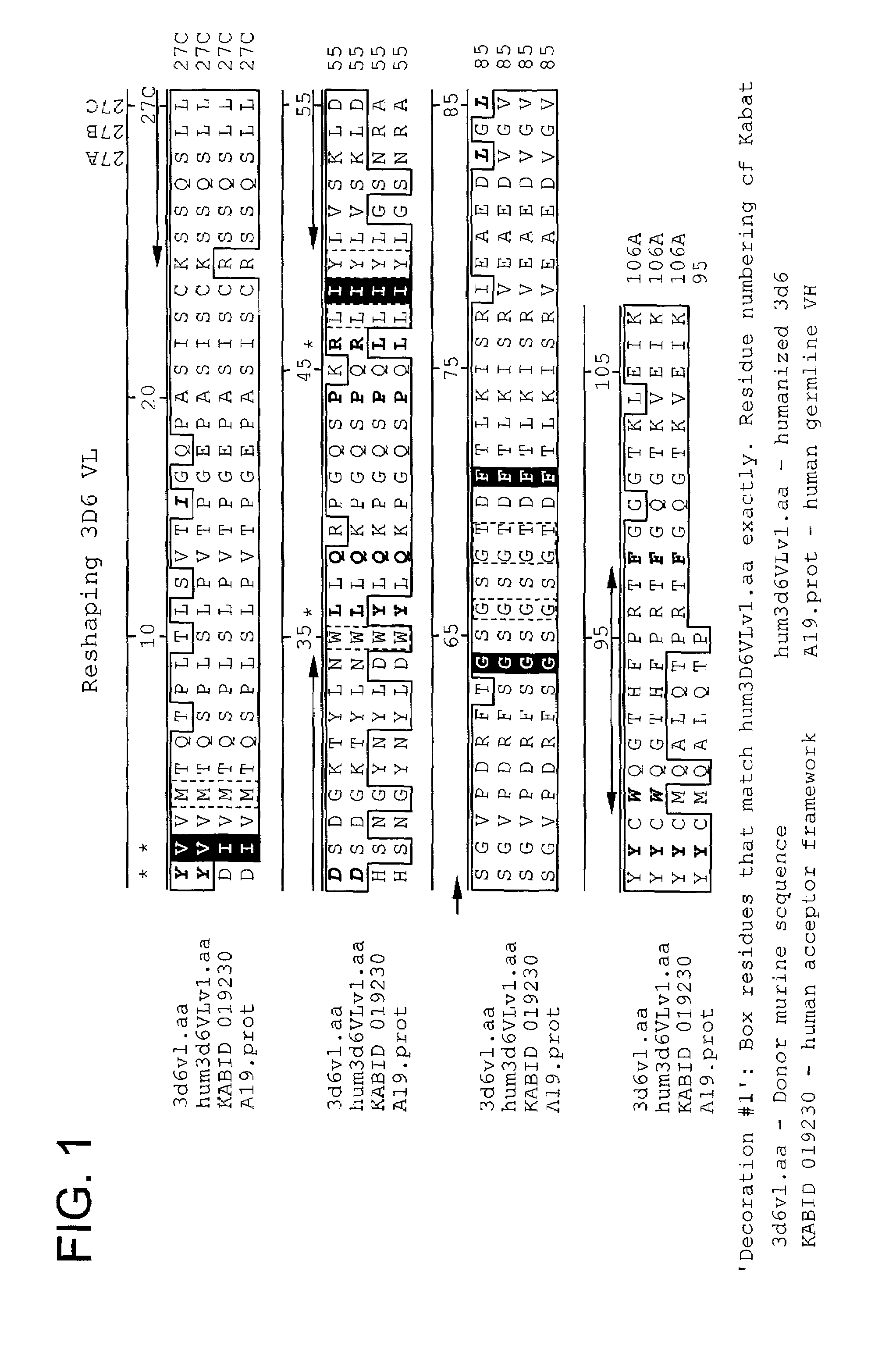
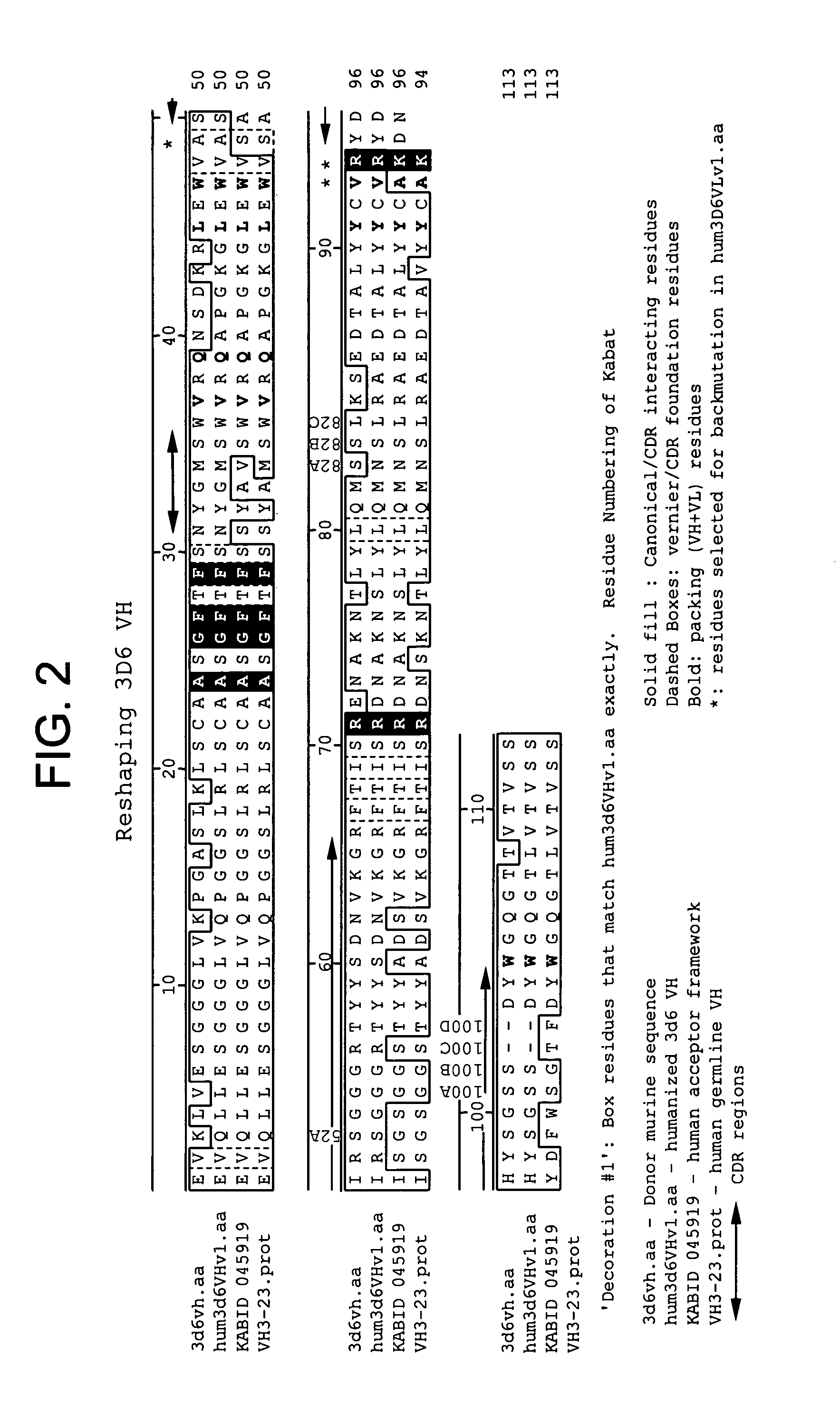
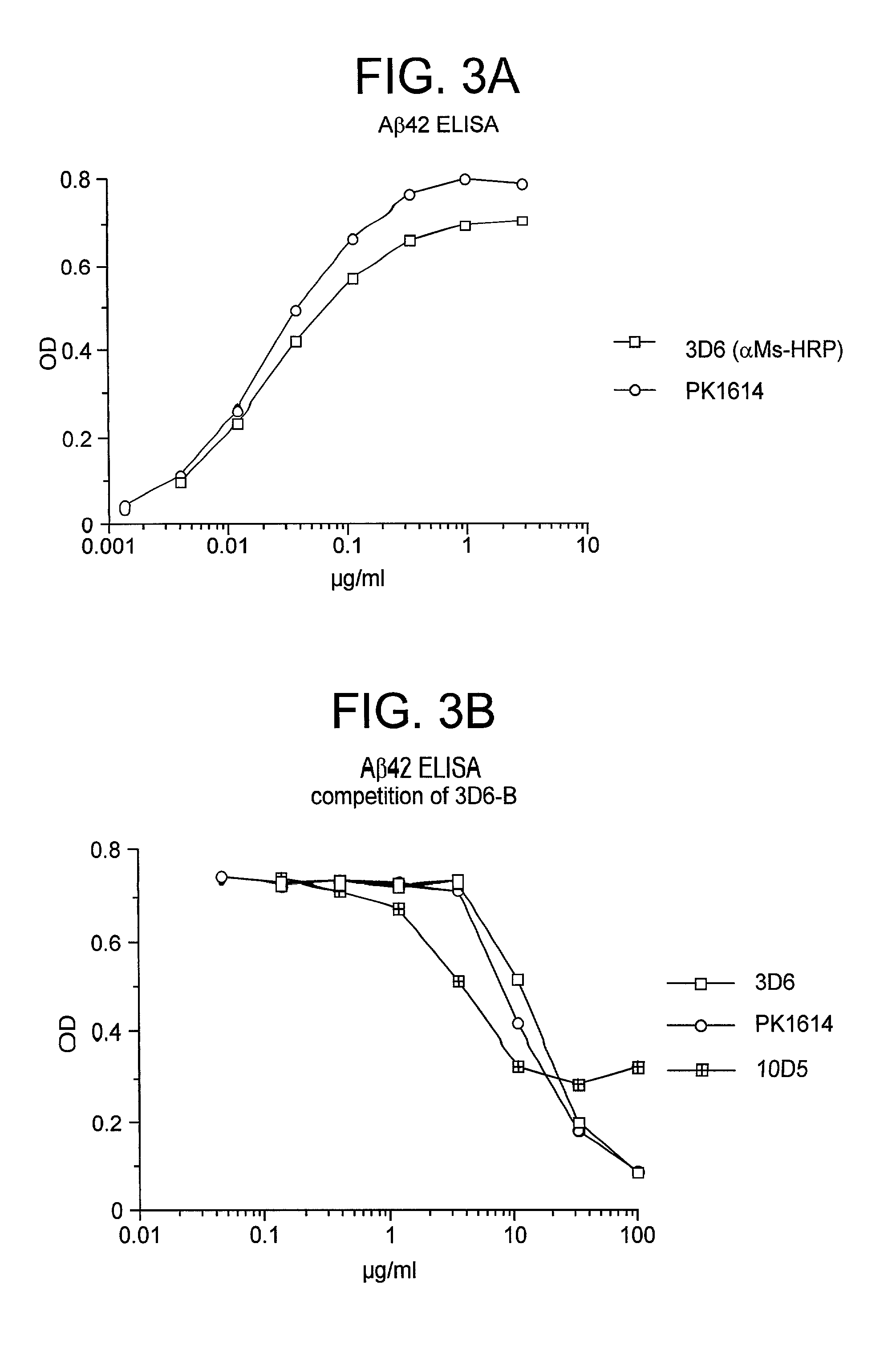
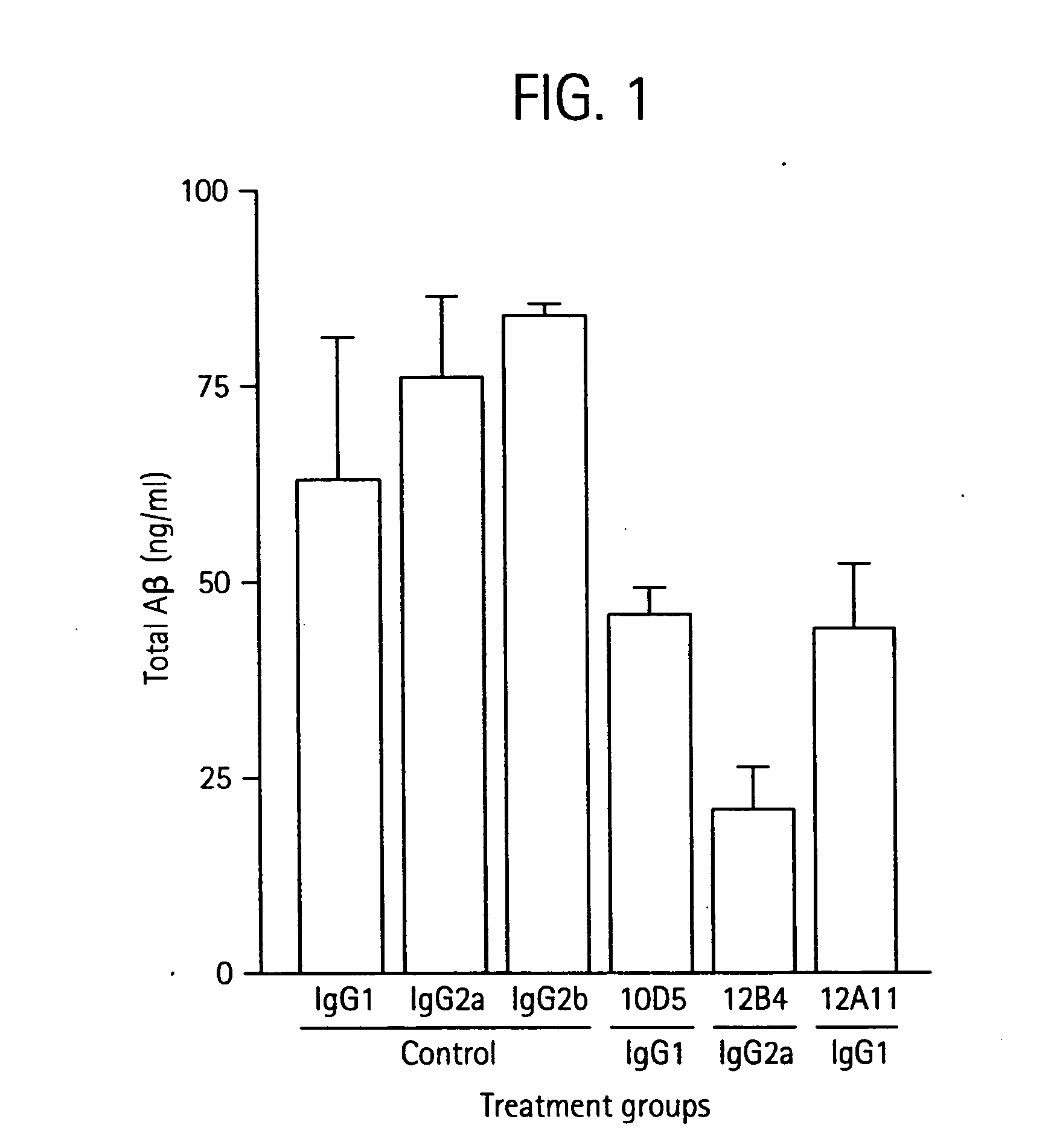
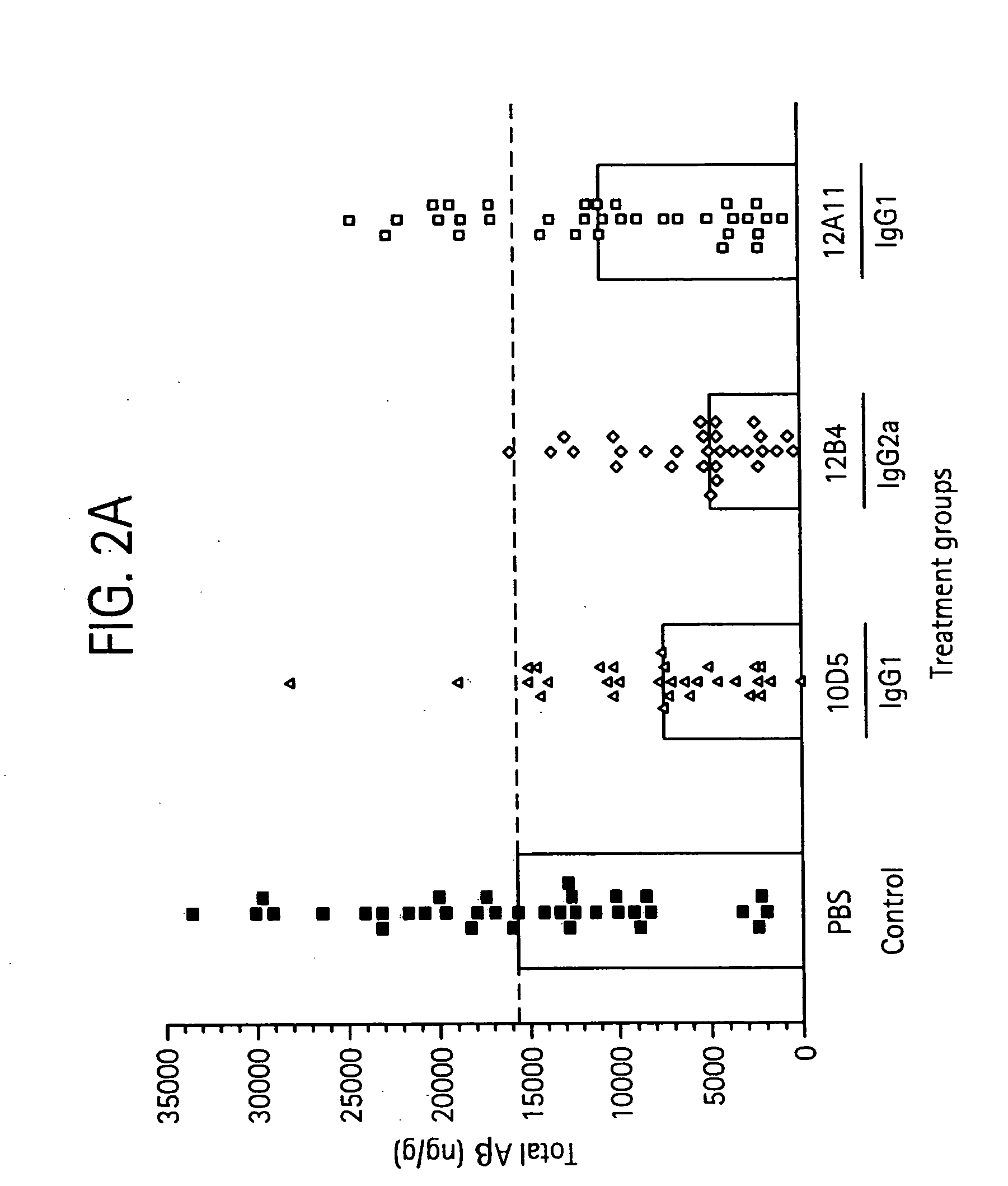
Humanized antibodies that sequester abeta peptide
A method to treat conditions characterized by formation of amyloid plaques both prophylactically and therapeutically is described. The method employs humanized antibodies which sequester soluble Aβ peptide from human biological fluids or which preferably specifically bind an epitope contained within position 13–28 of the amyloid beta peptide Aβ.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO +1
Polynucleotides encoding humanized antibodies against human 4-1BB
A humanized antibody that binds to human 4-1BB and that allows binding of human 4-1BB to a human 4-1BB ligand. In one aspect, the antibody is an IgG4 antibody. Also provided is a method for treating cancer in a subject comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of the antibody to said subject.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Humanized antibodies against human 4-1BB
ActiveUS6887673B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentation4-1BB ligandHumanized antibody
A humanized antibody that binds to human 4-1BB and that allows binding of human 4-1BB to a human 4-1BB ligand. In one aspect, the antibody is an IgG4 antibody. Also provided is a method for treating cancer in a subject comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of the antibody to said subject.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Humanized antibodies that recognize beta amyloid peptide
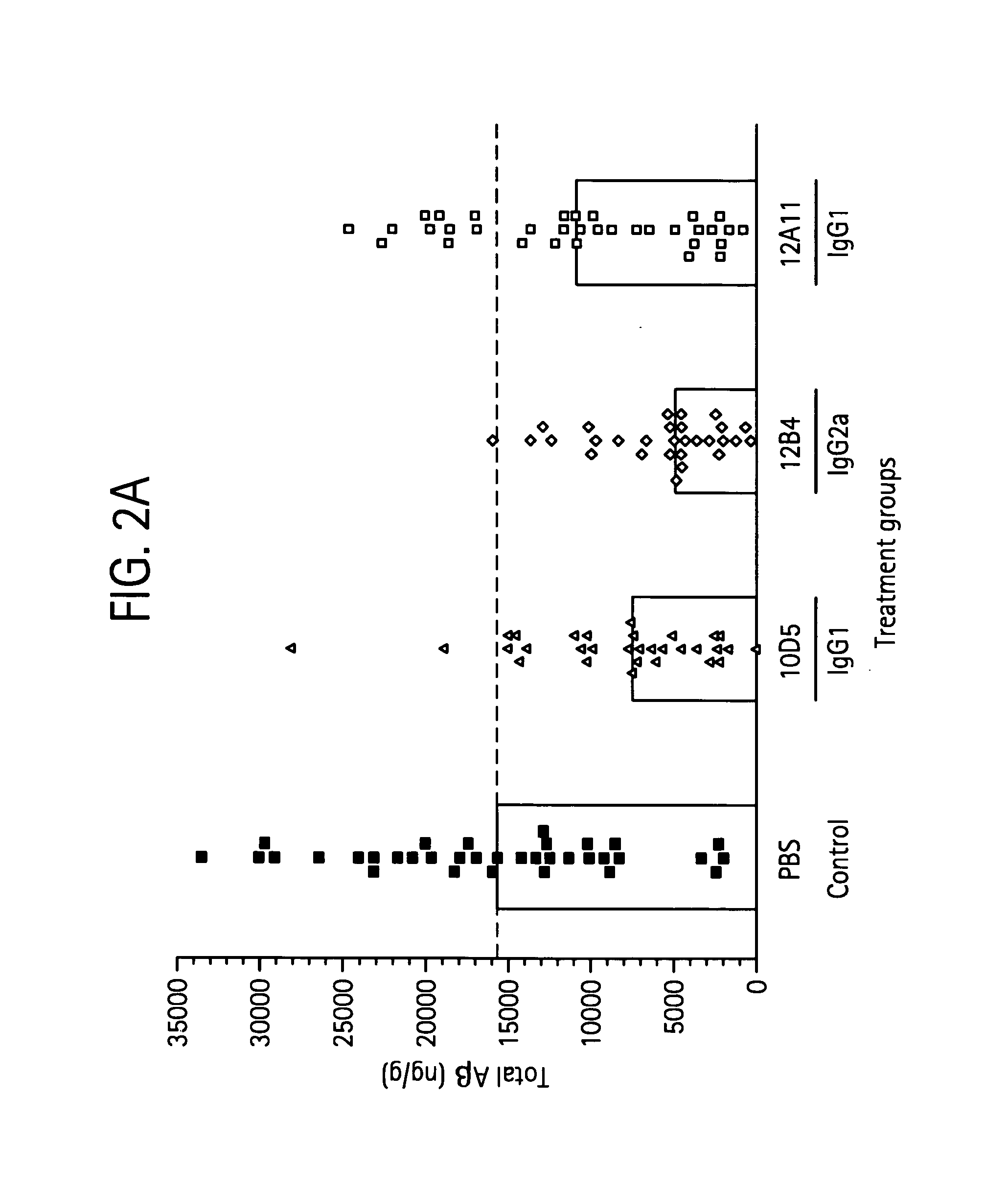
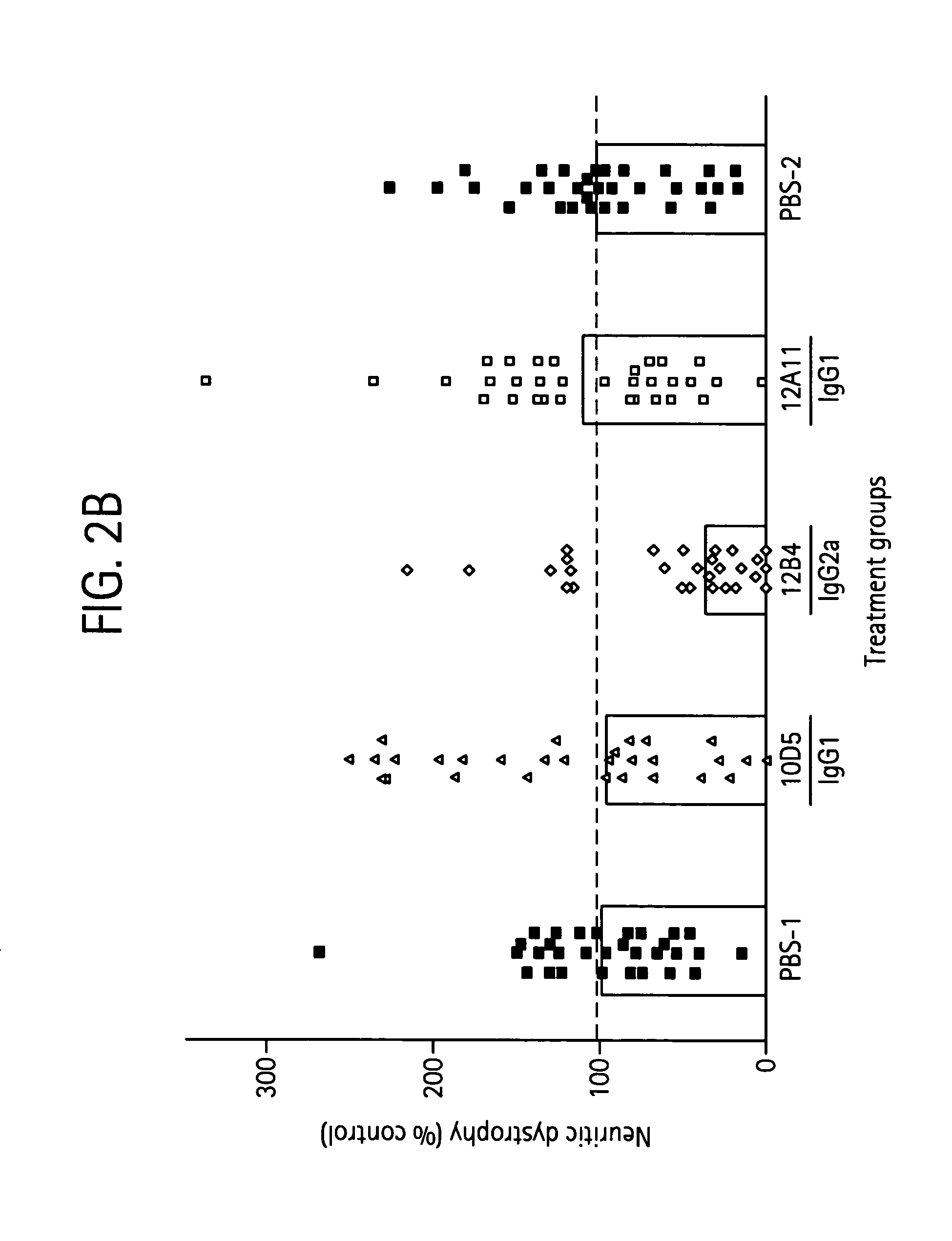
InactiveUS7179892B2Reduce the burden onReducing the neuritic dystrophyNervous disorderGenetically modified cellsHumanized antibodyΒ amyloid peptide
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with amyloid deposits of Aβ in the brain of a patient. Preferred agents include humanized antibodies.
Owner:WYETH LLC +1
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
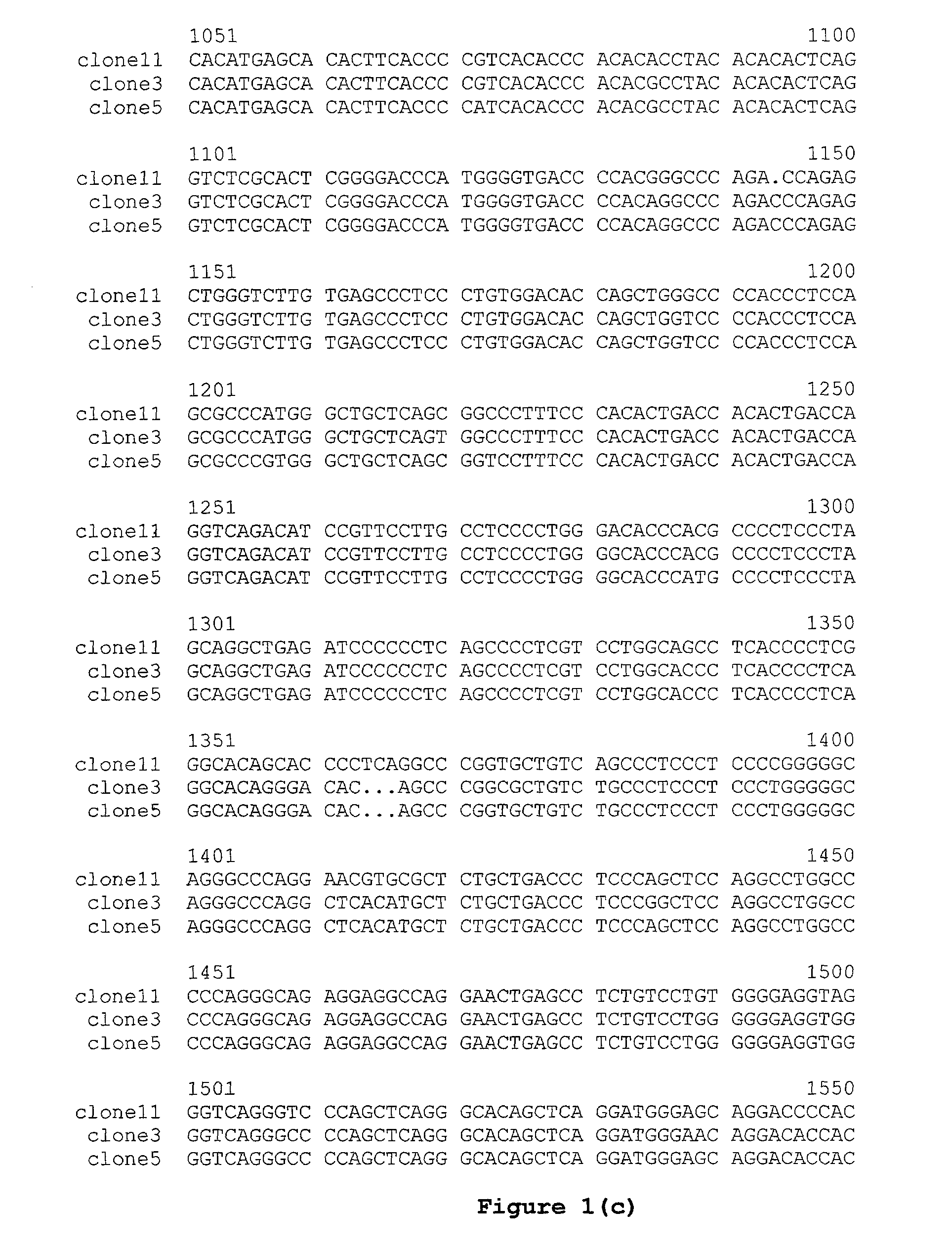
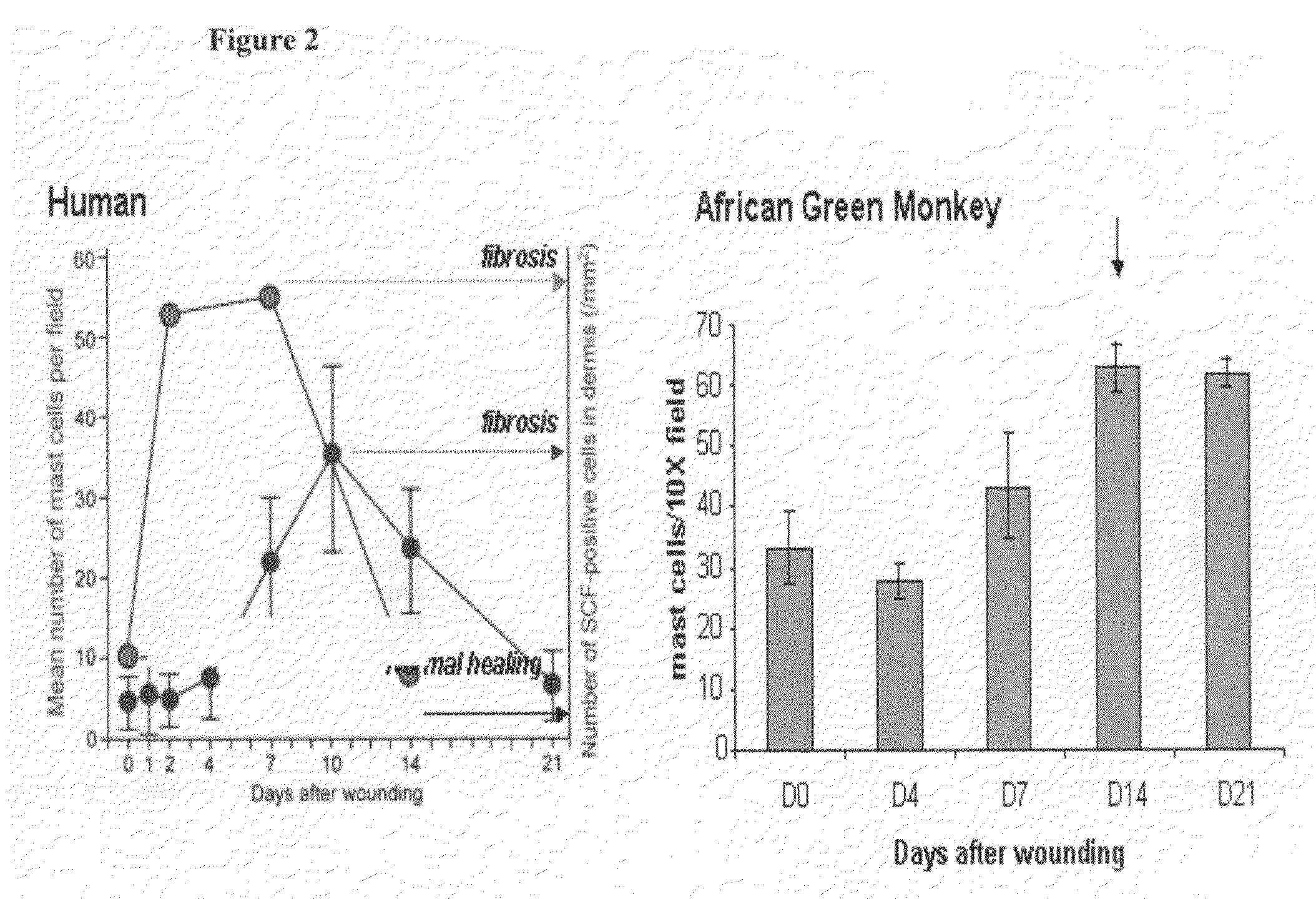
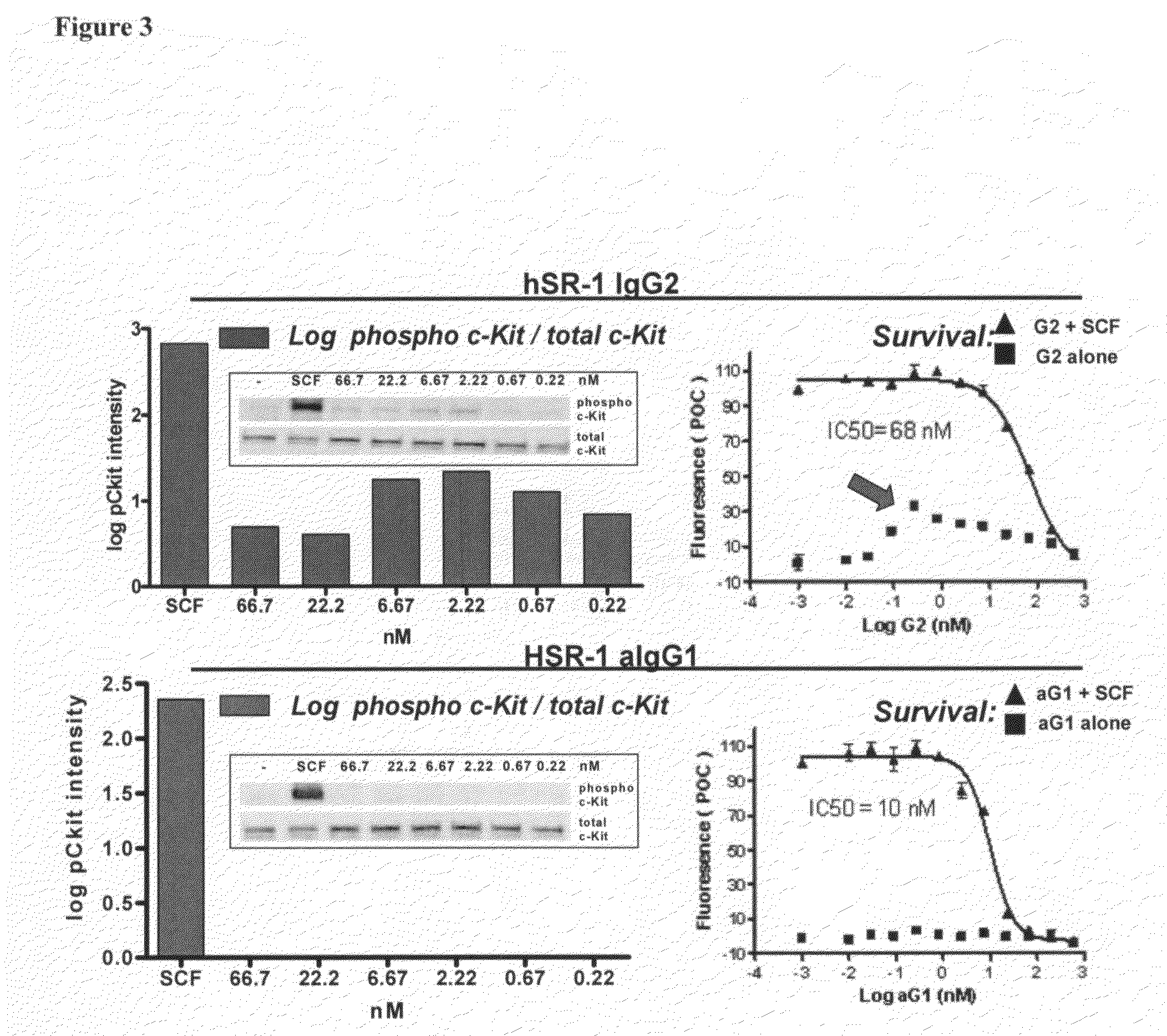
Humanized c-Kit antibody
This invention relates to compositions and methods for treating c-Kit associated disorders such as fibrosis, and more particularly, to compositions containing humanized c-Kit antibodies.
Owner:AMGEN INC
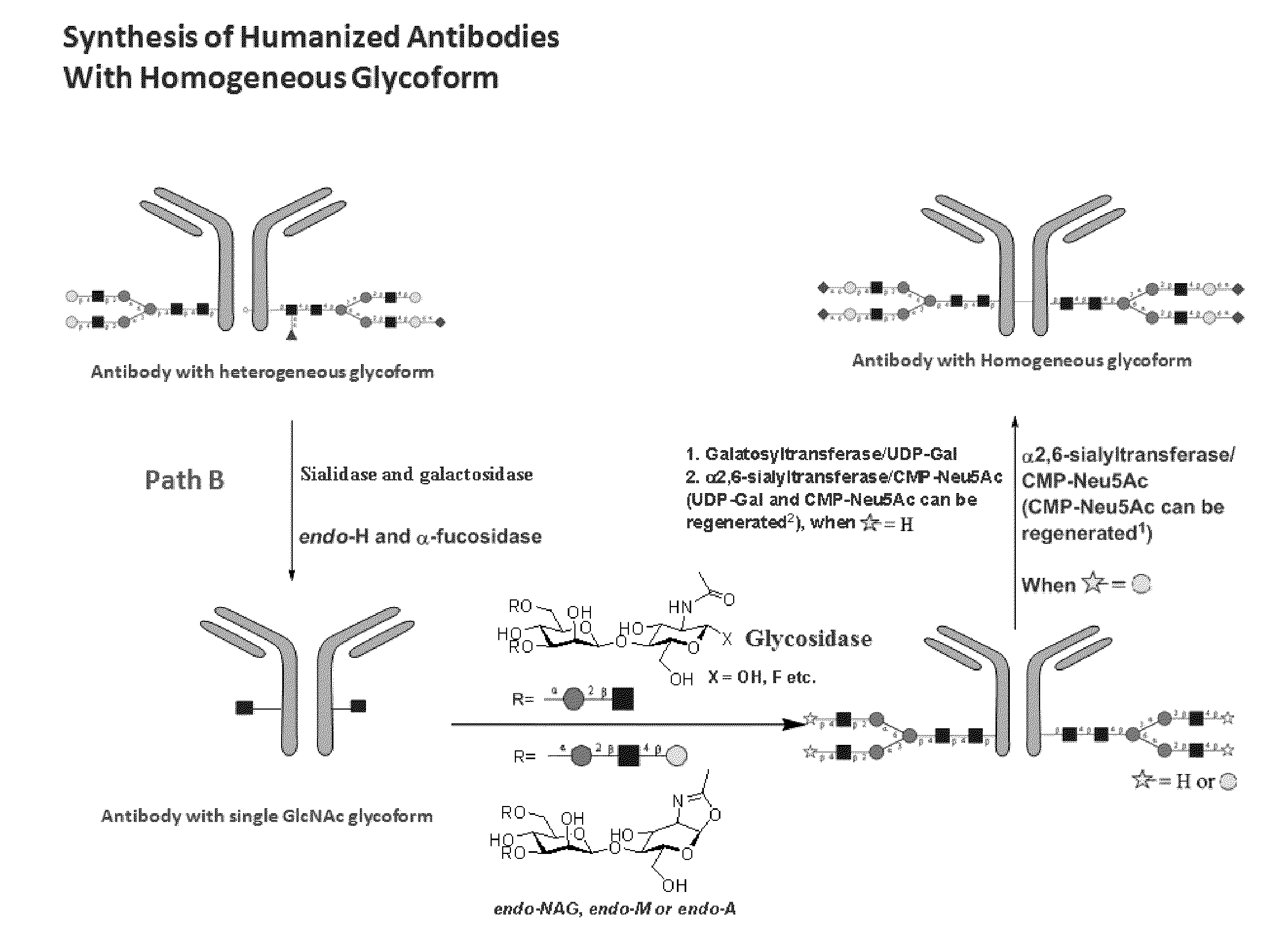
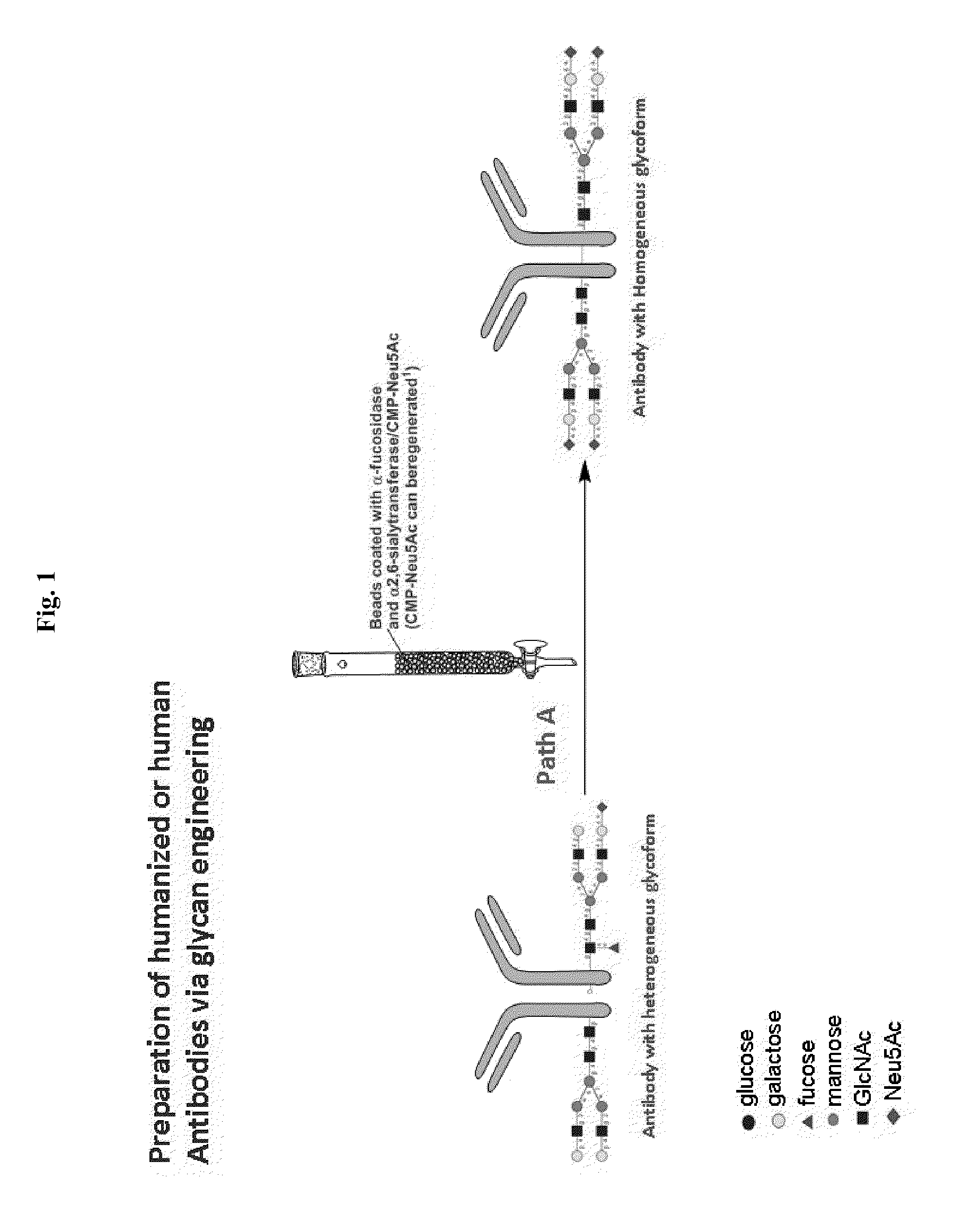
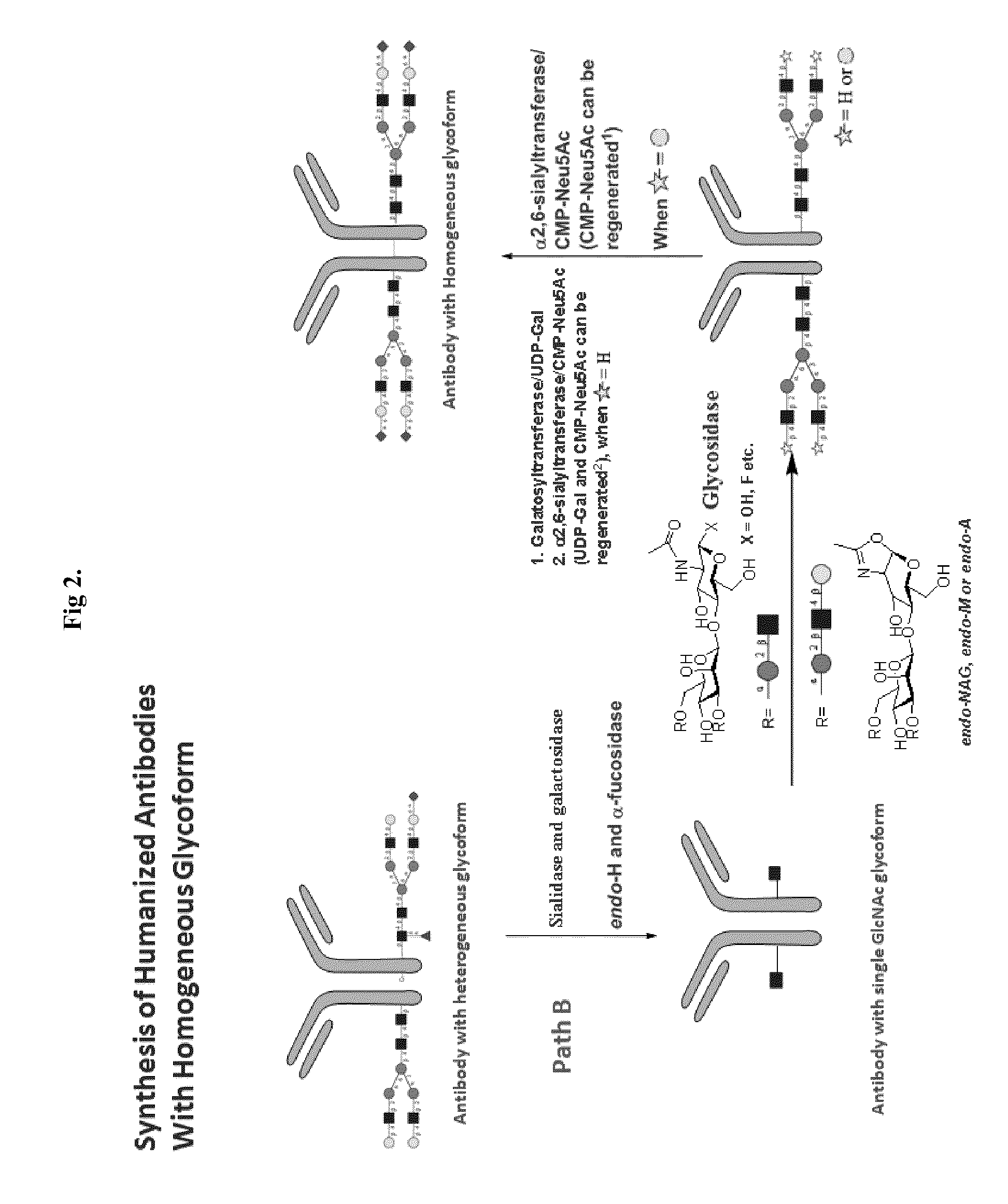
Methods for modifying human antibodies by glycan engineering
ActiveUS20110263828A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityImmunoglobulinsFermentationGlycanAntibody fragments
Modified Fc regions of antibodies and antibody fragments, both human and humanized, and having enhanced stability and efficacy, are provided. Fc regions with core fucose residues removed, and attached to oligosaccharides comprising terminal sialyl residues, are provided. Antibodies comprising homogeneous glycosylation of Fc regions with specific oligosaccharides are provided. Fc regions conjugated with homogeneous glycoforms of monosaccharides and trisaccharides, are provided. Methods of preparing human antibodies with modified Fc using glycan engineering, are provided.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Humanized antibodies that recognize beta amyloid peptide
ActiveUS20050118651A1Reduce the burden onAnimal cellsNervous disorderGreek letter betaHumanized antibody
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with amyloid deposits of Aβ in the brain of a patient. Preferred agents include antibodies, e.g., humanized antibodies.
Owner:WYETH LLC +1
Humanized antibodies that recognize beta amyloid peptide
InactiveUS7256273B2Reducing plaque burdenReduce the burden onHybrid immunoglobulinsNervous disorderHumanized antibodyΒ amyloid peptide
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with amyloid deposits of Aβ in the brain of a patient. Preferred agents include humanized antibodies.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
Non-human mammals for the production of chimeric antibodies
ActiveUS20110236378A1Improve representationEfficiently rearrangedPeptide librariesSugar derivativesMammalHumanized antibody
The invention provides knock-in non-human cells and mammals having a genome encoding chimeric antibodies and methods of producing knock-in cells and mammals. Certain aspects of the invention include chimeric antibodies, humanized antibodies, pharmaceutical compositions and kits. Certain aspects of the invention also relate to diagnostic and treatment methods using the antibodies of the invention.
Owner:ABLEXIS LLC
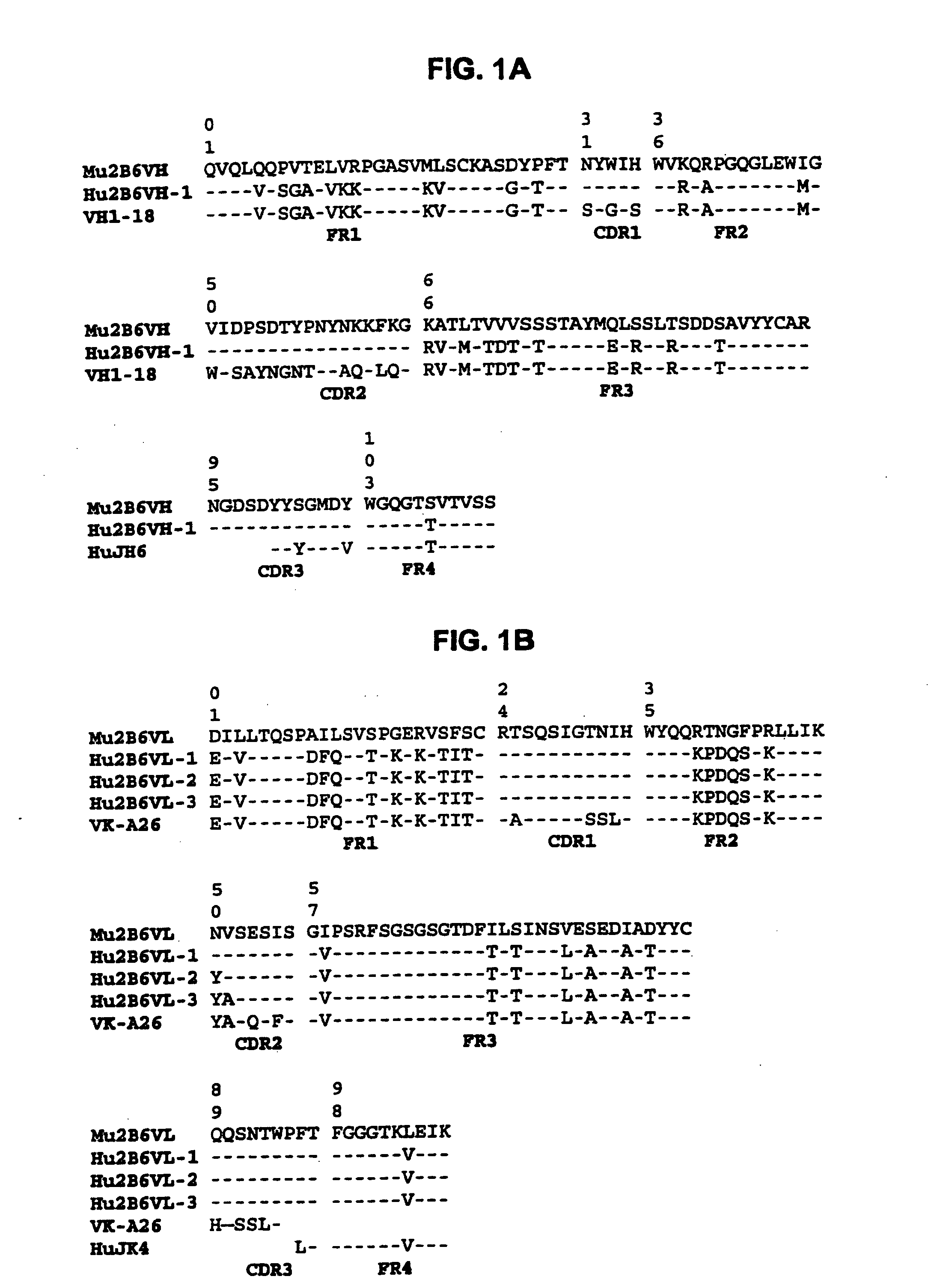
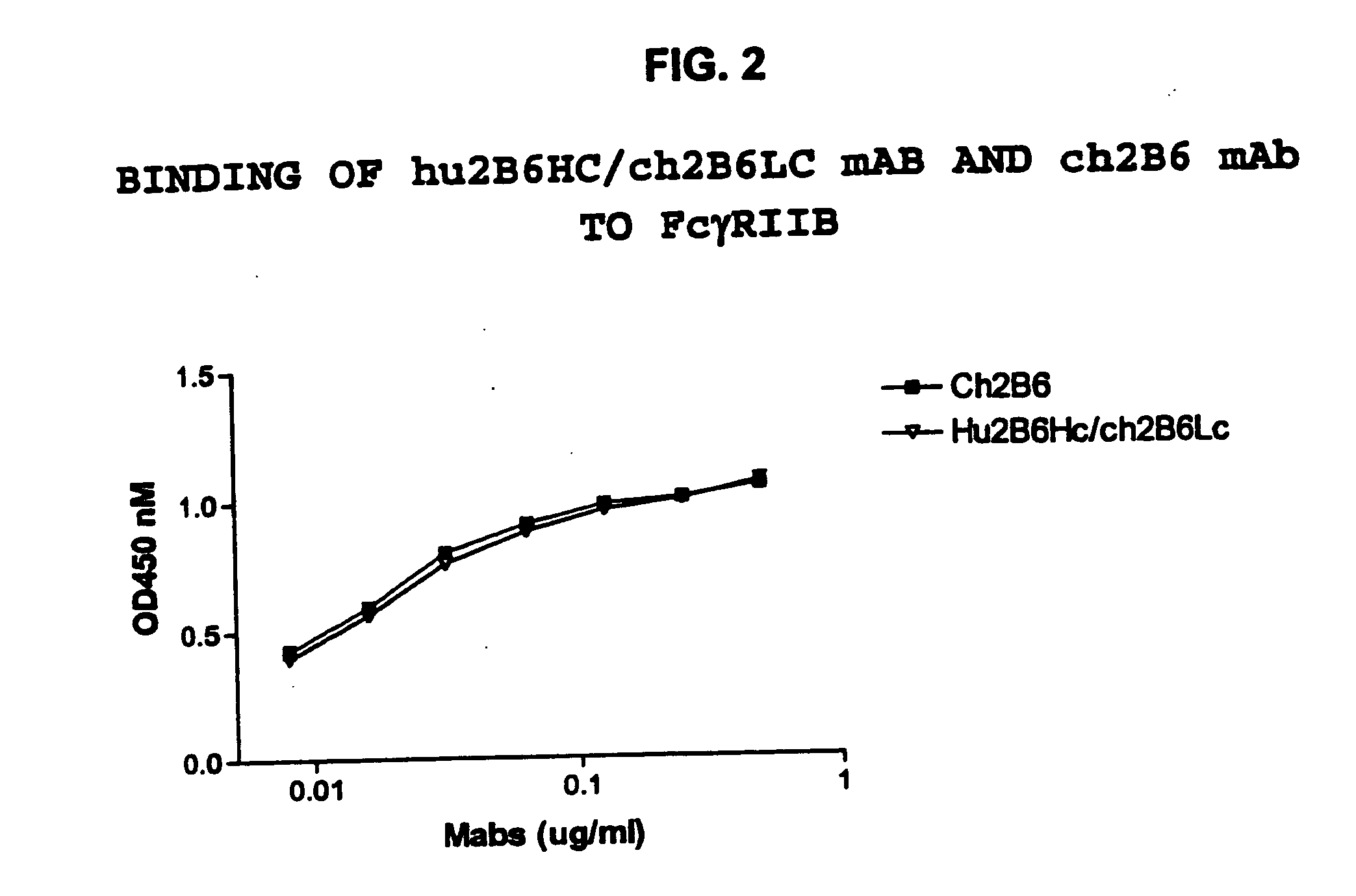
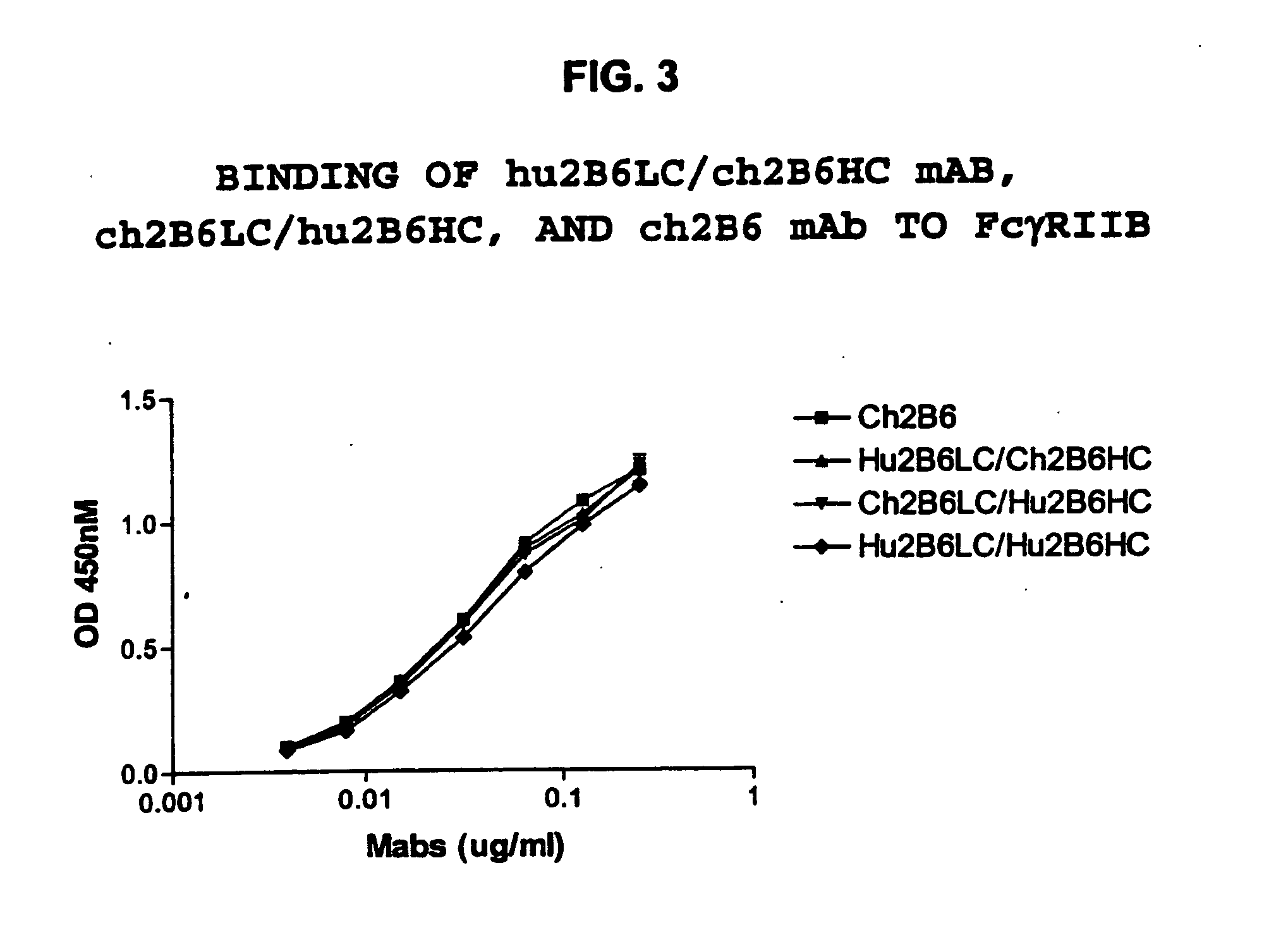
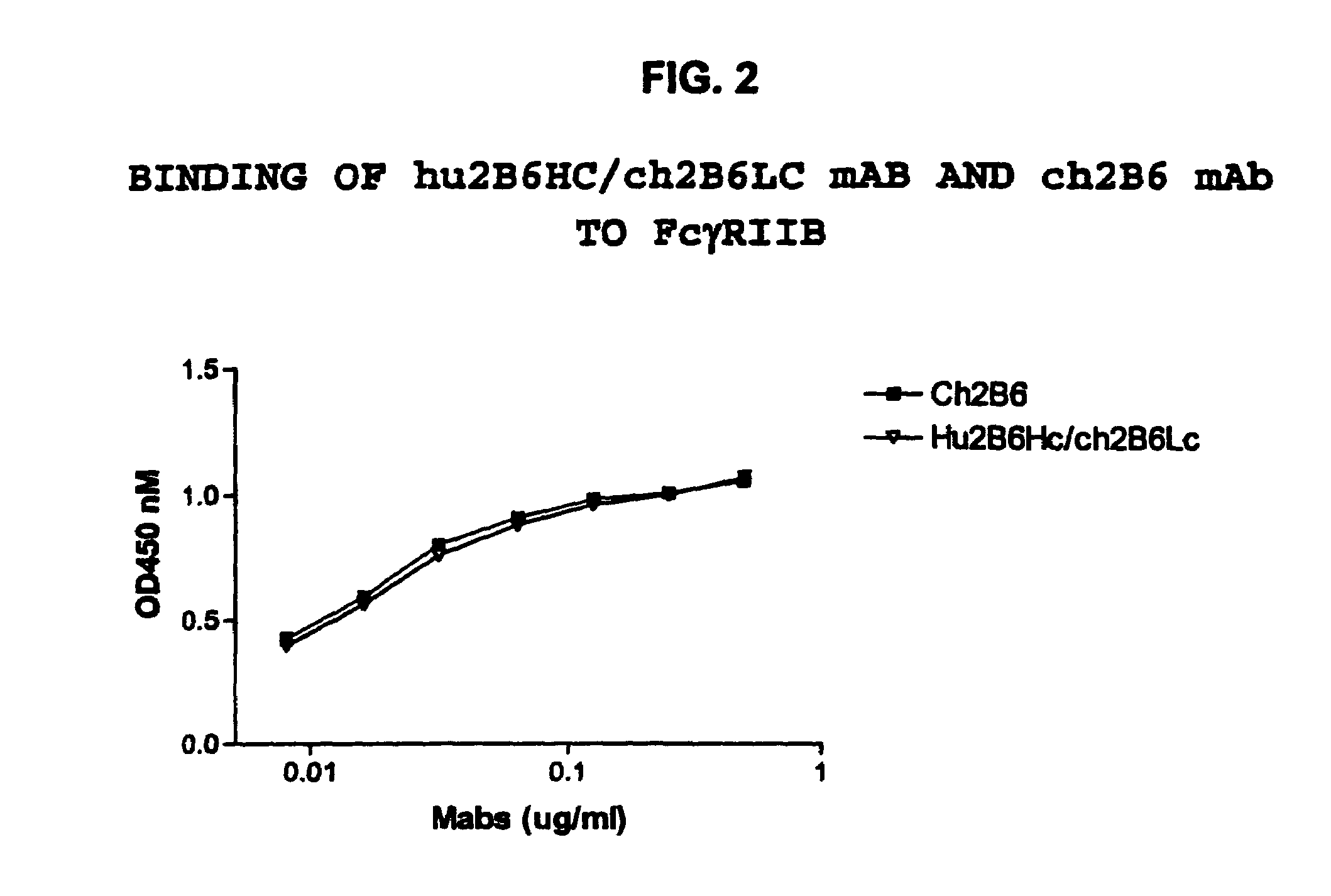
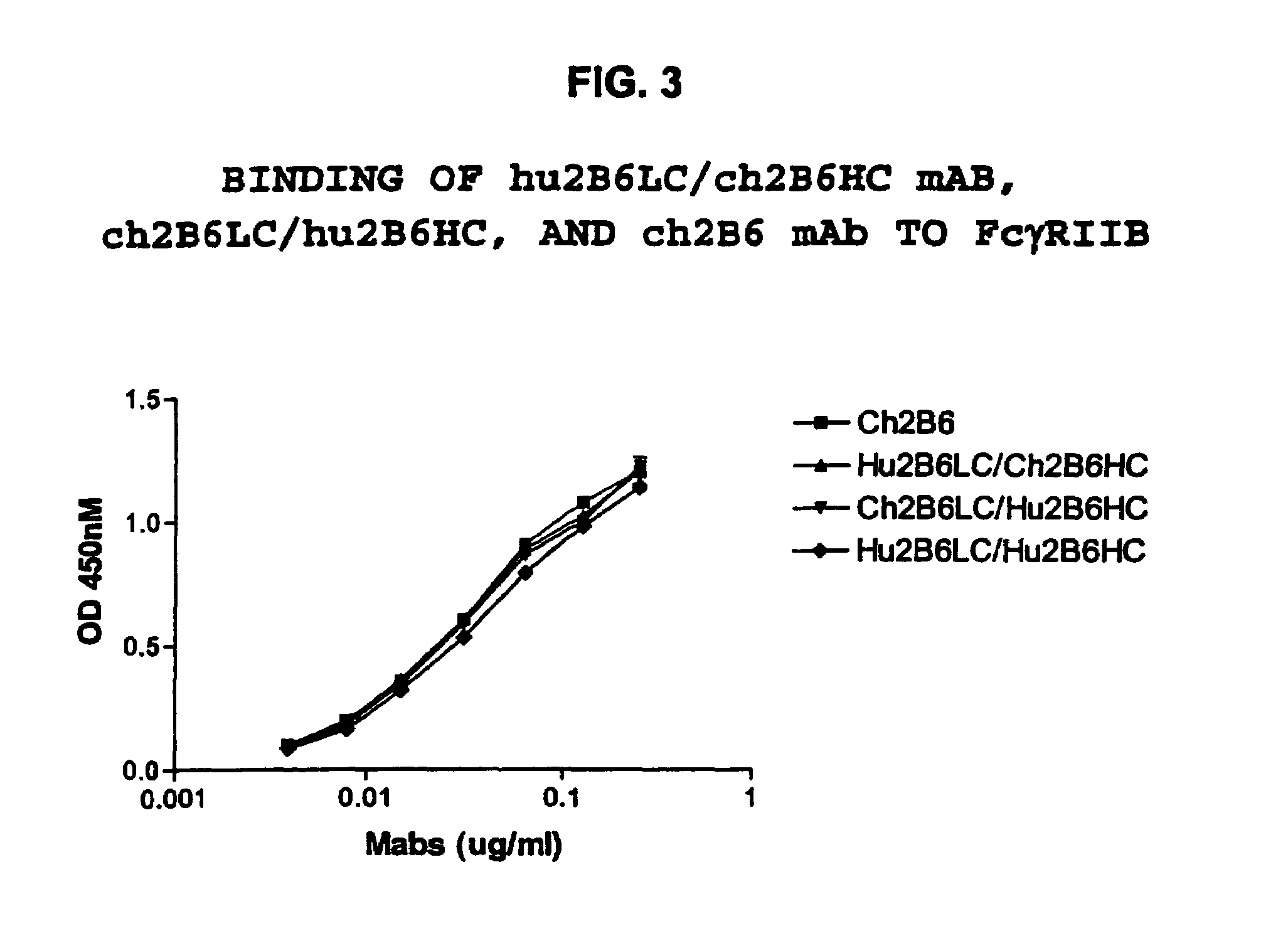
Humanized FcgammaRIIB-specific antibodies and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20060013810A1Good curative effectConvenient treatmentSenses disorderNervous disorderFc(alpha) receptorDisease
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Humanized antibodies that recognize beta amyloid peptide
InactiveUS20050009150A1High binding affinityLow immunogenicityFungiNervous disorderHumanized antibodyΒ amyloid peptide
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with amyloid deposits of Aβ in the brain of a patient. Preferred agents include humanized antibodies.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
Humanized FcgammaRIIB-specific antibodies and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7521542B2Immune responseAvoid immune responseSenses disorderNervous disorderFc(alpha) receptorTherapeutic antibody
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
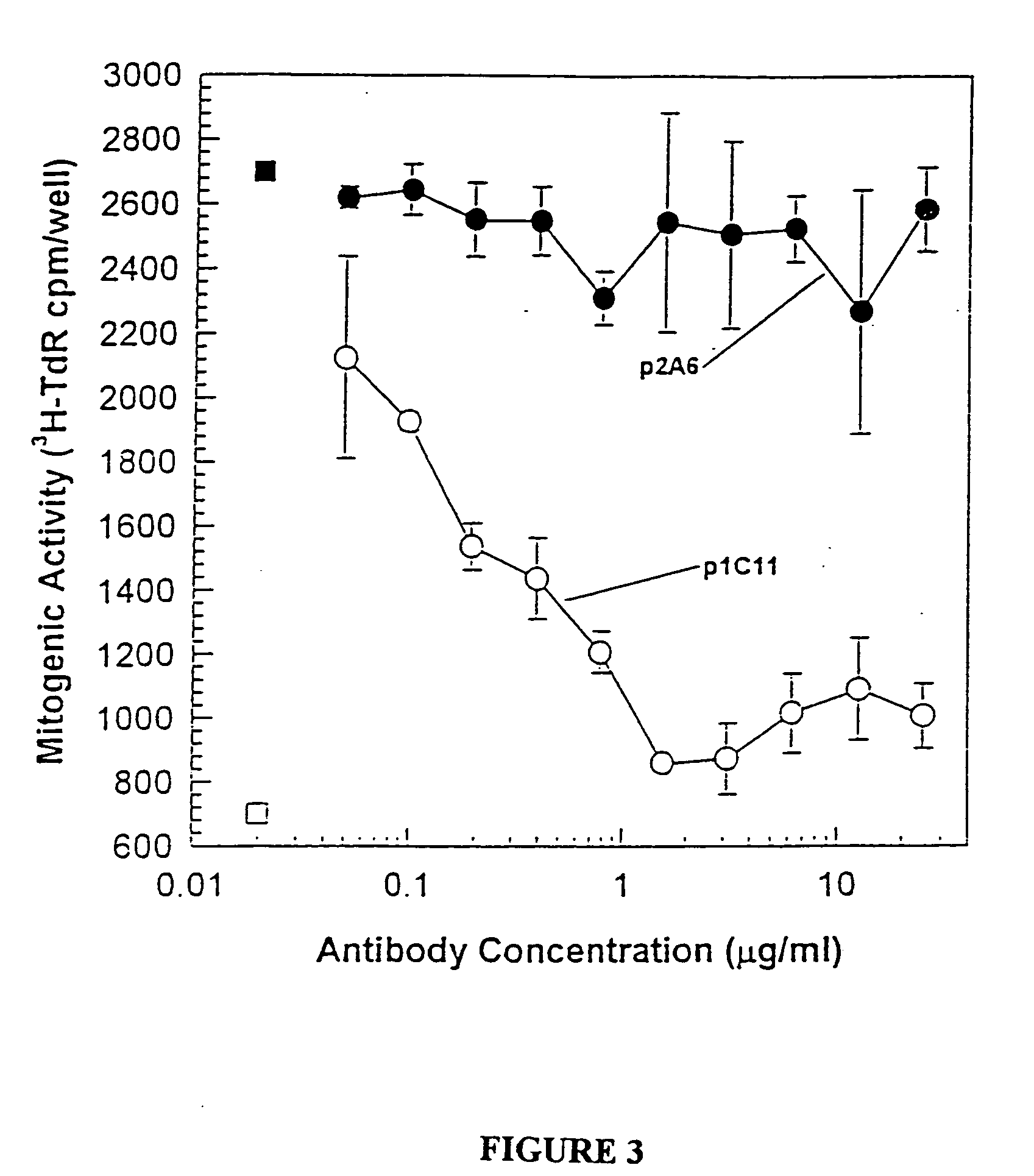
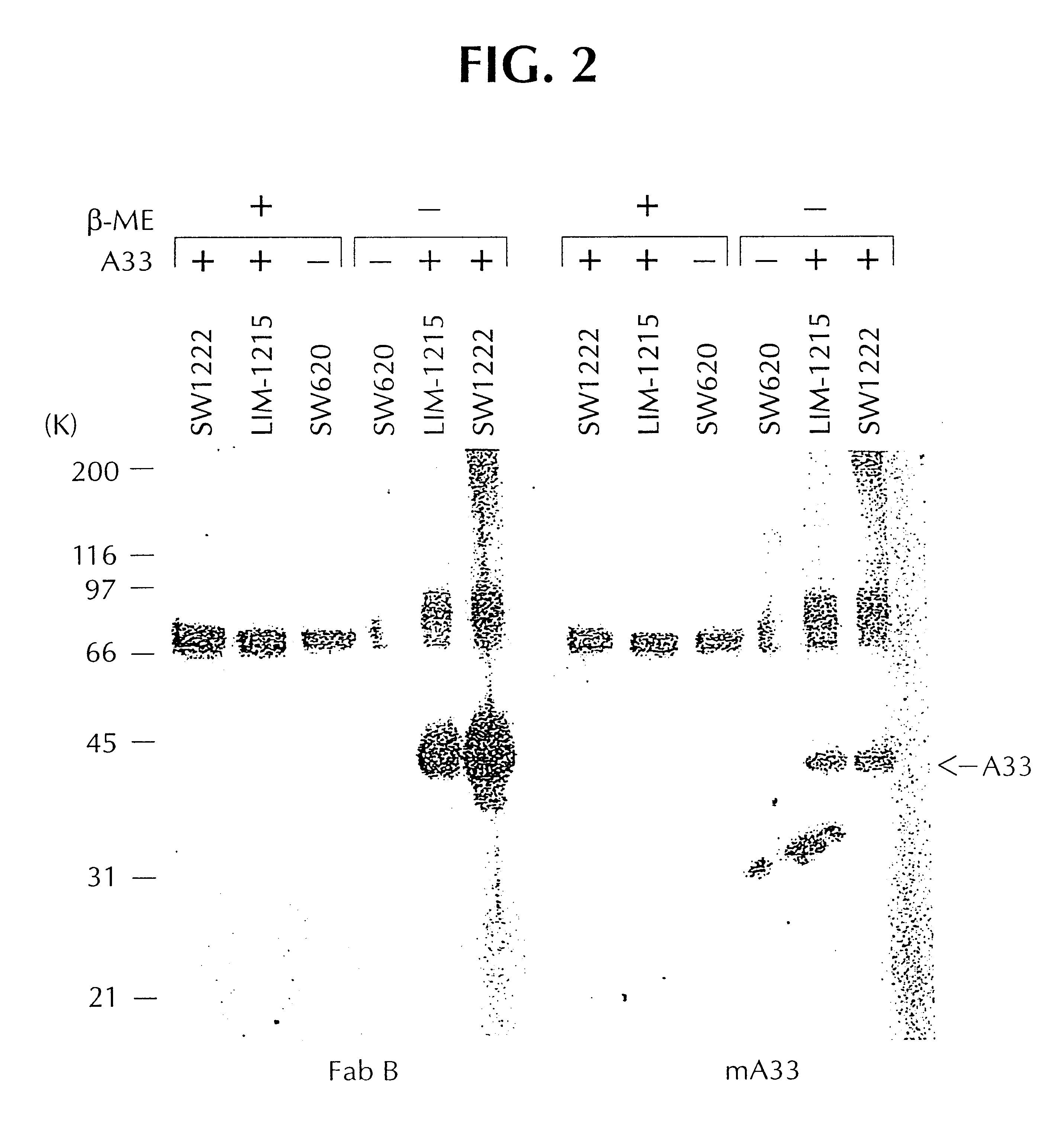
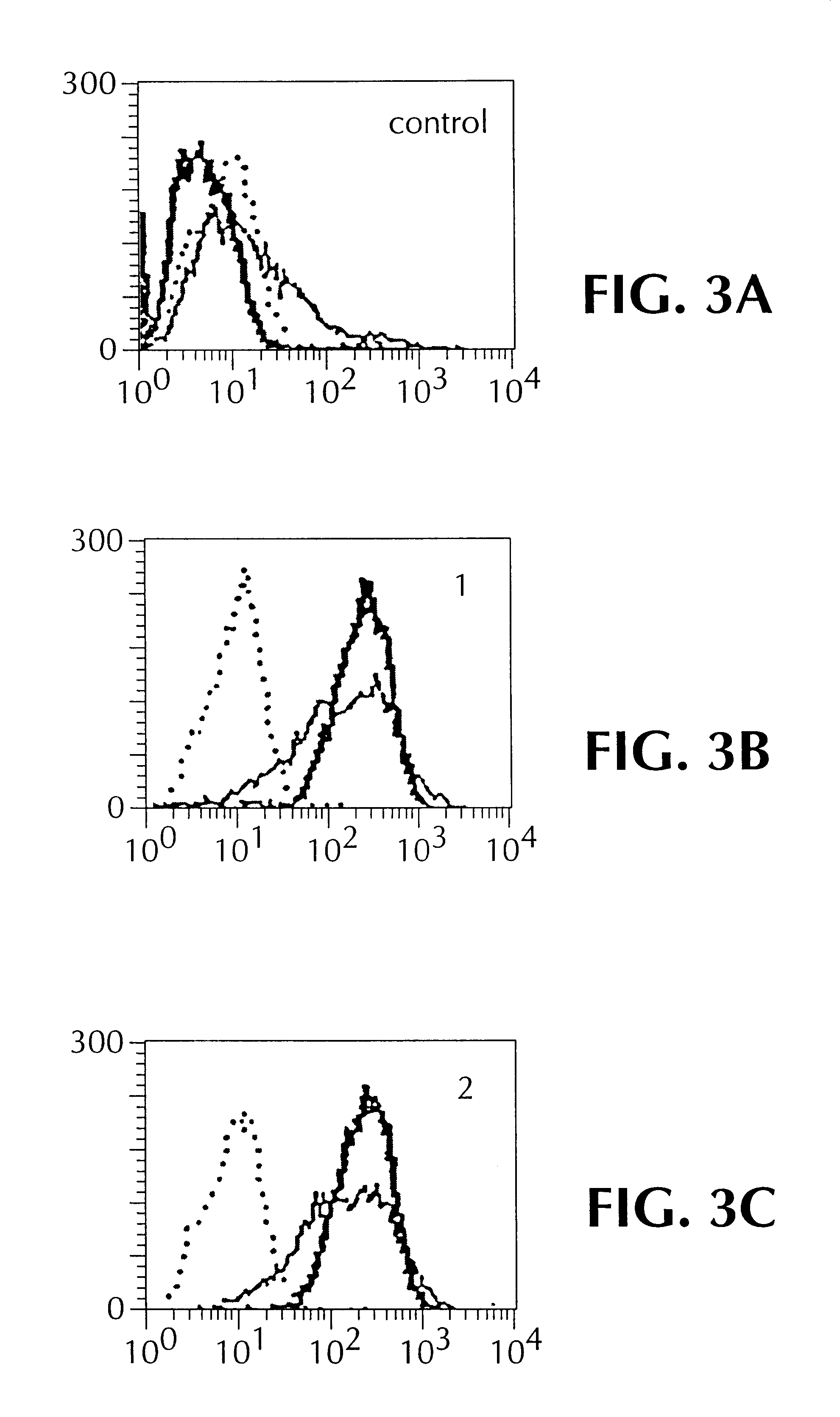
Humanized antibodies directed against A33 antigen
InactiveUS6307026B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCross-linkLymphatic Spread
A33 antigen binding proteins are described for use in the diagnosis or treatment of colorectal tumors and metastases arising therefrom. The binding protein may be a humanized A33 antibody, including complete antibody molecules, fragments thereof, and particularly, multivalent monospecific proteins comprising two, three, four or more antibodies or fragments thereof, bound to each other by a cross-linking agent. For diagnosis or therapy, the humanized A33 antibody may be linked to a reporter or effector molecule.
Owner:CELLTECH LTD
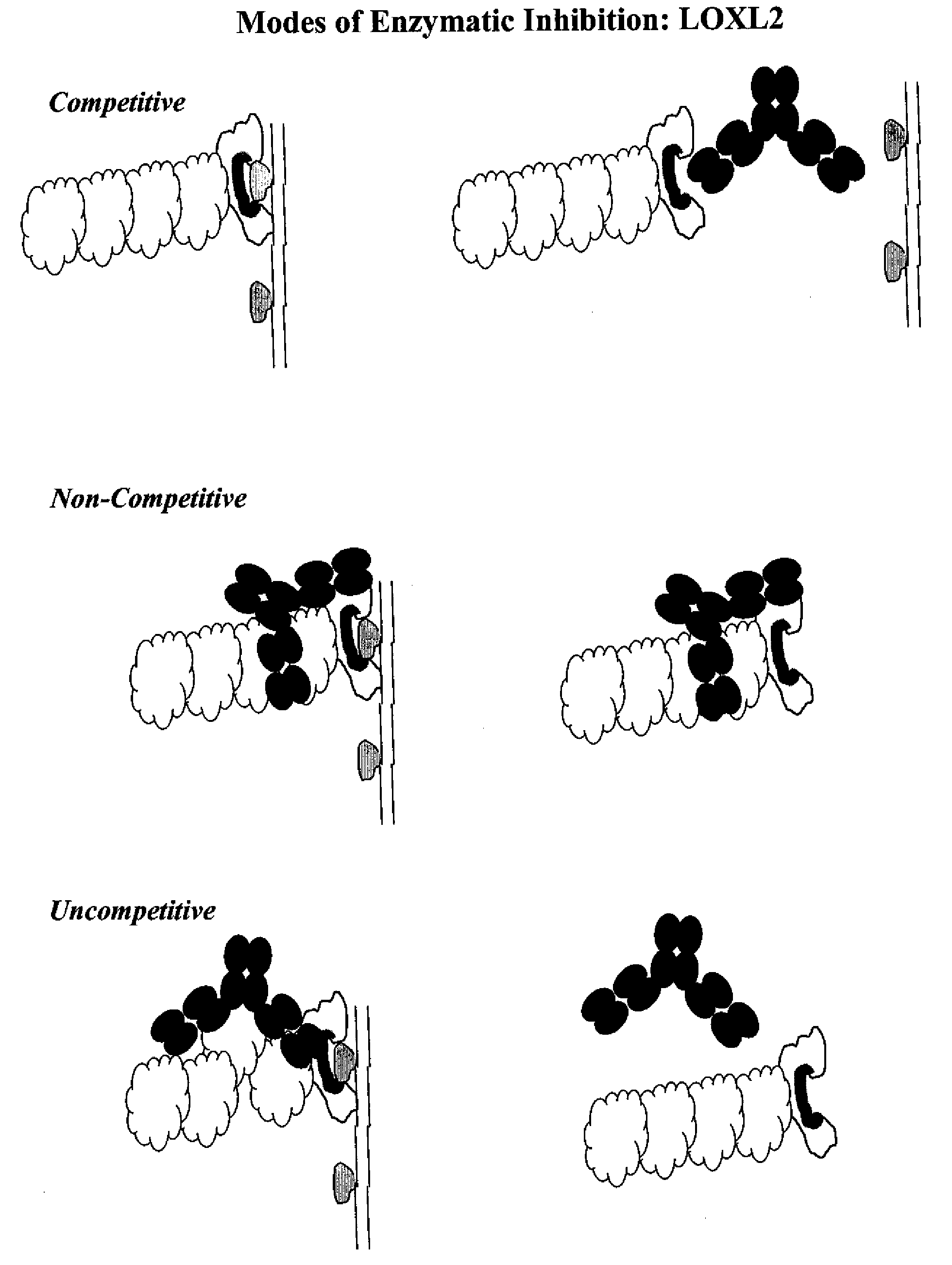
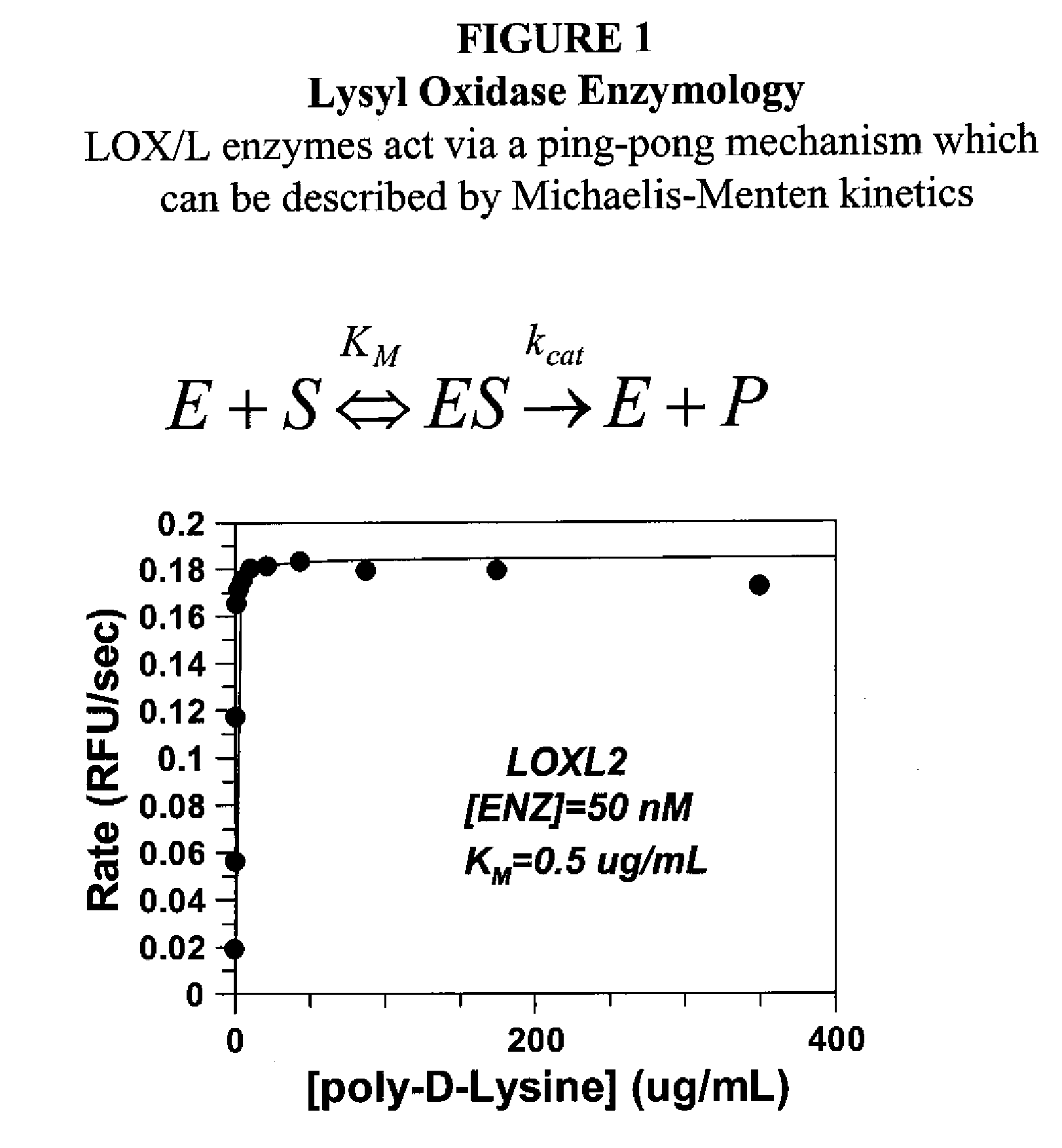
Lox and loxl2 inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090053224A1Block enzymatic activitySlow tumor growthNervous disorderMuscular disorderAngiogenesis growth factorFibrosis
The present application relates to anti-LOX and anti-LOXL2 antibodies and their use in purification, diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Antibodies include monoclonal antibodies, humanized antibodies and functional fragments thereof. Anti-LOX and anti-LOXL2 antibodies can be used to identify and treat conditions such as a fibrotic condition, angiogenesis, or to prevent a transition from an epithelial cell state to a mesenchymal cell state.
Owner:GILEAD BIOLOGICS
Humanized antibodies against CD3
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Humanized Fc.gamma.RIIB-Specific Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080044417A1Good curative effectEnhanced effector functionDisease diagnosisTissue cultureFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The present invention relates to humanized FcγRIIB antibodies, fragments, and variants thereof that bind human FcγRIIB with a greater affinity than said antibody binds FcγRIIA. The invention encompasses the use of the humanized antibodies of the invention for the treatment of any disease related to loss of balance of Fc receptor mediated signaling, such as cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The invention provides methods of enhancing the therapeutic effect of therapeutic antibodies by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention to enhance the effector function of the therapeutic antibodies. The invention also provides methods of enhancing the efficacy of a vaccine composition by administering the humanized antibodies of the invention. The invention encompasses methods for treating an autoimmune disease and methods for elimination of cancer cells that express FcγRIIB.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Humanized antibodies that recognize beta amyloid peptide
InactiveUS7189819B2Reduce the burden onReducing the neuritic dystrophyFungiNervous disorderHumanized antibodyΒ amyloid peptide
The invention provides improves agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with amyloid deposits of Aβ in the brain of a patient. Preferred agents include humanized antibodies.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +3
Anti-glypican 3 antibody
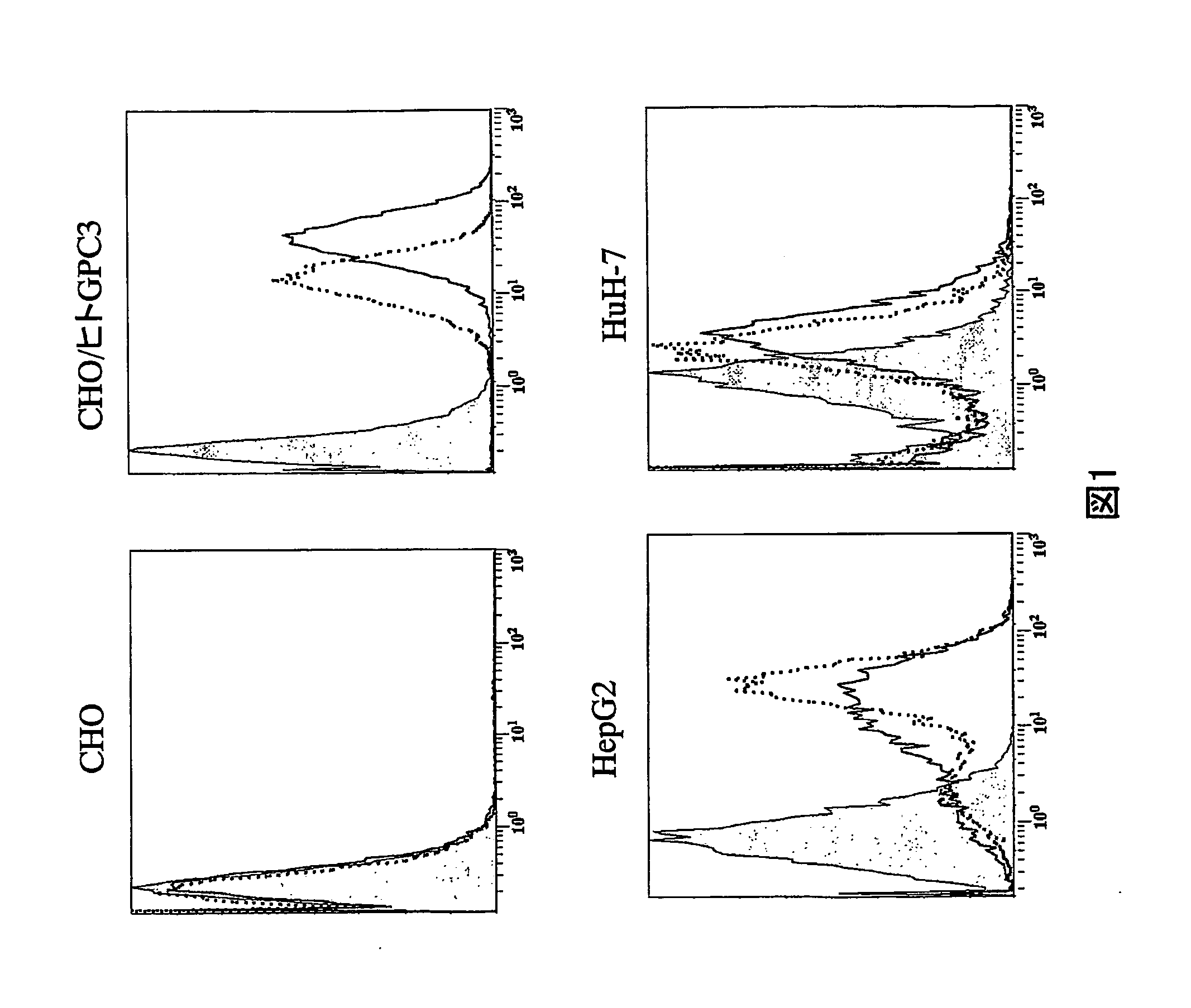
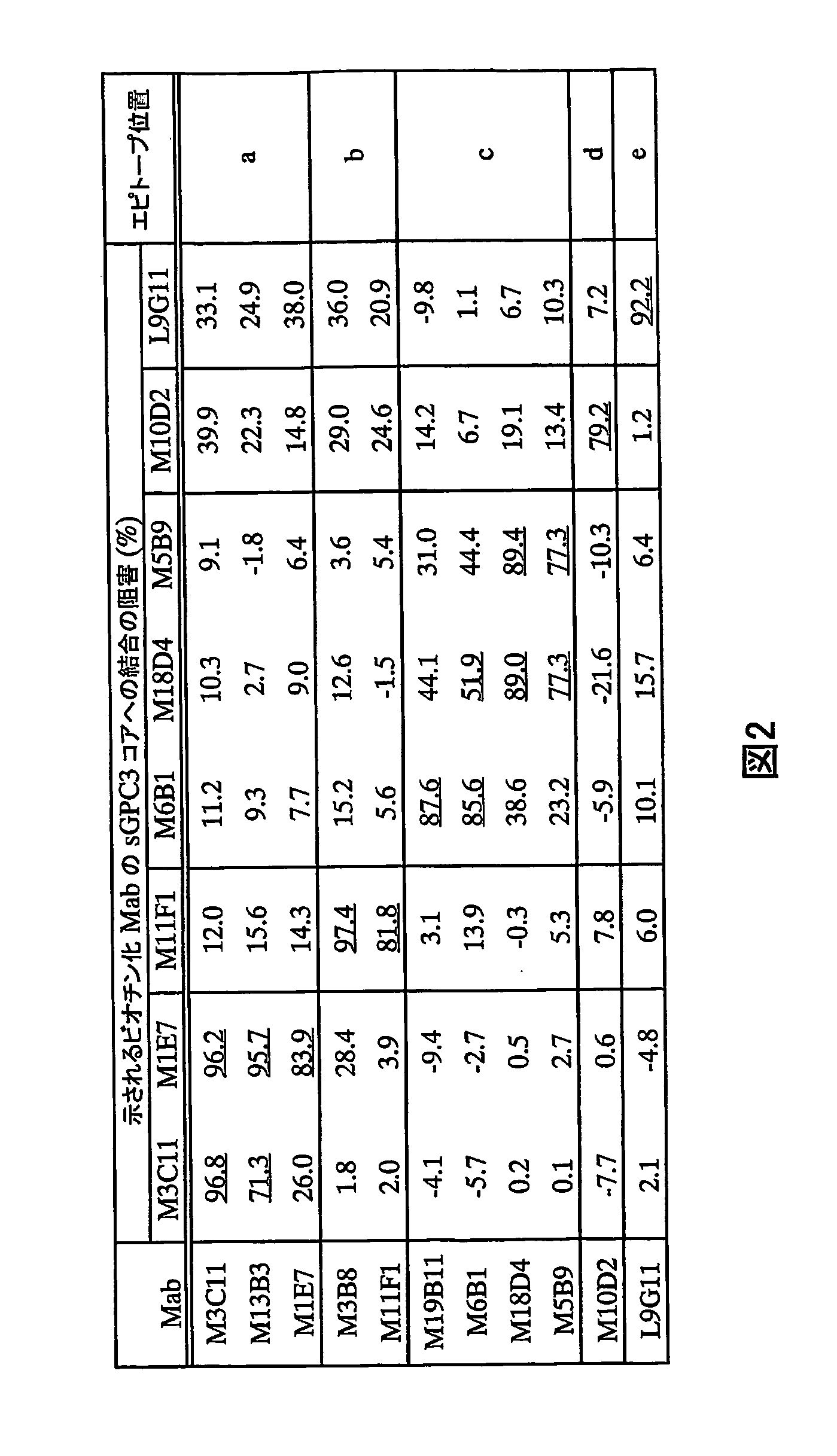
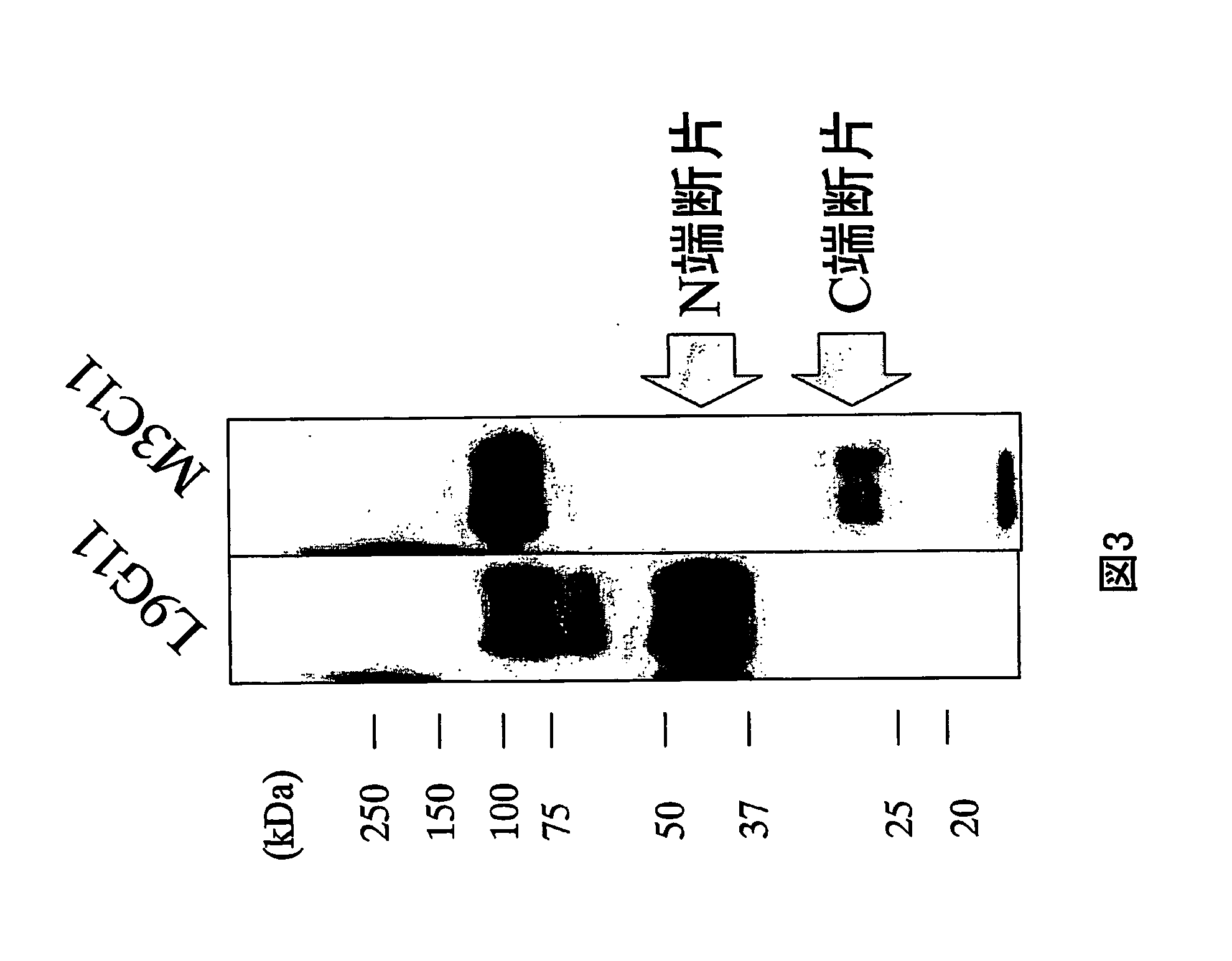
ActiveUS20070190599A1High cytotoxic activityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAnticarcinogenHumanized antibody
An antibody capable of binding to a specific region of glypican 3, as well as a humanized antibody created based on that antibody are disclosed. The anti-GPC3 antibody of the invention has a higher ADCC activity and CDC activity compared with those of a conventional antibody. The antibody of the present invention is useful as a cell growth inhibitor, an anticancer agent and an agent for diagnosis of cancers.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Humanized Abeta antibodies for use in improving cognition
InactiveUS20060198851A1Increase awarenessReduce the burden onNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with beta amyloid (Aβ). Preferred agents include antibodies, e.g., humanized antibodies specific for Aβ.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
Antibodies specific to KDR and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050214860A1Inhibit tumor growthCompound screeningVirusesSingle-Chain AntibodiesAngiogenesis growth factor
The invention provides an immunoglobulin molecule which binds KDR with an affinity comparable to human VEGF, and that neutralizes activation of KDR. Immunoglobulin molecules include monovalent single chain antibodies, multivalent single chain antibodies, diabodies, triabodies, antibodies, humanized antibodies and chimerized antibodies. The invention further provides nucleic acid molecules that encode these immunoglobulin molecules. The invention also provides a method of making the immunoglobulin molecules mentioned above. The invention further provides a method of neutralizing the activation of KDR, a method of inhibiting angiogenesis in a mammal and a method of inhibiting tumor growth in a mammal with such immunoglobulin molecules.
Owner:ZHU ZHENPING +1
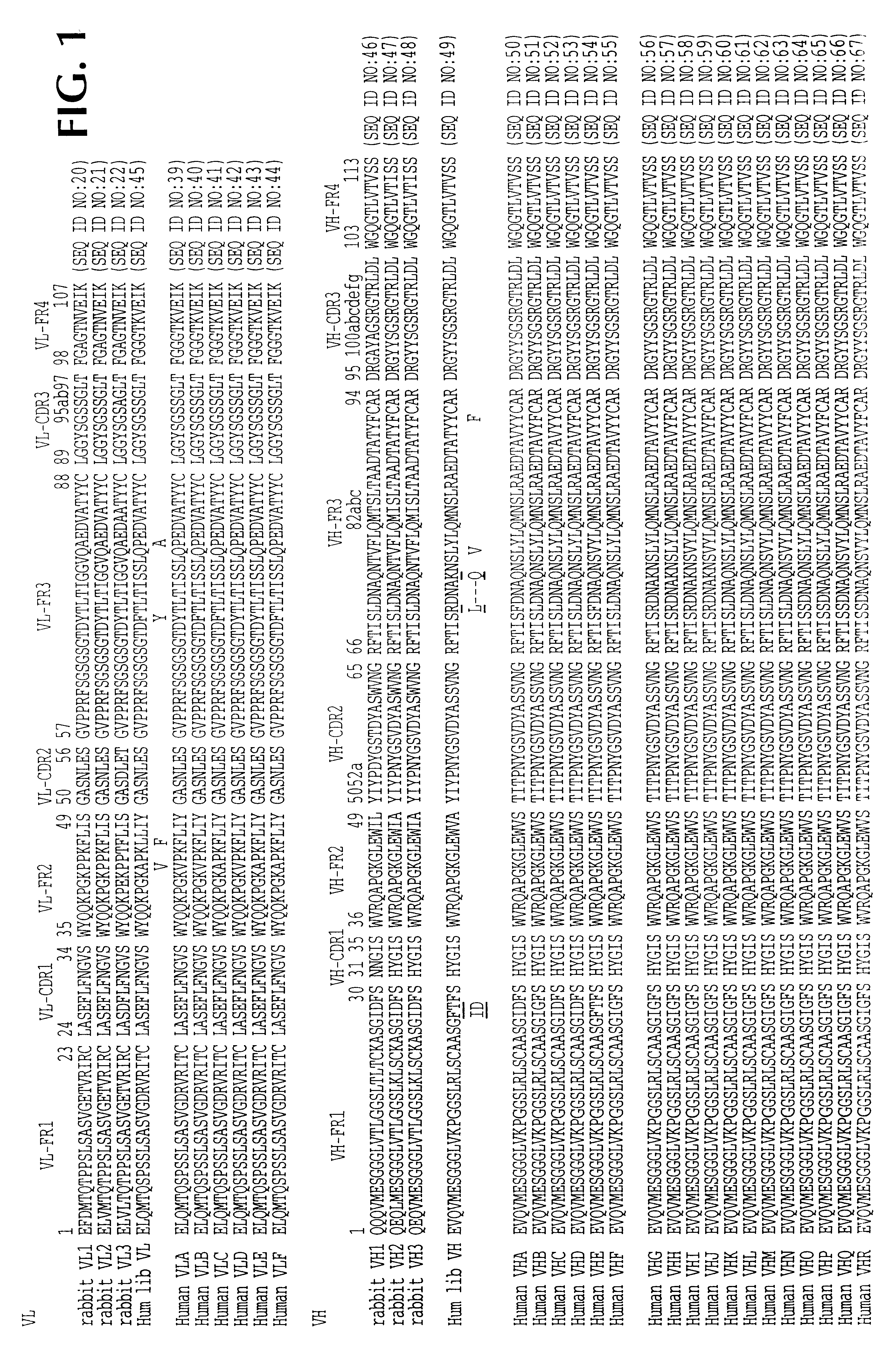
A33 antigen specific immunoglobulin products and uses thereof
InactiveUS6342587B1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunglobulin eBacteriophage
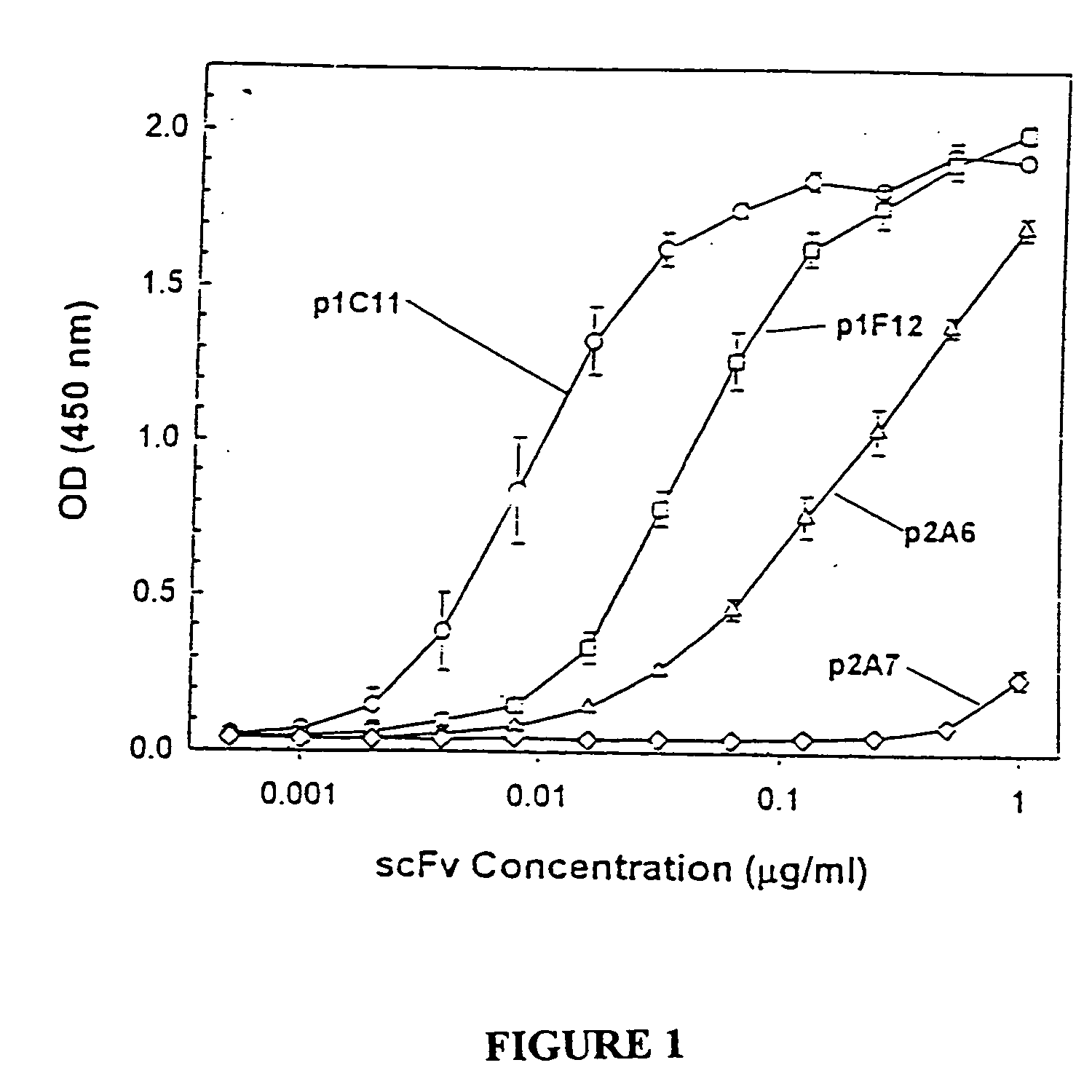
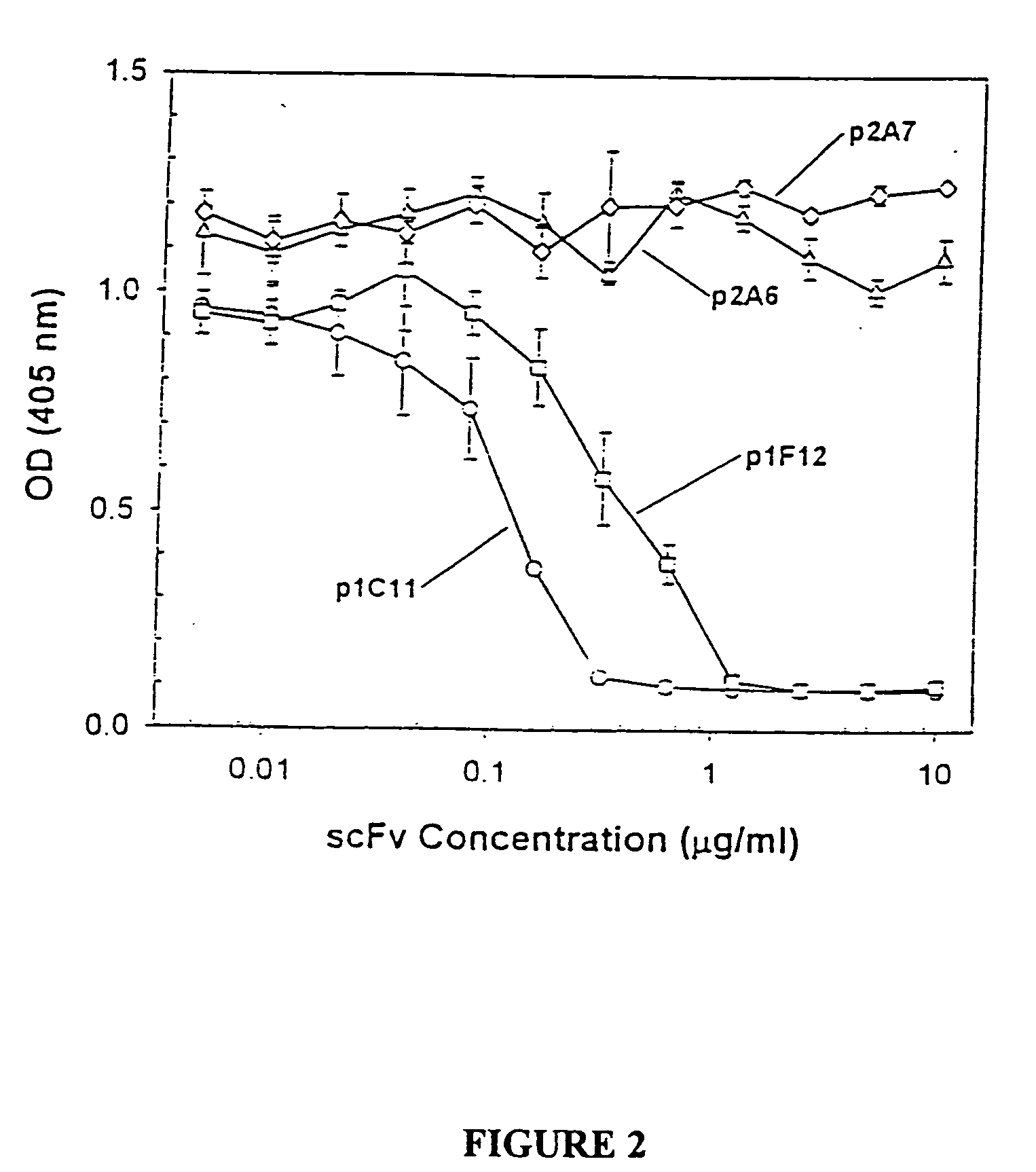
The invention is directed to novel CDRs and immunoglobulin products that bind to A33 antigens and methods for their use. The invention also involves a method for making humanized antibodies, using a rabbit as a host animal, and phage display library methodologies, and the antibodies themselves. The methodology is useful, for example, in generating humanized antibodies against molecules associated with cancer, such as A33, which is associated with colon cancer.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com