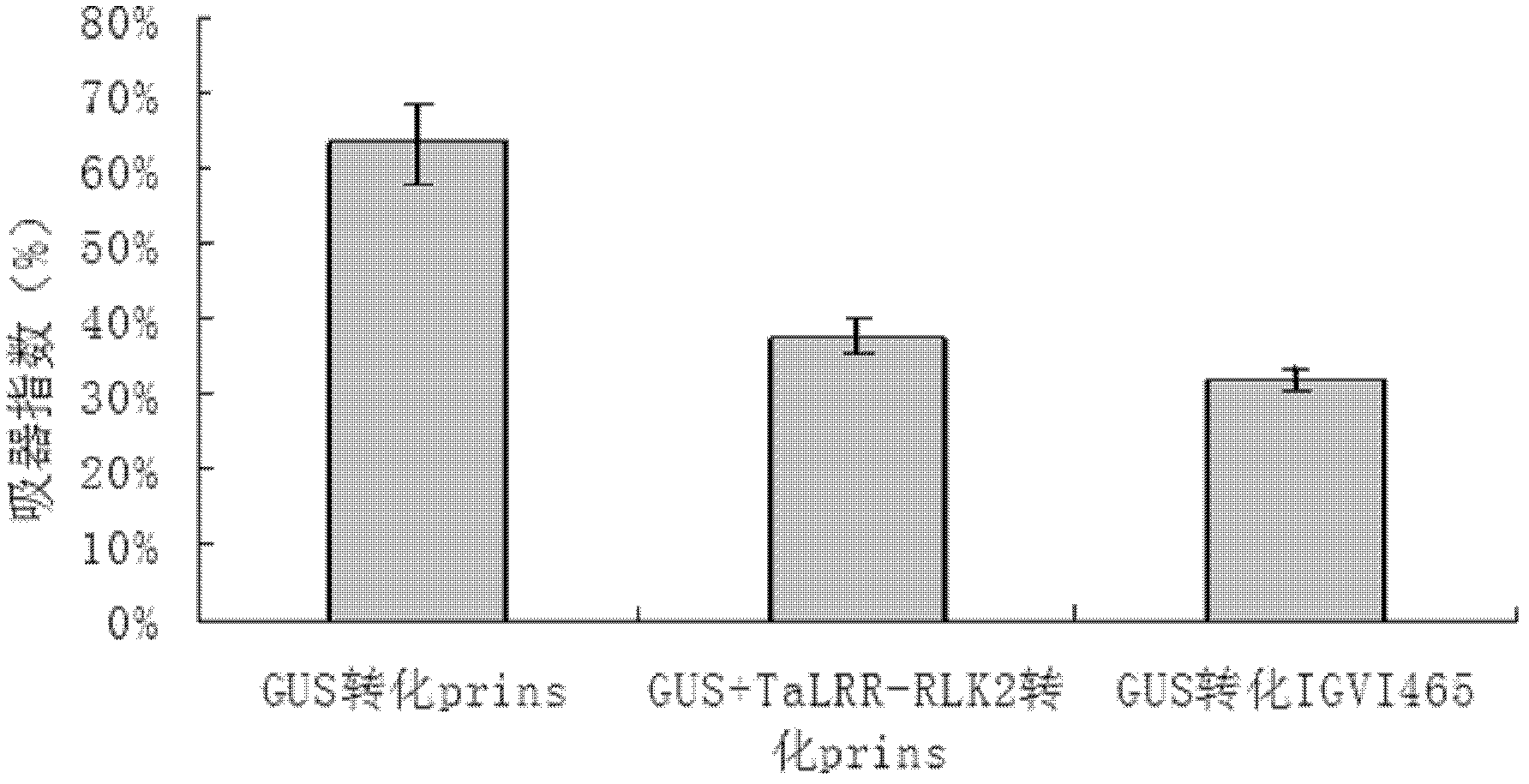Patents
Literature
626 results about "Gene conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene conversion is the process by which one DNA sequence replaces a homologous sequence such that the sequences become identical after the conversion event. Gene conversion can be either allelic, meaning that one allele of the same gene replaces another allele, or ectopic, meaning that one paralogous DNA sequence converts another.
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20030017534A1Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
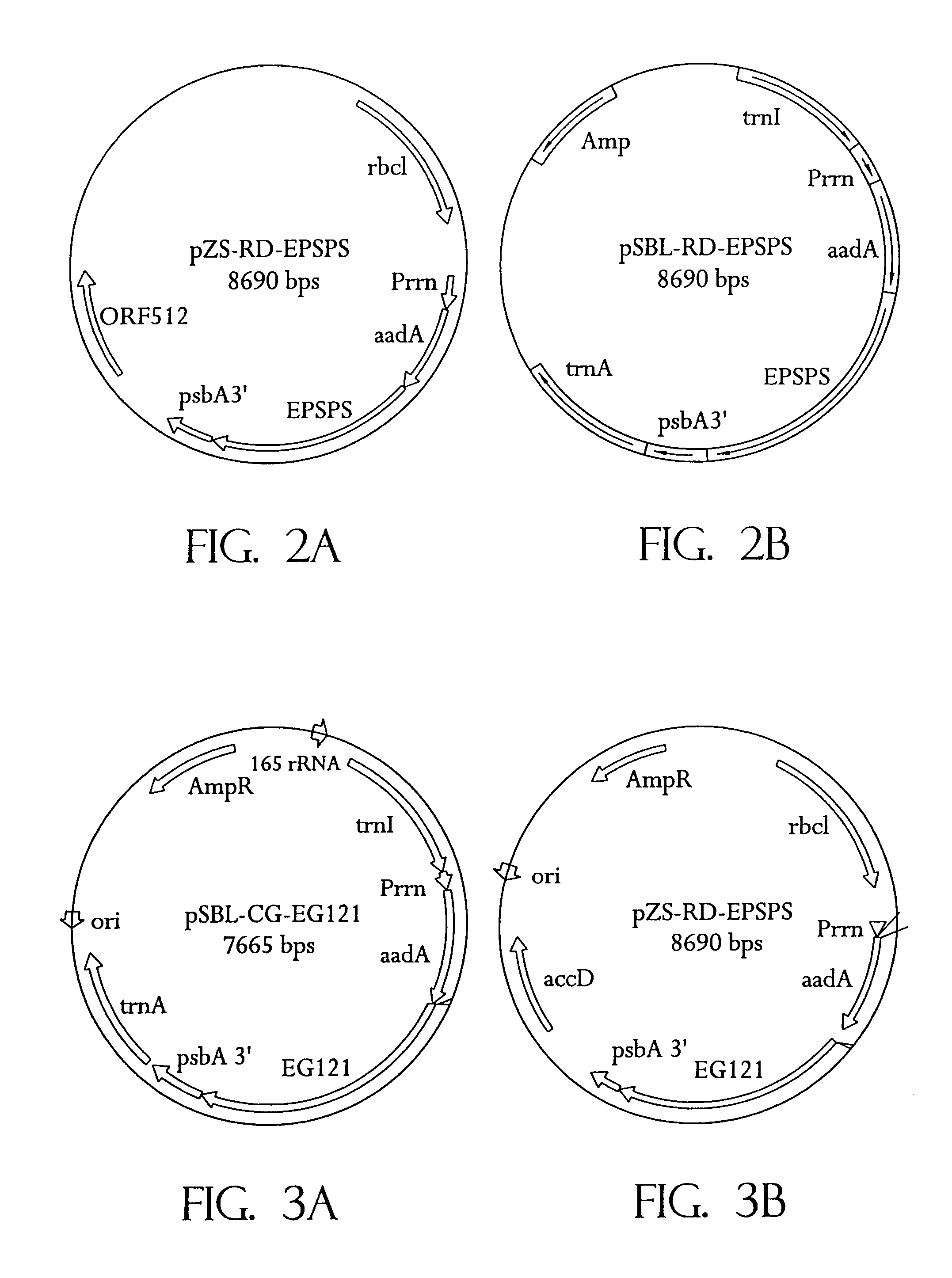
Glyphosate-tolerant 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthases
InactiveUSRE39247E1Reduce amount of overproductionGlyphosate toleranceSugar derivativesTransferasesPhosphateGenetically modified crops
Genes encoding Class II EPSPS enzymes are disclosed. The genes are useful in producing transformed bacteria and plants which are tolerant to glyphosate herbicide. Class II EPSPS genes share little homology with known, Class I EPSPS genes, and do not hybridize to probes from Class I EPSPS's. The Class II EPSPS enzymes are characterized by being more kinetically efficient than Class I EPSPS's in the presence of glyphosate. Plants transformed with Class II EPSPS genes are also disclosed as well as a method for selectively controlling weeds in a planted transgenic crop field.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Trophic conversion of obligate phototrophic algae through metabolic engineering
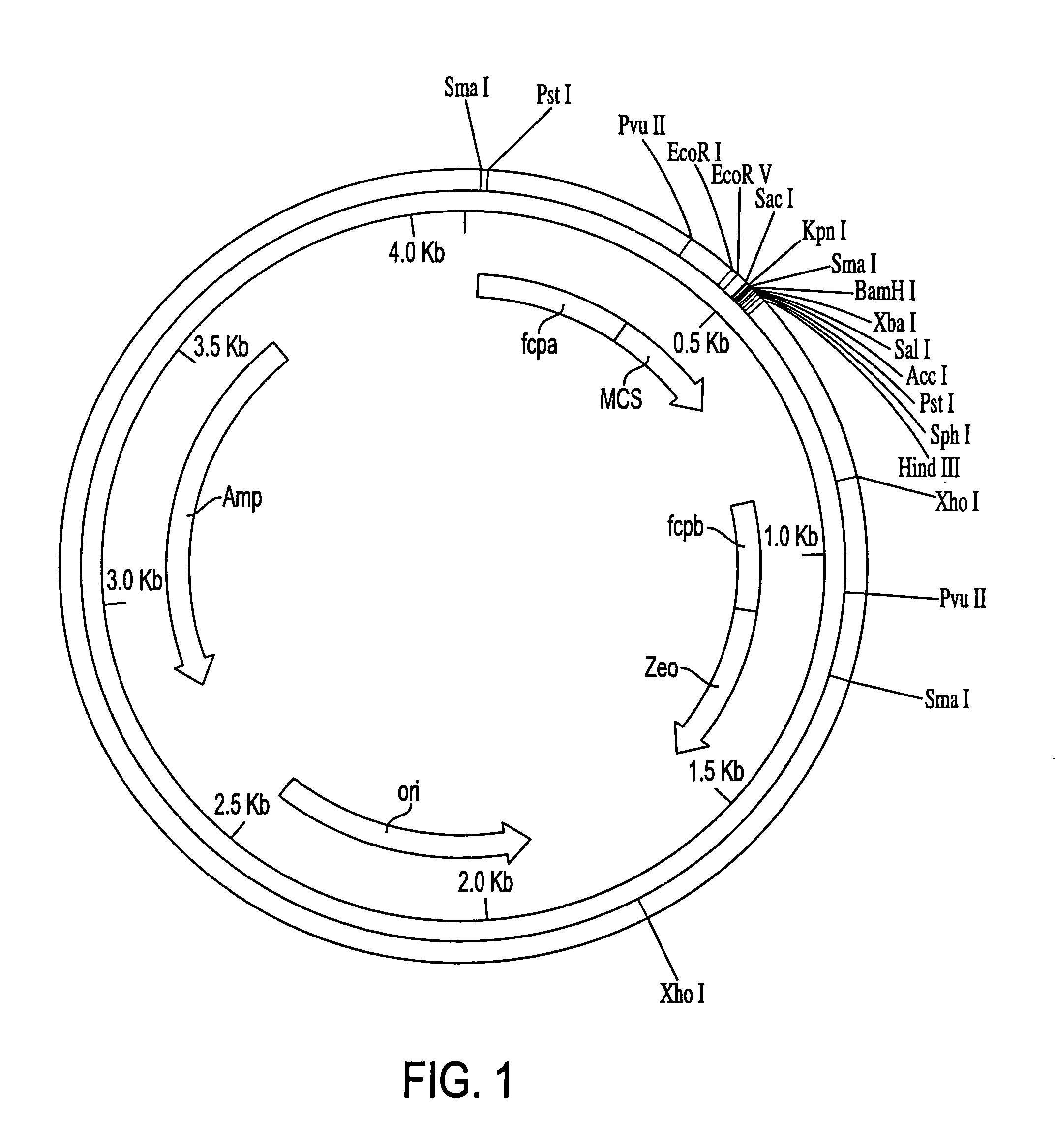
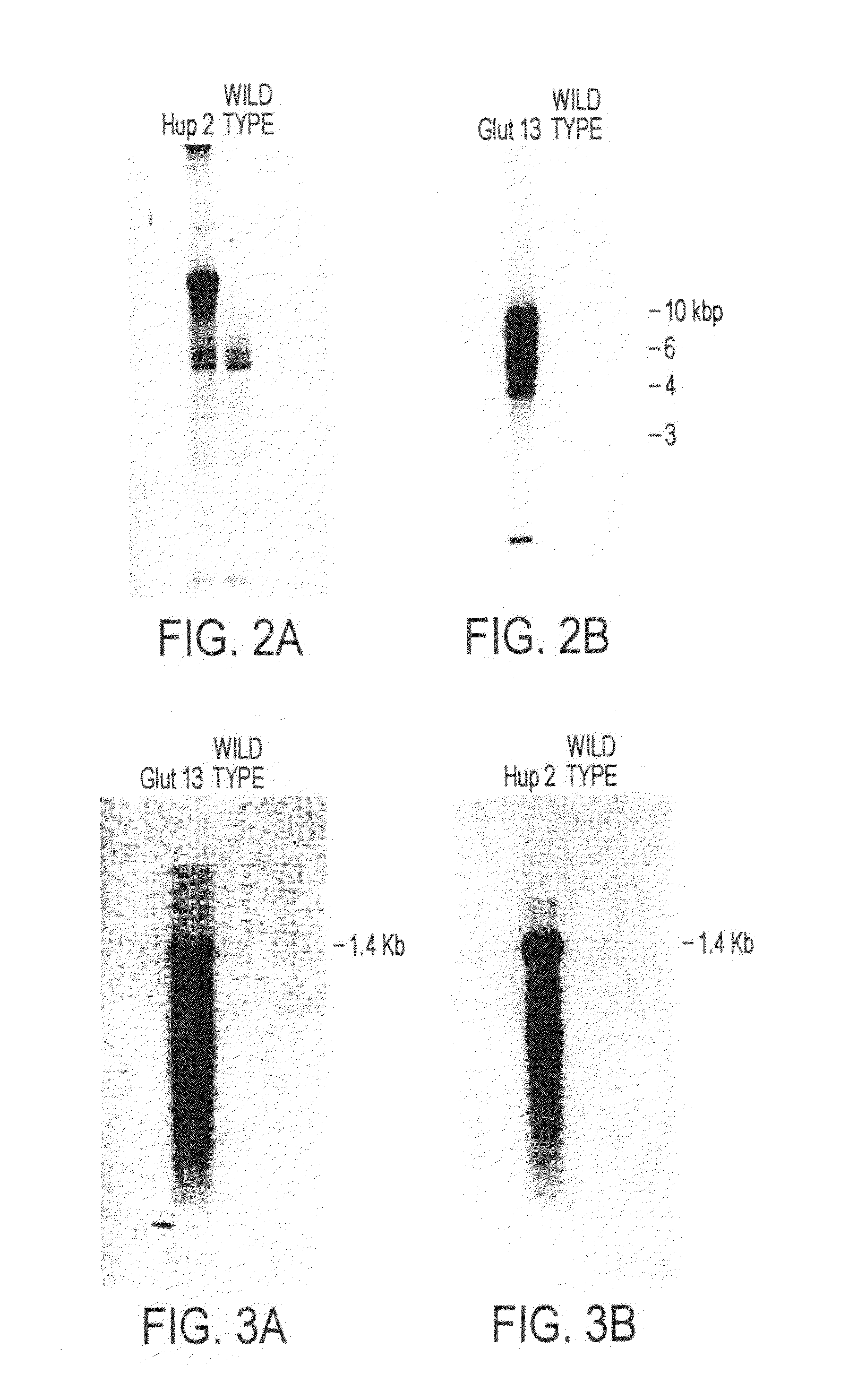
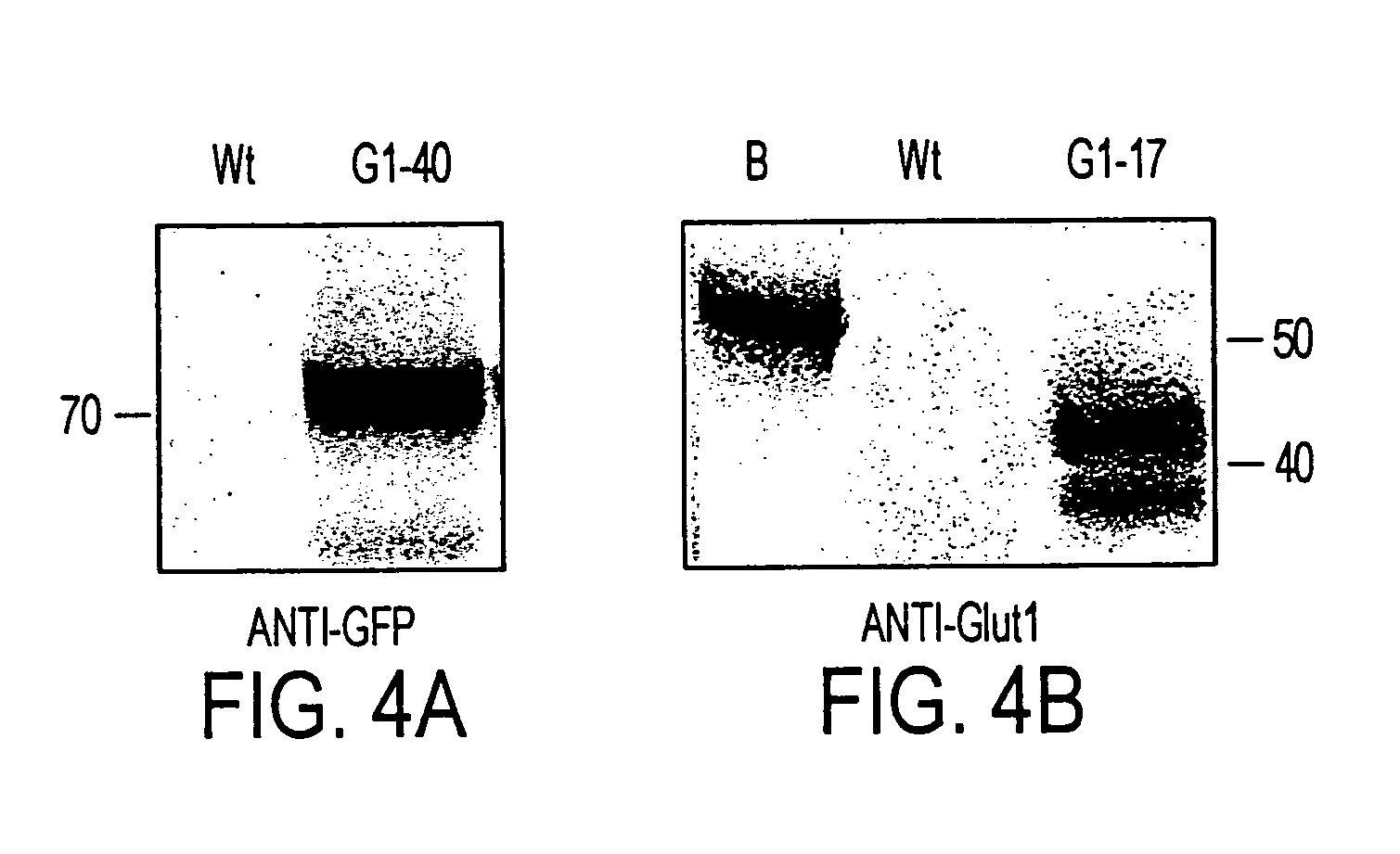
Most microalgae are obligate photoautotrophs and their growth is strictly dependent on the generation of photosynthetically-derived energy. In this study it is shown that the microalga Phaeodaclylurn tricornutum can be engineered to import glucose and grow in the dark through the introduction of genes encoding glucose transporters. Both the human and Chlorella kessleri glucose transporters facilitated the uptake of glucose by P. tricornutum, allowing the cells to metabolize exogenous organic carbon and thrive, independent of light. This is the first successful trophic conversion of an obligate photoautotroph through metabolic engineering, and it demonstrates that methods of cell nourishment can be fundamentally altered with the introduction of a single gene. Since strains transformed with the glucose transport genes are able to grow non-photosynthetically, they can be exploited for the analysis of photosynthetic processes through mutant generation and characterization. Finally, this work also represents critical progress toward large-scale commercial exploitation of obligate phototrophic algae through the use of microbial fermentation technology, eliminating significant limitations resulting from light-dependent growth.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Expression of phytase in plants
The present invention provides for the expression of phytase in transgenic plants or plant organs and methods for the production of such plants. DNA expression constructs are provided for the transformation of plants with a gene encoding phytase under the control of regulatory sequences which are capable of directing the expression of phytase. These regulatory sequences include sequences capable of directing transcription in plants, either constitutively, or stage and / or tissue specific, depending on the use of the plant or parts thereof. The transgenic plants and plant organs provided by the present invention may be applied to a variety of industrial processes either directly, e.g. in animal feeds or alternatively, the expressed phytase may be extracted and if desired, purified before application.
Owner:SYNGENTA MOGEN BV +1
Gene and its application in treatment of quinoline contaminant
The invention discloses a new gene purE1 which has high degradability on quinoline. Experiment shows that by using the purE1 gene to transform a microbe, the microbe can obtain degradation activity on quinoline, and the maximal degradation concentration of the degradation activity of the microbe provided by the purE1 gene and its coded protein is up to 850 mg / L. The invention has very important practical application value for the treatment of quinoline contaminants.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
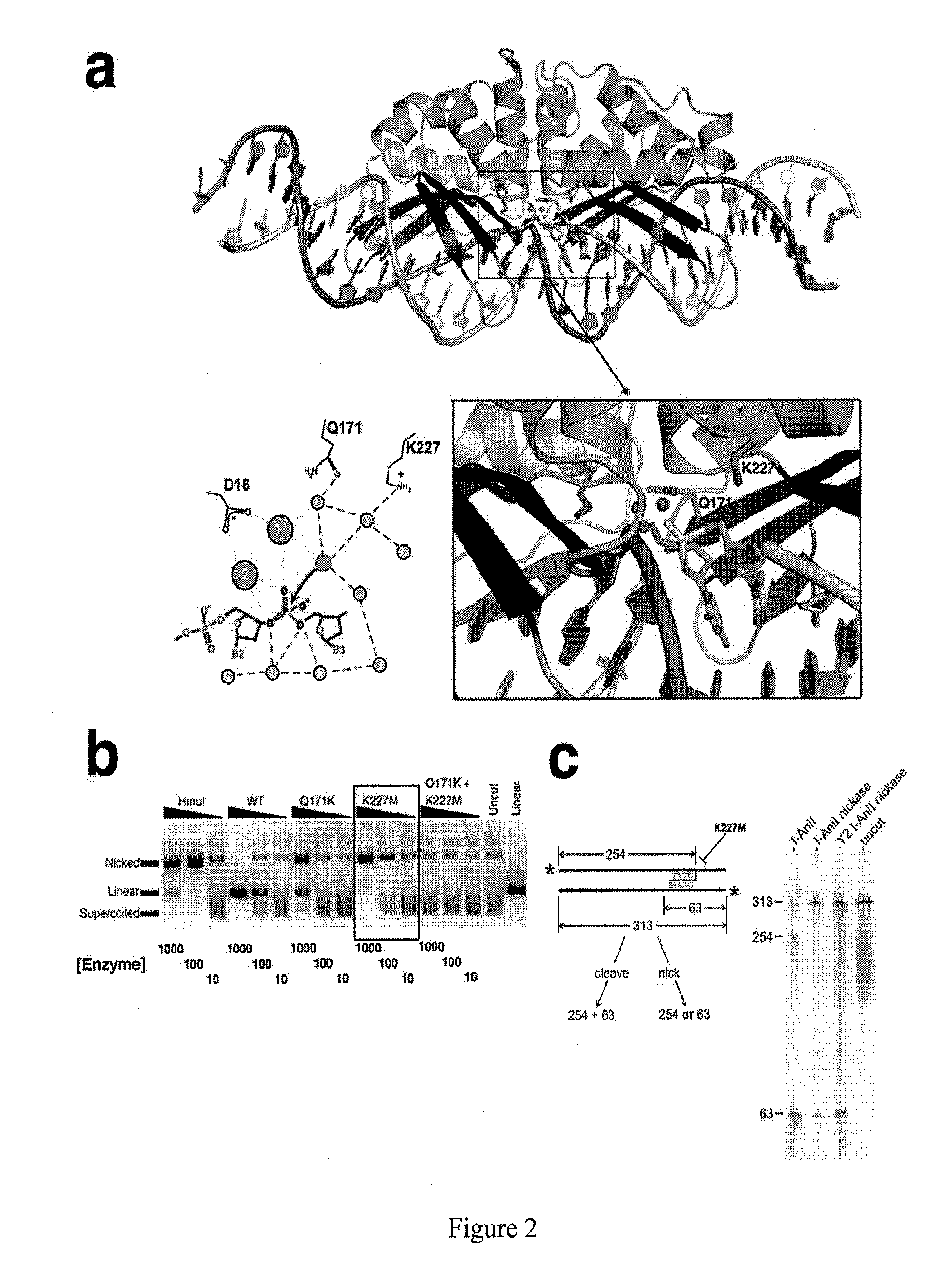
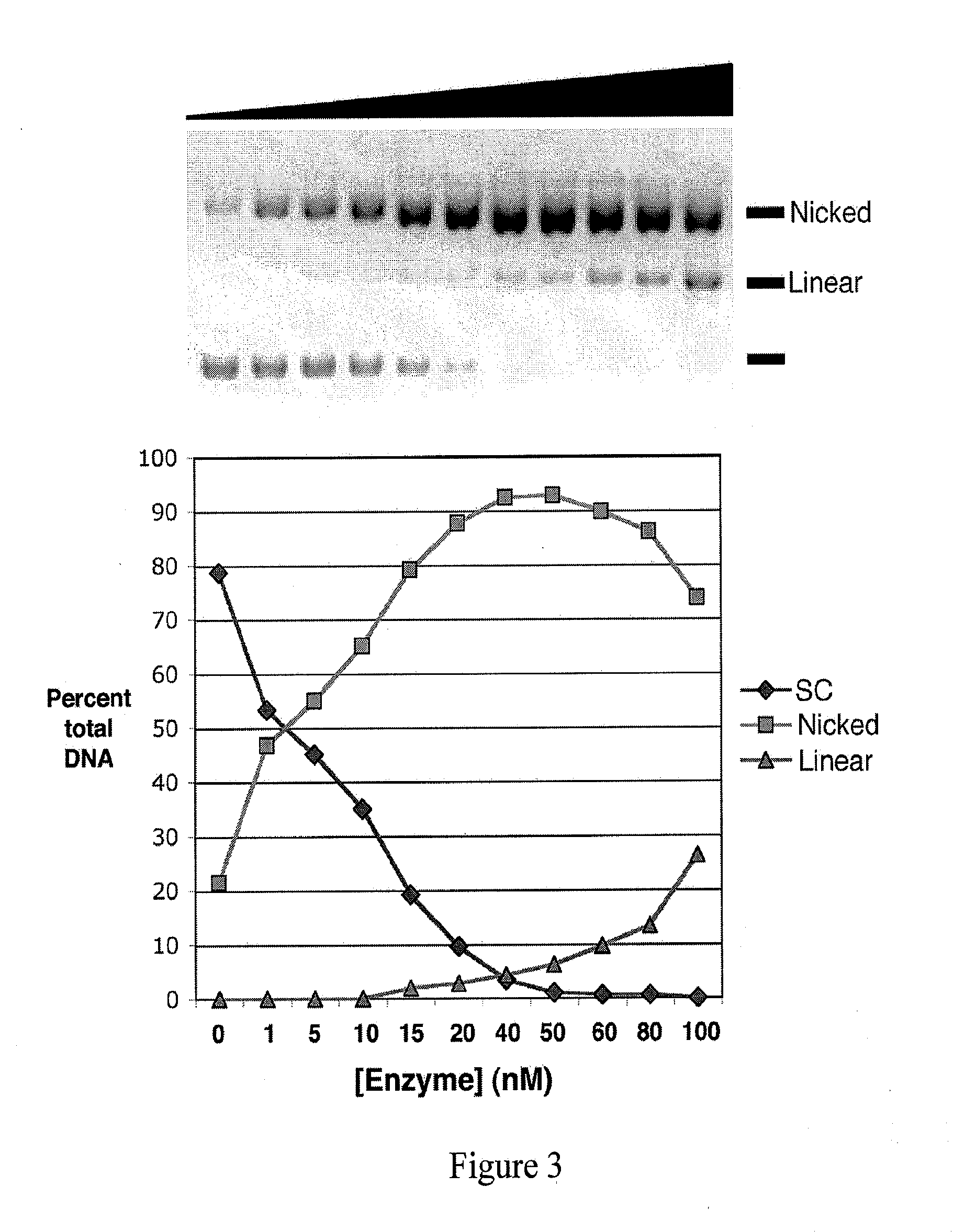
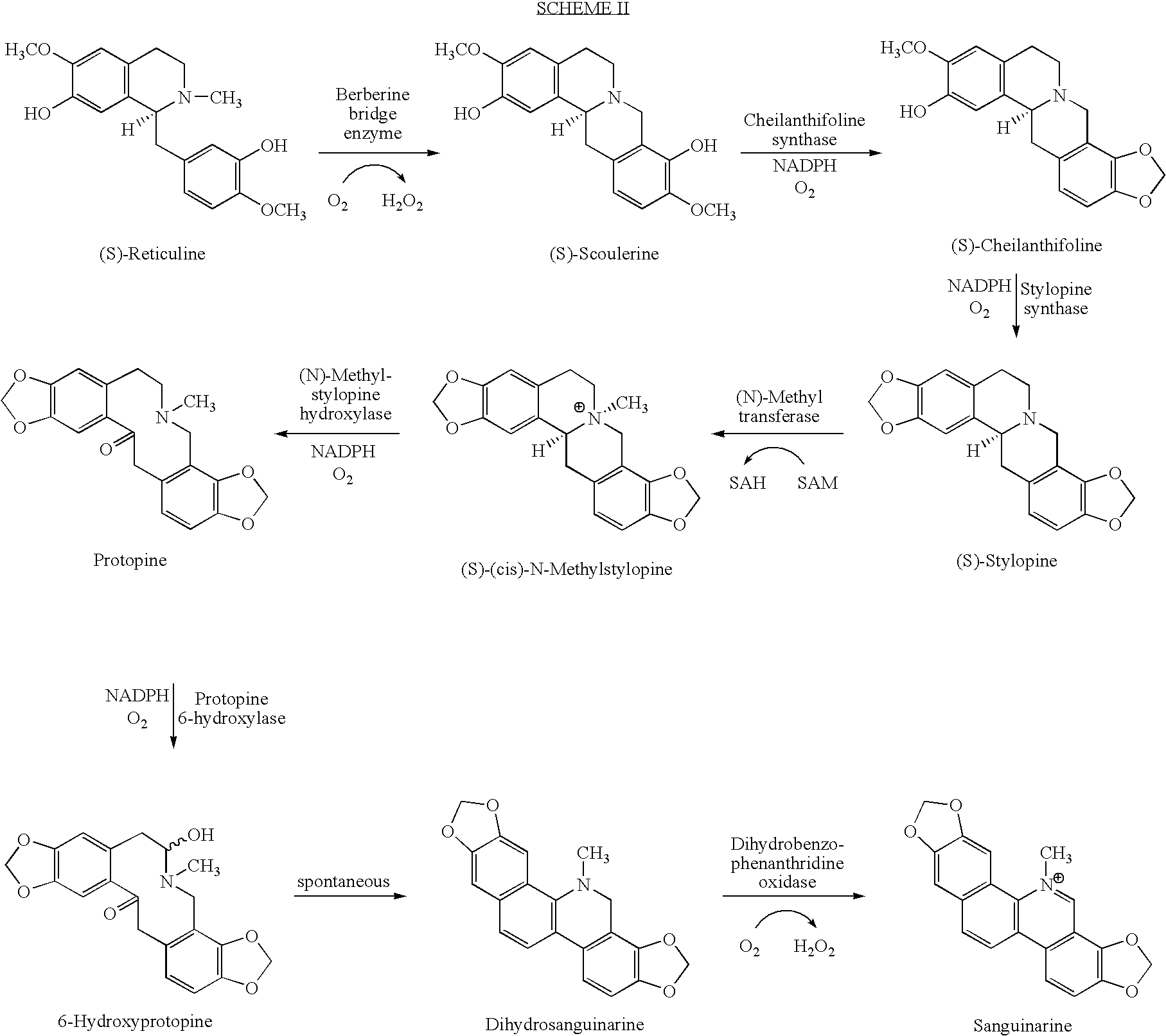
DNA nicking enzyme from a homing endonuclease that stimulates site-specific gene conversion
An engineered highly specific DNA-cleavage enzyme delivers a site-specific nick in a double stranded DNA, to cleave one DNA strand within its target site while leaving the opposing DNA strand intact. The engineered enzyme provides the ability to induce a gene conversion event in a mammalian cell. An engineered sequence-specific nickase derived from a LAGLIDADG homing endonuclease is altered by a single amino acid residue, wherein the amino acid residue is involved in the polarization of solvent molecules and acid-base catalysis in the active site without affecting direct contacts between the enzyme and either the bound DNA or bound metal ions. Engineered, site-specific nickase variants, such as of I-AniI and other homing endonucleases, are particularly useful in targeted genome engineering as well as therapeutic, targeted gene repair.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Method of preparing transgenic organism with use of methylation and system therefor
InactiveUS20070022485A1Improve conversion efficiencyEfficient productionAnimal cellsHydrolasesGene conversionOrganism
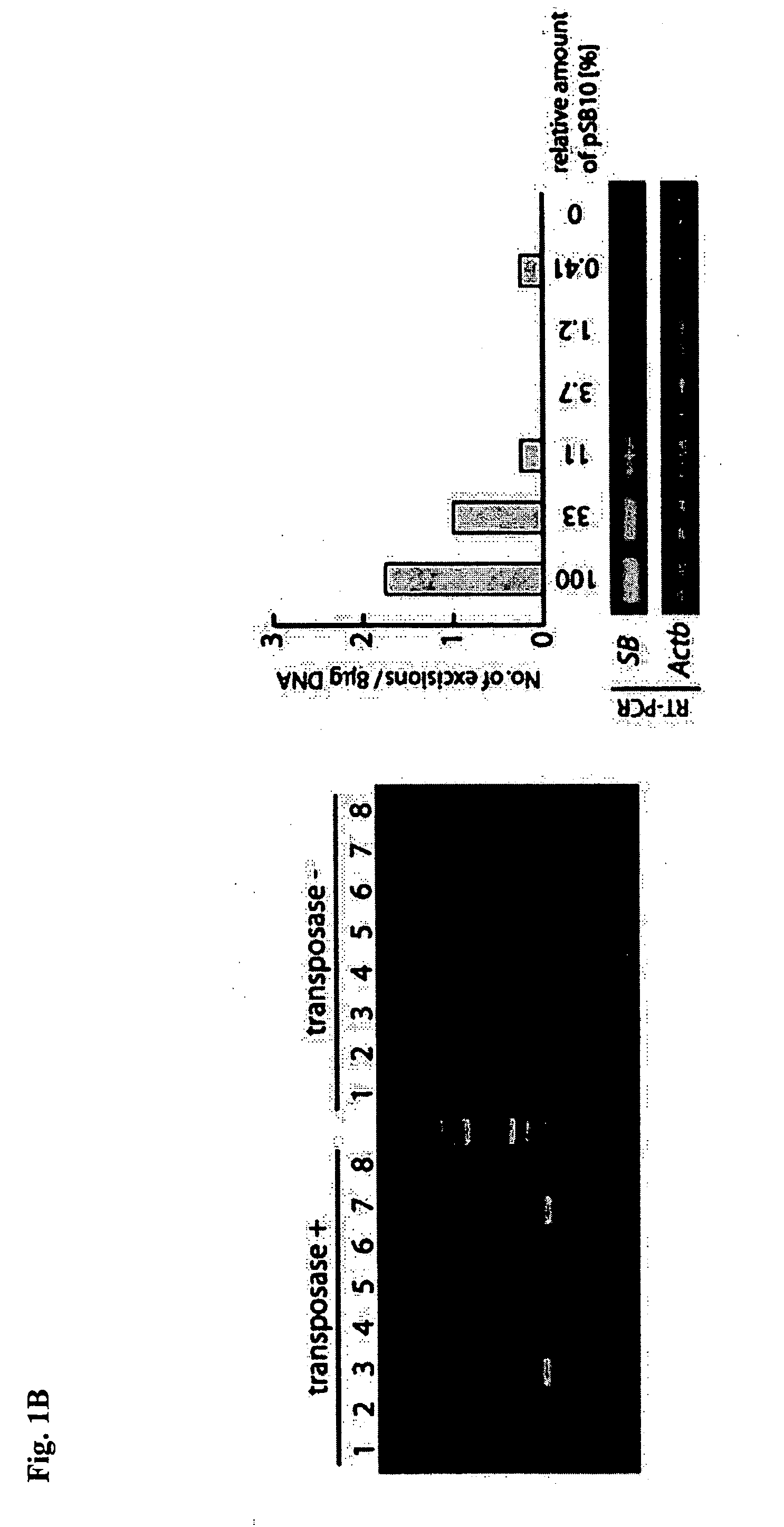
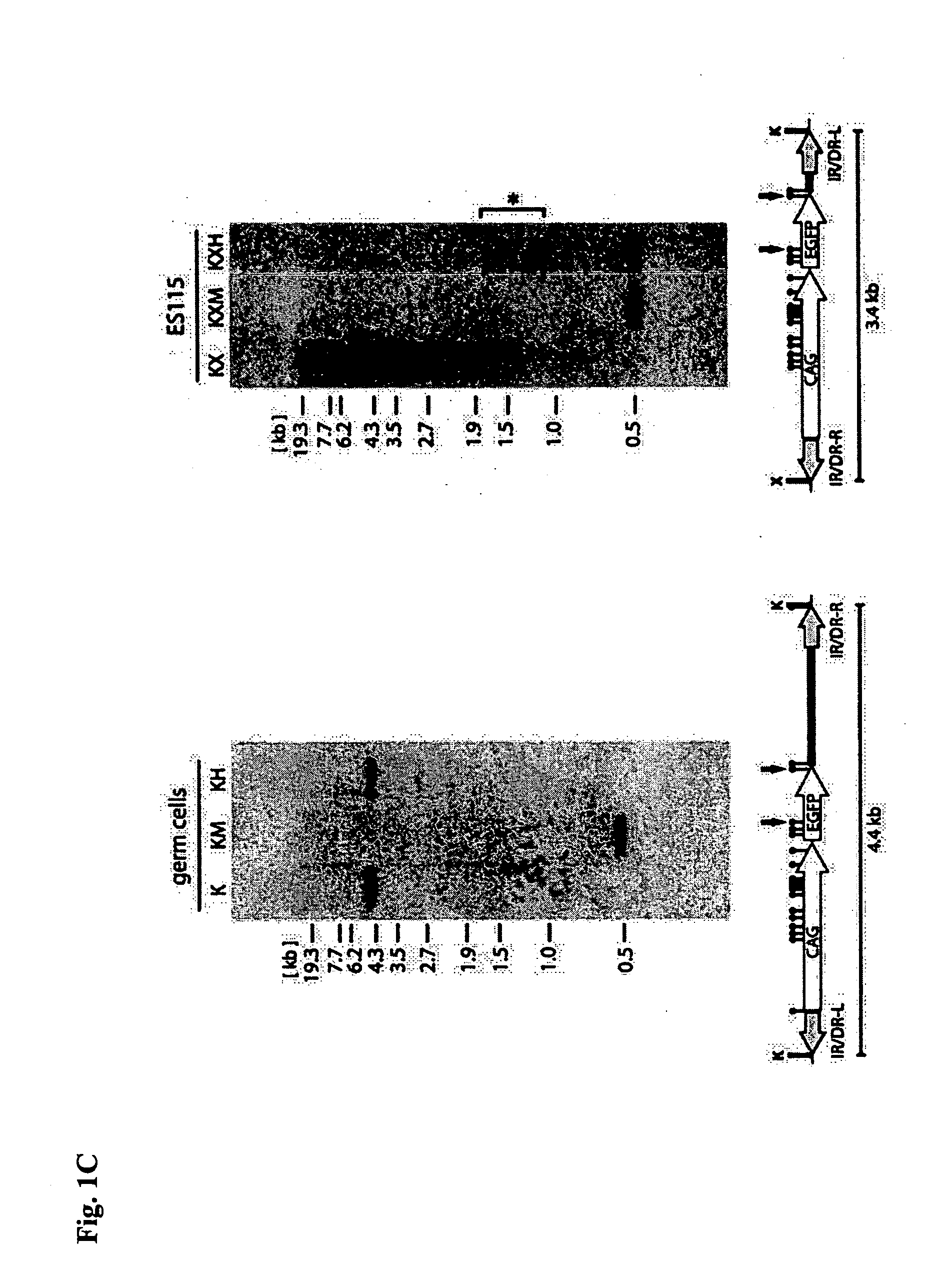
A technique for efficiently introducing a foreign gene into cells with the use of transposons. In particular, a technique for efficiently preparing a transgenic organism with the use of a transposon having its transposition activity strikingly enhanced through methylation of a sequence containing the transposon. The methylation is retained even after incorporation in a genome, and now can be utilized in actual gene incorporation in a genome. This technique can realize strikingly efficient gene transformation as compared with the a method of preparing a transgenic organism with the use of conventional transposons.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Regulation of heterologous recombinant protein expression in methylotrophic and methanotrophic bacteria
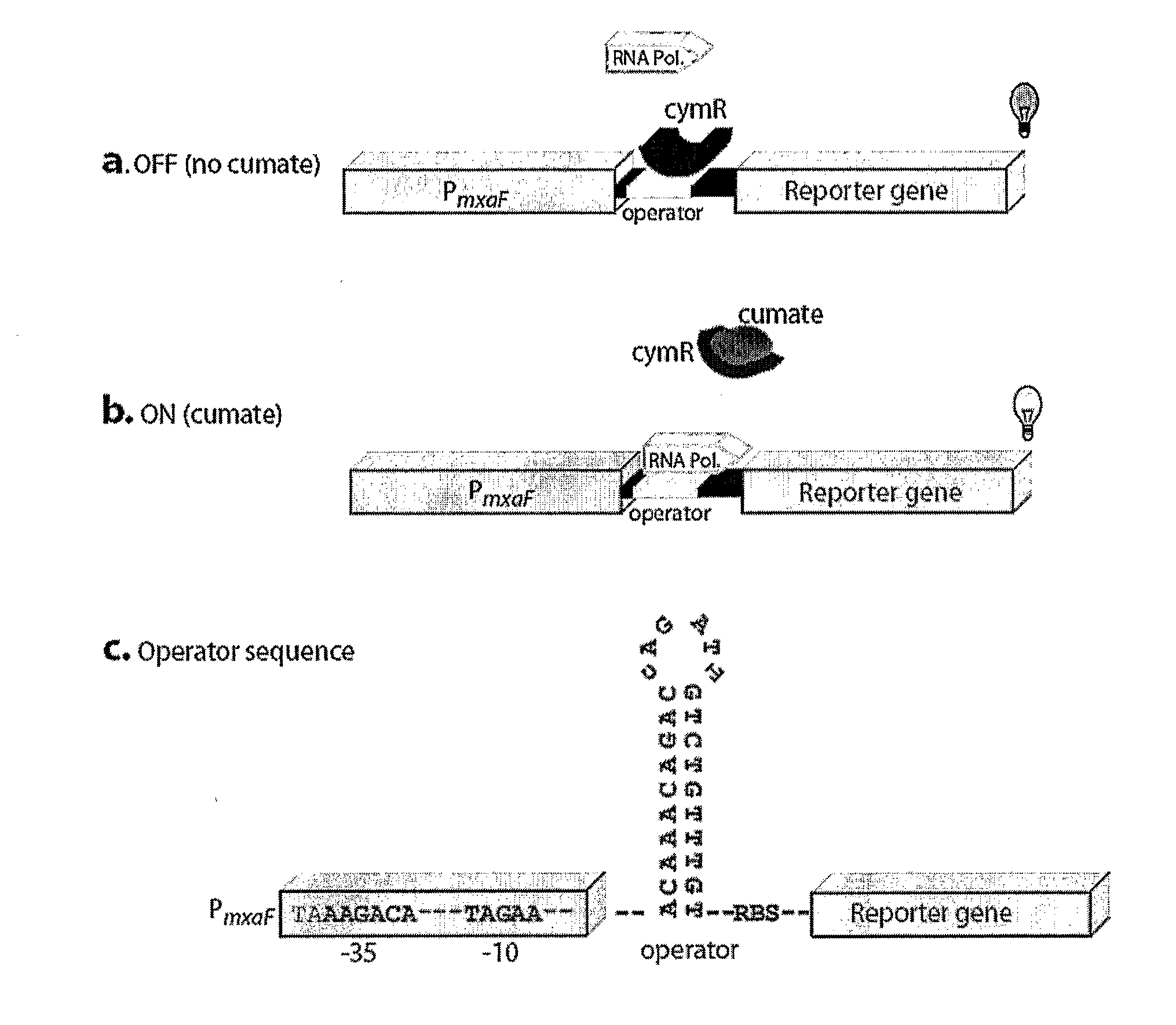
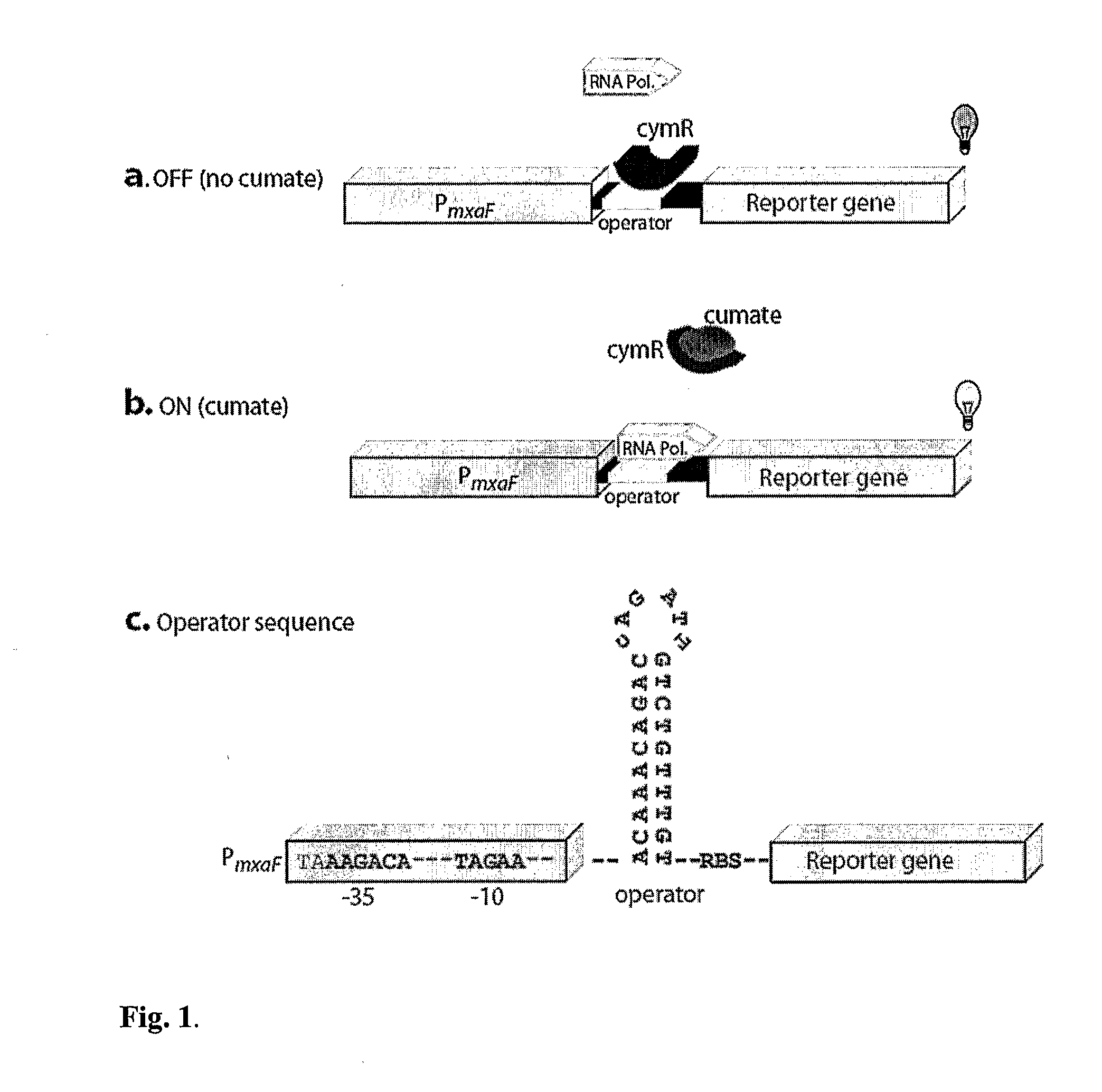
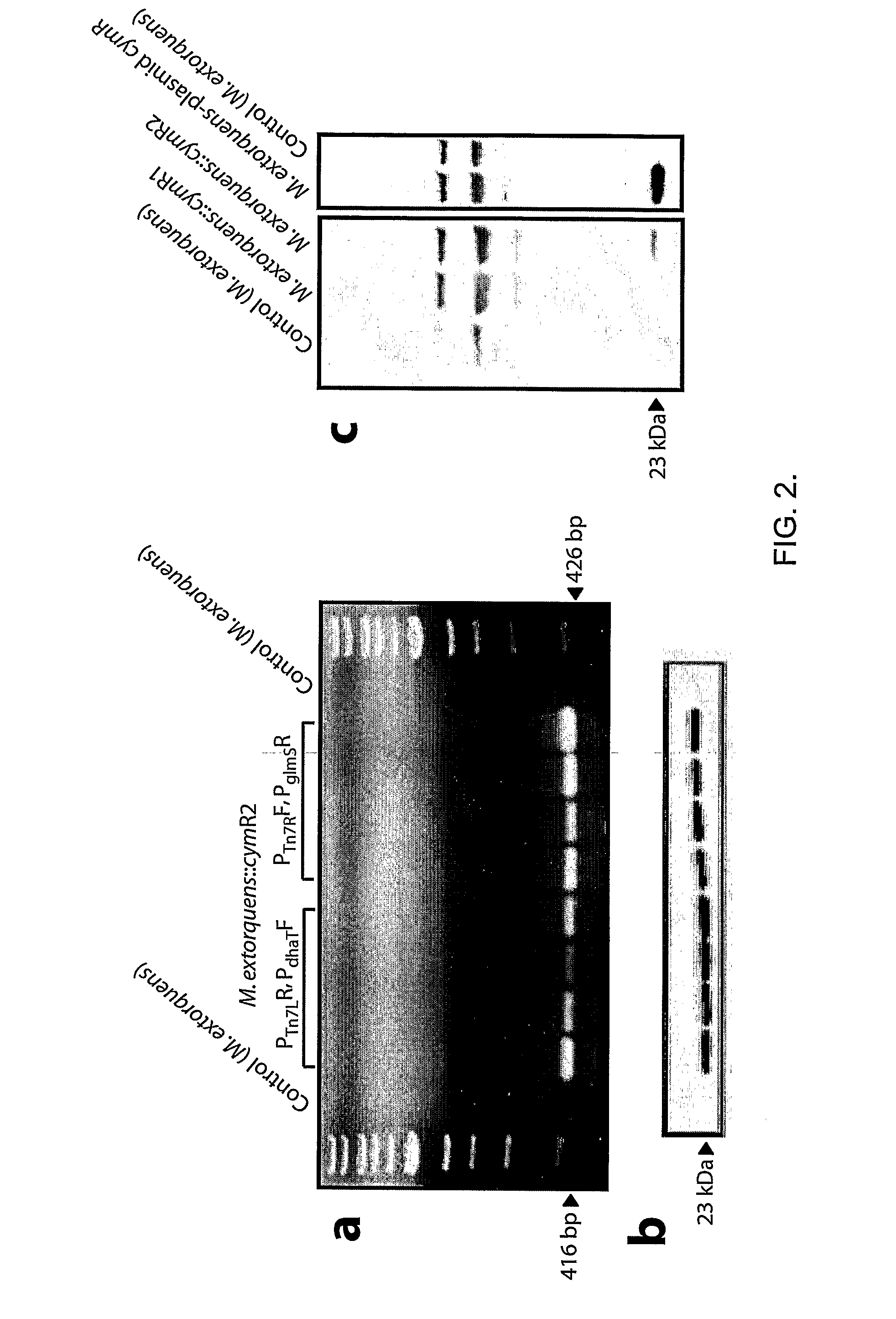
Methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria such as Methylobacterium are transformed with a gene of interest, and expression of the gene is regulated by means of a cumate repressor protein and an operator sequence which is operatively linked to the gene of interest, and the addition of an external agent. Specifically, the cymR repressor and cmt operator from Pseudomonas putida may serve to regulate gene expression in methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria with the addition of cumate.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
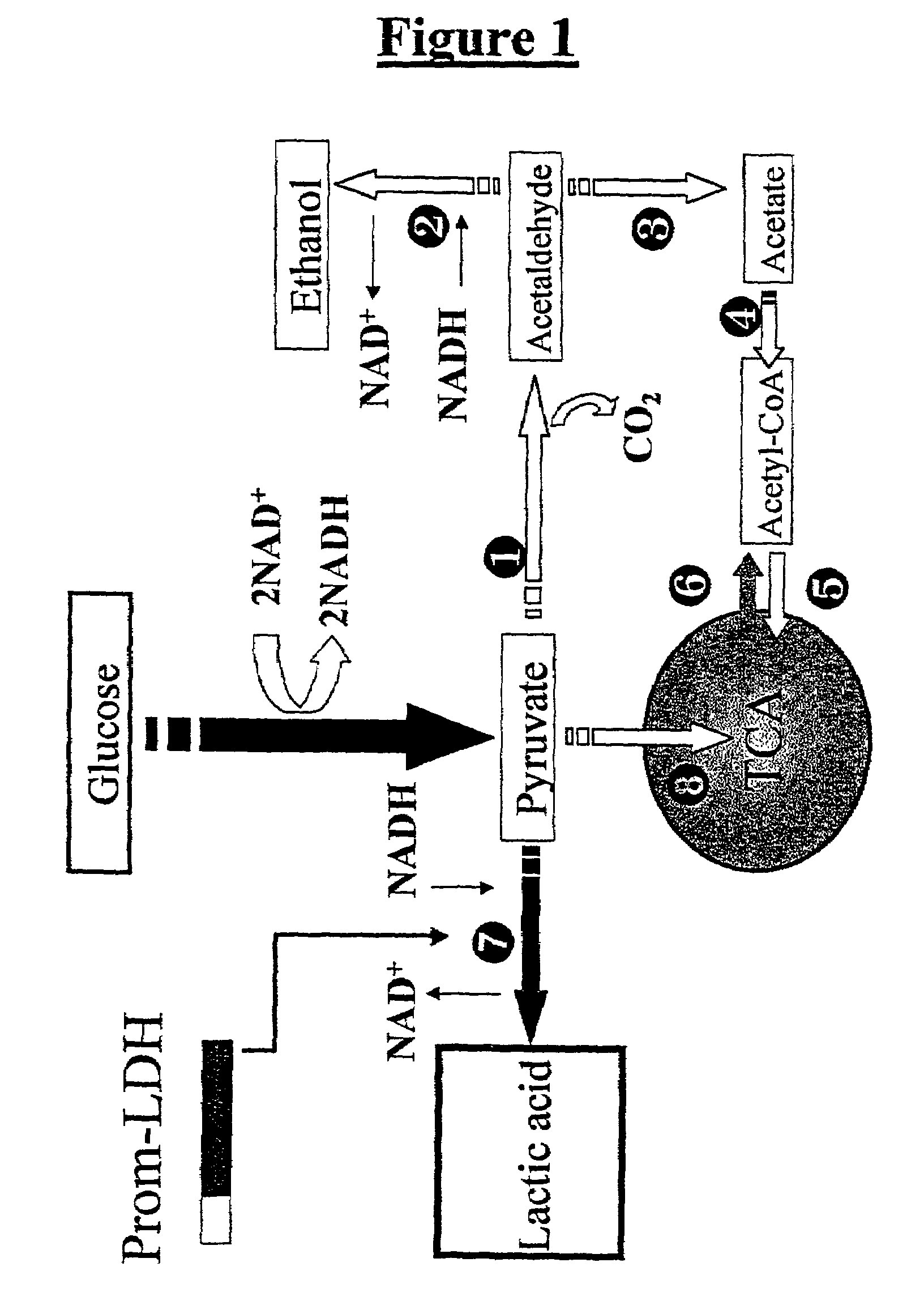
Processes for producing lactic acid using yeast transformed with a gene encoding lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Clone and application of a gene improving rice drought tolerance and relative with ABA synthesis
ActiveCN101173287AAffect normal growthAffect economyPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGene conversion
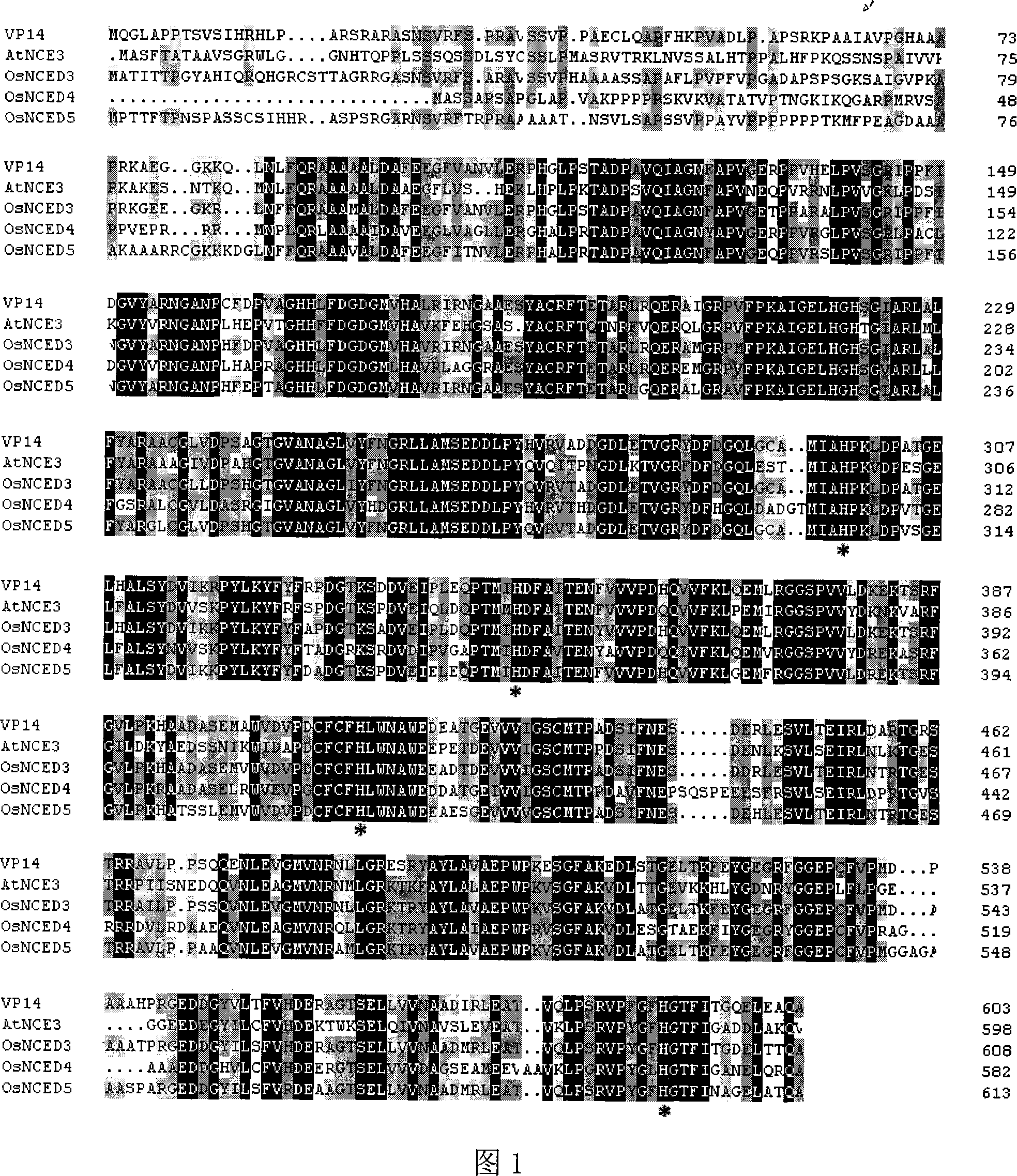
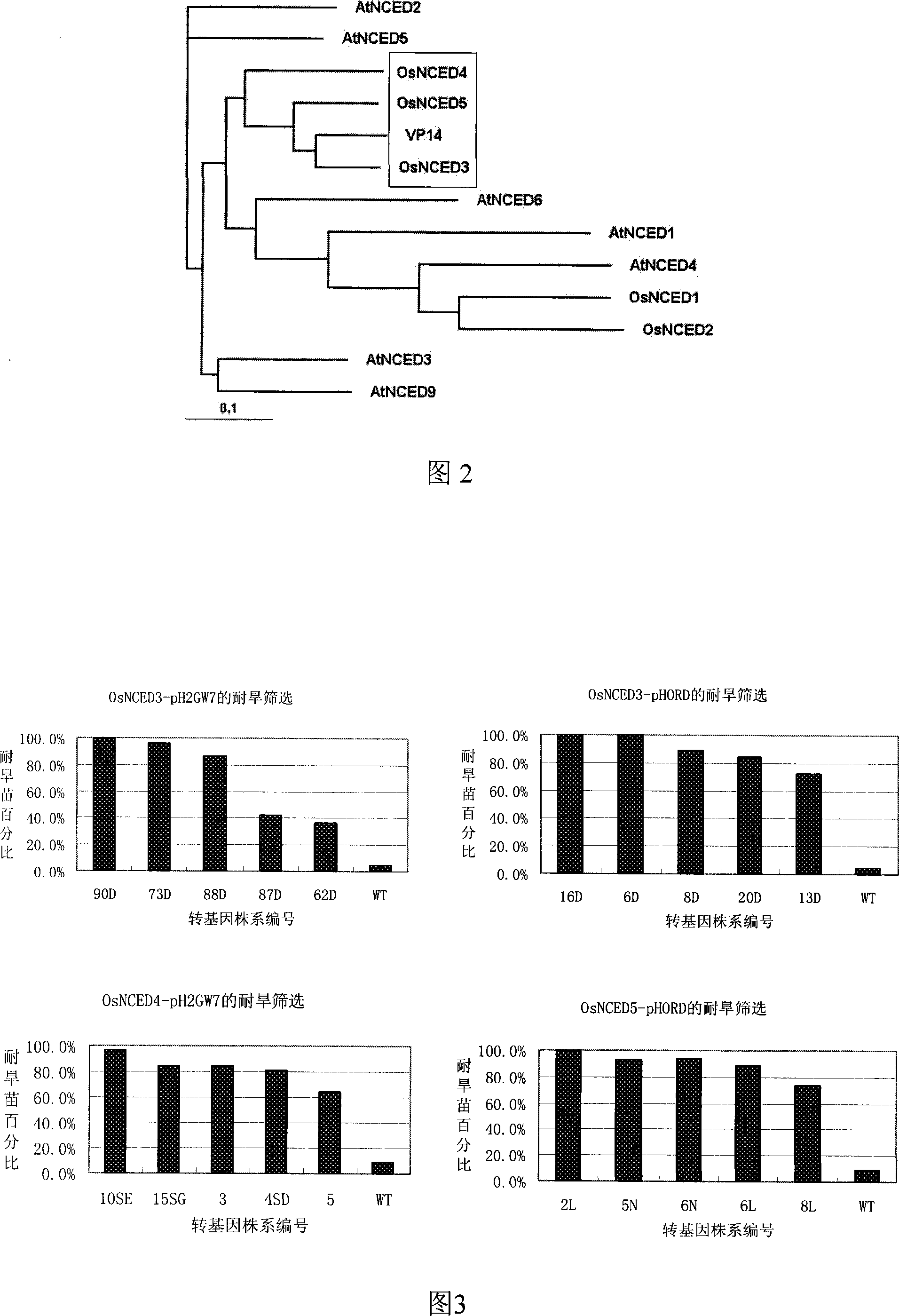
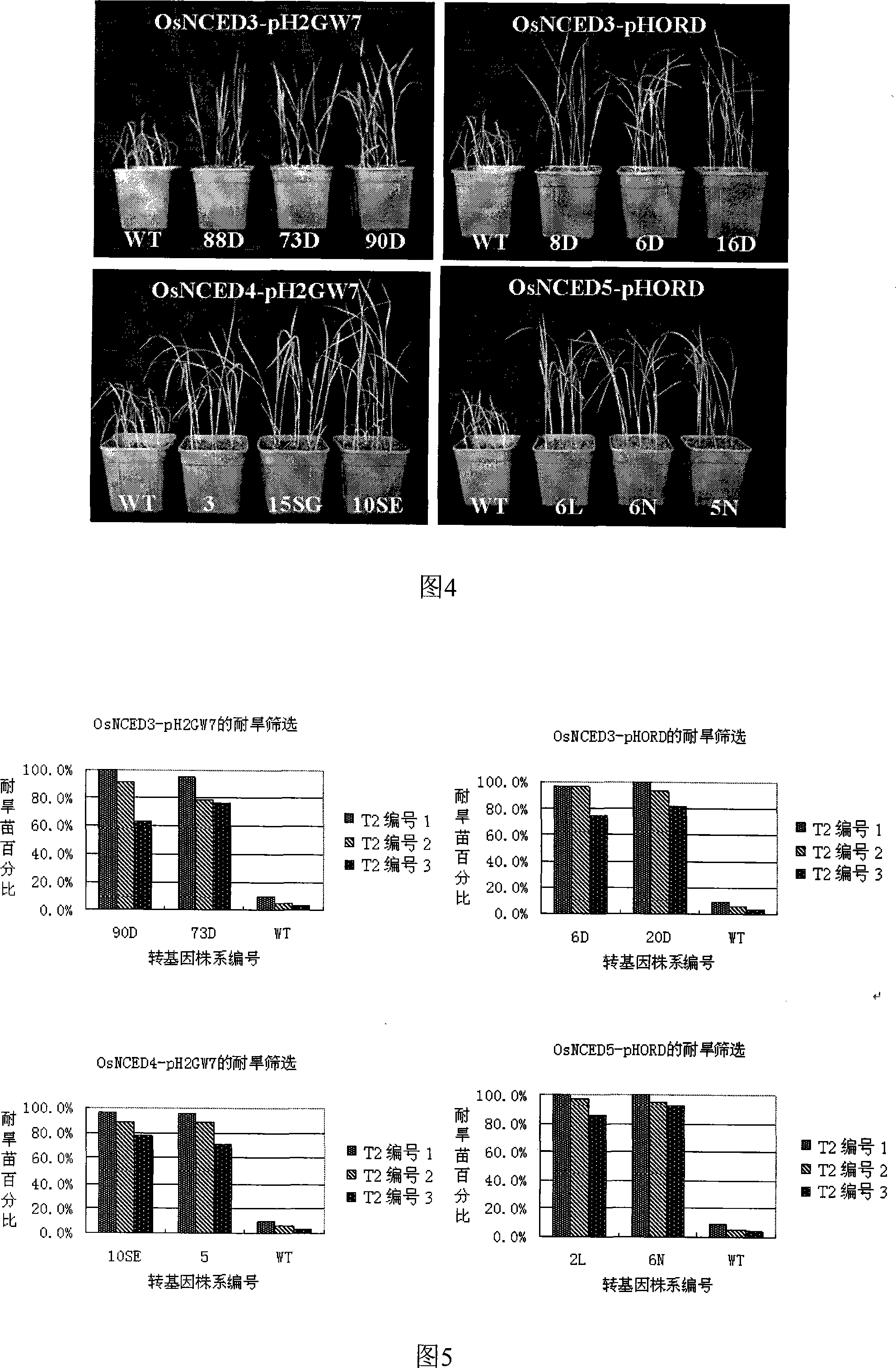
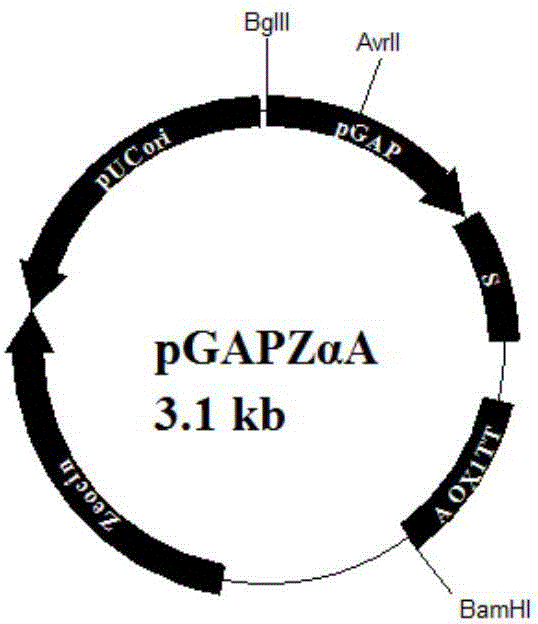
The invention discloses an OsNCEDs gene relative to drought resistance originating from rice. Coded protein has one of the following amino acid sequences: 1). SEQ ID NO: 1, 3 or 5 in sequence list; 2). The amino acid residue sequence for the SEQ ID NO: 1, 3 or 5 in the sequence list pass through replacing, lacking or adding of one to ten amino acid residue and derived protein has the function of controlling drought resistance of plants. The experiment proves that: the gene conversion rice can obviously improve drought resistance of rice. The invention has the advantages of having an important theory and actual meaning upon research of drought resistance mechanism for plants and improving drought resistance and relative characteristics, playing an important role in drought resistance gene engineering improvement for plants (especially for rice crops) and having wide application prospect.
Owner:未名三农生物农业技术有限公司
Method for improving expression amount of secretory foreign protein in pichia pastoris
ActiveCN104152484AHigh expressionPromotes proper foldingFungiMicroorganism based processesForeign proteinSecretion expression
The invention aims to provide a method for improving the expression amount of secretory foreign protein in pichia pastoris. Byintracellular co-expression of double genes of HAC1 and ERO1 or three genes of HAC1, ERO1 and BIP in pichia pastoris, the expression amount of secretory foreign protein in pichia pastoris is effectively improved. According to the invention, double genes of HAC1 and ERO1 or three genes of HAC1, ERO1 and BIP are transformed into pichia pastoris secreting and expressing exogenous xylanase to obtain recombinant pichia pastoris strains, thereby significantly increasing the expression amount of the exogenous xylanase. During co-expression of double genes of HAC1 and ERO1 in pichia pastoris, the secretion expression amount of exogenous xylanase is generally increased by 15%-25% compared with the initial level; and during the co-expression of three genes HAC1, ERO1 and BIP, the secretion expression amount of xylanase is increased by 45%-57% compared with the initial level.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
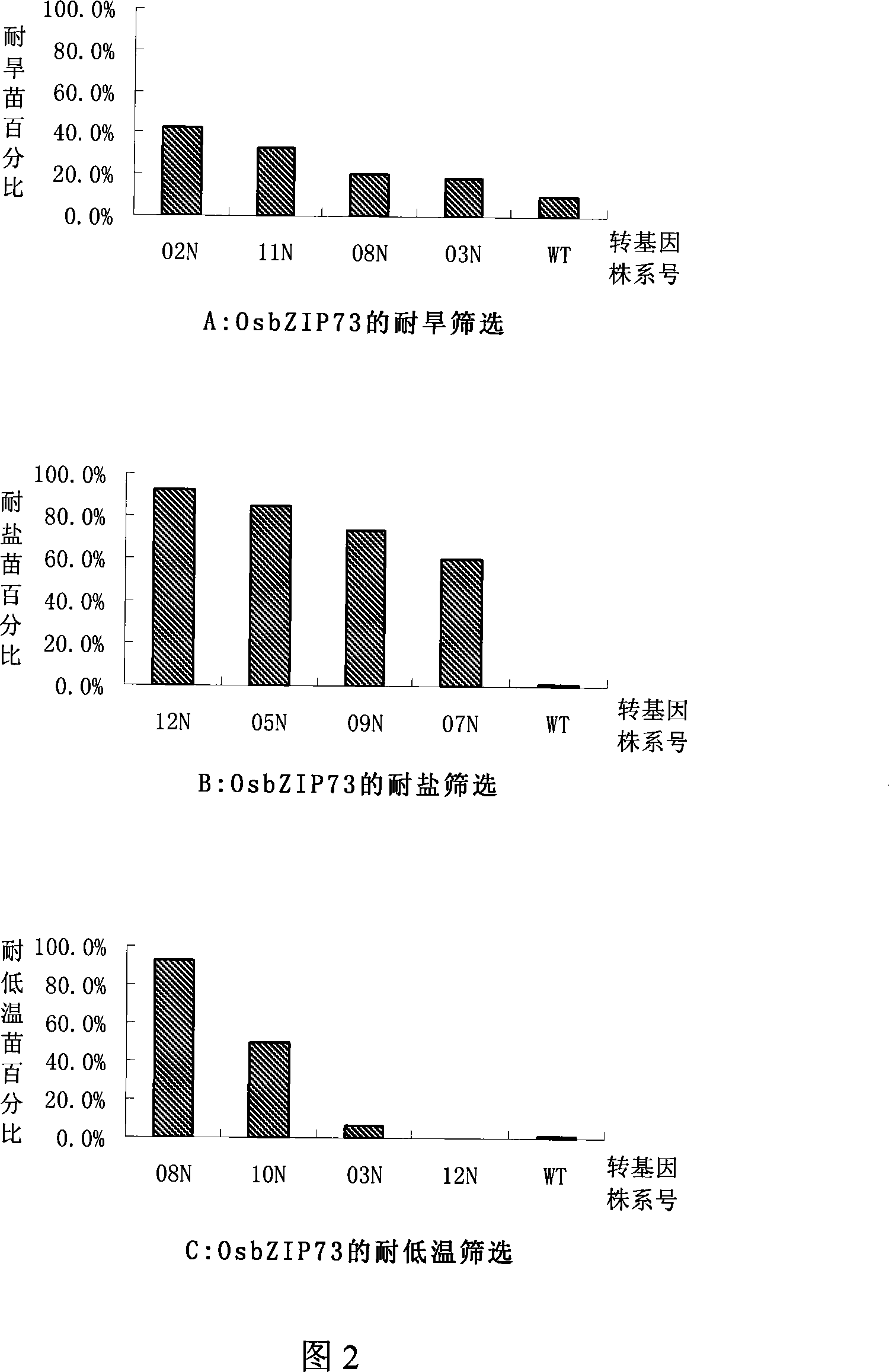
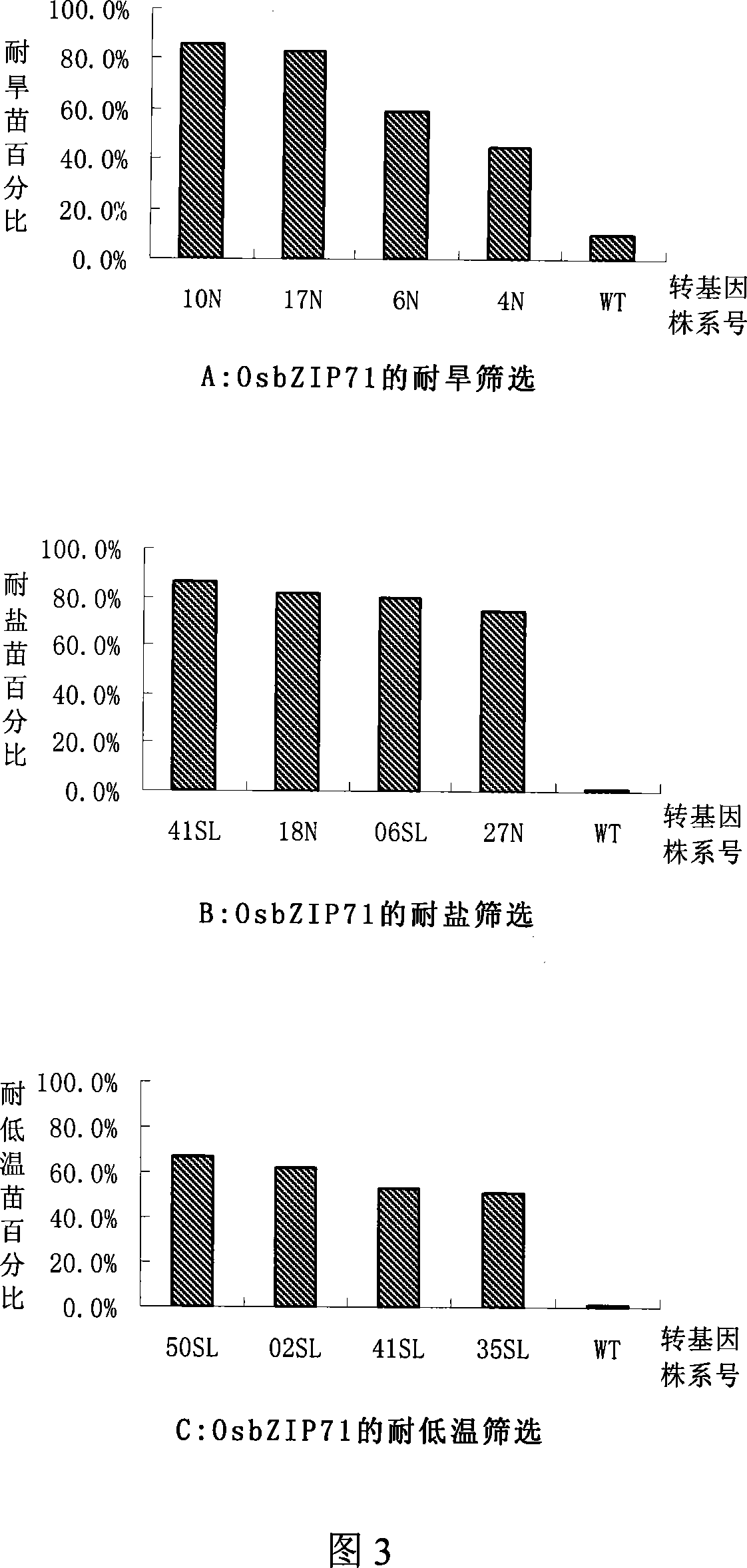
Rice bZIP and application of the same in improving stress tolerance of plants
ActiveCN101220363AImprove toleranceNo apparent effect on normal growthPlant peptidesFermentationNormal growthGene conversion
The invention discloses a group of bZIP genes which are derived from rice and are related with stress tolerance, the encoded protein has one of the following amino acid sequences: 1) the SEQ ID No:1, 3 or 5 in a sequence table; 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the SEQ ID No:1, 3 or 5 in the sequence table is treated with the substitution, deletion or adding of one to ten amino acid residues and the derived protein has the effect of regulating the performance of plant stress tolerance. The experiments proves that the transgenic rice of the invention can improve the tolerance of the rice to high-salt, drought and low-temperature adversity threats and have no apparent impacts on the normal growth and the economic traits of the rice. The protein and the encoded genes of the invention have important theoretical and practical significances on the research of a plant stress tolerance mechanism, the improvement of the plant stress tolerance and the improvement of the related traits, thereby playing an important role in the stress tolerance genetic engineering improvement of plants (more particularly cereal crops) and having broad application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
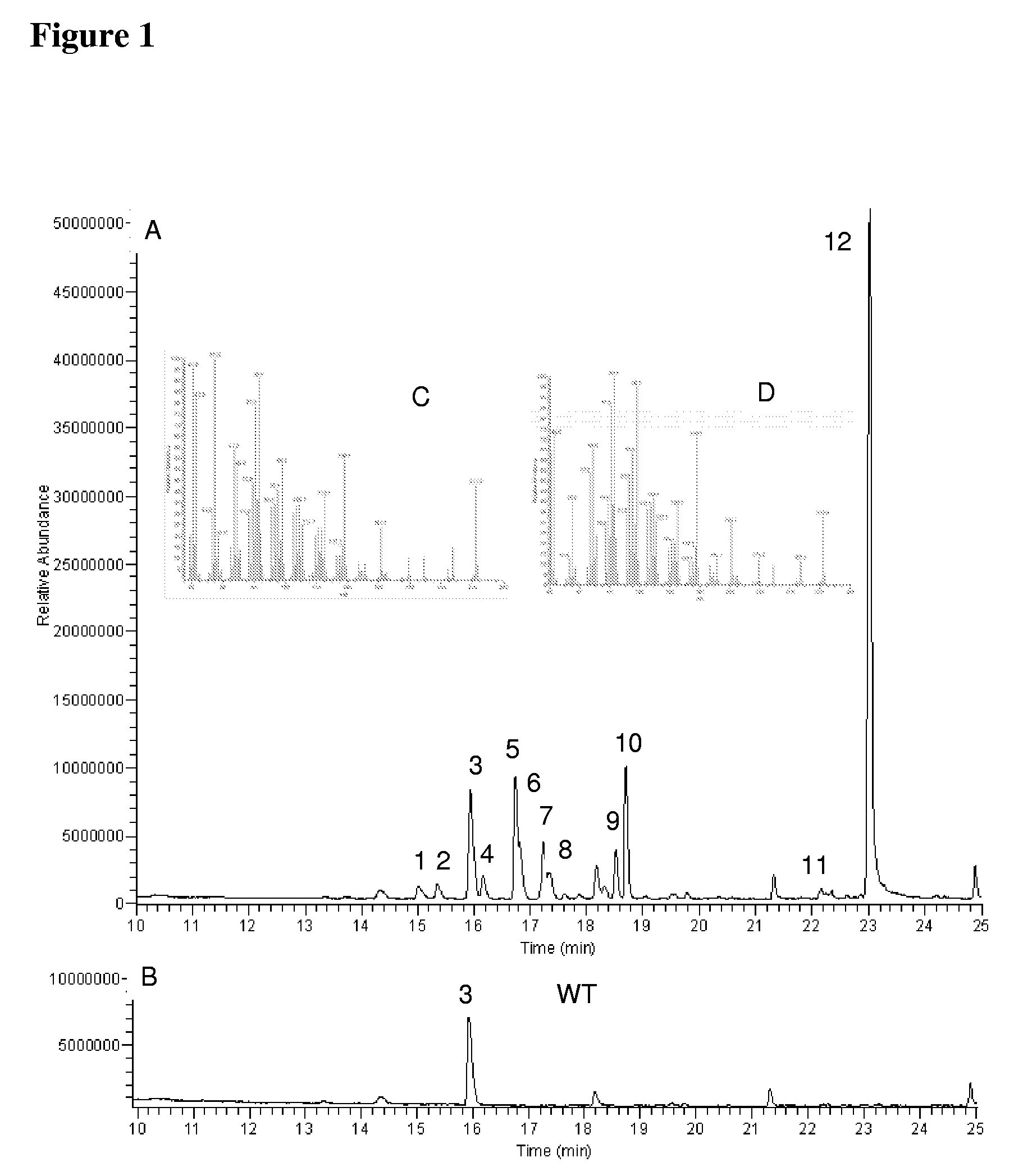
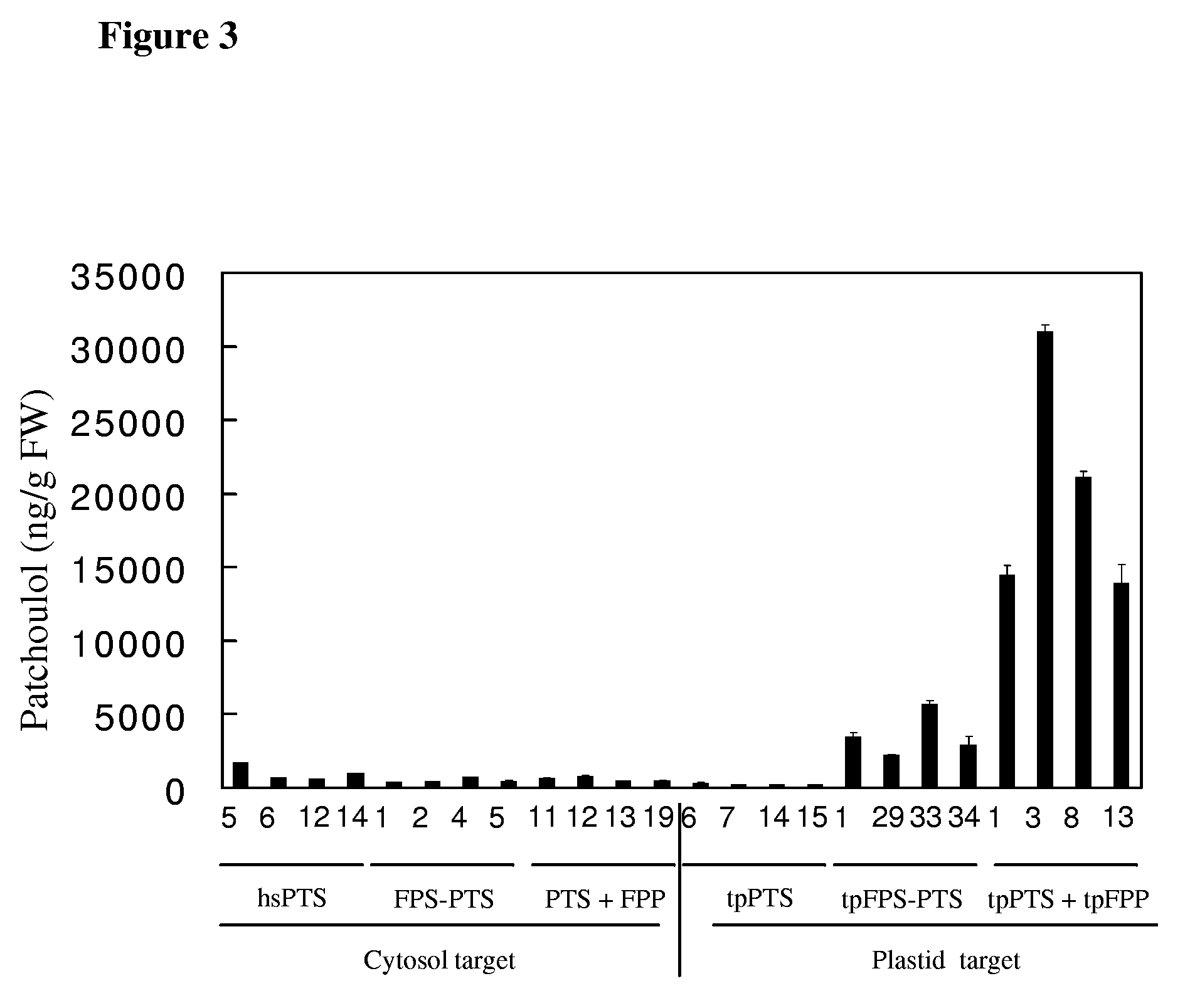
Transformed plants accumulating terpenes
InactiveUS20090123984A1Increase contentHigh yieldTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesTerpene synthaseGene conversion
The present invention relates to transformed plants with an altered terpene content, preferably over-accumulating a mono- or sesqui-terpene. By transformation of plants with genes encoding terpene synthases (TS), and prenyl transferases (PRT), plants accumulating at least 1000 ng / per g of fresh leaf of a specific terpene were obtained. The present invention provides an advantageous system for production of terpenes in that any desired mono- or sesqui-terpene at the choice of the skilled person can be produced in plants. Preferably, the transformed plants contain at least one recombinant plastid targeted TS and PRT.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane
InactiveCN102154364AOvercome serious shortfalls in conversionAddress serious deficienciesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMetal ArtifactTransformation efficiency
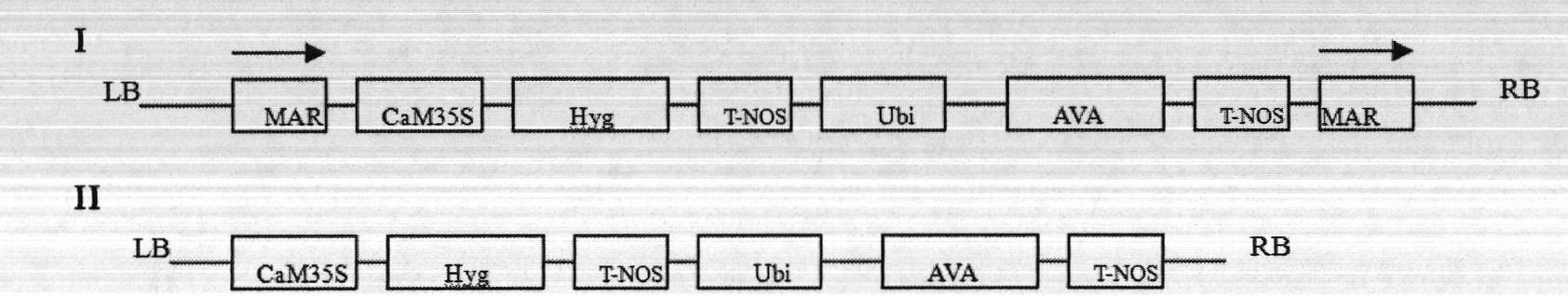
The invention discloses a method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane. The method comprises the steps: leading agrobacterium tumefaciens liquor carrying plant expression vectors to infect embryogenic callus of the sugarcane; and selecting and proliferating resistant calli to induce the resistant calli to obtain the resistant buds of the sugarcane, wherein matrix attachment region sequences are connected at two sides of a gene expression box of the plant expression vector. According to the method, MARs (metal artifact reduction) sequences are built at two sides of the gene expression box of the plant expression vector, thus greatly improving the exogenous gene transformation efficiency and seedling rate of the sugarcane, and being simple in process flow and low in cost.
Owner:广西作物遗传改良生物技术重点开放实验室
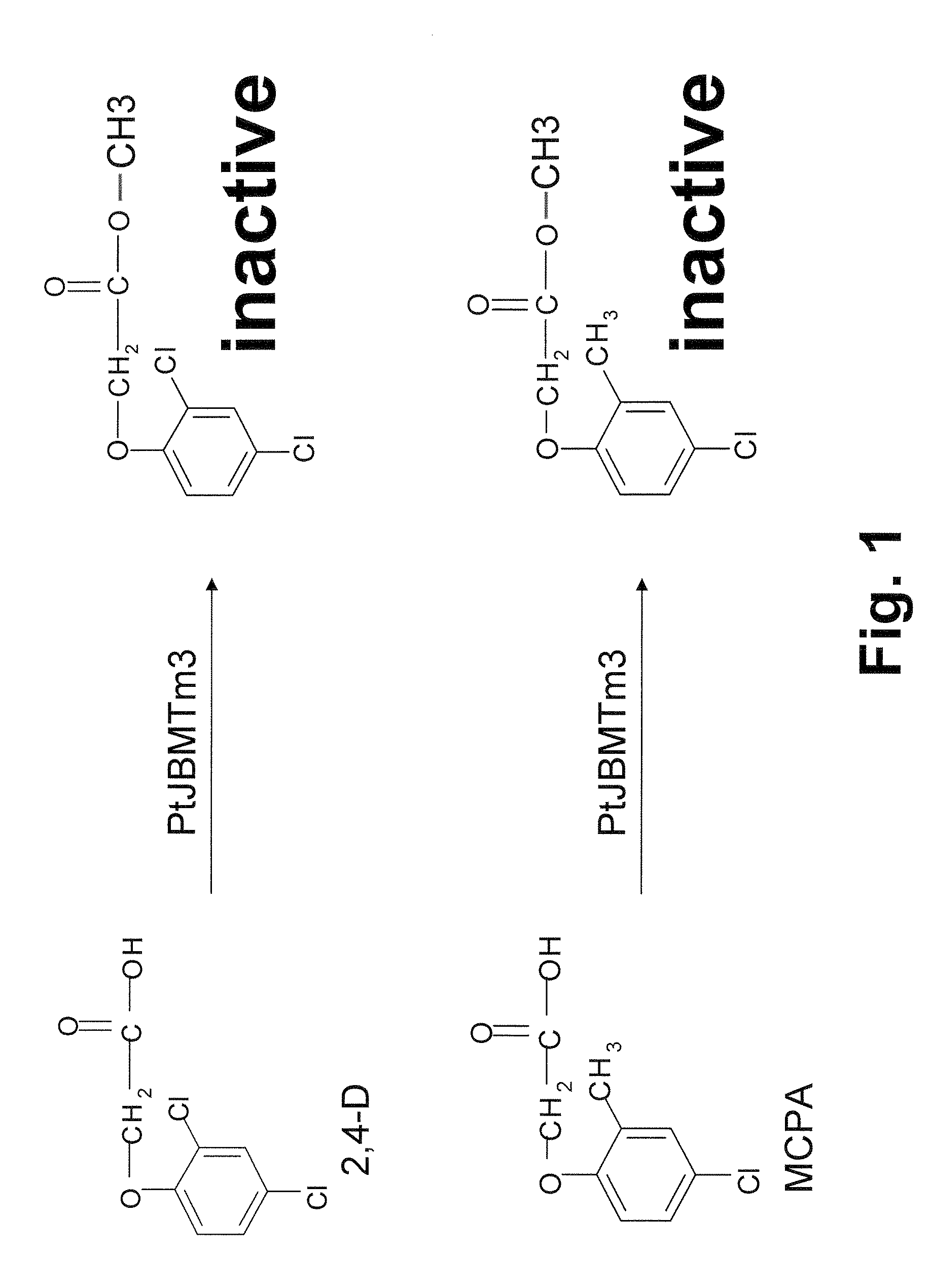
Novel herbicide resistance gene
The subject invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoding a methyltransferase. The subject invention provides novel plants that express the methyltrasferase disclosed herein and are resistant to auxin-based herbicides. The subject invention also provides transgenic plants have been transformed with one or more other herbicide resistance genes such that the plants are resistant to the application of auxin-based herbicides and one or more other herbicides.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Immune protective antigen of haemophilus parasuis
ActiveCN102864157AGood protective antigen proteinAntibacterial agentsBacteriaProtective antigenEscherichia coli
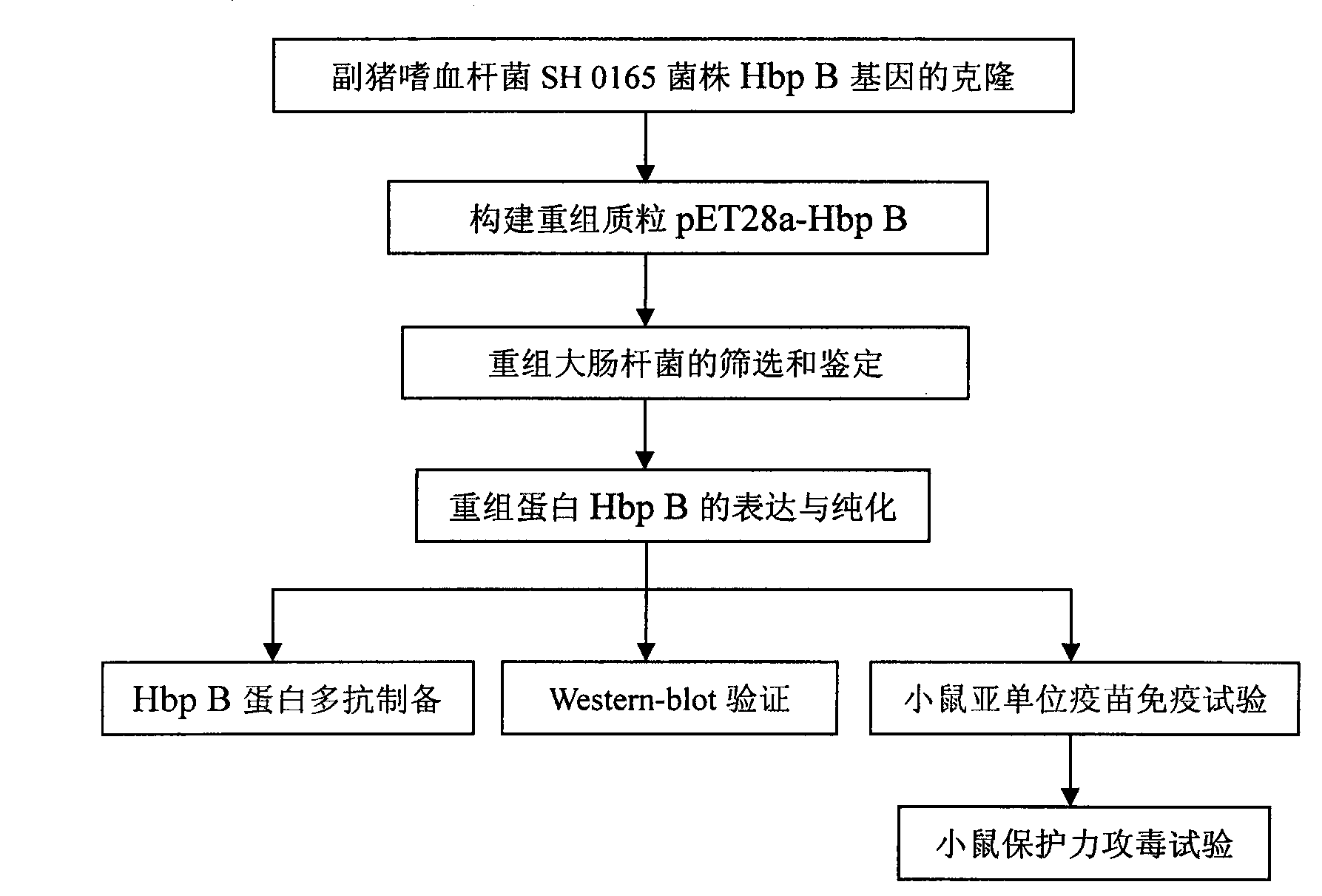
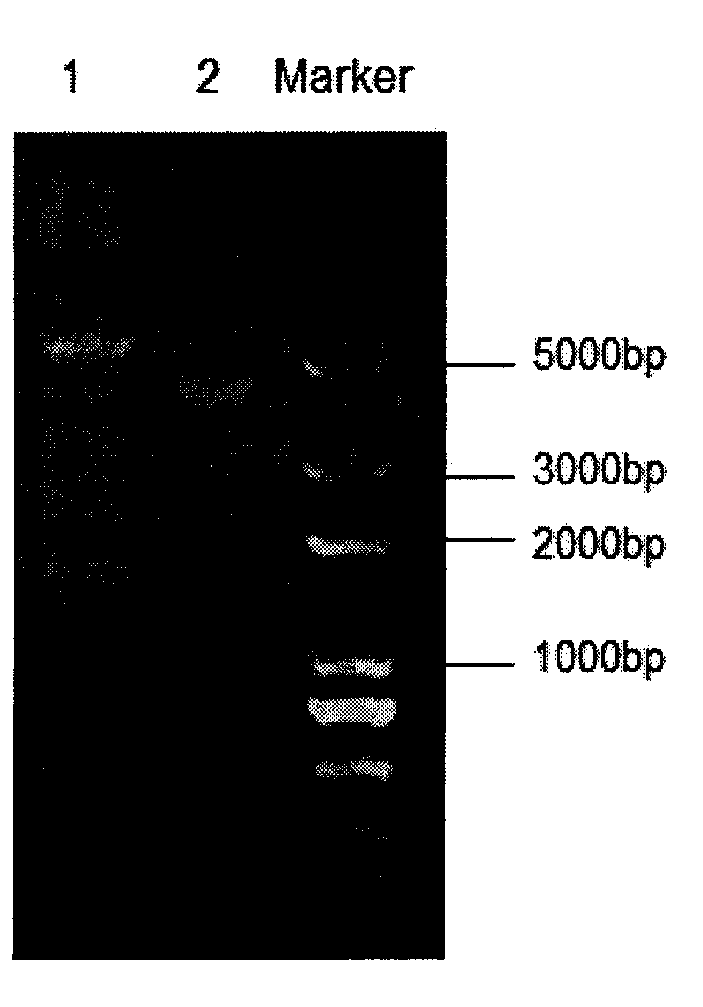
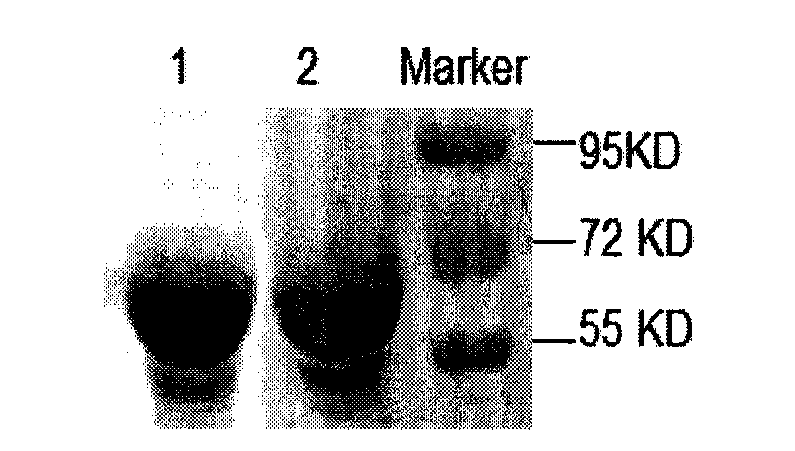
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal-borne disease subunit vaccine preparation and relates to preparation and application of the immune protective antigen of the haemophilus parasuis. Outer membrane protein Hbp B genes of the haemophilus parasuis are cloned, a nucleotide sequence is indicated as SEQID NO:1, and the sequence of gene code is indicated as SEQ ID NO:2. Recombination Escherichia coli BL21 / Pet-28a-Hbp B (preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2011228) is built and comprises genes in a sequence table SEQ ID NO:1. Antigen protein of the haemophilus parasuis is obtained and expressed through gene transformation Escherichia coli in the SEQ ID NO:1. The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the recombination Escherichia coli. The haemophilus parasuis subunit vaccine has good safety, and an immune protection effect reaches 83%.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
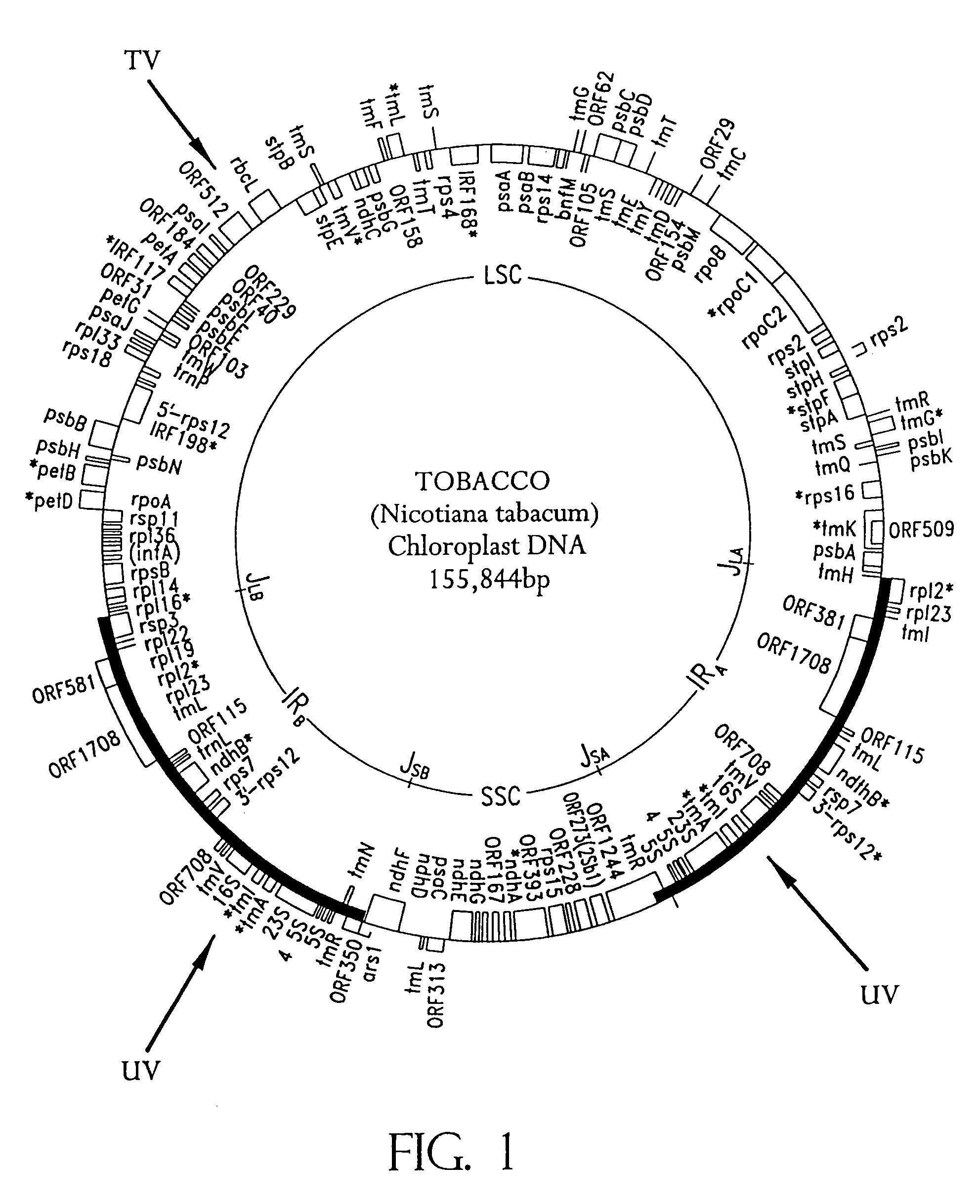
Universal chloroplast integration and expression vectors, transformed plants and products thereof
InactiveUS7803991B2Easy to identifyClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesChloroplastOrganism
The invention provides universal chloroplast integration and expression vectors which are competent to stably transform and integrate genes of interest into chloroplast genome of multiple species of plants. Transformed plants and their progeny are provided. Monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants are transformed which have never been transformed heretofore. Plants transformed with a synthetic gene express valuable biodegradable protein-based polymers (PBPs). Transformed plants produce high value molecules. Resistance is provided to agricultural crops against the major classes of chemical herbicides. Herbicide resistance is used as a lethal selectable marker for chloroplast transformation. The transformed plants are capable of expressing in addition to the targeted trait, a desirable, secondary non-targeted trait. Insect resistance is provided to transformed plants, both against insects that are susceptible to Bt toxins and against insects that have developed resistance to Bt toxins.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
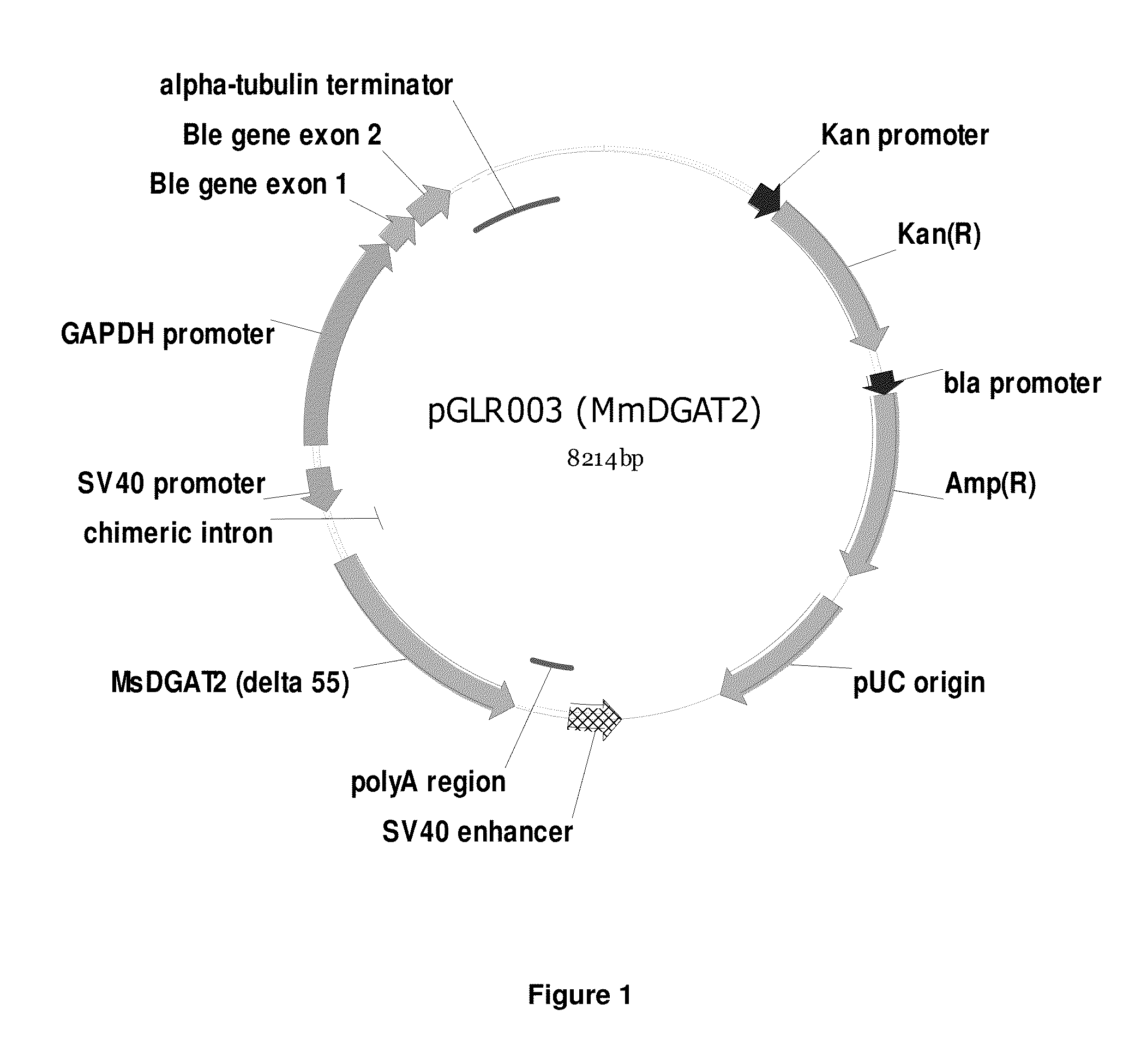
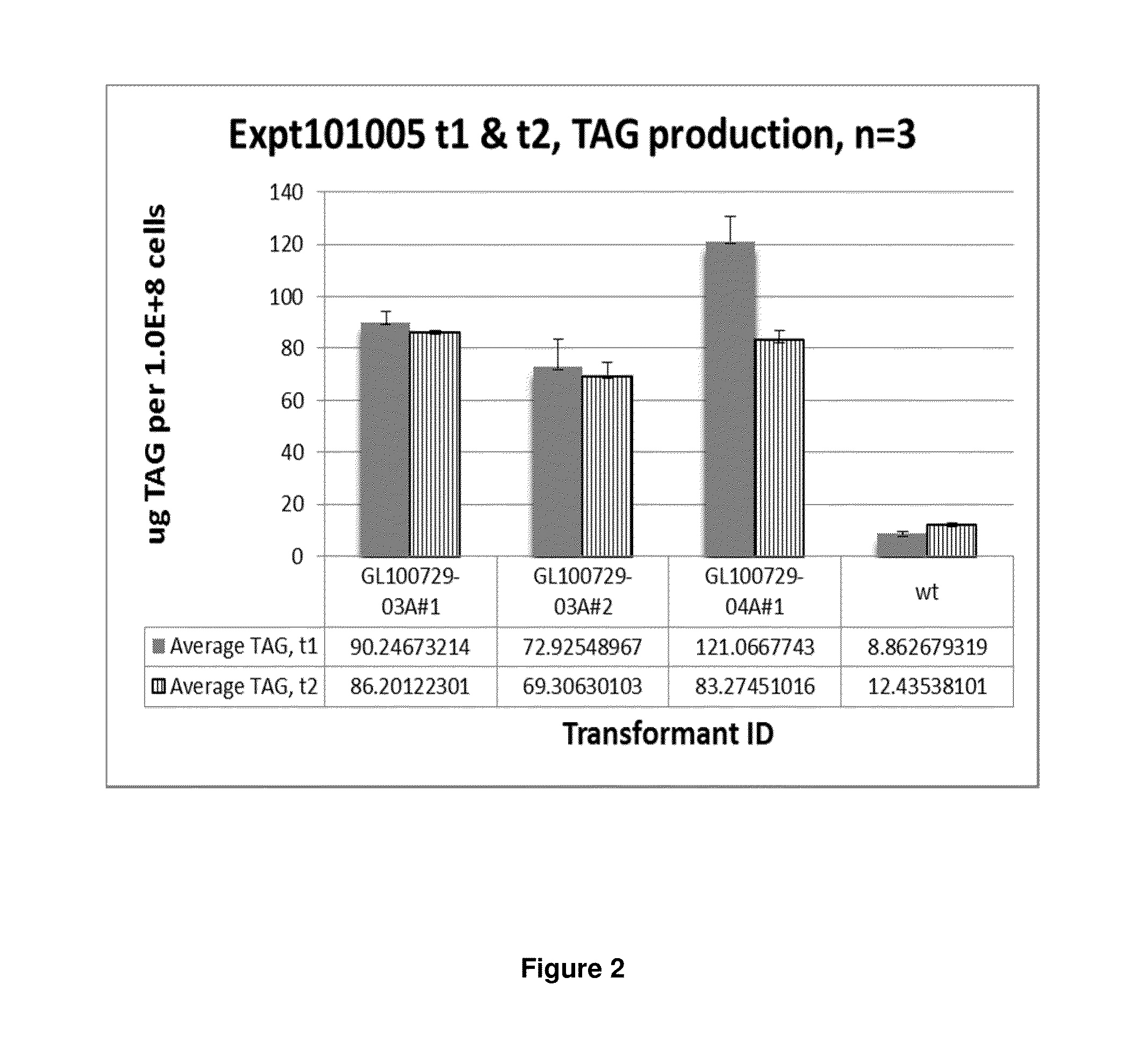
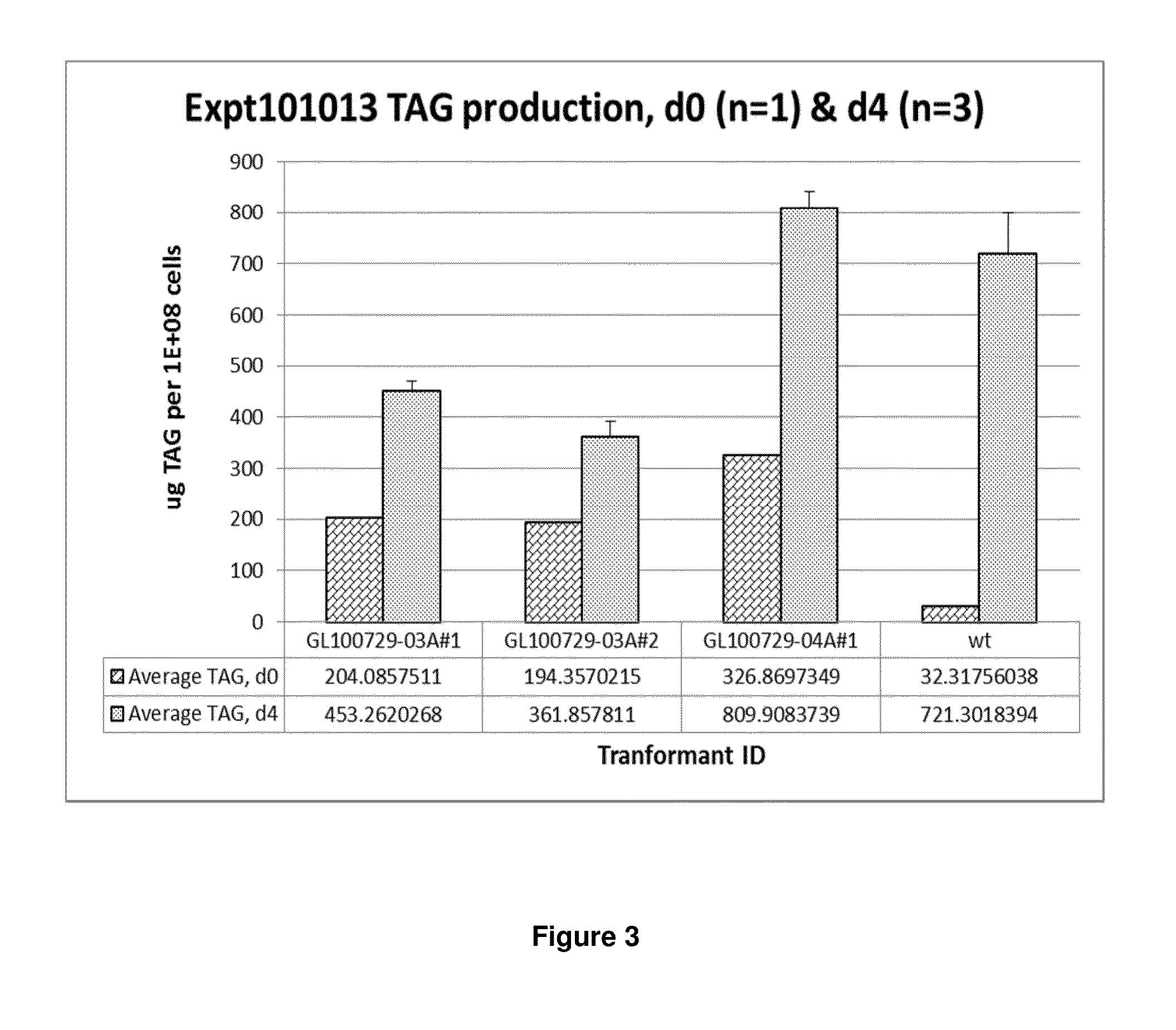
DGAT genes and methods of use for triglyceride production in recombinant microorganisms
ActiveUS20140106417A1Reduce expensesReduce riskSugar derivativesUnicellular algaeMicroorganismTriglyceride
The present invention provides novel diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) genes, including novel genes encoding localization peptides. The present invention also provides recombinant cells, such as algae, transformed with DGAT genes and methods of using such recombinant cells to produce triglyceride.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
L-cysteine producing bacterium and method for producing L-cysteine
L-cysteine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium in which intracellular serine acetyltransferase activity is increased by transformation with a gene coding for serine acetyltransferase, such modification of an expression control sequence of a gene coding for serine acetyltransferase that expression of the gene in a cell should be enhanced and for forth, preferably in which L-cysteine decomposition system is further suppressed, in a medium to produce and accumulate L-cysteine in culture and collecting the L-cysteine from the culture.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
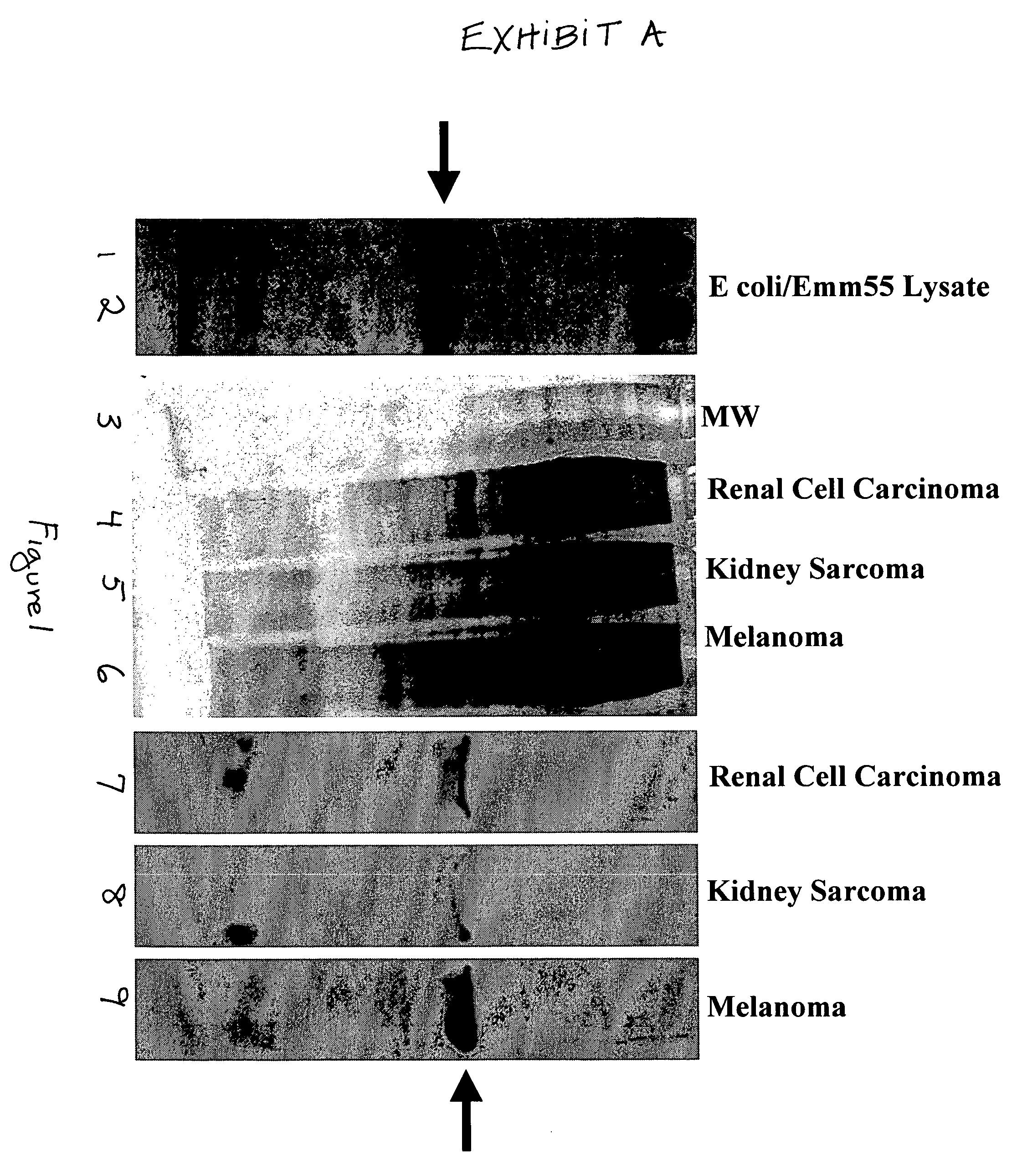
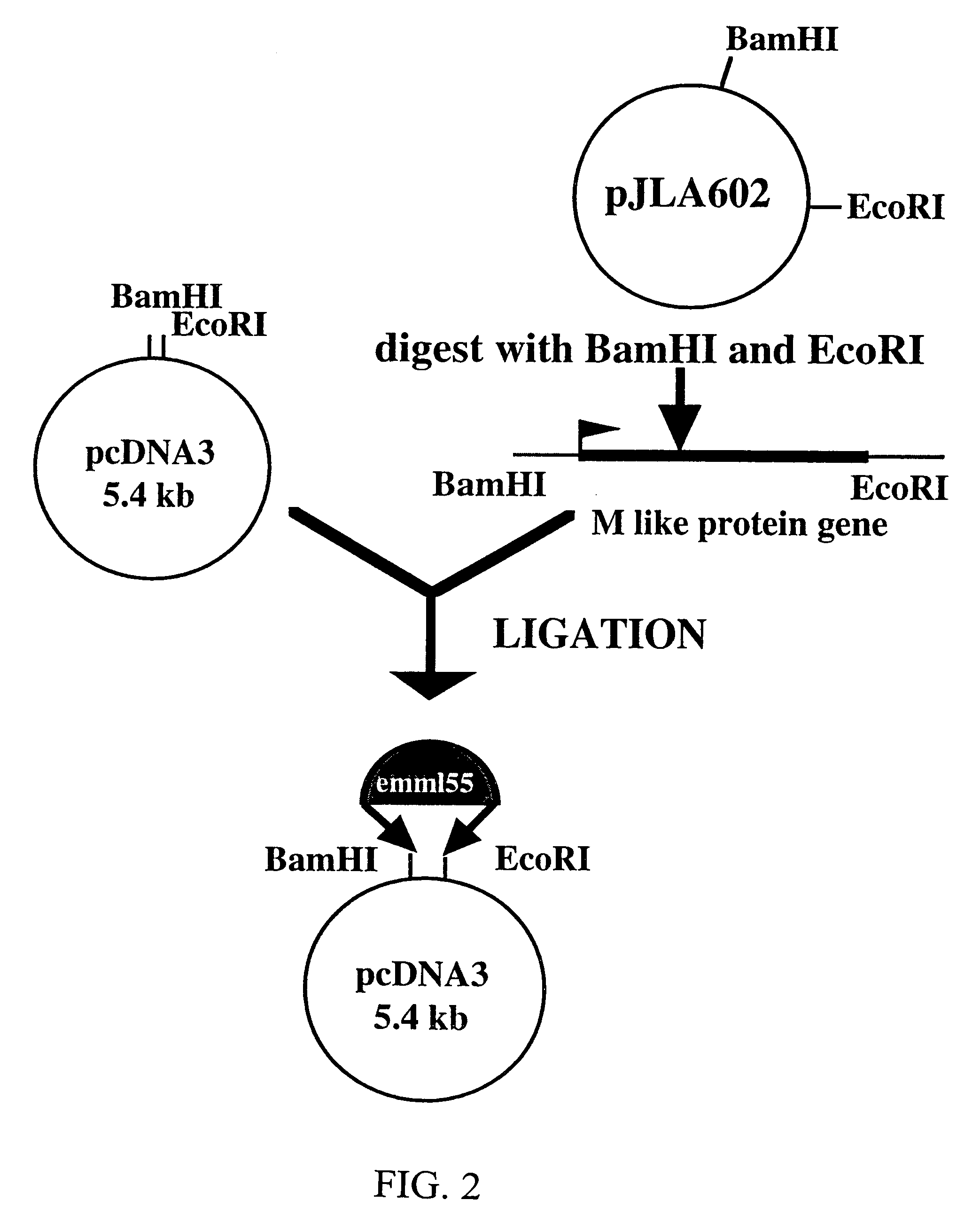
Materials and methods for treating oncological disease
Novel methods are disclosed for treating oncological disorders in an individual or animal using a superantigen expressed in tumor cells. A gene encoding a superantigen, such as an M-like protein of group A streptococci, can be introduced into a tumor cell in order to make the tumor cell more immunogenic in the host. Also contemplated are methods wherein a cell expresses a superantigen or superantigens, and immunogenic or immunostimulatory proteins, such as foreign MHC, cytokines, porcine-derived hyperacute rejection antigen, Mycobacterium-derived antigens, and the like. The subject invention also pertains to cells transformed with polynucleotides encoding a superantigen and foreign MHC antigen, cytokines, and other immunogenic or immunostimulatory proteins. Transformed cells according to the subject invention are then provided to an individual or animal in need of treatment for an oncological disorder. The immune response to tumor cells transformed according to the present invention inhibits in vivo tumor growth and results in subsequent tumor regression. The subject invention also pertains to cell lines transformed with genes encoding a superantigen and, optionally, a foreign Class II MHC antigen and / or a cytokine.
Owner:MORPHOGENESIS
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene from plants
InactiveUS20050193446A1Increase TAG contentChange ratioTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesPlanting seedAdemetionine
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of the plant diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) gene and genetic products. The invention includes isolated and purified DGAT DNA and relates to methods of regulating seed oil content, the ratio of diacylglycerol / triacylglycerol proportions in the seed oil, fatty acid synthesis, seed oil acyl composition, seed size / weight and carbon flux into other seed components, using the gene, and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of the invention, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
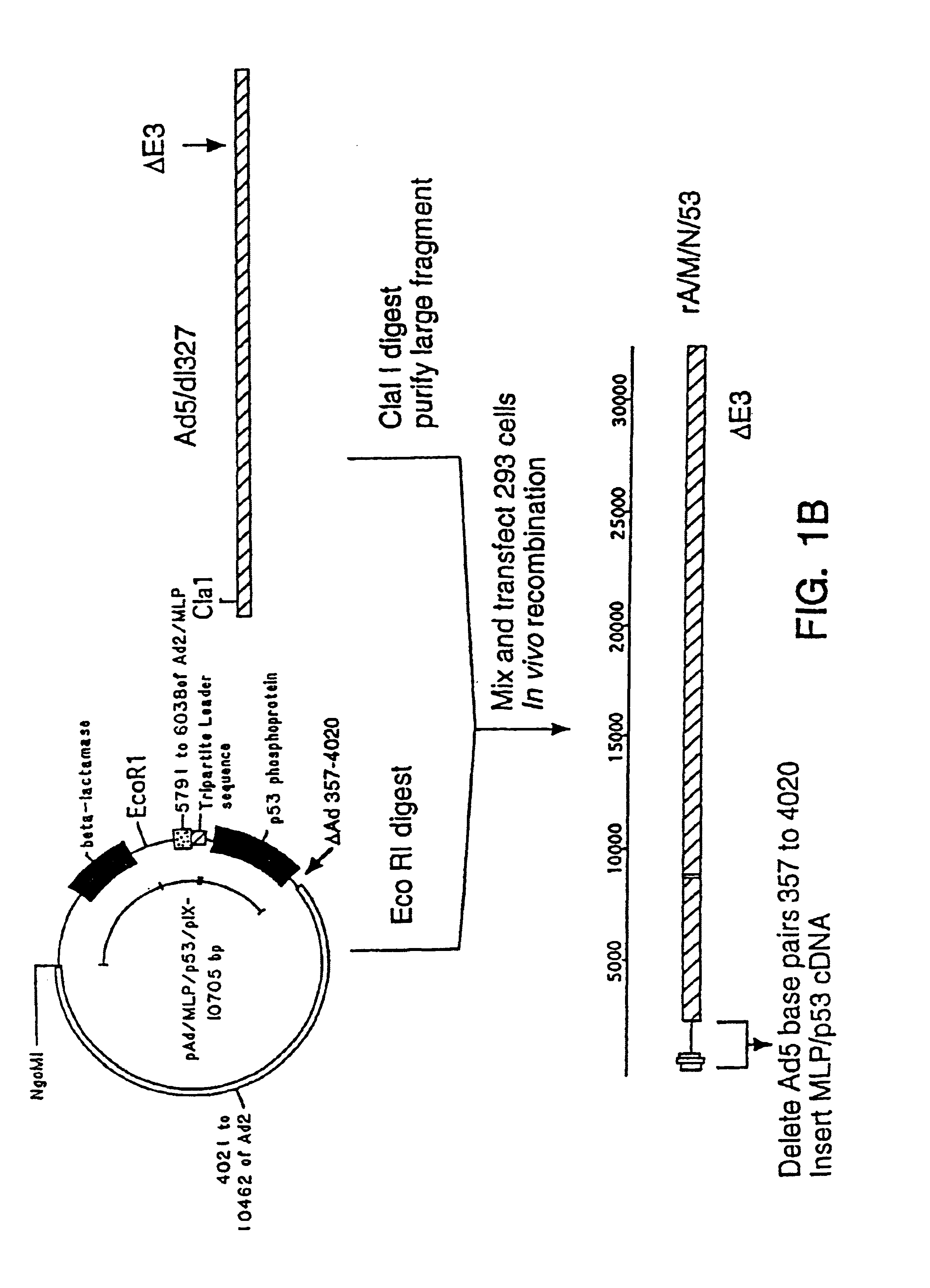
Recombinant adenoviral vector and method of use
This invention provides a recombinant adenovirus expression vector characterized by the partial or total deletion of the adenoviral protein IX DNA and having a gene encoding a foreign protein or a functional fragment or mutant thereof. Transformed host cells and a method of producing recombinant proteins and gene therapy also are included within the scope of this invention. Thus, for example, the adenoviral vector of this invention can contain a foreign gene for the expression of a protein effective in regulating the cell cycle, such as p53, Rb, or mitosin, or in inducing cell death, such as the conditional suicide gene thymidine dinase. (The latter must be used in conjunction with a thymidine kinase metabolite in order to be effective.)
Owner:CANJI
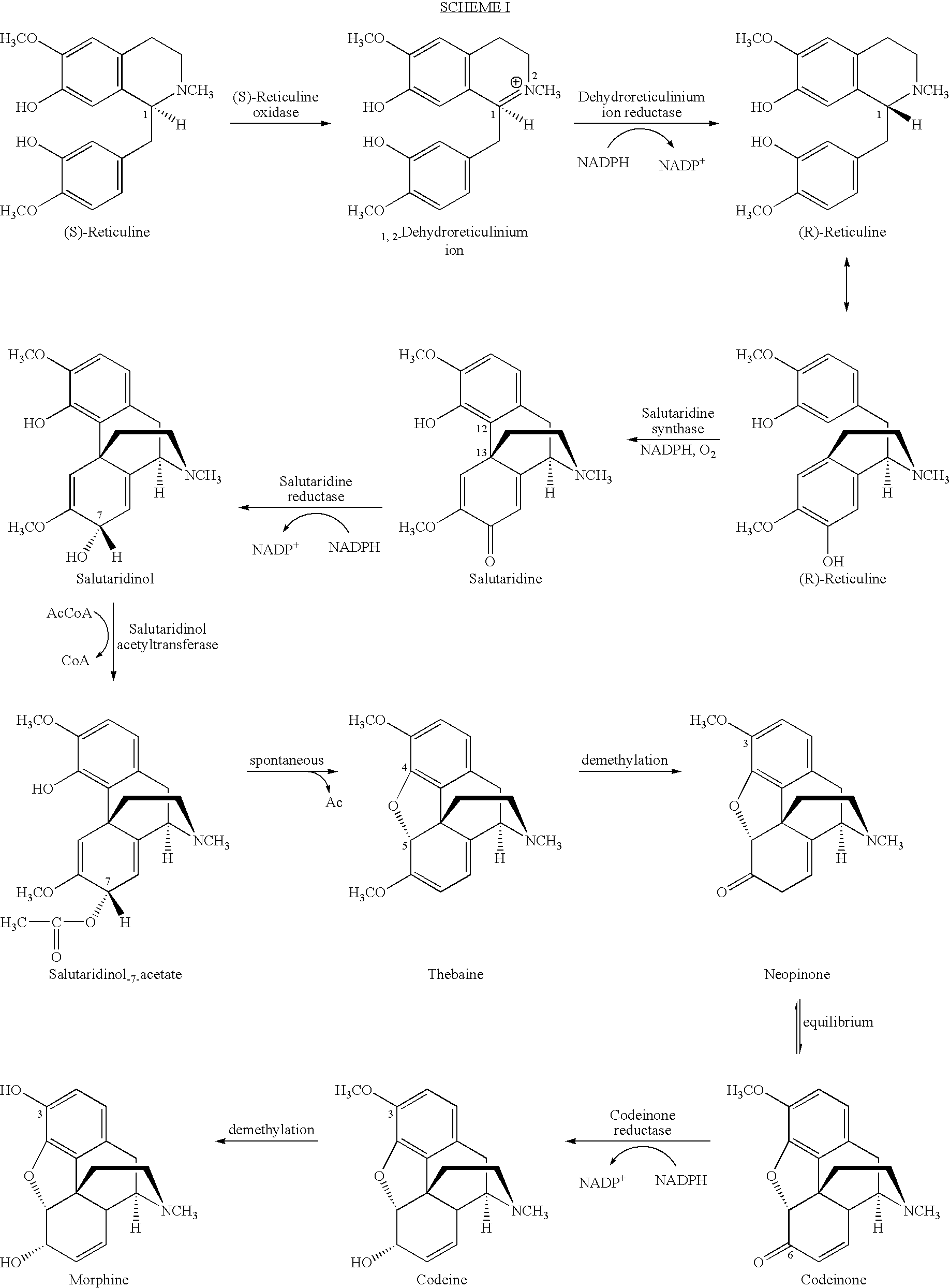
Cytochrome P450 reductases from poppy plants
InactiveUS7037674B1Alleviating “ bottleneck ”Increase productionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytochrome P450 reductaseCytochrome P450
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON RES PTY LTD
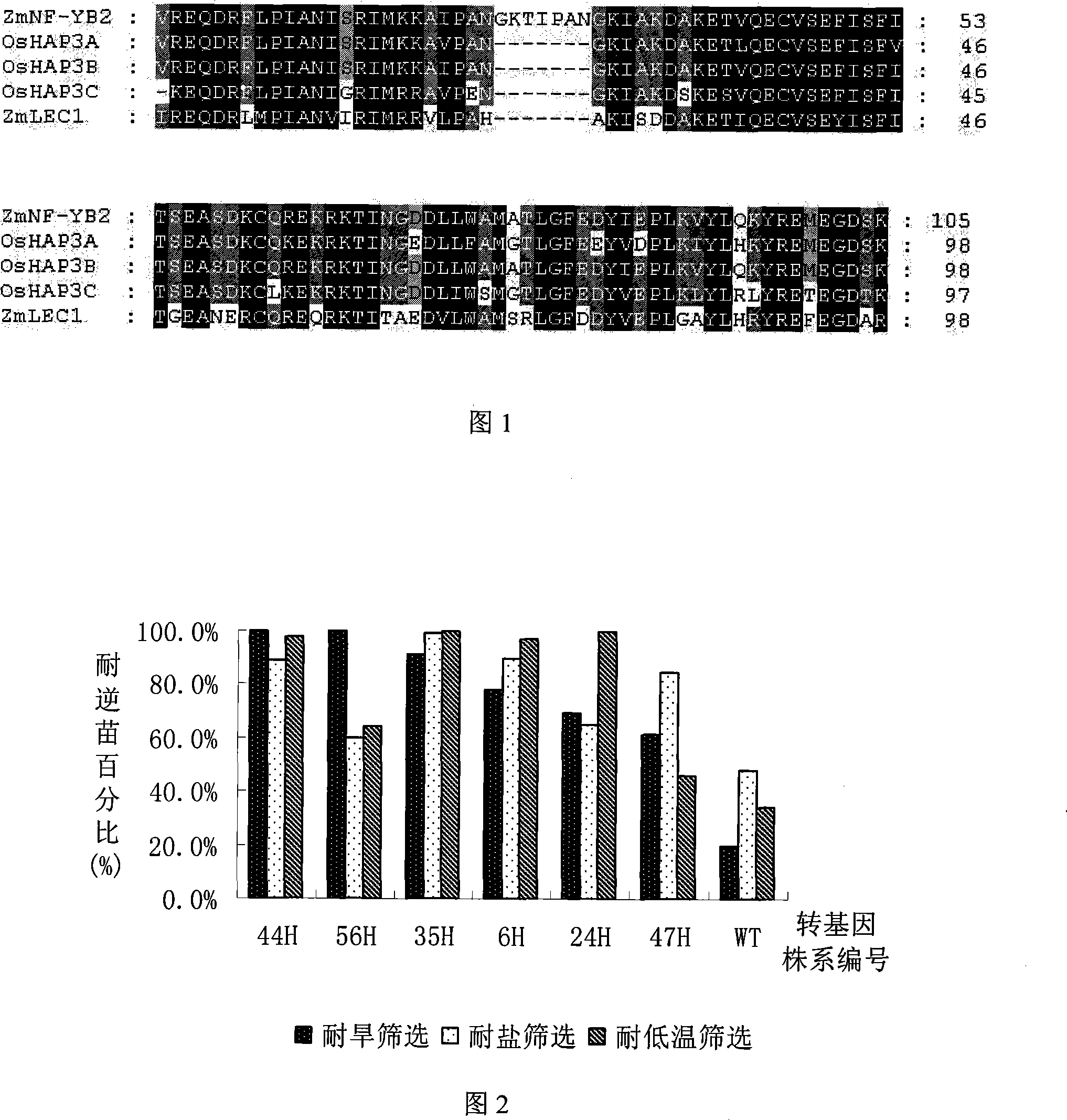
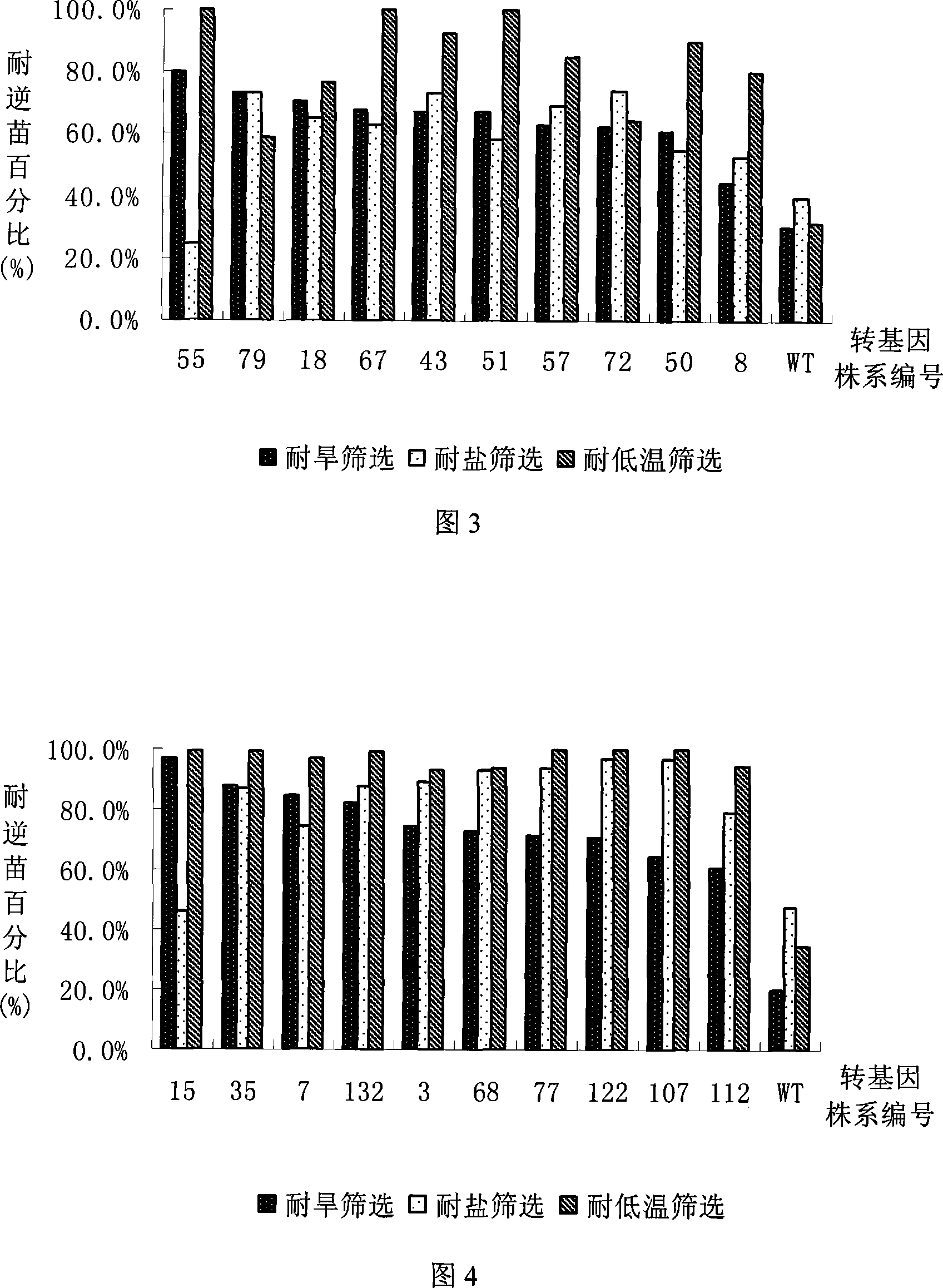
Rice HAP3 and application of the same in improving stress tolerance of plants
ActiveCN101220364AImprove toleranceImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationNormal growthGene conversion
The invention discloses a group of HAP3 genes which are derived from rice and are related with stress tolerance, the encoded protein has one of the following amino acid sequences: 1) the SEQ ID No:1, 3 or 5 in a sequence table; 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the SEQ ID No.:1, 3 or 5 in the sequence table is treated with the substitutes, deletes or adds of one to ten amino acid residues and the derived protein has the effect of regulating the performance of plant stress tolerance. The experiments proves that the transgenic rice of the invention can improve the tolerance of the rice to the high-salt, drought and low-temperature adversity threats and have no apparent impacts on the normal growth and the economic traits of the rice. The protein and the encoded genes of the invention have important theoretical and practical significances on the research of a plant stress tolerance mechanism, the improvement of the plant stress tolerance and the improvement of the related traits, thereby playing an important role in the stress tolerance genetic engineering improvement of plants (particularly cereal crops) and having broad application prospect.
Owner:FRONTIER LAB OF SYST CROP DESIGN CO LTD
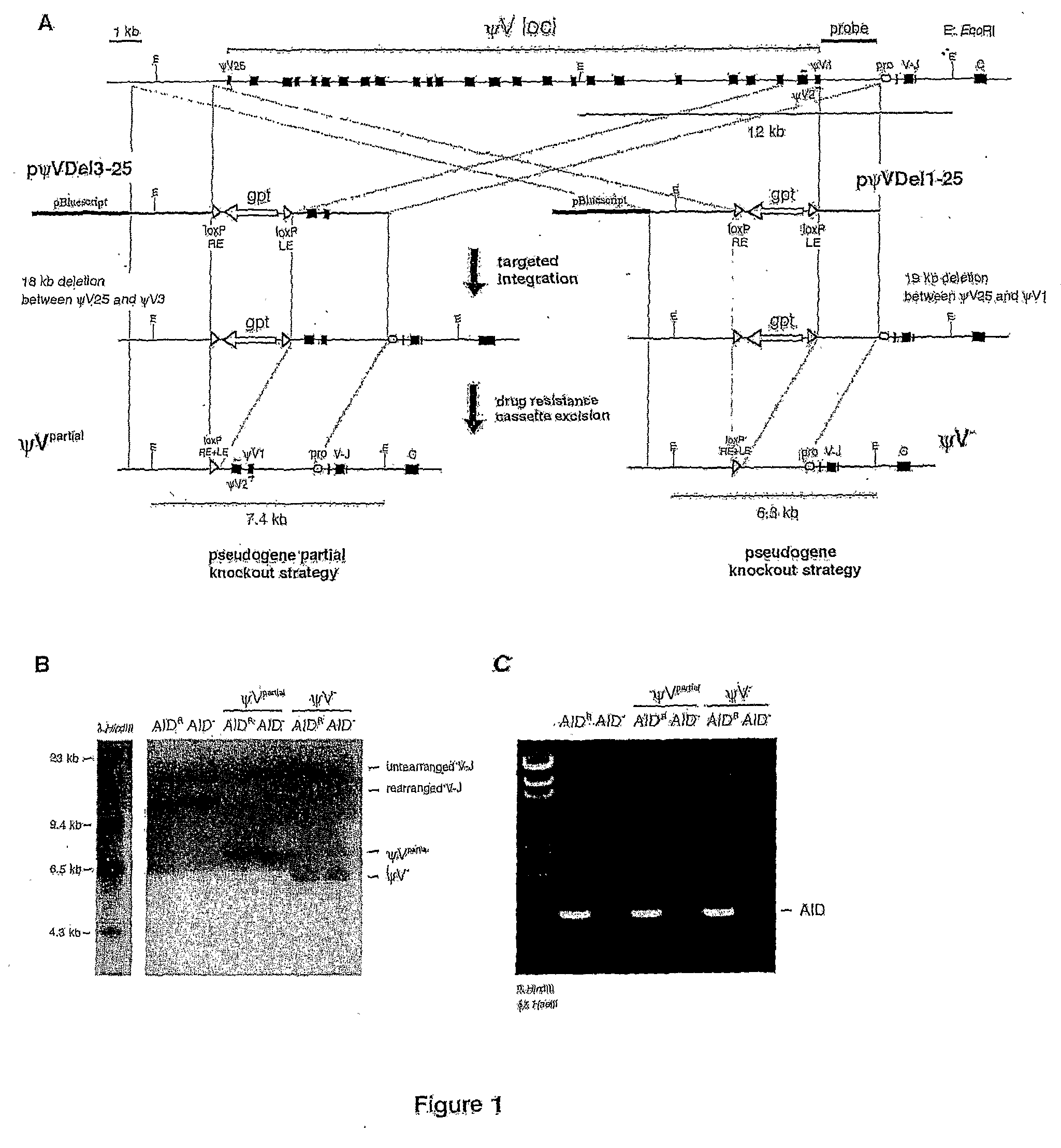
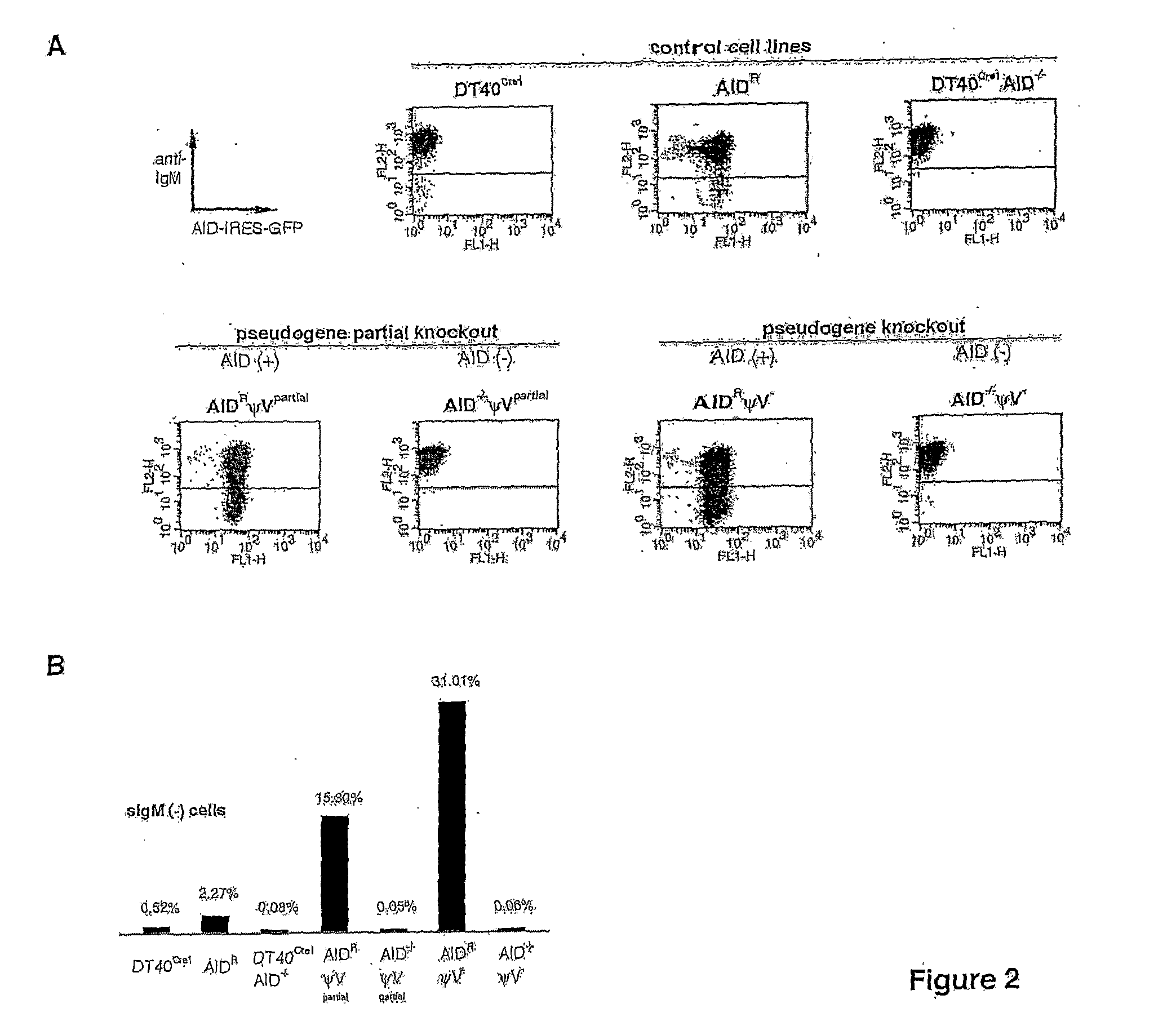
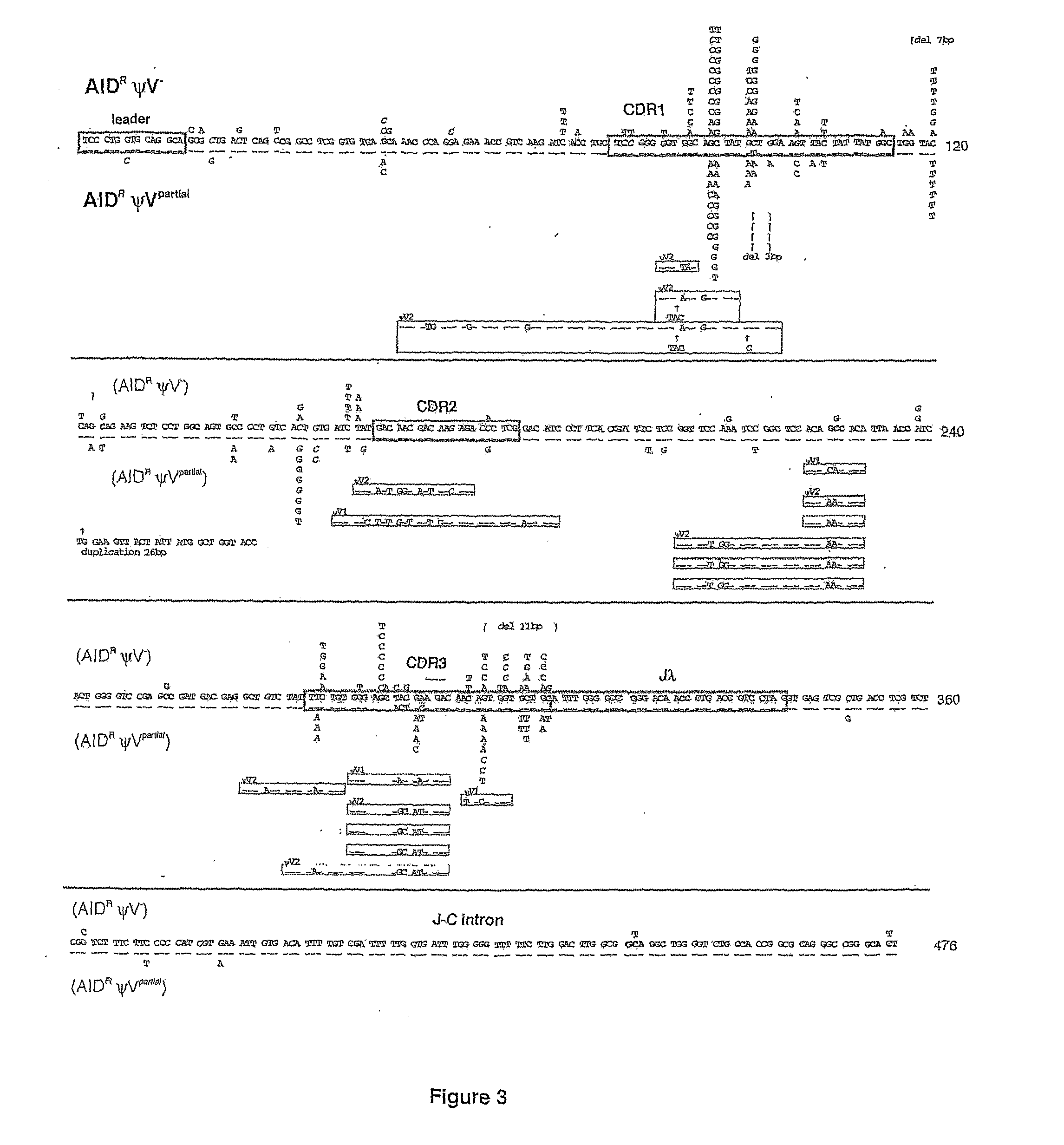
Methods for genetic diversification in gene conversion active cells
ActiveUS20070186292A1Increase contentModify diversificationGenetic material ingredientsMutant preparationHeavy chainGene conversion
The invention relates to a modified lymphoid cell having gene conversion fully or partially replaced by hypermutation, wherein said cell has no deleterious mutations in genes encoding paralogues and analogues of the RAD51 protein, and wherein said cell is capable of directed and selective genetic diversification of a target nucleic acid by hypermutation or a combination of hypermutation and gene conversion. The invention also relates to a method for diversifying any transgenic target gene in said cell. Preferably, the target gene is integrated into the immunoglobulin light or heavy chain locus by targeted integration.
Owner:CHIOME BIOSCIENCE INC
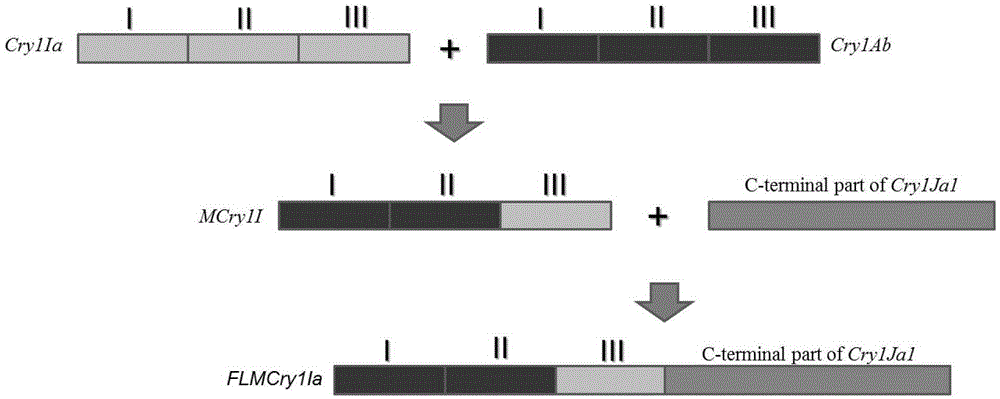
Artificially synthesized Bt insecticidal gene FLIa as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides an artificially synthesized Bt insecticidal gene FLIa as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of insecticidal protein and biosafety. The nucleotide sequence of the Bt insecticidal gene FLIa is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence of encoded protein of the Bt insecticidal gene FLIa is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in a sequence table. The preparation method of the Bt insecticidal gene FLIa comprises the steps of exchanging and fusing Domain I and Domain II of a insecticidal gene CrylAb and Domian III of a insecticidal gene CrylIa to obtain a recombinant insecticidal gene MCrylI; on the basis of the recombinant insecticidal gene MCrylI, connecting the carbon terminal of a insecticidal gene CrylJal at a 3minute terminal to obtain a recombinant insecticidal gene FLMCrylIa; performing codon reconstruction on the recombinant insecticidal gene FLMCrylIa to obtain the Bt insecticidal gene FLIa. The Bt insecticidal gene FLIa can be stably inherited and expressed in transformation plants, and is high in expression quantity, and obtained transgenic plants are good in insect resistance. The gene is used for transforming crops of corn, cotton, rice, vegetables and the like, and enabling the same to have corresponding insect-resistant activity, so that the using amount of pesticides is reduced and environment pollution and production cost are reduced.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Dominant selectable marker for gene transformation and disruption in yeasts
InactiveUS20010031724A1Good antifungal activityGene manipulationFungiBacteriaAntifungal drugCandida famata
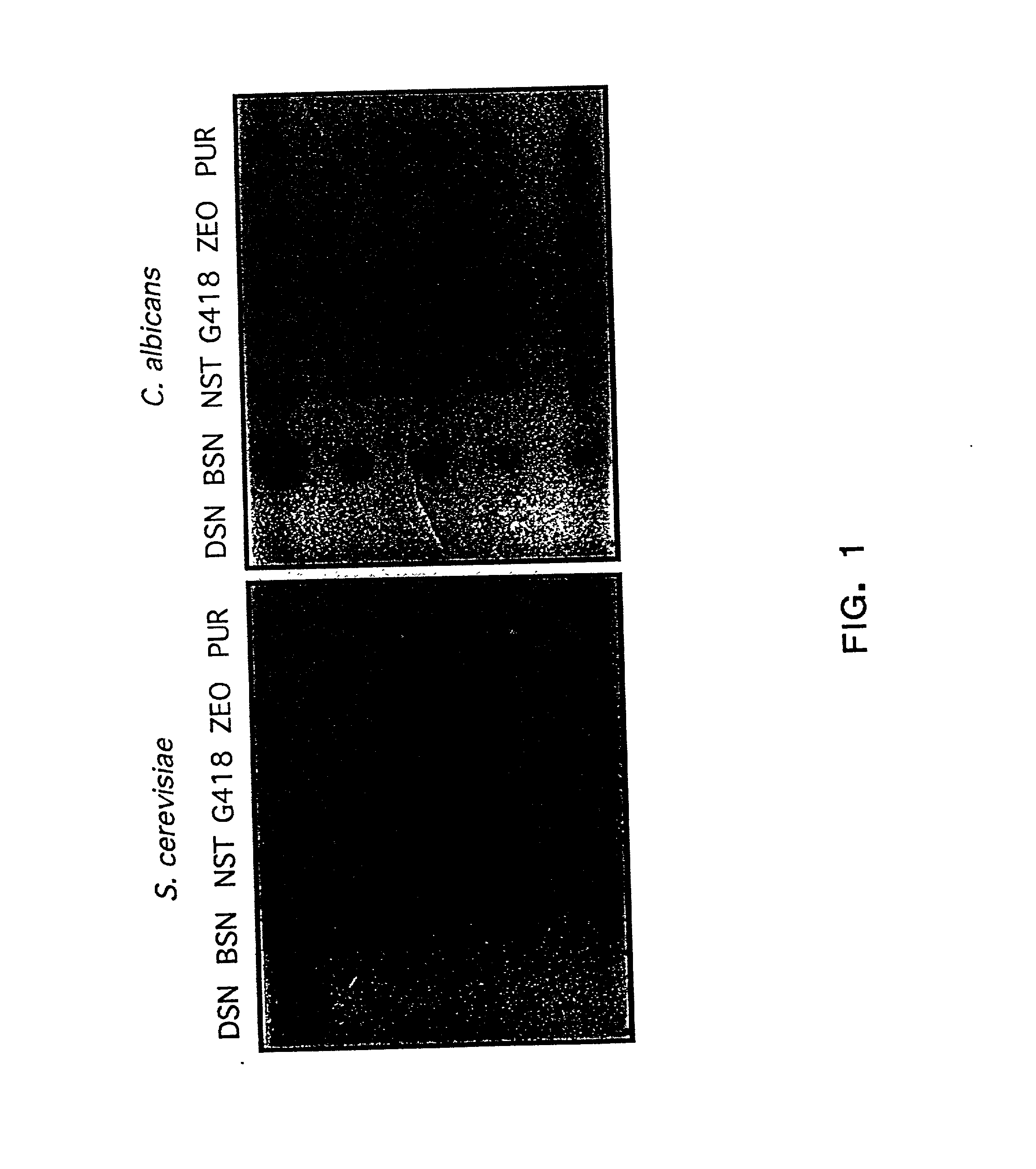
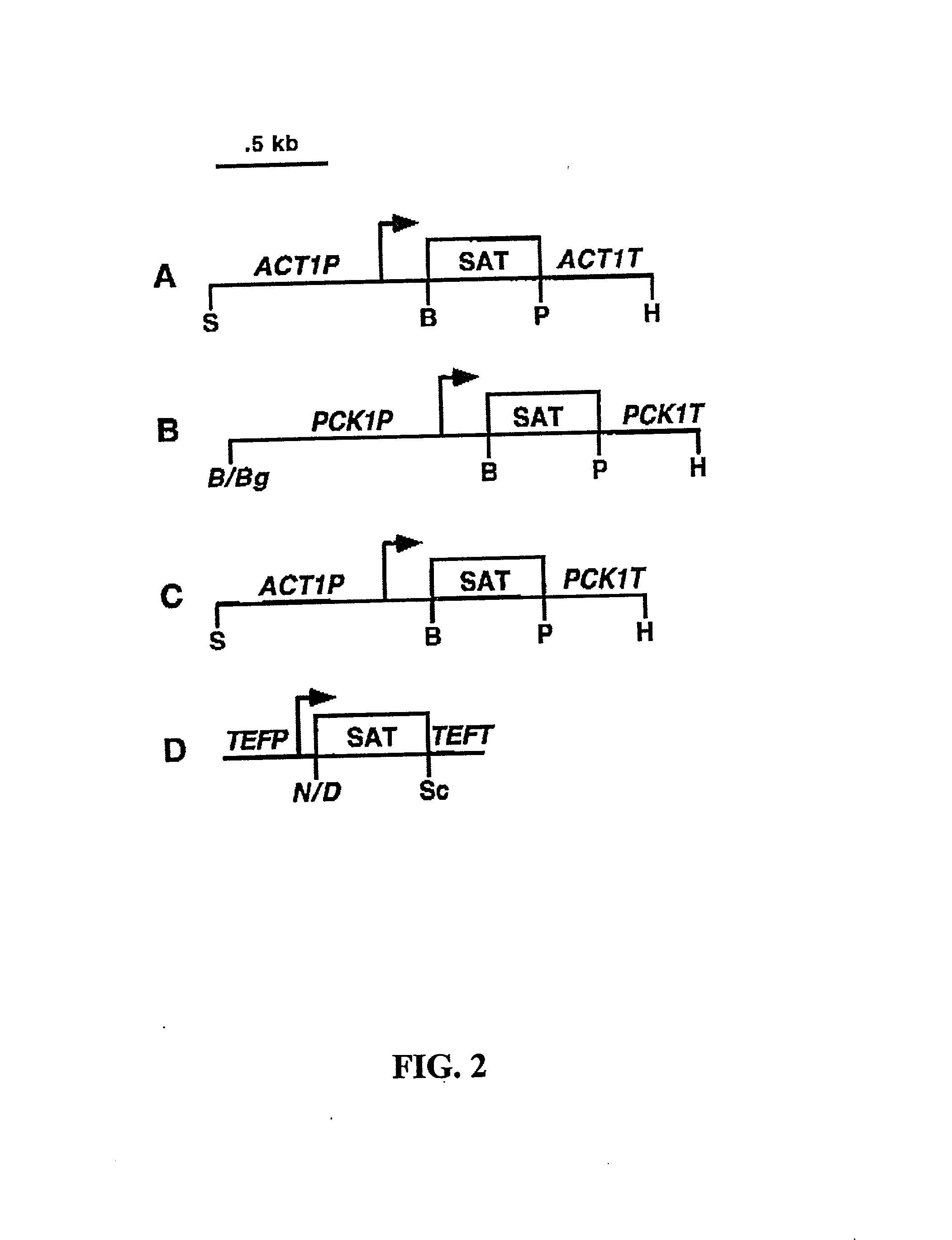
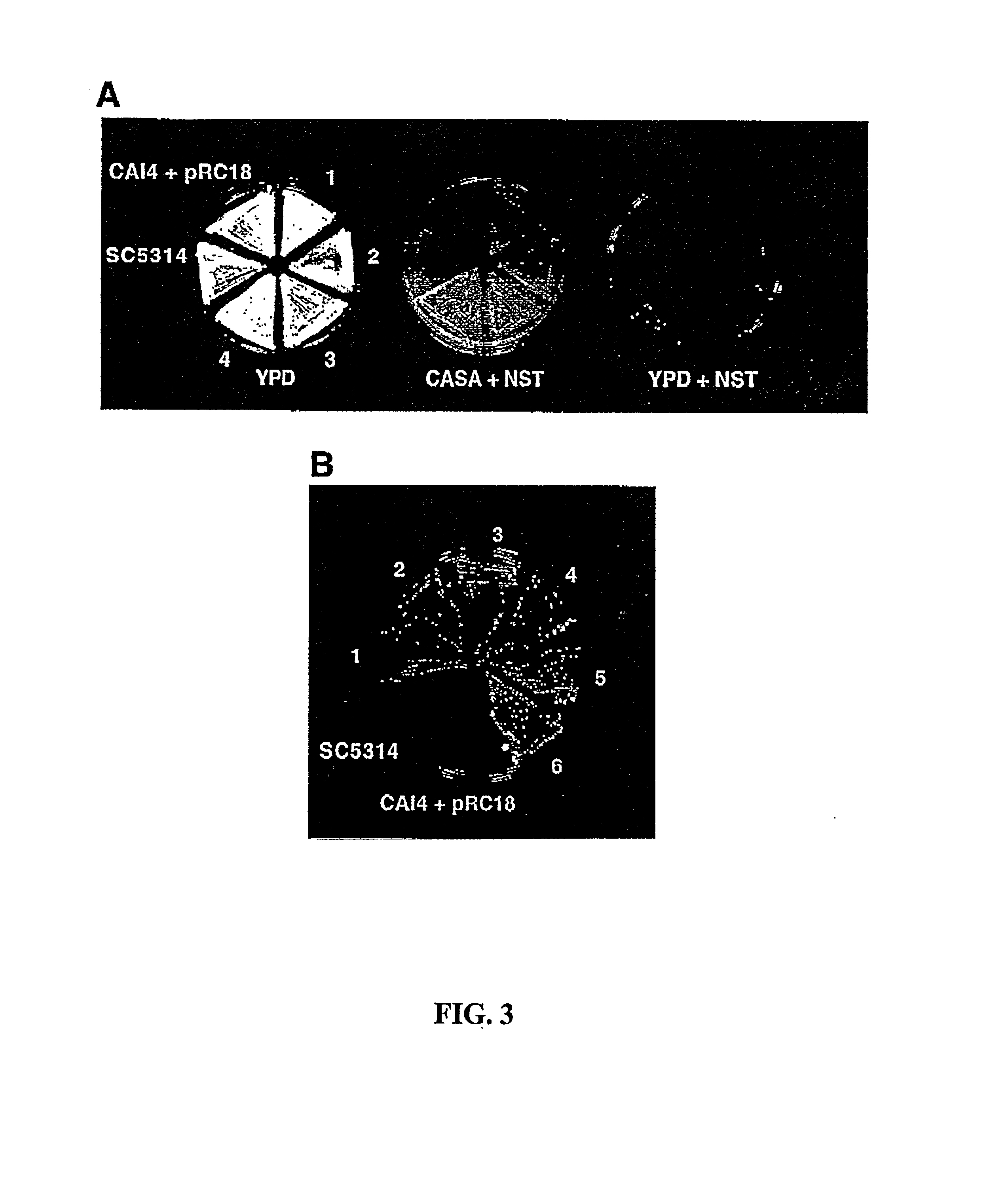
The present invention provides a novel dominant selectable marker system in yeast that is based on an aminoglycoside, nourseothricin (NST). This compound possesses a powerful antifungal activity against Candida albicans and S. cerevisiae. The invention provides a cognate drug resistance marker for use in gene transformation and disruption experimentation in Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In particular, the invention presents: 1) direct utility for gene manipulations in both clinically and experimentally relevant strains regardless of genotype and without affecting growth rate, or hyphal formation; and 2) applicability to antifungal drug discovery, including target validation and various forms of drug screening assays.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Receptor-like protein kinase gene, and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102533812AIncrease resistancePowdery mildew resistantTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyGene conversion
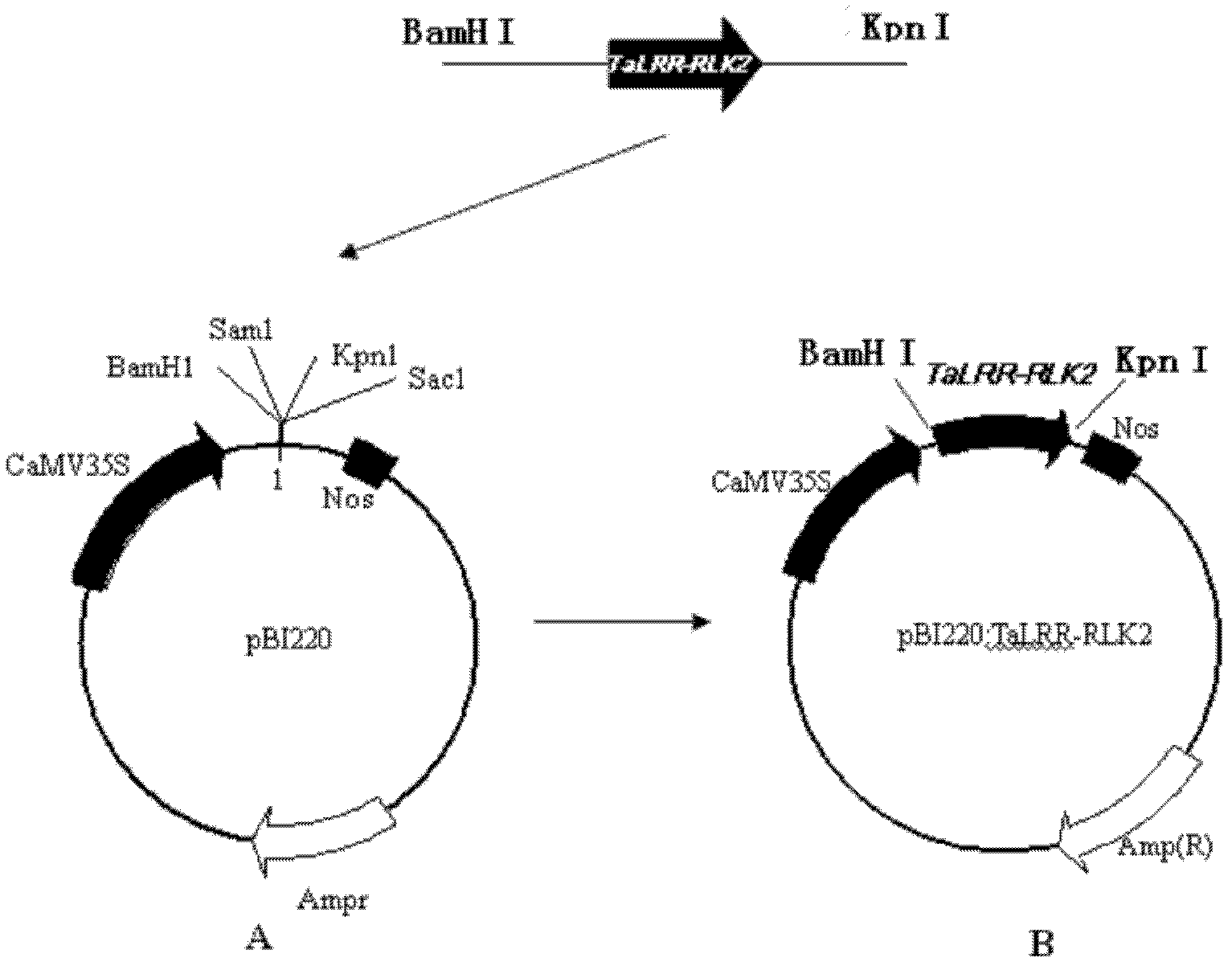
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a receptor-like protein kinase gene, and an expression vector and application thereof. The cDNA sequence of the receptor-like protein kinase gene TaLRR-RLK2 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and an ammonia acid sequence coded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The gene comes from a Triticum aestivum L. Prins-T. timopheevi Zhuk introgression line IGVI465, and is reported in wheat for the first time. The gene transforms susceptible wheat variety Prins through transient expression, and a result shows that the over-expression of the TaLRR-RLK2 can reduce the haustorium index of the Prins. Therefore, the TaLRR-RLK2 can be expected to be used for genetically engineered breeding, and can improve the powdery mildew resistance of wheat after the gene is transferred into a powdery mildew susceptible wheat variety.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Corn borer resistant transgenetic ultra-sweet corn regeneration system and construction method thereof
InactiveCN1763207AEfficient and stable acquisitionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGene conversionTransgene
The present invention provides one kind of maize borer resisting transgenic super sweet maize regeneration system and its establishment method. The establishment method includes the following steps: inducing callus of super sweet maize, establishing embryonic callus, genetic gun transformation of embryonic callus cell, culture and screening of the transformed callus, and plant differentiation and transplanting. The method has high super sweet maize cell transforming regeneration rate, and the present invention provides one kind of super sweet maize cell transforming regeneration system and can obtain transgenic regenerated plant at high efficiency and high stability.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com