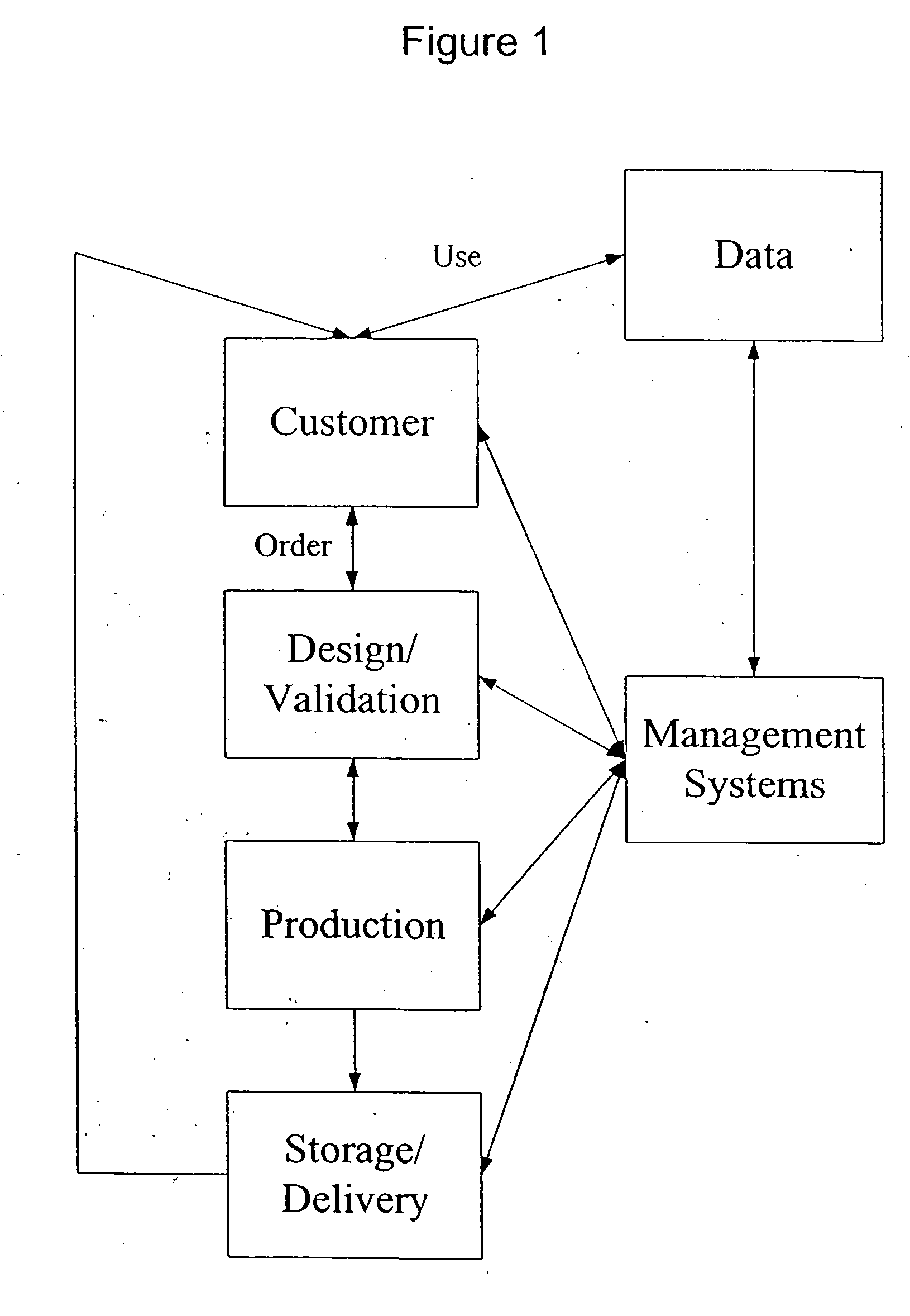
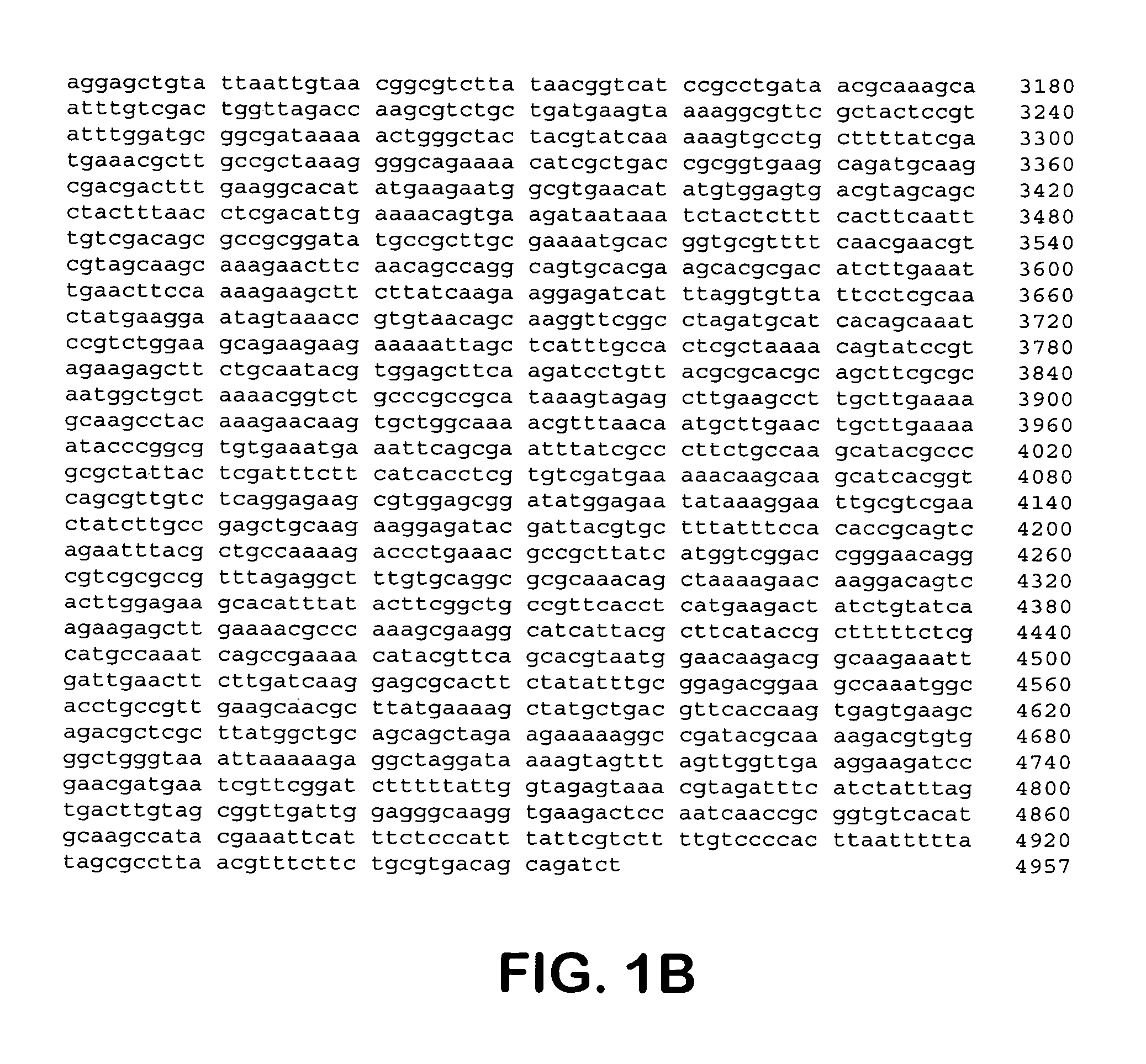
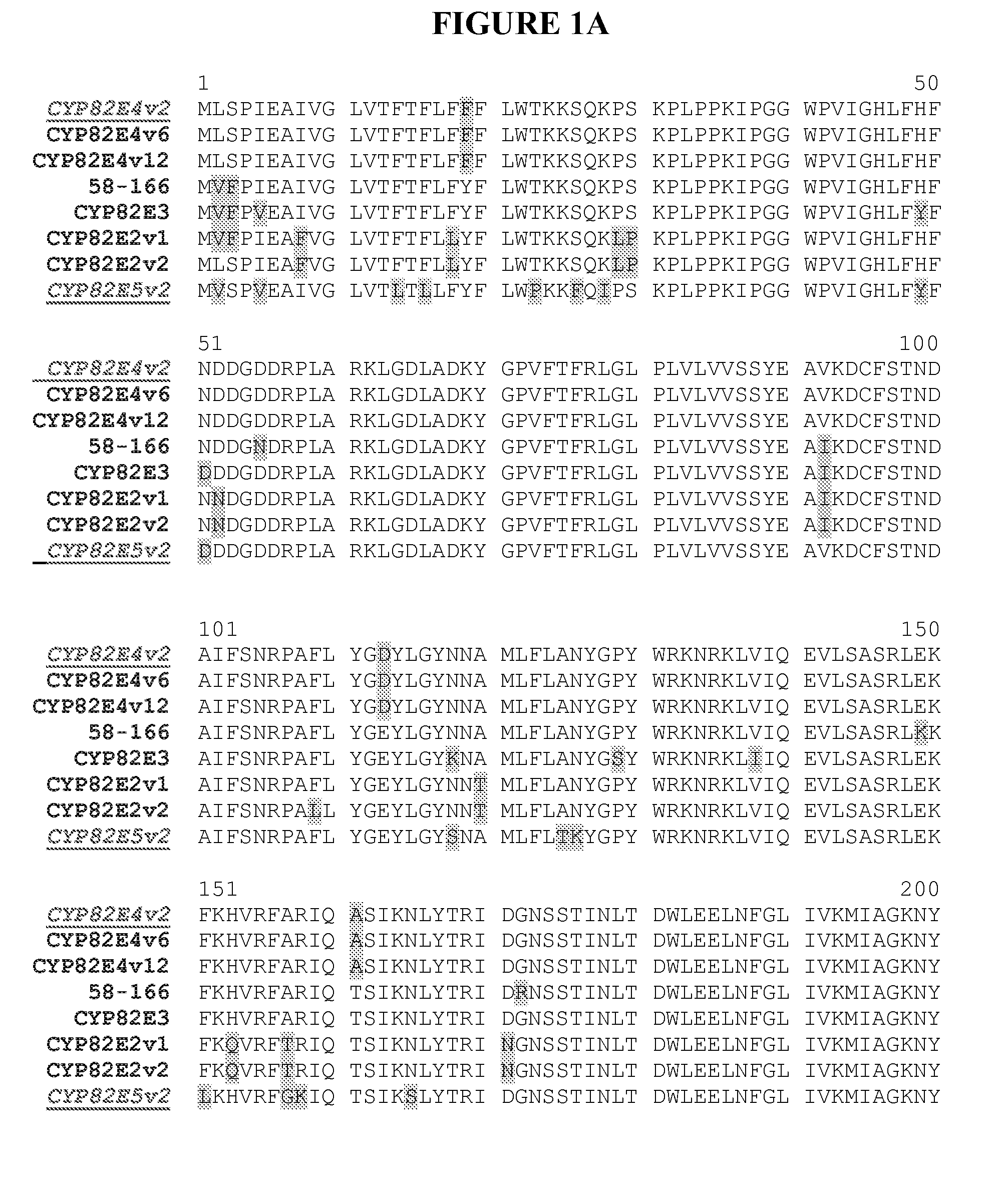
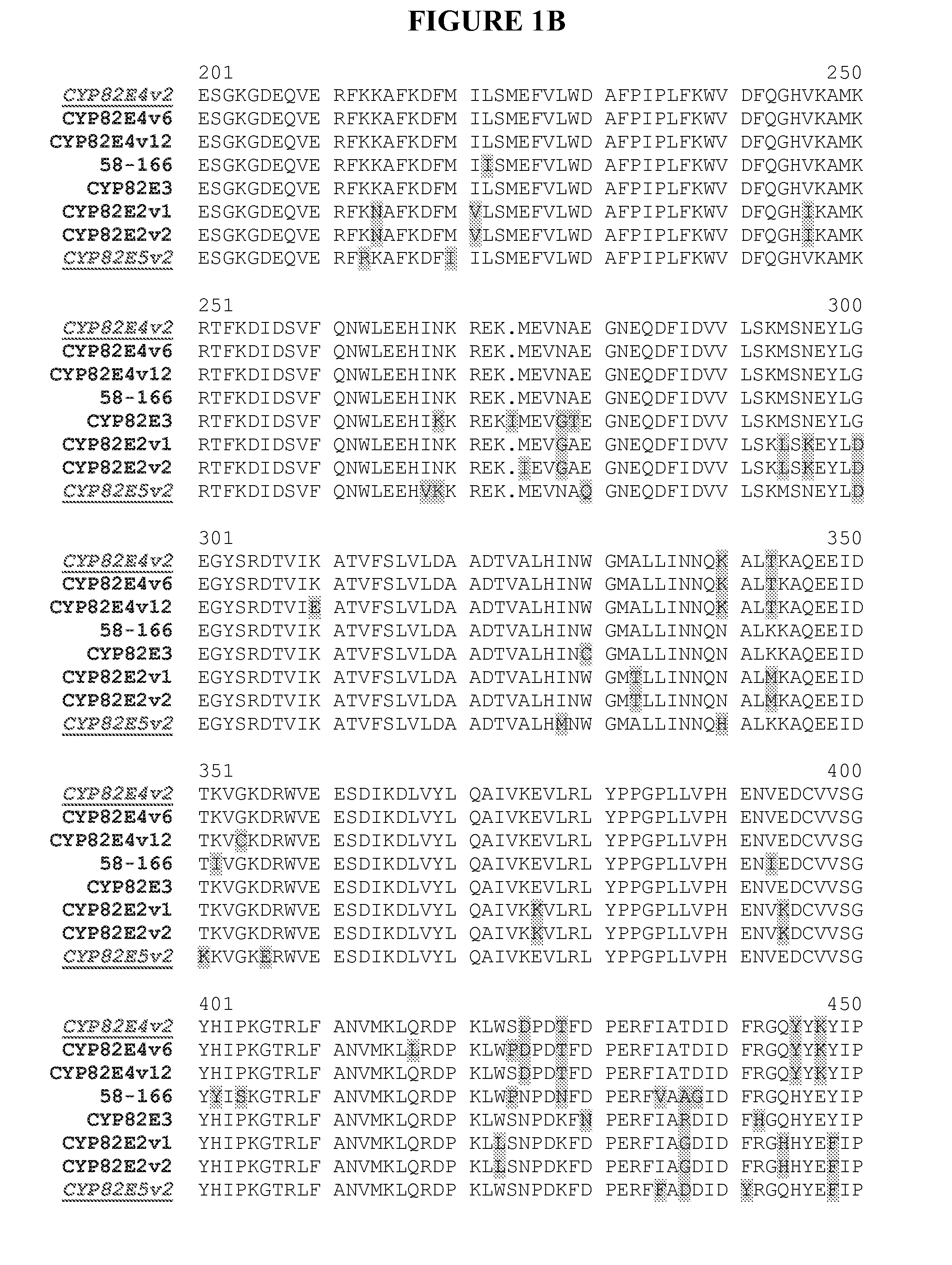
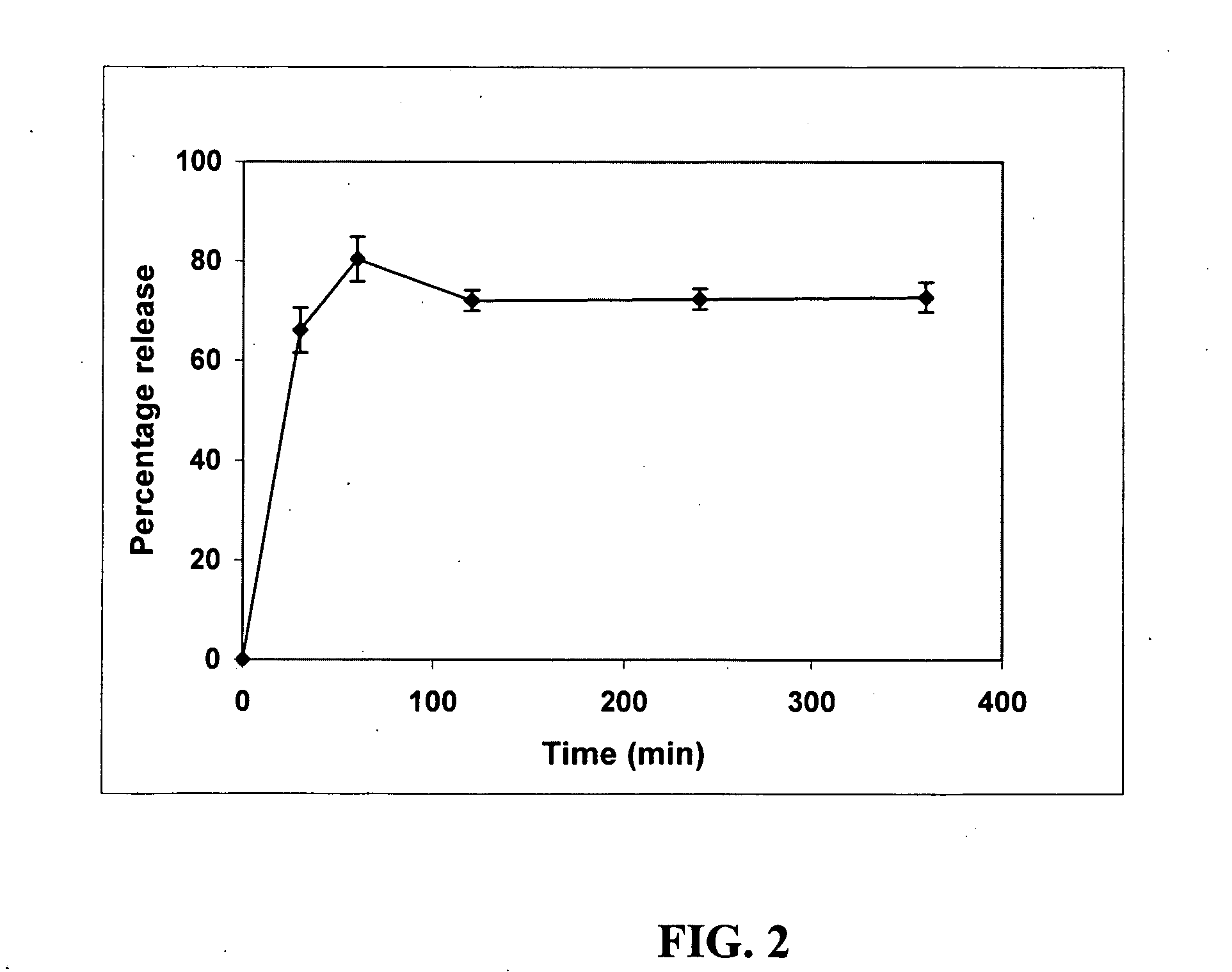
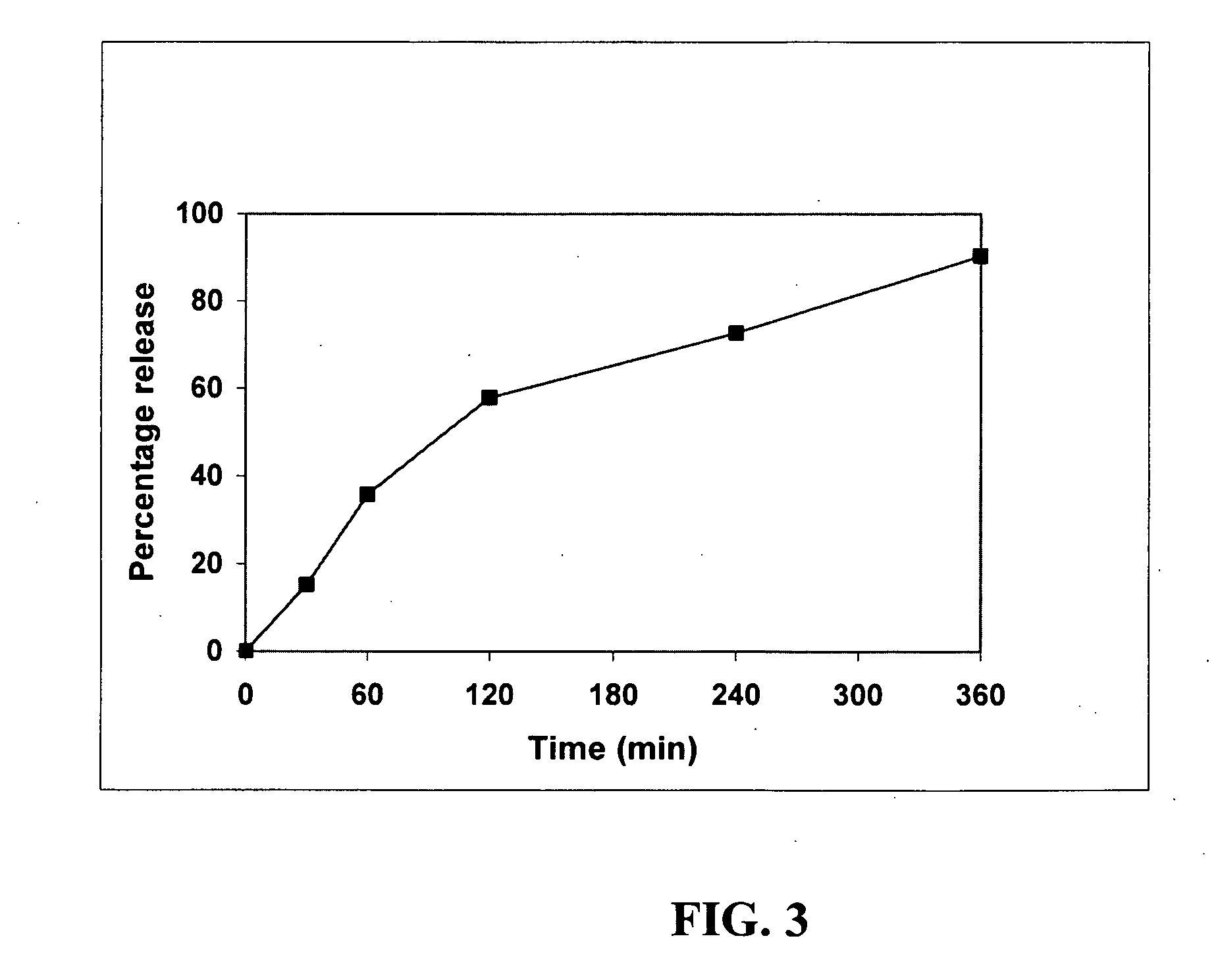
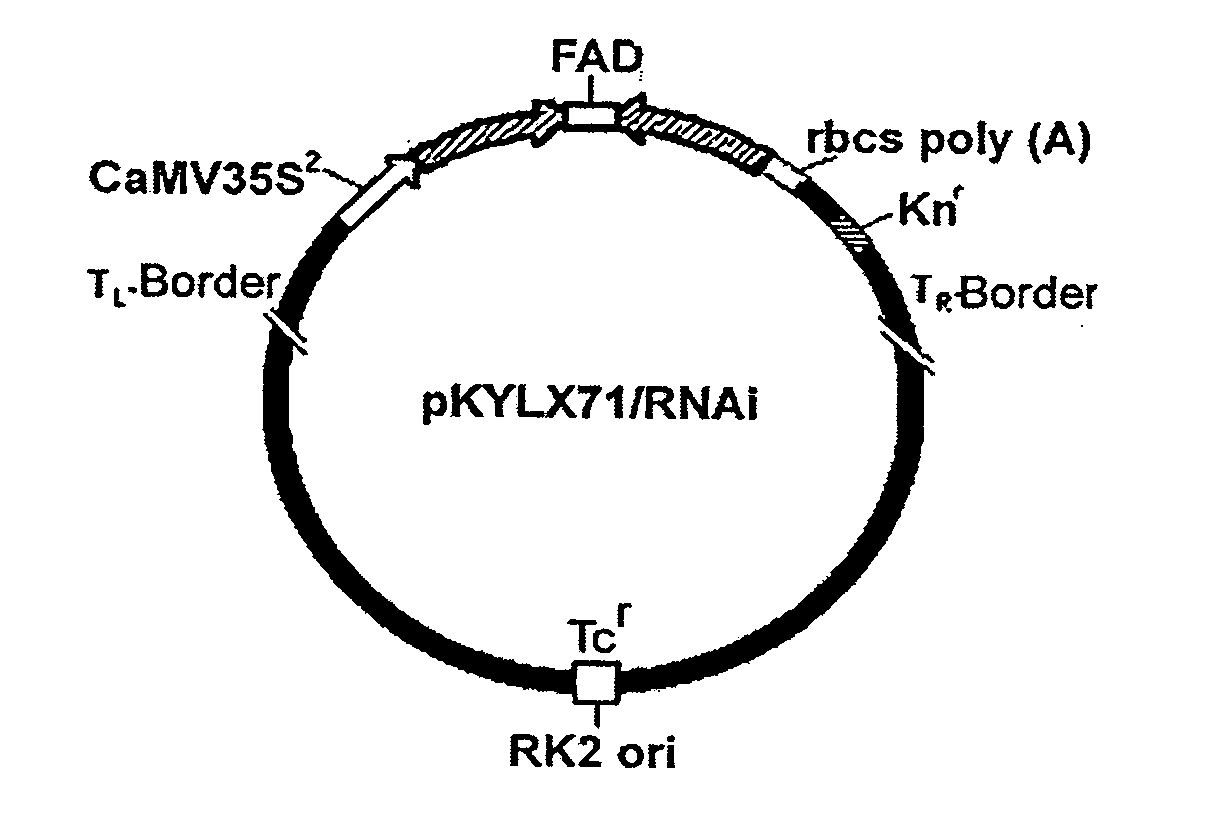
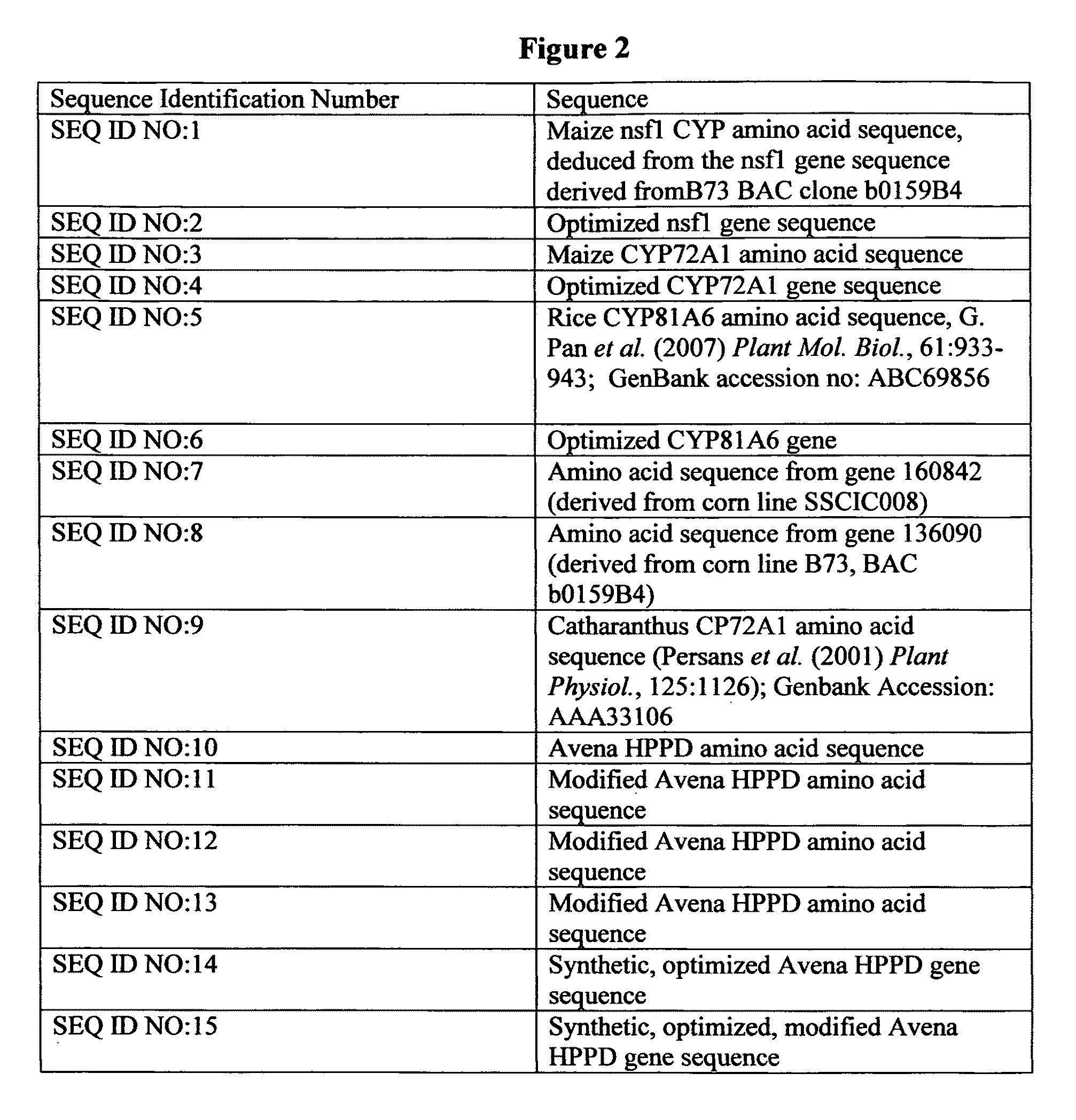
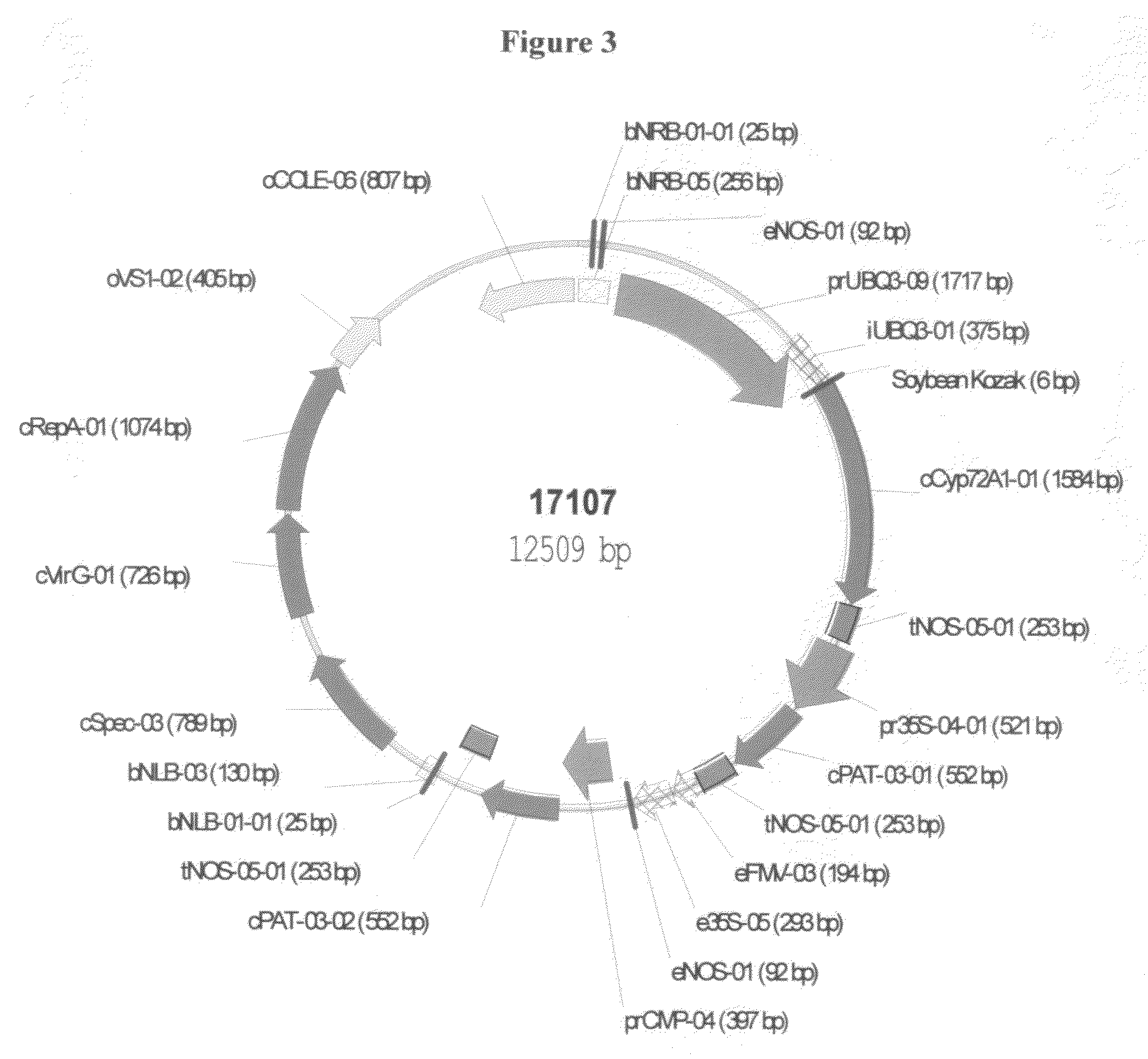
Patents
Literature
311 results about "Cytochrome P450" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
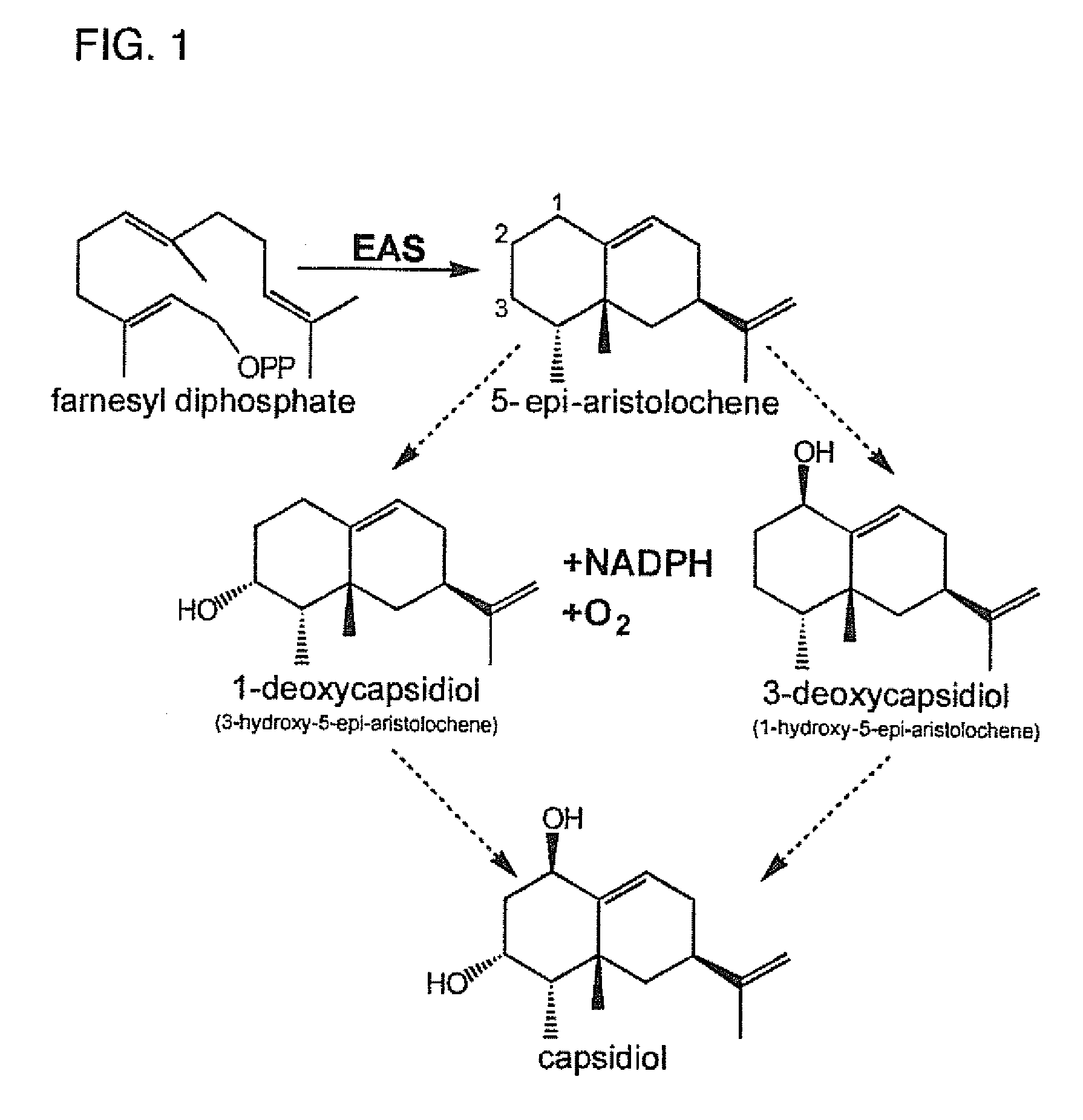
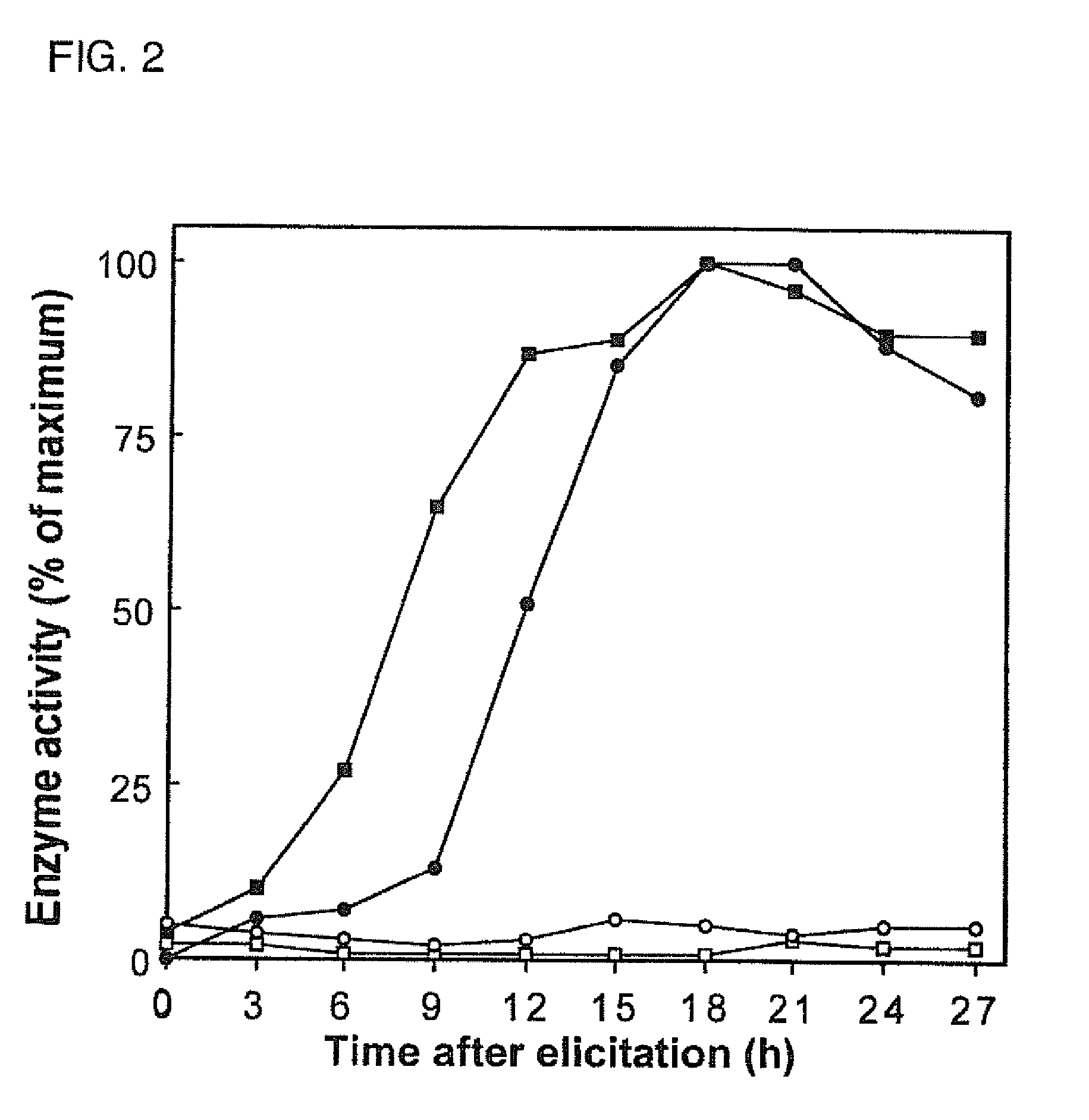
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a family of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.
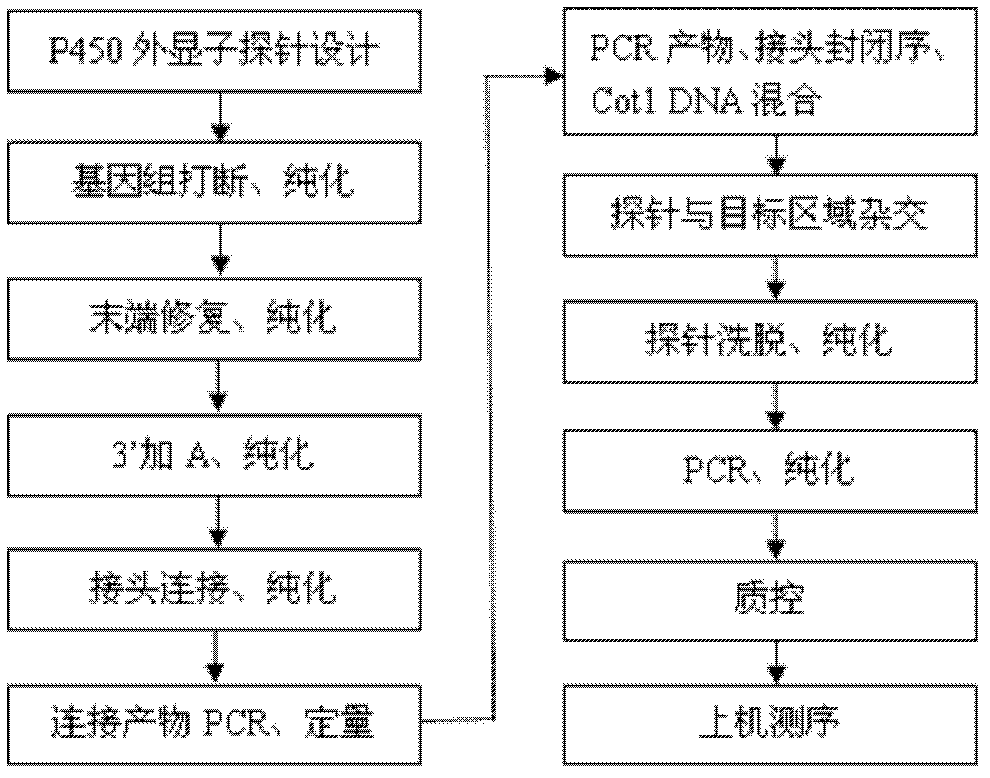
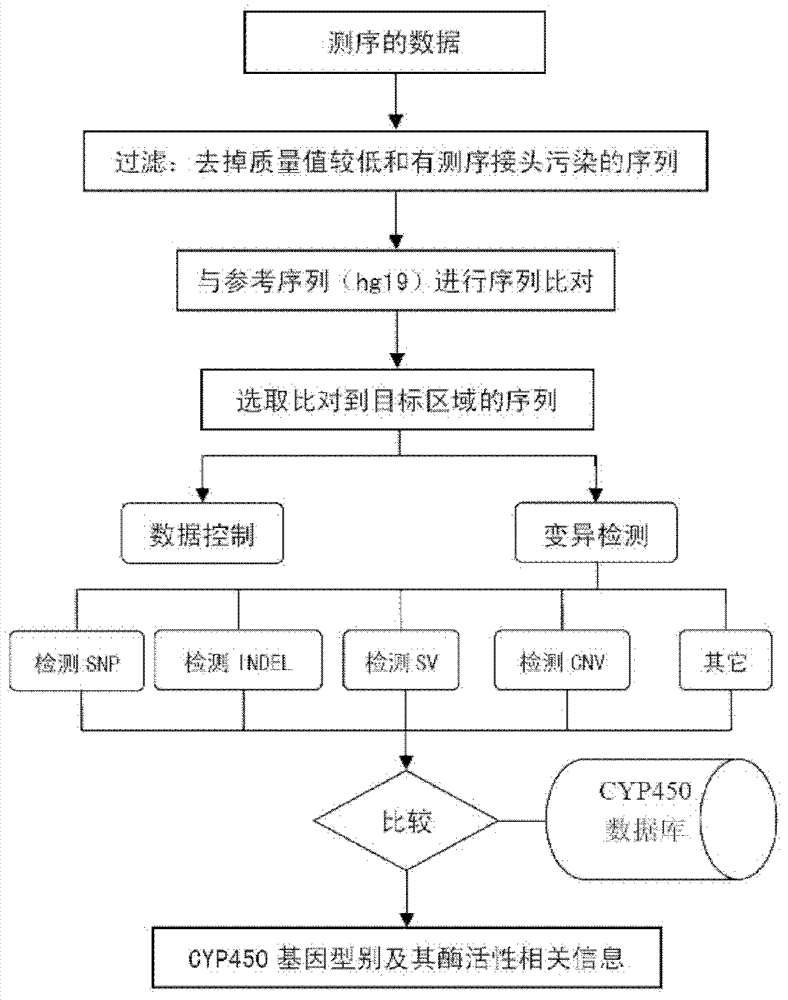
Analysis of genetic polymorphisms and gene copy number
InactiveUS6468744B1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsCytochrome P450Drug biotransformation
The invention provides methods for detecting variations in polymorphic sites and / or variations in gene copy number. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of biotransformation genes, such as cytochromes P450.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Delivery of tetrahydrocannabinol
InactiveUS20070104741A1Avoiding hepatic first-pass metabolismGood choiceBiocideNervous disorderChylomicronTG - Triglyceride
A self-emulsifying drug delivery system to improve dissolution, stability, and bioavailability of drug compounds of dronabinol or other cannabinoids. The drug compound(s) are dissolved in an oily medium (e.g. triglycerides and / or mixed glycerides and / or free fatty acids containing medium and / or long chain saturated, mono-unsaturated, and / or poly-unsaturated free fatty acids) together with at least one surfactant. The surfactant promotes self-emulsification, thereby promoting targeted chylomicron delivery and optimal bioavailability to a mammalian intestinal lumen. A dosage form can optionally include co-solvents, anti-oxidants, viscosity modifying agents, cytochrome P450 metabolic inhibitors, P-GP efflux inhibitors, and amphiphilic / non-amphiphilic solutes to induce semi-solid formation for targeted release rates.
Owner:MURTY PHARMA
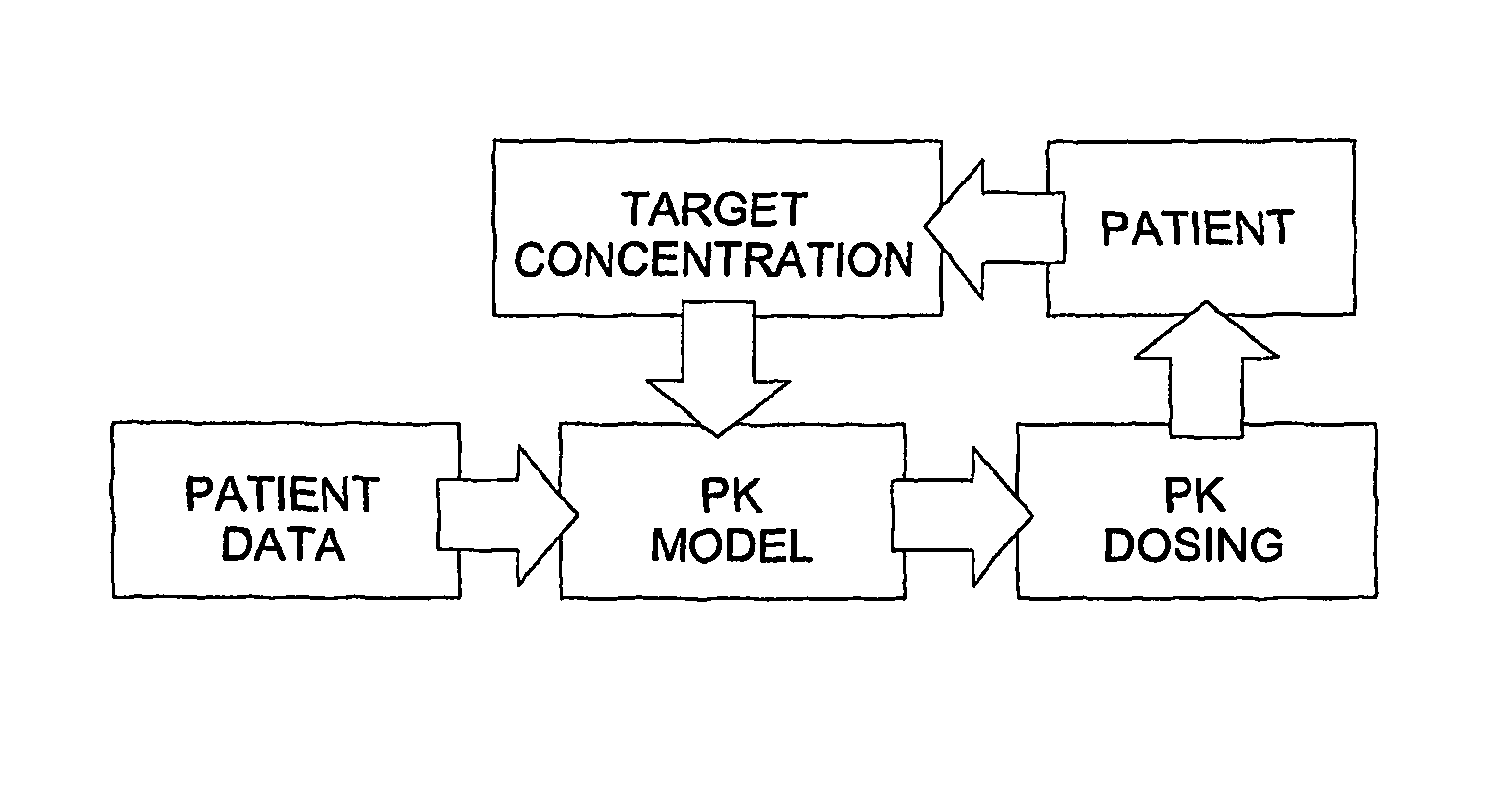
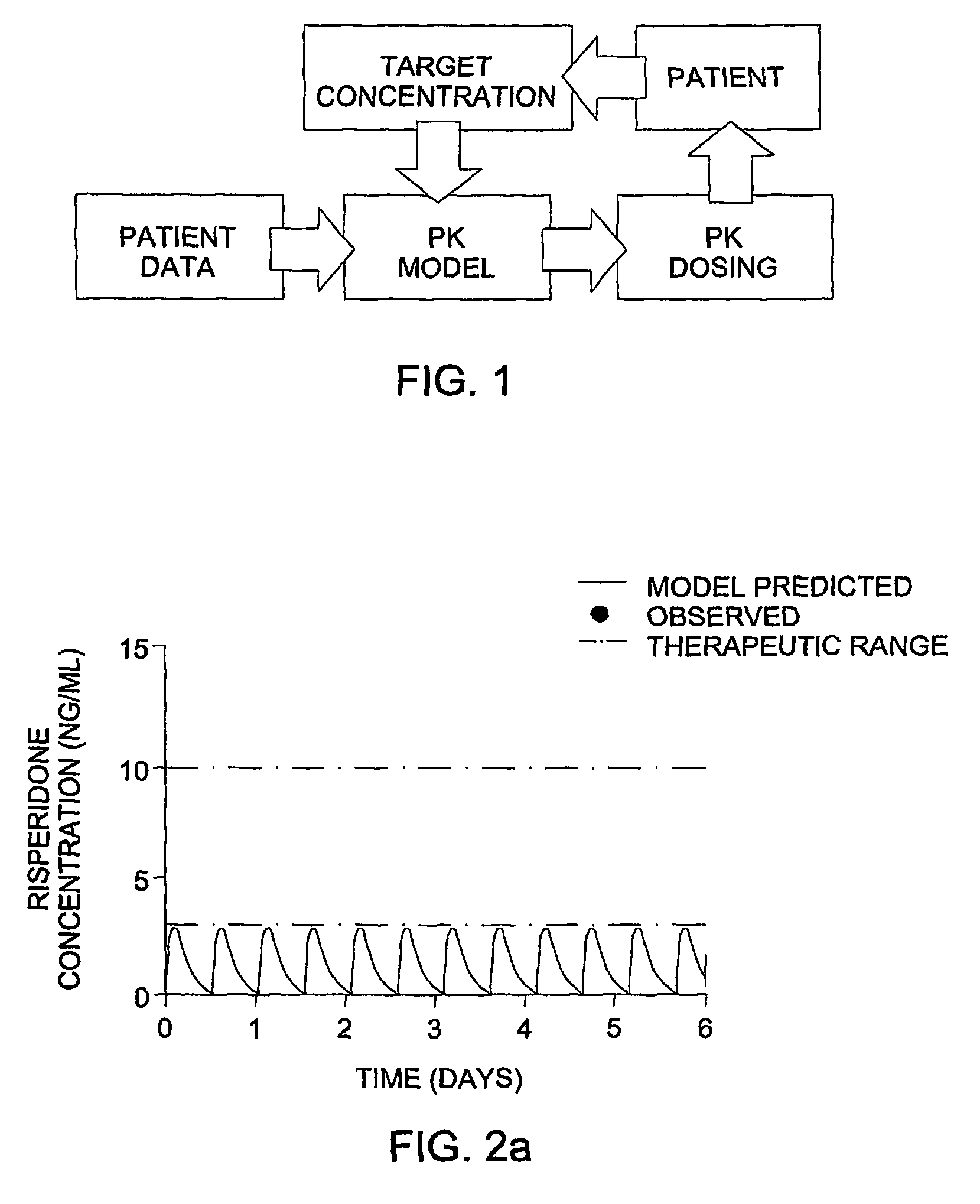
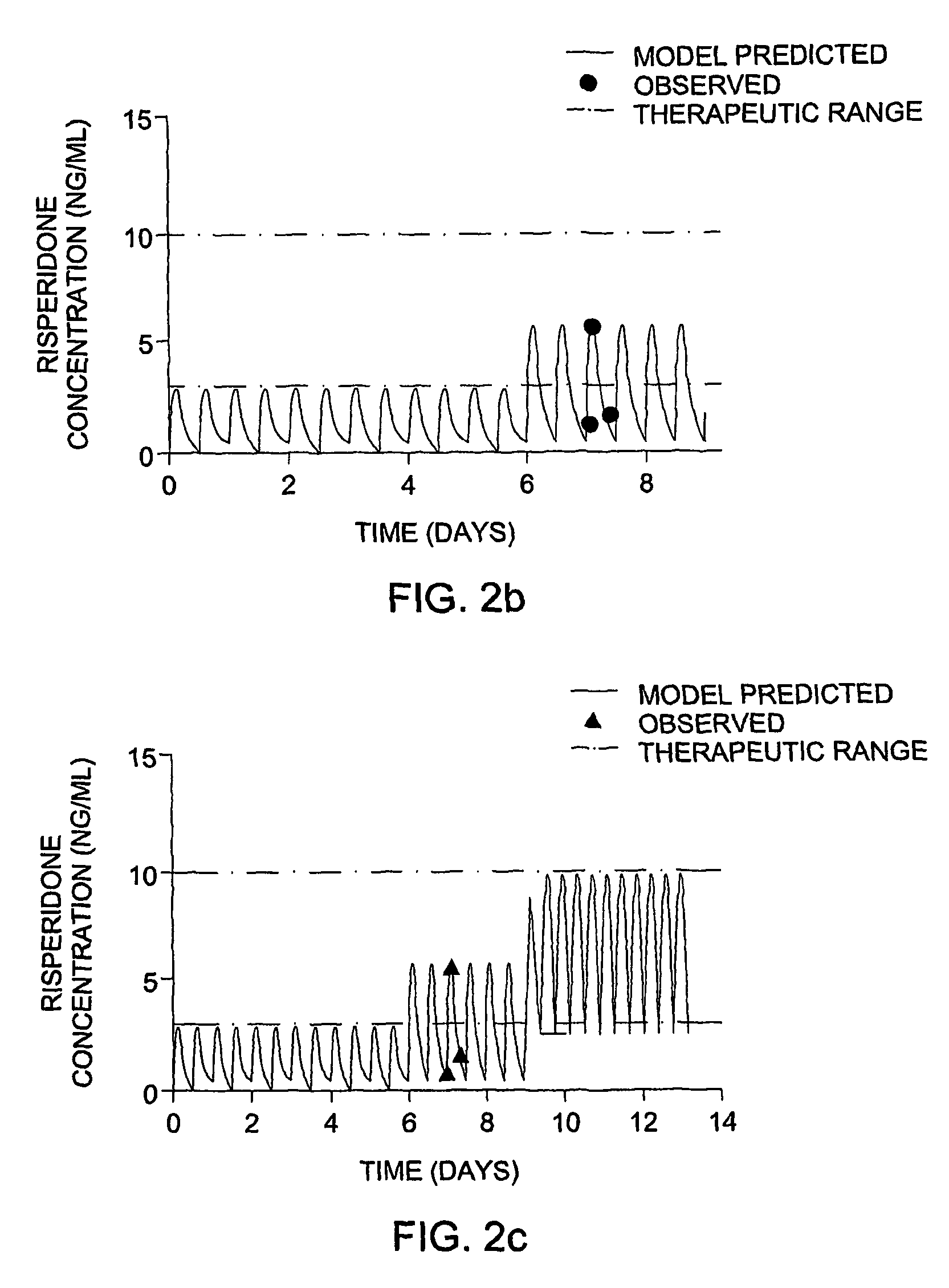
Optimization and Individualization of Medication Selection and Dosing
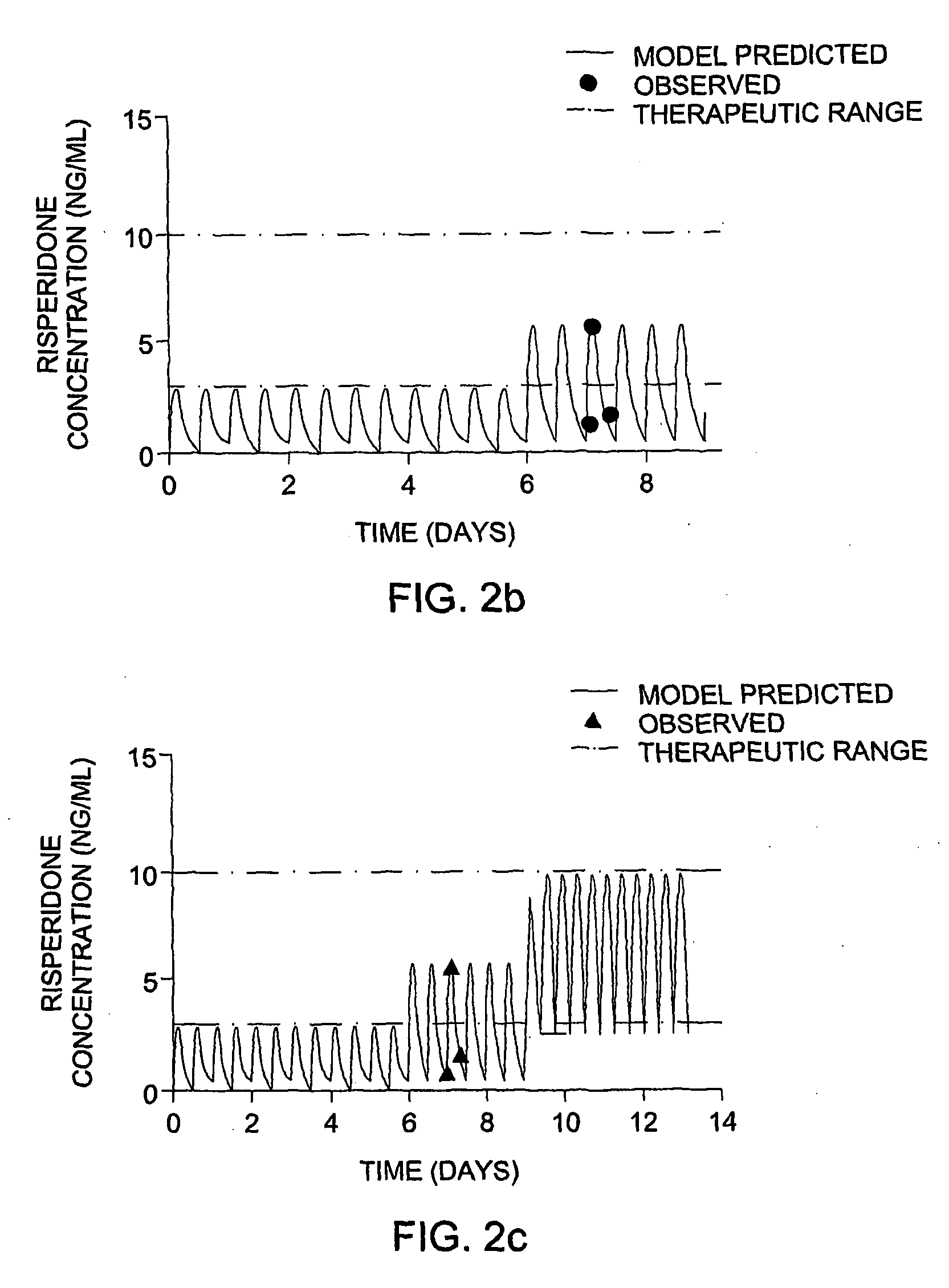
ActiveUS20090171697A1Easy to understandEasy to recommendationDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationDosing regimen
The invention provides population models, methods, and algorithms for targeting a dosing regimen or compound selection to an individual patient. The methods and algorithms of the invention utilize population models that incorporate genotype information for genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes for one or more compounds of interest. The methods allow integration of genotype information for one or more genes encoding a drug metabolizing enzyme, particularly a cytochrome P450 gene with patient data. The methods allow integration of genotype information and the effect of one or more compounds on one or more drug metabolizing enzymes. The methods allow iterative feedback of drug metabolizing data obtained from a patient into the process of generating a dosage regimen recommendation for a compound of interest for an individual patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
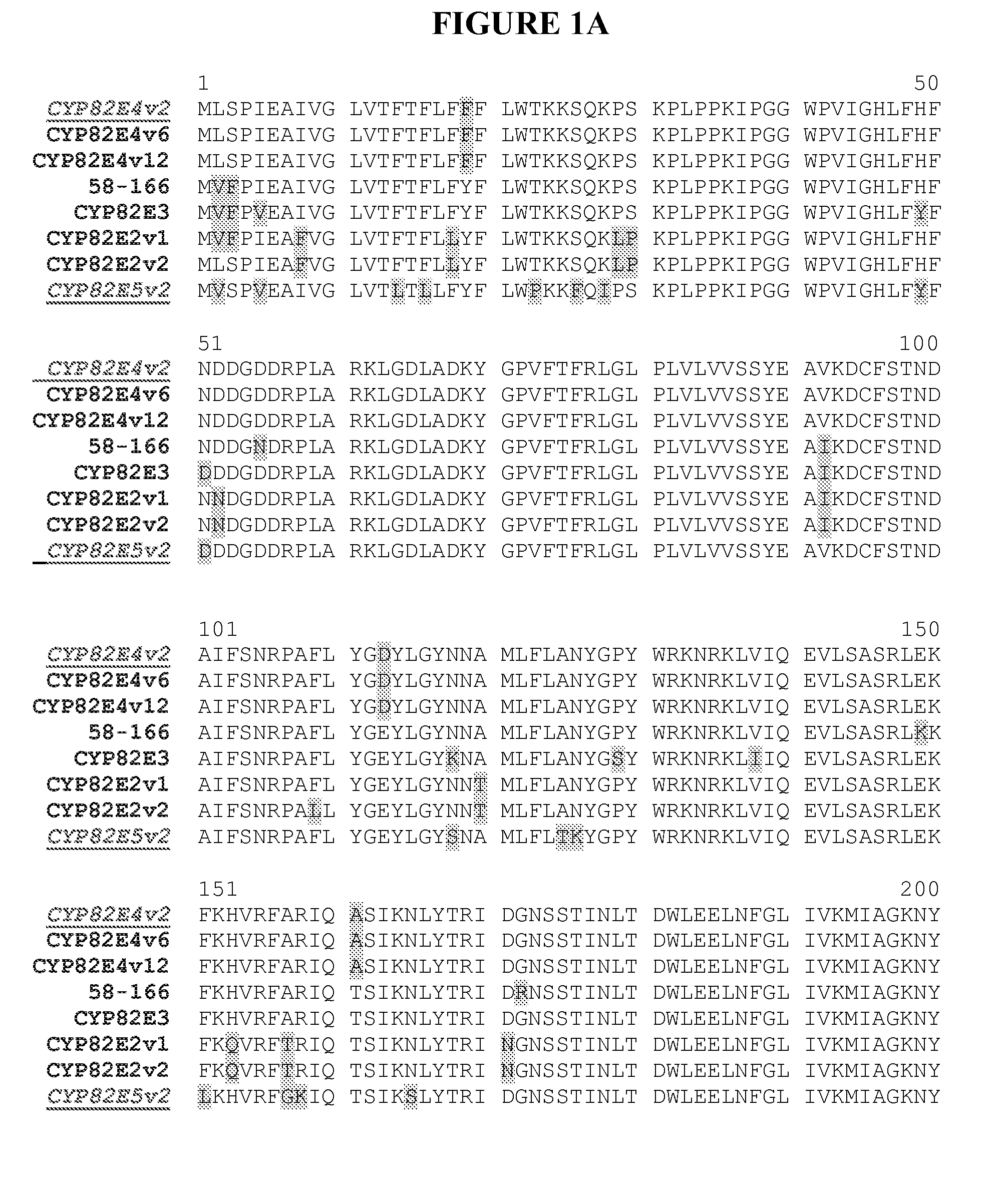
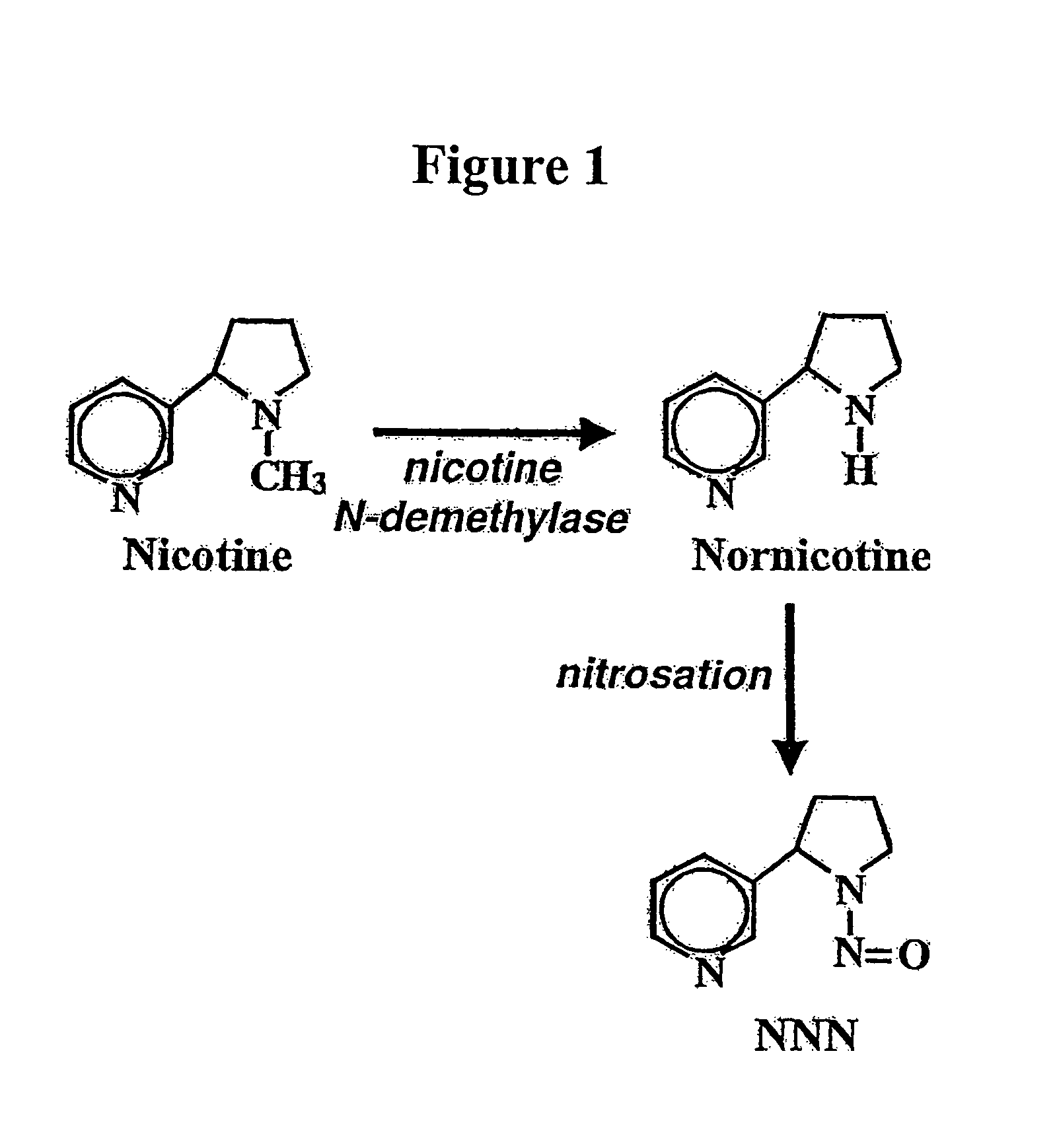
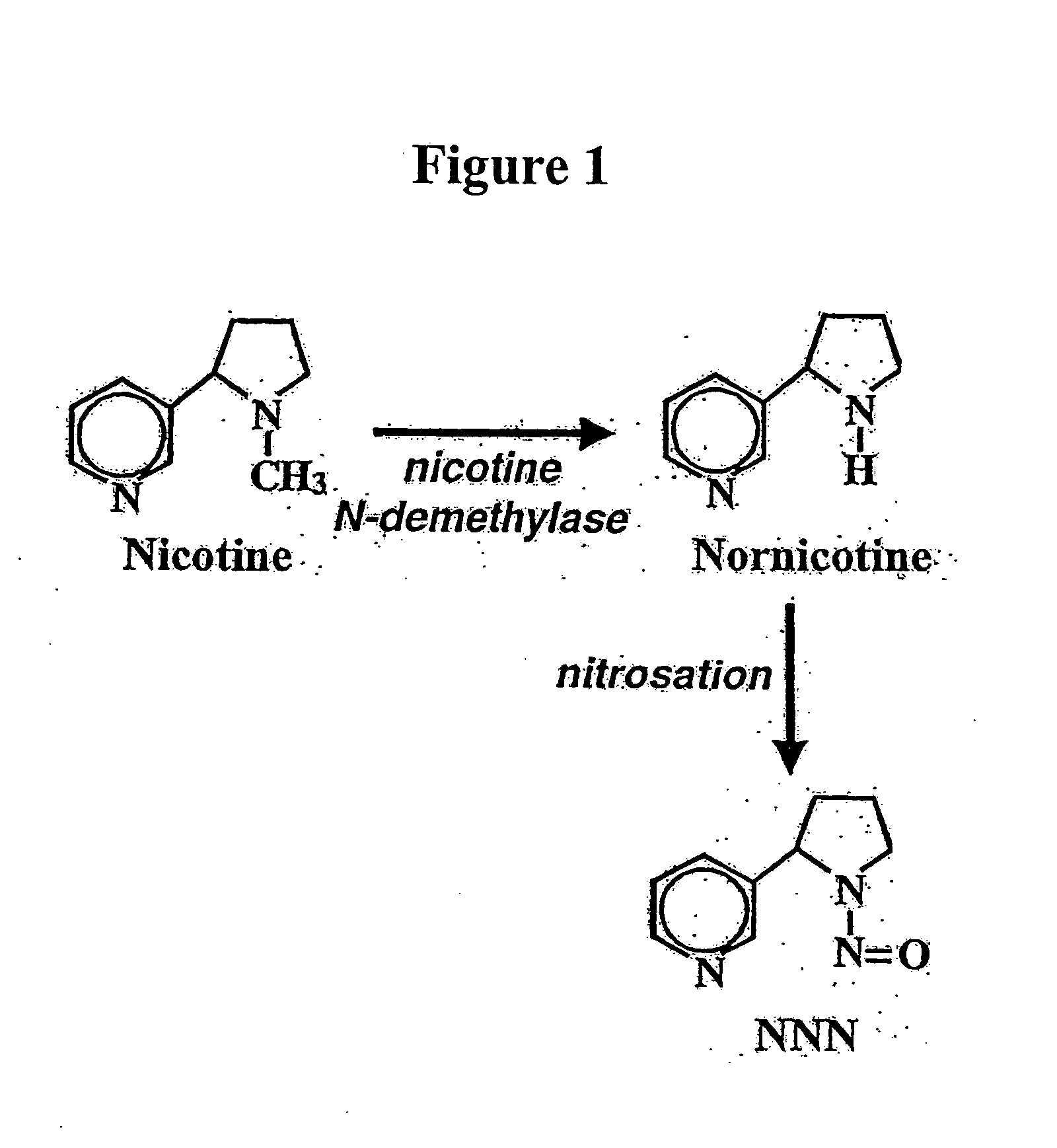
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS8124851B2Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS7884263B2Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsTobacco treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Pharmacogenetic DME detection assay methods and kits
InactiveUS20060160074A1Increase nucleic acid synthesis reaction rateHeating evenlySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismPharmacogenetics
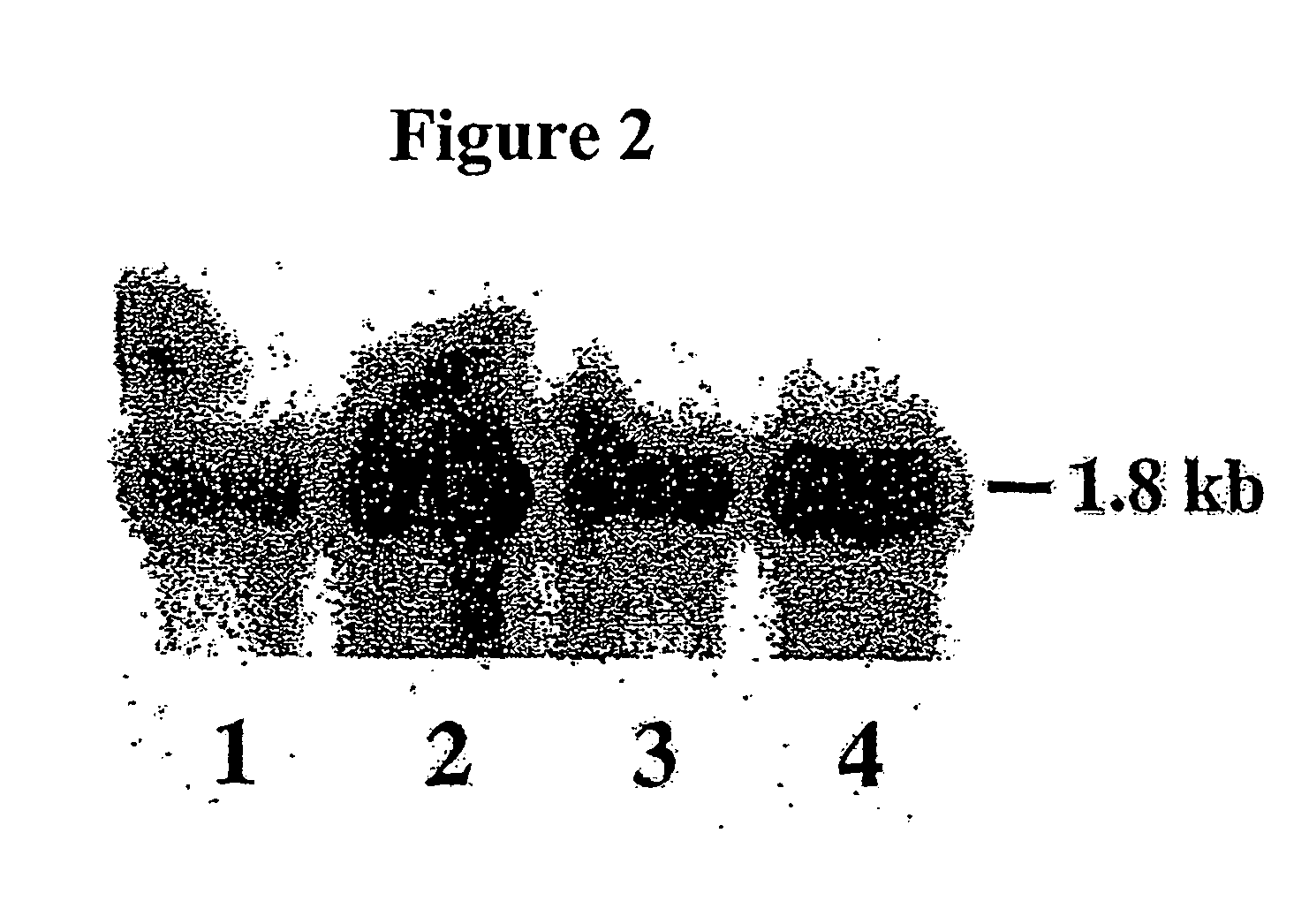
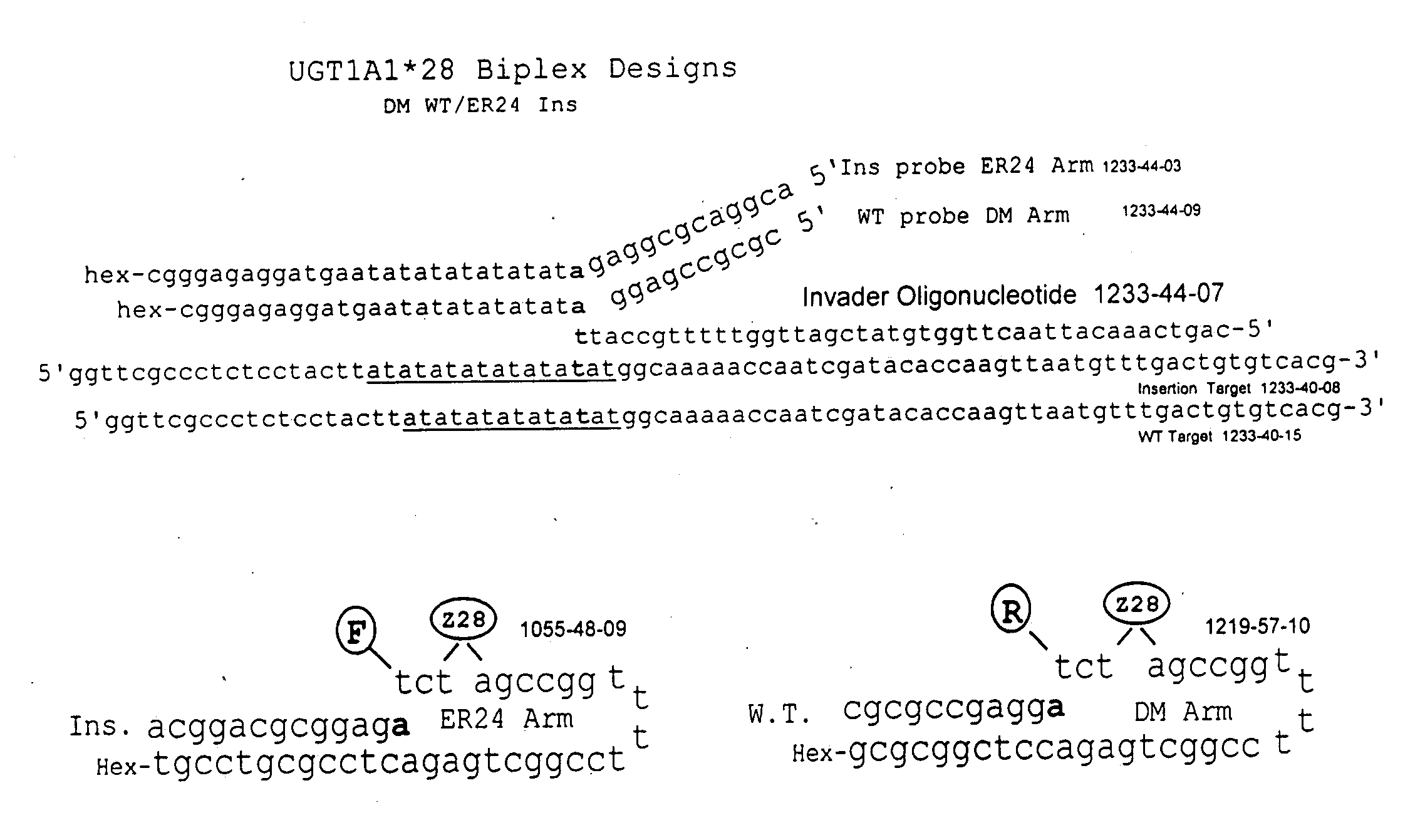
The present invention relates to methods for detecting polymorphisms in enzymes related to drug metabolizm (Drug Metabolizing Enzymes or DMEs) such as uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) gene promoter, cytochrome p450, with a non-amplified oligonucleotide detection assays. The present invention also relates to pharmacogenetic DME detection assay kits.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
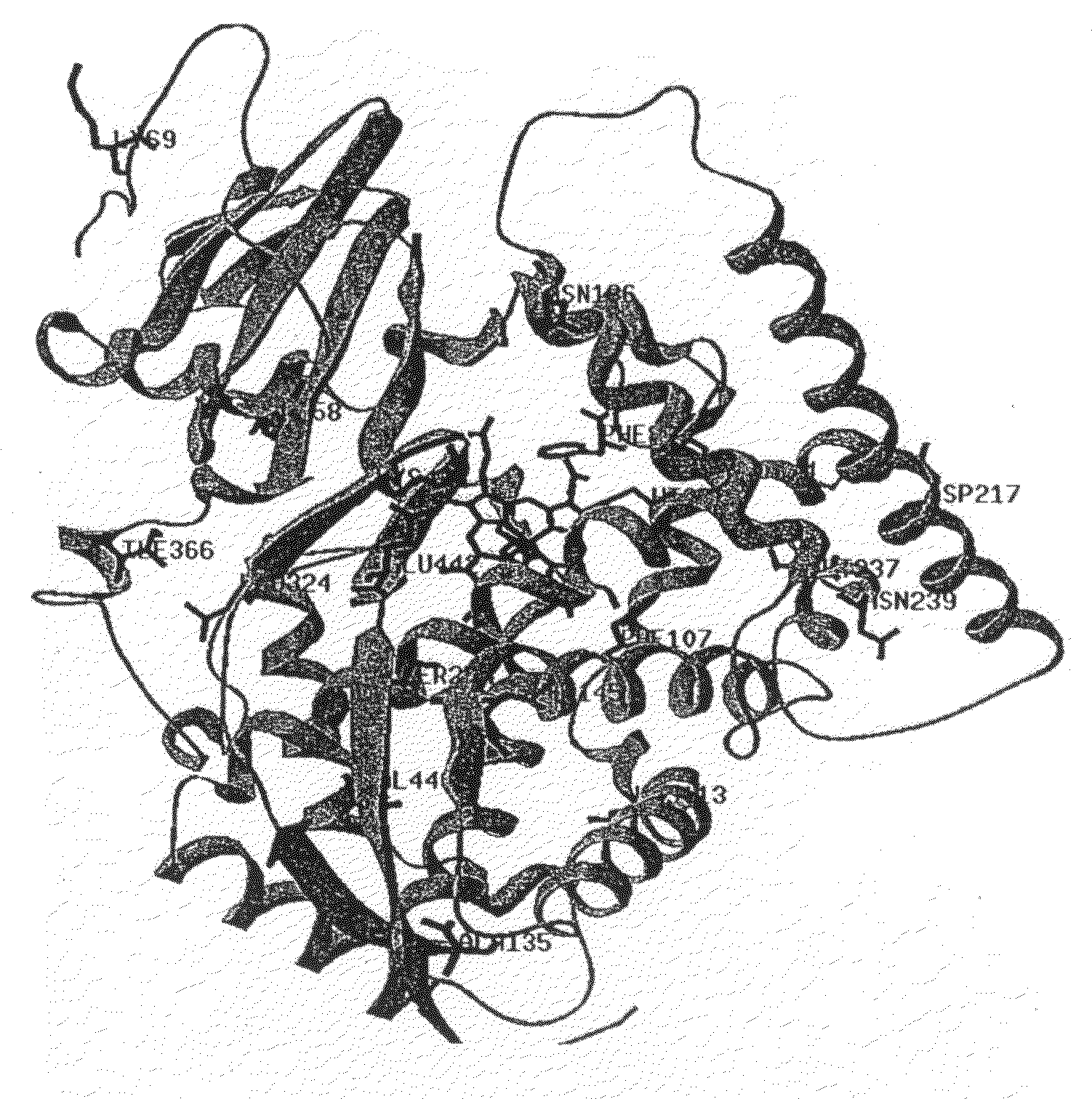
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
InactiveUS20050202419A1Improve abilitiesImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesOxygenaseHeme
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome p450 genes
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in Nicotiana plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for cytochrome P450s that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Expression cassettes, vectors, plants, and plant parts thereof comprising inhibitory sequences that target expression or function of the disclosed cytochrome P450 polypeptides are also provided. Methods for the use of these novel sequences to inhibit expression or function of cytochrome P450 polypeptides involved in this metabolic conversion are also provided. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Optimization and individualization of medication selection and dosing
ActiveUS8589175B2Easy to understandEasy to recommendationDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationDosing regimen
The invention provides population models, methods, and algorithms for targeting a dosing regimen or compound selection to an individual patient. The methods and algorithms of the invention utilize population models that incorporate genotype information for genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes for one or more compounds of interest. The methods allow integration of genotype information for one or more genes encoding a drug metabolizing enzyme, particularly a cytochrome P450 gene with patient data. The methods allow integration of genotype information and the effect of one or more compounds on one or more drug metabolizing enzymes. The methods allow iterative feedback of drug metabolizing data obtained from a patient into the process of generating a dosage regimen recommendation for a compound of interest for an individual patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Oral Dosage Form Of Tetrahydrocannabinol And A Method Of Avoiding And/Or Suppressing Hepatic First Pass Metabolism Via Targeted Chylomicron/Lipoprotein Delivery
ActiveUS20110092583A1Easy to transportPromote lymphatic transportBiocideSenses disorderChylomicronCytochrome P450
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems are provided to improve dissolution, stability, and bioavailability of drug compounds of dronabinol or other cannabinoids. The drug compound(s) are dissolved in an oily medium (e.g. triglycerides and / or mixed glycerides and / or free fatty acids containing medium and / or long chain saturated, mono-unsaturated, and / or poly-unsaturated free fatty acids) together with at least one surfactant. The surfactant promotes self-emulsification, thereby promoting targeted chylomicron / lipoprotein delivery and optimal bioavailability through the mammalian intestinal tract. A dosage form can optionally include co-solvents, anti-oxidants, viscosity modifying agents, cytochrome P450 metabolic inhibitors, P-GP efflux inhibitors, and amphiphilic / non-amphiphilic solutes to induce semi-solid formation for targeted release rates.
Owner:MURTY RAM B +1
Composition for Treatment of Pain Specification
InactiveUS20080096872A1Easy to useRelief the painBiocideNervous disorderCytochrome P450Treatment pain
A method for the treatment of pain and / or inflammation in a subject by the administration of N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) or derivative thereof and a pain and / or anti-inflammatory medication. The pain or anti-inflammatory medication is metabolized by the action of the cytochrome p450 system. The pain medication includes N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist(s). NAC and the pain medicine can be administered concurrently or sequentially. The joint administration can result in the use of lower dosages than typical dosage of the pain and / or anti-inflammatory medication or in enhanced relief from the treated condition.
Owner:FRIEDMAN ROBERT S
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS20080202541A1Lower Level RequirementsReducing nornicotine levelTobacco treatmentTobacco devicesMetaboliteNornicotine
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in Nicotiana plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for cytochrome P450s that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Expression cassettes, vectors, plants, and plant parts thereof comprising inhibitory sequences that target expression or function of the disclosed cytochrome P450 polypeptides are also provided. Methods for the use of these novel sequences to inhibit expression or function of cytochrome P450 polypeptides involved in this metabolic conversion are also provided. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
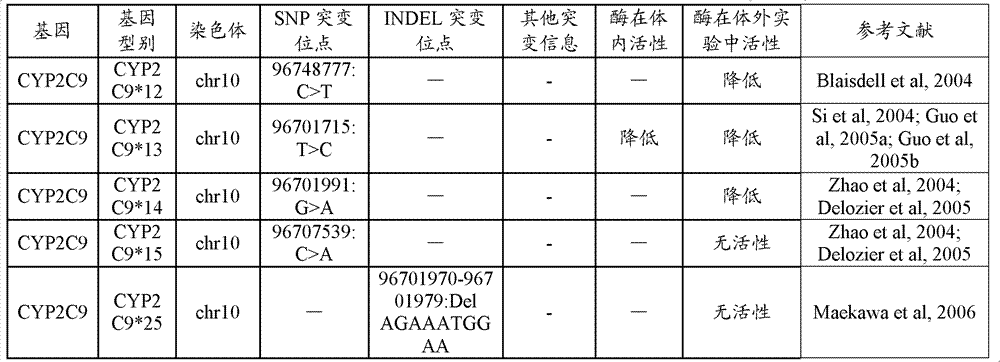
CYP450 gene type database and gene typing and enzymatic activity identification method
ActiveCN103198236AGive quickly and accuratelyAccurate judgment basisMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDiseaseGene type
The invention discloses a method for building a standard CYP450 (cytochrome p450) gene type database. The method comprises the steps as follows: comparing a specific sequence corresponding to mutation information of a CYP450 gene type with a standard human whole genome sequence to obtain a corresponding relation between the specific sequence and the standard human whole genome sequence; and converting the CYP450 gene type into a gene type taking the standard human whole genome sequence as a reference sequence according to the corresponding relation. The invention further discloses a database built by the method and a CYP450 gene typing and enzymatic activity identification method based on the database. The database is convenient for research of CYP450; the gene typing method provides unified standards for CYP450 gene typing and provides more accurate judgment criterions for diseases, drugs or the like; unknown mutation sites in CYP450 genes can be effectively detected; hundreds of samples can be detected at the same time; and the coverage range is comprehensive and wide.
Owner:北京六合华大基因科技有限公司
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Membrane receptor reagent and assay
InactiveUS7288368B2Improve developmentImprove overall utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyLipid formationFluorescence
A membrane receptor reagent and assay is disclosed in which liposomes are bound to an evanescent wave emitting surface. Membrane receptors on the liposome's fluid lipid bilayer membrane are labeled with a fluorescent or luminescent moiety. These membrane receptors are free to diffuse randomly throughout the liposome surface, and thus tend to redistribute according to externally applied forces. The evanescent wave-emitting surface additionally contains reagents that reversibly bind to the membrane receptors, tending to bring them closer to region of high evanescent wave intensity. Test analytes that disrupt or promote the association between the membrane receptors and the surface reagents act to change the average distance between the membrane receptors and the evanescent wave emitting surface, resulting in a change in the fluorescent or luminescent signal. This reagent and assay system functions with physiologically important membrane receptors such as GPCR receptors, other 7-tm receptors, drug transport proteins, cytochrome P450 membrane proteins and other clinically important membrane components. The reagent and assay methods may be incorporated into microarrays, capillaries, flow cells and other devices, and used for drug discovery, ADMET, and other biomedically important assays.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
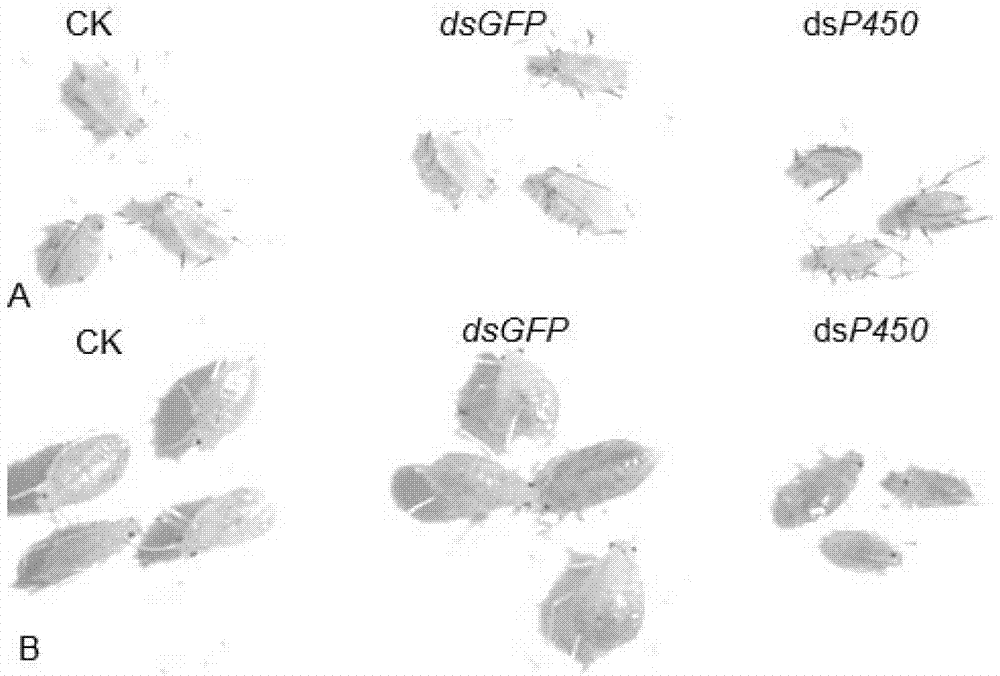
Cytochrome P450 dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application to aphid growth inhibition
The invention discloses dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application to aphid growth inhibition. The dsRNA provided by the invention is dsRNA as expressed by 1) or 2) as follows: 1) dsRNA consisting of ribonucleic acid as shown by a sequence 4 in a sequence table and ribonucleic acid as shown by a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 4; and 2) dsRNA consisting of ribonucleicacid as shown by a sequence 5 in the sequence table and ribonucleic acid as shown by a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 5. According to experiments, the obtained dsRNA of a conserved sequence of cytochrome P450cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of English grain aphids and green peach aphids can inhibit growth and development of the English grain aphids and the green peach aphids and can cause a lethal effect by adopting a method of feeding the dsRNA in vitro and using an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interfere) technology to silence the in-vivo cytochrome p450 of the English grain aphids and the green peach aphids.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Thermostable peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants and methods of use
InactiveUS20090264311A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove abilitiesSugar derivativesLibrary screeningOxygenaseHeme
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have at least one mutation improving their ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. The variants also have at least one mutation improving thermostability as compared to the parent enzyme or corresponding wild-type enzyme. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain variants having L52I, I58V, F87A, H100R, S106R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, A184V, N239H, S274T, L324I, V340M, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Genome editing of cytochrome p450 in animals
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences encoding cytochrome P450 (CYP) proteins. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. The invention also provides zinc finger nucleases that target chromosomal sequence encoding CYP proteins, as well as methods of using the genetically modified animals or cells disclosed herein to screen agents for toxicity and other effects.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
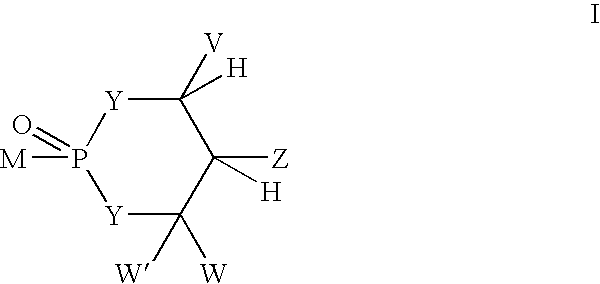
Method for improving pharmacokinetics of protease inhibitors and protease inhibitor precursors
InactiveUS20060287316A1Preventing and reducing and probabilityPreventing and reducing riskBiocideAntiviralsProteinase activityDepressant
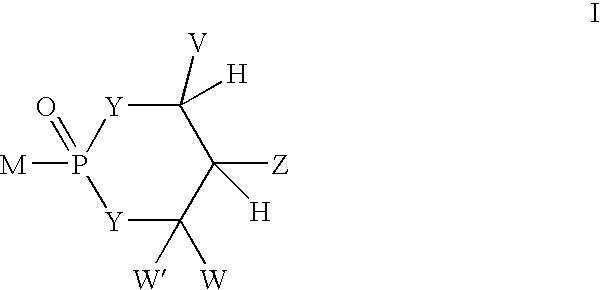
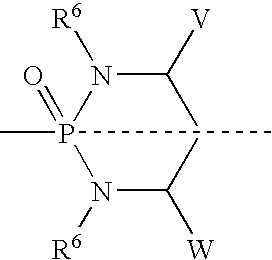
The present invention provides methods for improving the pharmacokinetics of protease inhibitors and protease inhibitor precursors and pharmaceutical composition comprising protease inhibitors or protease inhibitor precursors of formula I and a cytochrome P450 monooxigenase inhibitor; when the compound of formula I comprises an amino group, pharmaceutically acceptable ammonium salts thereof, wherein R1 may be, for example, (HO)2P(O)—, (NaO)2P(O)—, alkyl-CO— or cycloalkyl-CO—, wherein X may be, for example, F, Cl, and Br, and wherein R2 and R3 are as defined herein.
Owner:AMBRILIA BIOPHARMA INC
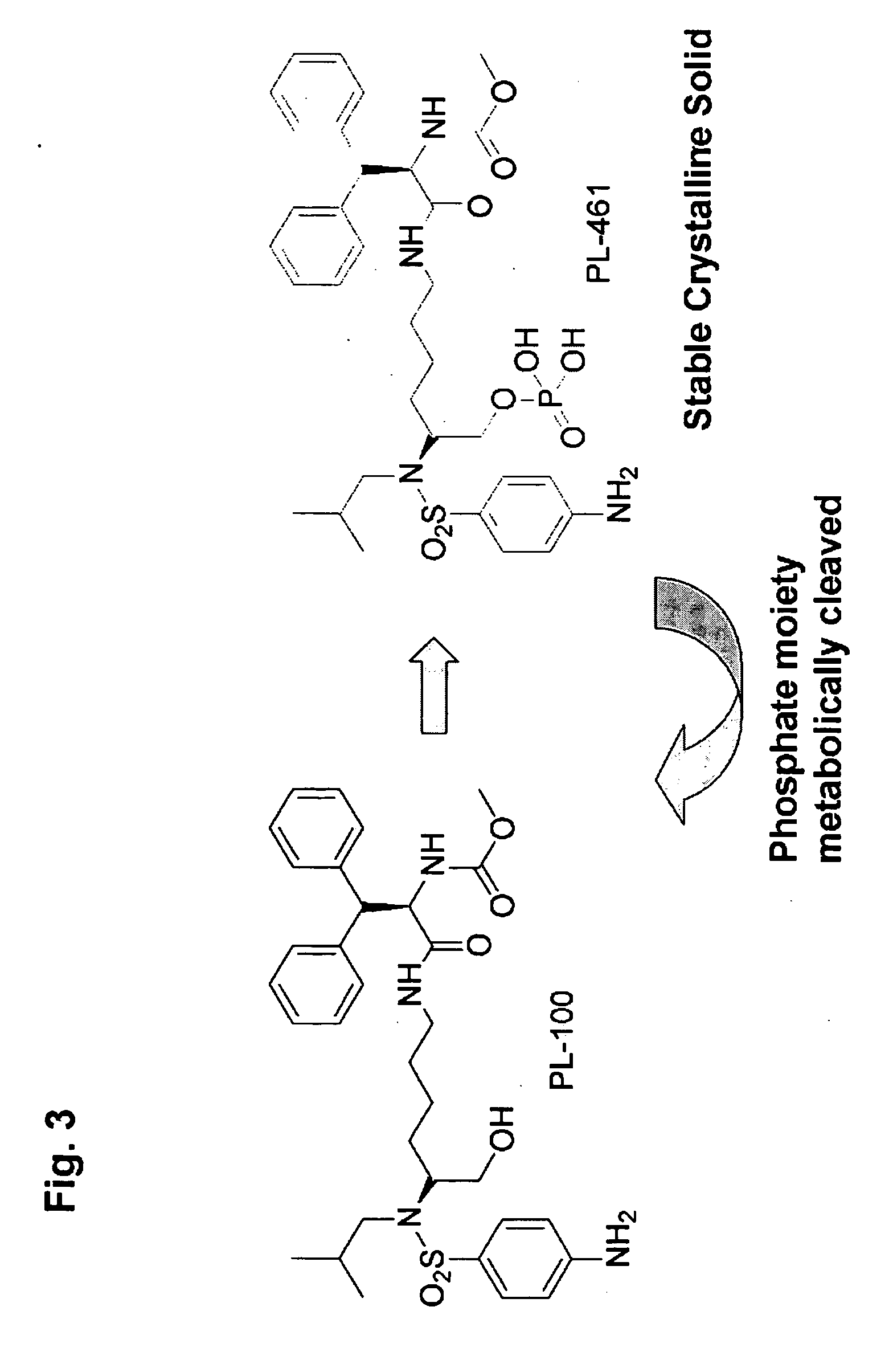
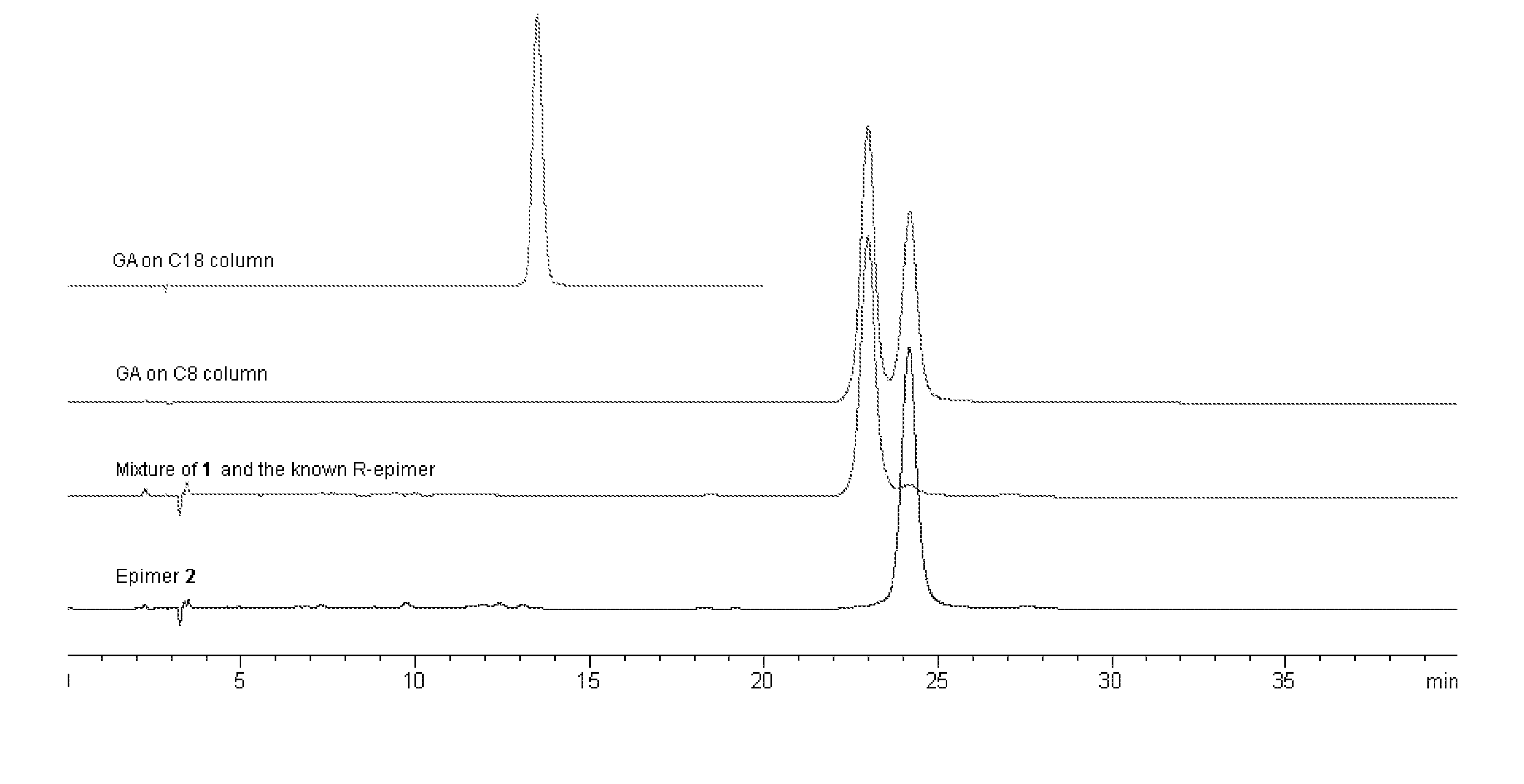
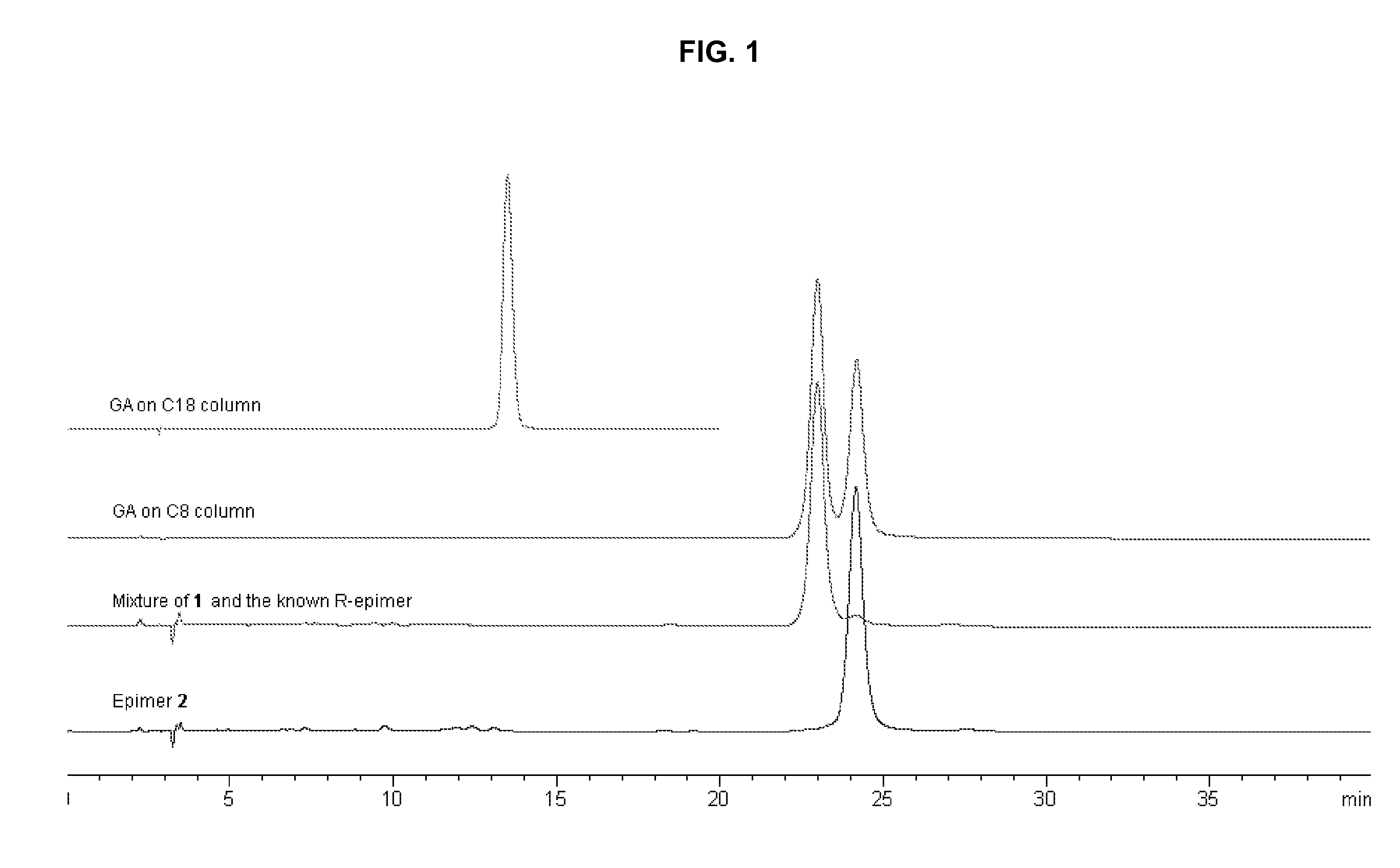
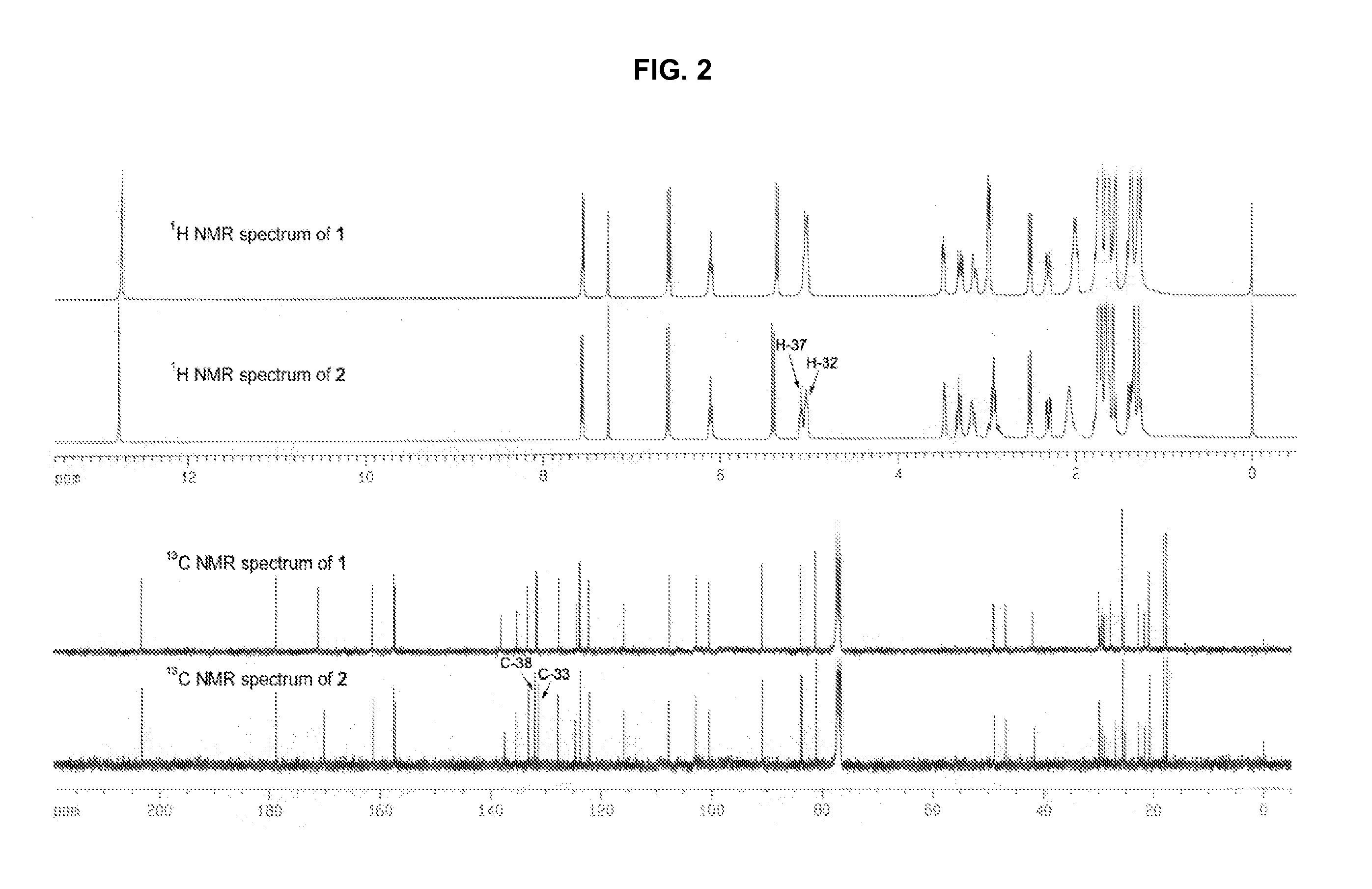
Novel compounds from garcinia hanburyi, their use in treating cancer and method of separating epimers thereof
InactiveUS20070149610A1Little inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryCytochrome P450Xanthone
Three pairs of C-2 epimeric xanthones isolated from Garcinia hanburyi and method for efficiently separating the xanthone compounds into individual epimers, each of which possesses varying biological effects. The compounds are useful for their anticancer effects, particularly because they are shown to be non-substrates of the multidrug-resistance transporter. Some of the epimers have significant inhibitory effects on cytochrome P450 systems. The xanthone compounds of the present invention are gambogic acid, epigambogic acid, isogambogic acid, isoepigambogic acid, 30-hydroxygambogic acid and 30-hydroxyepigambogic acid.
Owner:HONG KONG JOCKEY CLUB INST OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Cytochrome P450 genes conferring herbicide resistance
ActiveUS8097774B2Reduce residue levelsConfer resistanceBiocideOther foreign material introduction processesSulfonylureaPlant cell
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include transgenic plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds that have been transformed with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a cytochrome P450 or variant thereof that confers herbicide resistance or tolerance, alone or in combination with one or more additional nucleic acid molecules encoding polypeptides that confer desirable traits. In particular, the cytochrome P450 or variant thereof confers resistance or tolerance to HPPD inhibitors, benzothiadiazinones, sulfonylureas, and other classes of herbicides. The additional polypeptide may also confer resistance or tolerance to an herbicide, including HPPD inhibitors and other herbicides. Methods are also provided for the production and use of the herbicide resistant or tolerant plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds of the invention.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Prodrugs for liver specific drug delivery
The present invention is directed towards novel cyclic phosph(oramid)ate prodrugs of alcohol-, amine-, and thiol-containing drugs, their preparation, their synthetic intermediates, and their uses. Another aspect of the invention is the use of the prodrugs to treat diseases that benefit from enhanced drug distribution to the liver and like tissues and cells that express cytochrome P450, including hepatitis, cancer, liver fibrosis, malaria, other viral and parasitic infections, and metabolic diseases where the liver is responsible for the overproduction of the biochemical end product, e.g. glucose (diabetes); cholesterol, fatty acids and triglycerides (hyperlipidemia) (atherosclerosis) (obesity). In one aspect, the invention is directed towards the use of the prodrugs to enhance oral drug delivery. In another aspect, the prodrugs are used to prolong pharmacodynamic half-life of the drug. In addition, the prodrug methodology of the current invention is used to achieve sustained delivery of the parent drug. In another aspect, the prodrugs are used to increase the therapeutic index of the drug. In another aspect of the invention, a method of making these prodrugs is described. In another aspect, the prodrugs are also useful in the delivery of diagnostic imaging agents to the liver.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Cytochrome p450s and uses thereof
The invention features isolated cytochrome P450 polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules, as well as expression vectors and transgenic plants containing these molecules. In addition, the invention features uses of such molecules in methods of increasing the level of resistance against a disease caused by a plant pathogen in a transgenic plant, in methods for producing altered compounds, for example, hydroxylated compounds, and in methods of producing isoprenoid compounds.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
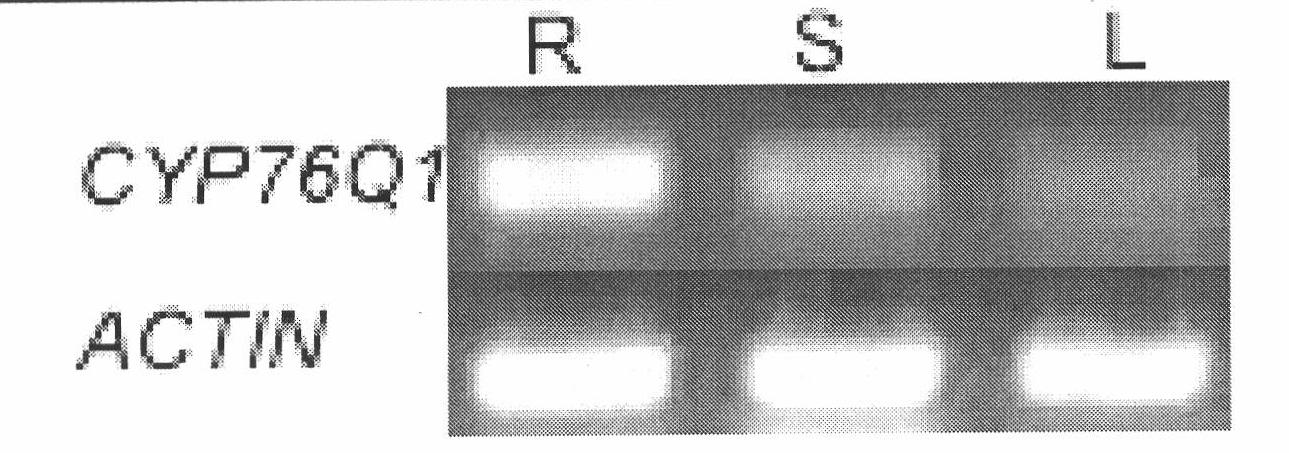
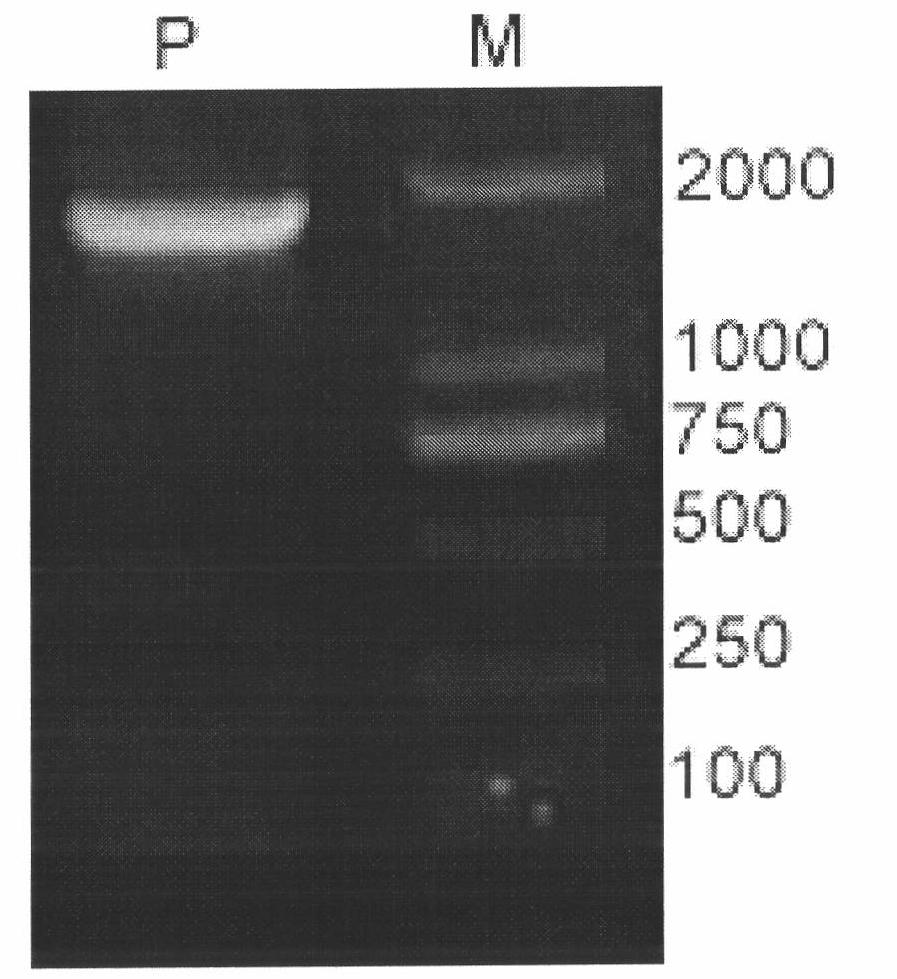
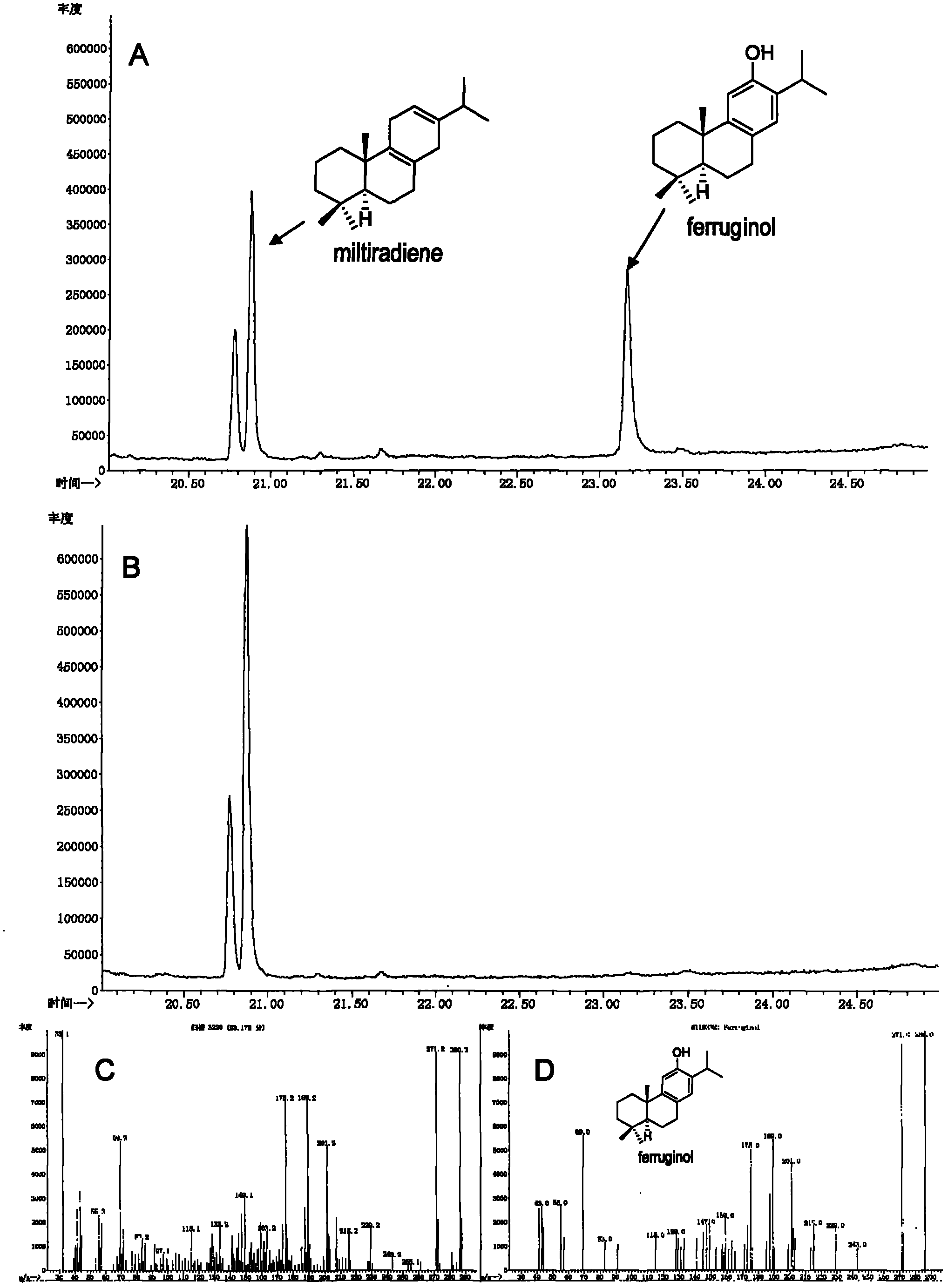
CYP450 (Cytochrome P450) gene participating in tanshinone biosynthesis and coded product as well as application thereof
The invention discloses a CYP450 (Cytochrome P450) gene participating in tanshinone biosynthesis and a coded product as well as application thereof, and belongs to the field of medicinal plant genetic engineering. The gene is firstly obtained through cloning from salvia miltiorrhiza bunge, is a key enzyme gene for a biosynthesis pathway of a tanshinone compound and is a key step of catalyzing miltiradiene to ferruginol. The CYP76Q1 gene provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID NO. 1. Protein coded by the gene has an amino acid residue sequence shown by SEQ ID No. 2 in a sequence table and protein with the same activity as that of the amino acid residue sequence shown by the SEQ ID No. 2 and derived from the SEQ ID No. 2. The CYP76Q1 gene provided by the invention is closely associated with biosynthesis of the tanshinone compound, has great theoretical and actual significance to regulating and producing a plant diterpene compound and improving the content of the diterpene active ingredient tanshinone in the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge through a biotechnology, contributes to quality improvement of the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge medicinal material and variety selection, also has the capacity of producing ferruginol monomer with pharmacological activity by constructing engineering bacteria using the gene, and has excellent application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Prodrugs for liver specific drug delivery
InactiveUS20050101775A1Enhanced drug distributionProlong pharmacodynamic half-lifeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHalf-lifeImaging agent
The present invention is directed towards novel cyclic phosph(oramid)ate prodrugs of alcohol-, amine-, and thiol-containing drugs, their preparation, their synthetic intermediates, and their uses. Another aspect of the invention is the use of the prodrugs to treat diseases that benefit from enhanced drug distribution to the liver and like tissues and cells that express cytochrome P450, including hepatitis, cancer, liver fibrosis, malaria, other viral and parasitic infections, and metabolic diseases where the liver is responsible for the overproduction of the biochemical end product, e.g. glucose (diabetes); cholesterol, fatty acids and triglycerides (hyperlipidemia) (atherosclerosis) (obesity). In one aspect, the invention is directed towards the use of the prodrugs to enhance oral drug delivery. In another aspect, the prodrugs are used to prolong pharmacodynamic half-life of the drug. In addition, the prodrug methodology of the current invention is used to achieve sustained delivery of the parent drug. In another aspect, the prodrugs are used to increase the therapeutic index of the drug. In another aspect of the invention, a method of making these prodrugs is described. In another aspect, the prodrugs are also useful in the delivery of diagnostic imaging agents to the liver.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Insect cytochrome P450 gene and application thereof
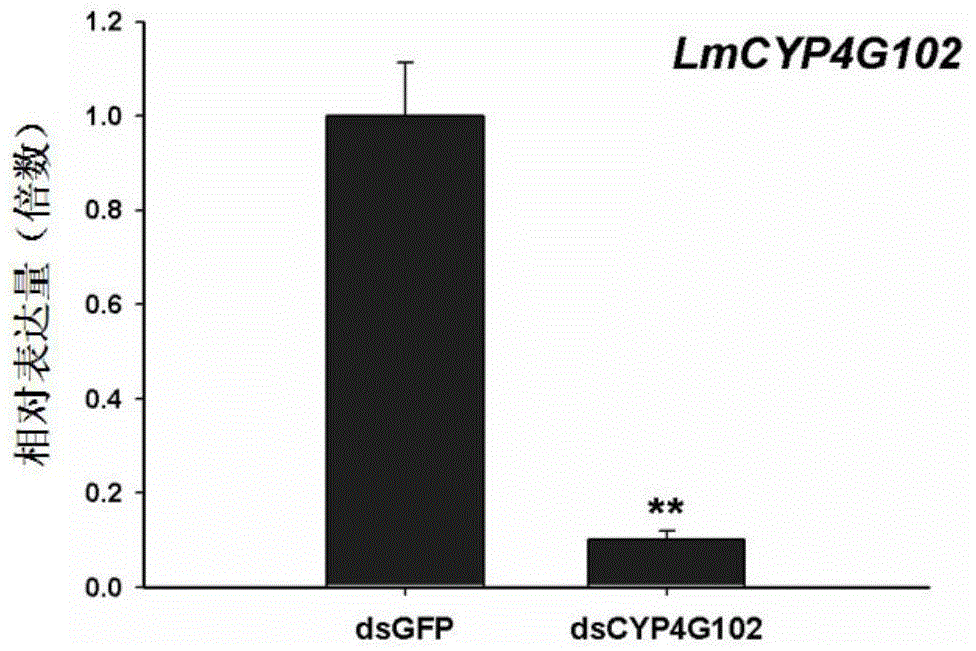
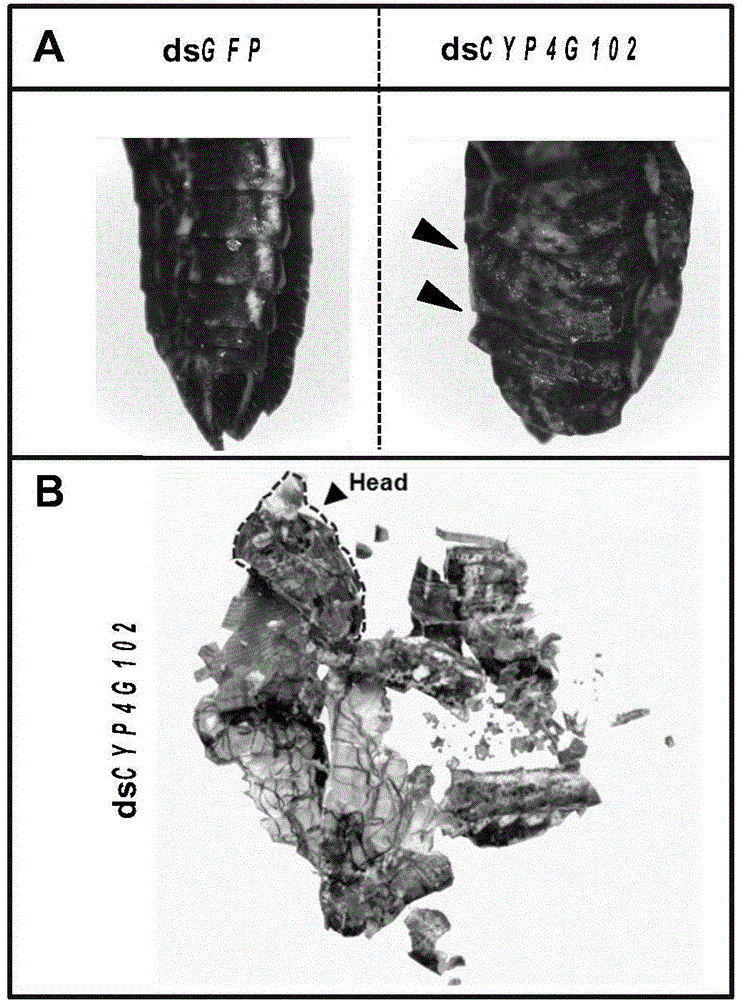
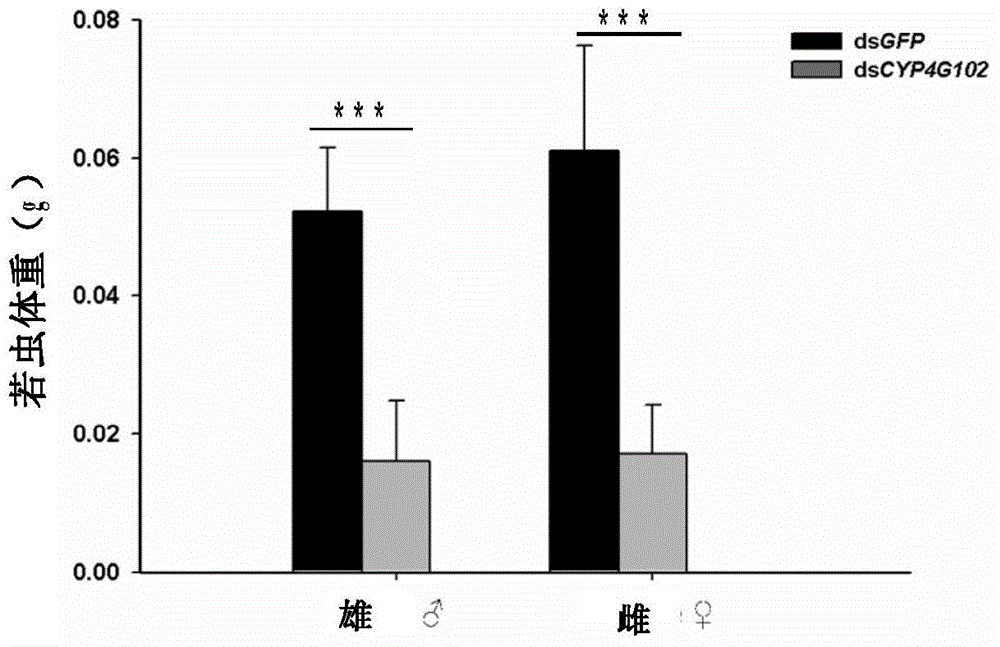
The invention provides an insect cytochrome P450 gene and the application thereof, and particularly relates to the insect cytochrome P450 gene, gene fragments, dsRNA and the application of the dsRNA to killing pests. Firstly, the cytochrome P450 gene of a migratory locust is cloned and sequenced to obtain a CYP4G102 gene, an overall nucleotide sequence of the CYP4G102 gene is SEQ ID NO:1, and an amino acid sequence of the CYP4G102 gene is SEQ ID NO:2; secondly, the gene fragments of which the sequence is SEQ ID NO:3 are obtained and used for synthesizing the dsRNA. After the synthesized dsRNA is injected into the body cavity of the migratory locust, the insect dies due to excessive in-vivo water loss caused by the fact that the water retention capacity of the body wall is reduced after ecdysis, and the death rate reaches 100 percent. The insect cytochrome P450 gene provides a molecular target or pest control based on RNA interference and can be used for the pest control.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
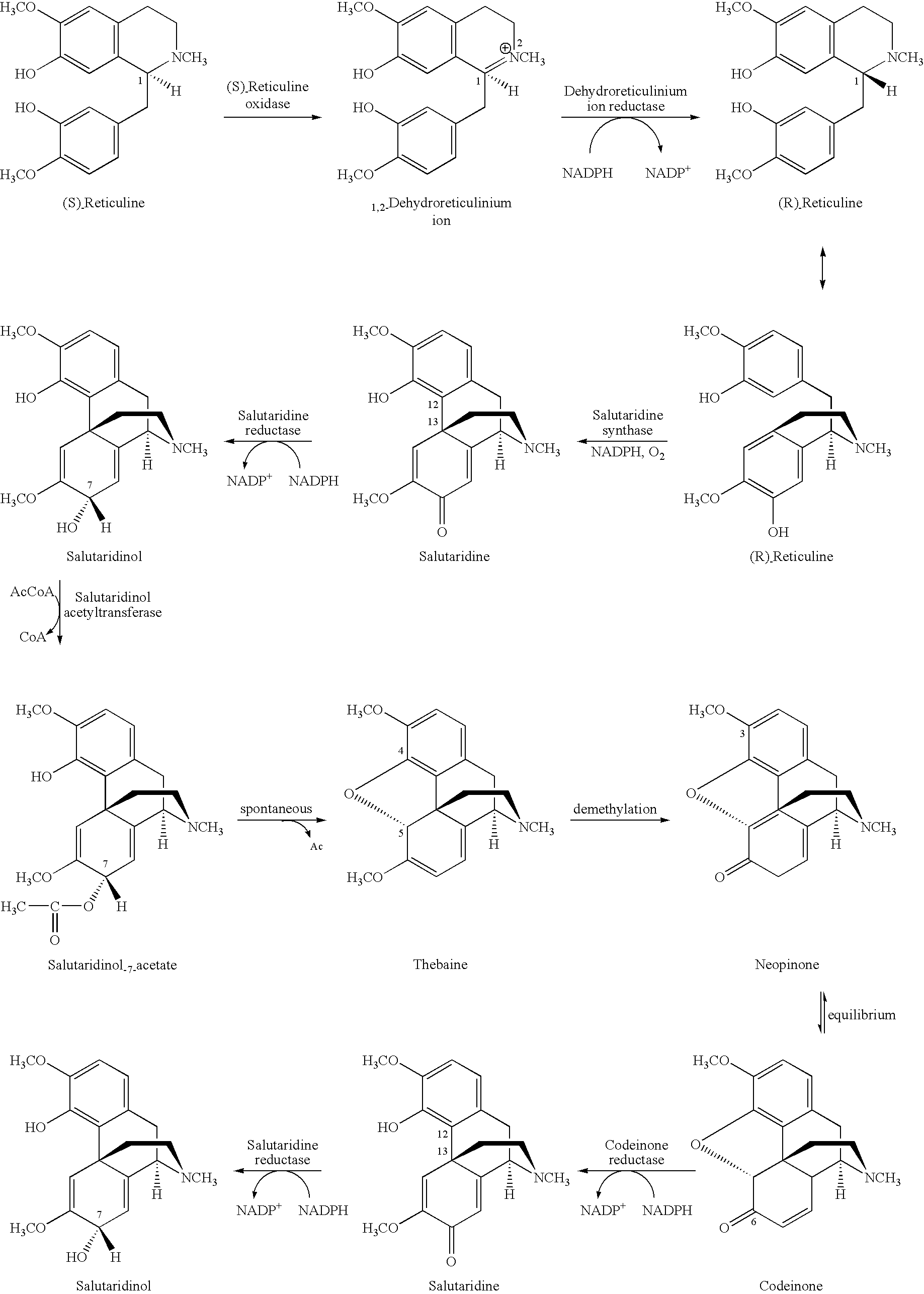
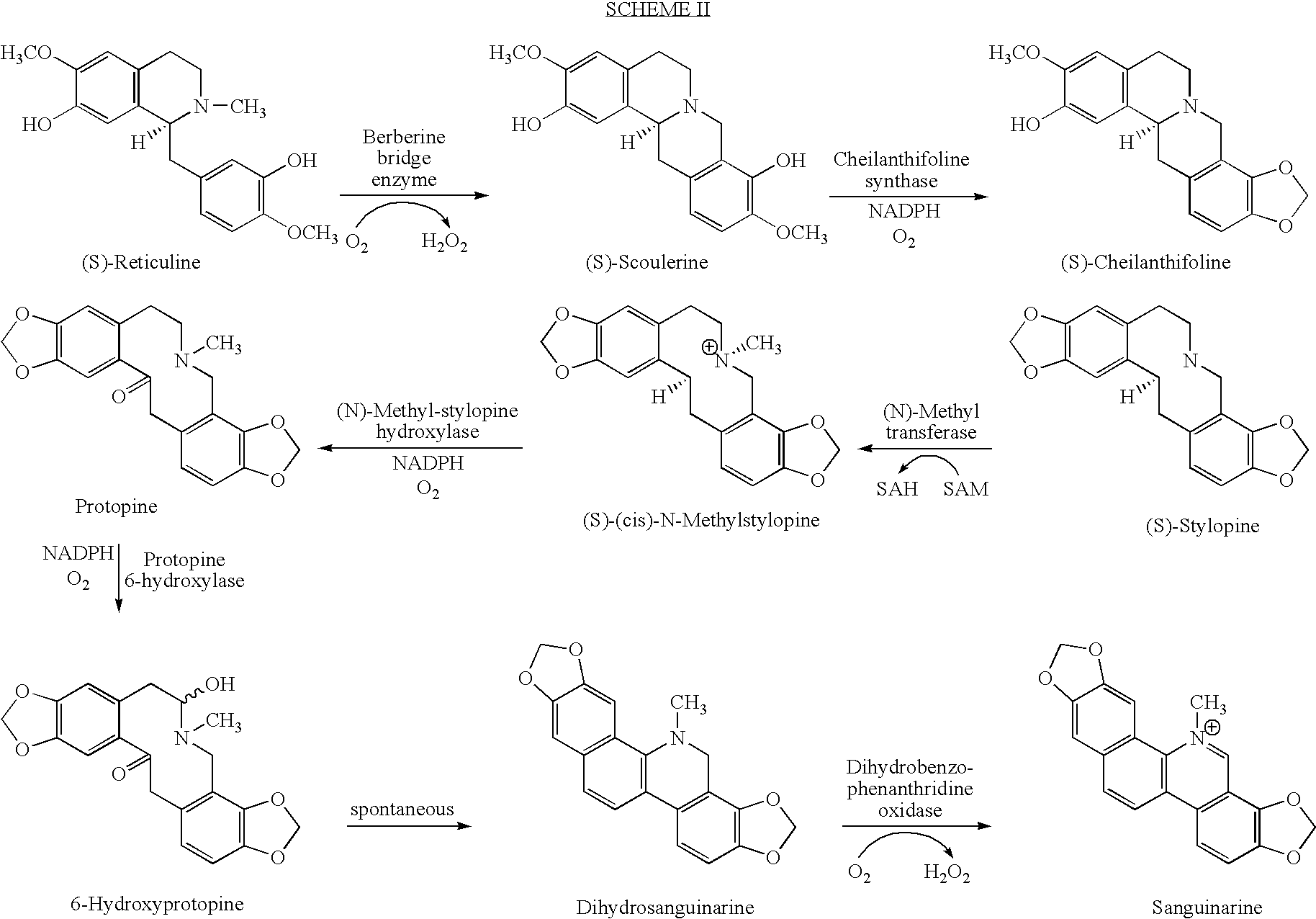
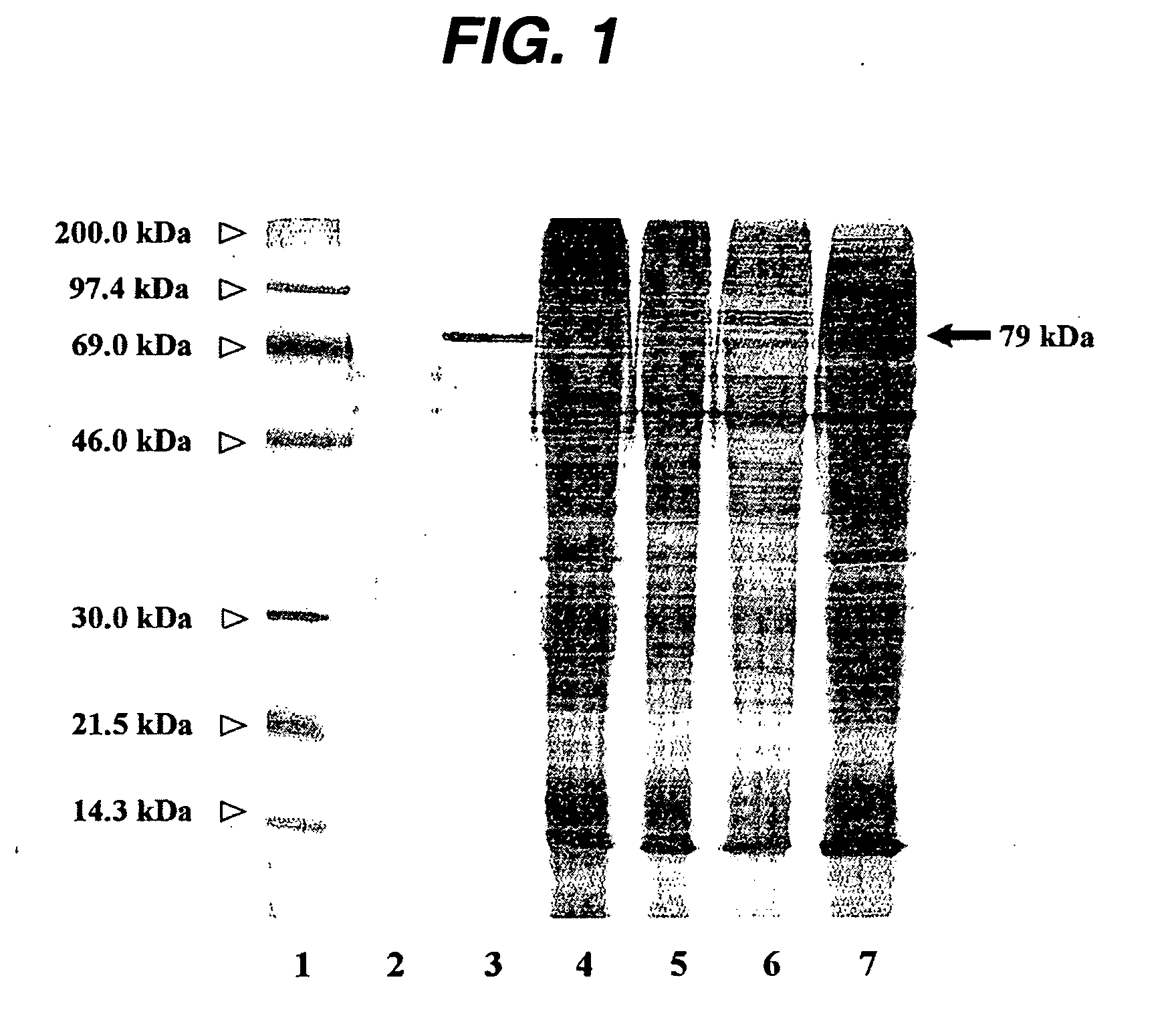
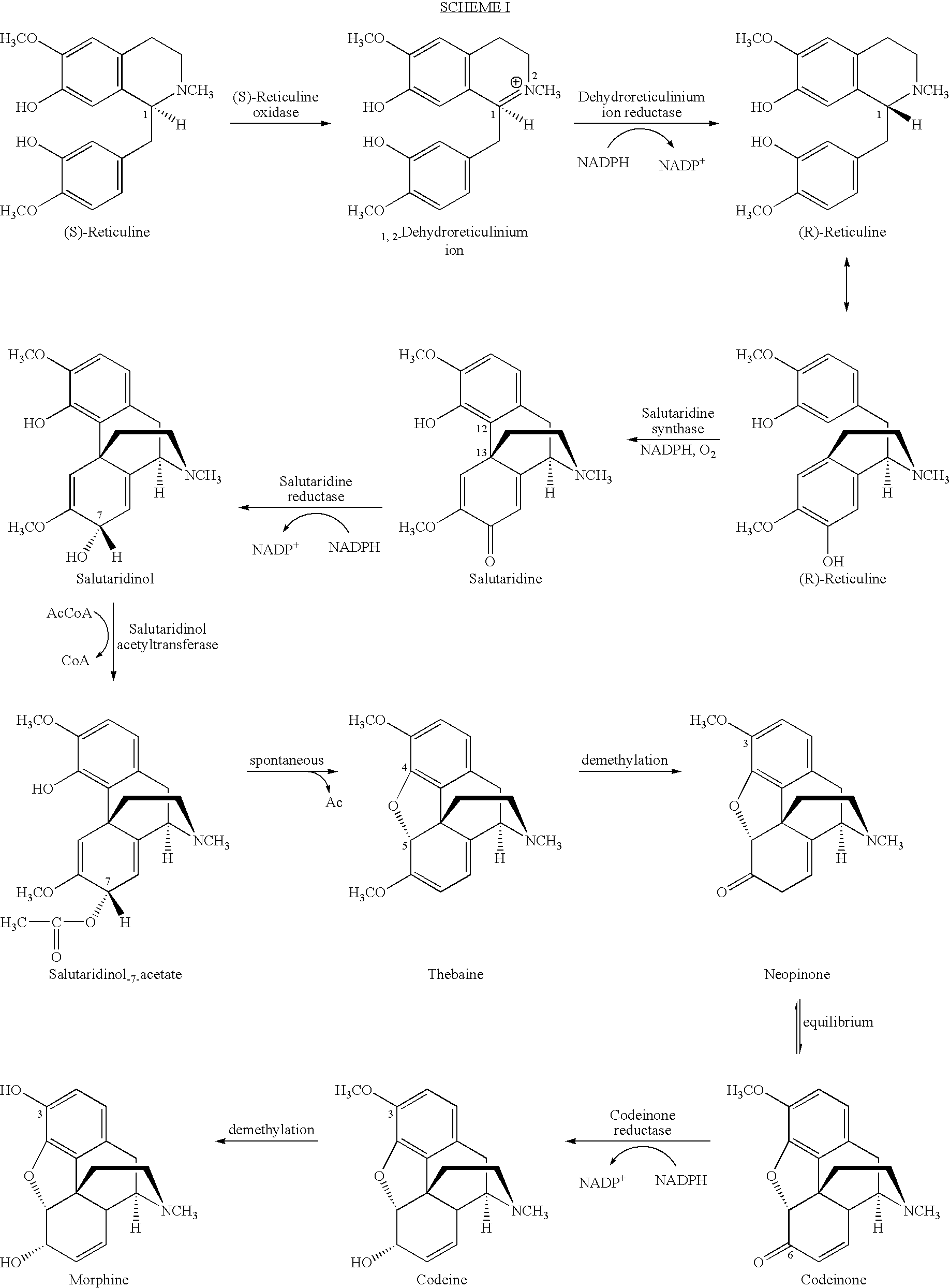
Cytochrome P450 reductases from poppy plants
InactiveUS20060185032A1Alleviating “ bottleneck ”Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCytochrome P450 reductaseCytochrome P450
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON RES PTY LTD
Cytochrome P450 reductases from poppy plants
InactiveUS7037674B1Alleviating “ bottleneck ”Increase productionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytochrome P450 reductaseCytochrome P450
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON RES PTY LTD
Human hepatocyte-like cells and uses thereof
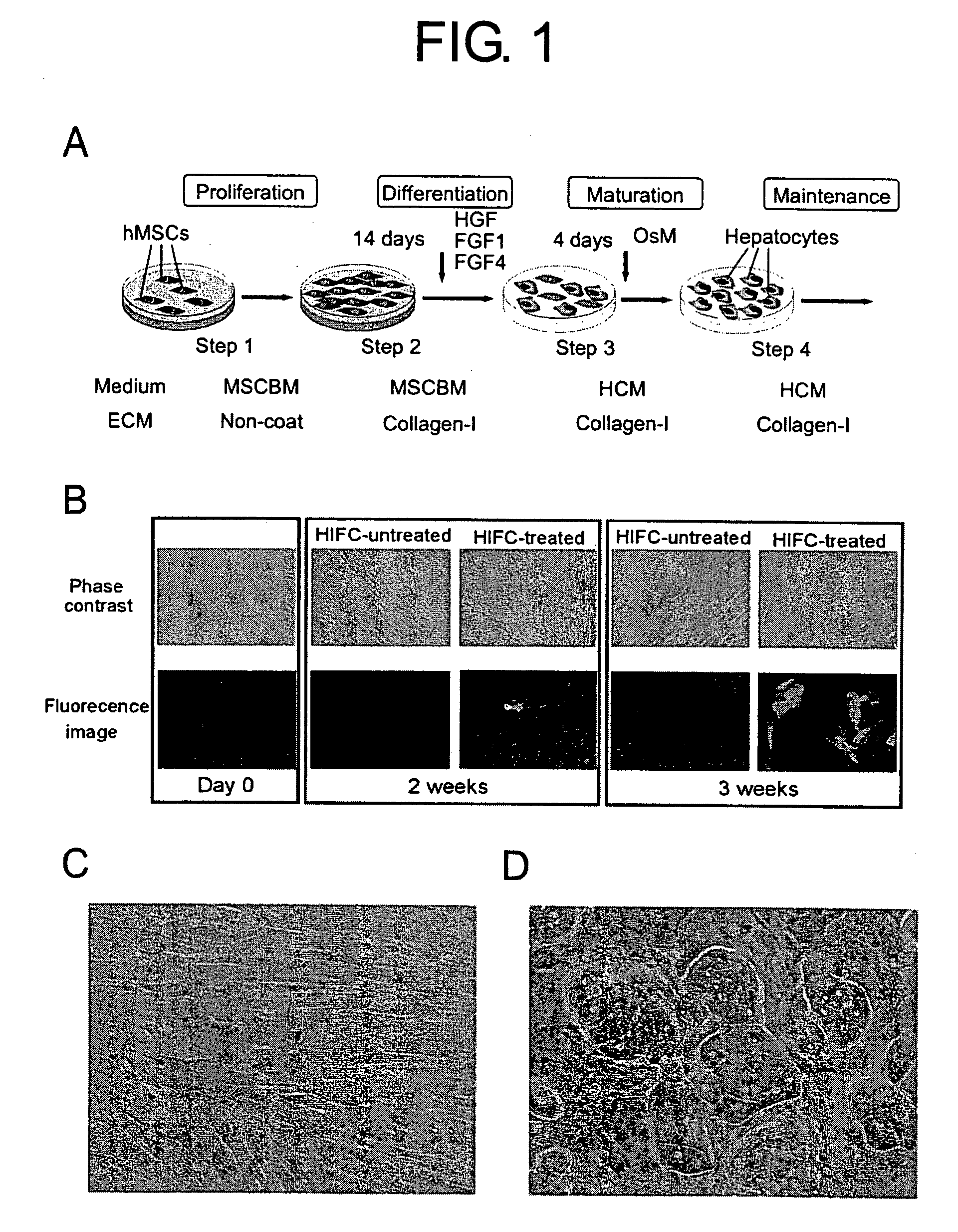
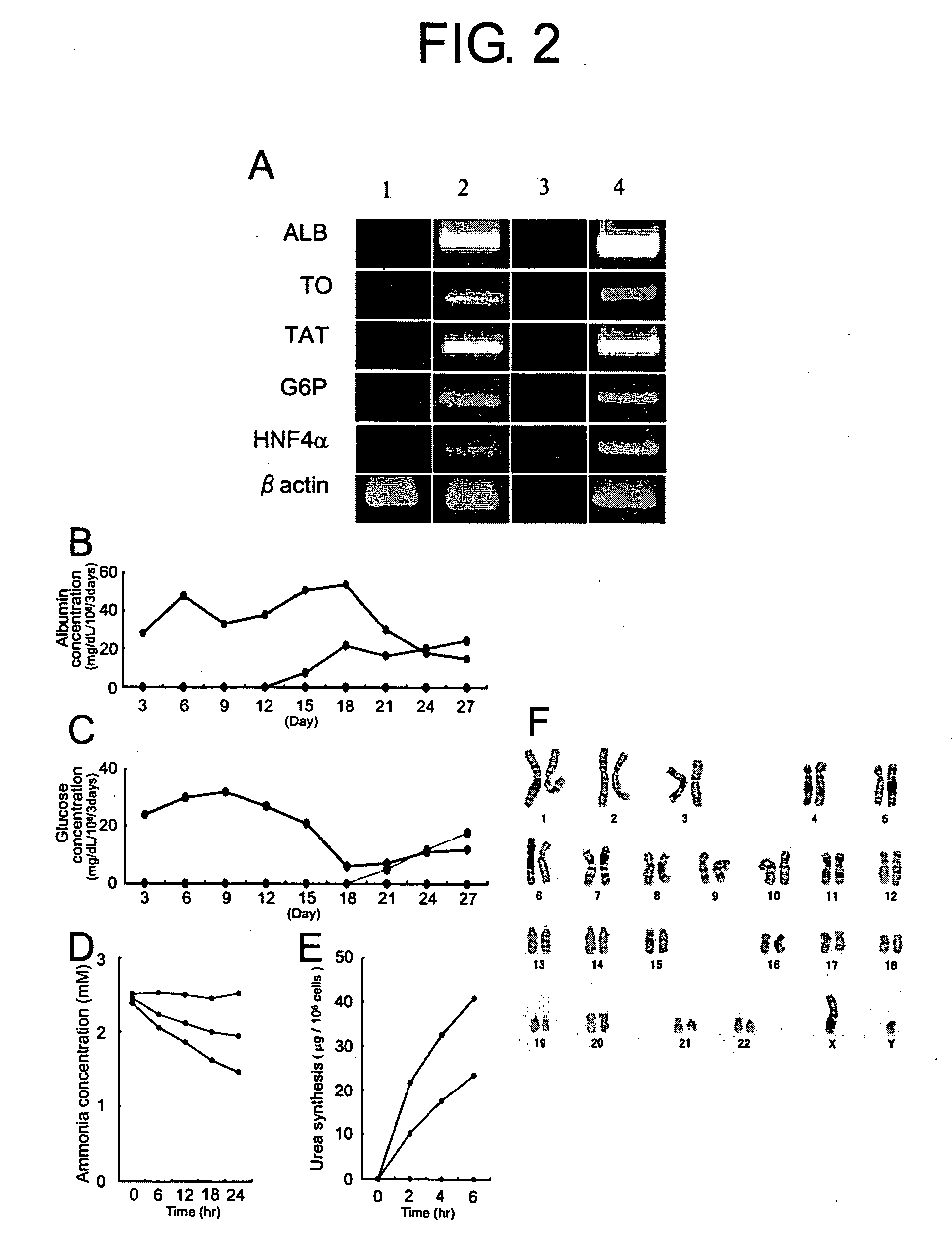
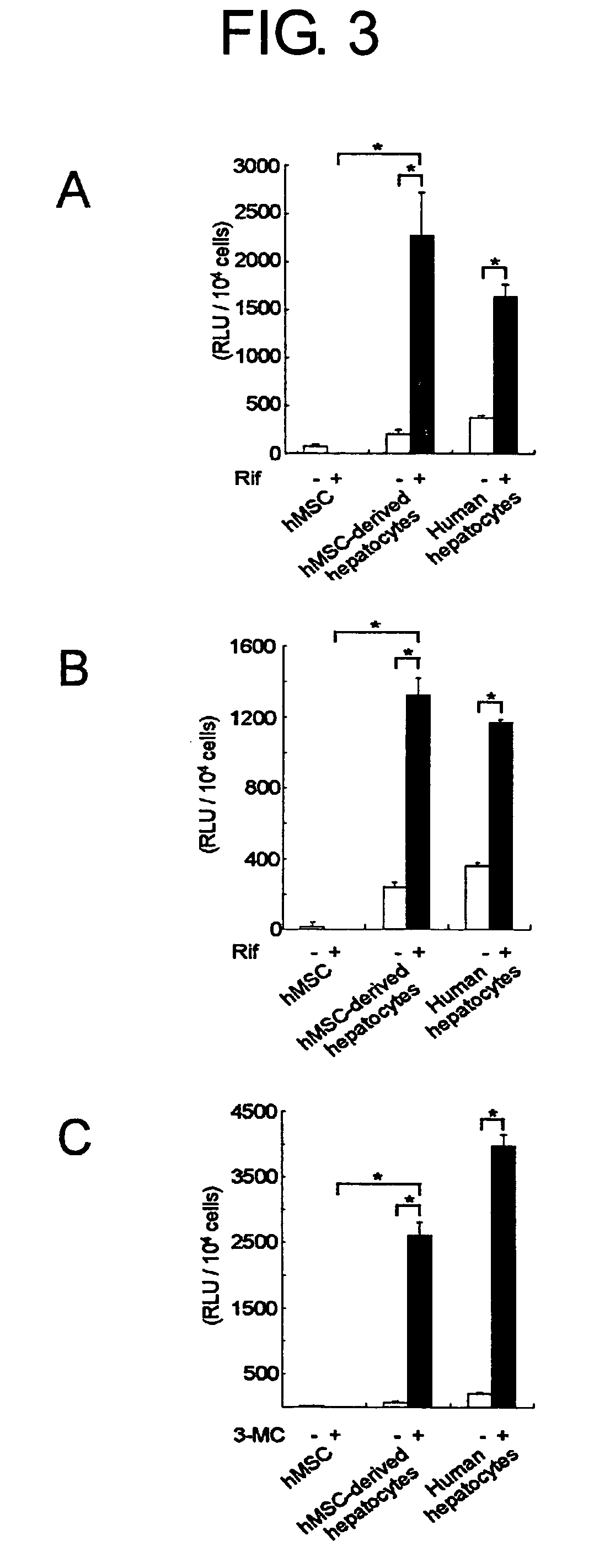
InactiveUS20060154235A1Improve efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsCytochrome P450Culture mediums
The present invention provides modified methods of producing human hepatocyte-like cells which exhibit phenotypes more similar to those of human hepatocytes. The present invention also provides the human hepatocyte-like cells and uses thereof. The methods of the present invention comprises a prolonged incubation period and addition of dexamethasone to the culture medium. The methods of the inventors produce human hepatocyte-like cells whose morphology is more similar to that of human hepatocytes, compared with the conventional system. The cells produced have both morphological and functional features of primary culture cells from normal human liver, including cytochrome P450 (CYP), multi-drug resistance-associated protein (MRP), and multi-drug protein (MDR). The use of human hepatocyte-like cells of the present invention enables, without using any animal model, assessment of metabolism and hepatotoxicity of test compounds, which are drug candidates, and screening for therapeutic agents for hepatic diseases, inhibitors to hepatitis virus infection, and therapeutic agents for viral hepatitis.
Owner:EFFECTOR CELL INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com