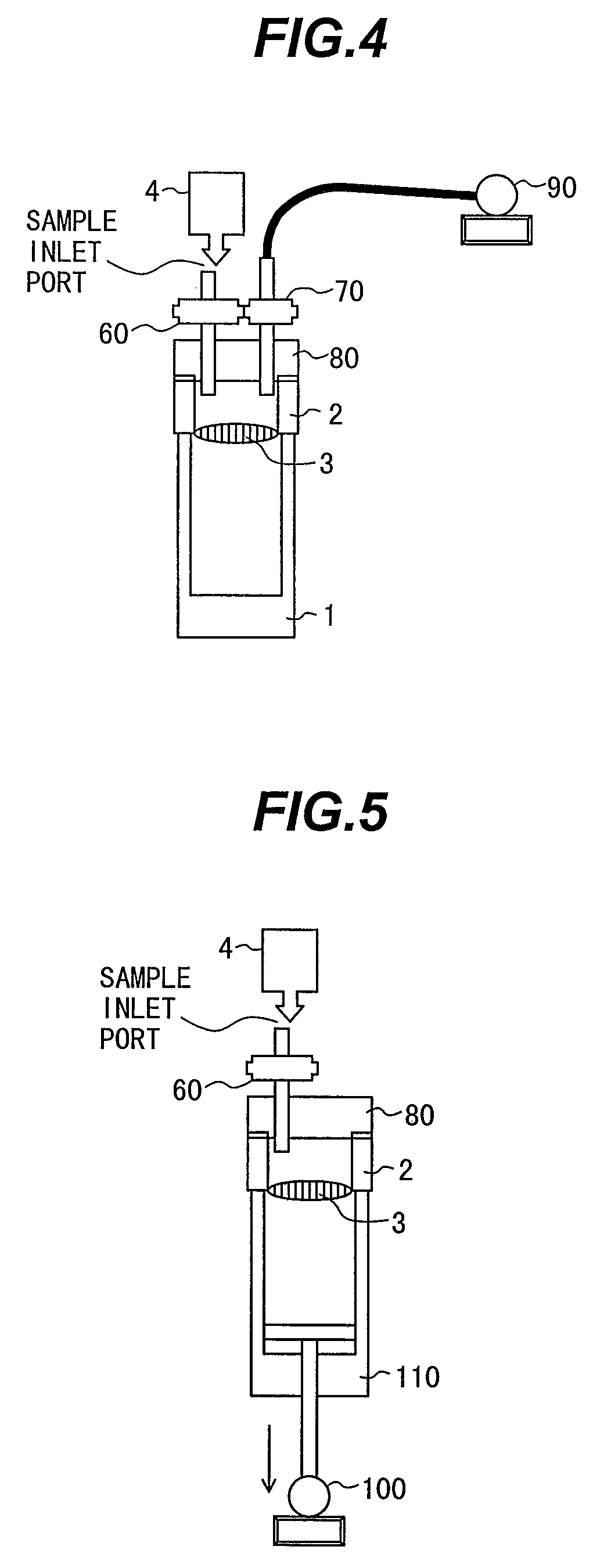
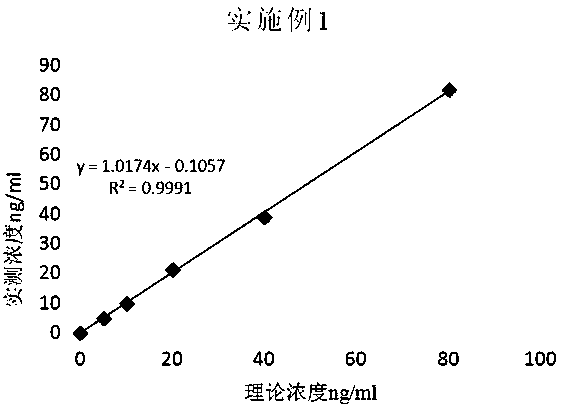
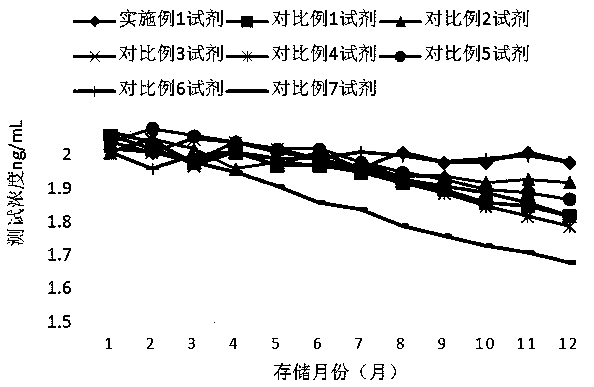
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Chylomicron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning juice (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning small particle) are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). Due to their density relative to lipoproteins, they are also commonly known as ultra low density lipoproteins (ULDL) in modern usage. They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. ULDLs are one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (sorted by density) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. A protein specific to chylomicrons is ApoB48.
Delivery of tetrahydrocannabinol
InactiveUS20070104741A1Avoiding hepatic first-pass metabolismGood choiceBiocideNervous disorderChylomicronTG - Triglyceride
A self-emulsifying drug delivery system to improve dissolution, stability, and bioavailability of drug compounds of dronabinol or other cannabinoids. The drug compound(s) are dissolved in an oily medium (e.g. triglycerides and / or mixed glycerides and / or free fatty acids containing medium and / or long chain saturated, mono-unsaturated, and / or poly-unsaturated free fatty acids) together with at least one surfactant. The surfactant promotes self-emulsification, thereby promoting targeted chylomicron delivery and optimal bioavailability to a mammalian intestinal lumen. A dosage form can optionally include co-solvents, anti-oxidants, viscosity modifying agents, cytochrome P450 metabolic inhibitors, P-GP efflux inhibitors, and amphiphilic / non-amphiphilic solutes to induce semi-solid formation for targeted release rates.
Owner:MURTY PHARMA
Method of regulating glucose metabolism, and reagents related thereto
InactiveUS20030153509A1Reduce insulin resistanceExcellent hostBiocideDipeptide ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaChylomicron
The present invention provides methods and compositions for modification and regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, generally to reduce insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoprotein-emia (such as chylomicrons, VLDL and LDL), and to regulate body fat and more generally lipid stores, and, more generally, for the improvement of metabolism disorders, especially those associated with diabetes, obesity and / or atherosclerosis.
Owner:1149336 ONTARIO +2
Dual glucose-turbidimetric analytical sensors
InactiveUS20060051738A1Simple data analysisImprove compatibilityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceChylomicronTurbidity
Diagnostic dry reagent tests capable of reacting with a single drop of whole blood and reporting both glucose and light-scattering analytes, such as chylomicrons, are taught. Such dry reagent tests may employ electrochemical detection methodologies, optical detection methodologies, or both methodologies. These tests alert diabetics to excessive levels of postprandial lipemia caused by meals with excessive amounts of fat, and thus can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Oral Dosage Form Of Tetrahydrocannabinol And A Method Of Avoiding And/Or Suppressing Hepatic First Pass Metabolism Via Targeted Chylomicron/Lipoprotein Delivery
ActiveUS20110092583A1Easy to transportPromote lymphatic transportBiocideSenses disorderChylomicronCytochrome P450
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems are provided to improve dissolution, stability, and bioavailability of drug compounds of dronabinol or other cannabinoids. The drug compound(s) are dissolved in an oily medium (e.g. triglycerides and / or mixed glycerides and / or free fatty acids containing medium and / or long chain saturated, mono-unsaturated, and / or poly-unsaturated free fatty acids) together with at least one surfactant. The surfactant promotes self-emulsification, thereby promoting targeted chylomicron / lipoprotein delivery and optimal bioavailability through the mammalian intestinal tract. A dosage form can optionally include co-solvents, anti-oxidants, viscosity modifying agents, cytochrome P450 metabolic inhibitors, P-GP efflux inhibitors, and amphiphilic / non-amphiphilic solutes to induce semi-solid formation for targeted release rates.
Owner:MURTY RAM B +1
Method of regulating glucose metabolism, and reagents related thereto
InactiveUS20040176307A1Long-term abatementLong-term reductionBiocideDipeptide ingredientsLipid storageChylomicron
The present invention provides methods and compositions for modification and regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, generally to reduce insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoprotein-emia (such as chylomicrons, VLDL and LDL), and to regulate body fat and more generally lipid stores, and, more generally, for the improvement of metabolism disorders, especially those associated with diabetes, obesity and / or atherosclerosis.
Owner:1149336 ONTARIO +2
Assay system and method for direct measurement of LDL cholesterol
ActiveUS20050221502A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChylomicronPrecipitation
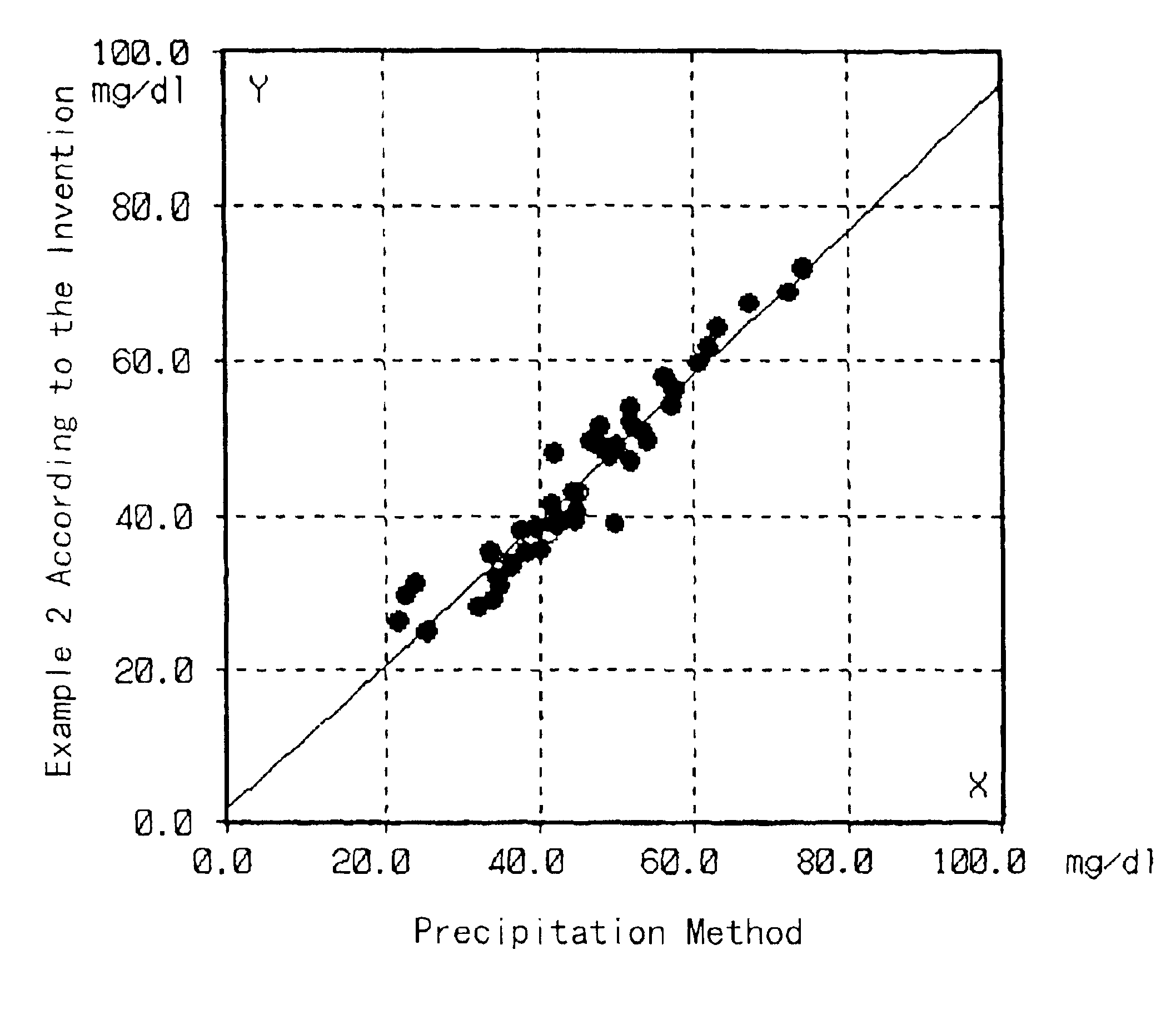
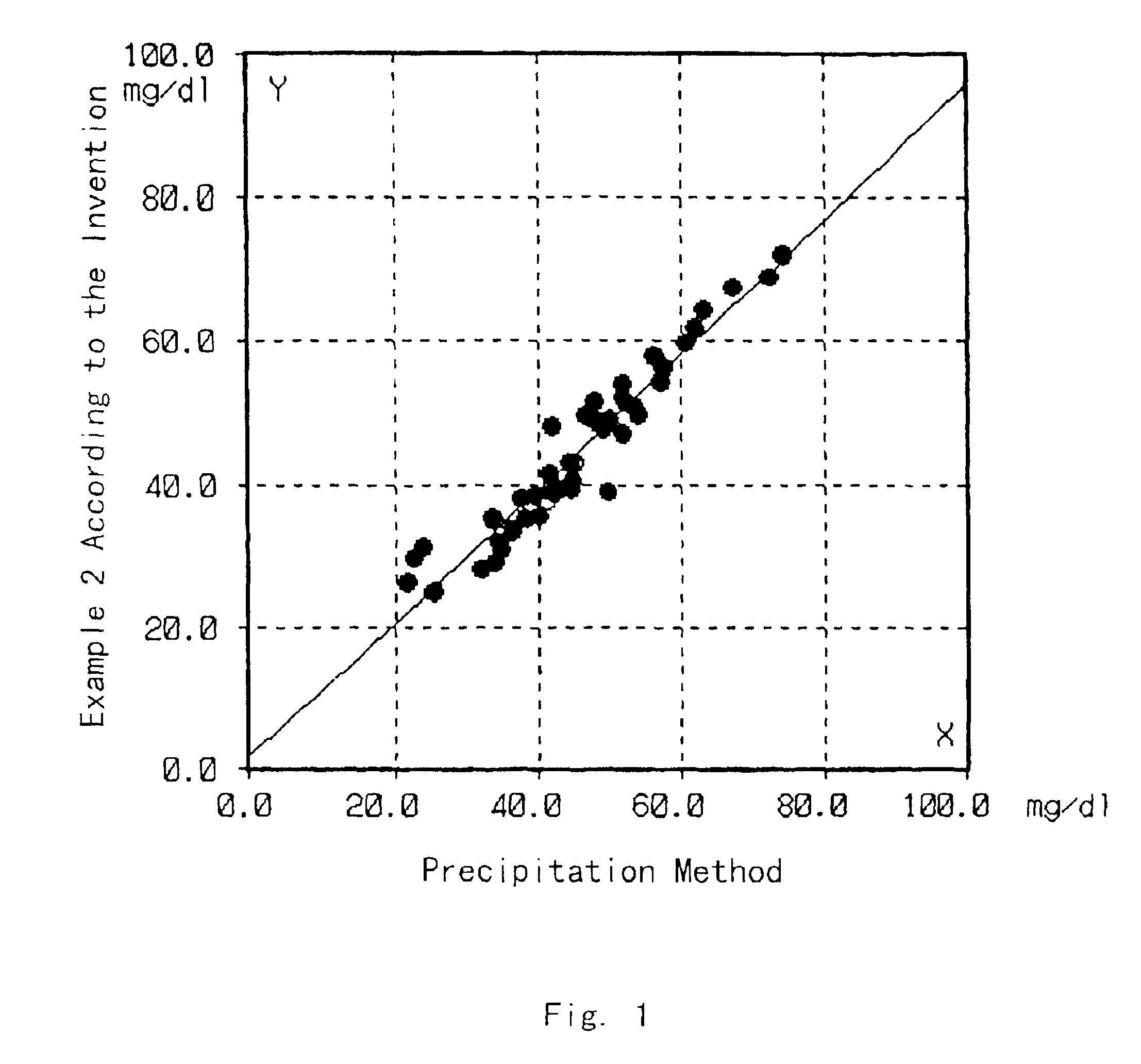
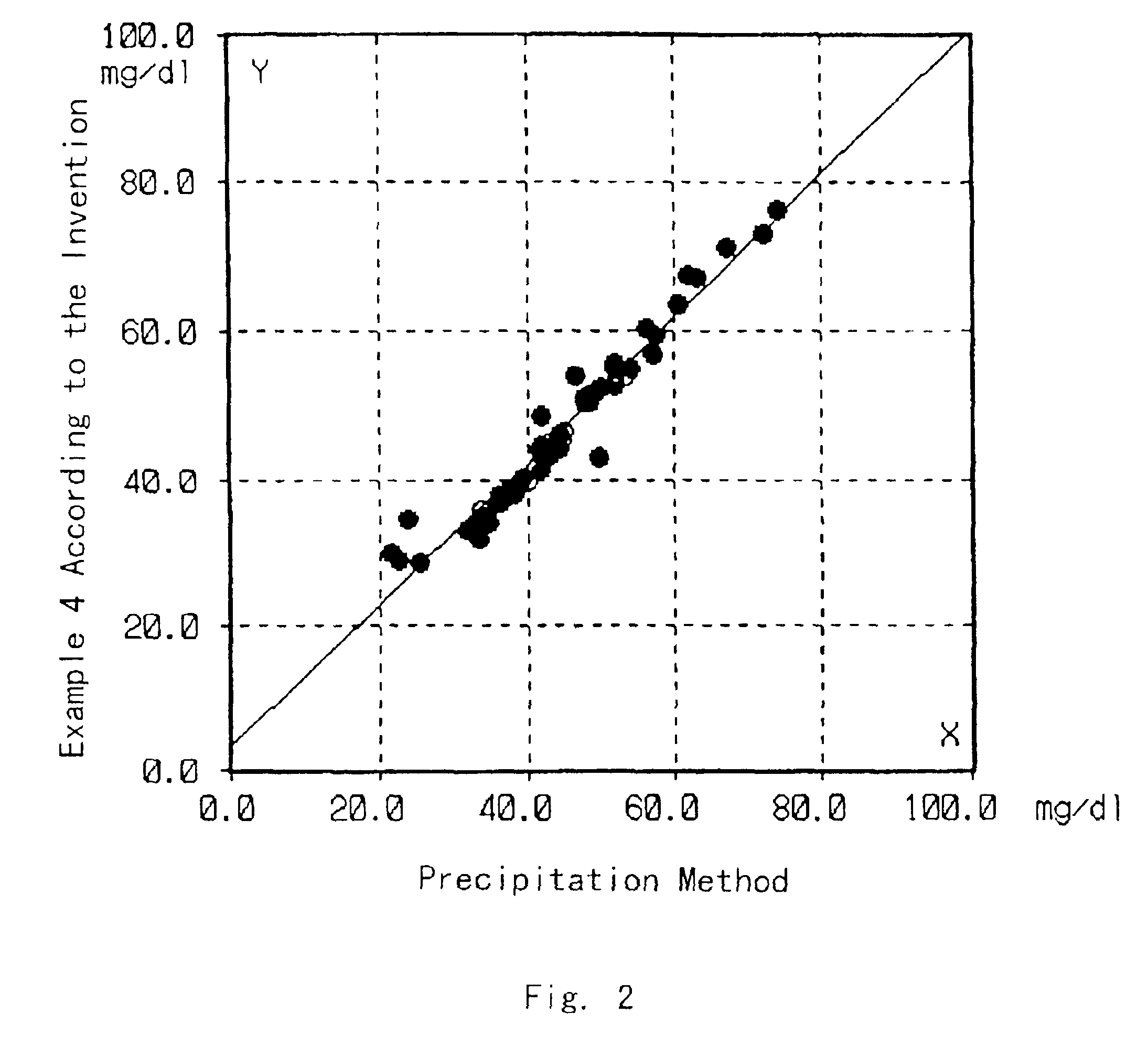
An assay device and method for measuring the concentration of LDL-associated cholesterol in a blood-fluid sample are described. The method employs selective precipitation of VLDL and chylomicrons and immunoseparation of HDL from a blood fluid sample. The assay device allows the assay to be performed entirely in a flow strip fornat.
Owner:ALERE SAN DIEGO INC
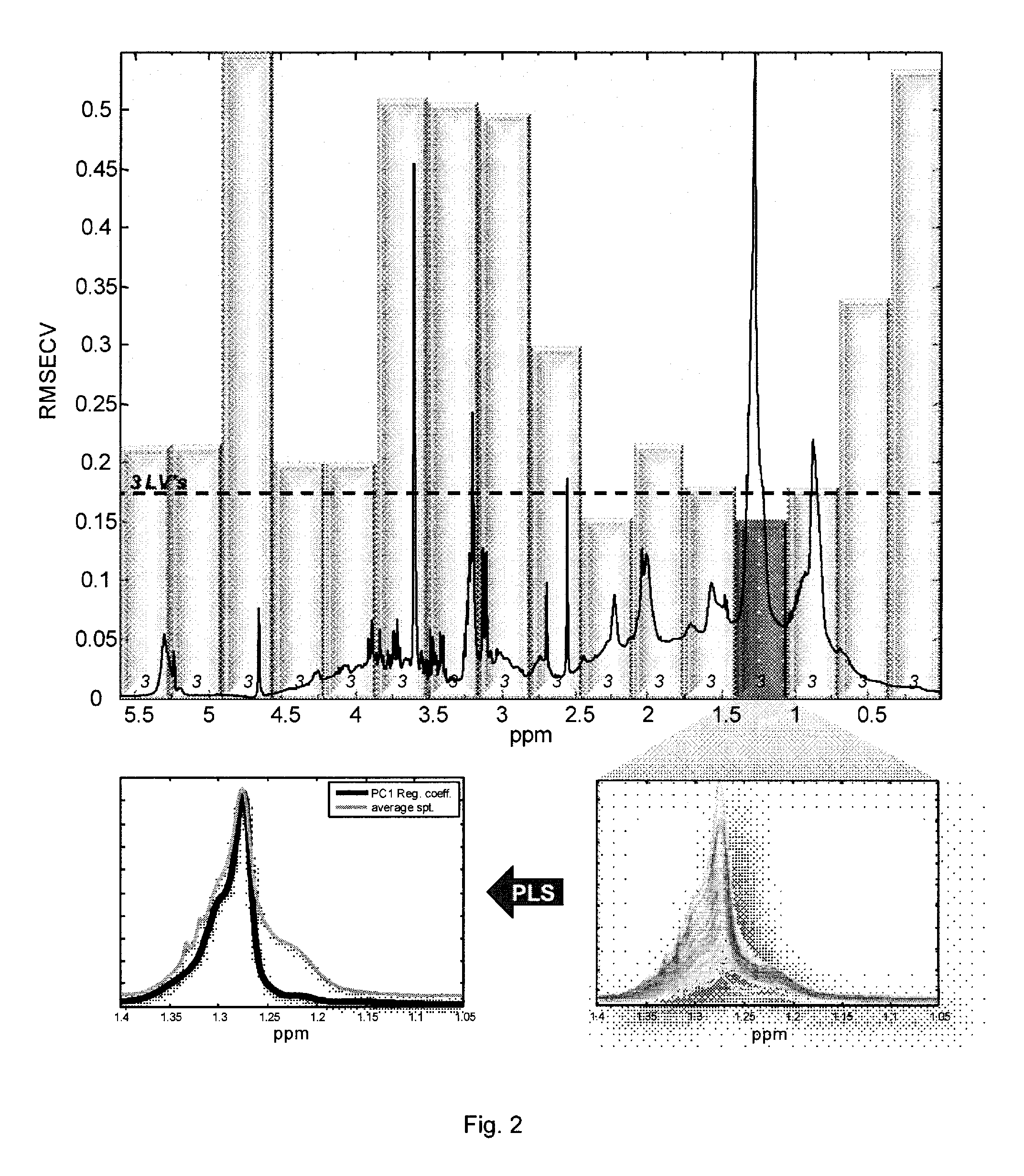
Method for prediction of lipoprotein content from nmr data
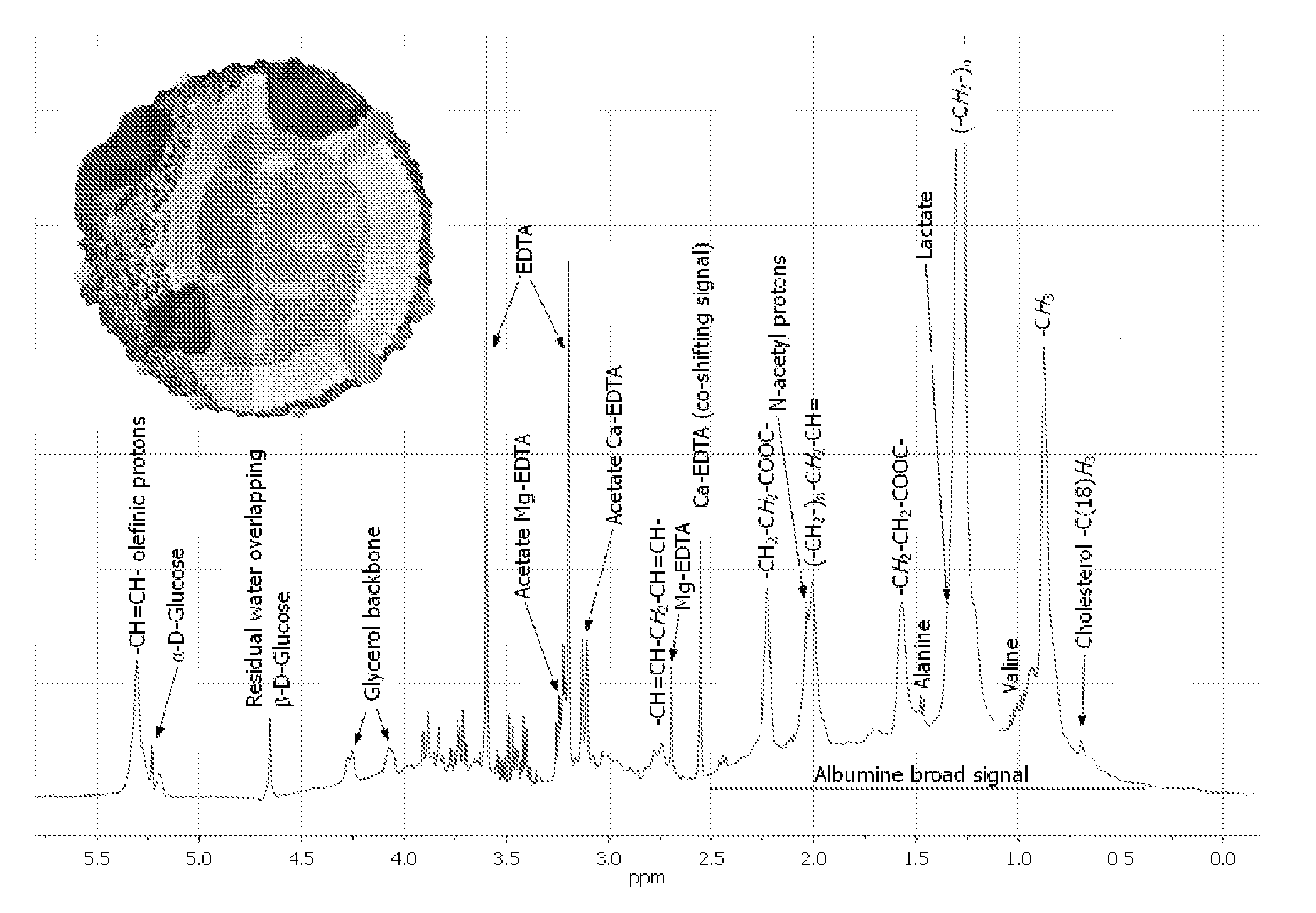
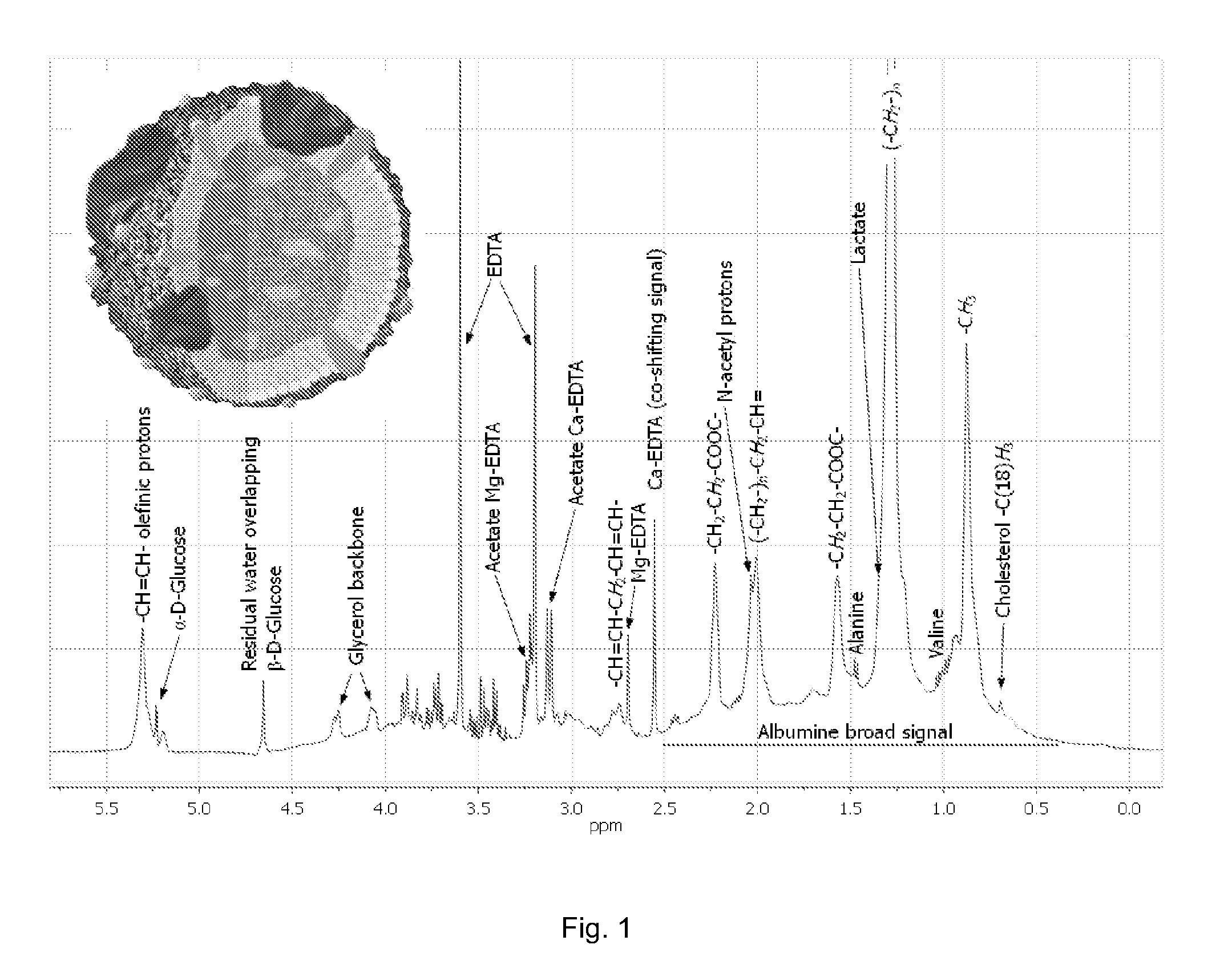
InactiveUS20110004453A1Enhancing its regressionGood estimateMagnetic measurementsAnalogue computers for chemical processesChylomicronA lipoprotein
The invention concerns a method of preparing regression coefficients in a multivariate analysis for predicting the quantity of a component of a lipoprotein entity in a biological sample from NMR spectral data and a method of predicting the quantity of a component of a lipoprotein entity in a biological sample from NMR spectral data, which is based on the regression coefficients. The invention is especially useful for predicting the triacylglycerol level in chylomicrons of a patient.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
Oral dosage form of tetrahydrocannabinol and a method of avoiding and/or suppressing hepatic first pass metabolism via targeted chylomicron/lipoprotein delivery
ActiveUS9265724B2Promote self-emulsificationImprove bioavailabilityBiocideSenses disorderChylomicronTG - Triglyceride
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems are provided to improve dissolution, stability, and bioavailability of drug compounds of dronabinol or other cannabinoids. The drug compound(s) are dissolved in an oily medium (e.g. triglycerides and / or mixed glycerides and / or free fatty acids containing medium and / or long chain saturated, mono-unsaturated, and / or poly-unsaturated free fatty acids) together with at least one surfactant. The surfactant promotes self-emulsification, thereby promoting targeted chylomicron / lipoprotein delivery and optimal bioavailability through the mammalian intestinal tract. A dosage form can optionally include co-solvents, anti-oxidants, viscosity modifying agents, cytochrome P450 metabolic inhibitors, P-GP efflux inhibitors, and amphiphilic / non-amphiphilic solutes to induce semi-solid formation for targeted release rates.
Owner:MURTY RAM B +1
Method for quantifying cholesterol in high density lipoprotein
InactiveUS6893832B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementChylomicronTest sample
Owner:DENKA SEIKEN CO LTD
Enteral compositions for the prevention and/or treatment of sepsis
The present invention relates to an enteral composition containing phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesterol or precursors thereof, which can be used in the treatment of sepsis. With the composition of the invention the natural level of chylomicrons is maintained, in particular in gut associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which ensures that most of LPS and / or LTA which are released in the body can be neutralized, substantially decreasing the risk of locally occurring high levels of LPS and / or LTA and thus sepsis.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Lipoprotein detection kit
ActiveCN107942081AEliminate interferenceAccurate measurementBiological testingChylomicronMicrosphere
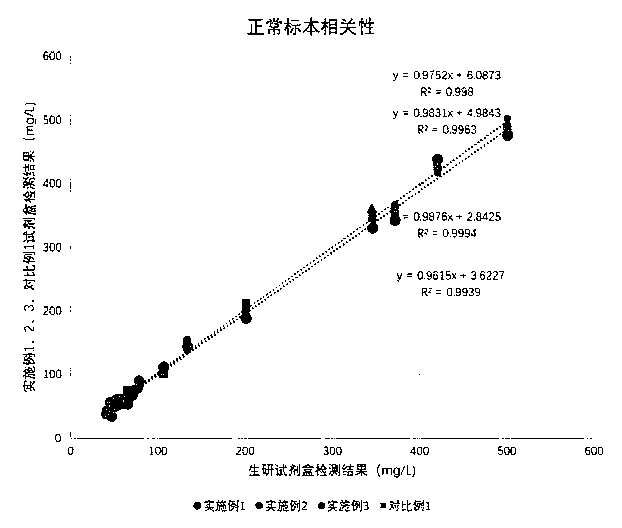
The invention relates to the technical field of medical detection, in particular to a lipoprotein detection kit. The kit comprises a R1 reagent and a R2 reagent, wherein the R1 reagent is prepared from a buffer solution, BSA (Bull Serum Albumin), chylomicron dissociation agents, surfactants, sodium chloride and preservatives; the R2 reagent is prepared from a buffer solution, lipoprotein multiresistant latex microspheres, aminopropionic acid, EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), BSA, sugar and preservatives. The kit can effectively eliminate the interference effect of chylomicrons in samples to be tested; the accurate determination of lipoprotein in specimens with high chylomicron contents is realized; the sensitivity is high; the linear detection range is wide.
Owner:SINOCARE
Apparatus for measuring high density lipoproteins and method of separating high density lipoproteins
InactiveUS7838631B2Easy to separateSimple configurationApolipeptidesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCelluloseChylomicron
The present invention provides a method of separating lipoproteins other than high density lipoproteins from a biological fluid. The method can quickly measure HDL cholesterol with a simple configuration and without the need of providing additional complicated devices. In this method, high density lipoproteins not generating any precipitate are fractionated from low density lipoproteins, very-low density lipoproteins, and chylomicrons generating precipitates. Then the precipitates are removed not by centrifugal separation based on the conventional technology, but by filtration using a filter to separate high density lipoproteins in blood serum. A hydrophilic cellulose-mixed ester is preferable as a material for the filter, and the pore diameter is 0.8 μm or below. When the filtering method is employed, it is possible to eliminate the complicated operations required in the conventional centrifugal separation, and to shorten the time it takes for separation of the high density lipoproteins.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Sensitive and stable serum procalcitonin determination kit as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111337691ASpecificEasy to operateBiological material analysisBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesChylomicron
The invention provides a procalcitonin (PCT) determination kit. The kit contains a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 is prepared from the following components: a piperazine-1, 4-diethylsulfonic acid (PIPES) buffer solution, NaCl, MgCl2, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid, a surfactant and a preservative. And the reagent R2 is prepared from piperazine-1, 4-diethylsulfonic acid (PIPES) buffer solution, goat anti-human PCT antibody coated latex particles, a suspending aid, a stabilizer and a preservative. The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the kit, the kit can effectively avoid interference of chyle particles, latex particles of different specifications, novel surfactants and different protective agents and suspending agents are adoptedat the same time, and the kit is a liquid kit which is high in stability, high in sensitivity, good in repeatability and low in cost.
Owner:中拓生物有限公司 +1
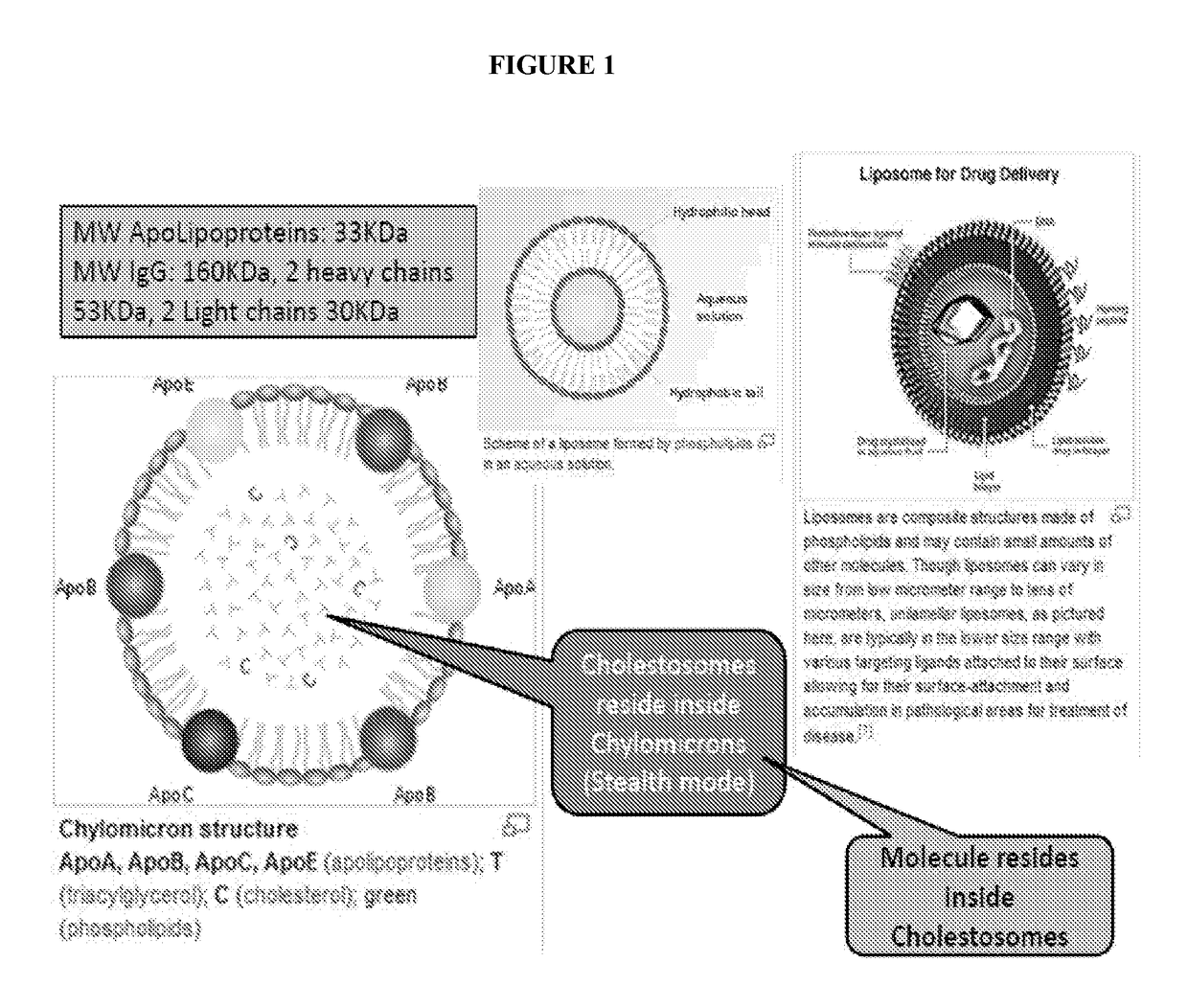
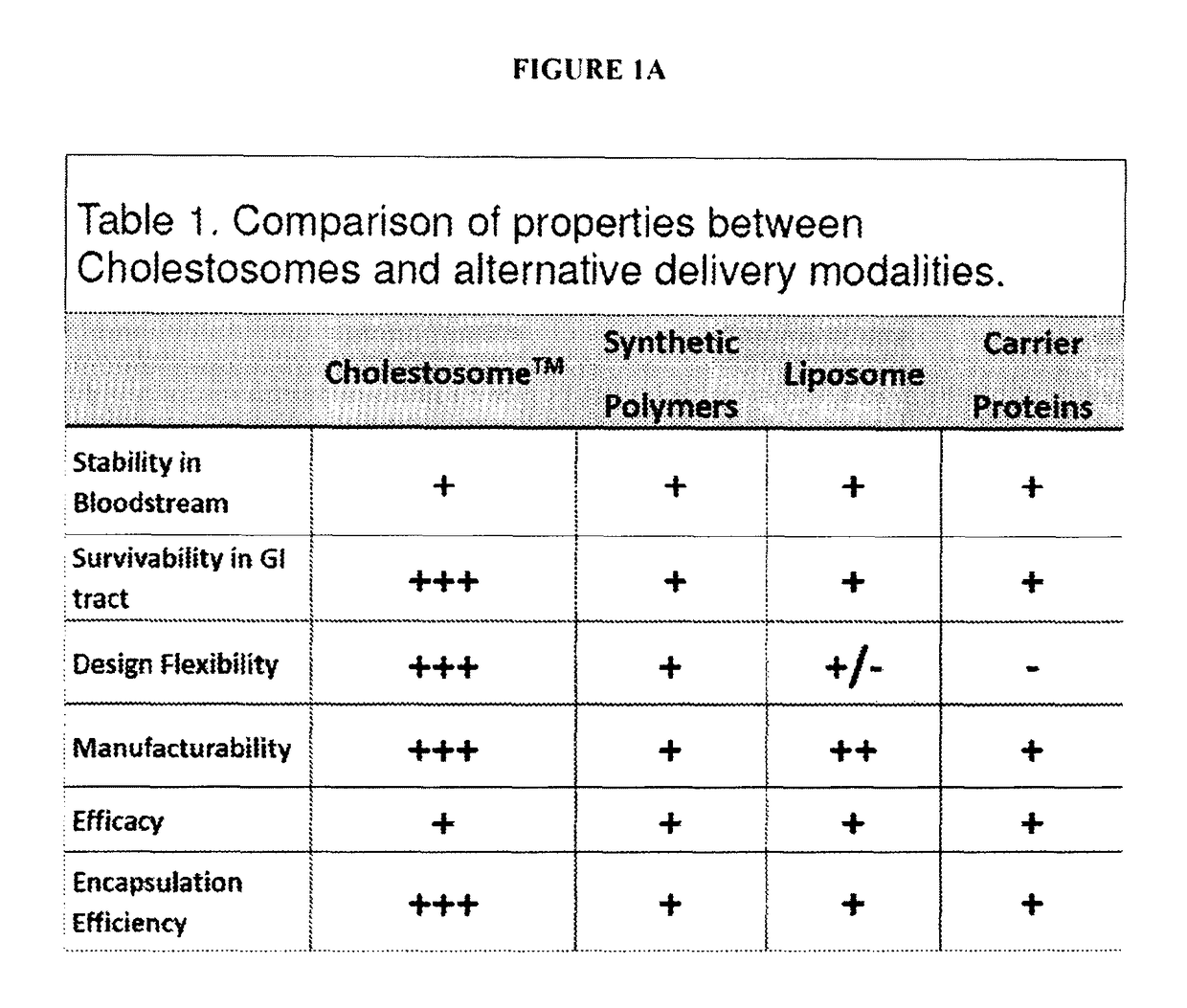
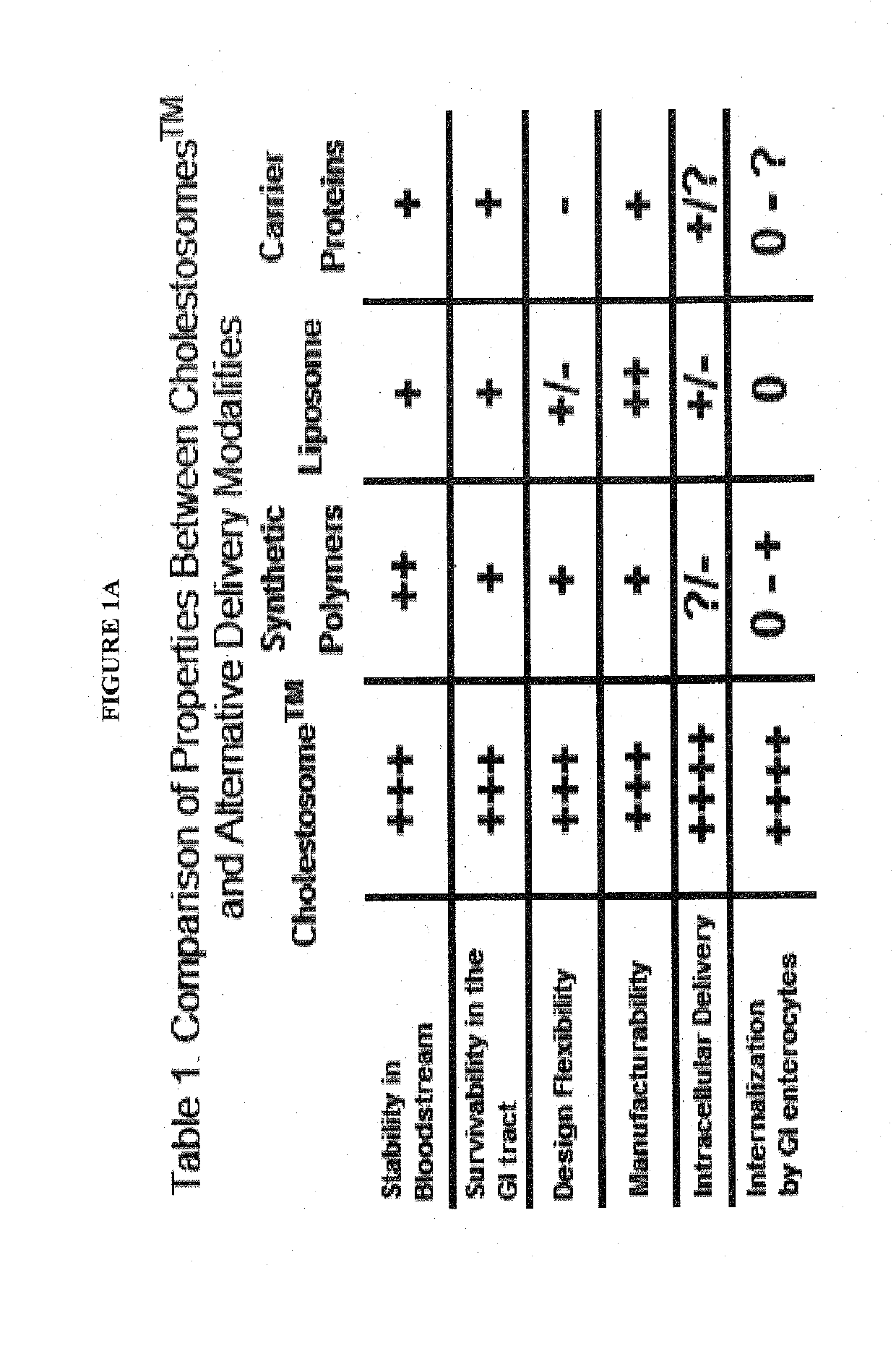
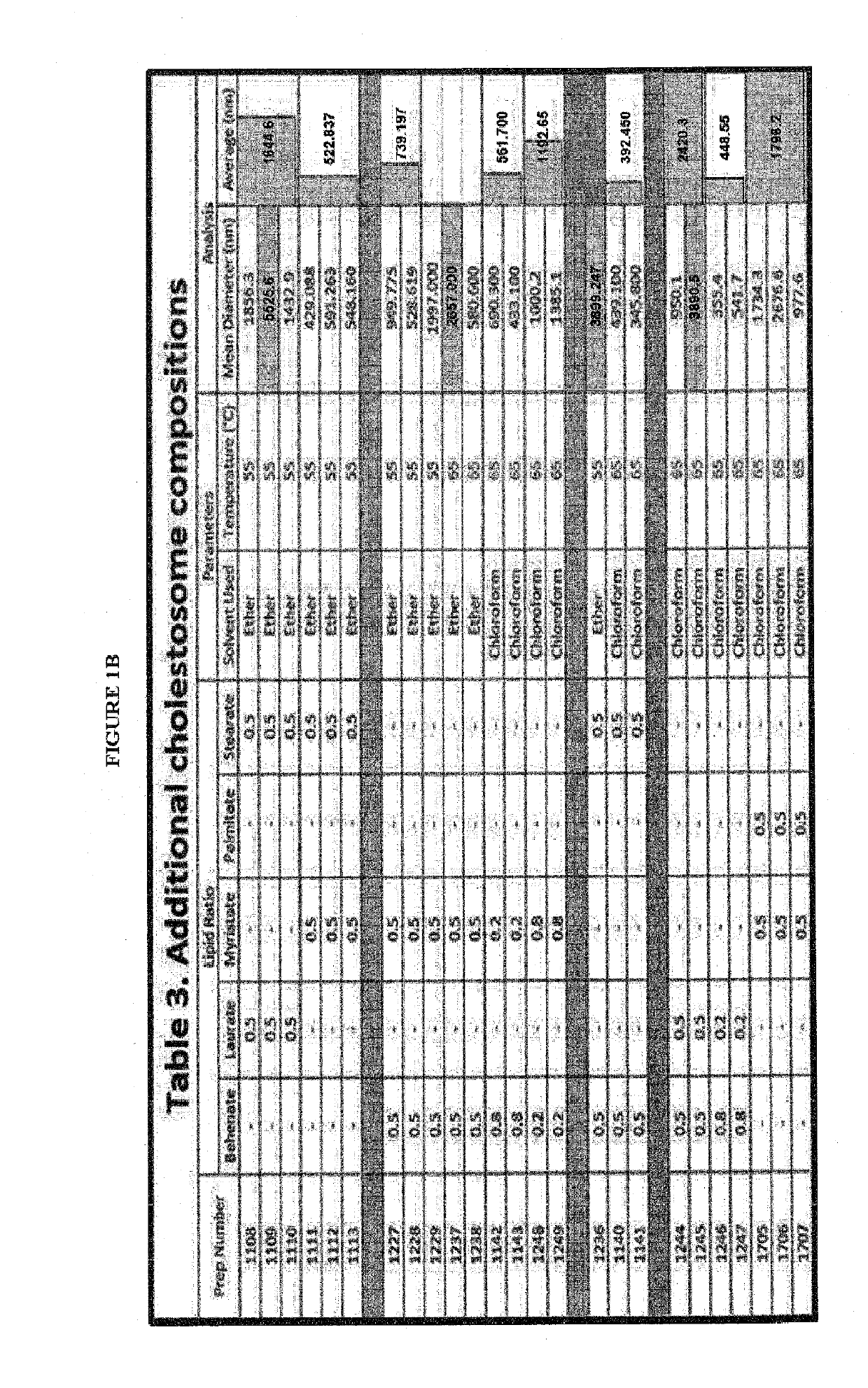
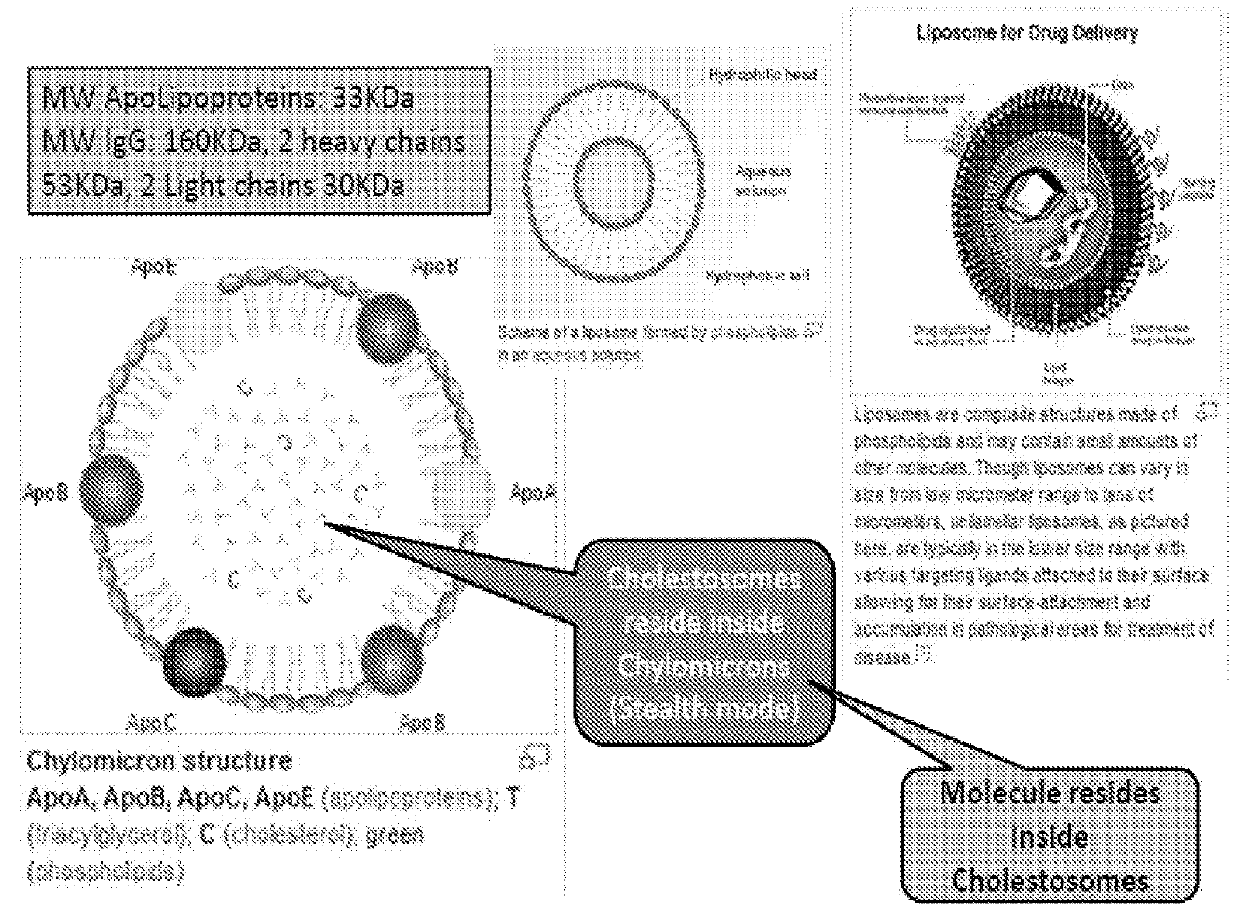
Cholestosome vesicles for incorporation of molecules into chylomicrons
The present invention is directed to a cargo-loaded cholesteryl ester nanoparticle with a hollow compartment (“cholestosome”) consisting essentially of at least one non-ionic cholesteryl ester and one or more encapsulated active molecules which cannot appreciably pass through an enterocyte membrane in the absence of said molecule being loaded into said cholestosome, the cholestosome having a neutral surface and having the ability to pass into enterocytes in the manner of orally absorbed nutrient lipids using cell pathways to reach the golgi apparatus. Pursuant to the present invention, the novel cargo loaded cholestosomes according to the present invention are capable of depositing active molecules within cells of a patient or subject and effecting therapy or diagnosis of the patient or subject.
Owner:THERASYN SENSORS
Cholesteryl ester vesicles loading peptides, proteins and nucleic acids into chylomicrons and body cells
InactiveUS20190175515A1Improve oral bioavailabilityImprove surface propertiesLyophilised deliveryAntineoplastic agentsIntestinal structureChylomicron
The present invention is directed to one or more macromolecules in a lipid vesicle oral formulation which targets intracellular receptors, in particular for peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and mixtures thereof, optionally in combination with small molecules. The invention encapsulates said macromolecules in a neutral lipid vesicle comprised of one or more cholesteryl esters. Unique properties of macromolecules encapsulated in said vesicles include high oral bioavailability, defined herein as in at least 50%, i.e., often in excess of 50% on the basis of oral to parenteral AUC. Non-limiting examples are provided, for large hydrophilic molecules such as peptides, proteins and nucleic acids which heretofore have been very poorly absorbed by the mammalian intestine. In prior art; said molecules are generally less than 25% bioavailable, even with protective coatings and optionally absorption enhancing component substances in the formulation. An additional feature of the present invention is high tissue concentrations after oral use, a result of rapid uptake of cholestosomes delivered by chylomicrons to body cells. A preferred embodiment is disclosed for insulin, where with cholestosome encapsulation oral bioavailability is at least 66%. Prior to the present invention, oral bioavailability of insulin and other peptides and proteins was maximally 25% and usually between 5% and 10%. Additional preferred examples are provided for one or more macromolecules useful in the treatment of cancer and in particular intracellular targeting in the practice of cancer immunotherapeutics.
Owner:THERASYN SENSORS
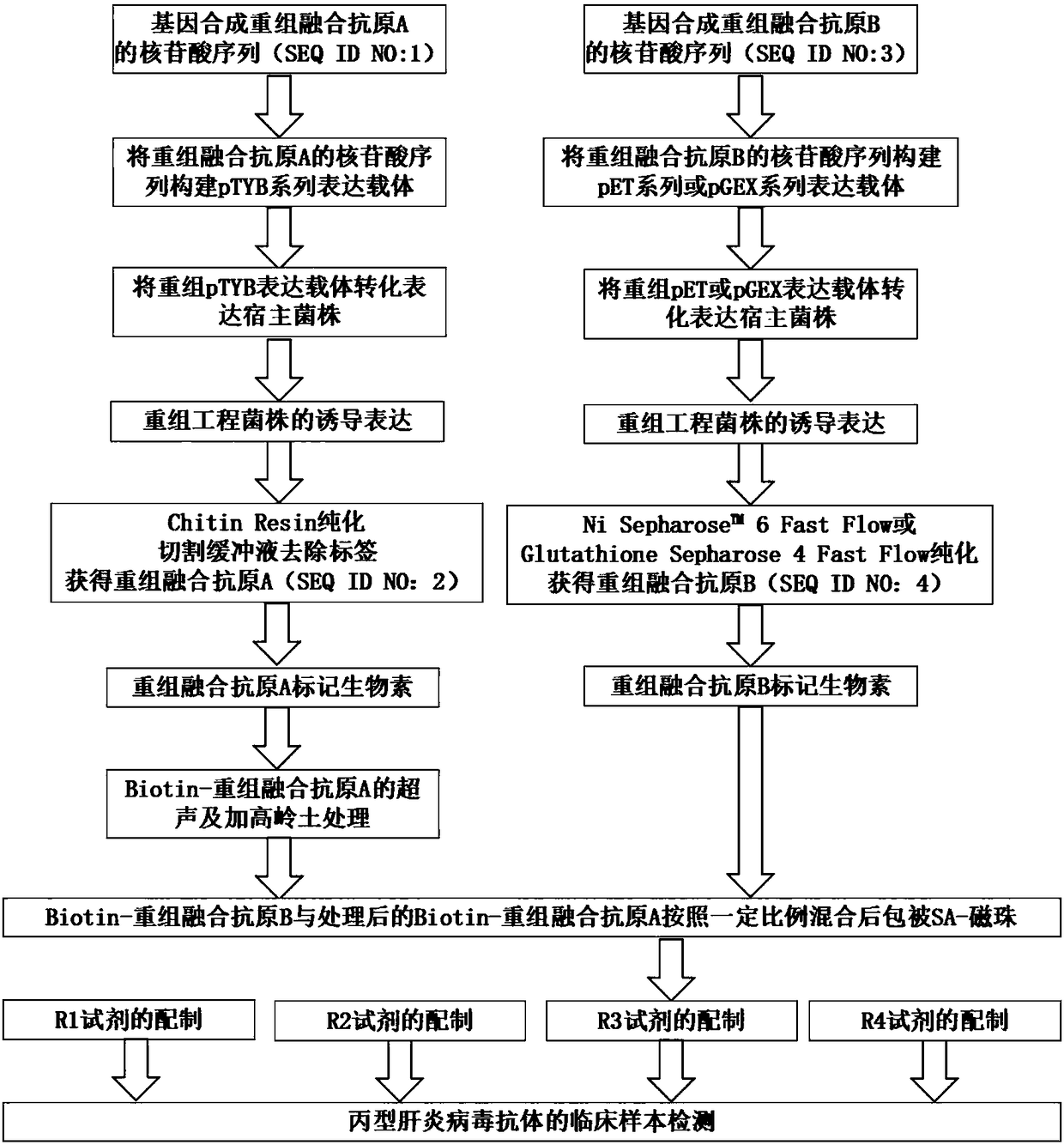
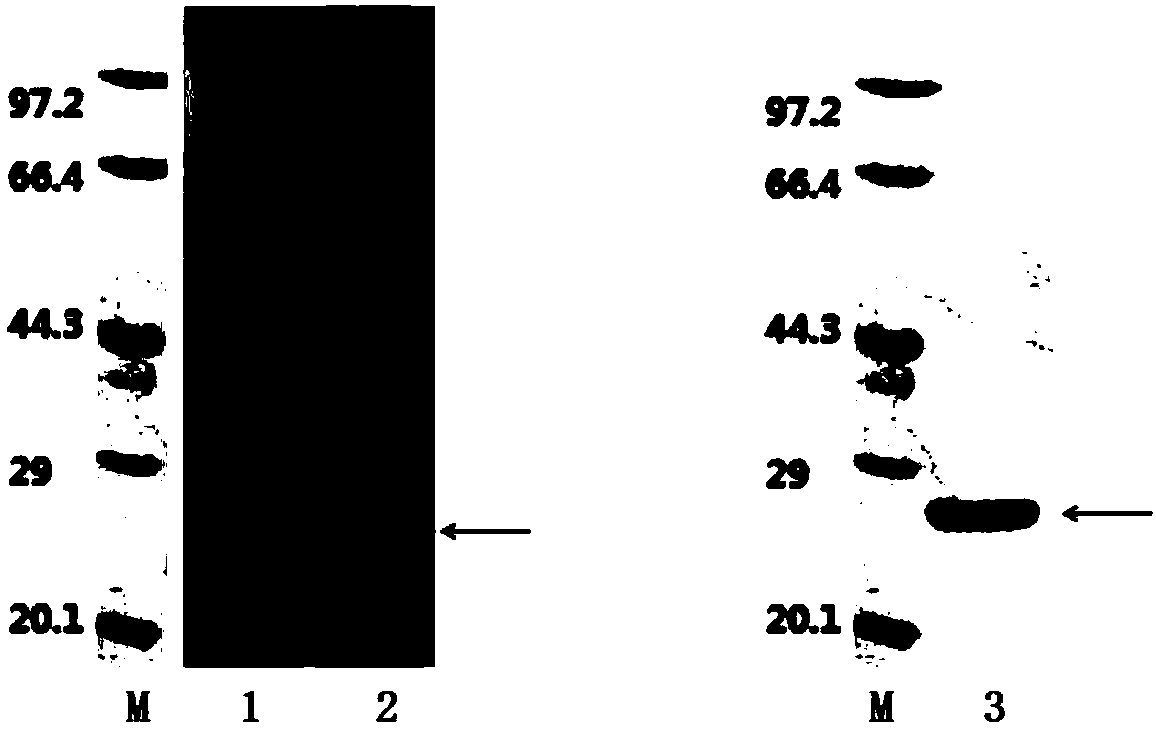
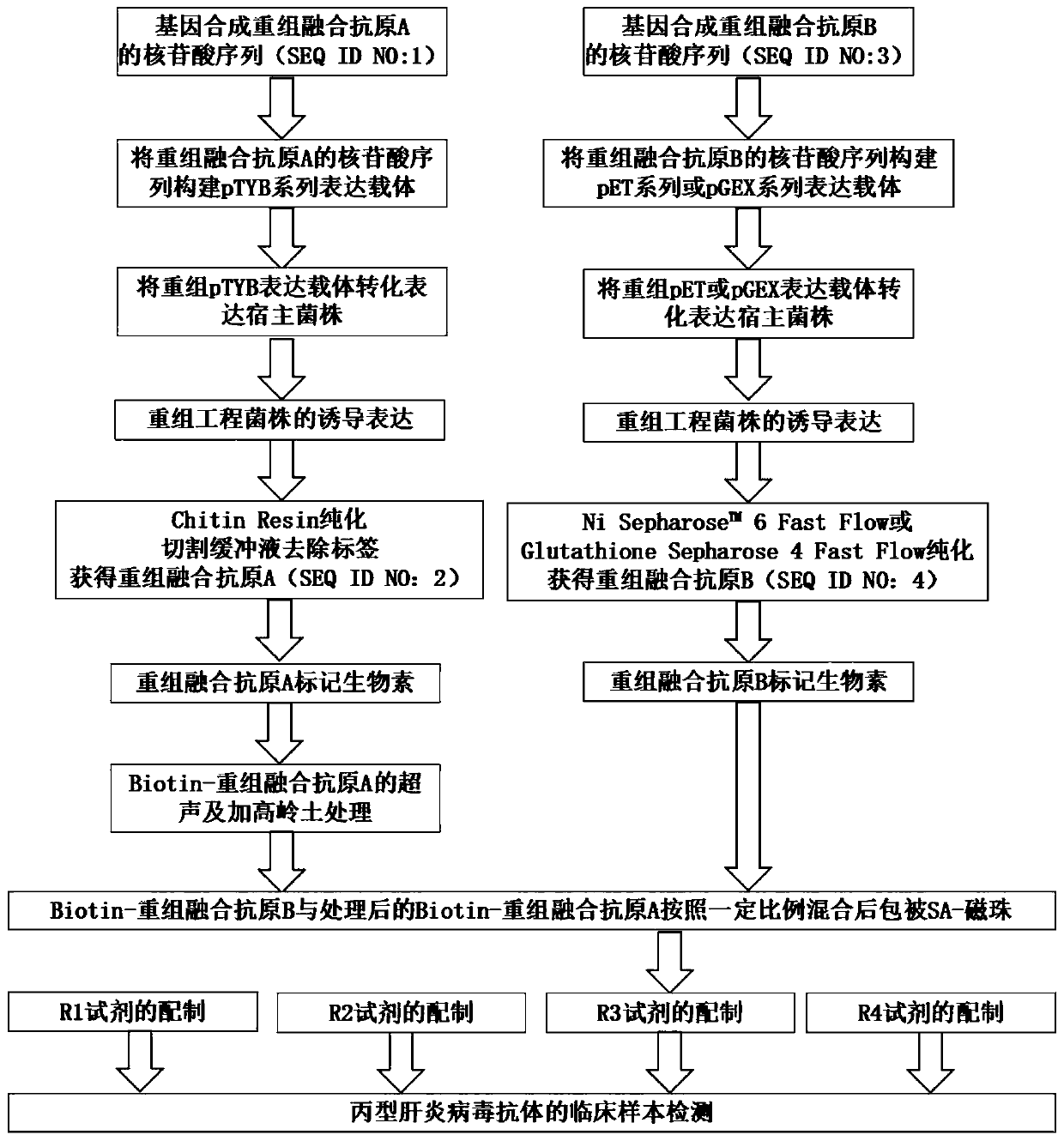
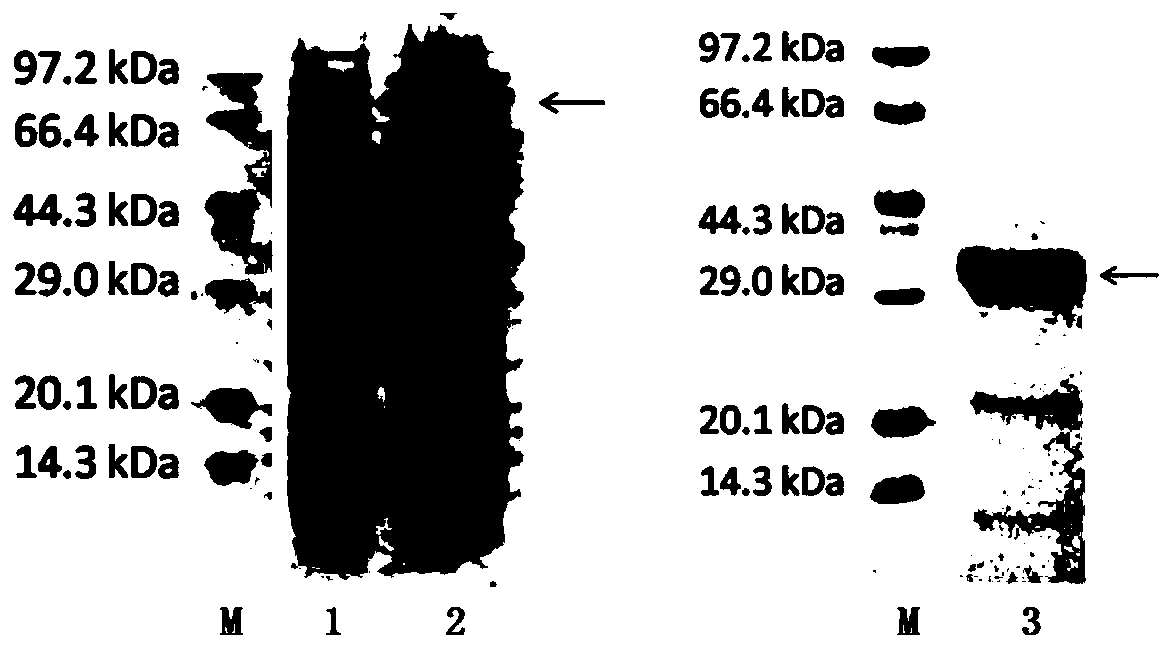
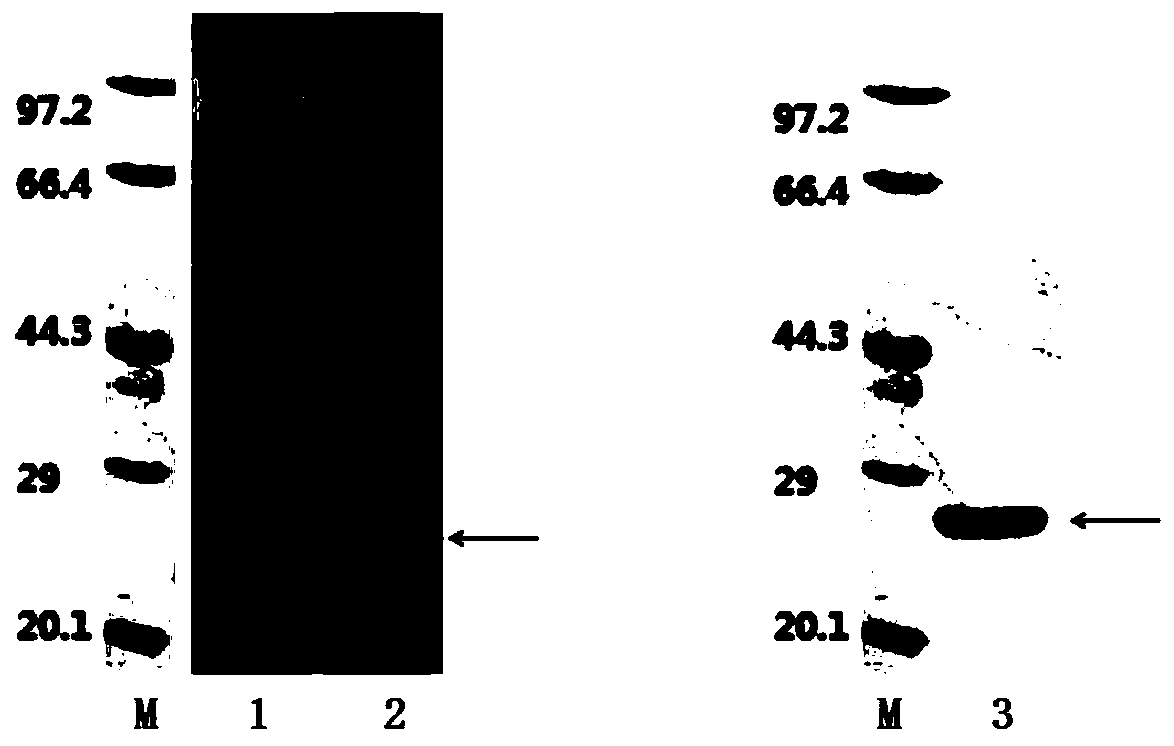
HCV (hepatitis c virus) antibody detection reagent containing recombinant fusion antigens A and B, application and recombinant fusion antigens A and B
ActiveCN108196069AImprove solubilityFold preciselySsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsChylomicronHCV Antibody
The invention relates to an HCV (hepatitis c virus) antibody detection reagent containing recombinant fusion antigens A and B, an application and the recombinant fusion antigens A and B, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the HCV antibody detection reagent containing the recombinant fusion antigens A and B, the recombinant fusion antigen A contains an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; the recombinant fusion antigen B contains an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4; the detection reagent comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2, a reagent R3 anda reagent R4. The detection reagent has the following advantages: the two recombinant fusion antigens have the characteristics of high specificity and good stability and can be used for preparing thehepatitis C virus antibody detecting reagent by mixing in a certain ratio, and the clinical detection effect of the reagent is remarkable. Meanwhile, the detection reagent has high anti-interference capacity to chylomicron, bilirubin and hemoglobin, and can greatly meet requirements of clinical diagnosis of HCV.
Owner:深圳德睿生物科技有限公司
DNA encoding human monocyte-macrophage apolipoprotein B receptor gene and protein
InactiveUS6194558B1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesChylomicronTG - Triglyceride
The present invention provides an isolated DNA molecule that codes for a cell-surface binding protein in human monocytes and macrophages. In addition, an amino acid sequence derived from the nucleotide sequence is provided. The newly-identified cell-surface binding protein described herein is instrumental in the apoB-mediated cellular uptake of plasma chylomicrons and remnants and hypertriglyceridemic tryglyceride-rich lipoproteins in an ApoE- and lipoprotein lipase- and heparin sulfate proteoglycan-independent pathway. The present invention also provides evidence that the ligand for the receptor is within the N-terminal region of apoB-48 or B-100 at or near the lipoprotein lipase binding domain and not in a heparin binding domain.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Dual glucose-turbidimetric analytical sensors
InactiveUS7758744B2Minimize cross-talkAccurate estimateAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceChylomicronTurbidity
Diagnostic dry reagent tests capable of reacting with a single drop of whole blood and reporting both glucose and light-scattering analytes, such as chylomicrons, are taught. Such dry reagent tests may employ electrochemical detection methodologies, optical detection methodologies, or both methodologies. These tests alert diabetics to excessive levels of postprandial lipemia caused by meals with excessive amounts of fat, and thus can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Cholestosome vesicles for incorporation of molecules into chylomicrons
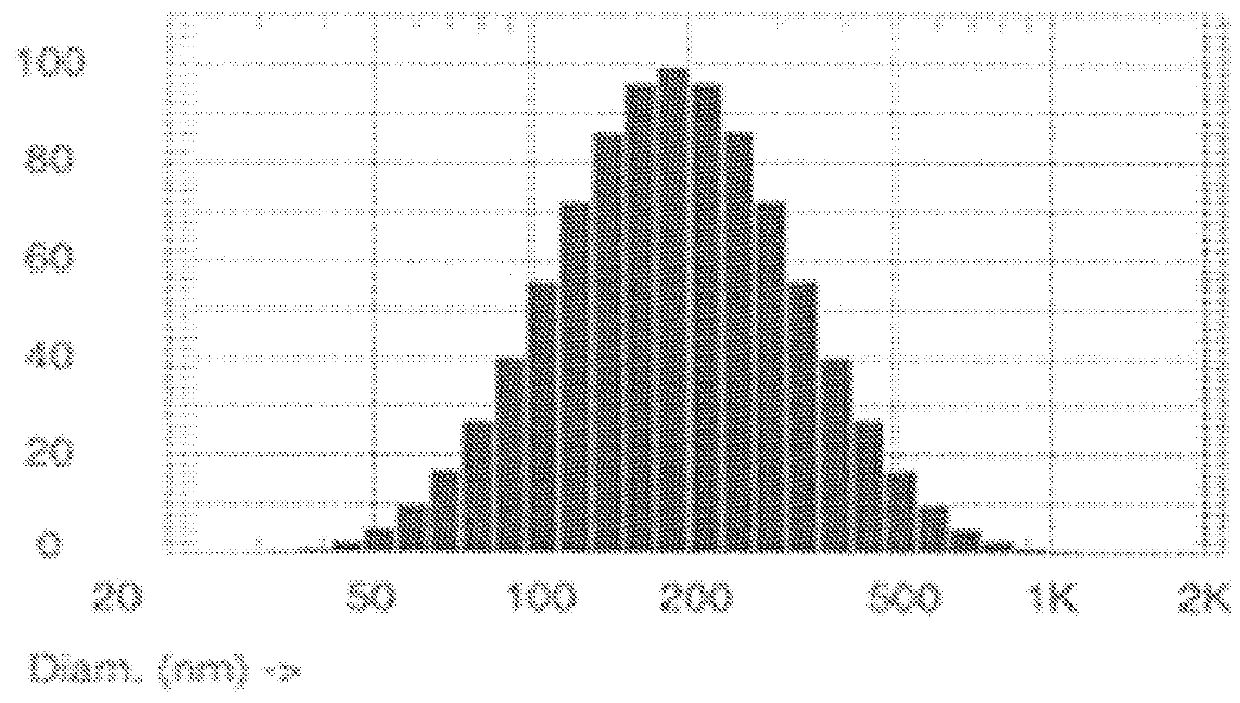
ActiveUS20160030361A1Increase milk productionSimple structureAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChylomicronNanoparticle
The present invention is directed to a cargo-loaded cholesteryl ester nanoparticle with a hollow compartment (“cholestosome”) consisting essentially of at least one non-ionic cholesteryl ester and one or more encapsulated active molecules which cannot appreciably pass through an enterocyte membrane in the absence of said molecule being loaded into said cholestosome, the cholestosome having a neutral surface and having the ability to pass into enterocytes in the manner of orally absorbed nutrient lipids using cell pathways to reach the golgi apparatus. Pursuant to the present invention, the novel cargo loaded cholestosomes according to the present invention are capable of depositing active molecules within cells of a patient or subject and effecting therapy or diagnosis of the patient or subject.
Owner:THERASYN SENSORS
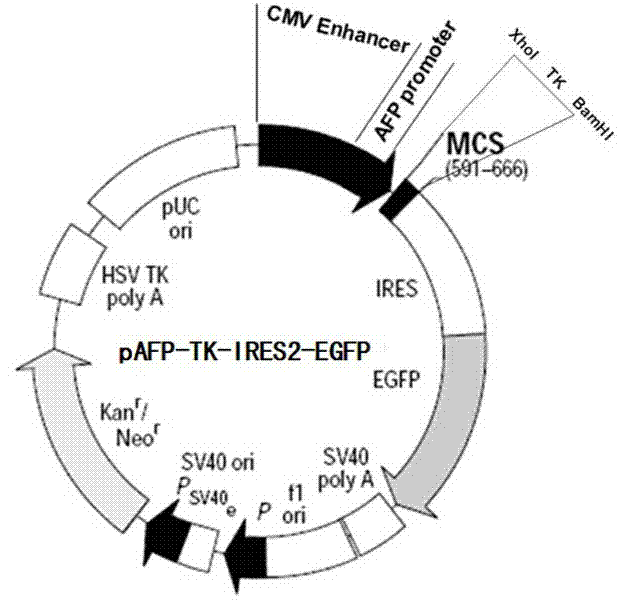
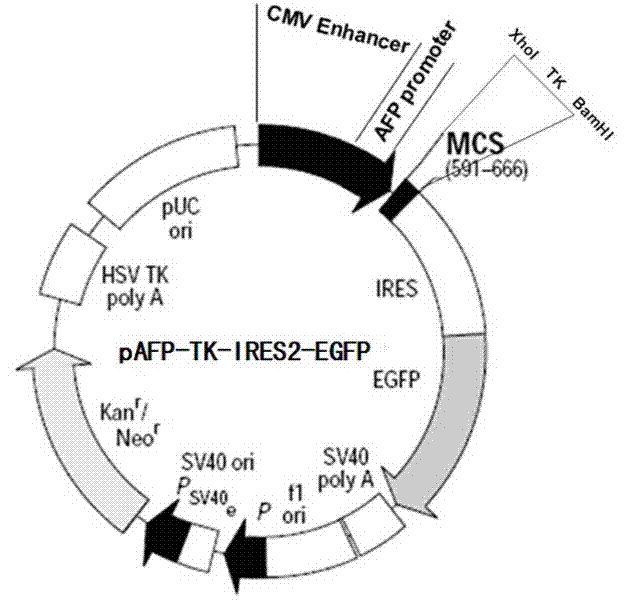
Dual-targeting gene treatment vector for liver cancer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102198277AStrong targetingLethalGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsApolipoprotein e4Chylomicron
The invention relates to a dual-targeting gene treatment vector for liver cancer, which is a complex consisting of chylomicron and an eukaryotic expression plasmid vector containing an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) promoter and a suicide gene. Apolipoprotein E (apo E) is contained in the chylomicron, and apo E receptors present on membrane surfaces of liver cells and liver cancer cells, and can identity and combine the apo E specifically, so the plasmid vector can be carried by the chylomicron specifically to be oriented to the liver cells and the liver cancer cells without being absorbed by other cells of bodies; and the eukaryotic expression plasmid vector contains the AFP promoter for promoting gene expression, and the promoter can be promoted only under the specific AFP promoting environment to promote the gene expression at the downstream of the eukaryotic expression plasmid vector, so the dual-targeting gene treatment vector has high and obvious liver cell targeting, and can be promoted and expressed only in the liver cancer cells.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for separating plasma chylomicrons
The invention relates to the technical field of medical treatment, in particular to a method for separating plasma chylomicrons. The method comprises the following steps of A, freezing plasma, whereina plasma bag containing plasma is frozen, freezing time is 2-8 hours, and the freezing temperature is 40 DEG C-10 DEG C; B, standing plasma, wherein the frozen plasma bag in step A is placed upside down, and standing is conducted at 0 DEG C-4 DEG C for 8-12 hours; C, centrifuging, wherein after standing in step B, the plasma is centrifuged in a centrifuge, the centrifuge has a centrifugal force of 3900 g-4200 g, the centrifugation time is 8-12 minutes, and the centrifugation temperature is 0 DEG C-4 DEG C; D, separating, wherein the plasma in the plasma bag after centrifugation in step C is extracted to achieve separation of the plasma and the chylomicrons. The method solves the problem of separating the chylomicrons from the plasma.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Anticholesterol immunoglobulin to treat lipid raft diseases
Immunoreactive compositions and methods for immunizing animal, including, humans, cows, and fowl, against cholesterol and cholesterol derivatives, including cholesterol oxides, and their use in methods for reducing and preventing lipid raft-based diseases, including, but not limited to HIV-1, SARS, prion formation in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, and neutralizing oxidized modified lipoproteins, specifically, oxidized-LDL, oxidized-VLDL / IDL, and oxidized-chylomicrons, which contribute to the formation of fatty streaks and atherosclerotic plaques, are described.
Owner:ORIGO FOODS
System for delivering nucleic acids for suppressing target gene expression by utilizing endogenous chylomicron
ActiveUS20100234282A1Suppressing a target gene expression in vivo more safely and efficientlySafe and efficientOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryDiseaseChylomicron
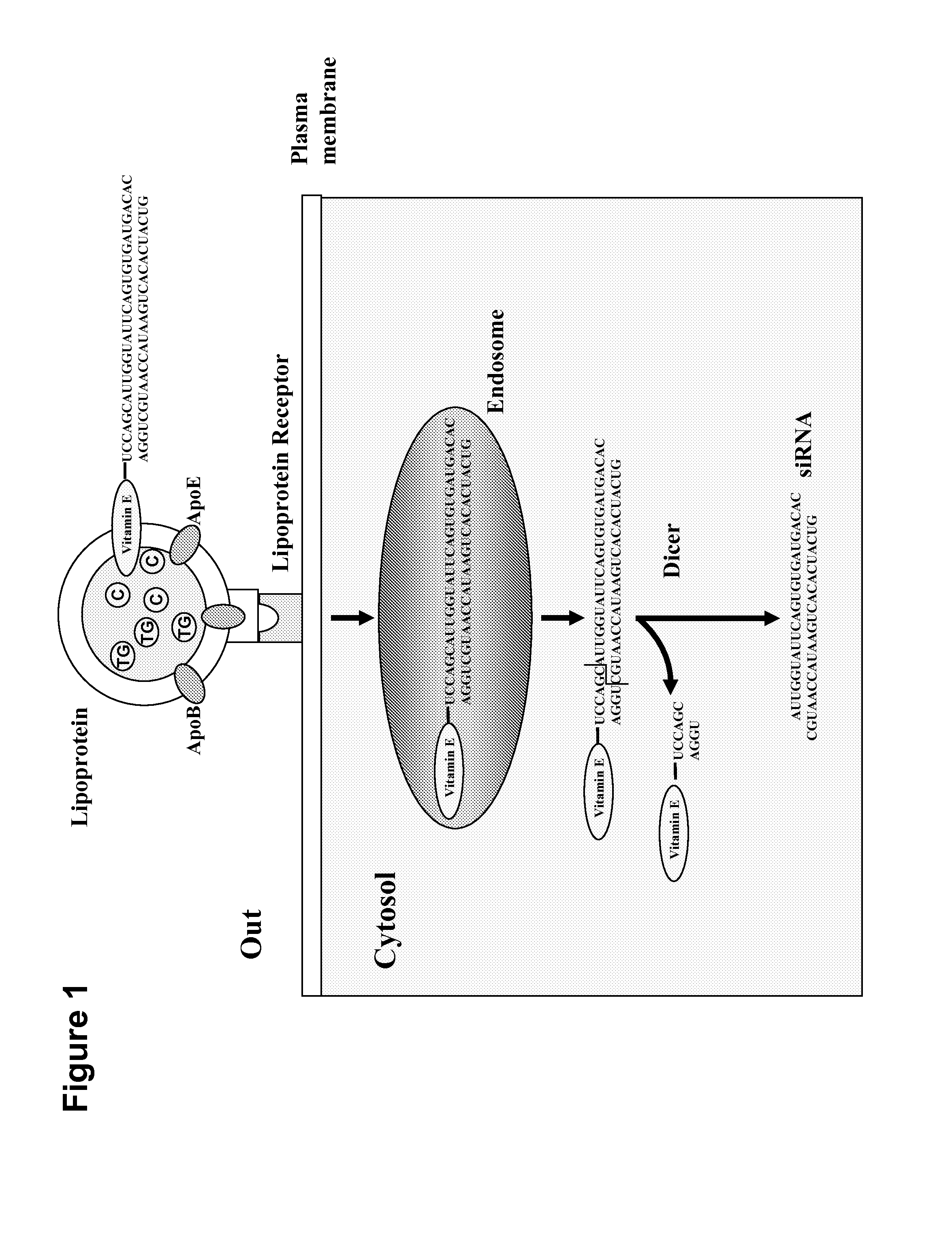
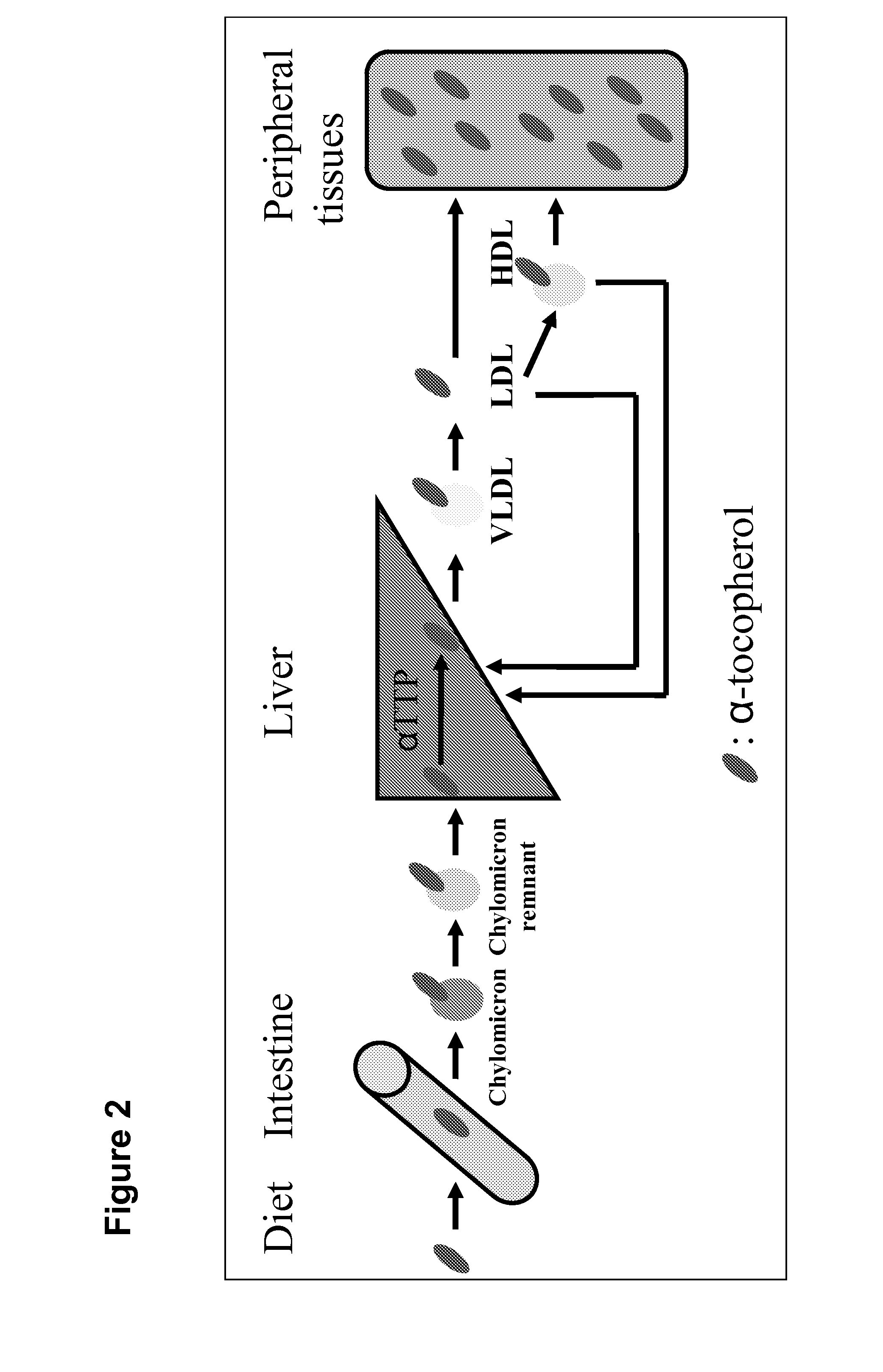
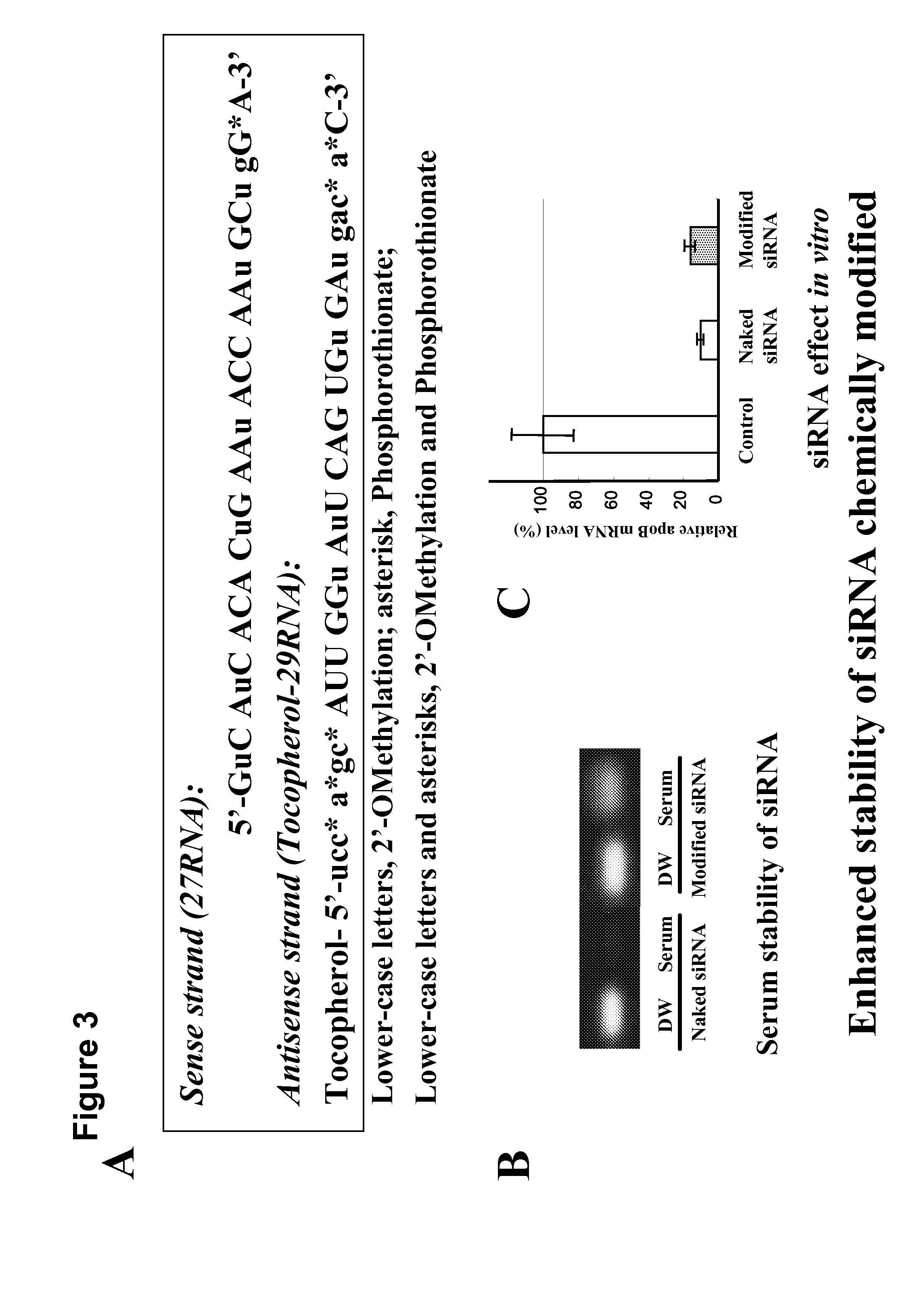
The object of present invention is to provide a system that can deliver in vivo nucleic acids such as an siRNA for suppressing a target gene expression in vivo more safely and efficiently, and to provide an expression-suppressing agent and a pharmaceutical composition utilizing the system. An introduction substance into chylomiclon, particularly nucleic acids to which an alpha-tocopherol is bound for suppressing a target gene expression, can be delivered more safely and efficiently into hepatic cells in vivo by administering the nucleic aids under the condition where the production of chylomicron is induced in the body. Alternatively, alpha-tocopherol-bound nucleic acids are mixed with extracted chylomiclon, and then they are administered. Consequently, a target gene expression is suppressed, thereby a disease caused by an elevated expression of the target gene can be treated more safely and efficiently.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO MEDICAL & DENTAL UNIV
Preparation method and use of artificial cannabidiol chylomicron
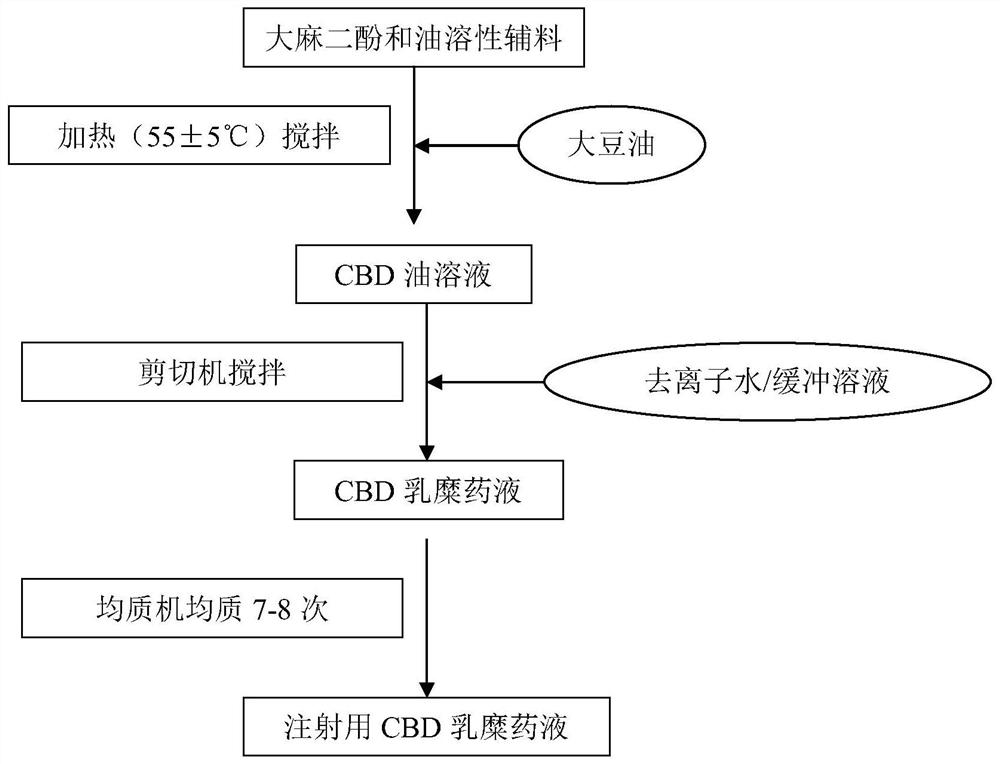
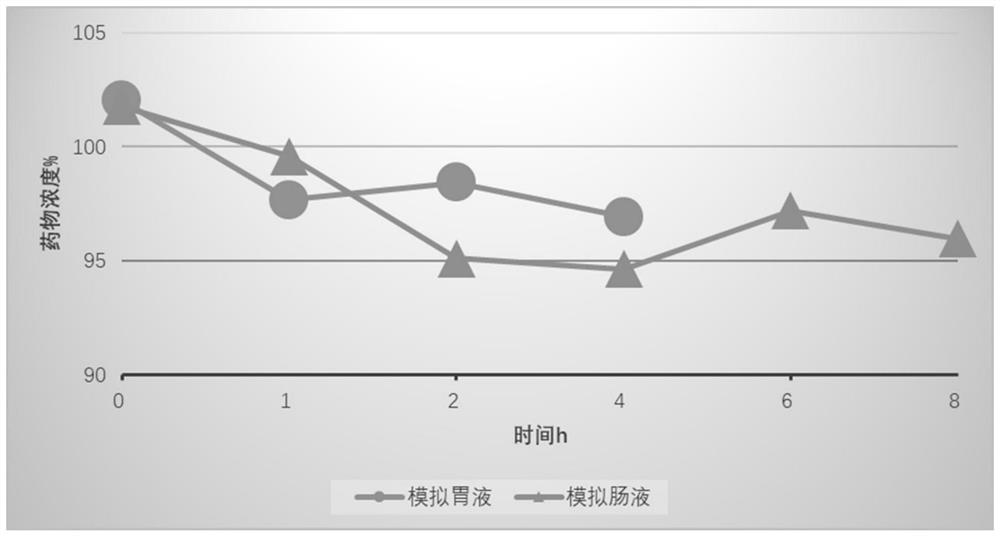
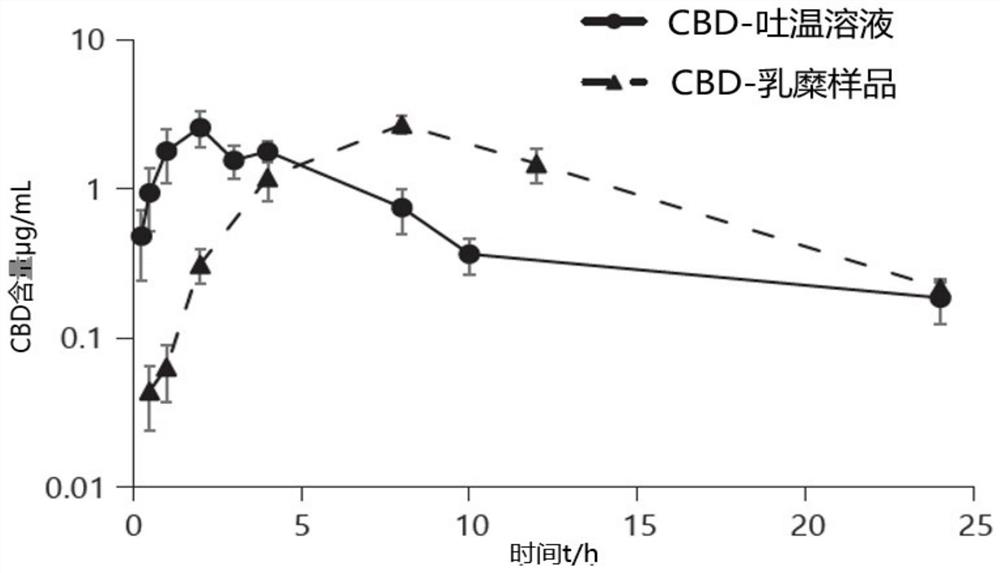
PendingCN112336705APromote absorptionSolve the problem of water solubilityNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsCholic acidMonoglyceride
The present invention provides a preparation method and use of artificial cannabidiol chylomicron. Cannabidiol is wrapped in oil-phase cores of emulsion droplets on the premise of keeping a basic composition of simplified chylomicron. The artificial chylomicron wrapping the cannabidiol comprises the following main components: a phospholipid emulsifier, a fatty acid monoglyceride co-emulsifier, a fatty acid diglyceride co-emulsifier, cholesterol or cholic acid, cannabidiol (CBD) and a liquid oil phase. The artificial cannabidiol chylomicron can wrap the CBD in inner cores of the chylomicron, solves water solubility of the CBD and also ensures chemical stability of the CBD.
Owner:西安力邦医美科技有限公司
Application of chylomicron as liver targeting gene treatment vector
ActiveCN102198276AGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsChylomicronCytotoxicity
The invention relates to new application of chylomicron as a vector of a gene treatment medicament, in particular to application of chylomicron as a vector of a liver targeting gene treatment medicament. Apolipoprotein E (apo E) is contained in the chylomicron, and apo E receptors present on membrane surfaces of liver cells and liver cancer cells, and can identity and combine the apo E specifically, so a plasmid vector can be carried by the chylomicron specifically to be oriented to the liver cells and the liver cancer cells without being absorbed by other cells of bodies; and the chylomicronhas high liver cell targeting, and can be metabolized in the liver cells and the liver cancer cells without residues, so the problem of cytotoxicity is solved.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of high purity and low density lipoprotein
InactiveCN109323910AAchieve layer-by-layer separationIncrease concentrationPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingChylomicronPhosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of material extraction, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a high purity and low density lipoprotein. Chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins in blood plasma are centrifuged and removed according to different densities, remain blood plasma is extracted and added withpotassium bromide and the density is adjusted to 1.045g / mL, centrifugation is carried out again to obtain a normal low density lipoprotein located at the uppermost layer, and a phosphate buffer salt solution is used for dialyzing to reduce K+ concentration; and aresultof the K+ concentration of the low density lipoprotein before and after dialyzing measured by a full-automatic biochemical analyzer is compared with a result measured by an osmotic pressure analyzer, if the K+ concentration of the low density lipoprotein is dialyzed to be with no obvious differences with the osmotic pressure of the phosphate buffer salt solution, the potassium bromide is considered to be completely dialyzed, and then the high purity and low density lipoprotein is obtained. The preparation method of the high purity and low density lipoprotein can obtain the high purity and low density lipoprotein to meet of existing experimentalrequirements.
Owner:XUZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
Artificial chylomicron containing medicine carrying compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
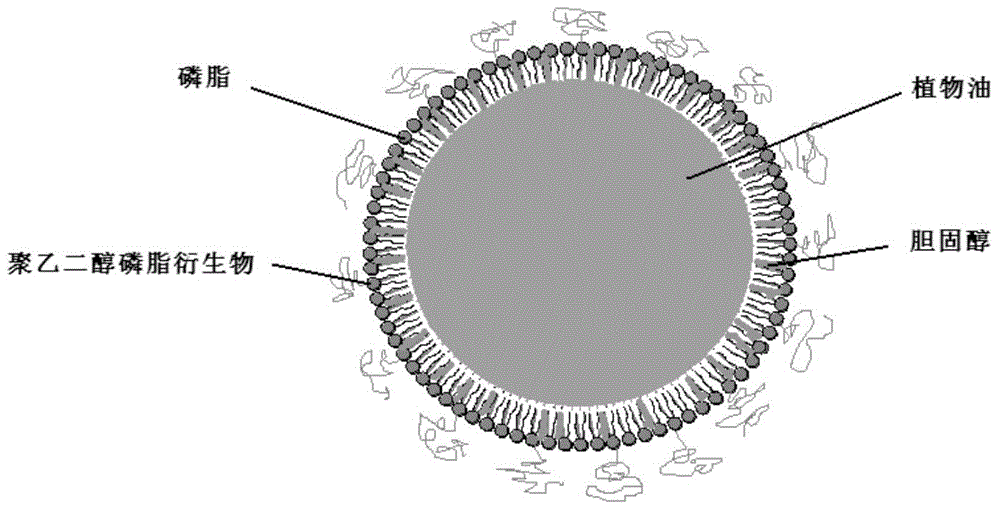
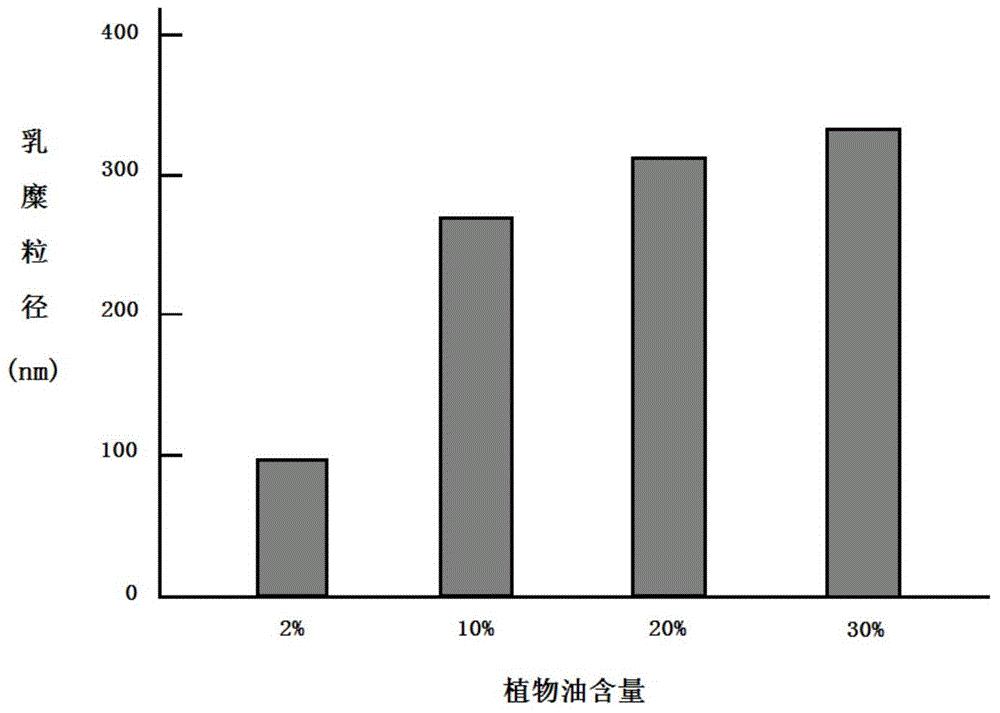
ActiveCN104524583AGuaranteed stabilityAdd passive targeting functionMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMonoglycerideChylomicron
The invention relates to a novel drug carrying and delivering system and particularly relate to a formula and a preparation method of an artificial chylomicron containing medicine carrying compound. The artificial chylomicron is prepared from the following main components: an animal oil, a vegetable oil, an oily medicine or an oil-soluble medicine, phospholipid which serves as an emulsifier, cholesterol or steroid which serves as a stabilizer, a shape control agent or a biological modifier, oleic acid or an oleate which serves a stabilizer or a co-emulsifier, fatty monoglyceride and fatty diglyceride which serve as co-emulsifiers, polyethylene glycol phospholipid derivatives (artificial chylomicron membrane protein substitutes) which serve as stabilizers and emulsifiers and are used for prolonging the half-life period of artificial chylomicron in blood, vitamin E which serves as an anti-oxidant; (8) a complex which serves as a controlling metal ion and glycerol or a carbohydrate for regulating the isotonicity of a medicinal preparation.
Owner:XIAN LIBANG ZHAOXIN BIOTECH CO LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions of carotenoid
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising a chylomicron and a carotenoid. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising a micelle and a carotenoid, suspended in an aqueous solution and suitable for intravenous administration. The bioavailability of the carotenoid of the pharmaceutical composition is higher relative to the bioavailability of free carotenoid.
Owner:JYONG BIOTECH INT PTE LTD
Methods and compositions for treating hypertriglyceridemia
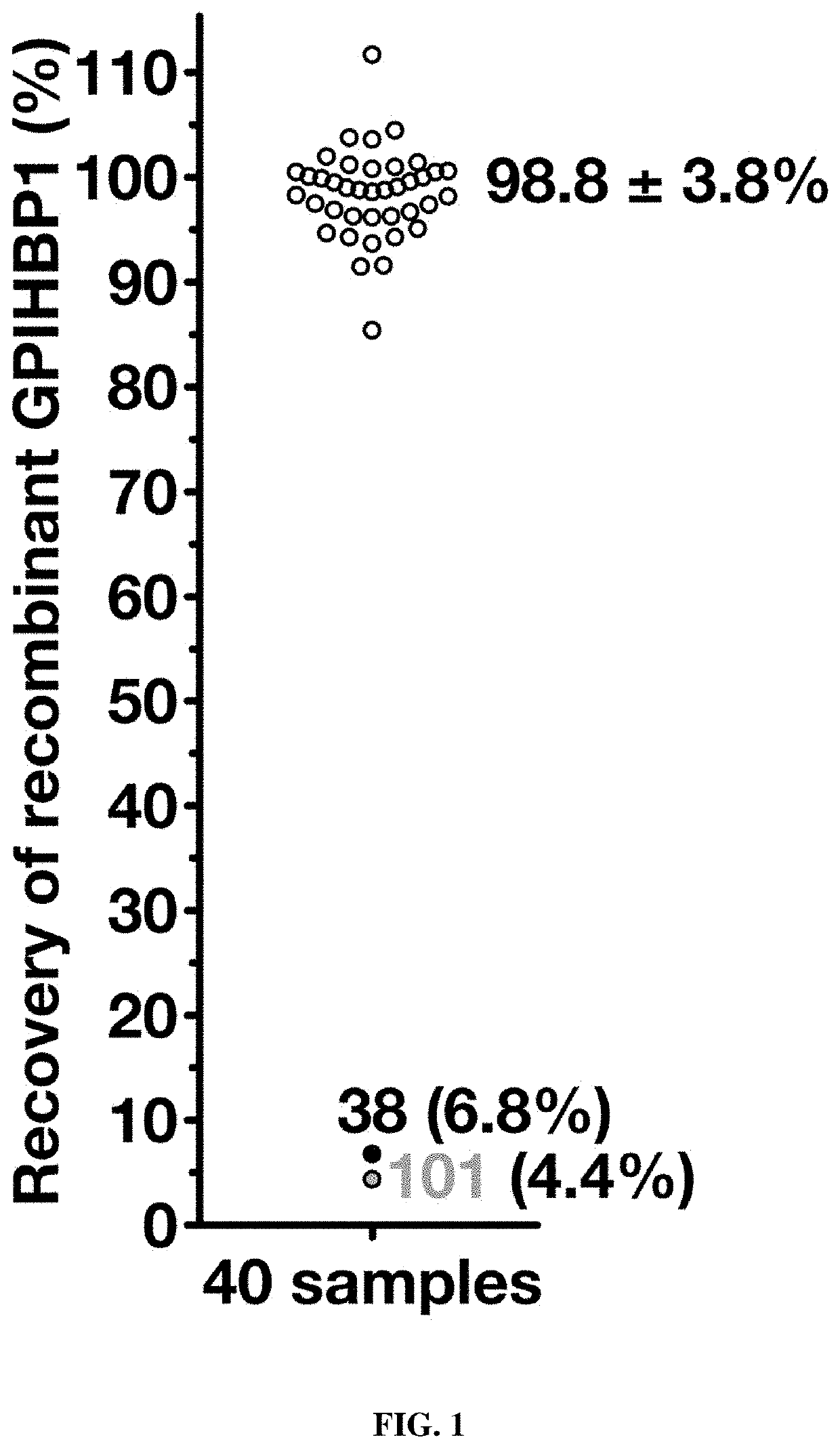
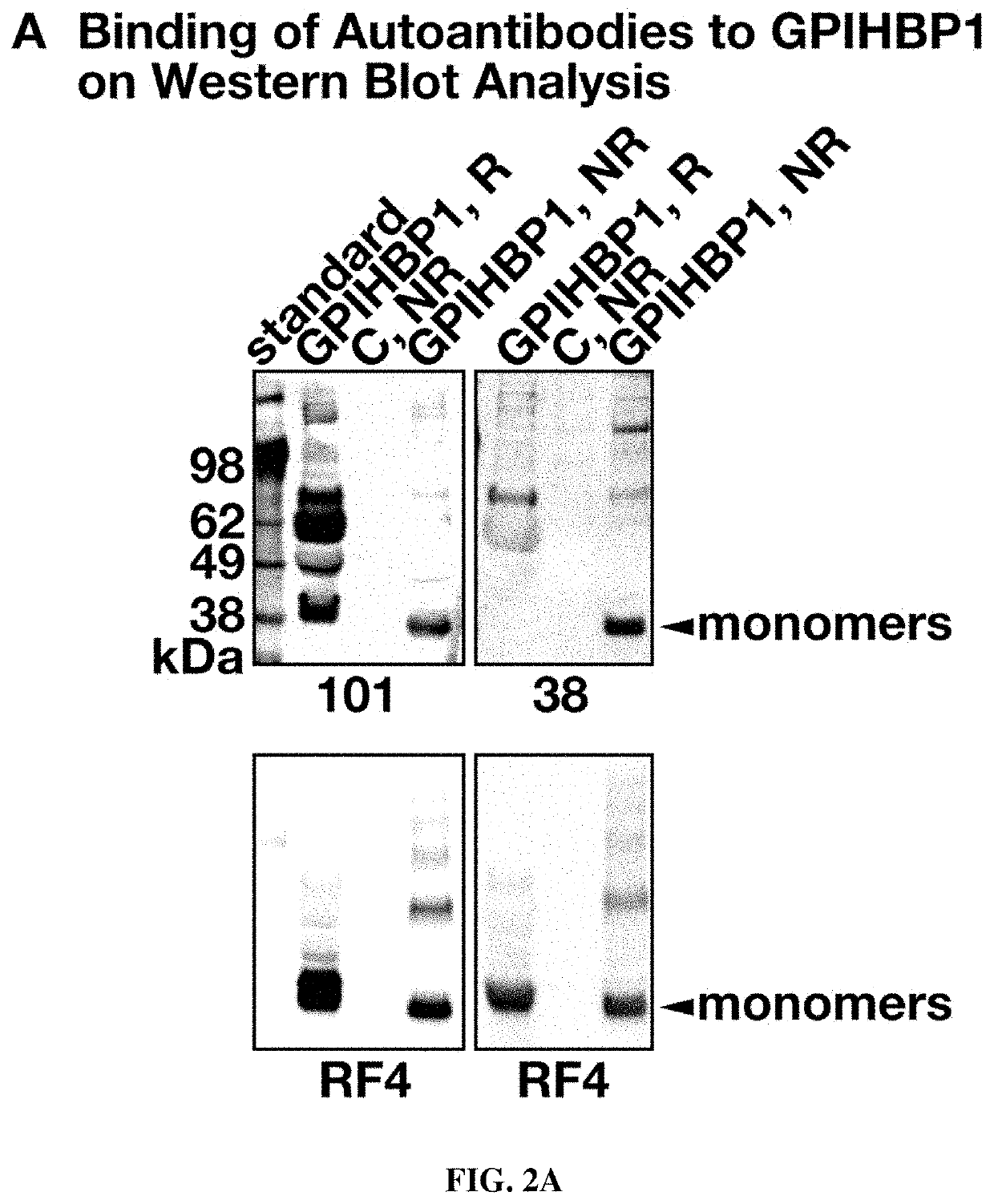
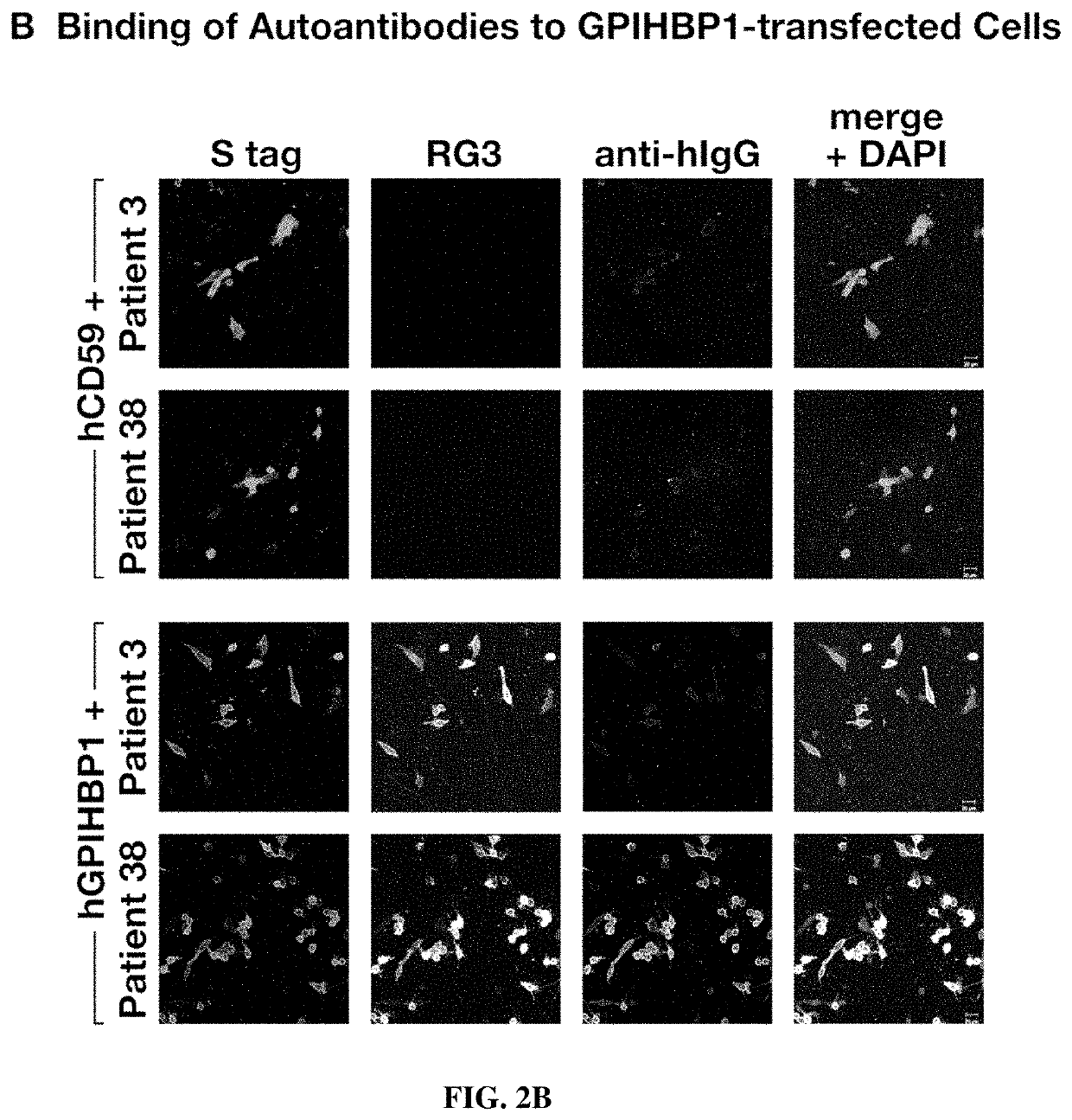
This application describes novel therapeutic strategies for treating patients with hypertriglyceridemia and / or chylomicronemia based on the presence of GPIHBP1 autoantibodies. It was unexpectedly found that autoantibodies to GPIHBP1, a GPI anchored protein of capillary endothelial cells that shuttles lipoprotein lipase to its site of action in the capillary lumen, were found to be present in patients with hypertriglyceridemia, and that the autoantibodies blocked the binding of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) to GPIHBP1. Patients having hypertriglyceridemia and / or chylomicronemia and also having GPIHBP1 autoantibodies may be treated with a therapeutically effective amount of an immunosuppressive treatment and / or GPIHBP1 activator.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY +1
A hepatitis C virus antibody detection reagent comprising recombinant fusion antigen a and b and its application and recombinant fusion antigen a and b
ActiveCN108196069BImprove solubilityFold preciselySsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsChylomicronHcv hepatitis c virus
The invention relates to an HCV (hepatitis c virus) antibody detection reagent containing recombinant fusion antigens A and B, an application and the recombinant fusion antigens A and B, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the HCV antibody detection reagent containing the recombinant fusion antigens A and B, the recombinant fusion antigen A contains an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; the recombinant fusion antigen B contains an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4; the detection reagent comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2, a reagent R3 anda reagent R4. The detection reagent has the following advantages: the two recombinant fusion antigens have the characteristics of high specificity and good stability and can be used for preparing thehepatitis C virus antibody detecting reagent by mixing in a certain ratio, and the clinical detection effect of the reagent is remarkable. Meanwhile, the detection reagent has high anti-interference capacity to chylomicron, bilirubin and hemoglobin, and can greatly meet requirements of clinical diagnosis of HCV.
Owner:深圳德睿生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com