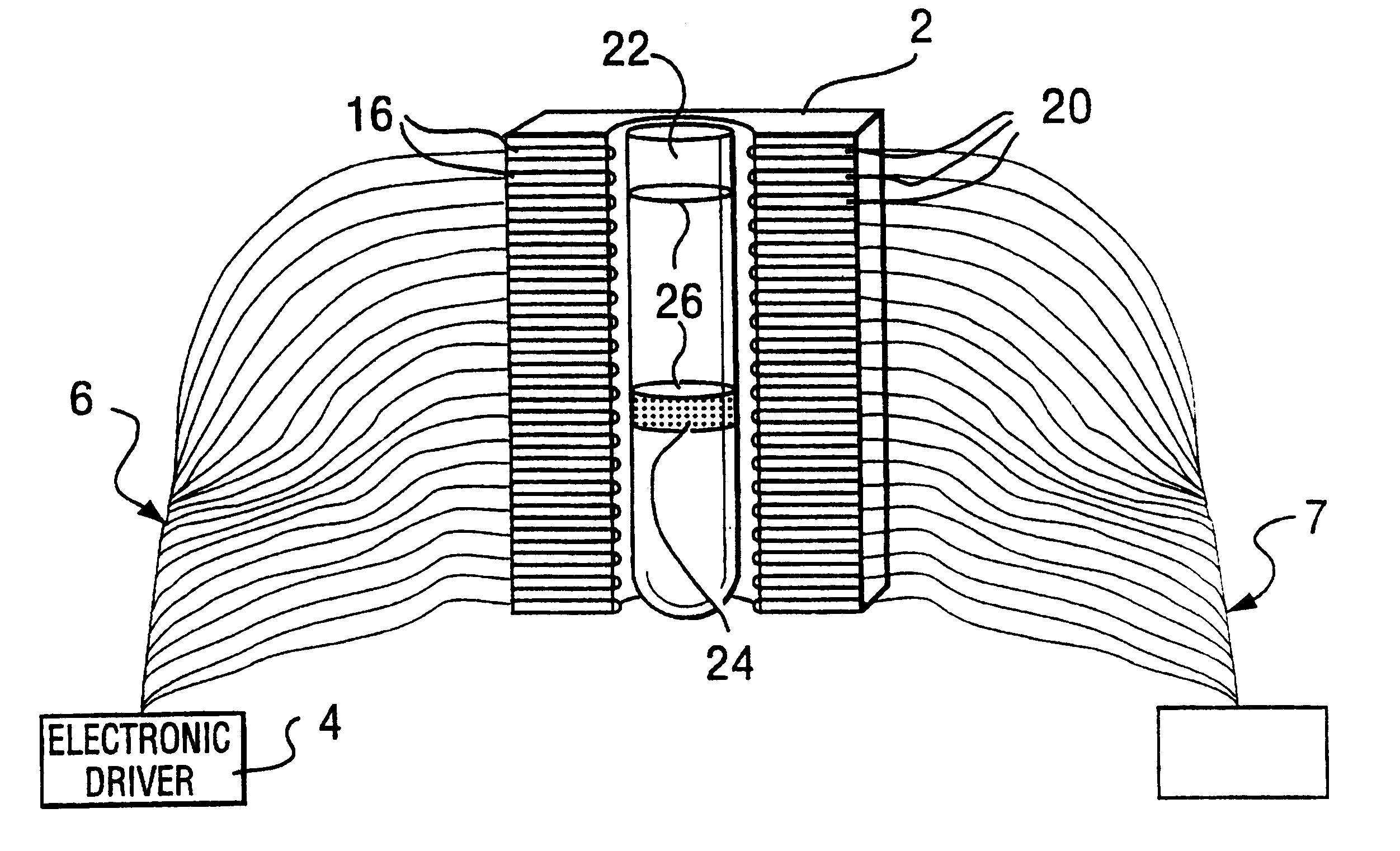
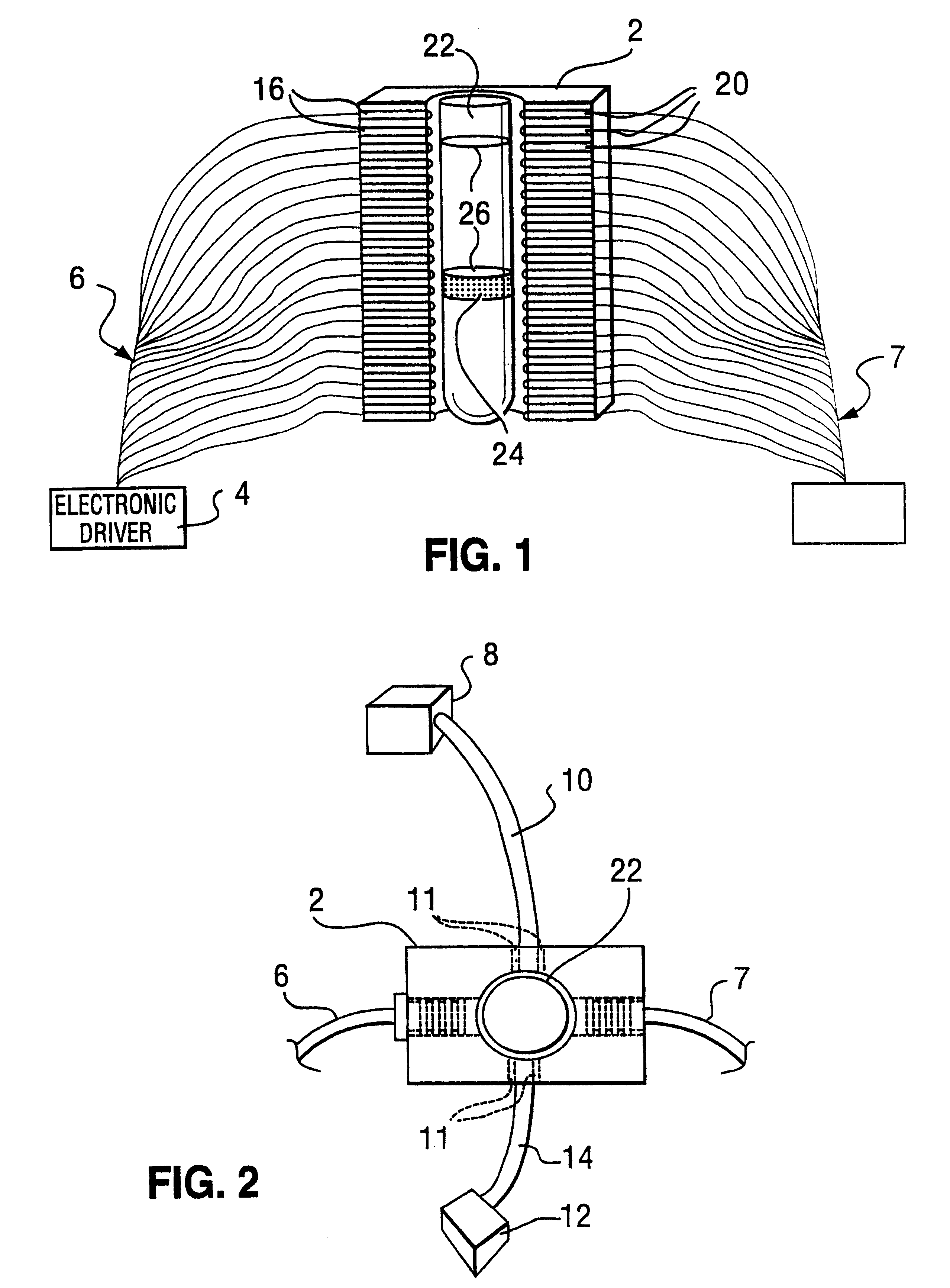
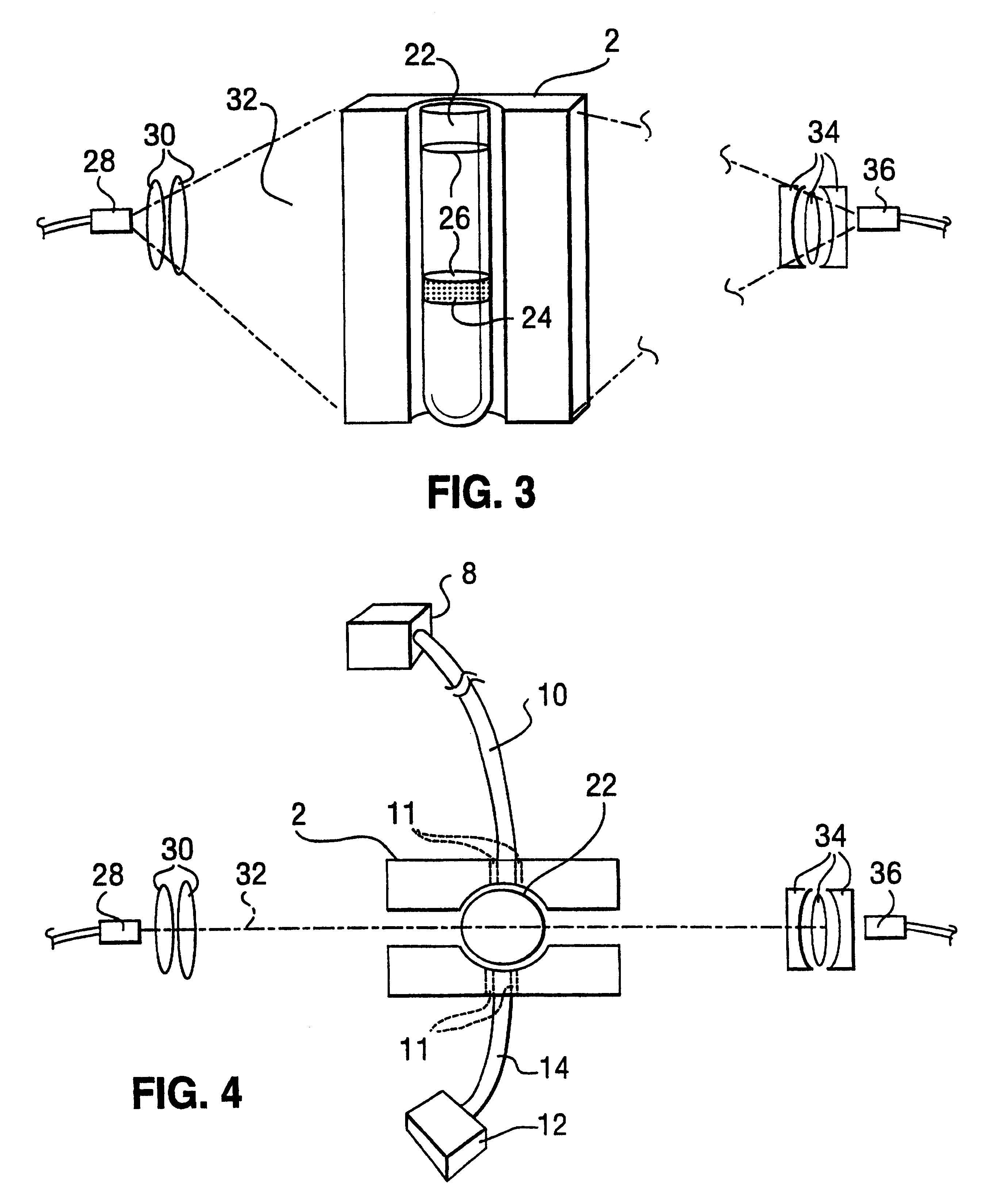
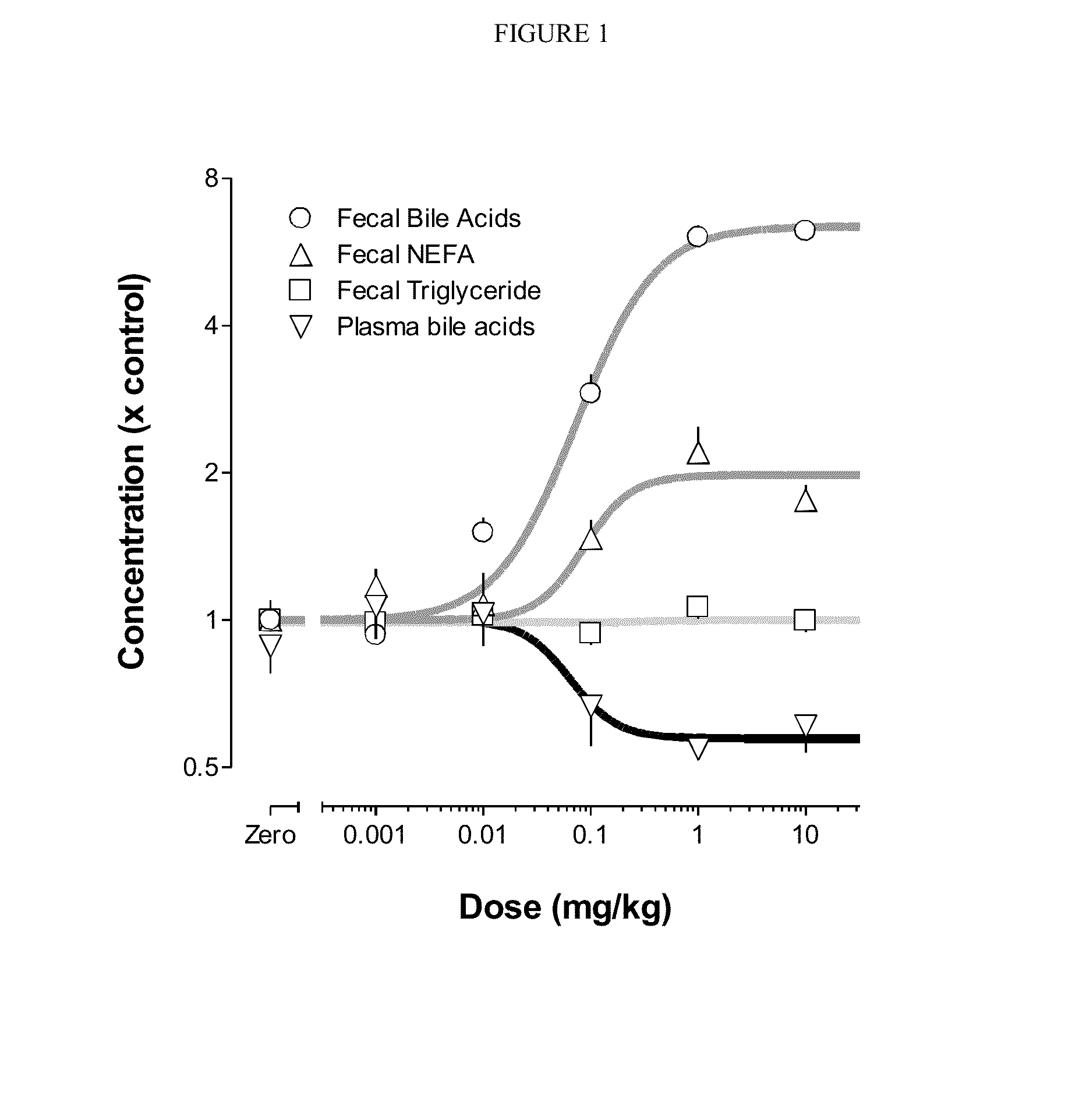
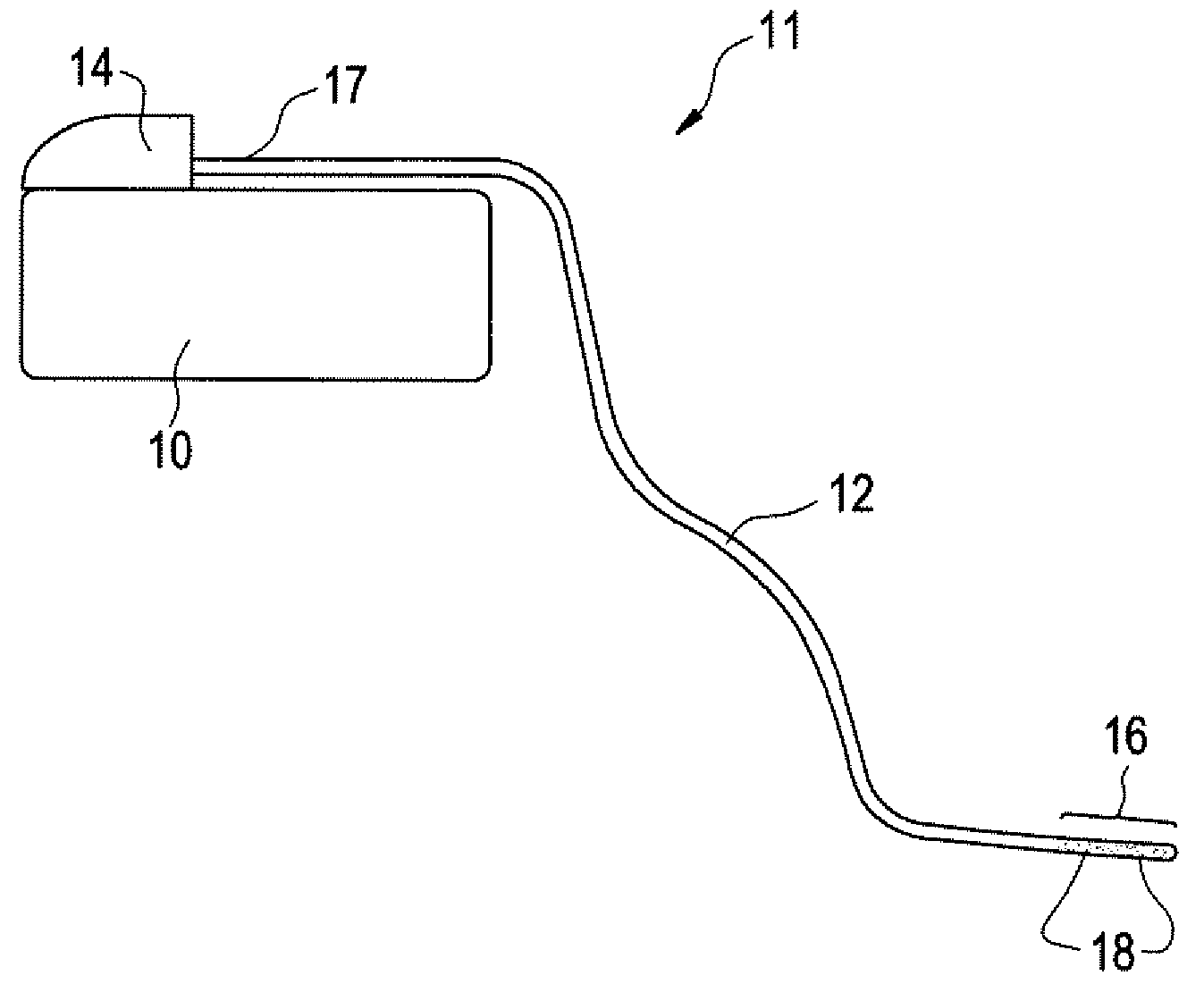
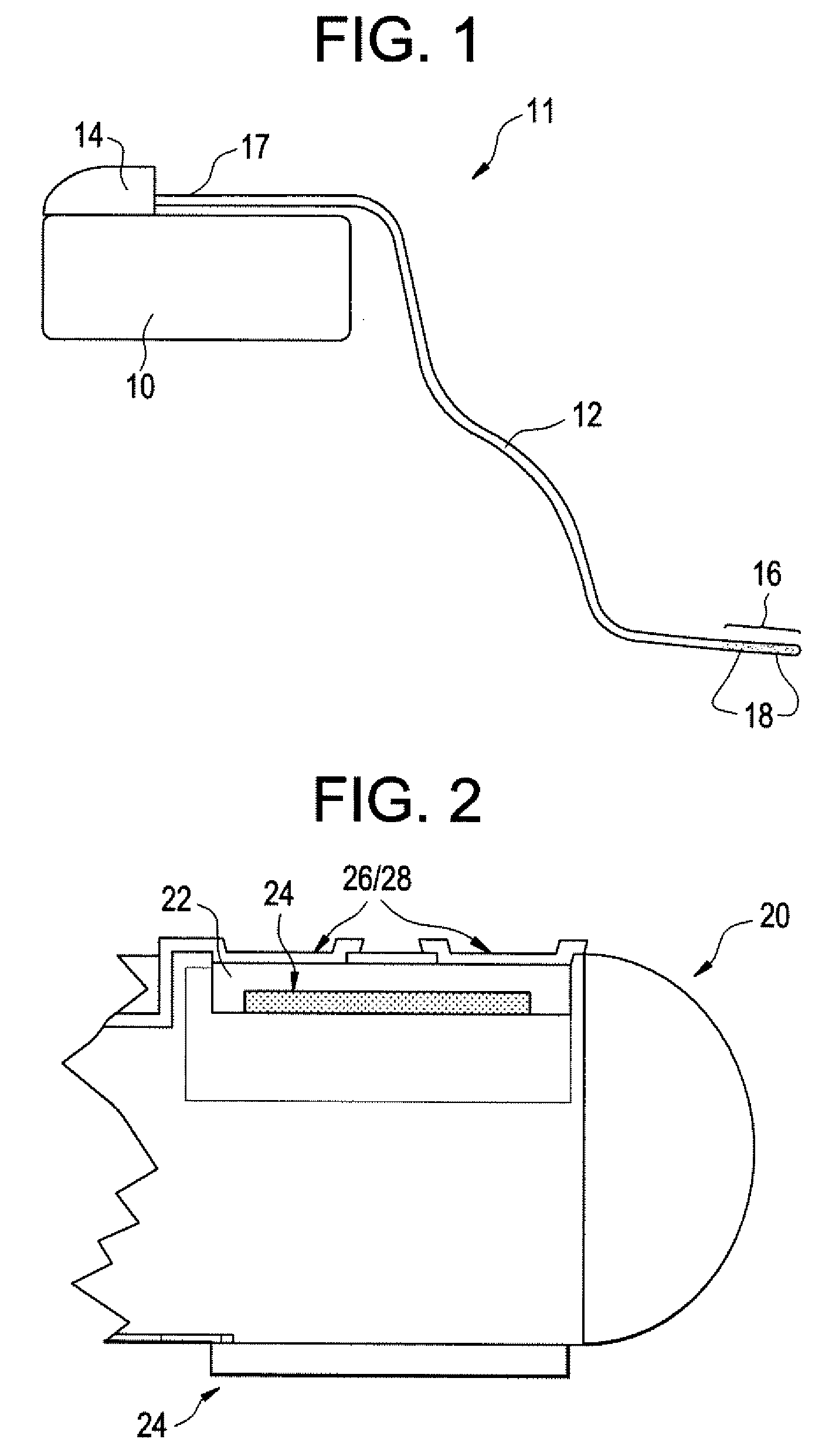
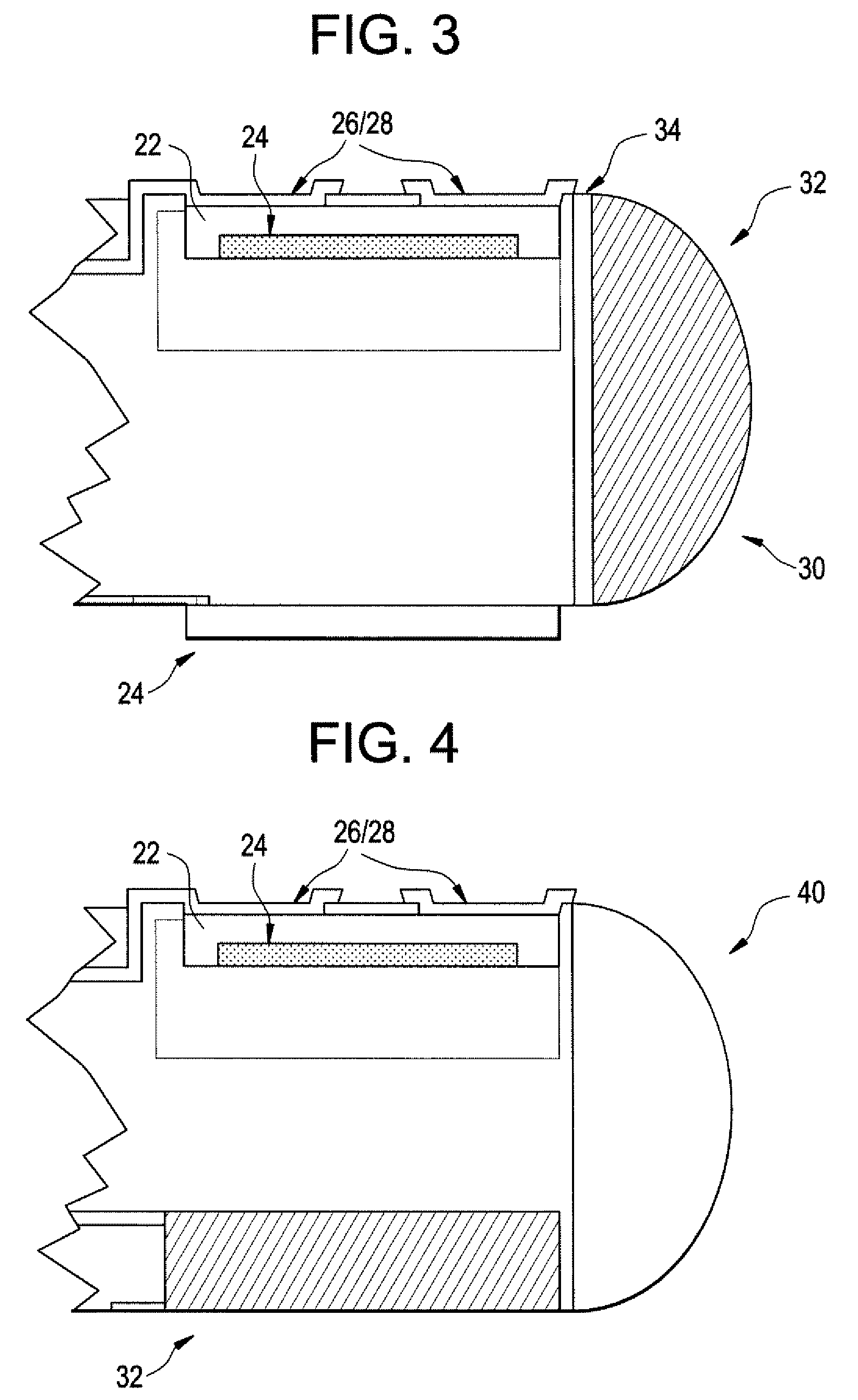
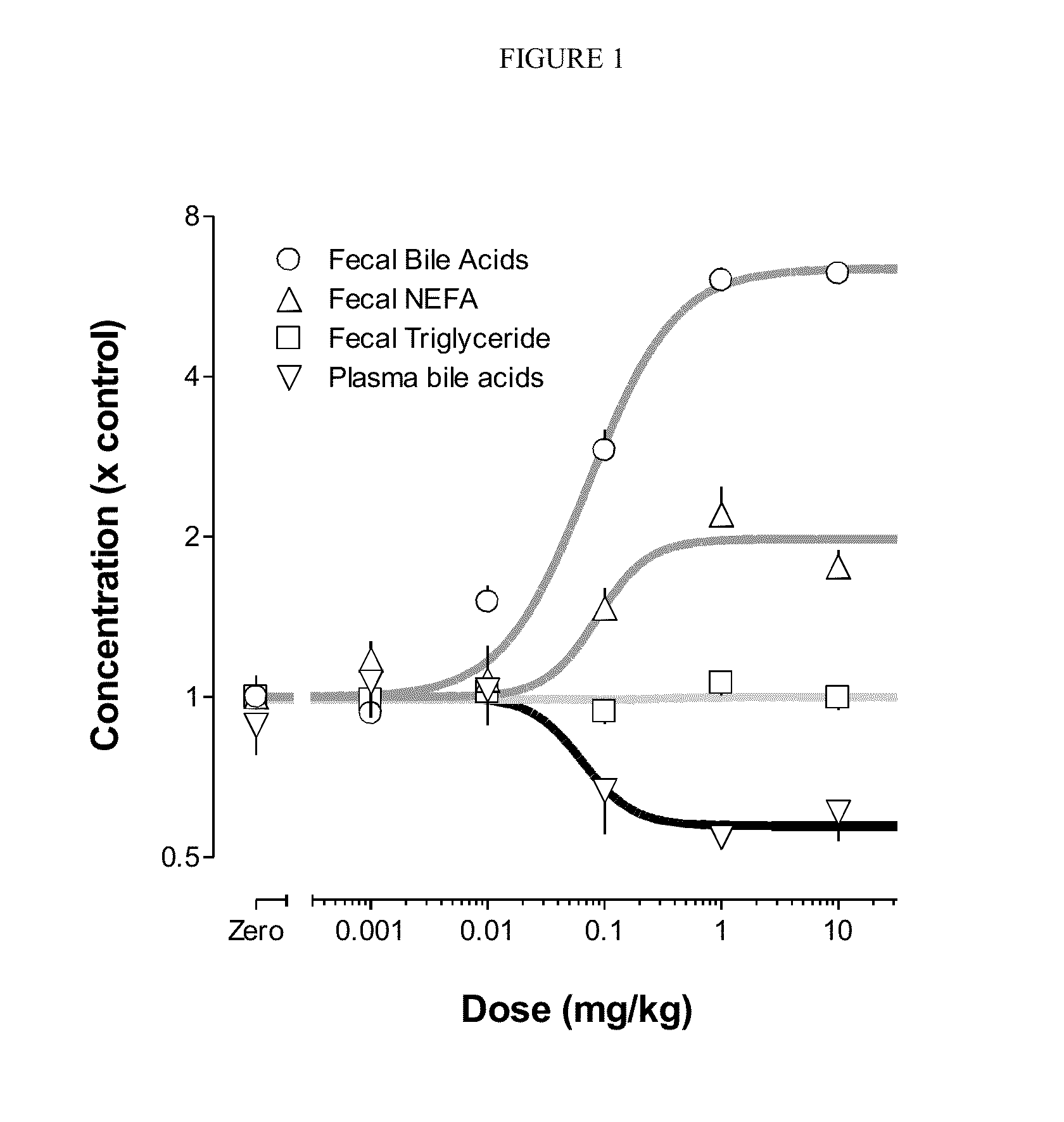
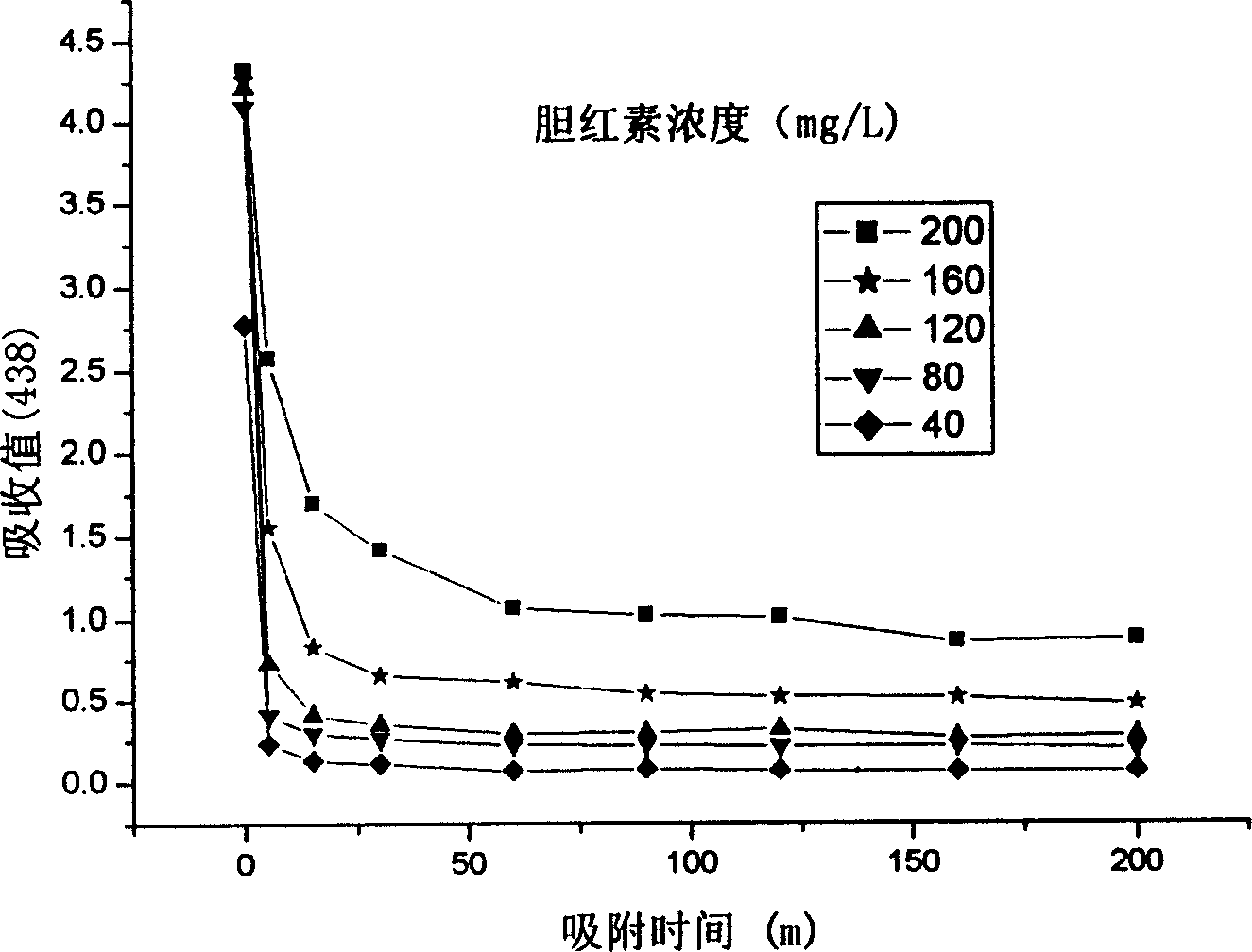
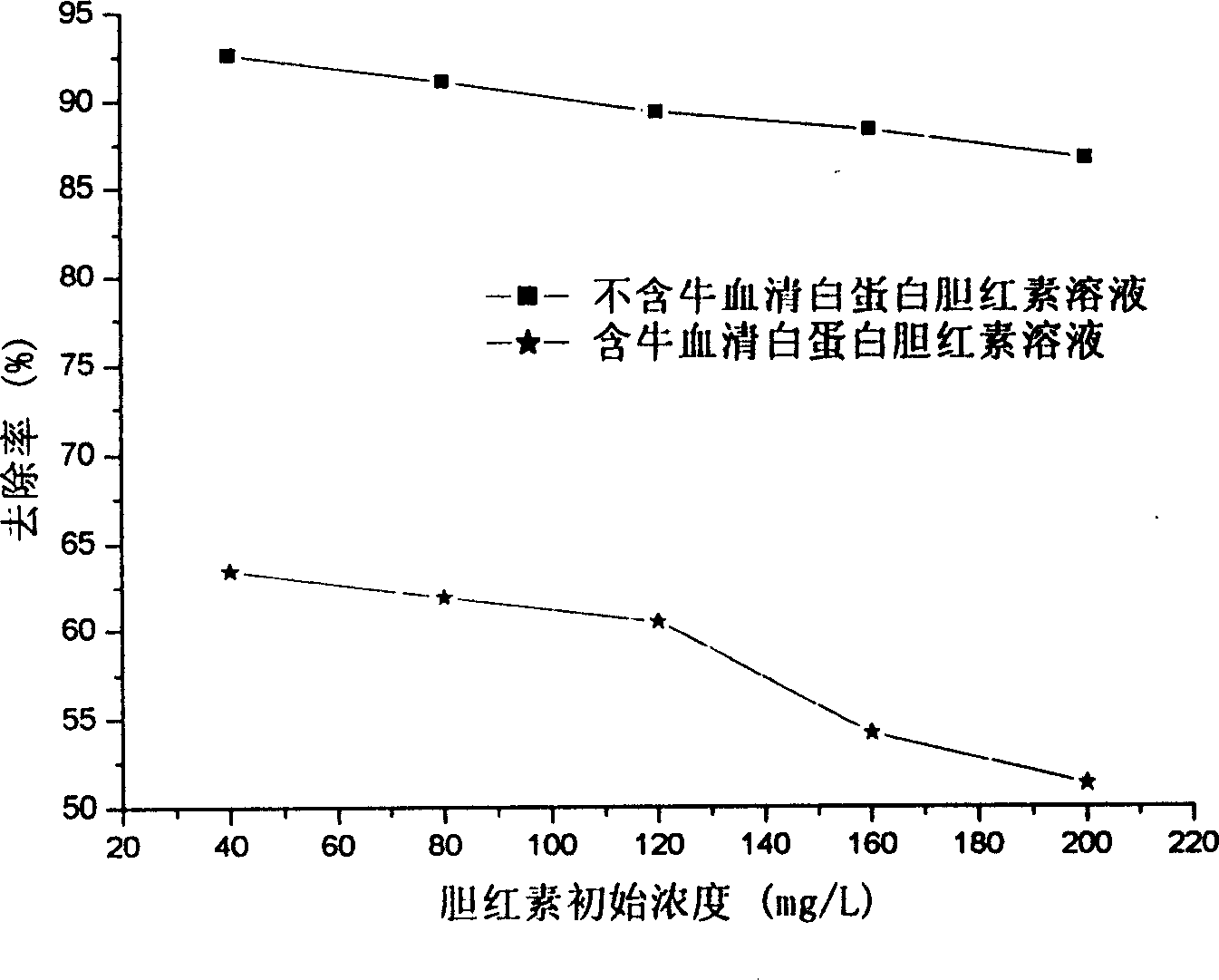
Patents
Literature
453 results about "Bilirubin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
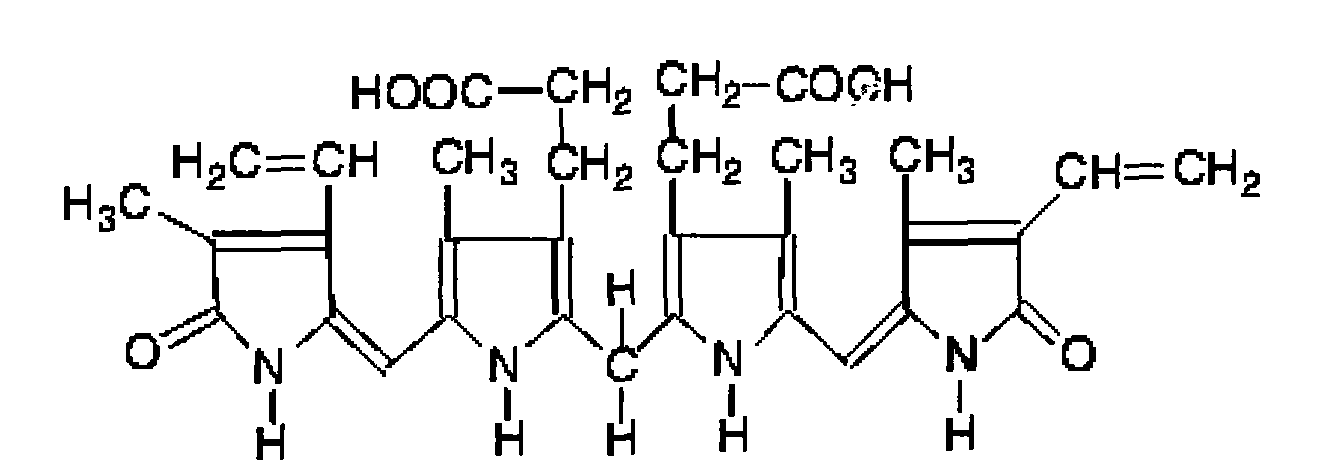
Bilirubin is a yellow compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the destruction of aged or abnormal red blood cells. First the hemoglobin gets stripped of the heme molecule which thereafter passes through various processes of porphyrin catabolism, depending on the part of the body in which the breakdown occurs. For example, the molecules excreted in the urine differ from those in the feces. The production of biliverdin from heme is the first major step in the catabolic pathway, after which the enzyme biliverdin reductase performs the second step, producing bilirubin from biliverdin.
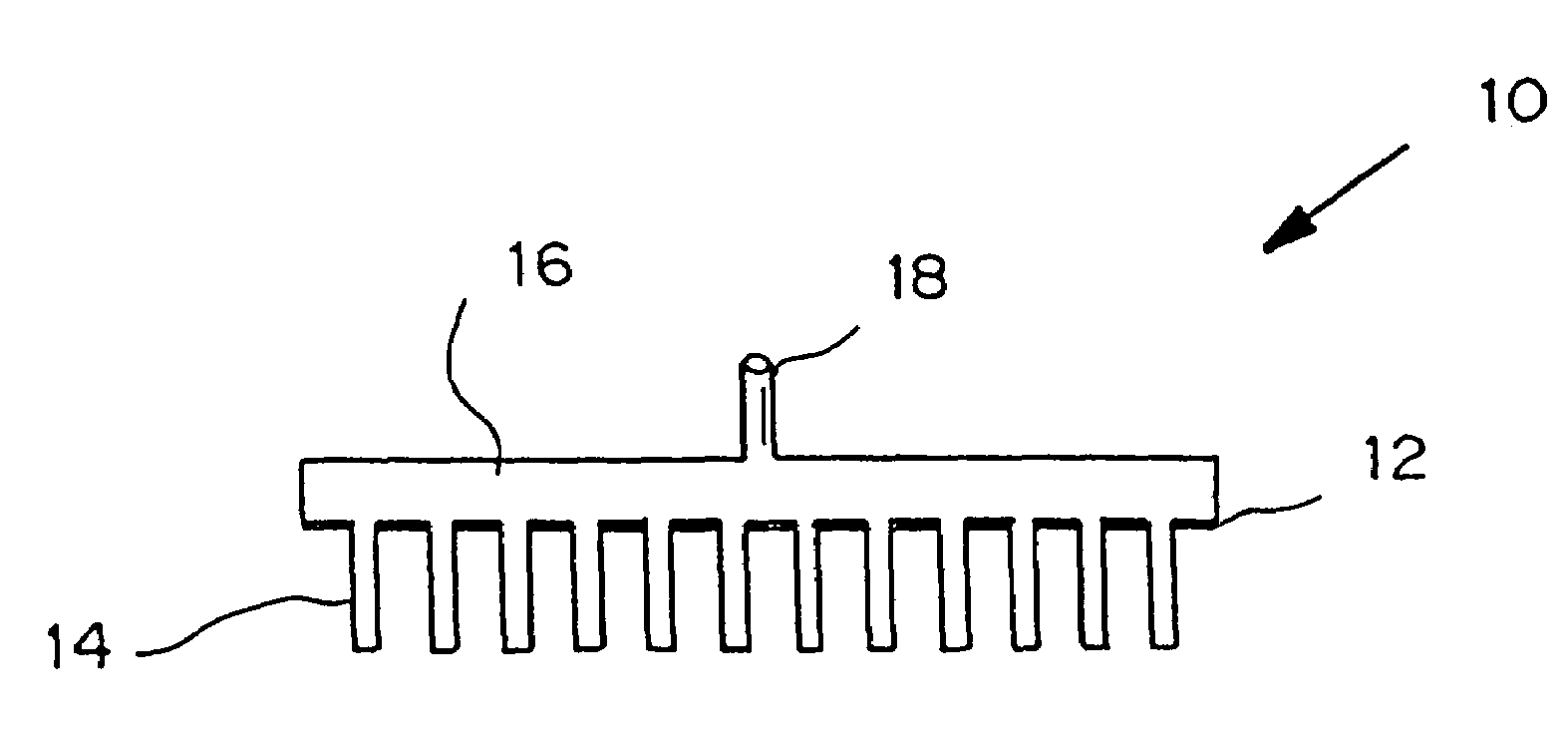
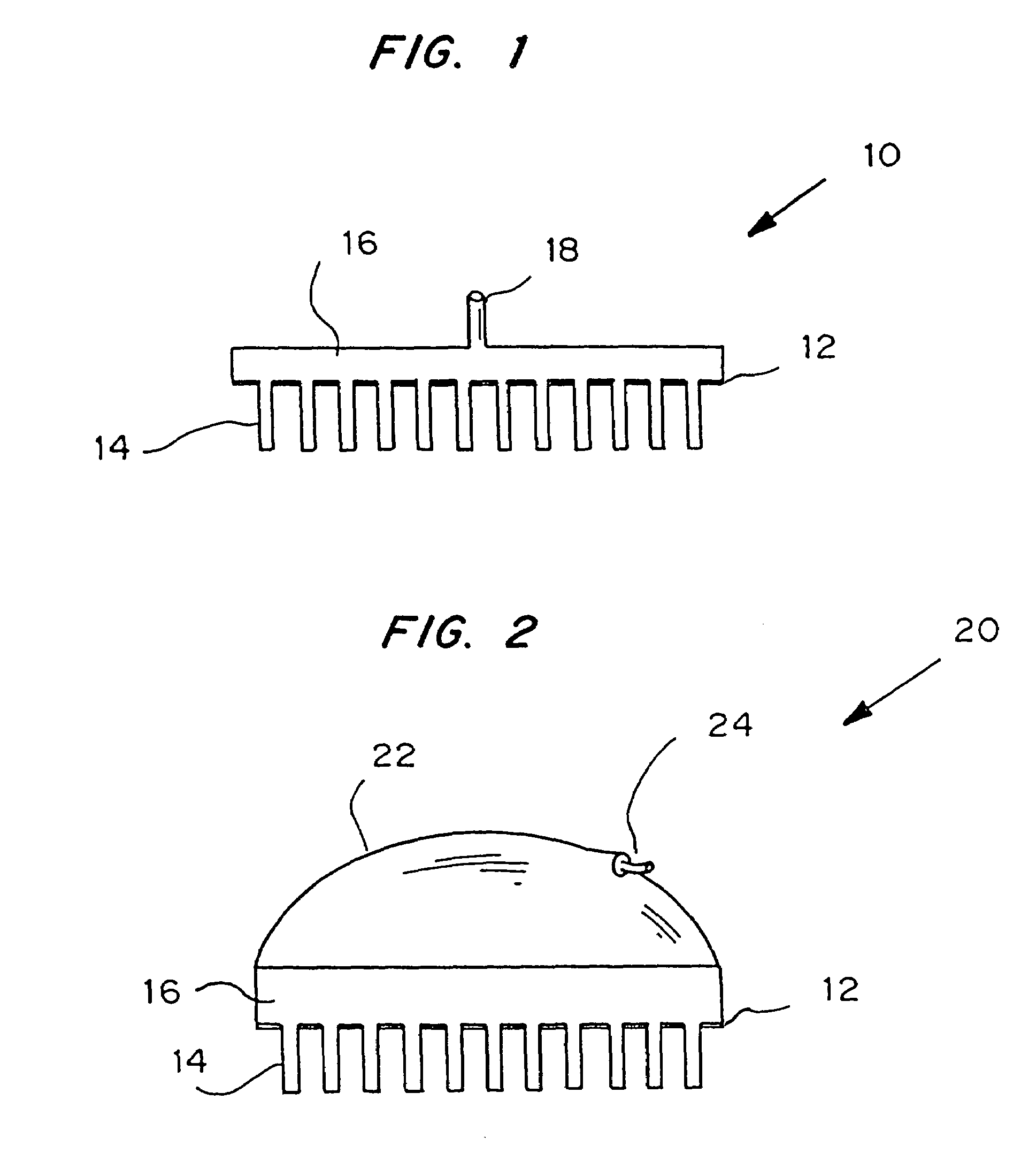
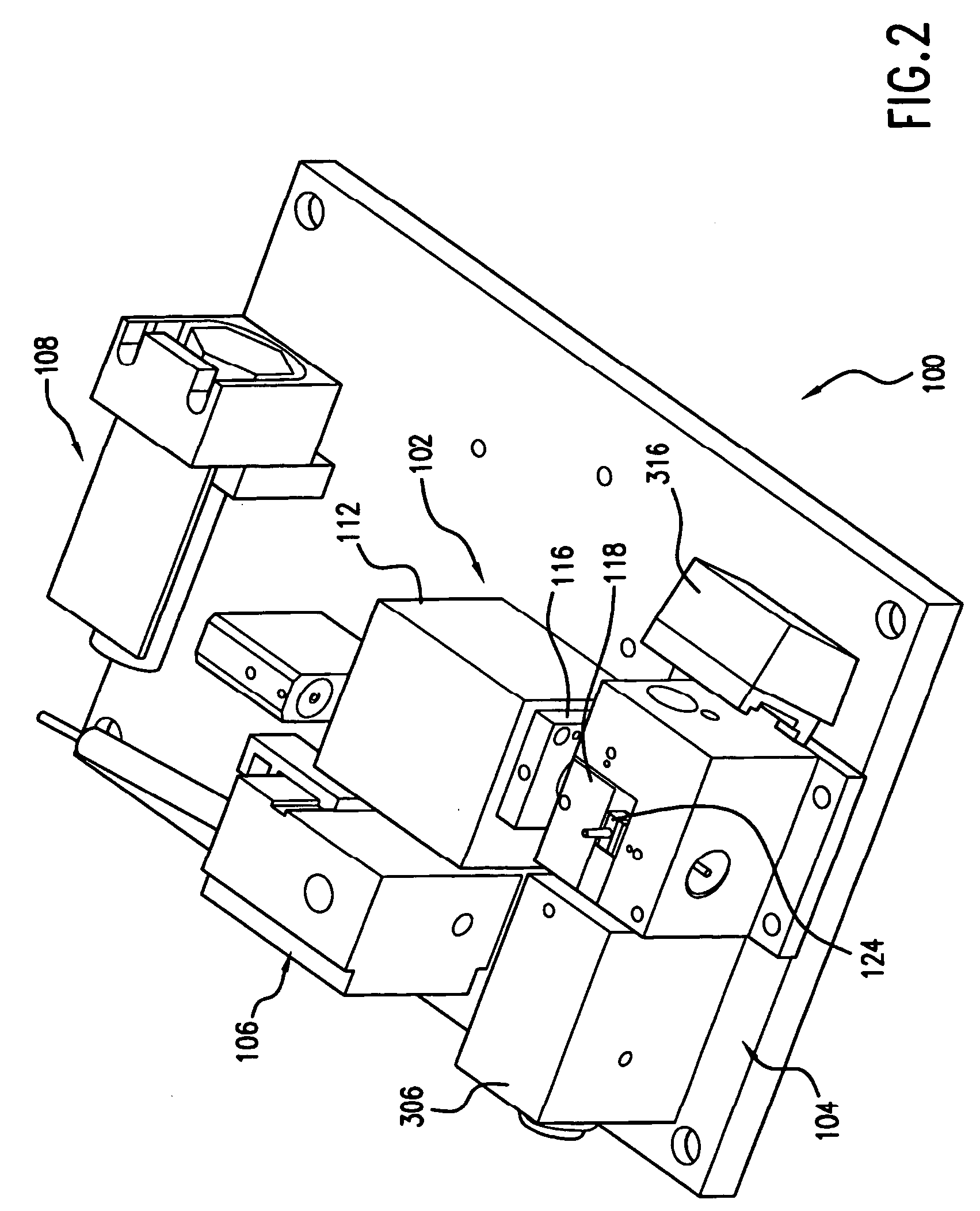
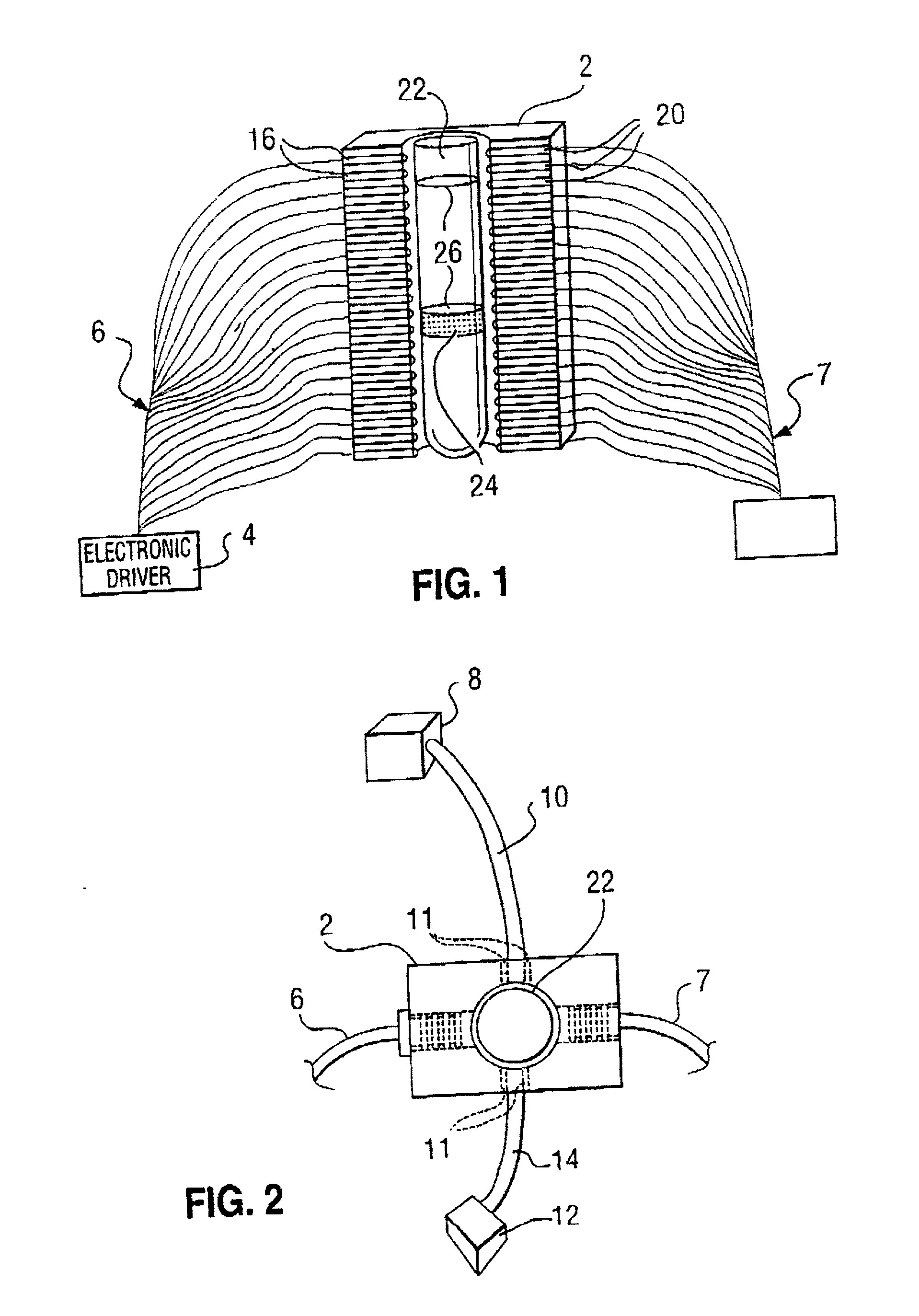
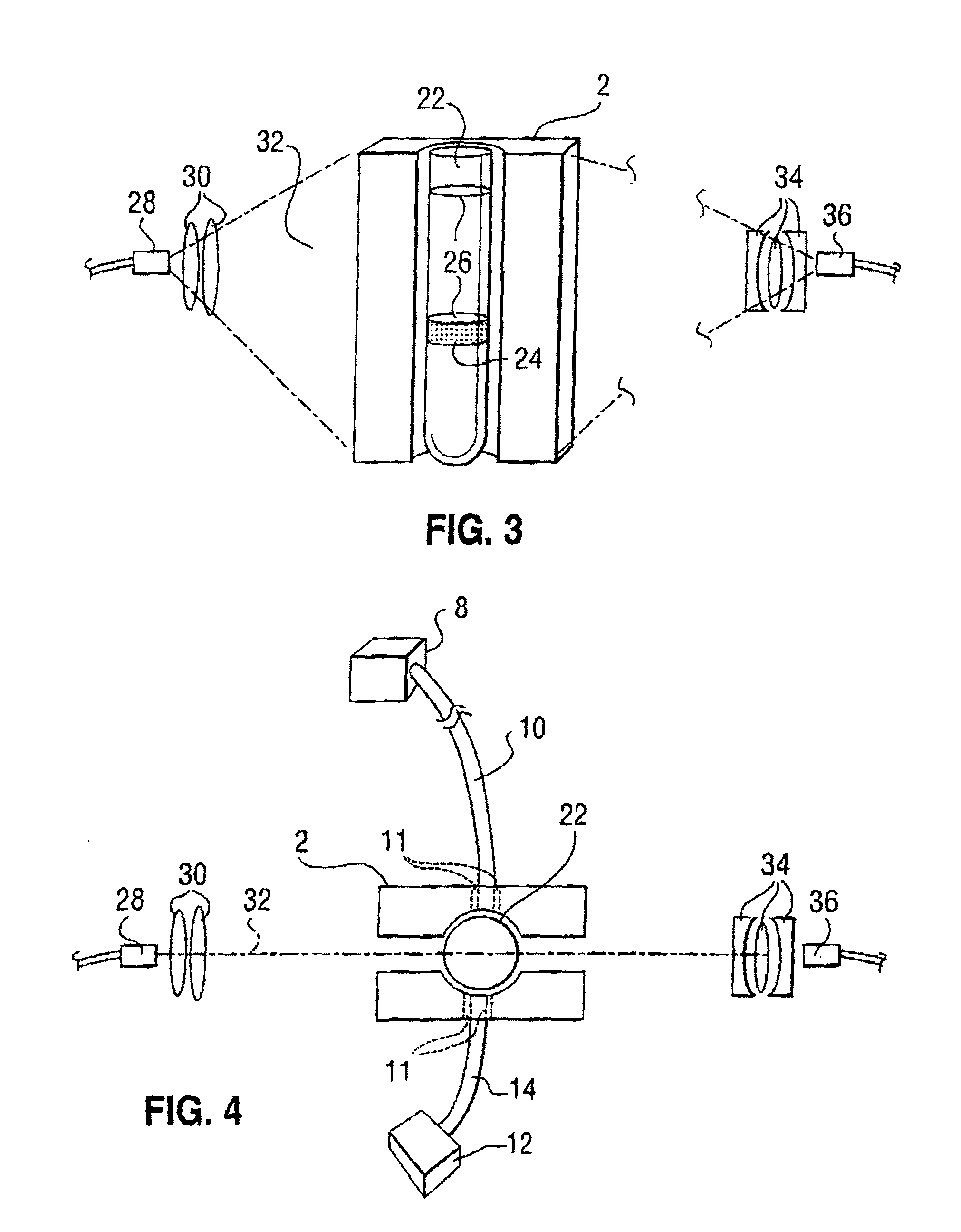
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
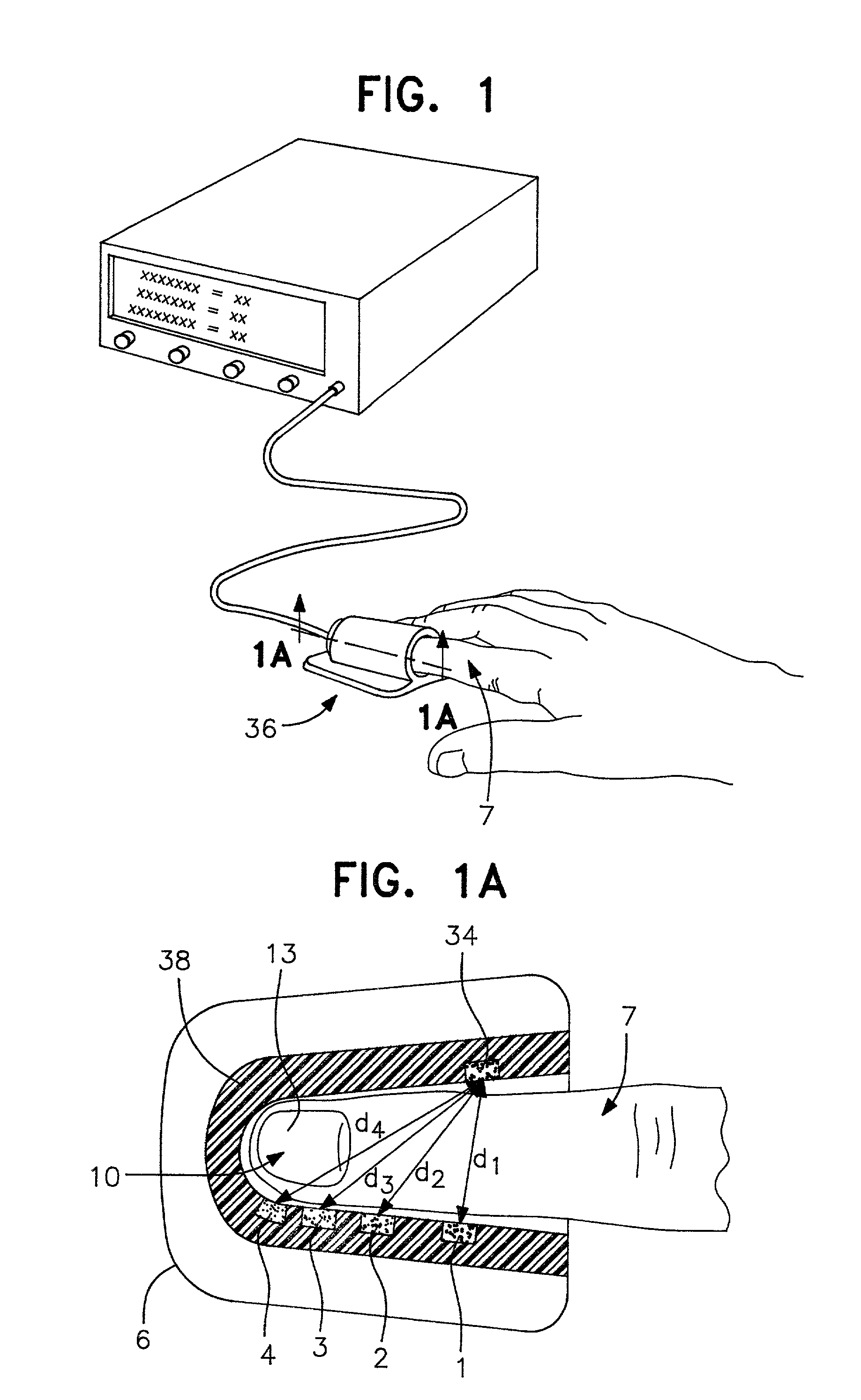
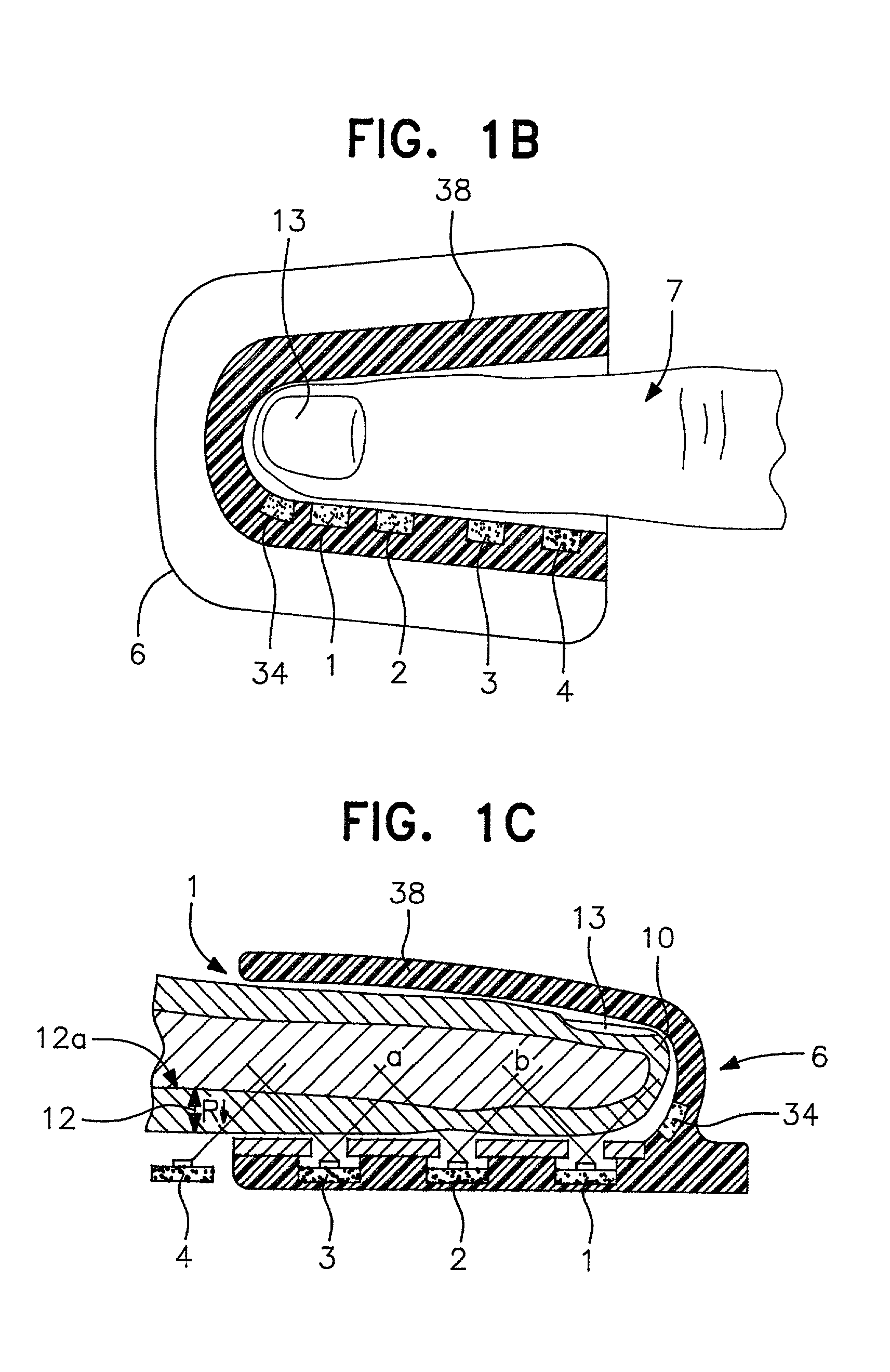
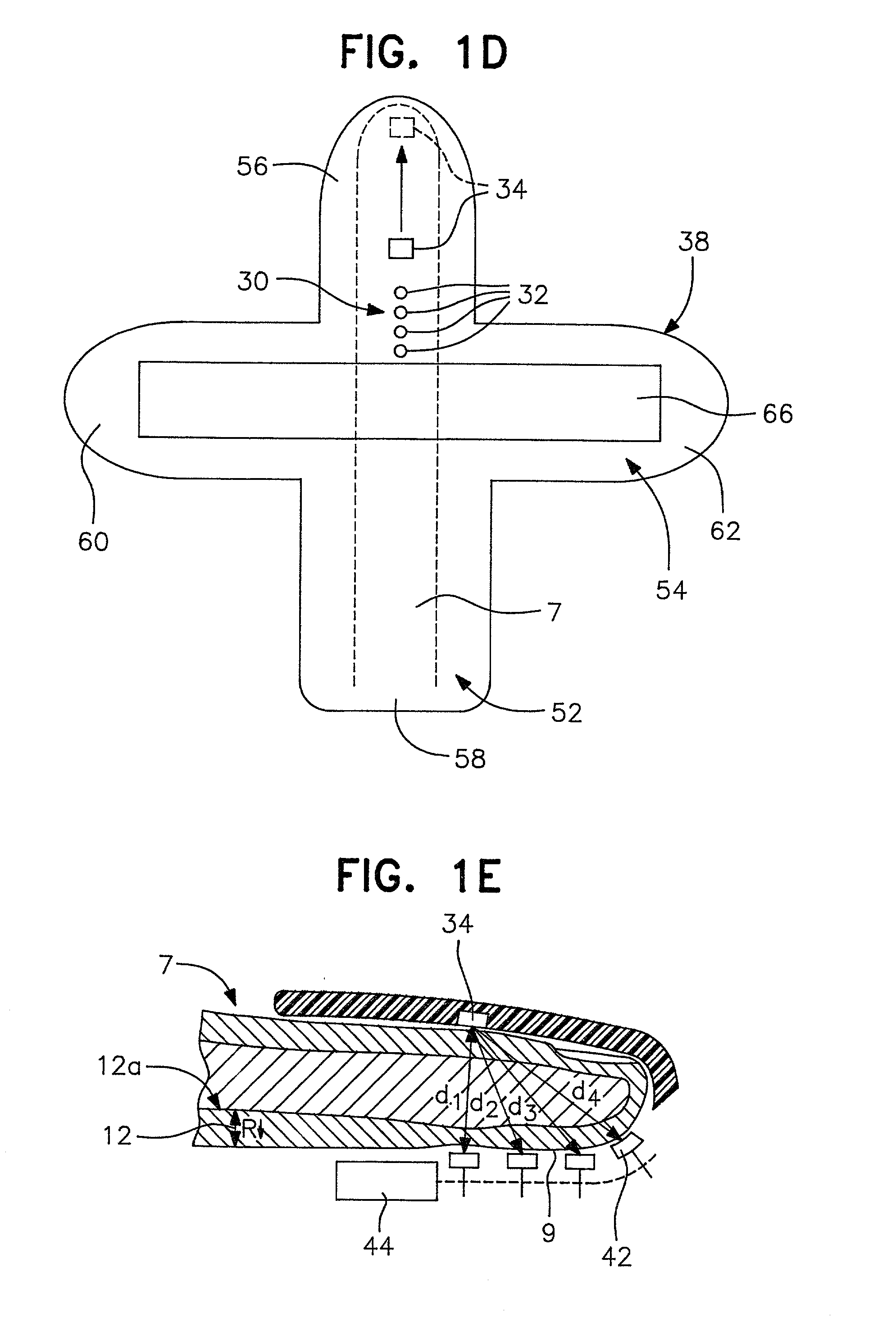
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS6181958B1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveHemoglobin G Szuhu
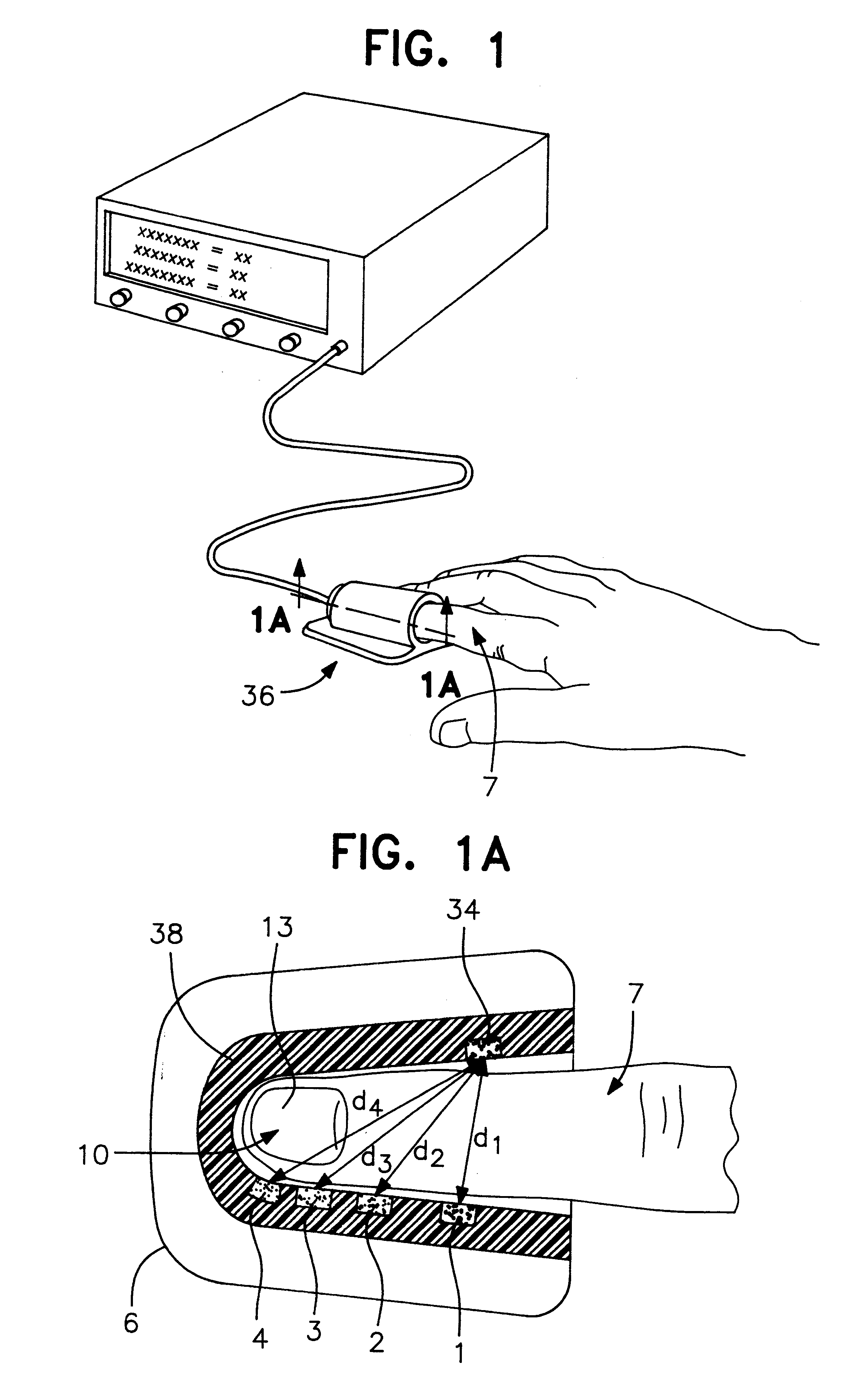
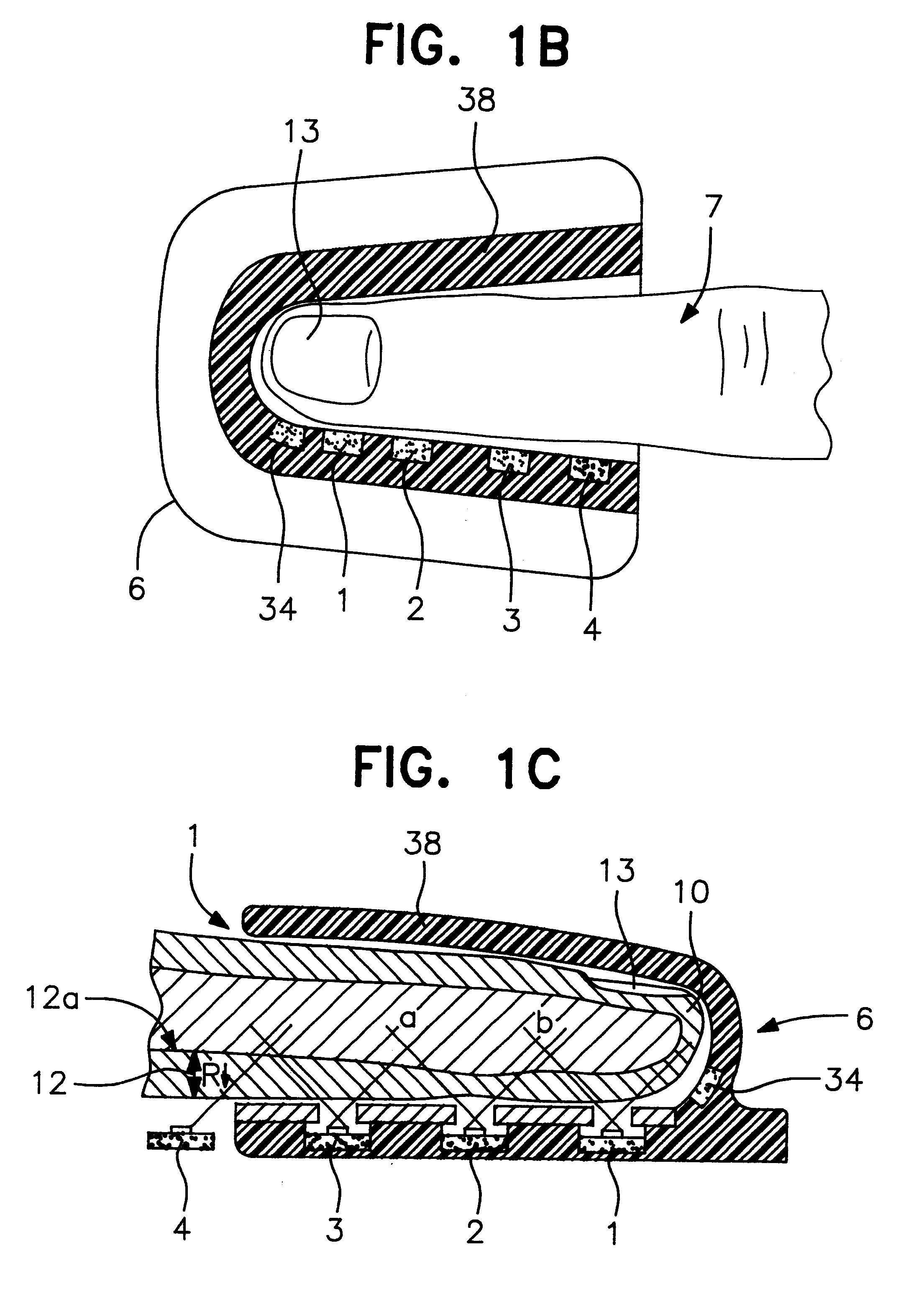
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
Reagentless analysis of biological samples by applying mathematical algorithms to smoothed spectra
InactiveUS7303922B2Improve accuracyImprove automationPhase-affecting property measurementsRaman scatteringCreatinine riseRefractive index
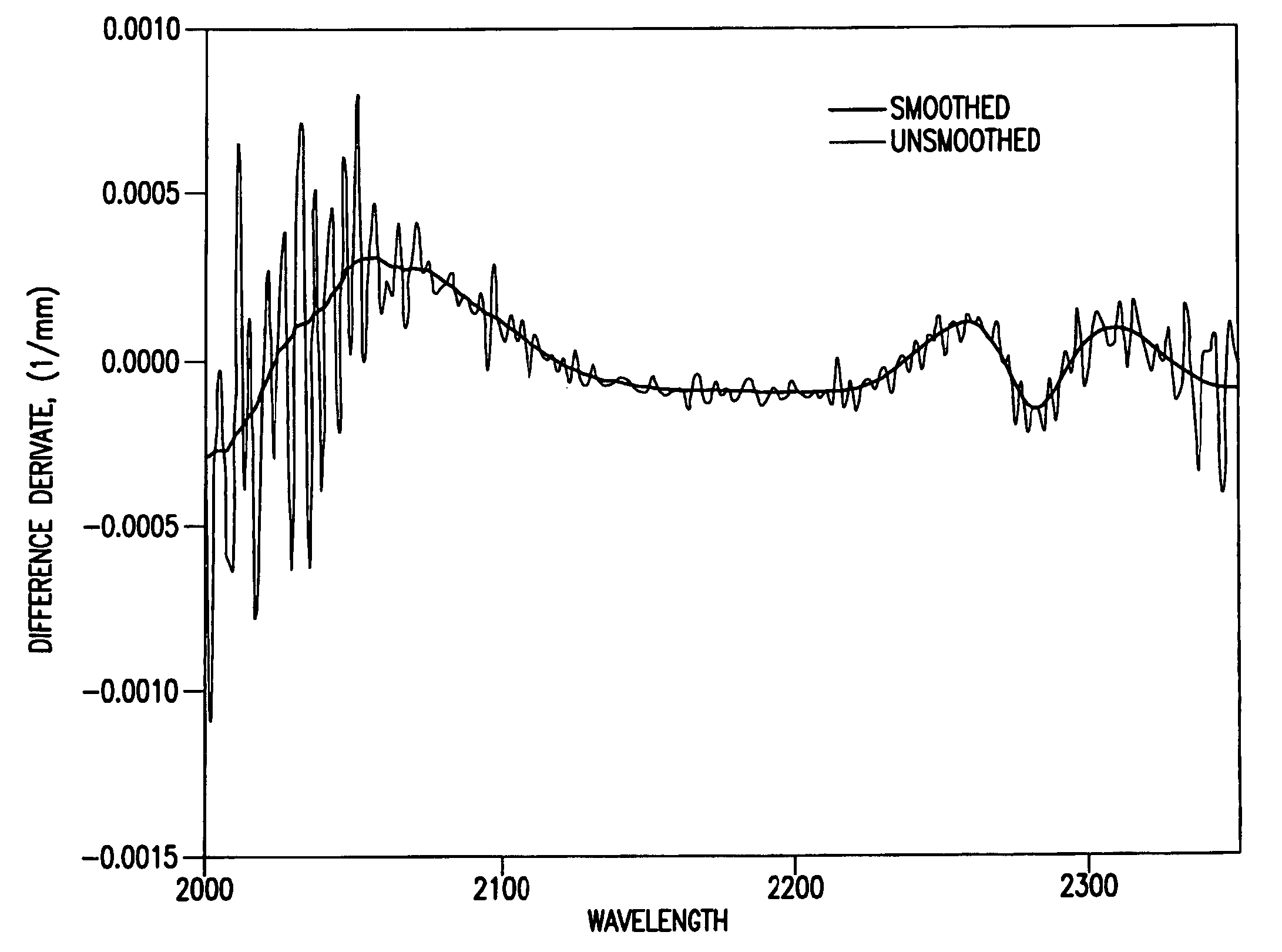
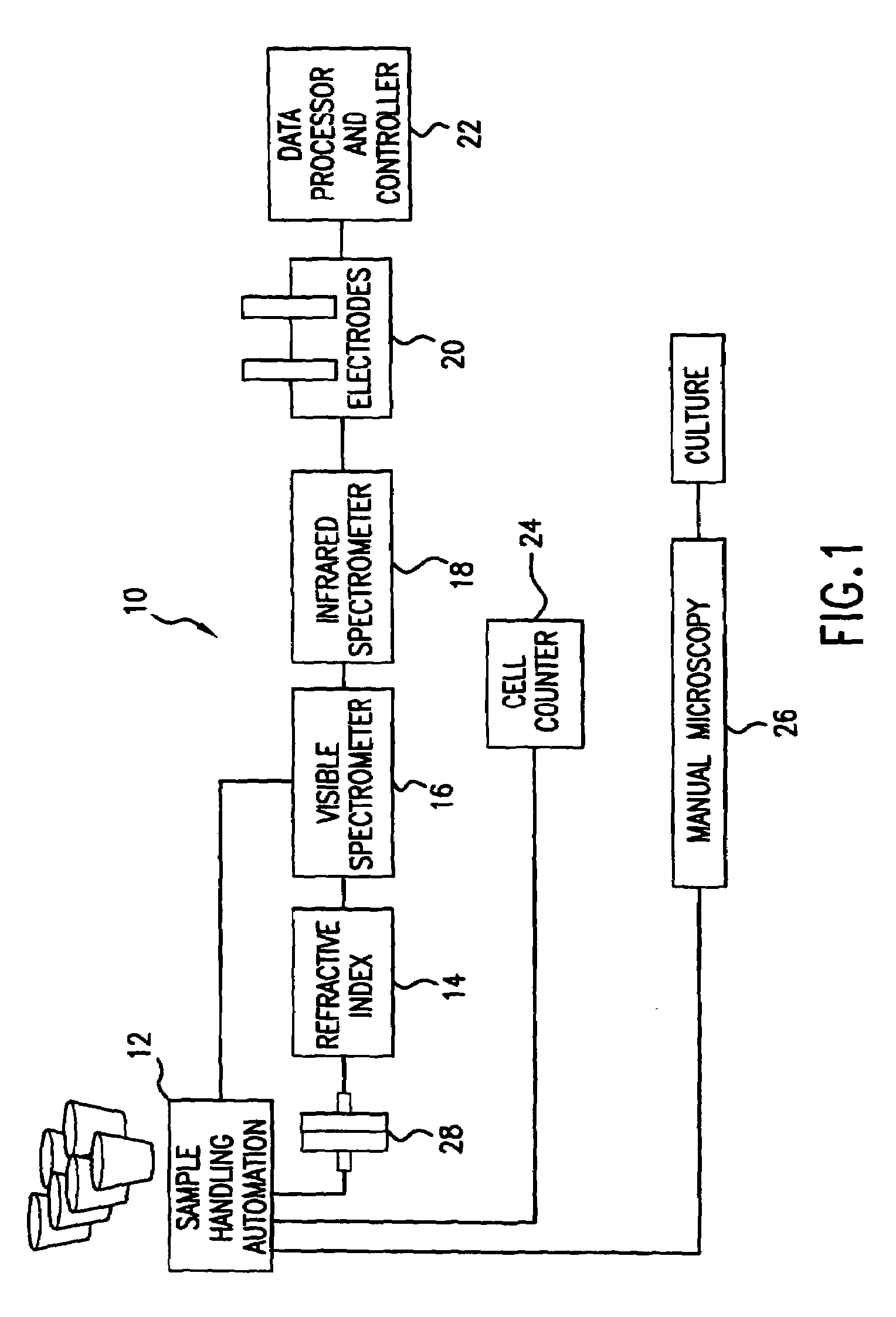
Apparatus and method for determining at least one parameter, e. g., concentration, of at least one analyte, e. g., urea, of a biological sample, e. g., urine. A biological sample particularly suitable for the apparatus and method of this invention is urine. In general, spectroscopic measurements can be used to quantify the concentrations of one or more analytes in a biological sample. In order to obtain concentration values of certain analytes, such as hemoglobin and bilirubin, visible light absorption spectroscopy can be used. In order to obtain concentration values of other analytes, such as urea, creatinine, glucose, ketones, and protein, infrared light absorption spectroscopy can be used. The apparatus and method of this invention utilize one or more mathematical techniques to improve the accuracy of measurement of parameters of analytes in a biological sample. The invention also provides an apparatus and method for measuring the refractive index of a sample of biological fluid while making spectroscopic measurements substantially simultaneously.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS20010039376A1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveTwo step
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
Apparatus and method for rapid spectrophotometric pre-test screen of specimen for a blood analyzer
InactiveUS6195158B1The process is fast and accurateWithdrawing sample devicesTransmissivity measurementsLipid formationHematology analyzer
A method and apparatus for use in respect of samples which are assessed for quality prior to testing in a clinical analyzer. The method and apparatus identify parameters such as gel level and height of fluid above the gel in blood samples, where appropriate, for the purposes of positioning the specimen for determination of interferents. Such interferents include hemoglobin (Hb), total bilirubin and lipids. These interferents are determined by measurement of absorption of different wavelengths of light in serum or plasma, or other specimens, which are then compared with values obtained through calibration using reference measurements for the respective interferents in serum or plasma or other type of specimen. Determinations of temperature of the specimen, as well as specimen type, for example whether the specimen is urine or plasma or serum, may also be carried out.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
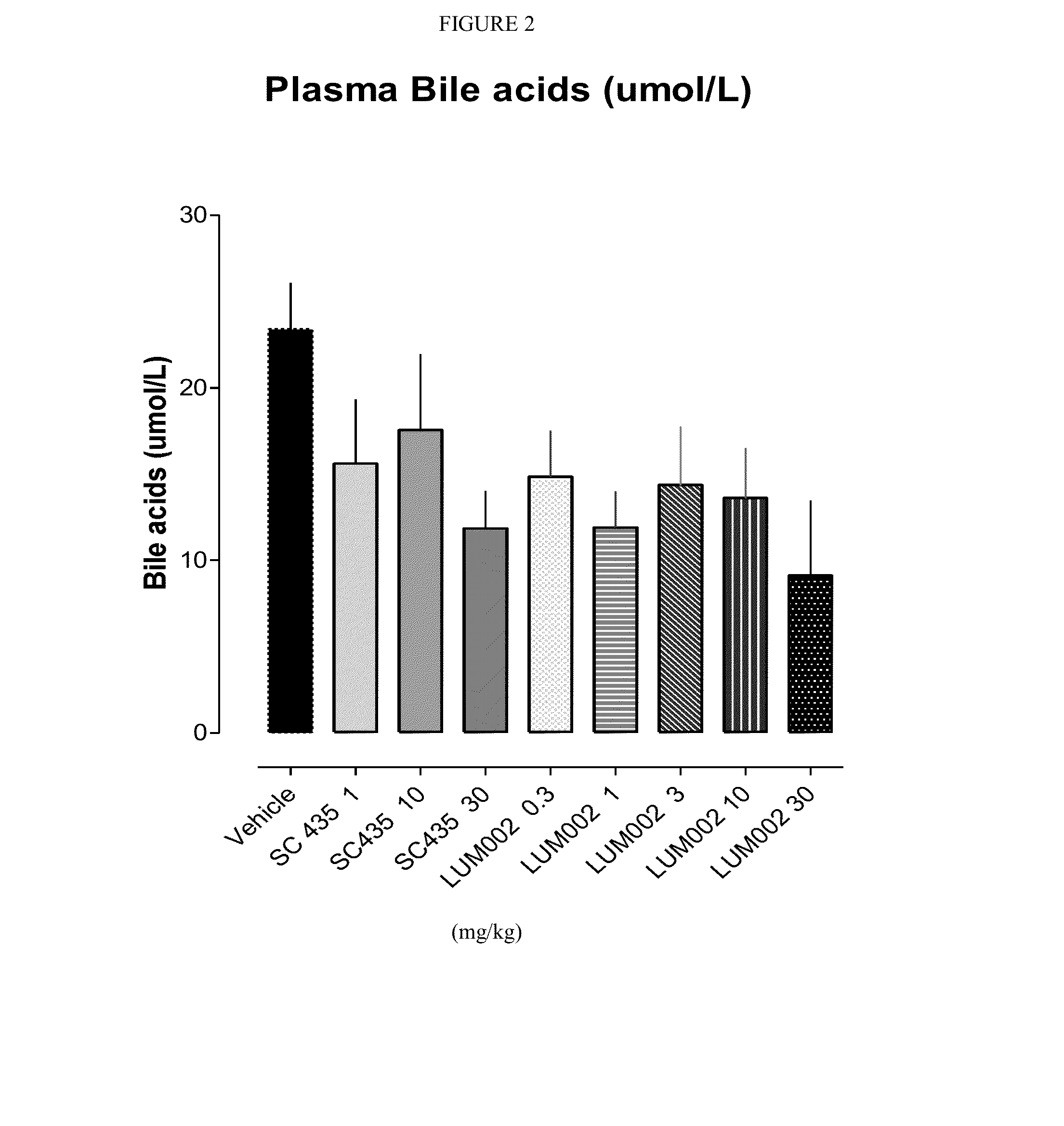
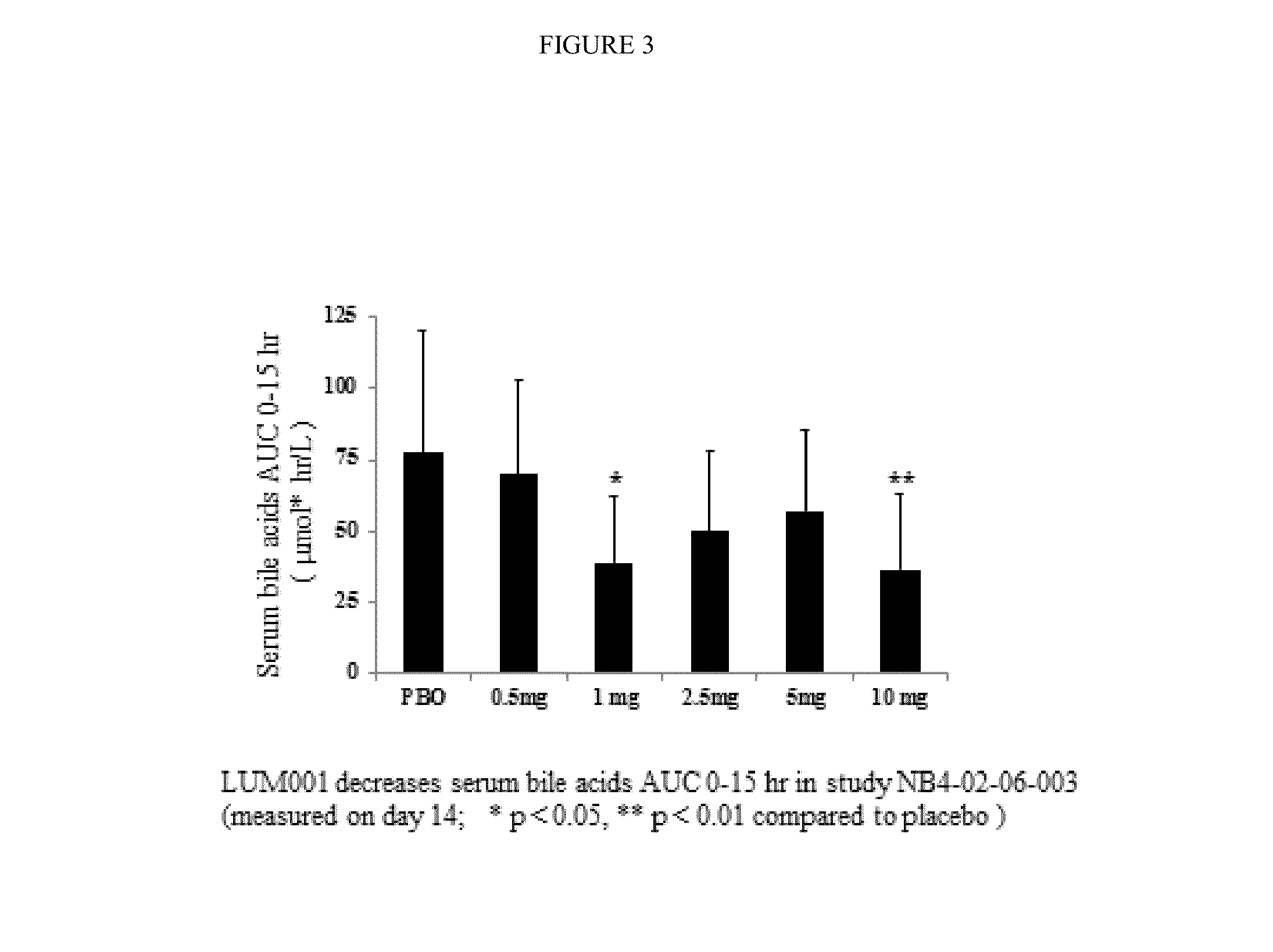
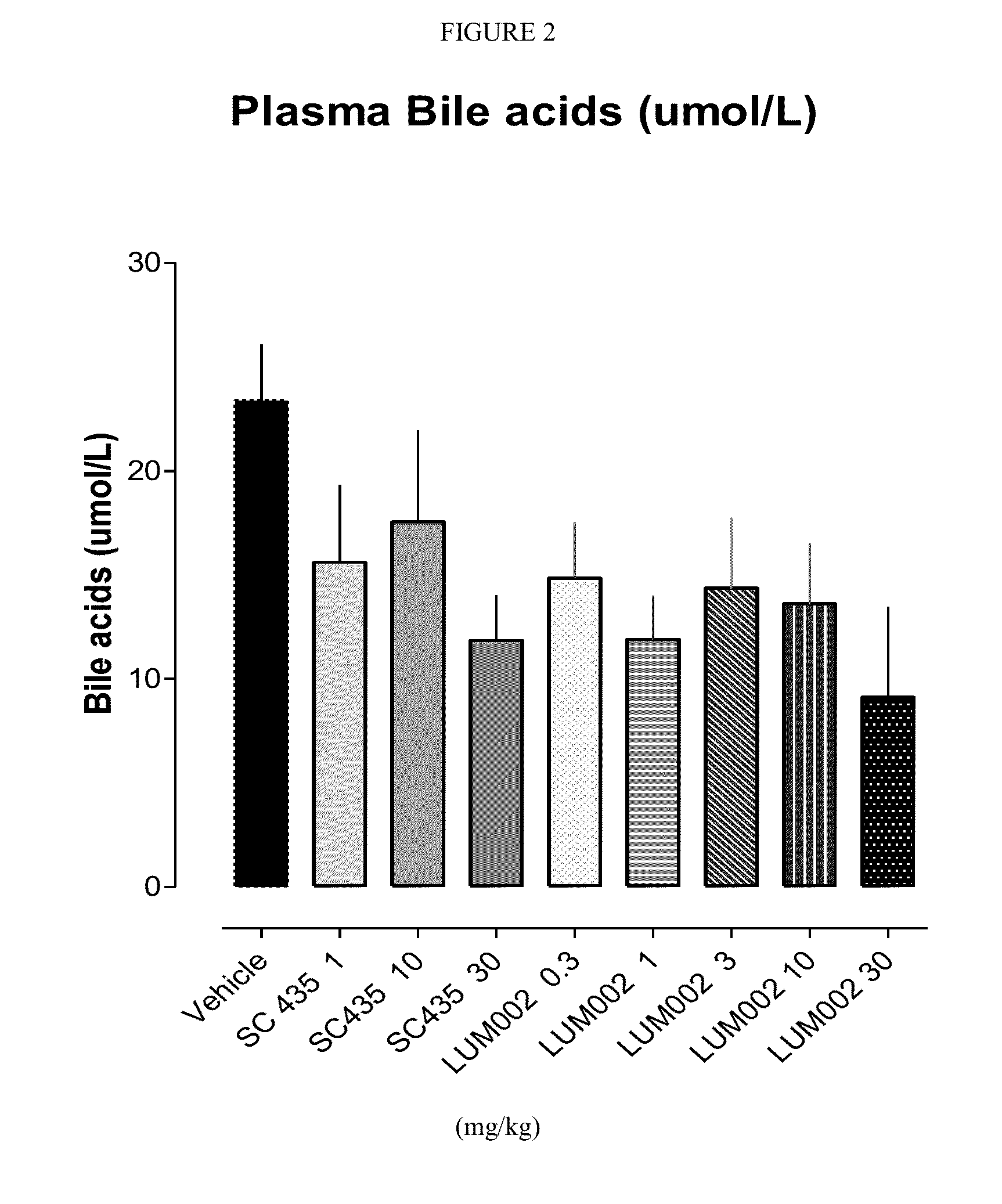
Bile Acid Recycling Inhibitors for Treatment of Hypercholemia and Cholestatic Liver Disease
InactiveUS20130108573A1Relieve symptomsReduce recurrenceBiocideCyclic peptide ingredientsDiseaseHepatic bile
Provided herein are methods of treating or ameliorating hypercholemia or a cholestatic liver disease by administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of an Apical Sodium-dependent Bile Acid Transporter Inhibitor (ASBTI) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Also provided are methods for treating or ameliorating a liver disease, decreasing the levels of serum bile acids or hepatic bile acids, treating or ameliorating pruritis, reducing liver enzymes, or reducing bilirubin comprising administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of ASBTI or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:LUMENA PHARMA INC
Intra-serum and intra-gel for modeling human skin tissue
InactiveUS6475800B1Diagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsConfocalCrosslinking reagent
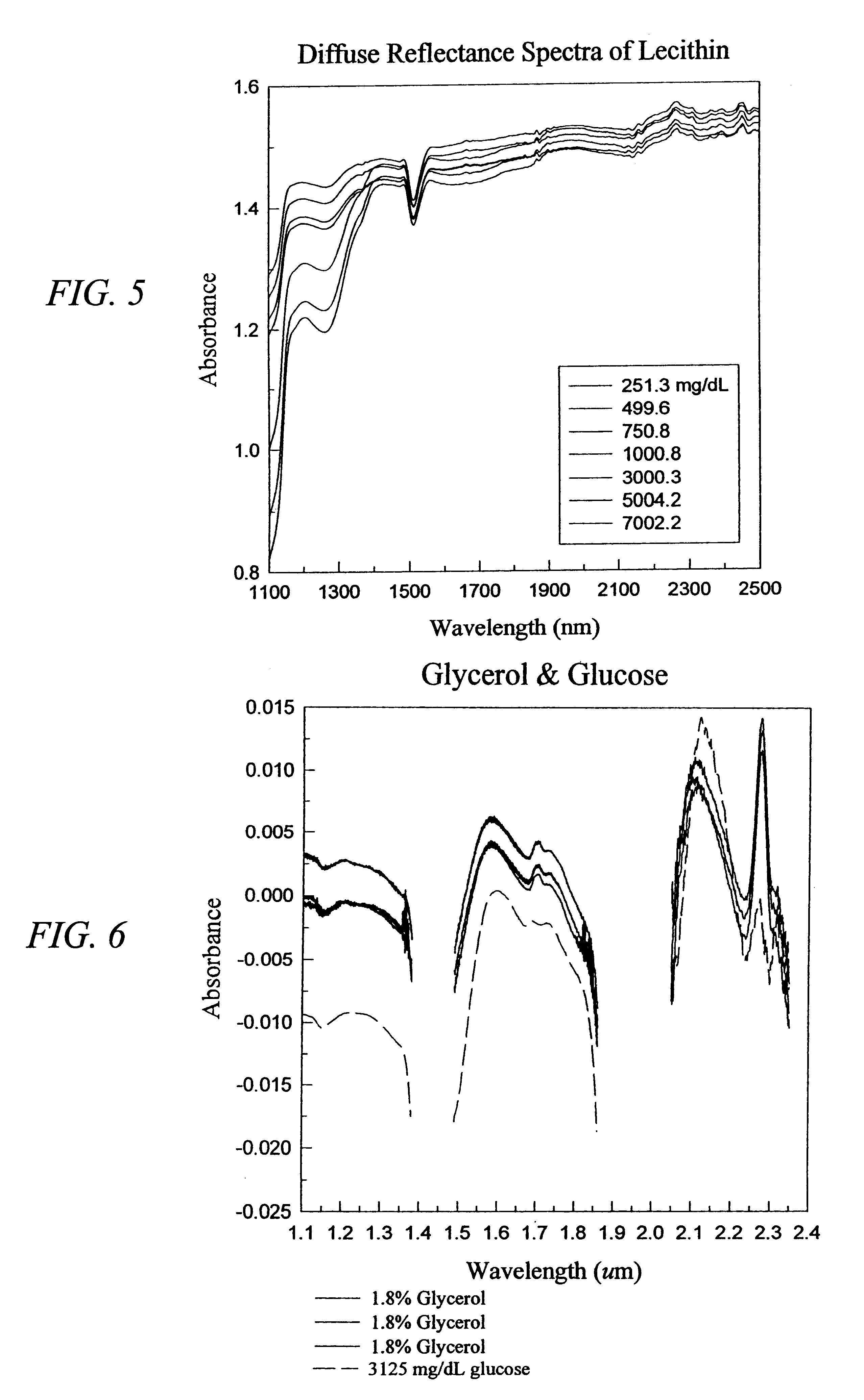
The invention provides a class of samples that model the human body. This family of samples is based upon emulsions of oil in water with lecithin acting as the emulsifier. These solutions that have varying particle sizes may be spiked with basis set components (albumin, urea and glucose) to simulate skin tissues further. The family of samples is such that other organic compounds such as collagen, elastin, globulin and bilirubin may be added, as can salts such as Na+, K+ and Cl-. Layers of varying thickness with known index of refraction and particle size distributions may be generated using simple crosslinking reagents, such as collagen (gelatin). The resulting samples are flexible in each analyte's concentration and match the skin layers of the body in terms of the samples reduced scattering and absorption coefficients, mums and muma. This family of samples is provided for use in the medical field where lasers and spectroscopy based analyzers are used in treatment of the body. In particular, knowledge may be gained on net analyte signal, photon depth of penetration, photon radial diffusion, photon interaction between tissue layers, photon density (all as a function of frequency) and on instrument parameter specifications such as resolution and required dynamic range (A / D bits required). In particular, applications to delineate such parameters have been developed for the application of noninvasive glucose determination in the near-IR region from 700 to 2500 nm with an emphasis on the region 1000 to 2500 nm (10,000 to 4,000 cm-1).
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
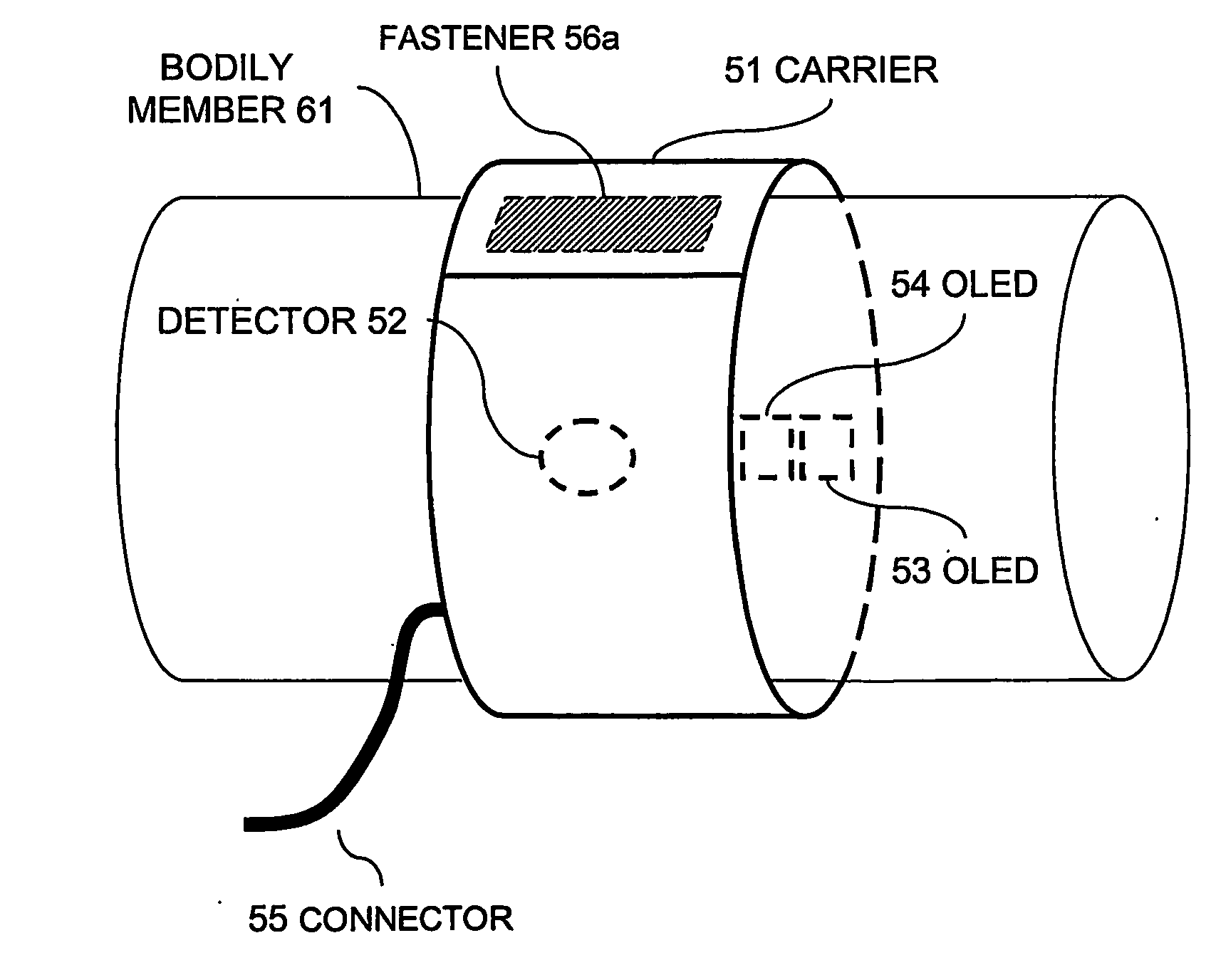
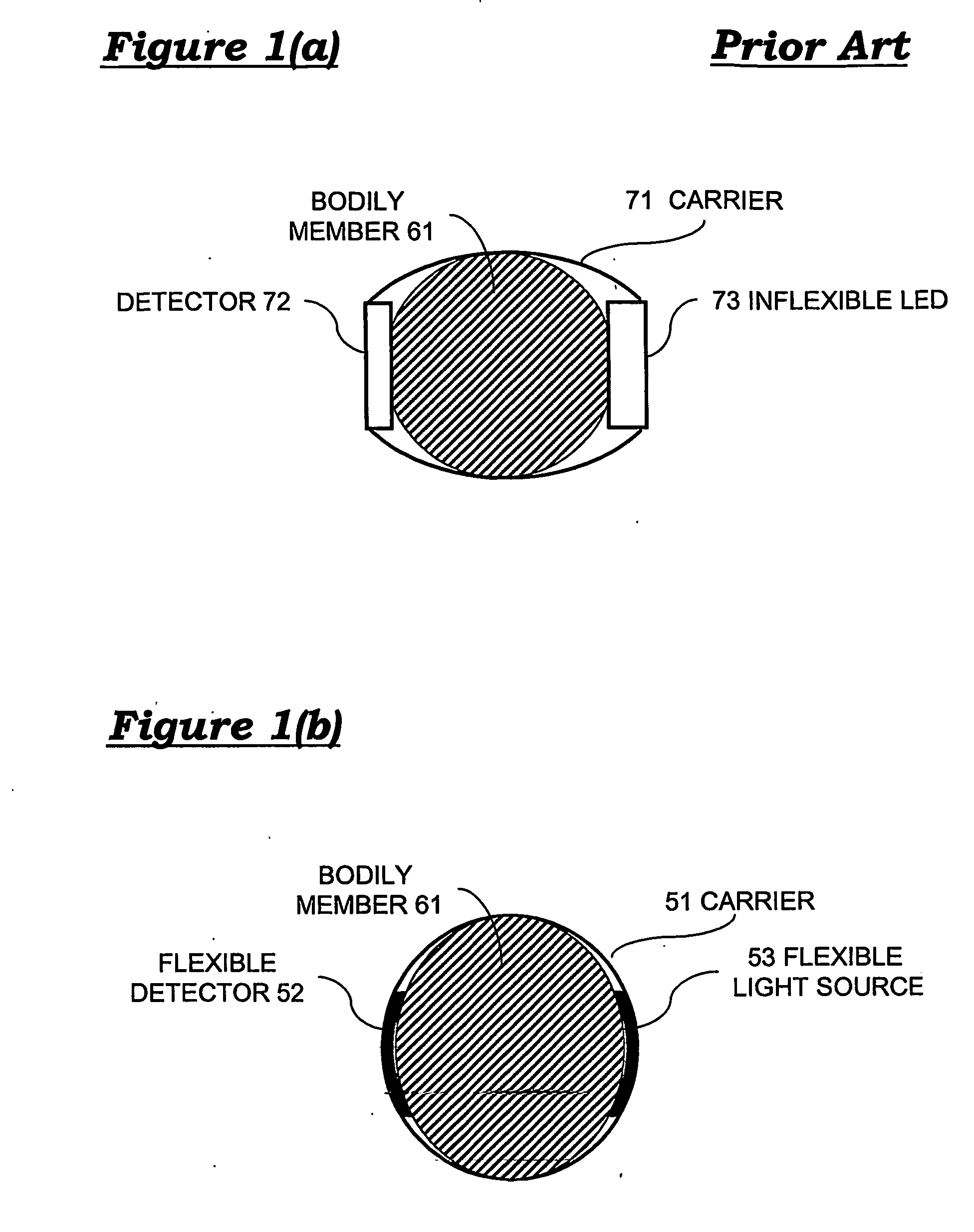
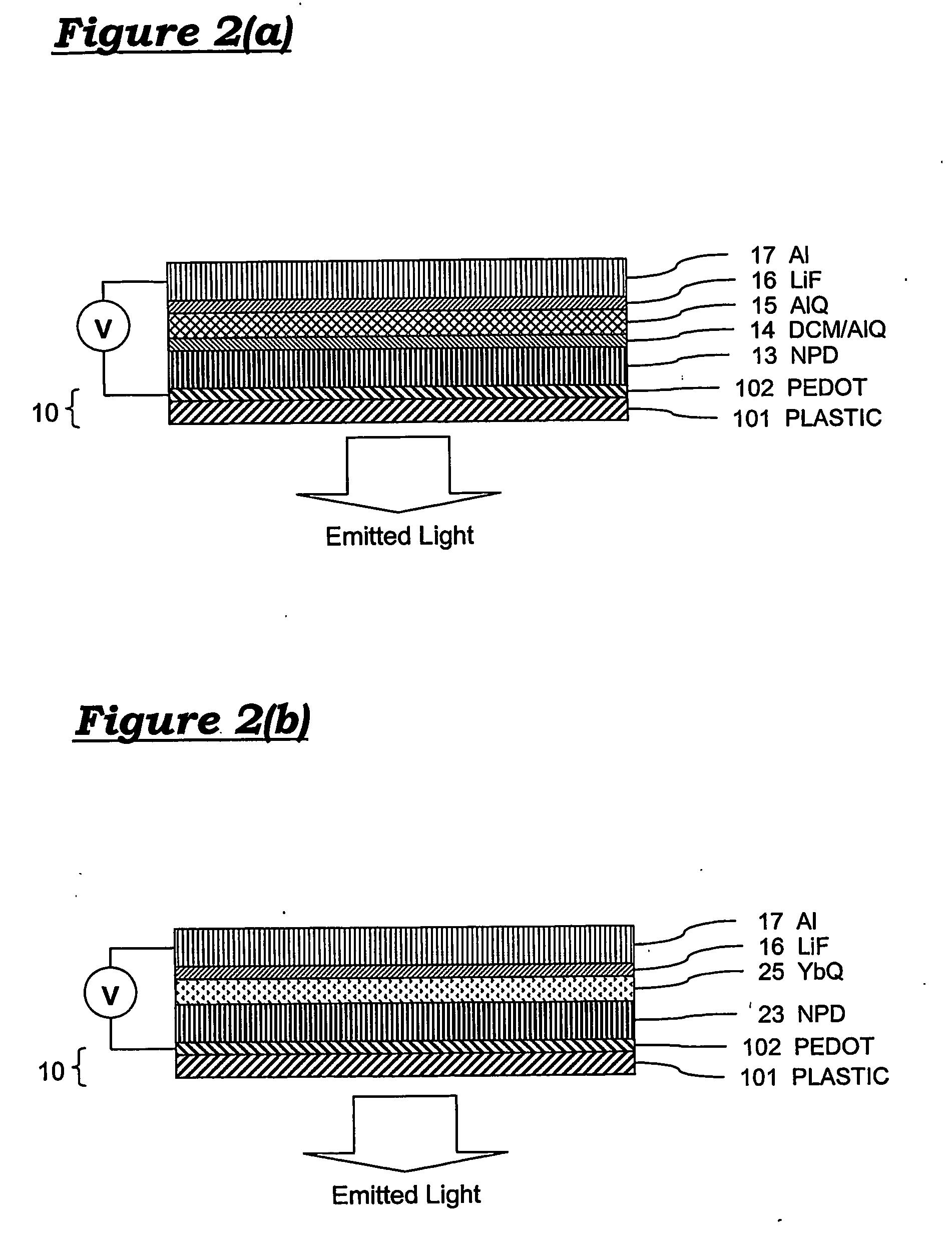
Flexible light sources and detectors and applications thereof
Flexible and conformal medical light sources and related diagnostic devices directed to monitoring blood characteristics (e.g. levels of CO, oxygen, or bilirubin) and photo-therapeutic devices for treatment of ailments such as psoriasis and some forms of cancer. The flexible light source preferably comprises one or more organic light emitting diodes on a flexible substrate. Light sources may also be used for purposes of treatment. The substrate can also form a integral strap for attachment of the device over or around the patient's body. Optionally, the device comprises a photo-detector arranged to detect and monitor emissions from the sources. Flexible and conformal medical light detectors and devices are also provided.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Cardiac Biosensor Devices and Methods
Implantable medical devices for cardiac care are provided that include a housing having a power source and control electronics; at least one lead extending from the housing and having one or more discrete reservoirs therein, each reservoir having an opening to an outer surface of the lead; one or more sensors, which monitor or detects an analyte, biomarker, or physical parameter that is associated with cardiac health, located in the reservoirs and in operable communication with said control electronics; and at least one selectively disintegratable reservoir cap sealing each of the reservoir openings, wherein the reservoir cap is operably connected to the power source and control electronics to disintegrate the reservoir cap and expose the sensors in vivo. The sensor may detect an analyte or biomarker selected from potassium ion, sodium ion, lithium ion, magnesium ion, ammonium ion, ionized calcium, lactate, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and creatinine, urea, BUN, and bilirubin.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
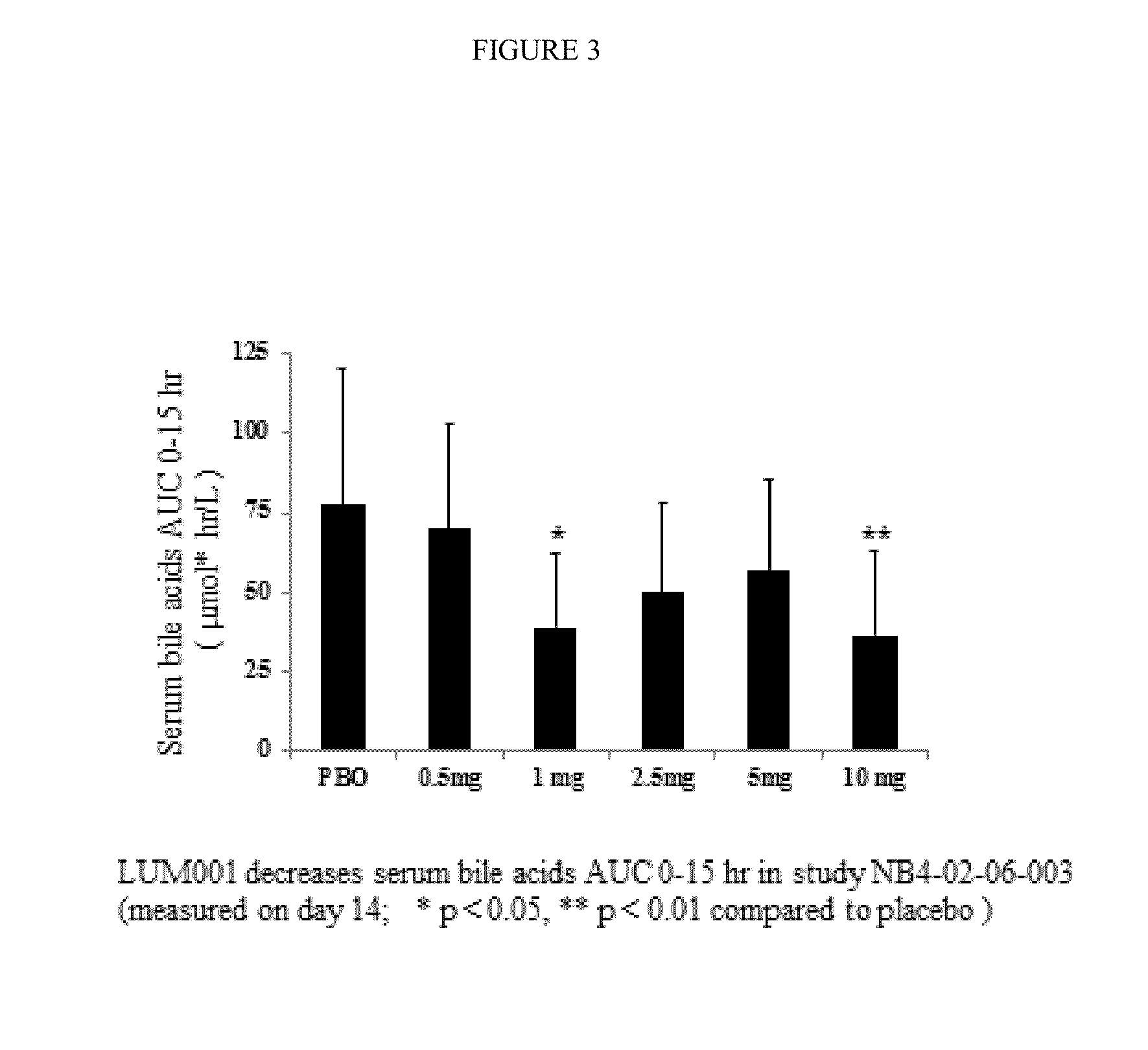
Bile Acid Recycling Inhibitors for Treatment of Pediatric Cholestatic Liver Diseases
InactiveUS20130109671A1Reduces and inhibits recyclingReduce harmBiocidePill deliveryHepatic DiseasesHepatic bile
Provided herein are methods of treating or ameliorating a pediatric cholestatic liver disease by non-systemically administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a pediatric formulation comprising an Apical Sodium-dependent Bile Acid Transporter Inhibitor (ASBTI) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Also provided are methods for treating or ameliorating a pediatric liver disease, decreasing the levels of serum bile acids or hepatic bile acids, treating or ameliorating pruritis, reducing liver enzymes, or reducing bilirubin comprising non-systemically administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a pediatric formulation comprising an ASBTI or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:LUMENA PHARMA INC
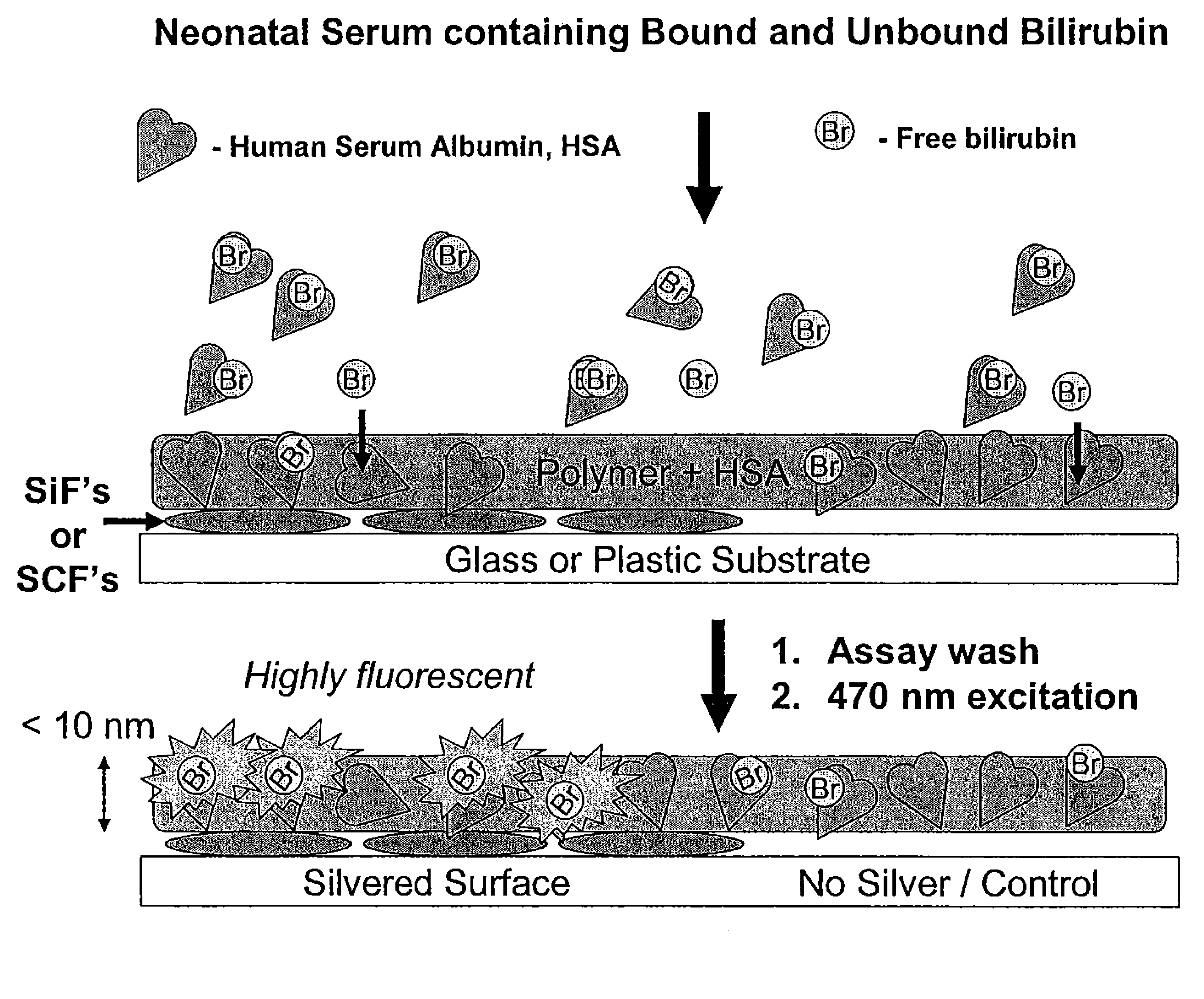
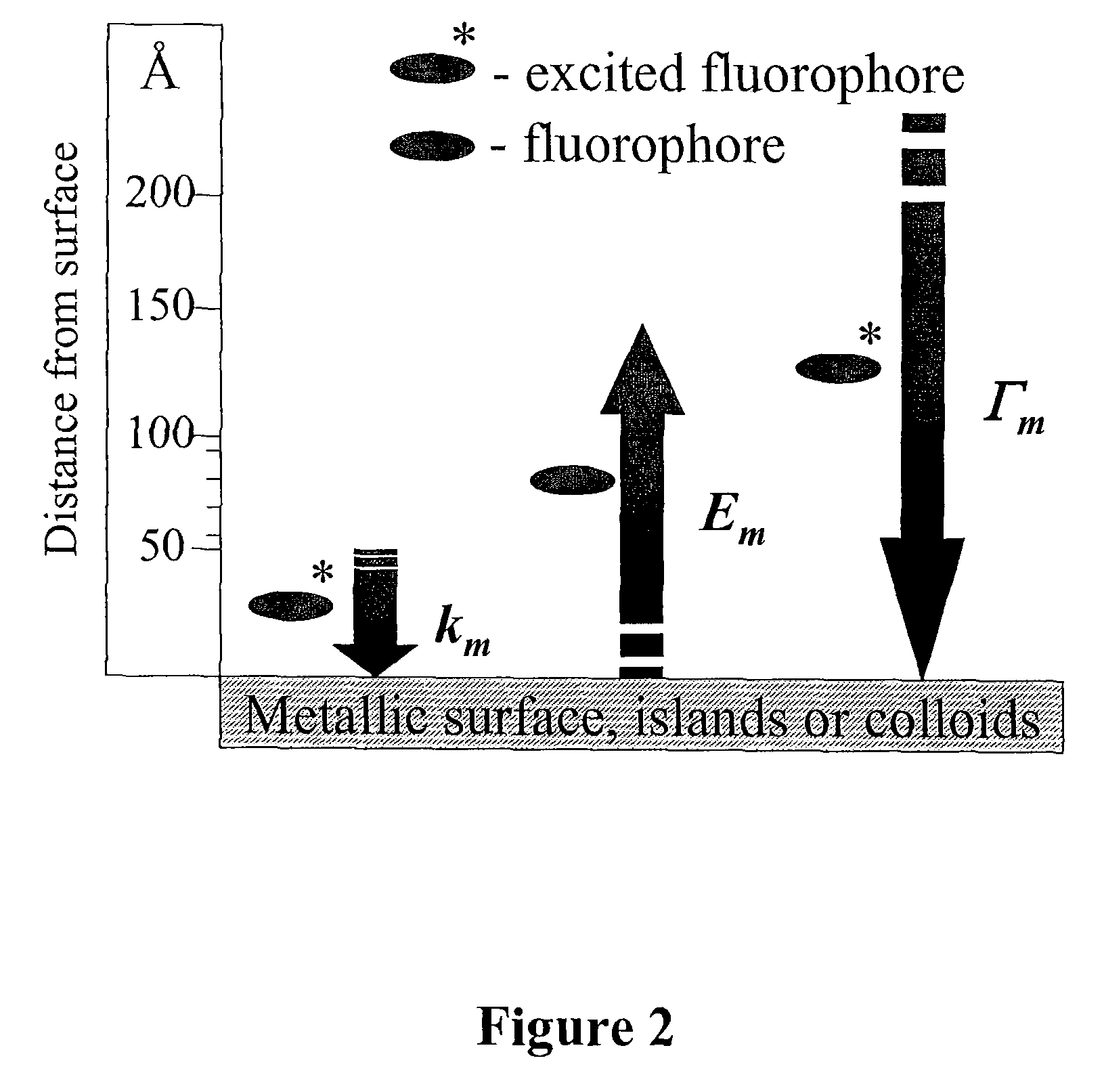
Metal enhanced fluorescence-based sensing methods
InactiveUS7939333B2Fluorescence enhancementAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by electrical excitationFluorescenceNucleotide sequencing
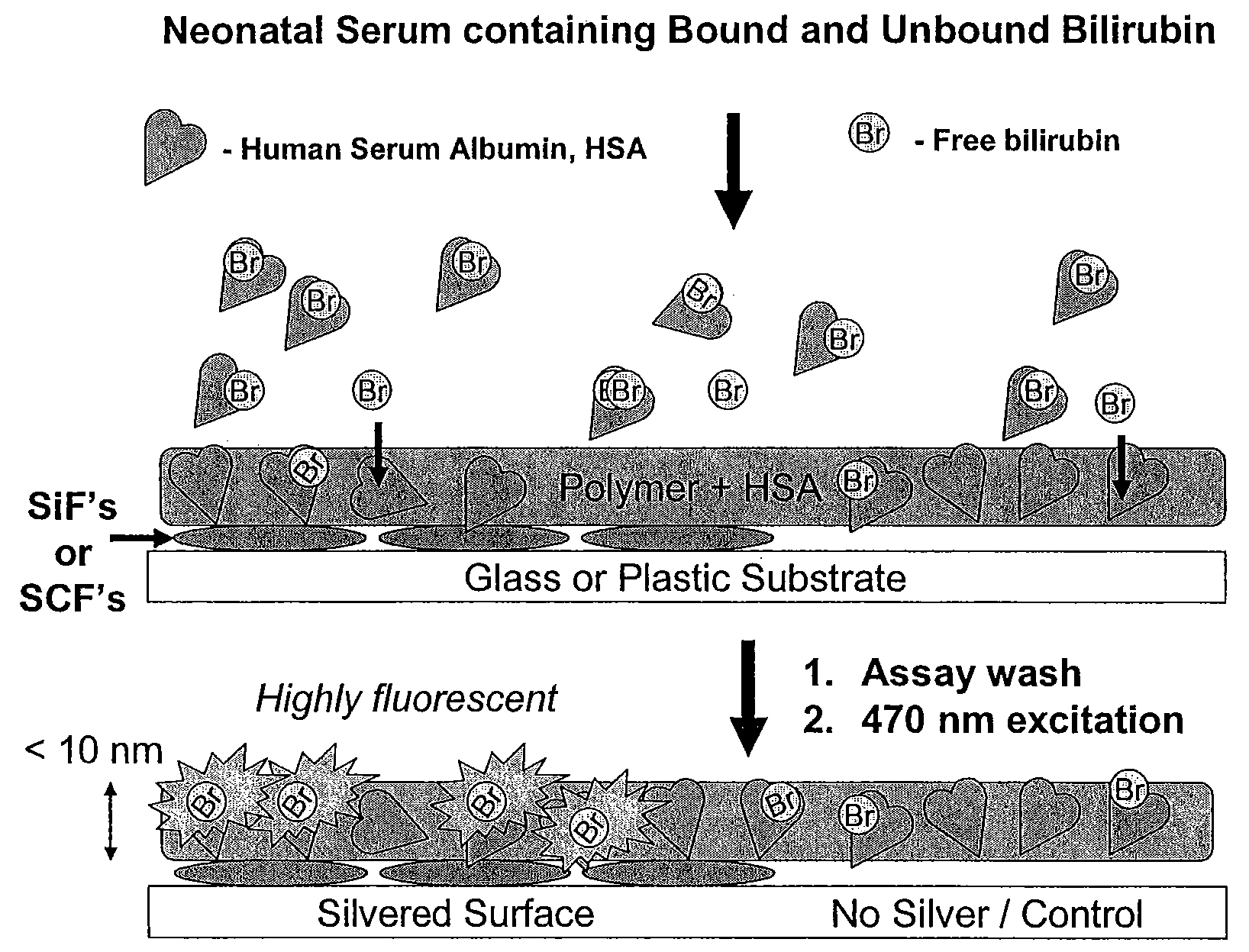
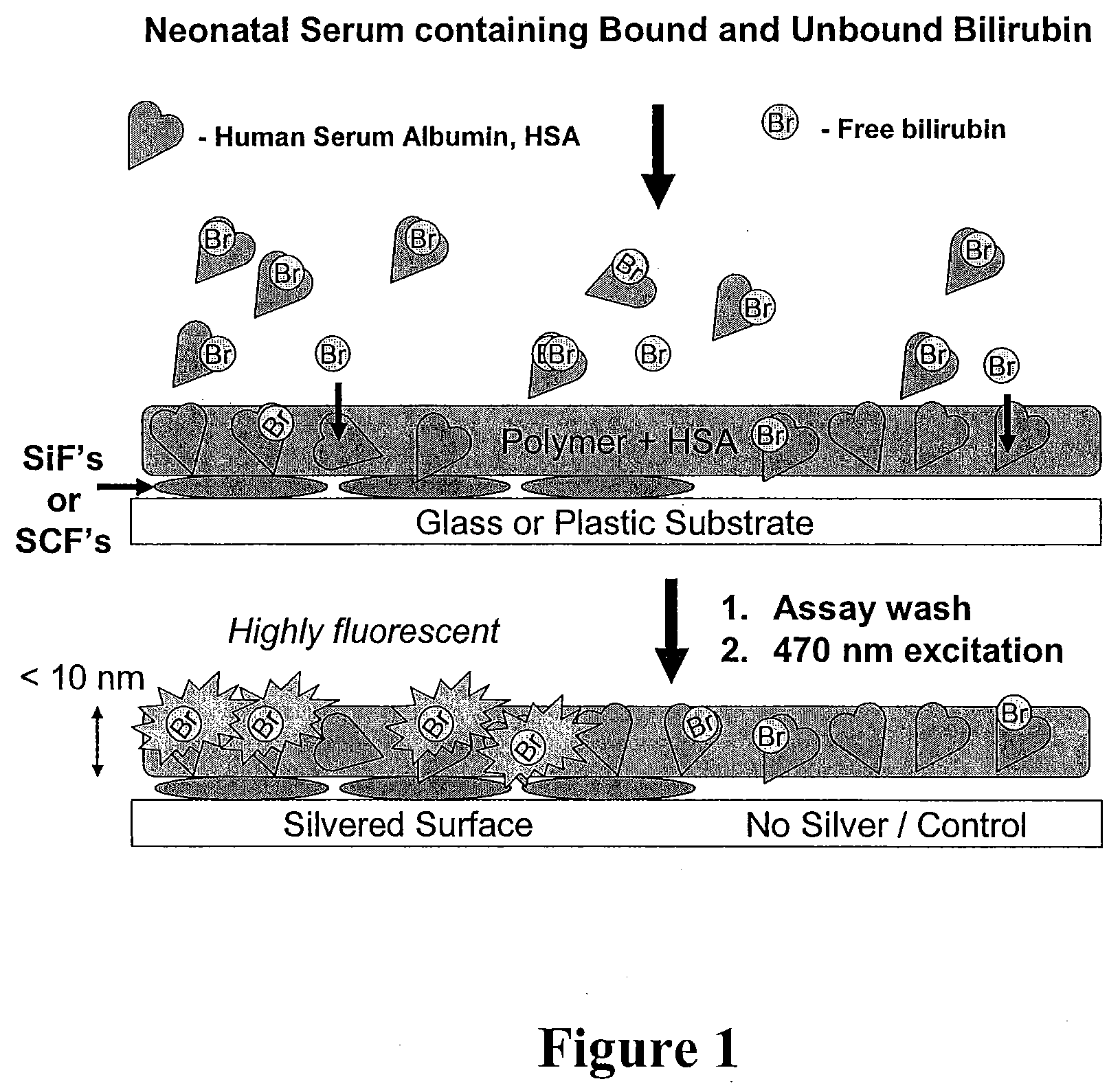
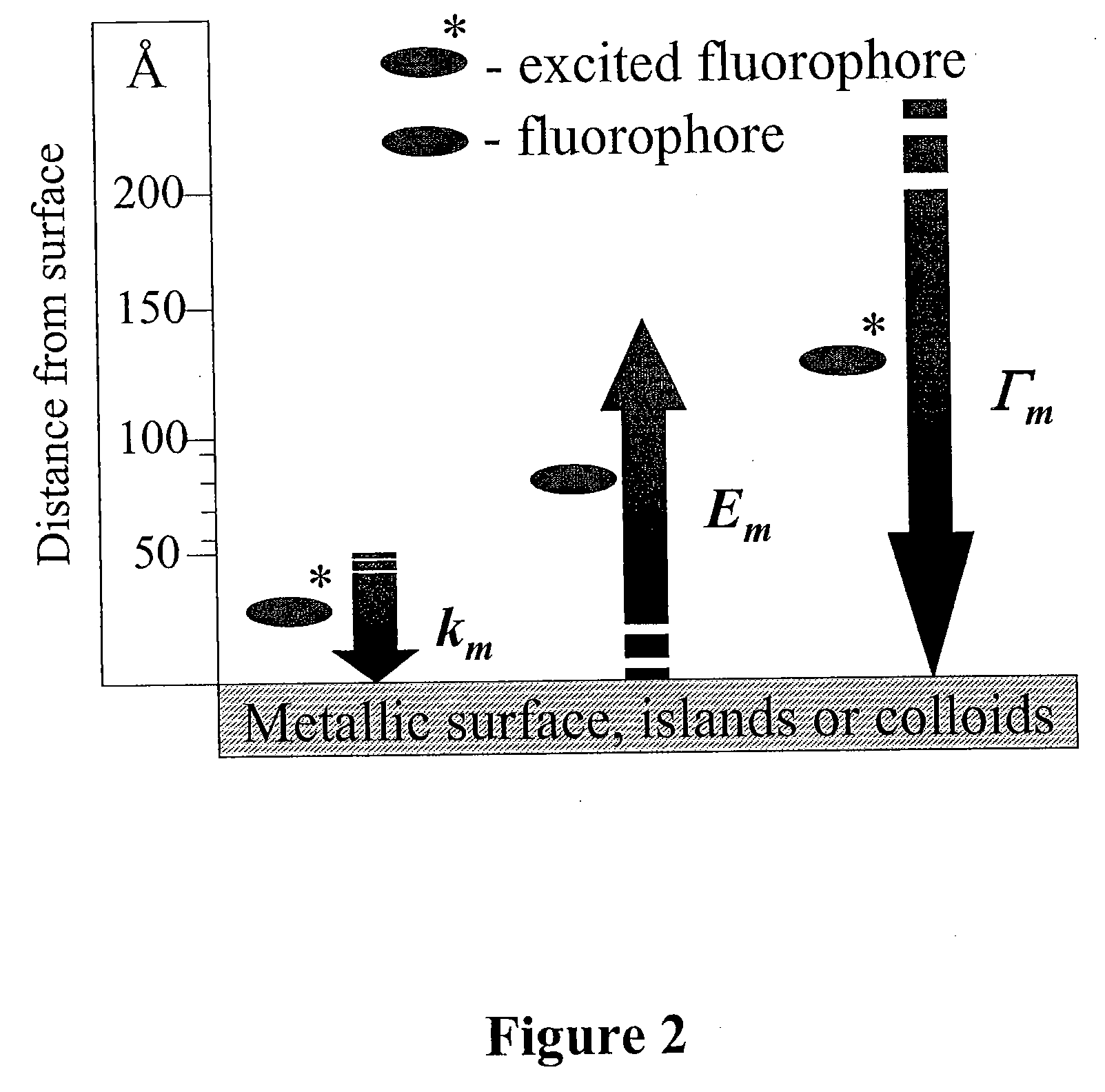
The present invention relates to metallic-surface detection systems for determining target substances including free bilirubin in neonatal serum in the presence of a predominantly high background of bilirubin bound Human Serum Albumin (HSA) or sensing and isolating target nucleotide sequences wherein a fluorescence signal is enhanced by close proximity of the target substances near metallic surfaces.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +1
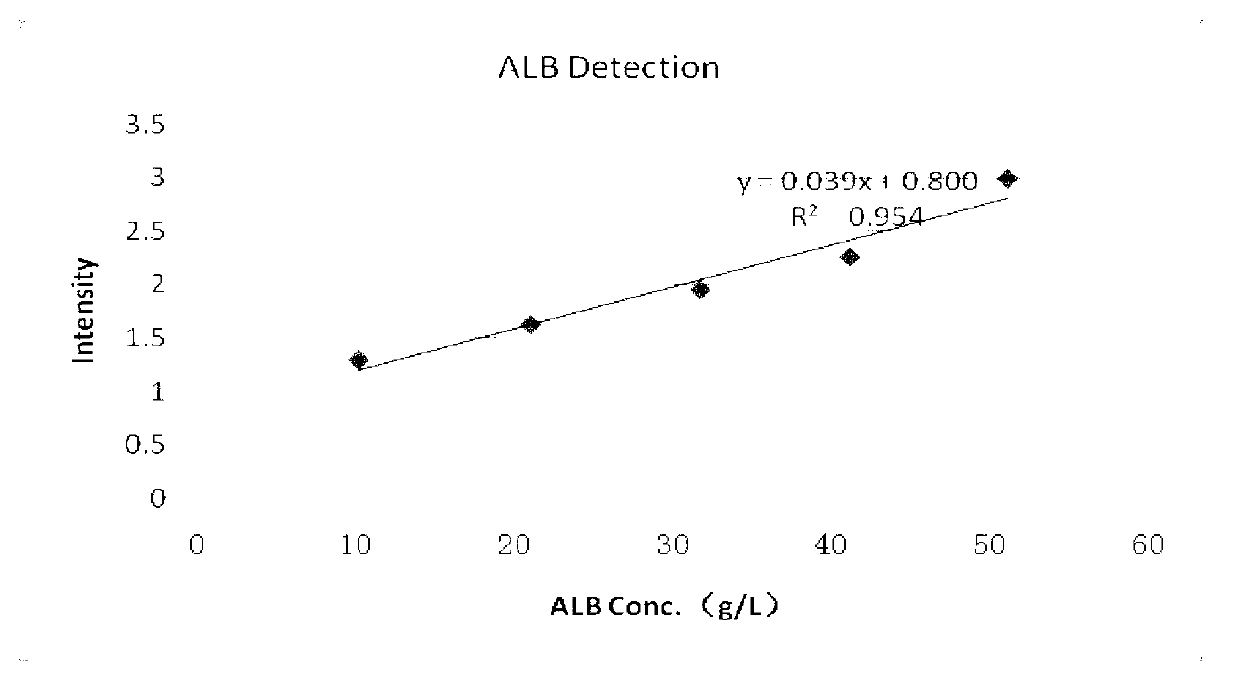
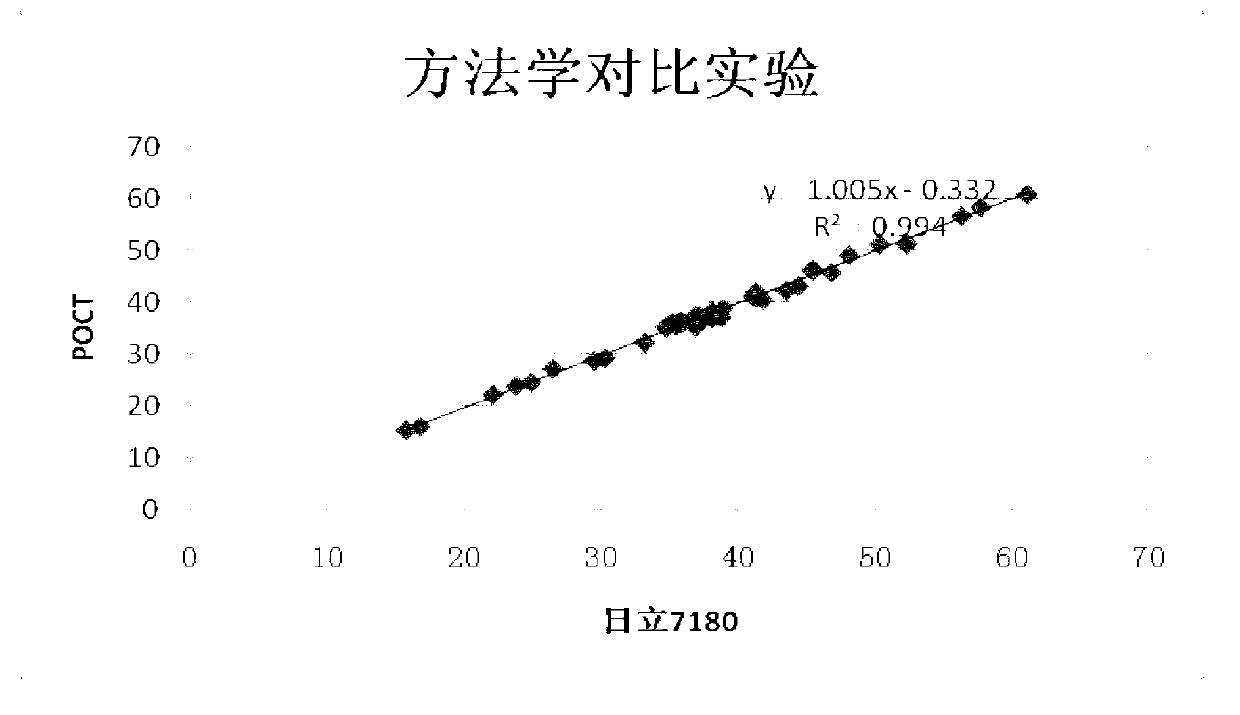
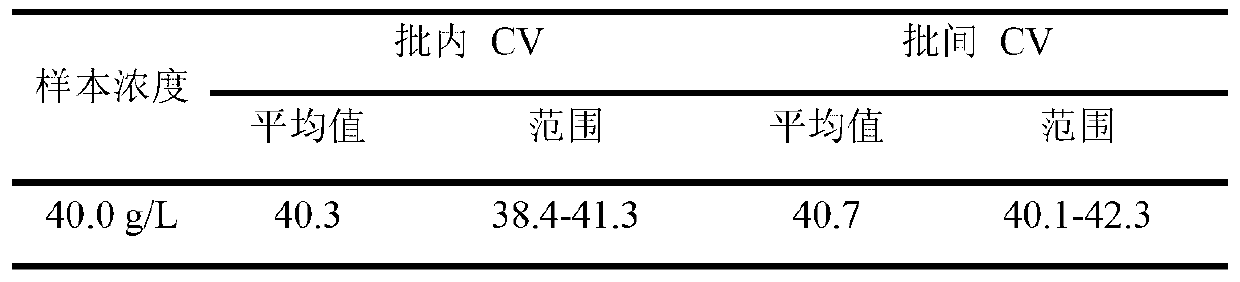
Albumin detection reagent
The invention discloses an albumin detection reagent which comprises a diluent and a reaction reagent, wherein the diluent is composed of trihydroxymethyl amino buffer, surfactant, preservative, anti-bilirubin interference agent and vitamin C oxidase; and the reaction reagent is composed of buffer, surfactant, bromocresol green and freeze-drying protective agent. The detection reagent disclosed by the invention has favorable sensitivity, accuracy, precision and linearity, and can completely satisfy the clinical examination requirements.
Owner:宁波美康盛德医学检验所有限公司
Method for automatically detecting factors that disturb analysis by a photometer
ActiveUS7663738B2Easy to detectCost effectiveBiological material analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansClinical chemistryMedicine
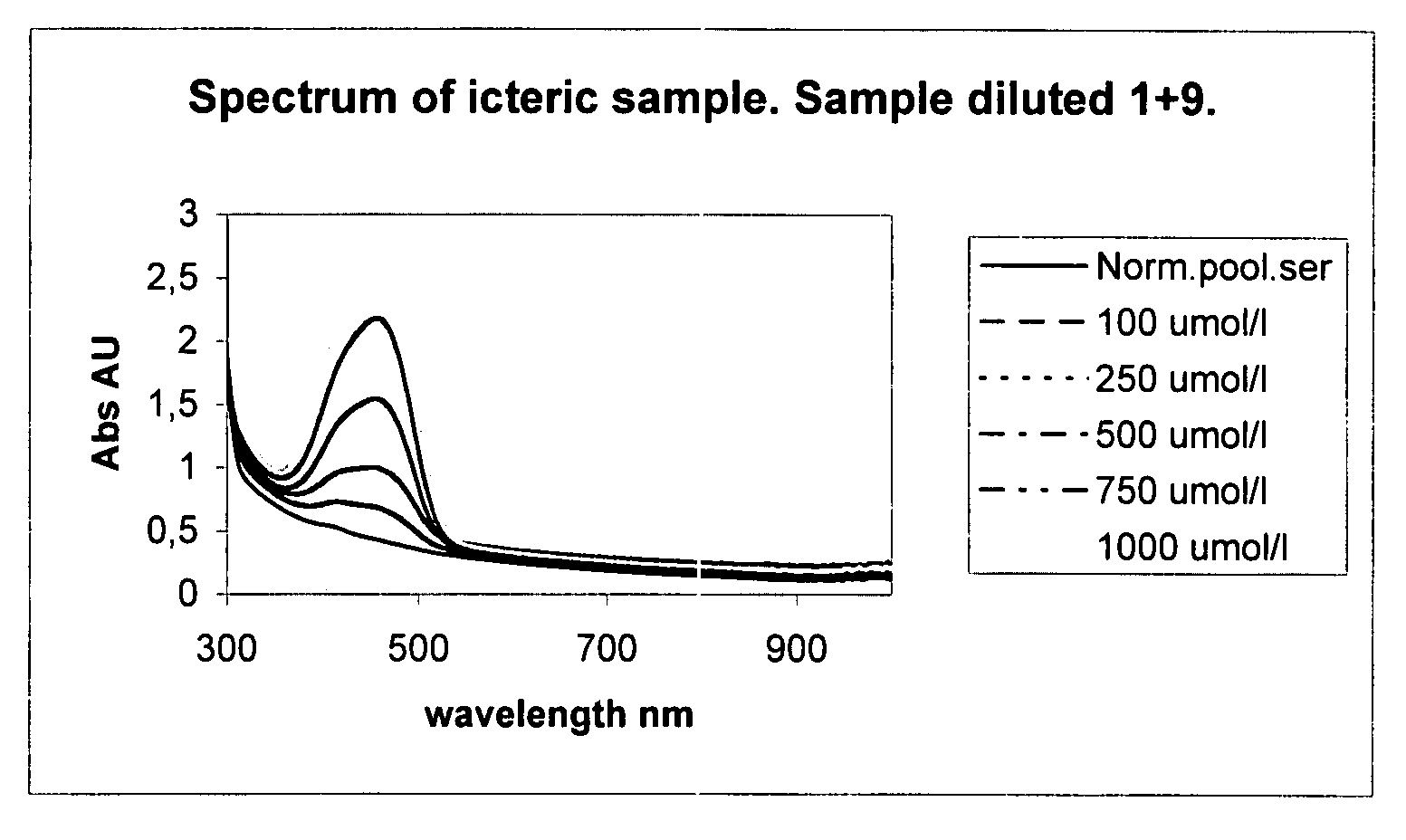
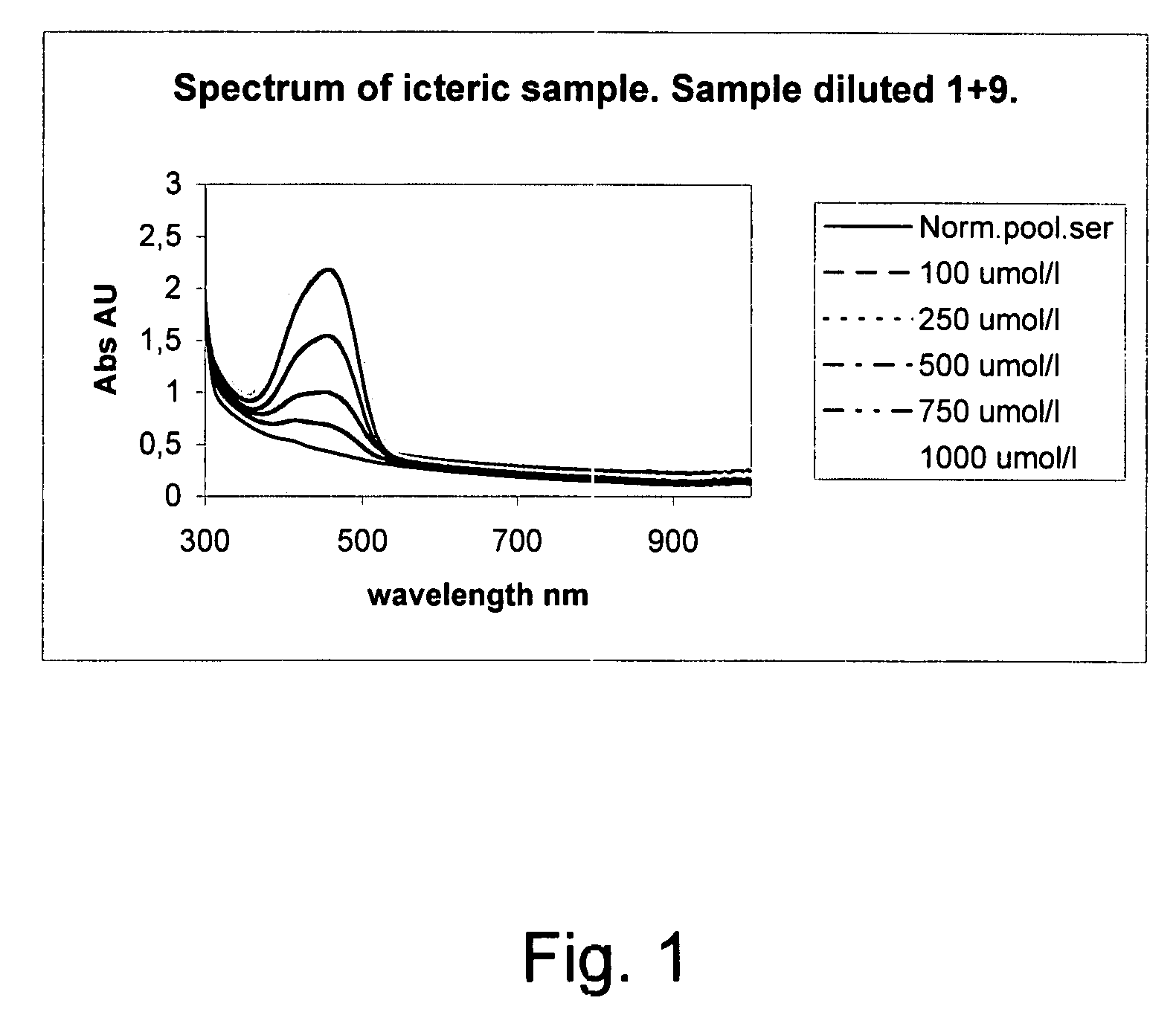
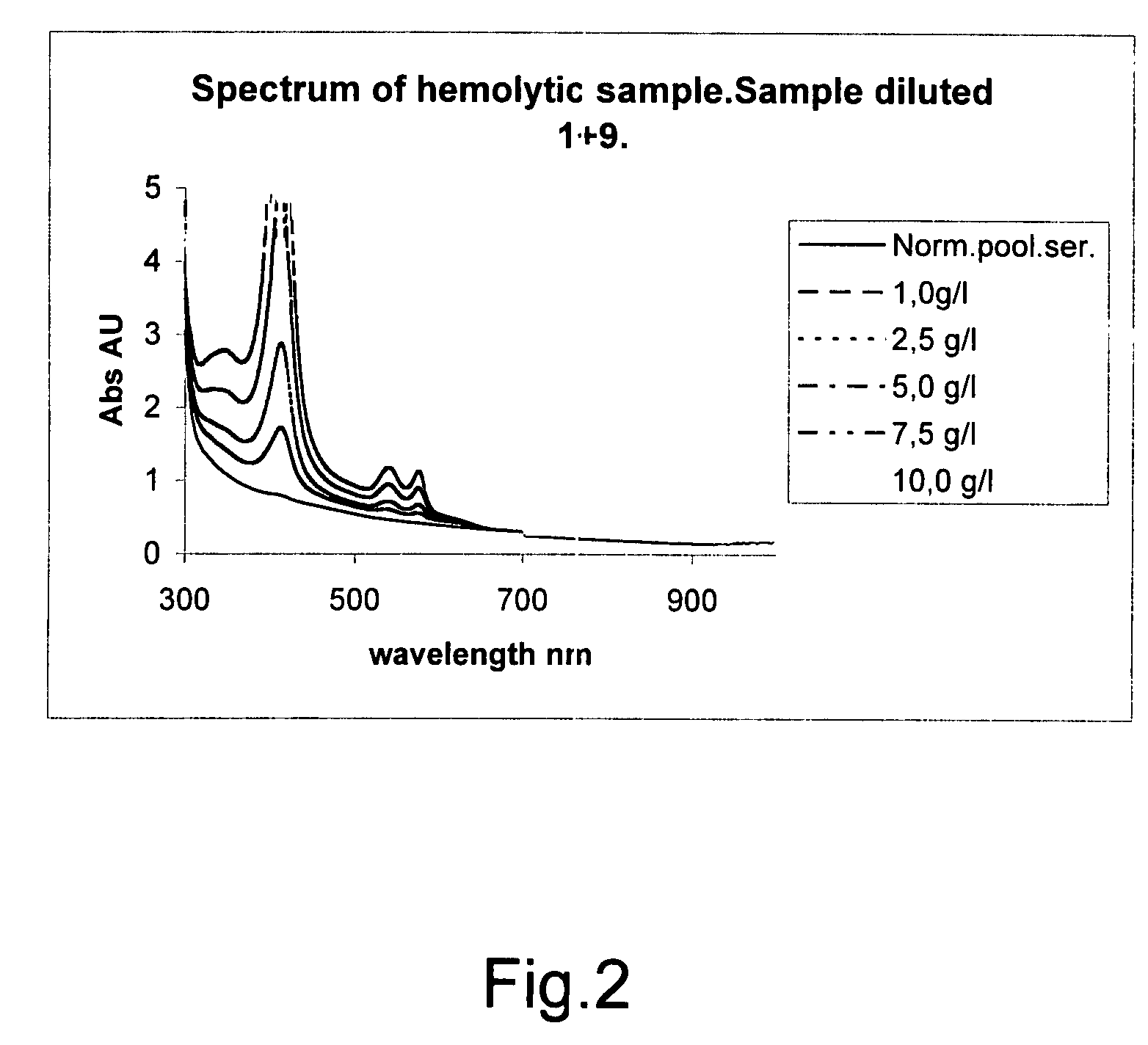
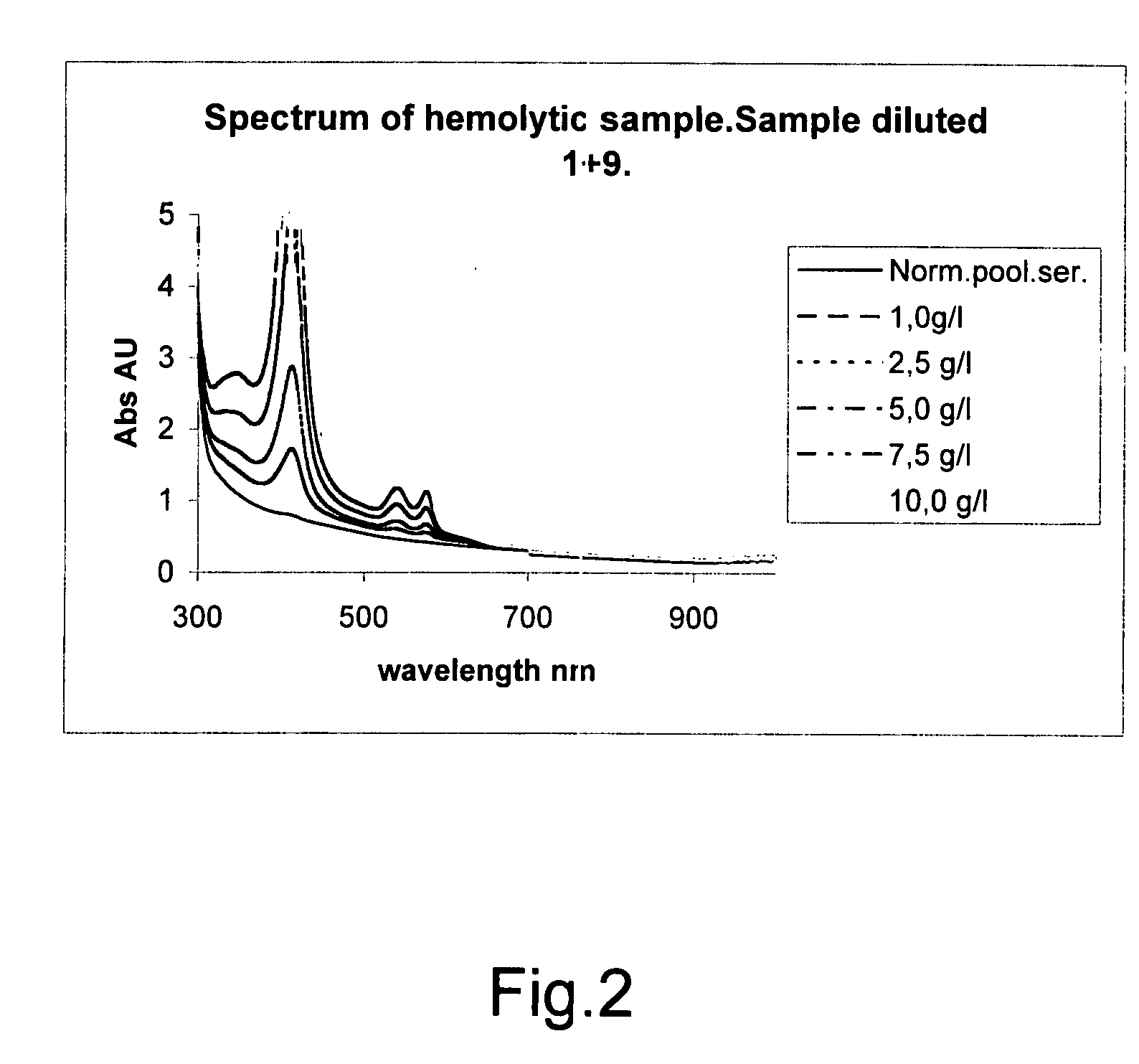
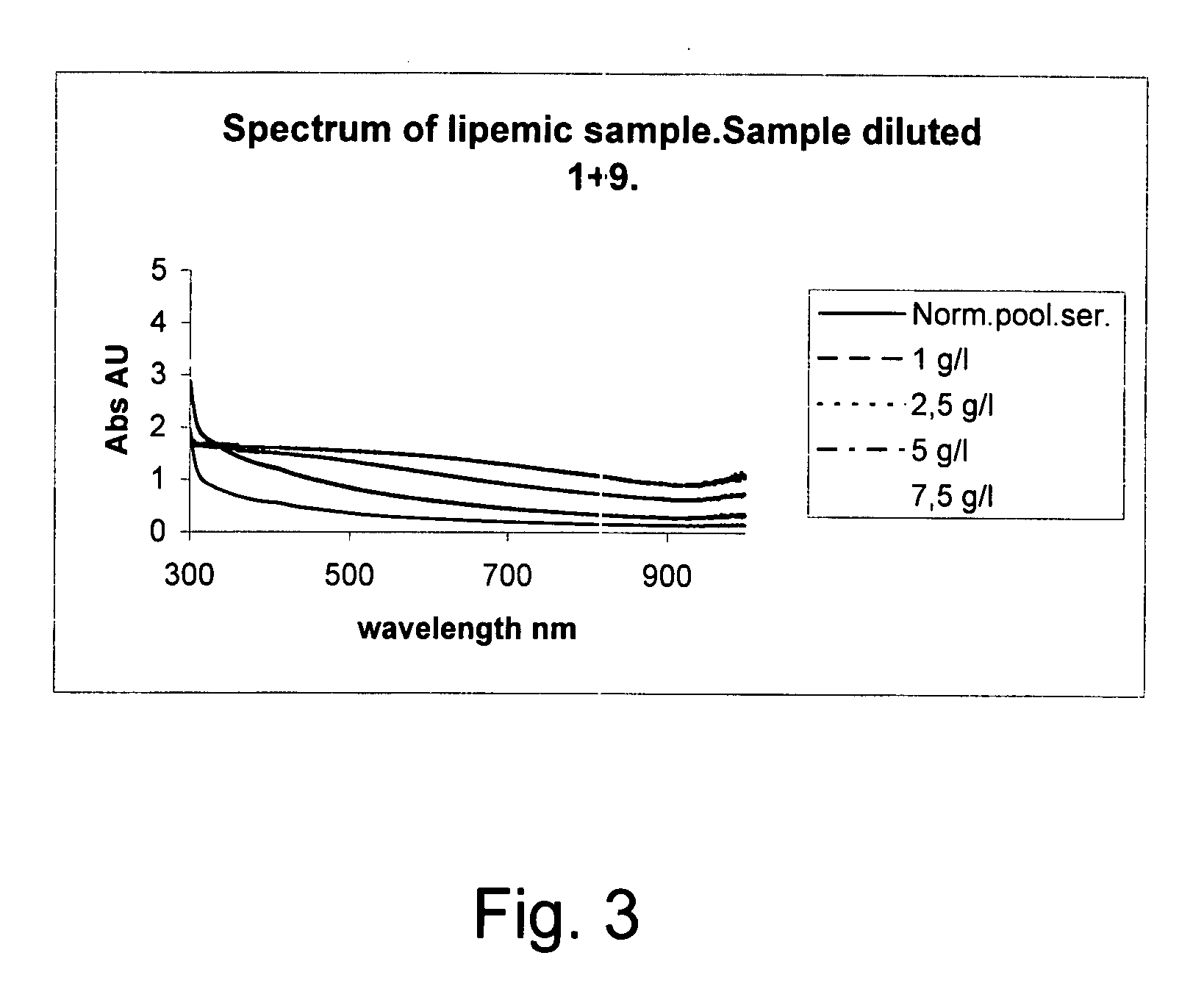
The invention concerns a method for detecting the amounts of substances that may disturb chemical analysis performed by an analyzer for clinical chemistry. The presence and concentration of hemoglobin, bilirubin and lipemia are detected by measuring the absorbance or reflectance on at least two, preferably six, different wavelengths over the measured spectrum. The measurements are performed at two wavelengths for each substance, preferably on the absorbance peaks of the specific substance and on the root of the specific peaks. Since the three substances mentioned above each have at least one peak in the spectrum, the measurement is done on three peaks and three root positions respectively when three substances have to be measured.
Owner:THERMO FISCHER SCI OY
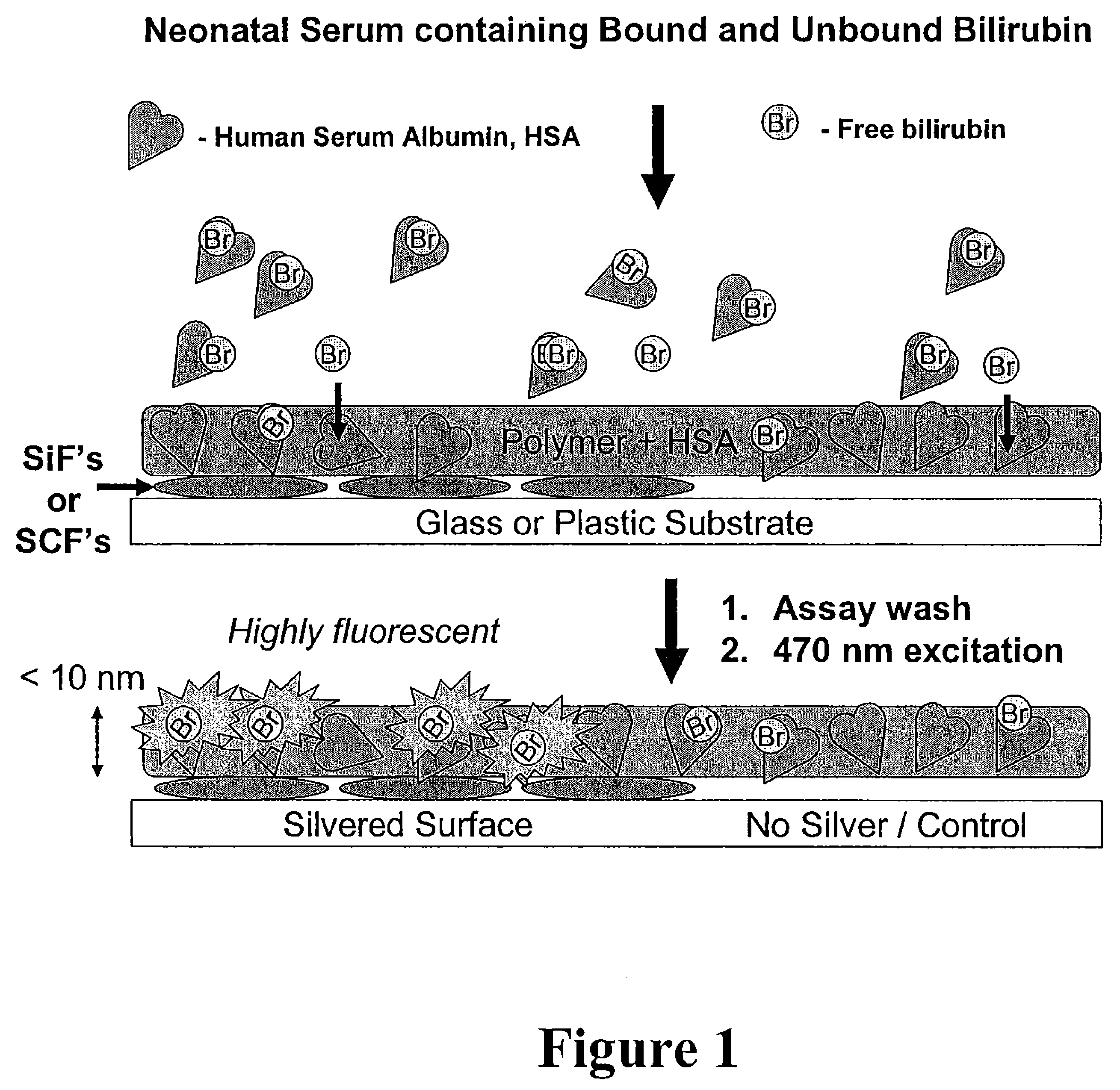
Metal enhanced fluorescence-based sensing methods
InactiveUS20090142847A1Fluorescence enhancementAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by electrical excitationFluorescenceNucleotide sequencing
The present invention relates to metallic-surface detection systems for determining target substances including free bilirubin in neonatal serum in the presence of a predominantly high background of bilirubin bound Human Serum Albumin (HSA) or sensing and isolating target nucleotide sequences wherein a fluorescence signal is enhanced by close proximity of the target substances near metallic surfaces.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
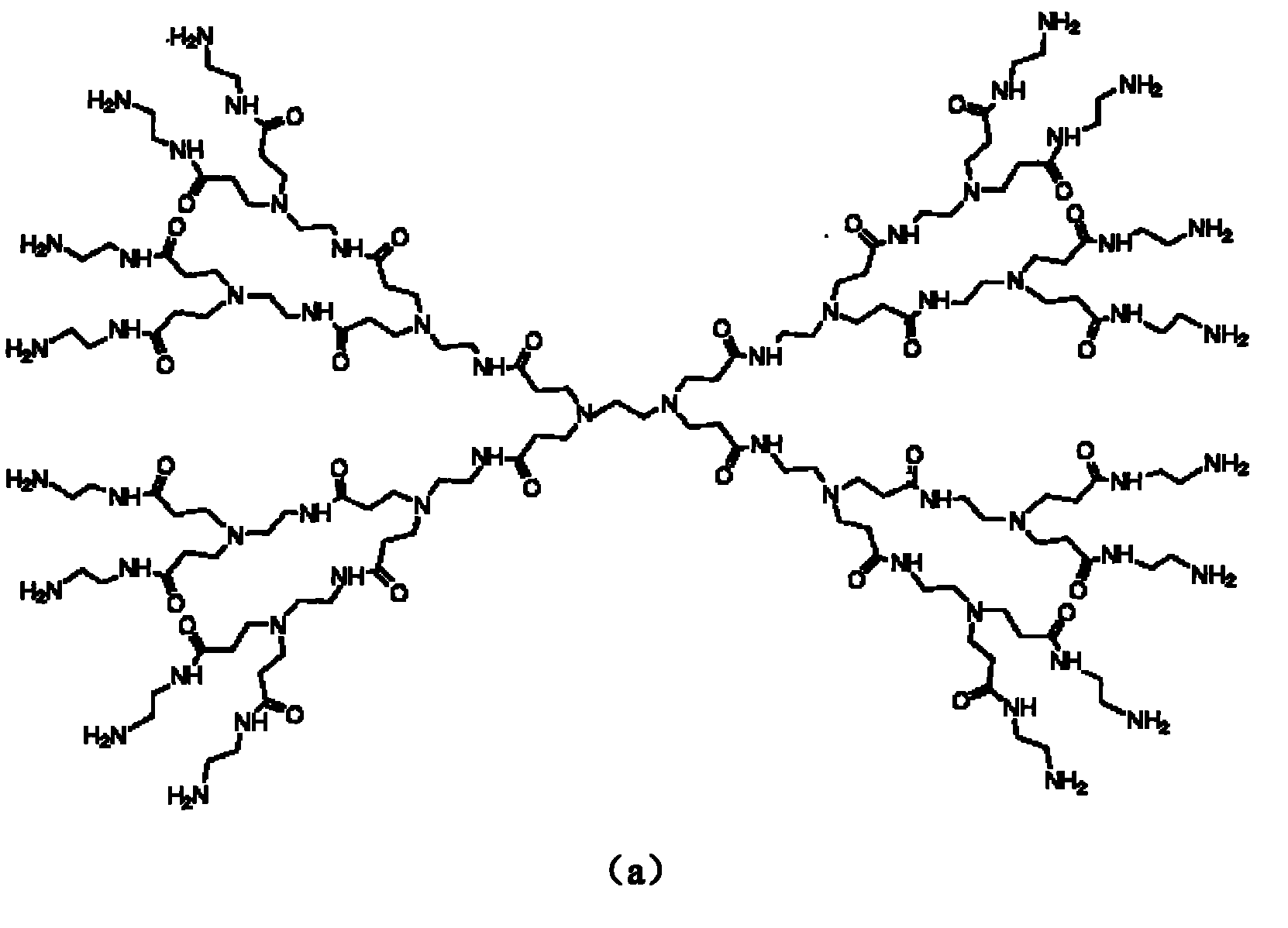
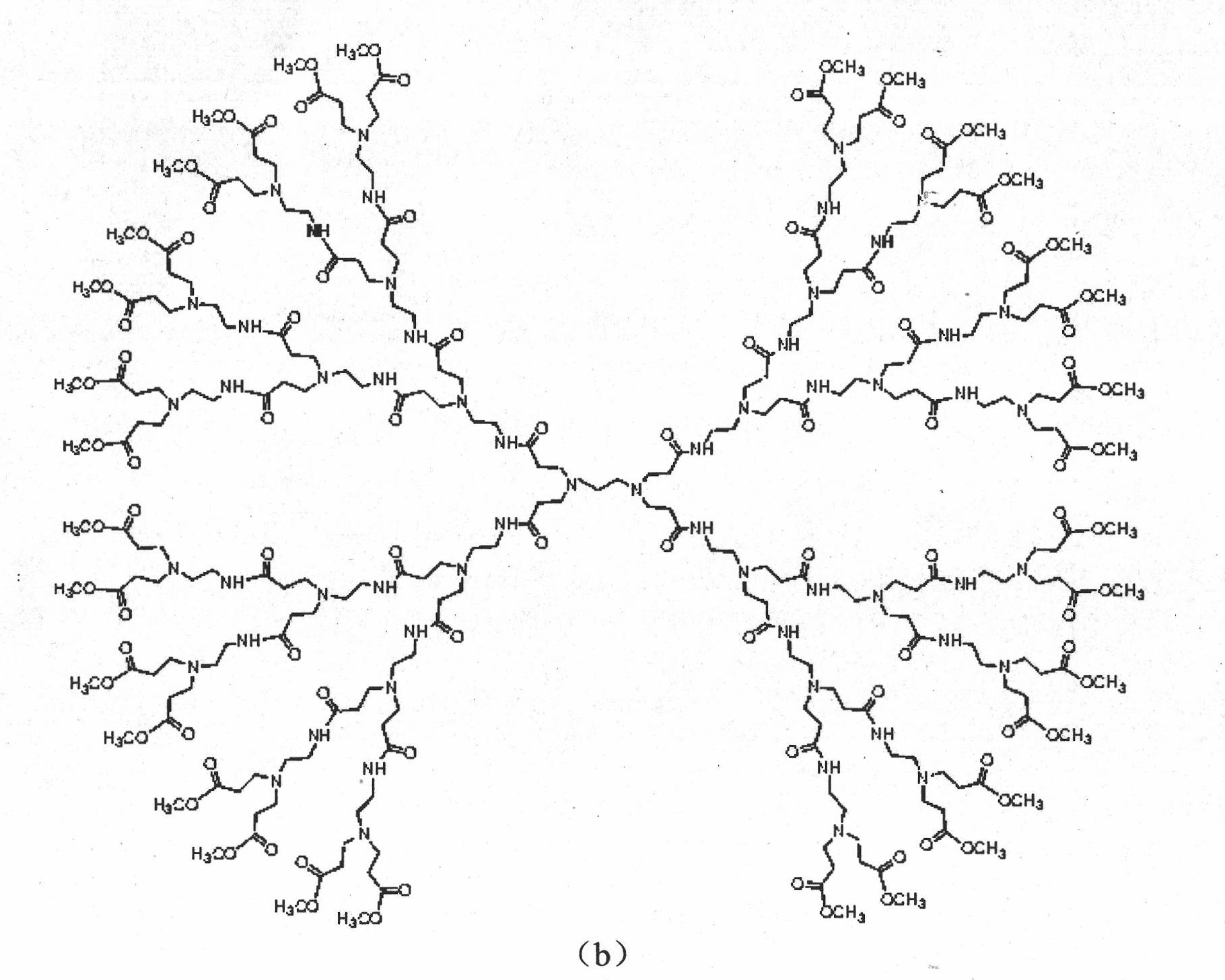
Polyamido-amine dendrimers -modified macroporous crosslinked chitosan microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101817932AImprove adsorption capacityHigh amino contentOrganic active ingredientsOther chemical processesDendrimerCrosslinked chitosan
The invention relates to a polyamido-amine dendrimers-modified macroporous crosslinked chitosan microsphere and a preparation method thereof, specifically a low-generation (Generation is not more than 3) polyamide-amine (Poluamidoamine, short for PAMAM) dendrimers (Dendrimers)-modified macroporous crosslinked chitosan microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The macroporous crosslinked chitosan microsphere is prepared by means of inverse suspension reaction by using chitosan as raw material, sucrose as pore forming agent, glutaric dialdehyde as crosslinking agent, and is then chemically modified by using low-generation (generation is not more than 3) polyamide-amine dendrimer as amination agent. The microsphere has the average particle diameter of 100 to 170 microns. The modified macroporous crosslinked chitosan microspheres CS-G0, CS-G1.0, CS-G2.0 and CS-G3.0 respectively have the content of amino: 4.63, 5.30, 5.41 and 4.84mmol / g. The microsphere has the advantages of: simple steps of the material preparation method thereof, increased amino content after the modification thereof, and higher adsorption performance than unmodified chitosan microspheres when being used for the adsorption of bilirubin in aqueous solution.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
High efficiency technique for extracting bilirubin and bile acid by using animal bile as raw material
The present invention relates to process of extracting cholic acid, deoxycholic acid and bilirubin from bile of pig, ox and sheep. Bile of pig, ox and sheep consists of water in about 97 %, bile acid in about 2.5 % and bilirubin in about 0.4 %; and contains also phospholipid, cholesterol, Na, K, Ca, phosphate, carbonate, small amount of protein, and other components. Fresh bile is treated through cooling, filtering to defat, basic hydrolysis, acidification and organic solvent extracting to obtain bilirubin; the rest solution is further treated through deep saponification, acidification and organic solvent precipitation to obtain the mixture of cholic acid and deoxycholic acid; and the mixture is re-crystallization separated to obtain high purity cholic acid and deoxycholic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing high-purity hyodeoxycholic acid by pig bile
InactiveCN101037463AReduce the difficulty of purificationLow impurity contentDigestive systemUnknown materialsBenzeneHyodeoxycholic acid
The invention relates to a method for extracting the hyodeoxycholic acid from the leftovers of pig bile or extracted bilirubin, including saponify the leftovers with alkali, adjusting pH value, acetic ester extraction, decoloring with active carbon; concentrating the mother liquid to a proper volume, precipitating deposit, separating the deposit and drying to get coarse hyodeoxycholic acid; esterifying the coarse product, then doing an addition reaction with benzene, separating the methylhyodeoxycholanate-benzene addition compound; decomposing the addition compound with alkali, adjust pH value, getting the purified deoxycholic acid. The obtained mother liquid can be further extracted to get precious chenodeoxycholic acid. The craft has a lot of material, a low pollution, safety and no poison, a low cost, a high product purity and is suitable for industry production in a large scale.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparing macromolecule resin type bilirubin sorbent
InactiveCN1557538AImprove mechanical propertiesAvoid the danger of blood pressure dropsOther chemical processesCross-linkSorbent
The present invention features that the bilirubin adsorbent is synthesized by selecting well biocompatible polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer as carrier, PHEMA as coating agent, epichlorohydrin for activating the functional hydroxy radical of PHEMA, and glutaraldehyde as cross-linking agent for cross-linking functional cyclodextrin molecule. The bilirubin adsorbent has biocompatibility and adsorption capacity superior to active carbon and cationic resin adsorbing material, and has no adsorbent molecule falling resulting in immunological dysfunction. Animal experiment shows that the novel bilirubin adsorbent may be used to eliminate bilirubin from blood, blood plasma and albumin solution effectively.
Owner:杭州科锐净化工程有限公司
Creatinine detection reagent
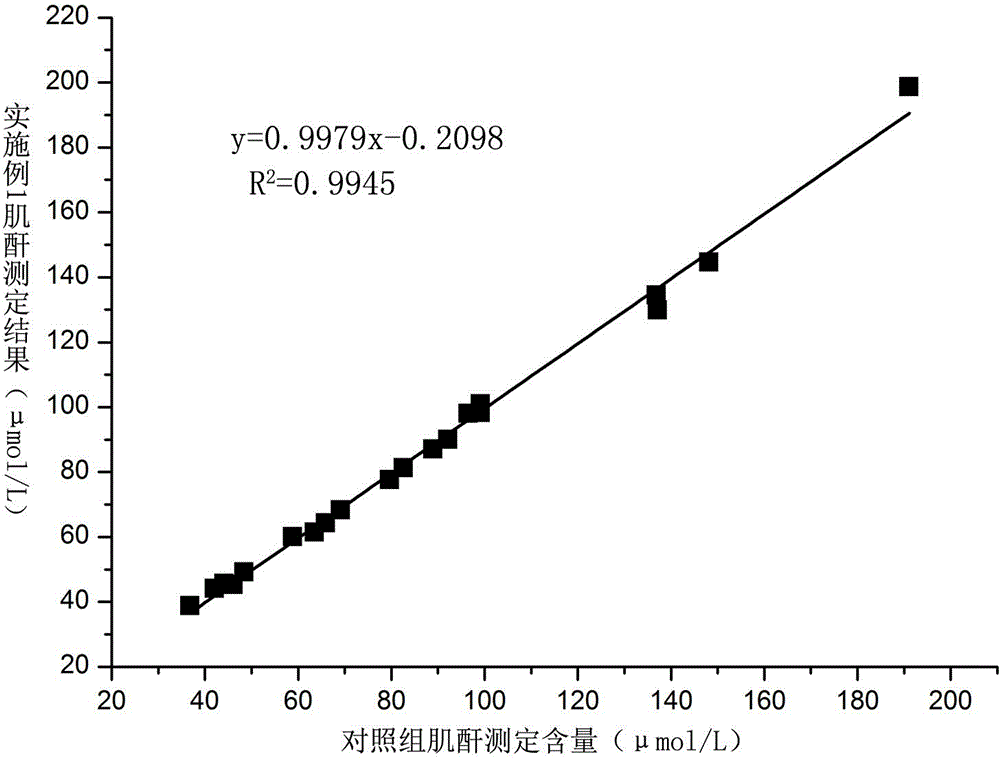
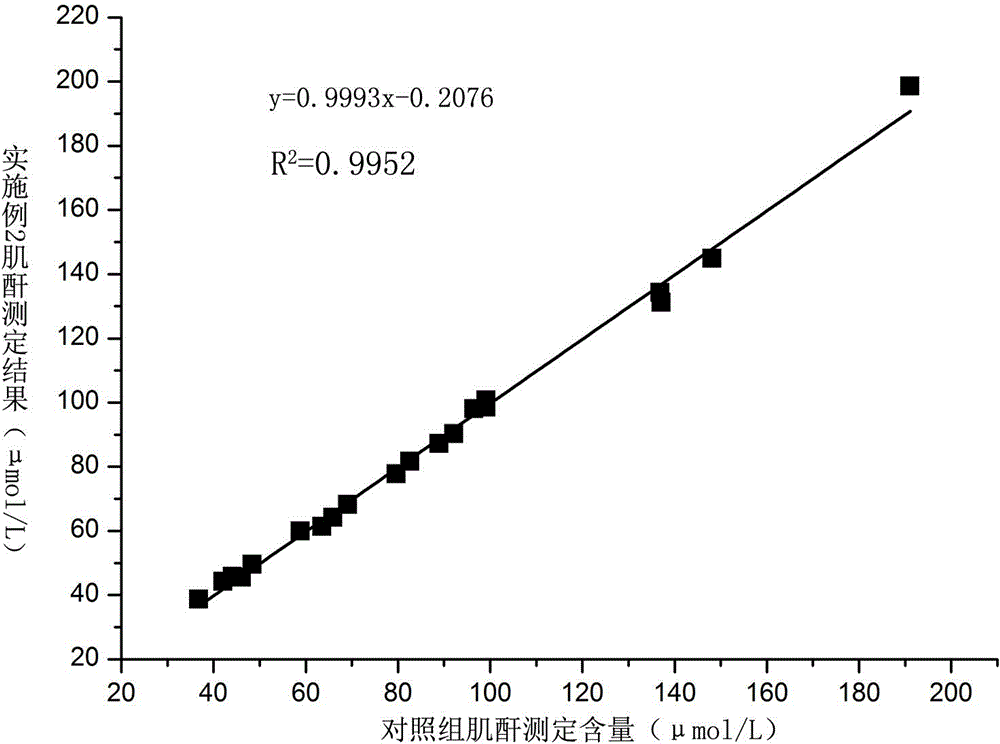
ActiveCN103278468AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsMethylanilineCreatininase
The invention discloses a creatinine detection reagent which is characterized by comprising a diluent and a reaction reagent, wherein the diluent is composed of buffer, surfactant, preservative, anti-bilirubin interference agent and vitamin C oxidase; and the reaction reagent is composed of buffer, creatinase, sarcosine oxidase, peroxidase, N-ethyl-N-(3-propylsulfo)-3-methylaniline, creatininase, 4-aminoantipyrine, preservative and freeze-drying protective agent. The detection reagent disclosed by the invention has favorable sensitivity, accuracy, precision and linearity, and can completely satisfy the clinical examination requirements.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Cyclodextrin cross-linking polymeric microsphere capable of absorbing bilirubin and its preparation and application
InactiveCN1541761AHigh selectivityImprove removal efficiencyOther chemical processesCross-linkCyclodextrin
The present invention relates to the removal of bilirubin from blood, and is especially cyclodextrin crossed polymer microsphere for adsorbing bilirubin and its preparation and application. The microsphere is prepared with diisocyanate as crosslinking agent and through condensation with cyclodextrin monomer. The polymer microsphere of the present invention has low cost and results in simplified experiment process, and the efficient removal of bilirubin with the polymer microsphere shows that the said material has excellent clinical application latent.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anion resin for bilirubin absorption and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102049242AHigh affinityGood dispersionOther chemical processesOther blood circulation devicesCross-linkPreferential adsorption
The invention relates to anion resin for bilirubin absorption and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, in the anion resin for bilirubin absorption, styrene is adopted as monomers, divinyl benzene is adopted as a cross-linking agent, maleic anhydride copolymer microspheres and organic small molecules are adopted as a pore-forming agent, and oil dispersible hyperoxide is adopted as an initiating agent; porous microspheres are prepared through suspension polymerization; and the anion resin with preferential bilirubin adsorption ability is obtained through quaternary ammoniation treatment, wherein the theoretical crosslinking degree of the resin is 4-20%, the average pore size of total pores is 80-120nm, and functional groups are quaternary ammonium salt groups. Accordingto the invention, the anion resin with uniform pore sizes, good permeability, good blood compatibility, high preferential adsorption of bilirubins, is obtained, and the problems in the prior art, such as poor absorption selectivity, high prices of imports, and the like, are solved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KONCEN BIOSCI
Preparation method of nitrogen-doped hierarchical pore carbon materials
InactiveCN103537262AQuality improvementWith tunable specific surface areaOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesAluminum IonBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of nitrogen-doped hierarchical pore carbon materials. The method comprises the steps of soaking waste banana peel, which serves as a nitrogen source and a carbon source, into an aluminum nitrate aqueous solution with a certain concentration, thus forming a multi-pore-channel metalloid organic skeleton coordination complex material through coordination and modification of metal aluminum ions; constructing a large mesoporous mesostructure by using the multi-pore-channel metalloid organic skeleton coordination complex material as a template; carrying out microstructure regulation and guidance by using an amphiphilic triblock copolymer Planck F127 as a soft template to prepare a series of nitrogen-doped hierarchical pore carbon materials with high specific surface area, large pore volume and adjustable average mesoporous size. The raw materials are cheap, easily available and environment-friendly; the preparation method is simple and mild in condition; the obtained hierarchical pore carbon materials have stable quality, can be applied to CO2 gas adsorption with high selectivity, can also be applied to bilirubin adsorption with high selectivity, large adsorption capacity and excellent biocompatibility, and are expected to be a potential blood purification and separation medium material in the aspect of clinical medicine.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Apparatus and method for rapid spectrophotometric pre-test screen of specimen for a blood analyzer
InactiveUS20010004285A1The process is fast and accurateColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingBlood specimenHemoglobin hb
A method and apparatus for use in respect of samples which are assessed for quality prior to testing in a clinical analyzer. The method and apparatus identify parameters such as gel level and height of fluid above the gel in blood samples, where appropriate, for the purposes of positioning the specimen for determination of interferents. Such interferents include hemoglobin (Hb), total bilirubin and lipids. These interferents are determined by measurement of absorption of different wavelengths of light in serum or plasma, or other speciments, which are then compared with values obtained through calibration using reference measurements for the respective interferents in serum or plasma or other type of specimen. Determination of temperature of the specimen, as well as specimen type, for example whether the specimen is urine or plasma or serum, may also be carried out.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
System for estimating state of critically ill patient in obstetrical department
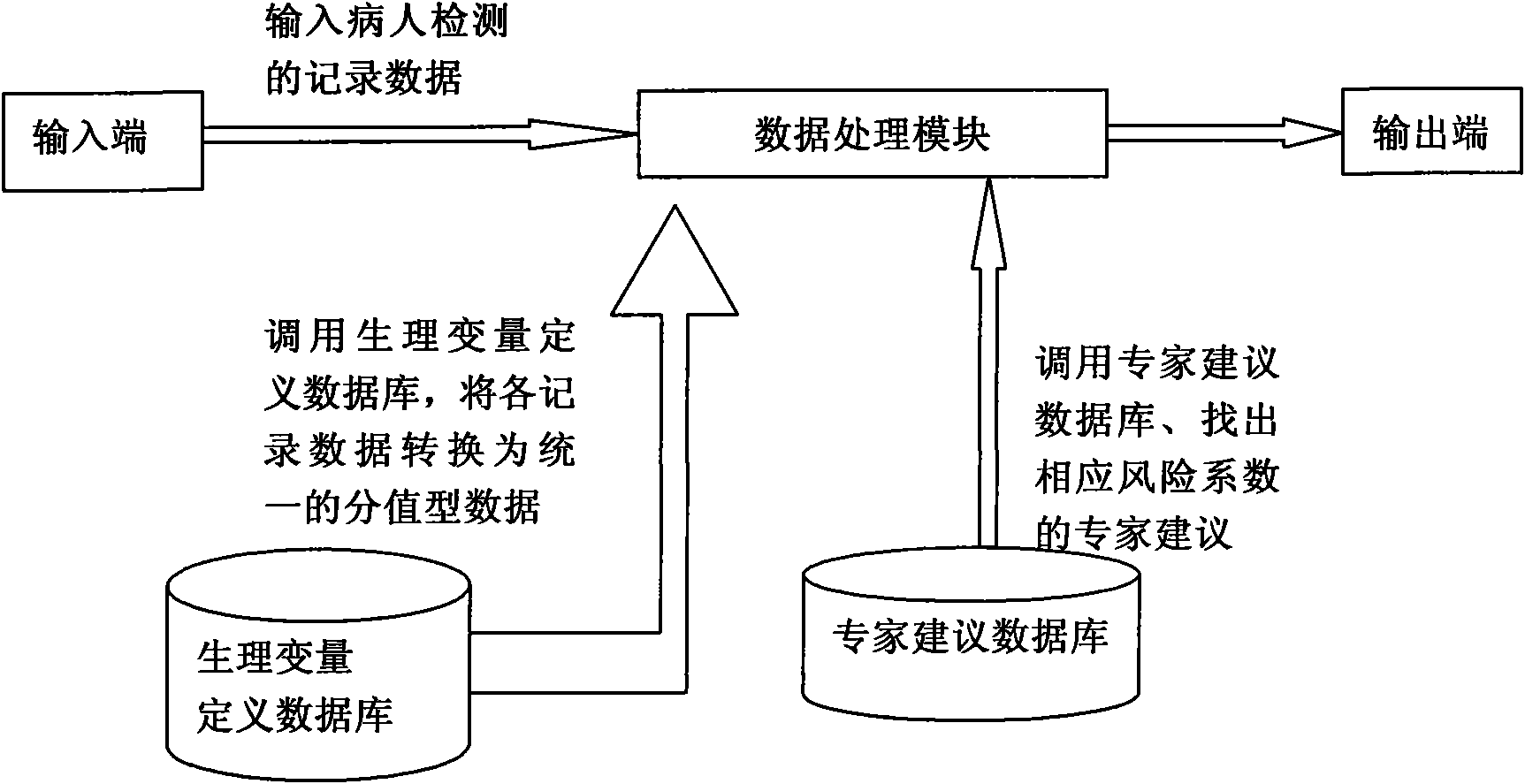
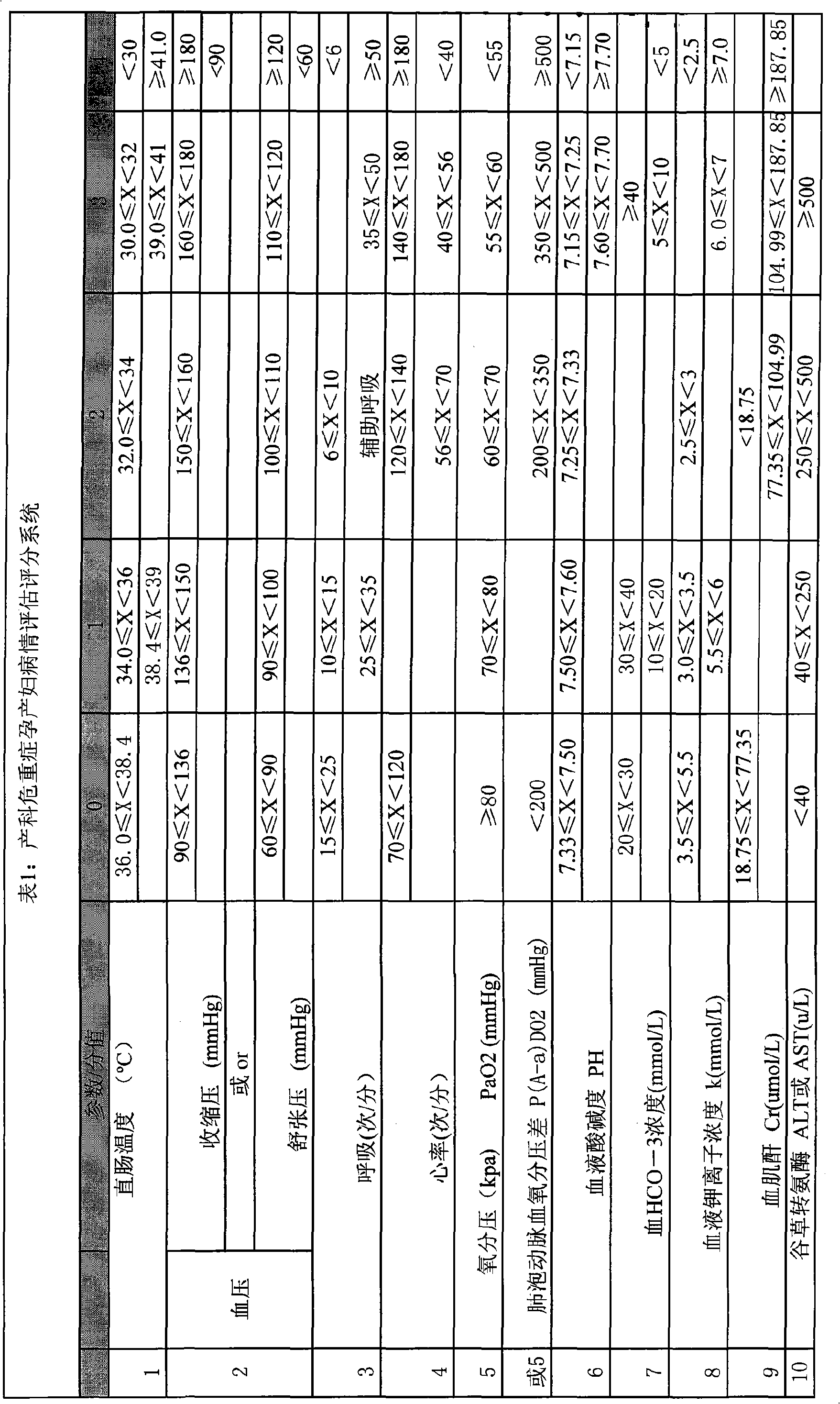
InactiveCN101554322AImprove the level of treatmentReduce mortalitySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringNervous systemCritically ill
The invention discloses a system for estimating the state of a critically ill patient in an obstetrical department, which comprises an input end, an output end and a data processing module. Firstly, measured heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, breathing rate, pH, blood HCO-3 concentration, oxygen partial pressure, alveolar arterial blood oxygen tension difference, potassium ion concentration, hematokrit, white cell count, platelet count, fibrinogen, glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, albumin, bilirubin, creatinine, blood glucose concentration and nervous system grading data are input the system through the input end; the data processing module evaluates a death risk factor; and at last, the output end directly reflects the result of the patient and the expert suggestion. The invention can not only accurately evaluate the critical degree of the state of the patient and predict the death risk, but also can provide quantitative indexes for changing to a three-class hospital, and is beneficial to improve the treatment level of the critical state of the obstetrical department and lower the death rate of pregnant and lying-in women and perinatal infants.
Owner:陈敦金 +1
Preparation of polystyrene-divinylbenzene microspheres for blood purification
InactiveCN101612543AEvenly distributed diameterGood repeatabilityMicroballoon preparationSuction devicesLipid formationCross-link
The invention provides a method for preparing polystyrene-divinylbenzene microspheres 60 to 100 microns in diameter, and a use thereof for blood purification. Polymer microspheres prepared are synthesized by swelling and polymerizing seed emulsion. Seeds microspheres used are large-diameter linear polystyrene microspheres 6 to 8 microns in diameter. Monomer and cross-linking agent used are styrene and divinyl benzene respectively. Pore-forming agents used are toluene, ethylbenzene, o-phthalic acid lipids, n-heptane, n-octane, n-heptanol or a mixture of the substances. The polymer microspheres prepared are used to remove bilirubin during blood purification. The microspheres prepared have the characteristics of cross-linked multihole, high specific surface area (between 100 and 1,000 m<2> / g), stable mechanical strength, high yield of preparation process, use for blood purification and bilirubin adsorption, small pressure drop of adsorption column, high removal rate and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for automatically detecting factors that disturb analysis by a photometer
ActiveUS20090009750A1Easily and reliably detectedReliable analysisBiological material analysisTransmissivity measurementsClinical chemistryMedicine
The invention concerns a method for detecting the amounts of substances that may disturb chemical analysis performed by an analyzer for clinical chemistry. The presence and concentration of hemoglobin, bilirubin and lipemia are detected by measuring the absorbance or reflectance on at least two, preferably six, different wavelengths over the measured spectrum. The measurements are performed at two wavelengths for each substance, preferably on the absorbance peaks of the specific substance and on the root of the specific peaks. Since the three substances mentioned above each have at least one peak in the spectrum, the measurement is done on three peaks and three root positions respectively when three substances have to be measured.
Owner:THERMO FISCHER SCI OY
Separation purification preparation method of chenodeoxycholic acid in pig's bile
InactiveCN1869044ASimple and fast operationLow costUnknown materialsSteroidsCholic acidChenodeoxycholic acid
A process for separating the chenodeoxycholic acid from pig's gall and purifying it includes such steps as preparing general cholic acid from the mother liquid generated by extracting the cholerythrin from pig's gall, saponifying, regulating pH value to obtain crude chenodeoxycholic acid, decoloring, defatting, preparing the deposit of barium chenodeoxycholate, reacting on potassium carbonate to remove Ba, regulating pH value, and purifying by silicon gel column.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Serum creatinine detecting reagent
The invention discloses a serum creatinine detecting reagent, and belongs to the technical field of clinical in-vitro detection. According to the serum creatinine detecting reagent, gamma-Fe2O3 nano-particles are added into a reagent R1, so that the activity of peroxidase and the specificity to a substrate are enhanced, and the interferences of reducing substances, such as ascorbic acid, uric acid, glutathione and bilirubin, are reduced; meanwhile, the gamma-Fe2O3 nano-particles also serve as a catalyst of a reaction; the interference of endogenous creatine is effectively eliminated by the combination action of the gamma-Fe2O3 nano-particles and the peroxidase. In addition, the serum creatinine detecting reagent adopts N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxy-3-sulfonated propyl)-3-methylaniline sodium salt (TOOS) as a chromogen, so that the reagent is more stable; the analysis sensitivity is high. The substances, such as lipase and lipoprotein lipase, are also added into the reagent R1, so that the influence of lipid turbidity can be removed effectively; therefore, the reagent of the invention has higher anti-jamming capability and stability.
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
Kit for mensurating total bilirubin through chemistry oxidation process
ActiveCN1959415ALarge linear upper limitImprove anti-interference abilityColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAcetic acidSulfate
A kit using chemical oxidation method to analyze total bilirubin is composed of reagent A prepared from 0.5-3g / L monopotassium phosphate (MP), 16-82g / L of dibasic sodium phosphate ( DSP), 2.5-12.5g / L sodium chloride, 1-30g / L of PVP, 0.2-1g / L of complexone IV B, 5-3ml / L of quton 1000, 0.05-0.25g / L of merthiolate and pH value 7.6-8.4 of MP-DSP buffer liquid; reagent B prepared from 1-5.5g / L of DPS, 0.25-1.5g / L of MP, 12.5-65g / L of superpotassium sulfate, 4.5-22.5g / L of sodium chloride, 0.05-0.25g / L of merthiolate and pH value 6.8-7.6 of MP-DSP buffer liquid.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Analyte system and method for determining hemoglobin parameters in whole blood
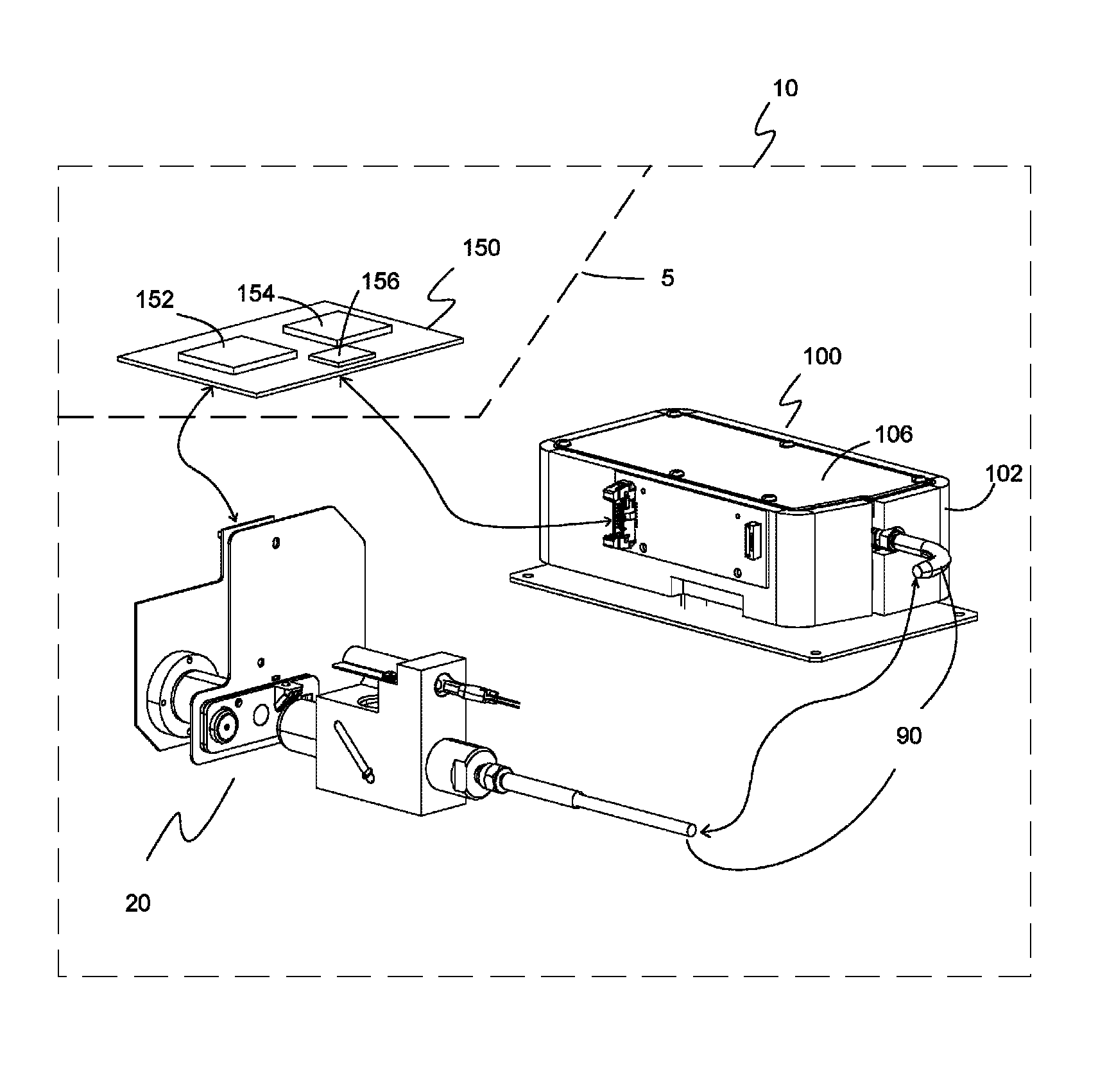
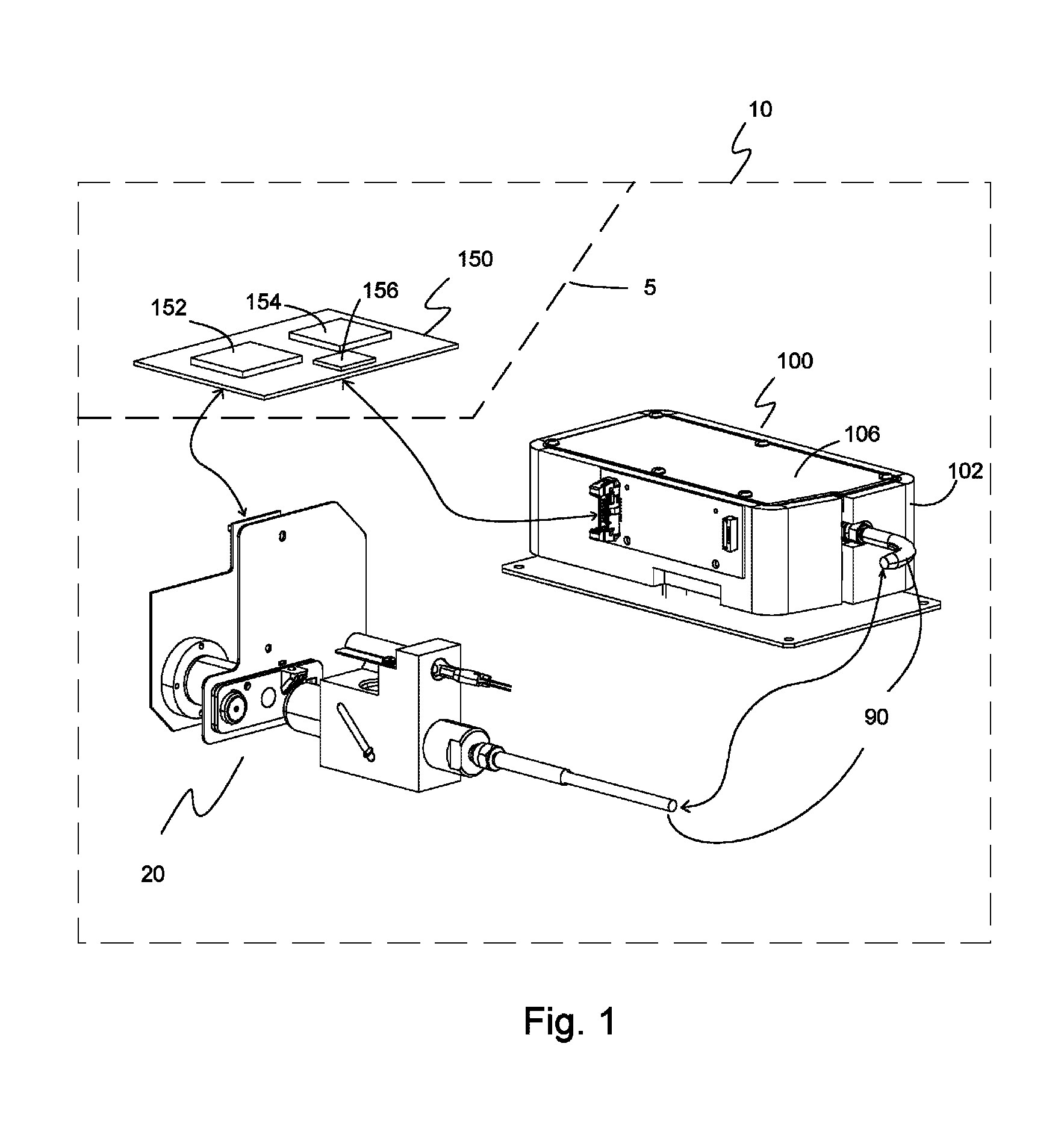
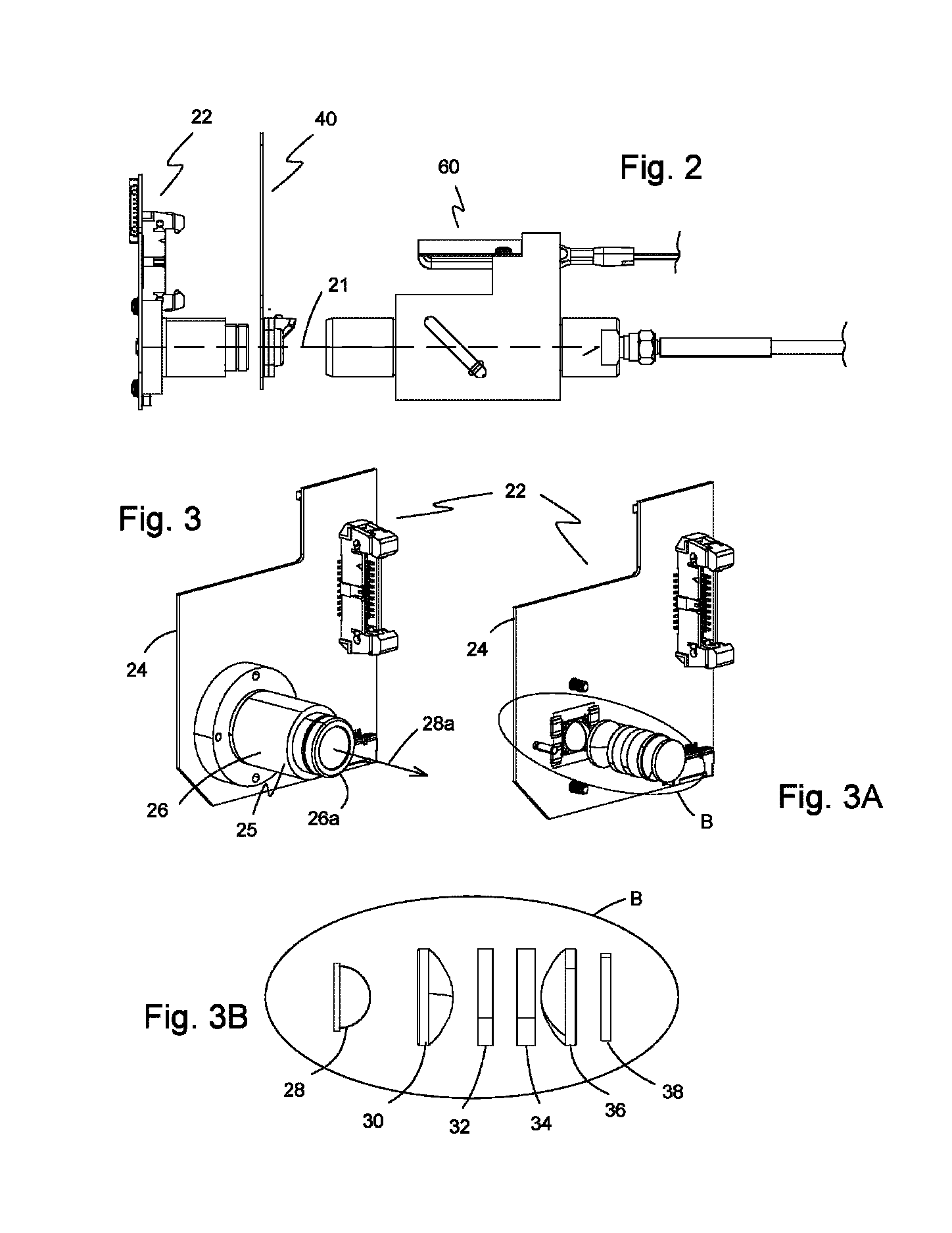
ActiveUS9535053B1Light throughputMinimize thermal drift effects on the spectral responseAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsWhole blood sampleSpectrometer
A system of measuring hemoglobin and bilirubin parameters in a whole blood sample using optical absorbance. The system includes an optical-sample module, a spectrometer module, an optical fiber module optically connecting the optical-sample module to the spectrometer module, and a processor module. The optical-sample module has a light-emitting module having a LED light source, a cuvette and a calibrating-light module. The processor module receives and processes an electrical signal from the spectrometer module and transforms the electrical signal into an output signal useable for displaying and reporting hemoglobin parameter values and / or total bilirubin parameter values for the whole blood sample.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com