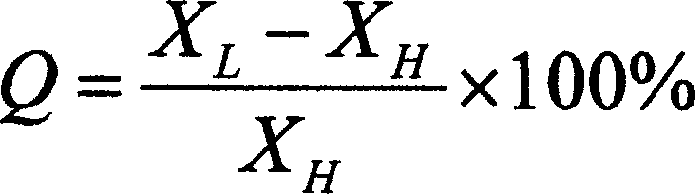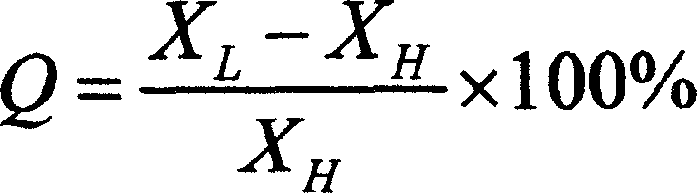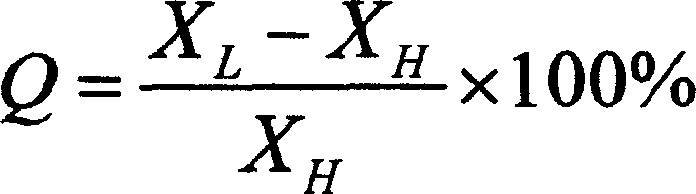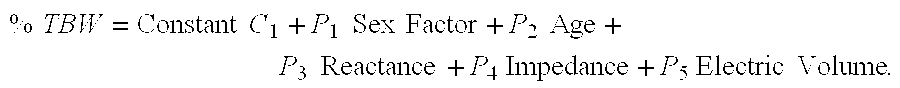Patents
Literature
57 results about "Intracellular Fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The fluid inside CELLS.
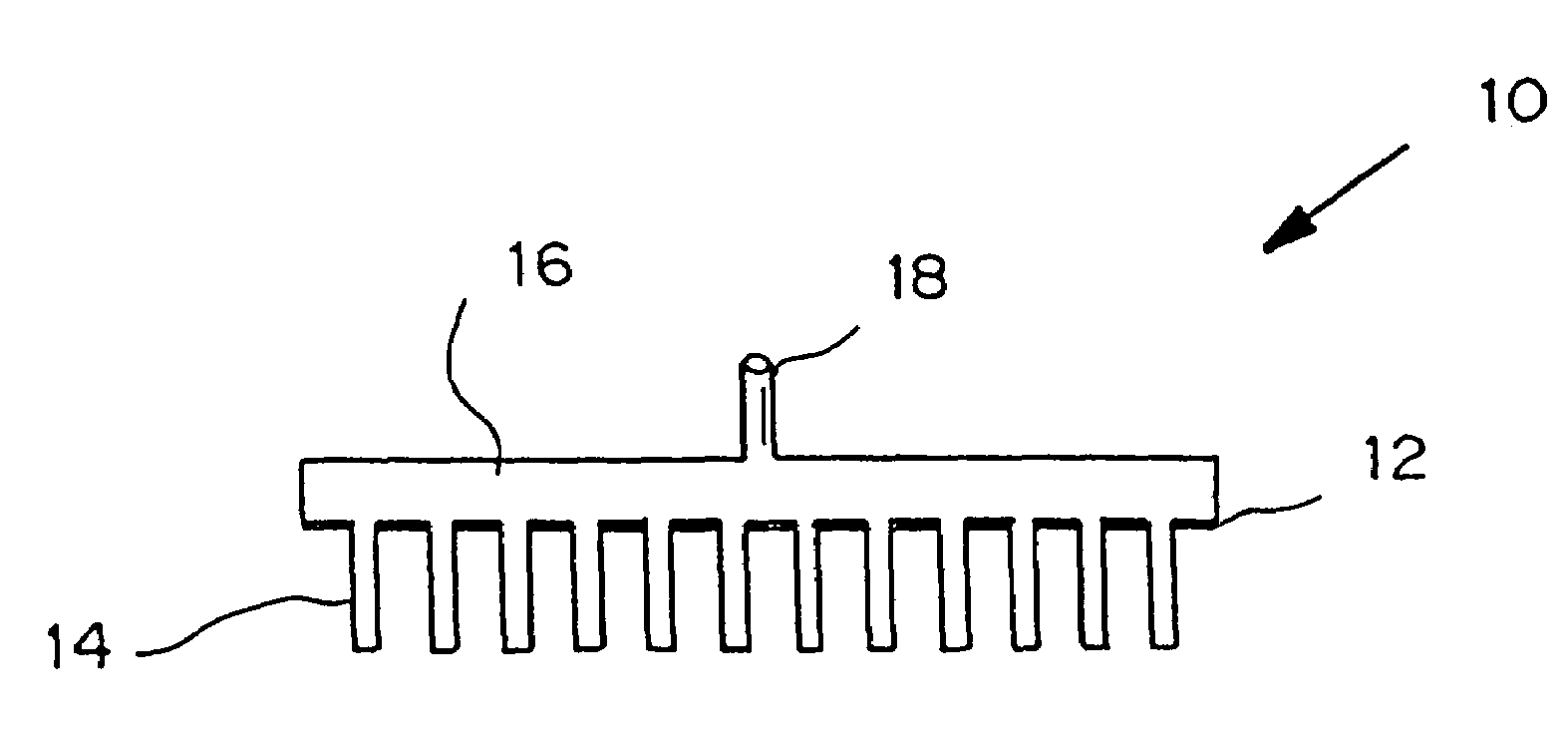
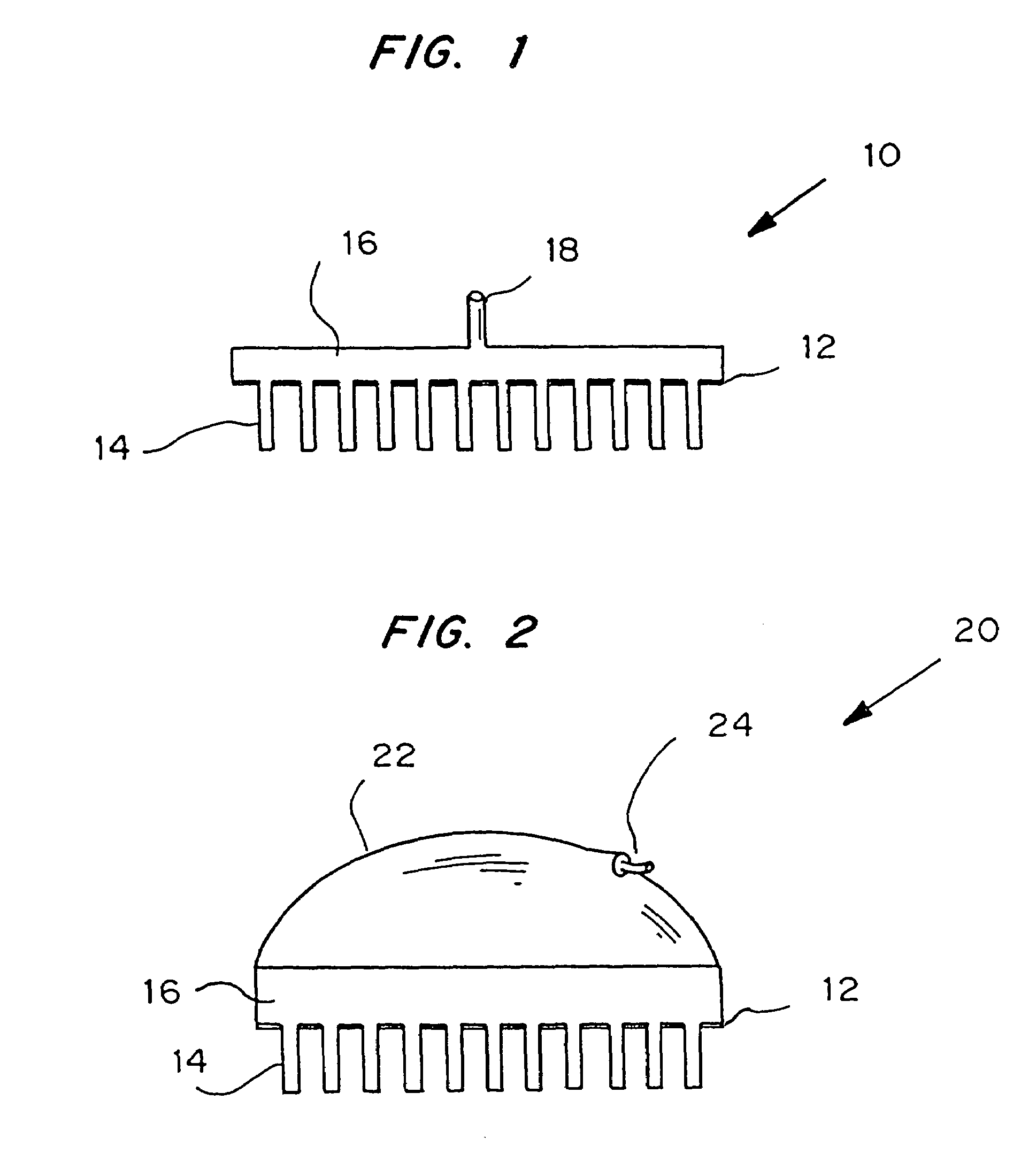
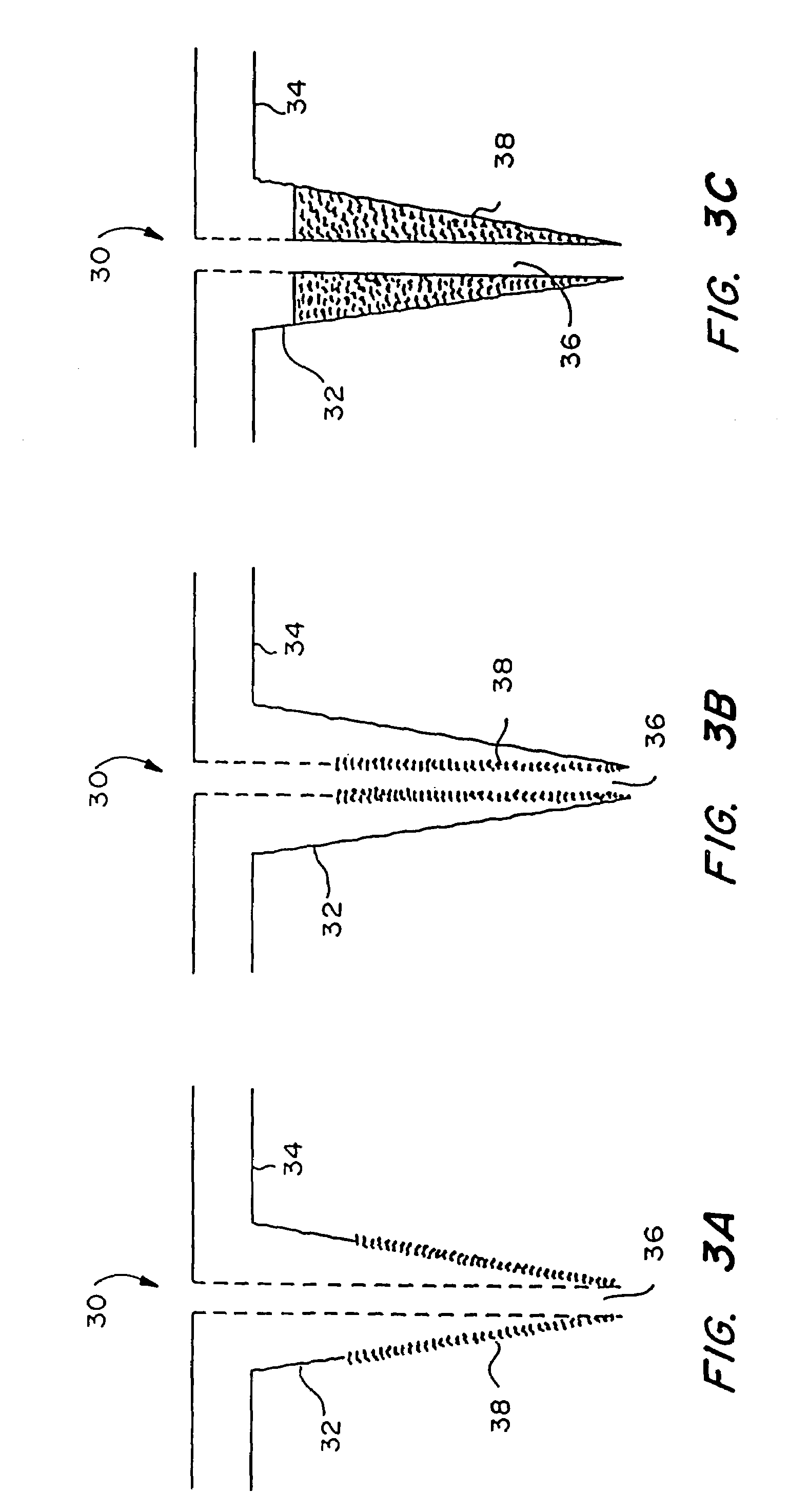
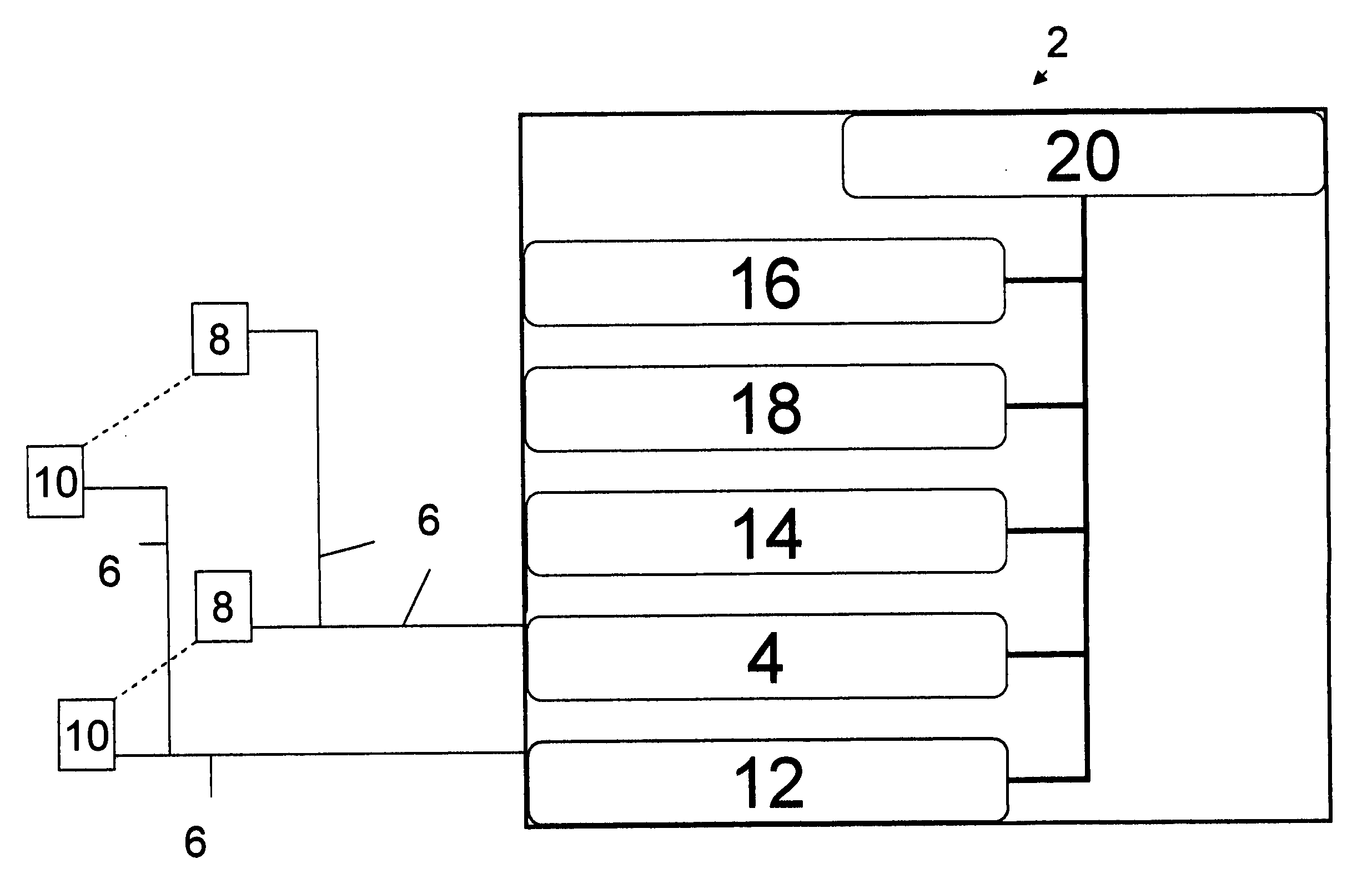
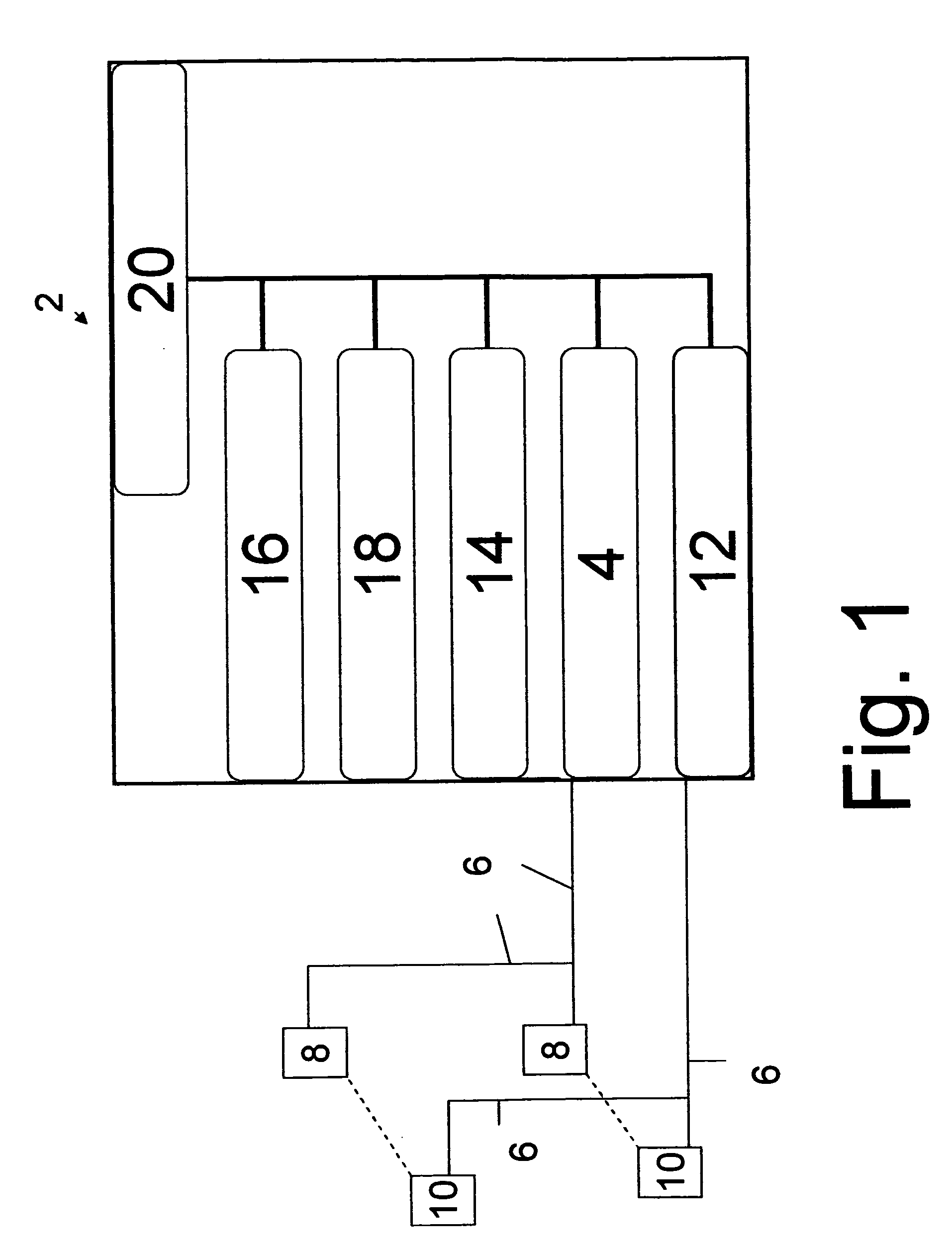
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
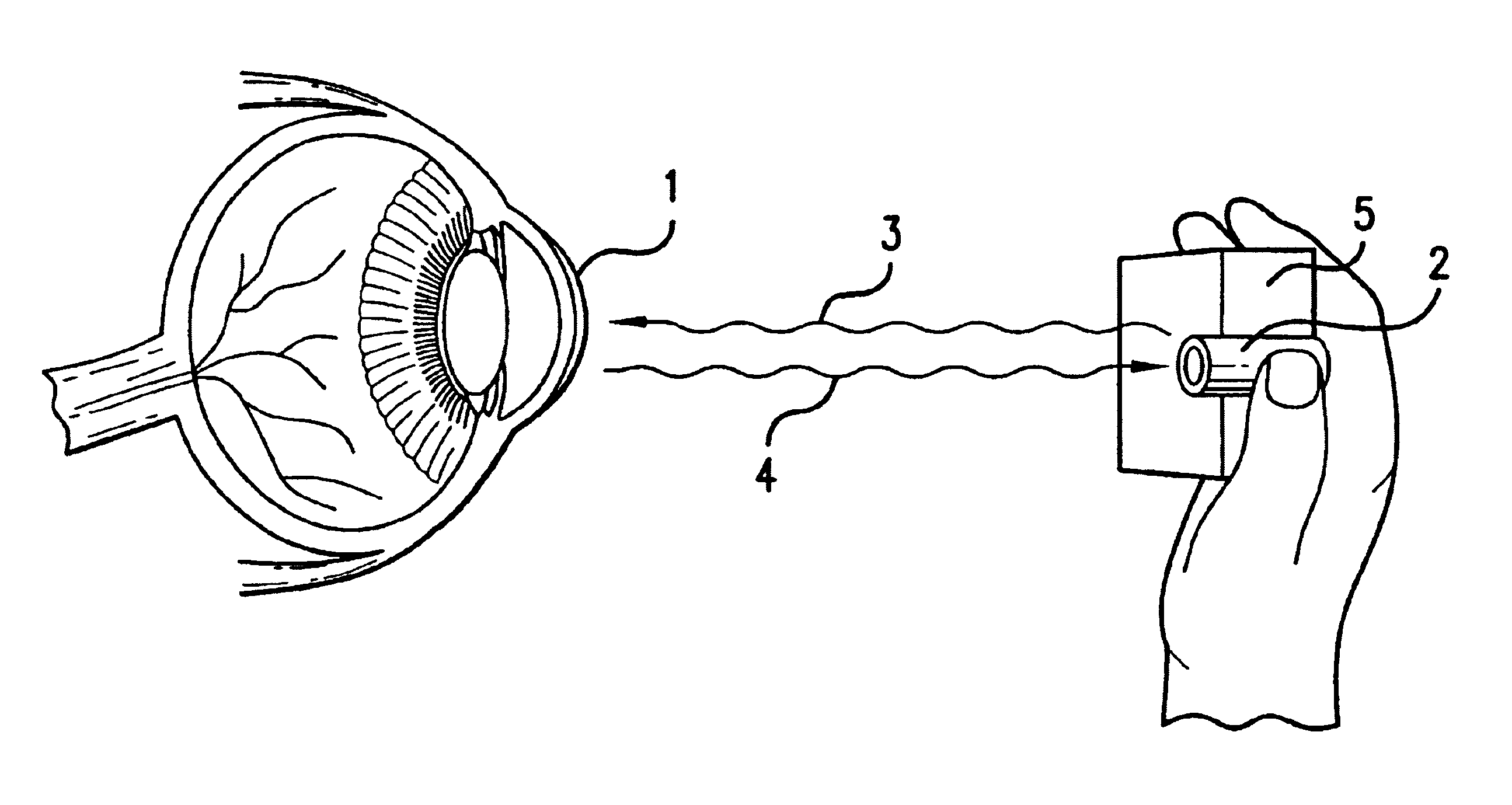
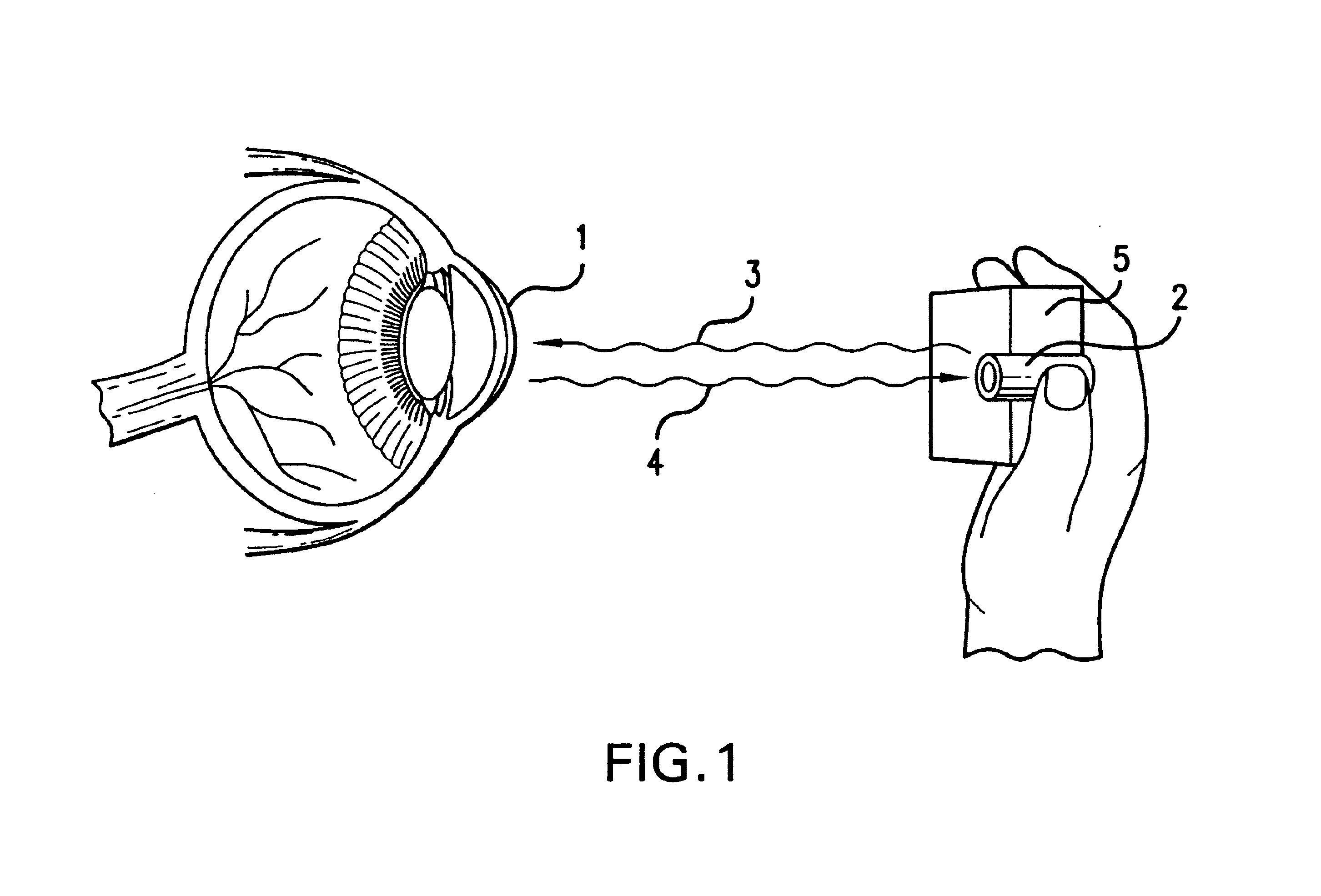
Ocular analyte sensor
An ophthalmic lens comprising a receptor moiety can be used to determine the amount of an analyte in an ocular fluid. The receptor moiety can bind either a specific analyte or a detectably labeled competitor moiety. The amount of detectably labeled competitor moiety which is displaced from the receptor moiety by the analyte is measured and provides a means of determining analyte concentration in an ocular fluid, such as tears, aqueous humor, or interstitial fluid. The concentration of the analyte in the ocular fluid, in turn, indicates the concentration of the analyte in a fluid or tissue sample of the body, such as blood or intracellular fluid.
Owner:EYESENSE AG
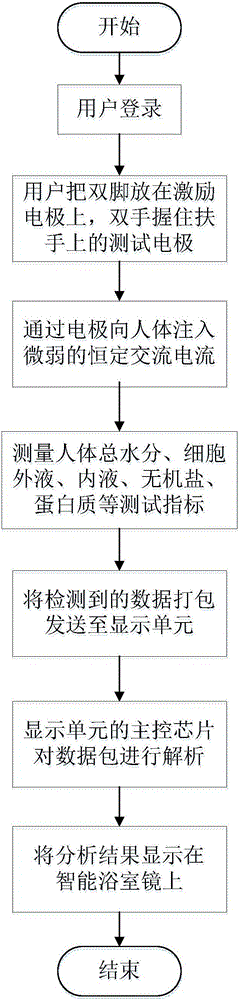
Human body component detection and analysis method applied on intelligent healthy stool
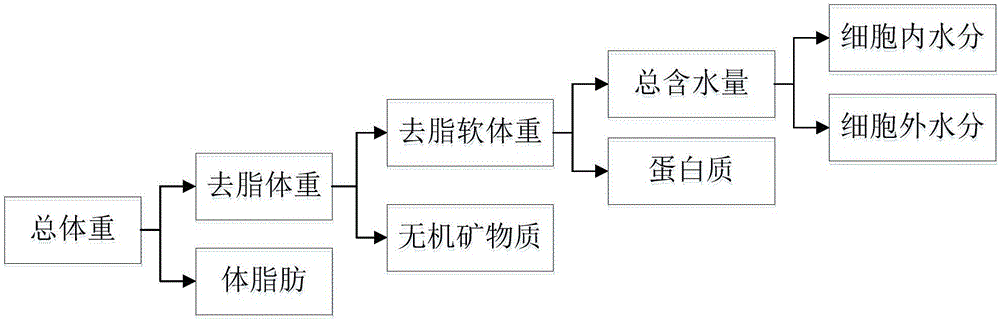
The invention relates to a human body component detection and analysis method applied on an intelligent healthy stool. The method comprises the steps of user logging-on, inputting information of gender, age, height and body weight; placing two feet on electrodes on floor in front of the stool by the user, gripping electrodes on two armrests at two sides of the stool by two hands, and applying a weak constant AC current on the human body through the electrodes; measuring testing indexes of total water, extracellular fluid, intracellular fluid, inorganic salt, protein, fat content, muscle amount, body fat rate, bone mass and body weight of the human body, and packing the detected human body component data and transmitting the packet to a displaying unit; analyzing the human body component data packet by the displaying unit, generating an evaluation report on the human body health of the user according to an analysis result, and displaying the evaluation report on an intelligent bathroom mirror. A controller according to the invention can perform analysis on user health according to the detected user body component information and furthermore displays an analysis report to the user on the displaying unit. The method of the invention can be used for performing daily health monitoring on the user body.
Owner:CAS HEFEI INST OF TECH INNOVATION
Wearable multi-physiological parameter monitoring method and device thereof
InactiveCN106137169AEasy to useFacilitates continuous routine monitoringStethoscopeSensorsLiquid glucoseEmergency medicine
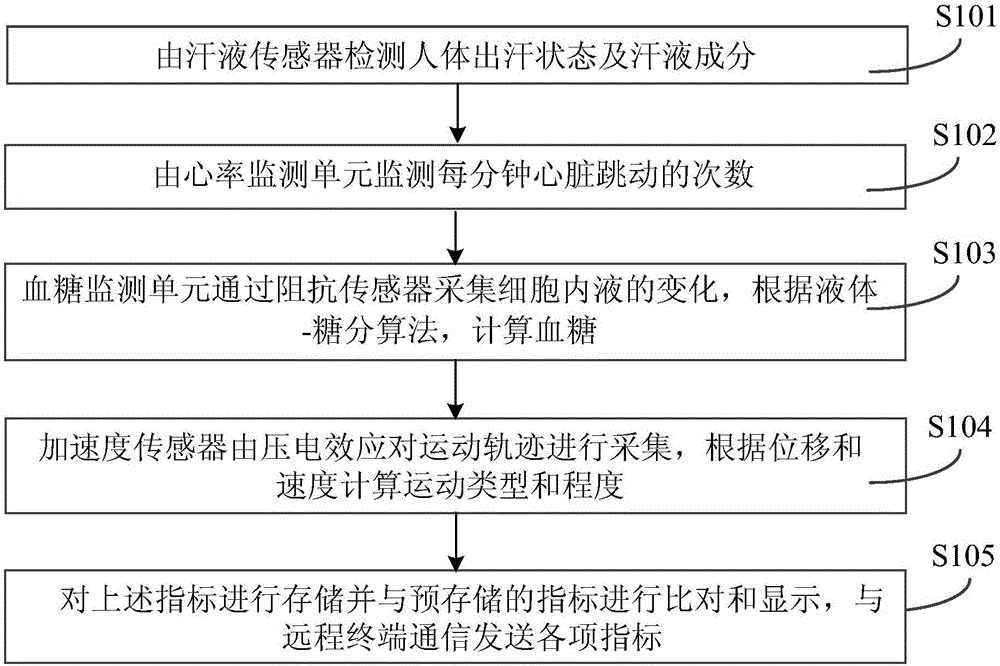
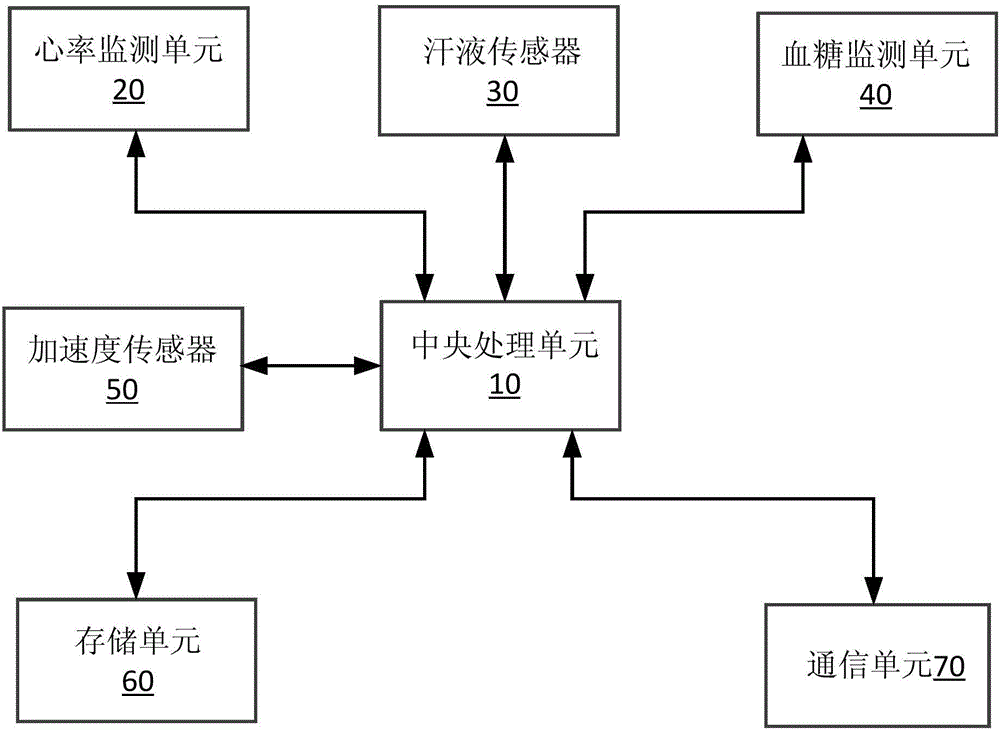
The invention discloses a wearable multi-physiological parameter monitoring method and a device thereof. In an embodiment of the invention, a sweat sensor, a heart rate monitoring unit, a blood glucose monitoring unit and an acceleration sensor are arranged on an integrated wearable suite. The method comprises the following steps: the sweat sensor detects the sweating state and the sweat composition of a human body; the heart rate monitoring unit monitors the heart beating times per minute, and the blood glucose monitoring unit collects the change of intracellular fluid through the impedance sensor and calculates the blood glucose according to a liquid-glucose algorithm; the acceleration sensor collects the movement track by a piezoelectric effect, and calculates the movement type and degree according to the displacement and speed; and the physiological parameters are stored and compared with the pre-stored physiological parameters and displayed, and all physiological parameters are sent through communication with a remote terminal. The method and device disclosed by the invention can realize classified monitoring of multiple physiological parameters of the human body and are convenient and quick and simple and practical.
Owner:HANGZHOU TONGQUAN IOT TECH CO LTD
High-throughput micron particle circular sorting and concentrating device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN107020164ASimple structure and processSimple preparation processLaboratory glasswaresPeristaltic pumpHigh concentration
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Fast discrimination method for iced fish and unfrozen fish
The present invention discloses fast identifying method of freshly frozen fish and defrozen fish in food identifying range. Based on the principle that the freezing of fish will cause the concentration change of intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid of muscle fibril, the transfer of intracellular and extracellular water, the change in cell shape and change in conducting characteristic of muscle medium, the conducting characteristic of fish is detected with an impedance measuring instrument at the conditions of 1000-16000 Hz frequency and voltage 3-9 V, the defrozen fish has Q value lower than 10 % and the freshly frozen fish has Q value higher than 20 %. The present invention makes it possible to detect freshly frozen fish and defrozen fish within 2 min without damage to fish, and the present invention has identification accuracy over 95 % and low cost.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Judgment method for appropriate rolling degree of red tea
The invention discloses a judgment method for an appropriate rolling degree of red tea. The judgment method is characterized in that the rolling comprises the compressing steps of air compressing, light compressing, middle compressing and heave compressing, wherein a stage is finished after each four compressing steps are finished; sampling is carried out once in each step of each stage; obtained samples are subjected to complex impedance Z value measurement and complex impedance Z values are recorded; the recorded complex impedance Z values are from big to small, the decreasing speeds of the complex impedance Z values are from fast to slow, and when the complex impedance Z values decrease, tend towards a stable state and rise again for the first time, the complex impedance Z value is the appropriate rolling degree. According to the judgment method, the normal intercellular permeability of the rolled leaves is broken along with the rolling, the intracellular fluid seeps outwards, the ion concentration of extracellular fluid is increased, and the complex impedance Z values decrease to be stable; the plasticity and flexibility of the rolled leaves are sequentially increased and decreased by the rolling, leave blades or leaf stalks are ruptured and broken, the bulk weights of the rolled leaves are increased, and the complex impedance Z values rise again. Thus, the appropriate rolling degree can be effectively judged according to the complex impedance Z values, and the high-quality tea having high cell breakage rate and strip forming rate can be obtained.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Dendrobium officinale health-care product
InactiveCN106798328ASignificant effectImprove the immunityFood scienceAdditive ingredientCedrela sinensis
The invention relates to the dendrobium officinale processing field, and discloses a dendrobium officinale health-care product prepared from the following raw materials: fresh dendrobium officinale, dried dendrobium officinale flowers, hibiscus tiliaceus, basil, rambutan, dandelion, naseberry, mulberry, mockstrawberry, wax apple, rose apple, cedrela sinensis, ashitaba, and sedum aizoon; the fresh dendrobium officinale is subjected to stir-frying processing, so water is removed, the loss of effective ingredients is prevented, and the effects of promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis are better; and with compounding of other auxiliary materials with the fresh dendrobium officinale, the product has a magical effect on postoperative recovery, has the health-care effects of participating in synthesis of collagen in a body, increasing the human body resistance, resisting virus infection, promoting wound healing, regulating the human body intracellular fluid balance, helping create new cells and promoting cell metabolism, and also has a blood-enriching function.
Owner:ANHUI MULONGSHAN ECOLOGY TRAVEL DEV
Compound sodium acetate Ringer's injection and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108066360AAvoid hyponatremiaAvoid hypocalcemiaMetabolism disorderInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsSodium acetatePotassium
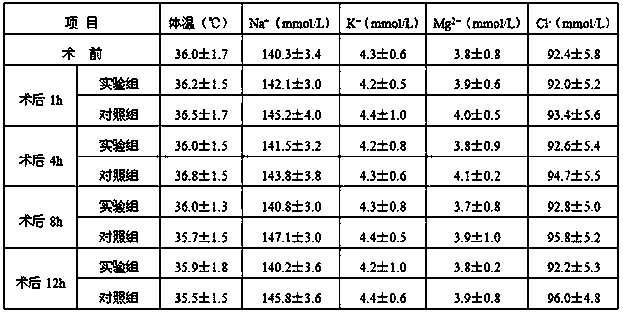
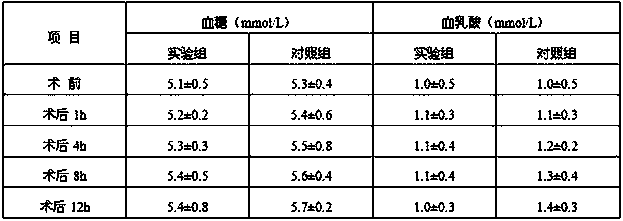
The invention discloses a compound sodium acetate Ringer's injection and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of injections. 1L of the injection is prepared from raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 0.800-0.900 g of sodium chloride, 0.700-0.800 g of potassium chloride, 0.280-0.350 g of magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 1.000-1.200 g of calcium gluconate monohydrate, 1.300-1.400 g of monopotassium phosphate, 1.500-1.700 g of sodium acetate trihydrate and 90-110 g of anhydrous dextrose. The invention further provides the preparation method of the injection. The injection is a hypotonic electrolyte glucose injection, belongs to an intracellular fluid replenisher, supplements moisture and electrolytes to intracellular fluid, extracellular fluid and intercellular fluid simultaneously after entering a human body, and is mainly used for maintaining balance of moisture and electrolytes and supplying energy to the organism when oral intake cannot be performed orenergy intake is insufficient.
Owner:HUAREN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
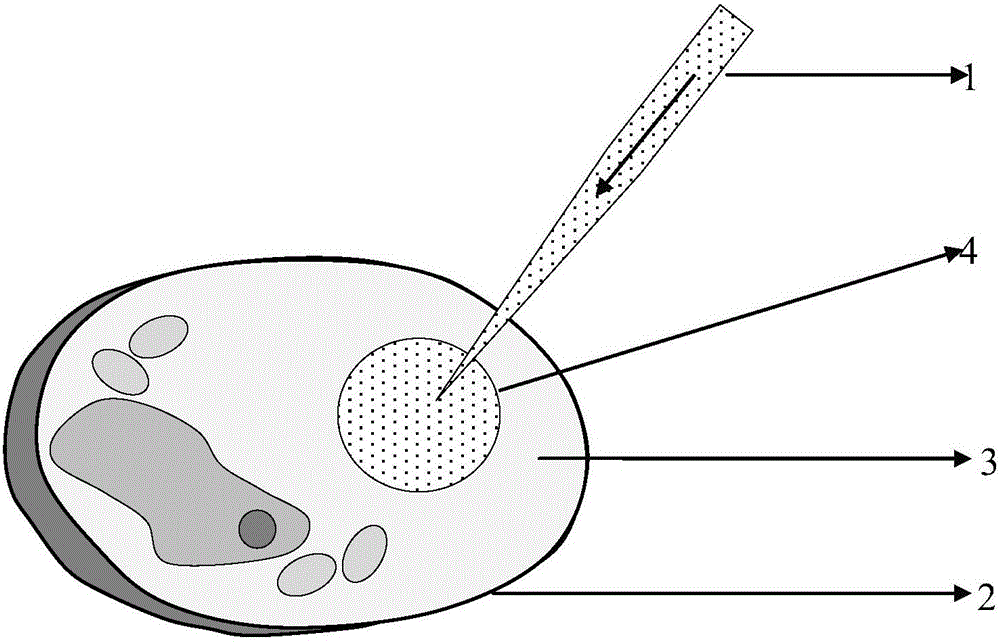
Preparation and application method for liquid fluorescent microsphere with cell tracing function
ActiveCN105778916AEasy to set upEasy to operatePowder deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsPhthalateCell tracking
The invention provides a preparation method and an application method for liquid fluorescent microspheres with a cell tracing function. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding nano crystal NaYF4:Yb<3+> and Er<3+> into an organic solvent cyclohexane, wherein the cyclohexane can be uniformly dispersed; adding an organic solvent dioctyl phthalate into a mixed solution, wherein the nano crystal is uniformly dispersed in the dioctyl phthalate after cyclohexane is volatilized; by using a capillary injection tube, and injecting the dioctyl phthalate in which the nano crystal is uniformly dispersed into in-vitro culture cells so as to form liquid microspheres in intracellular fluid; injecting cells with the liquid microspheres into a biological body by using a cell syringe. The nano crystal which is uniformly dispersed in the liquid microspheres can emit green fluorescence under the excitation of laser of 980nm, and has a cell tracking function. The invention discloses a completely new in-vivo cell tracing mode which has significant clinical meanings for studying migration, proliferation, metabolism, distribution regulation and the like of cells in bodies.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Cornea metaphase preserving fluid without serum component
The invention relates to cornea metaphase preserving fluid without a serum component. The cornea metaphase preserving fluid is prepared from an compound electrocular irrigating solution, sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, monopotassium phosphate, chondroitin sulfate, sodium hyaluronate, a HEPES buffer solution, hydrochloric acid dexamethasone, reduced glutathione and levofloxacin. The cornea metaphase preserving fluid is reddish and transparent liquid with a specific electrolyte ionic concentration, a pH value, crystalloid osmotic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure. Needed raw materials are easy to get, the cornea metaphase preserving fluid does not contain the serum component, the risks of infecting special viruses is avoided, osmotic pressure of intracellular fluid and osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid are balanced through various ions, and the preservation effect is remarkable.
Owner:拜欧迪赛尔成都生物科技有限公司
Methods and Solutions for Tissue Preservation
InactiveUS20080286745A1Promote resultsReduce ischemic, hypothermic and reperfusion injuringDead animal preservationHeart transplantationReperfusion injury
Described herein are compositions and methods particularly useful in the medical arts. The compositions and methods may be used in connection with the preservation of a portion of a mammal, for example, tissues, organs, appendages, limbs, extremities, stem cells, myocytes, bone marrow, skeletal muscle as well as an array of other medical procedures, such as cardiac surgery, transplantation and / or preservation. In various embodiments, the inventive composition may be hyperoxygenated and be formulated to resemble the biochemistries of natural intracellular fluids. The inventive composition includes active ingredients to reduce ischemic, hypothermic and reperfusion injury during transplantation, thereby resulting in improved post-transplant graft function and quality, when used in connection with organ transplantation and storage procedures, for example cardiac transplantation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Tonoplast localization sequence and its application
The invention relates to a tonoplast localization sequence and its application. The inventor, for the first time, separates a segment of signal sequence for specific location of cell tonoplast, i.e. a tonoplast targeting sequence (TTS). The sequence can lead accurate and efficient location of protein on intracellular tonoplast. The sequence can be utilized to perform localization transformation on target protein, and expression of the target protein at other sites other than the tonoplast can be reduced or prevented.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation technology of pumpkin-coconut juice mixed drink
InactiveCN104041884AHas beauty effectReplenish intracellular fluidFood preparationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTMixed drink
The invention discloses a preparation technology of pumpkin-coconut juice mixed drink, belonging to the field of food. The pumpkin-coconut juice mixed drink comprises the following active ingredients by weight: 20kg of pumpkin pulp, 12kg of coconut juice, 7kg of mango pulp, 5.5kg of white granulated sugar, 65g of aspartame, 380g of citric acid, 30g of xanthan gum, 65g of carboxymethyl cellulose and 55kg of water, and the products can be obtained finally through certain procedures. The invention has the beneficial effects of providing a preparation technology of the pumpkin-coconut juice mixed drink, the drink has the effects of being capable of enhancing physical strength, supplementing intracellular fluid, expanding blood volume, moistening the skin, and retaining youthful looks and beautifying, and has certain effect of preventing common diseases such as myopia of the adolescent and the osteoporosis of the middle-aged and the old.
Owner:马国丰
Method and apparatus for measuring the state of hydration of hairy animals such as horses, camels, and the like
InactiveUS20100234754A1Simple equipmentSimple requirementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWhole bodyBlood plasma
A method and apparatus for measuring and analyzing the state of hydration of a horse, camel or other hairy animal including providing power to a transmitting circuit to transmit a signal to electrodes resulting in a potential difference across the electrodes causing a flow of current between the electrodes reflecting the impedance encountered and sending a signal reflecting such information to receiving circuits which pass that data to processing circuits which process that data with other external inputs to produce an output display reflecting an indication of the state of hydration of the animal, comprising:means for providing a voltage difference across two or more electrodes; means for maintaining said electrodes in a fixed spatial relation and in good electrical contact with the skin of the animal without penetrating the skin of the animal on which said measurements are to be made; means for measuring the impedance of said animal in the region of or between the electrodes; means for transmitting the measured data to processing circuits which process that data with other external inputs to produce an output display reflecting an indication of the state of hydration of the animal, wherein the other external inputs include one or more of the factors for sex, age, electrode gap, and heart girth; and the output display provides indications of one or more of the outputs produced by formulations of the data reflecting the percentage of total body water, the percentage of extracellular fluid volume, the percentage of plasma and the percentage of intracellular fluid volume and the analyzing monitoring unit may be selected from the group of embodiments consisting of software in a computer, hard wired circuits, printed circuits, integrated circuits, microcircuits, microchips, silicon chips, digital chips, analog chips, hybrid chips and combinations of any or all of the members of this group.
Owner:LATMAN NEAL S +4
Method for forming high-resistance seal with quick rupture of membrane by quickly improving membrane permeability
InactiveCN103571819AImprove permeabilityEffective dissolutionElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentElectrical/wave energy enzyme treatmentHigh resistanceMembrane permeability
The invention discloses a method for forming high-resistance seal with quick rupture of a membrane by quickly improving membrane permeability. The method comprises the following steps: infusing an extracellular fluid containing ivermectin into a quick chemical feed pipe, then infusing an intracellular fluid containing amphotericin into a microelectrode, thereafter clamping cells by utilizing the microelectrode of the intracellular fluid containing amphotericin to realize high-resistance seal, lifting the anchorage-dependent cells to the opening of the quick chemical feed pipe, opening the quick chemical feed pipe to culture the cells in the extracellular fluid containing ivermectin and reduce the Ra value of the cells to 10 at an electrophysiological test state, and then ending culturing. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly and efficiently dissolving amphotericin B in the intracellular fluid and combining the amphotericin B with the ivermectin to quickly improve the membrane permeability, so that quick rupture of the membrane is realized in the membrane clamp test to form high-resistance seal for experiments.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating burns and scalds and preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine composition
InactiveCN105031016AReduce exudationReduce the chance of infectionHydroxy compound active ingredientsAerosol deliverySide effectAngelica Sinensis Root
The invention relates to the field of traditional Chinese medicine preparations and particularly relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating burns and scalds. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of coptis chinensis, 5-15 parts of radix sanguisorbae, 5-15 parts of radix rehmanniae, 10-15 parts of angelica sinensis, 5-15 parts of rheum officinale, 1-3 parts of musk, 2-5 parts of borneol, 40-60 parts of beewax and 200-300 parts of sesame oil. The traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating burns and scalds is prepared according to the theory of traditional Chinese medicines. All the traditional Chinese medicines are combined and are mutually supplemented to take the curative effect of rapidly healing wounds of burns and scalds of skins; the traditional Chinese medicine preparation is low in toxic or side effect and capable of directly acting on the wounds and treating both symptoms and root causes. The traditional Chinese medicine composition disclosed by the invention has the advantages of softness, lubrication as well as no hardening and bonding discomfort. A layer of film is formed after the traditional Chinese medicine composition rapidly covers an injured wound, so that the seeped intracellular fluid of injured cells is effectively reduced, and the infection opportunity of exogenous bacteria is reduced. Meanwhile, the body movement of a patient is not influenced.
Owner:王斌
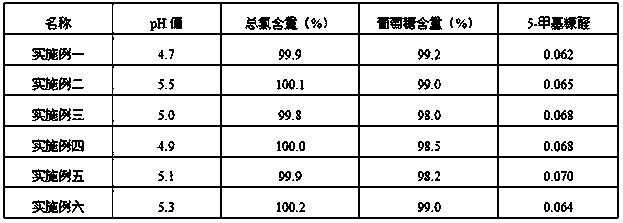
Method for detecting organic acid in intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN103698449AEasy to analyzeShorten the timeComponent separationGas phaseGas liquid chromatographic
The invention relates to a method for detecting organic acid in intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical test and measurement. The detecting method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) high speed centrifuging fermentation liquor, and respectively collecting intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid; (2) preparing an intracellular metabolin sample, cleaning the collected thallus through normal saline, dissolving the thallus in cold methanol, ultrasonic crushing, low temperature extracting, centrifuging to collect extract supernatant, adding internal standard substance, and vacuum drying at a low temperature; (3) preparing an extracellular fluid sample, removing protein in the extracellular fluid through acetonitrile, vortex oscillating, centrifuging to collect supernatant, adding internal standard substance, and vacuum drying at a low temperature; (4) deriving the sample, and adding a sugar derivating agent and an amino acid derivating agent; and (5) carrying out gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and collecting data. The detecting method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple sample treatment, simple and convenient operation, short detection time, high sensitivity, high repeatability of test results, capability of preparing a plurality of samples, and the like.
Owner:陈东
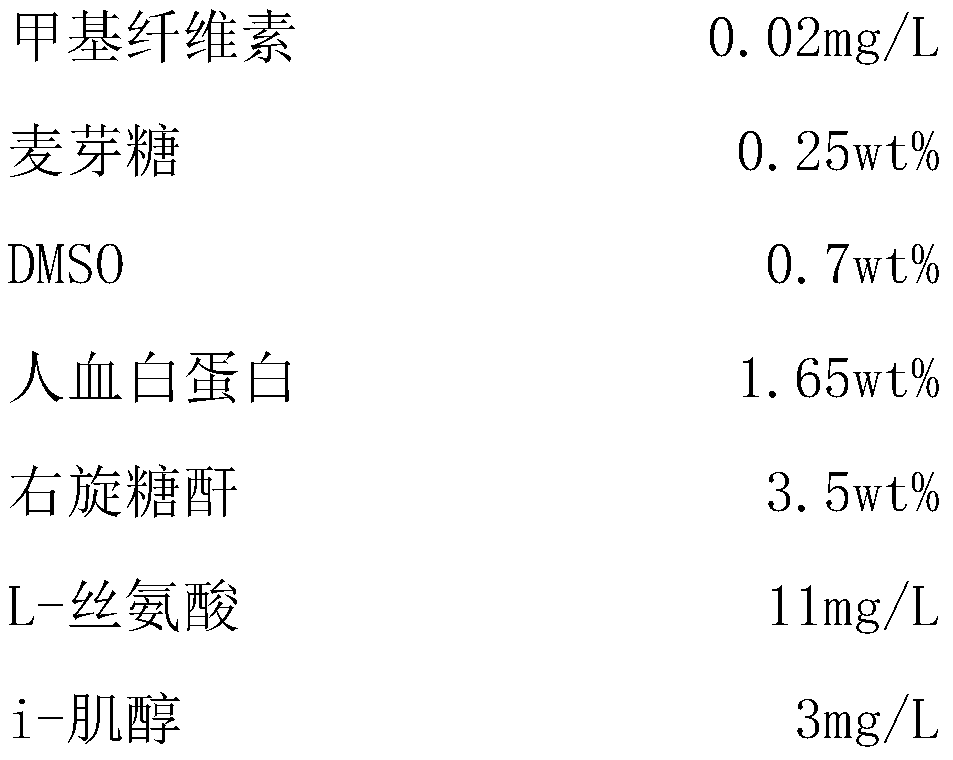
Cell cryopreservation solution and cryopreservation method
InactiveCN111345282AAvoid damageReduce harmDead animal preservationCelluloseSodium Chloride Injection
The invention relates to the technical field of cell cryopreservation. The invention relates to a cell cryopreservation solution and a cryopreservation method. Wherein the cell cryopreservation liquidis prepared from methyl cellulose, maltose, DMSO, human serum albumin, dextran, L-serine, i-inositol and sodium chloride injection, and in the cell cryopreservation solution, DMSO can prevent damagecaused by intracellular fluid ice crystal formation, osmotic pressure change, cell structure disorder and the like; methyl cellulose is used as a stabilizer and a tackifier, so that the damage to cells caused by ice crystals formed by free water in the cryopreservation process is reduced; maltose has good crystallization resistance and prevents damage of ice crystals to cells. Through the combination of the raw materials, the loss of cells caused by ice crystals can be prevented to the maximum extent, and the content of DMSO is reduced as much as possible, so that the cell cryopreservation solution has a relatively good protection capability on cells such as PBMC or stem cells or T lymphocytes, and is high in survival rate.
Owner:GUANGDONG PANGUARD CELL BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Cellulase-rich pest-resistant planting substrate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106577230AImprove protectionAnti-insect effectGrowth substratesCulture mediaBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTAllium sativum
The invention discloses a cellulase-rich pest-resistant planting substrate and a preparation method thereof. The cellulase-rich pest-resistant planting substrate is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: a cellulase preparation, a resin monomer mixture, soybean starch, sweet potato vines, garlic straws, cinnamomum camphora sawdust, leaf mold, matrine, diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate, sheep manure balls, humic acid powder, tomato leaves and an appropriate amount of water; and intracellular fluid of melia azedarach leaves, the tomato leaves and the like contains pest-repellent active ingredients. According to the planting substrate disclosed by the invention, materials are subjected to pulp grinding and crushing treatments, active ingredients are concentrated, starch grafted resin is used for performing adsorption at first, the stability of the resin provides a very good protective effect, so that a certain pest preventing effect can be achieved, and meanwhile, the added garlic straws have a certain preventive effect on pests.
Owner:蚌埠市亿丰生物有机肥有限公司
Preparation method of novel photosynthesis accelerant combined nitrogen-magnesium foliar fertilizer
InactiveCN108250000AEasy to optimizeImprove the preservation effectMagnesium fertilisersNitrogenous fertilisersSolventHigh pressure homogenization
The invention discloses a preparation method of novel photosynthesis accelerant combined nitrogen-magnesium foliar fertilizer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out amplification culture on photosynthetic bacteria to obtain amplification culture bacterium liquid; then carrying out cell crushing on the amplification culture bacterium liquid; carrying out secondary impurity removal to obtain supernatant; taking the extracted supernatant as a solvent and adding a nutrient element main body; after mixing, stirring and dissolving, adding mixed oil and a surfactant; emulsifying in a high-pressure homogenization machine to obtain emulsion. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, culture liquid containing photosynthetic bacterium intracellular fluid is used as a diluting agent of the foliar fertilizer, and the photosynthetic bacteria are bacteria with a function of producing aminolevulinic acid; the culture liquid containing the photosynthetic bacterium intracellular fluid has the effect of simulating an environment in a photosynthetic bacterium cell, and an active substance aminolevulinic acid is easy to form; the preservation effect and the acting effect are improved.
Owner:安徽金敦福农业科技有限公司
Method for coating skin abrasion, laceration, burn or oedema after surgery
ActiveUS10064975B2Inhibit productionReduce fatNon-adhesive dressingsAbsorbent padsAluminium chlorideInjury mouth
The present invention relates to a biological film-forming agent which is for facilitating wound healing and coating and protecting biological organs, and for coating and protecting damaged cells, wound surfaces, organs and damaged sites of organs, and wound surfaces reaching soft tissues such as muscle and facia, periosteum or bone cortex. Provided is a biological film-forming agent for suppressing exudation of intracellular fluid from damaged cells, suppressing expansion of inflammation reactions and secondary inflammation reactions resulting from production of fibrin and eliminating adverse effects caused by formation of stabilised fibrin on healing. Various problems can be solved by using the agent containing aluminium chloride, cyclodextrin and water as base components.
Owner:LILAC LAB
Preparation method and application of mammal bone marrow intracellular fluid
InactiveCN103463128ASignificant tumor suppressive effectUnknown materialsAntineoplastic agentsBone marrow cellCell membrane
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of mammal bone marrow intracellular fluid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding fresh isolated bone marrow cells into normal saline, wherein concentration is 108 to 109cell / ml; then repeatedly freezing and thawing to crack the bone marrow cells; and separating cell membranes from intracellular fluid by high speed centrifugation, then extracting surface supernatant, filtering to the aseptic state so as to obtain filtrate, i.e. the mammal bone marrow intracellular fluid, wherein the fresh isolated bone marrow cells are from a mammal. Current, tumor treatment modes comprise drug treatment, operative treatment and radiotherapy; the drug treatment further comprises chemical drug treatment, biological treatment and gene therapy, but the chemical drug treatment, the biological treatment and the gene therapy all cannot achieve a satisfied treatment effect; and particularly, chemotherapy is used as the main treatment method, but has a particularly serious killing effect on a human body, and thus, usually, tumor is not inhibited, but a patient is died. The mammal bone marrow intracellular fluid prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has no toxic or side effects on the body and has an obvious tumor inhibiting effect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ocular analyte sensor
An ocular lens including a receptor half can be used to determine the amount of analyte in eye fluid. The receptor half is capable of binding a specific analyte or a detectable labeled competitor half. The amount of detectably labeled competitor half displaced by analyte from the receptor half is measured, and a means is provided for determining the analyte concentration in ocular fluids, such as tears, aqueous fluid, or interstitial fluid. Analyte concentration in eye fluid is in turn indicative of the analyte concentration in body fluid or tissue samples, such as blood or intracellular fluid.
Owner:EYESENSE AG
8 electrode intelligent body fat bracelet
PendingCN110063720AThe test result is accurateShort test timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyWhole body
The invention discloses an 8 electrode intelligent body fat bracelet, and particularly relates to the technical field of intelligent wearable body fat measurement. The 8 electrode intelligent body fatbracelet comprises a ring body and a body fat scale. One end of the ring body is fixedly connected with a first ring belt, and the other end of the ring body is fixedly connected with a second ring belt. A current conversion module generates a testing mode of multi-frequency alternating current signals, according to alternating current signal testing in the testing mode, the alternating current signals are adopted for analyzing internal components of the human body, the alternating current signals can reflect the components of the human body more truly compared with direct current signals, according to another multi-frequency testing, the alternating current signals at multiple frequency bands are adopted for analysis, components of intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid can be distinguished, meanwhile, in combination with body fat measured data of the body fat scale, whole body detection is equivalently completed, thus, a precise detection result is obtained, compared with the previous direct current signal detection technology, the testing time is shorter, the product power consumption is lower, the detected data size is larger, and obtained analysis result data is more accurate.
Owner:深圳卓隆智能电子有限公司
Solution sterilization and alga removal device
PendingCN108850787AChange in permeabilityChange surface tensionFood electrical treatmentEngineeringCell wall
The invention discloses a solution sterilization and alga removal device. The solution sterilization and alga removal device comprises a sterilization and alga removal unit and a solution homogenization and conveying unit, wherein the solution homogenization and conveying unit comprises a liquid inlet spraying nozzle and a liquid storage groove arranged below the liquid inlet spraying nozzle; a middle pressurizing pump is arranged at an outlet end of the liquid storage groove; a powdered magnetic seed is arranged in the liquid storage groove; the sterilization and alga removal unit comprises ahigh-gradient magnetic field device and a high-frequency electric field device. According to the device provided by the invention, deflection and an electronic vortex are generated through the magnetic seed under the common effect of a high-gradient magnetic field and a high-frequency electric field, and the osmotic pressure and surface tension of a solution are changed instantly. The magnetic seed forms small deflection impact under the action of a magnetic field Lorentz force to damage cell walls. The cell walls are damaged due to osmotic pressure difference of tissue liquid inside and outside the cells walls and the impact of the electronic vortex, and intracellular fluid flows out, so that the effect of killing alga and bacteria in the solution is realized.
Owner:北京中电聚能新技术有限公司
A medium-term corneal preservation solution without serum components
The invention relates to cornea metaphase preserving fluid without a serum component. The cornea metaphase preserving fluid is prepared from an compound electrocular irrigating solution, sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, monopotassium phosphate, chondroitin sulfate, sodium hyaluronate, a HEPES buffer solution, hydrochloric acid dexamethasone, reduced glutathione and levofloxacin. The cornea metaphase preserving fluid is reddish and transparent liquid with a specific electrolyte ionic concentration, a pH value, crystalloid osmotic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure. Needed raw materials are easy to get, the cornea metaphase preserving fluid does not contain the serum component, the risks of infecting special viruses is avoided, osmotic pressure of intracellular fluid and osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid are balanced through various ions, and the preservation effect is remarkable.
Owner:拜欧迪赛尔成都生物科技有限公司
Separation and extraction method of amino acid in different forms of monocotyledons
ActiveCN108195656ATrue reflection distributionTrue reflection of transportationPreparing sample for investigationInsoluble proteinSlurry
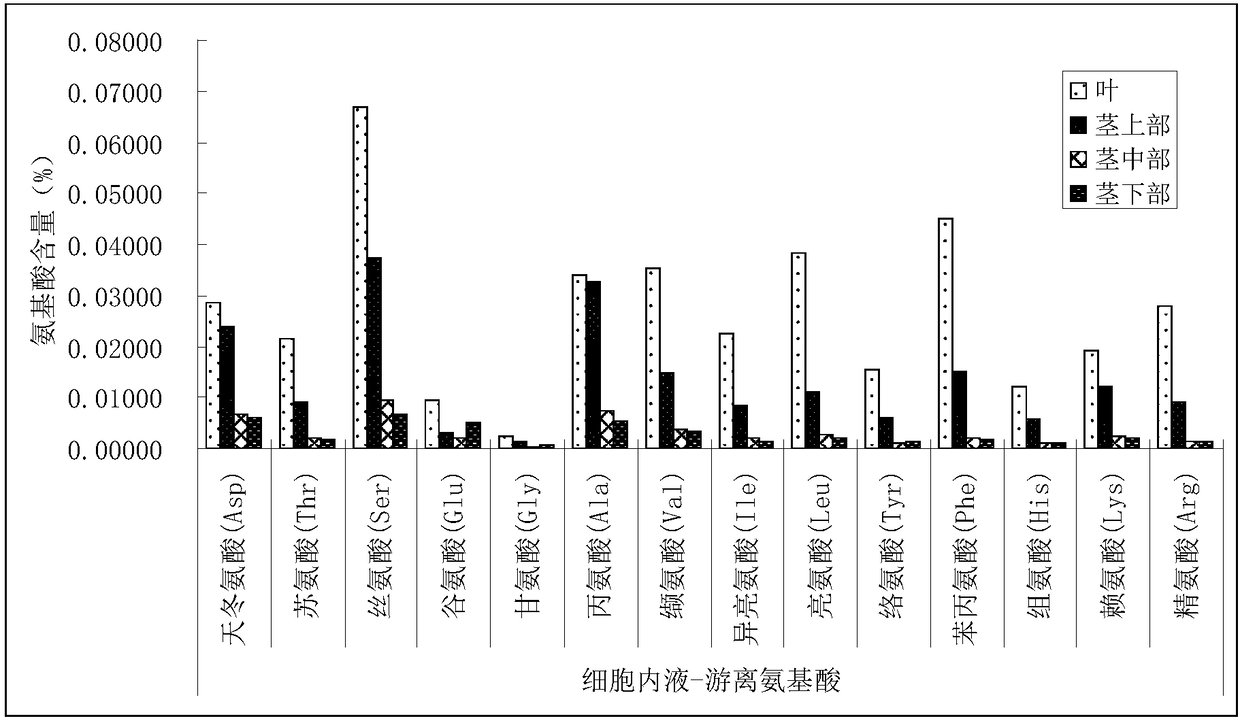
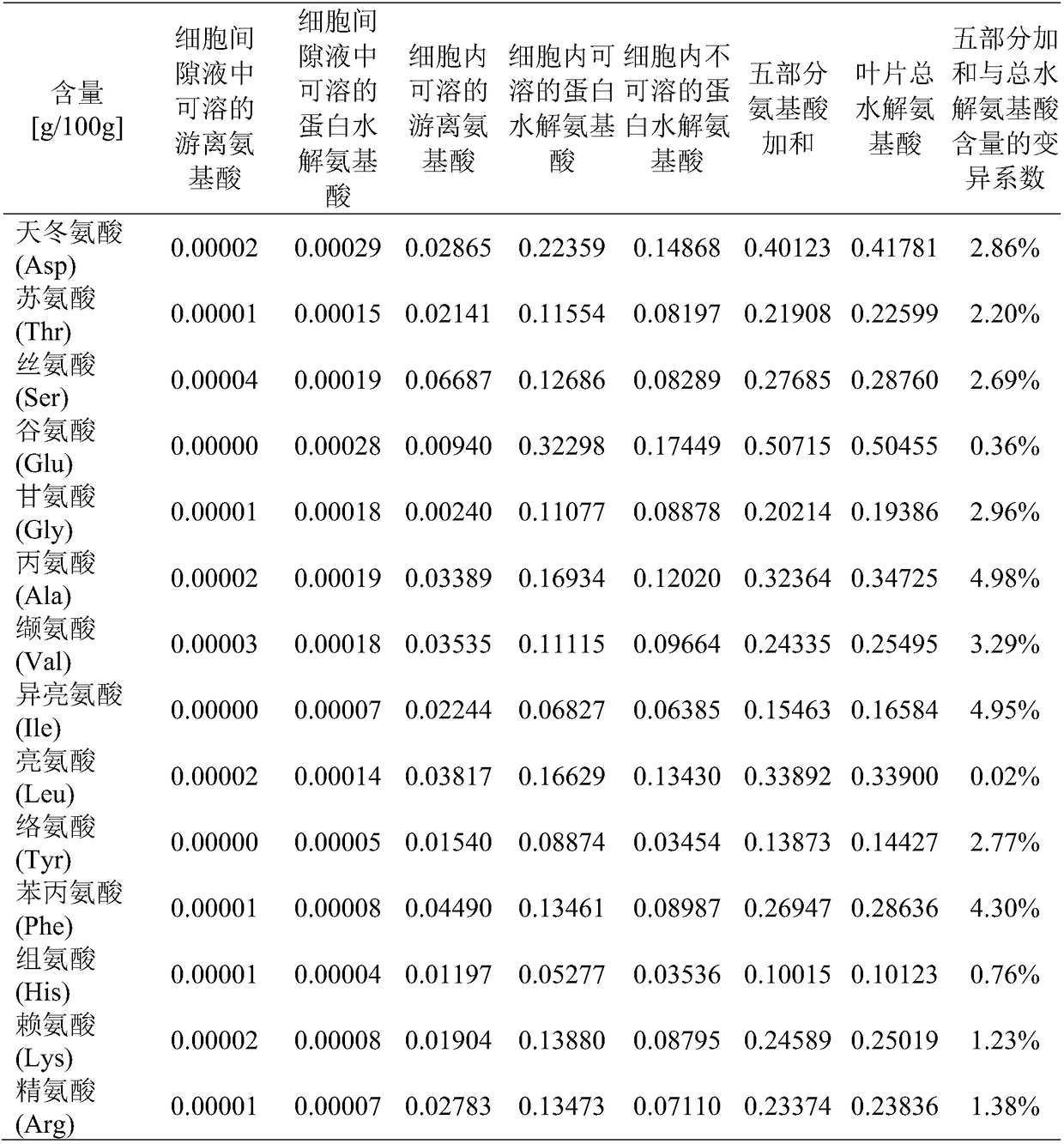
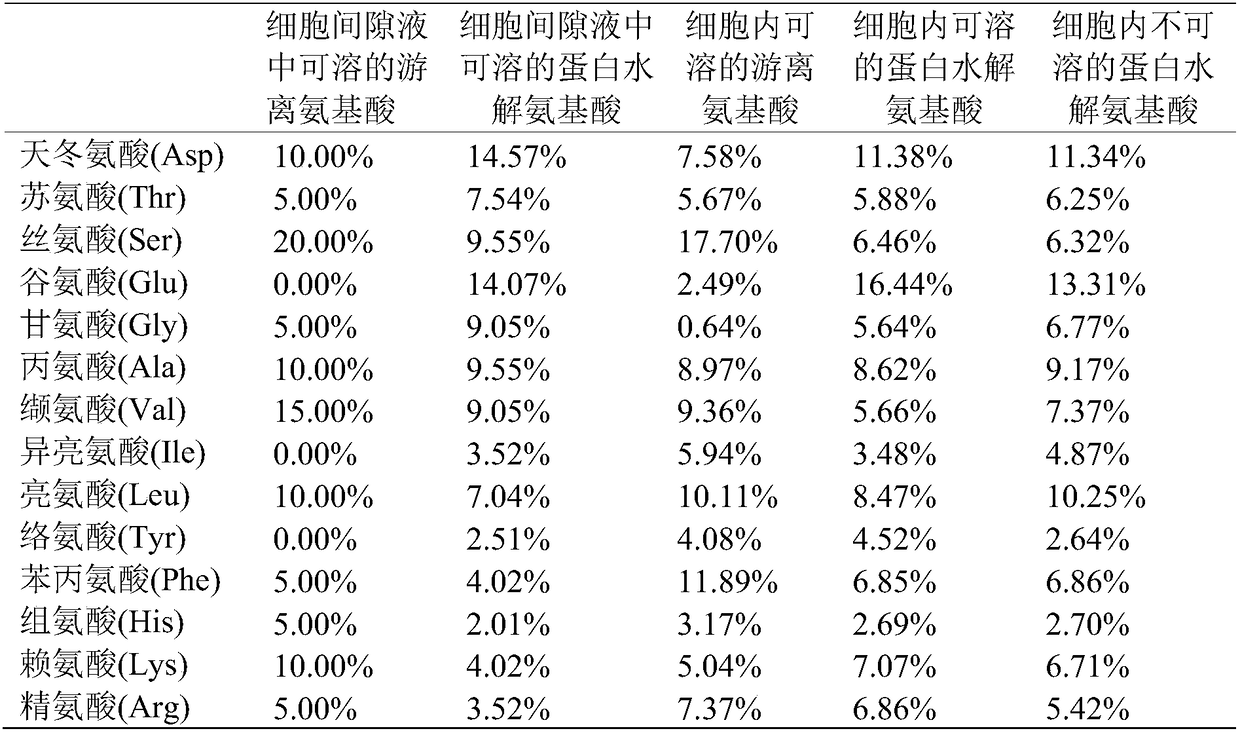
The invention discloses a separation and extraction method of amino acid in different forms of monocotyledons, and belongs to the technical field of separation and extraction of amino acid. The methodspecifically comprises the following steps: separating out intercellular washing fluid by carrying out water soaking, vacuumizing and centrifuging on stems or leaves of the monocotyledons; cutting the stems or the leaves from which the intercellular washing fluid is separated out into pieces, pulping in an ice bath and centrifuging the slurry to obtain intracellular fluid and solid residues; respectively detecting the content of soluble free amino acid in the intercellular washing fluid and soluble protein hydrolytic amino acid in the intracellular fluid; detecting the content of insoluble protein hydrolytic amino acid in the solid residues to obtain the content of amino acid in different forms. The method has the advantage that distribution and transportation of the amino acid in plantsare truly reflected, which has great theoretical and practical value for exploring physiology, metabolism and development of plants.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
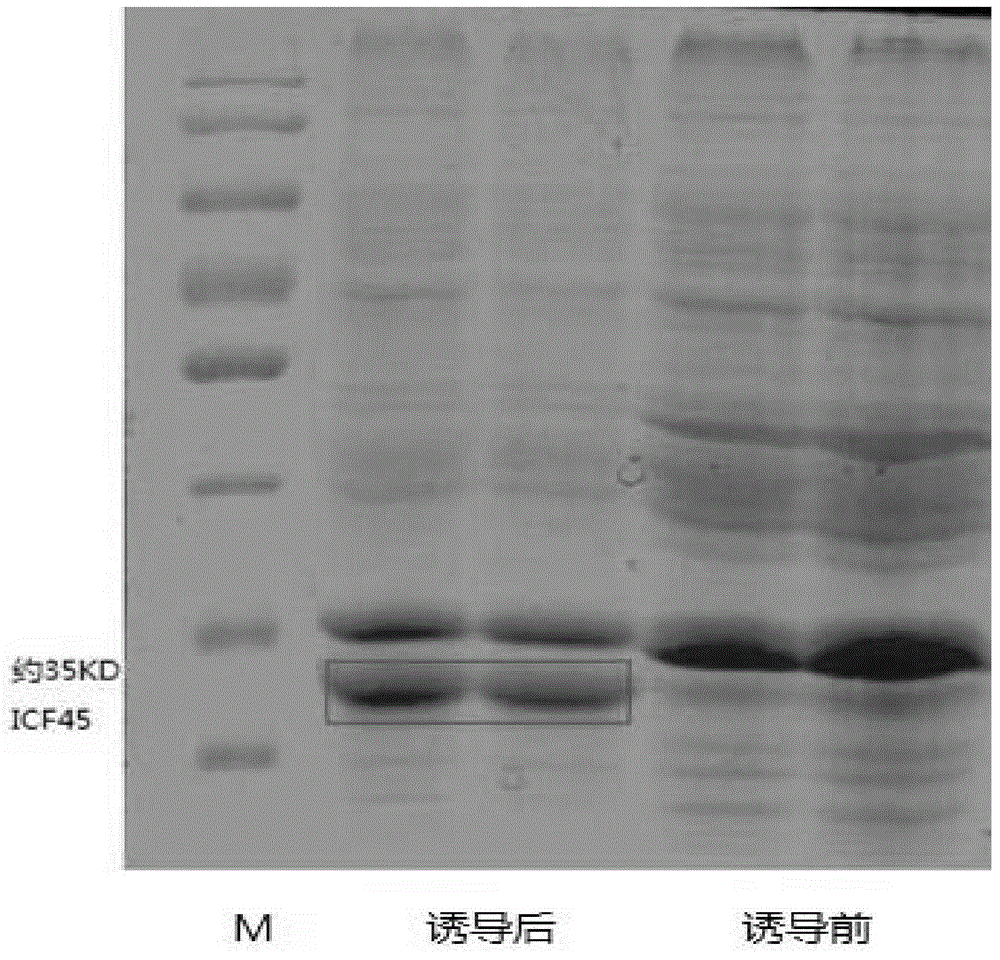
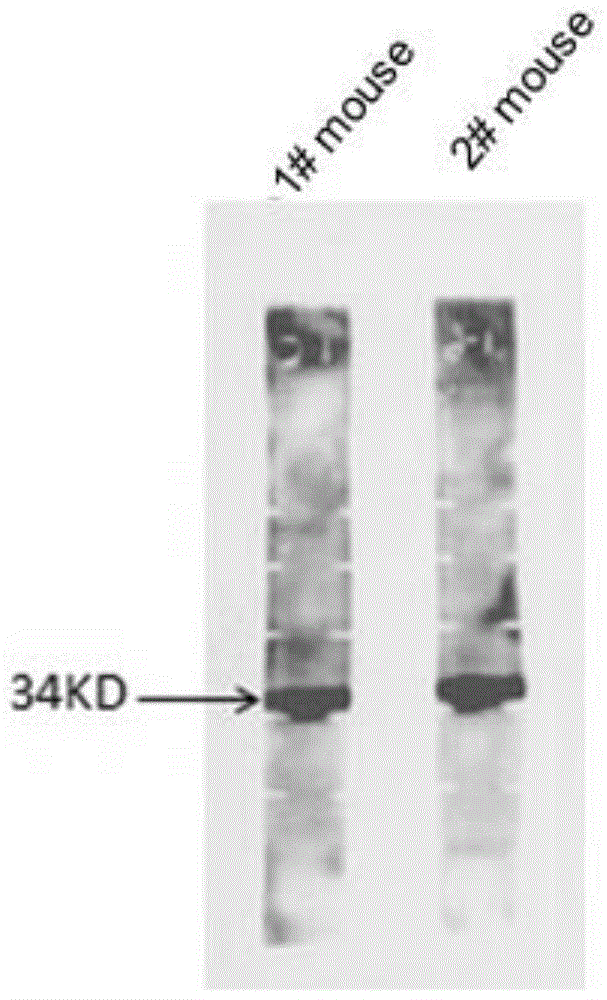
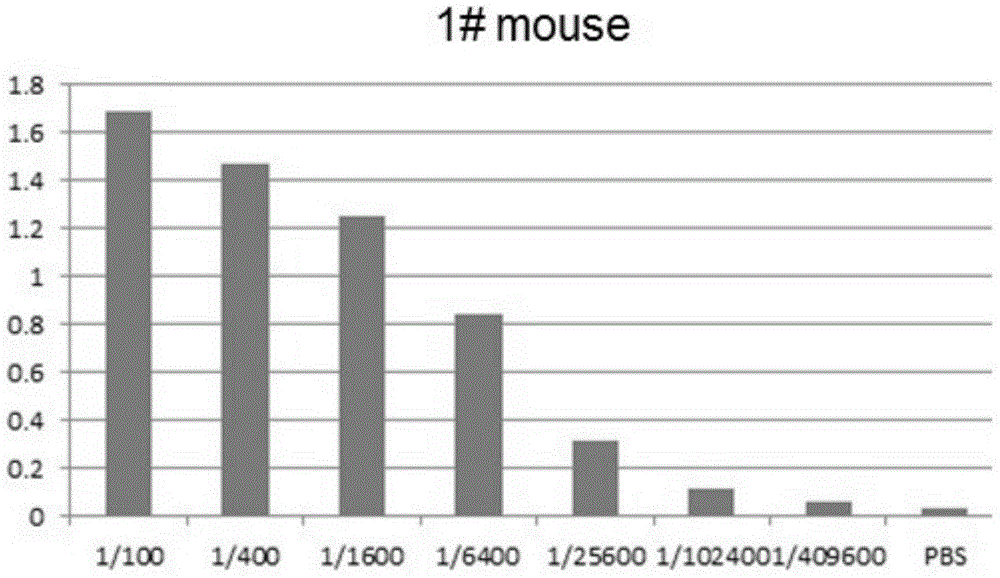
Preparation and application of a kind of human icf45 monoclonal antibody
The invention discloses preparation and method of a human ICF (Intracellular Fluid) 45 monoclonal antibody, provides mus musculus hybridoma (mus musculus hybridoma) F5H1D1H2 with the storage number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.8659, and also provides mus musculus hybridoma (mus musculus hybridoma) F5H1D1H2 with the storage number of CGMCC No.8659. The experience result shows that a mus musculus hybridoma (mus musculus hybridoma) F5H1D1H2 can be obtained by screening; and the mus musculus hybridoma (mus musculus hybridoma) F5H1D1H2 is subjected to biological characteristics identification in order to further research the influence of ICF45 at protein level on normal physiological process of the cell, and provide basis and build foundation for further study on the corresponding functional relation and function in diseases, tumor and allergic reaction, as well as prepare potential drug protein capable of inhibiting corresponding diseases.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Tonoplast localization sequence and its application
The invention relates to a tonoplast localization sequence and its application. The inventor, for the first time, separates a segment of signal sequence for specific location of cell tonoplast, i.e. a tonoplast targeting sequence (TTS). The sequence can lead accurate and efficient location of protein on intracellular tonoplast. The sequence can be utilized to perform localization transformation on target protein, and expression of the target protein at other sites other than the tonoplast can be reduced or prevented.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com