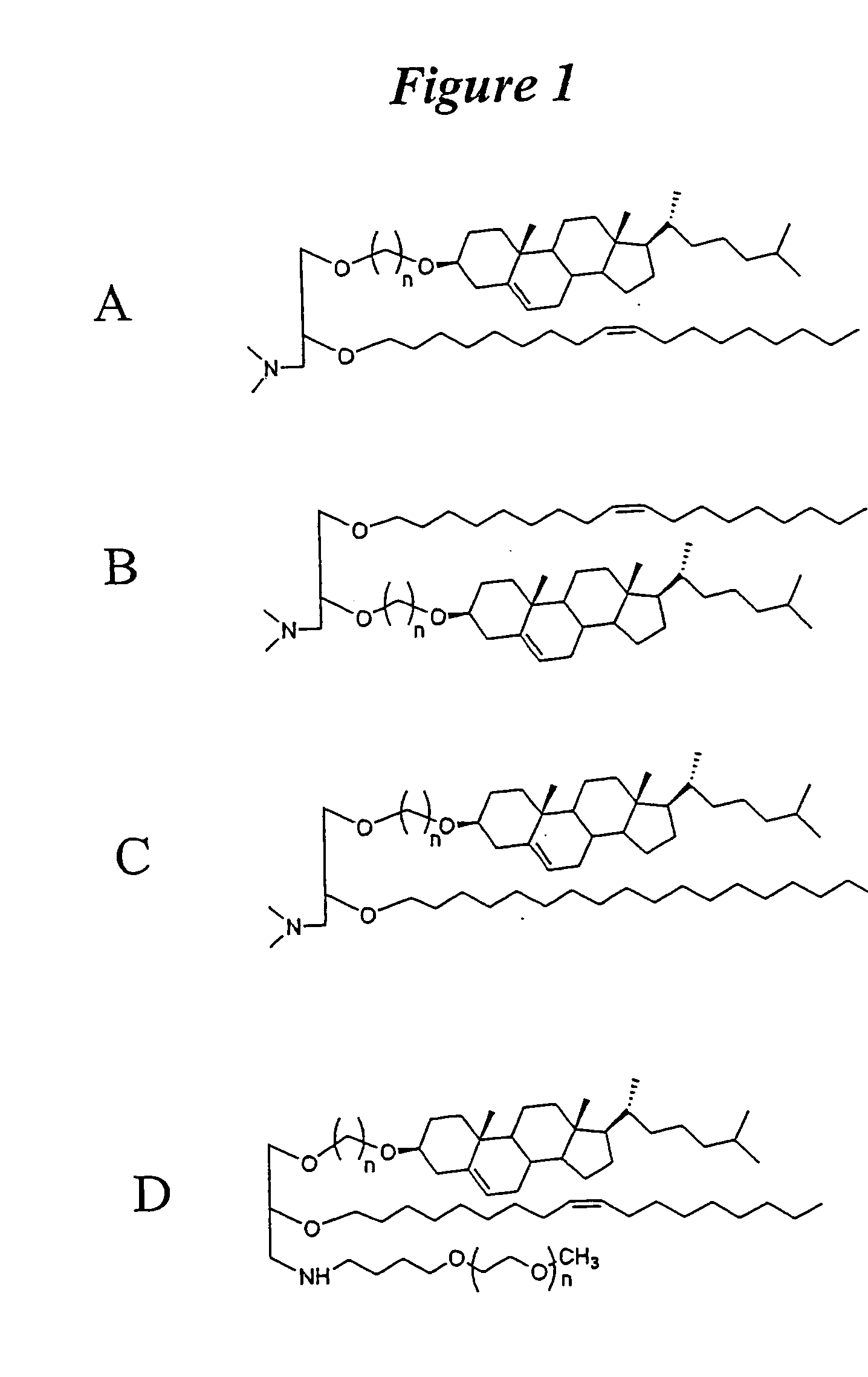
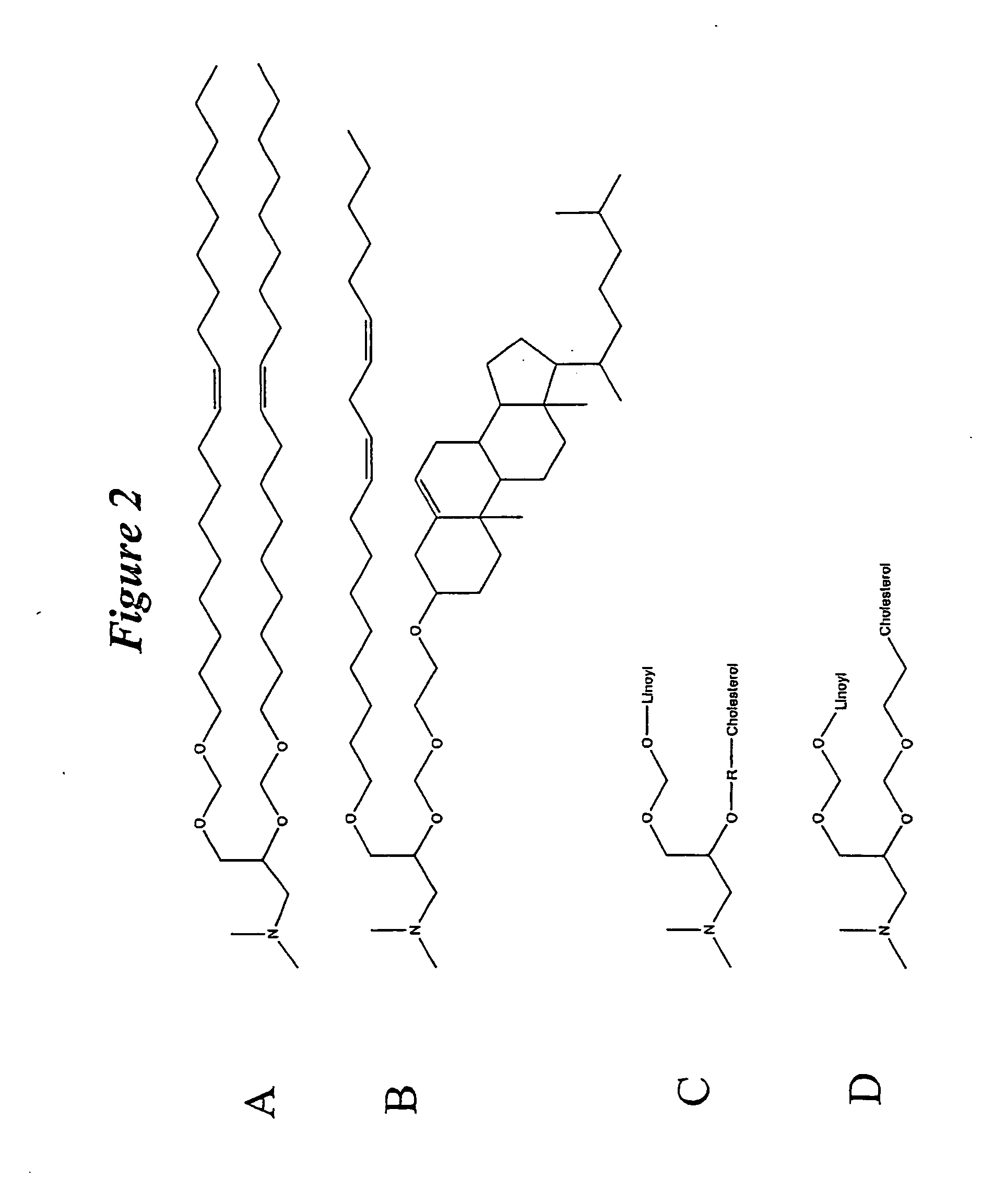
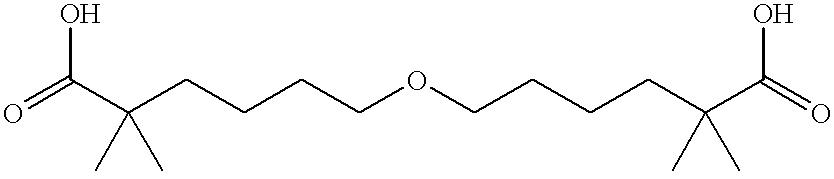
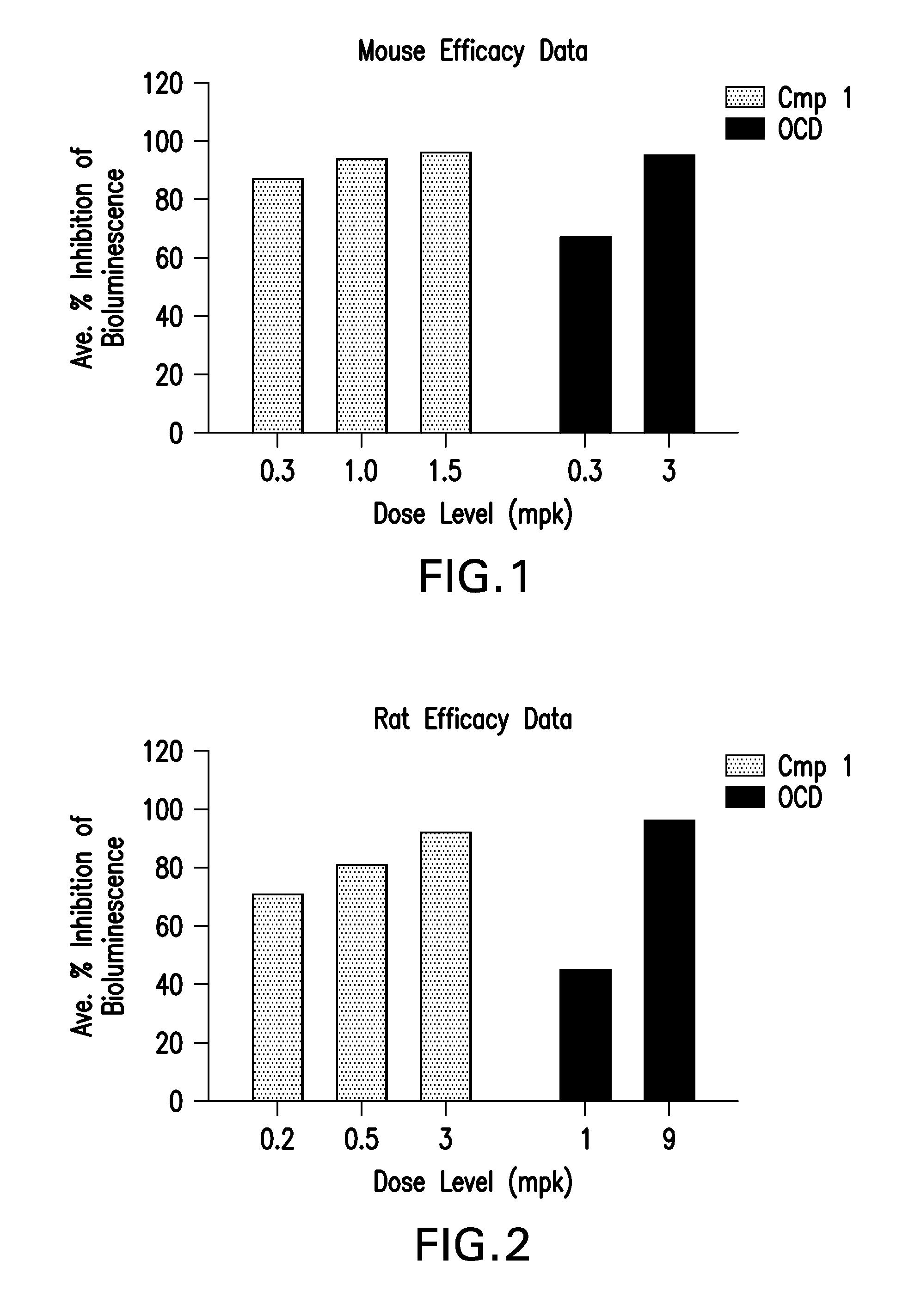
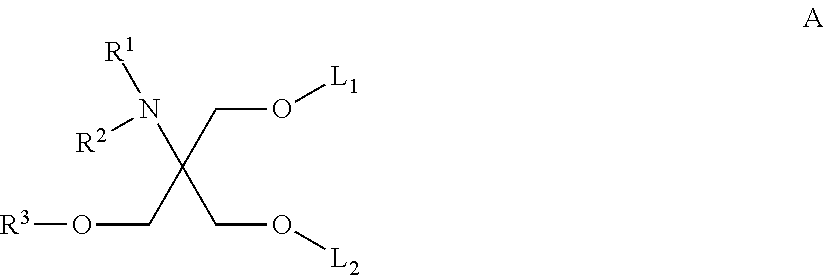
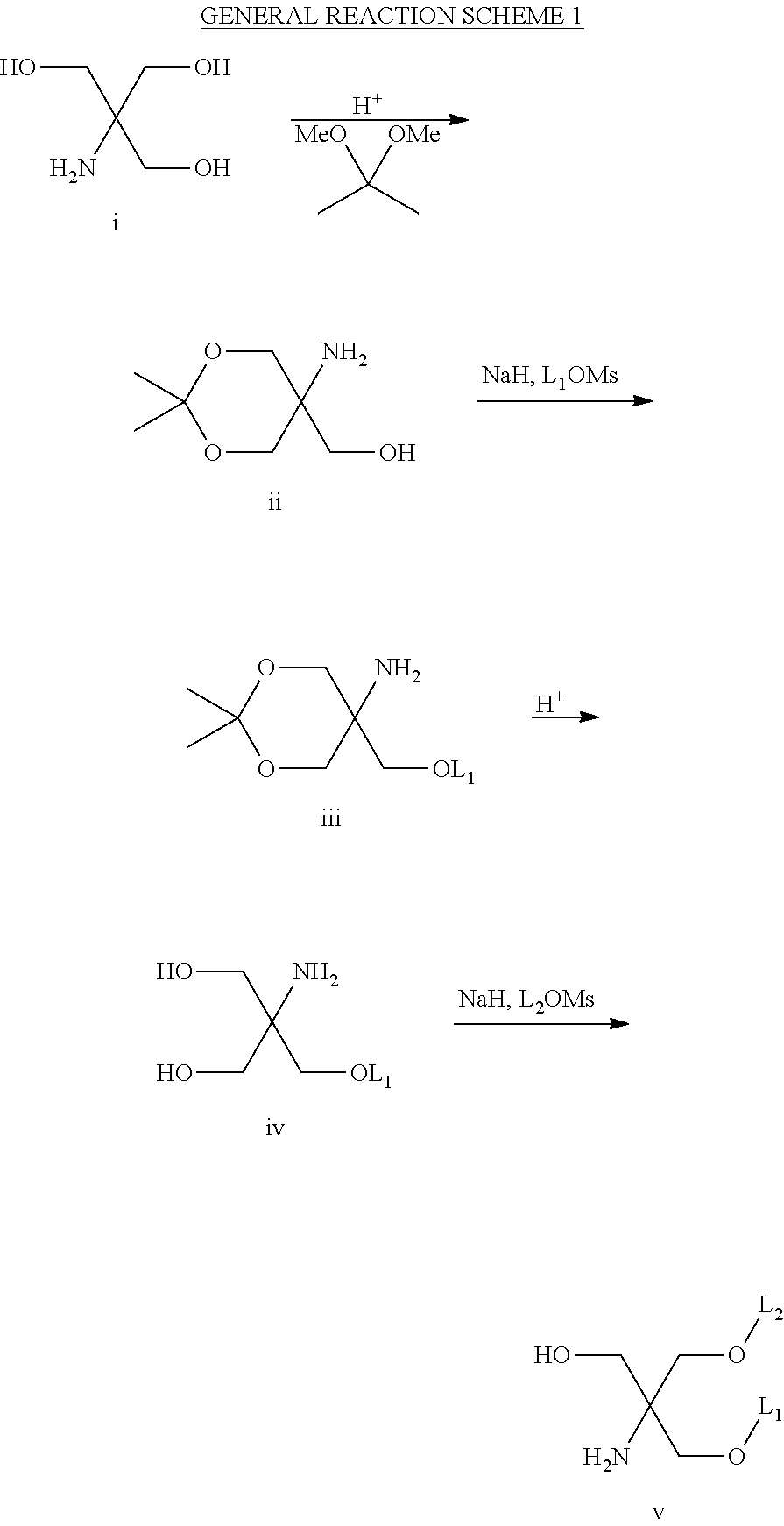
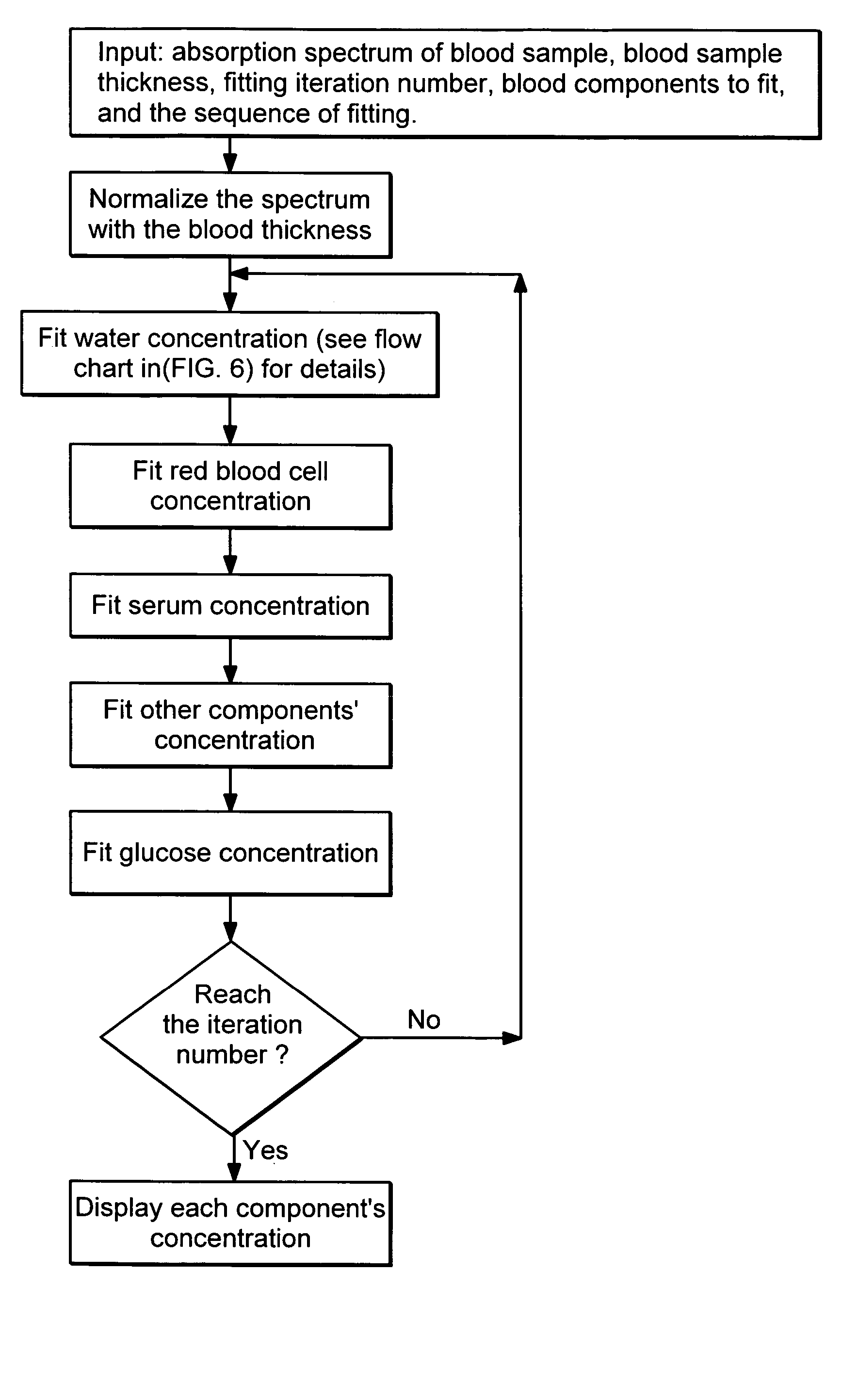
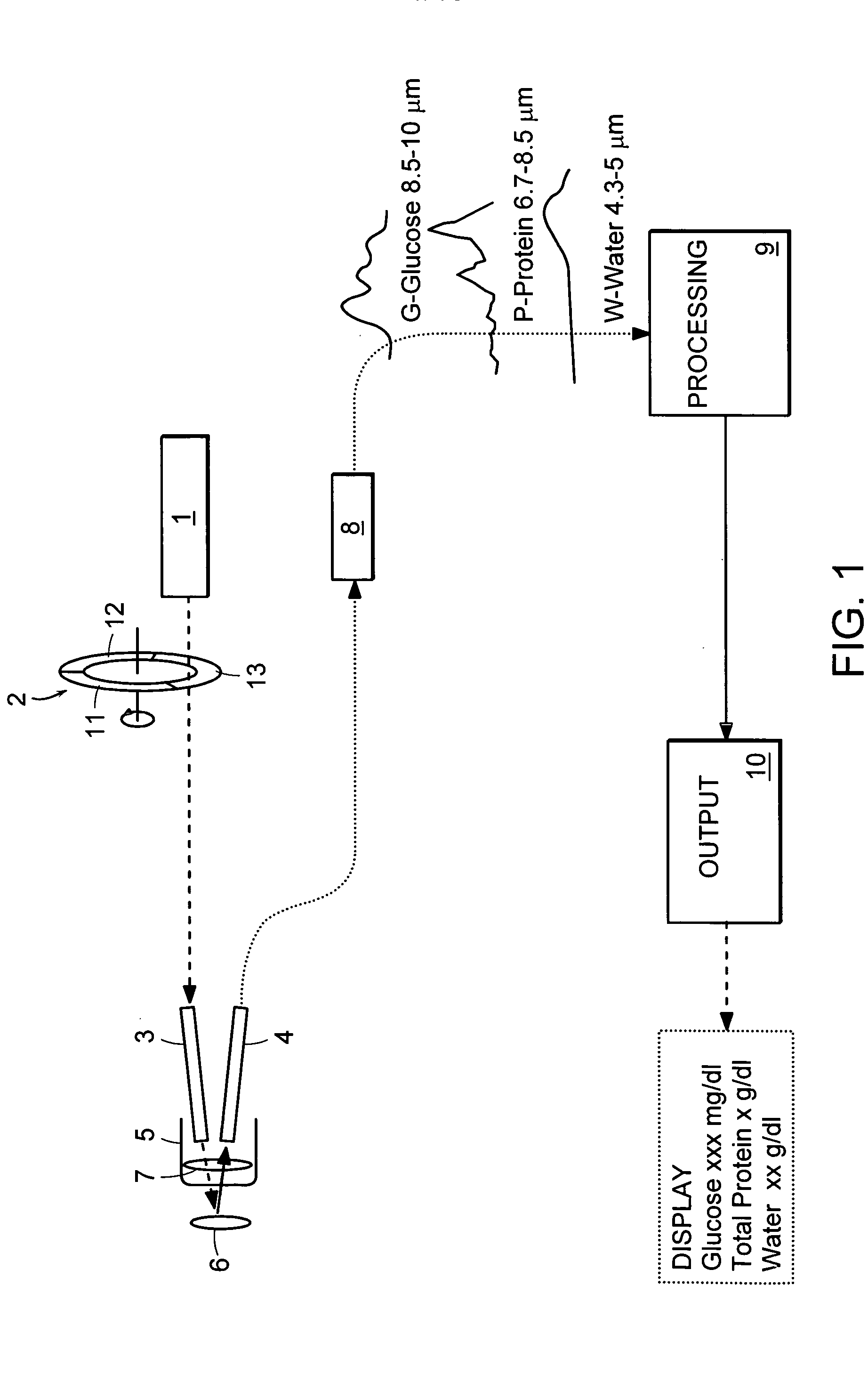
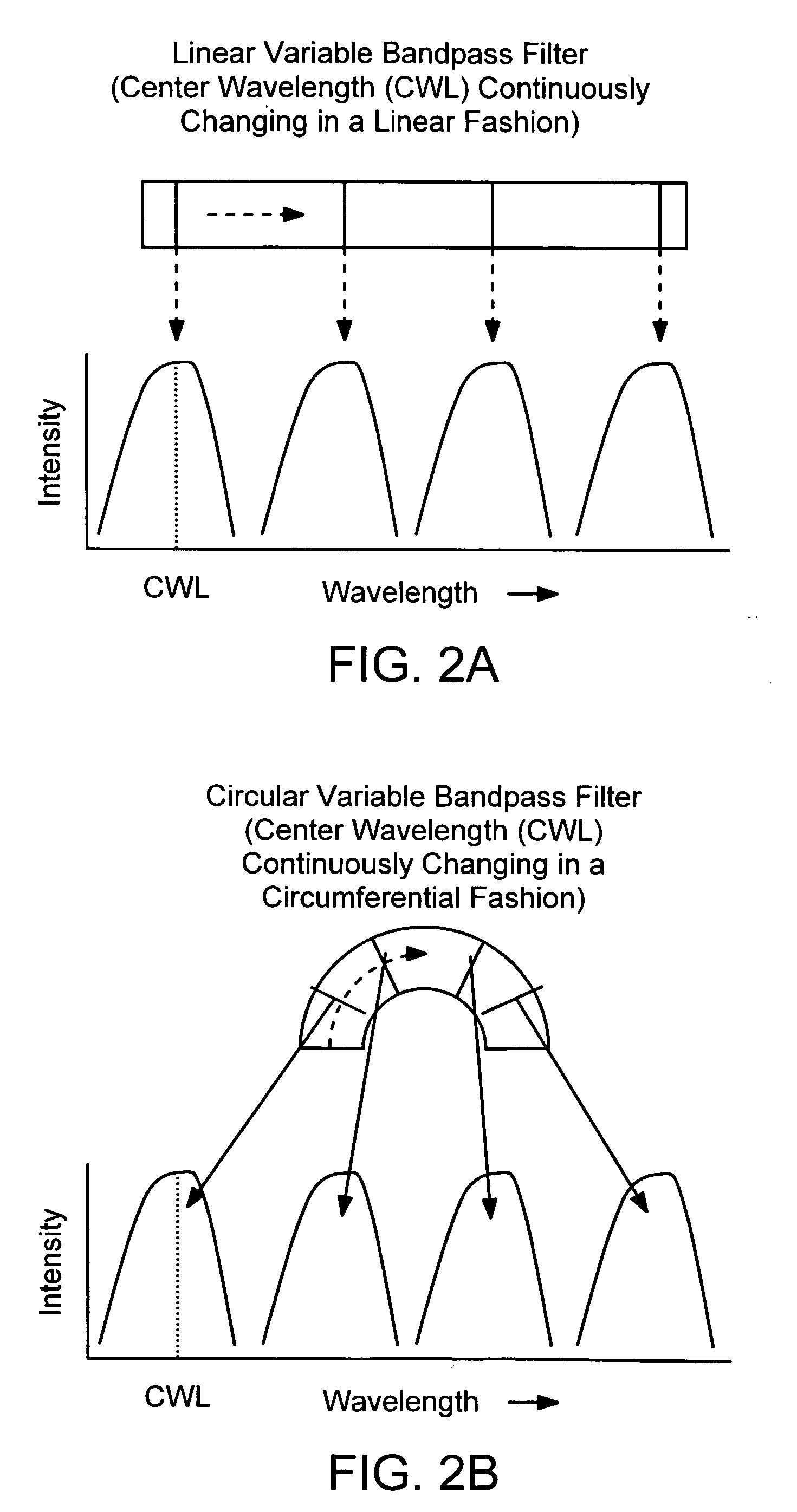
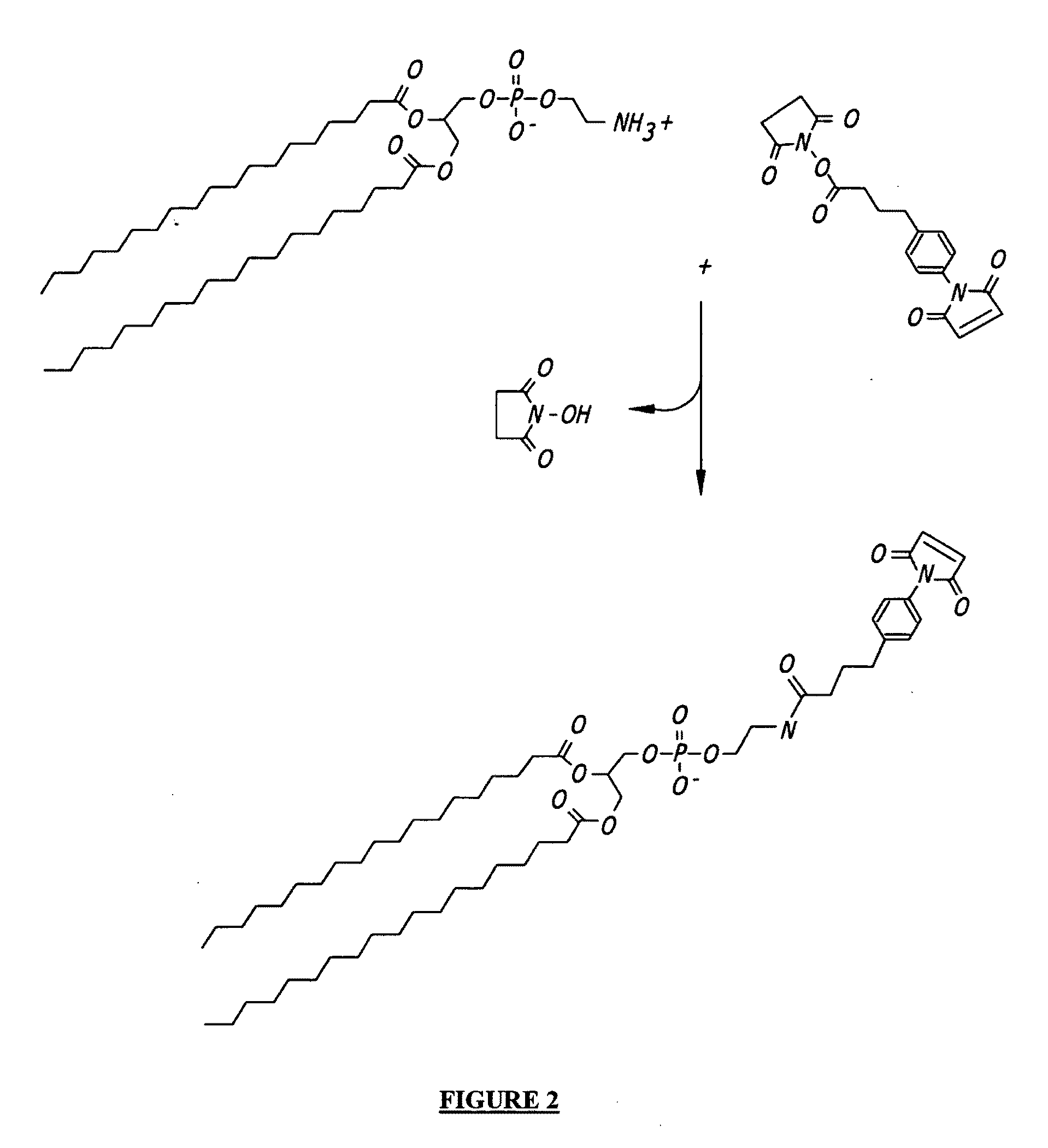
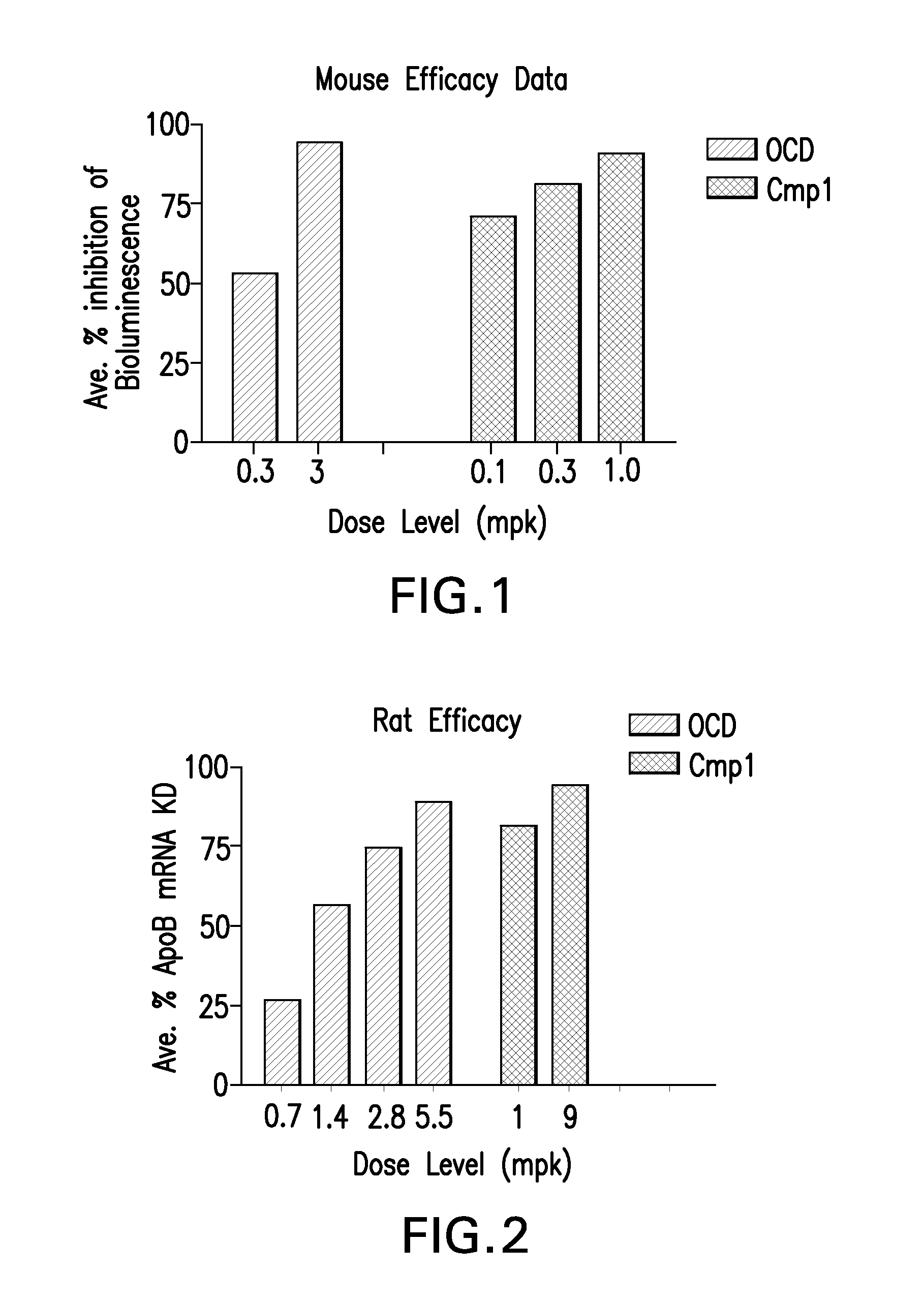
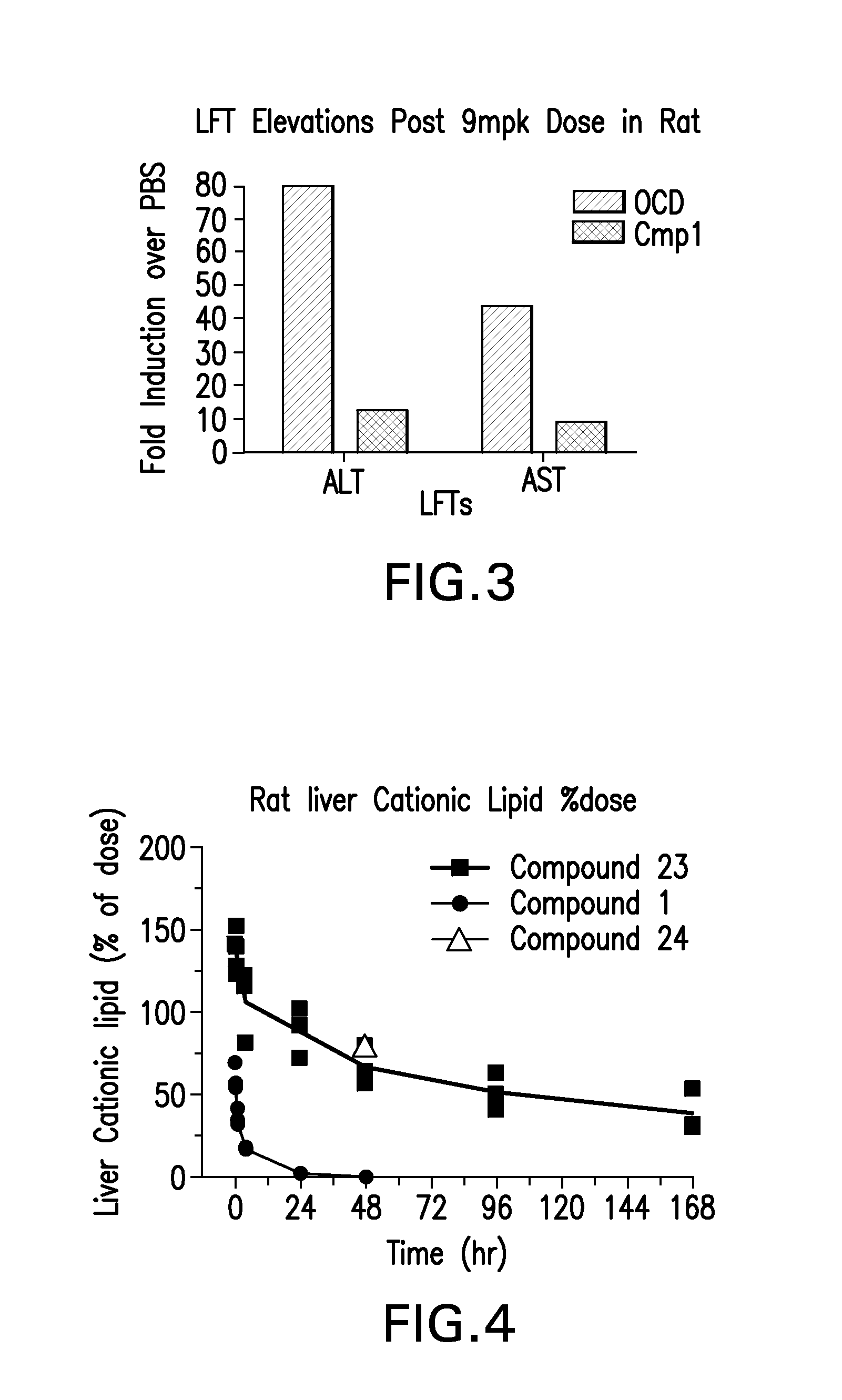
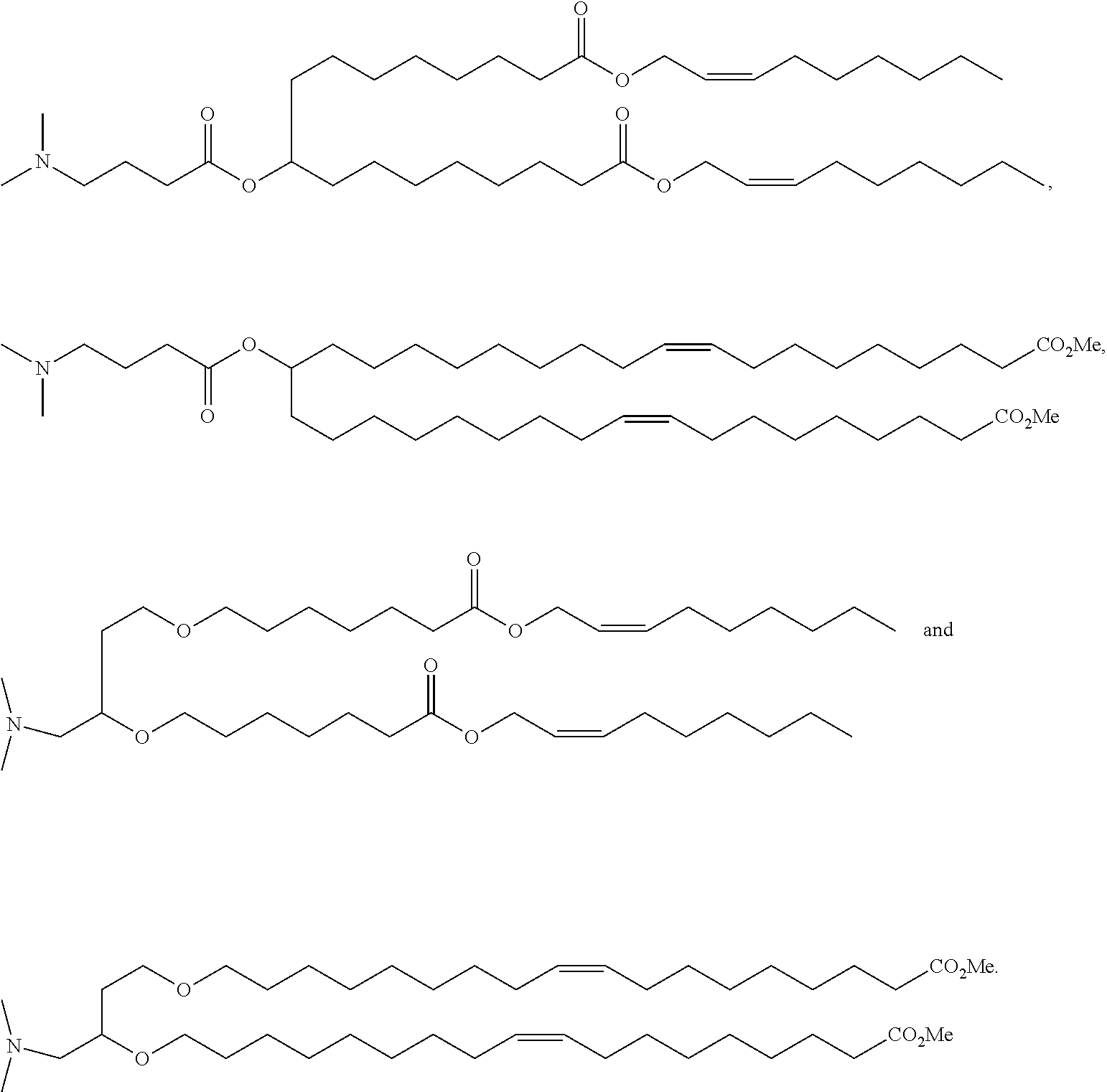
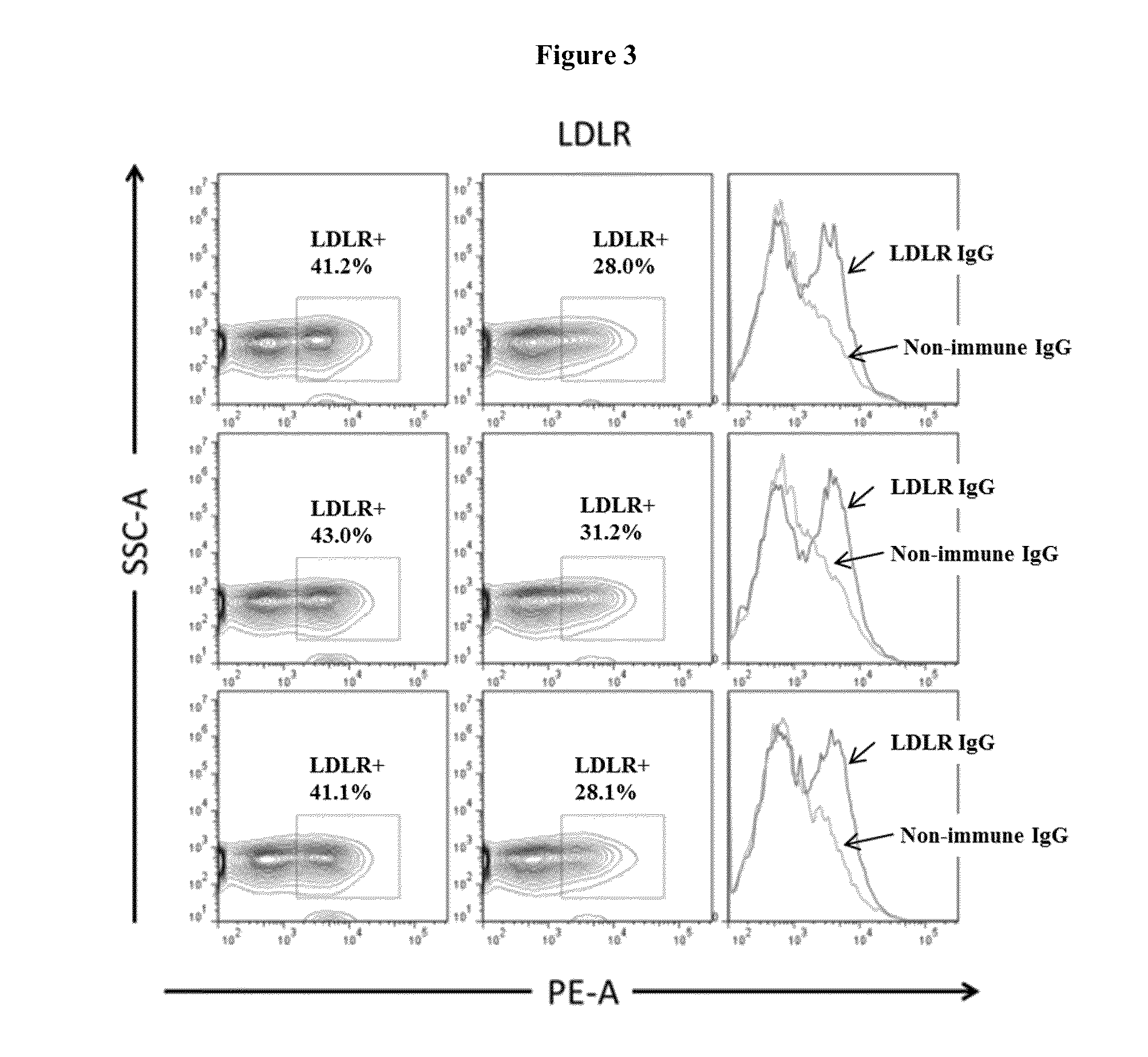
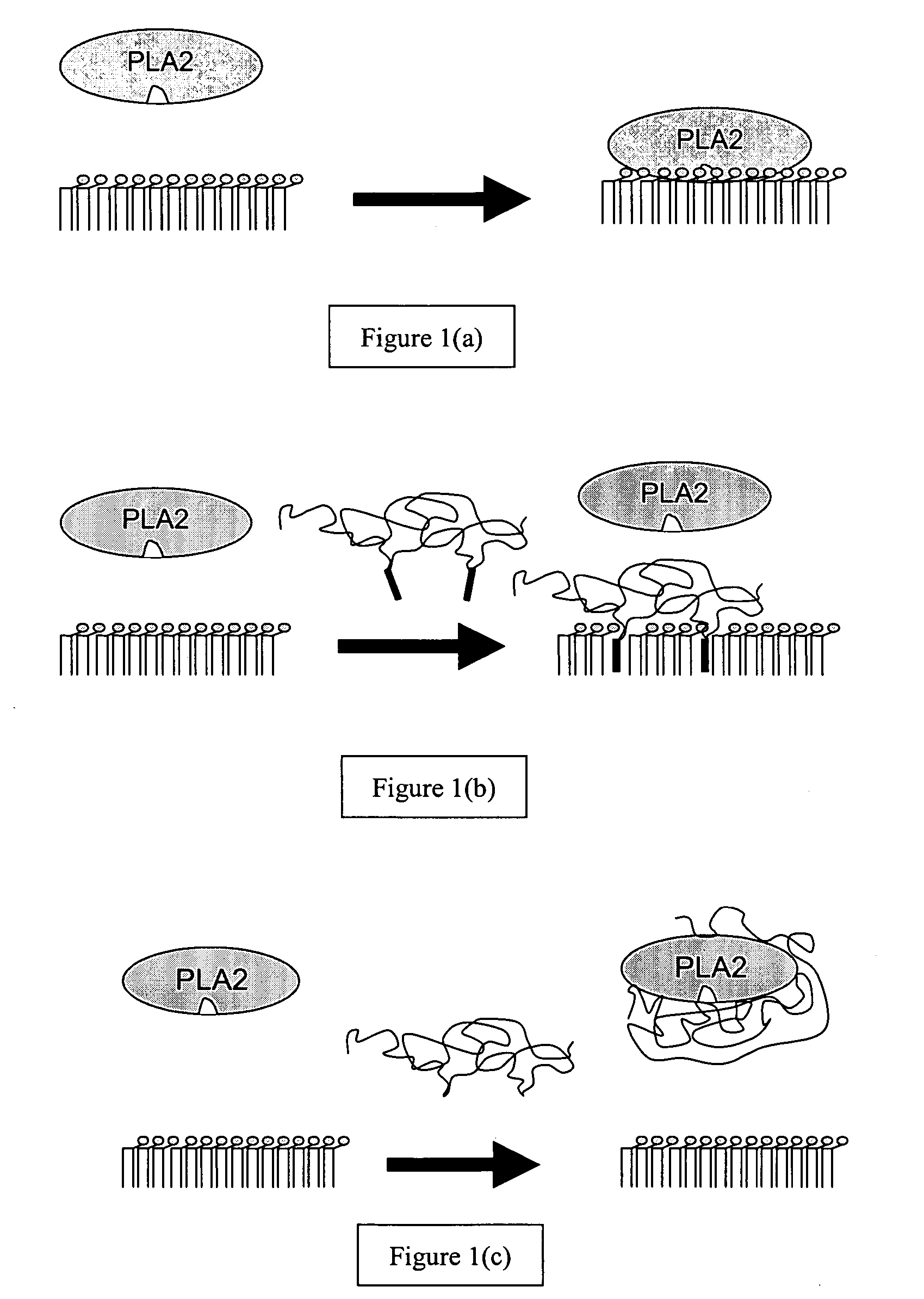
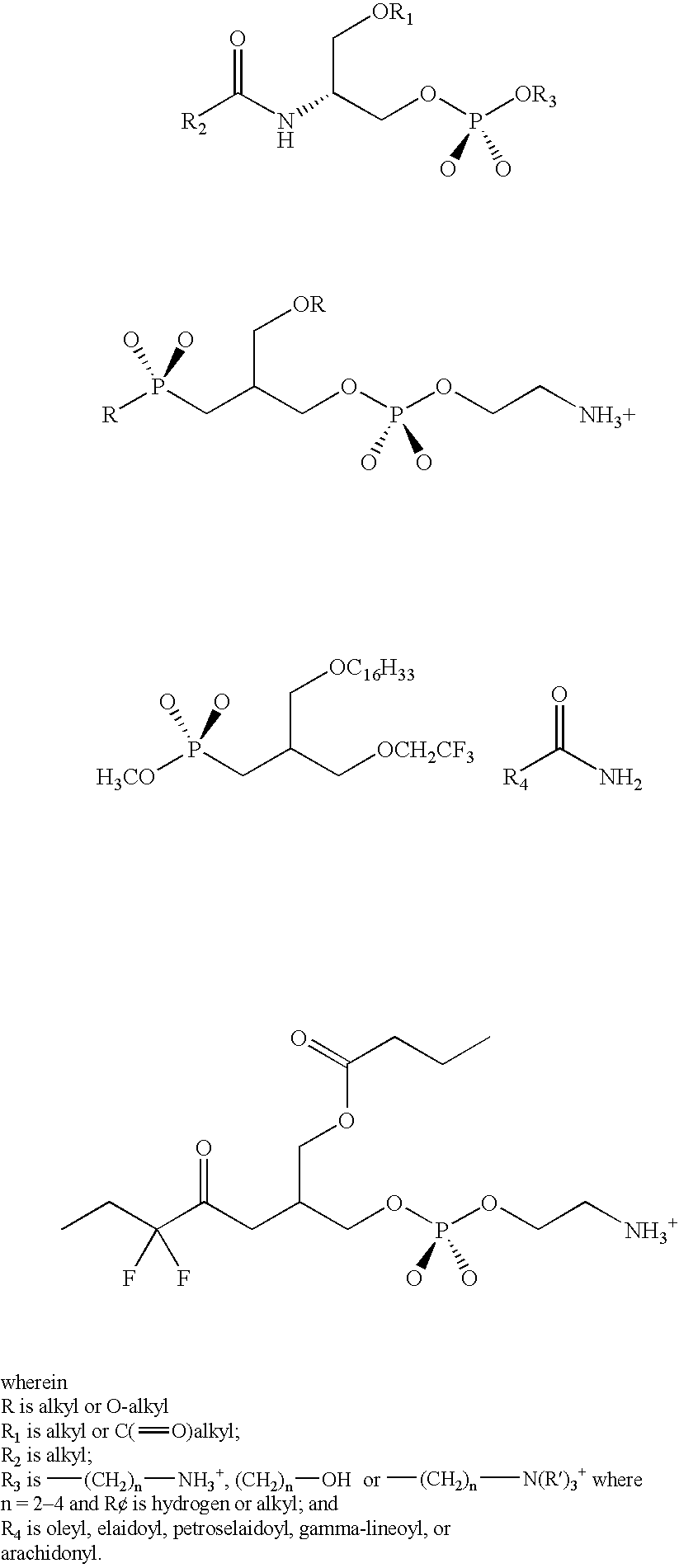
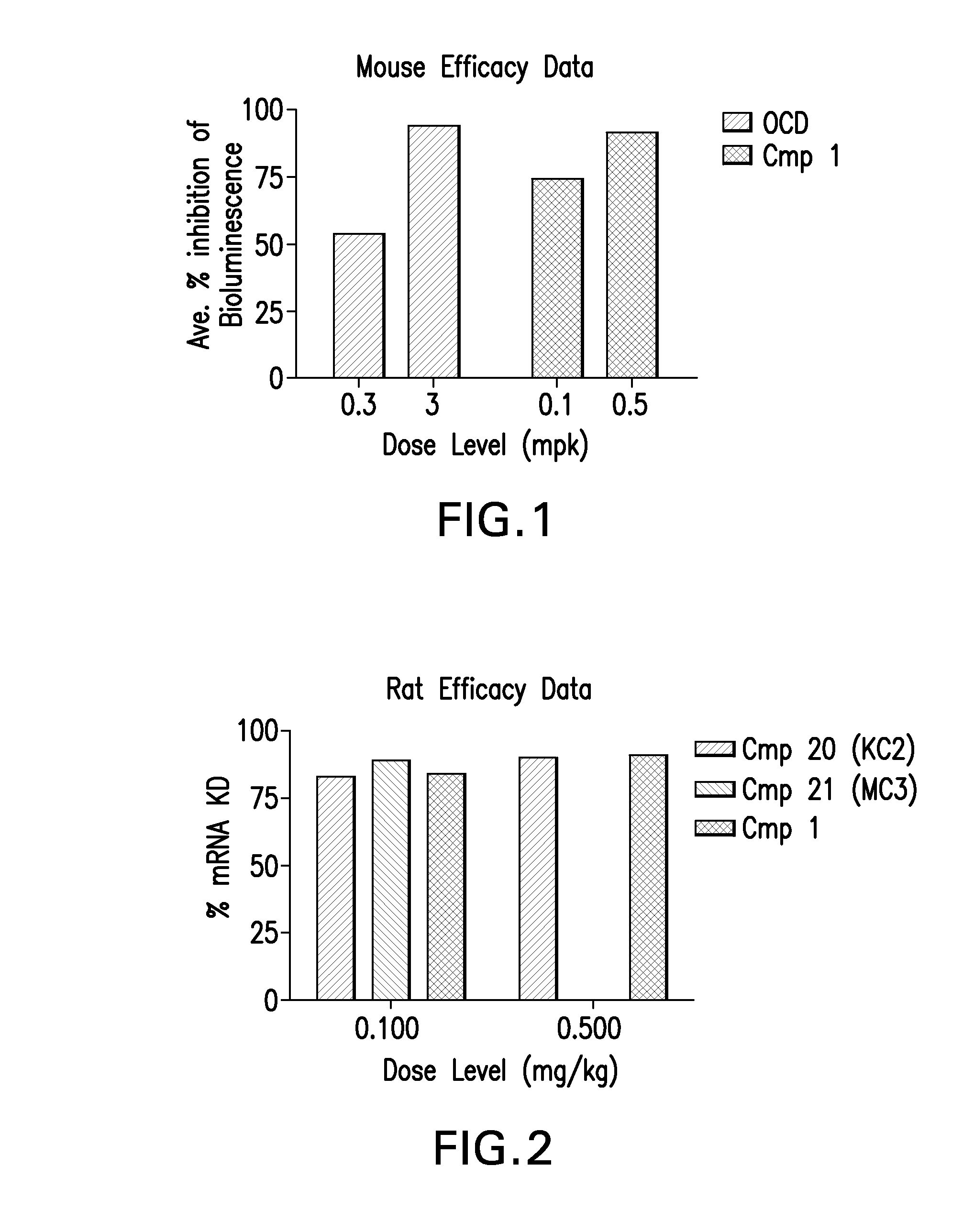
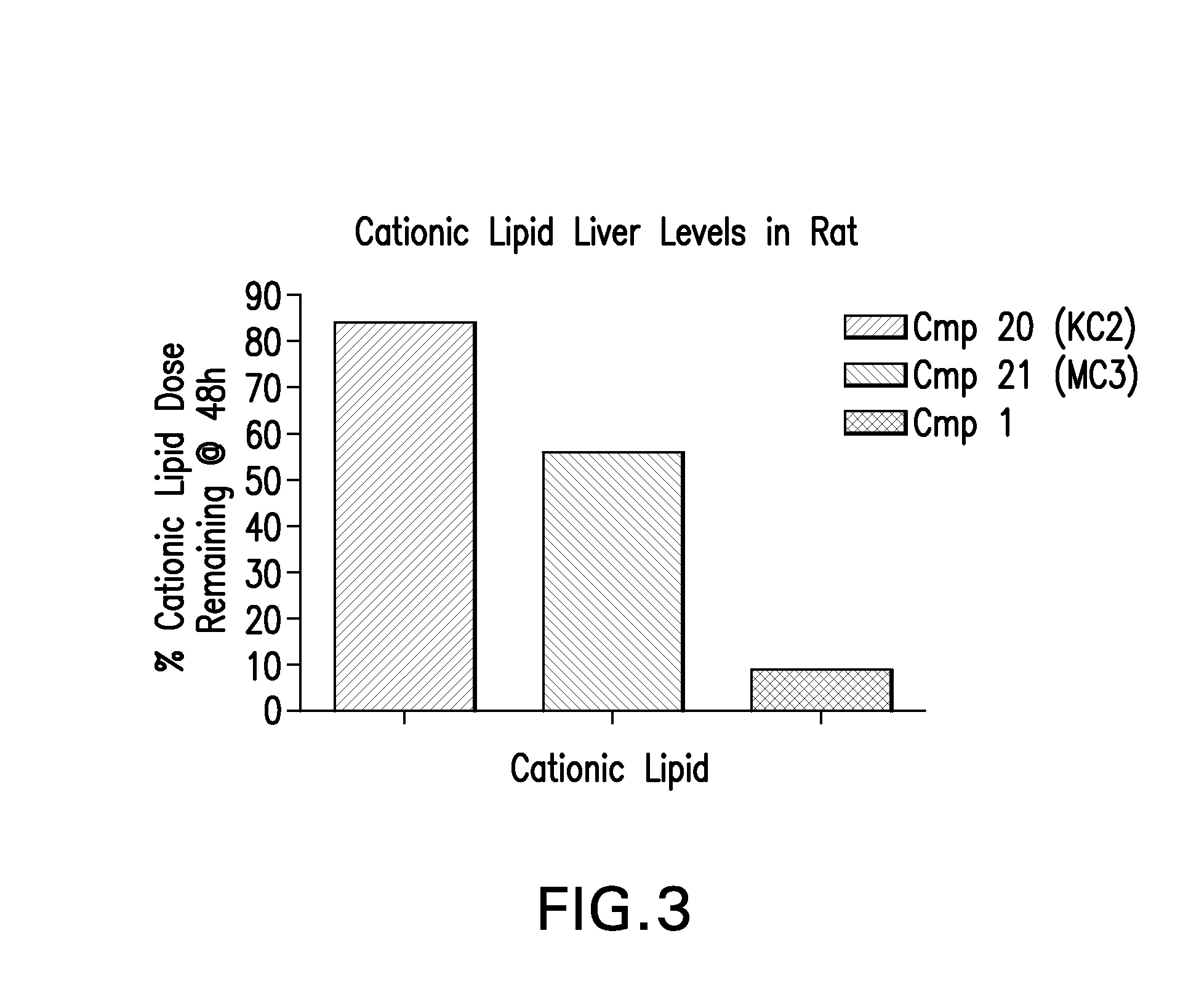
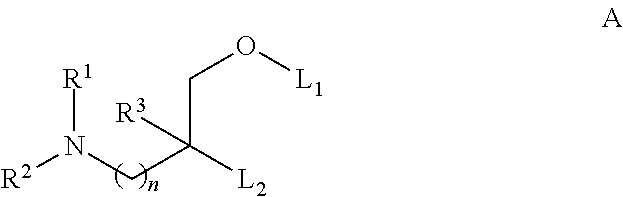
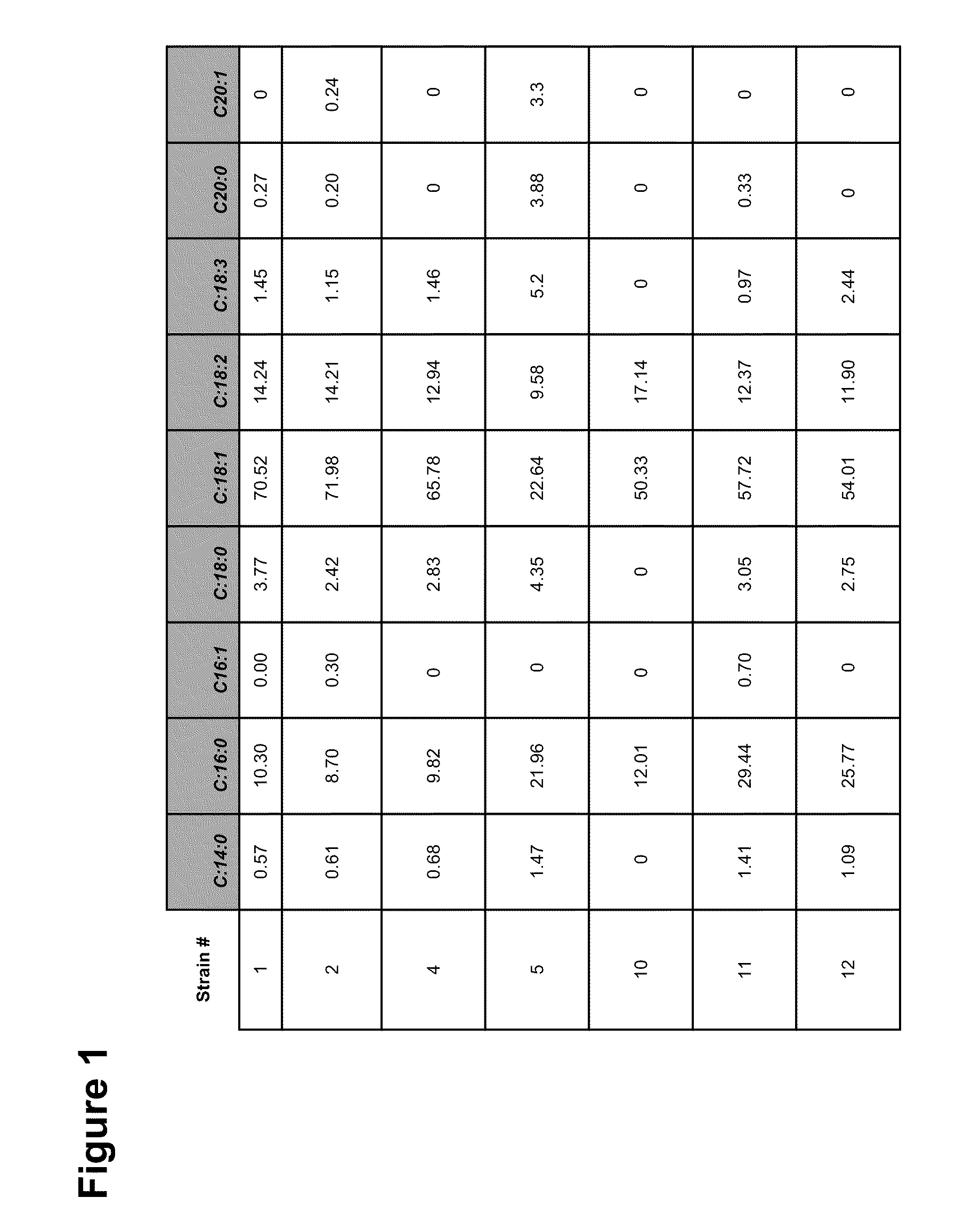
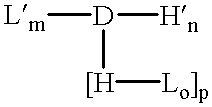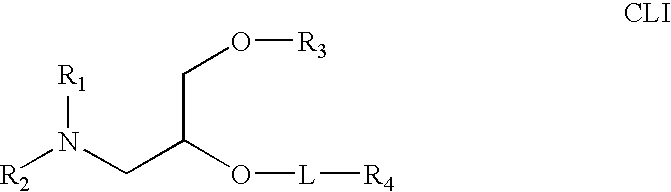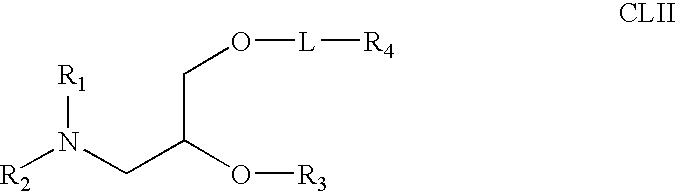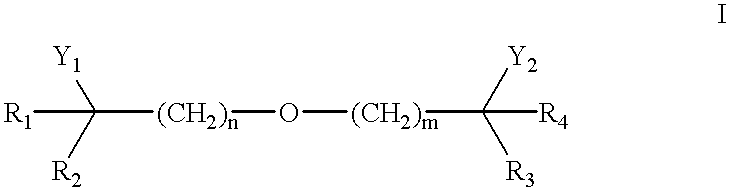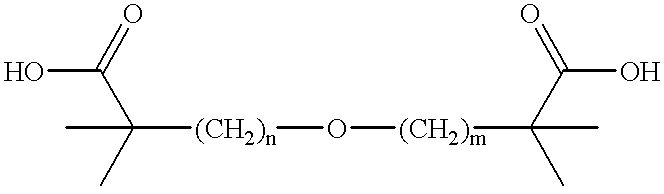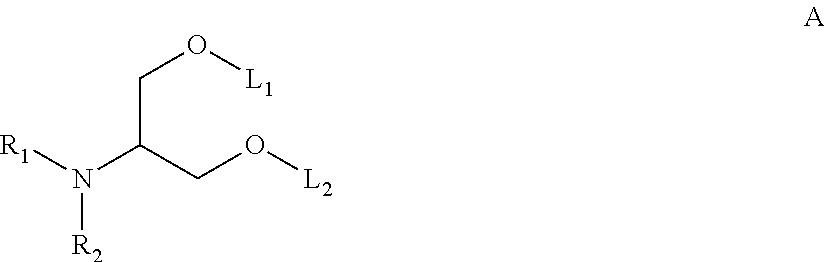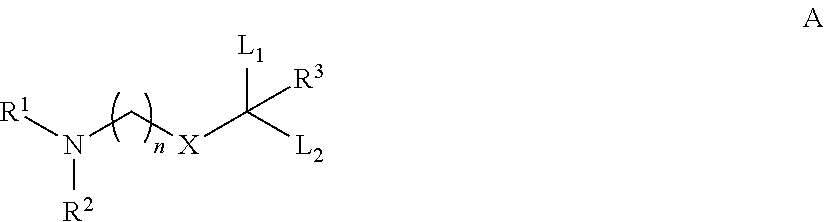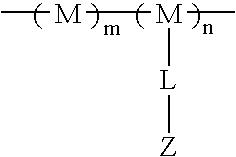Patents
Literature
6770 results about "Cholesterol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
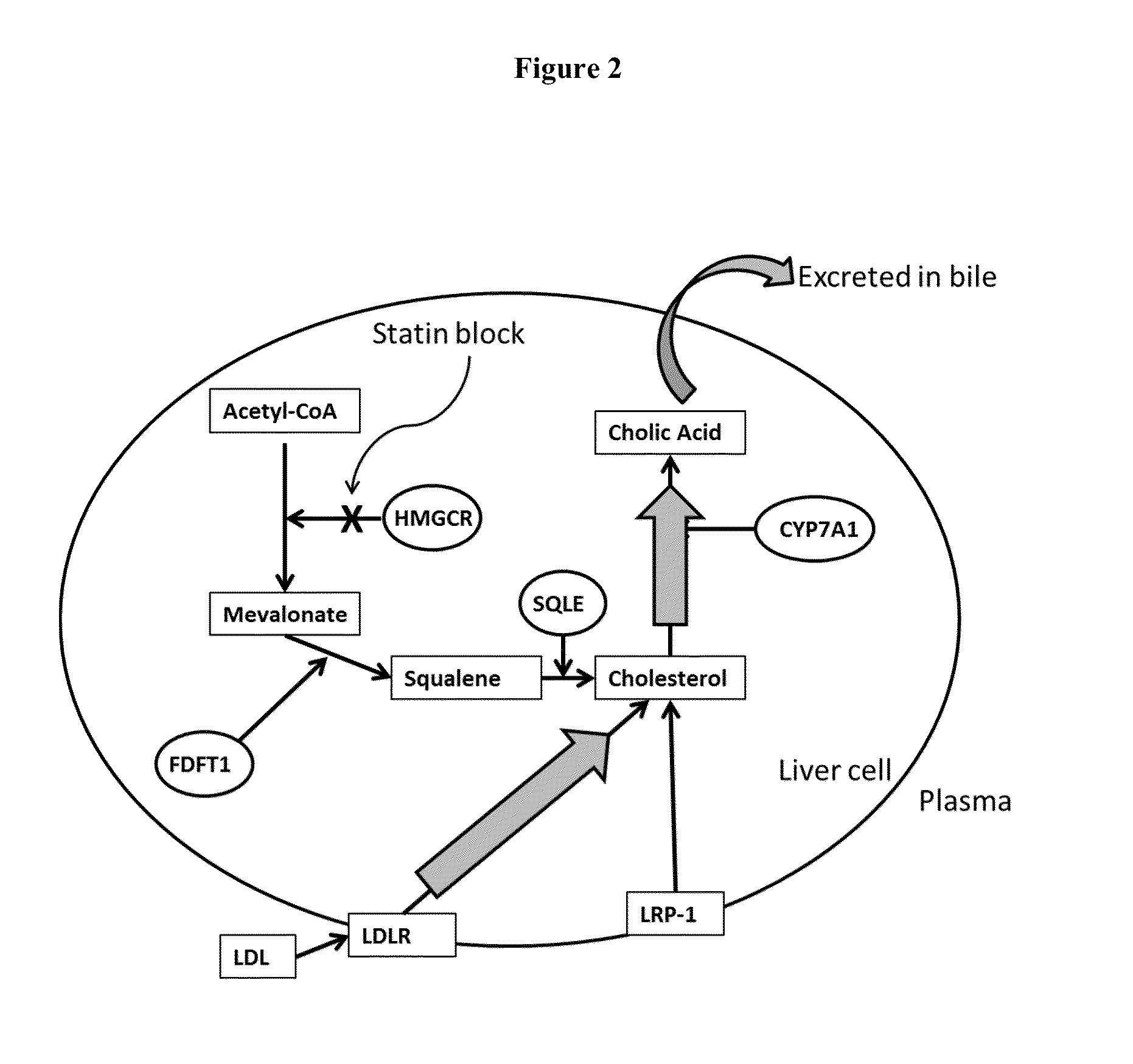
Cholesterol (from the Ancient Greek chole- (bile) and stereos (solid), followed by the chemical suffix -ol for an alcohol) is an organic molecule. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes.
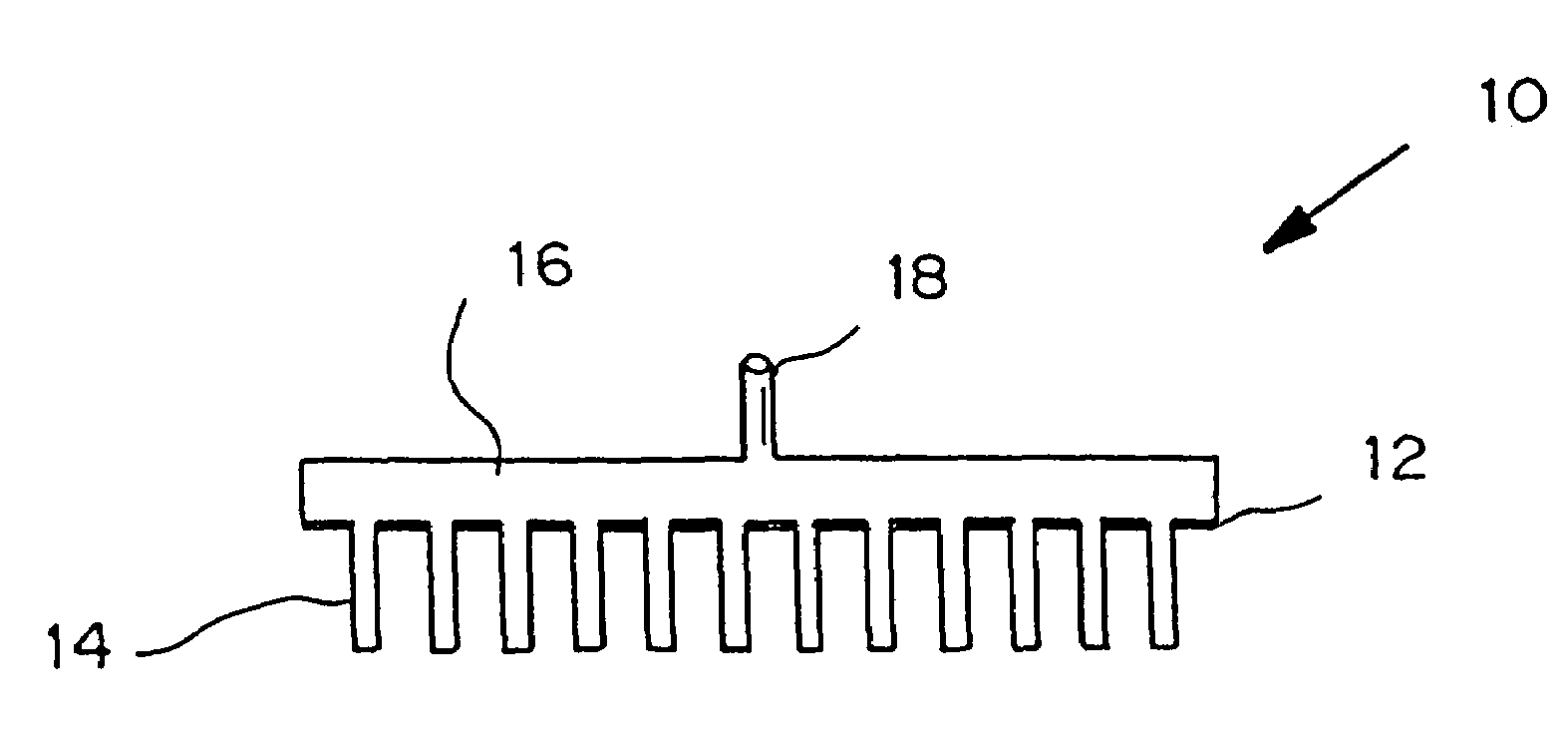
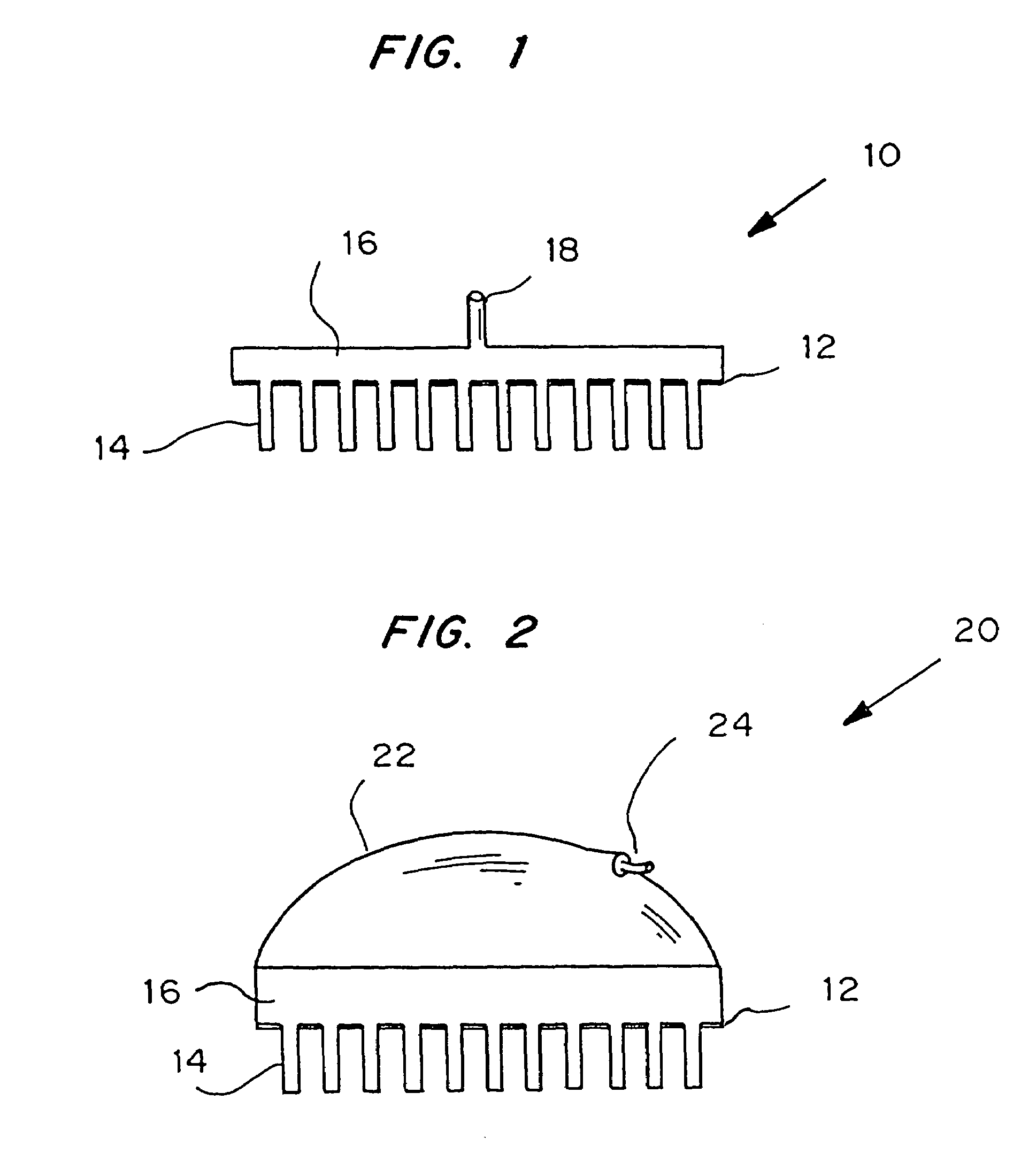
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates with hydroyzable lipophile components and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS6309633B1Reduce deliveryExtended durationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinCholesterol
The invention provides a drug-oligomer conjugate having the following general formula:wherein D is a therapeutic drug moiety; H and H' are each a hydrophilic moiety, independently selected from the group consisting of straight or branched PEG polymers having from 2 to 130 PEG subunits, and sugars; L is a lipophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups having 2-26 carbon atoms, cholesterol, adamantane and fatty acids; o is a number from 1 to the maximum number of covalent bonding sites on H; m+n+p together have a value of at least one and not exceeding the total number of covalent bonding sites on D for the -H', -L and -H-L substituents; the H-L bond(s) are hydrolyzable and the D-L' bond(s), when present, are hydrolyzable; the conjugate being further characterized by one of the following: (i) m is 0 and p is at least 1; (ii) n is 0 and p is at least 1; (iii) m and n are each 0 and p is at least 1; (iv) p is 0 and m and n are each at least 1. The therapeutic drug moiety is preferably a therapeutic protein or peptide, preferably insulin or a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Nucleic Acid-Lipopolymer Compositions
InactiveUS20090042829A1Increase efficiency and dosing flexibilityEfficiently be lyophilizedSpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCholesterolFiller Excipient
Compositions, methods, and applications that increase the efficiency of nucleic acid transfection are provided. In one aspect, a pharmaceutical composition may include at least about 0.5 mg / ml concentration of a nucleic acid condensed with a cationic lipopolymer suspended in an isotonic solution, where the cationic lipopolymer includes a cationic polymer backbone having cholesterol and polyethylene glycol covalently attached thereto, and wherein the molar ratio of cholesterol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10, and the molar ratio of polyethylene glycol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10. The composition further may include a filler excipient.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS20080020058A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLipid formationCholesterol
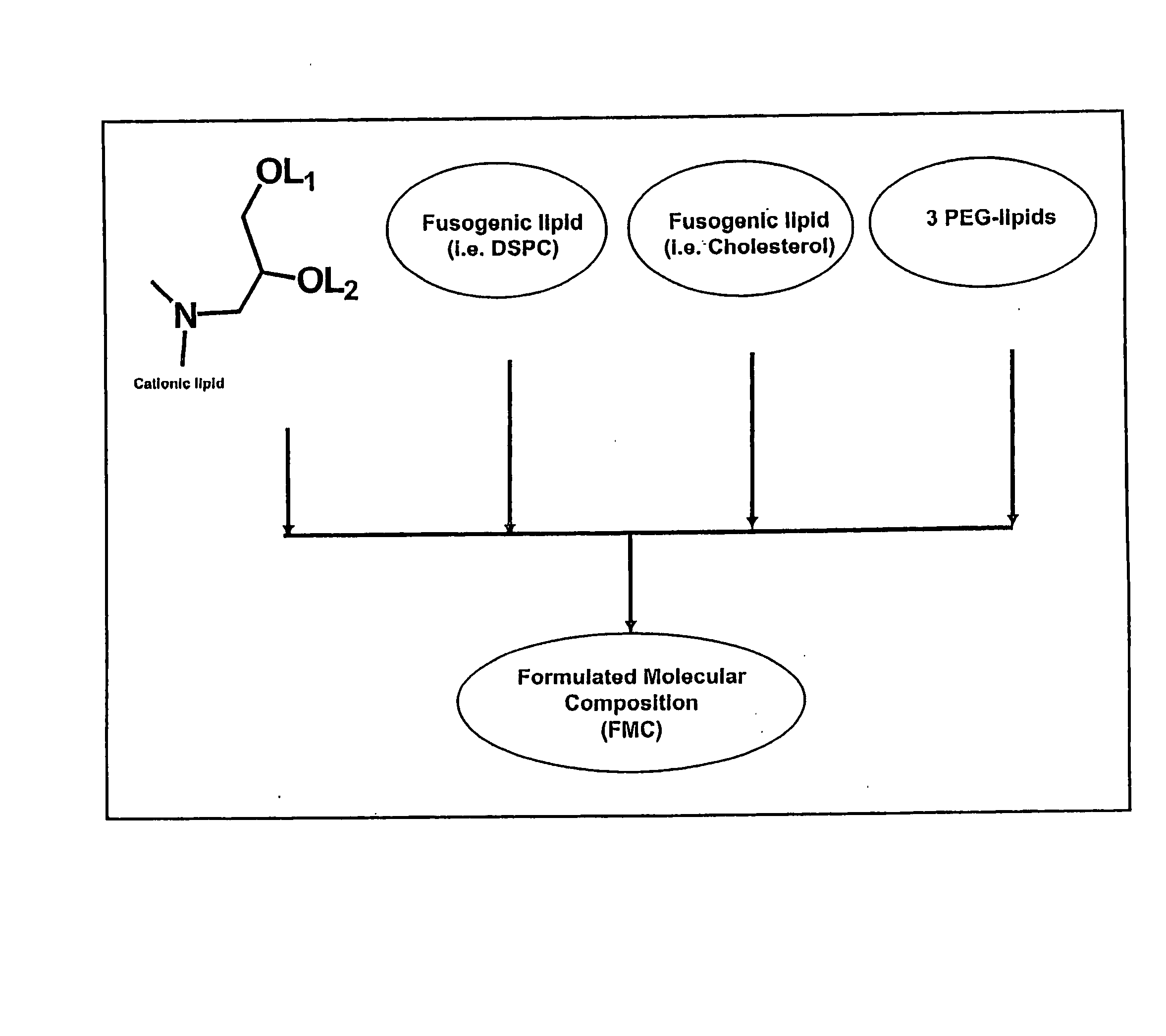
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and RNAi inhibitor molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Interactive, internet supported health and fitness management system
A wellness system monitors the controlled progress of patients under surveillance and includes a server base station which is generally off-site, a web-site interface and a local station at the point-of-use, which is generally a health or fitness center. A unique data base is created for each user and goals and objectives may be set with progress monitored. Typically, the user will respond to a survey or questionnaire to populate his specific database. This is combined with a professional assessment and an automated measurement of vital statistics such as weight, blood pressure and body composition as measured at the local station. Other data may be entered manually such as height, age and the like. In a more comprehensive system the invention is designed to monitor other data such as cholesterol and blood glucose, as well. The locally input data may be updated at will by the user or on behalf of the user by professional personnel.
Owner:VIRGIN PULSE INC
Novel low molecular weight cationic lipids for oligonucleotide delivery
ActiveUS20130178541A1Good curative effectReduce liver toxicityBiocideMicroencapsulation basedTolerabilityNanoparticle
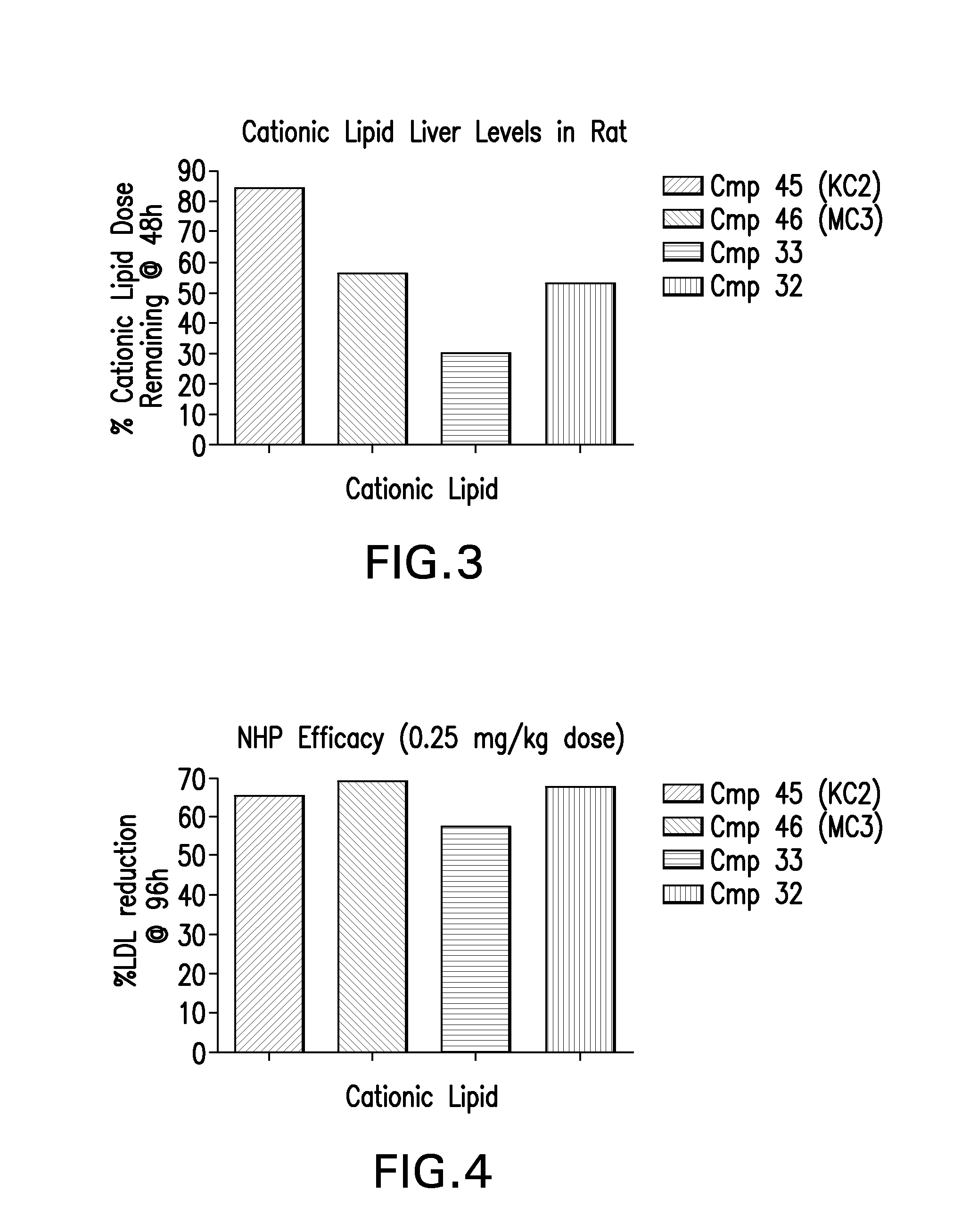
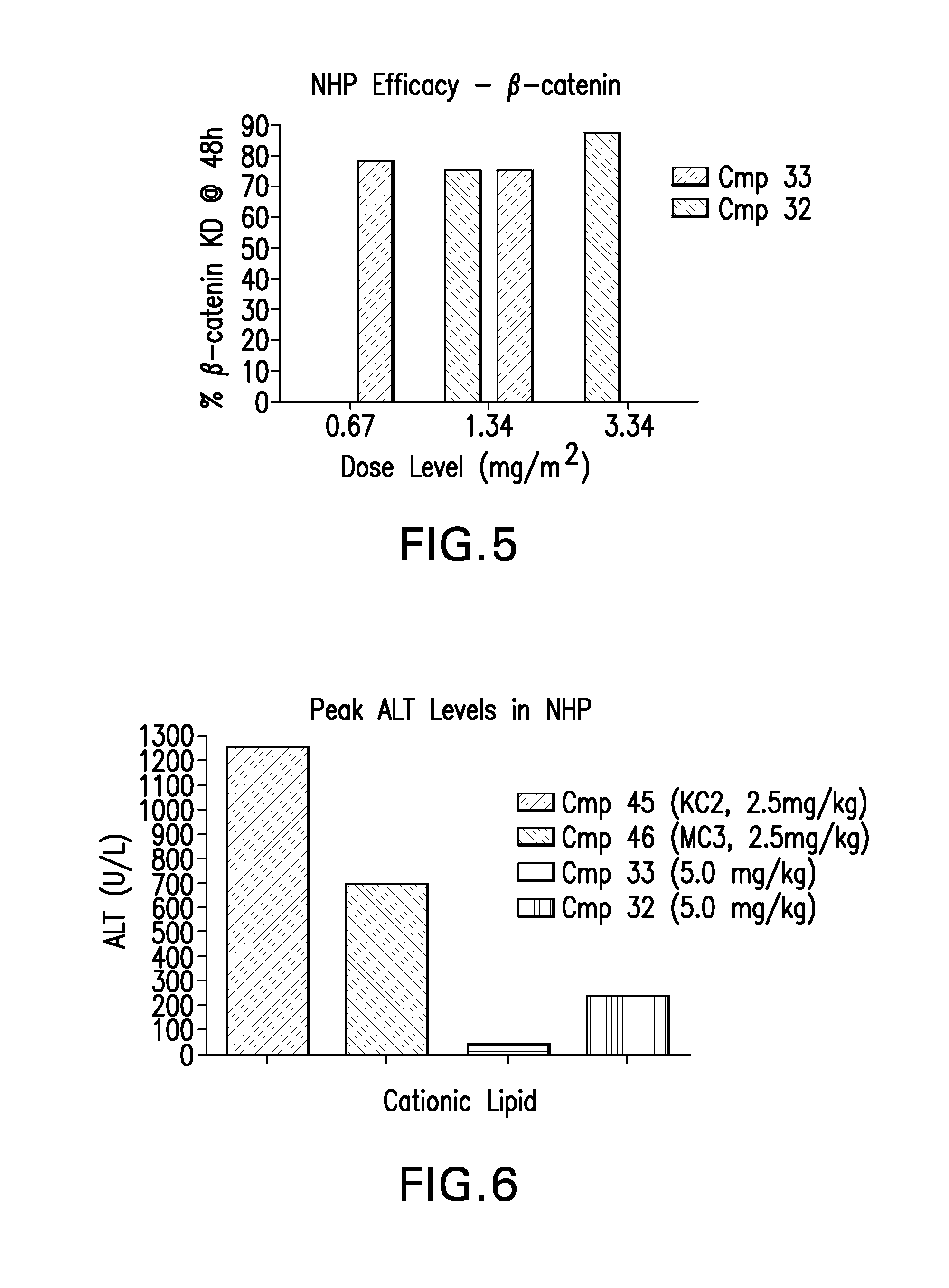
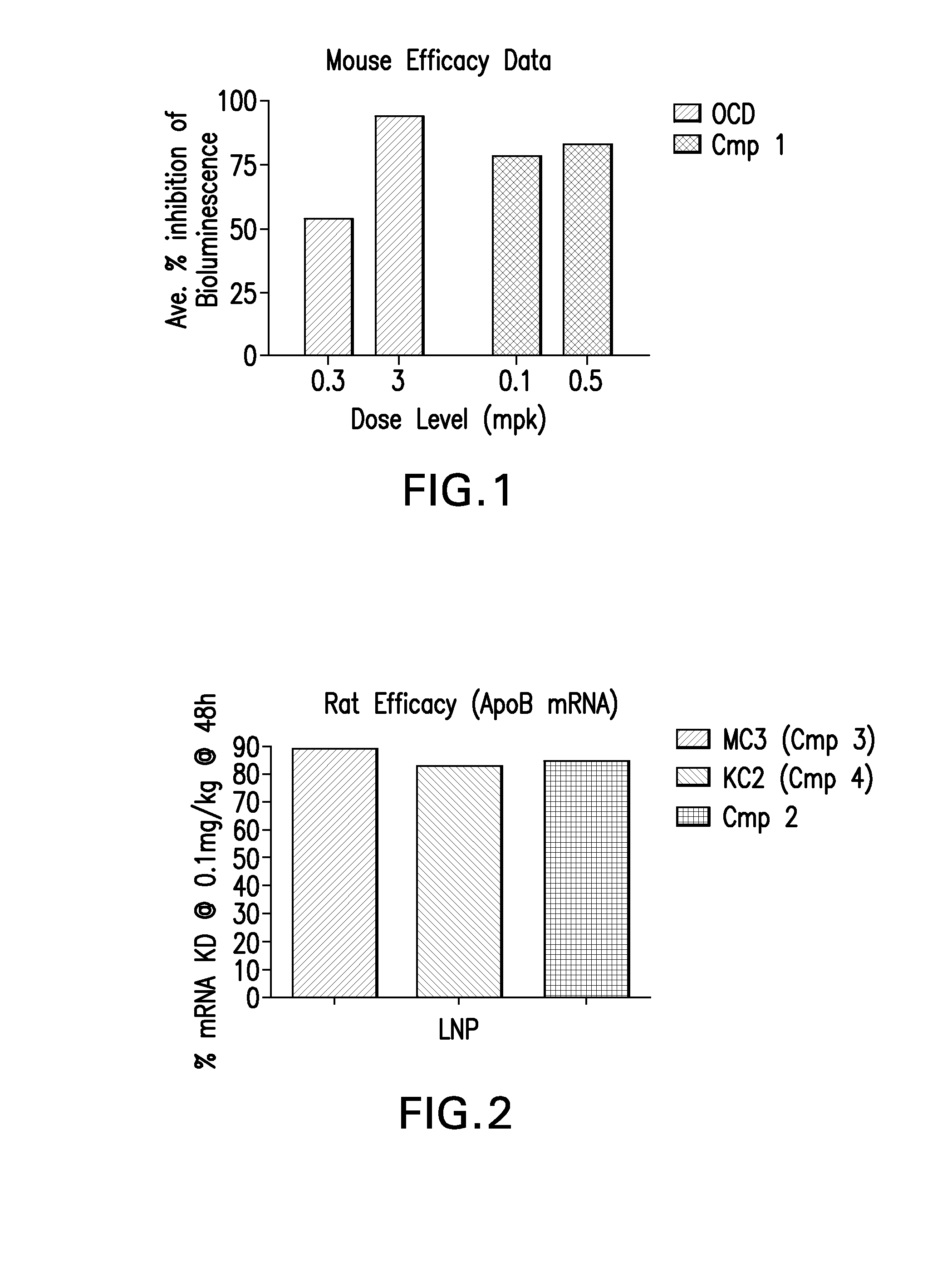
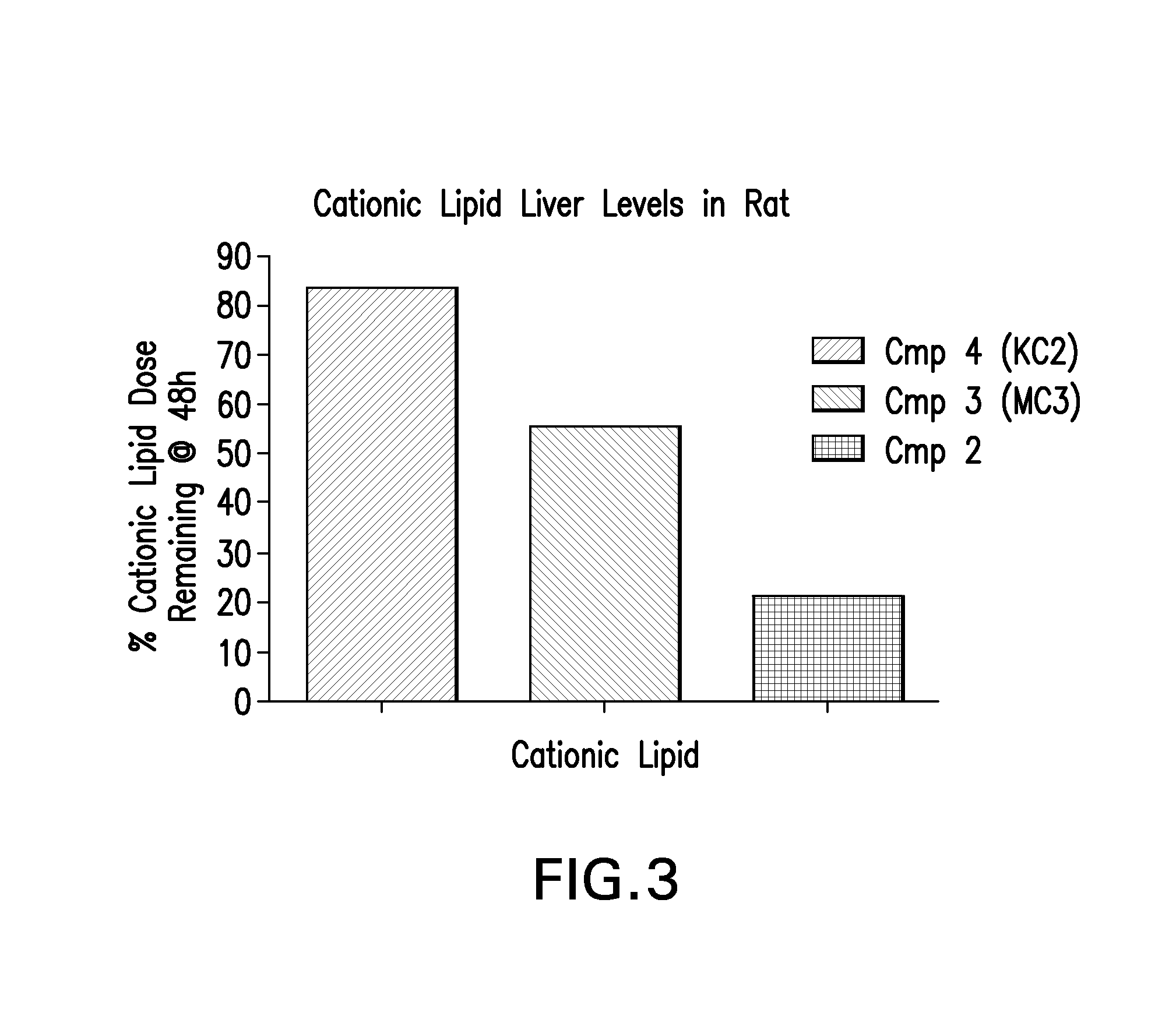
The instant invention provides for novel catiomc lipids that can be used in combination with other lipid components such as cholesterol and PEG-lipids to form lipid nanoparticles with oligonucleotides. It is an object of the instant invention to provide a cationic lipid scaffold that demonstrates enhanced efficacy along with lower liver toxicity as a result of lower lipid levels in the liver. The present invention employs low molecular weight cationic lipids with one short lipid chain to enhance the efficiency and tolerability of in vivo delivery of siRNA.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for treating alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20020055529A1Reduce vascular and cardiac diseaseBiocideAnimal repellantsCholesterolPlasma triglyceride level
The present invention provides a method for treating or preventing the onset of Alzheimer's Disease comprising administering to a mammal in need thereof an Alzheimer's Disease-preventing or treating amount of a plasma-triglyceride level-lowering agent. Optionally, the plasma-triglyceride level-lowering agent can be co-administered with a cholesterol level-lowering agent.
Owner:WARNER LAMBERT CO LLC
Novel Amino Alcohol Cationic Lipids for Oligonucleotide Delivery
ActiveUS20130150625A1Enhance efficiency of in vivo deliveryEfficaciousOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationAlcoholNanoparticle
The instant invention provides for novel cationic lipids that can be used in combination with other lipid components such as cholesterol and PEG-lipids to form lipid nanoparticles with oligonucleotides. It is an object of the instant invention to provide a cationic lipid scaffold that is more efficacious than traditional cationic lipids. The present invention employs amino alcohols to enhance the efficiency of in vivo delivery of siRNA.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Non-invasive blood component measurement system
Non-invasive, optical apparatus and methods for the direct measurement of hemoglobin derivatives and other analyte concentration levels in blood using diffuse reflection and transmission spectroscopy in the wavelength region 400-1350 nm which includes the transparent tissue window from approximately 610 to 1311 nanometers and, using diffuse reflection spectroscopy, the mid-infrared region from 4.3-12 microns in wavelength. Large area light collection techniques are utilized to provide a much larger pulsate signal than can be obtain with current sensor technology. Sensors used in separate or simultaneous precision measurements of both diffuse reflection and transmission, either separately or simultaneously, from pulsate, blood-perfused tissue for the subsequent determination of the blood analytes concentrations such as arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2), carboxyhemoglobin (COHb), oxyhemoglobin (OHb), deoxyhemoglobin (dOHb), methemoglobin (metHb), water (H2O), hematocrit (HCT), glucose, cholesterol and proteins such as albumin and other analytes components.
Owner:3WAVE OPTICS
Self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system
InactiveUS20090226525A1High binding affinityHigh affinityPowder deliveryMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationMedicine
A self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system for the delivery of various bioactive agents including peptides, proteins, nucleic acids or synthetic chemical drugs is provided. The self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system described herein includes viral capsid proteins, such as Hepatitis B Virus core protein, encapsulating the bioactive agent, a lipid layer or lipid / cholesterol layer coat and targeting or facilitating molecules anchored in the lipid layer. A method for construction of the self-assembling nanoparticle drug delivery system is also provided.
Owner:CHIMEROS
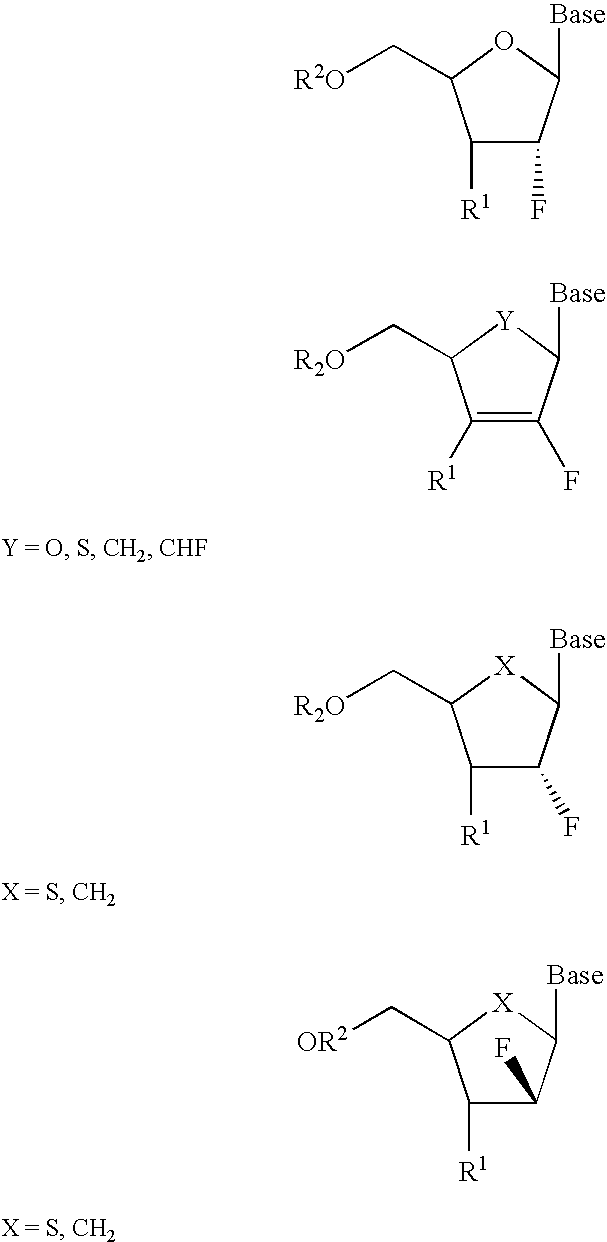
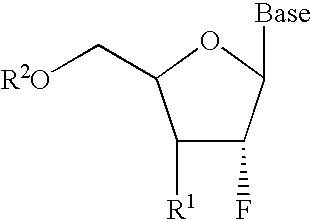
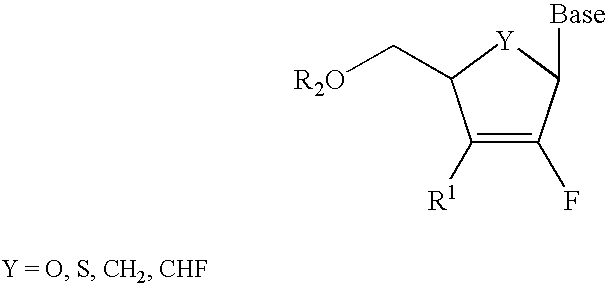
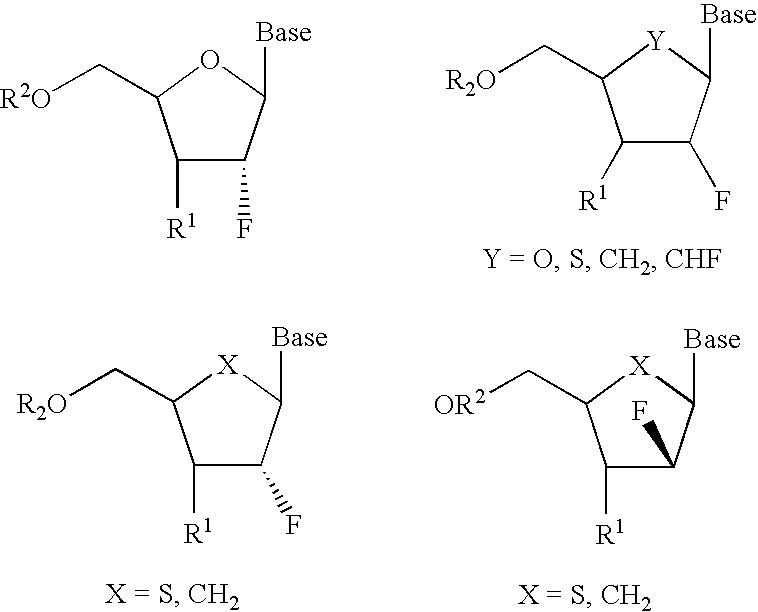
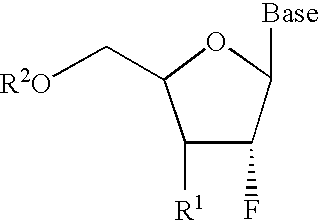
2′-fluoronucleosides
InactiveUS6911424B2Sure easyUseful in treatmentBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphoric Acid EstersPurine
A class of 2′-fluoro-nucleoside compounds are disclosed which are useful in the treatment of hepatitis B infection, hepatitis C infection, HIV and abnormal cellular proliferation, including tumors and cancer. The compounds have the general formulae: wherein[0001]Base is a purine or pyrimidine base;[0002]R1 is OH, H, OR3, N3, CN, halogen, including F, or CF3, lower alkyl, amino, loweralkylamino, di(lower)alkylamino, or alkoxy, and base refers to a purine or pyrimidine base;[0003]R2 is H, phosphate, including monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate, or a stabilized phosphate prodrug; acyl, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of providing a compound wherein R2 is H or phosphate; sulfonate ester including alkyl or arylalkyl sulfonyl including methanesulfonyl, benzyl, wherein the phenyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described in the definition of aryl given above, a lipid, an amino acid, peptide, or cholesterol; and[0004]R3 is acyl, alkyl, phosphate, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of being cleaved to the parent compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Novel Low Molecular Weight Cationic Lipids for Oligonucleotide Delivery
ActiveUS20130090372A1Good curative effectReduce liver toxicityOrganic compound preparationOther foreign material introduction processesTolerabilityNanoparticle
The instant invention provides for novel cationic lipids that can be used in combination with other lipid components such as cholesterol and PEG-lipids to form lipid nanoparticles with oligonucleotides. It is an object of the instant invention to provide a cationic lipid scaffold that demonstrates enhanced efficacy along with lower liver toxicity as a result of lower lipid levels in the liver. The present invention employs low molecular weight cationic lipids with one short lipid chain to enhance the efficiency and tolerability of in vivo delivery of siRNA.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods of altering cholesterol levels
ActiveUS20140275227A1Address poor treatment outcomesElevated cholesterolCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCholesterolPolynucleotide
Owner:MODERNATX INC
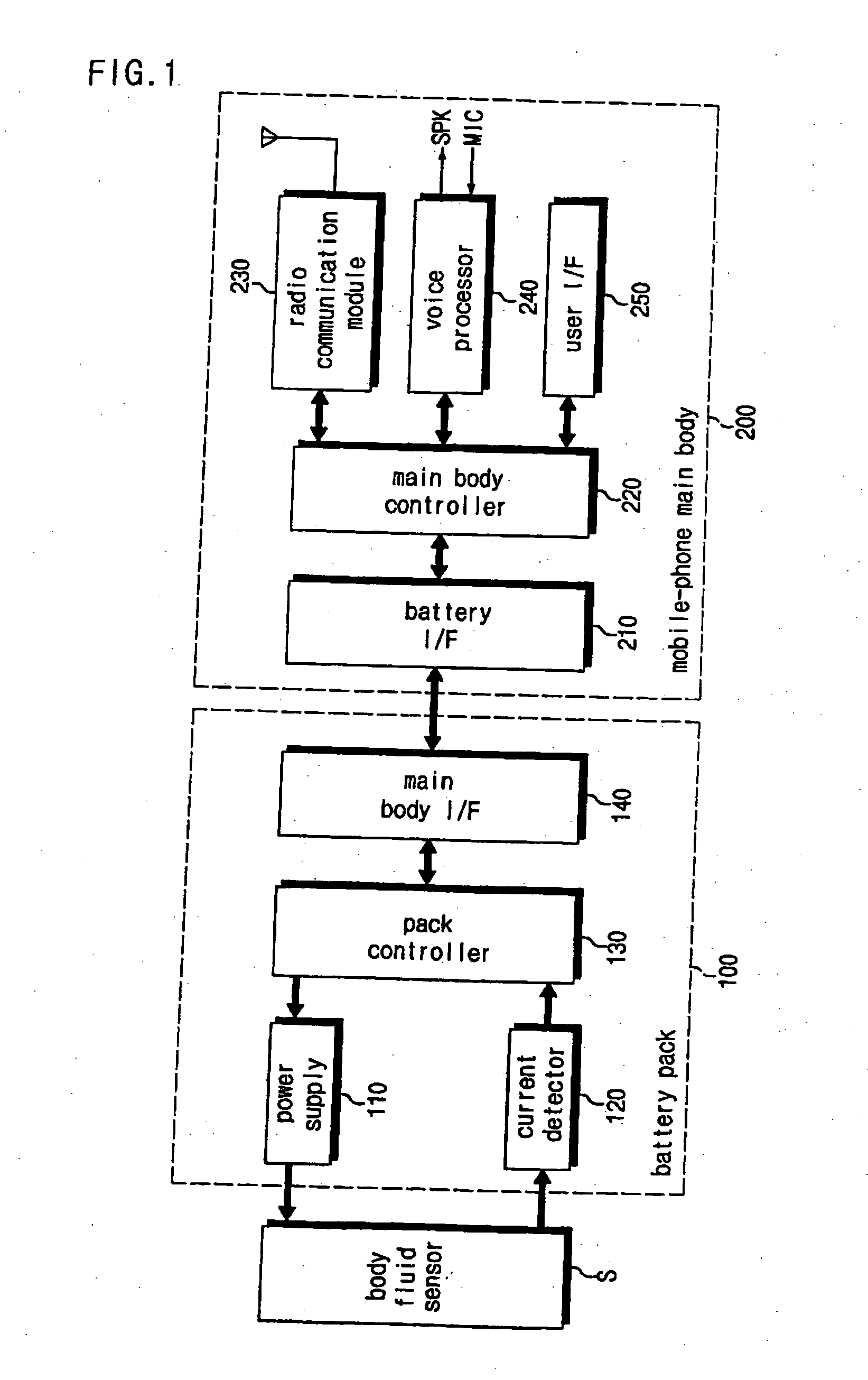
Battery pack of a mobile communication terminal to be capable of reading output of bio-sensors and self-diagnosis system
A battery pack for self-diagnosis and a system using the same, which can read a data value from a body fluid sensor (referred to as a biosensor) reacting with body fluid such as urine, and indicate a measurement value of a test item such as a blood glucose level, a cholesterol level or etc. The battery pack includes: a power supply for supplying electric power to a working electrode of the body fluid sensor; a current detector for detecting the amount of electric current flowing into the working electrode; a battery pack controller for controlling an electric power supply operation for the working electrode, reading, from a memory, the test item-based measurement value corresponding to the detected current amount, and outputting the read measurement value; and an interface for carrying out an interface function so that the test item-based measurement value outputted from the battery pack controller can be sent to the main body of the mobile communication terminal.
Owner:SEYFARTH SHAW
Novel Low Molecular Weight Cationic Lipids For Oligonucleotide Delivery
ActiveUS20130274504A1Good curative effectReduce liver toxicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTolerabilityNanoparticle
The instant invention provides for novel cationic lipids that can be used in combination with other lipid components such as cholesterol and PEG-lipids to form lipid nanoparticles with oligonucleotides. It is an object of the instant invention to provide a cationic lipid scaffold that demonstrates enhanced efficacy along with lower liver toxicity as a result of lower lipid levels in the liver. The present invention employs low molecular weight cationic lipids comprising at least one short lipid chain to enhance the efficiency and tolerability of in vivo delivery of siRNA.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
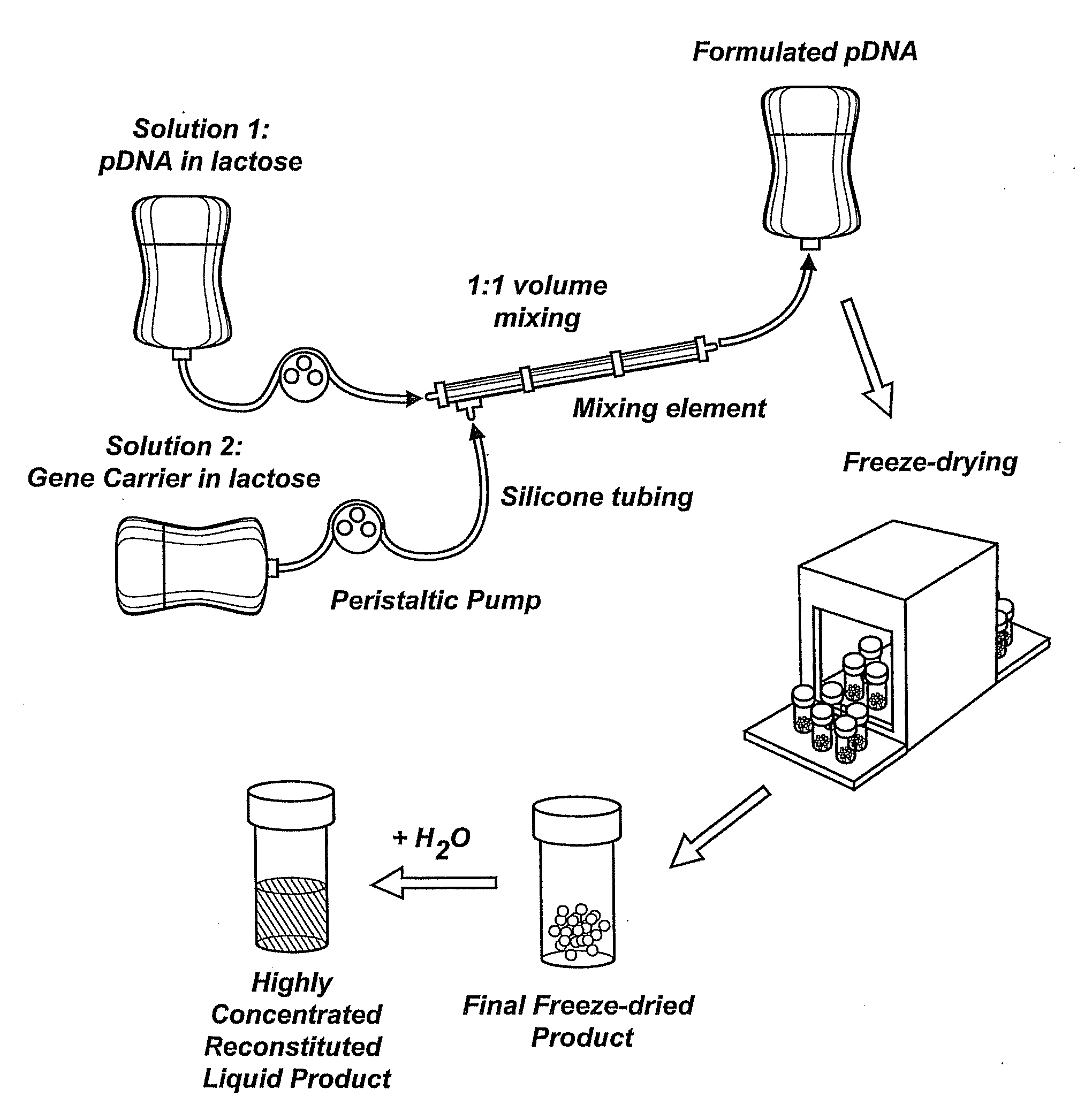
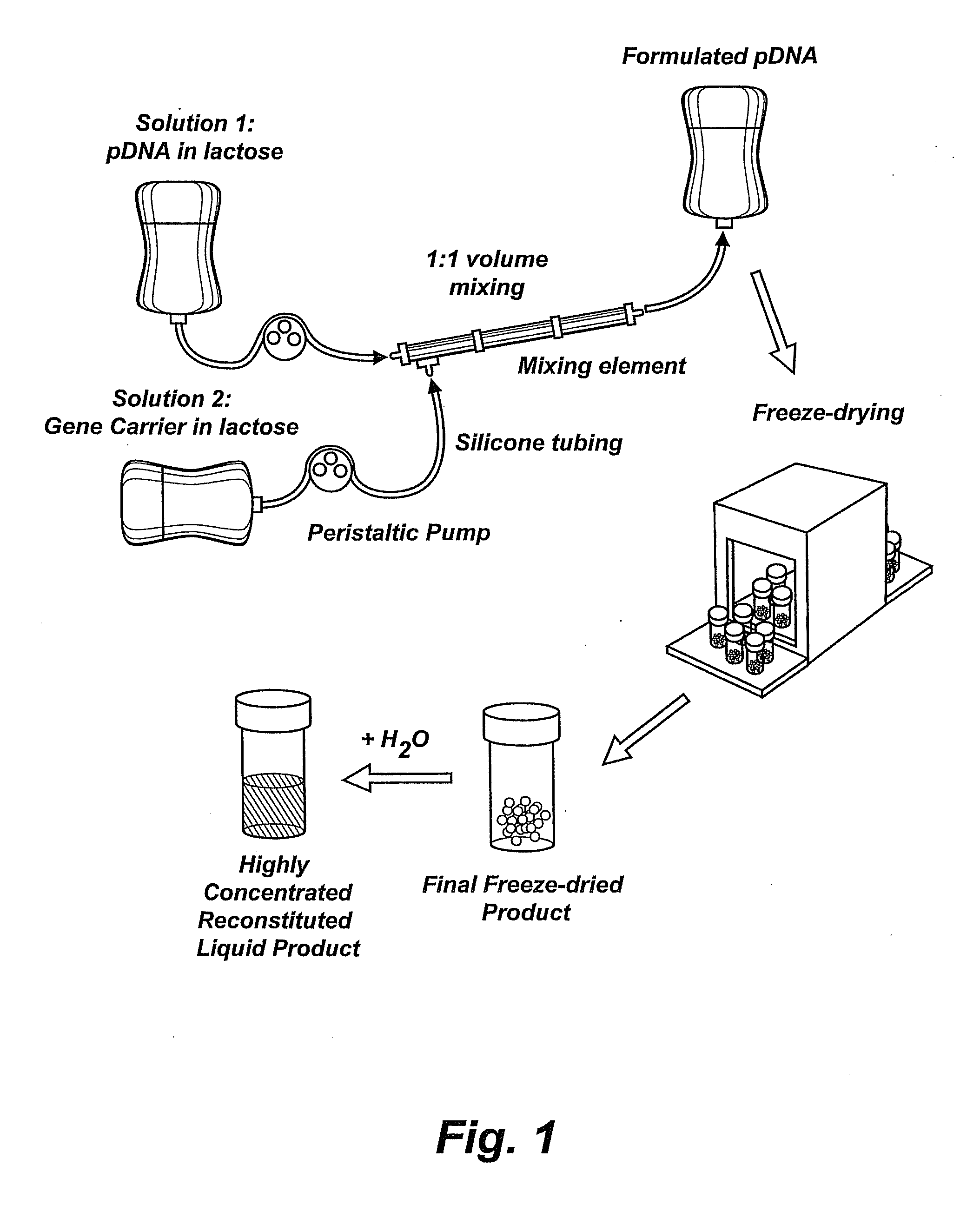
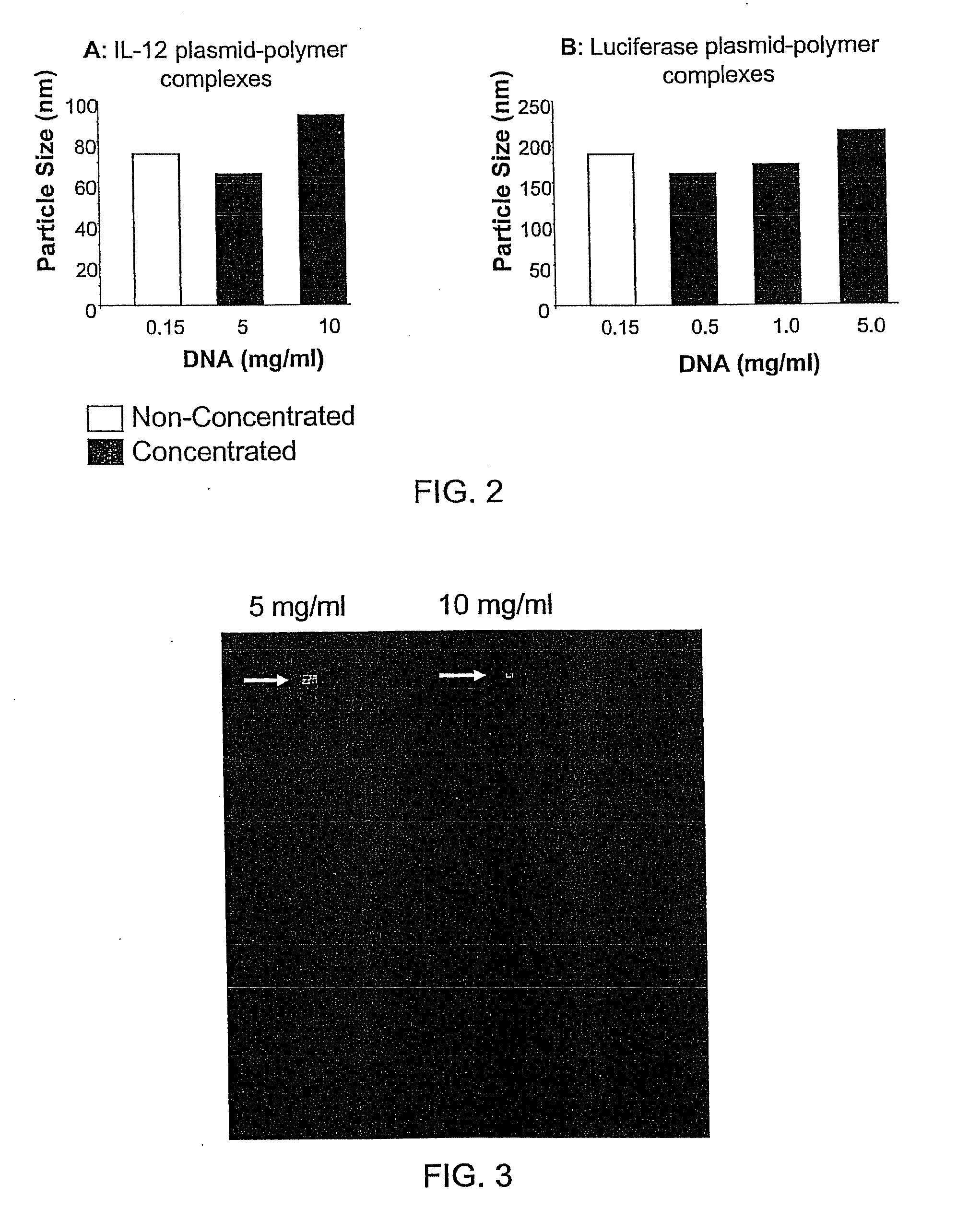
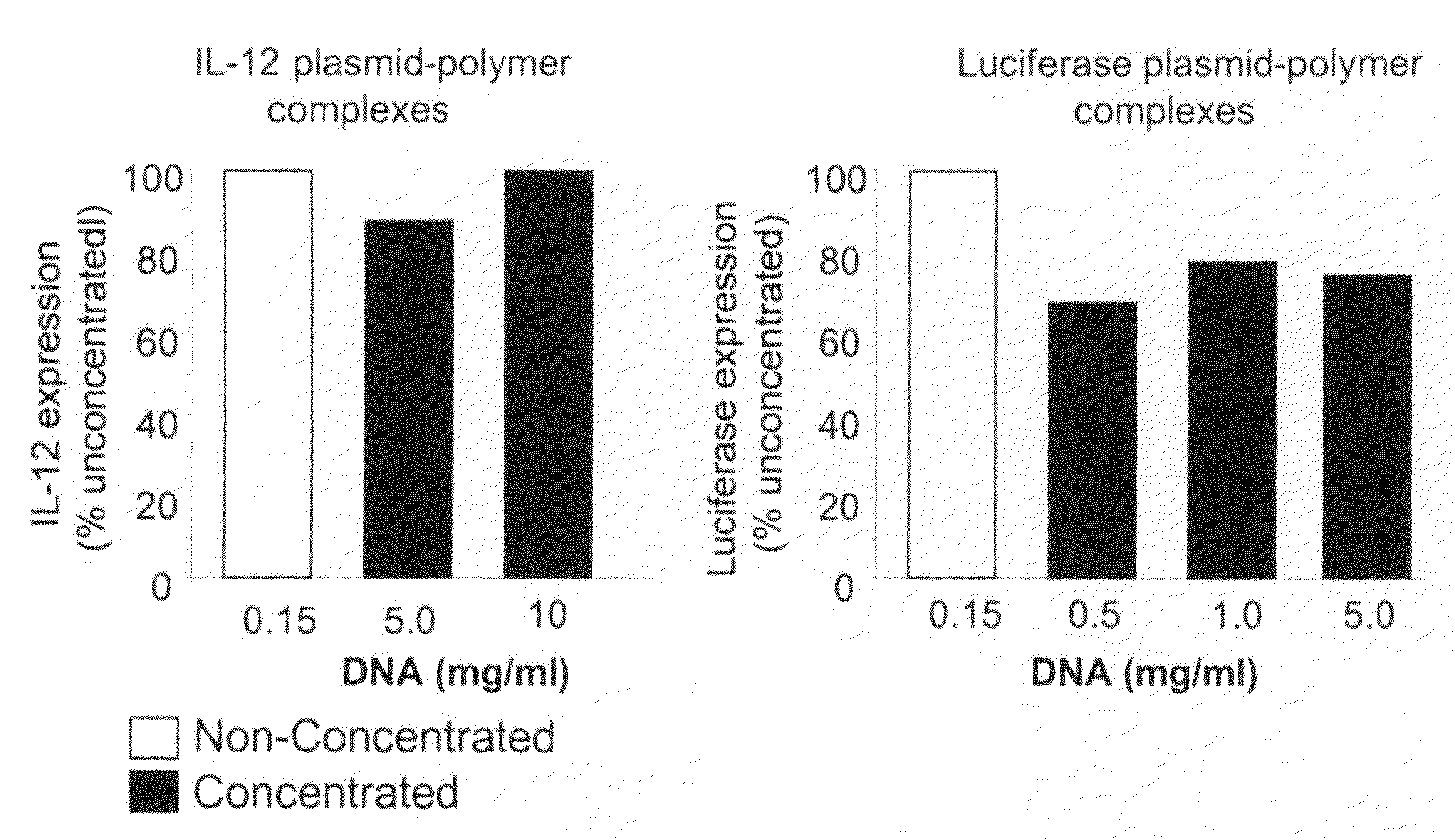
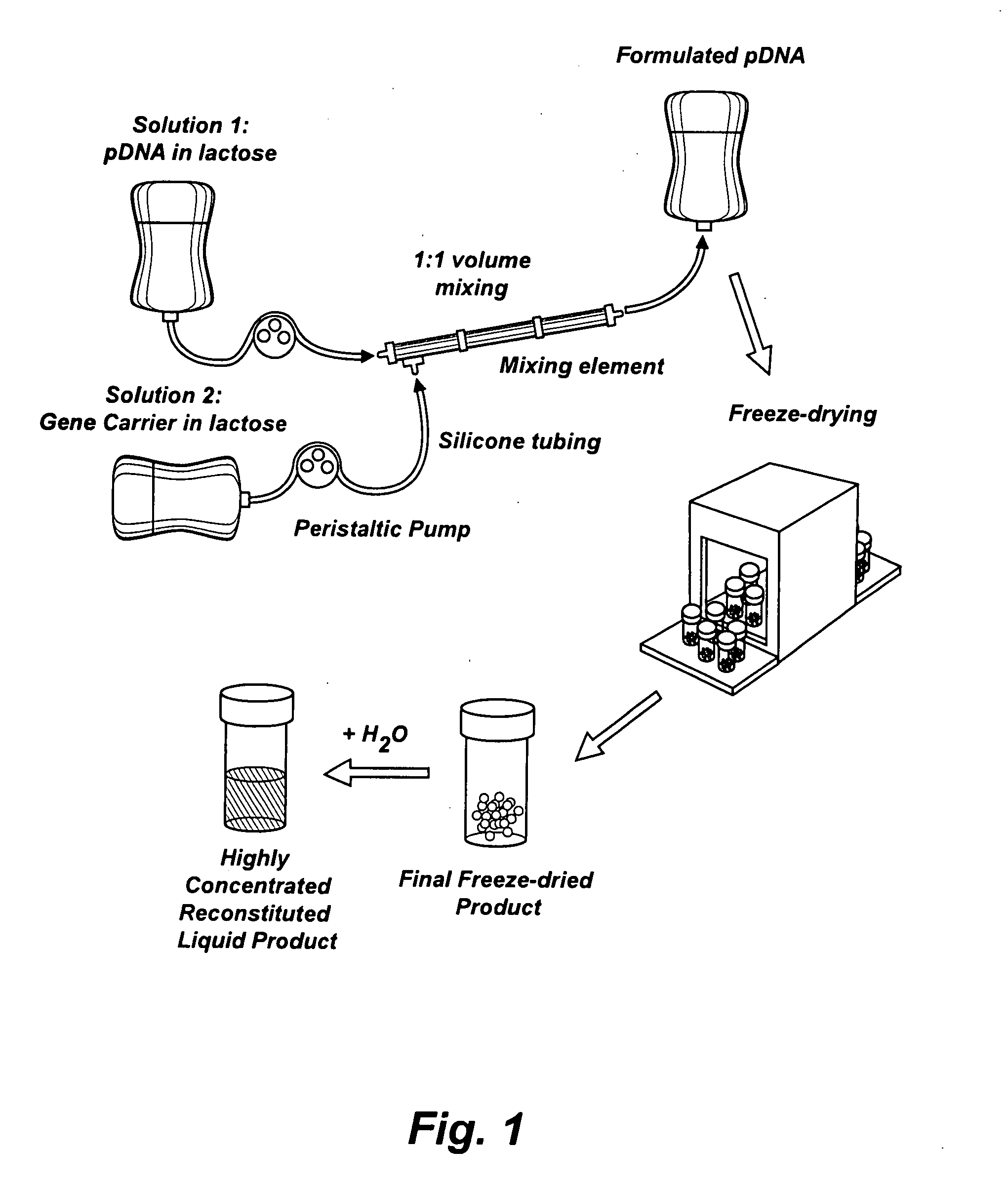
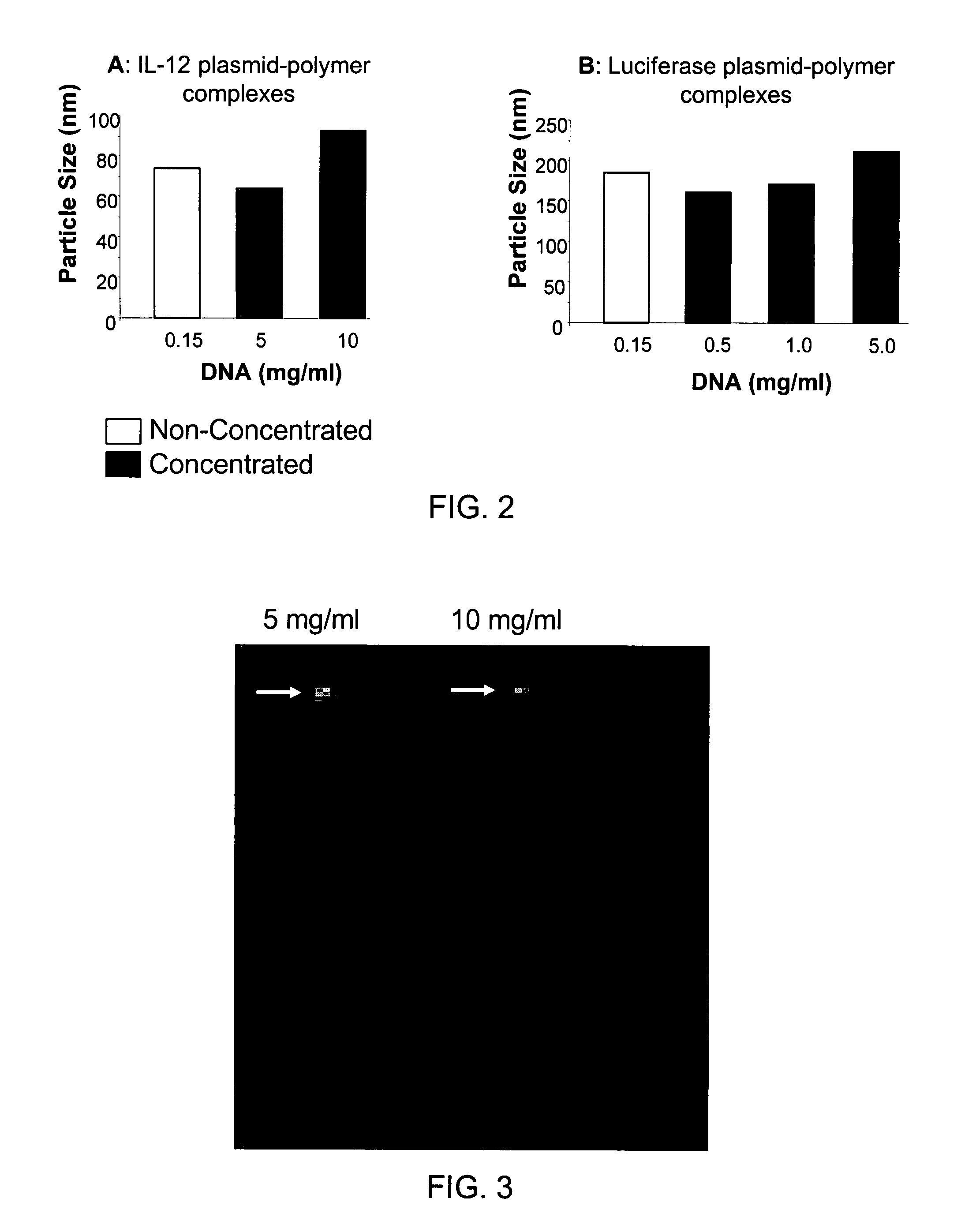
Composition, method of preparation & application of concentrated formulations of condensed nucleic acids with a cationic lipopolymer
UndeterminedUS20090042825A1Increase efficiency and dosing flexibilitySpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsFiller ExcipientCholesterol
Compositions, methods, and applications that increase the efficiency of nucleic acid transfection are provided. In one aspect, a pharmaceutical composition may include at least about 0.5 mg / ml concentration of a nucleic acid condensed with a cationic lipopolymer suspended in an isotonic solution, where the cationic lipopolymer includes a cationic polymer backbone having cholesterol and polyethylene glycol covalently attached thereto, and wherein the molar ratio of cholesterol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10, and the molar ratio of polyethylene glycol to cationic polymer backbone is within a range of from about 0.1 to about 10. The composition further may include a filler excipient.
Owner:EXPRESSION GENETICS INC
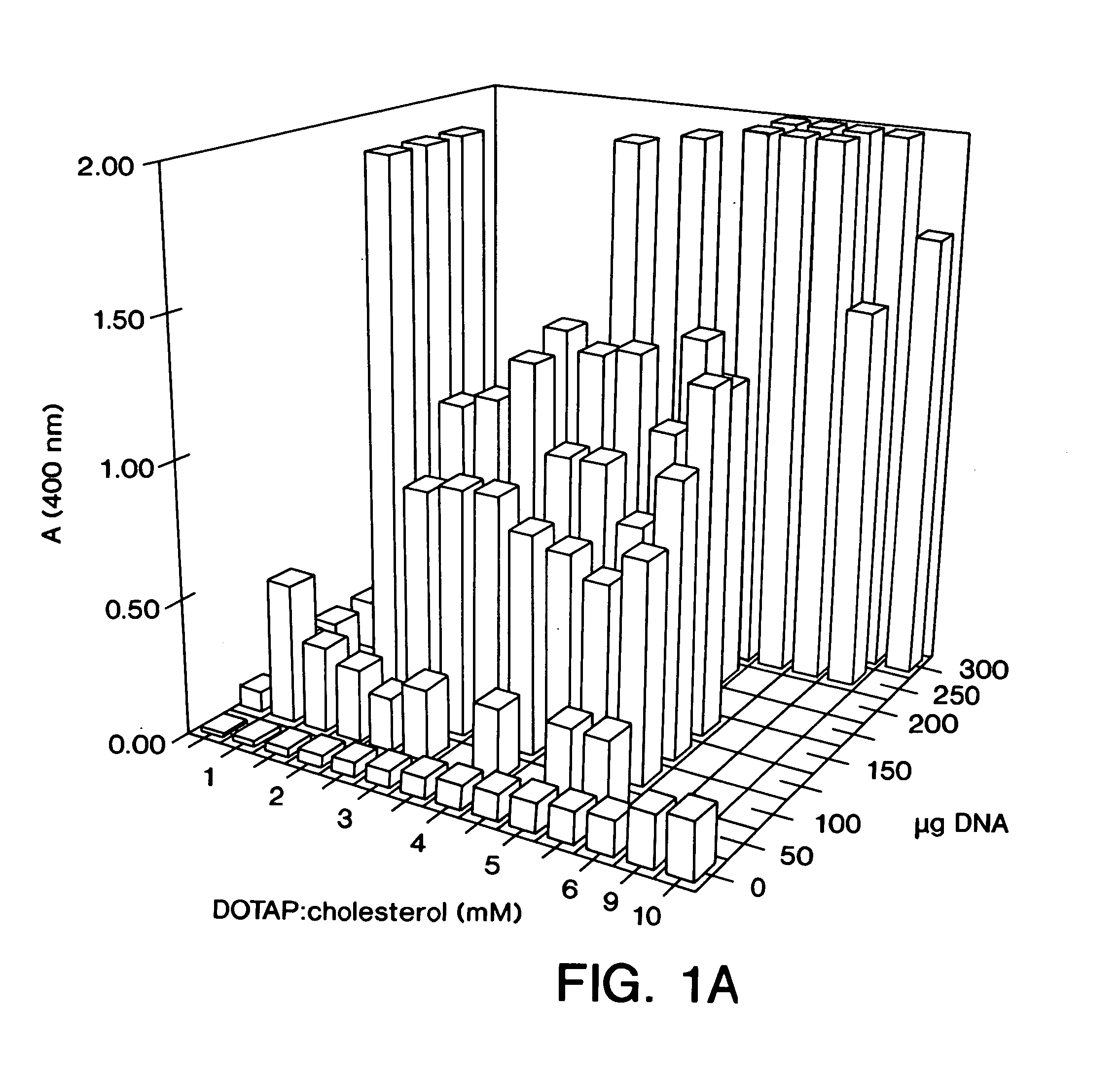
Novel liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery
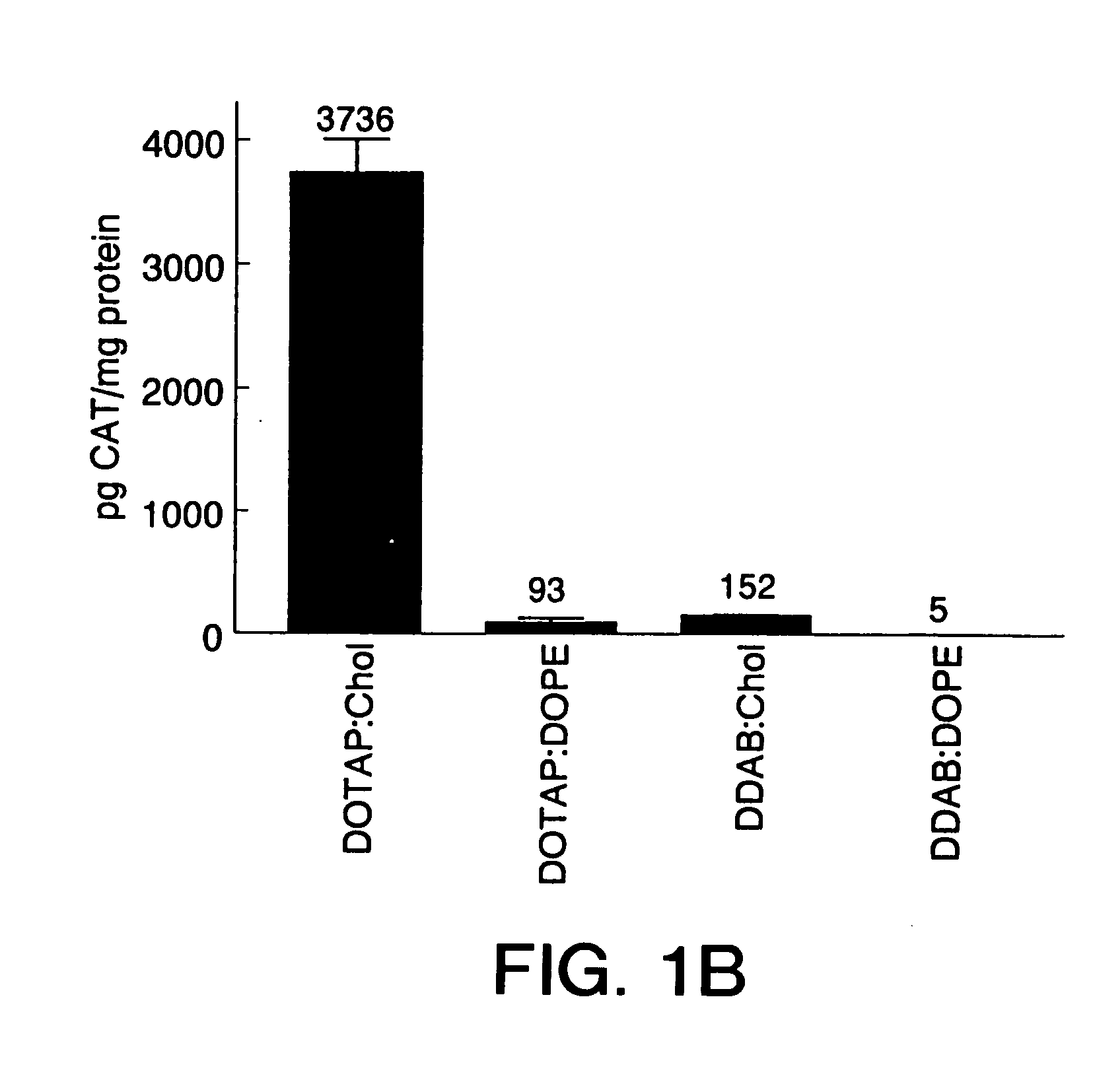
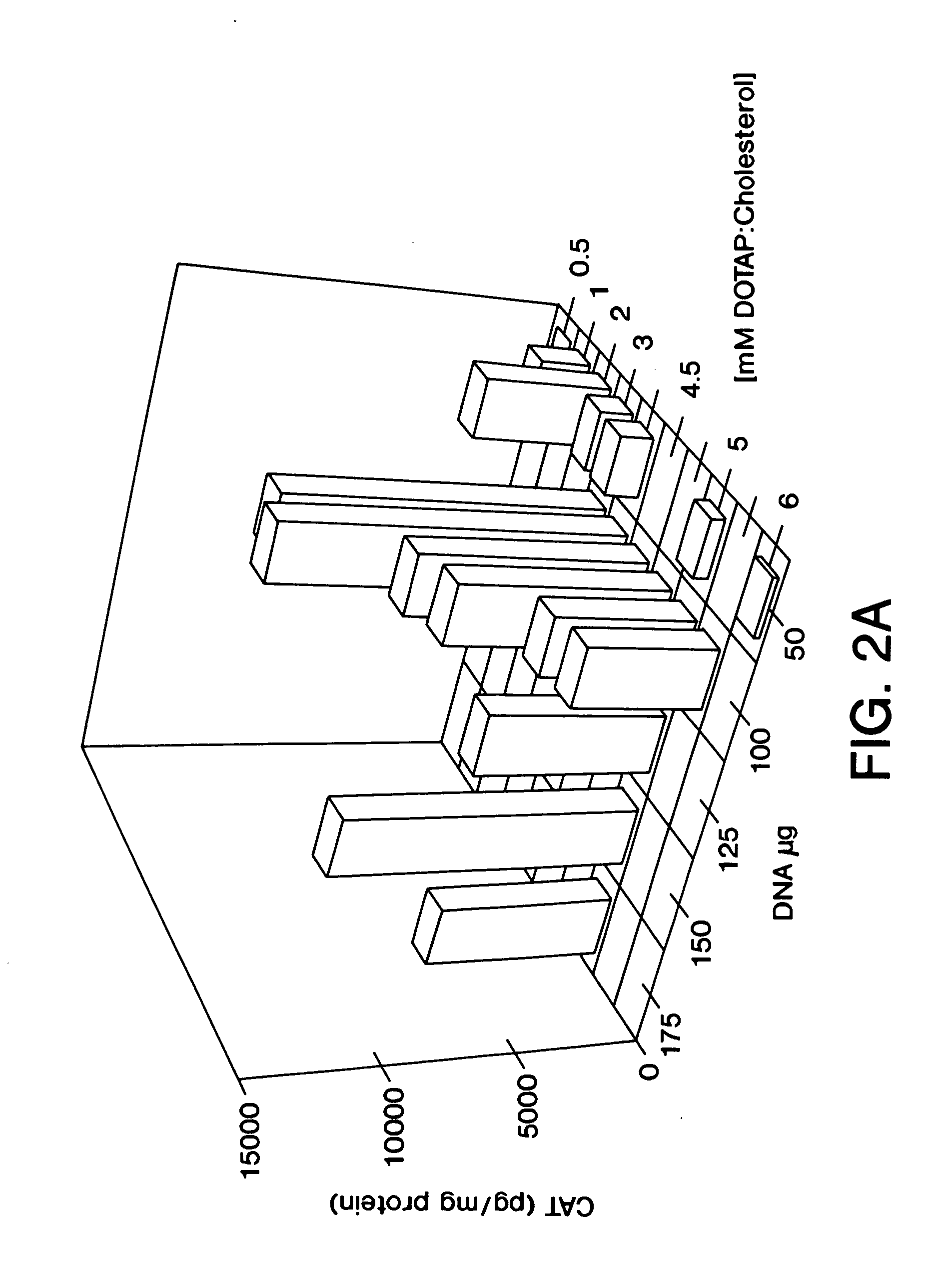
Highly efficient cationic liposomes have been developed as an improved delivery system for biologically-active reagents. A novel structure, the sandwich liposome, is formed and comprises one or more biologically active agents internalized between two bilomellar liposomes. This structure protects the incoming agent and accounts for the high efficiency of in vivo delivery and for the broad tissue distribution of the sandwich liposome complexes. These novel liposomes are also highly efficient carriers of nucleic acids. By using extruded DOTAP:cholesterol liposomes to form complexes with DNA encoding specific proteins, expression has been improved dramatically. Highest expression was achieved in the lung, while increased expression was detected in several organs and tissues.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Compositions and methods of altering cholesterol levels
InactiveUS20150005372A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsCholesterolPolynucleotide
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Phospholipase inhibitors localized in the gastrointestinal lumen
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the treatment of phospholipase-related conditions. In particular, the invention provides a method of treating insulin-related, weight-related conditions and / or cholesterol-related conditions in an animal subject. The method generally involves the administration of a non-absorbed and / or effluxed phospholipase A2 inhibitor that is localized in a gastrointestinal lumen.
Owner:ILYPSA
Liposomal products
InactiveUS6060080AHigh encapsulation efficiencyEasy to packLiposomal deliveryCholesterolWater soluble drug
A liposomal aqueous dispersion and method of making the liposomal aqueous dispersion is useful for encapsulation of drugs. The liposomal aqueous dispersion comprises: an aqueous suspension medium; multilamellar liposomes comprising an anionic phospholipid and cholesterol as essential components; neutral phospholipid in a mole ratio of 0 to 40% based on the total amount of said multilamellar liposomes; and a cation moiety-containing water-soluble drug, wherein the electrolyte concentration of said aqueous suspension medium is not more than 40 mM.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
Low molecular weight cationic lipids for oligonucleotide delivery
ActiveUS20130274523A1Good curative effectReduce liver toxicityPowder deliveryNanotechTolerabilityCholesterol
The instant invention provides for novel cationic lipids that can be used in combination with other lipid components such as cholesterol and PEG-lipids to form lipid nanoparticles with oligonucleotides. It is an object of the instant invention to provide a cationic lipid scaffold that demonstrates enhanced efficacy along with lower liver toxicity as a result of lower lipid levels in the liver. The present invention employs low molecular weight cationic lipids with one short lipid chain to enhance the efficiency and tolerability of in vivo delivery of siRNA.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
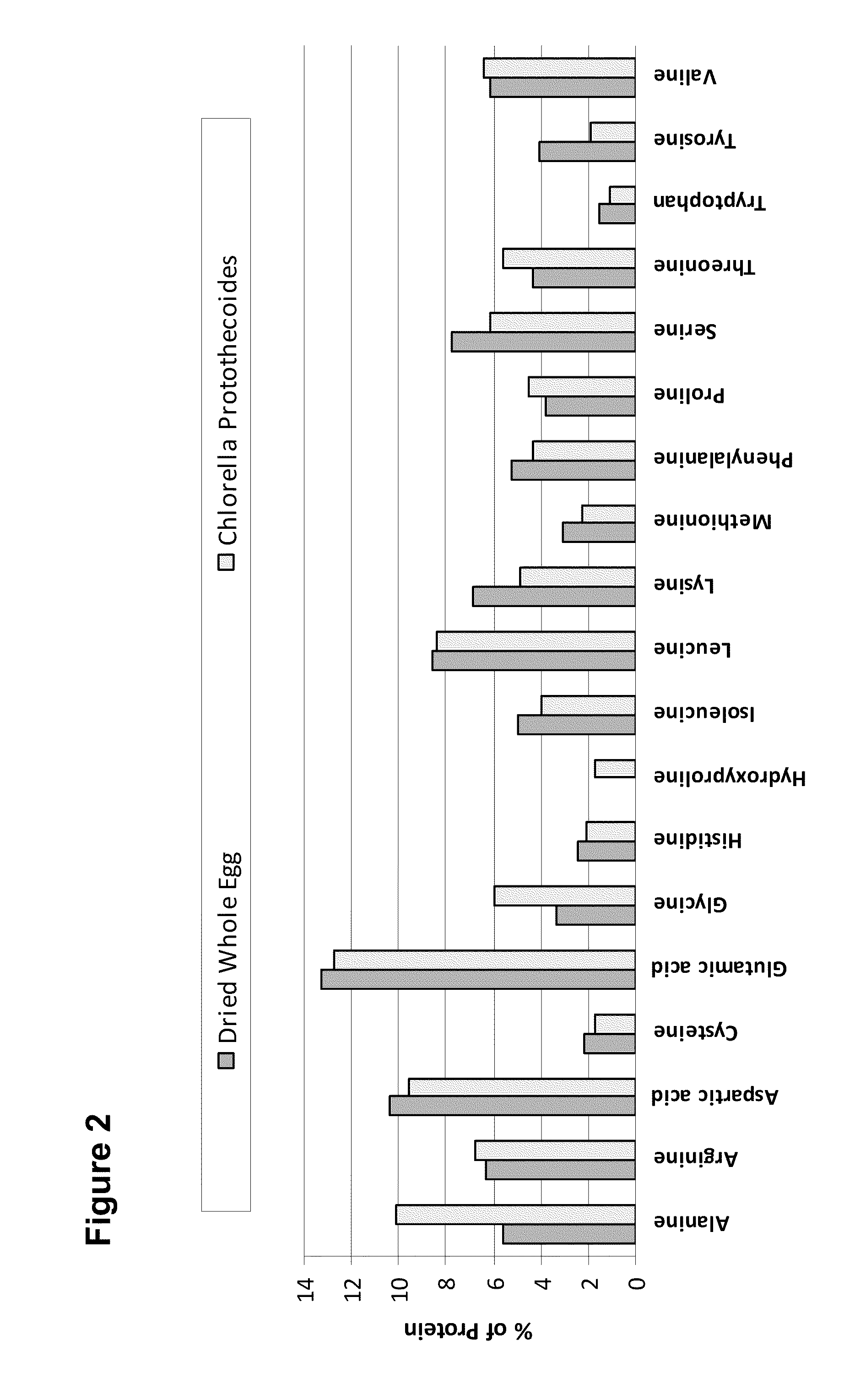
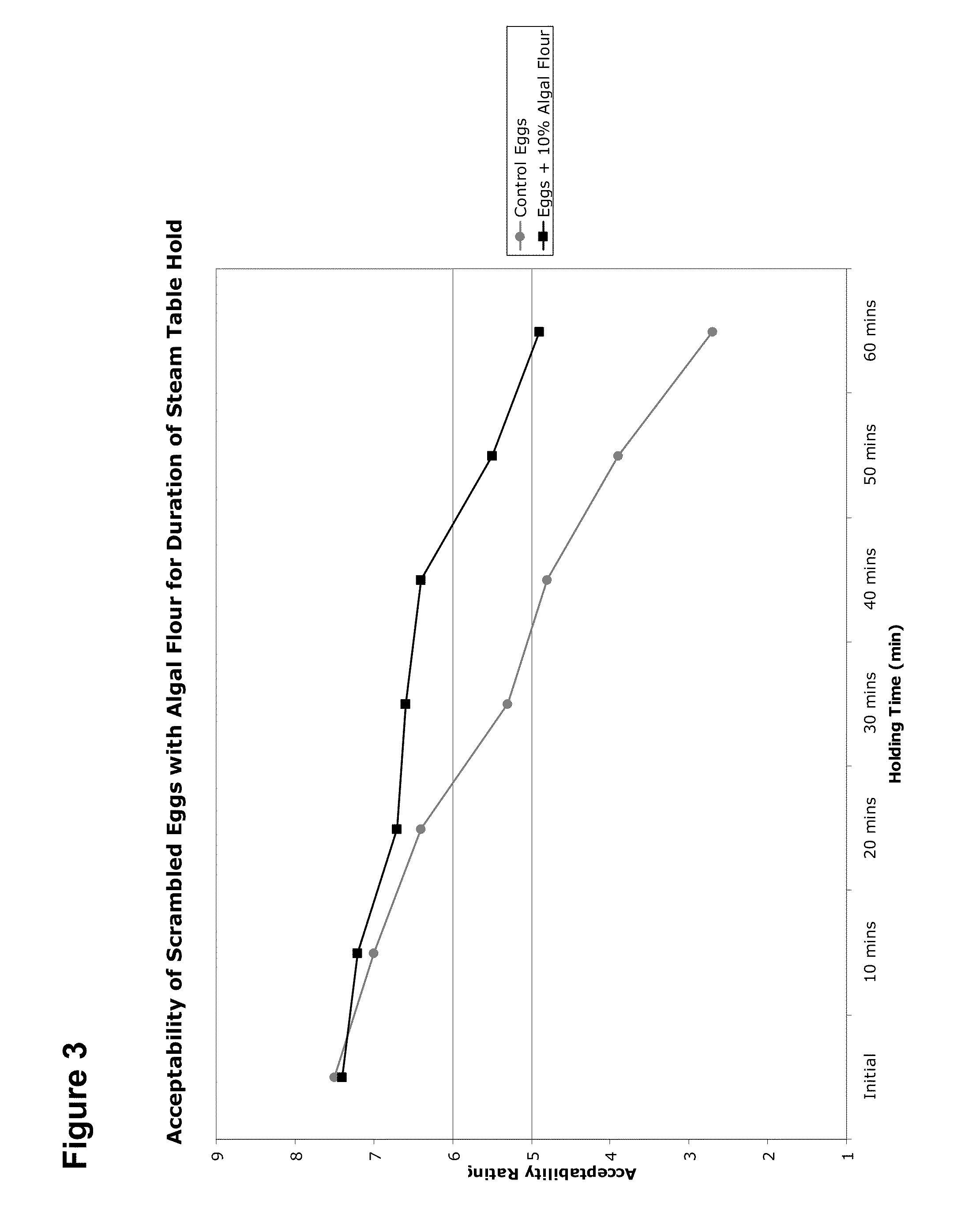
Gluten-free Foods Containing Microalgae
InactiveUS20100297323A1Improve health benefitsDesirable sensory propertySpread compositionsDough treatmentAdditive ingredientCholesterol
Disclosed herein are microalgae-containing gluten-reduced and gluten-free finished food compositions, as well as microalgae-containing food ingredients for the large-scale manufacture of gluten-reduced and gluten-free foods. Foods and ingredients of the invention, while reducing or eliminating gluten, also have increased health benefits through reduction or elimination of less healthy oils and fats via replacement of primarily monounsaturated algal oils. The novel food compositions also possess more desirable sensory properties and shelf life than previously existing gluten free foods. Foods and ingredients disclosed herein, whoch containing reduced or no gluten, also containing high dietary fiber levels, reduced or eliminated cholesterol, and healthier oil content than existing gluten free foods. Also disclosed are methods of reducing food allergies and symptoms of diseases such as Celiac-Sprue to address increasing rates of sensitivity to gluten-containing products. Also disclosed are methods of formulating and manufacturing microalgae-containing gluten-free foods and ingredients for the formulation of such foods.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
2′-Fluoronucleosides
InactiveUS7307065B2Sure easyUseful in treatmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphoric Acid EstersPhosphate
A class of 2′-fluoro-nucleoside compounds are disclosed which are useful in the treatment of hepatitis B infection, hepatitis C infection, HIV and abnormal cellular proliferation, including tumors and cancer. The compounds have the general formulae:whereinBase is a purine or pyrimidine base;R1 is OH, H, OR3, N3, CN, halogen, including F, or CF3, lower alkyl, amino, loweralkylamino, di(lower)alkylamino, or alkoxy, and base refers to a purine or pyrimidine base;R2 is H, phosphate, including monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate, or a stabilized phosphate prodrug; acyl, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of providing a compound wherein R2 is H or phosphate; sulfonate ester including alkyl or arylalkyl sulfonyl including methanesulfonyl, benzyl, wherein the phenyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described in the definition of aryl given above, a lipid, an amino acid, peptide, or cholesterol; andR3 is acyl, alkyl, phosphate, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of being cleaved to the parent compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Healthier Baked Goods Containing Microalgae
Provided herein are microalgae-containing baked goods with novel properties compared to preexisting products of the same type. Methods of formulating and manufacturing these foods to deliver reduced fat, reduced cholesterol, and increased fiber content are disclosed herein. Various embodiments include elimination or reduction of eggs, butter, animal fat, and saturated oils in favor of healthy oil-containing microalgae biomass and oils, including the manufacture of foods with lower calories than preexisting products of the same type. Methods of producing raw materials for the manufacture of novel processed baked foods and intermediates such as cake and bead mixes are also provided.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Nutritional supplement
A nutritional supplement comprising an infant milk formula having long chain poly unsaturated fatty acids, sialic acids, and cholesterol.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
Method for selectively combining multiple membranes for assembly into test strips
ActiveUS7129038B2Improve performanceReduce test strip lot rejectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCholesterolKetone
A method for selectively combining multiple membranes for assembly into test strips (such as visual blood glucose test strips with side-by-side membranes). The method includes first measuring a plurality of color parameters (e.g., L*, a* and b*color parameters) associated with membrane samples from at least two membrane lots. Next, response characteristics (e.g., blood glucose response levels) are simulated for a speculative test strip that includes, for purposes of the simulation, combined multiple membranes tentatively selected from the at least two membrane lots. The simulated response characteristics are based on the measured plurality of color parameters of the tentative selection of combined multiple membranes. Optionally, the simulated response characteristics can also be based on simulated color parameters of the tentative selection of combined multiple membranes. Subsequently, assembly of the at least two membrane lots into a test strip with combined membranes is contingent on acceptable simulated response characteristics. Any suitable color parameters can be employed. The method can be used to selectively combine two or more membranes based on any number of color parameters. The assembled test strips can be used to measure glucose, cholesterol, proteins, ketones, phenylalanine or enzymes in blood, urine, saliva or other biological fluid, as well as sample fluid characteristics (e.g., pH and alkalinity).
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Near infrared risk assessment of diseases
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for identifying the risk of a clinical condition in a human or animal by correlating Near Infrared (NIR) absorbance spectral data with one or several parameters including a concentration of one or more substances in the skin, a concentration of one or more substances in skin plus subdermal tissue, a score derived from one or more clinical tests like a stress test on a treadmill, coronary angiography, or intravascular coronary ultrasound. The method determines the concentration of a compound in the skin of a human or animal and comprises the steps of placing a part of the skin against a receptor, directing electromagnetic radiation (EMR) from the near-infrared spectrum onto the skin, measuring a quantity of EMR reflected by, or transmitted through, the skin with a detector; and performing a quantitative mathematical analysis of the quantity of EMR to determine the concentration of the compound, for example free and esterfied cholesterol. An example of a clinical condition is cardiovascular disease.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Oligonucleotides comprising a C5-modified pyrimidine
ActiveUS20050288244A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderBenzoic acidPhosphate
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one ligand. In certain embodiments, a ligand is bound to only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, both of the oligonucleotide strands of the double-stranded oligonucleotide independently comprise a bound ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, a phosphate linkage in one or both of the strands of the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the ligand is cholesterol or 5β-cholanic acid. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, a phosphate linkage of the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the ligand is cholesterol or 5β-cholanic acid. The ligand improves the pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
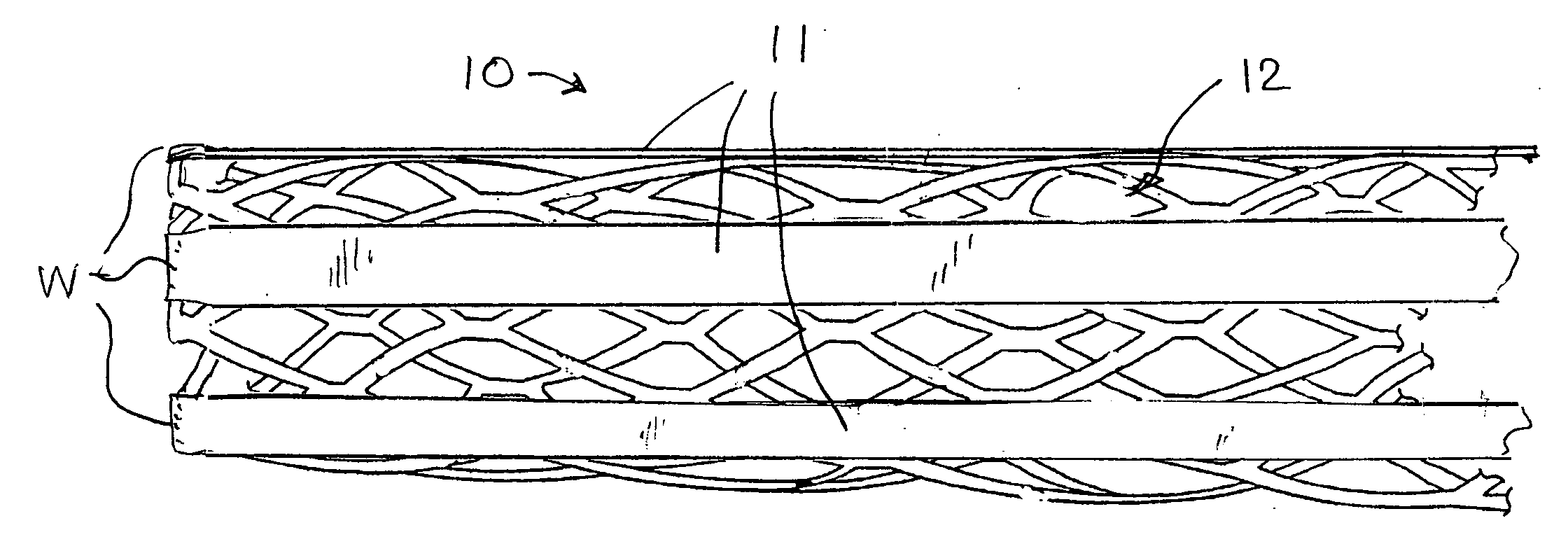
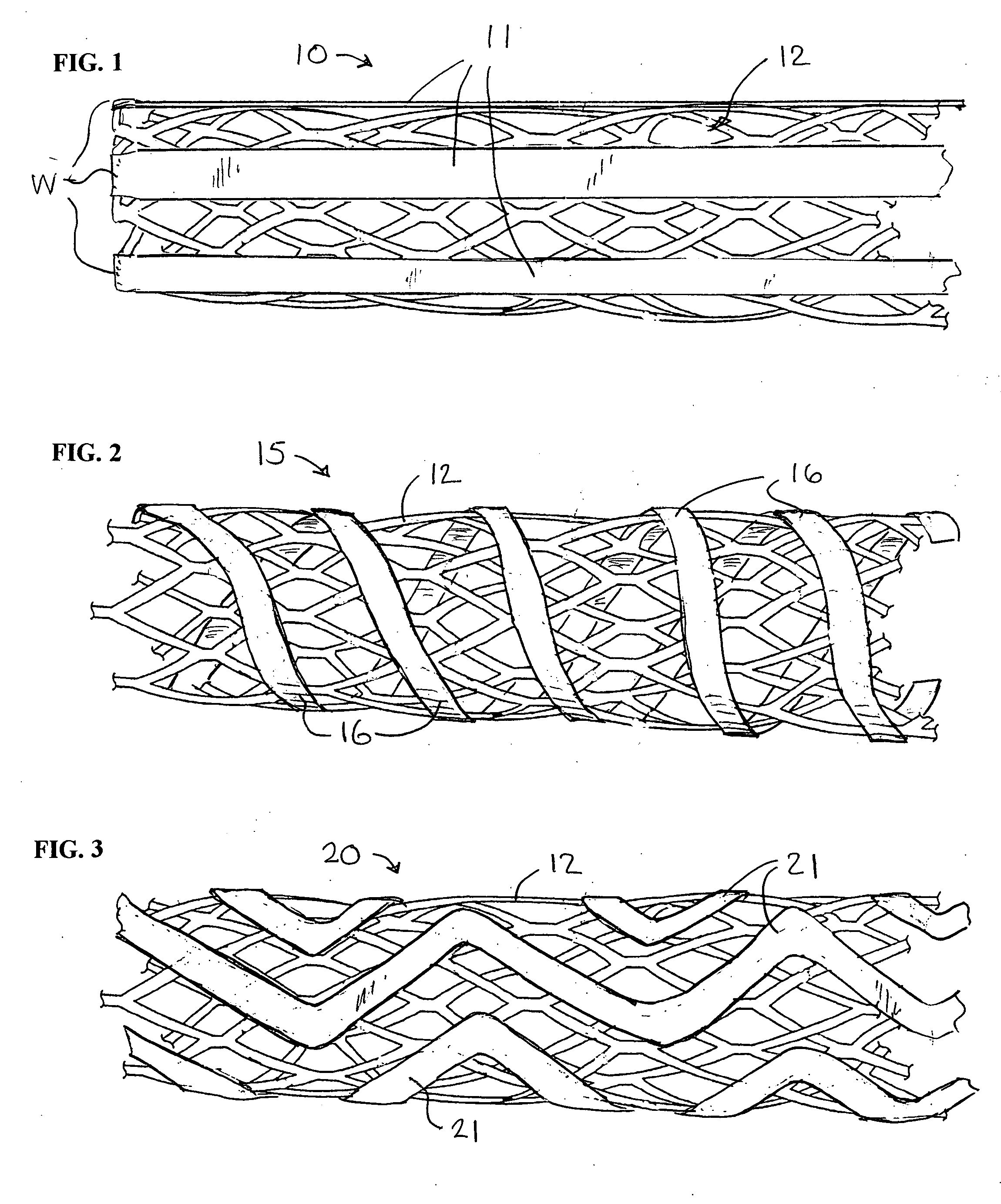
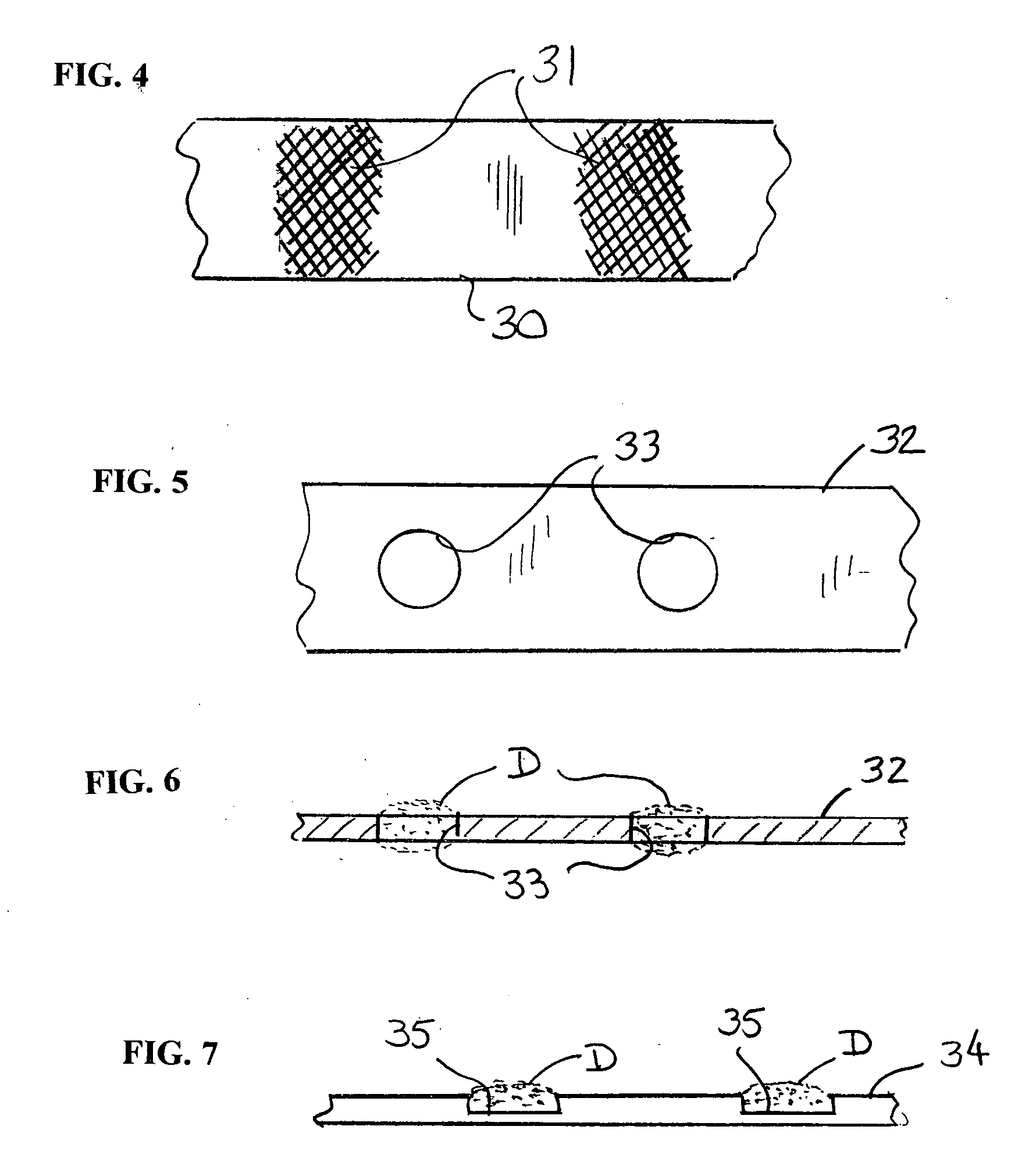
Stent with auxiliary treatment structure
InactiveUS20060085065A1Reduce fluid turbulenceAvoid problemsStentsBlood vesselsReticular formationCholesterol
A medical device for treatment of a stenosed body lumen, includes an open-ended cylindrical body carried on a distal end of a catheter for insertion of the device into the body lumen and placement at the stenosed site. The cylindrical body is movable between a collapsed position for insertion into the body lumen, and a radially expanded position pressed against the wall of the body lumen. In one embodiment the body sidewall is formed by a plurality of interconnected struts or elements defining openings therebetween, and at least one elongate ribbon is attached to an outer surface thereof for carrying a therapeutic agent. In another embodiment, the body is formed of interwoven elements defining a mesh-like structure, and the elements may comprise dissimilar materials, such as, e.g., copper and silver. In a further embodiment the body is formed of layers of different materials such as, e.g., copper, silver, and / or steel, laminated together. In a still further embodiment the device is designed for temporary placement of the catheter and body in a body lumen for treatment of a stenosed site, after which the catheter and body are withdrawn. In all forms the body may have an outwardly flared inlet end to reduce turbulence of fluid flowing through it, and / or a gel-like coating of a cholesterol-dissolving or blood clot dissolving agent may be placed on the device.
Owner:LIM WALTER K
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com