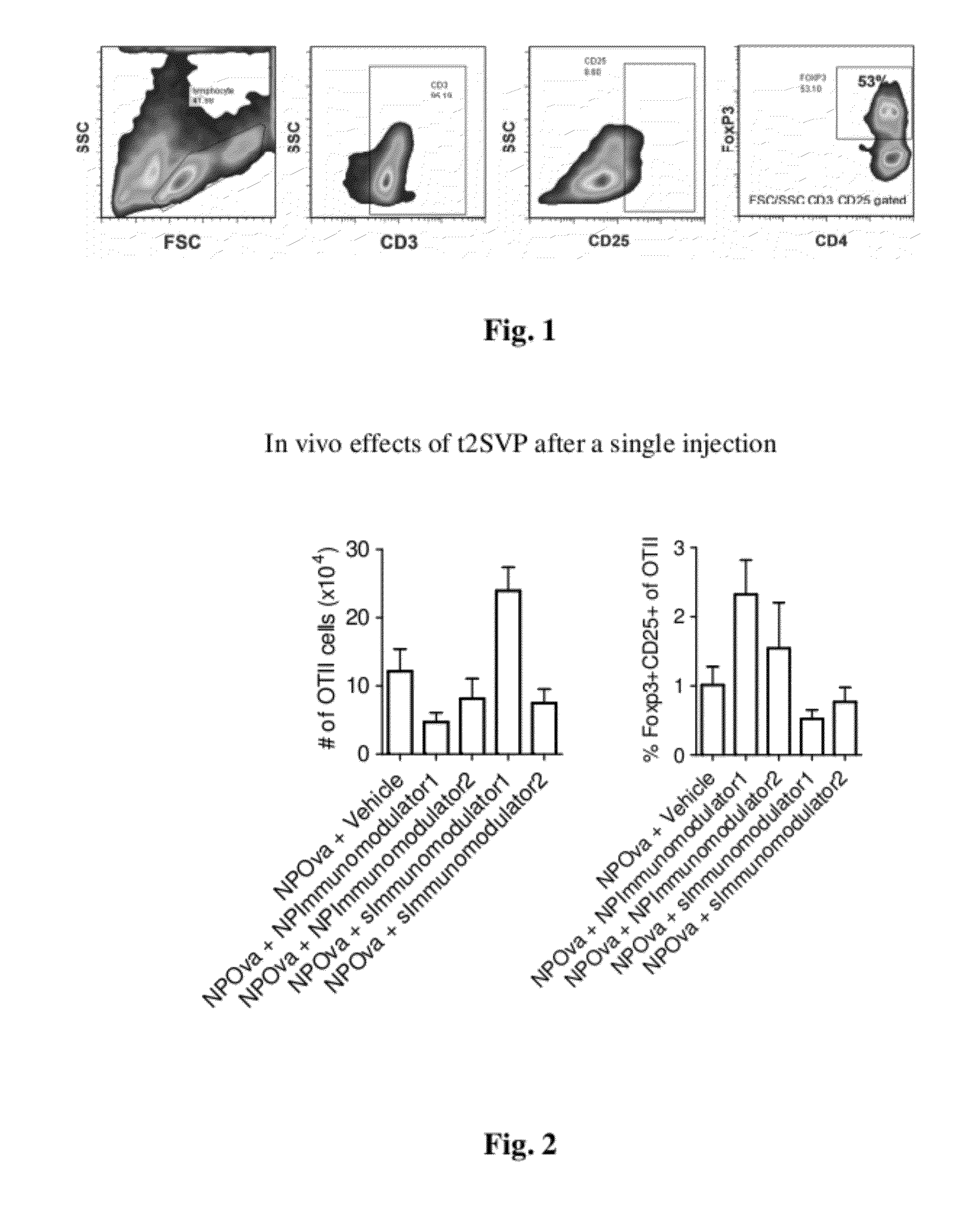
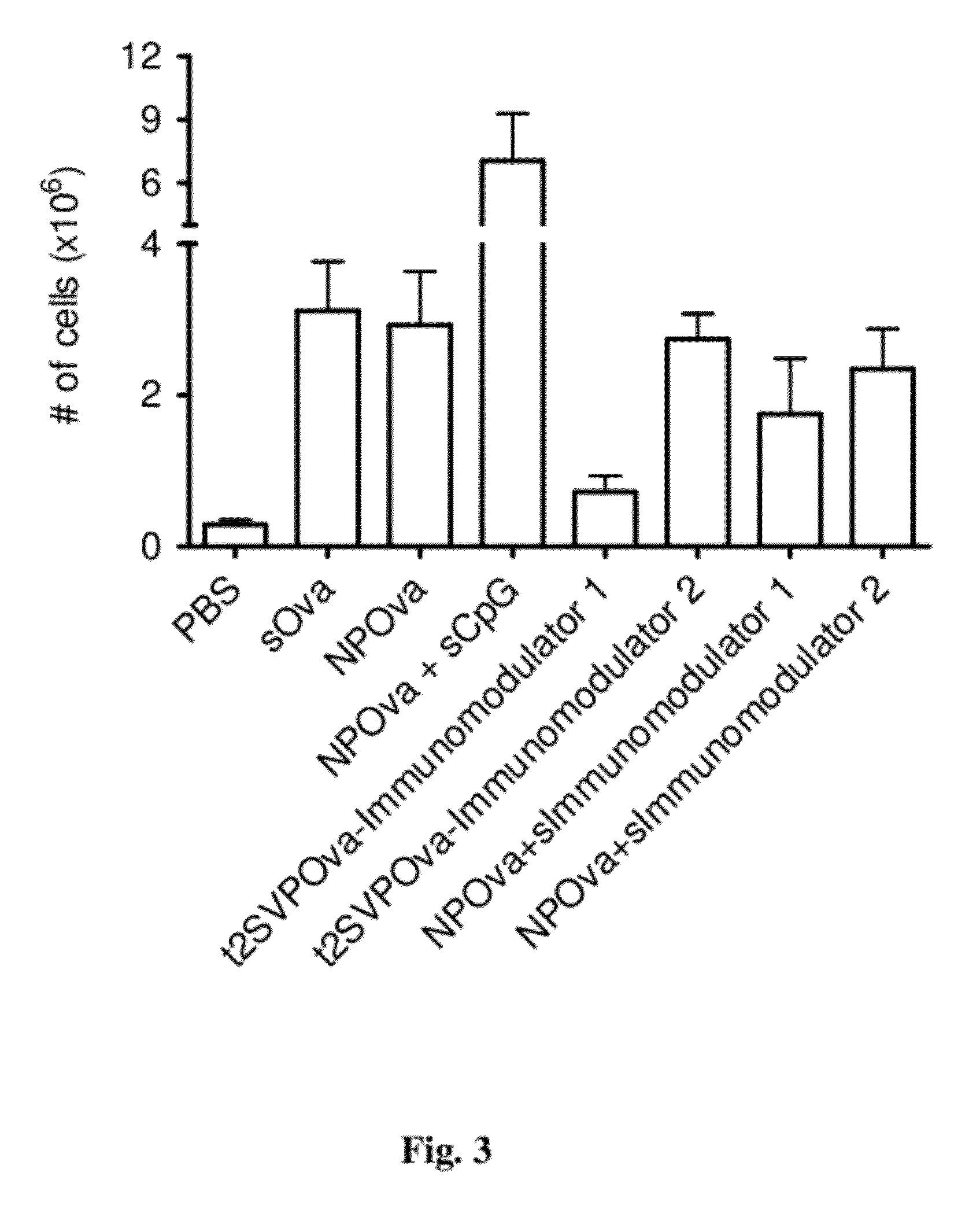
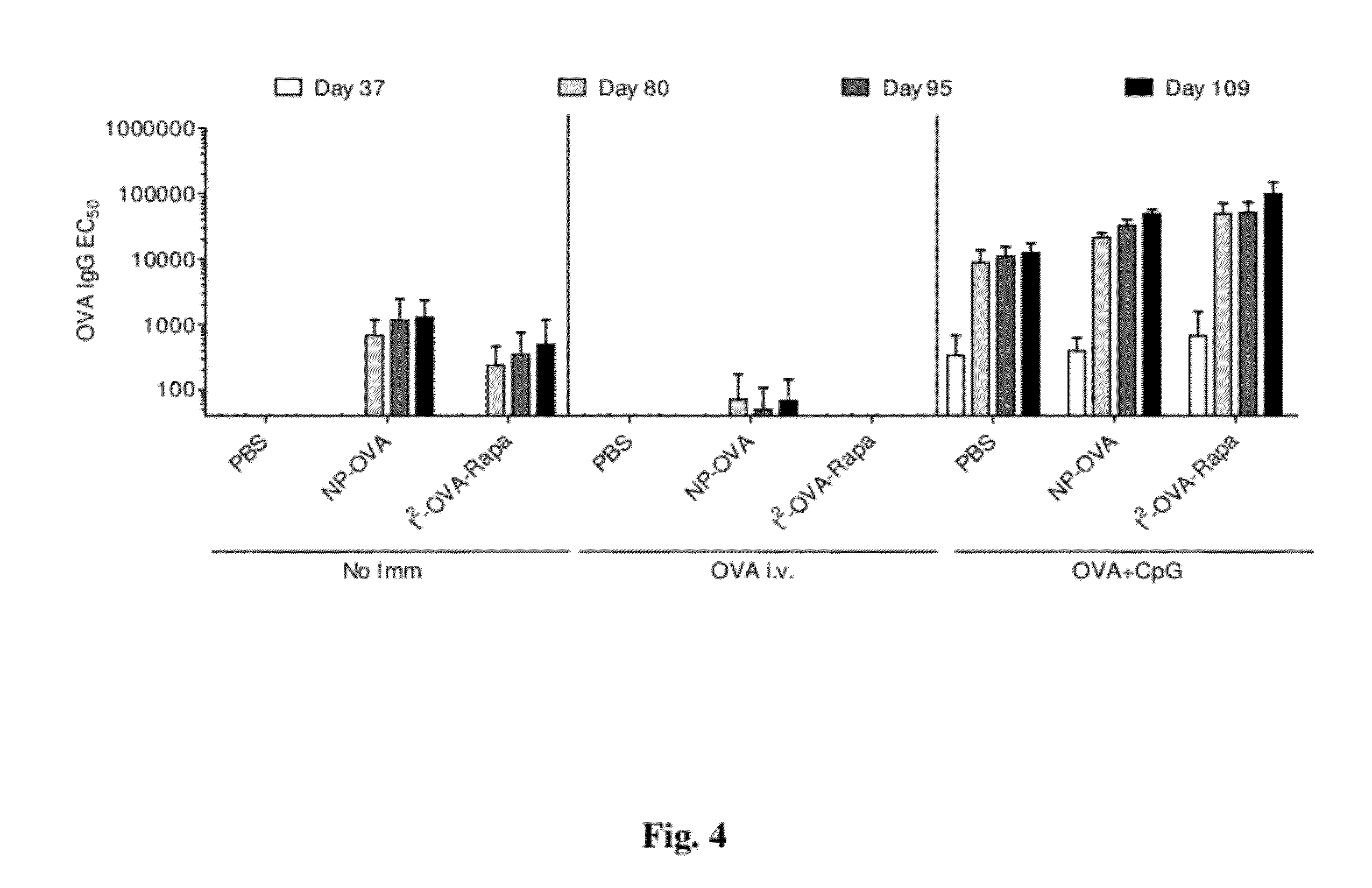
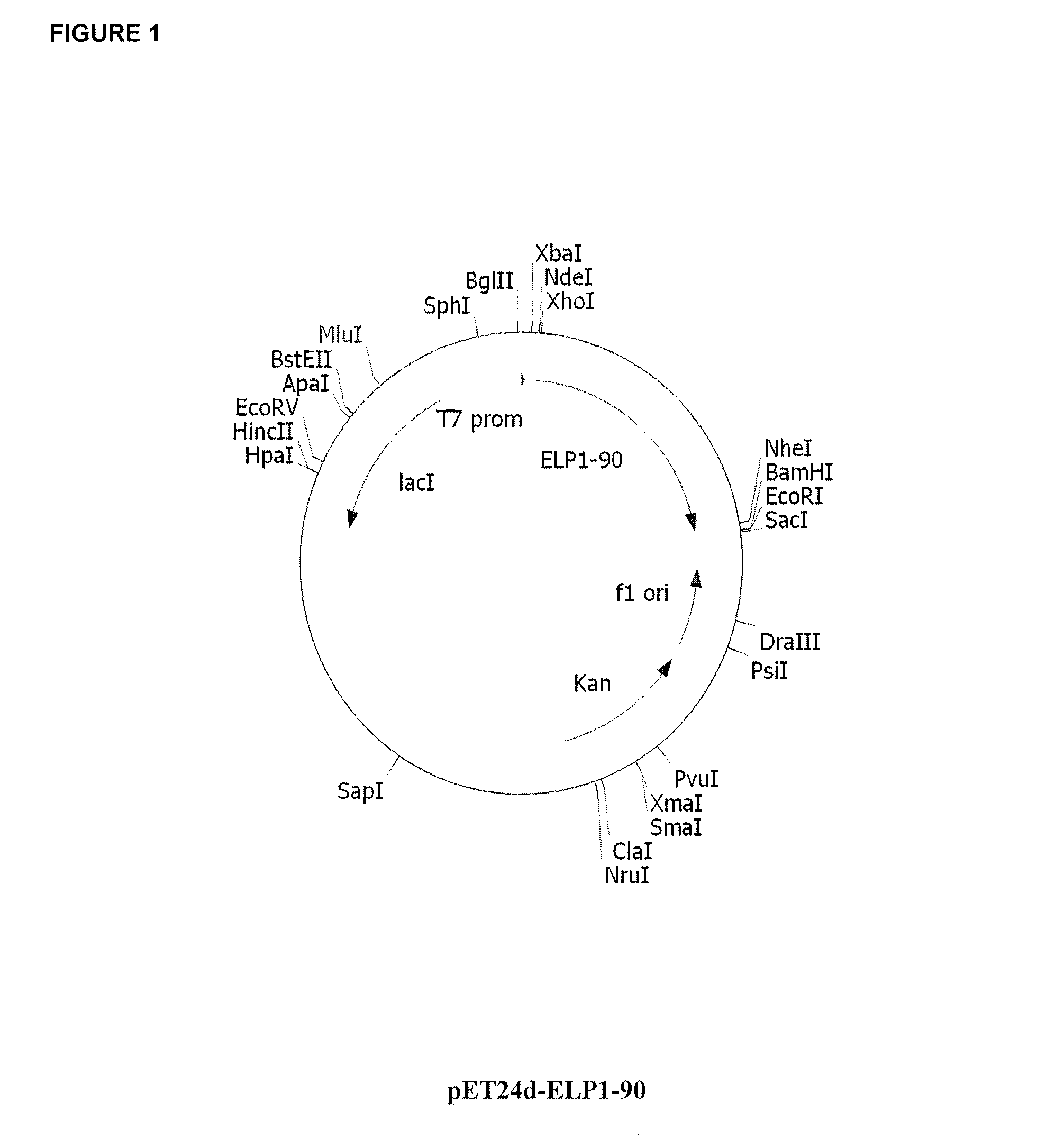
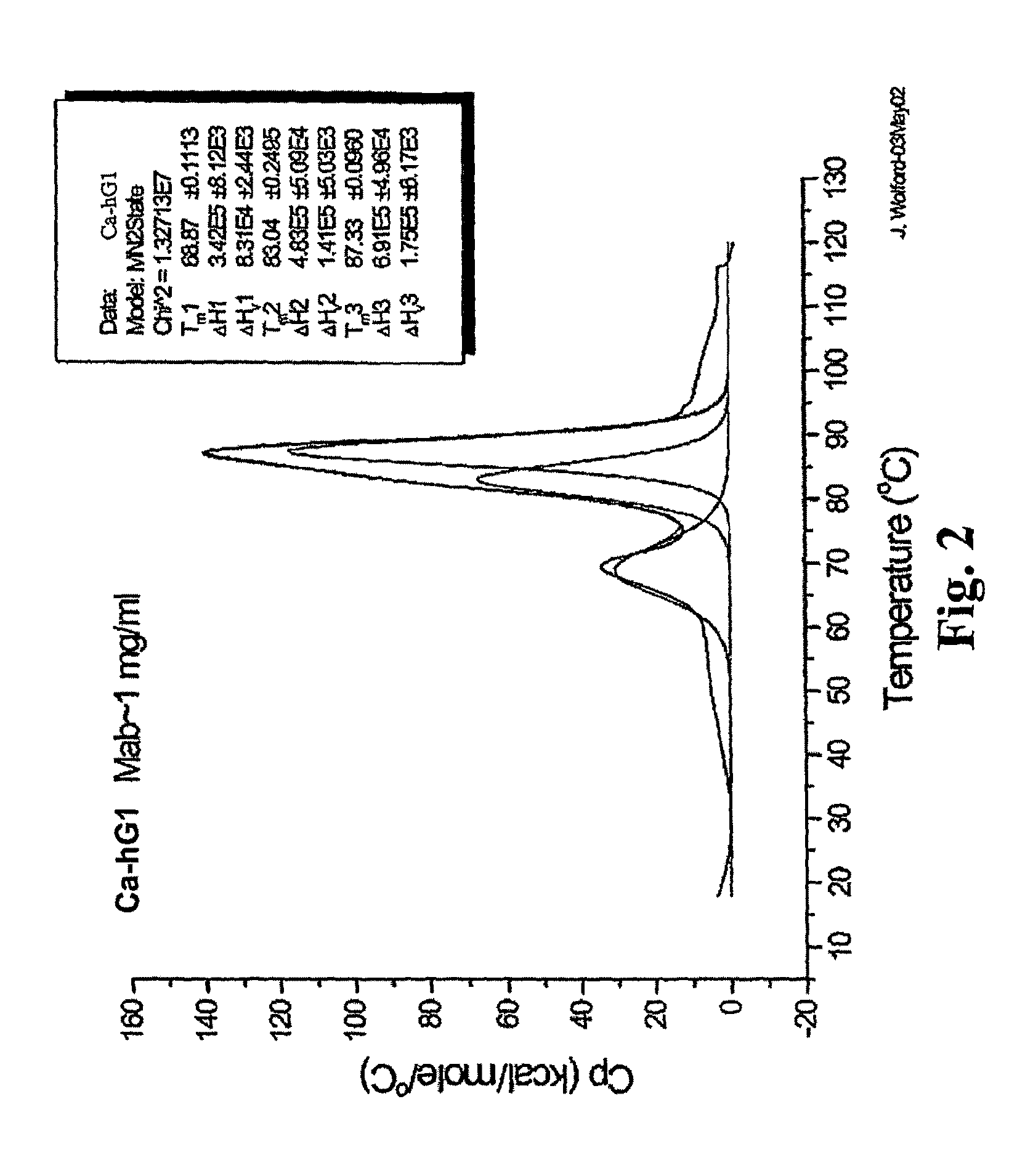
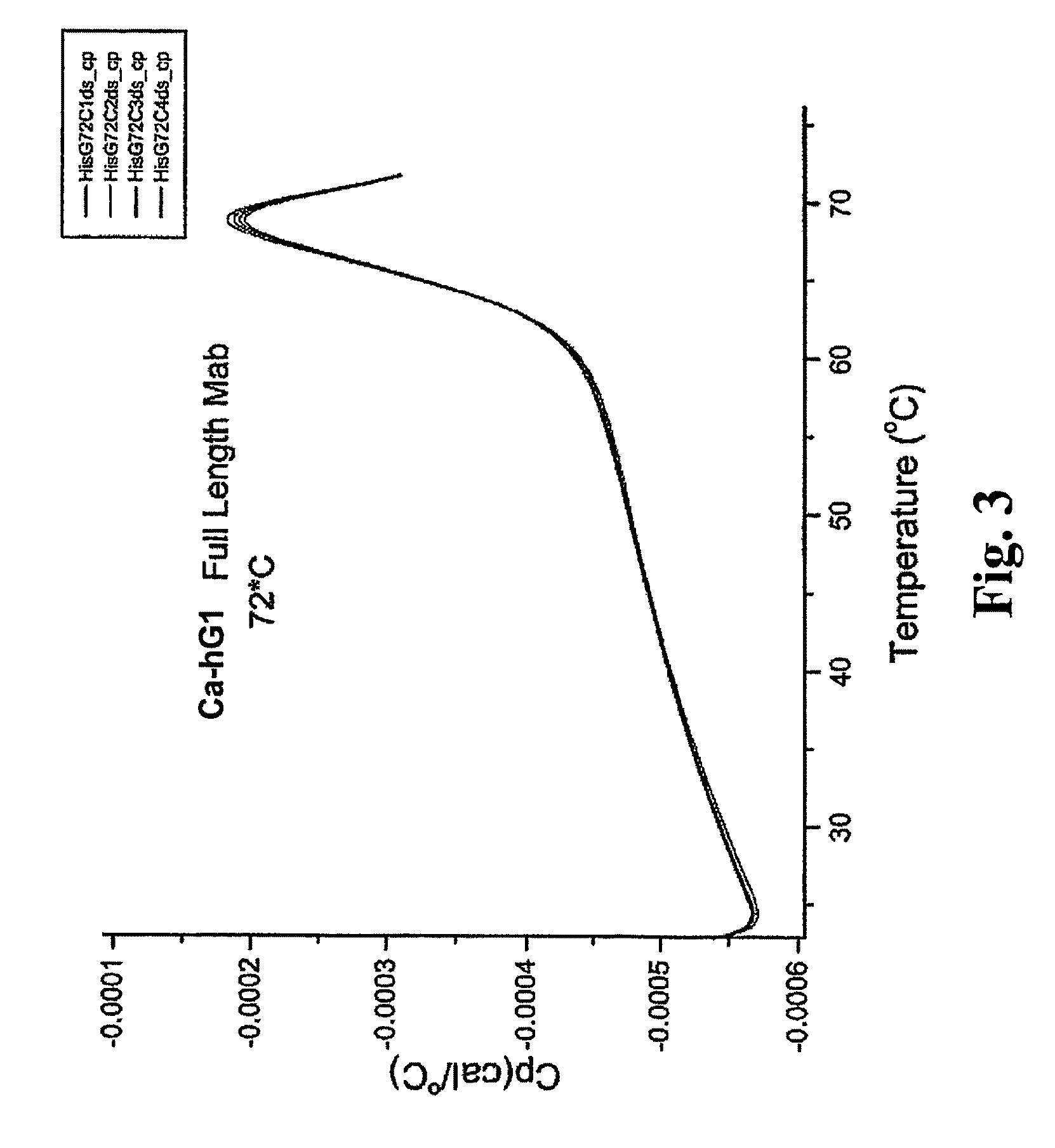
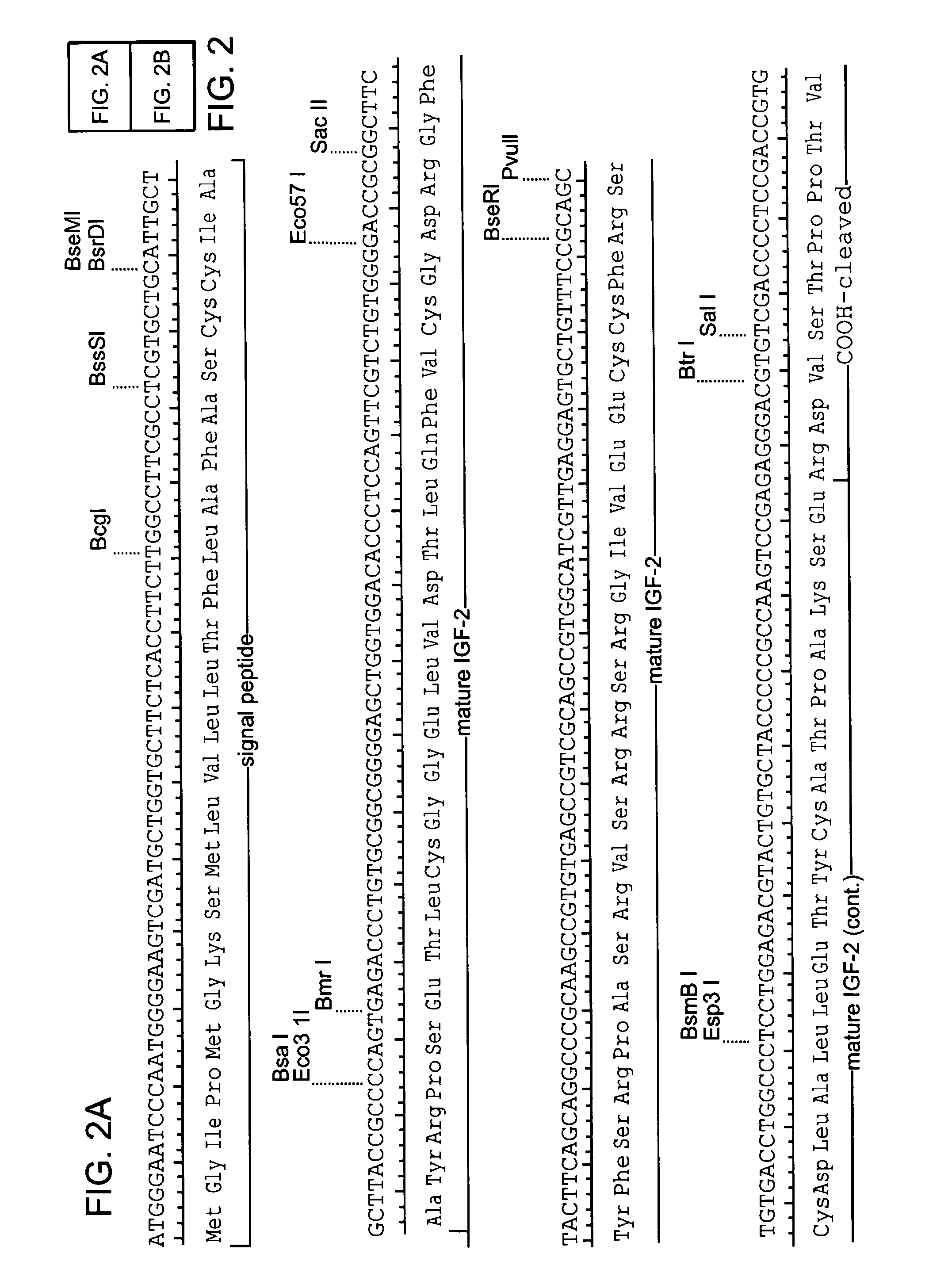
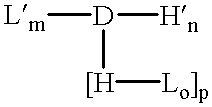Patents
Literature
572 results about "Therapeutic protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Therapeutic proteins act when they are delivered inside a body, such as through an injection. The body recognizes the protein as functional, and responds as if the protein was naturally occurring. Diseases that are controllable through therapeutic protein medications include certain types of anemia, specific forms of diabetes and hemophilia.
Amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates with hydroyzable lipophile components and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS6309633B1Reduce deliveryExtended durationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinCholesterol
The invention provides a drug-oligomer conjugate having the following general formula:wherein D is a therapeutic drug moiety; H and H' are each a hydrophilic moiety, independently selected from the group consisting of straight or branched PEG polymers having from 2 to 130 PEG subunits, and sugars; L is a lipophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups having 2-26 carbon atoms, cholesterol, adamantane and fatty acids; o is a number from 1 to the maximum number of covalent bonding sites on H; m+n+p together have a value of at least one and not exceeding the total number of covalent bonding sites on D for the -H', -L and -H-L substituents; the H-L bond(s) are hydrolyzable and the D-L' bond(s), when present, are hydrolyzable; the conjugate being further characterized by one of the following: (i) m is 0 and p is at least 1; (ii) n is 0 and p is at least 1; (iii) m and n are each 0 and p is at least 1; (iv) p is 0 and m and n are each at least 1. The therapeutic drug moiety is preferably a therapeutic protein or peptide, preferably insulin or a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Methods for rational pegylation of proteins
The present invention relates to the use of simulation technology to rationally optimize the locations and sizes of attached polymeric moieties for modification of therapeutic proteins and the proteins generated from this method.
Owner:XENCOR
Combinatorial DNA library for producing modified N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7449308B2The overall structure is closedHigh yieldSugar derivativesMicroorganismsHeterologousTherapeutic protein
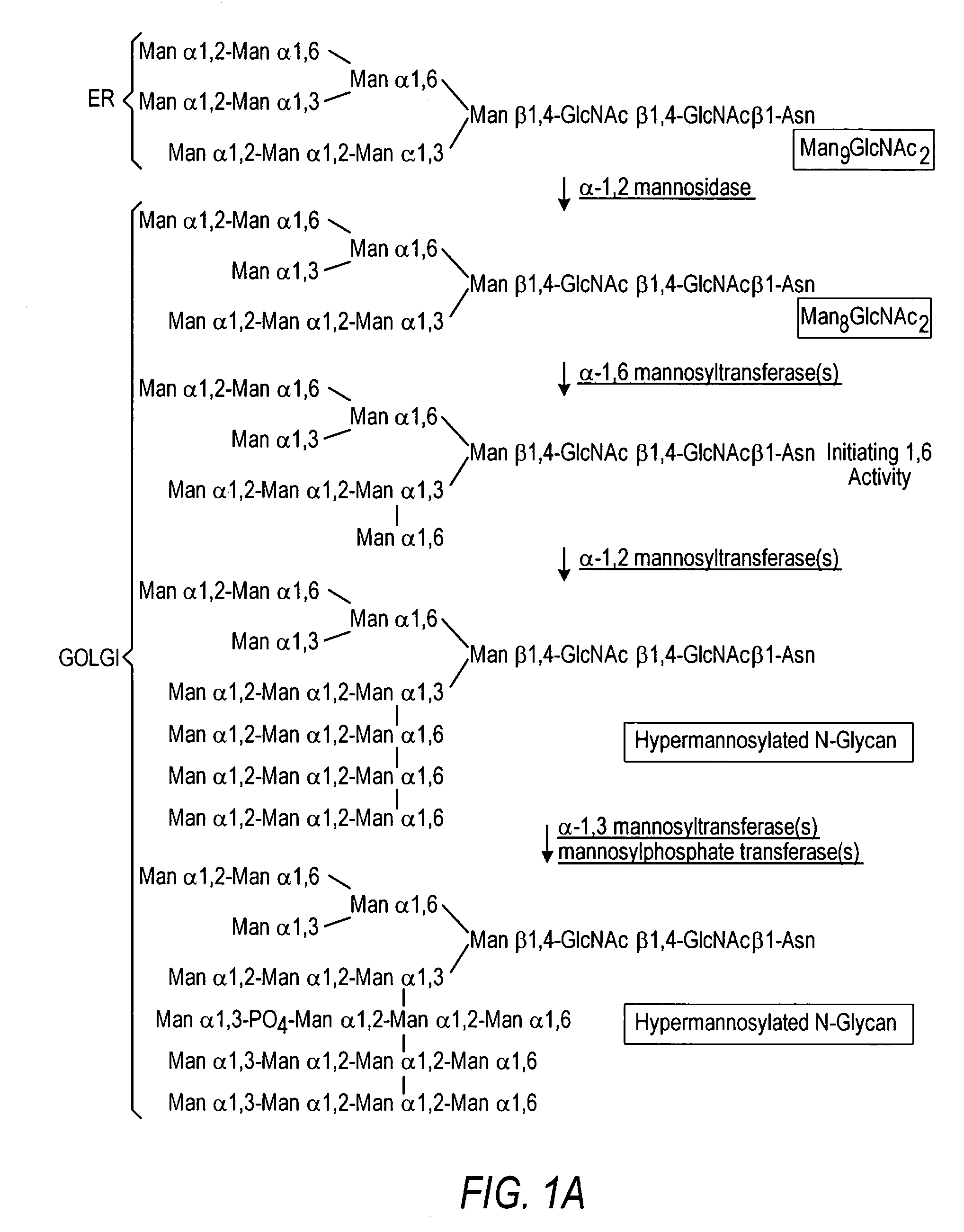
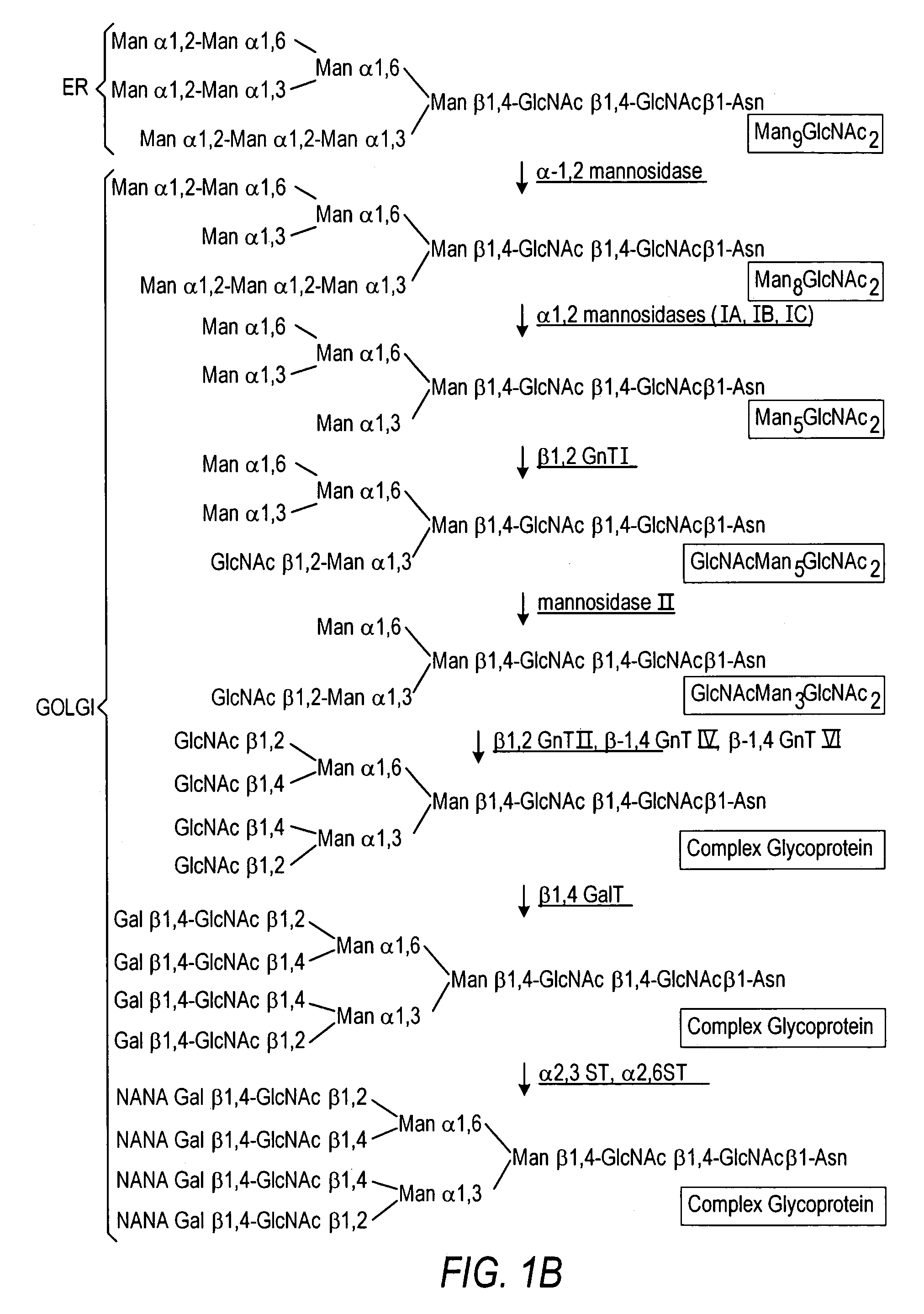
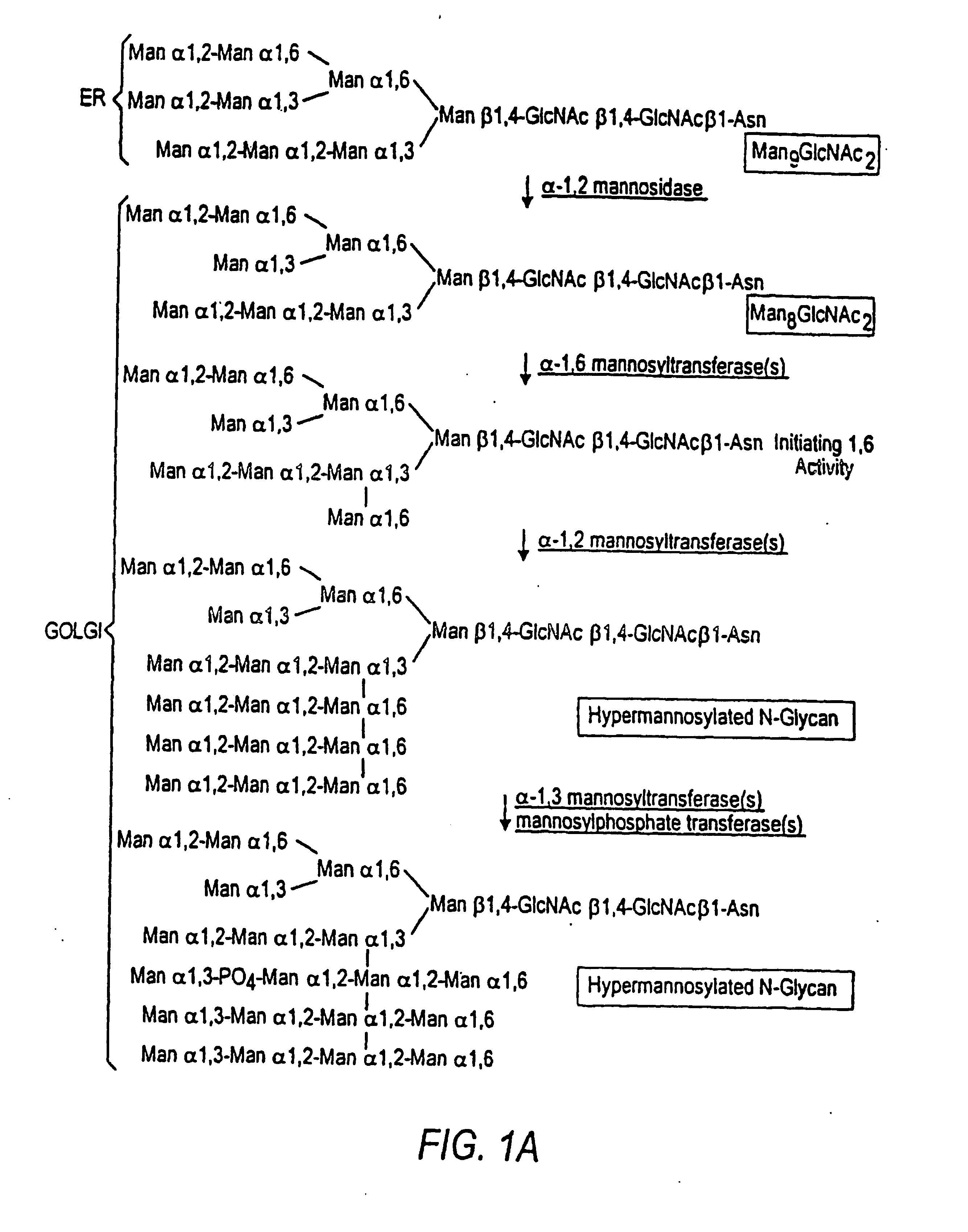
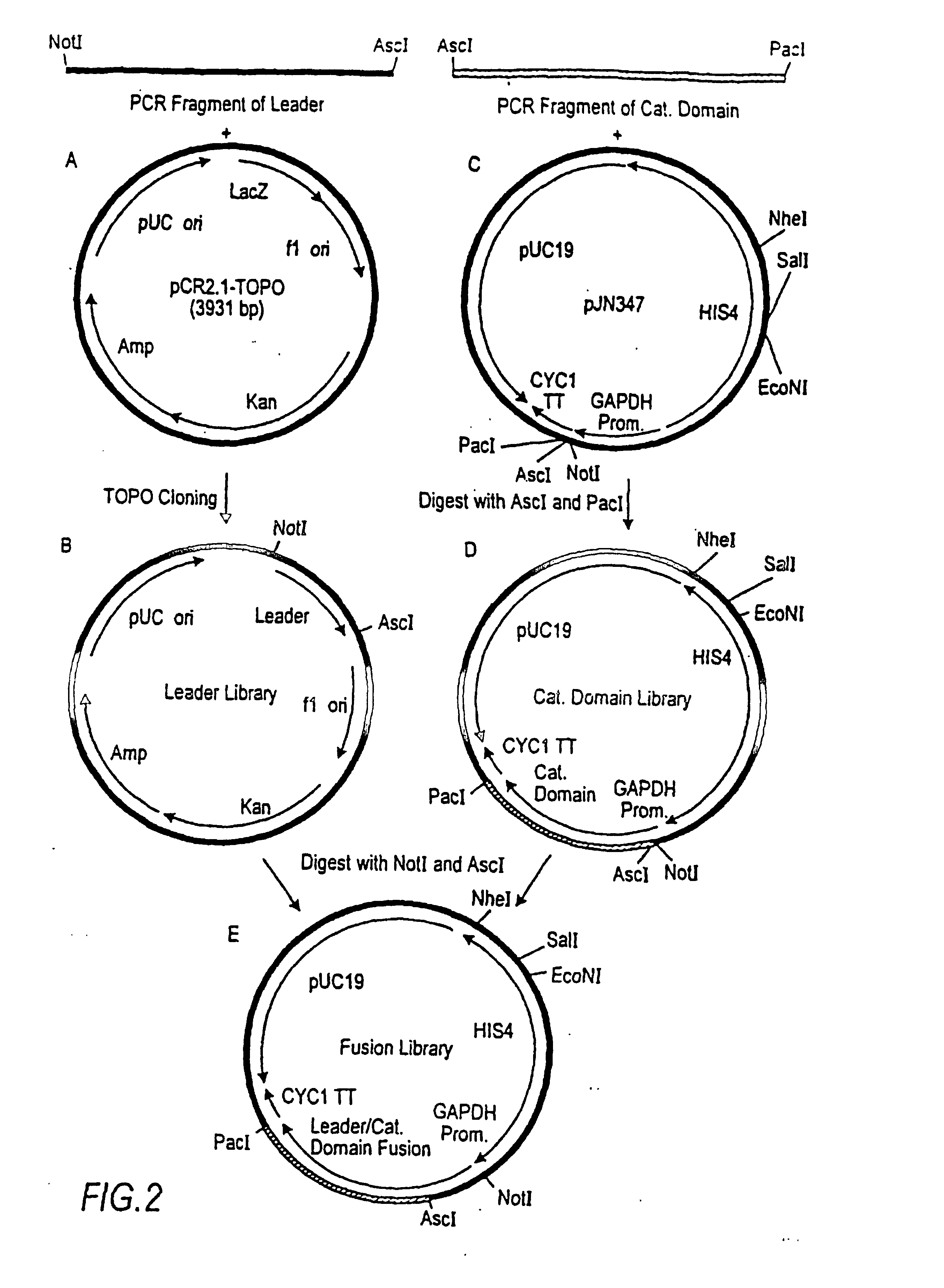
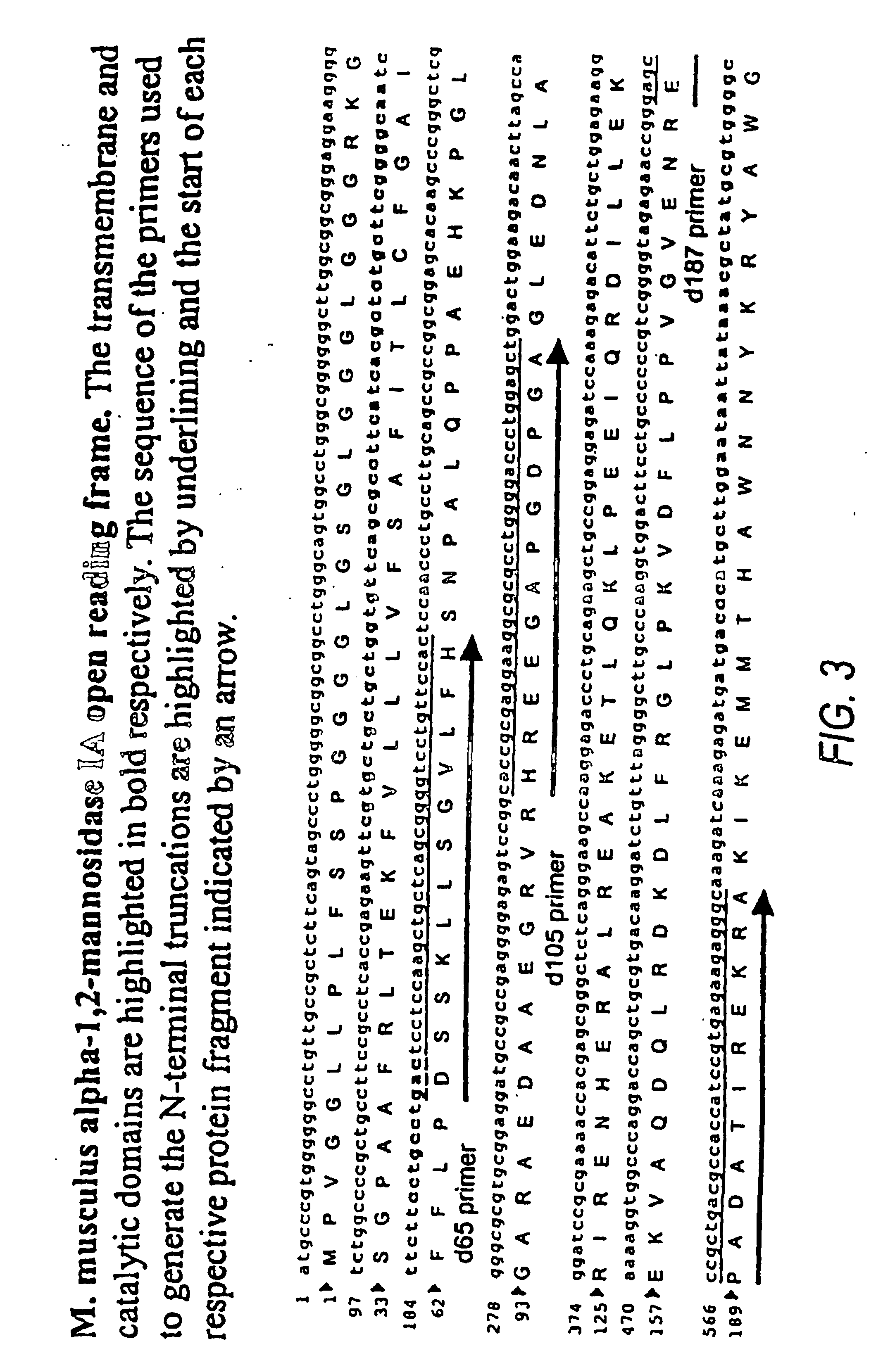
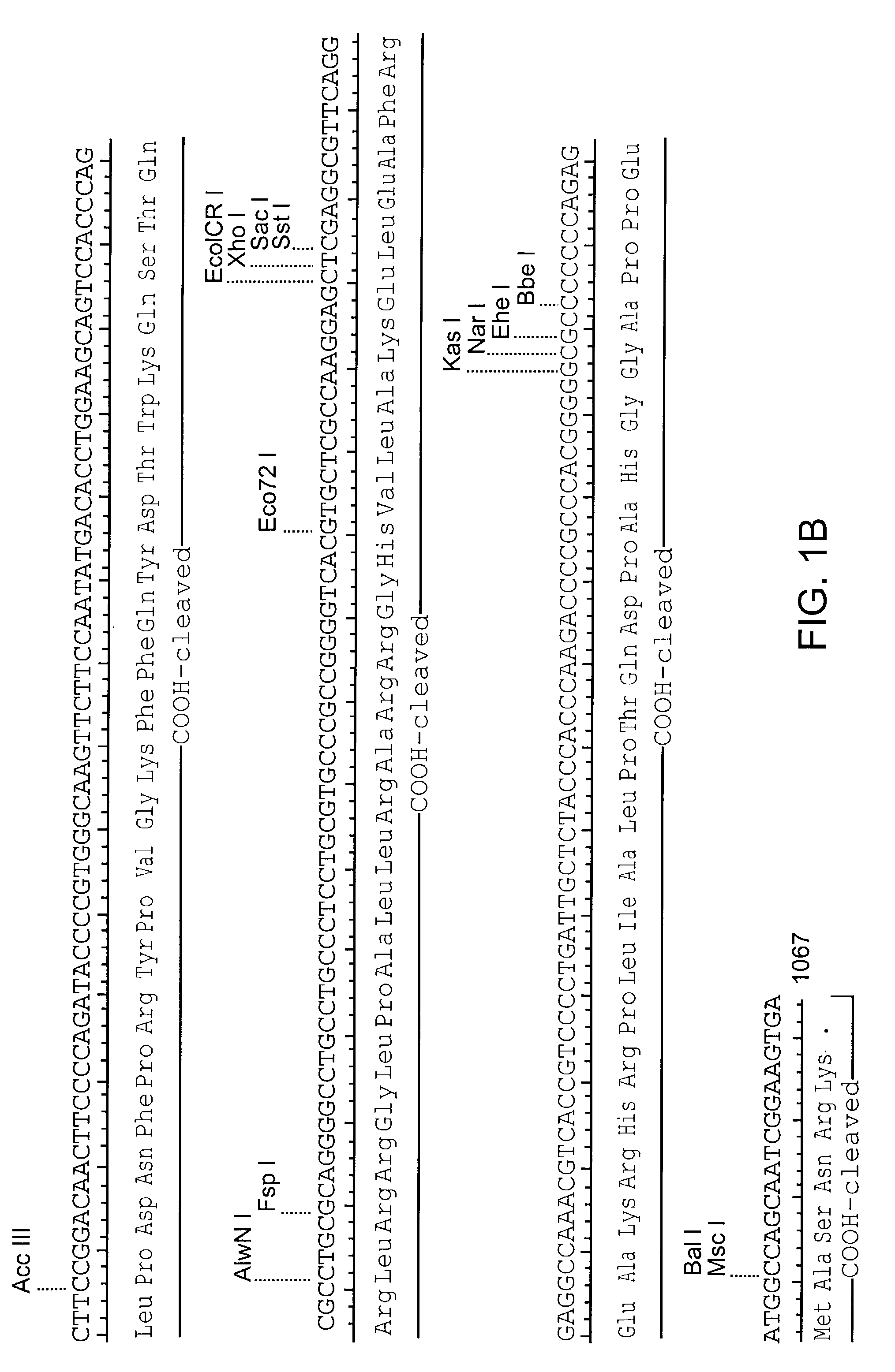
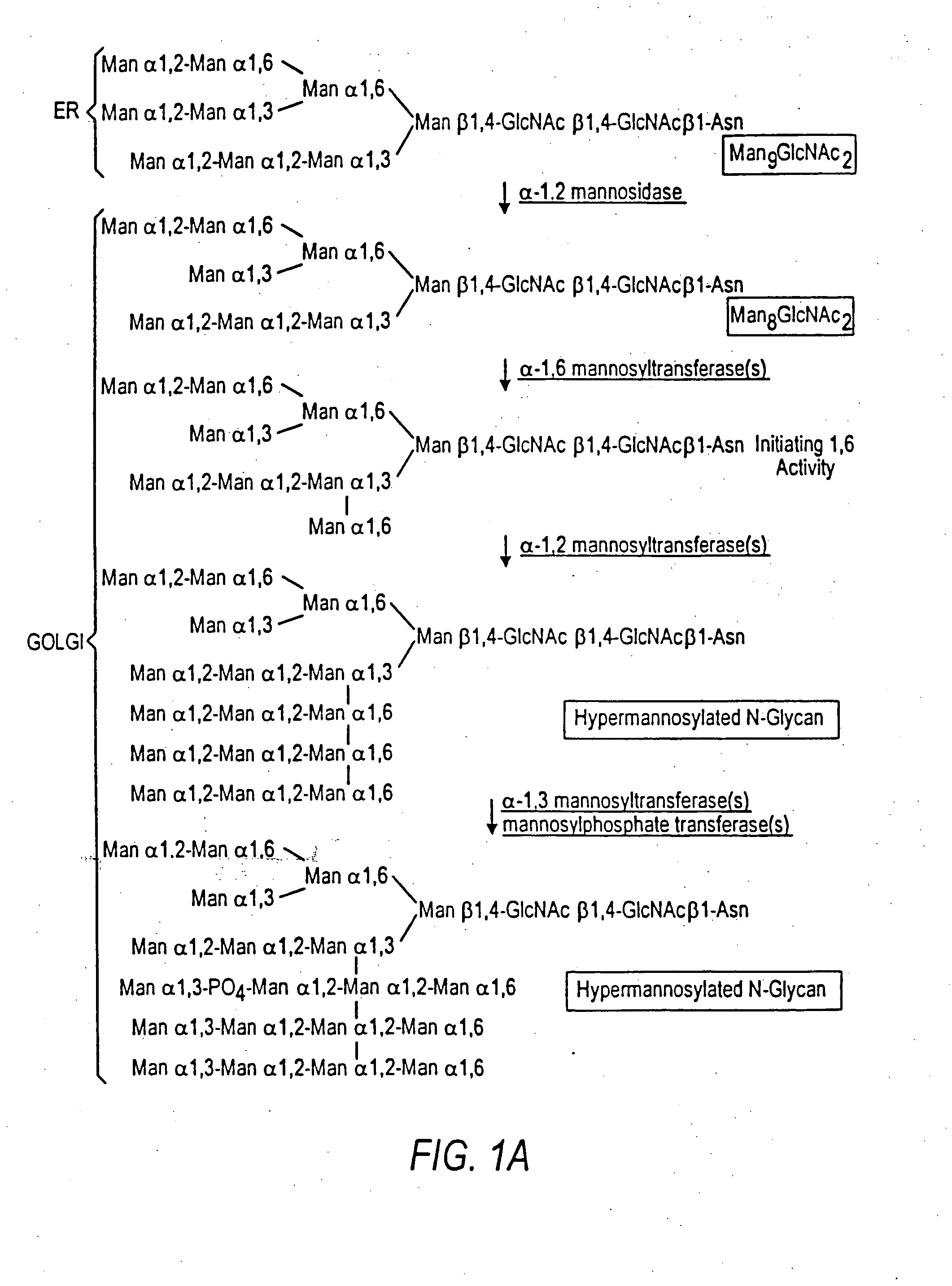
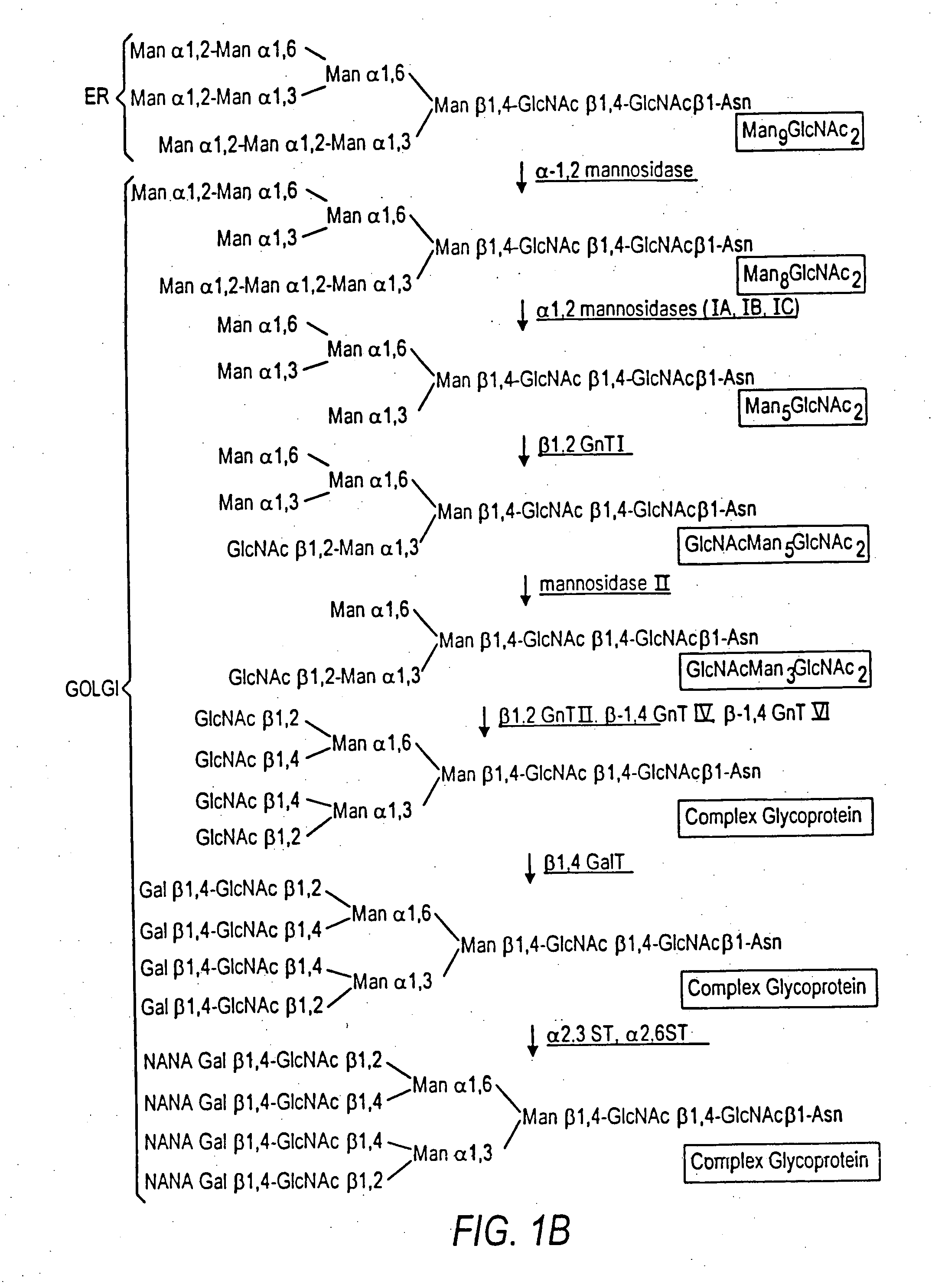
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities such as those involved in glycosylation to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells have a Man5GlcNAc2 core structure which may then be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS20050281805A1Extended half-lifeReduce the binding forcePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTherapeutic proteinLysosome
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
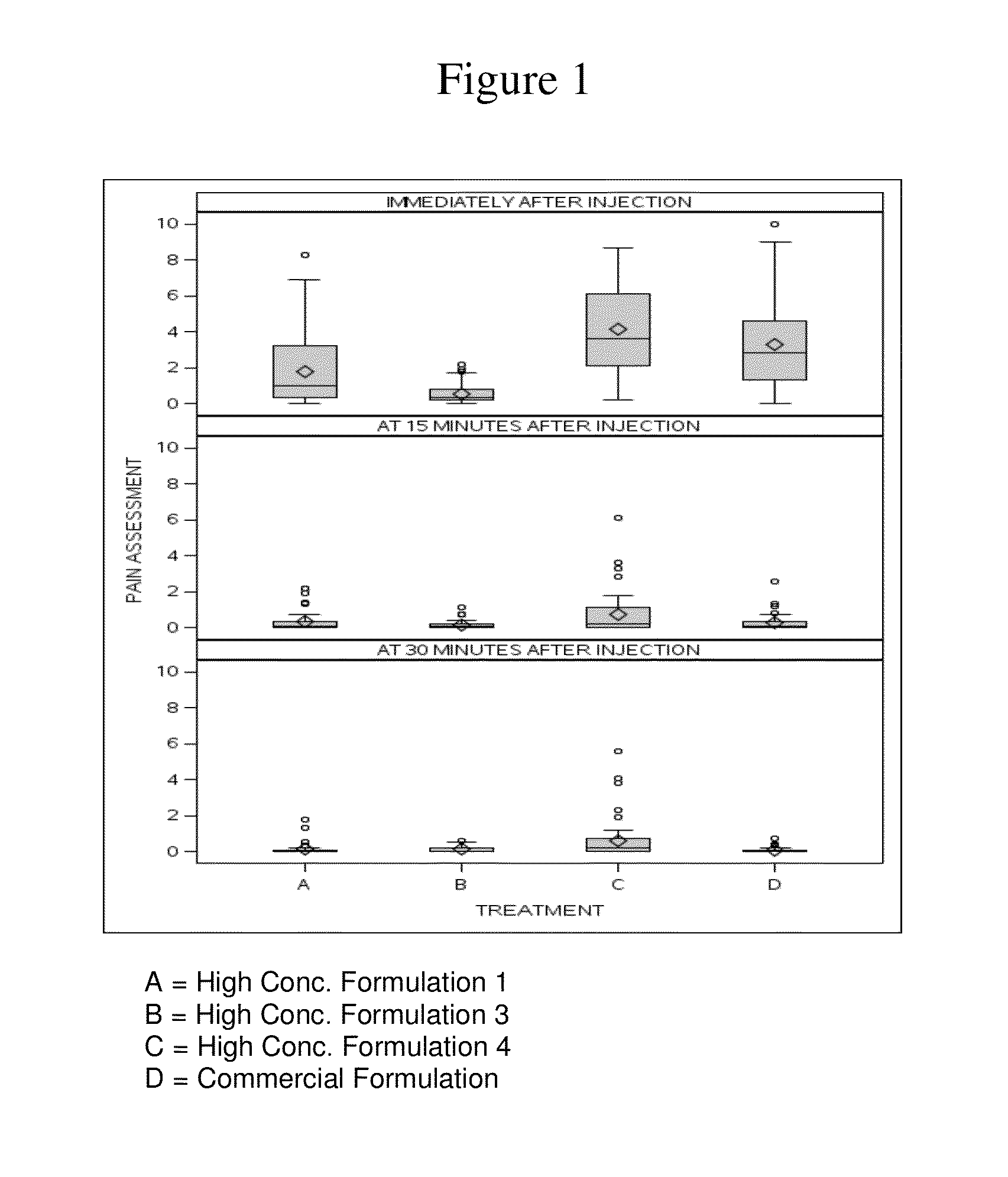
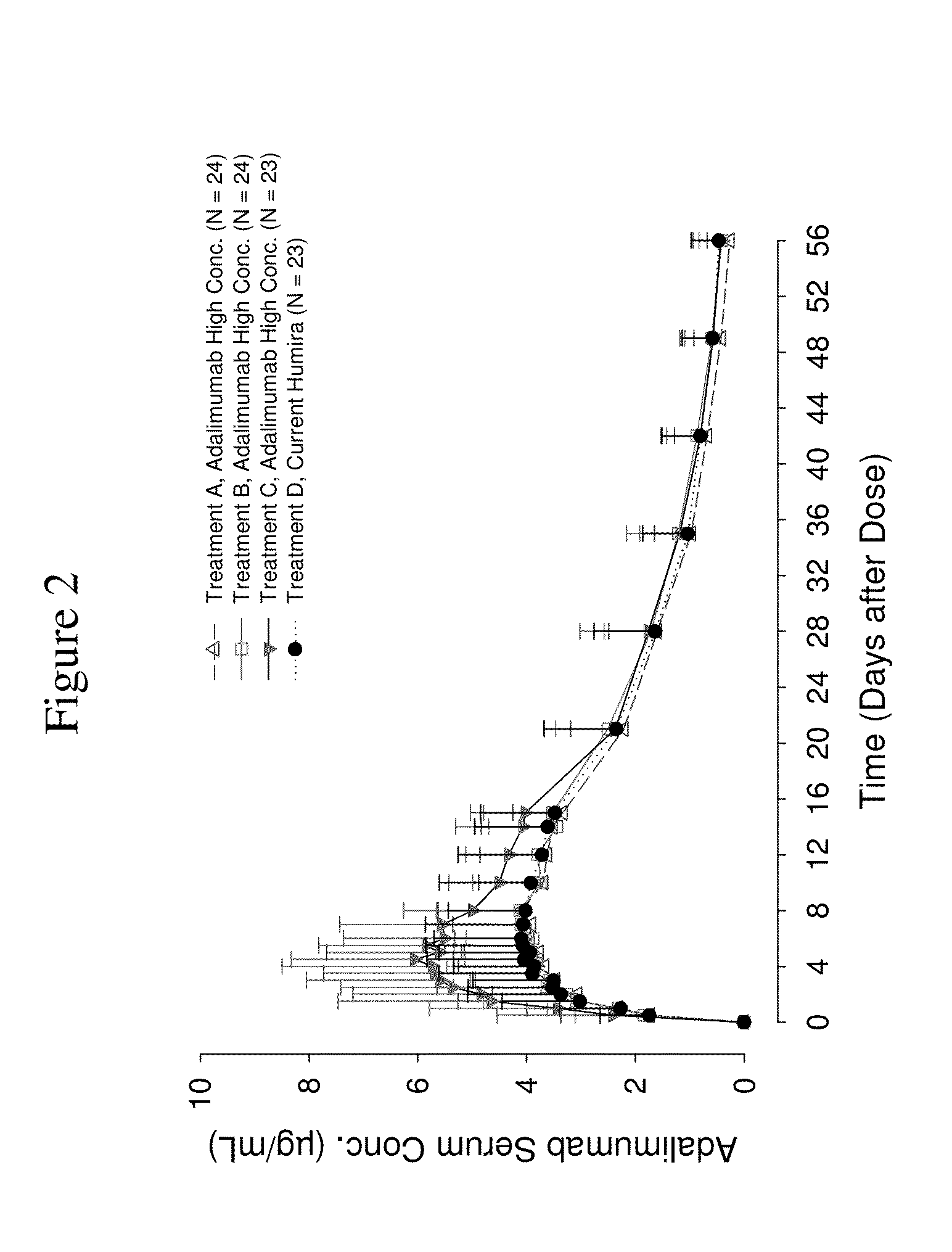
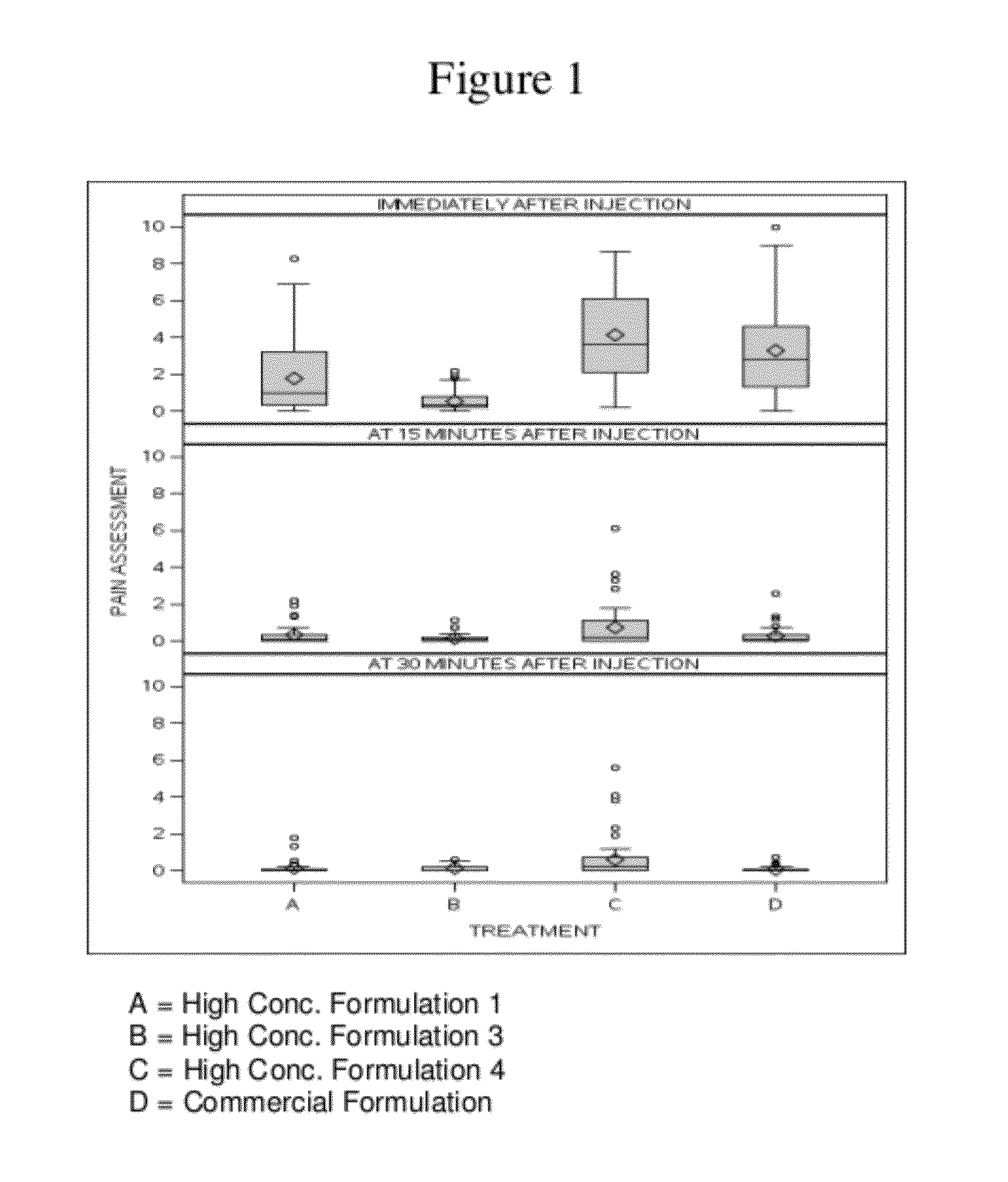
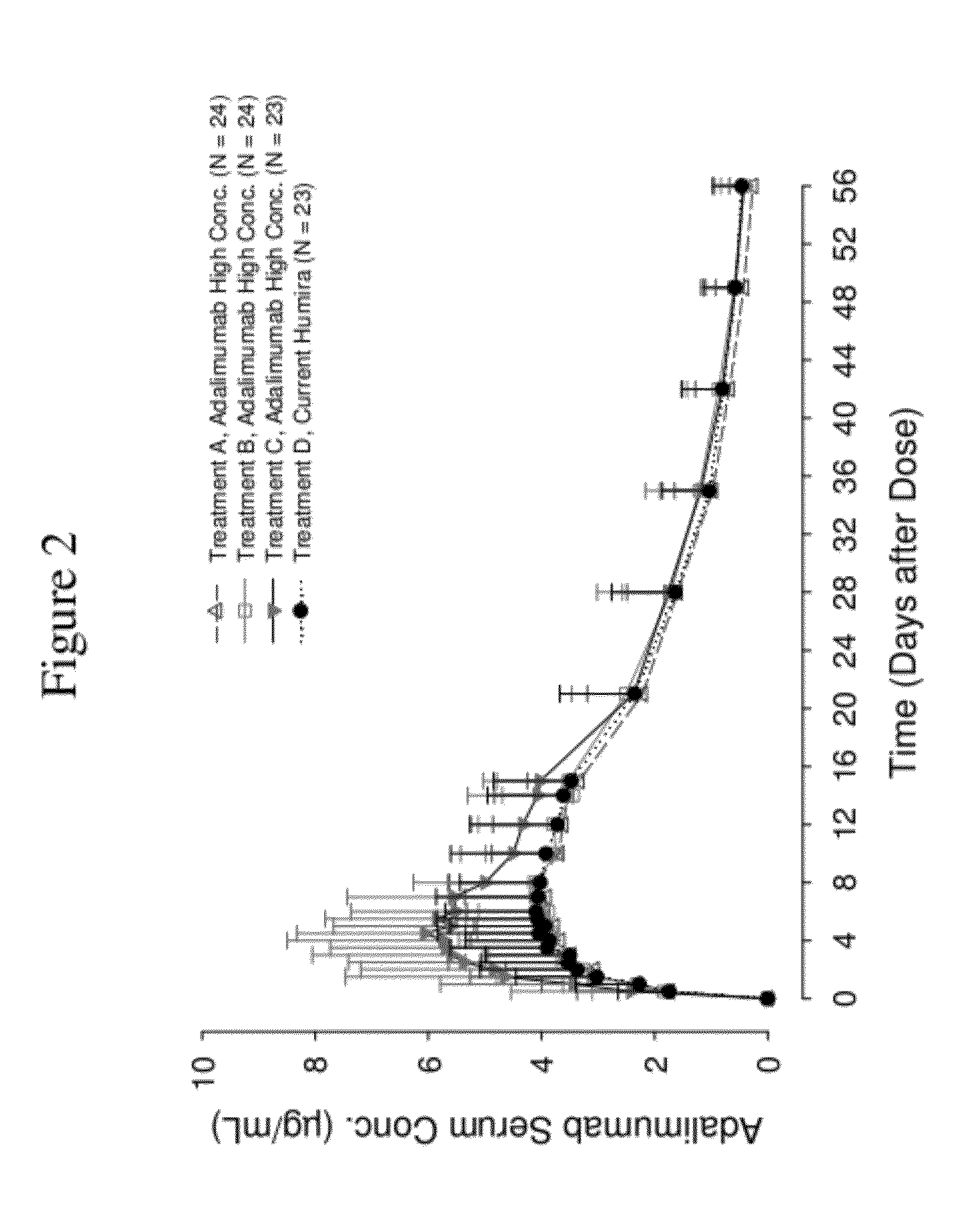
High concentration anti-TNFα antibody liquid formulations
ActiveUS8821865B2Improve bioavailabilityRelieve painSenses disorderNervous disorderAntiendomysial antibodiesTherapeutic protein
The invention provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, which reduces pain associated with injection in a subject by at least about 50% when compared to injecting an otherwise identical formulation comprising at least one salt and / or at least one buffer. The invention also provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, having increased bioavailability upon subcutaneous administration into a subject. The formulation may comprise a therapeutic protein, such as a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or an antigen-binding portion thereof, or a biosimilar thereof.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Method of treating immune cell mediated systemic diseases
InactiveUS20010056066A1Prolonged systemic exposureEnhance and create propertyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAntigenWhole body
An improved method of treating immune cell mediated systemic diseases, particularly T and B cell mediated diseases, is provided by increasing the systemic exposure, or bioavailibility, of a therapeutic protein. Such therapeutic protein is selected from the group consisting of a monoclonal antibody, a soluble receptor and a soluble ligand which binds to an antigen expressed on the surface of an immunce cell.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Production of modified glycoproteins having multiple antennary structures
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells, especially lower eukaryotic host cells, having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar and sugar nucleotide transporters to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII, GnTIV, GnTV, GnT VI or GnTIX activity, which produce bisected and / or multiantennary N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar, sugar nucleotide transporters, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Subcellular targeting of therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7396811B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
N-acetylglucosamintransferase III expression in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20050208617A1The overall structure is closedFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationHeterologous
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII activity, which produce bisected N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
HIGH CONCENTRATION ANTI-TNFalpha ANTIBODY LIQUID FORMULATIONS
ActiveUS20120263731A1Improve bioavailabilityRelieve painSenses disorderNervous disorderHigh concentrationBiosimilar Pharmaceuticals
The invention provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, which reduces pain associated with injection in a subject by at least about 50% when compared to injecting an otherwise identical formulation comprising at least one salt and / or at least one buffer. The invention also provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, having increased bioavailability upon subcutaneous administration into a subject. The formulation may comprise a therapeutic protein, such as a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or an antigen-binding portion thereof, or a biosimilar thereof.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS20080269070A1High yieldQuality improvementBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment, or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest, including therapeutic proteins, hormones, a growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PFENEX
Novel class of therapeutic protein based molecules
ActiveUS20050112751A1Prevent and inhibit adhesion and functionInhibitory responseAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderTherapeutic proteinViral infection
The present invention provides new compositions and methods for preventing and treating pathogen infection. In particular, the present invention provides compounds having an anchoring domain that anchors the compound to the surface of a target cell, and a therapeutic domain that can act extracellularly to prevent infection of a target cell by a pathogen, such as a virus. The present invention also comprises therapeutic compositions having sialidase activity, including protein-based compounds having sialidase catalytic domains. Compounds of the invention can be used for treating or preventing pathogen infection, and for treating and reducing allergic and inflammatory responses. The invention also provides compositions and methods for enhancing transduction of target cells by recombinant viruses. Such compositions and methods can be used in gene therapy.
Owner:ANSUN BIOPHARMA
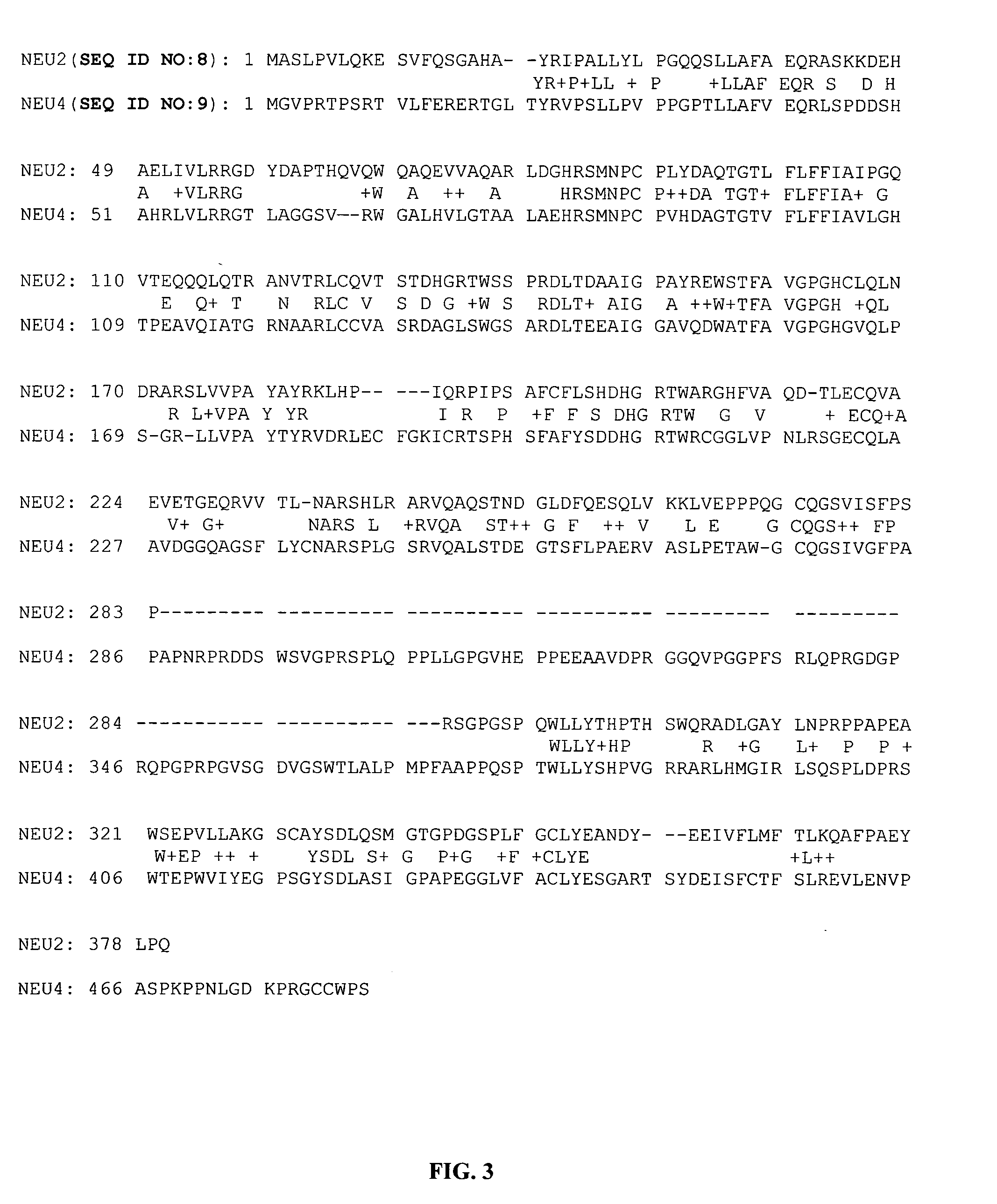
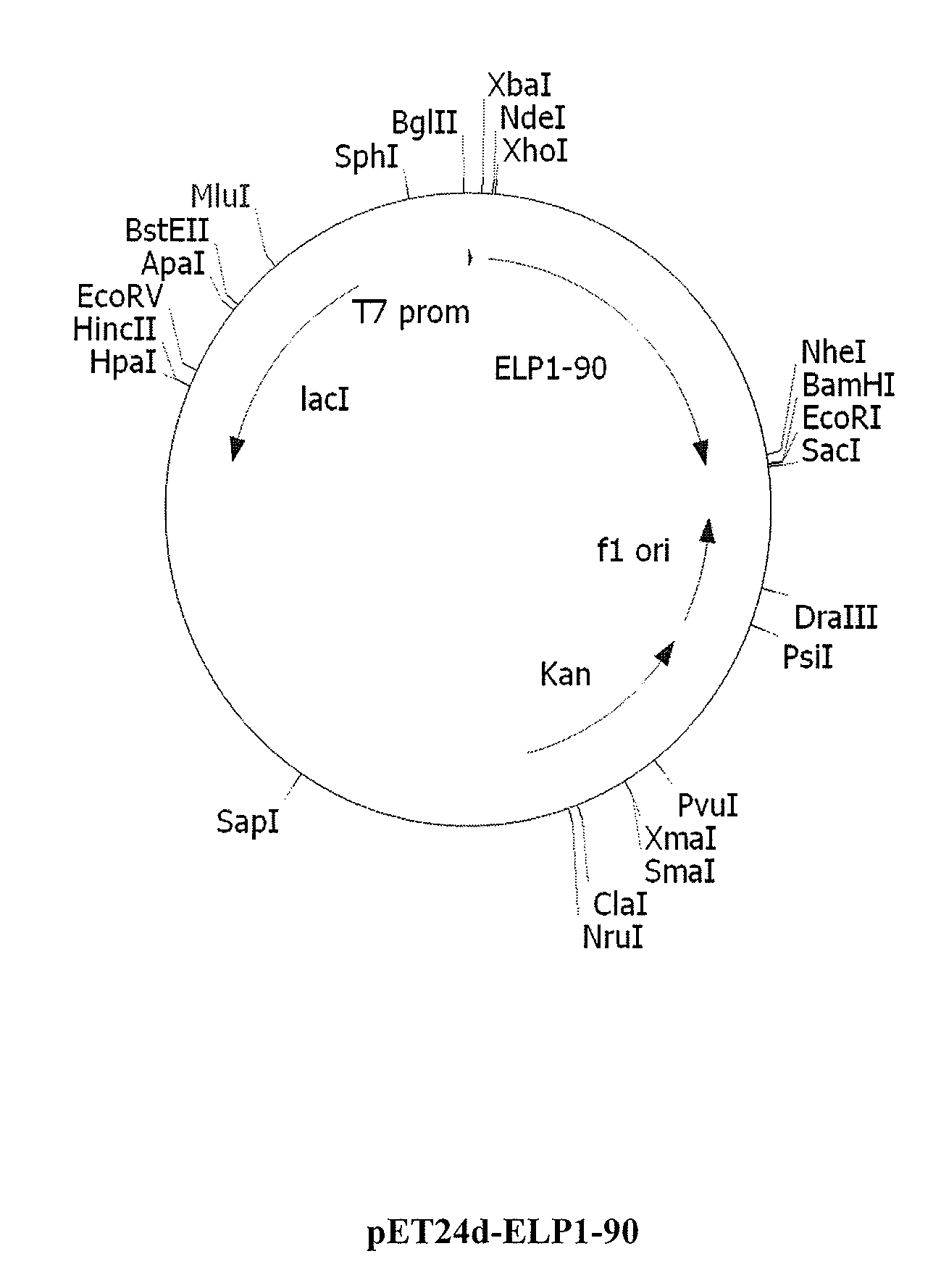
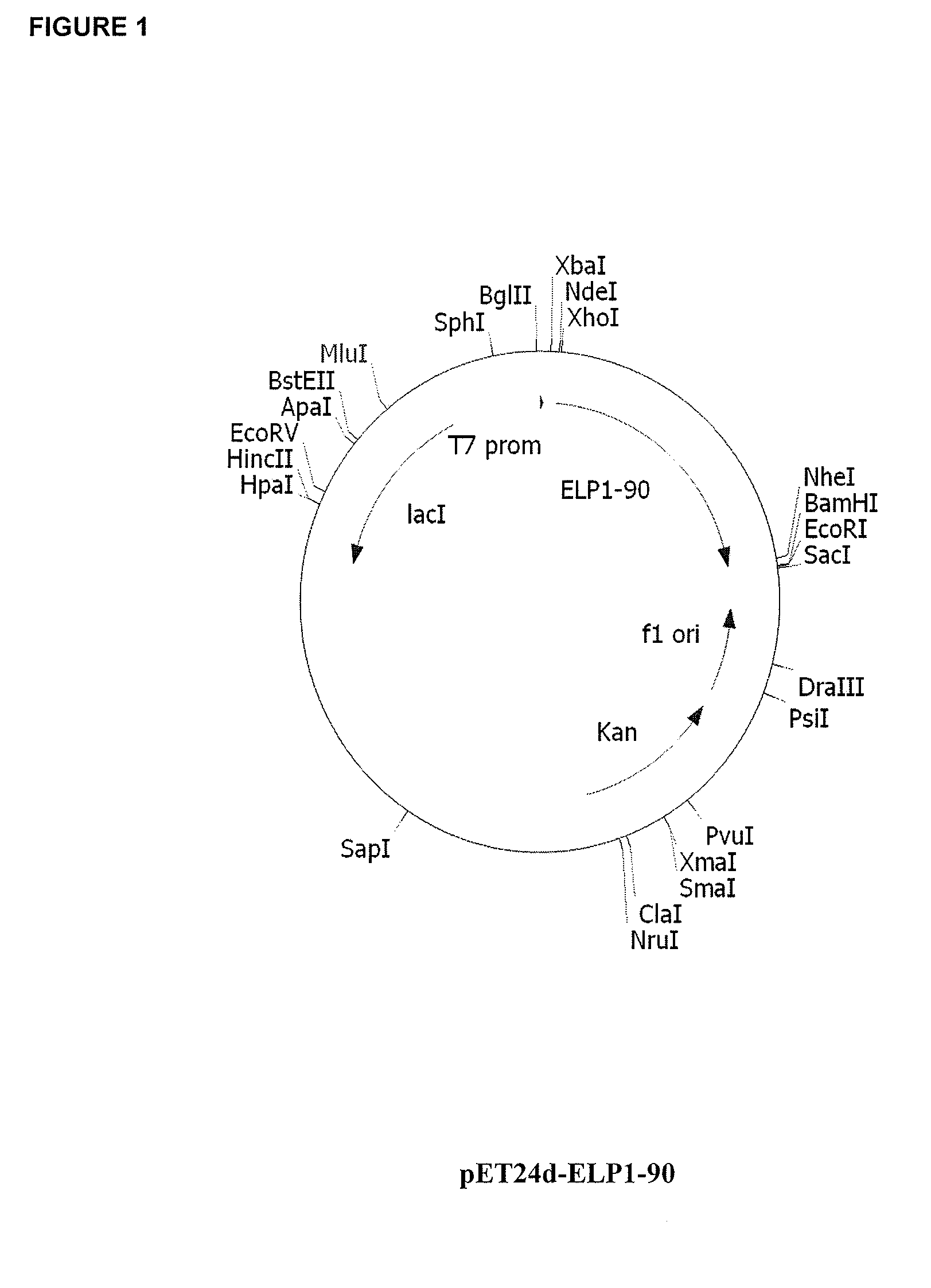
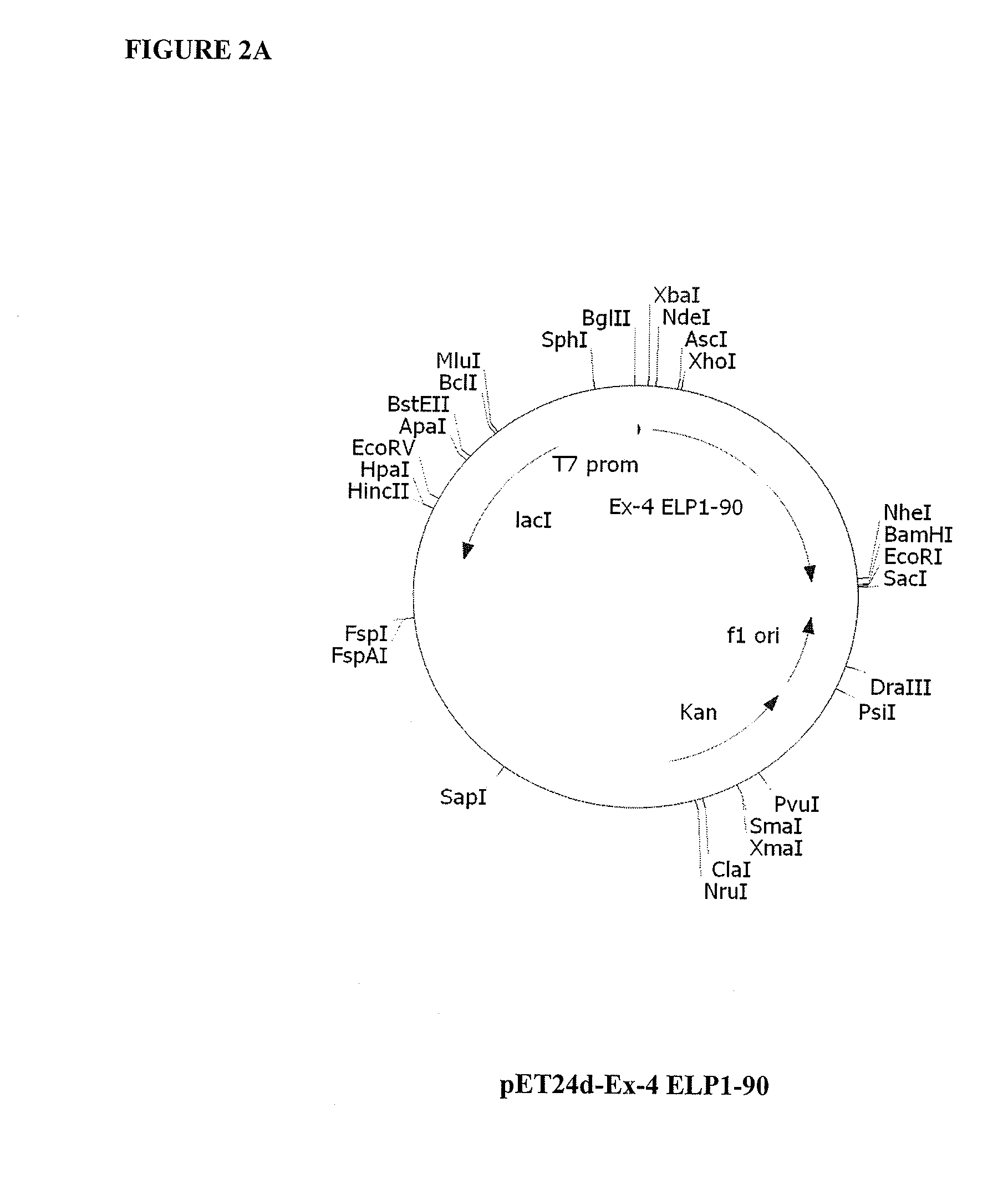
Therapeutic agents comprising elastin-like peptides
ActiveUS20100022455A1Enhanced advantageImprove stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityTherapeutic protein
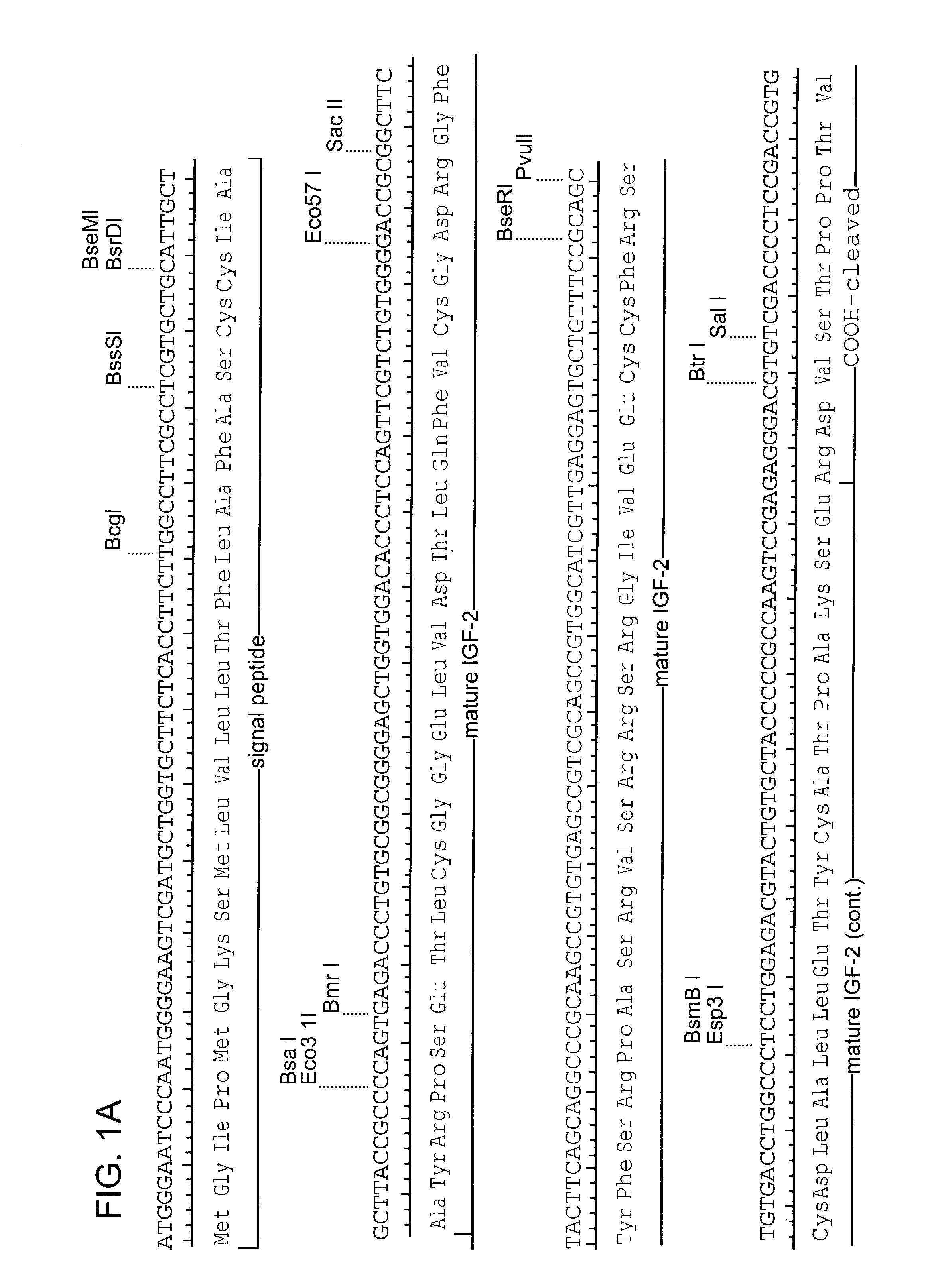
The present invention provides therapeutic agents and compositions comprising elastin-like peptides (ELPs) and therapeutic proteins. In some embodiments, the therapeutic protein is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, insulin, or Factor VII / VIIa, including functional analogs. The present invention further provides encoding polynucleotides, as well as methods of making and using the therapeutic agents. The therapeutic agents have improvements in relation to their use as therapeutics, including, inter alia, one or more of half-life, clearance and / or persistance in the body, solubility, and bioavailability.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Method of intra-operative coating therapeutic agents onto sutures, composite sutures and methods of use
InactiveUS20060287676A1Enhance anterior stabilitySuture equipmentsCoatingsTherapeutic proteinBiomedical engineering
Intra-operative coating of sutures with therapeutic proteins, particularly growth factors such as rhGDF-5. including contacting a suture to a device containing a therapeutic agent, methods of repairing soft tissue defects with coated sutures and composite sutures coated with therapeutic agents.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
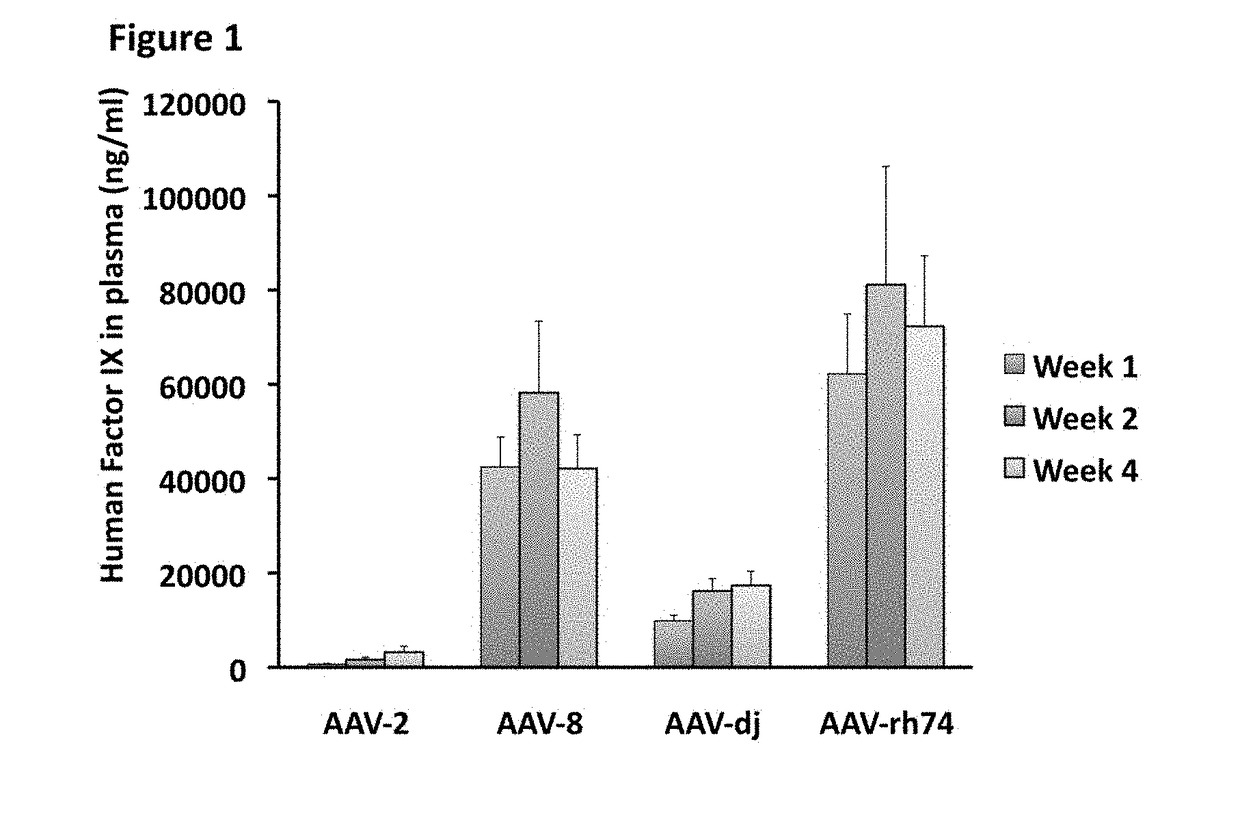
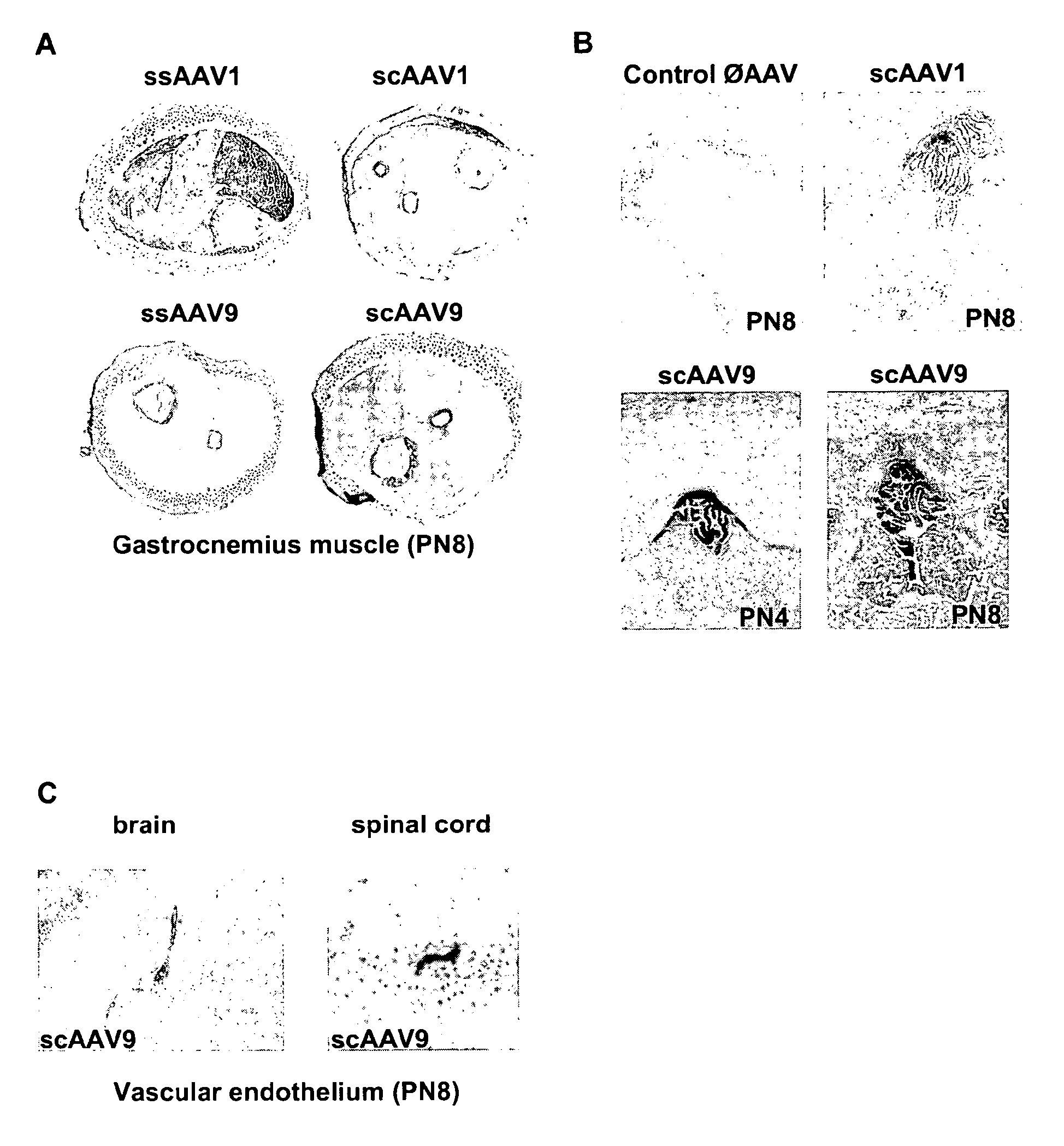
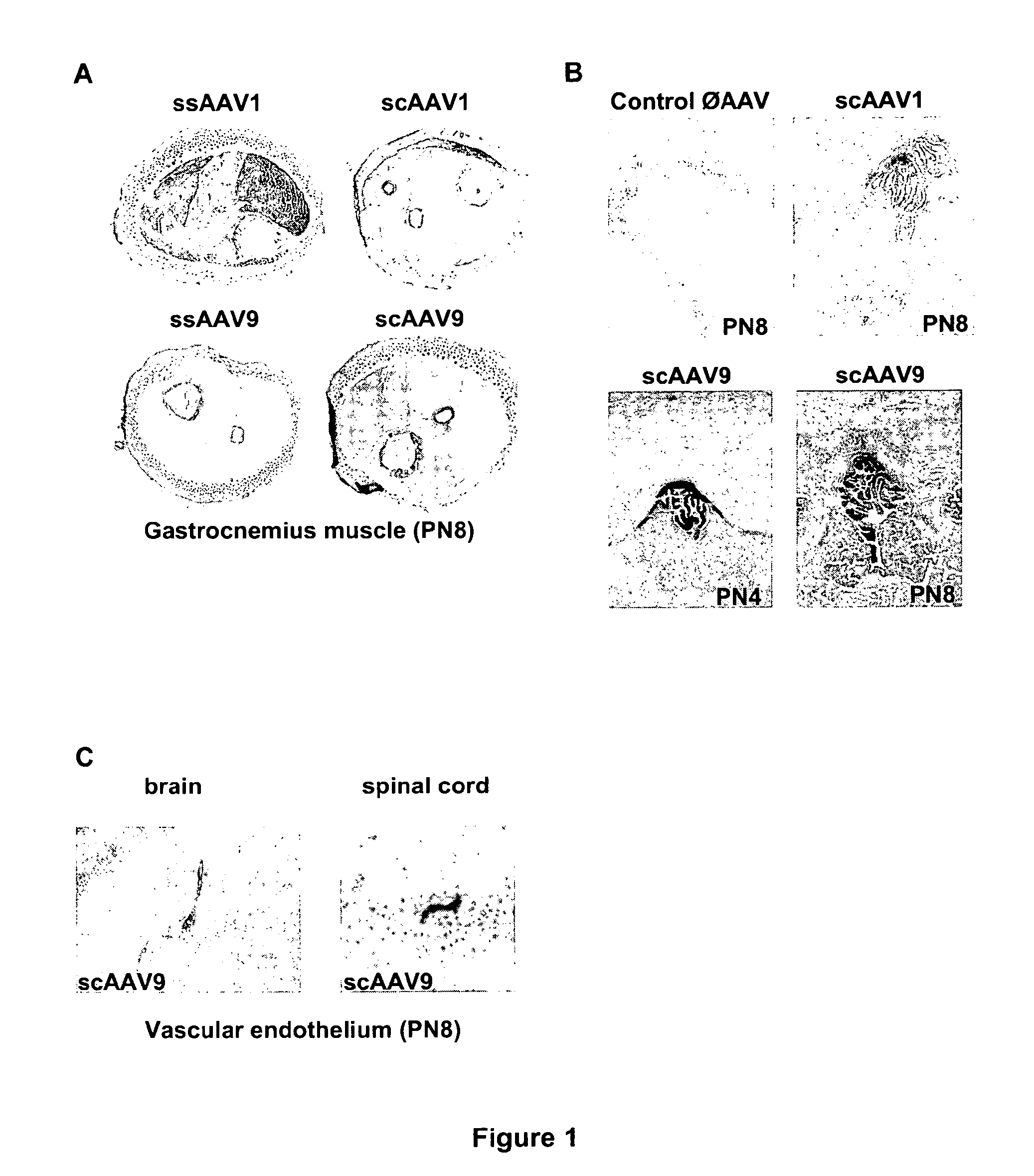
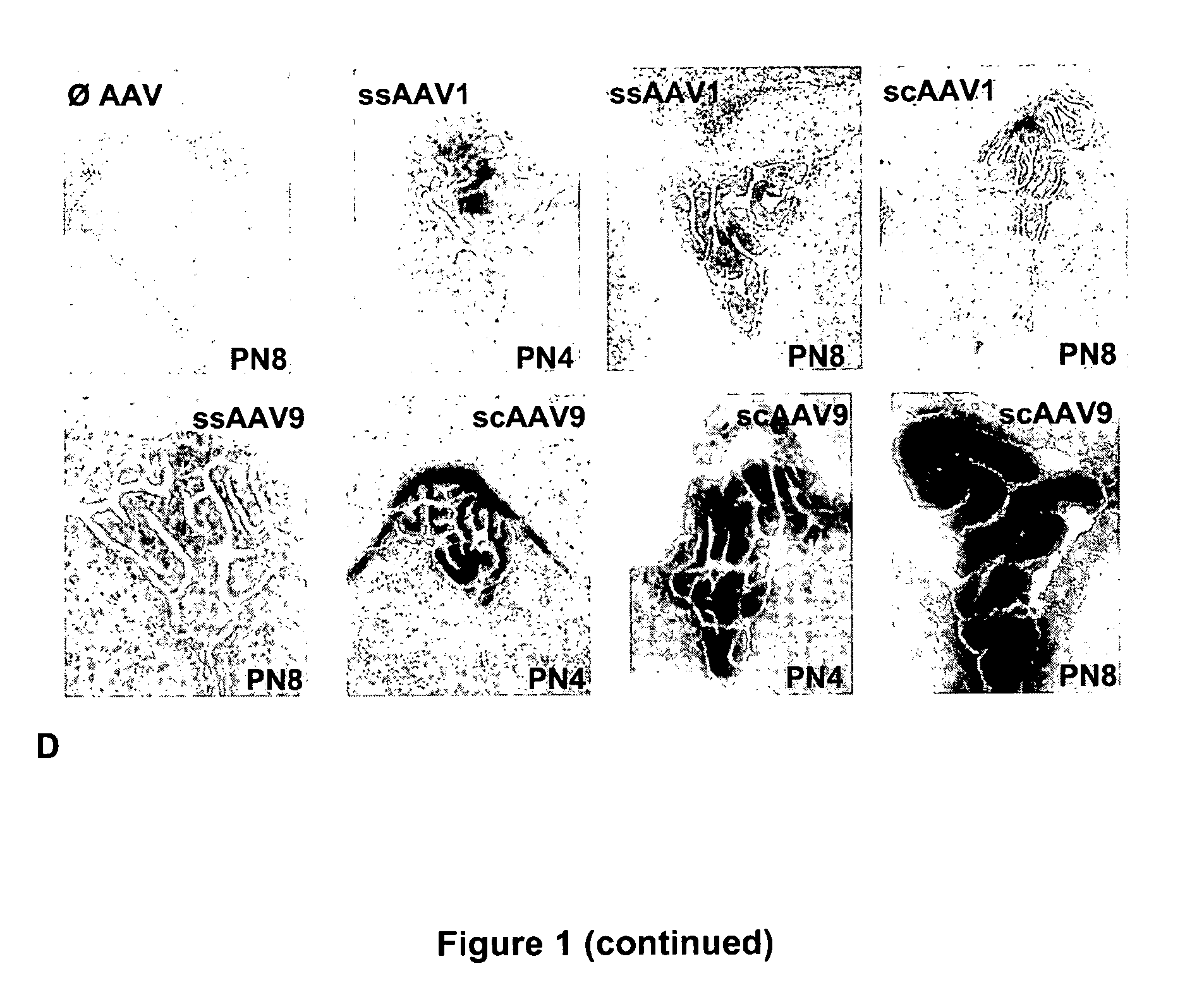
Variant AAV and compositions, methods and uses for gene transfer to cells, organs and tissues
ActiveUS9840719B2Reduce the possibilityCost of treatmentVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic proteinNucleic acid sequencing
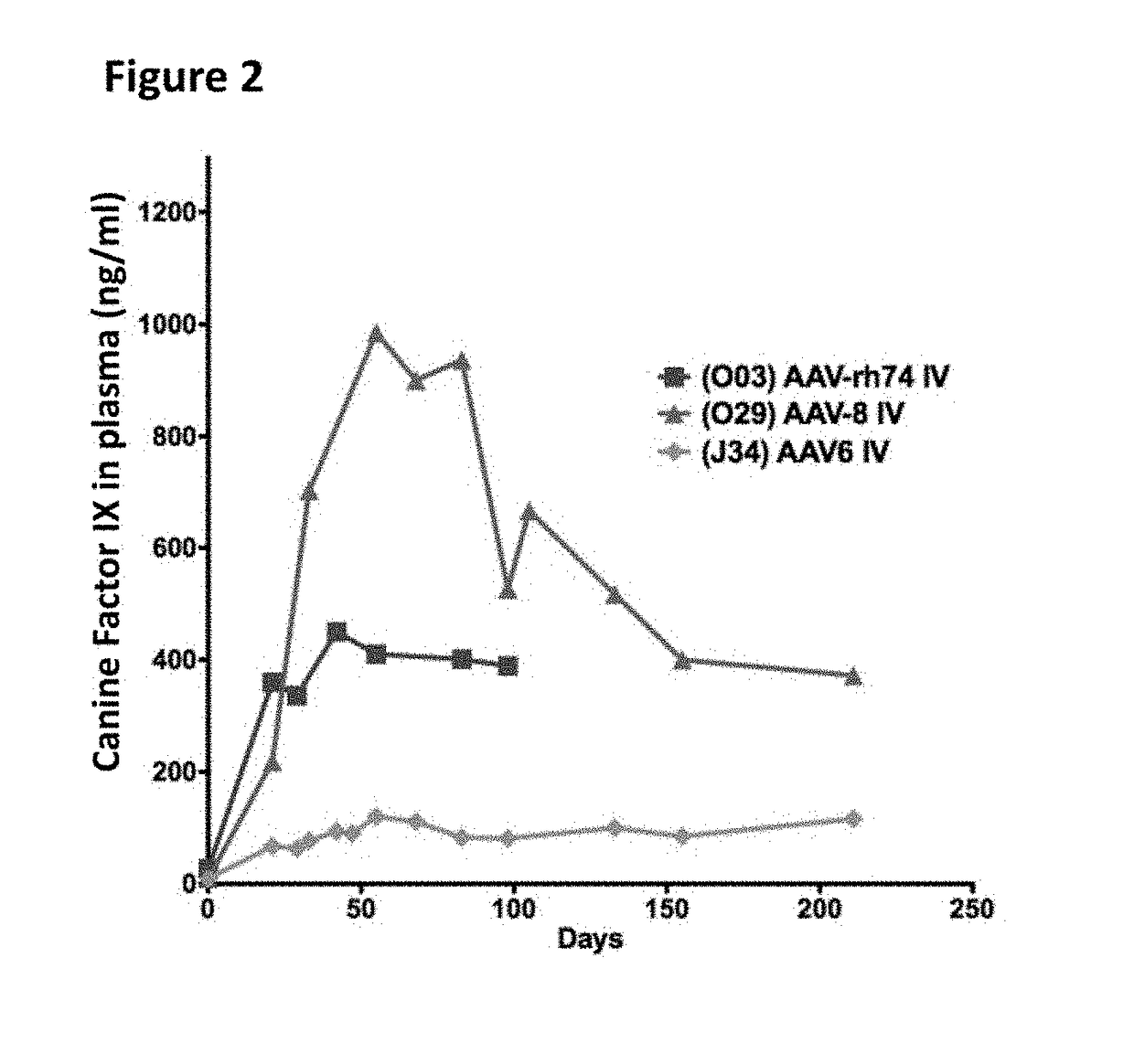
The invention relates to adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype AAV-Rh74 and related AAV vectors, and AAV-Rh74 and related AAV vector mediated gene transfer methods and uses. In particular, AAV-Rh74 and related AAV vectors target polynucleotides to cells, tissues or organs for expression (transcription) of genes encoding therapeutic proteins and peptides, and polynucleotides that function as or are transcribed into inhibitory nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Complementing cell lines
InactiveUS6974695B2Low efficiencyEfficient disseminationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousVaccination
A packaging cell line capable of complementing recombinant adenoviruses based on serotypes from subgroup B, preferably adenovirus type 35. The cell line is preferably derived from primary, diploid human cells (e.g., primary human retinoblasts, primary human embryonic kidney cells and primary human amniocytes) which are transformed by adenovirus E1 sequences either operatively linked on one DNA molecule or located on two separate DNA molecules, the sequences being operatively linked to regulatory sequences enabling transcription and translation of encoded proteins. Also disclosed is a cell line derived from PER.C6 (ECACC deposit number 96022940), which cell expresses functional Ad35 E1B sequences. The Ad35-E1B sequences are driven by the E1B promoter or a heterologous promoter and terminated by a heterologous poly-adenylation signal. The new cell lines are useful for producing recombinant adenoviruses designed for gene therapy and vaccination. The cell line can also be used for producing human recombinant therapeutic proteins such as human growth factors and human antibodies. In addition, the cell lines are useful for producing human viruses other than adenovirus such as influenza virus, herpes simplex virus, rotavirus, measles virus.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Tolerogenic synthetic nanocarriers to reduce immune responses to therapeutic proteins
ActiveUS20120276109A1Reduce frequencyHigh frequencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryAntigenIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTS
Disclosed are synthetic nanocarrier compositions, and related methods, comprising therapeutic protein APC presentable antigens and immunosuppressants that provide tolerogenic immune responses specific to therapeutic proteins.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
Therapeutic agents comprising a GLP-1 receptor agonist and elastin-like peptide
ActiveUS8178495B2Improve stabilityImprove solubilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityTherapeutic protein
The present invention provides therapeutic agents and compositions comprising elastin-like peptides (ELPs) and therapeutic proteins. In some embodiments, the therapeutic protein is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, insulin, or Factor VII / VIIa, including functional analogs. The present invention further provides encoding polynucleotides, as well as methods of making and using the therapeutic agents. The therapeutic agents have improvements in relation to their use as therapeutics, including, inter alia, one or more of half-life, clearance and / or persistance in the body, solubility, and bioavailability.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Polymerized solid lipid nanoparticles for oral or mucosal delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides
InactiveUS20080311214A1Powder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigen deliveryTherapeutic protein
The present invention encompasses lipid nano / micro particles, which have been modified, preferably on their surface, to contain a molecule or ligand, which targets the nano / micro particles to a specific site. The invention also encompasses the use of the modified lipid nano / micro particles for the oral delivery of drugs and antigen delivery systems.
Owner:TRANSGENE BIOTEK
Method of intraoperative coating therapeutic agents onto sutures
InactiveUS20060286289A1Enhance anterior stabilitySuture equipmentsPretreated surfacesTherapeutic proteinBiomedical engineering
Intra-operative coating of sutures with therapeutic proteins, particularly growth factors such as rhGDF-5. including contacting a suture to a device containing a therapeutic agent.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
Therapeutic antibodies
InactiveUS20040258677A1Reduce the binding forceImprove bindingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTherapeutic antibodyAntibody combining site
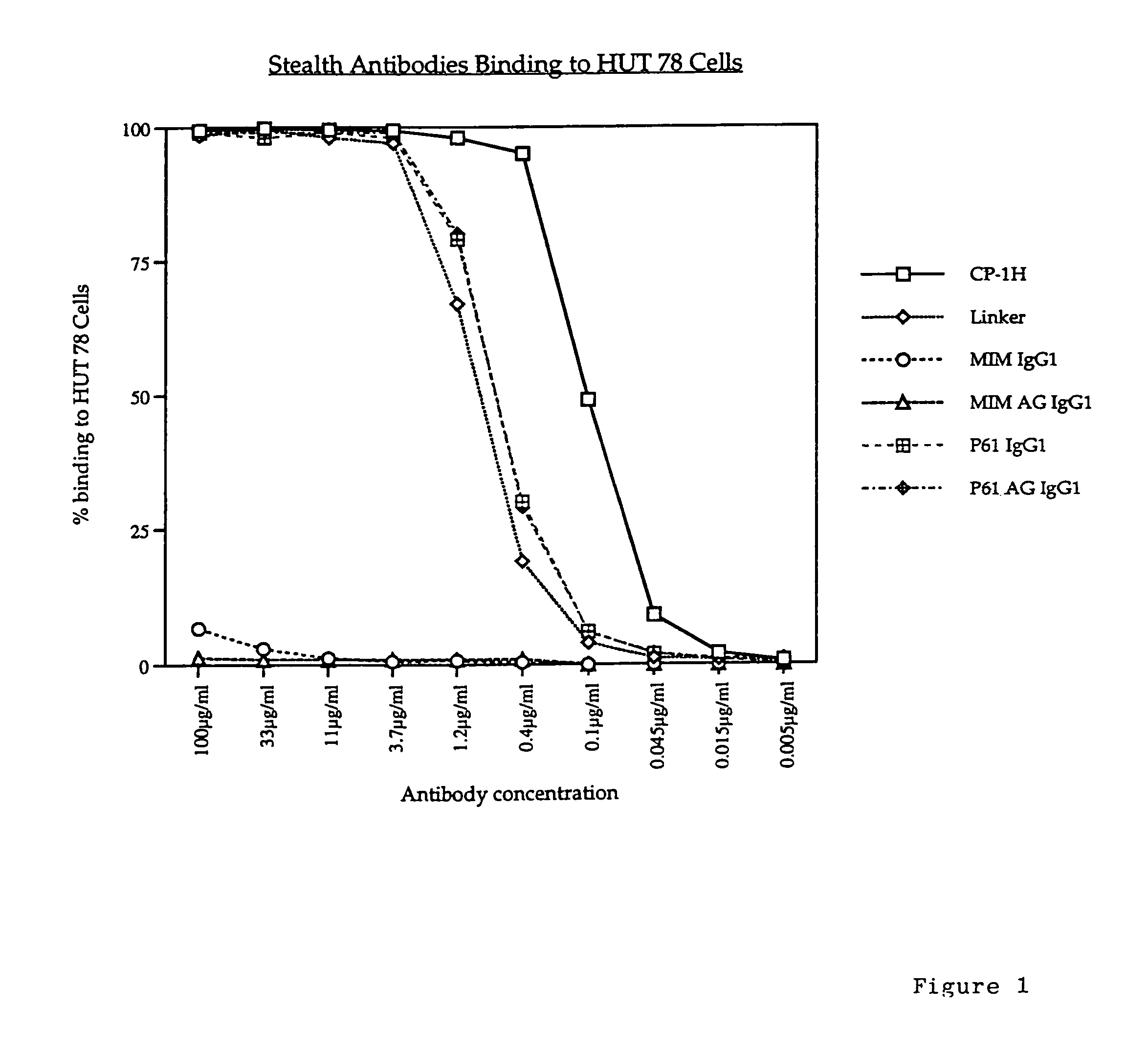
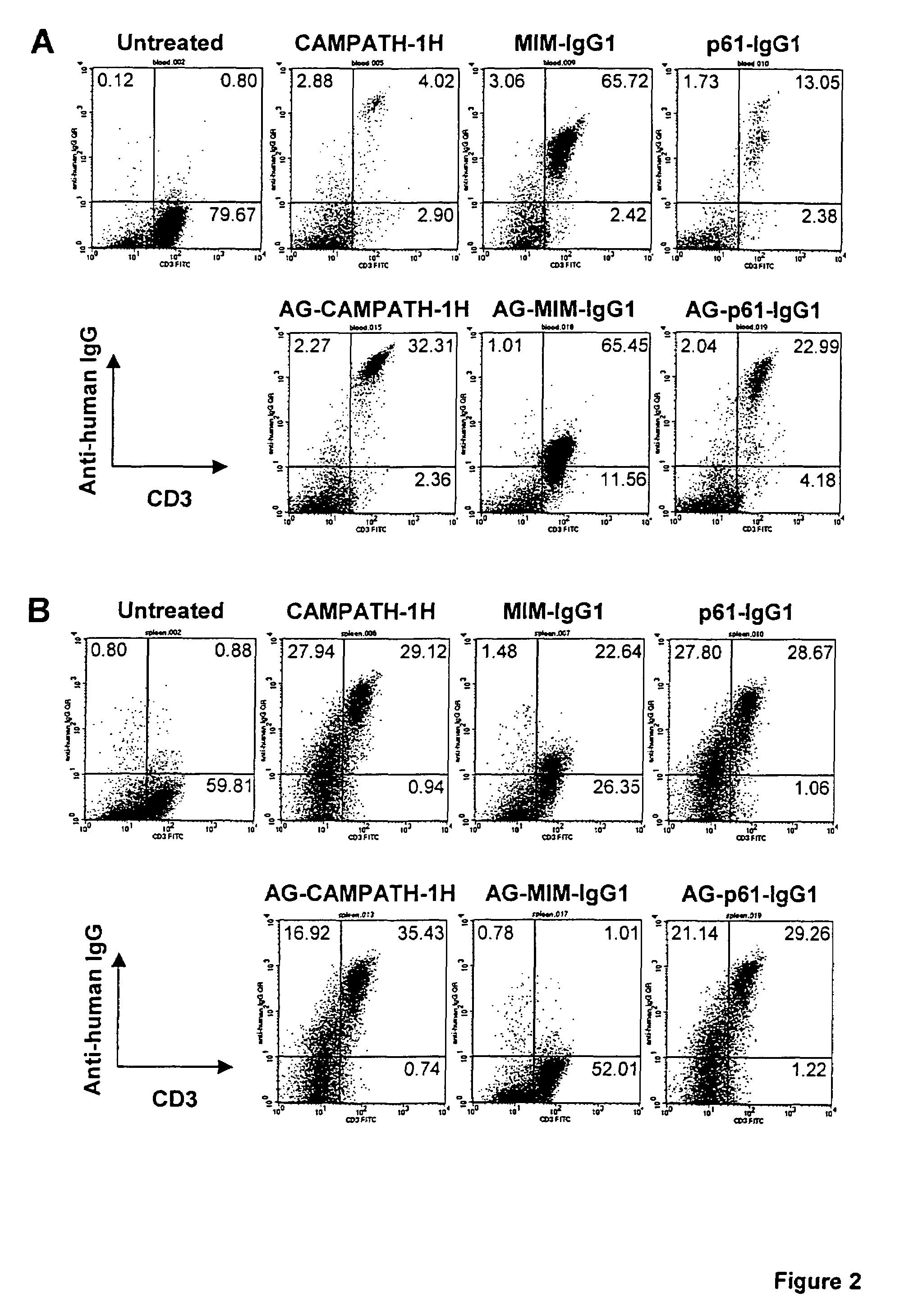
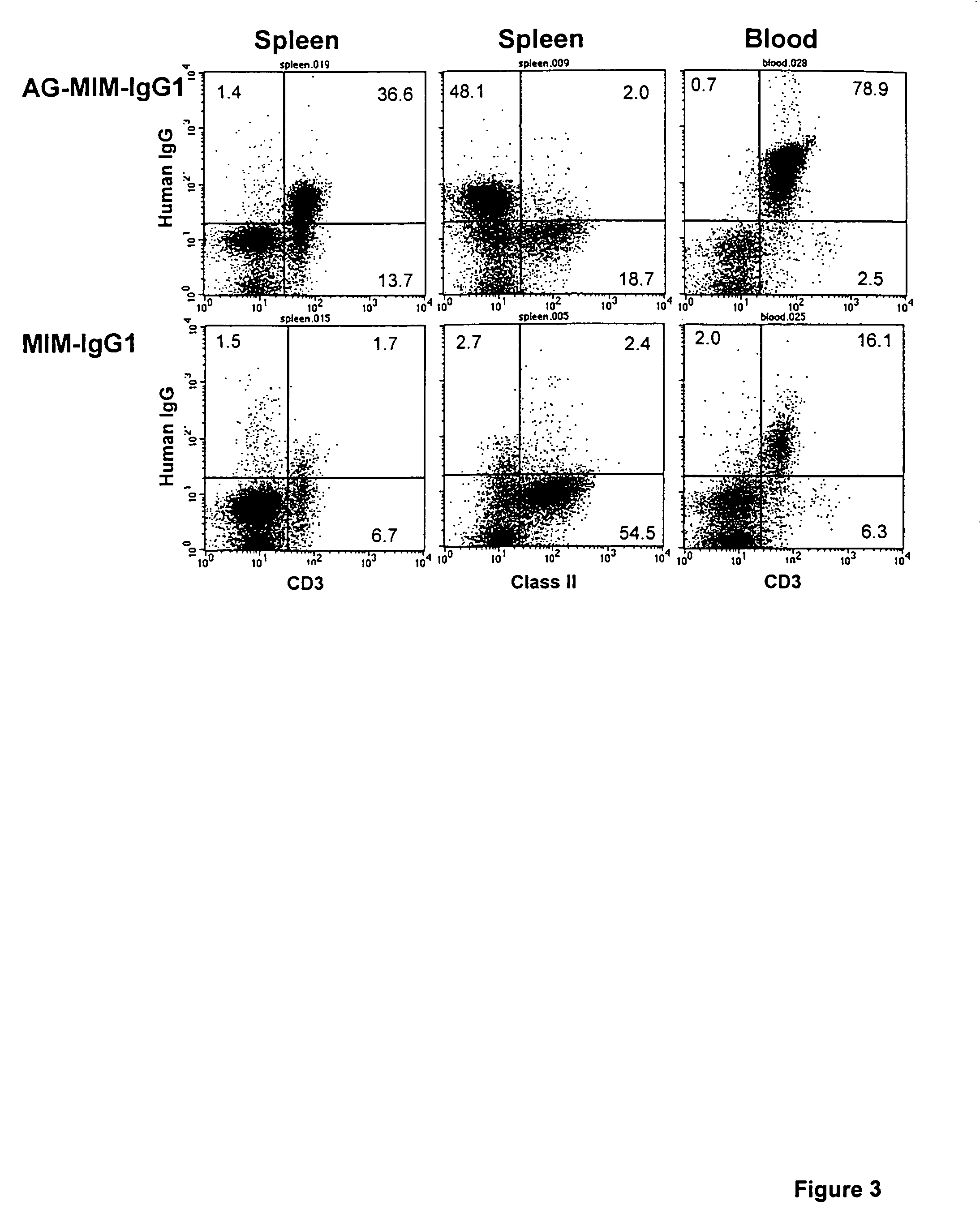
A pharmaceutical comprising a therapeutic protein that binds to a therapeutic target, the protein being modified with a compound that inhibits binding of the protein to the therapeutic target, the modified protein being effective for reducing an immune response against the protein and for producing a therapeutic effect by binding to the therapeutic target. The therapeutic protein may be an antibody that includes an antibody combining site that binds to the therapeutic target.
Owner:CYTOMX THERAPEUTICS
Integrated approach for generating multidomain protein therapeutics
InactiveUS8309690B2Good curative effectImprove development efficiencyAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsThermal denaturationTherapeutic protein
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7560424B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Genetically modified tumor cells as cancer vaccines
InactiveUS20060165668A1Convenient treatmentEasy to detectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for electroporation-mediated gene transfer to cancer cells. The transfected cancer cells are genetically modified to express one or more therapeutic proteins. In certain embodiments, the cancer cells are modified to express one or more cytokines capable of enhancing the immunogenicity of the transfected cancer cell. Administering the transfected cancer cell to a subject will lead to enhanced immune-cell mediated killing of tumors. Accordingly, the present invention provides methods and compositions for improved treatment and prevention of cancer and other hyperproliferative diseases.
Owner:MAXCYTE
CNS gene delivery using peripheral administration of aav vectors
ActiveUS20100130594A1Safe and convenientSuitable as therapeuticOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGene deliveryTherapeutic protein
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the delivery of therapeutic proteins to the CNS using recombinant AAV vectors. More specifically, the invention relates to compositions and methods for delivering proteins into the cerebrospinal fluid of mammalian subjects through peripheral administration of AAV vectors. The invention may be used to treat various disorders of the central nervous system, including degenerative diseases and motor neuron diseases.
Owner:GENETHON +1
Method of intra-operative coating therapeutic agents onto sutures composite sutures and methods of use
InactiveUS20060287675A1Enhance anterior stabilitySuture equipmentsCoatingsTherapeutic proteinBiomedical engineering
Intra-operative coating of sutures with therapeutic proteins, particularly growth factors such as rhGDF-5. including contacting a suture to a device containing a therapeutic agent, methods of repairing soft tissue defects with coated sutures and composite sutures coated with therapeutic agents.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Treating heart failure
Heart cells in a subject can be treated, for example, by introducing, into the heart of the subject, an adeno-associated virus subtype 6 (AAV6) viral delivery system that includes a functional nucleic acid. For example, the functional nucleic acid encodes a non-viral therapeutic protein, thereby treating the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
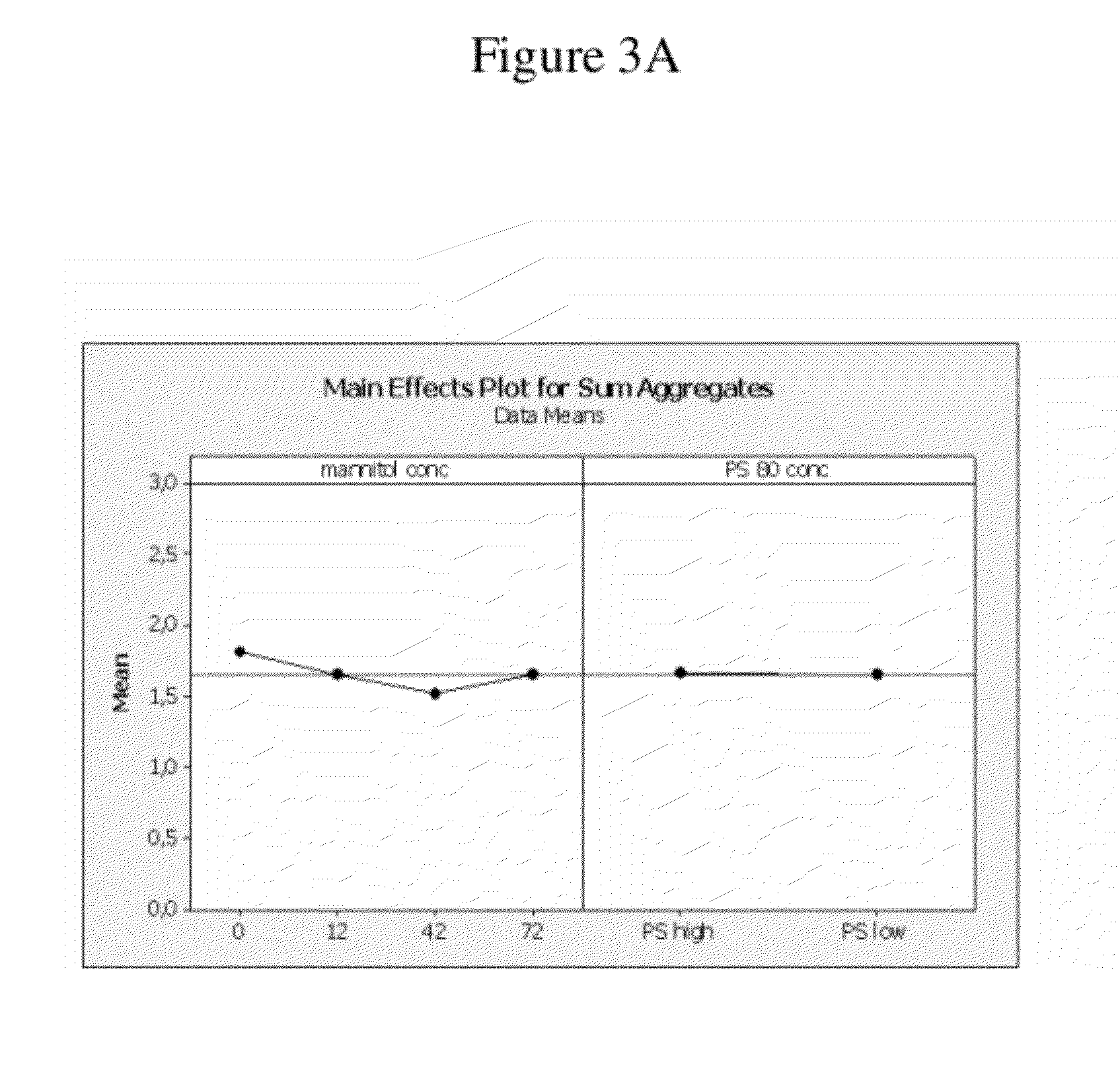
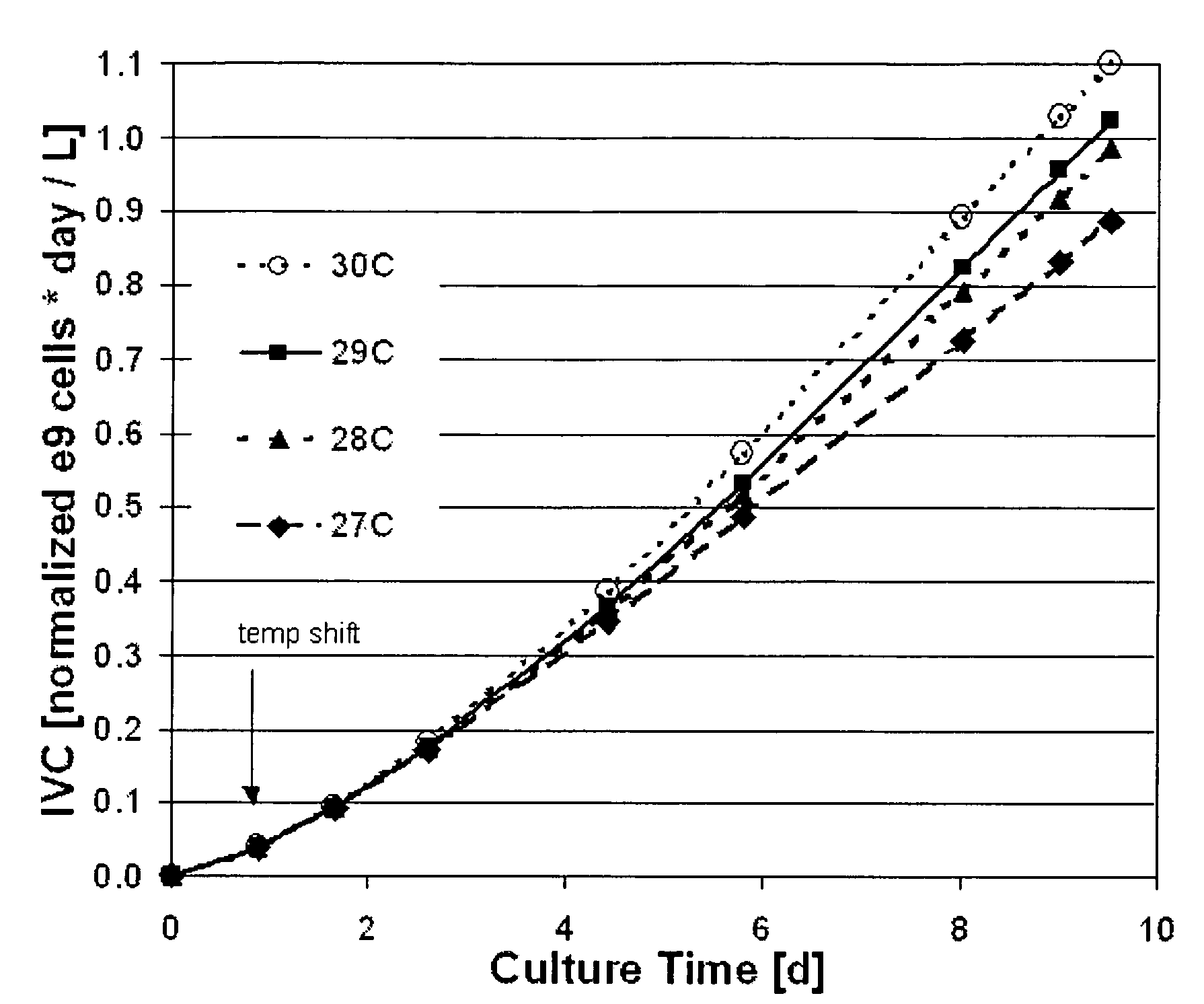
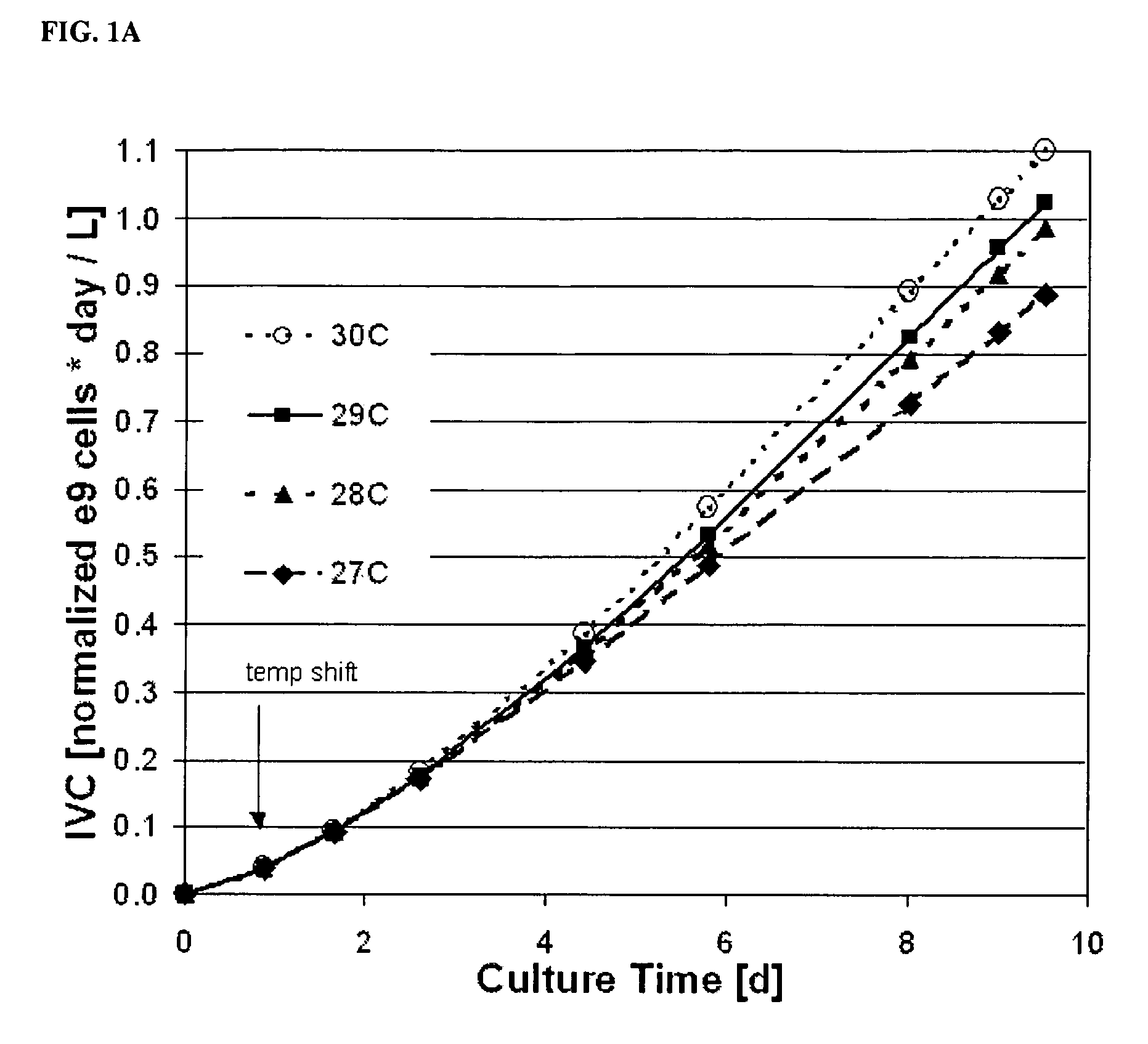
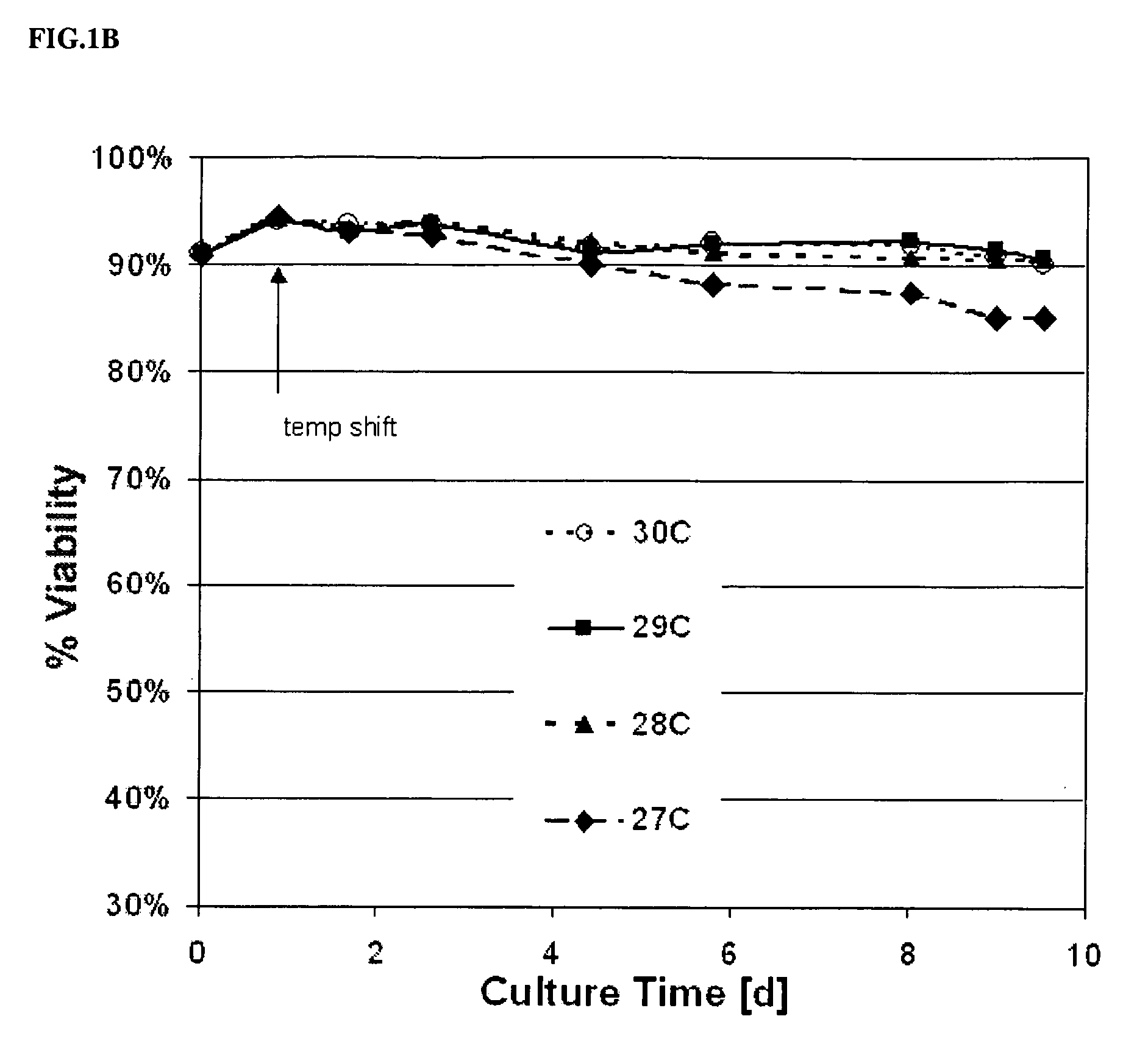
Use of low temperature and/or low ph in cell culture
ActiveUS20080269132A1Reduce productionReduce the temperaturePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetically modified cellsCulture cellTherapeutic protein
The present invention provides a novel method of reducing protein misfolding and aggregation in the cell culture by growing the cell culture at a reduced temperature and / or reduced pH. As a result, the quality of the protein produced in the cell culture is greatly improved. Thus, the present invention facilitates improvements in the efficacy of therapeutic proteins produced in cell culture.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Mirac proteins
This disclosure relates to a method of generating conditionally active biologic proteins from wild type proteins, in particular therapeutic proteins, which are reversibly or irreversibly inactivated at the wild type normal physiological conditions. For example, evolved proteins are virtually inactive at body temperature, but are active at lower temperatures.
Owner:BIOATLA LLC
Therapeutic antibodies
InactiveUS7465790B2Low immunogenicityEliminate generationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTherapeutic antibodyAntibody combining site
A pharmaceutical comprising a therapeutic protein that binds to a therapeutic target, the protein being modified with a compound that inhibits binding of the protein to the therapeutic target, the modified protein being effective for reducing an immune response against the protein and for producing a therapeutic effect by binding to the therapeutic target. The therapeutic protein may be an antibody that includes an antibody combining site that binds to the therapeutic target.
Owner:CYTOMX THERAPEUTICS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com