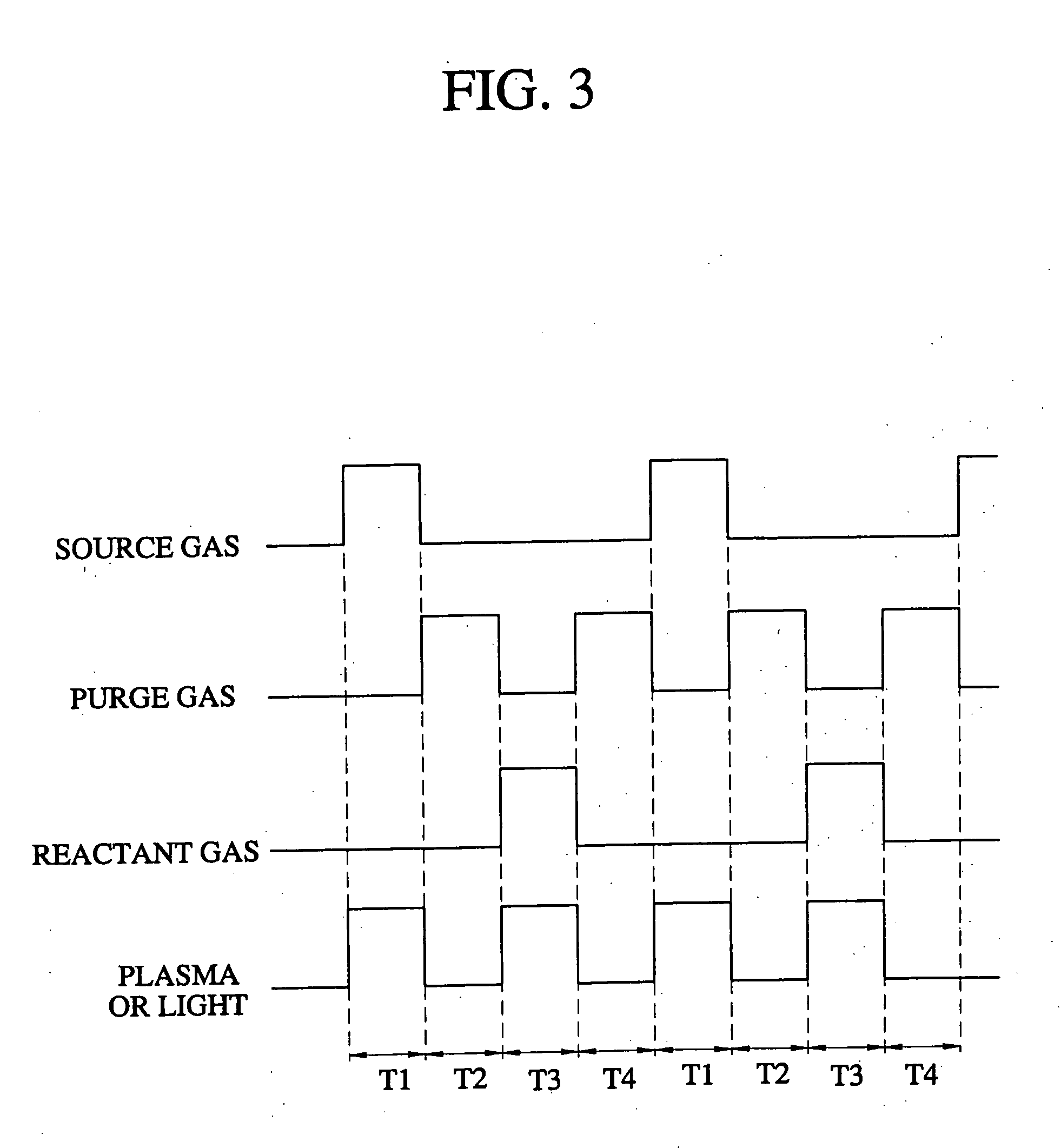
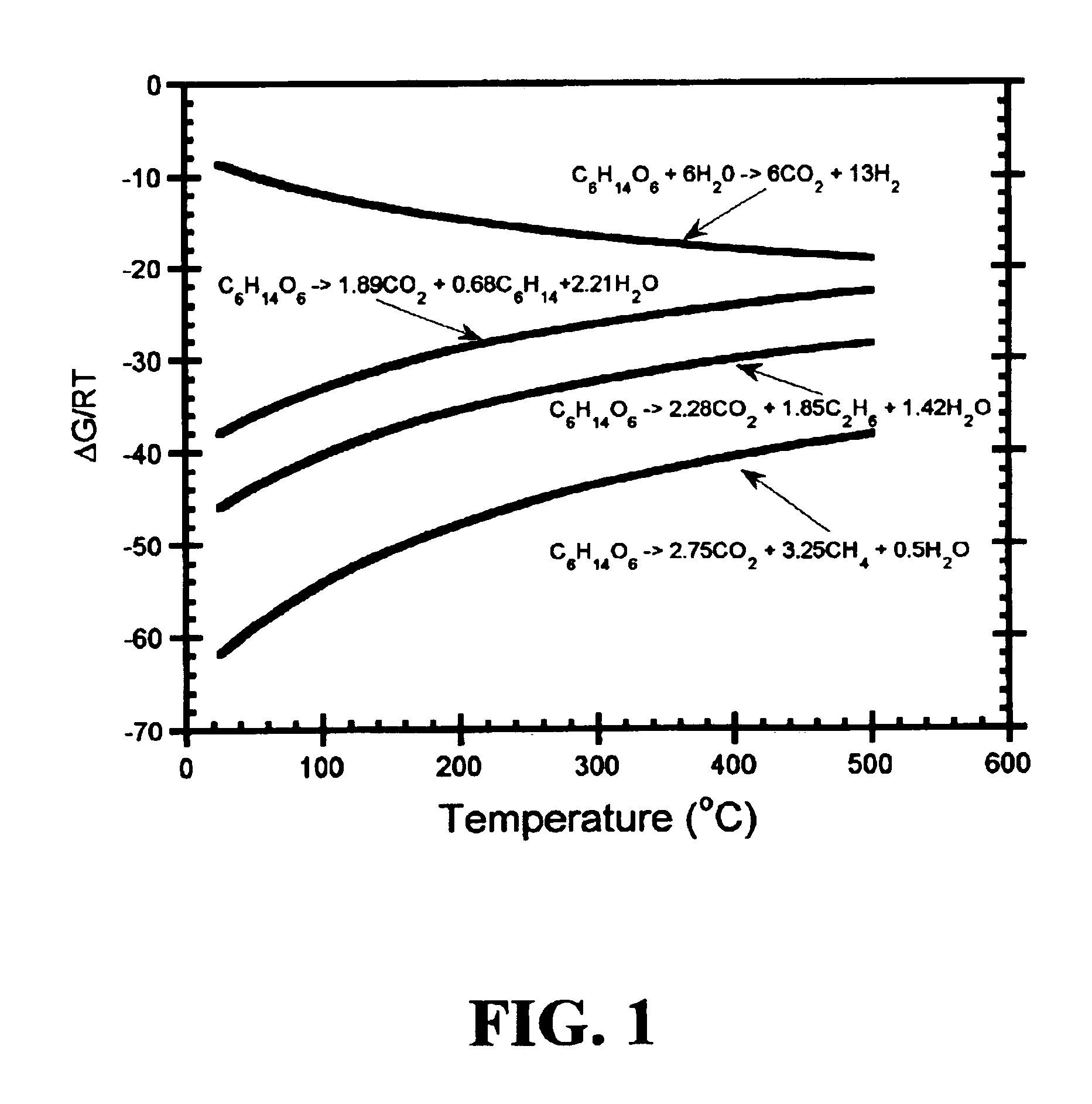
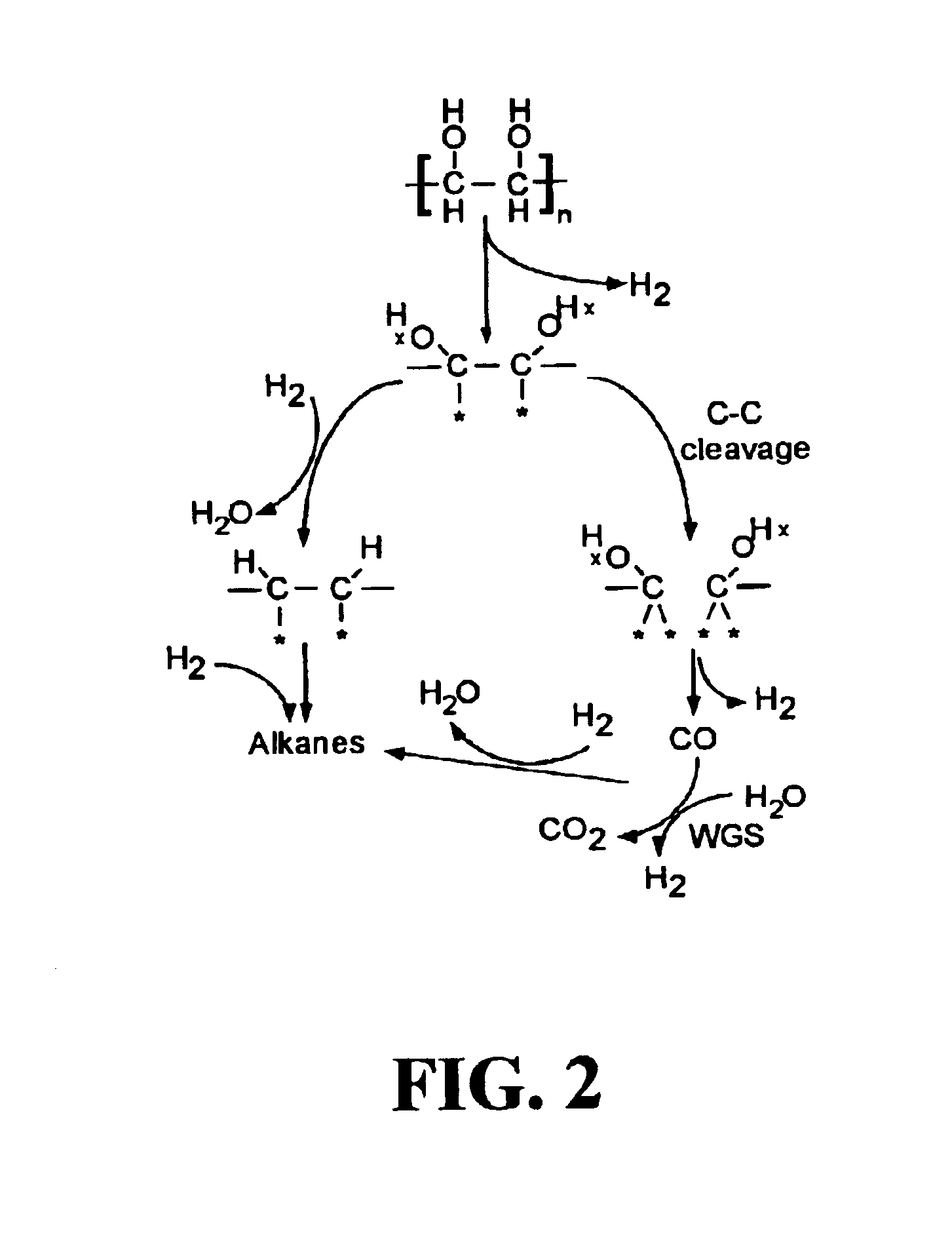
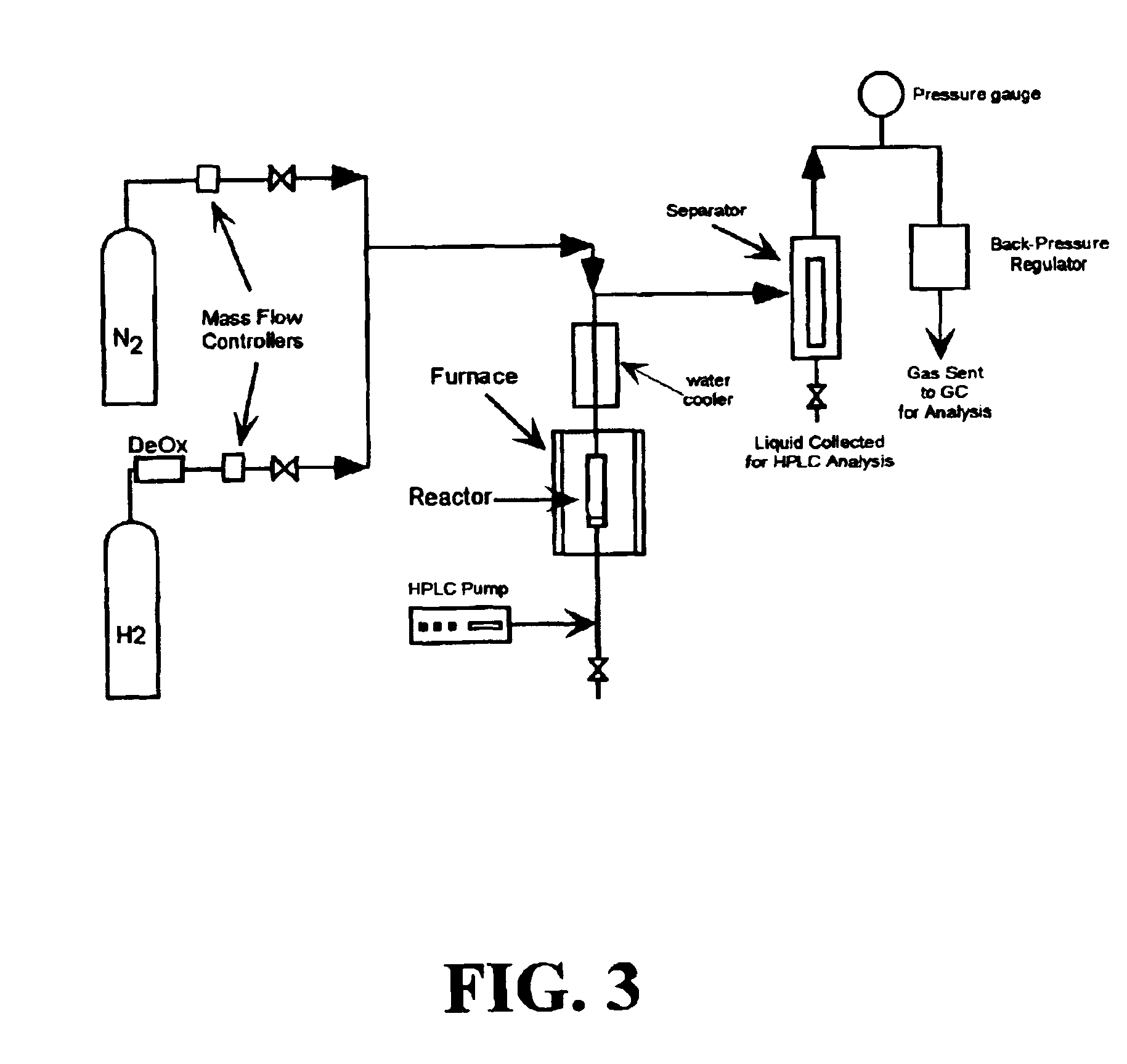
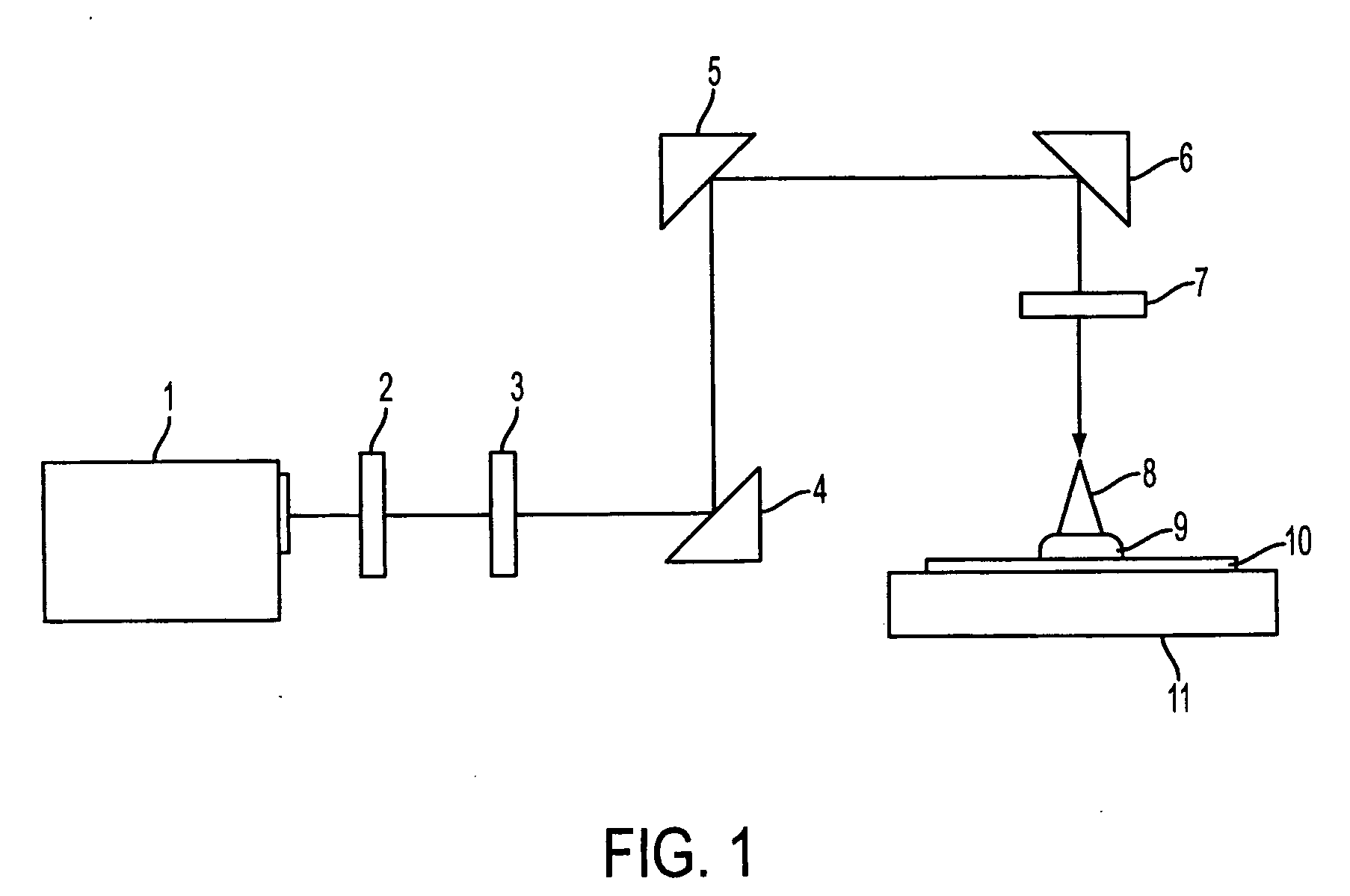
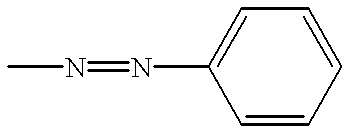
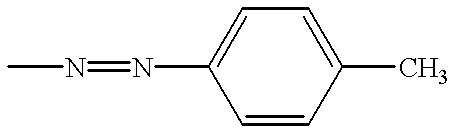
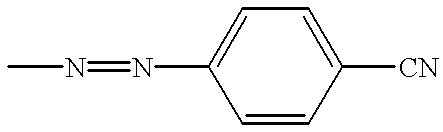
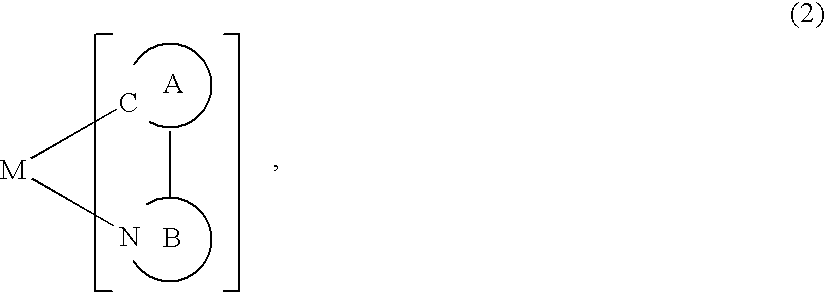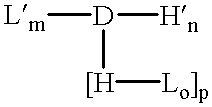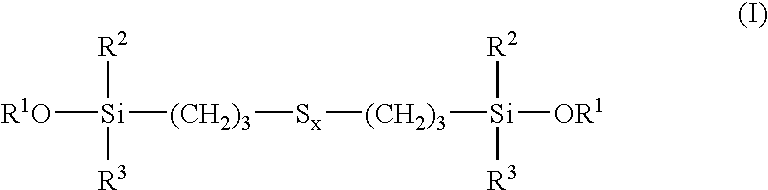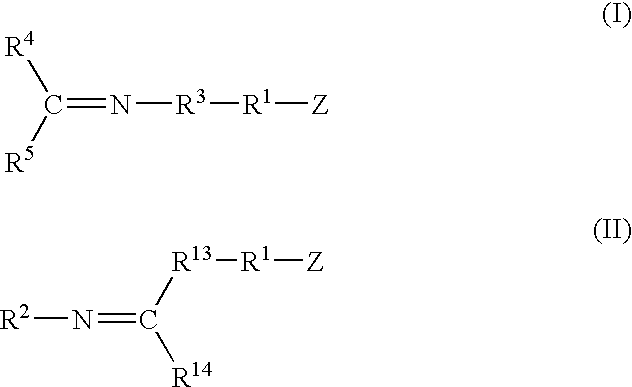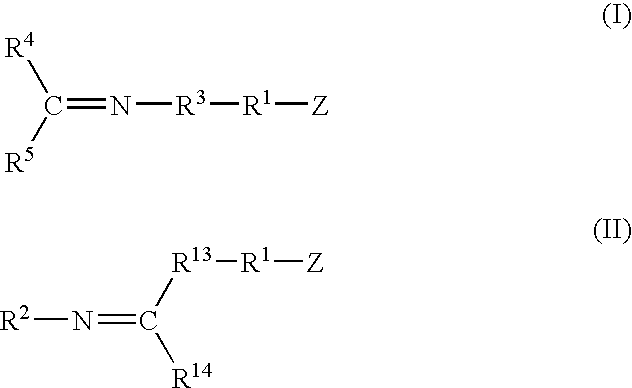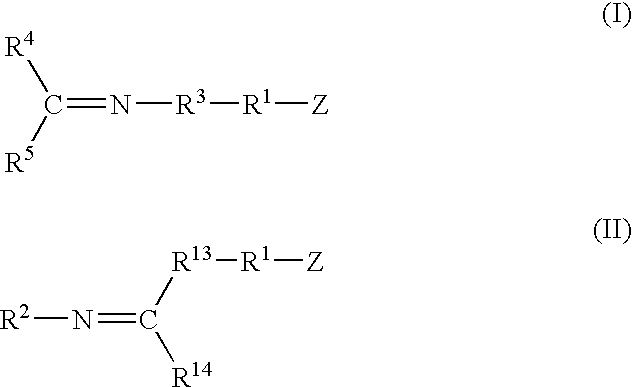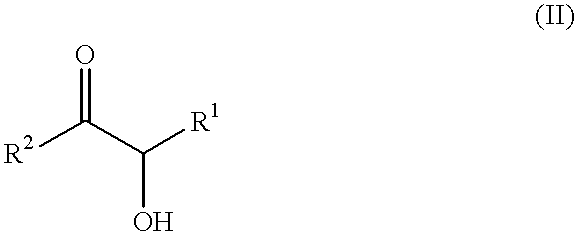Patents
Literature
27240 results about "Carbon atom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
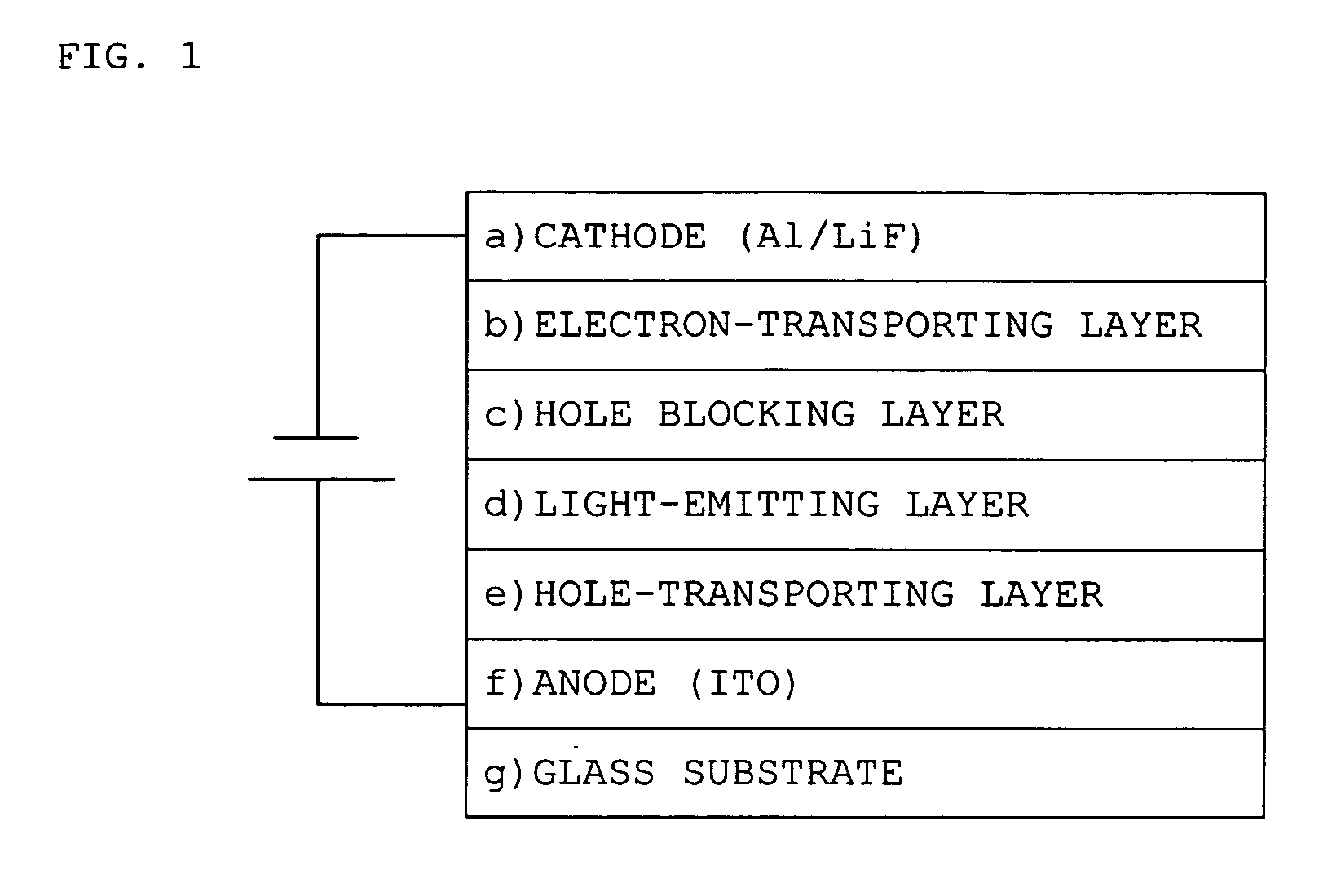
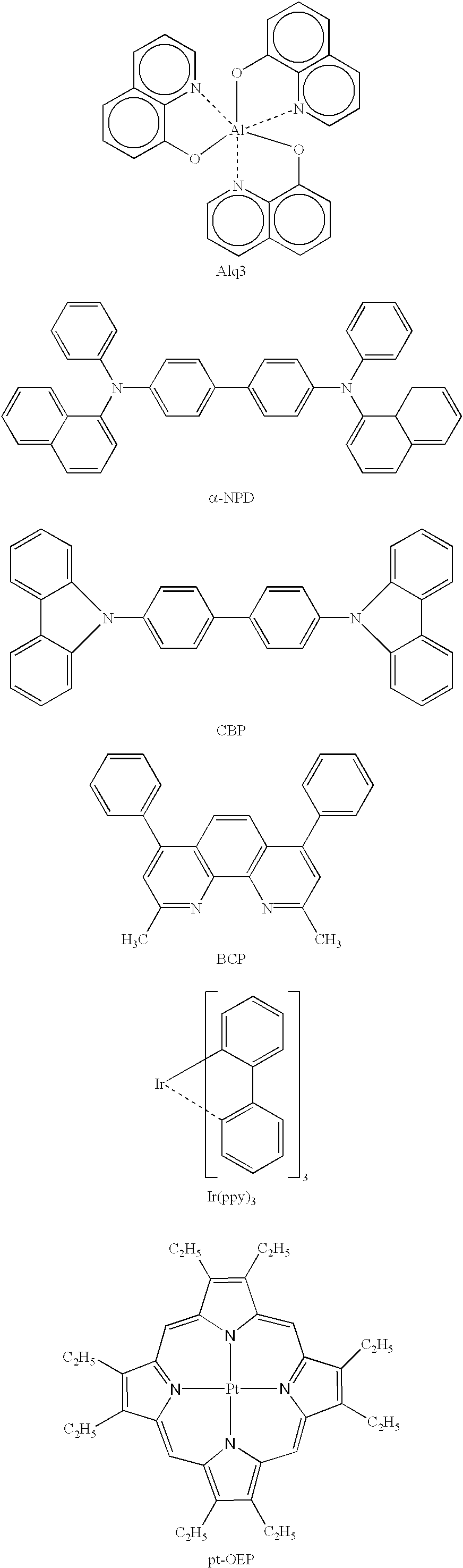
Luminescence device and display apparatus
InactiveUS20030068526A1High efficiency luminescenceExtend device lifeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensHigh luminanceLight emitting device
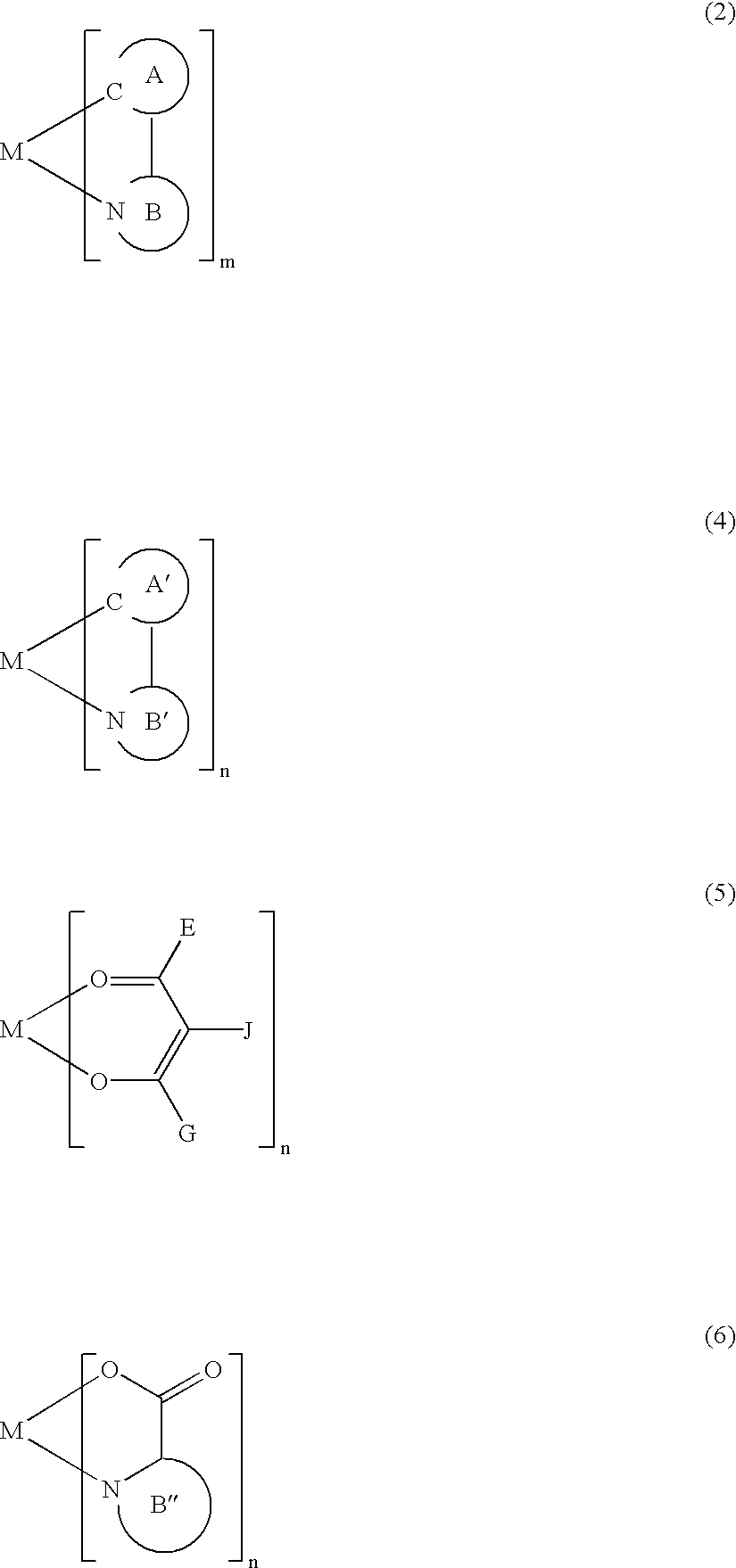
A luminescence device having a layer containing a metal coordination compound which has a partial structure MLm of formula (2) below and is preferably entirely represented by formula (3) below:MLmL'n (3),wherein M denotes a metal atom of Ir, Pt, Rh or Pd; represent mutually different bidentate ligands; m is 1 or 2 or 3; n is 0 or 1 or 2 with the proviso that m+n=2 or 3; the partial structure MLm is represented by formula (2) below (wherein B is an isoquinolyl group bonded to the metal M with its N and including a position-1 carbon atom bonded to a cyclic group A which includes the C bonded to the metal M), and the partial structure ML'n is represented by formula (4), (5) or (6) shown below. There is provided a luminescence device capable of high-efficiency luminescence and long-term high luminance and adapted to red luminescence.
Owner:CANON KK
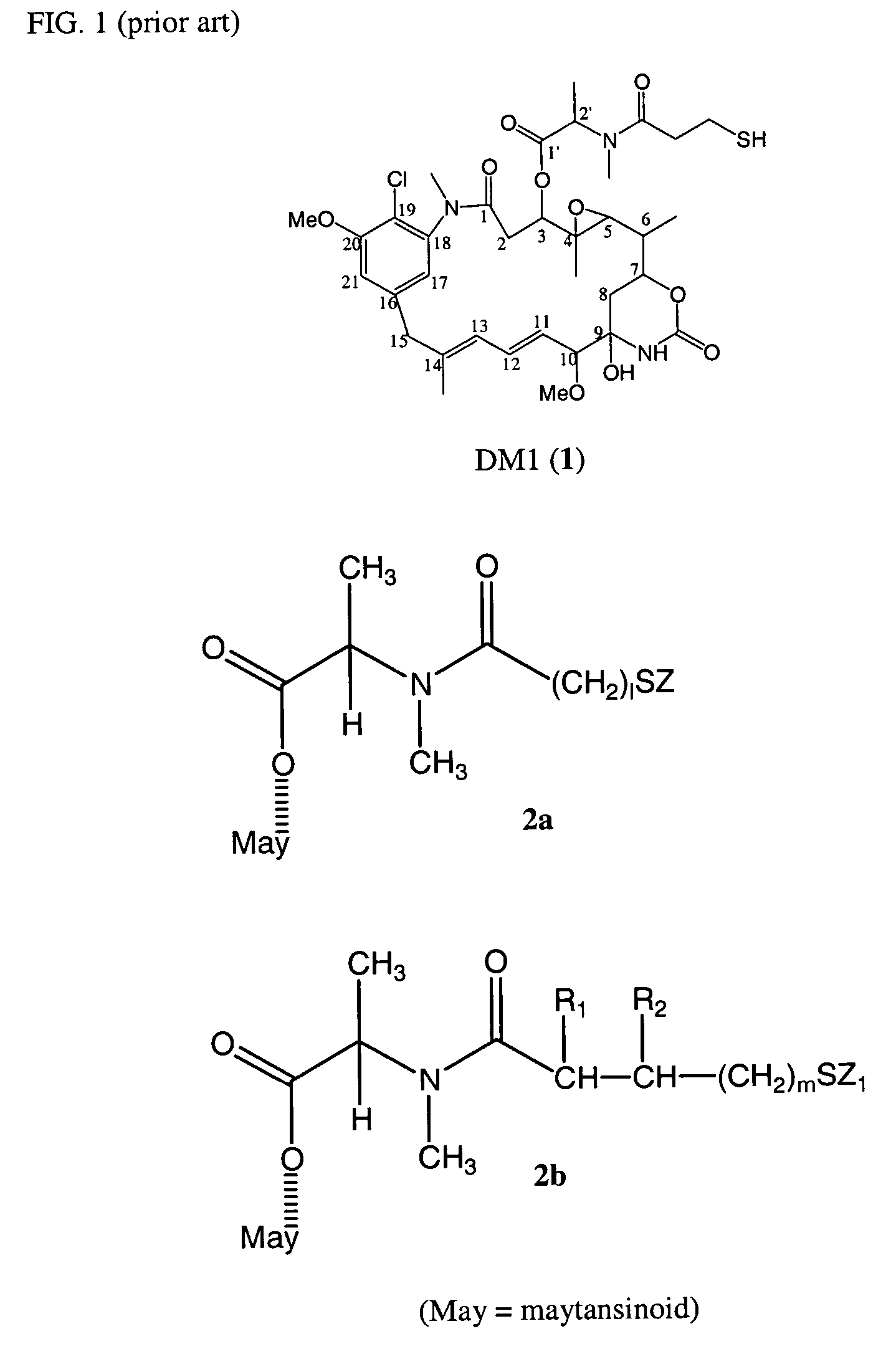
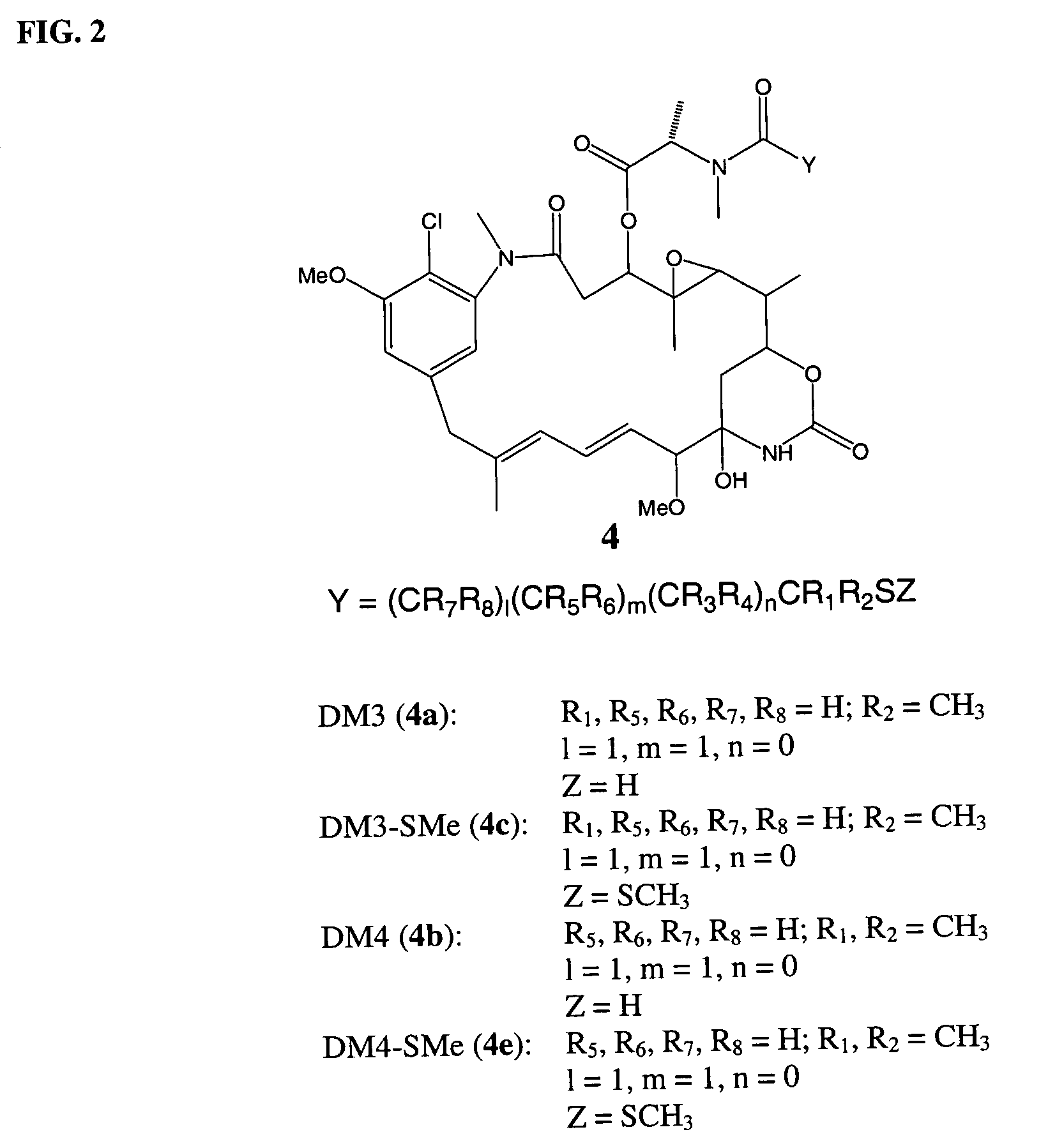
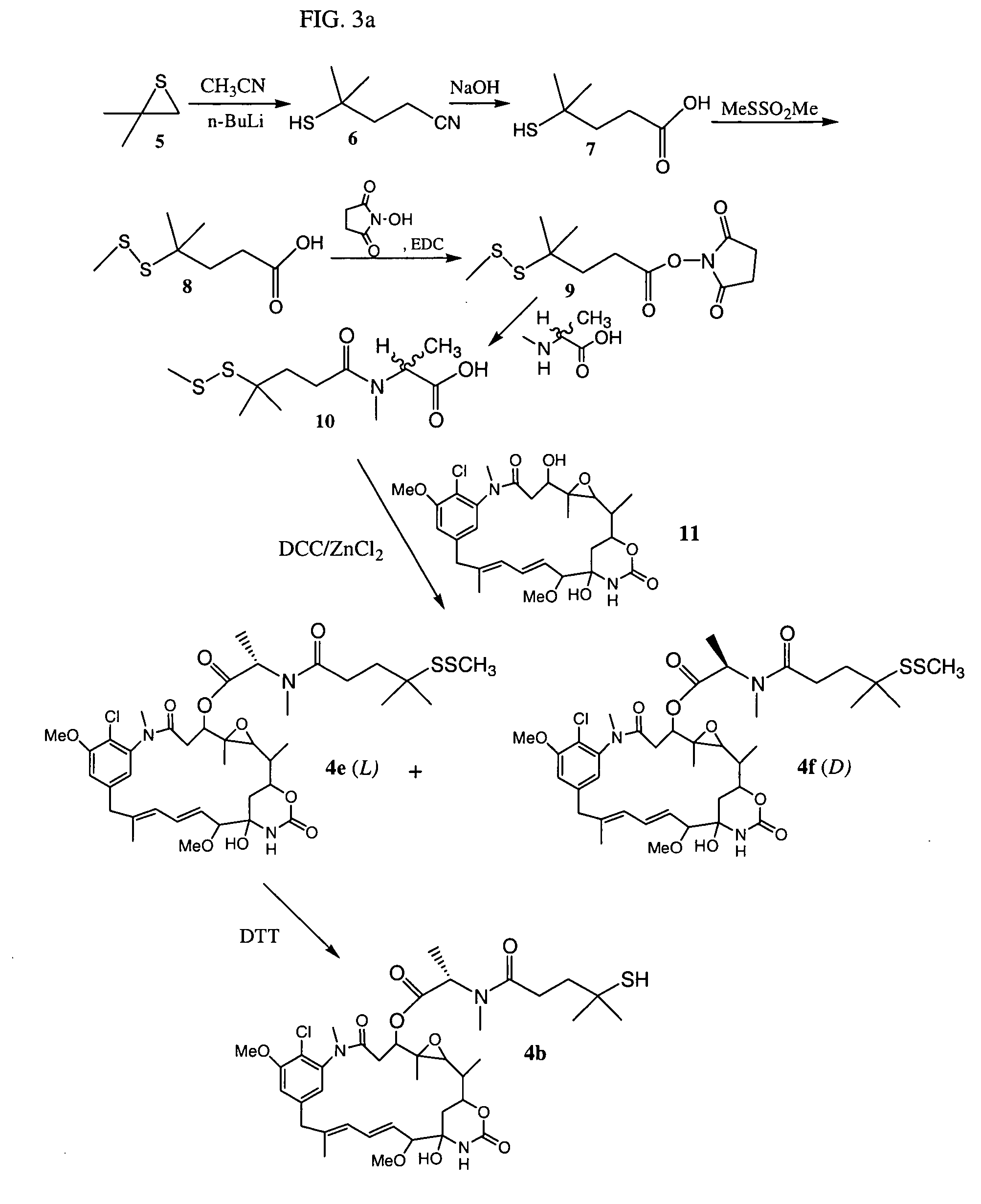
Cytotoxic agents comprising new maytansinoids
ActiveUS7276497B2Improve anti-tumor activityImprove biological activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnimal tumorEfficacy
New thiol and disulfide-containing maytansinoids bearing a mono or di-alkyl substitution on the α-carbon atom bearing the sulfur atom are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for the synthesis of these new maytansinoids and methods for the linkage of these new maytansinoids to cell-binding agents. The maytansinoid-cell-binding agent conjugates are useful as therapeutic agents, which are delivered specifically to target cells and are cytotoxic. These conjugates display vastly improved therapeutic efficacy in animal tumor models compared to the previously described agents.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Nano-scaled graphene plates
A nano-scaled graphene plate material and a process for producing this material. The material comprises a sheet of graphite plane or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane. The graphite plane is composed of a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms and the plate has a length and a width parallel to the graphite plane and a thickness orthogonal to the graphite plane with at least one of the length, width, and thickness values being 100 nanometers or smaller. The process for producing nano-scaled graphene plate material comprises the steps of: a). partially or fully carbonizing a precursor polymer or heat-treating petroleum or coal tar pitch to produce a polymeric carbon containing micron- and / or nanometer-scaled graphite crystallites with each crystallite comprising one sheet or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane; b). exfoliating the graphite crystallites in the polymeric carbon; and c). subjecting the polymeric carbon containing exfoliated graphite crystallites to a mechanical attrition treatment to produce the nano-scaled graphene plate material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
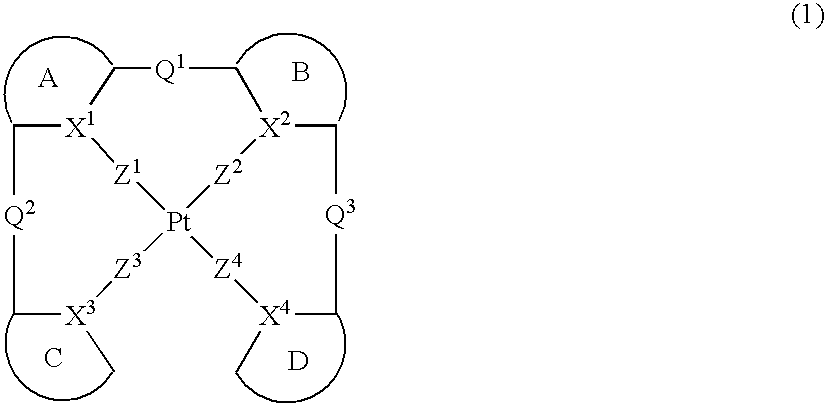
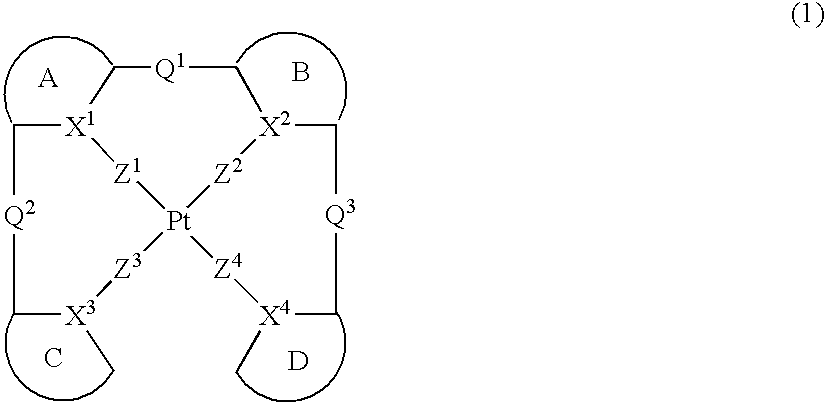
Platinum complex and light emitting device
ActiveUS20070103060A1Enhanced glowSolve low luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOxygenLight emission
Provision of a novel platinum complex which is useful as a material for a light-emitting device of good light emission characteristic and light emission efficiency, and a novel light-emitting material that may be utilized in various fields. A platinum complex represented by the following general formula (1): (in which two rings of ring A, ring B, ring C, and ring D represent nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings which may have a substituent and the remaining two rings of them represent aryl rings or hetero aryl rings which may have a substituent, the ring A and the ring B, the ring A and the ring C or / and the ring B and the rind D may form condensed rings. Two of X1, X2, X3, and X4 represent nitrogen atoms coordination bonded to a platinum atom and the remaining two of them represent carbon atoms or nitrogen atoms. Q1, Q2, and Q3 each represents a bond, oxygen atom, sulfur atom or bivalent group, two of Z1, Z2, Z3, and Z4 represent coordination bonds, and the remaining two of them represent covalent bonds, oxygen atoms or sulfur atoms), and a light-emitting device containing the platinum complex.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Amphiphilic drug-oligomer conjugates with hydroyzable lipophile components and methods for making and using the same
InactiveUS6309633B1Reduce deliveryExtended durationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinCholesterol
The invention provides a drug-oligomer conjugate having the following general formula:wherein D is a therapeutic drug moiety; H and H' are each a hydrophilic moiety, independently selected from the group consisting of straight or branched PEG polymers having from 2 to 130 PEG subunits, and sugars; L is a lipophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of alkyl groups having 2-26 carbon atoms, cholesterol, adamantane and fatty acids; o is a number from 1 to the maximum number of covalent bonding sites on H; m+n+p together have a value of at least one and not exceeding the total number of covalent bonding sites on D for the -H', -L and -H-L substituents; the H-L bond(s) are hydrolyzable and the D-L' bond(s), when present, are hydrolyzable; the conjugate being further characterized by one of the following: (i) m is 0 and p is at least 1; (ii) n is 0 and p is at least 1; (iii) m and n are each 0 and p is at least 1; (iv) p is 0 and m and n are each at least 1. The therapeutic drug moiety is preferably a therapeutic protein or peptide, preferably insulin or a functional equivalent thereof.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Organometallic Complex, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
InactiveUS20140246656A1Improve efficiencyHigh sublimabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesHydrogenEmission efficiency
As a novel substance having a novel skeleton, an organometallic complex having high emission efficiency and improved color purity is provided. The color purity is improved by reducing the half width of an emission spectrum. The organometallic complex is represented by General Formula (G1). In General Formula (G1), at least one of R1 to R4 represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and the others each independently represent hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Note that the case where all of R1 to R4 represent alkyl groups each having 1 carbon atom is excluded. Further, R5 to R9 each independently represent hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Precursors for CVD silicon carbo-nitride films
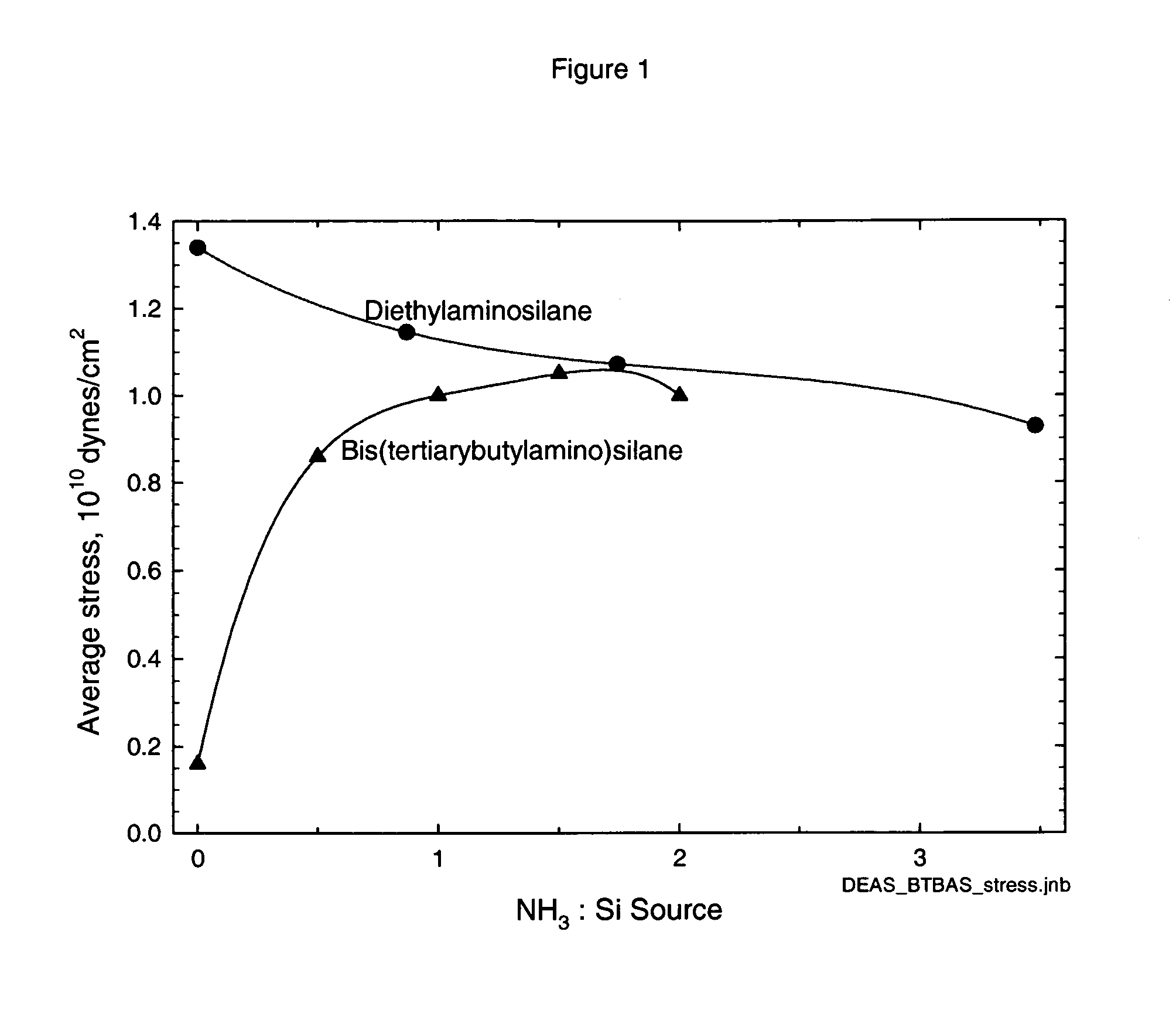
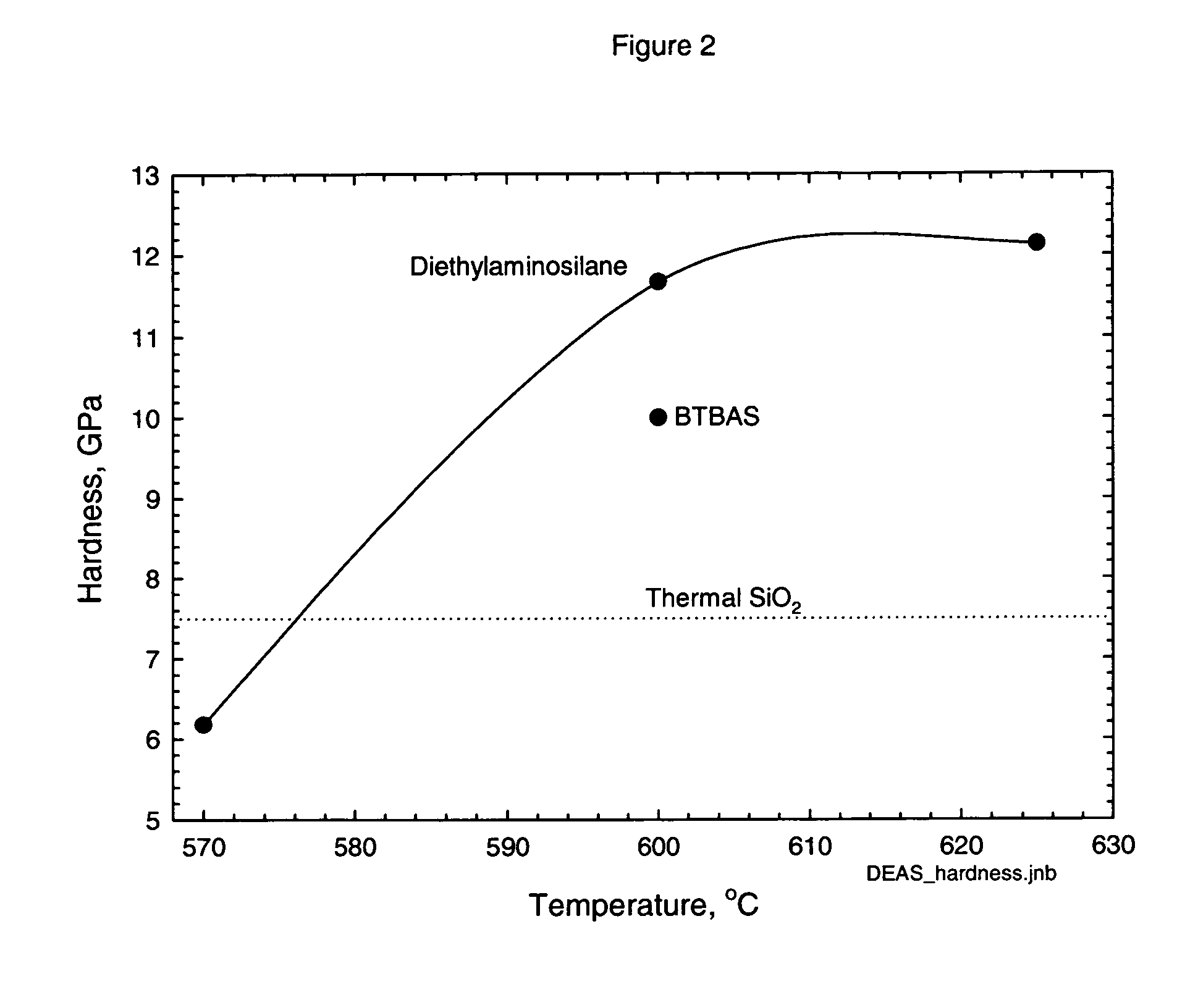
ActiveUS20060258173A1Easy to movePromote formationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesRoom temperature
Classes of liquid aminosilanes have been found which allow for the production of silicon carbo-nitride films of the general formula SixCyNz. These aminosilanes, in contrast, to some of the precursors employed heretofore, are liquid at room temperature and pressure allowing for convenient handling. In addition, the invention relates to a process for producing such films. The classes of compounds are generally represented by the formulas: and mixtures thereof, wherein R and R1 in the formulas represent aliphatic groups typically having from 2 to about 10 carbon atoms, e.g., alkyl, cycloalkyl with R and R1 in formula A also being combinable into a cyclic group, and R2 representing a single bond, (CH2)n, a ring, or SiH2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
New condensed polycyclic compound and organic light-emitting element using the same
InactiveUS20130175519A1Improve light emission efficiencyReduce the driving voltageOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPolycyclic compoundAryl
The present invention provides a stable new condensed polycyclic compound which is not likely to form a molecular association. In addition, the present invention also provides an organic light-emitting element having a high light-emitting efficiency and a low drive voltage. In the condensed polycyclic compound in Claim 1 represented by the general formula [1], R1, R2 and R5 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an aryl group, and a heterocyclic group. R3 and R4 each represent an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. The aryl group and the heterocyclic group each may have at least one of an alkyl group, an aralkyl group, an aryl group, a heterocyclic group, an amino group, and an alkoxy group as a substituent.
Owner:CANON KK
Organic-electroluminescence-material-containing solution, method for forming thin film of organic electroluminescence material, thin film of organic electroluminescence material and organic electroluminescence device
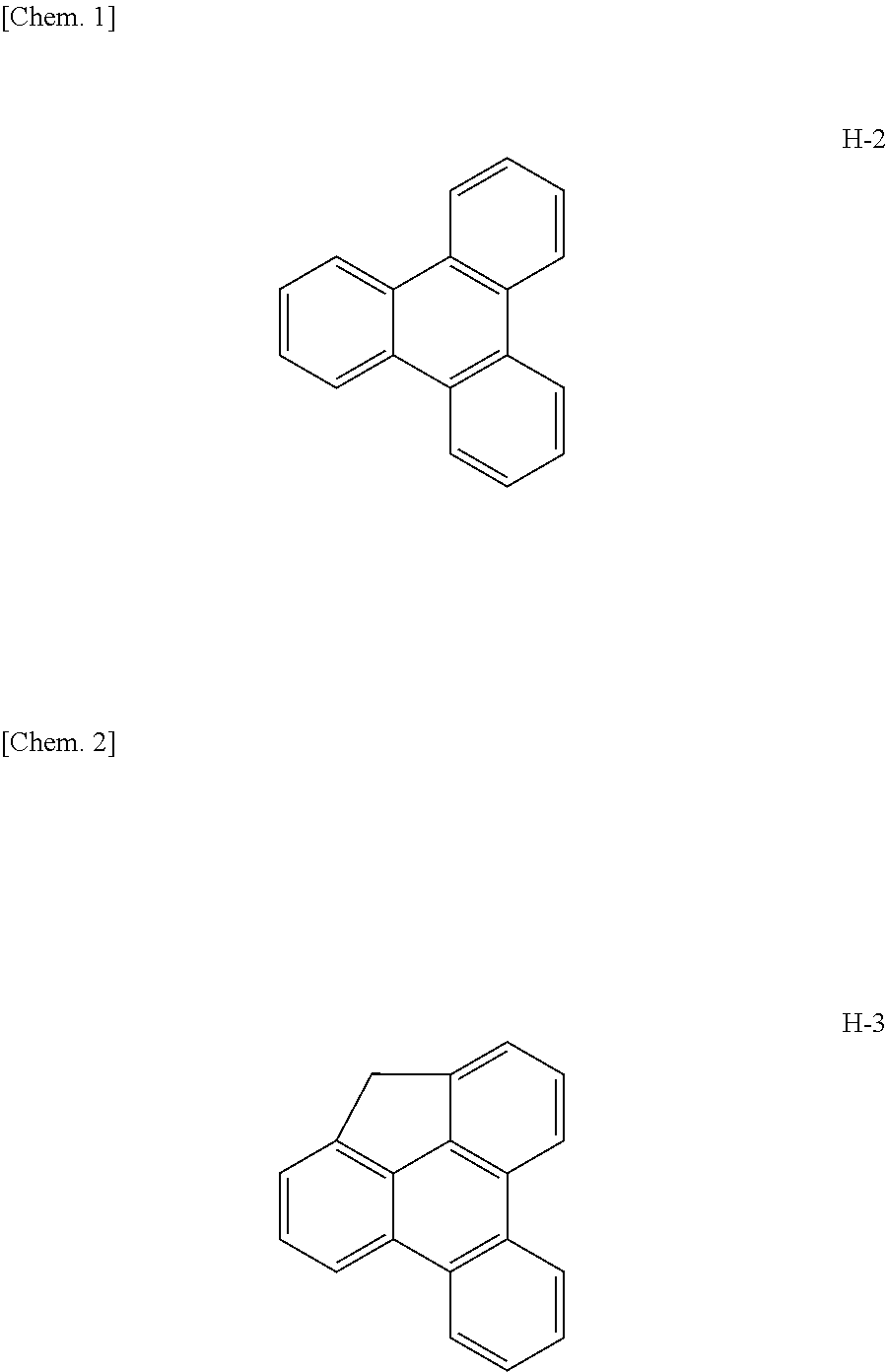
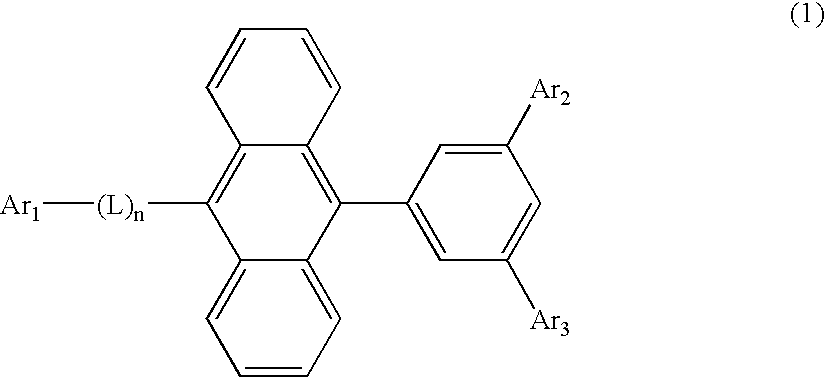
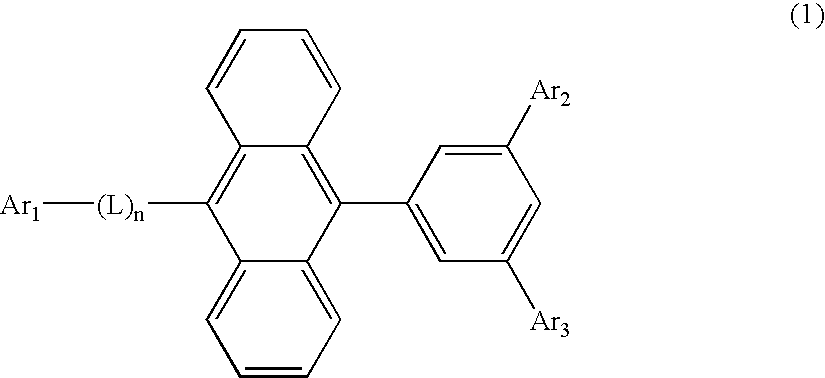
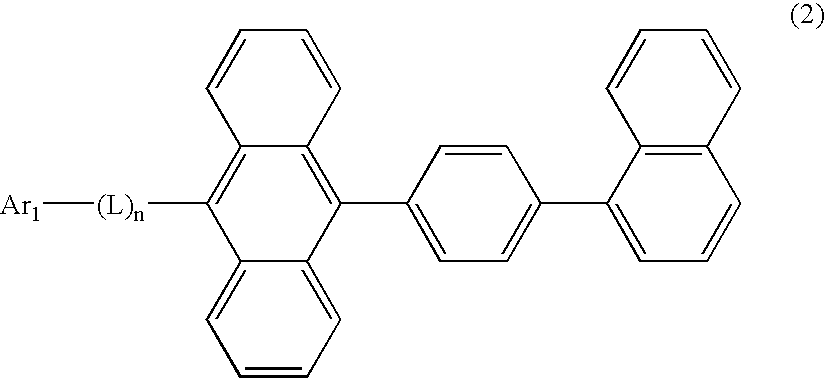
An organic EL material-containing solution contains an organic EL material, a solvent and a viscosity control agent. The organic EL material contains a host and a dopant.The host is a compound shown by Formula (1) below and has a solubility of 2 wt % or higher in the solvent. The solvent is an aromatic solvent, while the viscosity control agent is an alcohol type solution or an alkyl-substituted aromatic solution having 4 or more carbon atoms.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
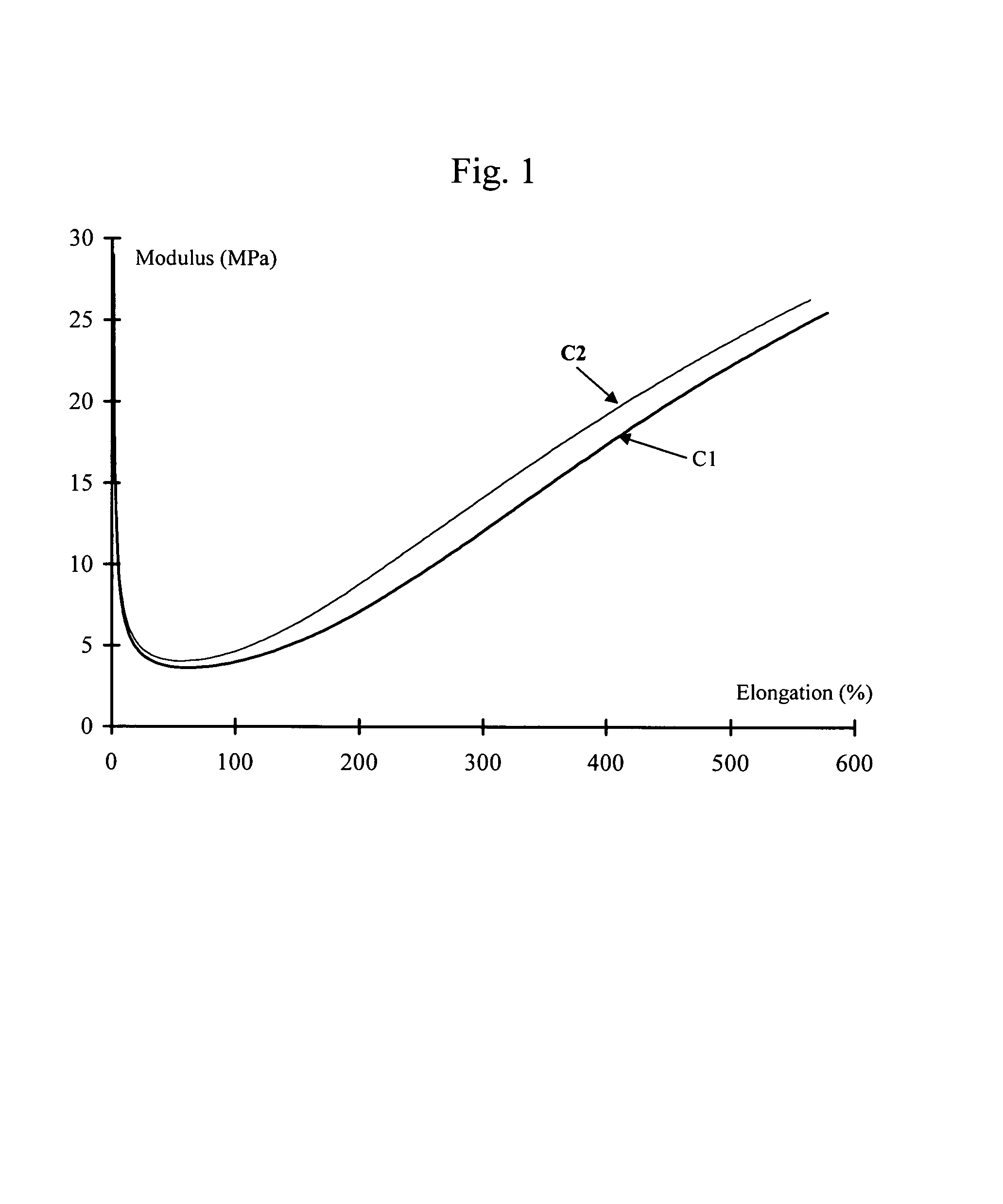
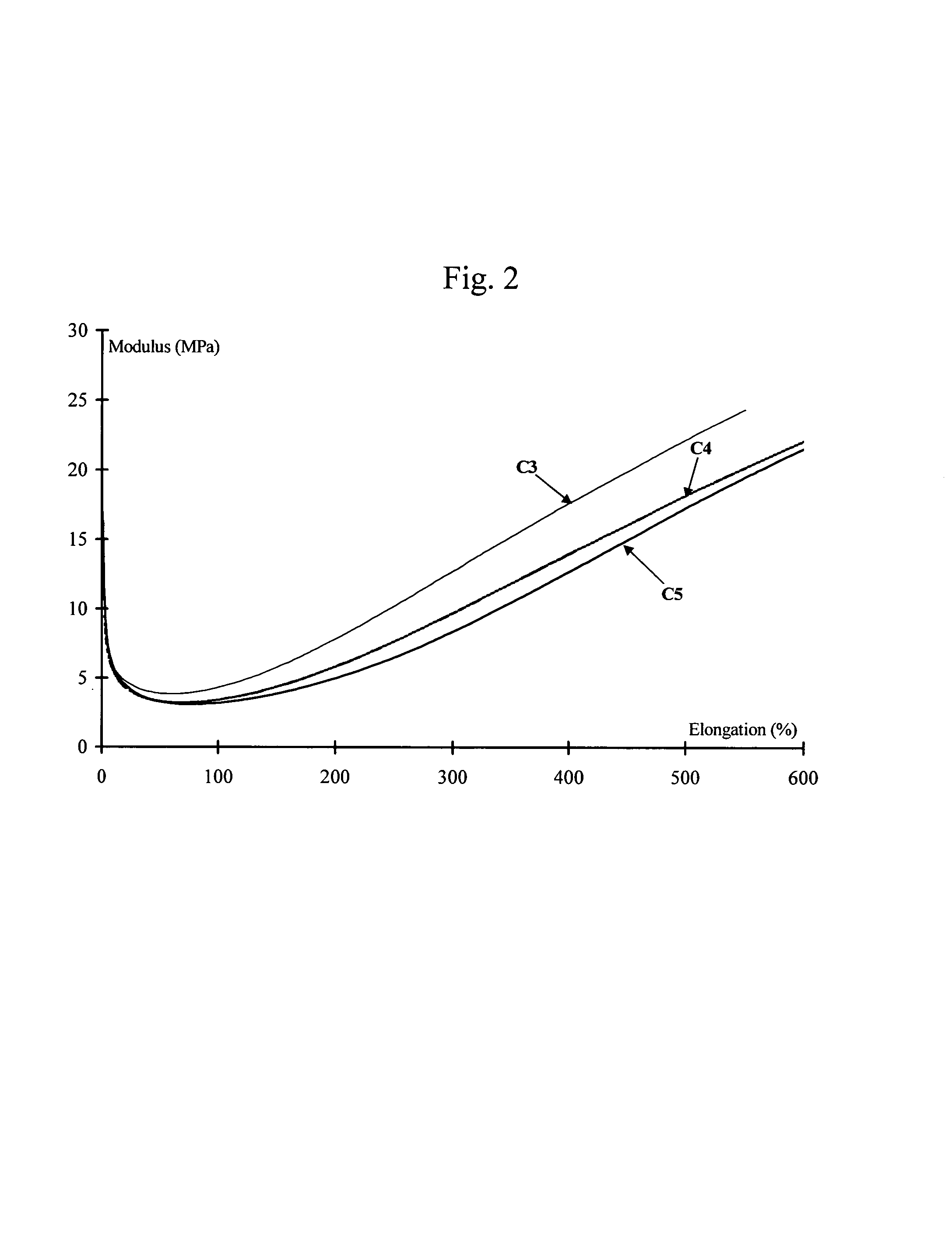
Tire and tread comprising a bis-alkoxysilane tetrasulfide as coupling agent
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
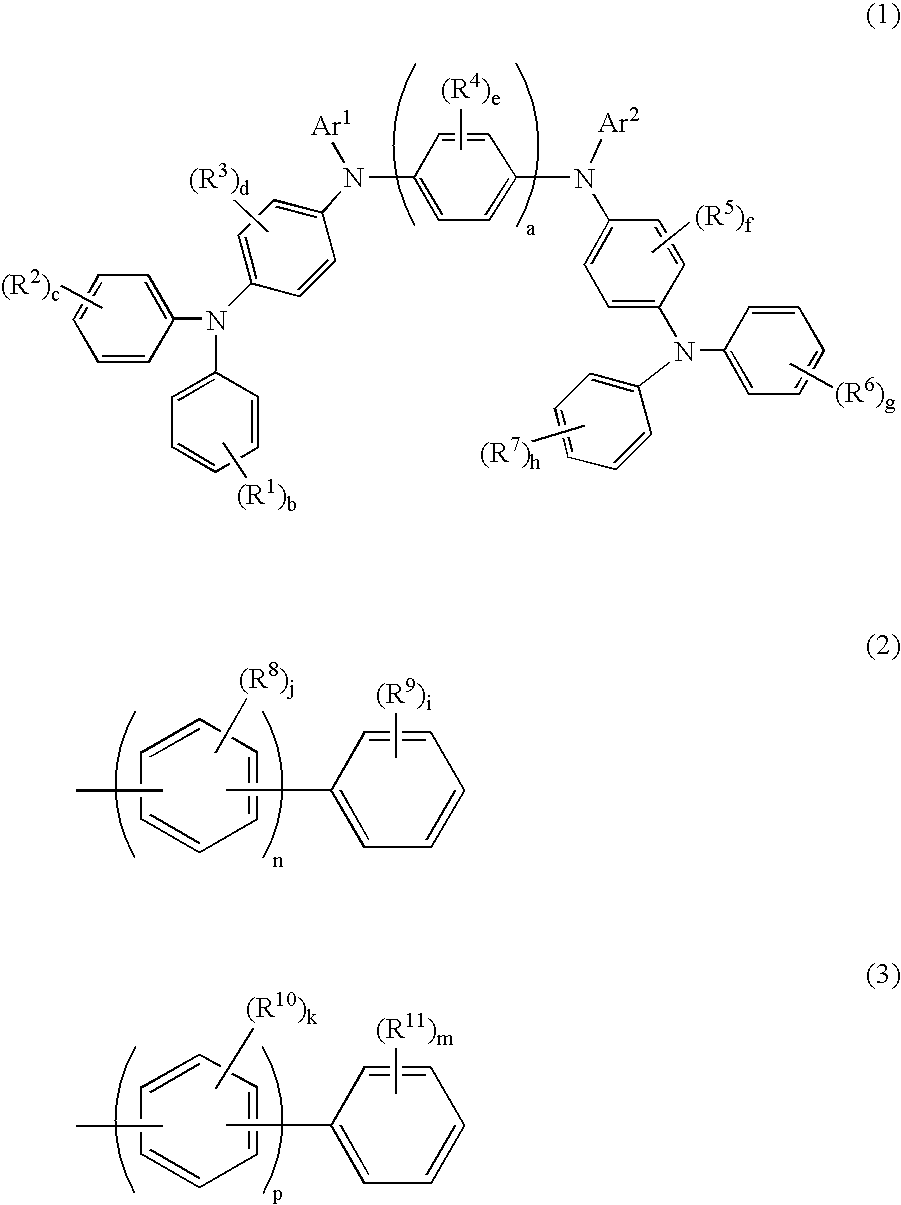
Aromatic amine derivative and organic electroluminescence device using the same
InactiveUS20080145707A1Small increase in driving voltageSolution to short lifeOrganic chemistryLayered productsArylHydrogen atom
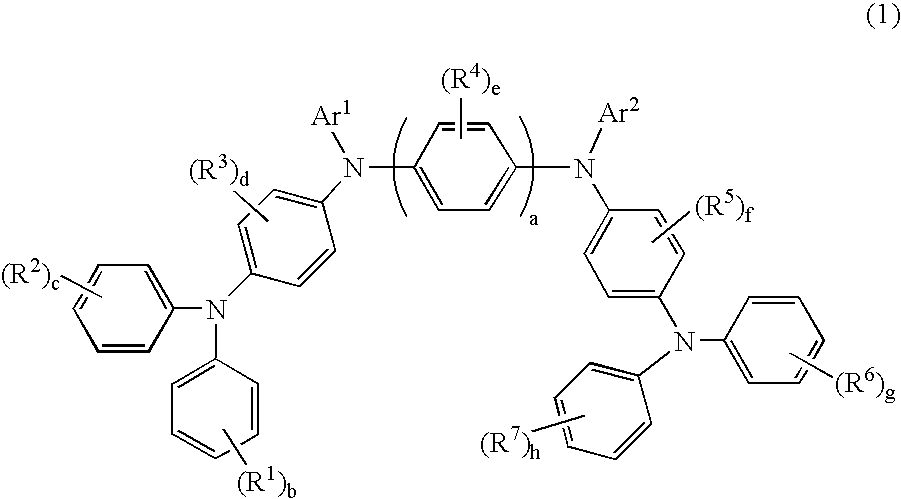
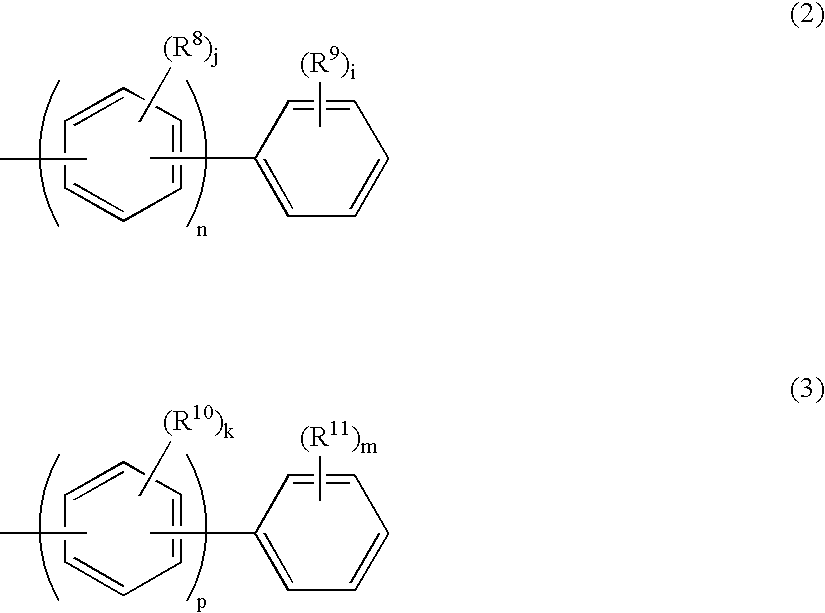
The present invention provides a novel aromatic amine derivative enabling to obtain an organic electroluminescence device which is driven under a low voltage, exhibits small increase in the driving voltage after continuous driving for a long time and has a long life. The amine derivative is represented by the following general formula (1). In the formula, R1 to R7 each represent, for example, hydrogen atom or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group having 5 to 50 nuclear carbon atoms; a represents an integer of 1 or greater; b, c, g and h each represent an integer of 1 to 5, and d, e and f each represent an integer of 1 to 4; and Ar1 and Ar2 represent a group represented by following general formulae (2) and (3), respectively, and the groups represented by Ar1 and Ar2 are not same with each other. R8 to R11 each represent, for example, hydrogen atom; and i and m each represent an integer of 1 to 5, j and k each represent an integer of 1 to 4, n and p each represent an integer of 0 or greater, and n≠p.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Methods for forming aluminum containing films utilizing amino aluminum precursors
ActiveUS20050003662A1Security benefitsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical structureHydrogen
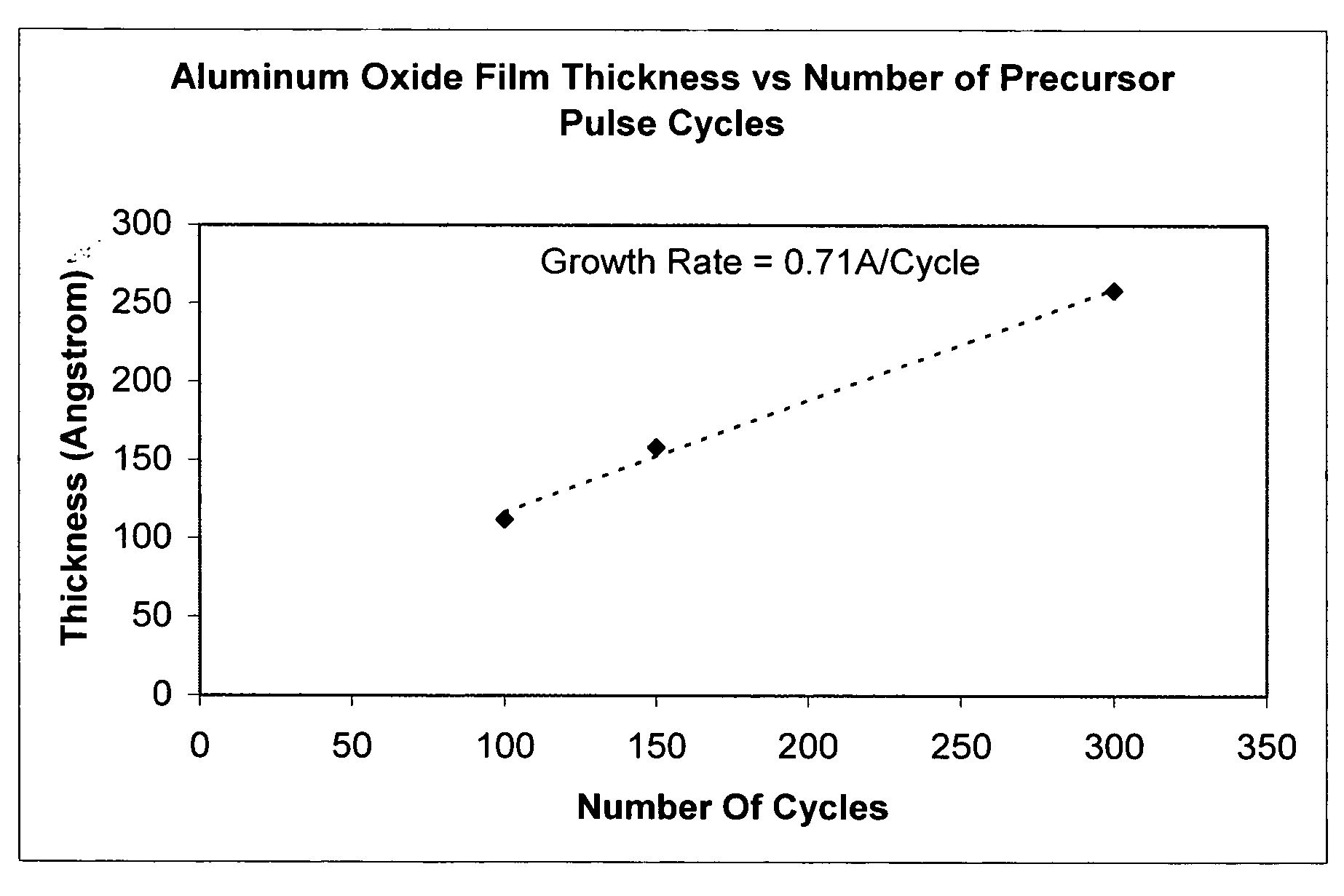
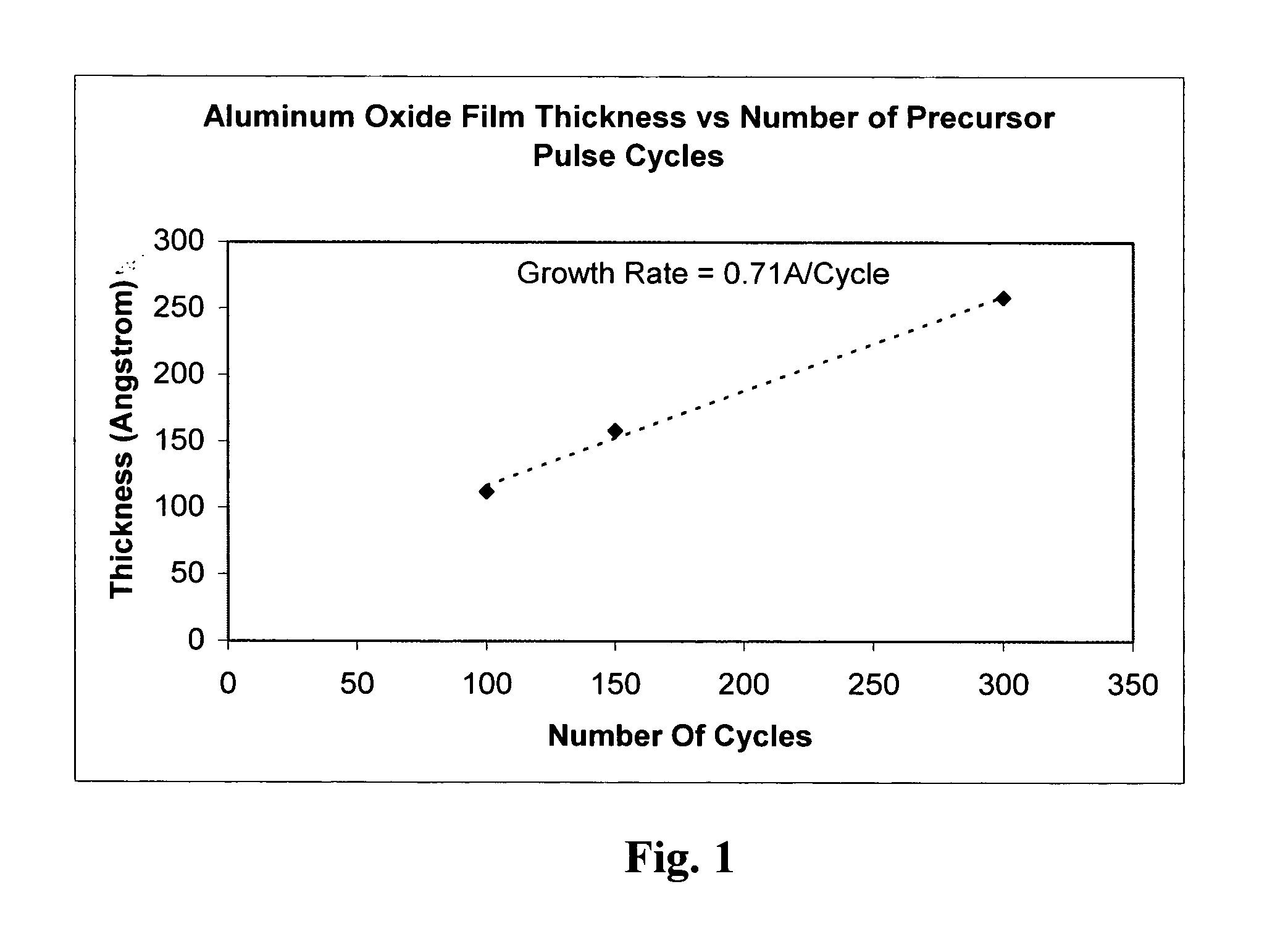
A method of forming an aluminum containing film on a substrate includes providing a precursor having the chemical structure: Al(NR1R2)(NR3R4)(NR5R6); where each of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and an alkyl group including at least two carbon atoms. The precursor is utilized to form a film on the substrate including at least one of aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride and aluminum oxy-nitride. Each of the R1-R6 groups can be the same or different and can by straight or branched chain alkyls. An exemplary precursor that has is useful in forming aluminum containing films is tris diethylamino aluminum.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Modified polymers prepared with lanthanide-based catalysts
A method for preparing a functionalized polymer comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, where said pseudo-living polymer is characterized by having greater than about 85 percent of the polymer in the cis microstructure and less than about 3 percent of the polymer is in the 1,2- or 3,4-microstructure, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with at least one functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) or (II) where Z is a substituent that will react or interact with organic or inorganic fillers; R1 is a single bond or a divalent organic group; R2 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R13 or R14; R3 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R4 or R5; R13 is a single bond, a divalent organic group, or a trivalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R14; R4 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R5; R14 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R2 or R13; and R5 is a monovalent organic group or a divalent organic group that forms a cyclic organic group with R3 or R4; with the proviso that each group attached to the imino carbon is attached via a carbon atom and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R13, R14 and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Process for producing single wall nanotubes using unsupported metal catalysts
InactiveUS6221330B1Continuous and efficient productionMaterial nanotechnologyFibre chemical featuresHydrogenGas phase
A process for producing hollow, single-walled carbon nanotubes by catalytic decomposition of one or more gaseous carbon compounds by first forming a gas phase mixture carbon feed stock gas comprising one or more gaseous carbon compounds, each having one to six carbon atoms and only H, O, N, S or Cl as hetero atoms, optionally admixed with hydrogen, and a gas phase metal containing compound which is unstable under reaction conditions for said decomposition, and which forms a metal containing catalyst which acts as a decomposition catalyst under reaction conditions; and then conducting said decomposition reaction under decomposition reaction conditions, thereby producing said nanotubes.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a fluorinated surfactant
InactiveUS20070015866A1Low toxicityGood chemical stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsFibre treatmentEmulsion polymerizationEther
The present invention provides an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers including gaseous fluorinated monomers using a perfluoro ether surfactant as an emulsifier. The perfluoro ether surfactants correspond to formula (I) Rf—O—CF2CF2—X (I) wherein Rf represents a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1, 2, 3 or 4 carbon atoms and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. In a further aspect, the invention also provides an aqueous fluoropolymer dispersion comprising the perfluoro ether surfactant and the use of such dispersion in the coating or impregnation of substrates.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
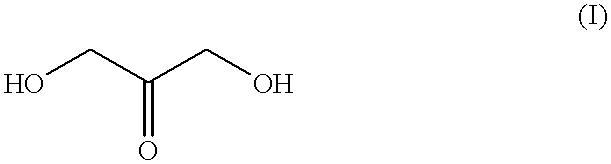
Self-tanning dihydroxyacetone formulations having improved stability and providing enhanced delivery
A composition is provided which is useful for self-tanning skin coloring and is characterized by improved stability, which comprises from about 0.5% to about 20.0% by weight, based on total weight of said composition, of a self-tanning skin coloring agent subject to chemical instability, which is preferably dihydroxyacetone; from about 2.0% to about 40.0% by weight of a polyethoxyglycol, which is preferably ethoxydiglycol; and from about 0.1% to about 15.0% by weight of a polyol comprising a polyhydric compound having at least three hydroxyl groups and at least three carbon atoms, which is preferably D-sorbitol. The self-tanning composition may further optionally contain from about 0.1% to about 8.0% by weight of a water soluble dihydroxyl compound having at least two, and up to eight carbon atoms, which is preferably ethylene glycol; and the self-tanning composition may still further optionally contain an acidifying agent in amount sufficient to maintain the pH of said total composition at from about 3.5 to about 4.5, which is preferably sorbic acid. Cosmetologic products and methods of tanning are also provided.
Owner:SCHERING PLOUGH HEALTHCARE PRODUCTS INC
Breathable polyurethanes, blends, and articles
InactiveUS6897281B2Improve breathabilityImprove moisture vapor transmission rateSynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsGramSide chain
A breathable polyurethane having an upright moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) of more than about 500 gms / m2 / 24 hr comprises:(a) poly(alkylene oxide) side-chain units in an amount comprising about 12 wt. % to about 80 wt. % of said polyurethane, wherein (i) alkylene oxide groups in said poly(alkylene oxide) side-chain units have from 2 to 10 carbon atoms and are unsubstituted, substituted, or both unsubstituted and substituted, (ii) at least about 50 wt. % of said alkylene oxide groups are ethylene oxide, and (iii) said amount of said side-chain units is (i) at least about 30 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is less than about 600 grams / mole, (ii) at least about 15 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is from about 600 to about 1,000 grams / mole, and at least about 12 wt. % when the molecular weight of said side-chain units is more than about 1,000 grams / mole, and(b) poly(ethylene oxide) main-chain units in an amount comprising less than about 25 wt. % of said polyurethane.Coatings and films for textiles and other articles and applications using such polyurethanes have excellent breathability, i.e., high moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR).
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Acid generator, sulfonic acid, sulfonic acid derivatives and radiation-sensitive resin composition
A novel photoacid generator containing a structure of the following formula (I), wherein R is a monovalent organic group with a fluorine content of 50 wt % or less, a nitro group, a cyano group, or a hydrogen atom, and Z1 and Z2 are individually a fluorine atom or a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1-10 carbon atoms, is provided. When used in a chemically amplified radiation-sensitive resin composition, the photoacid generator exhibits high transparency, comparatively high combustibility, and no bioaccumulation, and produces an acid exhibiting high acidity, high boiling point, moderately short diffusion length in the resist coating, and low dependency to mask pattern density.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Nanoporous silicone resins having low dielectric constants
InactiveUS6541107B1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsDead plant preservationOrganic solventCarbon–carbon bond
Nanoporous silicone resins and silicone resin films having low dielectric constants and a method for preparing such nanoporous silicone resins. The silicone resin comprises the reaction product of a mixture comprising(A) 15-70 mol % of a tetraalkoxysilane described by formula where each R1 is an independently selected alkyl group comprising 1 to about 6 carbon atoms,(B) 12 to 60 mol % of a hydrosilane described by formula where each X is an independently selected hydrolyzable substituent,(C) 15 to 70 mole percent of an organotrialkoxysilane described by formula where R2 is a hydrocarbon group comprising about 8 to 24 carbon atoms or a substituted hydrocarbon group comprising a hydrocarbon chain having about 8 to 24 carbon atoms and each R3 is an independently selected alkyl group comprising 1 to about 6 carbon atoms; in the presence of(D) water,(E) hydrolysis catalyst, and(F) organic solvent for the reaction product.The silicone resin is cured and heated in an inert atmosphere at a temperature sufficient to effect thermolysis of carbon-carbon bonds of the R2 groups thereby forming a nanoporous silicone resin.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Material for organic electroluminescent device, organic electroluminescent device, and organic electroluminescent display
ActiveUS8044390B2Improve heat resistanceDeposition stabilityOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesHalogenHydrogen
A material for an organic electroluminescent device including an imine derivative represented by the following formula (Ia) or (Ib),wherein Y1 to Y4 are independently a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom; R1 to R4 are independently hydrogen, an alkyl group, an aryl group, a heterocycle, a halogen atom, a fluoroalkyl group or a cyano group; and R1 and R2, or R3 and R4 may be bonded together to form a ring.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD +1
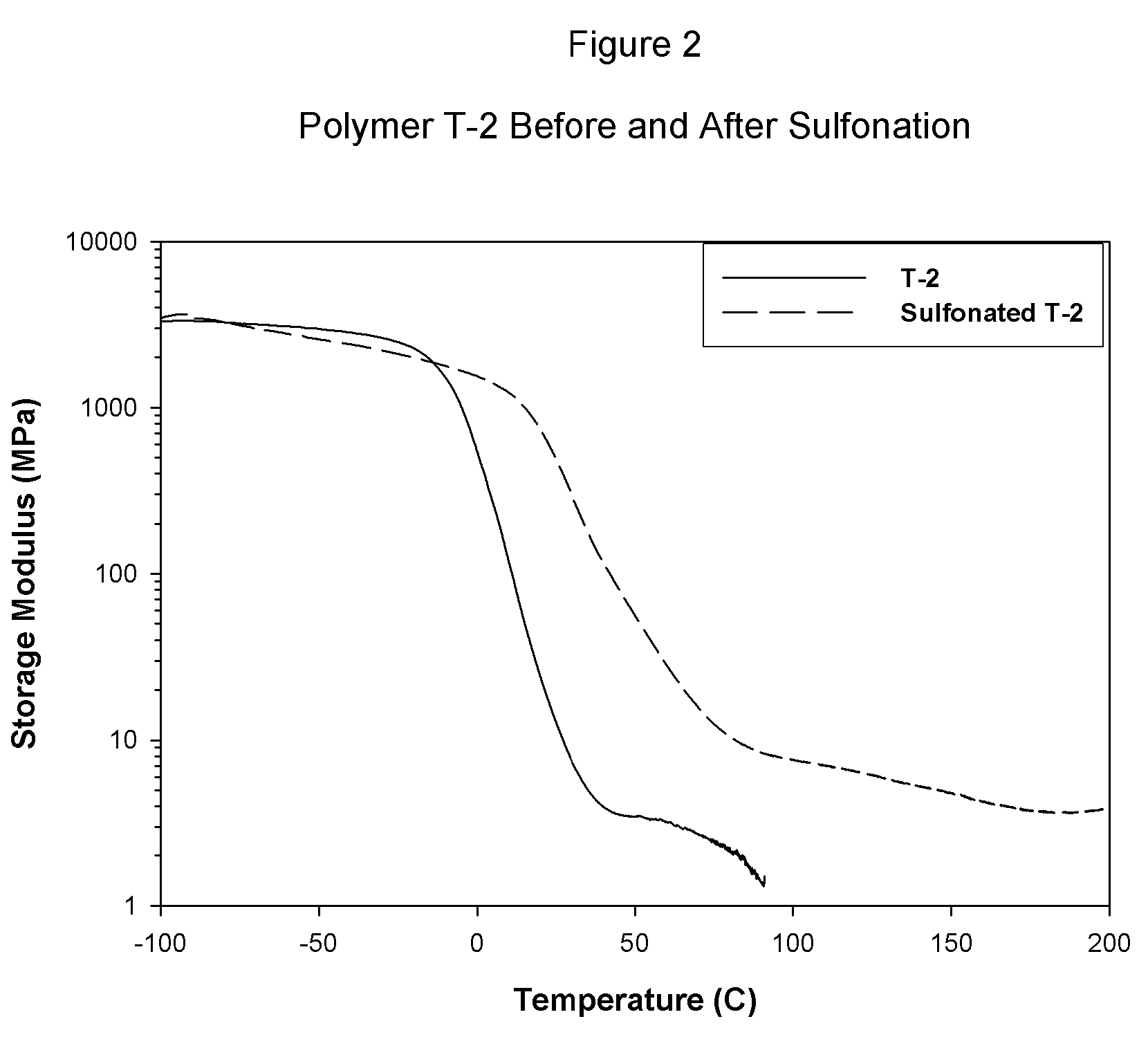
Sulfonated block copolymers, method for making same, and various uses for such block copolymers
ActiveUS7737224B2Reduced responseHigh propertySemi-permeable membranesNegative electrodesMethacrylatePolymer science
The present invention is a, solid block copolymer comprising at least two polymer end blocks A and at least one polymer interior block B wherein each A block is a polymer block resistant to sulfonation and each B block is a polymer block susceptible to sulfonation, and wherein said A and B blocks do not contain any significant levels of olefinic unsaturation. Preferably, each A block comprising one or more segments selected from polymerized (i) para-substituted styrene monomers, (ii) ethylene, (iii) alpha olefins of 3 to 18 carbon atoms; (iv) hydrogenated 1,3-cyclodiene monomers, (v) hydrogenated monomers of conjugated dienes having a vinyl content less than 35 mol percent prior to hydrogenation, (vi) acrylic esters, (vii) methacrylic esters, and (viii) mixtures thereof; and each B block comprising segments of one or more polymerized vinyl aromatic monomers selected from (i) unsubstituted styrene monomers, (ii) ortho-substituted styrene monomers, (iii) meta-substituted styrene monomers, (iv) alpha-methylstyrene, (v) 1,1-diphenylethylene, (vi) 1,2-diphenylethylene and (vii) mixtures thereof. Also claimed are processes for making such block copolymers, and the various end uses and applications for such block copolymers.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Metal coordination compound, luminescence device and display apparatus
InactiveUS20020094453A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen atomNitrogen
A metal coordination compound suitable as an organic material for a luminescent device is represented by the following formula (1): wherein M denotes Ir, Pt, Rh or Pd; n is 2 or 3; Y denotes an alkylene group having 2-6 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S- or -CO- and capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with a linear or branched alkyl group which has 1-10 carbon atoms and is capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with fluorine atom; and CyN denotes a cyclic group containing nitrogen atom connected to M and capable of having a substituent selected from the group consisting of halogen atom; nitro group; phenyl group; trialkylsilyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms; and a linear or branched alkyl group having 1-20 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CO-O-, -O-CO-, -CH=CH- or -C=C- and capable of including hydrogen atom which can be replaced with fluorine atom.
Owner:CANON KK
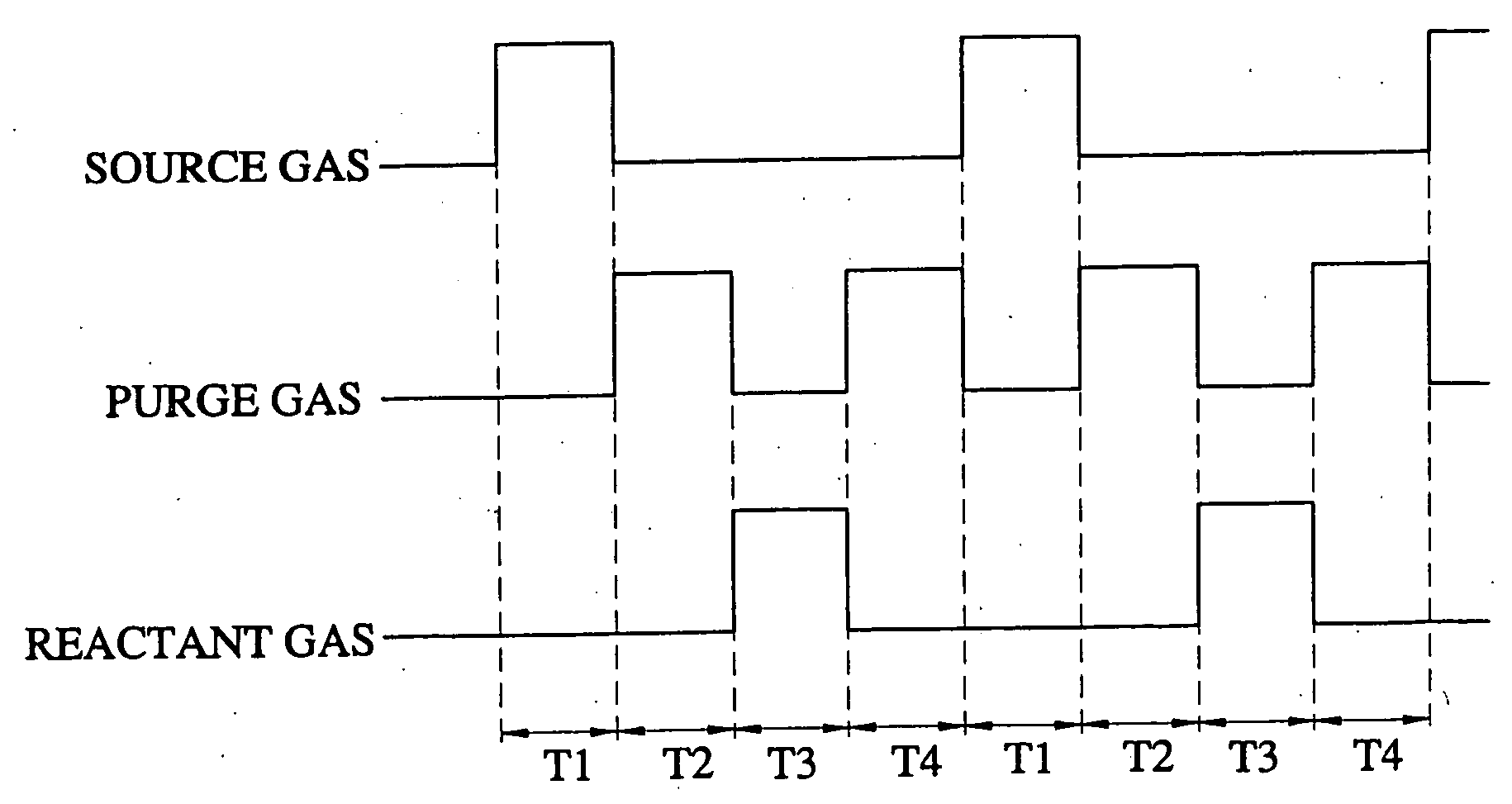
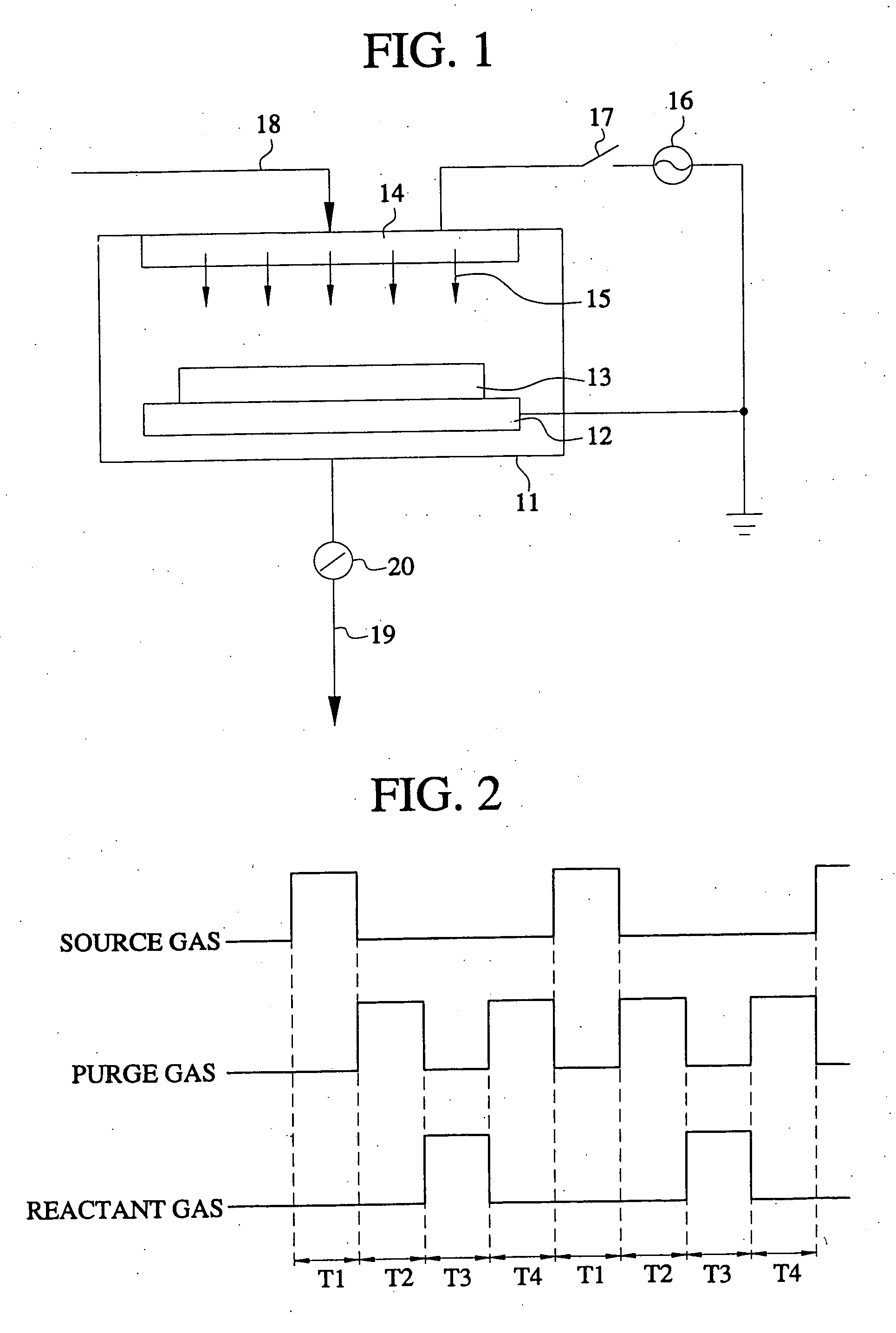
Method of forming a carbon nano-material layer using a cyclic deposition technique
ActiveUS20050003089A1Well formedEasy to disassemblePolycrystalline material growthChemical vapor deposition coatingChemisorptionCarbon nanomaterials
A method of forming a carbon nano-material layer may involve a cyclic deposition technique. In the method, a chemisorption layer or a chemical vapor deposition layer may be formed on a substrate. Impurities may be removed from the chemisorption layer or the chemical vapor deposition layer to form a carbon atoms layer on the substrate. More than one carbon atoms layer may be formed by repeating the method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for producing aromatic amino compound
InactiveUS7250532B2High yieldEasy to eliminateOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationArylCompound a
A method for producing aromatic amino compound (V):by synthesizing intermediate compound (IV):by the reaction of compound (I): H2N—R1 with a mixture of halogenated aryl compounds (II): Ar1—X and (III): Ar2—X in the presence of a noble metal catalyst, followed by eliminating the substituent R1 from the nitrogen atom in compound (IV) under an acidic condition or an alkaline condition or by addition of a reducing agent or an oxidizing agent. (R1: a substituent having 2 to 50 carbon atoms; Ar1 and Ar2: a substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbon group or heterocyclic group having 6 to 50 carbon atoms and the same with or different from each other; and X: a halogen group). The aromatic amino compound useful as the charge transporting material can be produced efficiently at a great yield without using highly toxic raw materials.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Low-temperature hydrocarbon production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrocarbons from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as glycerol, glucose, or sorbitol. The method can take place in the vapor phase or in the condensed liquid phase (preferably in the condensed liquid phase). The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon having at least two carbon atoms, in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. These metals are supported on supports that exhibit acidity or the reaction is conducted under liquid-phase conditions at acidic pHs. The disclosed method allows the production of hydrocarbon by the liquid-phase reaction of water with biomass-derived oxygenated compounds.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Photoresists, polymers and processes for microlithography
InactiveUS6849377B2Improve balanceHigh transparencyOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsResistChemical compound
Photoresists and associated processes for microlithography in the extreme, far, and near UV are disclosed. The photoresists in some embodiments comprise (a) a fluorine-containing copolymer derived from at least one polycyclic ethylenically unsaturated compound and at least one compound having at least one fluorine atom covalently attached to an ethylenically unsaturated carbon atom; and (b) at least one photoactive component. In other embodiments, the photoresists comprise a fluorine-containing copolymer derived from at least one polycyclic ethylenically unsaturated compound having at least one atom or group covalently attached to a carbon atom contained within a ring structure and separated from each ethylenically unsaturated carbon atom of the ethylenically unsaturated compound by at least one covalently attached carbon atom, wherein the atom or group is selected from the group consisting of fluorine perfluoroalkyl and perfluoroalkoxy.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Positive type resist composition for use in liquid immersion exposure and a method of forming the pattern using the same
ActiveUS20060008736A1Inhibition formationLess leachingOrganic chemistryRadiation applicationsActinic RaysPositive type
A positive type resist composition for use in liquid immersion exposure comprises: (A) a resin having a monocyclic or polycyclic cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon structure, the resin increasing its solubility in an alkali developer by an action of acid; (B) a compound generating acid upon irradiation with one of an actinic ray and a radiation; (C) an alkali soluble compound having an alkyl group of 5 or more carbon atoms; and (D) a solvent.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Liquid crystal composition comprising liquid crystal molecules and alignment promoter
InactiveUS20020039627A1Easy alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsSingle bondCarbon atom
A liquid crystal composition comprises liquid crystal molecules and an alignment promoter. The alignment promoter is represented by the formula (I). <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>(Hb-L1-)nBl (I) < / in-line-formula>In the formula (I), Hb is an aliphatic group having 4 to 40 carbon atoms, an aromatic group having 6 to 40 carbon atoms or an aliphatic substituted oligosiloxanoxy group having 1 to 40 carbon atoms. L1 is a single bond or a divalent linking group, and n is an integer of 2 to 12. Bl is an n-valent group comprising at least two rings.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Functionalized high cis-1,4-polybutadiene prepared using novel functionalizing agents
InactiveUS20060004131A1High ci microstructureLower glass transition temperatureInksActive polymerPolymer science
A functionalized polymer prepared by a process comprising the steps of preparing a pseudo-living polymer by polymerizing conjugated monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst, and reacting the pseudo-living polymer with a functionalizing agent defined by the formula (I) A-R1-Z (I) where R1 is a divalent bond or divalent organic group comprising from 0 to about 20 carbon atoms, A is a substituent that will undergo an addition reaction with a pseudo-living polymer, and Z is a substituent that will react or interact with silica or carbon black reinforcing fillers, with the proviso that A, R1, and Z are substituents that will not protonate a pseudo-living polymer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Thermoplastic Elastomer Composition, Method for Producing Same and Formed Article
The invention provides a thermoplastic elastomer composition having mechanical properties equivalent or superior to those of conventional thermoplastic elastomer compositions and having excellent heat resistance and oil resistance and a preparation process thereof, and molded or formed products making use of this thermoplastic elastomer composition. The thermoplastic elastomer composition according to the present invention contains a thermoplastic resin having a polar group and an ethylene•α-olefin elastomer having a functional group. The ethylene•α-olefin elastomer having the functional group is preferably a random copolymer obtained by copolymerizing ethylene, an α-olefin having 3 to 10 carbon atoms, an unsaturated monomer having the functional group and an optional non-conjugated diene.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com