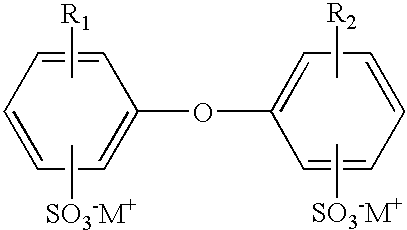
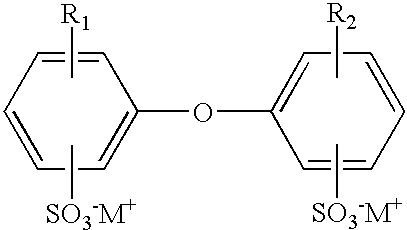
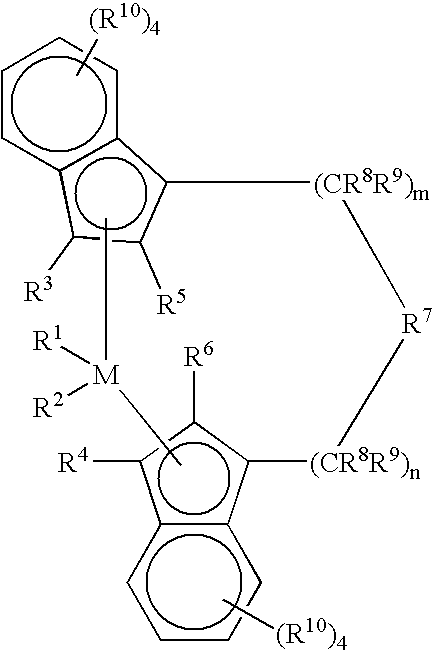
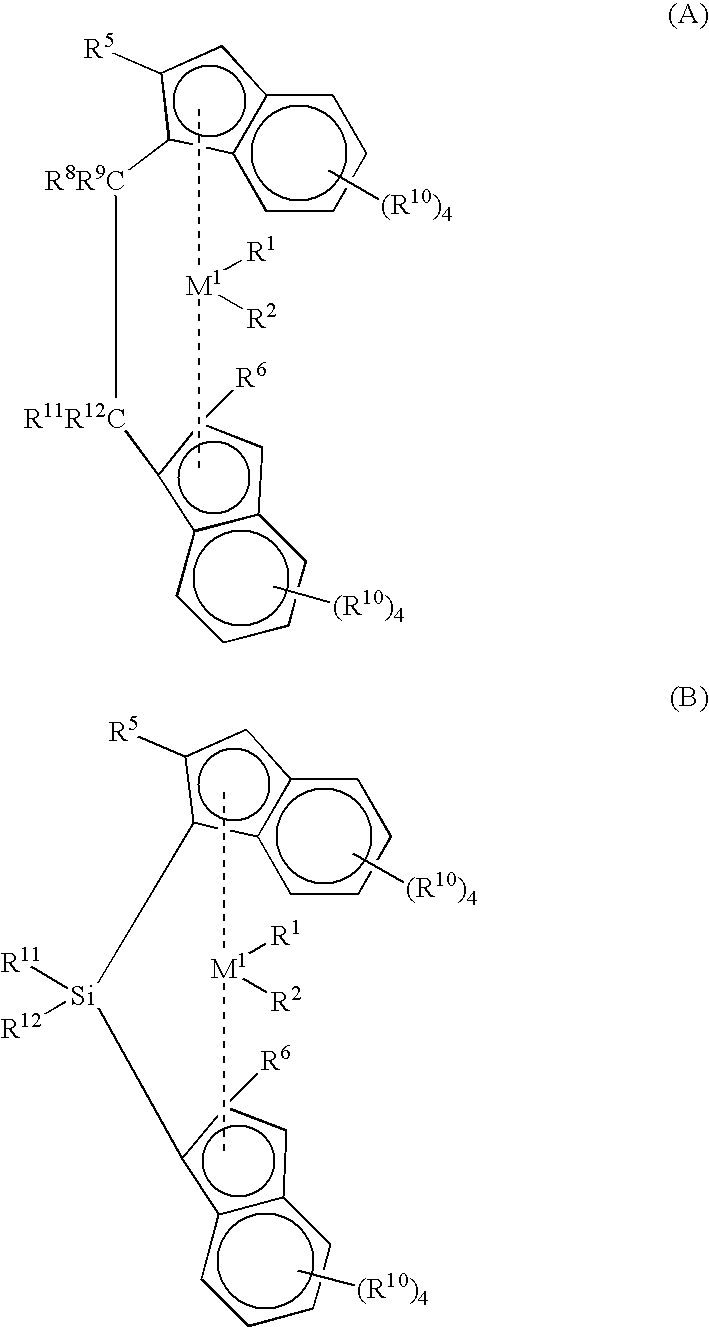
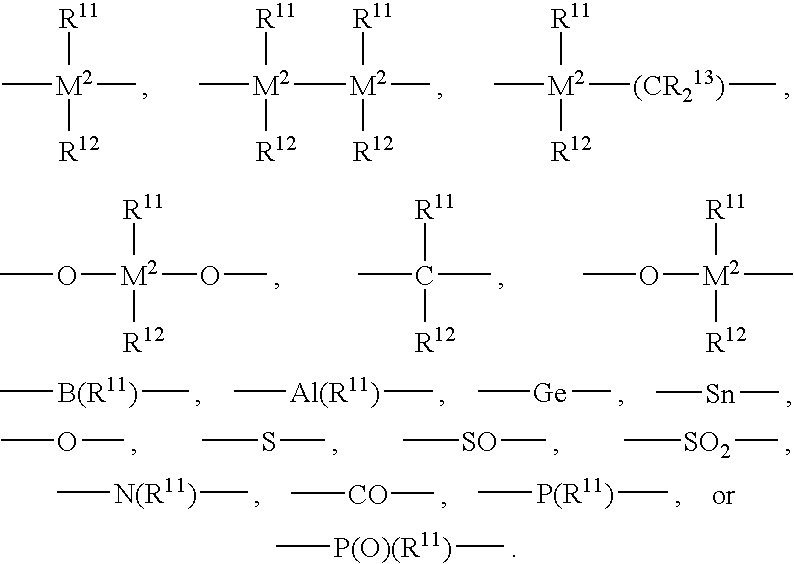Patents
Literature
4467 results about "Emulsion polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Emulsion polymerization is a type of radical polymerization that usually starts with an emulsion incorporating water, monomer, and surfactant. The most common type of emulsion polymerization is an oil-in-water emulsion, in which droplets of monomer (the oil) are emulsified (with surfactants) in a continuous phase of water. Water-soluble polymers, such as certain polyvinyl alcohols or hydroxyethyl celluloses, can also be used to act as emulsifiers/stabilizers. The name "emulsion polymerization" is a misnomer that arises from a historical misconception. Rather than occurring in emulsion droplets, polymerization takes place in the latex/colloid particles that form spontaneously in the first few minutes of the process. These latex particles are typically 100 nm in size, and are made of many individual polymer chains. The particles are prevented from coagulating with each other because each particle is surrounded by the surfactant ('soap'); the charge on the surfactant repels other particles electrostatically. When water-soluble polymers are used as stabilizers instead of soap, the repulsion between particles arises because these water-soluble polymers form a 'hairy layer' around a particle that repels other particles, because pushing particles together would involve compressing these chains.
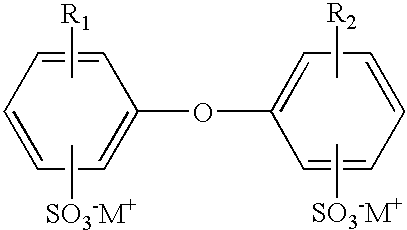
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a perfluoropolyether surfactant
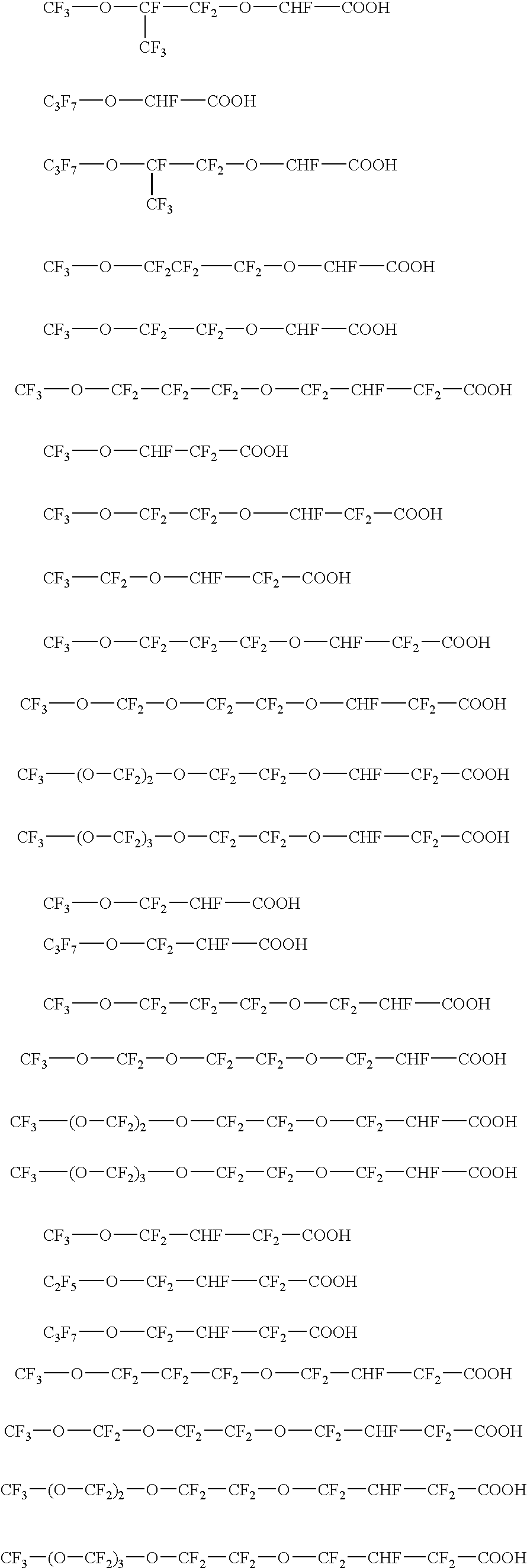
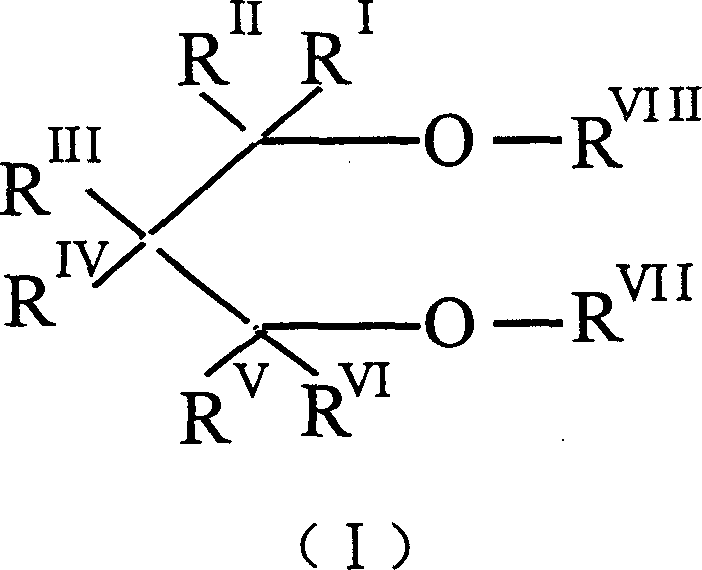
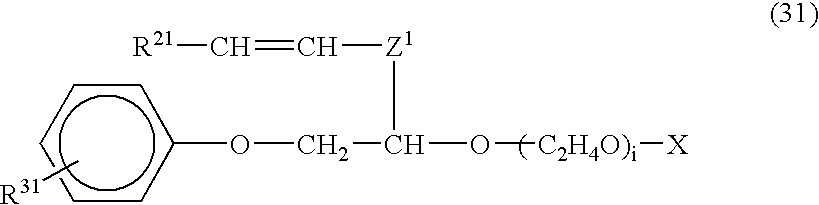
The invention relates to an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using perfluoropolyethers of the following formula (I) or (II). In particular, the perfluoropolyether surfactants correspond to formula (I) or (II) CF3—(OCF2)m—O—CF2—X (I) wherein m has a value of 1 to 6 and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof, CF3—O—(CF2)3—(OCF(CF3)—CF2)z—O-L-Y (II) wherein z has a value of 0, 1, 2 or 3, L represents a divalent linking group selected from —CF(CF3)—, —CF2— and —CF2CF2— and Y represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. The invention further relates to an aqueous dispersion of a fluoropolymer having the aforementioned perfluoropolyether surfactant(s).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Fluorinated surfactants for making fluoropolymers
ActiveUS20070142541A1Easy to preparePrepared cost-effectivelyLiquid surface applicatorsTransportation and packagingEmulsion polymerizationFluoropolymer
The invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula: [Rf—(O)t—CHF—(CF2)n—COO—]iXi+ (I) wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, t is 0 or 1 and n is 0 or 1, Xi+ represents a cation having a valence i and i is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant can be used in emulsion polymerization of fluoromonomers to prepare fluoropolymers.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a fluorinated surfactant
InactiveUS20070015866A1Low toxicityGood chemical stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsFibre treatmentEmulsion polymerizationEther
The present invention provides an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers including gaseous fluorinated monomers using a perfluoro ether surfactant as an emulsifier. The perfluoro ether surfactants correspond to formula (I) Rf—O—CF2CF2—X (I) wherein Rf represents a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1, 2, 3 or 4 carbon atoms and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. In a further aspect, the invention also provides an aqueous fluoropolymer dispersion comprising the perfluoro ether surfactant and the use of such dispersion in the coating or impregnation of substrates.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Fluorinated surfactants for use in making a fluoropolymer
InactiveUS20070117914A1Convenient and easy preparationPrepared cost-effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationEmulsion polymerizationCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula:[Rf—(O)t—CQH—CF2—O]n—R-G (I)wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, Q is CF3 or F, R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon group, G represents a carboxylic or sulphonic acid or salt thereof, t is 0 or 1 and n is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant is particularly useful in polymerizing fluorinated monomers in an aqueous emulsion polymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous dispersions containing multi-stage emulsion polymers
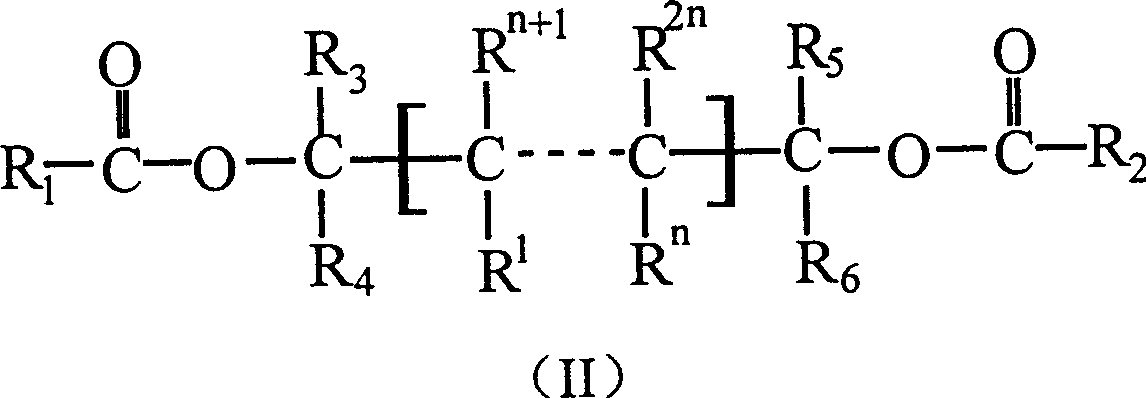
Aqueous dispersions are disclosed, having a minimum film formation temperature no greater than about 50° C., that include a multi-stage emulsion polymer made by a process that includes a first polymerization stage, in which a first monomer mixture having a calculated glass transition temperature of at least about 50° C. is polymerized via free radical emulsion polymerization to obtain a first-stage emulsion polymer, and a second polymerization stage, in which a second monomer mixture, having a calculated glass transition temperature from about −30° C. to about 10° C., is polymerized via free radical emulsion polymerization, in the presence of the first-stage emulsion polymer. The dispersions are useful in a variety of coating compositions that exhibit improved block resistance.
Owner:HEXION INC
Inkjet printing ink
ActiveUS20120306976A1Quality improvementLow viscosityMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsFiberEmulsion
An inkjet printing ink having properties of crosslinking and being fixed on a fiber by heating, characterized in that in an ink composition consisting of (A) a pigment dispersion having a mean particle diameter of 200 nm or less and a maximum particle diameter of 500 nm or less, consisting of a pigment, a water-soluble pigment dispersant and a hydrophilic solvent, (B) a water-soluble fixing agent, and (C) a crosslinking agent, the water-soluble pigment dispersant in (A) is a specific emulsion polymer neutralized by a basic substance; the water-soluble fixing agent (B) is the one having a crosslinking functional group; and the crosslinking agent (C) is the one having a functional group that crosslinks the crosslinking functional group of the water-soluble pigment dispersant in (A) with the crosslinking functional group of the water-soluble fixing agent (B) at a temperature of 100° C. or more.
Owner:MATSUI SHIKISO KAGAKU INDSHO
Method for making polysiloxane emulsions
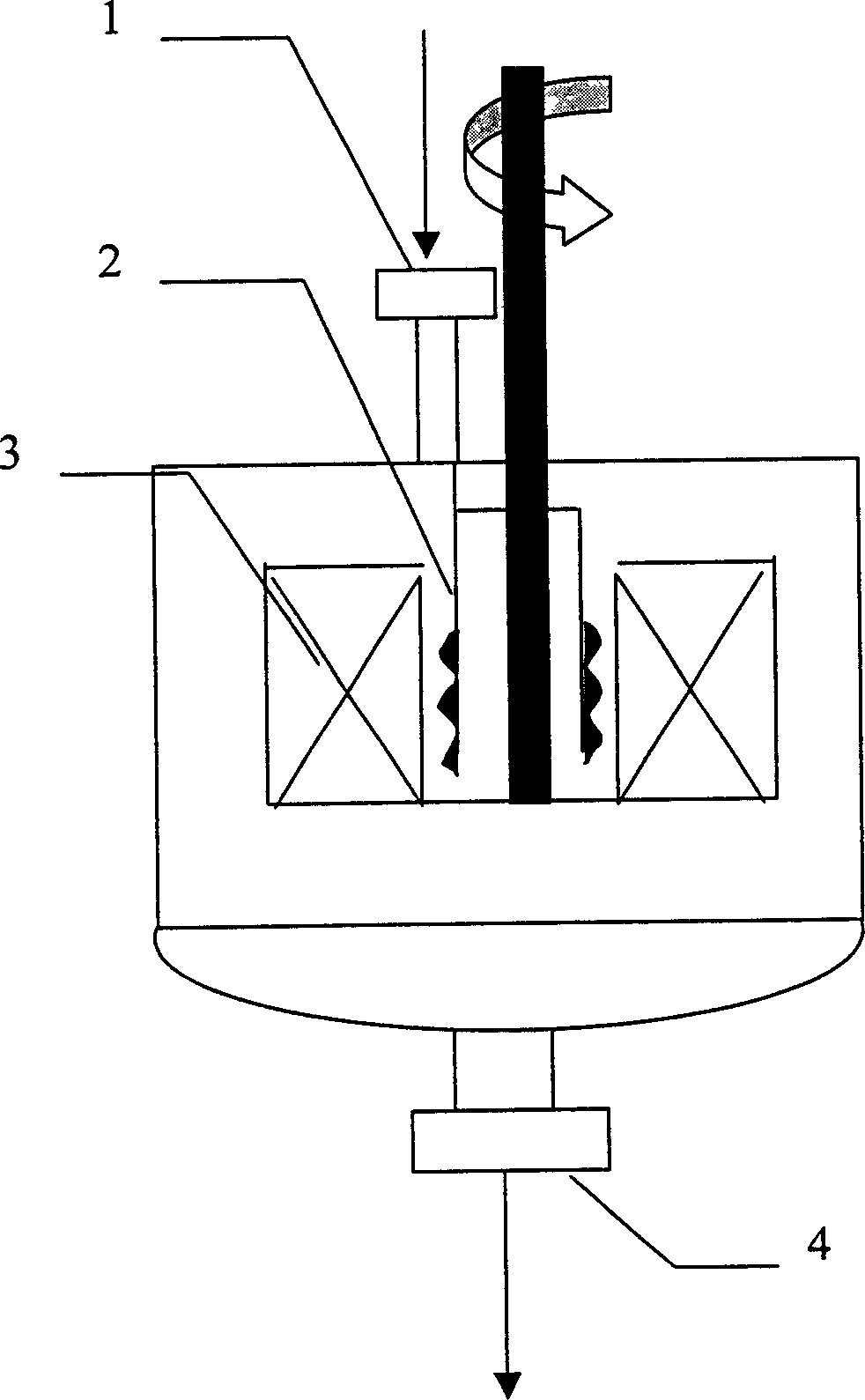
A method for making oil free polysiloxane standard, fine and microemulsions using emulsion polymerization is disclosed. The method comprises reacting a cyclicsiloxane in the presence of a catalyst, ionic surfactant and nonionic surfactant within a certain operating window. Emulsions containing silicone copolymers can also be produced using the method of the instant invention.
Owner:DOW SILICONES CORP
Profile control oil-displacement agent for core-shell type inorganic/organic polymer composite microballoon
InactiveCN102485830AGood expansion performanceGood temperature and salt resistanceDrilling compositionCross-linkMicrosphere
The invention discloses a profile control oil-displacement agent for a core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon. A preparation method of the core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon comprises the following steps of carrying out surface modification of inorganic cores of inorganic nano-particles such as silica particles and magnetic particles, and carrying out graft polymerisation by a dispersion polymerization method or an inverse emulsion polymerization method to form polymer shells (such as polyacrylamide cross-linked copolymers) on the surfaces of the inorganic cores. The inorganic components and the organic components bind by chemical bonds so that the core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon has very stale structure. The core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon retains the advantages of polymer microballoons and inorganic particles, and has strong heat-resistant and mineralization-resistant capabilities, high plugging strength and good dilatancy. The core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon can move in rock pores and can plug the rock pores. When a plugging pressure difference is improved to a certain degree, elastic deformation of the core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon can be produced and the deformed core-shell type inorganic / organic polymer composite microballoon sequentially moves to a deep rock stratum part so that a liquid flow direction is changed gradually and a crude oil yield is improved. The profile control oil-displacement agent provided by the invention has a large potential.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Globular catalyst component used for olefine polymerization and its catalyst
ActiveCN1718595AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsAlcoholEmulsion polymerization
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Process for preparing microencapsulated pigment, microencapsulated pigment, aqueous dispersion, and ink for ink jet recording
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a microencapsulated pigment, which comprises adding a polymerizable surfactant having a hydrophilic group, a hydrophobic group and a polymerizable group, a polymerization initiator and an aqueous medium to a wet pigment, and conducting emulsion polymerization to encapsulate pigment particles with a polymer. Also disclosed are a microencapsulated pigment obtained by using this preparation process and an ink for ink jet recording containing at least the microencapsulated pigment and water.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Hydrophilic polymeric material and method of preparation
InactiveUS6218440B1Allows preparationStable maintenanceOther chemical processesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The present invention relates to a porous crosslinked hydrophilic polymeric material having cavities joined by interconnecting pores wherein at least some of the cavities at the interior of the material communicate with the surface of the material. The present invention also relates to a process for producing the polymeric material. This process involves combining a hydrophilic monomer phase with an oil discontinuous phase to form an emulsion, and polymerizing the emulsion. The emulsion can be a high internal phase emulsion (i.e., a "HIPE"). The polymeric material can be produced in a variety of forms. In one embodiment the emulsion is suspended in an oil suspension medium, and emulsion droplets are polymerized to produce polymeric microbeads.
Owner:SUNSTORM RES CORP
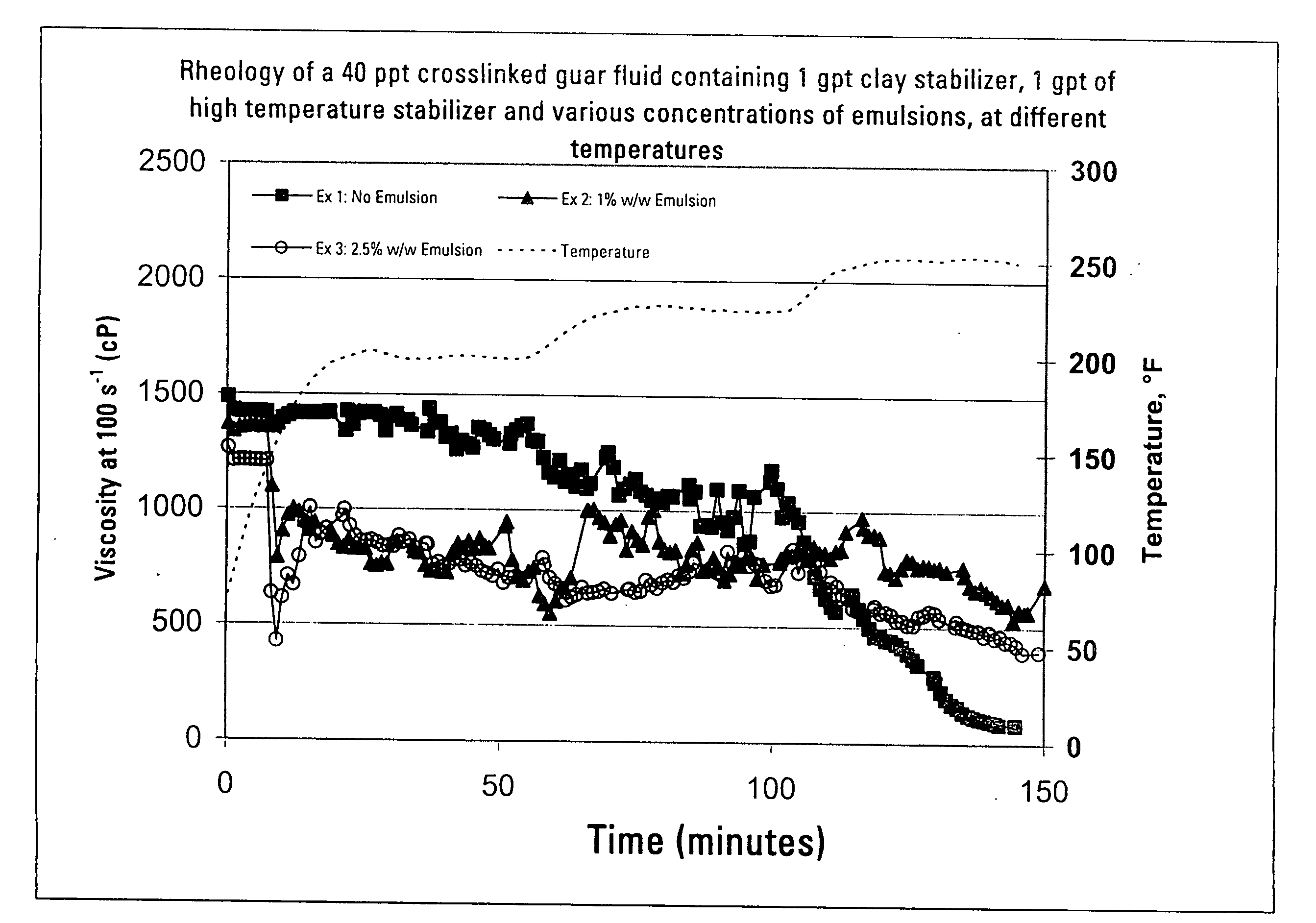
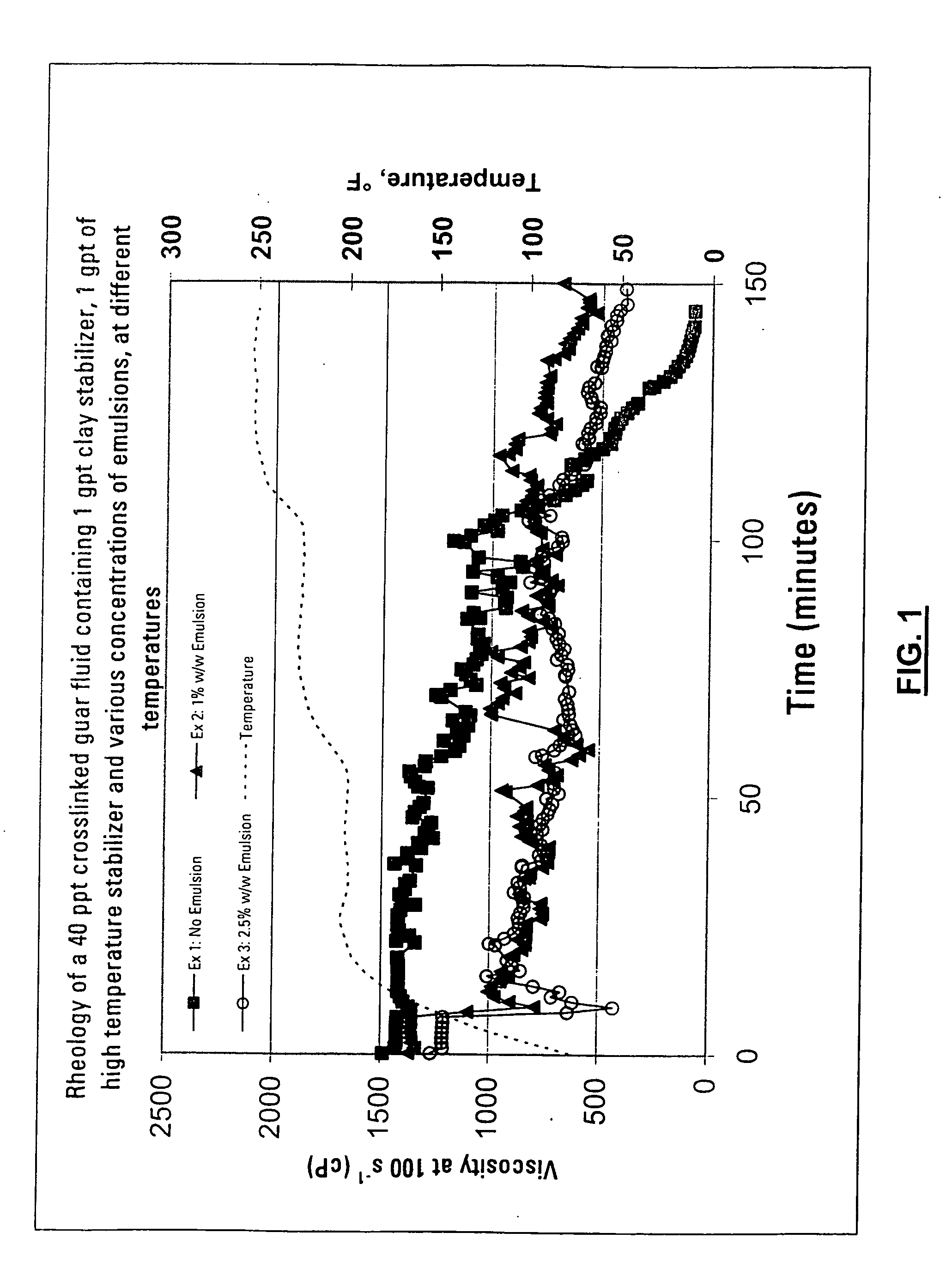
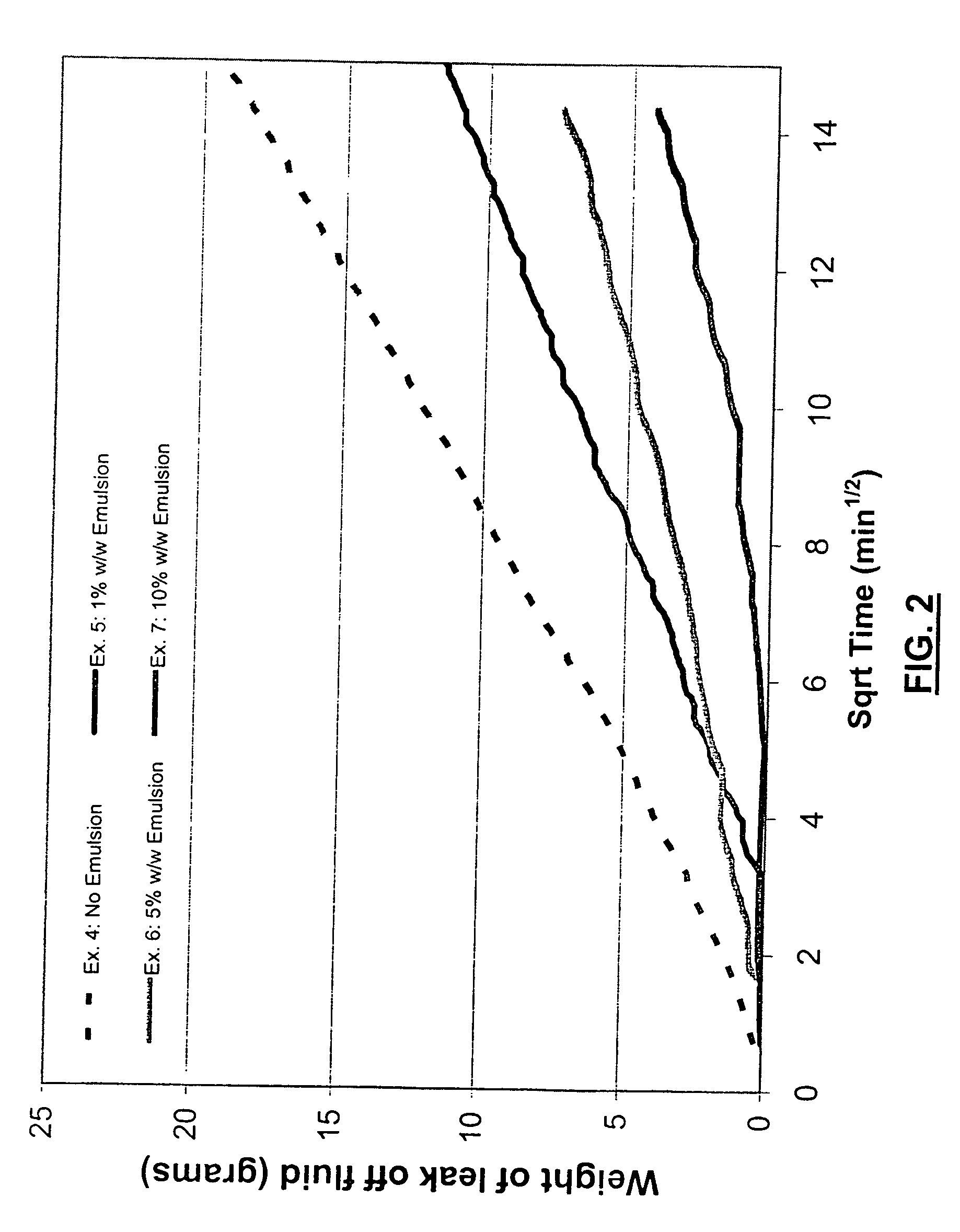
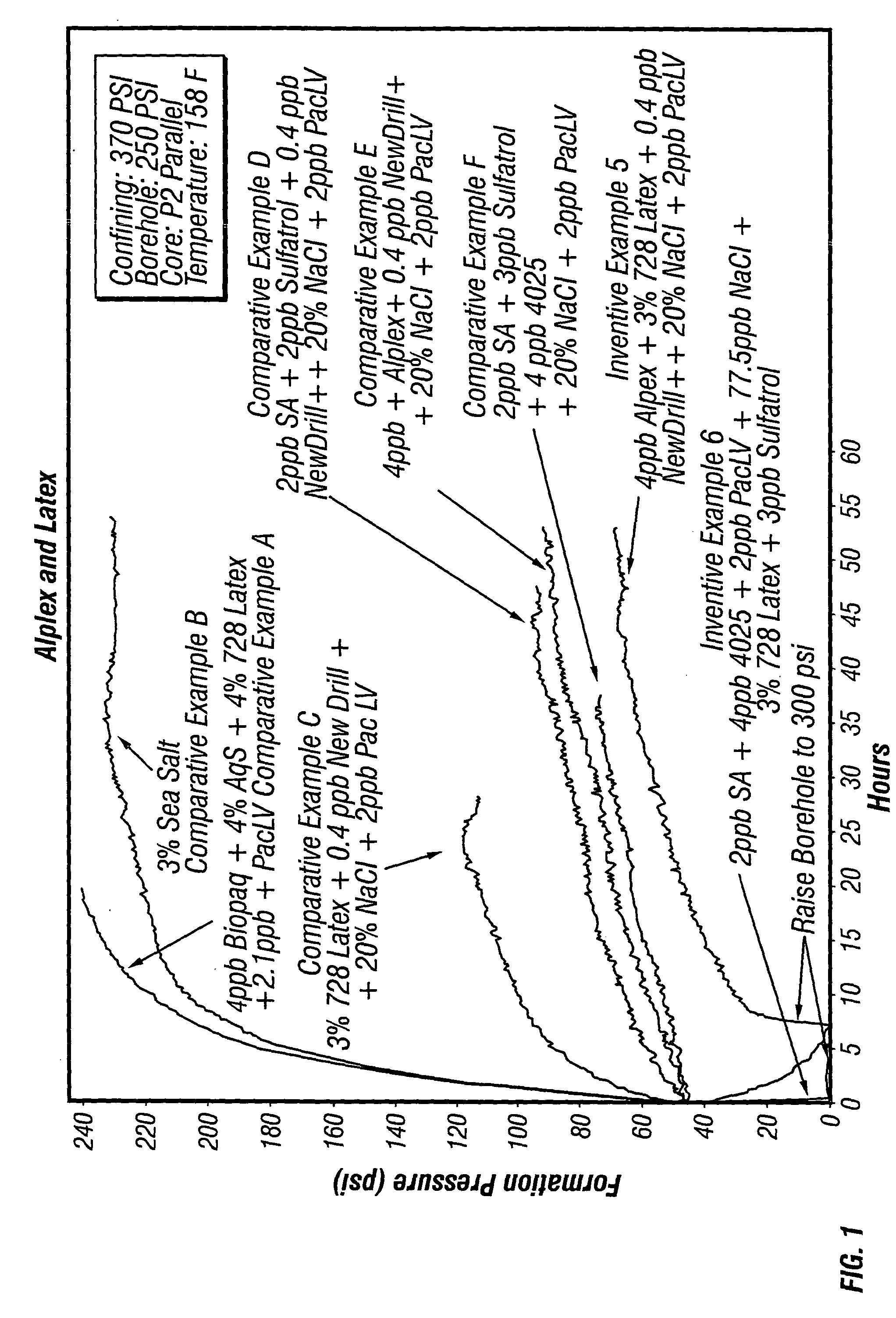
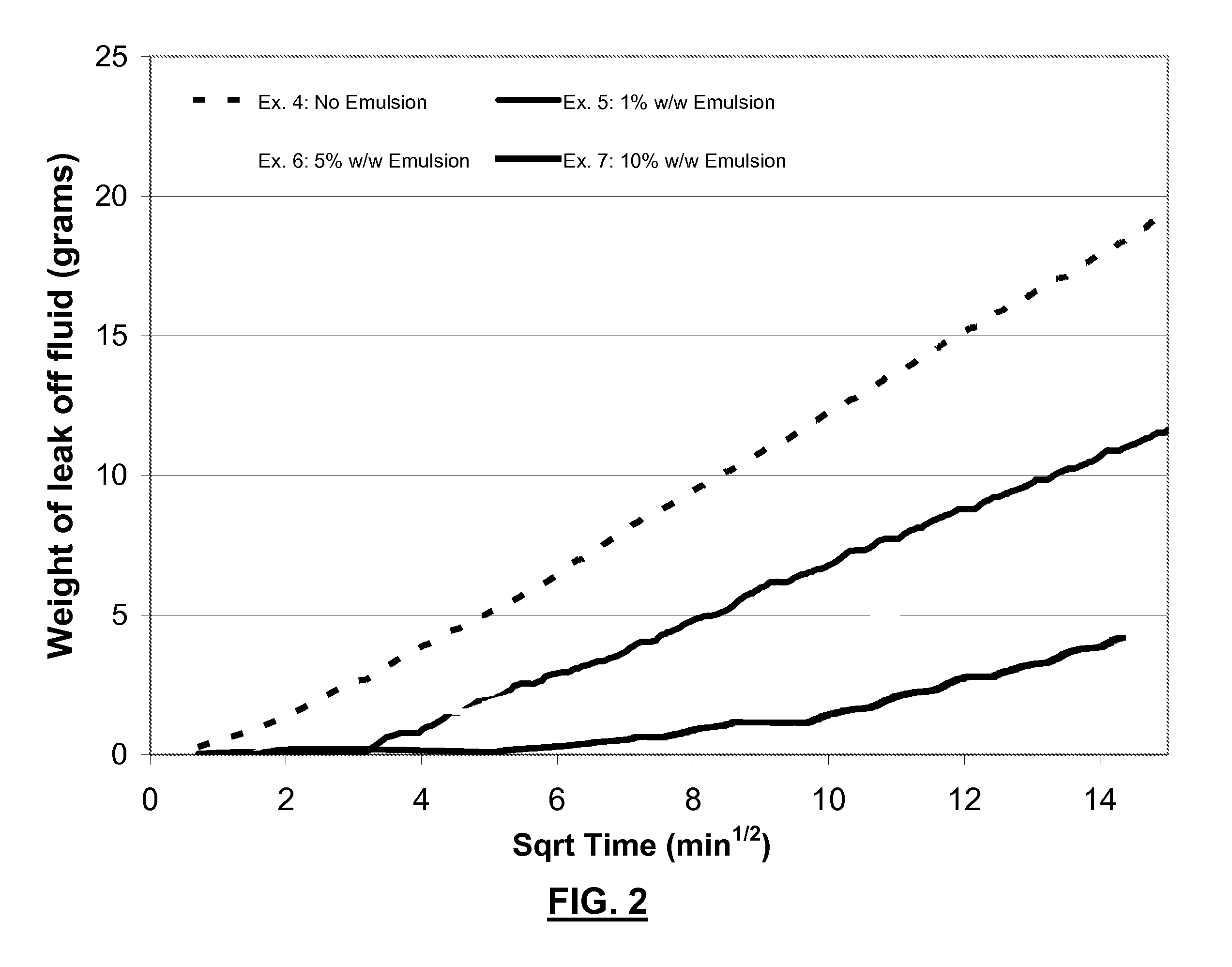
Methods of Limiting Leak Off and Damage In Hydraulic Fractures
InactiveUS20080289828A1Improve cleanupEnhanced hydrocarbon productionFluid removalDrilling compositionMatrix damageEmulsion
Methods for treating a formation penetrated by a wellbore which improves fluid loss control during treatment. In some aspects, the treatments include preparing an aqueous fluid including one or more water inert degradable polymers and an optional viscosifier, injecting the aqueous fluid into the wellbore at a pressure equal to or greater than the formation's fracture initiation pressure, and thereafter injecting into the wellbore a proppant laden fluid at a pressure equal to or greater than the formation's fracture initiation pressure. The water inert degradable polymer may be a polymer such as an emulsion polymer or a latex polymer. Some methods of the invention use a fluid which may have a normalized leak off coefficient (Cw / sqrt(K)) equal to or less than about 0.0022, 0.0014, or 0.0010. A conventional fluid loss additive may or may not be used in conjunction with the treatment fluid and / or the proppant laden fluid. The water inert degradable polymer may or may not substantially enter formation pores. In another aspect, methods for reducing matrix damage to a formation during a treatment operation include preparing an aqueous treatment fluid formed of at least one water inert degradable polymer, and injecting the fluid at a pressure equal or greater than the formation's fracture initiation pressure.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Latex processes
InactiveUS6503680B1Improve performanceImprove featuresDevelopersEmulsion paintsGlass transitionPolymer chemistry
A process for the preparation of a latex polymer consistent with E / A (emulsion / aggregation / coalescence) toner manufacture. The process utilizes a standard (universal) latex composition and involves chain-transfer agent partitioning, emulsion polymerization that provides a latex polymer with a wide range of molecular properties. In particular, the process customizes a wide range Mw (weight average molecular weight) latex, without substantially varying the Mn (number average molecular weight) and hence, without substantially varying Tg (glass transition temperature) such that good toner performance is maintained. In a preferred process, a latex polymer is prepared by mixing a seed particle latex, generated by aqueous emulsion polymerization of a first portion of a monomer emulsion, with a second portion of the monomer emulsion and at least one chain-transfer agent. The mixing is done in the presence of a free-radical initiator and heated, and wherein the monomer emulsion comprises a mixture of polymerization reagents of at least one monomer, at least one chain-transfer agent, at least one surfactant, and water. This process may be applied to core-shell polymerization as well. These latex polymers are ideally suited in the manufacture of toner and developer for electrophotographic imaging and printing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Multi-staged binder for use in elastomeric coatings, caulks and sealants
InactiveUS6060532ALower Level RequirementsLow temperature flexibilityImpression capsOther chemical processesElastomerEmulsion
A method for using a thermoplastic elastomeric composition which contains a multi-staged emulsion polymer binder is provided. An elastomeric composition which contains a multi-staged emulsion polymer binder and a photosensitive composition and a method for using the elastomeric composition in elastomeric coatings, caulks, or sealants is also provided.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Preparation of high closeness polyacrylacid ester dispersion
The invention relates to a high-sealing polyacrylic ester dispersoid and a preparation method thereof; a multi-element emulsifier system which consists of an anionic emulsifier and a compound non-ionic emulsifier is adopted for controlling the charging process and components of the emulsifier in different polymerization periods, and the room-temperature self-crosslinking high-sealing polyacrylic ester dispersoid is prepared by a semi-continuous seeding emulsion polymerization process. The dispersoid has small particle size, good electrolyte-resistance (calcium ion) stability and high tolerance to various film forming accessory ingredients (various organic solvents with high boiling point). The dispersoid is used as seal coat of water-based wood coating and has good sealing performance to various woods; harmful volatile organic compounds (VOC) such as formaldehyde, and the like sealed against escaping from plates to pollute indoor environment, and the colored compounds such as turpentine, pine oil and tannin and the like are sealed against dissolving out of the plates to pollute pure top coating and white top coating of a water-based wooden ware; and in addition, the dispersoid can be used in water-based leather finishing agents.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Atom or group transfer radical polymerization
A polymerization process comprising initiating a first polymerization of monomers using an initiator functionalized with an ATRP initiating site, wherein the first polymerization is selected from the group of cationic polymerization, anionic polymerization, conventional free radical polymerization, metathesis, ring opening polymerization, cationic ring opening polymerization, and coordination polymerization to form a macroinitiator comprising an ATRP initiating site and further initiating an ATRP polymerization of radically polymerizable monomers using the macroinitiator comprising an ATRP initiating site. Novel block copolymers may be formed by the disclosed method.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Method for preparing hollow microsphere with hydrogel microsphere as stencil
InactiveCN101121112ASafe preparationSimple and fast operationMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationStrong acidsSilicon dioxide
The present invention discloses a hollow microsphere preparation method, which uses a hydrogel microsphere as a template. The preparation method is that an emulsion or inverse emulsion polymeric method is adopted to synthesize the hydrogel microsphere with electric charge. A surfactant with inverse electric charge and hydrophobic monomer are added into the hydrogel microsphere suspension, and the hydrogel microsphere is coated by a polymer crust layer of the hydrophobic monomer by a seed emulsion polymerization method to form a core-shell microsphere with an inner layer of hydrogel and an outer layer of polymer; a hydrolyzation of a silicon dioxide or titanium dioxide precursor is used to form the core-shell microsphere with the outer layer of inorganic matter and the inner layer of hydrogel. The core-shell microsphere is dried to obtain the hollow microsphere. The method of the present invention does not need removing the template by organic impregnant dissolving, strong acid or strong alkali etching or high temperature calcining; the preparation process is safe and the operation is simple; and the hollow microsphere with different chemical components can be obtained by changing core or shell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
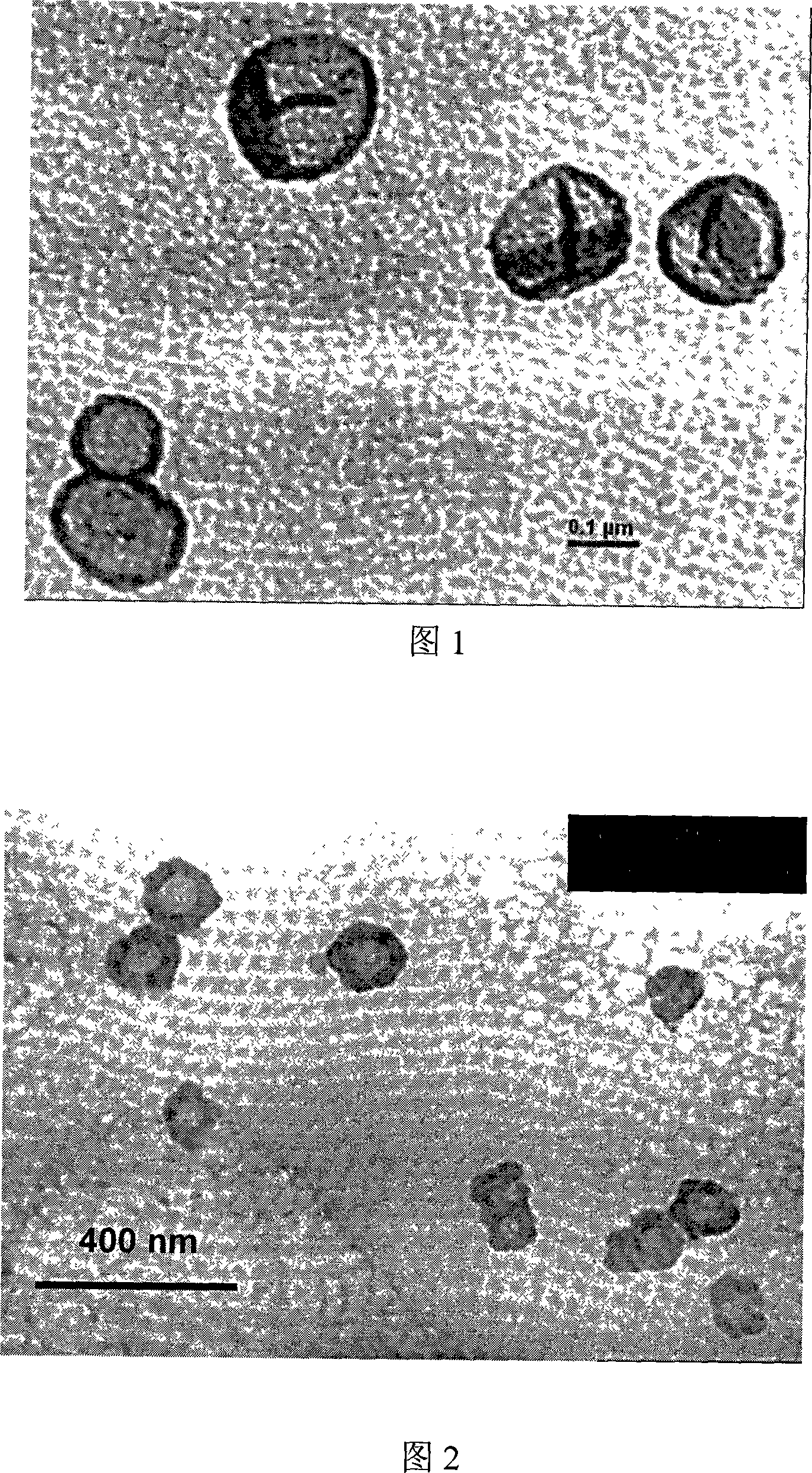
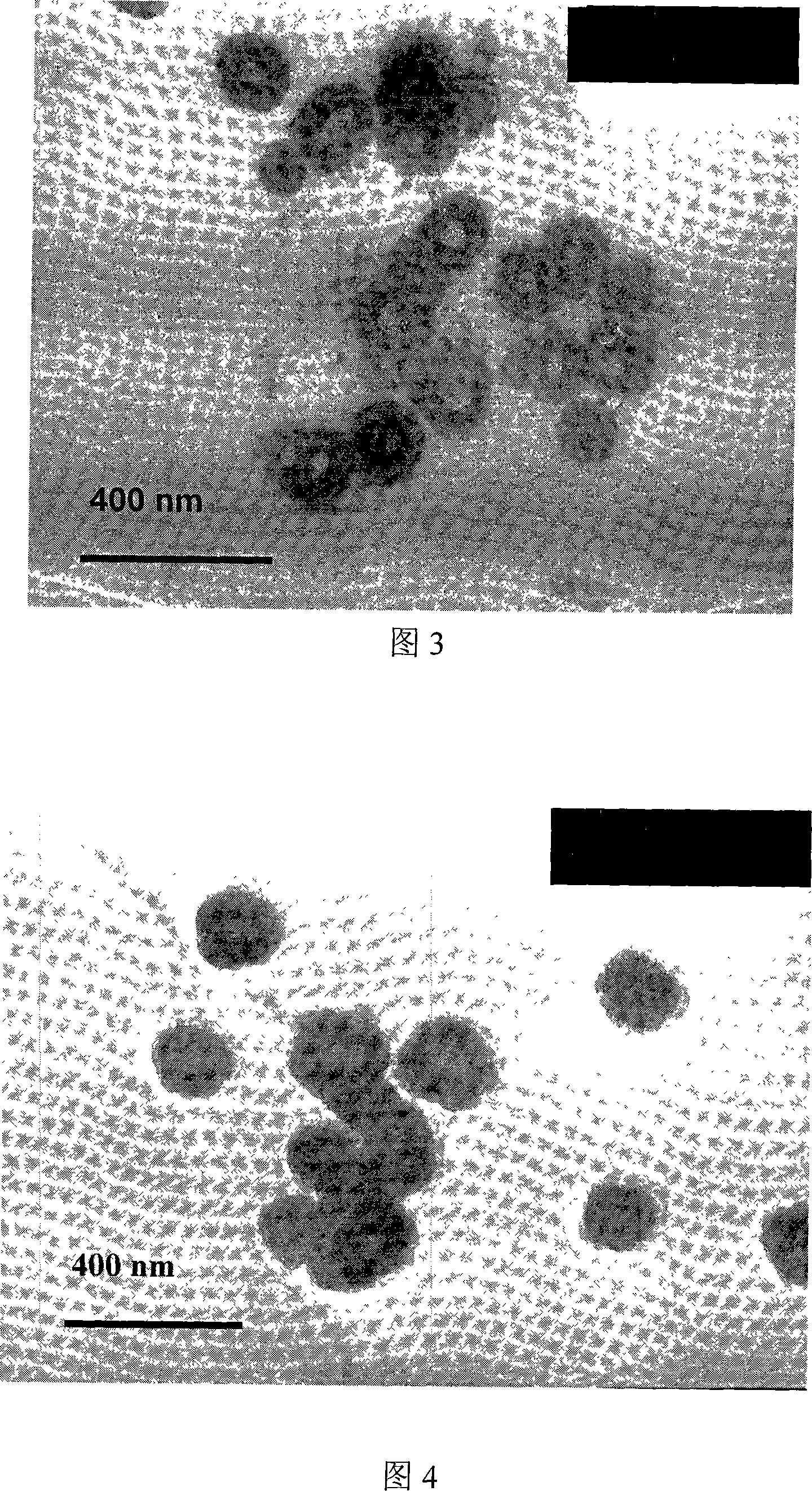
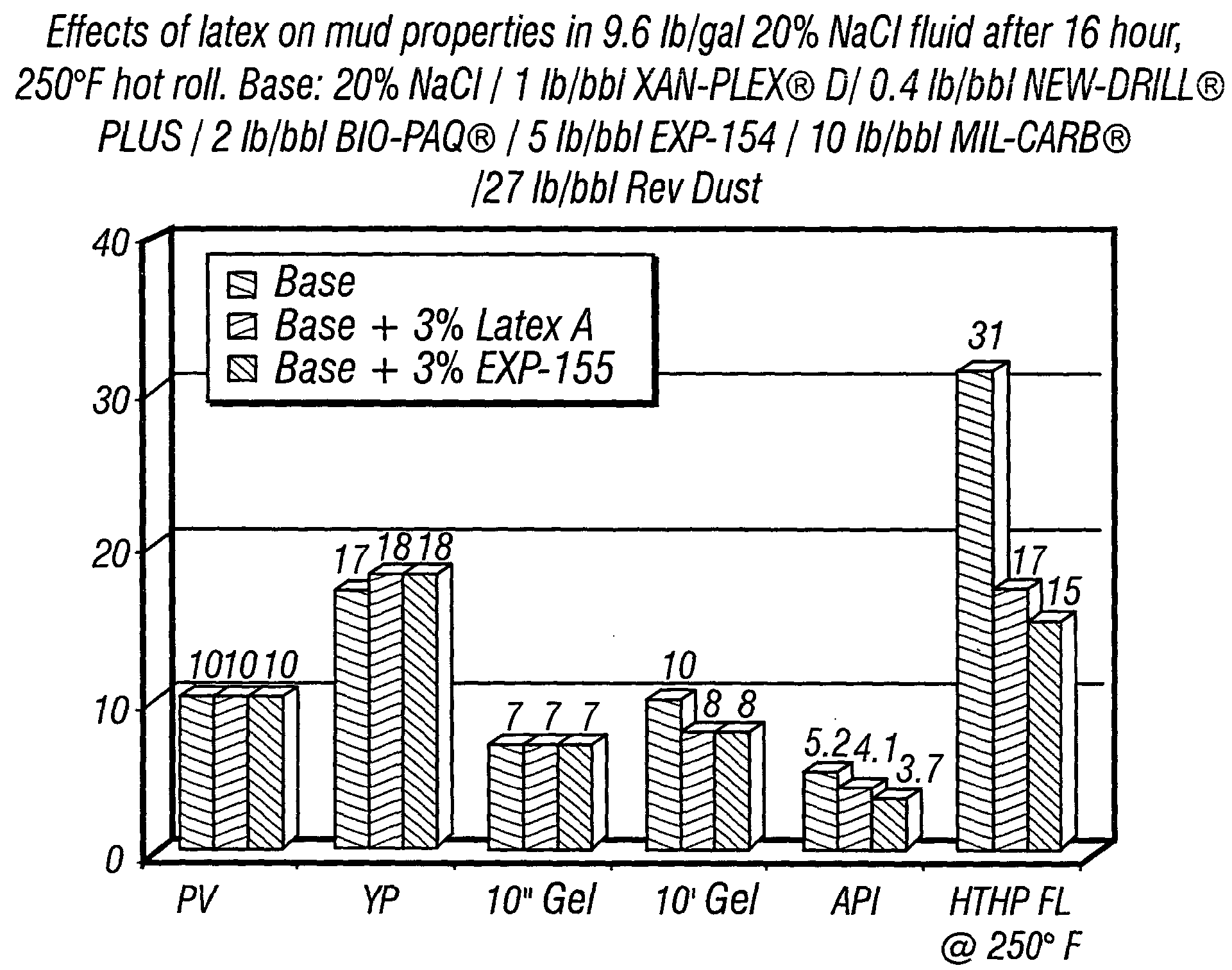
Fluid loss control and sealing agent for drilling depleted sand formations
InactiveUS7271131B2Reduce probabilityIncrease pressure blockage reliabilityFlushingDrilling compositionEmulsion polymerizationSealant
An oil-based drilling fluid having a polymer latex capable of providing a deformable latex film on at least a portion of a subterranean sand formation has been discovered to inhibit or control fluid loss and act as a sealing agent when used to drill in sand formations for hydrocarbon recovery operations. Typically, the polymer latex is an aqueous suspension of particles formed by emulsion polymerization that is in turn emulsified into a hydrocarbon base fluid. The polymer particles of suitable size precipitate onto the pores of a subterranean sand formation to at least partial seal the formation with a deformable polymer film.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Environmentally-friendly acrylic ester coating printing adhesive emulsion and preparation method
InactiveCN101928367AThe polymerization process is stableEvenly distributedEster polymer adhesivesDyeing processEpoxyFunctional monomer
The invention discloses environmentally-friendly acrylic ester coating printing adhesive emulsion and a preparation method. An emulsion polymerization process is adopted. The emulsion comprises the following raw materials in part by weight: 50 to 90 parts of soft monomer, 10 to 20 parts of hard monomer, 2 to 10 parts of functional monomer, 2 to 5 parts of emulsifying agent, 0.2 to 0.5 part of initiator, 0.2 to 0.5 part of pH buffer, 80 to 120 parts of deionized water and a proper amount of pH adjustor, wherein the total amount of the soft monomer, the hard monomer and the functional monomer is 100 parts by weight. The three monomers are cooperatively used as functional monomers for generating carboxyl crosslinking, hydroxy crosslinking, epoxy crosslinking and the like so that the obtained printing adhesive emulsion has excellent water tolerance and mechanical property. The crosslinking monomers and the emulsifying agent do not contain the components such as N-methylol acrylamide, APEO and the like, so the emulsion does not release formaldehyde during baking and using and is suitable for high-grade environmentally-friendly printing adhesive.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Room temperature self-crosslinking acrylic ester emulsion
InactiveCN102585072AHigh glossImprove wear resistanceAqueous dispersionsCoatingsMethacrylateFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a room temperature self-crosslinking acrylic ester emulsion. The emulsion comprises deionized water, an initiator, an emulsifier, a vinyl aromatic compound, carboxyl-containing olefin monomers, alkyl acrylate unsaturated monomers of C4-C12, methacrylate unsaturated monomers of C4-C20 and functional monomers. The emulsion is prepared with an emulsion polymerization method by adding a pH regulator, a curing agent and a metallic cross linker. The emulsion has the advantages of high glossiness, good abrasive resistance, water resistance and alcohol resistance, has good dryness under high humidity, can be applied to different coating fields and is also suitable for floor wax formulas of polishing-free wax, spray cleaning, cleaning wax polish and the like. The emulsion can be applied to various rigid base materials such as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), boards and composite boards and has good balance between detergent resistance and removability.
Owner:NANJING REGAL POLYMER
Nano silicasol / acrylic ester composite emulsion and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a nanometer silica sol / acrylic ester composite latex and a preparation method thereof. The composite latex is formed by polymerizing acrylic ester monomers with nanometer silica sol and alkylol solvent; emulsion particles in the composite latex are in a nanometer nucleus-shell structure taking silicon dioxide granules as nucleus and acrylic ester multipolymer as shells; and the preparation method adopts a seed emulsion polymerization method or in situ polymerization method. The composite latex has higher tensile-strength and tearing strength and better performances of acid durability, weather resisting property, wearing resistance, ultraviolet aging resistance, anti-pollution resistance, and the like, can be applied to various aspects of inner and outer wall dope, ground and terrace dope, ground coating of specialty sports fields, and the like, is green and environment-friendly, and has wide market foreground.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUNRISE CHEMISTRY CO LTD
Methods of Limiting Leak Off and Damage in Hydraulic Fractures
Methods for treating a formation penetrated by a wellbore which improves fluid loss control during treatment. In some aspects, the treatments include preparing an aqueous fluid including one or more water inert polymers and an optional viscosifier, injecting the aqueous fluid into the wellbore at a pressure equal to or greater than the formation's fracture initiation pressure, and thereafter injecting into the wellbore a proppant laden fluid at a pressure equal to or greater than the formation's fracture initiation pressure. The water inert polymer may be a polymer such as an emulsion polymer or a latex polymer. Some methods of the invention use a fluid which may have a normalized leak off coefficient (Cw / sqrt(K)) equal to or less than about 0.0022, 0.0014, or 0.0010. A conventional fluid loss additive may or may not be used in conjunction with the treatment fluid and / or the proppant laden fluid. The water inert polymer may or may not substantially enter formation pores. In another aspect, methods for reducing matrix damage to a formation during a treatment operation include preparing an aqueous treatment fluid formed of at least one water inert polymer, and injecting the fluid at a pressure equal or greater than the formation's fracture initiation pressure.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Single-component low temperature self-crossing emulsion adhesive for paper and plastic compounds and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101928534ALess slagHigh affinityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEster polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
The invention discloses a single-component low temperature self-crossing emulsion adhesive for paper and plastic compounds and a preparing method thereof. The raw materials of the self-crossing emulsion adhesive comprise the following components in part by weight: 100-150 parts of de-ionized water, 0.8-3.0 parts of emulsifier, 20-40 parts of nuclear layer monomer, 30-50 parts of interlayer monomer, 20-40 parts of shell layer monomer, and 0.2-0.6 part of initiator. The invention uses a small amount of anionic emulsifier to prepare nuclear emulsion, uses polymerisable emulsifier to prepare interlayer and shell layer pre-emulsion, and adopts semi-continuous seeded low emulsion polymerization process to prepare emulsion particles that have a three-layer core-shell microstructure to obtain the exquisite and stable emulsion. The product has no organic solvent, and does not release methanal, contains no APEO and no phthalate; the film coating has high transparency, high water resistance and high heat and humidity resistance; and the emulsion adhesive is applied to plastic and paper compounds, has high adhesive strength, peel strength and permanent adhesion, is also compatible to oil and ink and has high oil / ink transferring rate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Paper surface sizing agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101148842AIncreased ring compressive strengthLose weightWater-repelling agents additionPaper/cardboardCross-linkEmulsion
The present invention relates to paper surface treating agent, and is especially one kind of paper surface sizing agent and its preparation process. The paper surface sizing agent is prepared with cationic monomer, cross-linking monomer, (methyl) acrylate monomer and (methyl) styrene, and through free radical emulsion polymerization in mixture emulsion comprising dispersant, emulsifier and initiator. It has high performance and environment friendship. It is applied in sizing paper surface together with starch to raise the compression strength of paper, raise Cobb value and improve other performance of paper.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGSHENG NEW MATERIALS
Process for preparing lattices stabilized by polyvinyl alcohol
ActiveUS20070112117A1Efficient removalSuitably producedNon-fibrous pulp additionColloidal chemistry detailsPolymer sciencePolyvinyl alcohol
A process for preparing polymer dispersions stabilized by polyvinyl alcohol includes a step of emulsion polymerization. The polymerization occurs such that at least 60% of the total conversion occurs at a temperature from 100° C. to 140° C.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Spherical encoded beads
InactiveUS20090032592A1Increase chanceHighly suitableSequential/parallel process reactionsPretreated surfacesEmulsion polymerizationCompound (substance)
The present application discloses a composition comprising a plurality of spherical beads, wherein a radiofrequency chip operating at a frequency of in the range of 2.2-2.7 GHz is embedded within each of said beads and wherein essentially each of said beads is individually identifiable on the basis of radiofrequency identification. Alternatives utilizing a ultrasonic identification chip are also disclosed. The beads are preferably made of polymeric material and can for example be used for the synthesis of e.g. solid-phase chemical libraries. Preferred materials include some that minimise interference in biochemical assays (fouling). The invention also relates to batch and continuous methods of producing such compositions, including emulsion-polymerisation methods. In a further aspect, the present invention relates to an apparatus for analysing radiofrequency-encoded beads. Also provided are methods for detecting and / or analysing and / or sorting beads, as well as methods for processing beads once they have been analysed and / or sorted.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Polymerization process with mixed catalyst compositions
InactiveUS7192902B2Selectively activateEffectively tailor-makeOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationEmulsion polymerizationOlefin polymerization
The application describes a mixed olefin polymerization catalyst composition comprising a support, a reaction product of at least one first organometallic compound and a first activator capable of rendering the first organometallic compound active for insertion polymerization, and at least one second organometallic compound, the activator incapable of rendering the second organometallic compound active for polymerization of the monomers. The mixed catalyst composition can be used to prepare a first polymer component in a first polymerization reactor stage and then, when an effective activator is added for the second organometallic compound, the catalyst composition can be used to prepare a second polymer composition that is homogeneously blended with the first polymer component.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalyst used for olefine polymerization or copolymerization, its preparation method and application
A catalyst for the polymerization or copdymerization of olefin is composed of Ti-contained solid component A, organoaluminium compound B and organosilicon compound C. Said A is prepared through dissolving magnesium halide in the mixture of organic epoxy compound, organophosphorus compound and inertial diluent, adding educing agent and magnesium halide or its derivatives to educe out Mg / Ti contained deposit, and carrying a surface modifier, a titanium halide or derivative and an electronic doner. It can be used for the polymerization of propene or copolymerization of propene-ethene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Shale gas acid fracturing drag reducer and reparation method thereof
InactiveCN103694984AImprove acid resistanceImprove stabilityDrilling compositionEthylenediamineOil phase
The invention discloses a shale gas acid fracturing drag reducer and a reparation method of the shale gas acid fracturing drag reducer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing monomer acrylic acid and 2-acrylamide-2 methyl propane sulfonic acid, dissolving in water, subsequently adding acrylamide, and finally adding ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium to prepare into a water phase; mixing and dissolving a compounded surfactant with base oil to form an oil phase; performing inverse emulsion polymerization on the oil phase and the water phase to prepare the shale gas acid fracturing drag reducer. As a great amount of acid resistance monomers are introduced into the drag reducer, the acid resistance of the dreg reducer is greatly improved; the dreg reducer is milk white emulsion in appearance, is high in stability, non-ignitable, non-explosive, safe to transport and store, rapid to dissolve in water and free of fisheye; the requirements of continuous blending in shale gas acid fracturing can be met; the resistance reduction rate of a dreg reducer solution with the mass percentage of 0.2% can be greater than 70%.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Crosslinked polymer gels for filter cake formation
This invention relates to methods of preparing crosslinked polymer gels useful in subterranean well operations, to compositions comprising such polymers, and to the use of such compositions in treating subterranean formations. In certain exemplary embodiments, the crosslinked polymer gels are produced from emulsion polymerization reactions.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com