Patents
Literature
3851 results about "In situ polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In polymer chemistry, in situ polymerization is a preparation method that occurs "in the polymerization mixture" and is used to develop polymer nanocomposites from nanoparticles. There are numerous unstable oligomers (molecules) which must be synthesized in situ (i.e. in the reaction mixture but cannot be isolated on their own) for use in various processes. The in situ polymerization process consists of an initiation step followed by a series of polymerization steps, which results in the formation of a hybrid between polymer molecules and nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are initially spread out in a liquid monomer or a precursor of relatively low molecular weight. Upon the formation of a homogenous mixture, initiation of the polymerization reaction is carried out by addition of an adequate initiator, which is exposed to a source of heat, radiation, etc. After the polymerization mechanism is completed, a nanocomposite is produced, which consists of polymer molecules bound to nanoparticles.
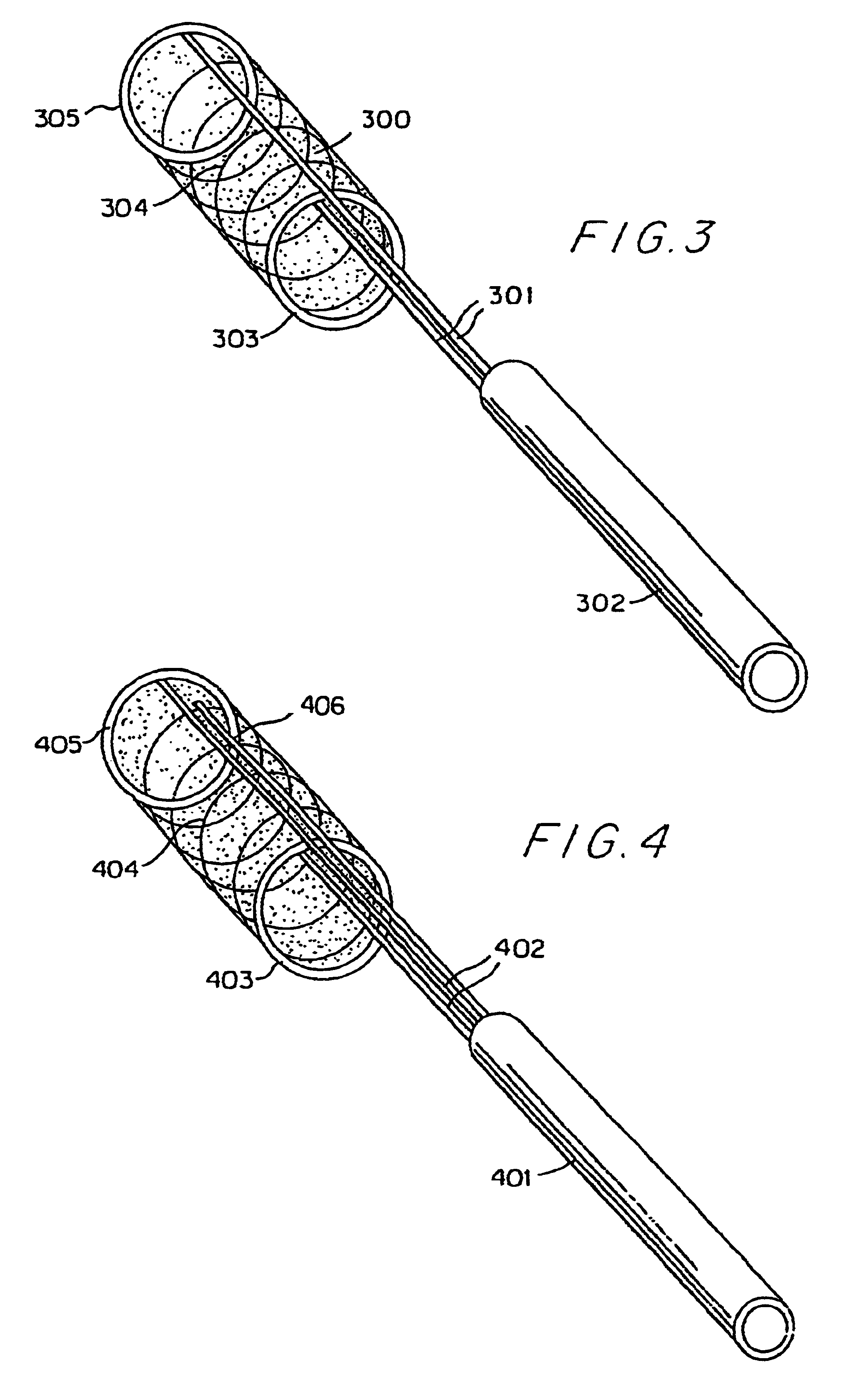
Endovascular thin film devices and methods for treating and preventing stroke
InactiveUS6605111B2Treating and preventing ischemic and hemorrhagic strokeInhibit migrationStentsCatheterIn situ polymerizationProsthesis
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Endovascular thin film devices and methods for treating and preventing stroke
InactiveUS20030060782A1Safely and permanently excludingPreventing initial or recurrent aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhageStentsCatheterIn situ polymerizationProsthesis
Devices for excluding aneurysms and treating atherosclerotic disease, for intra-aneurysmal occlusion; and devices for preventing distal emboli. The devices are generally pliable and collapsible thin film devices which can be delivered via a microcatheter into the desired location where they are deployed and undergo either a shape memory phase transformation or in situ polymerization to assume the stable configuration of a permanent endoluminal prosthesis. Prior to being caused to assume their final shape, the devices remain soft, collapsible and pliable to ensure atraumatic delivery through the vascular system. Upon reaching the endoluminal defect in the vessel, the device is extruded from the microcatheter. Devices are also provided for retrieving clots.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Endovascular thin film devices and methods for treating and preventing stroke
InactiveUS6666882B1Treating and preventing ischemic and hemorrhagic strokeInhibit migrationStentsOcculdersIn situ polymerizationDistal embolization
Devices for excluding aneurysms and treating atherosclerotic disease, for intra-aneurysmal occlusion, and devices for preventing distal emboli. The devices are generally pliable and collapsible thin film devices which can be delivered via a microcatheter into the desired location where they are deployed and undergo either a shape memory phase transformation or in situ polymerization to assume the stable configuration of a permanent endoluminal prosthesis. Prior to being caused to assume their final shape, the devices remain soft, collapsible and pliable to ensure atraumatic delivery through the vascular system. Upon reaching the endoluminal defect in the vessel, the device is extruded from the microcatheter. Devices are also provided for retrieving clots.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Surgical adhesive and uses therefore
InactiveUS20050129733A1Controlled strengthLess erosiveSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIn situ polymerizationEnteroceles
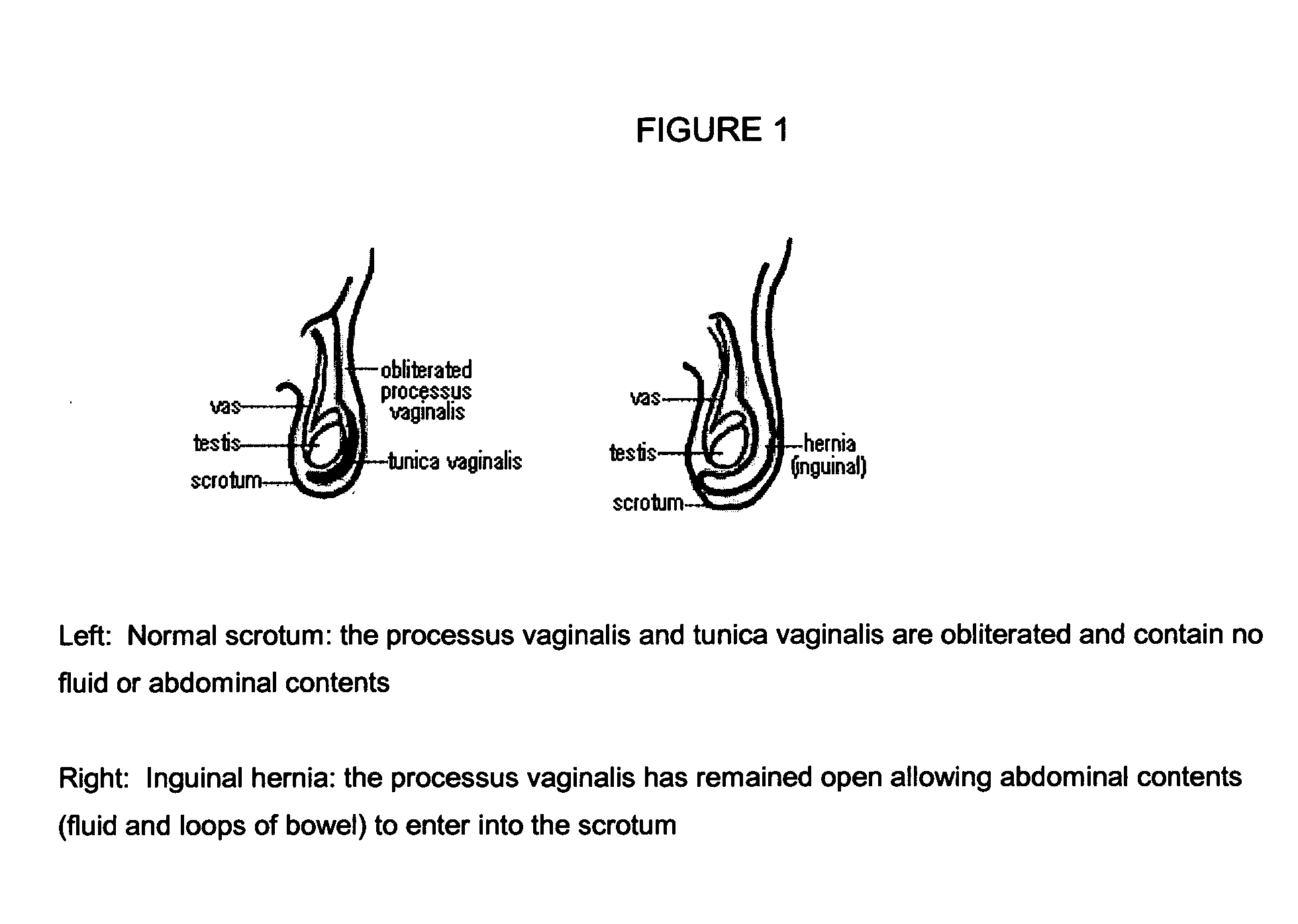
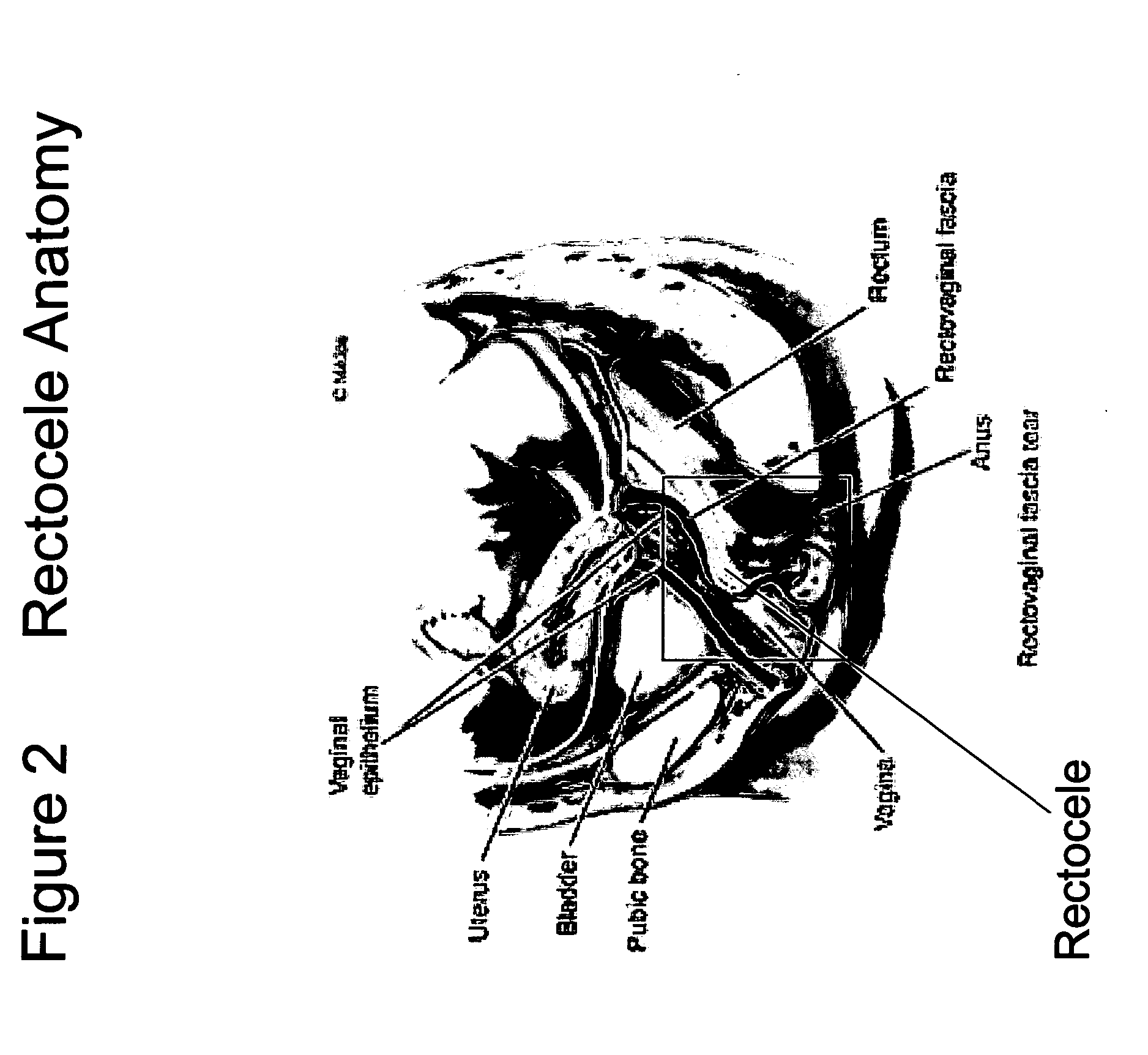
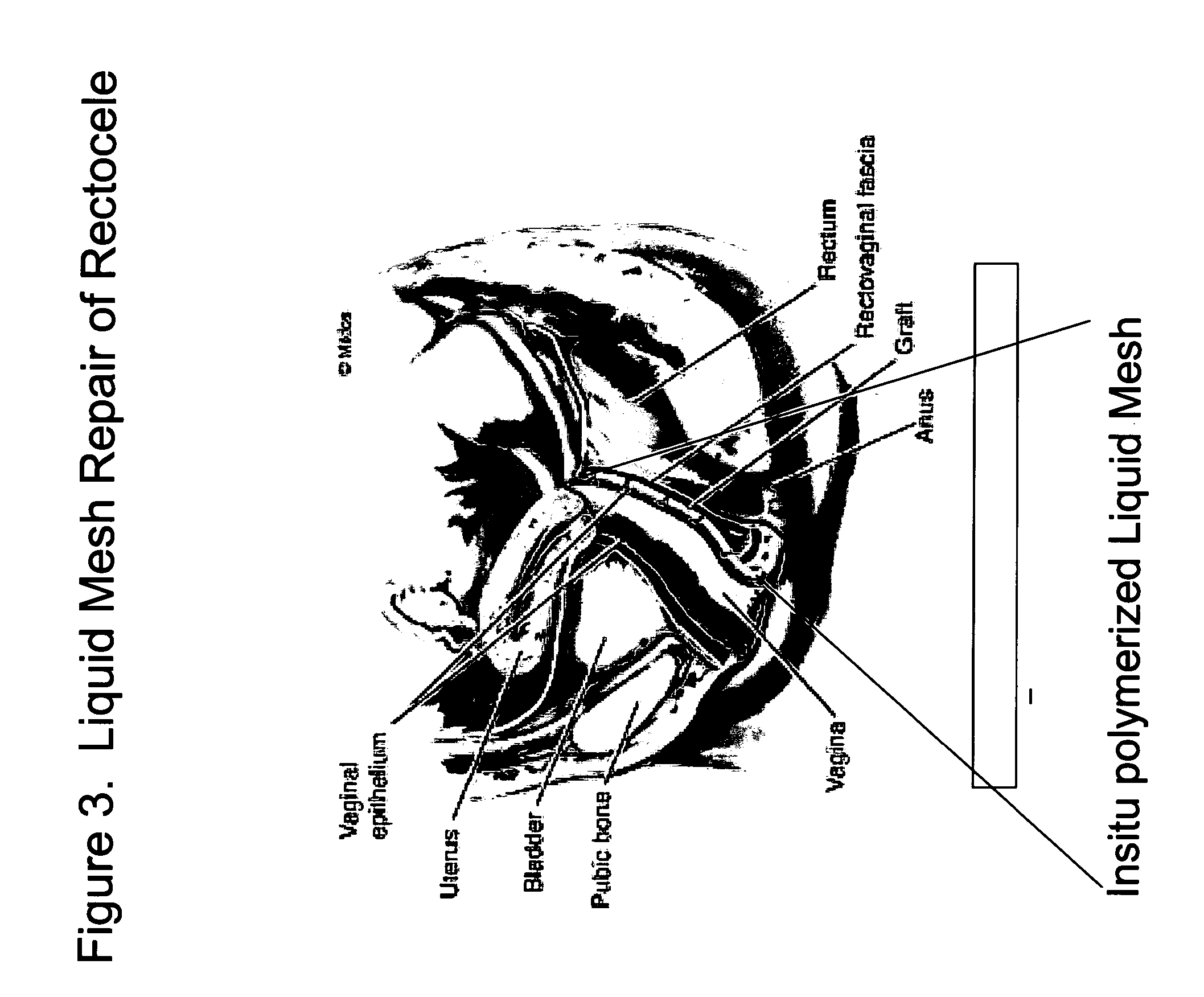
The present invention provides a liquid polymer composition which can be implanted into a living mammal and which forms a solid hydrogel by in situ polymerization upon contact with body fluid and tissue. The composition also can be used as a coating on a medical device, or for the formation of a medical device. Formation of a solid implant or coating involves crosslinking of the adhesive with itself and with surrounding tissue. The liquid implant, by itself or in conjunction with various prostheses, can be used for many purposed, including fixation of the urethra for providing treatment for incontinence, and repair of herniations in the abdominal cavity, including rectocele, cystocele, enterocele, and inguinal hernia. The adhesive may be used to establish adhesion prevention during such repairs, in part by coating or being the material of a repair mesh.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
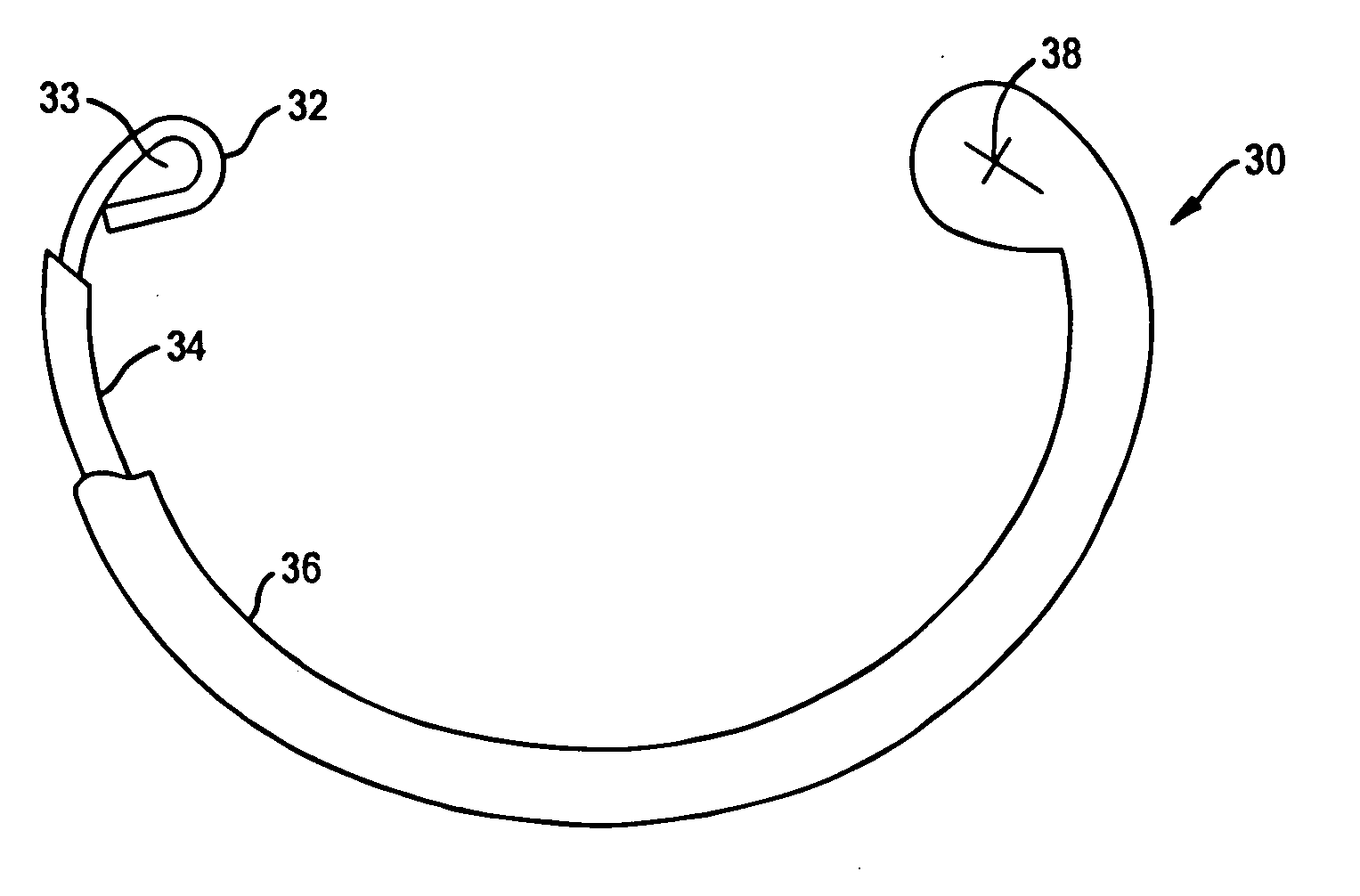
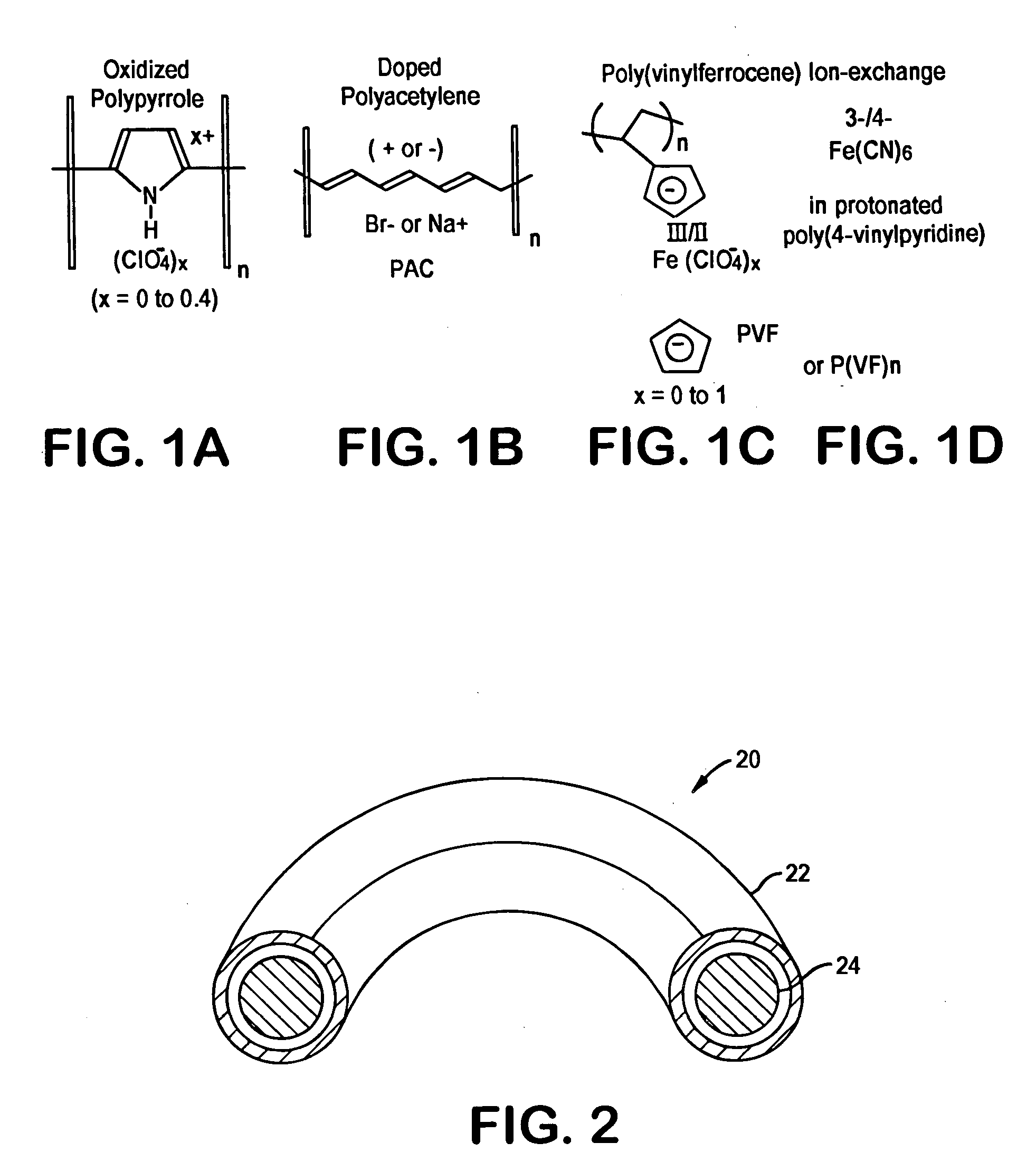
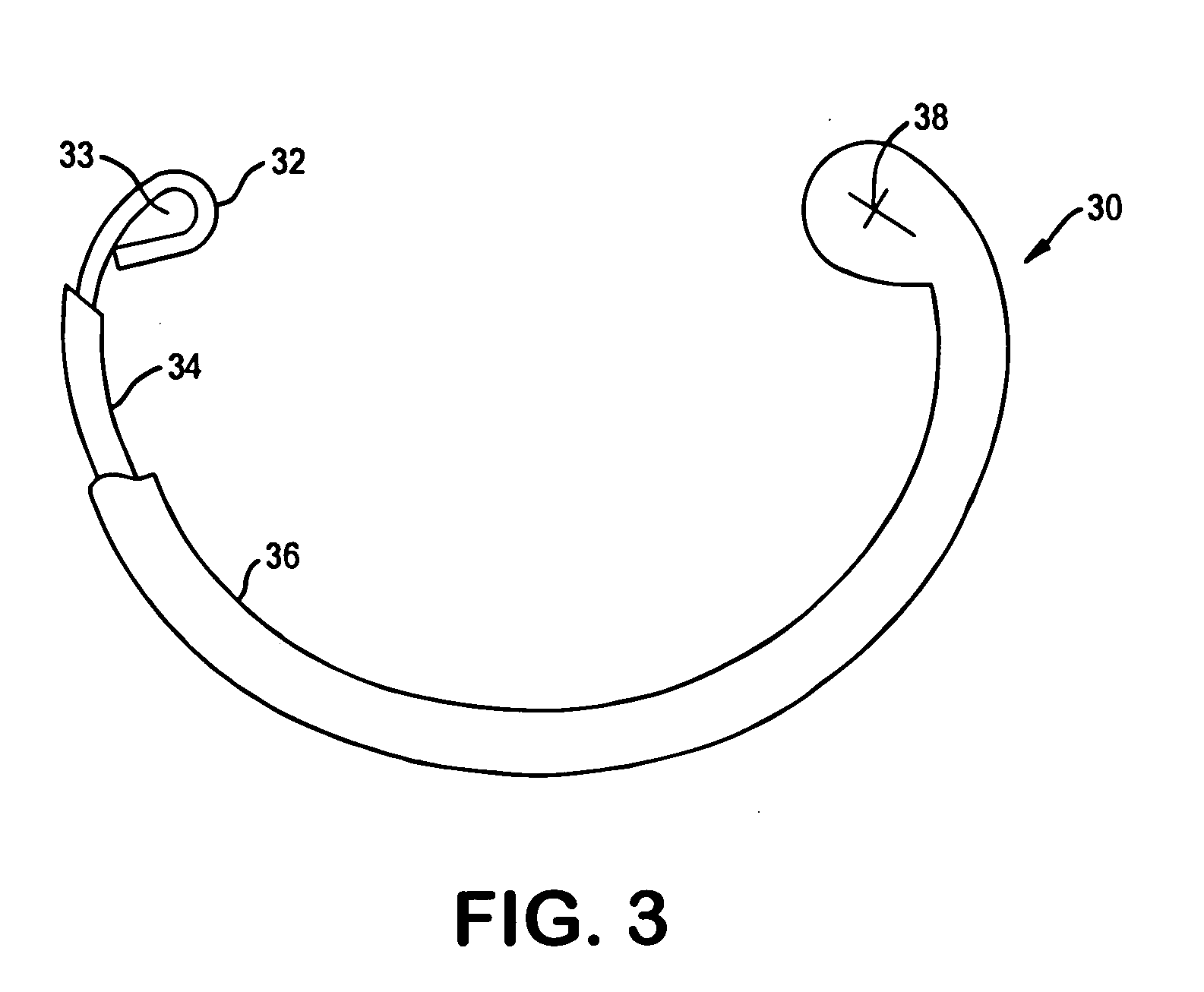
Implantable heart valve prosthetic devices having intrinsically conductive polymers
A heart valve sewing prosthesis including an intrinsically conductive polymer. The invention includes annuloplasty rings and bands, and sewing rings or cuffs for prosthetic heart valves. Some annuloplasty rings and sewing rings include fabric that is coated with an intrinsically conductive polymer. The coating can be formed over individual filaments or fibers, or on the fabric surface as a surface layer. One intrinsically conductive polymer is polypyrrole. The intrinsically conductive polymer can be doped to facilitate the intrinsic conductivity. Some devices have a polypyrrole surface layer doped with dialkyl-napthalene sulfonate. The intrinsically conductive polymer can be deposited on a fabric using in-situ polymerization of monomeric or oligomeric species, together with a dopant. Animal studies using implanted annuloplasty rings having an intrinsically conductive polymer coating have demonstrated a substantial reduction in pannus formation and inflammatory response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
In vivo tissue engineering with biodegradable polymers
The present invention relates generally to the utilization of in situ polymers or copolymers to form a porous microcellular scaffold for the delivery, attachment, housing, protection, multiplication and growth of encapsulated cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to cells delivered using such a scaffold to augment, repair or replace in vivo diseased, damaged or otherwise compromised tissues or organs of a living body.
Owner:DERMAGENESIS
Bioprosthetic tissue preparation with synthetic hydrogels
ActiveUS20050119736A1Reduce calcificationReduce stiffnessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for treating xenogenic tissue for implantation into a human body including in-situ polymerization of a hydrogel polymer in tissue, and tissue treated according to those methods, where the polymerization takes place in tissue that has not been fixed with glutaraldehyde. The polymerization may only fill the tissue, bind the polymer to the tissue, or cross-link the tissue through the polymer, depending on the embodiment. One method includes free radical polymerization of a first vinylic compound, and can include cross-linking through use of a second compound having at least two vinyl groups. Another method utilizes nucleophilic addition polymerization of two compounds, one of which can include PEG and can further include hydrolytically degradable regions. In one embodiment, applicants believe the in-situ polymerization inhibits calcification, and that the polymerization of tissue un-fixed by glutaraldehyde allows for improved penetration of the polymer. The methods find one use in the treatment of porcine heart valve tissue, intended to extend the useful life of the valves by inhibiting calcification. The incorporation of degradable hydrogel regions may initially fill the tissue and reduce any initial inflammatory response, but allow for later infiltration by cells to remodel the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
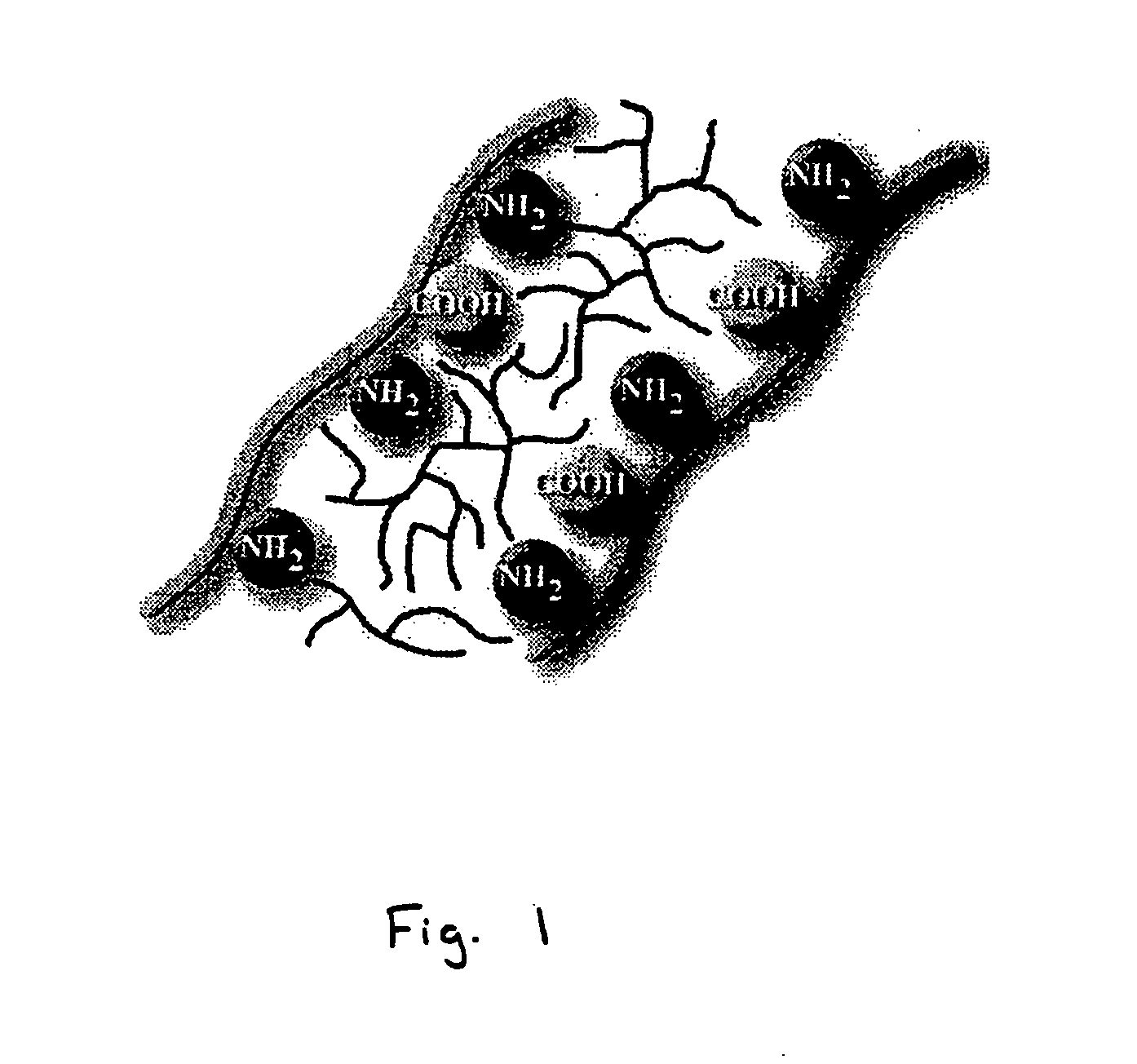
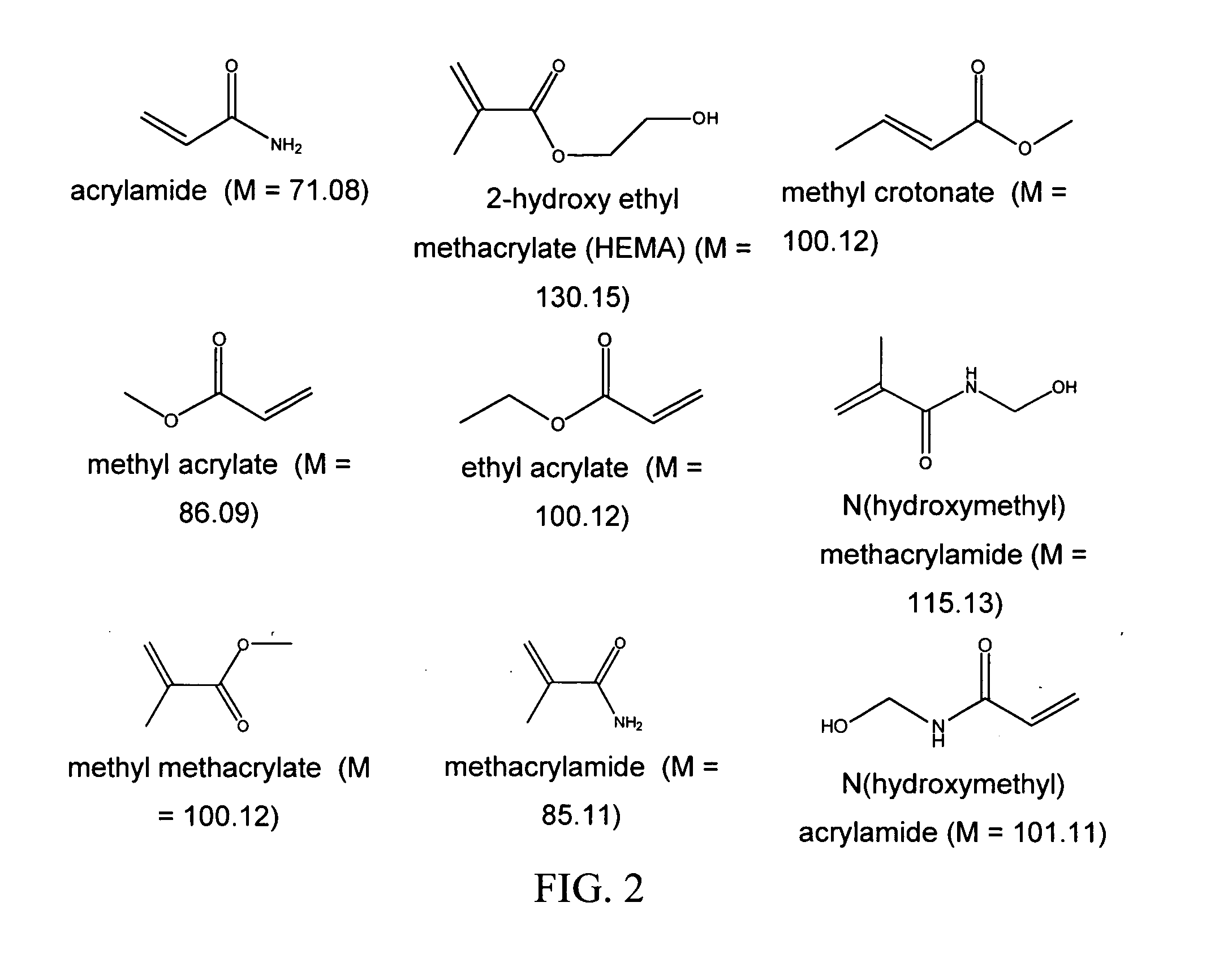
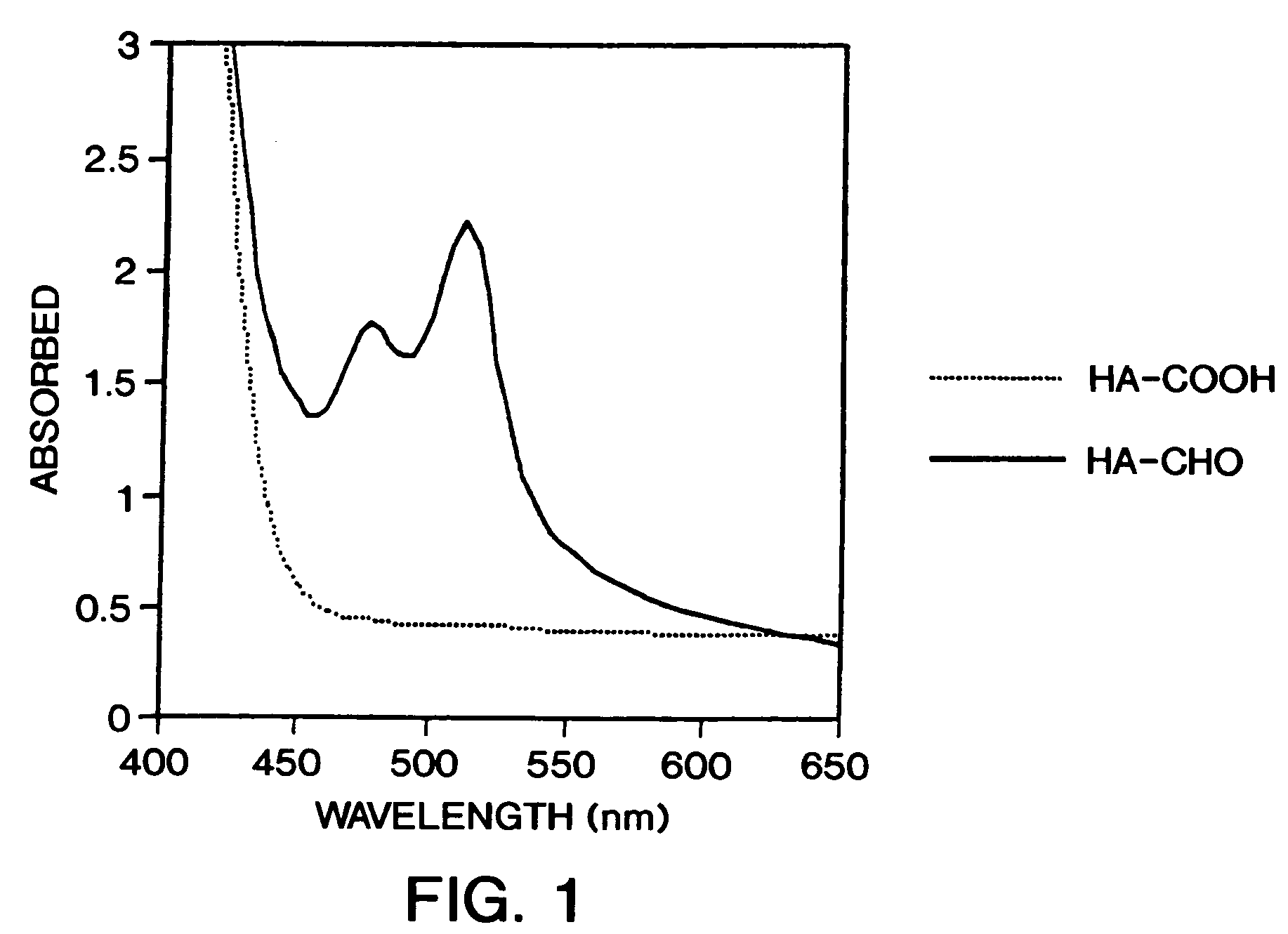
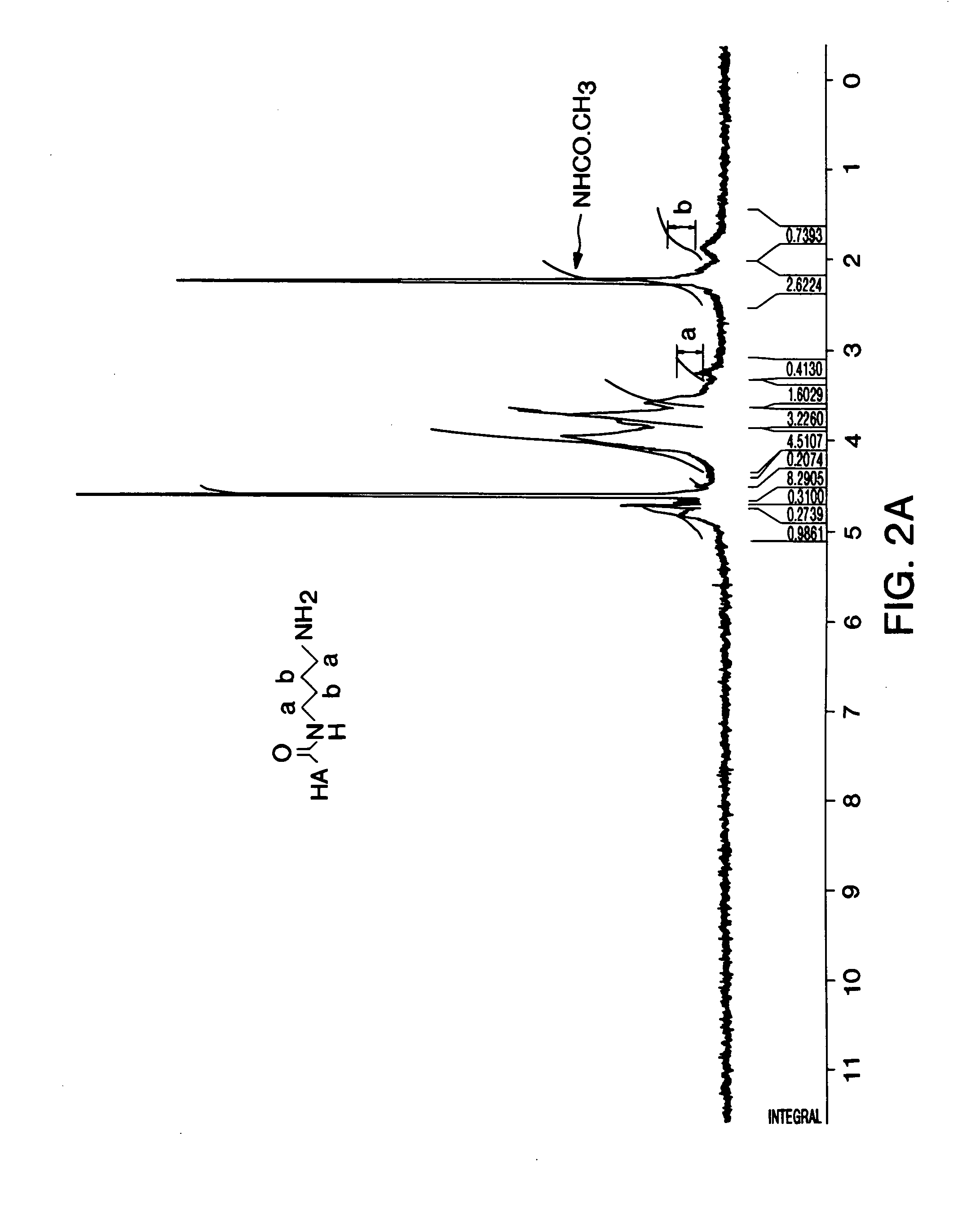
Functionalized derivatives of hyaluronic acid, formation of hydrogels in situ using same, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS7196180B2Good physical propertiesSimple structureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for chemical modification of hyaluronic acid, formation of amine or aldehyde functionalized hyaluronic acid, and the cross-linking thereof to form hydrogels are provided. Functionalized hyaluronic acid hydrogels of this invention can be polymerized in situ, are biodegradable, and can serve as a tissue adhesive, a tissue separator, a drug delivery system, a matrix for cell cultures, and a temporary scaffold for tissue regeneration.
Owner:ORTHOGENE
Graphene/metal oxide composite cathode material for lithium ion battery and preparation
InactiveCN102646817APromote circulationExcellent rate performanceCell electrodesHigh energyIn situ polymerization
The invention belongs to the fields of material synthesis and energy technology, and especially relates to a graphene / metal oxide composite cathode material for lithium ion batteries and a preparation method thereof. Grapheme is dispersed into various metal oxide precursor salt solutions; a graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained directly by a hydrothermal method, or an graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained by a liquid in-situ polymerization method or a coprecipitation process; and the graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained by heat treatment or hydrothermal treatment. In the invention, the novel three-dimensional composite cathode material of graphene-coated metal oxide or graphene-anchored metal oxide is prepared by carrying metal oxide particles with graphene as a carrier. The obtained composite material can be used as a lithium ion battery cathode, which has a high specific capacity, excellent cycle stability and rate capability, and is expected to be used as a lithium ion battery cathode material with a high energy density and a high power density.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
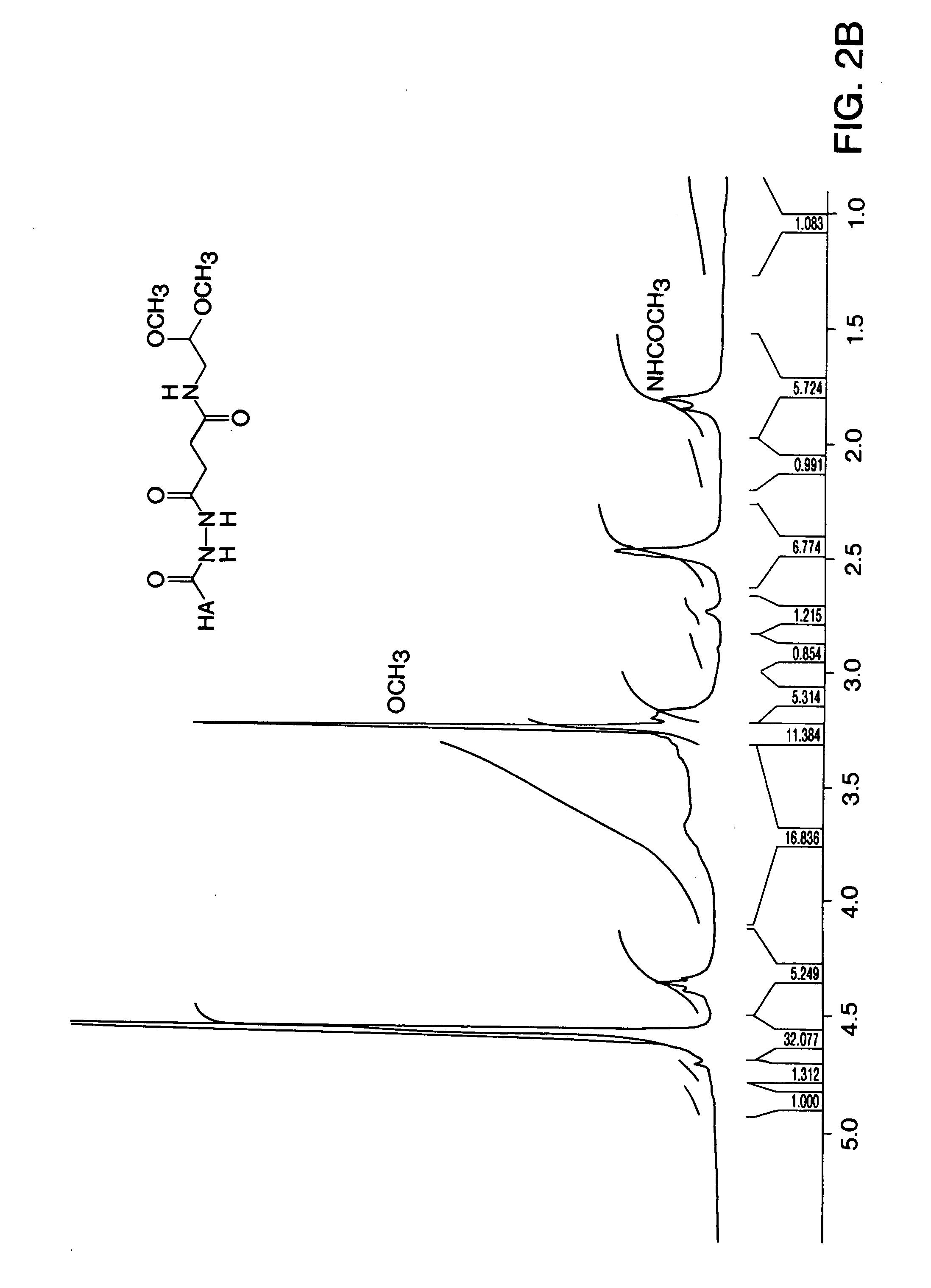
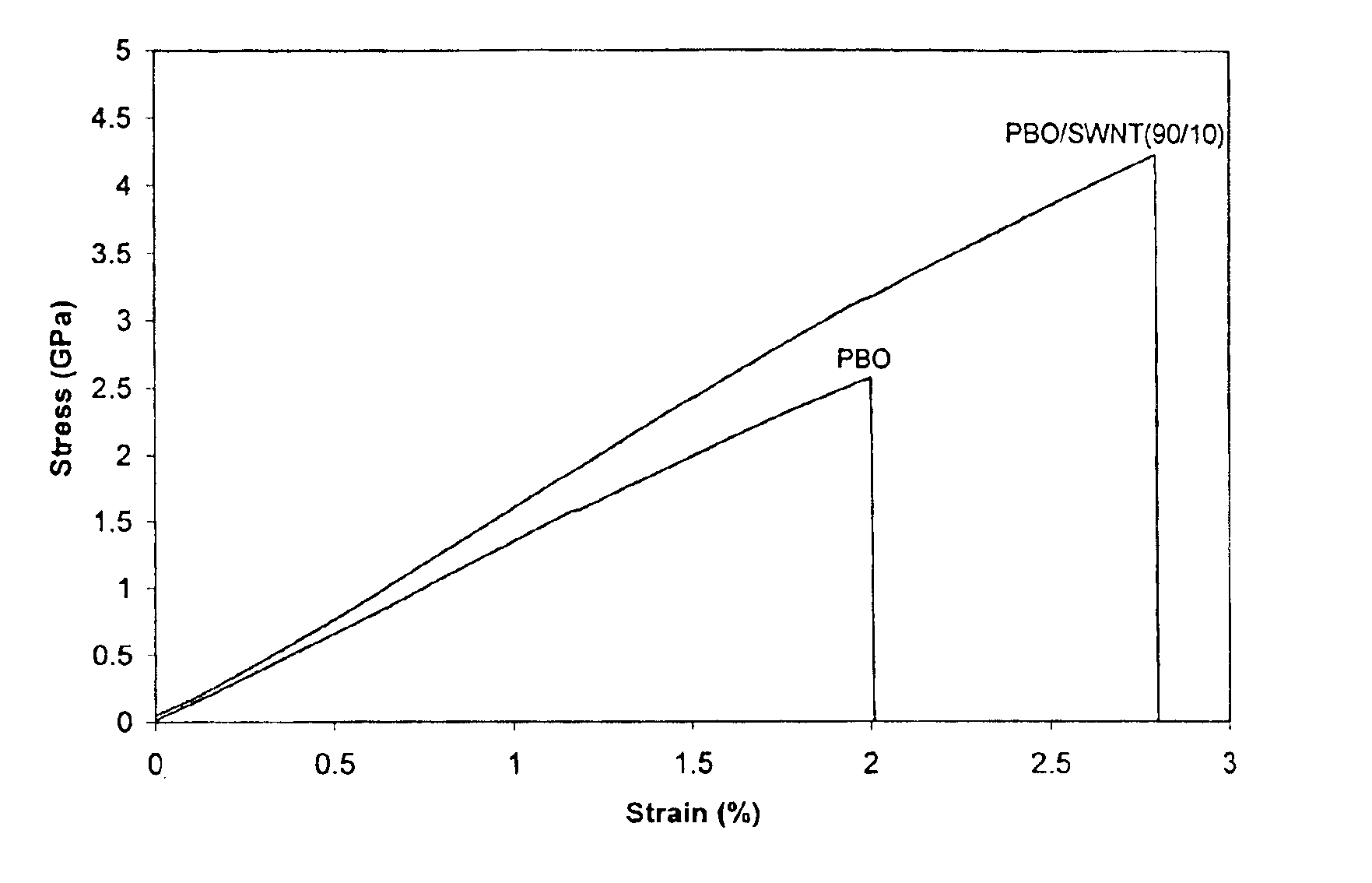
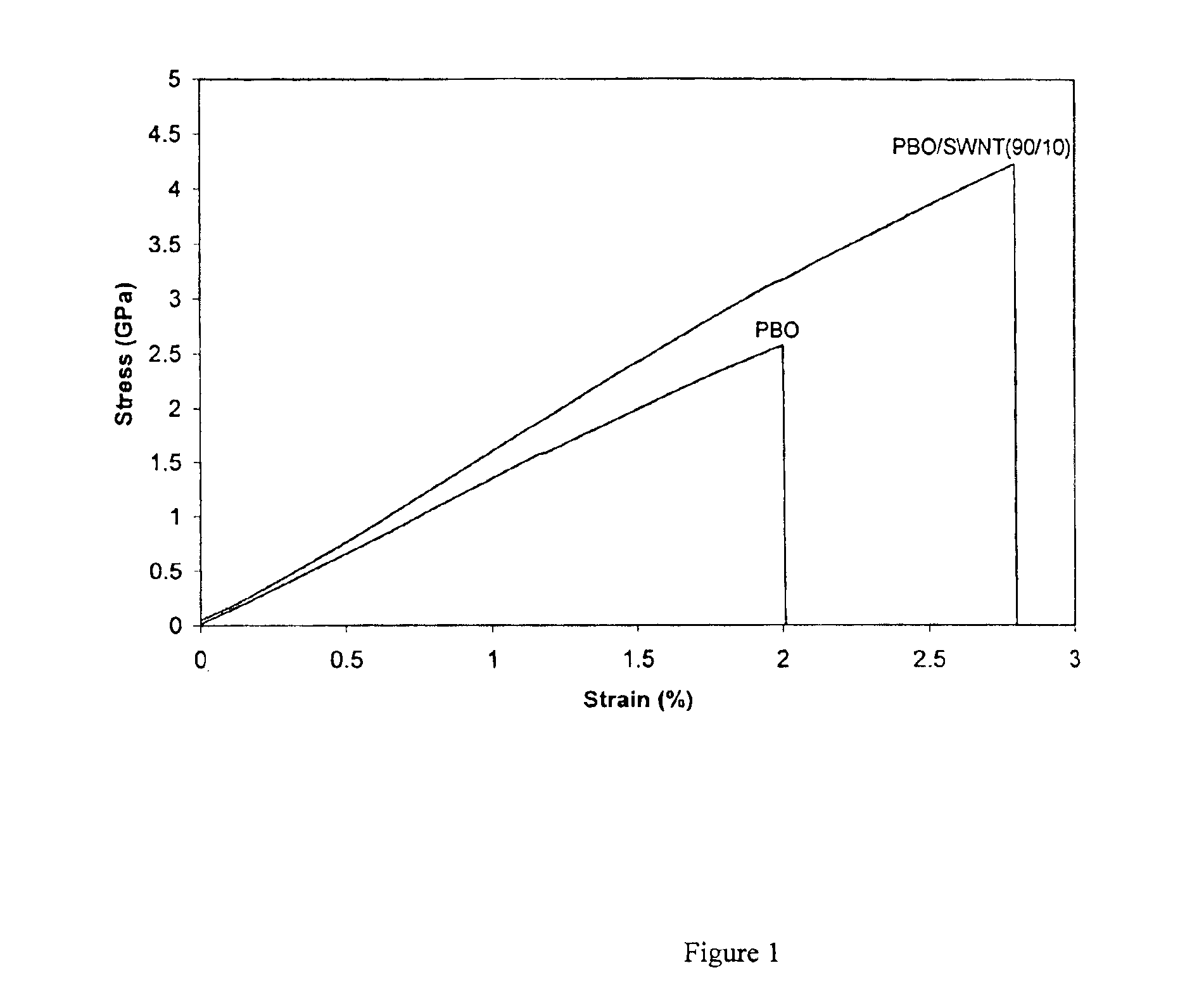
Compositions comprising rigid-rod polymers and carbon nanotubes and process for making the same
InactiveUS6900264B2High modulusHigh stiffnessMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresFiberLiquid crystalline
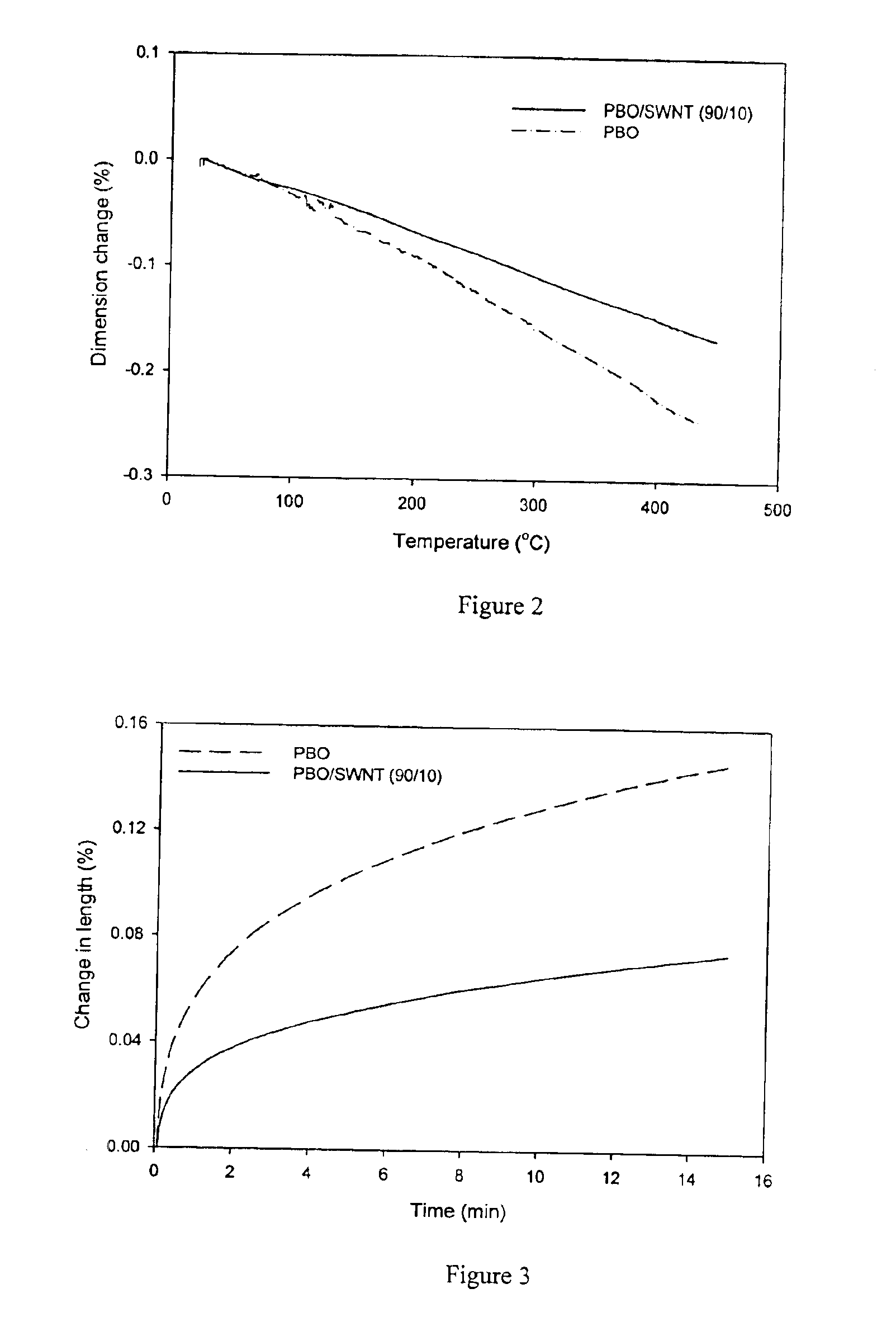
The present invention relates to compositions comprising rigid-rod polymers and carbon nanotubes. The compositions comprise dispersed carbon nanotubes aligned with rigid-rod polymers. The alignment of the nanotubes and polymers can be liquid crystalline. The rigid-rod polymers of this invention include, but are not limited to, polymers and copolymers comprising benzobisazole, pyridobisimidazole and benzamidazobenzo-phenanthroline repeat units. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes is achieved by in-situ polymerization in the presence of the carbon nanotubes, which may be either single-wall or multi-wall or a combination of both. The polymer compositions comprising carbon nanotubes may be spun into fibers or formed into films. The strength of the resulting fibers of the present invention is significantly greater than that of fibers without carbon nanotubes.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Composite Articles Comprising In-Situ-Polymerisable Thermoplastic Material and Processes for their Construction
InactiveUS20100062238A1Reliable constructionLow costFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesTurbine bladeIn situ polymerization
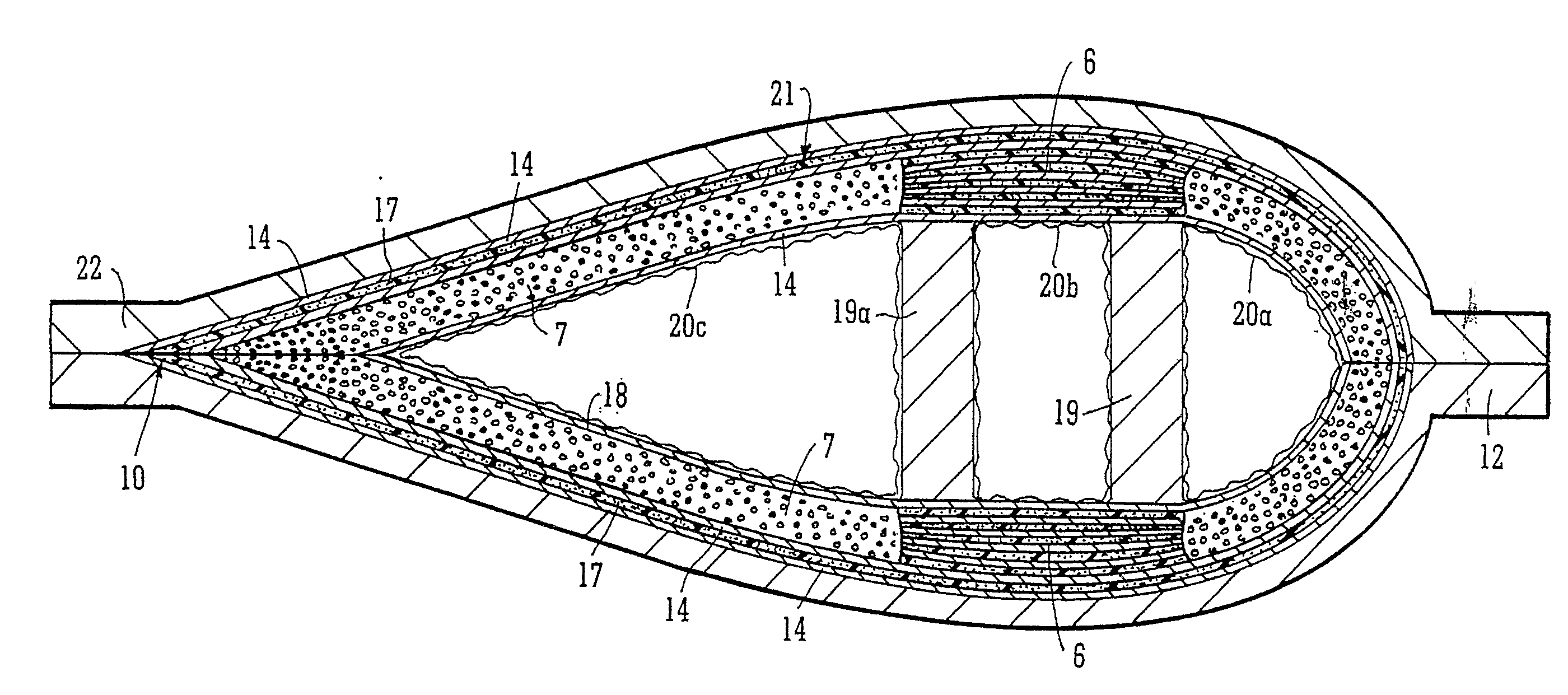
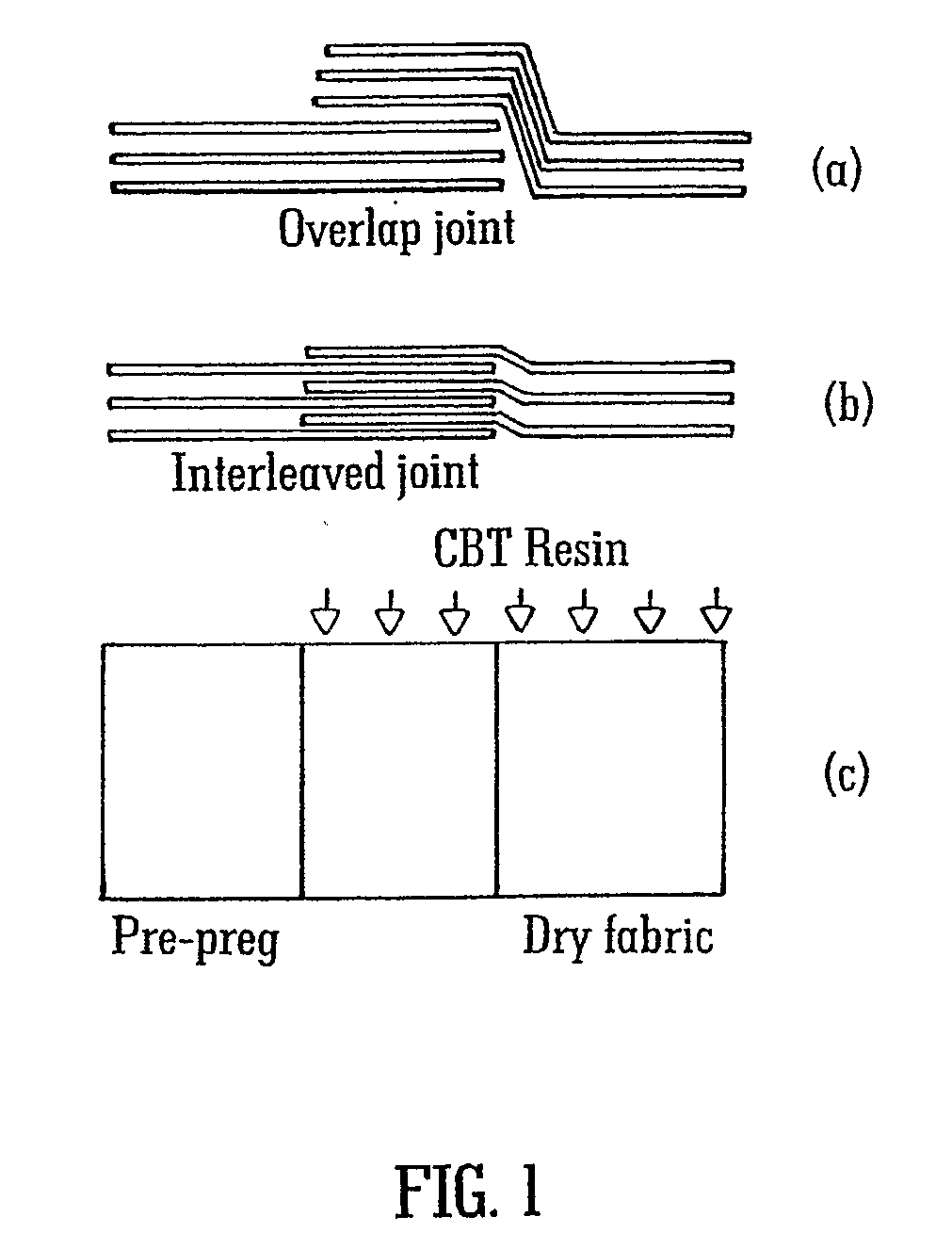
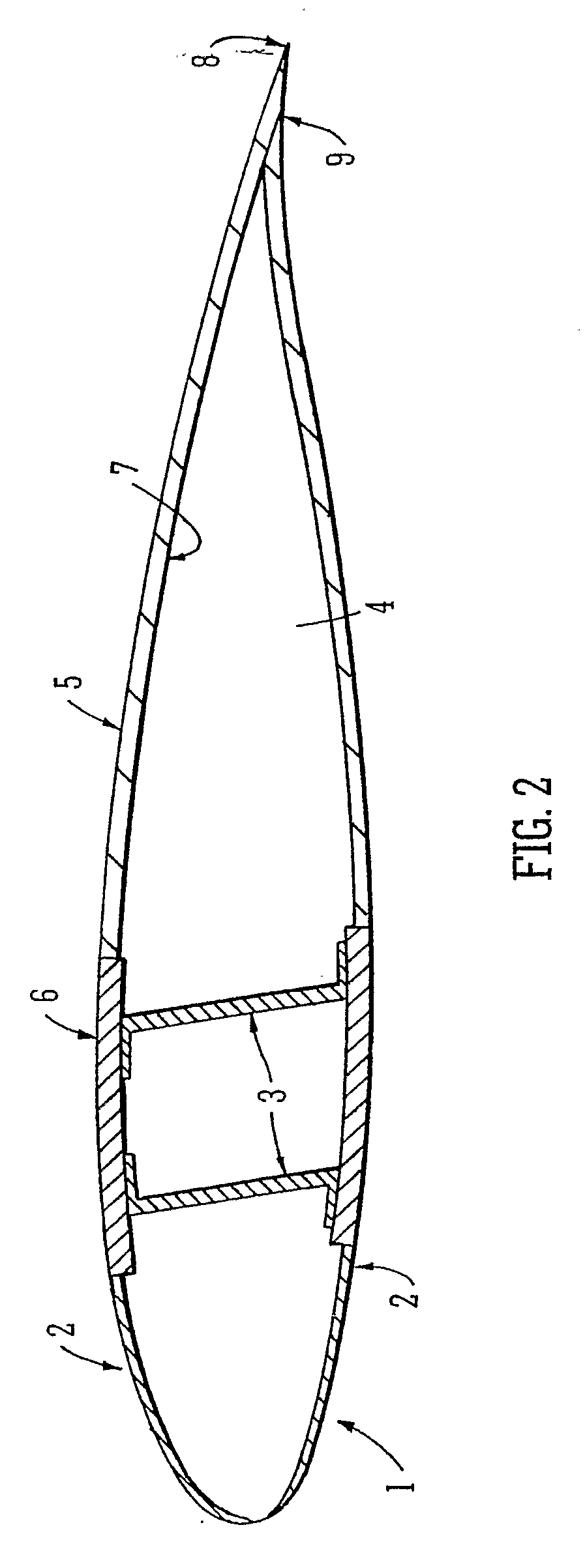
A process for the manufacture of a composite article is described wherein the process comprises the steps of (i) providing on a tool (22) a fibrous material (14) having associated therewith in at least one region thereof an in-situ polymerisable non-fibrous form of a thermoplastic material; (ii) applying heat and a vacuum to said material; and additionally (iii) drawing into the fibrous material, from a source external to the tool, additional thermoplastic pre-polymer material. The process described is particularly useful for the manufacture of a large composite structure such as thermoplastic composite wind turbine blade, for example.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK +2
Nano transparent insulating paint and its preparing process
InactiveCN101108946AGood dispersionImprove stabilityFireproof paintsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsInfraredIn situ polymerization
The invention relates to a nano transparent heat insulation coating, which comprises the following components: inorganic nano particle hybrid high molecular resin, coating additive and thinner. Wherein, the inorganic nano particle hybrid high molecular resin is the resin with core / shell structure and synthesized by inorganic nano heat insulation powder and high molecular resin through in-situ polymerization and the high molecular resin covers the nano heat insulation powder. The invention also provides a preparation method of the nano transparent heat insulation coating. The nano transparent heat insulation coating film forming material is the inorganic nano particle hybrid high molecular resin and is characterized by strong adhesive force, transparency and shielding infrared for heat insulation, which can be coated on the surfaces of glass, metals and cement and is especially for glass of cars or buildings. The invention adopts the inorganic nano particle hybrid high molecular resin with core / shell structure prepared through in-situ polymerization, which is simple and easy and has good coating properties.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
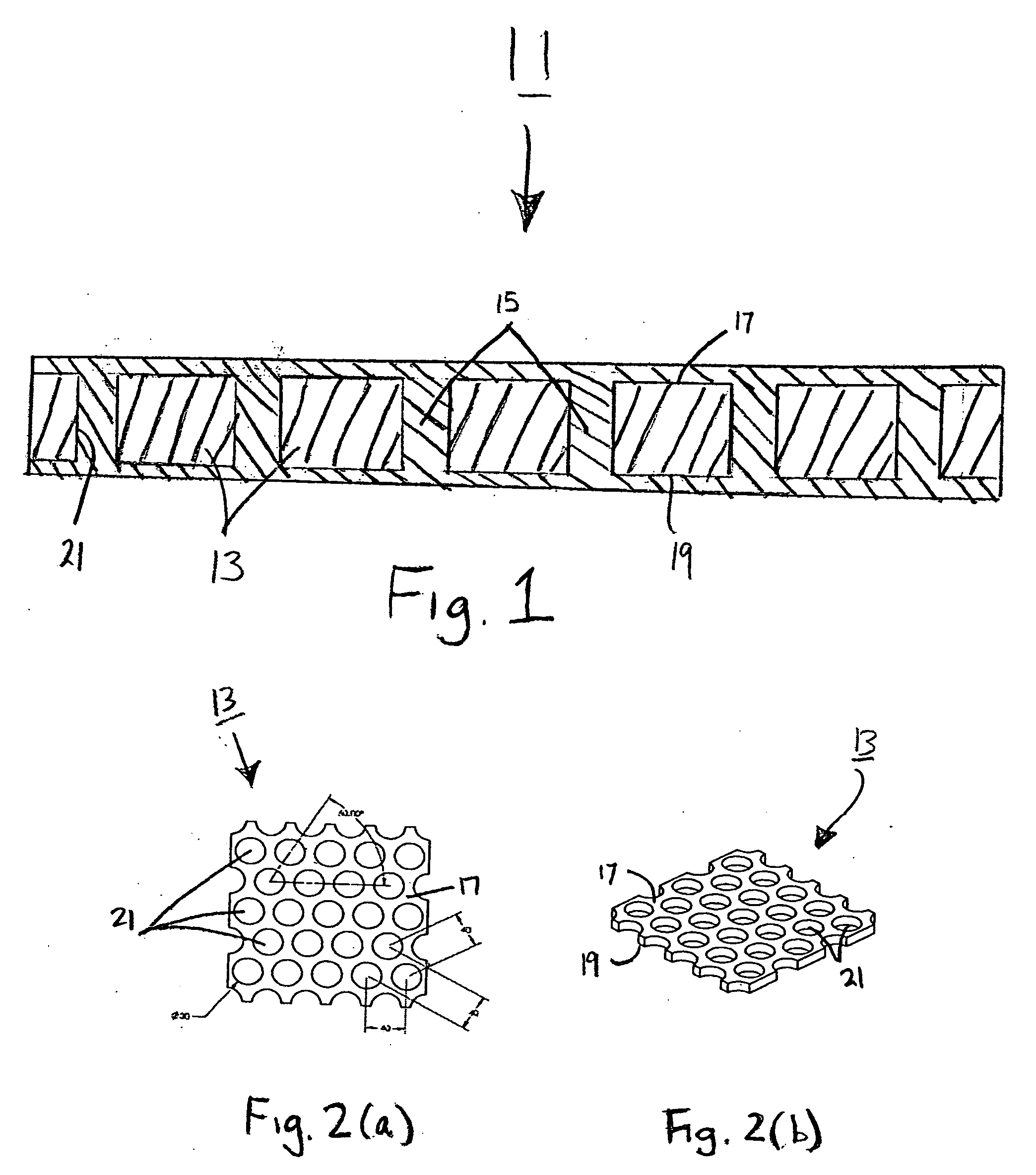
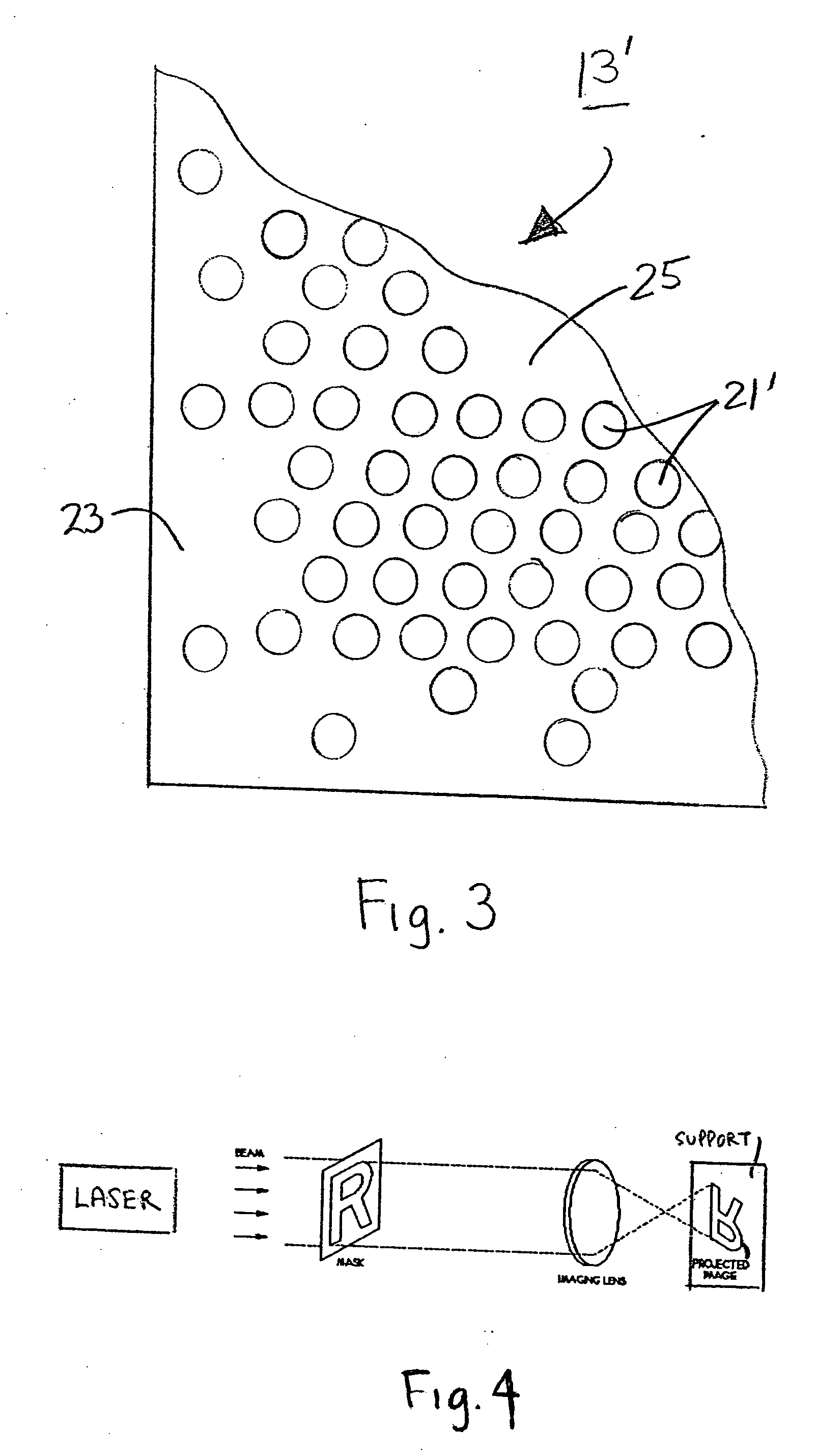
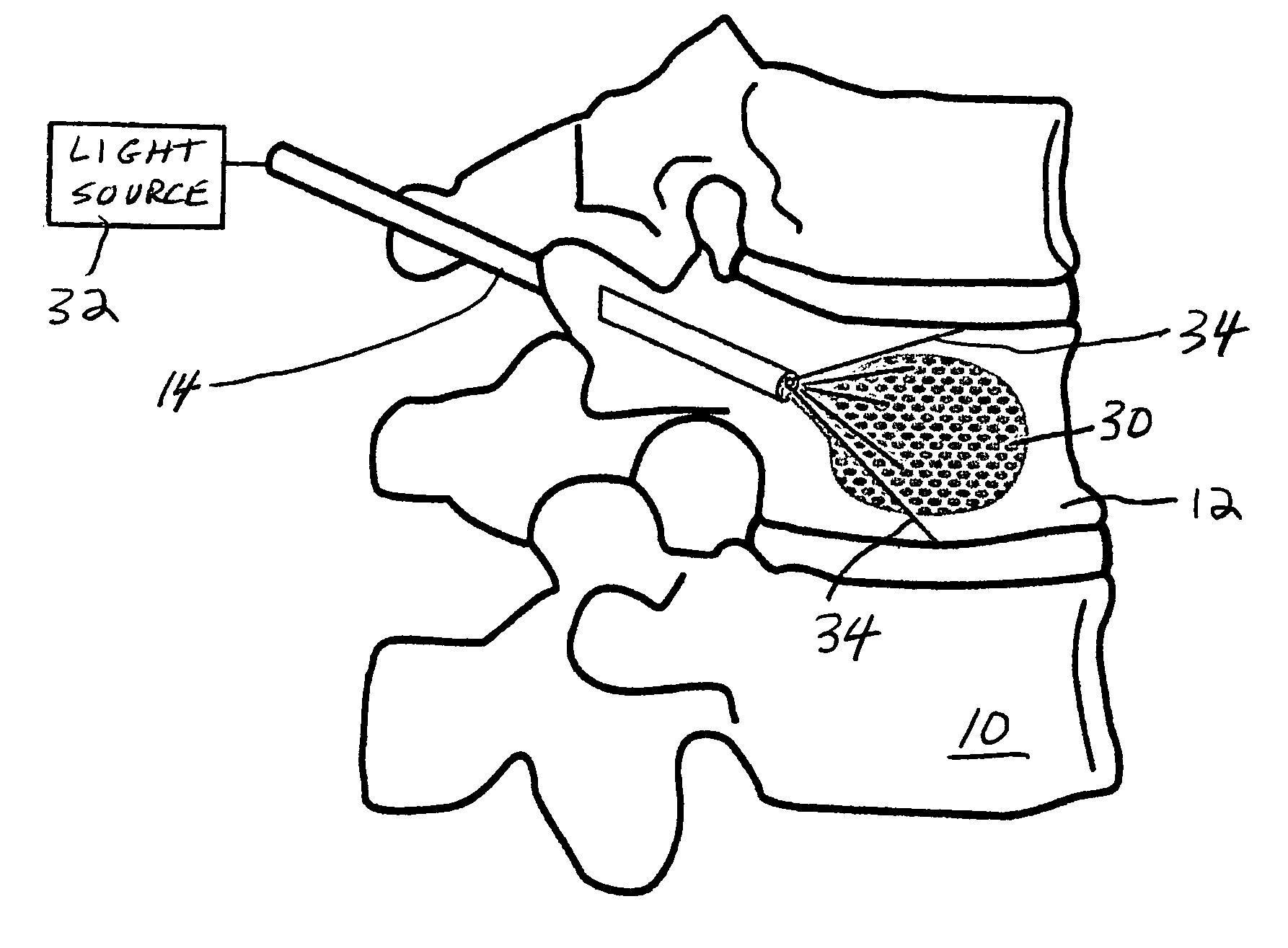
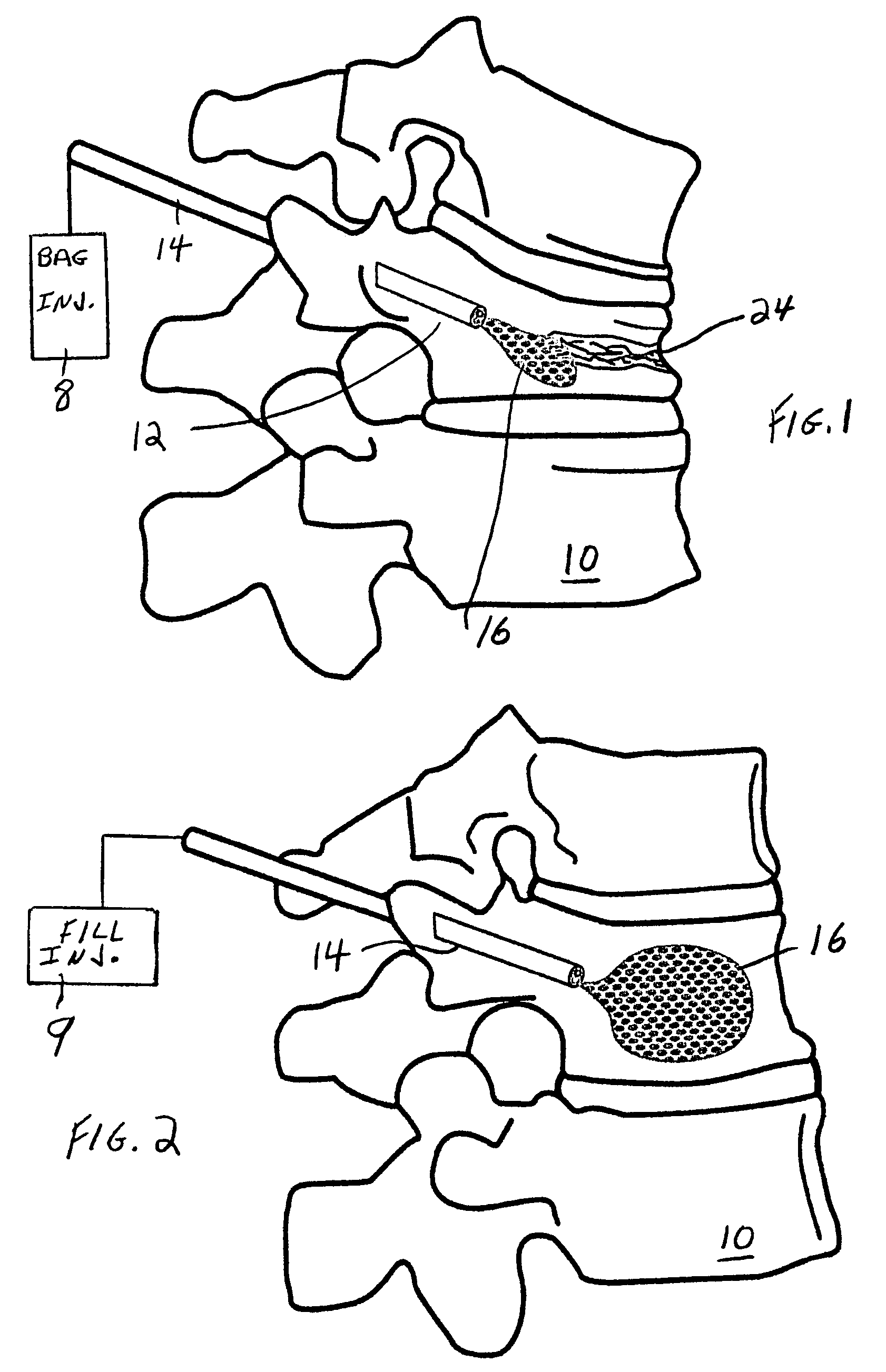
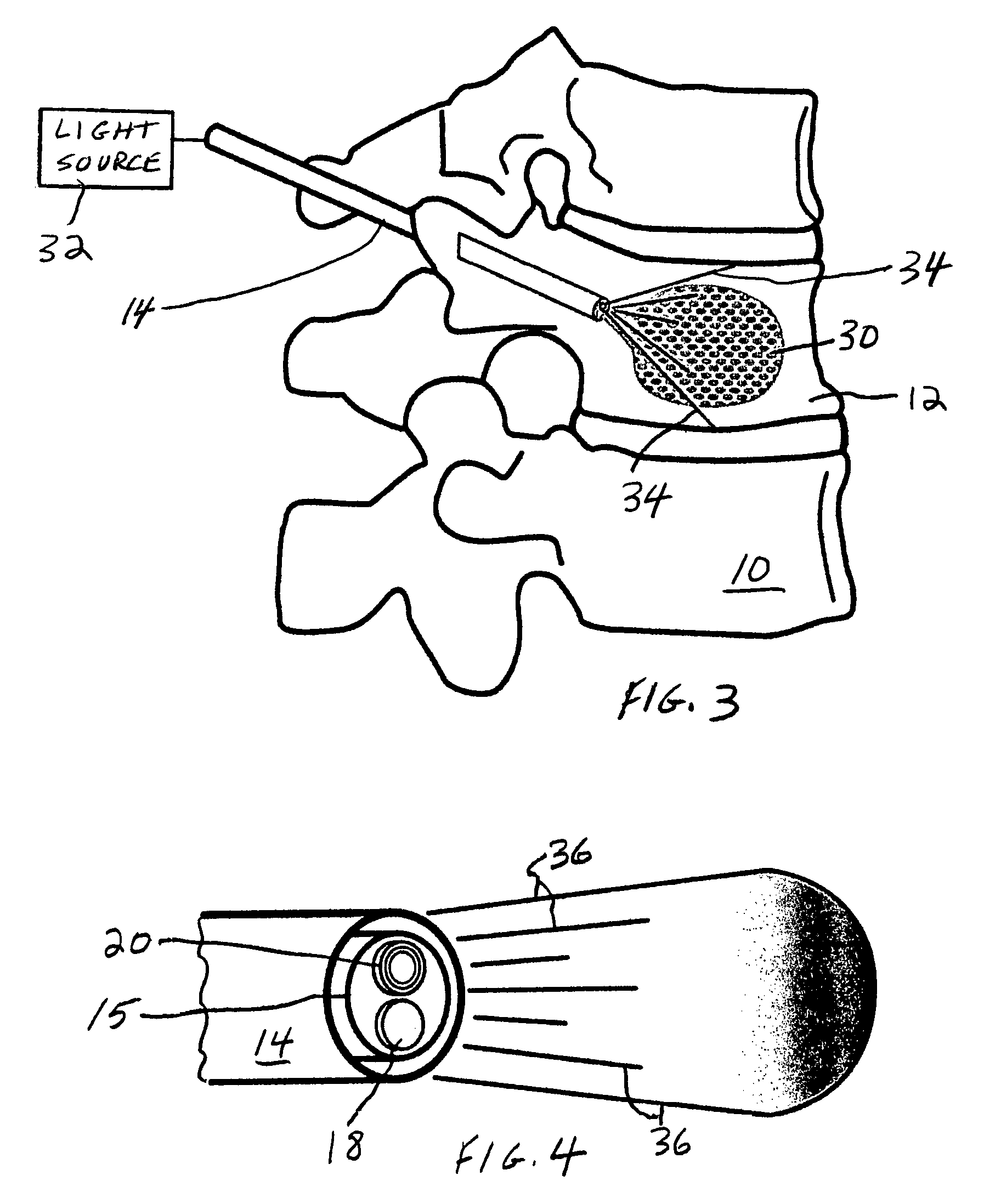
Spinal fill for disk surgery
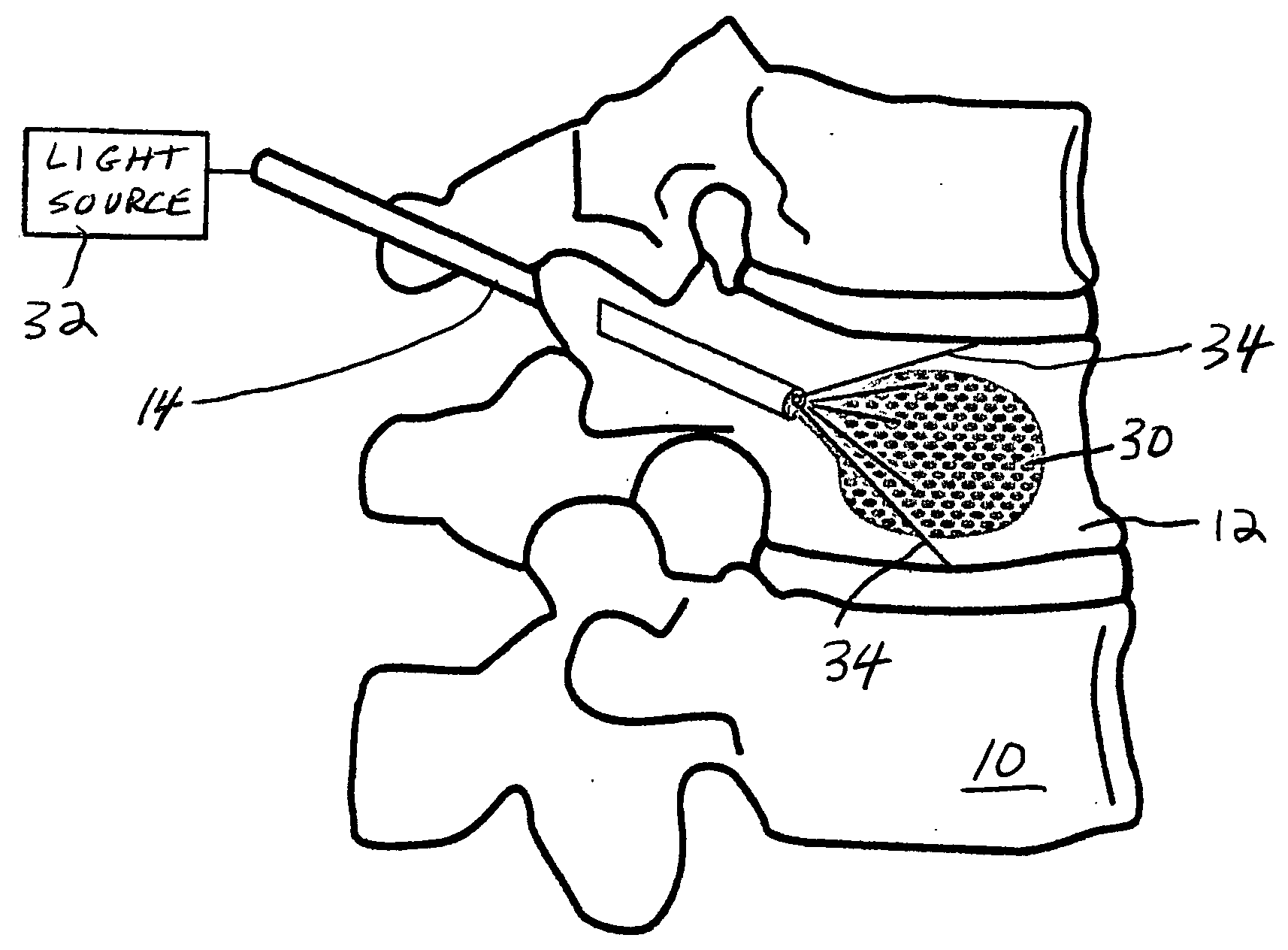
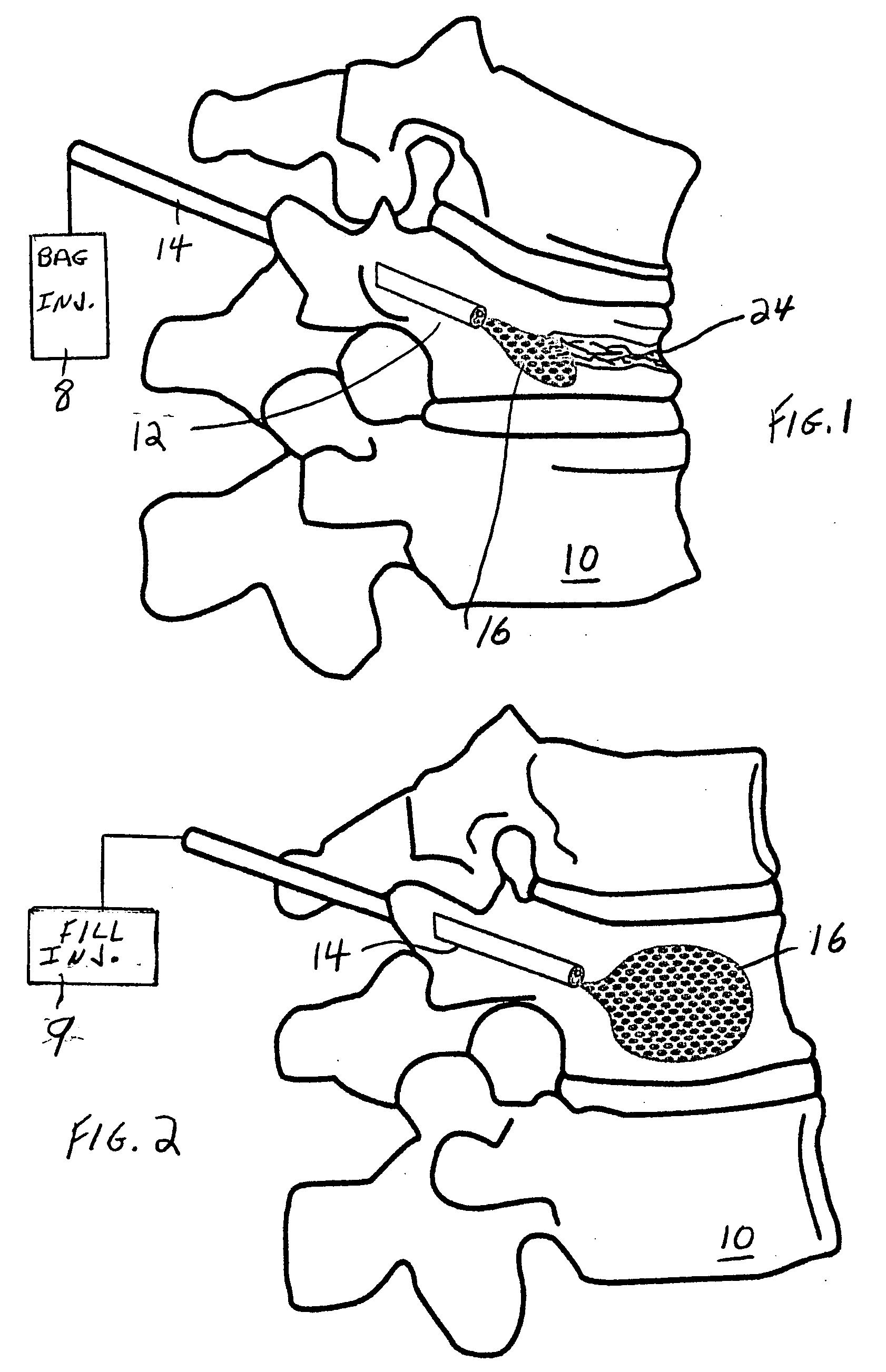
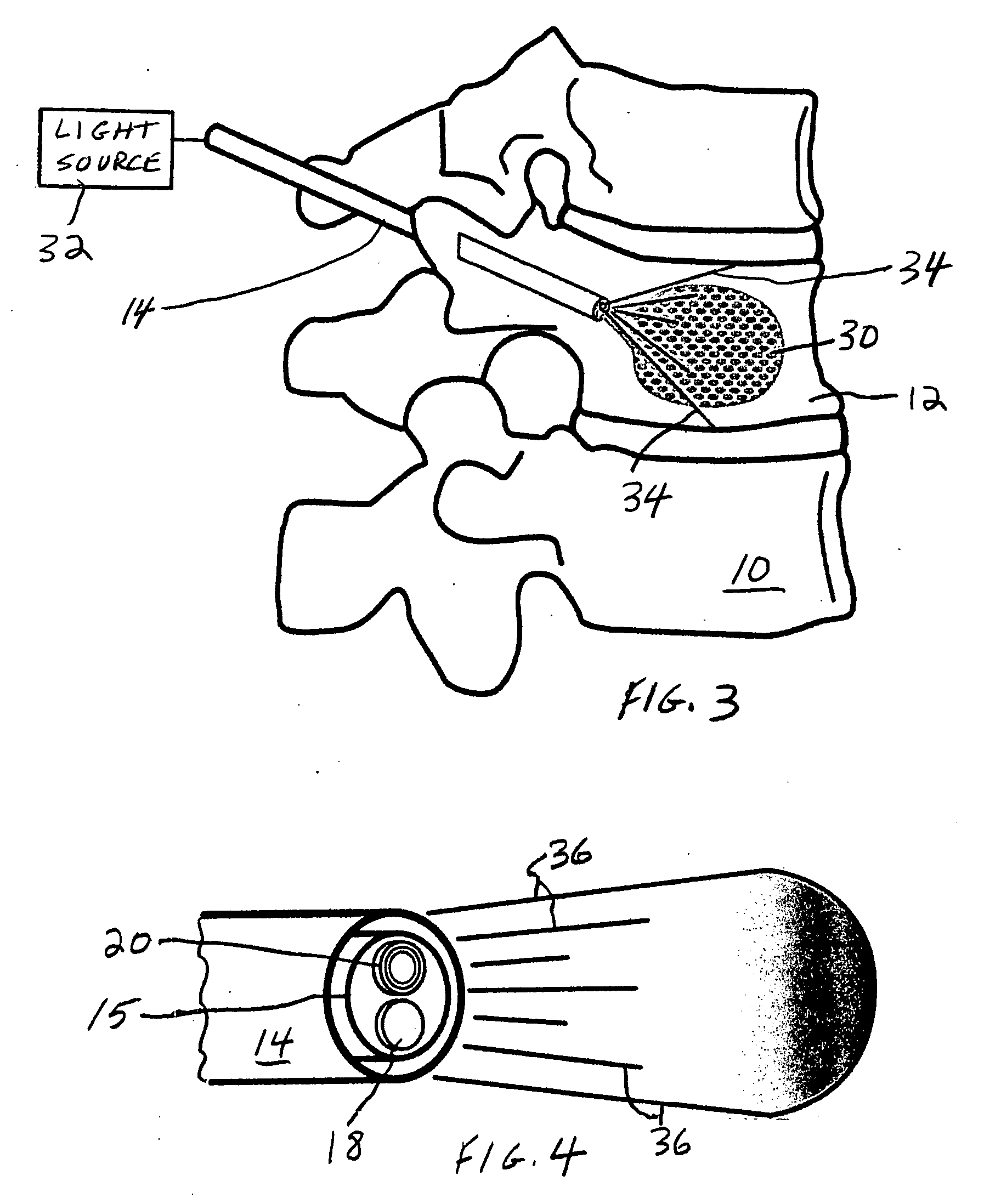
The invention is based on the use of polyisobutylmethacrylate instead of PMMA as an adhesive or spinal fill material for treating diseases of the spine. Polyisobutylmethacrylate has several advantages over PMMA, mainly less heat is developed during the in situ polymerization process. When using any spinal adhesive of fill material that is light activated, a tube can be used to transmit activating light to the light-activated adhesive or spinal polymerizable fill material at the surgical site. In addition, a mesh bag comprising optical fibers or similar light transmitting material can be employed to receive the injected light-activated fill, with the mesh bag, irradiated externally, for directing the light via the bag to the polymerizable fill.
Owner:ELLIQUENCE
Carbon nanotube-filled composites prepared by in-situ polymerization
ActiveUS7153903B1Material nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationIn situ polymerizationCarbon nanotube
A method of forming carbon nanotube-filled composites using miniemulsion polymerization. The carbon nanotubes are preferably single-walled carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes are highly dispersed within and associated with the polymer comprising the composite.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
In situ polymerization for hair treatment
InactiveUS20080066773A1Effective for long period of timeImprove hair strengthCosmetic preparationsHair removalSolubilityIn situ polymerization
Hair care products represent a world-wide multi-billion dollar industry. Pre-formed polymers are commonly used in a variety of hair care products including shampoos, conditioners, gels, and hair sprays. The present invention provides technology for polymerizing monomers on hair in situ to produce desired hair characteristics. This eliminates the solubility and application issues found with some polymers. The polymerization of monomers on hair is typically initiated using a thermal or photoinitiatied free radical initiator. In certain embodiments, the monomers are fluorinated thereby producing a fluorinated polymer on the hair upon polymerization. The invention provides monomers, initiators, methods, and kits for use in treating hair with polymers.
Owner:LIVING PROOF INC
Porous titanium dioxide/graphene composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103143338ANarrowing of the forbidden bandLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsIn situ polymerizationAniline
The invention discloses a porous titanium dioxide / graphene composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: adding aniline and graphene into a surfactant-containing protonic acid solution according to a certain ratio; preparing a nanometer polyaniline / graphene composite material through an in-situ polymerization method; preparing titanium dioxide sol by using a sol-gel method; adding 0.05-0.20g of nanometer polyaniline / graphene composite material into 50mL of sol, uniformly mixing; standing and aging the sol for 3-5 days; drying in a drying oven at the temperature of 60-120 DEG C; milling; calcining the obtained composite for 30 minutes -2 hours at the temperature of 200-550 DEG C; and removing the polyaniline, thereby obtaining the porous titanium dioxide / graphene composite material. According to the invention, the porous titanium dioxide / graphene is prepared by utilizing the nanometer polyaniline and the titanium dioxide is deposited on the graphene, so that the contact area of the titanium dioxide and pollutants is increased, the separating efficiency of photo-generated electrons and holes is improved and the photocatalytic efficiency is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Benzoxazine intermediate containing N-allyl and composition and preparation thereof
A benzoxazine intermediate containing N-allyl is prepared from allyltriamine, phenols and aldehydes. Its composition is prepared from said benzoxazine intermediate, thermosetting resin and / or filler through mixing or in-situ polymerizing. They have excellent high temp resistance, chemical performance, flame-retarding behaviour and machinability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Solid polymer electrolyte composite membrane comprising porous ceramic support
ActiveUS20060183011A1Electrolysis componentsElectrolytic capacitorsPolymer electrolytesIn situ polymerization
A solid polymer electrolyte composite membrane and method of manufacturing the same. The composite membrane comprises a porous ceramic support having a top surface and a bottom surface. The porous ceramic support may be formed by laser micromachining a ceramic sheet or may be formed by electrochemically oxidizing a sheet of the base metal. A solid polymer electrolyte fills the pores of the ceramic support and preferably also covers the top and bottom surfaces of the support. Application of the solid polymer electrolyte to the porous support may take place by applying a dispersion to the support followed by a drying off of the solvent, by hot extrusion of the solid polymer electrolyte (or by hot extrusion of a precursor of the solid polymer electrolyte followed by in-situ conversion of the precursor to the solid polymer electrolyte) or by in-situ polymerization of a corresponding monomer of the solid polymer electrolyte.
Owner:PLUG POWER
Spinal fill for disk surgery
Owner:ELLIQUENCE
Electropolymerization molecular imprinting technology-based double-parameter composite micro-sensor and preparation thereof
Relating to sensors and molecular imprinting technologies, the invention discloses an electropolymerization molecular imprinting technology-based double-parameter composite micro-sensor and a preparation thereof. According to the invention, three electrochemical microelectrode systems are integrated on a same chip, and each electrochemical microelectrode system has its independent micro-electrochemical reaction pool. Through encapsulation by a sealant, the integrated chip can form an open composite measurement pool containing three electrochemical microelectrode systems. In the micro-reaction pool of each electrochemical microelectrode system, by injecting a solution from the outside, a molecular imprinting procedure containing in situ polymerization and ultrasonic elution of template molecules can be implemented separately, thus obtaining a molecularly imprinted sensor. The left and right microelectrode systems of the composite micro-sensor respectively recognize two corresponding molecules due to different molecularly imprinted sensitive membranes, and the electrochemical microelectrode system positioned in the middle is used as a differential detection reference so as to deduct background signals and environmental effects of a test system. The composite micro-sensor provided in the invention can recognize two molecules simultaneously.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of phase change microcapsule with graphene-modified wall material
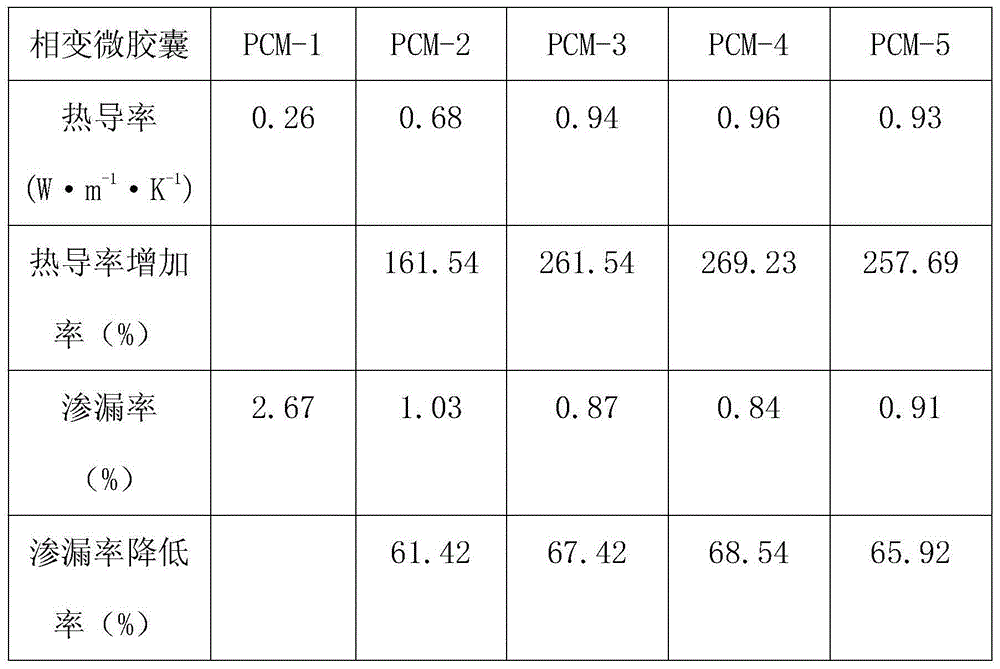
InactiveCN104861934AImprove thermal conductivityReduce leak rateHeat-exchange elementsMicroballoon preparationState of artIn situ polymerization
The invention discloses a preparation method of a phase change microcapsule with a graphene-modified wall material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a graphene oxide solution; preparing a graphene-modified wall material pre-polymer; emulsifying a phase change material; preparing the phase change microcapsule with the graphene-modified wall material. A solid-liquid phase change material serves as a core material of the phase change microcapsule prepared by using an in-situ polymerization method, and a graphene-modified polymer serves as the wall material. Compared with the prior art in which graphene is not added for modification, the preparation method in which the graphene is added into the wall material has the advantages that the heat conductivity of the phase change microcapsule is improved, and the leakage rate is lower.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
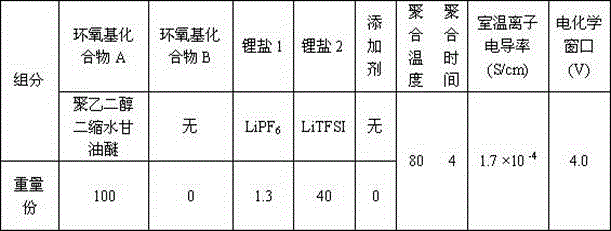
Preparation method of all-solid polymer electrolyte through in-situ ring opening polymerization of epoxy compound, and application of the all-solid polymer electrolyte in all-solid lithium battery
ActiveCN105914405AIncrease contactImprove interface compatibilityFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsEpoxySolid state electrolyte
The invention discloses a preparation method of an all-solid polymer electrolyte through in-situ ring opening polymerization of an epoxy compound, and an application of the all-solid polymer electrolyte in an all-solid battery. The preparation method is characterized in that a liquid-state epoxy compound, a lithium salt, a battery additive and the like are employed as precursors and are injected into between a positive pole sheet and a negative pole sheet of the battery, and under a heating condition, in-situ polymerization solidification is carried out to form the all-solid polymer electrolyte, and furthermore, the all-solid battery is produced. The ionic conductivity at room temperature of the all-solid polymer electrolyte can reach from 1*10<-5> S / cm to 9*10<-3> S / cm and electric potential window is 3.5-5 V. The all-solid polymer electrolyte is prepared through the in-situ copolymerization method, so that the all-solid polymer electrolyte has excellent contact with electrodes, thereby greatly improving interface compatibility of the solid-state battery, reducing interface wetting and modification steps of the solid-state battery, reducing production cost of the solid-state battery and improving performances of the solid-state battery. The invention also discloses an all-solid polymer lithium battery assembled from the all-solid polymer electrolyte.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Graphene filled polymer matrix composite material and its preparation method
ActiveCN103087404AImprove conductivityImprove thermal conductivityIn situ polymerizationMechanical property
The invention discloses a graphene filled polymer matrix composite material. The composite material is prepared through using 90-99 parts by weight of a thermoplastic resin, 0.1-10 parts by weight of a graphene microchip, 0.01-1 part of a coupling agent, and 1-10 parts of a lubricant. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the graphene filled polymer matrix composite material. Compared with other carbon system filled composite materials, the graphene filled polymer matrix composite material has the advantages of easy processing, easy forming, less filler filling amount, wide raw material source, environmental protection and the like. The composite material has the characteristics of excellent electric conductivity, excellent thermal conductivity, good mechanical properties, good dimensional stability, good weather resistance and the like; and compared with present technologies for preparing a graphene / polymer composite material through in-situ polymerization or solution polymerization, the melt blending method for preparing the graphene filled polymer matrix composite material in the invention has the advantages of continuous production, suitableness for the large-scale production, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
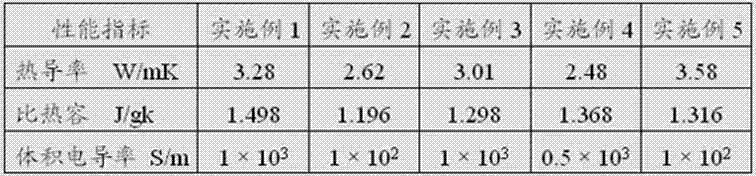
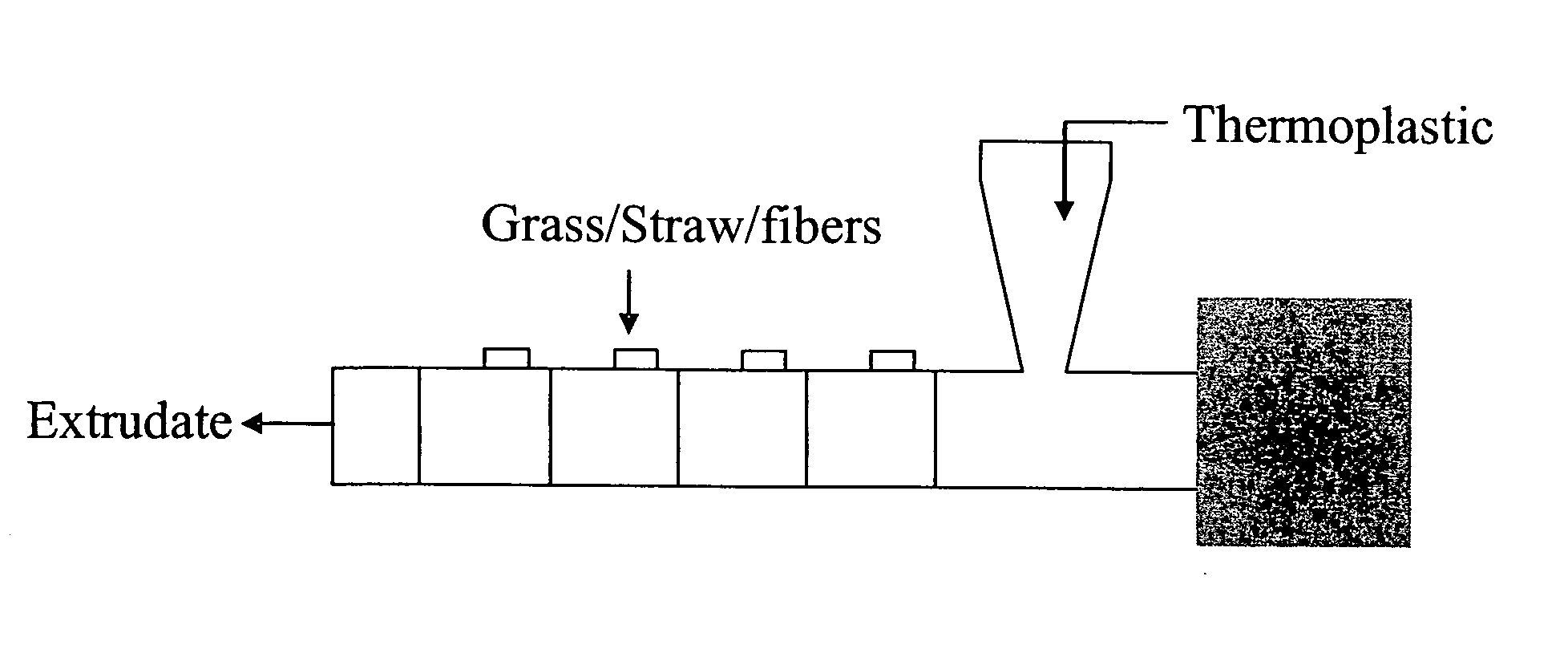
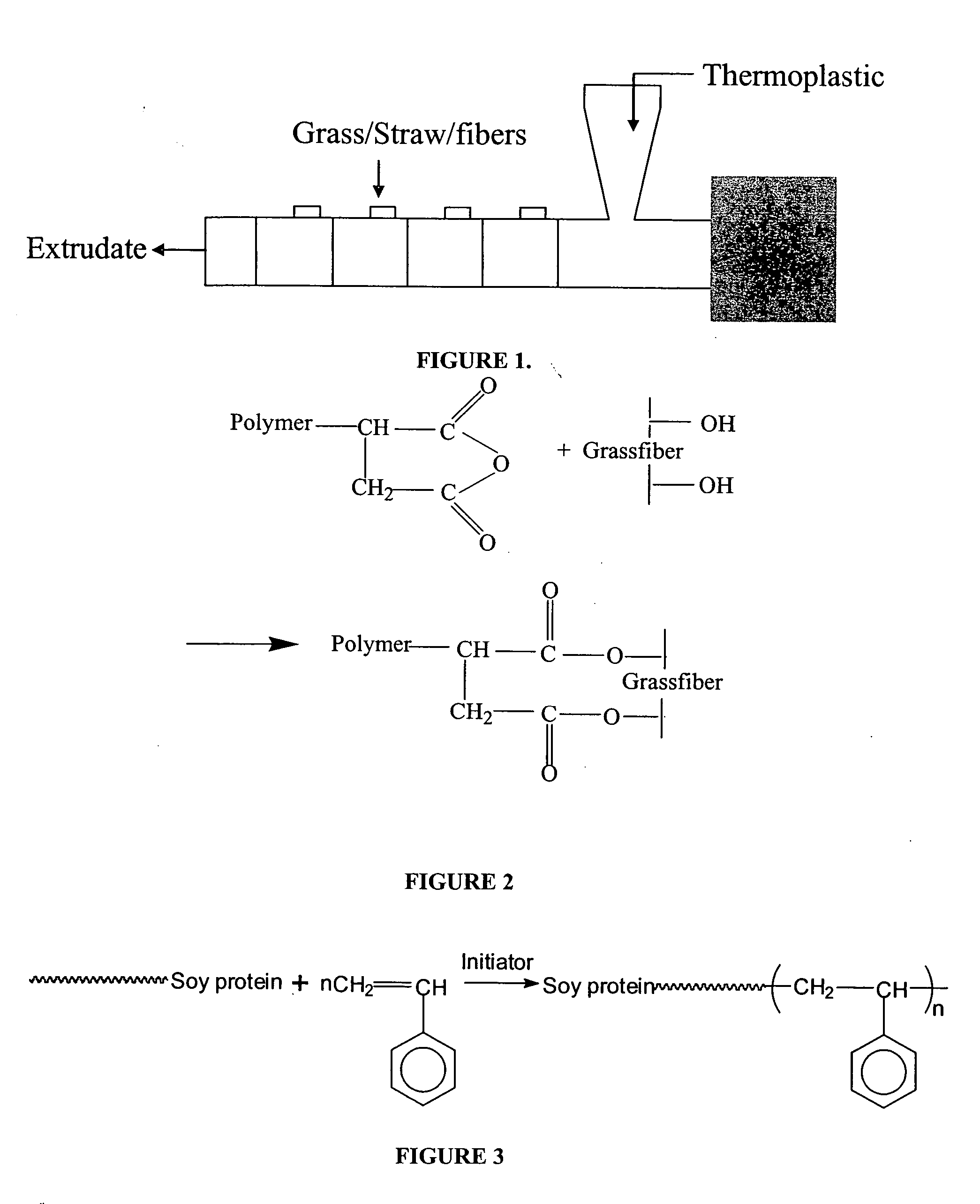
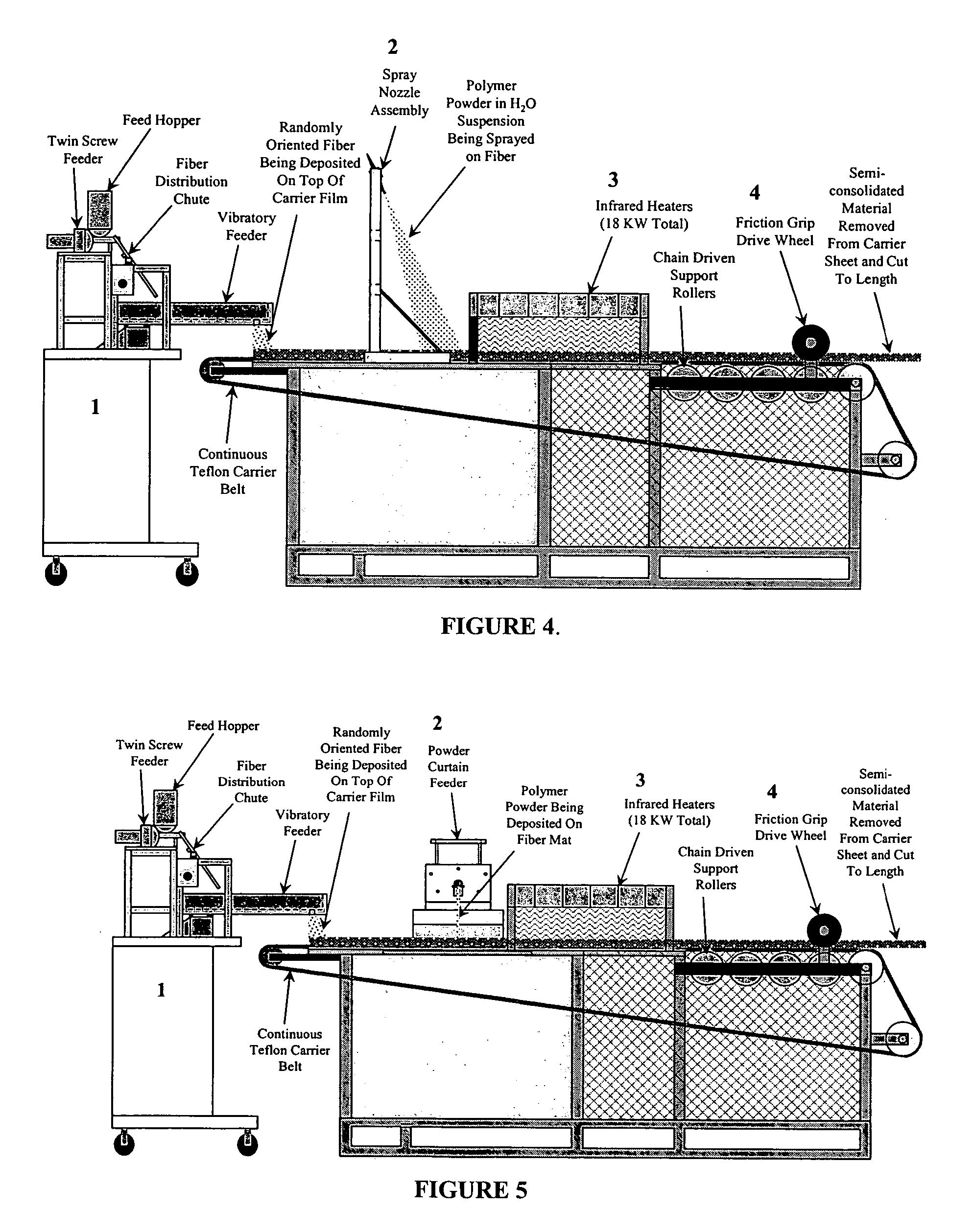
Cellulosic biomass soy flour based biocomposites and process for manufacturing thereof
A process for the manufacture of natural fiber and polymer composites is described. Thermoplastically processed plasticized soy flour based plastics are used with thermoplastic polymers. Polymers of soy flour and an in situ polymerized polyvinyl polymer which links proteins and carbohydrates in the flour to form the polymer are used. The composites are useful in engineering materials.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
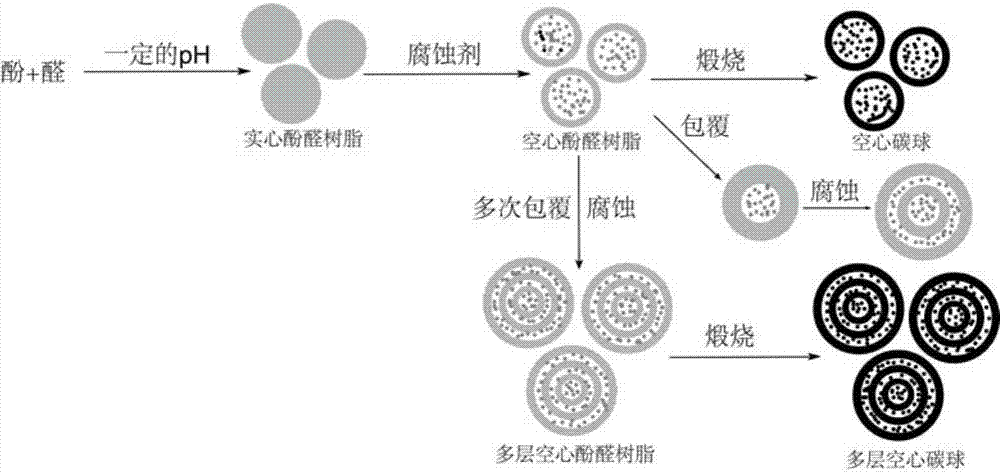
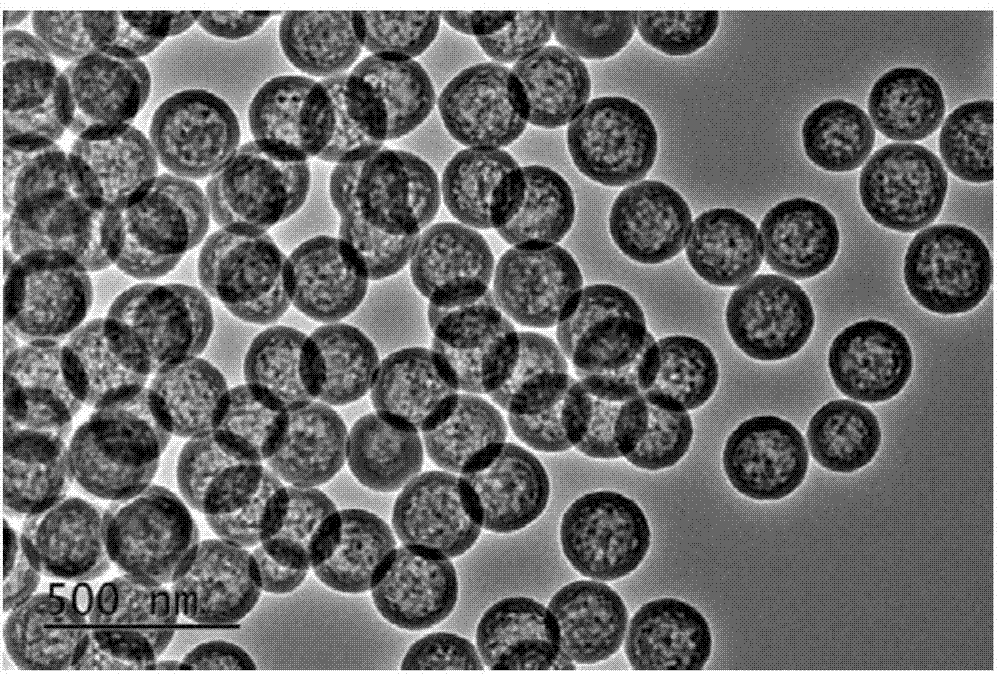
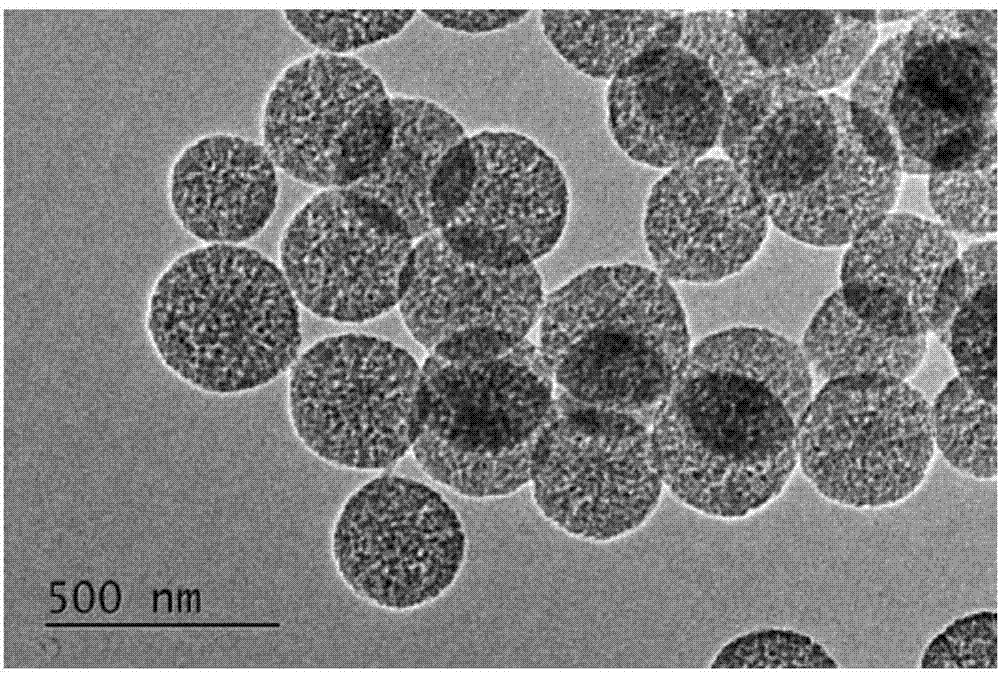
Single-layer and multi-layer hollow carbon nanosphere and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104843665AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsMaterial nanotechnologySolubilityIn situ polymerization
The invention discovers and proposes a characteristic that interior species of phenolic resin are nonuniform in distribution in a polymerization process, and discloses a method for preparing a hollow carbon sphere by utilizing the characteristic of phenolic resin. The method comprises: (1) putting phenol into water or a solvent, adjusting the pH, then adding aldehyde and stirring at a certain temperature for a period of time; (2) adding a corrosive agent in a reaction system, stirring at a certain temperature, and selectively removing a part with a relatively low polymerization degree inside a polymer by utilizing a solubility difference of interior species for different solvents, to obtain an intermediate product, that is, a hollow sphere of phenolic resin polymer; and (3) calcining the intermediate product that is obtained in step (2) in an inertia or reducing atmosphere, naturally cooling to room temperature, and thus completing preparation of the hollow carbon sphere. The method is simple and practicable, and the prepared hollow carbon sphere is uniform in shape and controllable in dimension. Moreover, by utilizing a characteristic that the phenolic resin can be in-situ polymerized on surfaces of different nanometer particles, on one hand, a multi-layer hollow structure can be prepared in a multi-cladding and layer-by-layer corrosion manner, and on the other hand, the different nanometer particles can also be packaged in a cavity in an in-situ mode, so as to prepare a nuclear shell or egg yolk-nuclear structure. The prepared hollow carbon sphere has a potential application value in aspects of silicon-carbon negative electrode material, Li-S battery, supercapacitor, heavy metal ion adsorption, and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
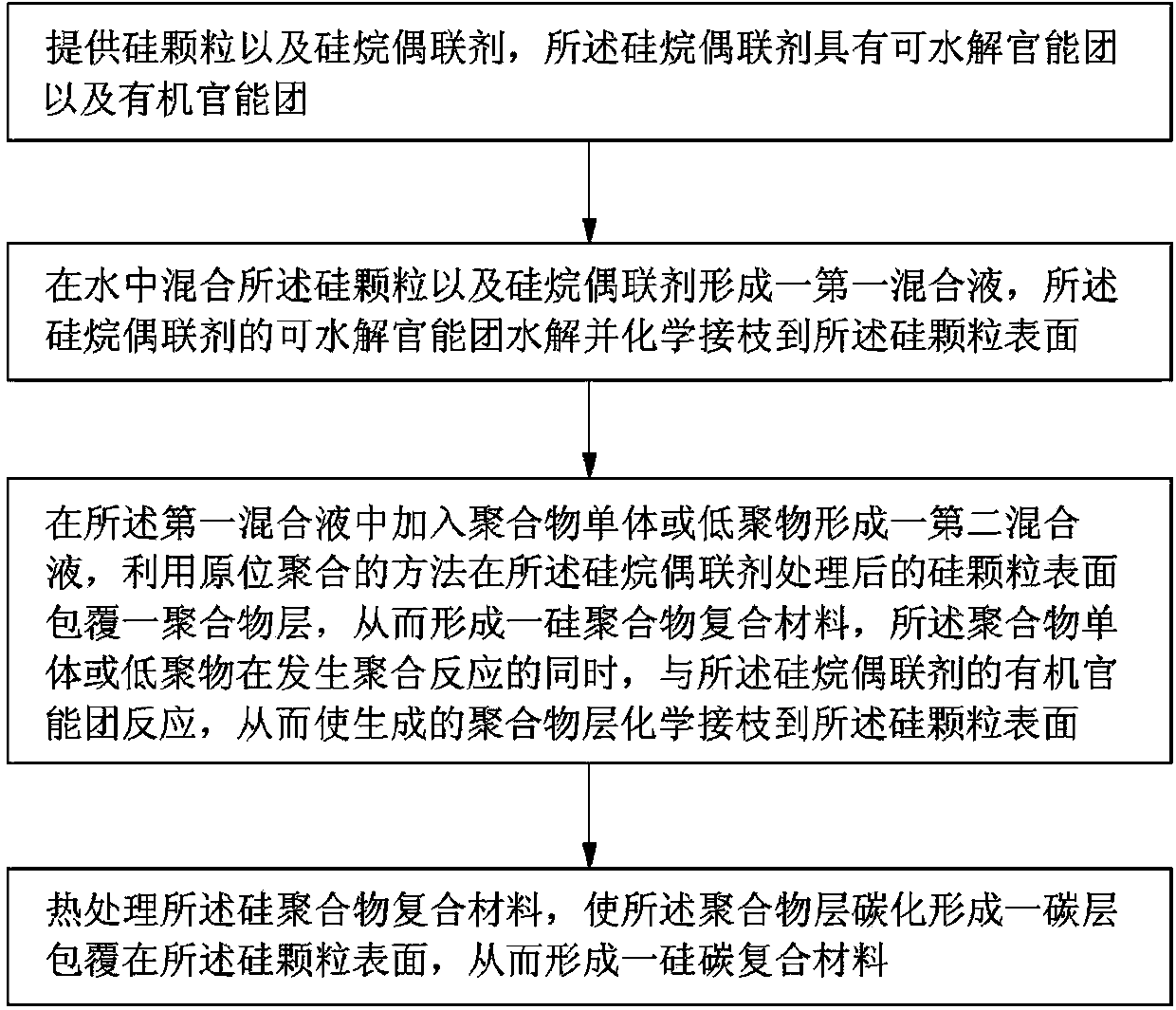
Preparation method for negative electrode active material of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN103474666AImprove conductivityImprove structural stabilityElectrode thermal treatmentSecondary cellsCarbon compositesCarbon layer
The invention relates to a preparation method for a negative electrode active material of a lithium ion battery. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing a silicon particle and a silane coupling agent which has a hydrolyzable functional group and an organic functional group; mixing the silicon particle with the silane coupling agent in water to form a first mixed liquor, wherein the hydrolyzable functional group of the silane coupling agent is hydrolyzed and chemically grafted onto the surface of the silicon particle; adding a polymer monomer or oligomer into the first mixed liquor to form a second mixed liquor, coating a polymer layer on the surface of the silicon particle by using in situ polymerization so as to form a silicon / polymer composite and allowing the polymer monomer or oligomer to react with the organic functional group of the silane coupling agent during polymerization so as to allow the generated polymer layer to be chemically grafted onto the surface of the silicon particle; and subjecting the silicon / polymer composite to heat treatment to carbonize the polymer layer so as to form a carbon layer coated on the surface of the silicon particle, thereby forming a silicon carbon composite.
Owner:JIANGSU HUADONG INST OF LI ION BATTERY +1
Graphene/carbon black thermoplastic resin master batch with high dispersibility and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a graphene / carbon black thermoplastic resin master batch with high dispersibility and a preparation method thereof. The graphene / carbon black compound in the master batch is formed in an electrostatic self-assembly manner, and comprises 10-50% of graphene, 5-20% of carbon black, 0.5-10% of surfactant, 10-65% of carrier resin and 2-10% of assistant. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) compounding and dispersing graphene by adopting the surfactant to control the positive electricity of the graphene surface; (2) forming a stable graphene / carbon black compound from the modified graphene and carbon black with positive electricity through electrostatic incorporation in a self-assembly manner; (3) preparing the graphene / carbon black thermoplastic resin master batch with high dispersibility by matching with a solution blended process, a melt-blending method and an in-situ polymerization method; (4) adding the assistant to extrude and pelletize, so as to prepare the graphene / carbon black / thermoplastic resin master batch particles after processing the master batch. By adopting the obtained master batch, the problems of difficult charging of graphene powder, uneven dispersion, dust pollution, unstable product performance and the like are solved.
Owner:XIAMEN KNANO GRAPHENE TECH CORP
Nano silicasol / acrylic ester composite emulsion and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a nanometer silica sol / acrylic ester composite latex and a preparation method thereof. The composite latex is formed by polymerizing acrylic ester monomers with nanometer silica sol and alkylol solvent; emulsion particles in the composite latex are in a nanometer nucleus-shell structure taking silicon dioxide granules as nucleus and acrylic ester multipolymer as shells; and the preparation method adopts a seed emulsion polymerization method or in situ polymerization method. The composite latex has higher tensile-strength and tearing strength and better performances of acid durability, weather resisting property, wearing resistance, ultraviolet aging resistance, anti-pollution resistance, and the like, can be applied to various aspects of inner and outer wall dope, ground and terrace dope, ground coating of specialty sports fields, and the like, is green and environment-friendly, and has wide market foreground.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUNRISE CHEMISTRY CO LTD
Preparing method for infrared response high-strength hydrogel for cartilago articularis repair
InactiveCN105107019AImprove mechanical propertiesEfficient photothermal conversion effectProsthesisCross-linkSide chain
The invention discloses a preparing method for infrared response high-strength hydrogel for cartilago articularis repair. The preparing method mainly includes the operation steps that polysaccharide or protein is modified in a double bond forming mode through methacrylic acid, methacrylic anhydride and methacrylate substances, so that the polysaccharide or the protein has a double-bond group in a side chain and is capable of being polymerized to form the hydrogel. Under the action of an initiator and a cross-linking agent, N-isopropyl acrylamide and the polysaccharide or the protein modified in the double bond forming mode form the double-network high-strength hydrogel through in-situ polymerization. The prepared infrared response high-strength hydrogel is high in biocompatibility and excellent in mechanical property and has good application prospects in the field of cartilago articularis repair.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Carbon nano tube-containing sulfur-based composite cathode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101891930AIncrease contentImprove power characteristicsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesIn situ polymerizationAcrylonitrile
The invention discloses a carbon nano tube-containing sulfur-based composite cathode material and a preparation method thereof. The sulfur-based composite cathode material is a ternary composite material AxByCz, wherein A is a dehydrocyclization product of an acrylonitrile-itaconic acid copolymer; B is elemental sulfur; C is a carbon nano tube; x is more than or equal to 30 weight percent and less than or equal to 60 weight percent; y is more than or equal to 30 weight percent and less than or equal to 60 weight percent; and z is more than or equal to 1 weight percent and less than or equal to 20 weight percent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: in-situ polymerizing an acrylonitrile-itaconic acid monomer on the surface of the multi-wall carbon nano tube, and performing thermal treatment on both of the acrylonitrile-itaconic acid copolymer and the elemental sulfur, so that the sulfur is uniformly dispersed in a substrate formed by the dehydrocyclization of the acrylonitrile-itaconic acid copolymer. The carbon nano tube-containing sulfur-based composite cathode material and a lithium cathode form a secondary lithium-sulfur battery which is charged and discharged at the room temperature. The carbon nano tube-containing sulfur-based composite cathode material has the reversible specific capacity of 697 mAh / g and high cyclical stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com