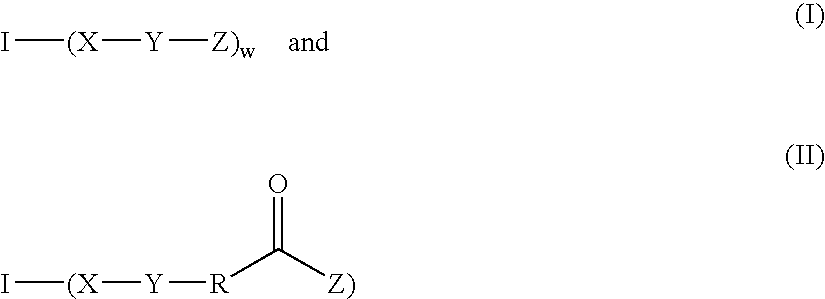Patents
Literature
144885 results about "Oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An oxide /ˈɒksaɪd/ is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O²⁻ atom. Metal oxides thus typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of solid oxides, the result of elements being oxidized by the oxygen in air or in water. Hydrocarbon combustion affords the two principal carbon oxides: carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al₂O₃ (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion. Individual elements can often form multiple oxides, each containing different amounts of the element and oxygen. In some cases these are distinguished by specifying the number of atoms as in carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, and in other cases by specifying the element's oxidation number, as in iron(II) oxide and iron(III) oxide. Certain elements can form many different oxides, such as those of nitrogen. other examples are silicon, iron, titanium, and aluminium oxides.
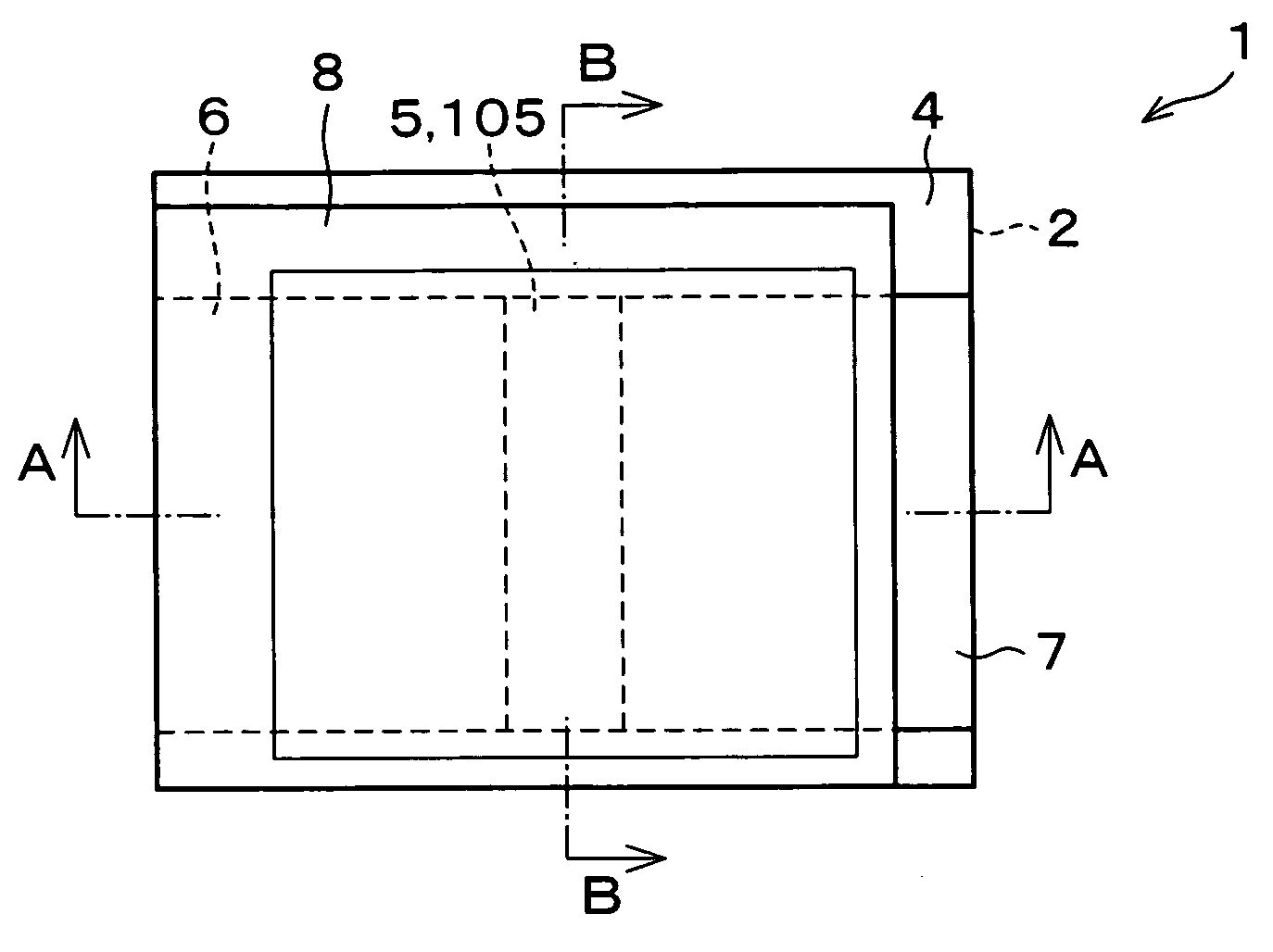
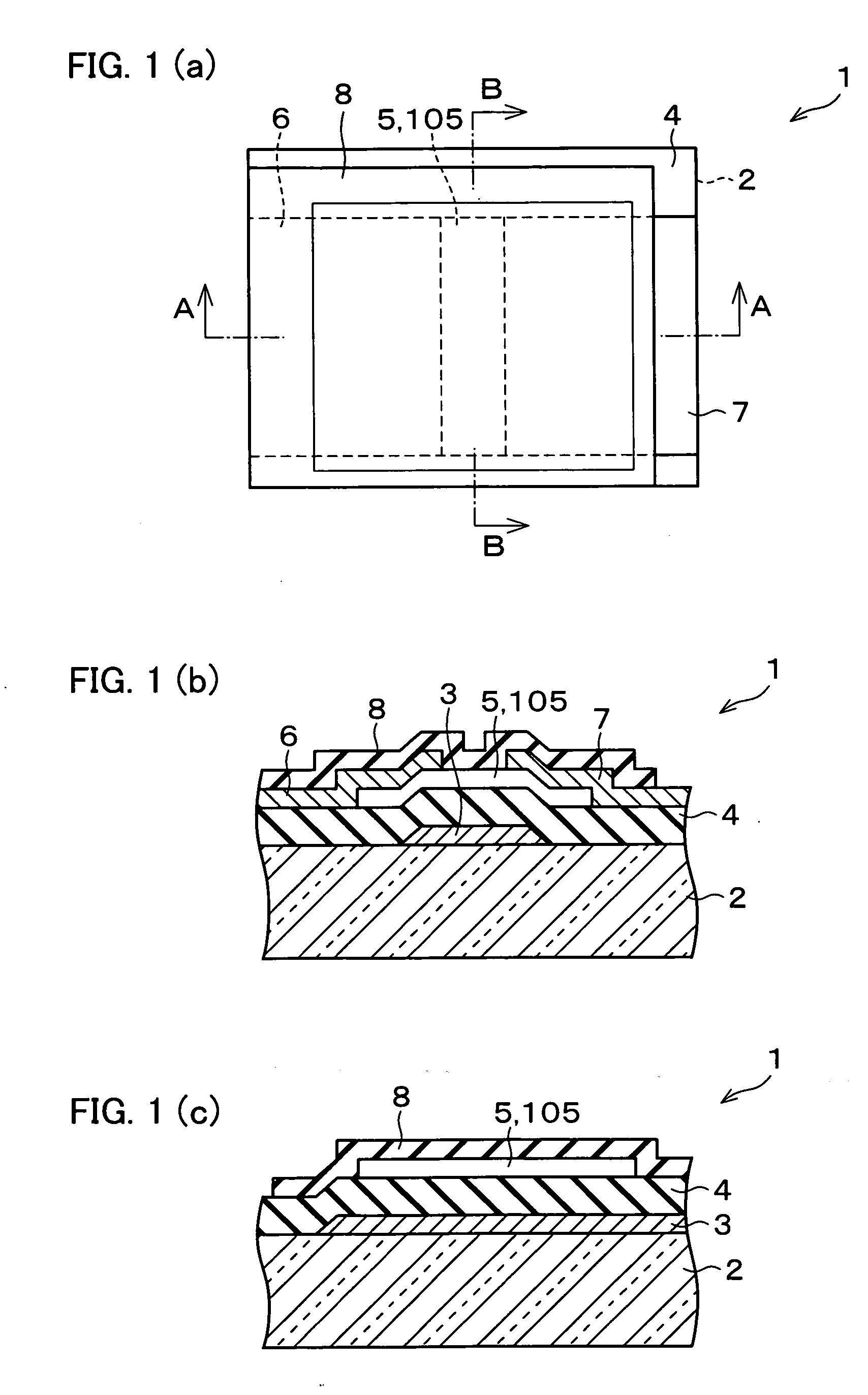
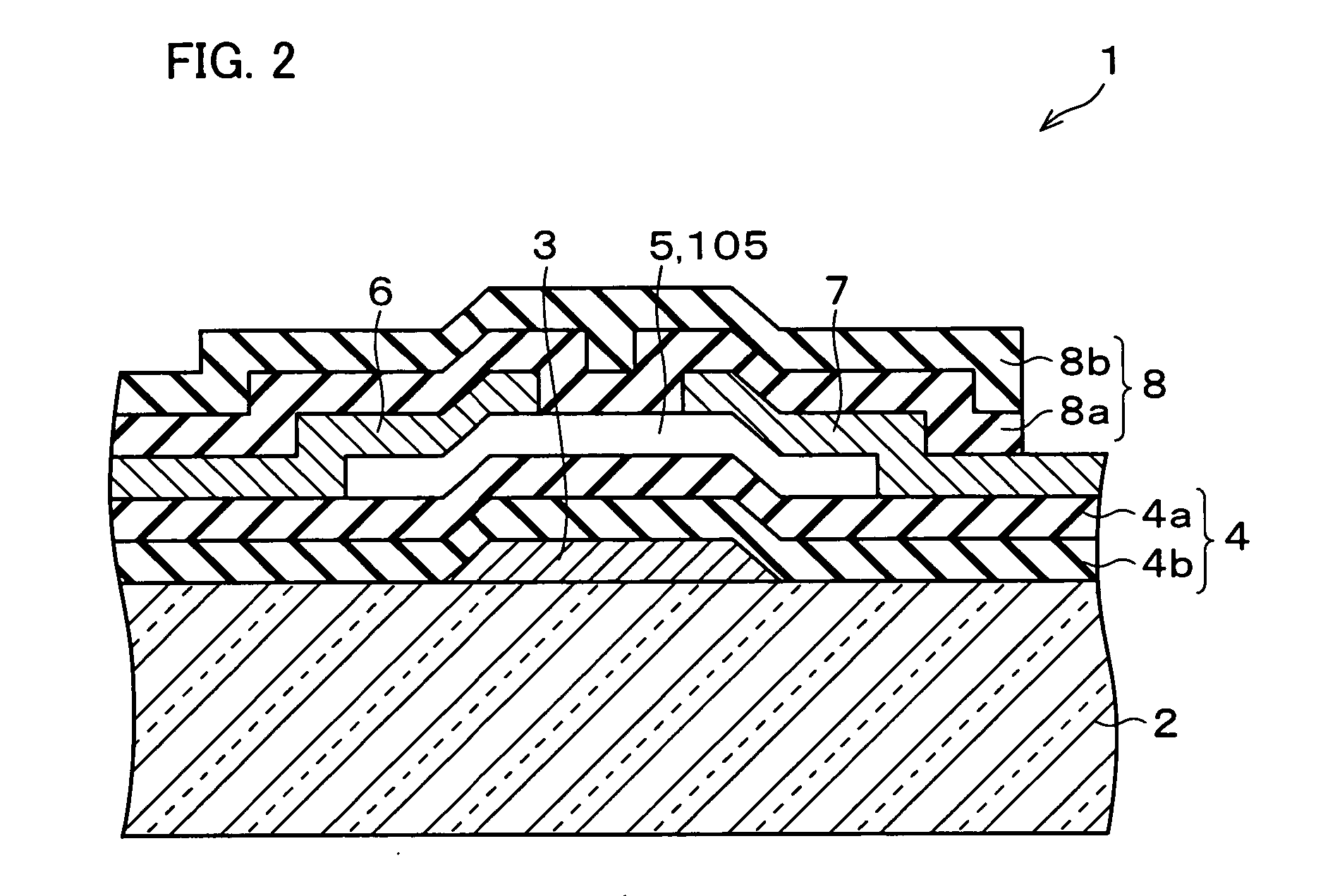
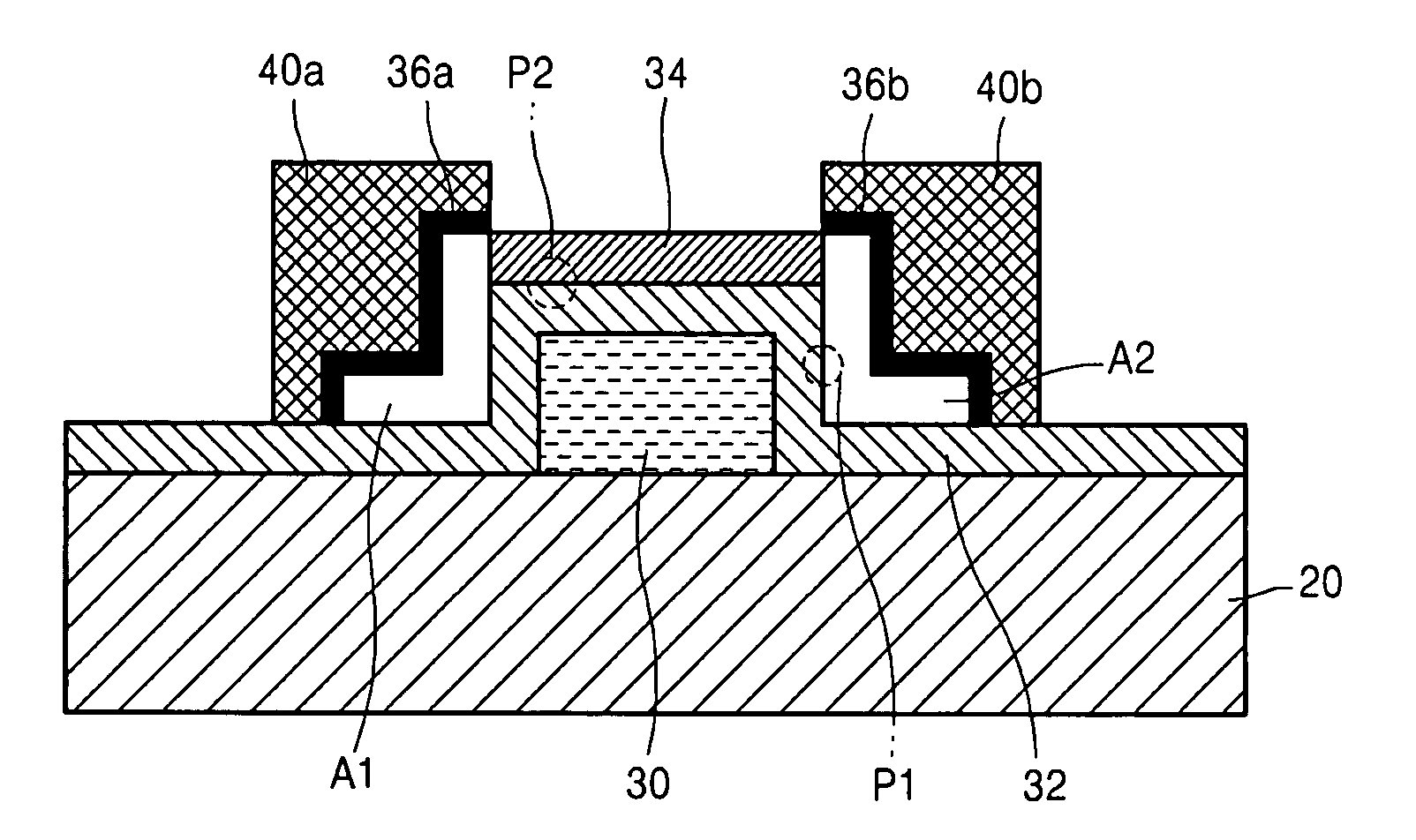
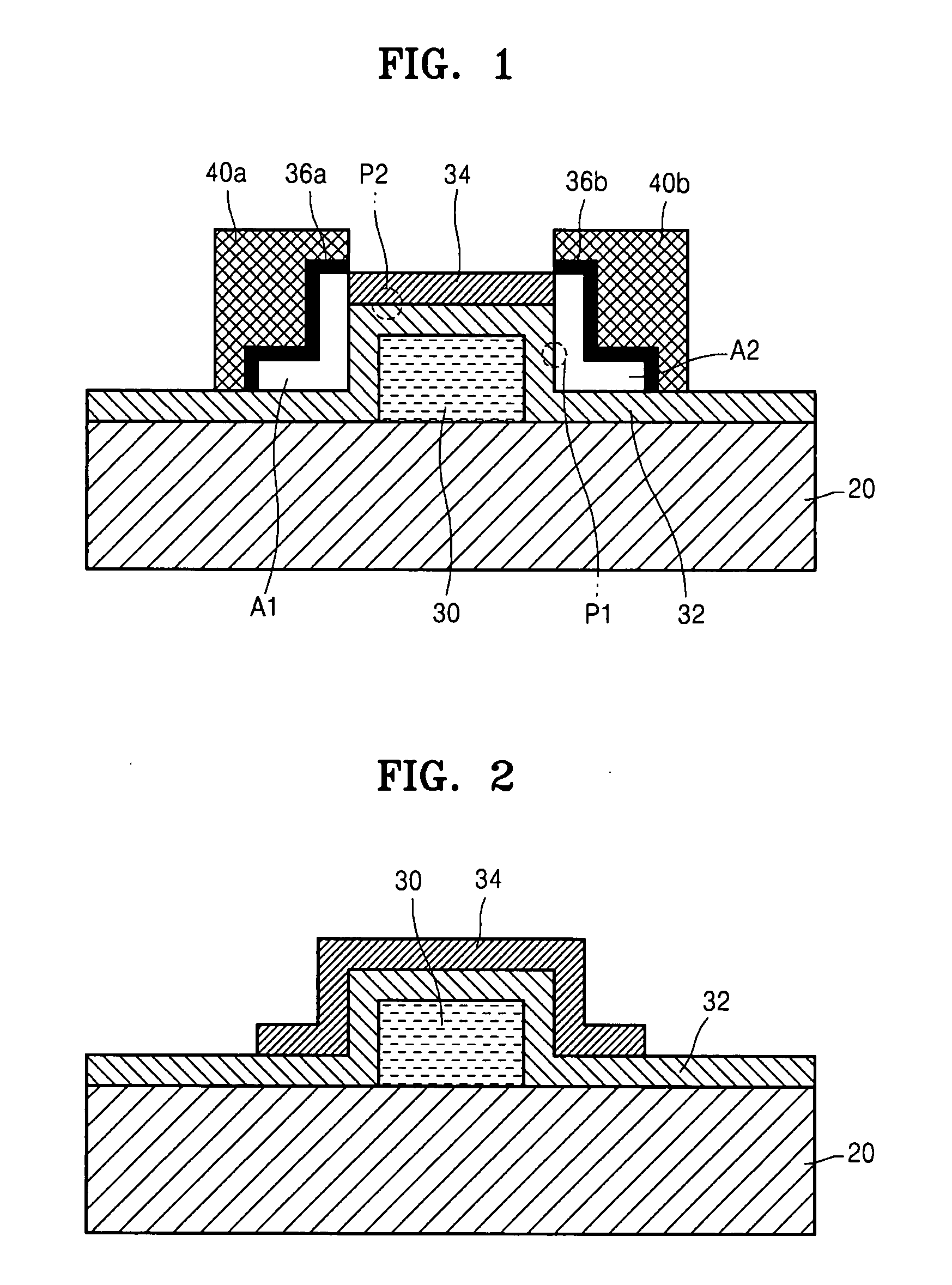
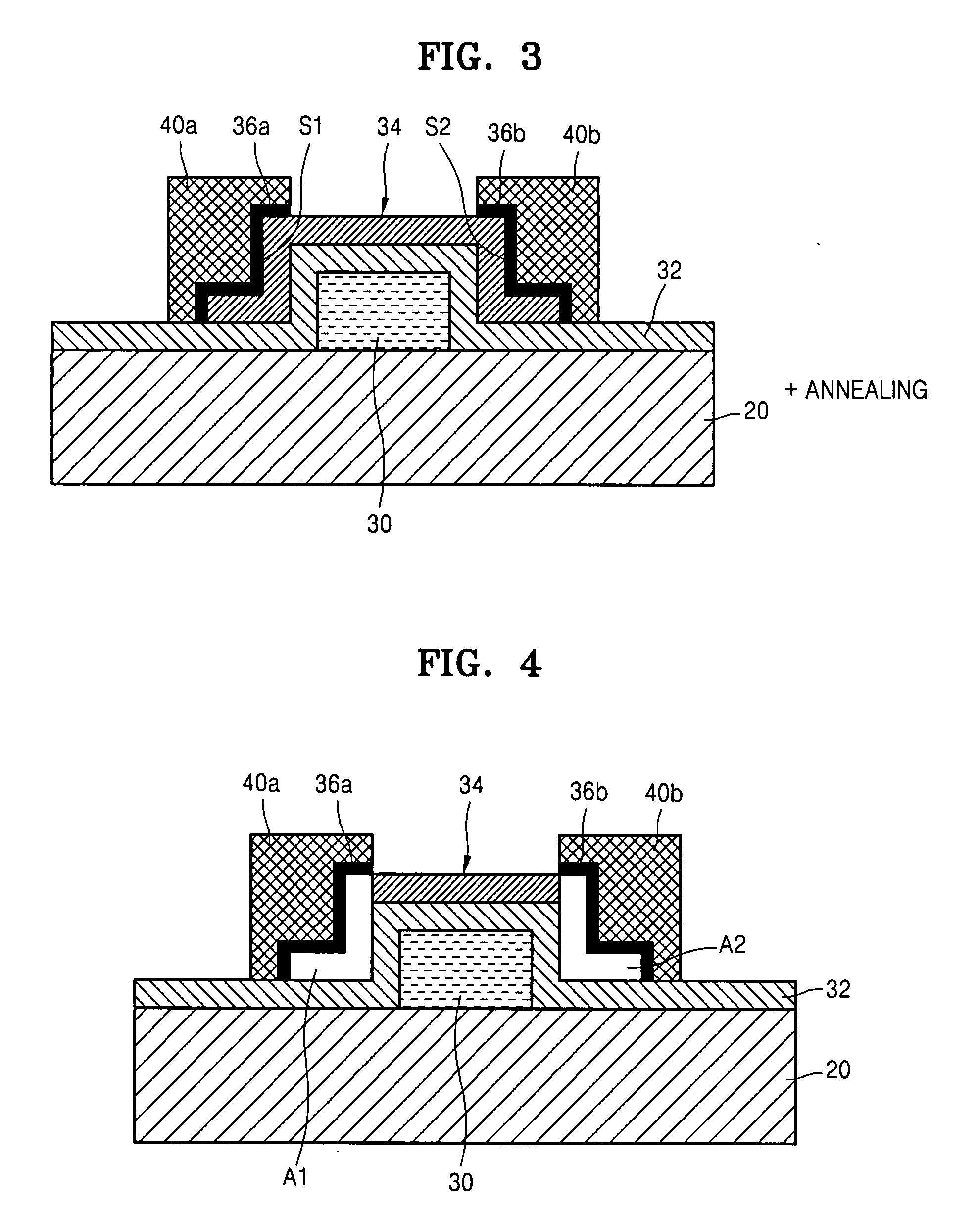
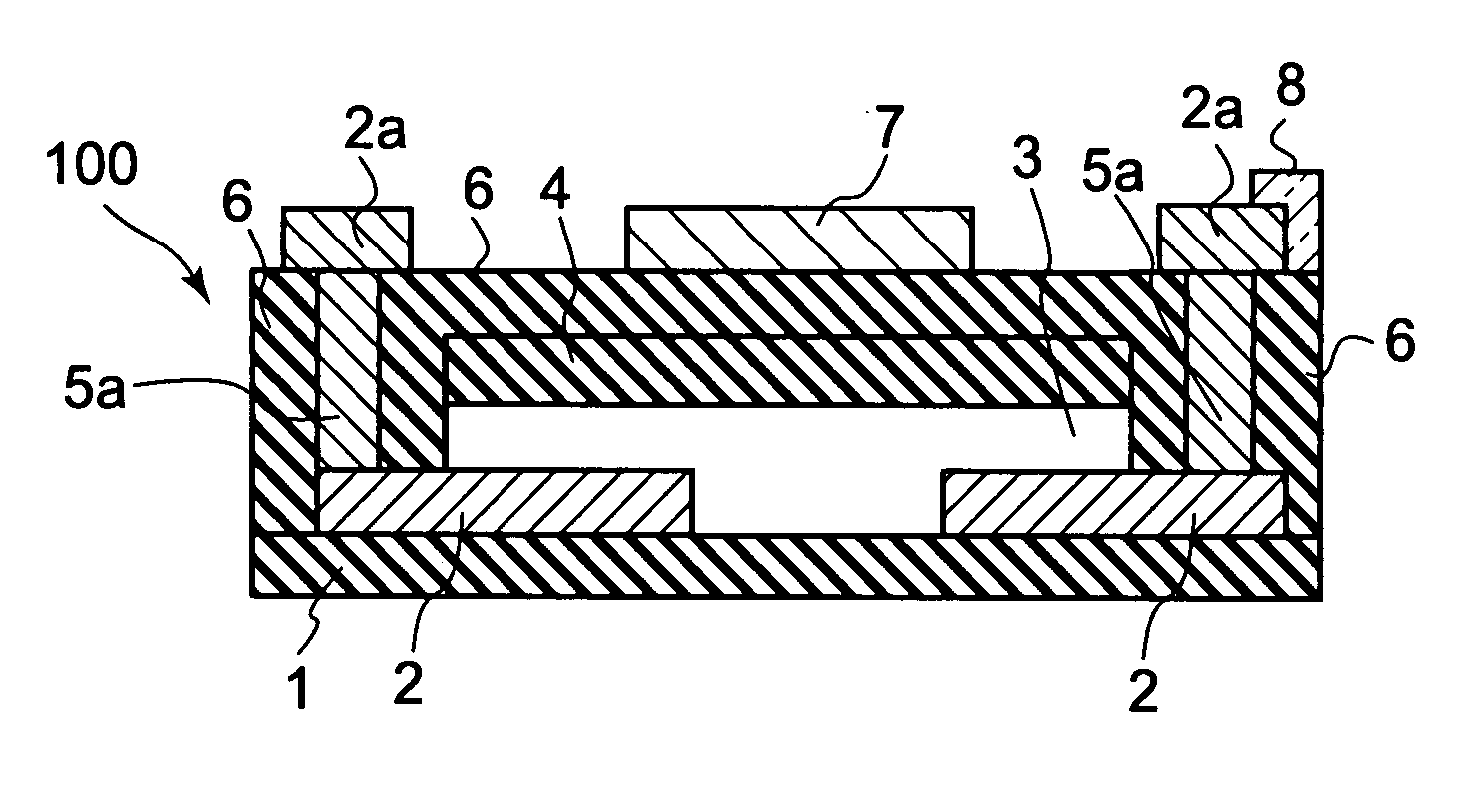
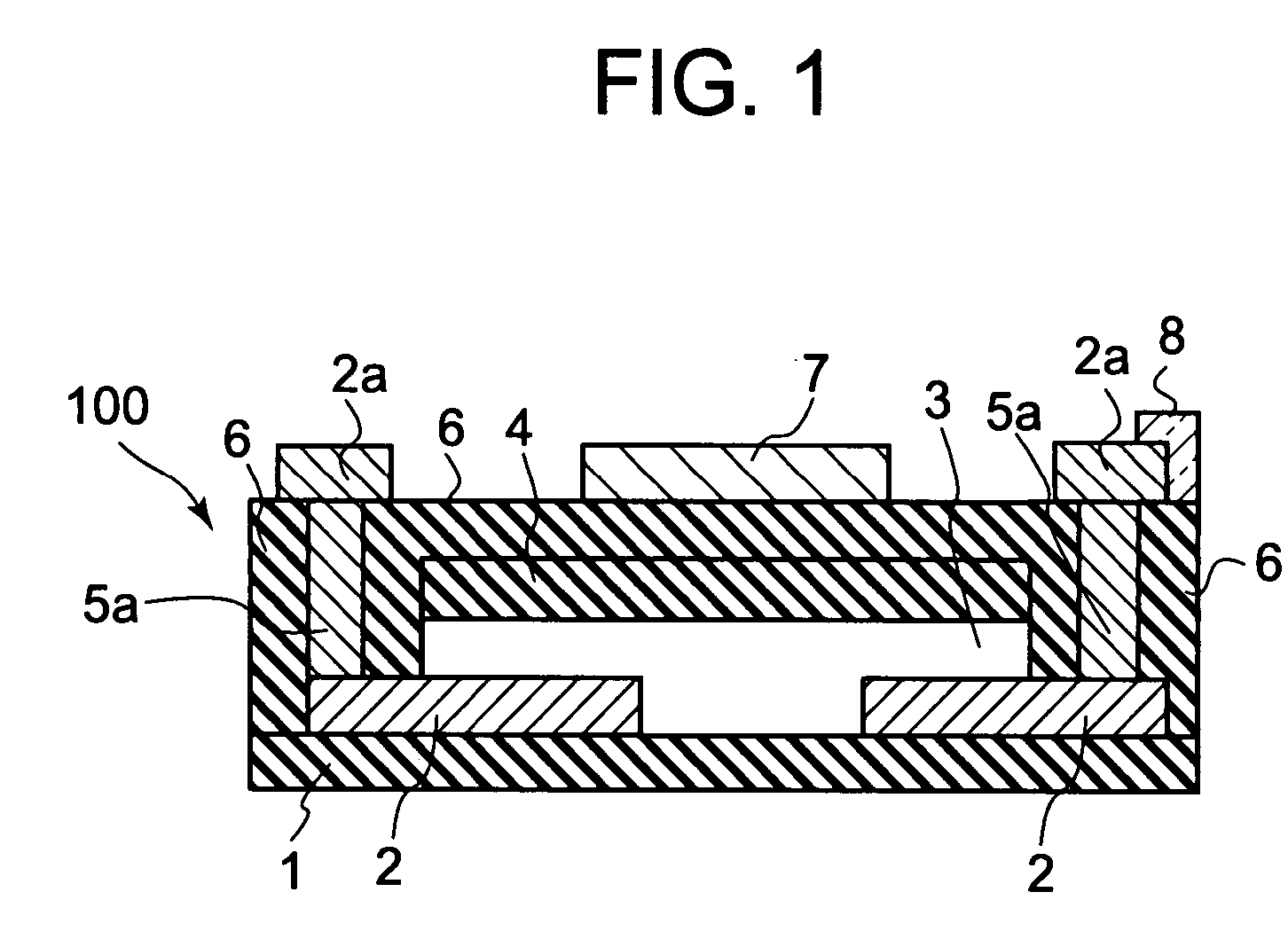
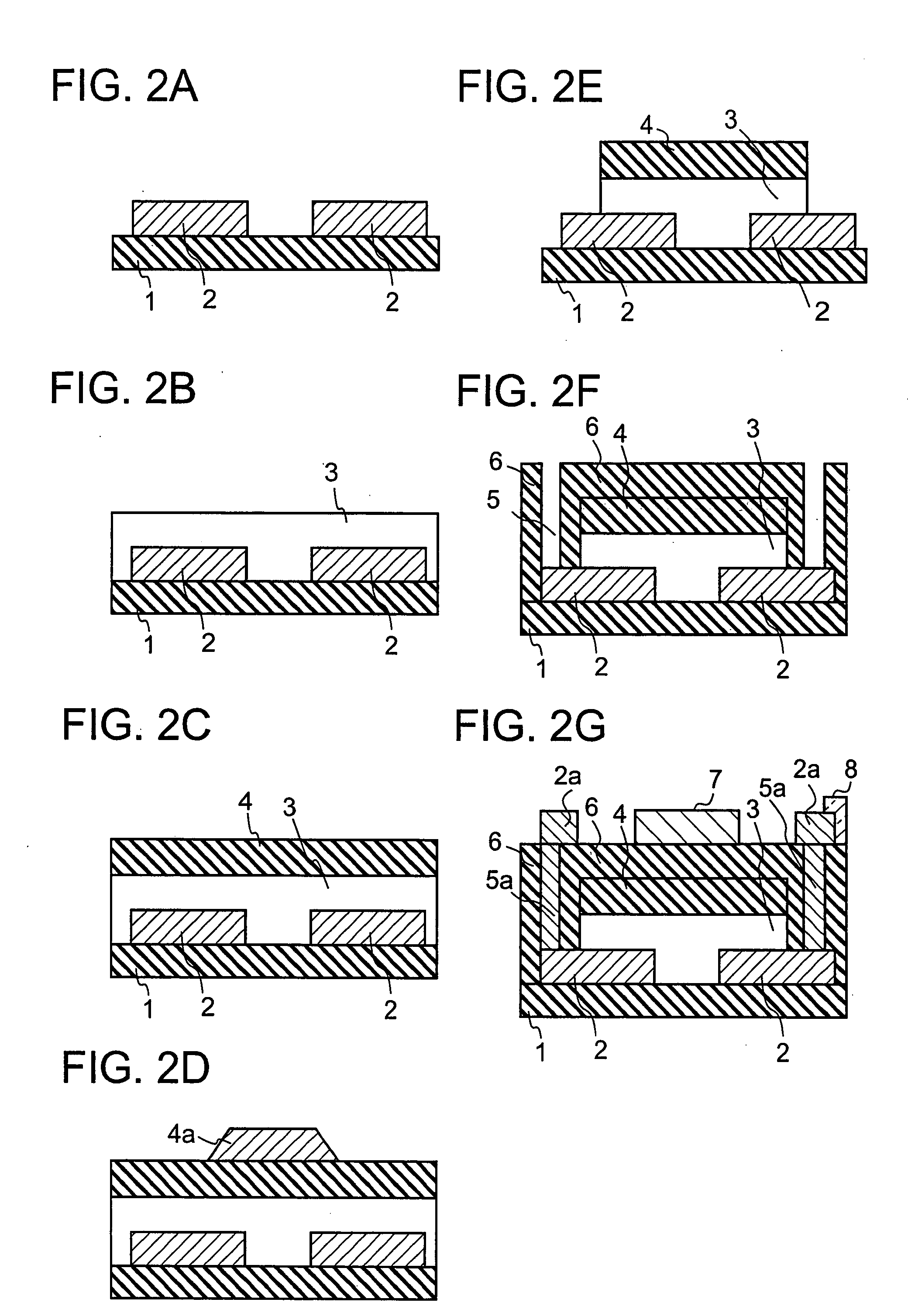
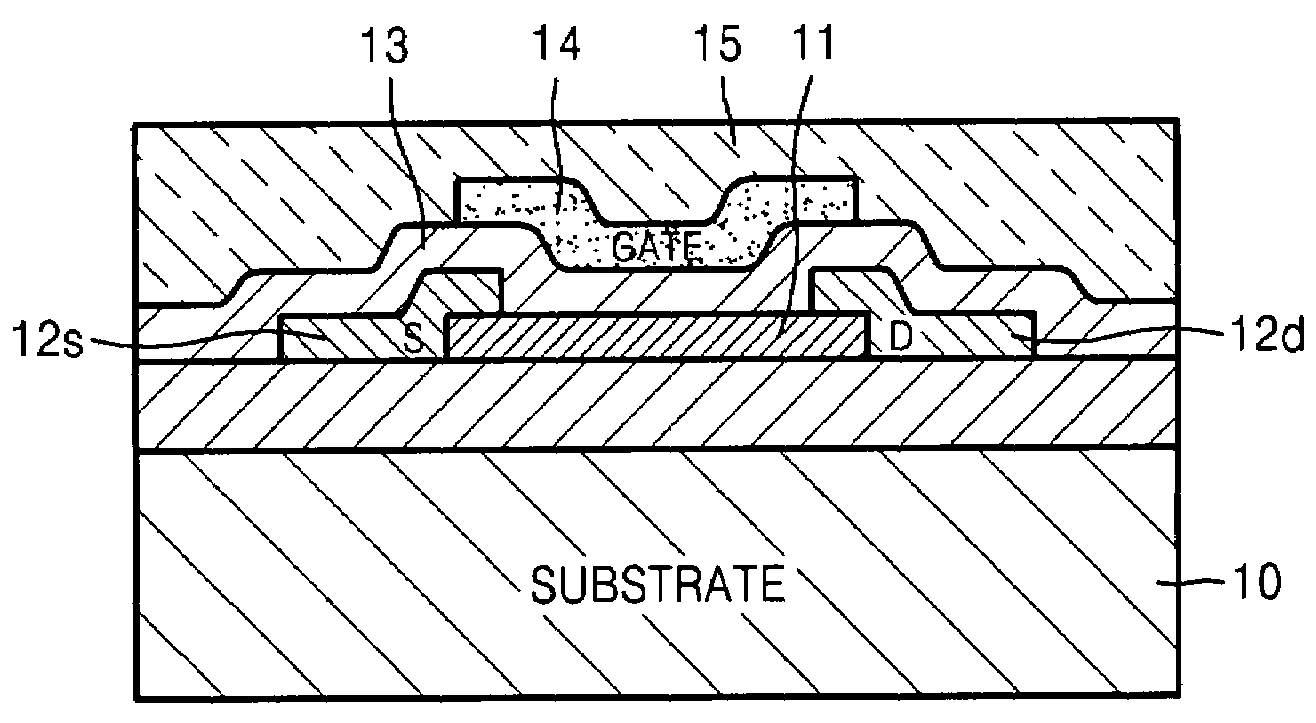
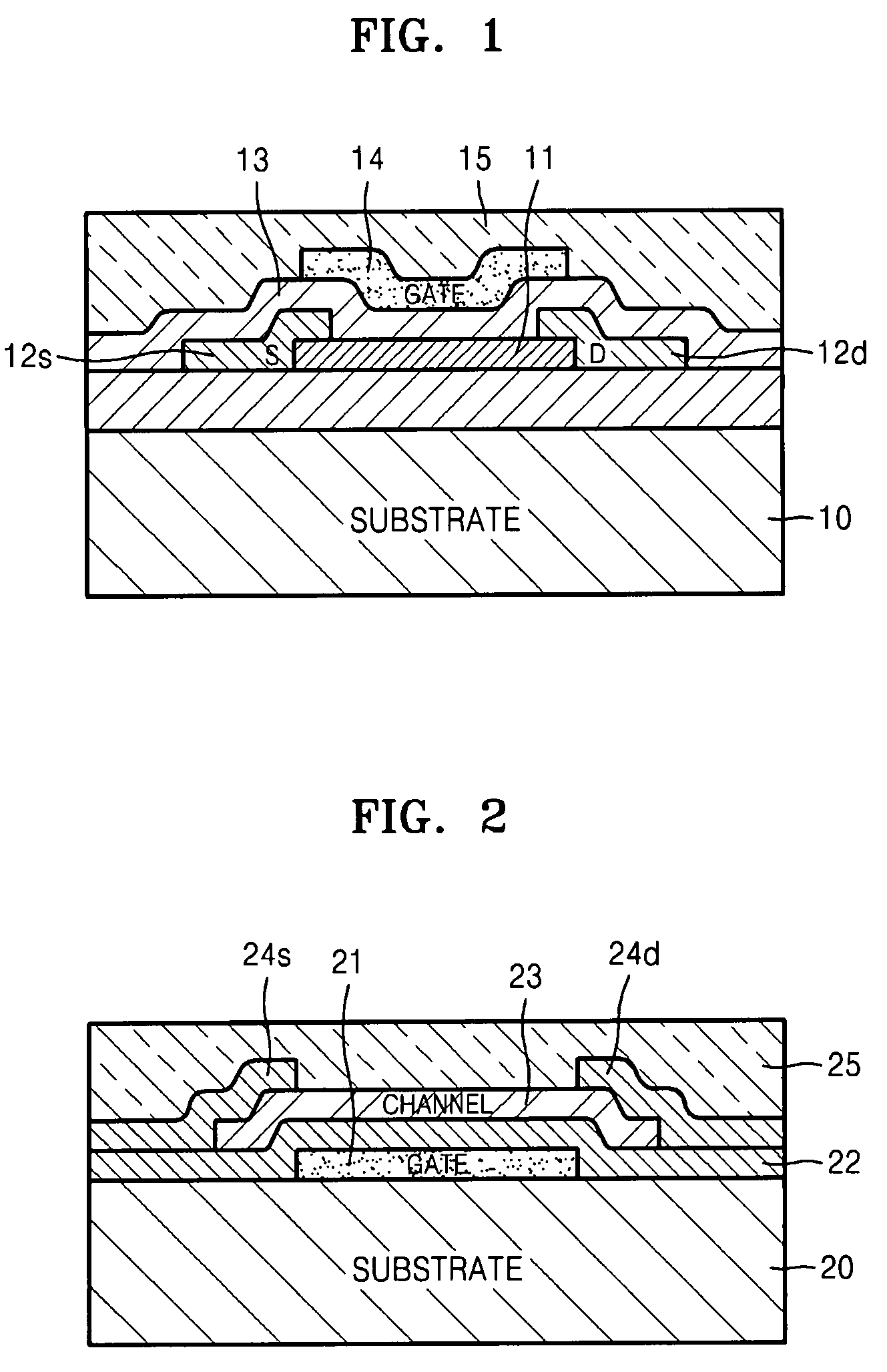
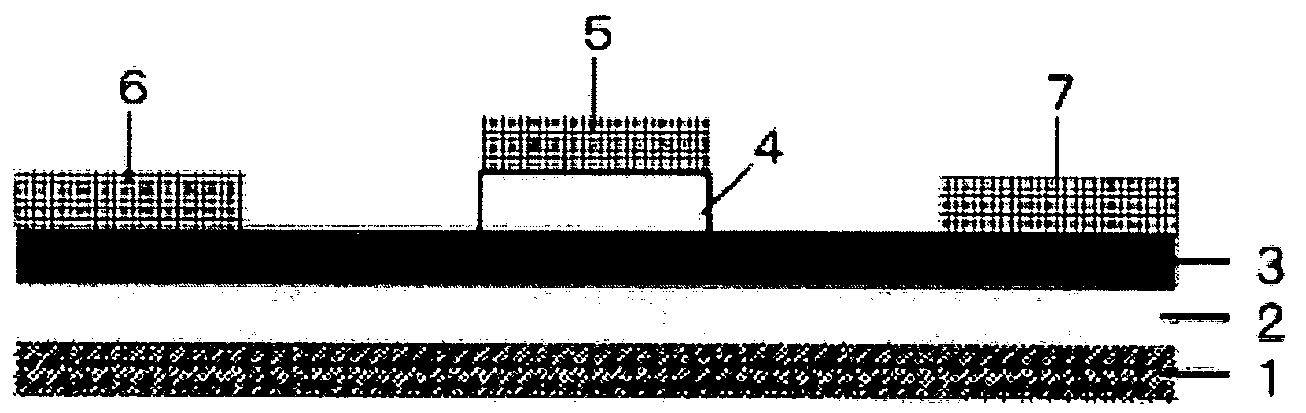
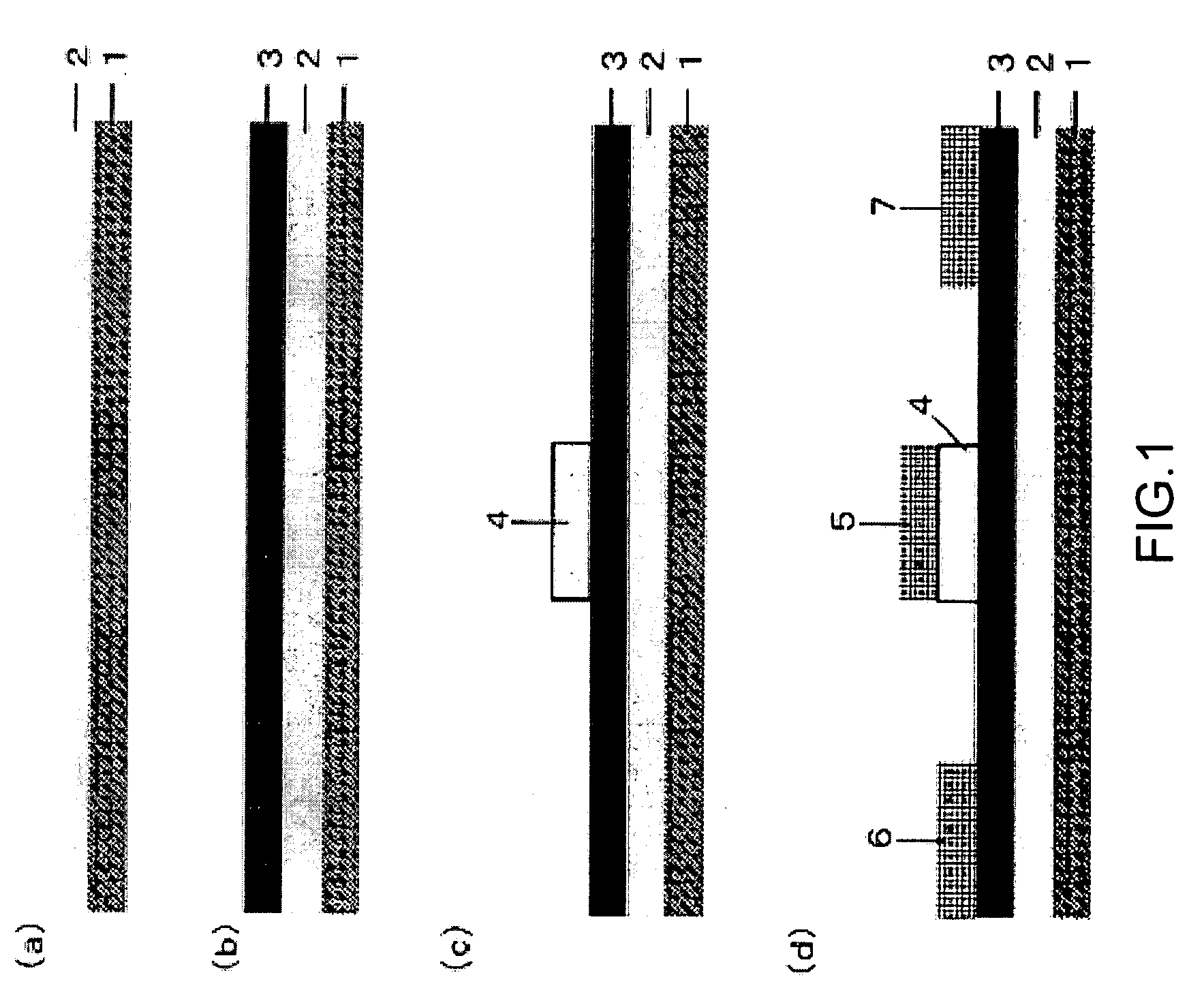
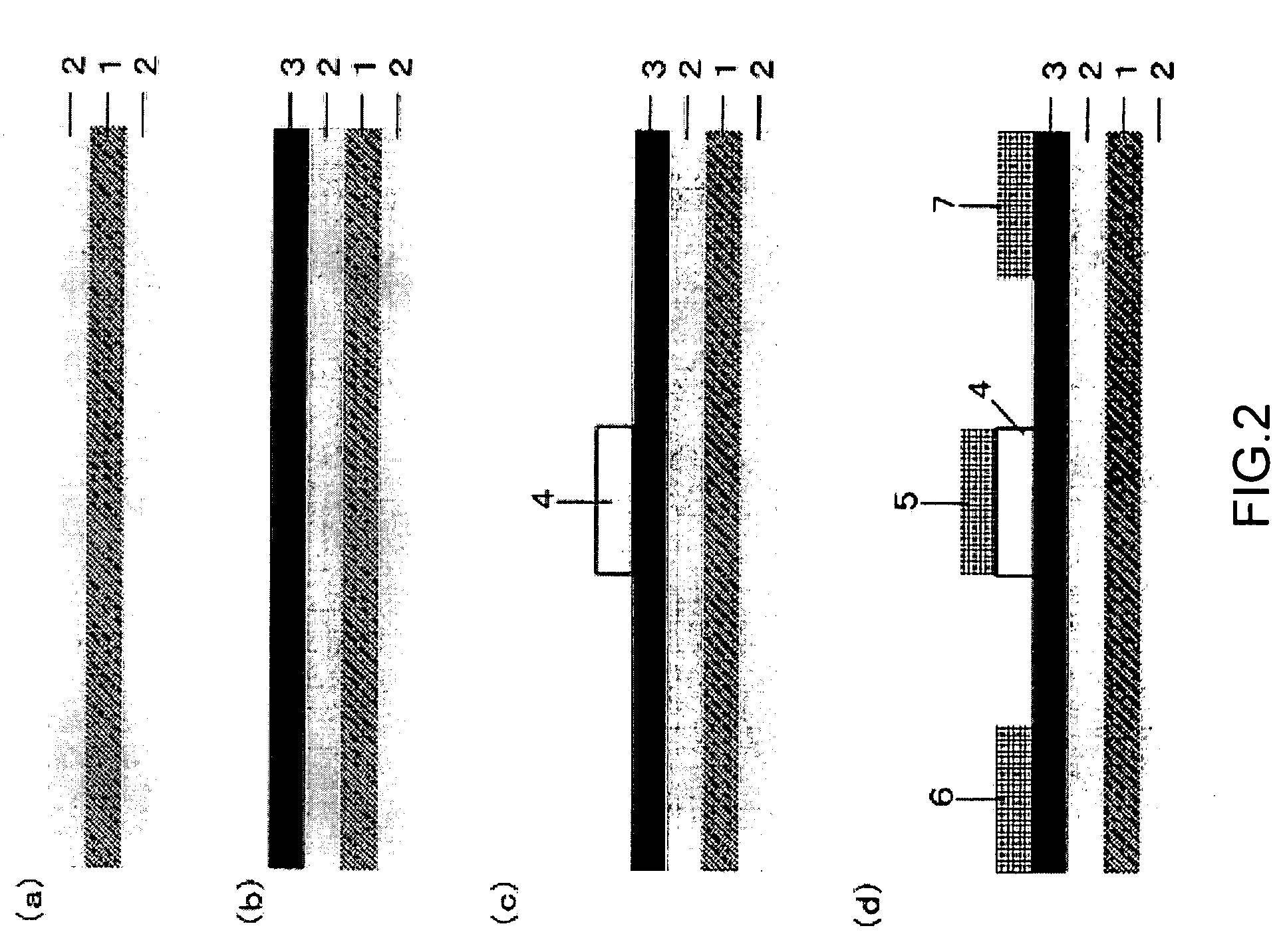
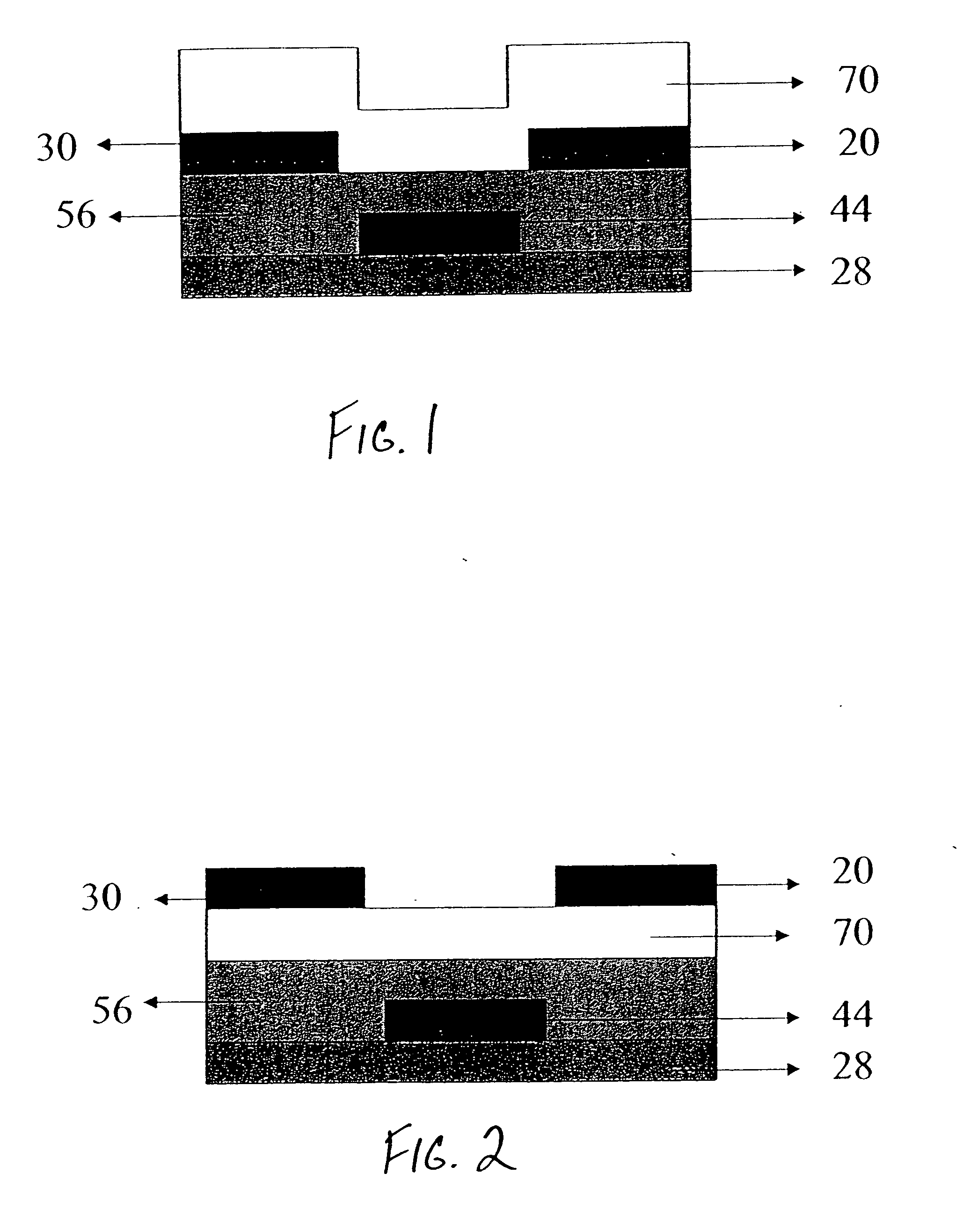
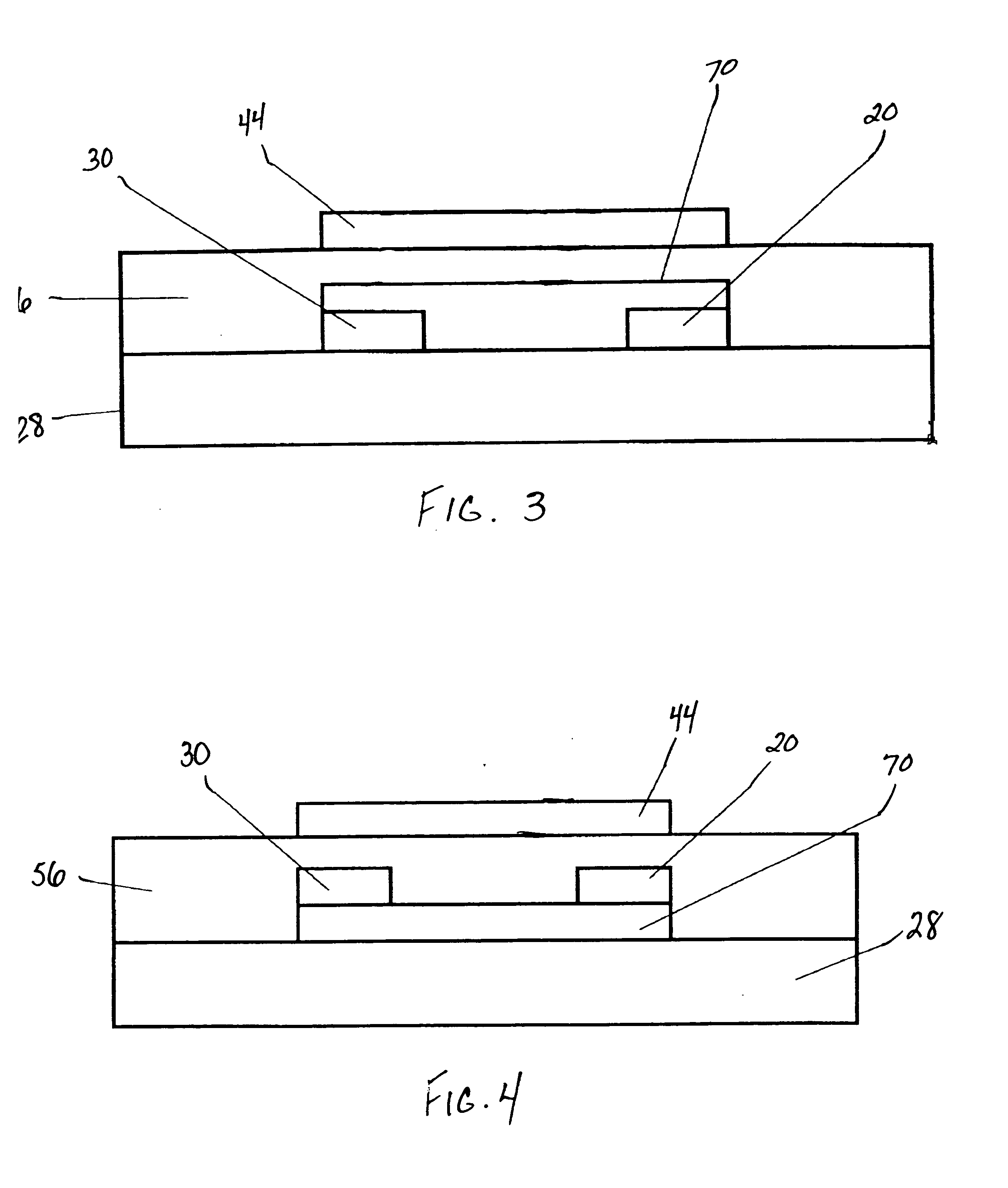
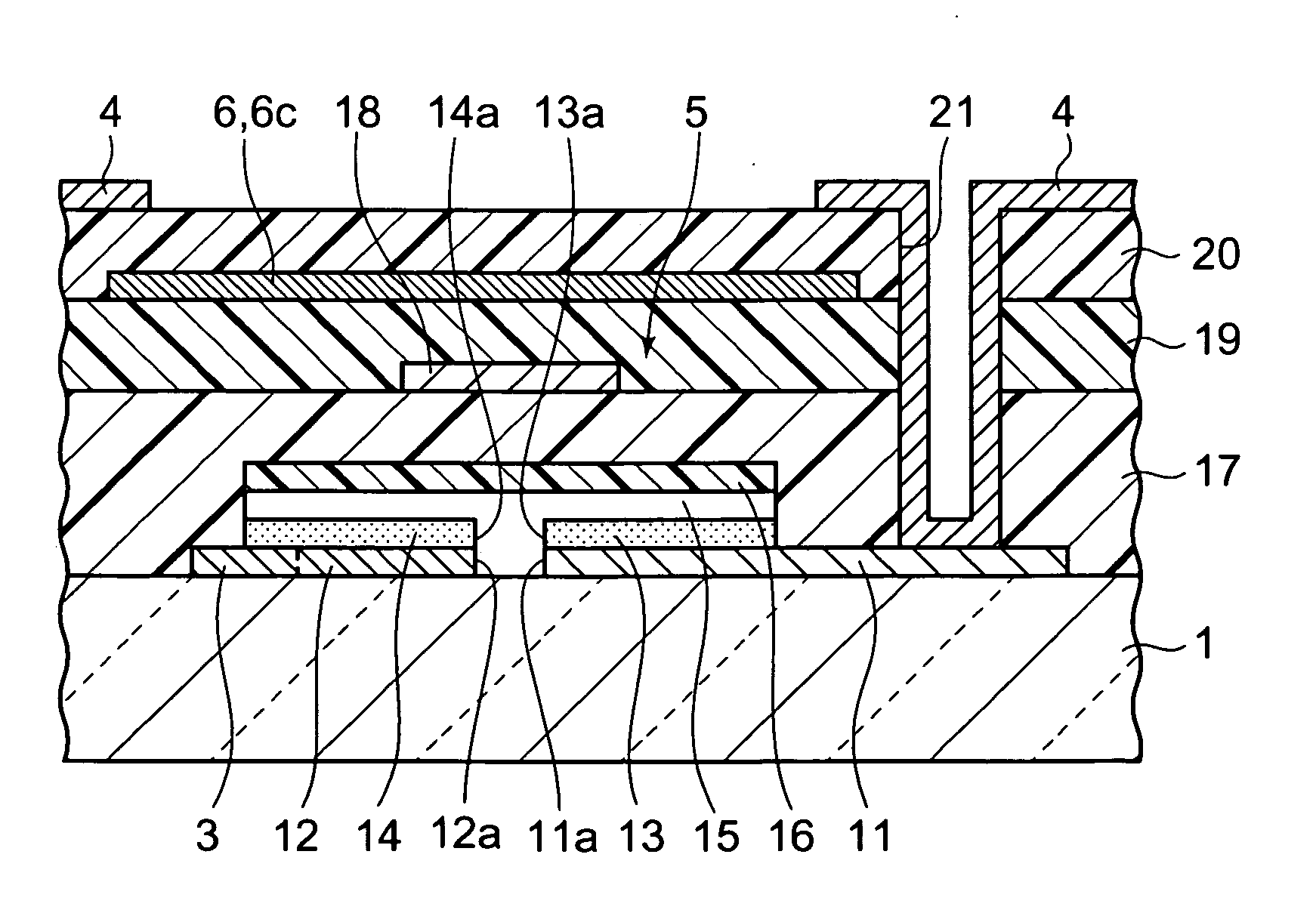
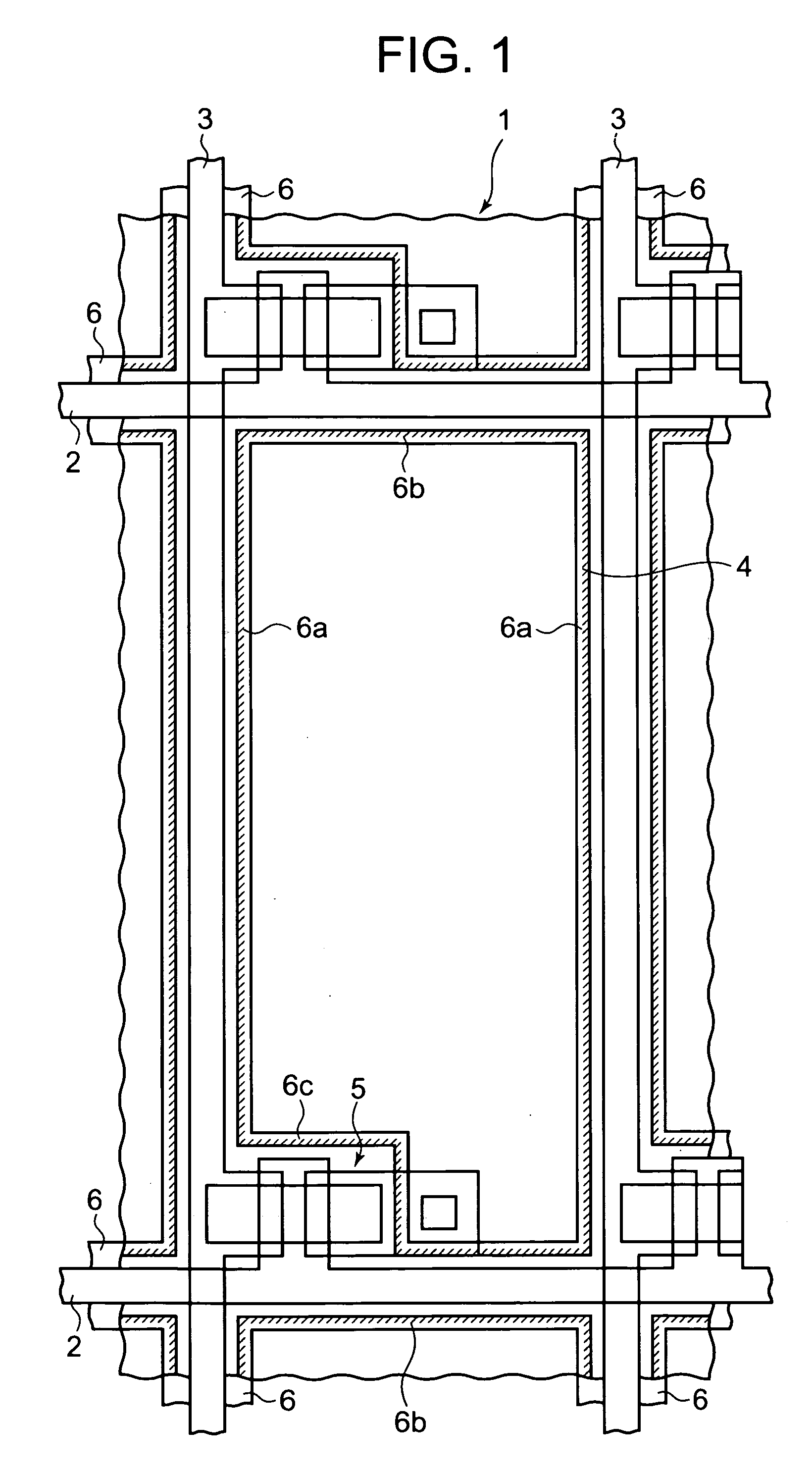
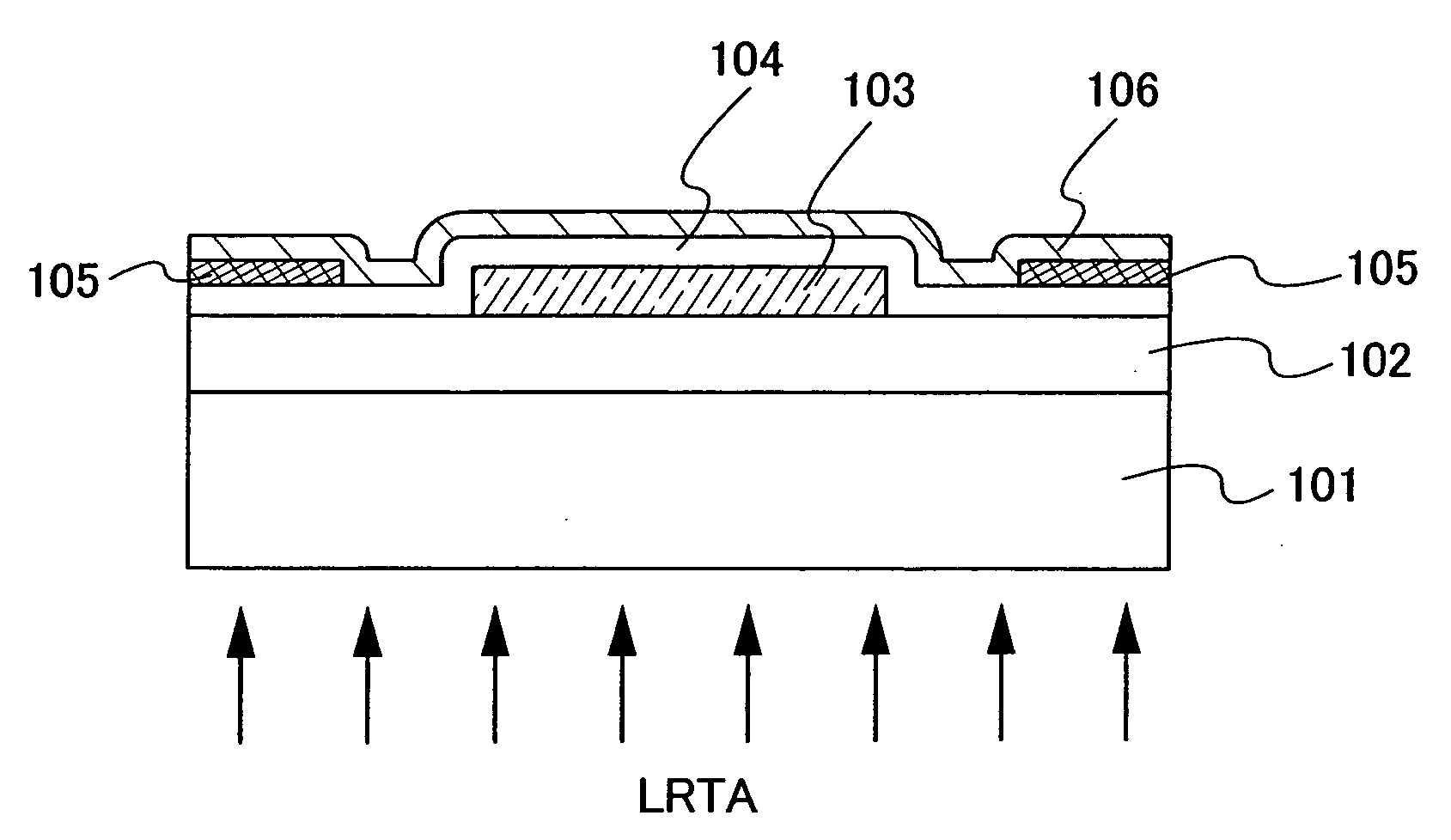
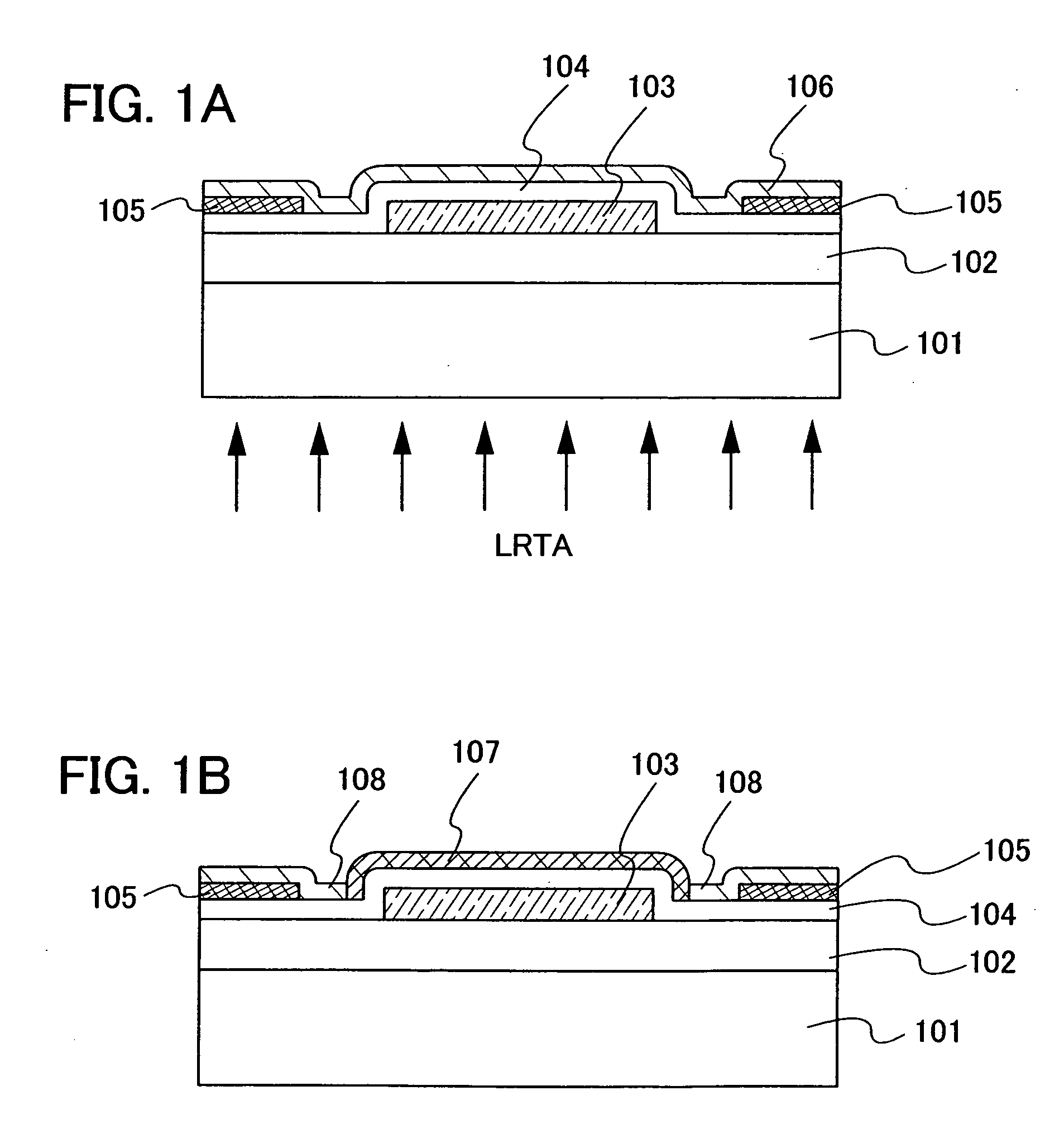
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method, and electronic device
ActiveUS20060244107A1Stabilize element propertyEasy to manufactureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface levelIntrinsic resistance
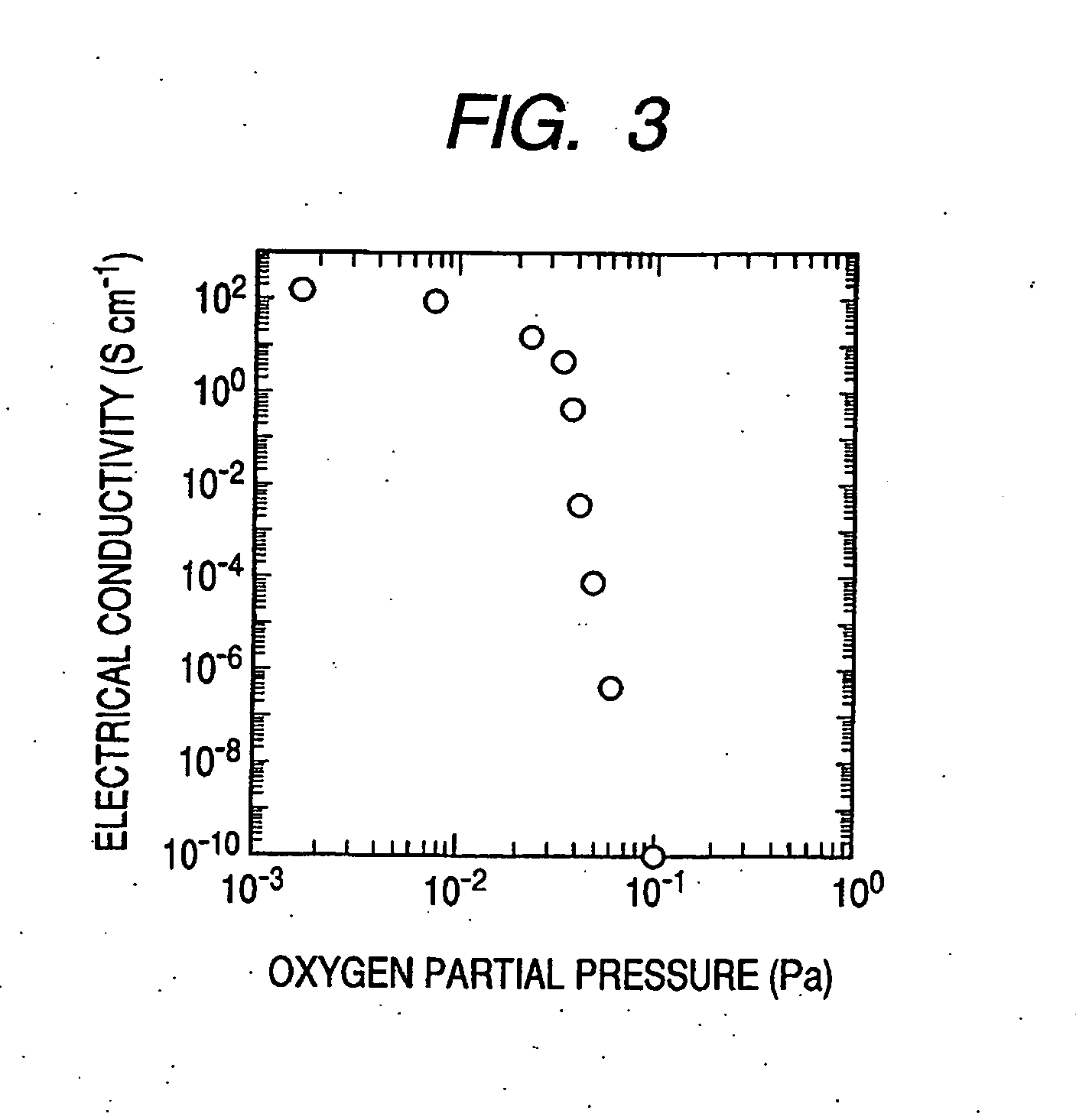
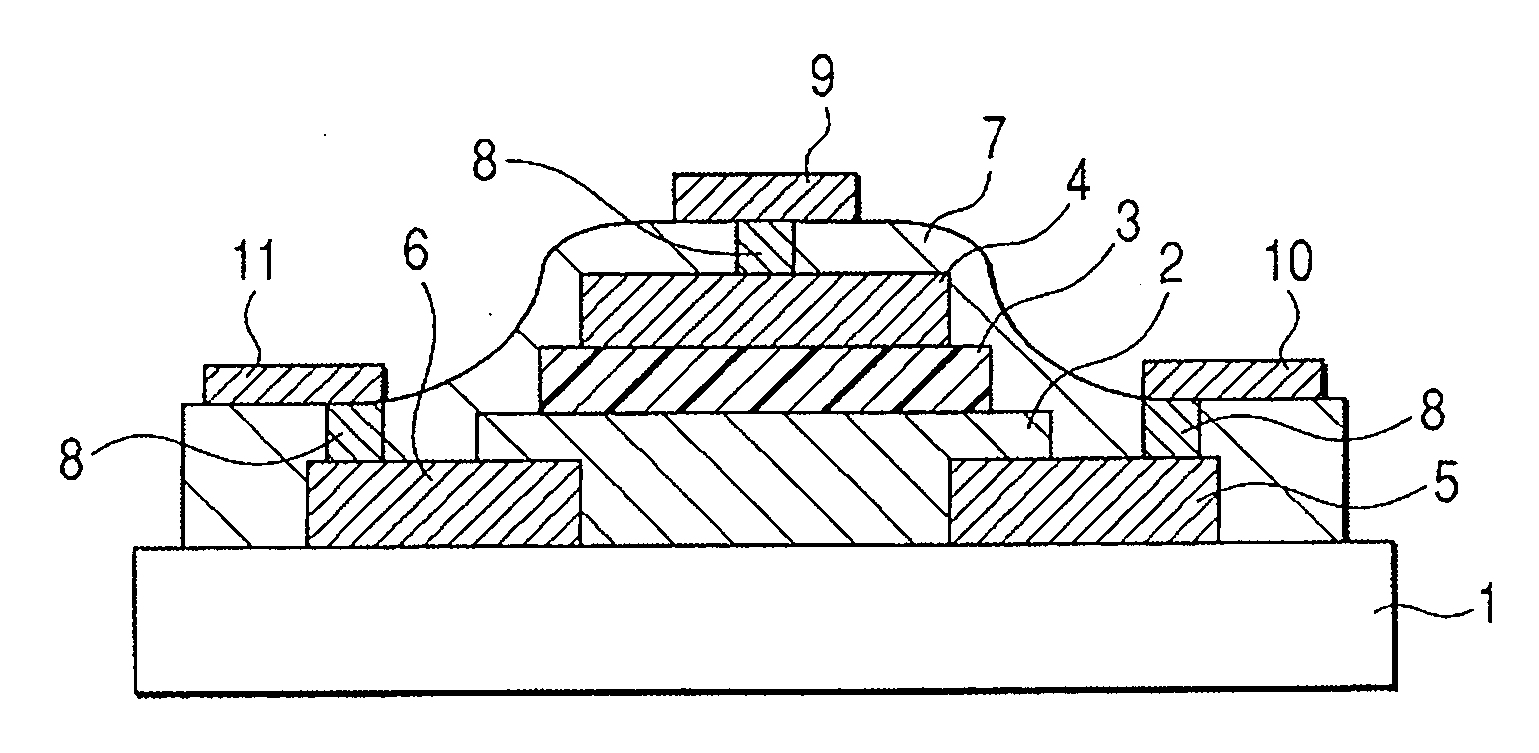
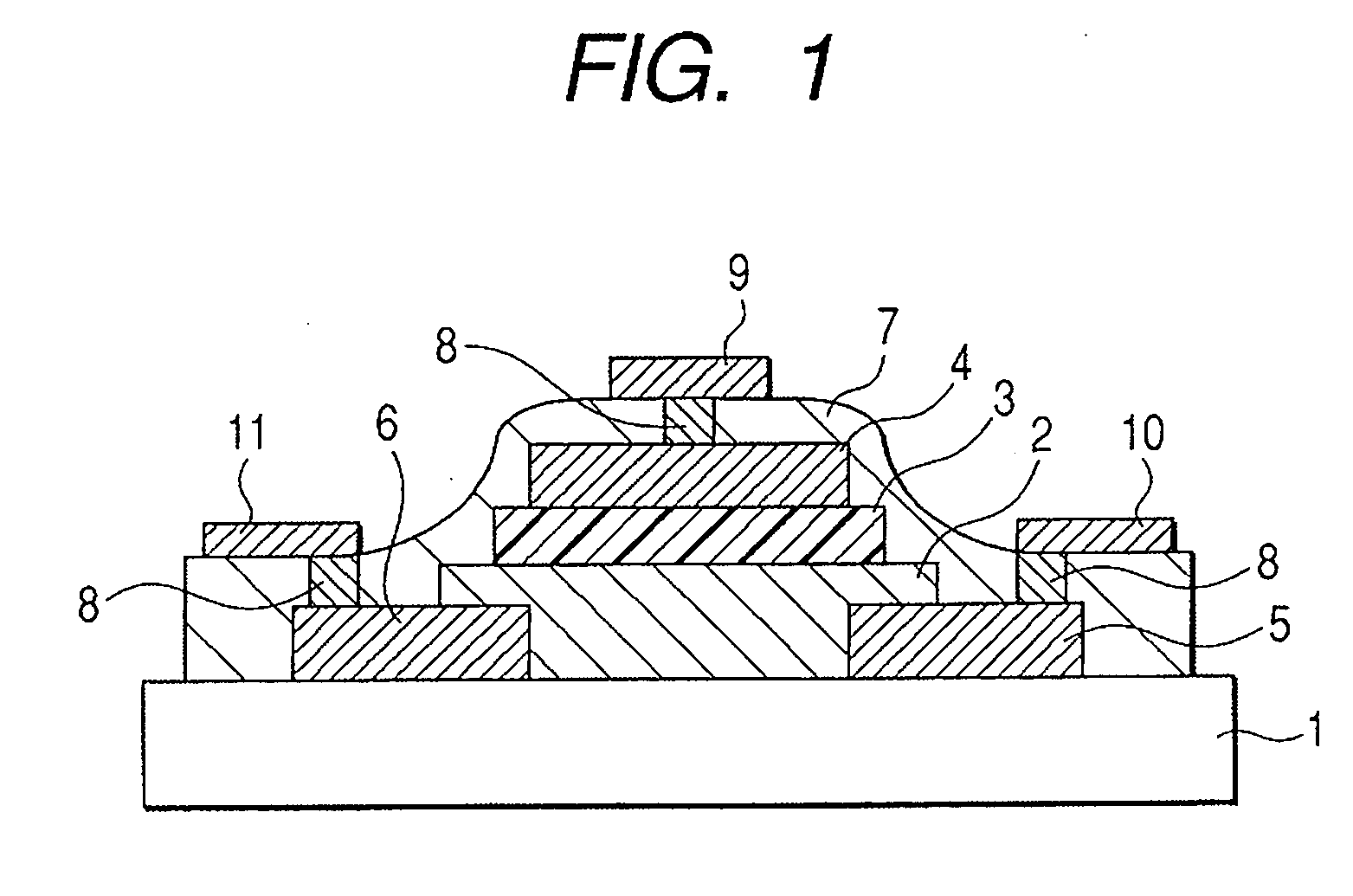
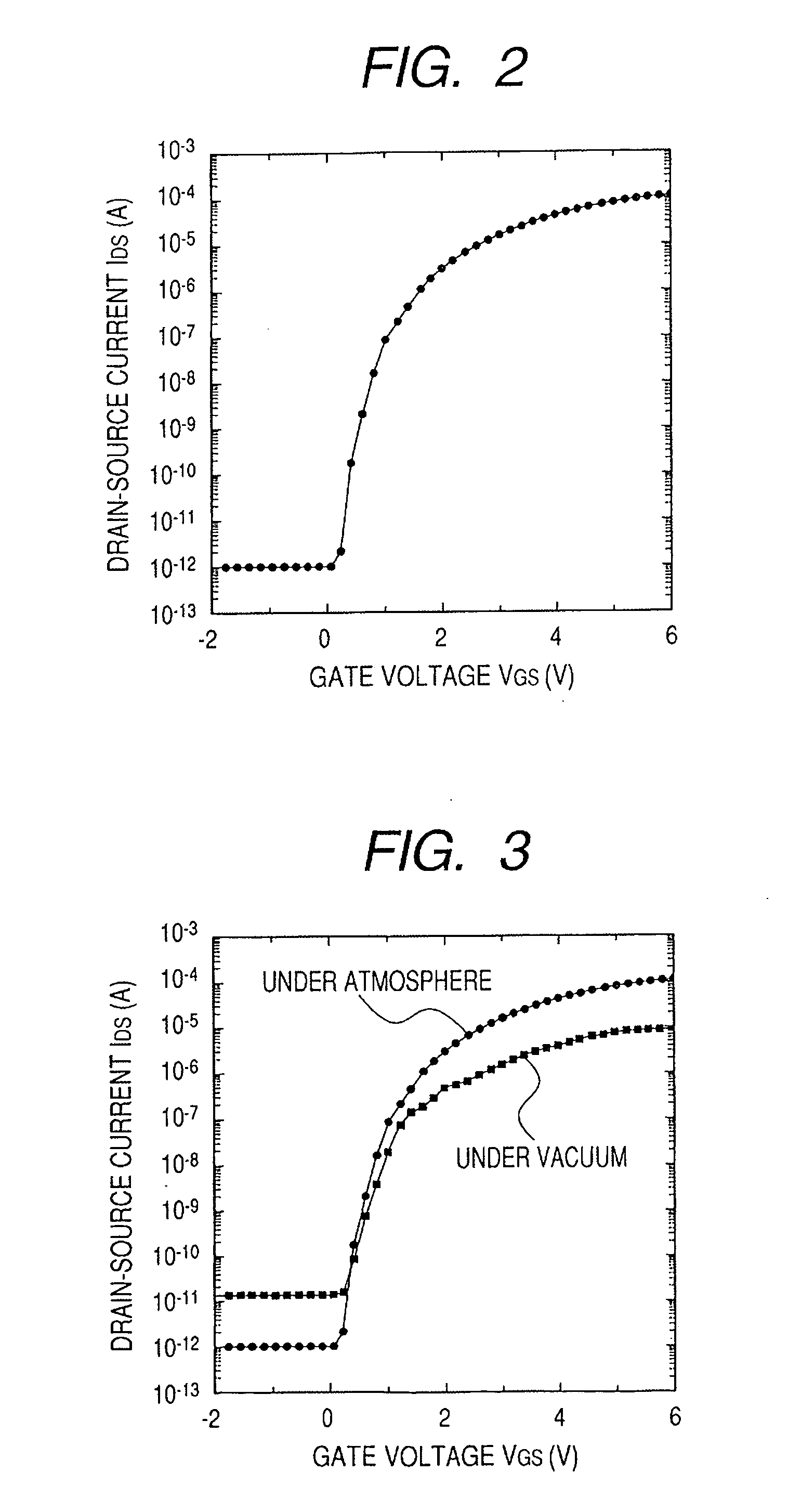
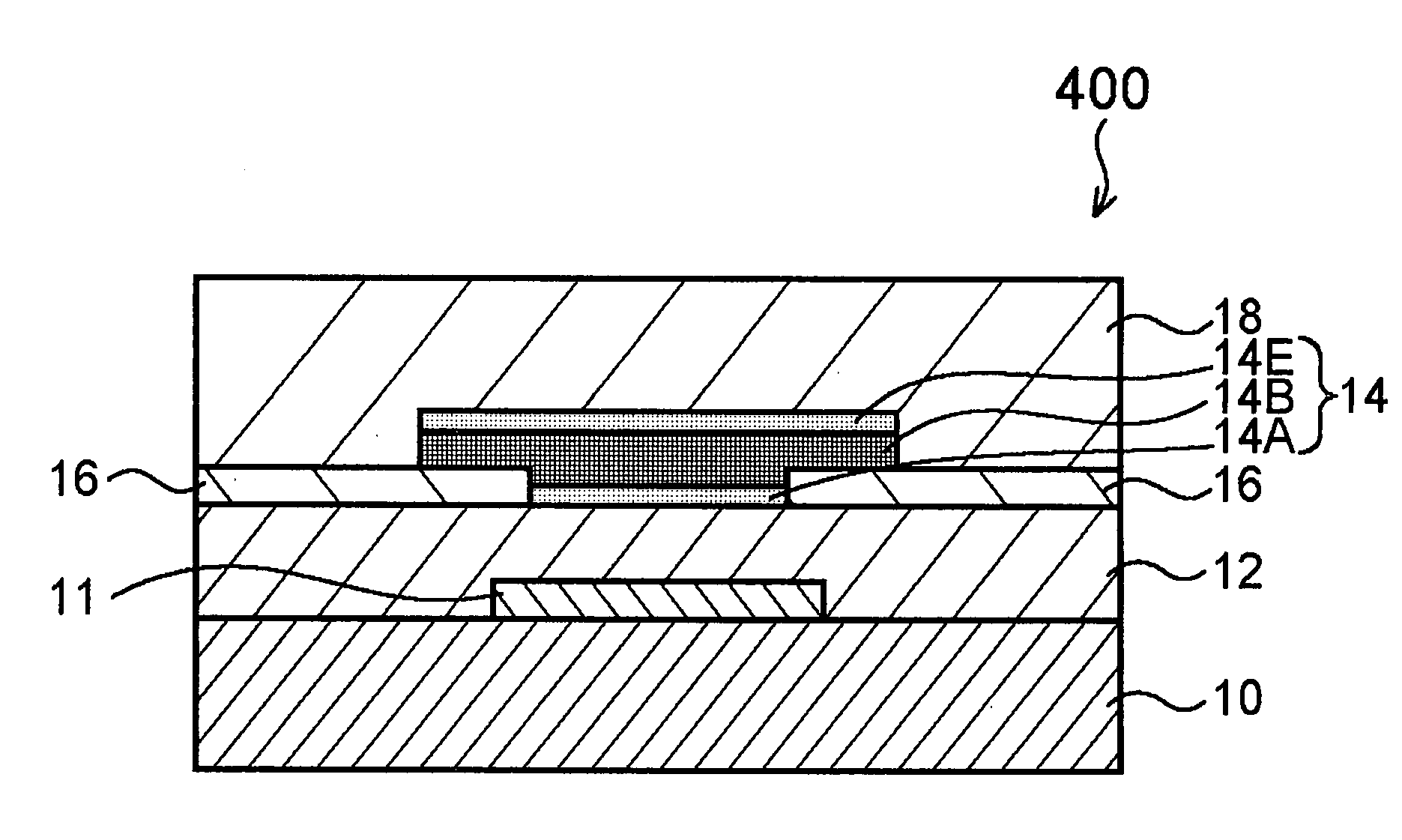
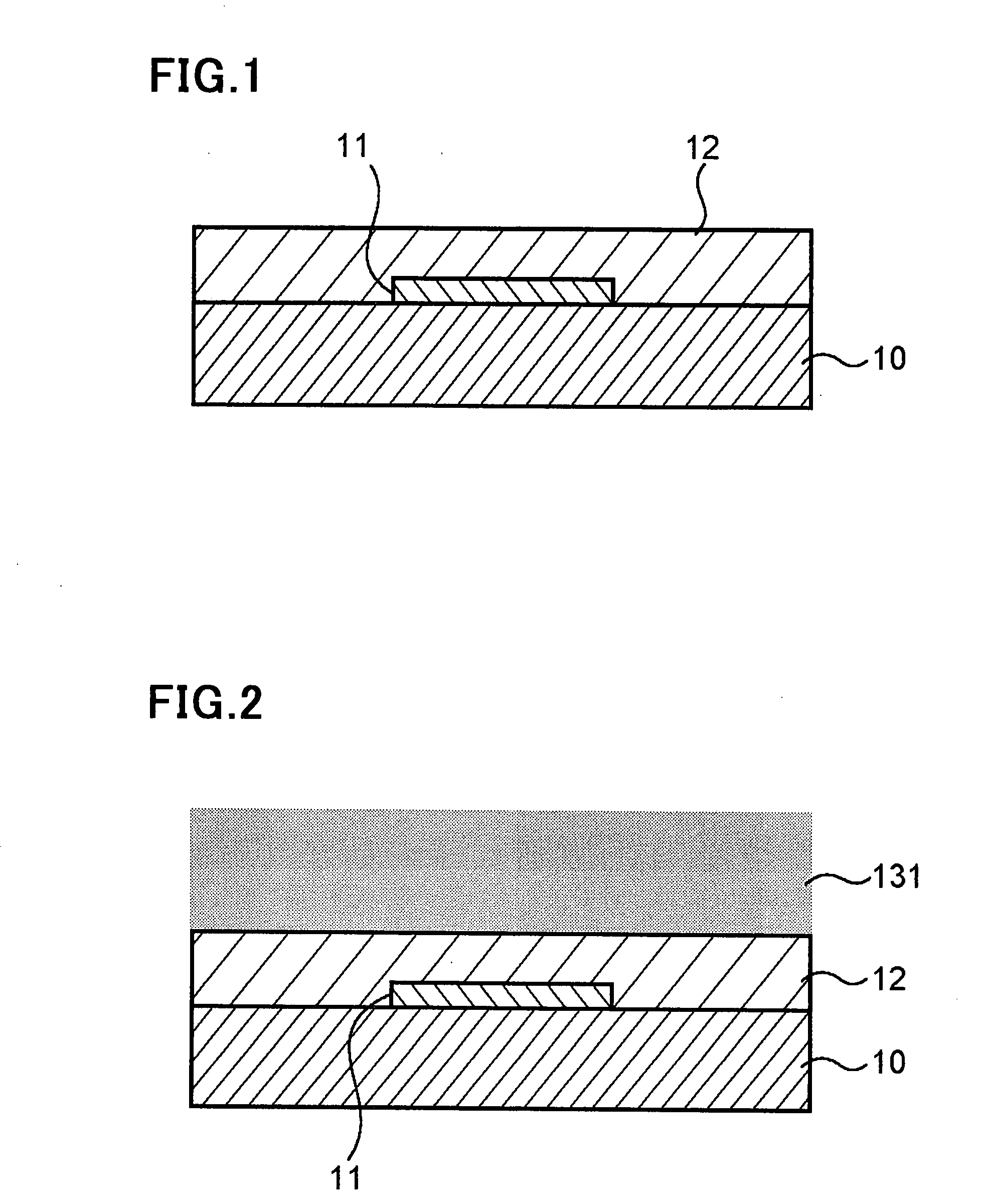
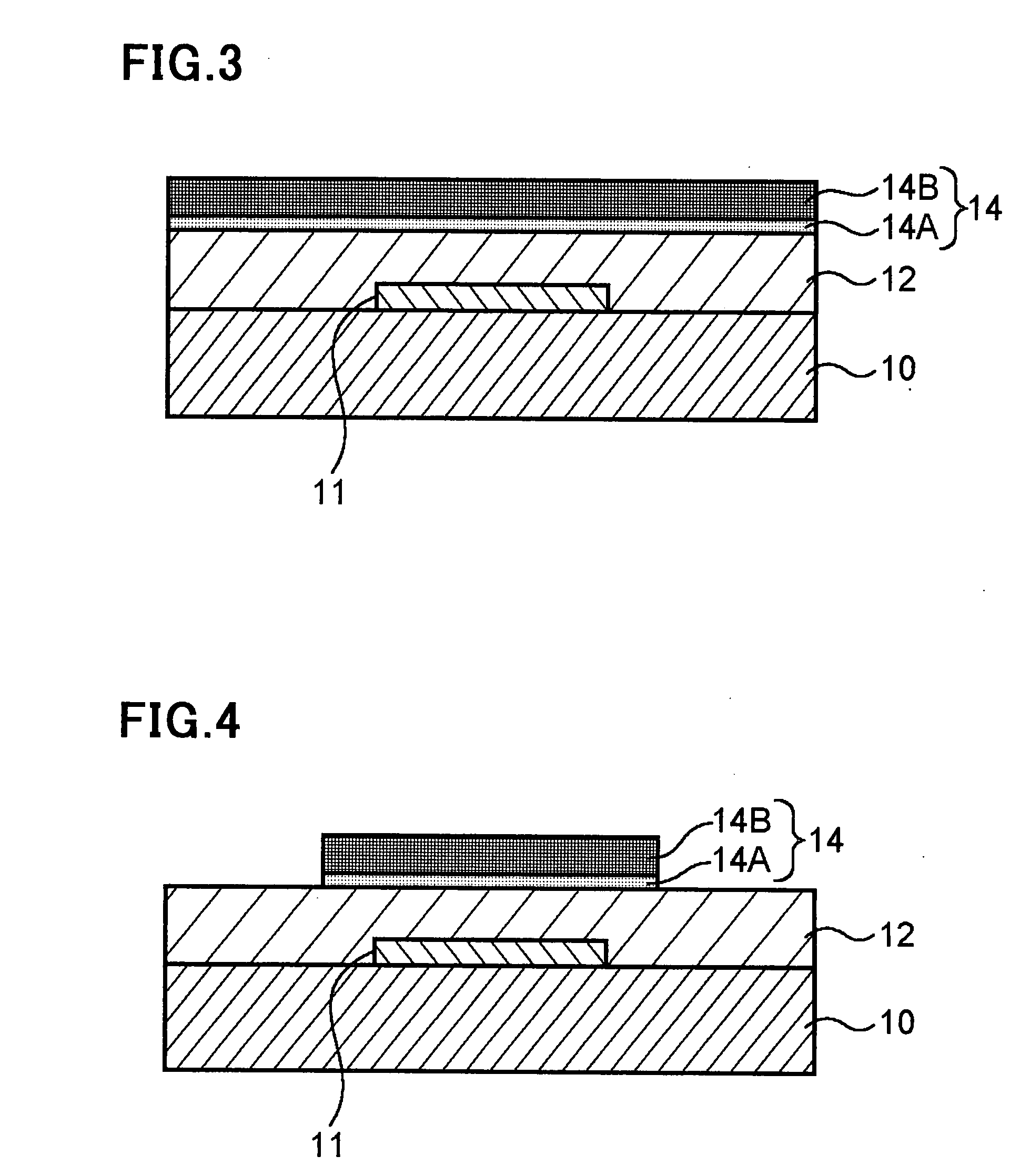
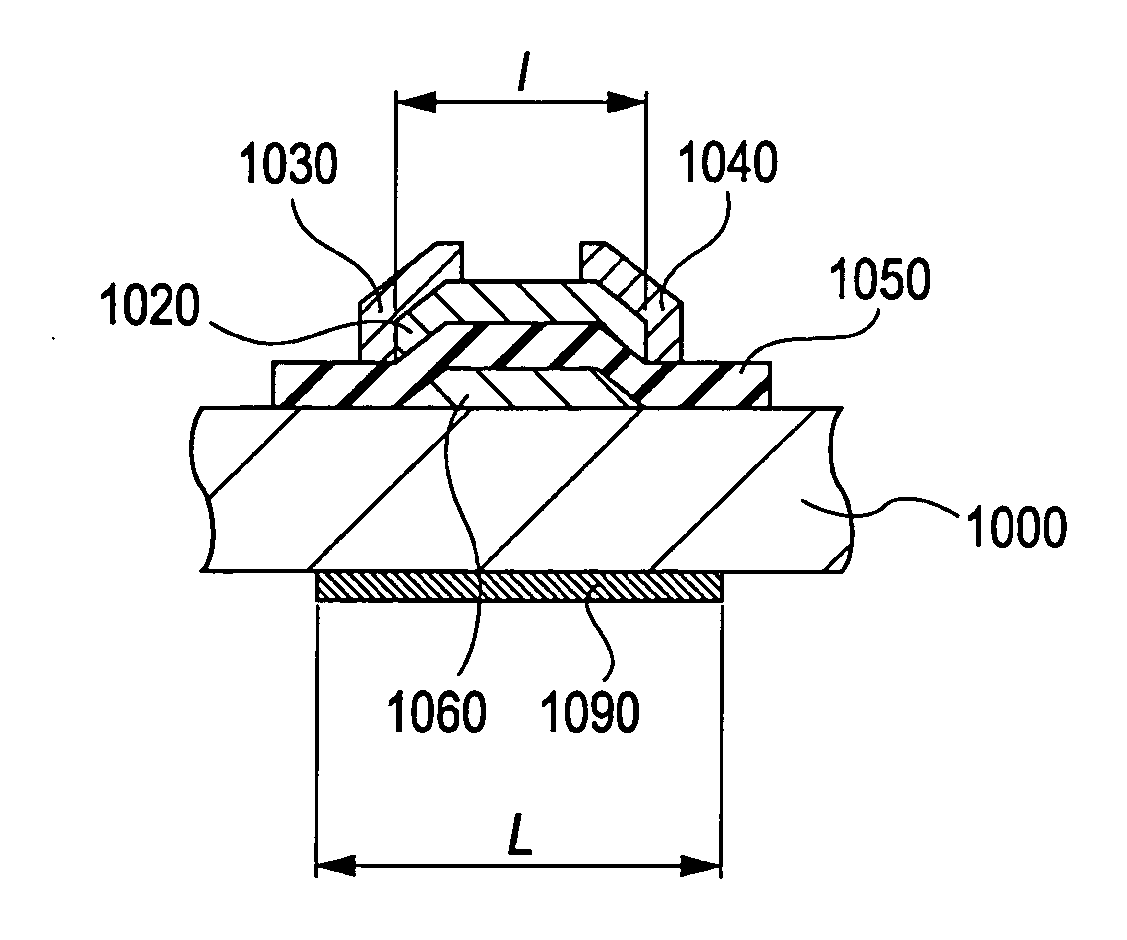
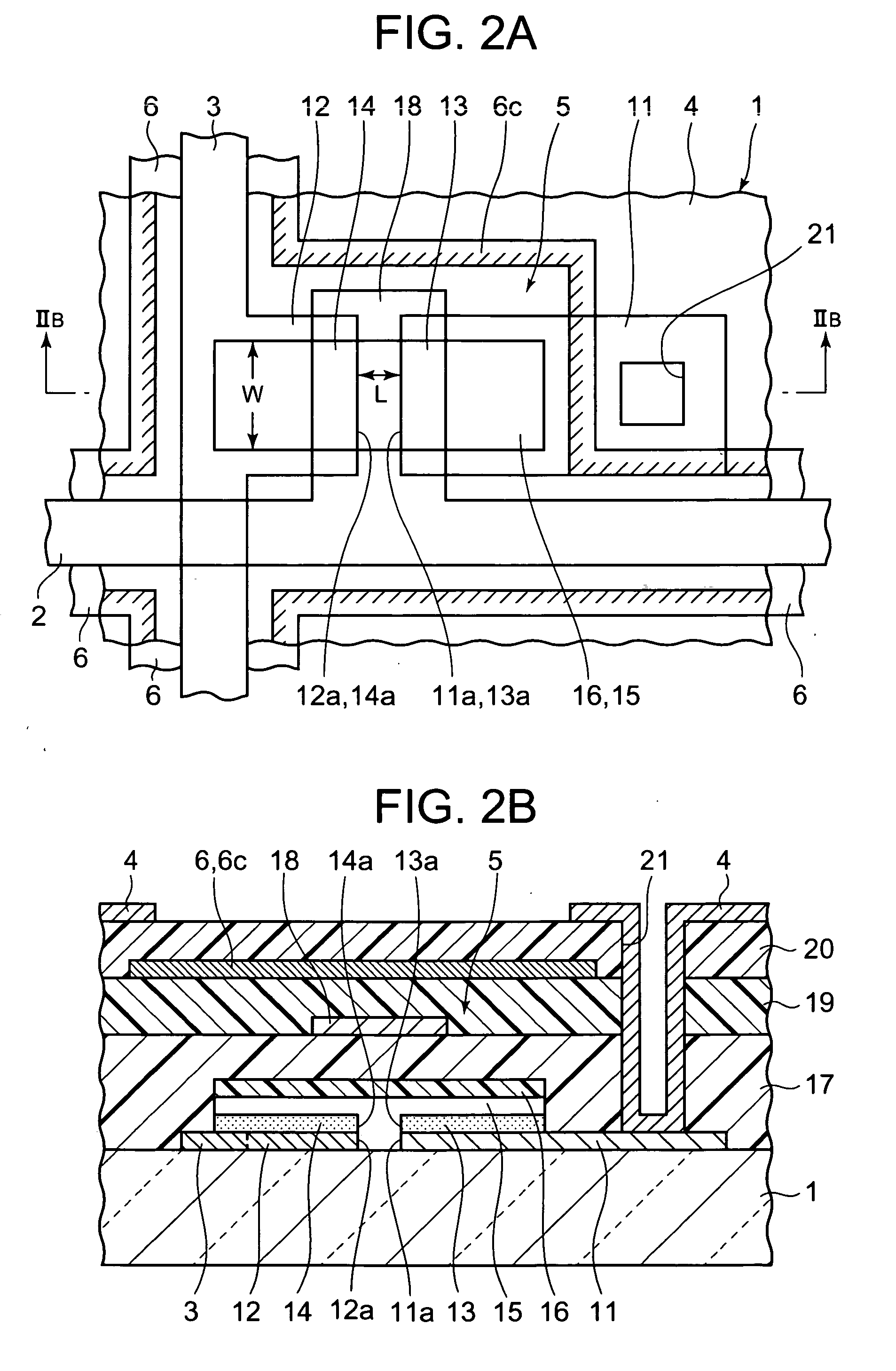
In a thin film transistor (1), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on a gate electrode (3) formed on an insulating substrate (2). Formed on the gate insulating layer (4) is a semiconductor layer (5). Formed on the semiconductor layer (5) are a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7). A protective layer (8) covers them, so that the semiconductor layer (5) is blocked from an atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is made of, e.g., a semiconductor containing polycrystalline ZnO to which, e.g., a group V element is added. The protective layer (8) thus formed causes decrease of a surface level of the semiconductor layer (5). This eliminates a depletion layer spreading therewithin. Accordingly, the ZnO becomes an n-type semiconductor indicating an intrinsic resistance, with the result that too many free electrons are generated. However, the added element works on the ZnO as an accepter impurity, so that the free electrons are reduced. This decreases a gate voltage required for removal of the free electrons, so that the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor (1) becomes on the order of 0V. This allows practical use of a semiconductor device which has an active layer made of zinc oxide and which includes an protective layer for blocking the active layer from an atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Transistor and semiconductor device
A transistor is provided, which is entirely and partially transparent by the use of a transparent channel layer made of zinc oxide or the like. A channel layer 11 formed of a transparent semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO. A transparent electrode is used for all of a source 12, a drain 13 and a gate 14, or a part of them. As the transparent electrode, a transparent conductive material such as conductive ZnO doped with, for example, group III elements is used. As a gate insulating layer 15, a transparent insulative material such as insulative ZnO doped with elements capable of taking a valence of one as a valence number or group V elements is used. If a substrate 16 must be transparent, for example, glass, sapphire, plastic or the like can be used as a transparent material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
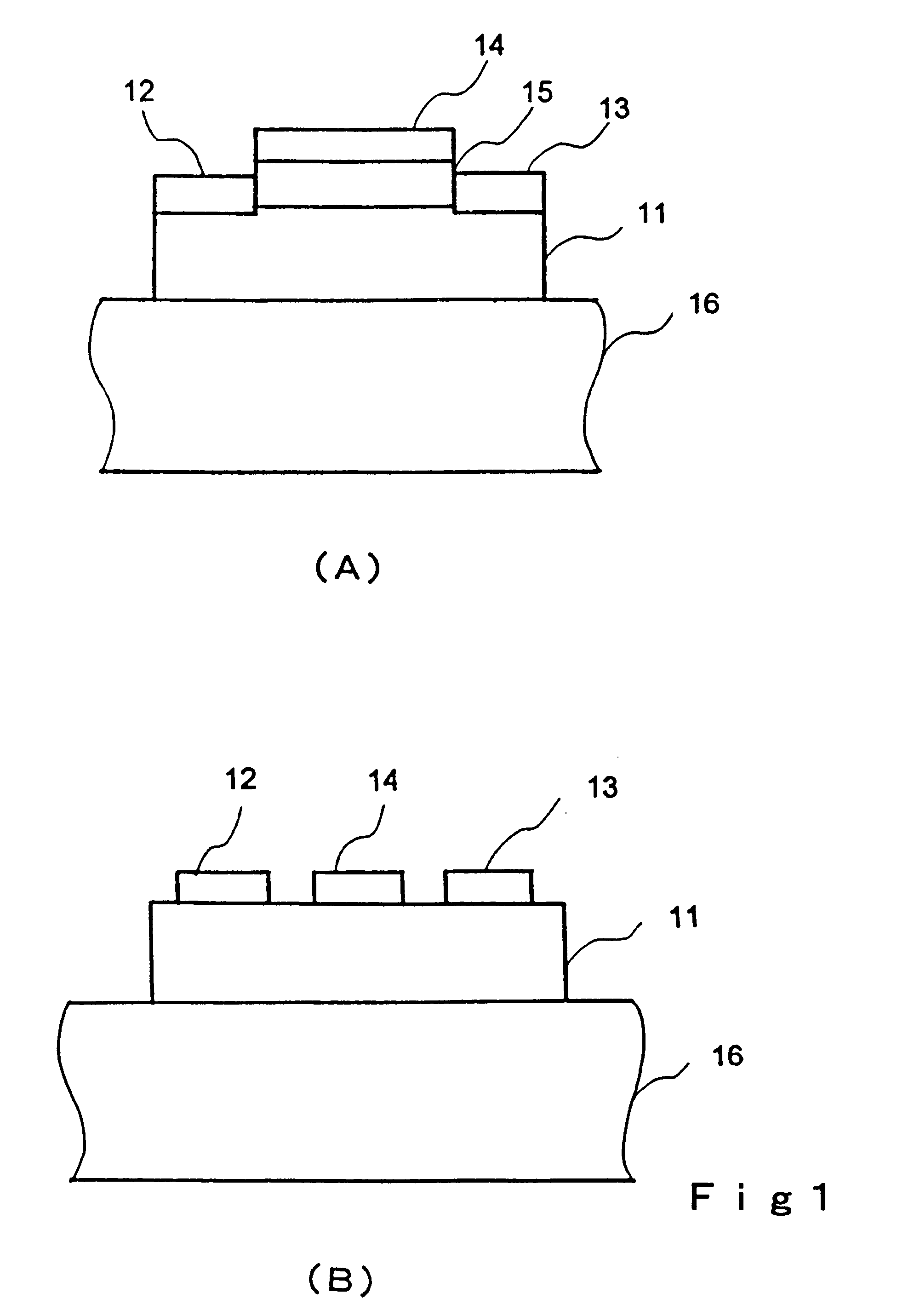
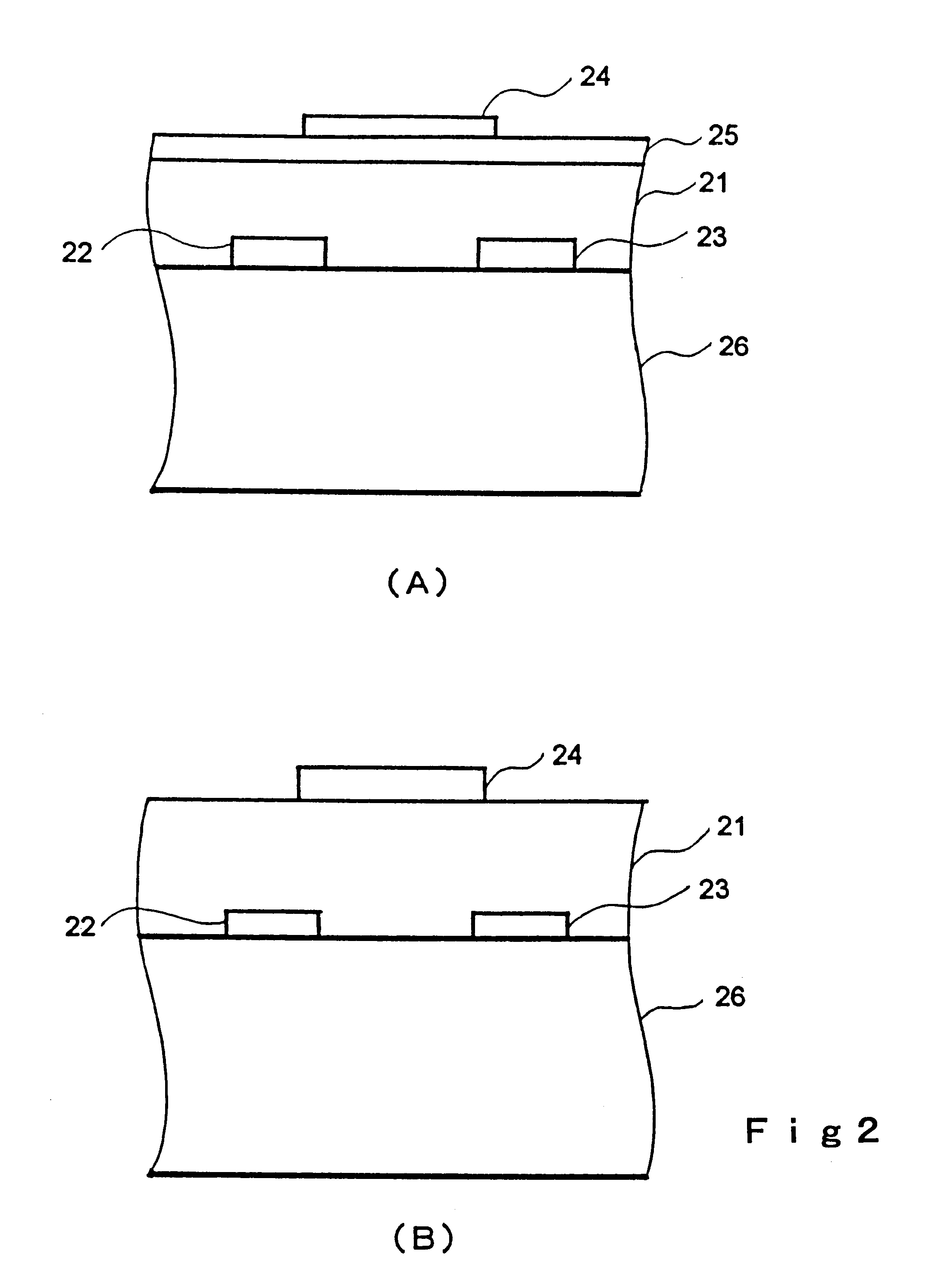
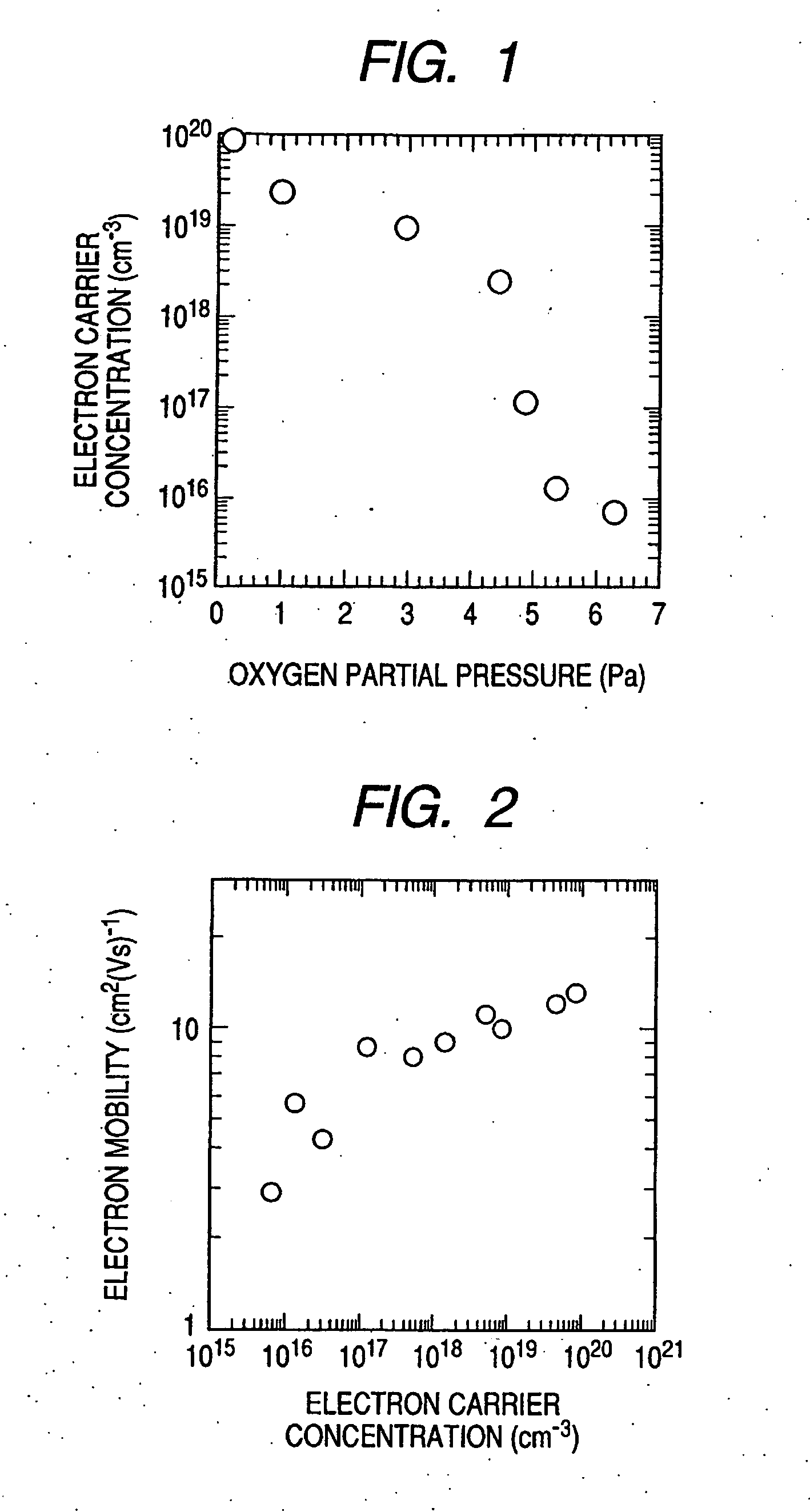
Electric elements and circuits utilizing amorphous oxides
Semiconductor devices and circuits with use of transparent oxide film are provided. The semiconductor device having a P-type region and an N-type region, wherein amorphous oxides with electron carrier concentration less than 1018 / cm3 is used for the N-type region.
Owner:CANON KK +2
Oxide semiconductor thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070052025A1Improve reliabilityUnstability of may lessenSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Provided is a thin film transistor comprising a channel layer comprised of an oxide semiconductor containing In, M, Zn, and O, M including at least one selected from the group consisting of Ga, Al, and Fe. The channel layer is covered with a protective film.
Owner:CANON KK
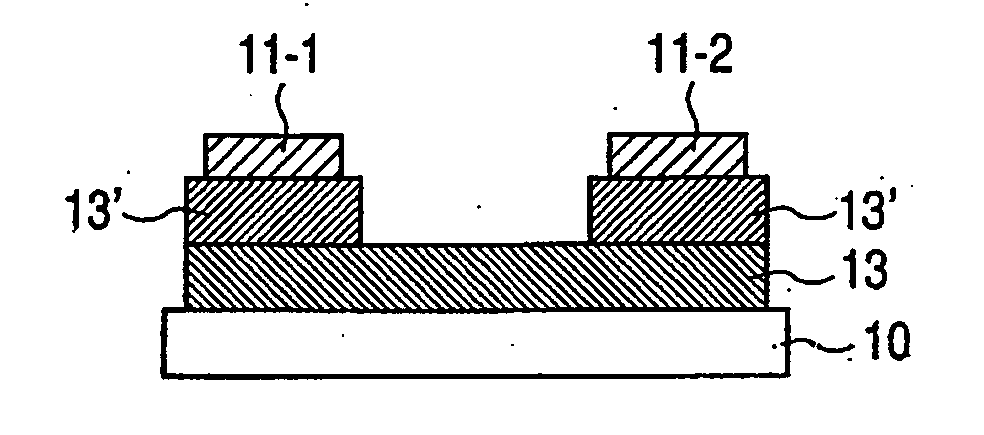
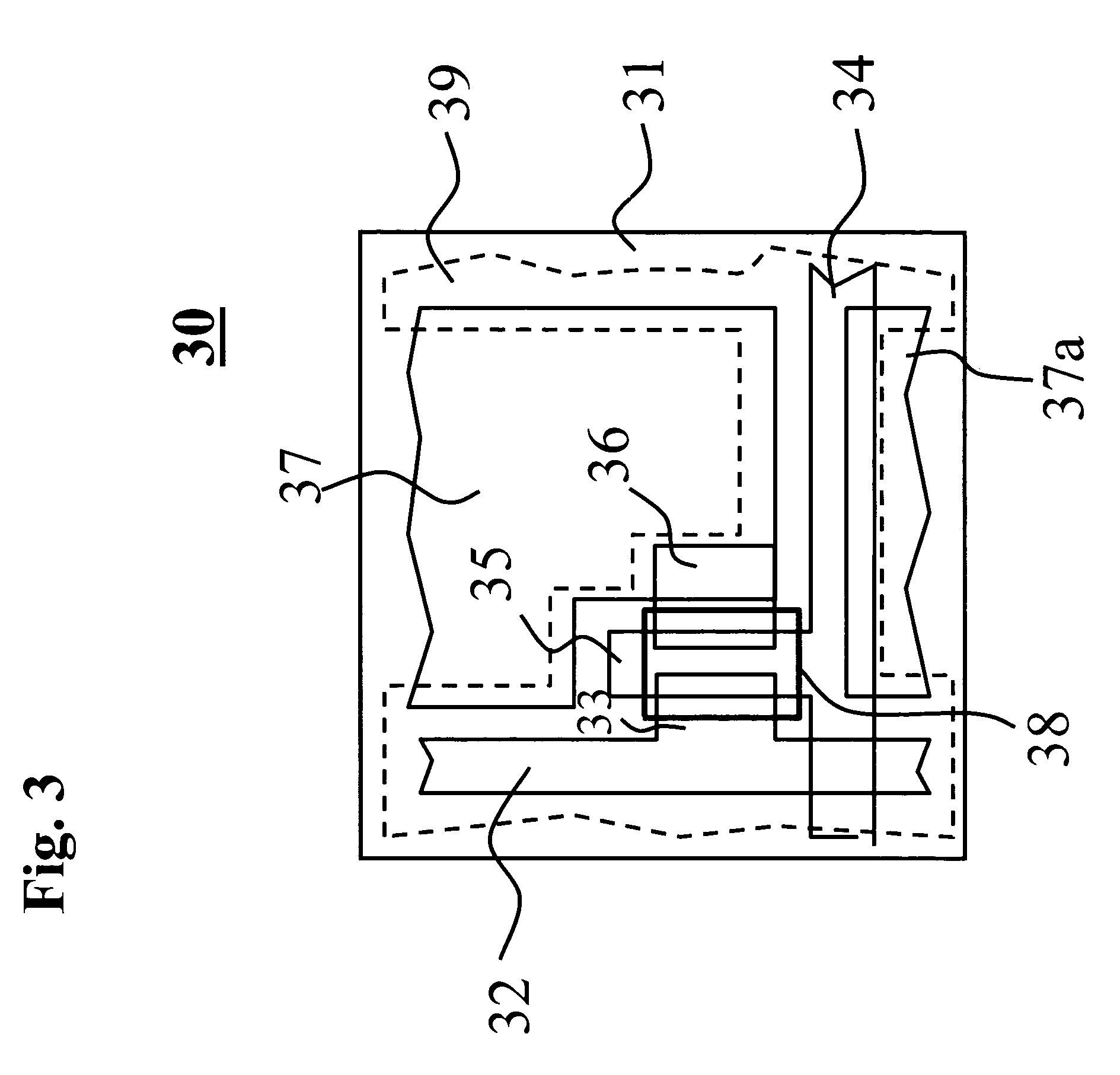
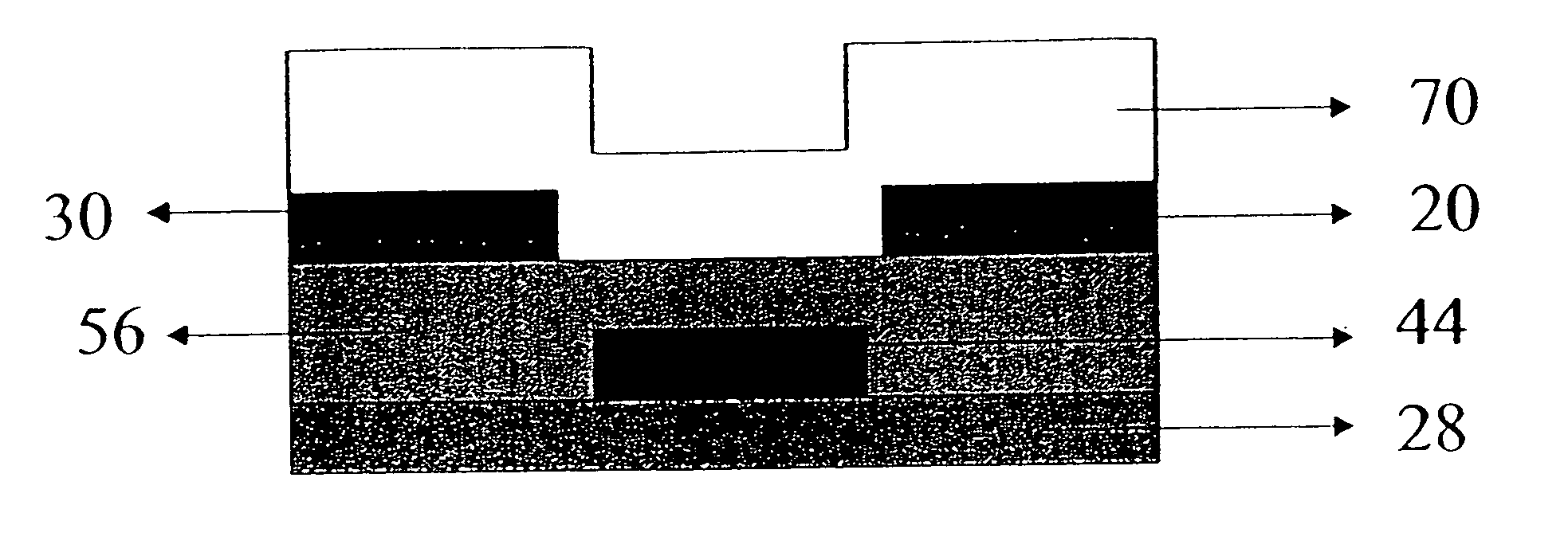
Thin-film device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20080038882A1Low densityGood reproducibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOxide semiconductorOxide
A thin-film device includes a first electrical insulator, an oxide-semiconductor film formed on the first electrical insulator, and a second electrical insulator formed on the oxide-semiconductor film, the oxide-semiconductor film defining an active layer. The oxide-semiconductor film is comprised of a first interface layer located at an interface with the first electrical insulating insulator, a second interface layer located at an interface with the second electrical insulator, and a bulk layer other than the first and second interface layers. A density of oxygen holes in at least one of the first and second interlayer layers is smaller than a density of oxygen holes in the bulk layer.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
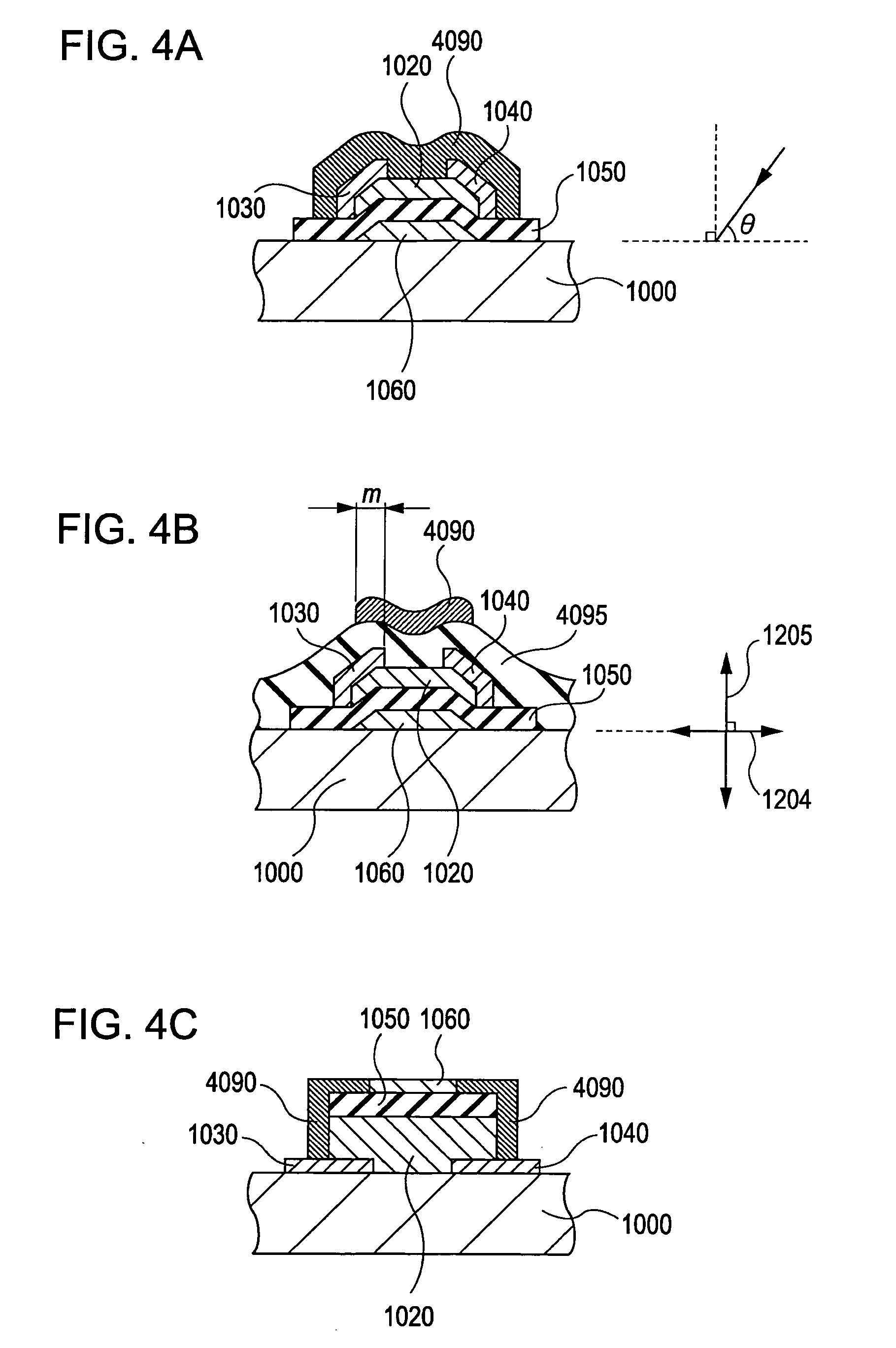
Field-effect transistor including transparent oxide and light-shielding member, and display utilizing the transistor
A field-effect transistor includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode, a gate-insulating film, and an active layer. The active layer contains an oxide having a transmittance of 70% or more in the wavelength range of 400 to 800 nm. A light-shielding member is provided as a light-shielding structure for the active layer, for example, on the bottom face of the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Indium oxide-based thin film transistors and circuits
In electronic displays or imaging units, the control of pixels is achieved by an array of transistors. These transistors are in a thin film form and arranged in a two-dimensional configuration to form switching circuits, driving circuits or even read-out circuits. In this invention, thin film transistors and circuits with indium oxide-based channel layers are provided. These thin film transistors and circuits may be fabricated at low temperatures on various substrates and with high charge carrier mobilities. In addition to conventional rigid substrates, the present thin film transistors and circuits are particularly suited for the fabrication on flexible and transparent substrates for electronic display and imaging applications. Methods for the fabrication of the thin film transistors with indium oxide-based channels are provided.
Owner:SHIH YI CHI +3
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
ActiveUS7402506B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsZinc
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
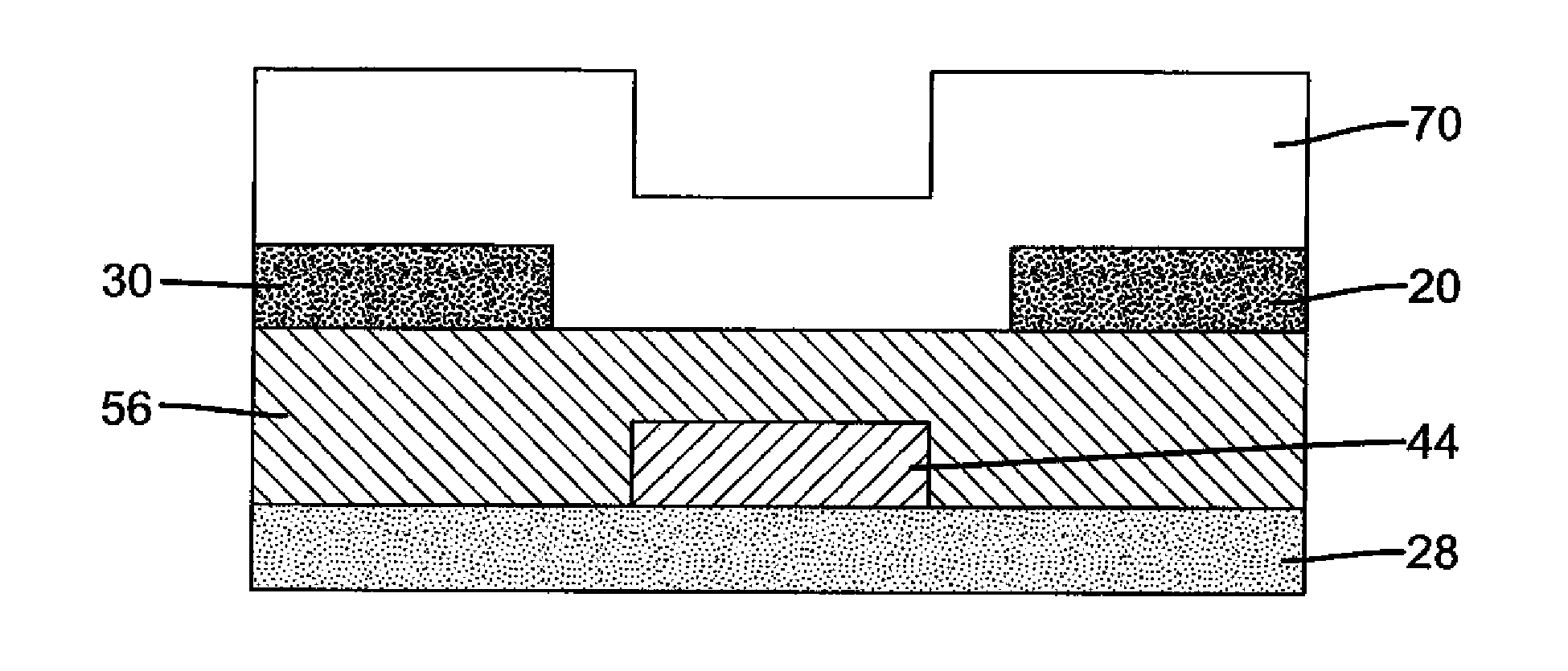
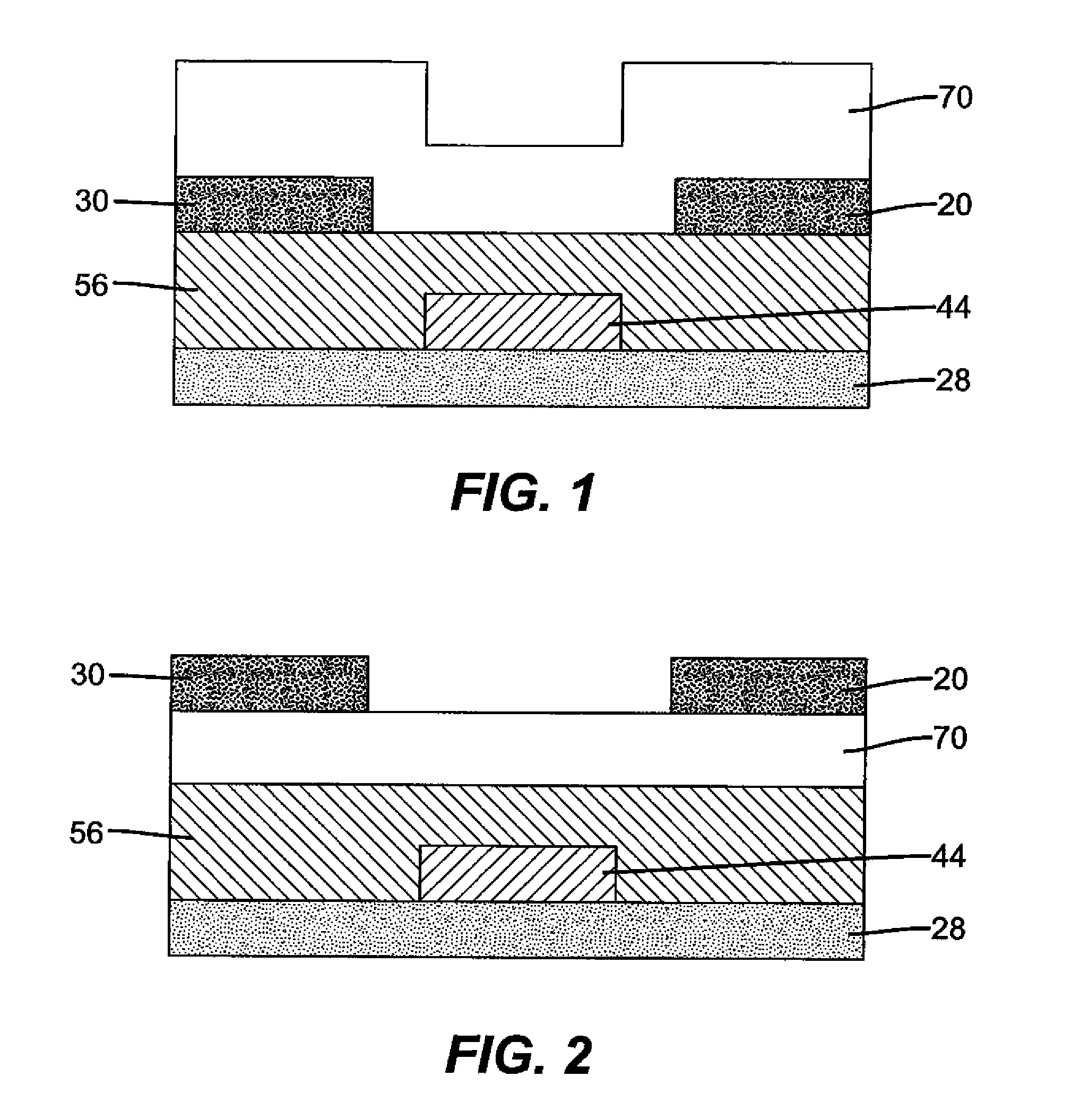
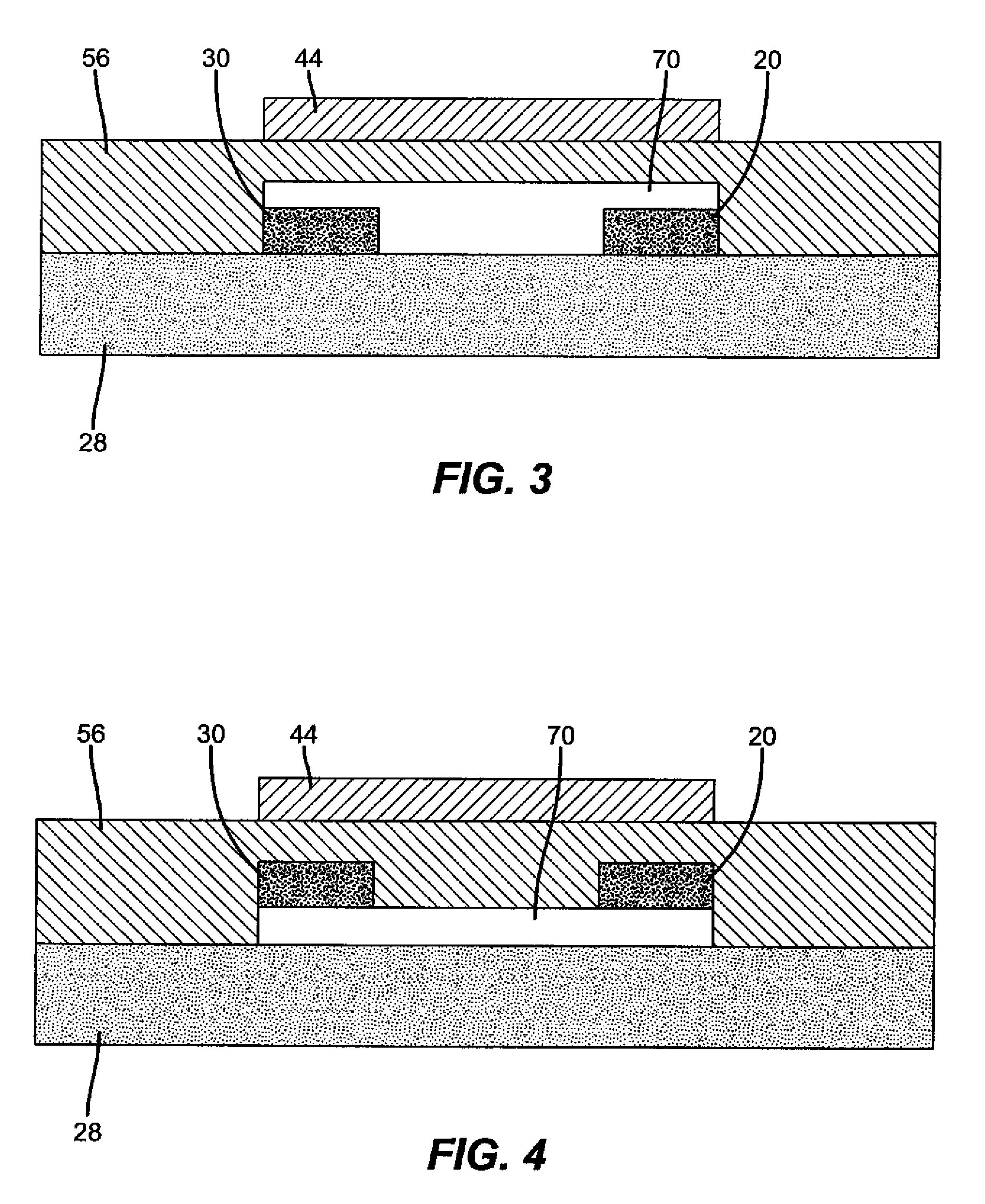
Field-effect transistor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7411209B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenField-effect transistor
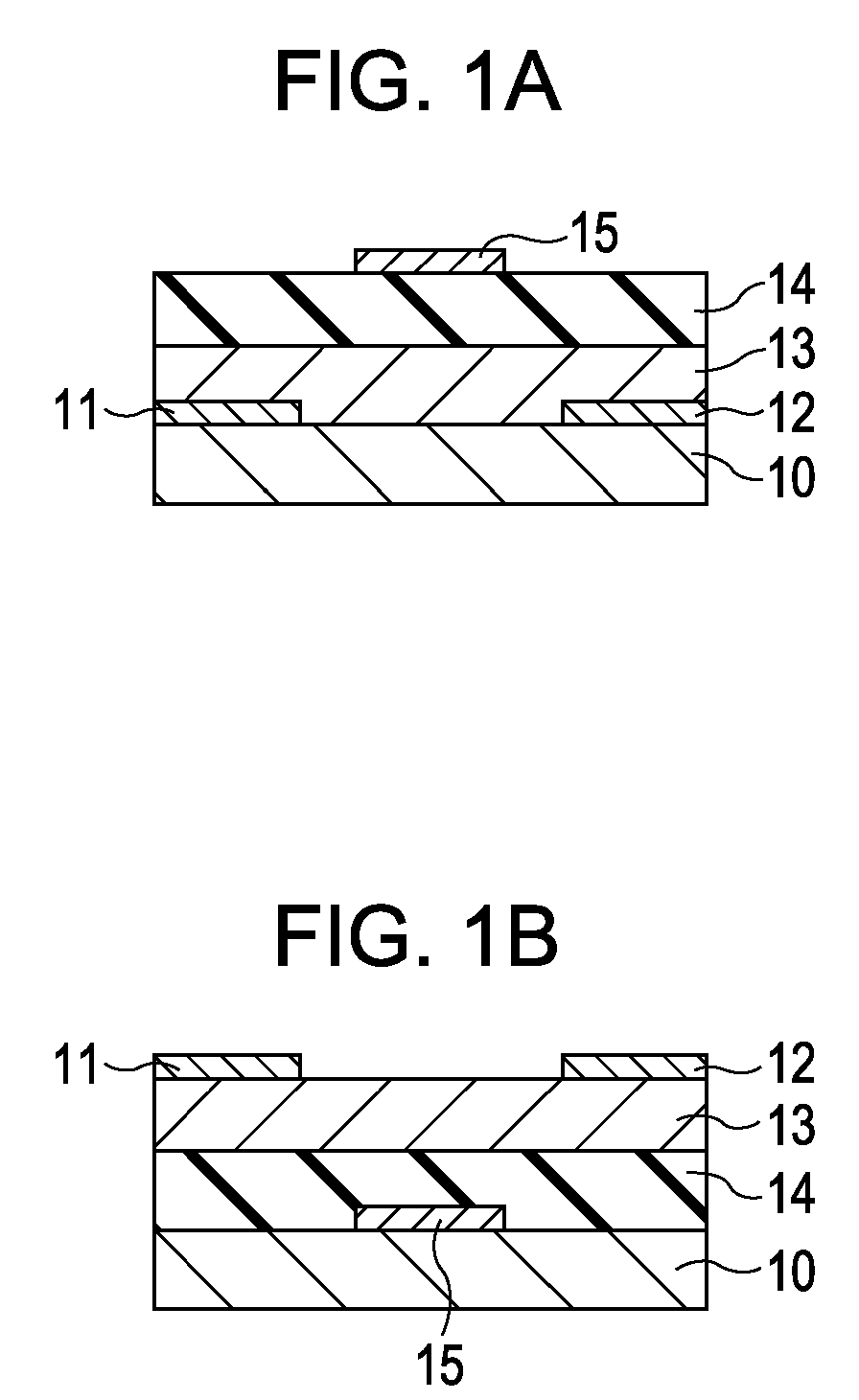
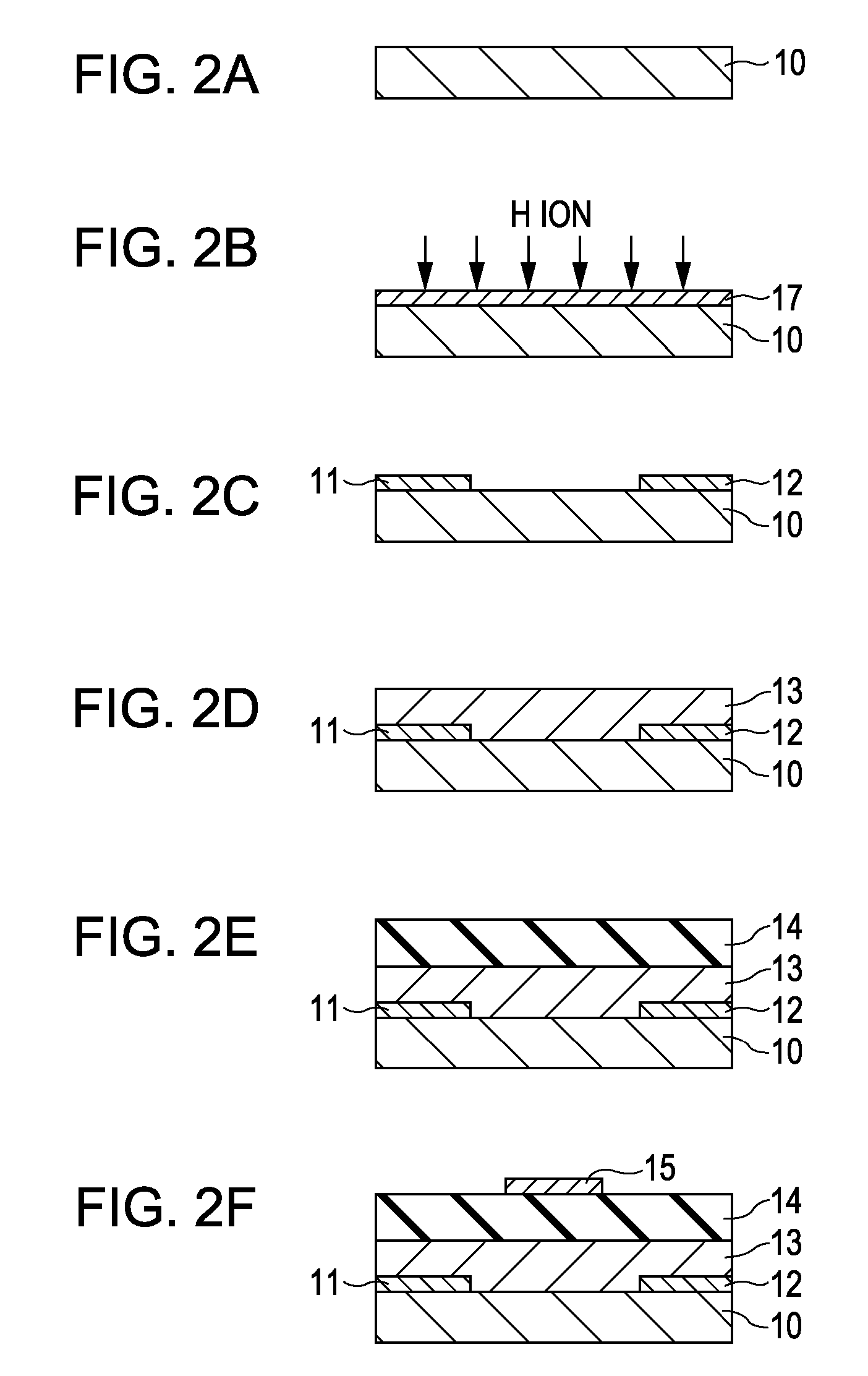
A method for manufacturing a field-effect transistor includes the steps of forming a source electrode and a drain electrode each containing hydrogen or deuterium; forming an oxide semiconductor layer in which the electrical resistance is decreased if hydrogen or deuterium is added; and, causing hydrogen or deuterium to diffuse from the source electrode and the drain electrode to the oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Fused nanocrystal thin film semiconductor and method
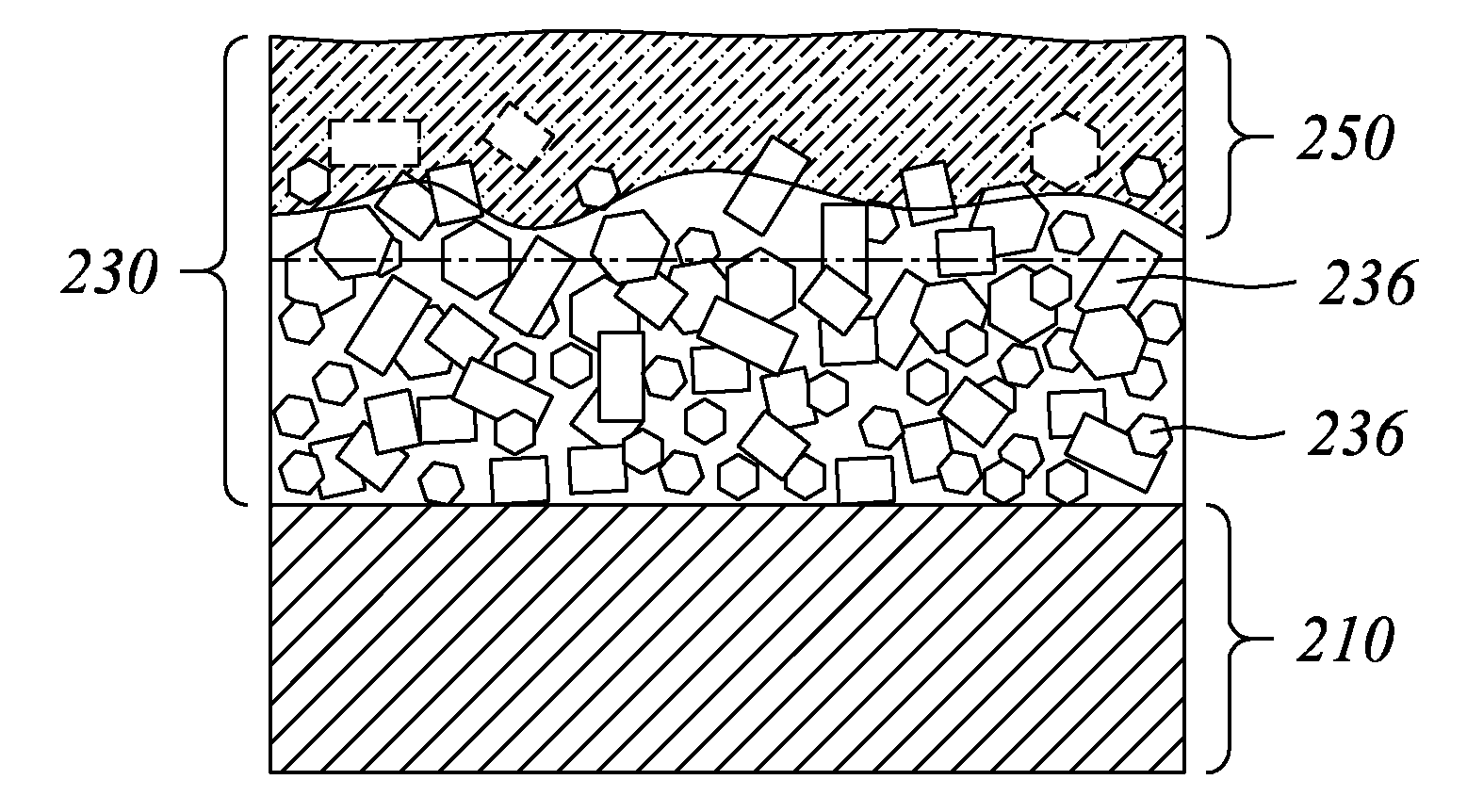
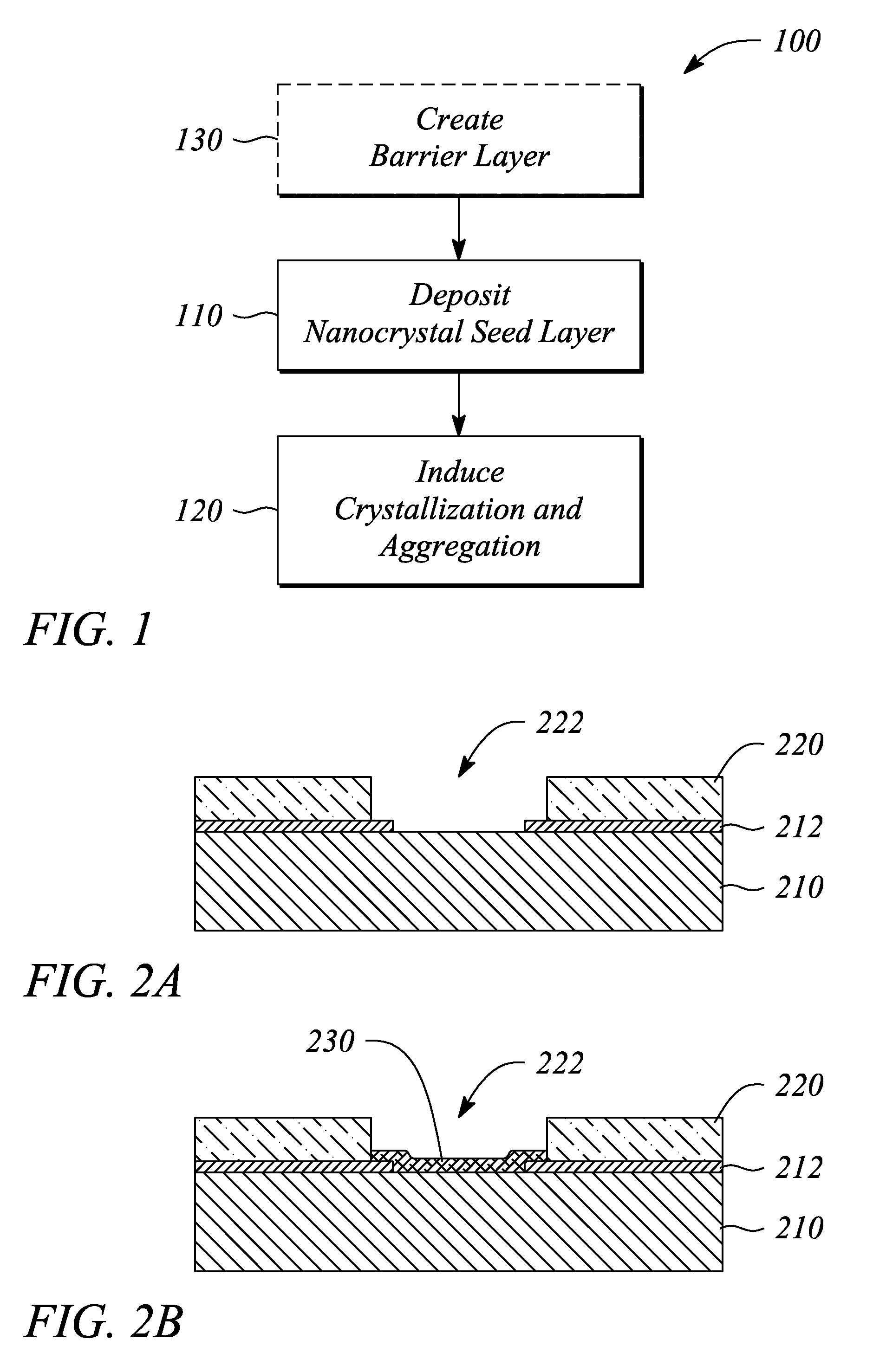
A thin film semiconductor and a method of its fabrication use induced crystallization and aggregation of a nanocrystal seed layer to form a merged-domain layer. The nanocrystal seed layer is deposited onto a substrate surface within a defined boundary. A reaction temperature below a boiling point of a reaction solution is employed. A thin film metal-oxide transistor and a method of its production employ the thin film semiconductor as a channel of the transistor. The merged-domain layer exhibits high carrier mobility.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Process for atomic layer deposition
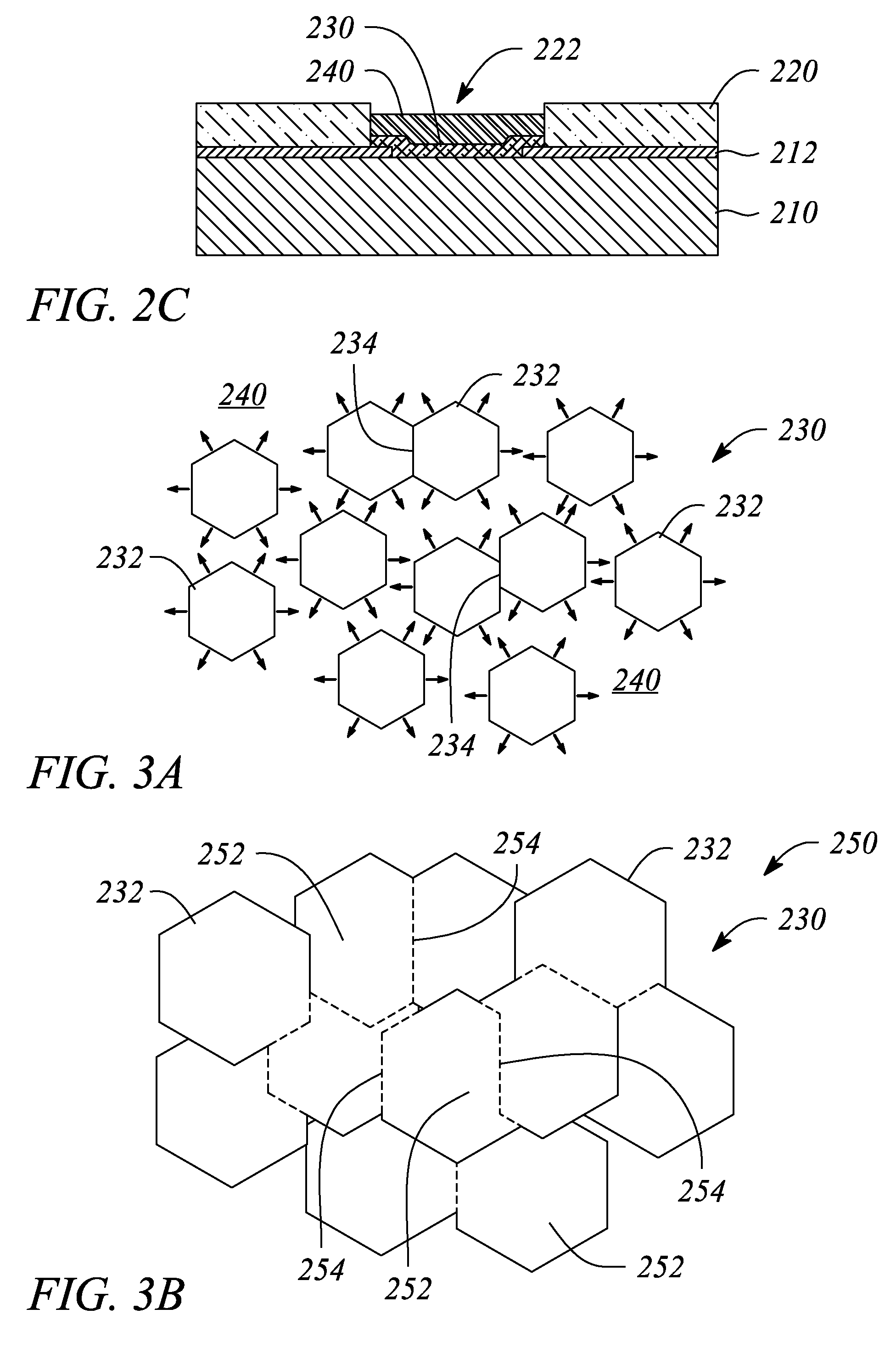
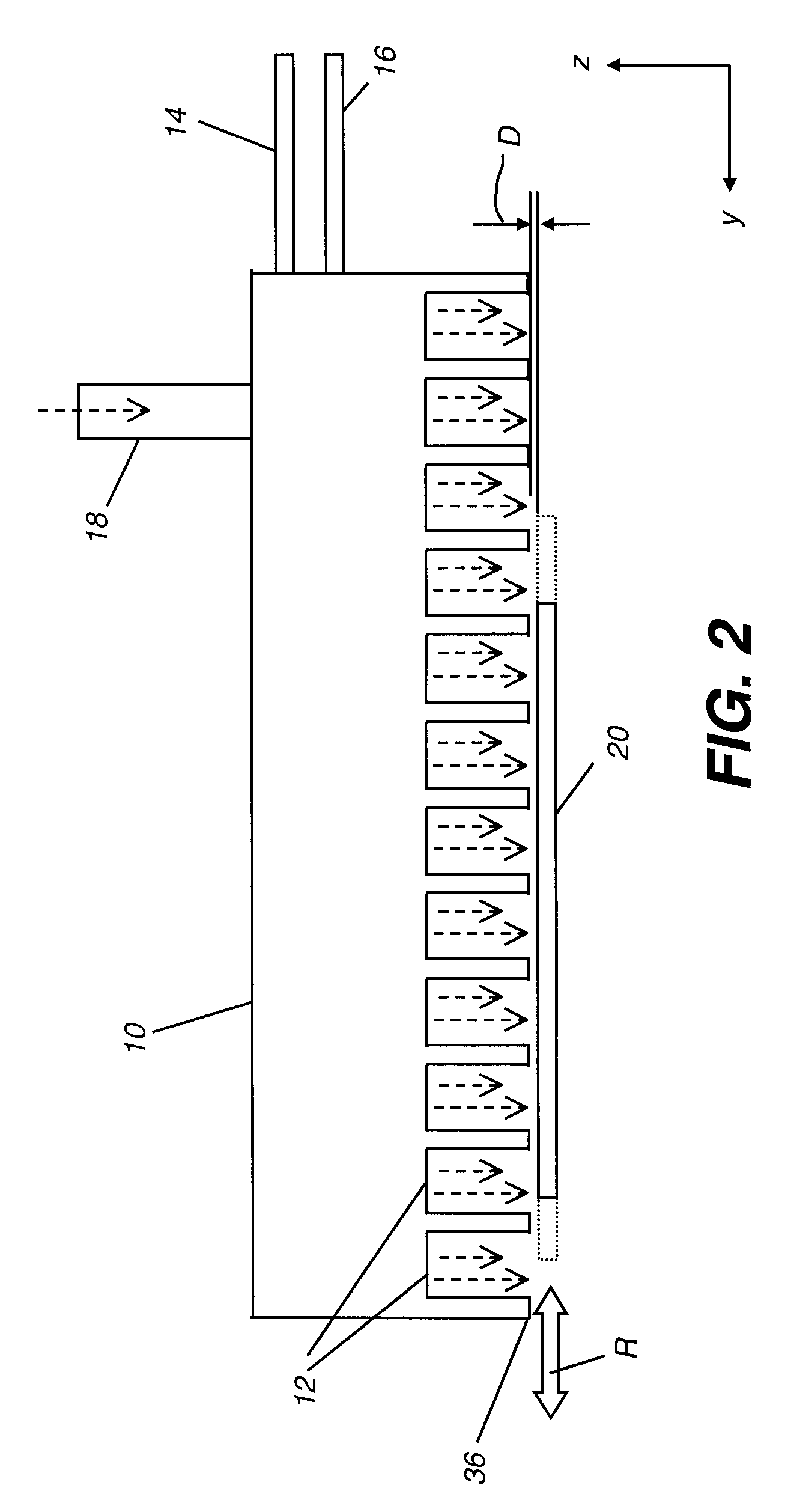
ActiveUS20080182358A1Suitable for processingAllowed to operateAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZincAtomic layer deposition
The present invention relates to a process of making a zinc-oxide-based thin film semiconductor, for use in a transistor, comprising thin film deposition onto a substrate comprising providing a plurality of gaseous materials comprising at least first, second, and third gaseous materials, wherein the first gaseous material is a zinc-containing volatile material and the second gaseous material is reactive therewith such that when one of the first or second gaseous materials are on the surface of the substrate the other of the first or second gaseous materials will react to deposit a layer of material on the substrate and wherein the third gaseous material is inert with respect to reacting with the first or second gaseous materials.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
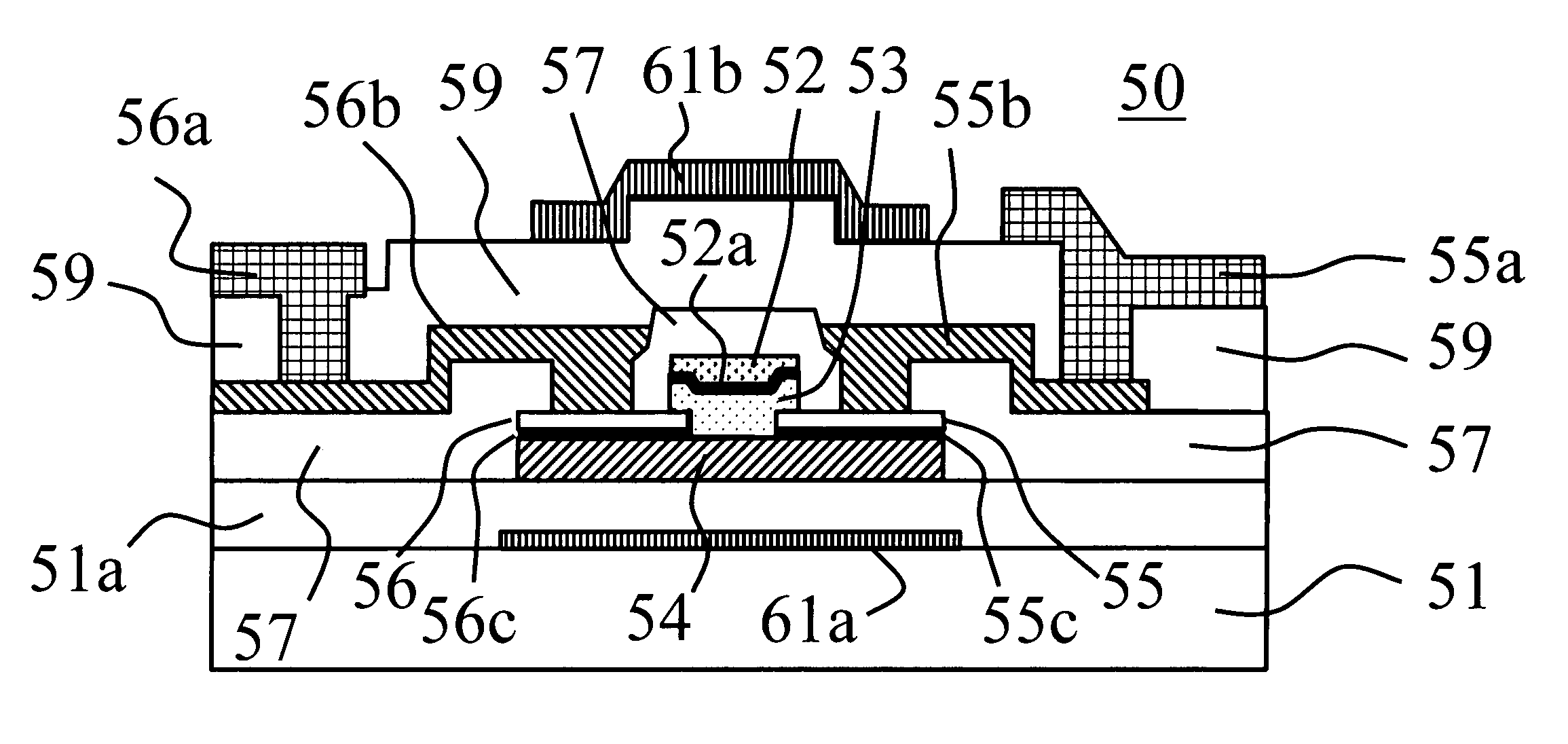
Thin film transistor including selectively crystallized channel layer and method of manufacturing the thin film transistor
ActiveUS20080258140A1Stable contact characteristicHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringIon implantation
Provided are a thin film transistor (TFT) including a selectively crystallized channel layer, and a method of manufacturing the TFT. The TFT includes a gate, the channel layer, a source, and a drain. The channel layer is formed of an oxide semiconductor, and at least a portion of the channel layer contacting the source and the drain is crystallized. In the method of manufacturing the TFT, the channel layer is formed of an oxide semiconductor, and a metal component is injected into the channel layer so as to crystallize at least a portion of the channel layer contacting the source and the drain. The metal component can be injected into the channel layer by depositing and heat-treating a metal layer or by ion-implantation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
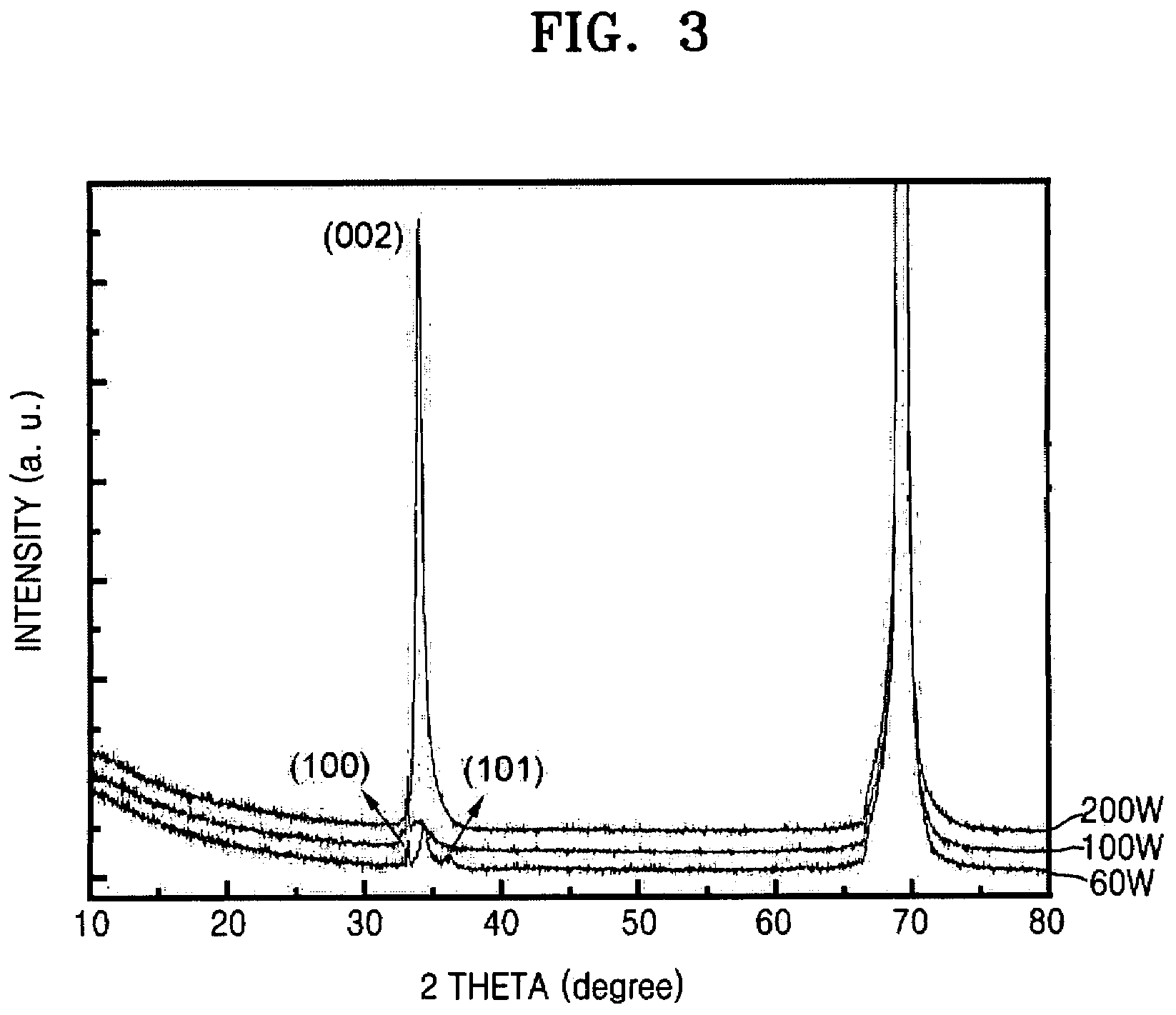
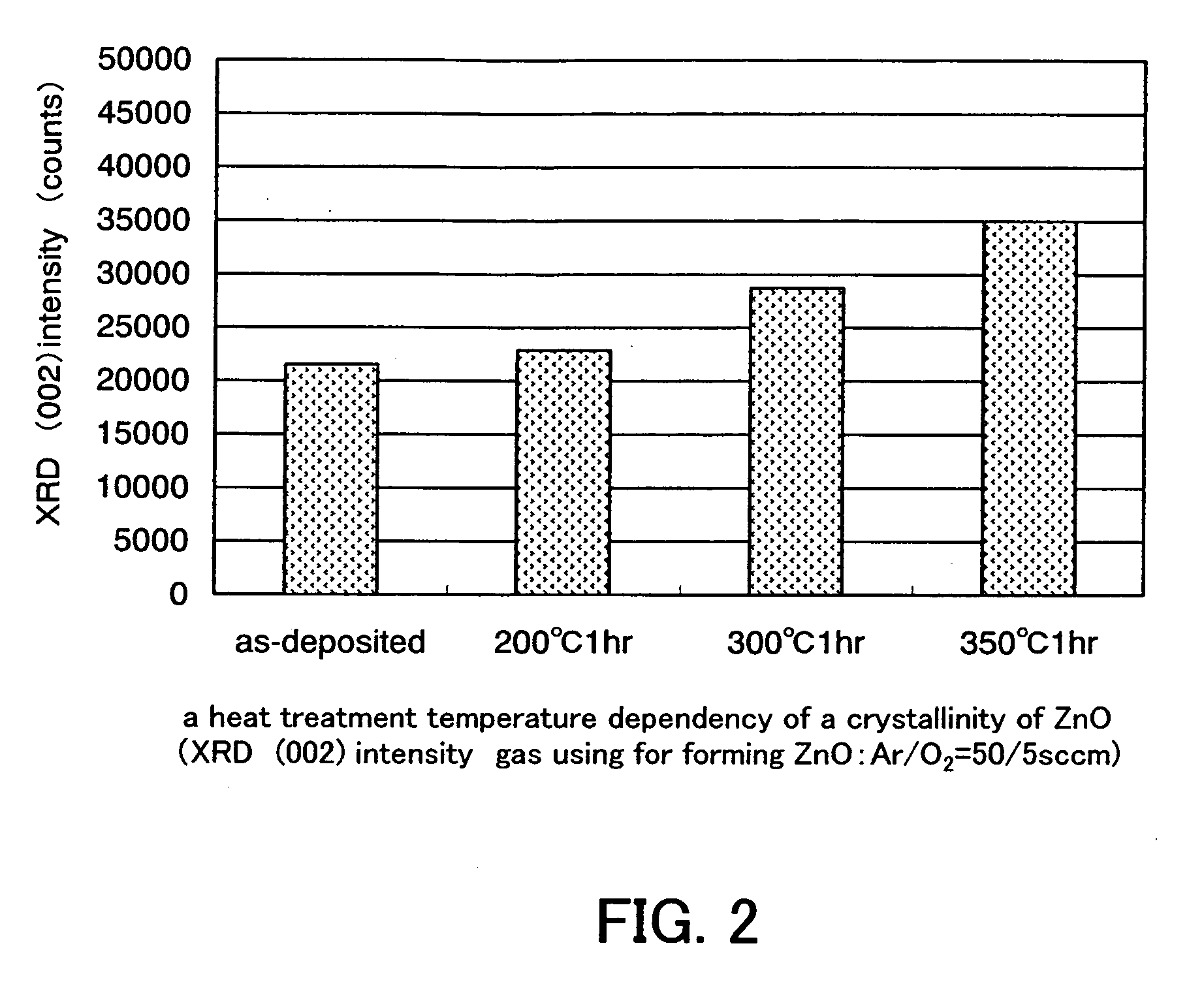
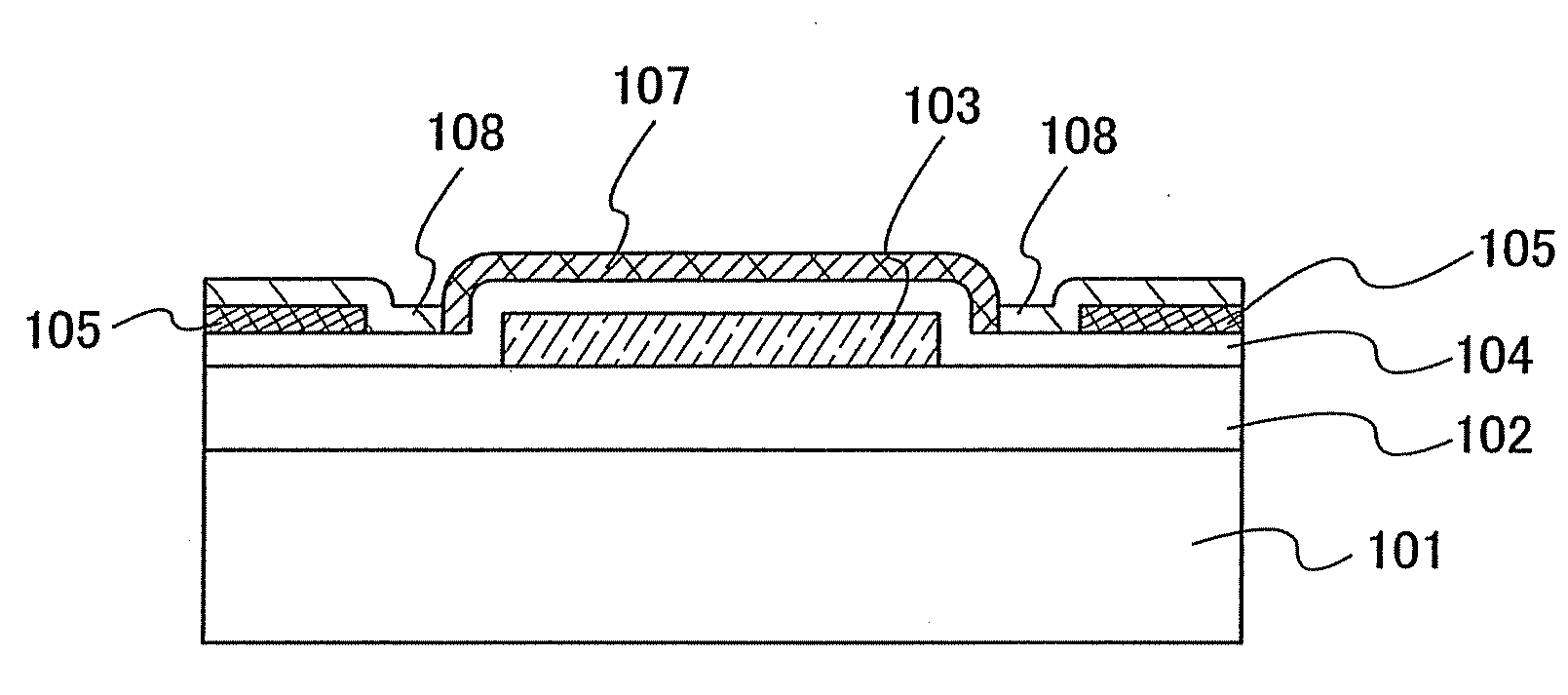
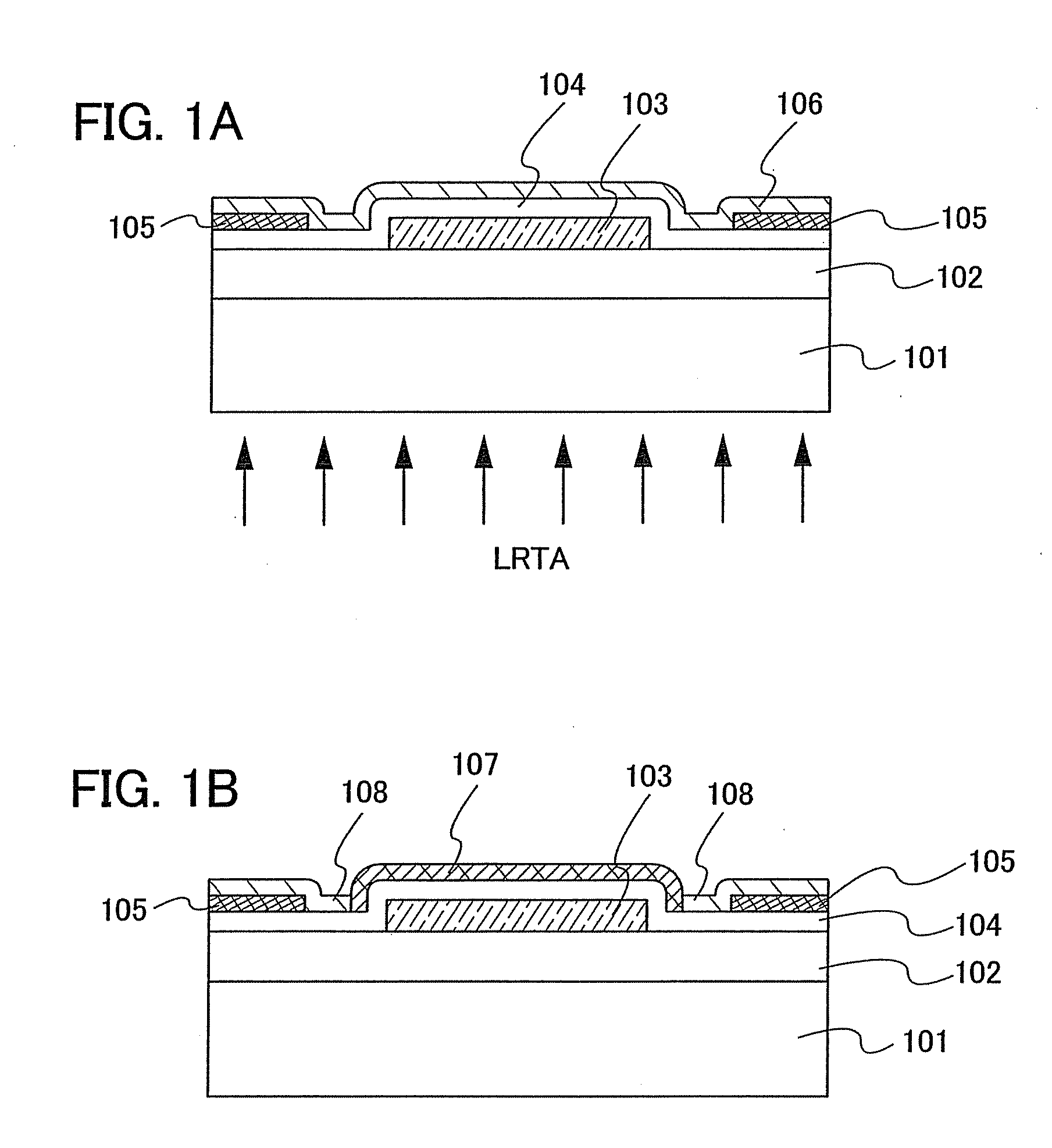
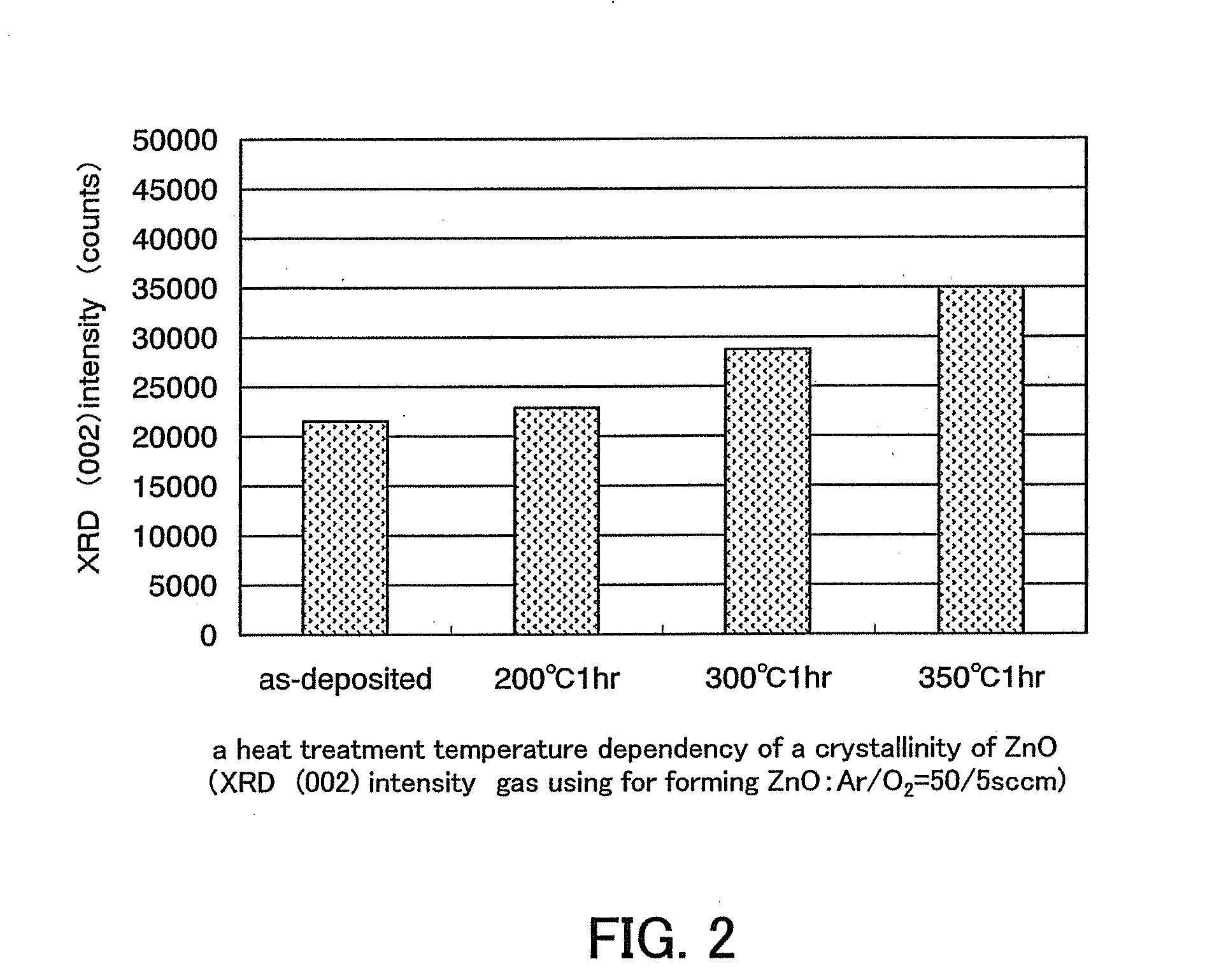
Semiconductor device including active layer made of zinc oxide with controlled orientations and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070187678A1Improve heat resistanceImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesZincActive layer
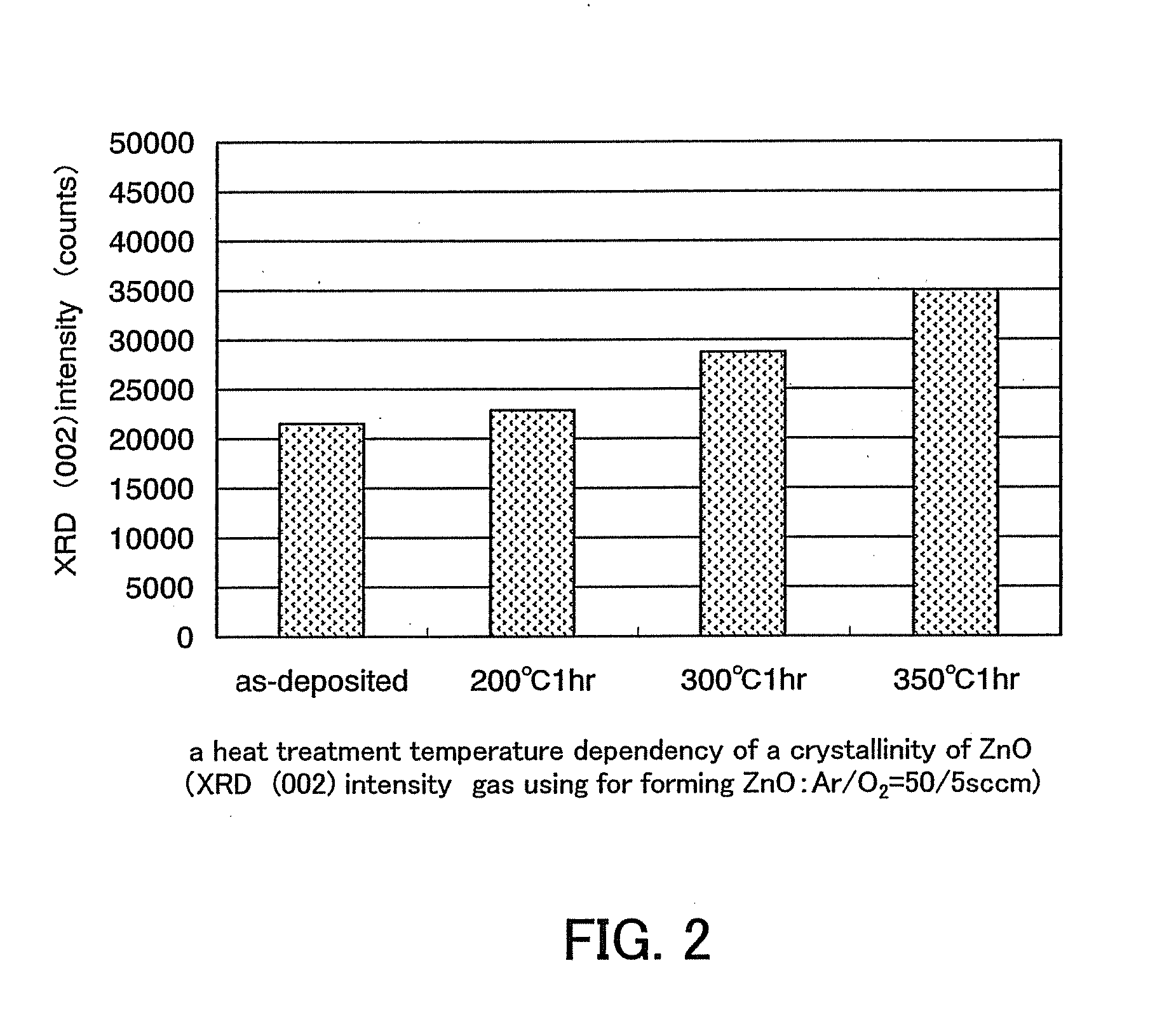
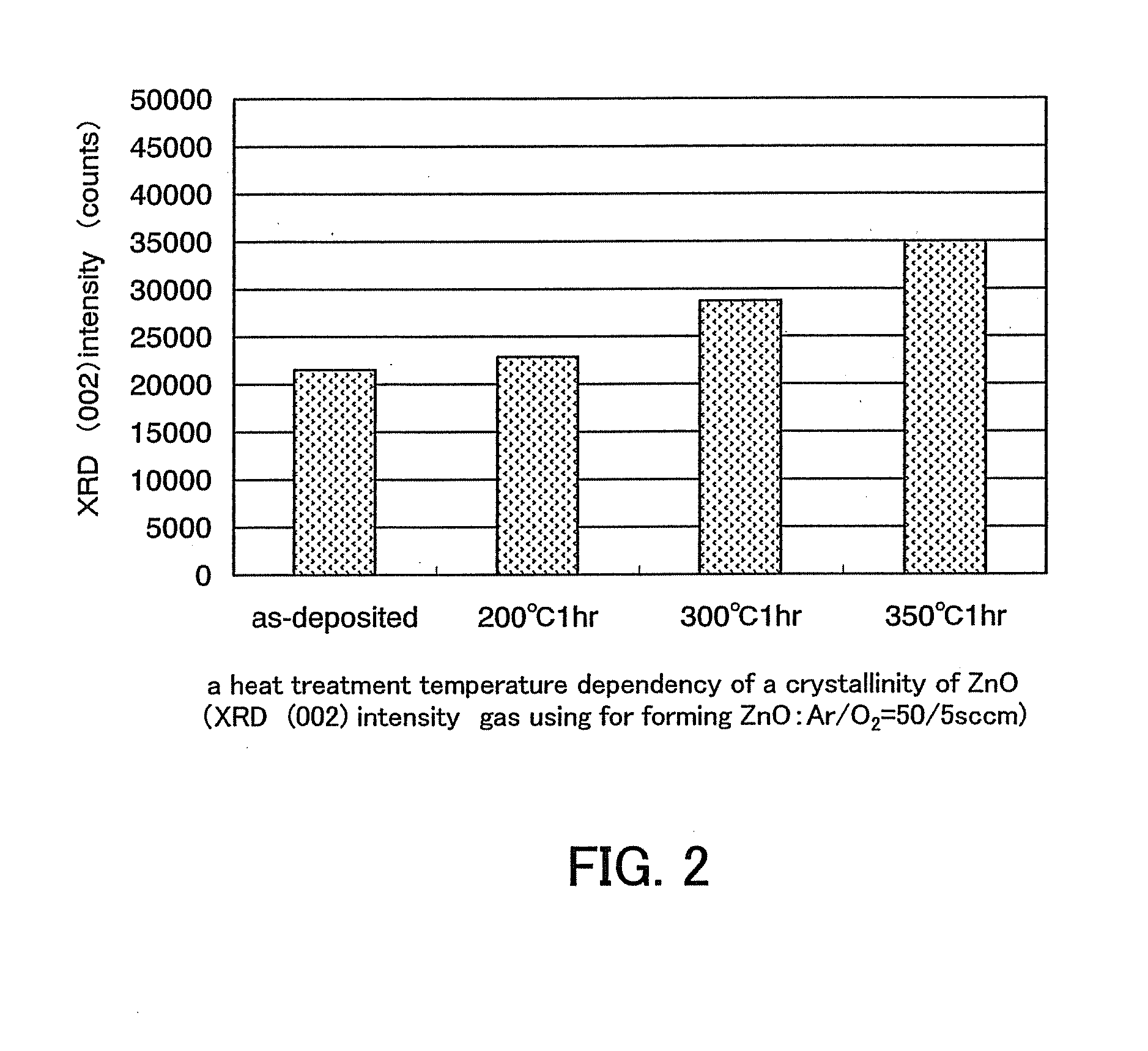
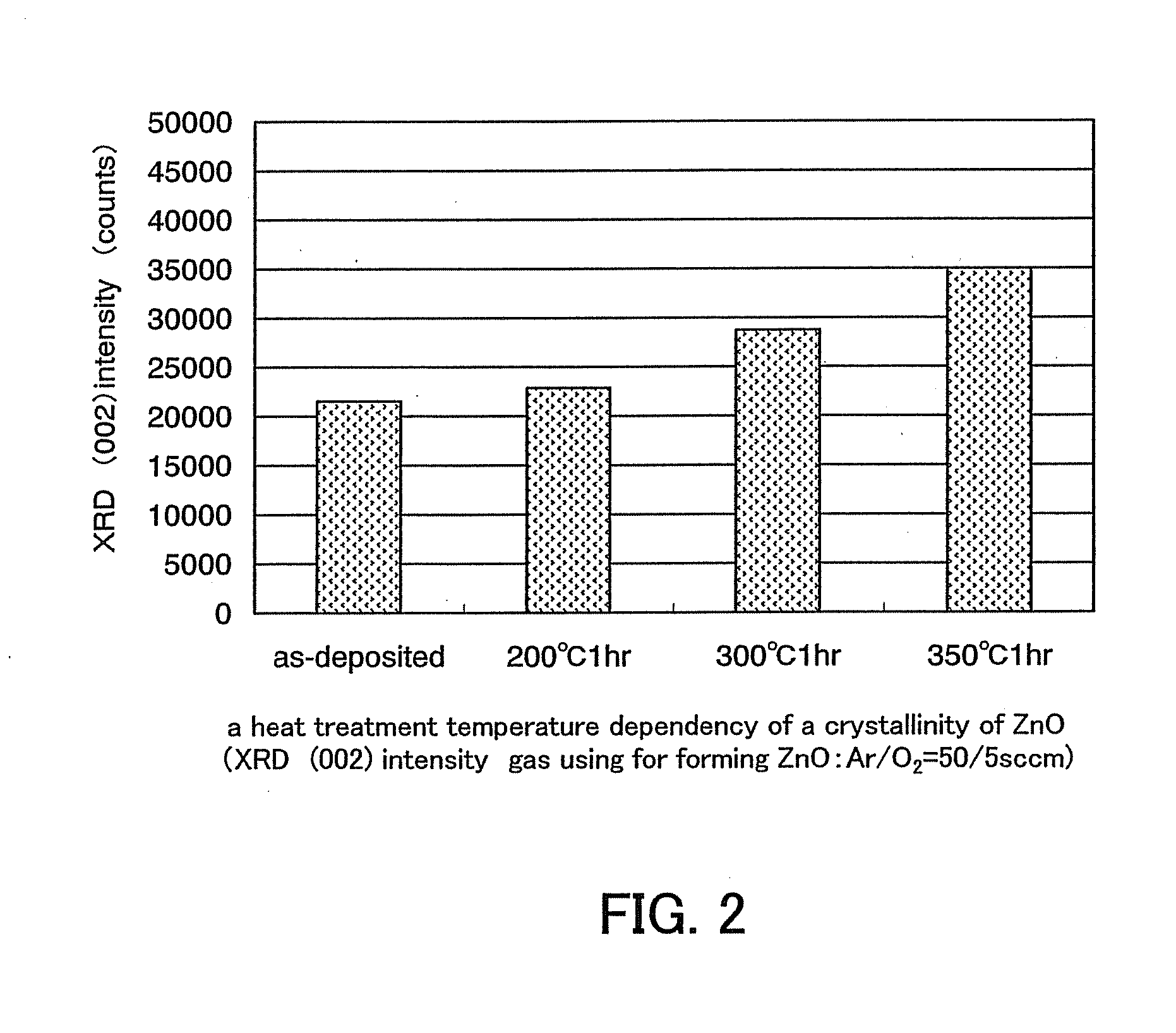
A semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor thin film layer primarily including zinc oxide having at least one orientation other than (002) orientation. The zinc oxide may have a mixed orientation including (002) orientation and (101) orientation. Alternatively, the zinc oxide may have a mixed orientation including (100) orientation and (101) orientation.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
Semiconductor device in which zinc oxide is used as a semiconductor material and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS7501293B2Improve surface smoothnessHigh crystallinityTransistorLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having excellent crystallinity and excellent electric characteristics includes a ZnO thin film having excellent surface smoothness. ZnO-based thin films (an n-type contact layer, an n-type clad layer, an active layer, a p-type clad layer, and a p-type contact layer) primarily including ZnO are formed sequentially by an ECR sputtering method or other suitable method on a zinc-polar surface of a ZnO substrate. A transparent electrode and a p-side electrode are formed by an evaporation method or other suitable method on a surface of the p-type contact layer, and an n-side electrode is formed on an oxygen-polar surface of the ZnO substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method of fabricating oxide semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070054507A1Efficient solutionReduce conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorMaterials science
A method for fabricating a device using an oxide semiconductor, including a process of forming the oxide semiconductor on a substrate and a process of changing the conductivity of the oxide semiconductor by irradiating a predetermined region thereof with an energy ray.
Owner:CANON KK
Transparent conductive film and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080050595A1Improve economyConductive layers on insulating-supportsSynthetic resin layered productsRocking curveFull width at half maximum
A ZnO-based transparent conductive film has practicable moisture resistance, desired characteristics of a transparent conductive film, and excellent economy. The transparent conductive film is produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate and has a region with a crystal structure in which a c-axis grows along a plurality of different directions. The transparent conductive film produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate has a ZnO (002) rocking curve full width at half maximum of about 13.5° or more.ZnO is doped with a group III element oxide so that the ratio of the group III element oxide in the transparent conductive film is about 7% to about 40% by weight.The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate with a SiNx thin film provided therebetween.The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate by a thin film formation method with a bias voltage applied to the substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
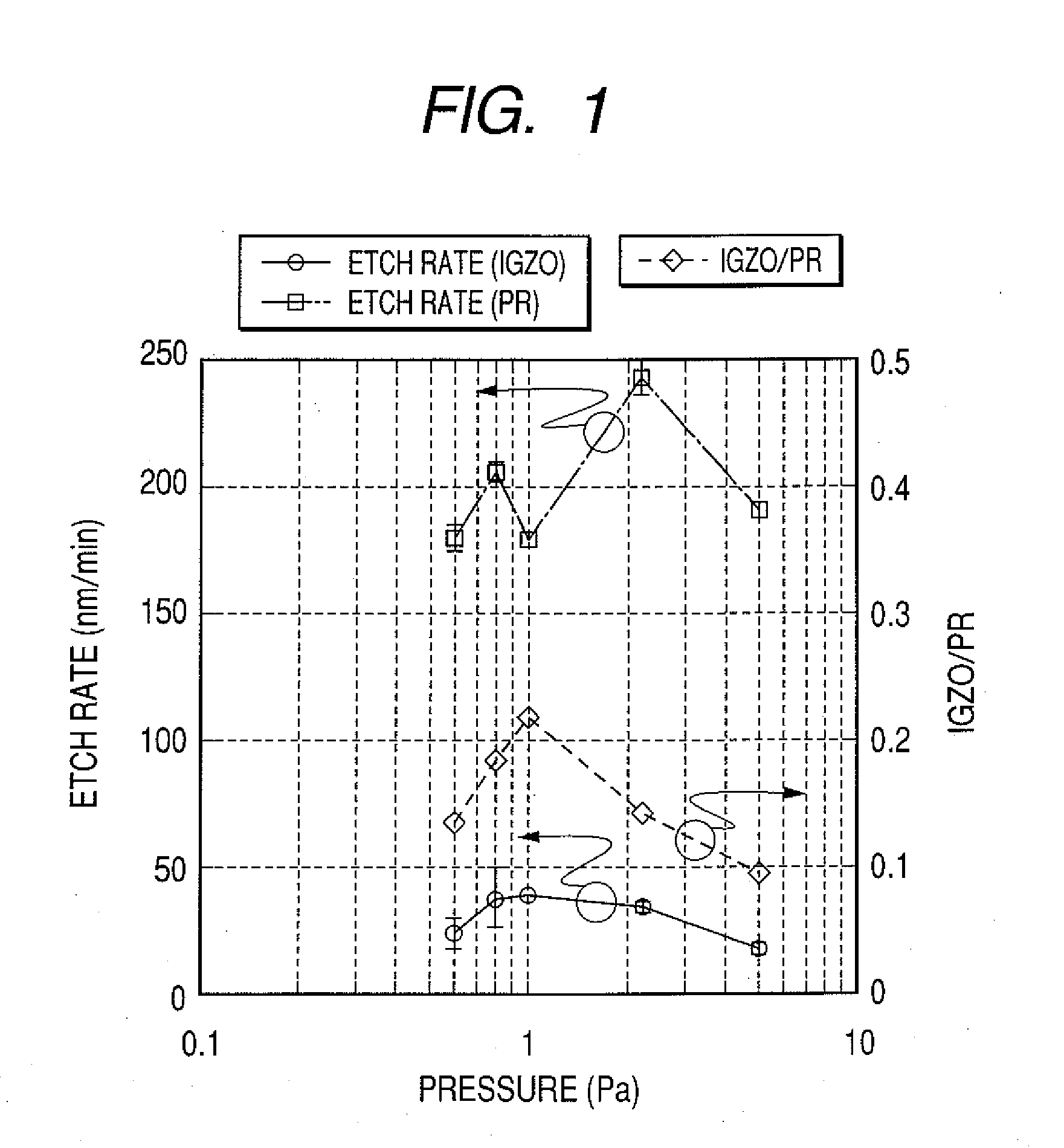
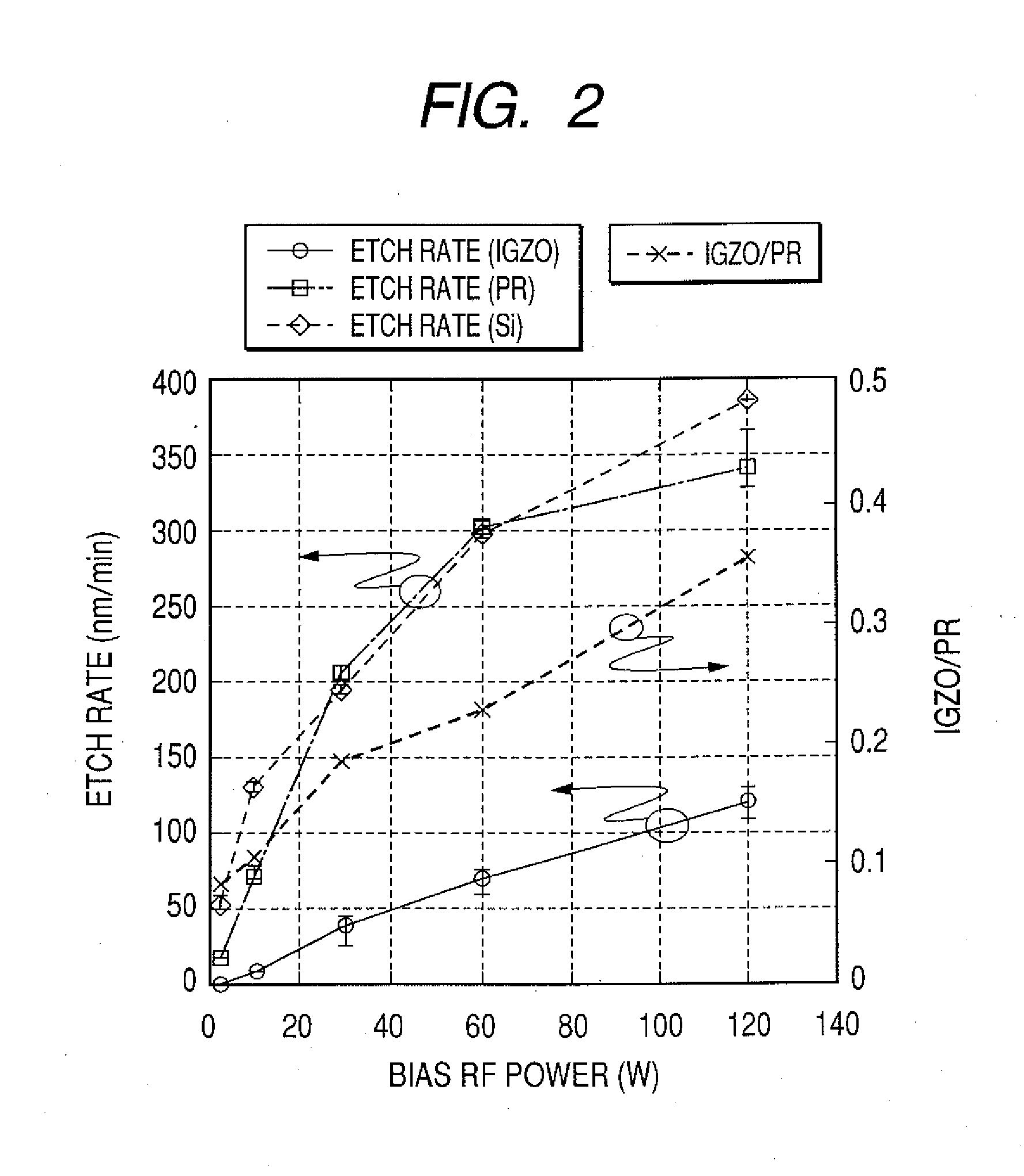
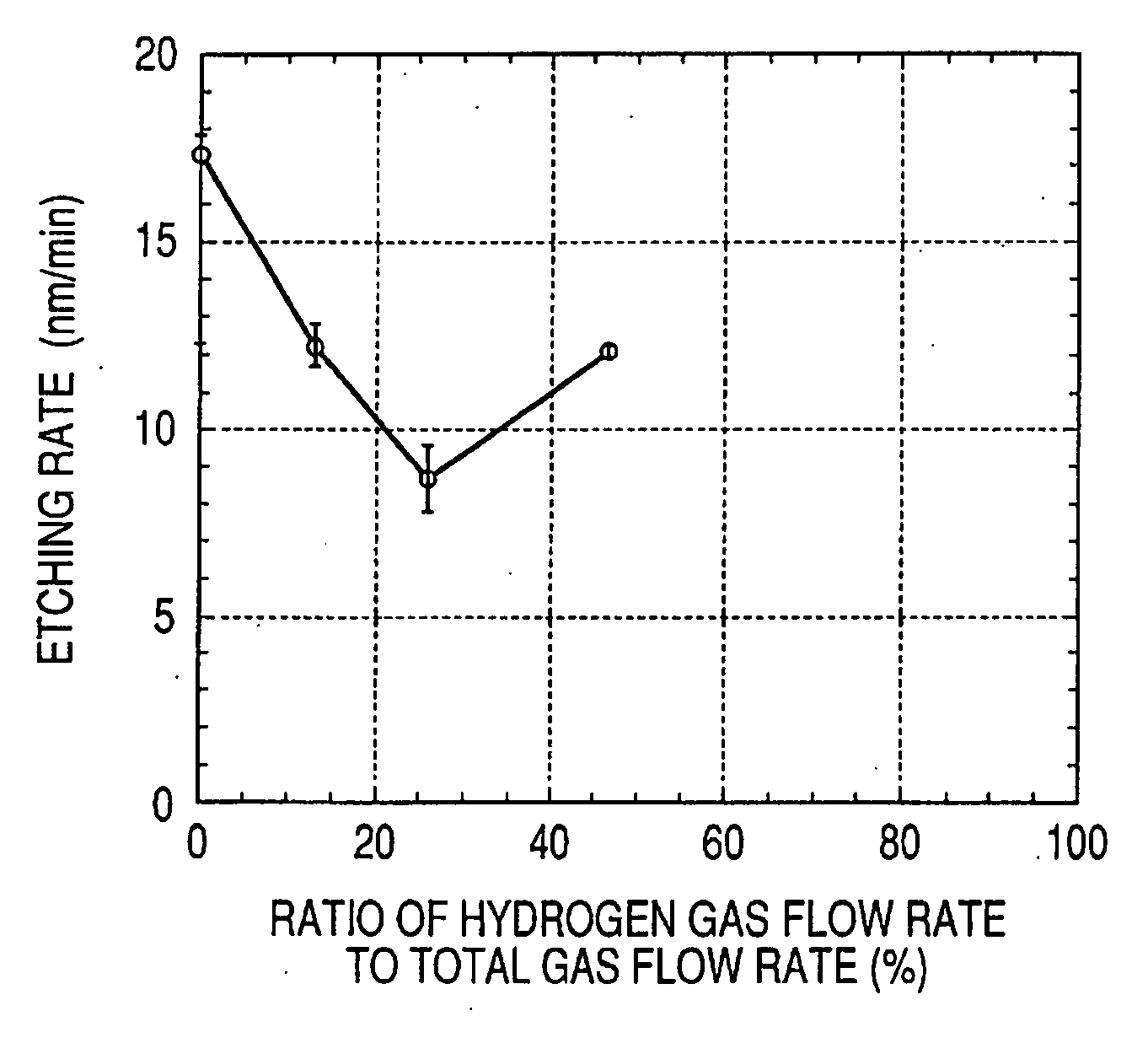
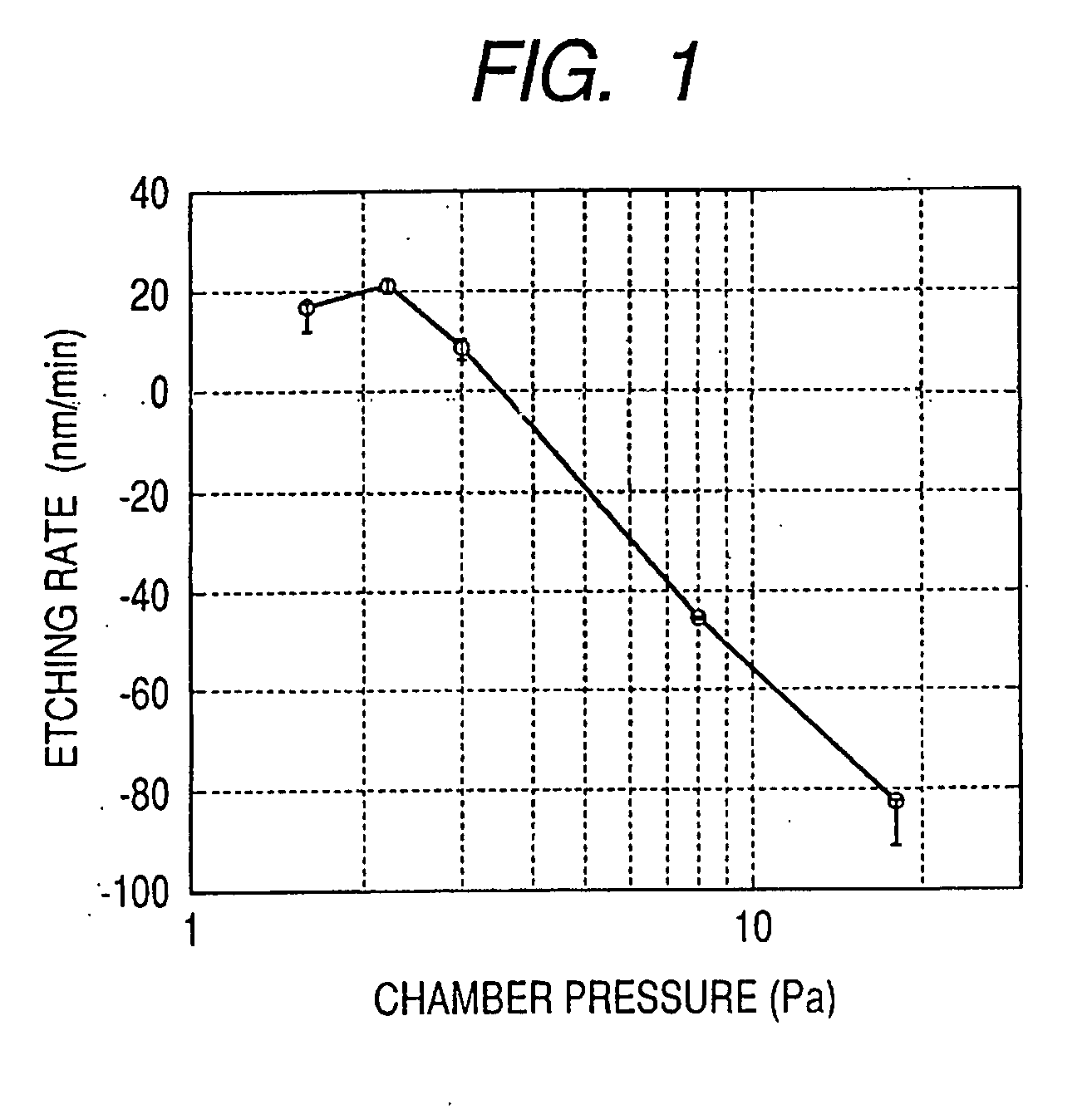
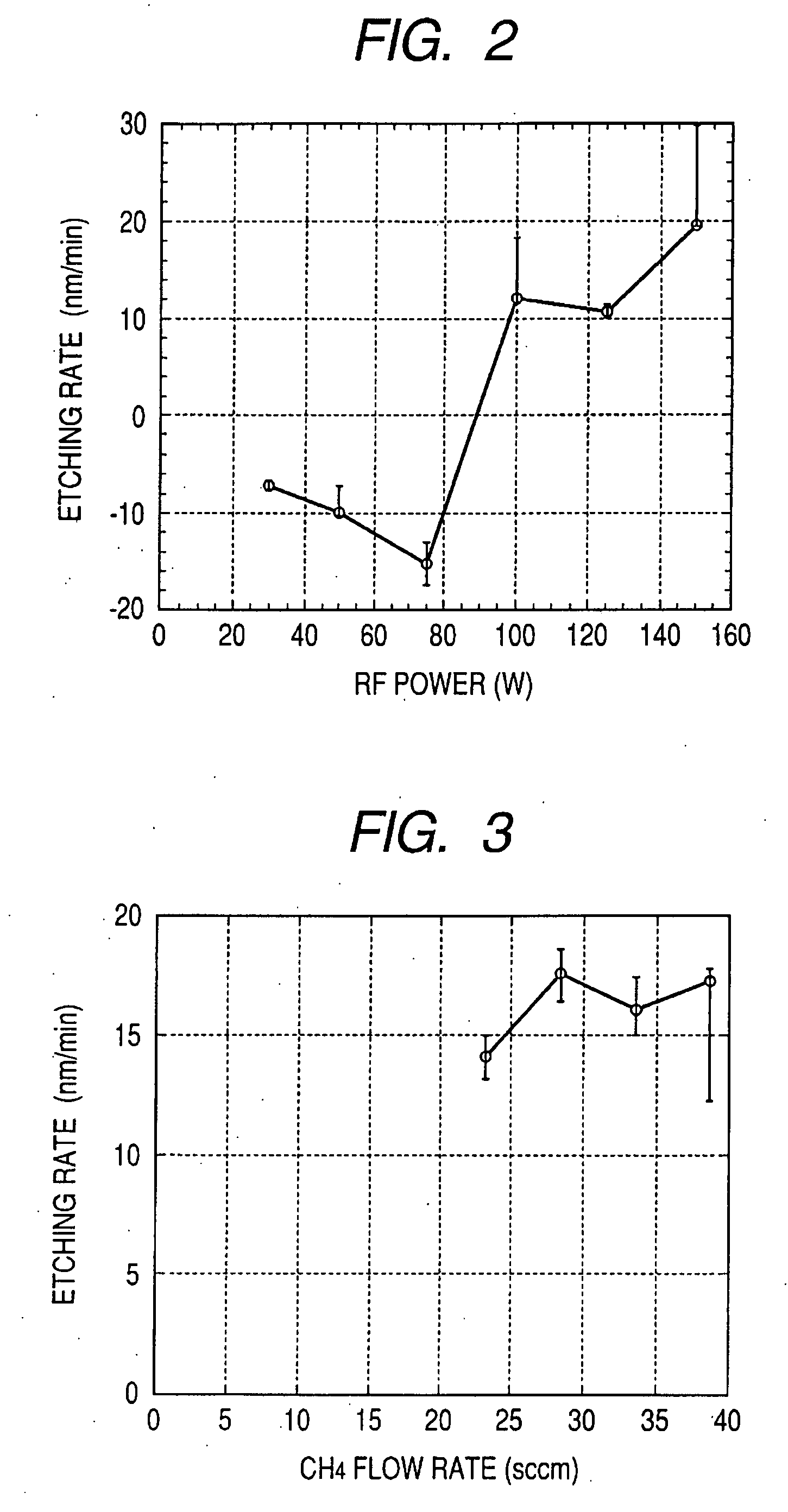
Method of dry etching oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20080038929A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorDry etching
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film containing at least In, Ga, and Zn, which includes etching an oxide semiconductor film in a gas atmosphere containing a halogen-based gas.
Owner:CANON KK
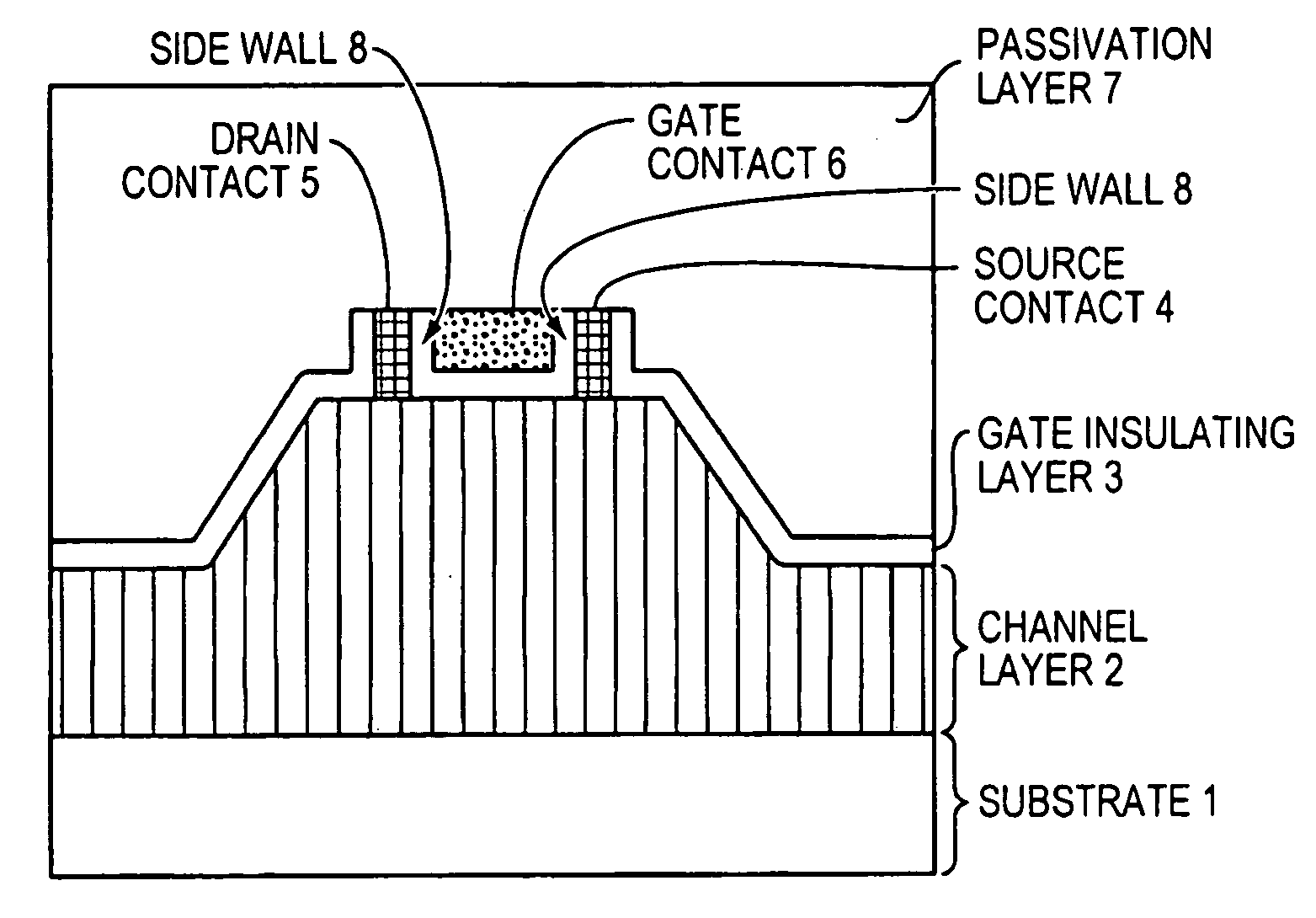
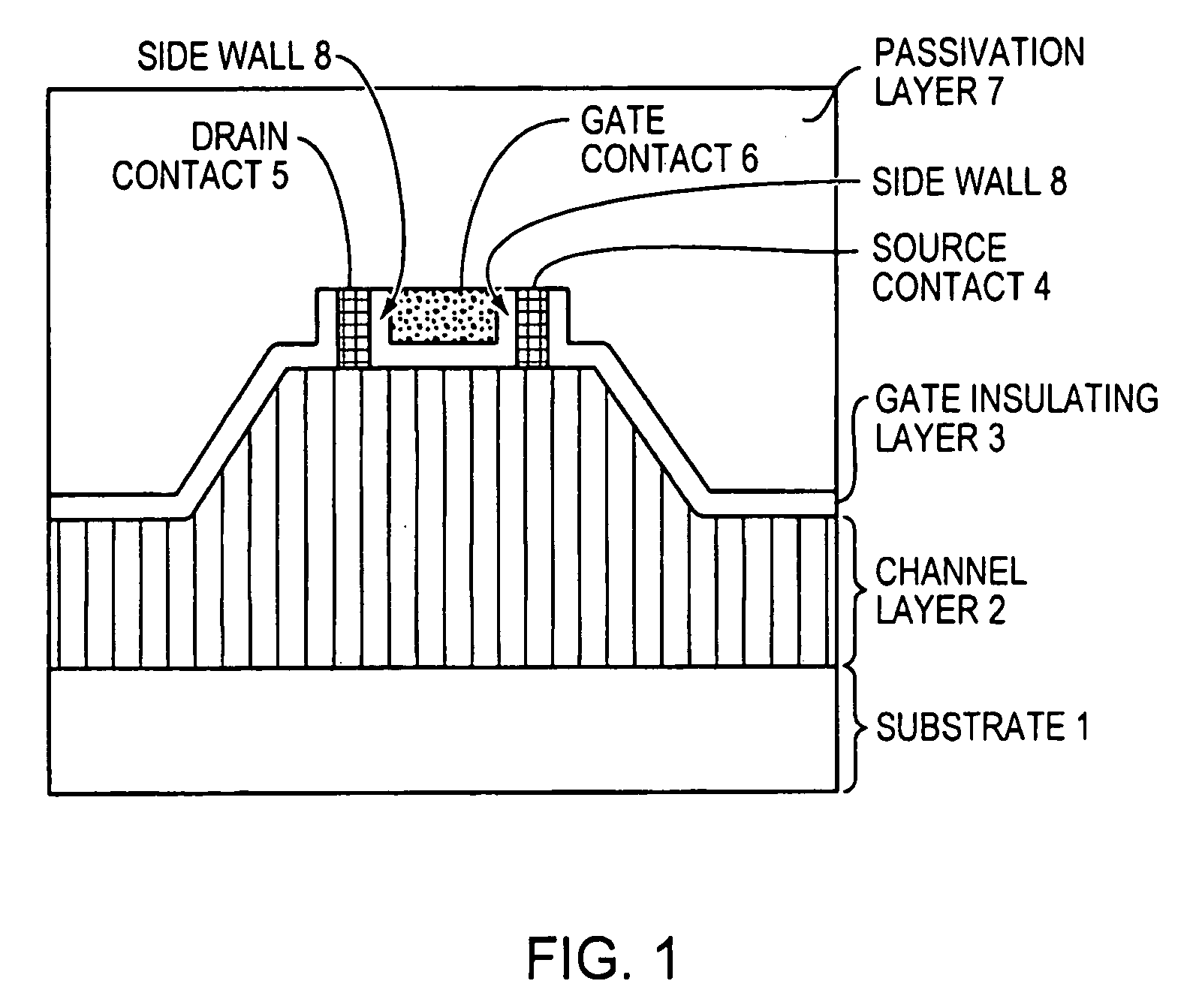
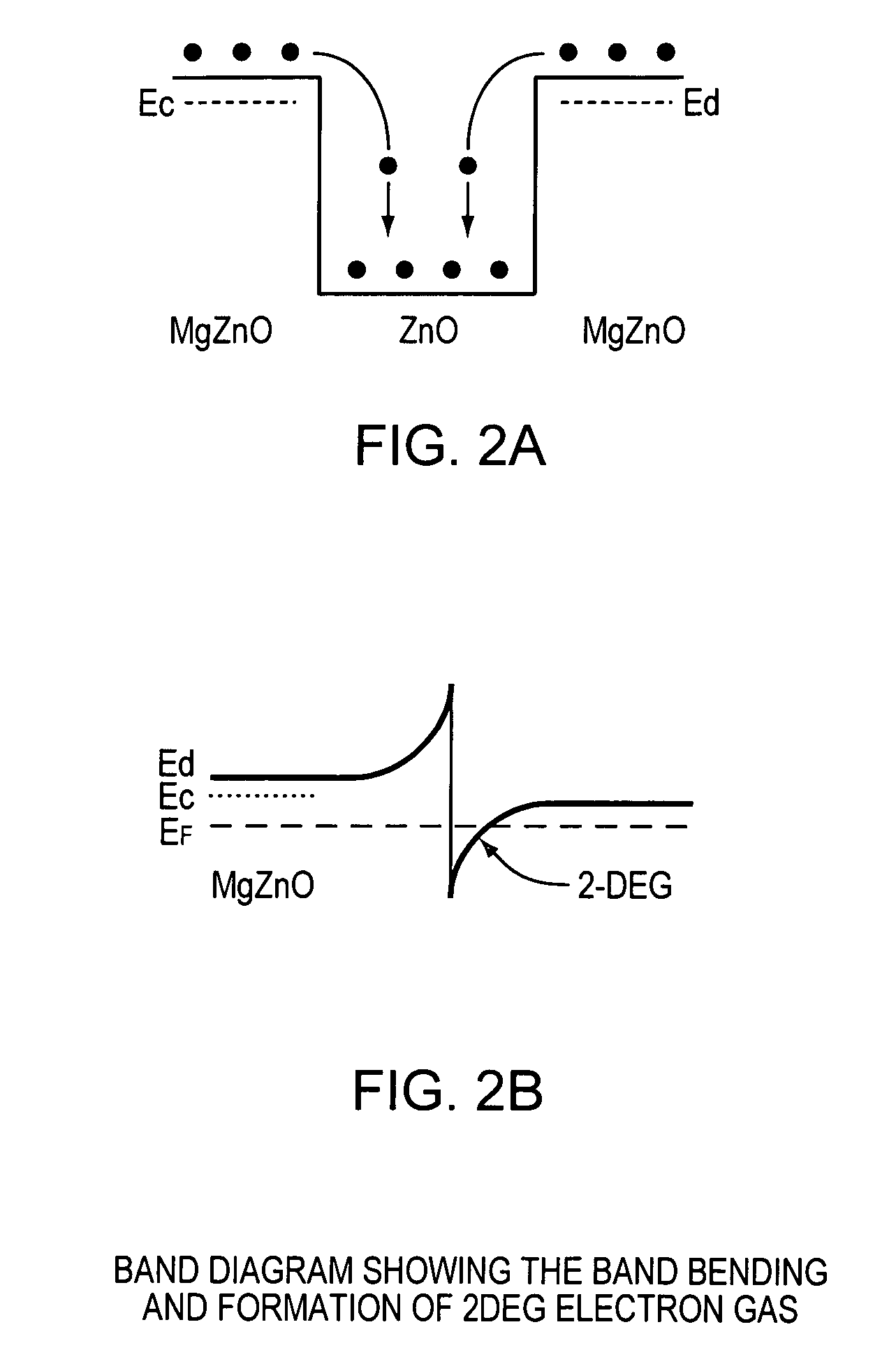
High-electron mobility transistor with zinc oxide
InactiveUS7105868B2Increase heightHigh electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierField-effect transistor
A zinc oxide (ZnO) field effect transistor exhibits large input amplitude by using a gate insulating layer. A channel layer and the gate insulating layer are sequentially laminated on a substrate. A gate electrode is formed on the gate insulating layer. A source contact and a drain contact are disposed at the both sides of the gate contact and are electrically connected to the channel layer via openings. The channel layer is formed from n-type ZnO. The gate insulating layer is made from aluminum nitride / aluminum gallium nitride (AlN / AlGaN) or magnesium zinc oxide (MgZnO), which exhibits excellent insulation characteristics, thus increasing the Schottky barrier and achieving large input amplitude. If the FET is operated in the enhancement mode, it is operable in a manner similar to a silicon metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (Si-MOS-type FET), resulting in the formation of an inversion layer.
Owner:NAUSE CATHERINE D
ZnO thin film transistor and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20070272922A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate insulatorEngineering
A zinc oxide (ZnO) thin film transistor (TFT) and method of forming the same are provided. The ZnO may include a ZnO semiconductor channel, a conductive ZnO gate forming an electric field around the ZnO semiconductor channel, an ZnO gate insulator interposed between the conductive ZnO gate and the ZnO semiconductor channel and an insulating ZnO passivation layer on the ZnO semiconductor channel, the conductive ZnO gate and the ZnO gate insulator to protect the ZnO semiconductor channel, the conductive ZnO gate, and the ZnO gate insulator. A thin film transistor (TFT) may be formed by forming a semiconductor channel, forming a conductive gate having an electric field around the semiconductor channel, forming a gate insulator between the conductive gate and the semiconductor channel, and forming an insulating passivation layer on the semiconductor channel, the conductive gate and the gate insulator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Structure with transistor
ActiveUS20080258139A1Improve mobilityOn/off ratio highSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A structure with a transistor is disclosed comprising a substrate, a gas barrier layer on the substrate, and a transistor on the gas barrier layer. The transistor can include an oxide semiconductor layer. The oxide semiconductor layers can comprise In—Ga—Zn—O. A display, such as a liquid crystal display, can have such a structure.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Thin film transistor having oxide semiconductor layer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060284172A1Etch resistance of resist is lowPromote meltingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZincSemiconductor
A thin film transistor has a semiconductor thin film including zinc oxide, a protection film formed on entirely the upper surface of the semiconductor thin film, a gate insulating film formed on the protection film, a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film above the semiconductor thin film, and a source electrode and drain electrode formed under the semiconductor thin film so as to be electrically connected to the semiconductor thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Dry etching method for oxide semiconductor film
InactiveUS20070287296A1Improve processing accuracyIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDry etchingSemiconductor
Provided is a dry etching method for an oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O, in which an etching gas containing a hydrocarbon is used in a dry etching process for the oxide semiconductor film made of In—Ga—Zn—O formed on a substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
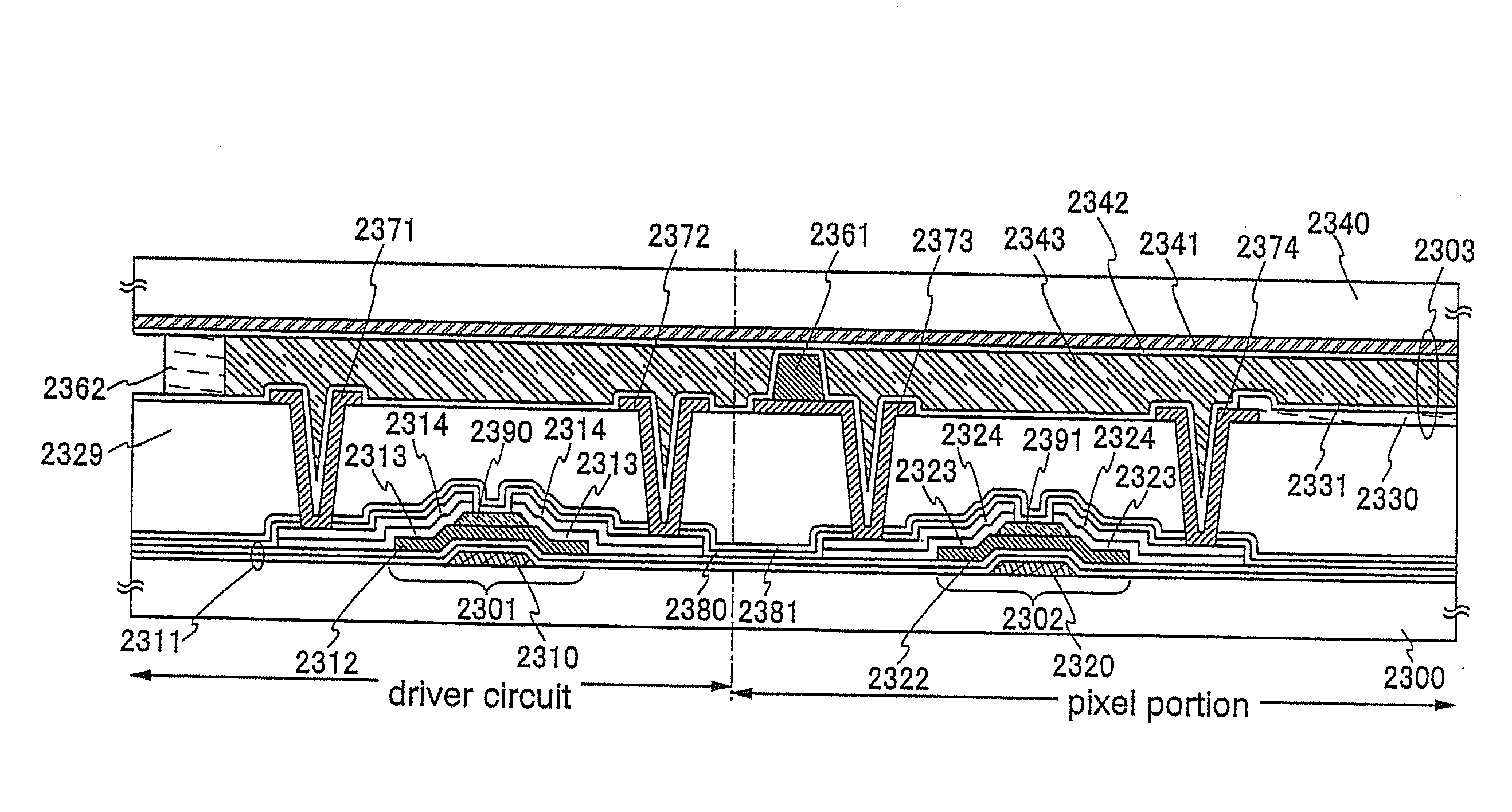
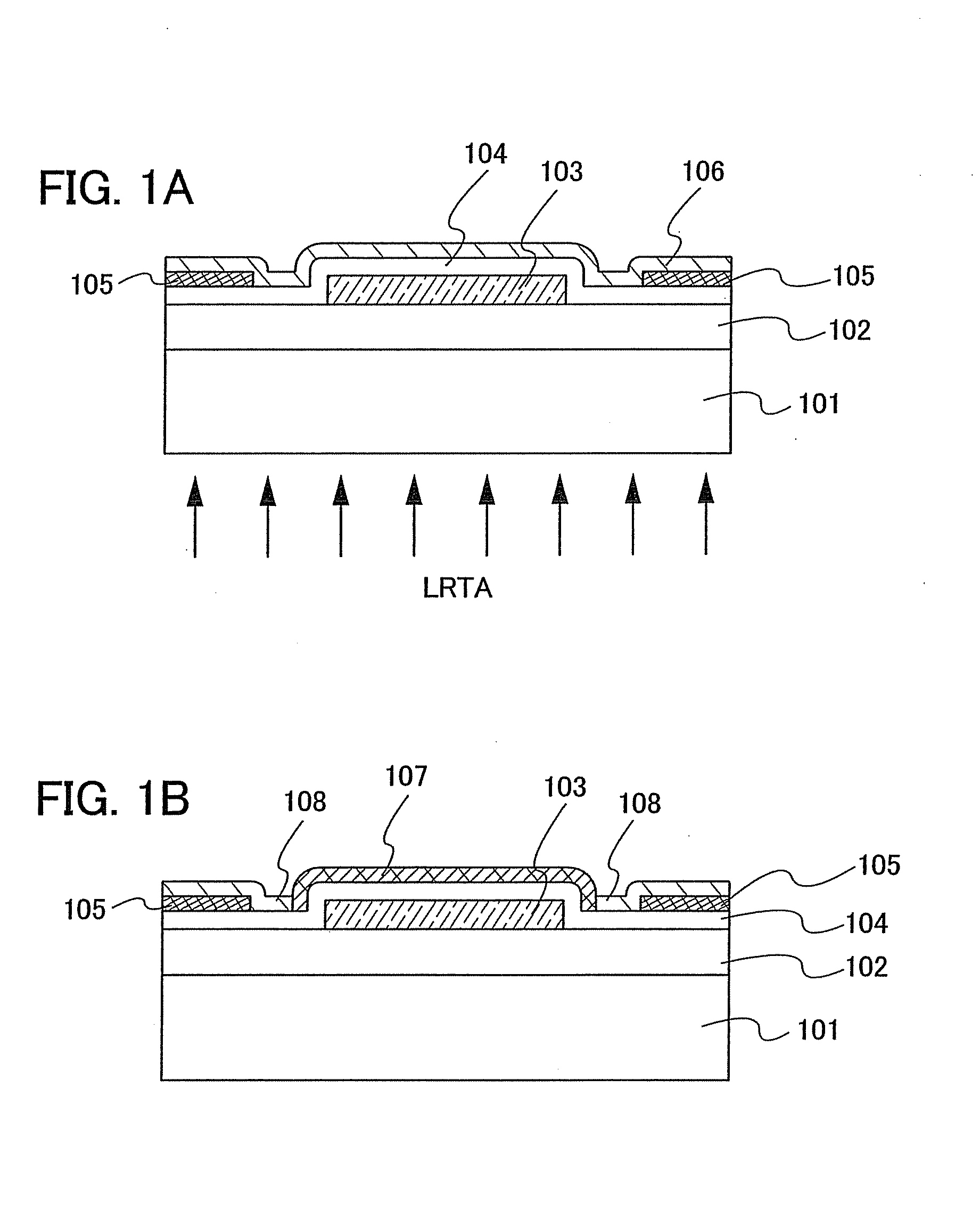
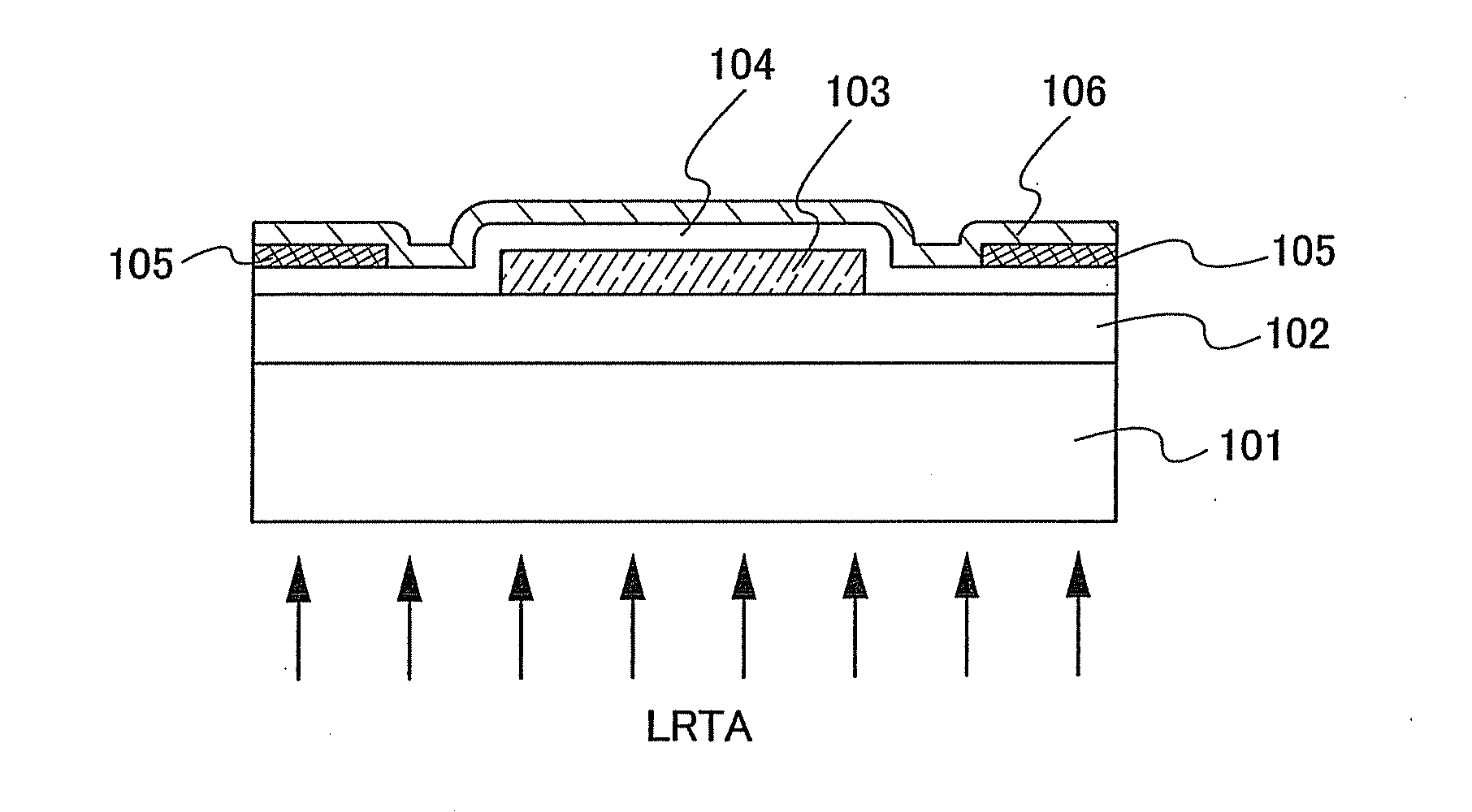
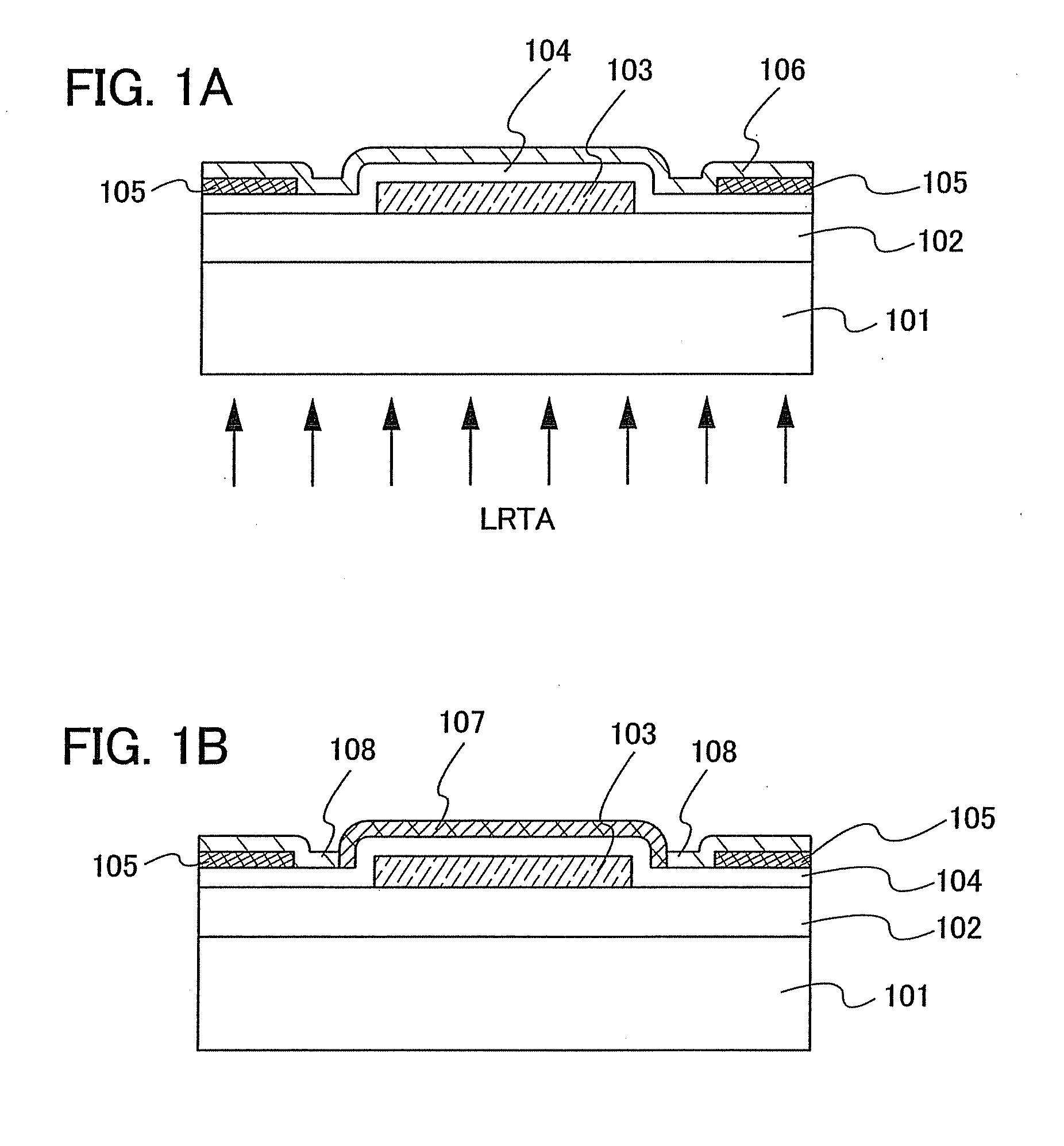
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
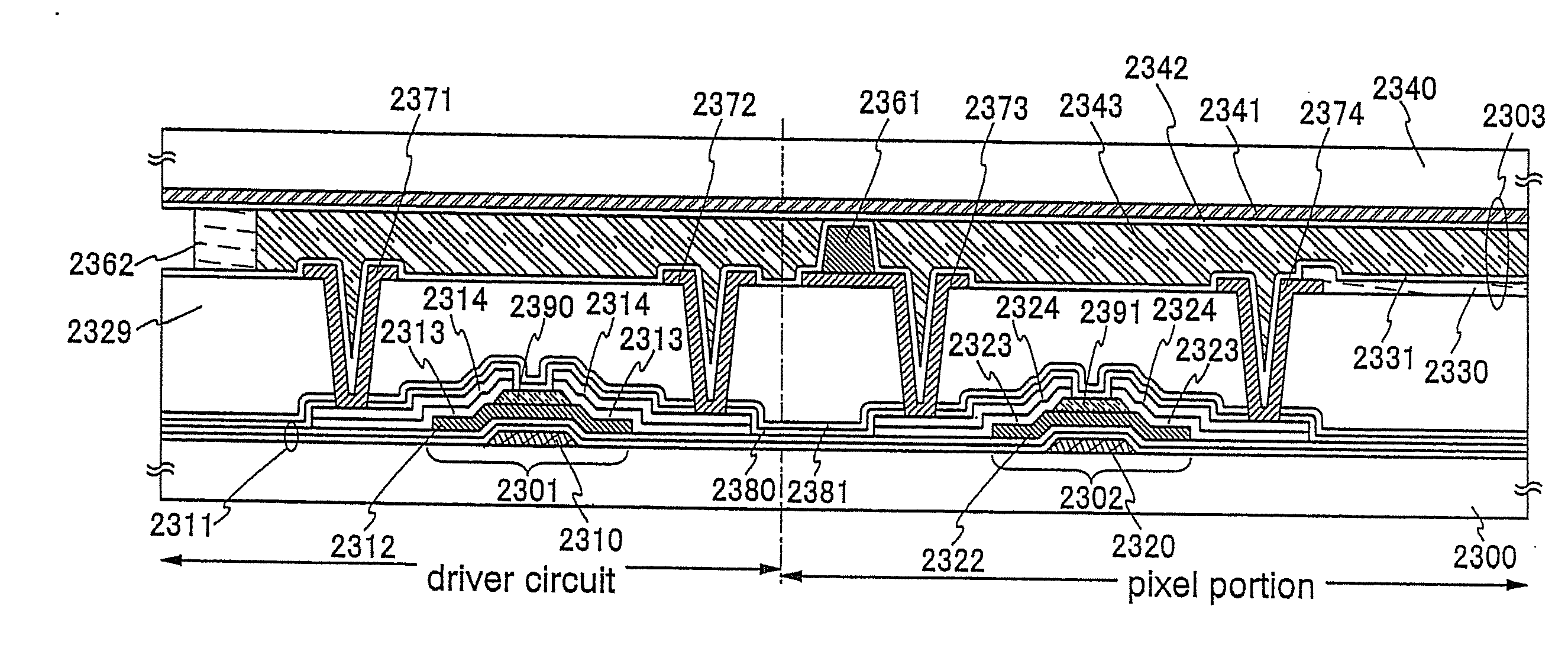
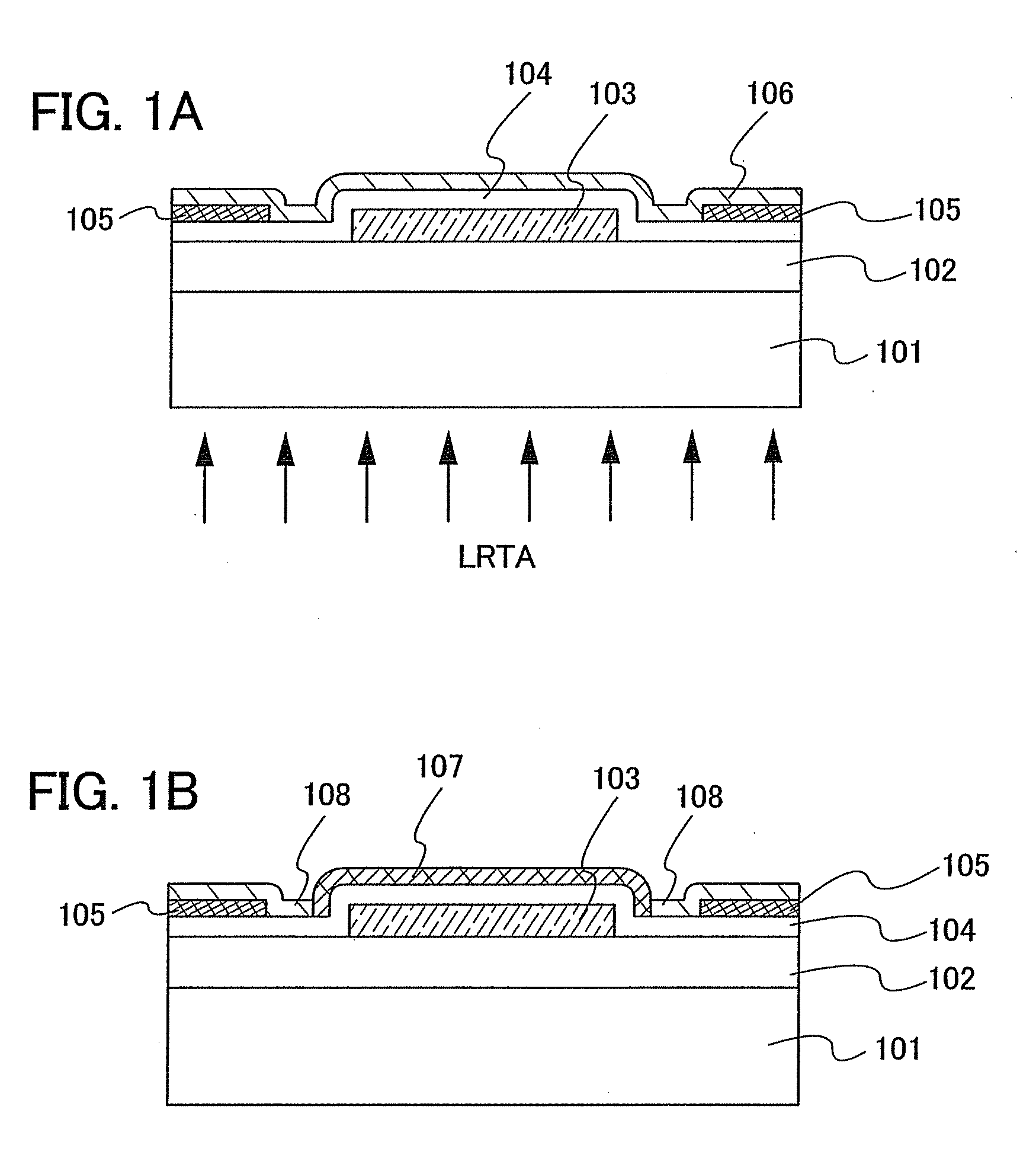
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of producing a sustained-release preparation
InactiveUS6197350B1Reduce the number of stepsSuitable for industrializationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood concentrationOrganic solvent
A method of producing sustained-release microcapsules which comprises dispersing a physiologically active polypeptide into a solution of a biodegradable polymer and zinc oxide in an organic solvent, followed by removing the organic solvent; which provides a sustained-release preparation showing a high entrapment ratio of the physiologically active polypeptide and its constant high blood concentration levels over a long period of time.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080308797A1High yieldReduce the ratioTransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensEngineeringZinc
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Adhesive formulatiions
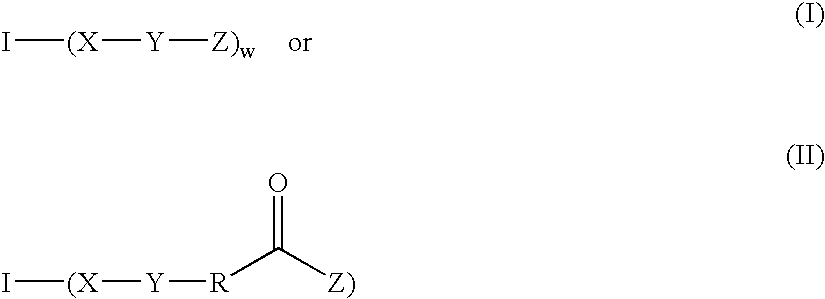
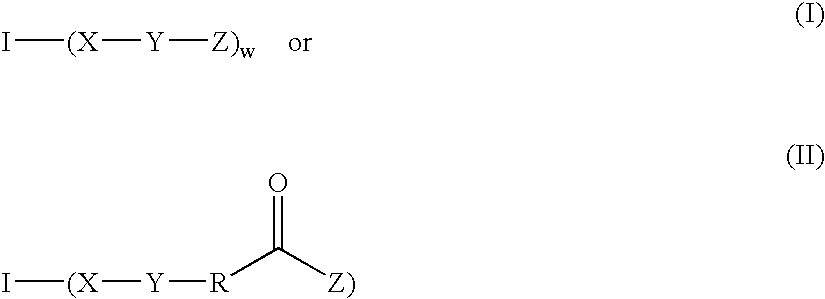
The disclosure relates to biocompatible components useful for forming compositions for use as medical / surgical synthetic adhesives and sealants. Biocompatible components of the present disclosure may include a multifunctional amine or multifunctional polyol core, with isocyanate and / or polyalkylene oxide arms, which may optionally be capped with electrophilic or nucleophilic groups. These biocompatible components may, in embodiments, be combined with optional cross linkers to form adhesive and / or sealant compositions.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com