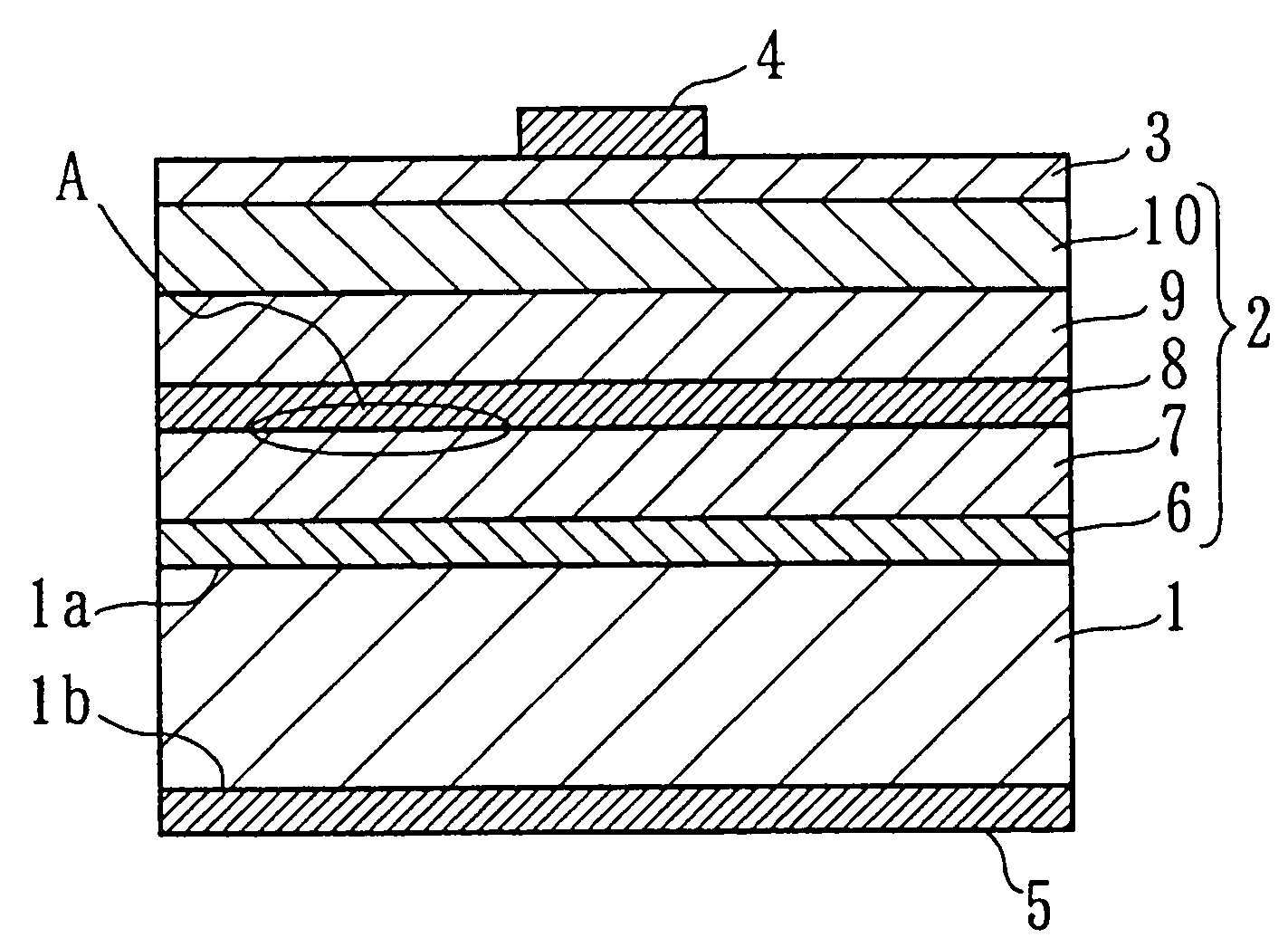
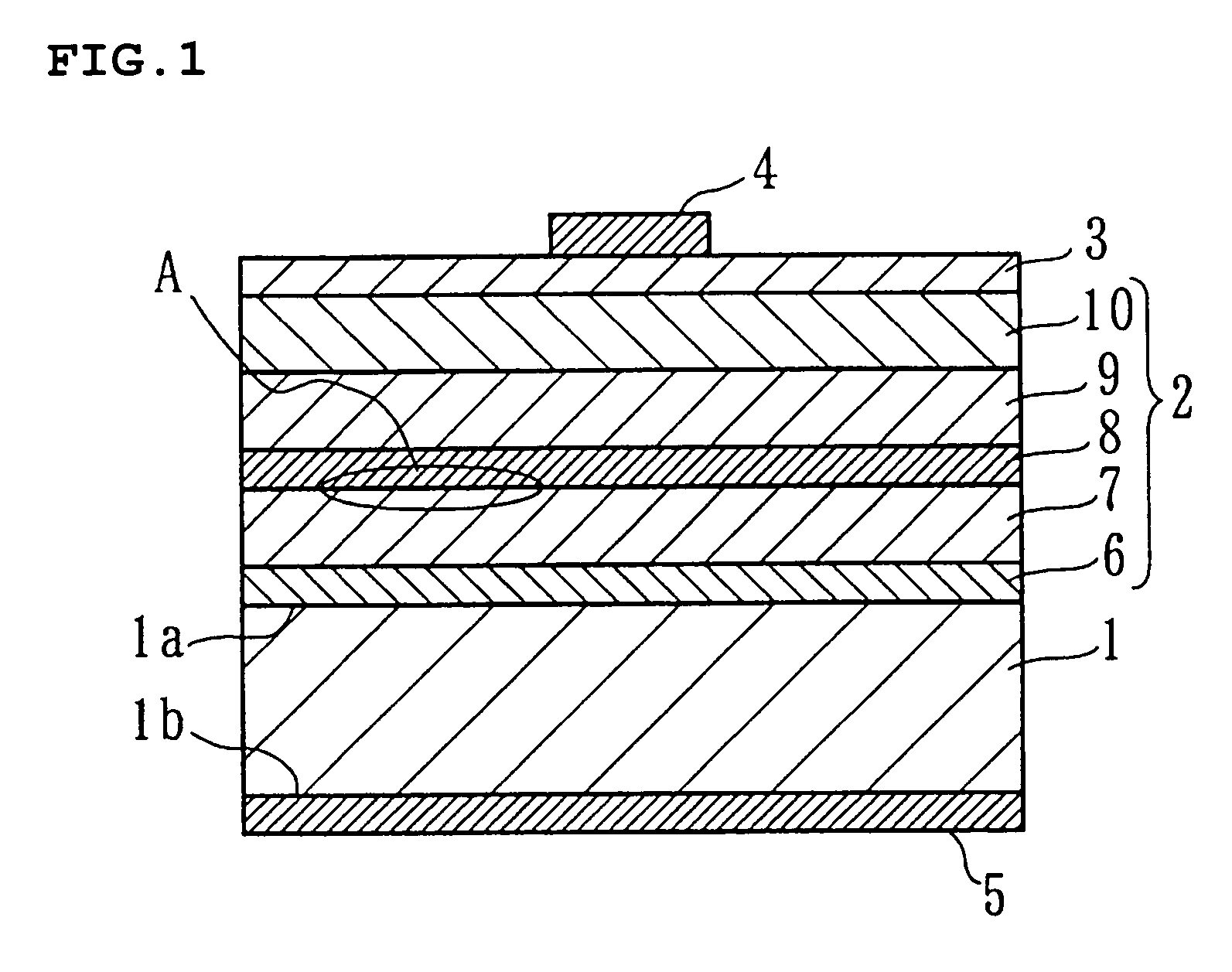
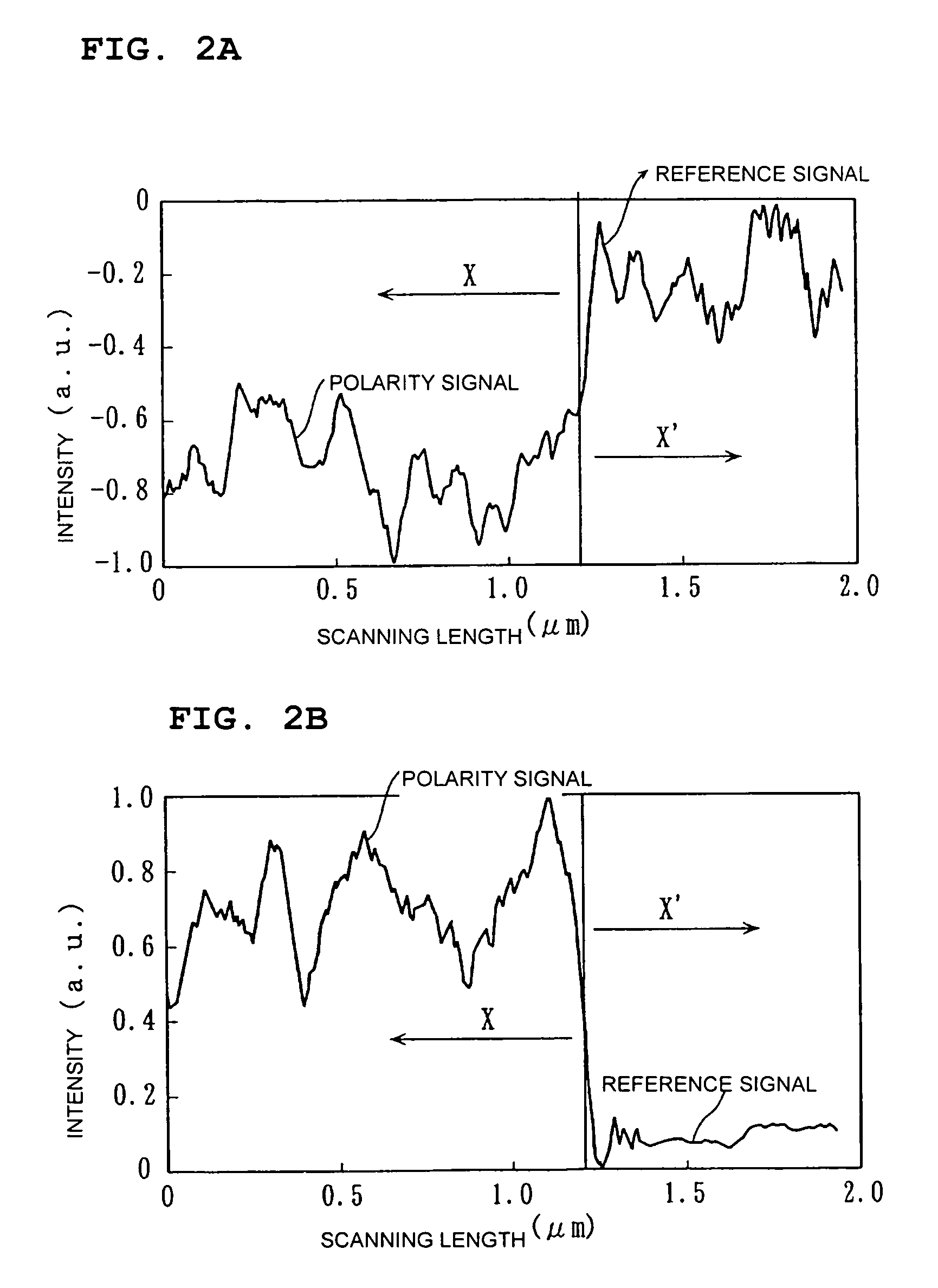
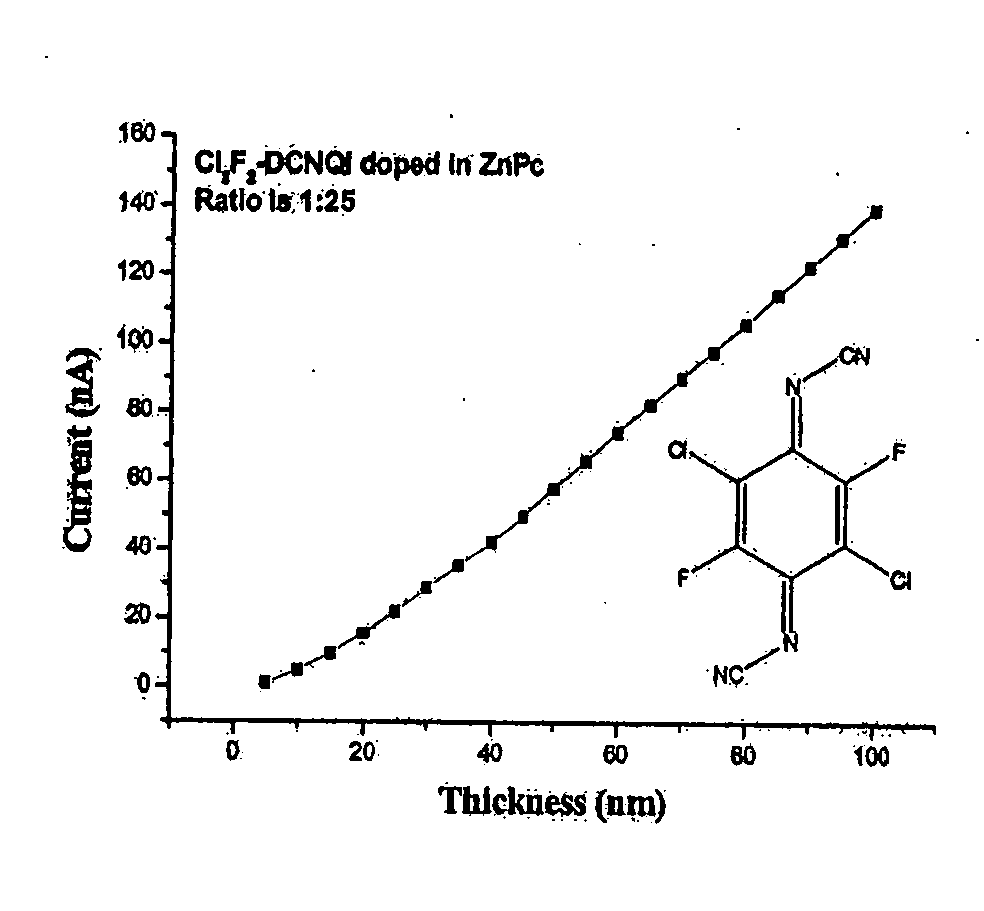
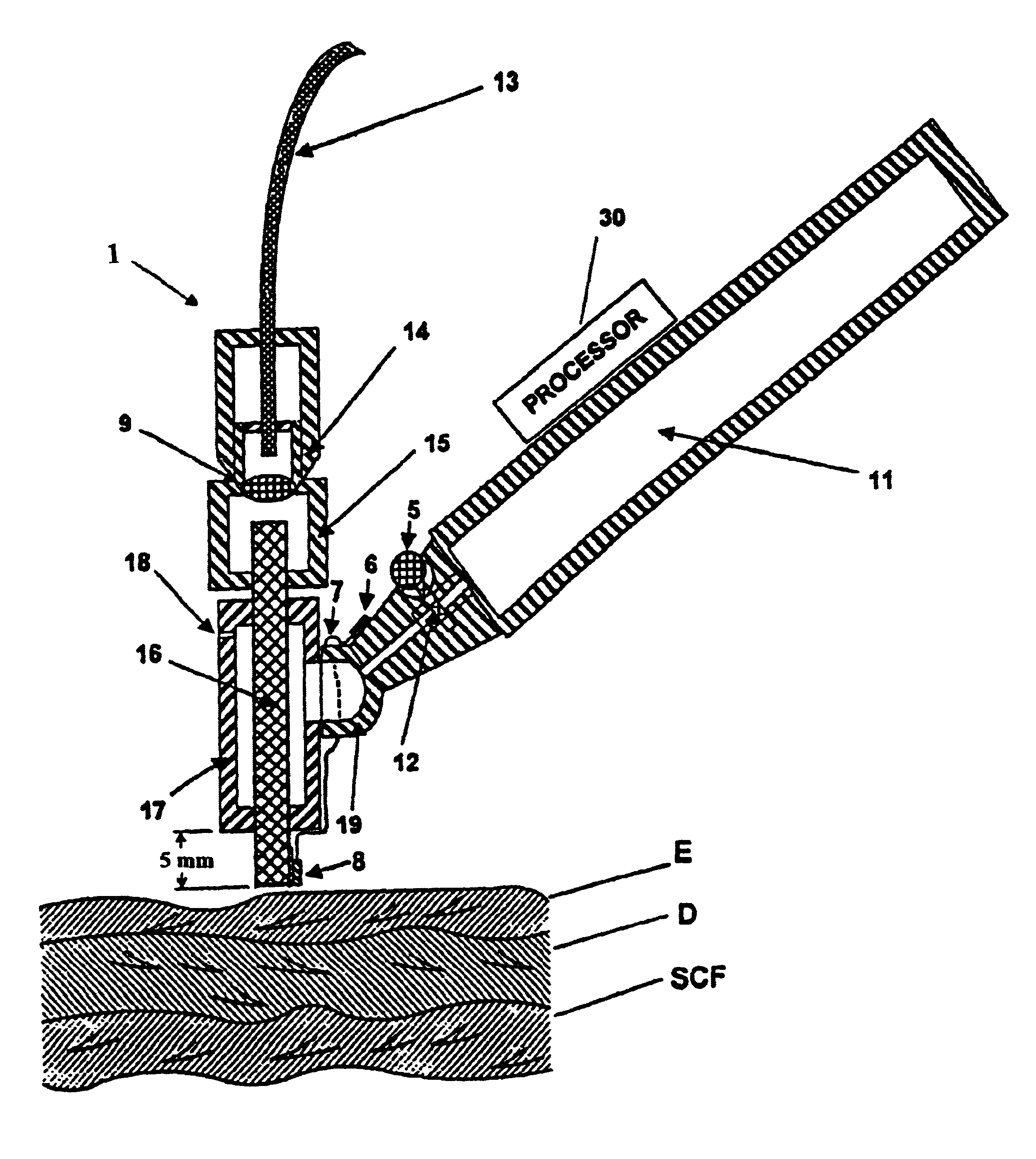
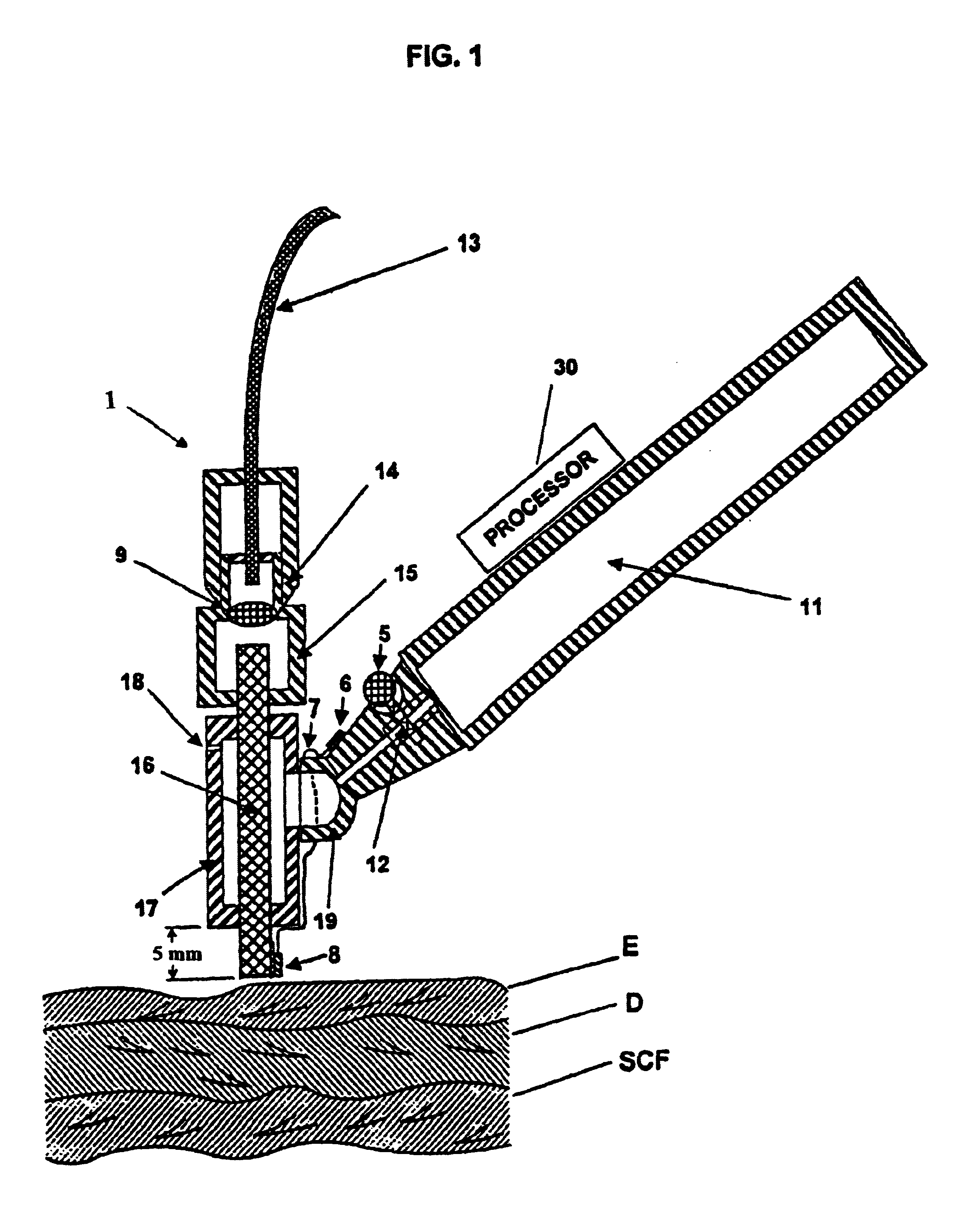
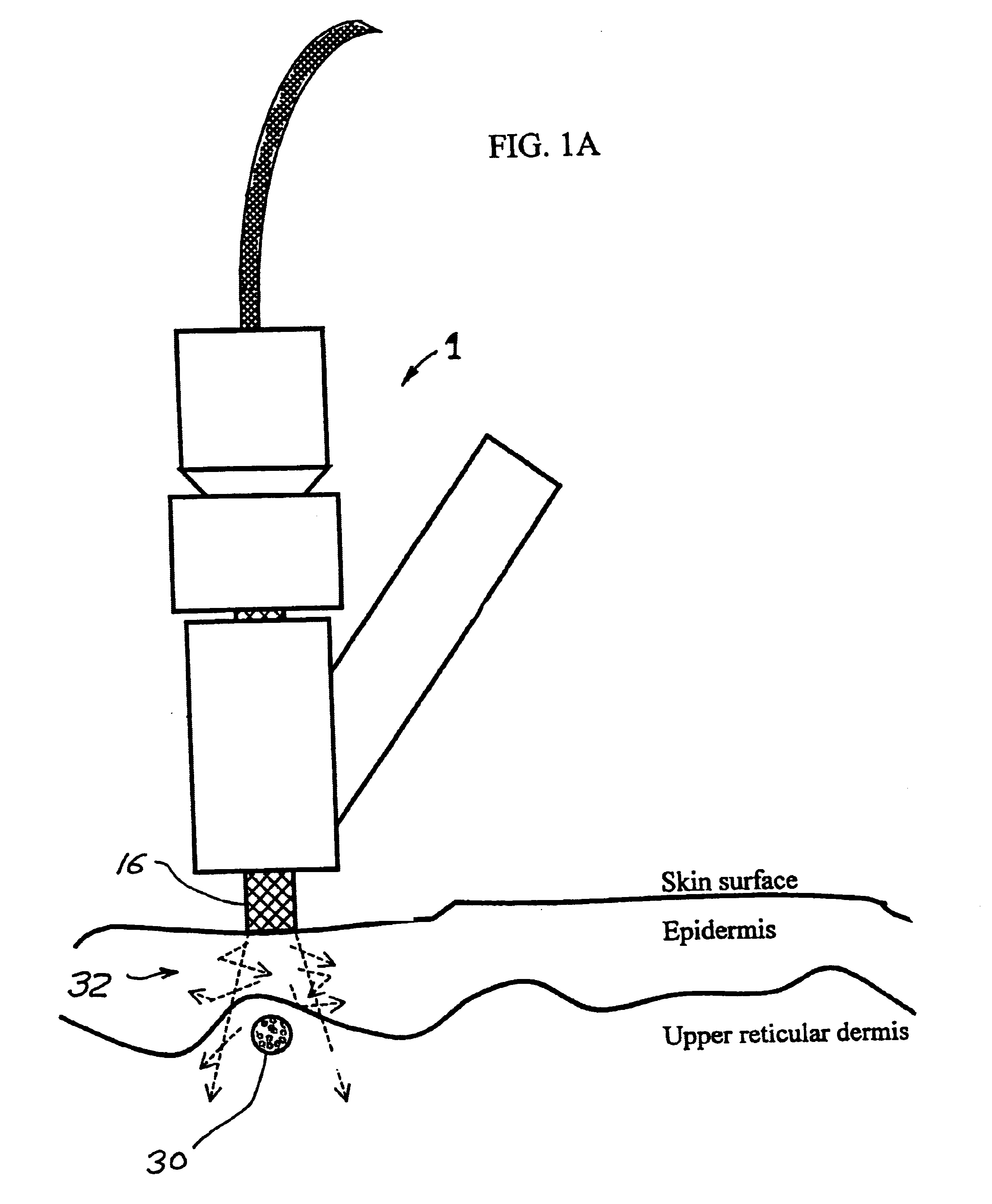
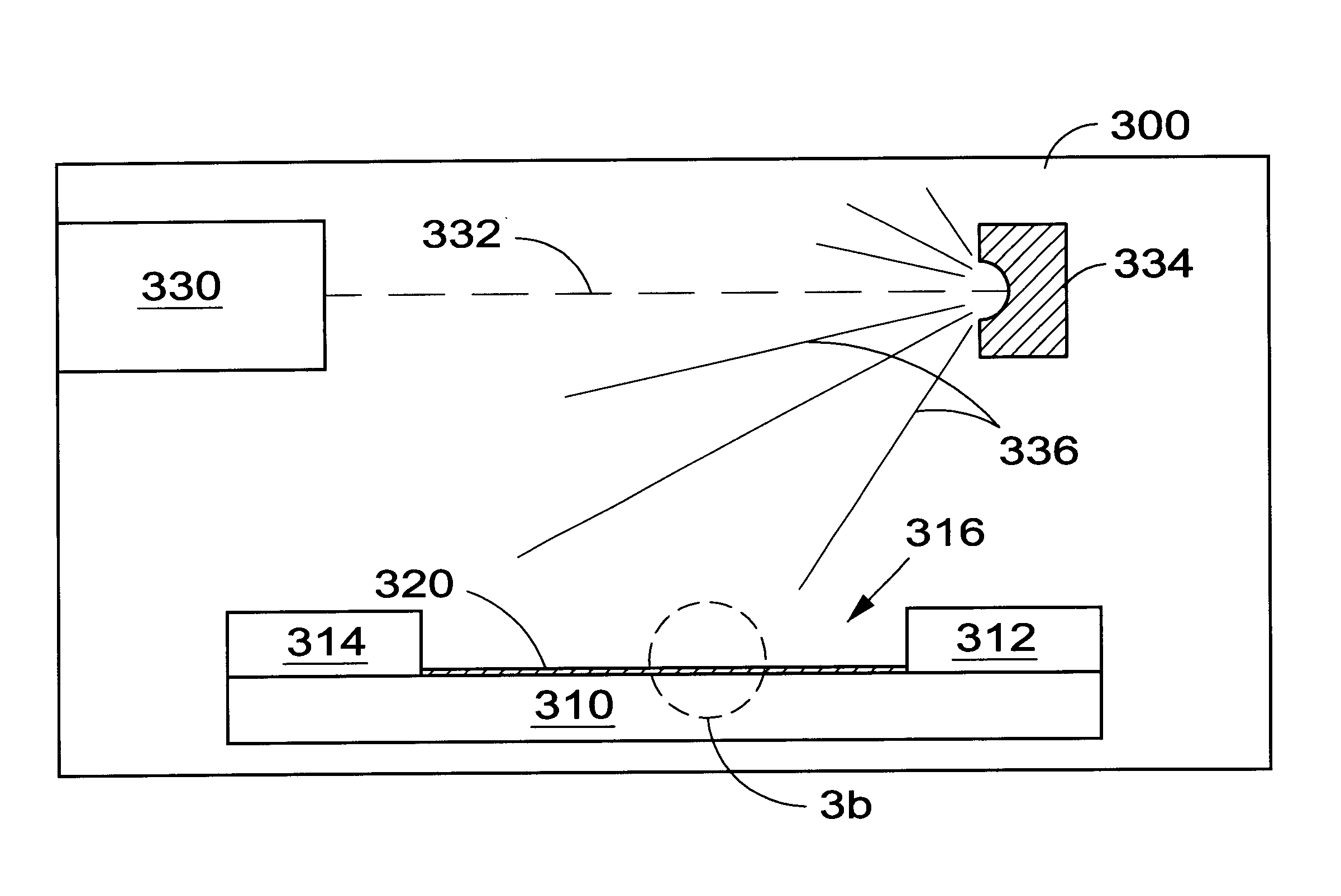
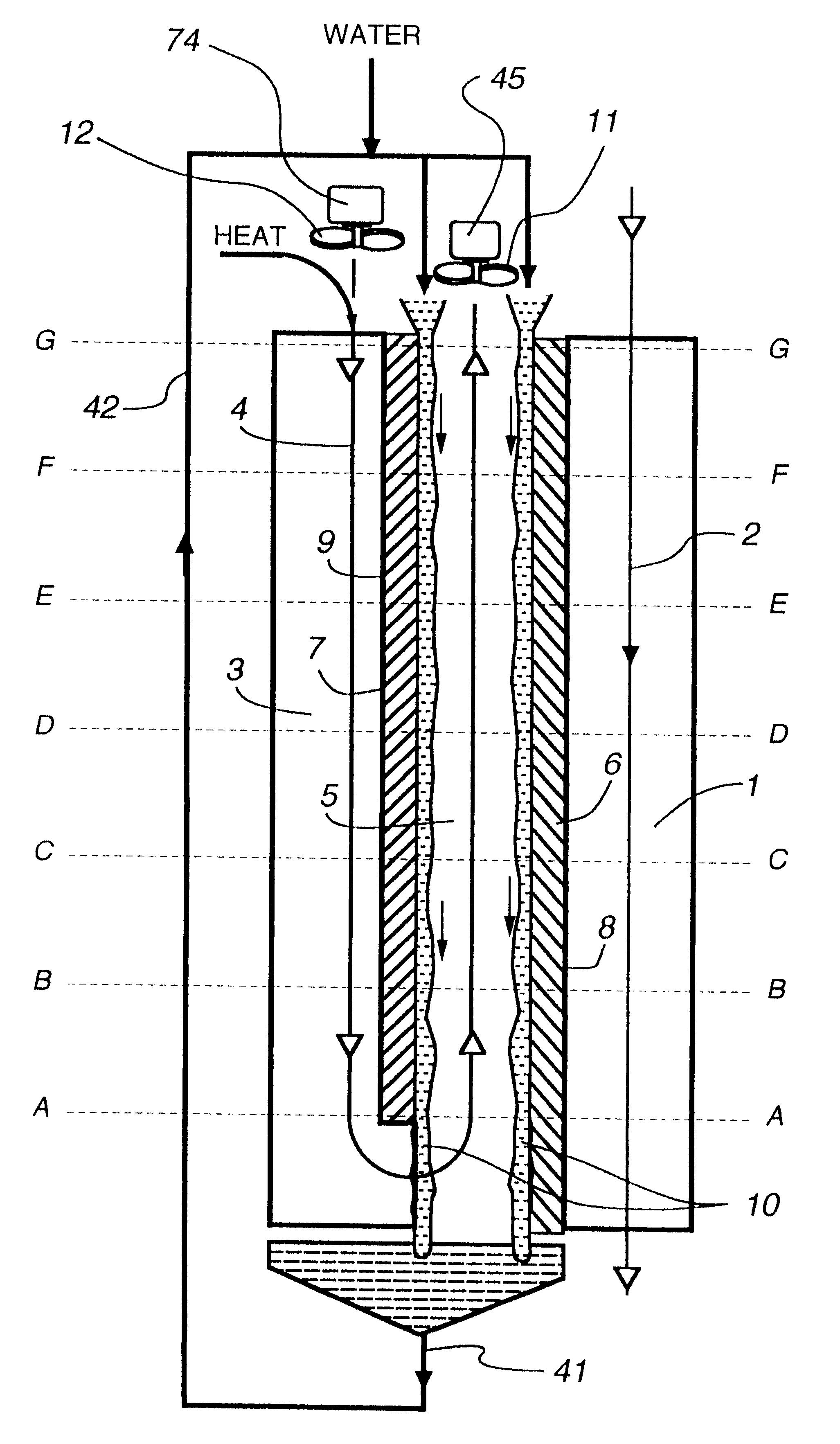
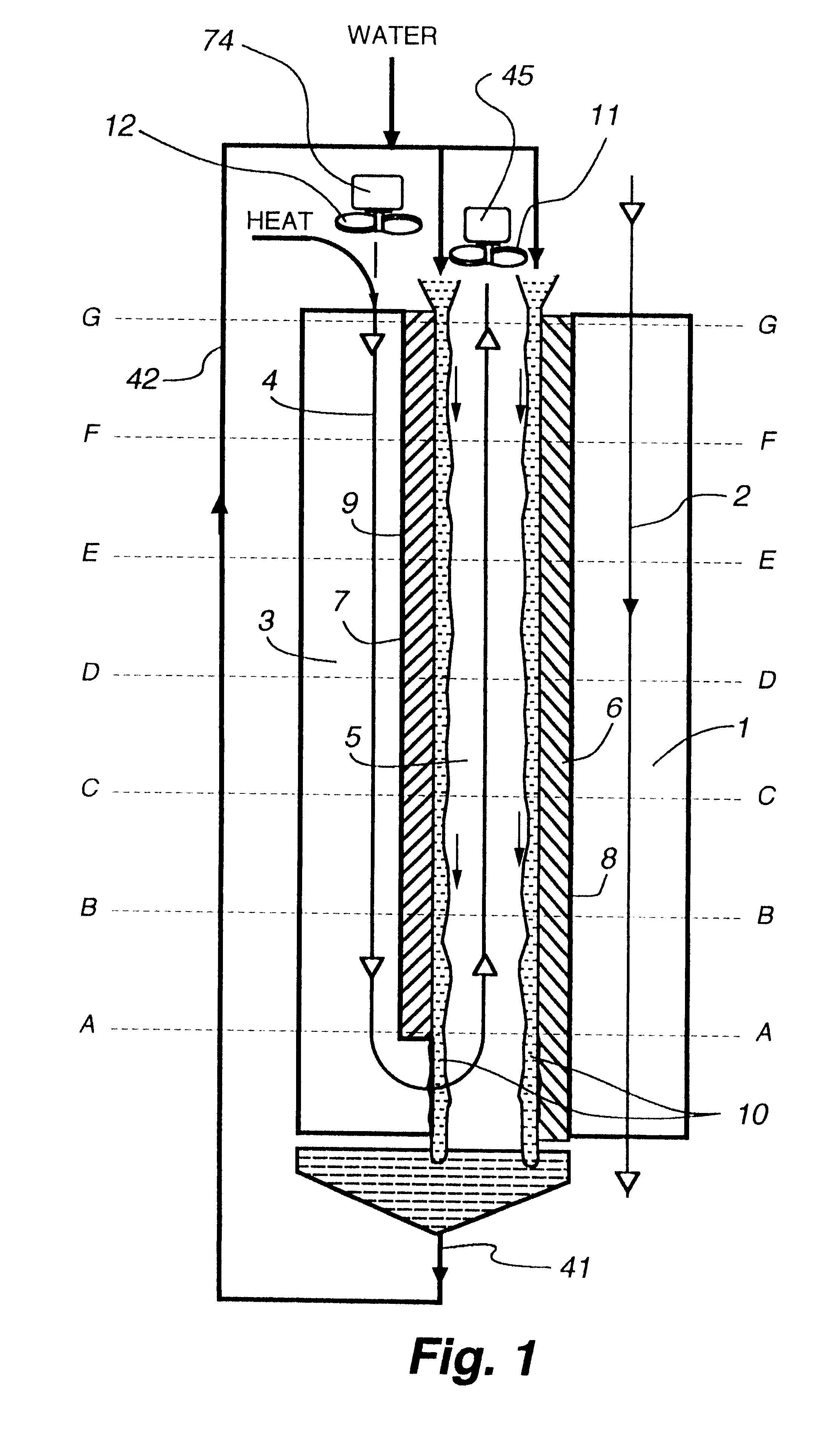
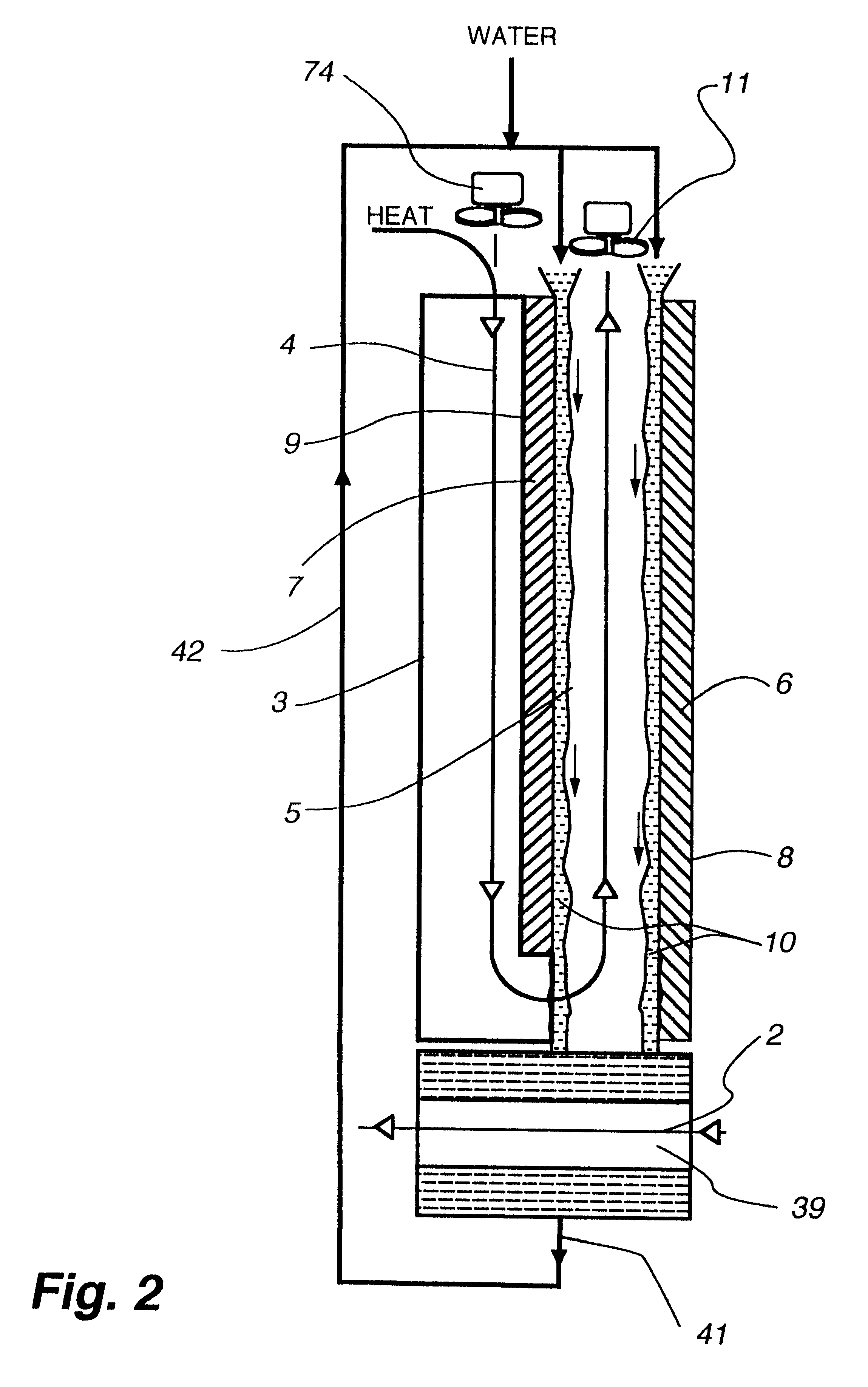
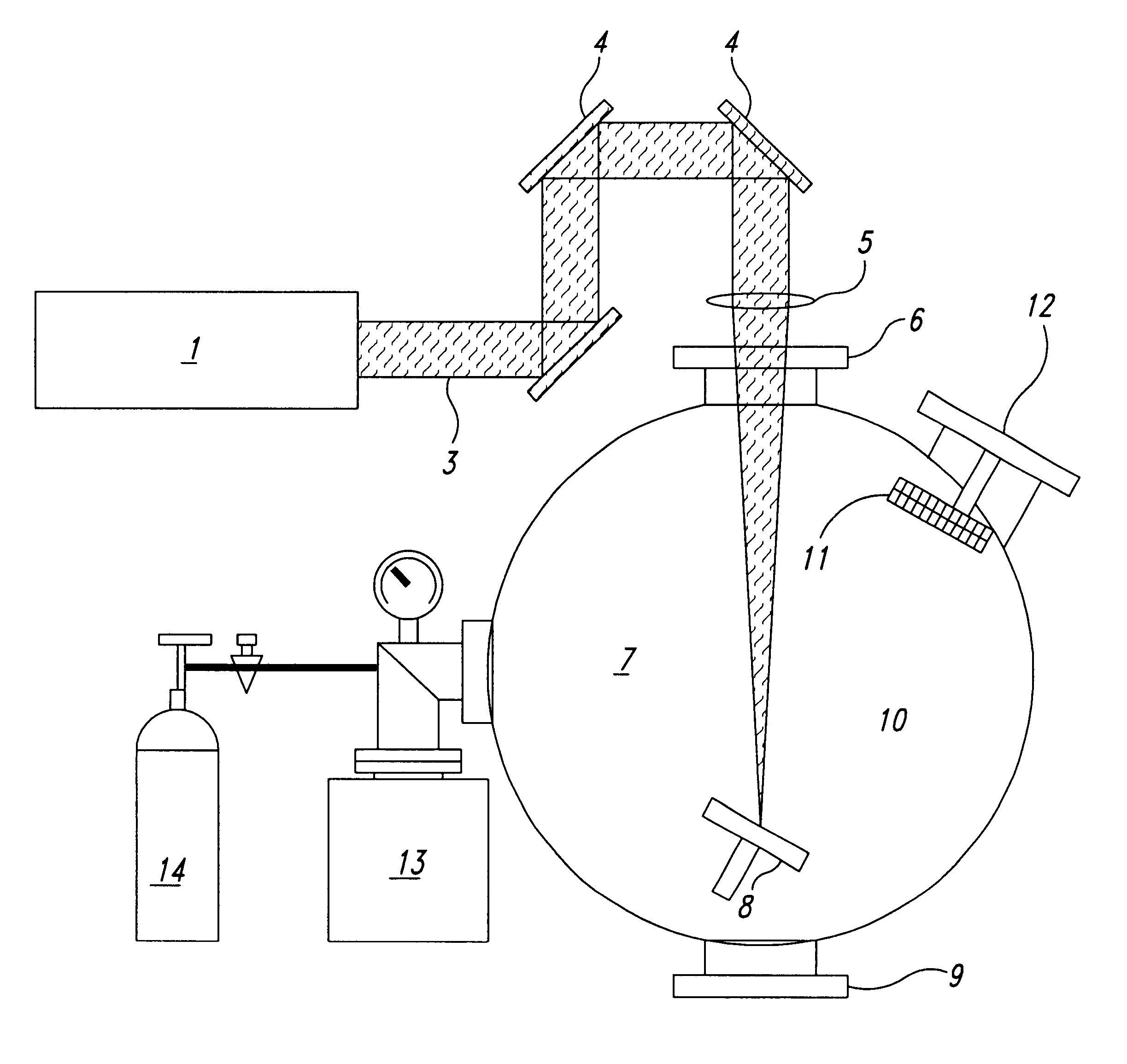
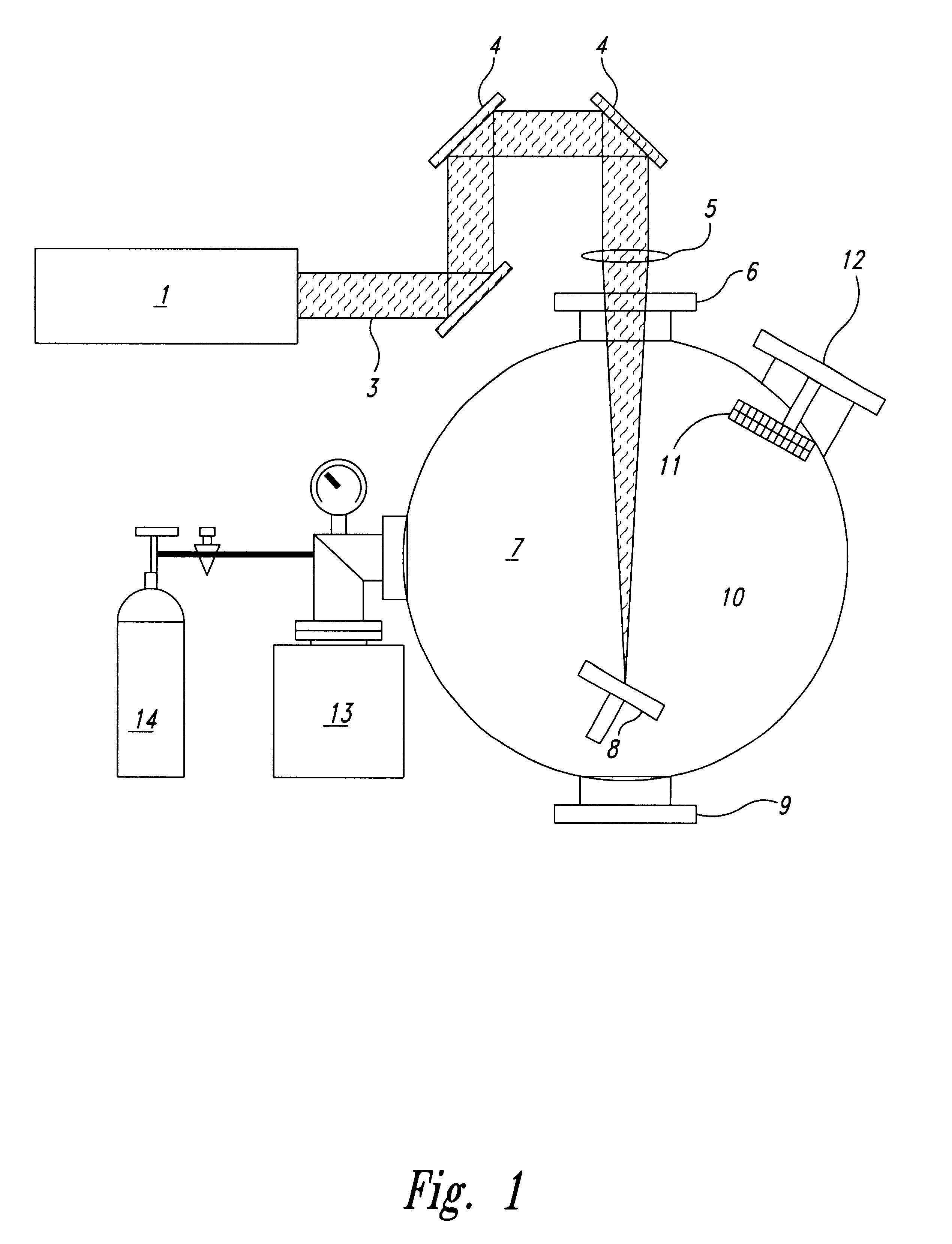
Patents
Literature
32867 results about "Evaporation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. The surrounding gas must not be saturated with the evaporating substance. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide with each other. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling.
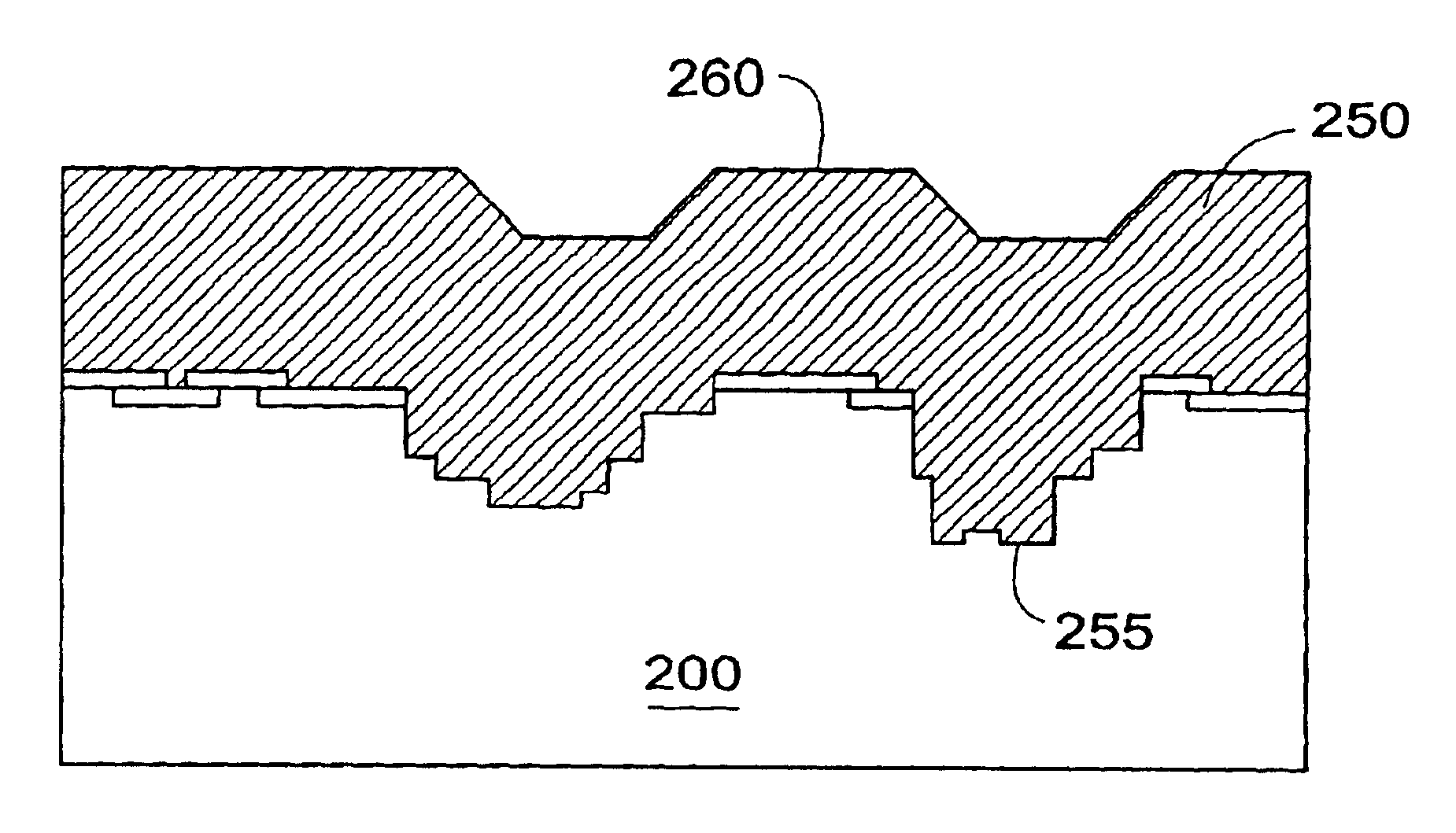
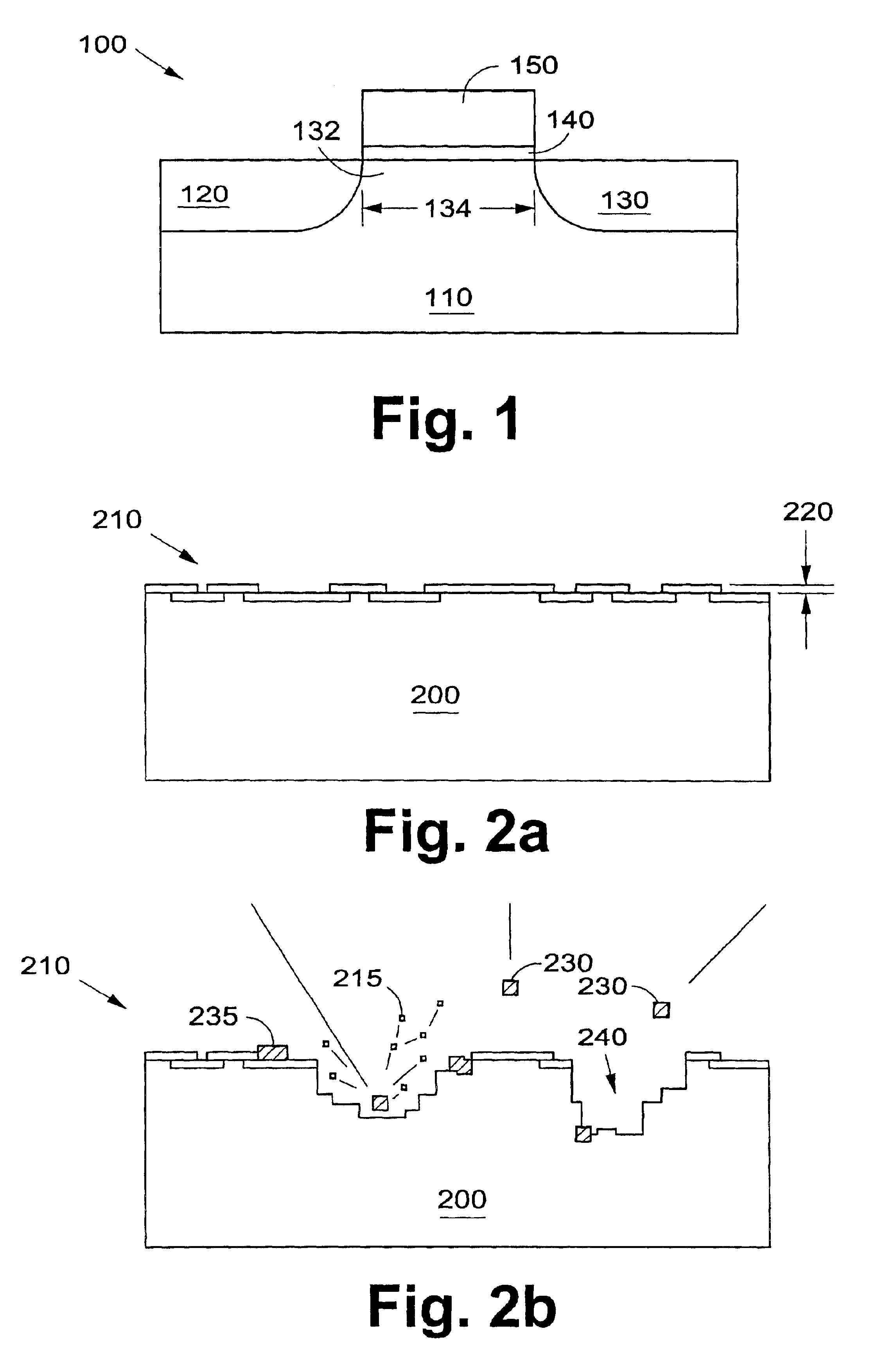
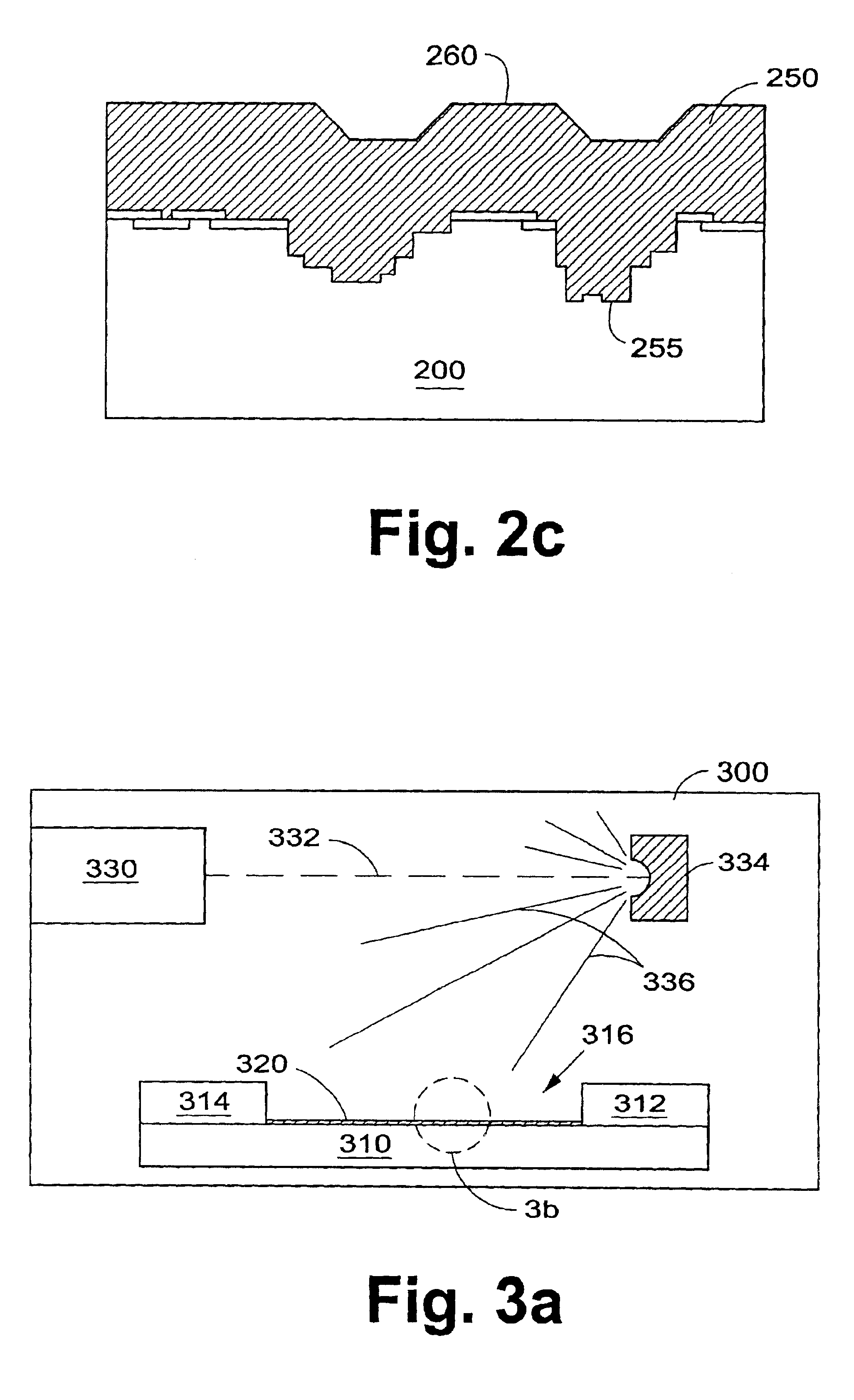
Semiconductor device in which zinc oxide is used as a semiconductor material and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS7501293B2Improve surface smoothnessHigh crystallinityTransistorLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having excellent crystallinity and excellent electric characteristics includes a ZnO thin film having excellent surface smoothness. ZnO-based thin films (an n-type contact layer, an n-type clad layer, an active layer, a p-type clad layer, and a p-type contact layer) primarily including ZnO are formed sequentially by an ECR sputtering method or other suitable method on a zinc-polar surface of a ZnO substrate. A transparent electrode and a p-side electrode are formed by an evaporation method or other suitable method on a surface of the p-type contact layer, and an n-side electrode is formed on an oxygen-polar surface of the ZnO substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method of doping organic semiconductors with quinone derivatives and 1, 3, 2 - dioxaborine derivatives
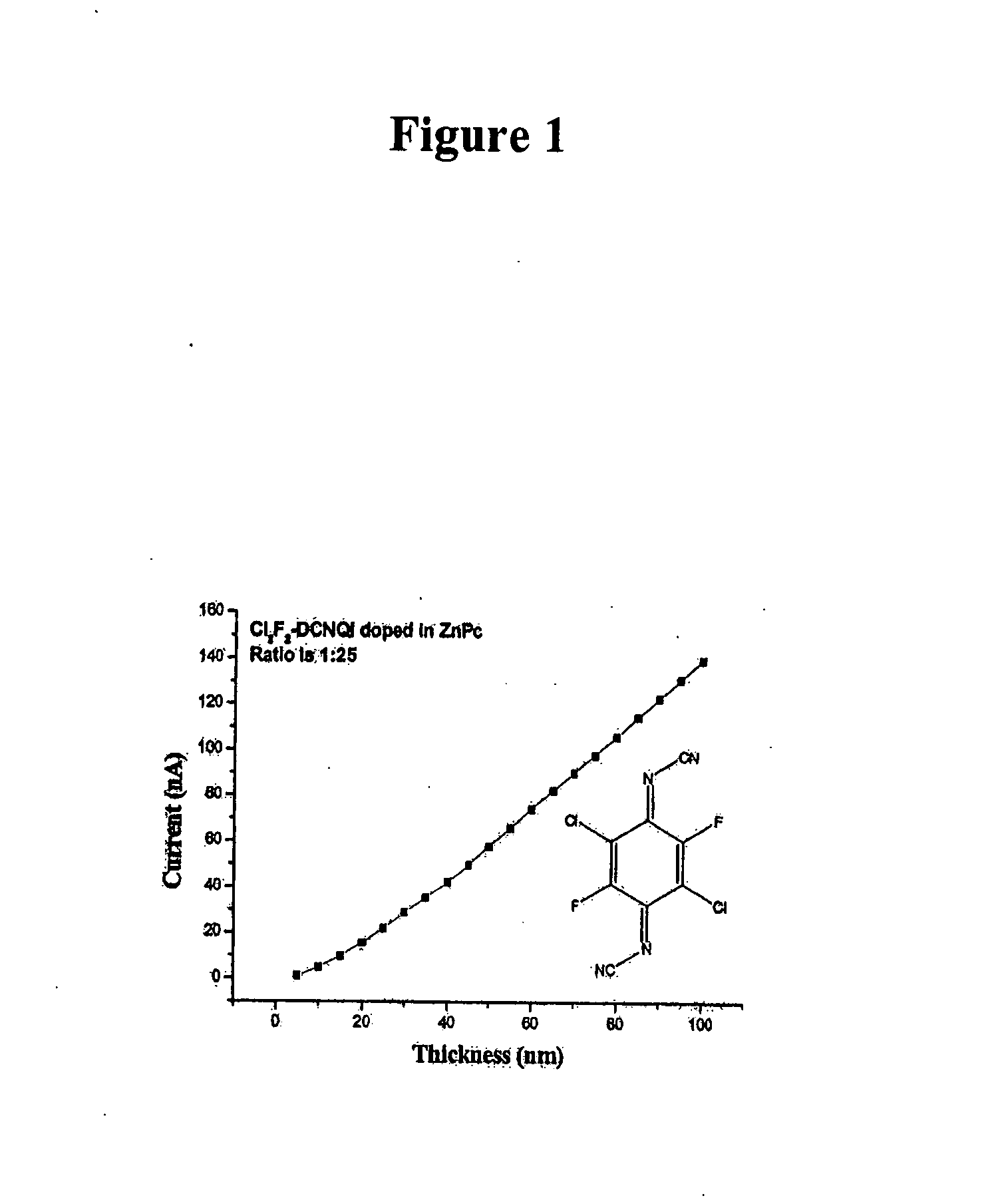
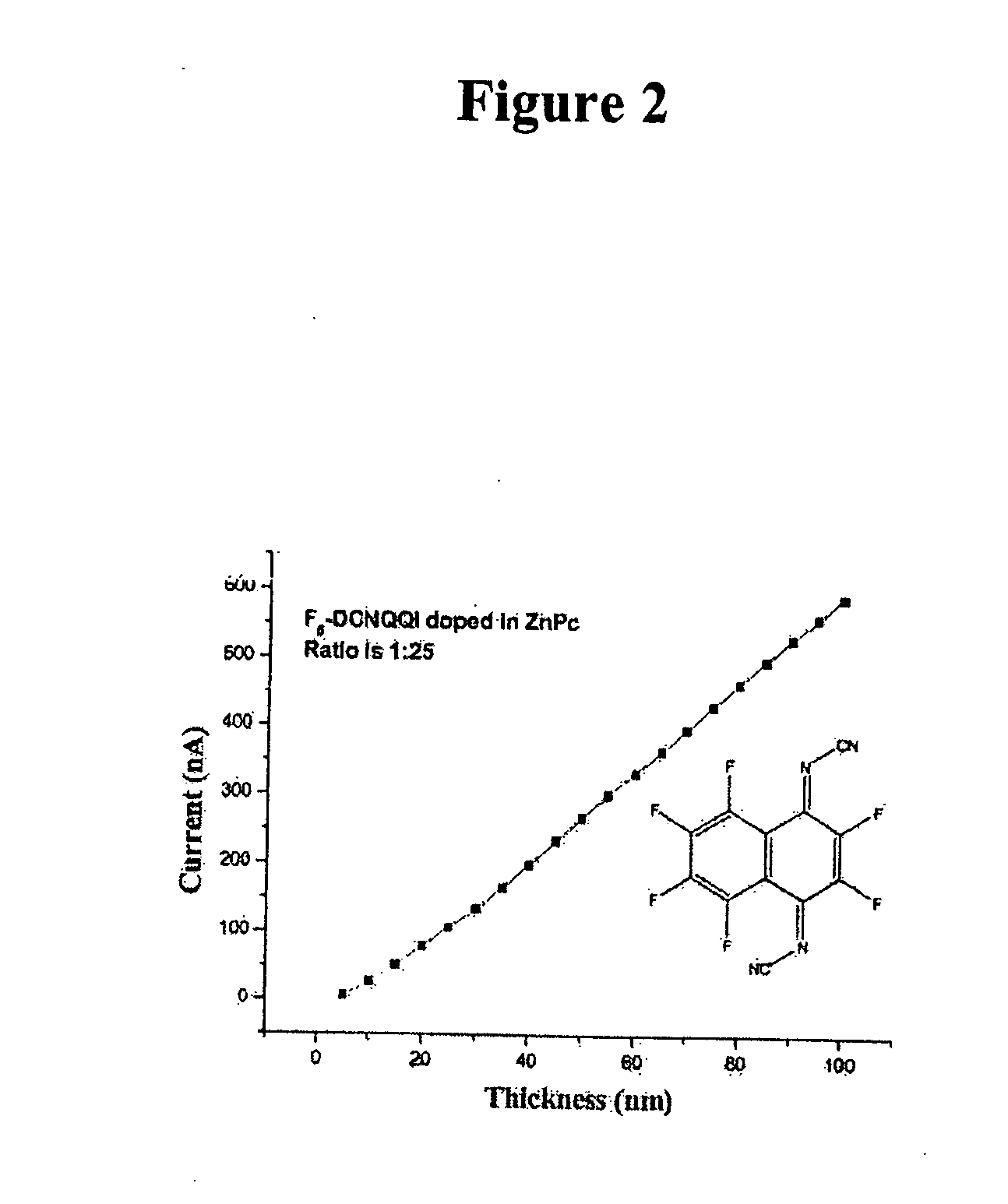
The invention relates to the use of an organic mesomeric compound as organic dopant for doping an organic semiconducting matrix material for varying the electrical properties thereof. In order to be able to handle organic semiconductors more easily in the production process and to be able to produce electronic components with doped organic semiconductors more reproducibly, a quinone or quinone derivative or a 1,3,2-dioxaborine or a 1,3,2-dioxaborine derivative may be used as a mesomeric compound, which under like evaporation conditions has a lower volatility than tetrafluorotetracyanoquinonedimethane (F4TCNQ).
Owner:KUEHL OLAF +4
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070066010A1Good step coverageReduce leakage levelTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEvaporation
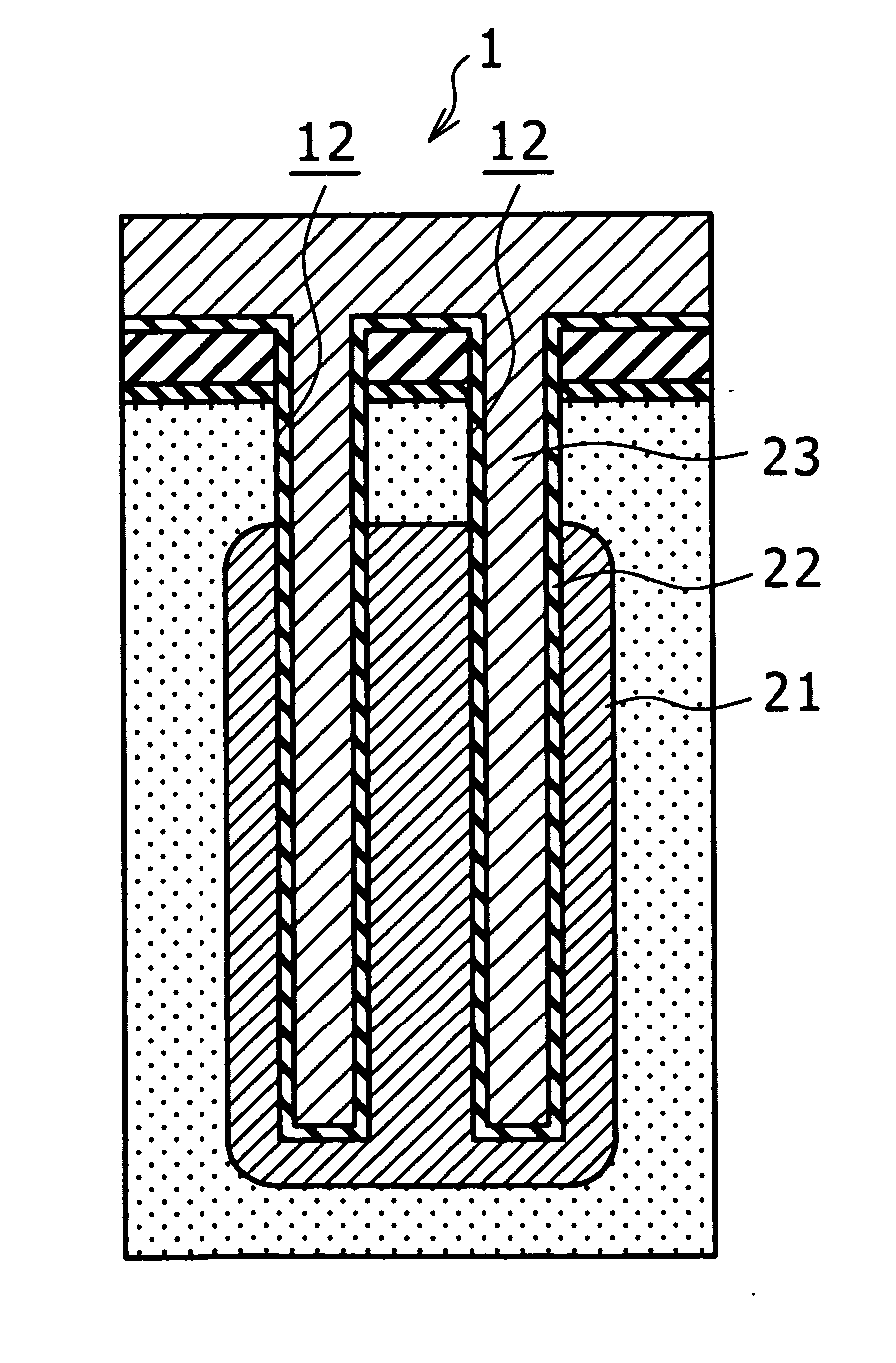
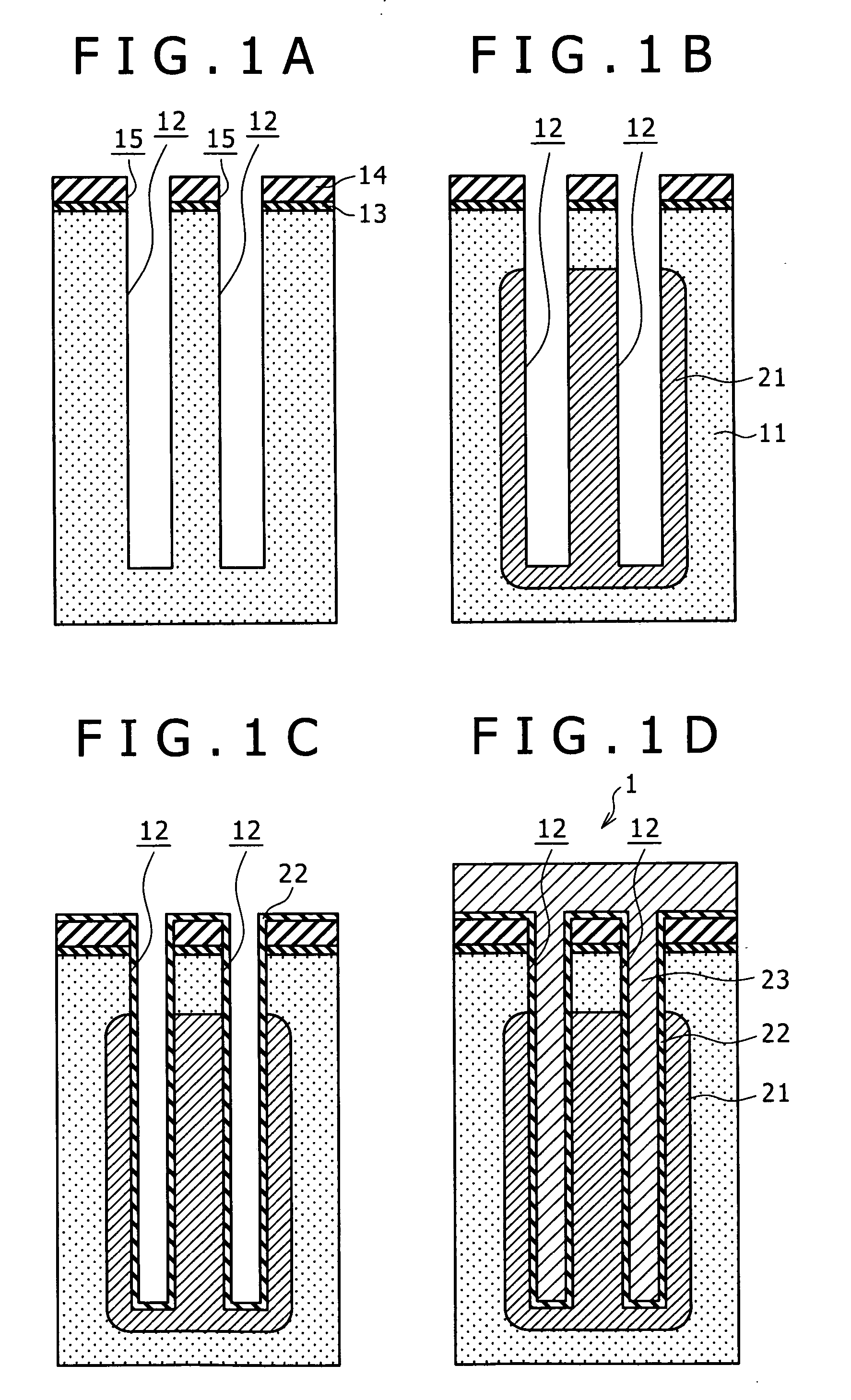
The invention aims at enabling leakage current characteristics and a step coverage property to be improved by depositing a hafnium silicate film by utilizing an atomic layer evaporation method using a hafnium raw material, a silicon raw material and an oxidizing agent. Disclosed herein is a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having a trench capacitor including a first electrode formed on an inner surface of a trench, a capacitor insulating film formed on a surface of the first electrode, and a second electrode formed on a surface of the capacitor insulating film. The method includes the step of depositing the capacitor insulating film in a form of a hafnium silicate film by utilizing an atomic layer deposition method using a hafnium raw material, a silicon raw material and an oxidizing agent.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for reducing particle contamination in a deposition system
ActiveUS20070215048A1Reduce particle pollutionChemical vapor deposition coatingDistribution systemEvaporation
A method and system is described for reducing particle contamination of a substrate in a deposition system. The deposition system comprises one or more particle diffusers disposed therein and configured to prevent or partially prevent the passage of film precursor particles, or break-up or partially break-up film precursor particles. The particle diffuser may be installed in the film precursor evaporation system, or the vapor delivery system, or the vapor distribution system, or two or more thereof.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for reducing particle formation in a vapor distribution system
InactiveUS20070218200A1Reduce particle pollutionChemical vapor deposition coatingDistribution systemEvaporation
A method and system is described for reducing particle contamination in a vapor distribution system. The vapor distribution system comprises a housing and a vapor distribution head comprising a plurality of openings configured to introduce a film precursor vapor to a deposition system. The housing and vapor distribution head define a plenum coupled to a film precursor evaporation system, and configured to receive the film precursor vapor from the evaporation system and distribute the film precursor vapor within the deposition system through the plurality of openings. In order to reduce particle contamination, the vapor distribution system is designed to reduce the difference, or ratio, between the pressure in the plenum and the pressure in the deposition system. For example, the plenum pressure can be less than twice the pressure in the process space, or can be less than 50 mTorr, 30 mTorr or even 20 mTorr than the pressure in the process space.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
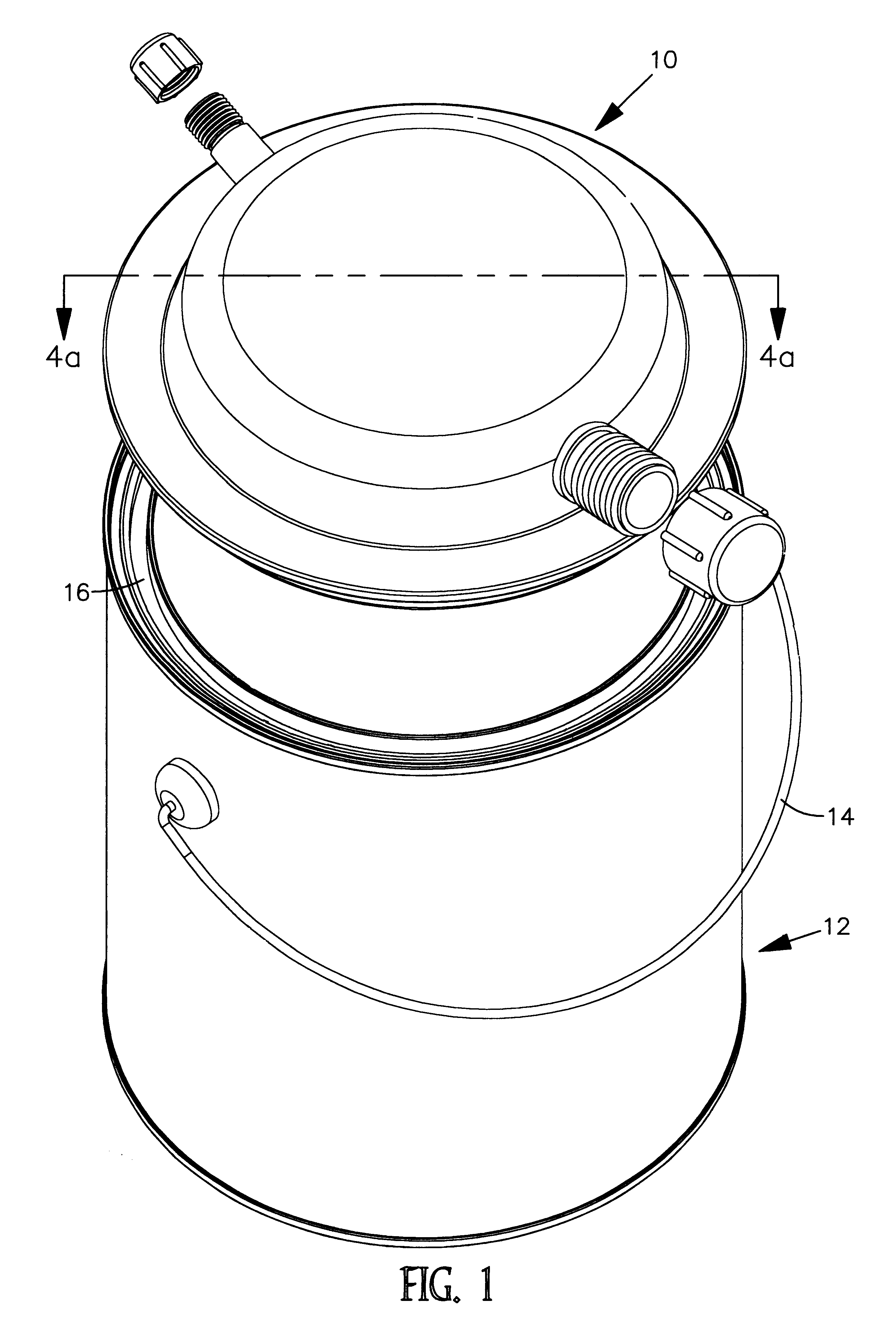
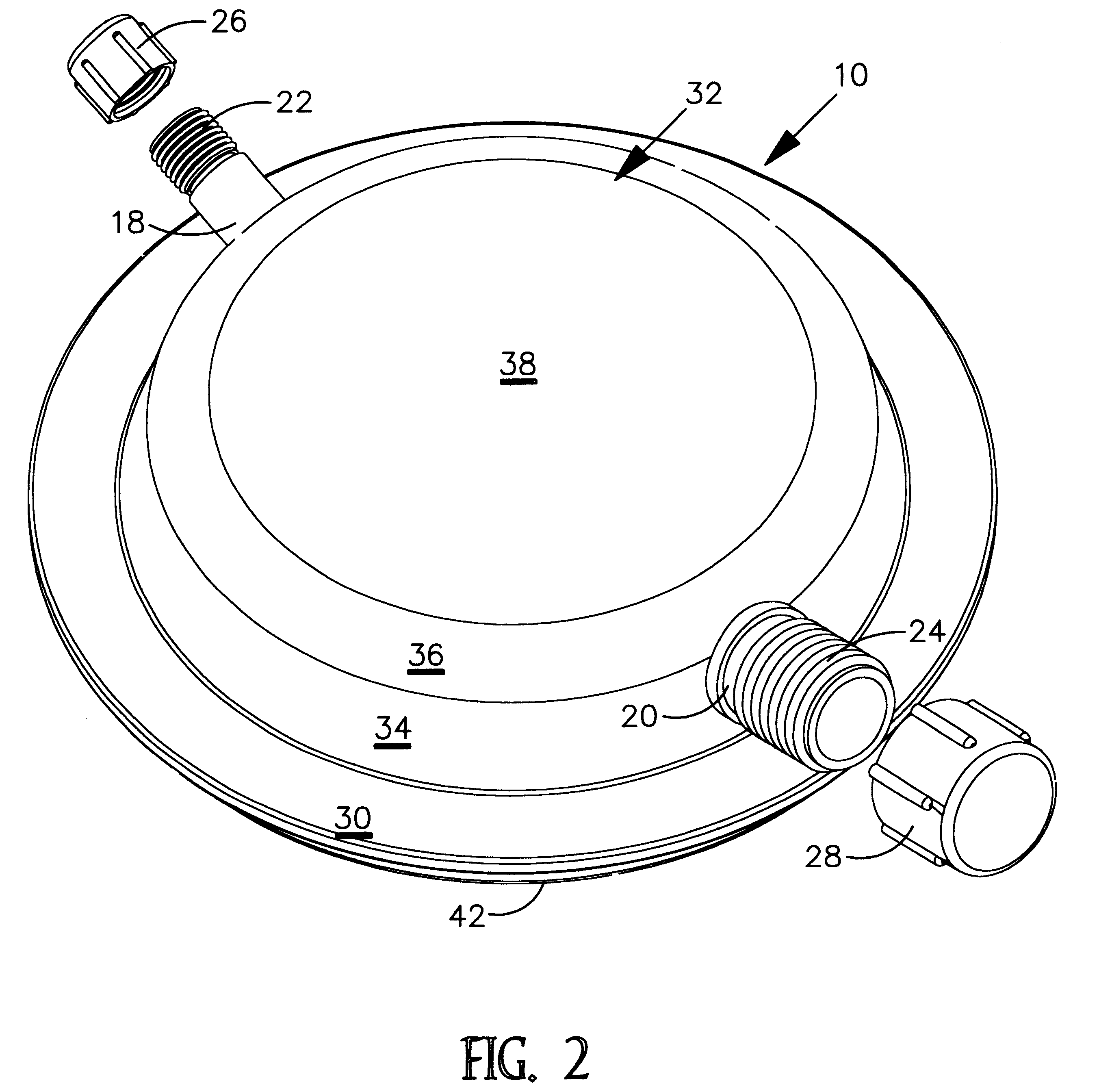
Stackable container cover
InactiveUS6269977B1Safely and conveniently sealsPackage recyclingLiquid flow controllersEvaporationEngineering
A stackable and reusable, container cover is disclosed for safe, sealed, and protected confinement of fluid contents therein to prevent, among other matters, spillage, contamination, evaporation and hardening of the fluid contents. The cover consists of a single molded disc shaped device with an elevated flat surface, platform for supporting another container thereon. The cover also provides for multiple and different sized spouts for various and particular flow rates and flow confinements, and angled in such manner for easy drip less pouring. In addition, the cover provides for a significant step in providing a very convenient snap on, attachment, and snap off, detachment means for reuse of the cover on yet another container.
Owner:MOORE KIM IRA
Phase change material thermal capacitor clothing
InactiveUS6855410B2Good thermal controlFast regenerationExothermal chemical reaction heat productionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSOCKSThermal insulation
An apparatus and method for metabolic cooling and insulation of a user in a cold environment. In its preferred embodiment the apparatus is a highly flexible composite material having a flexible matrix containing a phase change thermal storage material. The apparatus can be made to heat or cool the body or to act as a thermal buffer to protect the wearer from changing environmental conditions. The apparatus may also include an external thermal insulation layer and / or an internal thermal control layer to regulate the rate of heat exchange between the composite and the skin of the wearer. Other embodiments of the apparatus also provide 1) a path for evaporation or direct absorption of perspiration from the skin of the wearer for improved comfort and thermal control, 2) heat conductive pathways within the material for thermal equalization, 3) surface treatments for improved absorption or rejection of heat by the material, and 4) means for quickly regenerating the thermal storage capacity for reuse of the material. Applications of the composite materials are also described which take advantage of the composite's thermal characteristics. The examples described include a diver's wet suit, ski boot liners, thermal socks, gloves and a face mask for cold weather activities, and a metabolic heating or cooling blanket useful for treating hypothermia or fever patients in a medical setting and therapeutic heating or cooling orthopedic joint supports.
Owner:BUCKLEY THERESA M
Co-evaporation system comprising vapor pre-mixer
InactiveUS20130302520A1Uniform depositionUniform composition ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSource materialEvaporation
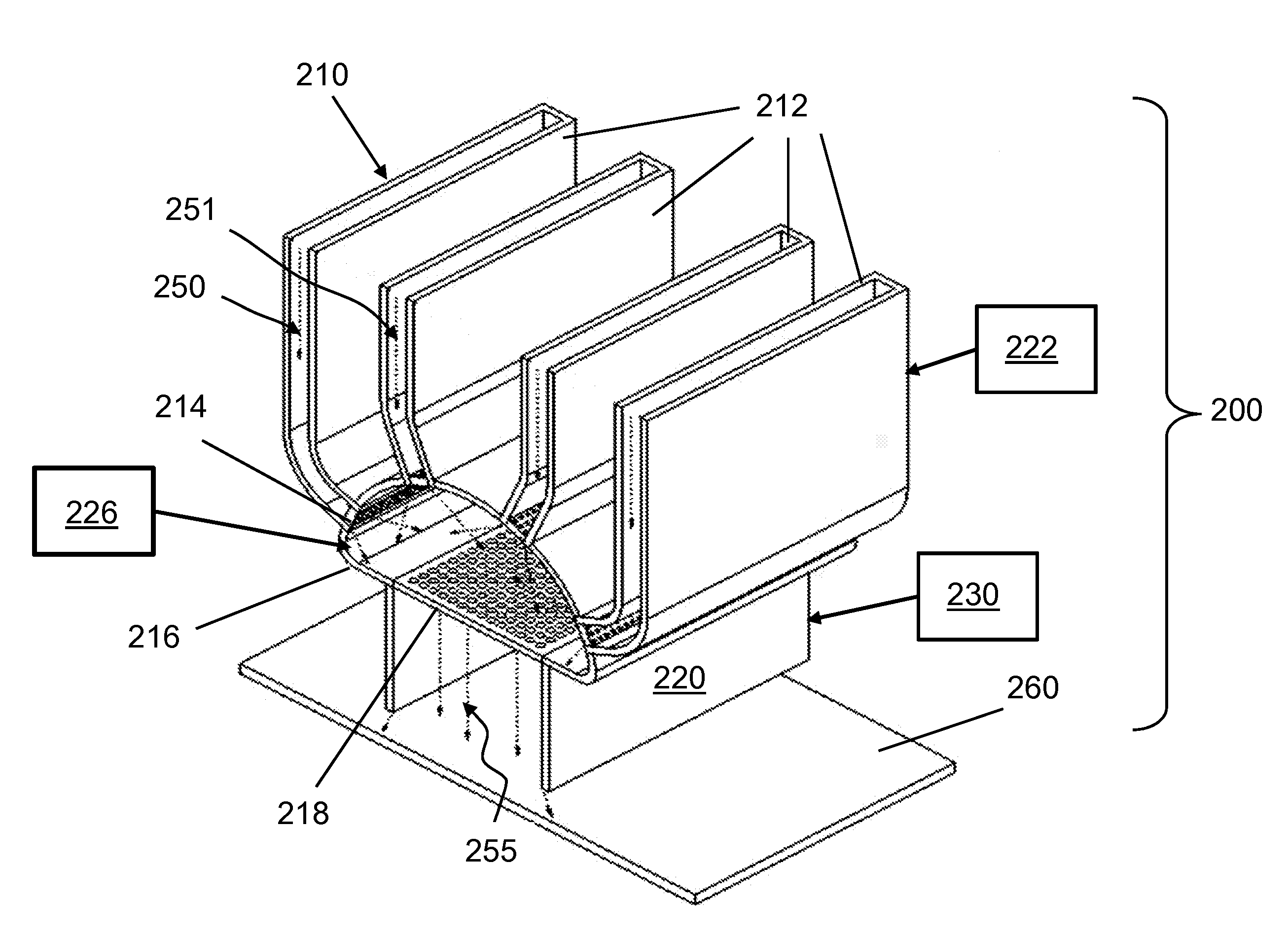
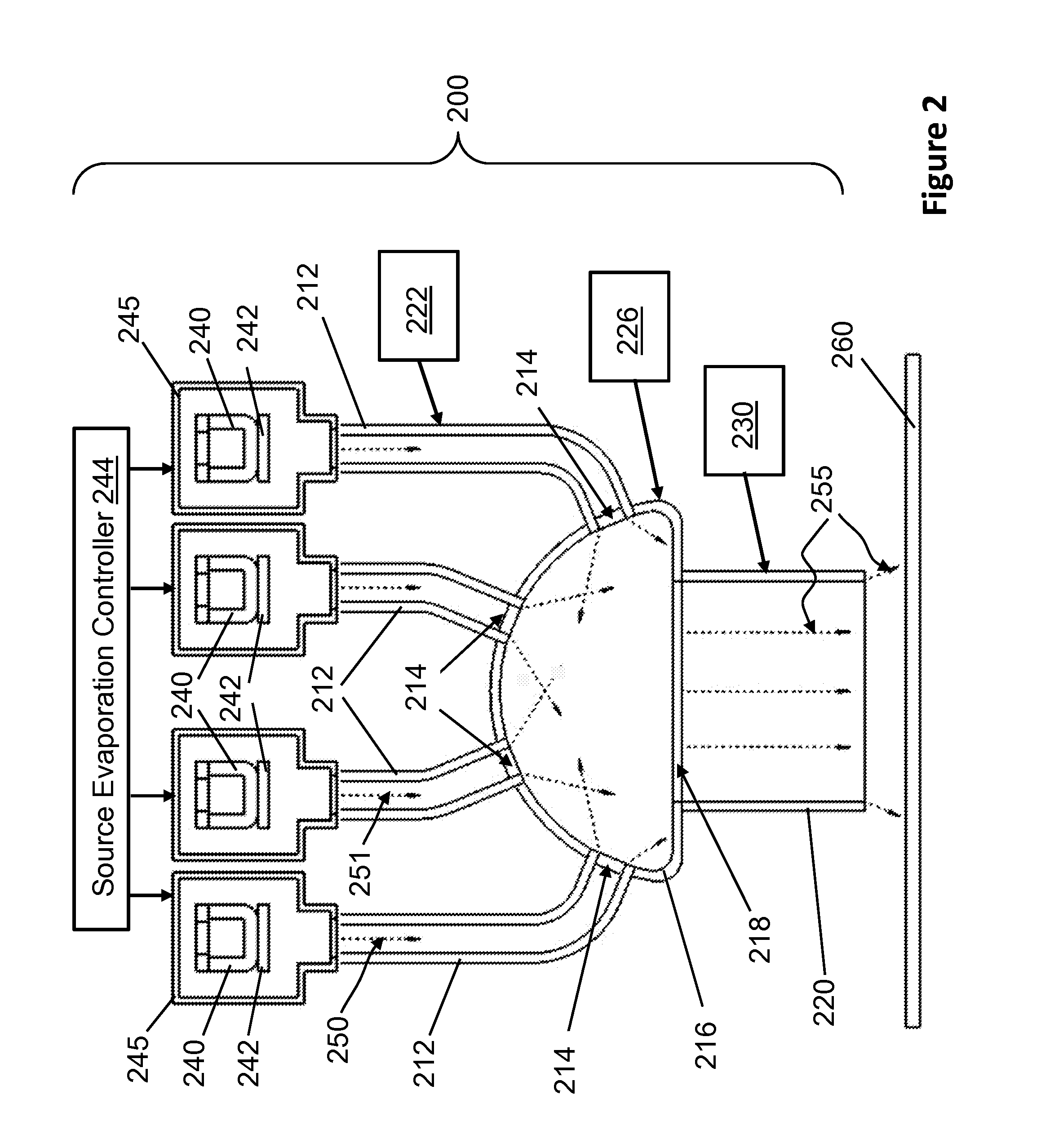
A processing system for depositing a plurality of source materials on a substrate, includes a first thermal evaporation source that can evaporate a first source material to produce a first vapor, a second thermal evaporation source that can evaporate a second source material to produce a second vapor, a vapor mixing chamber that allows the first vapor and the second vapor to be mixed to produce a mixed vapor, and conduits that can separately transport the first vapor and the second vapor to the vapor mixing chamber. The mixed vapor can be directed toward a substrate to deposit a mixture of the first source material and the second source material on the substrate. The processing system can also include vapor filters configured to regulate flows of the first vapor and the second vapor, and a mixed vapor filter to regulate flow of the mixed vapor.
Owner:WANG KAI AN +4
Gate oxides
InactiveUS6844203B2Improve surface roughnessSmooth surface roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEquivalent oxide thicknessGadolinium
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset of 2 eV or greater. Gate oxides formed from elements such as yttrium and gadolinium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
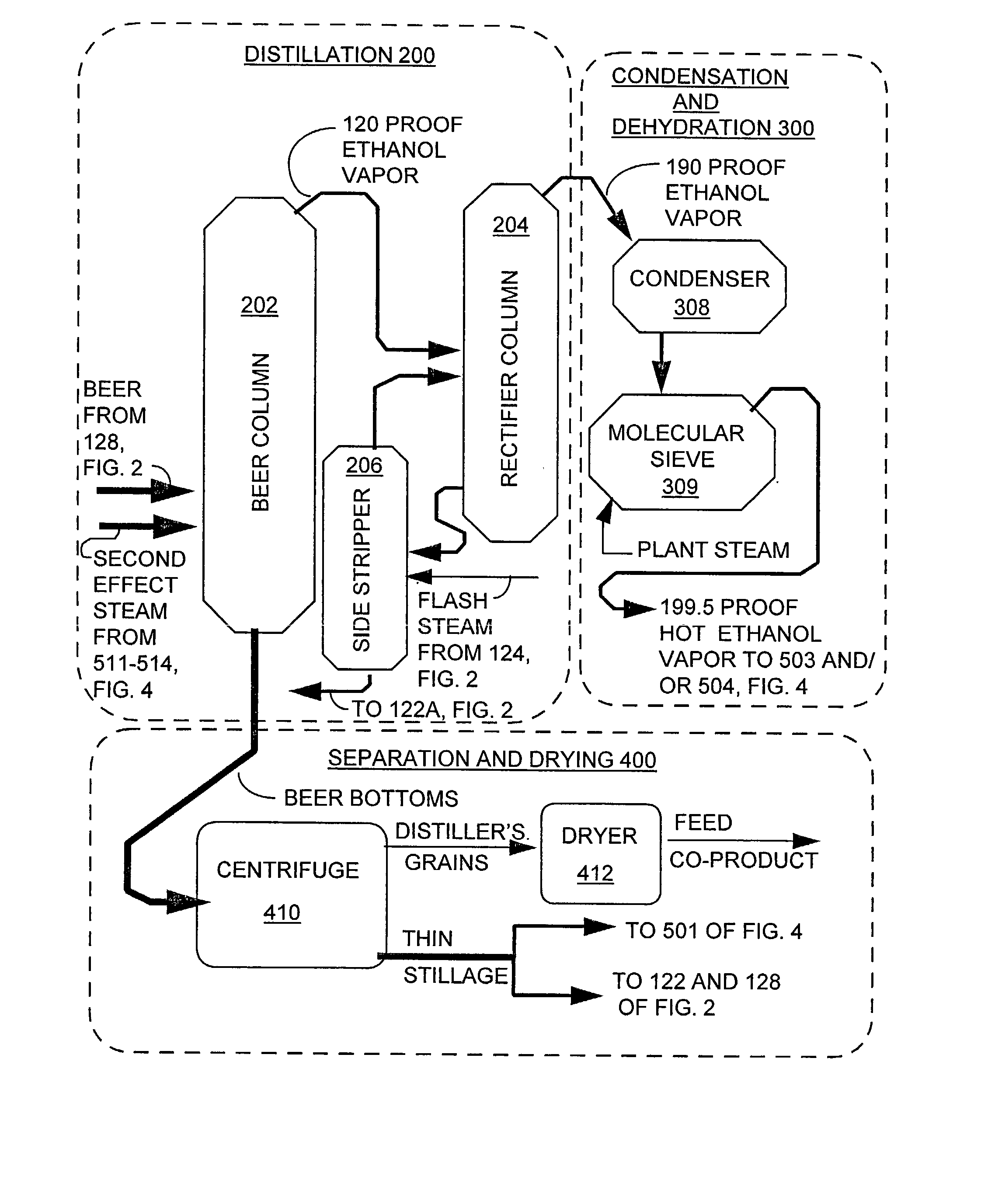
Ethanol distillation process
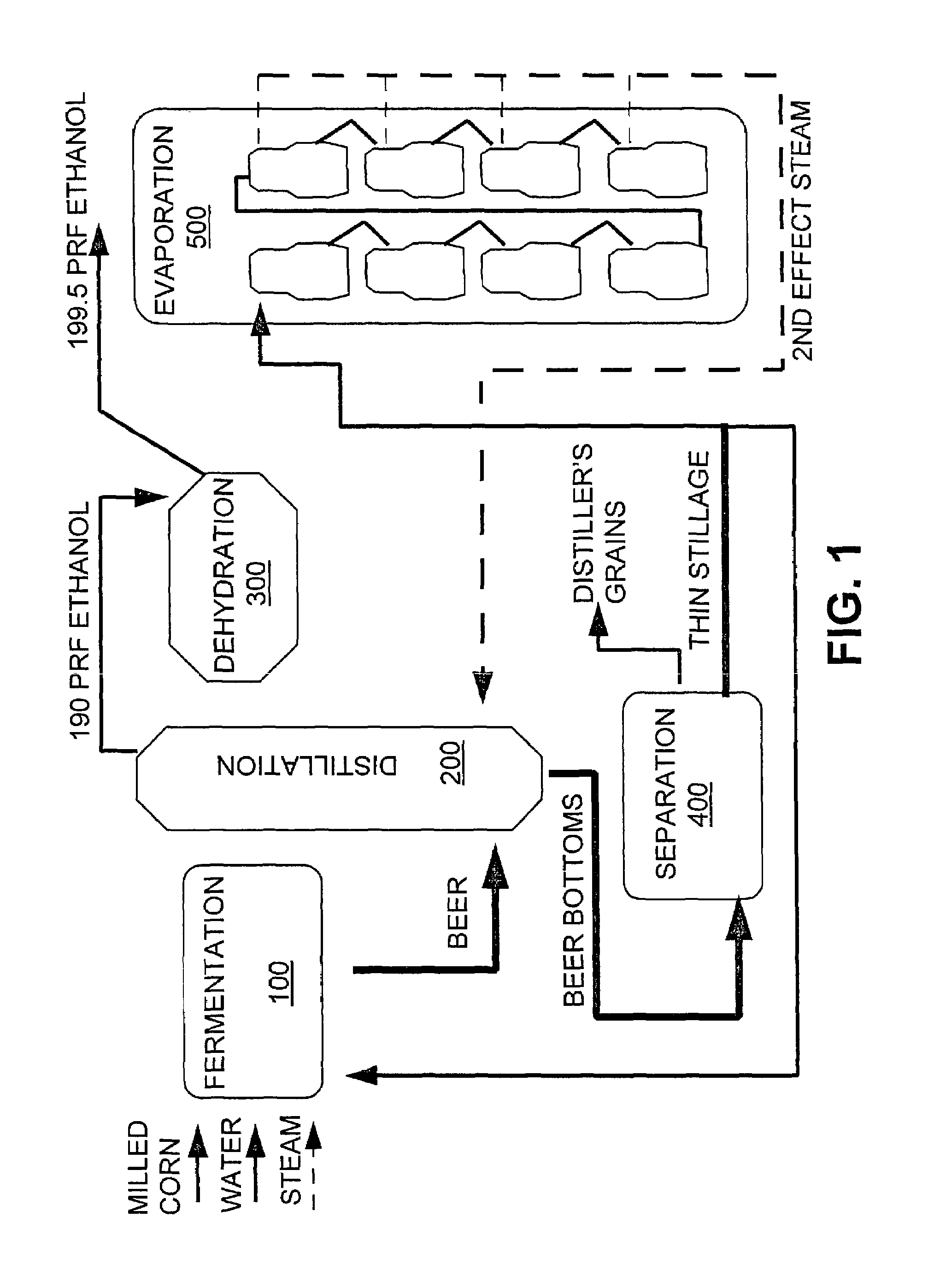
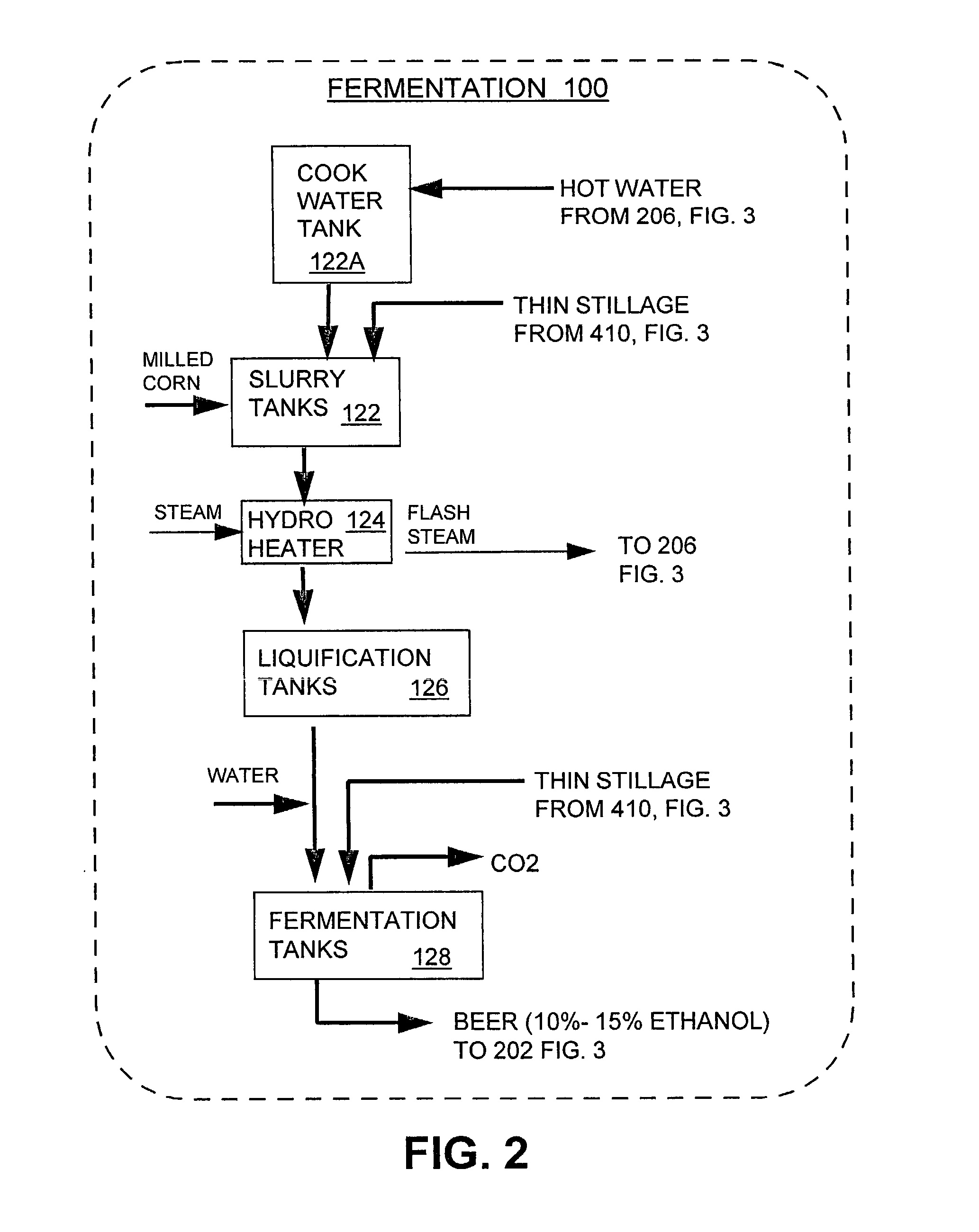
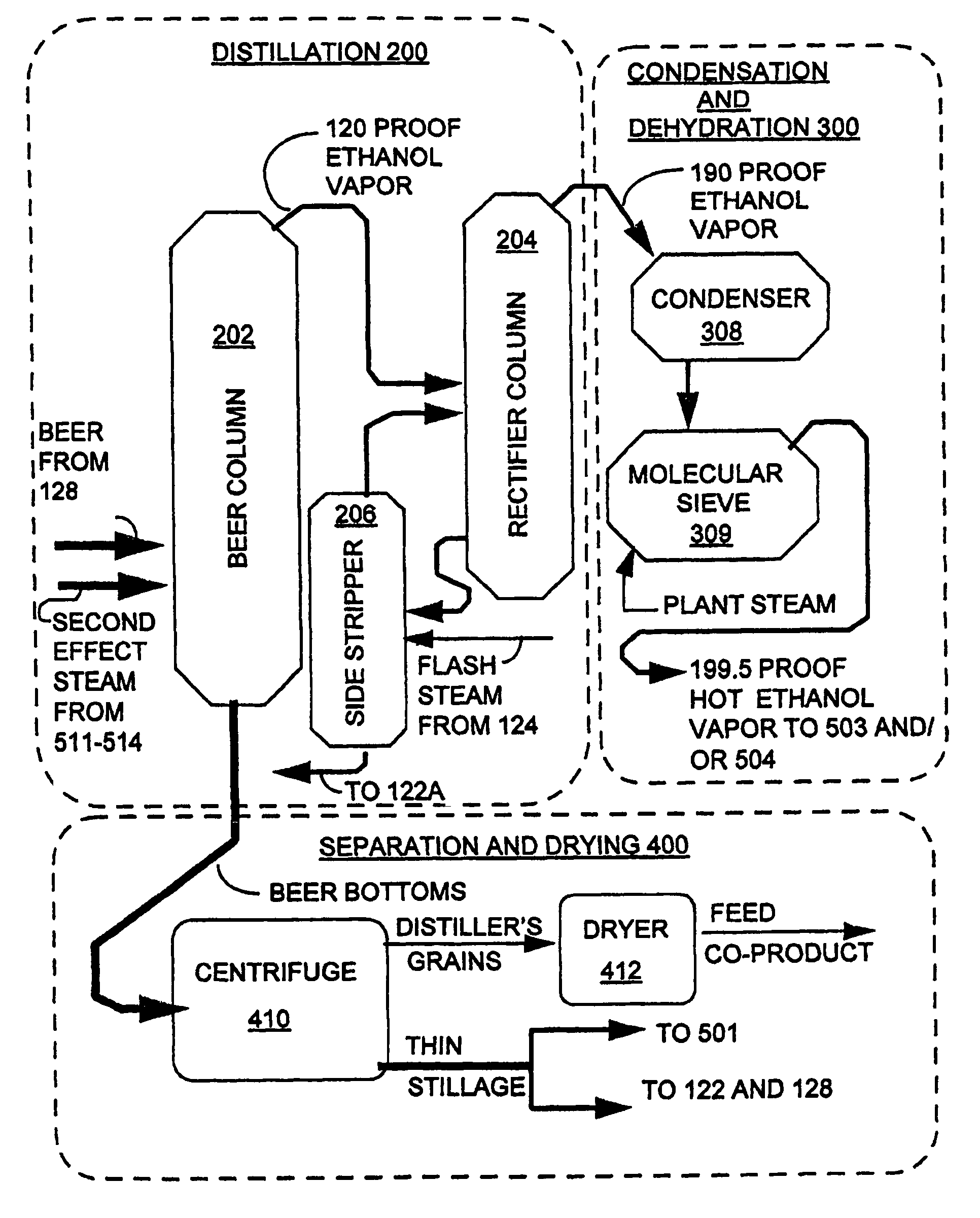
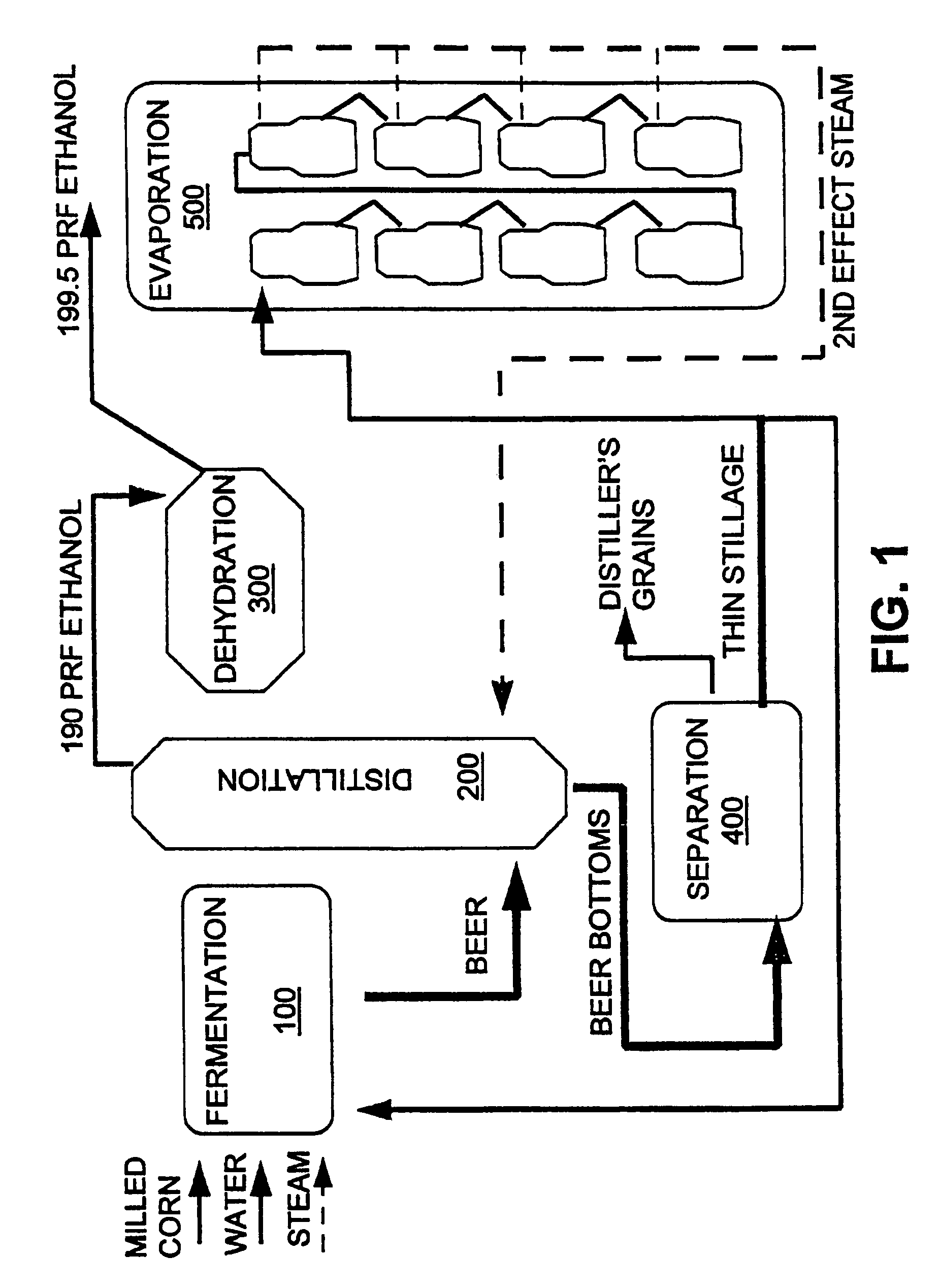
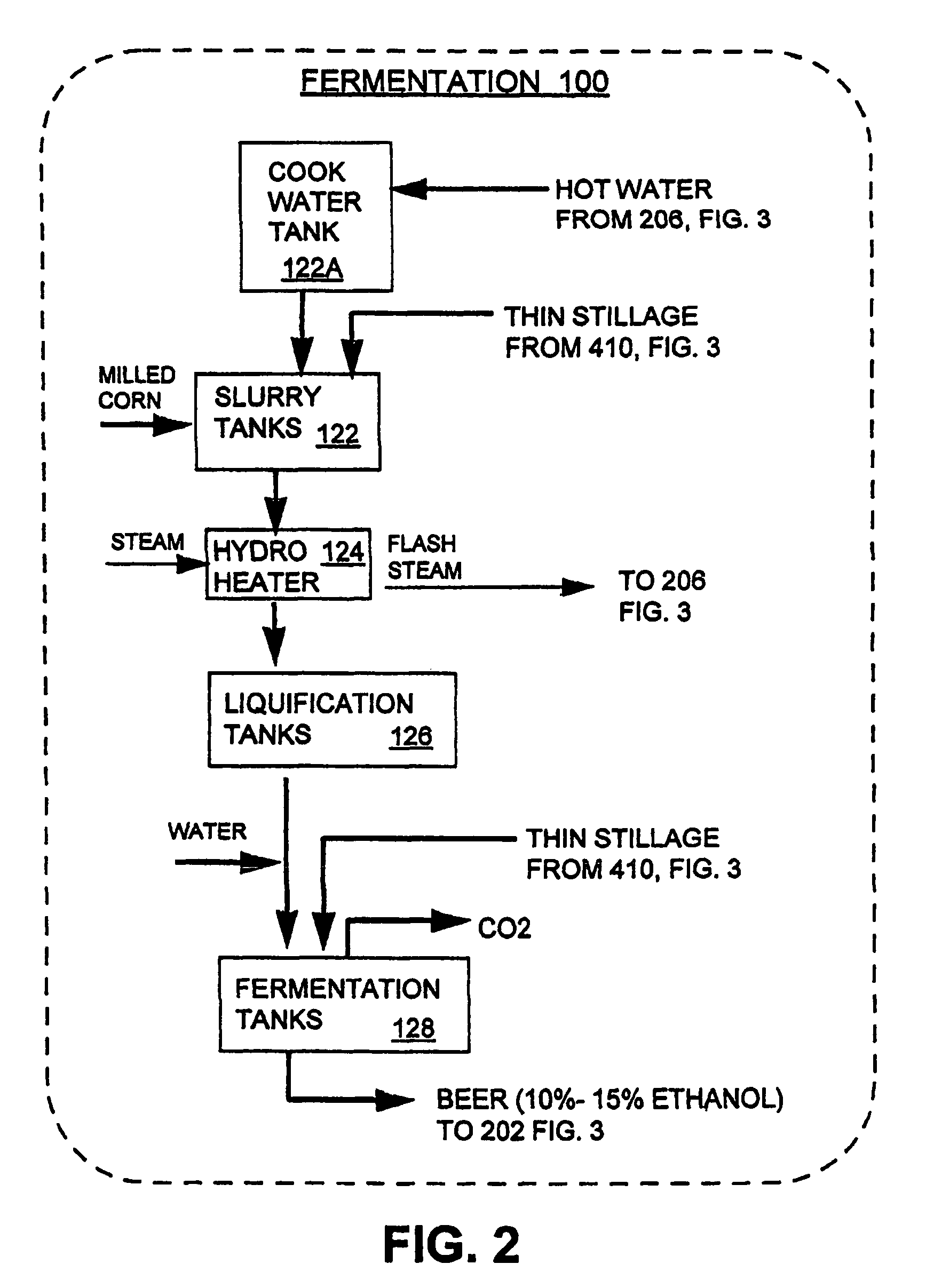
InactiveUS7297236B1Avoid insufficient heatingShorten the timeFermented solutions distillation/rectificationDistillation in boilers/stillsDistillationEvaporation
A process arrangement for distilling fuel grade ethanol includes a fermentation portion, a distillation portion, a condensation and dehydration portion, a separation and drying portion and an evaporation portion. The fermentation portion produces beer. The distillation portion, the condensation and dehydration portion and the separation and drying portion receives beer from the fermentation portion and produces hot ethanol vapor and thin stillage. In the evaporation portion, a set of first effect evaporators which are heated either by plant steam or hot ethanol vapor, concentrate thin stillage into mid stillage while producing first effect steam. The first effect steam from the first effect evaporators provides heat to a set of second effect evaporators which concentrate the mid stillage into a syrup for further drying. The second effect evaporators produce second effect steam which is used to heat the distillation portion of the process arrangement. The multiple evaporators of the first and second effects of the evaporation portion can be selectively taken off-line for maintenance while the evaporation portion and the remainder of the process arrangement continue to operate at full capacity.
Owner:ICM
Controlled patterning and growth of single wall and multi-wall carbon nanotubes
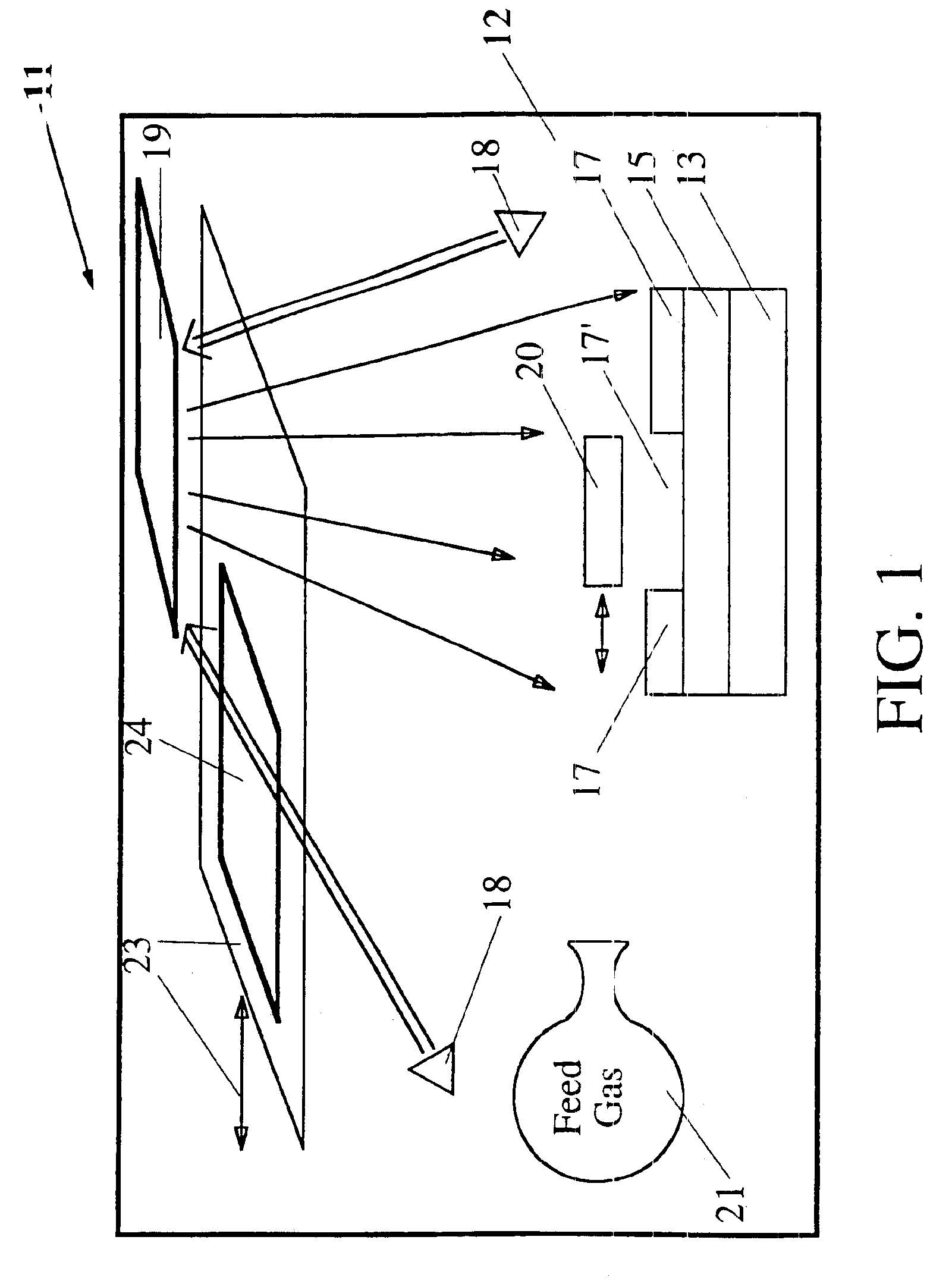
Method and system for producing a selected pattern or array of at least one of a single wall nanotube and / or a multi-wall nanotube containing primarily carbon. A substrate is coated with a first layer (optional) of a first selected metal (e.g., Al and / or Ir) and with a second layer of a catalyst (e.g., Fe, Co, Ni and / or Mo), having selected first and second layer thicknesses provided by ion sputtering, arc discharge, laser ablation, evaporation or CVD. The first layer and / or the second layer may be formed in a desired non-uniform pattern, using a mask with suitable aperture(s), to promote growth of carbon nanotubes in a corresponding pattern. A selected heated feed gas (primarily CH4 or C2Hn with n=2 and / or 4) is passed over the coated substrate and forms primarily single wall nanotubes or multiple wall nanotubes, depending upon the selected feed gas and its temperature. Nanofibers, as well as single wall and multi-wall nanotubes, are produced using plasma-aided growth from the second (catalyst) layer. An overcoating of a selected metal or alloy can be deposited, over the second layer, to provide a coating for the carbon nanotubes grown in this manner.
Owner:NASA +1
Ethanol distillation process
InactiveUS7572353B1Shorten the timeLess rapidlyFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationDistillationEvaporation
Owner:ICM
Liquid atomizing device with reduced settling of atomized liquid droplets
ActiveUS7775459B2Increase evaporation rateIncrease temperatureMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesVena contracta diameterEvaporation
A liquid atomizing device for dispensing liquid droplets includes a container for holding a liquid, the container having a porous wick positioned to communicate the liquid from the container, and an orifice plate with apertures, the orifice plate being vibrated by a piezoelectric element to cause liquid communicated from the container to be atomized and dispensed as liquid droplets through the apertures. The device employs a unique placement and design of heaters or fans to promote evaporation and dispersion of the atomized liquid while the liquid is airborne.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Method for producing multilayers on a substrate
InactiveUS20060083280A1Limited amountReduce riskLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEvaporationOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a method for producing a multilayer on a receiving substrate, including the following steps: the formation of an initial substrate comprising a first material layer formed on the surface of a supporting substrate made of a second material, molecular adhesion bonding of the surface of the initial substrate comprising the first material layer to the bonding surface of a receiving substrate to obtain a bonded structure, partial removal of the initial substrate so as to leave a thin film of said second material on the first material layer, evaporation of the second material thin film with a selective stop on the first material layer, growth of at least one layer from the first material layer bonded to the receiving substrate, with the evaporation step and the growth step being carried out in the same technological apparatus.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based compositions
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Tissue cooling rod for laser surgery
A laser treatment device and process with controlled cooling. The device contains a cooling element with high heat conduction properties, which is transparent to the laser beam. A surface of the cooling element is held in contact with the tissue being treated while at least one other surface of the cooling element is cooled by the evaporation of a cryogenic fluid. The cooling is coordinated with the application of the laser beam so as to control the temperatures of all affected layers of tissues. In a preferred embodiment useful for removal of wrinkles and spider veins, the cooling element is a sapphire plate. A cryogenic spray cools the top surface of the plate and the bottom surface of the plate is in contact with the skin. In preferred embodiments the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen so that absorption in targeted tissue is low enough so that substantial absorption occurs throughout the targeted tissue. In a preferred embodiment for treating large spider veins with diameters in the range of 1.5 mm, Applicants use an Er:Glass laser with a wavelength of 1.54 microns.< / PTEXT>
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
Low-temperature grown high-quality ultra-thin praseodymium gate dielectrics
InactiveUS6900122B2Inhibition formationSave budgetVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEquivalent oxide thicknessGate dielectric
A praseodymium (Pr) gate oxide and method of fabricating same that produces a high-quality and ultra-thin equivalent oxide thickness as compared to conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. The Pr gate oxide is thermodynamically stable so that the oxide reacts minimally with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit a Pr layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Automotive lighting assembly cooling system
InactiveUS6910794B2Point-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsMobile vehicleEffect light
An automotive lighting assembly cooling system includes a heat pipe with an evaporation area proximate to a heat generating component, such as a Light Emitting Diode (LED), and a condensing area located remote from the evaporation area. Evaporation of fluid within the heat pipe transfers heat away from the heat generating component. The efficiency of the cooling system in one embodiment is increased by including fins associated with the condensing area and placing the fins in an area where air flow external to a moving vehicle assists in cooling the fins.
Owner:GUIDE
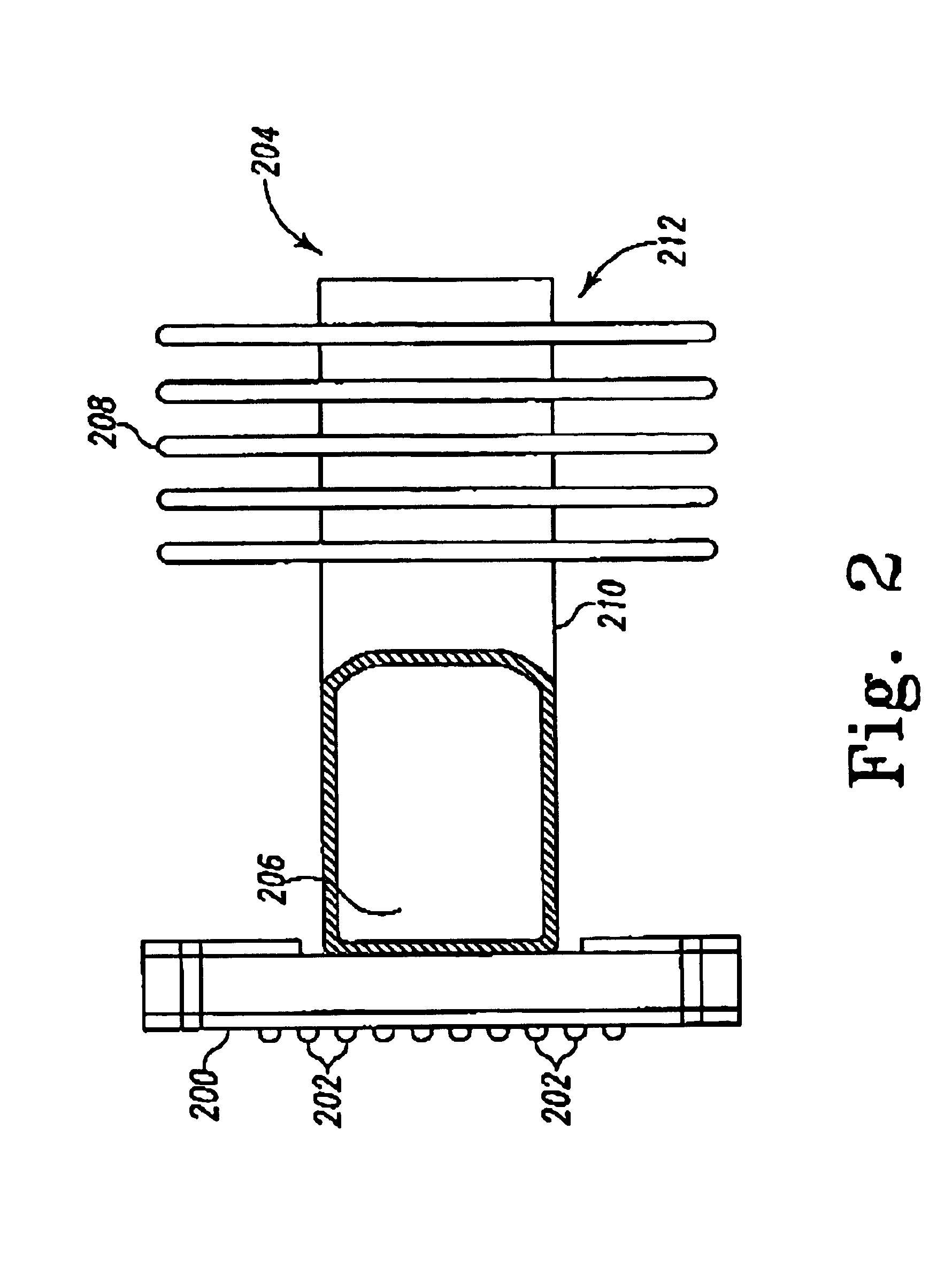
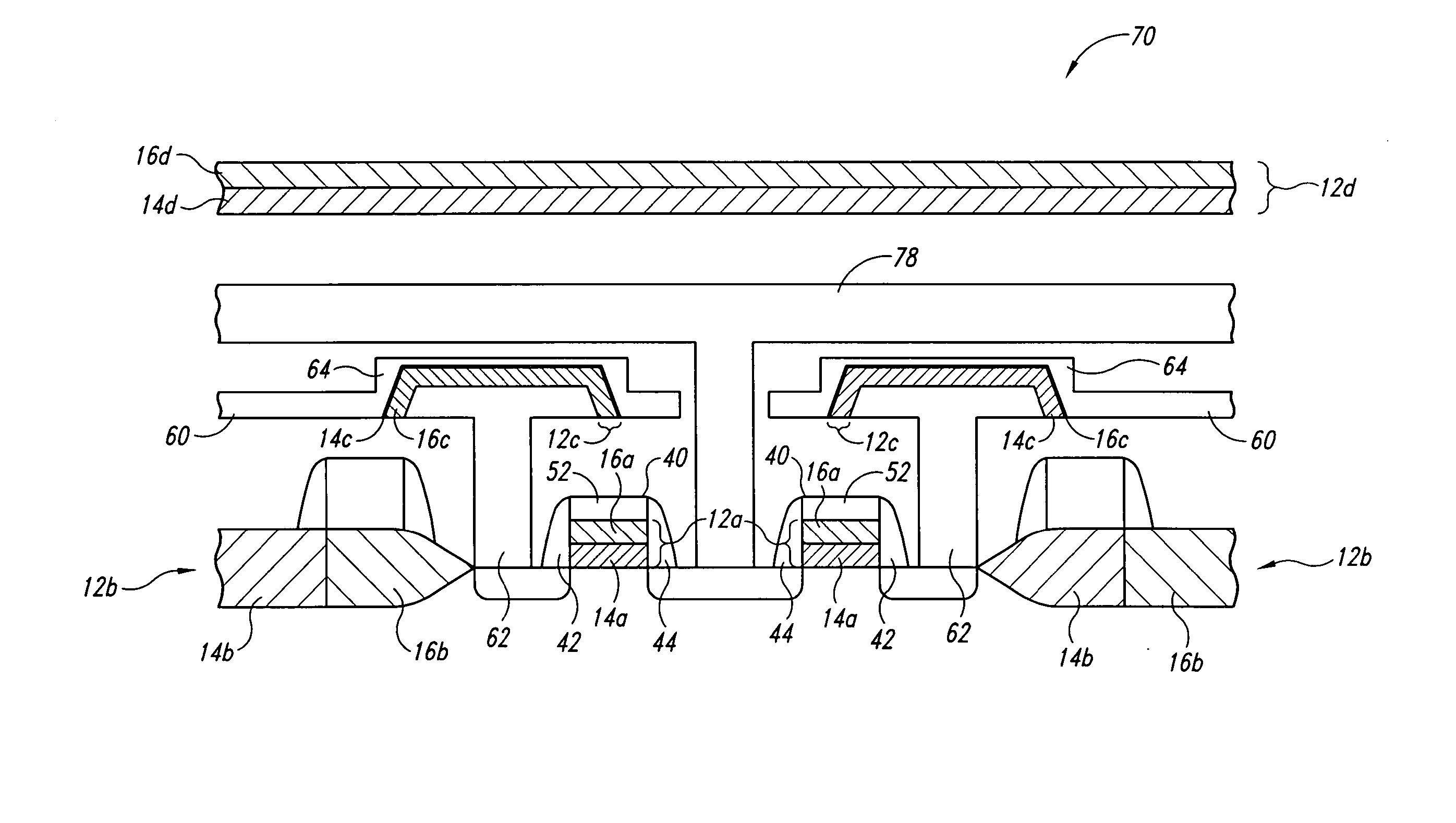
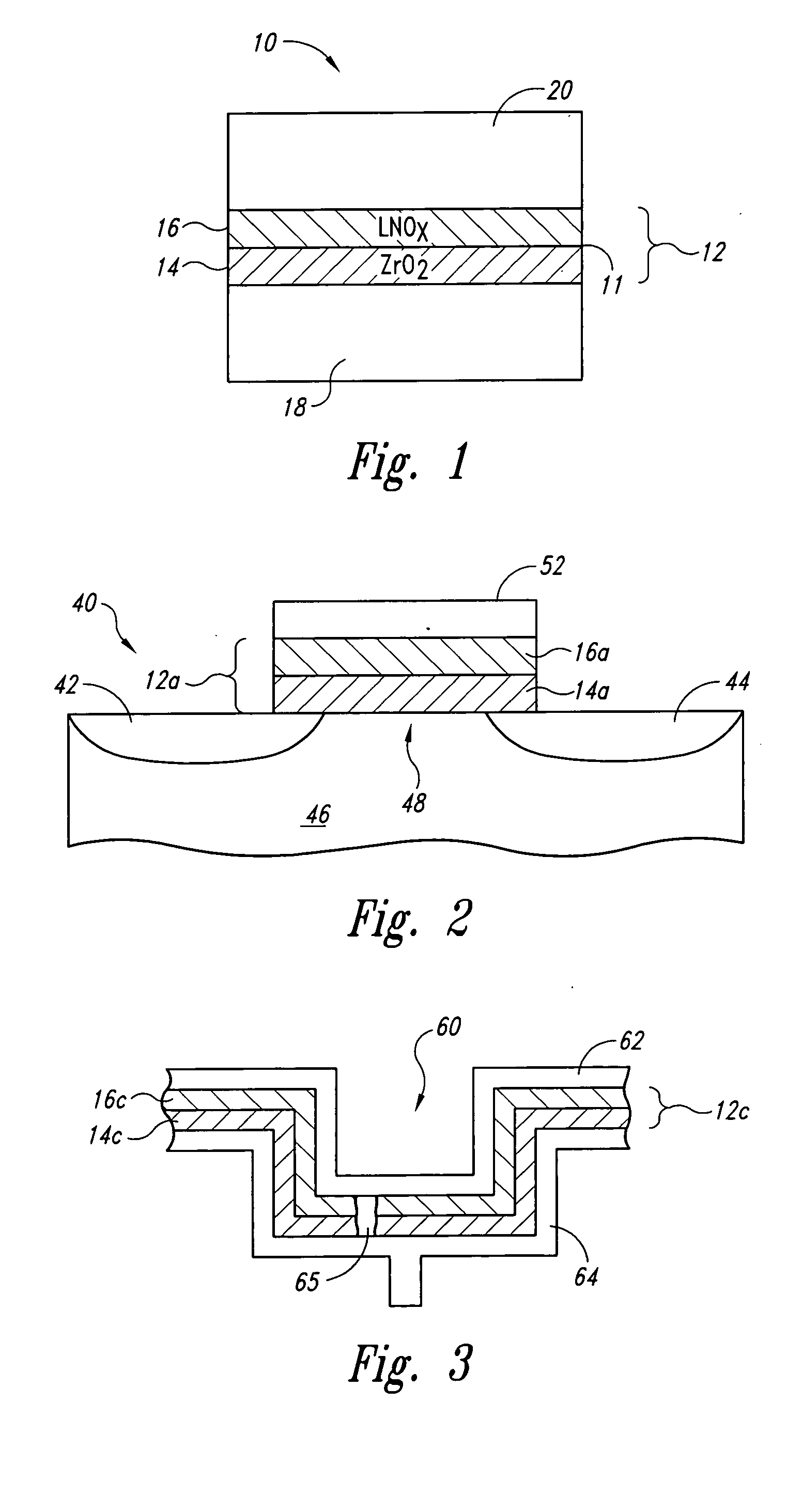
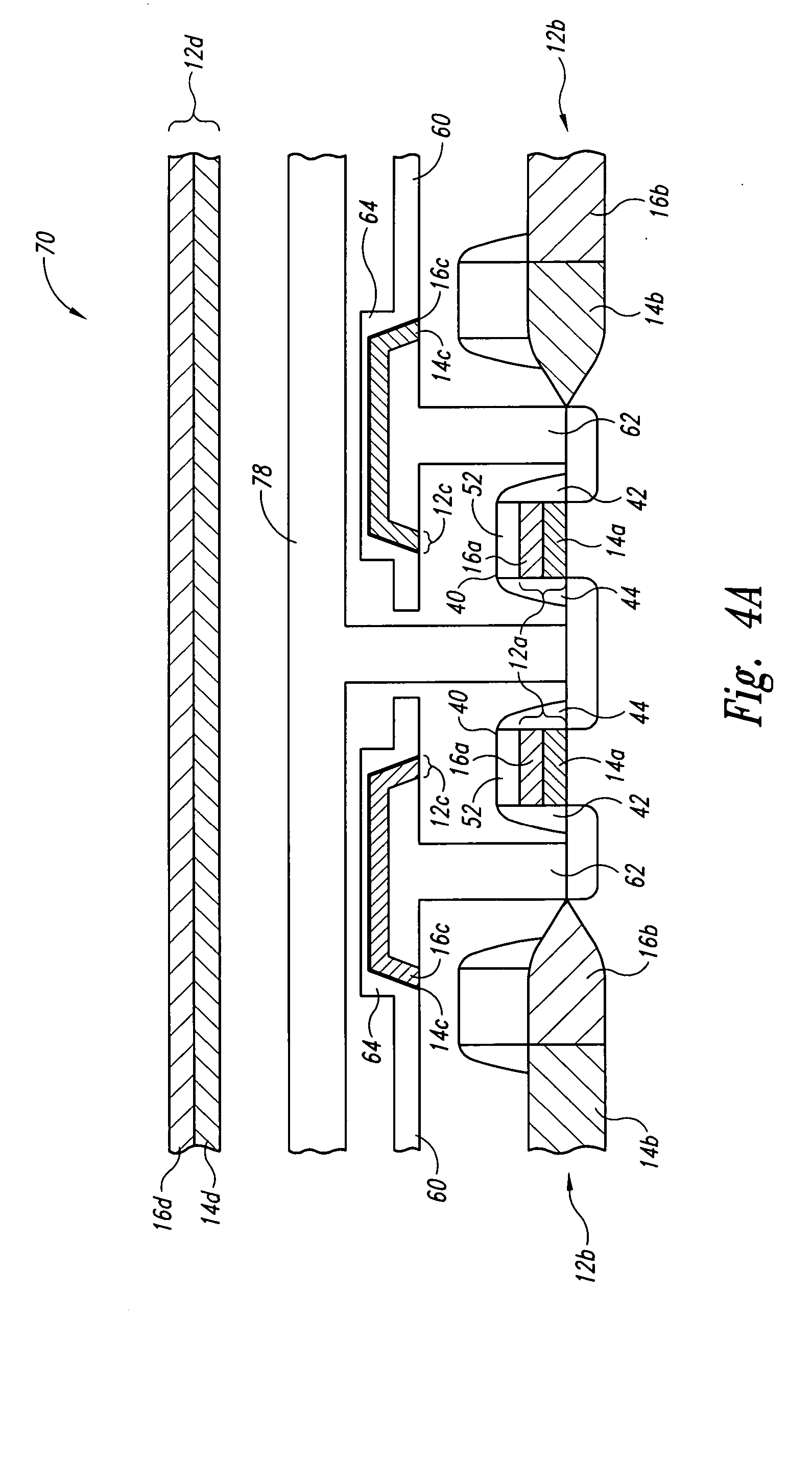
Lanthanide oxide/zirconium oxide atomic layer deposited nanolaminate gate dielectrics
The invention provides a laminated dielectric layer for semiconductor devices formed by a combination of ZrO2 and a lanthanide oxide on a semiconductor substrate and methods of making the same. In certain methods, the ZrO2 is deposited by multiple cycles of reaction sequence atomic layer deposition (RS-ALD) that includes depositing a ZrI4 precursor onto the surface of the substrate in a first pulse followed by exposure to H2O / H2O2 in a second pulse, thereby forming a thin ZrO2 layer on the surface. After depositing the ZrO2 layer, the lanthanide oxide layer is deposited by electron beam evaporation. The composite laminate zirconium oxide / lanthanide oxide dielectric layer has a relatively high dielectric constant and can be formed in layers of nanometer dimensions. It is useful for a variety of semiconductor applications, particularly for DRAM gate dielectric layers and DRAM capacitors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method of attaching layer material and forming layer in predetermined pattern on substrate using mask
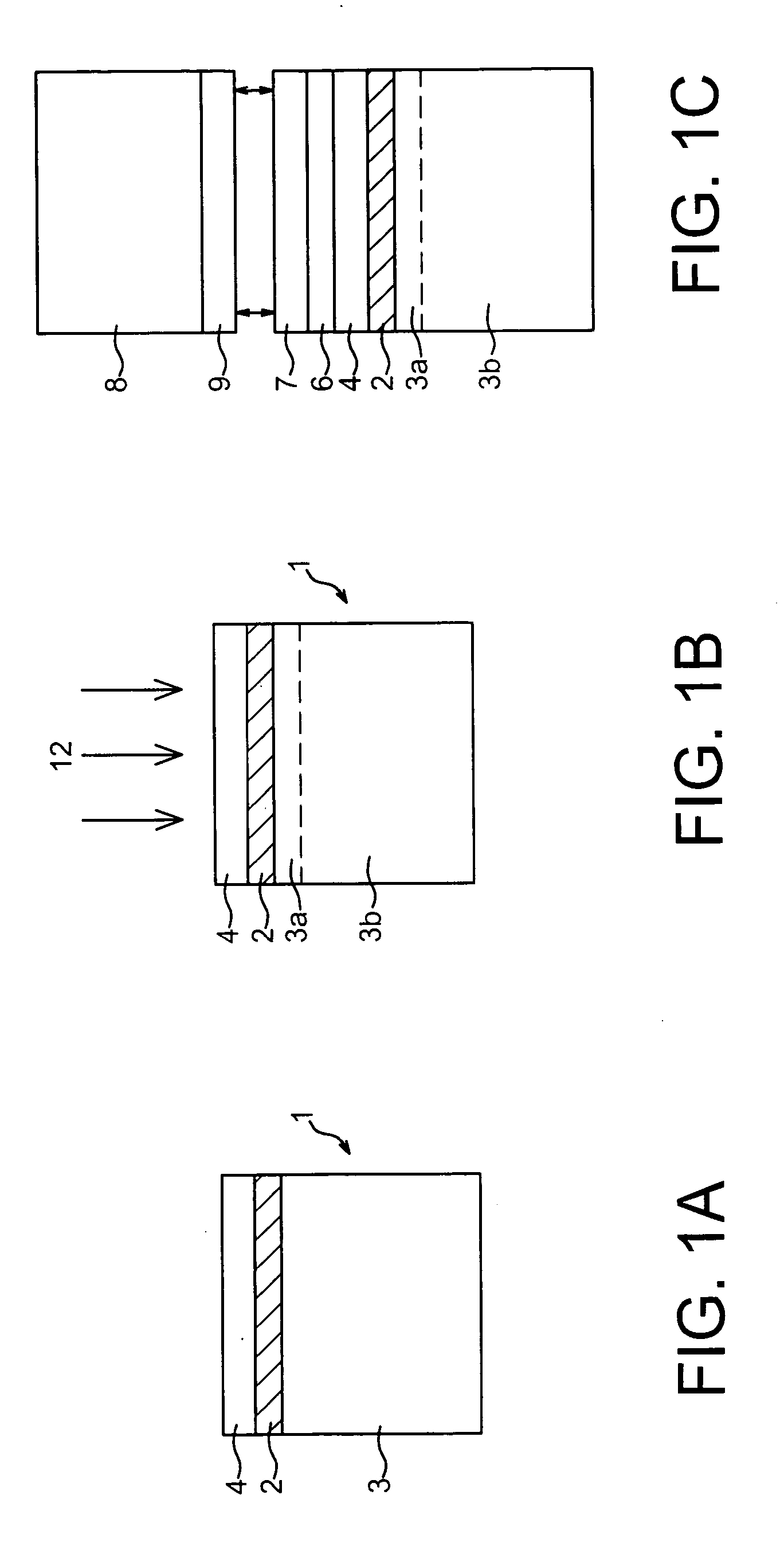
InactiveUS20020076847A1Improve accuracyProlong lifeElectroluminescent light sourcesVacuum evaporation coatingEvaporationOptoelectronics
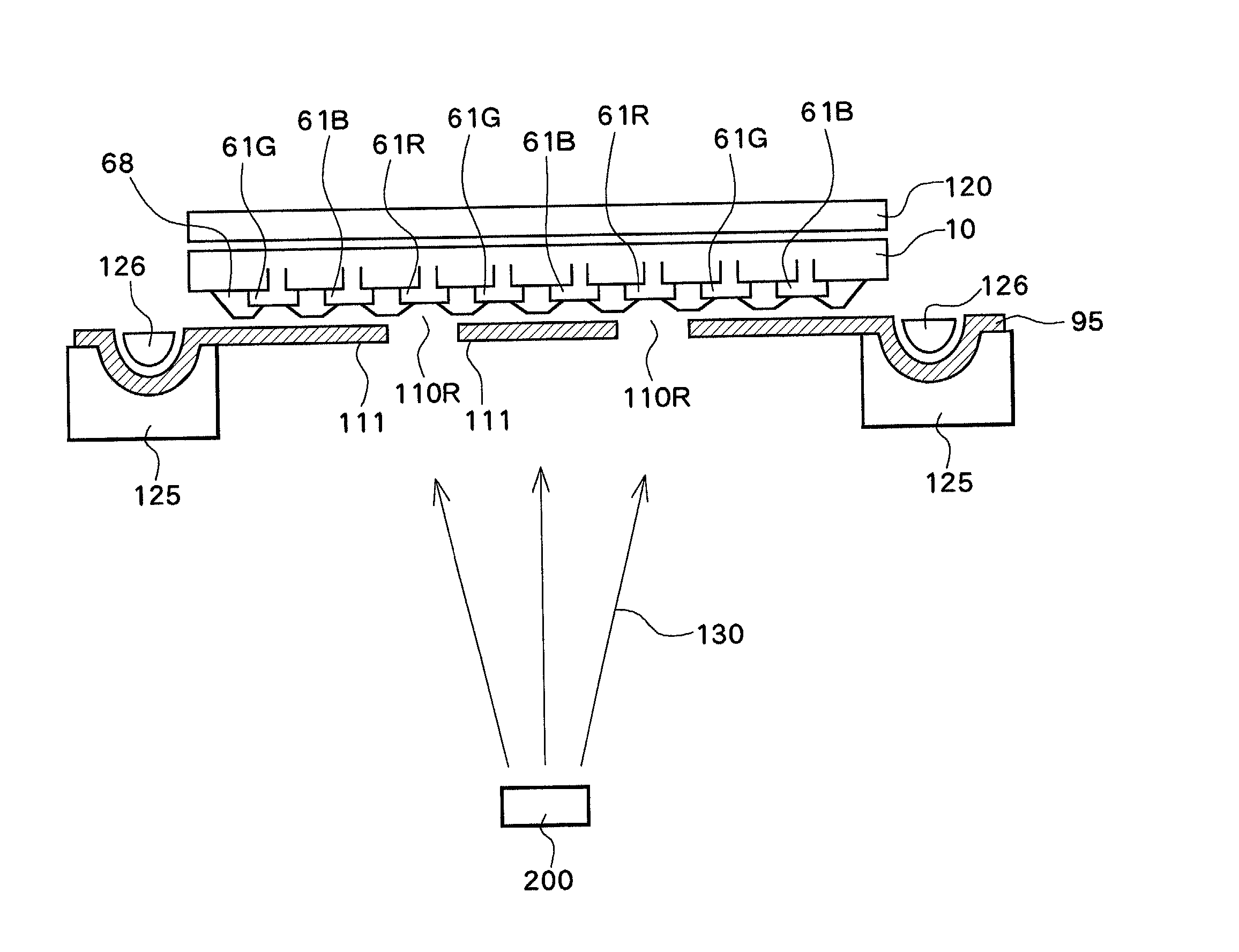
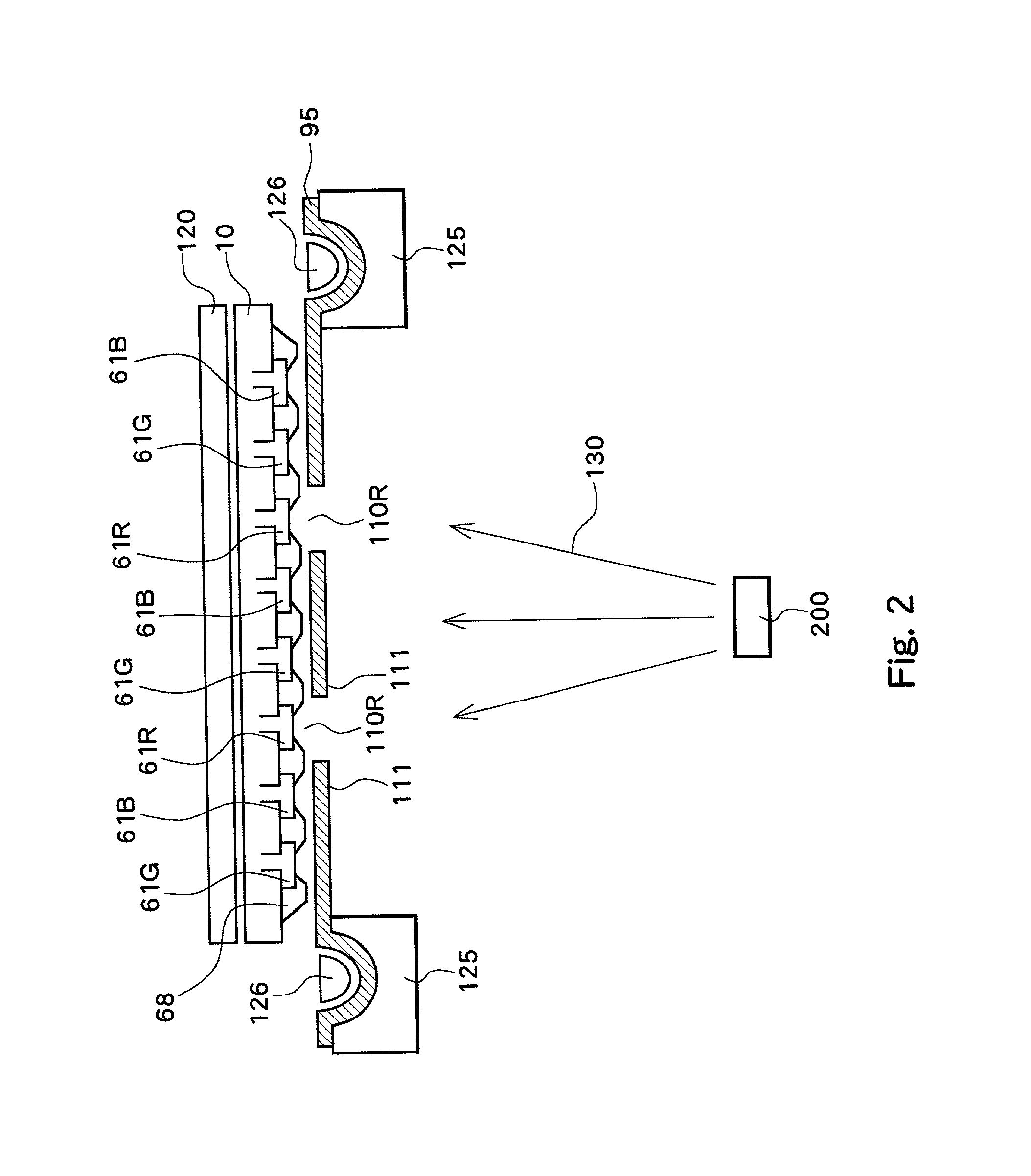
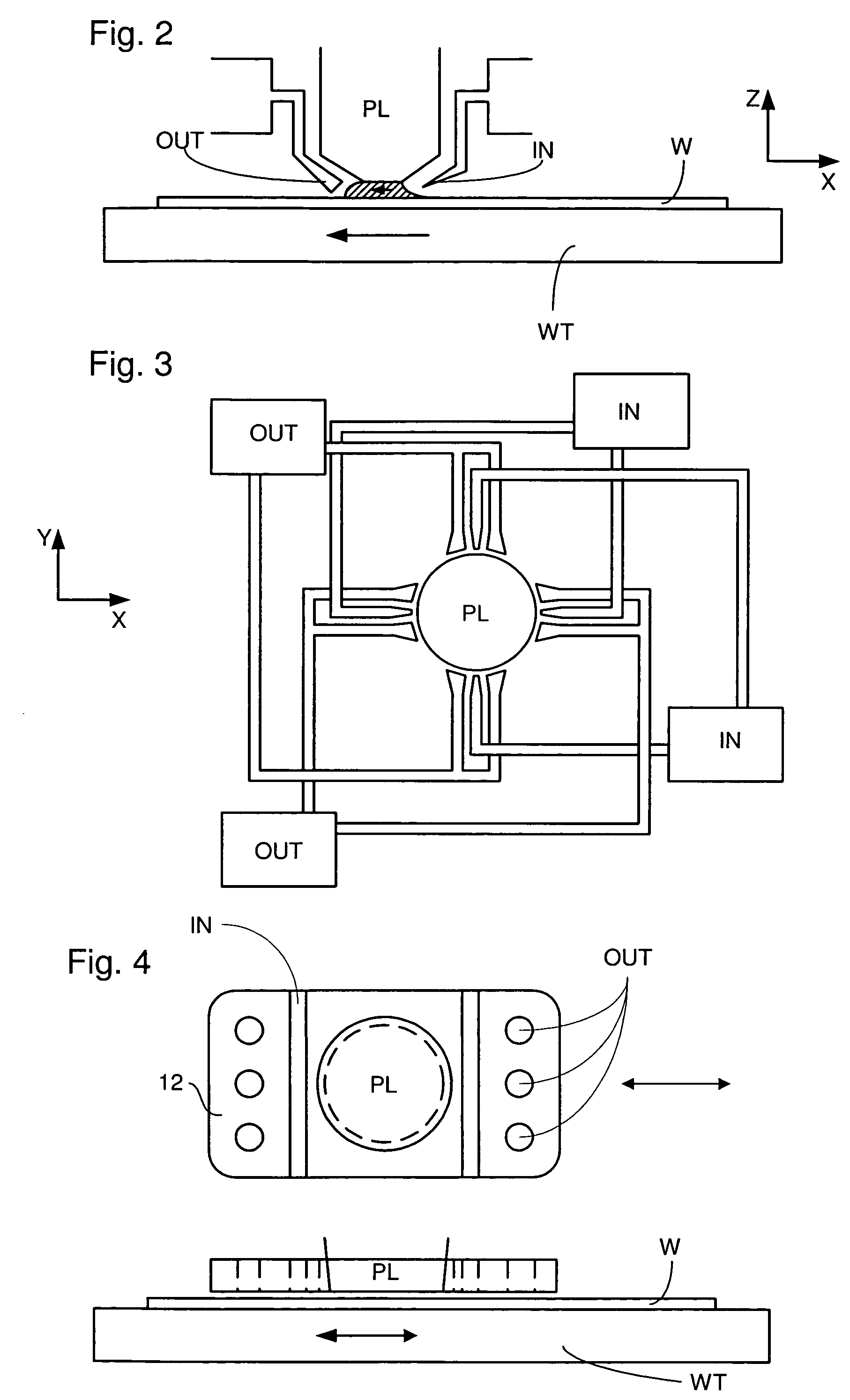
Upon formation of a layer such as an emissive layer of an organic EL element by attaching an emissive material onto a substrate (10), an evaporation mask (100) including an opening (110) corresponding to the layer formed to have a plurality of individual patterns and having an area, for example, smaller than the substrate is disposed between the substrate (10) and a material source (200). A relative position between the mask (100) and the material source (200), and the substrate (10) is slid by a predetermined pitch corresponding to the size of a pixel of the substrate (10), thereby forming a material layer (such as the emissive layer 64) in a predetermined region of the substrate. As a result, the material layer can be formed on the substrate through, for example, evaporation with a high accuracy.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Crystalline or amorphous medium-K gate oxides, Y2O3 and Gd2O3
InactiveUS20050032292A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEquivalent oxide thicknessGadolinium
A gate oxide and method of fabricating a gate oxide that produces a more reliable and thinner equivalent oxide thickness than conventional SiO2 gate oxides are provided. Also shown is a gate oxide with a conduction band offset of 2 eV or greater. Gate oxides formed from elements such as yttrium and gadolinium are thermodynamically stable such that the gate oxides formed will have minimal reactions with a silicon substrate or other structures during any later high temperature processing stages. The process shown is performed at lower temperatures than the prior art, which further inhibits reactions with the silicon substrate or other structures. Using a thermal evaporation technique to deposit the layer to be oxidized, the underlying substrate surface smoothness is preserved, thus providing improved and more consistent electrical properties in the resulting gate oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
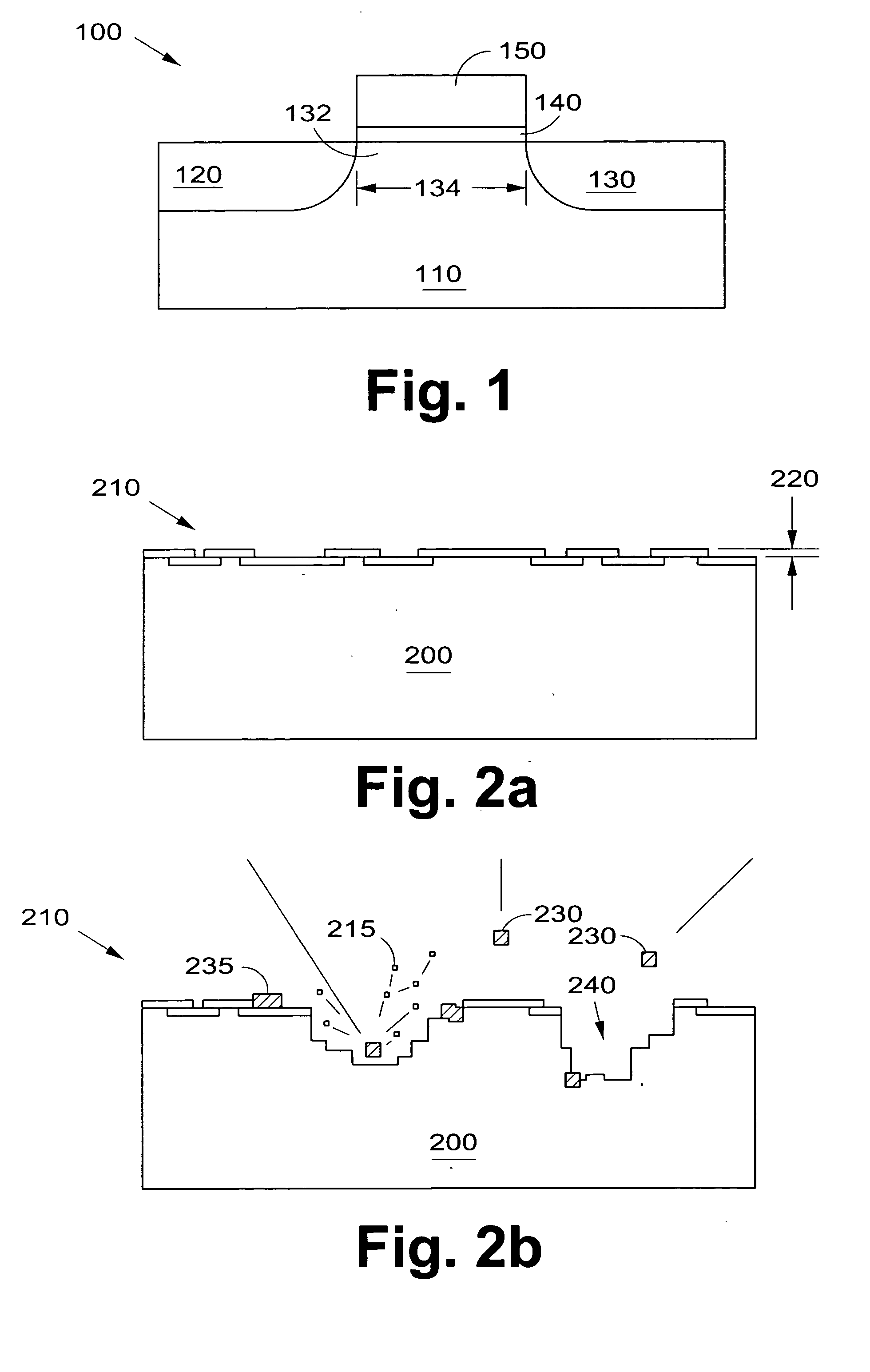
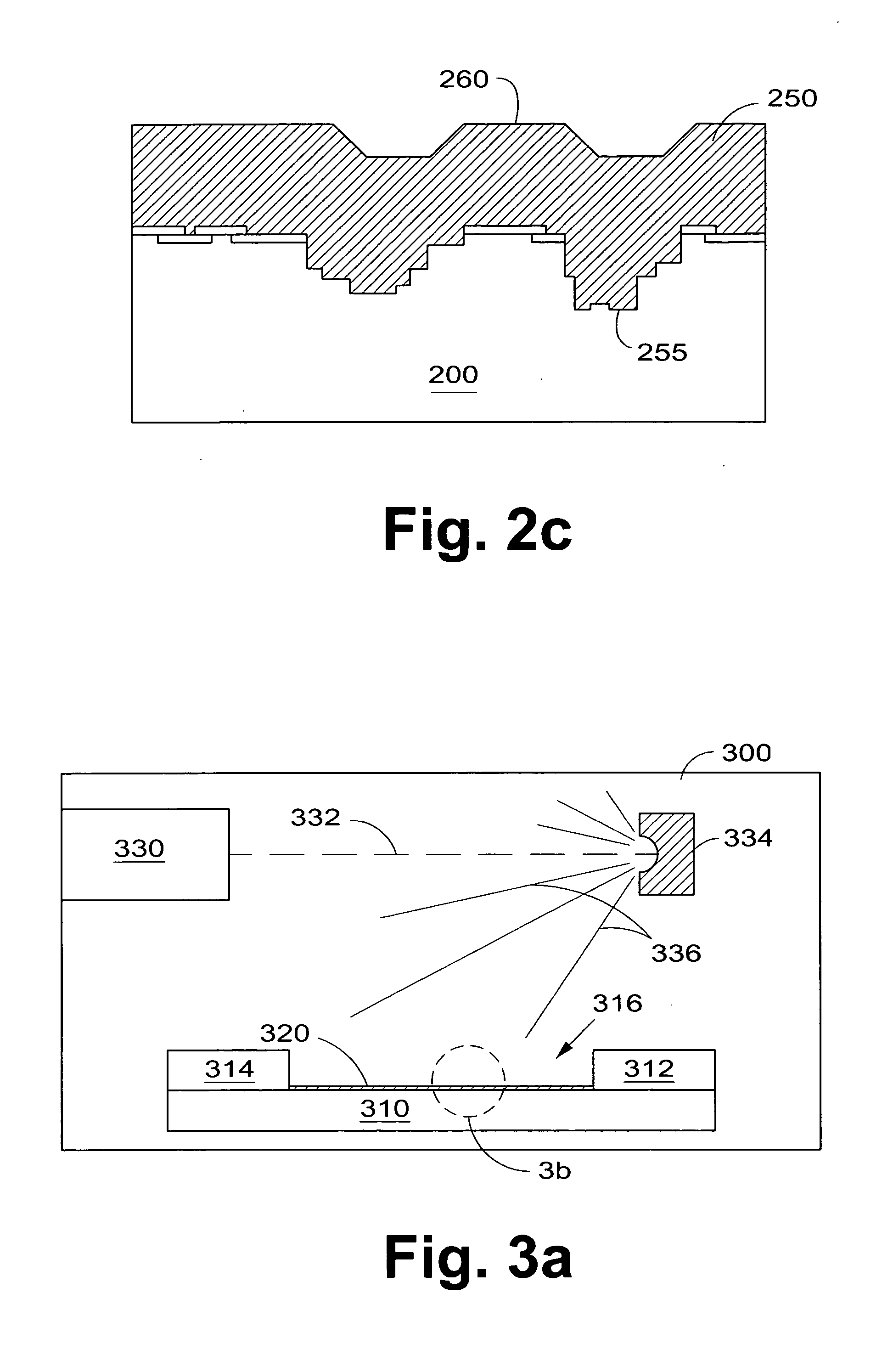
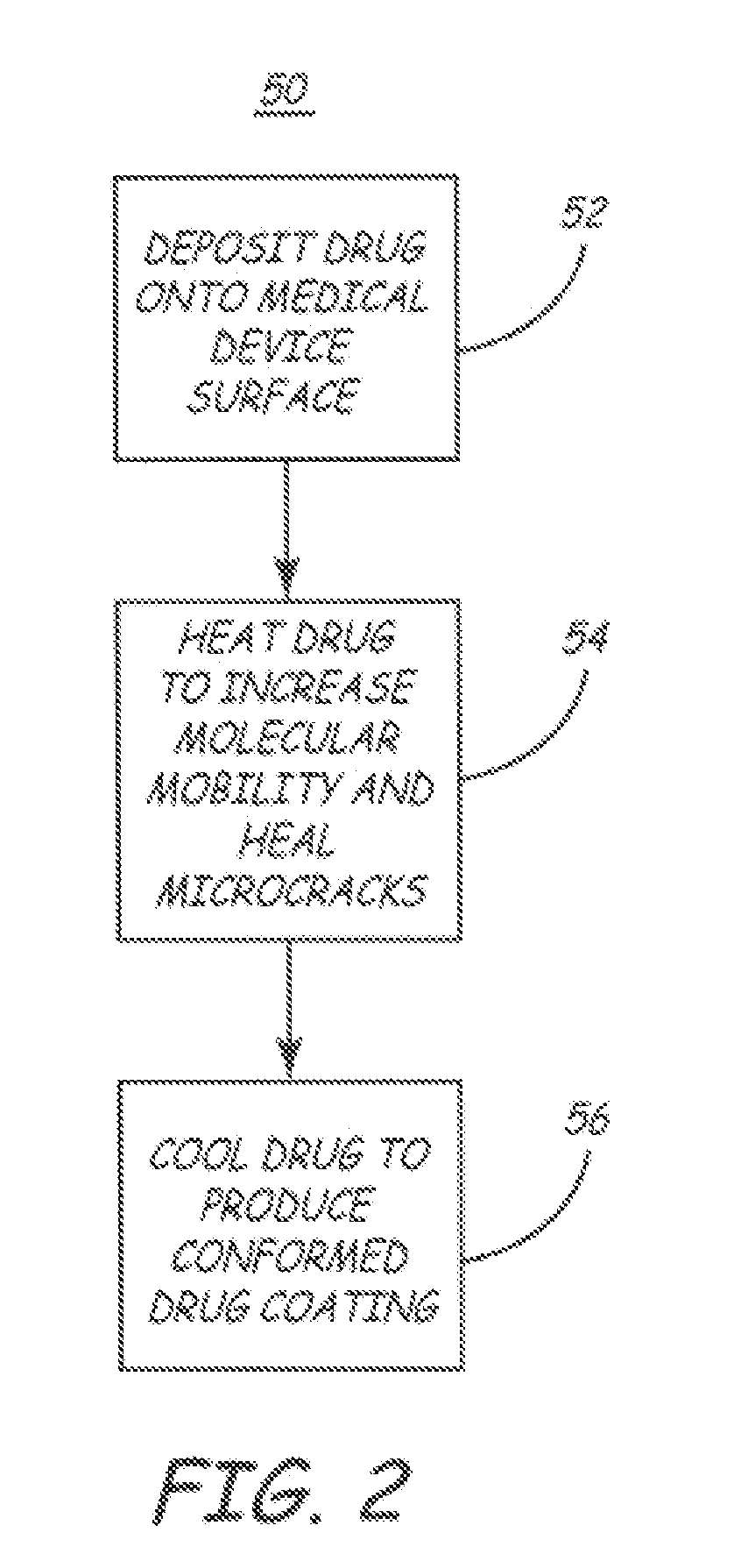
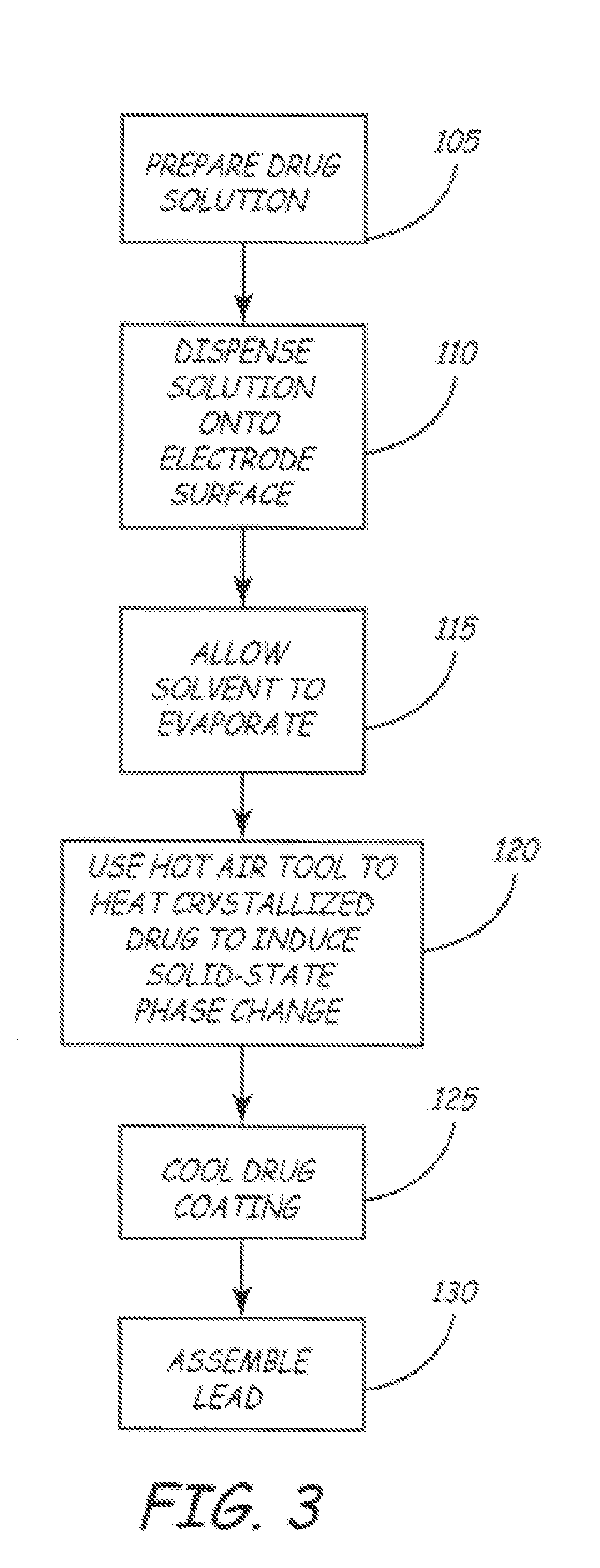
Method for applying a drug coating to a medical device
A method for coating a medical device with a drug is provided. Energy, preferably thermal energy, is applied to a crystalline deposit of a drug on the surface of a medical device to increase the molecular mobility and form a conformable drug coating with a low density of micro-cracks and other mechanical defects that can degrade the coating toughness and effective adhesion to the device surface. In a preferred embodiment, solution evaporation methods are used to deposit a crystalline coating of an anti-inflammatory steroid on a medical electrode. Heat applied at a controlled temperature, for a predetermined amount of time, induces a solid-state phase change of the drug coating providing a smooth, uniform, well-attached, conformable coating to form a layer that will elute from the electrode over time when implanted in a patient's body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for assembling nano objects
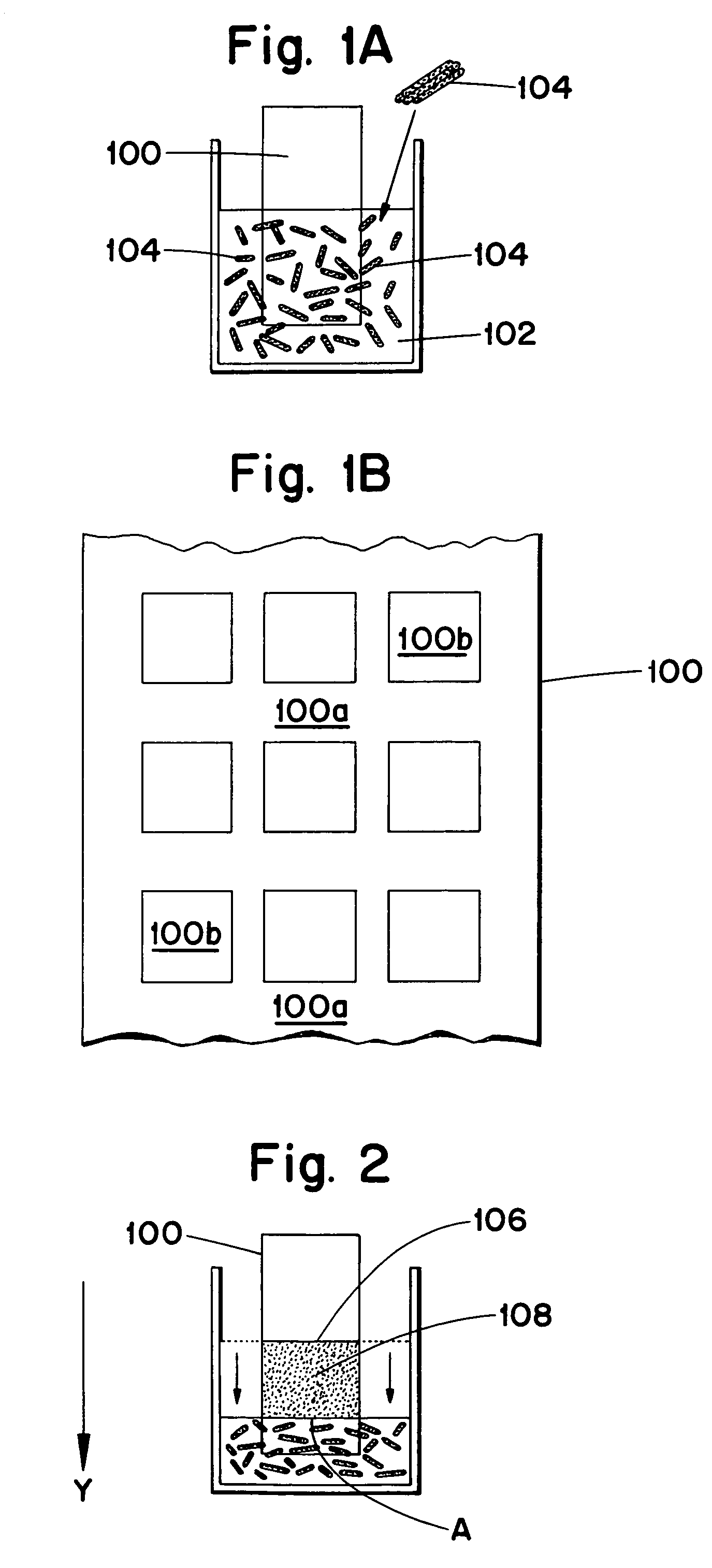
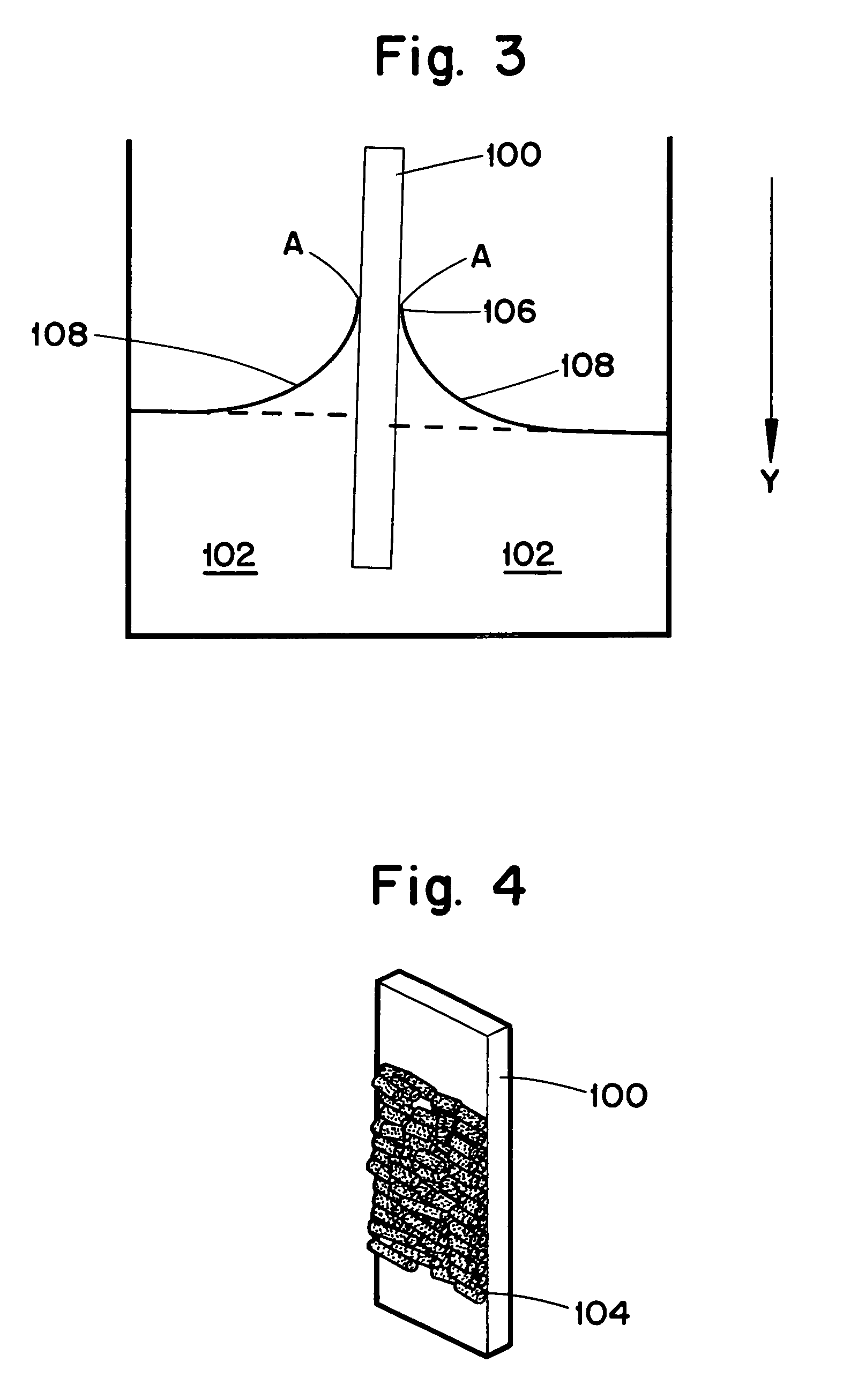
InactiveUS7147894B2Orientation can be controlledEfficient assemblyMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureEvaporationSolvent
A method for the self assembly of a macroscopic structure with a pre-formed nano object is provided. The method includes processing a nano object to a desired aspect ratio and chemical functionality and mixing the processed nano object with a solvent to form a suspension. Upon formation of the suspension, a substrate is inserted into the suspension. By either evaporation of the solvent, changing the pH value of the suspension, or changing the temperature of the suspension, the nano objects within the suspension deposit onto the substrate in an orientational order. In addition, a seed crystal may be used in place of the substrate thereby forming single-crystals and free-standing membranes of the nano-objects.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
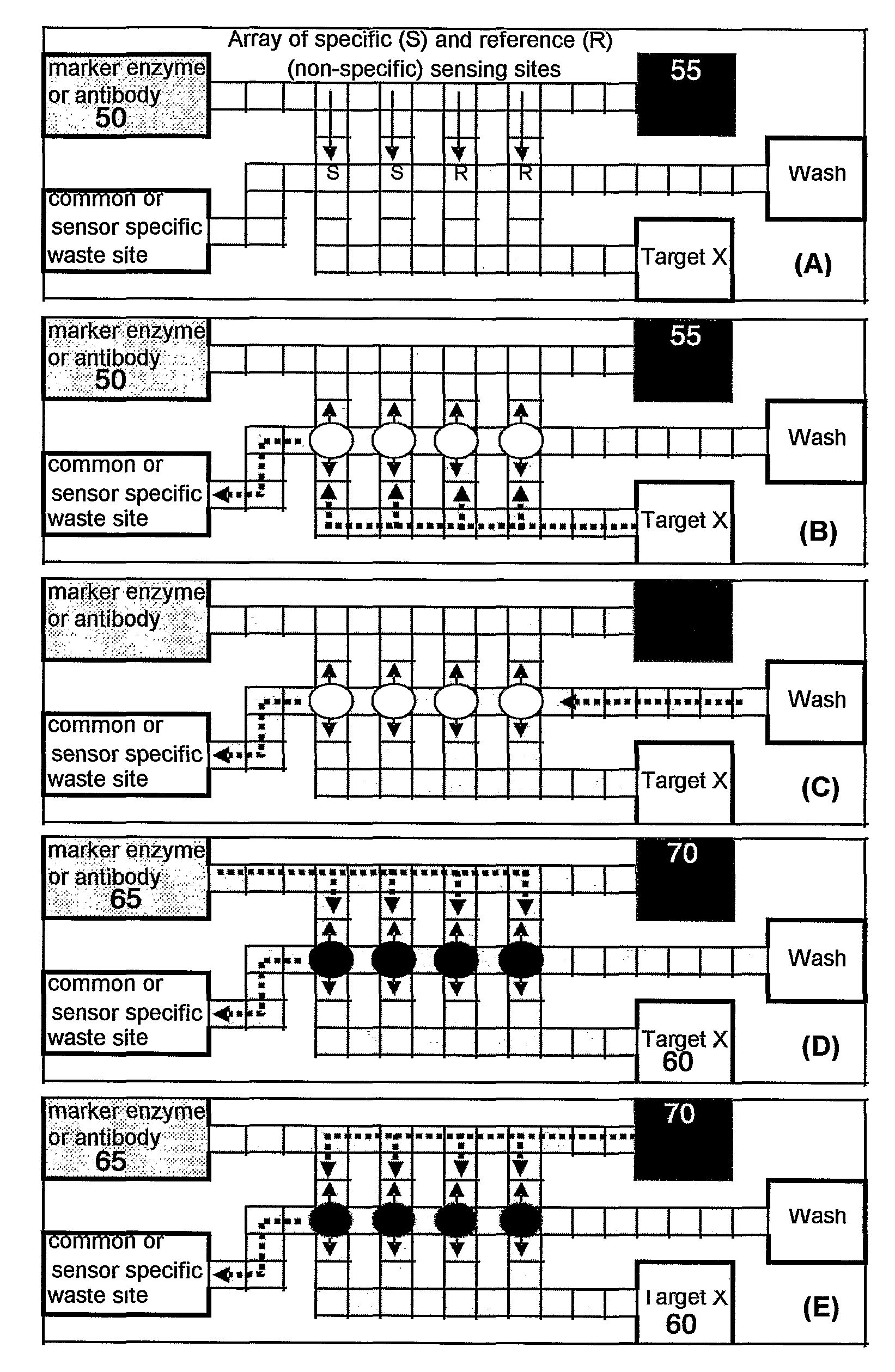
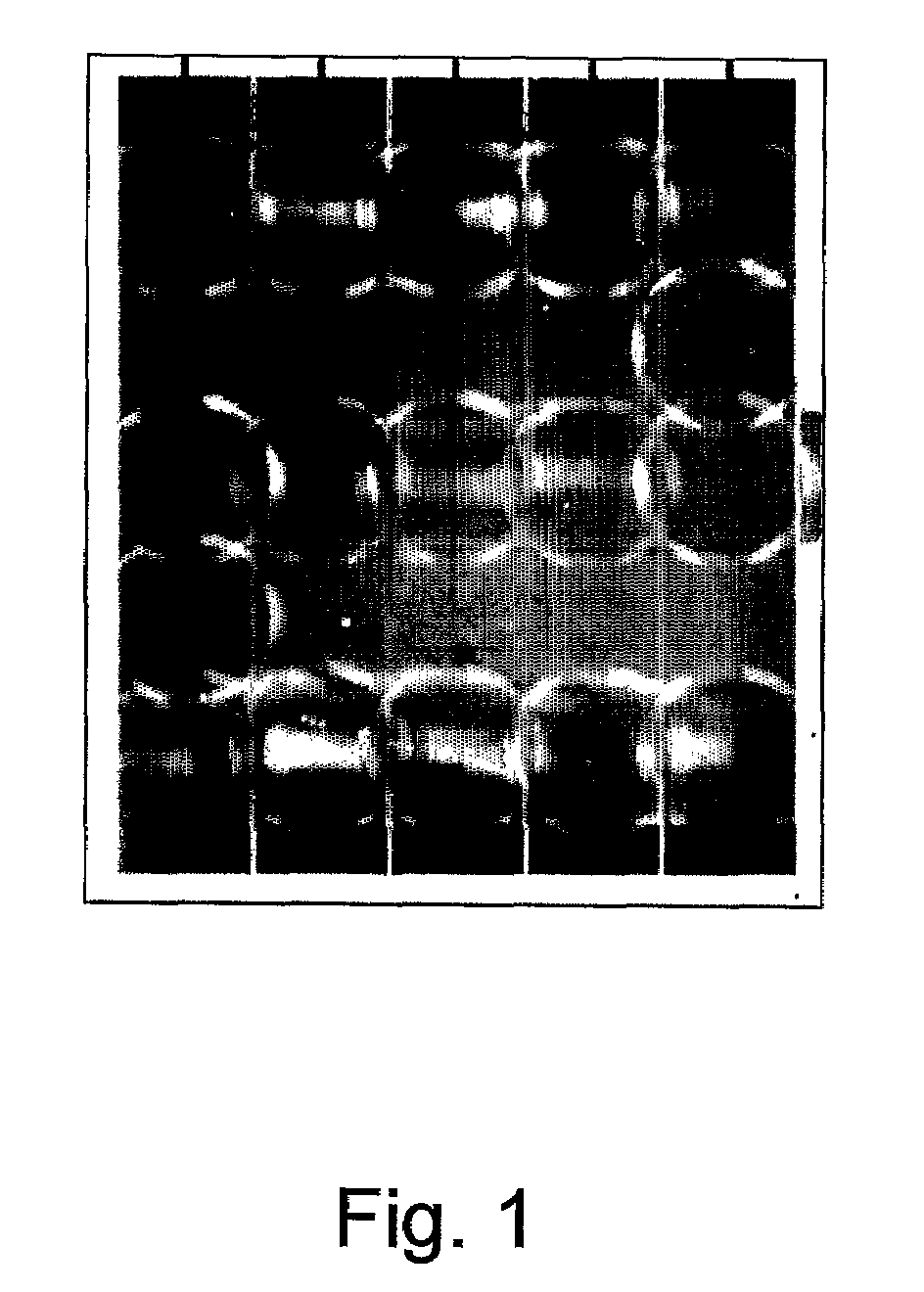
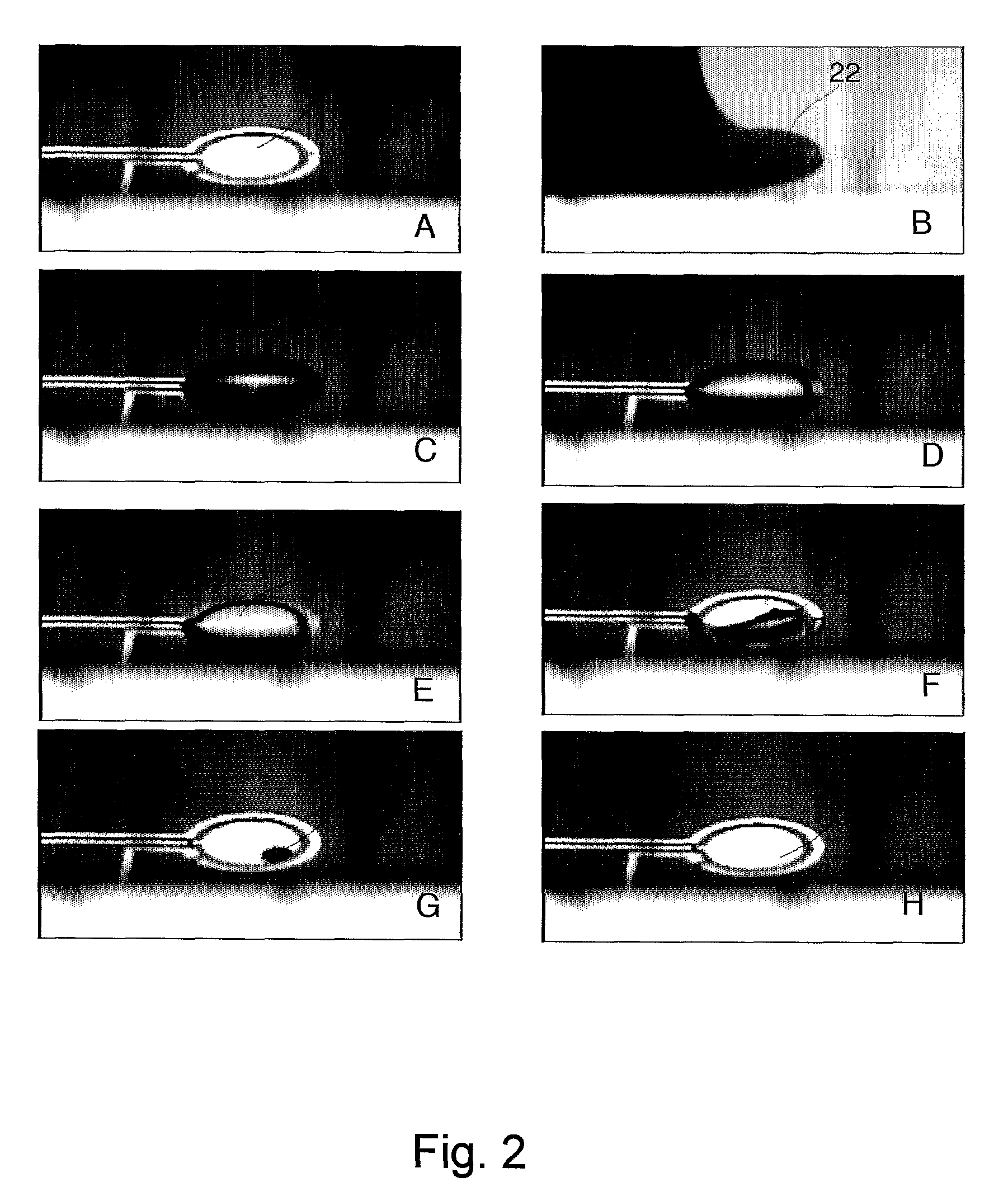
Biosensor Detection By Means Of Droplet Driving, Agitation, and Evaporation
InactiveUS20090042319A1More dataLow costSamplingTransportation and packagingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Analyte
Methods of improving microfluidic assays are disclosed. Assays can be improved (better signal to noise ratio) by using sessile drop evaporation as an analyte concentration step (enhanced signal) and repeated passes of wash droplets as a means to reduce non-specific binding (noise reduction). In addition multiple massively parallel analyses improve the statistical precision of the analyses.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Sheets having a starch-based binding matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix, optionally reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, a cellulosic ether, optionally fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the cellulosic ether to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and cellulosic ether form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060033898A1Reduces lithography errorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEvaporationEngineering
A lithographic apparatus is disclosed having a liquid supply system configured to at least partly fill a space between a projection system of the lithographic apparatus and a substrate with liquid, a barrier member arranged to substantially contain the liquid within the space, and one or more elements to control and / or compensate for evaporation of liquid from the substrate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Vapor deposition method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090017192A1Improve cooling effectAvoid misalignmentVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesGas phaseEvaporation
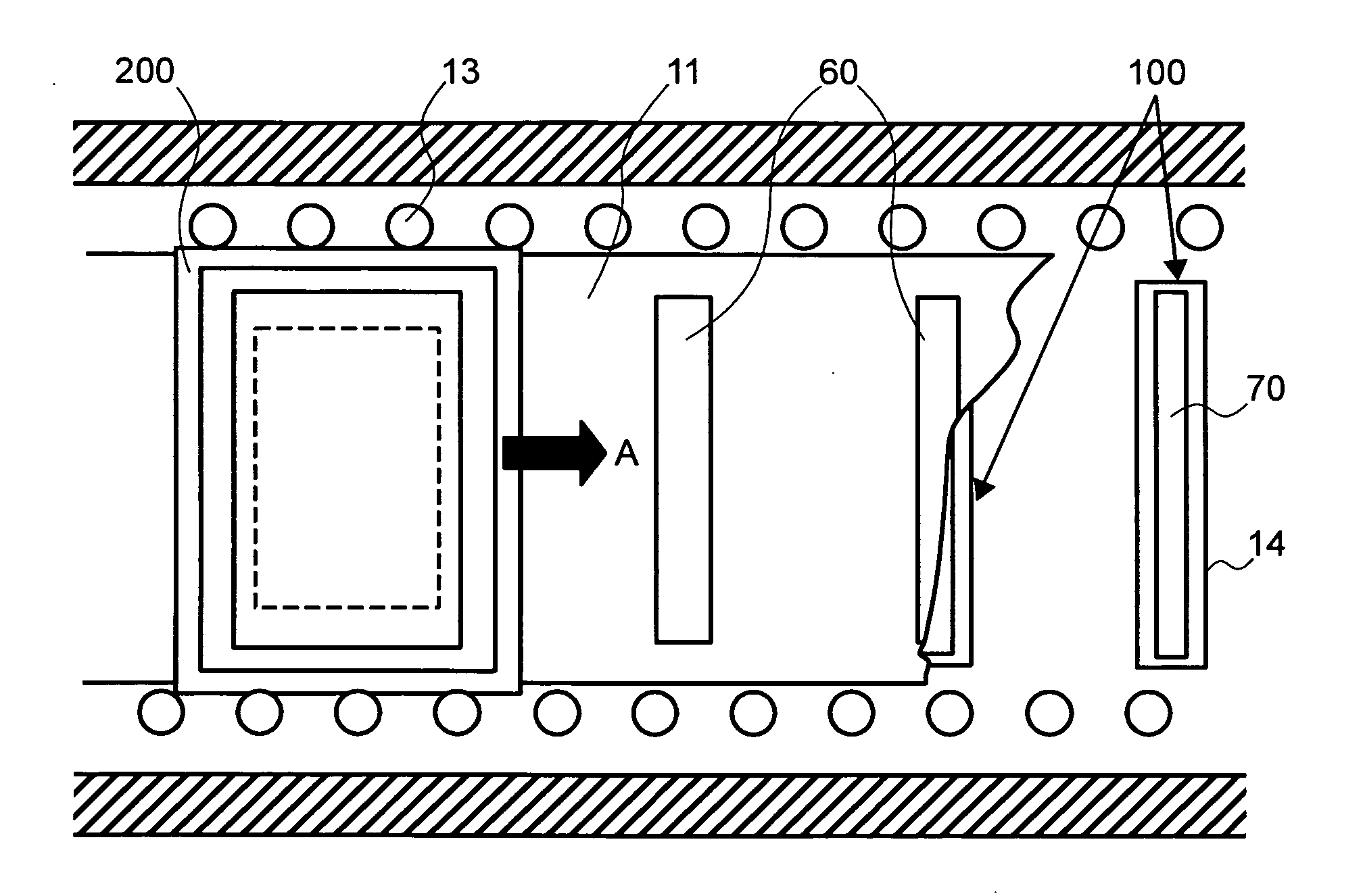
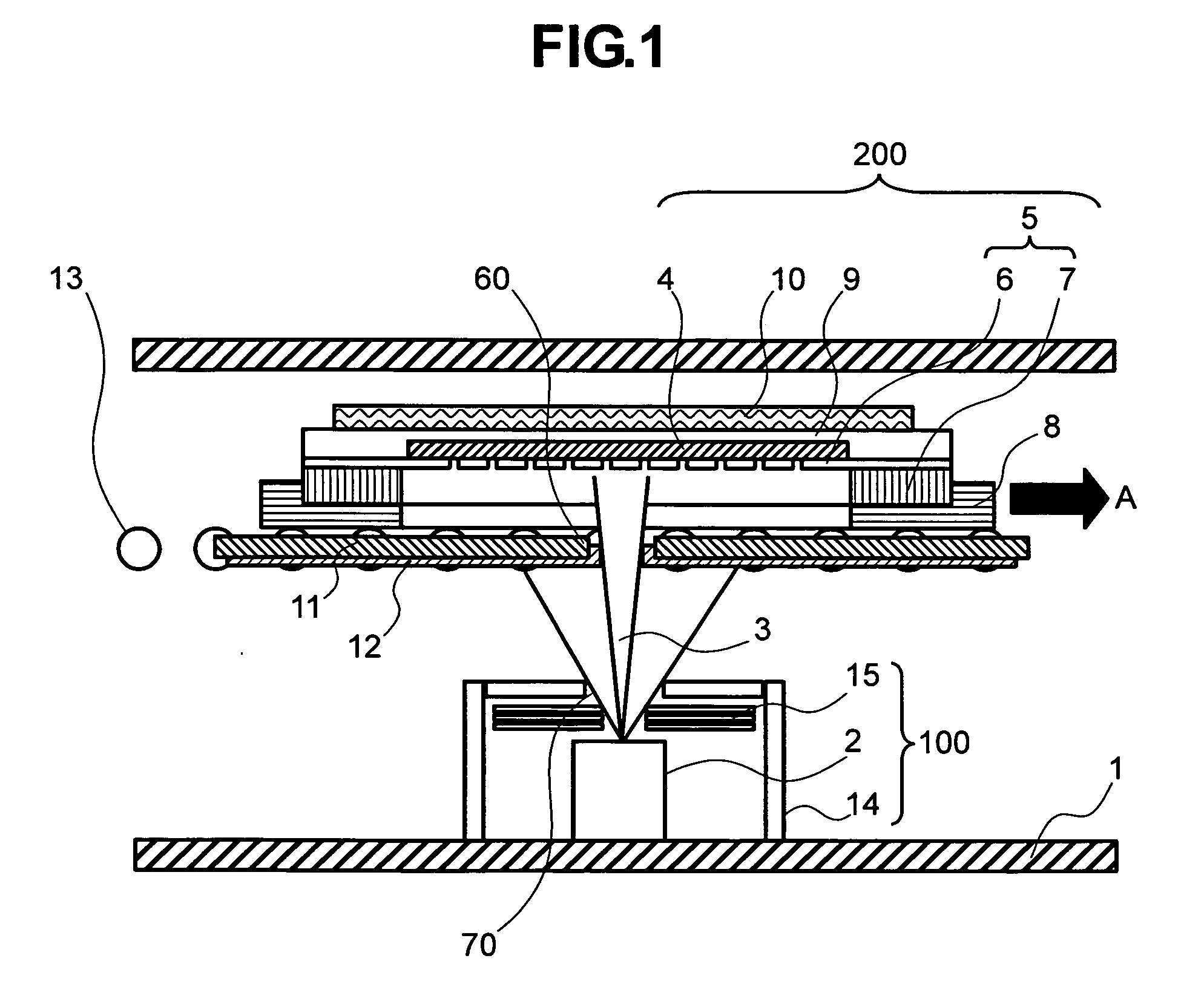
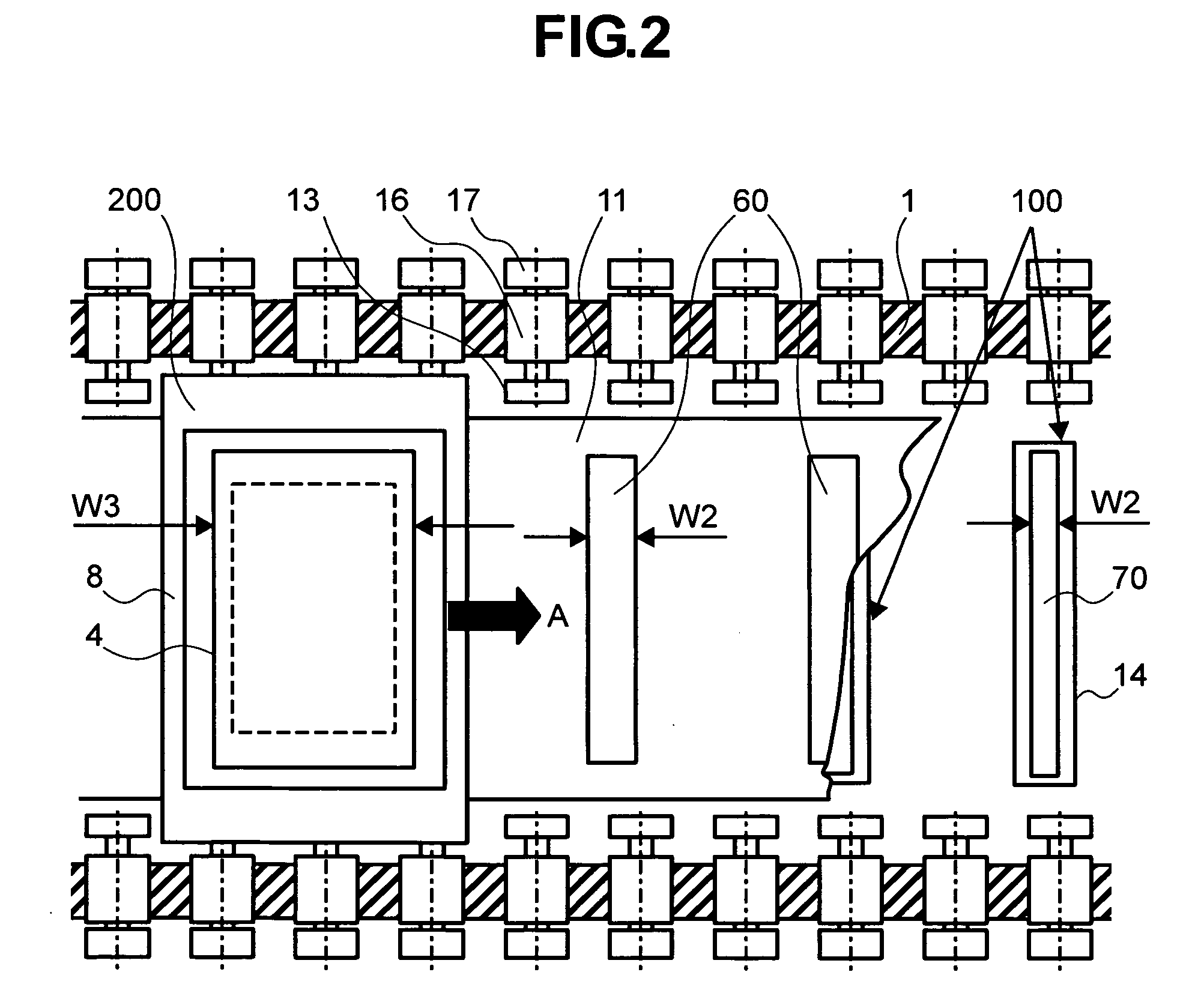
Provided is a method for moving, in a vacuum chamber carrying therein a fixedly-provided evaporation source, a substrate toward the evaporation source together with a mask closely attached to the substrate surface, and onto the surface substrate, evaporating a material vaporized in the evaporation source through an aperture formed to the mask. In this method of the invention, means for moving the substrate toward the evaporation source is provided with cooling means not to come in contact with but to be in proximity to a surface of the mask on the evaporation source side, and a cooling plate formed with an aperture proximal to the evaporation source is disposed. With such a configuration, the steam of the material coming from the evaporation source is directed to the mask and the substrate through the aperture of the cooling plate. As such, the material film evaporated on the substrate surface shows a satisfactory distribution of film thickness, and any possible misalignment from desired positions of evaporation can be accordingly suppressed.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS +1
Method and apparatus of indirect-evaporation cooling
InactiveUS6497107B2Less energyHigh energy costFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesWorking fluidEvaporation
The within invention improves on the indirect evaporative cooling method and apparatus by making use of a working fluid that is pre-cooled with and without desiccants before it is passed through a Wet Channel where evaporative fluid is on the walls to take heat and store it in the working fluid as increased latent heat. The heat transfer across the membrane between the Dry Channel and the Wet Channel may have dry, solid desiccant or liquid desiccant and may have perforations, pores or capillary pathways. The evaporative fluid may be water, fuel, or any substance that has the capacity to take heat as latent heat. The Wet Channel or excess cooled fluid is in heat transfer contact with a Product Channel where Product Fluid is cooled without adding any humidity. An alternative embodiment for heat transfer between adjacent channels is with heat pipes.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
Method of deposition of thin films of amorphous and crystalline microstructures based on ultrafast pulsed laser deposition
InactiveUS6312768B1Improve surface qualityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingMacroscopic scaleCarbon nanotube
Powerful nanosecond-range lasers using low repetition rate pulsed laser deposition produce numerous macroscopic size particles and droplets, which embed in thin film coatings. This problem has been addressed by lowering the pulse energy, keeping the laser intensity optional for evaporation, so that significant numbers of the macroscopic particles and droplets are no longer present in the evaporated plume. The result is deposition of evaporated plume on a substrate to form thin film of very high surface quality. Preferably, the laser pulses have a repetition rate to produce a continuous flow of evaporated material at the substrate. Pulse-range is typically picosecond and femtosecond and repetition rate kilohertz to hundreds of megahertz. The process may be carried out in the presence of a buffer gas, which may be inert or reactive, and the increased vapour density and therefore the collision frequency between evaporated atoms leads to the formation of nanostructured materials of increasing interest, because of their peculiar structural, electronic and mechanical properties. One of these is carbon nanotubes, which is a new form of carbon belonging to the fullerene (C60) family. Carbon nanotubes are seamless, single or multishell co-axial cylindrical tubules with or without dome caps at the extremities. Typically diameters range from 1 nm to 50 nm with a length >1 mum. The electronic structure may be either metallic or semiconducting without any change in the chemical bonding or adding of dopant. In addition, the materials have application to a wide range of established thin film applications.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com