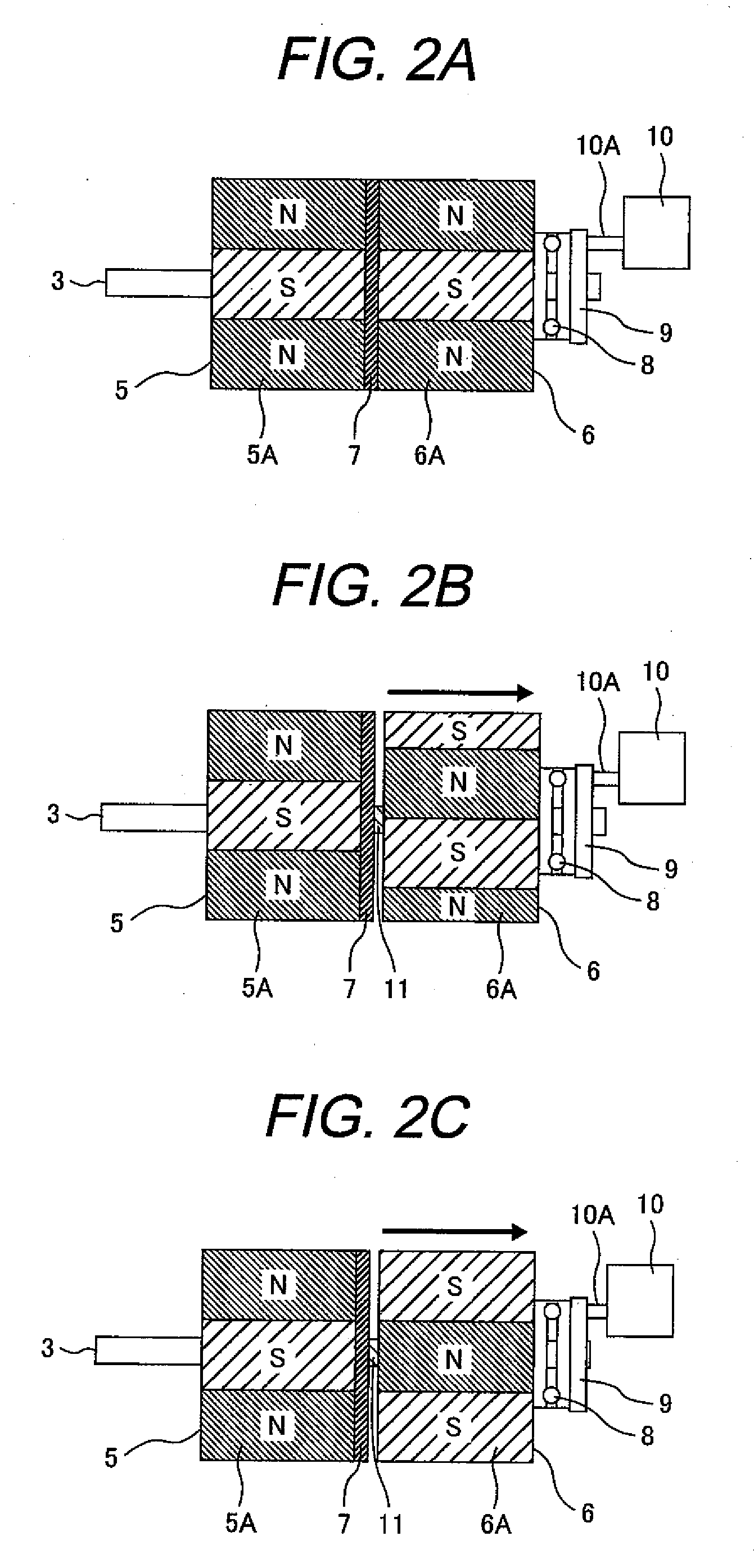
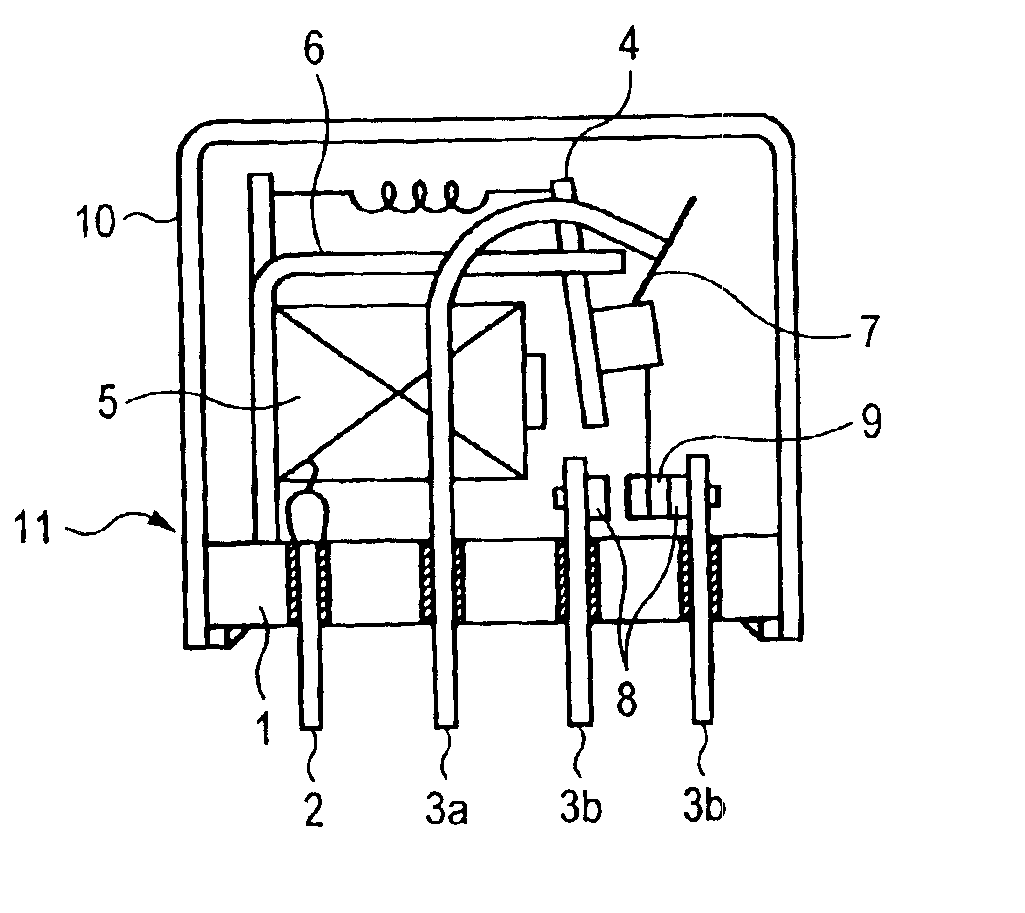
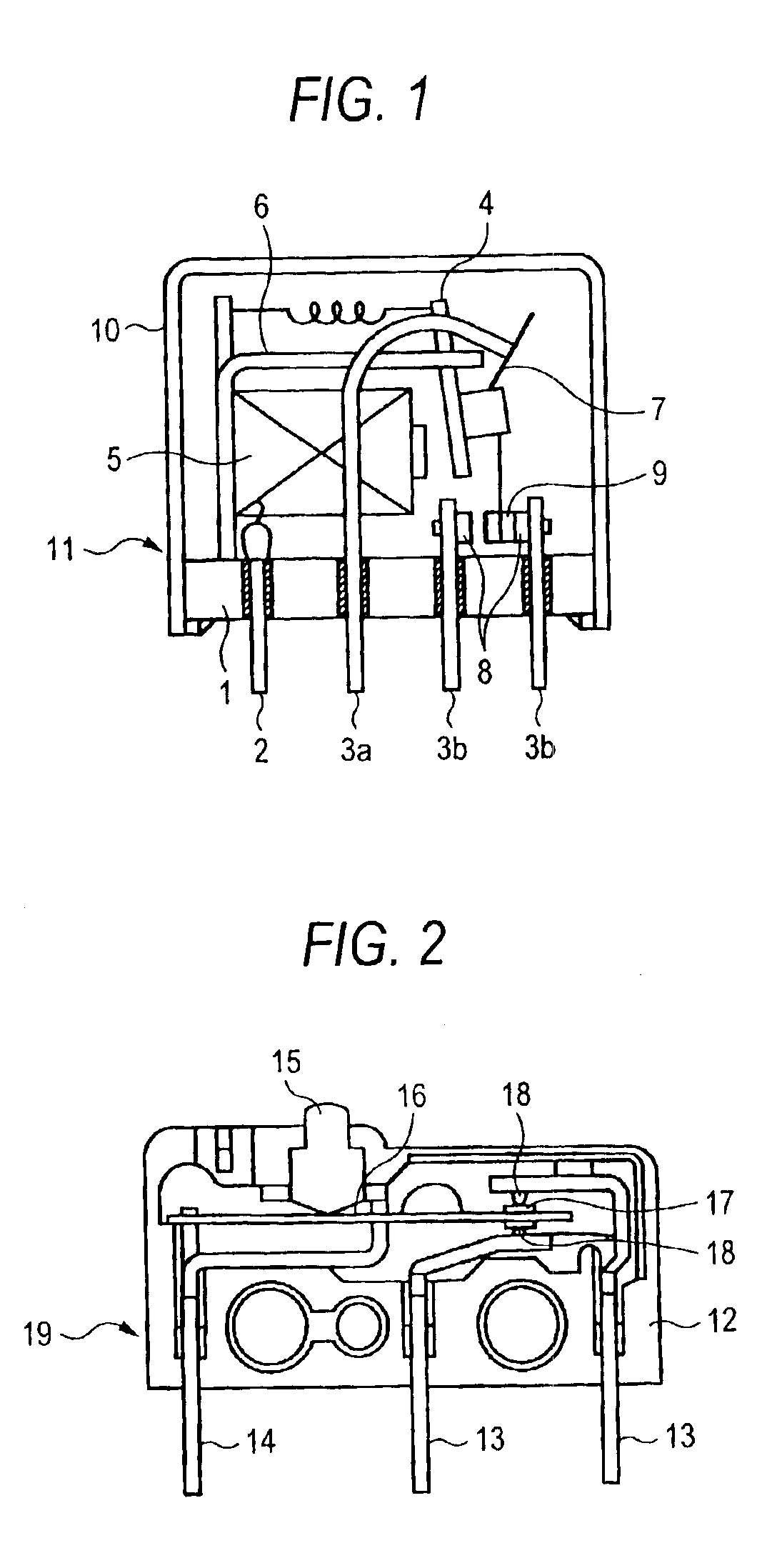
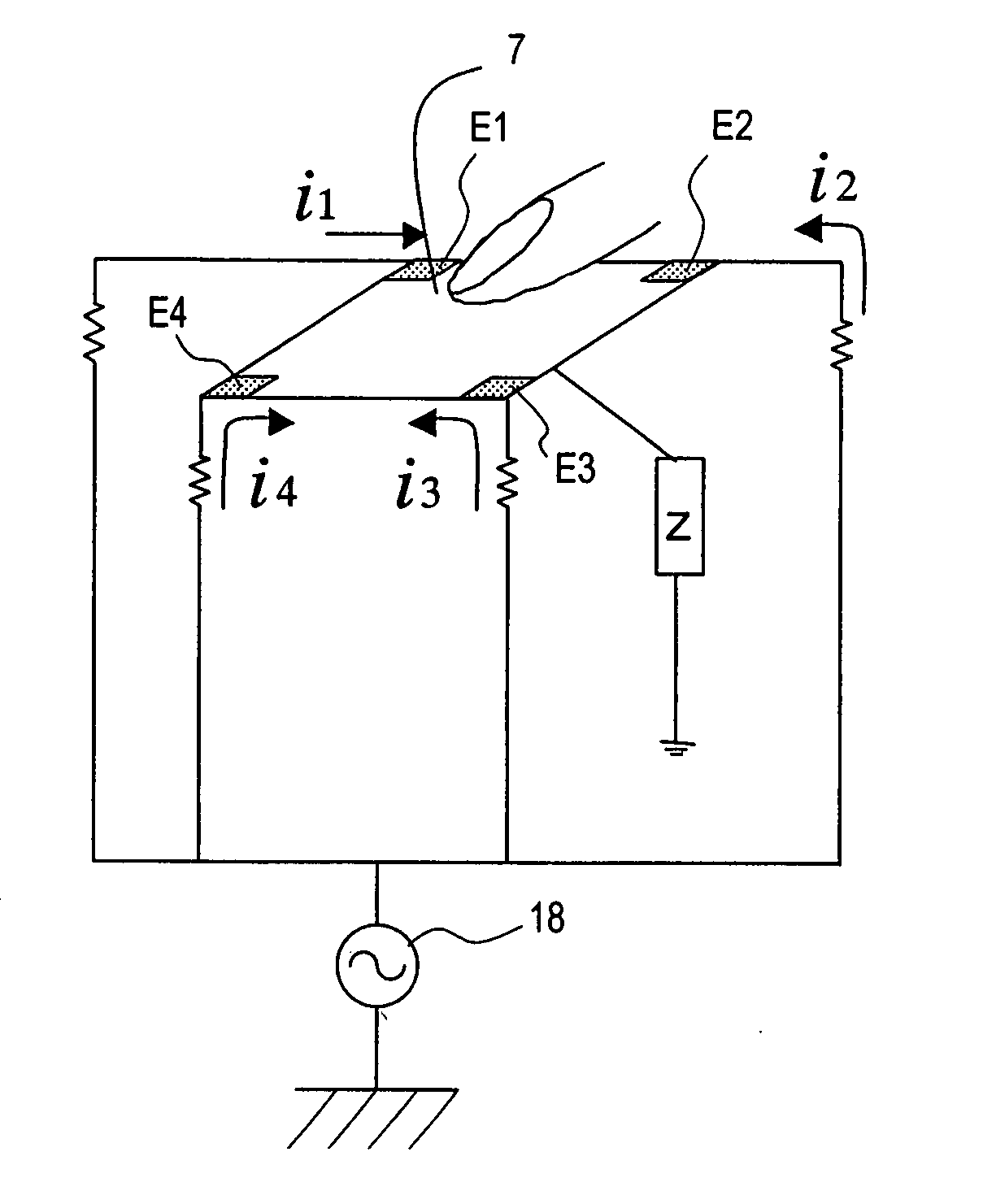
Patents
Literature
19403 results about "Electrical polarity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrical polarity is a term used throughout industries and fields that involve electricity. There are two types of poles: positive (+) and negative (−). This represents the electrical potential at the ends of a circuit. A battery has a positive terminal (+ pole) and a negative terminal (− pole). Interconnection of electrical device nearly always require correct polarity to be maintained. Correct polarity is essential for the operation of vacuum tube and semiconductor devices, many electric motors, electrochemical cells, electrical instruments, and other devices.
Semiconductor device in which zinc oxide is used as a semiconductor material and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS7501293B2Improve surface smoothnessHigh crystallinityTransistorLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having excellent crystallinity and excellent electric characteristics includes a ZnO thin film having excellent surface smoothness. ZnO-based thin films (an n-type contact layer, an n-type clad layer, an active layer, a p-type clad layer, and a p-type contact layer) primarily including ZnO are formed sequentially by an ECR sputtering method or other suitable method on a zinc-polar surface of a ZnO substrate. A transparent electrode and a p-side electrode are formed by an evaporation method or other suitable method on a surface of the p-type contact layer, and an n-side electrode is formed on an oxygen-polar surface of the ZnO substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
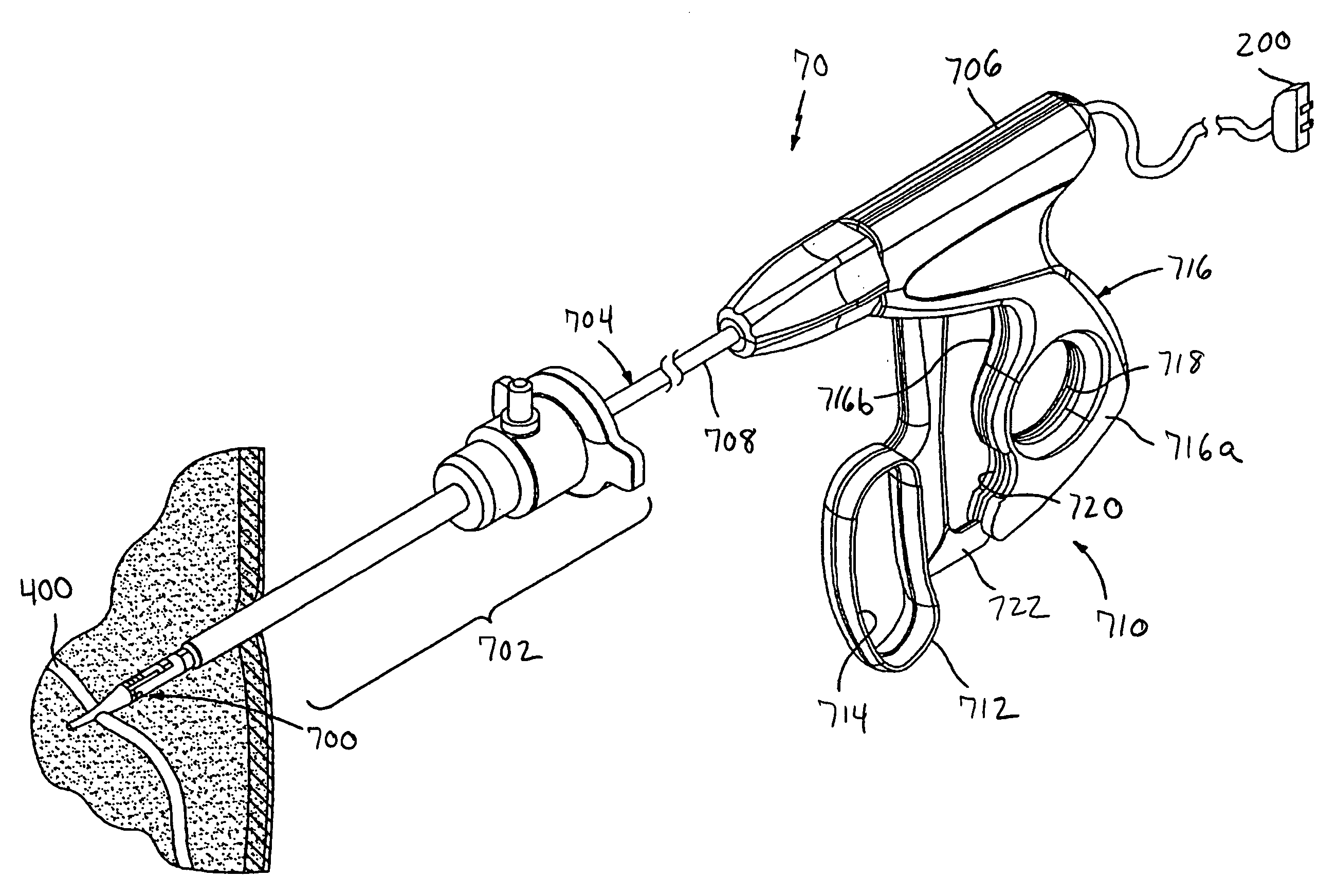
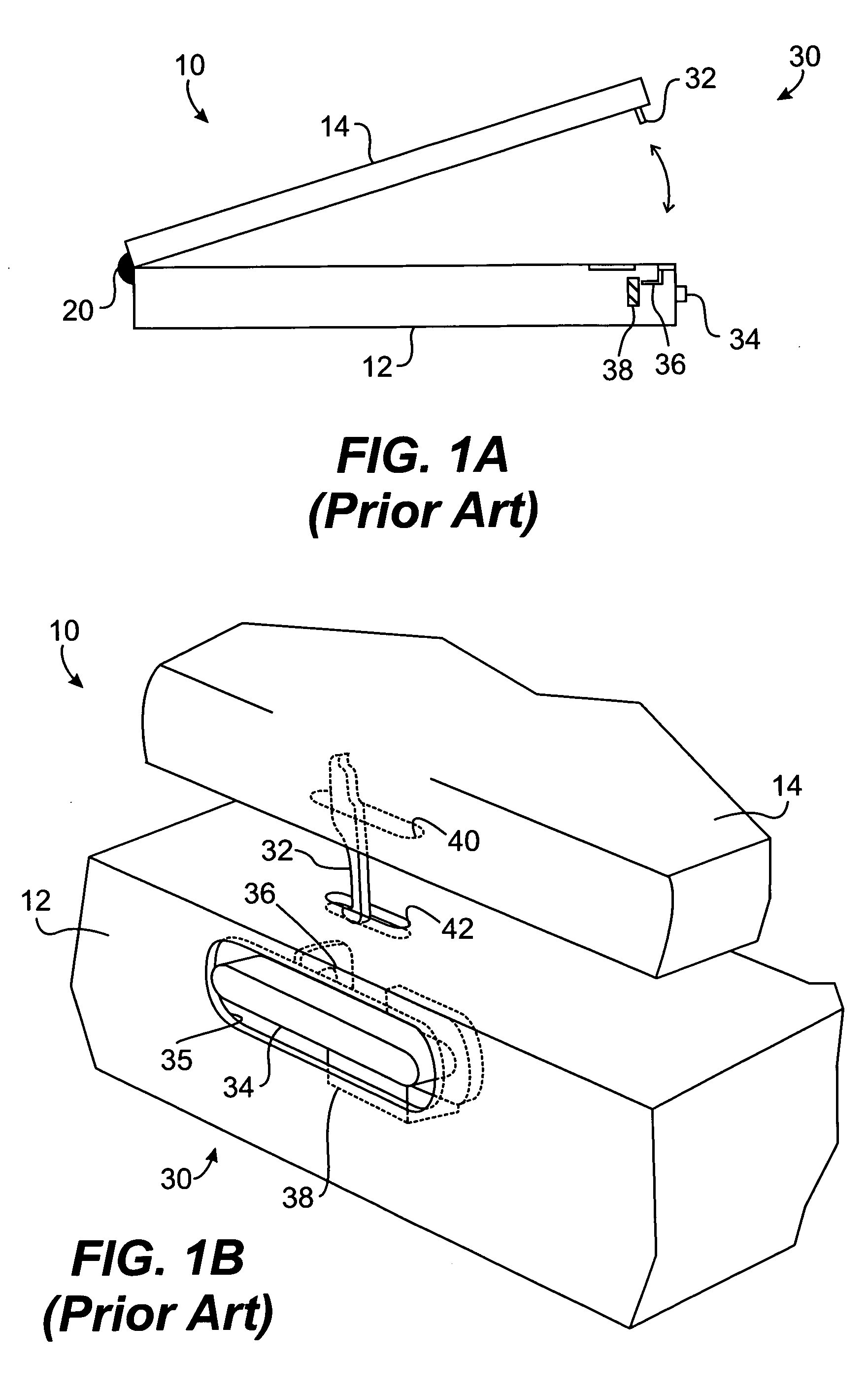
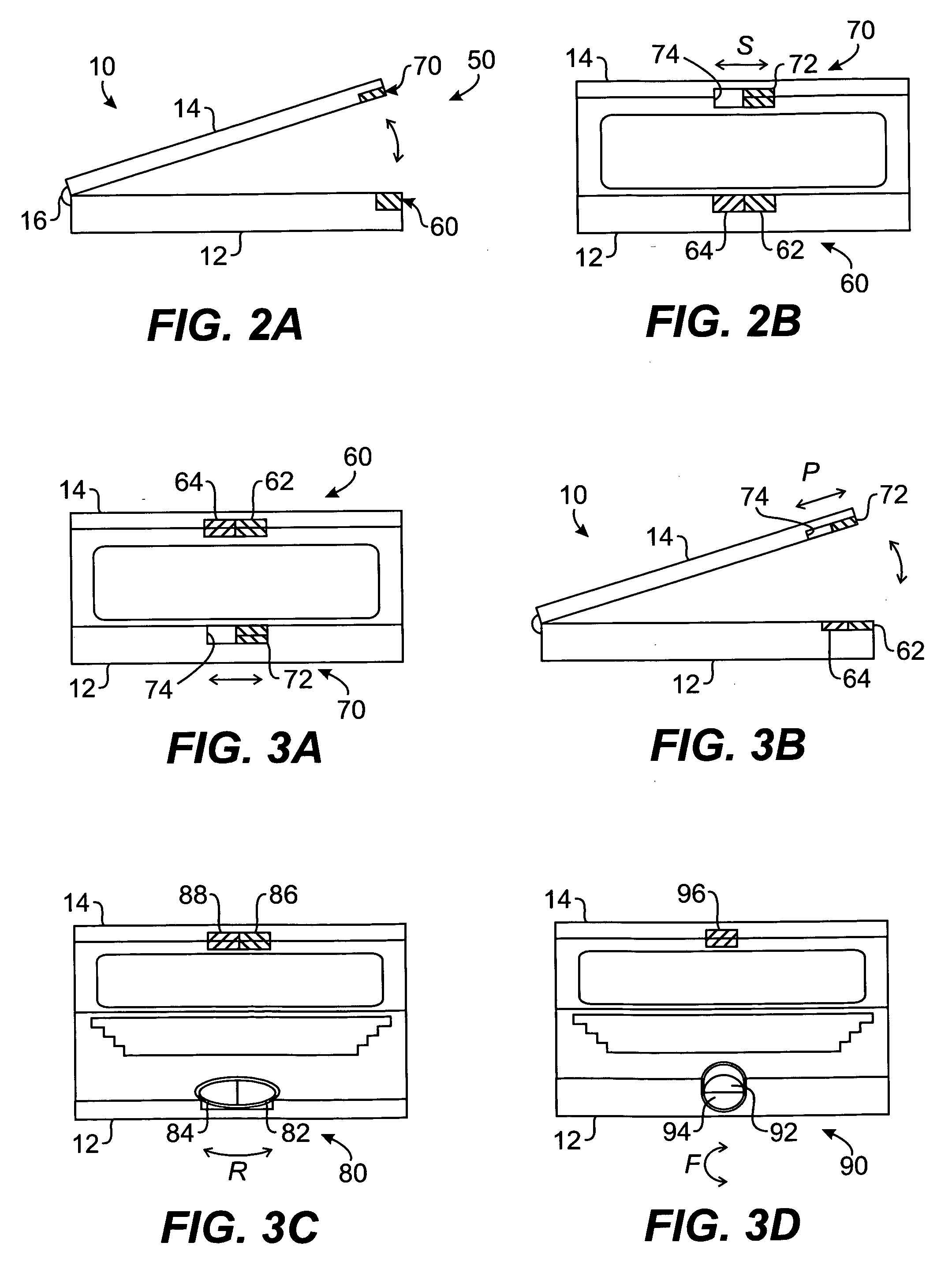
Bipolar surgical instruments having focused electrical fields
InactiveUS6514252B2Reduce capacityLower impedanceSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingElectricitySurgical device
A bipolar surgical device comprises a pair of actuable jaws. A first electrode member which optionally includes a line of electrically coupled tissue-penetrating elements is formed on one of the jaws, and a second electrode member which optionally includes a line of electrically coupled tissue-penetrating elements is formed on the same or the other jaw. The electrode members are laterally spaced-apart and arranged in a parallel, usually linear manner so that the lateral distance therebetween remains generally constant. In operation, tissue may be grasped between the jaws so that the electrode members contact and / or the tissue-penetrating elements enter into the tissue. By energizing the electrode members at opposite polarities using a high frequency energy source, tissue between the jaws will be heated, coagulated, and / or necrosed, while heating of tissue outside of the lines will be minimized.
Owner:PERFECT SURGICAL TECHN
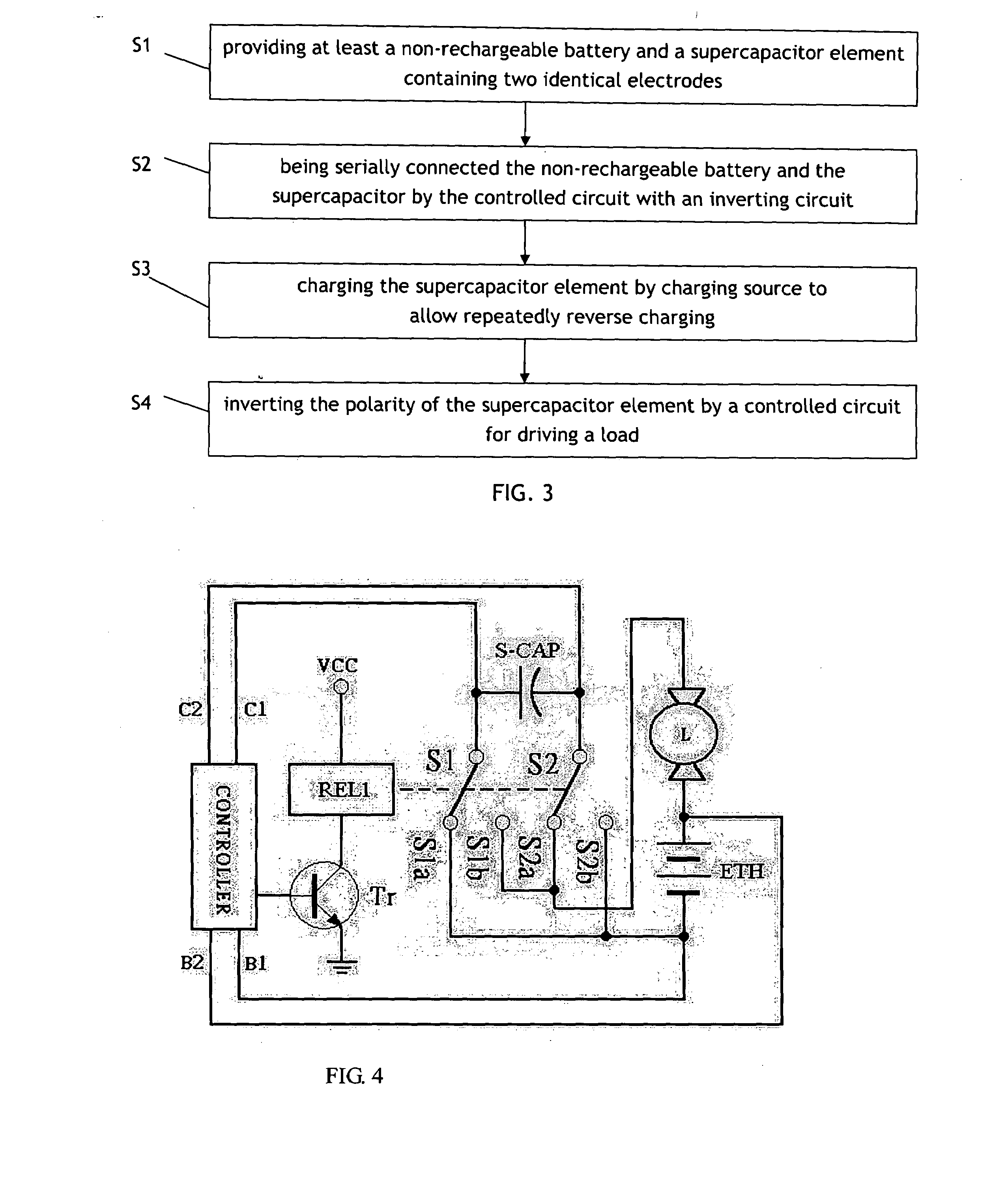
Battery energy reclamation apparatus and method thereby
InactiveUS20080129253A1Extended use timeLong workingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectrical polaritySupercapacitor
An energy-reclamation apparatus of the present invention including at least a supercapacitor element connected with a charging source and a controlled circuit. After the supercapacitor element is charged to the potential of the charging source, the supercapacitor element and the charging source will work in series to conduct a repetitive polarity reversal of the supercapacitor element through a controlled circuit. As the supercapacitor element discharges, it is reversely charged concurrently. In other words, while the voltage of the supercapacitor element is decreasing on the side, a negative potential is complementarily developing on the other side. By repeatedly reversing the polarity of the supercapacitor element, more energy from the serially connected charging source can be reclaimed and reused.
Owner:GAINIA INTELLECTUAL ASSET SERVICES
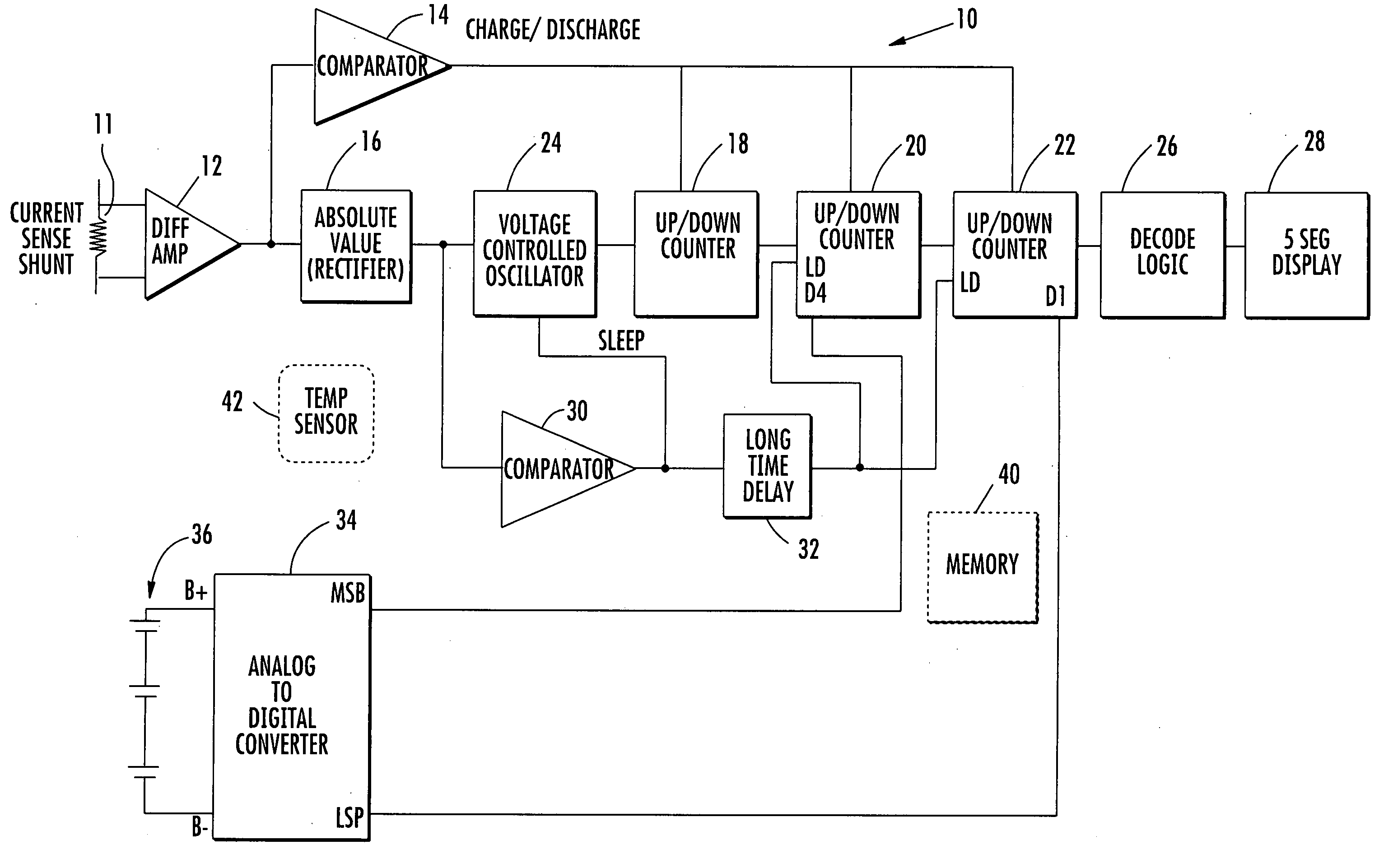
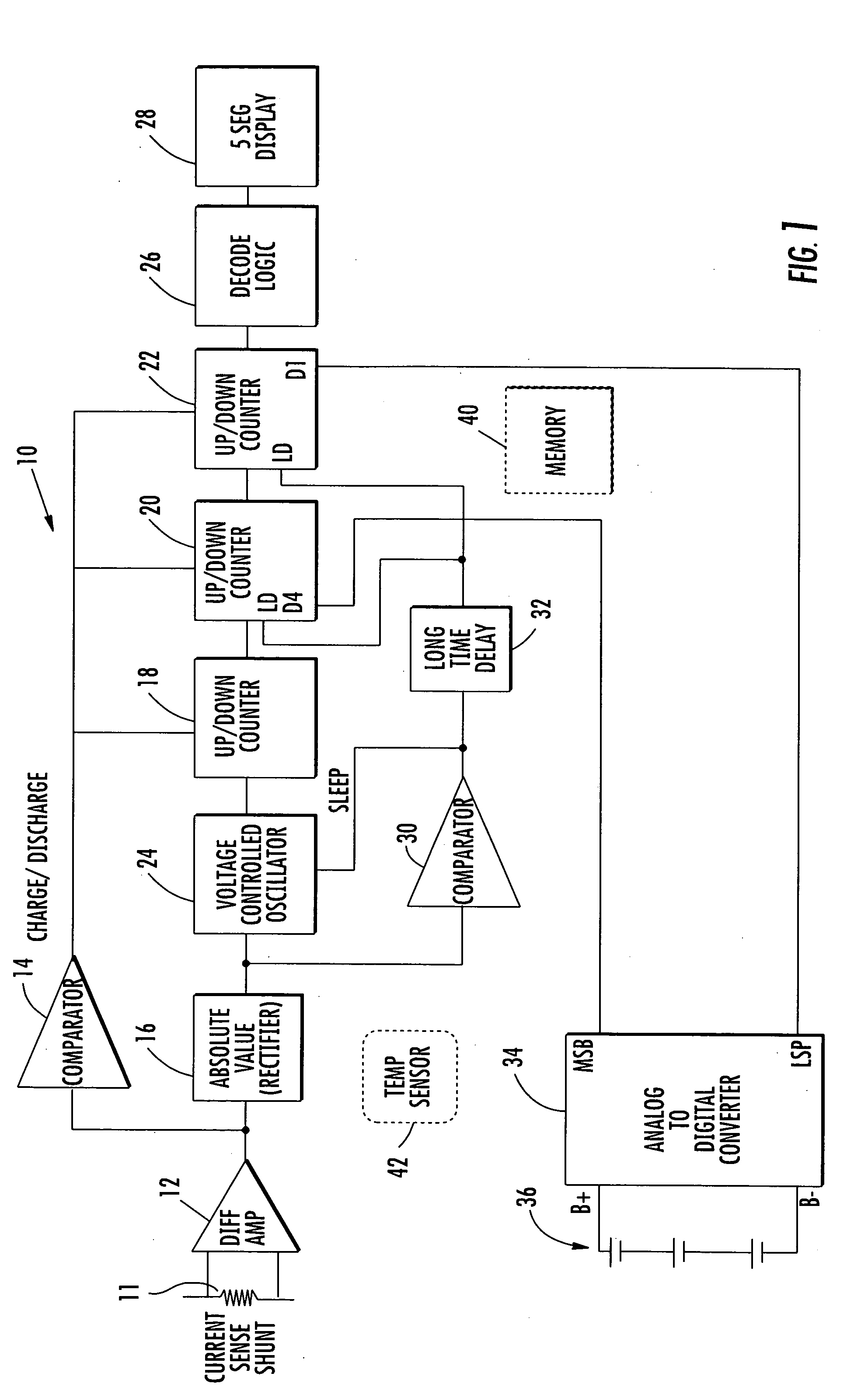
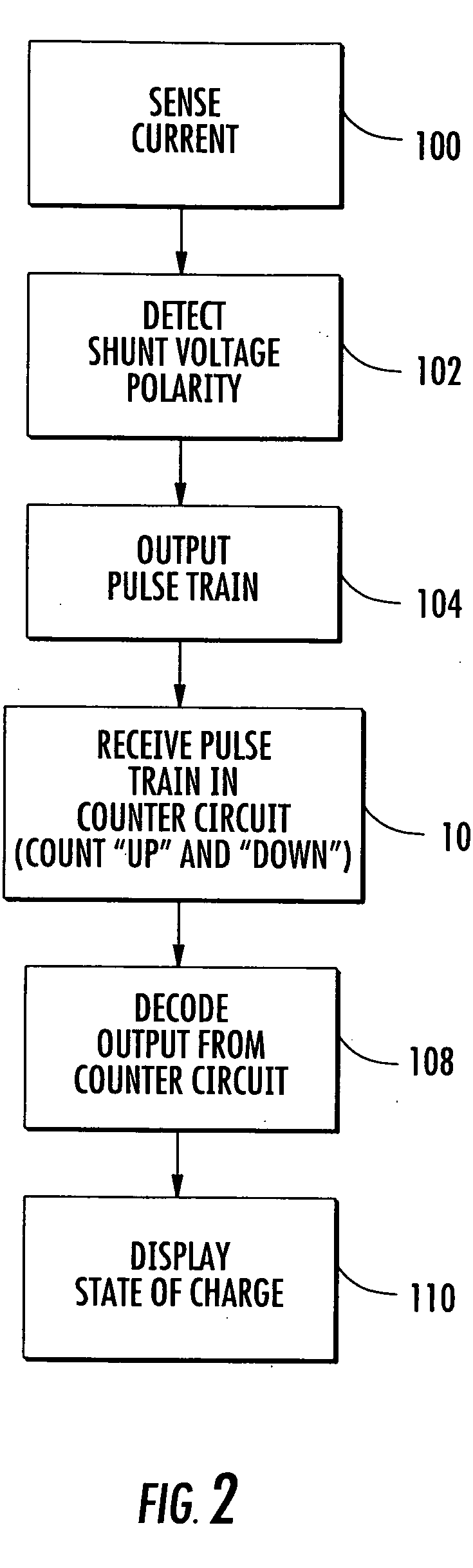
State of charge indicator for battery
InactiveUS20060097699A1Circuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitBattery state of chargeBipolar voltage
A state of charge indicator includes a current sensing circuit for sensing and converting charge or discharge current of a battery into a bipolar voltage. A counter circuit counts battery charge. A charge / discharge circuit is operatively connected to the current sensing and counter circuits and detects the voltage polarity from the current sensing circuit and sets the counter circuit to a count mode with an up or down count for a respective charge or discharge. A reset circuit is operative with the current sensing circuit, counter circuit and charge / discharge circuit for resetting the counter circuit to an actual state-of-charge of the battery after delay when the battery is idle representative of a battery open circuit voltage.
Owner:MATHEWS ASSOCS
Programmable metallization cell structure and method of making same
InactiveUS6084796ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A programmable metallization cell ("PMC") comprises a fast ion conductor such as a chalcogenide-metal ion and a plurality of electrodes (e.g., an anode and a cathode) disposed at the surface of the fast ion conductor and spaced a set distance apart from each other. Preferably, the fast ion conductor comprises a chalcogenide with Group IB or Group IIB metals, the anode comprises silver, and the cathode comprises aluminum or other conductor. When a voltage is applied to the anode and the cathode, a non-volatile metal dendrite grows from the cathode along the surface of the fast ion conductor towards the anode. The growth rate of the dendrite is a function of the applied voltage and time. The growth of the dendrite may be stopped by removing the voltage and the dendrite may be retracted by reversing the voltage polarity at the anode and cathode. Changes in the length of the dendrite affect the resistance and capacitance of the PMC. The PMC may be incorporated into a variety of technologies such as memory devices, programmable resistor / capacitor devices, optical devices, sensors, and the like. Electrodes additional to the cathode and anode can be provided to serve as outputs or additional outputs of the devices in sensing electrical characteristics which are dependent upon the extent of the dendrite.
Owner:AXON TECH +1
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
InactiveUS20080024482A1Good effectReduce or eliminate edge ghostingCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceElectrical polarity
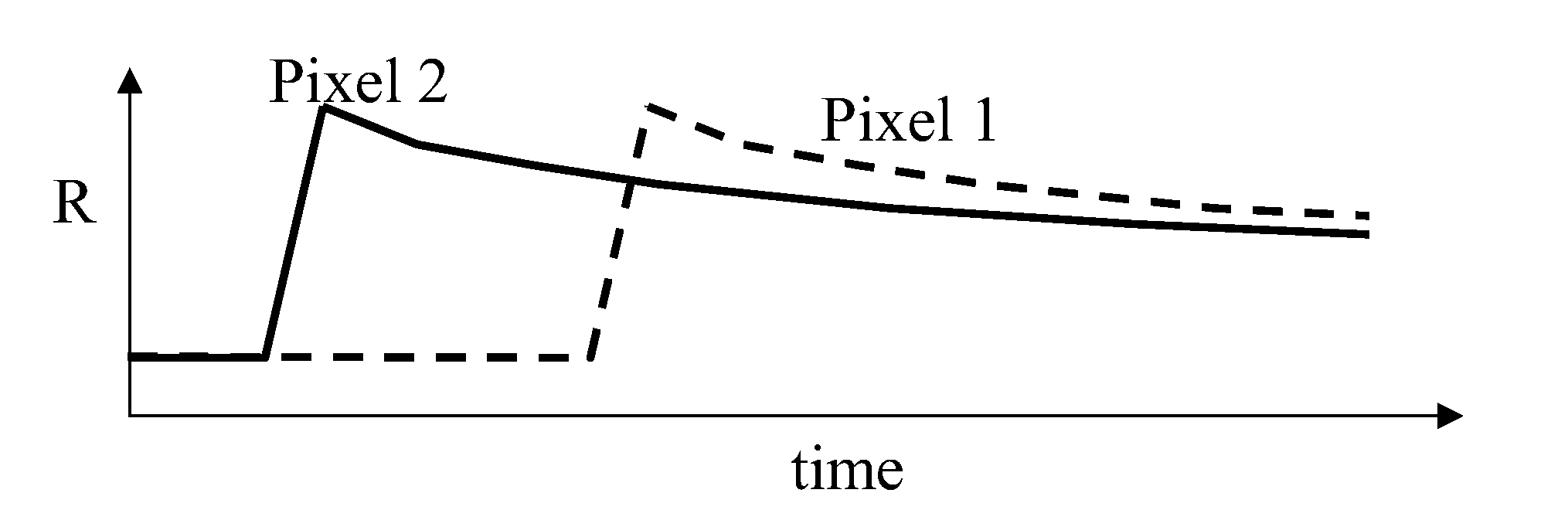
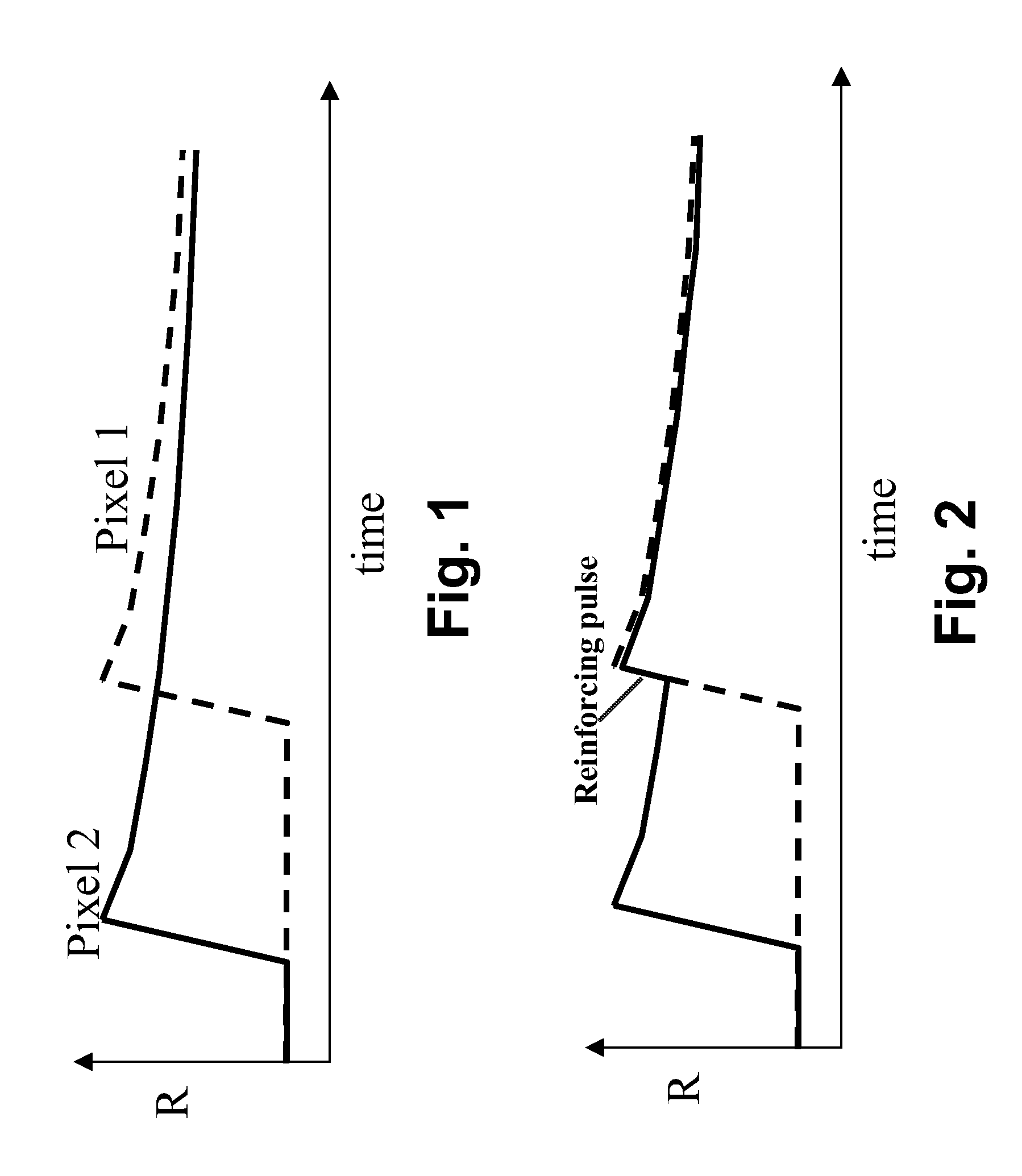
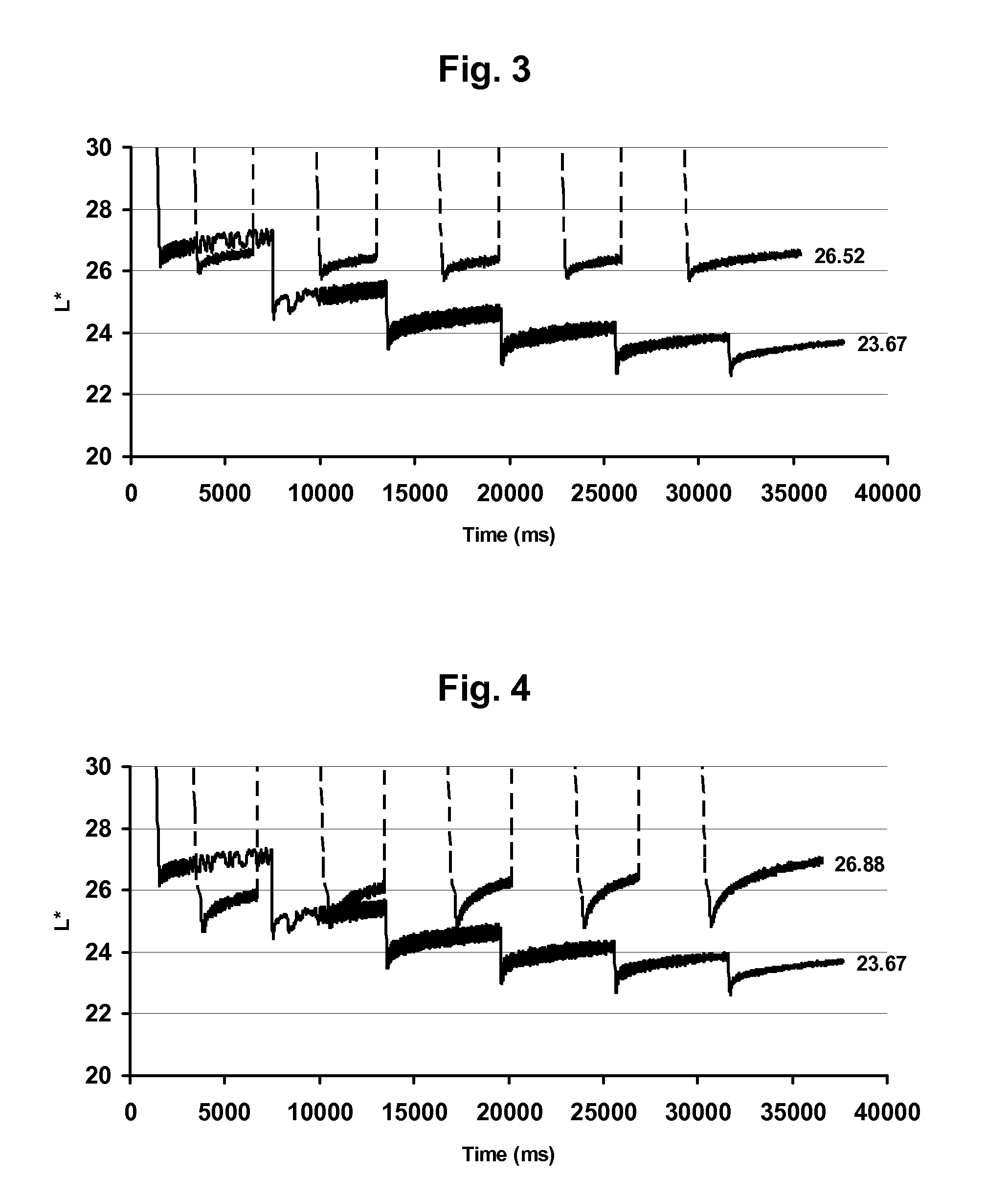
Methods are provided for of driving a bistable electro-optic display having at least first and second pixels separated by an inter-pixel gap. In one method, there is applied to the first pixel a drive pulse which drives the pixel to one extreme optical state, and there is applied to the second pixel, which is in this extreme optical state, a reinforcing pulse of the same polarity as the drive pulse. In a second method, a drive pulse applied to the first pixel drives that pixel away from one extreme optical state, and an inverse reinforcing pulse applied to the second pixel is of opposite polarity to the drive pulse. The drive methods reduce edge ghosting or blooming.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
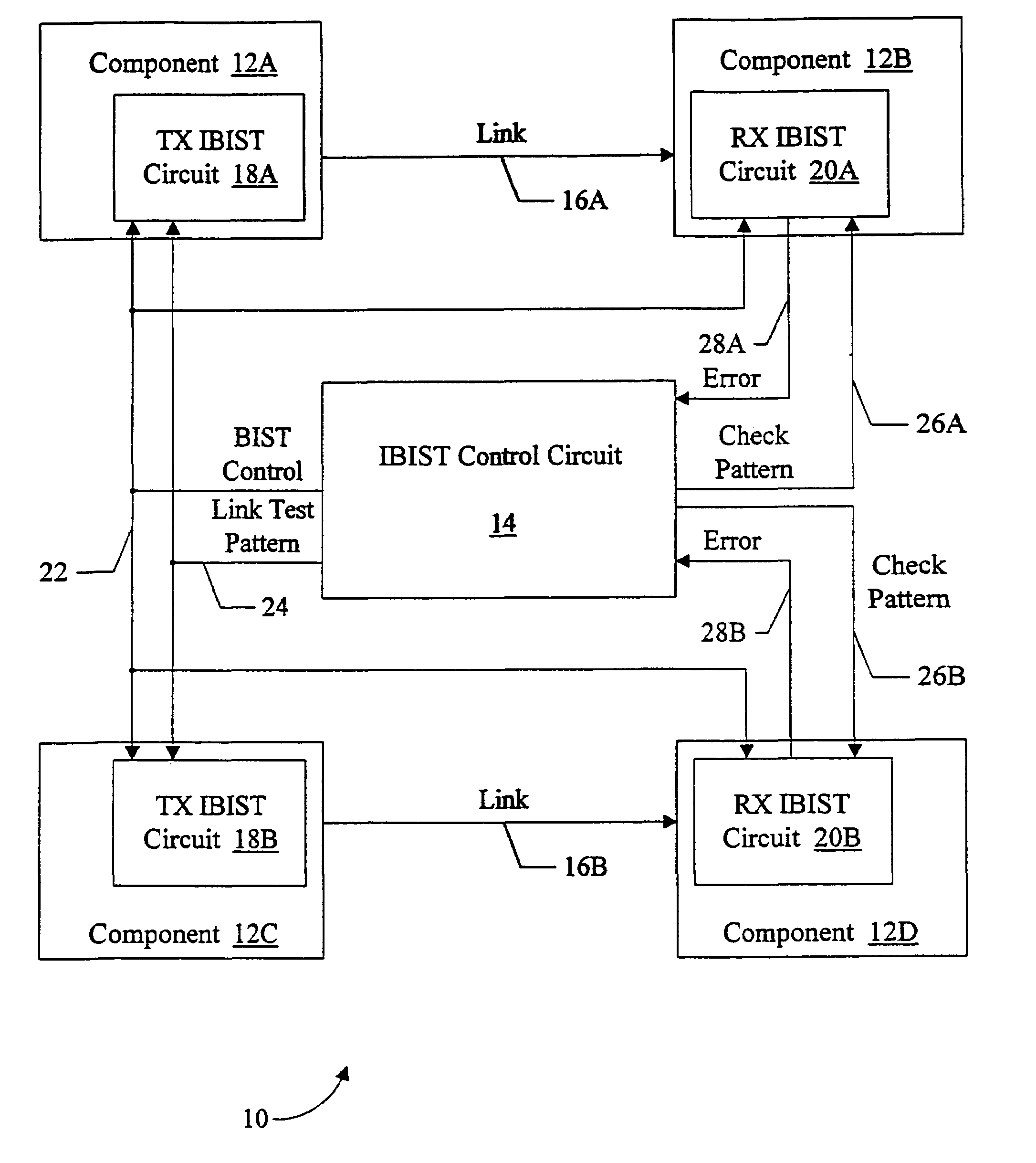
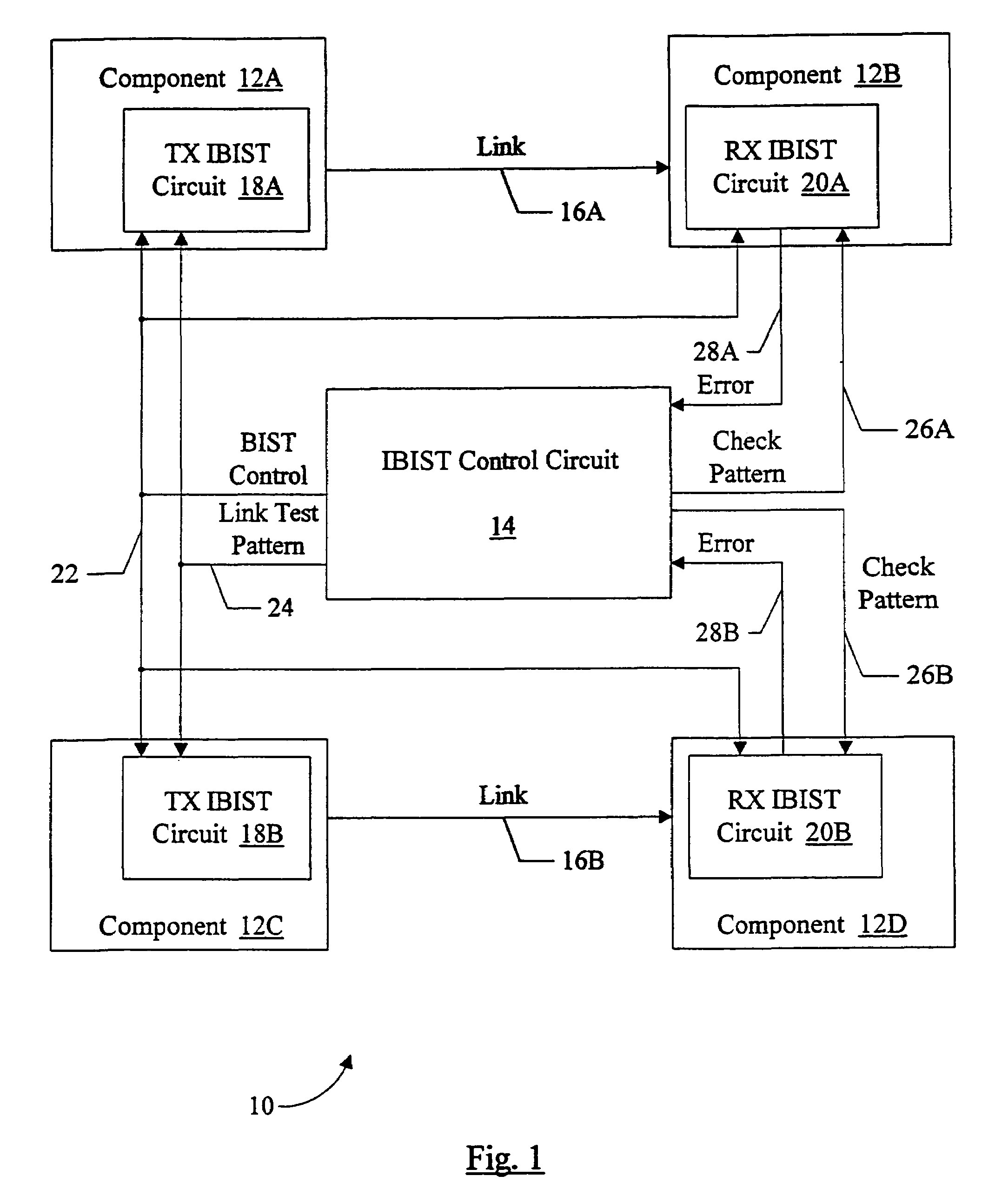
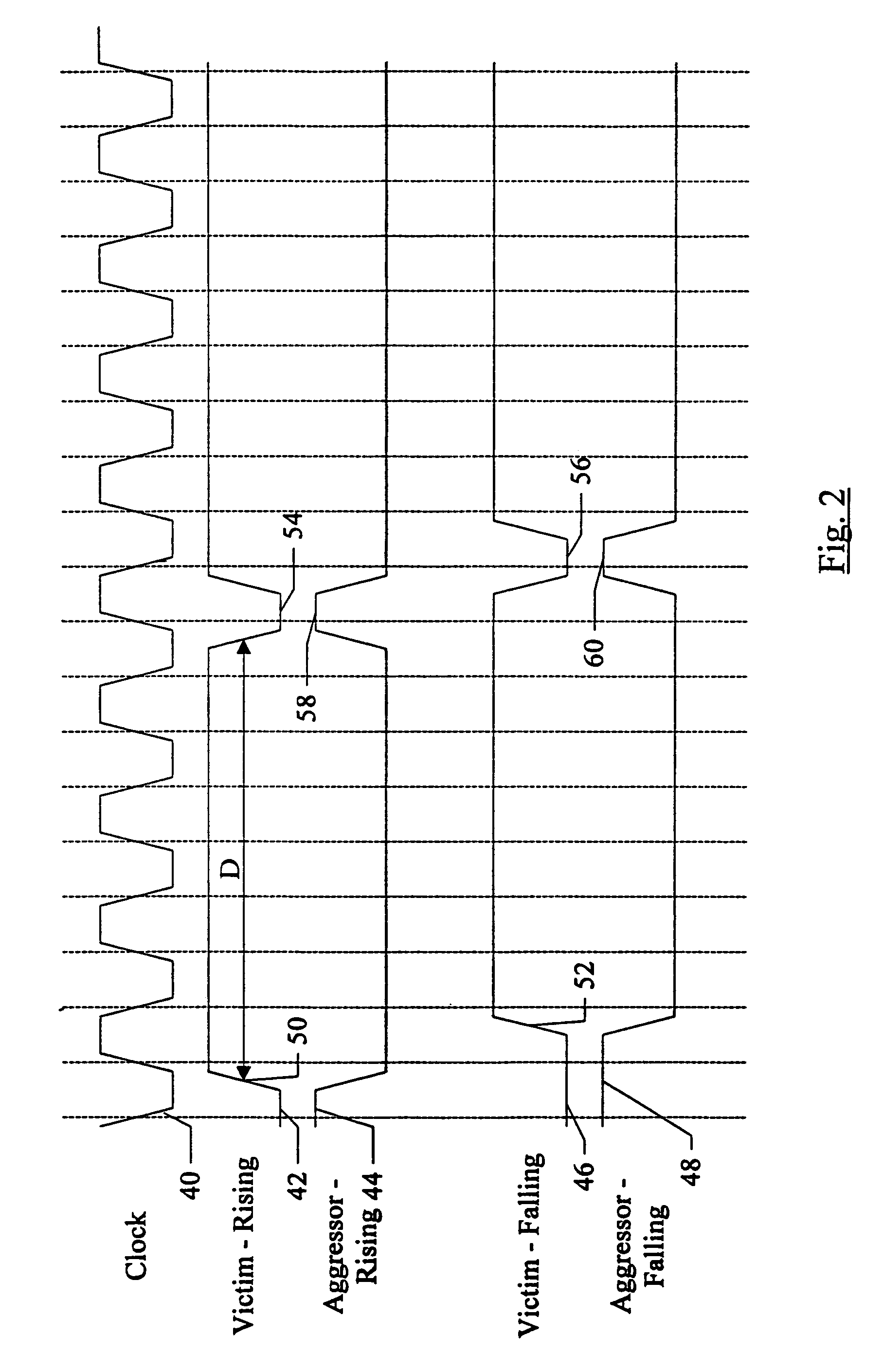
Source synchronous link integrity validation
InactiveUS6965648B1Flexible implementationCorrect operation testingElectronic circuit testingElectrical polaritySource-synchronous
A system may perform interconnect BIST (IBIST) testing on source synchronous links. The system may perform, at normal operating frequency, a source synchronous link test that tests a victim line on the source synchronous link using a transition weave pattern. The transition weave pattern causes interaction between a data transition on the victim line, previous transitions on the victim line, and transitions on the other lines of the link (the “aggressor” lines). The interaction caused may be: (i) a first crossing pulse on the victim line; (ii) a second crossing pulse of the opposite polarity on each aggressor line concurrent with the first crossing pulse on the victim line; and (iii) a reflection in the opposite direction of the first transition of the first crossing pulse, wherein the reflection results from a previous transition on the victim line.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
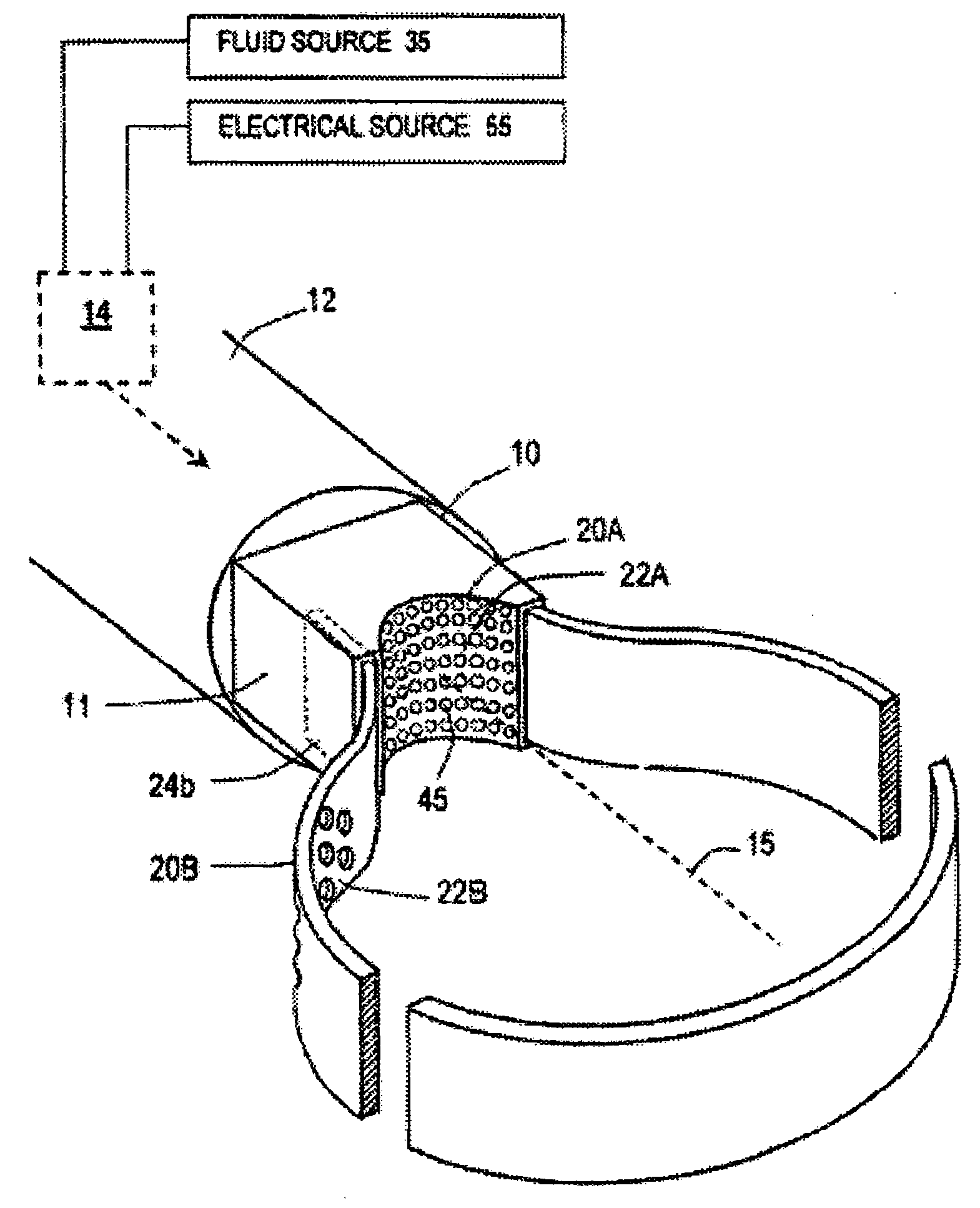
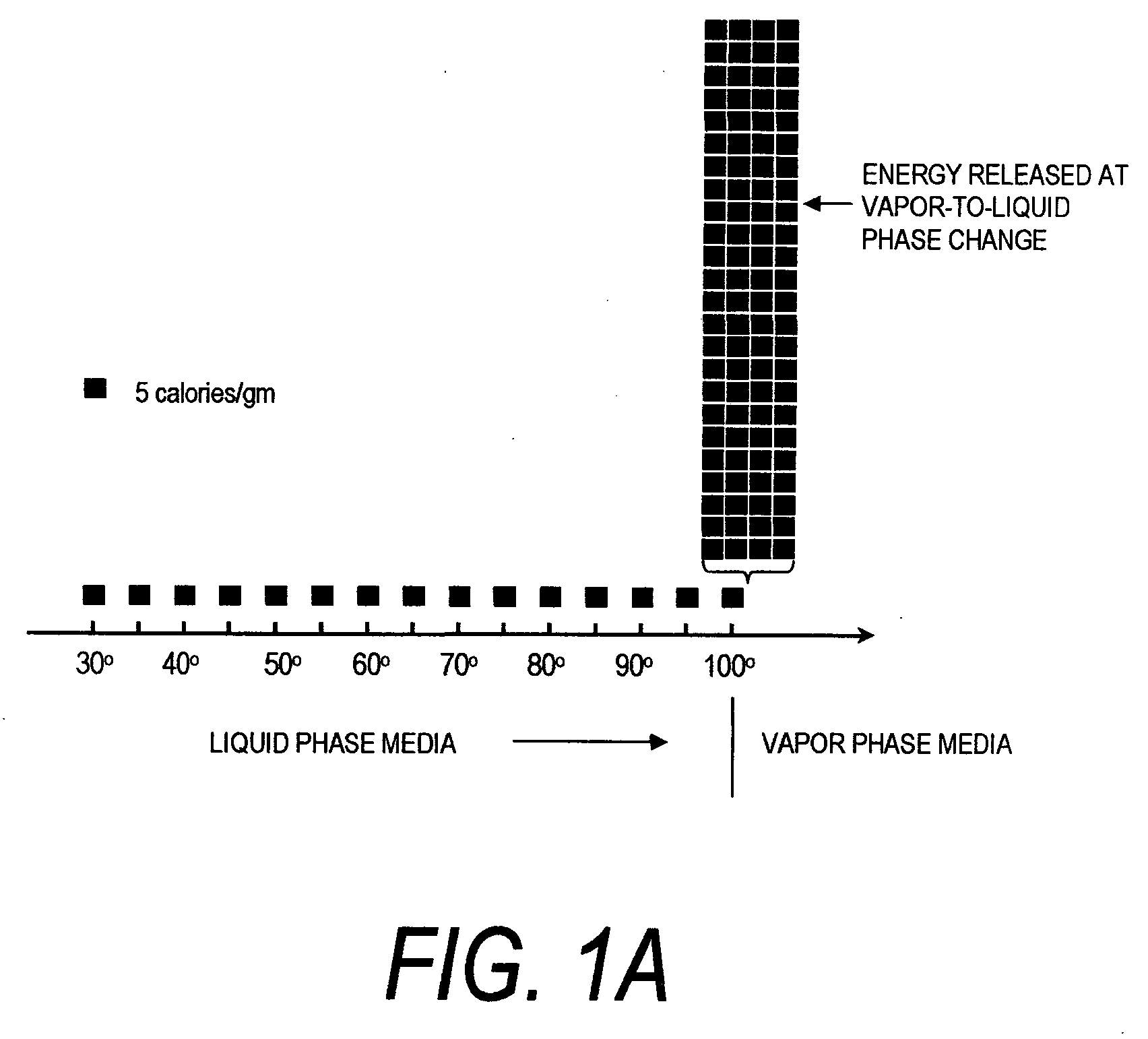
Medical instrument and method of use
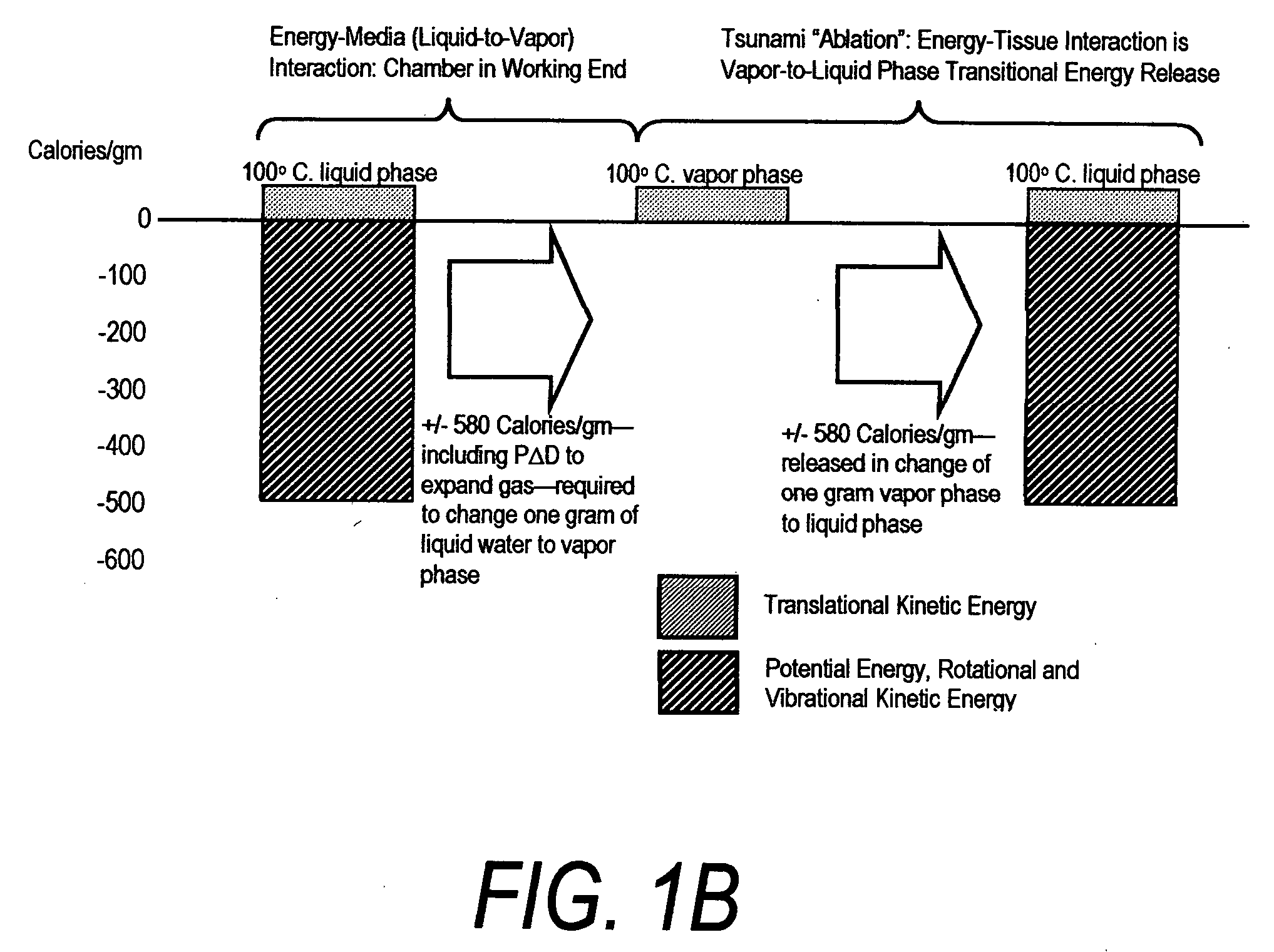
ActiveUS20060224154A1Prevents desiccationPrevents escharSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingThermal energyGas phase
An instrument for thermally-mediated therapies in targeted tissue volumes or for volumetric removal of tissue. In one embodiment, the instrument has an interior chamber that includes a diffuser structure for diffusing a biocompatible conductive fluid that is introduced under high pressure. The interior chamber further includes surfaces of opposing polarity electrodes for vaporizing the small cross-section diffused fluid flows created within a diffuser structure. In one embodiment, the diffuser structure includes a negative temperature coefficient of resistance material between the opposing polarity surfaces. The NTCR structure can self-adjust the lengths of current paths between the opposing polarities to insure complete vaporization of the volume of flow of conductive fluid. The non-ionized vapor phase media is ejected from a working surface of the instrument and a controlled vapor-to-liquid phase change in an interface with tissue applies thermal energy substantially equal to the heat of vaporization to ablate tissue. In another embodiment, the instrument provides voltage means for converting the non-ionized vapor phase media into an ionized media or plasma for applying energy to body structure.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Device and method for communicating data signals through multiple power line conductors
InactiveUS7075414B2Electric signal transmission systemsWireless systems/telephoneElectrical conductorElectrical polarity
The present invention provides a device for providing communications through power lines comprised of multiple conductors by transmitting the data signals through a plurality of the conductors. One embodiment of the present invention may be comprised of a transmit circuit communicatively coupled to a first energized conductor for applying a first voltage signal representing the data to the first energized conductor; the transmit circuit being communicatively coupled to a second energized conductor for applying a second voltage signal representing the data to the second energized conductor; and wherein the second voltage signal is opposite in polarity to said first voltage signal.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
RF active compositions for use in adhesion, bonding and coating
A susceptor composition that can bond two or more layers or substrates to one another and that can be used to coat or cut a substrate. The susceptor composition is activated in the presence of radio frequency (RF) energy. In one embodiment, the susceptor composition of the present invention comprises a susceptor and a carrier. The carrier and susceptor are blended with one another and form a mixture, preferably a uniform mixture. The susceptor is present in an amount effective to allow the susceptor composition to be heated by RF energy. In a preferred embodiment, the susceptor also functions as an adhesive. The susceptor is an ionic or polar compound and acts as either a charge-carrying or an oscillating / vibrating component of the susceptor composition. The susceptor generates thermal energy in the presence of an RF electromagnetic or electrical field (hereafter RF field).
Owner:AMBRELL CORP
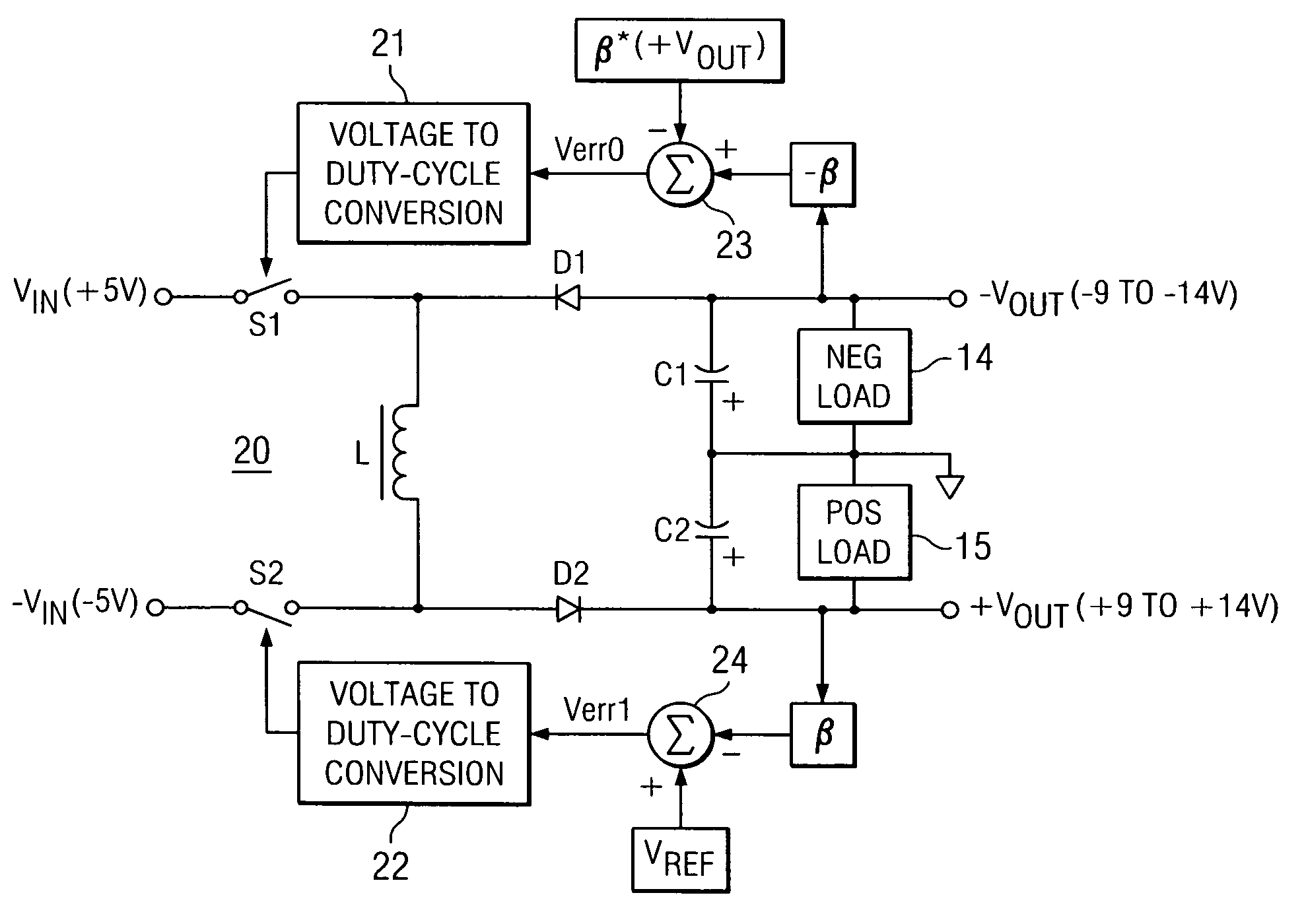
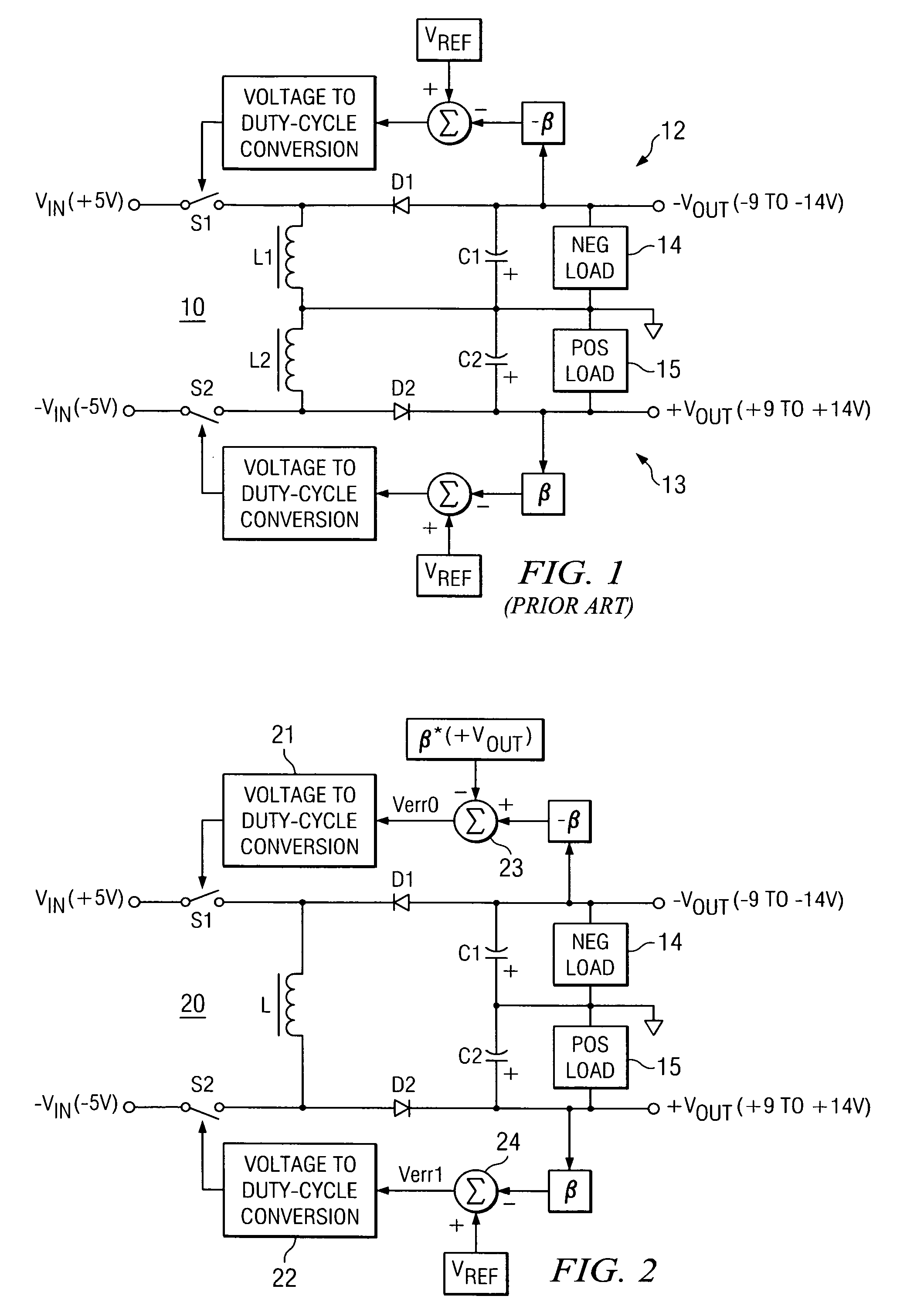
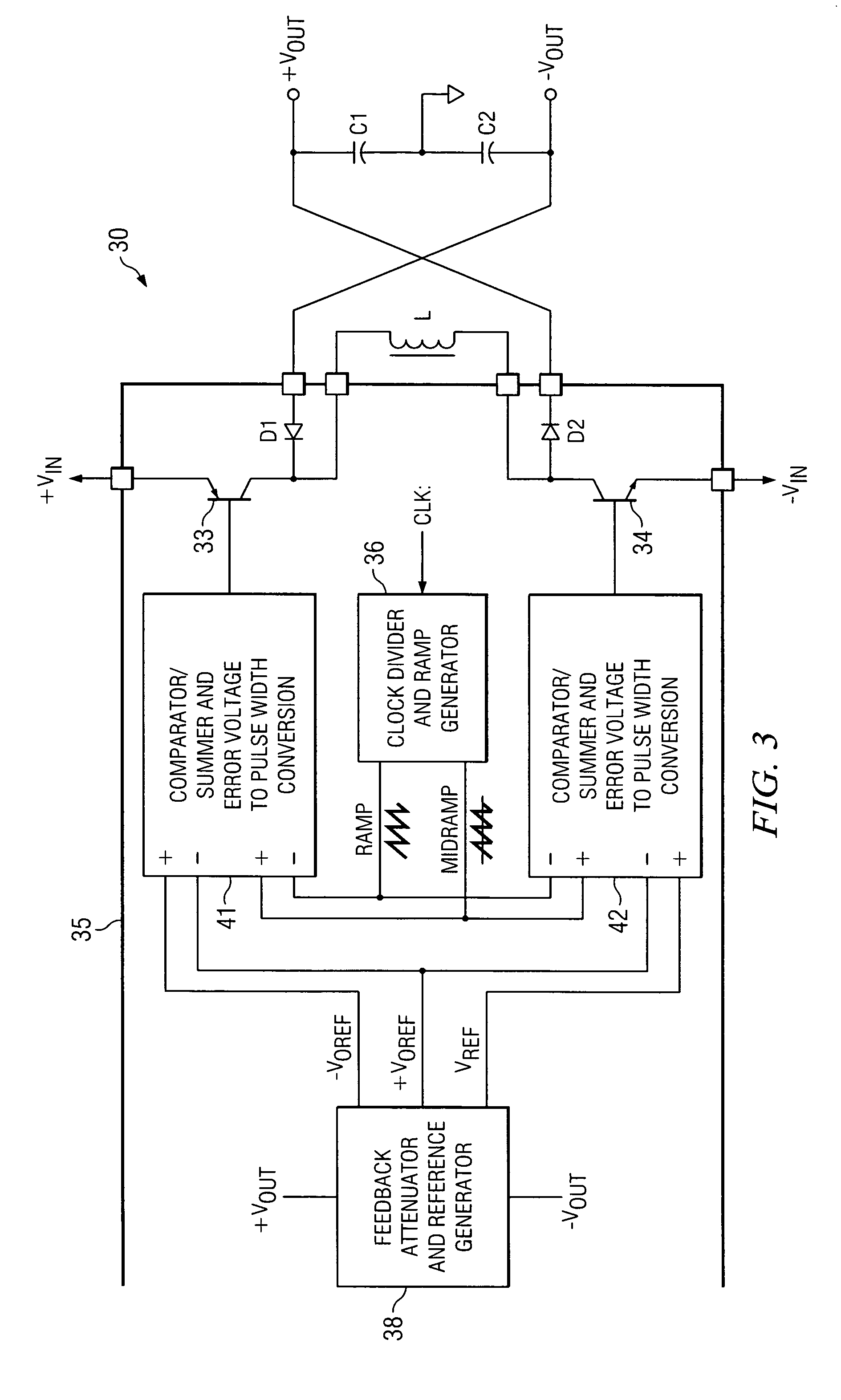
Dual buck-boost converter with single inductor
ActiveUS7276886B2Increase the pulse widthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitching cycleElectrical polarity
A dual output buck-boost power converter operates with a single inductor to achieve high efficiency with automatic or inherent load balancing. Switches associated with the opposite polarity outputs are driven based on feedback signals, with one feedback signal being a reference voltage and another feedback signal being related to an opposite polarity output. The opposite polarity feedback signal is provided to a comparator with a reversed polarity to achieve a simple balanced control that maintains polarity outputs. The power converter delivers power to each output with each switching cycle and uses a single inductor to achieve high efficiency performance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050045919A1Increase the areaFine granularitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A programmable semiconductor device has a switch element in an interconnection layer, wherein in at least one of the inside of a via, interconnecting a wire of a first interconnection layer and a wire of a second interconnection layer, a contact part of the via with the wire of the first interconnection layer and a contact part of the via with the wire of the second interconnection layer, there is provided a variable electrical conductivity member, such as a member of an electrolyte material. The via is used as a variable electrical conductivity type switch element or as a variable resistance device having a contact part with the wire of the first interconnection layer as a first terminal and having a contact part with the wire of the second interconnection layer as a second terminal. By varying the electrical conductivity of the switch element, the state of connection of the via with the wire of the first interconnection layer and the state of connection of the via with the wire of the second interconnection layer may be variably set to a shorted state, an open-circuited state or to an intermediate state A two-state switch element includes an ion conductor for conducting metal ions interposed between the first and second electrodes. The second electrode is formed of a material lower in reactivity than the first electrode. The electrical conductivity across the first and second electrodes is changed by the oxidation-reduction reaction of the metal ions. There are provided first and second transistors of opposite polarities, connected to the first electrode, and third and fourth transistors of opposite polarities, connected to the second electrode.
Owner:NEC CORP
Methods for driving electrophoretic displays
ActiveUS8174490B2Extension of timeReduce needStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisDisplay device
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Magnetic latching mechanism
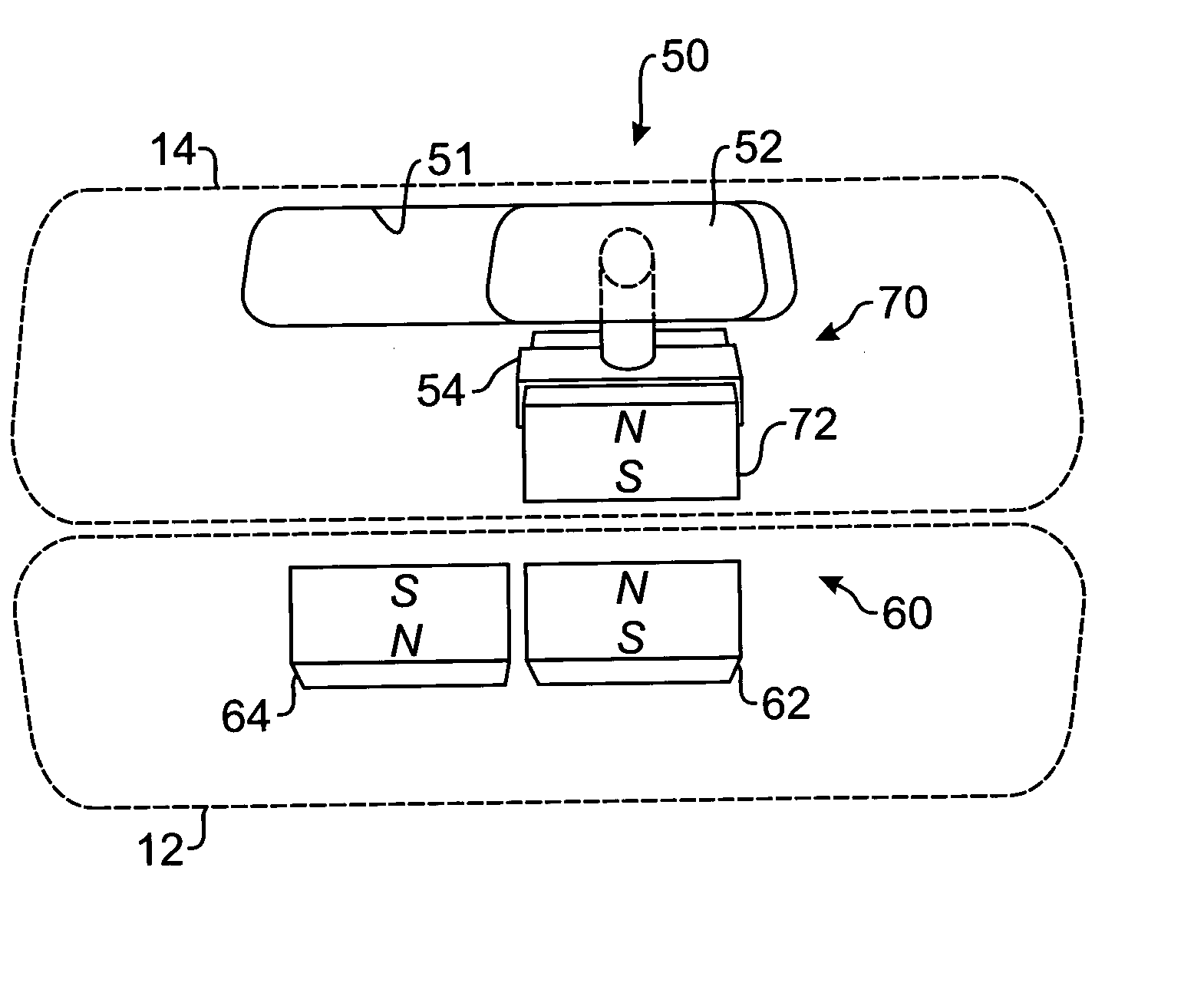
ActiveUS20070138806A1Easy to openWing fastenersDetails for portable computersElectrical polarityMagnetic poles
A magnetic latch for a display of a laptop computer is disclosed. The latch uses magnetic attraction to maintain the display closed and uses magnetic repelling forces to pop-up the display when opened. The latch includes one or more magnetic elements in the body of the laptop and at least one magnetic element in the display. When the display is closed, the magnet element in the display is positioned adjacent the magnet element in the body having an opposite polarity so that the magnet elements are attracted to one another. To pop-up the display, the user moves the magnetic element in the display so that it meets the magnetic pole in the body having the same polarity. When these meet, the repelling force between them causes the display to open slightly so that a user can then readily open the display.
Owner:APPLE INC
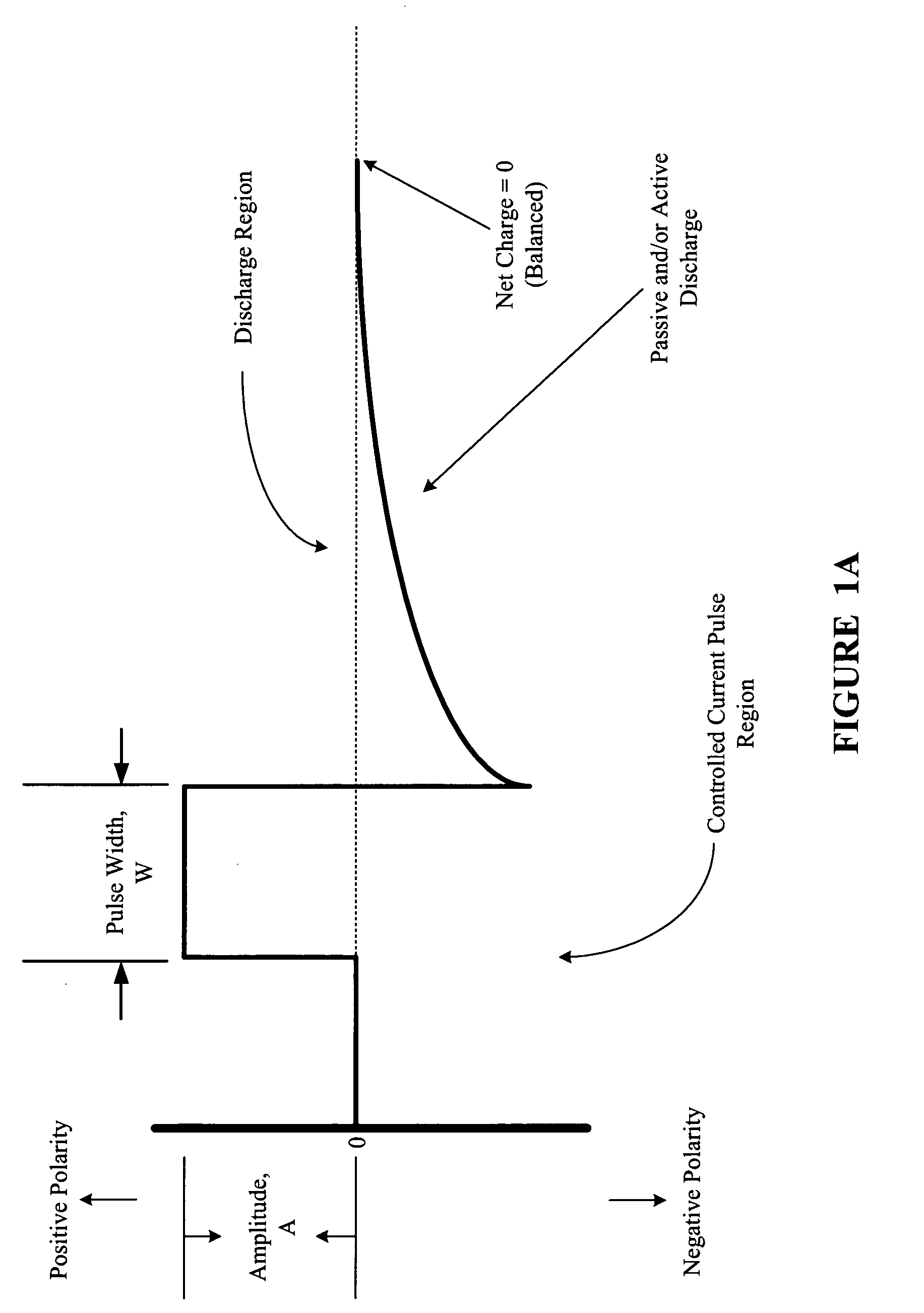
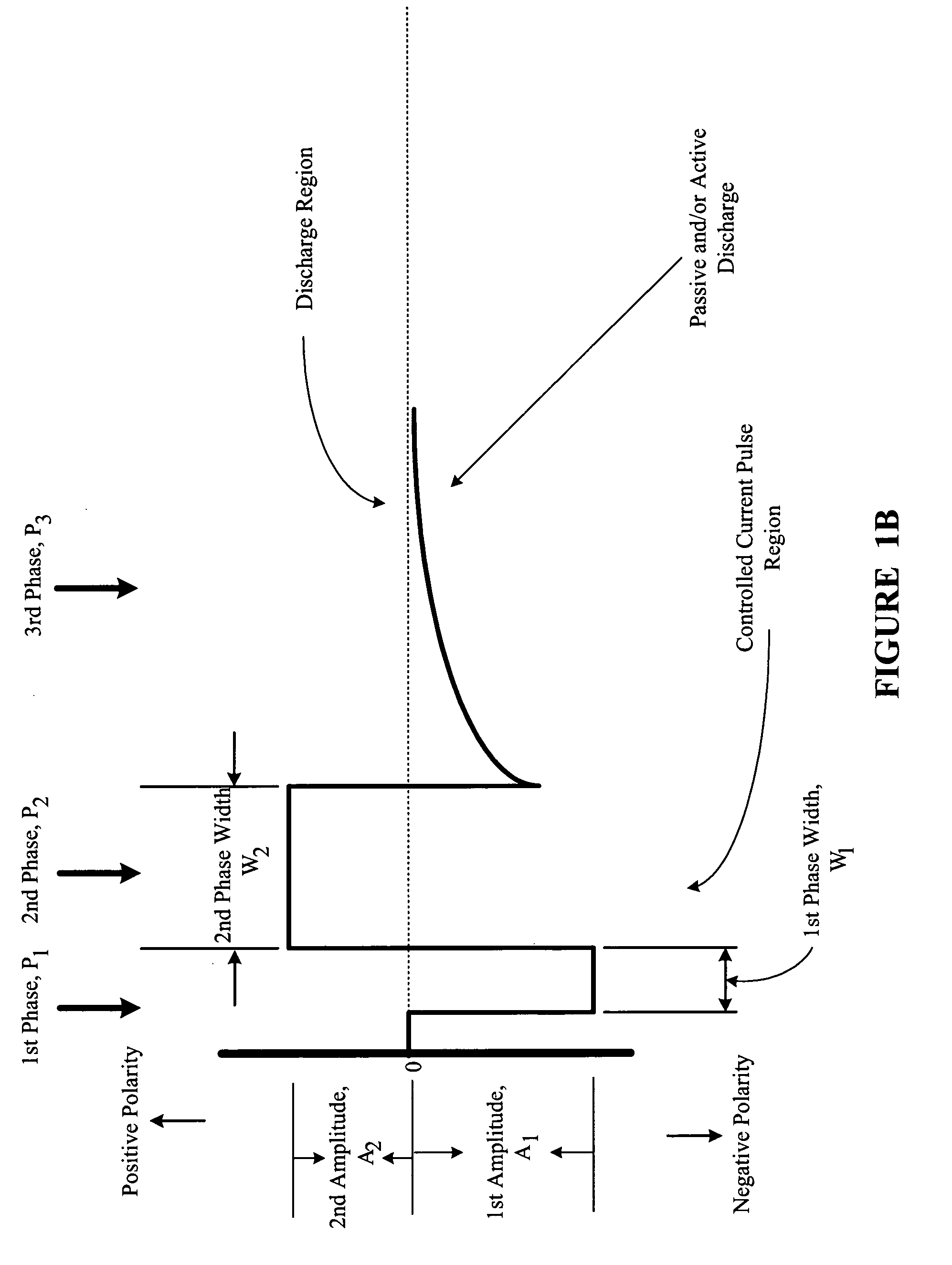
Multi-phasic signal for stimulation by an implantable device
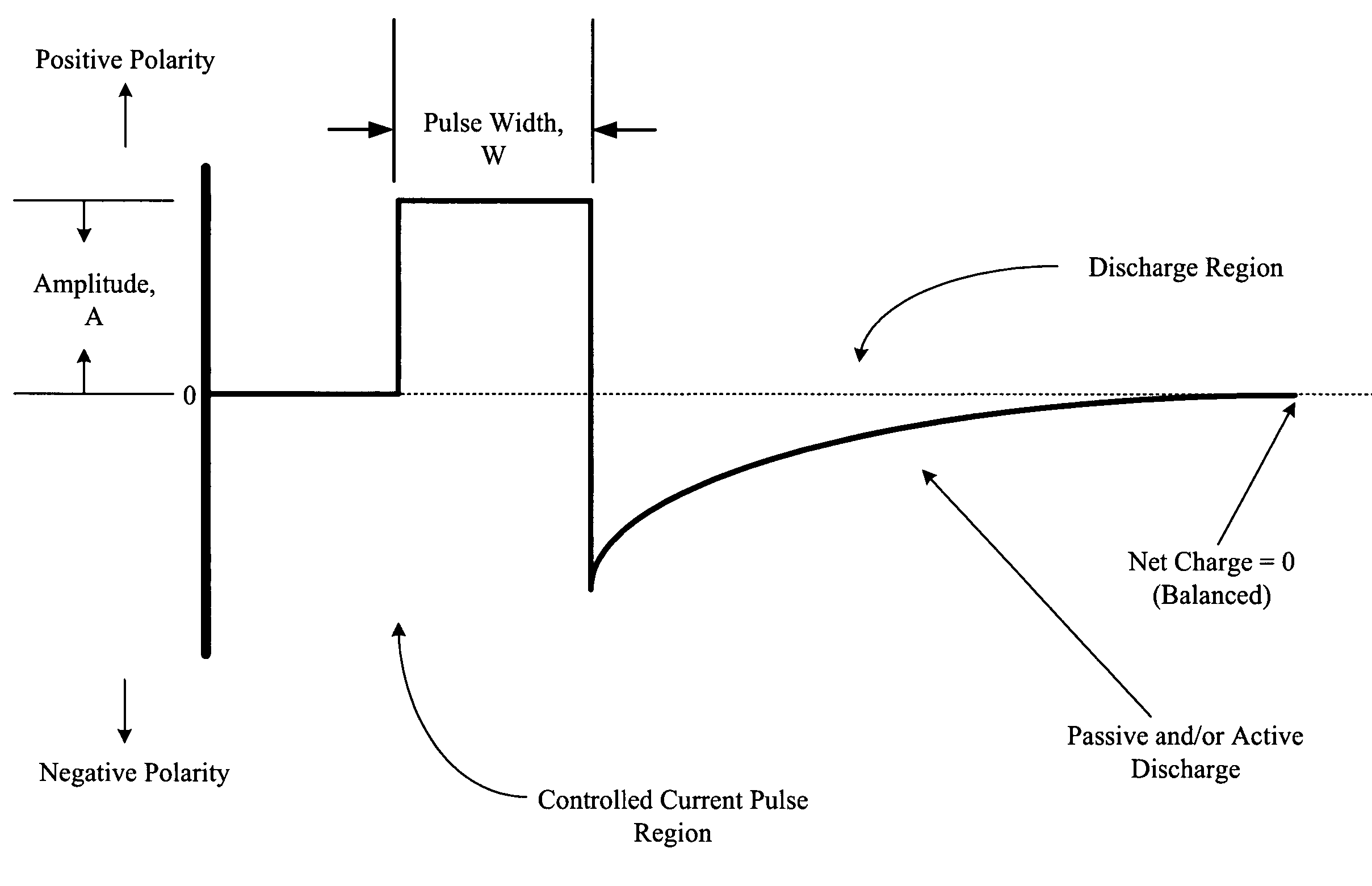
A method, system, and an apparatus for providing a multi-phasic stimulation signal for an implantable device are provided. An electrical pulse with a first characteristic that includes a first pulse width, a first pulse amplitude, a first pulse polarity, or a first pulse shape, is applied during a first time period to a portion of a vagus nerve using an implantable device. A controlled modification of the first characteristic of the electrical pulse is performed. The controlled modification is performed to provide a second characteristic for the electrical pulse during a second time period. The electrical pulse with the second characteristic is applied to the target portion of the vagus nerve.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
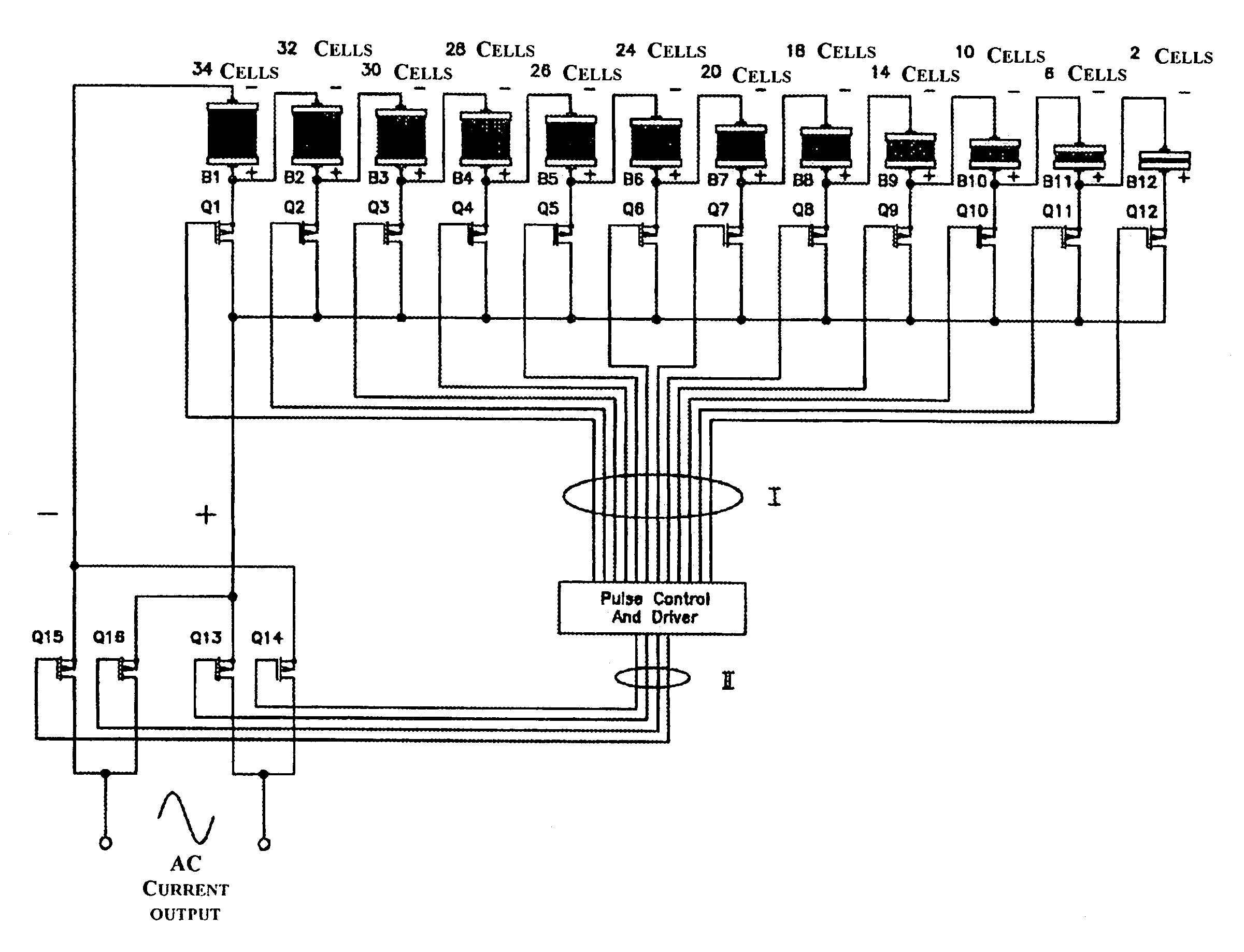
Transformerless static voltage inverter for battery systems
InactiveUS7046531B2Improve efficiencyReduce weightDc source parallel operationDc-ac conversion without reversalDc currentVoltage inverter
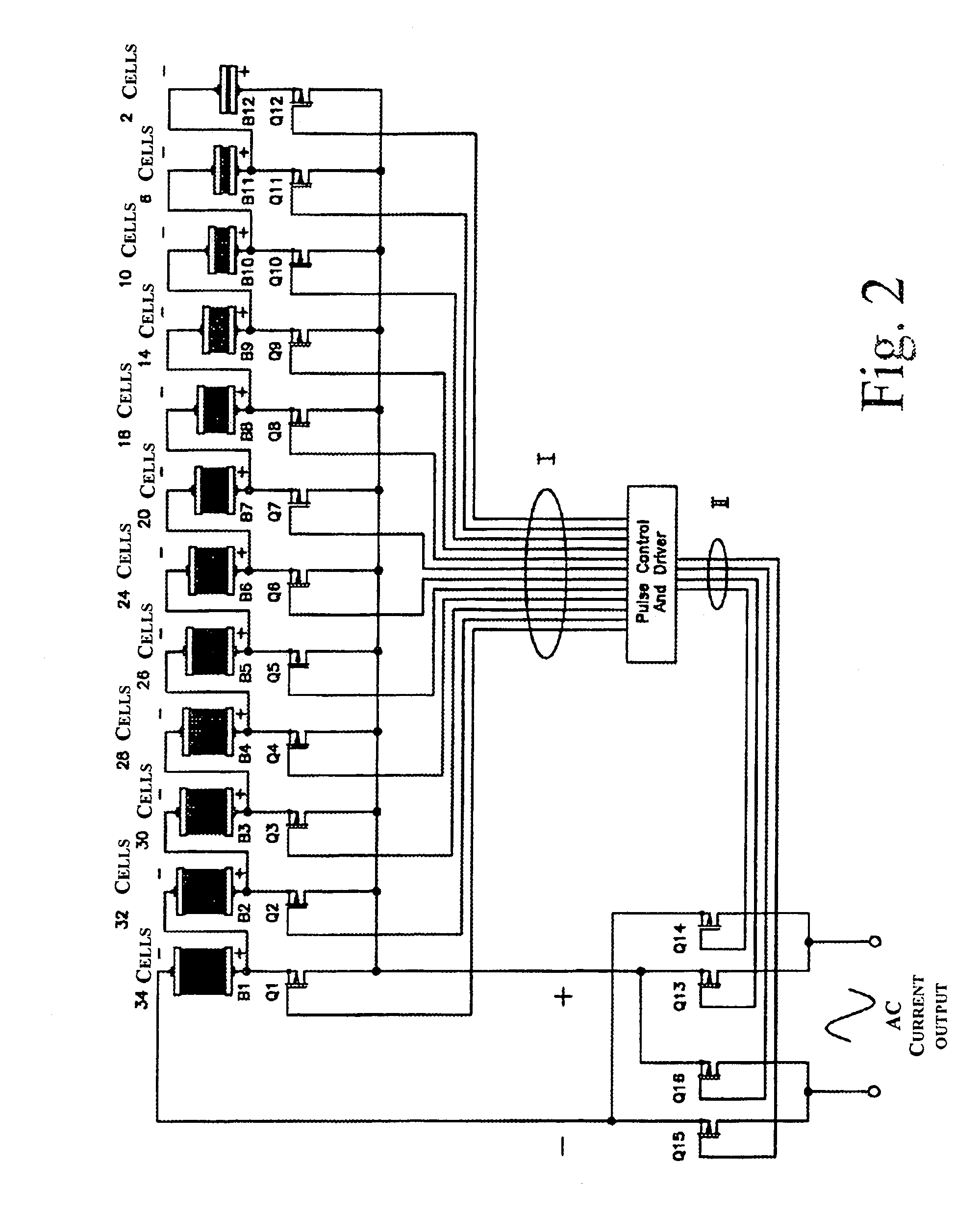
A static inverter for a battery of elementary, current sources or cells electrically in series and a number N of intermediate voltage taps along the chain of elementary DC current sources, wherein the number of elementary cells comprised between an intermediate tap and another intermediate tap adjacent to it or an end terminal of said chain is proportionate to the amplitude in the respective phase interval of a number N of discretization phases of the waveform of the AC voltage to be output in a quadrant; is implemented by arranging for: a number N of power switches each connecting a respective intermediate tap and a first end terminal of a first polarity of said chain of elementary cells in series to a common circuit node of said first polarity; an output bridge stage constituted by at least four power switches controlled in pairs for switching the current paths through the bridge stage, having a first pair of nodes coupled to said common circuit node of said first plurality and to the other end terminal of polarity opposite to said first polarity of said chain of elementary cells, respectively, and a second pair of nodes constituting an AC output; and a control circuit sequentially and cyclically turning on, in a continuous manner, one switch at the time of said N switches; each for a phase interval of 1 / (4N) times the period of said AC output, and alternately tuning on by pairs said four power switches of said output bridge stage at every half a period.
Owner:SQUIRREL HLDG
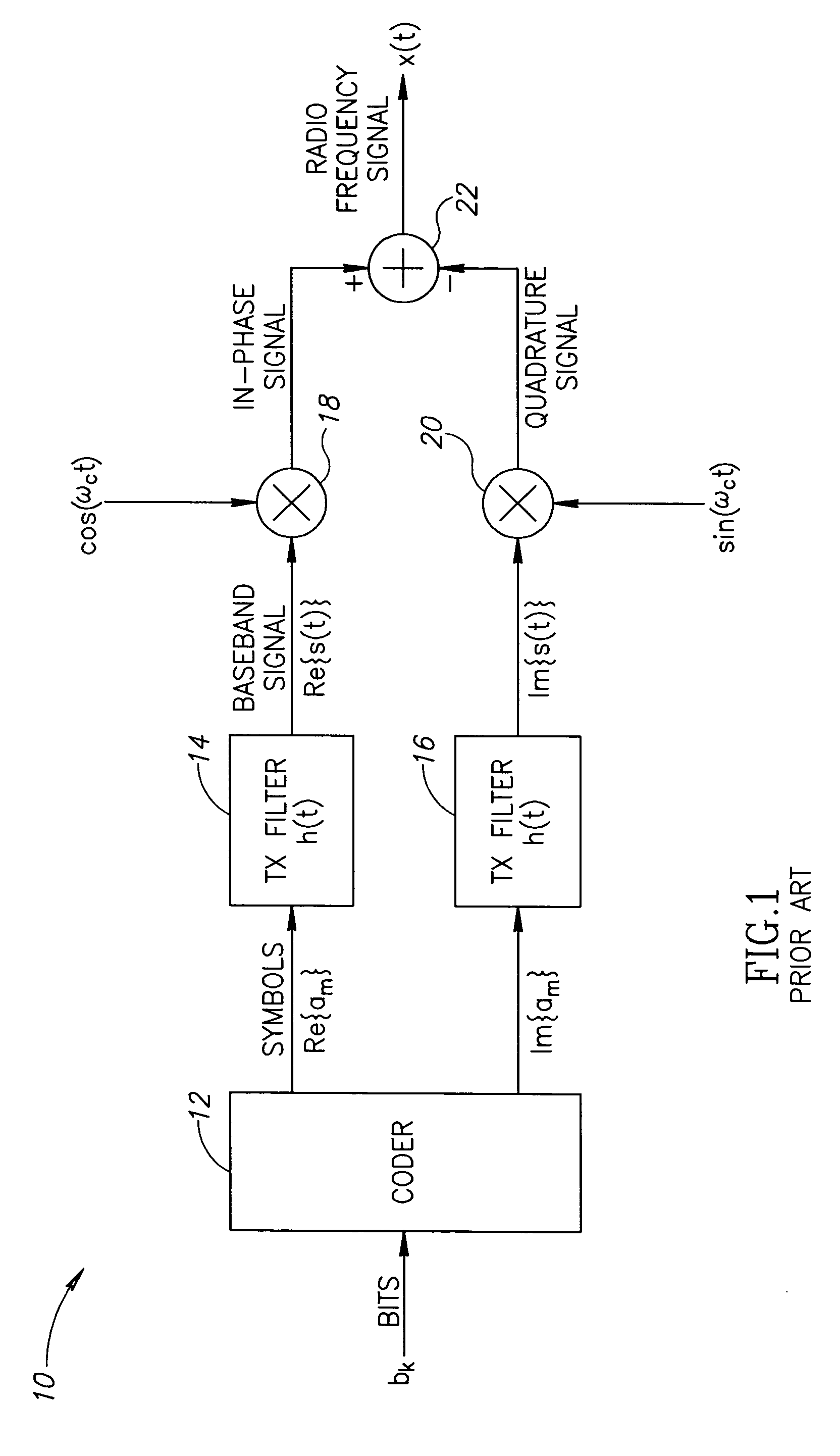
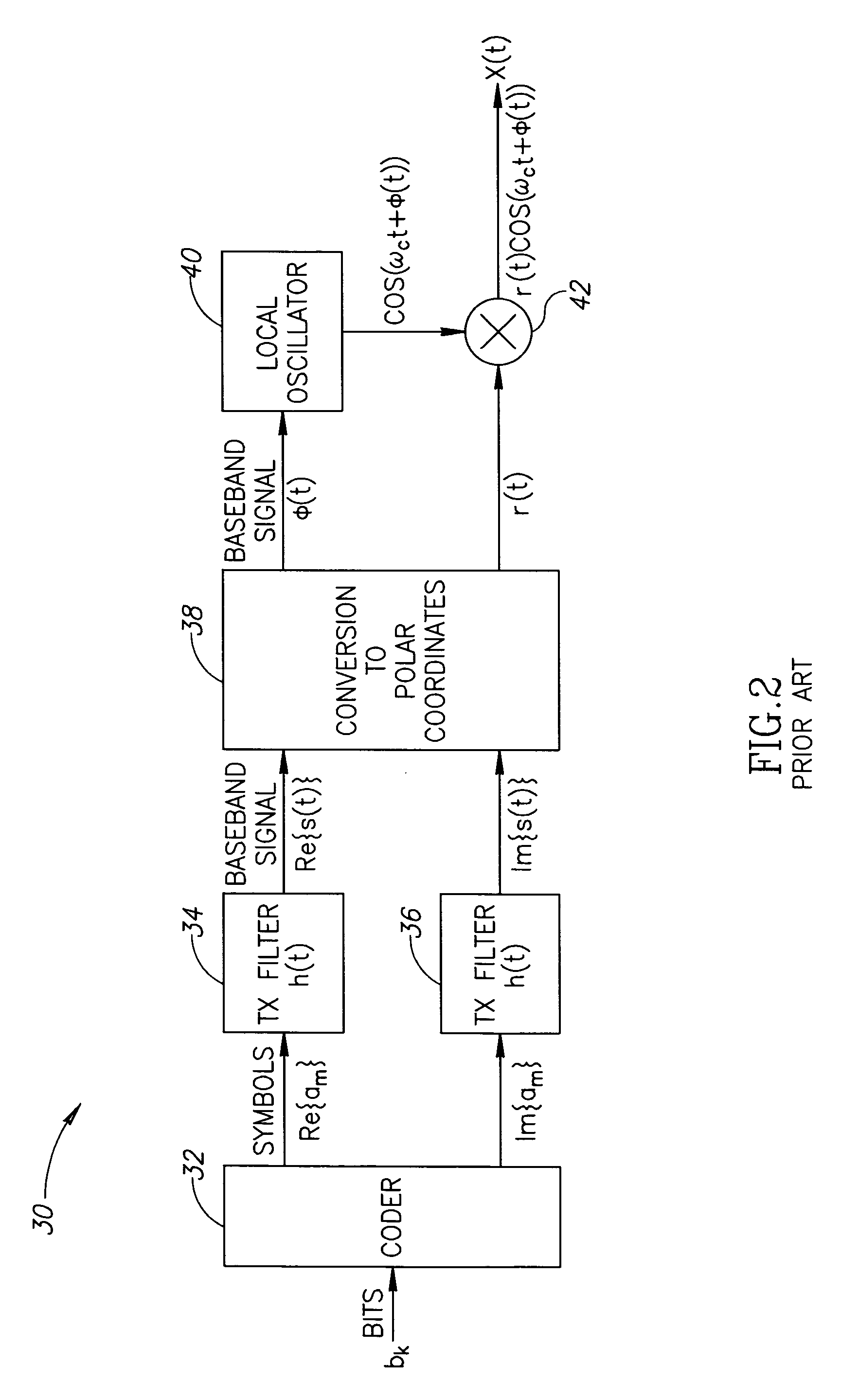
Method and apparatus for a fully digital quadrature modulator
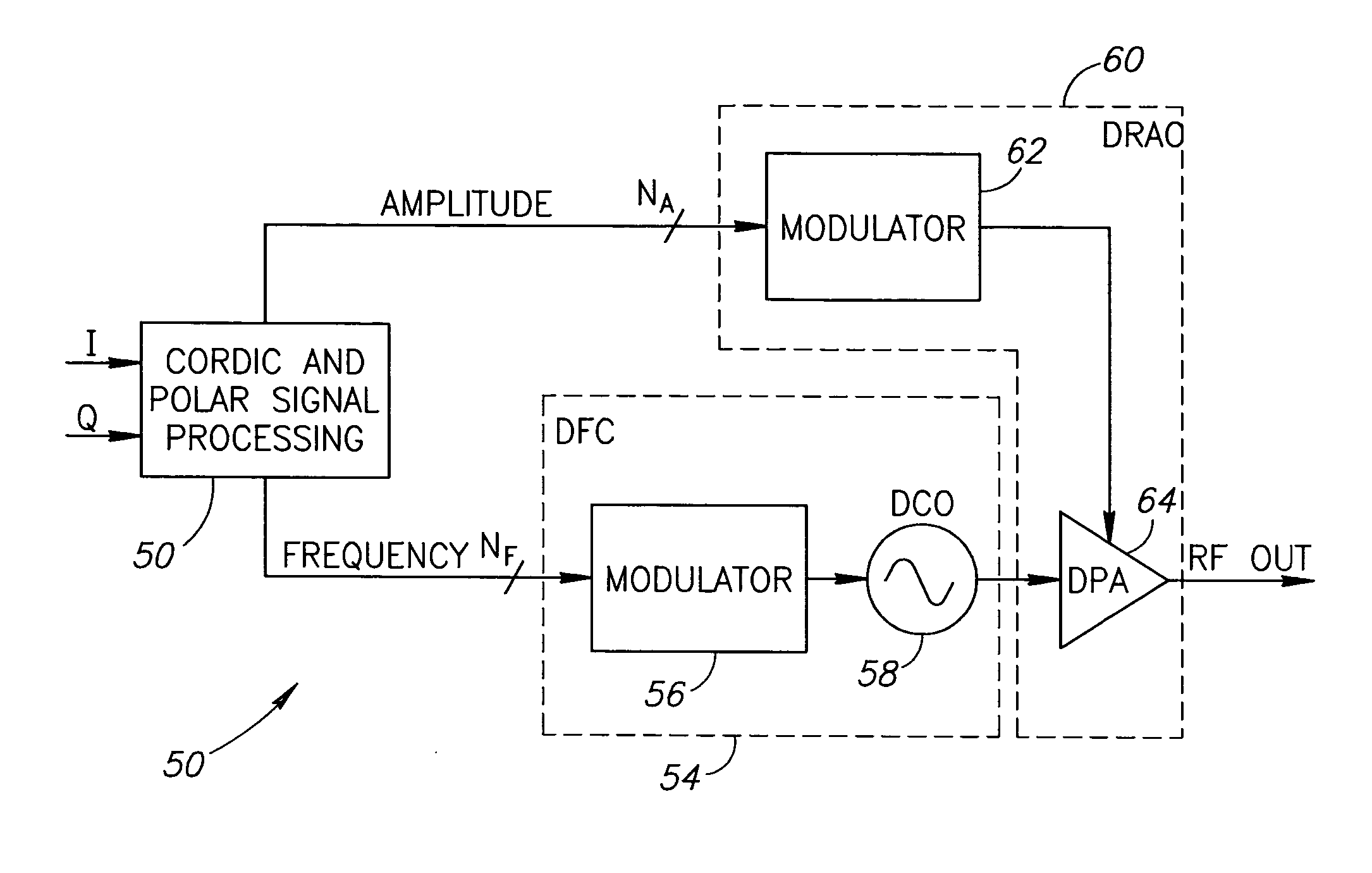
ActiveUS20060291589A1Little or no reuseMinimize impactSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersTransistor arrayQuadrature modulator
A novel apparatus and method for a fully digital quadrature architecture for a complex modulator. The complex modulator can substitute for existing prior art analog quadrature modulator structures and those based on a digital polar architecture (r, θ). The modulator effectively operates as a complex digital-to-analog converter where the digital inputs are given in Cartesian form, namely I and Q representing the complex number I+jQ, while the output is a modulated RF signal having a corresponding amplitude and phase shift. The phase shift being with respect to a reference phase dictated by the local oscillator, which is also input to the converter / modulator. Several embodiments are provided including modulators incorporating dual I and Q transistor arrays, a single shared I / Q transistor array, modulators with single ended and differential outputs and modulators with single and dual polarity clock and I / Q data signals.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Vessel sealing system using capacitive RF dielectric heating
ActiveUS20050197659A1Heating evenlyReduce heat spreadSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsCapacitanceVessel sealing
An electrosurgical system for sealing vessels using capacitive (RF) dielectric heating and a method thereof are provided. The system includes an electrosurgical instrument having an end effector with parallel plate electrodes that will clamp onto a vessel and maintain a specified gap distance; however, the electrodes will be coated with a non-conductive dielectric material. Such an end effector will ensure that direct conduction between the electrodes does not occur through tissue or fluids and effectively creates a parallel plate capacitor with a dielectric, e.g., tissue and coating, in between the plates. The electrosurgical instrument will be activated with an AC signal at a specified RF frequency, e.g., a Debye resonance frequency, via an electrosurgical generator. An effective AC current will flow through the tissue and cause heating due to fictional losses from rotating polar molecules in the tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Electronic device having magnetic latching mechanism
ActiveUS20070133156A1Easy to openPermanent magnetsDetails for portable computersMagnetic polesDisplay device
A magnetic latch for a display of a laptop computer is disclosed. The latch uses magnetic attraction to maintain the display closed and uses magnetic repelling forces to pop-up the display when opened. The latch includes one or more magnetic elements in the body of the laptop and at least one magnetic element in the display. When the display is closed, the magnet element in the display is positioned adjacent the magnet element in the body having an opposite polarity so that the magnet elements are attracted to one another. To pop-up the display, the user moves the magnetic element in the display so that it meets the magnetic pole in the body having the same polarity. When these meet, the repelling force between them causes the display to open slightly so that a user can then readily open the display.
Owner:APPLE INC
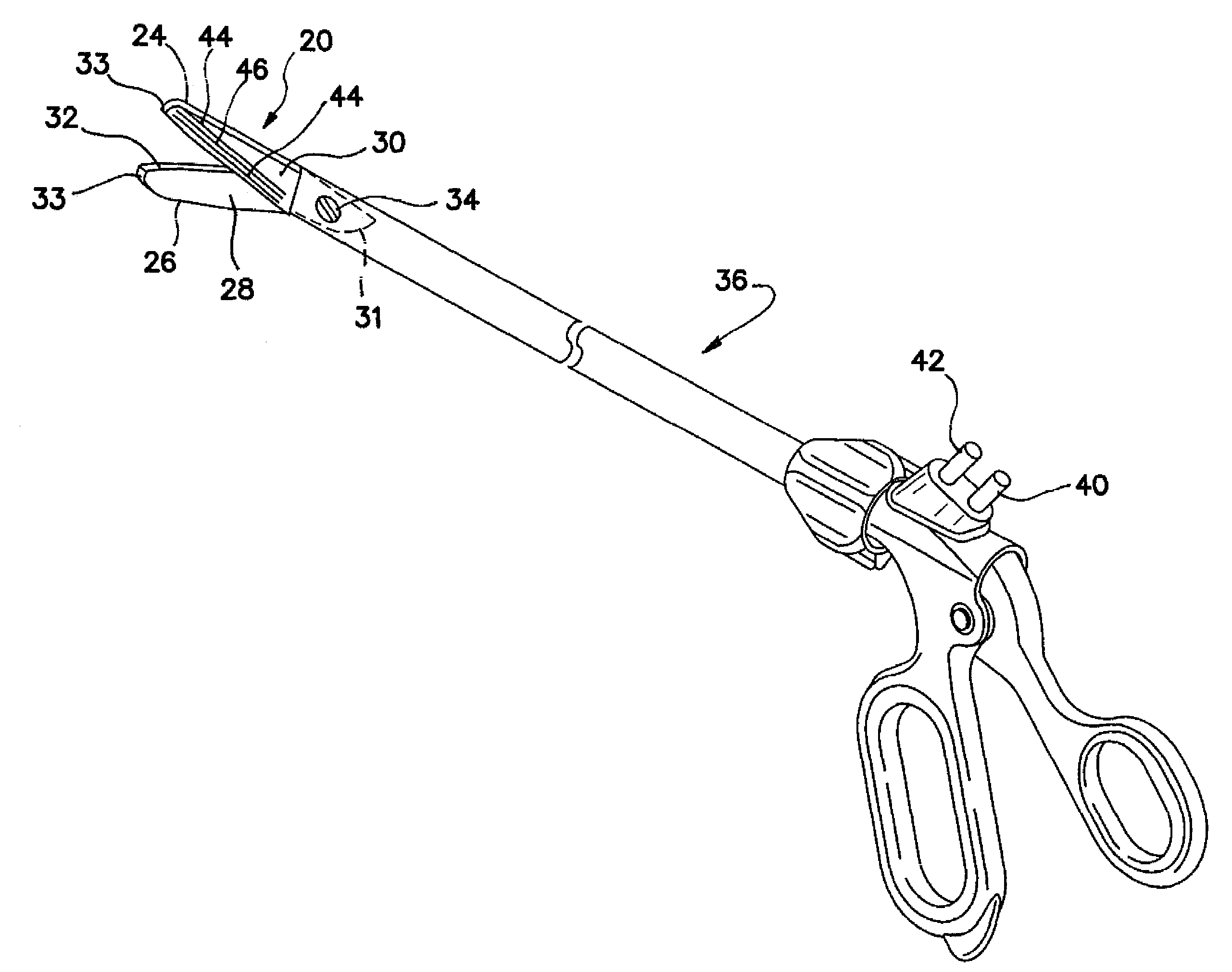
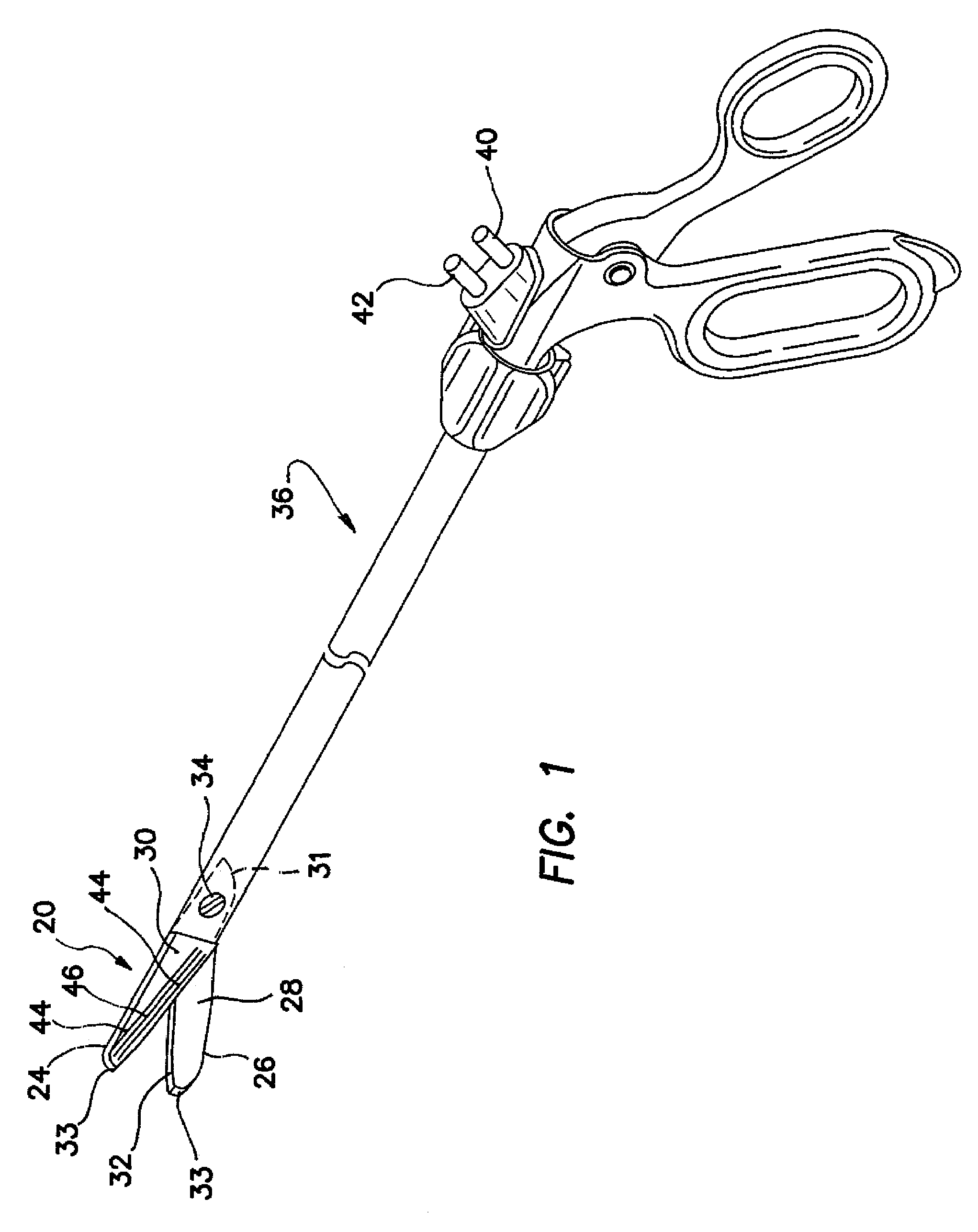
Bipolar electrosurgical scissors
ActiveUS7419490B2High dielectric strengthSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsBipolar electrosurgeryElectrical polarity
Bipolar electrosurgical scissors for treating biological tissue include first and second scissor blades. A shearing surface and cutting edge of each blade is electrically neutral. The scissors include a pair of electrical connections for receiving electrical currents of opposing polarities. Each blade includes at least one first electrode and at least one second electrode positioned on a surface opposite the shearing surface The at least one first electrode on the first blade and the at least one second electrode on the second blade are coupled to the first electrical connection. The at least one second electrode on the first blade and the at least one first electrode on the second blade are coupled to the second electrical connection. In a first energized state, the electrical connections deliver electrical current only to the first electrodes. In a second energized state, the electrical connections deliver electrical current to all of the electrodes.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Apparatus for intraoperative neural monitoring
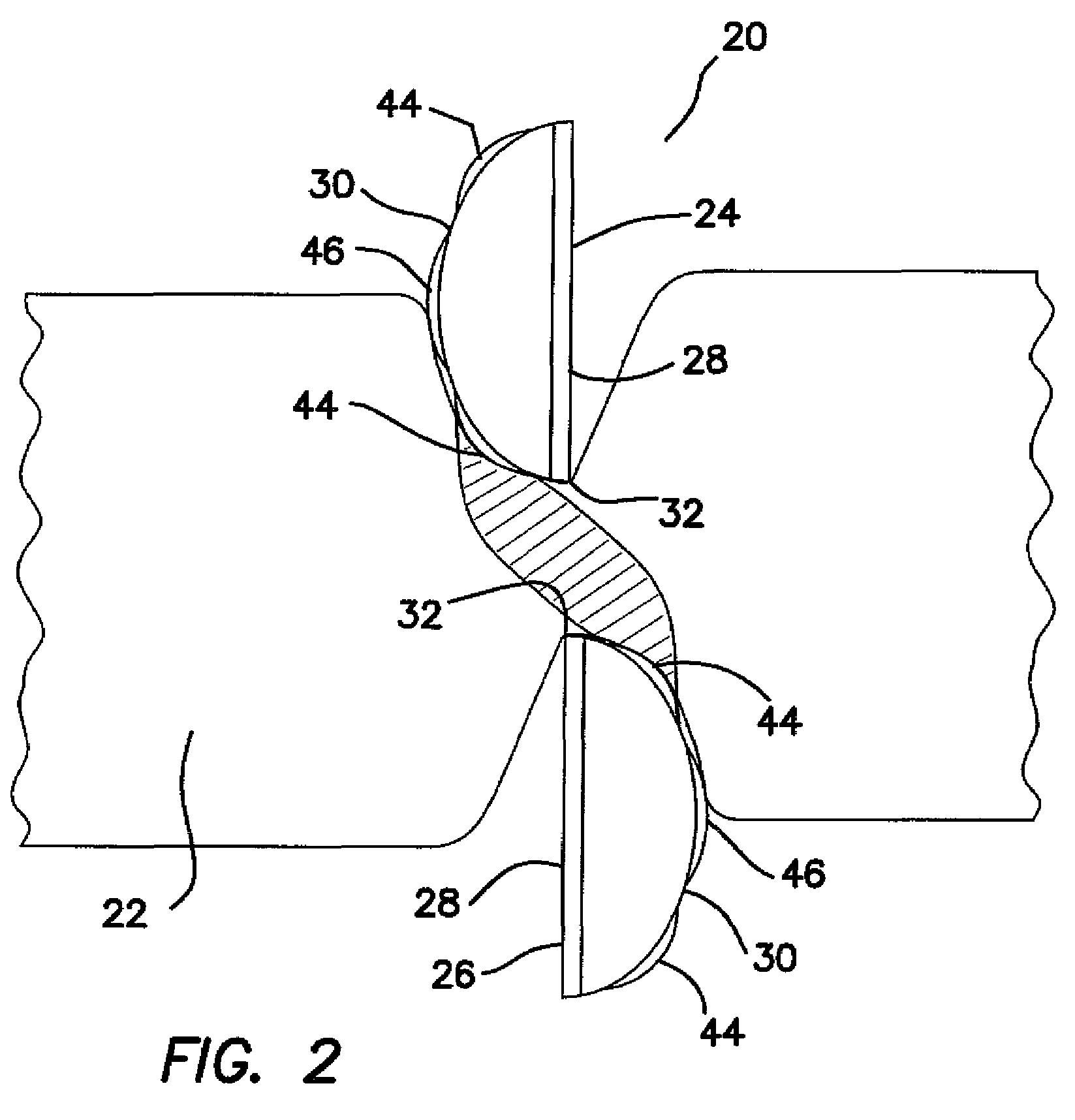
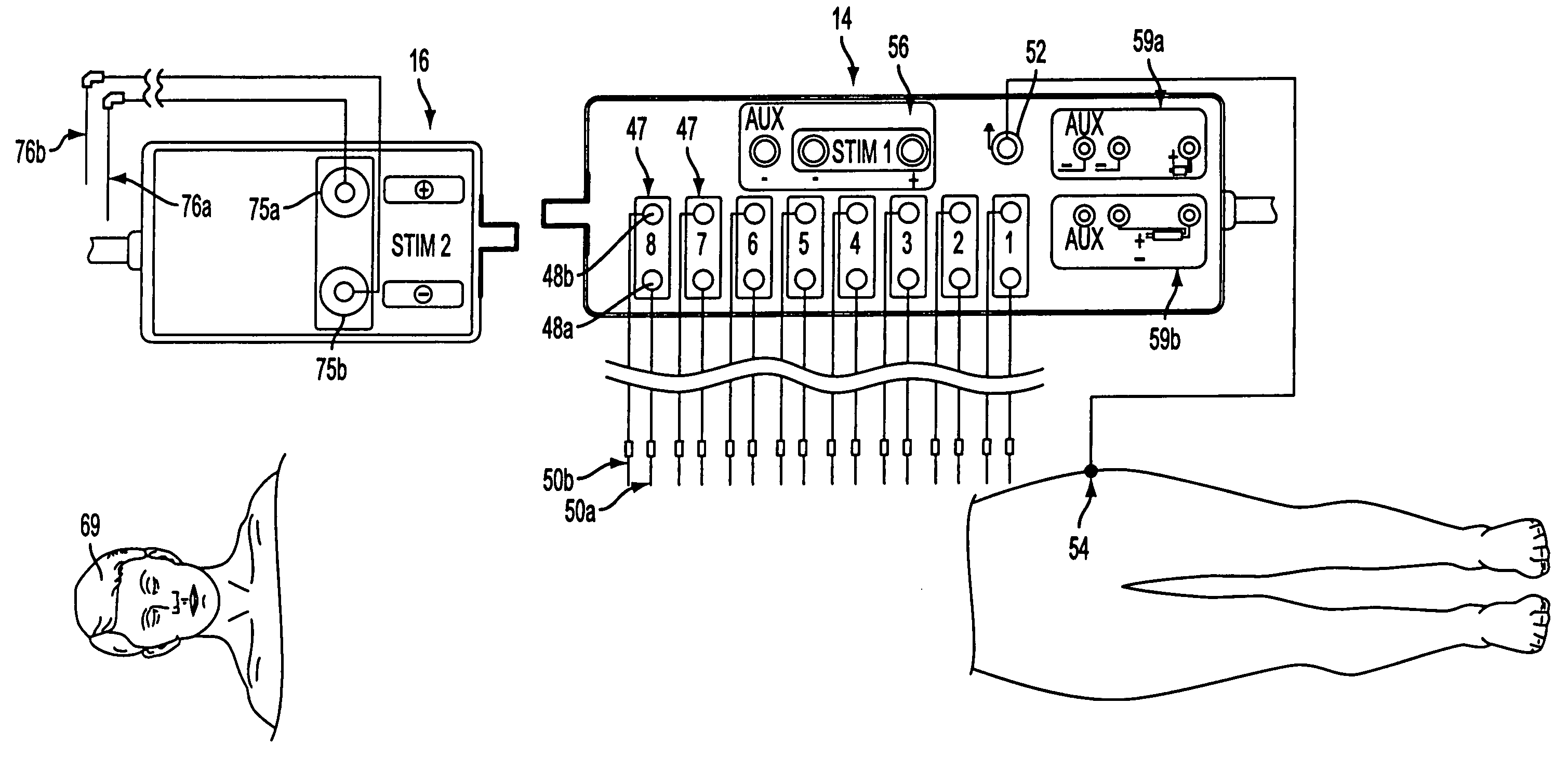
An intraoperative neural monitoring system includes a power source and a simulator powered by the power source to deliver a cycle of electrical stimulation to a patient as a first group of positive or negative phase pulses automatically followed by a second group of pulses of opposite phase or polarity to the pulses of the first group. An activation performed to initiate delivery of the first group of pulses is effective to deliver the entire cycle of stimulation. A method of intraoperative neural monitoring involves activating a simulator to deliver a biphasic cycle of electrical stimulation to a patient during an operative procedure, delivering the entire cycle of electrical stimulation to the patient in response to the activating step and detecting EMG activity in the patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Superluminescent diodes by crystallographic etching
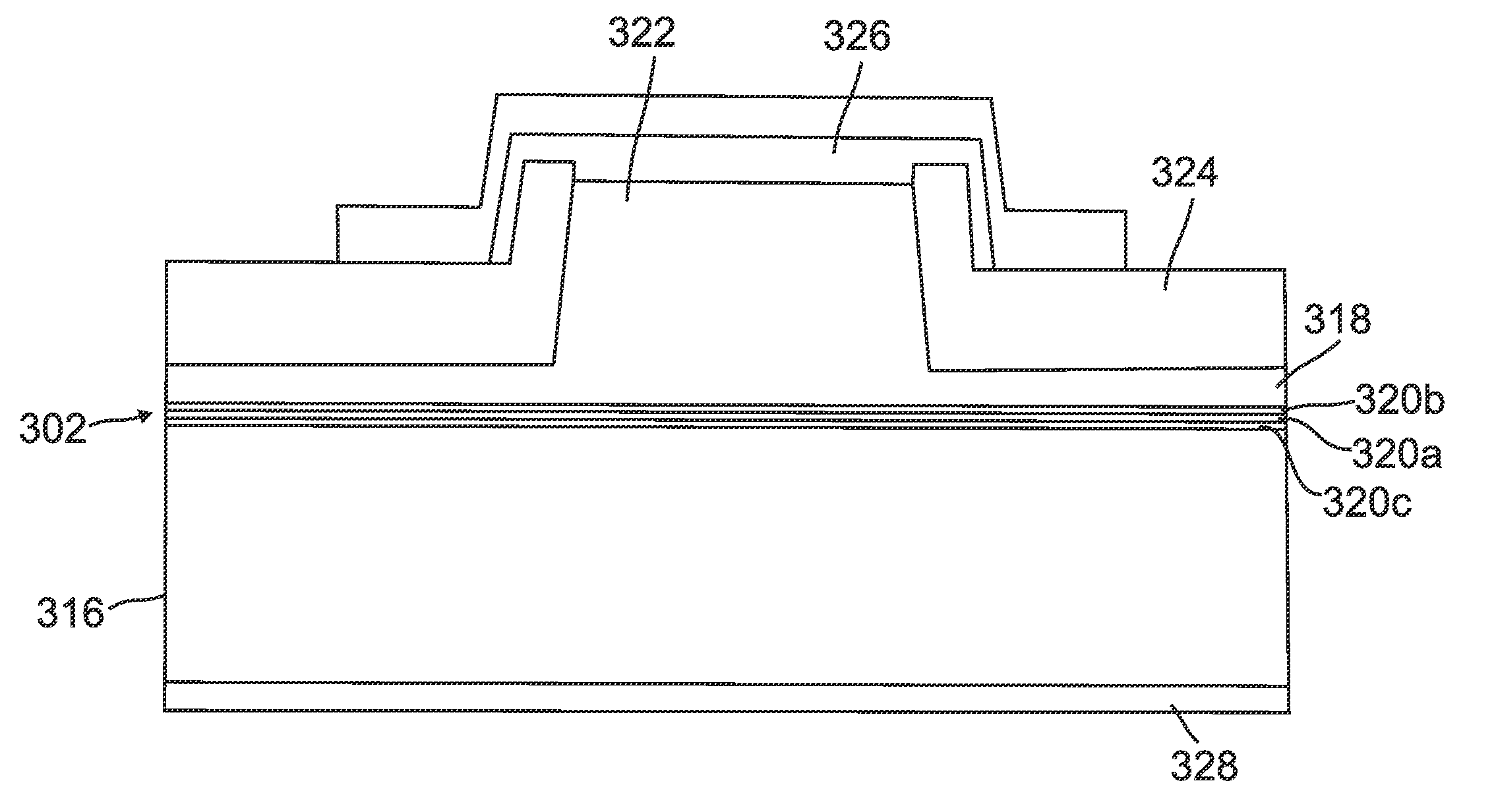
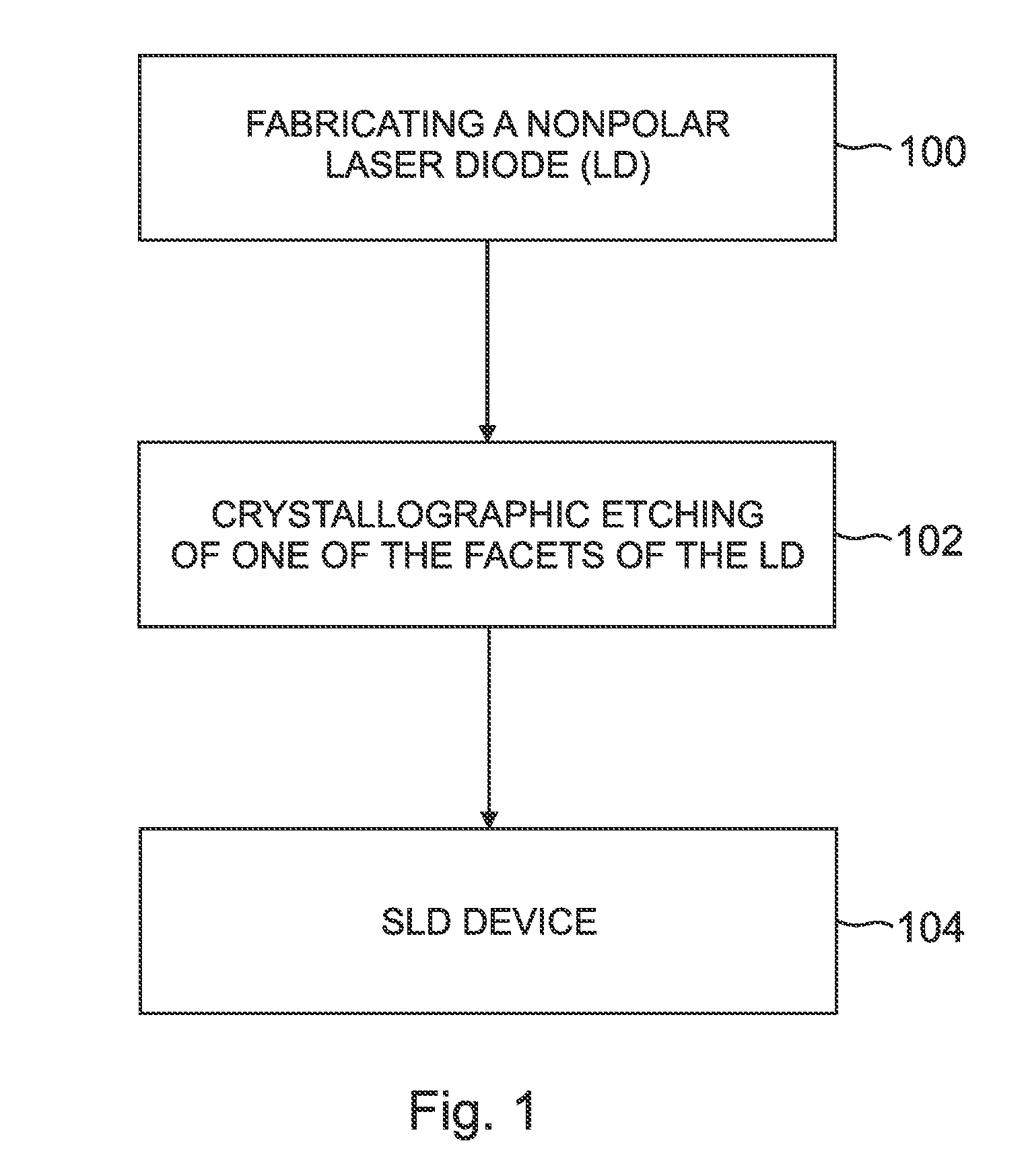
InactiveUS20110103418A1Reduce internal lossSignificant contributionOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSuperluminescent diodeEtching
An optoelectronic device, comprising an active region and a waveguide structure to provide optical confinement of light emitted from the active region; a pair of facets on opposite ends of the device, having opposite surface polarity; and one of the facets which has been roughened by a crystallographic chemical etching process, wherein the device is a nonpolar or semipolar (Ga,In,Al,B)N based device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
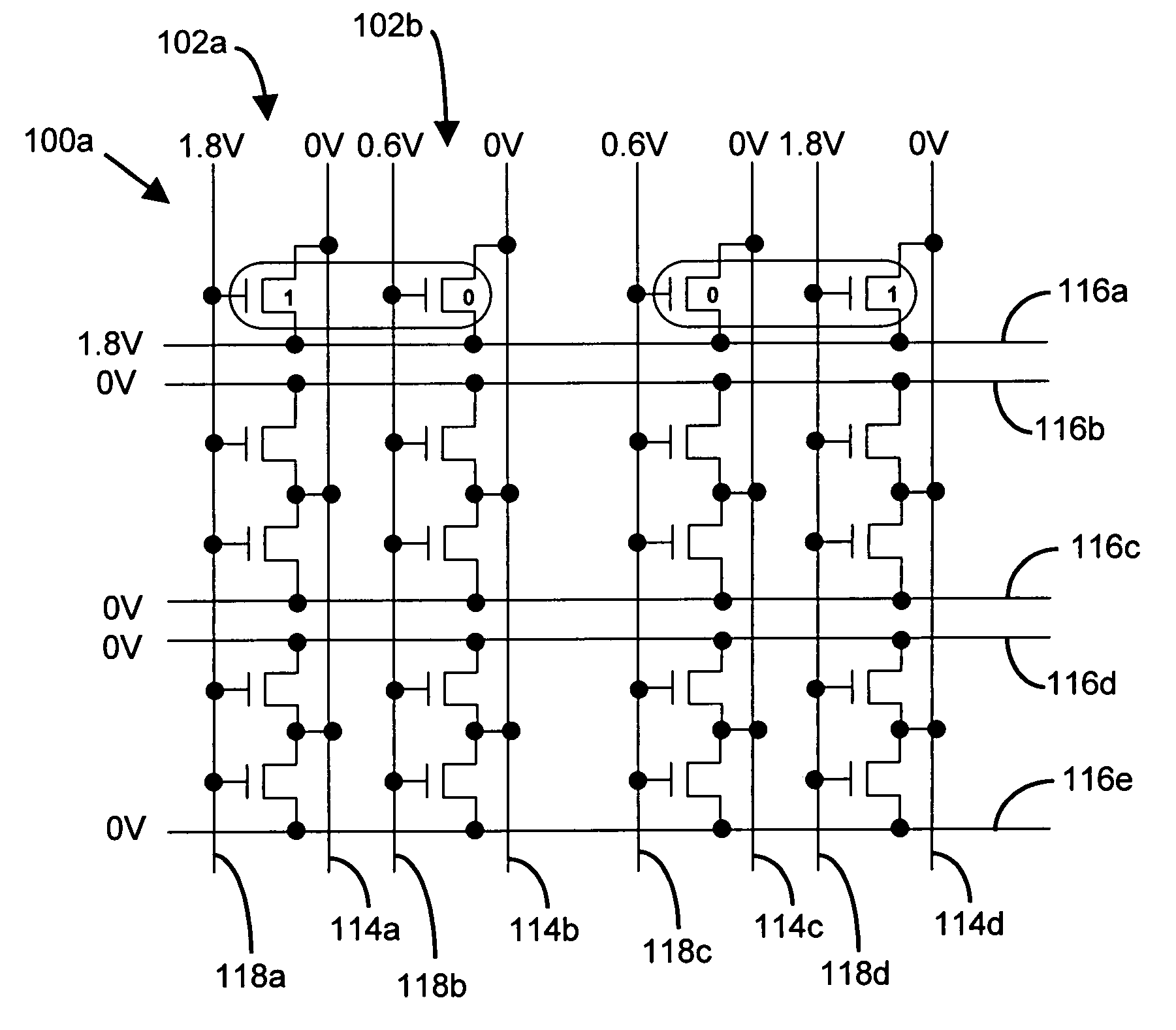
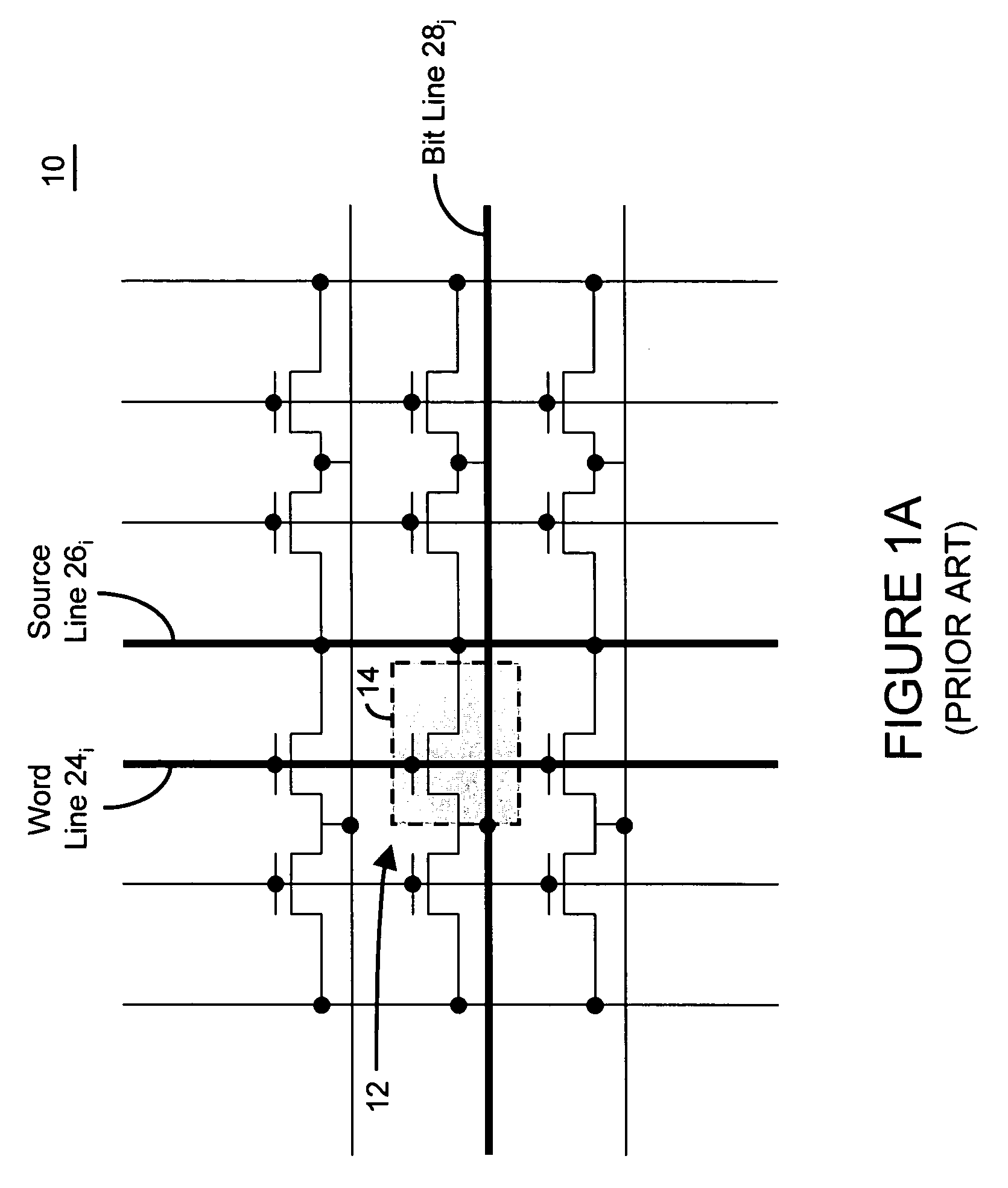
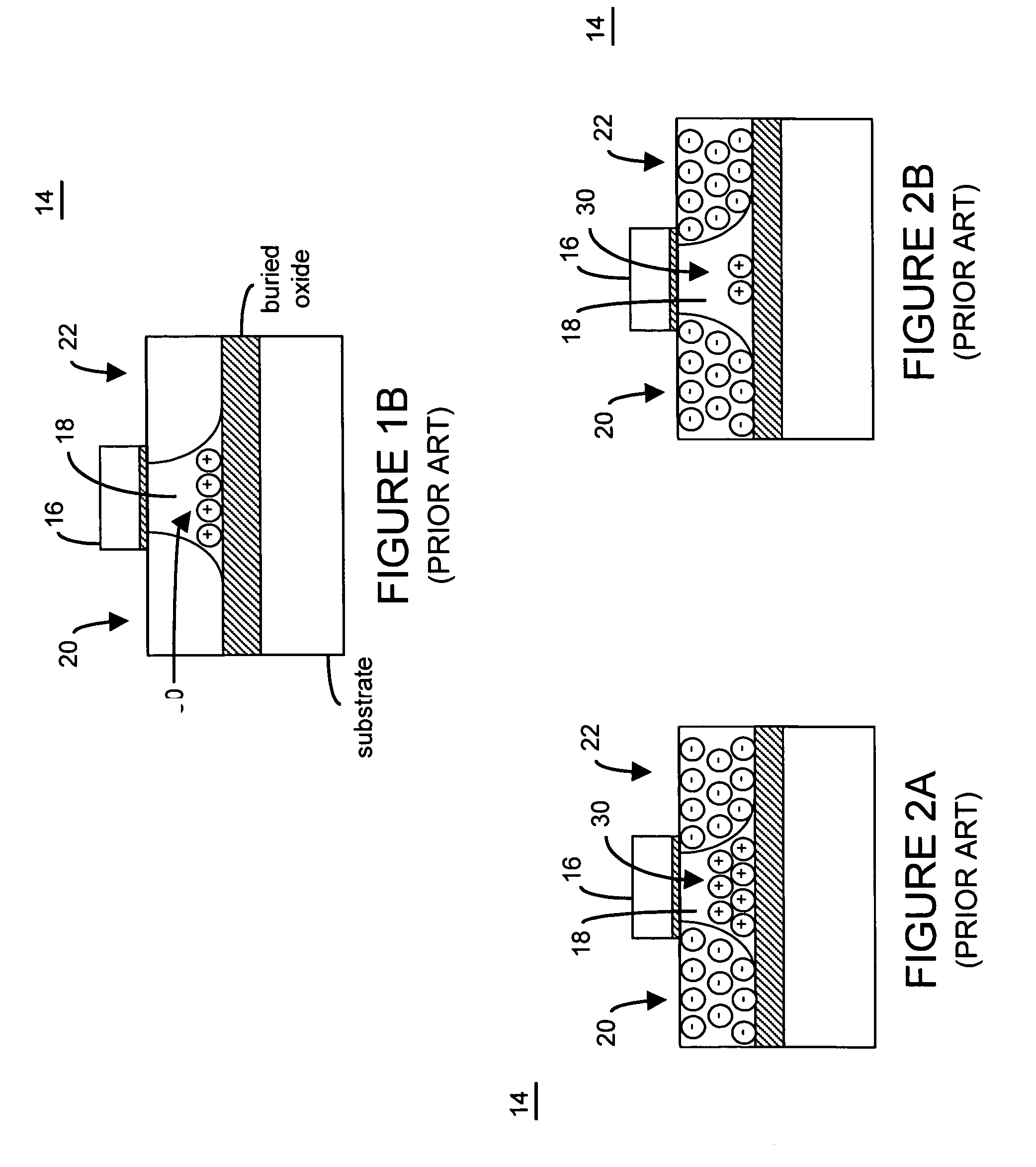
Semiconductor memory cell, array, architecture and device, and method of operating same
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In a first aspect, the present invention is directed to a memory cell and technique of reading data from and writing data into that memory cell. In this regard, in one embodiment of this aspect of the invention, the memory cell includes two transistors which store complementary data states. That is, the two-transistor memory cell includes a first transistor that maintains a complementary state relative to the second transistor. As such, when programmed, one of the transistors of the memory cell stores a logic low (a binary “0”) and the other transistor of the memory cell stores a logic high (a binary “1”). The data state of the two-transistor complementary memory cell may be read and / or determined by sampling, sensing measuring and / or detecting the polarity of the logic states stored in each transistor of complementary memory cell. That is, the two-transistor complementary memory cell is read by sampling, sensing measuring and / or detecting the difference in signals (current or voltage) stored in the two transistors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and system for data writing/reading onto/from and emulating a magnetic stripe
ActiveUS7591426B2Simplify complexityReduce complexitySensing record carriersRecord carriers used with machinesElectrical conductorElectrical polarity
A method of writing data on magnetic stripe of a smart card by imposing a magnetic field of a given polarity on each selected segment of the magnetic stripe, such that data on the magnetic stripe can be read by a magnetic card reader and interpreted as digital bits. The method includes providing a multi-dimensional conductor array placed proximate to the magnetic stripe, the number of conductors in the array is considerably smaller than the number of segments, and each segment is associated with two or more conductors. The method further includes providing current drivers for sending currents in a controlled direction through the conductor array. The system further includes sending currents, using said current drivers, through conductors of the array, such that for each one of the selected segment composite currents flowing through its associated two conductors overcome the coersivity of the segment on the magnetic stripe.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
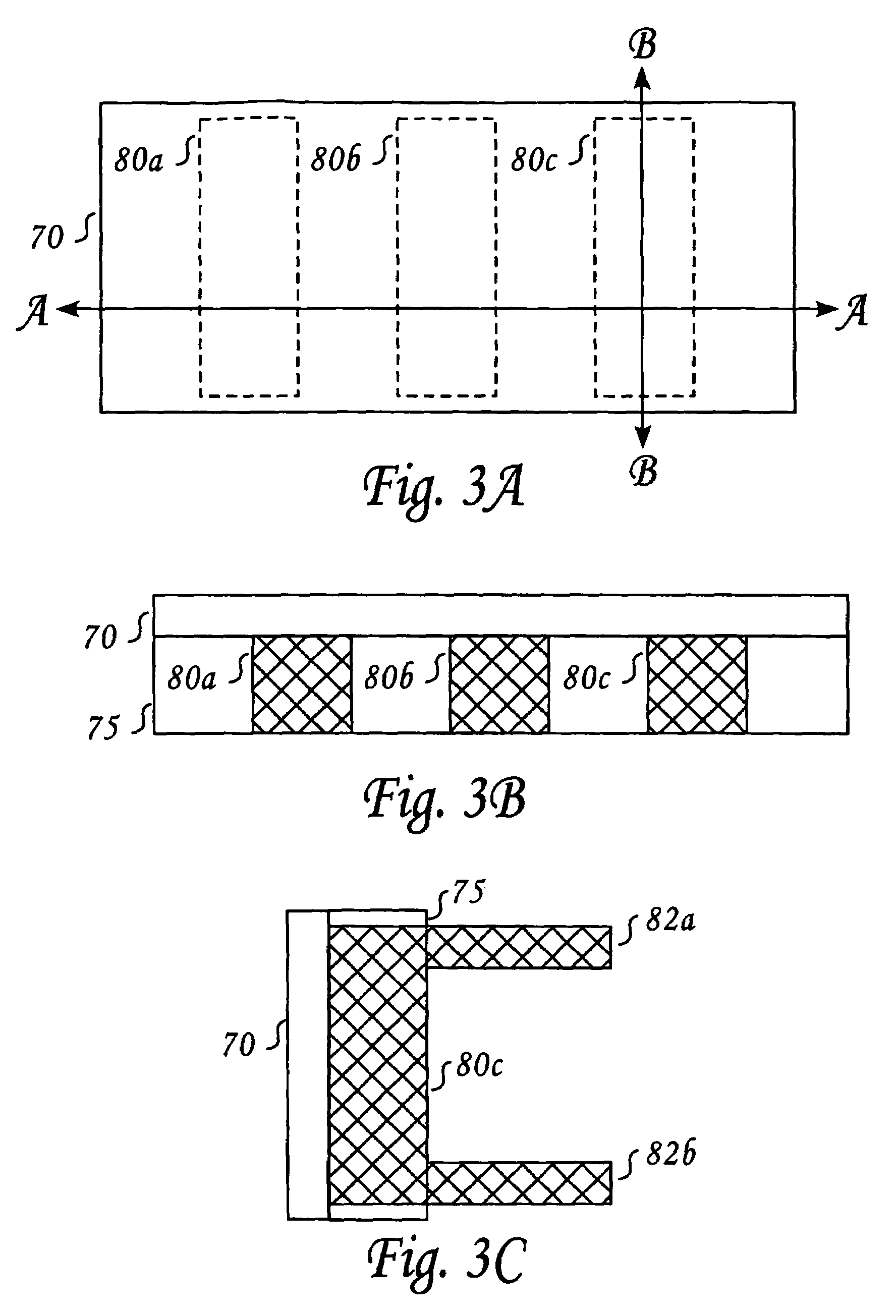
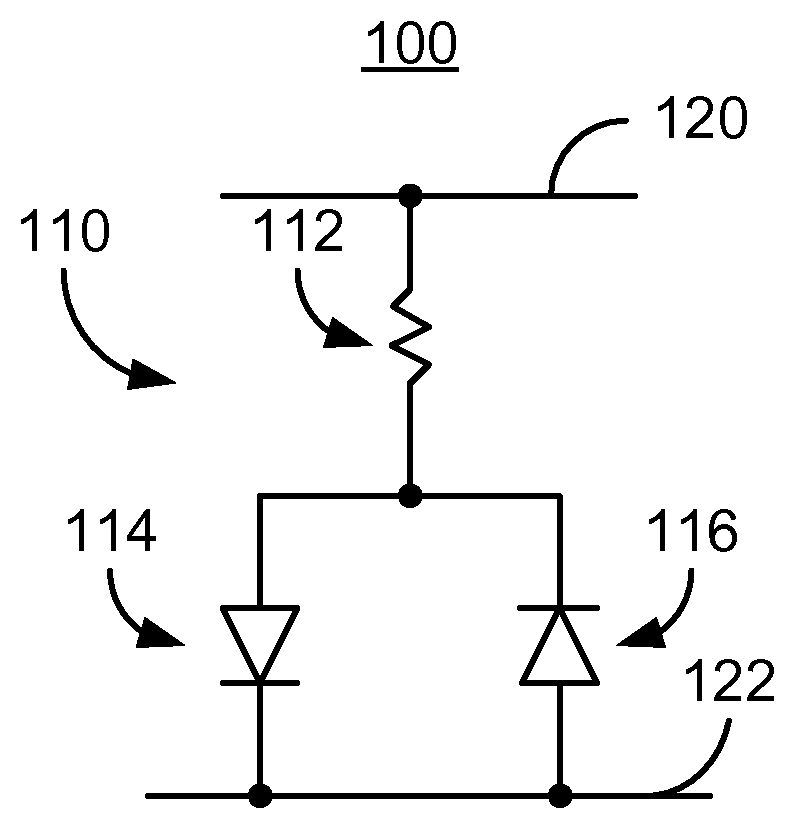
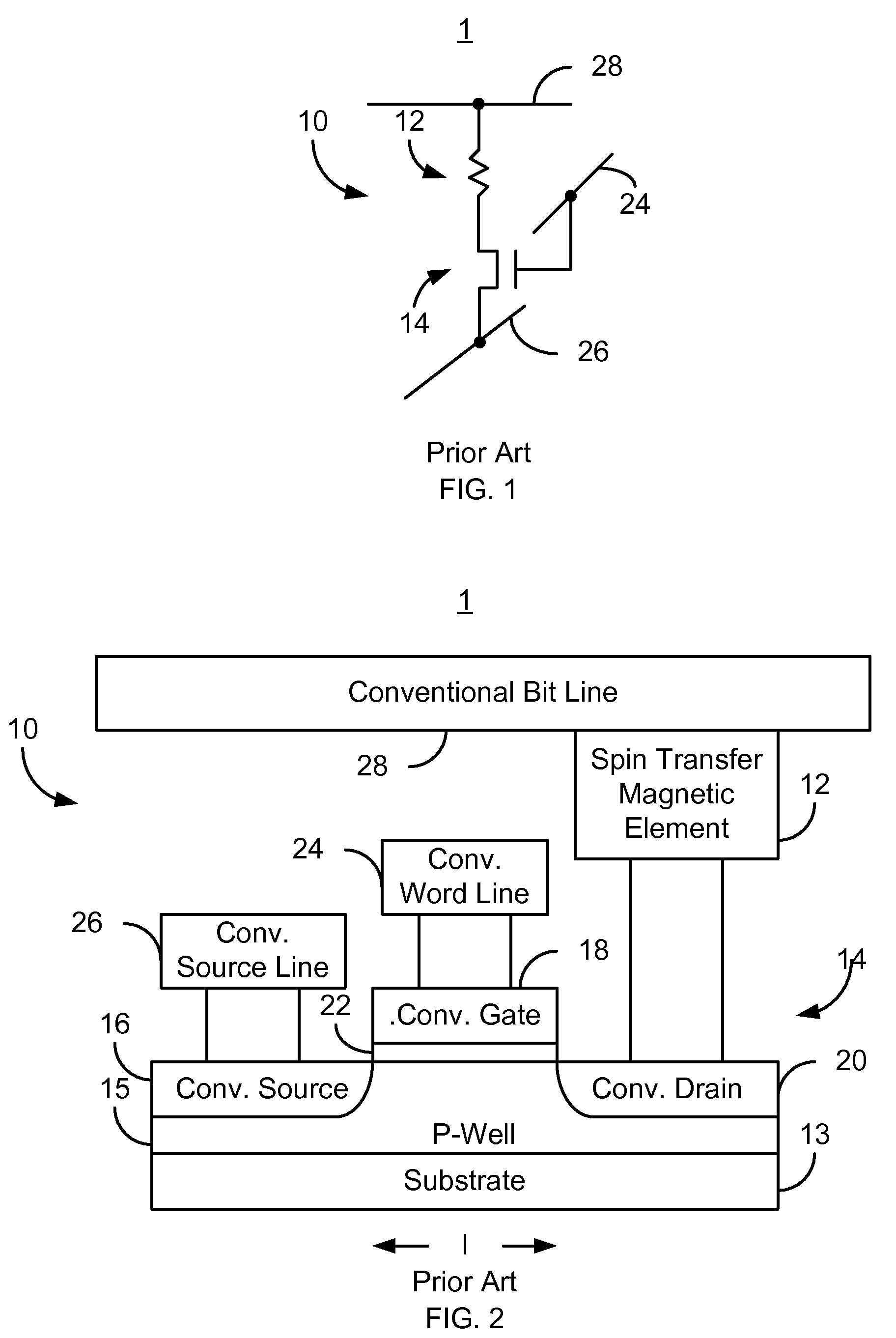
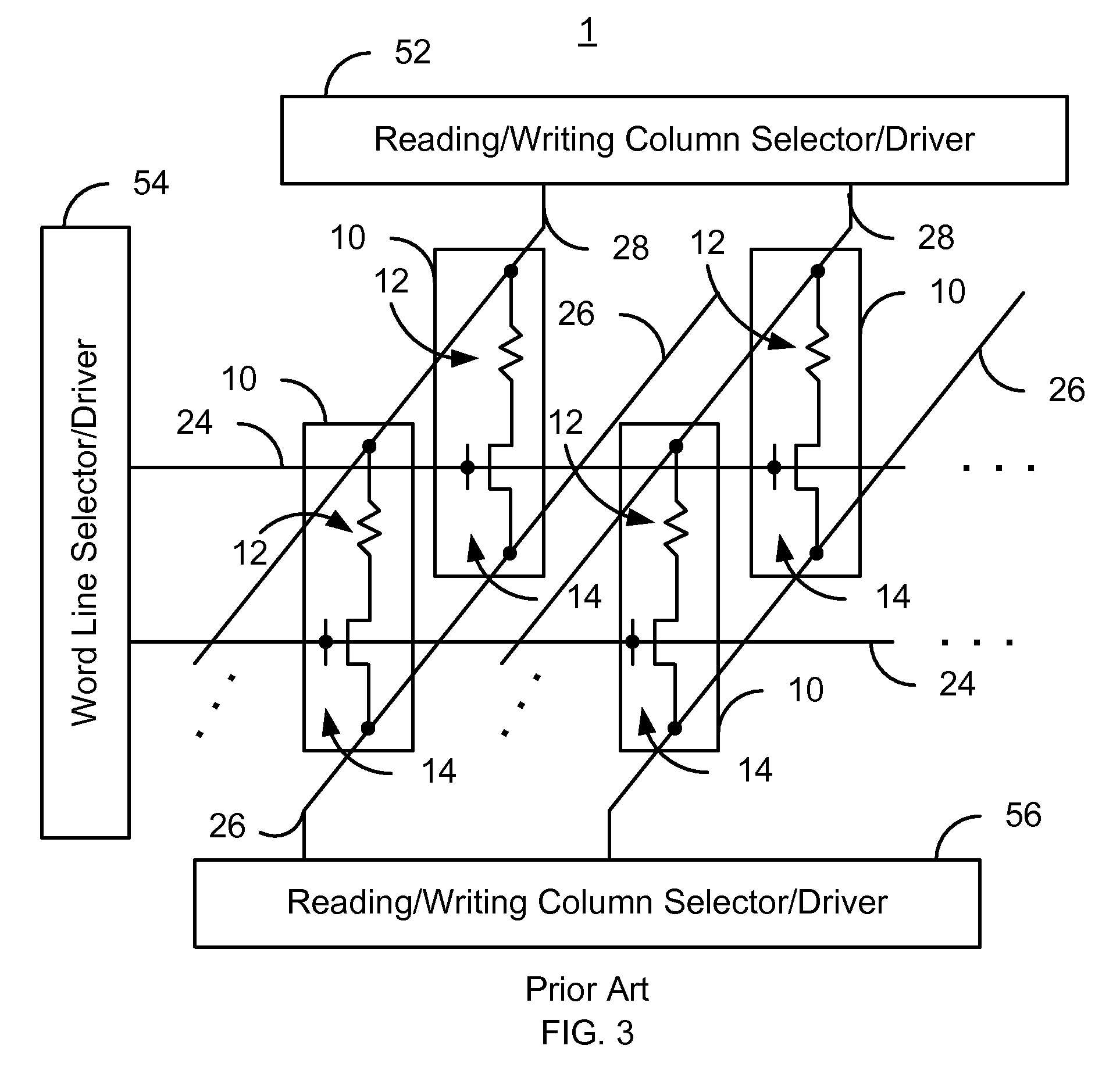
Method and system for providing spin transfer tunneling magnetic memories utilizing unidirectional polarity selection devices
A magnetic memory cell and a magnetic memory incorporating the cell are described. The magnetic memory cell includes at least one magnetic element and a plurality of unidirectional polarity selection devices. The magnetic element(s) are programmable using write current(s) driven through the magnetic element. The unidirectional polarity selection devices are connected in parallel and such that they have opposing polarities. The magnetic memory may include a plurality of magnetic storage cells, a plurality of bit lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells, and a plurality of source lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells.
Owner:GRANDIS
Gas distribution device for a wafer processing apparatus
ActiveUS20200056282A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingWaferingElectrical polarity
A reaction system is disclosed that may be used to prevent formation of contaminants. The reaction system includes a showerhead that may be configured with a gated nanochannel grid to prevent particular gaseous precursors from passing through depending on whether a voltage is applied. The gated nanochannel grid may allow for both polar and non-polar molecules to pass, or may be configured to allow just non-polar or just polar molecules to pass.
Owner:CANADAVFD CORP LTD +1
Magnetic buttons and structures thereof
This invention relates to a novel design of detachable / attachable magnetic buttons that can be used on clothes, accessories, and the like. Specifically, the invention also relates to a contact guiding structure of the button for a smooth detaching / attaching and an improved stability thereof.The magnetic button of the present invention is arranged so that the magnets on the flap and the body have opposite polarities from each other. Each magnet housing is placed around each magnet in order to make one magnet to be placed in that of the corresponding opposite button. Furthermore, to prevent magnets from slipping and to enhance their durability, a barrier is placed between the magnet and the housing. Hence, the stability of the contact portion of the button and the smooth detachment / attachment are more facilitated.
Owner:SHIN KYU HO
Variable magnetic flux electric rotary machine
InactiveUS20100164422A1Easy to operateWide operating speed rangeDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesElectrical polarityEngineering
An electric rotary machine is disclosed which can adjust relative angles of sub-rotors continuously and regardless of torque direction without generating an attractive force between the field magnets of the sub-rotors. The electric rotary machine includes: a stator having a winding; a dual rotor which is rotatably disposed with a gap from the stator and divided axially along a shaft into a first rotor and a second rotor each having field magnets with different polarities arranged alternately in a rotation direction; a mechanism for varying the axial position of the second rotor relative to the first rotor continuously; and a non-magnetic member located between the first rotor and the second rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Direct current load breaking contact point constitution and switching mechanism therewith
InactiveUS6934134B2Contact materialsCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical polarity
The invention intends to provide a direct current load breaking contact point constitution that can make and break an electrical circuit under both direct current loads of direct current resistance load and direct current inductance load over a long period of time without causing problems such as ① the conduction defect due to the consumption of the contact point, ② the locking due to material transfer from one contact point to the other contact point, ③ the welding between the contact points, and ④ the abnormal arc continuation, and a direct current load breaking switching mechanism such as a relay, a switch and so on that has the contact point constitution. The direct current load breaking contact point constitution according to the invention comprises a movable contact point and a stationary contact point that face each other; wherein the movable contact point is made of AgSnO2In2O3 alloy that contains at least Ag, 8 to 15% by weight in total of metal oxides including SnO2 and In2O3, 6 to 10% by weight of SnO2 and 1 to 5% by weight of In2O3; the stationary contact point is made of AgZnO alloy that contains at least Ag and 7 to 11% by weight of ZnO; and polarity of a movable side is (+) and that of a stationary side is (−).
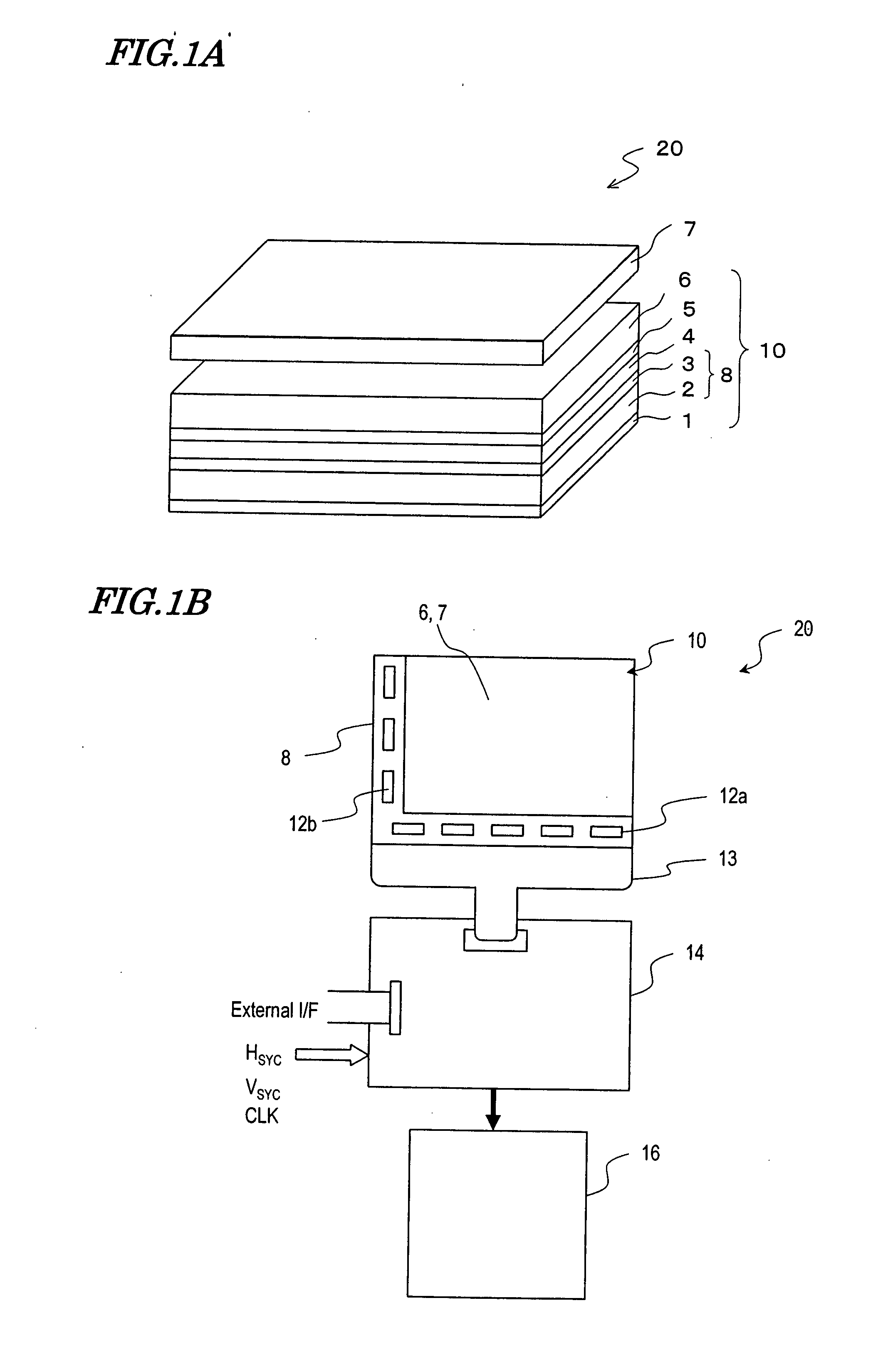
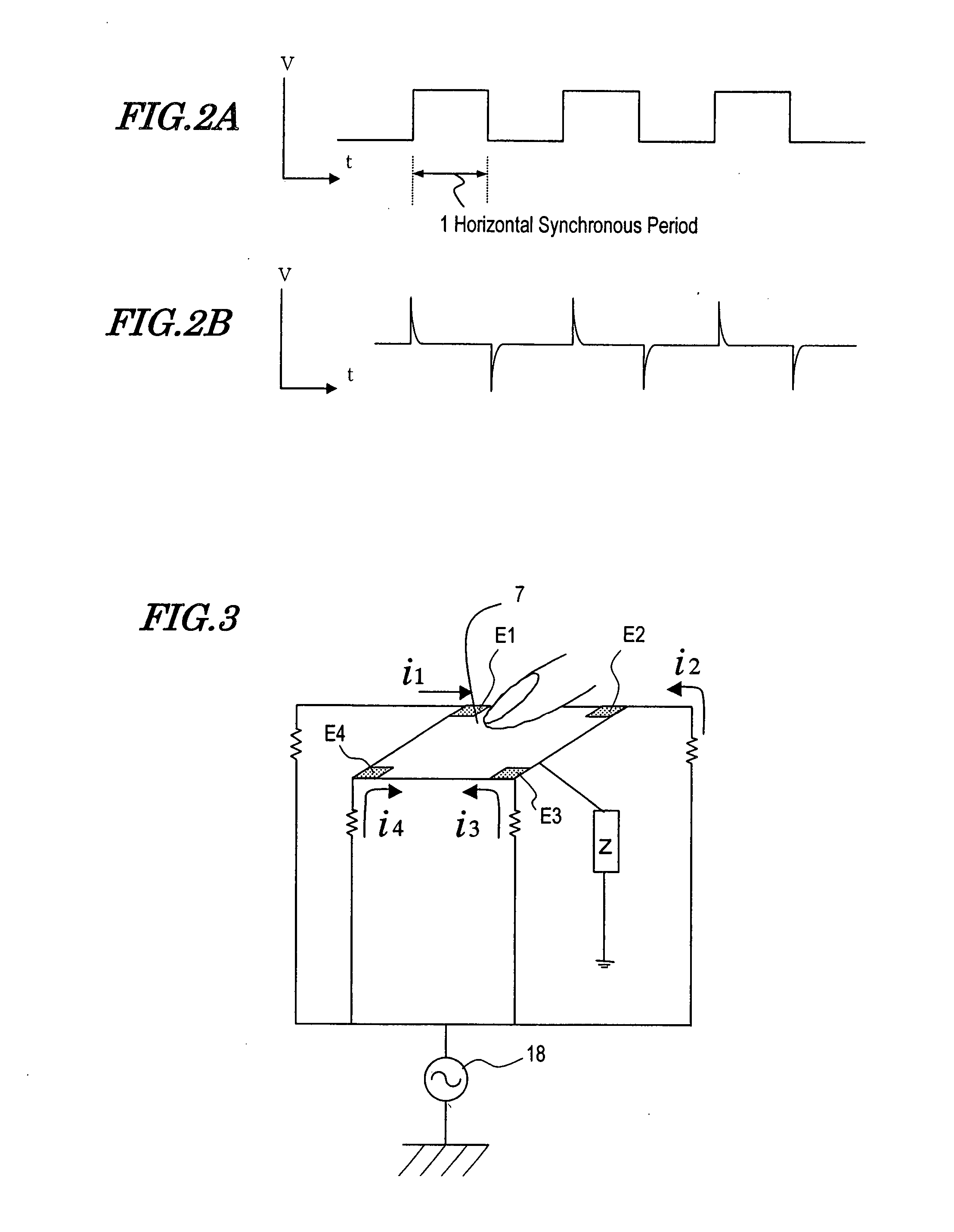
Display Device with Touch Sensor, and Drive Method for the Device
InactiveUS20070262966A1Raise the ratioImprove position detection accuracyInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixDisplay device
A touch-sensored display device 20 according to the present invention includes: a counter substrate 6 disposed on a viewer side of an active matrix substrate 8 via a display medium layer 4, the counter substrate 6 having a counter electrode 5 which opposes pixel electrodes; a display panel driving circuit 14 for supplying to the counter electrode 5 a common voltage which undergoes periodic inversion in polarity; a transparent conductive film 7 for position detection placed so as to oppose the counter electrode 5 via the counter substrate 6; a strobe signal generation circuit 32 for generating a strobe signal which is in synchronization with a polarity inversion period of the common voltage, and a noise-cut current signal generation circuit 30 for generating a noise-cut current signal which is obtained by eliminating based on the strobe signal a predetermined portion from a current flowing from a terminal connected to the transparent conductive film 7 for position detection.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com