Patents
Literature
3170 results about "Rotary machine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
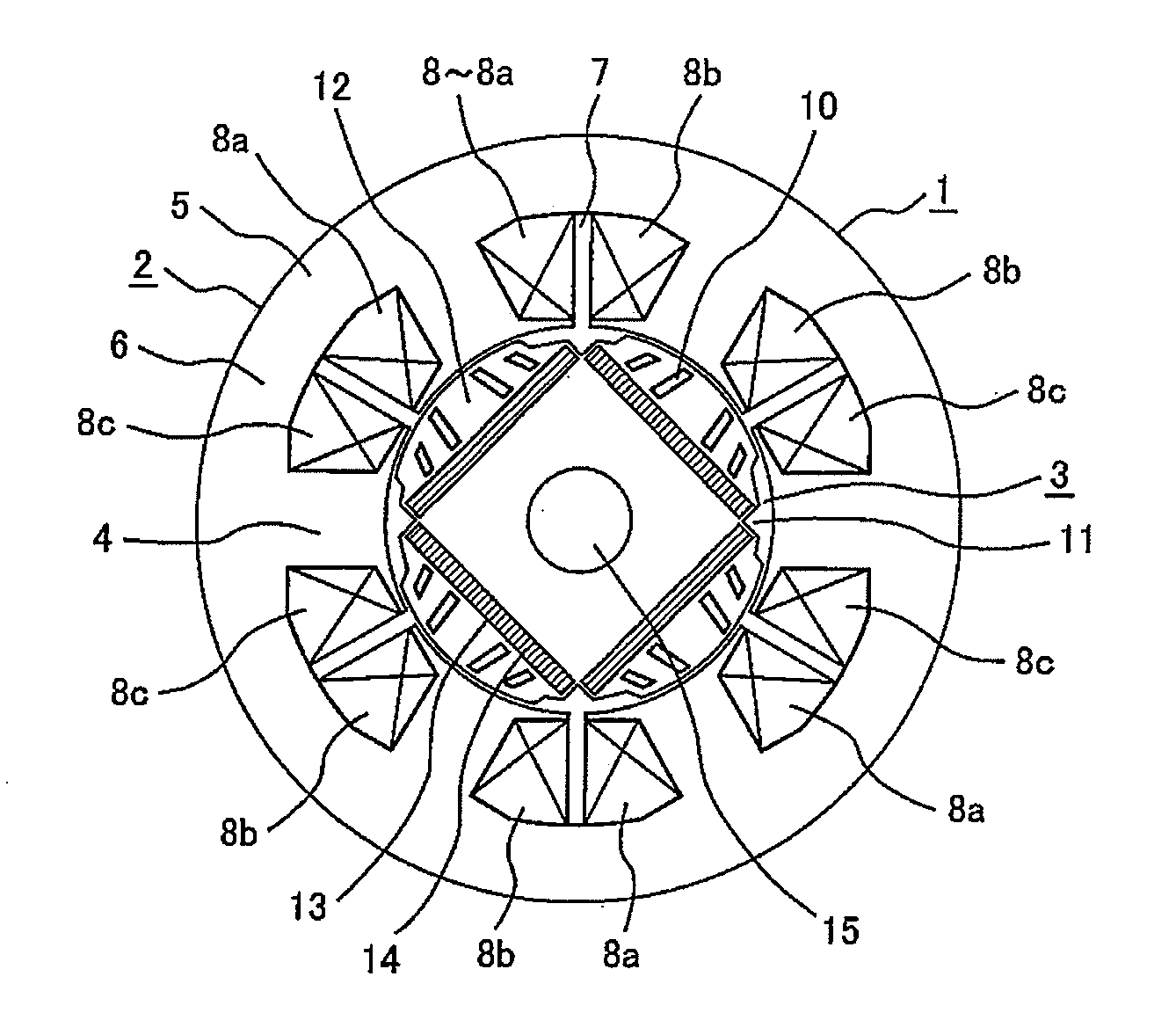
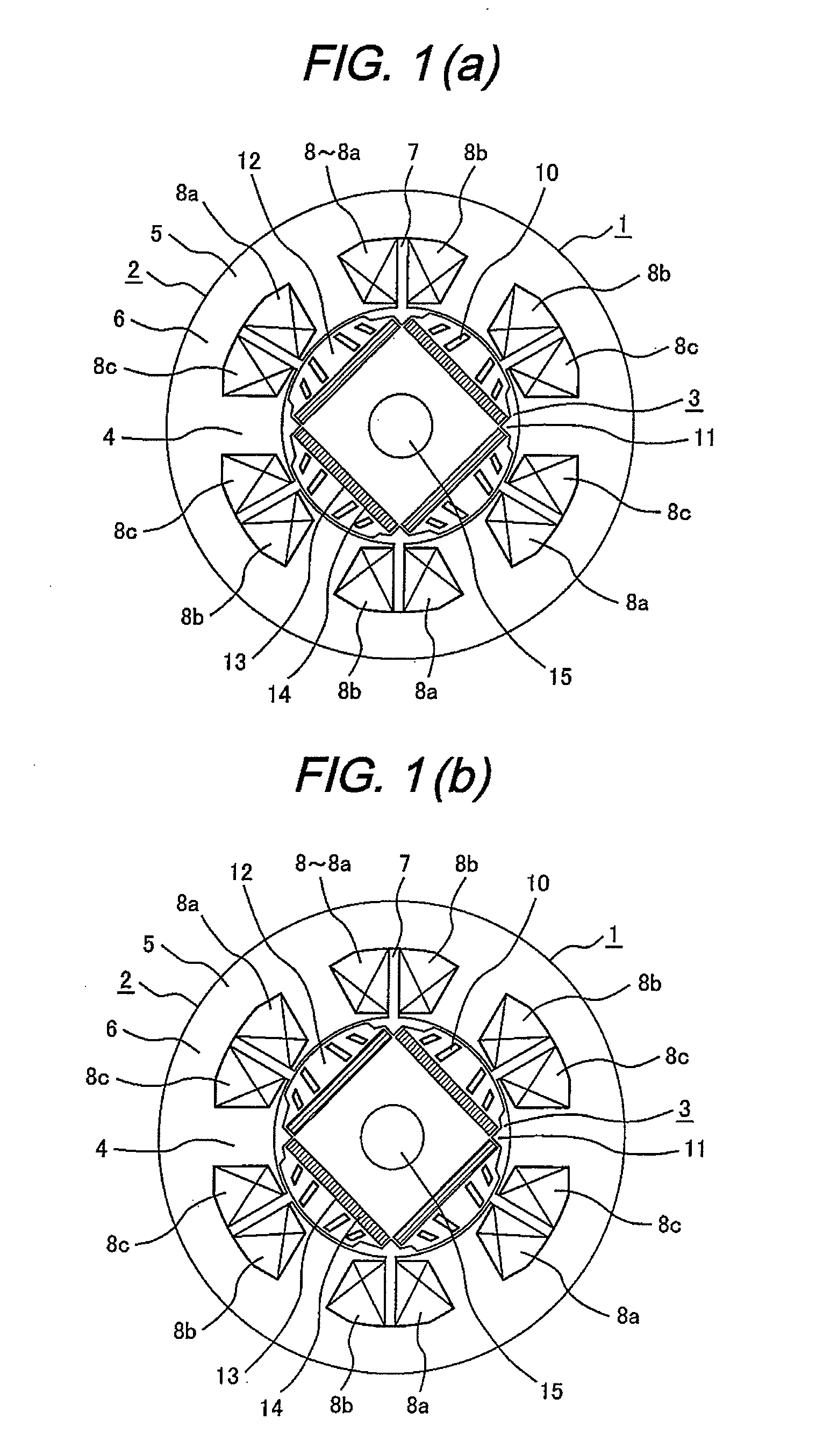
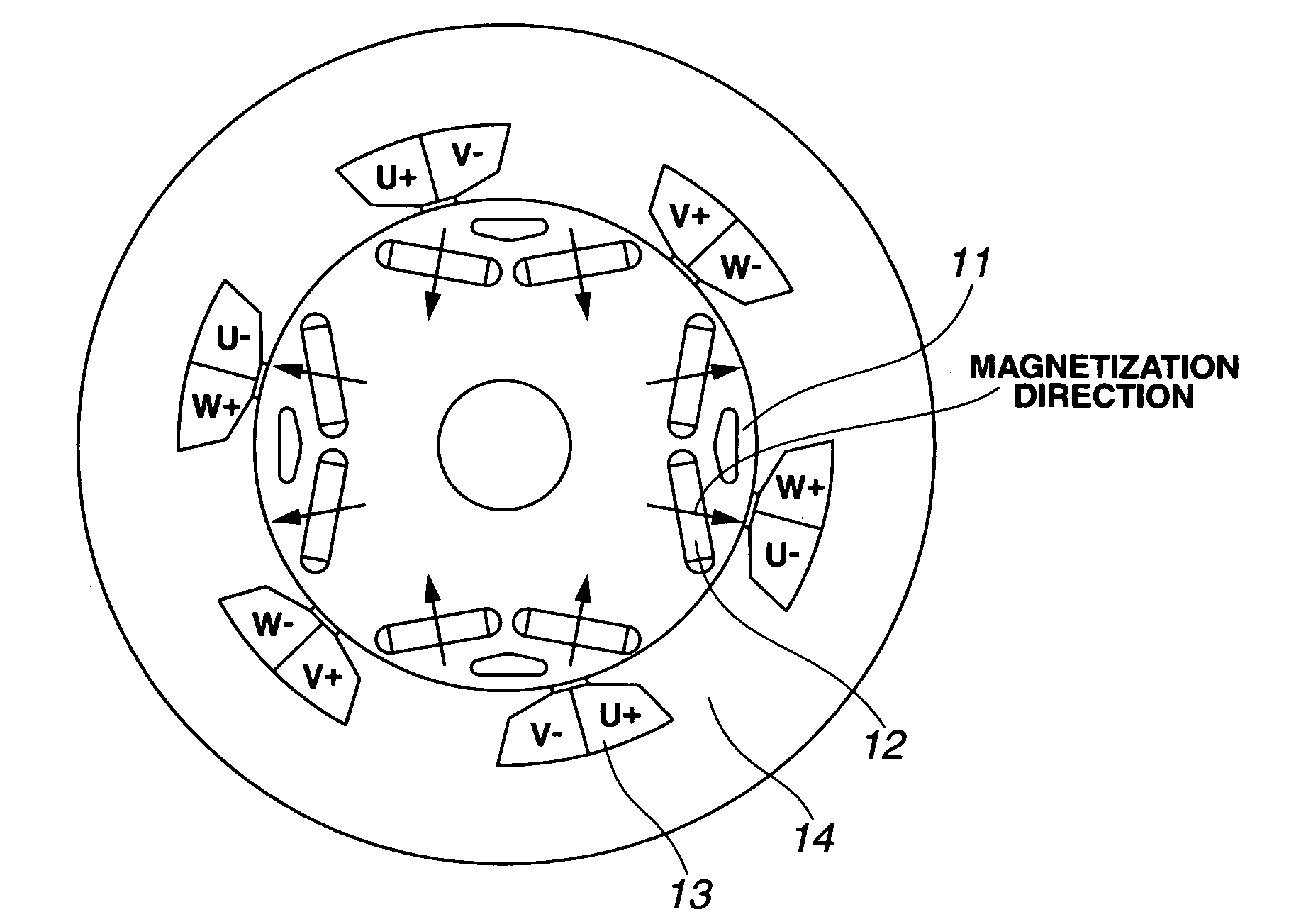
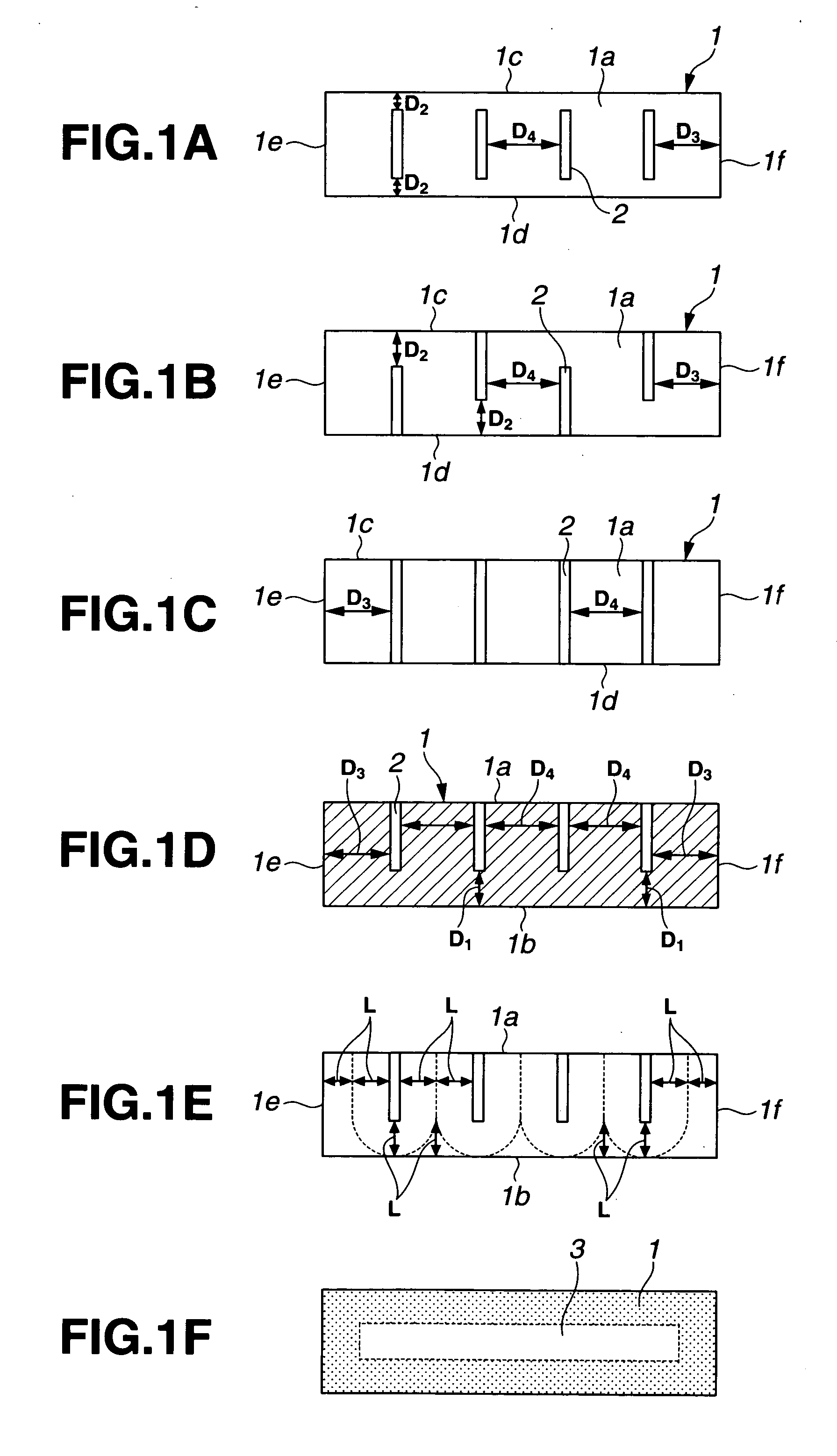
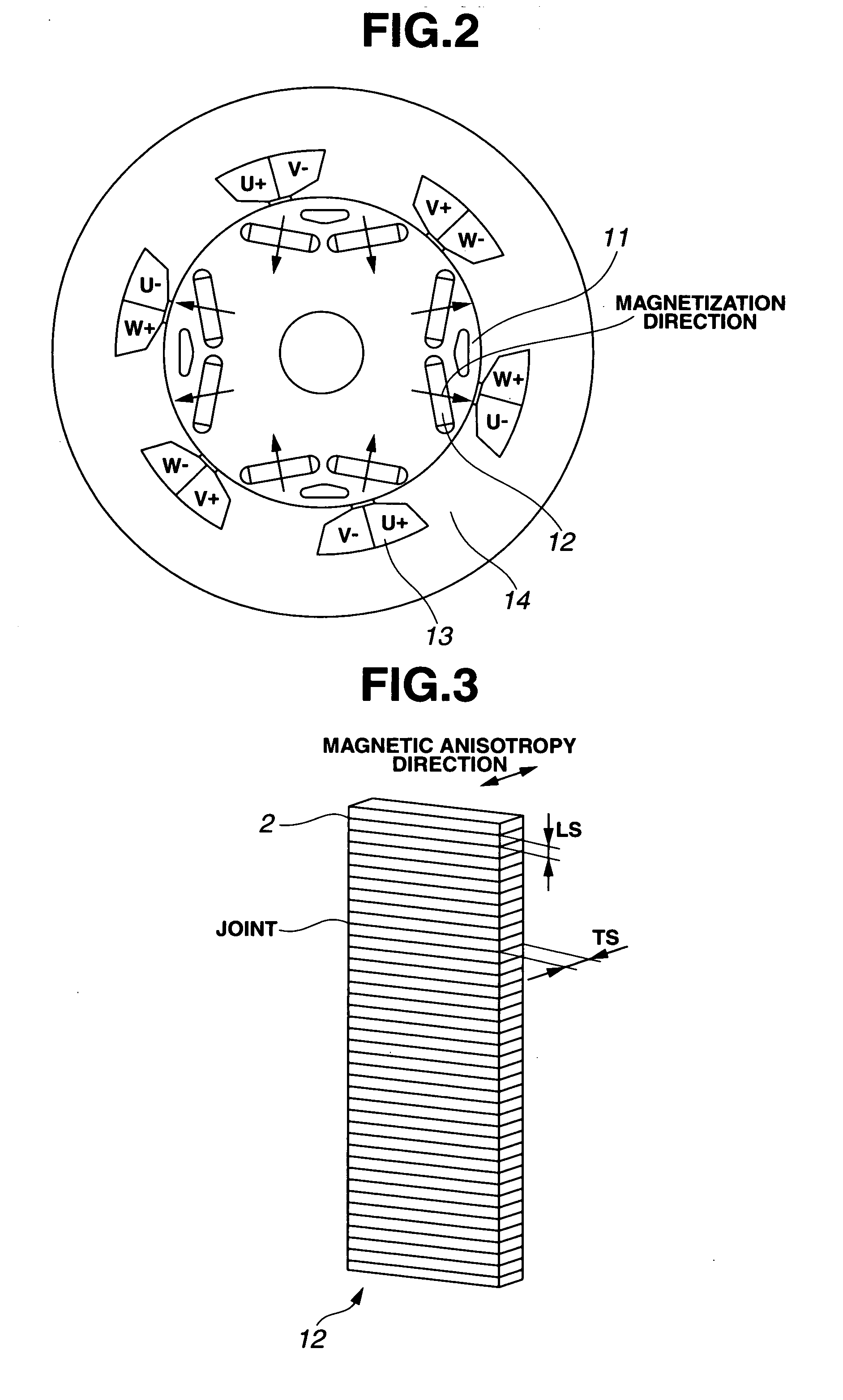
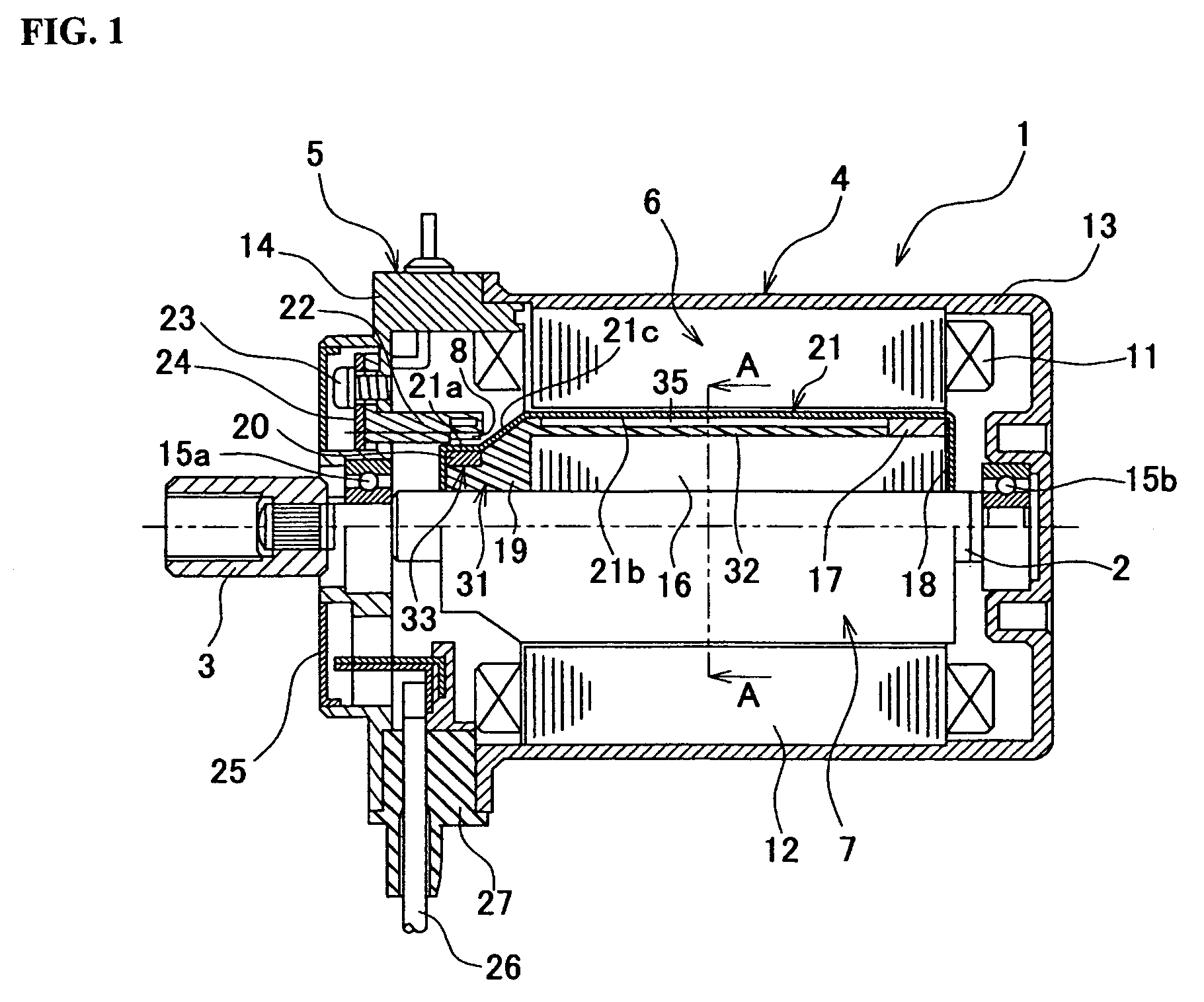
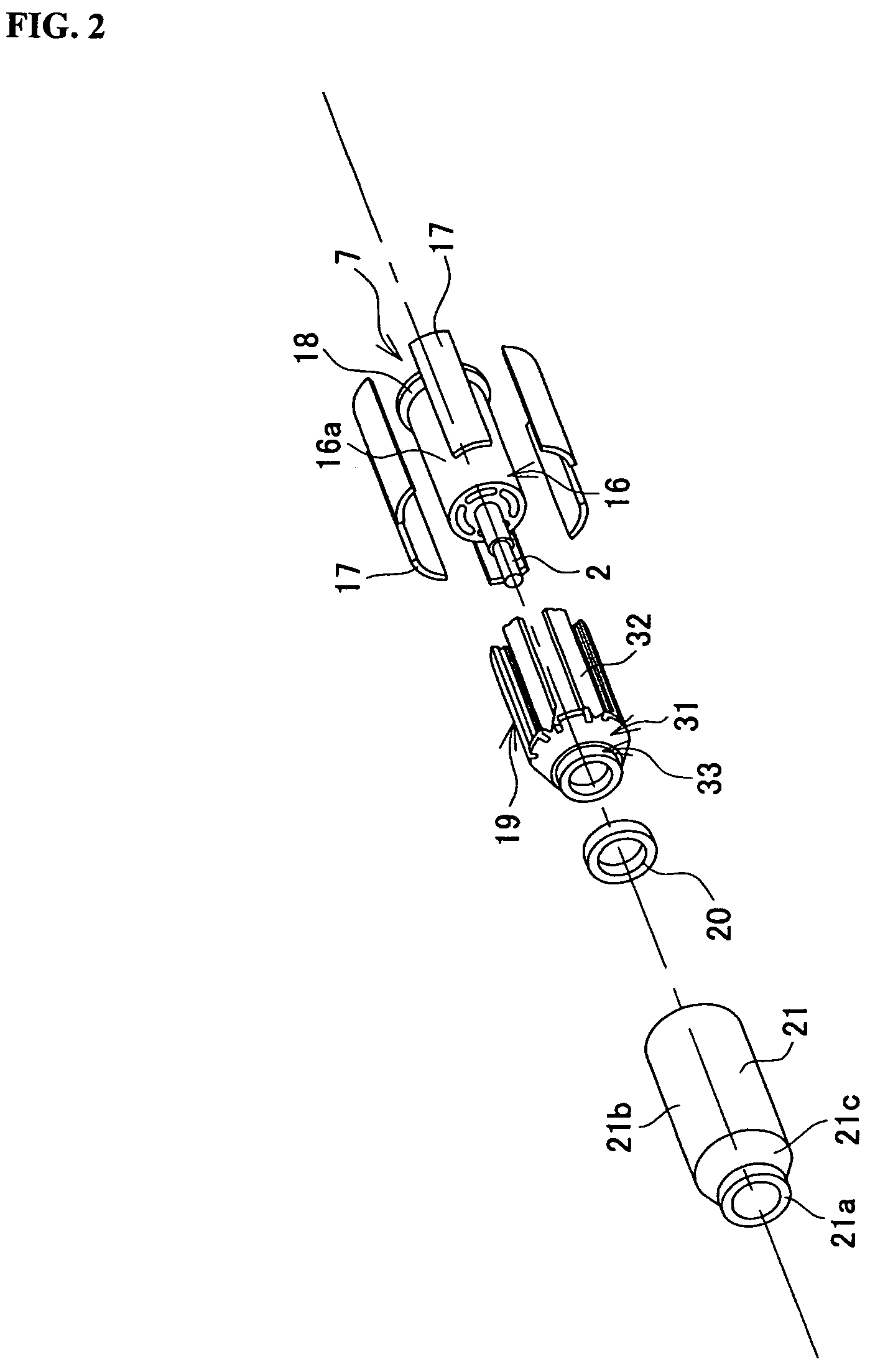
Variable magnetic flux electric rotary machine
InactiveUS20100164422A1Easy to operateWide operating speed rangeDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesElectrical polarityEngineering
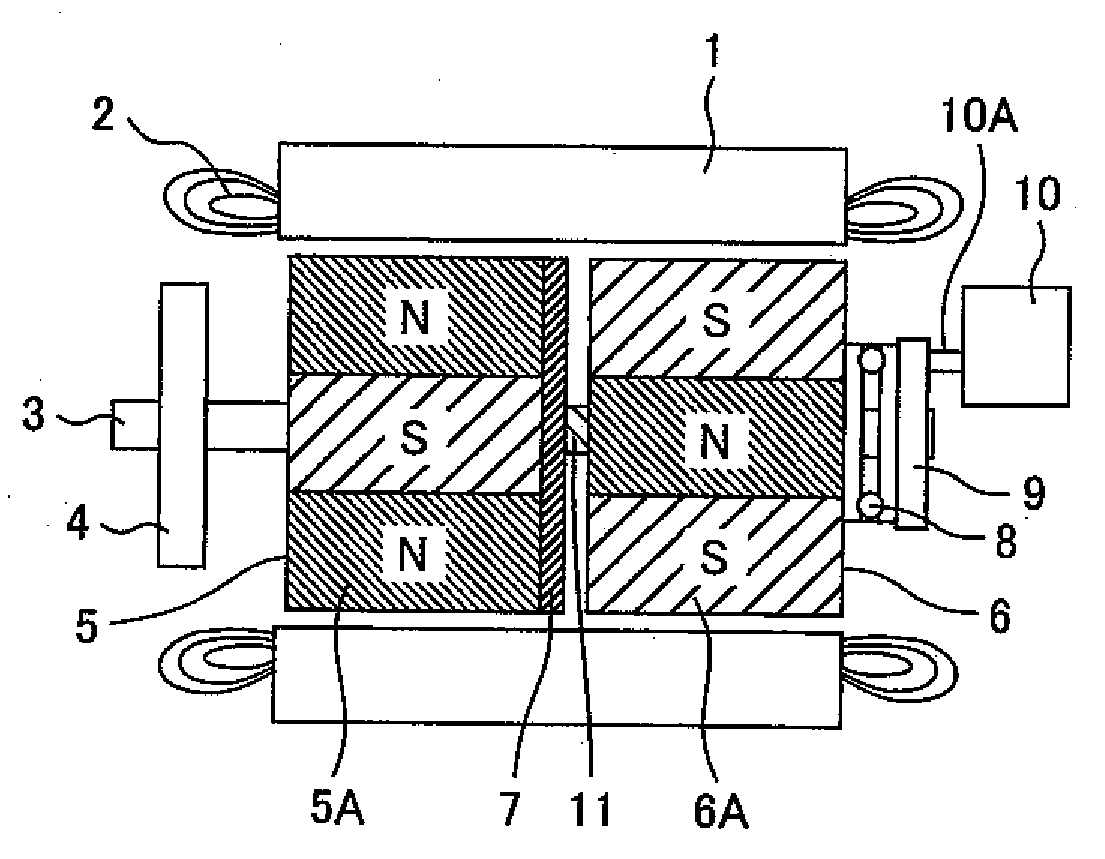
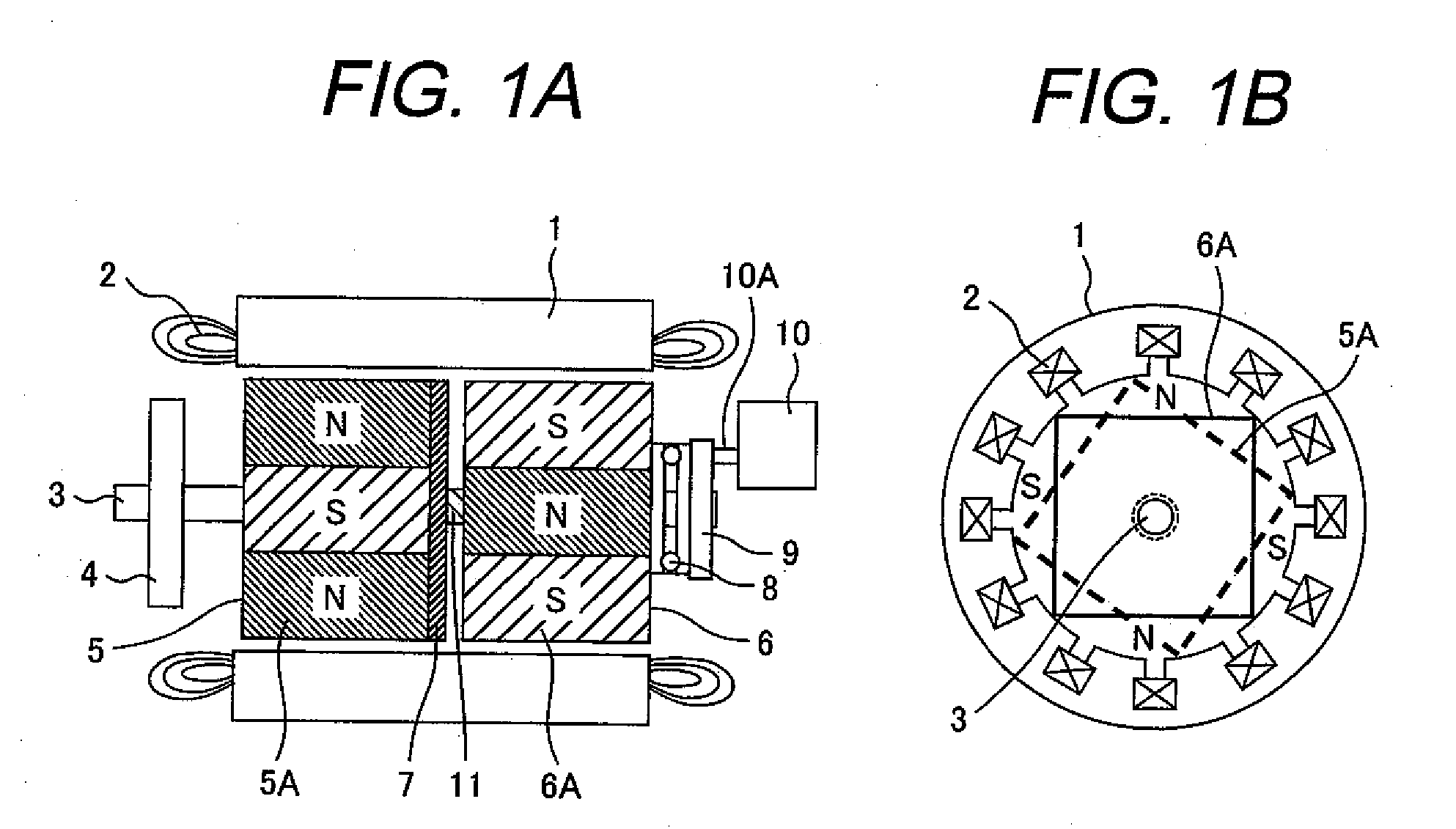
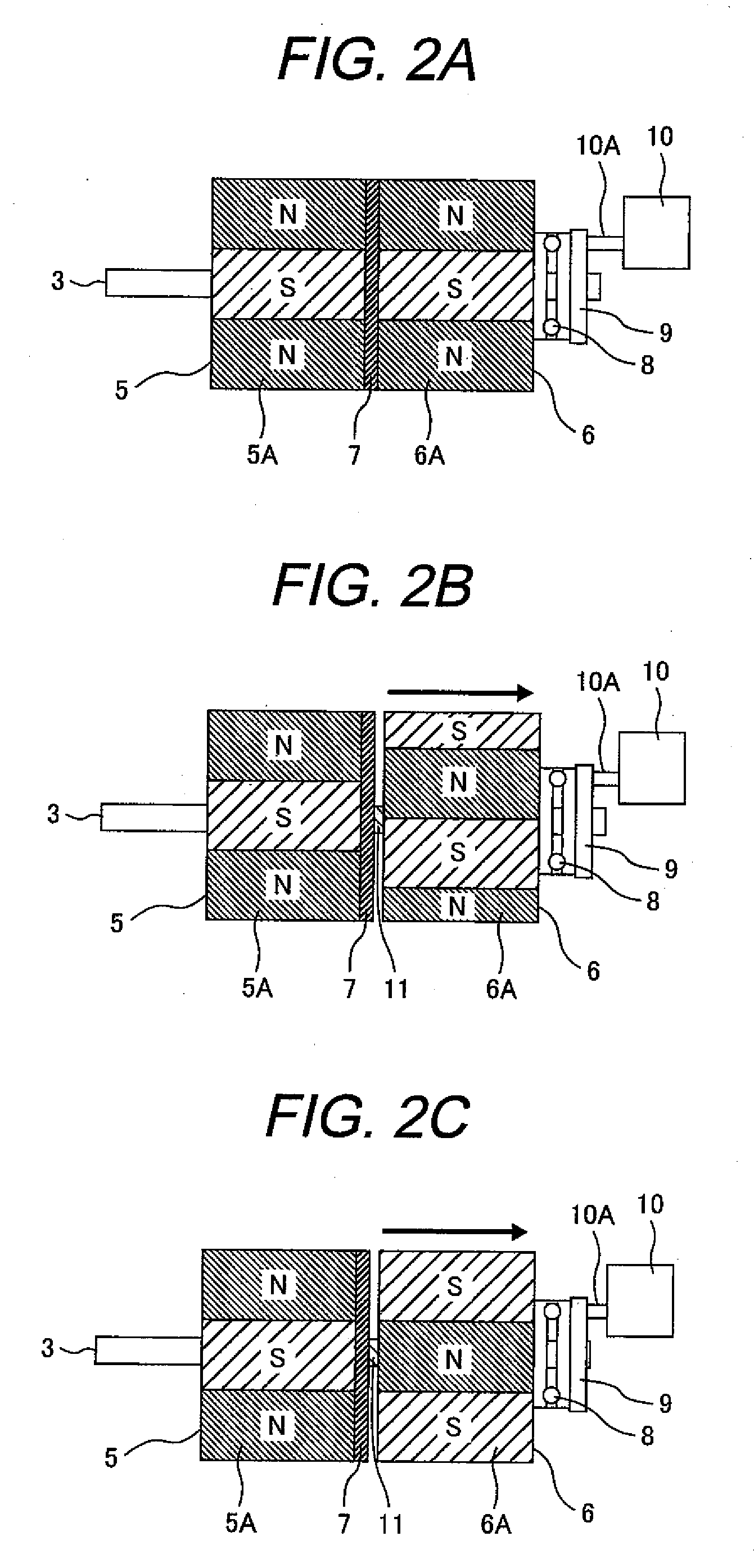
An electric rotary machine is disclosed which can adjust relative angles of sub-rotors continuously and regardless of torque direction without generating an attractive force between the field magnets of the sub-rotors. The electric rotary machine includes: a stator having a winding; a dual rotor which is rotatably disposed with a gap from the stator and divided axially along a shaft into a first rotor and a second rotor each having field magnets with different polarities arranged alternately in a rotation direction; a mechanism for varying the axial position of the second rotor relative to the first rotor continuously; and a non-magnetic member located between the first rotor and the second rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
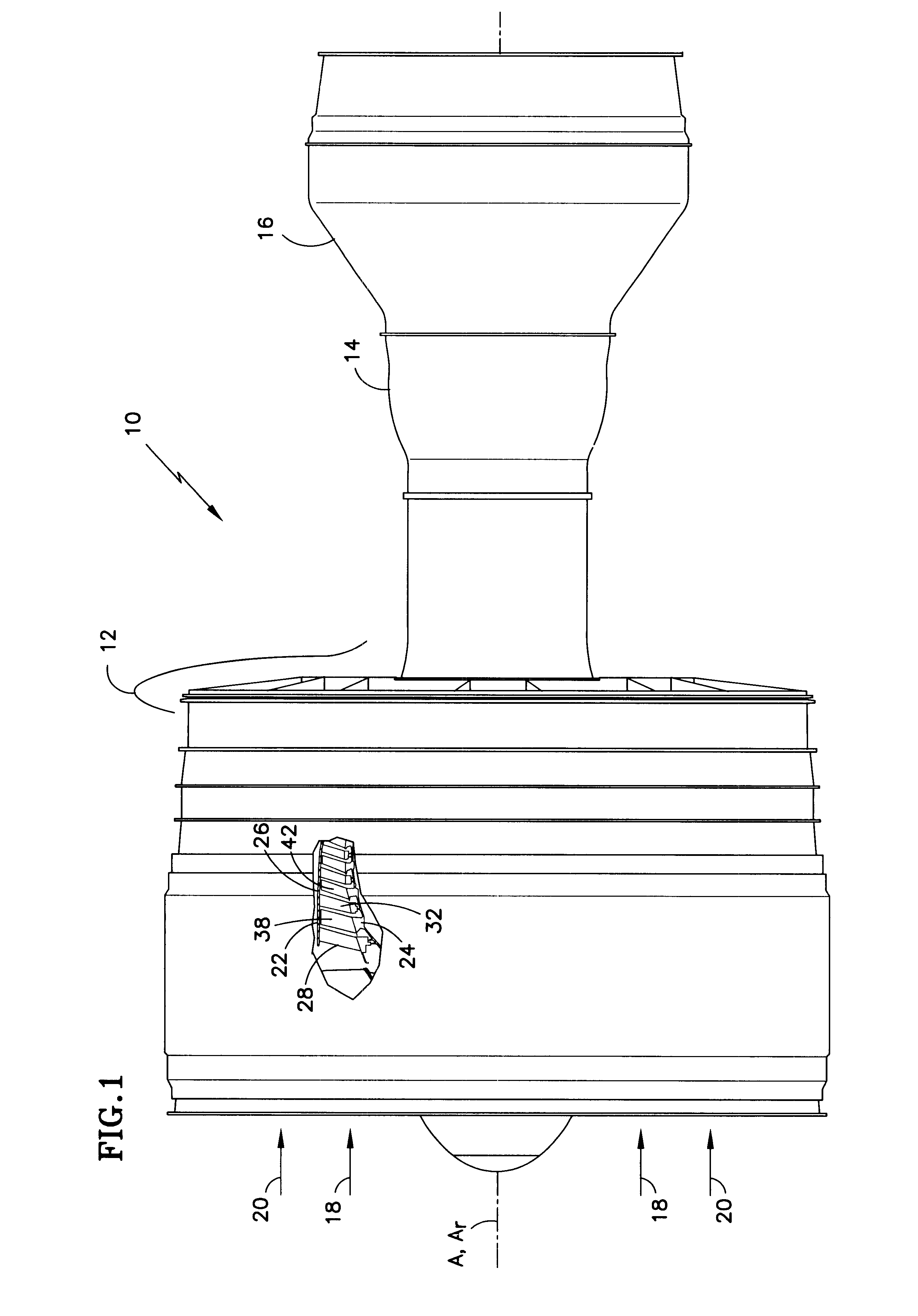
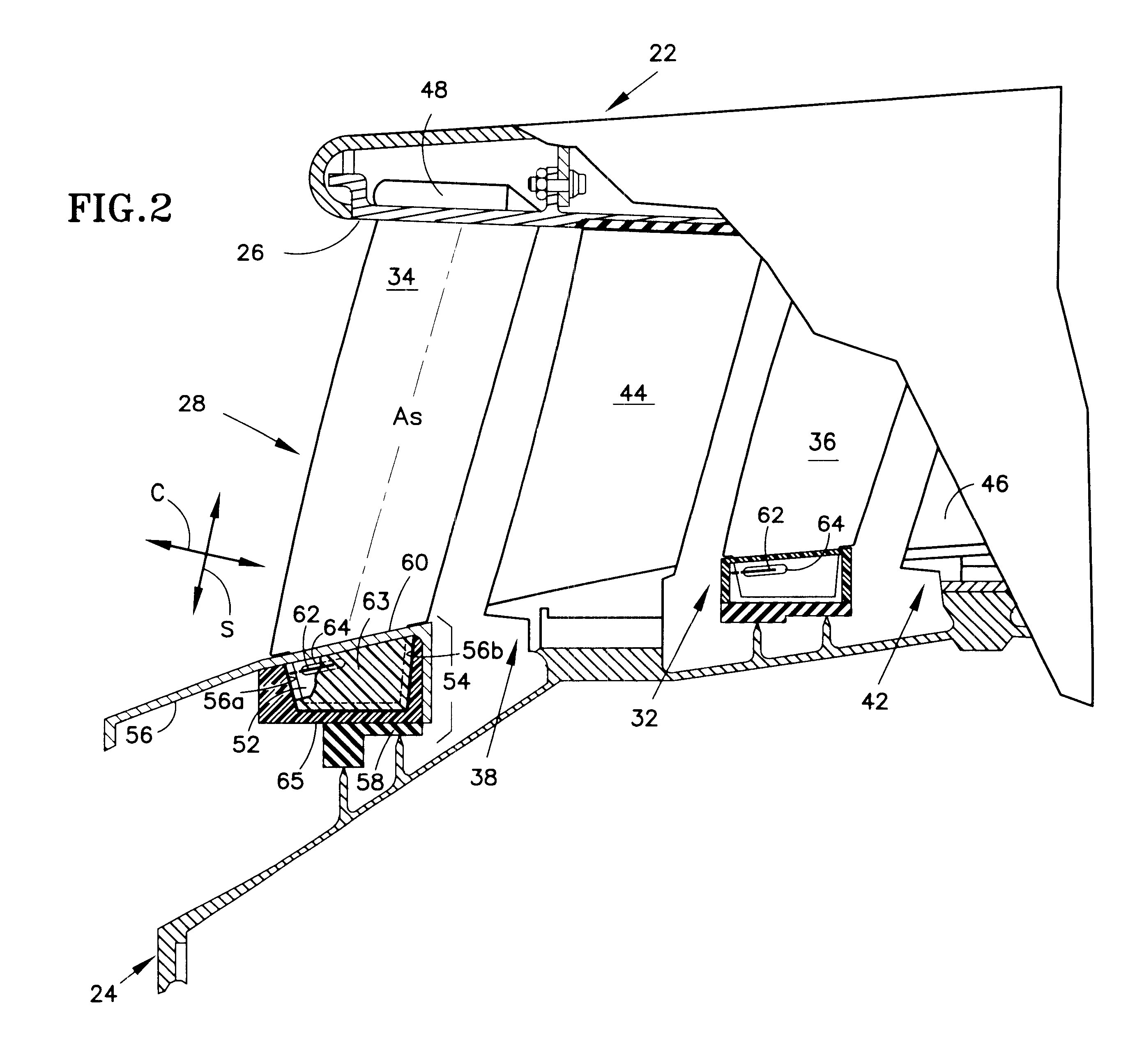
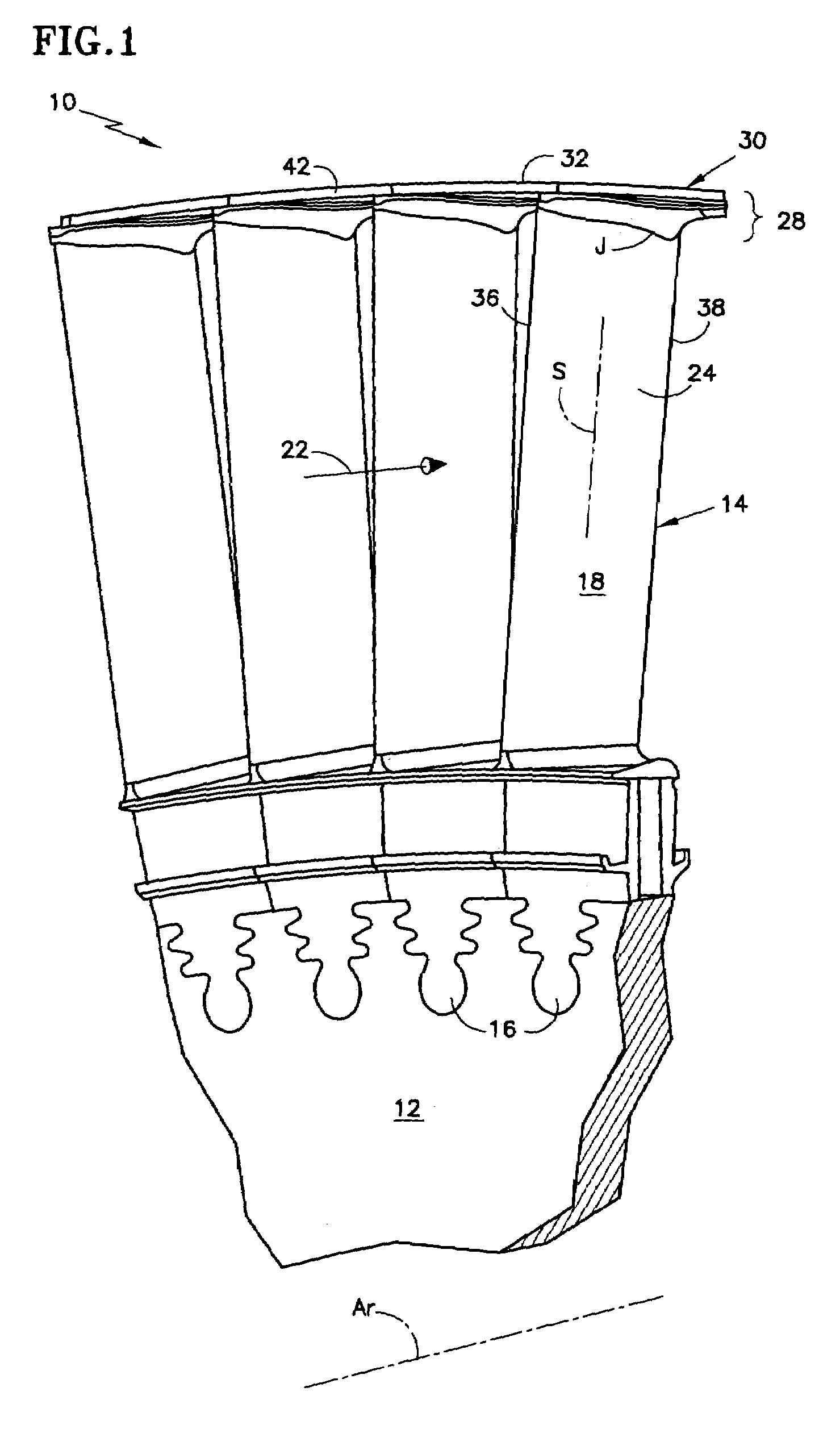
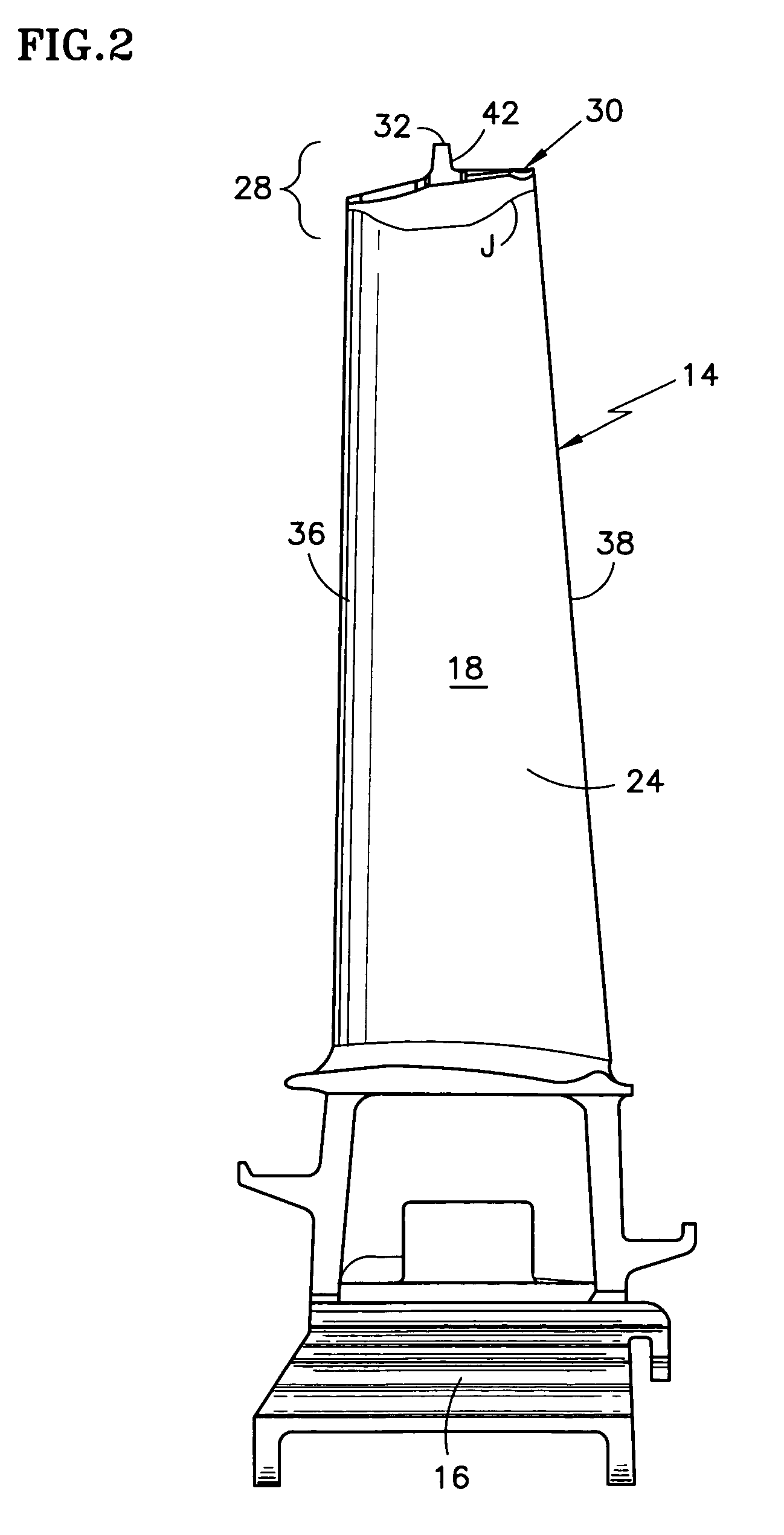
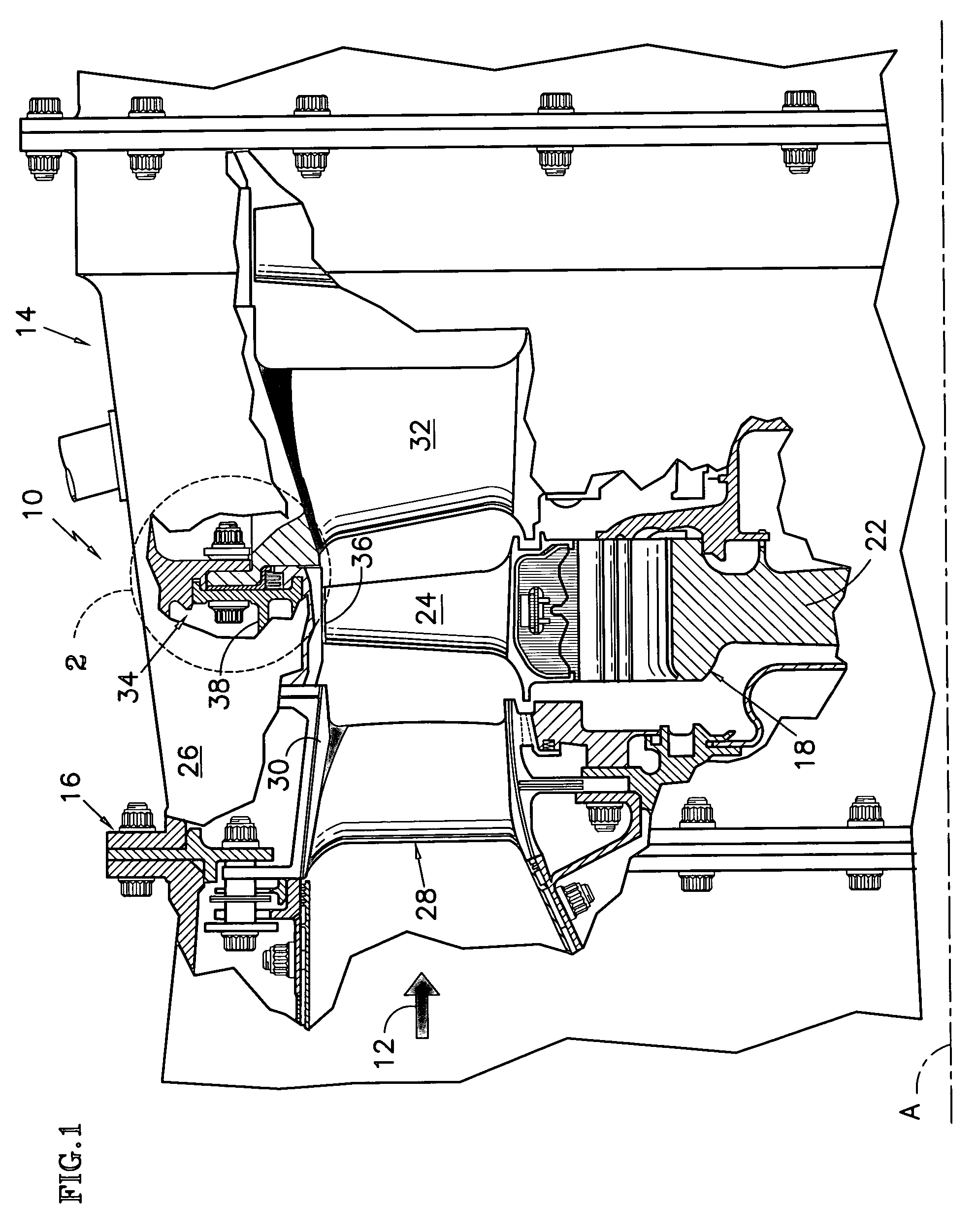
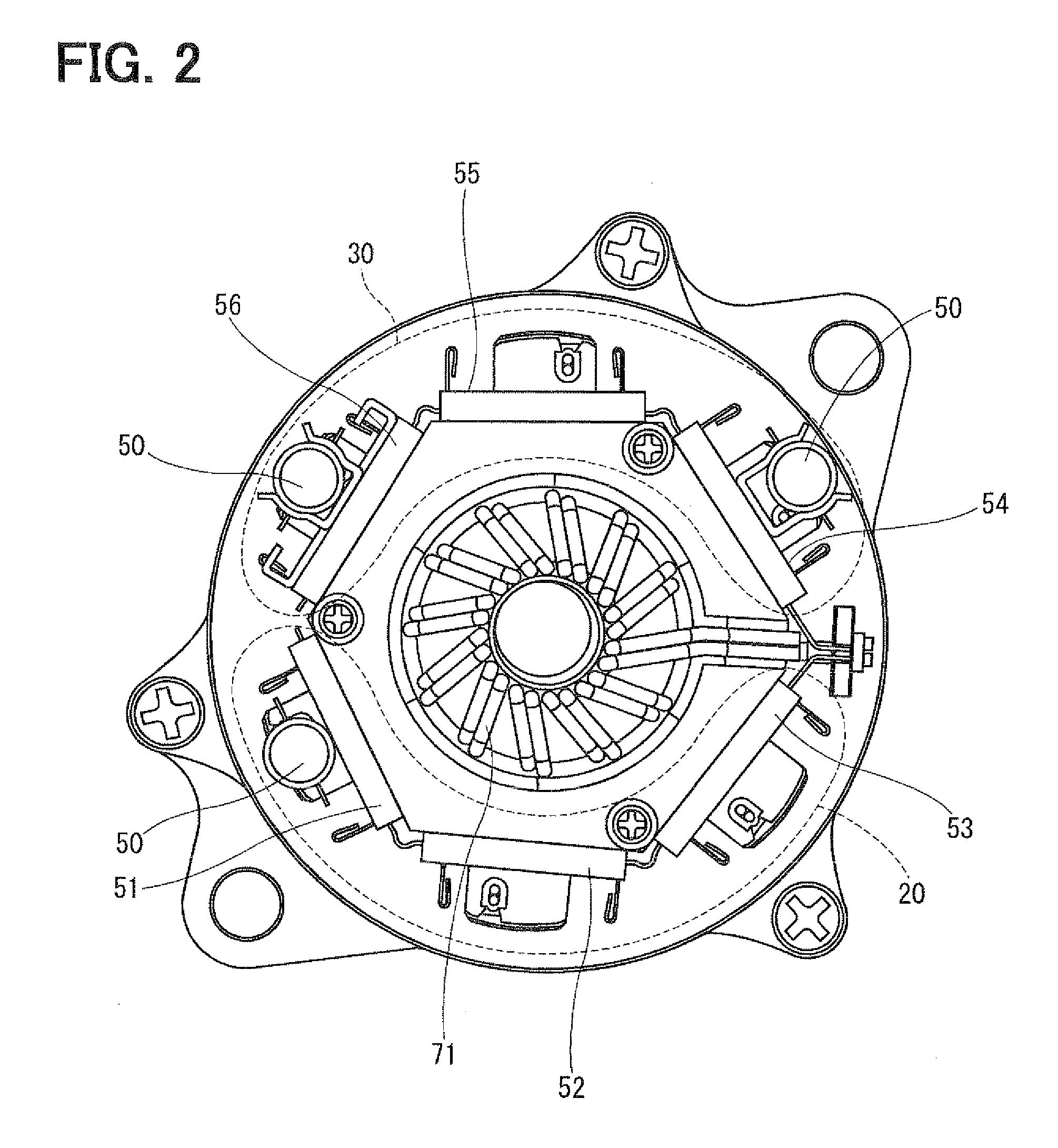
Stator assembly for a rotary machine and clip member for a stator assembly
InactiveUS6409472B1Reduce vibrationPump componentsReaction enginesMechanical engineeringRotary machine
A stator assembly for a rotary machine having a shroud for a stator vane is disclosed. Various construction details are developed which limit movement of the stator vane into the flowpath by reason of the stator vane being restrained by the shroud. In one particular embodiment, a clip member extends through an opening in the tip of the vane and is disposed at a location adjacent a nonflowpath surface of the shroud to restrain the tip of the vane against inward movement through the shroud.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
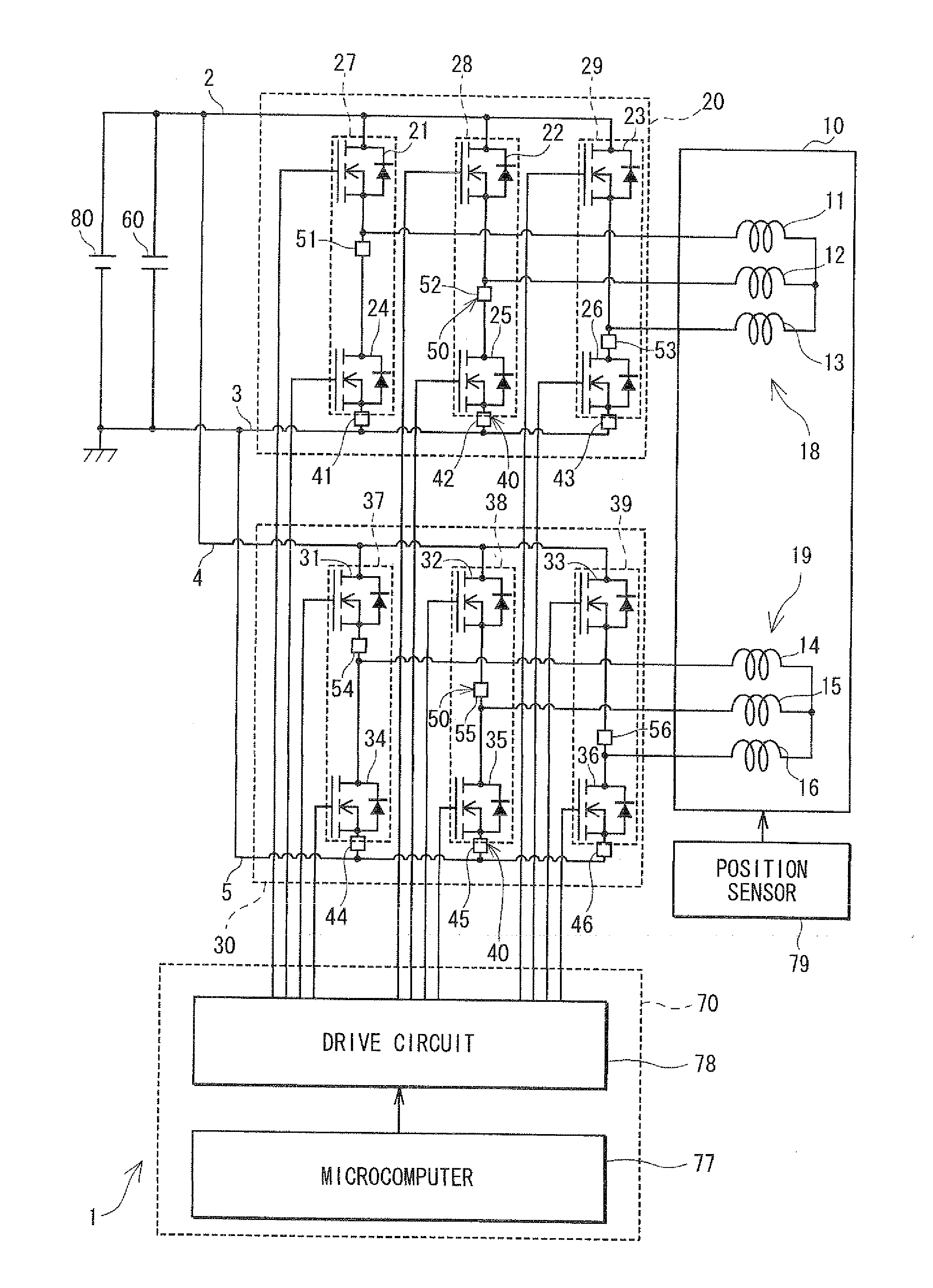
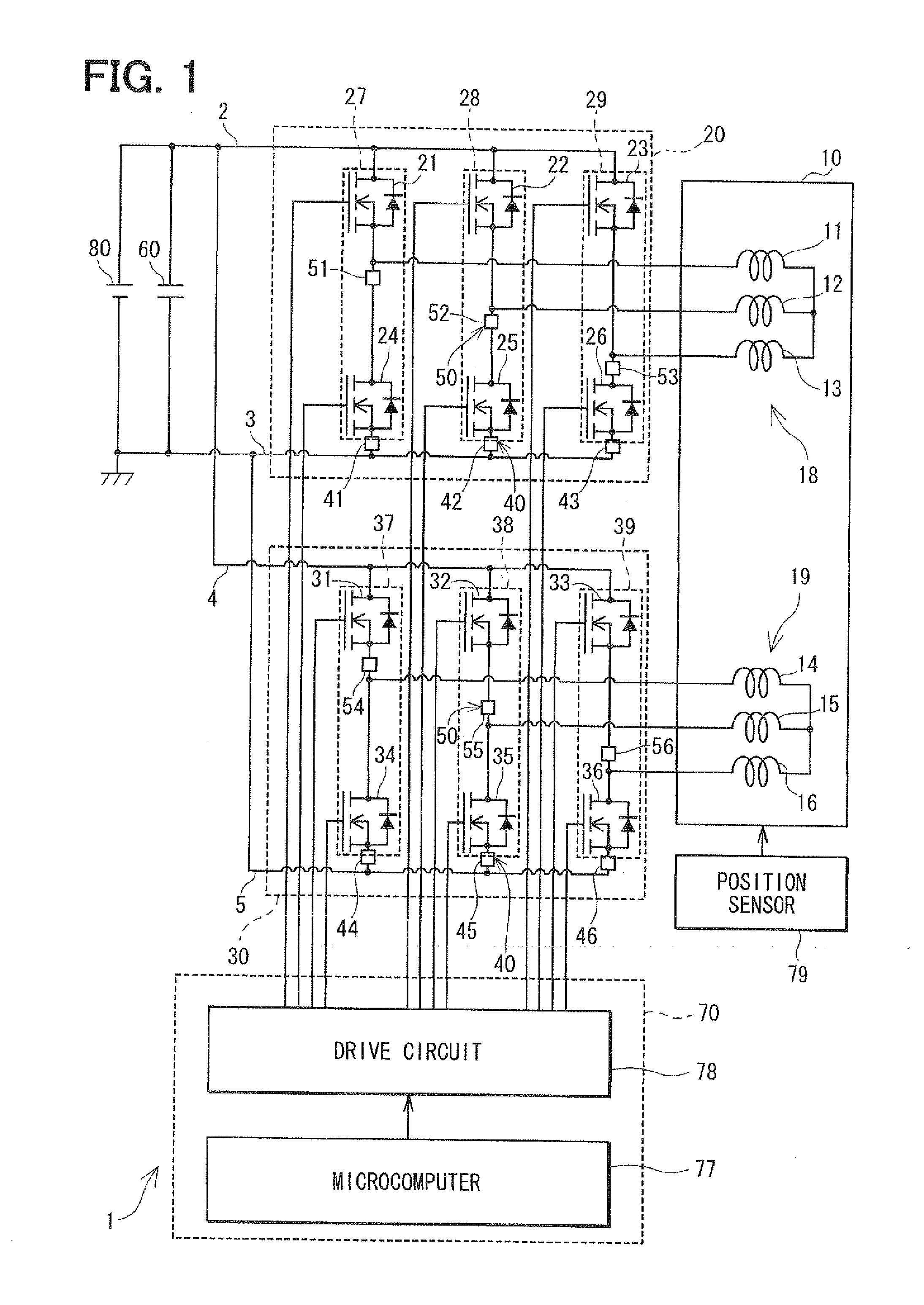
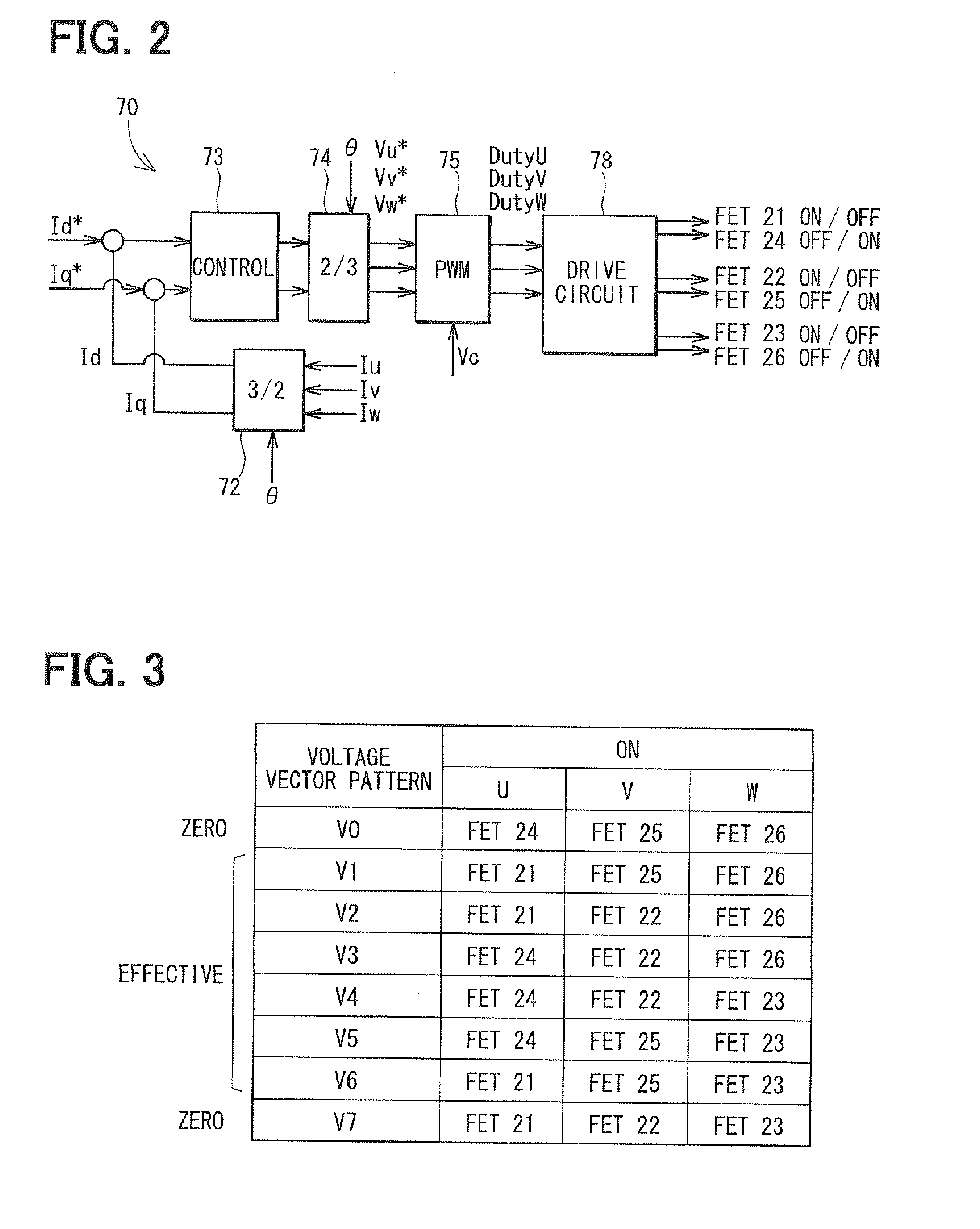
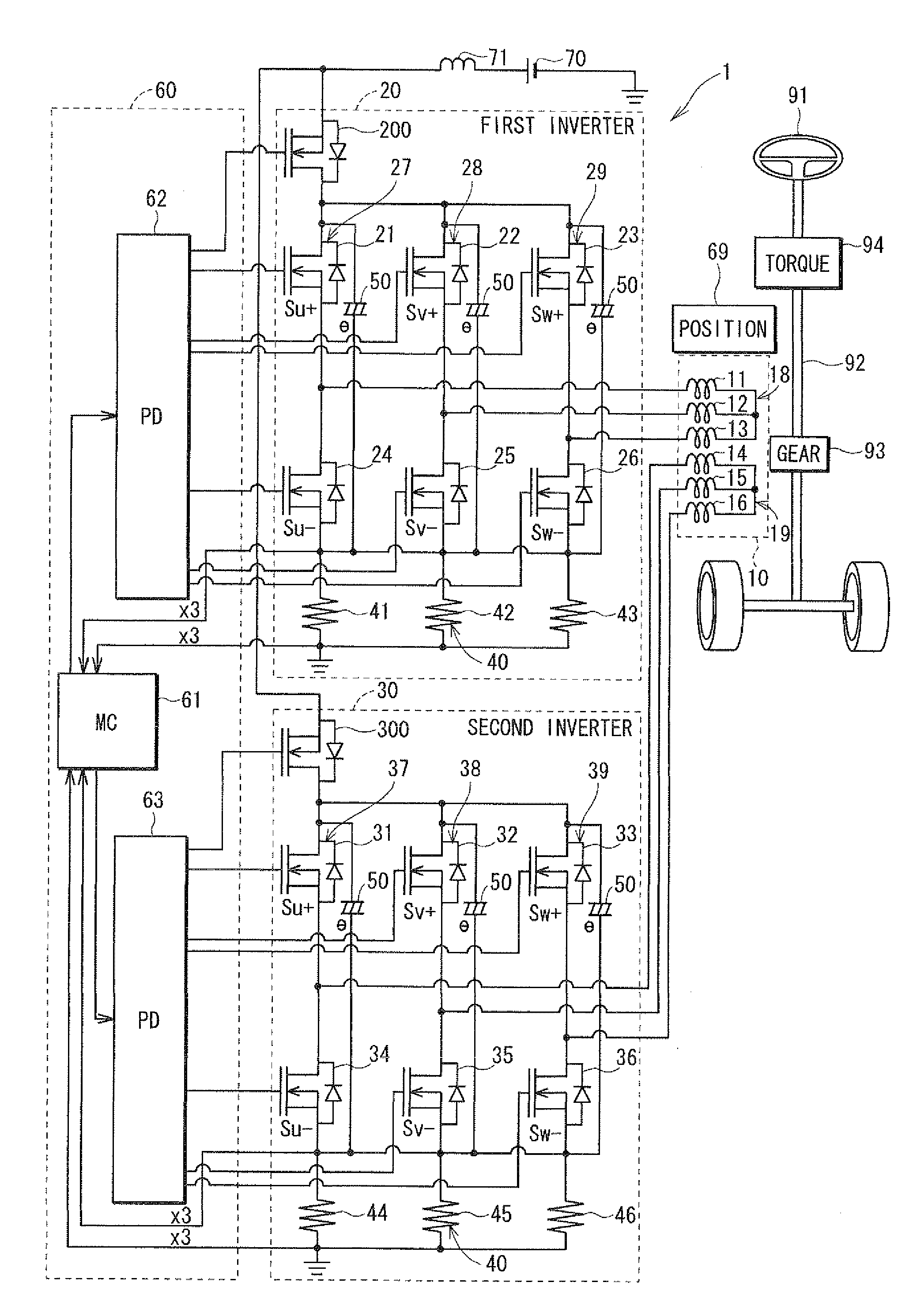
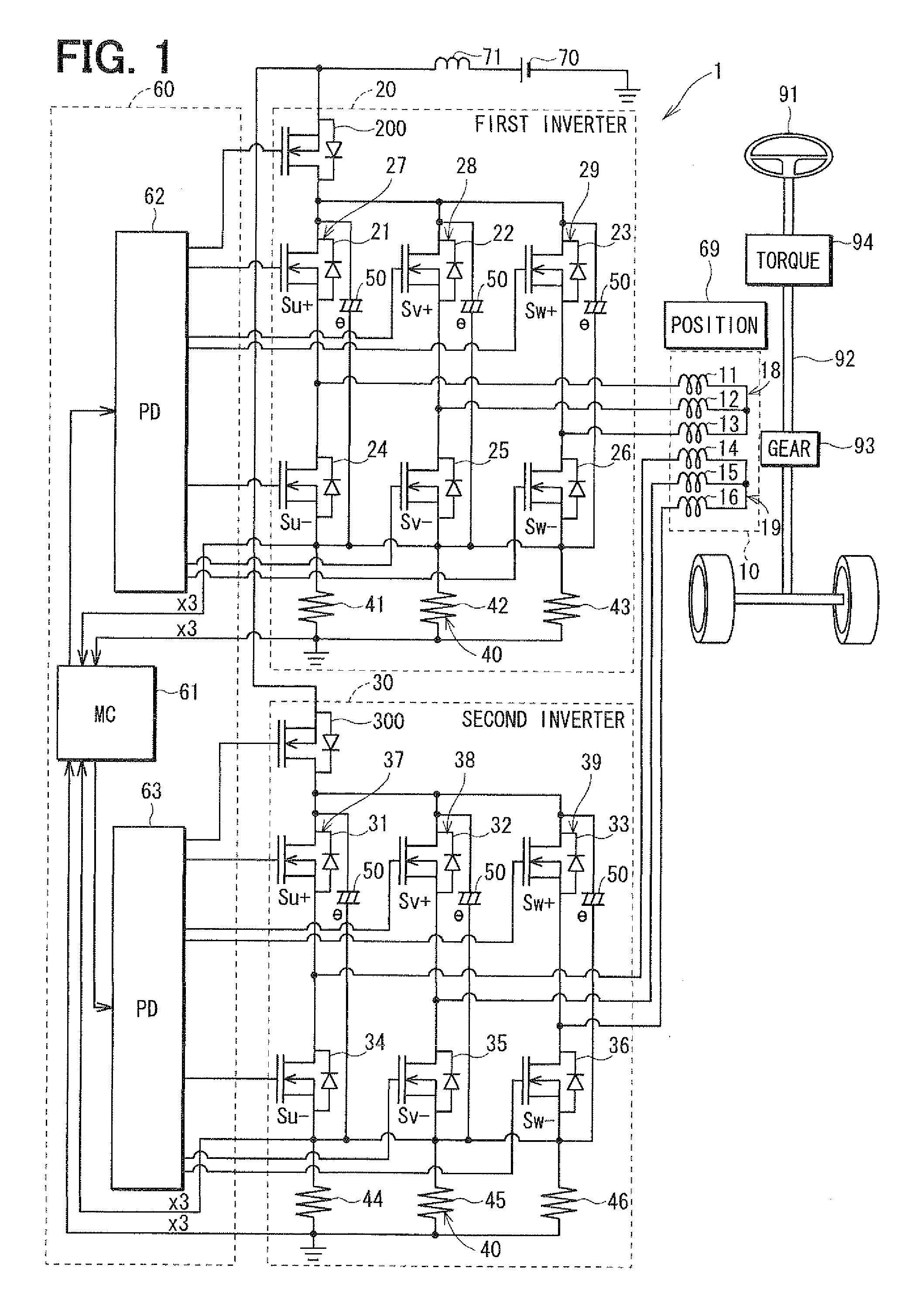
Control apparatus for multi-phase rotary machine and electric power steering system
ActiveUS20110074333A1Smooth rideInhibition effectCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlBrake torqueElectric power steering
A control apparatus for a multi-phase rotary machine includes a control unit and a plurality of power supply systems including respective inverter units. When a short-circuiting failure occurs in one of the systems due to an ON-failure in any one of FETs in an inverter unit of the failure system, the control unit stops driving of the rotary machine by bringing all the FETs in the failure system into the OFF state. The control unit controls FETs of the non-failure system such that a brake torque generated in the failure system is cancelled or the influence of the brake torque exerted on the driving of the motor is reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
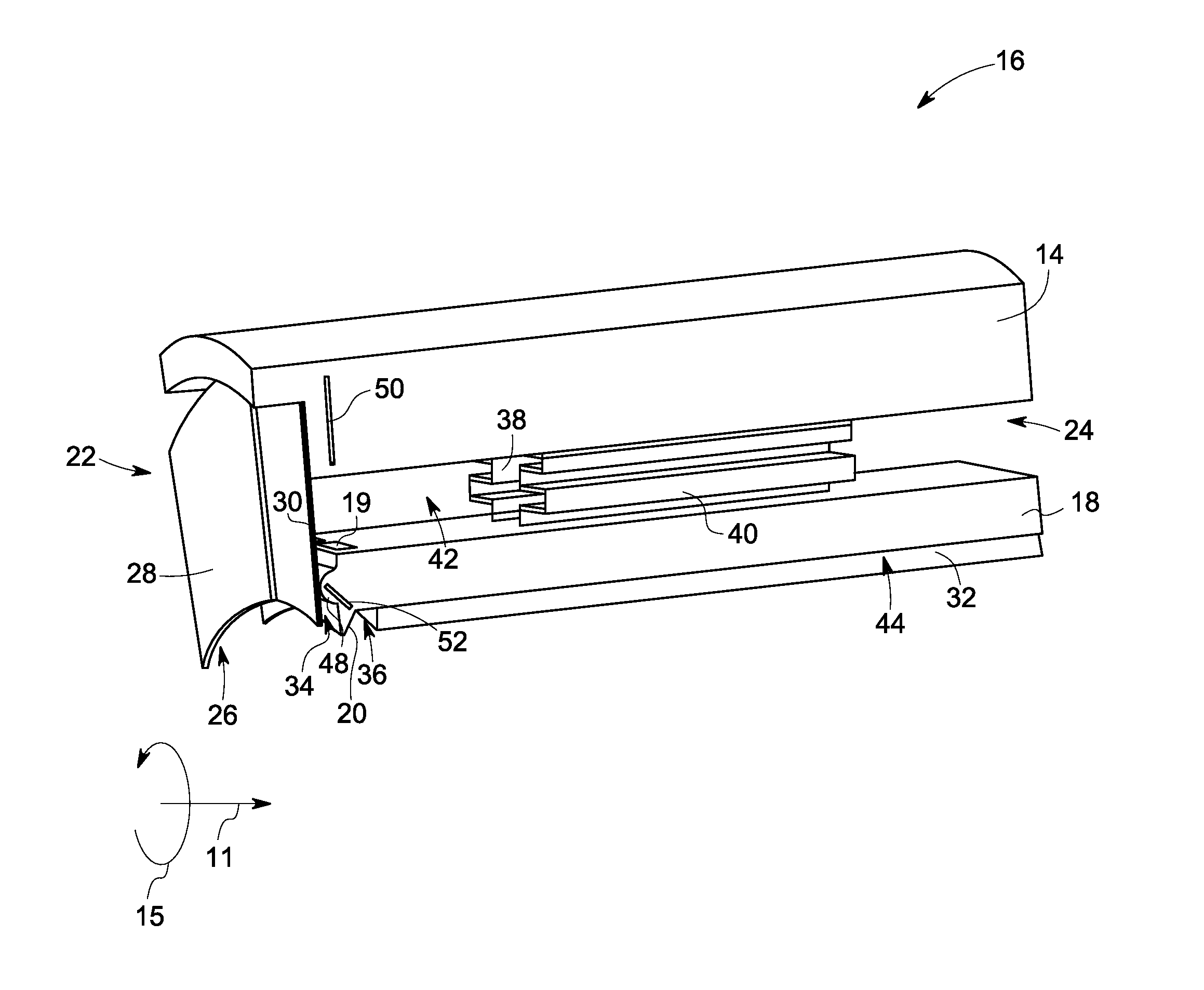
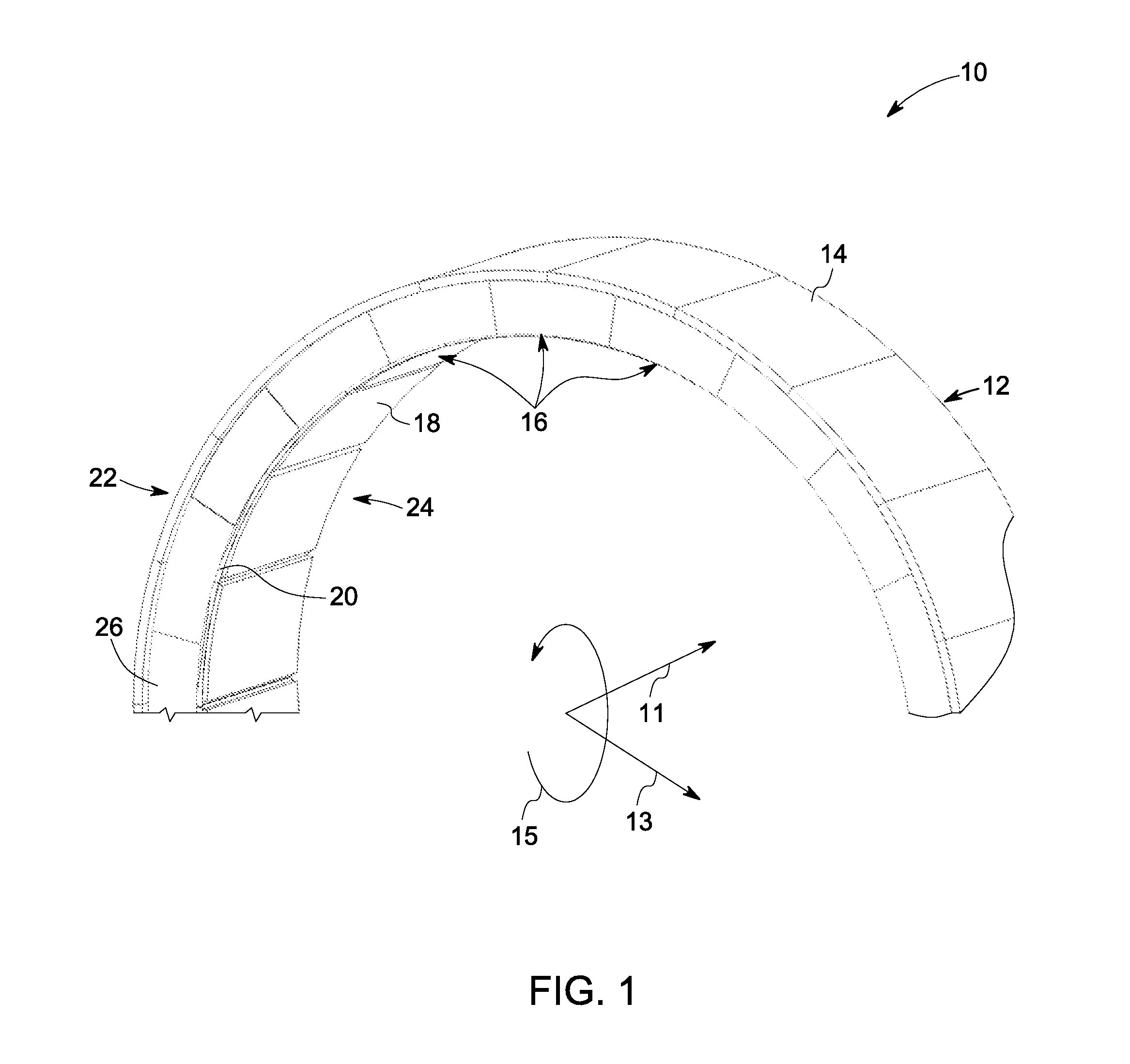
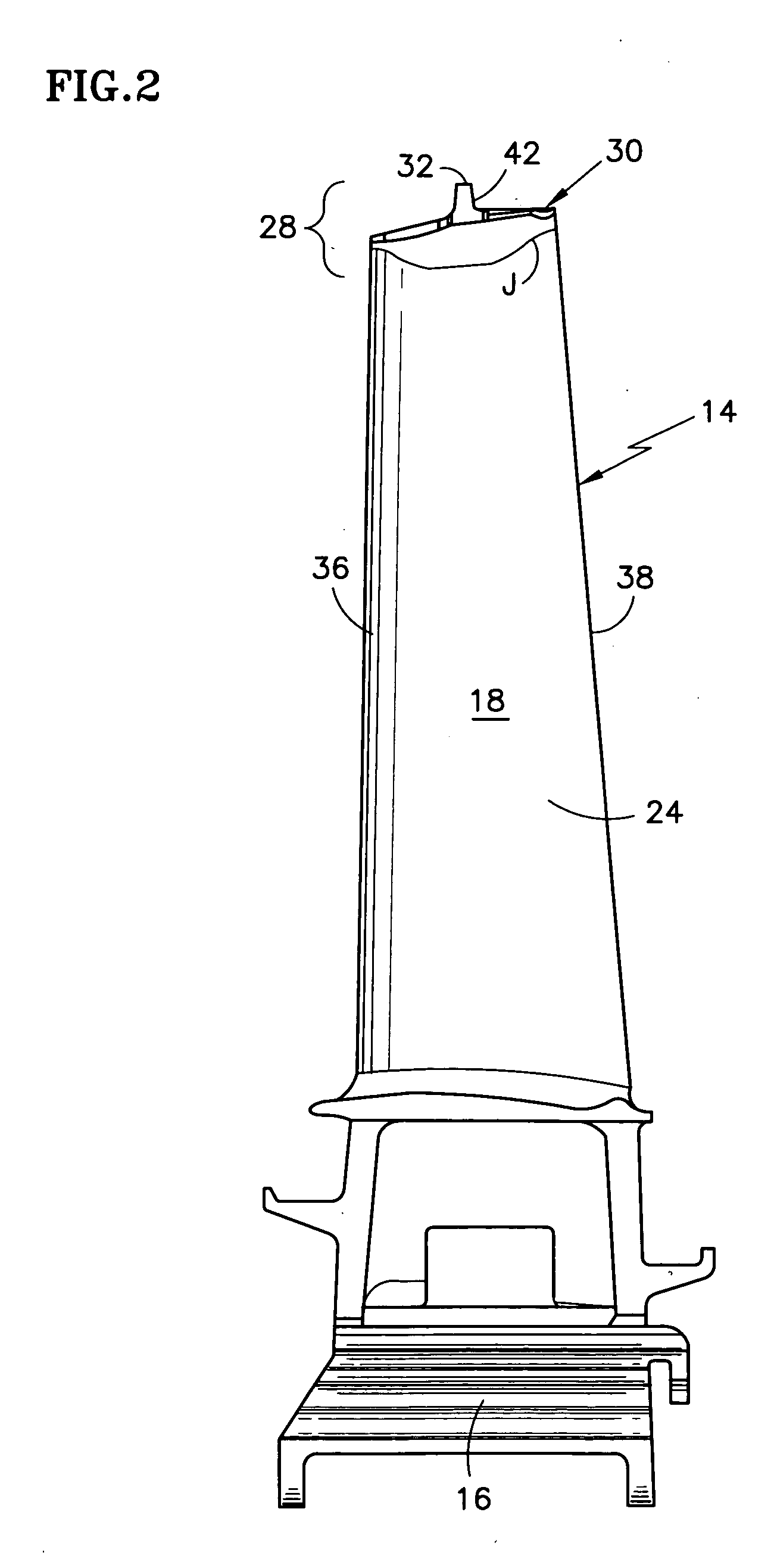
Stator assembly, module and method for forming a rotary machine
ActiveUS20070025837A1Engine efficiencyEasy to manufacturePump componentsBlade accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A stator assembly for a rotary machine having an array of wall segments for bounding a working medium flow path is disclosed. Various construction details which provide a sealing structure for the segments are developed. In one detailed embodiment, a removable seal retainer for a seal chamber bounded by wall segments traps a resilient seal member in the seal chamber. In one particular embodiment, a modular subassembly for the engine is an outer air assembly disposed in a fixture as the subassembly is assembled.
Owner:RTX CORP
Riding lawn mower
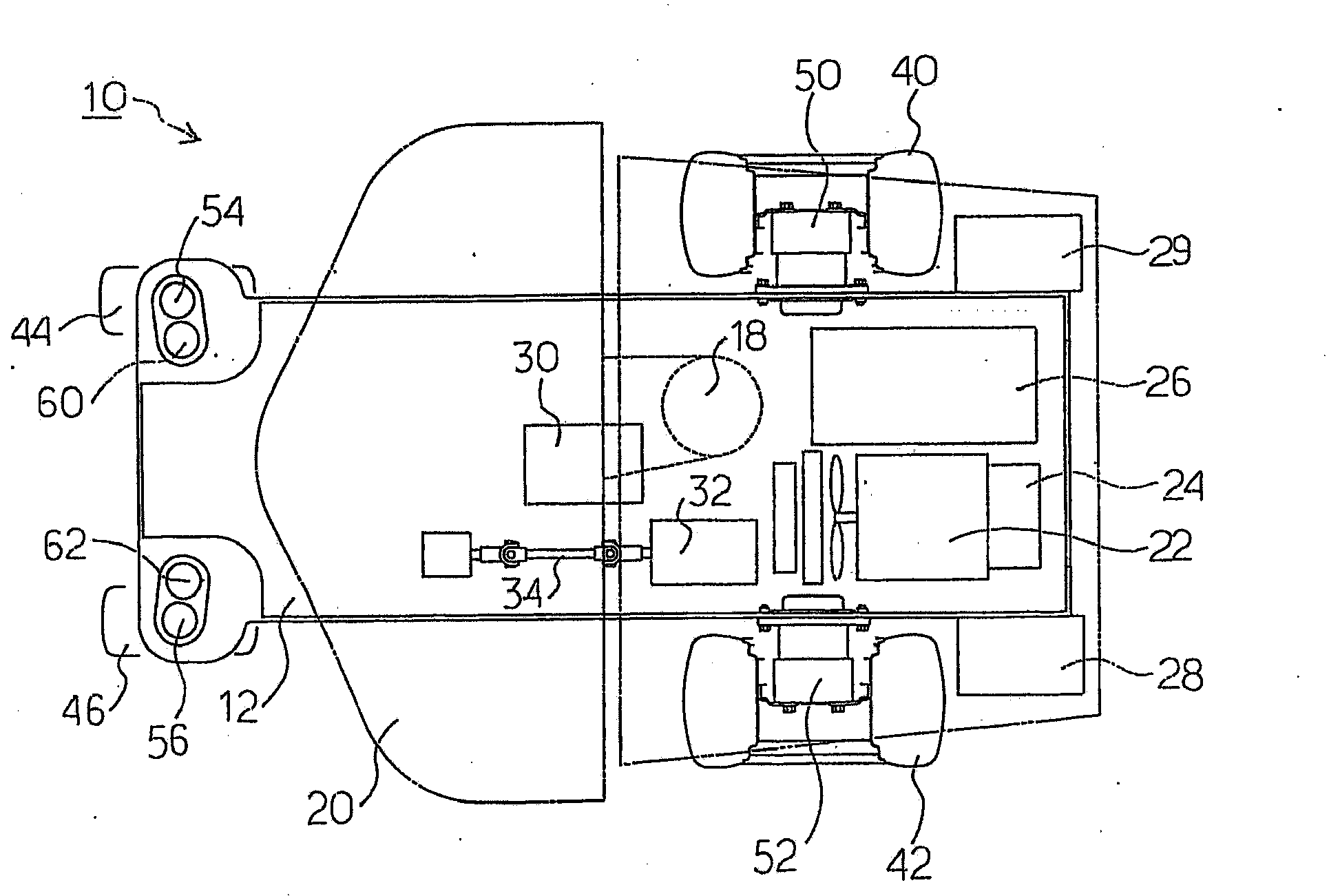
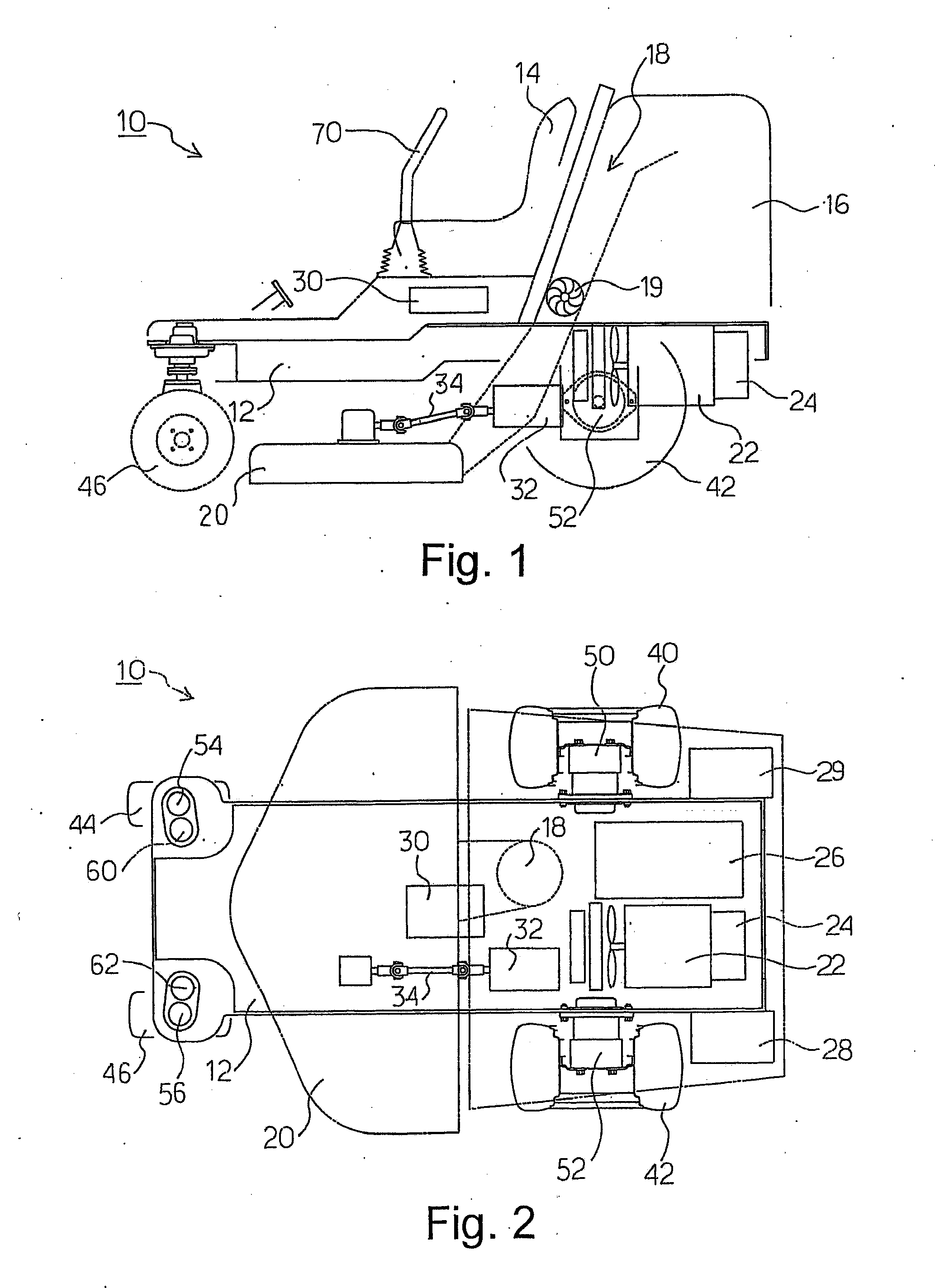
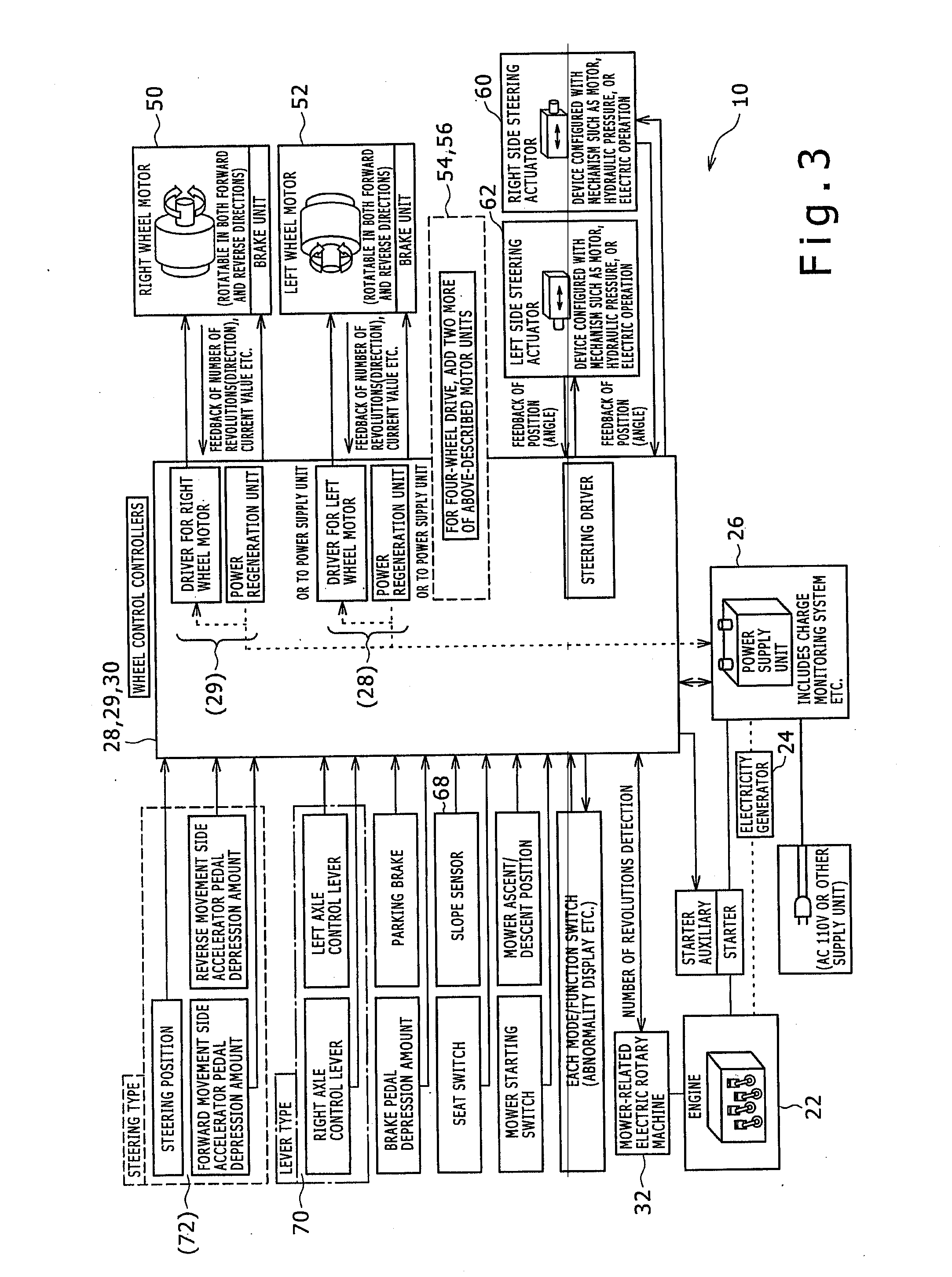
ActiveUS20090000839A1Preventing situationInhibitionDigital data processing detailsMowersKnife bladesEmbedded system
A riding lawnmower includes left and right wheels, at least one caster wheel, a lawnmower blade or reel, and a control section. The left and right wheels are independently driven by electric rotary machines to travel. The lawnmower blade or reel is driven for mowing. The control section, in response to turn instruction input by a turn operator, controls the left and right wheels according to preset standard setting conditions, or according to deceleration setting conditions which differ from the standard setting conditions, under which at least one of a vehicle movement speed and vehicle turning speed is decelerated more than under standard setting conditions. The riding lawnmower includes a section designating either standard setting conditions or deceleration setting conditions. In a riding lawnmower, left and right wheels are caused to turn around a turn center position corresponding to a turn instruction according to designated setting conditions.
Owner:KANZAKI KOKYUKOKI MFG
Apparatus and method for driving rotary machine
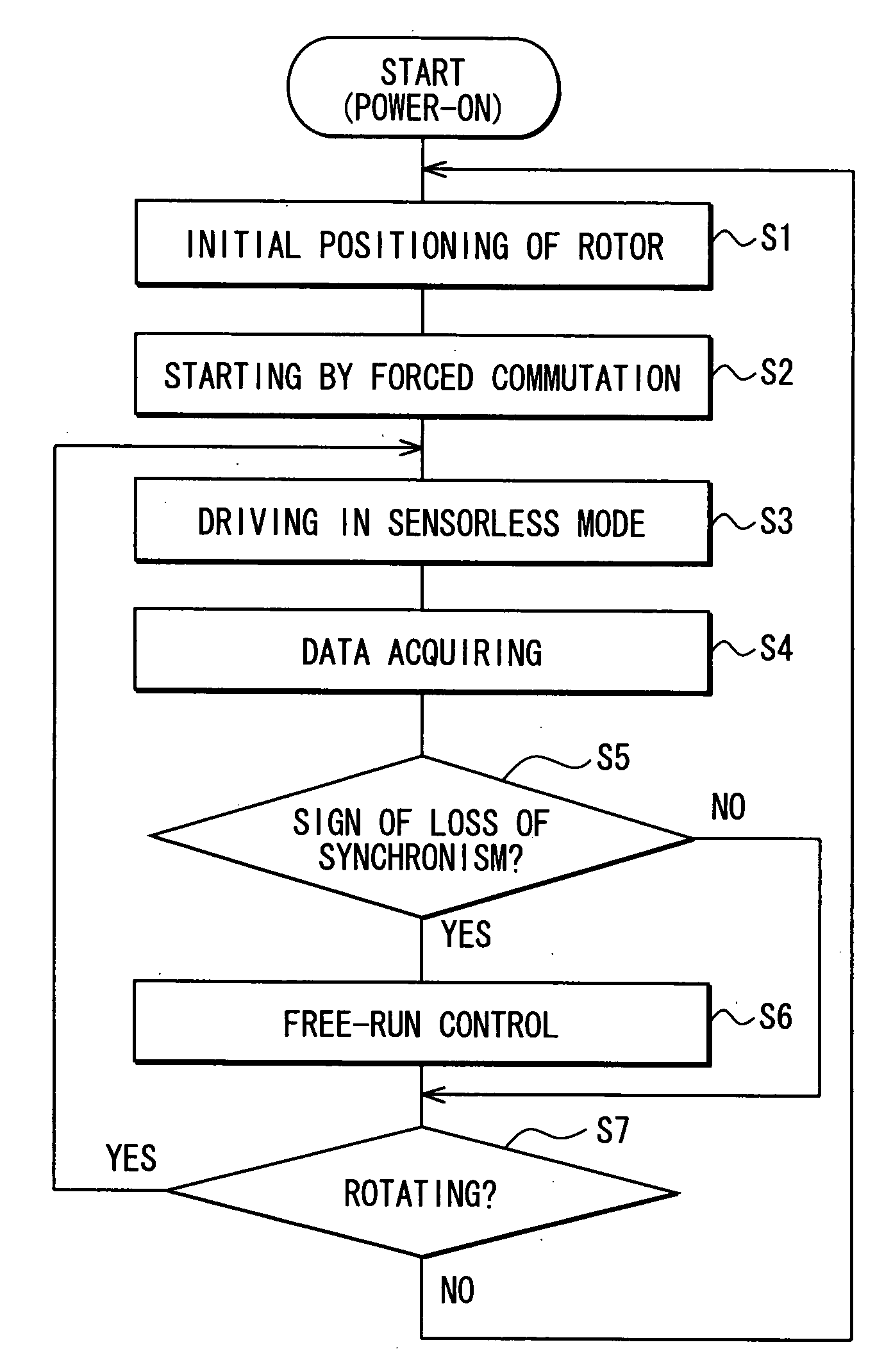
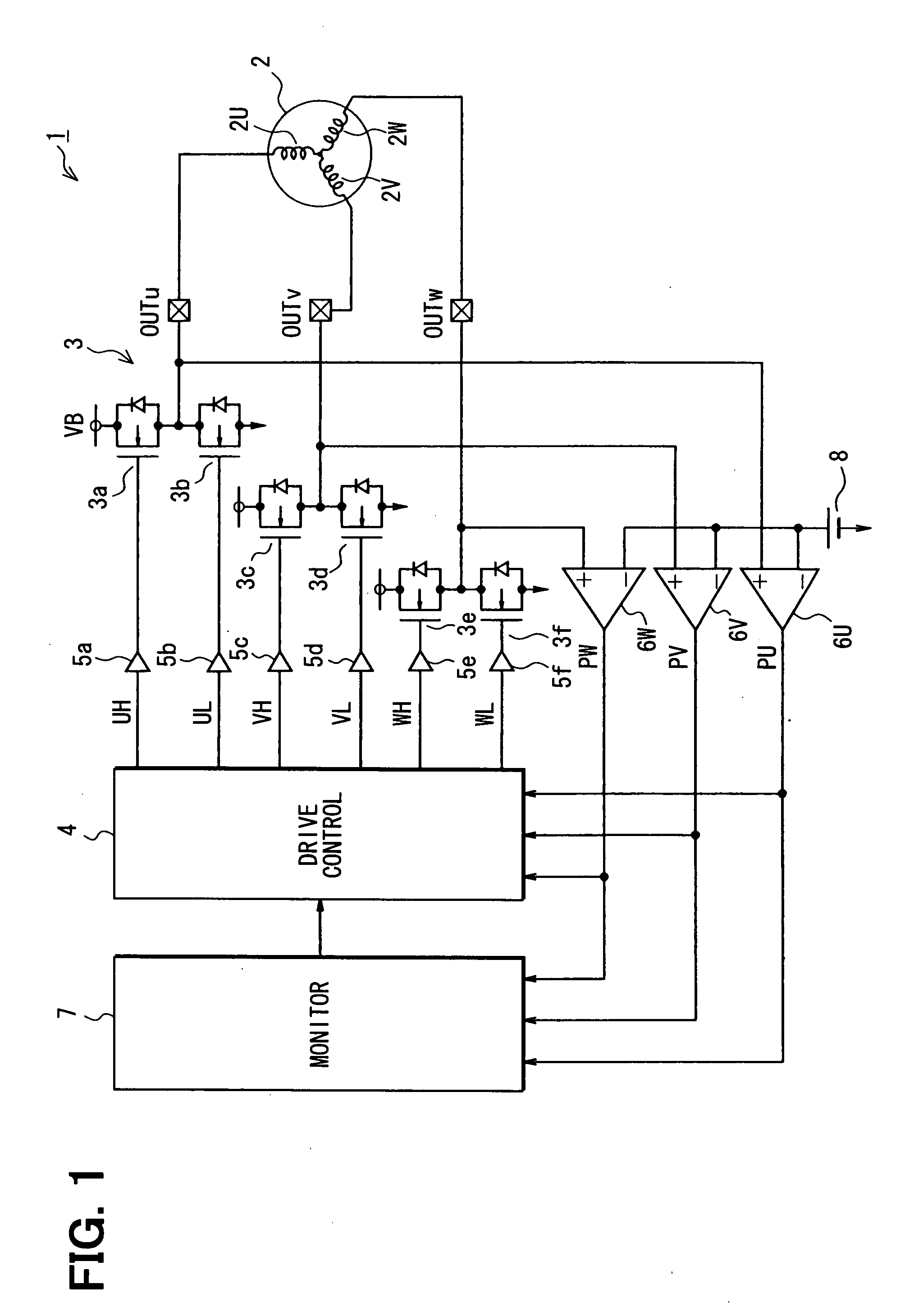
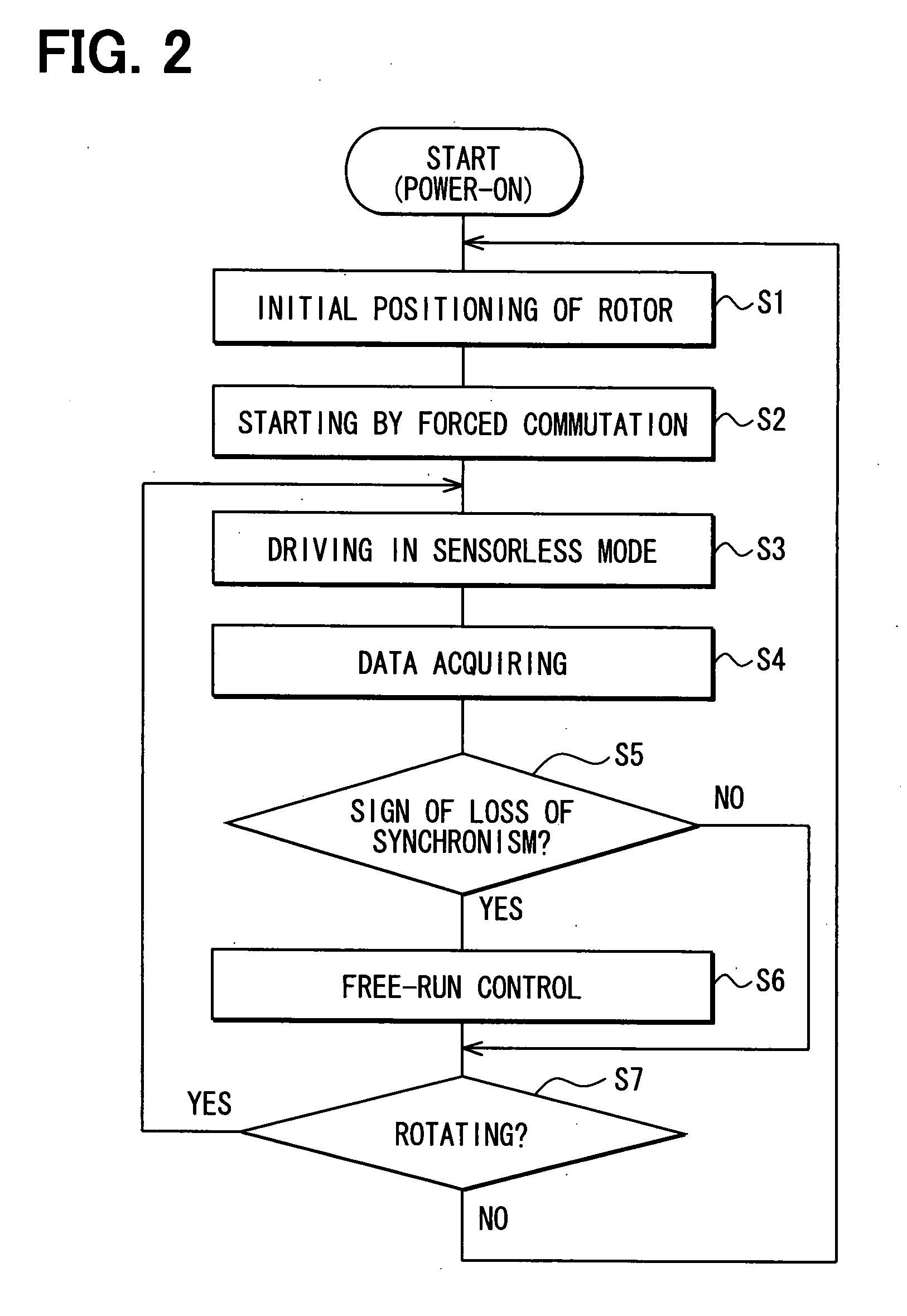
InactiveUS20080252242A1Loss of stateShort timeMotor/generator/converter stoppersCommutation monitoringRotary machineSynchronism
A motor driving apparatus has a loss-of-synchronism monitoring circuit that monitors the rotation of a rotary machine such as a brushless DC motor to detect a sign of transition to a state of loss of synchronism. When the sign is detected, an energization control circuit temporarily stops driving of the rotary machine to bring it into a free running state, and thereafter carries out control so as to resume driving of the rotary machine. Further, the motor driving apparatus has an inverter and a drive control circuit that controls switching operation of the inverter based on rotation of the rotary machine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Permanent magnet type electric rotary machine and compressor using the same
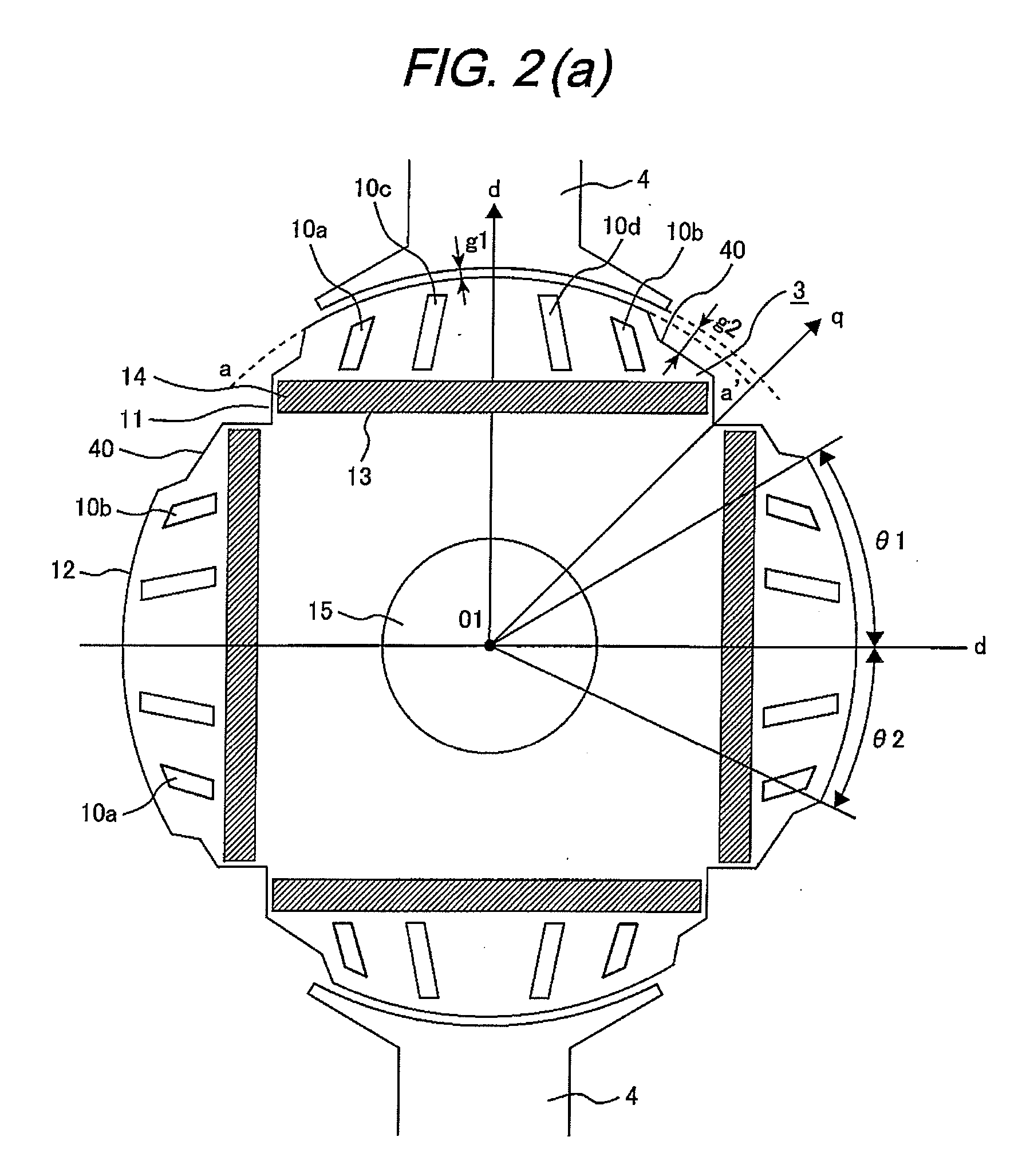
InactiveUS20080018190A1Reduce vibrationReduce noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineMagnetic flux
A permanent magnet type electric rotary machine includes a stator including a stator core having teeth and slots, and a rotor provided with permanent magnets as magnet poles in a rotor core. A pole core portion which between each of the permanent magnets and an outer surface of the rotor core is provided with a plurality of pole slits. A region of the pole core portion is defined by concave portions provided on q-axes to be interpolars on both sides of the pole core portion, and thereby configured that a gap between the outer surface on the q-axis of the rotor core and an inner surface of the stator core is larger than a gap between the outer surface on the d-axis of the pole core portion and the inner surface of the stator, so that magnetic fluxes from the permanent magnet pass through the pole core portion concentrately.
Owner:HITACHI IND EQUIP SYST CO LTD
Apparatus for carrying out improved control of rotary machine
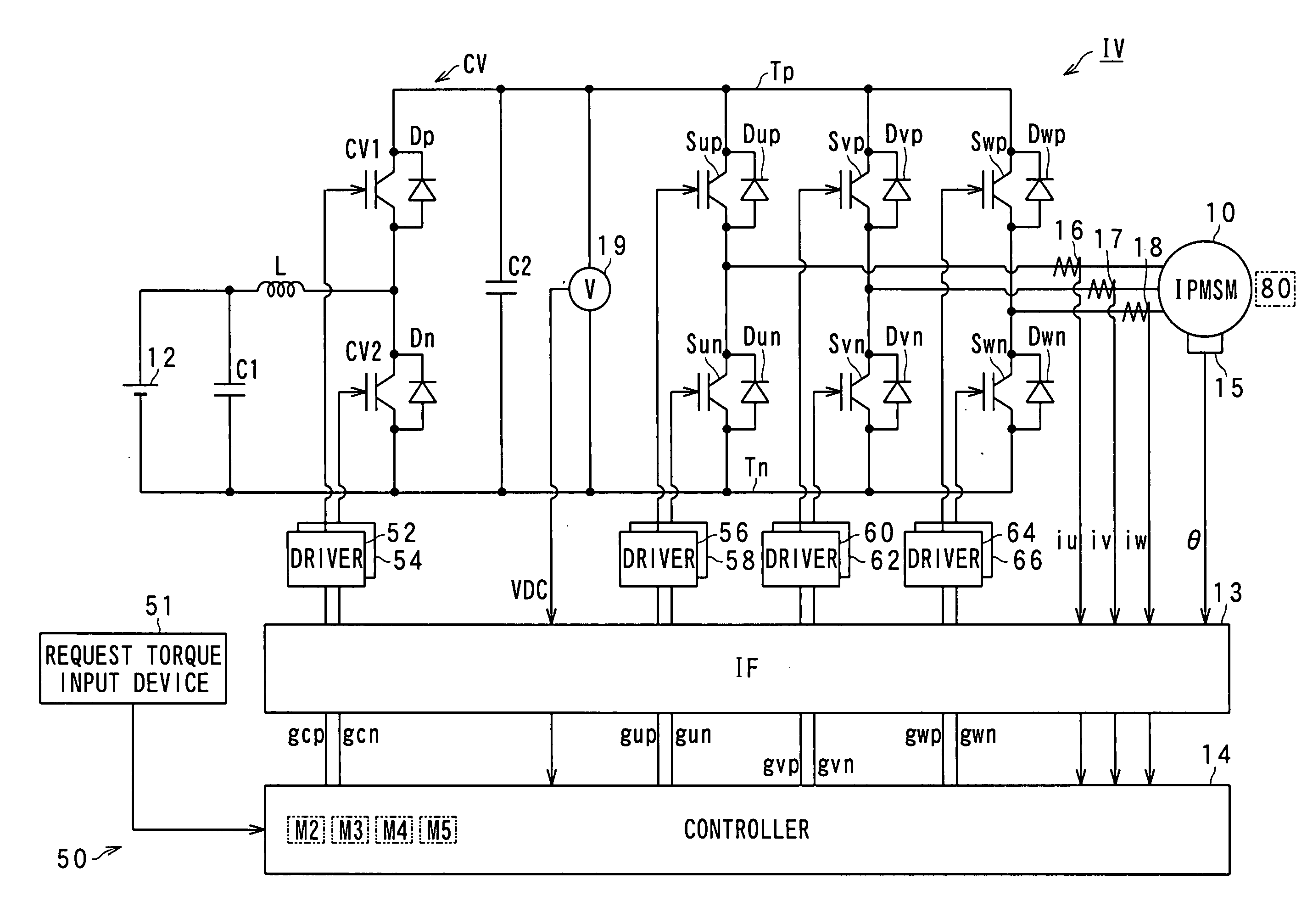
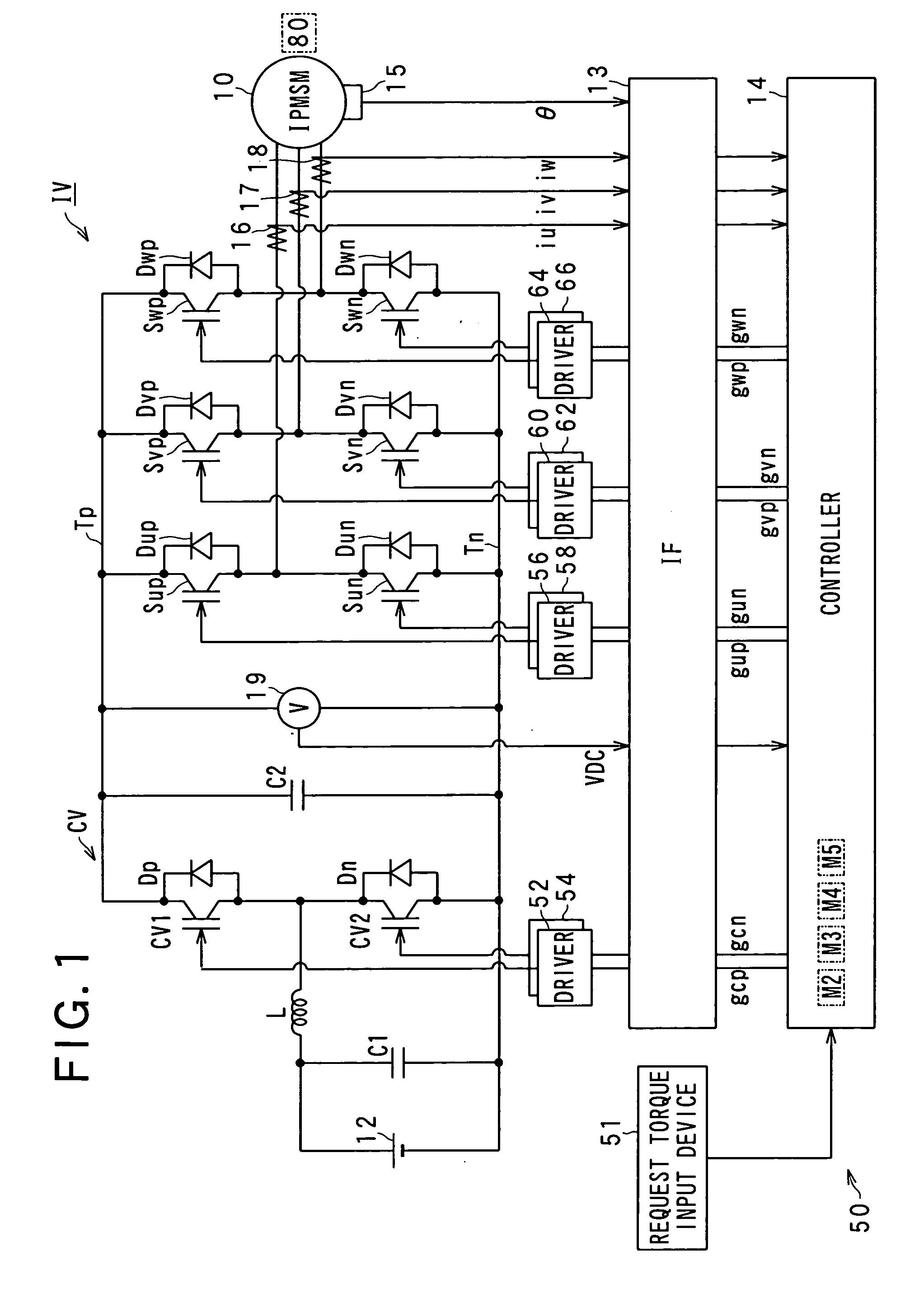
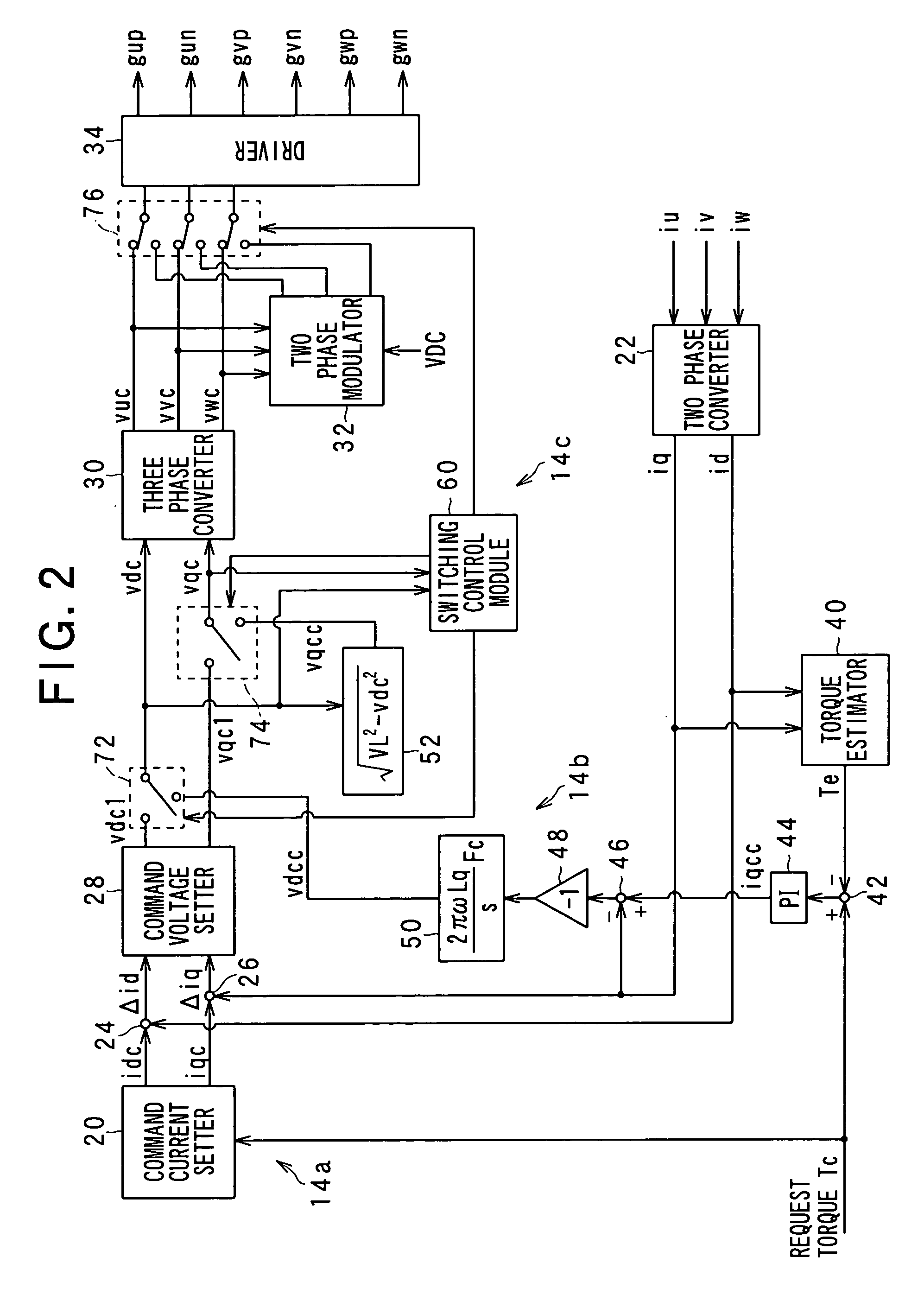
ActiveUS20090322264A1Easy maintenanceHigh levelCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlControl variableVoltage
In an apparatus, a first drive unit drives, in a first range of a voltage utilization factor, a switching member to thereby control an output voltage of the power converter to be matched with a command voltage. A second drive unit drives, in a second range of the voltage utilization factor, the switching member to thereby generate a value of a controlled variable of a rotary machine. The second range of the voltage utilization factor is higher than the first range thereof. An estimating unit estimates, during the switching member being driven by the second drive unit, a value of a parameter associated with the output voltage of the power converter. The estimated value is required for the first drive unit to generate the value of the controlled variable generated by the second drive unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
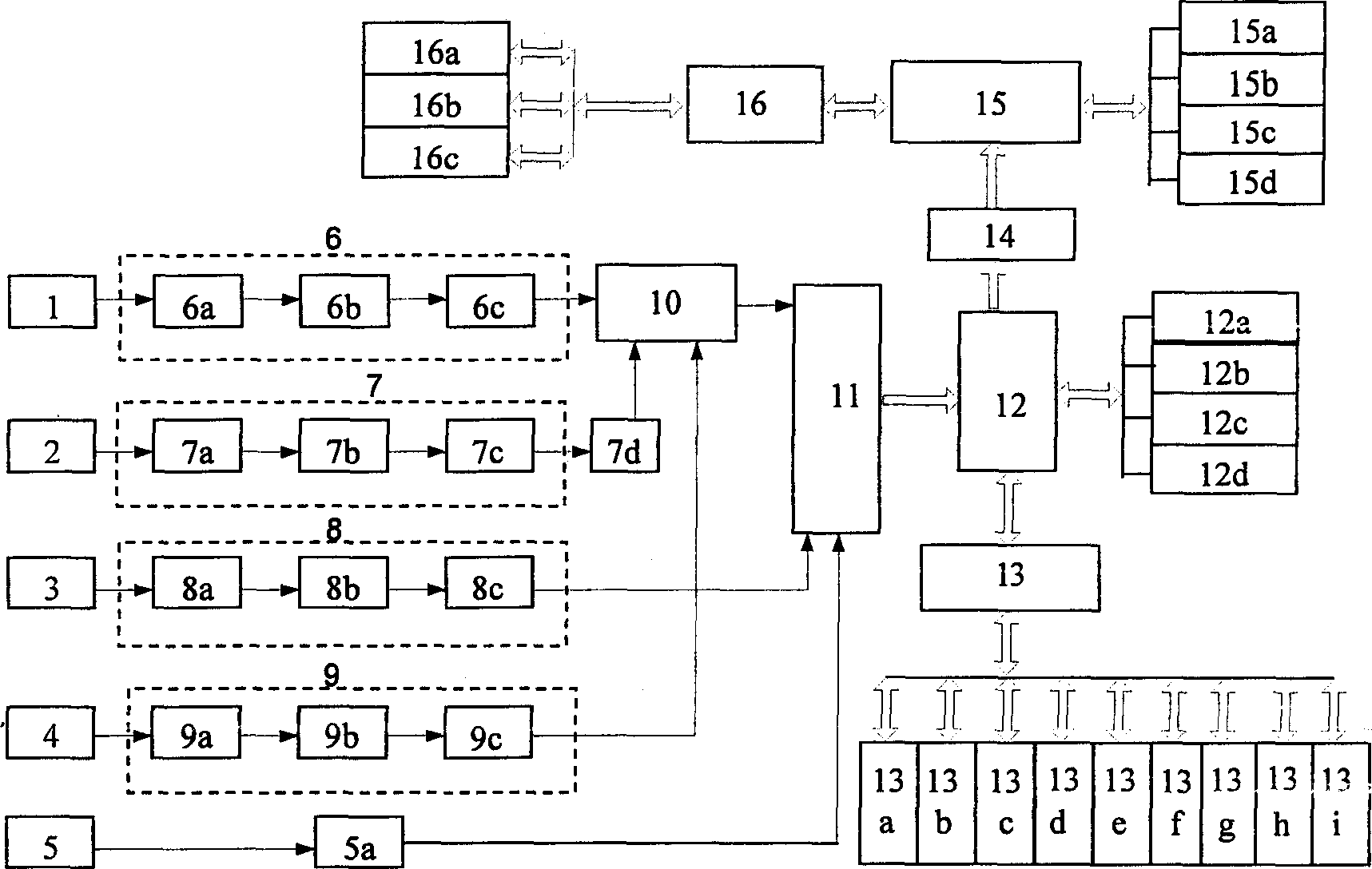
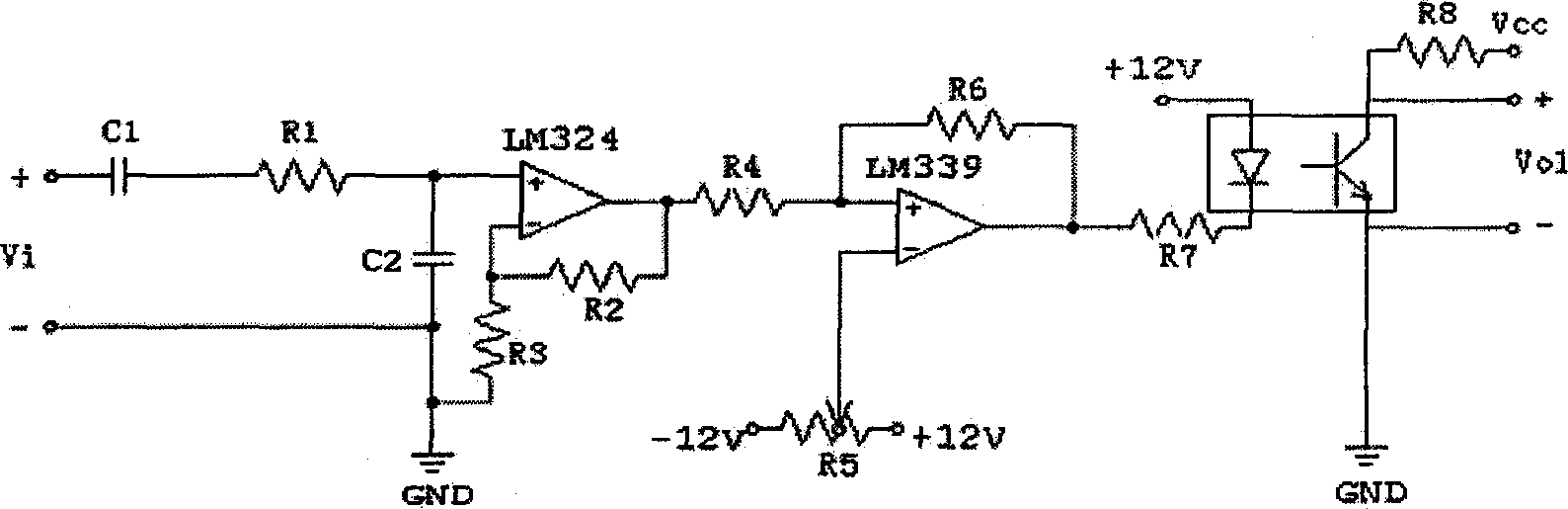
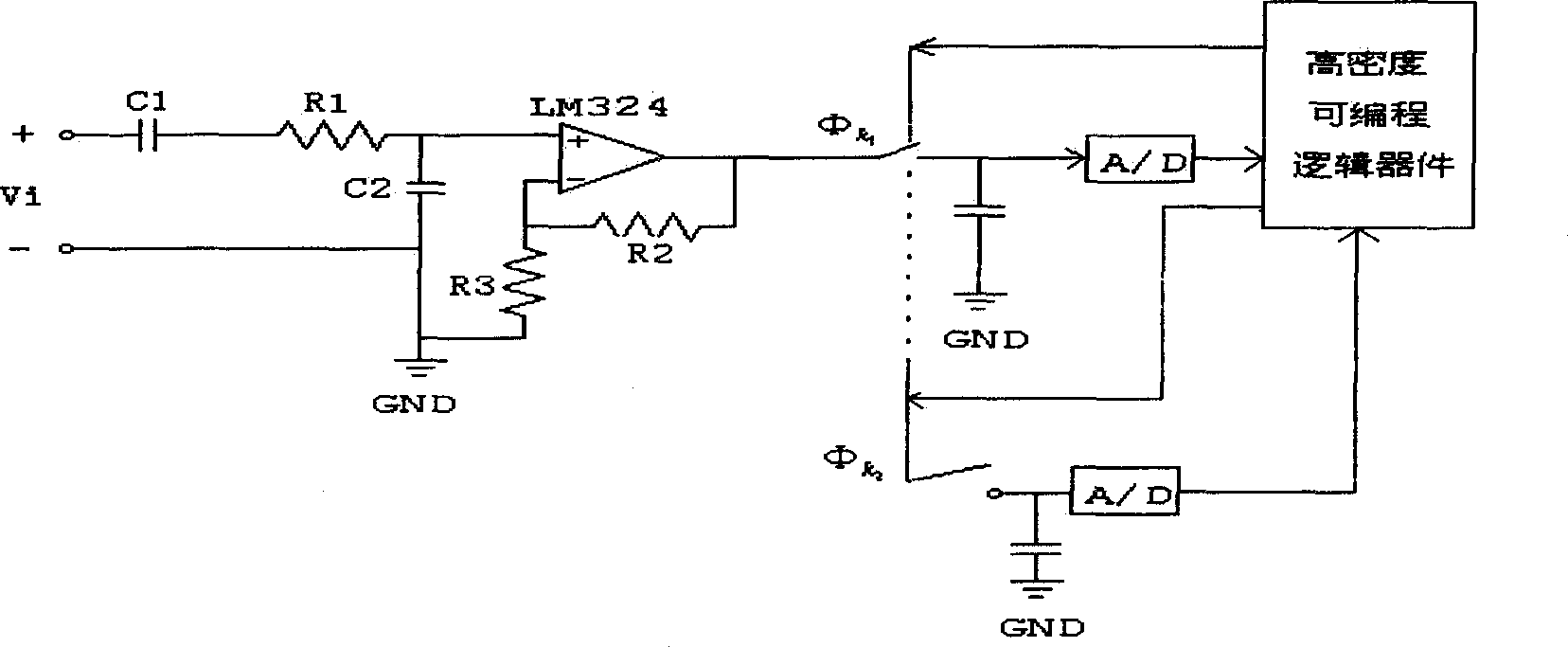
Rotary machine failure intelligent diagnosis method and device
InactiveCN1514209ARealize remote monitoring, analysis and diagnosisFully automatedBiological neural network modelsStructural/machines measurementLow speedTrend prediction
The system comprises preprocessing board connecting key phase signal to fast signal, key phase board controlling whole period of sampling, high speed collecting board for vibration signal, low speed data collecting board for graded signal. In the method, they are connected to down level server to fulfil data collection, signal analysis, and automatic identification as well as picking up characteristic parameters of operatino of machine set and down level server can make high speed communication with up level server through network card or IP protocol as up level server is equipped with an intelligent reasoning machine integrating professional knowledge rule, fuzzy logic and neural network in one component to carry trend prediction and intelligent diagnosis for operation and failure of machine.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
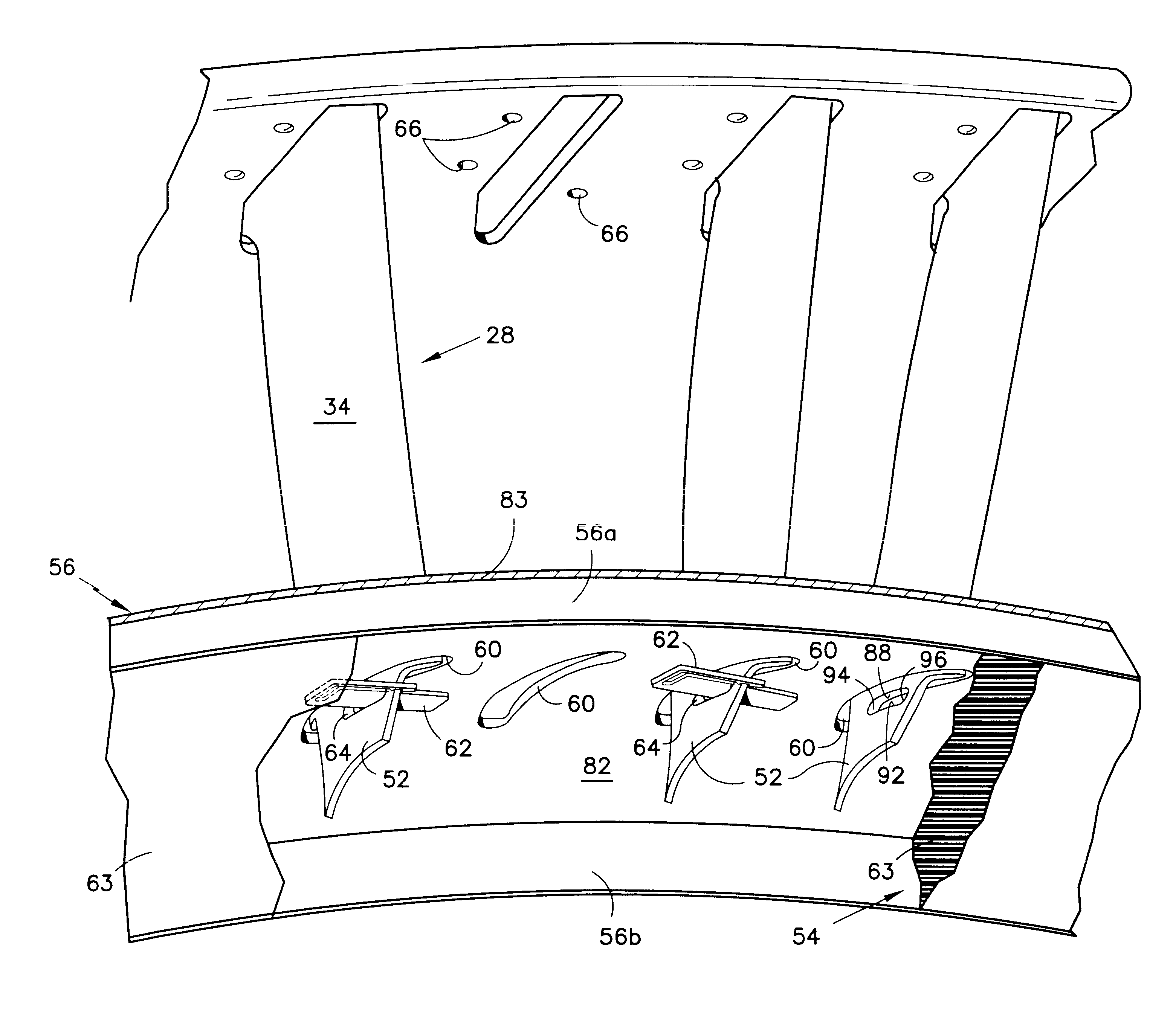
Rotor blade for a rotary machine
Owner:RTX CORP
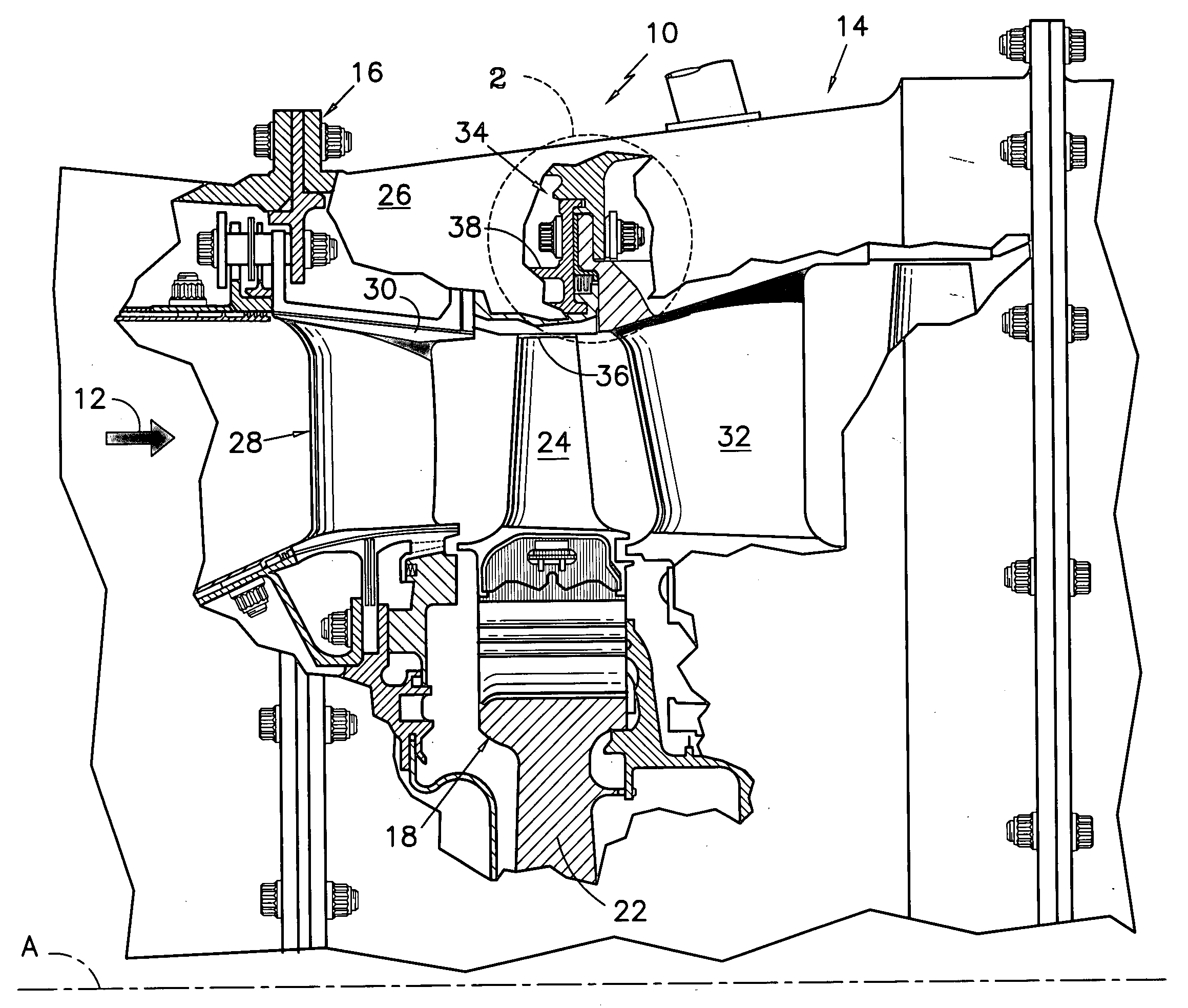
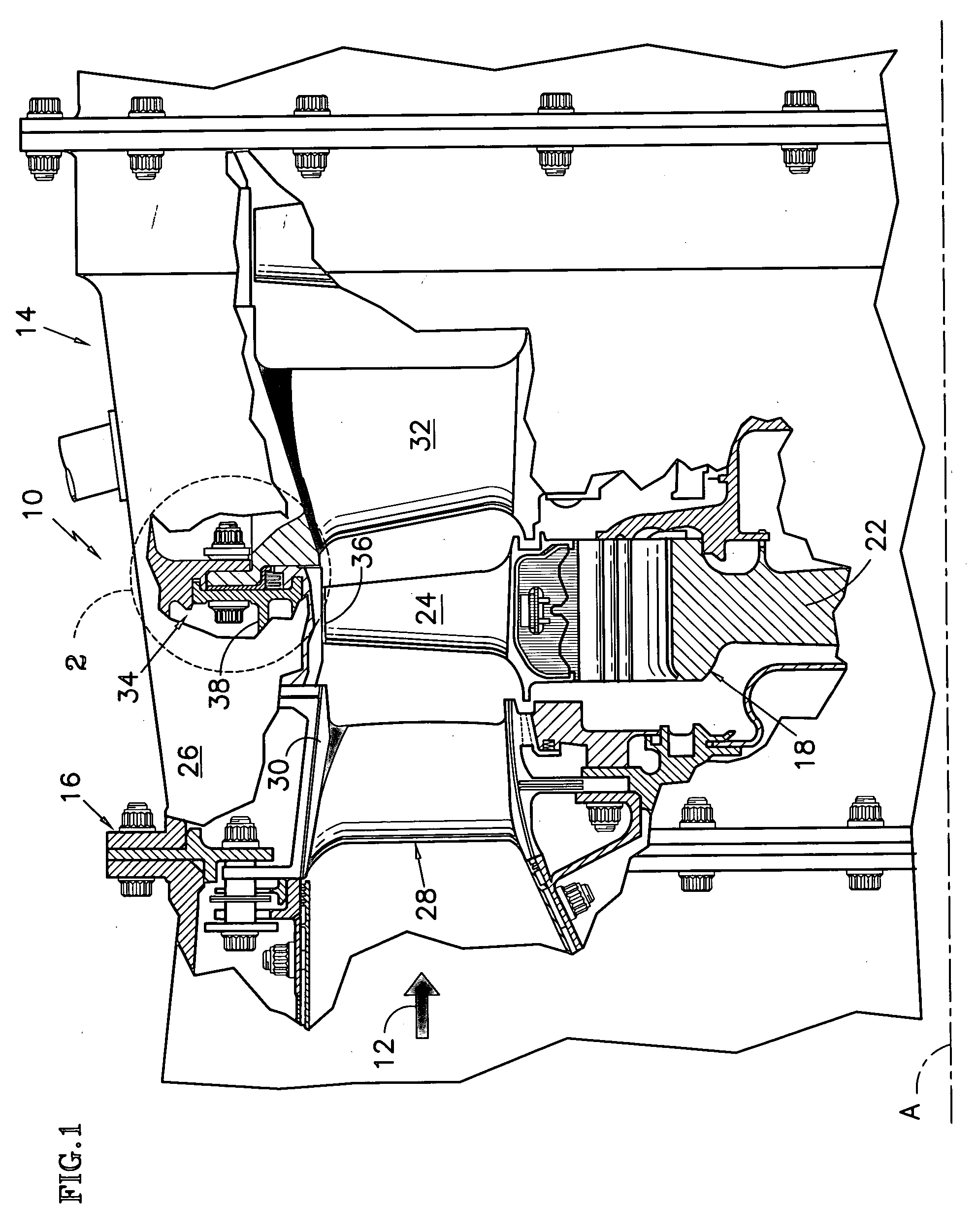
Film riding aerodynamic seals for rotary machines
A seal assembly for a rotary machine is provided. The seal assembly includes multiple sealing device segments disposed circumferentially intermediate to a stationary housing and a rotor. Each of the sealing device segments includes a stator interface element. The sealing device segment also includes a shoe plate having one or more labyrinth teeth facing the rotor and a load-bearing surface region, wherein the shoe plate allows a high pressure fluid to an upstream portion of the forwardmost labyrinth tooth and a low pressure fluid to a downstream portion of the aftmost labyrinth tooth. The sealing device segment further includes a secondary seal in contact with the stator interface element at a radially outer end and in contact with an elevated nose of the shoe plate on a radially inner end; and multiple bellow springs or flexures attached to the shoe plate and to the stator interface element.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sealing Ring, Especially Radial Shaft Seal
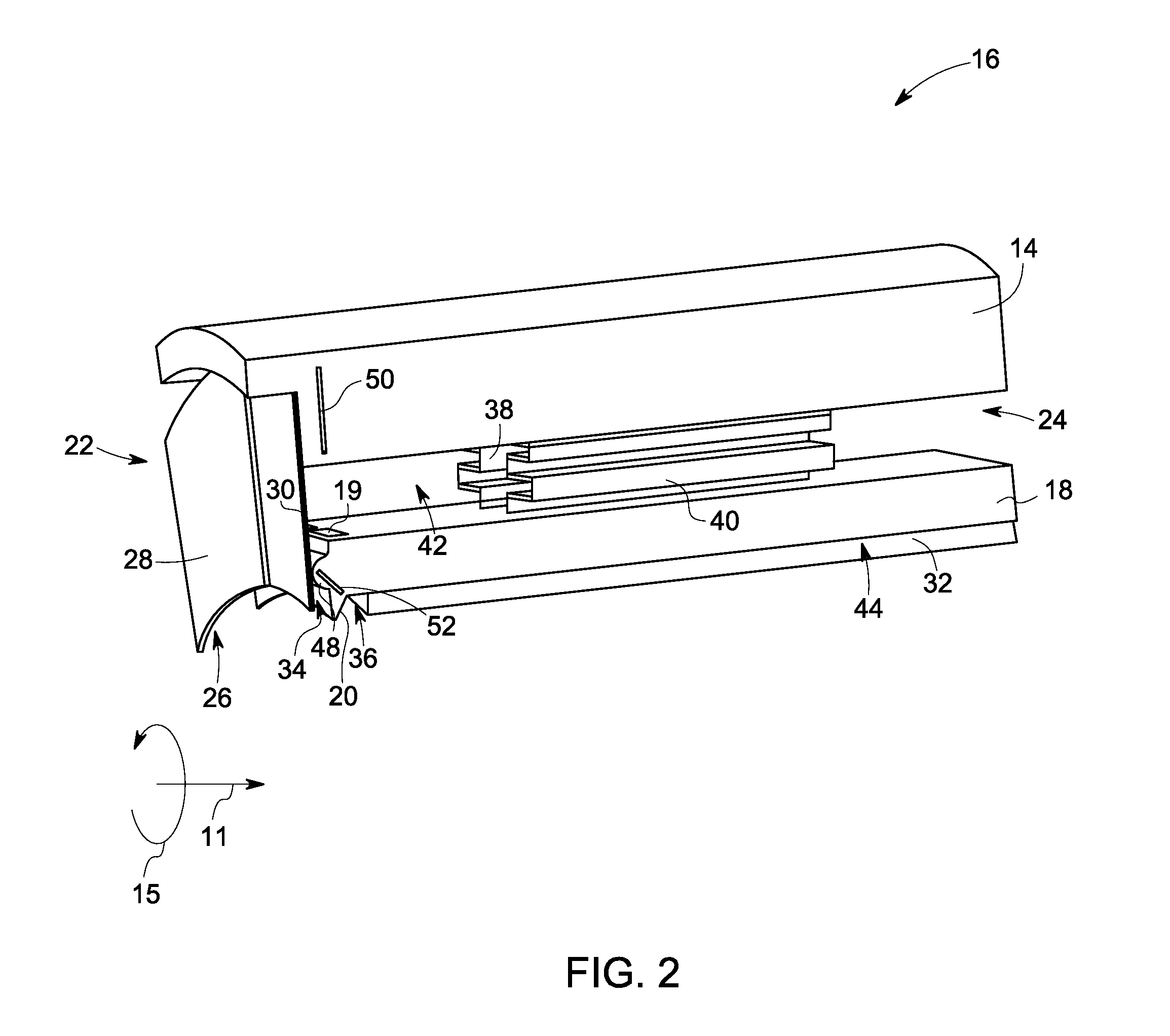
A sealing ring has a sealing disk having a fastening part and a seal part. The fastening part is connected to a first stationary machine part and the seal part seals a movable machine part and is oriented in an axial direction toward an atmosphere side or a medium side of the sealing ring. The seal part has a first sealing element and a second sealing element adjoining the first sealing element and oriented in a direction opposite to the first sealing element in a mounted position of the sealing ring. The second sealing part rests against the rotary machine part under a radial force.
Owner:KACO
Rare earth permanent magnet, making method, and permanent magnet rotary machine
ActiveUS20070017601A1Minimized eddy currentImprove remanenceMagnetic circuitInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
A rare earth permanent magnet is prepared from a sintered magnet body of a R1—Fe—B composition wherein R1 is a rare earth element inclusive of Y and Sc, by forming a plurality of slits in a surface of the magnet body, disposing a powder on the magnet body surface, the powder comprising an oxide of R2, a fluoride of R3, or an oxyfluoride of R4 wherein each of R2, R3, and R4 is a rare earth element, and heat treating the magnet body and the powder below the sintering temperature in vacuum or in an inert gas.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
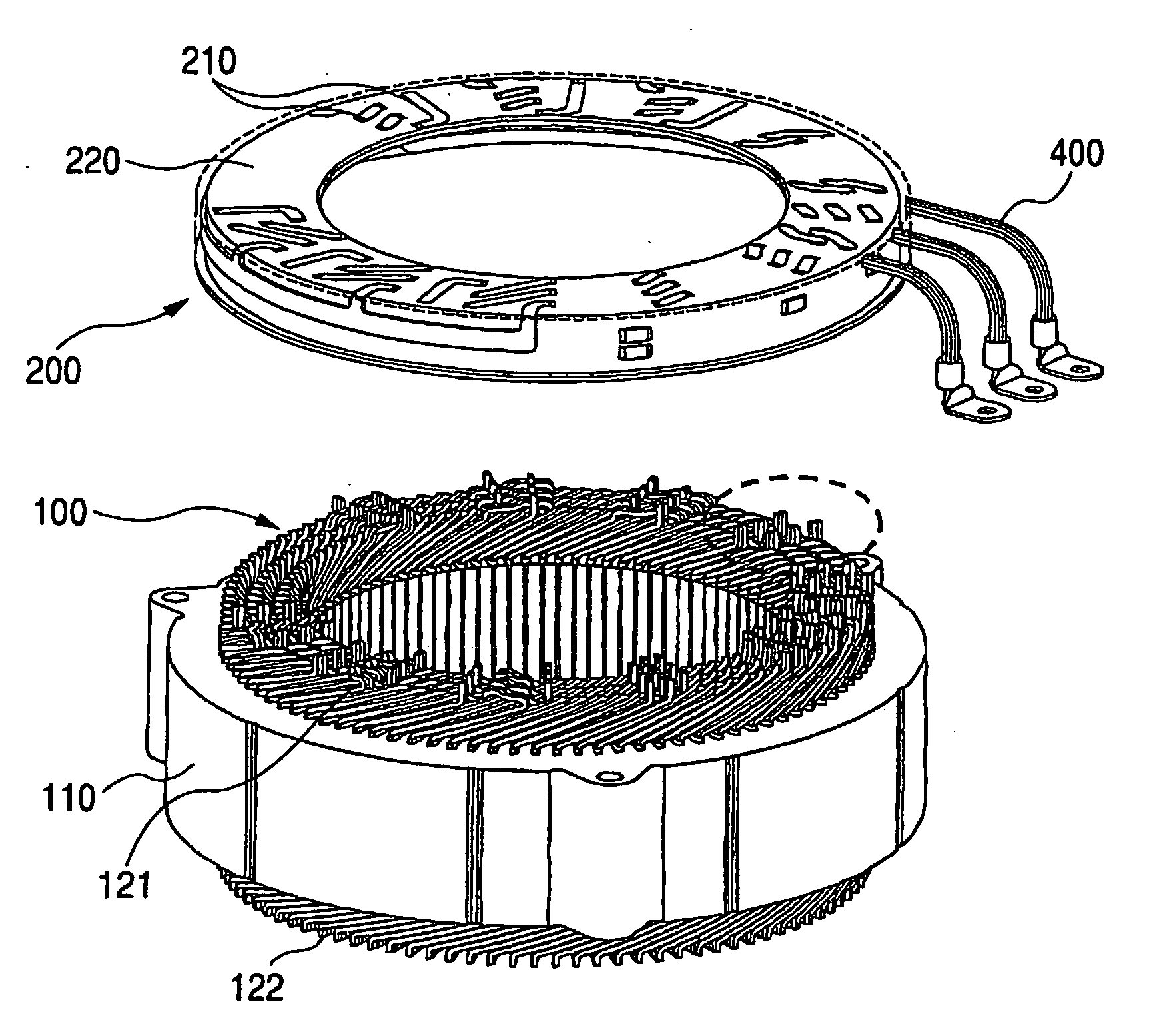
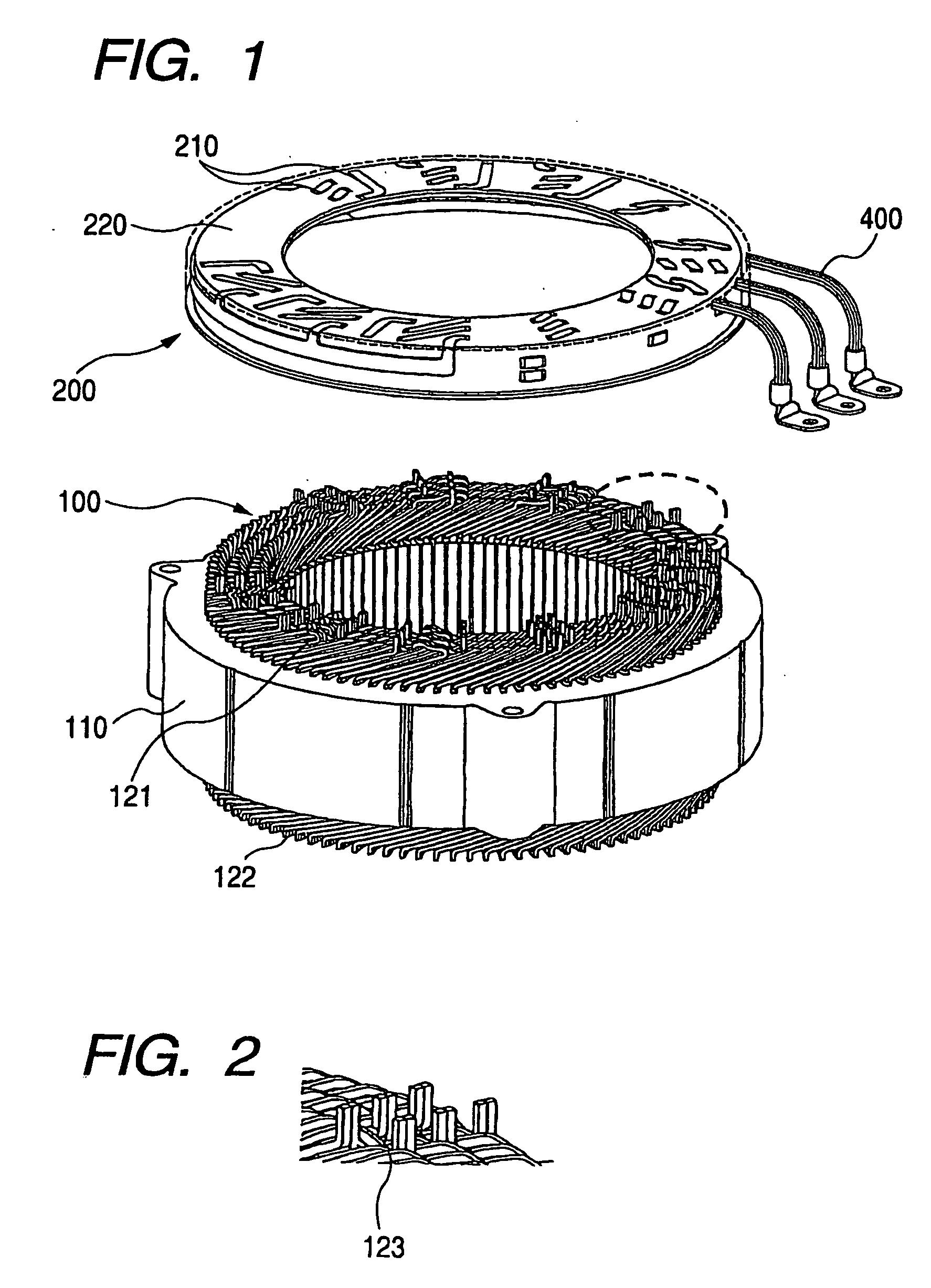
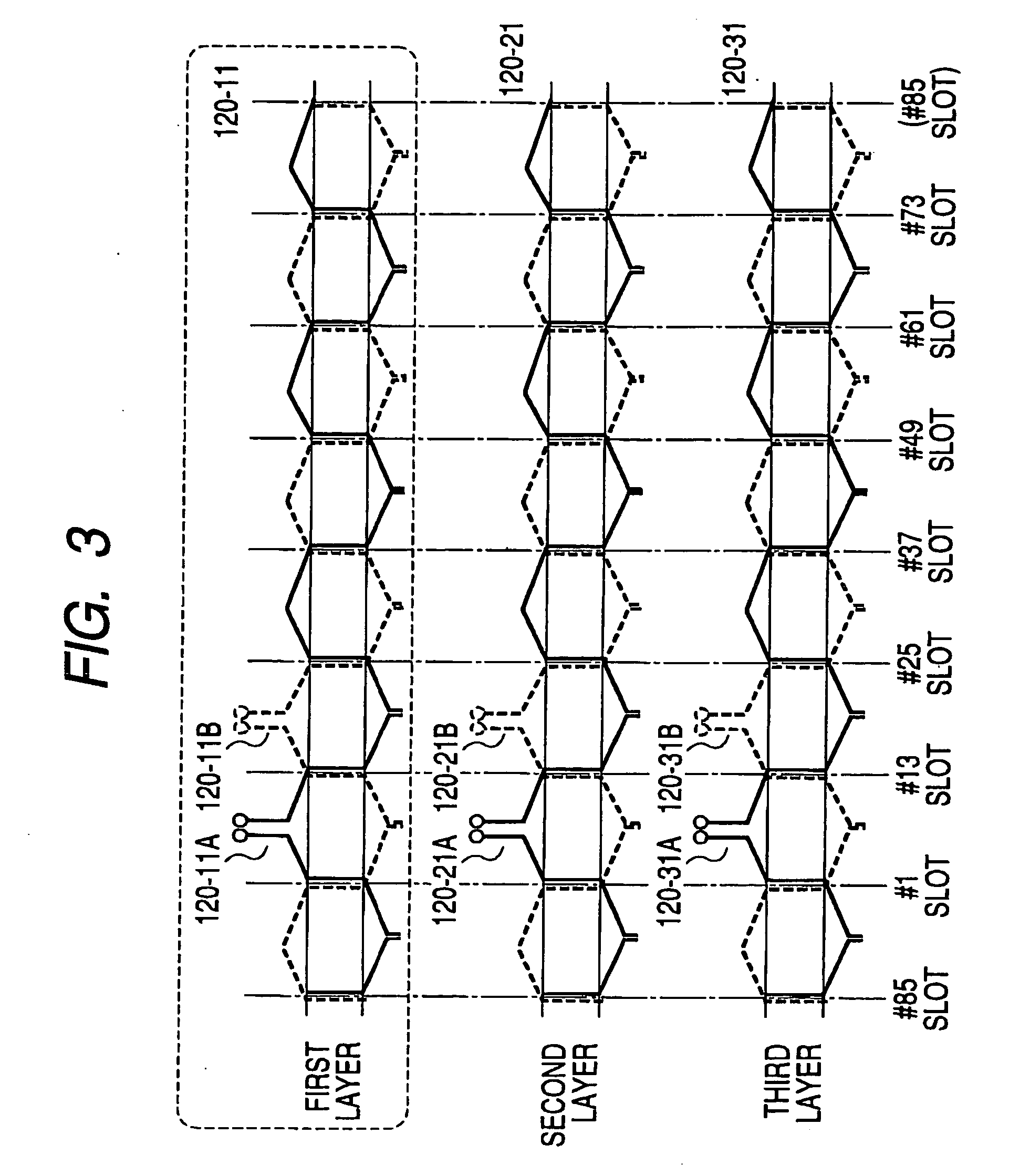
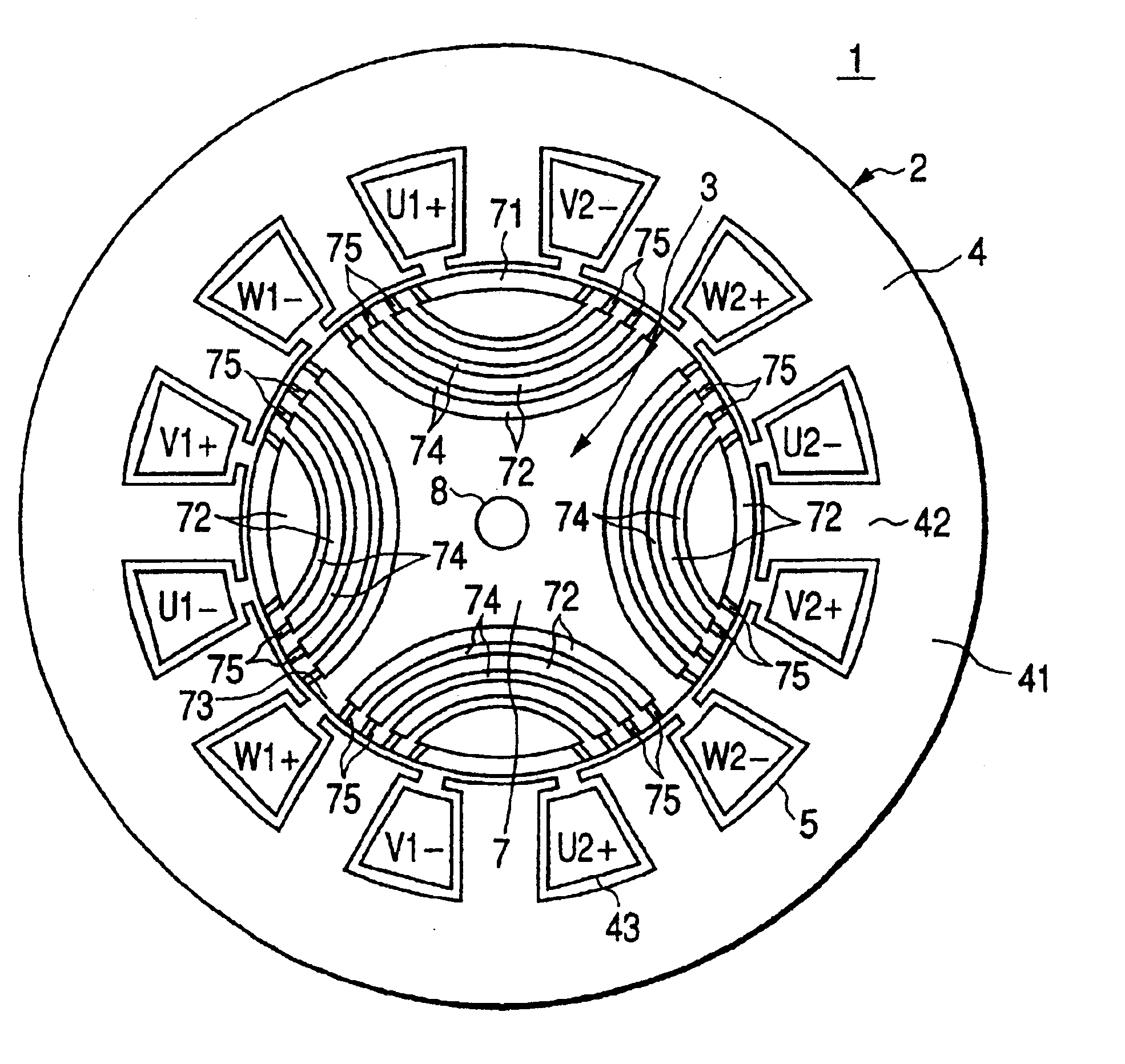
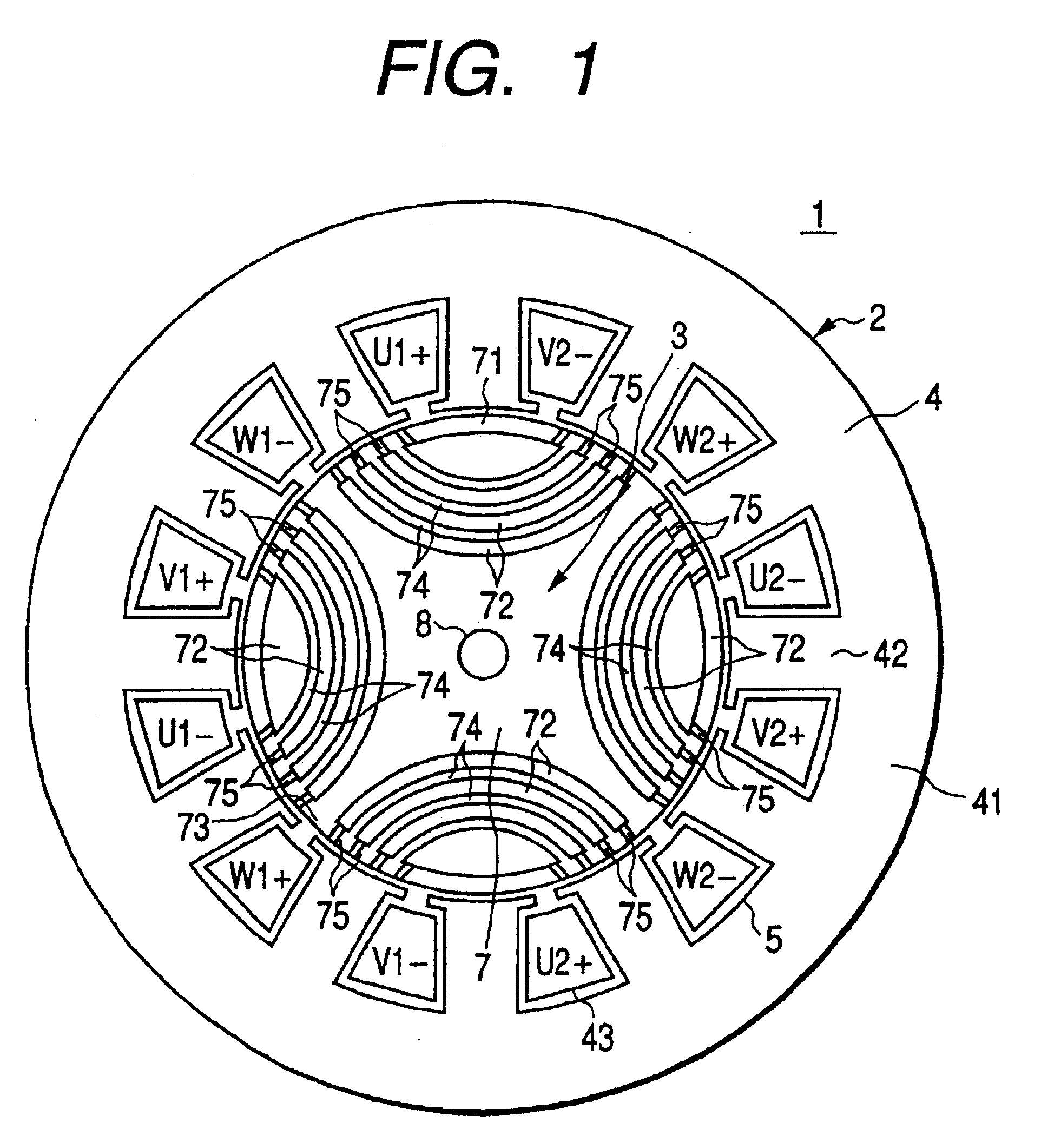
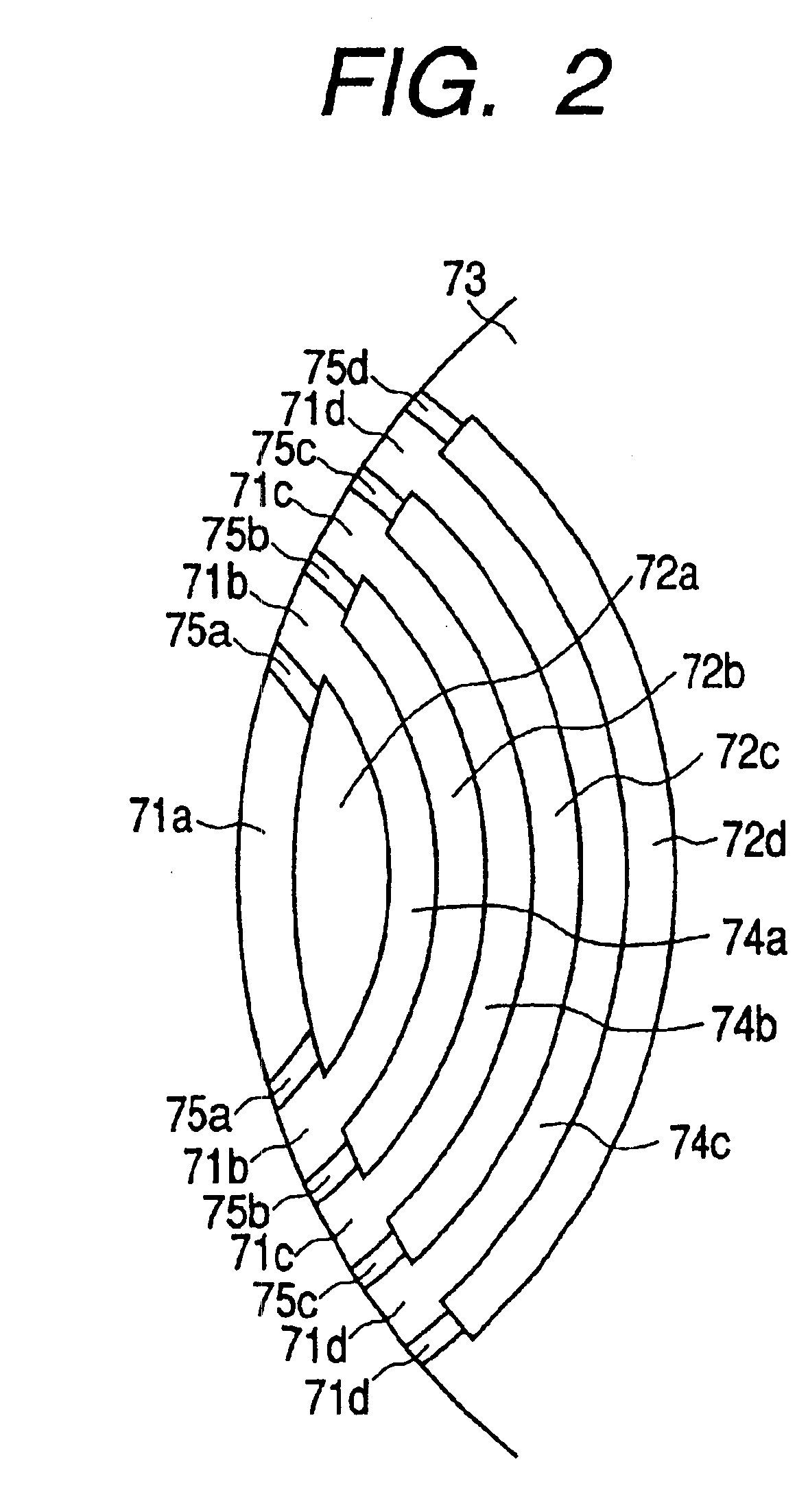
Stator coil including sequentially connected segment conductors preferably applicable to an electric rotary machine
ActiveUS20050253466A1Easy to changeSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitElectrical conductorStator coil
A stator coil includes a coil portion wound around a stator core and a terminal board serving as a bus bar array board. The coil portion is arranged by sequentially connected segment conductors. The terminal board is a molded ring plate member disposed adjacently to a head coil end of the coil portion in the axial direction and elongated in the radial direction. The turn number of the stator coil is easily adjustable by selecting an optimum one of a plurality of terminal boards.
Owner:DENSO CORP
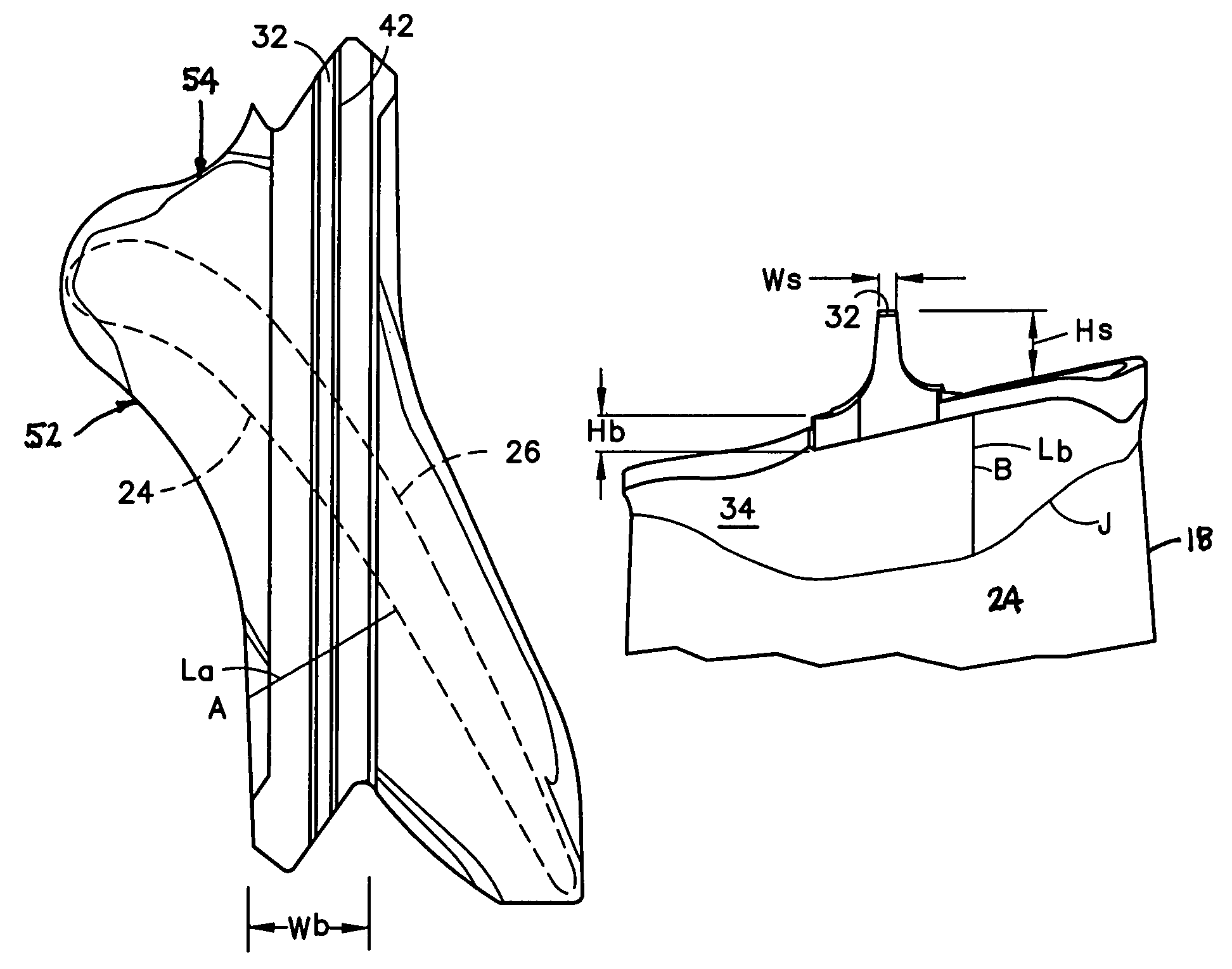
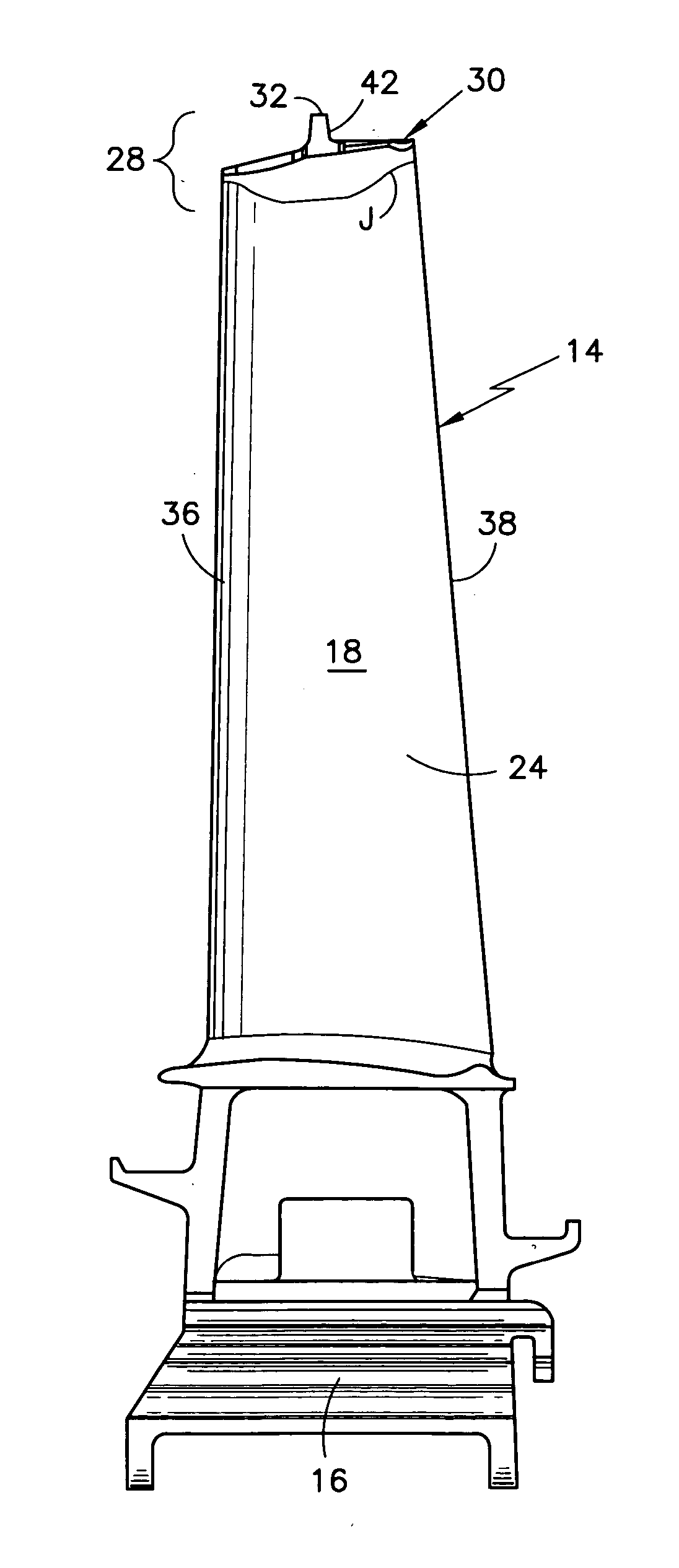
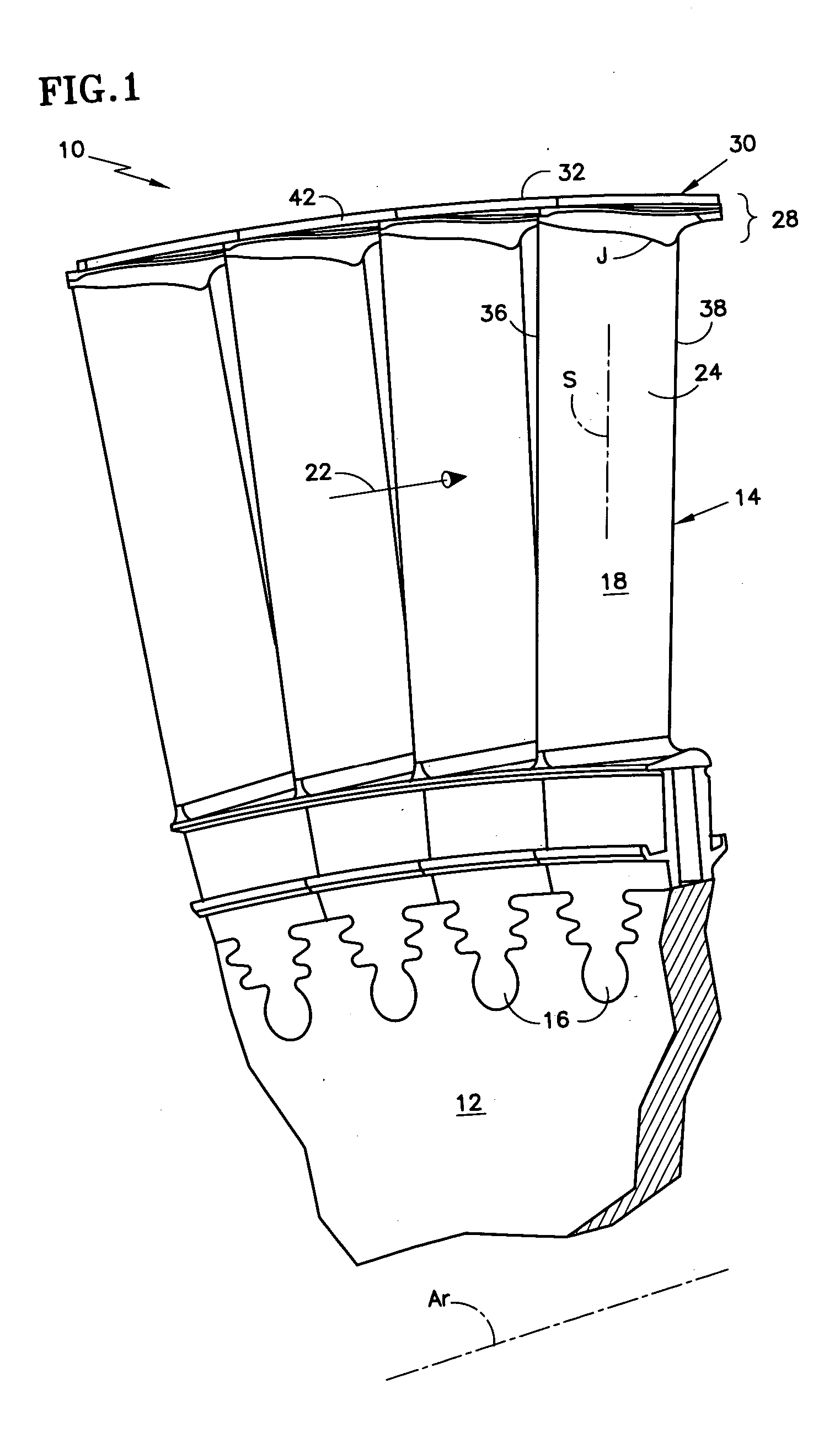
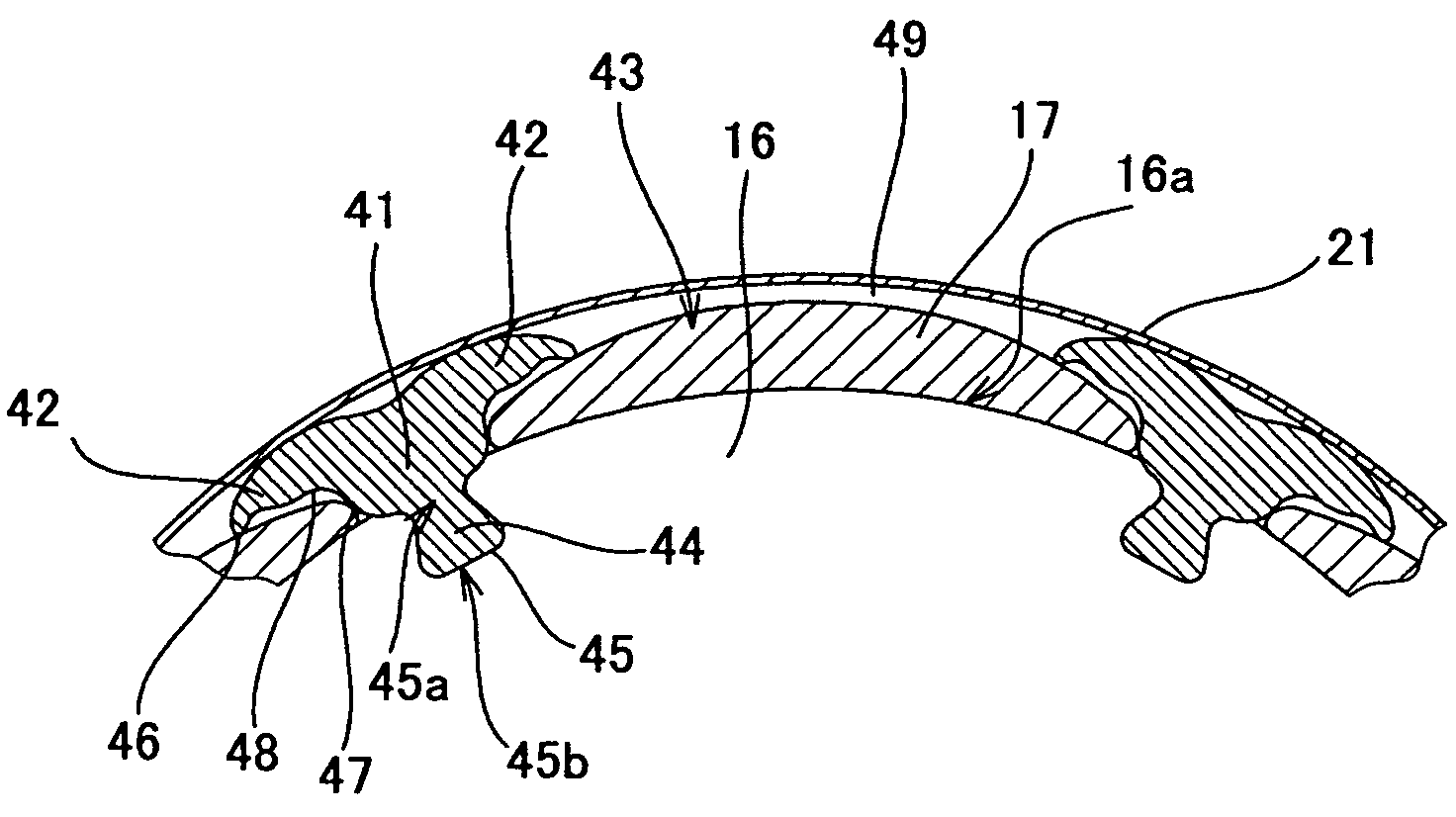
Rotor blade for a rotary machine
ActiveUS20050169761A1Reduce stress concentration factorReduce surface stressPropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTrailing edge
A rotor blade having a wing and beam construction for a tip shroud is disclosed. Various construction details are developed for providing a transition zone that extends from the suction side and pressure side of the airfoil to provide a flow path surface of the shroud. In one detailed embodiment, the transition zone over substantially all of its extent between the leading edge region and the trailing edge region is contoured to extend to the sides of the wings to provide a spanwise taper that extends to the side of the wing.
Owner:RTX CORP
Variable magnetic coupling of rotating machinery
ActiveUS7791235B2Reduce vibration transmissionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMechanical actuated clutchesCouplingEngineering
A system for transferring torque between a pair of independently, concurrently rotating shafts of a turbofan engine includes a magnetic gearbox. The magnetic gearbox has a first ring structure, a second ring structure and an intermediate ring structure. Each ring structure has an annular aperture therethrough and a plurality of permanent magnets embedded therein. The intermediate ring structure is disposed between the first and the second ring structures. Each ring structure is coaxially concentric with, and independently rotatable with respect to the remaining ring structures. The first and second ring structures are each coupled to separate ones of the rotating engine shafts, and the intermediate ring is operable to transfer torque between the pair of shafts. Preferably, the intermediate ring structure is coupled to a rotating machine. The rotating machine has a controller, and is operable for adjusting a ratio of torque transferred between the pair of shafts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotor shield for magnetic rotary machine
InactiveUS20020125779A1Total current dropCurrent lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsWind energy generationEddy currentEngineering
A magnet machine includes a magnet rotor. The rotor includes a sleeve and a magnet. The magnet is positioned within the sleeve. A highly electrically conductive, nonmagnetic shield surrounds the magnet. The shield reduces rotor eddy current losses and lowers rotor operating temperature, thereby improving efficiency of the machine.
Owner:CAPSTONE TURBINE
Method and device for reducing axial thrust in rotary machines and a centrifugal pump using same
InactiveUS6129507AReducing axial thrustReduce and even eliminate effectPump componentsReaction enginesRotation velocityAxial thrust
A method and device for reducing or eliminating axial thrust in a rotary machine such as a centrifugal pump or compressor by altering the fluid pressure in a cavity formed between a rotor and a housing. The device contains a disk placed along the rotor for subdividing the fluid in the cavity in such a way that all annular gap leakage flow is channeled and pumped through the space between that disk and the rotor from the center of the pump towards the periphery. As a result, the pressure in the cavity is altered to reduce and control the axial thrust on the rotor which becomes independent of the wear state of the shaft seals. In another embodiment, the step of flow subdividing is achieved by providing a set of braking vanes along the periphery of the cavity for reducing the rotational speed of the fluid coming from the cavity as well as from the annular gap and a stationary disk placed along the interior wall of the housing for directing the radial flow of that fluid towards the center of the pump.
Owner:TECH COMMLIZATION
Stator assembly, module and method for forming a rotary machine
ActiveUS7600967B2Engine efficiencyEasy to manufacturePump componentsBlade accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A stator assembly for a rotary machine having an array of wall segments for bounding a working medium flow path is disclosed. Various construction details which provide a sealing structure for the segments are developed. In one detailed embodiment, a removable seal retainer for a seal chamber bounded by wall segments traps a resilient seal member in the seal chamber. In one particular embodiment, a modular subassembly for the engine is an outer air assembly disposed in a fixture as the subassembly is assembled.
Owner:RTX CORP
Methods and systems for turning rotary components within rotary machines
A method and apparatus of turning rotary components of a rotary machine having a brake disc includes providing a turning gear assembly. The turning gear assembly includes a gear plate, a pinion gear and a gear motor coupled to the pinion gear. The method also includes coupling the turning gear assembly within the rotary machine using the gear plate such that the pinion gear engages with the brake disc, detecting a motion of the rotary machine, and rotating the brake disc using the pinion gear based on the detected motion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Aerodynamic seals for rotary machine
An aerodynamic seal assembly for a rotary machine is provided. The assembly includes multiple sealing device segments disposed circumferentially intermediate to a stationary housing and a rotor. Each of the segments includes a shoe plate with a forward-shoe section and an aft-shoe section having multiple labyrinth teeth therebetween facing the rotor. The shoe plate is configured to allow a high pressure fluid to a front portion of the plurality of the labyrinth teeth and a low pressure fluid behind the plurality of the labyrinth teeth and further configured to generate an aerodynamic force between the shoe plate and the rotor. The sealing device segment also includes multiple bellow springs or flexures connected to the shoe plate and to a top interface element, wherein the multiple bellow springs or flexures are configured to allow the high pressure fluid to occupy a forward cavity and the low pressure fluid to occupy an aft cavity. Further, the sealing device segments include a secondary seal attached to the top interface element at one first end and positioned about the multiple bellow springs or flexures and the shoe plate at one second end.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
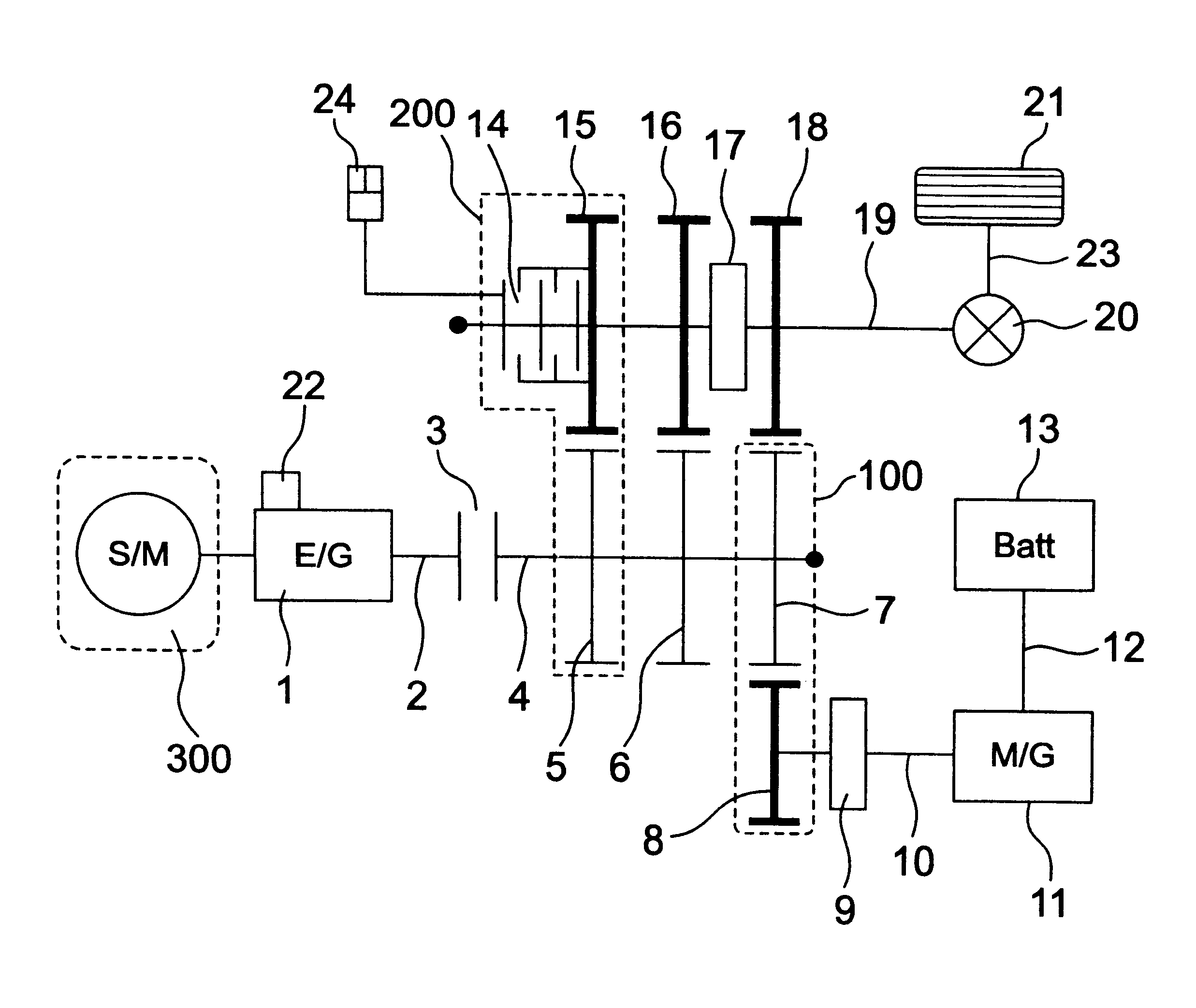
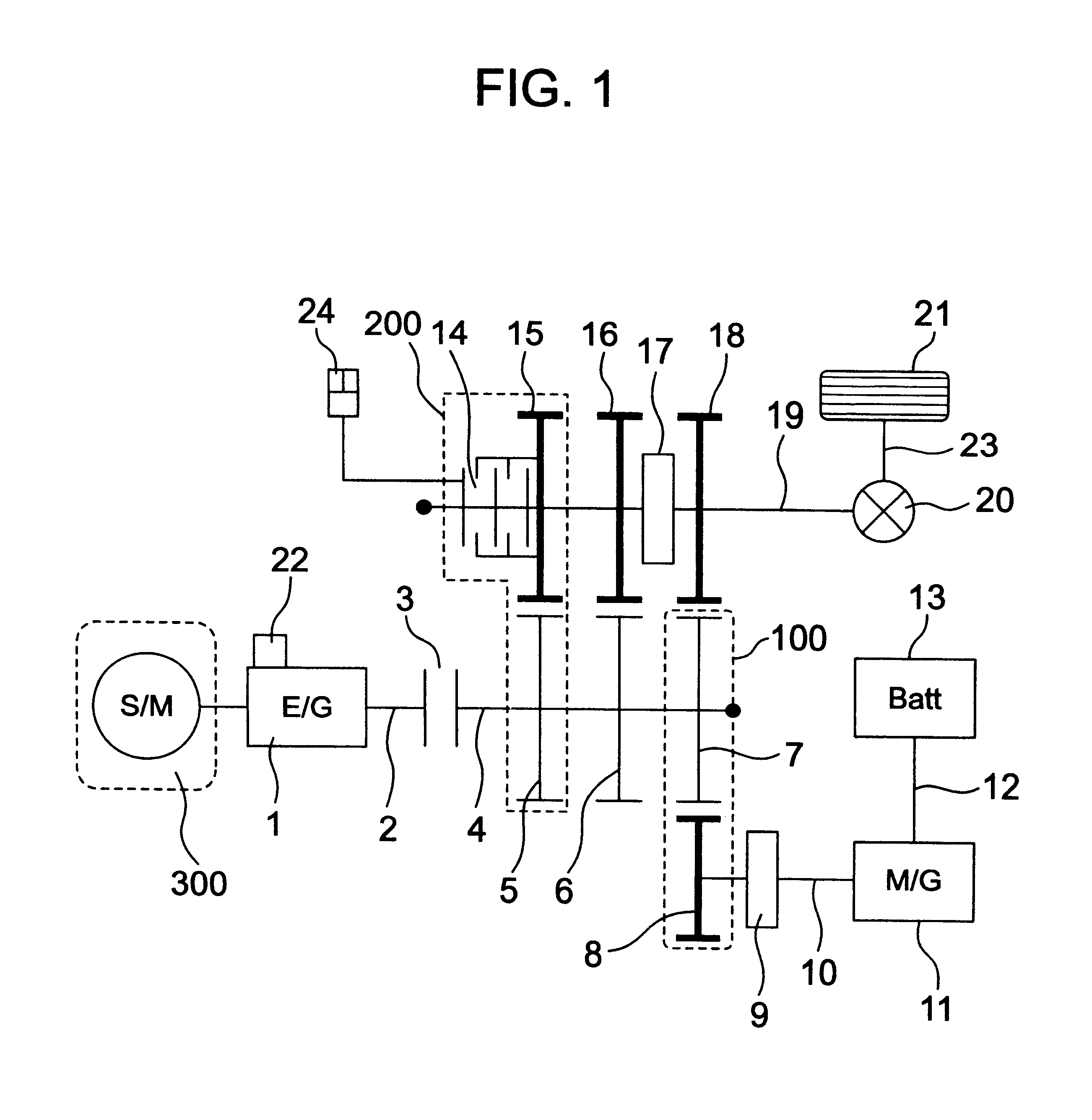
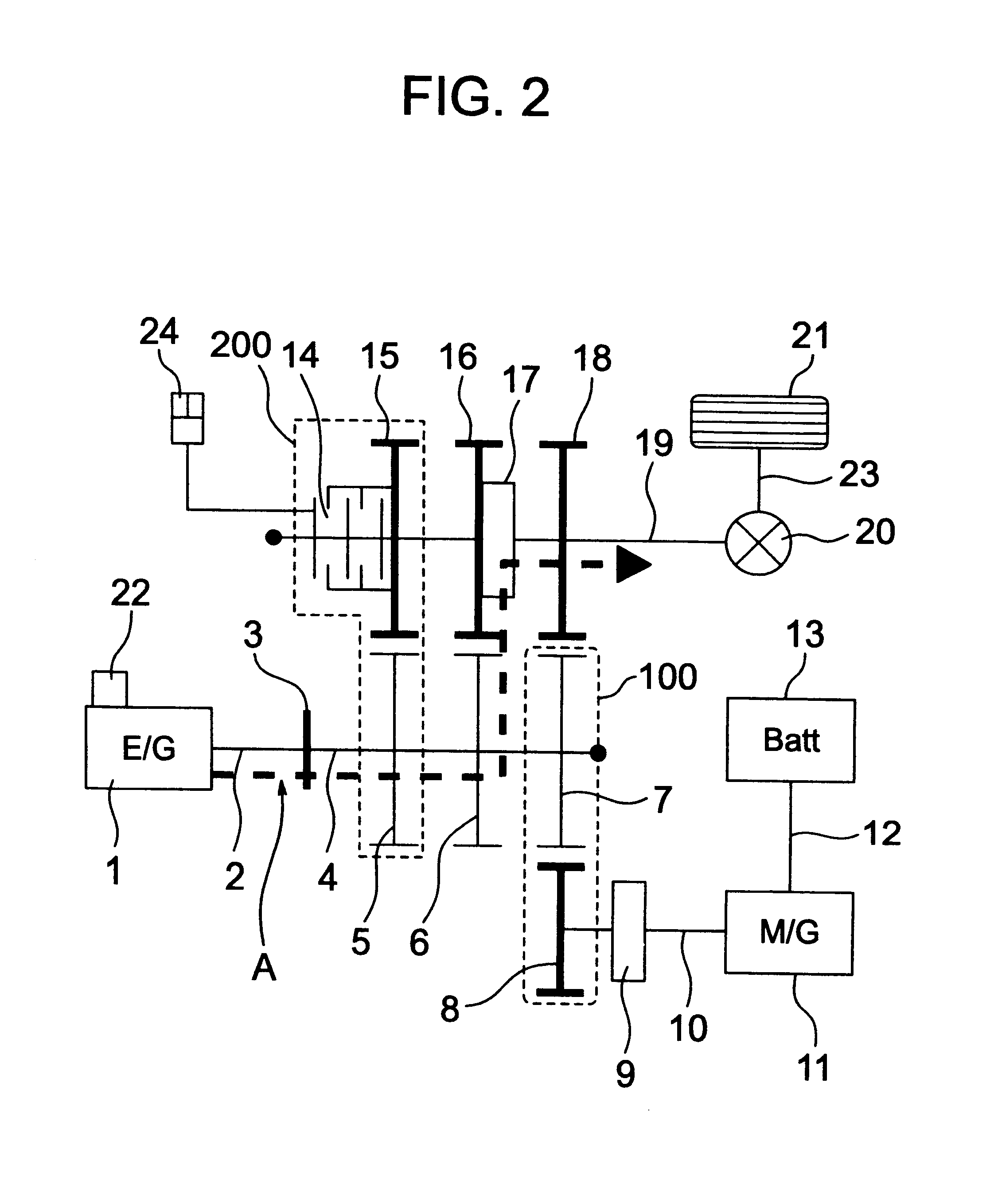
Power transmission apparatus of motor vehicles
InactiveUS7185722B1Improve transmission efficiencyReduce fuel consumptionElectric propulsion mountingFluid actuated clutchesMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
Disclosed is a power transmission apparatus of motor vehicles which has an engine, a gear change apparatus, an electric rotary machine to which a power is transmitted via the gear change apparatus, and a clutch provided between an input shaft and an output shaft of the gear change apparatus and adjusting a transmission torque between the input shaft and the output shaft.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Rotary machine having bypath magnetic path blocking magnetic barrier
InactiveUS6849983B2Increase torqueHigh mechanical strengthSpeed controllerSynchronous generatorsMagnetic barrierMagnetic poles
The rotary machine is composed of the rotor having magnetic poles and the stator having the stator yoke portion constituting the iron core tooth portion wound by the stator winding and the flux flow path of the magnetic poles. The rotor is composed of a metallic material having ferromagnetic parts and non-magnetic parts as a member and has a magnetic barrier area composed of the slit portion for blocking the bypath magnetic path in the periphery of the rotor and the non-magnetic parts. The rotary machine that produced torque can be increased sufficiently and the mechanical strength during high-speed running is improved and an electrical vehicle using it.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
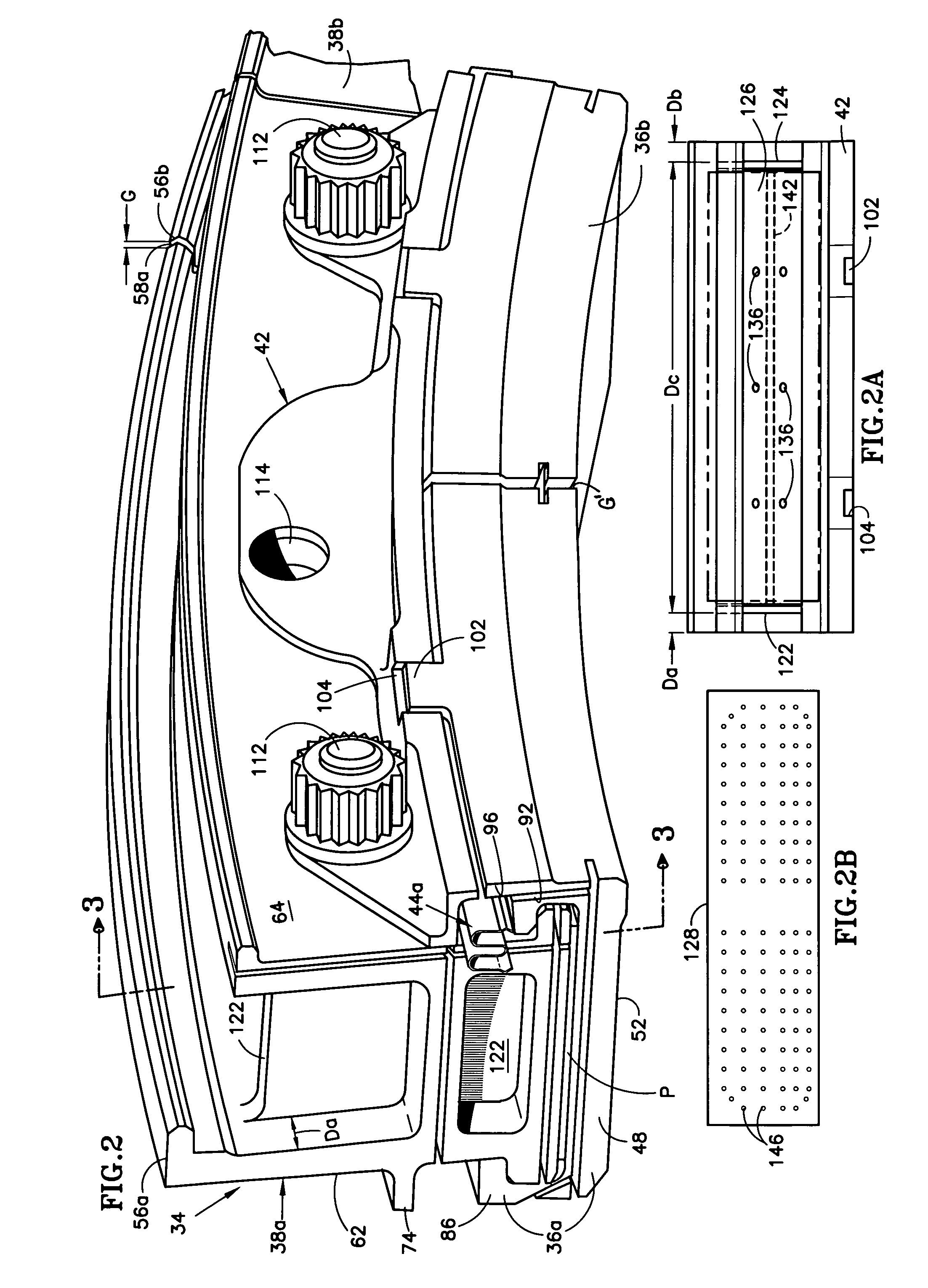
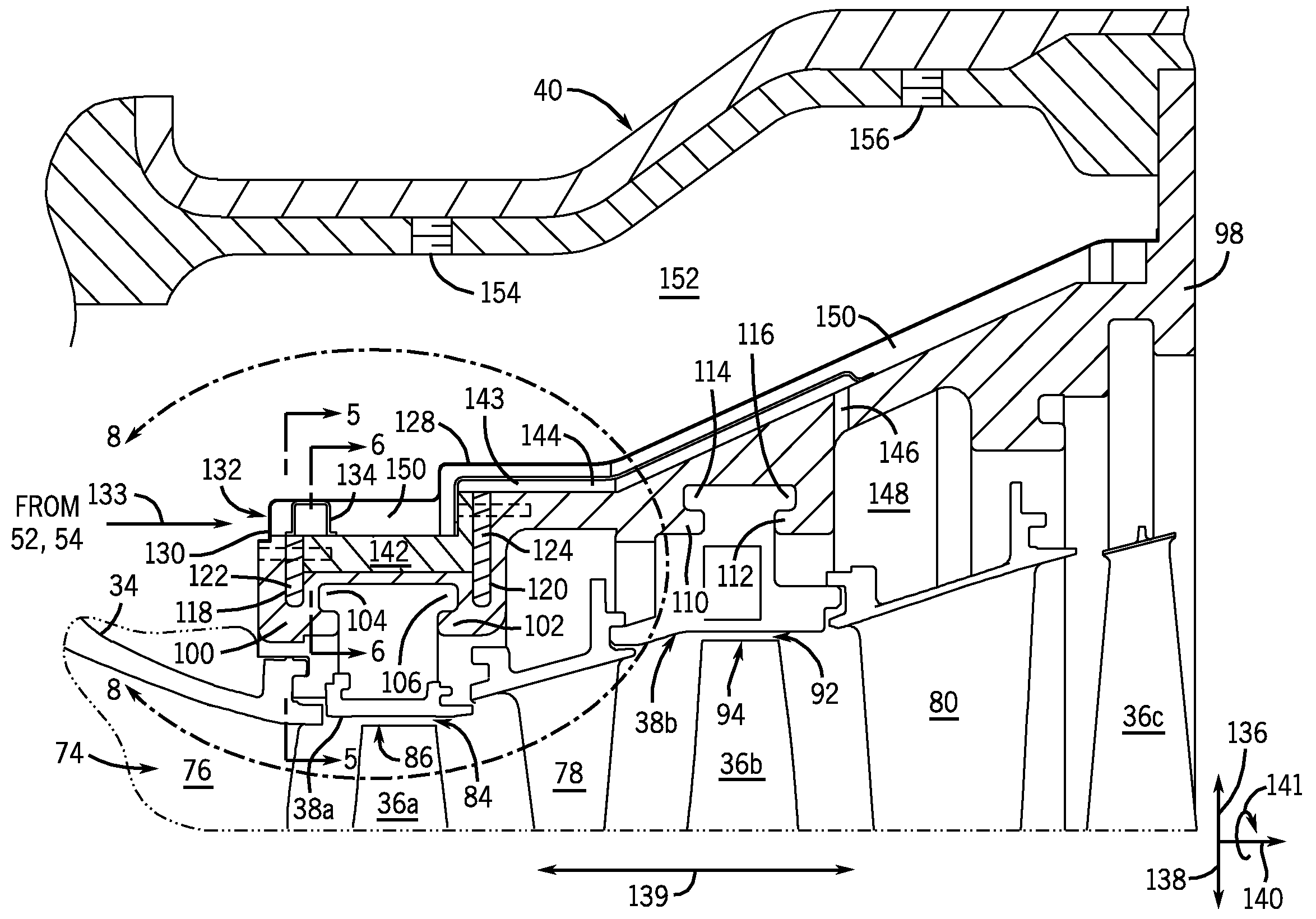
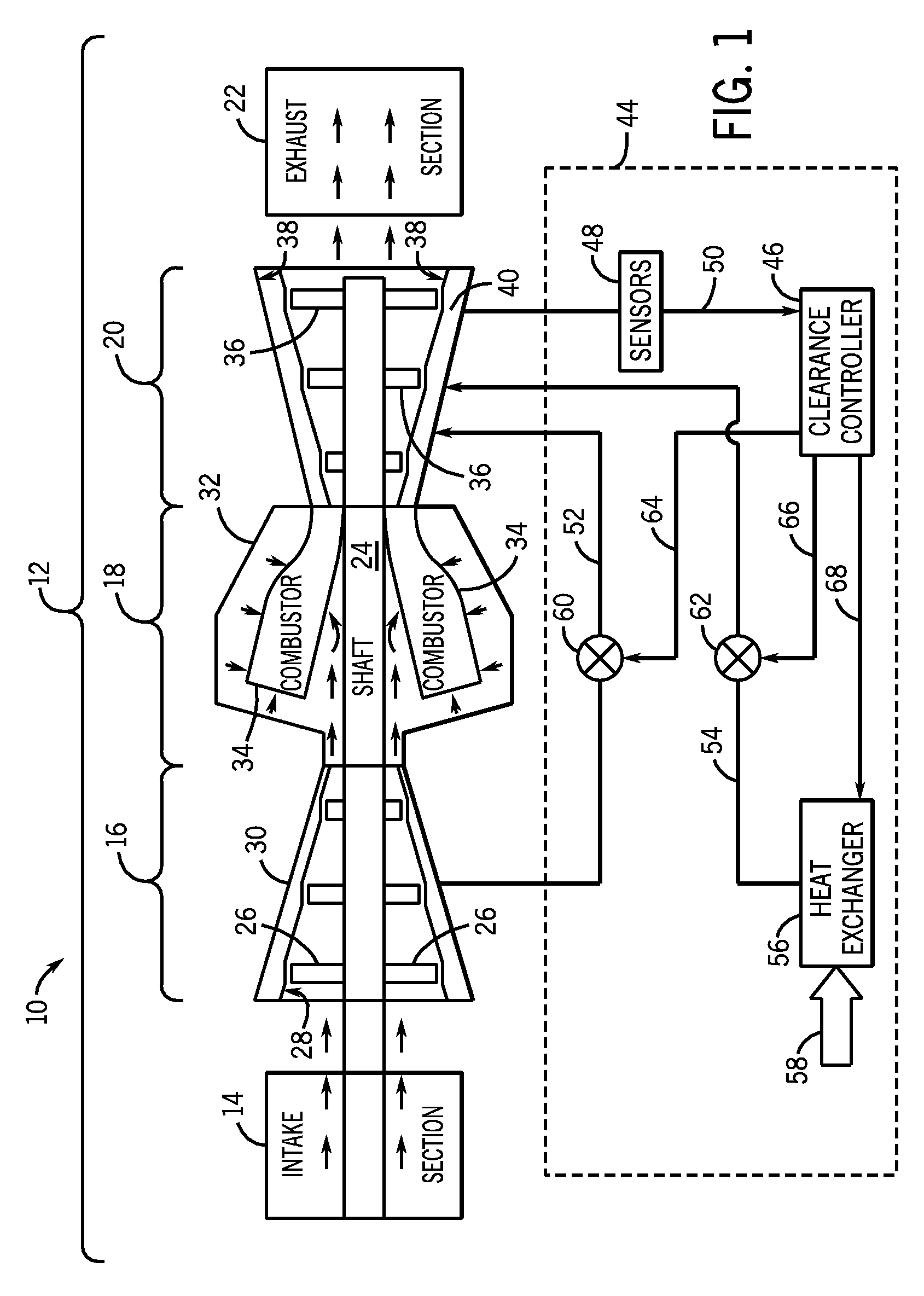
System and method for clearance control in a rotary machine
A system includes a turbine casing including a first hook configured to mate with a second hook to support a turbine shroud about a plurality of turbine blades. The turbine casing includes a coolant circuit configured to adjust clearance between the turbine shroud and the turbine blades based on coolant flow through the coolant circuit. The coolant circuit includes a first plurality of radial coolant passages extending into the first hook.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
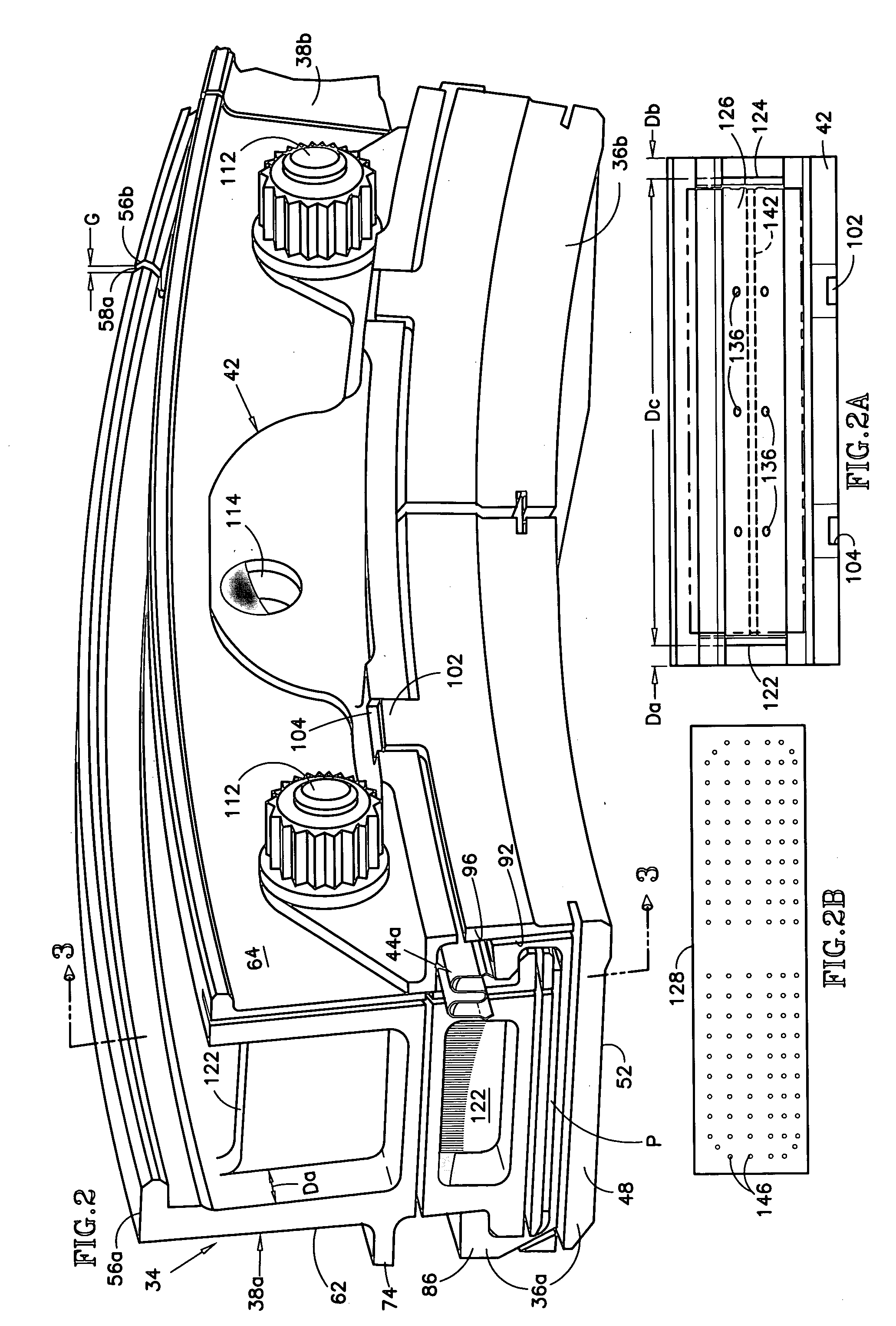
Moving-weight, dynamic balancing apparatus for a rotary machine, in particular for industrial fans
InactiveUS6210099B1Easy to implementLow costPropellersWind motor controlDynamic balanceSystem monitor
A moving-weight, dynamic balancing apparatus for a rotary machine, in particular an industrial fan, having a rotary shaft, and at least one rotor carried by the rotary shaft and provided with main rotor bearings to allow rotary movement thereof. The balancing apparatus includes at least one moving-weight balancing unit is carried by the rotary shaft, and at least one monitoring and correcting system having a drive assembly. The at least one monitoring and correcting system monitors and corrects the unbalanced state of the rotor, and acts continuously on the at least one moving-weight balancing unit when the rotor is rotating to monitor and correct for rotor unbalance. The at least one moving-weight balancing unit has at least two balancing masses mounted to be movable under drive from the drive assembly controlled by the monitoring and correction system. The at least one moving-weight balancing unit is situated axially at a distance from the rotor to be balanced beyond the main rotor bearings, and includes a ring and at least one guide assembly. The at least two balancing masses include respective carriages that are moveable in the ring, guided by the at least one guide assembly, independently of each other along trajectories that form closed circuits around the rotary shaft under drive from the drive assembly associated with each of said at least two balancing masses.
Owner:FLAKT SOLYVENT VENTEC
Online state monitoring and fault diagnosis device and method for rotary machine
InactiveCN102054179AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityStructural/machines measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionArray data structureDisplay device
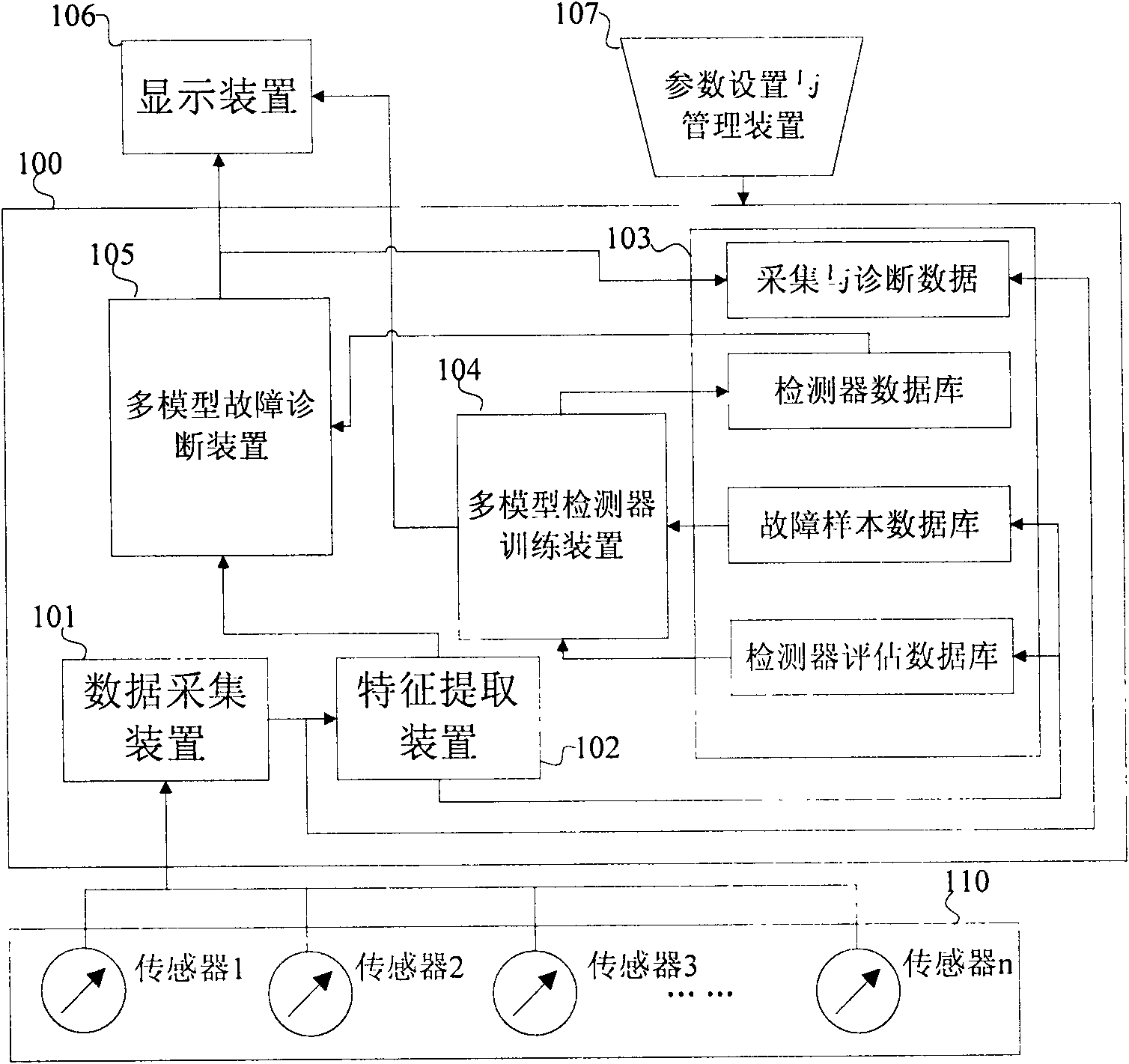
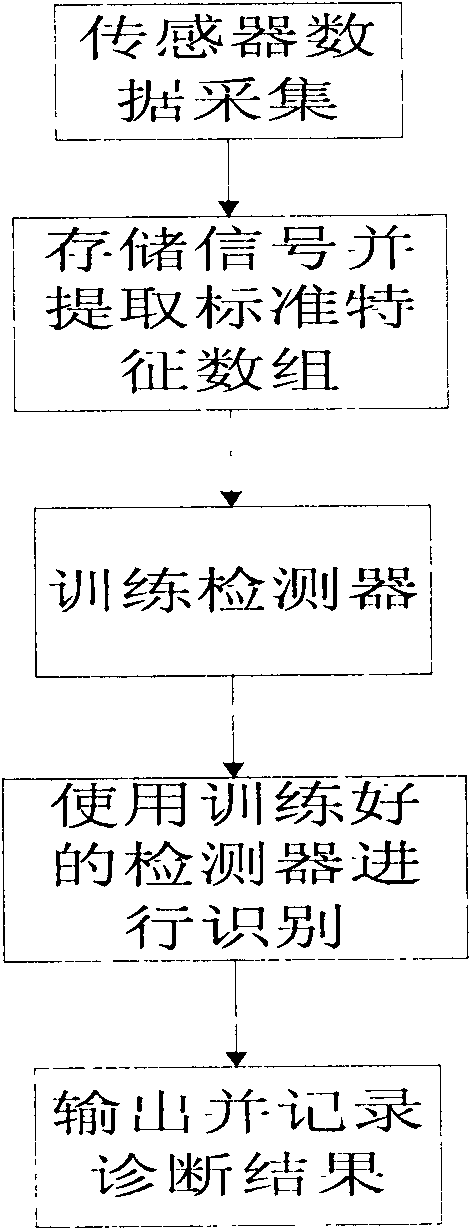
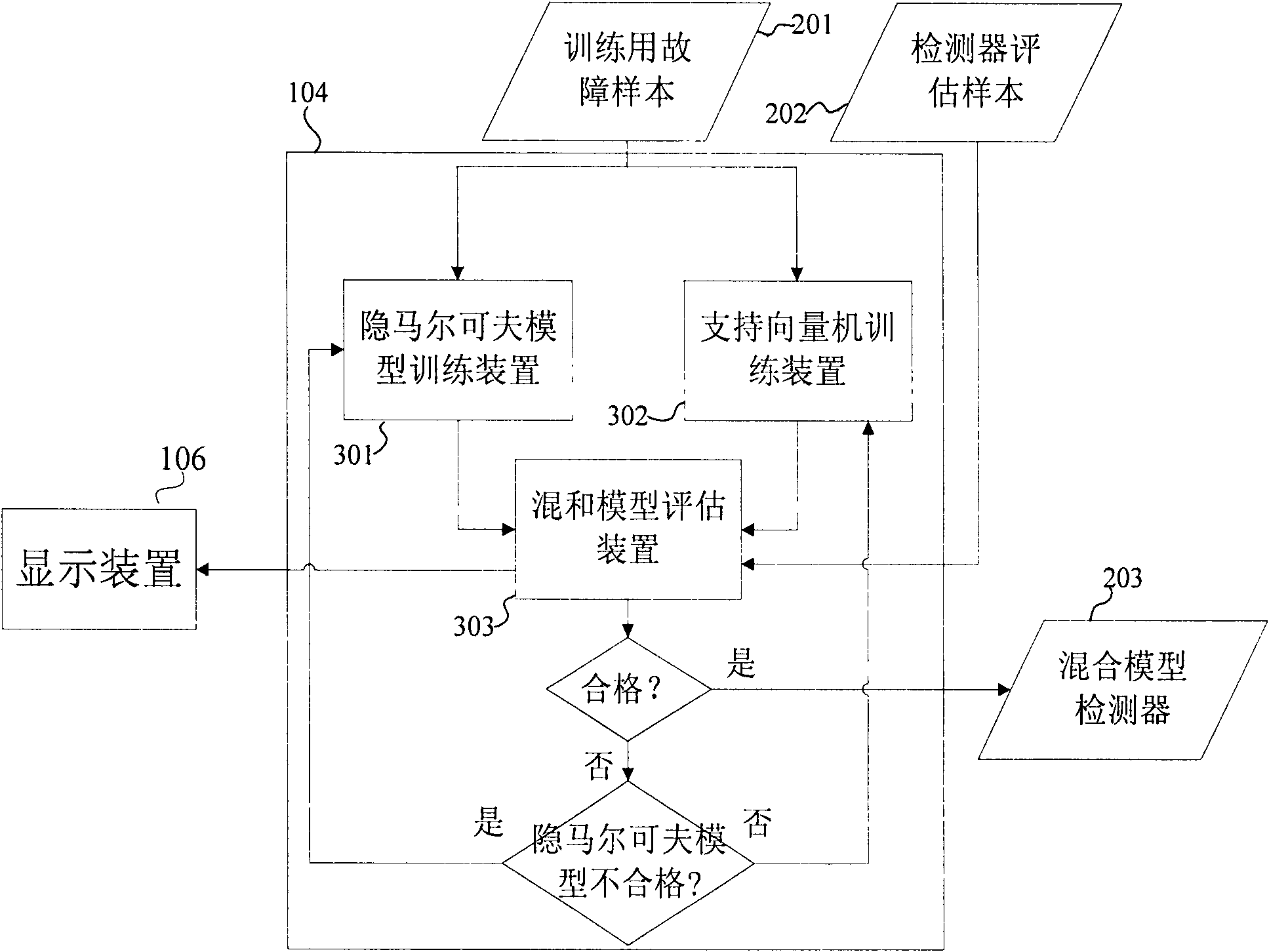
The invention relates to an online state monitoring and fault diagnosis device and an online state monitoring and fault diagnosis method for a rotary machine. The device comprises a data acquisition device 101, a feature extraction device 102, a data management device 103, a display device 106, a device 107 such as a mouse, a keyboard or the like for setting parameters and managing equipment by a user, a multi-model detector training device 104, and a multi-model fault diagnosis device 105. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring signals by using the data acquisition device; storing the signals, and extracting features of the signals by using the standard feature array extraction device; training a detector by using the training device for the detector for identification; performing identification by adopting the trained hybrid model detector; and outputting and recording the identification result. The device and the method can diagnose common rotary machine faults such as shaft eccentricity, bearing eccentricity, rolling body abrasion and the like, and have the advantages of high automation degree, capability of identifying multiple fault types, capability of realizing early diagnosis, good fault database expansibility and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
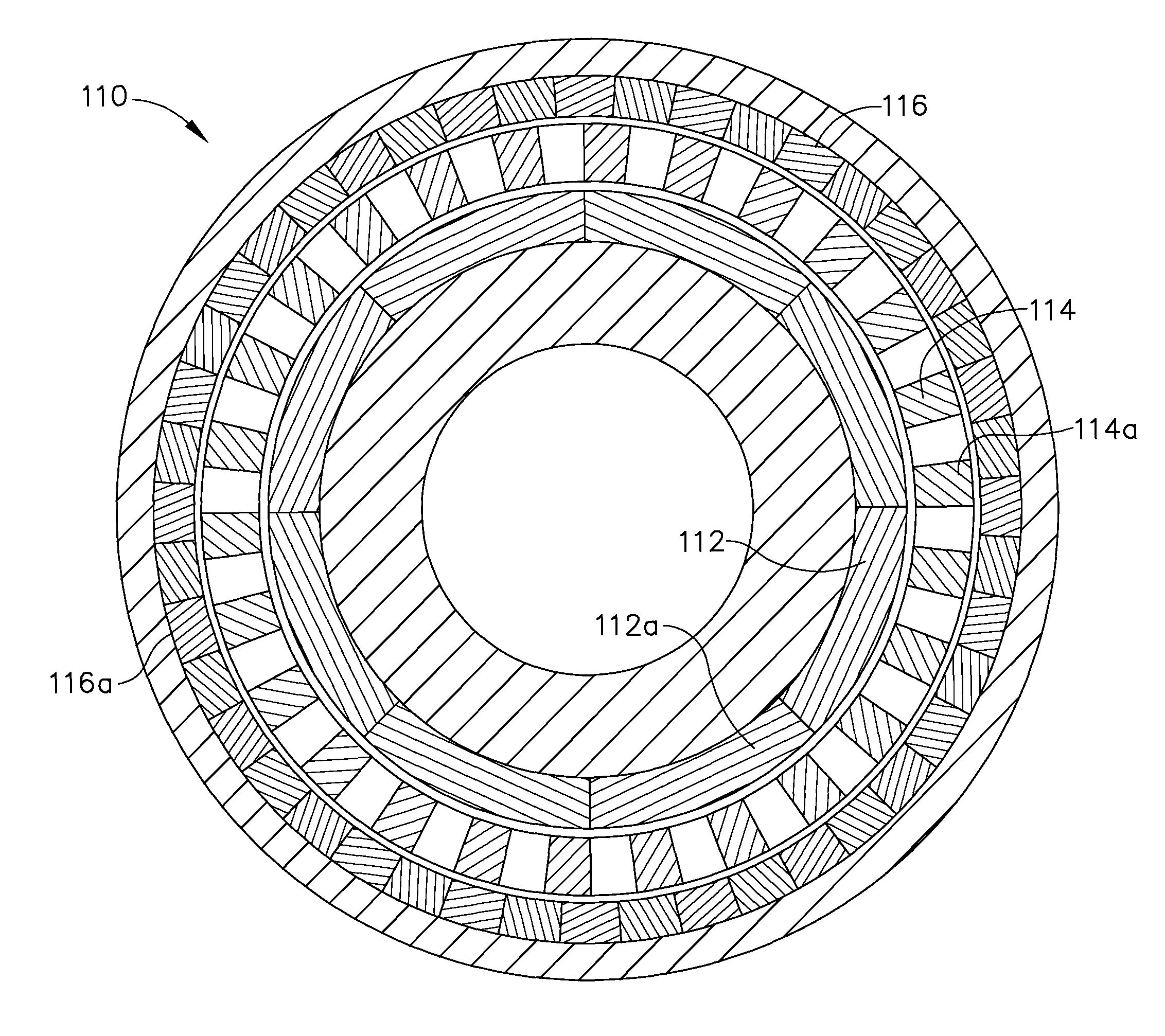
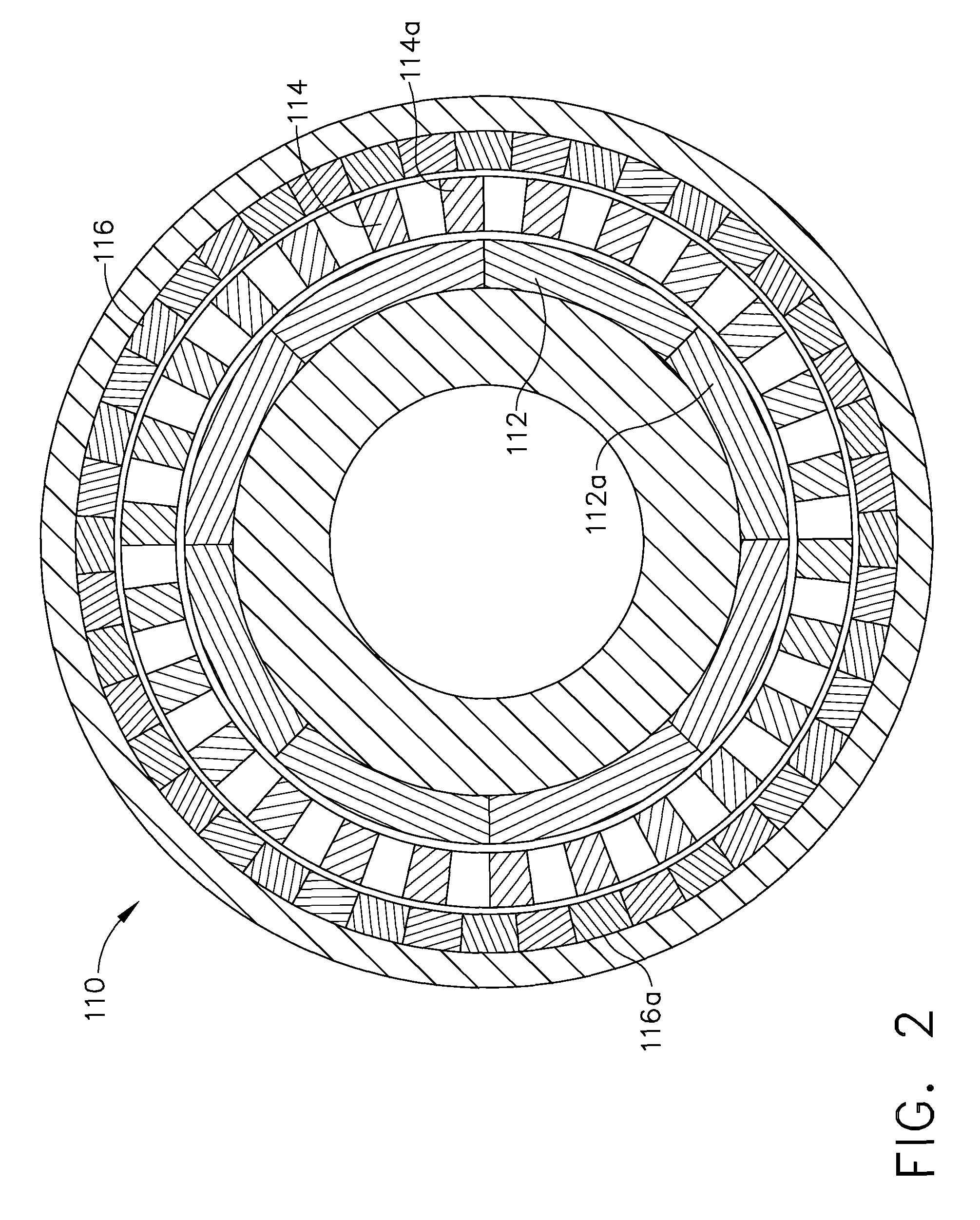
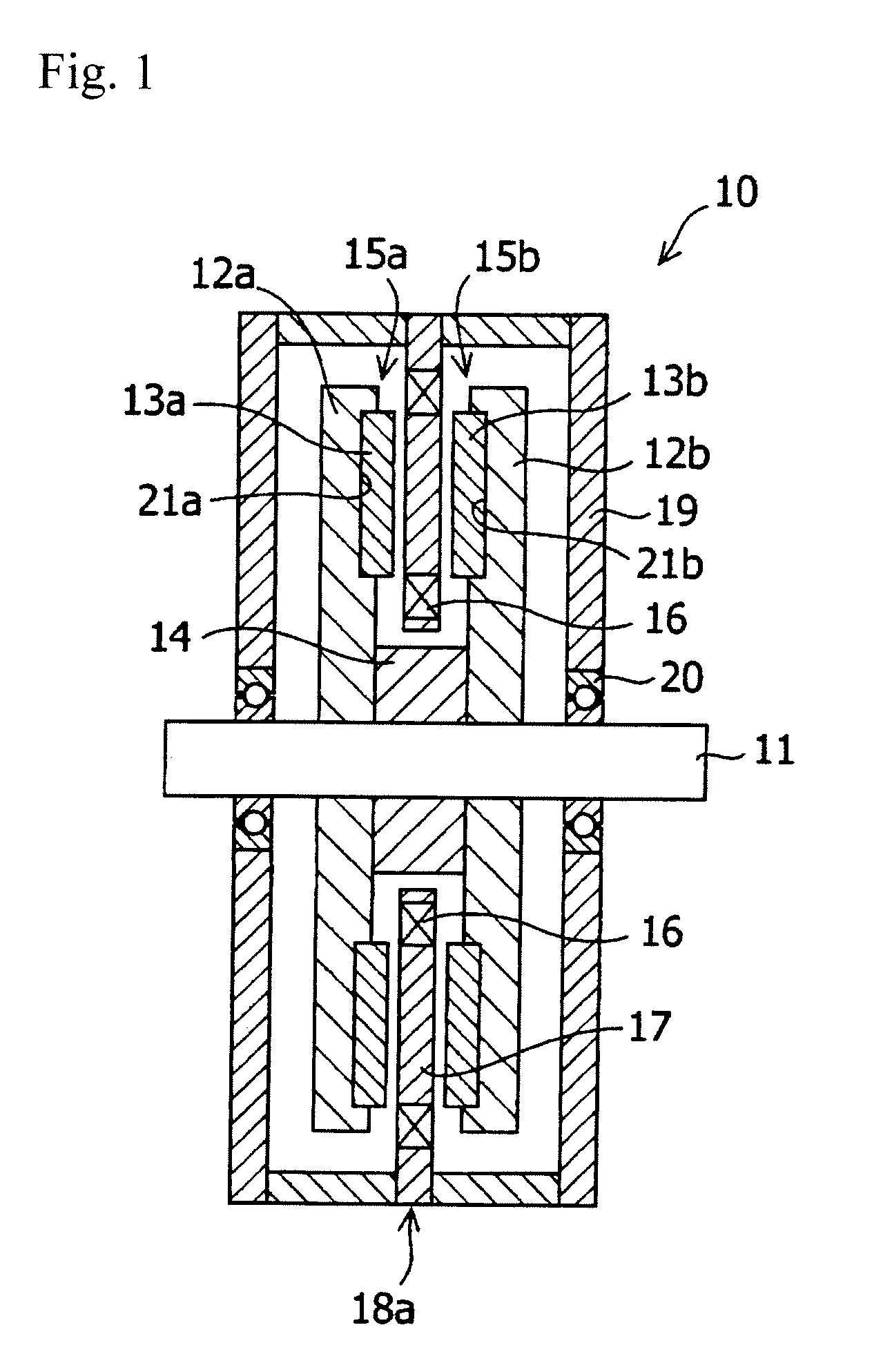
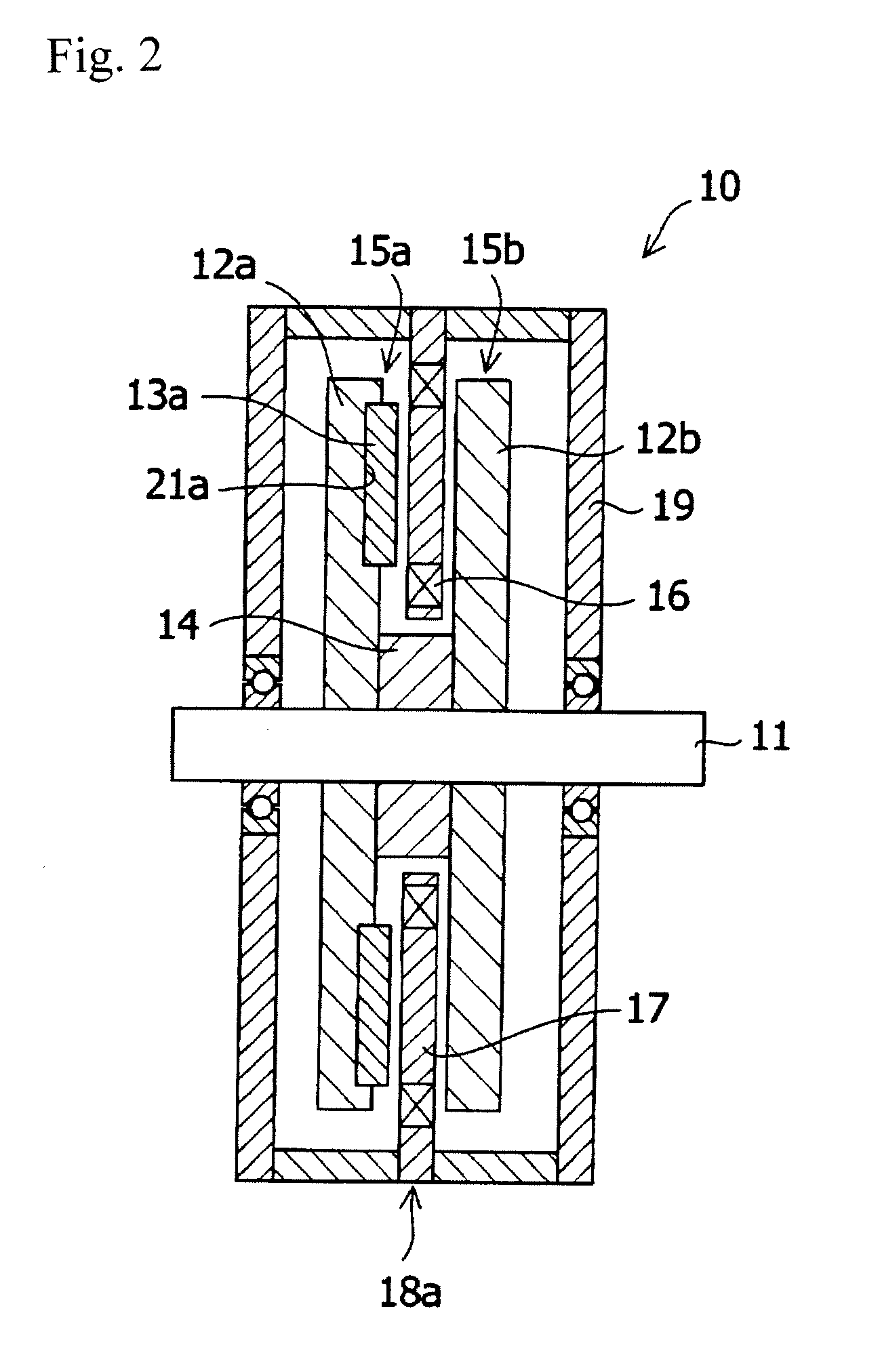
Axial gap type rotating machine
InactiveUS20100072850A1Without reducing magnetic fluxMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic fluxMagnet
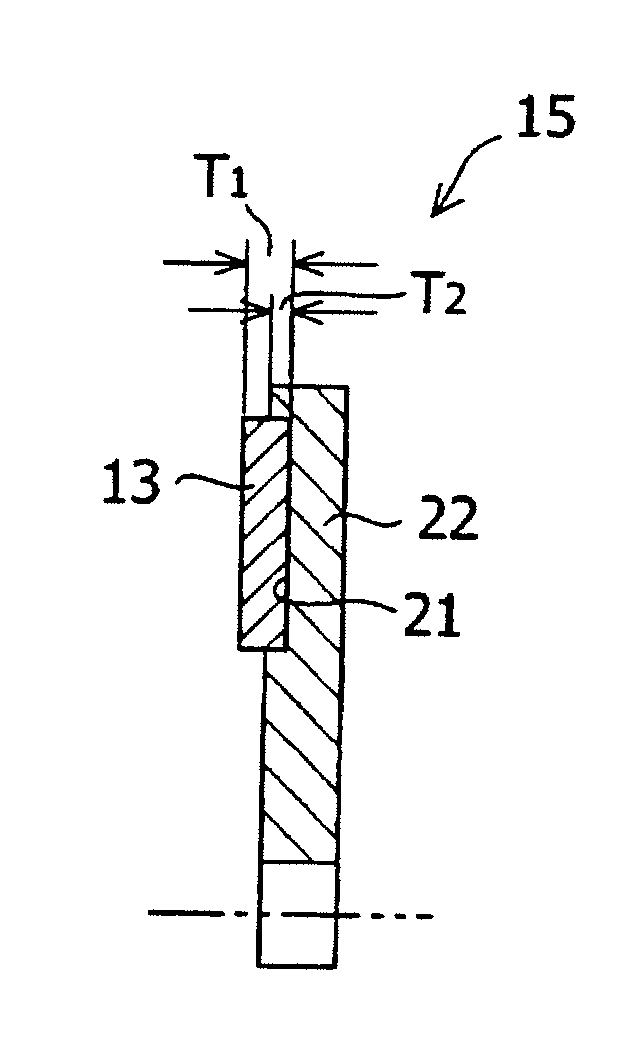
An axial gap type rotating machine rigidly fixing the permanent magnets without reducing the magnetic flux and having a high output is provided.An axial gap type rotating machine having: a housing 19; a rotating shaft 11 rotatably supported in the housing; two rotors (15a, 15b), having rotating disks (12a, 12b) rotatable integrally with the rotating shaft 11 as the central axis, and permanent magnets (13a, 13b) arranged concentrically in spaced relation to each other on at least one side of the surfaces of the rotating disks, wherein the surfaces having the permanent magnets face each other in spaced relation; and a stator 18 that is arranged between the rotors facing each other, the stator is spaced from the rotor, and fixed to the housing, the stator having a plurality of coils 16 disposed concentrically around said rotating shaft in spaced relation to each other; wherein magnetic flux generated from the permanent magnets of the rotors intermittently penetrates the interior of each of the coils 16 disposed concentrically around said rotating shaft 11 as it rotates, wherein the rotating disk has a concave portion 21 in the surface facing the stator and the permanent magnets are disposed at the concave portions so as to protrude above the surface of the rotating disk.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Multi-phase rotary machine control apparatus and electric power steering system using the same
ActiveUS20110074323A1Minimize output powerSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlElectric power steeringPhase currents
A failure identification part identifies a switching element pair having off-failure, in which a FET of the switching element pair in a first inverter part is disabled to turn on. A failure-time control part controls other switching element pairs and of the first inverter part based on failure-time phase current command values calculated as a function of a rotation position and a q-axis current command value. The failure-time control part controls a second inverter part normally. A motor is persistently driven with the minimum reduction in motor torque, even when the FET fails.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Magnet fixing structure for electric rotary machine
ActiveUS7687957B2Easy to degradeQuality improvementMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsEngineering
Holder anchoring grooves are arranged on the outer periphery of a rotor core so as to extend axially. A holder arm having a substantially T-shaped cross section is fitted to each of the holder anchoring grooves. The holder arm has a main body section, an engaging projection and magnet holding pieces. The engaging projection is engaged with the corresponding one of the holder anchoring grooves. Each of the magnet holding pieces includes a first contact section, a second contact section and a non-contact area. A magnet containing section is defined by the magnet holding pieces that are located vis-à-vis relative to each other of any two adjacently located holder arms and the outer peripheral surface of the rotor core. In the magnet containing sections, a rotor magnet is press fitted and anchored from the shaft direction. Thus, there is provided a magnet fixing structure that can accurately anchor magnets to a rotor core or the like at low cost.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Stator for rotary machine and method of manufacturing the stator
InactiveUS20020130582A1Improve cooling effectHigh insulation performanceSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionStator coilMechanical engineering
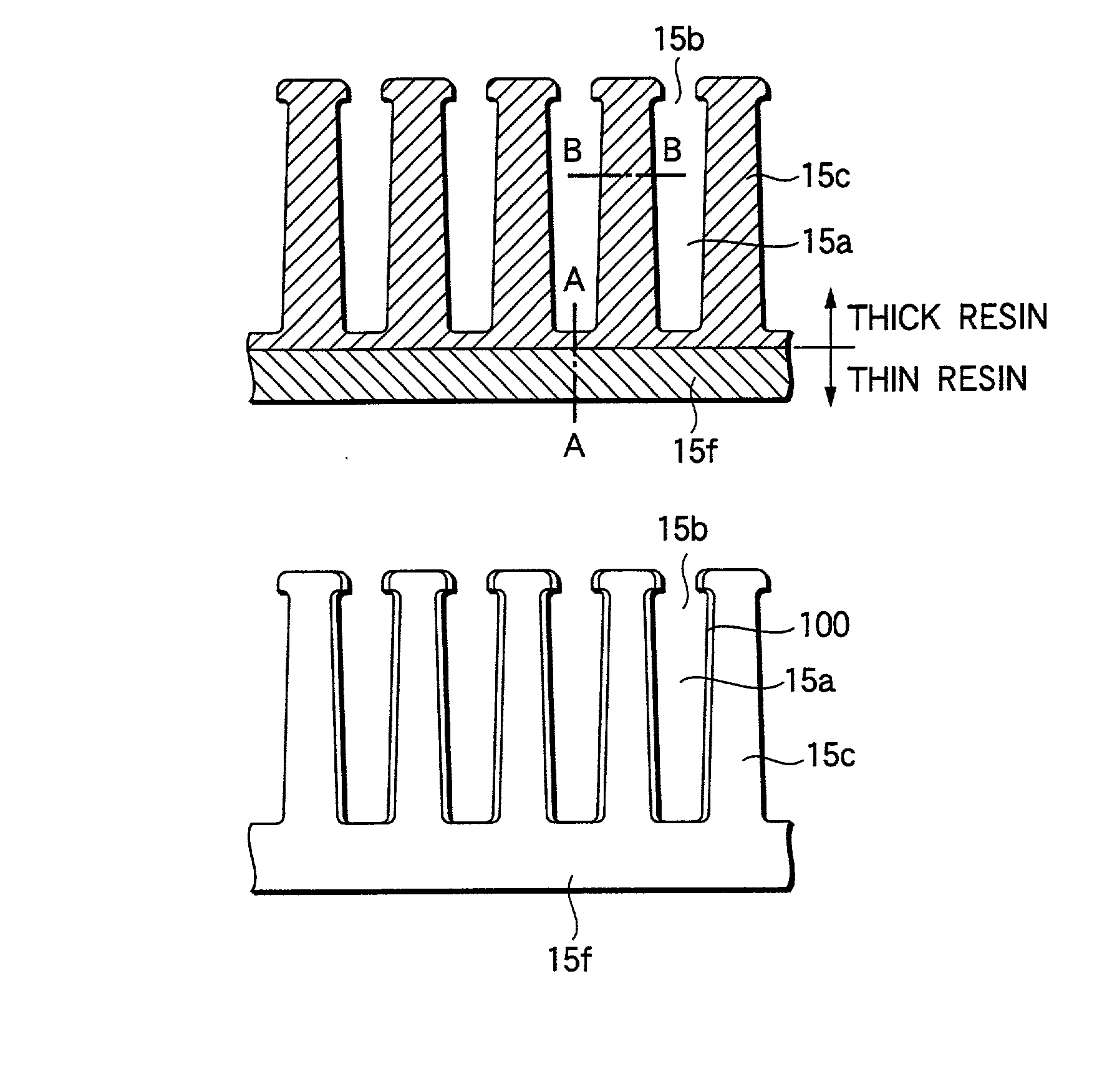
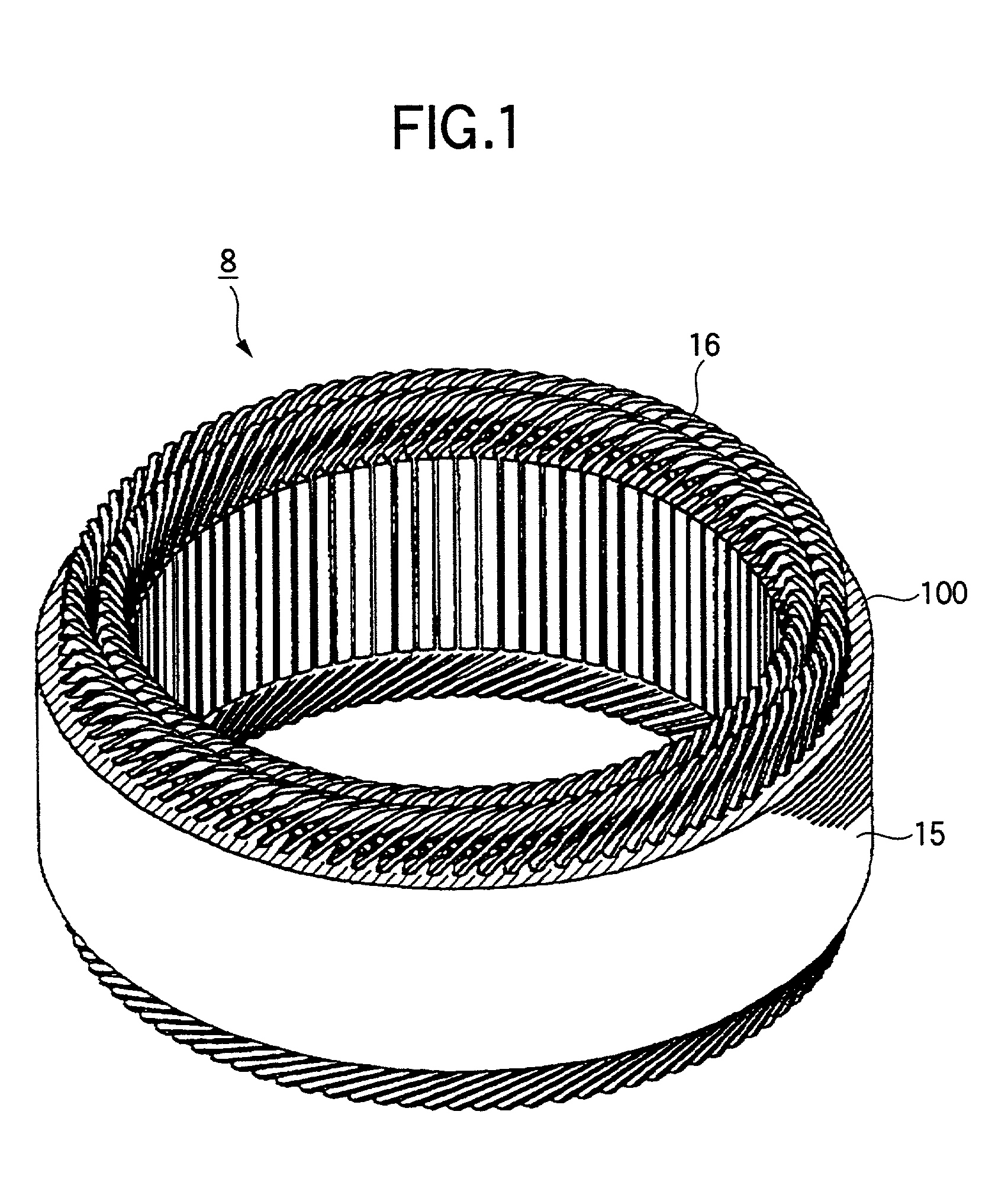
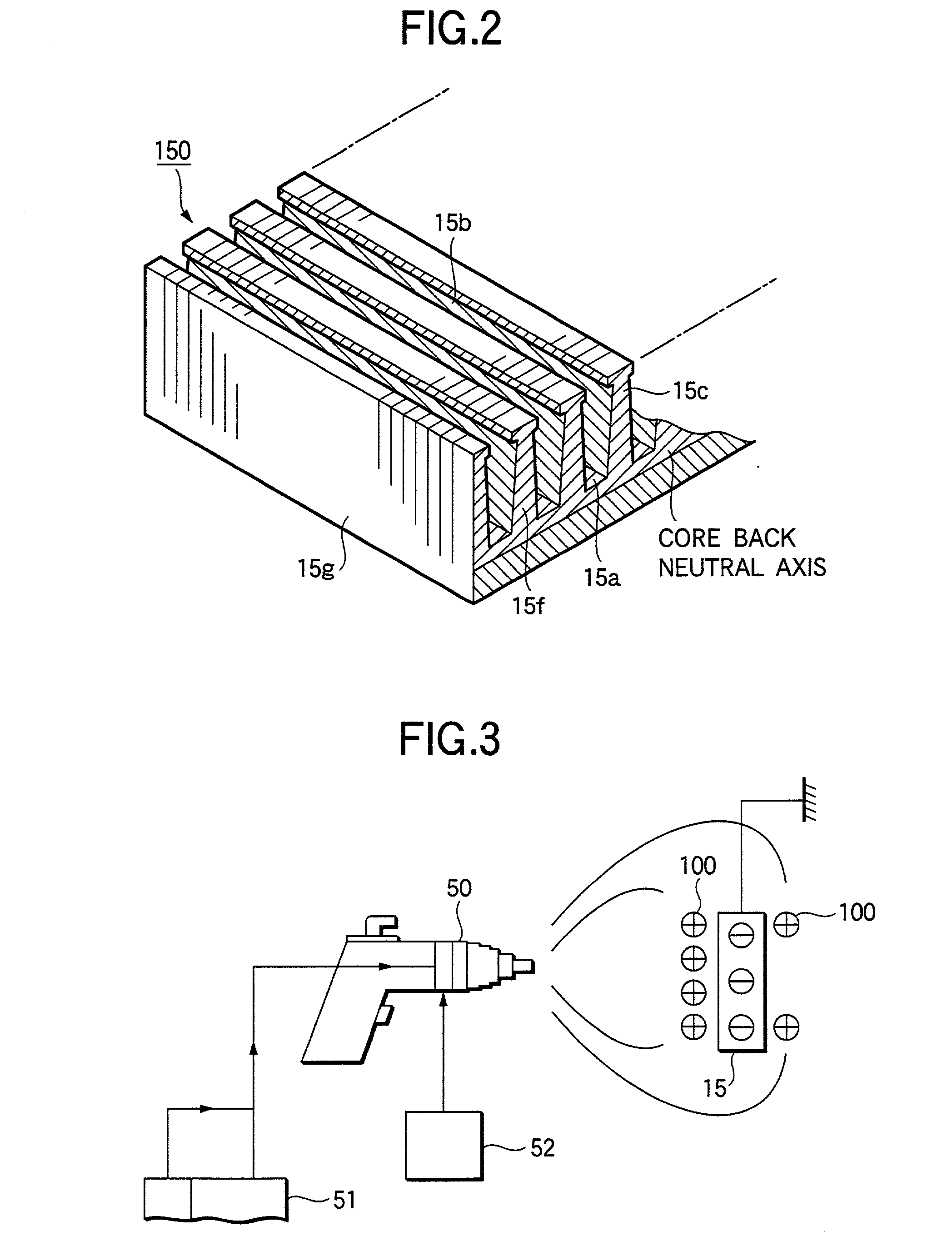
A stator for a rotary machine includes a rotor 7 and a stator 8 having a stator iron core 15 disposed oppositely around the outer circumference of the rotor 7 and a stator coil 16 fitted around the iron core 15, wherein the iron core 15 has a laminated iron core 150 with plural axially extending slots 15a formed circumferentially at predetermined pitches, an insulating resin 100 is coated on an axial end face 15f of the iron core 15 and an inner wall face of a slot 15a in the laminated iron core 150 to provide insulation between the iron core 15 and the stator coil 16, and the iron core is cylindrically shaped by bringing both circumferential end portions 15g of the laminated iron core 150 into contact to bend the laminated iron core 150 so that an opening face 15b of the slot 15a is directed inside.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com