Patents
Literature
606 results about "Tail rotor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
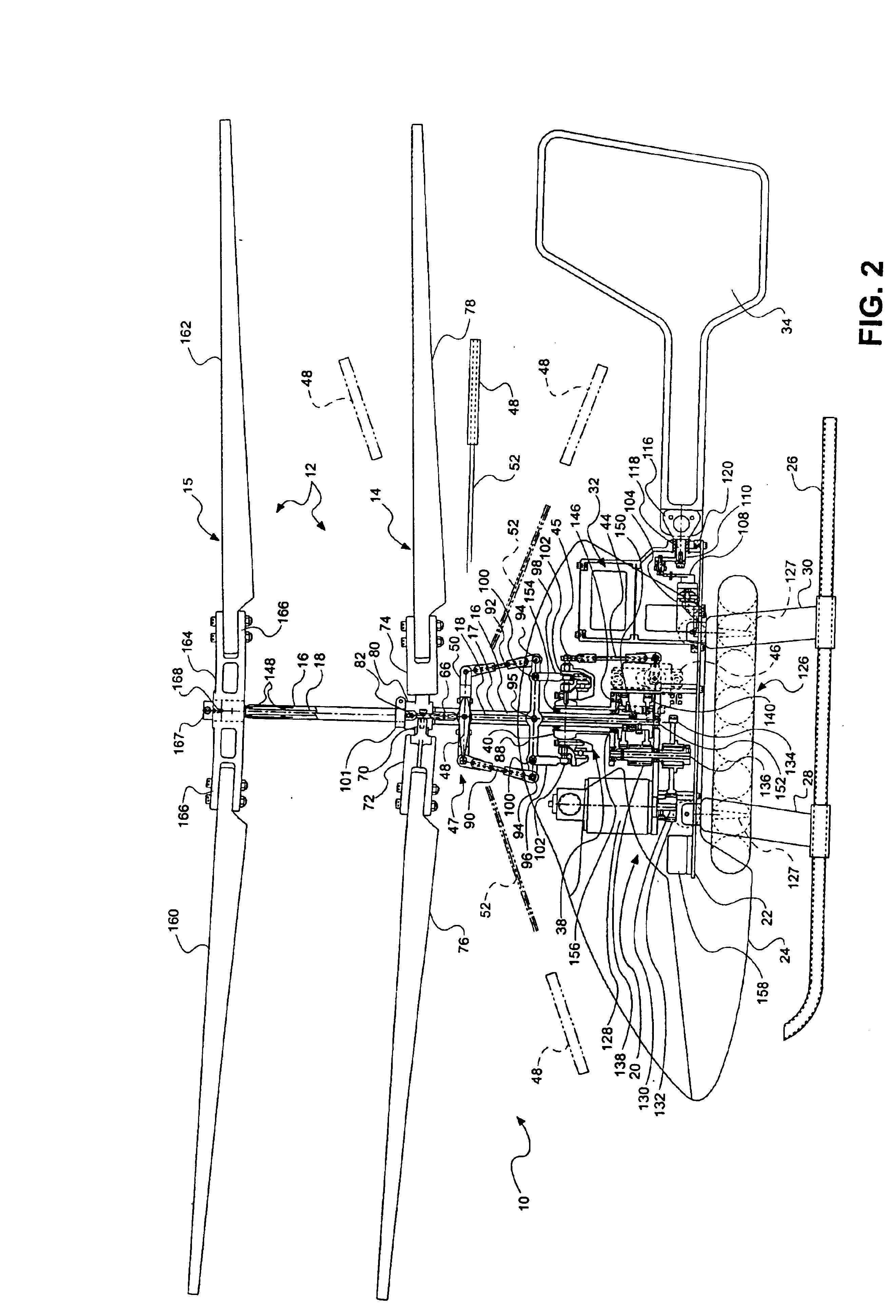
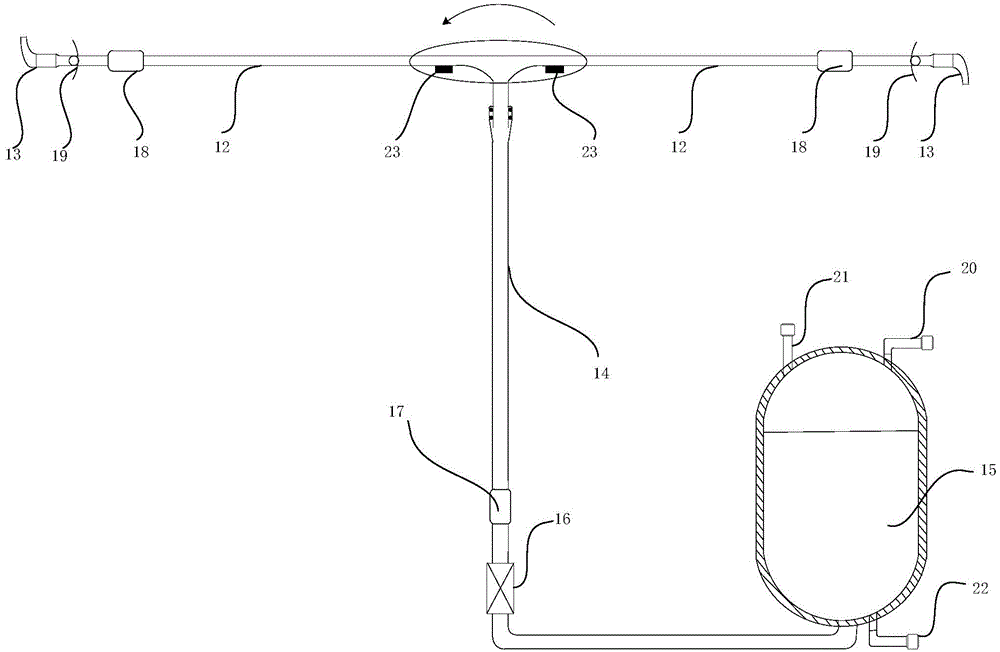
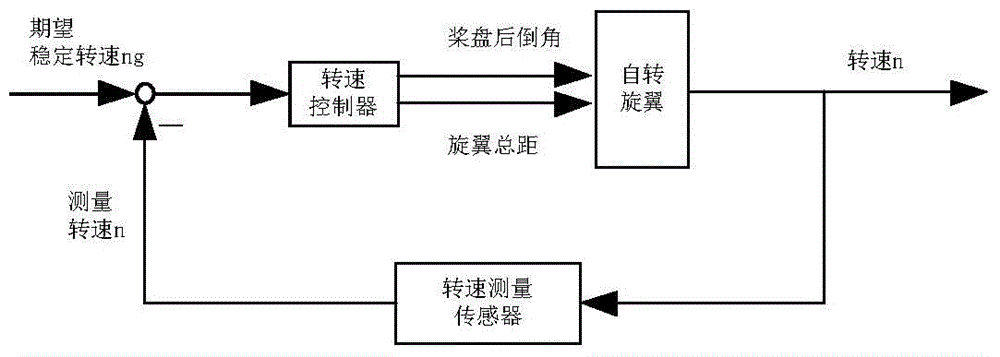
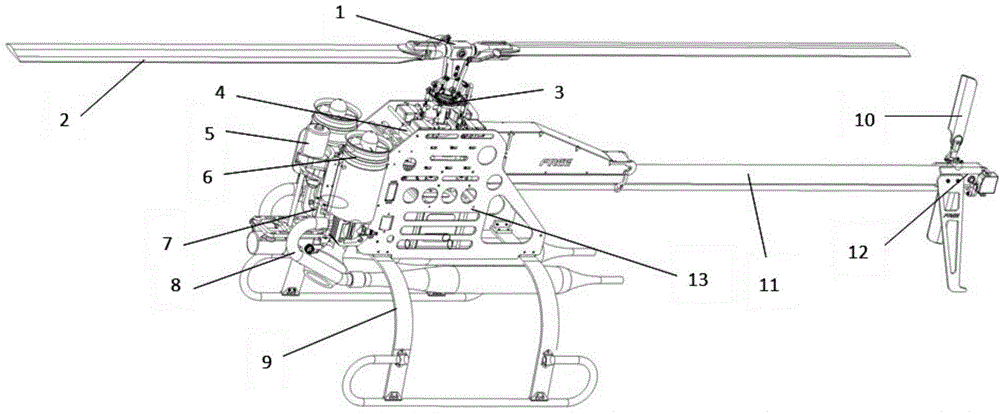
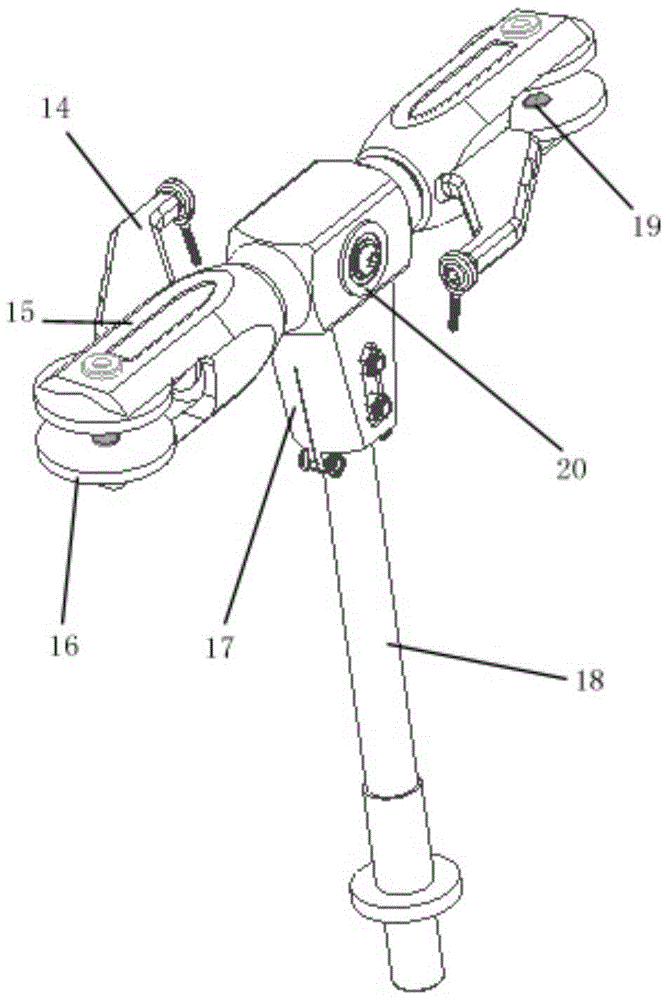
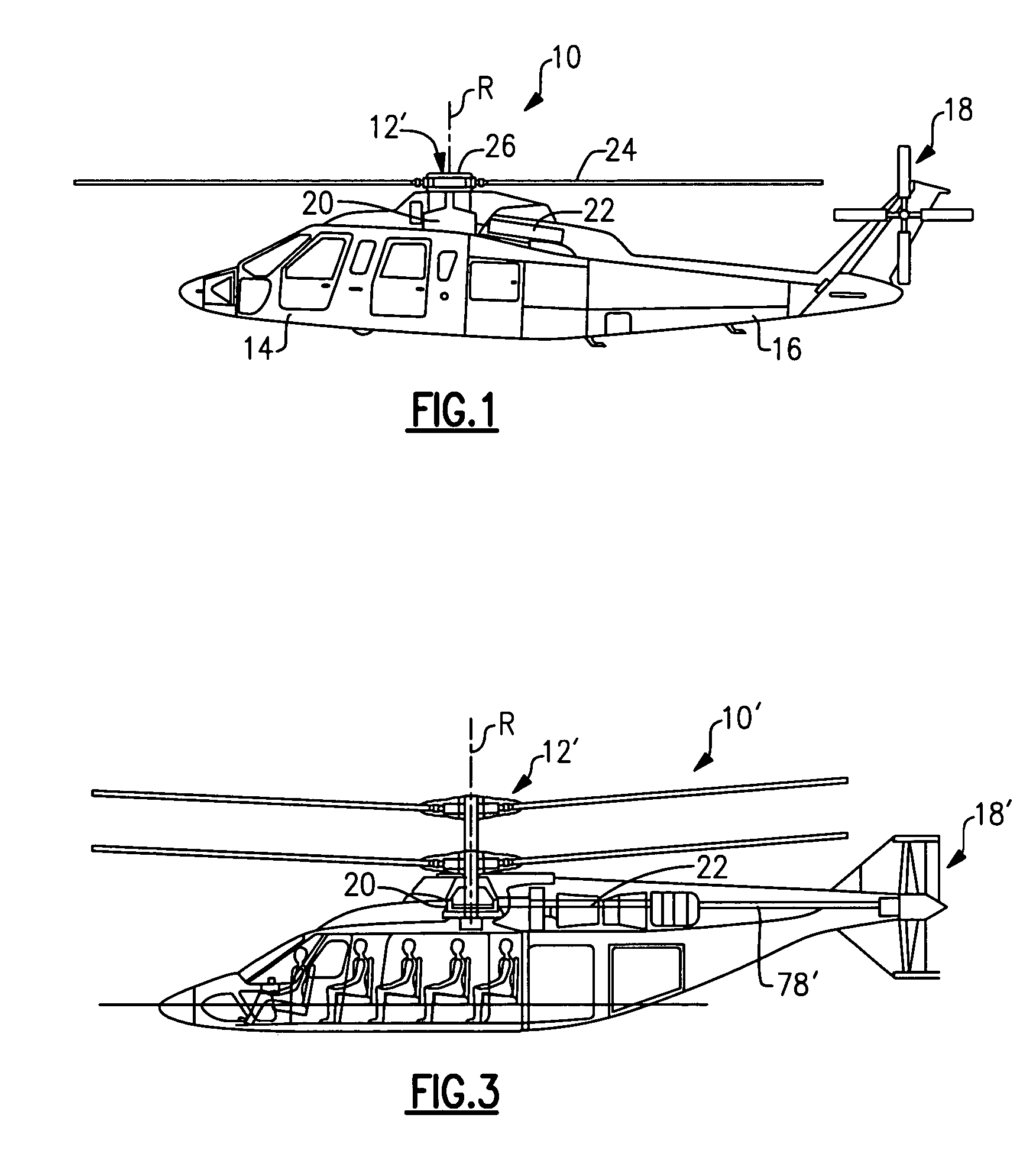
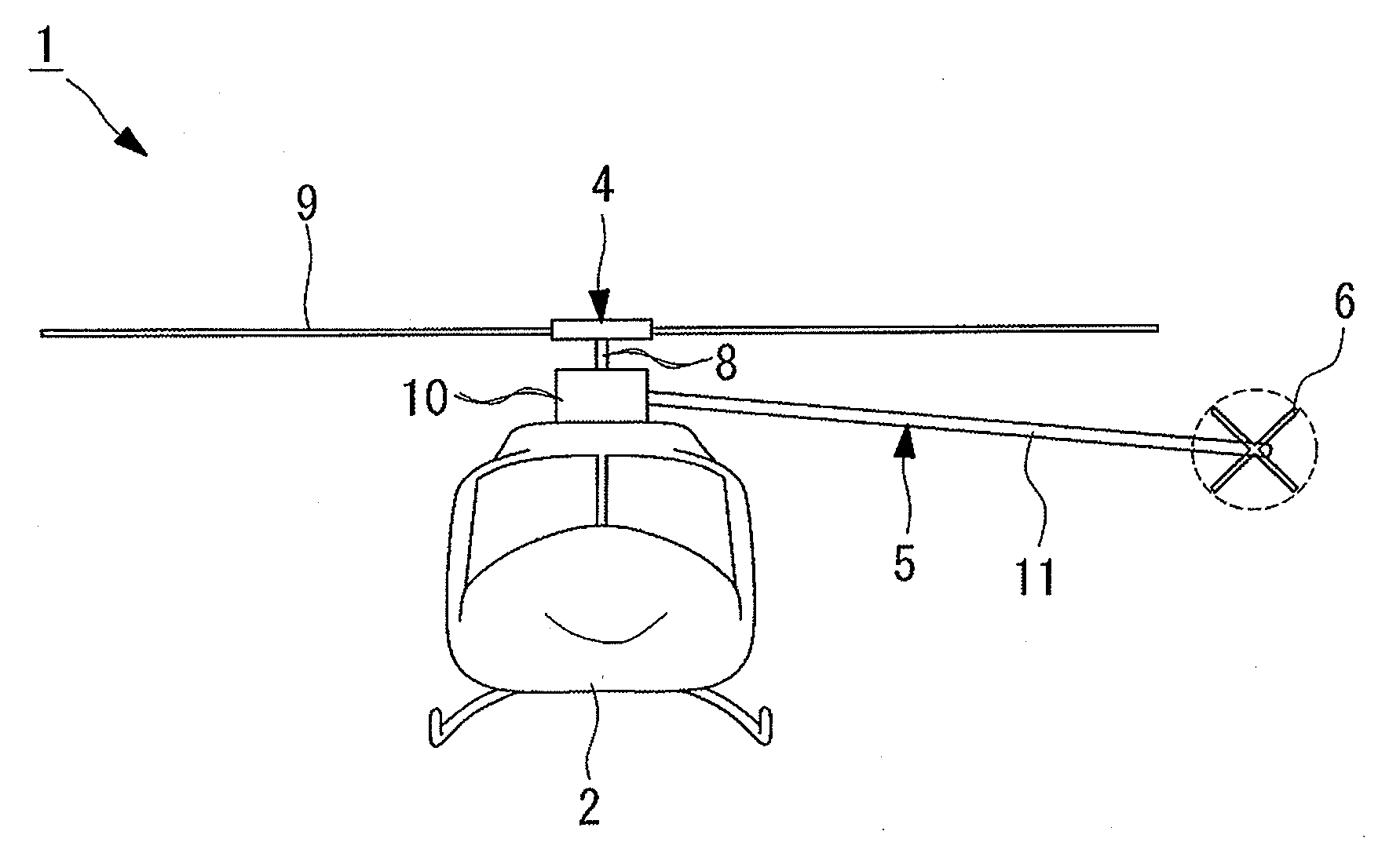
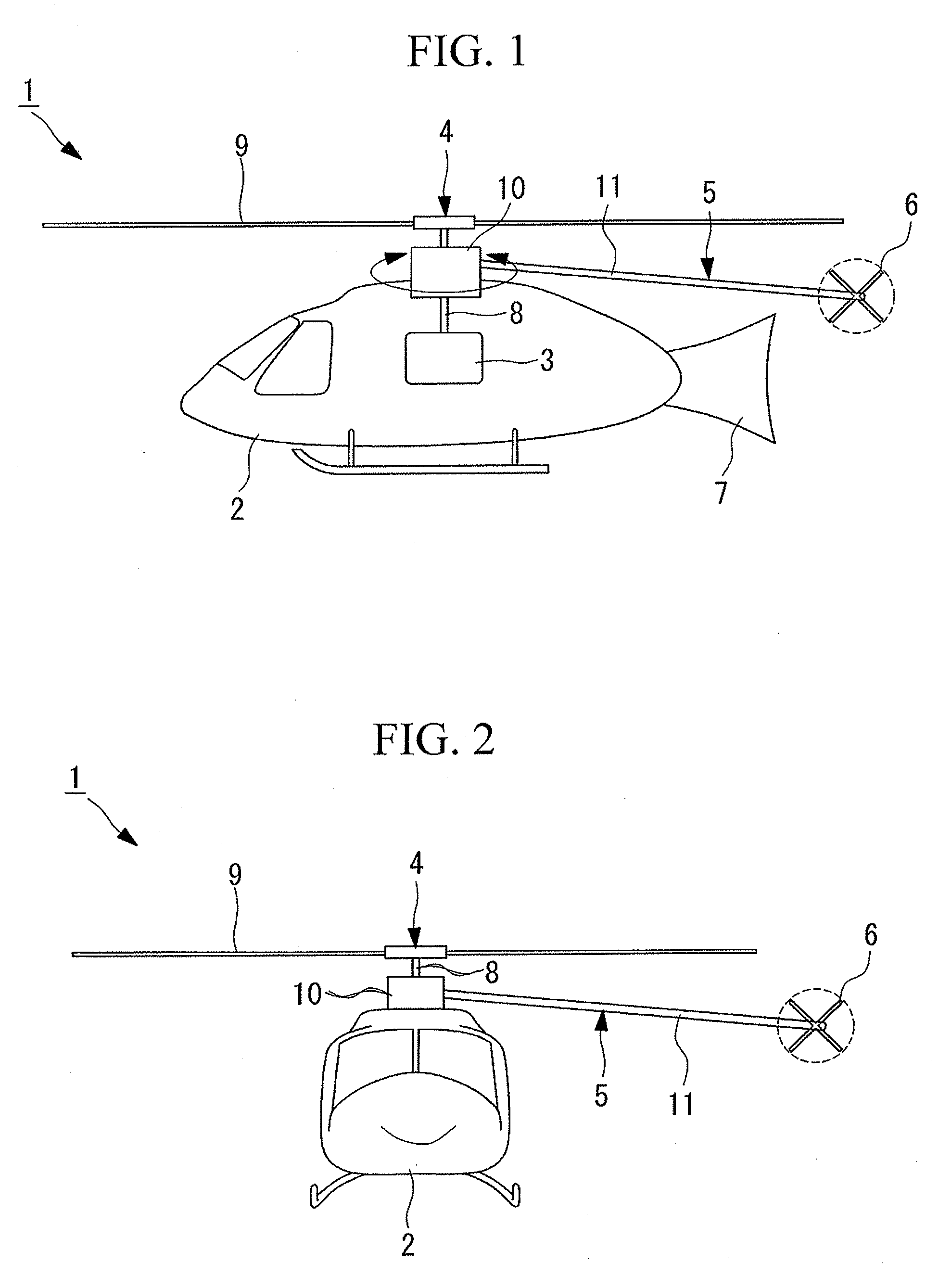
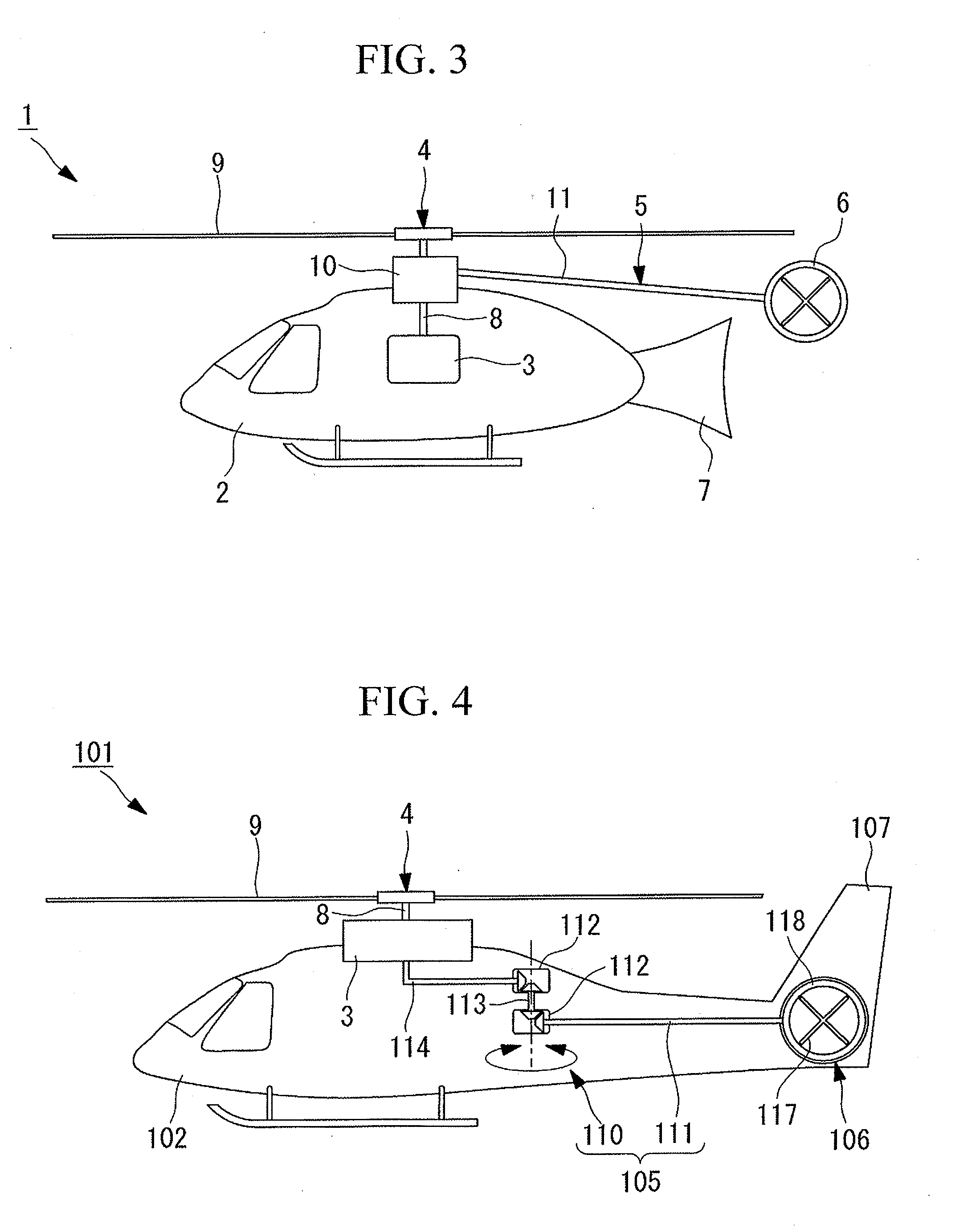
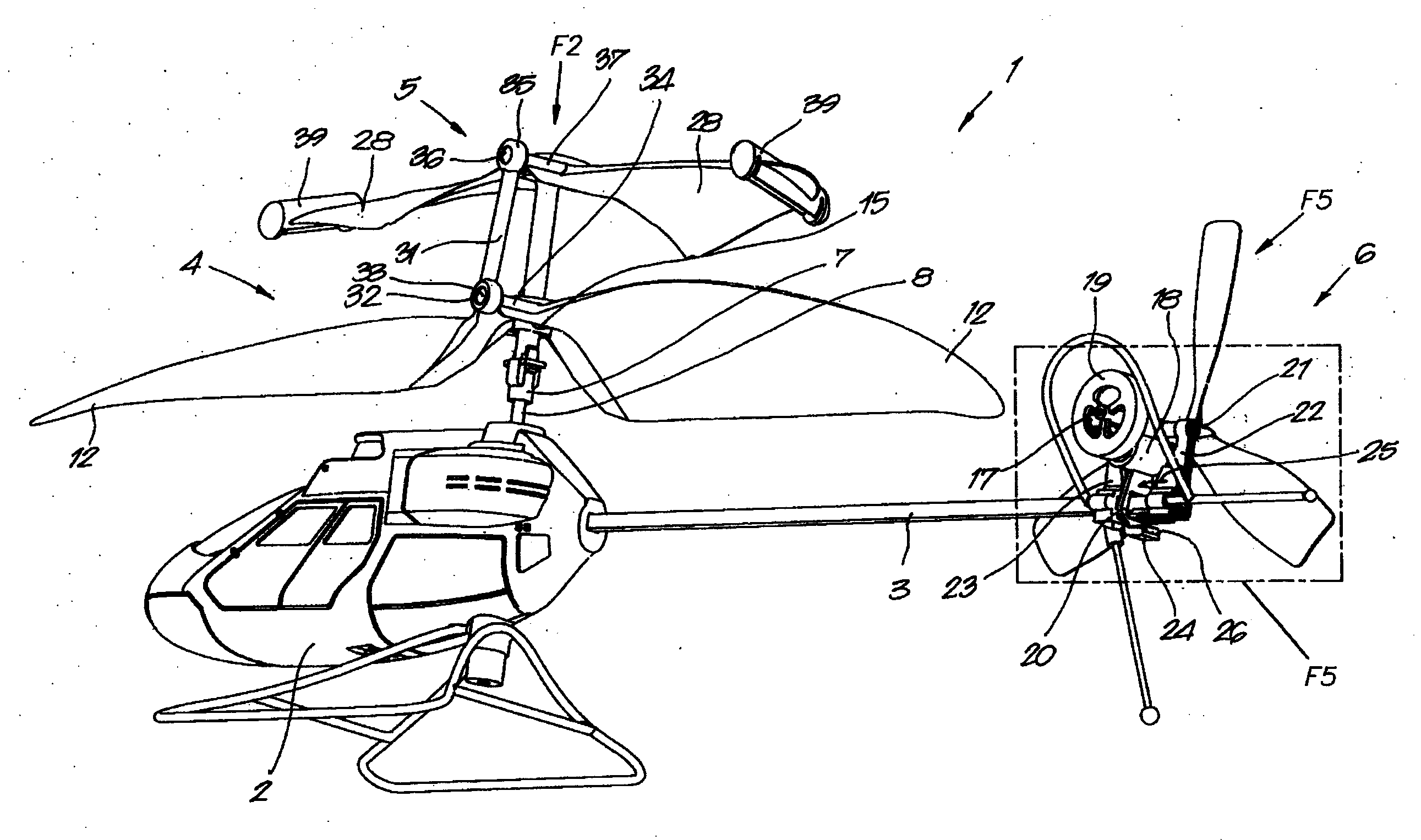
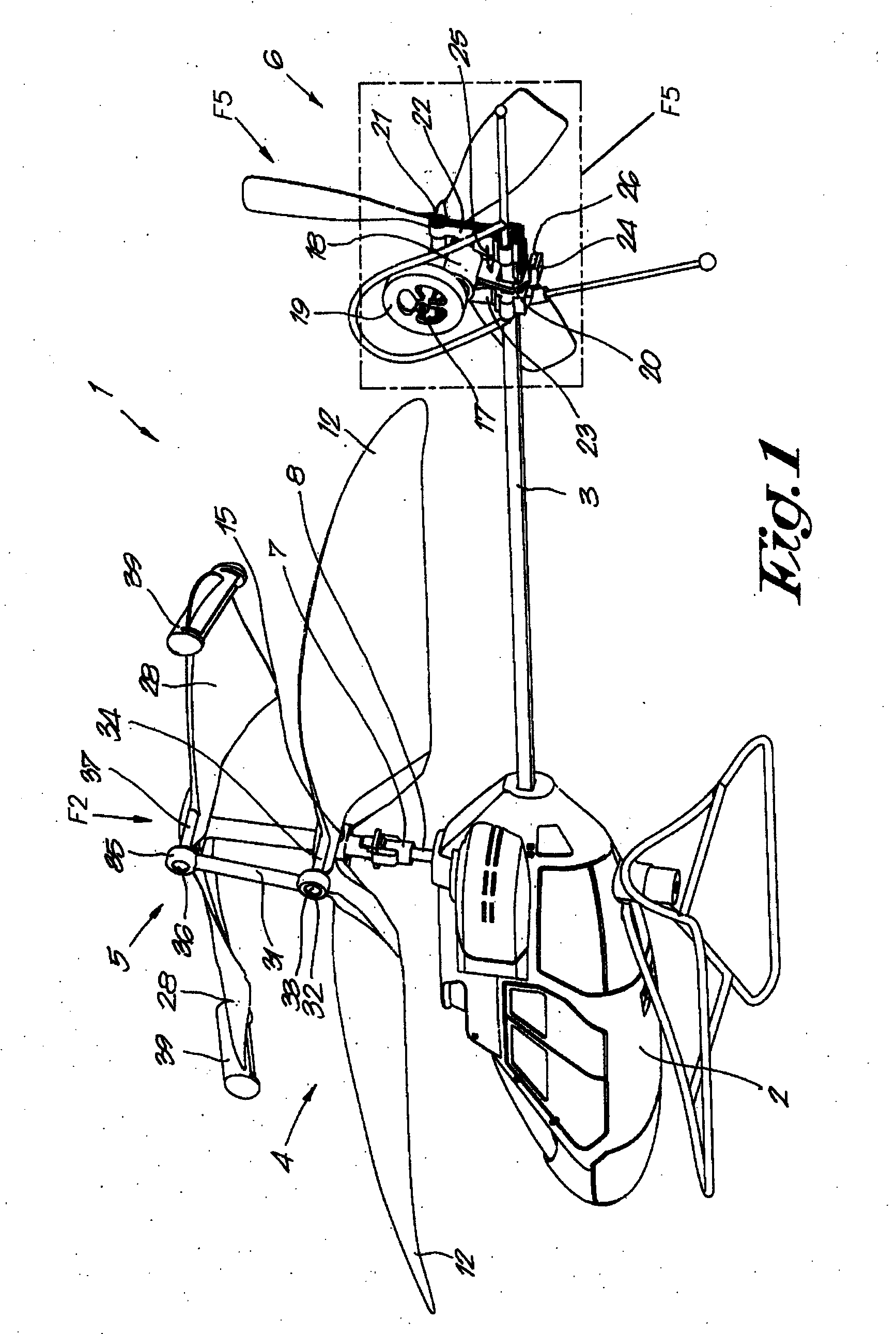
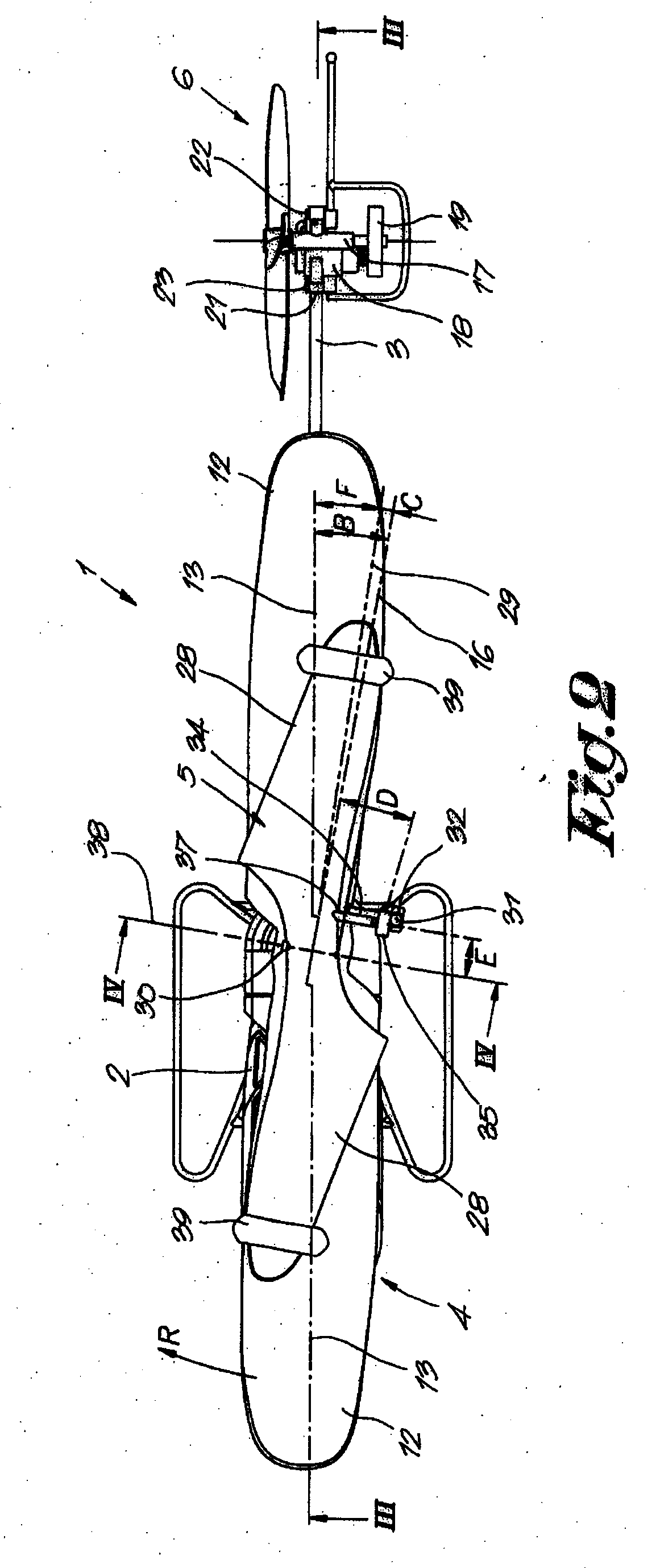
The tail rotor is a smaller rotor mounted so that it rotates vertically or near-vertically at the end of the tail of a traditional single-rotor helicopter. The tail rotor's position and distance from the center of gravity allow it to develop thrust in the same direction as the main rotor's rotation, to counter the torque effect created by the main rotor. Tail rotors are simpler than main rotors since they require only collective changes in pitch to vary thrust. The pitch of the tail rotor blades is adjustable by the pilot via the anti-torque pedals, which also provide directional control by allowing the pilot to rotate the helicopter around its vertical axis.
Variable magnetic flux electric rotary machine
InactiveUS20100164422A1Easy to operateWide operating speed rangeDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesElectrical polarityEngineering
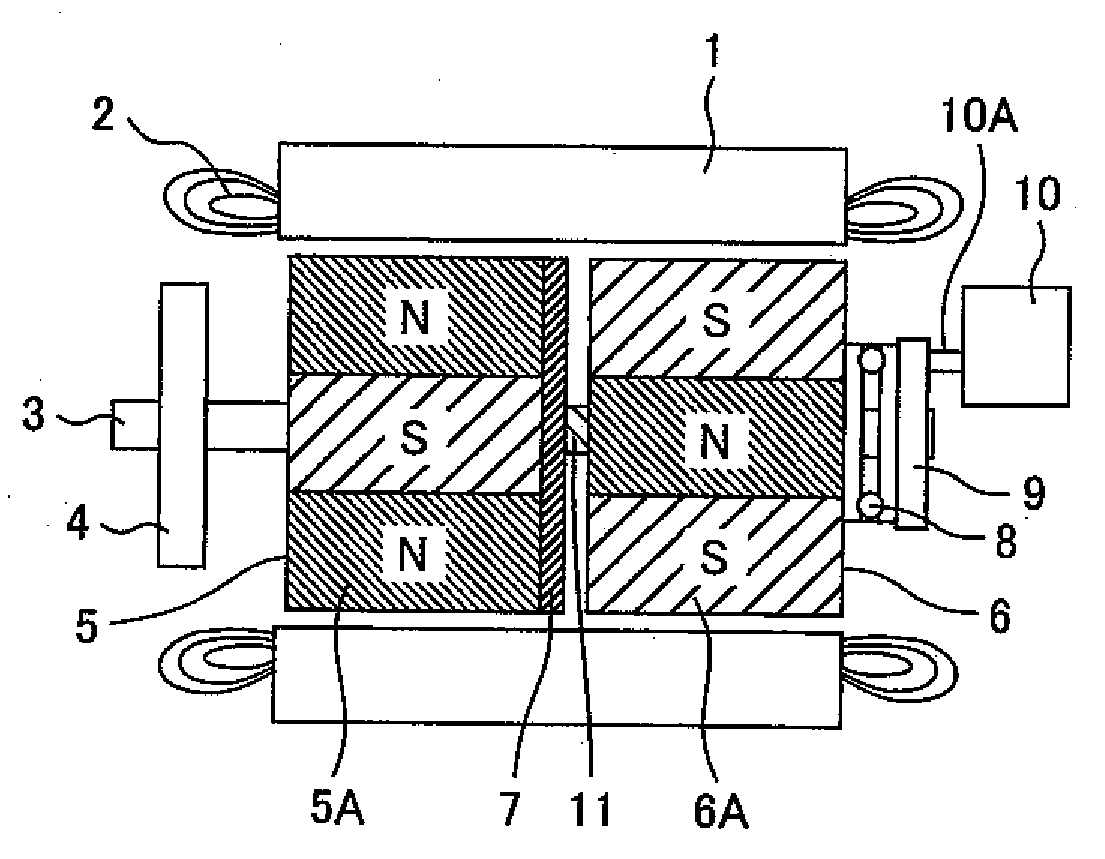
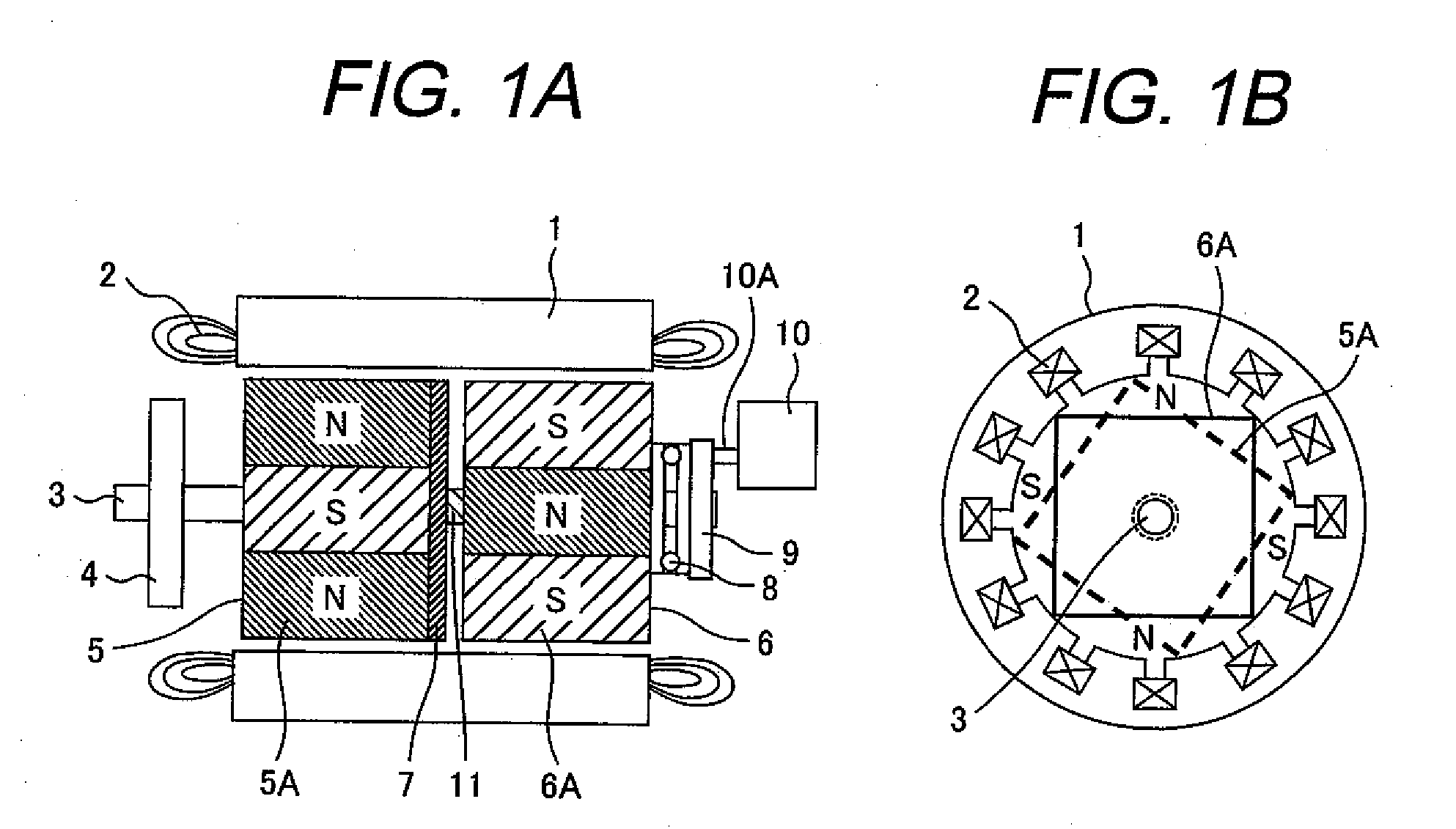
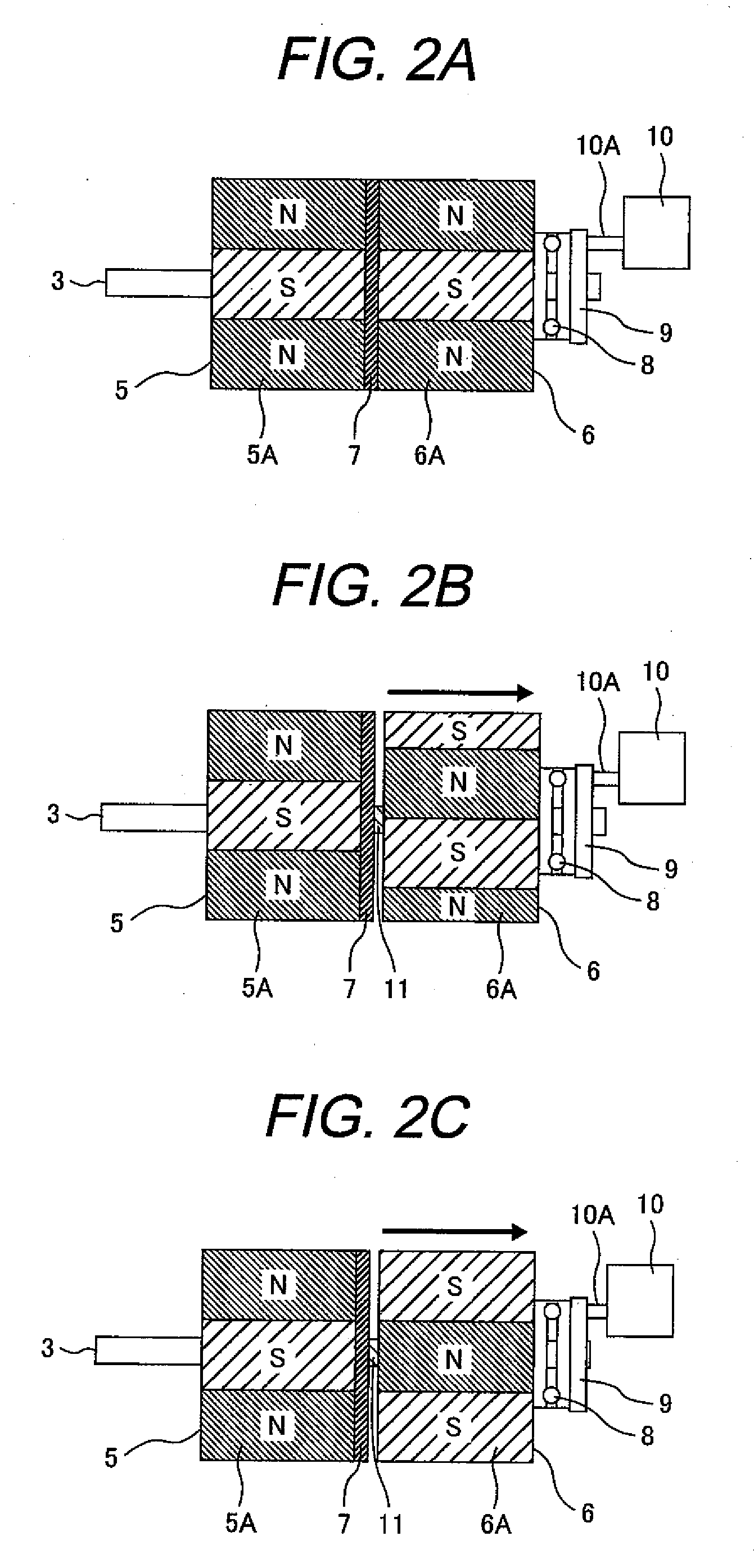
An electric rotary machine is disclosed which can adjust relative angles of sub-rotors continuously and regardless of torque direction without generating an attractive force between the field magnets of the sub-rotors. The electric rotary machine includes: a stator having a winding; a dual rotor which is rotatably disposed with a gap from the stator and divided axially along a shaft into a first rotor and a second rotor each having field magnets with different polarities arranged alternately in a rotation direction; a mechanism for varying the axial position of the second rotor relative to the first rotor continuously; and a non-magnetic member located between the first rotor and the second rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Tri-Rotor Aircraft Capable of Vertical Takeoff and Landing and Transitioning to Forward Flight
ActiveUS20160200436A1Increase rangeImprove enduranceAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesJet aeroplanePropeller
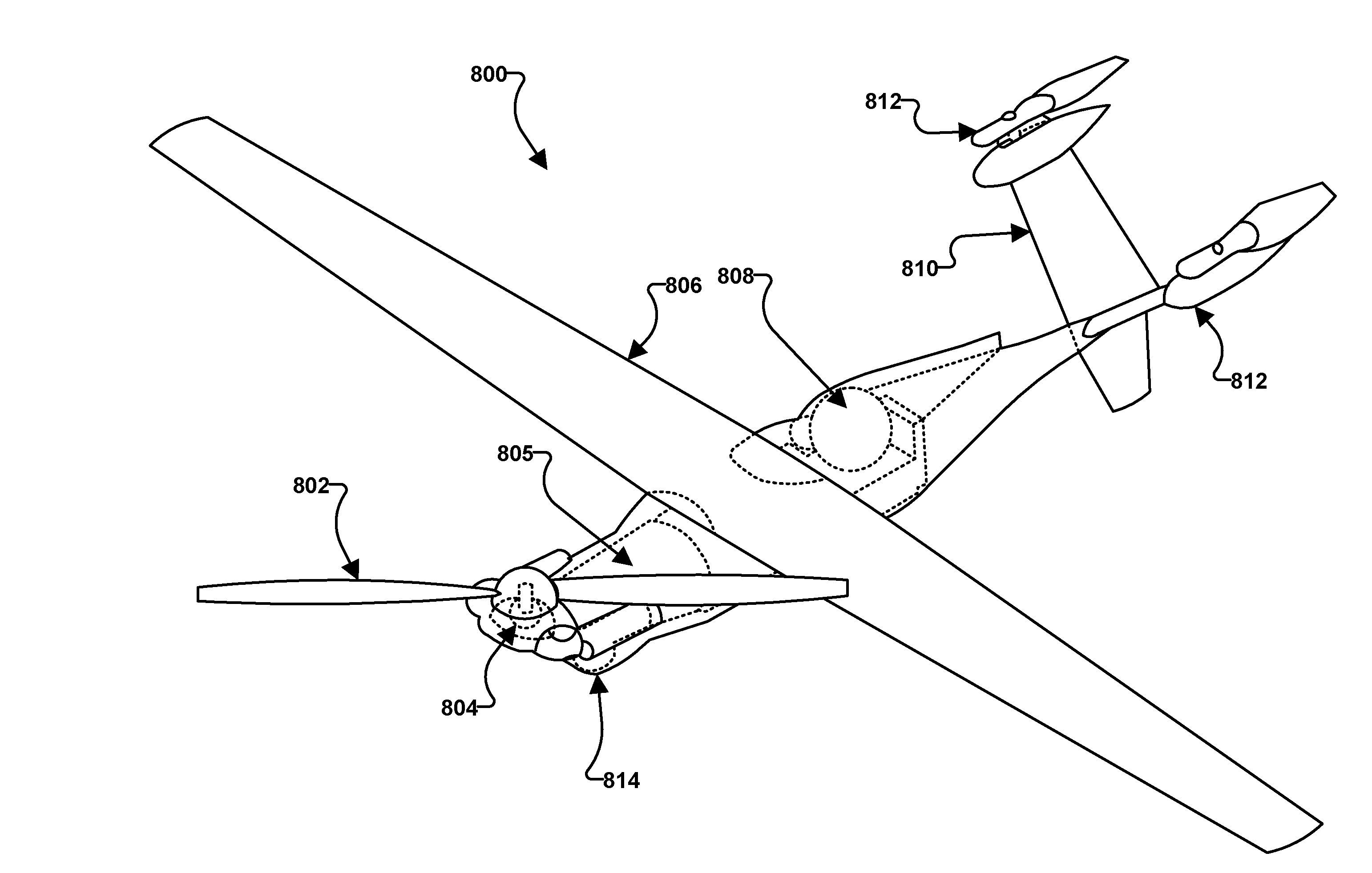
Systems, methods, and devices provide a vehicle, such as an aircraft, with rotors configured to function as a tri-copter for vertical takeoff and landing (“VTOL”) and a fixed-wing vehicle for forward flight. One rotor may be mounted at a front of the vehicle fuselage on a hinged structure controlled by an actuator to tilt from horizontal to vertical positions. Two additional rotors may be mounted on the horizontal surface of the vehicle tail structure with rotor axes oriented vertically to the fuselage. For forward flight of the vehicle, the front rotor may be rotated down such that the front rotor axis may be oriented horizontally along the fuselage and the front rotor may act as a propeller. For vertical flight, the front rotor may be rotated up such that the front rotor axis may be oriented vertically to the fuselage, while the tail rotors may be activated.
Owner:NASA
Coaxial helicopter
A coaxial helicopter, comprising a first rotor carried by a first shaft and a second rotor carried by a second shaft; wherein one of the first and second rotors has cyclic pitch control and the other rotor does not have cyclic pitch control, at least pitch and roll control being implemented by cyclic blade pitch control of only one rotor of the coaxial rotor set. Provisions for yaw control can include differential collective control of the first and second rotors, providing yaw paddles and / or a tail rotor, ducted fan, or an air jet configured for yawing the coaxial helicopter.
Owner:AEROTWIN MOTORS
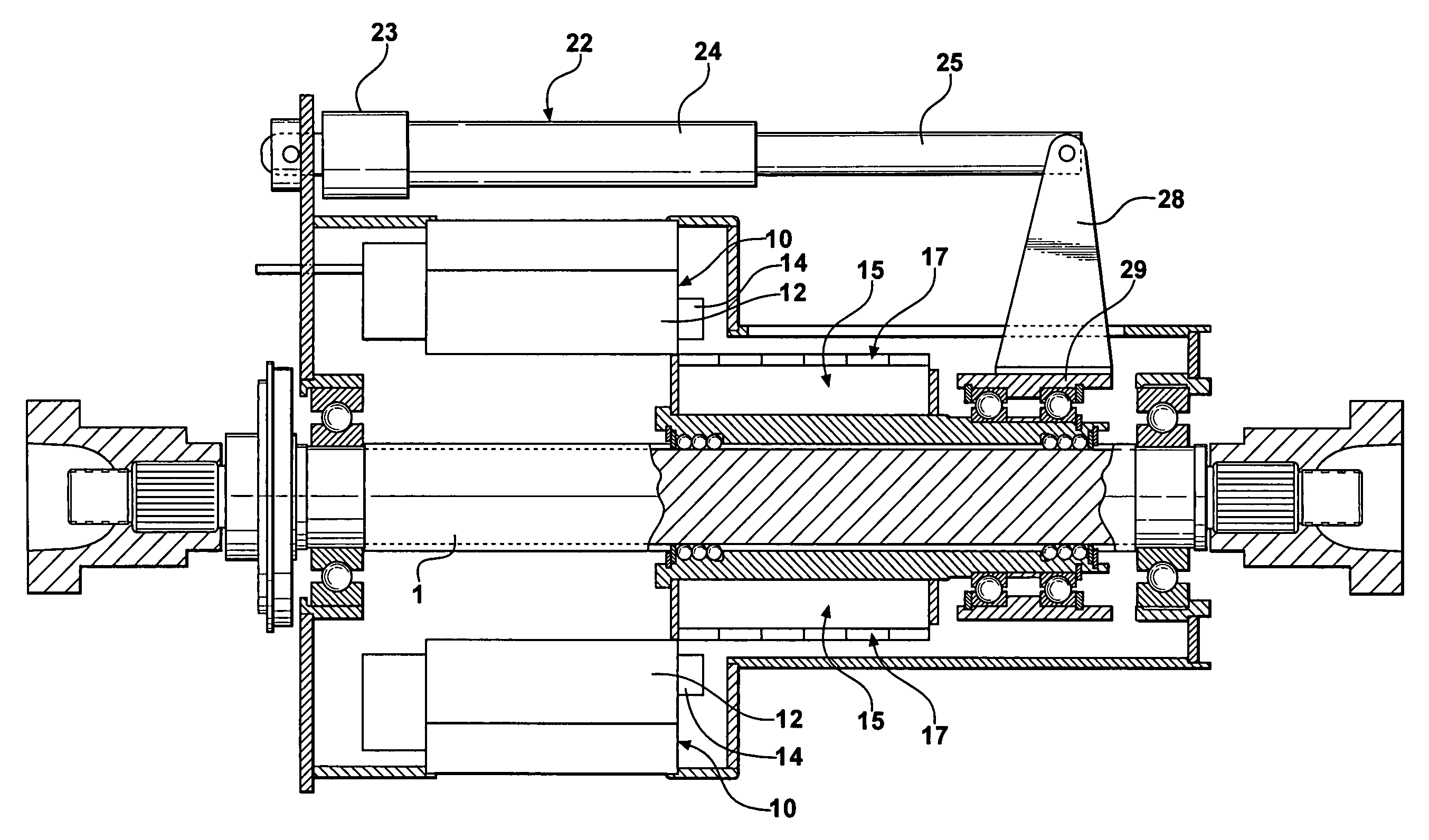
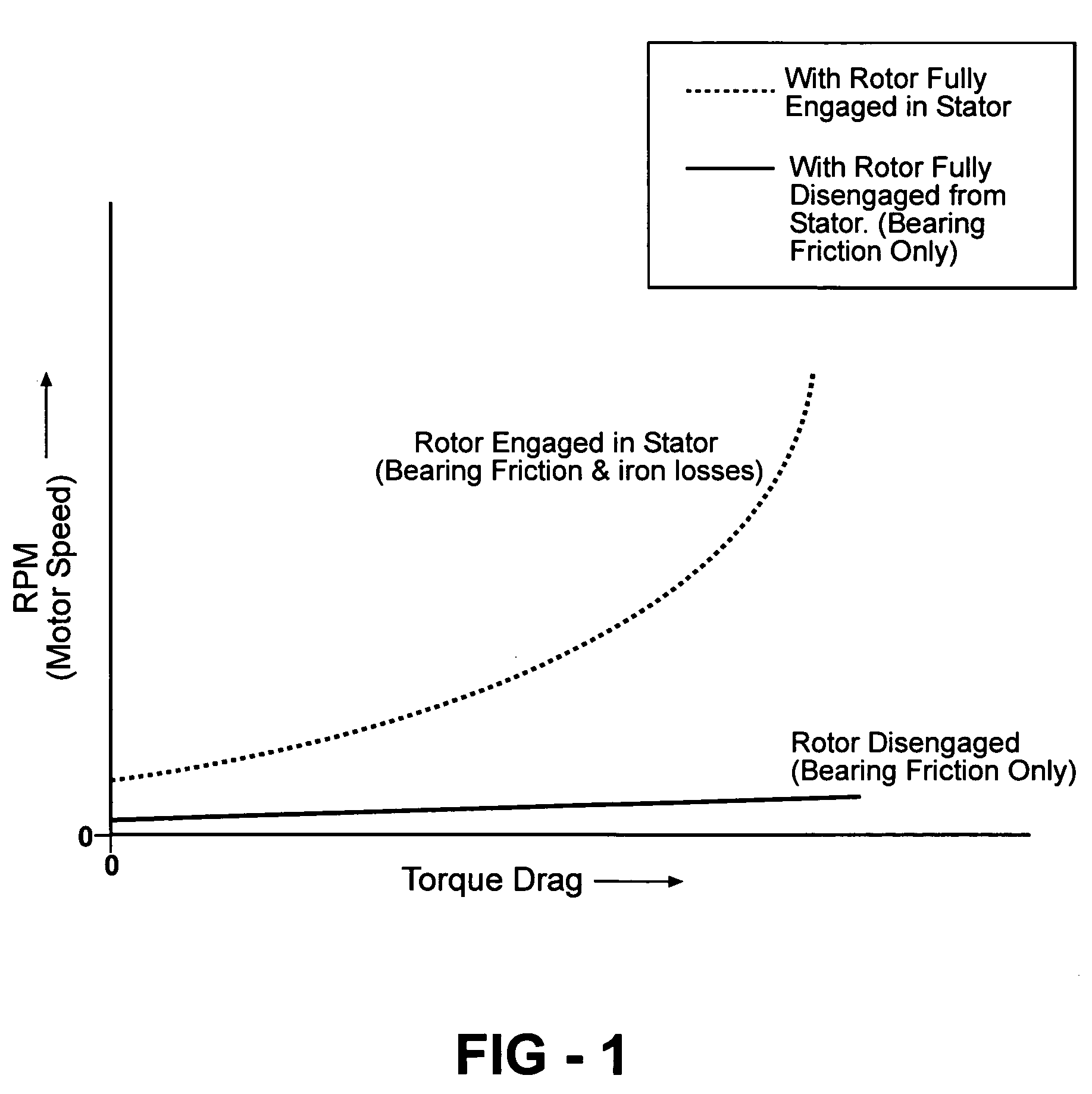
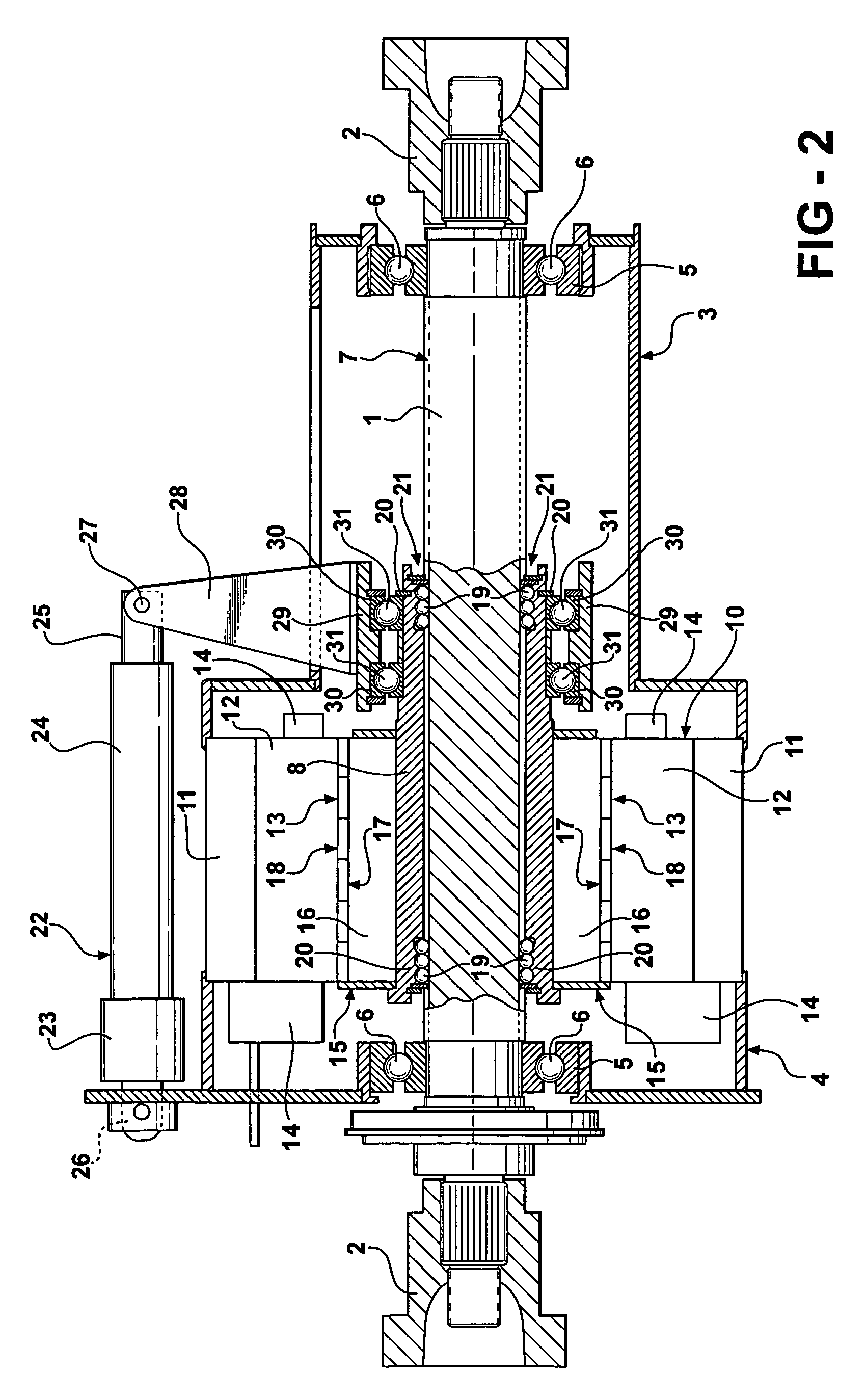
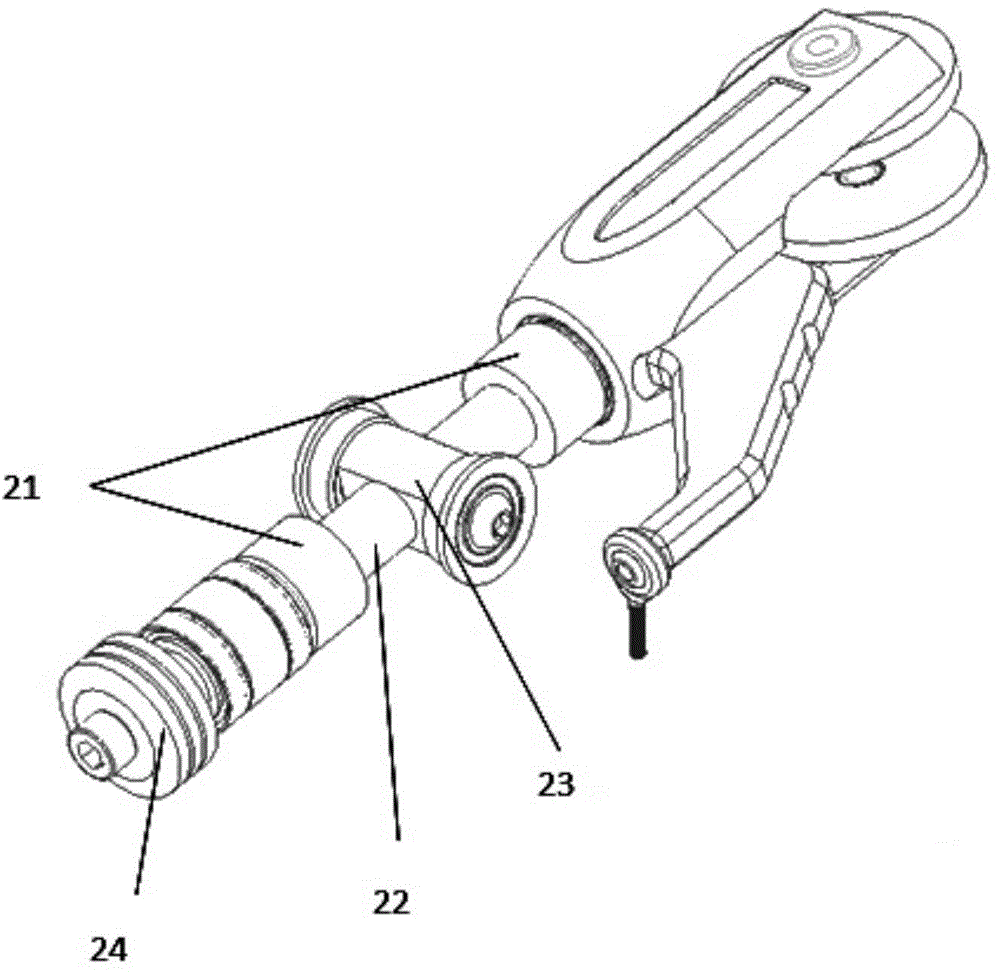
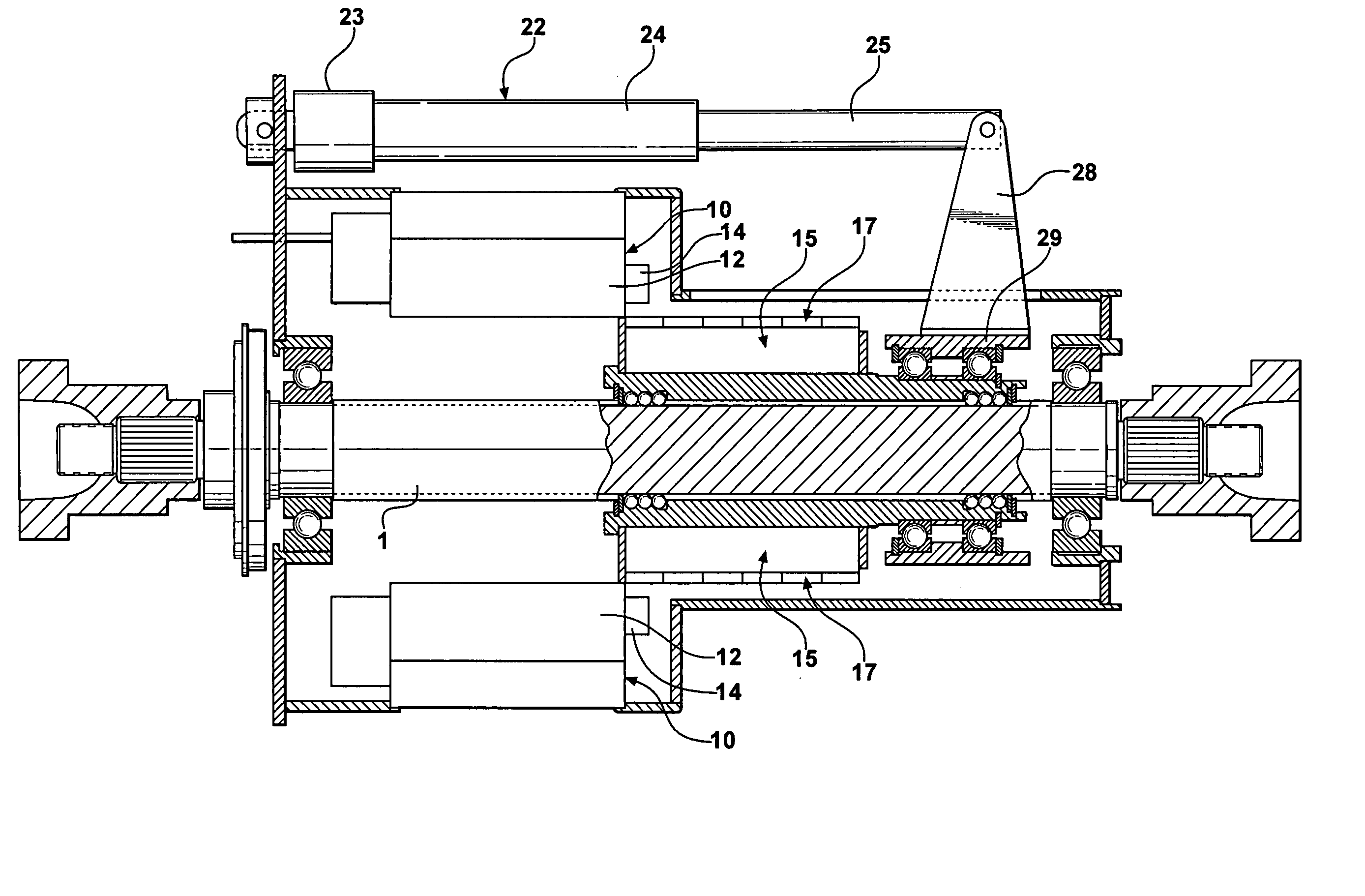
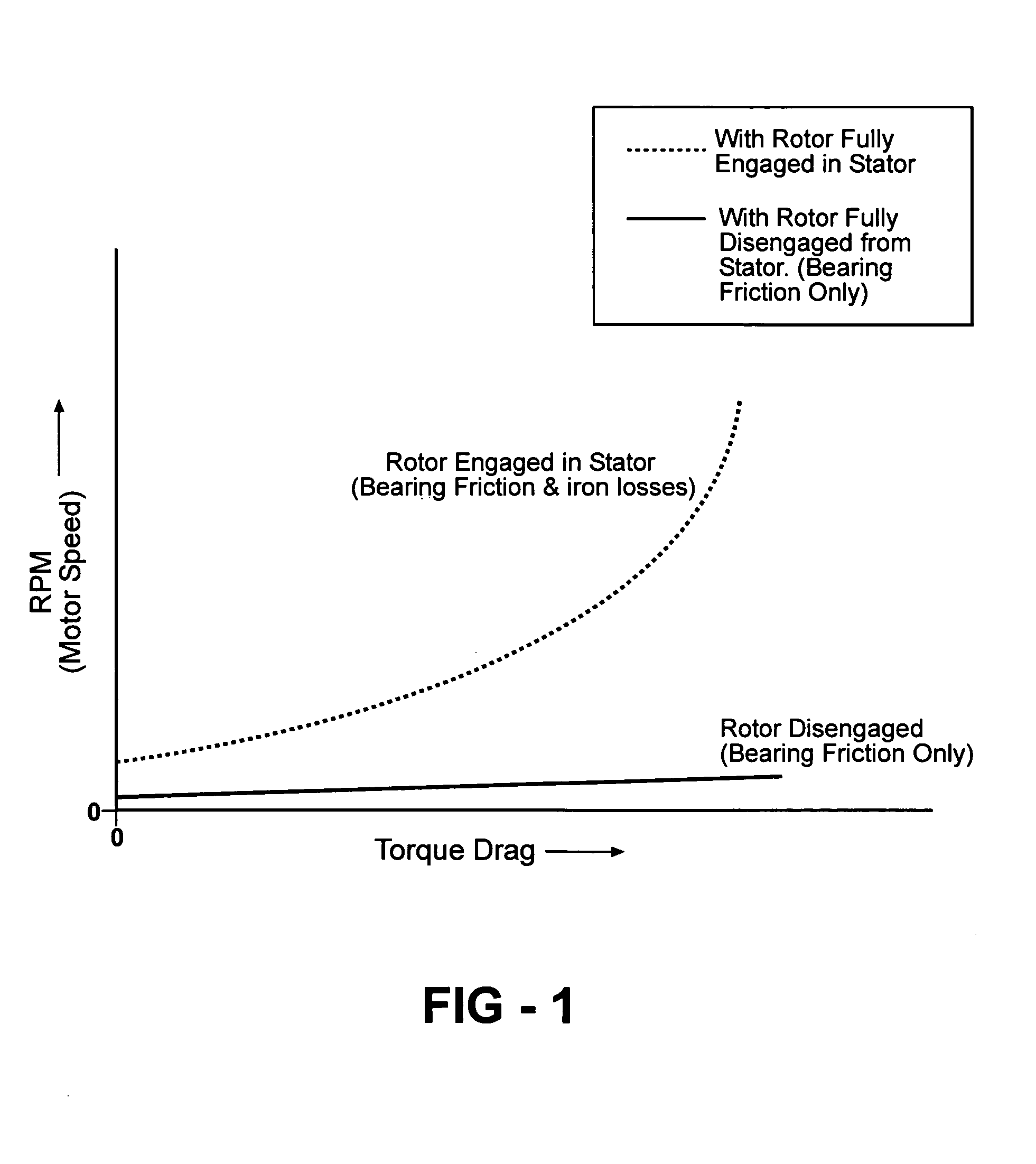
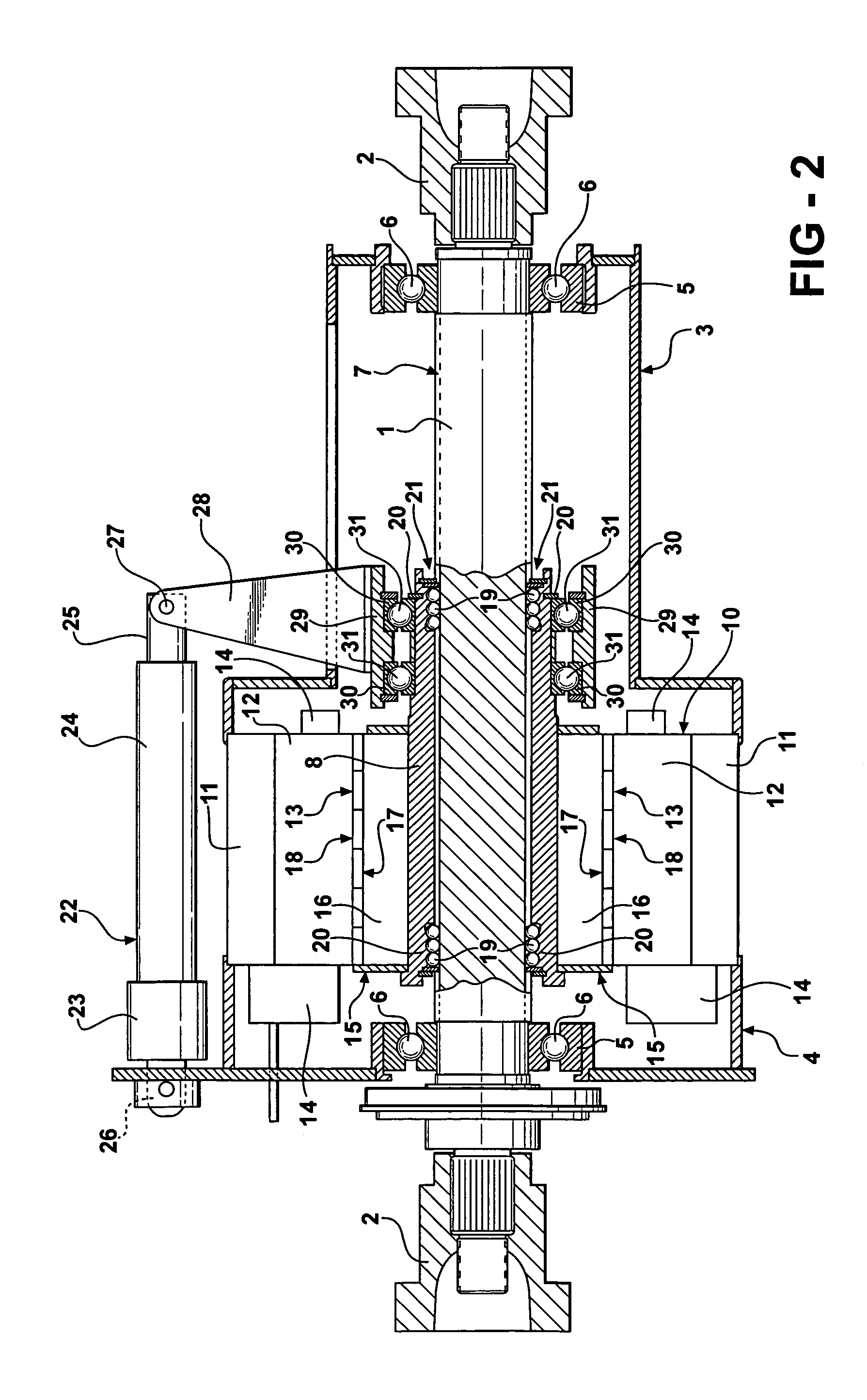
Brushless permanent magnet motor/generator with axial rotor decoupling to eliminate magnet induced torque losses
ActiveUS7863789B2Eliminate magnet induced torque dragSynchronous generatorsWindingsEngineeringPermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor / generator that includes a stator, a rotor provided with a plurality of permanent magnets at a peripheral surface thereof and having a central axis which coincides with the central axis of the stator, a rotatable shaft upon which the rotor is coupled, and an actuator for moving the rotor with respect to the stator axially along the rotatable shaft a sufficient distance to completely decouple the rotor from the stator so as to eliminate magnet induced torque drag. When the permanent magnet / generator is used in parallel hybrid vehicles, the ability to completely decouple the rotor from the stator greatly improves range and efficiency. In addition, by progressively engaging the rotor with the stator a desired voltage output can be obtained upon deceleration.
Owner:DURA TRAC MOTORS INC
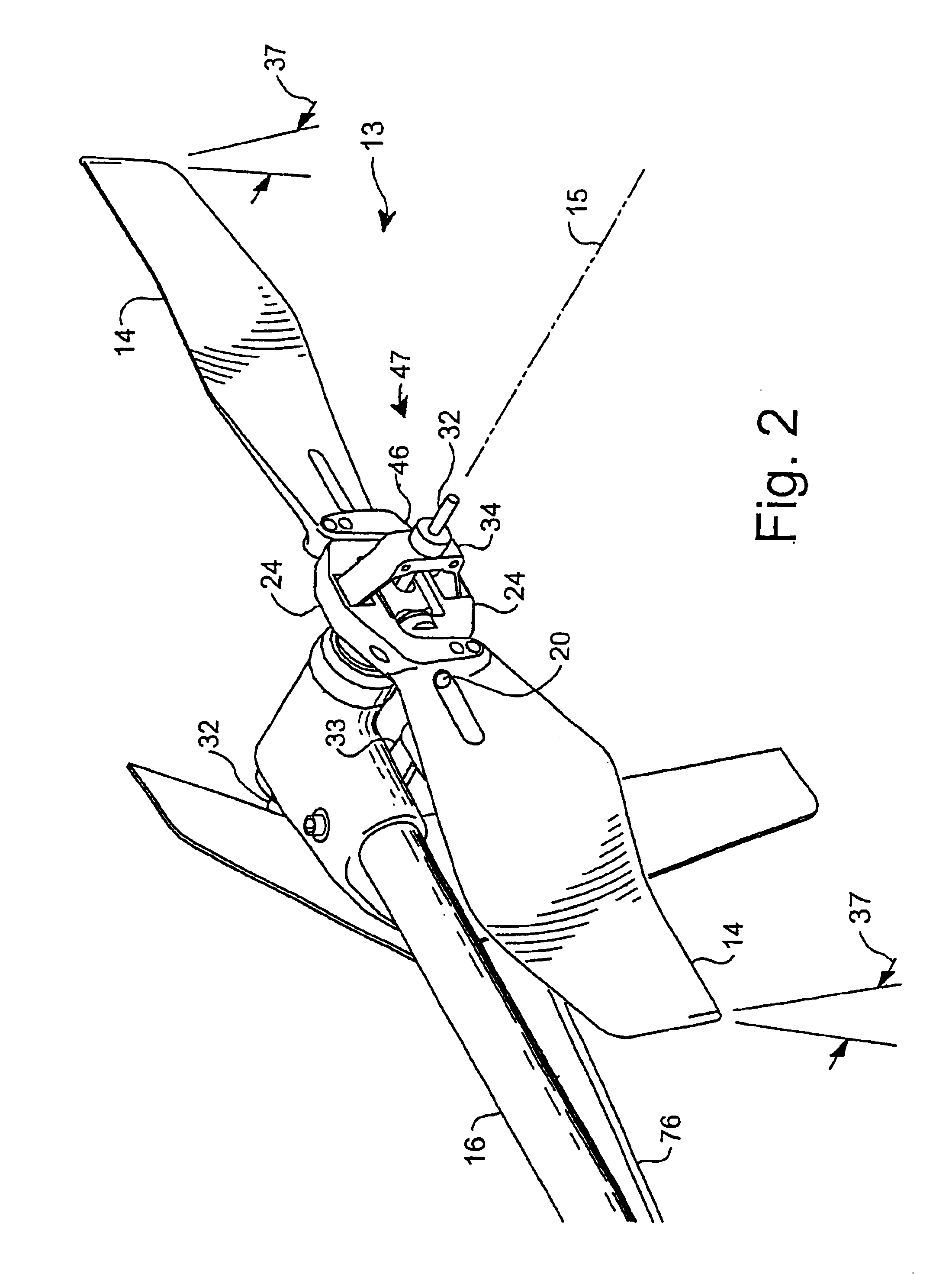
Blade pitch locking device for a main rotor of a rotary-wing aircraft
InactiveUS6032899AThe process is simple and effectiveLow costPropellersPump componentsTail rotorRotary wing
The present invention relates to a device for locking the pitch of the blades of a main rotor of a rotary-wing aircraft in which each blade is firstly rotated about an axis of rotation of the rotor by a rotor mast and is secondly constrained to pivot about a longitudinal pitch axis of the blade together with a pitch lever which is controlled by a pitch link connected to a rotary plate rotating with the rotor mast and belonging to a cyclic swash plate mechanism in which the rotary plate is rotatably mounted on a non-rotary plate capable of sliding axially along said rotor mast and of tilting in any direction relative to the rotor mast under the drive of at least three servo-controls each comprising a body fixed on a support secured to the aircraft and a rod having a free end secured to the non-rotary plate. The device includes immobilization means for holding the rod of each of the servo-controls relative to the corresponding body so as to lock the blades in a predetermined pitch position.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Miniature electric ducted propeller type intelligent unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN101934858AEasy to moveImprove efficiencyActuated automaticallyRotocraftMicrocontrollerTail rotor
The invention relates to a miniature electric ducted propeller type intelligent unmanned aerial vehicle, which consists of a ducted casing, a bracket, a coaxial counter propeller, a fairing, a battery, a motor, a driving control circuit and a microcontroller. The machine body has a dish-shaped appearance; and the ducted casing is arranged outside a rotor wing to eliminate flight safety threat caused by the traditional structure of the exposed rotor wing and improve the working efficiency of the propeller. The aerial vehicle adopts a design of the coaxial counter double-rotor wing, cancels the inertial rotation of the machine body without a tail rotor wing, saves materials and expands the operating space. The propeller is driven by the motor; the motor is under the servo control of the driving control circuit; and the horizontal motion of the aerial vehicle in the air is implemented by a deflectable guide plate below the propeller in a matching mode. In addition, a multi-azimuth convenient slot is formed inside the ducted casing of the aerial vehicle for mounting and detaching various sensors at any time; and the microcontroller comprehensively processes information fed back by each sensor and performs autonomous flight control according to a task.
Owner:王泽峰 +1
Tilt rotor aircraft adopting parallel coaxial dual rotors
The invention relates to a tilt rotor aircraft adopting parallel coaxial dual rotors, which comprises a fuselage, wings, an empennage, a pitch control scull system, a landing gear, a power and fuel system, a transmission system, a rotor system, a rotor nacelle and a tilt system, wherein the wings are arranged at the center section of the fuselage; the empennage and the pitch control scull system are arranged at the tail of the fuselage; the landing gear is positioned at the belly of the fuselage; the power and fuel system is arranged inside the center section of the fuselage and is connected with the rotor system and the pitch control scull system through the wings and the transmission system in the fuselage; the rotor system is arranged on the rotor nacelle at the tip of the wings; partial wing which is fixedly connected with the rotor nacelle and simultaneously can tilt is arranged at the inner side of the rotor nacelle; and the tilt system is arranged in the wings and is connected with the rotor nacelle and the partial wing which can tilt. The tilt rotor aircraft is mainly characterized by adopting the pitch control scull system, the parallel coaxial dual rotors and the partialwing which can tilt to realize flight status transformation and conventional taxiing and landing, thereby improving the forward speed and the propulsive efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
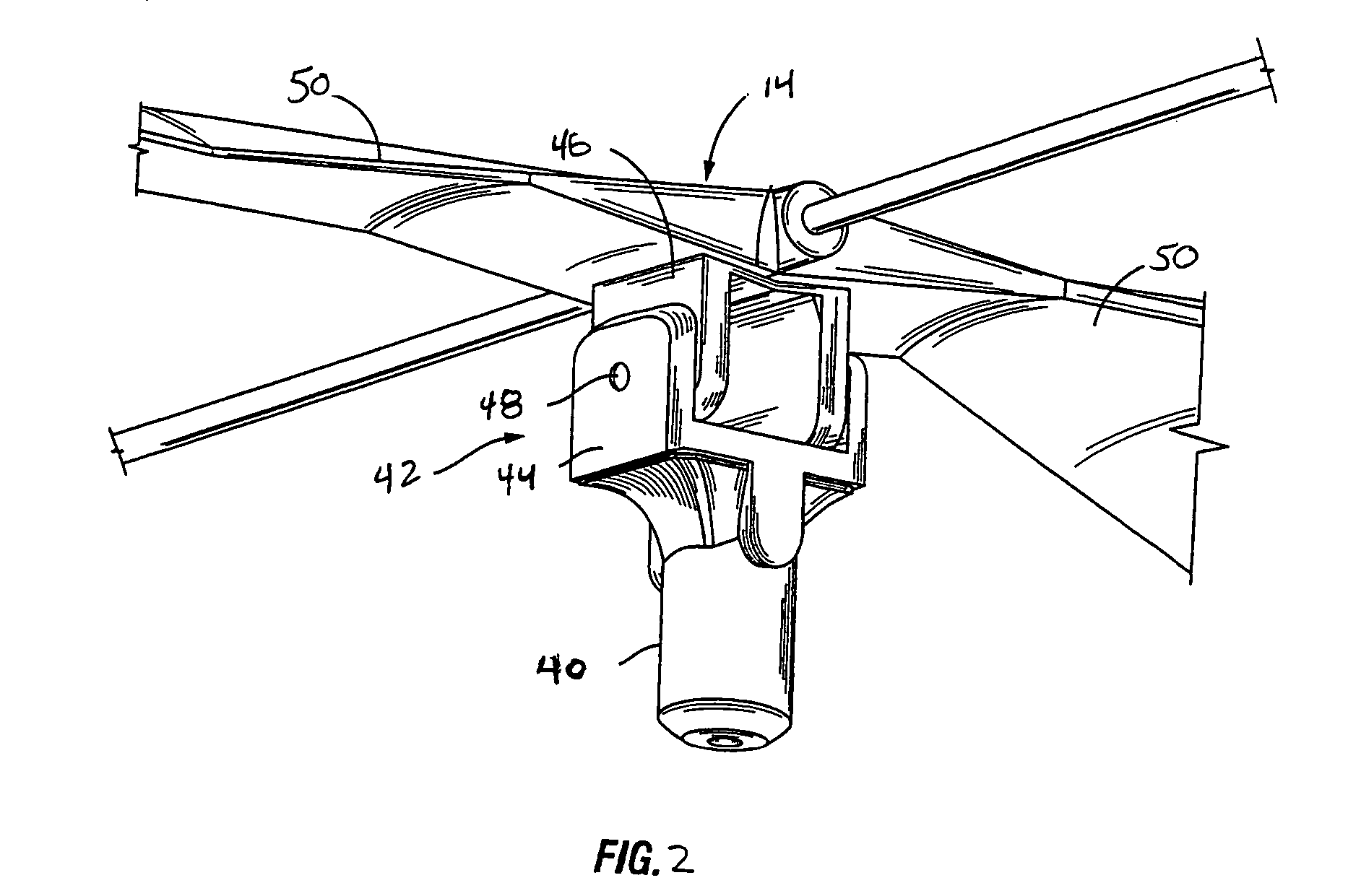
Rotor system for helicopters
A tail rotor system for a helicopter includes a gear box housing retainer (66) coupled to the tail boom (16) of the helicopter. The tail rotor system also includes a power-limiting device (50) configured to disconnect the tail rotor from a power plant for driving the tail rotor about a rotor axis of rotation.
Owner:ARLTON PAUL E
Vibration-reducing and noise-reducing spoiler for helicopter rotors, aircraft wings, propellers, and turbine blades
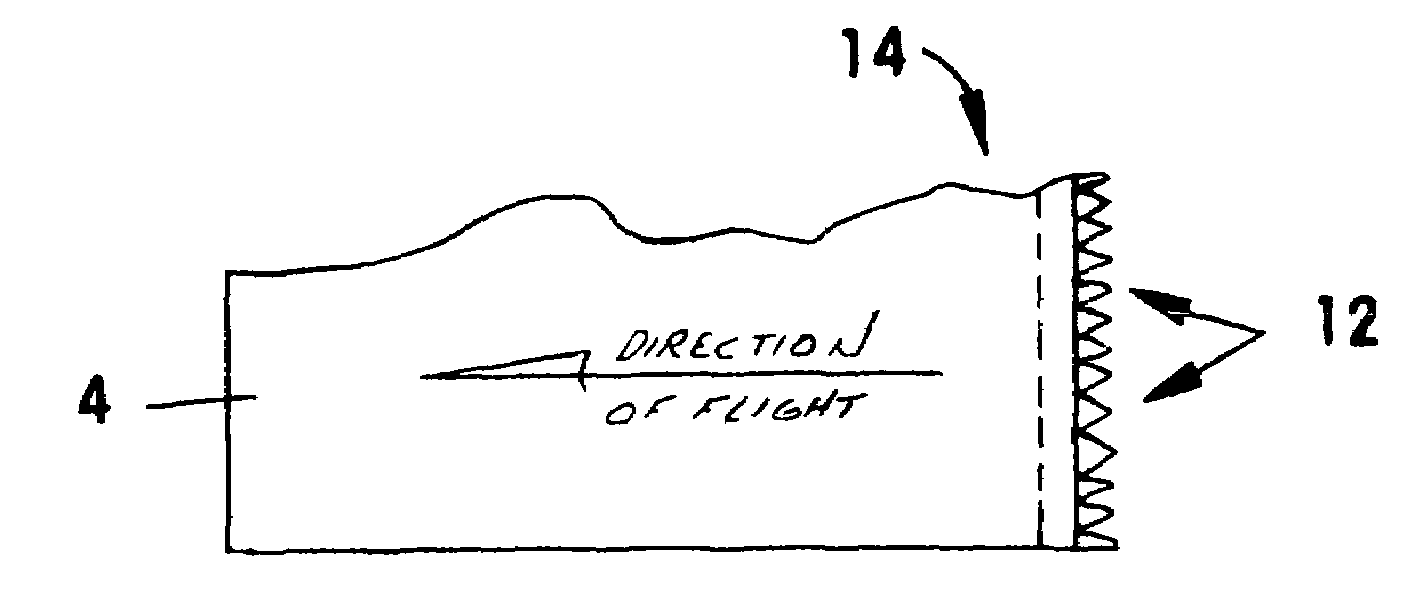
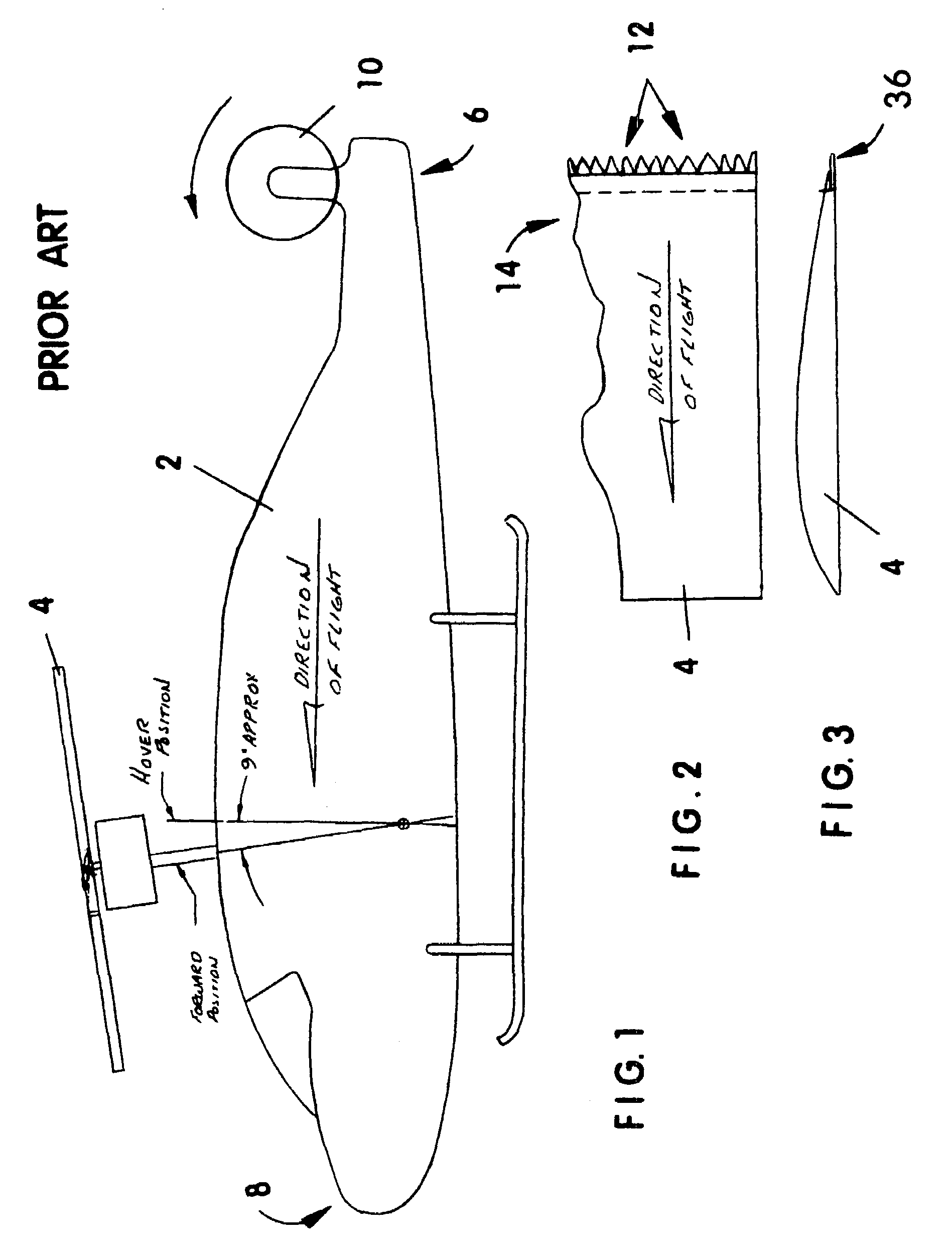
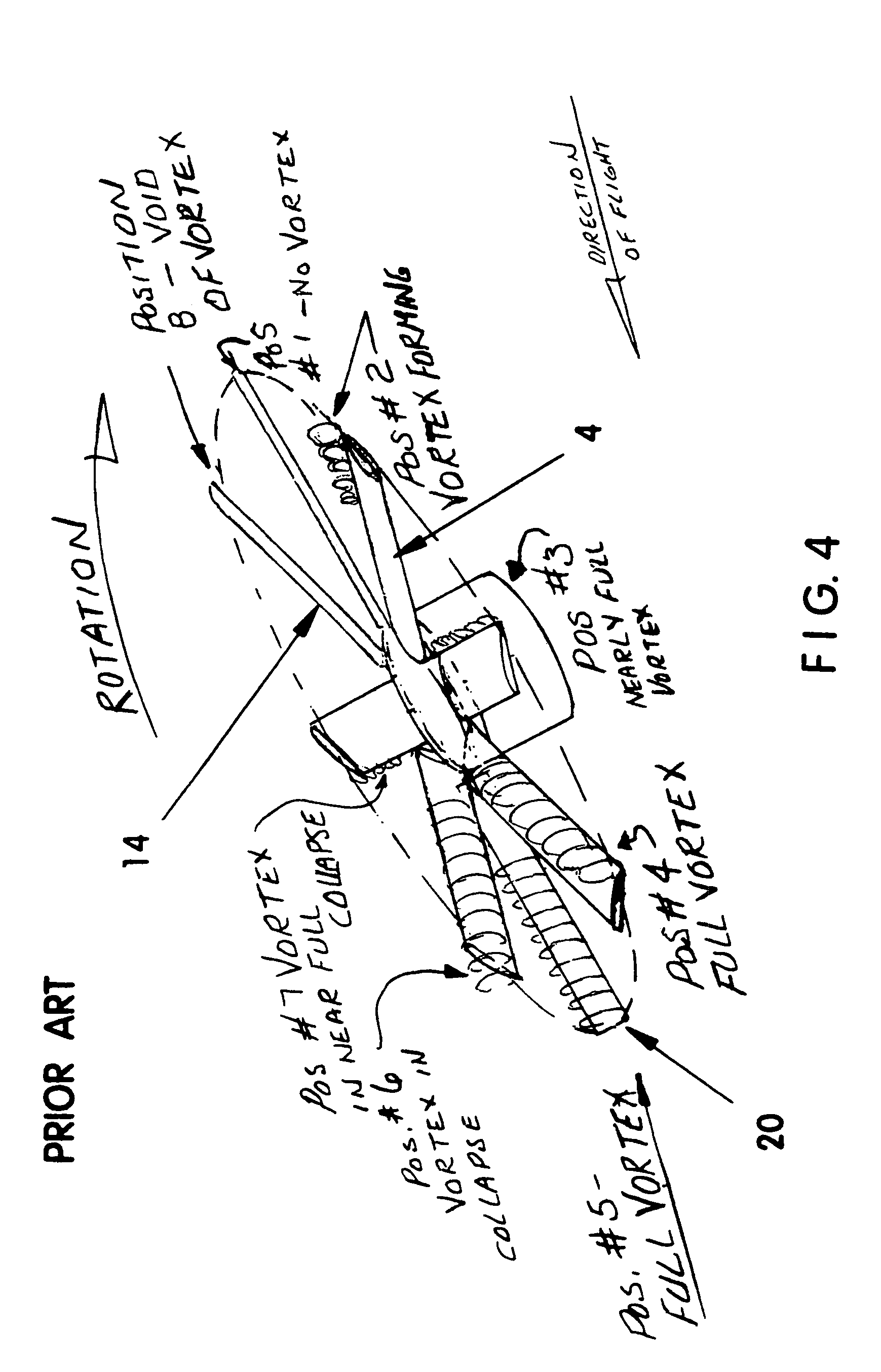
A spoiler attached to helicopter main rotor blades, tail rotor blades, propellers, aircraft wings, and machined into turbine blades, that reduces vibration and silences their operation. Also, when added to a substantial part of the trailing edges of its rotor blades, the spoiler eliminates the repetitive pop-pop sound common to current helicopter flight. Preferably, the spoiler is made from durable resilient materials that bend with resistance for high speed oscillation and it is secured on the top or bottom side, or both, of the trailing edge of a blade or wing. Further, the free edge of the spoiler exhibits a non-repeating pattern of feather-like projections that collectively break up vortex formation so that the next wing or blade traveling through the same location has clean air / fluid in which to move. In addition to noise reduction, the spoiler increases blade efficiency and wing lift.
Owner:TAFOYA SAMUEL B
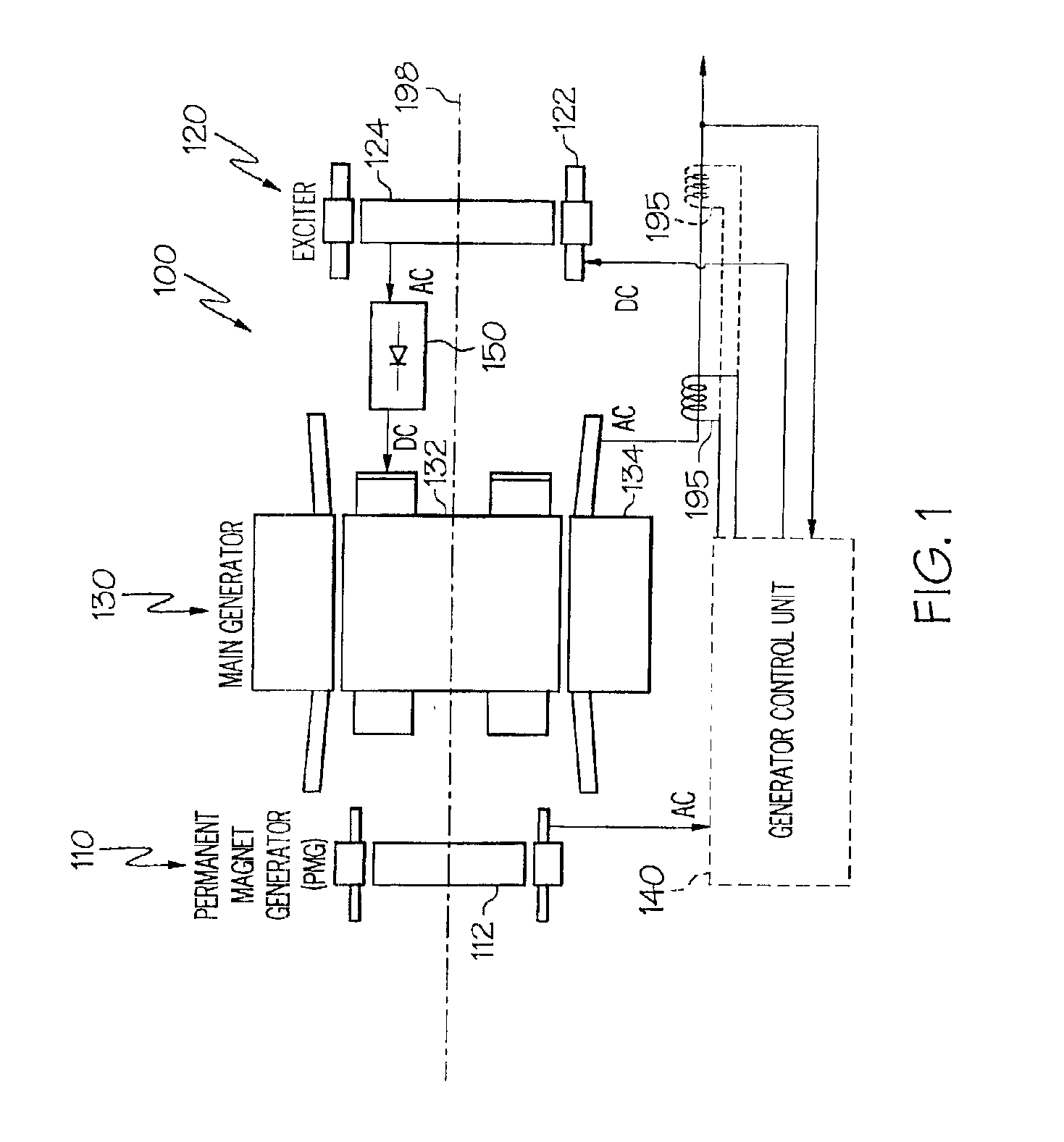
High speed generator with the main rotor housed inside the shaft
InactiveUS6897581B2Improves Structural IntegrityReduce material stressSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsEngineeringTail rotor
A high speed generator has its main rotor located within the main generator shaft assembly. The main rotor is mounted on a substantially hollow rotor shaft, which is also mounted within the main generator shaft assembly. The main stator surrounds at least a portion of the main generator shaft assembly. Main rotor cooling supply orifices extend through the rotor shaft. Main stator cooling supply orifices, which are in fluid communication with the main rotor cooling supply orifices, extend through the main generator shaft assembly. Cooling fluid is directed into the main generator shaft assembly, and flows through the main rotor cooling supply orifices and the main stator cooling supply orifices. The main rotor and main stator cooling supply orifices are configured to supply the main rotor and main stator with a cooling fluid spray. This configuration reduces the rotational fluid mass associated with flood-cooled rotors, which increases structural integrity, lowers material stresses, improves rotor dynamics.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
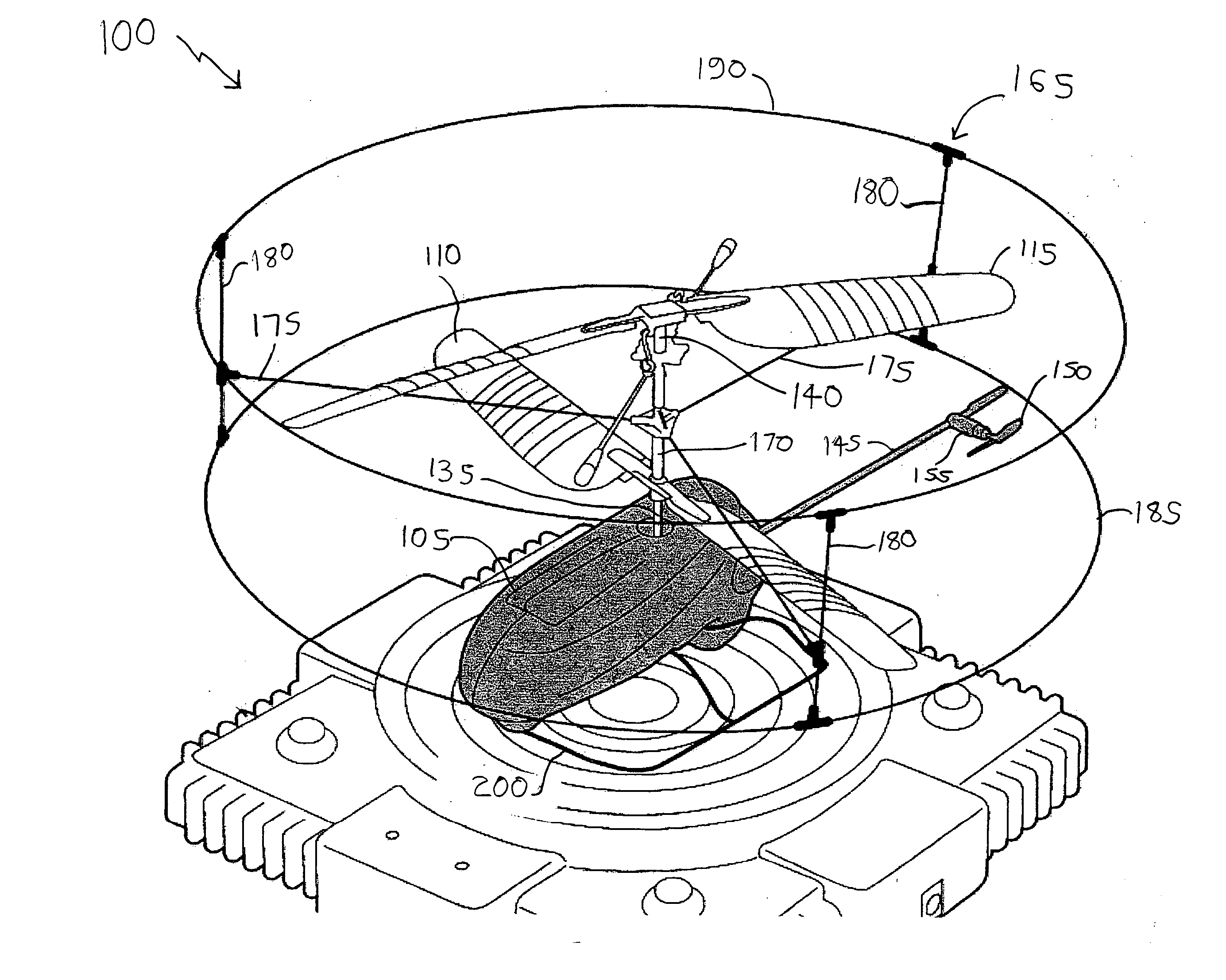
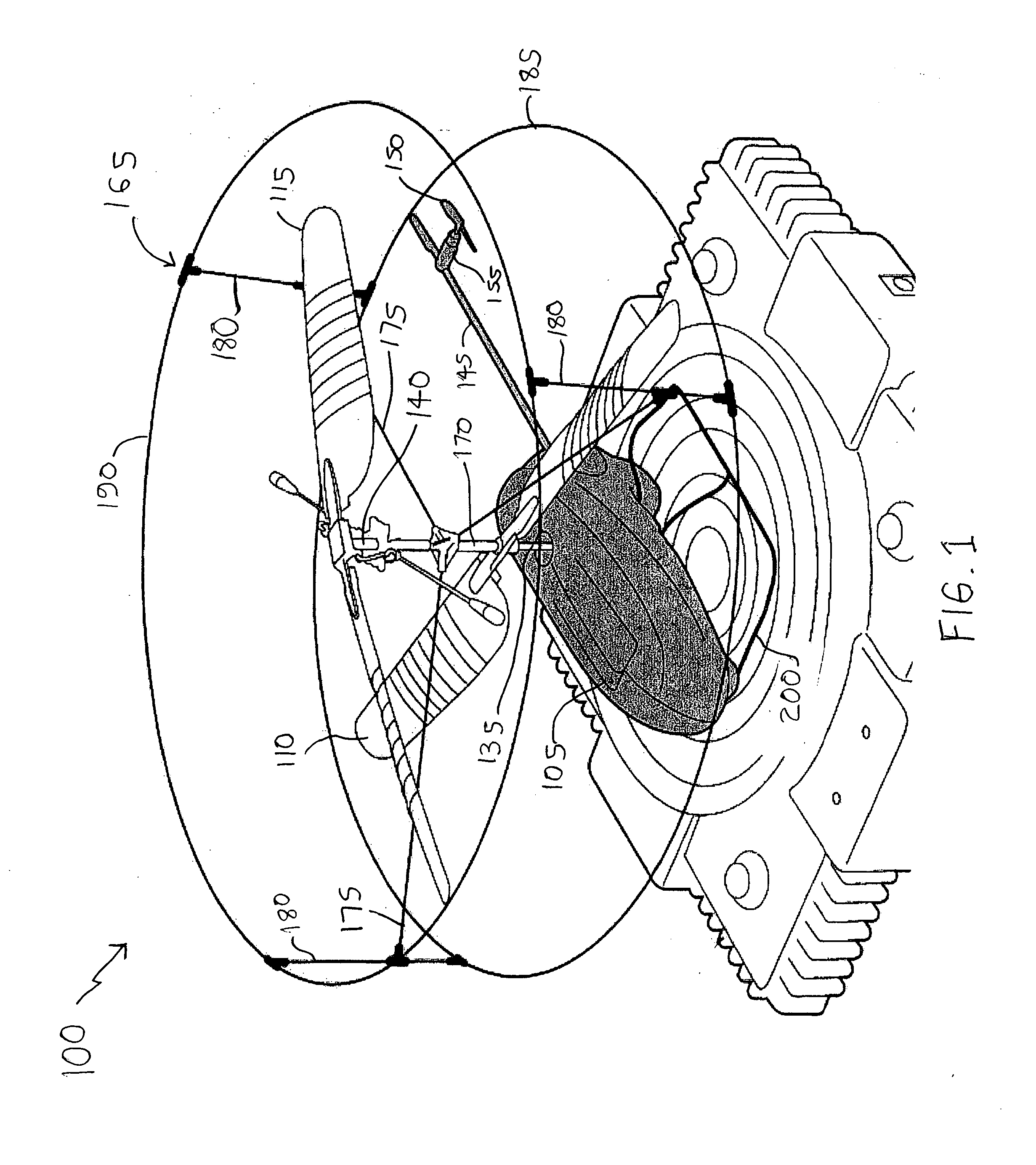
Radio controlled helicopter
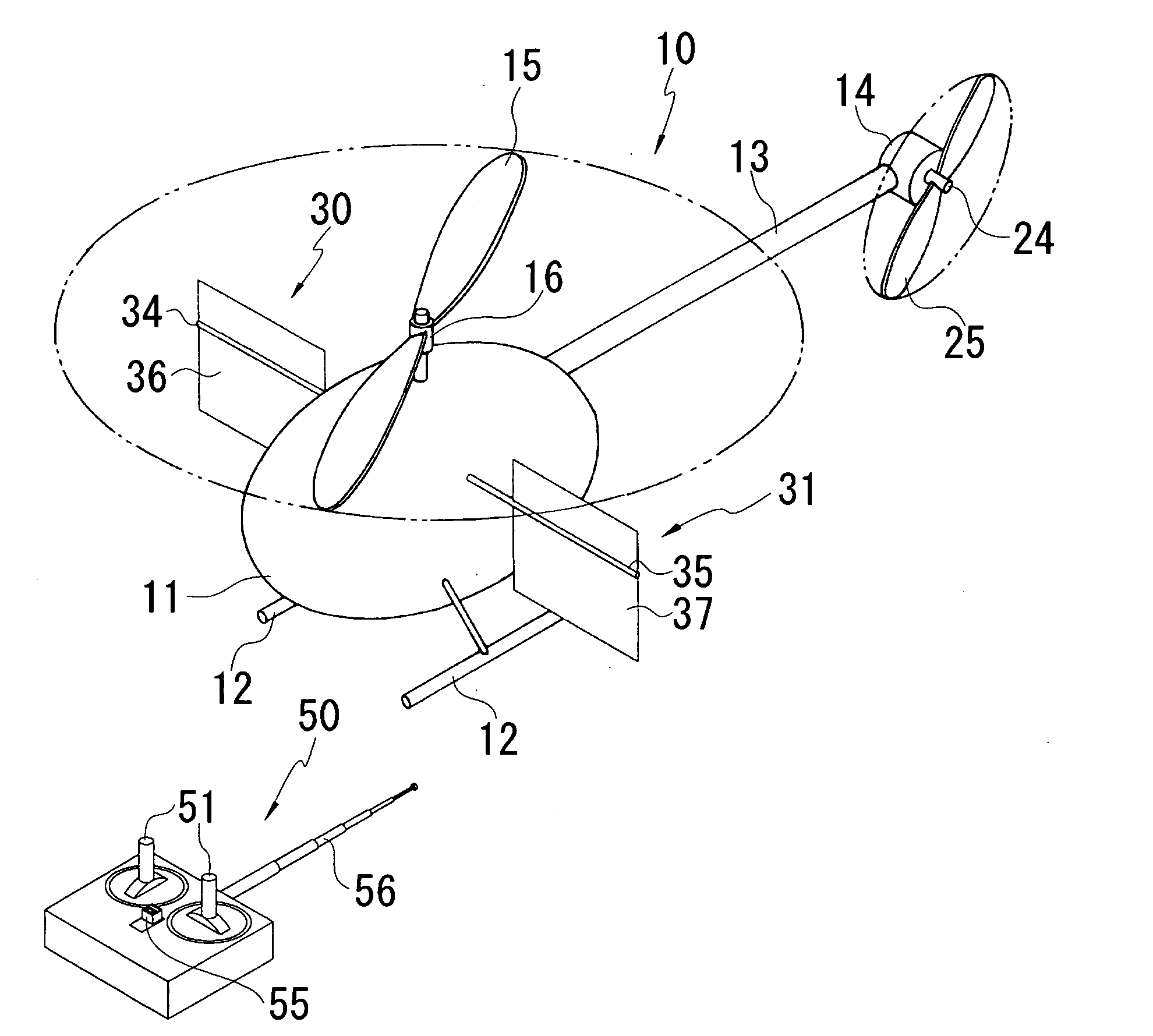
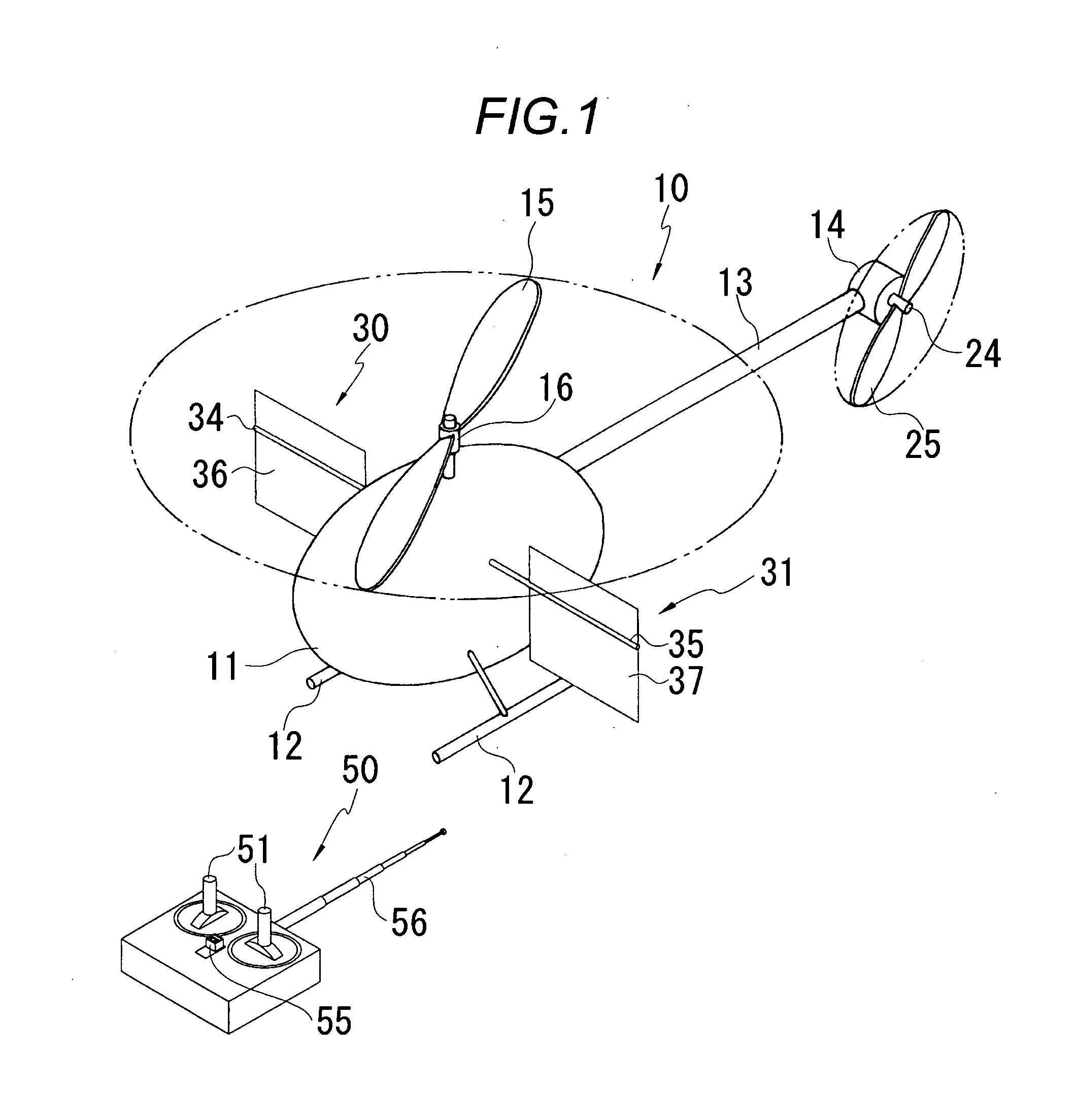
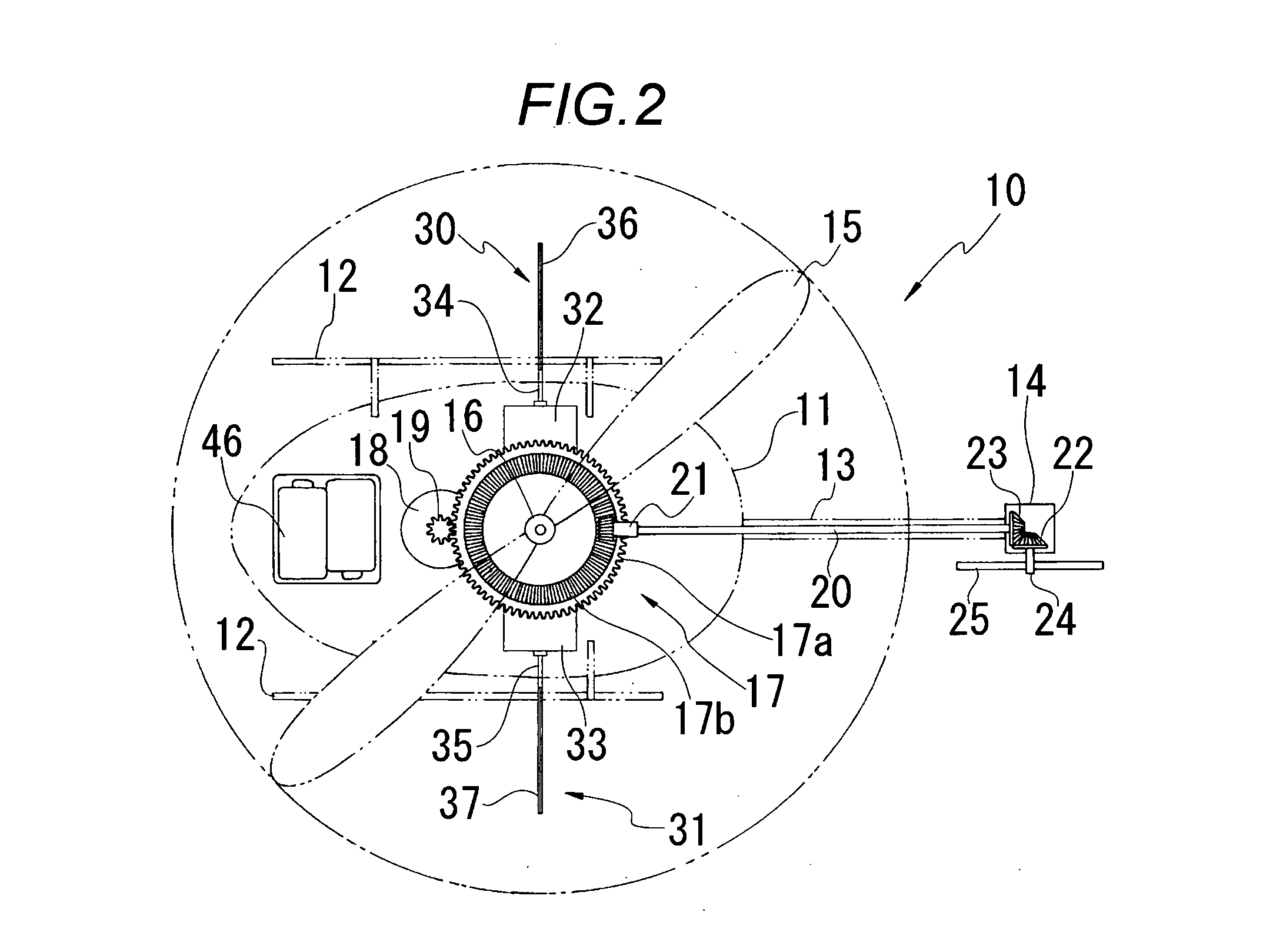
InactiveUS20070215750A1Least riskOperational securityToy aircraftsRemote-control toysTail rotorGravitation
A radio controlled helicopter is provided which eliminates or simplifies forward / reverse flight control for safe and easy indoor operation. Embodiments include a helicopter having a pair of counter rotating rotors which are driven at the same speed, a vertically aligned tail rotor driven by a reversible motor for controlling yaw, and a mass, such as a power supply battery, mounted for changing the center of gravity of the helicopter to adjust the tendency of the helicopter to move in a forward or reverse direction. The mass is either rigidly mounted, so that the helicopter is always moving forward during flight, or adjustably mounted so that the helicopter's forward or reverse direction can be adjusted prior to or during flight. A protective cage is provided to protect persons from injury from the rotors and to prevent damage to the rotors due to contact with objects during flight.
Owner:SHANTZ MICHAEL +1
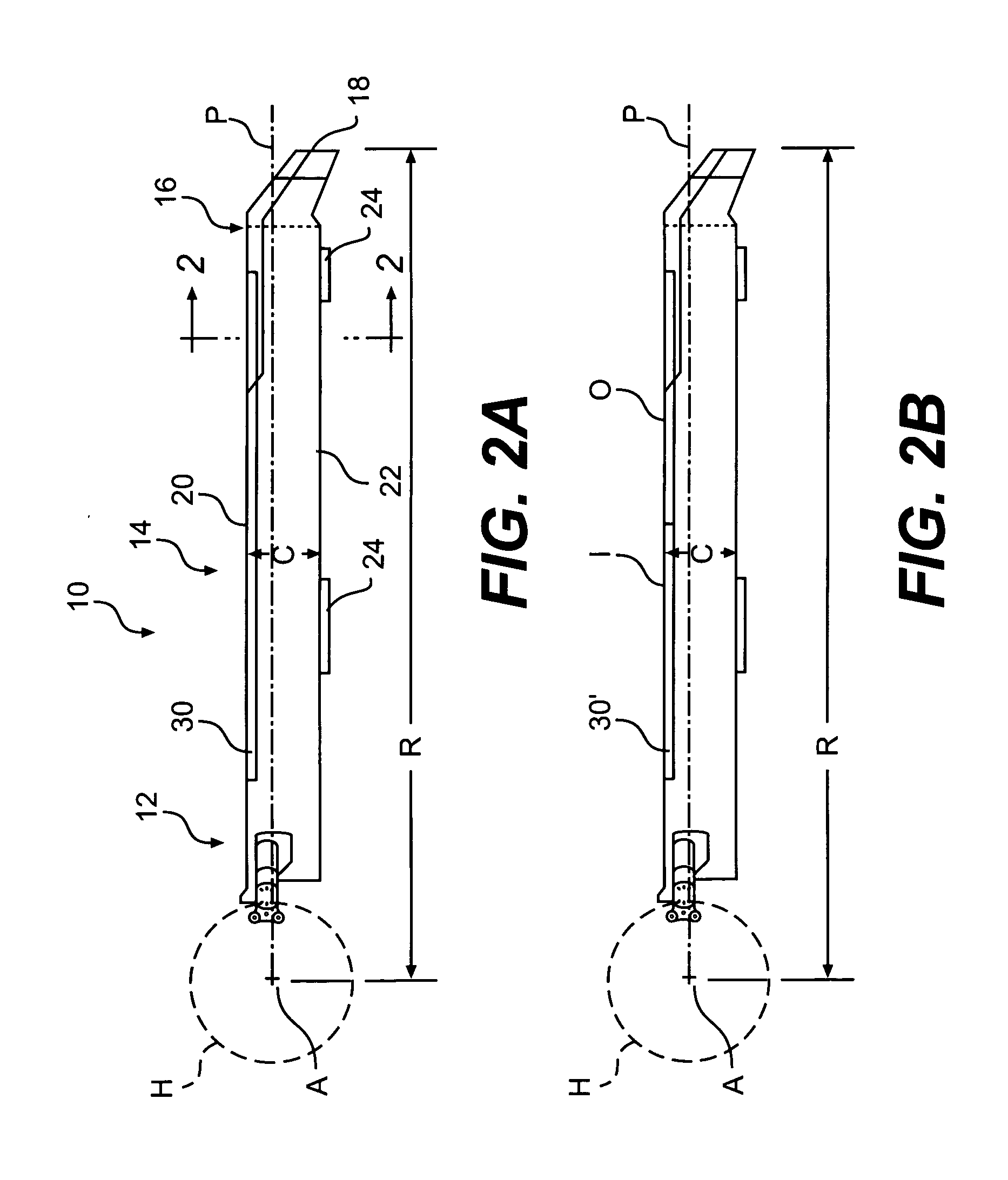
Compact co-axial rotor system for a rotary wing aircraft and a control system thereof
ActiveUS7083142B2Easy to separateReduce the overall heightPropellersPump componentsTip positionControl system
A dual, counter rotating, coaxial rotor system provides an upper and lower rotor system, with a reduced axial rotor separation distance along a common axis by way of rotor tip position sensing and rotor position controls to avoid tip contact.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
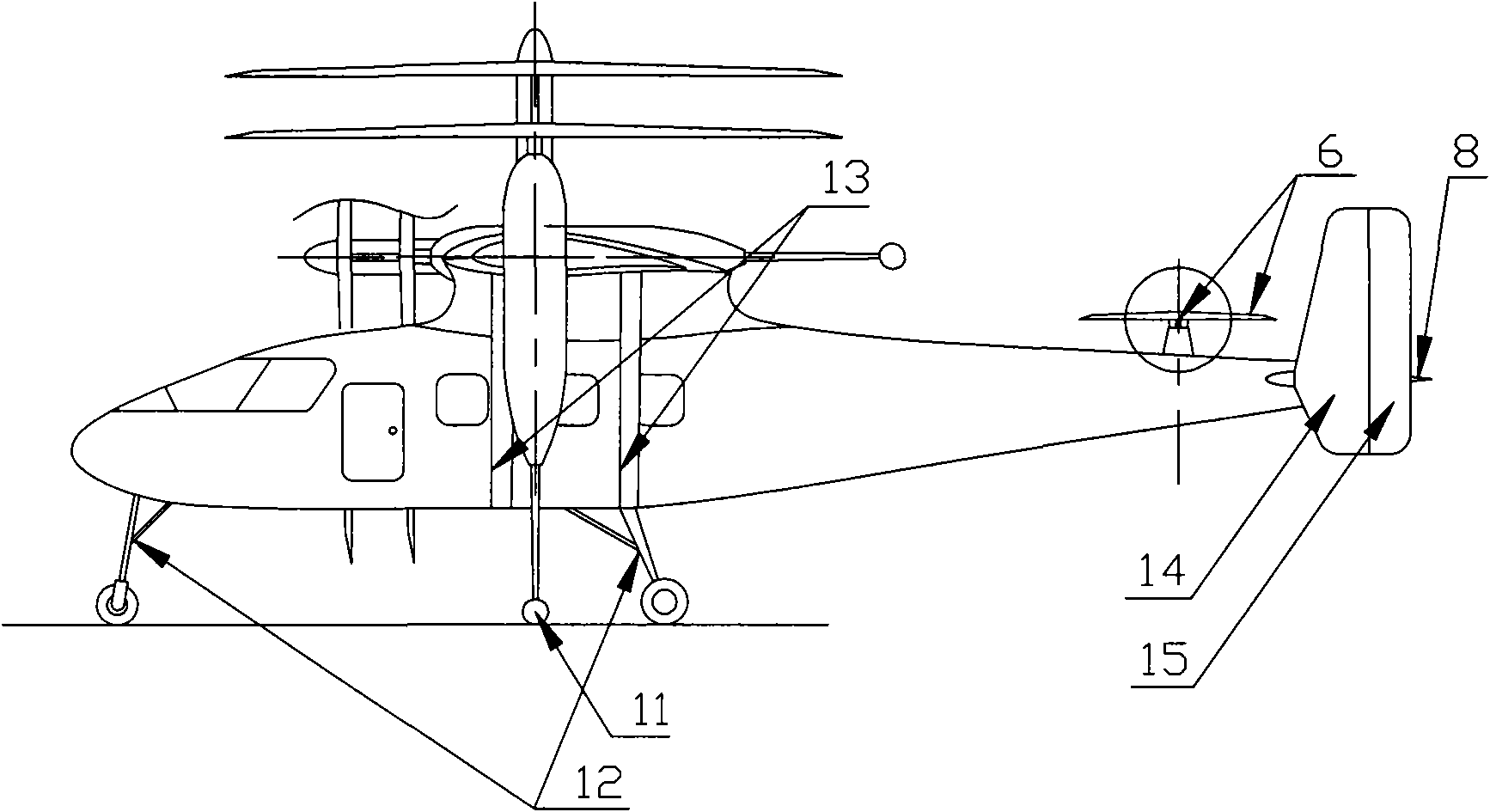
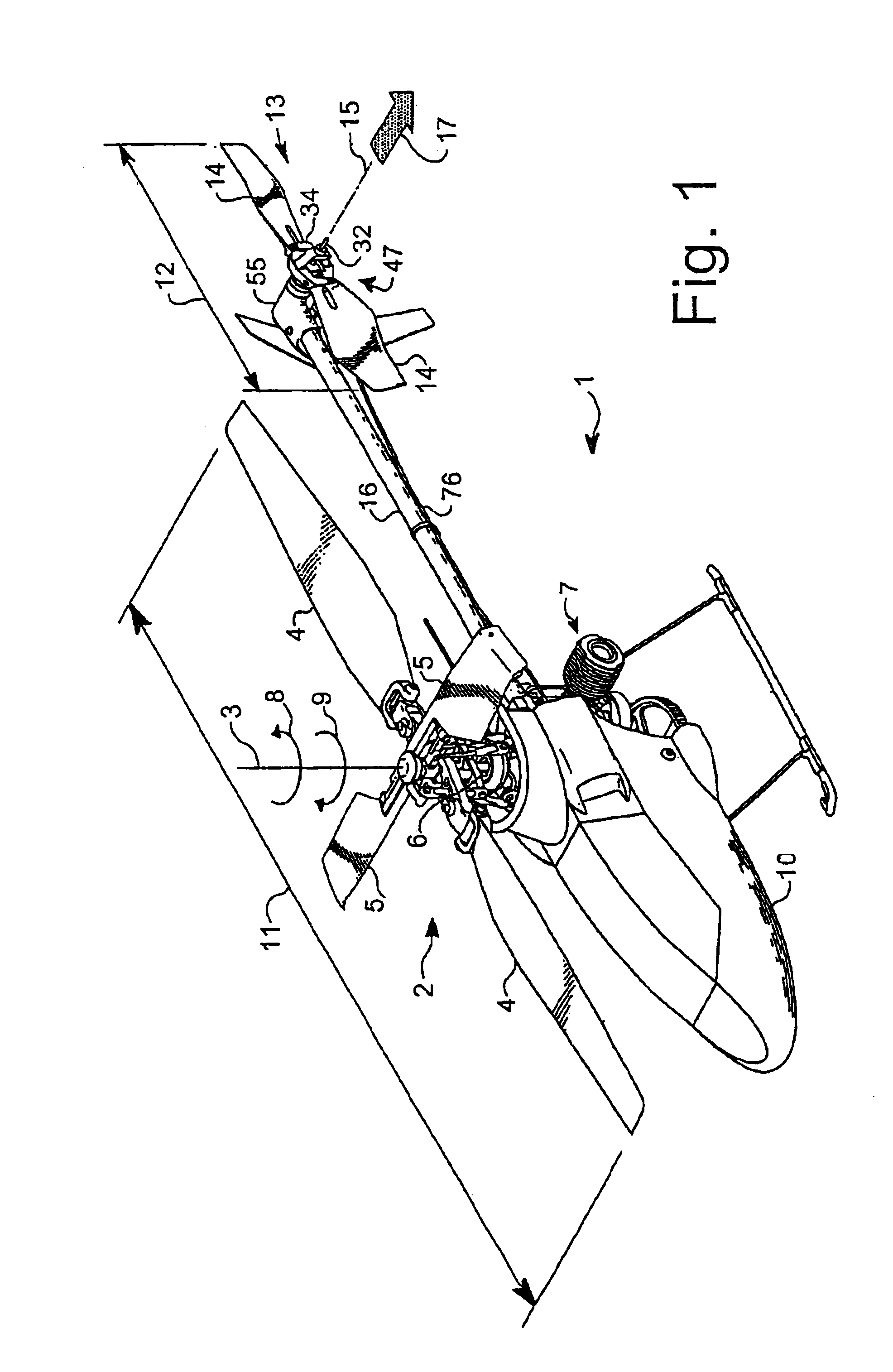
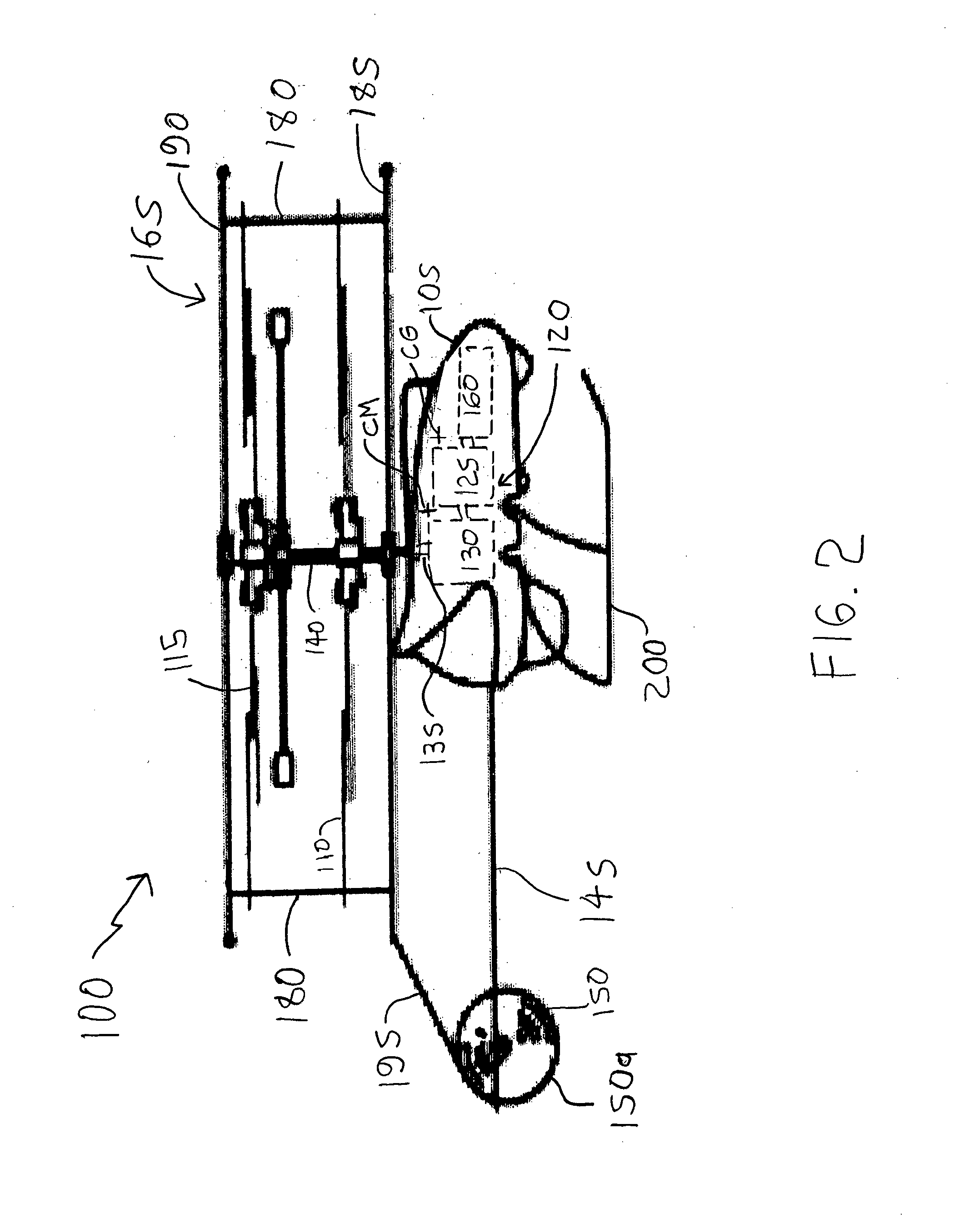
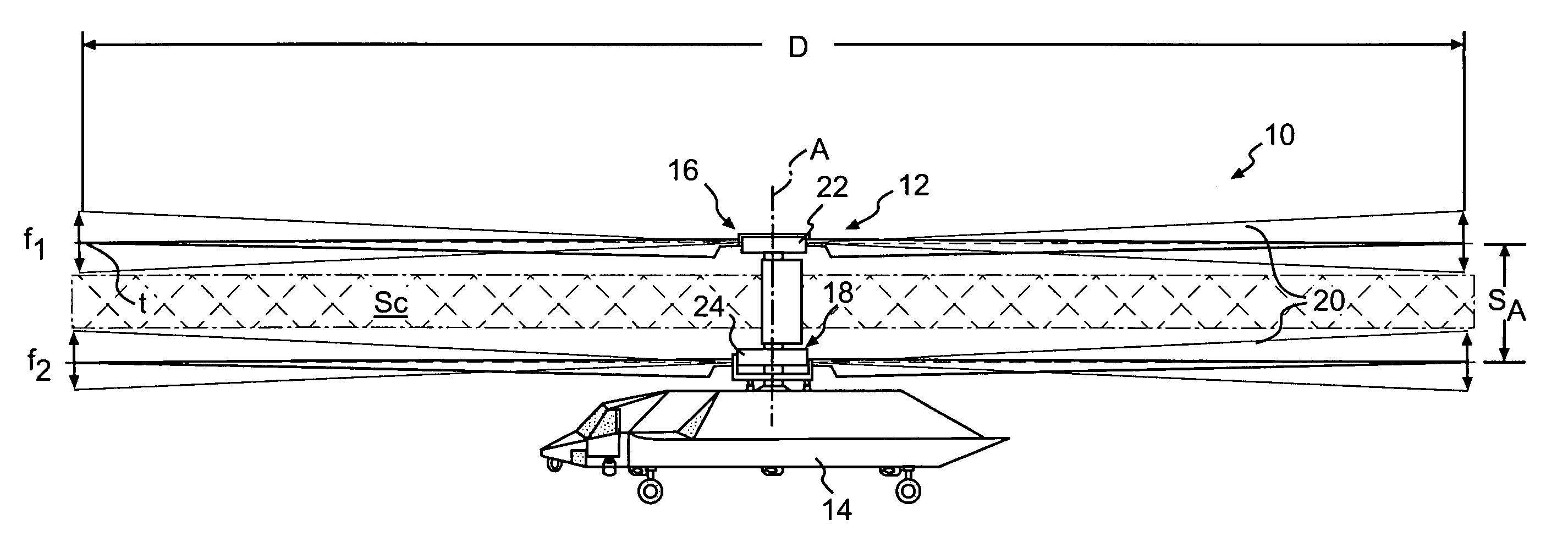
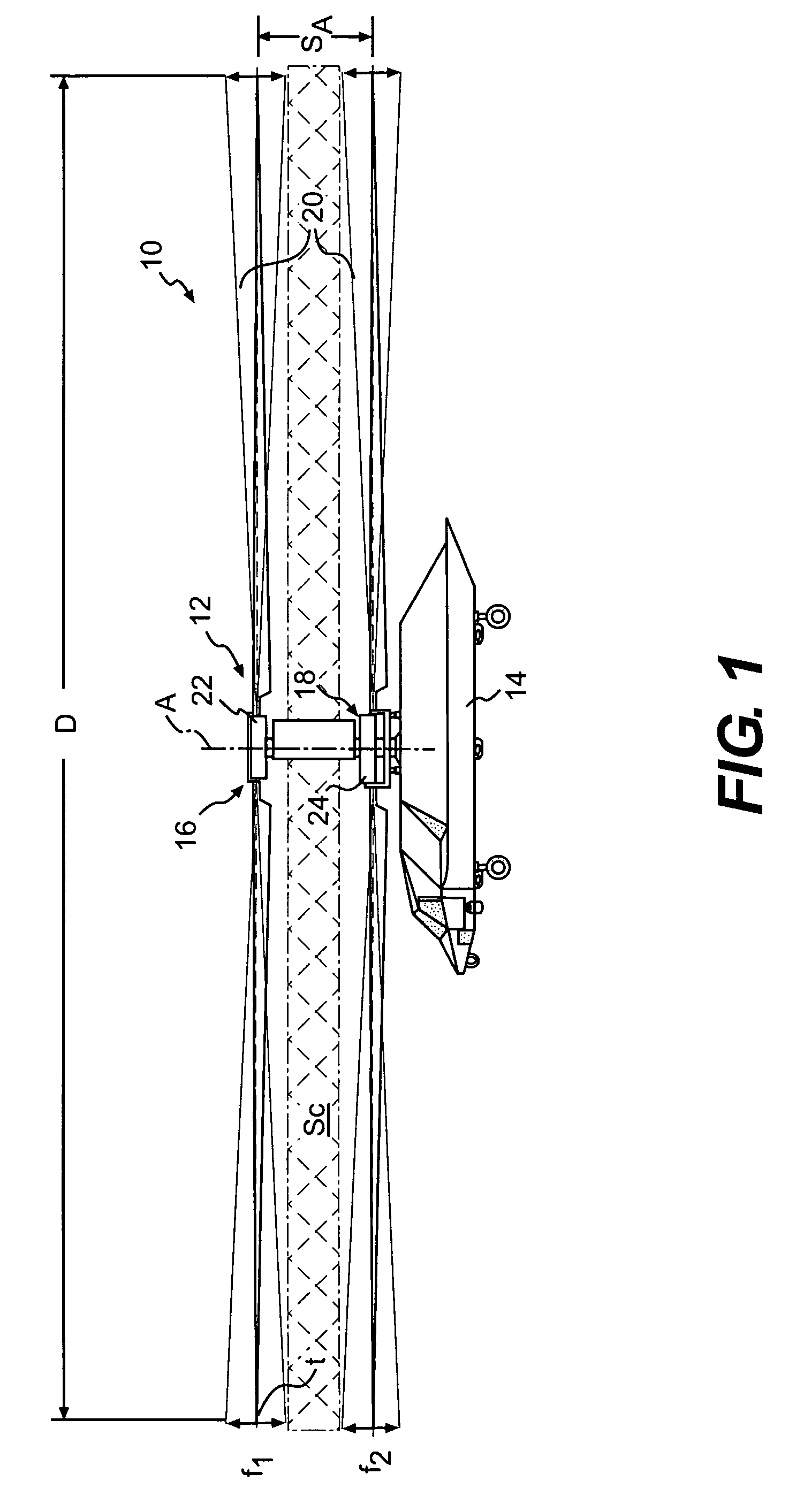
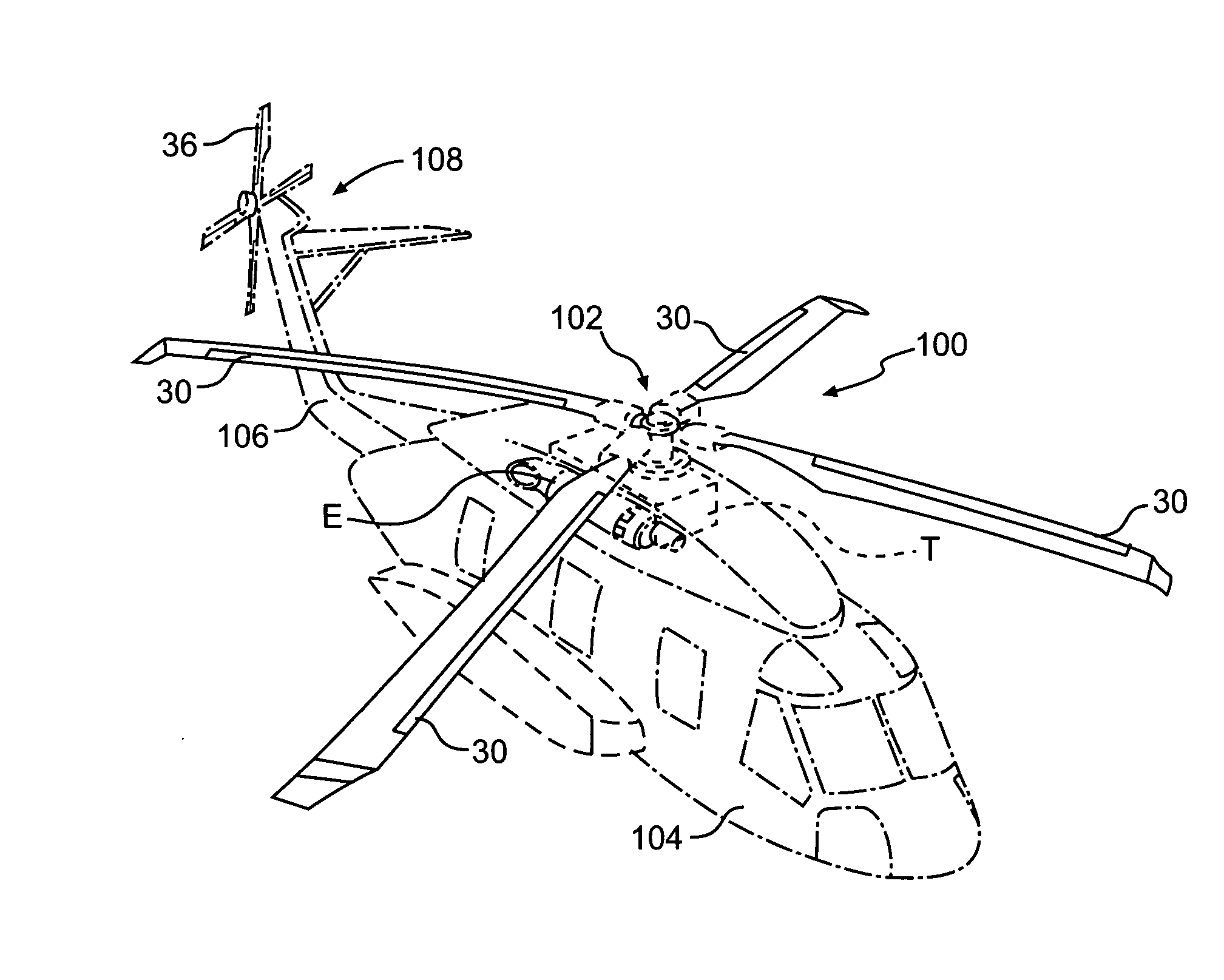
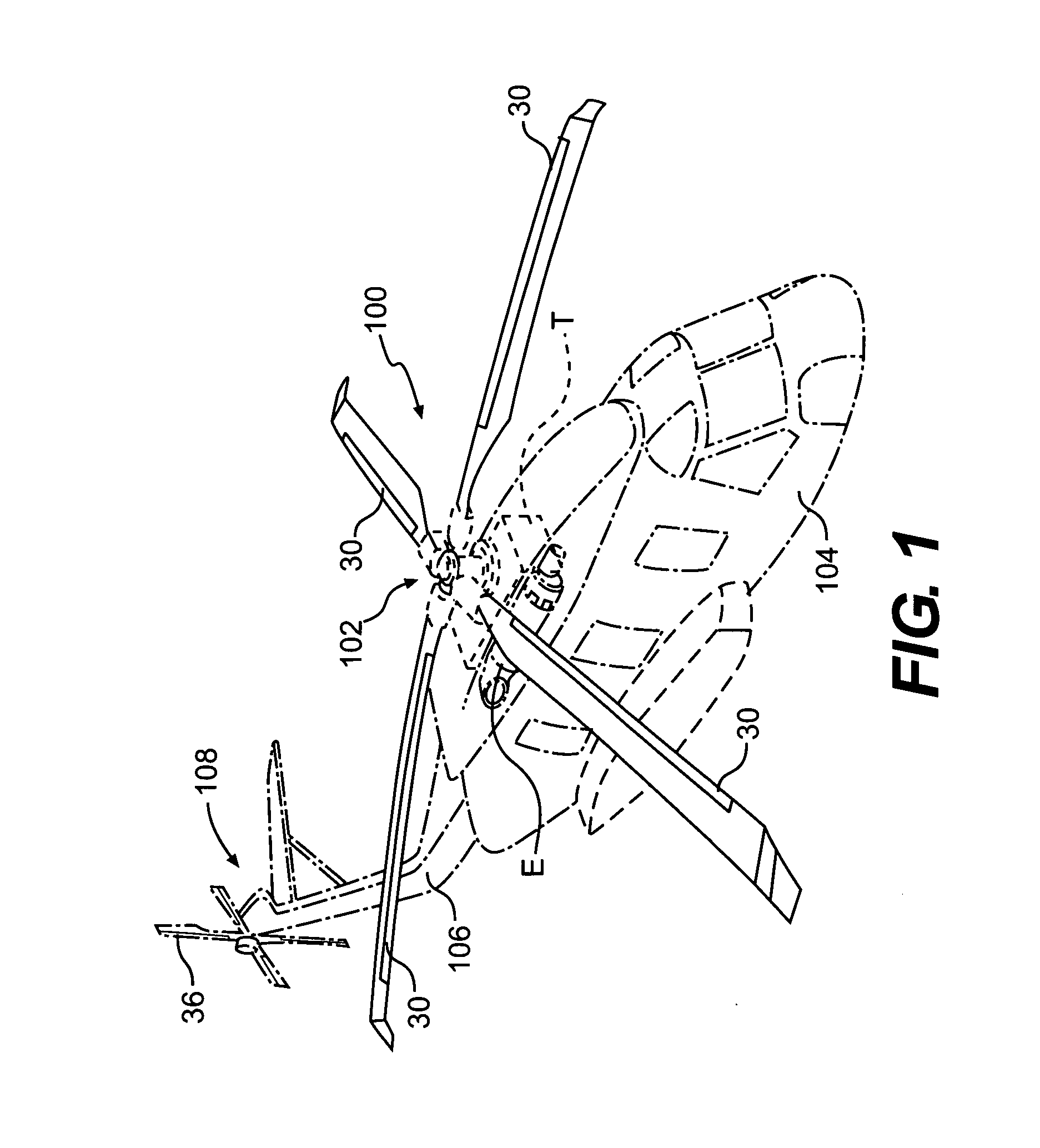
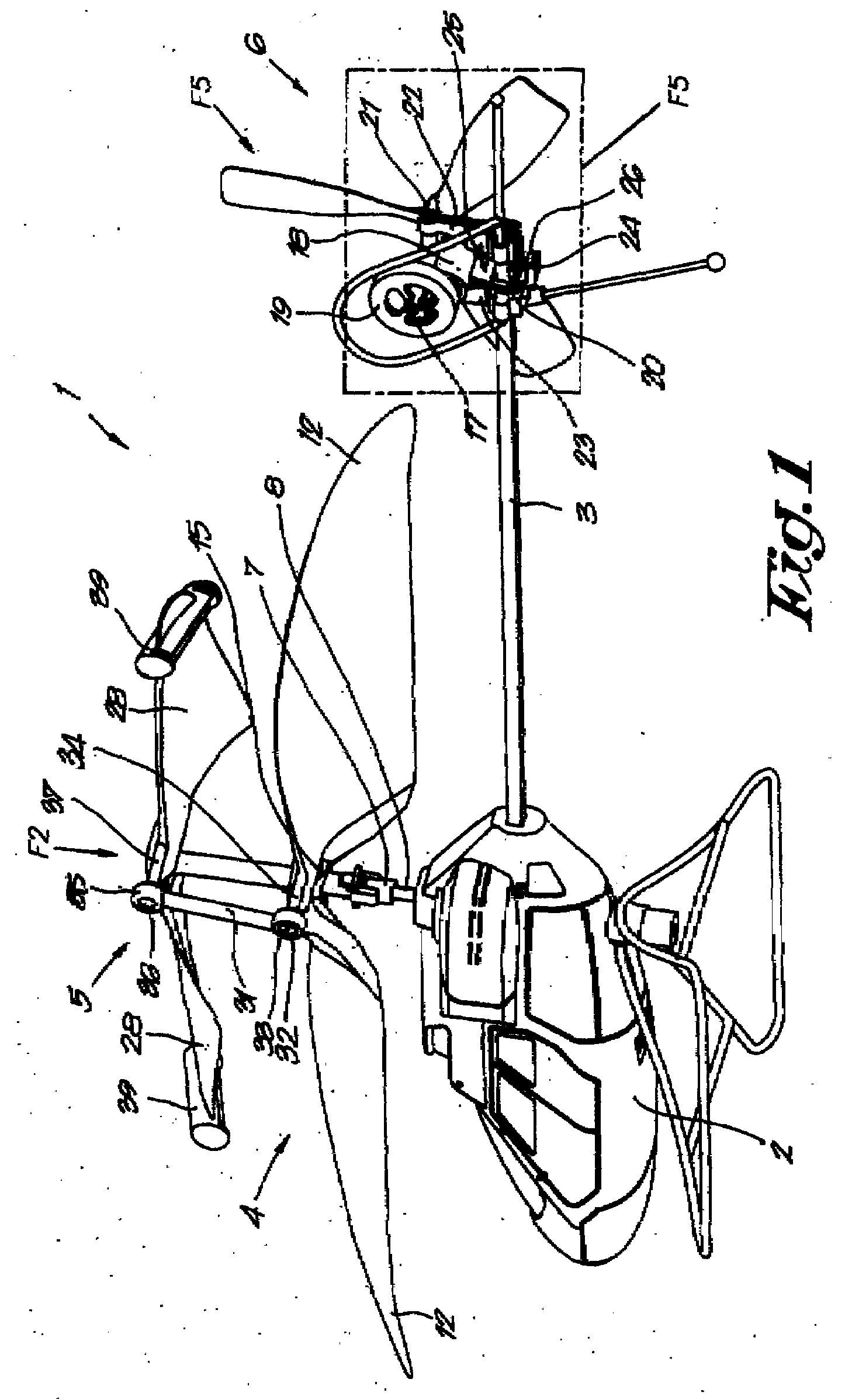
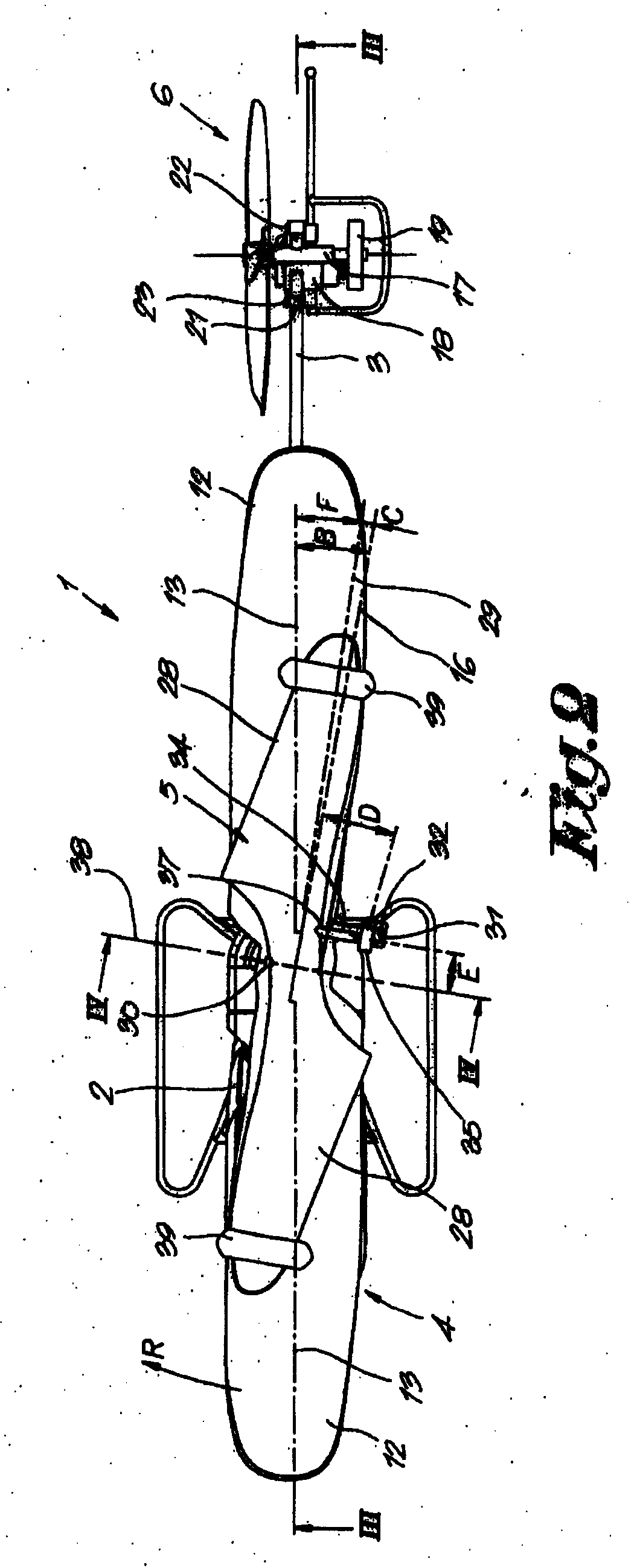
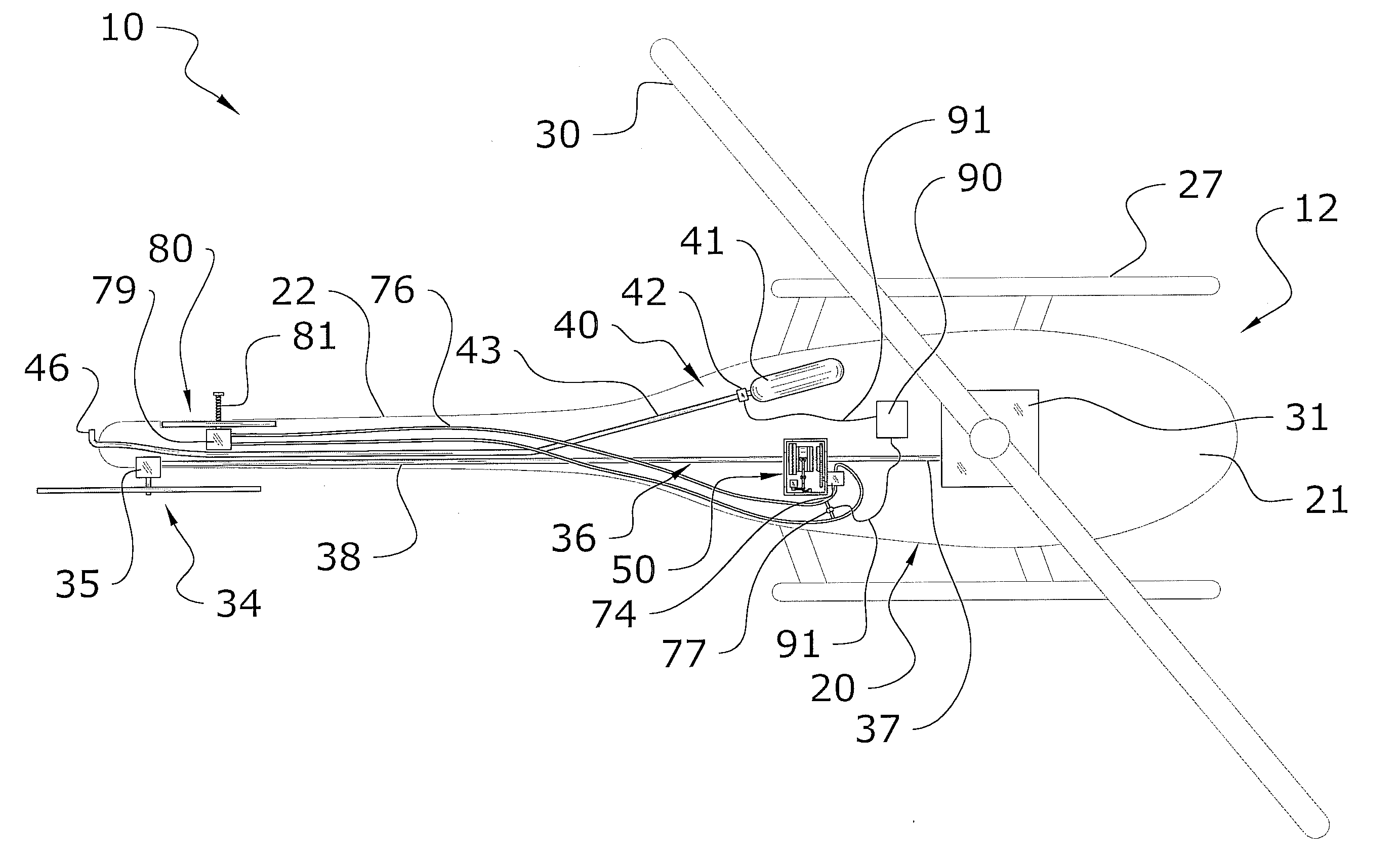
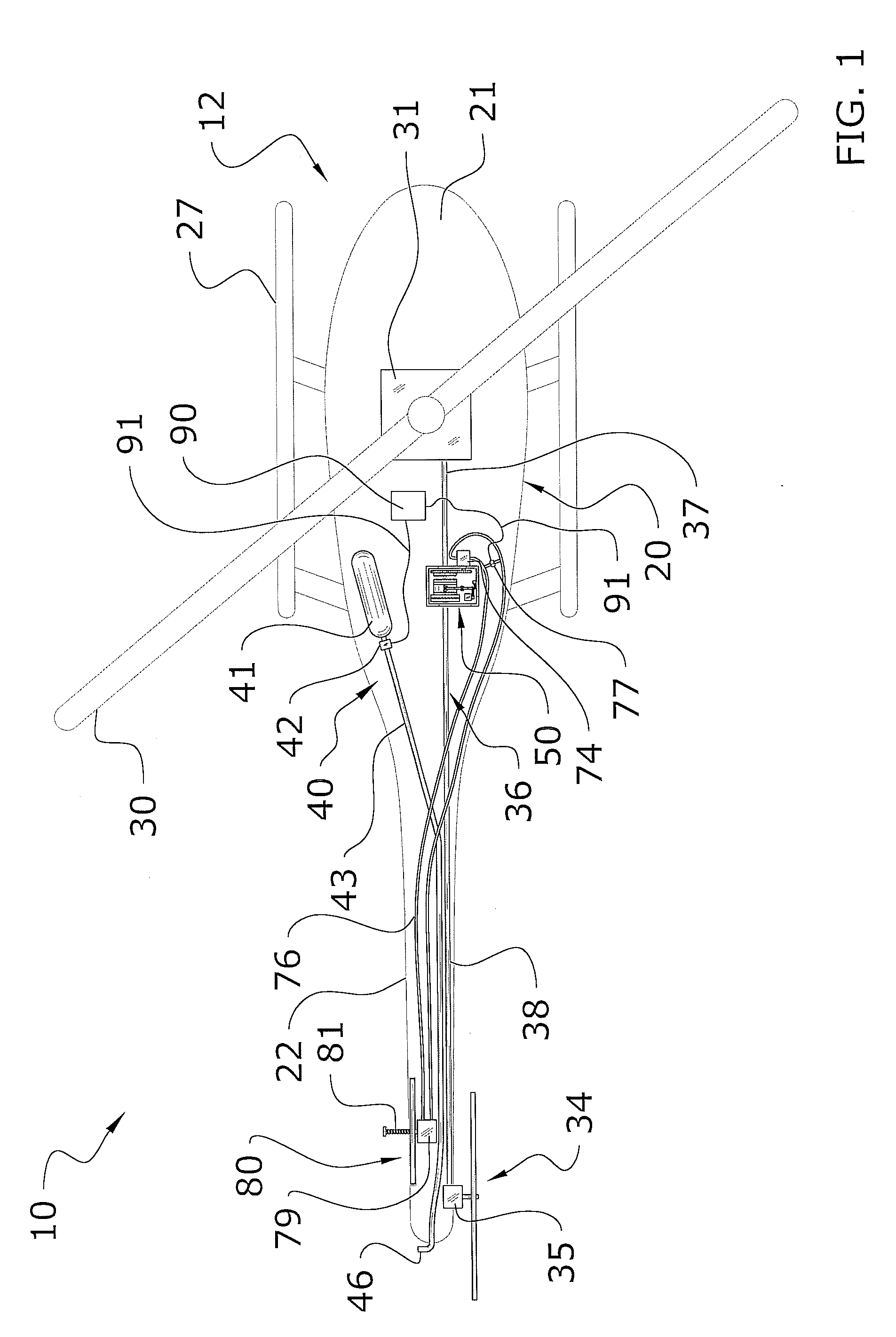
Rotary wing aircraft having a tail rotor, and a method of optimizing the operation of a tail rotor
InactiveUS20130264412A1Minimizes noise emissionOptimize flight durationPropellersPower installationsTail rotorRotary wing
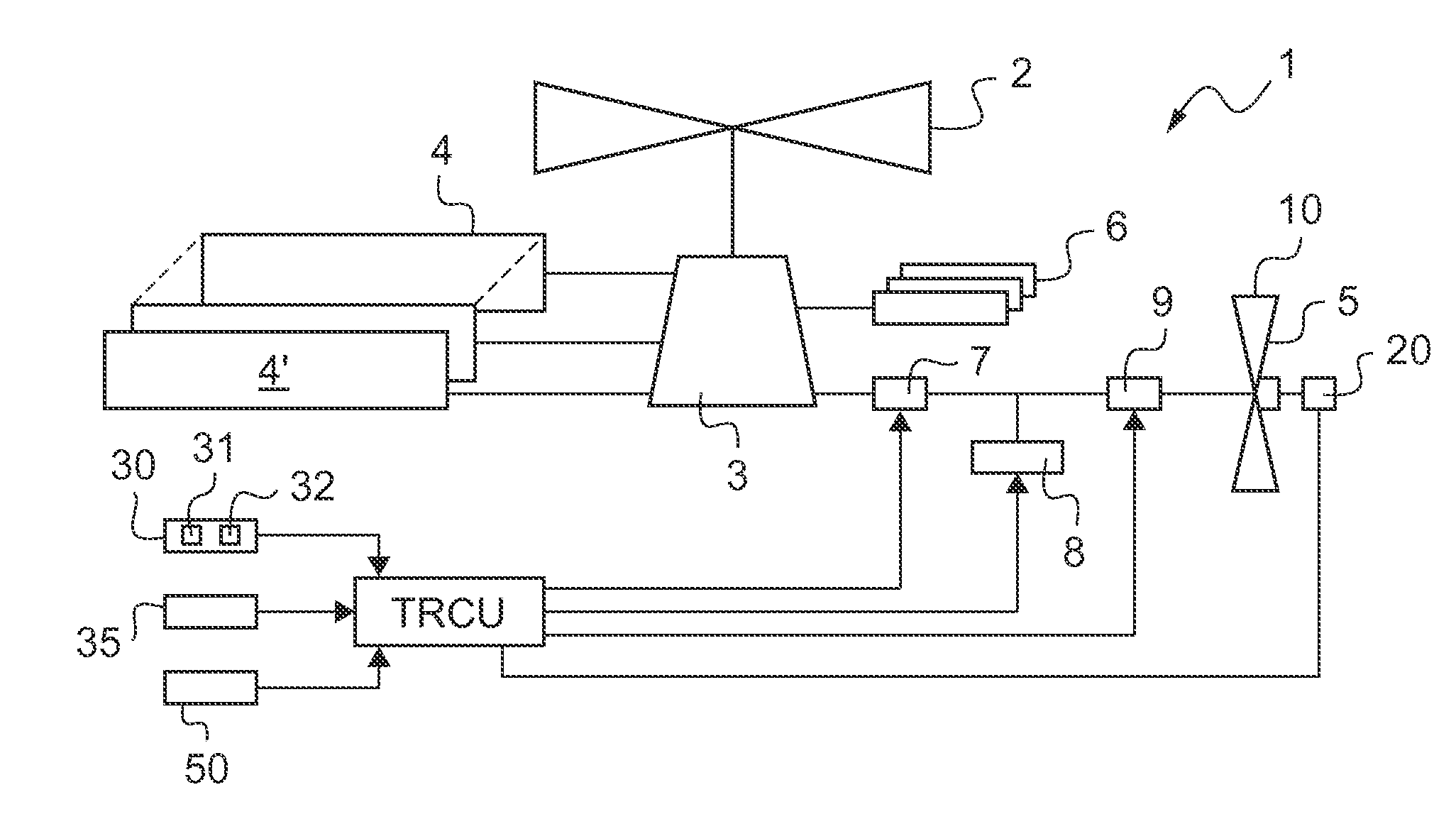
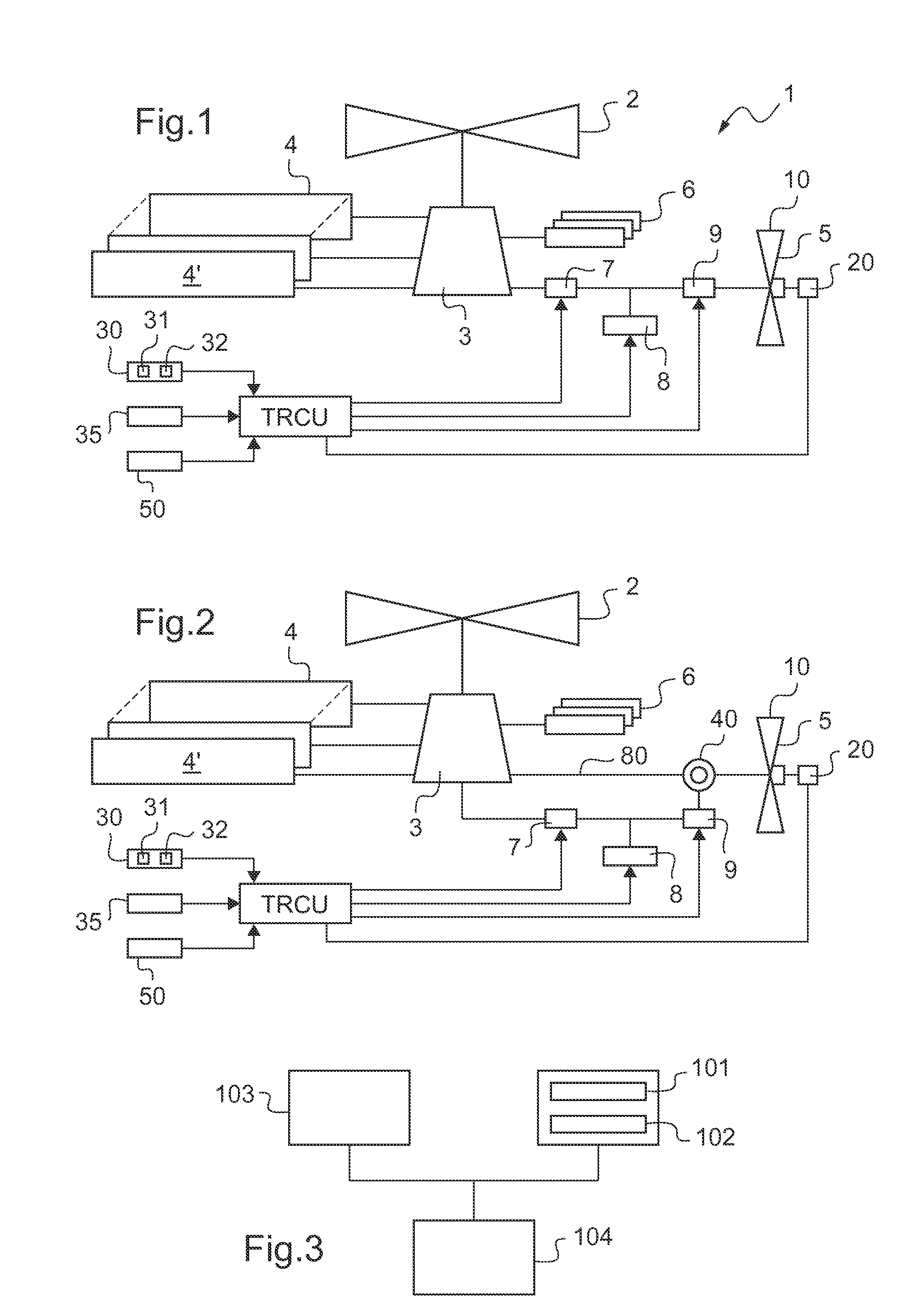
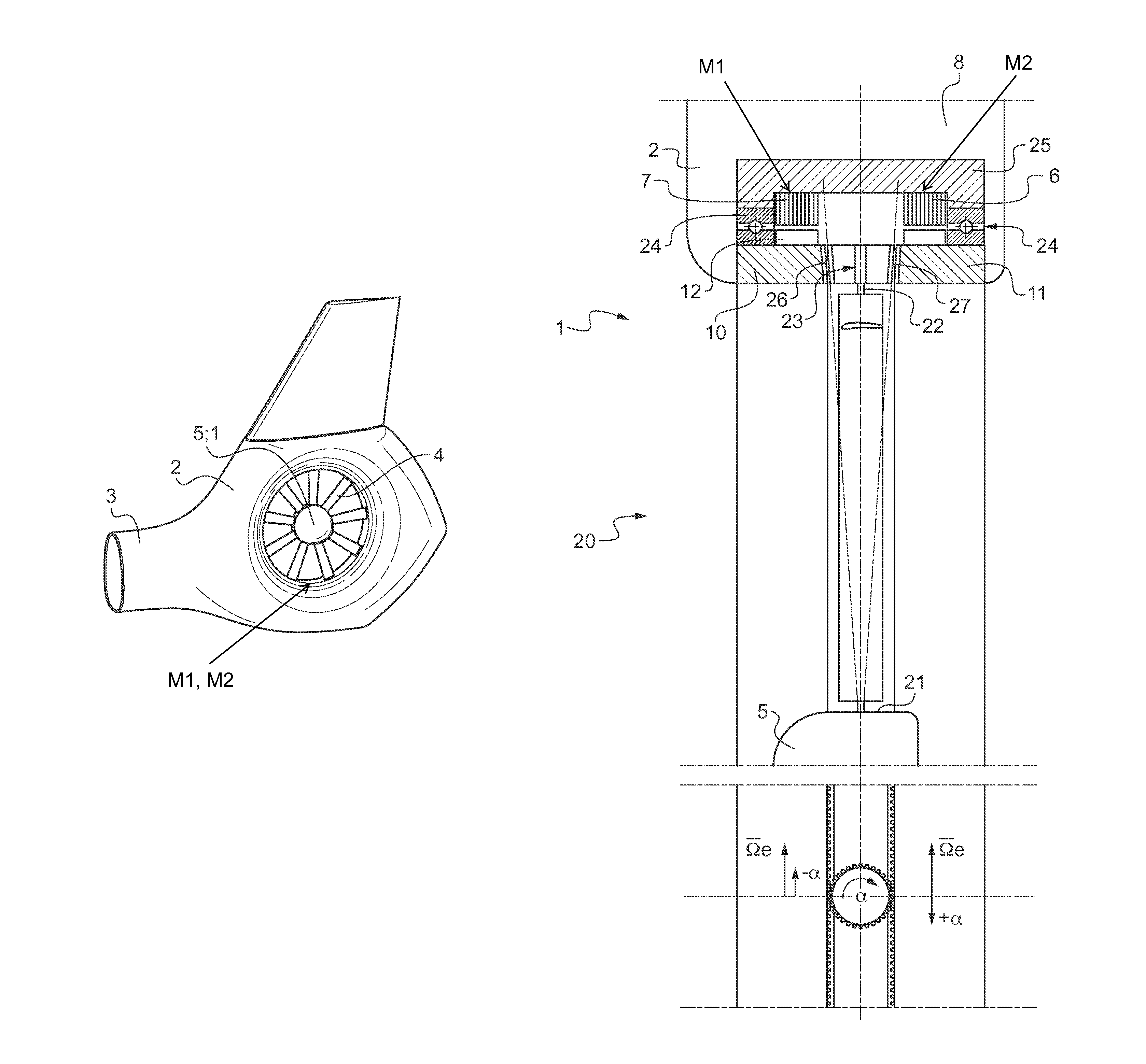
A rotary wing aircraft (1) provided with a main lift rotor (2), a tail rotor (5), and a power plant (4) driving a main gearbox (3) that co-operates with said main rotor (2), said tail rotor (5) being provided with a plurality of blades (10) of variable pitch (I) and with a pitch modification device (20), and said aircraft (1) having control means (30) for controlling said pitch modification device (20). The aircraft (1) includes an electric motor (9) for rotating said tail rotor (5) and regulator means (TRCU) connected to the control means (30) and also to the electric motor (9) and to the pitch modification device (20). The regulator means (TRCU) generate a first setpoint concerning pitch that is transmitted to the pitch modification device (20), and a second setpoint for controlling a motor parameter that is transmitted to the electric motor (9).
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Aircraft and hybrid with magnetic airfoil suspension and drive
InactiveUS7410123B2Better lifting capacityFlying saucersVertical landing/take-off aircraftsAlternatorGear wheel
An aircraft is disclosed that comprises a fuselage with first and second wings non-rotatably secured to and extending from sides of the fuselage. Inner and outer tracks are secured to and encircle the fuselage, and airfoils are operably secured between the inner and outer tracks. Means are provided for rotating the airfoils. The means for rotating the airfoils may be comprised of first and second drive coils, and first and second alternators may be operably coupled to the first and second drive coils, respectively, to provide redundant power supplies. Permanent magnets in the rotor hub may be arranged in a Halbach array or may be arranged to provide a series of alternating, opposite magnetic poles. Separate drive and suspension coils may be provided in the stator. The concept may find further application in a lift fan or tail section of conventional aircraft. In that regard, a lift fan or tail section may be provided in which a stator magnetically levitates a lift fan rotor or tail rotor. The stator may include suspension coils and drive coils to eliminate the need for a drive shaft and gears to power the lift fan rotor or tail rotor.
Owner:NUNNALLY WILLIAM C
Toy radio-controlled helicopter
InactiveUS20050121553A1Simplified piloting mechanismReduce manufacturing costToy aircraftsRemote-control toysTail rotorActuator
A toy radio-controlled helicopter includes: a main rotor, attached on the top of a fuselage and driven by a motor incorporated in the fuselage; a tail rotor that is driven by the motor and is attached to a tail unit provided at the end of a horizontally elongated boom that is extended from the rear of the fuselage; right and left movable wings, attached to the right and left sides of the fuselage below the main rotor, that can be rotated by respective actuators incorporated in the fuselage; and a receiver incorporated in the fuselage to control the operations of the motor and the actuators.
Owner:TAIYO KOGYO CORPORATION
Ducted coaxial multi-rotor type aircraft
The invention discloses a ducted coaxial multi-rotor type aircraft and belongs to the field of special aircrafts. The multi-rotor type aircraft comprises an airframe structure, a power system and a control system. The airframe structure comprises a central duct, a main rotor and a plurality of assistant rotors evenly distributed at the peripheral of the central duct. The main rotor comprises an upper propeller and a lower propeller. The upper and lower propellers are fixed in the central duct. The centers of the upper and lower propellers are at the same vertical axis and the directions of the upper and lower propellers are opposite. A rotation device is connected to the outside of a supporting structure. The assistant rotors are connected to the rotation device through retractable rocker arms. The rotation device controls the rocker arms to drive the assistant rotors to rotate around connection points of the assistant rotors and the supporting structure. The assistant rotors can rotate and move freely, and therefore the aircraft can change the lift force distribution of the aircraft according to flight needs and a good maneuvering characteristic of the aircraft is achieved. The assistant rotors can be retracted into the inside of the central duct so as to reduce the size of the aircraft, thus facilitating flight in narrow spaces.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Composite type multi-mode multi-purpose aircraft
InactiveCN104477377AImprove performanceWith verticalAircraft navigation controlWeight reductionFlight vehicleTail rotor
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Pilotless helicopter
ActiveCN104369862AGuaranteed effectIncrease payloadFuselage framesPower plant cooling arrangmentsTail rotorEngineering
The invention discloses a pilotless helicopter, comprising a main rotor system, a swash plate device, a drive system, a starting device, an engine, a body frame, a tail rotor device, a landing device and at least one auxiliary lift, anti-twisting force and cooling functional device, wherein the auxiliary lift, anti-twisting force and cooling functional device comprises ducts and a lift fan, the lift fan is annularly embraced in the ducts, and the ducts are arranged symmetrical about a central axis which is the advancing direction of the pilotless helicopter; the ducts are fixed above the engine, and an air guide passage is designed below the ducts and guides air to a cylinder of the engine; and the swash plate device is a four-channel hybrid control swash plate device. A part of additional lift and anti-twisting force are provided for the pilotless helicopter by using the power of the cooling engine, so that the pilotless helicopter has larger effective load and higher efficiency. Four steering engines of the four-channel hybrid control swash plate device are arranged in a manner of backing up each other, so that the stability is improved.
Owner:湖南星索尔航空科技有限公司
Brushless permanent magnet motor/generator with axial rotor decoupling to eliminate magnet induced torque losses
ActiveUS20070096581A1Eliminate magnet induced torque dragSynchronous generatorsWindingsEngineeringPermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor / generator that includes a stator, a rotor provided with a plurality of permanent magnets at a peripheral surface thereof and having a central axis which coincides with the central axis of the stator, a rotatable shaft upon which the rotor is coupled, and an actuator for moving the rotor with respect to the stator axially along the rotatable shaft a sufficient distance to completely decouple the rotor from the stator so as to eliminate magnet induced torque drag. When the permanent magnet / generator is used in parallel hybrid vehicles, the ability to completely decouple the rotor from the stator greatly improves range and efficiency. In addition, by progressively engaging the rotor with the stator a desired voltage output can be obtained upon deceleration.
Owner:DURA TRAC MOTORS INC
Dual-channel deicing system for a rotary wing aircraft
ActiveUS20060226292A1Minimize the possibilityReserved functionElectric heatingDe-icing equipmentsEngineeringTail rotor
A deicing system includes dual deice system components to provide a redundant deice system. Each redundant portion of the system generally includes a controller, an air data computer, an ice rate controller, and an ice rate probe. The controller communicating a heating cycle which defines a multiple of electric pulse trains to sequentially provides power to a multiple of heating elements in a designated blade set. Each electric pulse train is defined by an element on-time, a null time between the element on-time for this element and the next element, and an off-time between repetition of the heating cycle for the first heater element. The element on-time is a function of outside air temperature (OAT). The off-time is a function of liquid water content. The tail rotor heating cycle is a more straightforward version of the main rotor heating cycle as each of the tail rotor blade are activated simultaneously and there is only a single heating element on each tail rotor blade.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
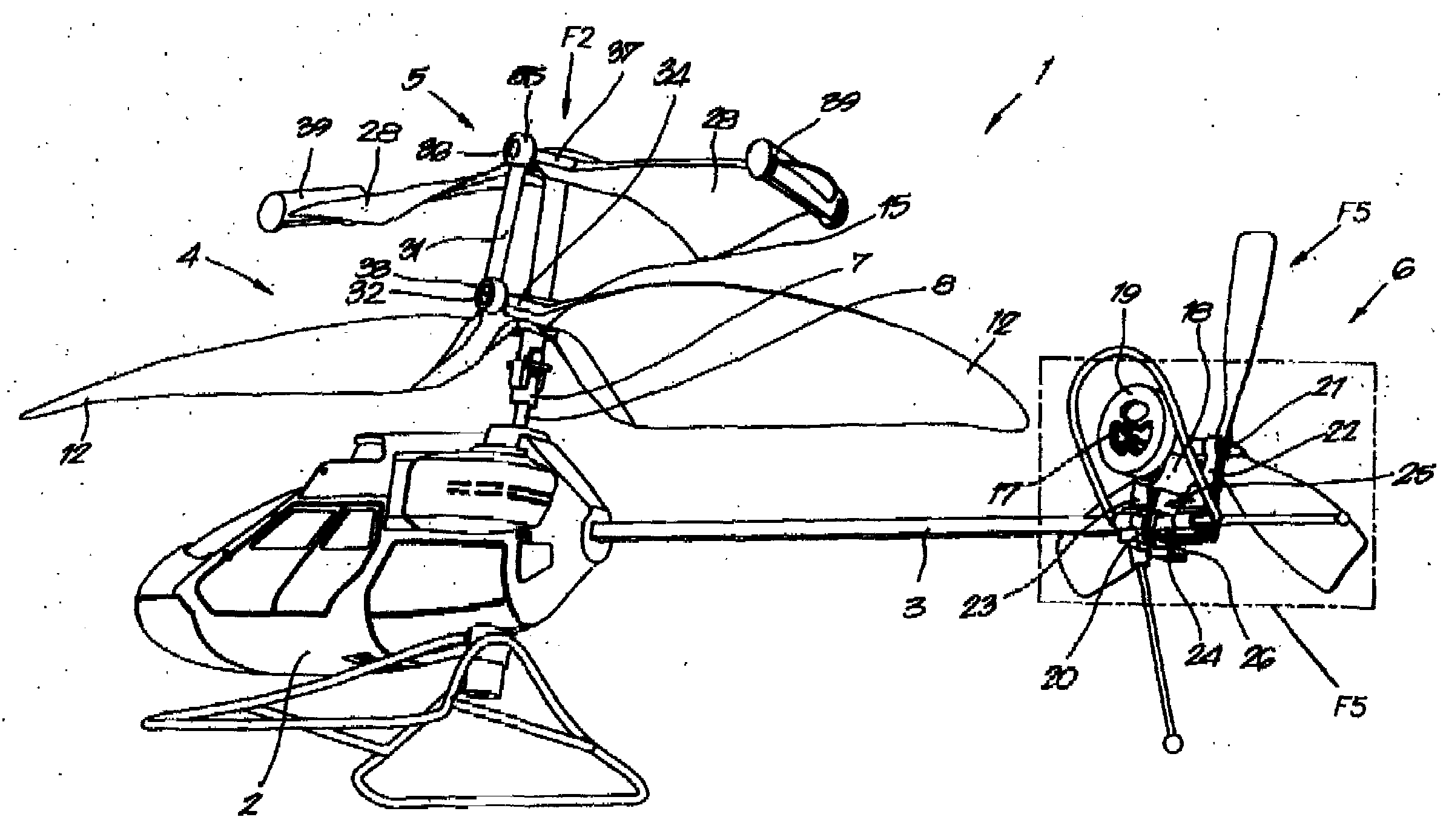
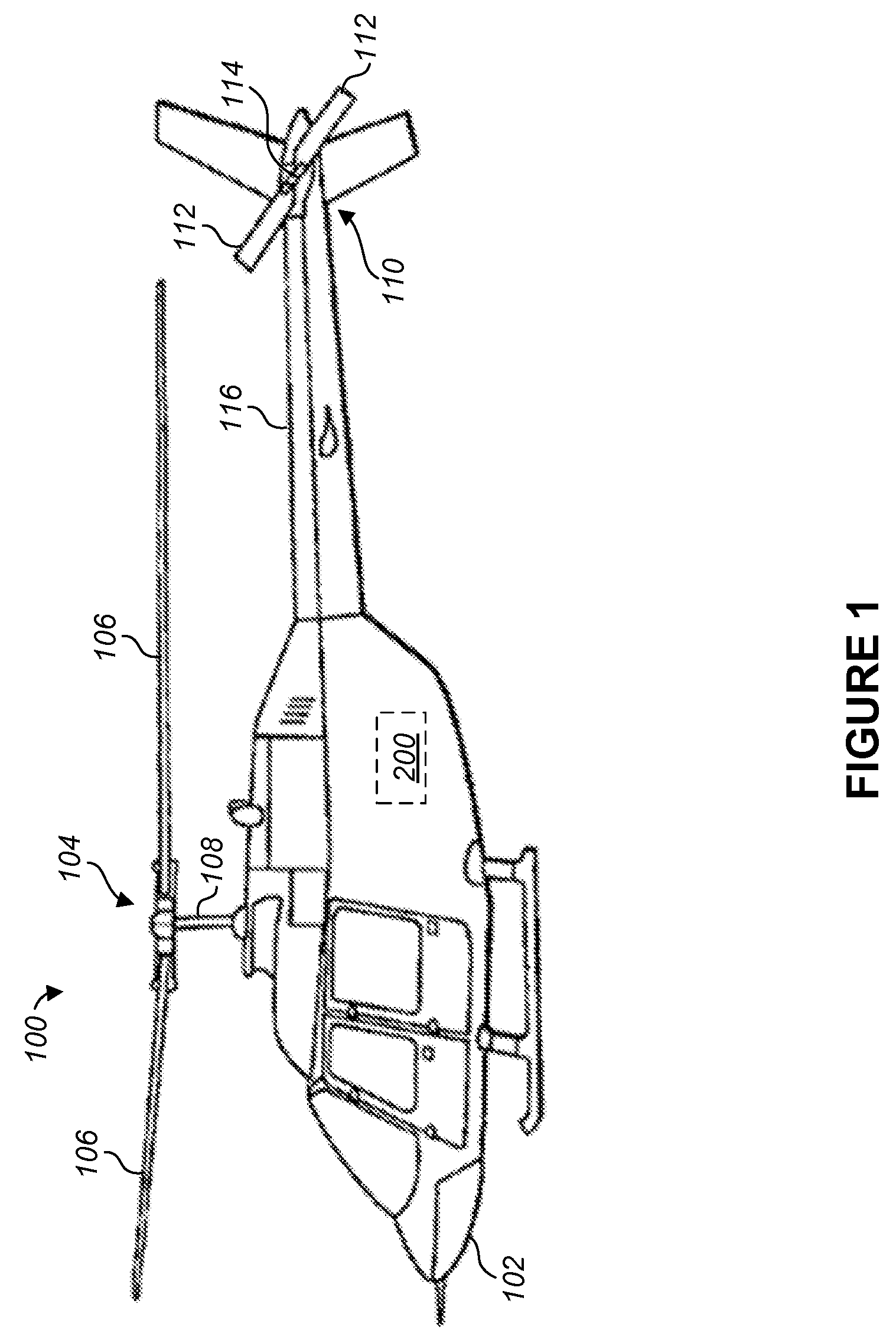
Helicopter
A helicopter has a main rotor with propeller blades which is driven by a rotor shaft and which is hinge-mounted to this rotor shaft. The angle between the surface of rotation of the main rotor and the rotor shaft may vary. A swinging manner on an oscillatory shaft is essentially transverse to the rotor shaft of the main rotor and is directed transversally to the longitudinal axis of the vanes. The main rotor and the auxiliary rotor are connected to each other by a mechanical link. The swinging motions of the auxiliary rotor controls the angle of incidence (A) of at least one of the propeller blades of the main rotor. There are wings from the body and a stabilizer at the tail.
Owner:SILVERLIT TOYS MANUFACTORY
Propellers and propeller related vehicles
InactiveUS7178758B2Reduce the possibilityIncrease centrifugal forceMachines/enginesToy aircraftsDrive shaftPropeller
Owner:REHCO LLC
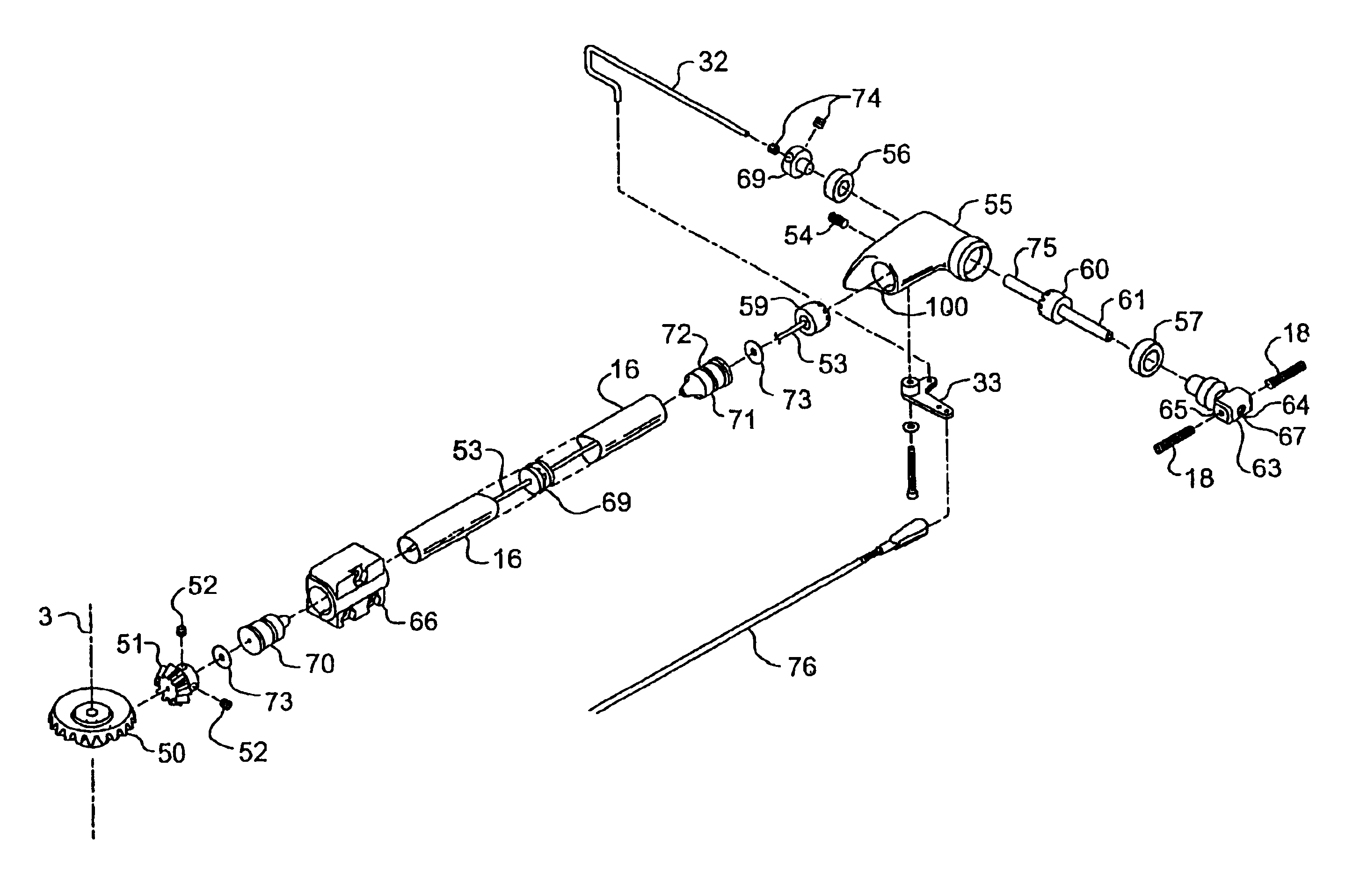
Rotor Blade Pitch Control
ActiveUS20080111399A1Simple and reliable processHigh harmonicPropellersPump componentsTail rotorActuator
A mechanical independent blade control (MIBC) mechanism for controlling the pitch of each of the blades of a rotor blade system or a main rotor of a rotor aircraft independently of the other blades includes a plurality of actuators disposed in the fuselage below the hub of the rotor, each being operable to selectively control the pitch of an associated one of the blades independently of the other blades, and a plurality of mechanical linkages disposed within the annulus of the rotor mast, each coupled between a blade and an actuator and operable to transmit a force output by the actuator to a pitch horn fixed to an inner end of the associated blade. The mechanism enables the direction of pitch of each blade to be changed more than twice during one revolution of the rotor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
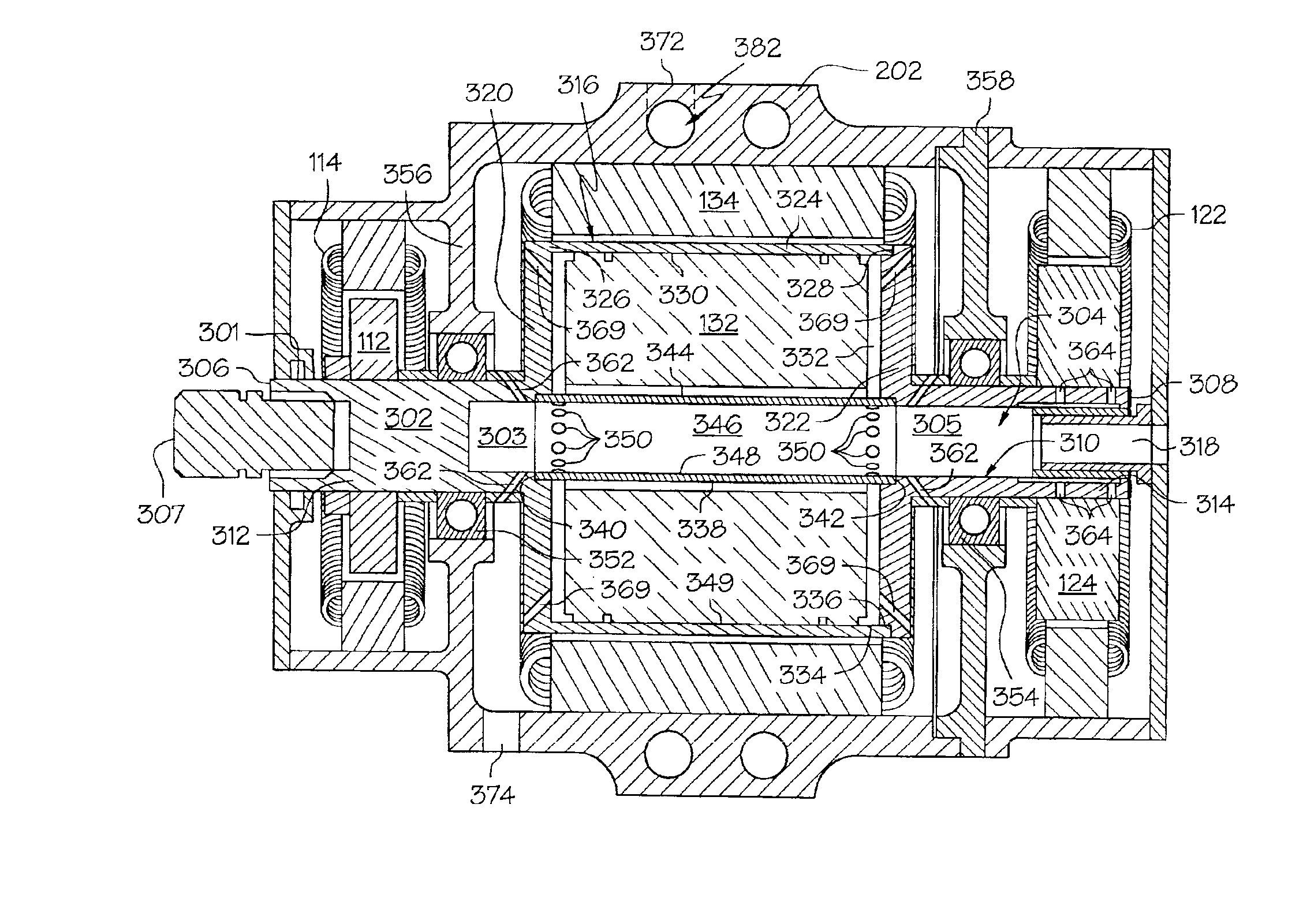
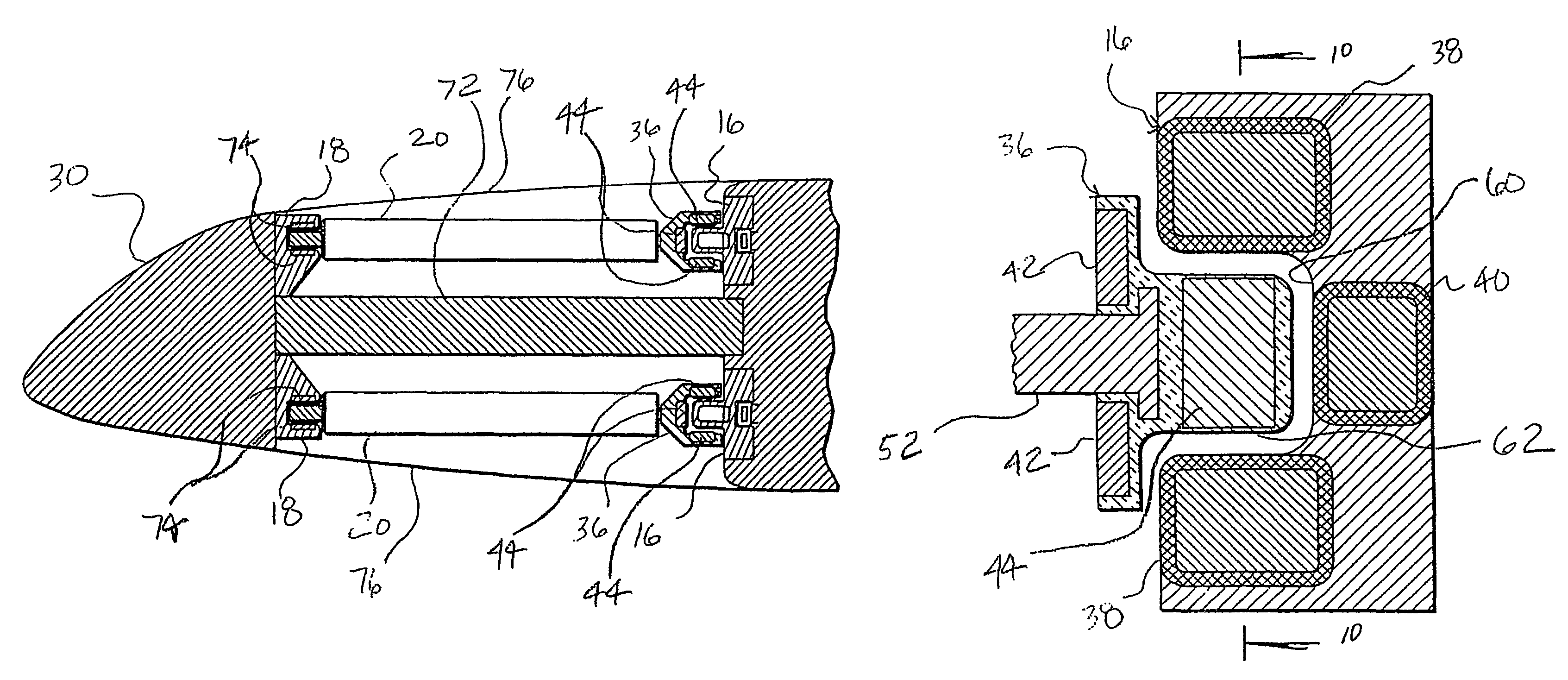
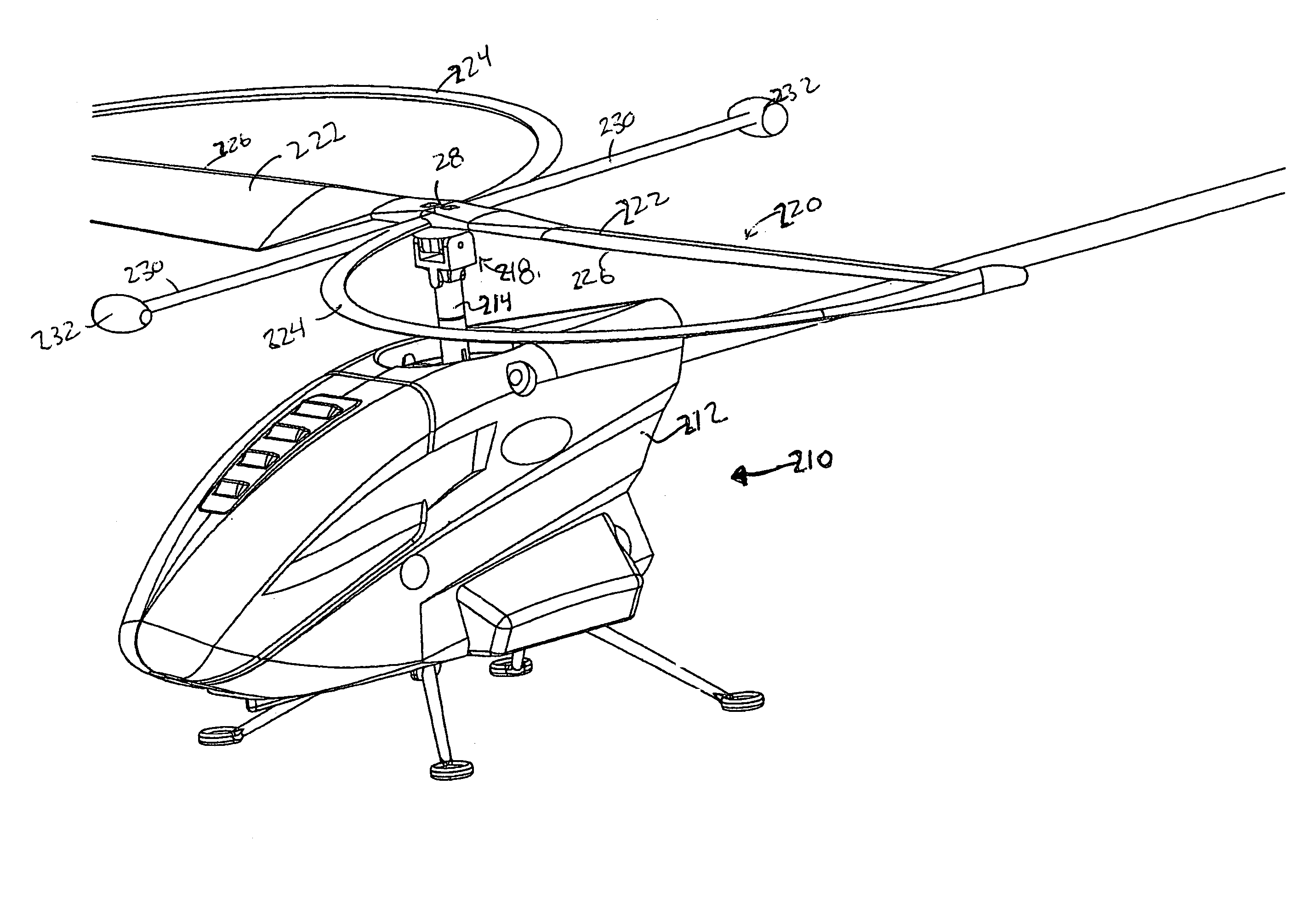
Electrical powered tail rotor of a helicopter
ActiveUS9174728B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the number of polesMagnetic circuit stationary partsMachines/enginesSynchronous motorEngineering
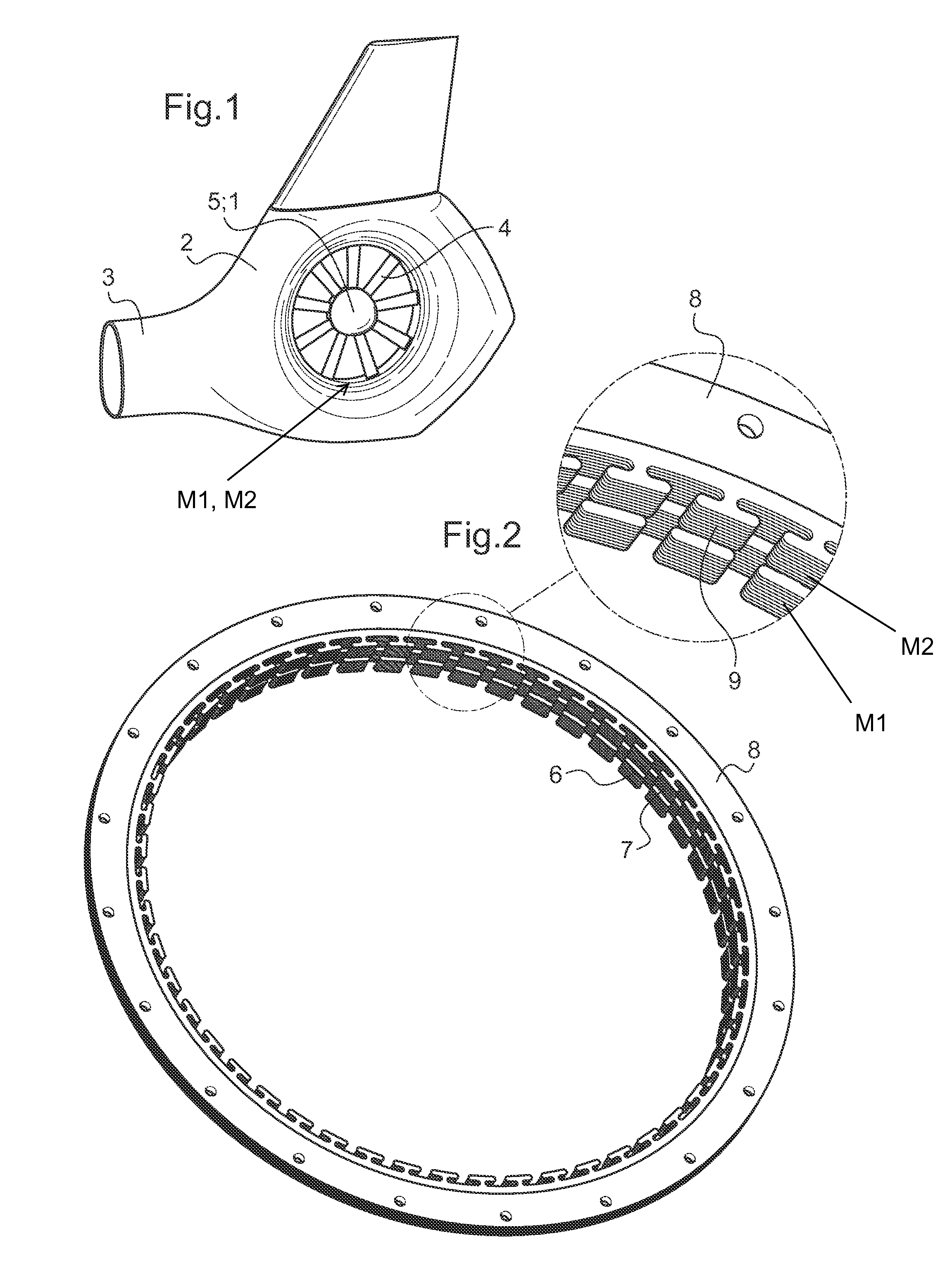
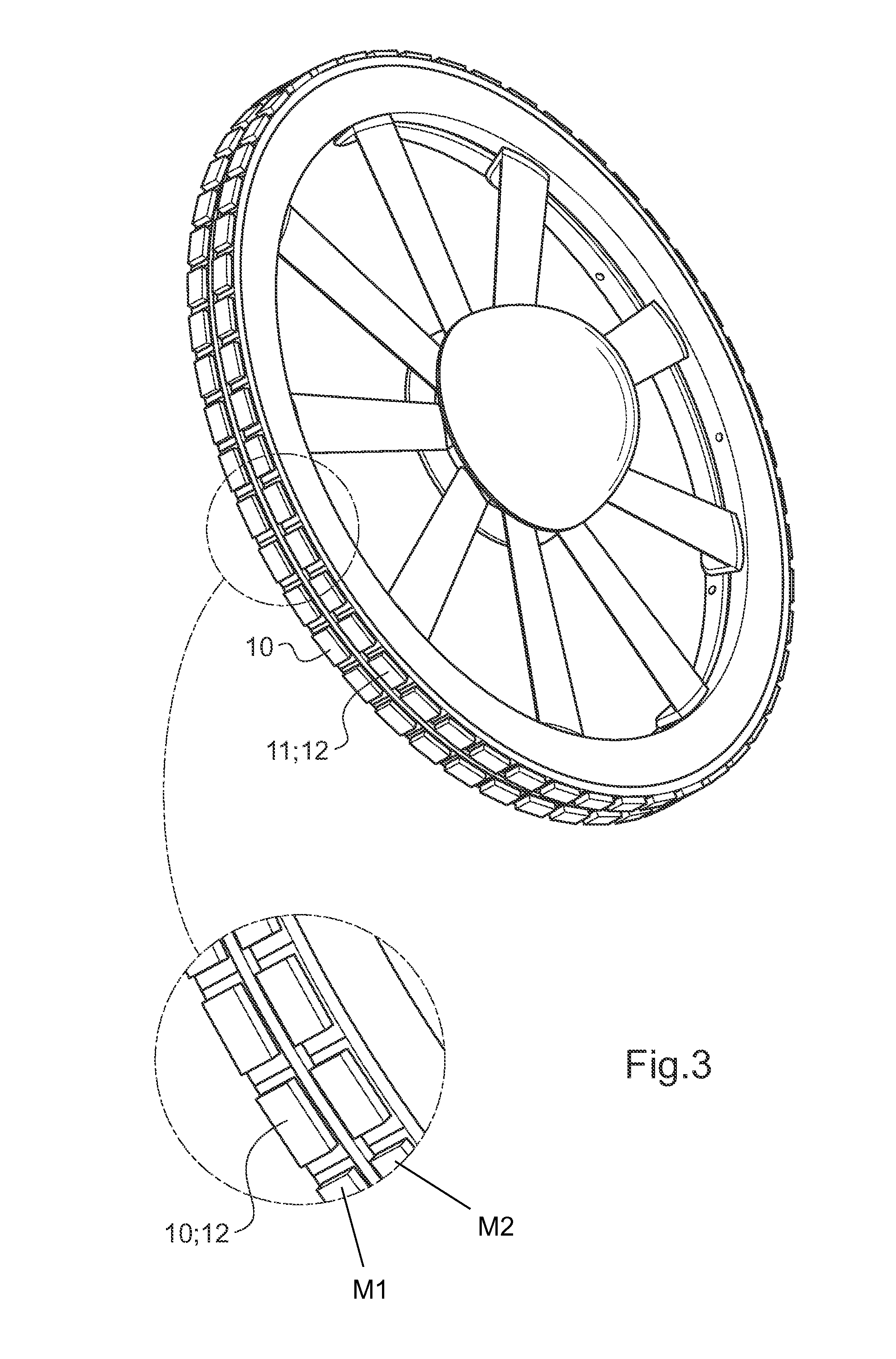
The invention is related to an electrical powered tail rotor (1) of a helicopter comprising a housing (2) around the tail rotor (1), and at least one permanent magnet energized synchronous motor with a stator (6, 7) with an increased number of poles (9). Said at least one synchronous motor is integrated as a torus (8) around an opening of the housing (2) encompassing the tail rotor (1). Blades (4) of the tail rotor (1) are fixed to at least one rotating component (10, 11) of said at least one synchronous motor. Supply means provide for electric energy to said at least one synchronous motor. Blade pitch control means are provided at the torus (8).
Owner:AIRBUS HELICOPTERS DEUT GMBH
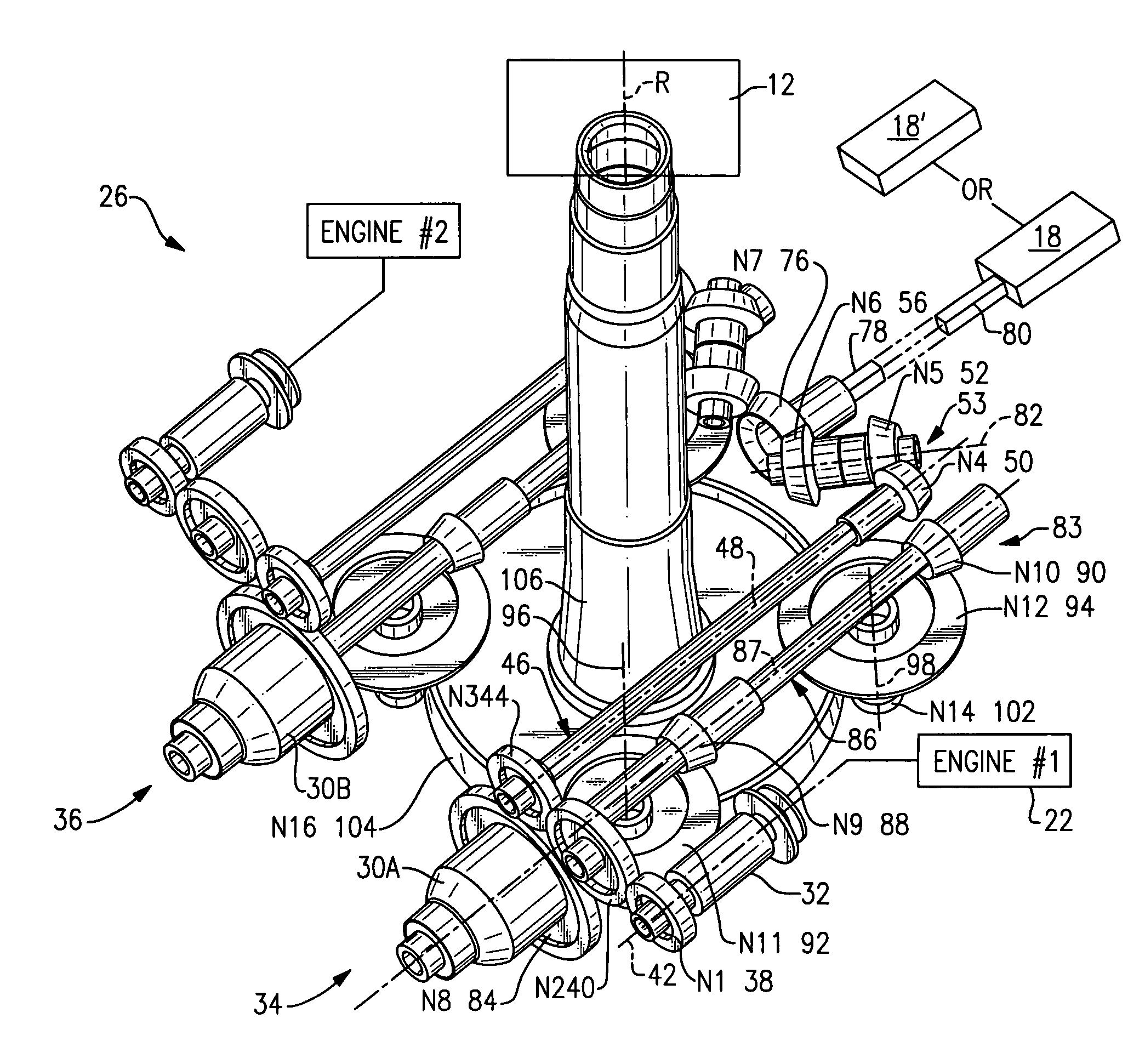
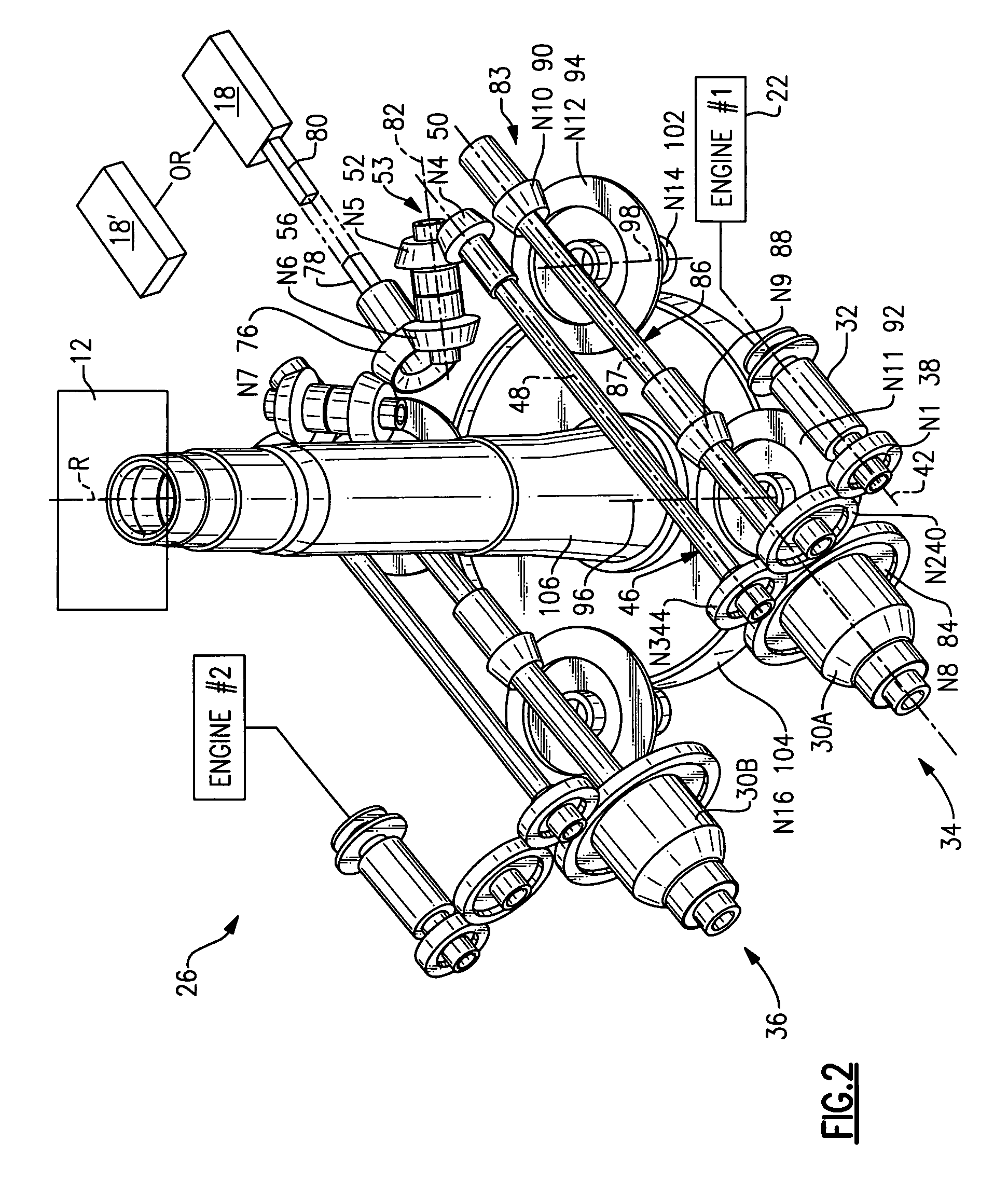
Variable speed gearbox with an independently variable speed tail rotor system for a rotary wing aircraft
InactiveUS7434764B2Shorten speedImprove abilitiesAircraft power transmissionRotocraftTail rotorRotary wing
A gearbox of a rotary-wing aircraft includes at least one variable speed system which optimizes the main rotor speed for different flight regimes such as a hover flight profile and a high speed cruise flight profile for any rotary wing aircraft while maintaining an independently variable tail rotor speed.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
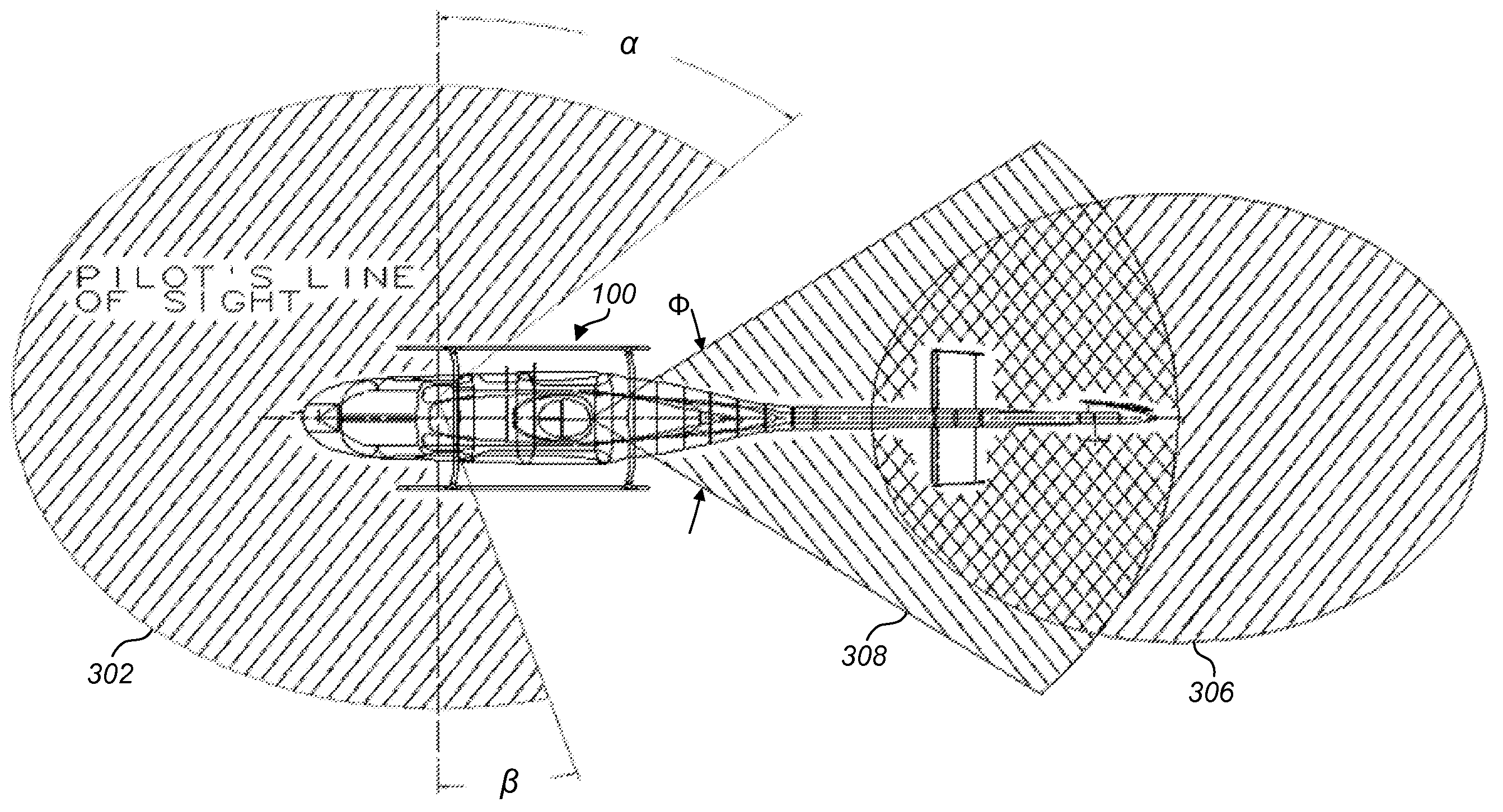
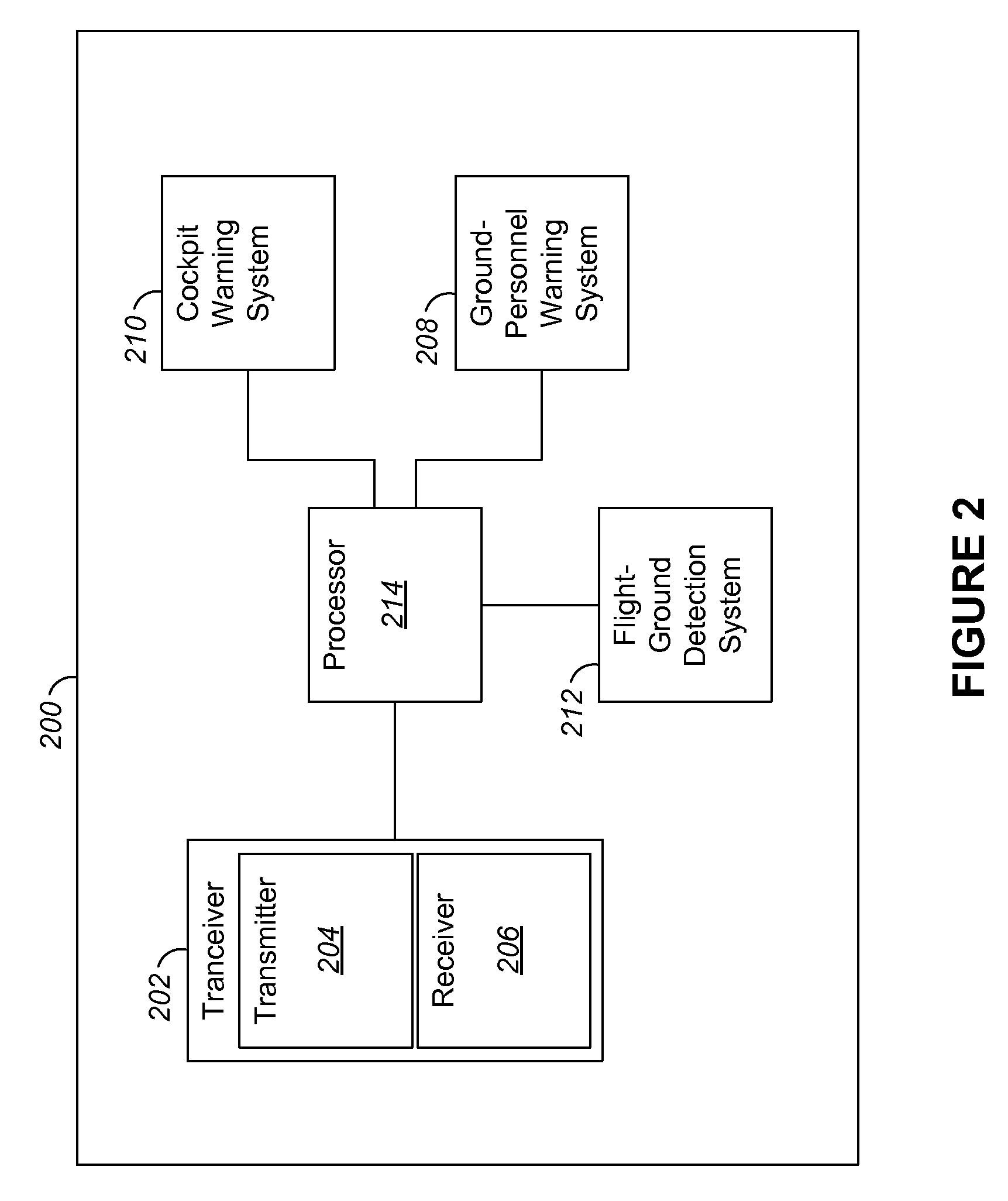
Collision avoidance and warning system
A collision avoidance and warning system for a helicopter uses a type of emitted energy, for example radio frequency radar, from a transceiver positioned to cover a selected field of view for detecting an object or pedestrian in the vicinity of the helicopter. For helicopters that include a tail rotor assembly, the selected field of view can include a region around the tail rotor assembly so that when the helicopter is running on the ground, an alarm can be issued to persons approaching the tail rotor assembly. When the helicopter is in flight, the collision avoidance and warning system can alert the pilot when a portion of the helicopter outside of the pilot's field of view is in danger of a collision with an object.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
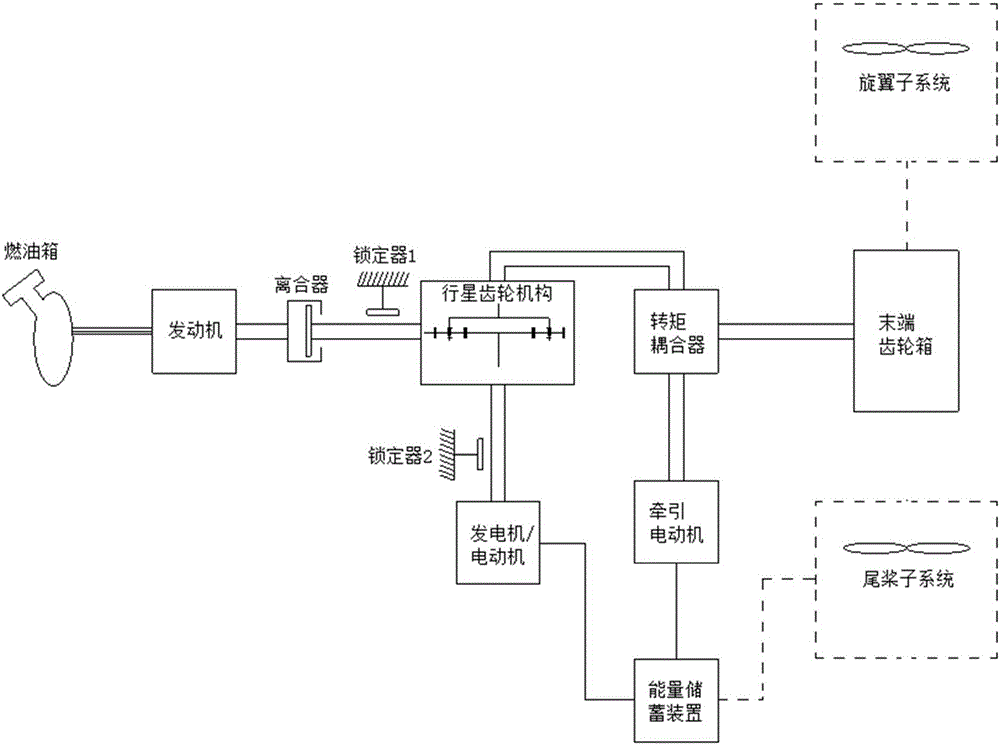
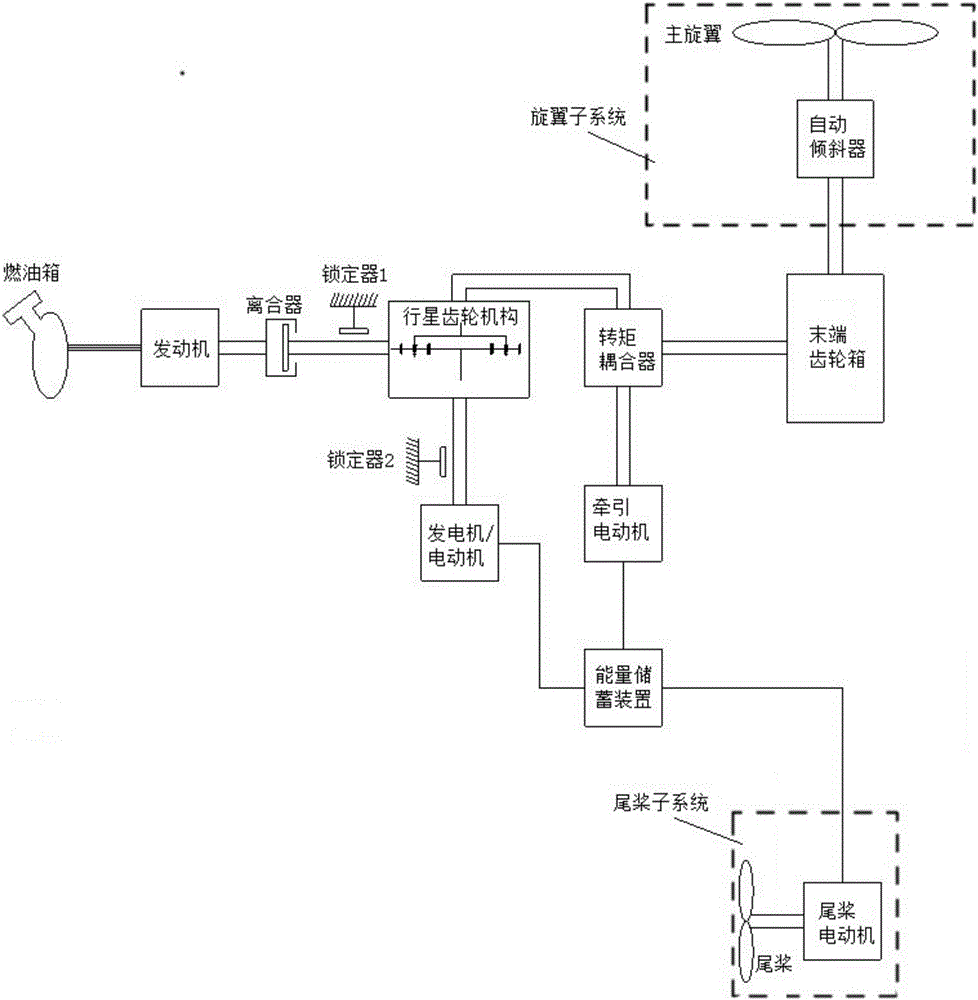
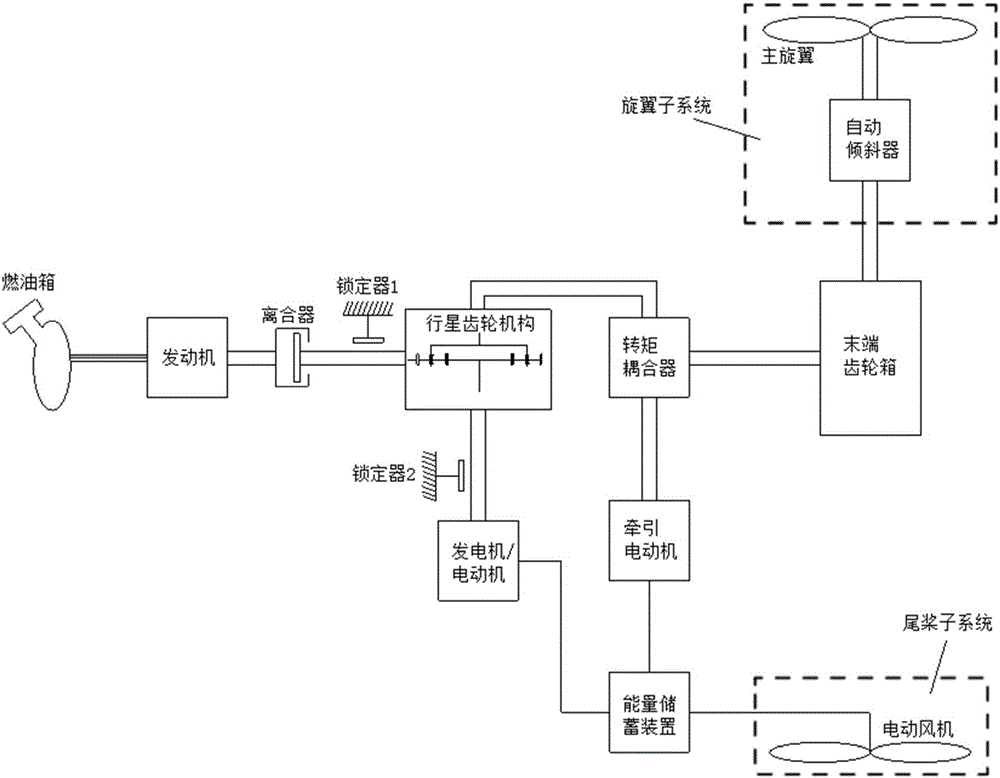
Driving mechanism and driving method of hybrid power helicopter
InactiveCN105836141AReduce weightFlying fastDepending on number of power plantsPower plant typeClutchTail rotor
The invention discloses a driving mechanism of a hybrid power helicopter. The driving mechanism of the hybrid power helicopter comprises a fuel tank, an engine, a clutch, a first locker, a planetary gear mechanism, an energy storage device, a generator / electric motor, a second locker, a second generator / electric motor, a torque coupler, a tail end gear box, a tail rotor subsystem, an swashplate and a rotor wing subsystem, wherein the clutch and the first locker are mounted between the engine and the planetary gear mechanism, and the second locker is mounted between the generator / electric motor and the planetary gear mechanism. Two power sources comprising a basic power source and an auxiliary power source are utilized, the two power sources are reasonably matched and selected when driving the helicopter, accordingly, the problems that the power source of a conventional helicopter is single, a drive system is complicated, a drive device is heavy, mechanical failure easily happens and the like are solved, and the safety and the maneuverability of the helicopter are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Helicopter
A helicopter capable of preventing an increase in size of an airframe and achieving high-speed flight is provided. Provided is an airframe for supporting a main rotor so as to be rotatable, a propeller having a plane of rotation intersecting a plane of rotation of the main rotor, a propeller supporting portion that supports the propeller so as to be movable between positions behind and at the side of the airframe, and a tail disposed on the airframe, having a surface intersecting the plane of rotation of the main rotor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Helicopter
InactiveUS20070164148A1Slow effectReduce needToy aircraftsRemote-control toysAngle of incidencePropeller
A helicopter has a main rotor with propeller blades which is driven by a rotor shaft and which is hinge-mounted to this rotor shaft. The angle between the surface of rotation of the main rotor and the rotor shaft may vary. A swinging manner on an oscillatory shaft is essentially transverse to the rotor shaft of the main rotor and is directed transversally to the longitudinal axis of the vanes. The main rotor and the auxiliary rotor are connected to each other by a mechanical link. The swinging motions of the auxiliary rotor controls the angle of incidence (A) of at least one of the propeller blades of the main rotor.
Owner:SILVERLIT TOYS MANUFACTORY LTD
Helicopter Auxilary Anti-Torque System
A helicopter auxilary anti-torque system for efficiently supplying thrust and control at the tail of a helicopter during failure of the helicopter tail rotor. The helicopter auxilary anti-torque system generally includes a fluid thrust assembly selectively engageable onboard the helicopter, an auxiliary tail rotor selectively engageable onboard the helicopter, and at least one controller to operate the fluid thrust assembly and the auxiliary tail rotor to effect a controlled anti-torque force of the tail boom during failure of the conventional helicopter tail rotor. The fluid thrust assembly projects a non flammable fluid from the tail boom of the helicopter. The auxiliary tail rotor is collapsible within the tail boom of the helicopter when not in use. The fluid thrust assembly and the auxiliary tail rotor may be automatically activated in the case of the primary tail rotor failure, or activated by the pilot of the helicopter via one or more switches.
Owner:BALKUS JR CARL E
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com