Patents
Literature
23879results about "Magnetic circuit rotating parts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
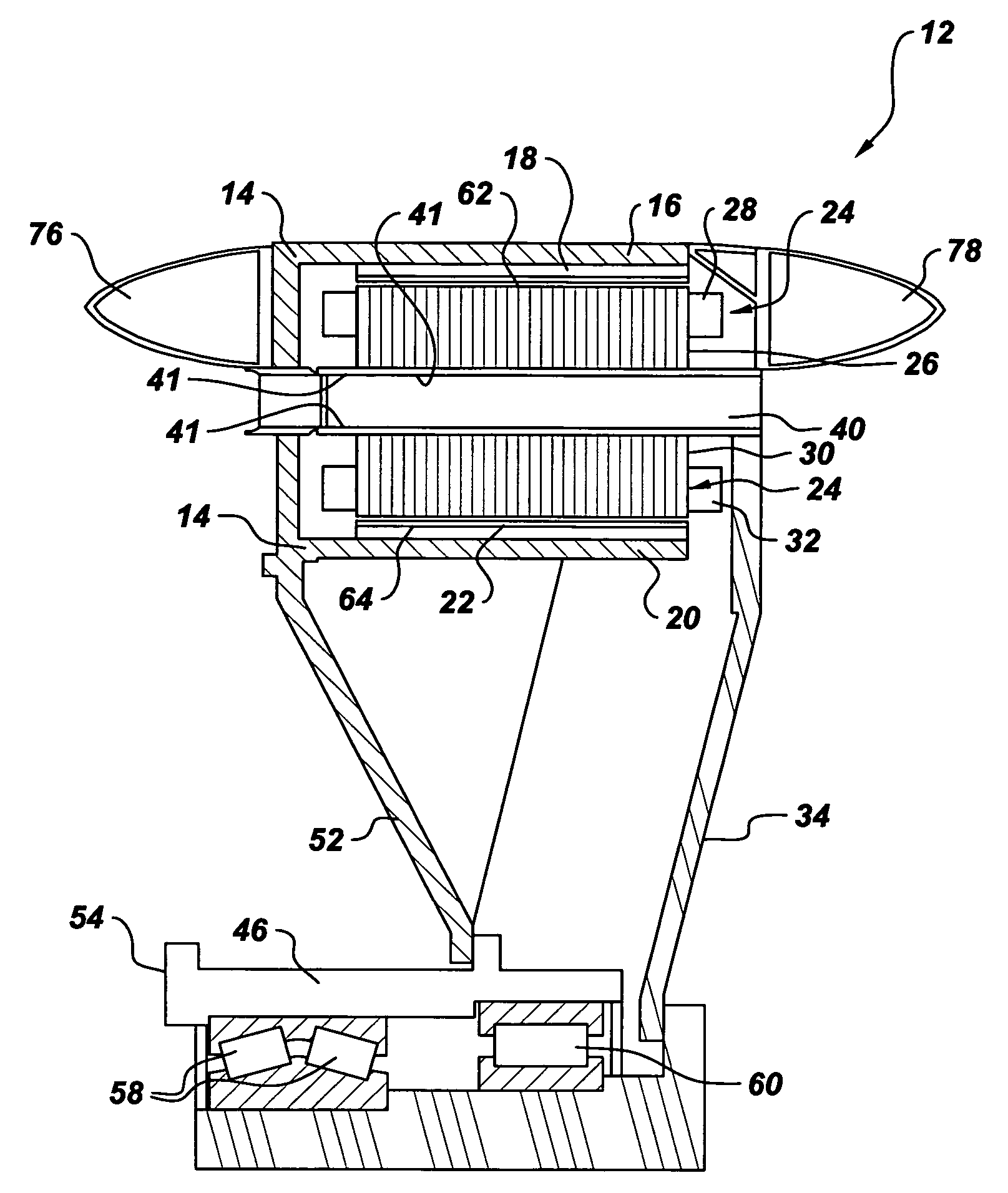
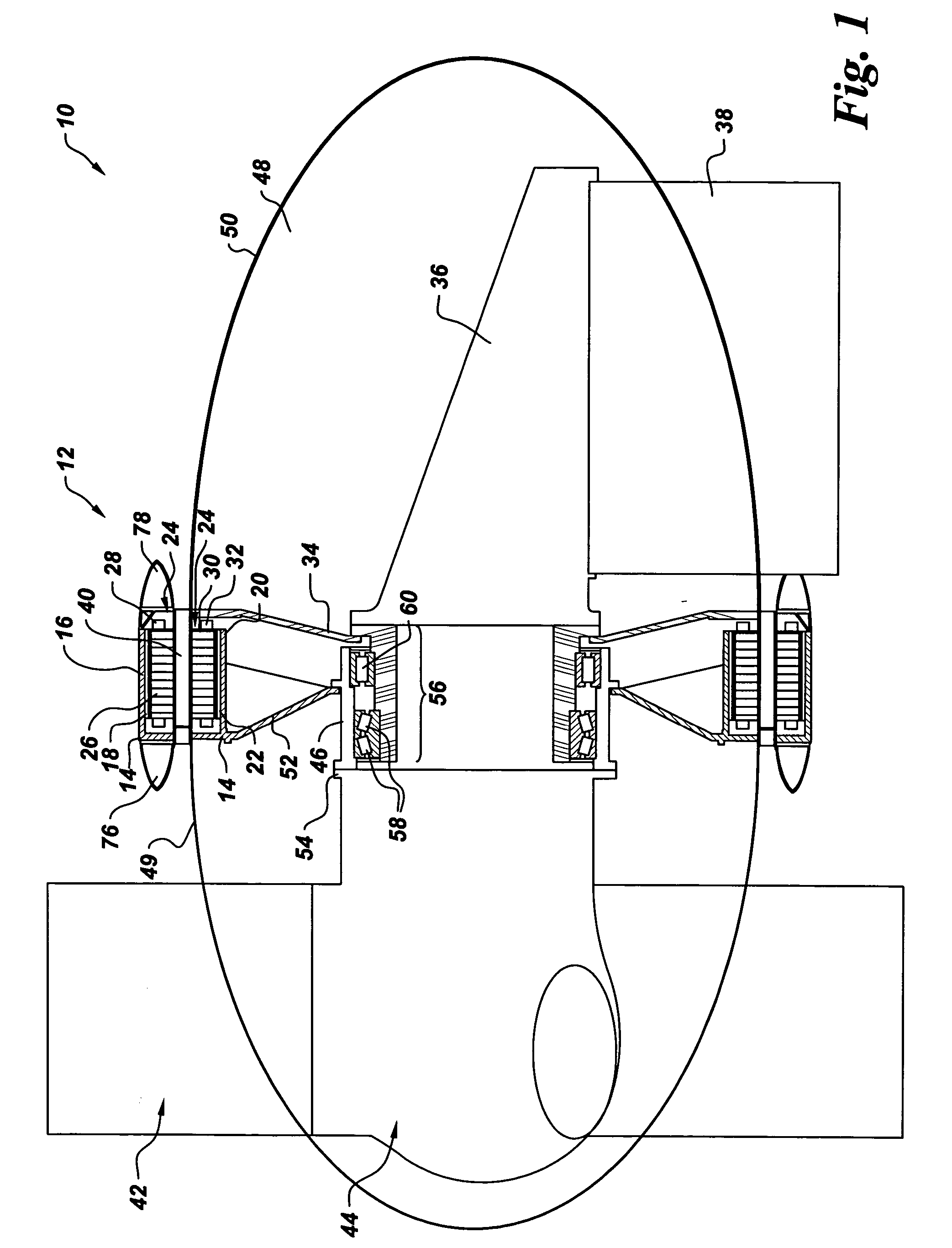
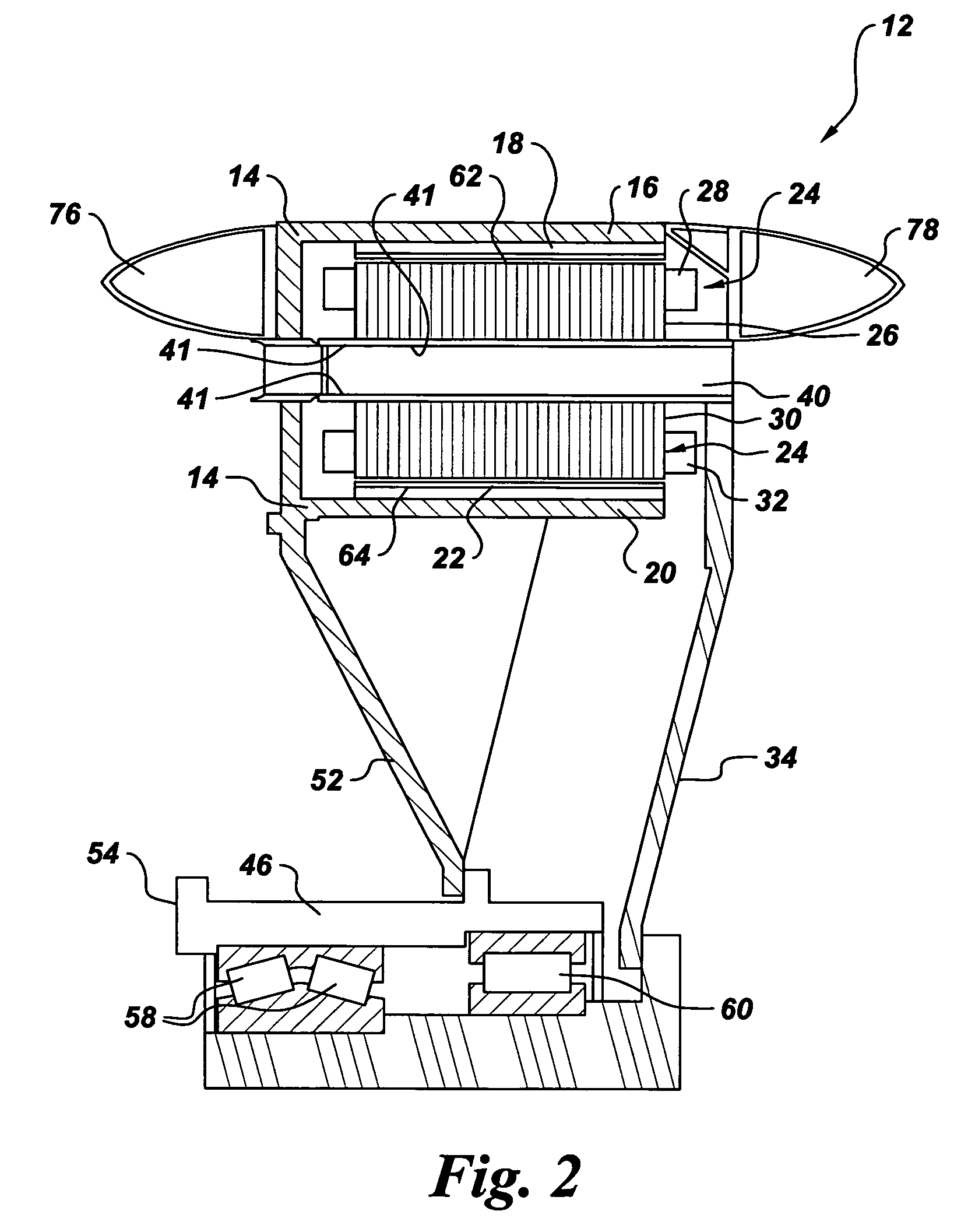
Transducer and transducer module
InactiveUS20130069483A1Enhanced Haptic FeedbackEnhance propagationMagnetic circuit rotating partsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerAcoustic propagation
Transducers and transducer modules having the transducers are disclosed. An embodiment discloses a transducer that includes a conductive layer having a U-shaped slit toward its swing end. The slit is configured to enhance a haptic feedback or an acoustic propagation, or adjust a resonant mode.
Owner:CHIEF LAND ELECTRONICS CO LTD
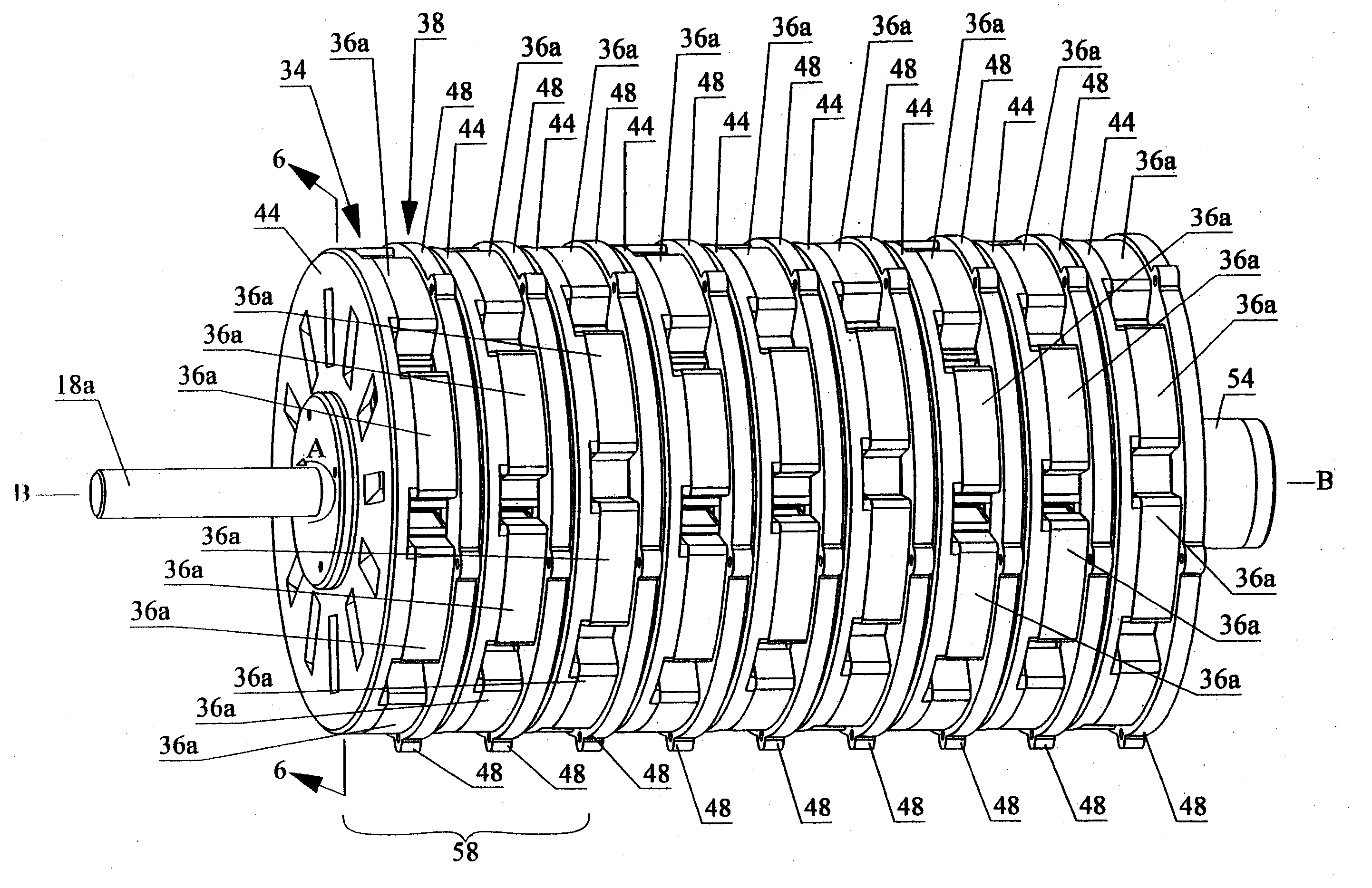
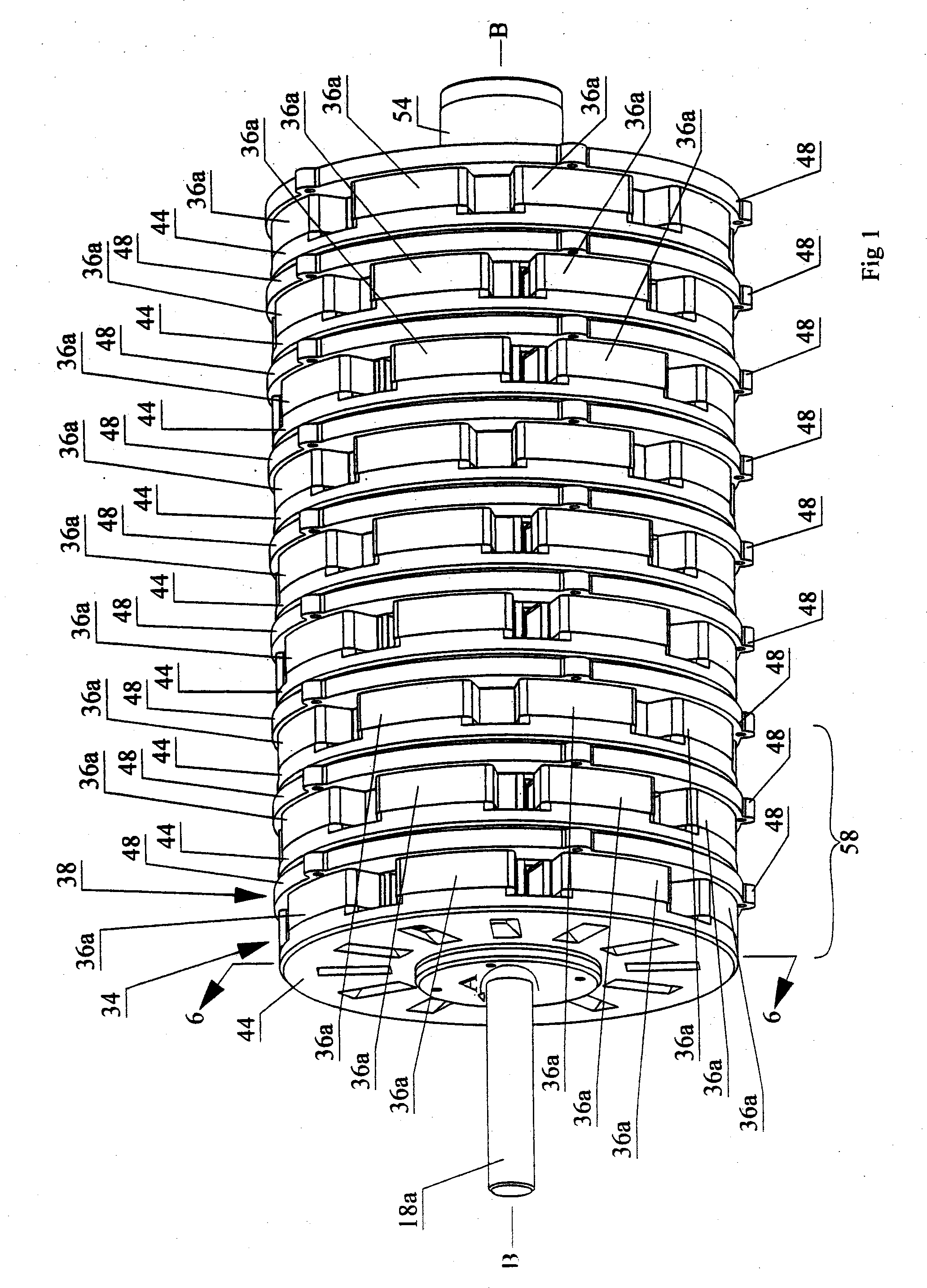
Variable magnetic flux electric rotary machine
InactiveUS20100164422A1Easy to operateWide operating speed rangeDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesElectrical polarityEngineering
An electric rotary machine is disclosed which can adjust relative angles of sub-rotors continuously and regardless of torque direction without generating an attractive force between the field magnets of the sub-rotors. The electric rotary machine includes: a stator having a winding; a dual rotor which is rotatably disposed with a gap from the stator and divided axially along a shaft into a first rotor and a second rotor each having field magnets with different polarities arranged alternately in a rotation direction; a mechanism for varying the axial position of the second rotor relative to the first rotor continuously; and a non-magnetic member located between the first rotor and the second rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Integrated electric drive unit including an electric motor and an electronic control and monitoring module
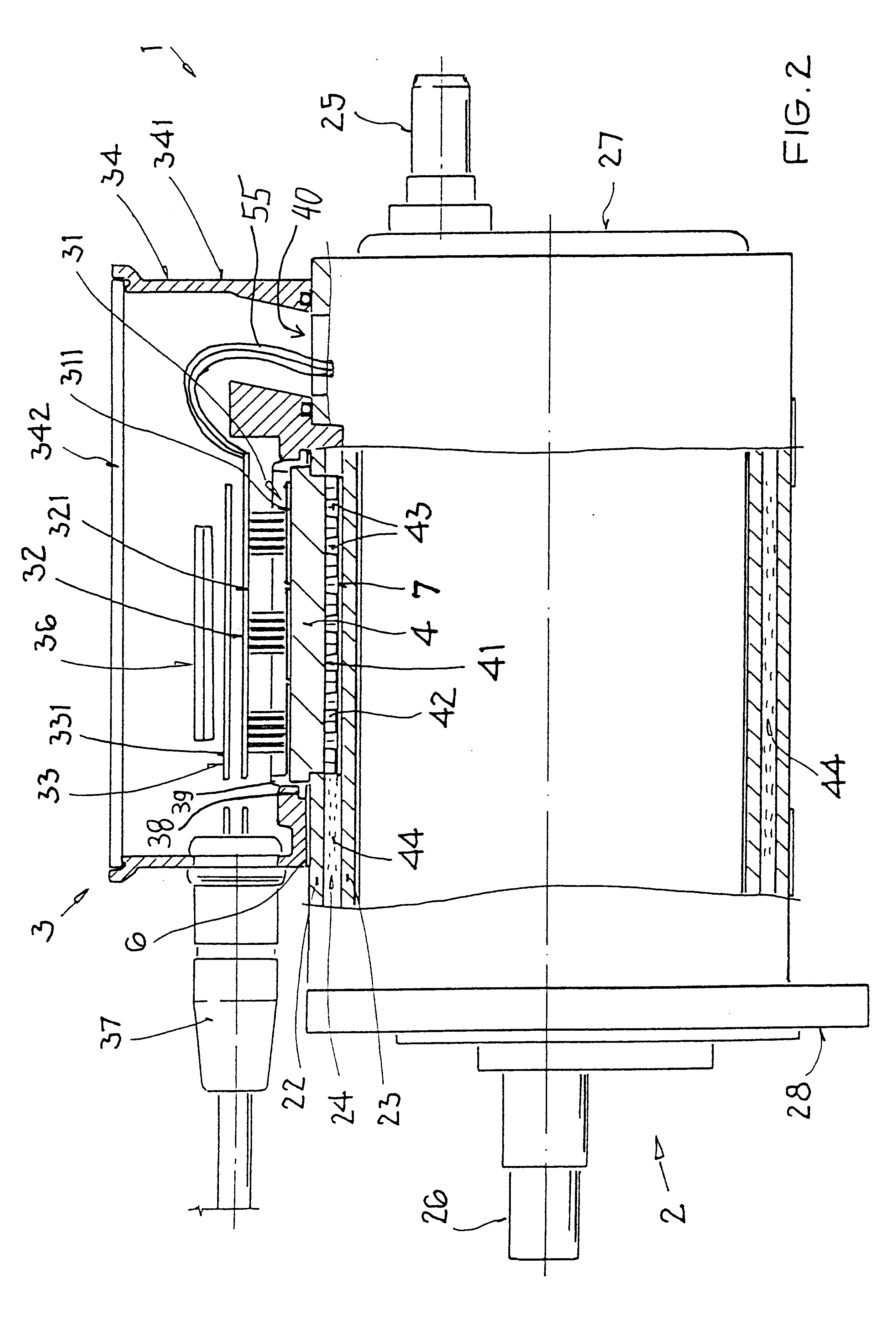
InactiveUS6198183B1Small structural installation volumeReduce manufacturing costAssociation with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectricityDouble wall
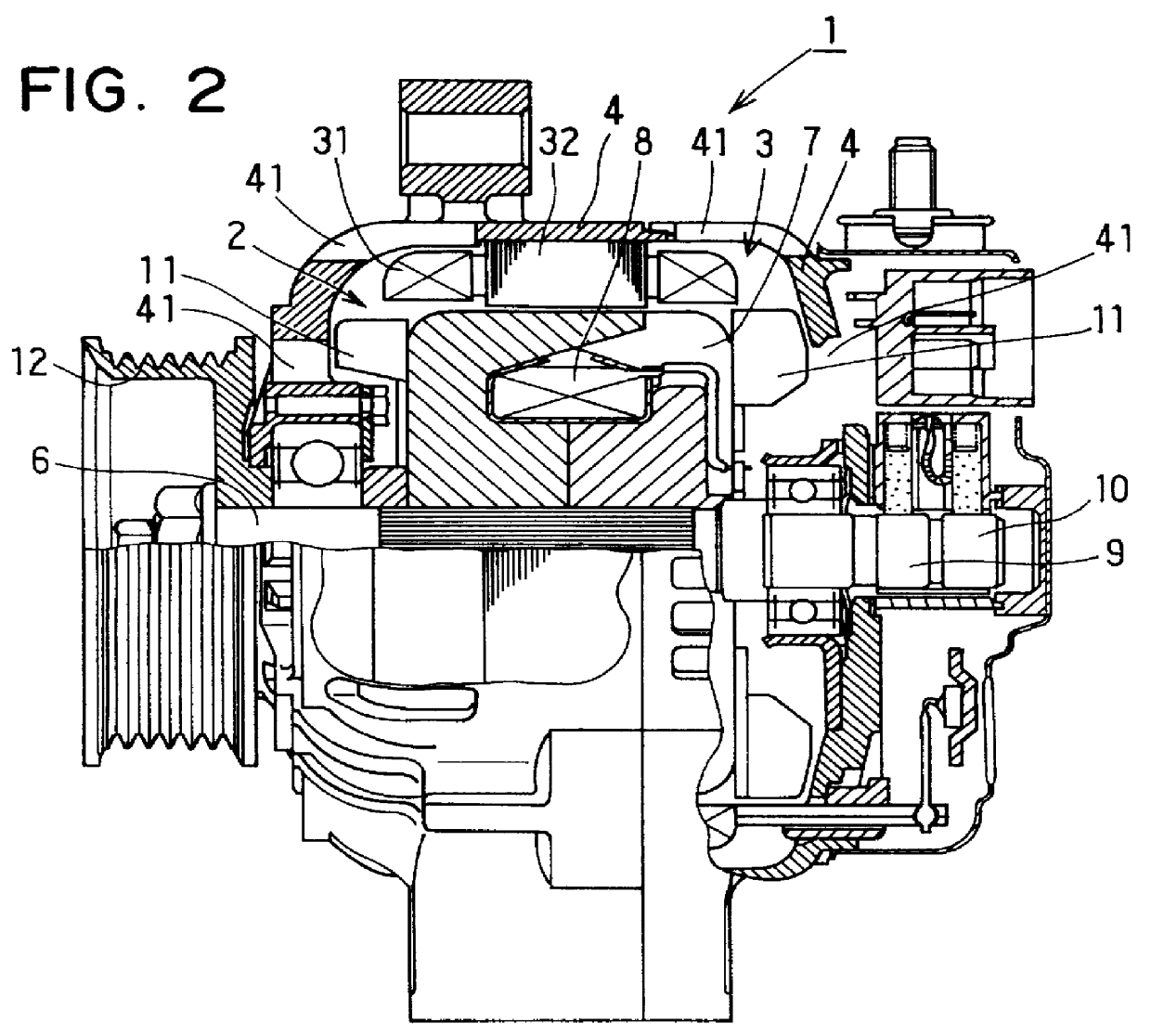
An electric drive unit includes an electronic control and monitoring module integrally connected to an electric motor. The housing of the electric motor has a double-walled construction to form a water jacket with cooling water passages therein. The electronic module includes at least one high power component that requires cooling. This component is mounted directly on a cooling insert that extends through a recess in the electronic module housing and is inserted in an opening provided in the outer wall of the motor housing. In this manner, the cooling insert is integrated into the water jacket of the motor housing and is directly cooled by the cooling water flowing in the cooling passages. A very compact and reliable construction is achieved, in which the electric motor and the electronic module share a common water cooling circuit. External water hoses and external electrical connections between the electric motor and the electronic module are avoided.
Owner:CONTI TEMIC MICROELECTRONIC GMBH
Magnetic coupling using halbach type magnet array
InactiveUS6841910B2Reduce leakageIncrease the magnetic field strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent-magnet clutches/brakesCouplingMagnetization
A magnetic coupling having two opposed annular arrays of angularly spaced permanent magnets magnetized to create magnetic north poles and magnetic south poles alternately spaced about each array. The north-pole and south-pole magnets of each array are tapered in cross-section from their surfaces at the gap to an annular surface of the array spaced from the gap, and permanent magnet spacer magnets completely fill in the space between the north-pole and south-pole magnets from the annular surface of the array at the gap to the spaced annular surface with the spacer magnets being magnetized generally transversely to the direction of magnetization of the adjacent north-pole, south-pole magnets so that the magnetic field created by the permanent magnets extends across the gap and annularly through each array to cause one of the arrays to rotate in synchronism with the other array.
Owner:QUADRANT TECH CORP
Motor rotor cooling with rotation heat pipes
InactiveUS20060066156A1Promote formationSmall sizeMagnetic circuit rotating partsCooling/ventillation arrangementInner loopEngineering
A heat pipe is partially-filled with a liquid, such as water, and is used to transfer heat from a rotating element, such as a rotor, via phase change and internal recycle of the liquid. Several heat pipes may be disposed radially around the rotating axis of the rotating element. The heat pipes may have a curved inner surface with a curvature not corresponding to the central axis of the heat pipe and positioned opposite the rotating axis so to experience greater centrifugal forces, to advance formation of a liquid film to improve heat transfer. For a rotor, the heat pipes, though individually placed as revolving heat pipes, in total exhibit behavior that approximates the favorable heat-transfer behavior of a single larger rotating heat pipe, but with heat-transfer surface area dispersed throughout the rotor, and without compromising structural integrity of the rotor shaft.
Owner:BALDOR ELECTRIC COMPANY
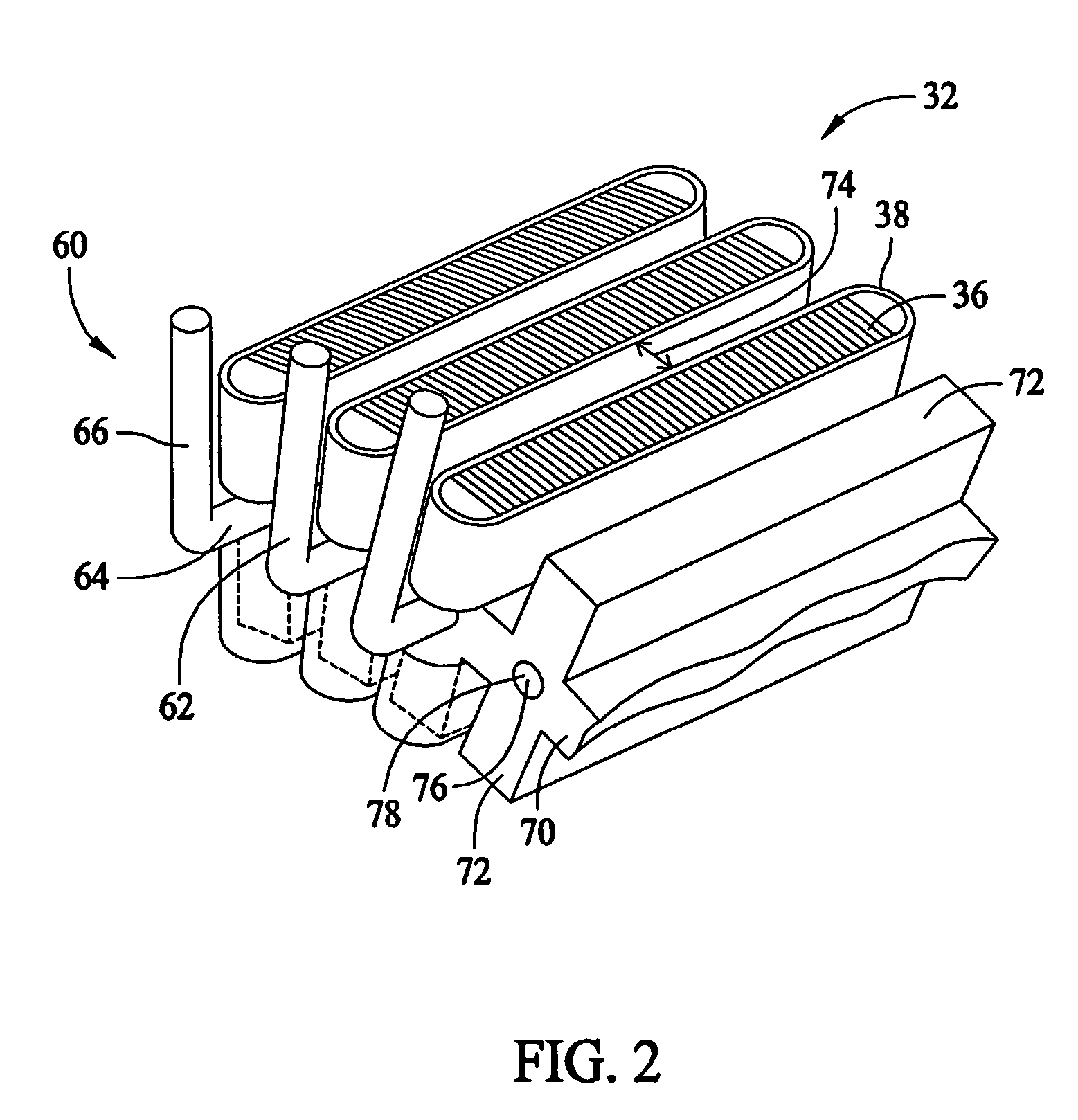
Conductor optimized axial field rotary energy device
ActiveUS7109625B1Association with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectrical conductorEngineering
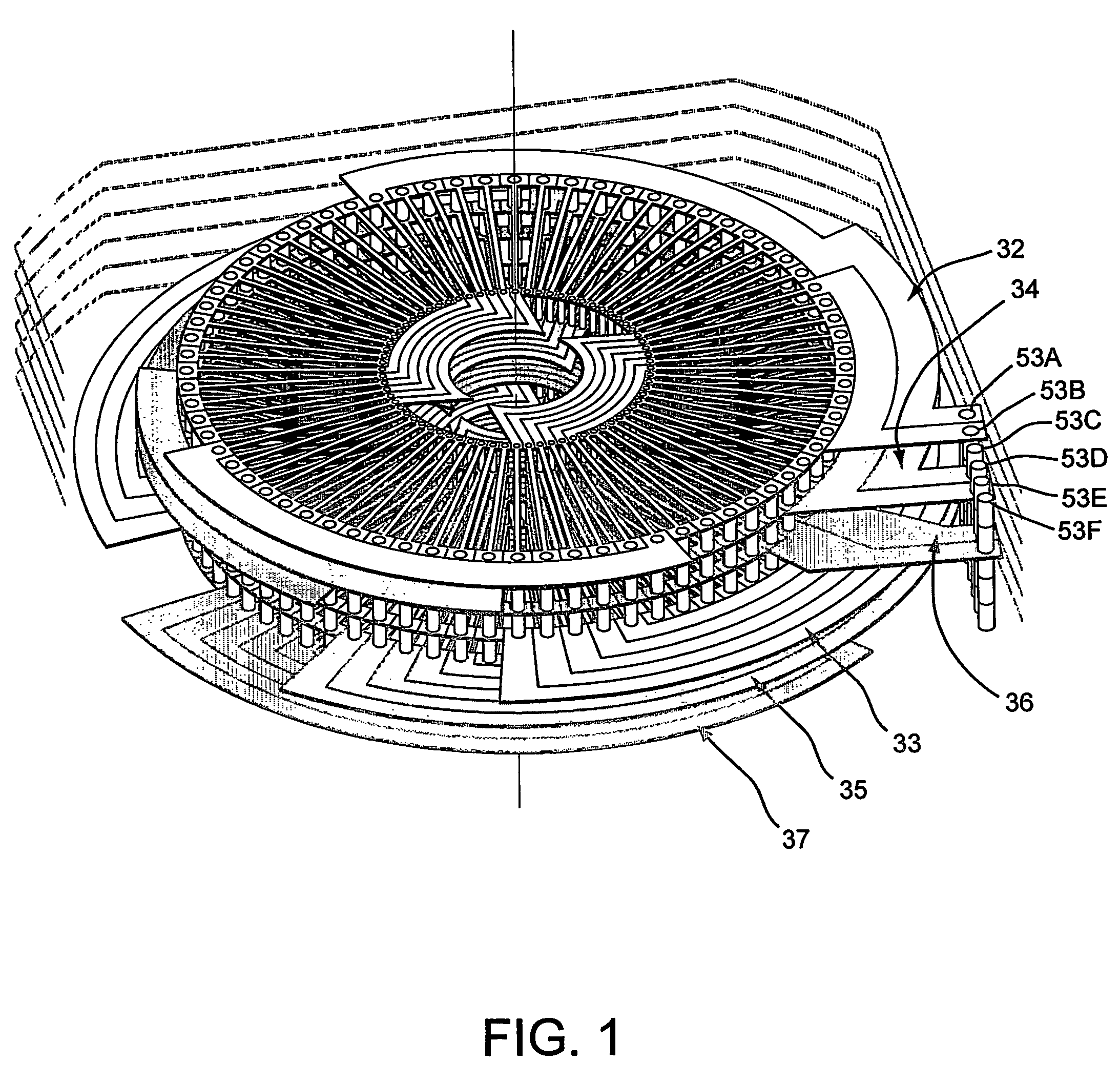
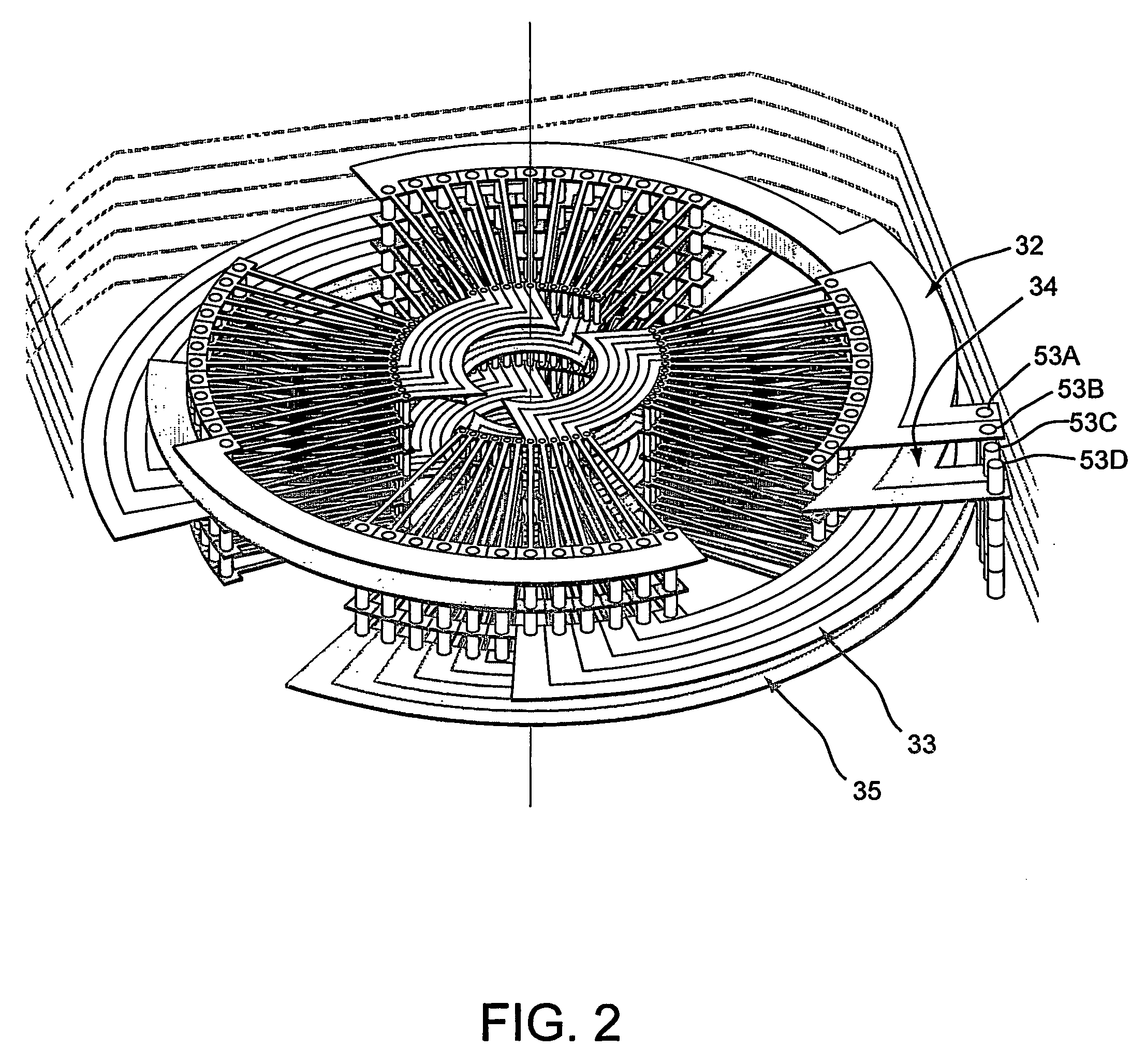
The present invention provides an axial rotary energy device which is arranged in a multi-phase electric current configuration. The device includes a rotor having a plurality of permanent magnet poles secured thereto and further includes a stator formed by stacking a plurality of printed circuit board working conductor layers together with a plurality of printed circuit board connecting layers. The stator having at least one working conductor layer for each phase of the electric current and at least one connecting conductor layer associated with one working conducting layer. The working conductor layer and the connecting conductor layer each having radial conductors extending from an inner diameter through-hole to an outer diameter through-hole. A plurality of via conductors are provided for electrically connecting selected ones of the radial connectors of the connecting conductor layer to selected ones of the radial connectors of the working conductor layers through the through-holes.
Owner:CORE MOTION
Motor mounted in a vehicle
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 02929 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 25, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 25, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 9, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 26700 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 24, 1997A motor mounted in a vehicle having a winding comprising a flat band-like copper wire is provided. The winding is wound on a projection that extends radially inward of a stator. The winding includes a first band-like section that is adapted to be wound on a radially inward portion of the projection of the stator. The winding also includes a connection section that is continuous with one longitudinal end of the first band-like section and extends radially outward along the radial direction of the projection of the stator. The winding further includes a second band-like section that is adapted to be wound on a radially outward portion of the projection of the stator. One longitudinal end of the second band-like section is continuous with the connection section. The first band-like section extends from a radially inward portion of the connection section and the second band-like section extends from a radially outward portion of the connection section. The first and second band-like sections extend from the connection section in opposite directions.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
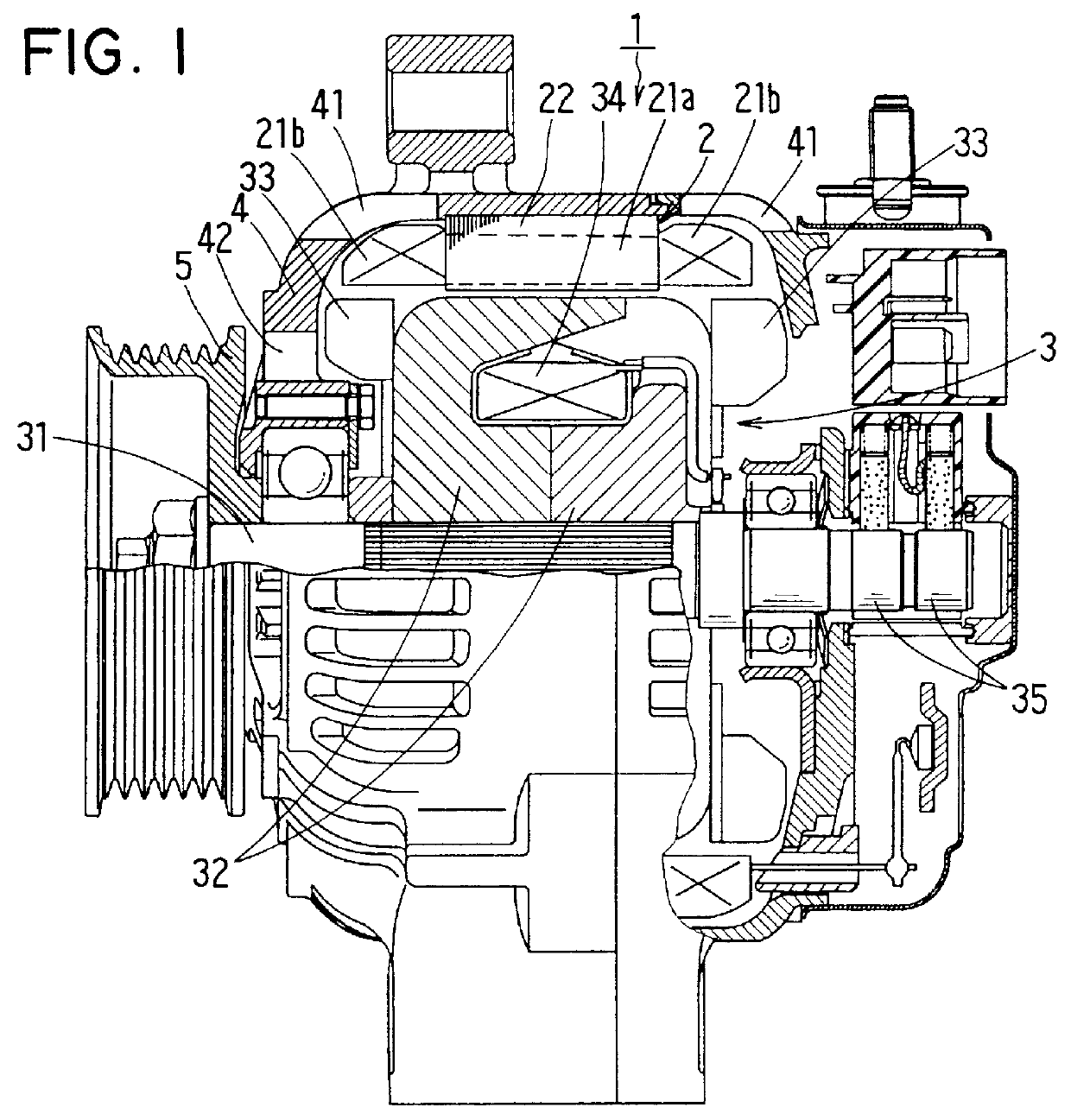
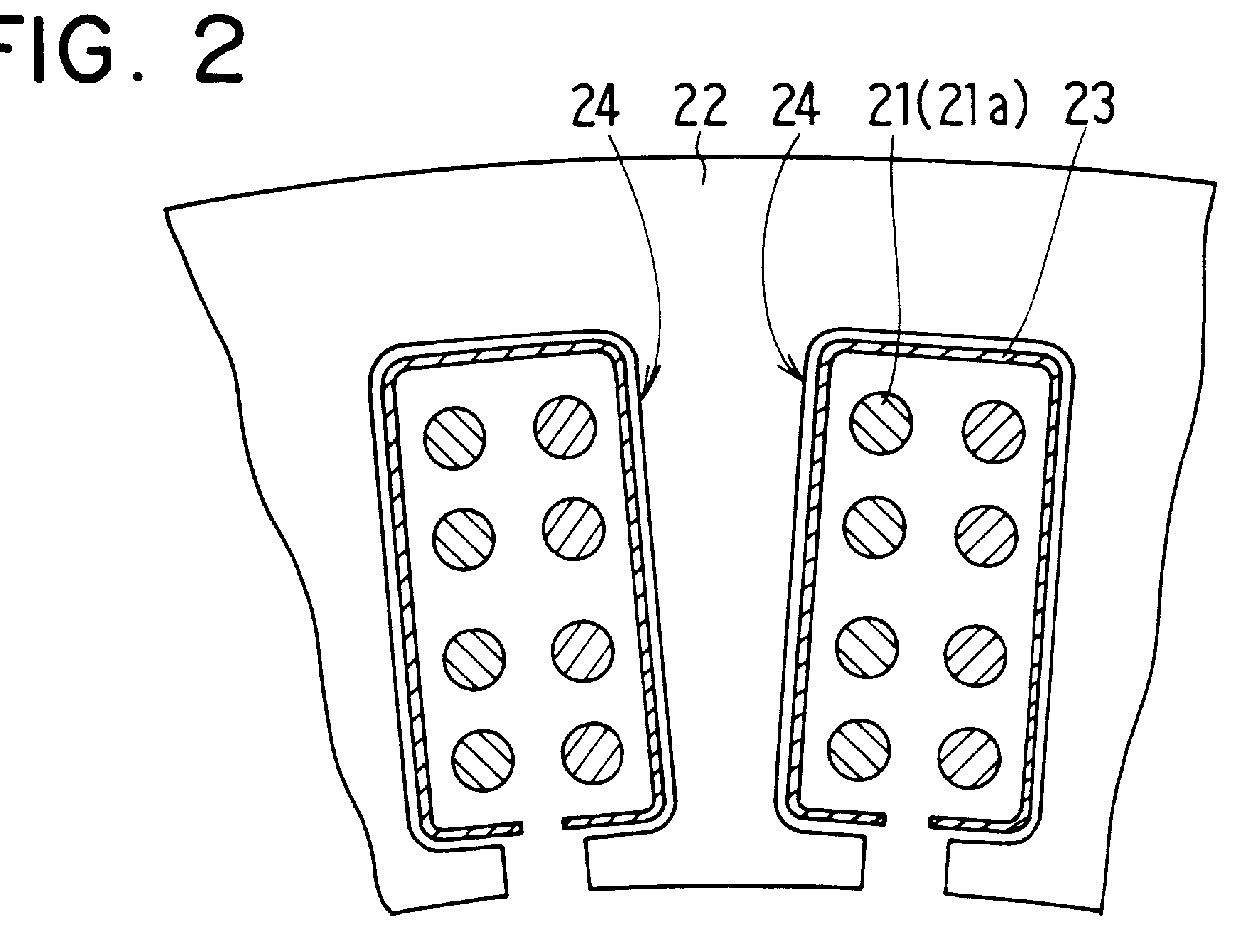
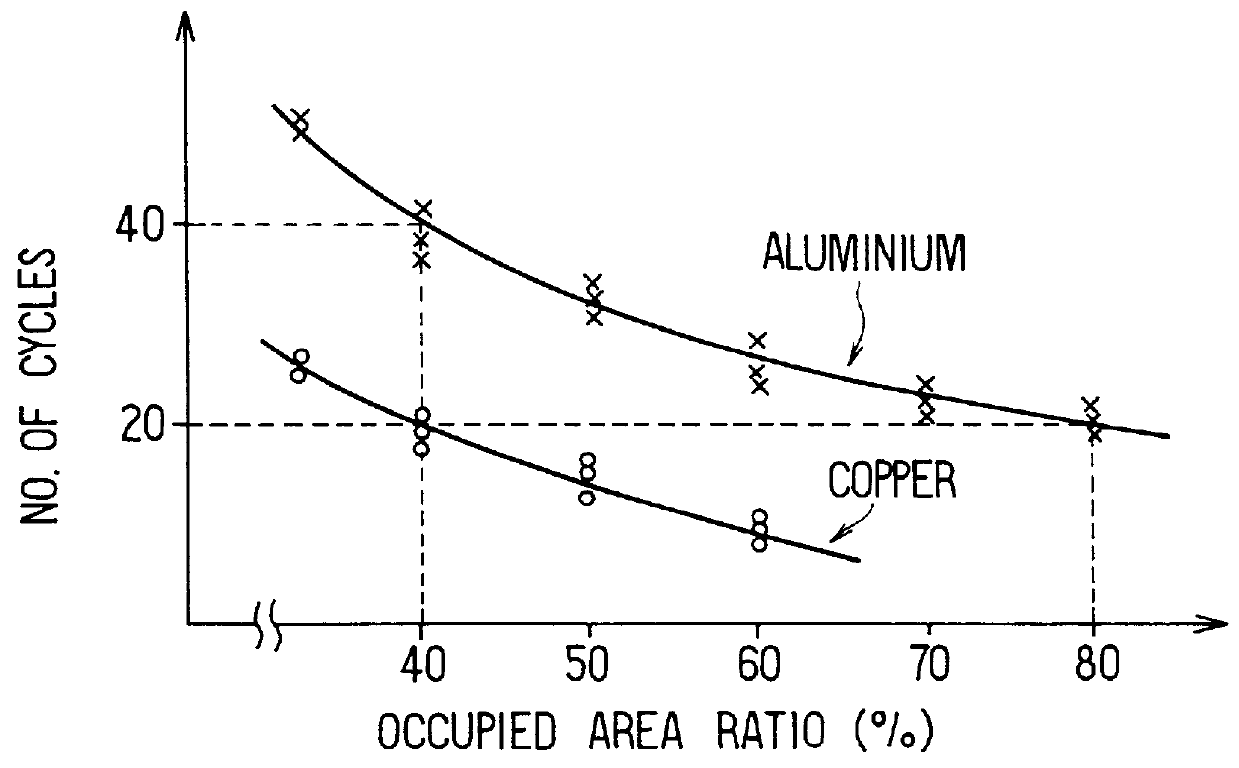
AC generator for vehicles
InactiveUS6137201ASynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsDynamoElectrical and Electronics engineering
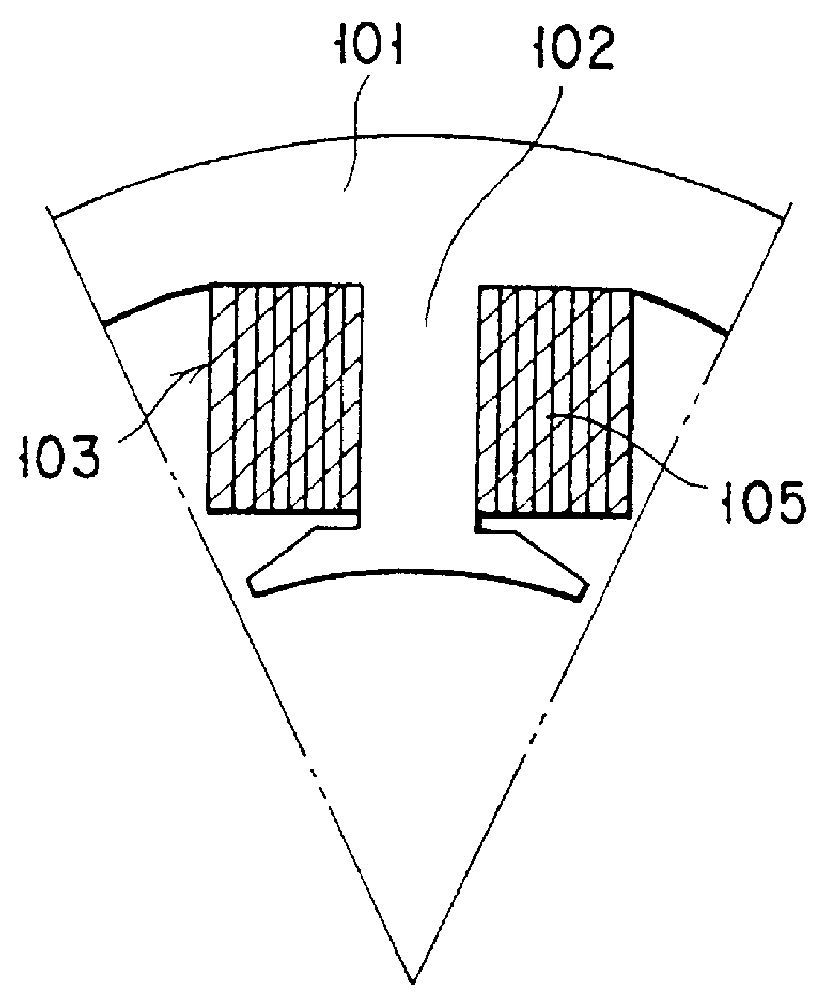
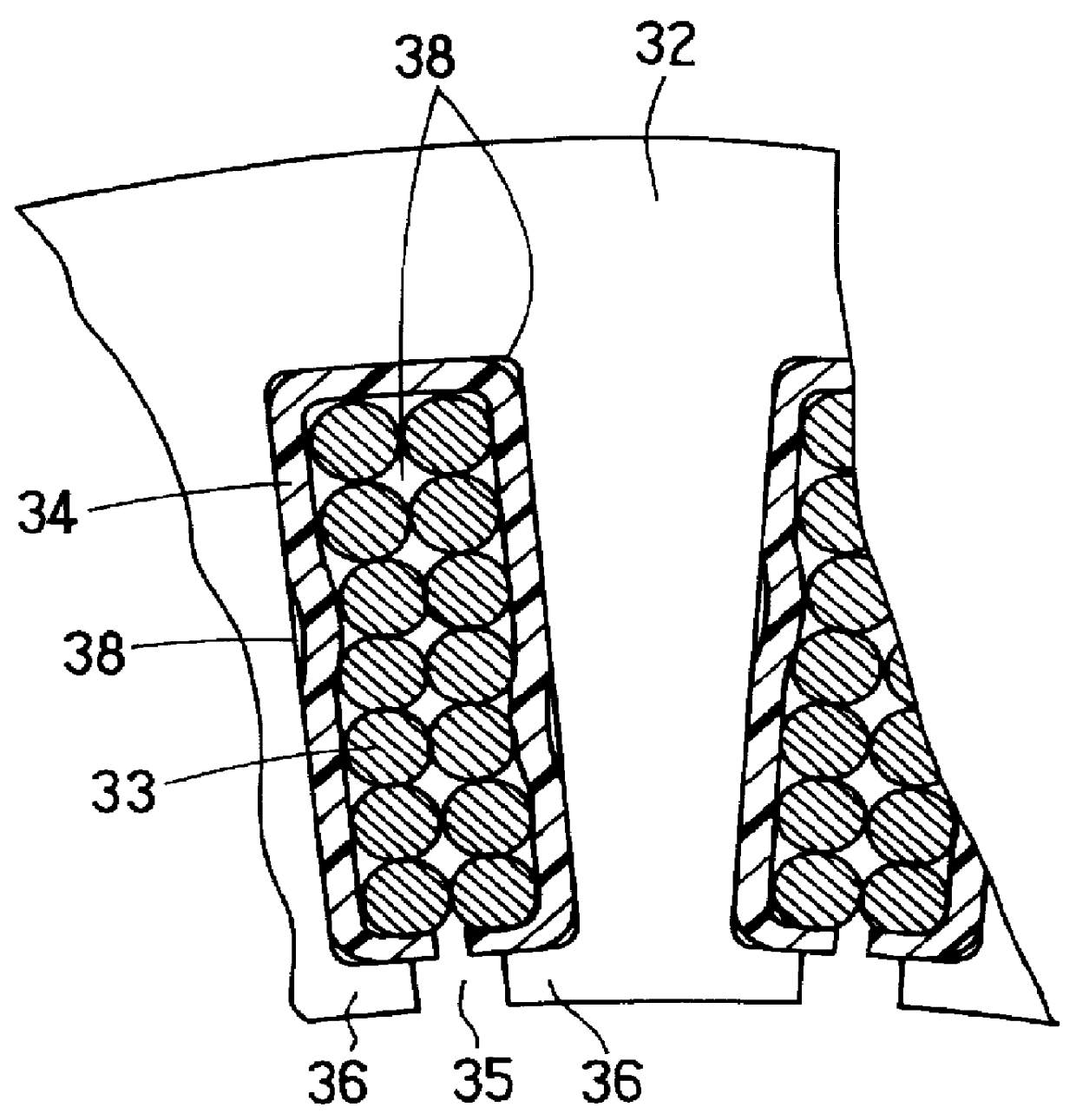
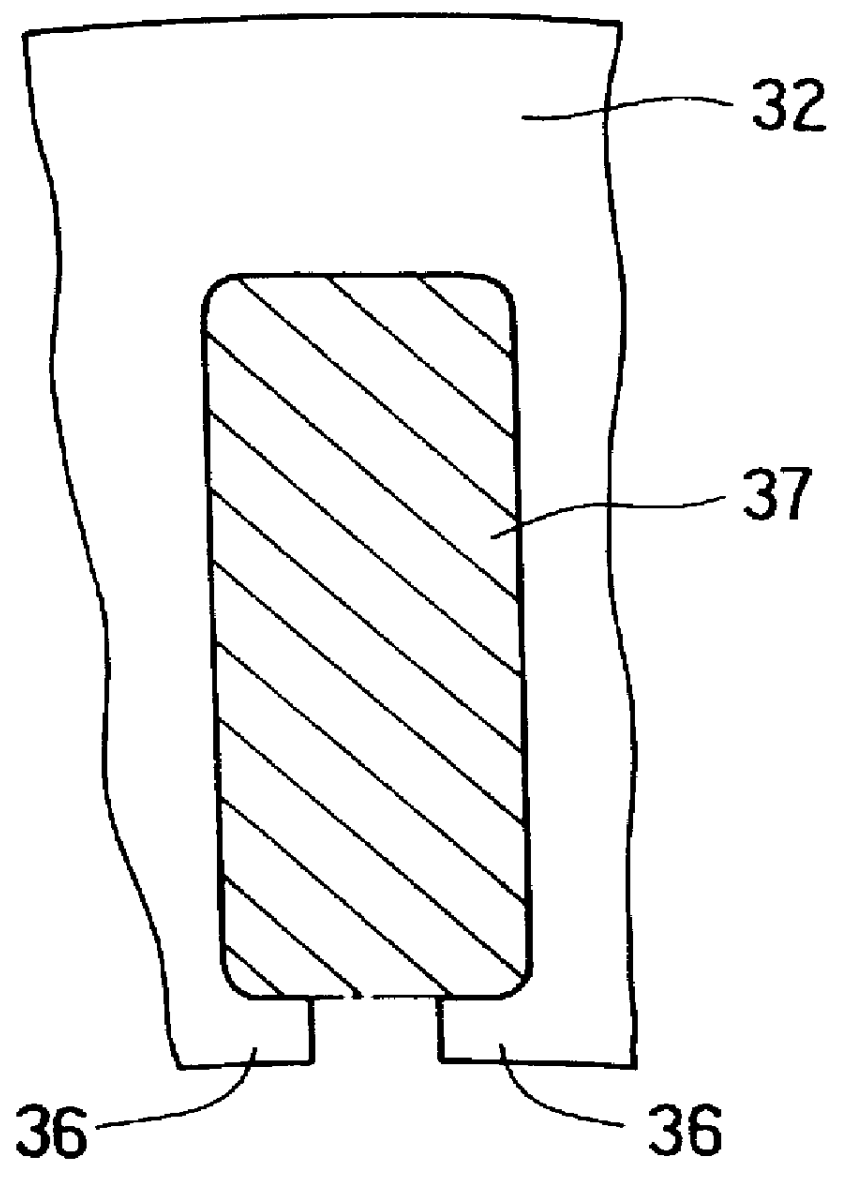
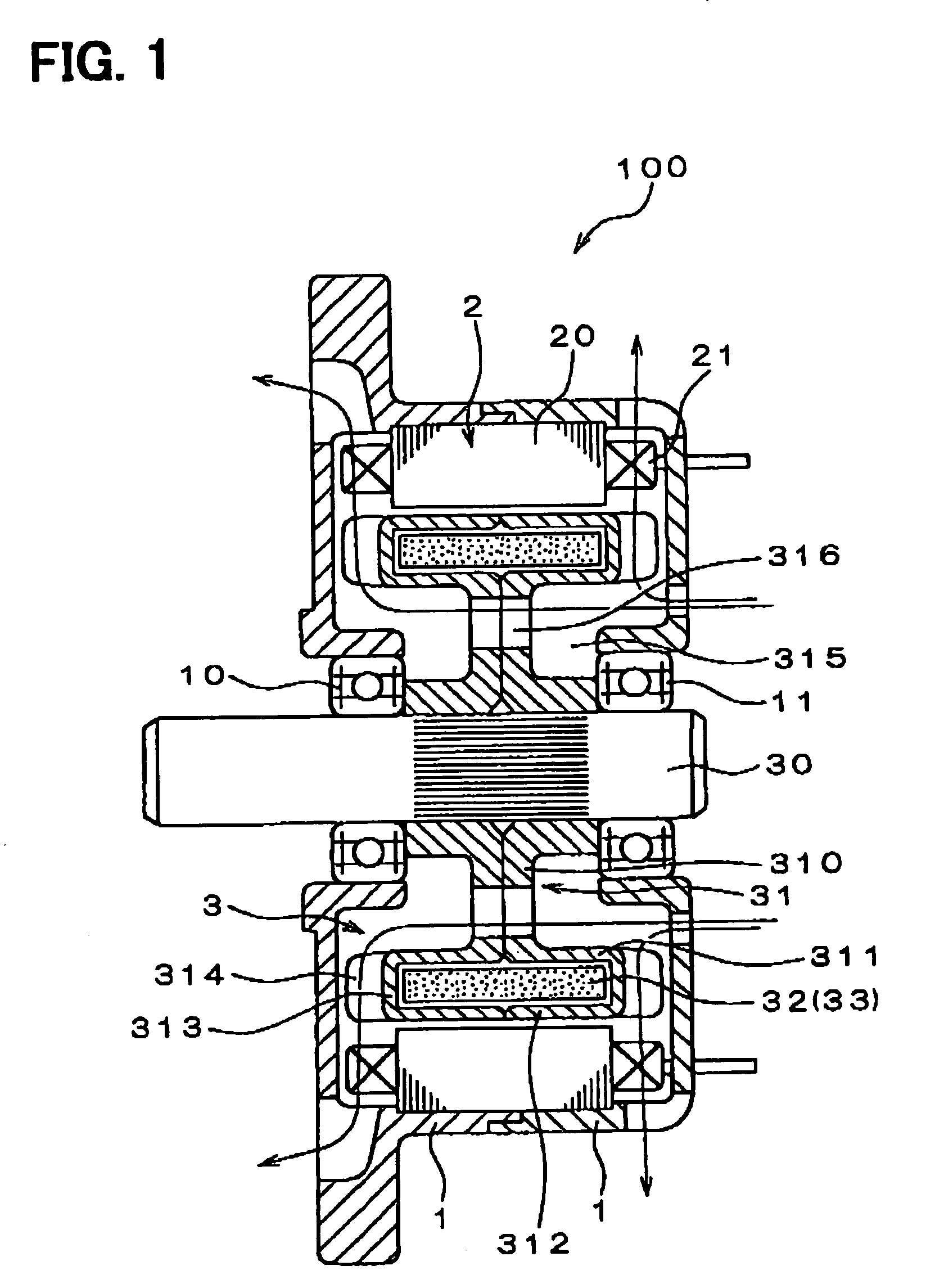
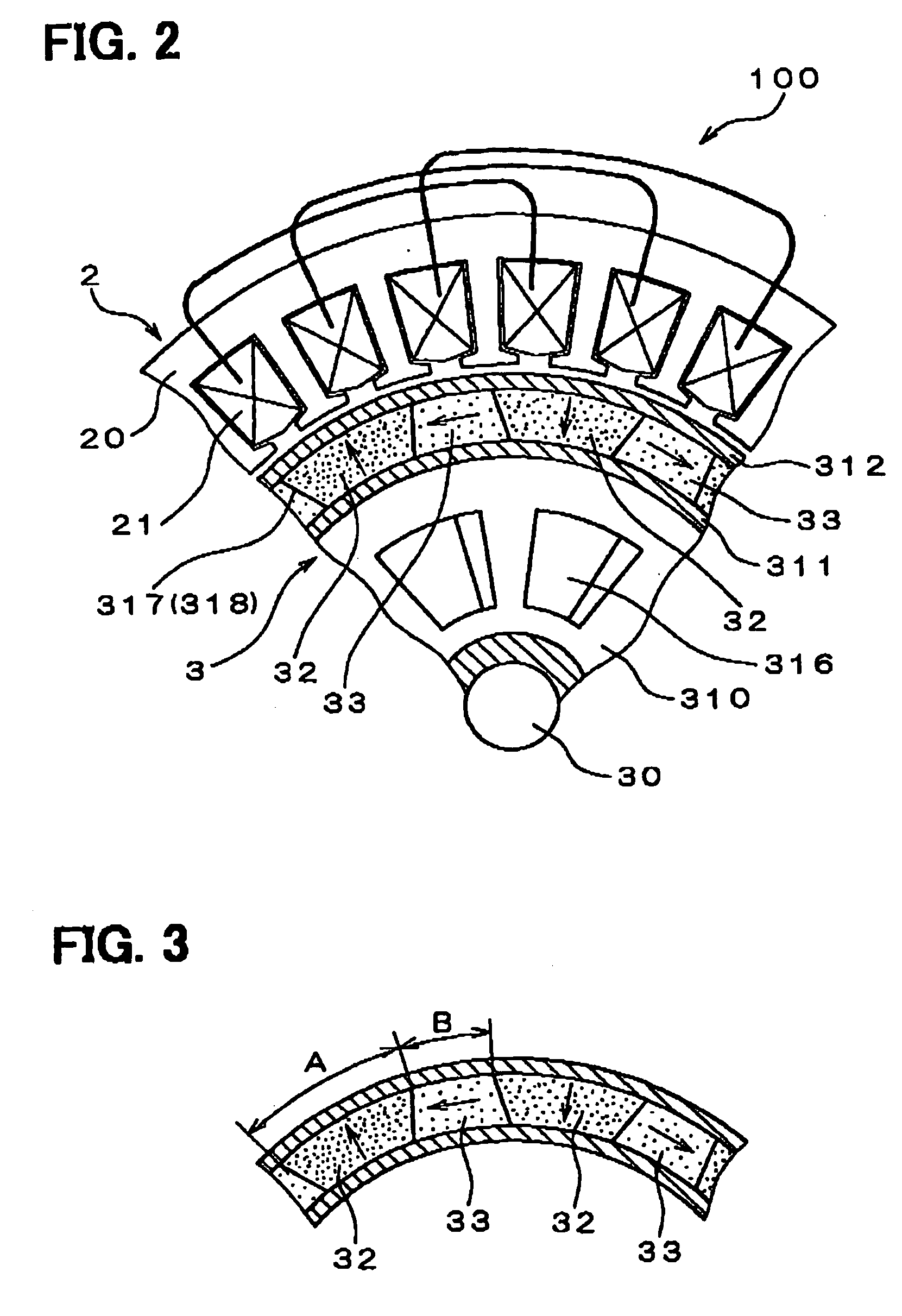
An AC generator for a vehicle including a rotor with a fan, a stator disposed around the outer periphery of the rotor, and a frame. The stator includes a laminated core having a plurality of slots, a plurality of electric conductors in the slots, and an insulator. There is a gap between the electric conductors and the insulator in a diametrical section of the slots, and an area ratio of the gap with respect to the sectional area of the slots is not more than 25%. A portion of the electric conductor positioned within the slot has a substantially rectangular shape along the shape of the slot.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electrical machine with double-sided stator
InactiveUS20060071575A1Increase rated powerReduce the overall diameterAsynchronous induction motorsMachines/enginesMarine propulsionTurbine
Machines useful for wind turbine and ship propulsion purposes include a wind turbine generator or a ship propulsion motor with two concentric air gaps. In one embodiment, the machine includes a rotor with an inner rotor core and an outer rotor core; and a double-sided stator with an inner stator side and an outer stator side. The double-sided stator is concentrically disposed between the inner rotor core and the outer rotor core.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
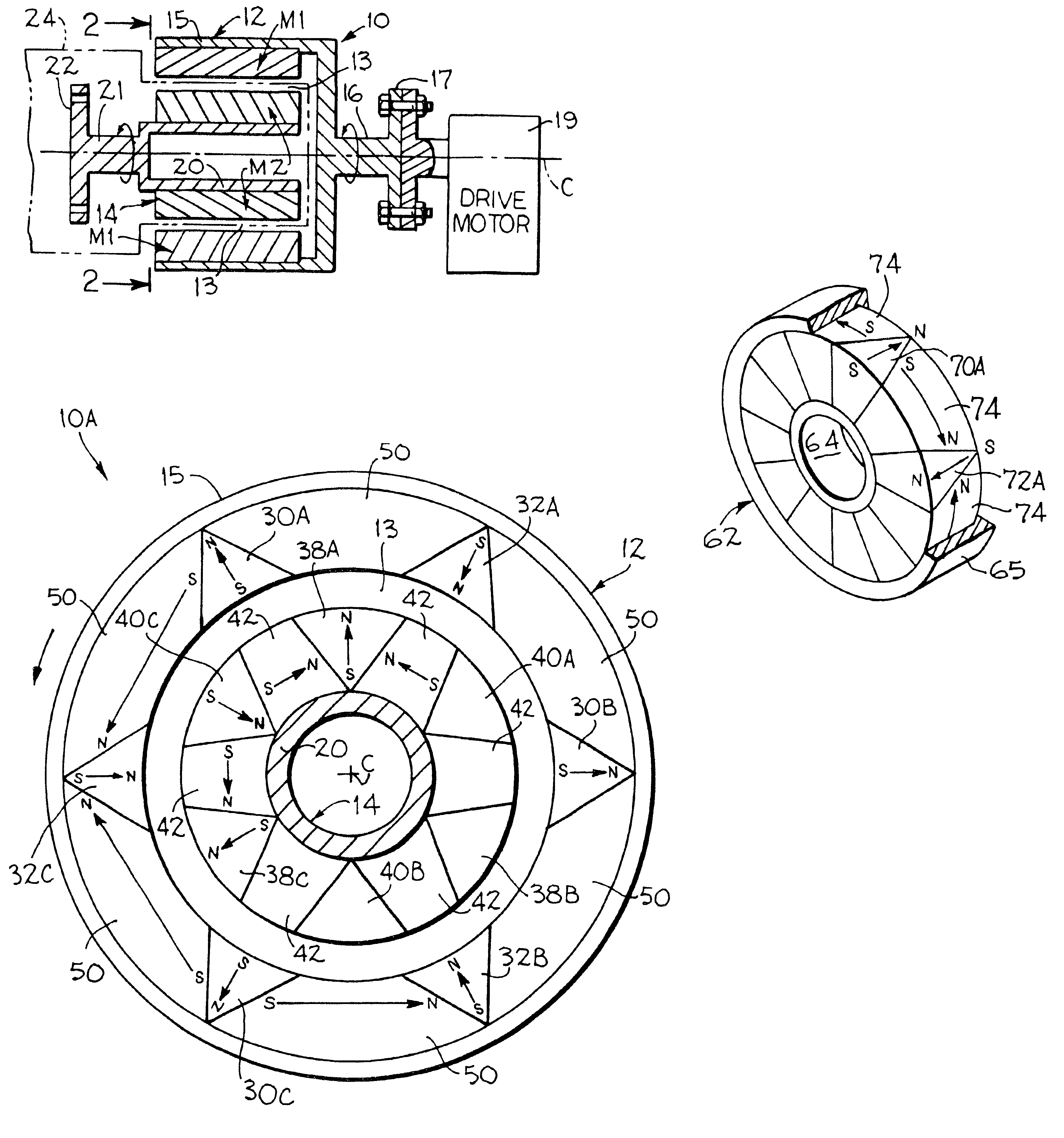
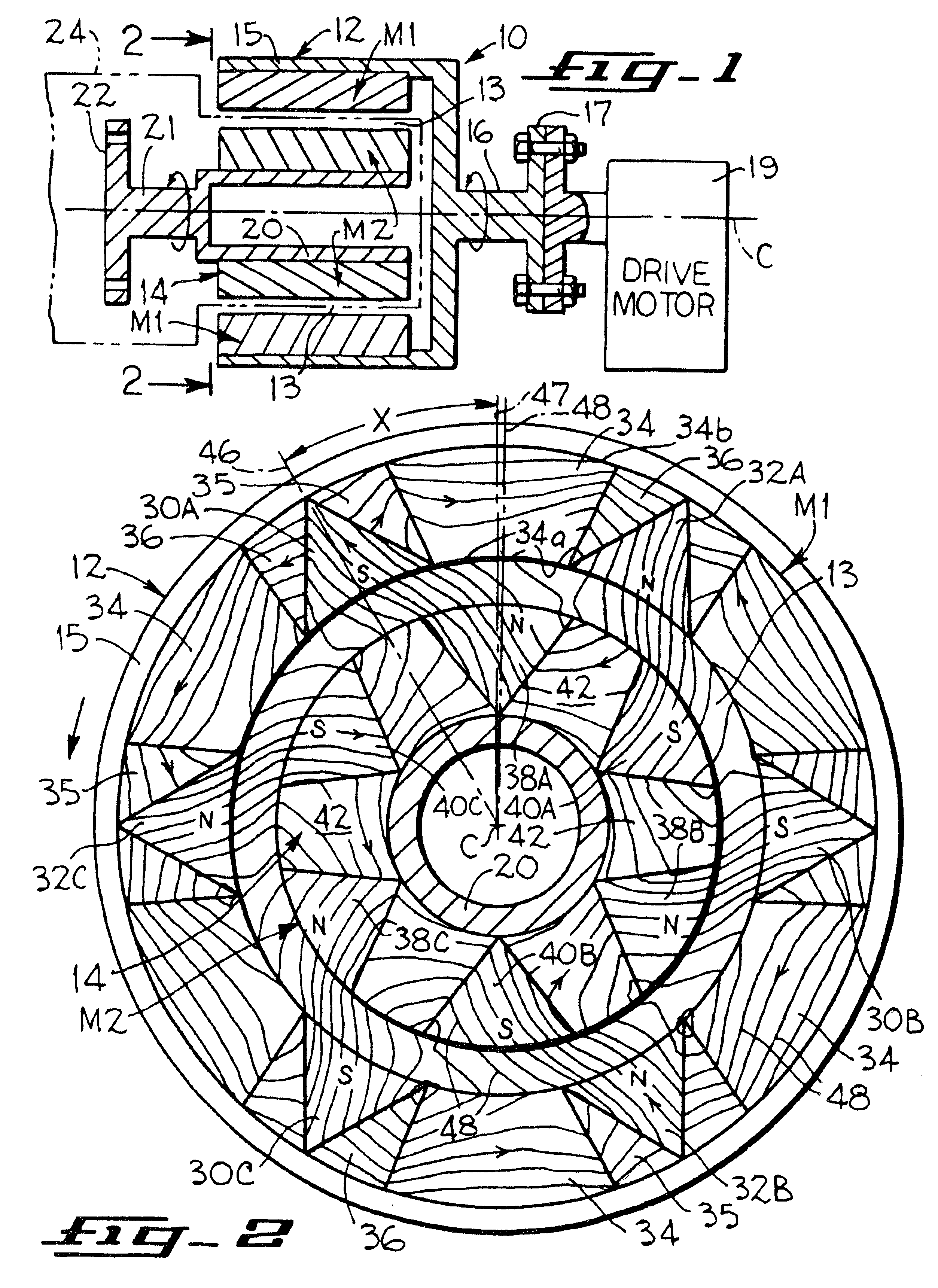
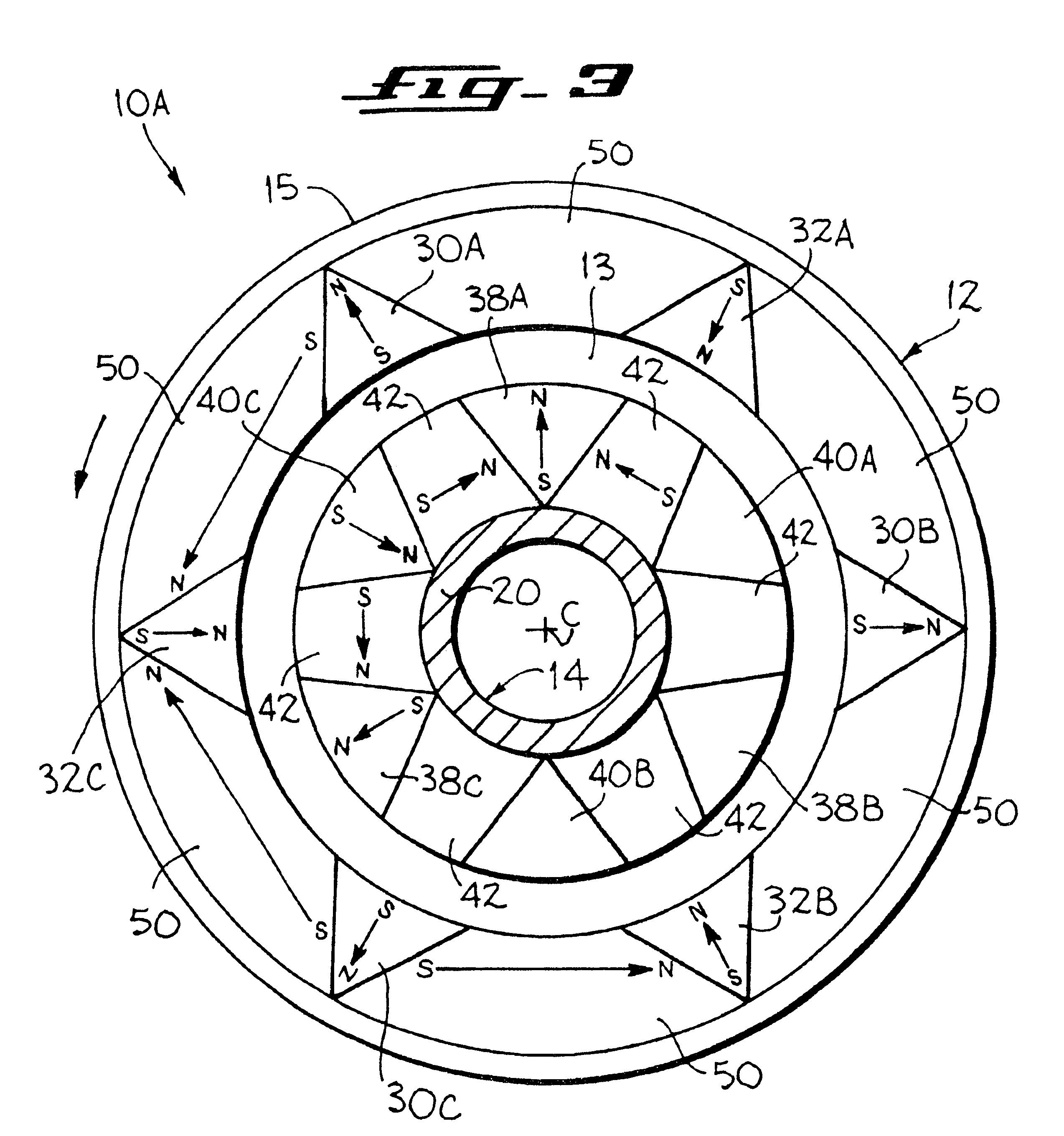
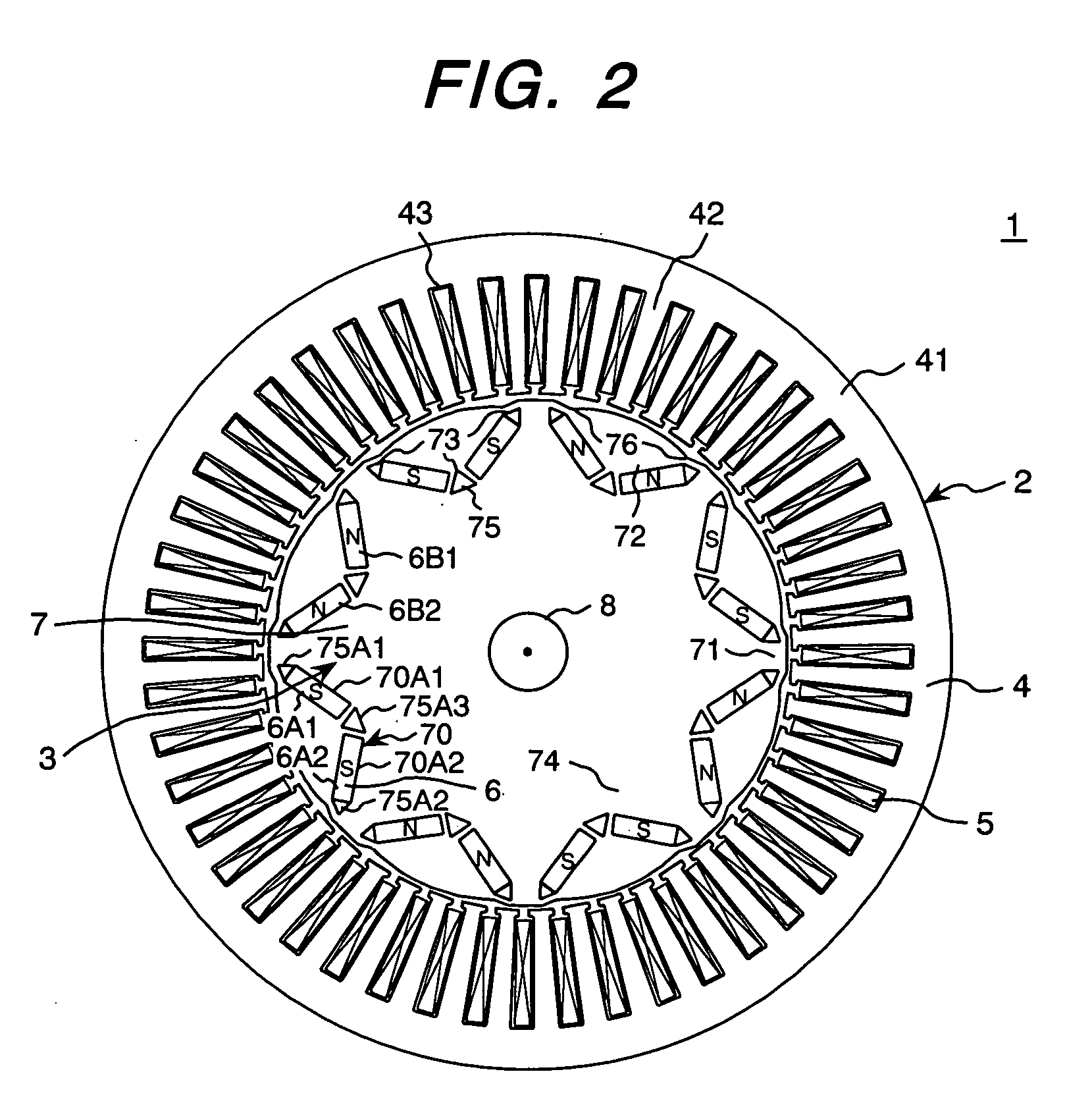
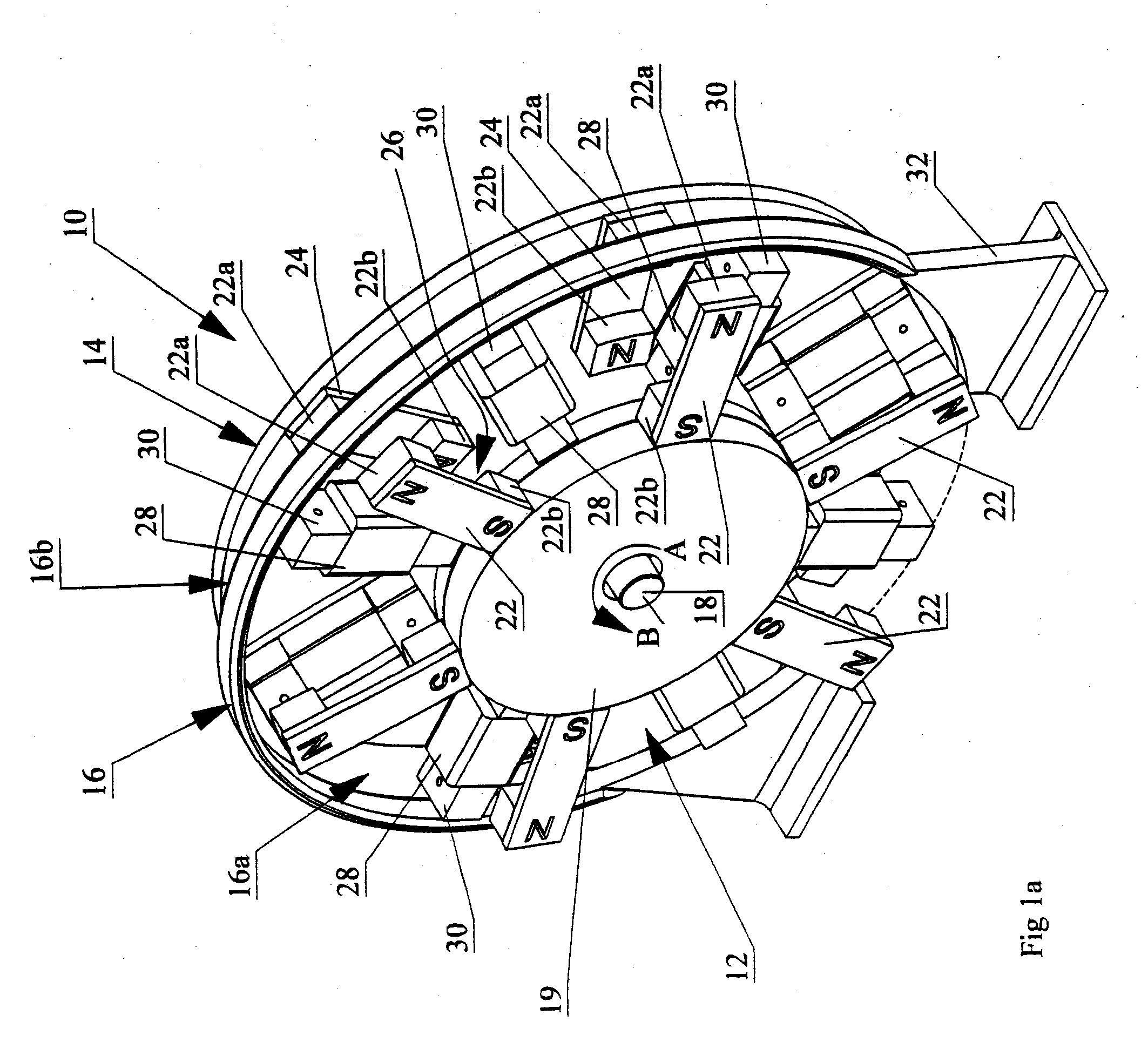
Permanent magnet electric rotating machine and electromotive vehicle using permanent magnet electric rotating machine
InactiveUS6208054B1Reduce pulsationMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetic flux density distribution
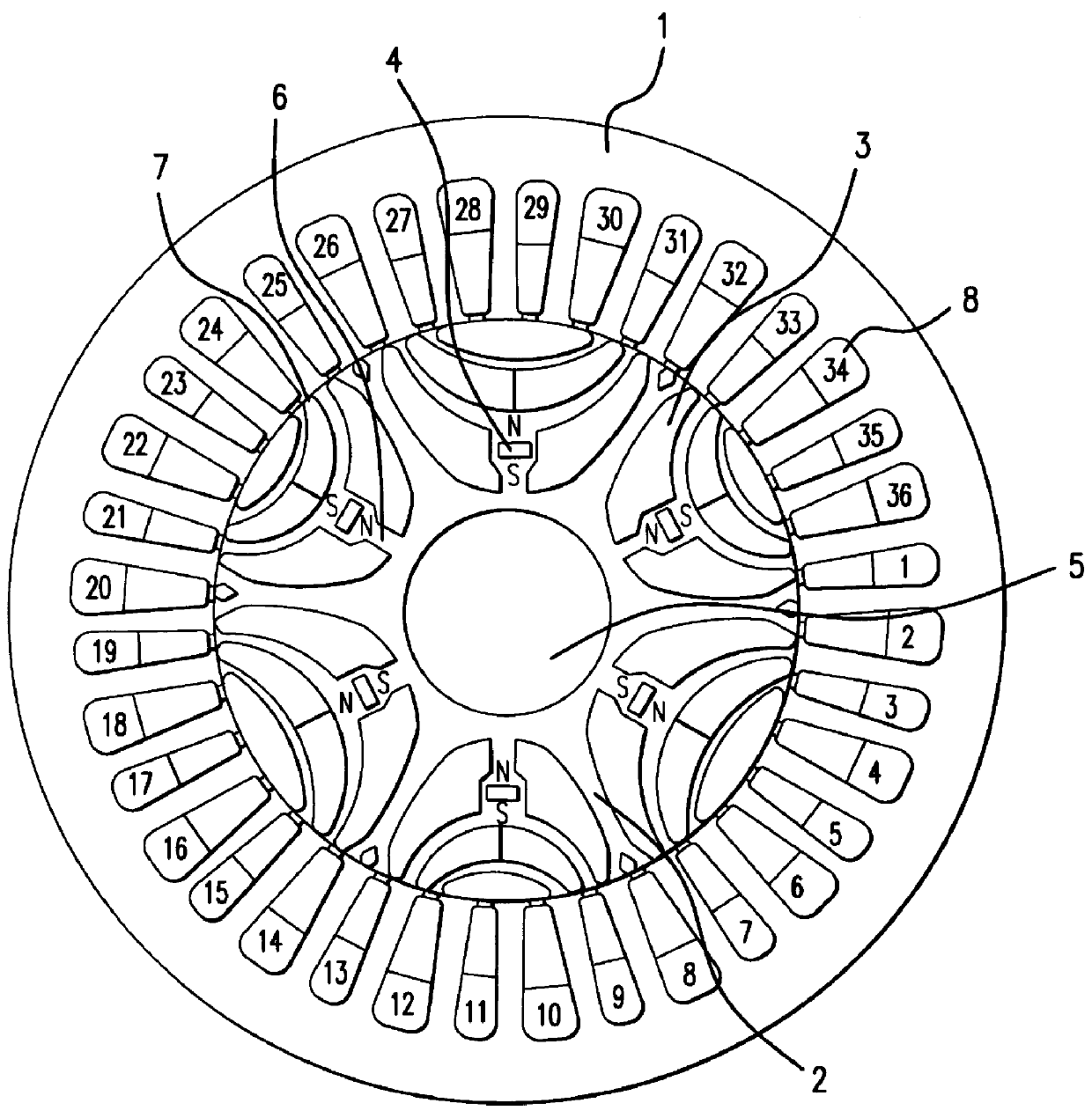
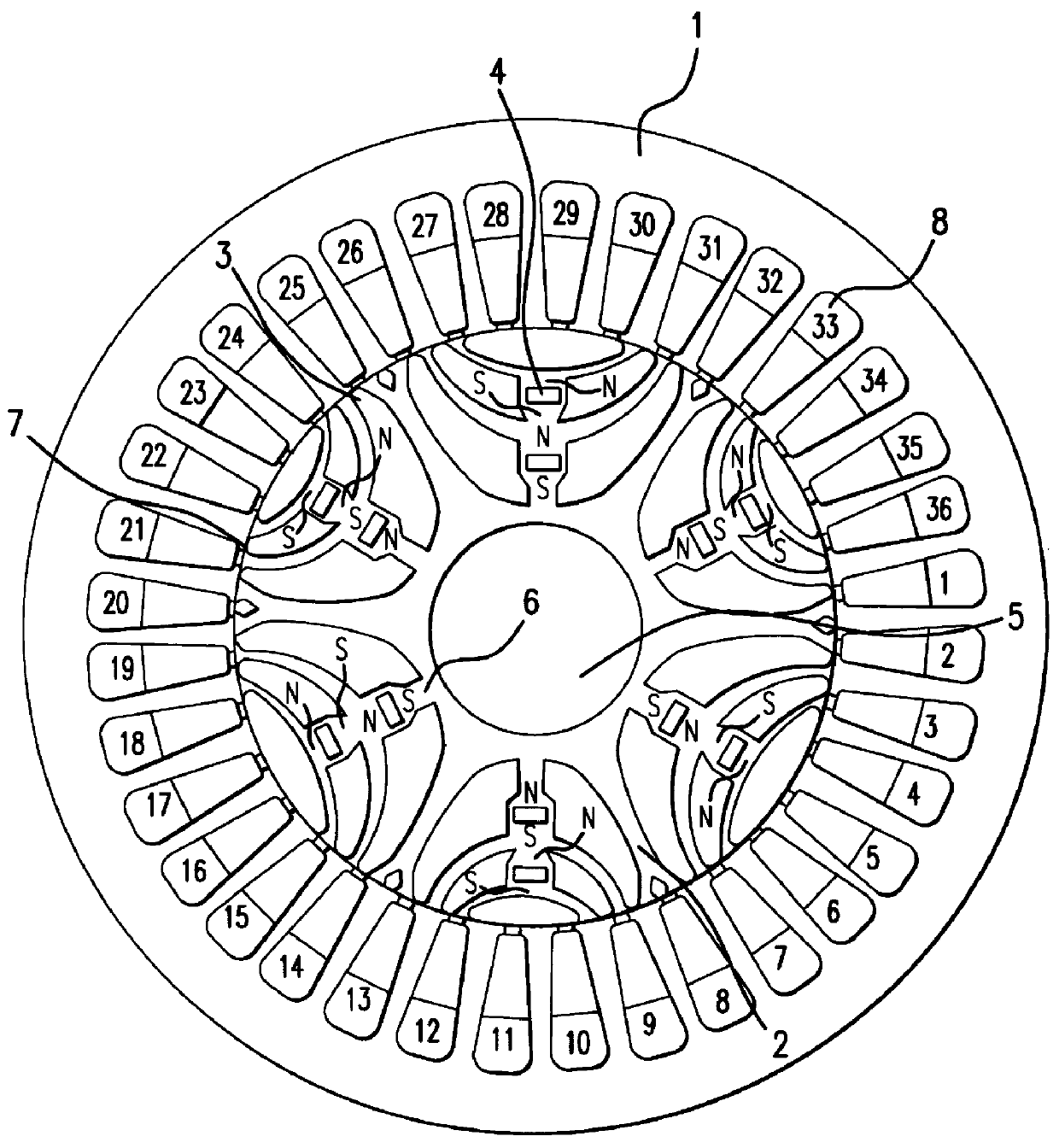
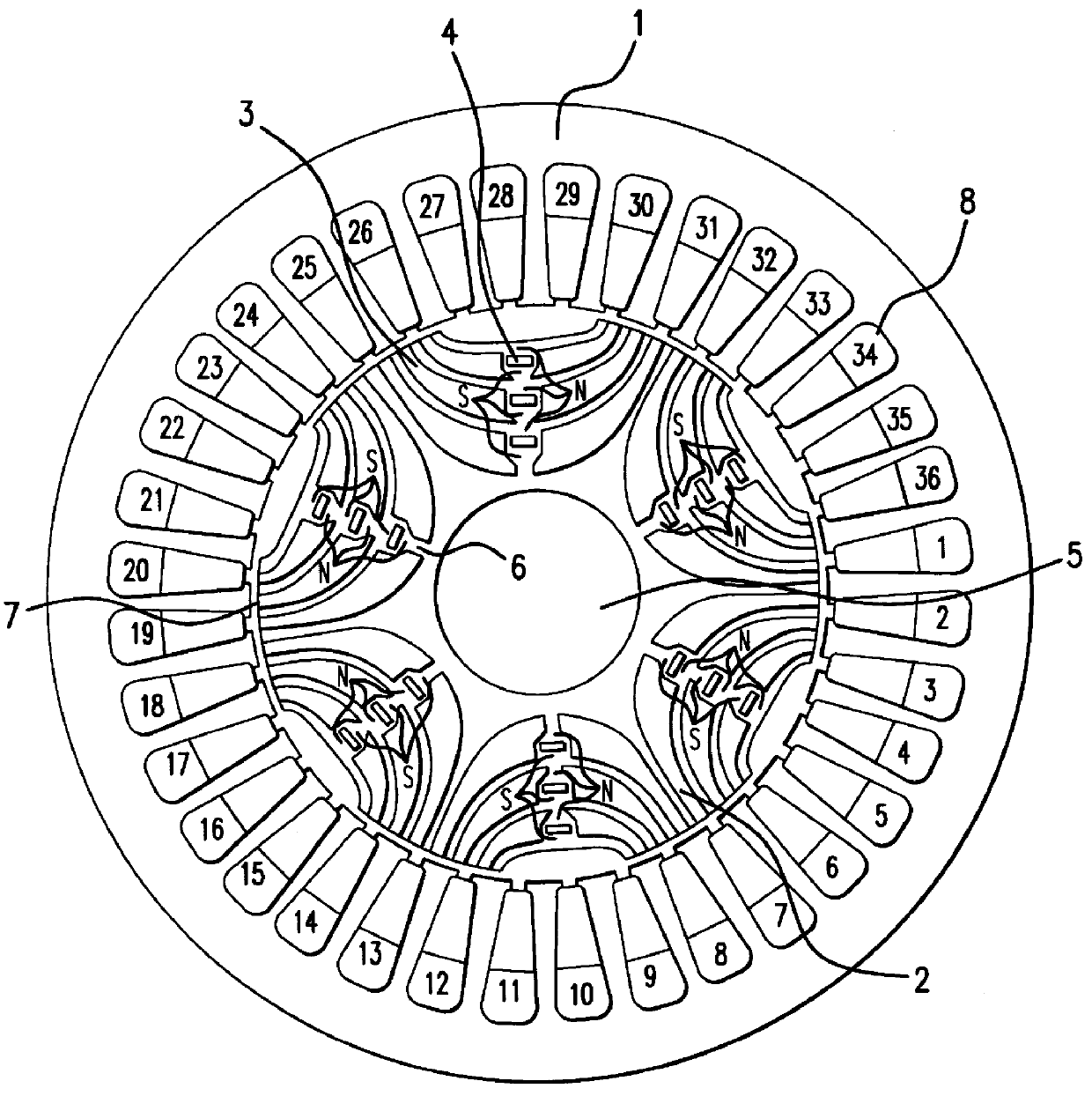
A magnetic gap is provided between a permanent magnet of a rotor and an auxiliary magnetic pole portion which is arranged adjacent to the permanent magnet in a peripheral direction. A gradual change in a magnetic flux density distribution of a surface of the rotor is obtained and a cogging torque and a torque pulsation are restrained. By obtaining a reluctance torque according to the auxiliary magnetic pole, a permanent magnet electric rotating machine in which the cogging torque and the torque pulsation are restrained can be obtained and further an electromotive vehicle having the permanent magnet electric rotating machine can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Permanent magnet rotating electric machine and electric car using the same
ActiveUS20050200223A1Reduce vibrationReduce noiseSpeed controllerMagnetic circuit rotating partsPhysicsElectric cars
A permanent magnet rotating electric machine comprises a stator having stator windings wound round a stator iron core and a permanent magnet rotor having a plurality of inserted permanent magnets in which the polarity is alternately arranged in the peripheral direction in the rotor iron core. The rotor iron core of the permanent magnets is composed of magnetic pole pieces, auxiliary magnetic poles, and a stator yoke, and furthermore has concavities formed on the air gap face of the magnetic pole pieces of the rotor iron core of the permanent magnets, gently tilting from the central part of the magnetic poles to the end thereof. In a permanent magnet rotating electric machine, effects of iron loss are reduced, and an electric car using highly efficient permanent magnet rotating electric machine are realized.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
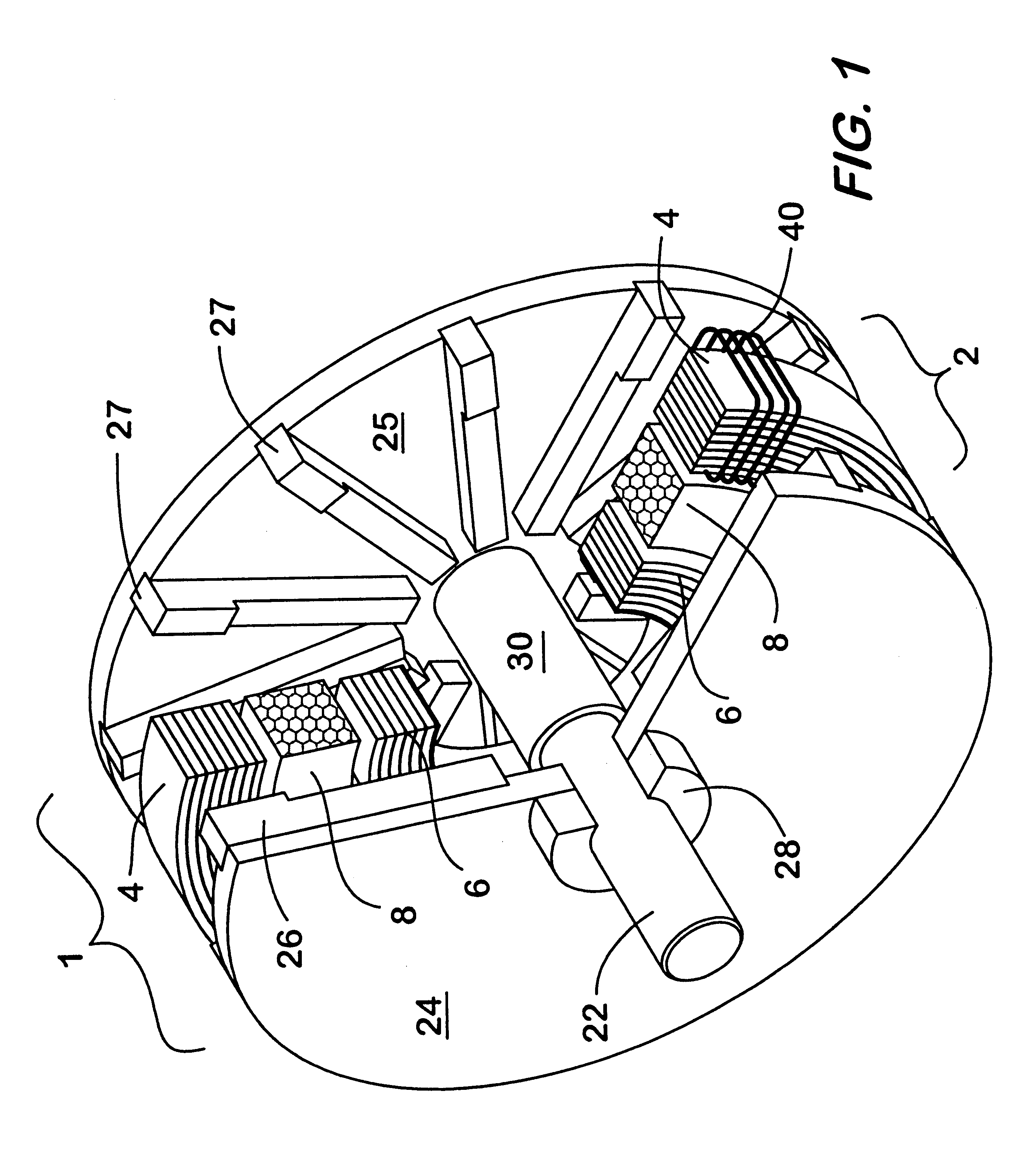
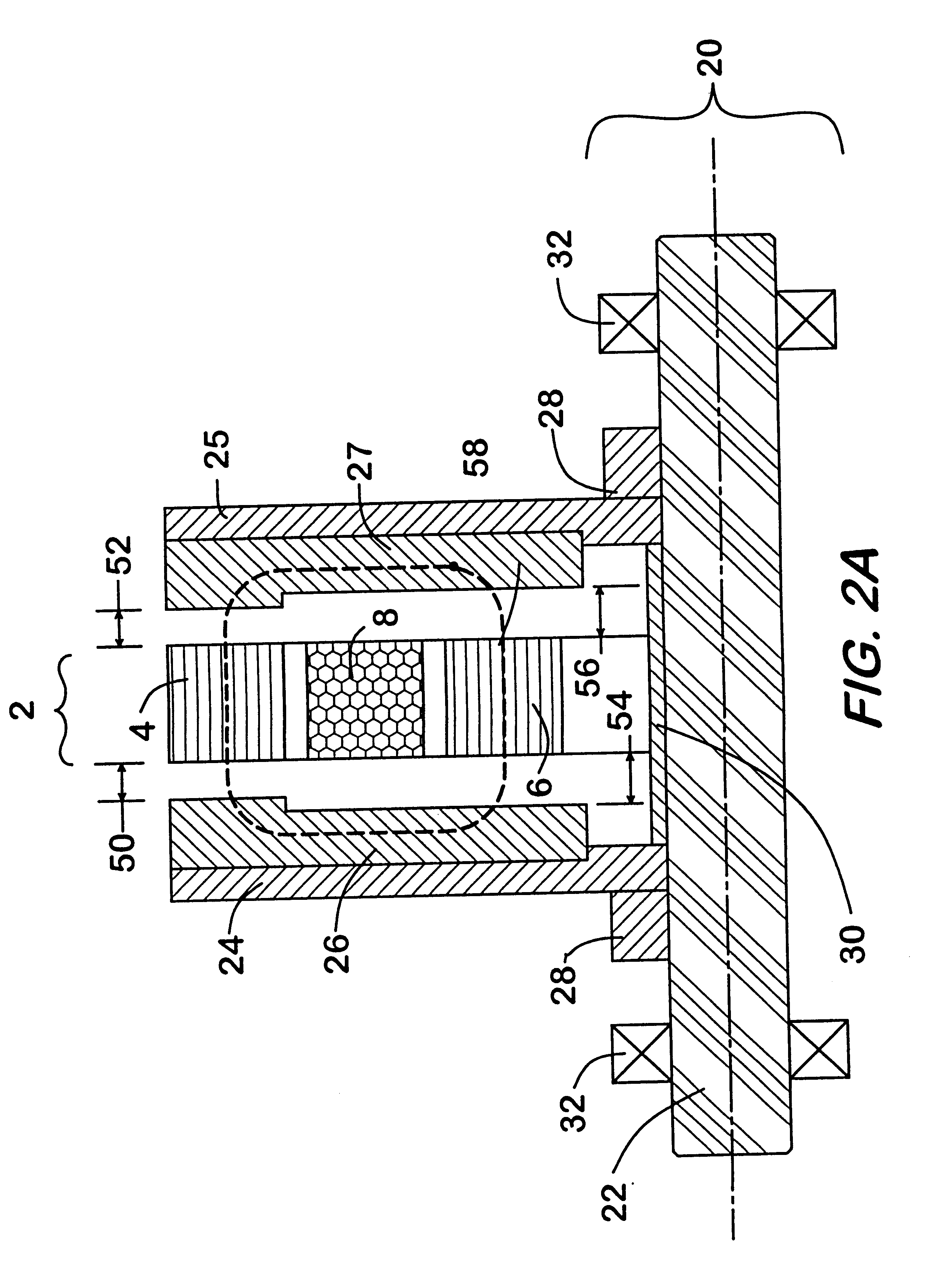
Low inductance electrical machine
A low inductance electrical machine that may be used as an alternator or motor with low armature inductance is disclosed. Arrangements of complementary armature windings are presented in which the fluxes induced by currents in the armature windings effectively cancel leading to low magnetic energy storage within the machine. This leads to low net flux levels, low core losses, low inductance and reduced tendency toward magnetic saturation. The inclusion of additional gaps in the magnetic circuit allows for independent adjustment of air gap geometry and armature inductance. Separately excited field arrangements are disclosed that allow rotor motion to effect brush-less alternator or brush-less motor operation. An exemplary geometry includes a stator including two annular rings and a concentric field coil together with a rotor structure separated from the stator by four air gaps.
Owner:RAVEN TECH
Permanent magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS20070126304A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMagnetic circuit rotating partsPiston pumpsMagnetic polesEngineering
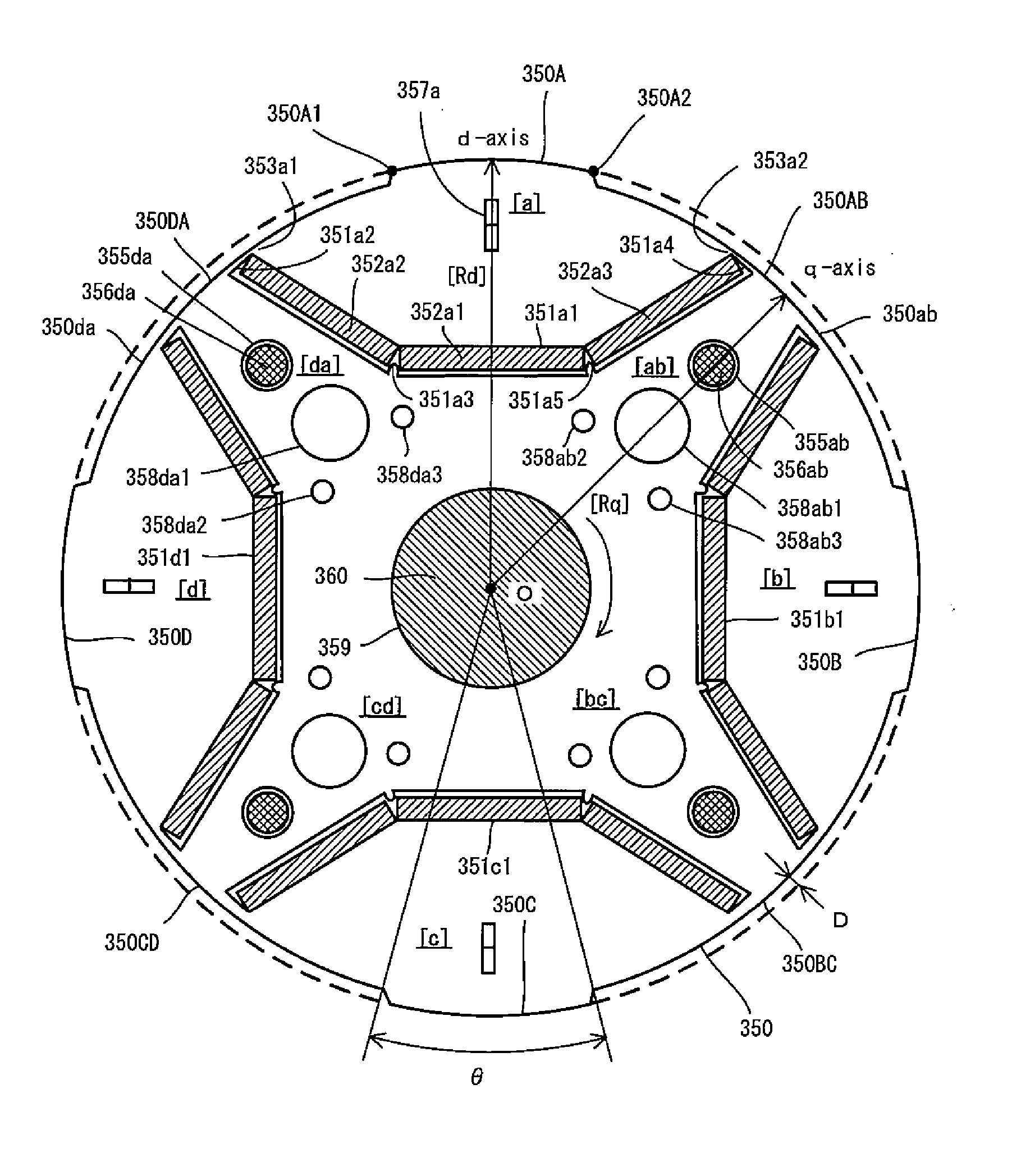
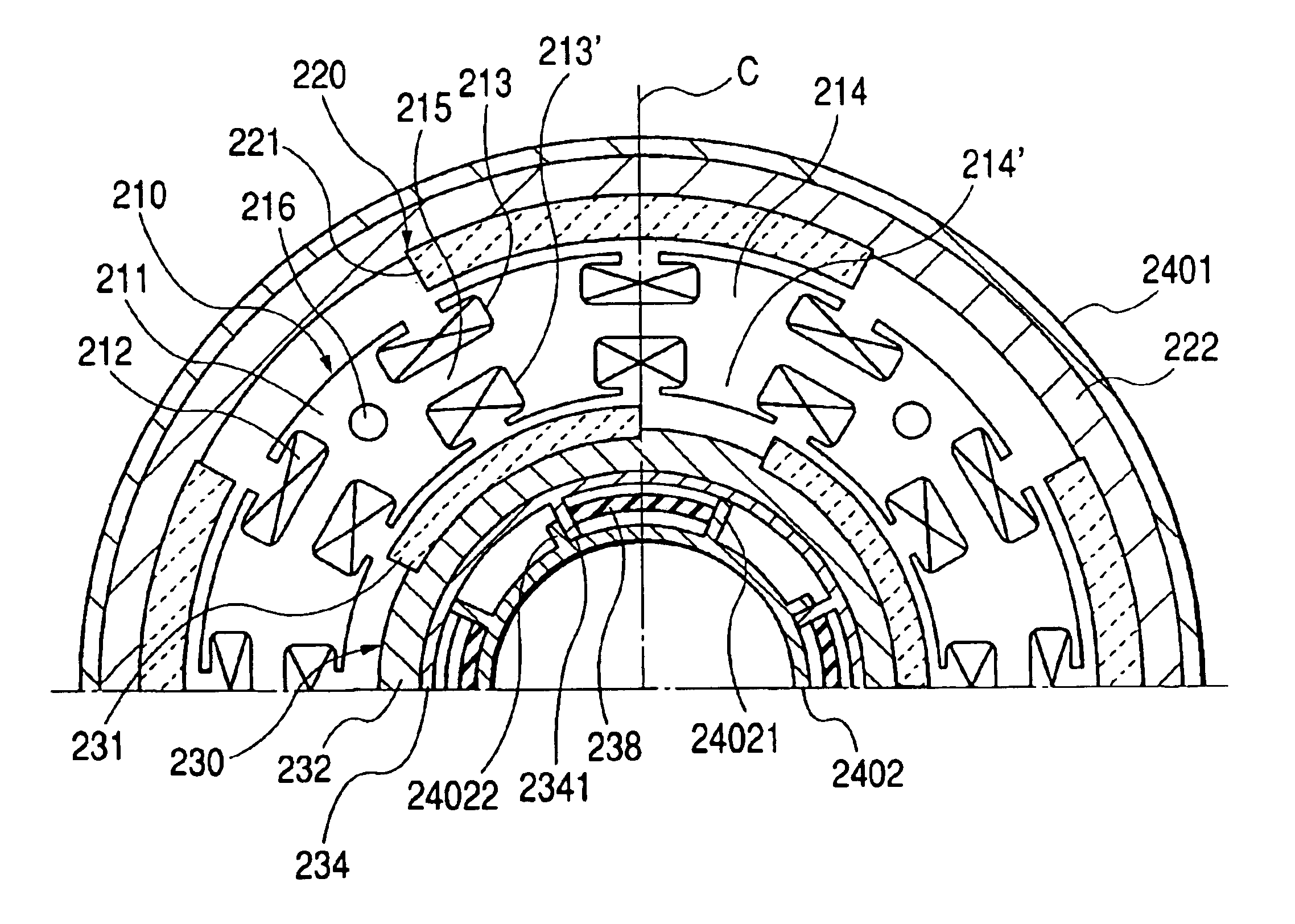
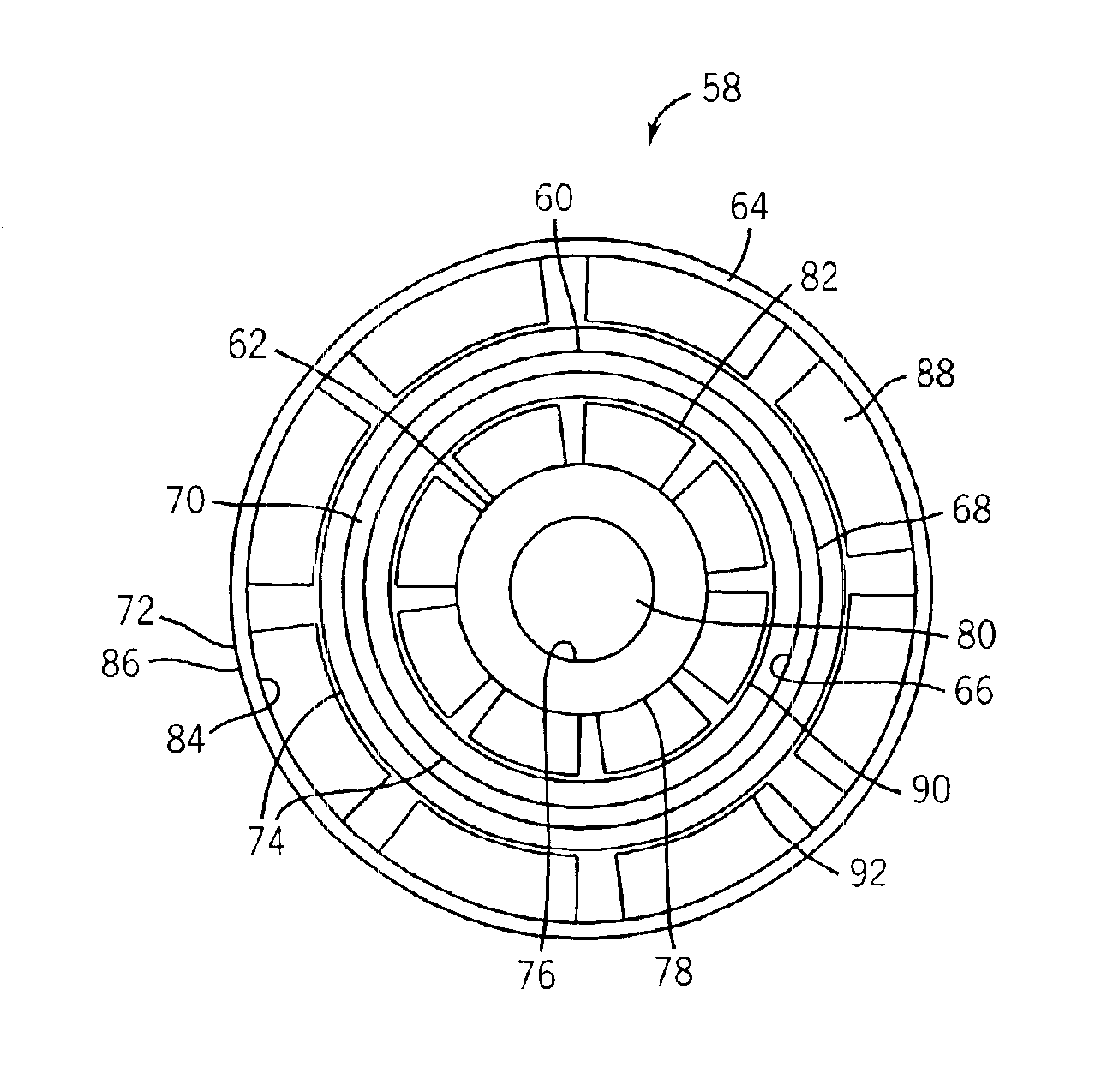
A rotary shaft 60 having an outside diameter larger than the bore diameter of a rotary shaft insert hole 59 of a rotor 50 is inserted into the rotary shaft insert hole 59. A magnet insert hole 51a1 is provided in a main magnetic pole [a] of the rotor 50. Permanent magnets 52a1 to 52a3 are inserted into the magnet insert hole 51a1 such that a gap is formed between the permanent magnets 52a1 to 52a3 and the magnet insert hole 51a1. A semi-tubular rivet insert hole 55a and interlocks 57a1, 57a2 elongated in the radial direction of the rotor are disposed radially outward of the magnet insert hole 51a in the rotor. A semi-tubular rivet 56a is inserted into the semi-tubular rivet insert hole 55a such that a gap is formed between the semi-tubular rivet 56a and the semi-tubular rivet insert hole 55a. Passage holes 58ab, 58da are provided in the auxiliary magnetic poles [ab], [da].
Owner:AICHI ELECTRIC
Rotary electric machine having a flux-concentrating rotor and a stator with windings on teeth
InactiveUS20020047425A1Increase powerReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machinePole piece
The invention relates to a rotary electric machine comprising a flux-concentrating rotor with permanent magnets disposed between pole pieces, and a stator with windings on teeth.
Owner:MOTEURS LEROY SOMER
Electric machine having a liquid-cooled rotor
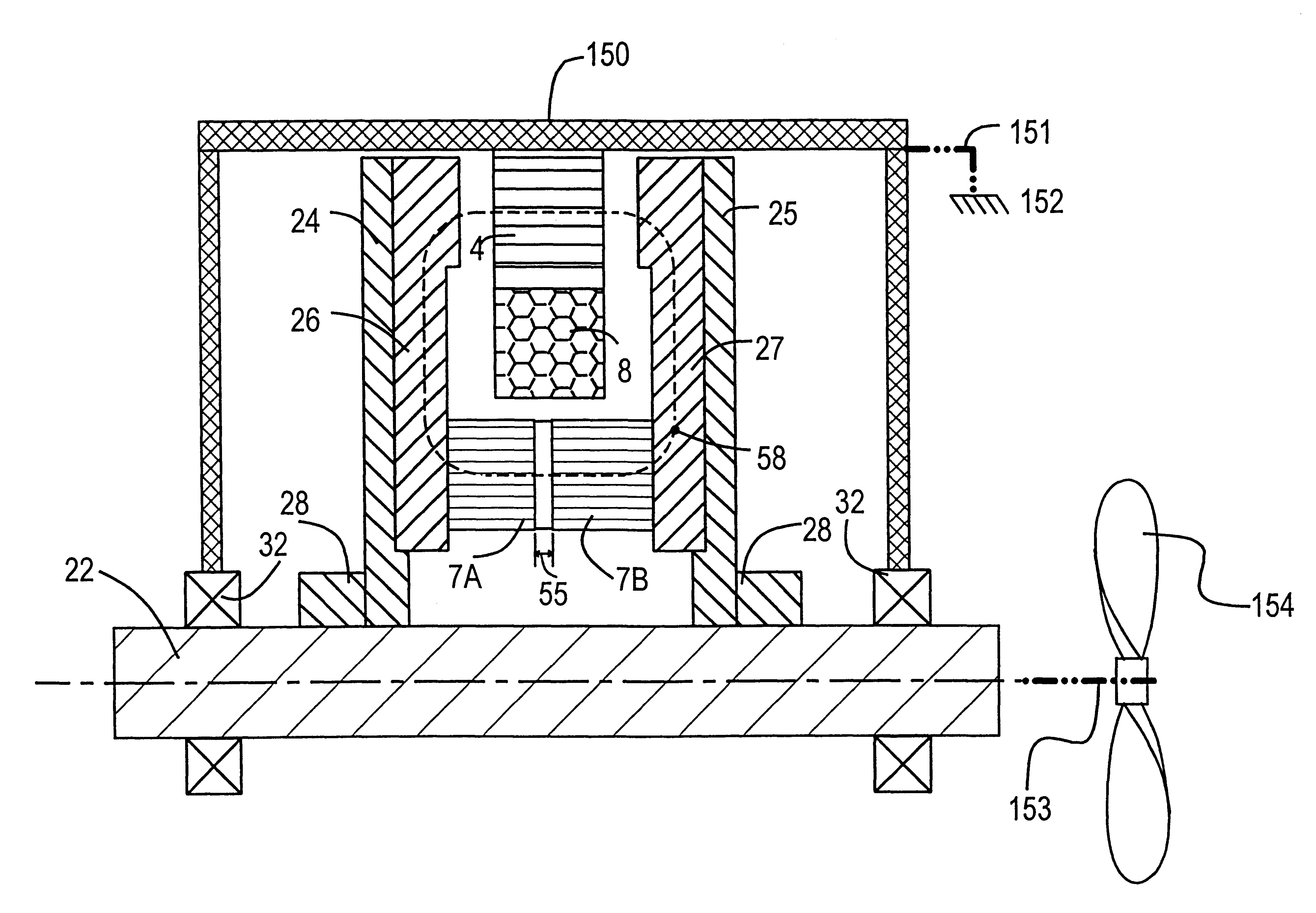
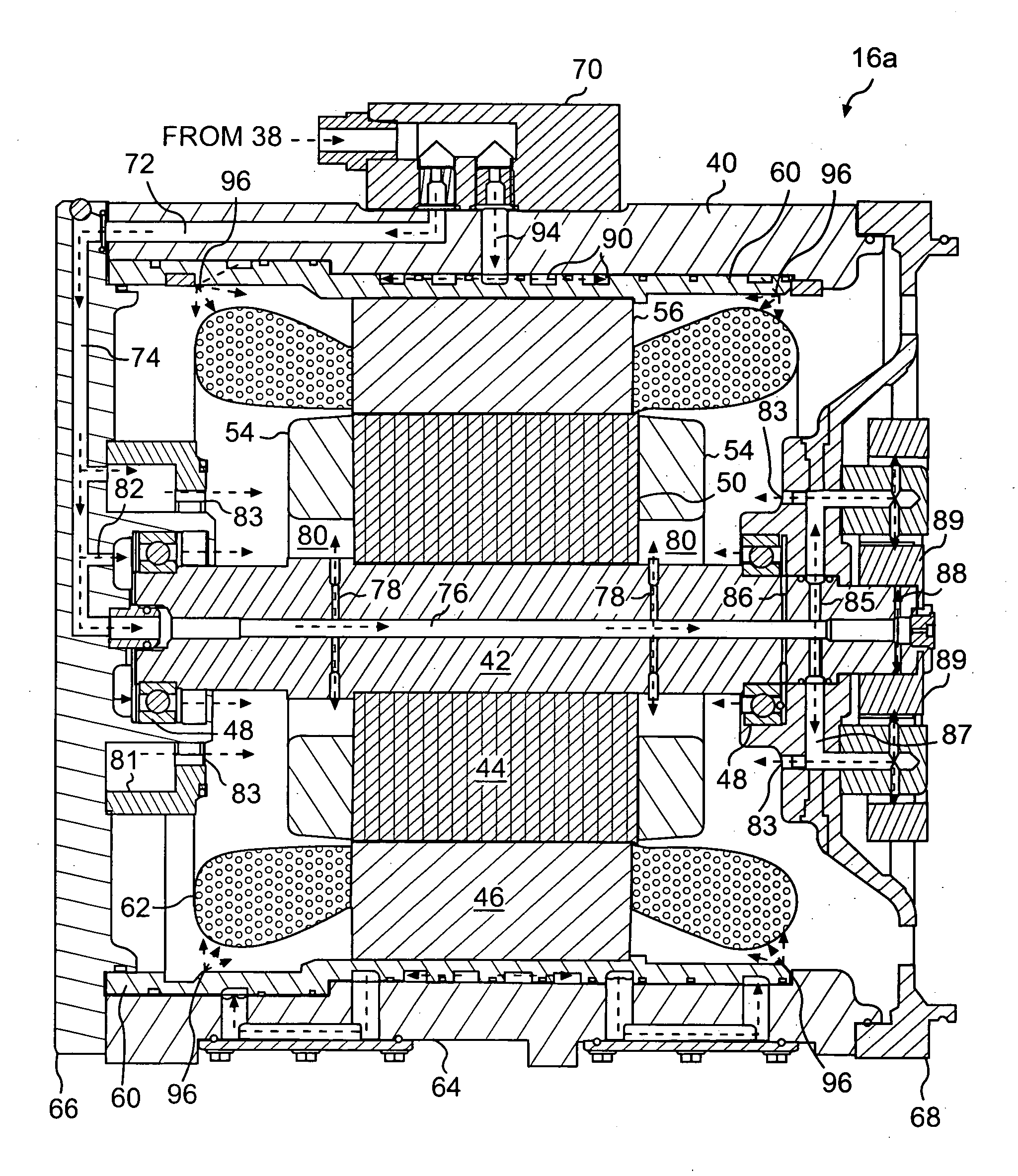
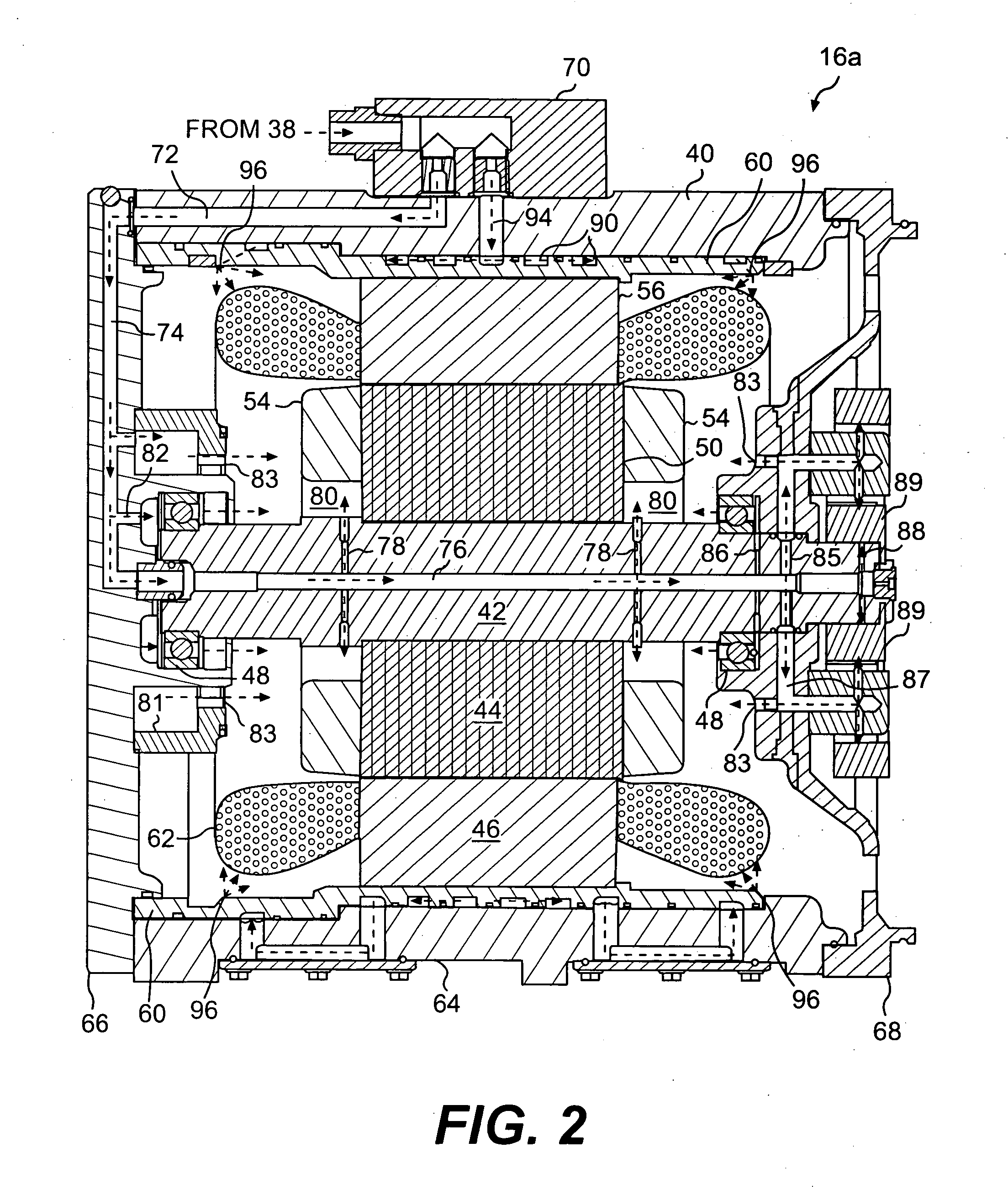
ActiveUS20080024020A1Propulsion by batteries/cellsVehicular energy storageElectric machineMechanical engineering
An electric machine for a power system is disclosed. The electric machine has a housing with a first end cap and a second end cap. The first end cap has a first fluid passageway, and the second end cap has a second fluid passageway. The electric machine also has a stator fixedly disposed within the housing, and a rotor rotationally disposed radially inward from the stator. The rotor has an axial passageway fluidly communicating the first fluid passageway with the second fluid passageway.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
AC generator for vehicles
InactiveUS6124660ASynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorEngineering
An AC generator for vehicles includes a field rotor, a stator disposed around said field rotor and a frame for supporting the rotor and the stator. The stator has a laminated core having a plurality of slots, aluminum conductors housed in the slots, and an electric insulator. The aluminum conductor is constituted by in-slot portion and a crossover portion for connecting an in-slot portion in one slot to another in-slot portion in a different slot to provide a winding as a whole. The frame is provided with a plurality of windows substantially in a whole periphery thereof at portions encircling the crossover portions and substantially in an outer diametrical direction opposite to the crossover portions.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Reluctance motor
InactiveUS6121706ASynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic polesReluctance motor
A reluctance motor is provided that reduces leaking magnetic flux. To generate magnetic flux between adjacent magnetic poles in a rotor 2, permanent magnets 4 are disposed in approximate centers of split magnetic paths near a borderline area between two magnetic poles in an internal portion of the rotor. Further, each of slots 8 in a stator 1 is wound with a coil of a corresponding phase such that the vector phase and amplitude expressed by the products of the number of coil turns and the amount of passing current, namely, ampere-turns, become almost identical for each of the slots. By reducing leaking magnetic flux according to this arrangement, generated torque can be increased. As the rotor mechanical strength is enhanced, the rotor can be safely driven at a higher speed. A practical motor is obtained that simultaneously achieves improved motor characteristics and reduced torque ripples.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Multi-rotor synchronous machine permitting relative movement between rotors
InactiveUS6998757B2Improve reliabilityCompact structureMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric motor startersRelative motionEngineering
A compact and reliable structure of a multi-rotor synchronous machine which may be employed as a generator / motor for automotive vehicles is provided. The machine includes an outer rotor having permanent magnets, an inner rotor having permanent magnets disposed to be rotatable relative to the outer rotor, a stator core having armature coils interlinking with field magnetic fluxes produced by the outer and inner rotors, and a rotor-to-rotor relative rotation controlling mechanism. A relative angle between the outer and inner rotors is controlled within a given angular range by controlling the phase and quantity of current flowing through the armature coils to rotate the inner rotor relative to the outer rotor through the rotor-to-rotor relative rotation controlling mechanism, thereby changing the magnetic fluxes interlinking with the armature coils as needed.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Dual-rotor, radial-flux, toroidally-wound, permanent-magnet machine
InactiveUS6924574B2Increased torque densityReduce the cost of the whole machineSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsSurface mountingElectric machine
The present invention provides a novel dual-rotor, radial-flux, toroidally-wound, permanent-magnet machine. The present invention improves electrical machine torque density and efficiency. At least one concentric surface-mounted permanent magnet dual-rotor is located inside and outside of a torus-shaped stator with back-to-back windings, respectively. The machine substantially improves machine efficiency by reducing the end windings and boosts the torque density by at least doubling the air gap and optimizing the machine aspect ratio.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Rotary electric motor having both radial and axial air gap flux paths between stator and rotor segments
InactiveUS6891306B1Low flux lossEliminate the effects ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesElectrical polarity
In a rotary electric motor, a stator contains a plurality of separate electromagnet core segments disposed coaxially about an axis of rotation. The core segments are affixed, without ferromagnetic contact with each other, to a non-ferromagnetic support structure. The rotor is configured in a U-shaped annular ring that at least partially surrounds the annular stator to define two parallel axial air gaps between the rotor and stator respectively on opposite axial sides of the stator and at least one radial air gap. Permanent magnets are distributed on each inner surface of the U-shaped rotor annular ring that faces an air gap. A winding is formed on a core portion that links axially aligned stator poles to produce, when energized, magnetic poles of opposite polarity at the pole faces.
Owner:BLUWAV SYST LLC
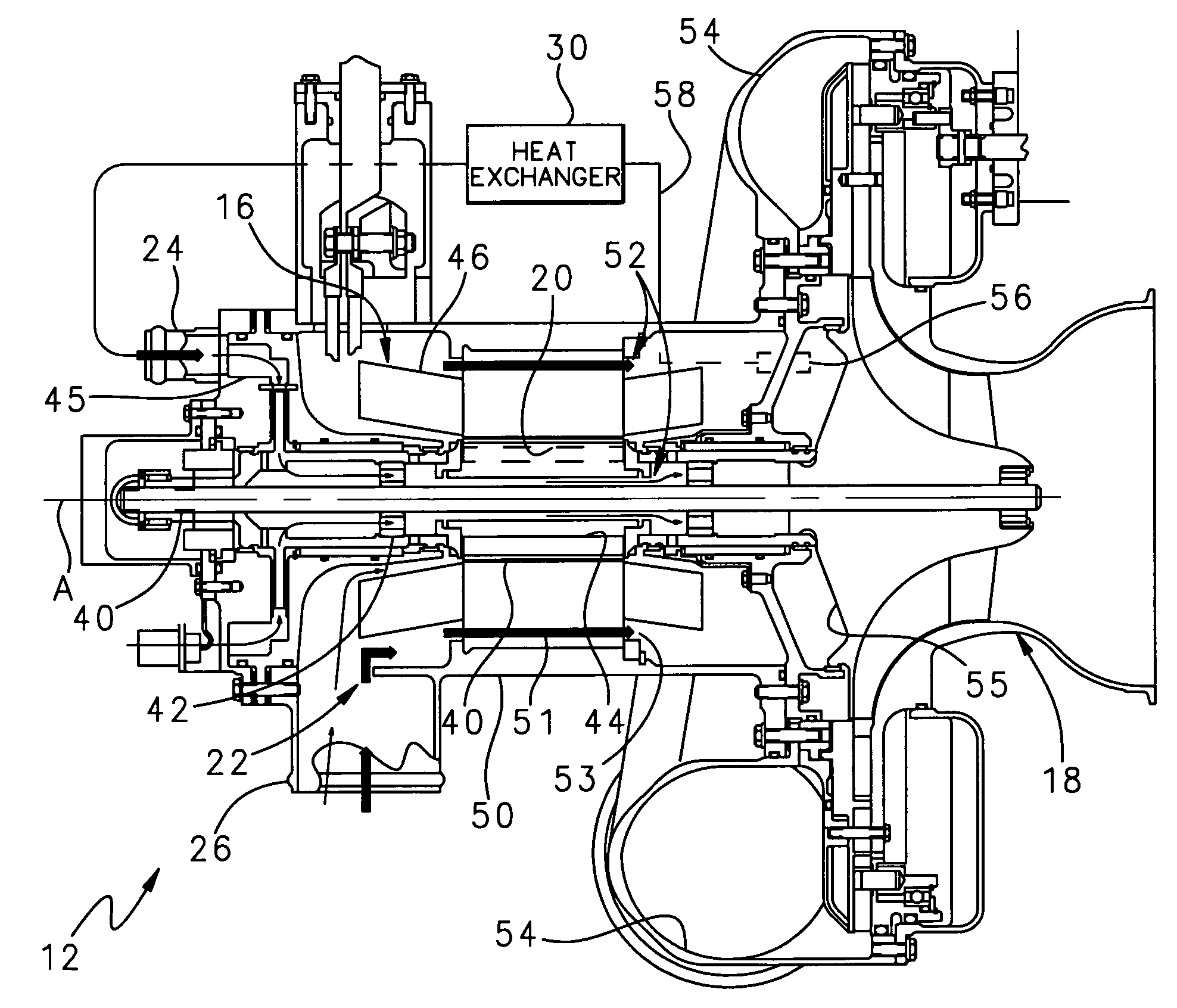
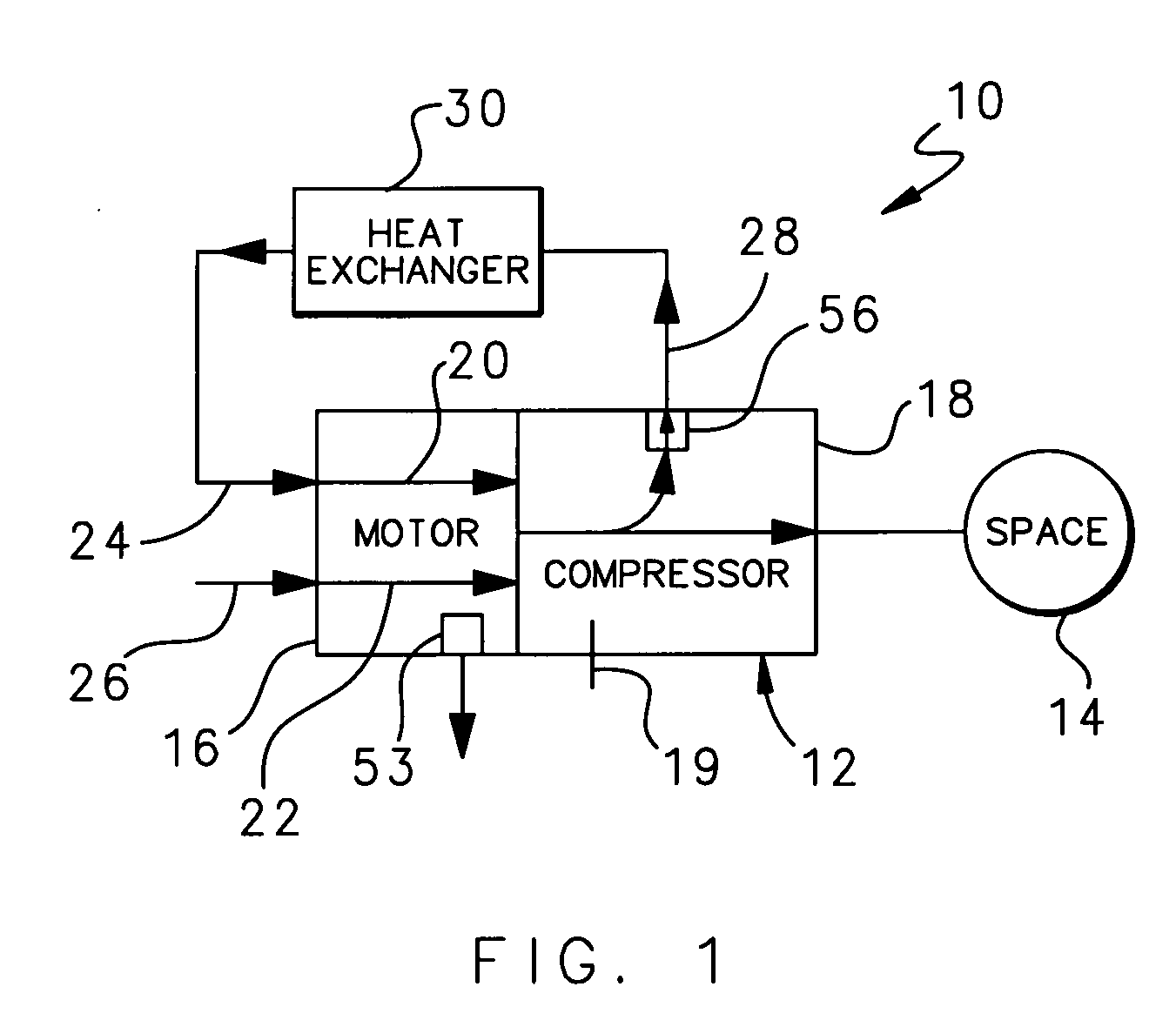
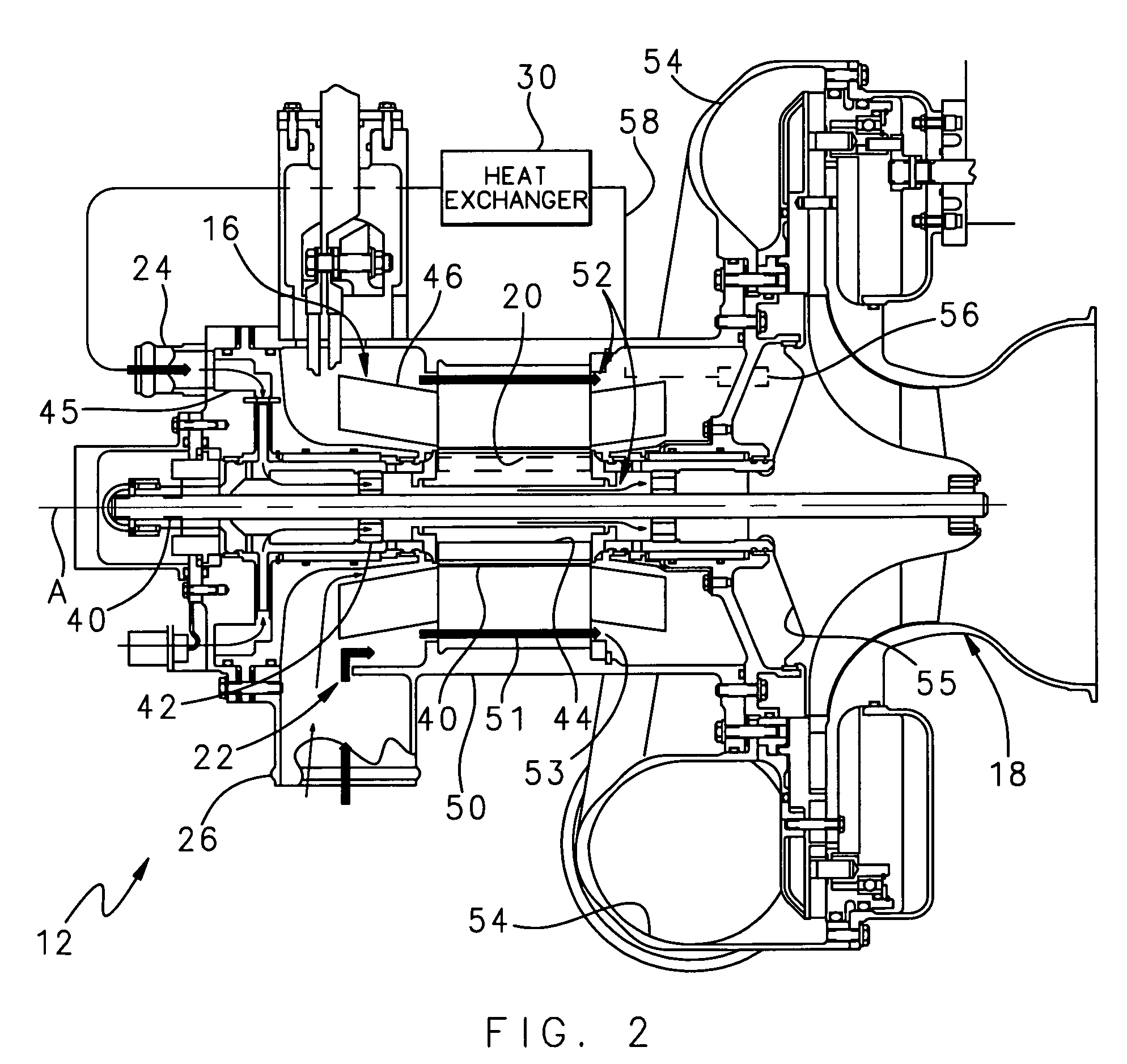
Internal thermal management for motor driven machinery
InactiveUS20070018516A1Efficient thermal managementMagnetic circuit rotating partsPump componentsRotational axisMotor drive
A motor driven assembly includes a motor having a motor shaft mounted for rotation about a rotational axis and a rotor radially located about the shaft. The motor drives a compressor that receives air from the motor, compresses the air, and circulates the compressed air to a space. The motor includes a first cooling flow passage and a second cooling flow passage that each receive air to provide internal cooling of the motor. A portion of the air compressed in the compressor is diverted from the compressor to a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger cools the compressed air from before the air circulates into the first cooling flow passage to cool the motor. The second cooling flow passage receives air from the environment surrounding the motor driven assembly to further cool the motor.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
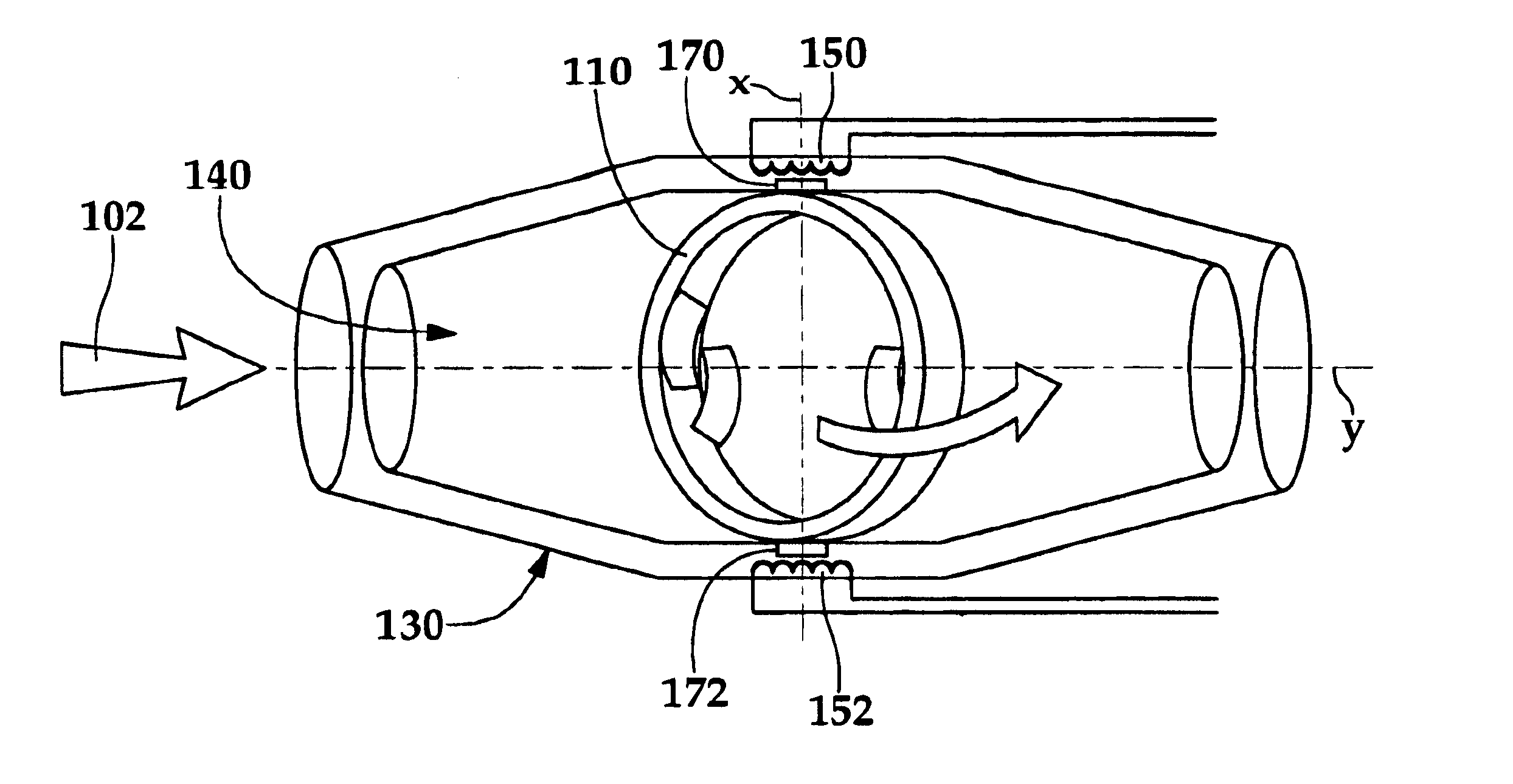
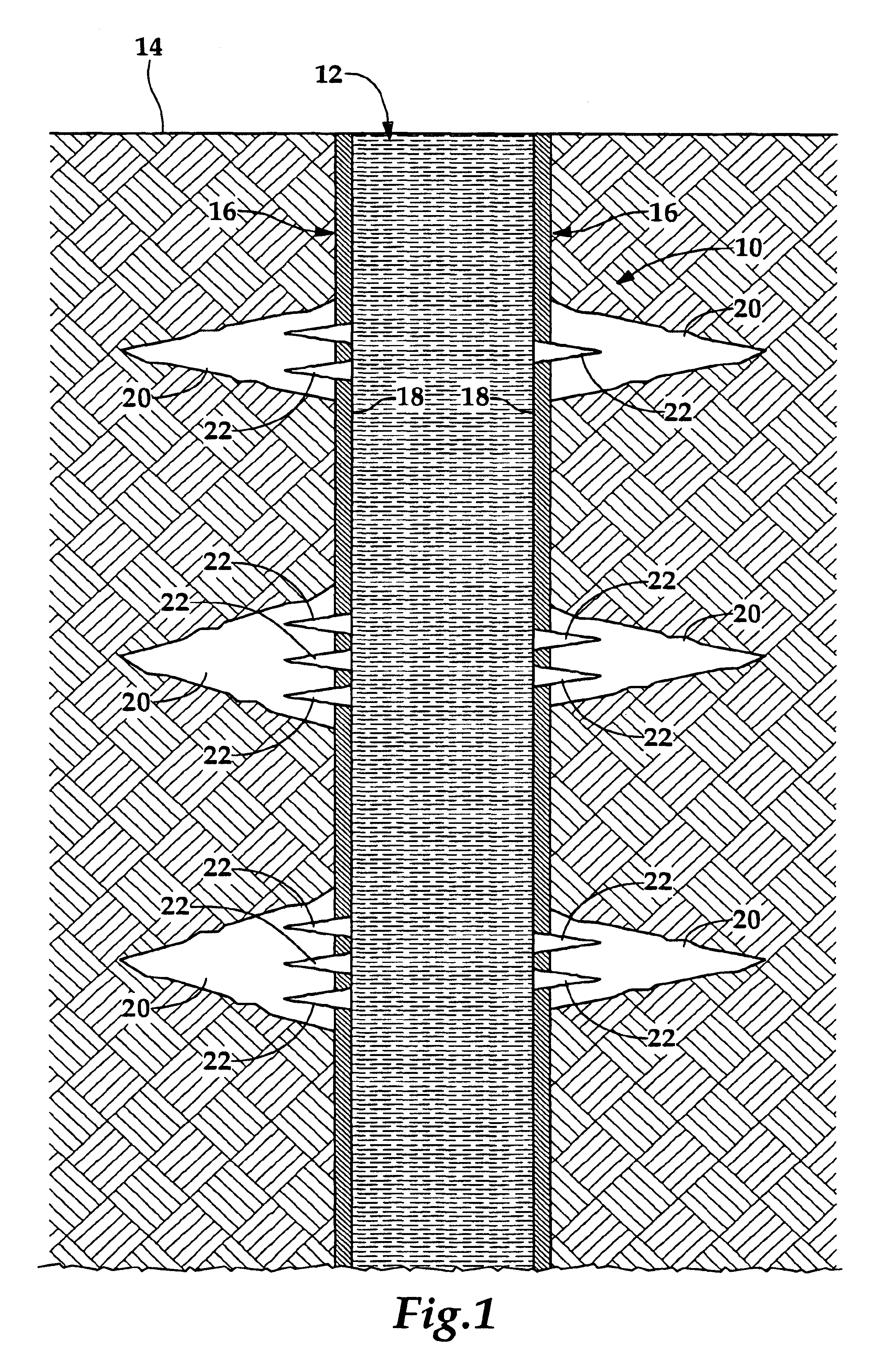
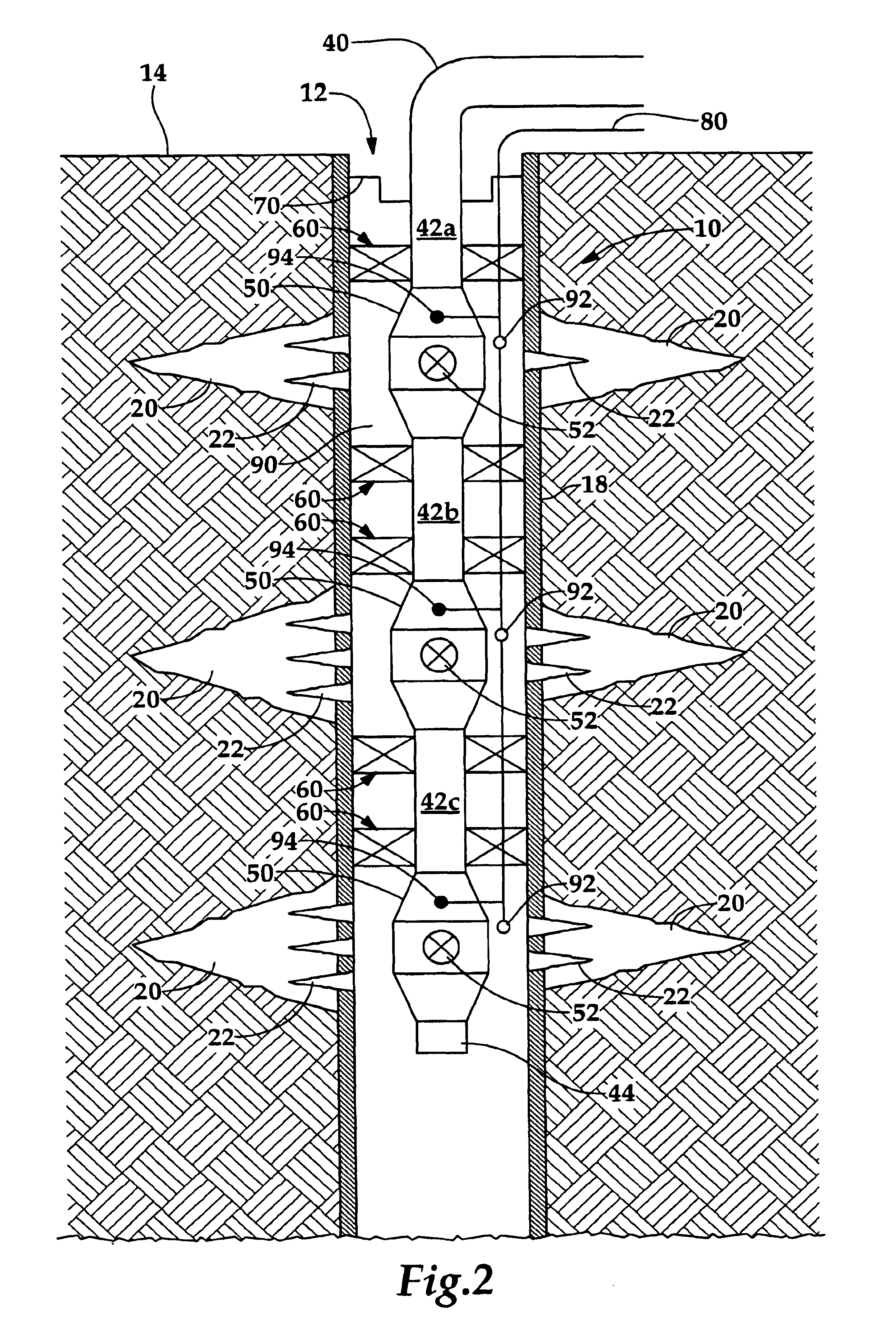
Wellbore power generating system for downhole operation
InactiveUS6848503B2Full accessSolution to short lifeMagnetic circuit rotating partsFluid removalElectricityPower conditioner
A power generating system (100) for a downhole operation (10) having production tubing (40) in a wellbore (12) includes a magnetized rotation member (110) coupled to the wellbore (12) within the production tubing (40), the rotation member (110) having a passageway (112) through which objects, such as tools, may be passed within the production tubing (40). Support braces (170, 172) couple the rotation member (110) to the production tubing (40) and allow the rotation member (110) to rotate within the production tubing (40). Magnetic pickups (150, 152) are predisposed about the rotation member (110) within the wellbore (12) and a power conditioner (200) is provided to receive currents from the magnetic pickups (150, 152) for storage and future use. The rotation member (110) rotates due to the flow of fluid, such as crude oil, through the production tubing (40) which causes the rotation member (110) to rotate and induce a magnetic field on the magnetic pickups (150, 152) such that electrical energy is transmitted to the power conditioner (200), the power conditioner able to store, rectify, and deliver power to any one of several electronic components within the wellbore (12).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Polyphasic multi-coil generator
ActiveUS7081696B2Reduce resistanceSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsDrive shaftAngular orientation
Owner:DPM TECH INC +1
Field controlled axial flux permanent magnet electrical machine
ActiveUS20070046124A1Implementing controlLess expensiveMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machinePole piece
An electrical machine is provided. The machine includes at least one rotor mounted for rotation about a central axis and at least two stator sections mounted axially adjacent to and on opposite sides of the rotor. The rotor includes two circumferentially arrayed rows of alternating segments of permanent magnet and ferromagnetic pole pieces. One of the rows is spaced radially inwardly from the other row. The permanent magnet and ferromagnetic pole pieces are separated by a non-ferromagnetic material. The pole pieces are arranged so that the permanent magnet segments in the first row are radially adjacent to ferromagnetic segments in the second row so that the N-S magnetic fields of the permanent magnet segments are aligned axially. Each stator section includes a ferromagnetic stator frame, at least a first AC winding wound in circumferential slots in the stator frame, and a DC field winding wound on the stator frame.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Permanent magnet rotor type electric motor with different permanent magnet materials
InactiveUS6025667AMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
In an electric motor, such as a DC brushless motor or the like, having a permanent magnet in a rotor, each magnetic pole is formed of three permanent magnets, and the permanent magnets are made of at least two kinds of magnetic materials represented by ferrite magnet and rare-earth magnet. Thus, in a permanent magnet rotor type electric motor, a reluctance torque and a magnetic flux density can be selectively established, and cost is reasonable, corresponding to the quality.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
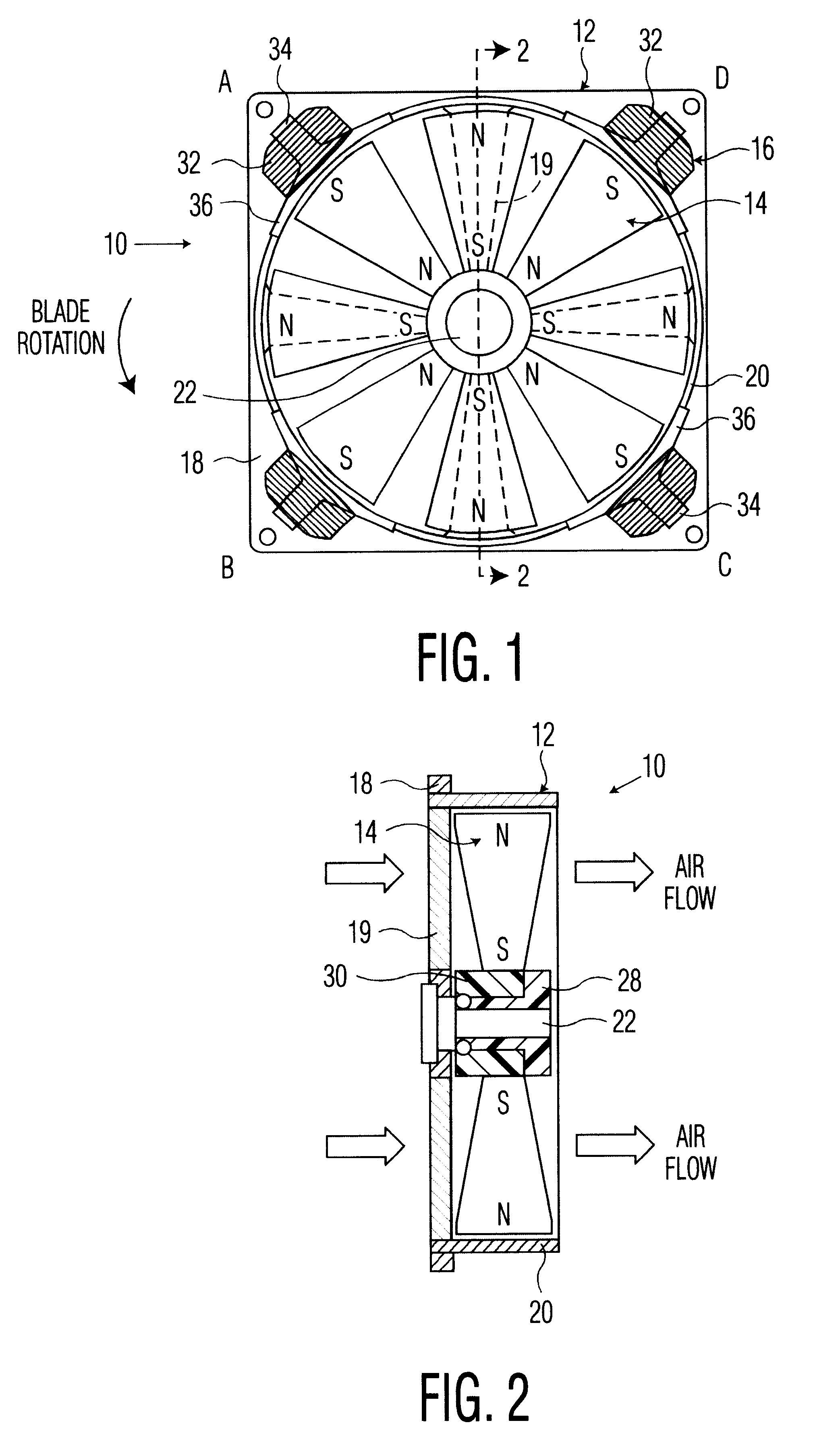
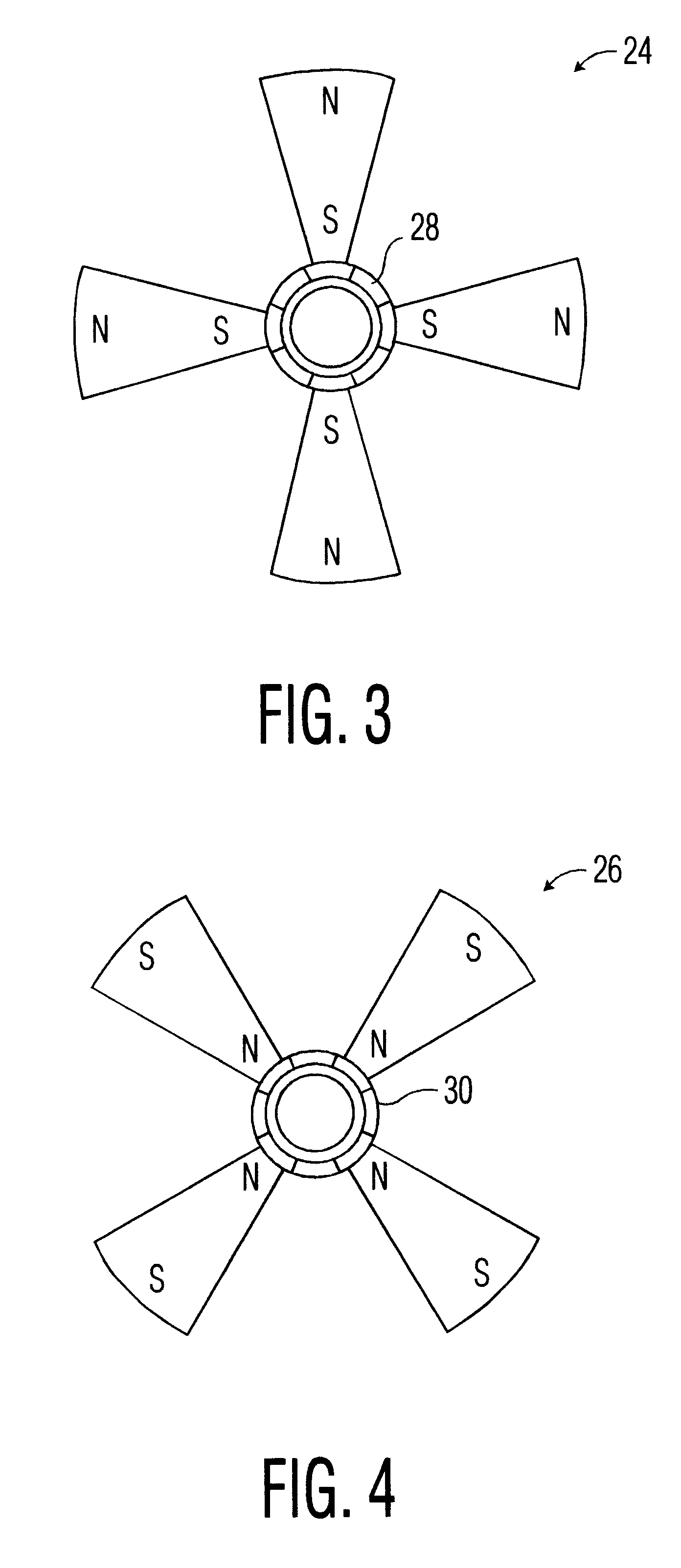
Fan with magnetic blades
InactiveUS6194798B1MiniaturizationReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsPump componentsStator coilEngineering
A DC driven fan with blades made of magnetized material and permanently magnetized in the radial direction and cooperating with a plurality of electromagnetic stator coils mounted external to the outer fan edges. Adjacent blades have alternate N-S, S-N radial magnetic orientations. In one embodiment, the blades are mounted in a non-ferrous hub and in an alternate embodiment they are mounted in a ferrous hub so that adjacent blades function like a U or V-shaped magnet. Blades can be made of magnetized ferrous, ferromagnetic, or magnetized plastic depending upon the application and blade strength specifications.
Owner:AIR CONCEPTS
Methods and apparatus for cooling wind turbine generators
A wind turbine generator includes a stator having a core and a plurality of stator windings circumferentially spaced about a generator longitudinal axis. A rotor is rotatable about the generator longitudinal axis, and the rotor includes a plurality of magnetic elements coupled to the rotor and cooperating with the stator windings. The magnetic elements are configured to generate a magnetic field and the stator windings are configured to interact with the magnetic field to generate a voltage in the stator windings. A heat pipe assembly thermally engaging one of the stator and the rotor to dissipate heat generated in the stator or rotor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Poly-phasic multi-coil generator
InactiveUS20080088200A1Reduce negative impactReduce harmSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsAngular orientationMulti coil
Owner:RITCHEY JONATHAN
Inner rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor
ActiveUS20080211326A1Improve efficiencyIncrease output powerMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxConductor Coil
Disclosed herein is an inner rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor, in which a laminated structure in an axial direction or in a radial shape is applied to a stator iron core so as to employ a small amount of permanent magnets compared with a conventional outer rotor type permanent magnet excited transverse flux motor, thus providing high output power, increasing the efficiency of power generation, and reducing noise and vibration.For this, the present invention provides an inner rotor type permanent magnetic excited transverse flux motor comprising: a stator including a stator powdered iron core press-molded using a mold, a stator laminated iron core laminated on upper and lower layer portions of the circumference of the stator powdered iron core at regular intervals, and a stator winding which winds the segmented stator powdered iron core in which a current flows is wound between the intervals; and a rotor in which a rotor permanent magnet and a rotor powdered iron core are arranged alternately to face each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
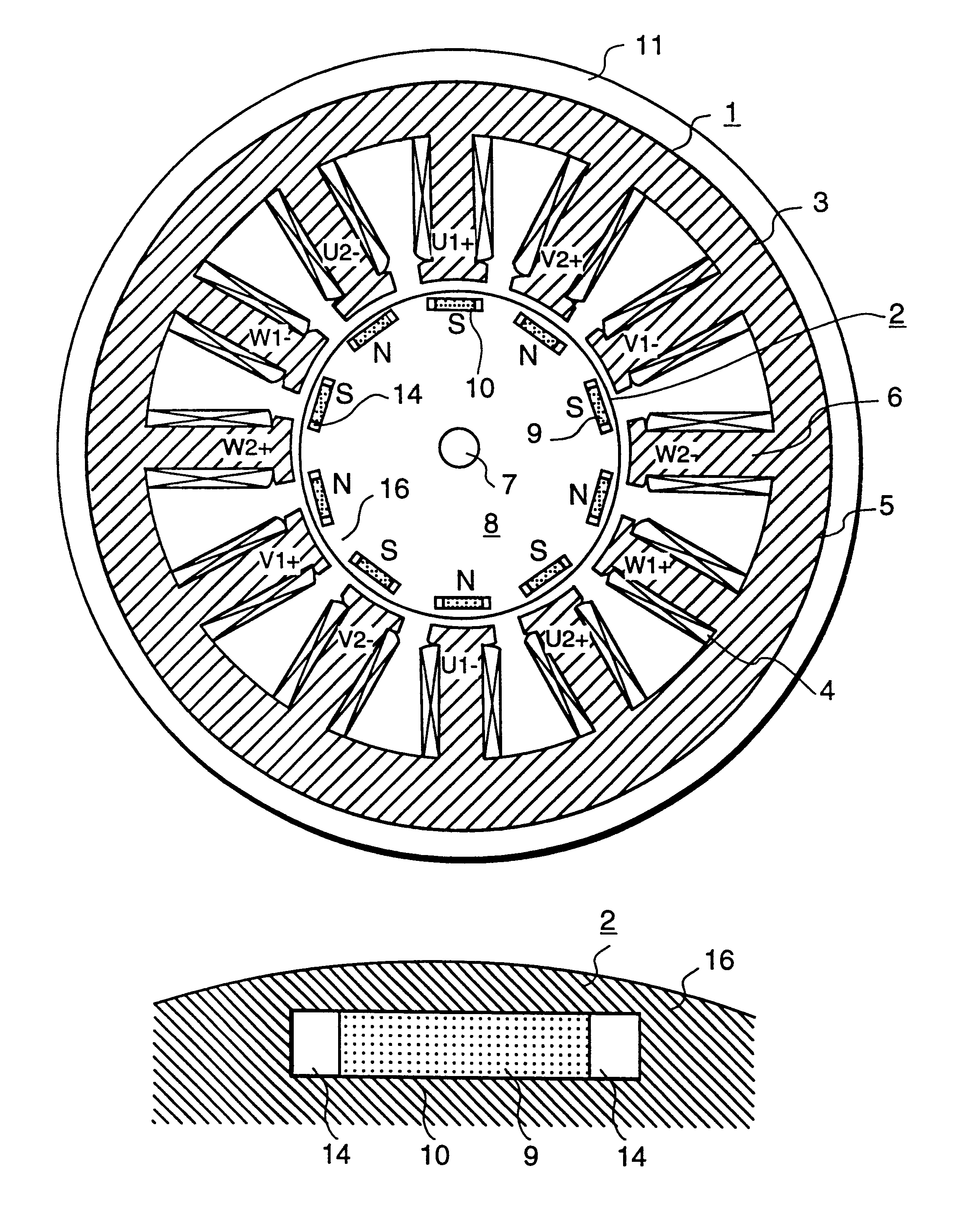
Rotary electric machine and a rotor of the same
ActiveUS20050040721A1Large armature reactionReliability to demagnetizationSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineElectrical polarity
In a rotor for a rotary electric machine, a predetermined number of main pole magnets and a predetermined number of yoke magnets are fixed in contact with a hub. Each main pole magnet is magnetized so that its radial inside portion and its radial outside portion have the opposite polarity from each other, of north pole and south pole. Also, each main pole magnet has its radial inside and radial outside polarities reversed from its closest main pole magnets. The yoke magnets are disposed to allow magnetic flux to flow through circumferential surfaces of the main pole magnets. The hub is provided as a heat radiating member and made of metal having high heat conductivity. The hub includes an inner cylindrical portion and an outer cylindrical portion, and forms an air passage spaces.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Popular searches
Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurement Solid-state devices Using electrical means Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device details Input/output processes for data processing Semiconductor devices Electric motor speed/torque regulation Dynamo-electric motors/converters starters Motor/generator/converter stoppers Synchronous machine details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com