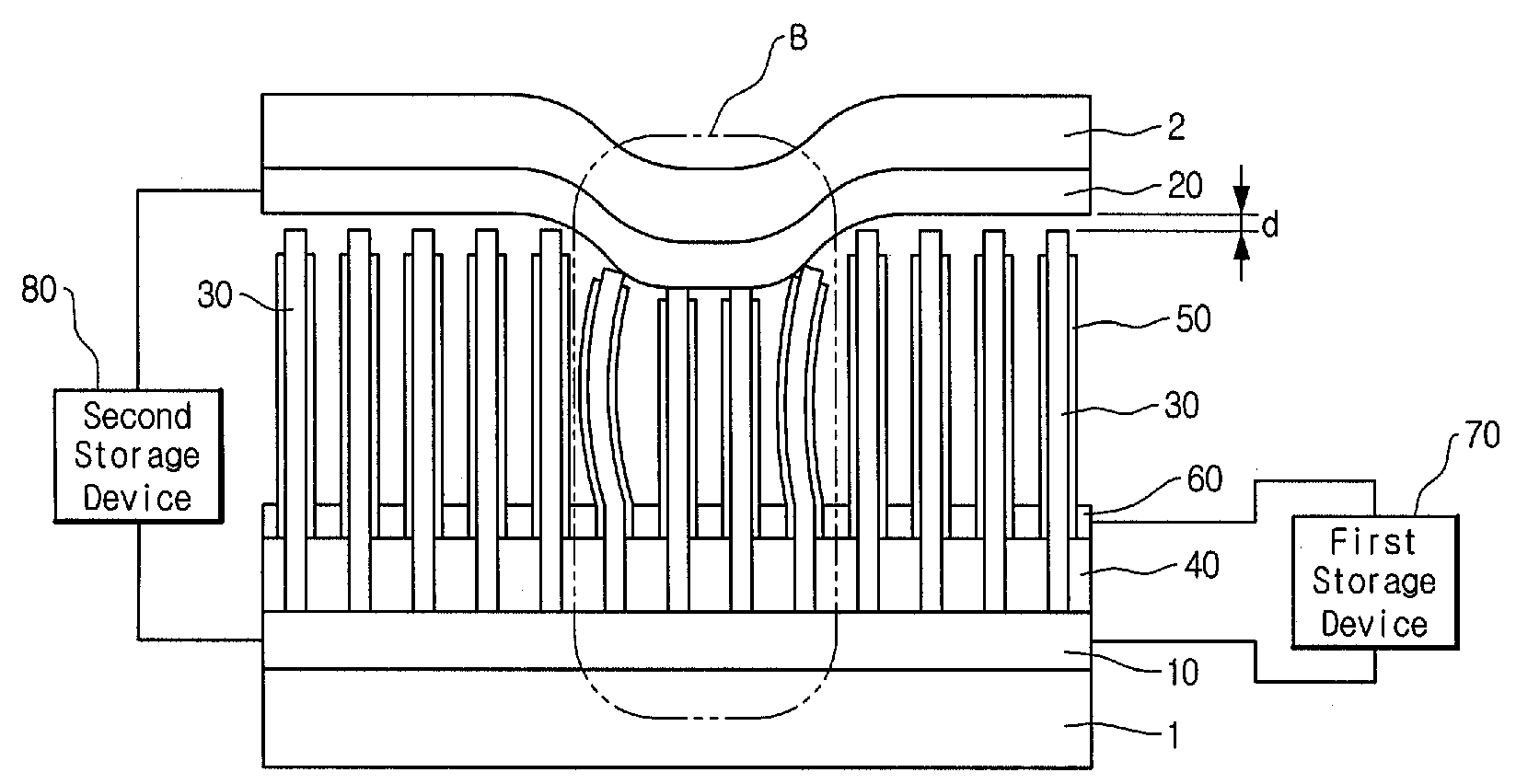
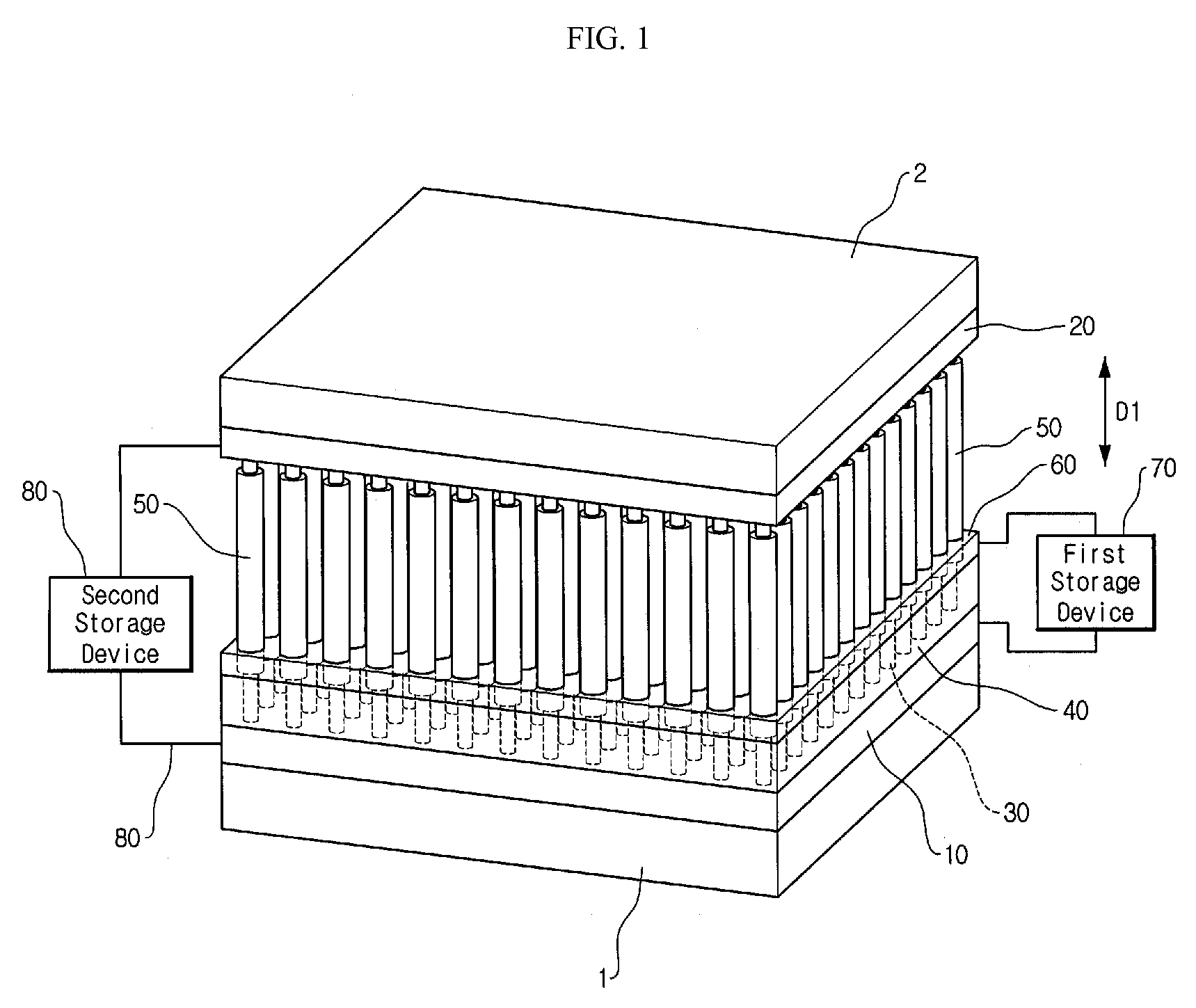
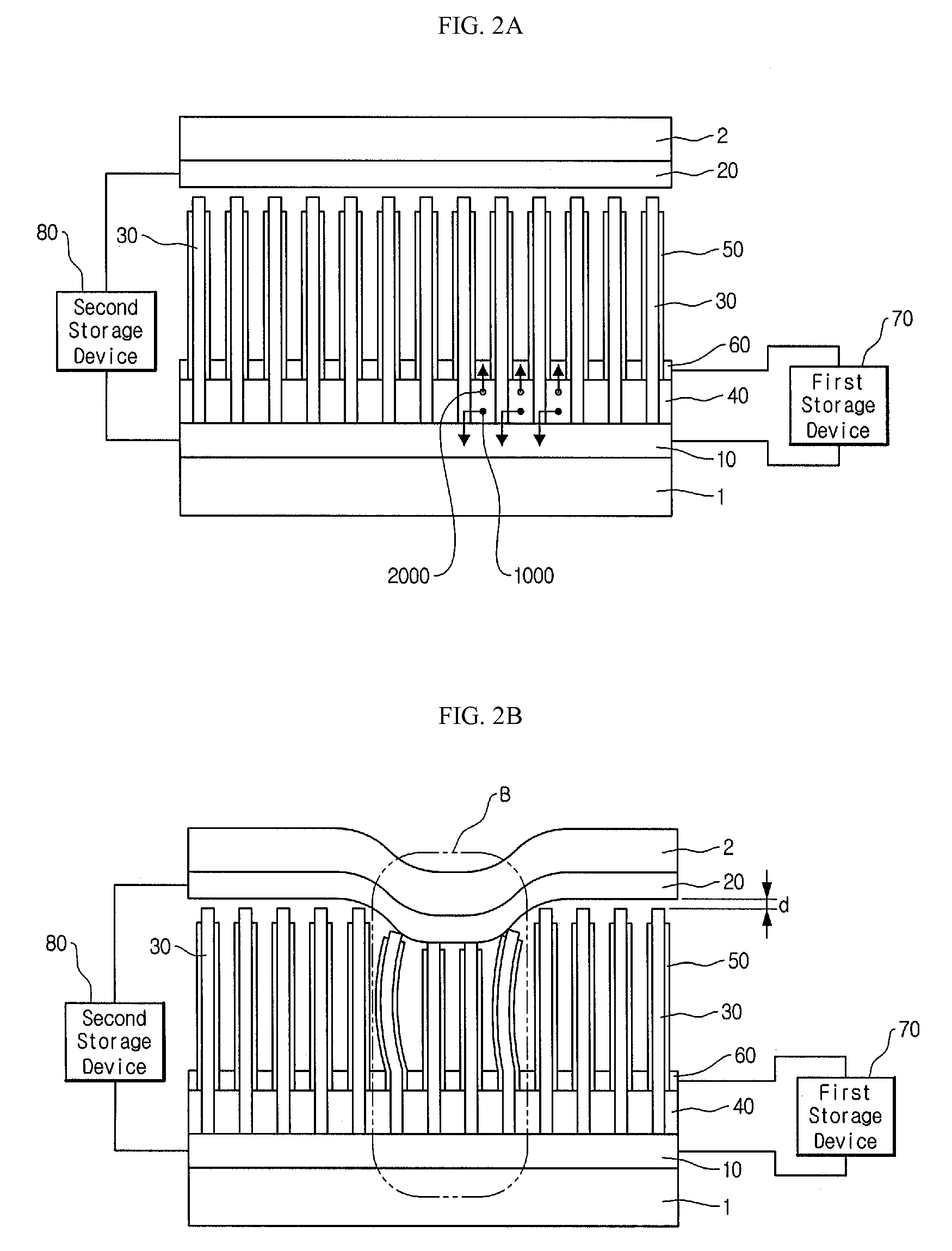
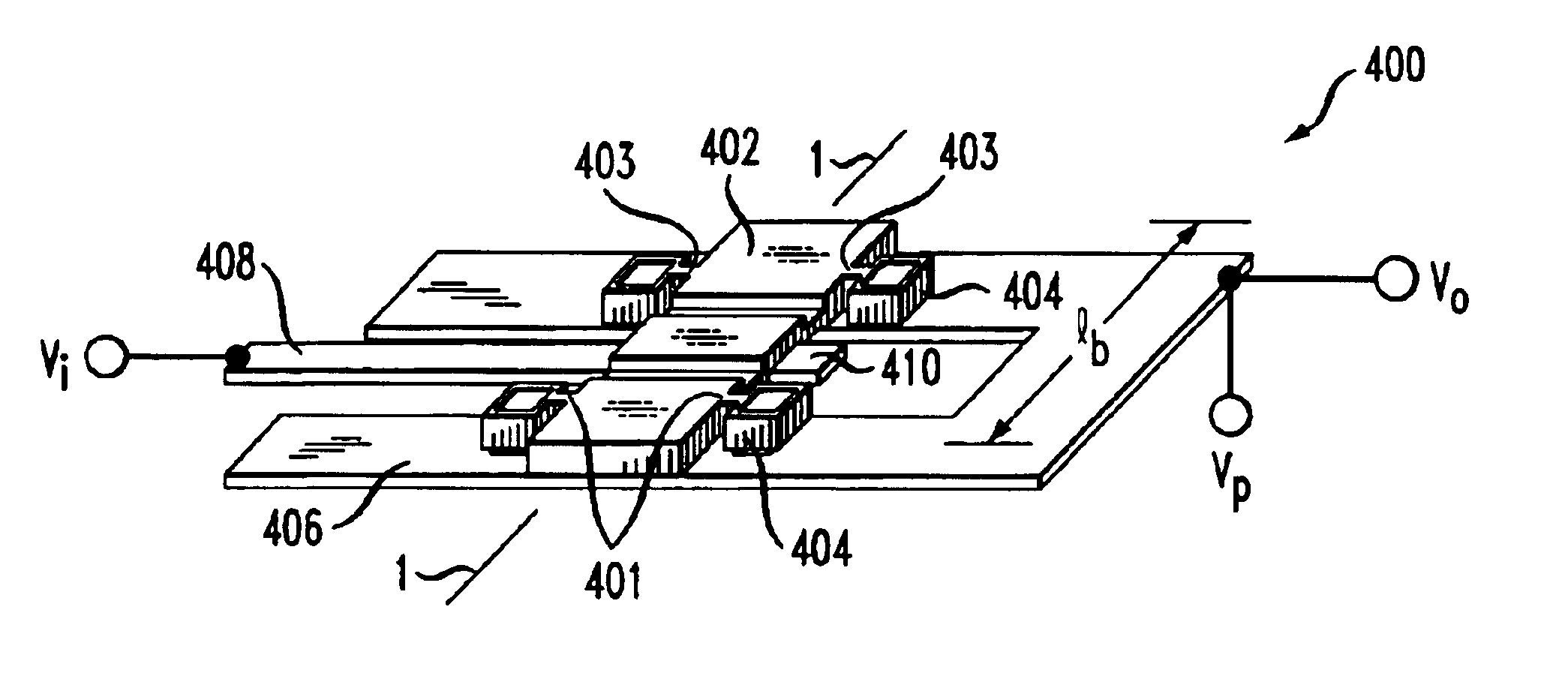
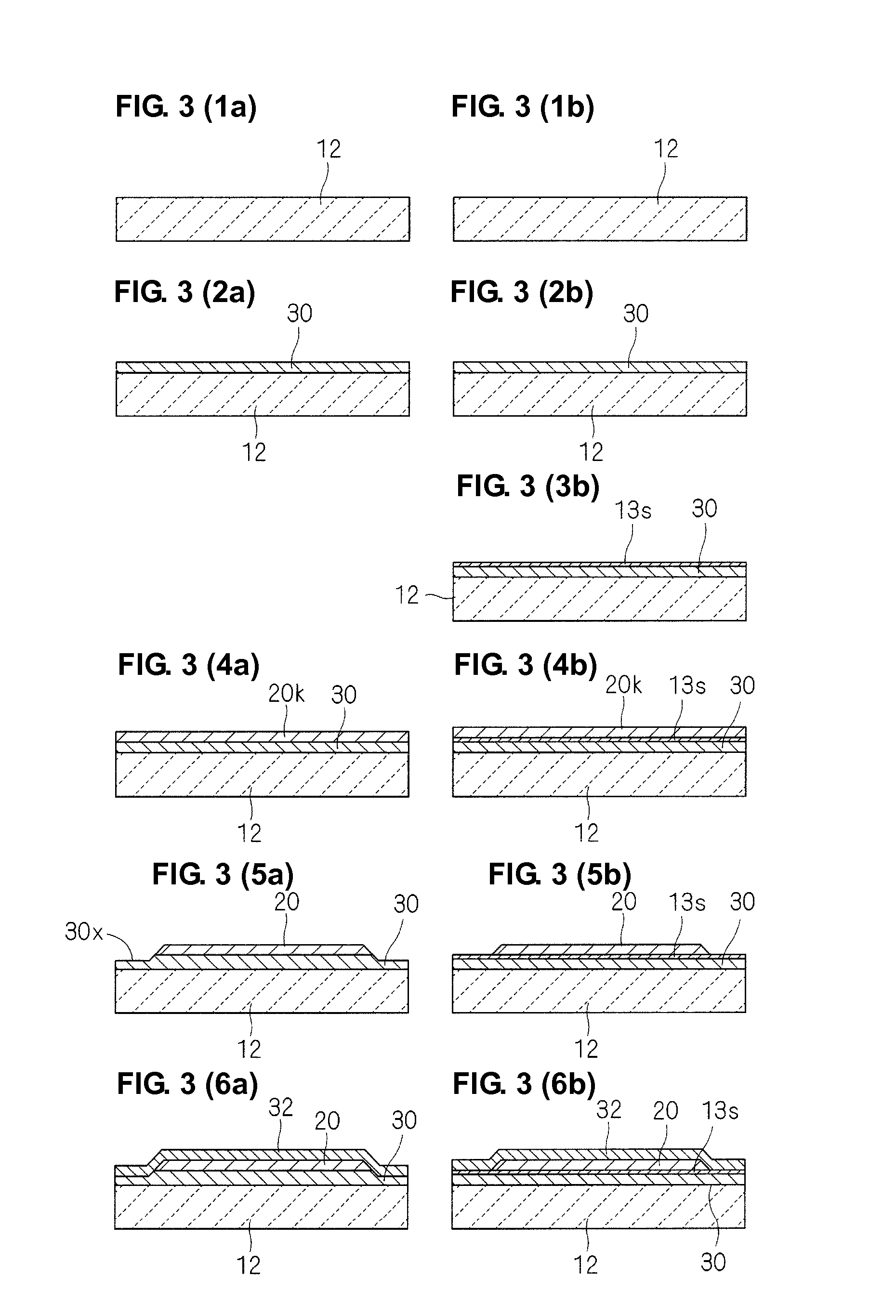
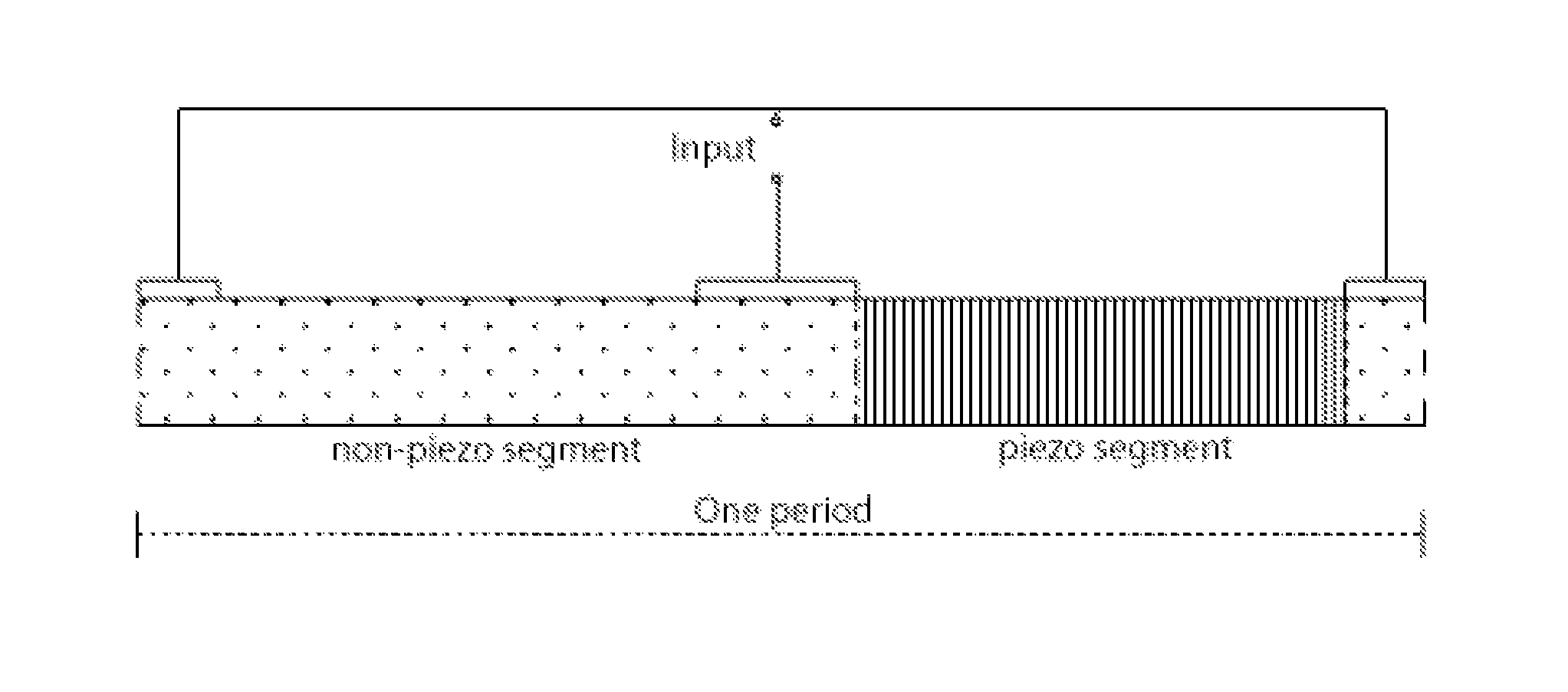
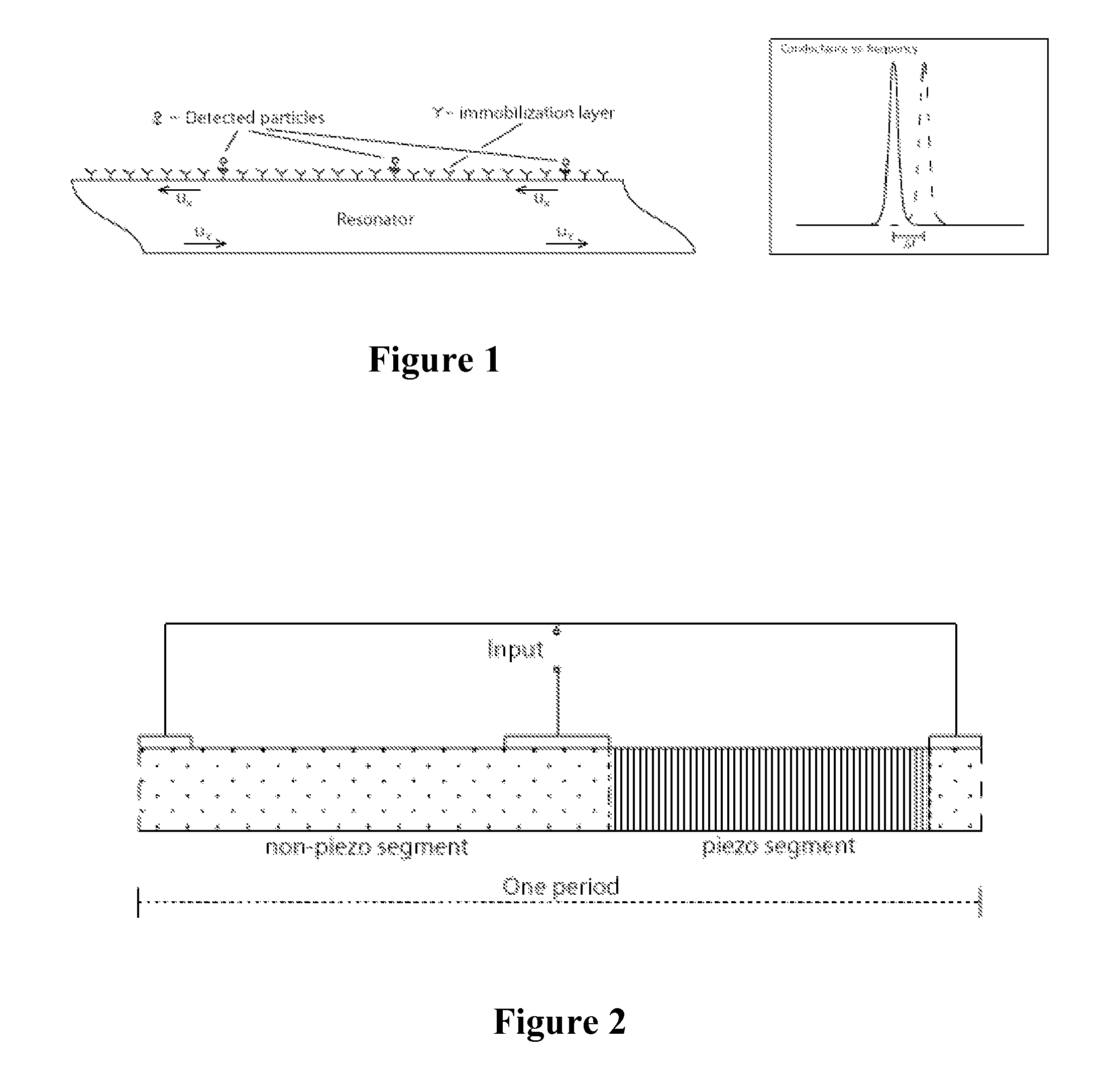
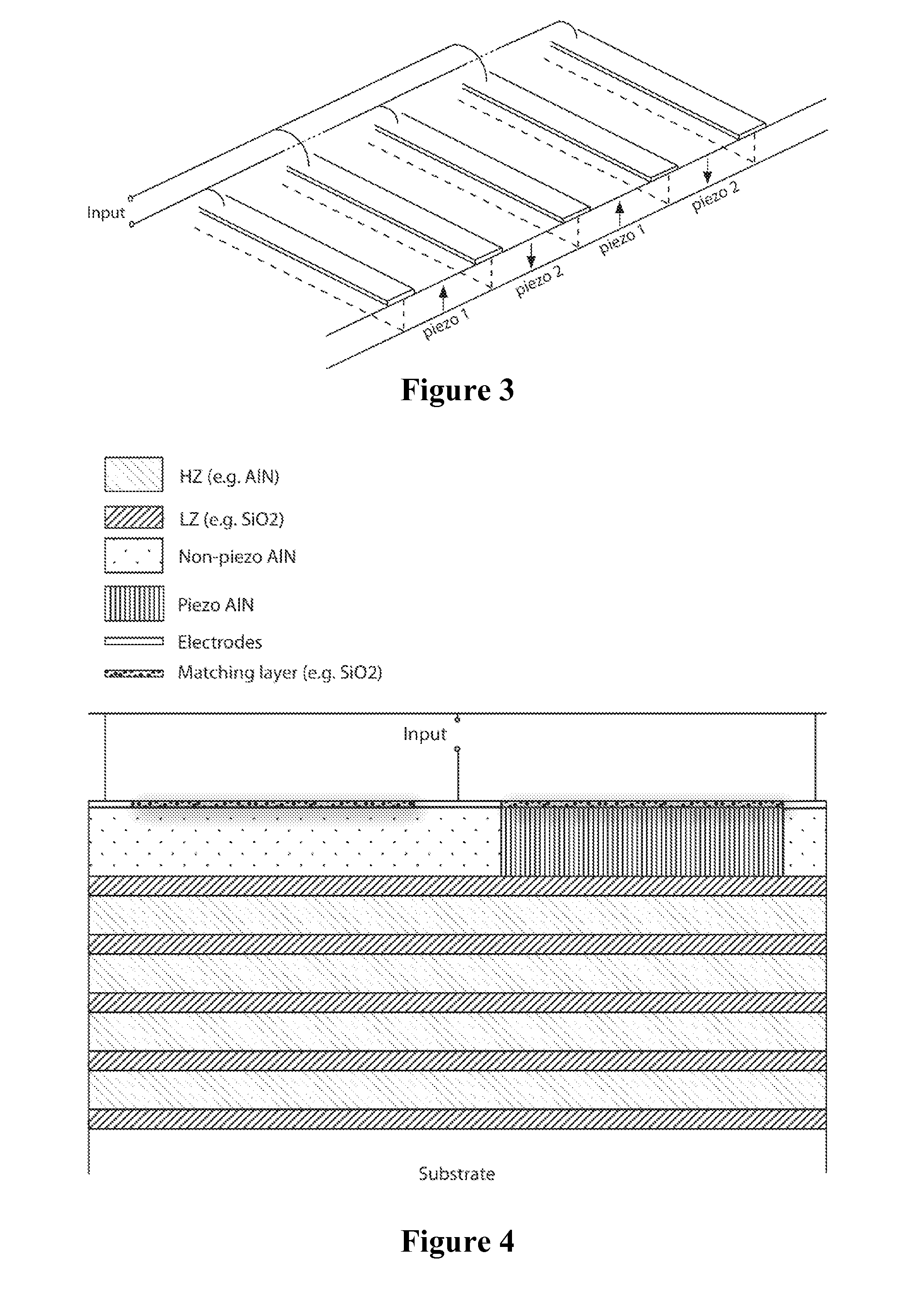
Patents
Literature
2074results about "Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
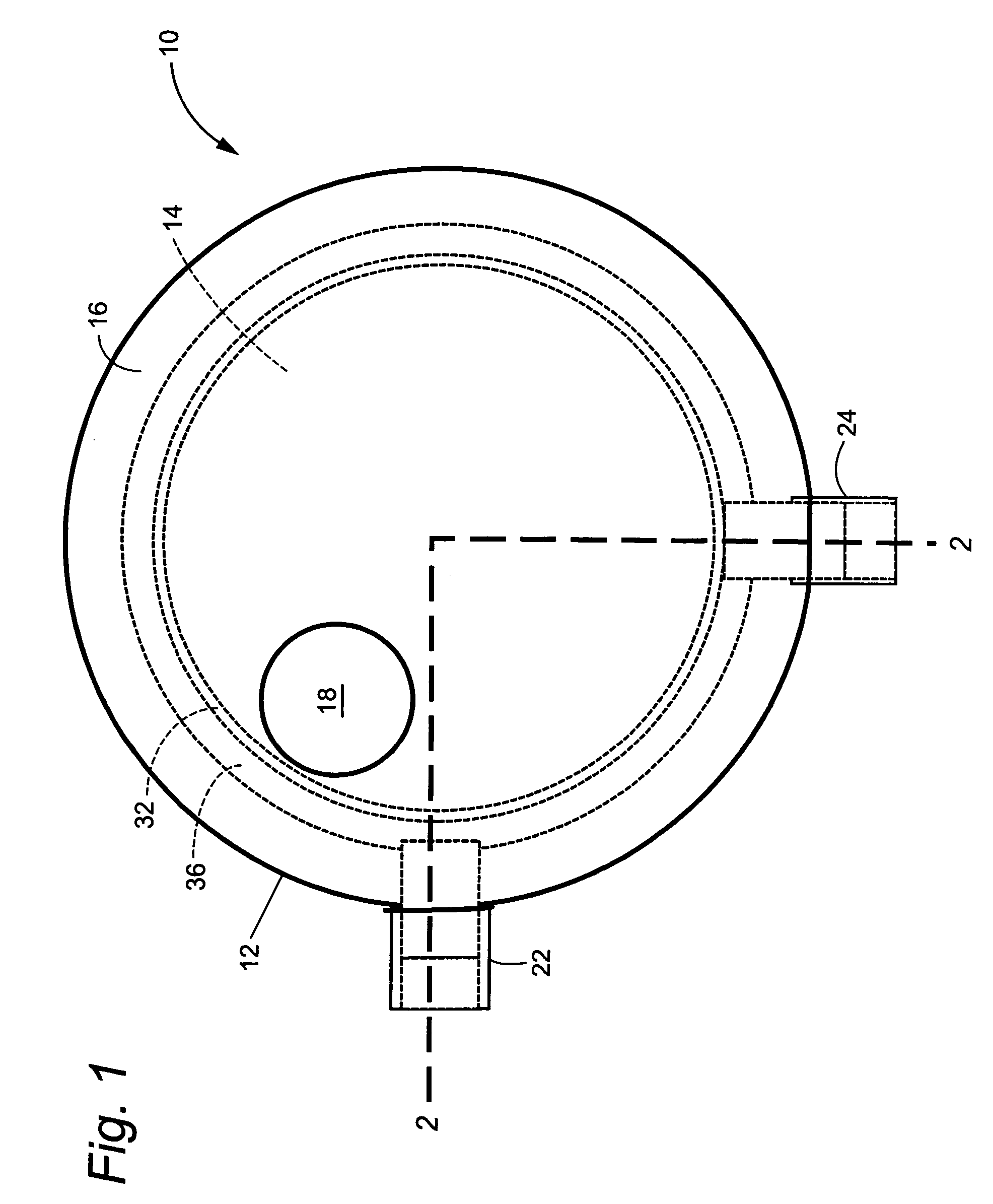
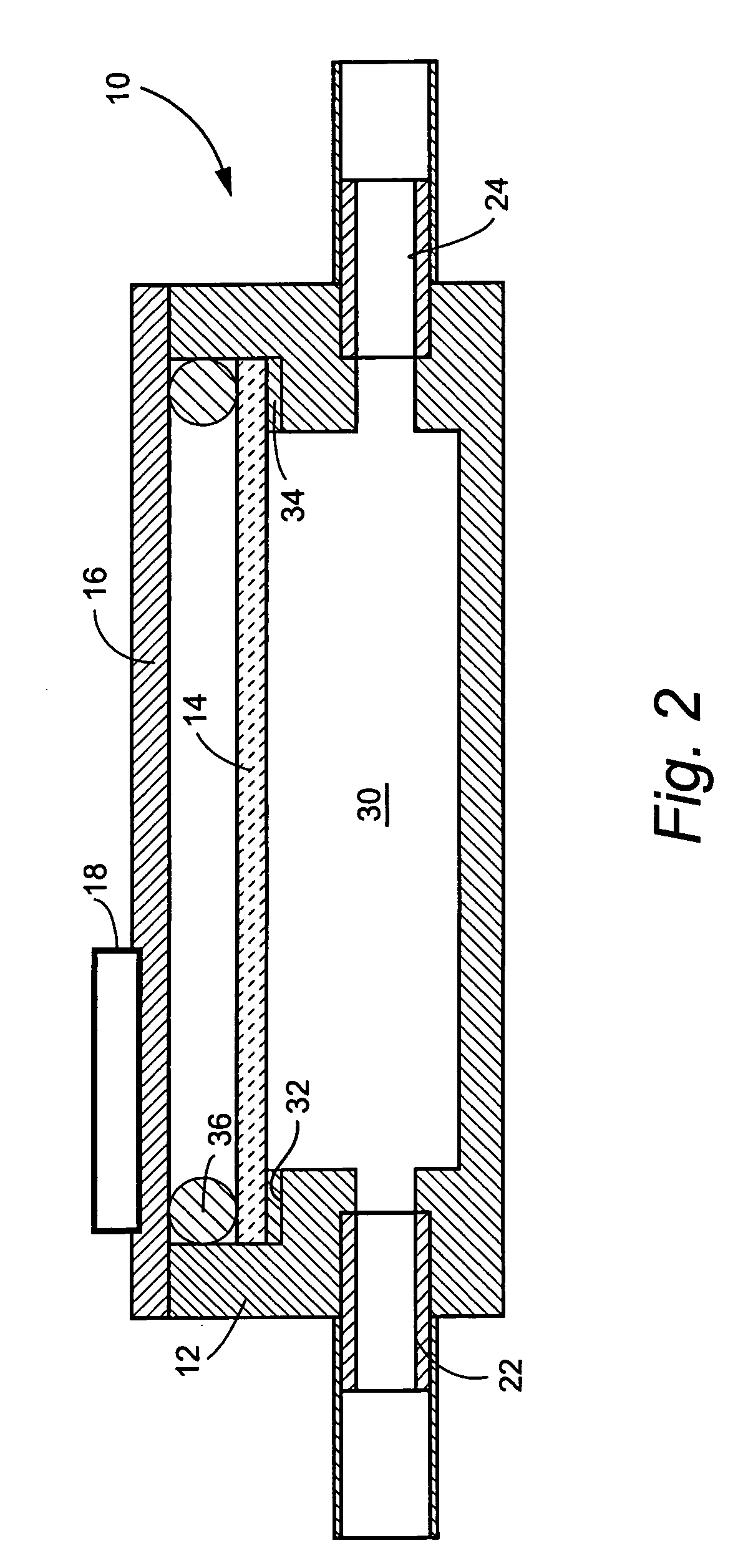
Transducer and transducer module
InactiveUS20130069483A1Enhanced Haptic FeedbackEnhance propagationMagnetic circuit rotating partsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerAcoustic propagation
Transducers and transducer modules having the transducers are disclosed. An embodiment discloses a transducer that includes a conductive layer having a U-shaped slit toward its swing end. The slit is configured to enhance a haptic feedback or an acoustic propagation, or adjust a resonant mode.
Owner:CHIEF LAND ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rolled electroactive polymers
InactiveUS6891317B2Increase conversionsImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPolymer scienceMechanical energy
The invention describes rolled electroactive polymer devices. The invention also describes employment of these devices in a wide array of applications and methods for their fabrication. A rolled electroactive polymer device converts between electrical and mechanical energy; and includes a rolled electroactive polymer and at least two electrodes to provide the mechanical / electrical energy conversion. Prestrain is typically applied to the polymer. In one embodiment, a rolled electroactive polymer device employs a mechanism, such as a spring, that provides a force to prestrain the polymer. Since prestrain improves mechanical / electrical energy conversion for many electroactive polymers, the mechanism thus improves performance of the rolled electroactive polymer device.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Ultrasonic transducer which is either crimped or welded during assembly
InactiveUS7876030B2Application of torsional stress and the like to piezoelectric elements can be suppressedAvoid distractionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurgeryUltrasonic sensorEngineering
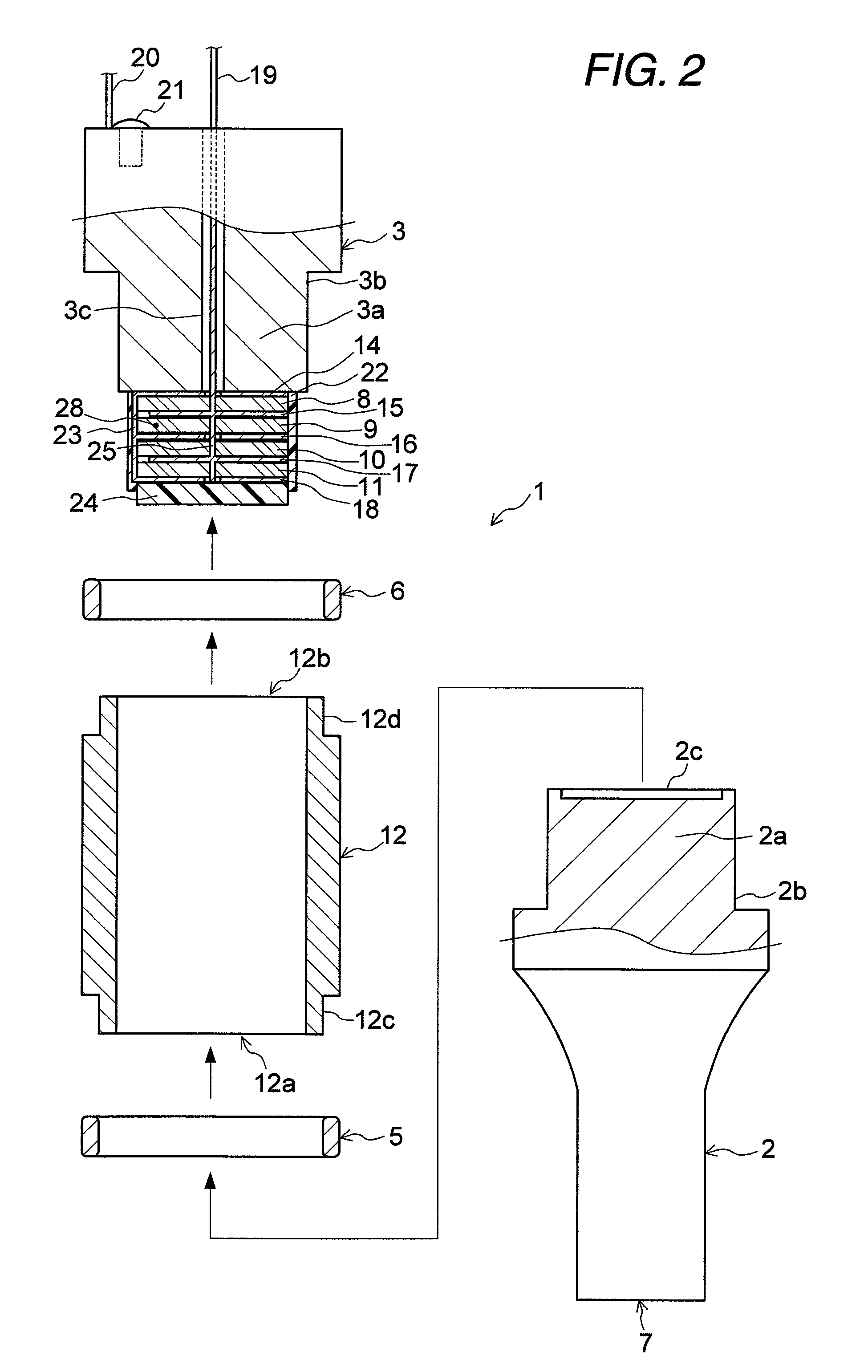
An ultrasonic transducer includes: piezoelectric elements; a pair of clamping members which clamp said piezoelectric elements; and a cover member which is crimped to at least one of said pair of clamping members in a state where said cover member cooperates with said pair of clamping members to surround said piezoelectric elements.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Ultrasonic lead screw motor
InactiveUS6940209B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPressure infusionUltrasonic vibrationAxial force
An apparatus for driving a threaded shaft assembly that contains a threaded shaft with an axis of rotation and, engaged therewith, a threaded nut. Subjecting the threaded nut to ultrasonic vibrations causes the threaded shaft to simultaneously rotate and translate in the axial direction. The threaded shaft is connected to a load that applies an axial force to the threaded shaft.
Owner:NEW SCALE TECH
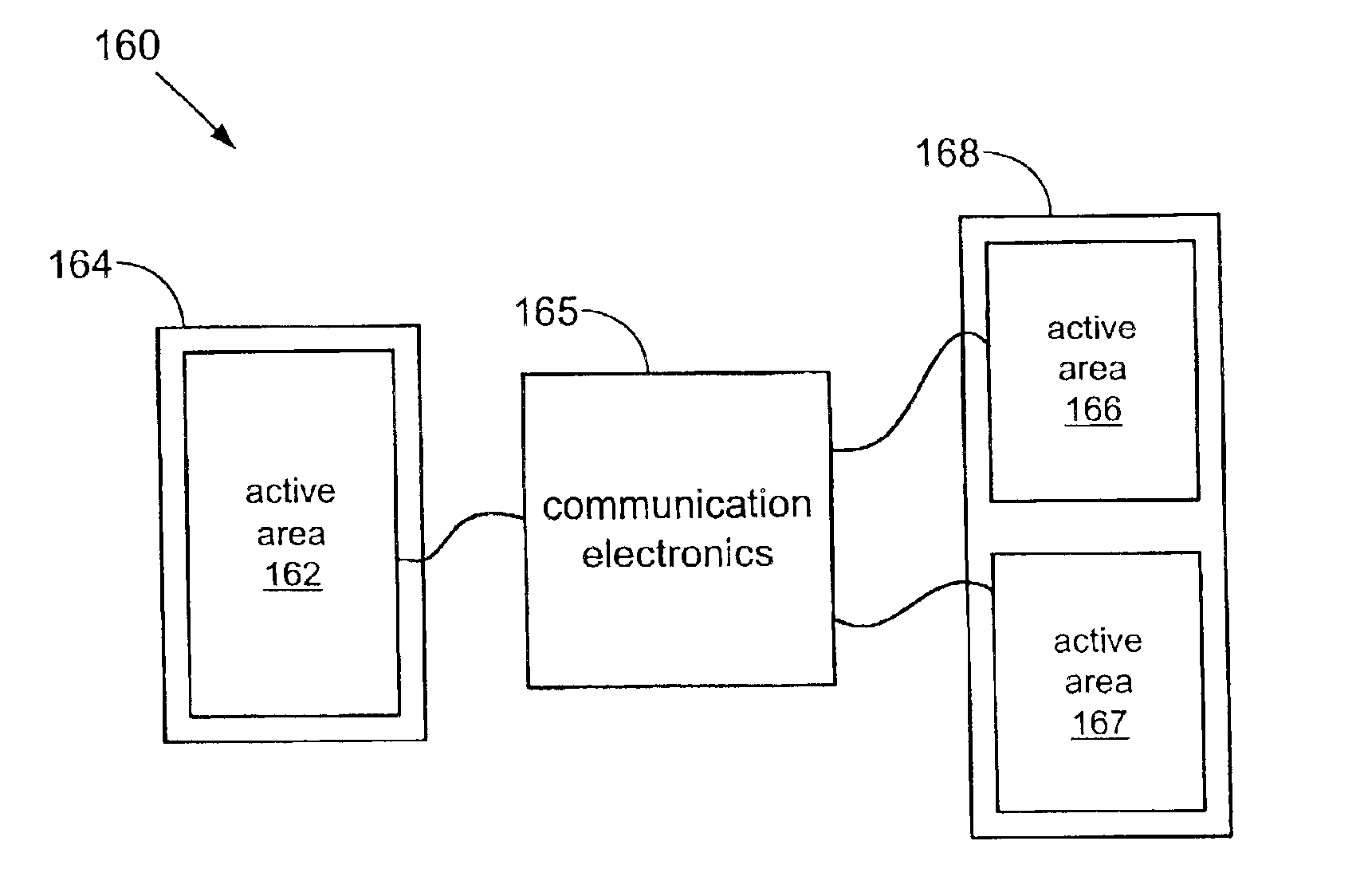
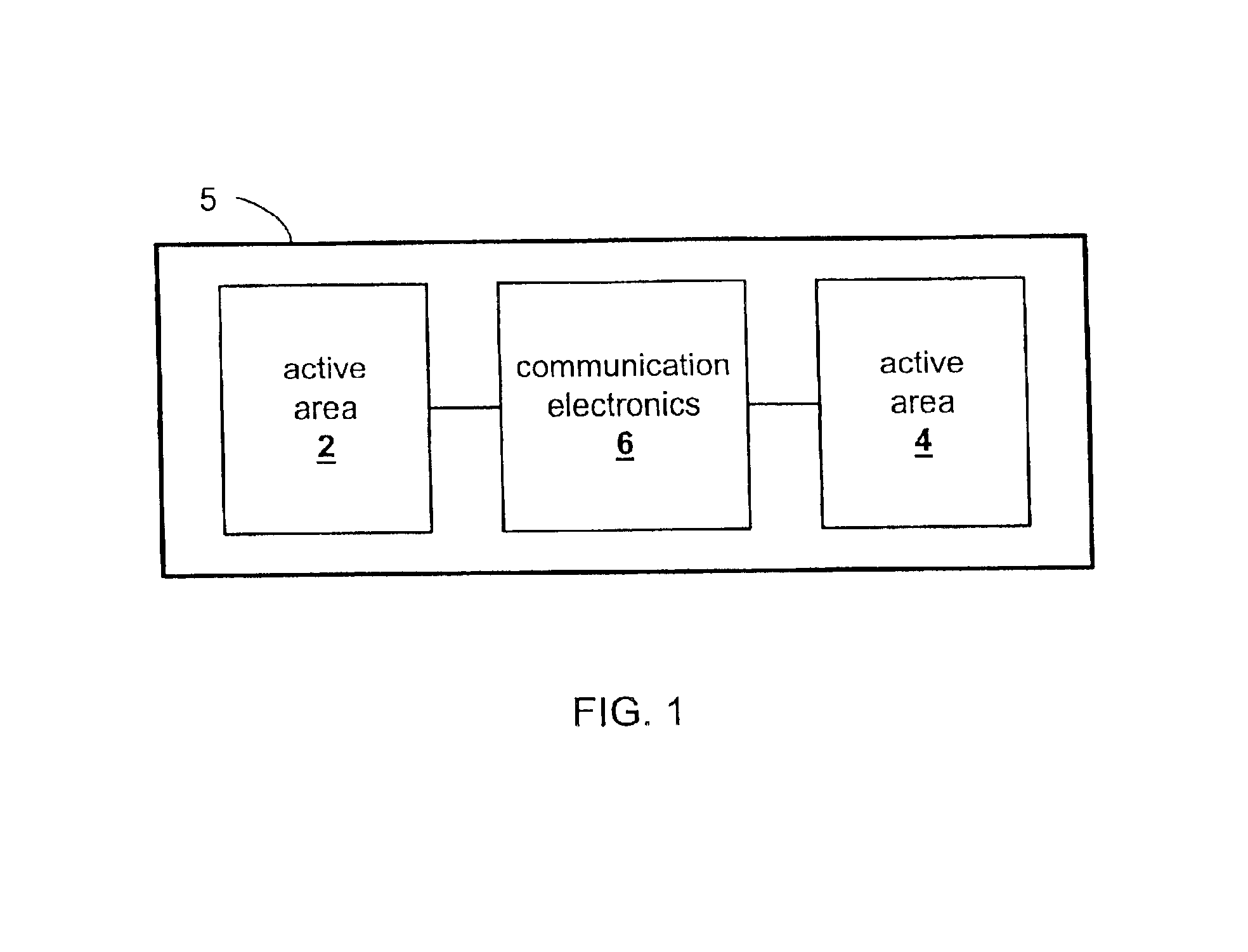
Master/slave electroactive polymer systems
InactiveUS6876135B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionActive polymerTransducer
The present invention relates to improved devices, systems and methods that convert between electrical and mechanical energy. An electroactive polymer transducer converts between electrical and mechanical energy. An active area is a portion of an electroactive polymer transducer. The active area comprises a portion of an electroactive polymer and at least two electrodes that provide or receive electrical energy to or from the portion. The present invention relates to transducers and devices comprising multiple active areas that are in electrically communication. More specifically, the present invention relates to master / slave arrangements for multiple active areas disposed on one or more electroactive polymers. In a master / slave arrangement, a first active area deflects (a ‘master’), and a second active area reacts (a ‘slave’). Communication electronics in electrical communication with electrodes for the first active area and in electrical communication with electrodes for the second active area transfer electrical energy between the two active areas.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
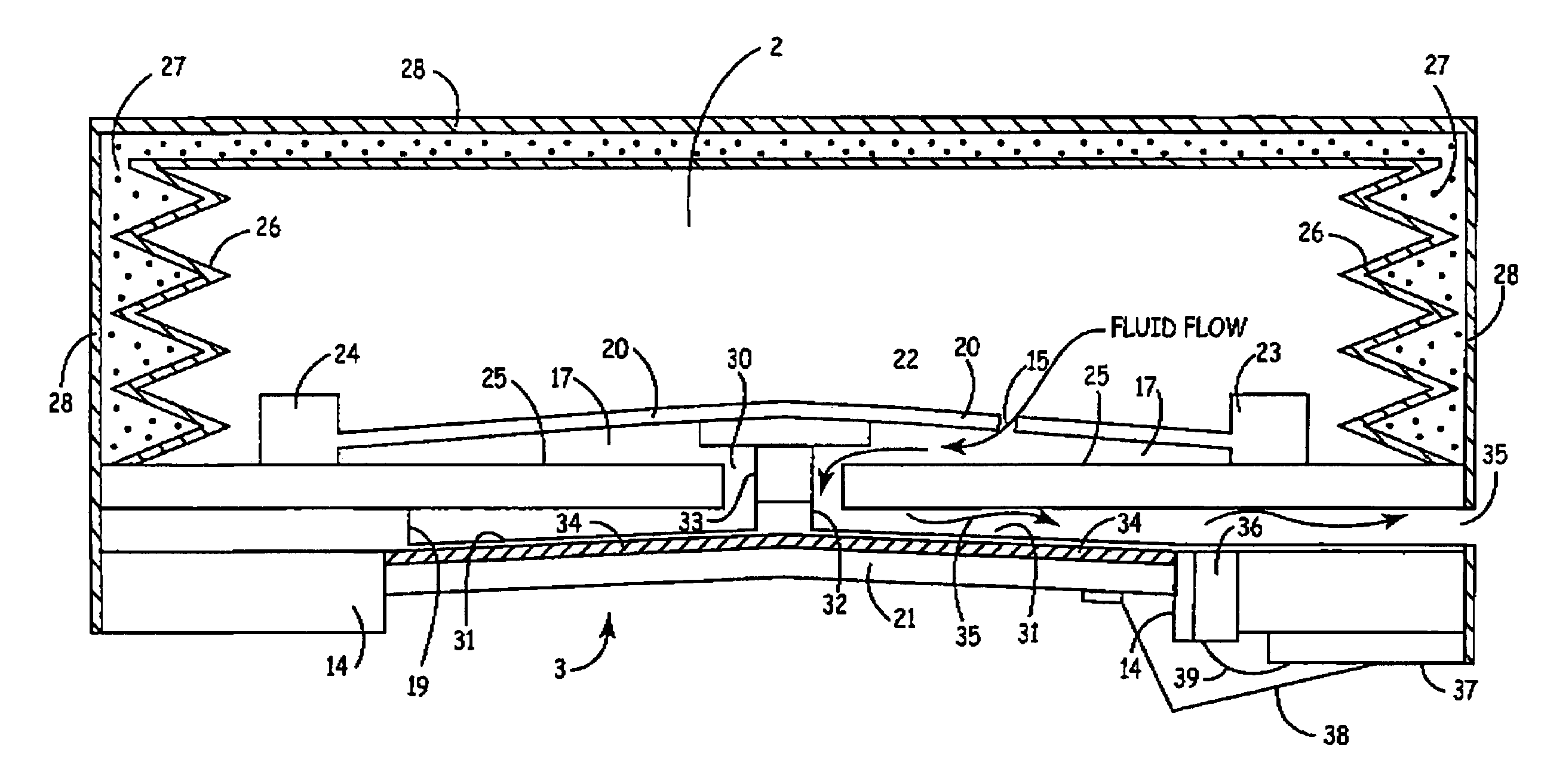
Drive circuit having improved energy efficiency for implantable beneficial agent infusion or delivery device
InactiveUS7070577B1Valve arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityEnergy recovery
An implantable beneficial agent infusion device featuring a unique energy recovery circuit and a deflectable energy storing member such as a piezo-electric membrane is disclosed. The circuit and deflectable energy storing member cooperate to permit electrical energy employed to activate the member to be at least partially recovered. In a preferred embodiment, the deflectable energy storing member is connected to a seal which is opened to permit the delivery or infusion of a pre-determined amount of a beneficial agent to a patient when the member is deflected or actuated through the application of a sufficiently high voltage thereacross. Charge stored on or in the deflectable energy storing member as a result of the voltage being applied thereacross is recovered by a novel circuit when the deflectable energy storing membrane is permitted to return to its non-actuated state or position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Multiple element electrode cMUT devices and fabrication methods
ActiveUS20050200241A1Optimizing receiptFacilitate transmissionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducersBiomedical engineering
Multiple electrode element capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (“cMUT”) devices and fabrication methods are provided. A cMUT device generally comprises a top electrode disposed within a membrane, a bottom electrode disposed on a substrate, and a cavity between the membrane and the bottom electrode. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, at least one of the first electrode and the second electrode comprises a plurality of electrode elements. The electrode elements can be positioned and energized to shape the membrane and efficiently transmit and receive ultrasonic energy, such as ultrasonic waves. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Transducer Having an Insulation Extension
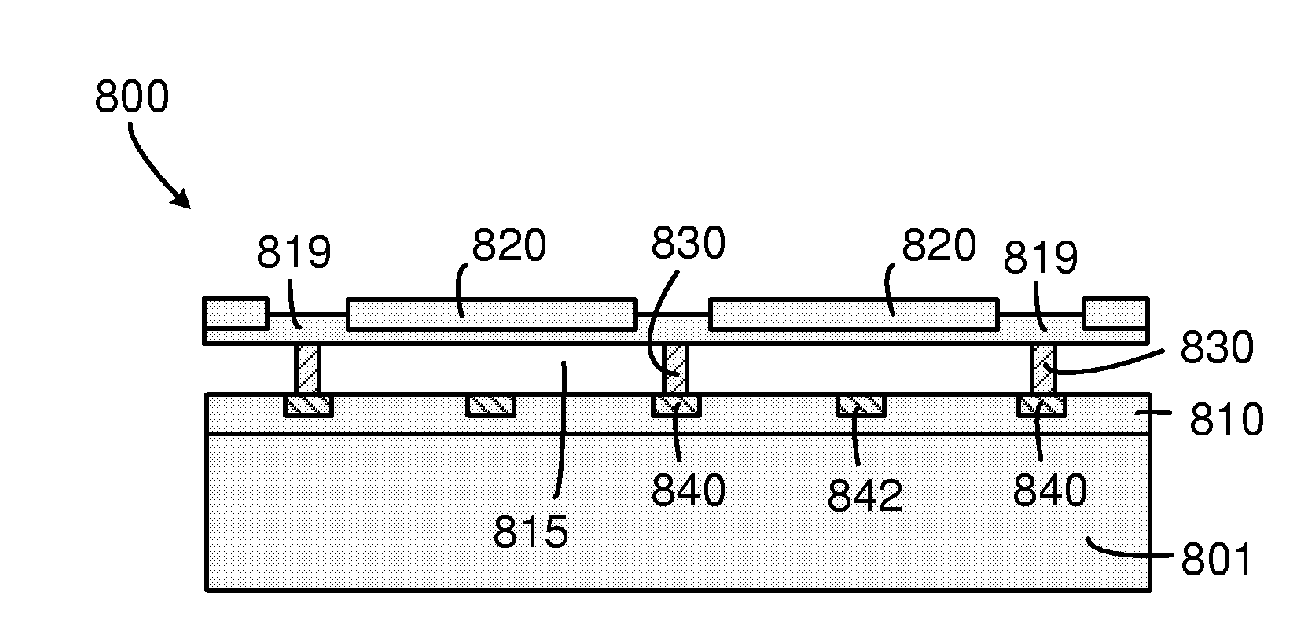
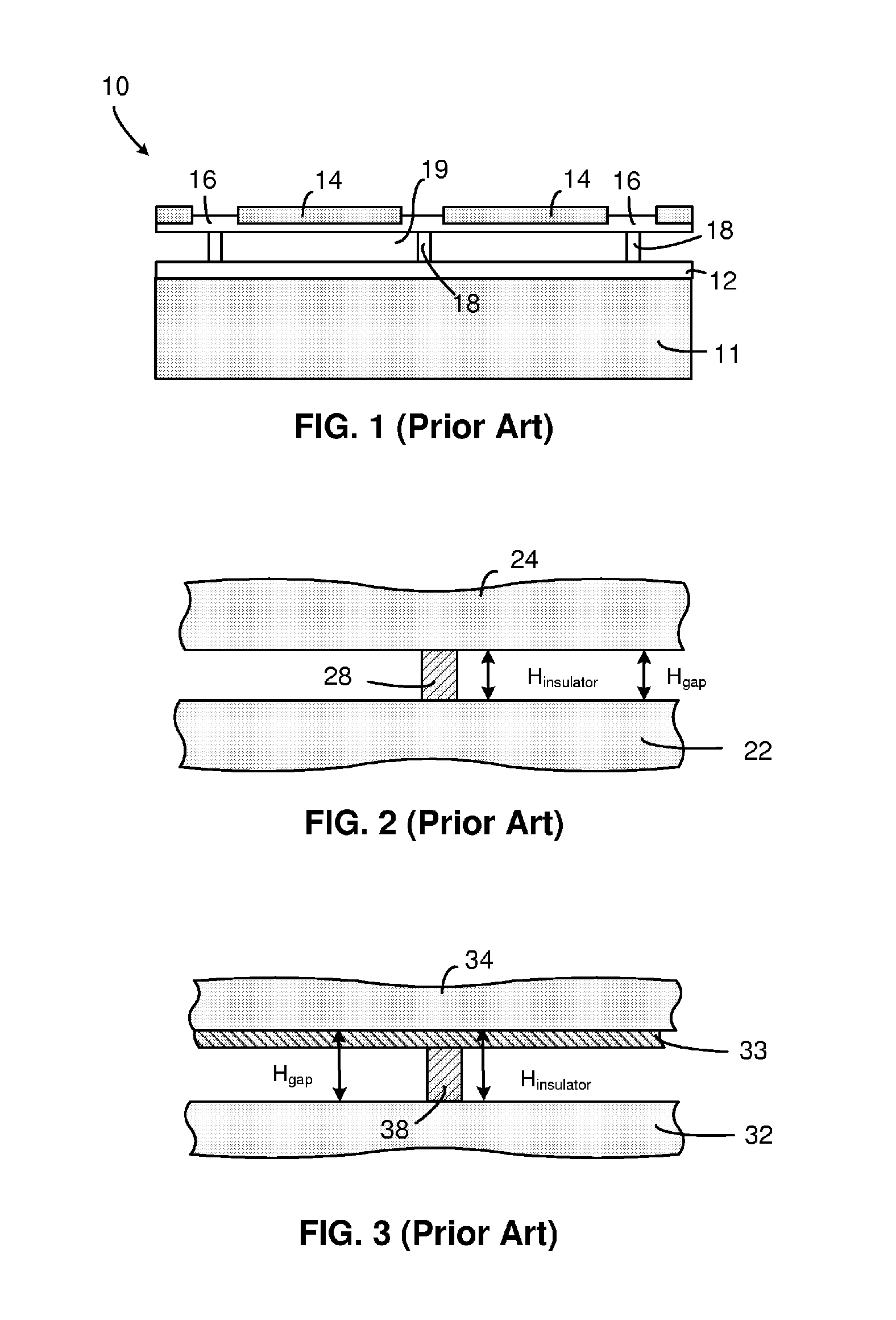
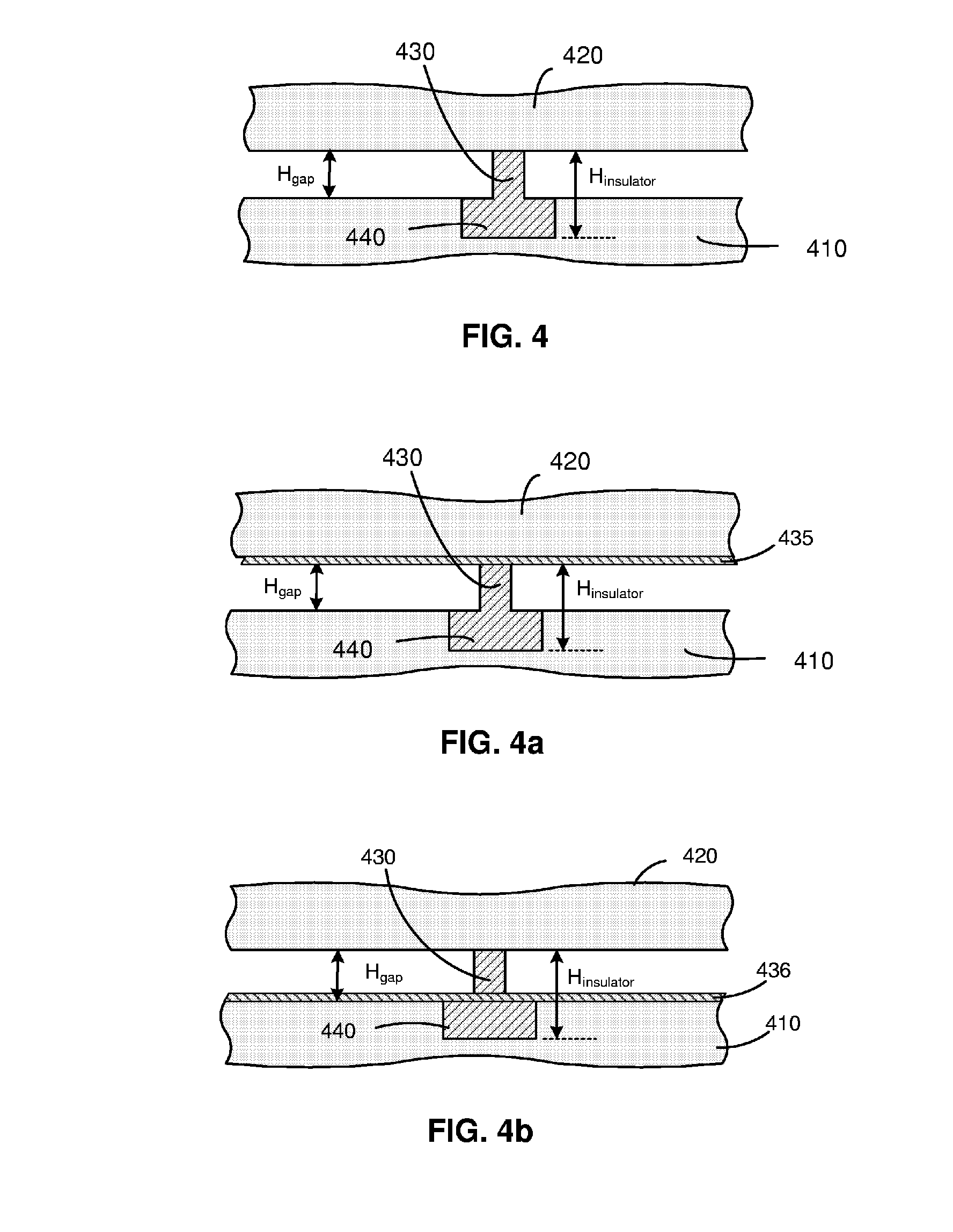
ActiveUS20080290756A1Effective insulationIncrease the gapElectrical transducersMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringElectromechanical transducer
A micro-electro-mechanical transducer (such as a cMUT) having two electrodes separated by an insulator with an insulation extension is disclosed. The two electrodes define a transducing gap therebetween. The insulator has an insulating support disposed generally between the two electrodes and an insulation extension extending into at least one of two electrodes to increase the effective insulation without having to increase the transducing gap. Methods for fabricating the micro-electro-mechanical transducer are also disclosed. The methods may be used in both conventional membrane-based cMUTs and cMUTs having embedded springs transporting a rigid top plate.
Owner:KOLO MEDICAL (SUZHOU) CO LTD
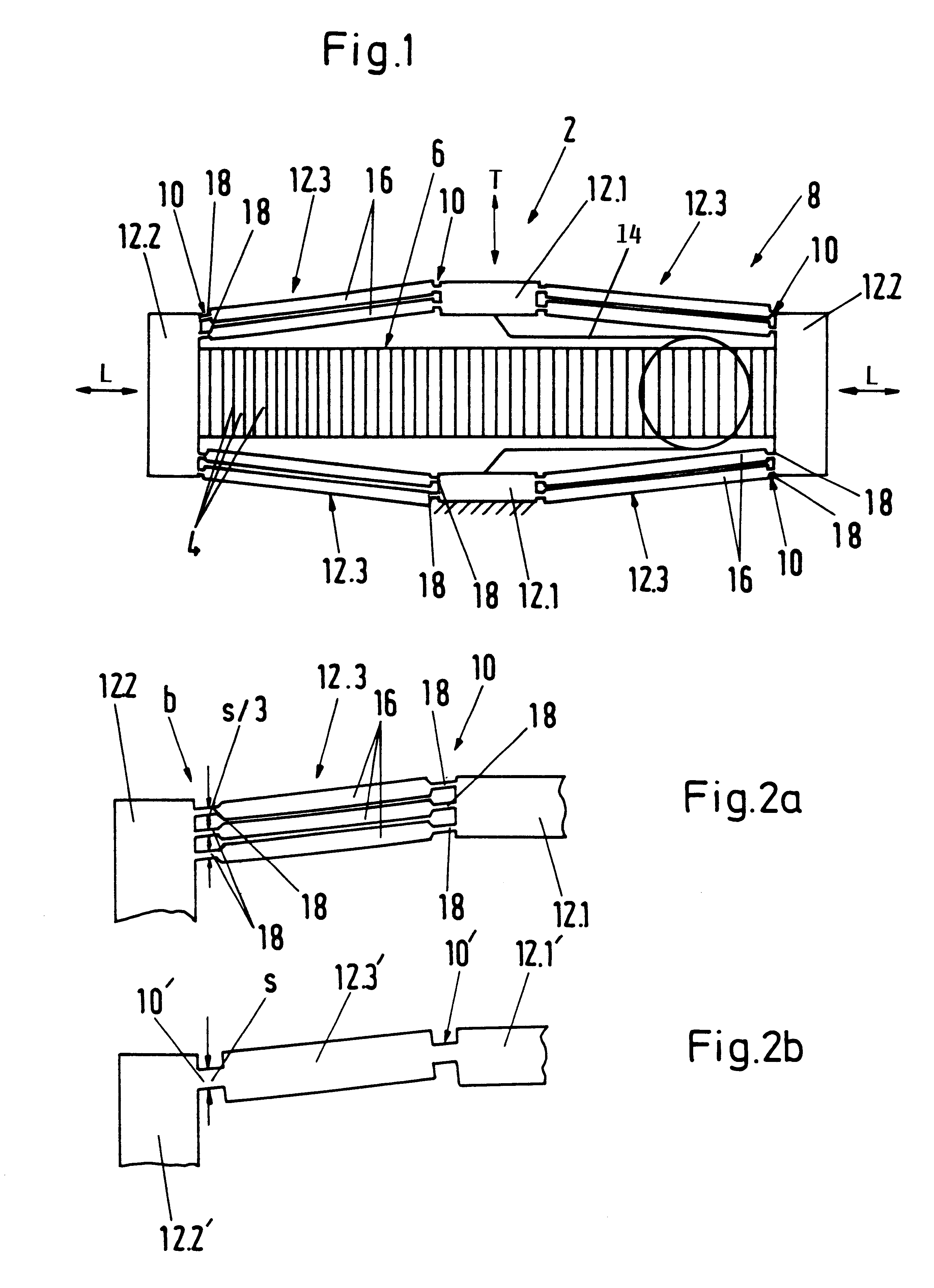
Electrostrictive or piezoelectric actuator device with a stroke amplifying transmission mechanism
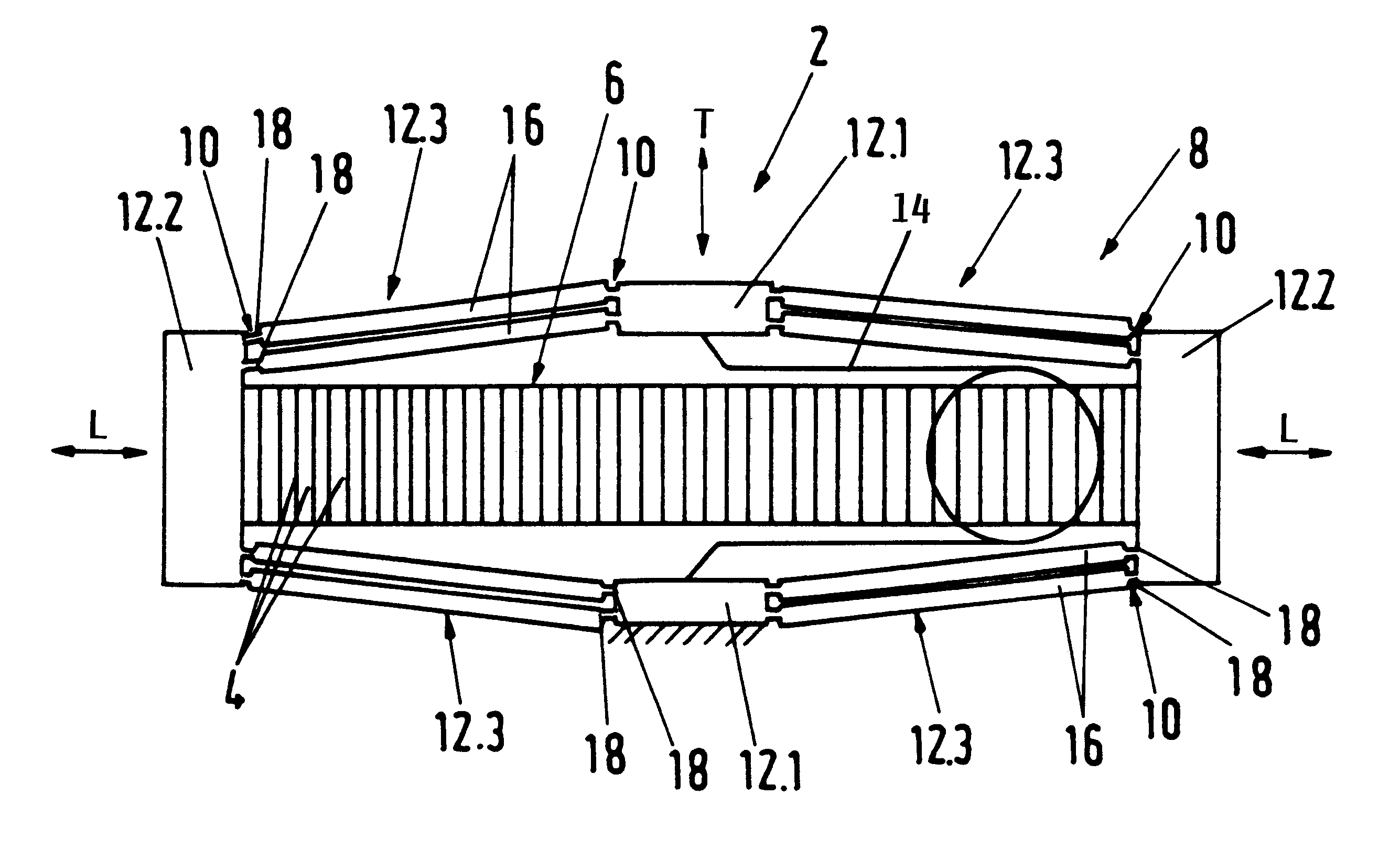
InactiveUS6294859B1Low bending stiffnessReduce joint stiffnessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGearingFiber strainPiezoelectric actuators
An actuator device (2) includes a piezoelectric or electro-strictive solid state actuator element (6) that is elongated upon application of an electric voltage thereto, and a transmission mechanism (8) that amplifies the stroke displacement of the actuator element. The transmission mechanism (8) includes a plurality of rigid frame members (12), including unitary frame members (12.1, 12.2) and divided frame members (12.3), and elastically flexible joints (10) that respectively interconnect the frame members. Each one of the divided frame members (12.3) is made up of a plurality of separate parallel link rods (16). Each flexible joint (10) is made up of a plurality of individual parallel hinge members (18) that respectively connect an end of each one of the link rods (16) to the adjacent unitary frame member (12.1, 12.2). By this division of the flexible joints and of the divided frame members into parallel sub-components, the cross-sectional thickness of each individual hinge member is reduced, and thereby the bending stiffness and the outer fiber strain of the material of the hinge members is significantly reduced while providing the same total tensile strength and tensile stiffness. The link rods of each divided frame member effectively form a parallelogram linkage for moving and guiding the output members (12.1) in a parallel manner.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
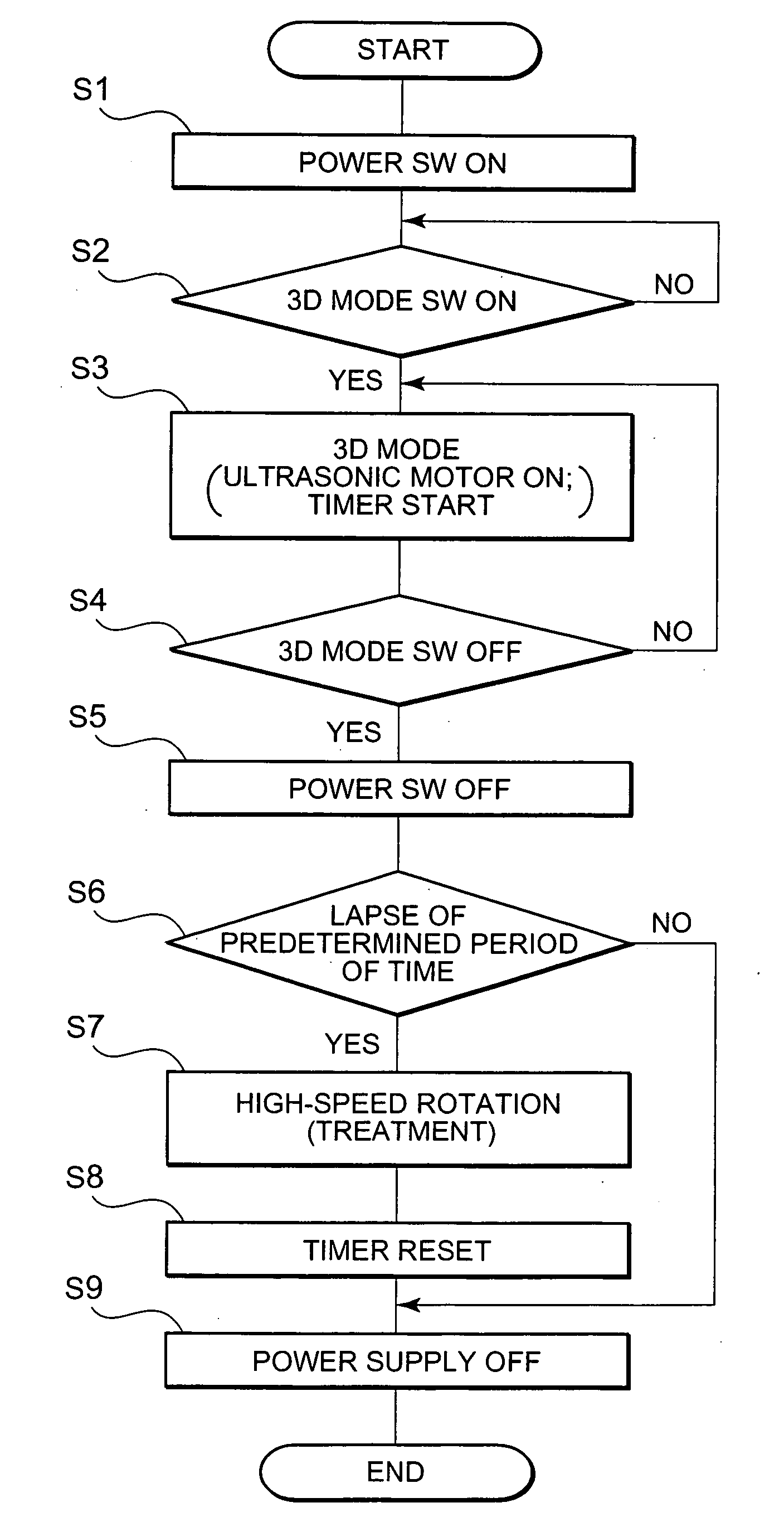
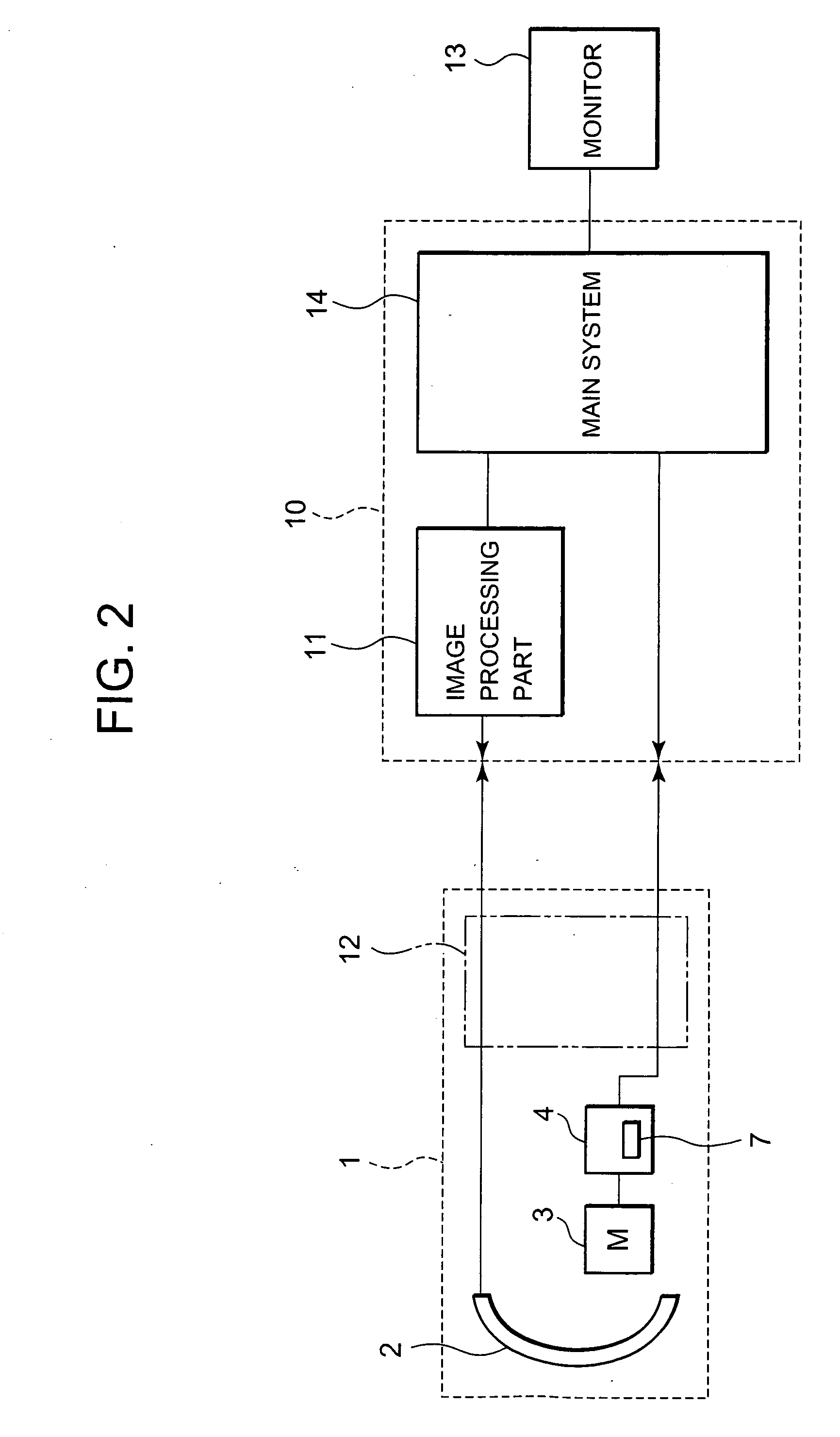
Ultrasonic motor driving device and ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus
InactiveUS20060250046A1Reduce stepsUnstable operationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyLow speedEngineering
A technology, wherein unstable operation of the ultrasonic motor is prevented, when the ultrasonic motor is driven at the lower speed out of at least two types of speeds, and life extension is attempted, is disclosed, and according to this invention, when the ultrasonic motor 3 is driven at a comparatively low-speed during normal driving, unstable operation due to driving at a comparatively low-speed can be prevented and life extension can be attempted by driving the ultrasonic motor at a comparatively high-speed every predetermined period of time.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
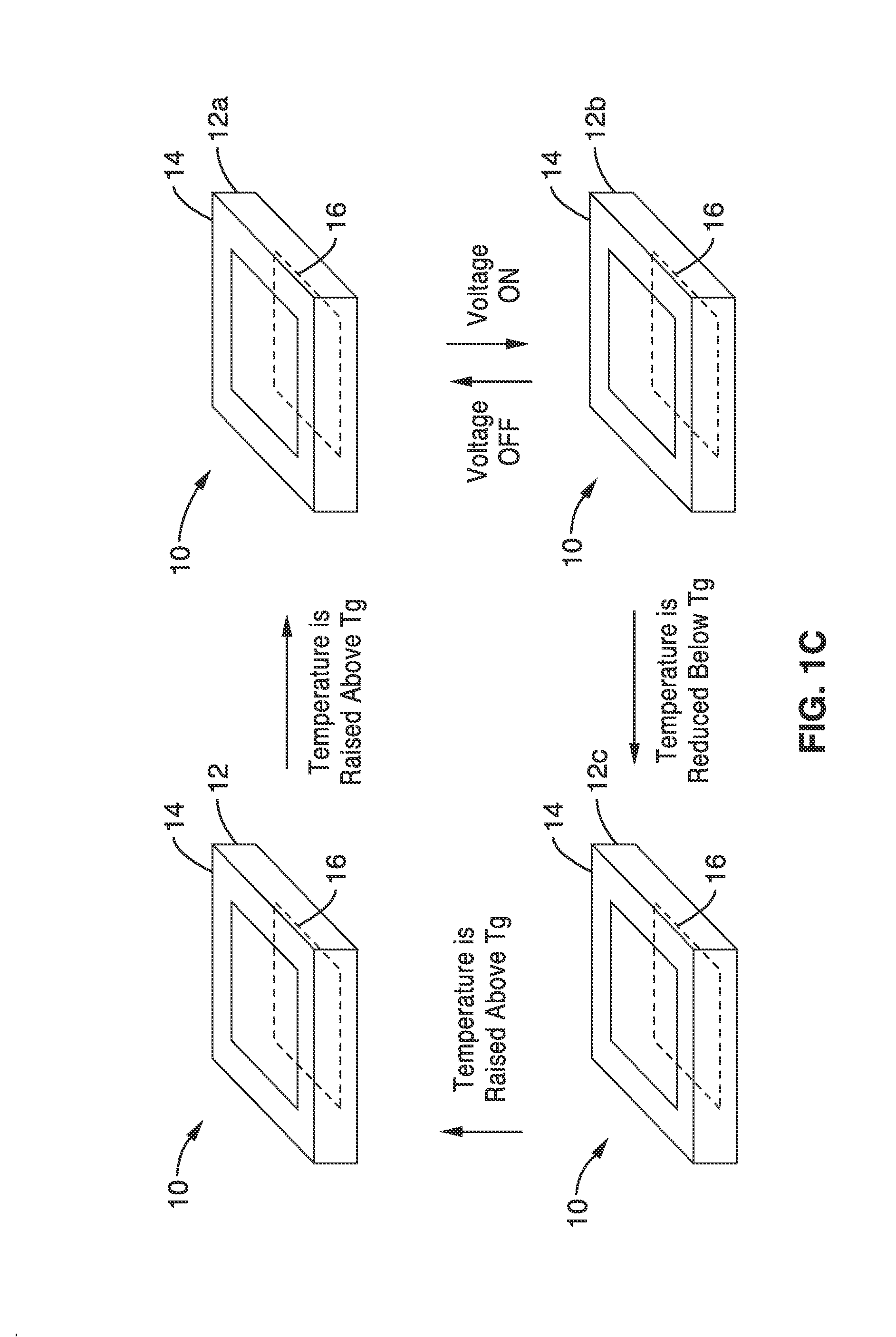
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS20100171393A1Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionHigh energyShock resistance
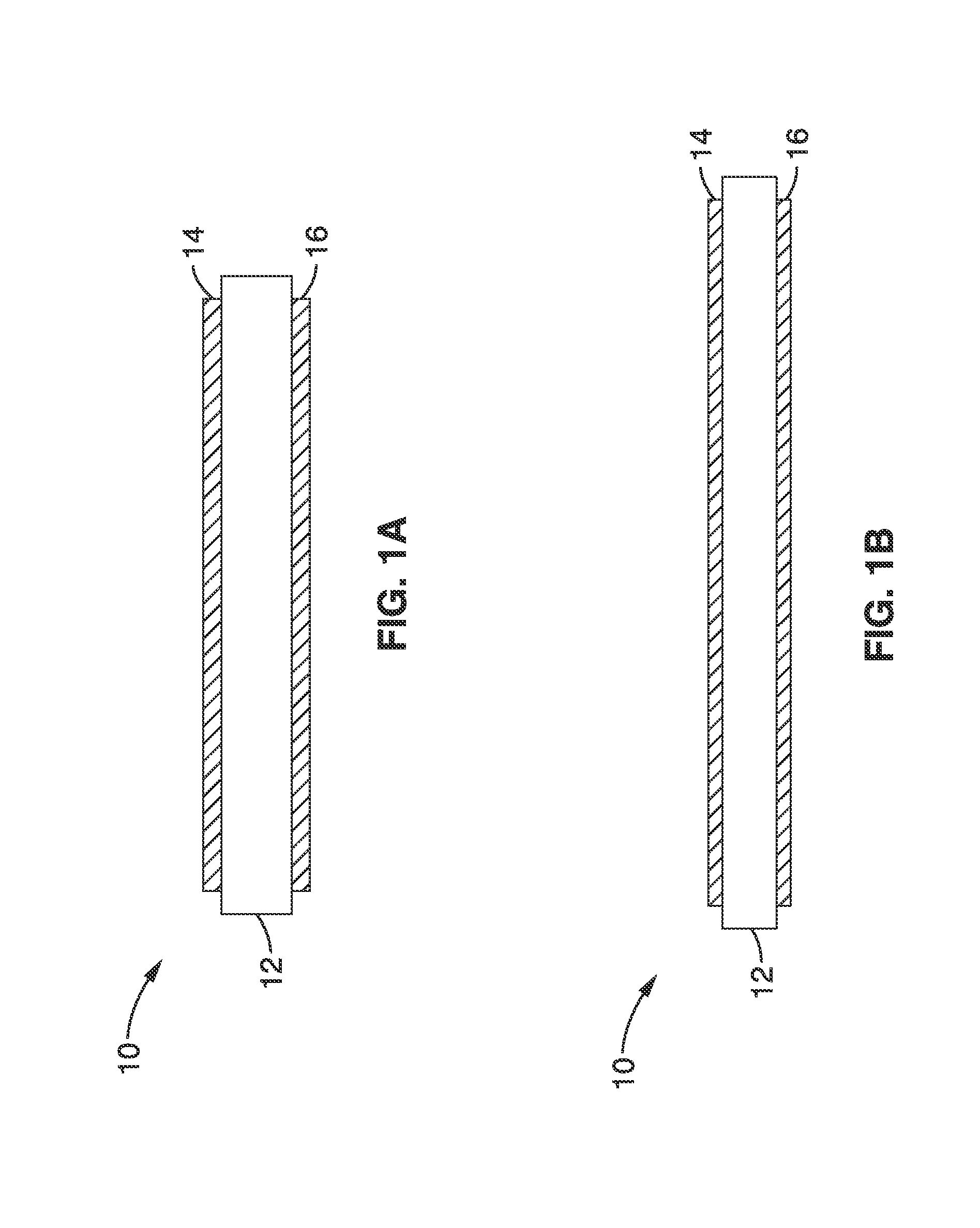
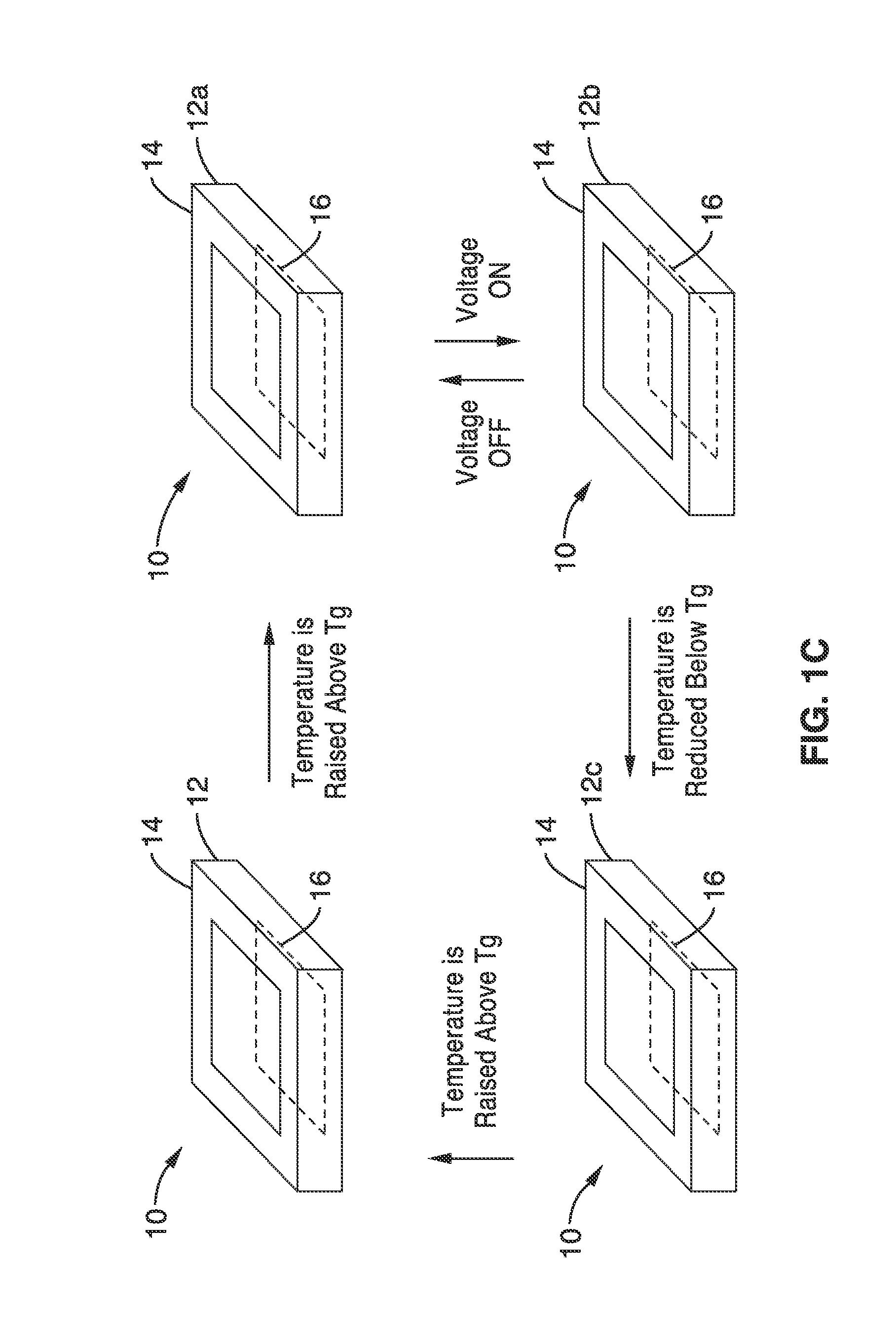
A bistable electroactive polymer transducer is provided for electrically actuated deformation of rigid electroactive polymer members. The polymers have glass transition temperatures (Tg) above ambient conditions and turn into rubbery elastomers above Tg and have high dielectric breakdown strength in the rubbery state. They can be electrically deformed to various rigid shapes with maximum strain greater than 100% and as high as 400%. The actuation is made bistable by cooling below Tg to preserve the deformation. The dielectric actuation mechanism includes a pair of compliant electrodes in contact with a dielectric elastomer which deforms when a voltage bias is applied between the pair of electrodes. In some of the transducers of the present invention, the dielectric elastomer is also a shape memory polymer. The deformations of such bistable electroactive polymers can be repeated rapidly for numerous cycles. The polymer transducers have such advantages as high energy and power densities, quietness, mechanical compliancy (for shock resistance and impedance matching), high efficiency, lightweight, and low cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tunable bulk acoustic wave mems microresonator
InactiveUS20050162040A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcousticsBulk acoustic wave
A suspended film bulk acoustic micro-resonator that includes a beam made of a piezoelectric material fixed to a support and sandwiched between excitation electrodes. The resonator also includes a mechanism modifying limiting conditions of the resonator composed of the excited beam to modify the micro-resonator resonant frequency.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Rolled electroactive polymers
InactiveUS7233097B2Improves mechanical/electrical energy conversionImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFlexible member pumpsPolymer scienceMechanical energy
The invention describes rolled electroactive polymer devices. The invention also describes employment of these devices in a wide array of applications and methods for their fabrication. A rolled electroactive polymer device converts between electrical and mechanical energy; and includes a rolled electroactive polymer and at least two electrodes to provide the mechanical / electrical energy conversion. Prestrain is typically applied to the polymer. In one embodiment, a rolled electroactive polymer device employs a mechanism, such as a spring, that provides a force to prestrain the polymer. Since prestrain improves mechanical / electrical energy conversion for many electroactive polymers, the mechanism thus improves performance of the rolled electroactive polymer device.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
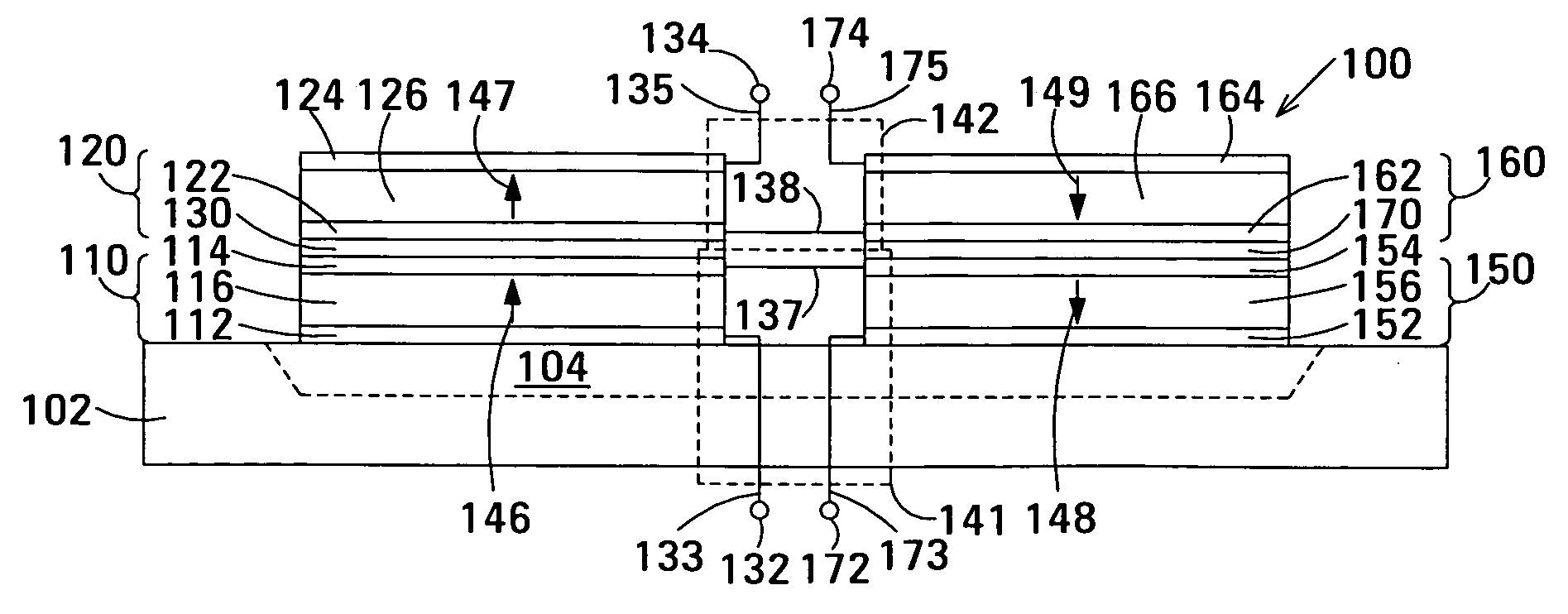
Piezoelectric actuator and micro-electromechanical device
InactiveUS20060055287A1Warpage suppressionImprove accuracyNanotechPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric actuatorsEngineering
A piezoelectric actuator includes a first beam including a first bottom electrode, a first piezoelectric film on the first bottom electrode, and a first top electrode on the first piezoelectric film, a fixed end assigned at an end of the first beam and fixed on a substrate, a connecting end assigned at another end of the first beam and suspended over a free space; and a second beam including a second piezoelectric film connected to the first piezoelectric film at the connecting end, a second bottom electrode under the second piezoelectric film, and a second top electrode on the second piezoelectric film, a working end assigned at an end of the second beam opposite to another end to which the connecting end is assigned and suspended over the free space; wherein a distance between centers of the fixed end and the working end is shorter than a distance from the working end to the connecting end.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Fault-tolerant electromechanical actuator having a torque sensing control system
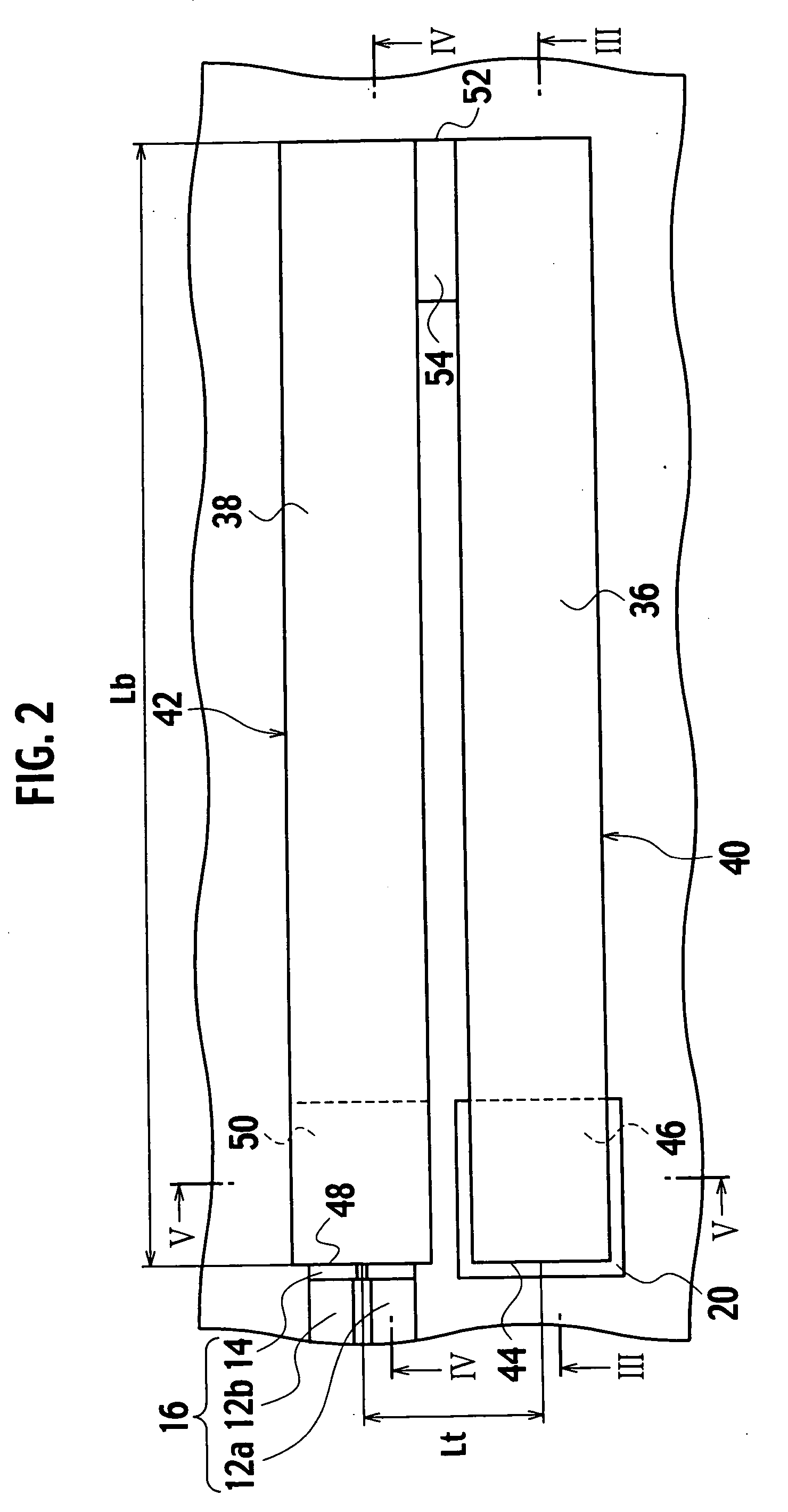
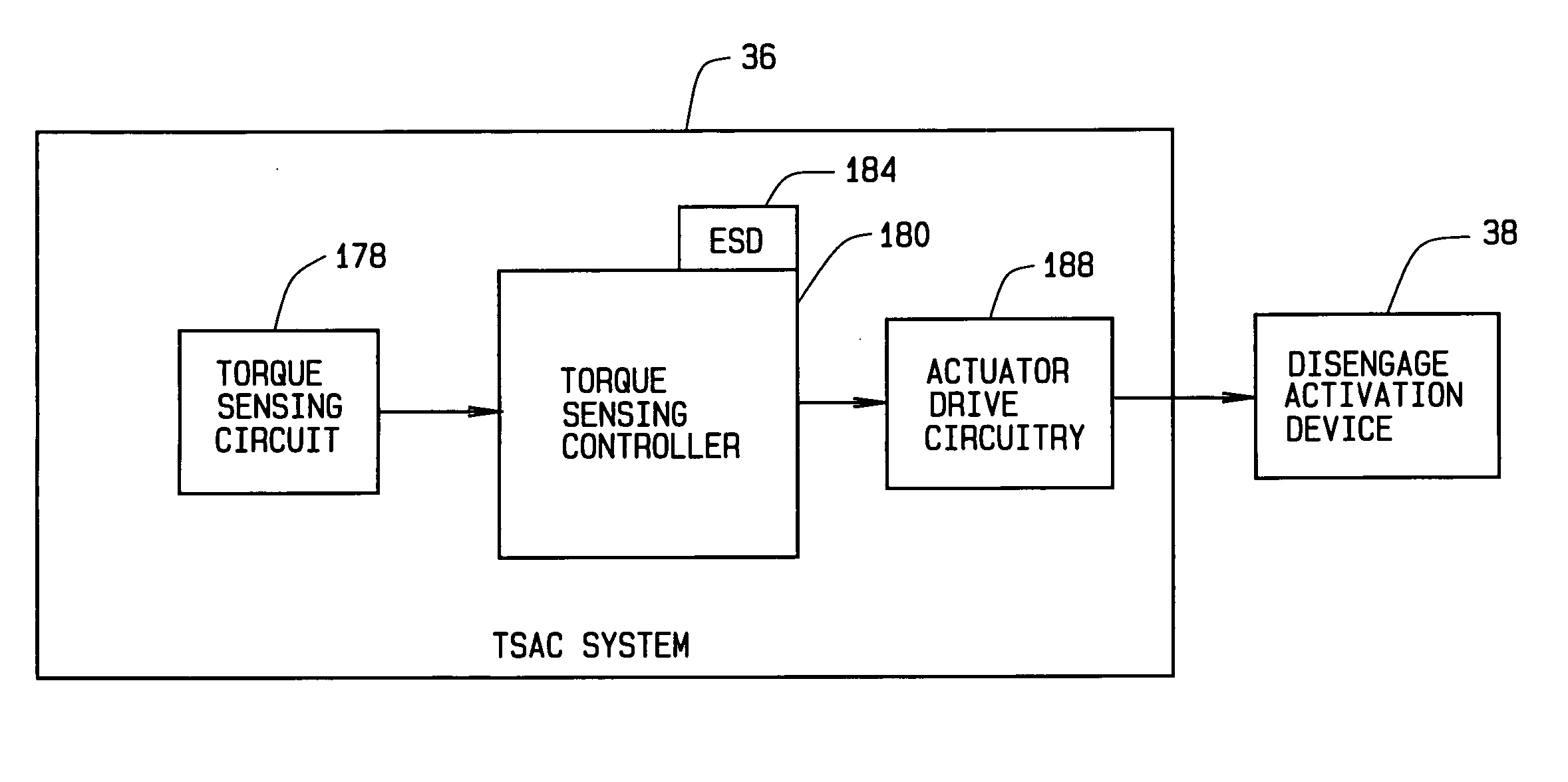
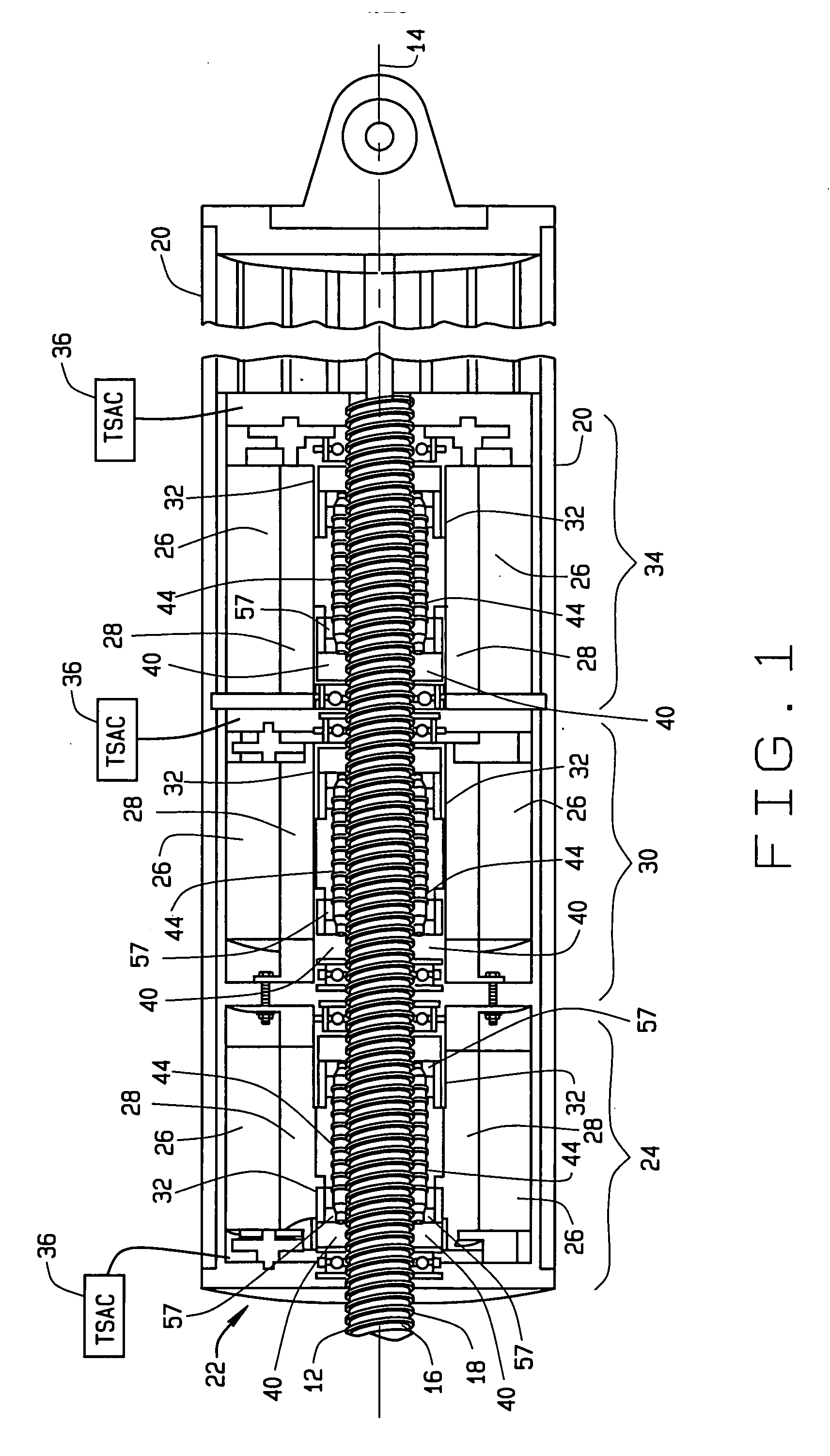
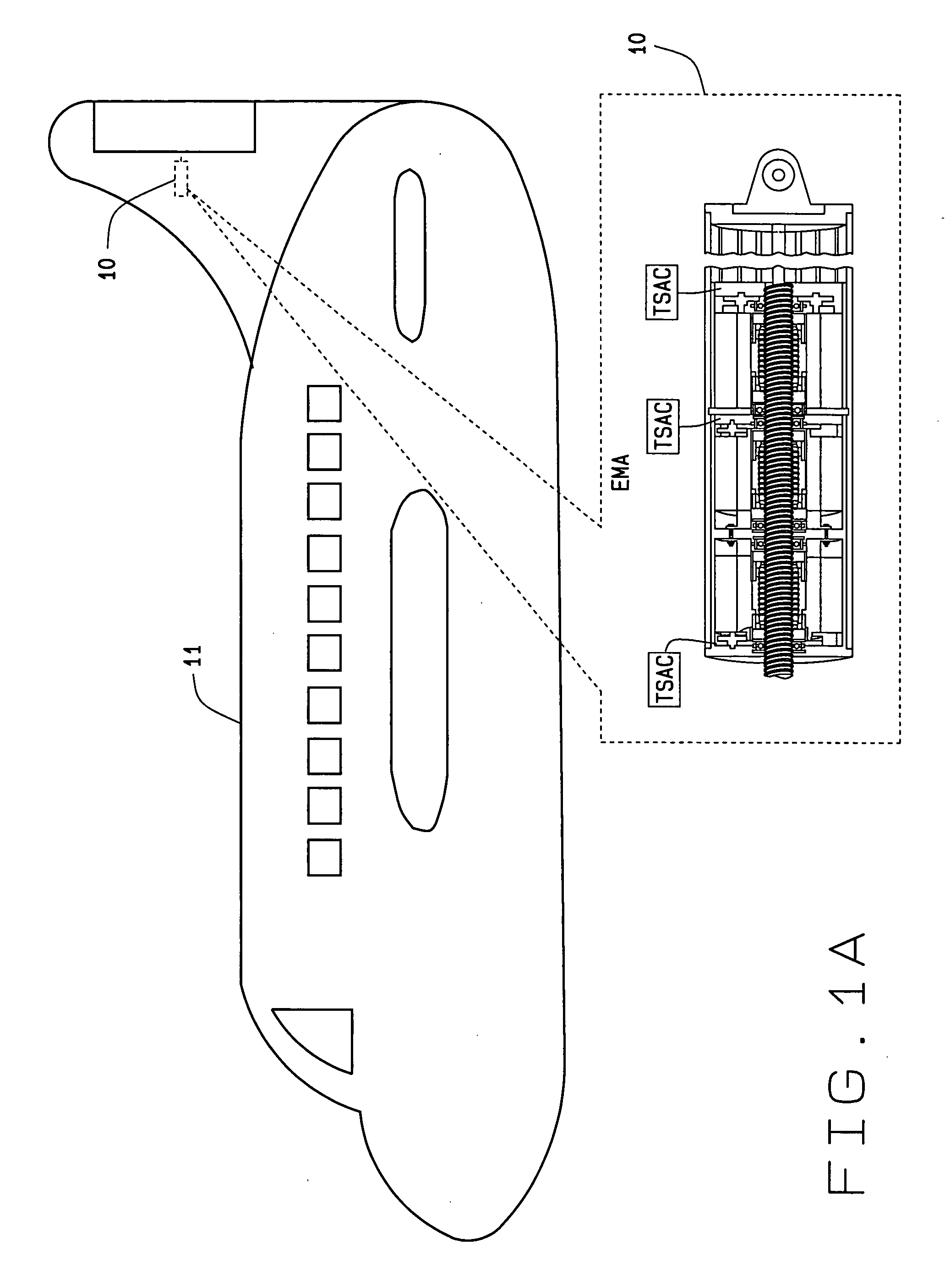
ActiveUS20060113933A1Low costEffectively prevent failureSynchronous generatorsDC motor speed/torque controlMechanical componentsControl system
An electromechanical actuator (EMA) is provided. The EMA includes a threaded output ram connectable to a mechanical component and at least one motor module engageable with the output ram for controllably translating the output ram along a linear axis of the output ram. The actuator further includes a torque sensing adaptive control (TSAC) system for monitoring torque within the motor module. The TSAC generates a disengagement command signal when the TSAC system determines torque within the motor module is outside an allowable motor module torque range. The disengagement command signal initiates disengagement of the motor module from the output ram.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Ultrasonic/acoustic transducer
ActiveUS20120163126A1Affect bandwidthValid matchPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionTransducerAcoustic wave
A transducer 1b comprising a vibrator body 2b for generating and / or receiving acoustic or ultrasonic waves, acoustically coupled to a second part 4 for generating and / or receiving acoustic or ultrasonic waves and, a matching layer 5 coupled to said vibrator body 2 so as, in use, to acoustically match the vibrator body 2b to a medium 6 contacting said matching layer 5.
Owner:CERAMTEC
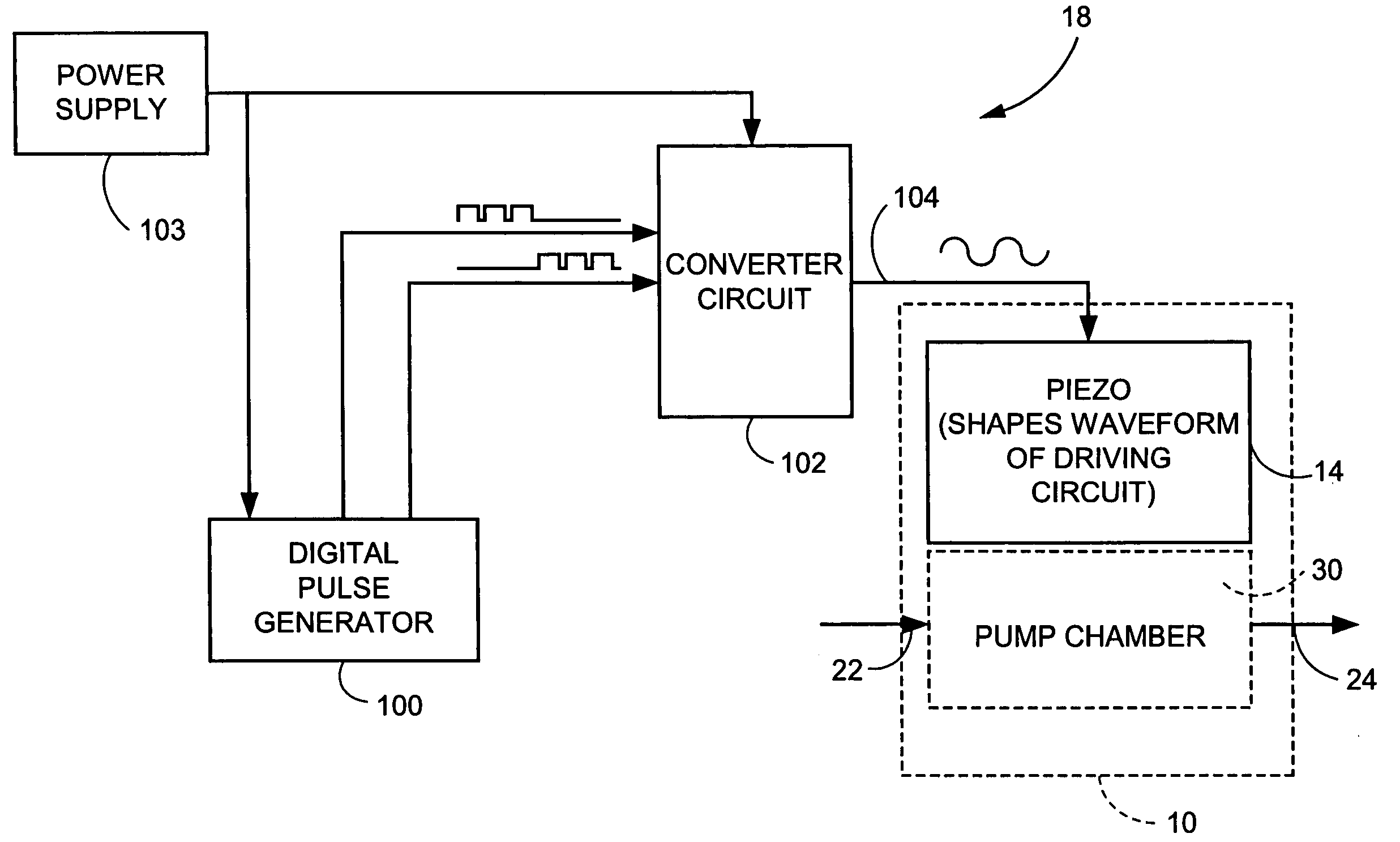
Piezoelectric devices and methods and circuits for driving same
A drive circuit (18) senses a parameter of a piezoelectric actuator (14) operating in a device (10) and adjusts a drive signal of the piezoelectric actuator in accordance with the parameter. The drive circuit comprises a controller (100) which controls a drive signal applied to the piezoelectric actuator (14); a feedback monitor (122) which obtains a feedback signal from the piezoelectric actuator while the piezoelectric actuator works; and, a processor (116) which uses the feedback signal to determine the parameter of the piezoelectric actuator. In one example mode, the parameter of the piezoelectric actuator which is determined by the piezoelectric actuator drive circuit is the capacitance or dielectric constant of the piezoelectric actuator. In other example modes, the parameter of the piezoelectric actuator which is determined by the piezoelectric actuator drive circuit is impedance or resonant frequency of the piezoelectric actuator.
Owner:PAR TECH
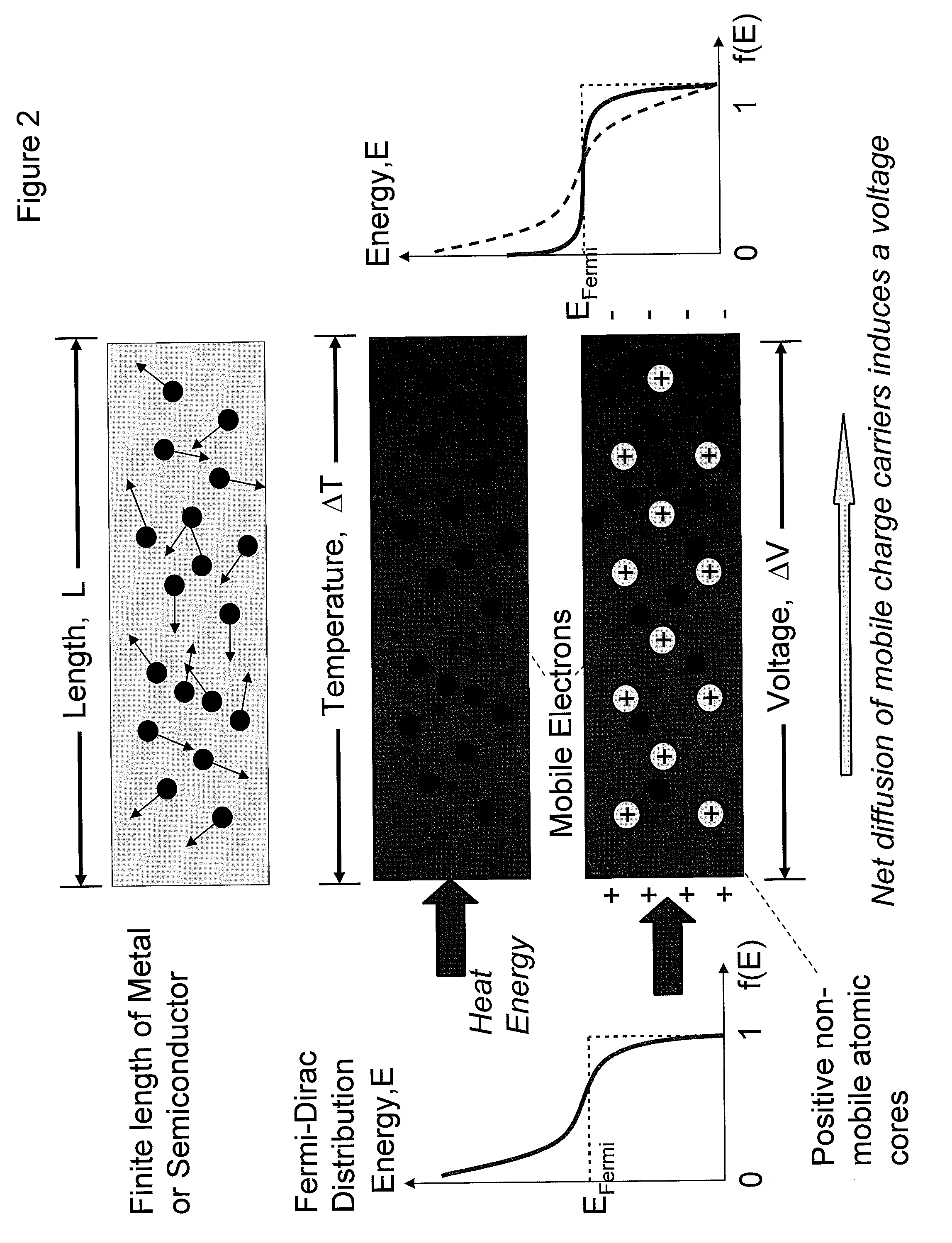
Thermoelectric and Pyroelectric Energy Conversion Devices
InactiveUS20080295879A1Improve efficiencyImprove thermoelectric conversion efficiencyRadiation pyrometryThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric materialsRare earth
New thermoelectric materials and devices are disclosed for application to high efficiency thermoelectric power generation. New functional materials based on oxides, rare-earth-oxides, rare-earth-nitrides, rare-earth phosphides, copper-rare-earth oxides, silicon-rare-earth-oxides, germanium-rare-earth-oxides and bismuth rare-earth-oxides are disclosed. Addition of nitrogen and phosphorus are disclosed to optimize the oxide material properties for thermoelectric conversion efficiency. New devices based on bulk and multilayer thermoelectric materials are described. New devices based on bulk and multilayer thermoelectric materials using combinations of at least one of thermoelectric and pyroelectric and ferroelectric materials are described. Thermoelectric devices based on vertical pillar and planar architectures are disclosed. The advantage of the planar thermoelectric effect allows utility for large area applications and is scalable for large scale power generation plants.
Owner:TRANSLUCENT PHOTONICS +1
Film acoustically-coupled transformers with two reverse c-axis piezoelectric elements
ActiveUS20050093396A1Low insertion lossSolve insufficient bandwidthImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorPlanar electrode
Embodiments of an acoustically-coupled transformer have a first stacked bulk acoustic resonator (SBAR) and a second SBAR. Each of the SBARs has a lower film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) and an upper FBAR, and an acoustic decoupler between the FBARs. The upper FBAR is stacked atop the lower FBAR. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes and a piezoelectric element between the electrodes. The piezoelectric element is characterized by a c-axis. The c-axes of the piezoelectric elements of the lower FBARs are opposite in direction, and the c-axes of the piezoelectric elements of the upper FBARs are opposite in direction. The transformer additionally has a first electrical circuit connecting the lower FBAR of the first SBAR to the lower FBAR of the second SBAR, and a second electrical circuit connecting the upper FBAR of the first SBAR to the upper FBARs of the second SBAR.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Film bulk acoustic device with integrated tunable and trimmable device
InactiveUS6924583B2Low costLower Reliability RequirementsImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceResonance
A film bulk acoustic device having integrated trimmable device comprises a FBAR and a integrated tunable and trimmable device being integrated on a common substrate, at least a common electrode or piezoelectric layer. By trimming the integrated trimmable device or the FBAR and alter either the capacitance or inductance of the integrated trimmable device until the film bulk acoustic device having integrated trimmable device achieves the target resonance frequency. By taking advantage of the electrostatic force, the integrated tunable device is capable of providing tuning until the film bulk acoustic device having integrated tunable device achieves the target resonance frequency.
Owner:ASIA PACIFIC MICROSYST
Thin film piezoelectric resonator and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveUS20050248232A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResonanceOptoelectronics
a thin film piezoelectric resonator includes a substrate having a cavity, and a resonance portion located on the substrate and right above the cavity. The resonance portion includes a lower electrode layer located at a side of the cavity, an upper electrode layer opposite to the lower electrode layer, and a piezoelectric thin film located between the upper electrode layer and the lower electrode layer. A side of the piezoelectric thin film and a side of the lower electrode layer are located in a common plane.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Apparatus for generating electrical energy and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100253184A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityNanowire
An apparatus for generating electrical energy may include; a first electrode, a second electrode spaced apart from the first electrode, a nanowire which includes a piezoelectric material and is disposed on the first electrode, an active layer disposed on the first electrode, a conductive layer disposed on the active layer, and an insulating film disposed between the conductive layer and the nanowire, wherein the nanowire and the active layer are electrically connected to each other. A method for manufacturing an apparatus for generating electrical energy may include; disposing a nanowire including a piezoelectric material on a first electrode, disposing an active layer, which is electrically connected to the nanowire, on the first electrode, disposing an insulating film on the nanowire, disposing a conductive layer on the active layer, and disposing a second electrode in proximity to the nanowire and substantially opposite to the first electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Micromechanical resonator having short support beams
InactiveUS6930569B2Reduce the possibilitySmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksLength waveBeam resonator
The illustrative embodiment of the present invention is a vertical-mode, free-free beam resonator, and micromechanical circuits that include one or more such resonators. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, the resonator comprises a movable beam that overlies a drive electrode. The movable beam is supported by a plurality of supports, the length of which is substantially less than one-quarter of a wavelength of the resonant frequency of the resonator.
Owner:MICREL
Piezoelectric resonator including an acoustic reflector portion
ActiveUS7868519B2Quality improvementImprove resonance characteristicsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResonanceAcoustics
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Piezoelectric resonator operating in thickness shear mode
InactiveUS8829766B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksElectrical polarityAcoustic wave
An acoustic wave resonator device comprising a resonant layer that comprises a series of side-by-side areas of first and second dielectric materials. In one embodiment the first dielectric material is a piezoelectric, in particular the first dielectric material can be a piezoelectric and the second dielectric material can be non-piezoelectric. In another embodiment, the first dielectric material is a piezoelectric of first polarity and the second dielectric material is a piezoelectric of opposite polarity or different polarity. Where needed, the resonant layer is supported on a reflector composed of series of layers of high acoustic impedance material(s) alternating with layers of low acoustic impedance material(s). For example, the reflector comprises AlN, Al2O3, Ta2O5, HfO2 or W as high impedance material and SiO2 as low impedance material.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Stepping actuator and method of manufacture therefore
InactiveUS20050146241A1Reduce air gapReduce pull-in voltageCapacitor with electrode distance variationMultiple capacitorsParallel plateActuator
An embodiment of the present invention provides a stepping actuator, comprising a suspended membrane comprising a plurality of movable electrodes connected by plurality of spring hinges to a payload platform; and anchors connecting said membrane to a substrate, said substrate comprising a plurality of fixed electrodes; wherein said movable electrodes of said suspended membrane and said fixed electrodes from said substrate form parallel-plate electrostatic sub-actuators.
Owner:WAN CHANG FENG
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS8237324B2Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesVitrificationActive polymer
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Composite piezoelectric apparatus and method
ActiveUS7109642B2Easy to disassemblePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesVacuum evaporation coatingTransducerVolume percent
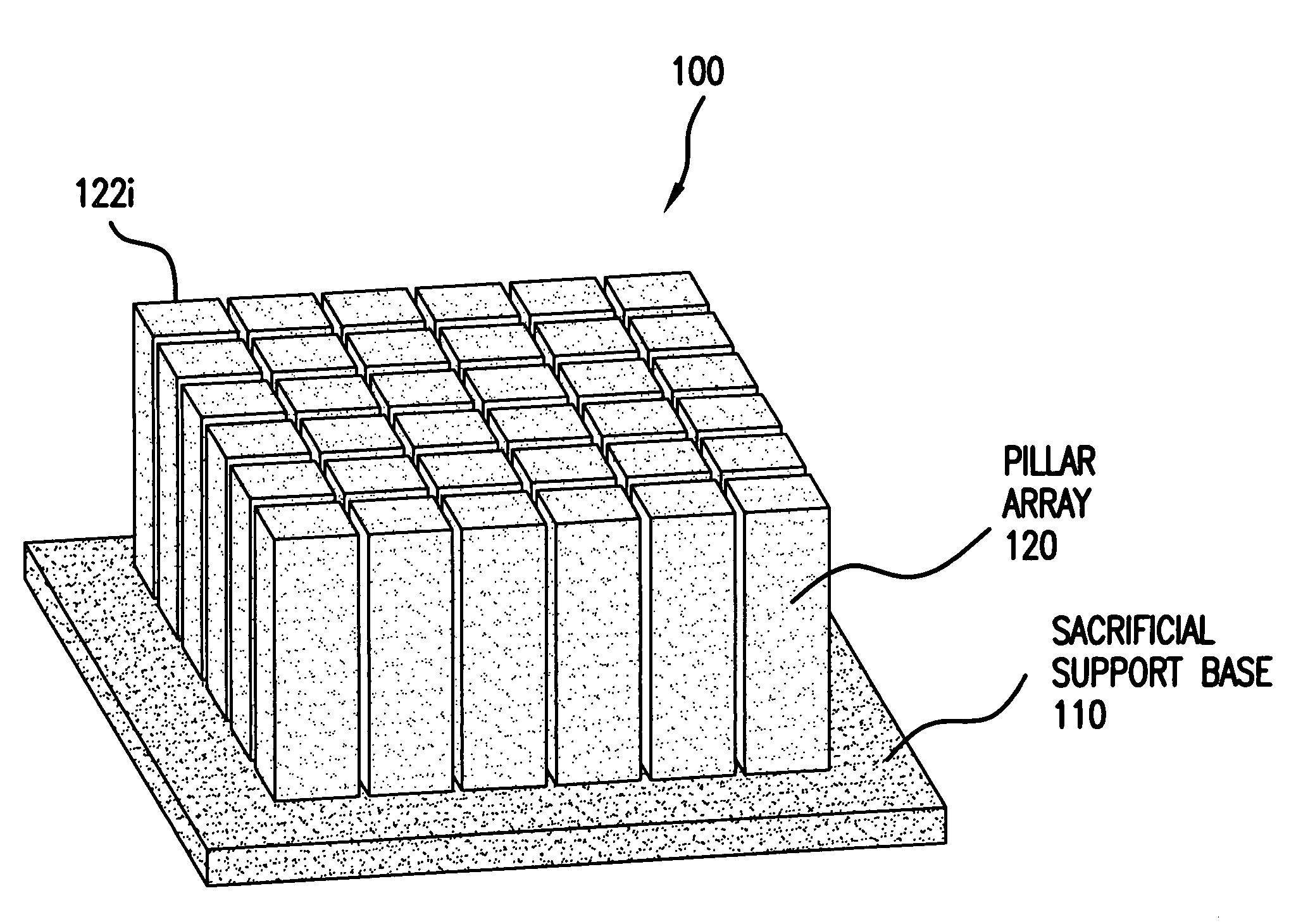
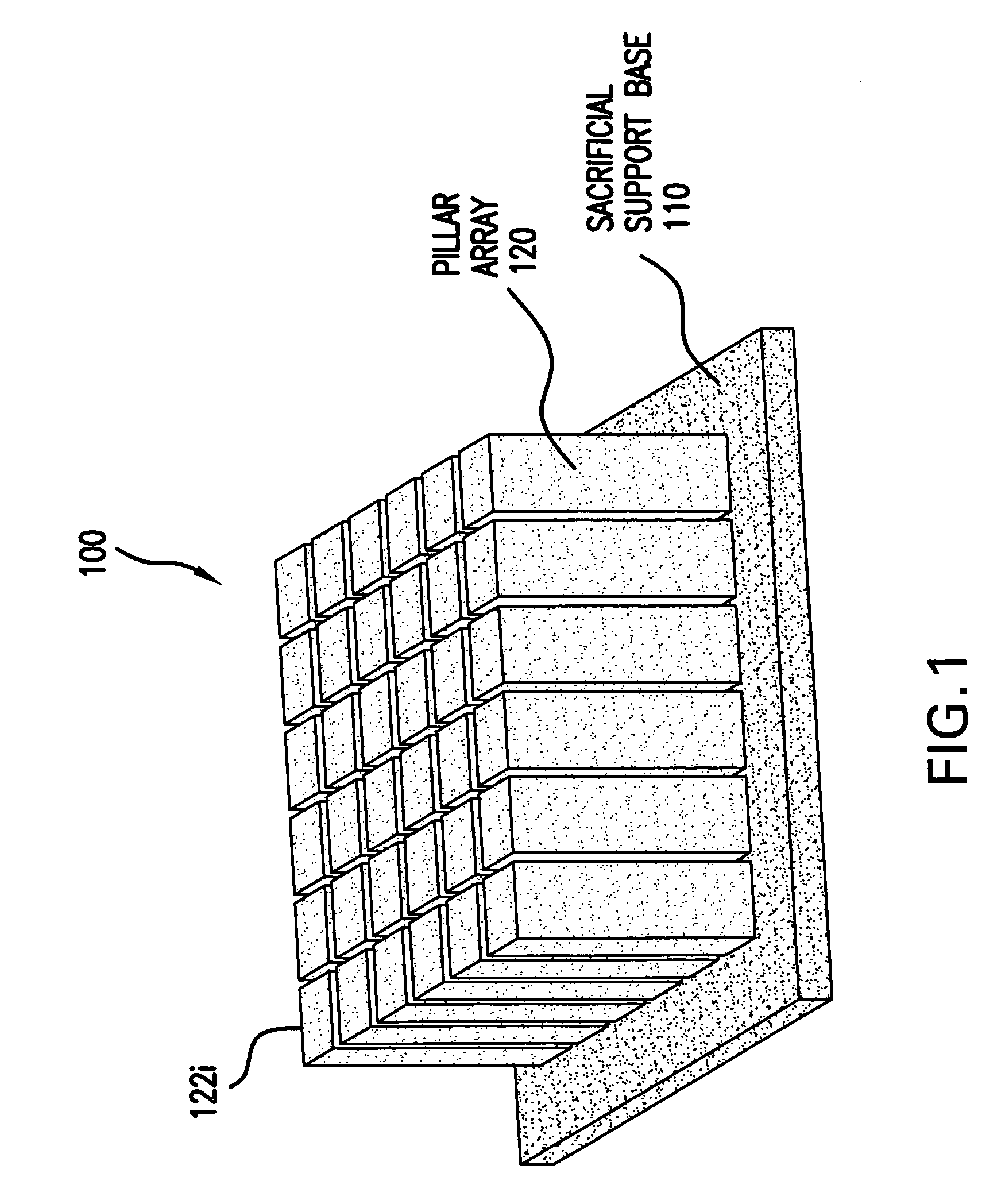
The present invention relates to composite piezoelectric apparatus, transducers and methods of manufacture. In an embodiment, a composite piezoelectric apparatus has a sacrificial base and pillar array. Different volume percents of piezoelectric material are used in the sacrificial base and pillar array. A first volume percent in the base is lower than the second volume percent in the pillar array. In this way, the sacrificial base can be easily removed from the pillar array after the base and pillar array are sintered in the manufacture of a final composite piezoelectric transducer. A method of manufacturing a composite piezoelectric transducer from a sacrificial base and pillar array and a composite piezoelectric transducer made by the method are provided. A composite piezoelectric transducer stack is provided.
Owner:SONAVATION INC
Multiple element electrode cMUT devices and fabrication methods
ActiveUS8008835B2Optimizing receiptFacilitate transmissionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for manufacturing a vibrating MEMS circuit
ActiveUS9369105B1Low temperature coefficientAccurate shapePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksElectromechanical coupling coefficientCrystal orientation
A method for making a micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) vibrating structure is disclosed. The MEMS is supported by a MEMS anchor system and includes a single-crystal piezoelectric thin-film layer that has a specific non-standard crystal orientation, which may be selected to increase an electromechanical coupling coefficient, decrease a temperature coefficient of frequency, or both. The MEMS vibrating structure may have dominant lateral vibrations or dominant thickness vibrations. The single-crystal piezoelectric thin-film layer may include Lithium Tantalate or Lithium Niobate, and may provide MEMS vibrating structures with precise sizes and shapes, which may provide high accuracy and enable fabrication of multiple resonators having different resonant frequencies on a single substrate.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com