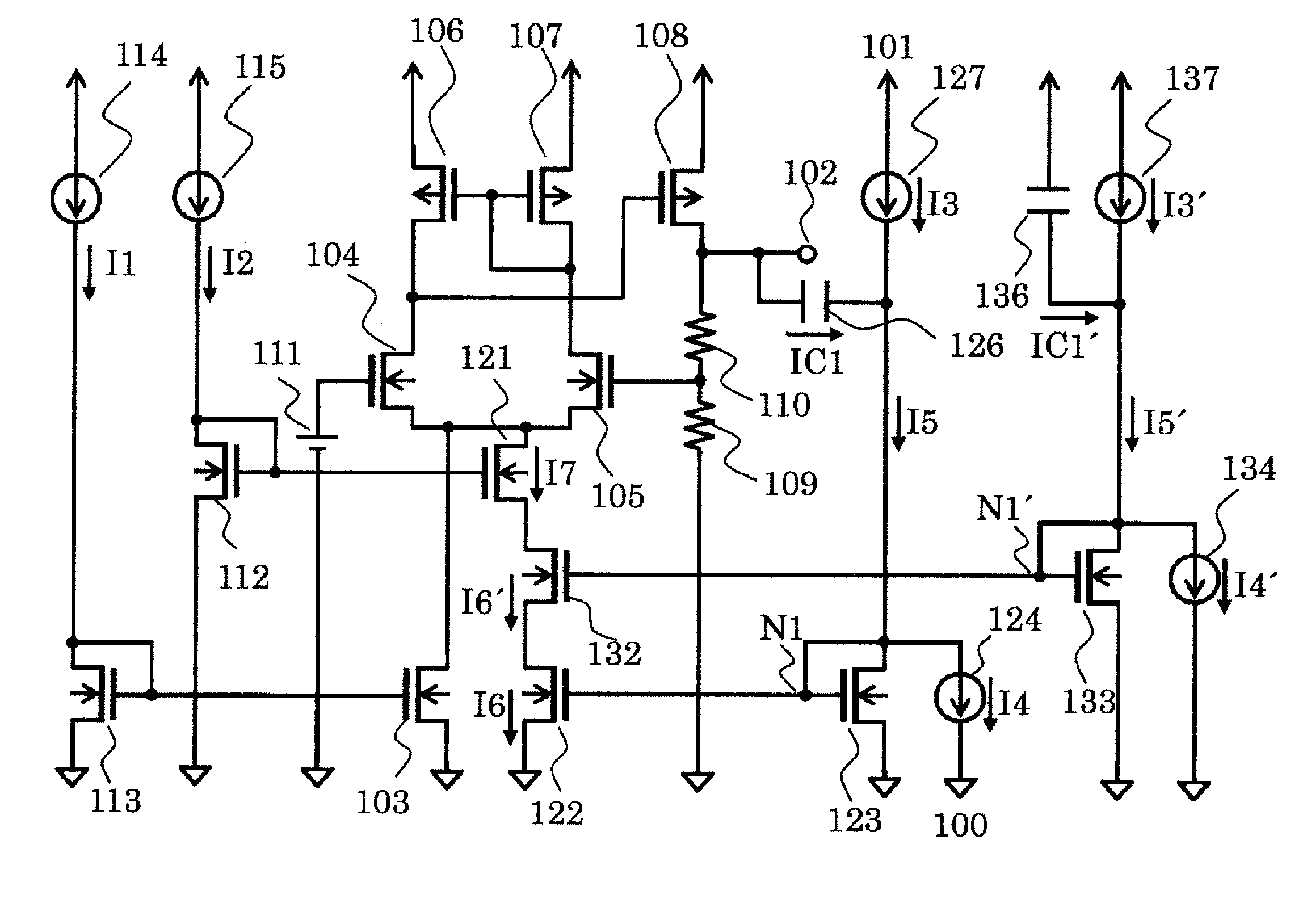
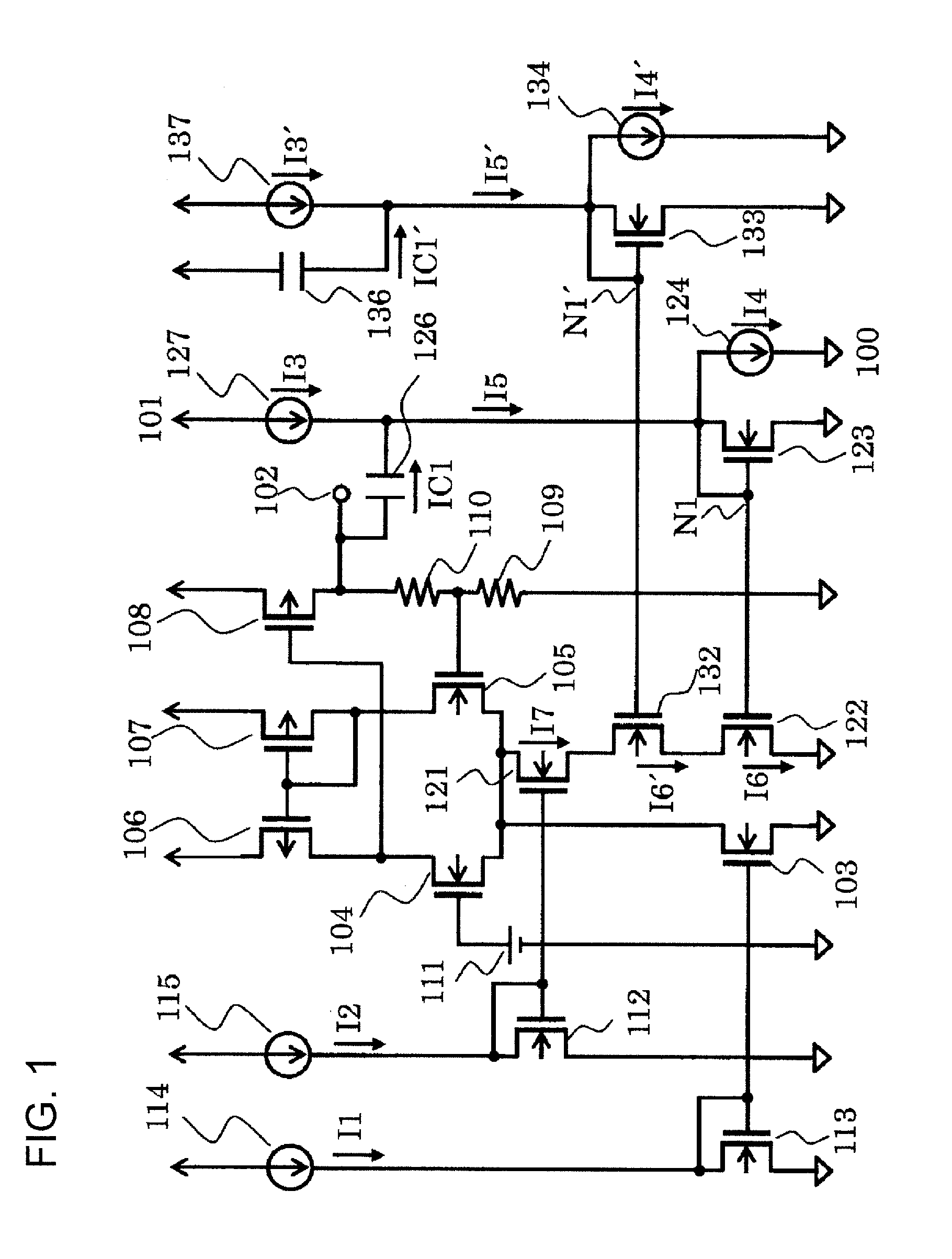
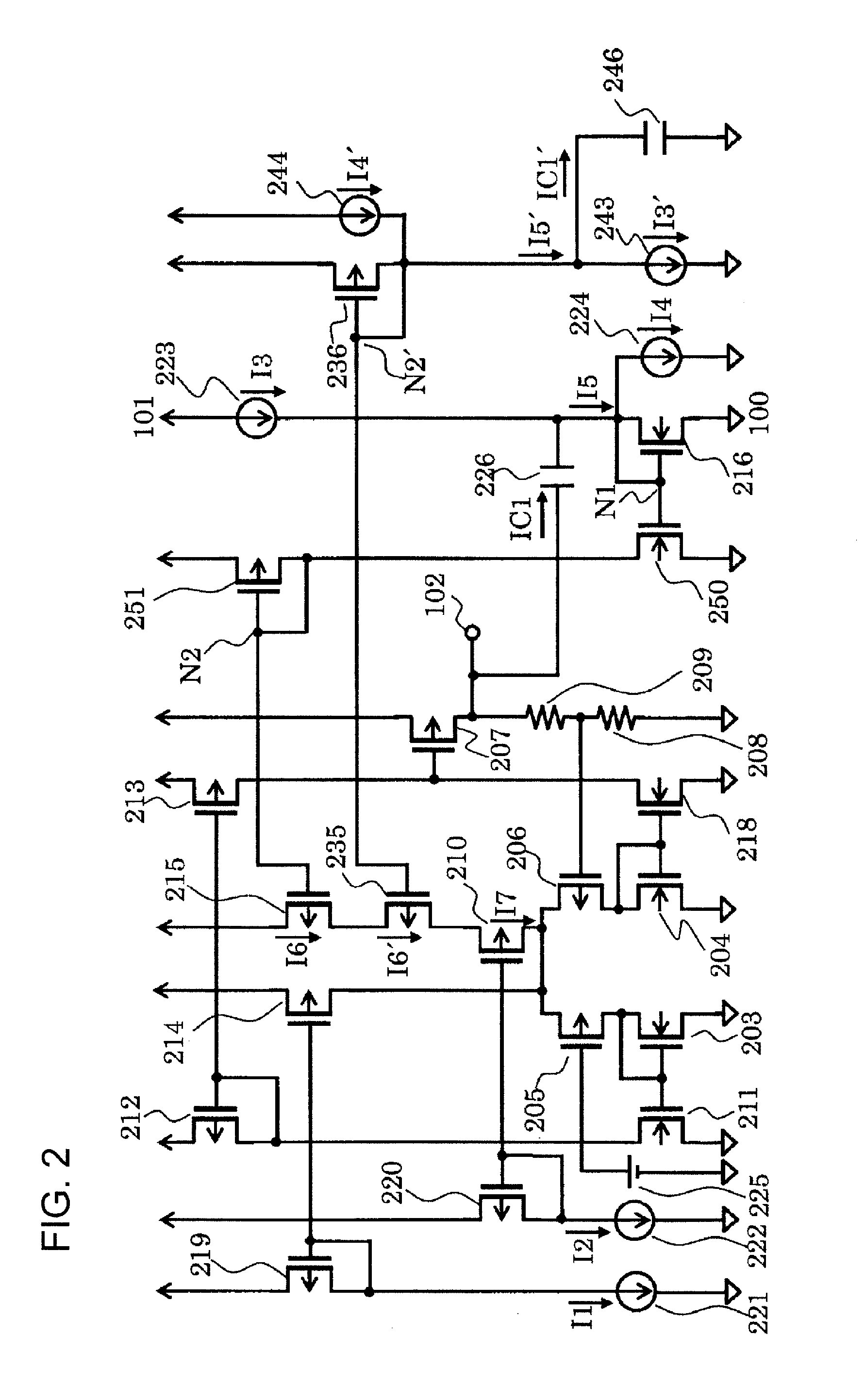
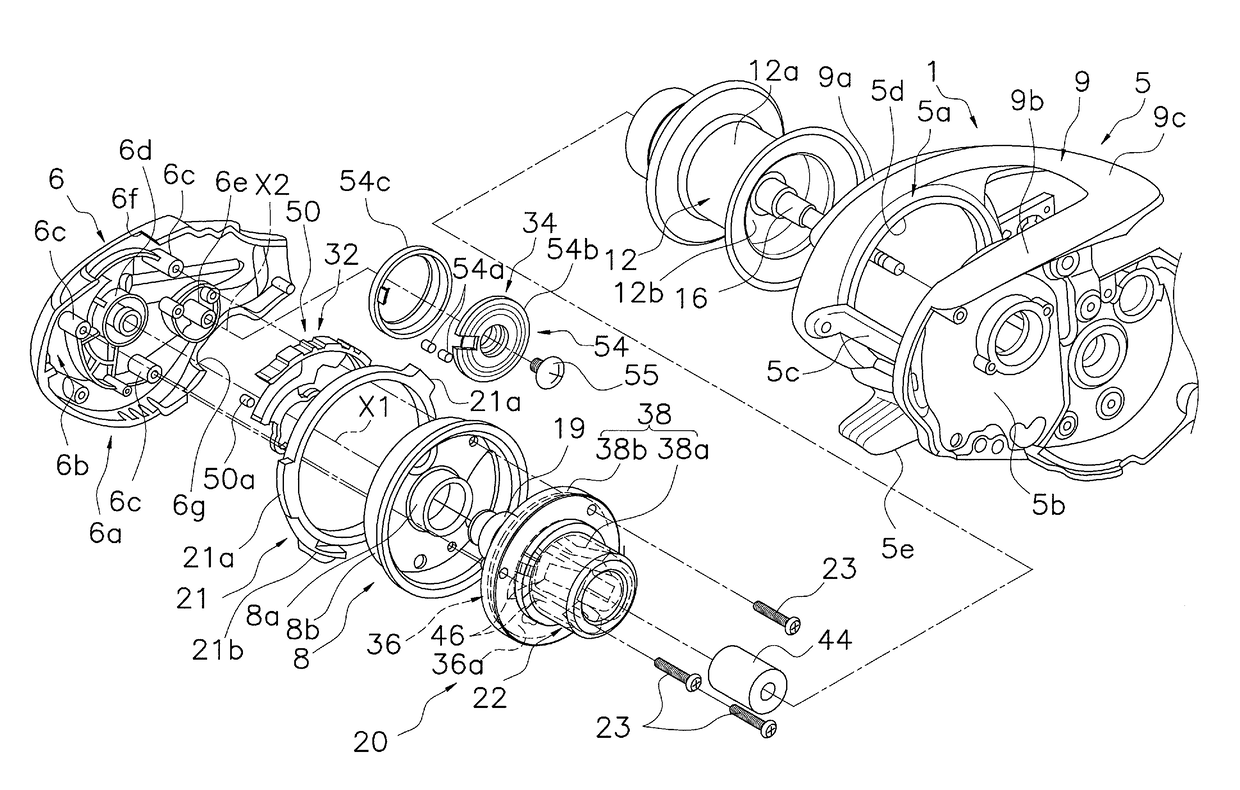
Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Unstable operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
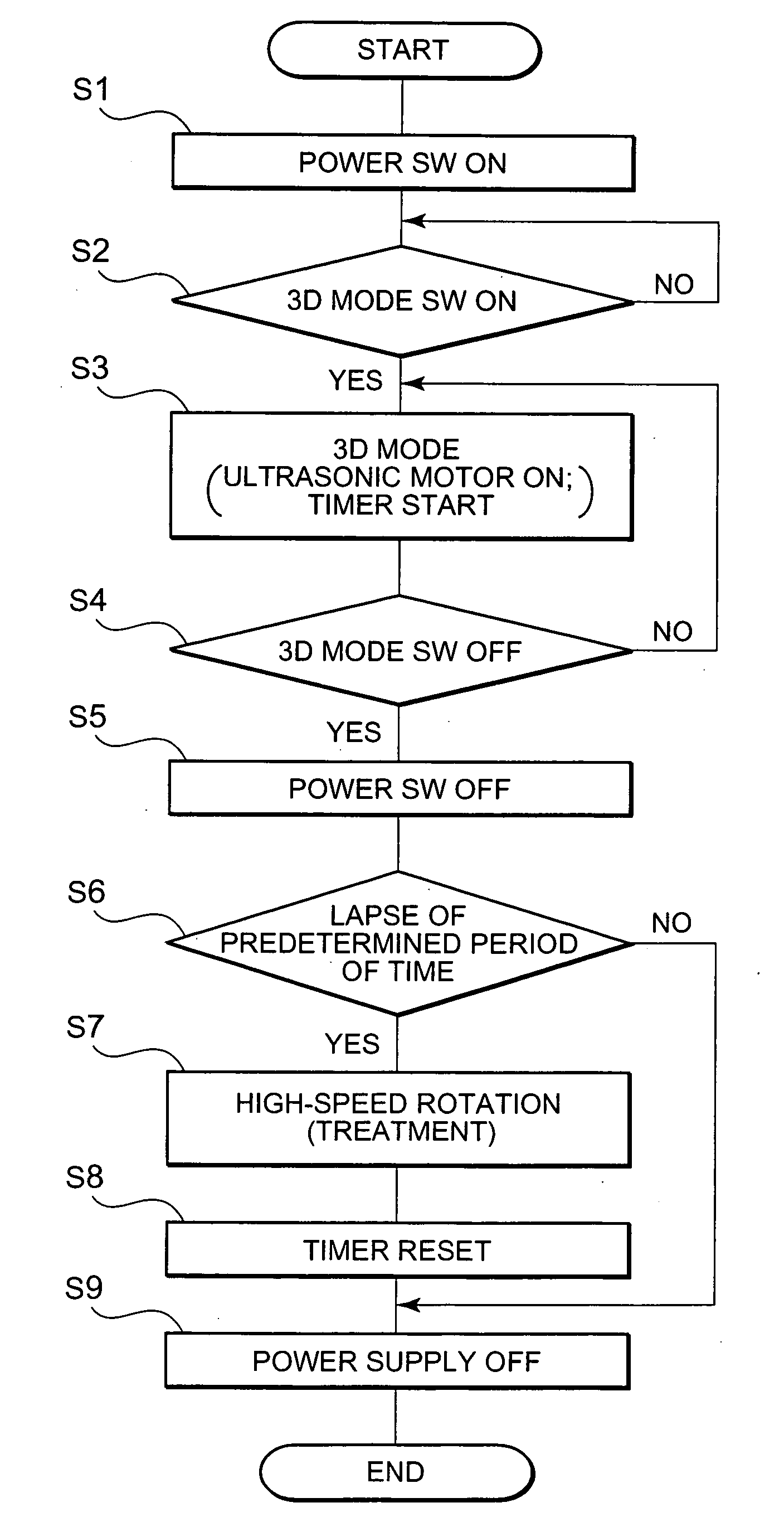
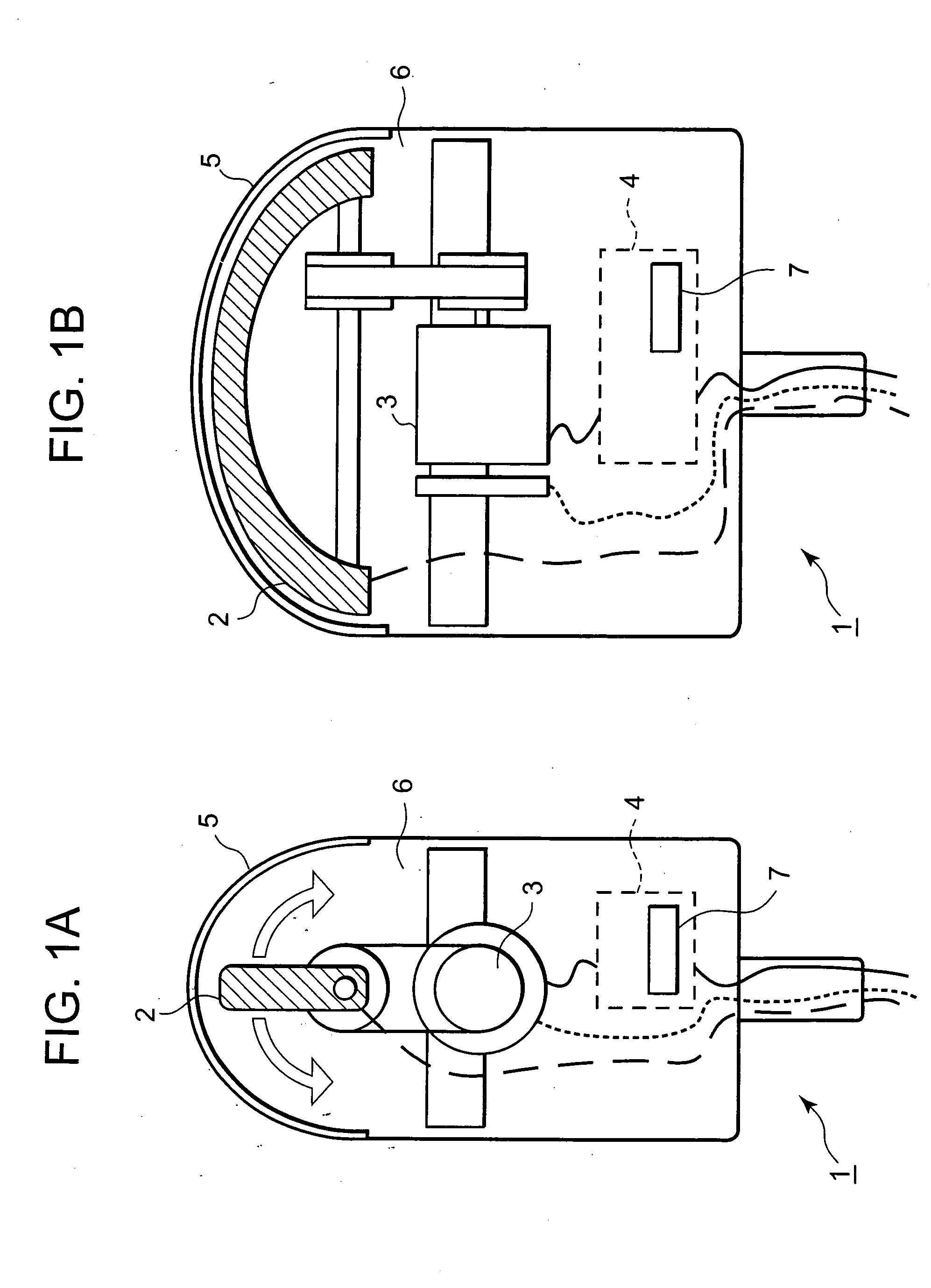
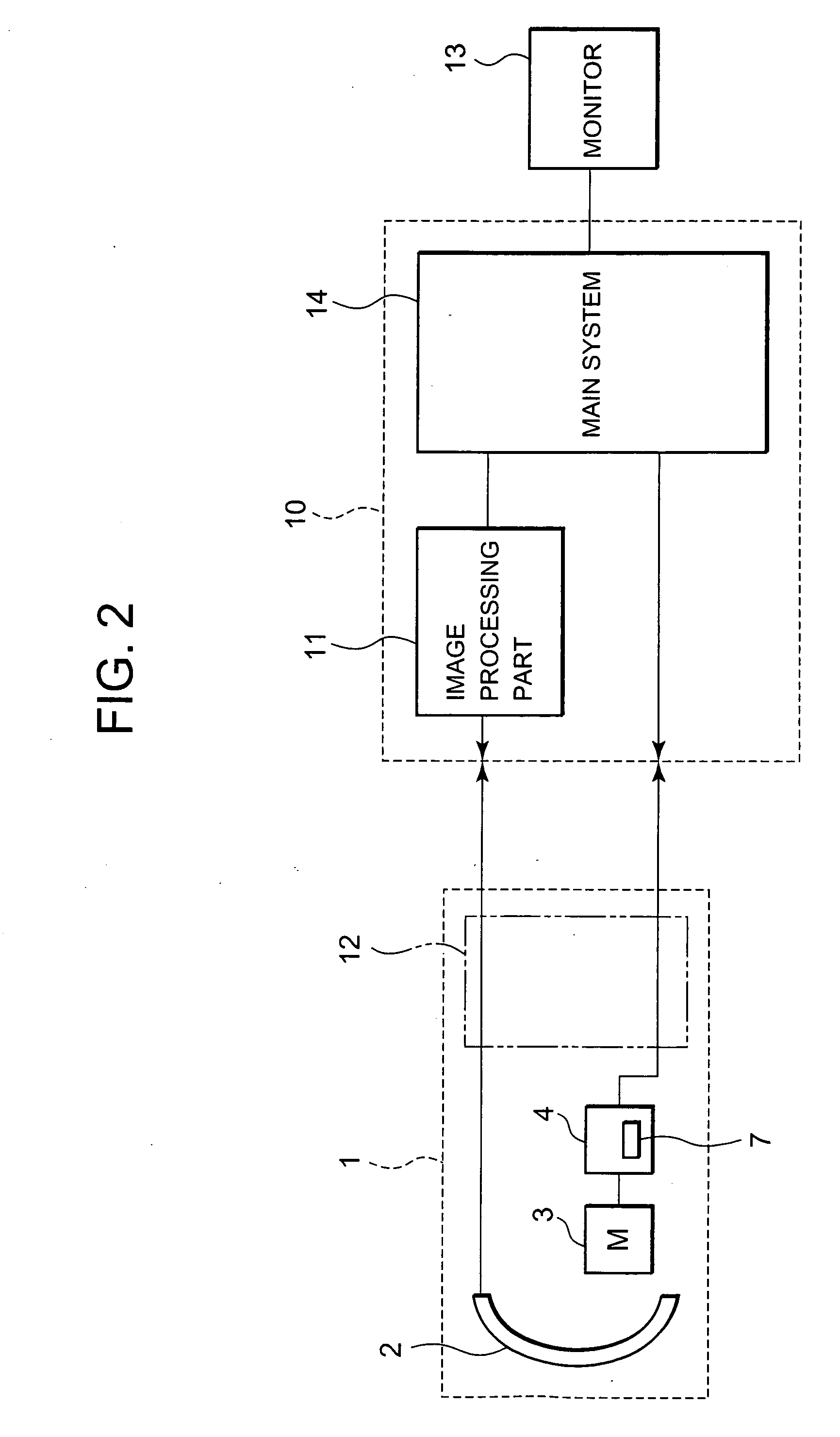
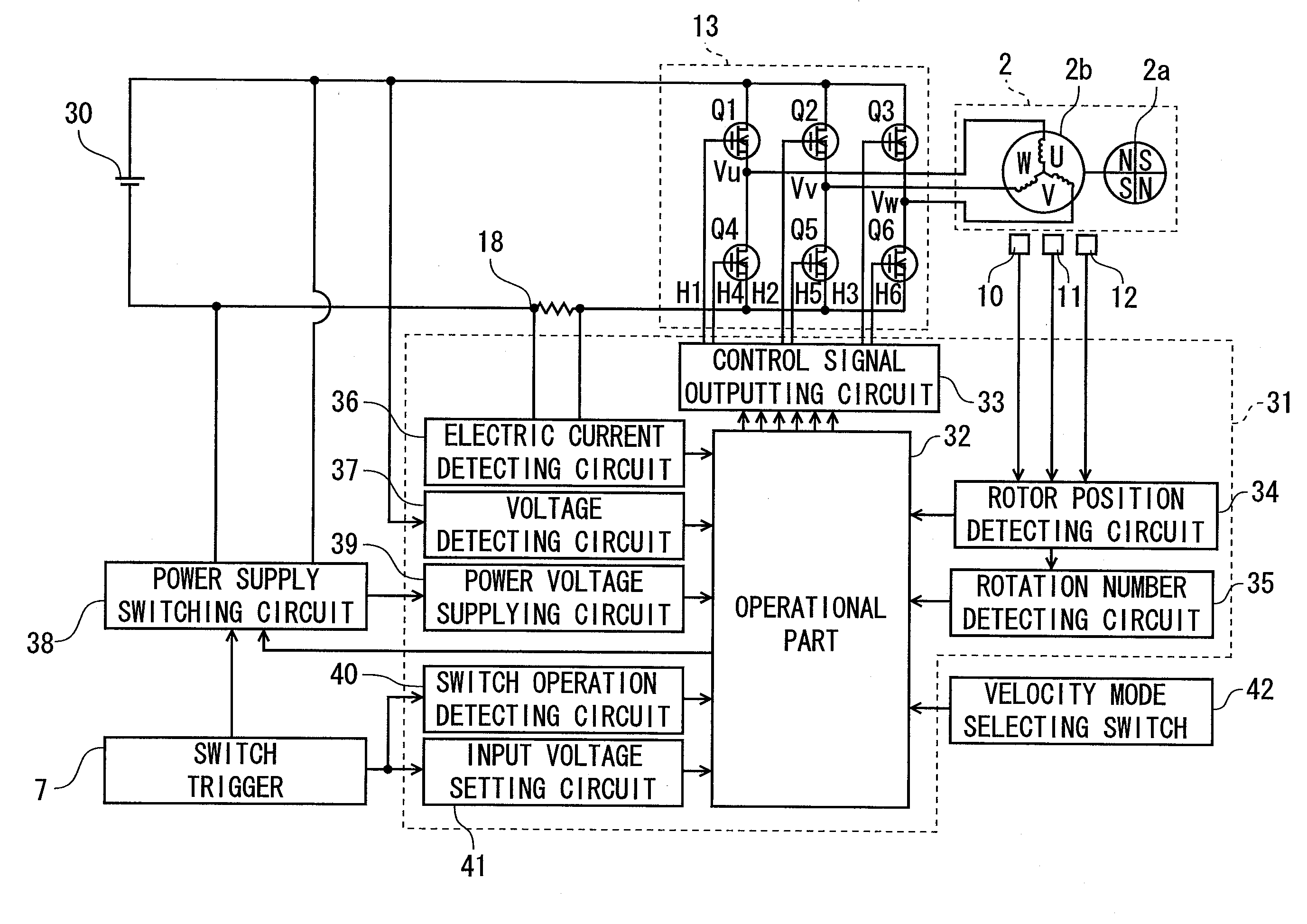
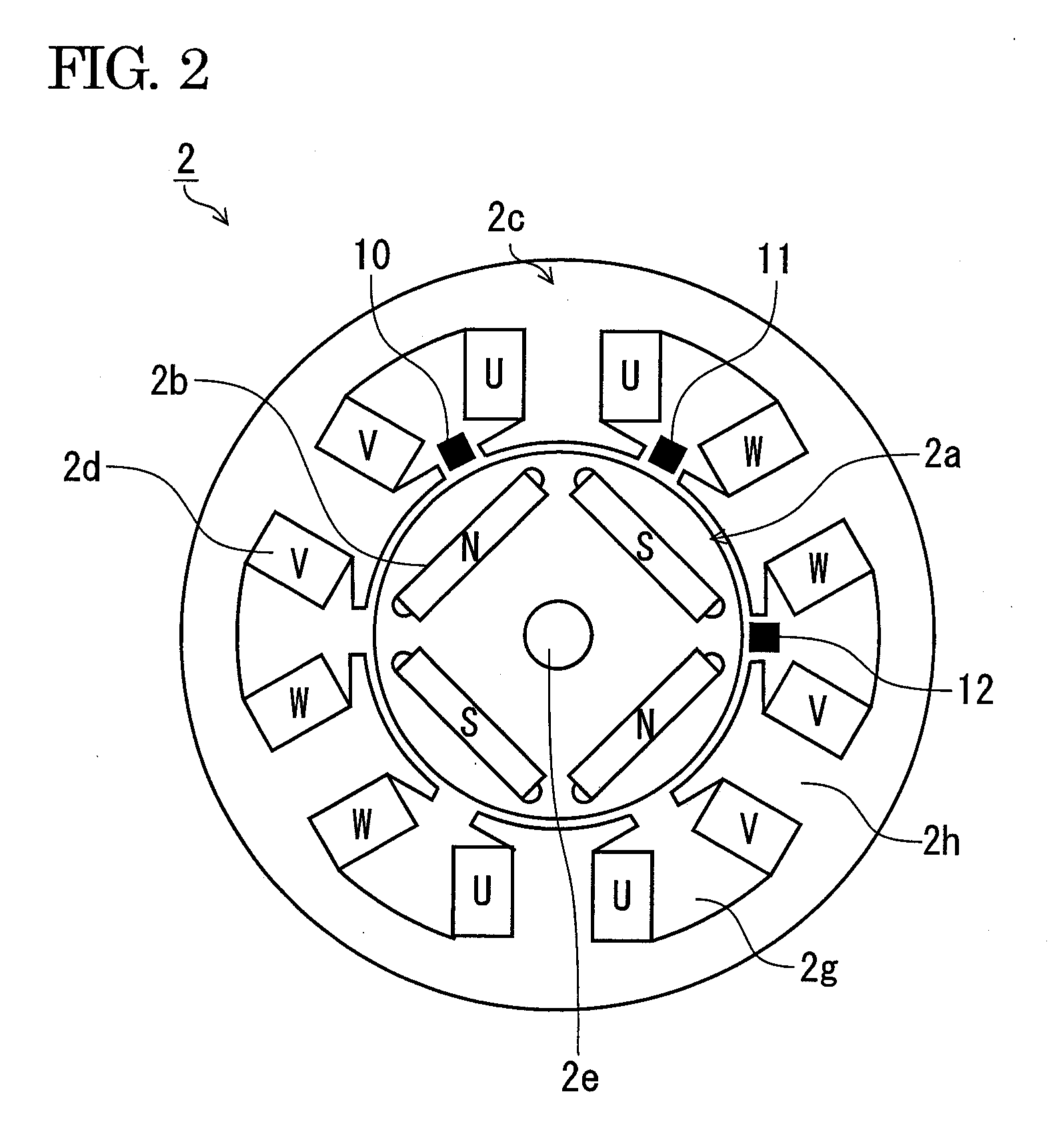
Ultrasonic motor driving device and ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus
InactiveUS20060250046A1Reduce stepsUnstable operationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyLow speedEngineering
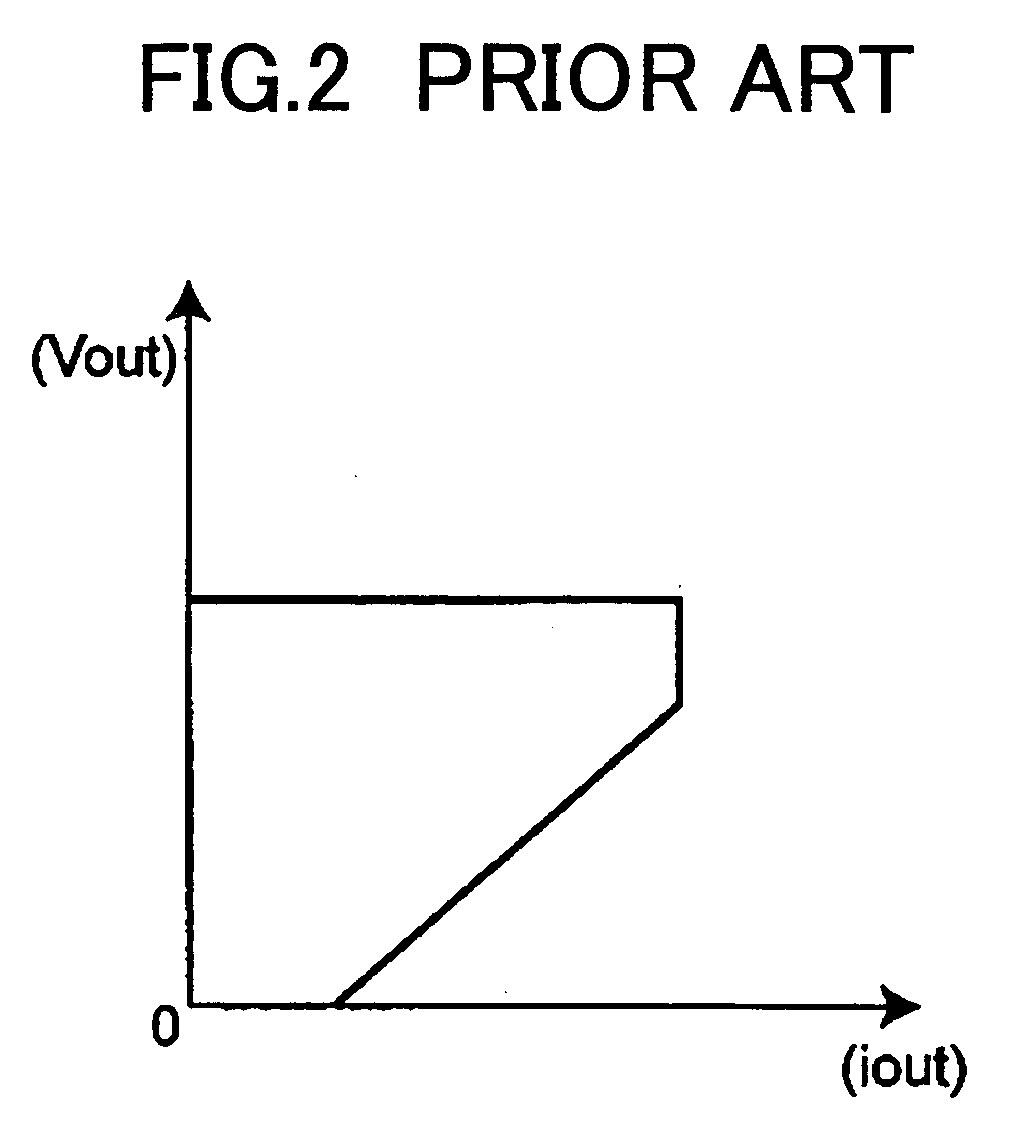
A technology, wherein unstable operation of the ultrasonic motor is prevented, when the ultrasonic motor is driven at the lower speed out of at least two types of speeds, and life extension is attempted, is disclosed, and according to this invention, when the ultrasonic motor 3 is driven at a comparatively low-speed during normal driving, unstable operation due to driving at a comparatively low-speed can be prevented and life extension can be attempted by driving the ultrasonic motor at a comparatively high-speed every predetermined period of time.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
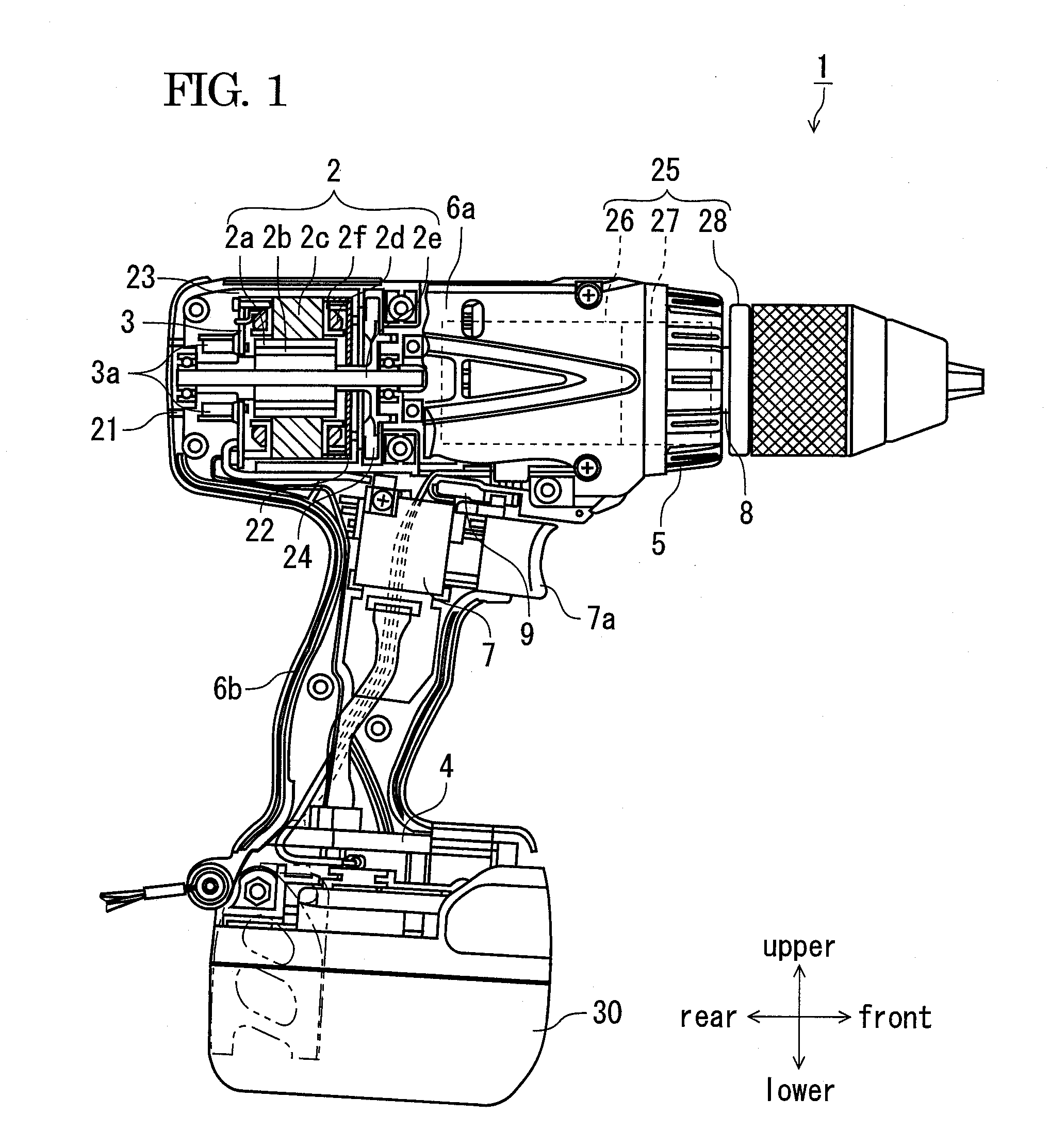
Power tool
InactiveUS20120191250A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlElectric power systemEngineering
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a power tool including: a motor; a driving circuit that supplies an electric power from a power supply to the motor; a control part that sets a target rotation number for the motor in accordance with a mode selected from a plurality of modes, each mode having a corresponding target rotation number; and a voltage detecting circuit that detects a voltage of the power supply, wherein the target rotation number is varied based on the detected voltage.
Owner:HITACHI KOKI CO LTD
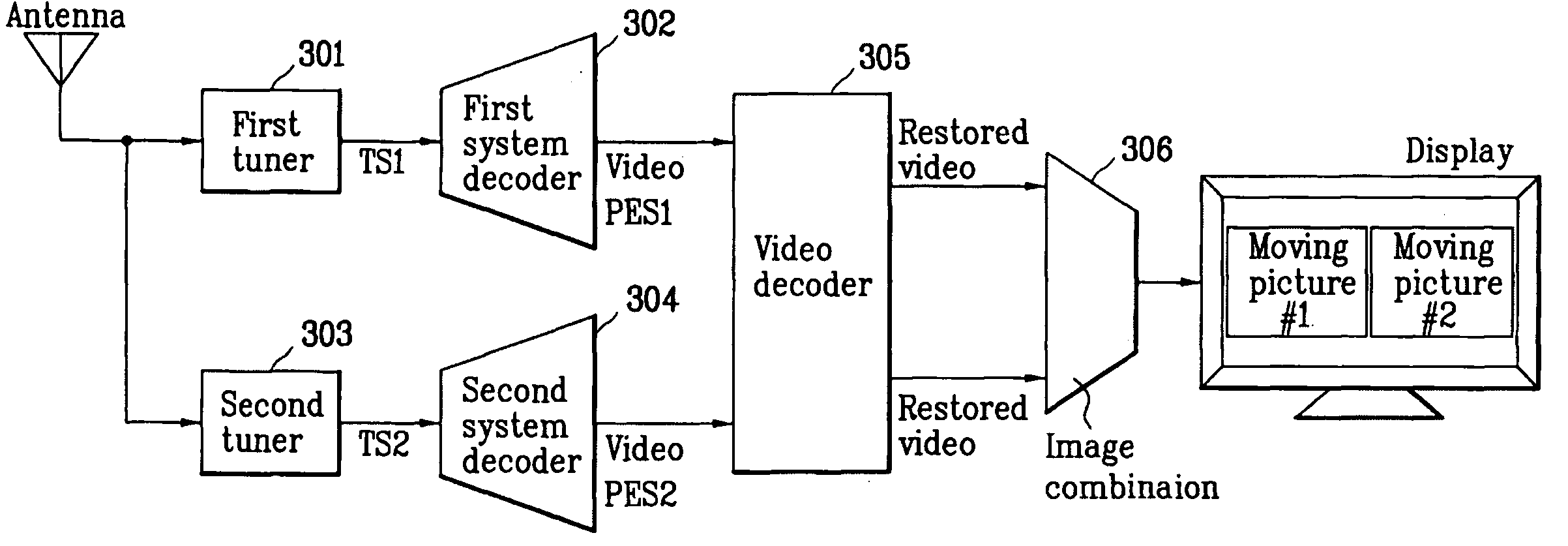
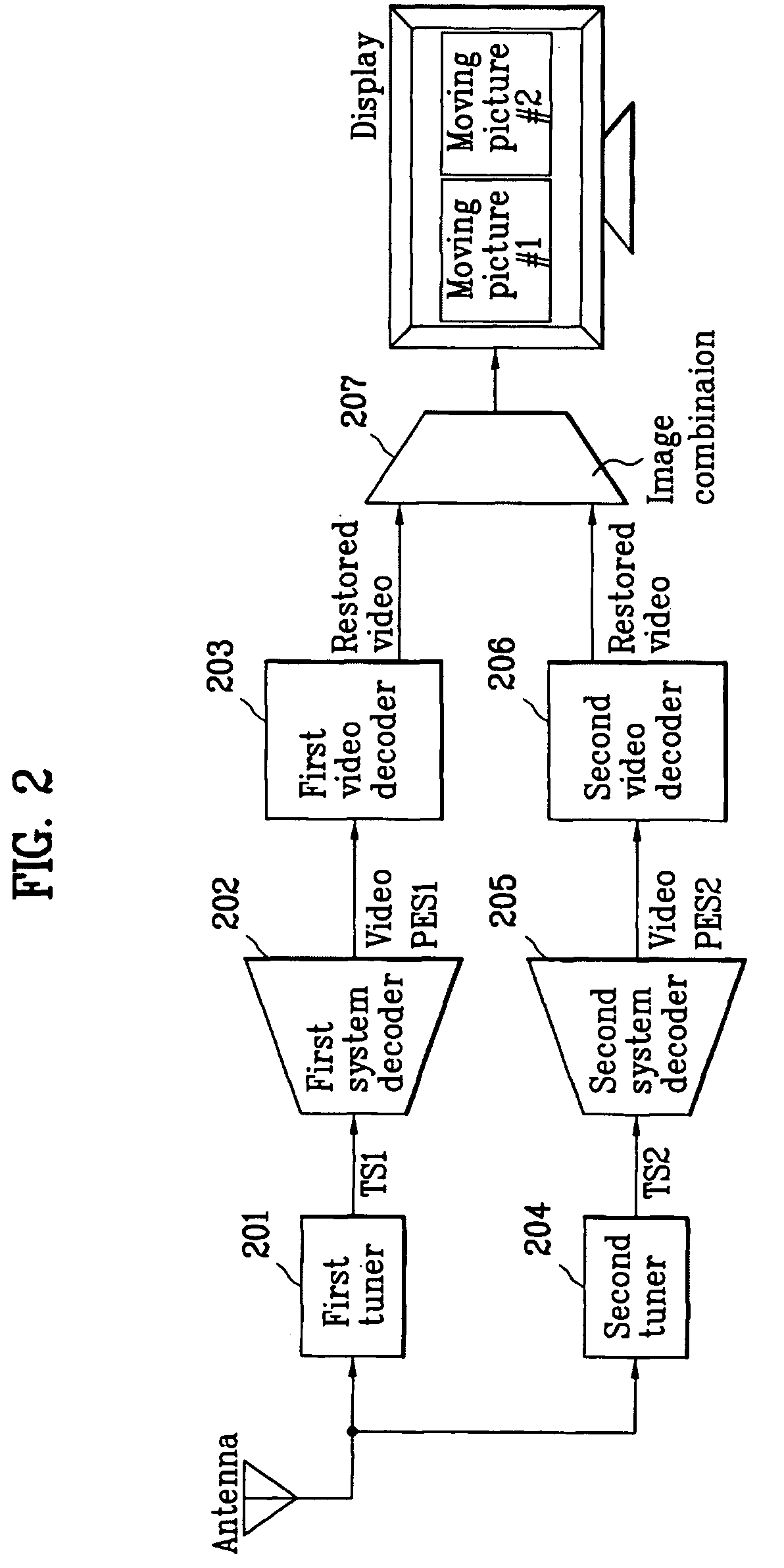
High-definition dual video decoder and decoding method, and digital broadcasting receiver using the same
InactiveUS20050117654A1Increase costHigh operating requirementsTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Control signal
A dual video decoder of a digital broadcasting receiver is provided. The decoder includes: a first PES decoder for decoding a first video PES outputted from a first system decoder, into a first video ES; a second PES decoder for decoding a second video PES outputted from a second system decoder, into a second video ES; a VBV (Video Buffer Verifier) buffer memory divided into a first video ES region and a second video ES region; a decoding controller for outputting a control signal to determine a to-be-decoded video ES among the first and second video ESs, and independently decode the first and second video ESs in a single decoding unit; and the single decoding unit for reading the to-be-decoded video ES from the corresponding region of the VBV buffer memory.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
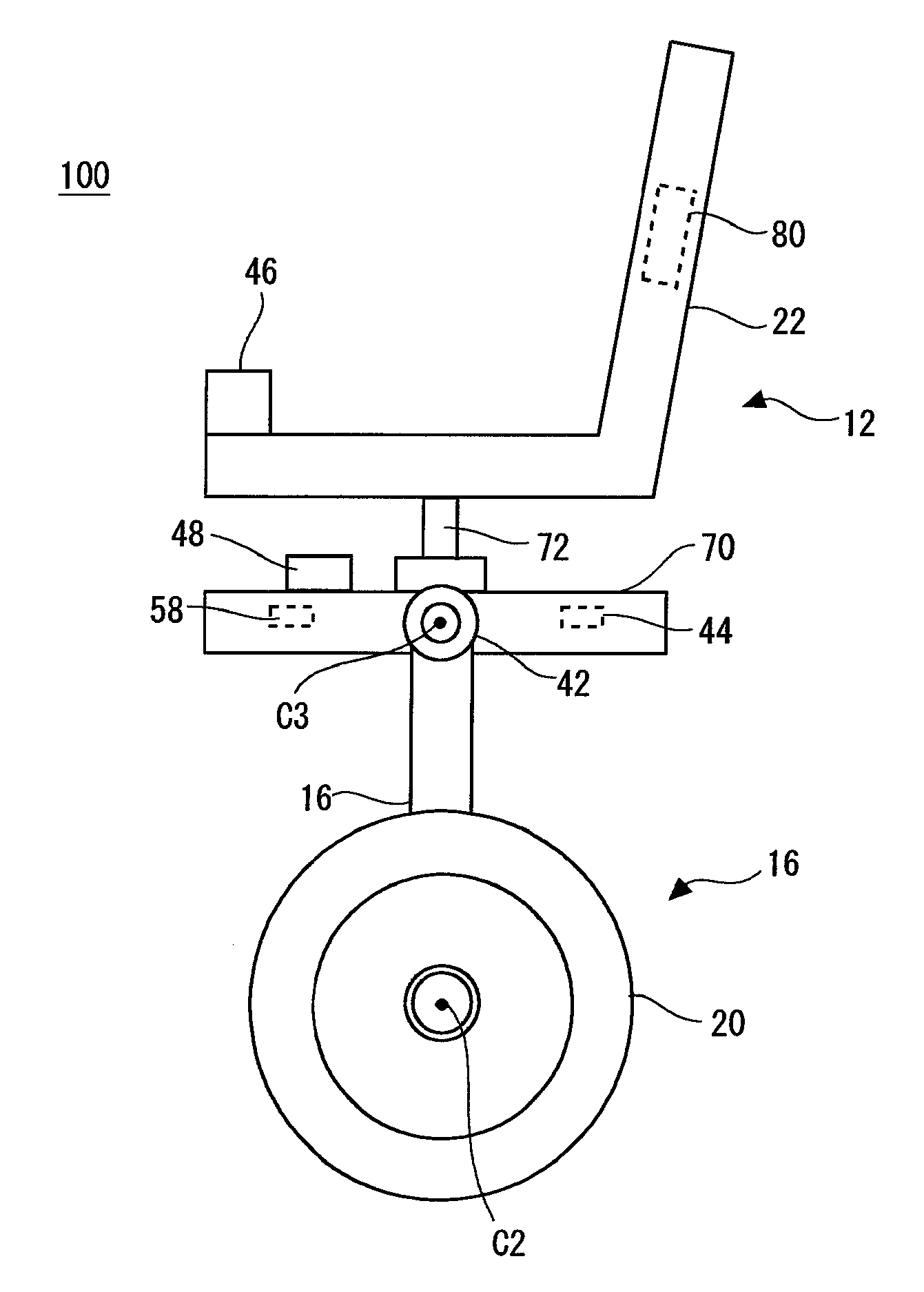
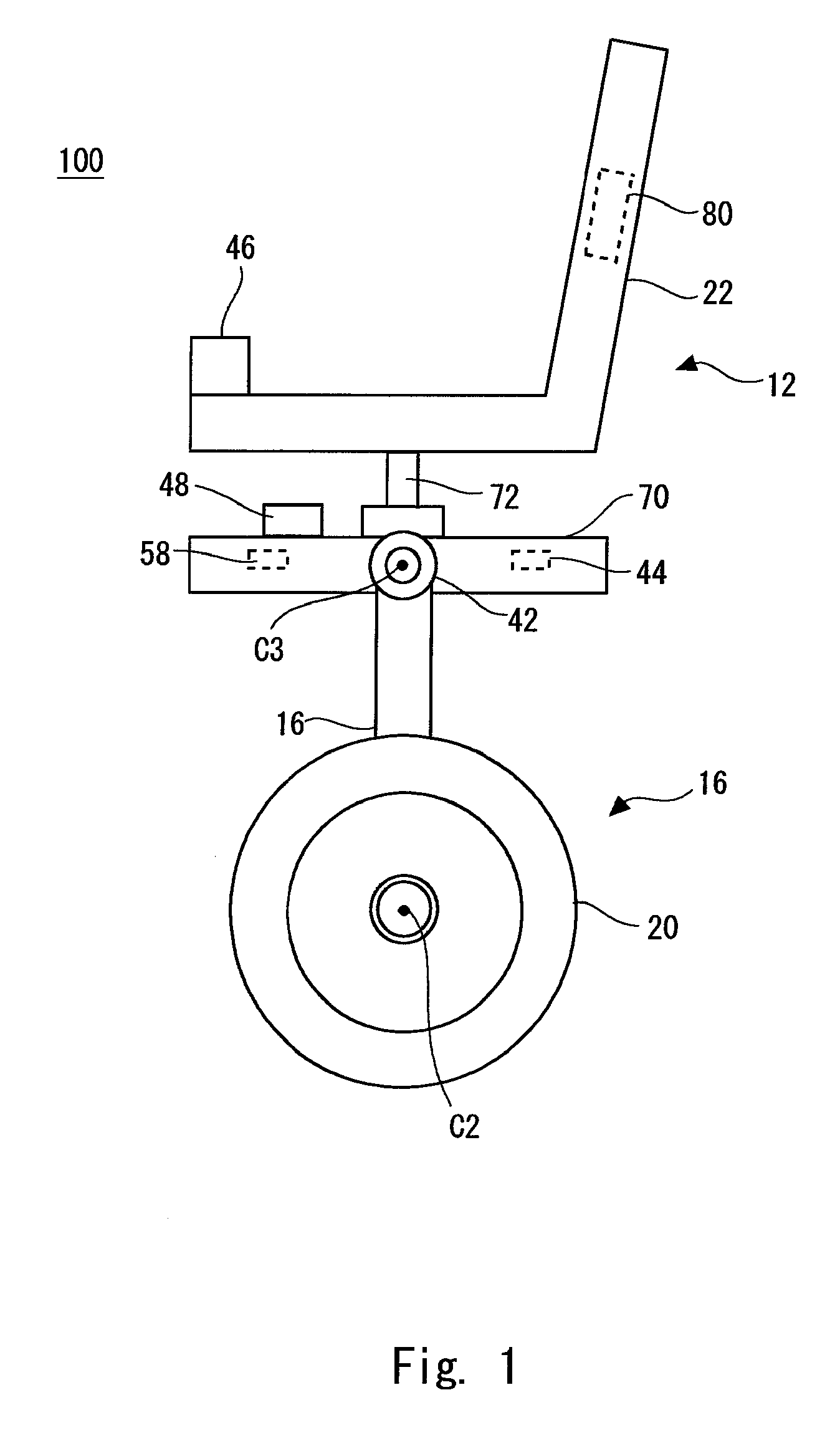
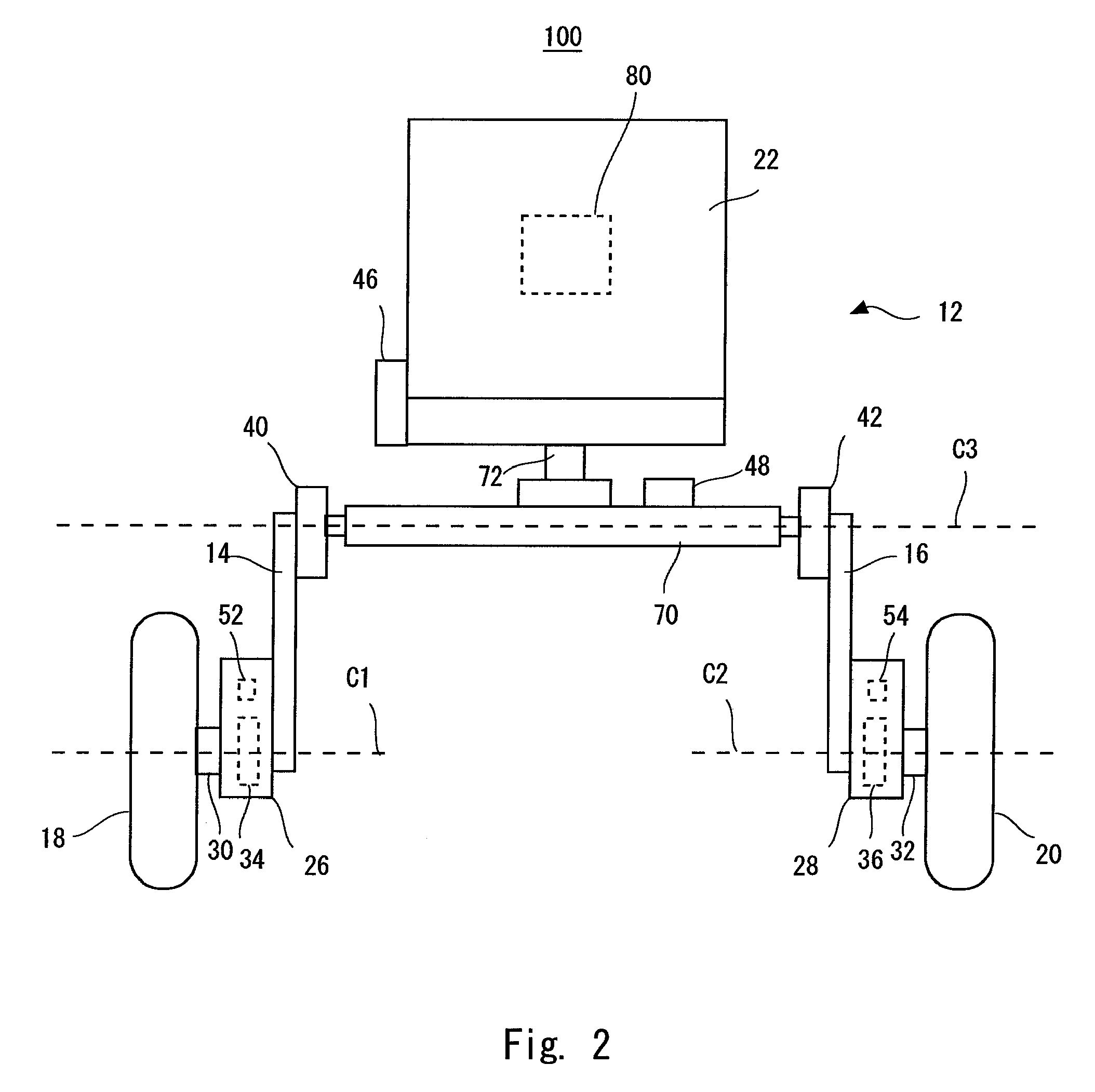
Inverted pendulum type moving body and method of controlling the same
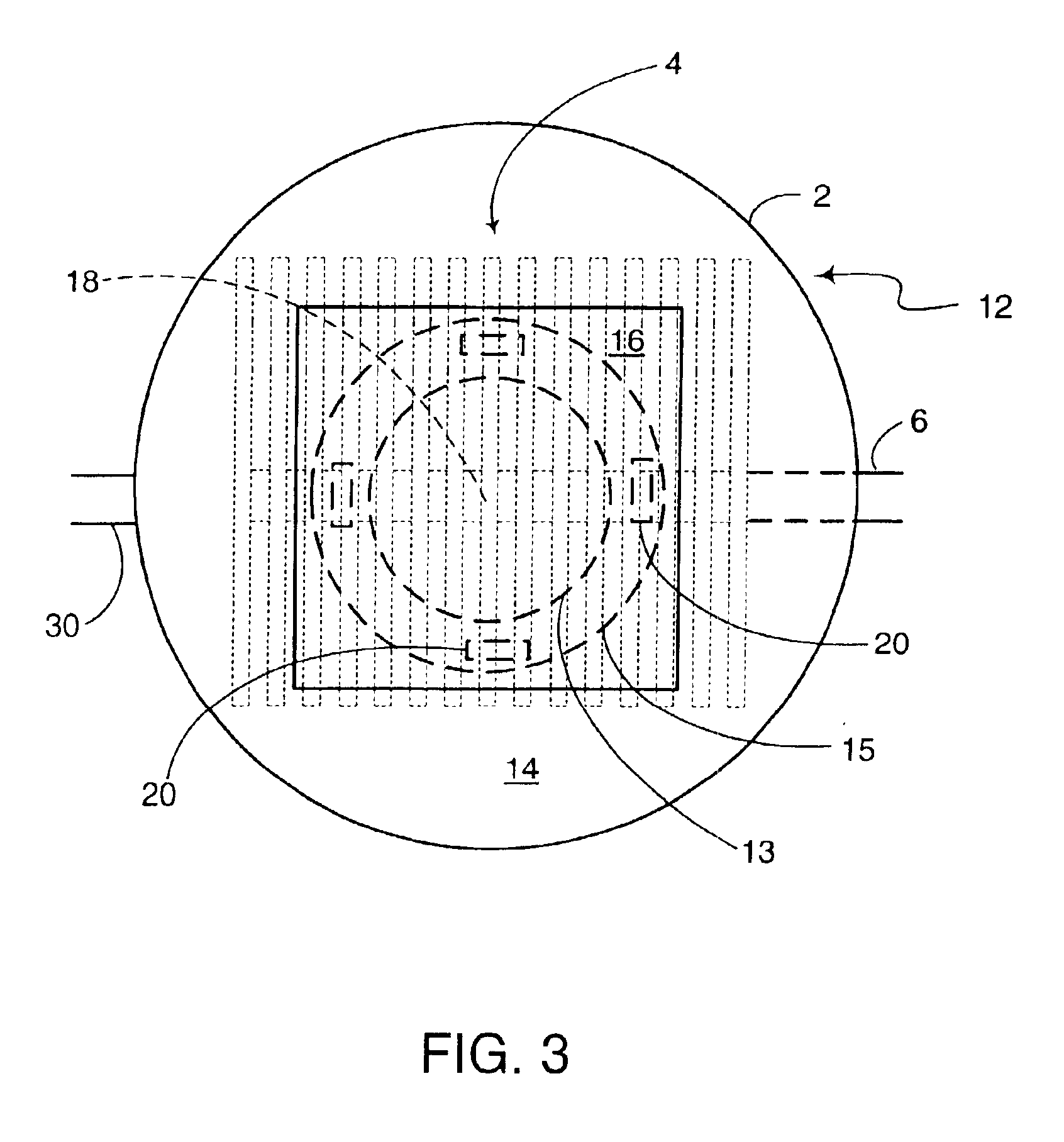
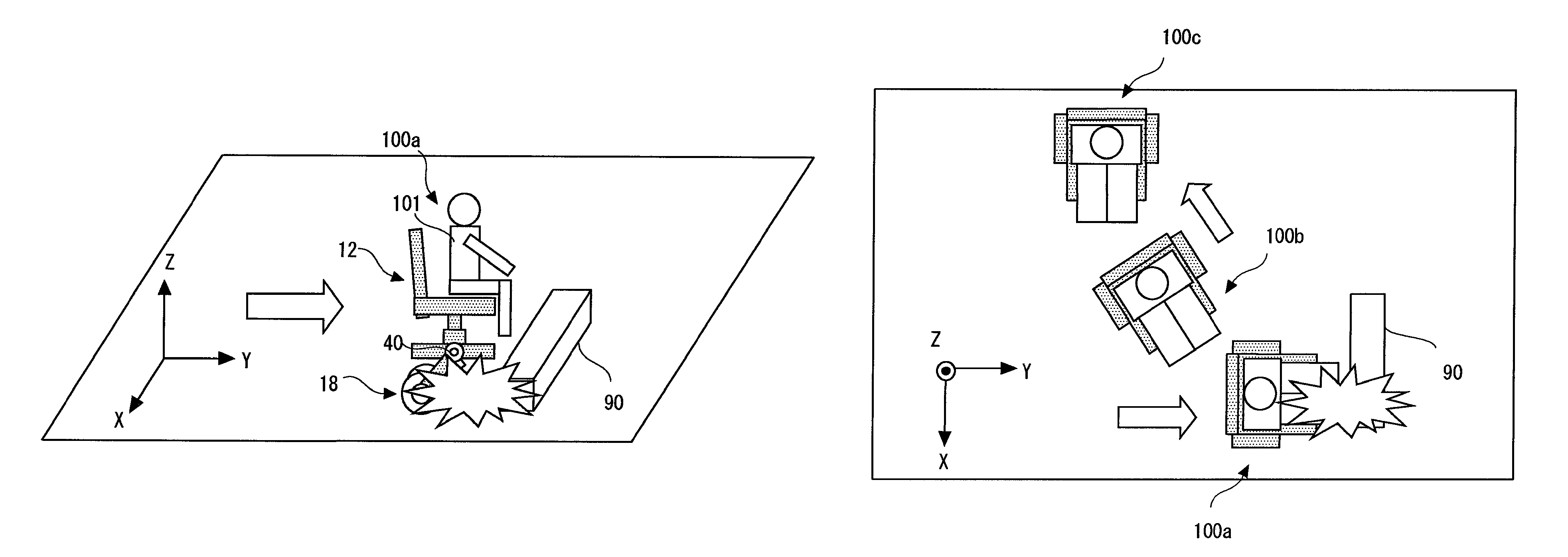
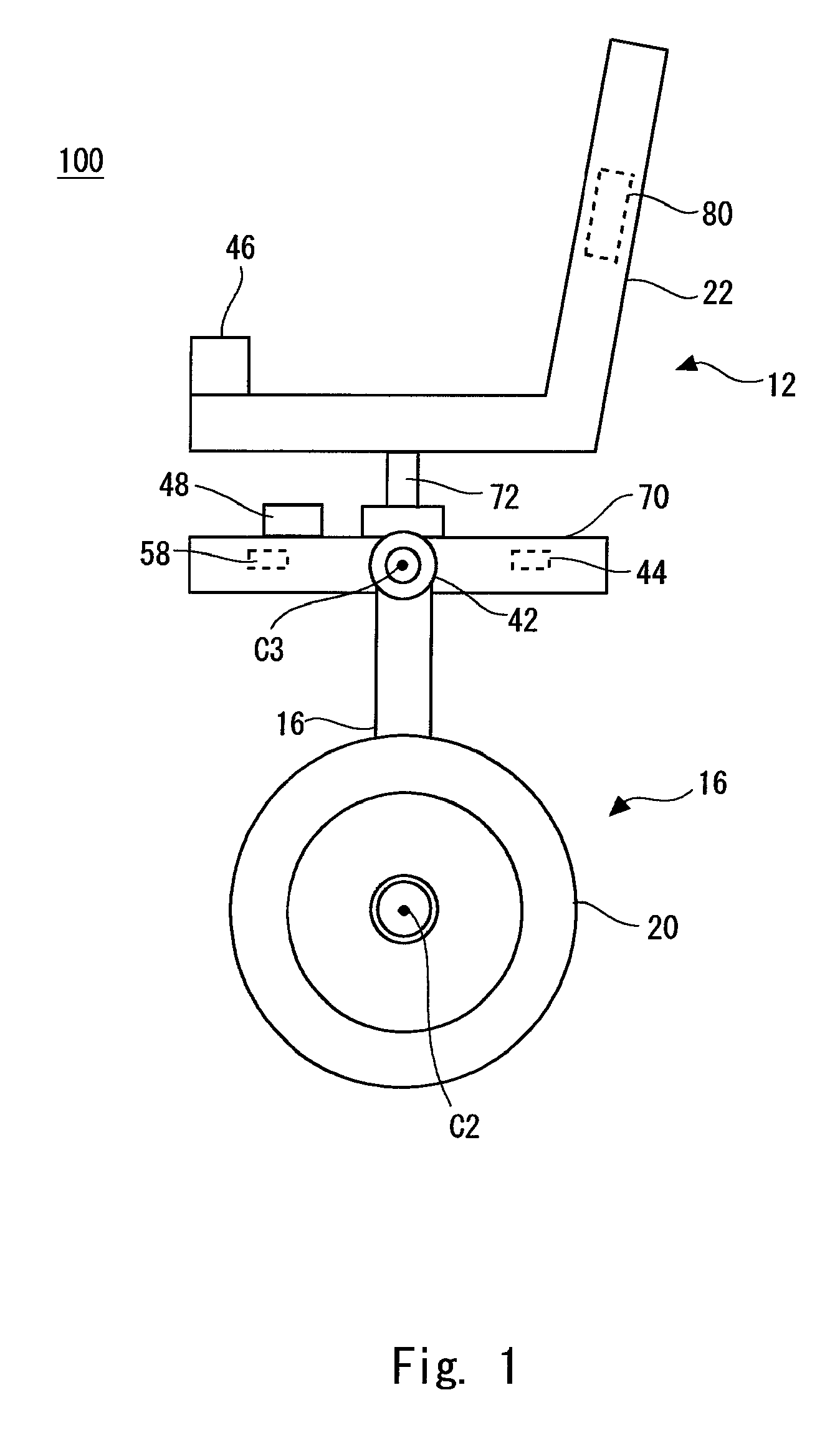
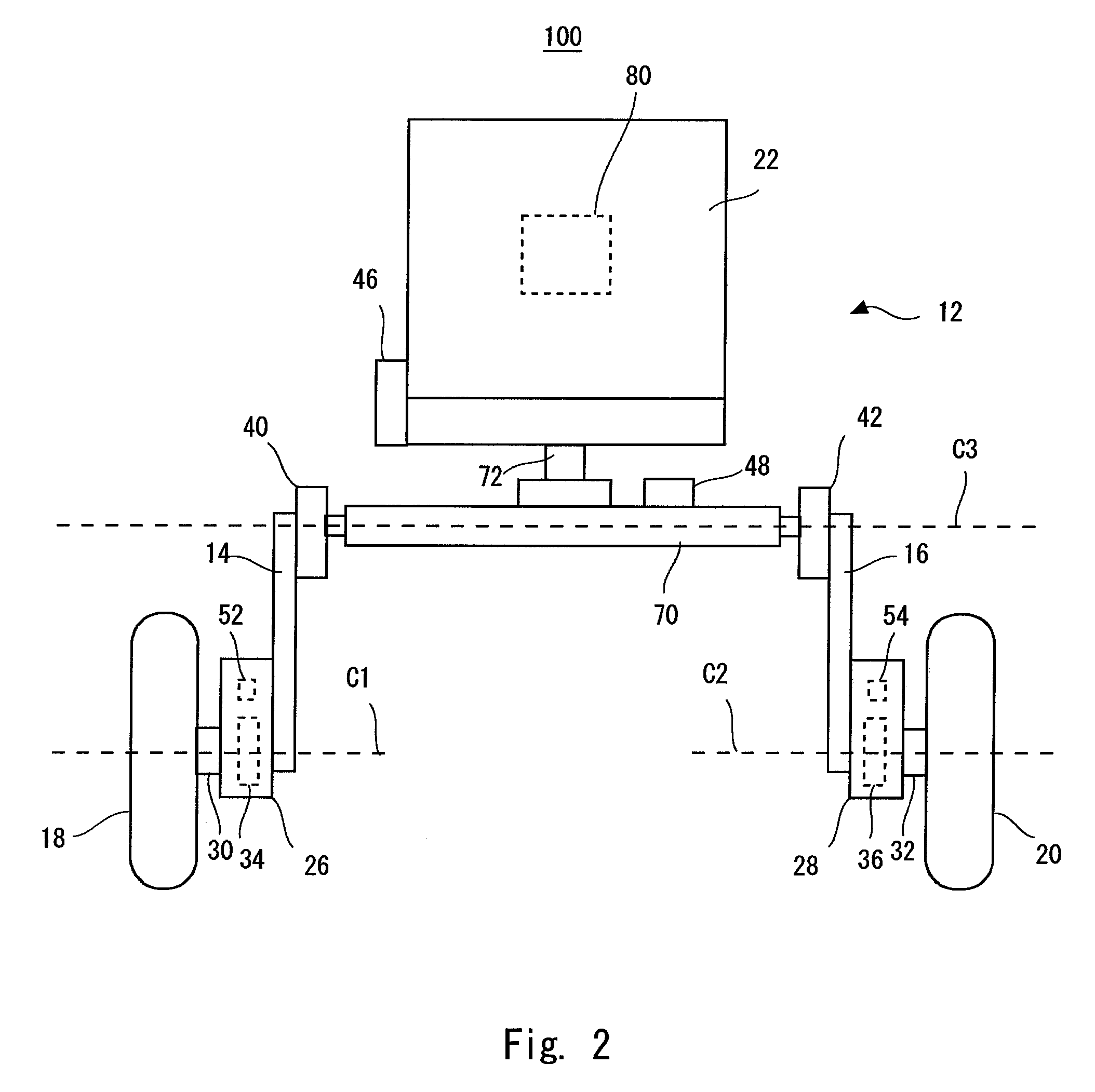
ActiveUS20090107240A1Improve responseImprove accuracyDigital data processing detailsWheelchairs/patient conveyanceDrive wheelMovement control
An inverted pendulum type moving body according to the present invention includes: first actuators that rotationally drive wheels each disposed on an axle; and a turning motion control portion that controls the first actuators when the inverted pendulum type moving body comes into contact with an obstacle so as to allow the inverted pendulum type moving body to perform a turning motion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Dedicated power supply apparatus, terminal. power supply system, and power supply method
ActiveUS20070046268A1Process safetySuppressing malfunction and unstable operationDigital data processing detailsLoad balancing in dc networkControl theoryComputer science
Owner:SONY CORP
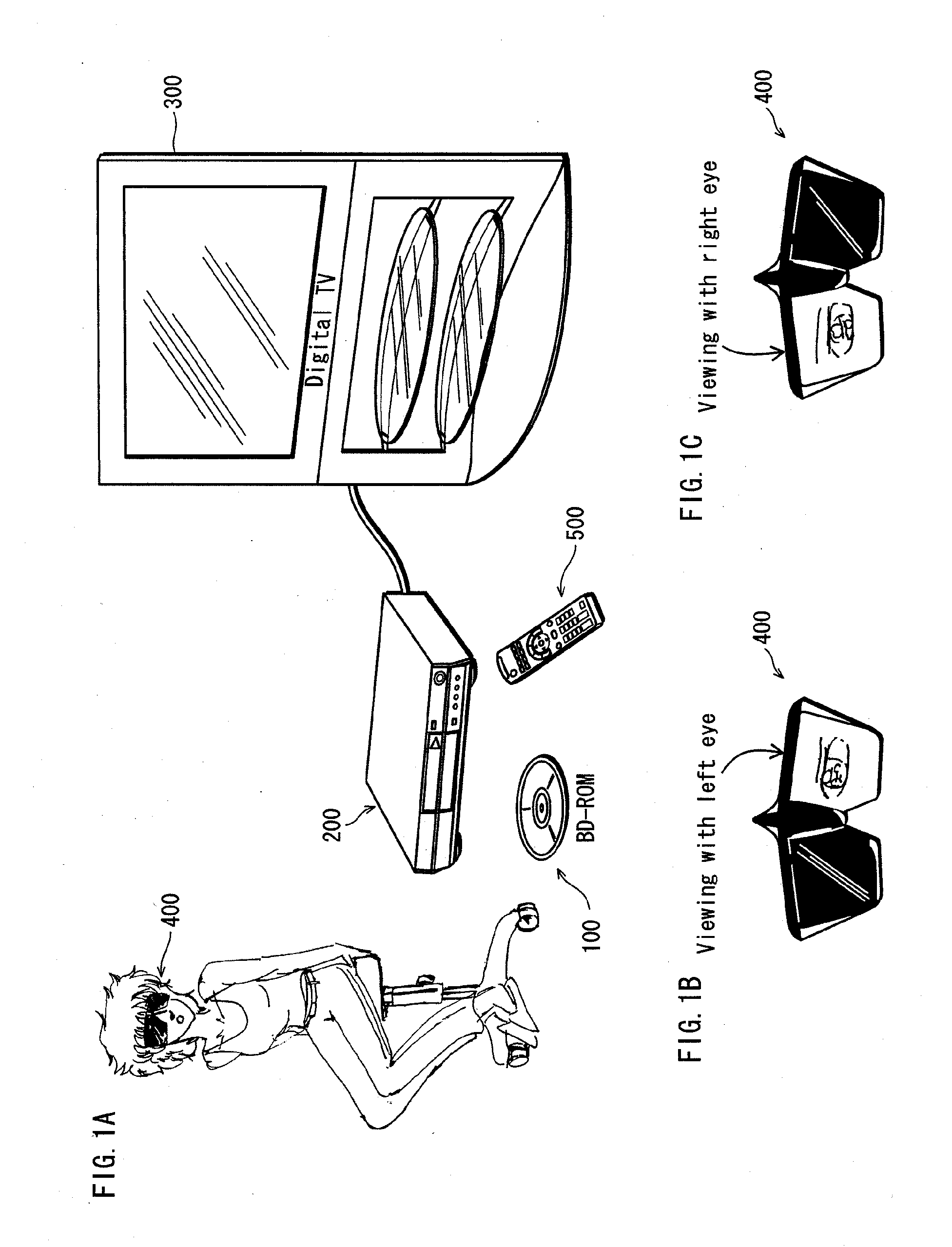
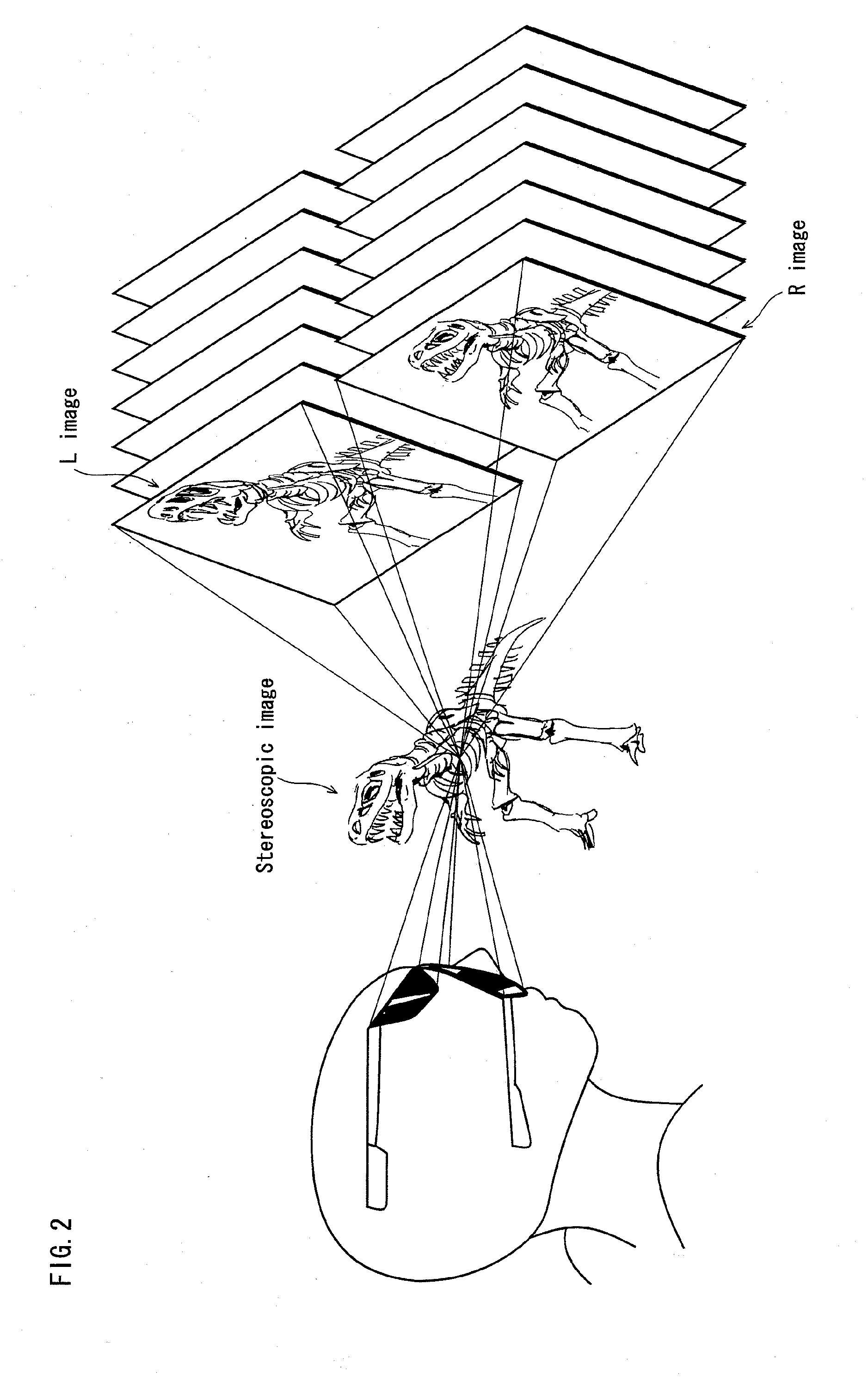
Recording medium, playback device, system lsi, playback method, glasses, and display device for 3D images
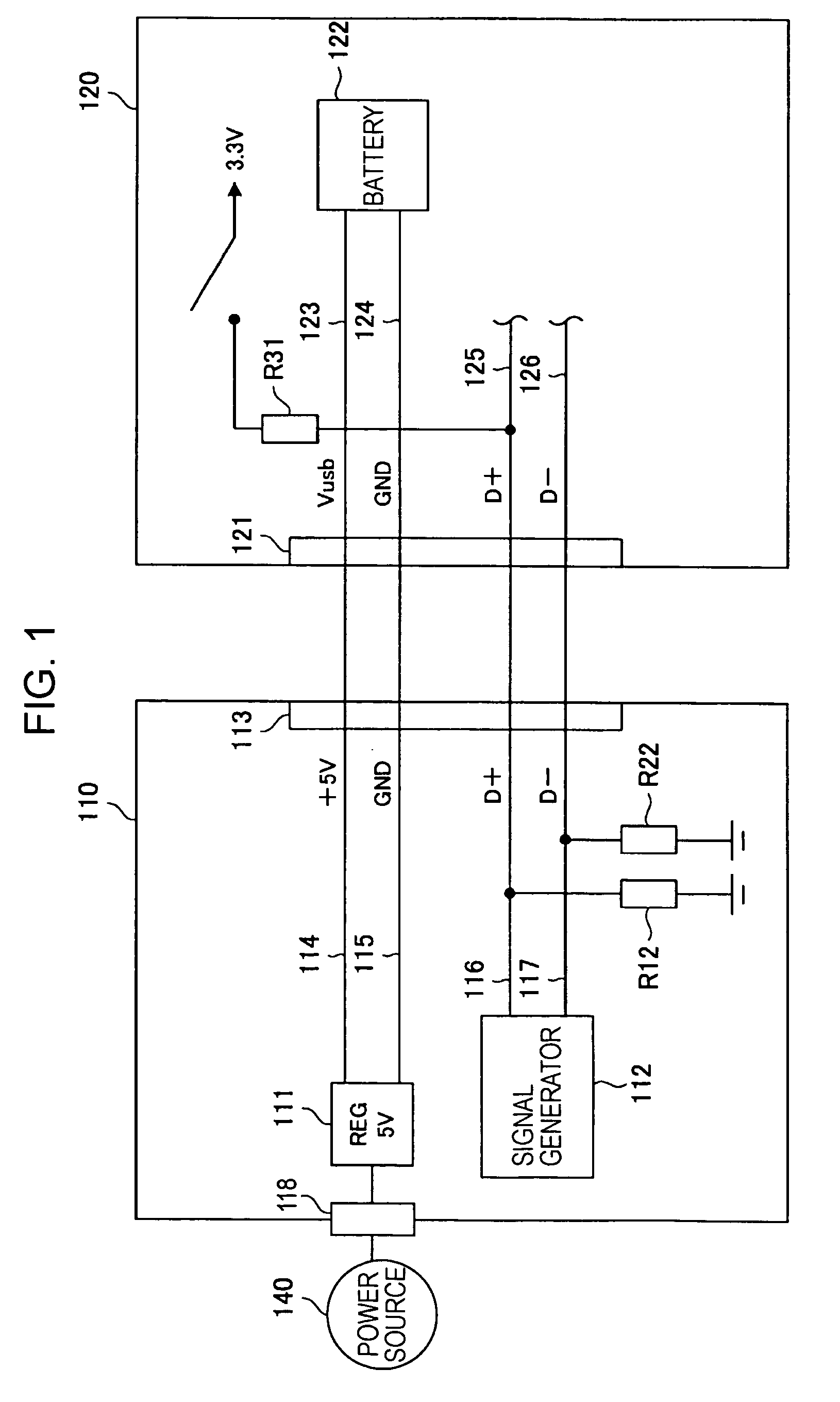
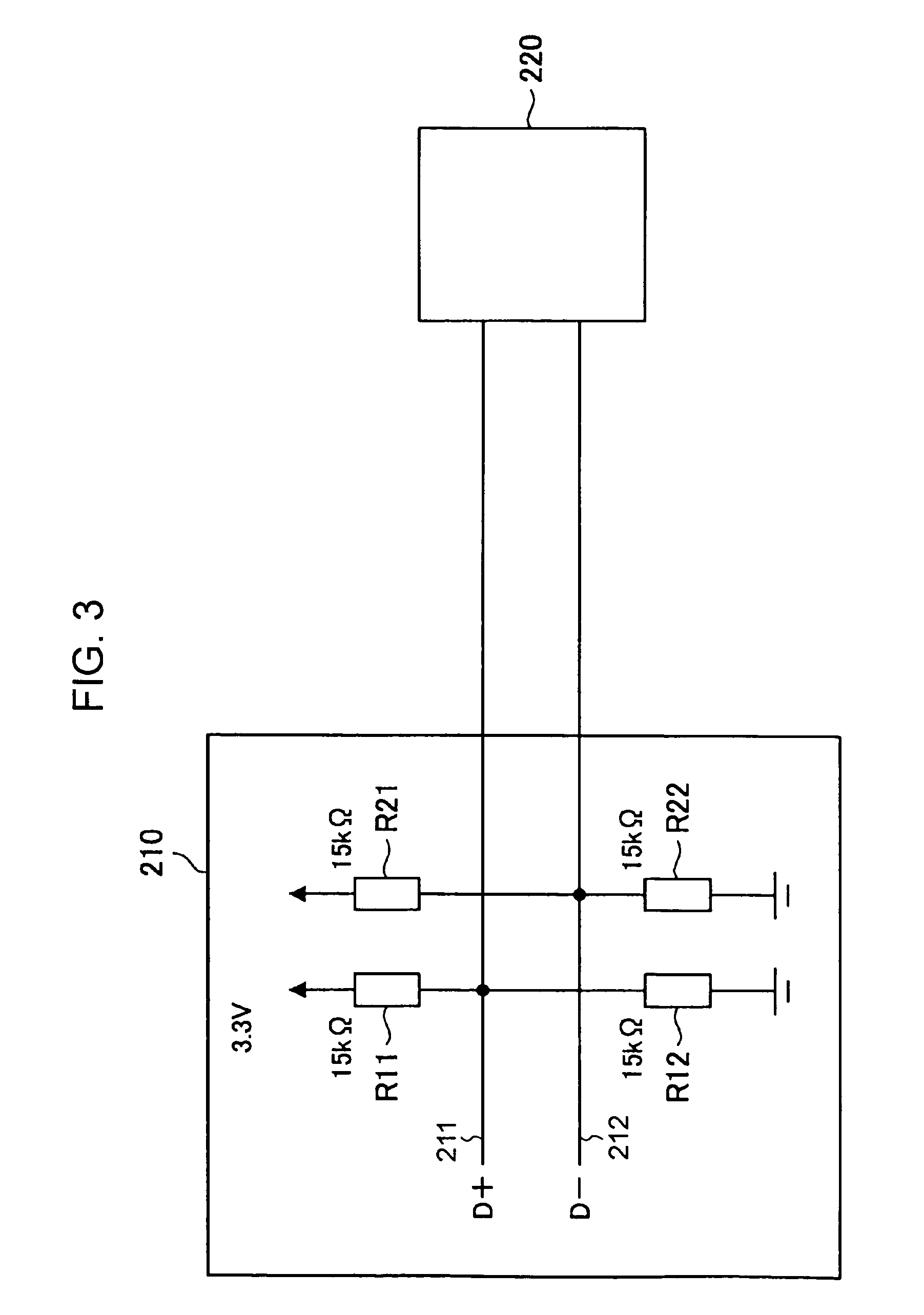
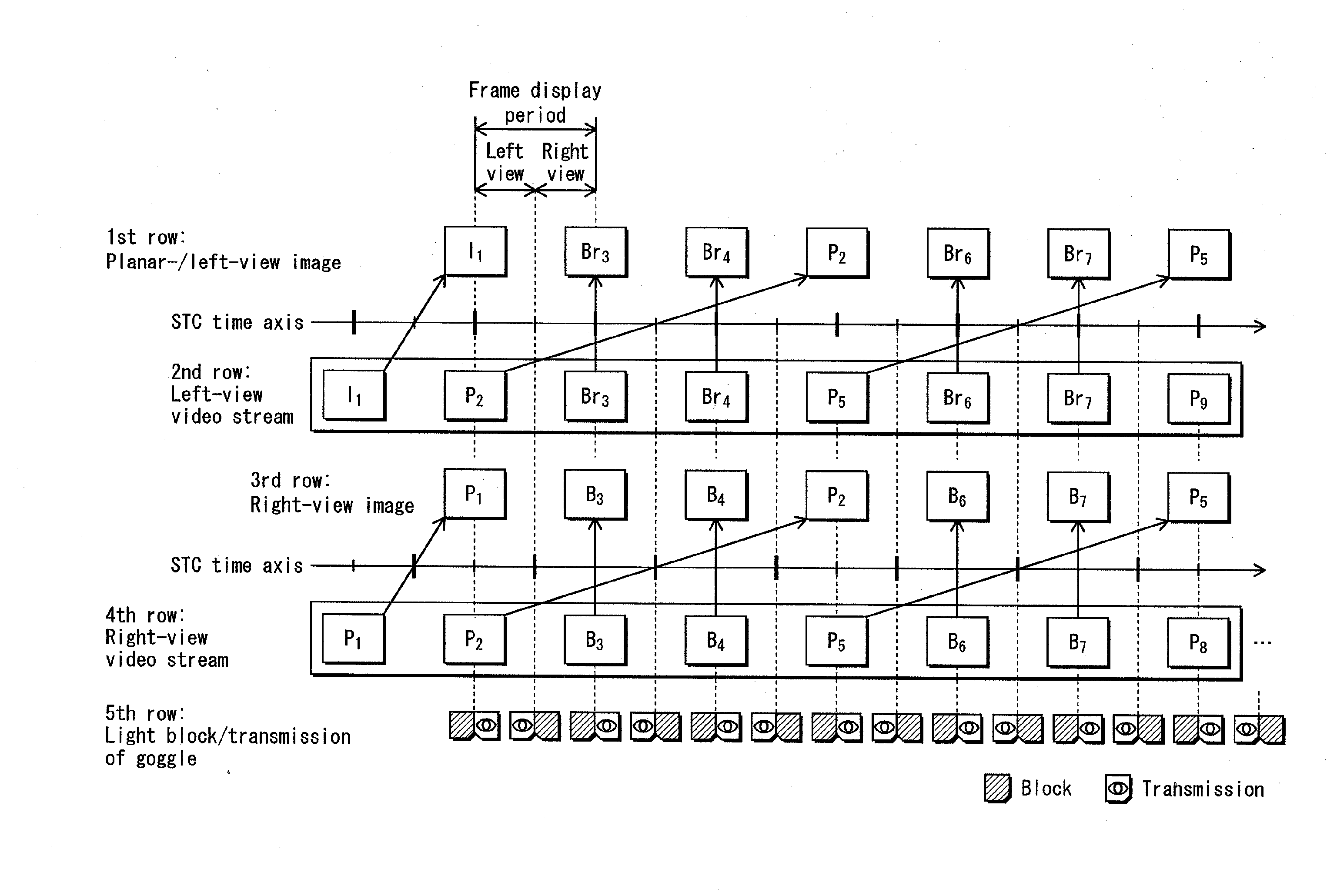
InactiveUS20120275765A1Unstable operationReduce troubleTelevision system detailsAudio/video recordingComputer hardwareFilename extension
A recording medium in which a left-view video stream and a right-view video stream are recorded in an interleaved transport stream file. The interleaved transport stream file is identified by a combination of (i) an equivalent identification number being equivalent with the file reference information and (ii) a file extension indicating that video streams are stored in the interleaved manner, the equivalent identification number. Among Extents that constitute the interleaved transport stream file, Extents constituting the left-view or right-view video stream are identified as a normal-format transport stream file by a combination of (i) the equivalent identification number being equivalent with the file reference information and (ii) a file extension indicating that video streams are stored in a normal manner.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
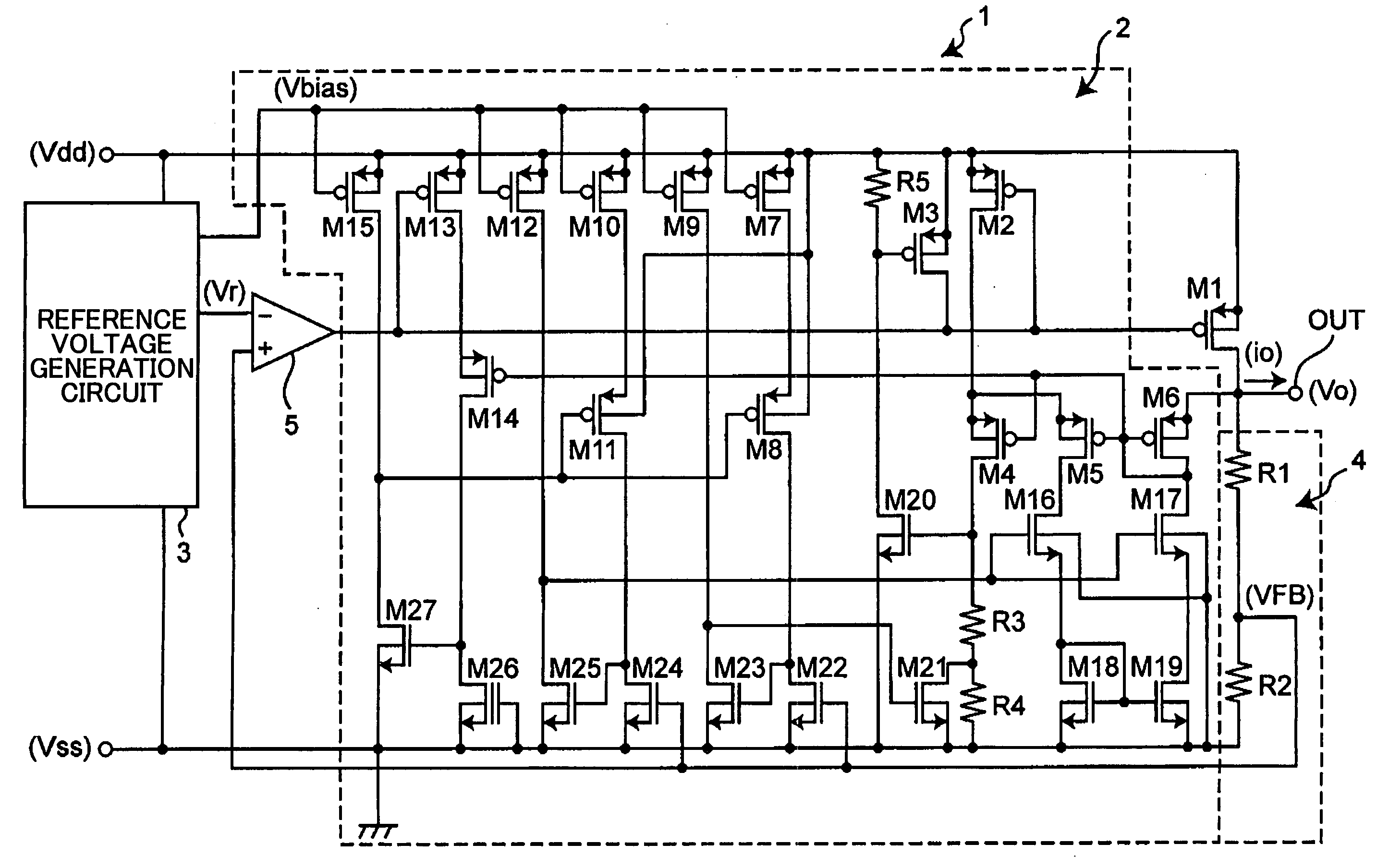
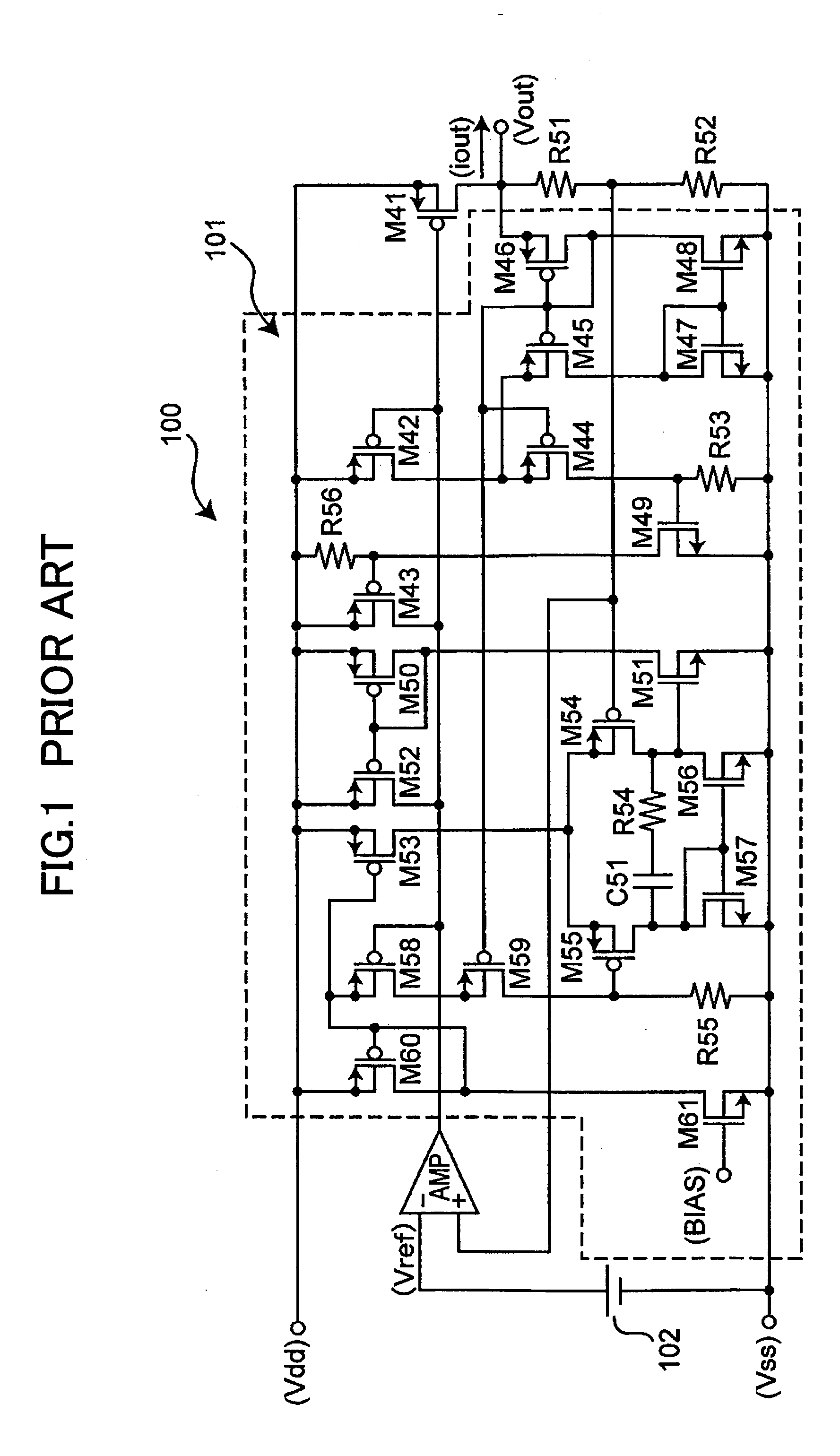
Constant voltage circuit
InactiveUS20050036246A1Reduce current consumptionEliminate disadvantagesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric variable regulationCurrent voltageEngineering
A constant voltage circuit is disclosed that includes an output control transistor and an overcurrent protection circuit. The overcurrent protection circuit includes a proportional current generation circuit part, a current division circuit part, a division ratio control circuit part, a current-voltage conversion circuit part, and an output current control circuit part. When the output voltage of the current-voltage conversion circuit part reaches a predetermined voltage, the output current control circuit part prevents an increase in the output current of the output control transistor so as to reduce a voltage output from an output terminal. When the voltage output from the output terminal is reduced to a predetermined limit voltage, the division ratio control circuit part changes the division ratio of the current division circuit part so that a current supplied to the current-voltage conversion circuit part increases so as to reduce the output current of the output control transistor.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
Temperature Fuse Protection Device
InactiveUS20080117016A1Unstable operationSolution to short lifeFuse device manufactureHeating/cooling contact switchesElectricityHot melt
A temperature fuse protection device uses a hot melt metal to rivet for connecting two terminals in the circuit that are separated for making the two terminals electrically-connected and the circuit complete. There is a spacing in between the two free ends of the two terminals when no external force is being imposed. When an electric overloading or high circuit temperature event occurs, the hot melt metal would be heated to melt and break, which would then make the free ends of the two terminals to be disconnected, and therefore, the circuit will be at “OFF” status.
Owner:YU TSUNG MOU
Communication device and communication method, computer program, and communication system
ActiveUS20120044904A1Satisfactorily perform communication operationImprove throughputModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionCommunications systemCommunication quality
A communication operation is suitably performed with application of Space Division Multiple Access in which wireless resources on a space axis are shared by a plurality of users.If a frequency width is narrowed to 20 MHz when the communication quality is high, the amount of transmittable data can be about half, and the frame length can be doubled. If the frame length is rather excessively long, switching is performed to a modulation scheme with the greater number of states to shorten the frame length. On the other hand, when the communication quality is low, switching is performed to a modulation scheme with the smaller number of states to lengthen the frame length. When the frame length is still insufficient, switching is performed to a narrow frequency width to lengthen the frame length.
Owner:SONY CORP
Inverter control device for driving a motor and an air conditioner
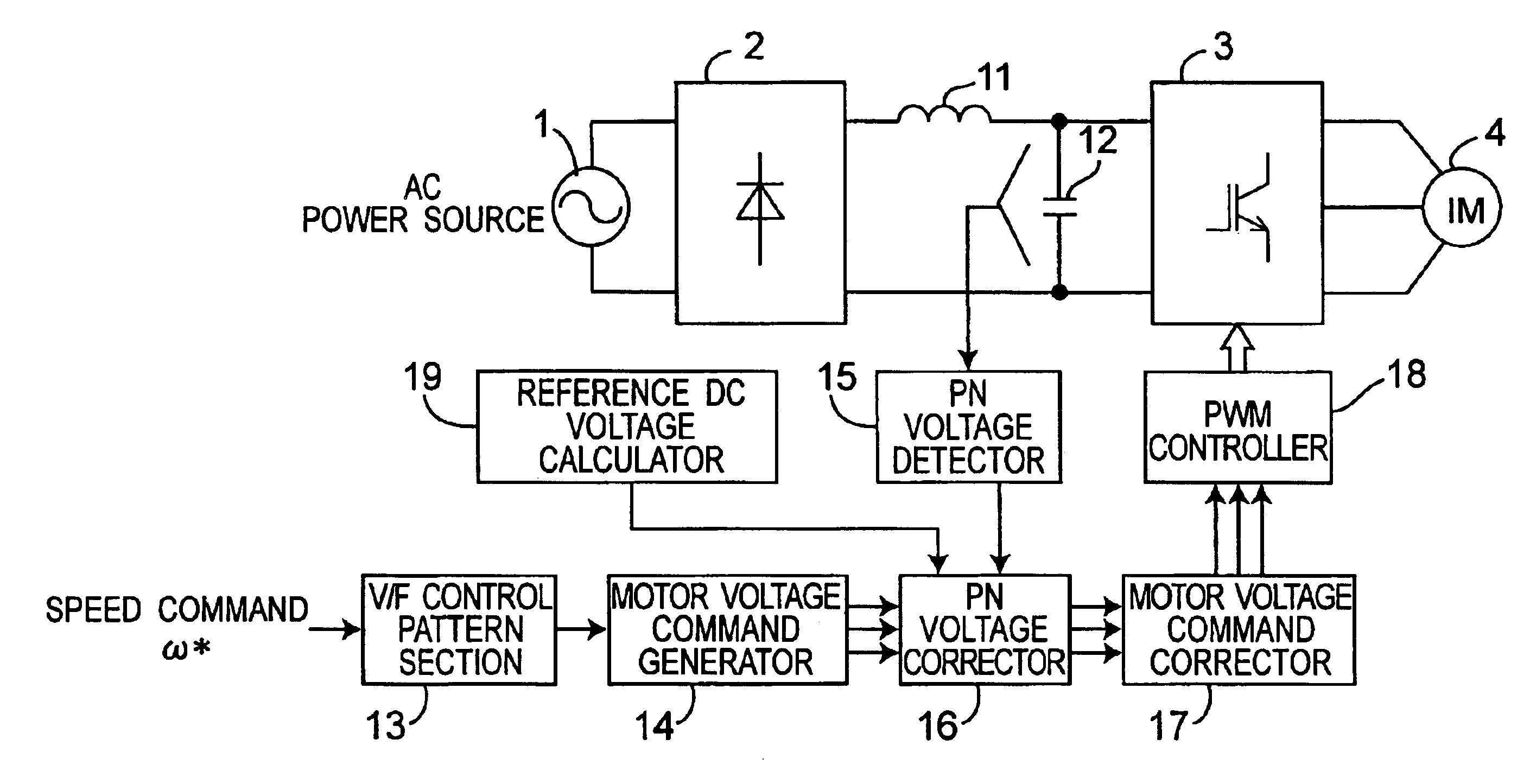
ActiveUS6972541B2Light weightImprove power factorElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringDc voltage
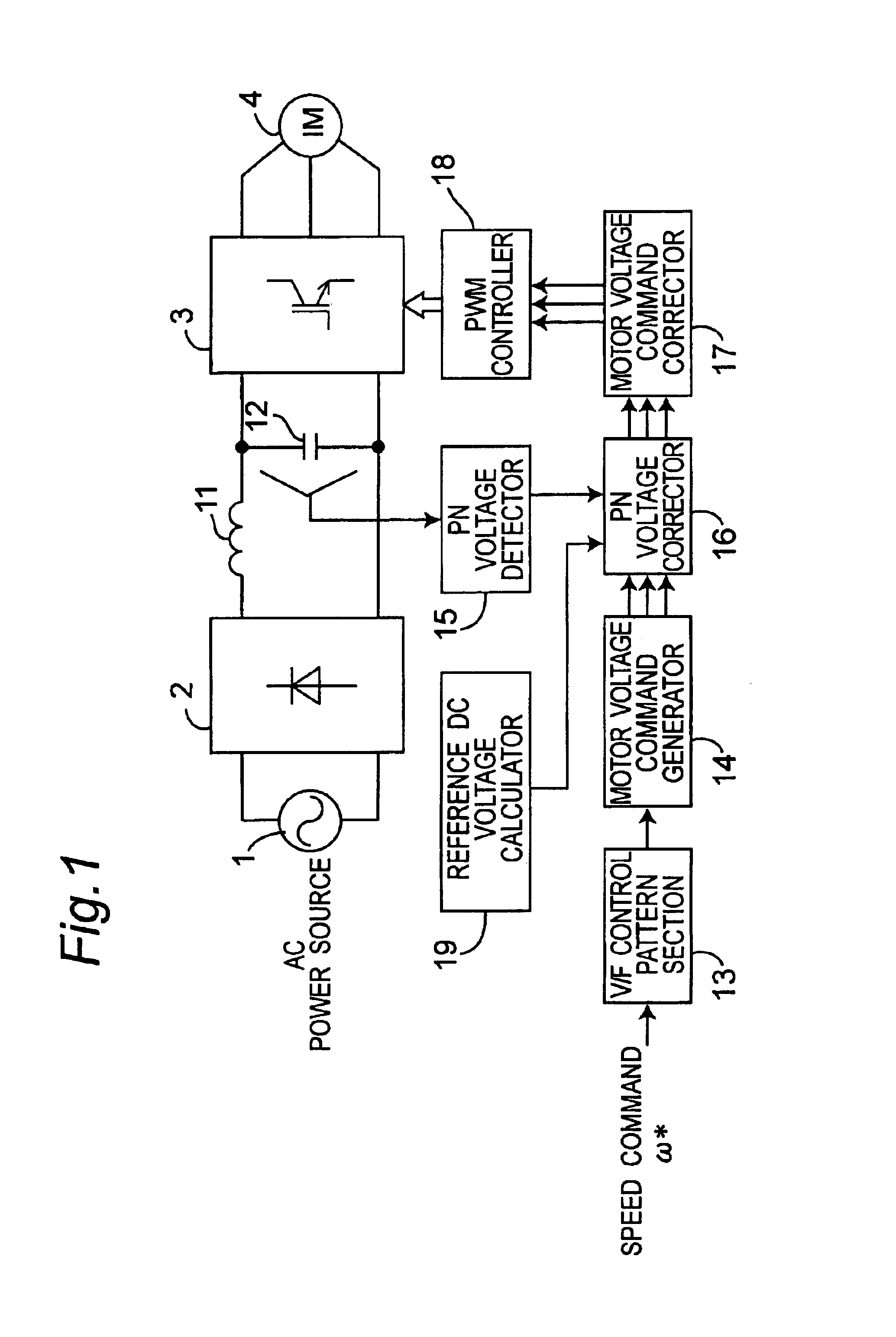
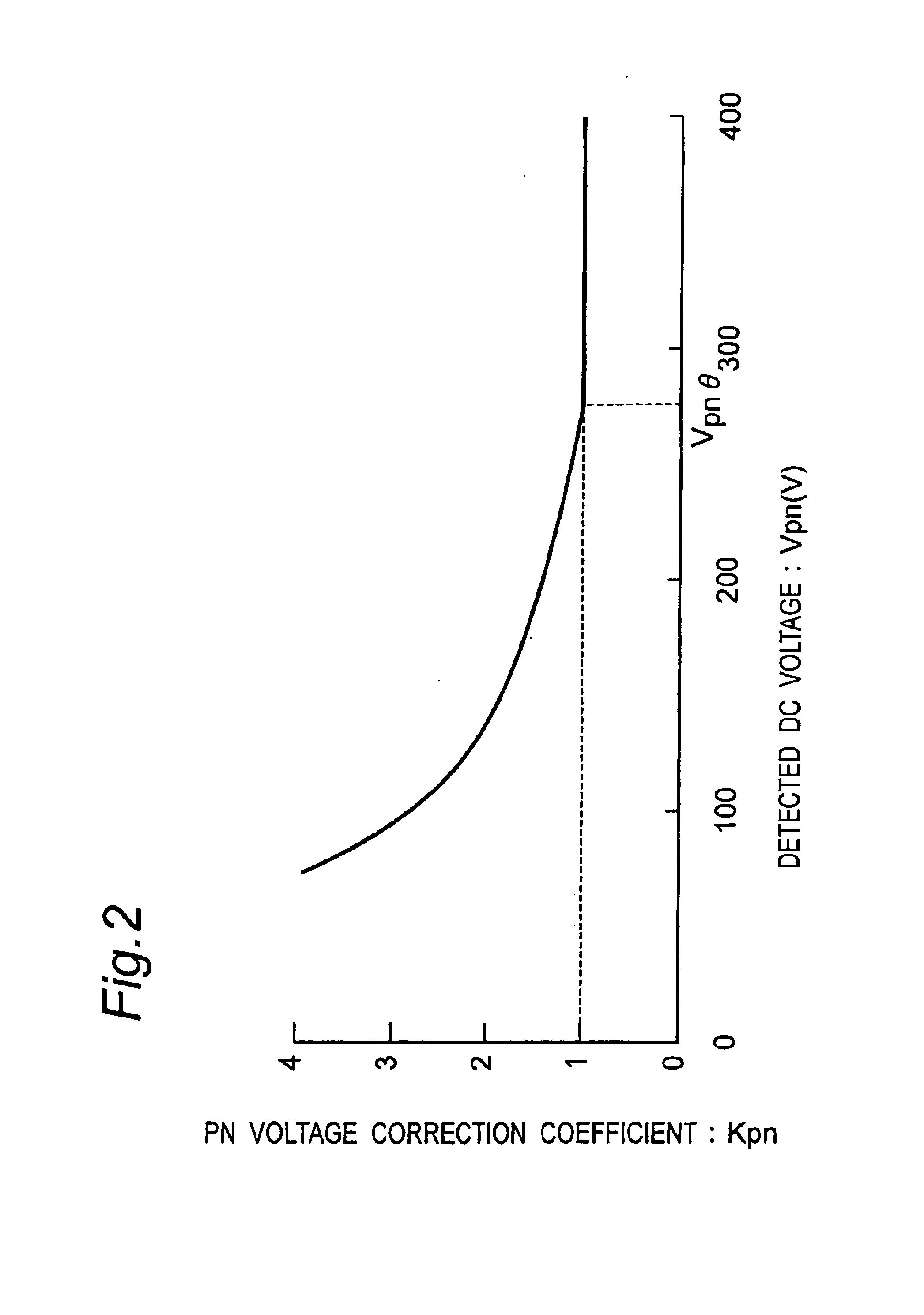
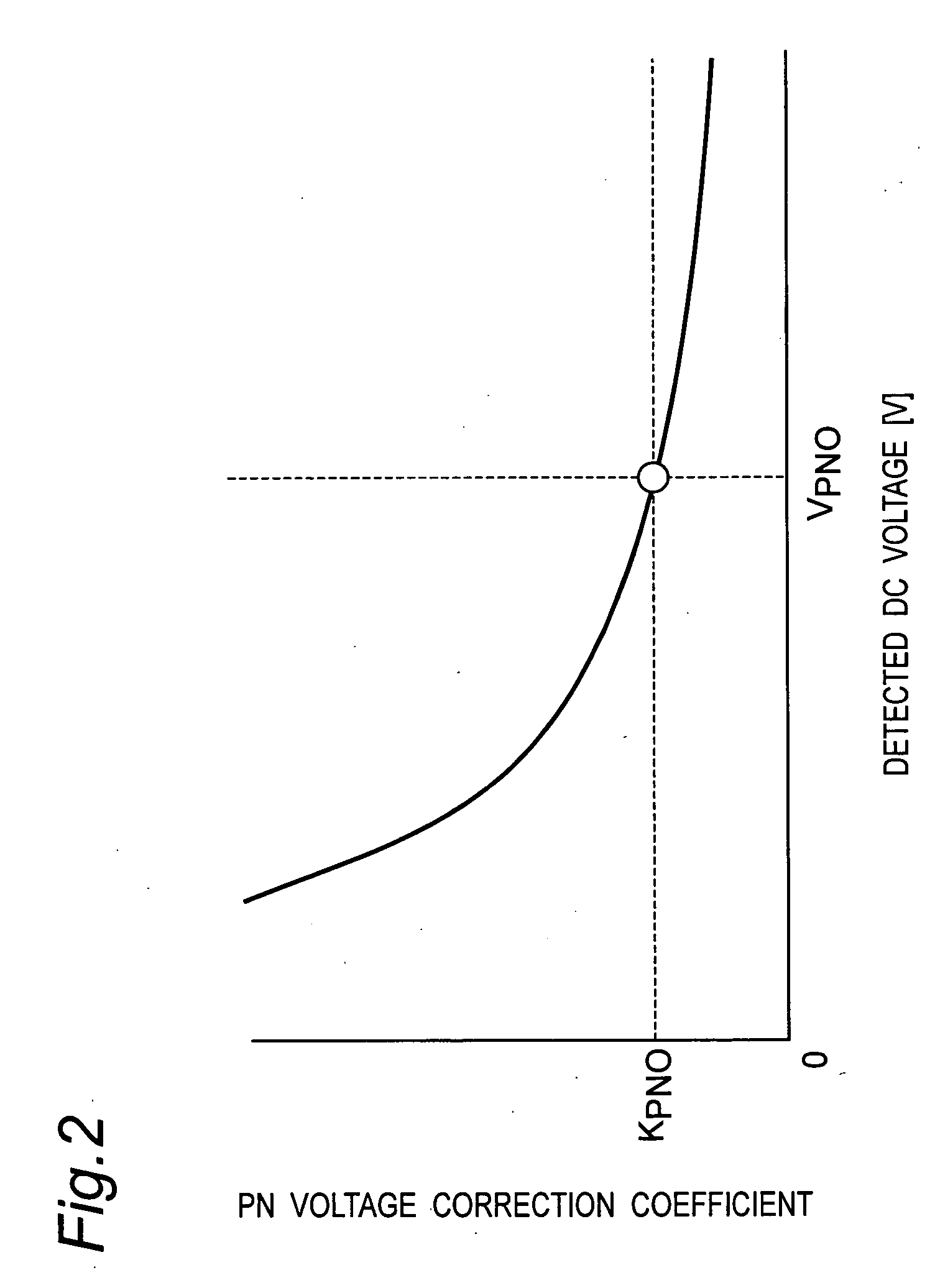
An inverter control device for driving a motor with small size, light weight and low cost is provided. The inverter control device generates PN voltage correction coefficient by dividing the reference DC voltage by the detected DC voltage, and corrects the voltage command of each phase by multiplying the voltage command of each phase obtained by the motor voltage command generator with the PN voltage correction coefficient output from the PN voltage corrector, thus resulting in the corrected motor voltage command. The inverter control device has, in generating PN voltage correction coefficient, a first mode in which the PN voltage correction coefficient is set to 1 when the DC voltage value is more than the reference DC voltage, and a second mode in which the value obtained by dividing the reference DC voltage by the detected DC voltage is set to the PN voltage correction coefficient.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Inverter control device for driving a motor and an air conditioner
InactiveUS20040228151A1Unstable operation of motor is preventedSmooth rideCompression machines with non-reversible cyclePower factor controlEngineeringControl theory
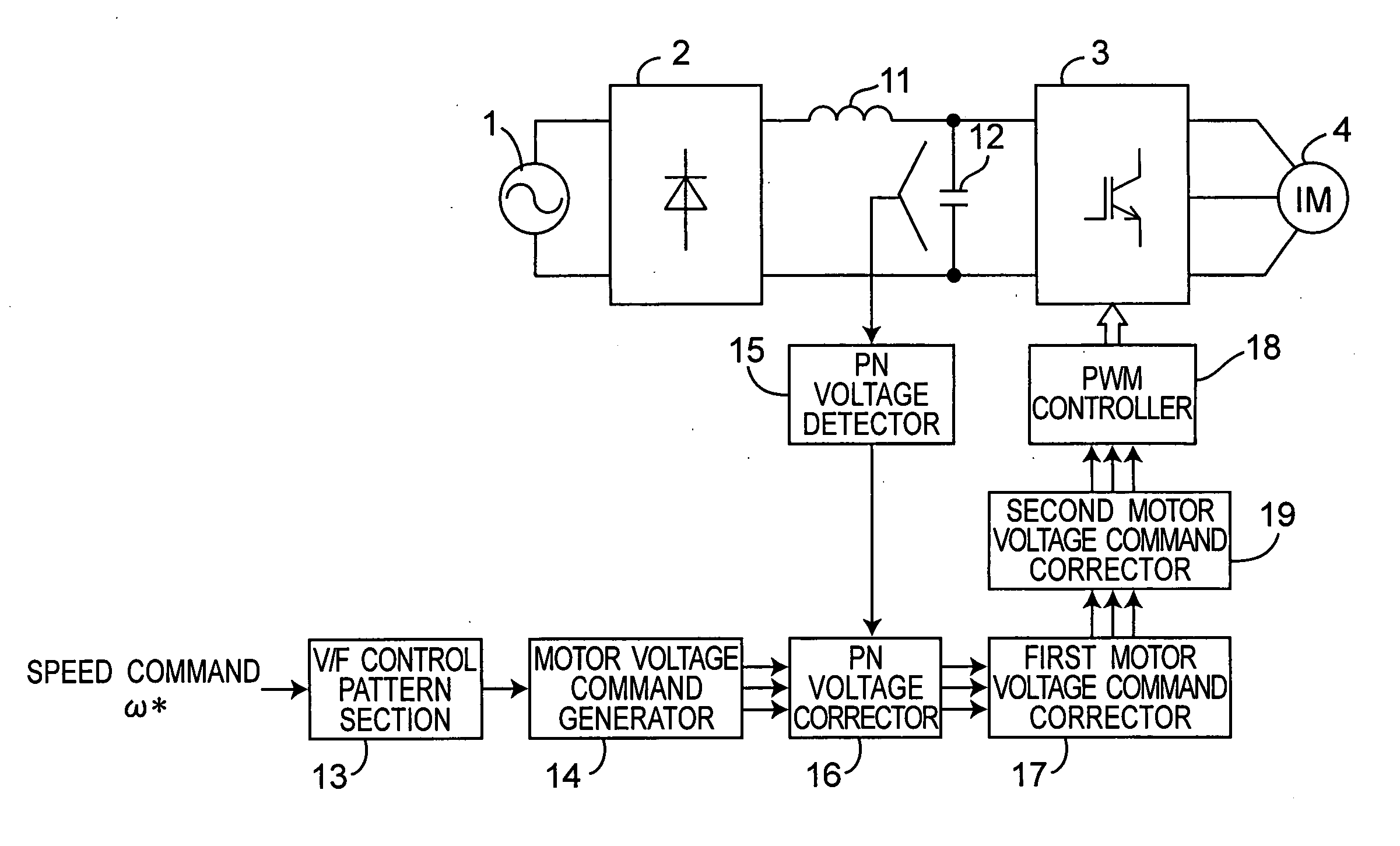
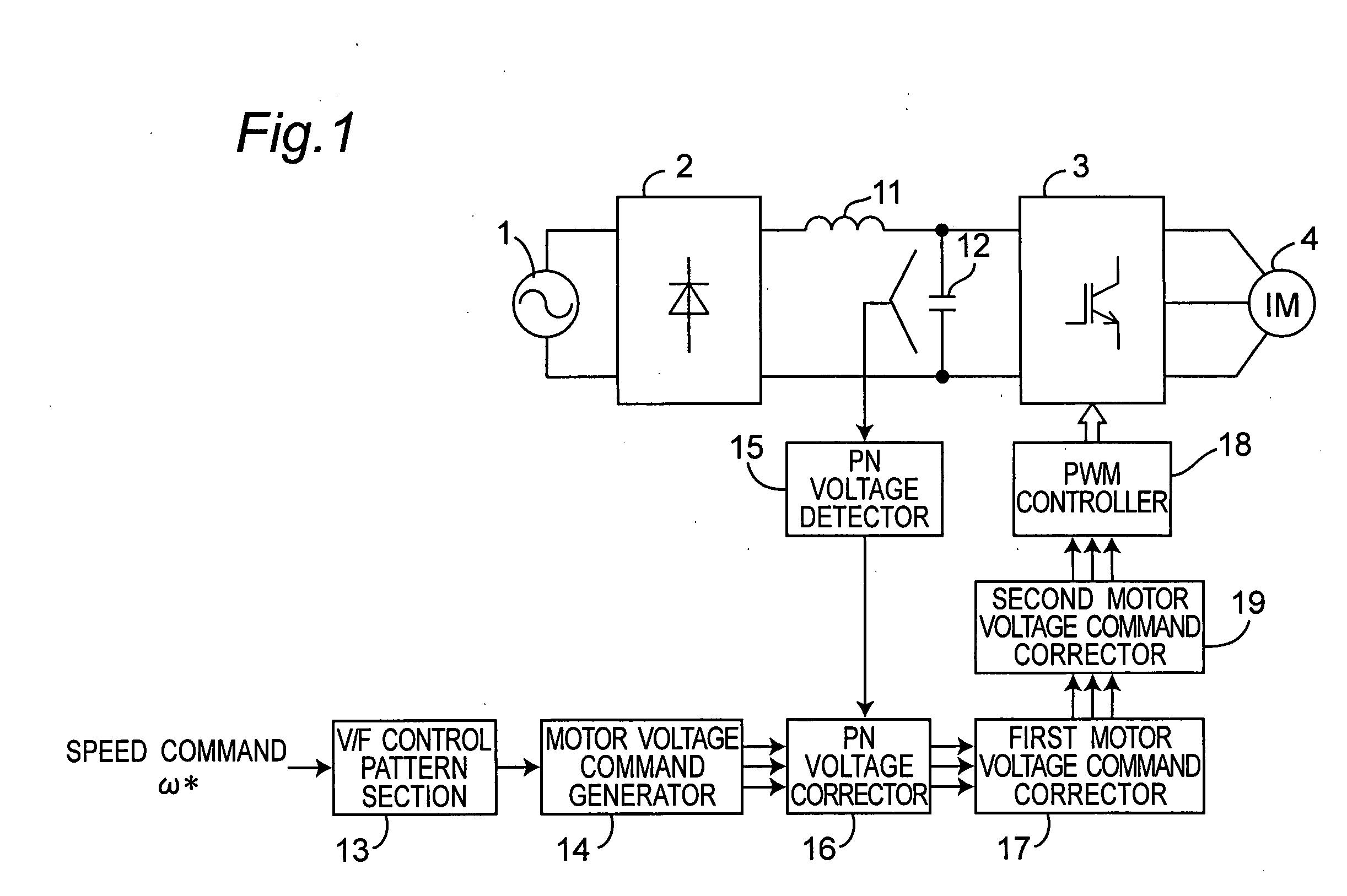
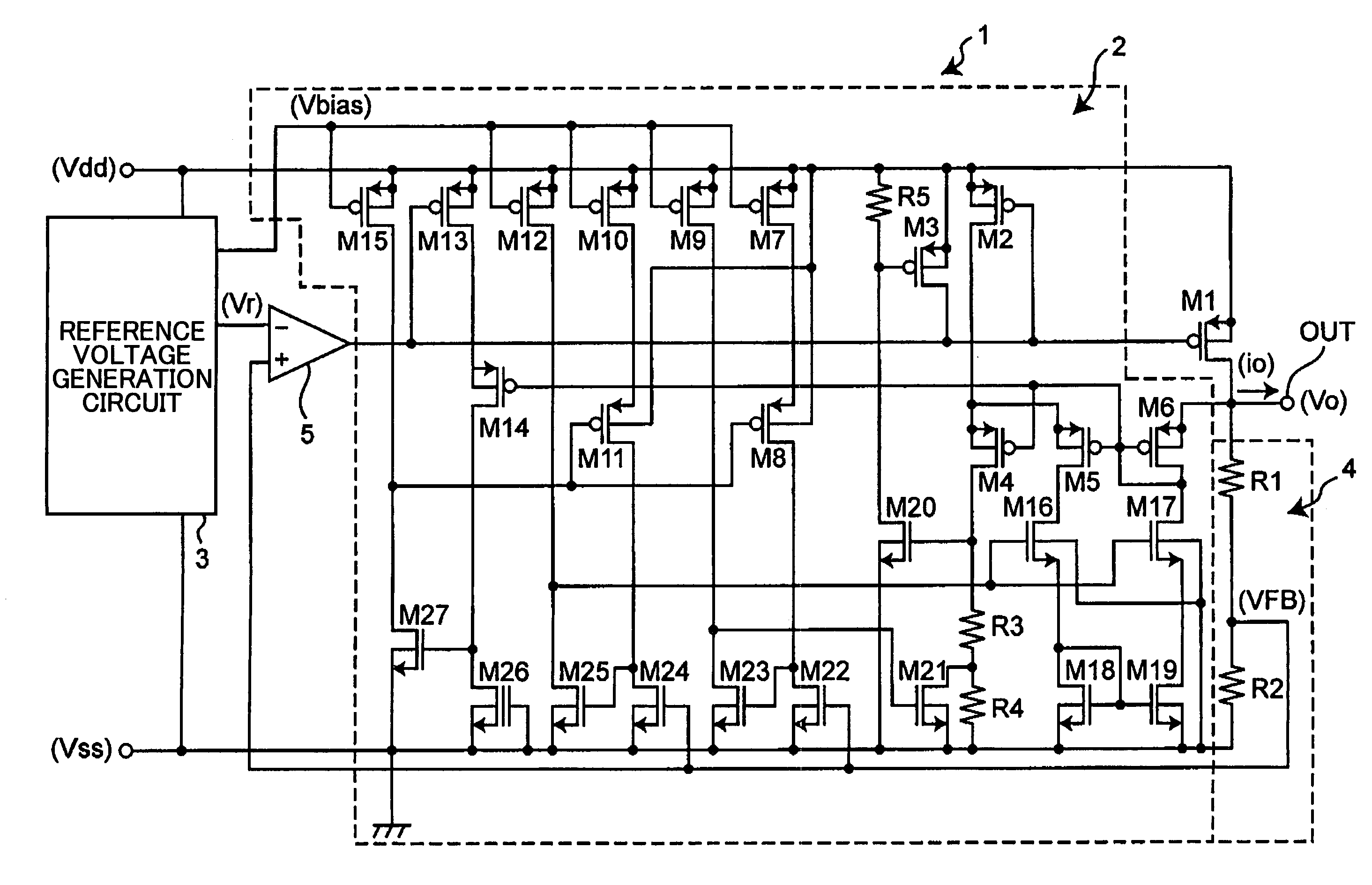
An inverter control device for driving a motor with small size, light weight and low cost is provided. The inverter control device includes a first motor voltage command corrector that corrects a voltage command of each phase by multiplying the each phase voltage command by a PN voltage correction coefficient, and a second motor voltage command corrector that corrects again the each phase voltage command once corrected by the first motor voltage command corrector, only when any one of the phase voltage commands corrected by the first motor voltage command corrector is larger than the inverter DC voltage, by multiplying the voltage command of each phase corrected by the first motor voltage command corrector by the inverter DC voltage value, and dividing the product of the multiplication by the maximum value of the phase voltage commands corrected by the first motor voltage command corrector.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Constant voltage circuit
InactiveUS7215180B2Eliminate disadvantagesTotal current dropEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric variable regulationCurrent voltageEngineering
A constant voltage circuit is disclosed that includes an output control transistor and an overcurrent protection circuit. The overcurrent protection circuit includes a proportional current generation circuit part, a current division circuit part, a division ratio control circuit part, a current-voltage conversion circuit part, and an output current control circuit part. When the output voltage of the current-voltage conversion circuit part reaches a predetermined voltage, the output current control circuit part prevents an increase in the output current of the output control transistor so as to reduce a voltage output from an output terminal. When the voltage output from the output terminal is reduced to a predetermined limit voltage, the division ratio control circuit part changes the division ratio of the current division circuit part so that a current supplied to the current-voltage conversion circuit part increases so as to reduce the output current of the output control transistor.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
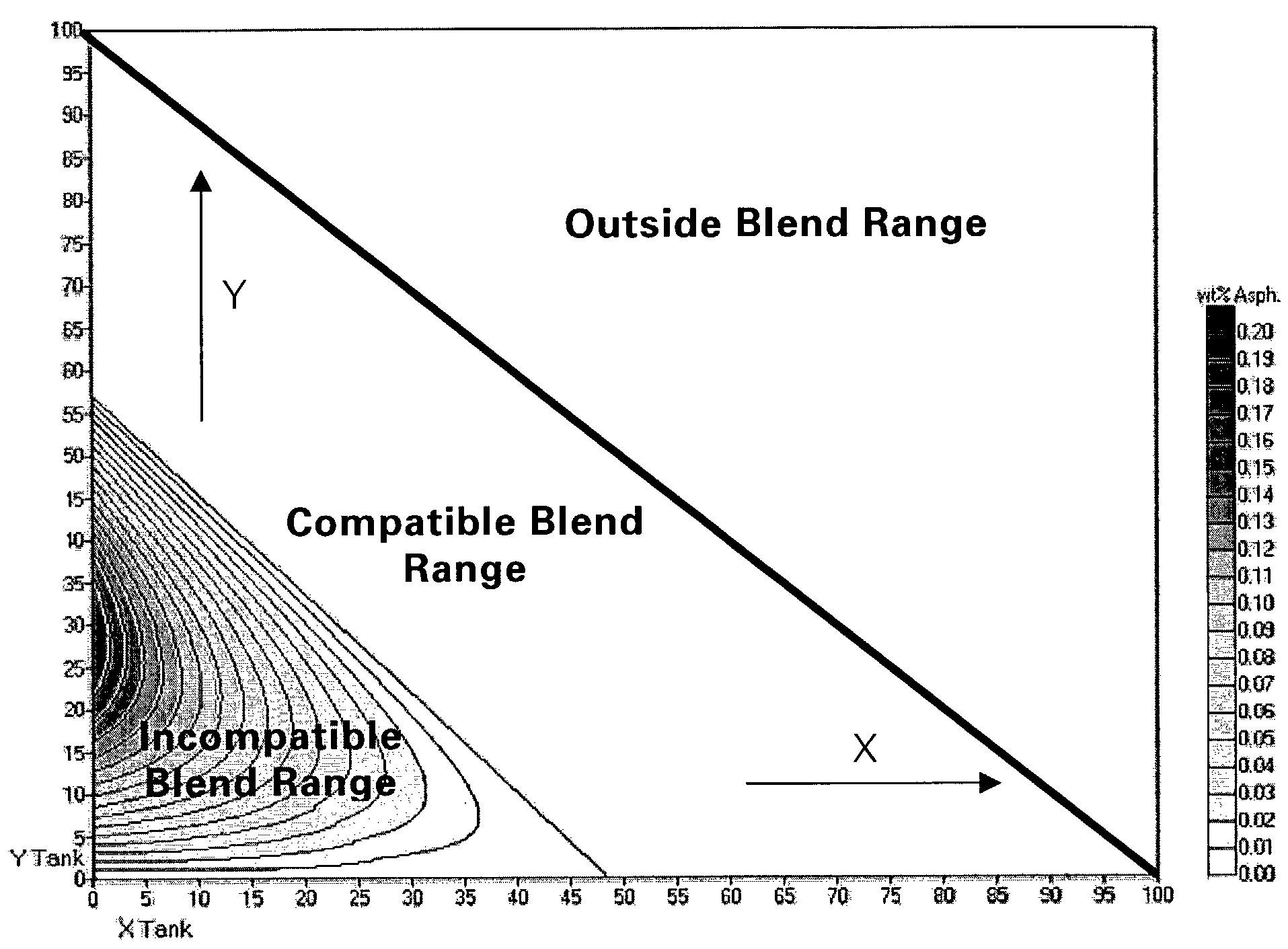
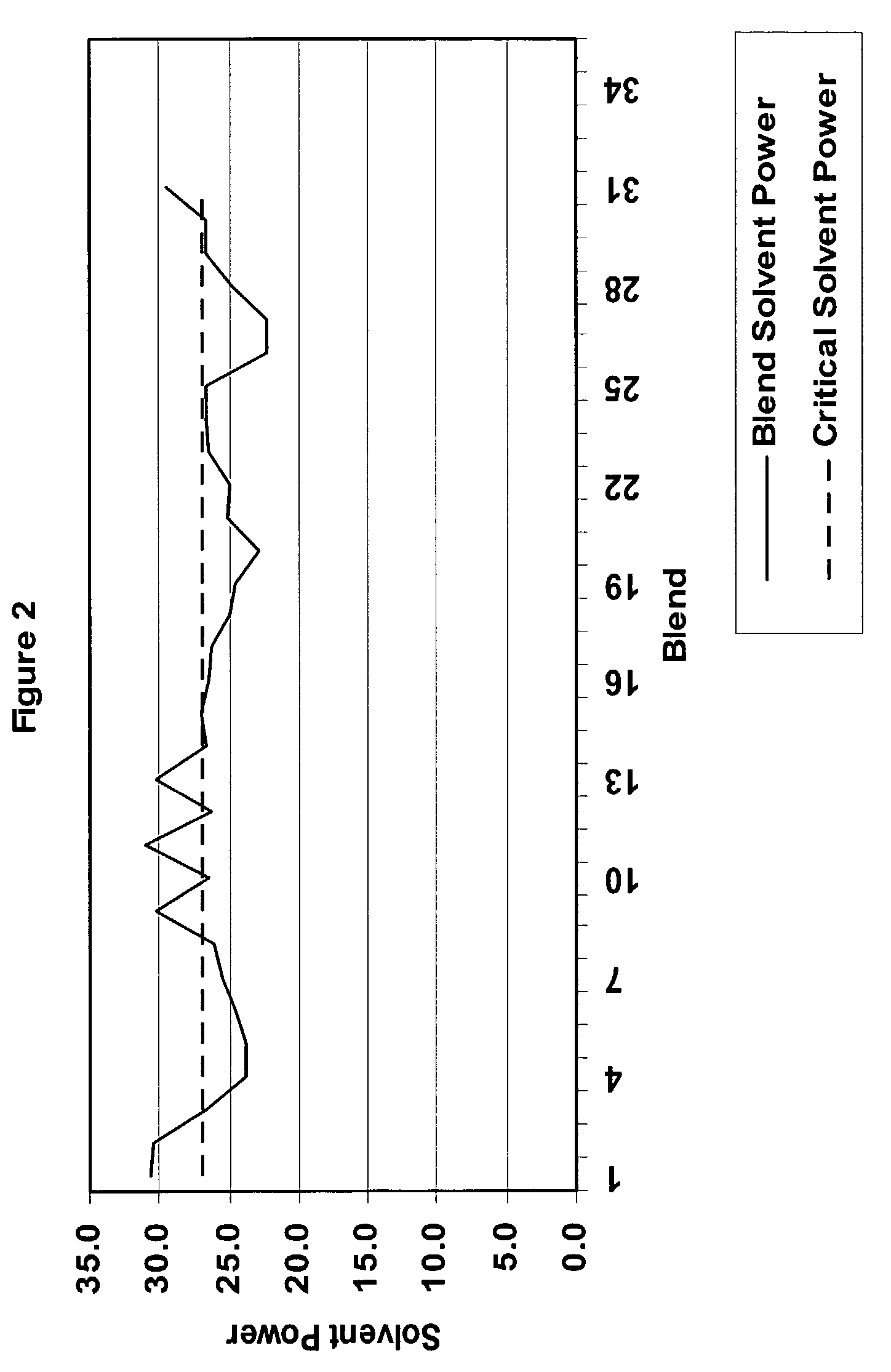
Predictive crude oil compatibility model
ActiveUS7618822B2Economical and practicalIncrease flexibilityWithdrawing sample devicesEarth material testingParaffin waxBoiling point
A method for blending at least two hydrocarbon liquids, the method comprising: (a) determining the critical solvent power for each hydrocarbon liquid by (i) mixing each hydrocarbon liquid with predetermined amounts of a paraffin; (ii) centrifuging each resulting mixture; (iii) recovering and weighing any resulting precipitated insolubles from step (ii); and (iv) correlating the weight of the insolubles in step (iii) to the solvent power at which asphaltenes begin to precipitate out of the hydrocarbon; (b) determining the solvent power for each hydrocarbon liquid by: (i) determining the distillation curve and density of each hydrocarbon liquid; (ii) numerically integrating the distillation curve of each hydrocarbon liquid, producing the volume average boiling point for each hydrocarbon liquid; (iii) calculating the characterization K factor for each hydrocarbon liquid using the volume average boiling point in step (ii); and (iv) determining the solvent power of each hydrocarbon liquid using the characterization K factor in step (iii), wherein heptane and toluene are used as solvent power references wherein heptane has a solvent power of zero and toluene has a solvent power of 100; and (c) blending the each crude oil into each other producing a crude oil blend wherein the solvent power of the crude oil blend is greater than the critical solvent power of the crude oil having the highest critical solvent power in the blend.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Temperature fuse protection device
InactiveUS7639114B2Solution to short lifeUnstable operationFuse device manufactureHeating/cooling contact switchesElectricityEngineering
Owner:YU TSUNG MOU
Shielding of heat exchangers in columns
InactiveUS6883788B1Unstable operationPressure drop unstableMixing methodsSteam/vapor condensersEngineeringVapor phase
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for exchanging heat in a column by passing a first vapor phase through a heat exchanger in the column to exchange heat with a first stream and produce a second vapor phase in the column. The second vapor phase is passed through a shielding device located above the heat exchanger and the shielding device prevents descending liquid from contacting the heat exchanger. The shielding device may be interposed between two heat exchangers in the column.
Owner:UOP LLC
Inverted pendulum type moving body and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS8265774B2Safely avoidedEasy to controlDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsDrive wheelActuator
An inverted pendulum type moving body according to the present invention includes: first actuators that rotationally drive wheels each disposed on an axle; and a turning motion control portion that controls the first actuators when the inverted pendulum type moving body comes into contact with an obstacle so as to allow the inverted pendulum type moving body to perform a turning motion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Exhaust gas recirculation apparatus of engine with supercharger
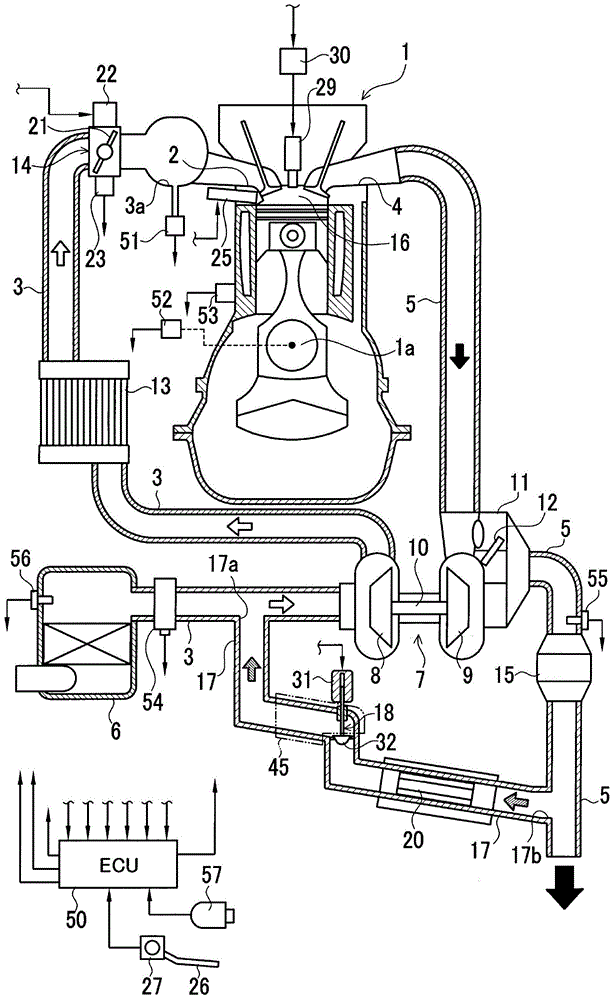
ActiveCN104454248AAvoid strandedAvoid corrosionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringExhaust gas recirculation
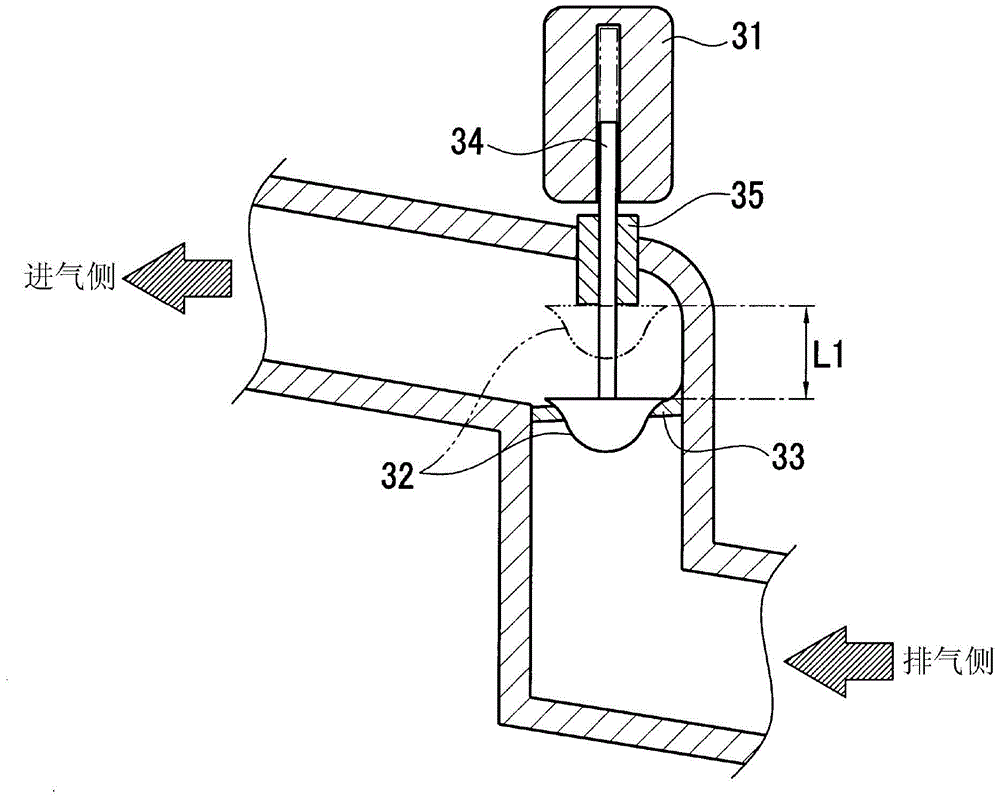
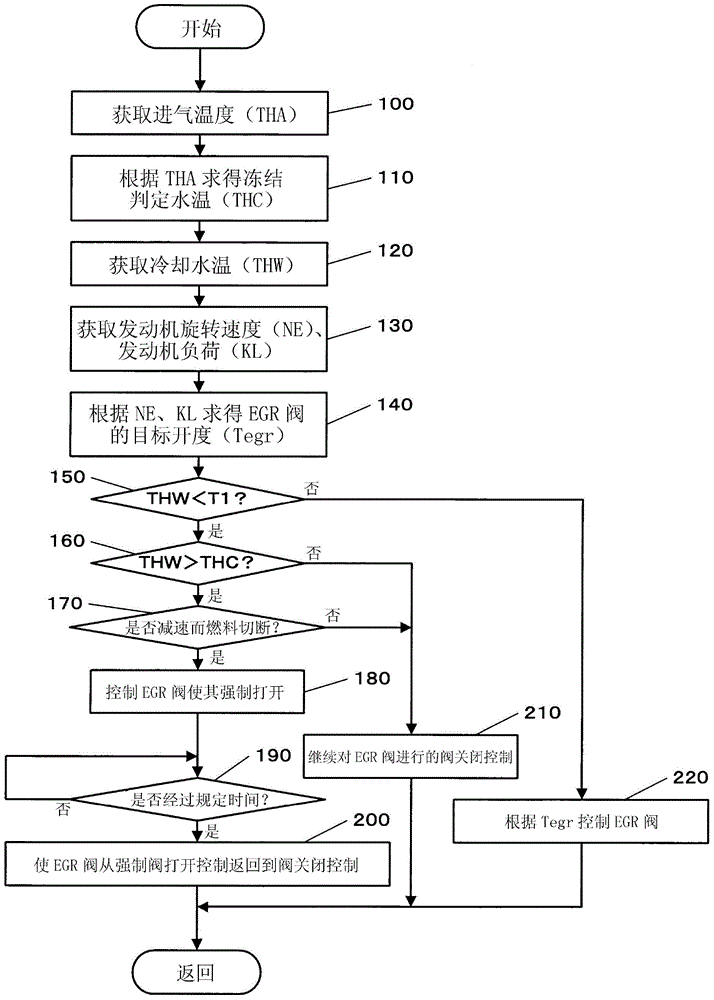
An exhaust gas recirculation apparatus of an engine with a supercharger, which prevents retention of a large amount of condensed water at the downstream side of an EGR valve, with the condensed water being generated by EGR gas leaked to the downstream side of the EGR valve during full closing of the EGR valve, is provided by the invention. The engine (1) is provided with the supercharger (7) and a low pressure loop EGR apparatus, wherein an electronic control unit (ECU) (50) controls the EGR valve (18) to be fully closed when a detected operating condition is a predetermined operating condition. An outlet (17a) of an EGR passage (17) is located at a higher position than an inlet (17b) in a vertical direction to allow condensed water to flow downward from downstream to upstream of the EGR valve (18) and flow downward through the EGR passage (17) to an exhaust passage (3). When the EGR valve (18) has to be controlled to be fully closed, to discharge the condensed water from a downstream side of the EGR valve (18), the ECU (50) forcibly opens the EGR valve (18) when a predetermined discharge condition is established.
Owner:AISAN IND CO LTD
Processing system and method for detecting hotkey activation
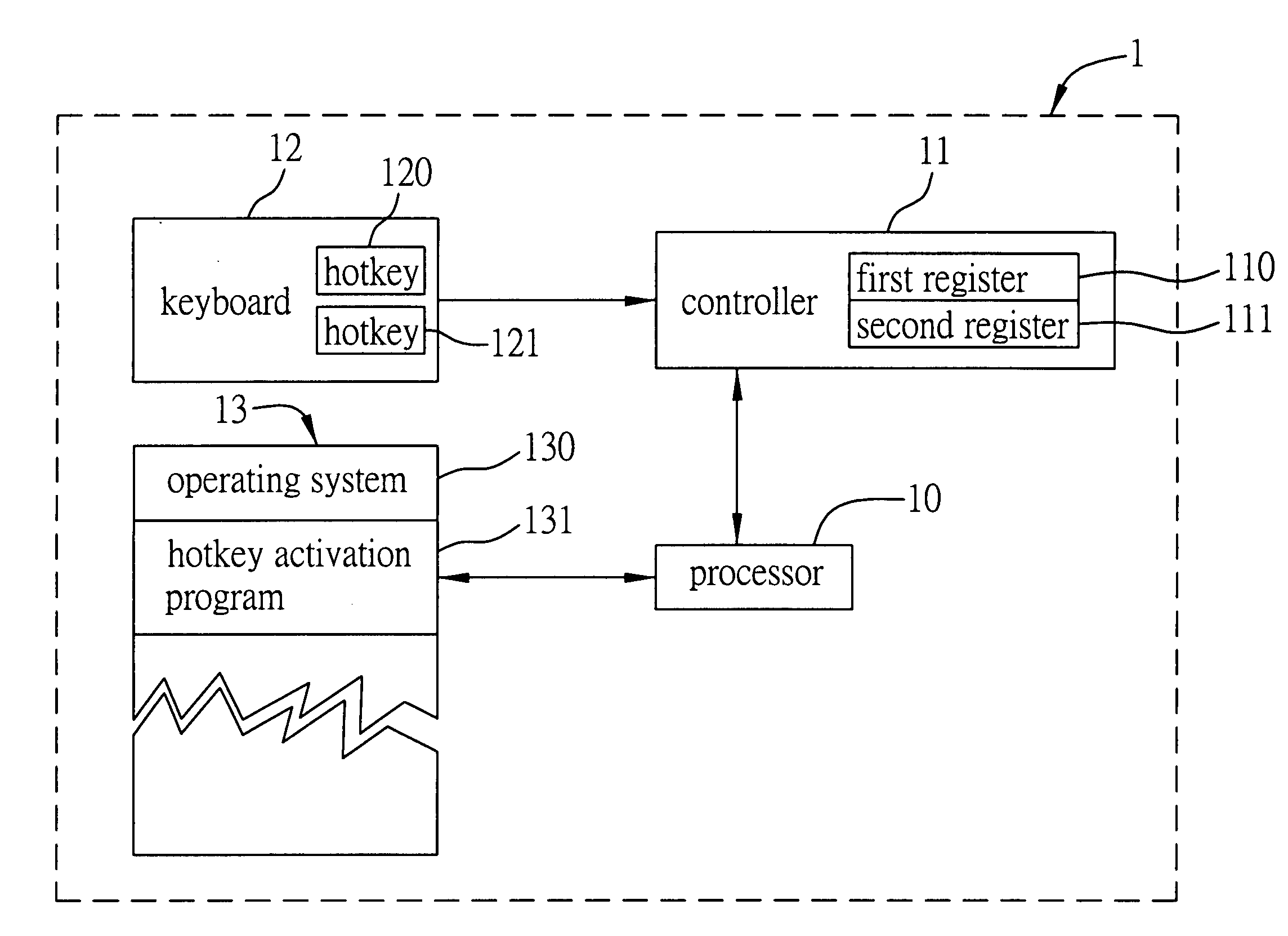
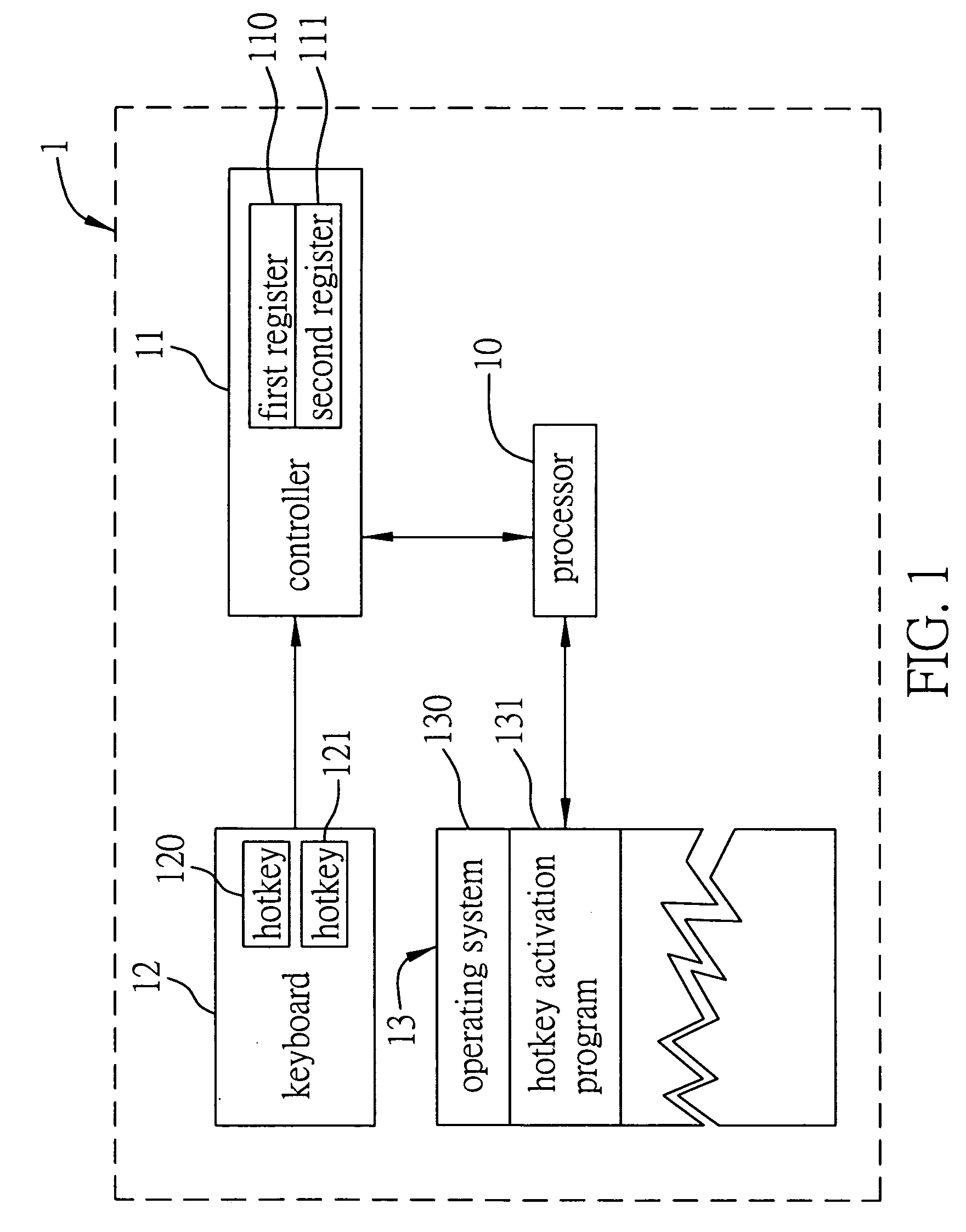
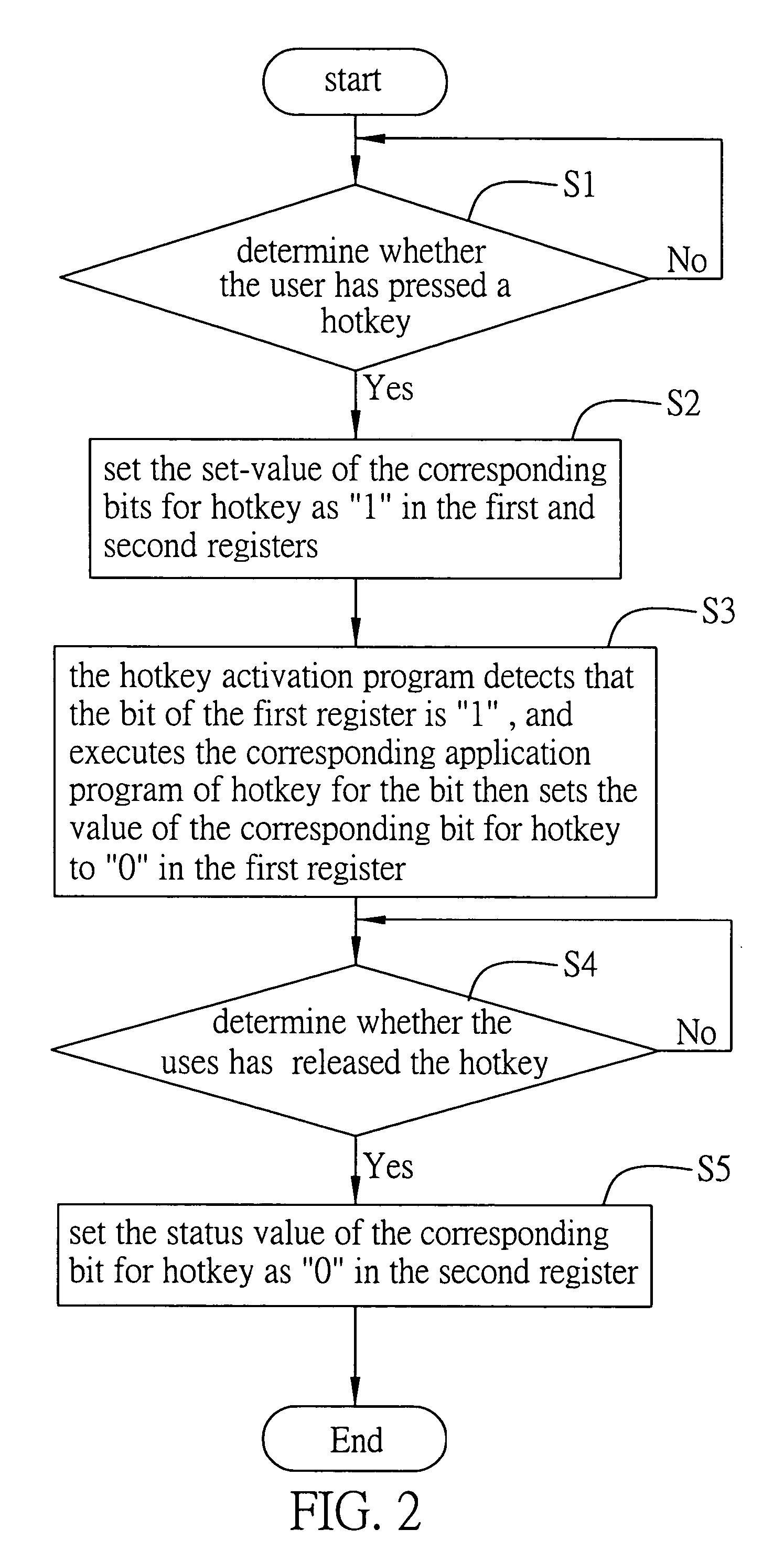
InactiveUS20060038787A1Unstable operation can be avoidedUnstable operationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsBiological activationHandling system
A processing system and method for detecting hotkey activation allows a computer device to determine whether a keyboard hotkey is activated by a user and to execute a corresponding application program associated with the hotkey if being activated. The system and method respectively associate each bit in a first register and a second register with each hotkey. Altering a value of the bit in the first register allows the computer device to identify if the hotkey is being pressed, and altering a value of the bit in the second register allows the computer device to identify if the hotkey has been released. The computer device thus detects the operating status of the hotkey in a polling manner via the first and second registers, thereby providing an active processing way for detecting hotkey activation to maintain the stability of the computer device.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
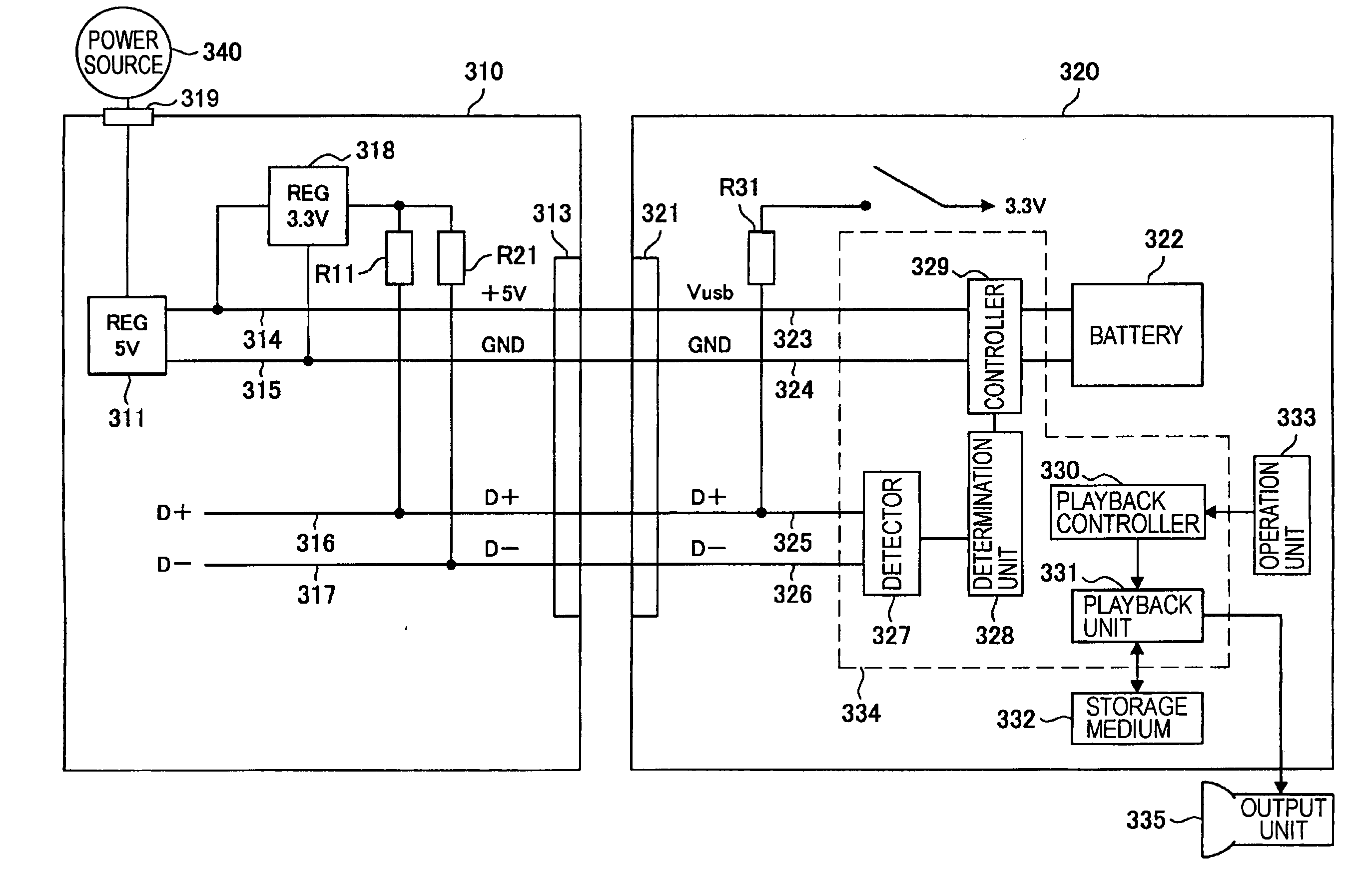
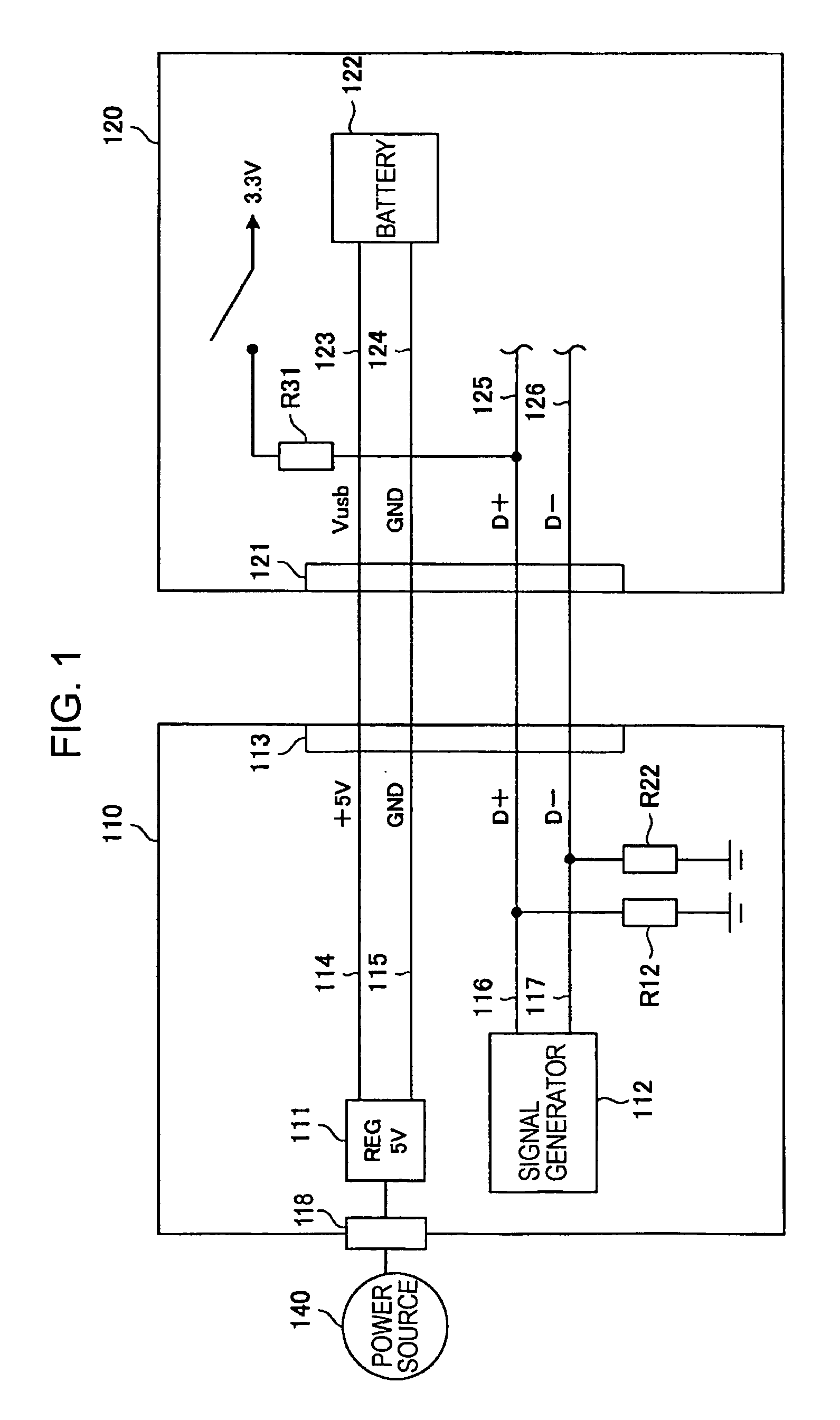
Dedicated power supply apparatus, terminal, power supply system, and power supply method
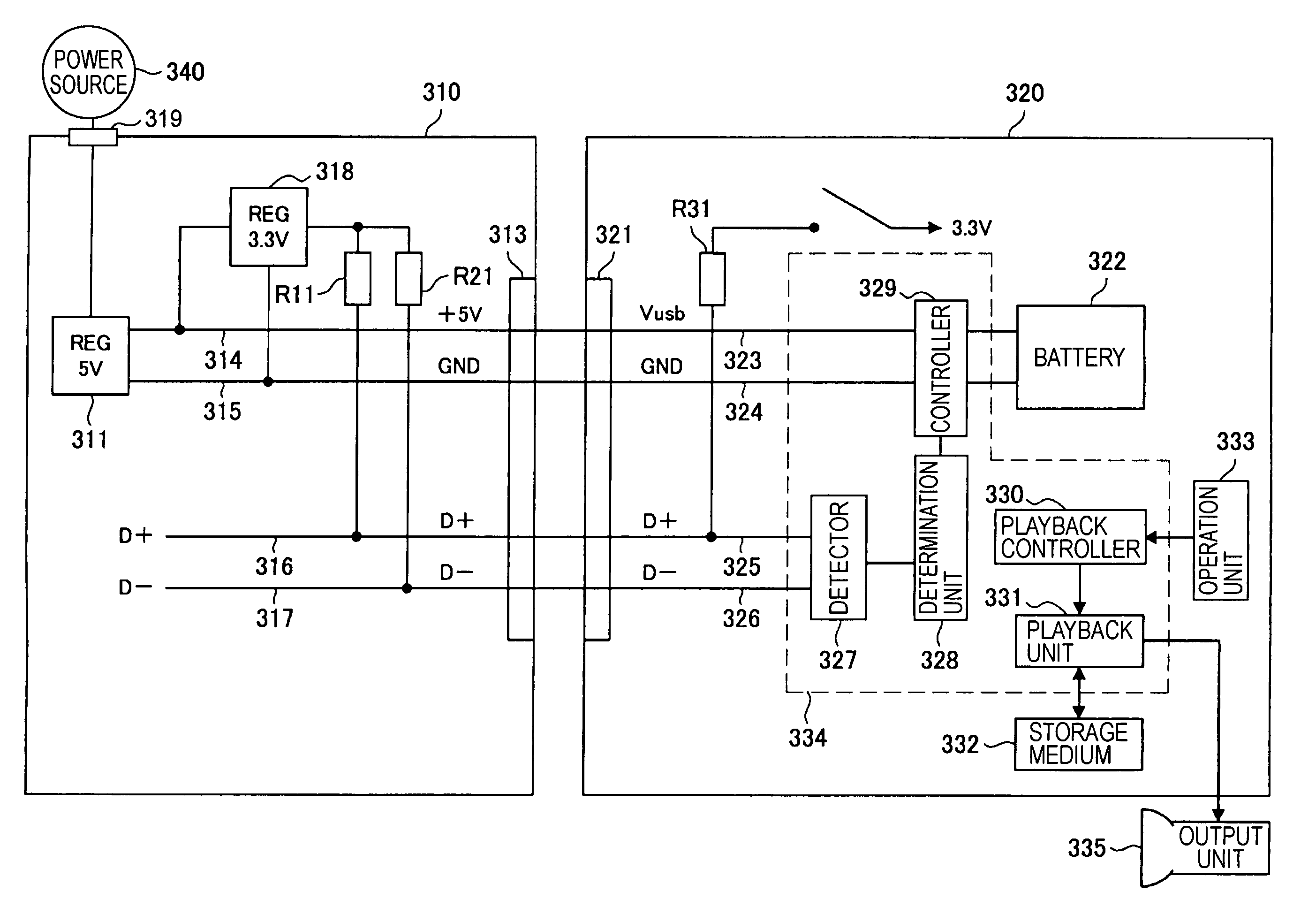
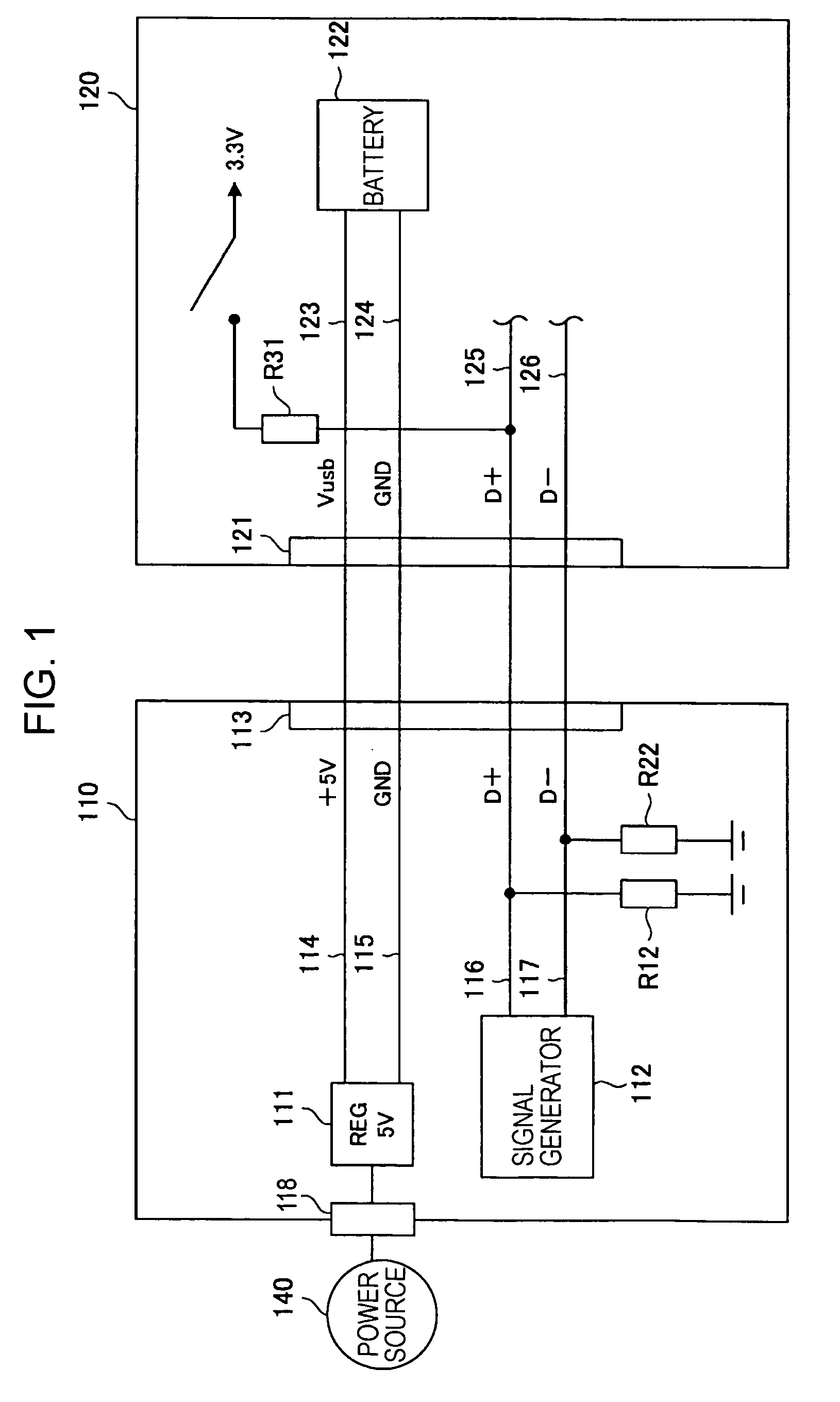
ActiveUS7631203B2Suppressing malfunction and unstable operationCharging safetyVolume/mass flow measurementLoad balancing in dc networkCharge currentElectrical battery
A terminal for a power supply system is disclosed. The terminal may have a connection portion, a battery that receives power from an external device via the connection portion, and a detector that detects a data signal from the external device. The terminal may also have a determination unit, a current converter that selectively converts an amount of charging current from a first current to a second current larger than the first current, and a controller that controls charging of the battery on the basis of a determination result. The controller is configured to control the current converter to charge the battery with the first current when the determination unit determines the external device is not a dedicated power supply, and to control the current converter to charge the battery with the second current when the determination unit determines the external device is a dedicated power supply.
Owner:SONY CORP
Fingerprint image reading apparatus
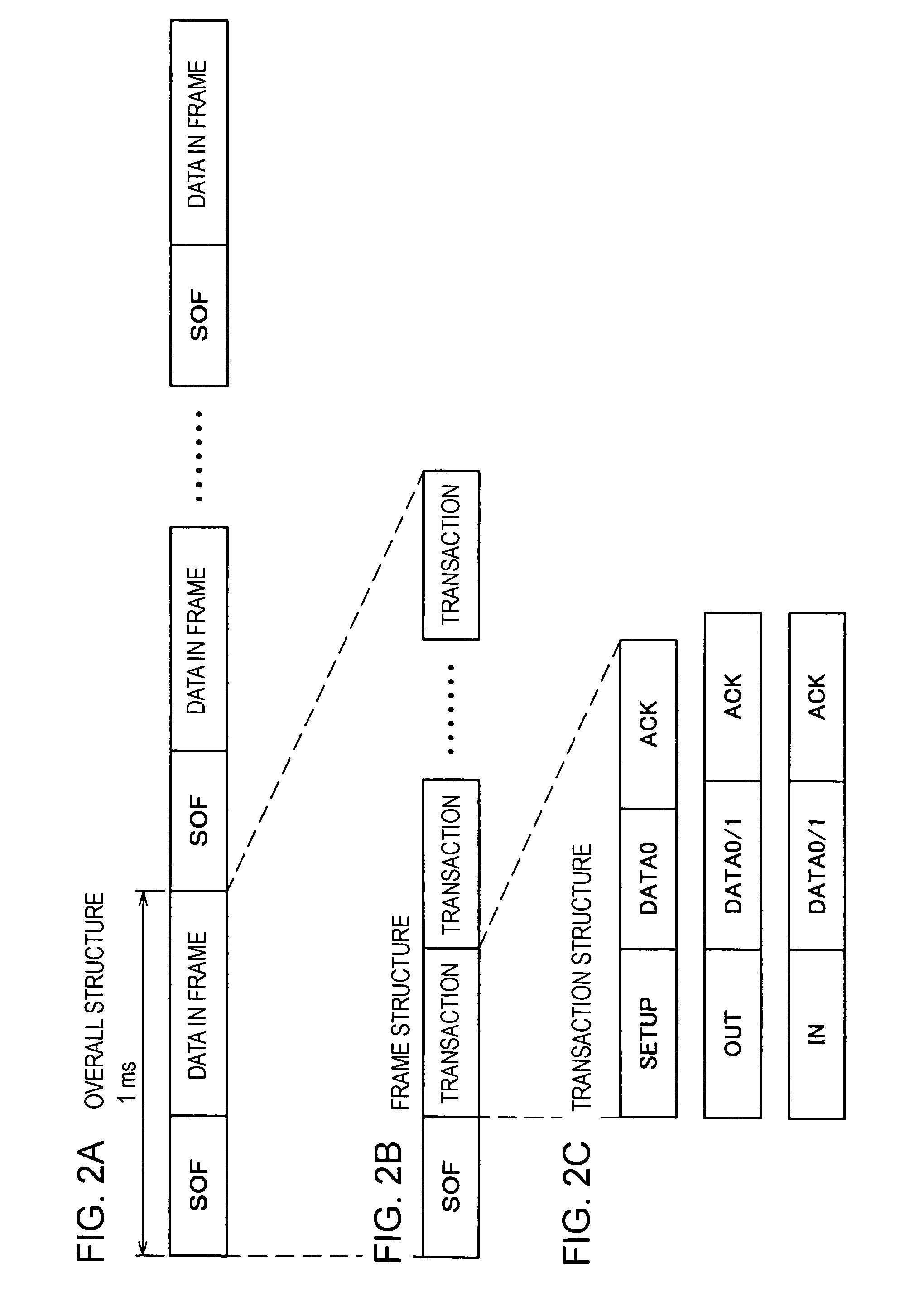
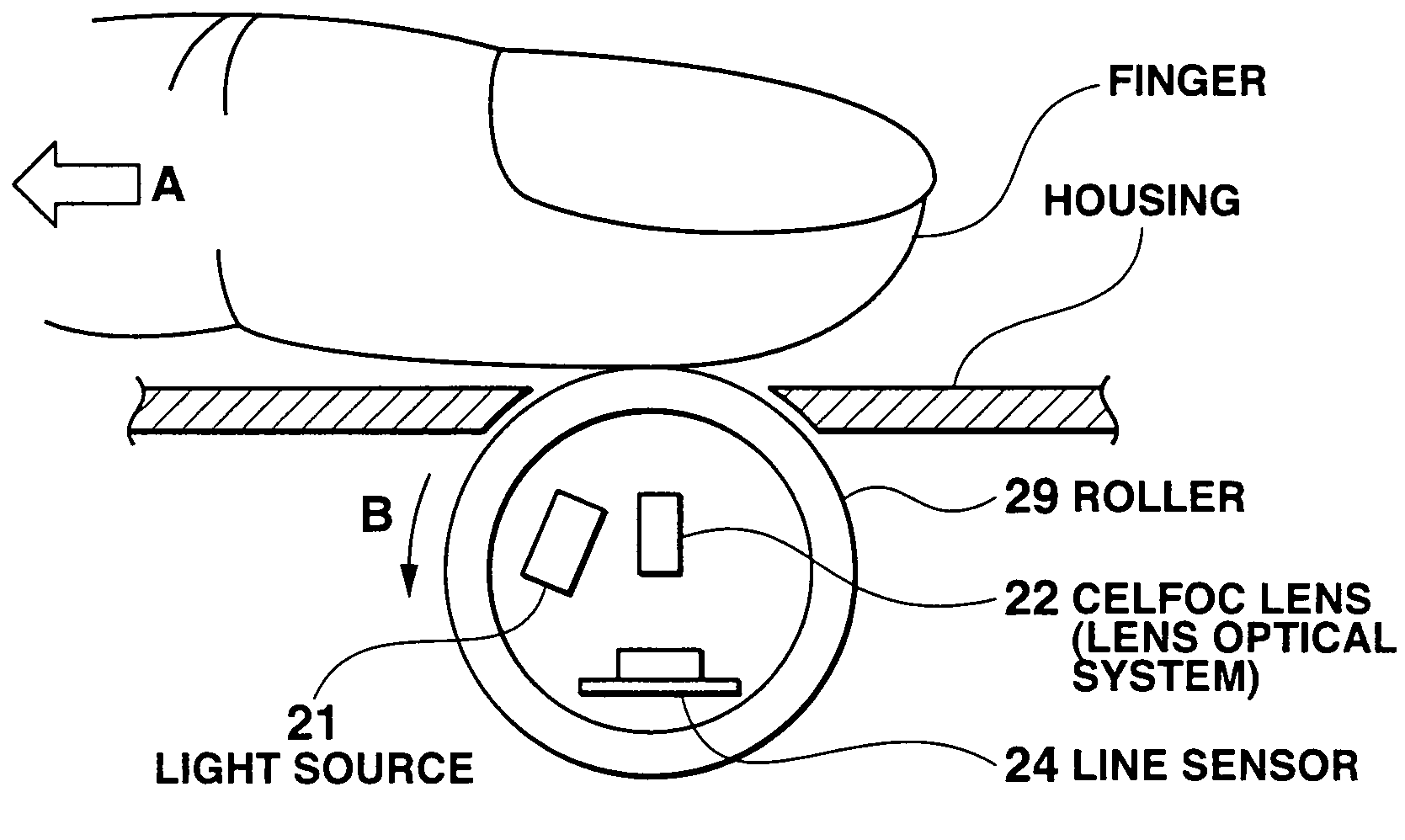
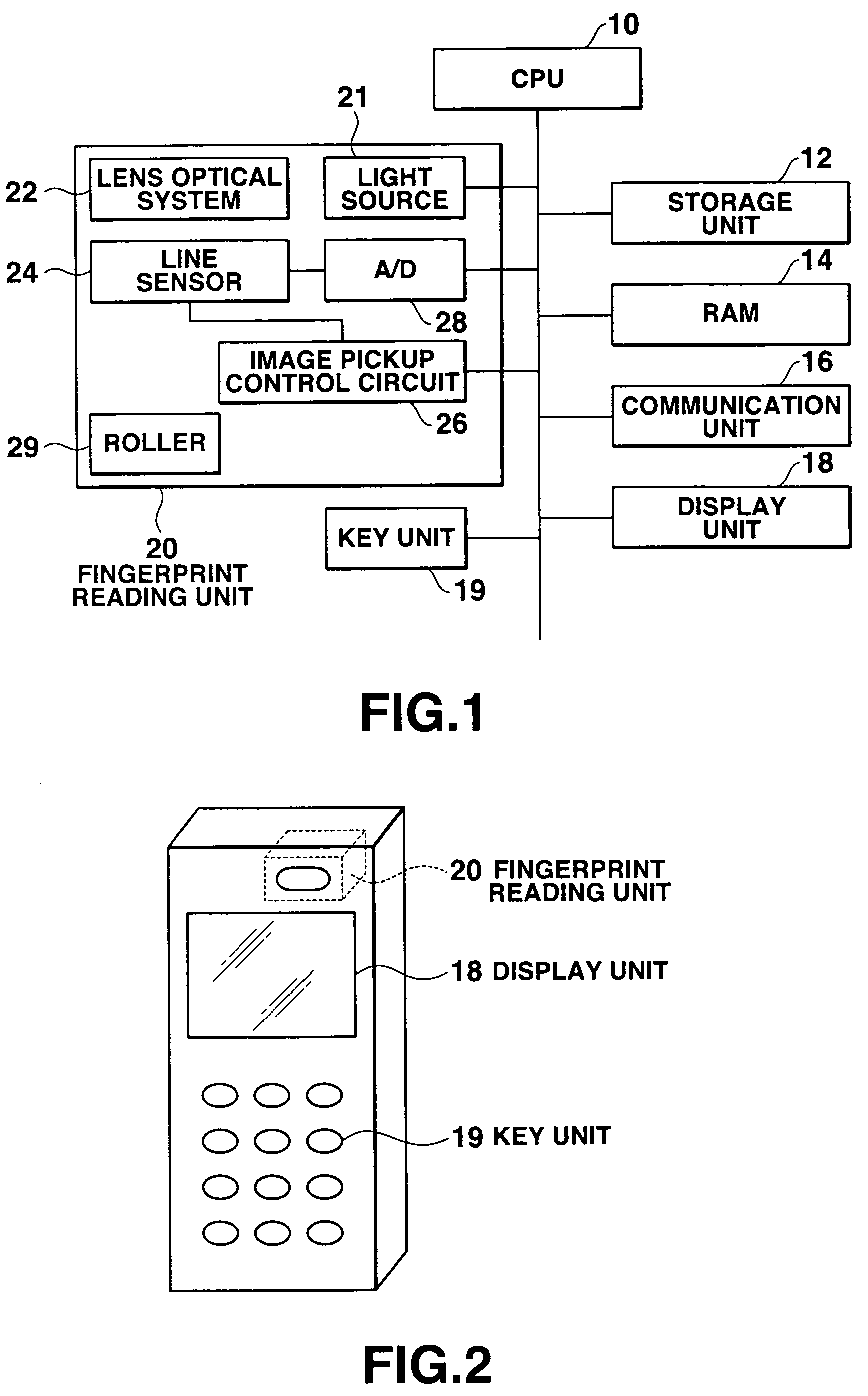
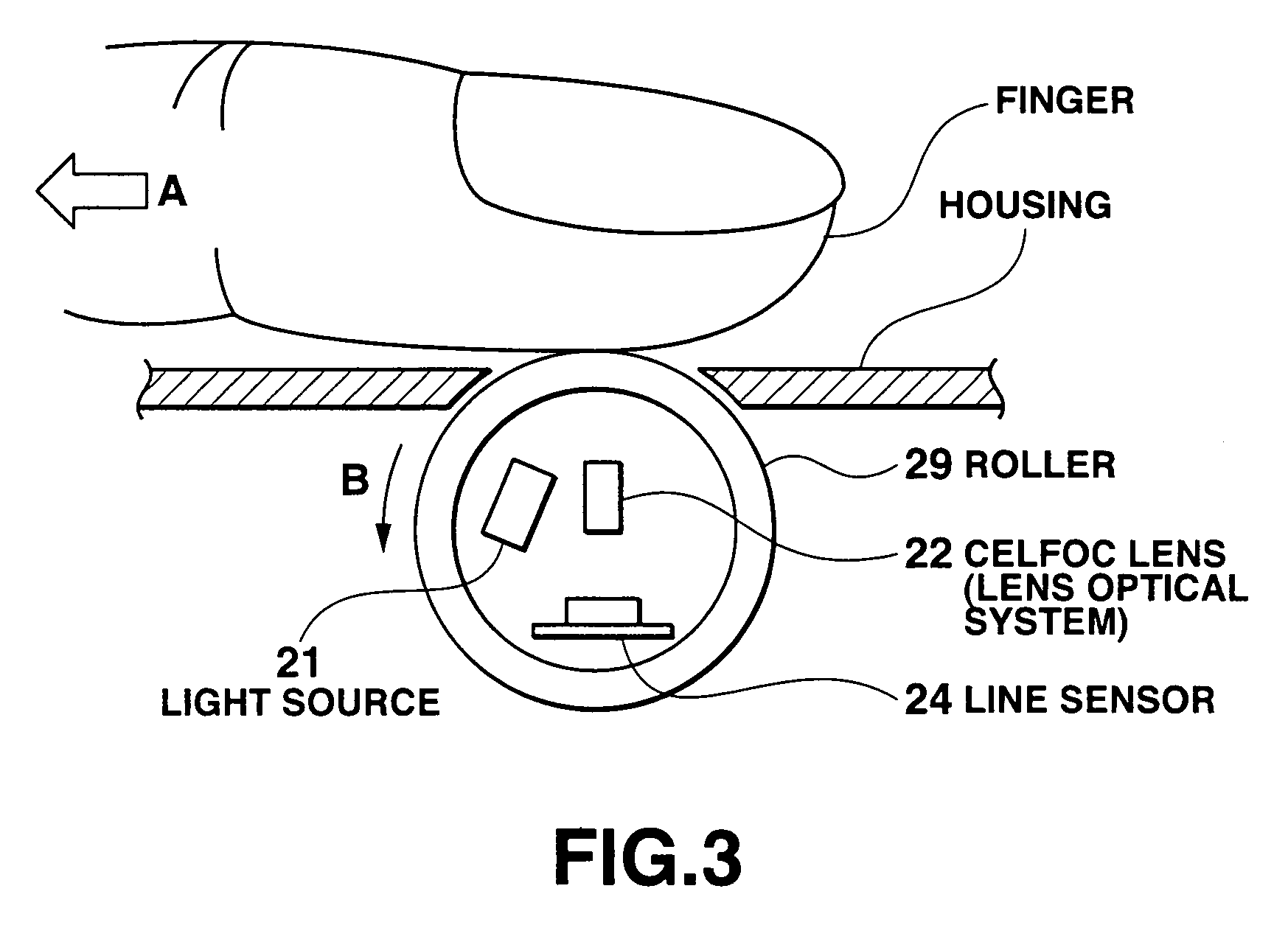
An image reading apparatus which reads a fingerprint image, includes a roller rotatably mounted to the image reading apparatus, a given pattern being printed on part of an outer surface of the roller in a circumferential direction, a line sensor including a plurality of image pickup elements which read a fingerprint image from a finger that touches with the roller as well as the pattern printed on the roller, a generating unit which generates a reference value to each of the image pickup elements corresponding to part of the line sensor, which reads the pattern, based on image data of the pattern, a rotation sensing image extracting unit which extracts a rotation sensing image based on the reference value, and a determination unit which determines capture timing of the fingerprint image based on variations in the rotation sensing image.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
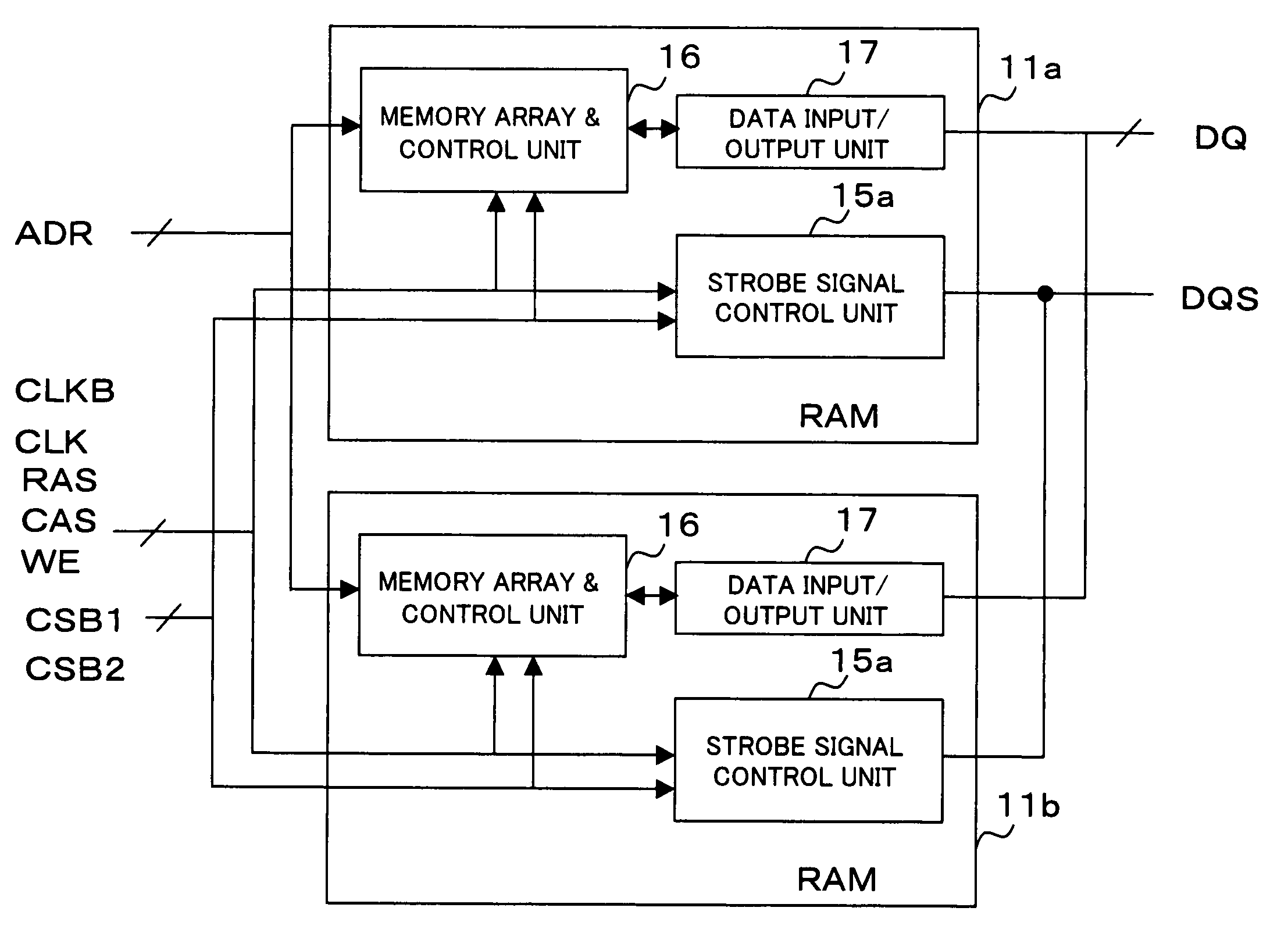
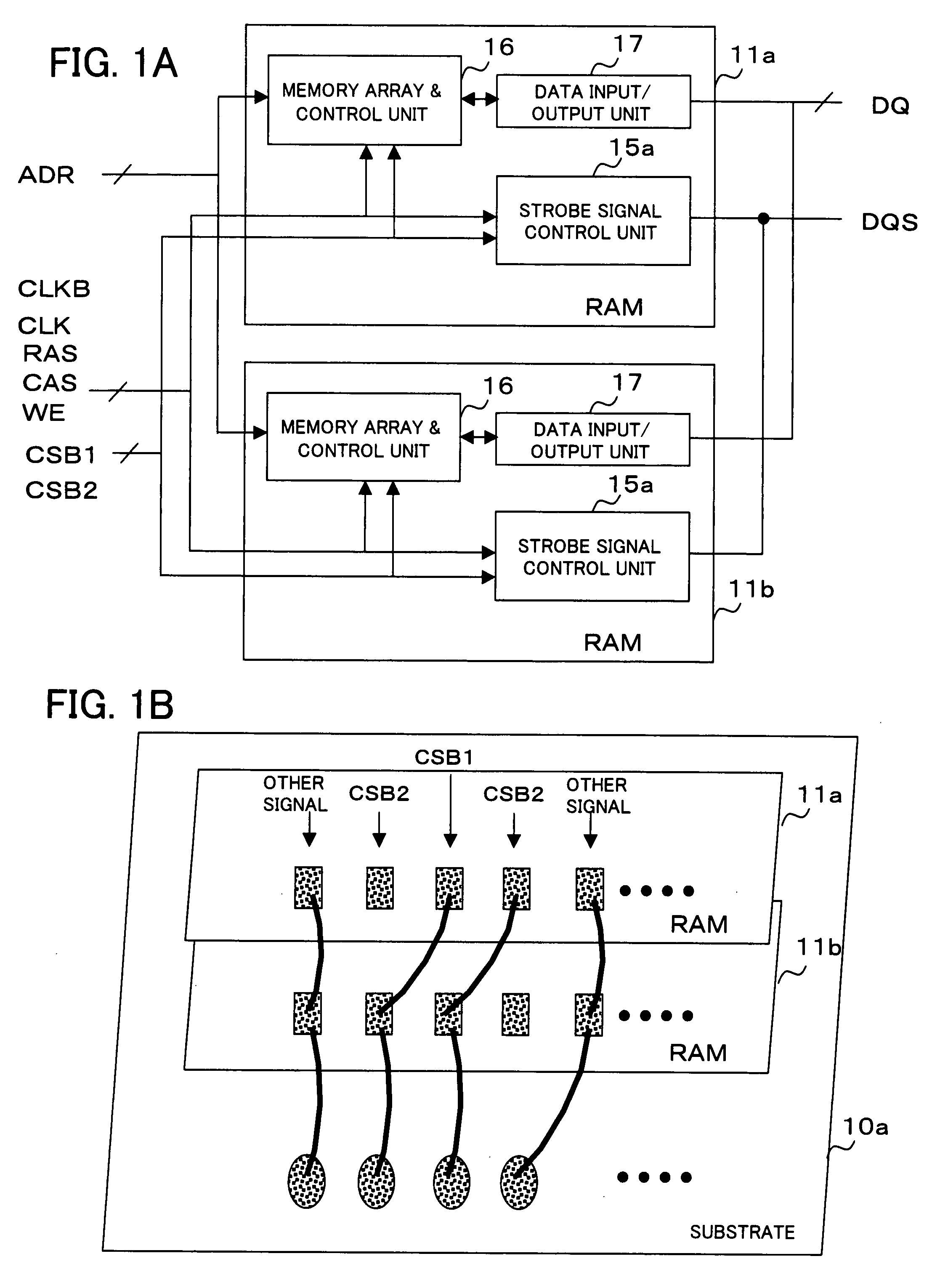
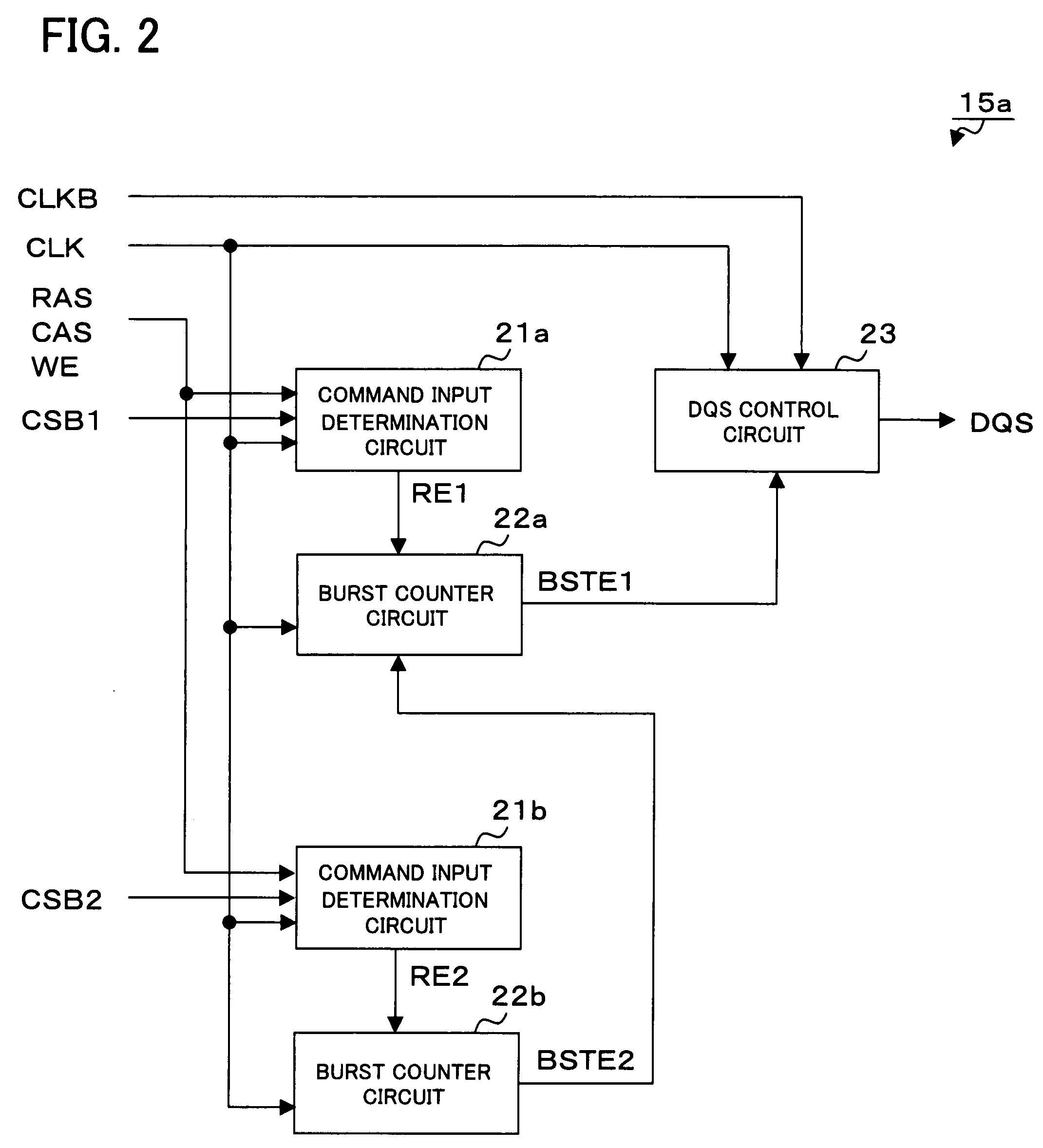
Semiconductor device and semiconductor chips outputting a data strobe signal
High-speed operation is achieved without increase in a circuit current and unstable operation of data strobe signal level due to collision between data strobe signals. Each of RAMs 11a and 11b outputs a data signal DQ and a data strobe signal DQS indicative of an output timing of the data signal. RAM 11a includes a strobe signal control unit 15a that determines whether RAM 11b connected in parallel with the RAM 11a is in a read state or not, and delays an output start timing of data strobe signal DQS when the RAM 11b is in the read state. Strobe signal control unit 15a of the RAM 11a controls output start timing so that a latter half portion of a preamble period of the data strobe signal DQS to be output coincides with a postamble period of the data strobe signal DQS output by the RAM 11b.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
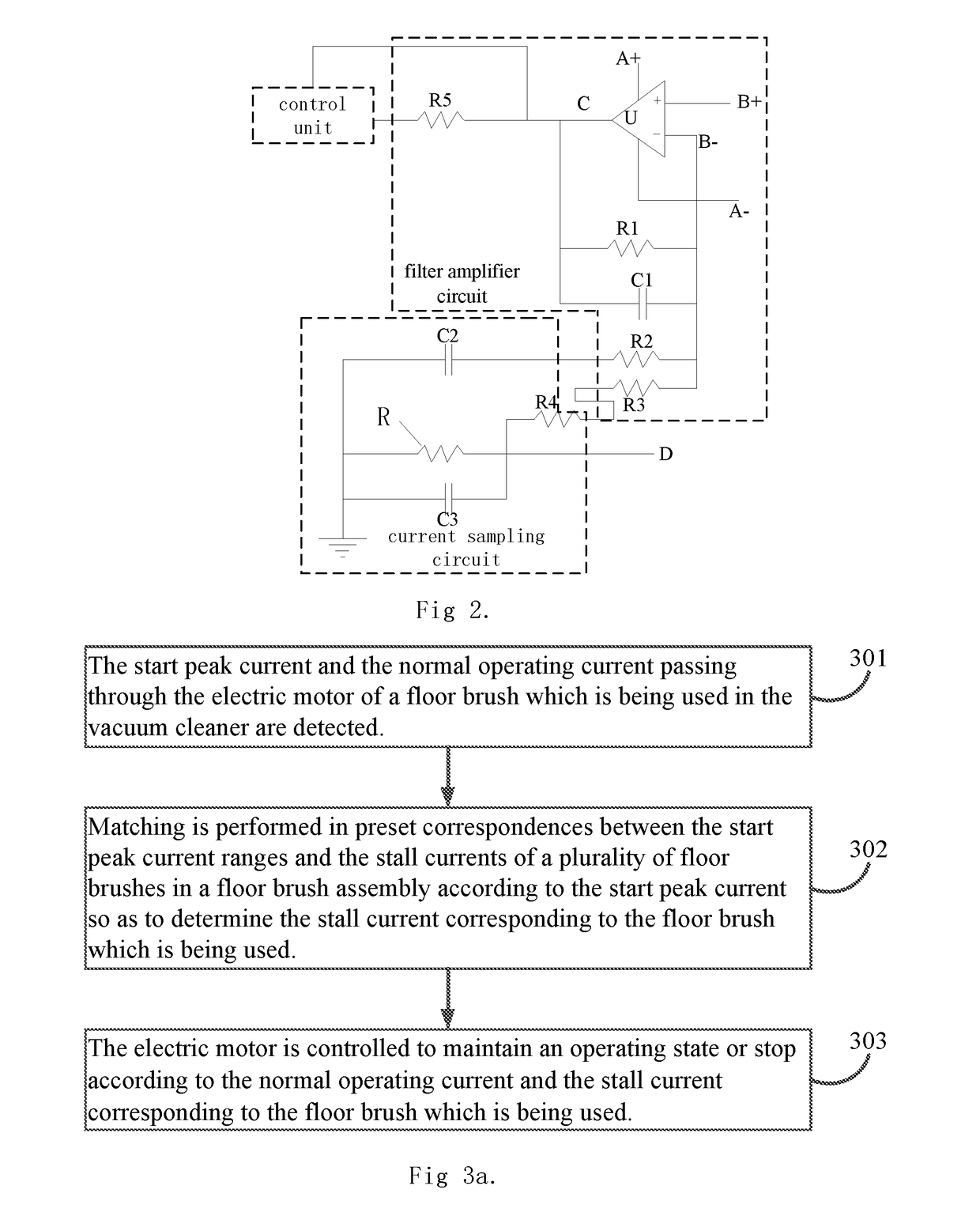
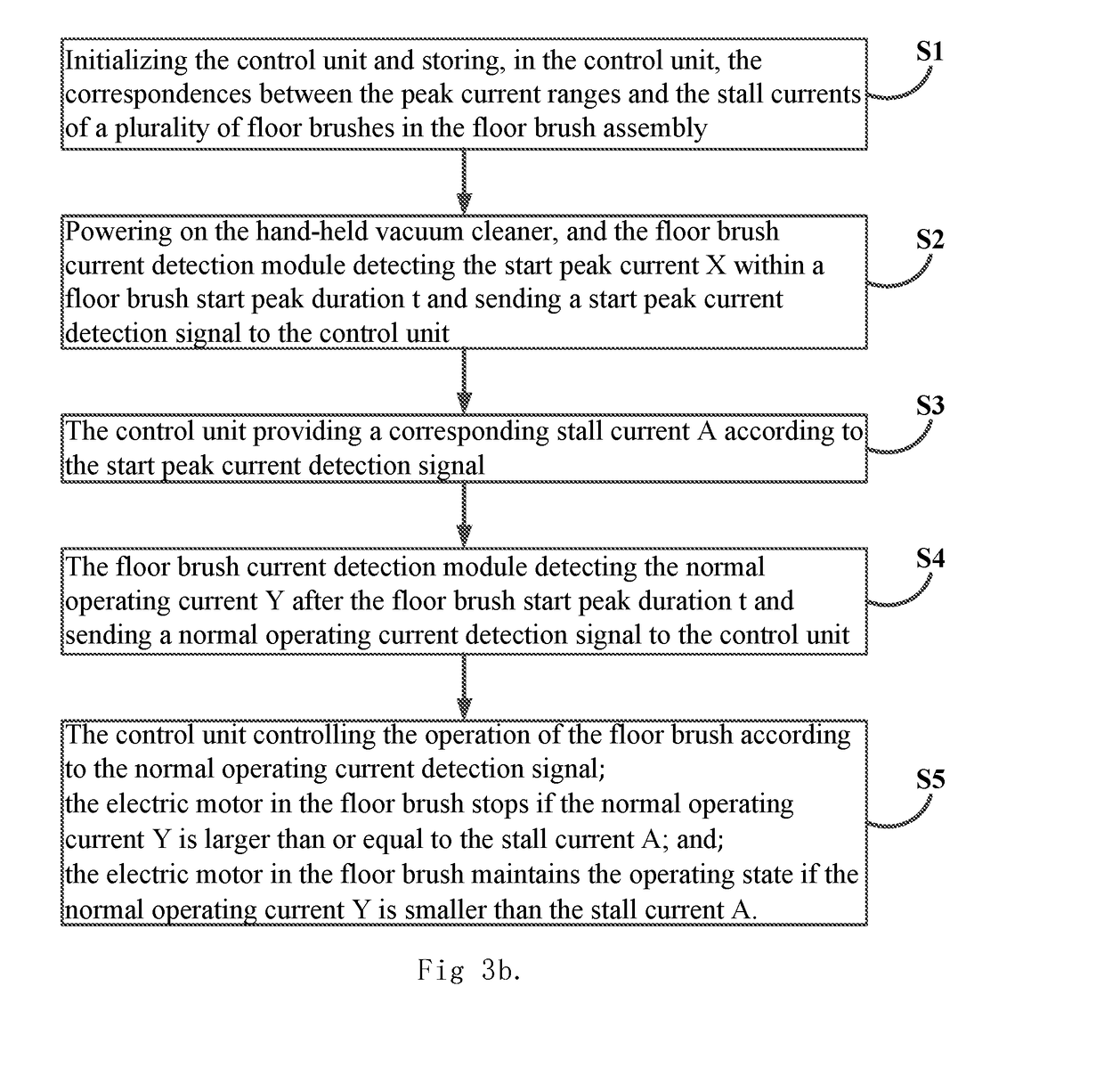
Vacuum cleaner and control method thereof
ActiveUS20190021567A1Potential safety hazardUnstable operationSuction nozzlesElectric equipment installationComputer moduleVacuum cleaner
A vacuum cleaner and a control method thereof, wherein the vacuum cleaner includes a vacuum cleaner body, a floor brush assembly, and an extension tube connecting the two together. The floor brush assembly comprises a plurality of different floor brushes for performing different cleaning work. The vacuum cleaner is further provided with a control unit and a detection unit. The detection unit comprises a floor brush current detection module for detecting current passing through an electric motor in a floor brush. The floor brush current detection module sends detection signals to the control unit, and the control unit controls the electric motor to maintain an operating state or stop the operating state according to the detection signals.
Owner:TINECO APPLIANCES CO LTD
Dedicated power supply apparatus, terminal, power supply system, and power supply method
ActiveUS20100045258A1Suppressing malfunction and unstable operationCharging safetyDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringElectric powerResistor
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
DC test apparatus
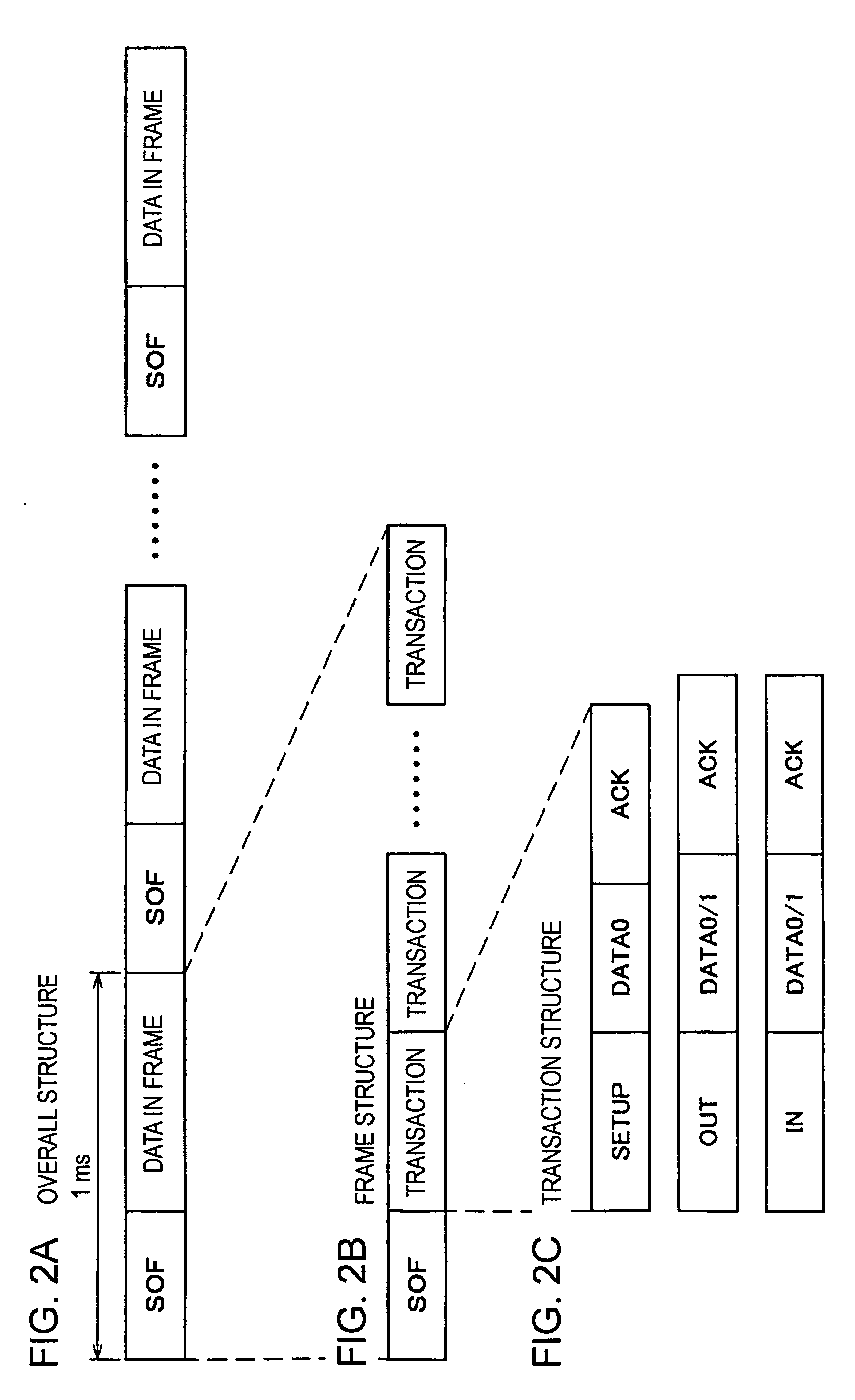
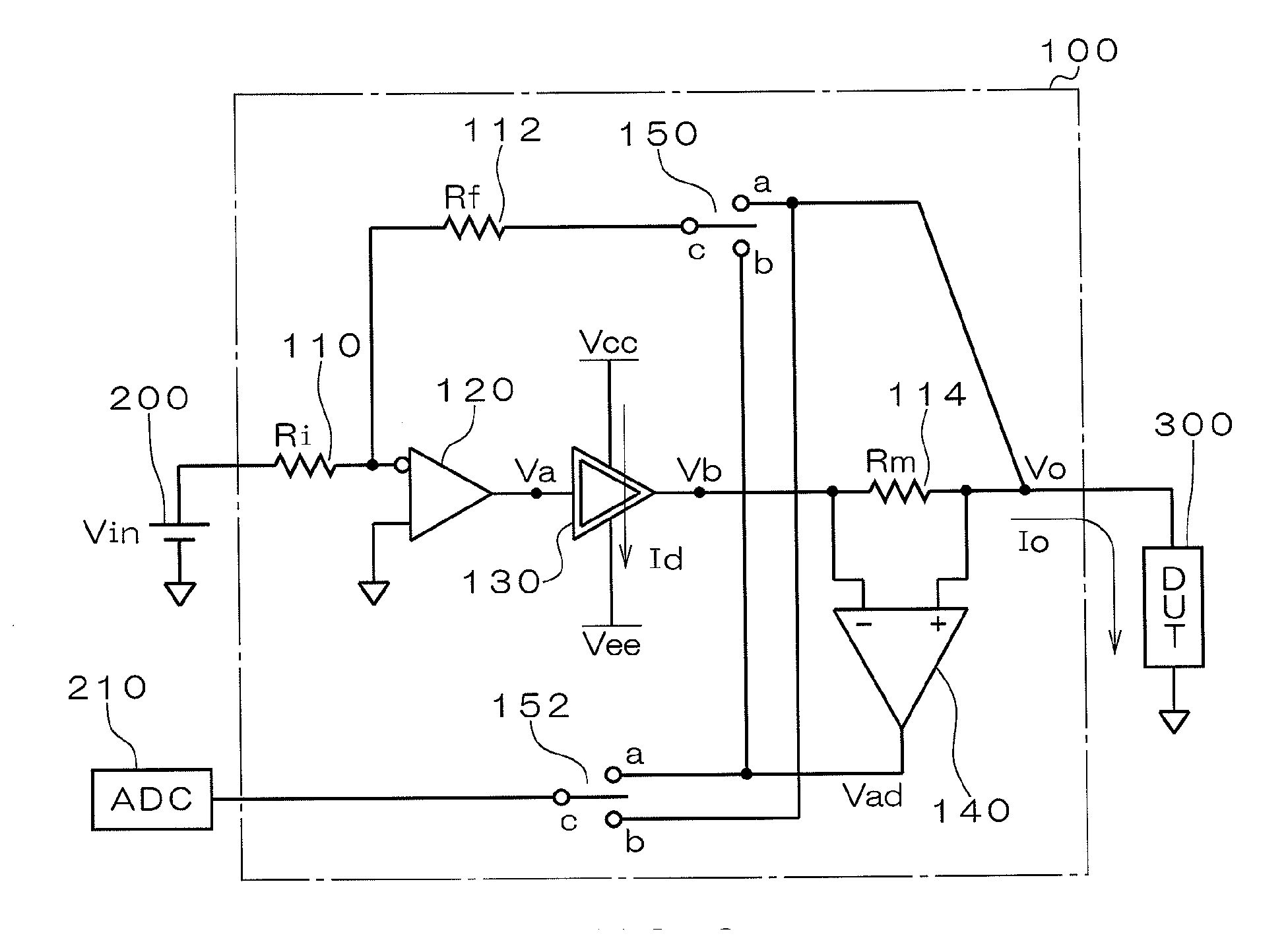
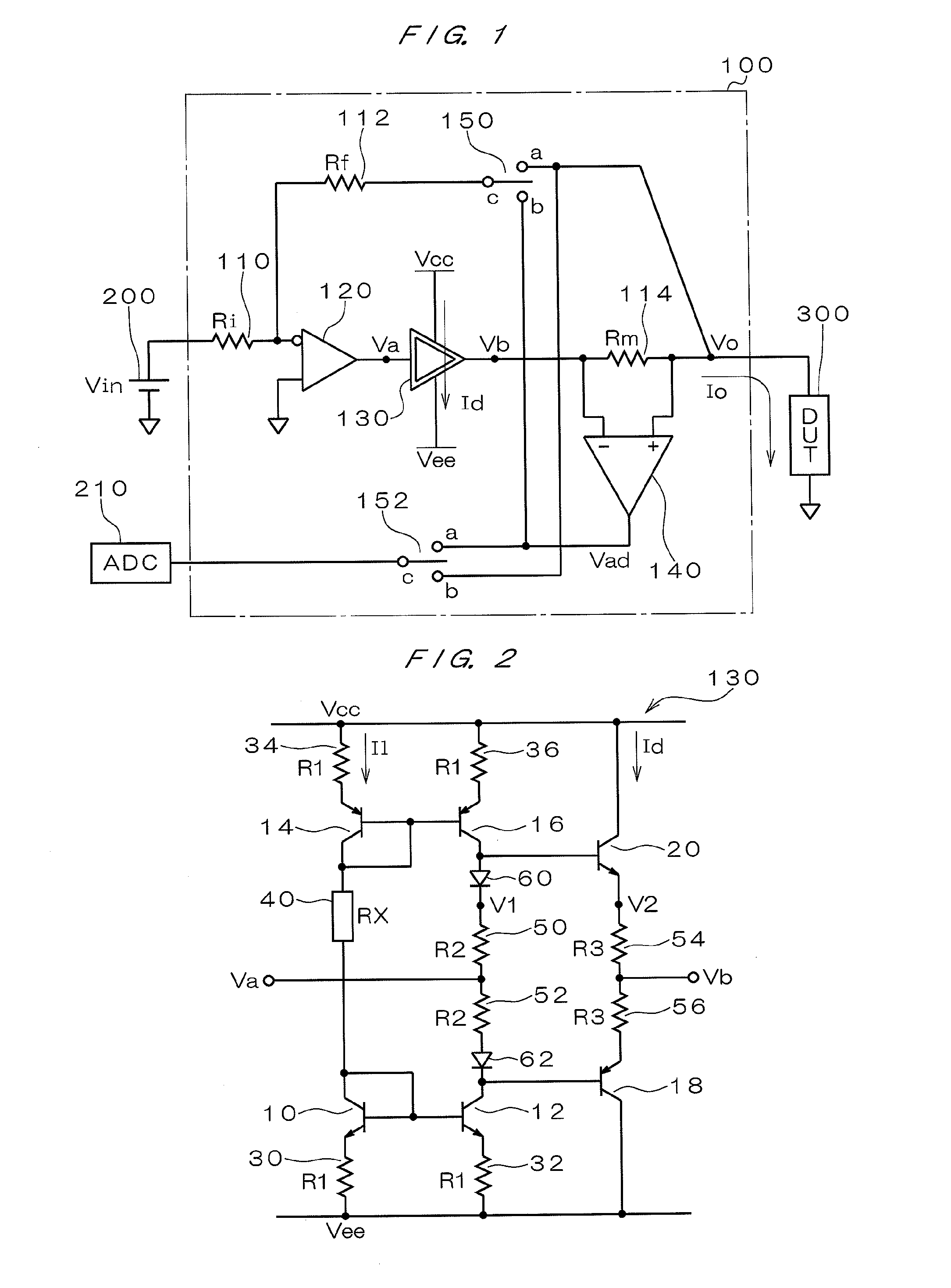
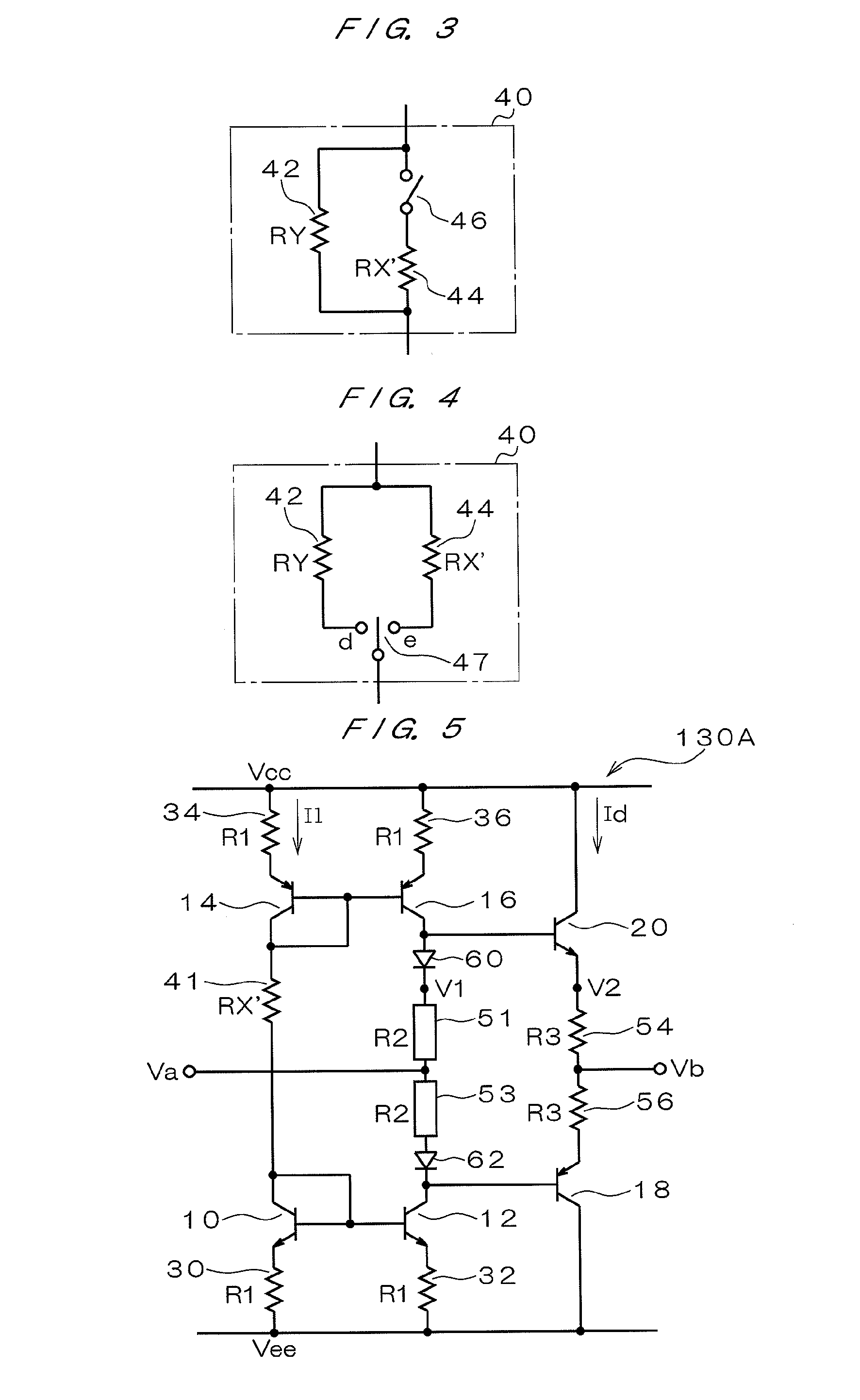
InactiveUS20070262778A1Reducing standbyReduce standby currentMaterial electrochemical variablesStandby powerAmplifier
An object of the present invention is to provide a DC test apparatus capable of reducing wasteful standby power consumption. The DC test apparatus has a power amplifier circuit 130 for supplying a current to a DUT during a test. The power amplifier circuit 130 is provided with transistors 18 and 20 for generating an output current appropriate for an input voltage during current supply, resistors 54 and 56, and a variable resistance circuit 40 for setting a standby current flowing through these transistors 18 and 20 and the like during current supply to a smaller value at any time other than during current supply.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Voltage regulator
ActiveUS20160342171A1Suppresses fluctuations in output voltageGuaranteed uptimeDc-dc conversionVoltage/current isolationVoltage regulationEngineering
Provided is a voltage regulator configured to suppress a fluctuation in output voltage even when a power supply voltage fluctuates, thereby realizing stable operation thereof. The voltage regulator includes a control circuit including a first input terminal connected to a drain of an output transistor, a second input terminal connected to a power supply terminal, an overshoot detection circuit connected to the first input terminal, and a power supply voltage detection circuit connected to the second input terminal, and being configured to cause a boost current to flow through an error amplifier circuit when an output voltage and a power supply voltage largely fluctuate with respect to a predetermined voltage.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Fishing reel
ActiveUS20170208788A1Unstable operationHigh voltageReelsBrake actuating mechanismsElectric power systemEngineering
A fishing reel forwardly releases a fishing line and includes a reel unit, a spool, a spool brake, an electric component, and a voltage booster circuit. The spool is rotatably supported by the reel unit. The spool brake generates an electric power upon a rotation of the spool, and applies a brake force to brake the spool using the electric power when the spool is rotated. The electric component operates using the electric power generated by the spool brake. The voltage booster circuit increases a voltage supplied to the electric component.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
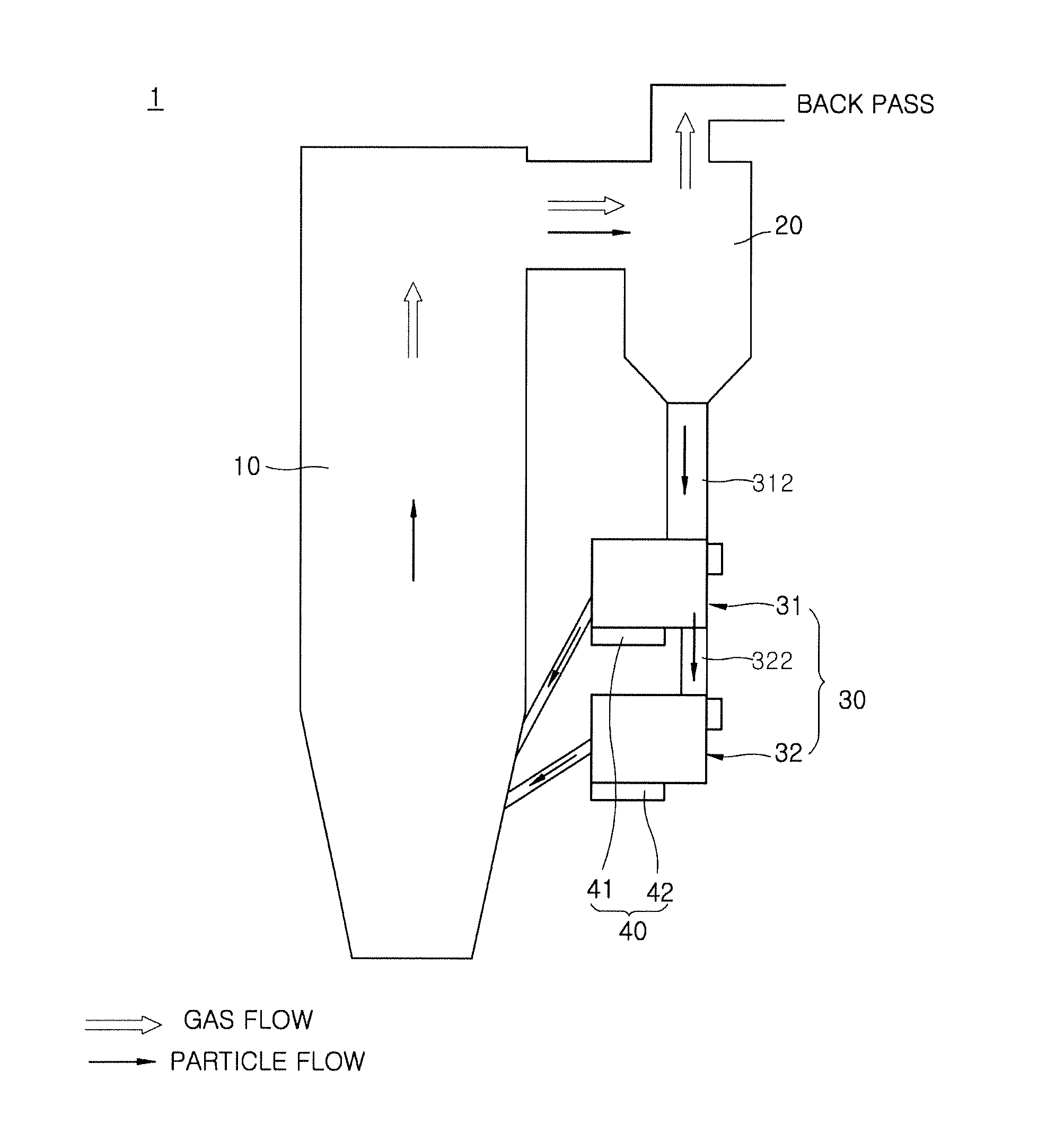
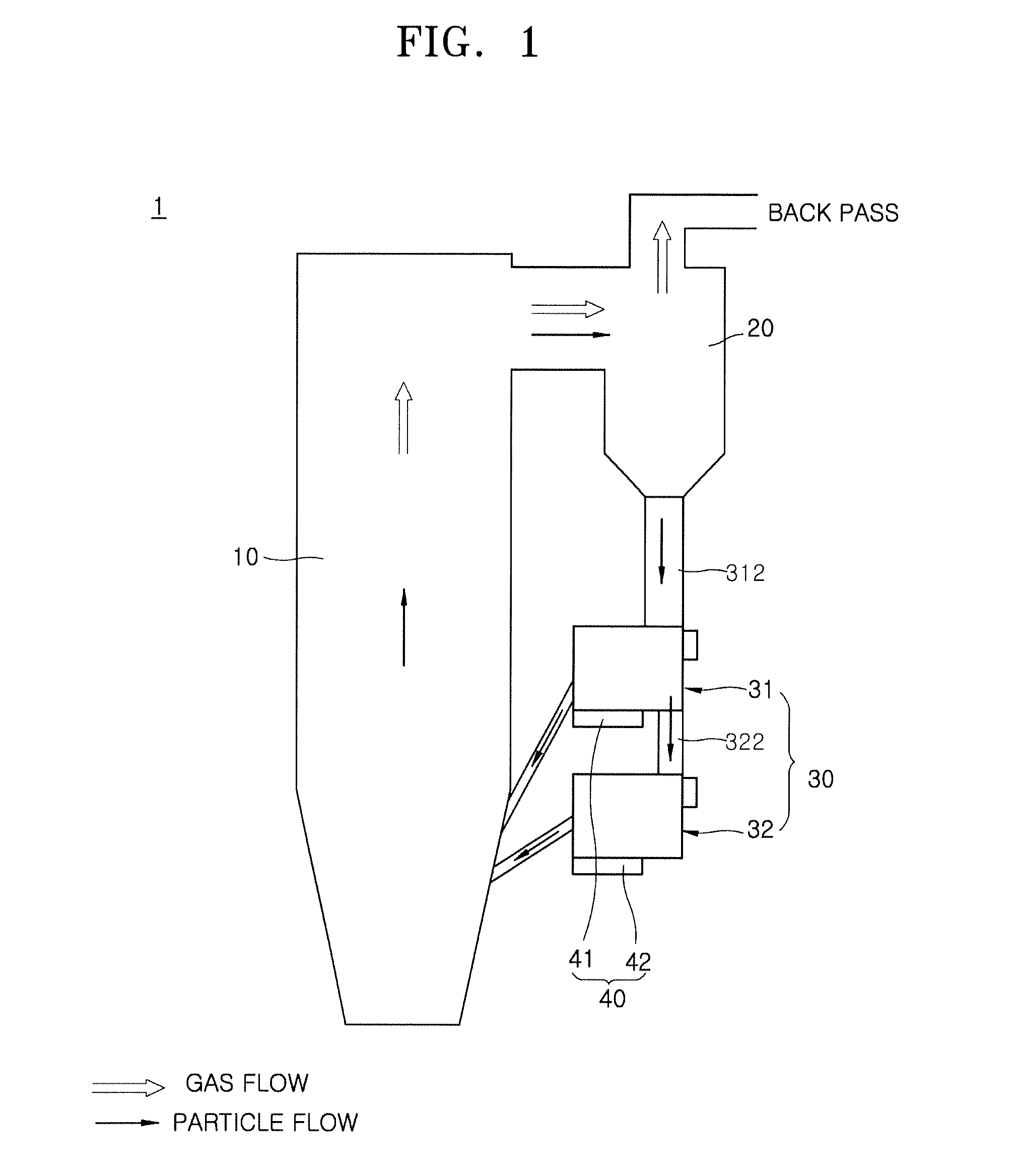
Heat exchange apparatus for circulating fluidized bed boilers
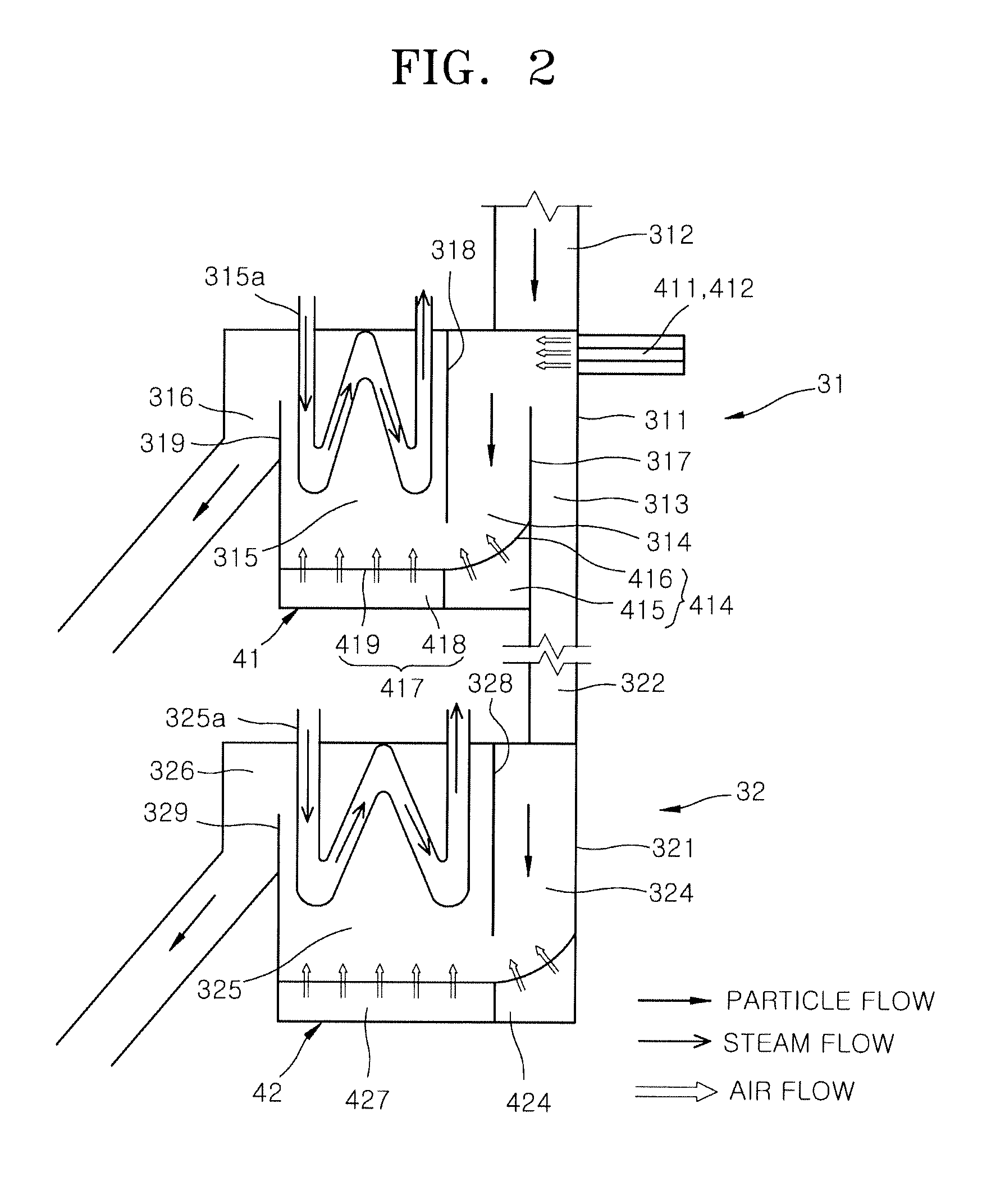
InactiveUS20160377351A1Improve acceleration performanceUnstable operationFluidized bed combustionAir supply regulationCombustionFluidized bed
A heat exchange apparatus for circulating fluidized bed boilers is disclosed. The heat exchange apparatus for circulating fluidized bed boilers includes a particle separator configured to separate an exhaust gas and a flow medium discharged from a combustion furnace, an external heat exchanger into which the flow medium collected in the particle separator flows and which is configured to heat a heat transfer medium by heat exchange with the flow medium, and a flow control unit installed at the external heat exchanger and configured to supply air to a flow path of the flow medium and to regulate an internal temperature of the external heat exchanger under the control of a flow direction and a flow quantity of the flow medium.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP +1
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory device
ActiveUS20180108390A1Unstable operationReduce adverse effectsNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeNanowire
A magnetoresistance effect element includes a recording layer containing a ferromagnetic body, and including a first fixed and second magnetization regions having magnetization components fixed substantially in a direction antiparallel to the in-plane direction to each other, and a free magnetization region disposed between the first and second fixed magnetization regions and having a magnetization component invertible in the in-plane direction, a domain wall disposed between the first fixed magnetization region and the free magnetization region, and being movable within the free magnetization region, and a magnetic nanowire having a width of 40 nm or less. The thickness of the recording layer is 40 nm or less and at least half but no more than twofold the width of the magnetic nanowire. The element further includes a barrier layer disposed on the recording layer, and a reference layer disposed on the barrier layer and containing a ferromagnetic body.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Film formation method, thin-film transistor and solar battery
InactiveUS20090140257A1Improve the immunityLow mobilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron temperatureHigh electron
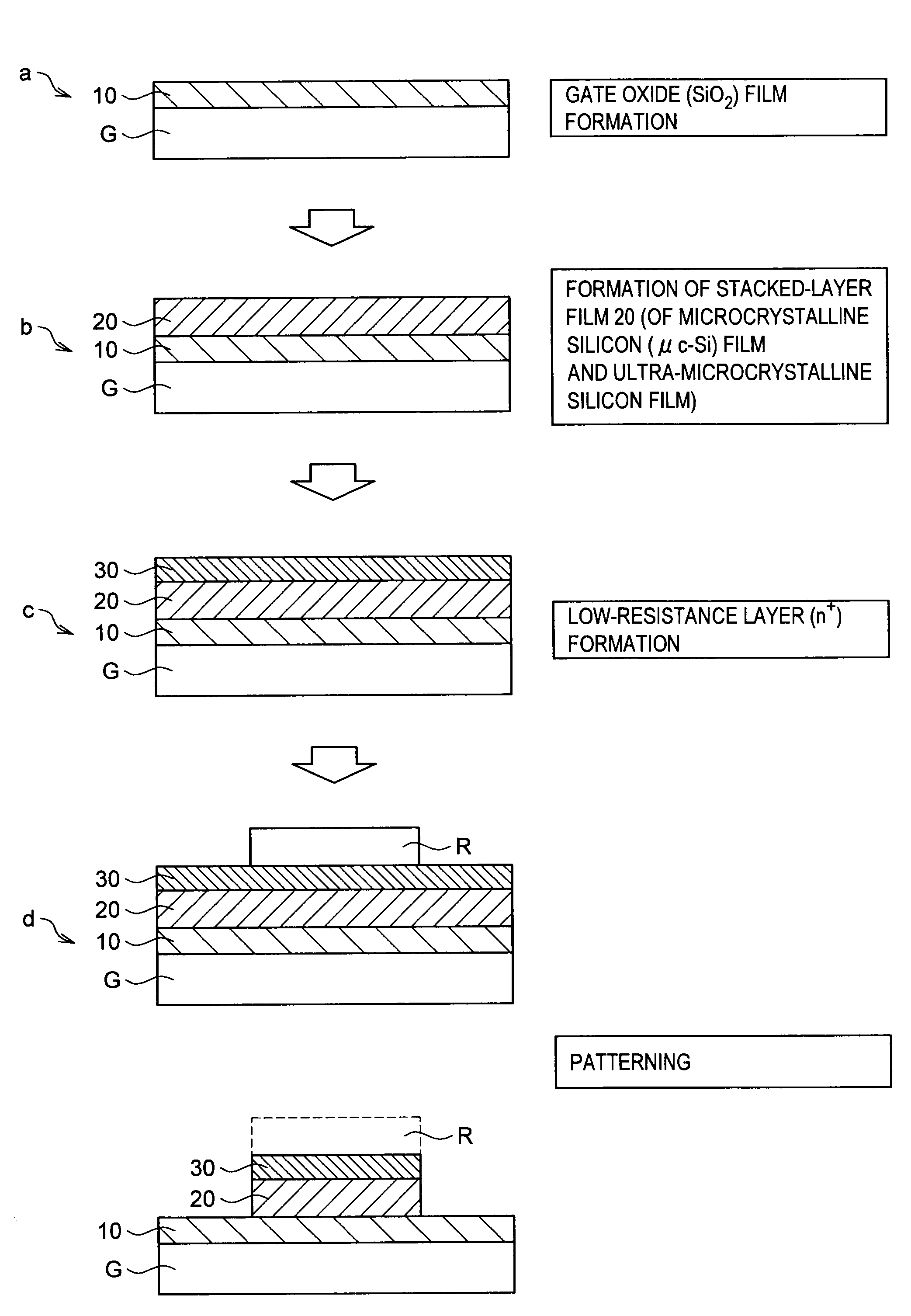
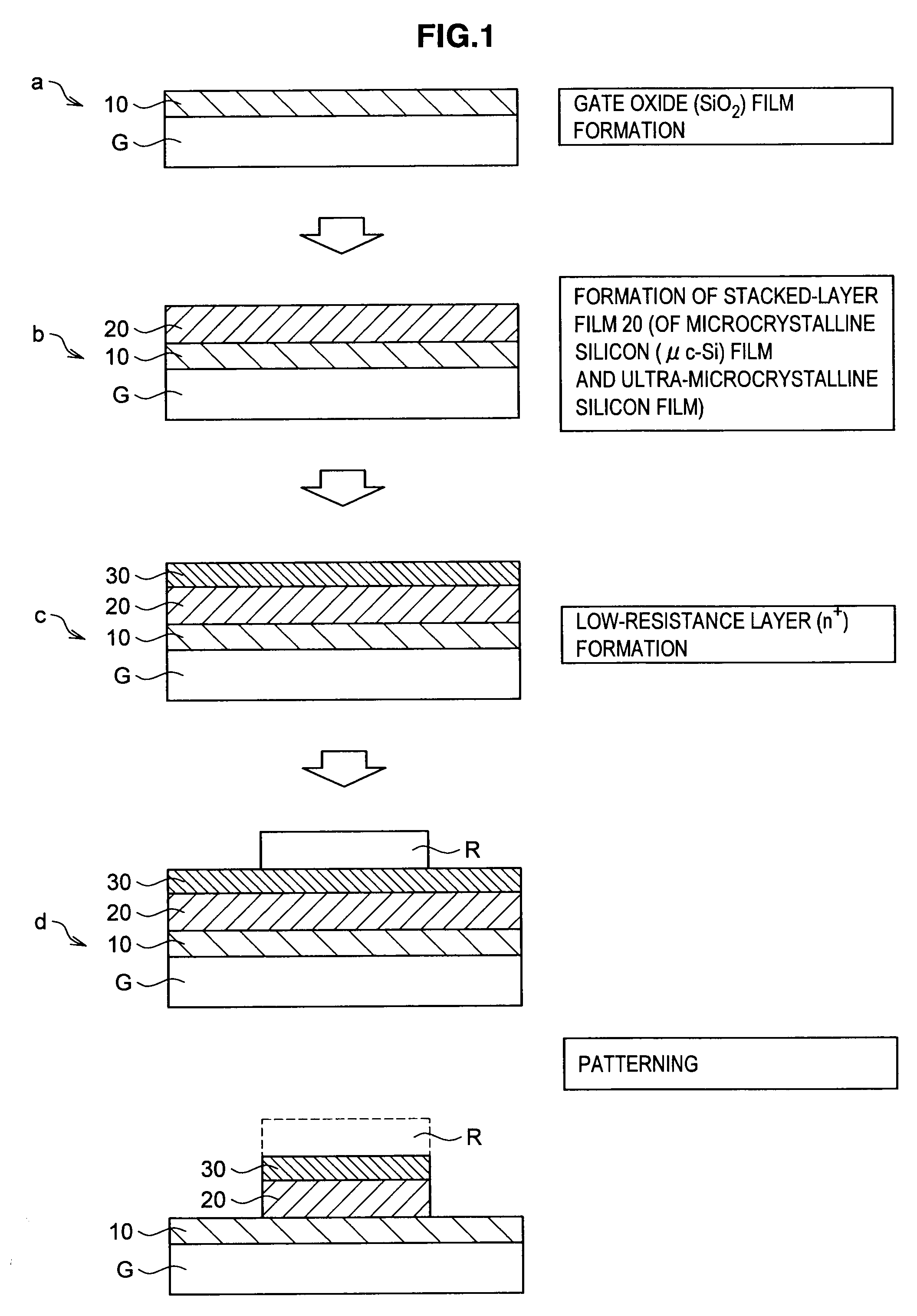
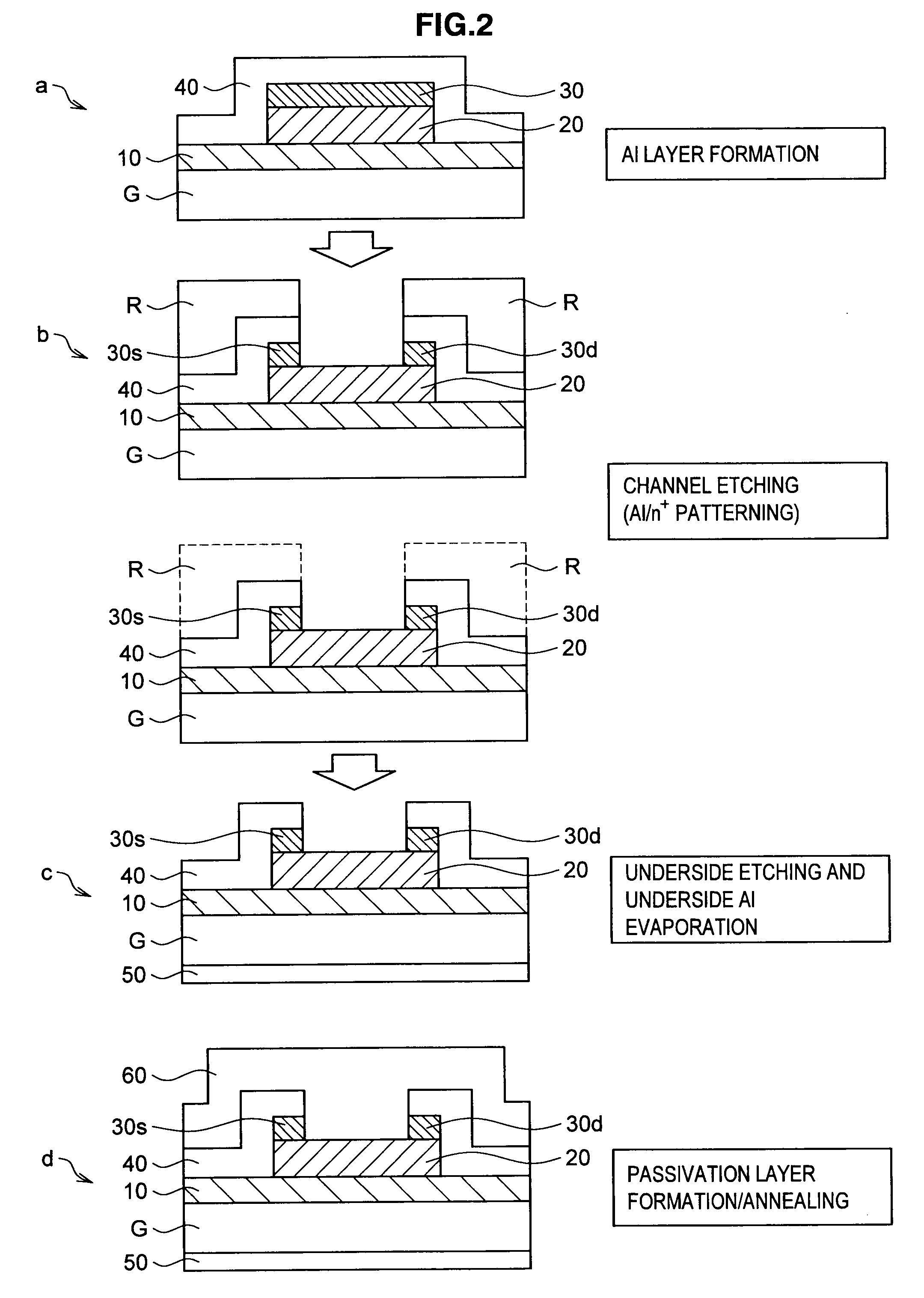
After a gate oxide film 10 has been formed on a silicon substrate G, a first step of forming a microcrystalline silicon film by high electron density plasma of an electron temperature of 2.0 eV or less and a second step of forming an ultra-microcrystalline silicon film by high electron density plasma of an electron temperature higher than 2.0 eV are repeated. A stacked-layer film 20 of the ultra-microcrystalline silicon film and the microcrystalline silicon film is thereby formed. With the film formation method described above, at least one of an n-channel thin-film transistor and a p-channel thin-film transistor with the stacked-layer film 20 functioned as an active layer may be manufactured.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Lighting Device
InactiveUS20130049624A1Not easy to failReliable lightingElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementFull bridgeEngineering
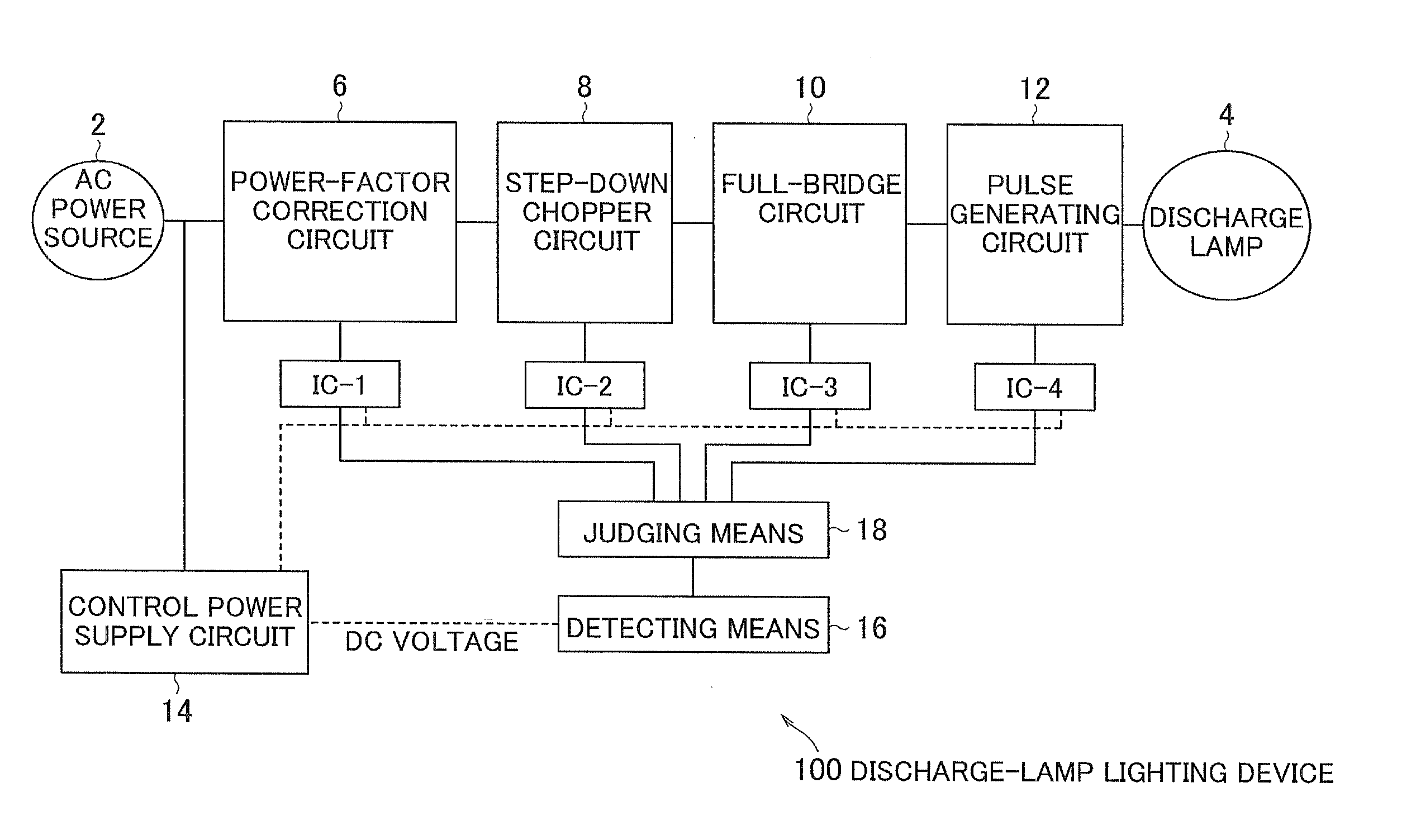
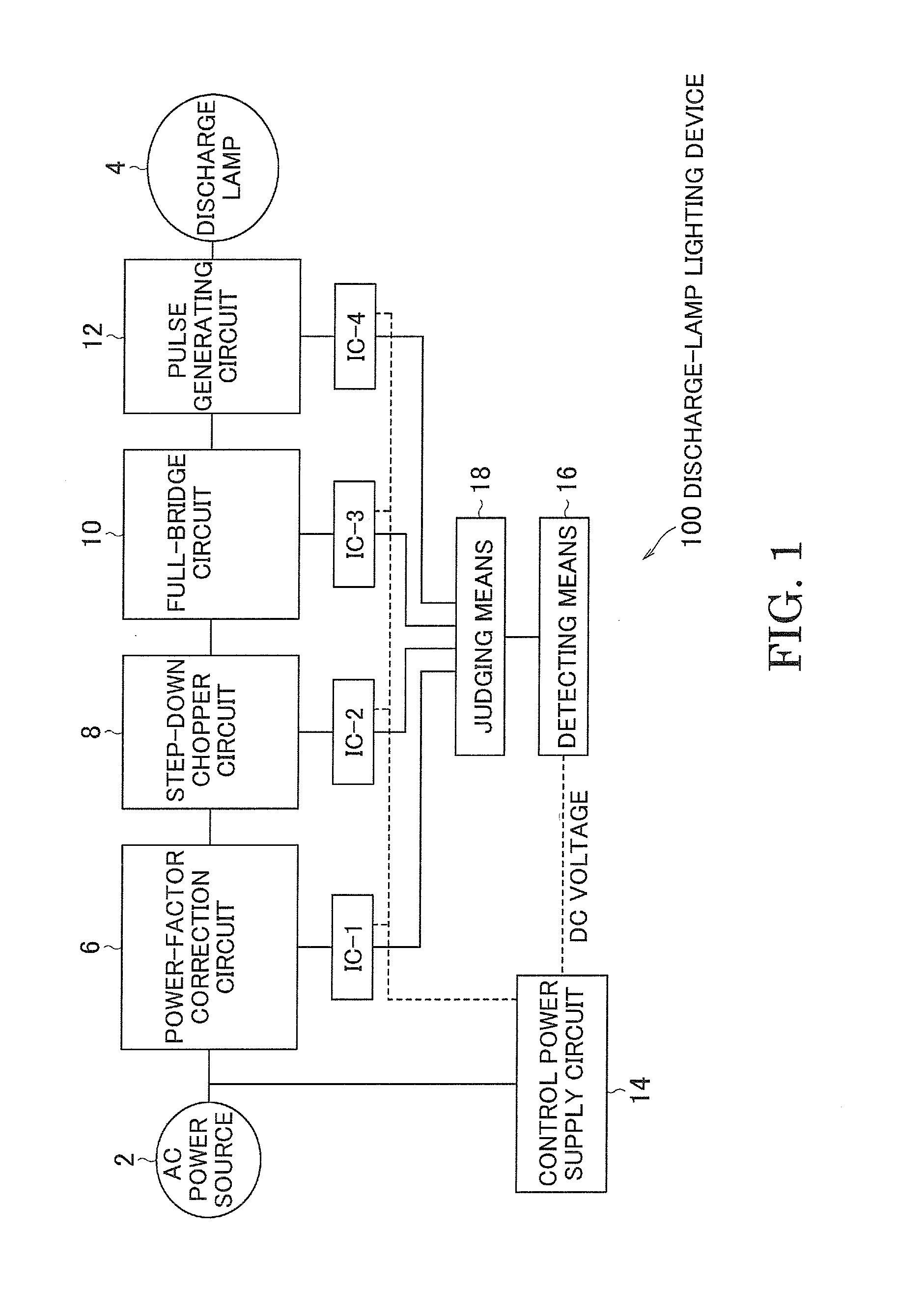
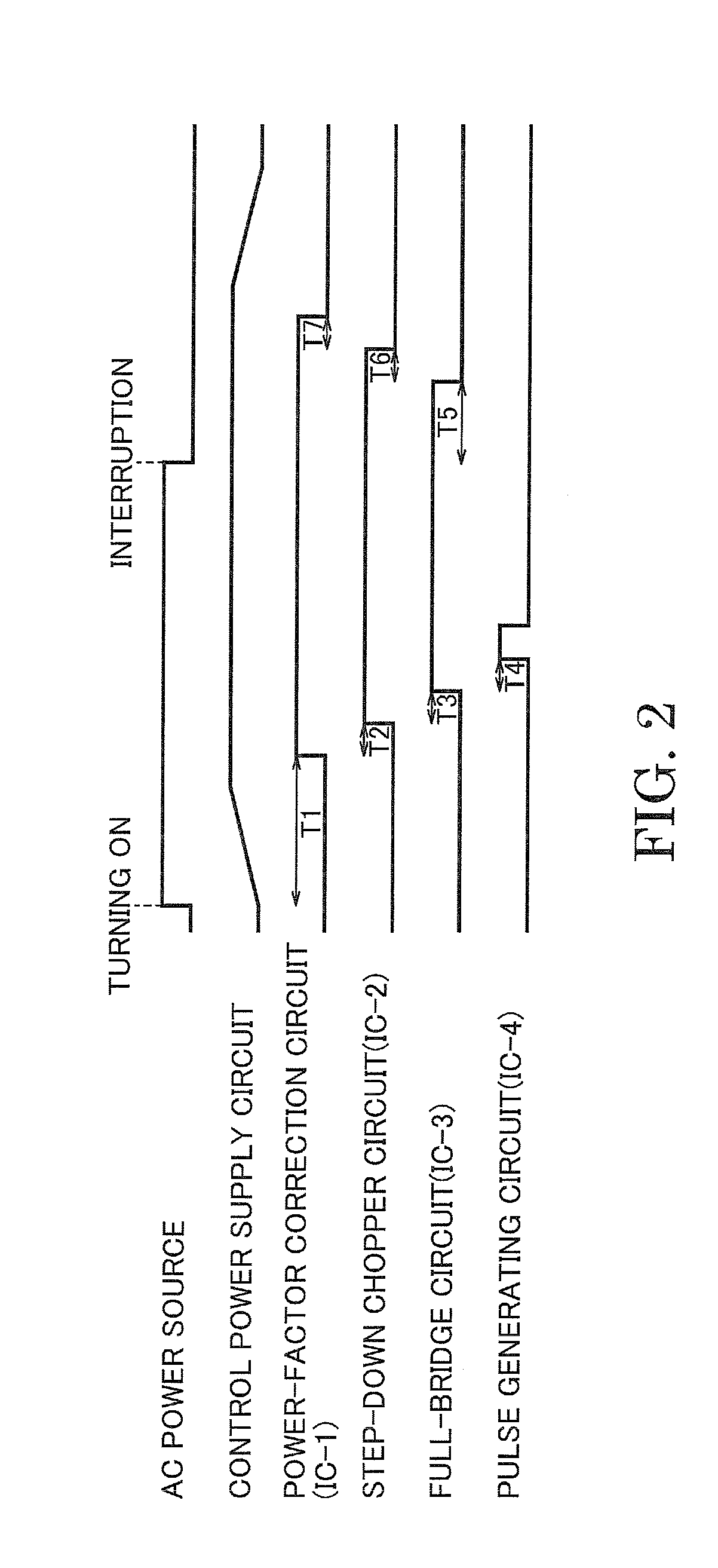
A lighting device has a power-factor correction circuit 6, a step-down chopper circuit 8, a full-bridge circuit 10, control ICs for these circuits and a driving-voltage supply circuit 14. The supply circuit 14 supplies a driving voltage to the control ICs. The control IC outputs the on / off driving voltage to a switching element of the corresponding circuit 6 to 10. The lighting device also has a detector 16 and judgment equipment 18. The detector 16 detects the driving voltage supplied from the supply circuit 14. The judgment equipment 18 instructs the control ICs to start outputting the on / off driving voltages in the order from the control IC close to the power source 2 to the control IC close to the discharge lamp 4 when the driving voltage detected by the detector 16 reaches a predetermined value during the time when the driving voltage supplied from the supply circuit 14 rises.
Owner:EYE LIGHTING SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com