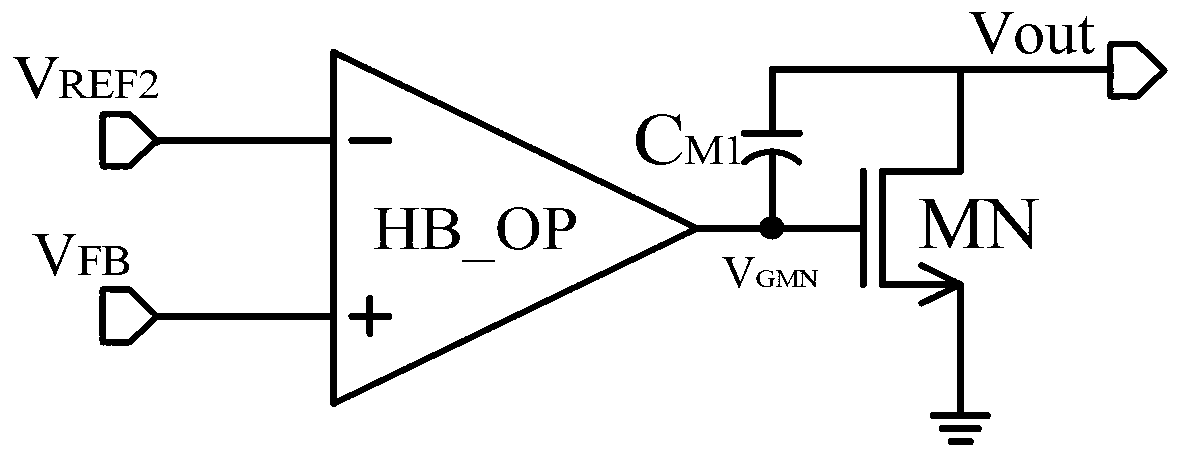
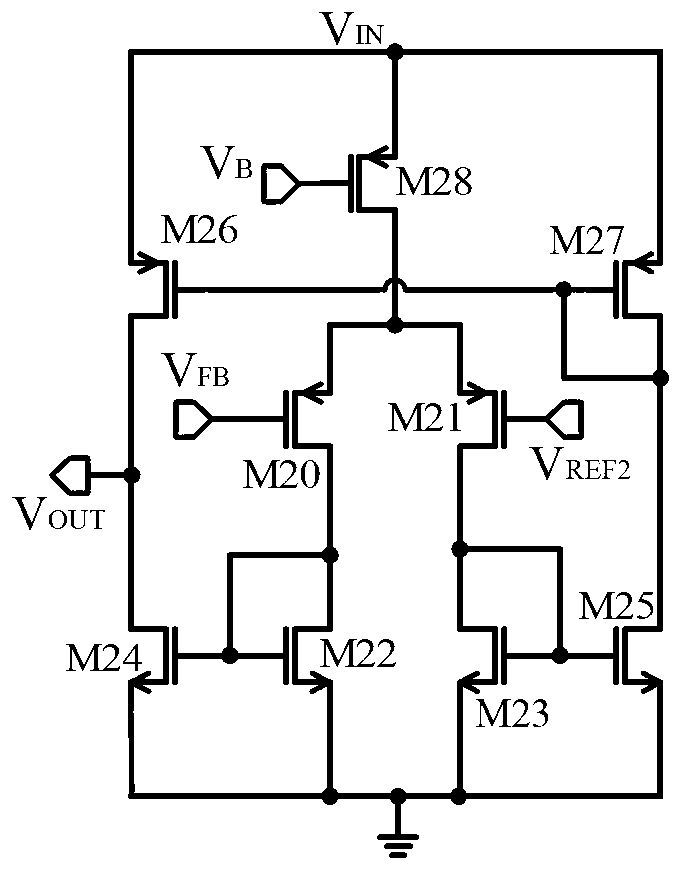
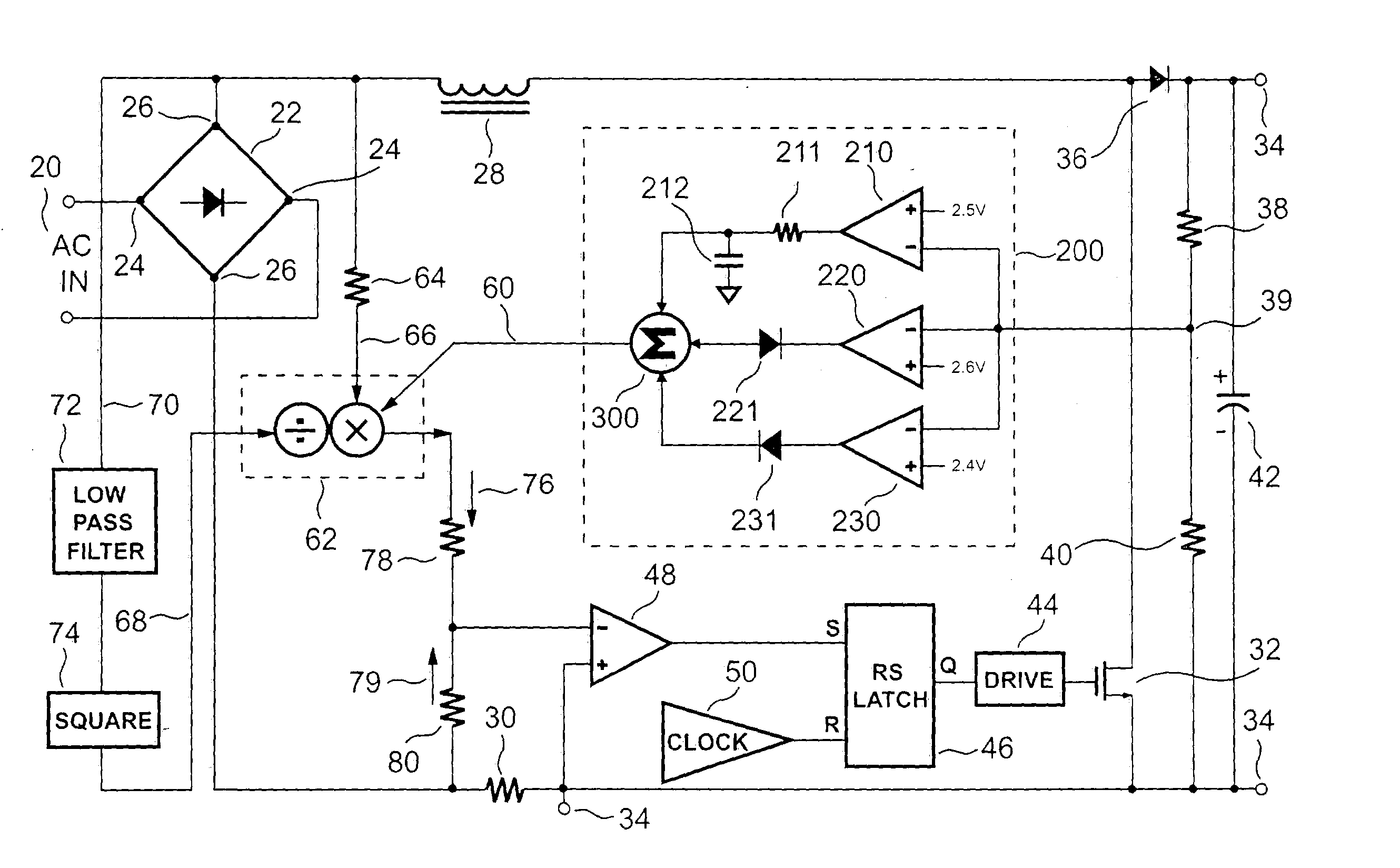
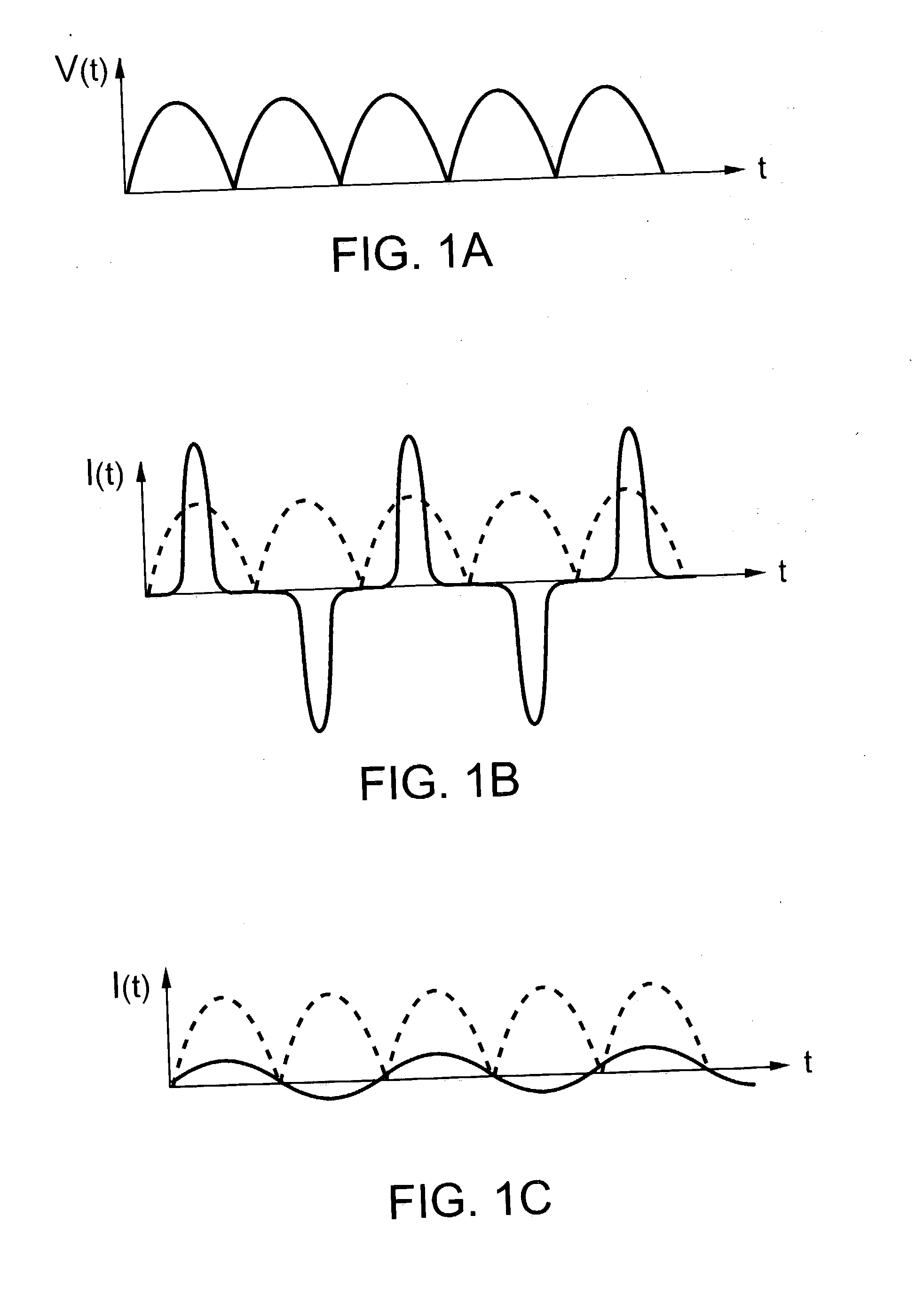
Patents
Literature
896 results about "Error amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
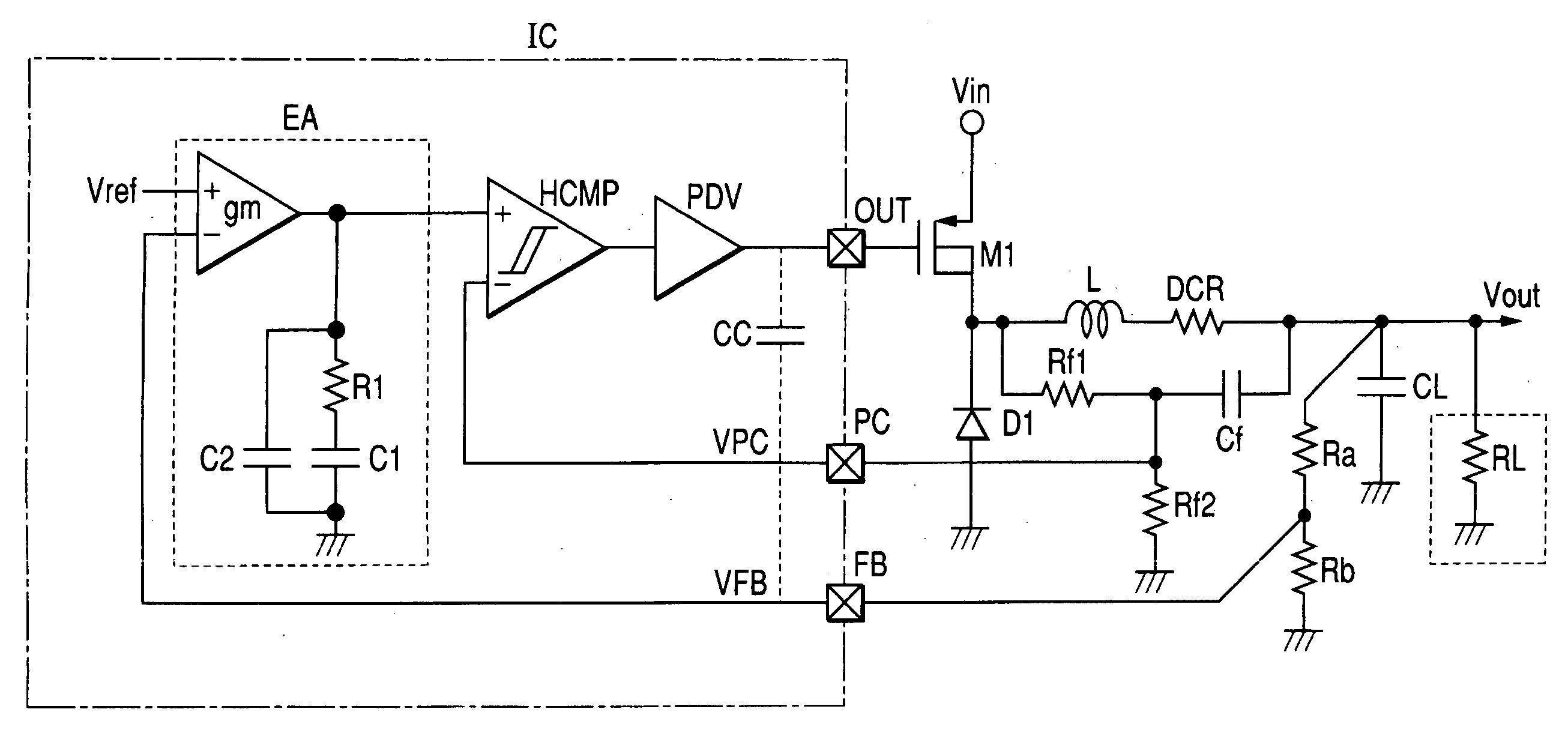
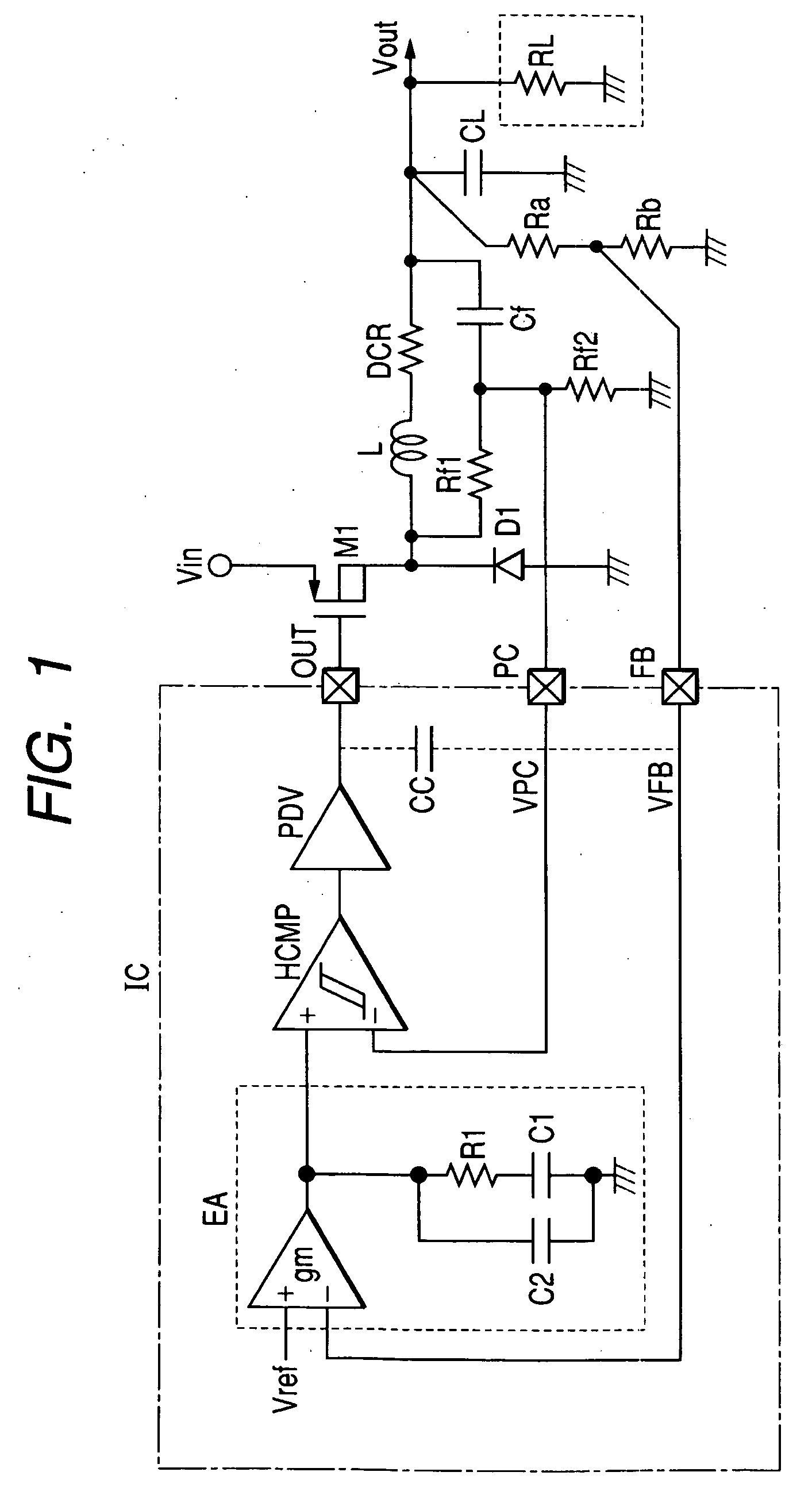
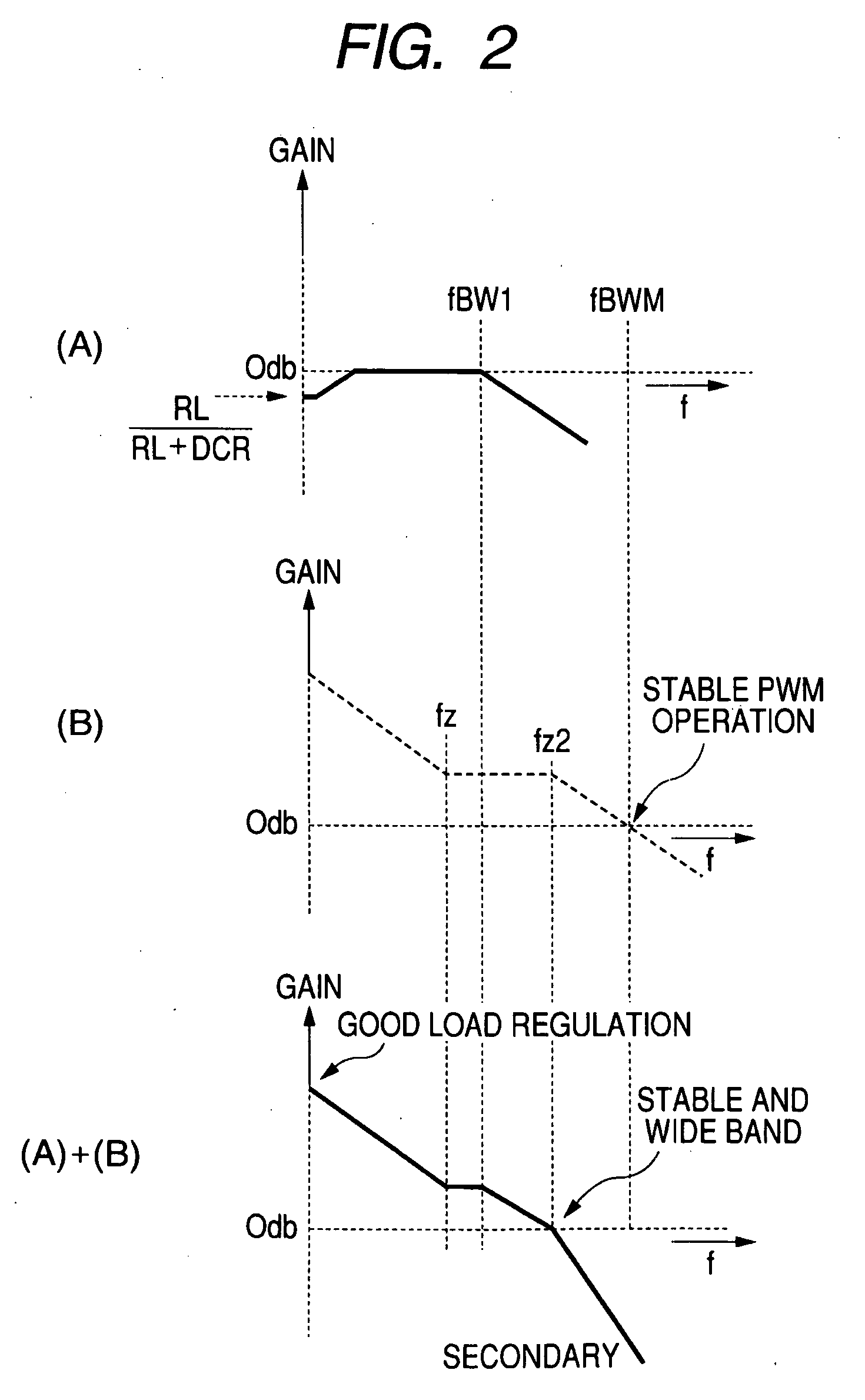
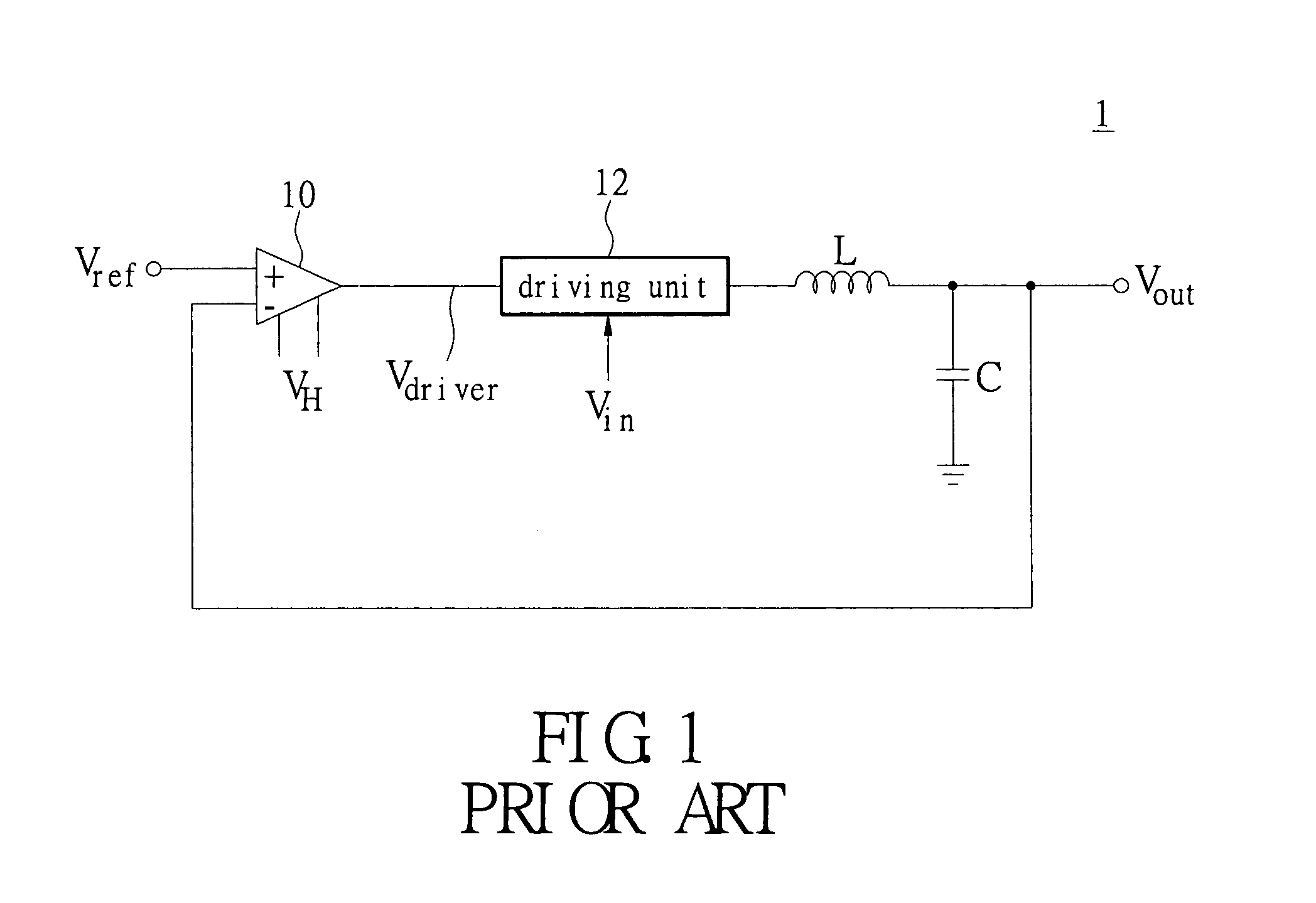
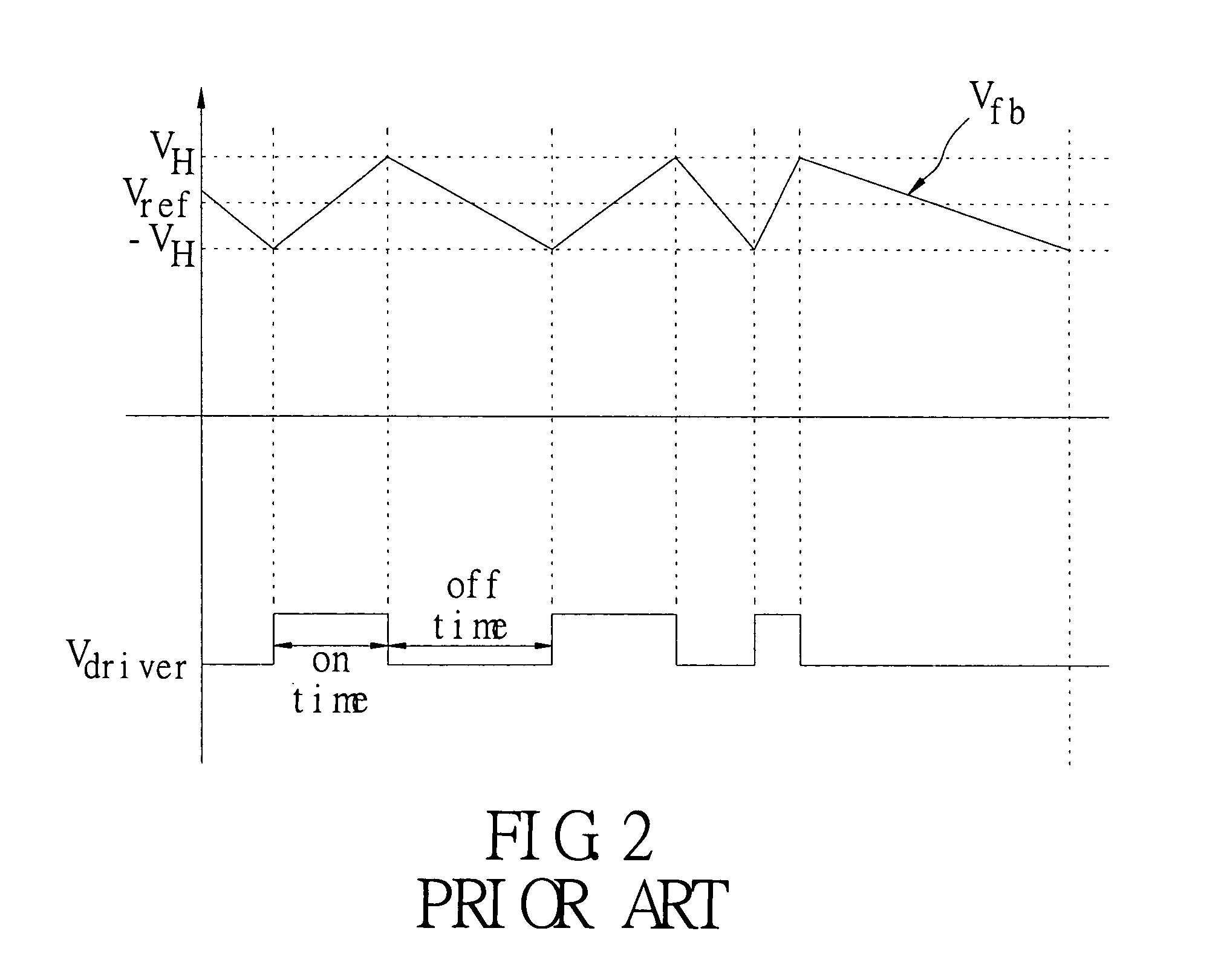
An error amplifier is most commonly encountered in feedback unidirectional voltage control circuits, where the sampled output voltage of the circuit under control, is fed back and compared to a stable reference voltage. Any difference between the two generates a compensating error voltage which tends to move the output voltage towards the design specification.
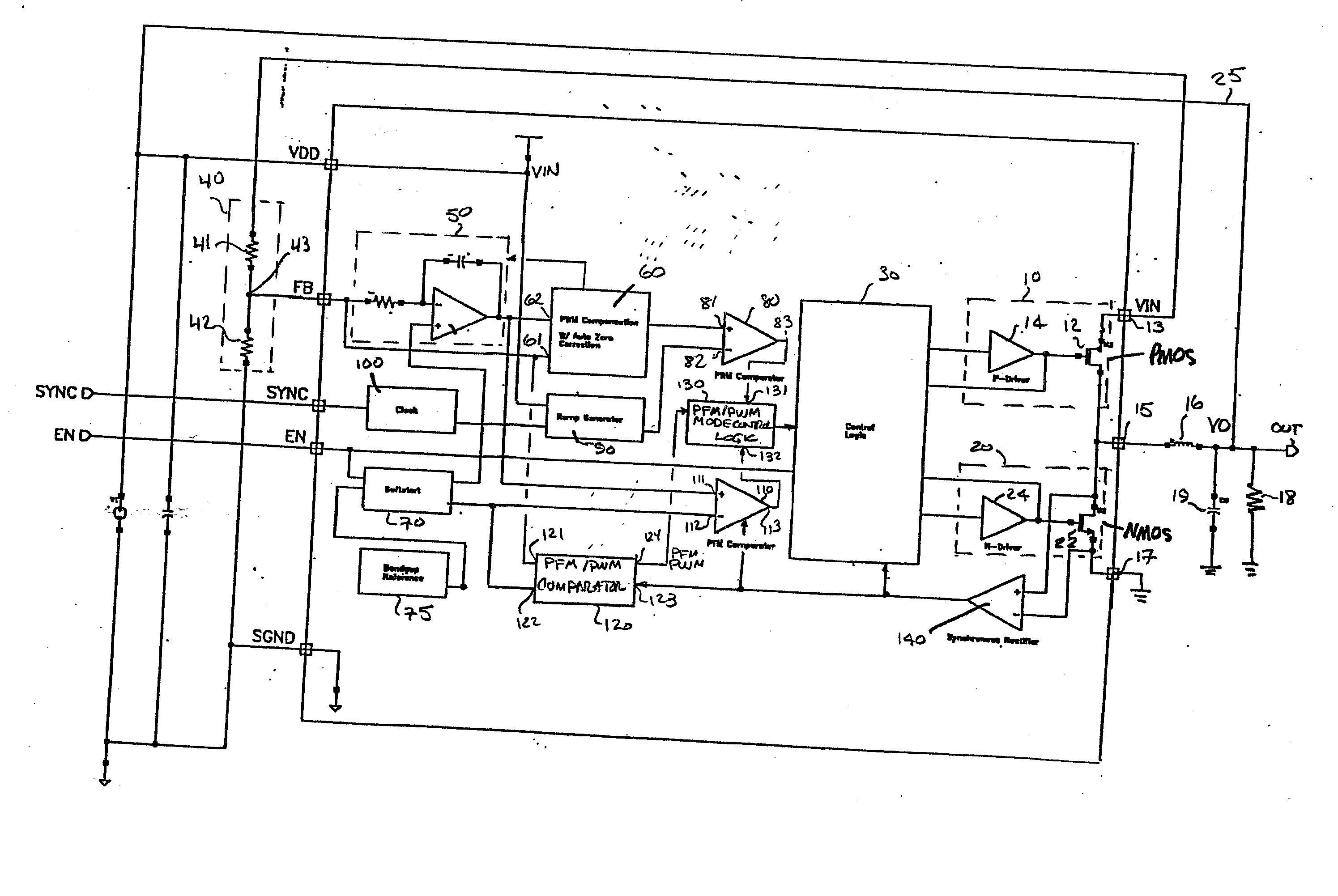
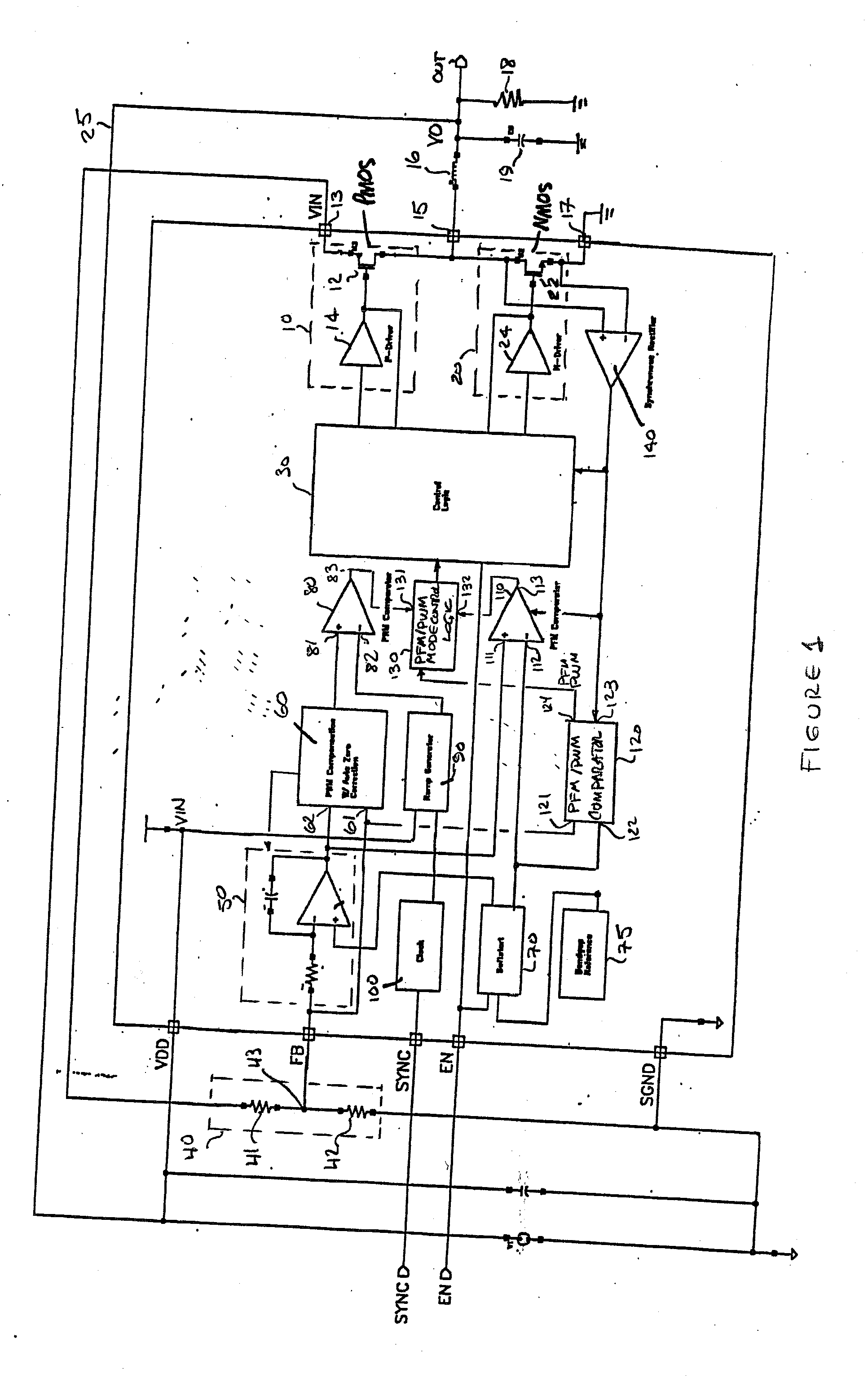
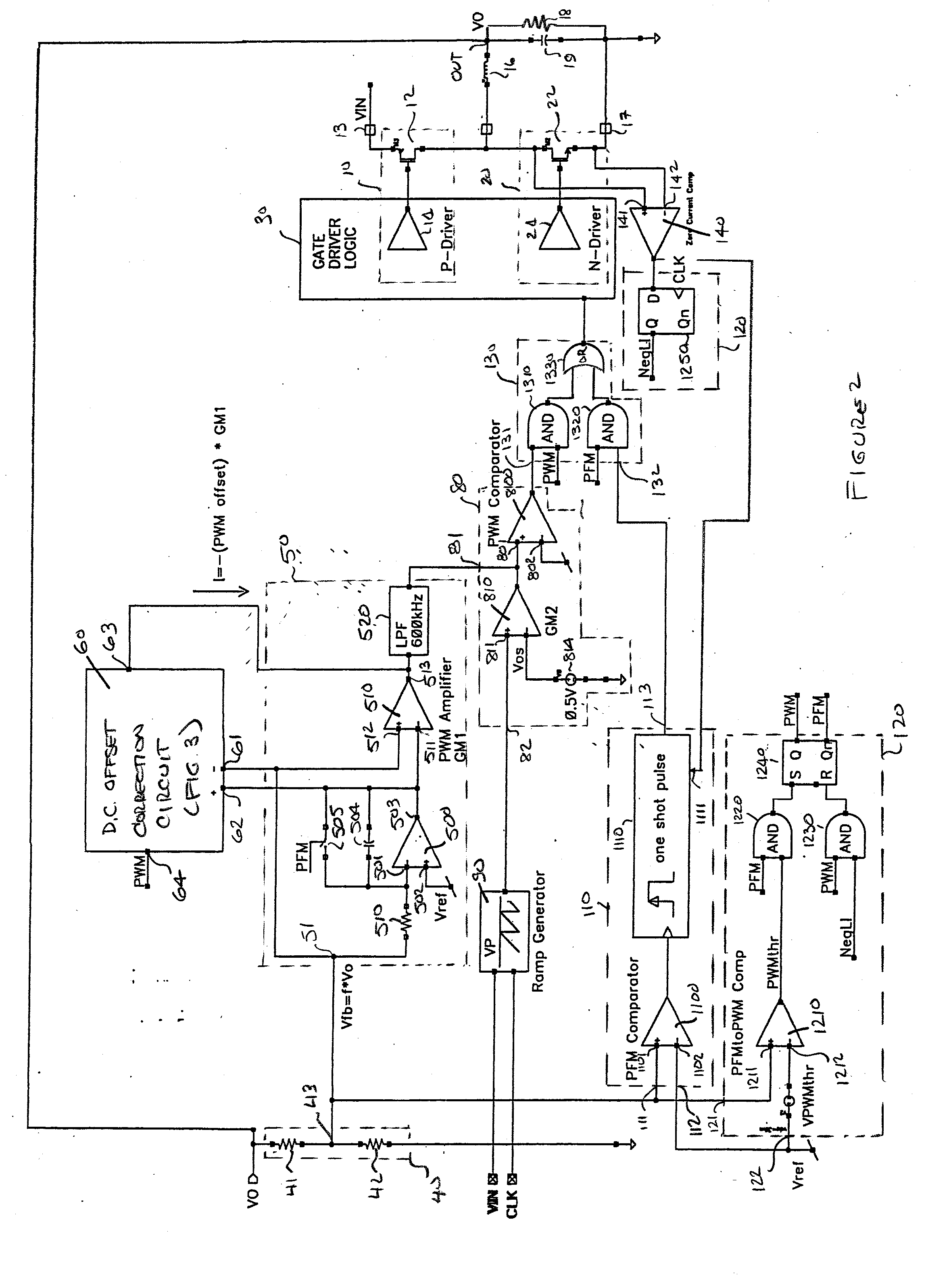
PFM-PWM DC-DC Converter Providing DC Offset Correction To PWM Error Amplifier And Equalizing Regulated Voltage Conditions When Transitioning Between PFM And PWM Modes
ActiveUS20060273772A1Accurate supervisionPrecise regulationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterVoltage regulation
To prevent a voltage glitch in the regulated DC output voltage of a PWM / PFM DC-DC converter when switching between PFM and PMW modes, the error amplifier of the converter's PWM regulation path is provided with a DC voltage offset correction mechanism. This mechanism “zeros-out” DC voltage offsets that may be present in the voltage regulation path, thereby enabling the error amplifier to accurately regulate the converter's output voltage. When the converter transitions between PFM and PWM modes, the DC offset correction mechanism establishes initial conditions of the error amplifier that effectively ensure that the converter's regulated output voltage at the beginning of a new “switched-to” PWM mode cycle is DC offset-free.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
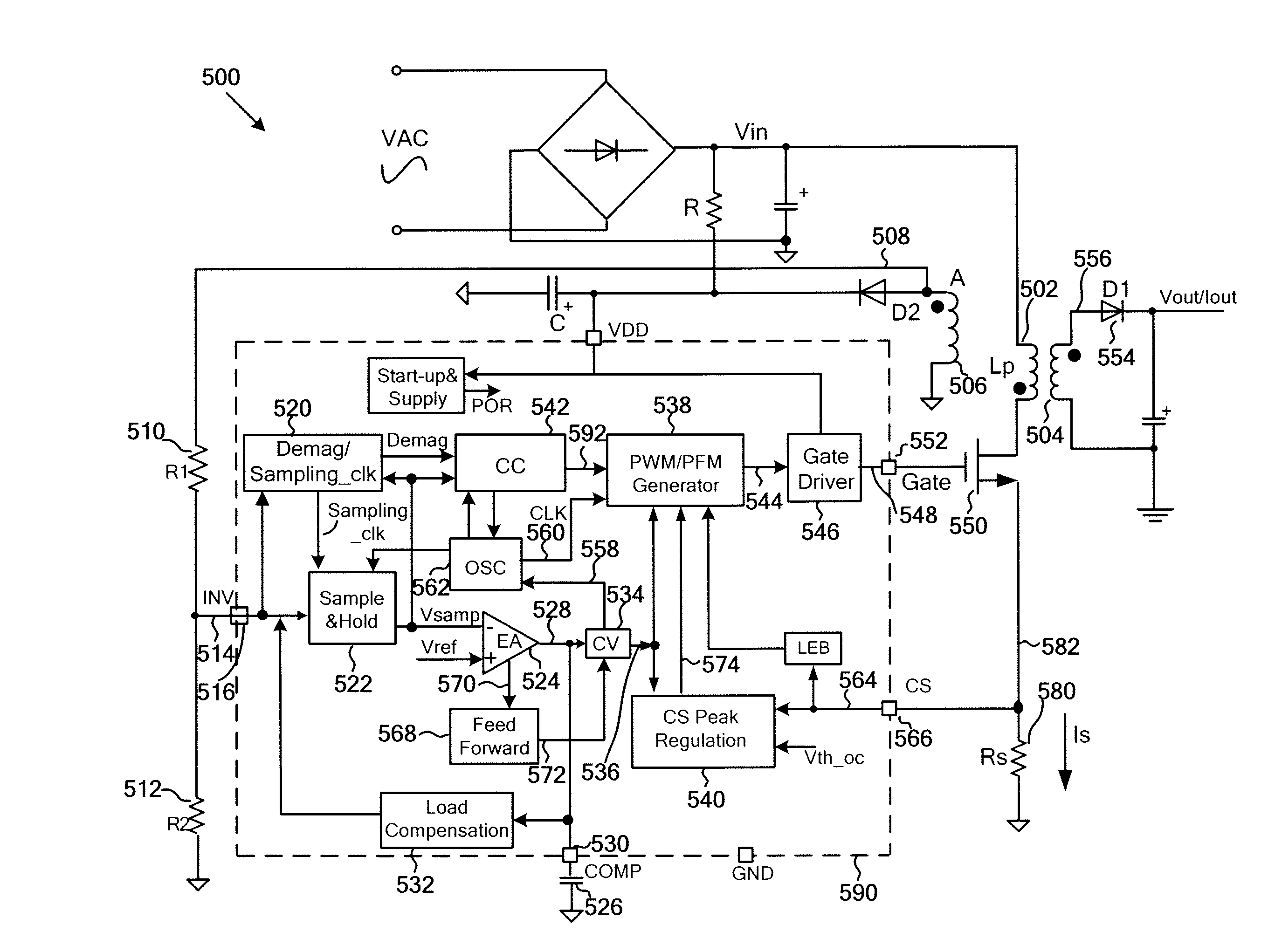
Systems and methods for constant voltage mode and constant current mode in flyback power converter with primary-side sensing and regulation
ActiveUS20100128501A1Reduce the number of partsReduce system costDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringSignal generator
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
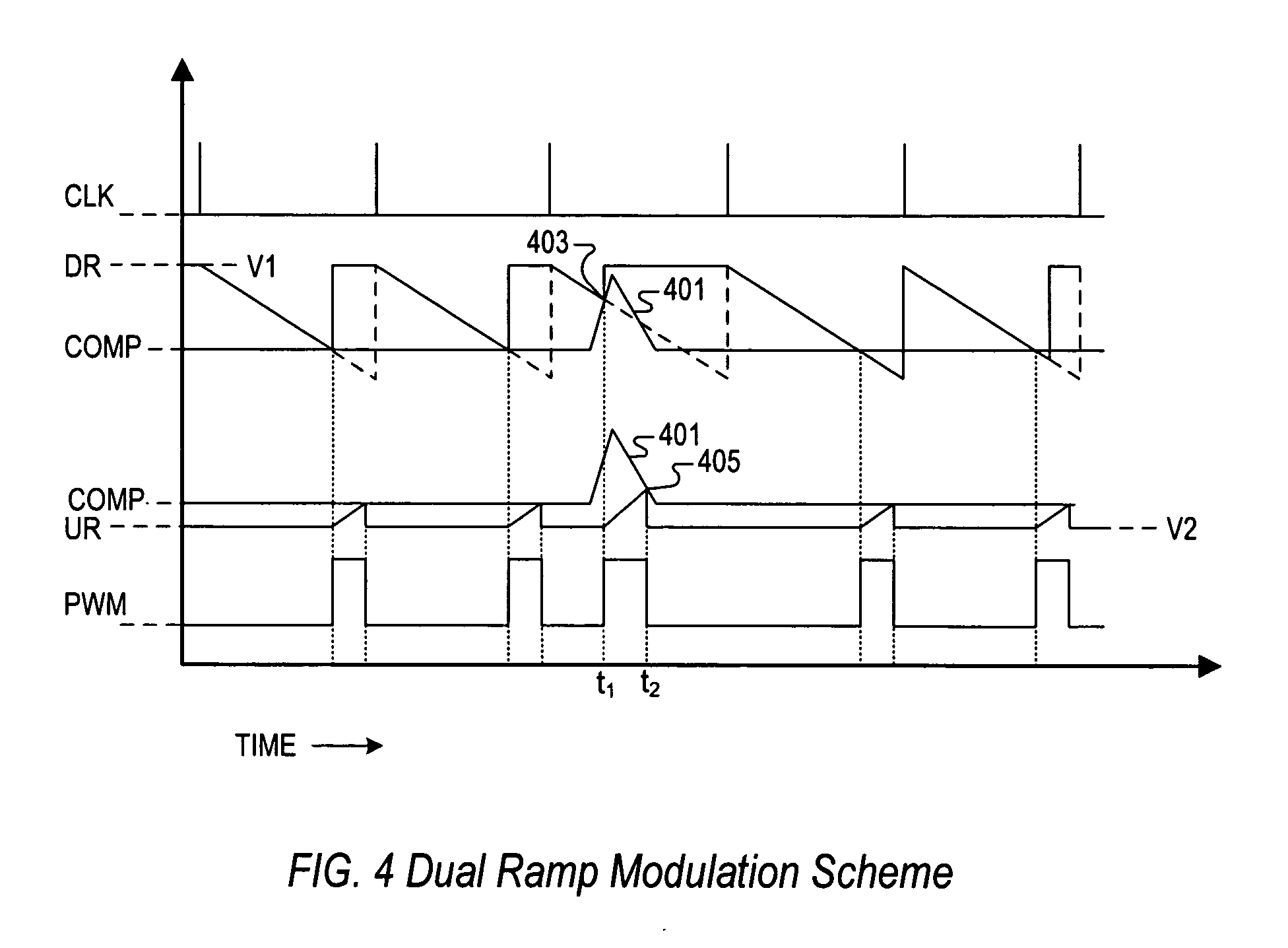
PWM controller with dual-edge modulation using dual ramps
ActiveUS20070013356A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLeading edgePulse control
A dual-edge modulation controller including first and second ramp circuits, first and second comparators, an error amplifier and pulse control logic. The first ramp circuit provides a leading-edge ramp synchronous with a clock. The error amplifier compares a feedback signal with a reference and provides a compensation signal. The first comparator compares the leading-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a set signal. The second ramp circuit provides a trailing-edge ramp that begins ramping when the set signal is asserted. The second comparator compares the trailing-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a reset signal. The pulse control logic asserts a PWM signal when the set signal is asserted and de-asserts the PWM signal when the reset signal is asserted. The controller may control multiple phases with current balancing. The slew rate of the ramps may be adjusted based on the number of PWM signal asserted.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Fixed-frequency current mode converter and control method thereof
InactiveUS20060043943A1Rapid responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationInductorCurrent mode
A fixed-frequency current mode converter comprises a power stage to produce an inductor current and an output voltage, an error amplifier to generate an error signal from the difference between the output voltage and a reference voltage varied with the inductor current, a comparator to compare the error signal with a ramp signal varied with the inductor current to generate a comparison signal, and a PWM generator to generate a PWM signal in response to a fixed-frequency clock and the comparison signal to drive the power stage. A second comparator is further comprised to compare the error signal with a second reference voltage varied with the inductor current, and generates a second comparison signal to reset the clock when the error signal is lower than the second reference voltage.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Electronic parts for high frequency power amplifier and wireless communication device
ActiveUS20070066250A1Improve controllabilityImprove dynamic rangeResonant long antennasGain controlCapacitanceHigh frequency power
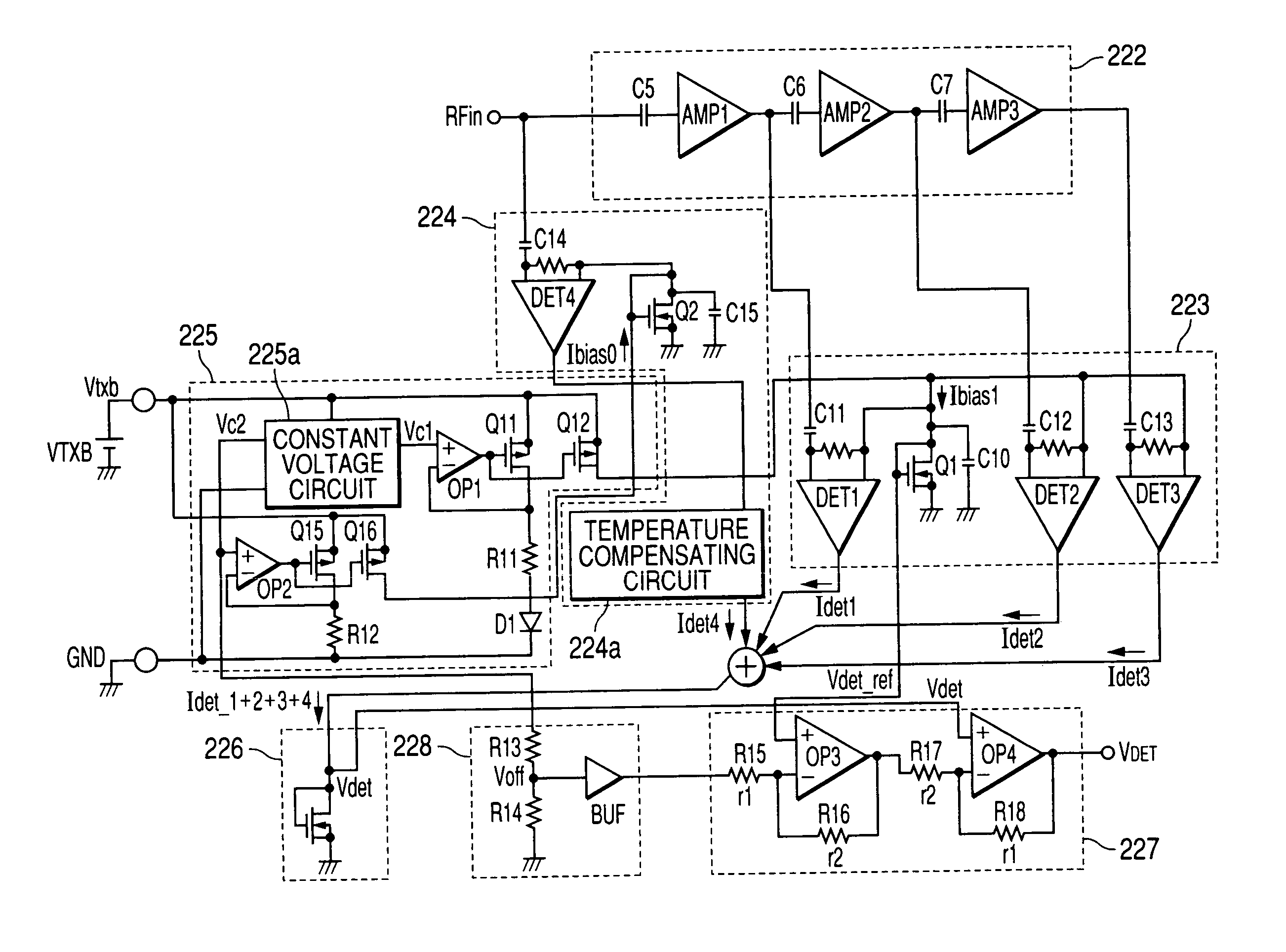
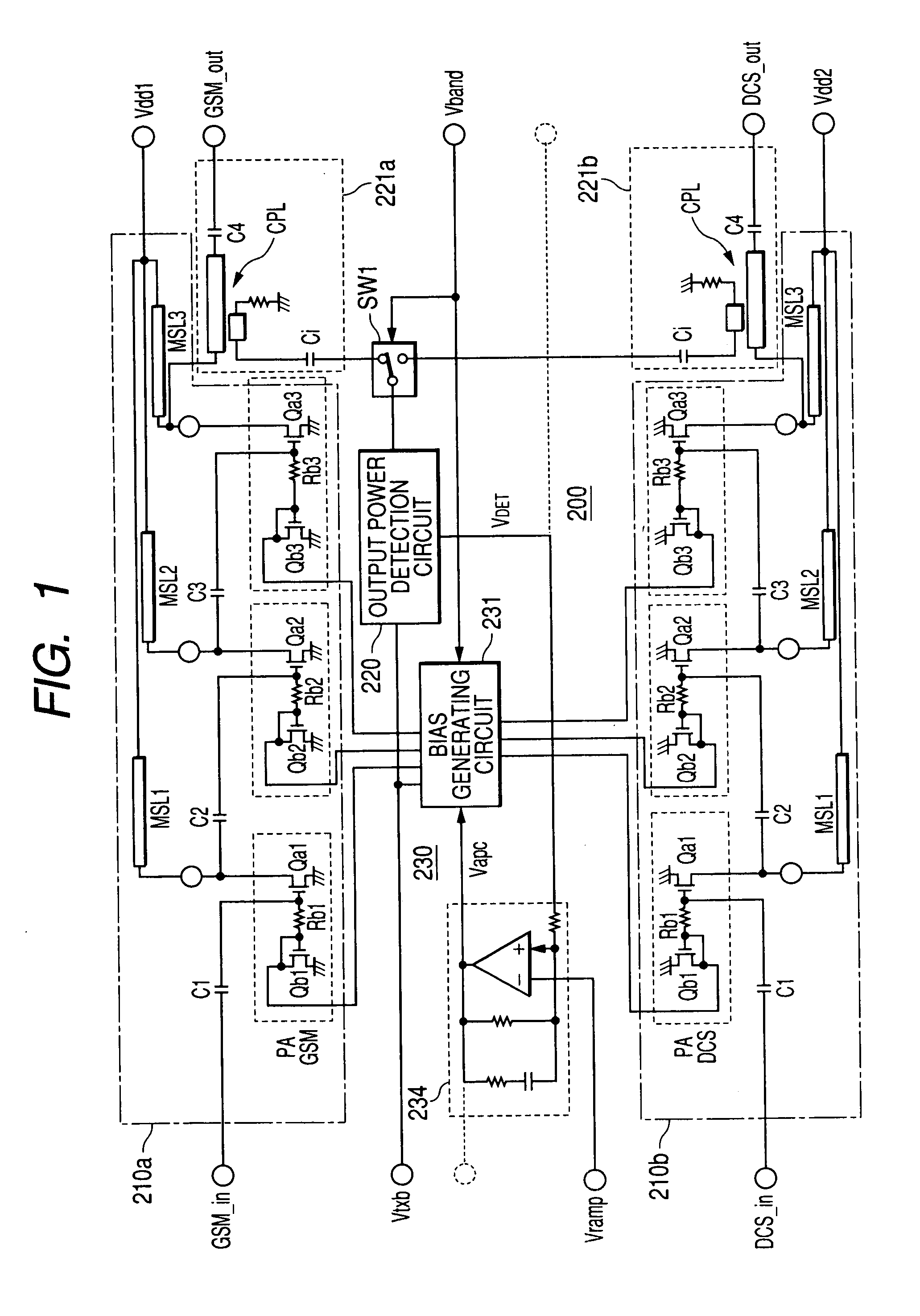
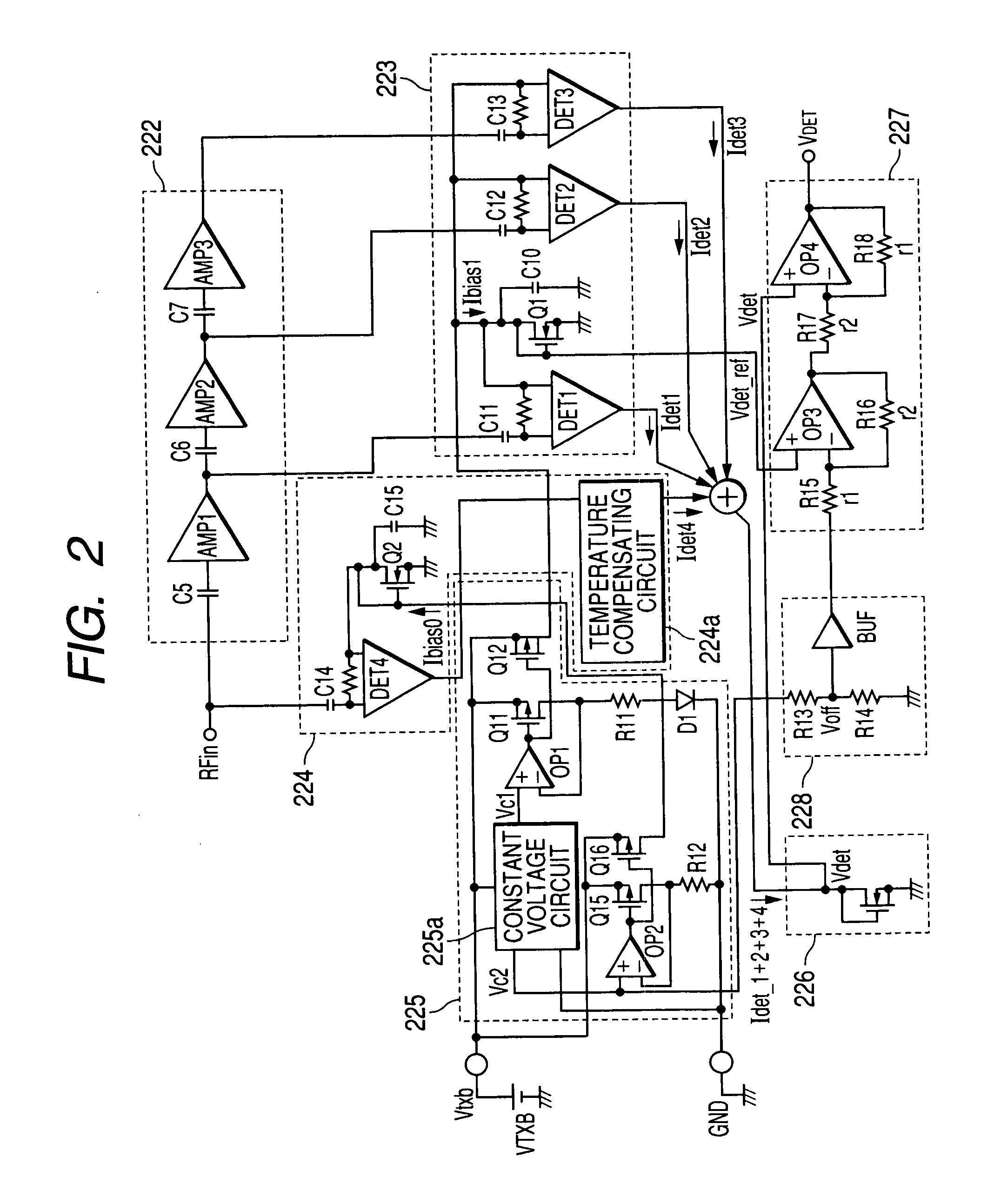
The present invention provides electronic parts for amplifying high frequency power capable of expanding a dynamic range of an output power detection circuit, obtaining a continuous detection output having no inflexion point from a low region of output power to its high region and thereby improving controllability of the output power. In a wireless communication system which controls output power of a high frequency power amplifier, based on an output power detection signal and a signal indicative of an output level, an output power detection circuit is provided with a multi-stage configured amplifier which amplifies a high frequency signal taken out via a coupler and capacitive elements. Further, a plurality of detection circuits which detect outputs of amplifiers of respective stages, and a detection circuit which detects the high frequency signal without passing through the multi-stage configured amplifier are provided. One obtained by combining the outputs of these detection circuits is inputted to an error amplifier for generating an output power control signal, as the output power detection signal to thereby generate a control signal for the high frequency power amplifier.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Variable-gain amplifier having error amplifier with constant loop gain
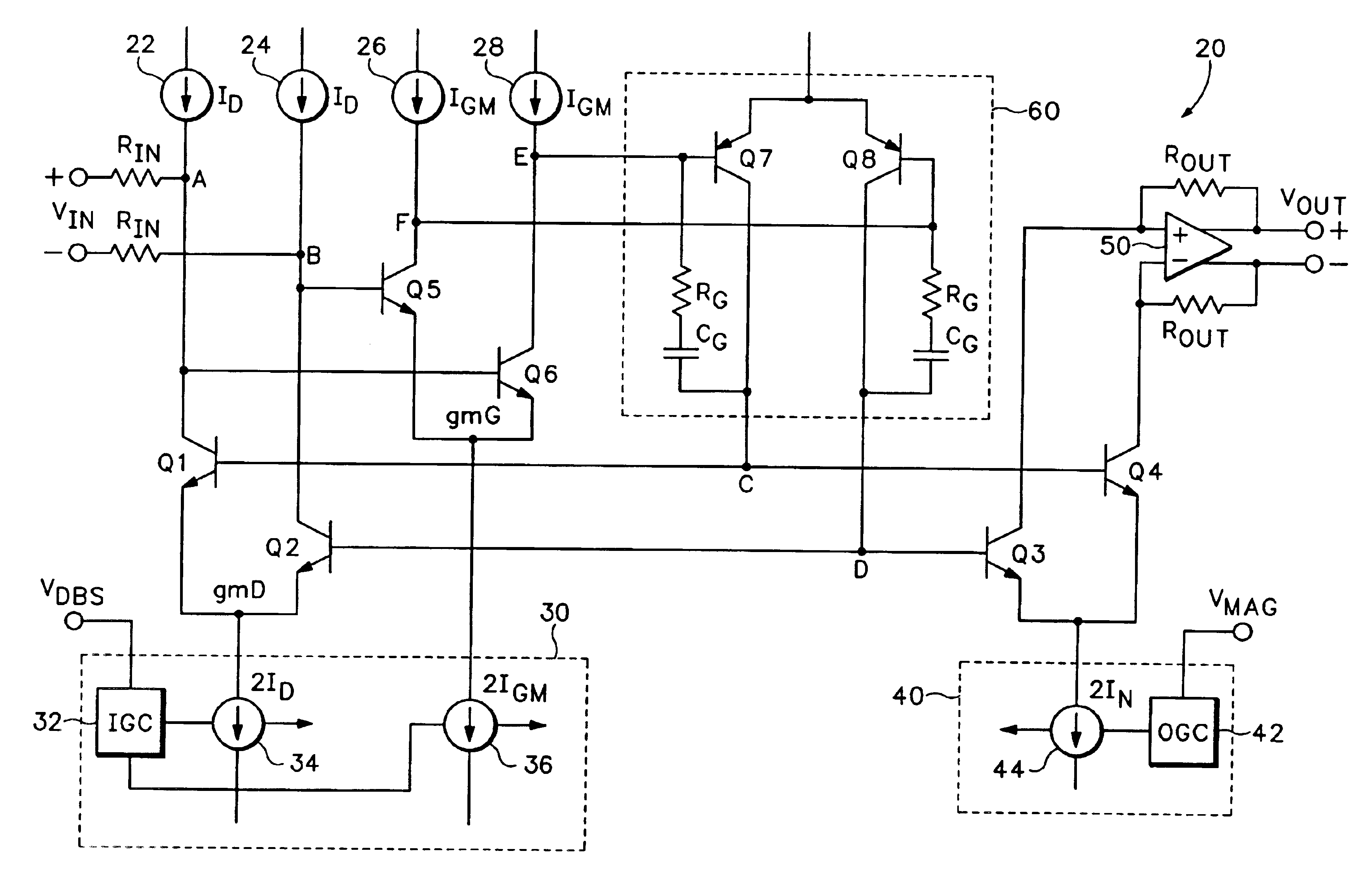
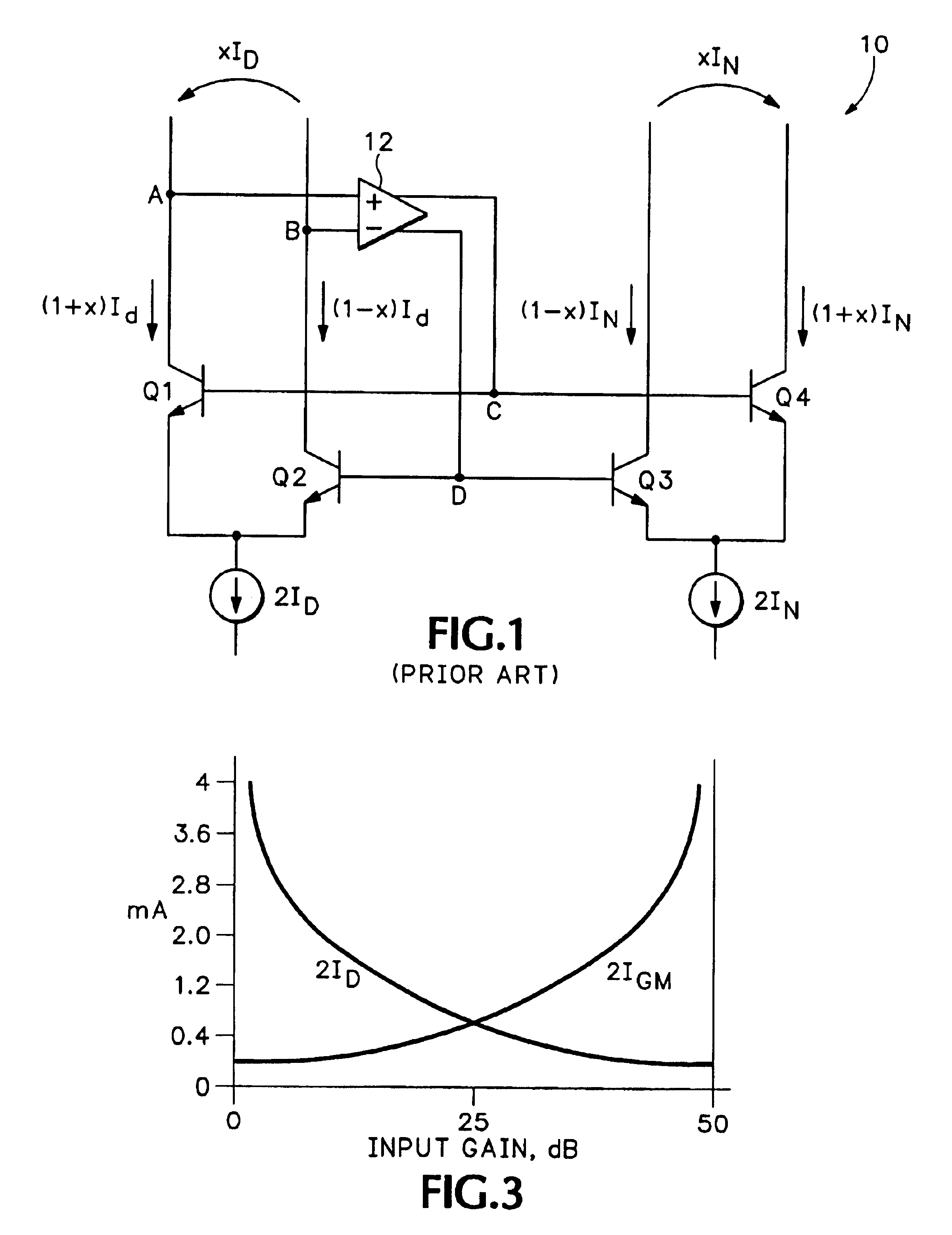
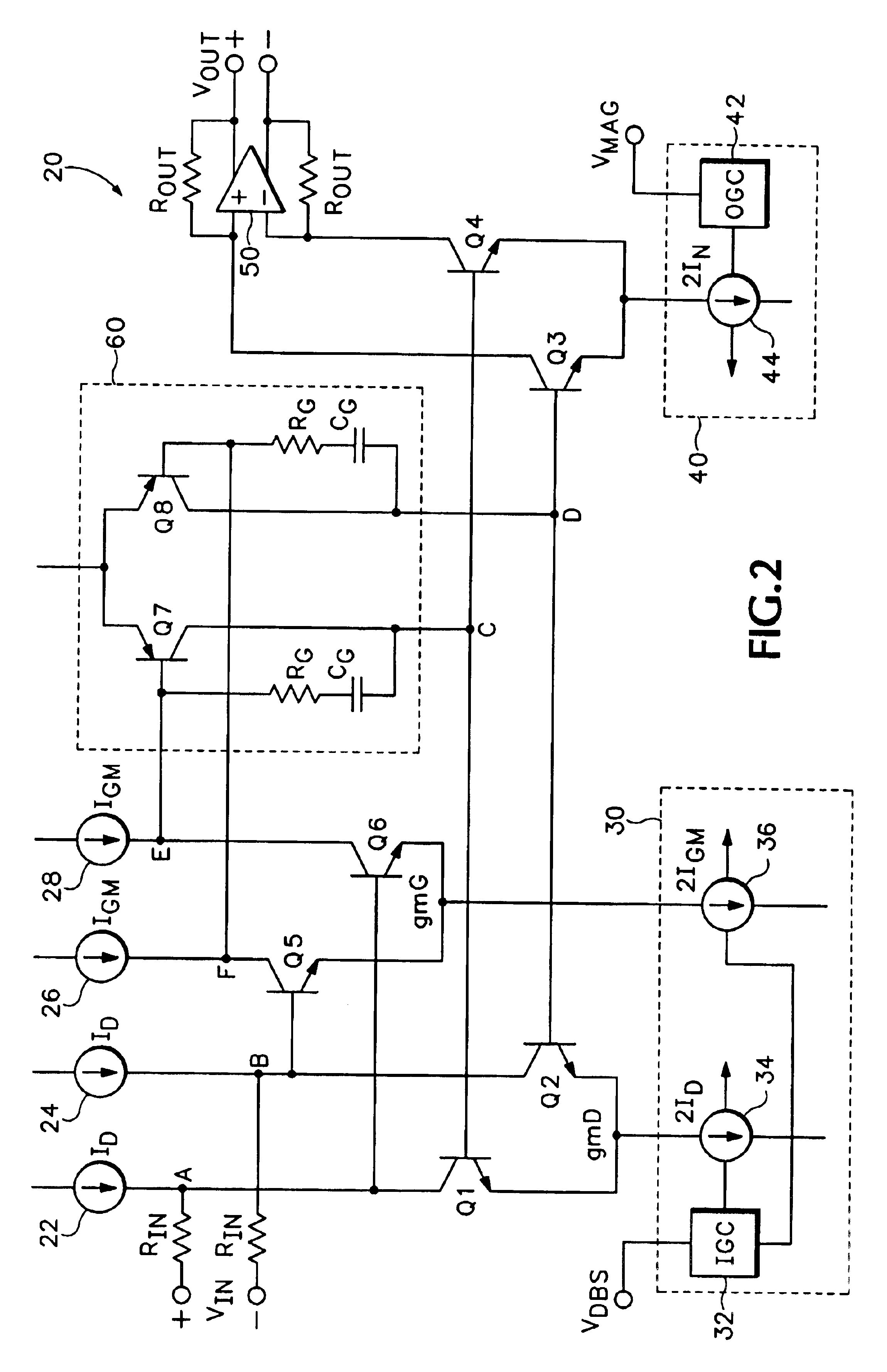
ActiveUS6894564B1Increase capacityImprove performanceDifferential amplifiersAmplification control detailsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A translinear amplifier is disclosed. A loop amplifier drives the bases of the input and output transistor pairs from the differential collector voltage of the input pair. The loop amplifier contains a third differential pair (a gain pair). The tail current of the gain pair is inversely related to the tail current of the input pair, such that loop amplifier gain remains stable when the transconductance of the input pair changes (due, e.g., to input gain changes). In one embodiment, a linear-in-dB interface is provided that adjusts input pair tail current exponentially (and gain pair tail current exponentially and inversely) to linear voltage changes at a gain input.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Linear voltage stabilizing circuit with low voltage difference
InactiveCN102681582ALower resistanceHigh inhibition ratioElectric variable regulationLow voltageHemt circuits
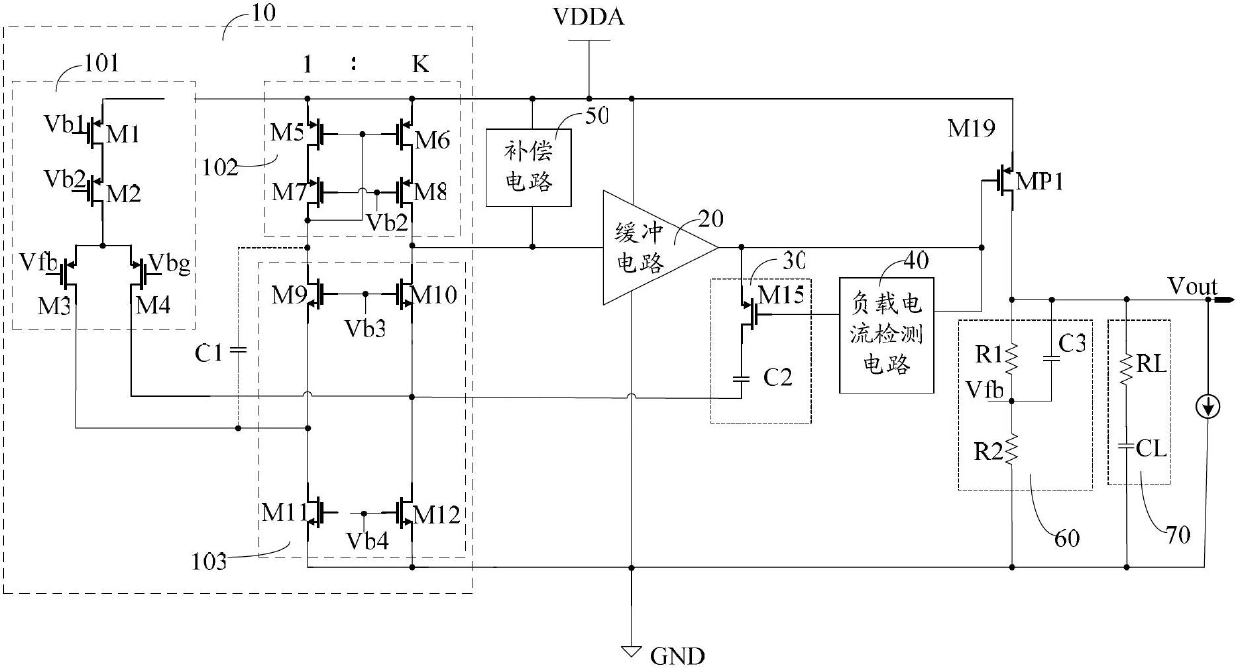
The invention provides a linear voltage stabilizing circuit with low voltage difference. The linear voltage stabilizing circuit with the low voltage difference is provided with high power supply rejection ratio and comprises an error amplifier, a buffer circuit, a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) regulating transistor, a compensation circuit, a voltage division feedback circuit and an output circuit. The error amplifier is a novel error amplifier. Ratio of width to length ratio of a fifth PMOS tube and a sixth PMOS tube, ratio of width to length ratio of a seventh PMOS tube and an eighth PMOS tube and ratio of width to length ratio of a ninth N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube and a tenth NMOS tube are all 1: K, and K is an integer greater than 1. The ratio of width to length ratio of the metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) tubes is changed, resistance of an output node of the error amplifier to a power supply is reduced, power interference enters from a current mirror low resistance point is amplified through current amplification technology, and power supply high frequency small signal interference in output signals of the error amplifier cannot be attenuated excessively. Therefore, the linear voltage stabilizing circuit with the low voltage difference enables power supply interference signals arriving at a PMOS regulating transistor grid to be varied according to variation of power supply voltage well, and improves the power supply rejection ratio of circuits.
Owner:BRIGATES MICROELECTRONICS KUNSHAN
Windowless h-bridge buck-boost switching converter
ActiveUS20140084883A1Reduce in quantityImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLogic circuitryError amplifier
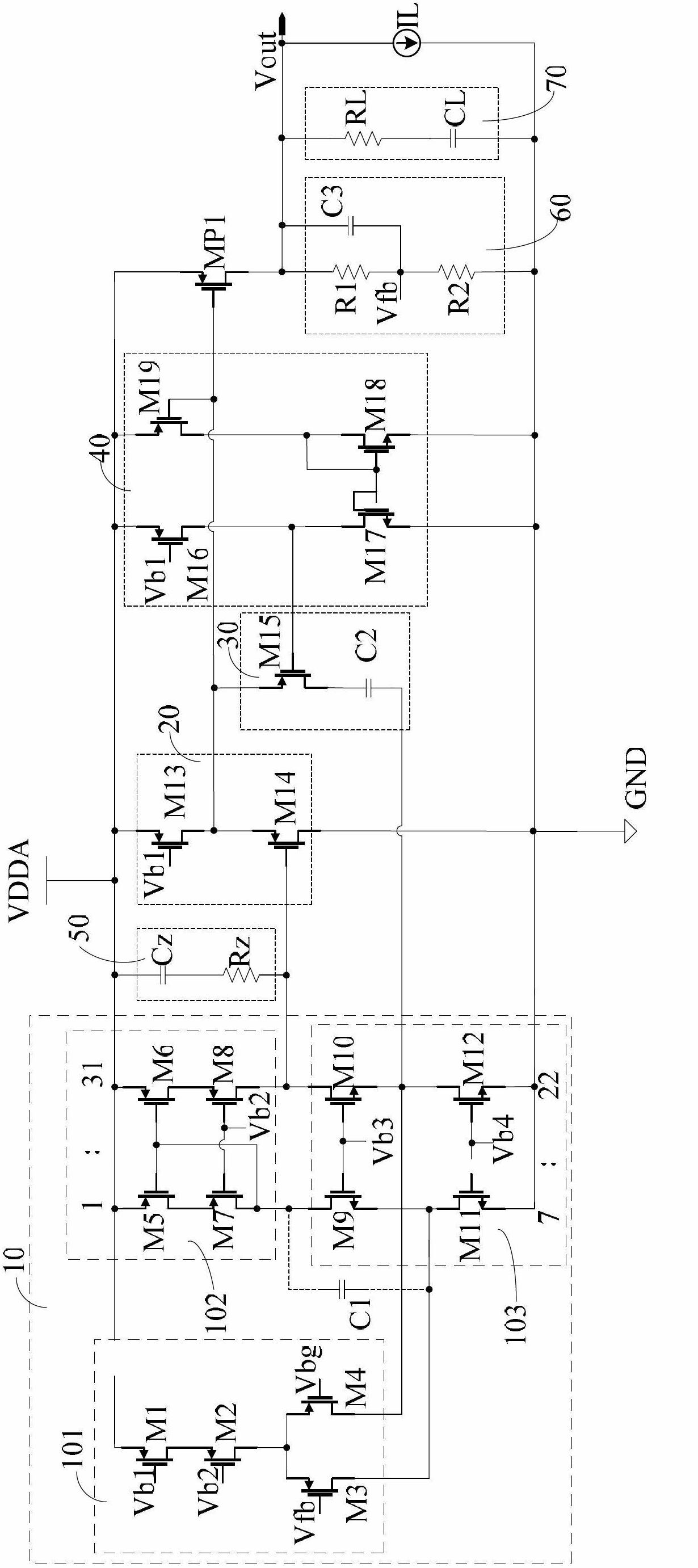
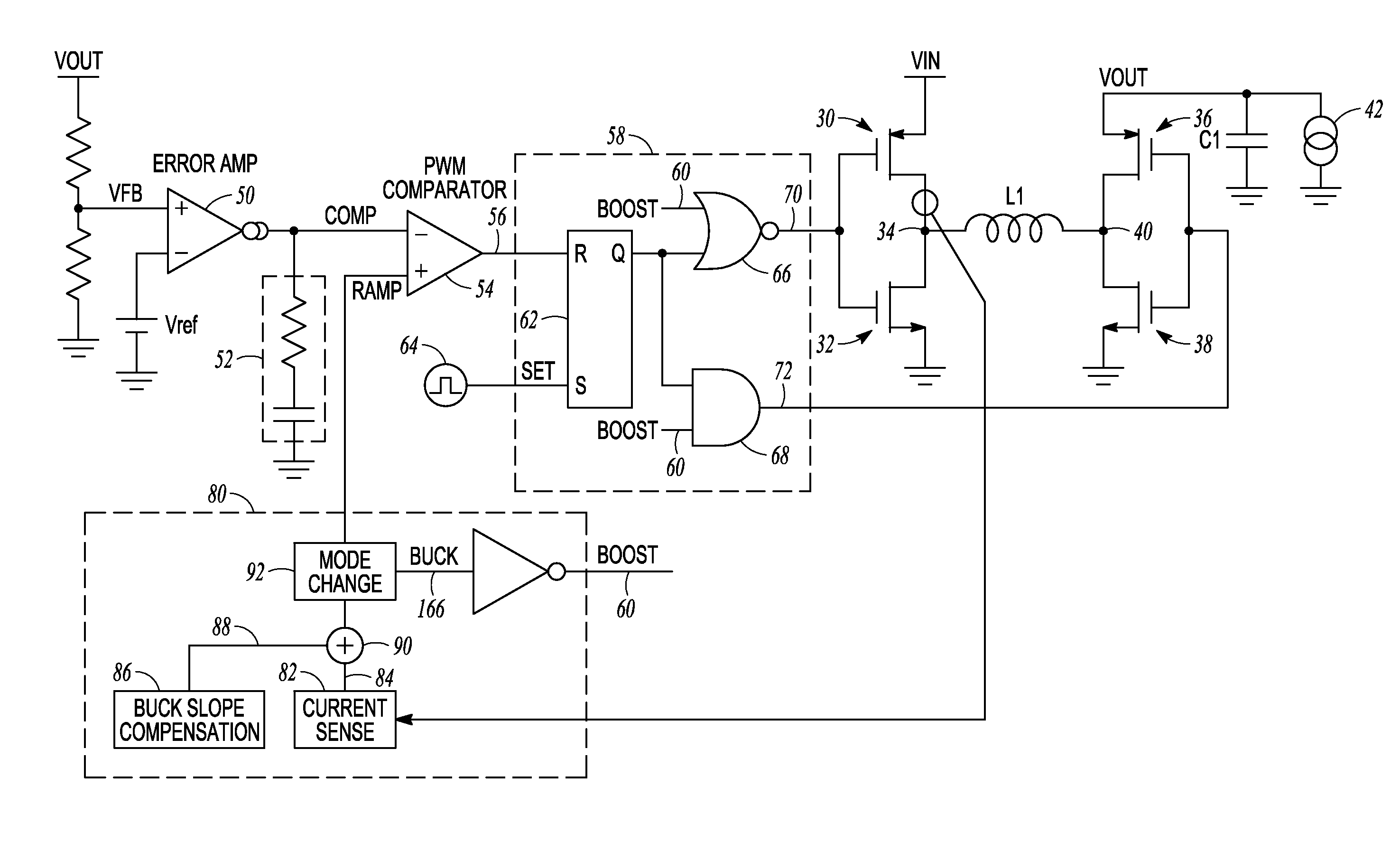
A “windowless” H-bridge buck-boost switching converter includes a regulation circuit with an error amplifier which produces a ‘comp’ signal, a comparison circuit which compares ‘comp’ with a ‘ramp’ signal, and logic circuitry which receives the comparison circuit output and a mode control signal indicating whether the converter is to operate in buck mode or boost mode and operates the primary or secondary switching elements to produce the desired output voltage in buck or boost mode, respectively. A ‘ramp’ signal generation circuit operates to shift the ‘ramp’ signal up by a voltage Vslp(p−p)+Vhys when transitioning from buck to boost mode, and to shift ‘ramp’ back down by Vslp(p−p)+Vhys when transitioning from boost to buck mode, thereby enabling the converter to operate in buck mode or boost mode only, with no need for an intermediate buck-boost region.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Low drop-out voltage regulator with common-mode feedback
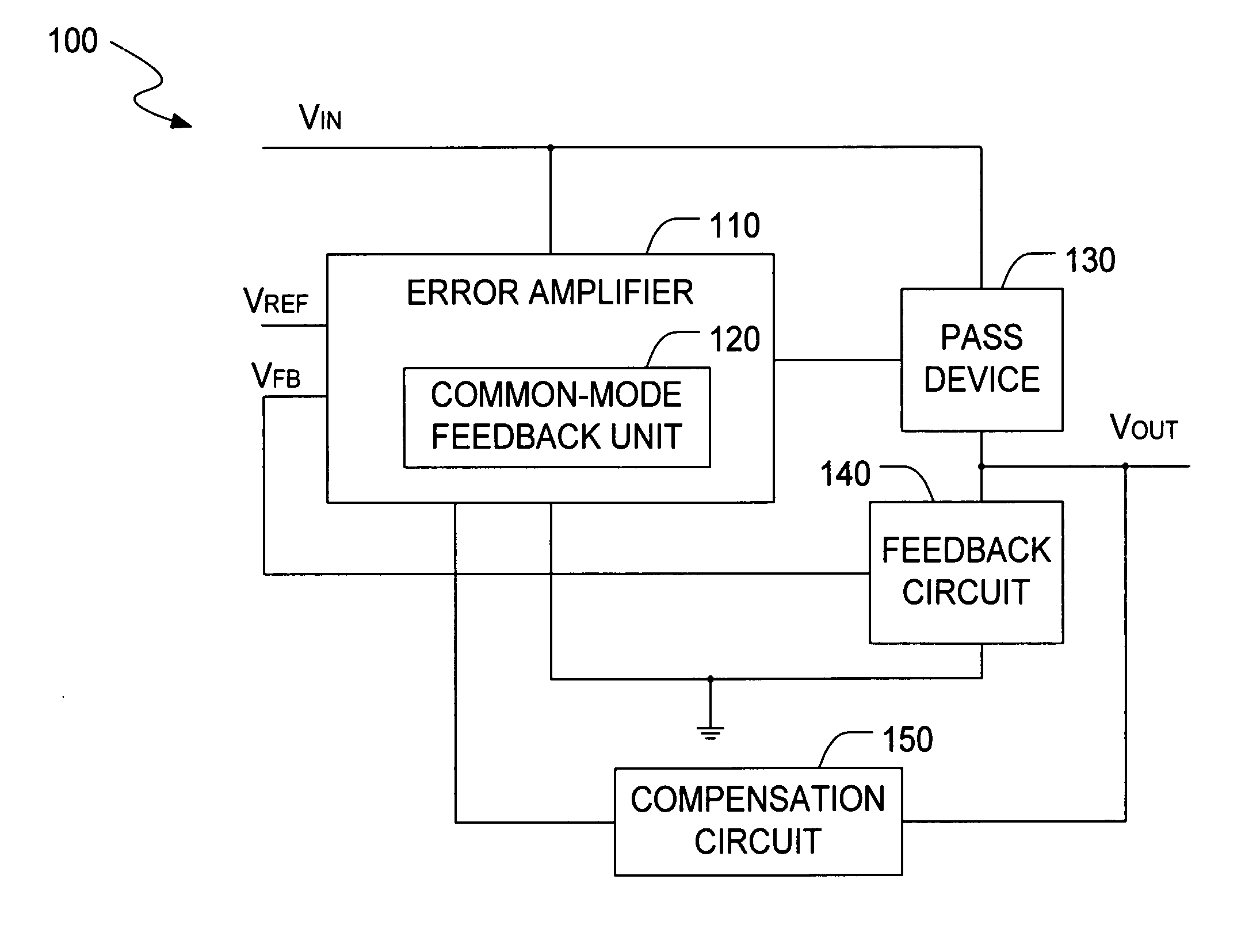
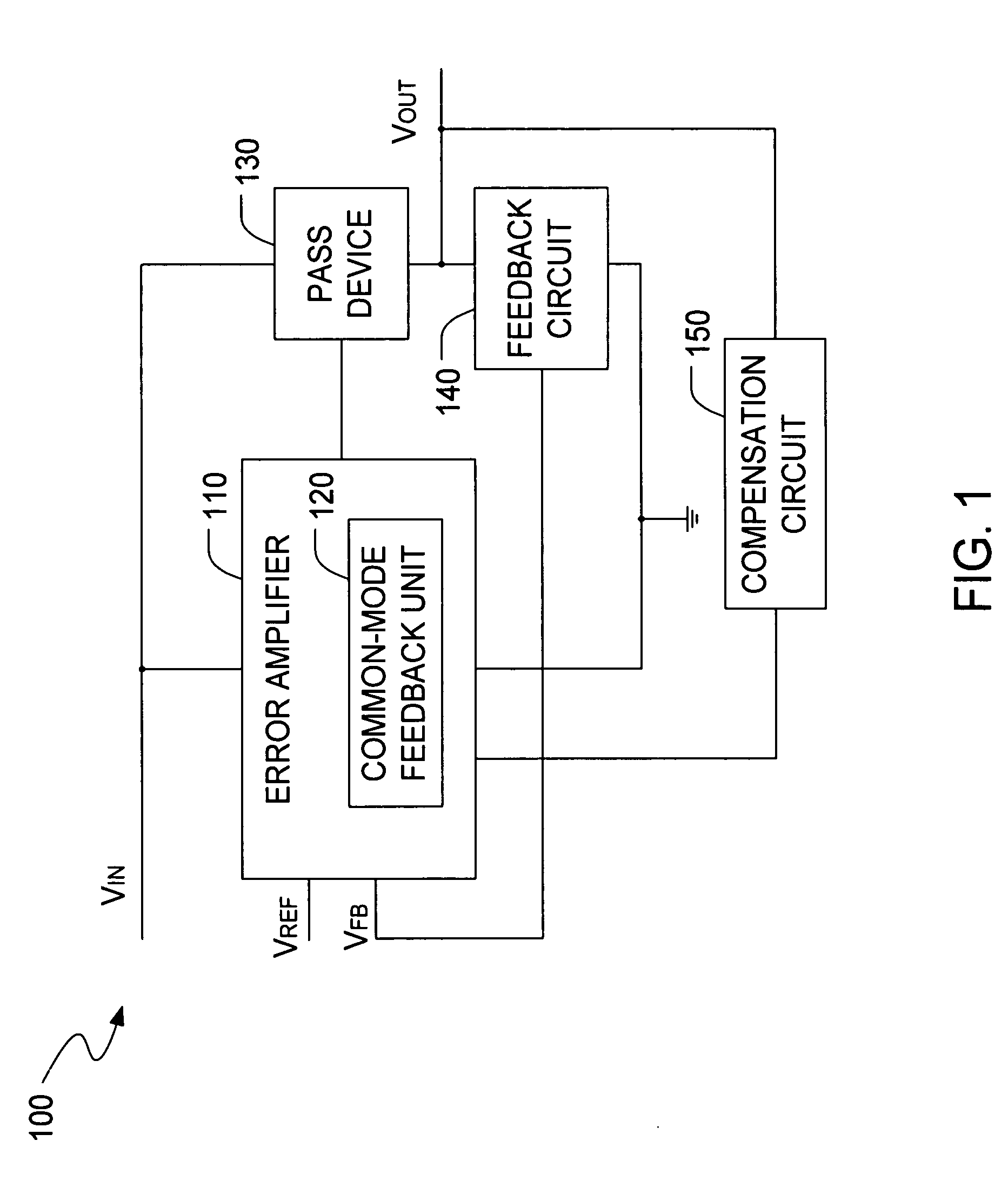
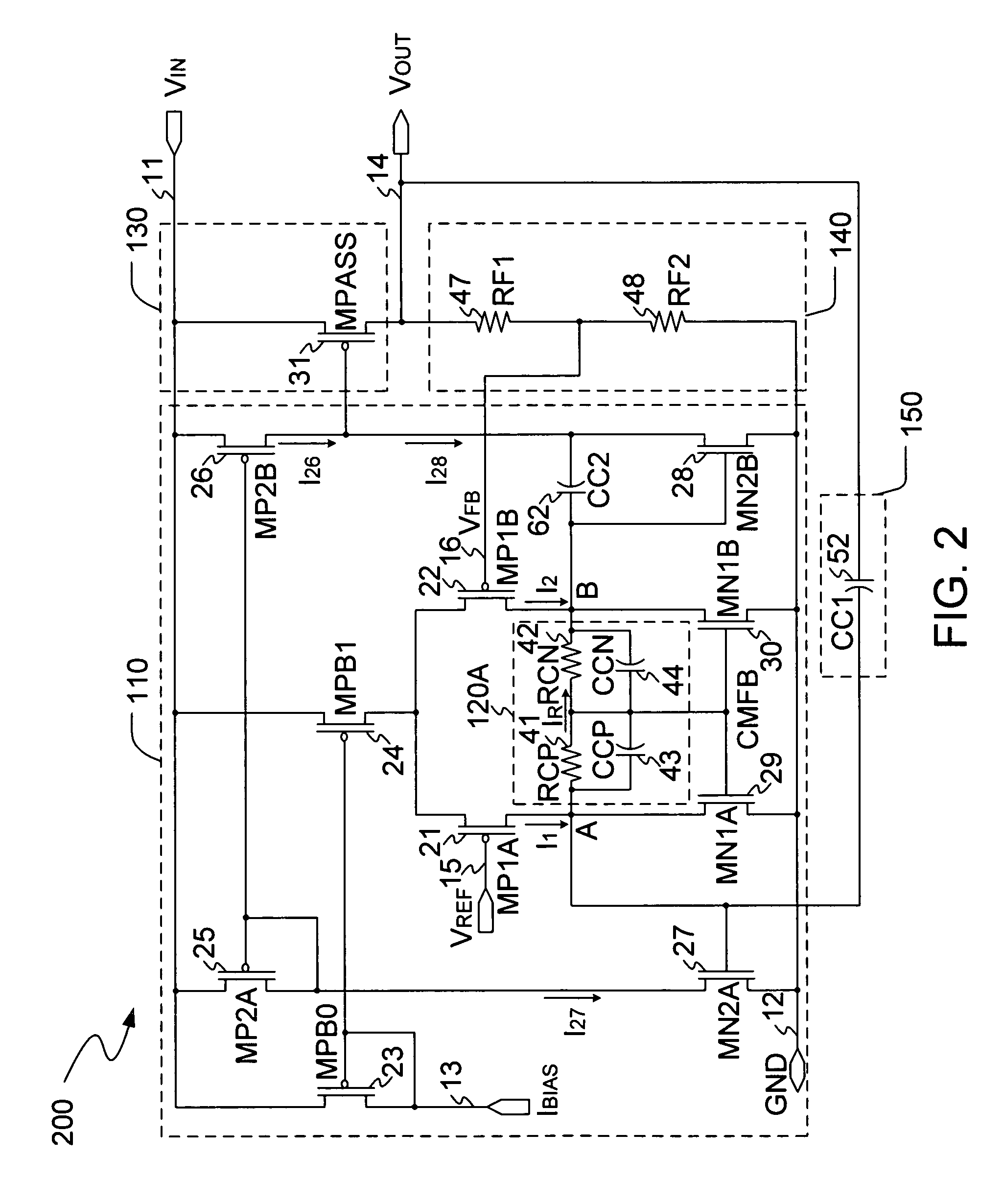
InactiveUS20060197513A1Increase conversion rateStable output voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
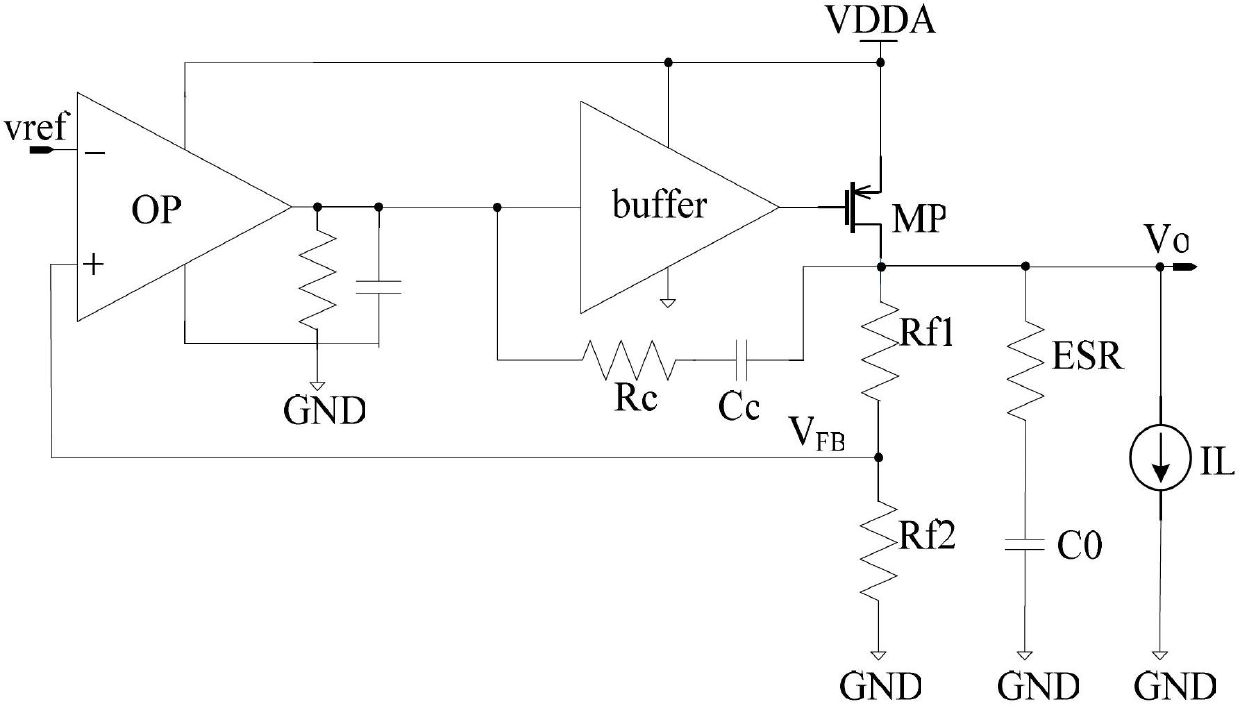
The present invention is a LDO voltage regulator circuit with common-mode feedback. The LDO voltage regulator includes an error amplifier with a common-mode feedback unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal to the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the pass device. A capacitor in the compensation unit provides frequency compensation to the LDO voltage regulator. The common-mode feedback unit incorporated into the error amplifier greatly improves a slew rate of a gate voltage of the pass device.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
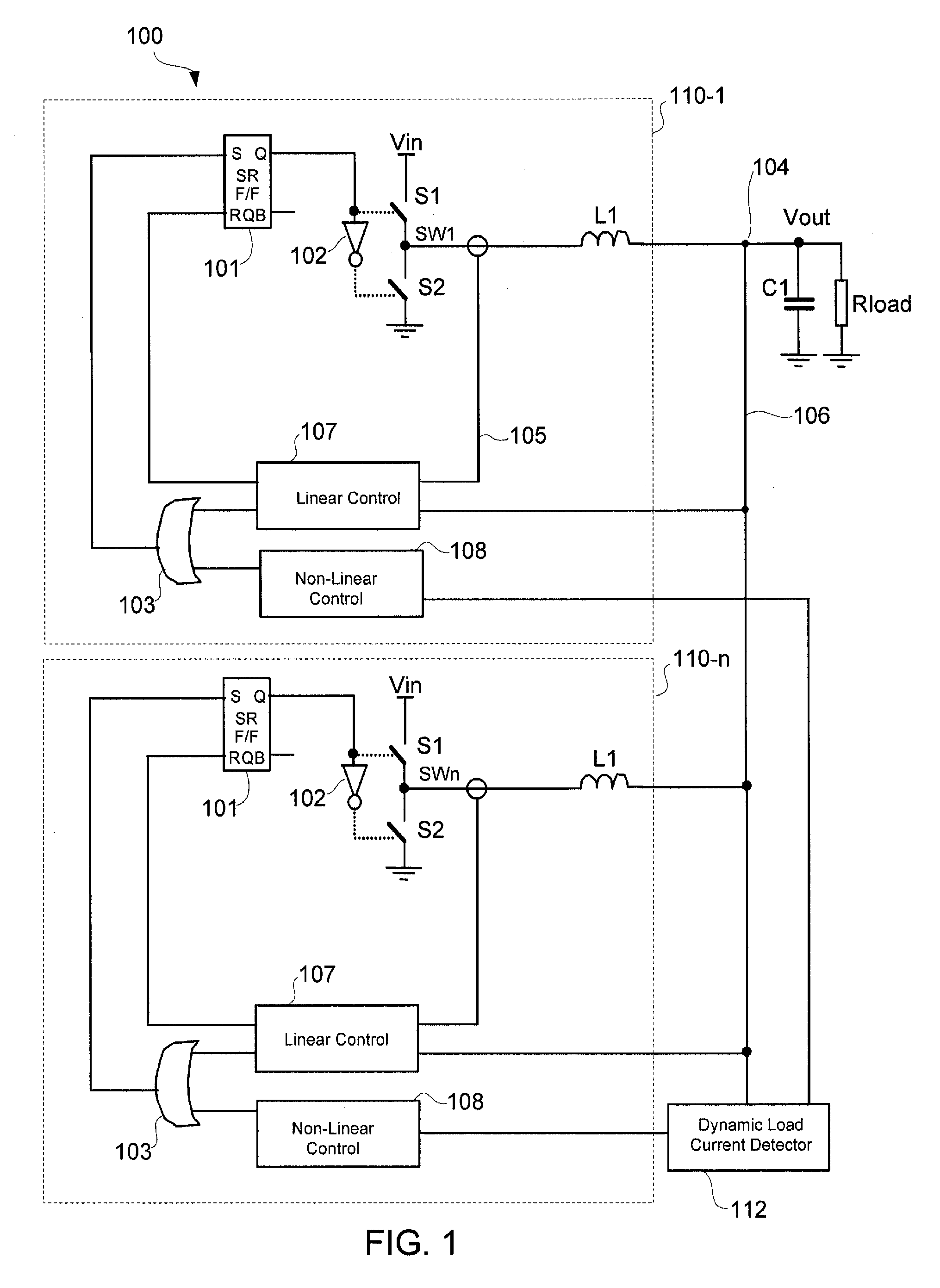
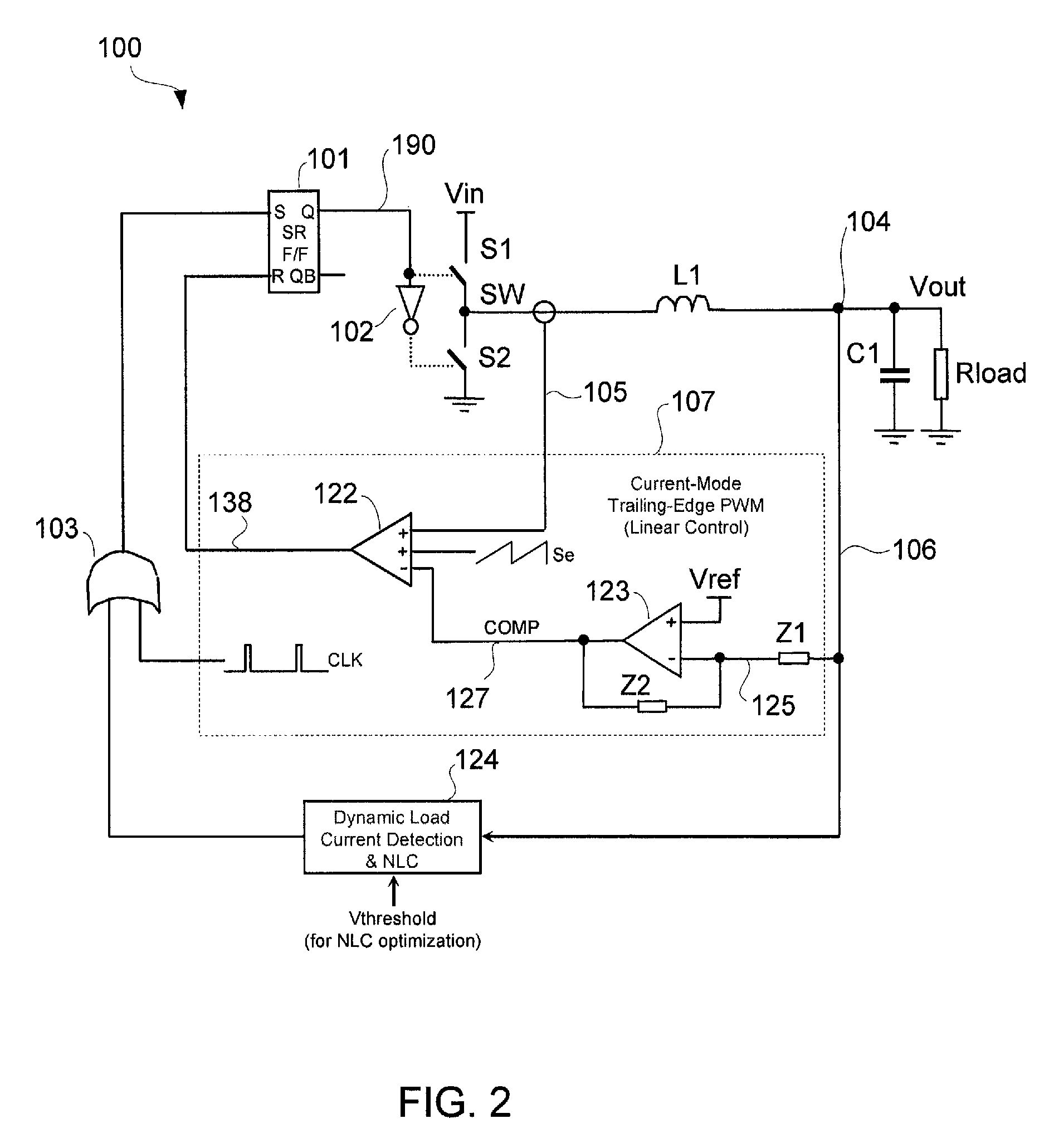
Non-linear control techniques for improving transient response to load current step change
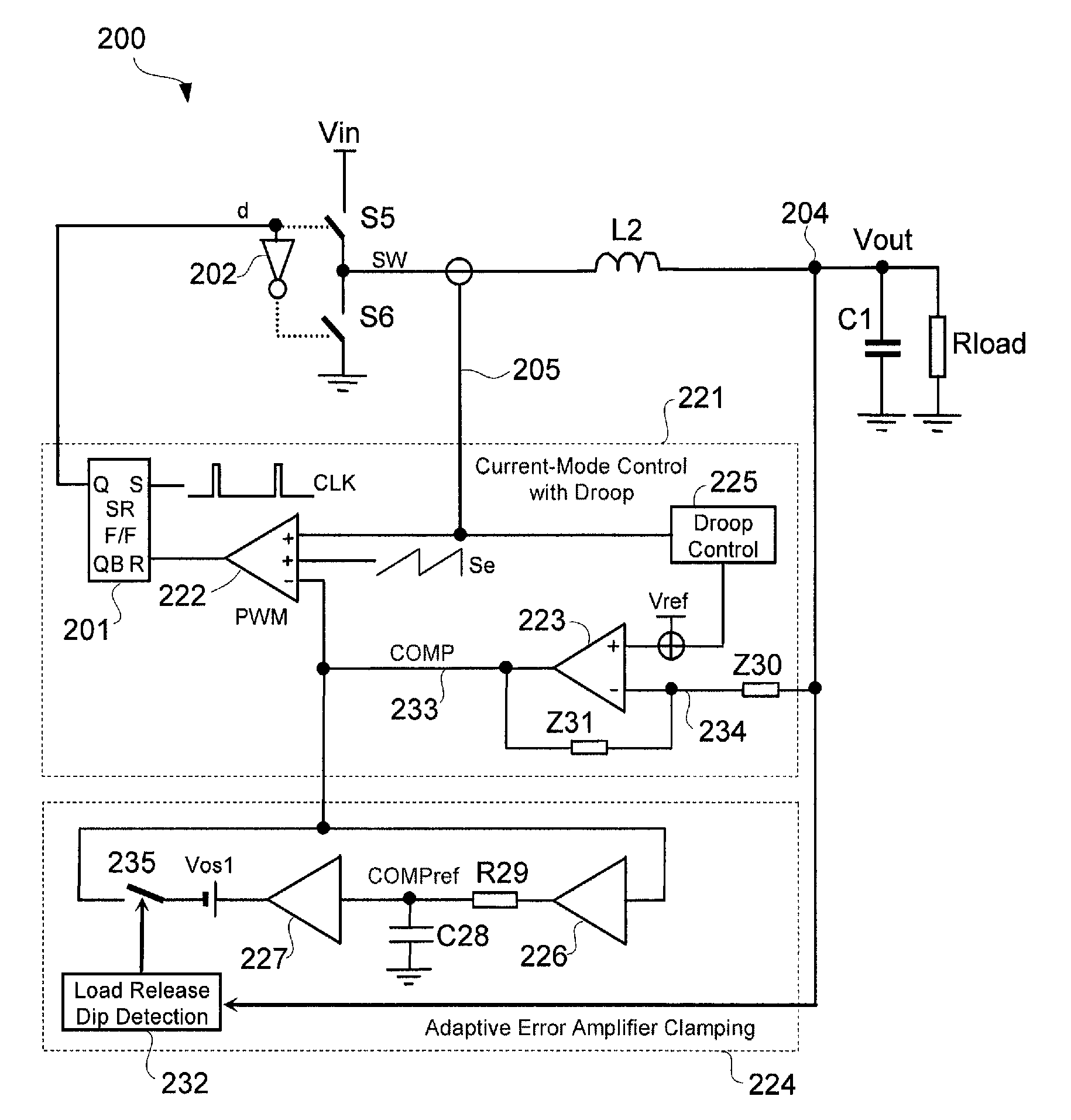
ActiveUS7863875B1Limited to controlled bandwidthAvoid output voltageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage overshootLinear control
A voltage regulator may be configured to detect variation in load current and control transient response when the load current has a high slew rate or varies at high repetition rates. A linear control circuit may be employed to control charging of an output capacitor and a load of the regulator. Upon detection of high load current step-up change at high slew rates, a non-linear control circuit may be activated. The fast load current step change may be detected by comparing an output voltage of the regulator to a feedback input of an error amplifier of the linear control circuit. The output of the error amplifier may be clamped to prevent output voltage ring-back when using the non-linear control circuit or to control load release dip. Output voltage overshoot may be controlled by turning OFF a top switch that charges the output capacitor before the inductor current becomes zero.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Plasma sterilizing-purifying device and method for air sterilizing and purifying
ActiveUS20120269677A1Improve reliabilityEasy to useMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusVoltage pulseNickel chromium alloy
The present invention belongs to the technical field of air sterilizing and purification and in particular relates to a plasma air sterilizing and purifying device and an air sterilizing and purifying method. The plasma air sterilizing and purifying device comprises a plasma reactor, a pulse power supply, a fan component, a control device, a power adaptor, and a housing case, wherein the reactor is provided with positive electrodes formed by several nickel-chromium alloy wires or nickel-chromium alloy belts, and the two ends of each positive electrodes are fixed in the corresponding grooves on the micro-discharge preventive conductor rail; and a pulse power supply has a digital control circuit with an oscillator, an error amplifier and a PWM comparator inside which converts signals into a digital control current to control the width of the high-voltage pulse.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANQING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Switching regulator
InactiveUS20070035281A1Improve stabilityImprove responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationHysteresisControl signal
The present invention provides a switching regulator having good stability compatible with a good response and an enhanced protection function. A first capacitor is placed between an output end of an inductor to generate an output voltage and a ground potential. From input voltage, a current is supplied to the inductor's input end by a first switch element. A first feedback path includes a hysteretic comparator. An output voltage added to a voltage proportional to the current flowing through the inductor is supplied to the hysteretic comparator which discriminates whether the voltage is appropriate by hysteresis characteristics and generates a PWM control signal in accordance with an output current variation. Moreover, a second feedback path is provided to feed back an error amplifier output voltage with greater gain in a low frequency domain and an attenuation loop around a PWM frequency band to the comparator's reference voltage input terminal. Feedback voltage through the second feedback path is used as a monitoring voltage in a protection circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
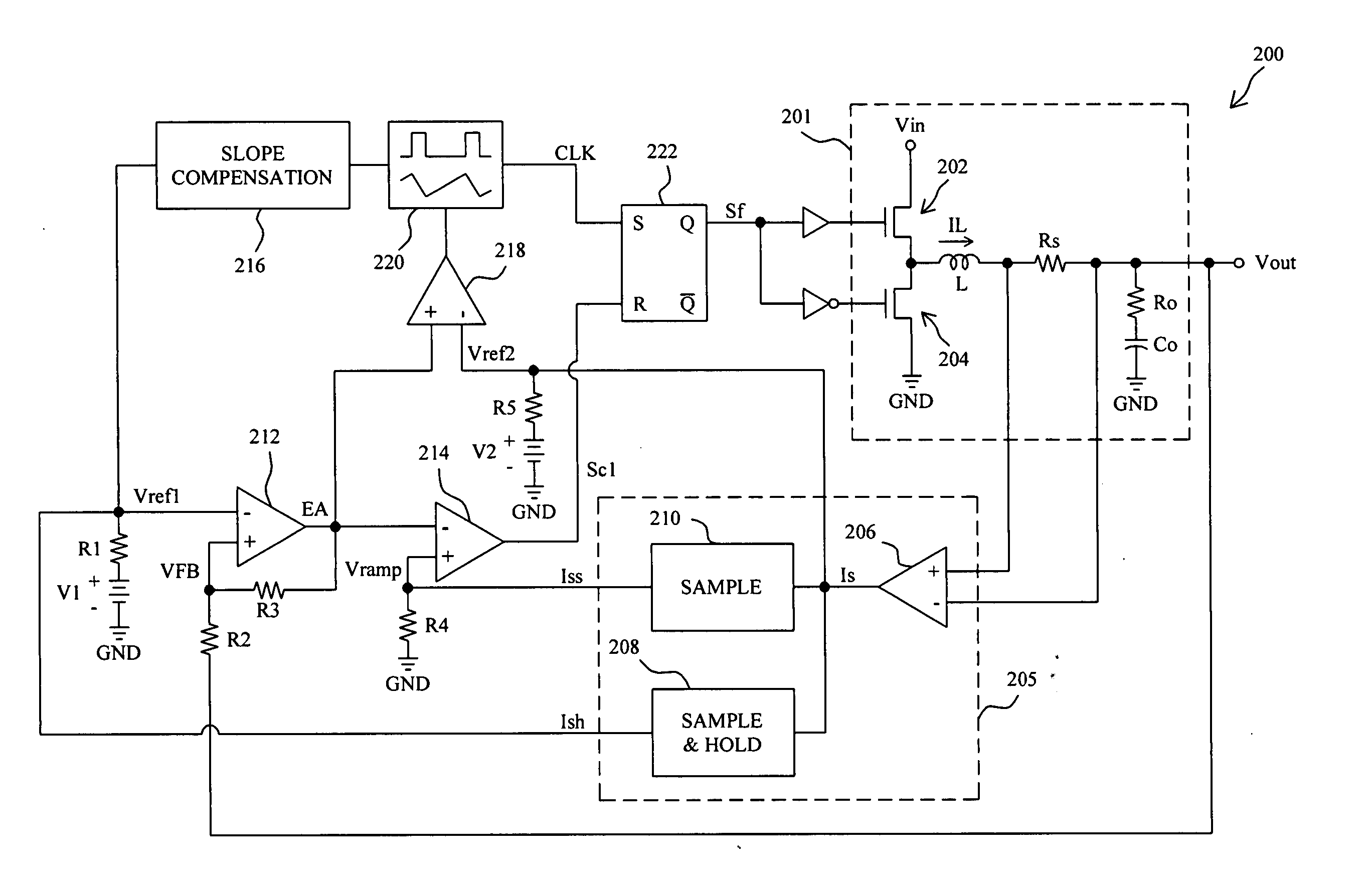
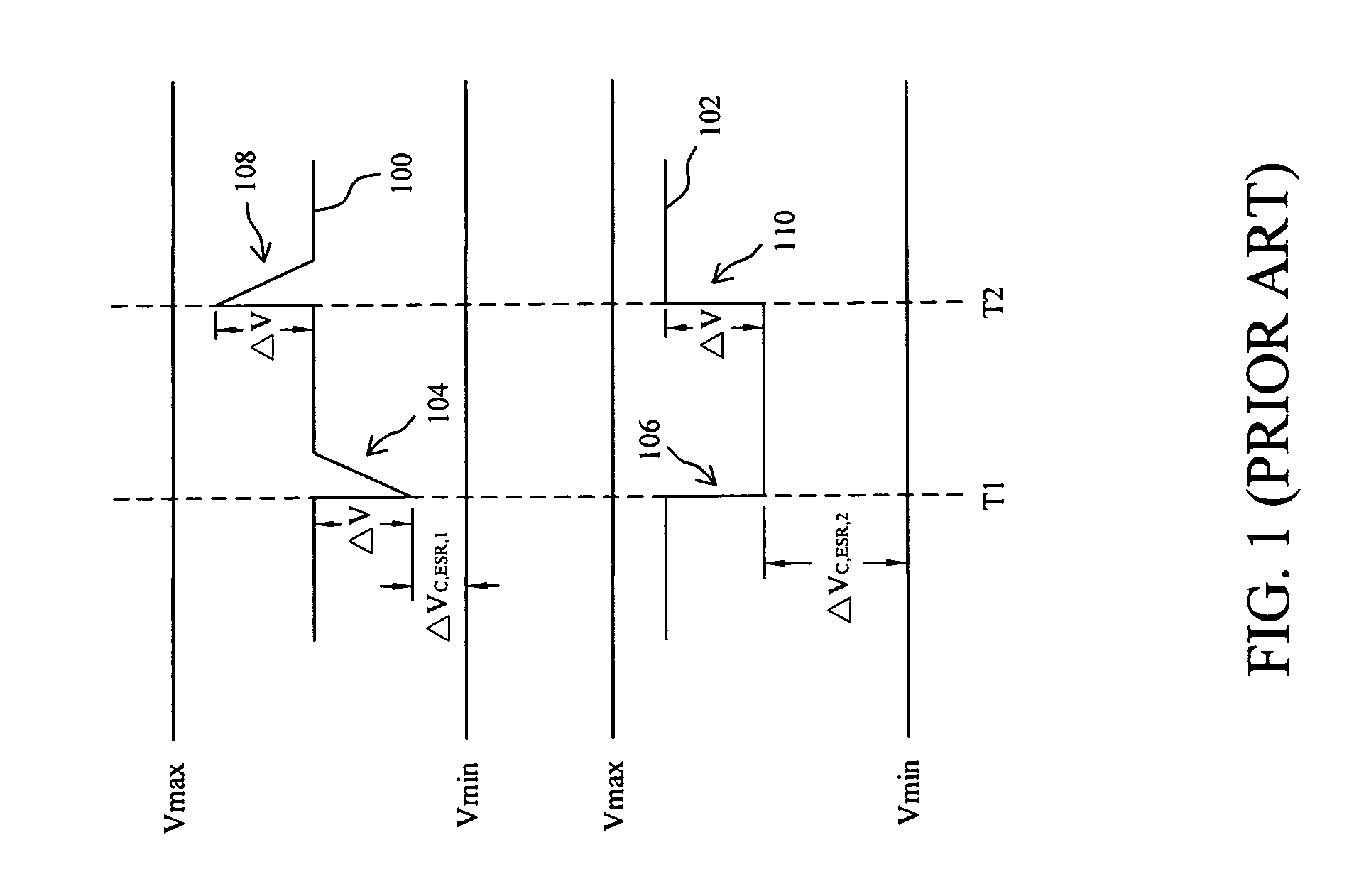
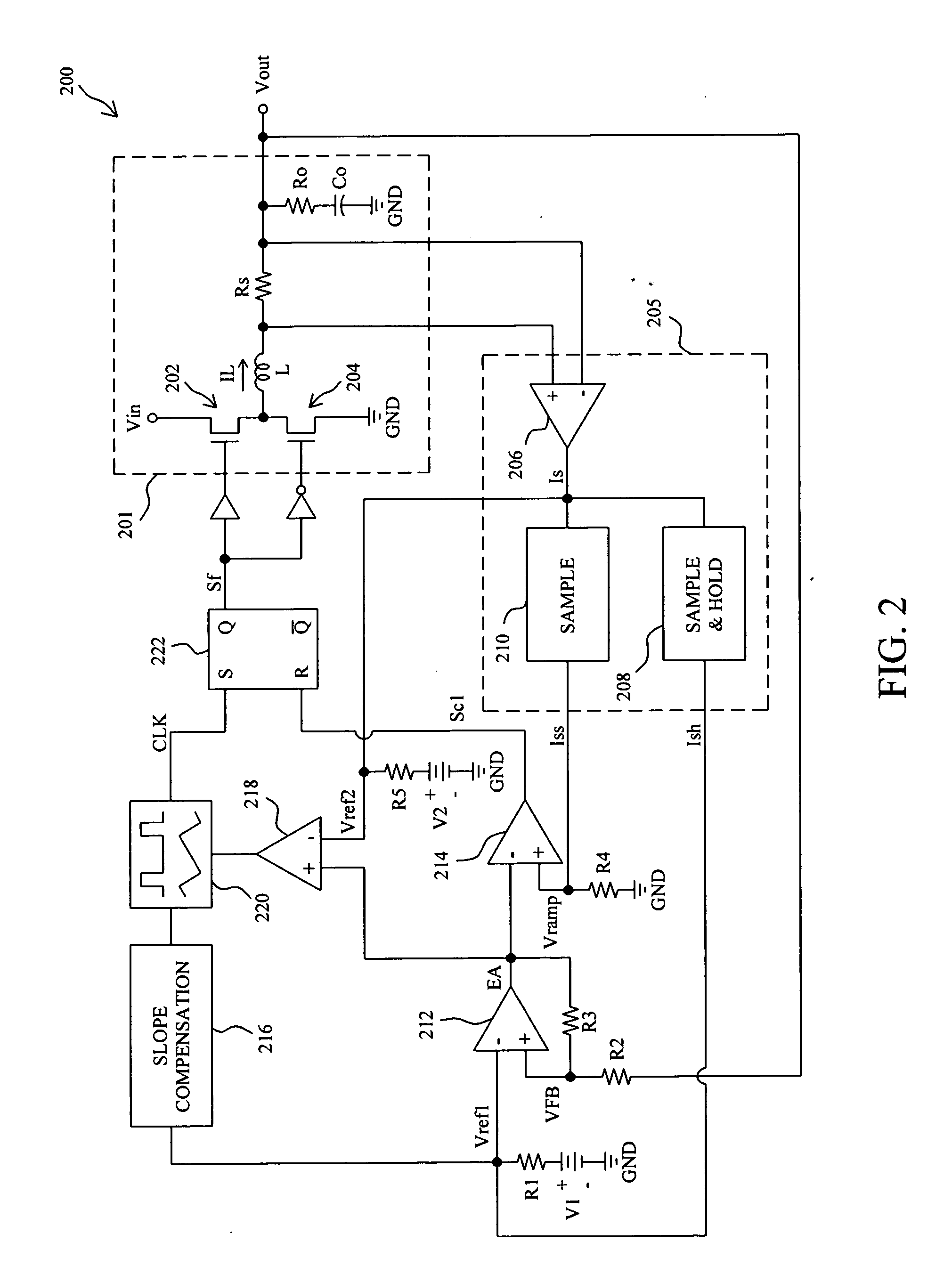
Power-supply device and hard disk drive using same
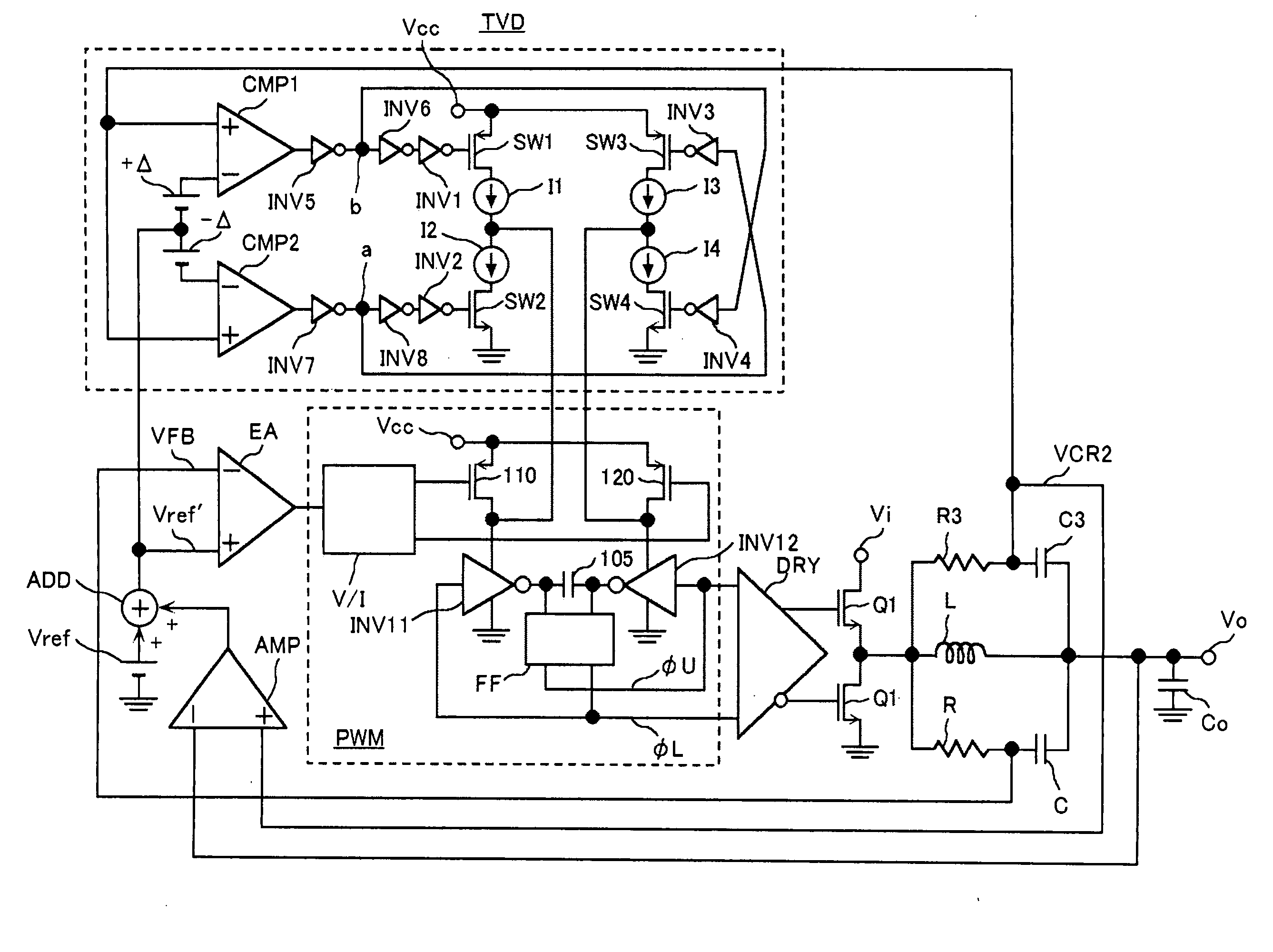
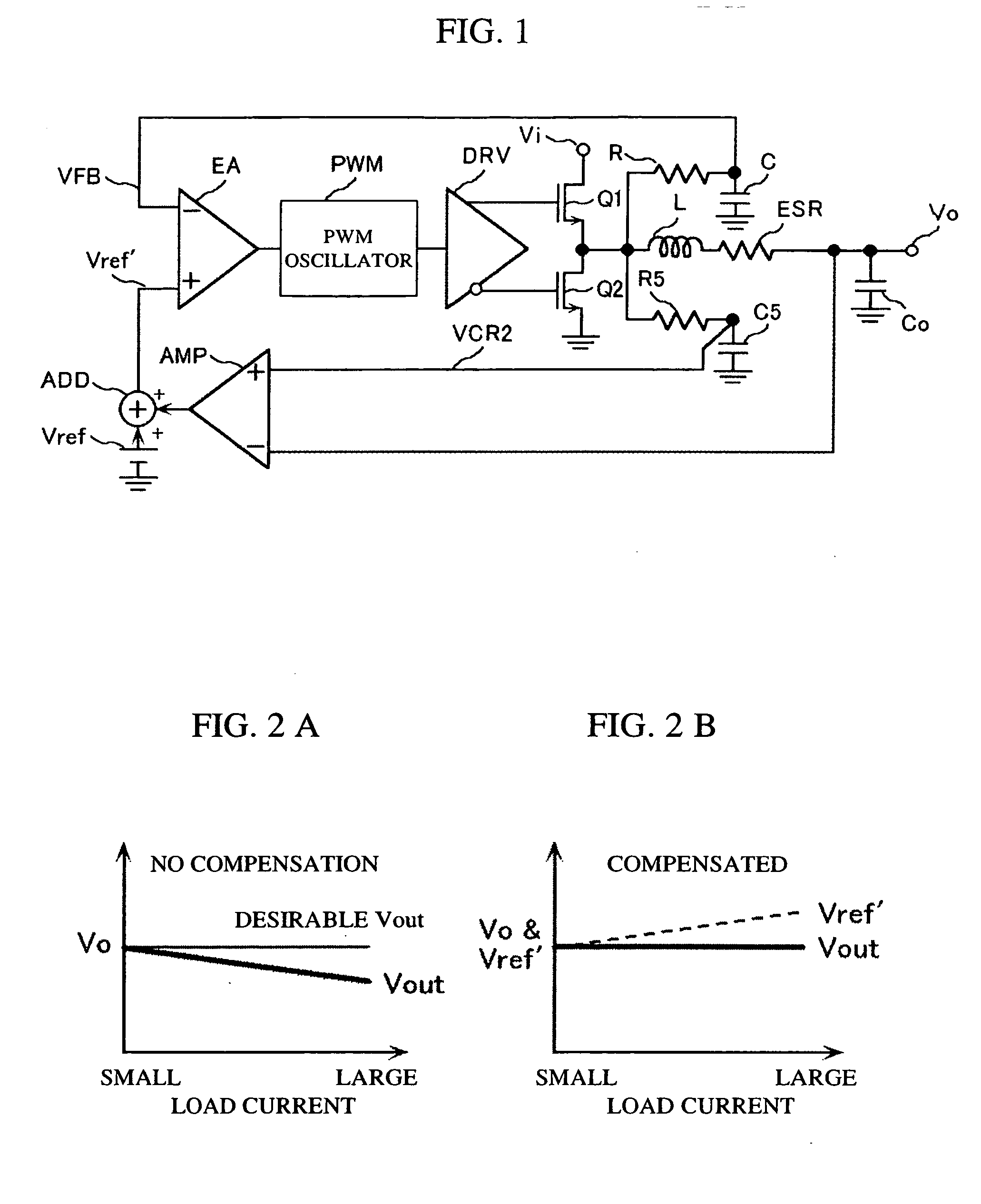
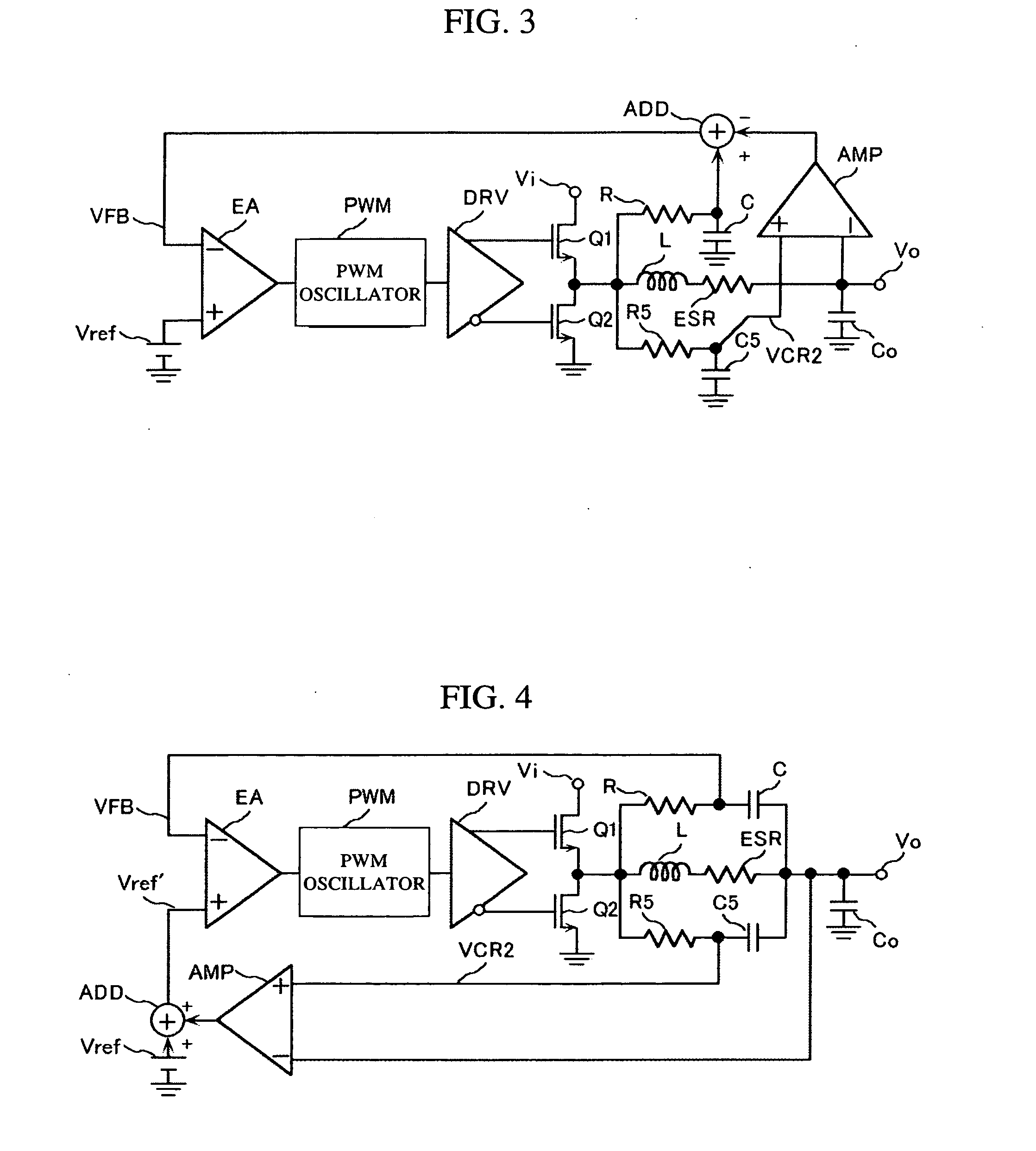
The object of the invention is to compensate an effect of a voltage drop emerging in output voltage by the equivalent series resistance of a power output filter in a power-supply device. To achieve the object, a power-supply device wherein the power output filter that passes output power and first and second filters provided separately from the power output filter are provided, the first filter provided separately and one input terminal of an error amplifier are connected, new reference voltage acquired by adding differential voltage between the output of the second filter provided separately and the output of the power output filter to reference voltage is input to the other input terminal of the error amplifier and an output signal is fed back to the error amplifier is provided. According to the power-supply device, a voltage drop by equivalent series resistance emerging the output voltage of the power-supply device can be compensated.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
High-speed PWM control apparatus for power converters with adaptive voltage position and its driving signal generating method
InactiveUS7109692B1Prevent overshootLower component costsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationHigh speed controlSwitching frequency
A high-speed PWM control apparatus with adaptive voltage position and a driving signal generating method thereof is provided. The present invention automatically detects a change in the loading and adjusts the voltage position instantaneously for stabilizing the voltage and reducing the loading output power consumption. The present invention does not require a clock signal to generate a driving signal and does not require an error amplifier to control the modulation. Therefore, the present invention has a fast transient response that responds to the change of the loading instantaneously and has a stabilizing effect. When the apparatus is on a continuous conduction mode (CCM), the switching frequency of the controller is still fixed even though the input voltage Vin and the output voltage Vout are changed. The electrical-magnetic noise disturbance is improved.
Owner:NIKO SEMICON +1
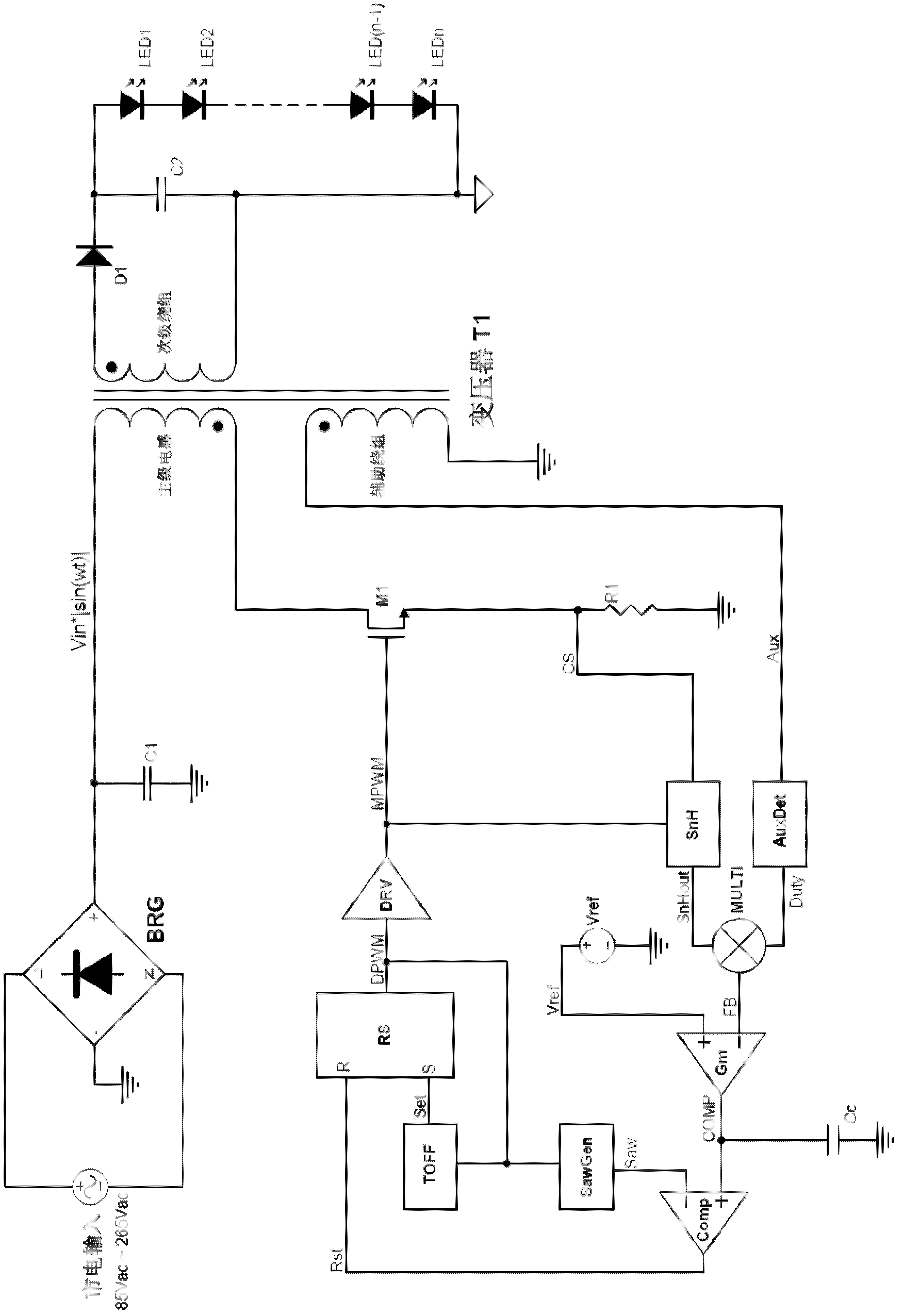
LED driver and power control circuit with spread spectrum frequency modulation function and display panel using the same
ActiveUS20100033110A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitElectromagnetic interference
The present invention relates to an LED driver, power control circuit and display panel using the same. The LED driver has the function of spread spectrum frequency modulation (SSFM). The circuit topology of the driver includes a power converter, an error amplifier, a feedback circuit, a saw-tooth generator and a driving circuit. The present invention adds the SSFM circuit in the saw-tooth generator to generate a time variant current according to time variant function, so that the saw-tooth wave could be changed by the time variant current as mentioned above. Therefore, the frequency of the driving pulse generated by the LED driver will be varied as time. As the result, the reduction of the electromagnetic interference (EMI) can be achieved.
Owner:ORISE TECH CO LTD
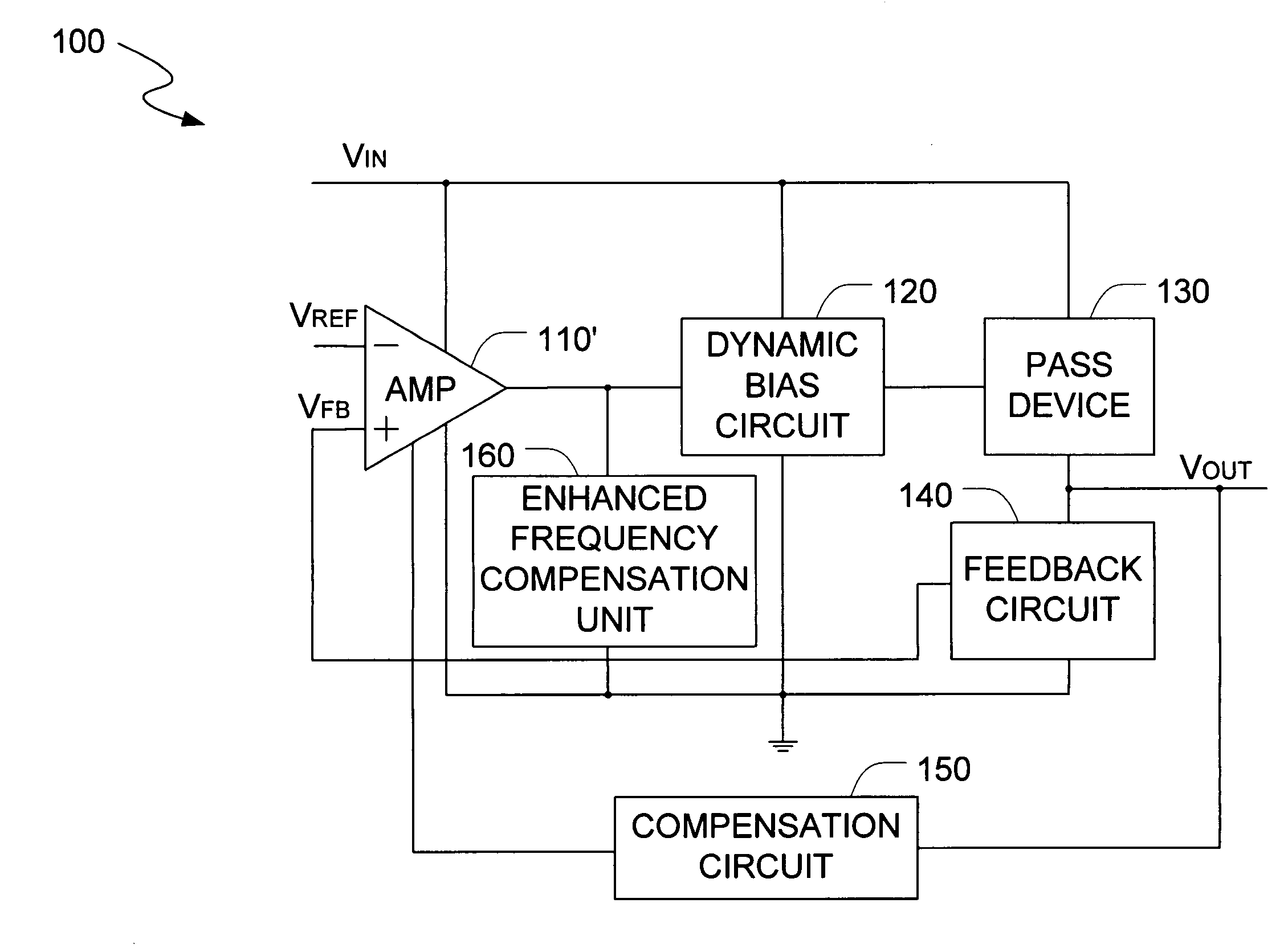
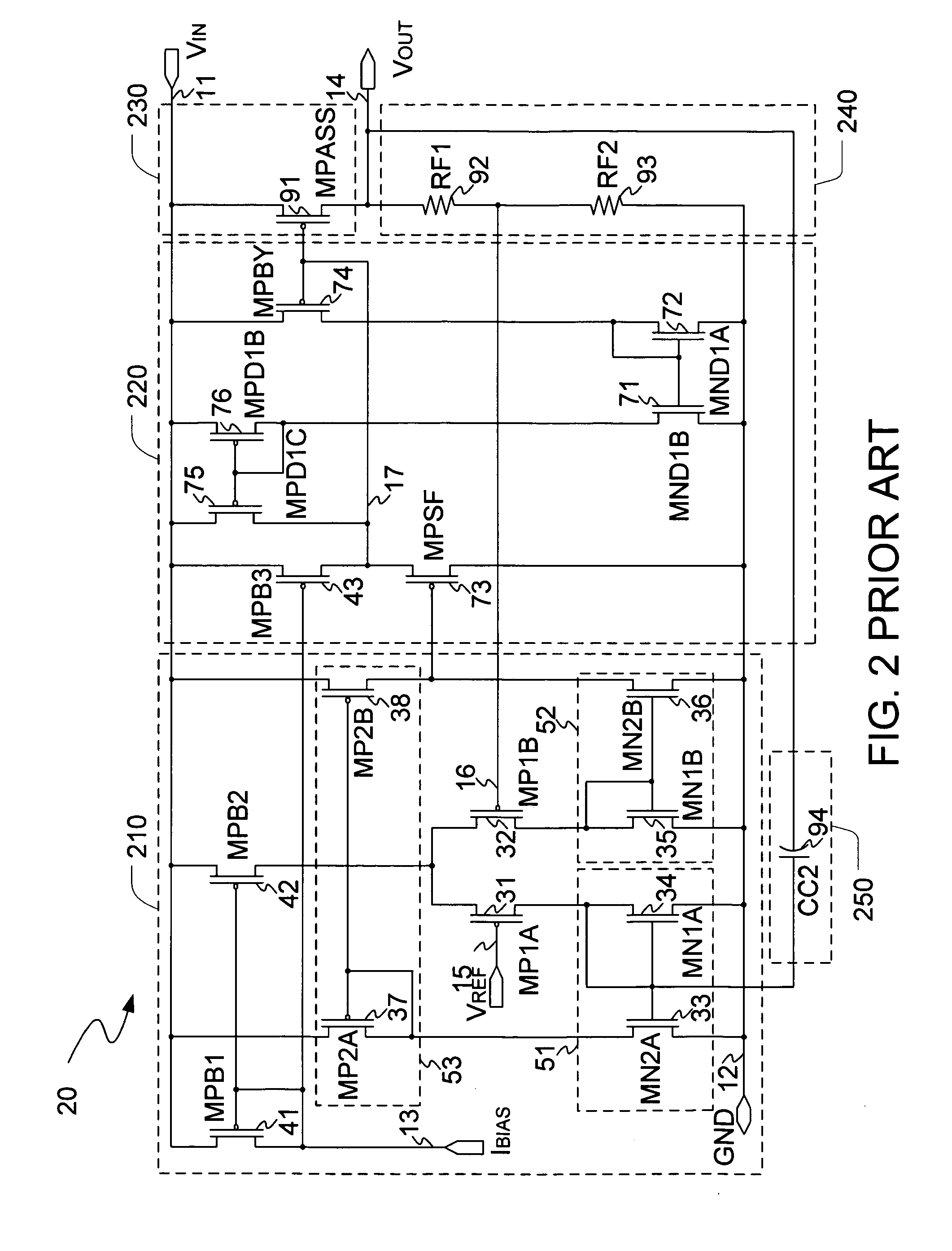
Low drop-out voltage regulator with enhanced frequency compensation
InactiveUS20060192538A1Enhanced frequency compensation capacityIncrease conversion rateElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
The present invention is a voltage regulator circuit with enhanced frequency compensation. The voltage regulator includes an error amplifier, a dynamic bias circuit, an enhanced frequency compensation unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal of the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the dynamic circuit and the enhanced frequency compensation unit. The enhanced frequency compensation unit is provided such that a zero reference value in a left-hand plane can be generated to optimize the compensation for the voltage regulator circuit. The error amplifier includes a capacitor for compensating an output voltage of the voltage regulator circuit.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Dc/dc converter and switching power supply
ActiveUS20170070149A1Increase input voltageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLinearityPwm signals
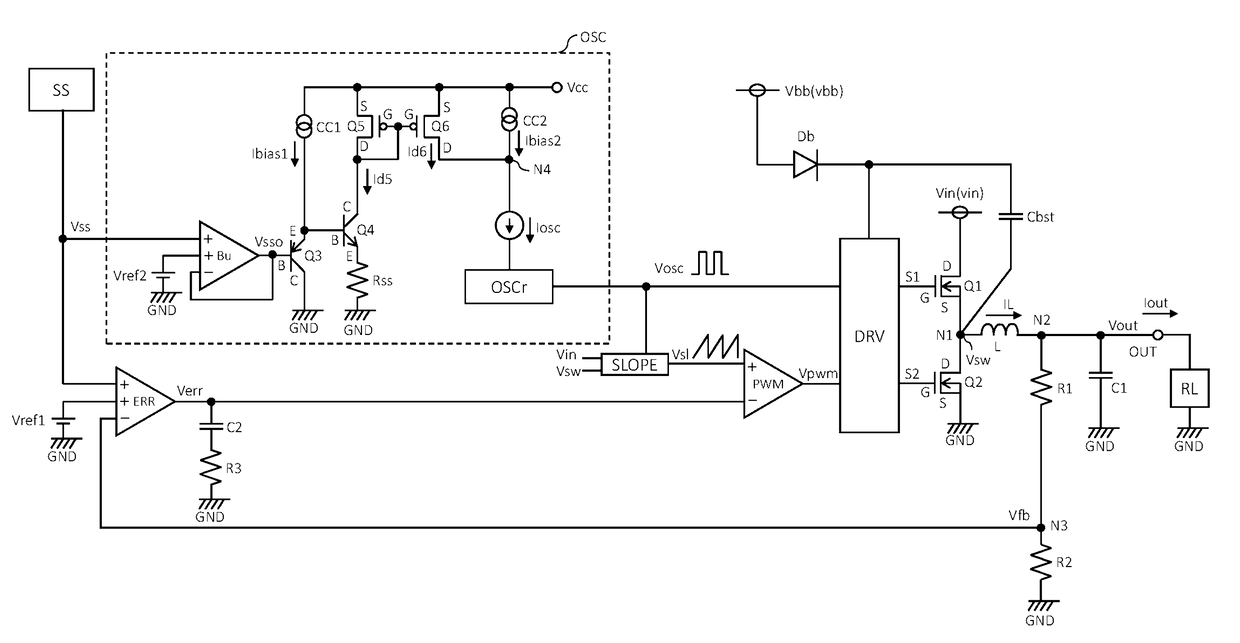
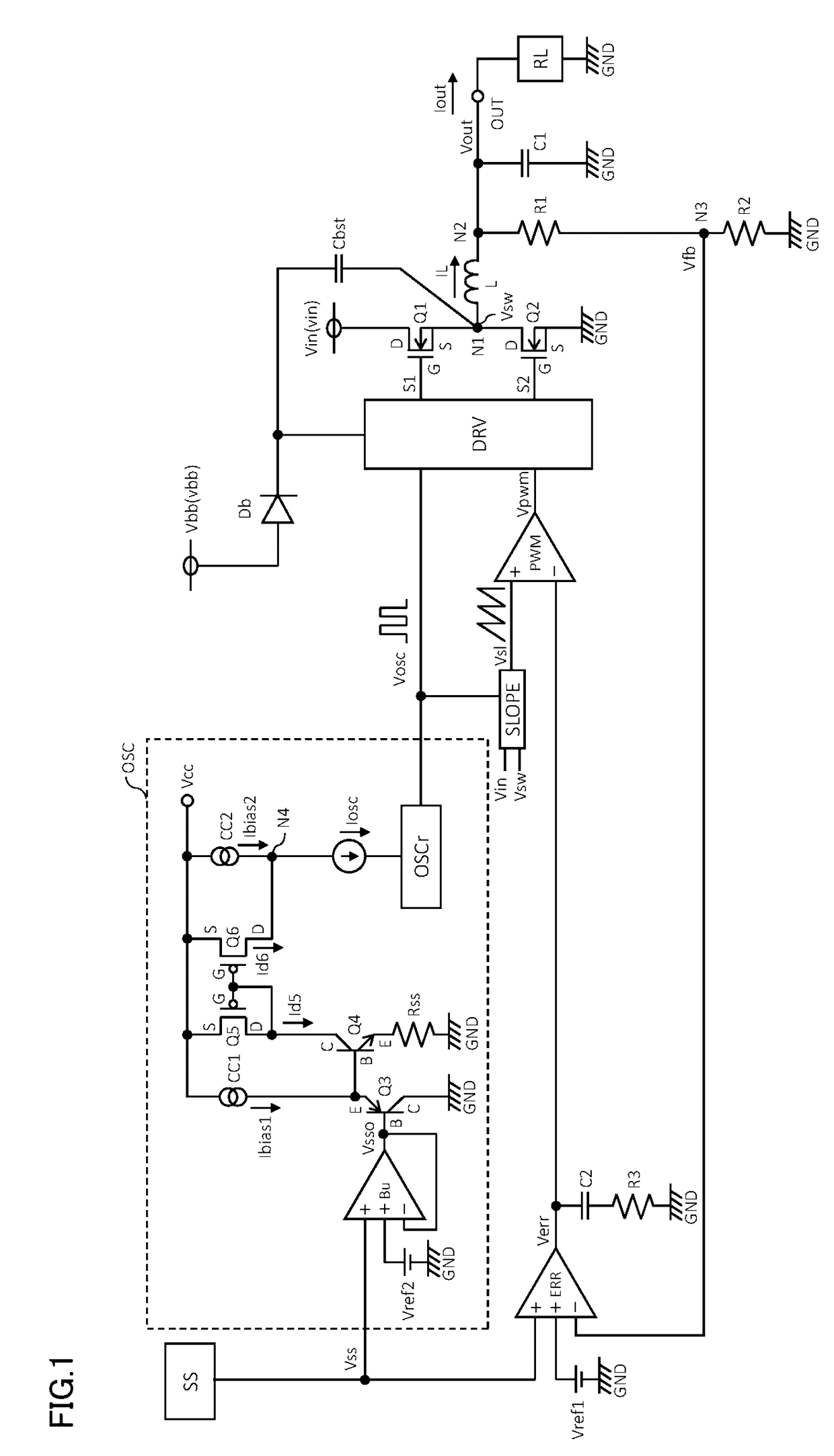
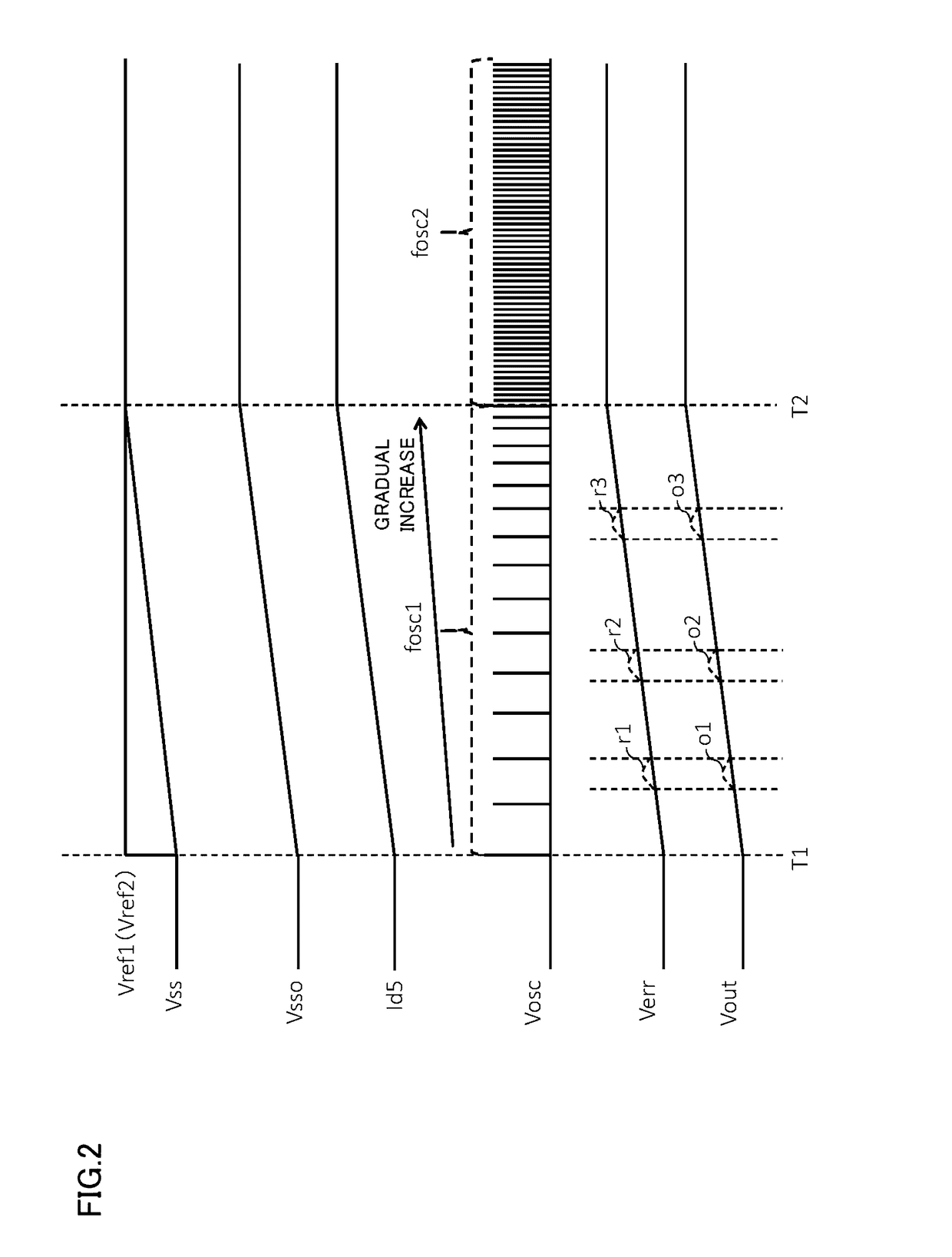
A DC / DC converter has: a soft-start circuit generating a soft-start input voltage increasing gradually; an error amplifier generating an error signal by comparing an output voltage or a feedback voltage with a reference voltage or the soft-start input voltage, whichever is lower; a variable current generator generating a variable current proportional to the soft-start input voltage or a soft-start output voltage; a constant current source generating a bias current; an oscillator generating a rectangular-wave signal whose frequency varies linearly with a soft-start current which is the sum of the variable current and the bias current; a slope circuit generating a slope signal based on the rectangular-wave signal; a PWM comparator generating a PWM signal based on the error signal and the slope signal; and a control circuit switching transistors alternately based on the PWM signal. Through switching operation of the transistors, an input voltage is converted into the output voltage.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Dynamic discharge circuit and LDO integrated with same
InactiveCN102707757AImprove transient responseReduce the maximumElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a dynamic discharge circuit and an LDO (Low Dropout Regulator) integrated with the same. The dynamic discharge circuit comprises a first error amplifier, a first MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube and a first capacitor. The LDO comprises a second error amplifier, a second PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube, a second capacitor, a first resistor and a second resistor. The dynamic discharge circuit provided by the invention, under the premise of not significantly increasing the static power consumption, can detect the change of voltage at the output terminal when the LDO load jumps from heavy load to light load, and form a discharge channel for leading the output of the LDO to be grounded, thereby greatly reducing the uprush maximum of the output; and the LDO integrated with the dynamic discharge circuit can greatly reduce the uprush maximum of output voltage, thereby shortening the recovery time of the LDO circuit from a transient state to a steady state and improving the transient response of the LDO circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Power supply having multi-vector error amplifier for power factor correction
ActiveUS20050007083A1Reduce distortion problemsIncrease control bandwidthEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionLow distortionEngineering
A regulated power supply having power factor correction control includes a multi-vector error amplifier. The multi-vector error amplifier provides an error signal that is used to regulate a switching mechanism of the power supply. The multi-vector error amplifier acts to provide a low distortion error signal during steady-state operation, while responding rapidly and smoothly to sudden load changes.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
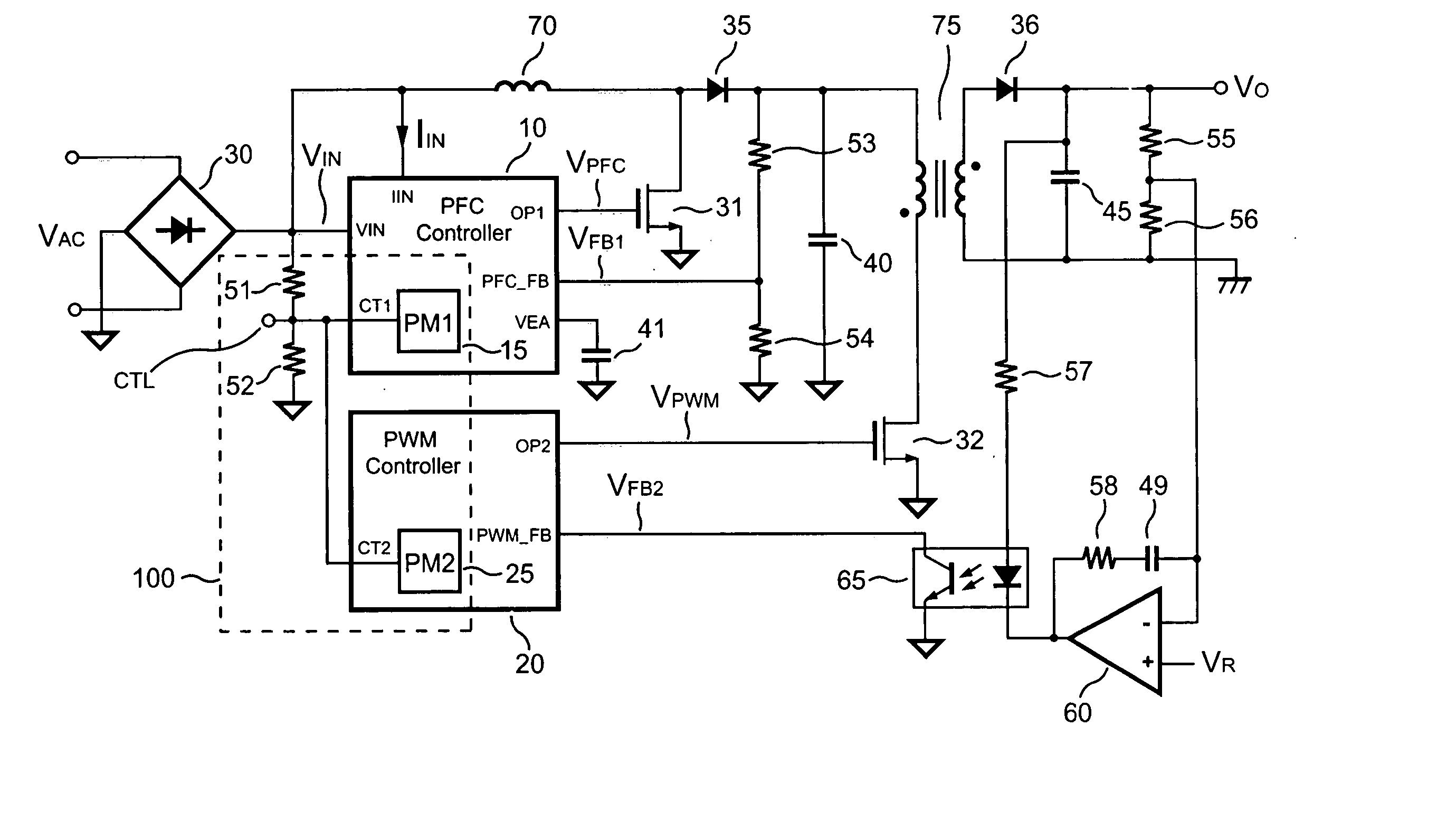
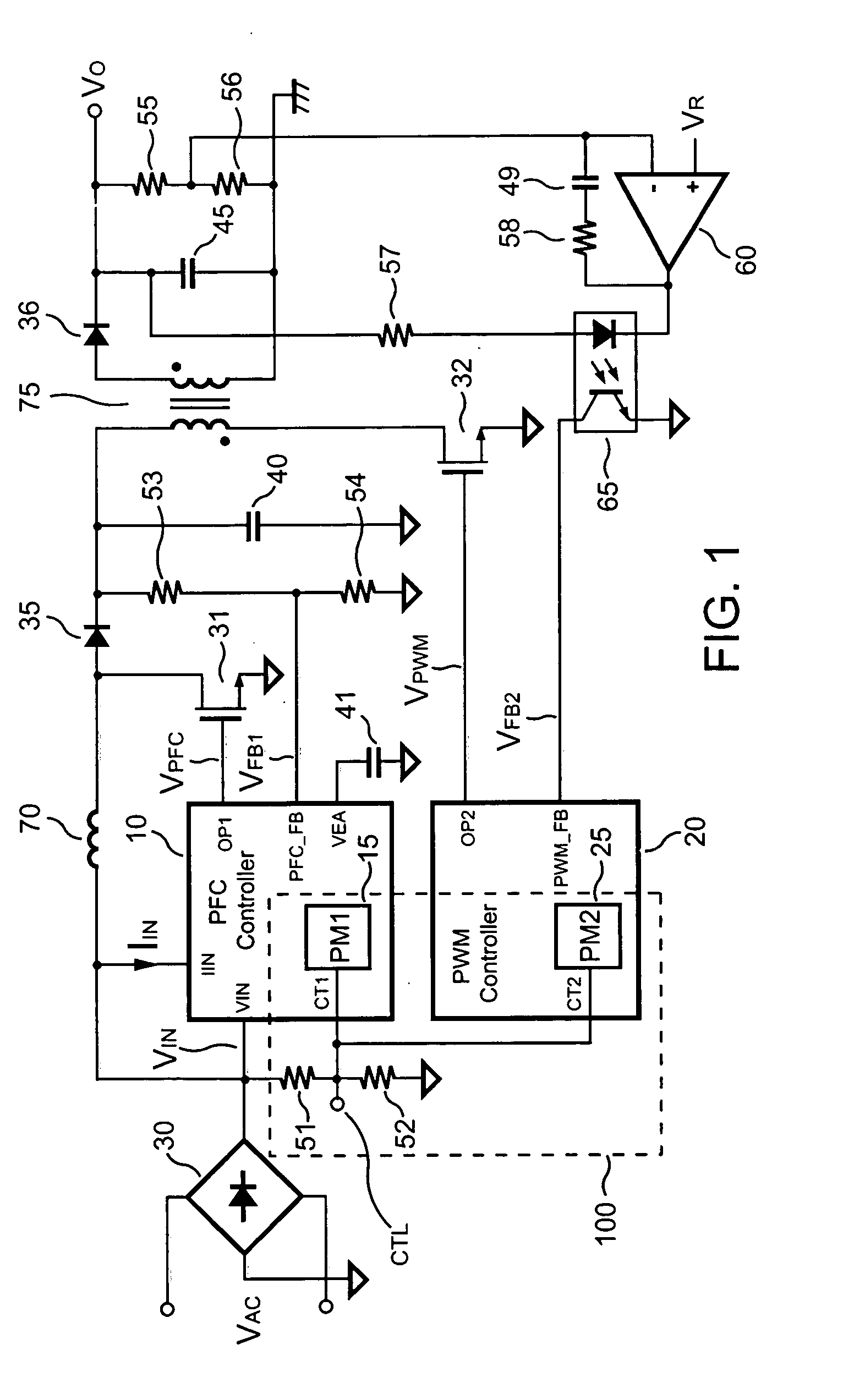
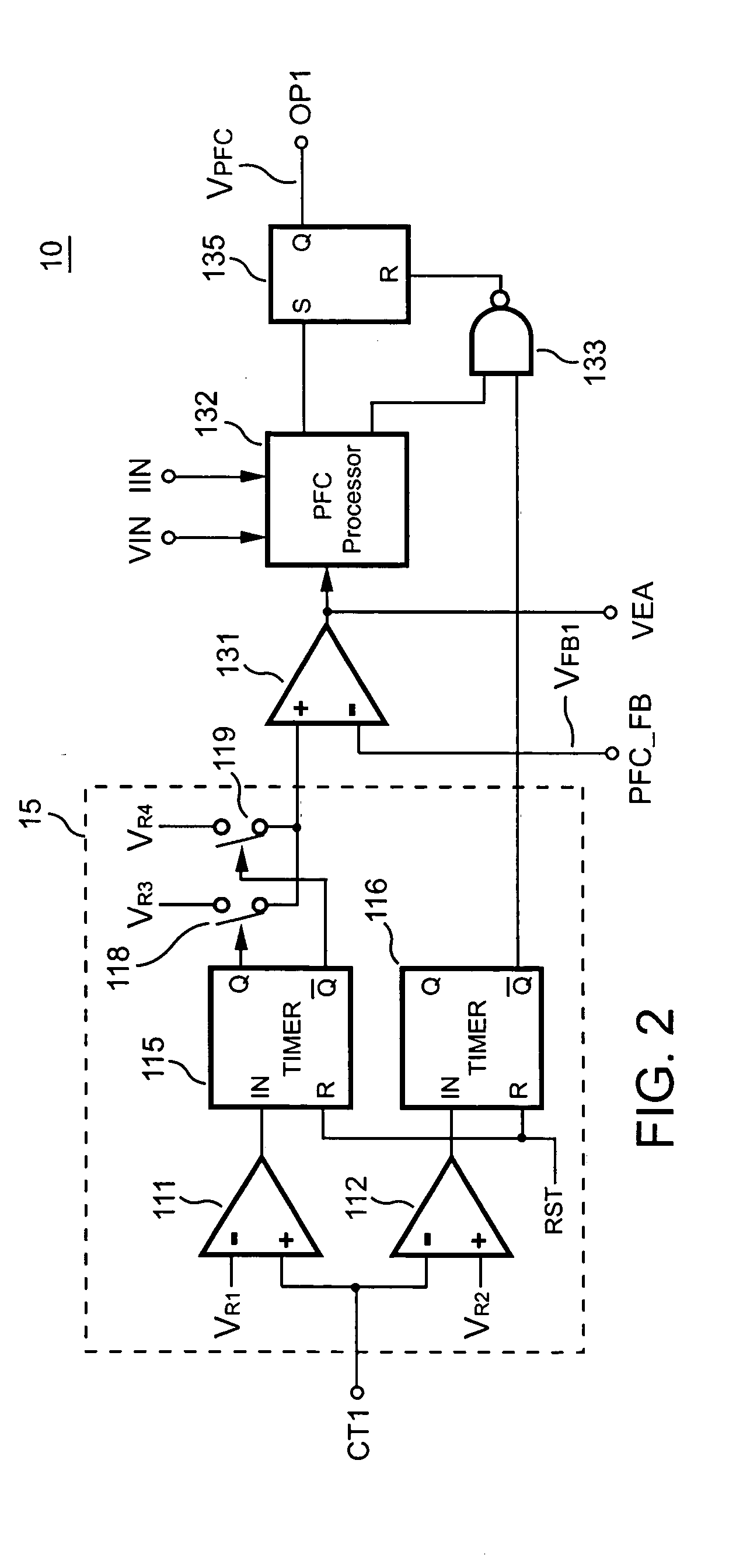
Apparatus for reducing the power consumption of a PFC-PWM power converter
ActiveUS20050128773A1Reduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionLow voltageControl signal
An apparatus for reducing the power consumption of a PFC-PWM power converter is described. The apparatus includes a control terminal used to detect a line-input voltage and to control a PFC signal and a PWM signal. The apparatus further includes a PFC power-manager and a PWM power-manager. The PFC power-manager of the PFC controller determines a PFC-reference voltage for an error amplifier of the PFC controller. The PFC-reference voltage is generated in response to the voltage at the control terminal. The PFC power-manager will disable the PFC signal whenever the voltage at the control terminal drops below a low-voltage threshold voltage. The PWM power-manager will disable the PWM signal whenever the voltage at the control terminal drops below a programmable threshold voltage. Furthermore, the PWM power-manager will pull the voltage at the control terminal low to disable the PFC circuitry during light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Overcurrent protection circuit
InactiveUS20060012932A1Fast sensingWithout loss of stability of circuitTransistorDc-dc conversionVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
The voltage generator circuit includes a regulator, a first sensor circuit, and a second sensor circuit. The first sensor circuit includes a first transistor, a first resistor, and an error amplifier. When V1>Vth, the error amplifier senses an overcurrent condition to provide feedback to the operational amplifier to limit an output current. The second sensor circuit includes a second transistor, a second resistor, and a sensing transistor. When the output current exceeds a sense threshold current, the sensing transistor is turned ON to provide feedback to the operational amplifier 12 to limit the output current. The second sensor circuit has a higher setting of sense threshold current than does the first sensor circuit, while having a higher setting of sensing speed than does the first sensor circuit.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Current-limiting circuitry
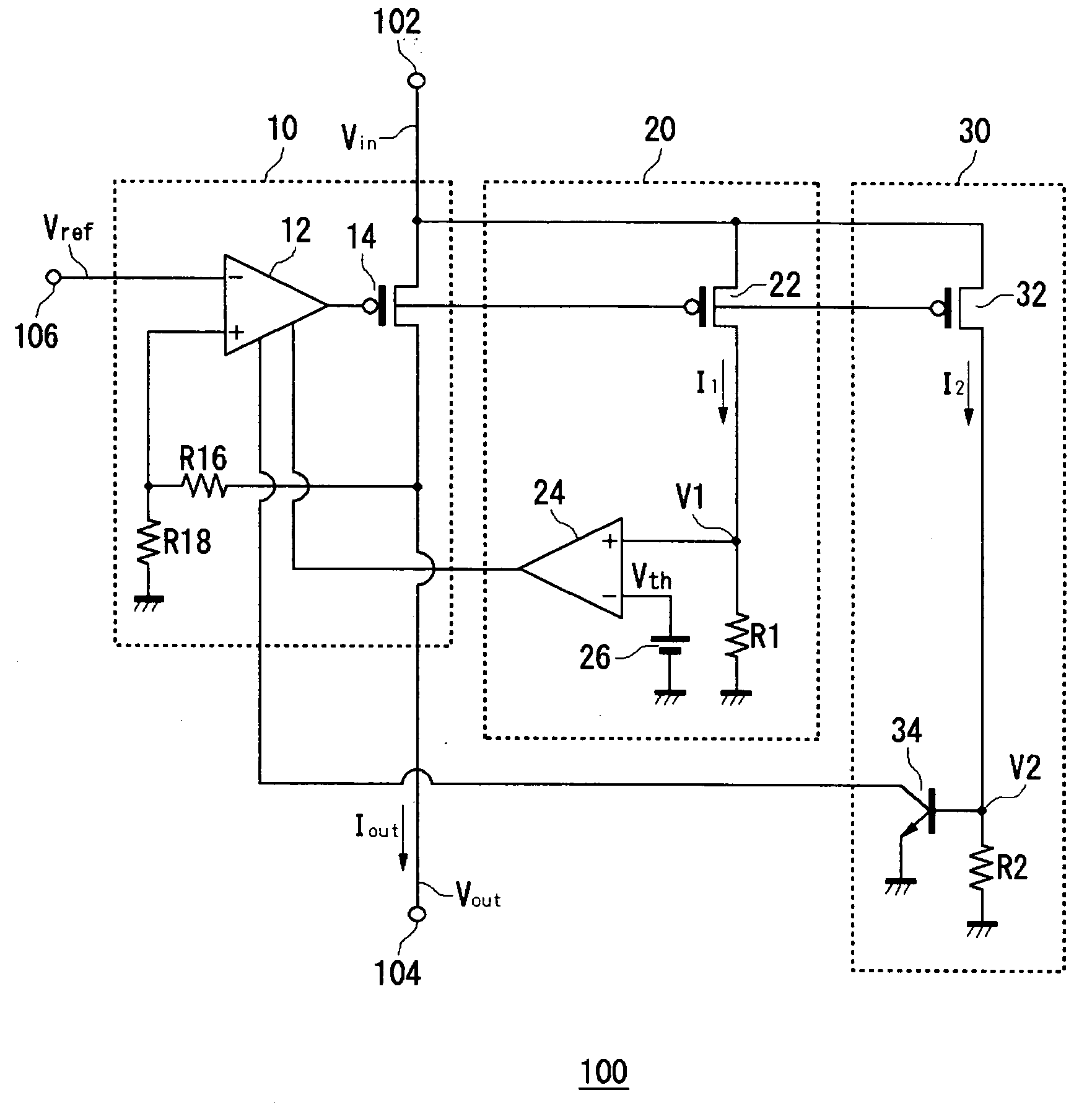
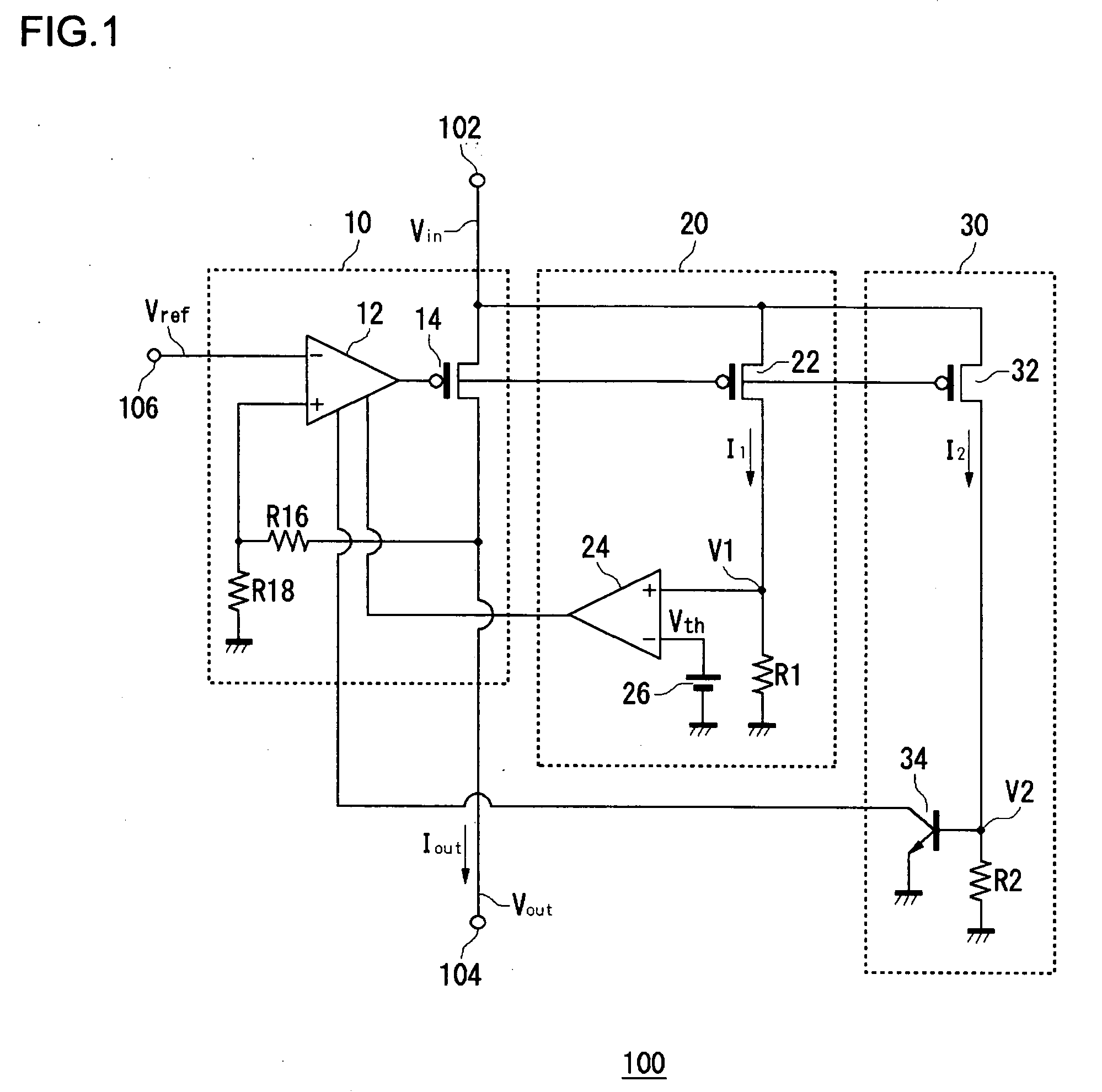
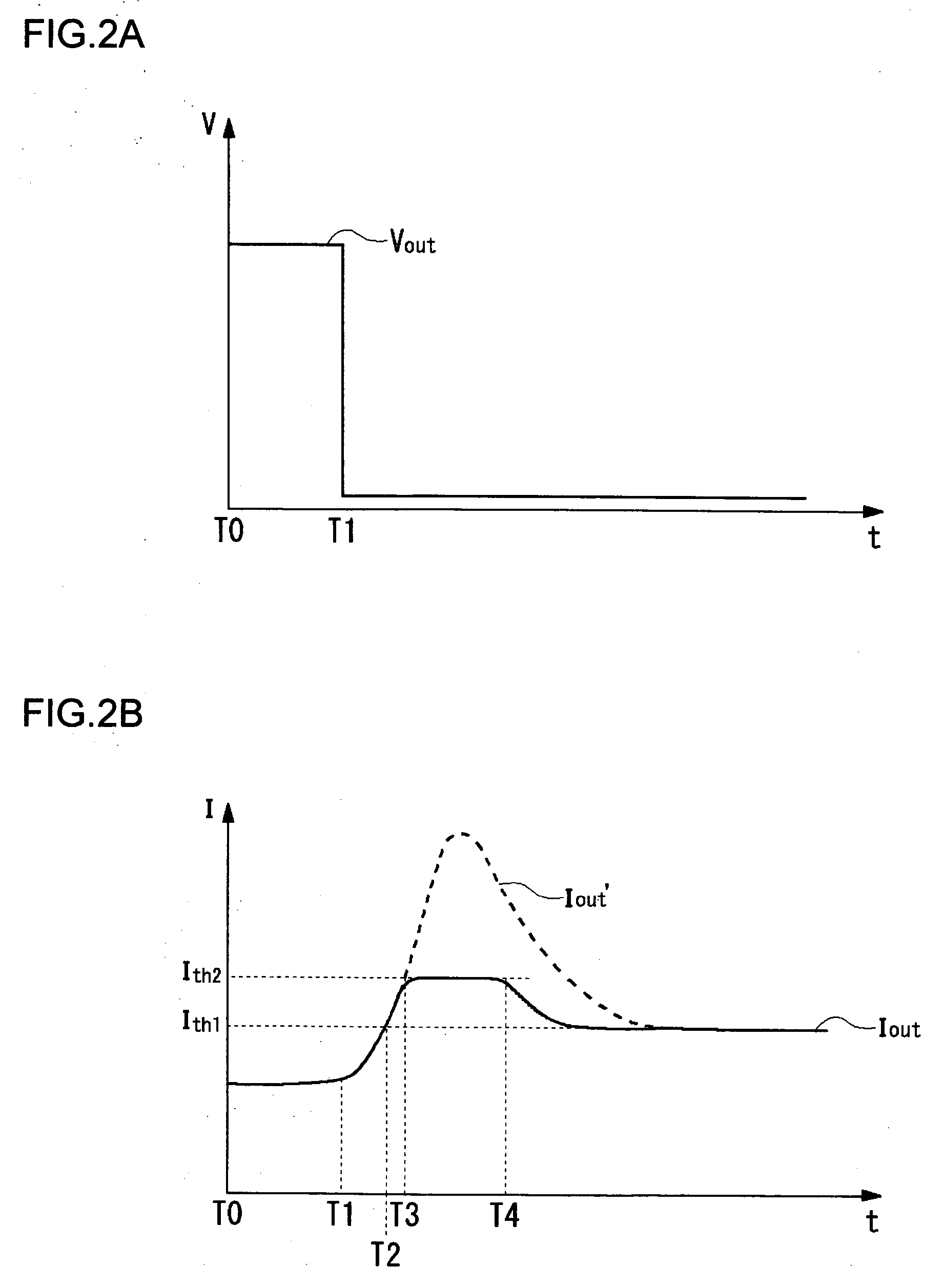
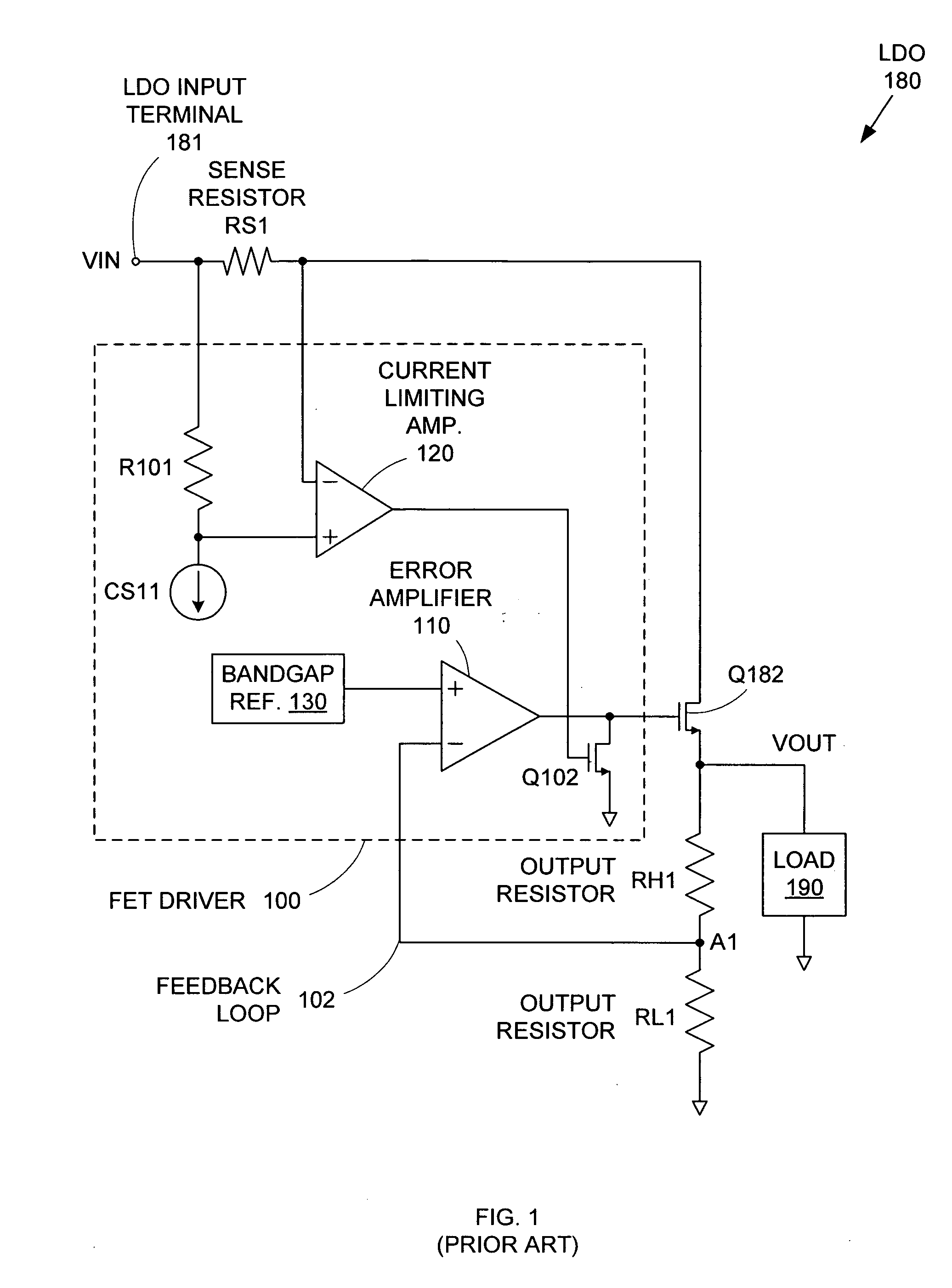
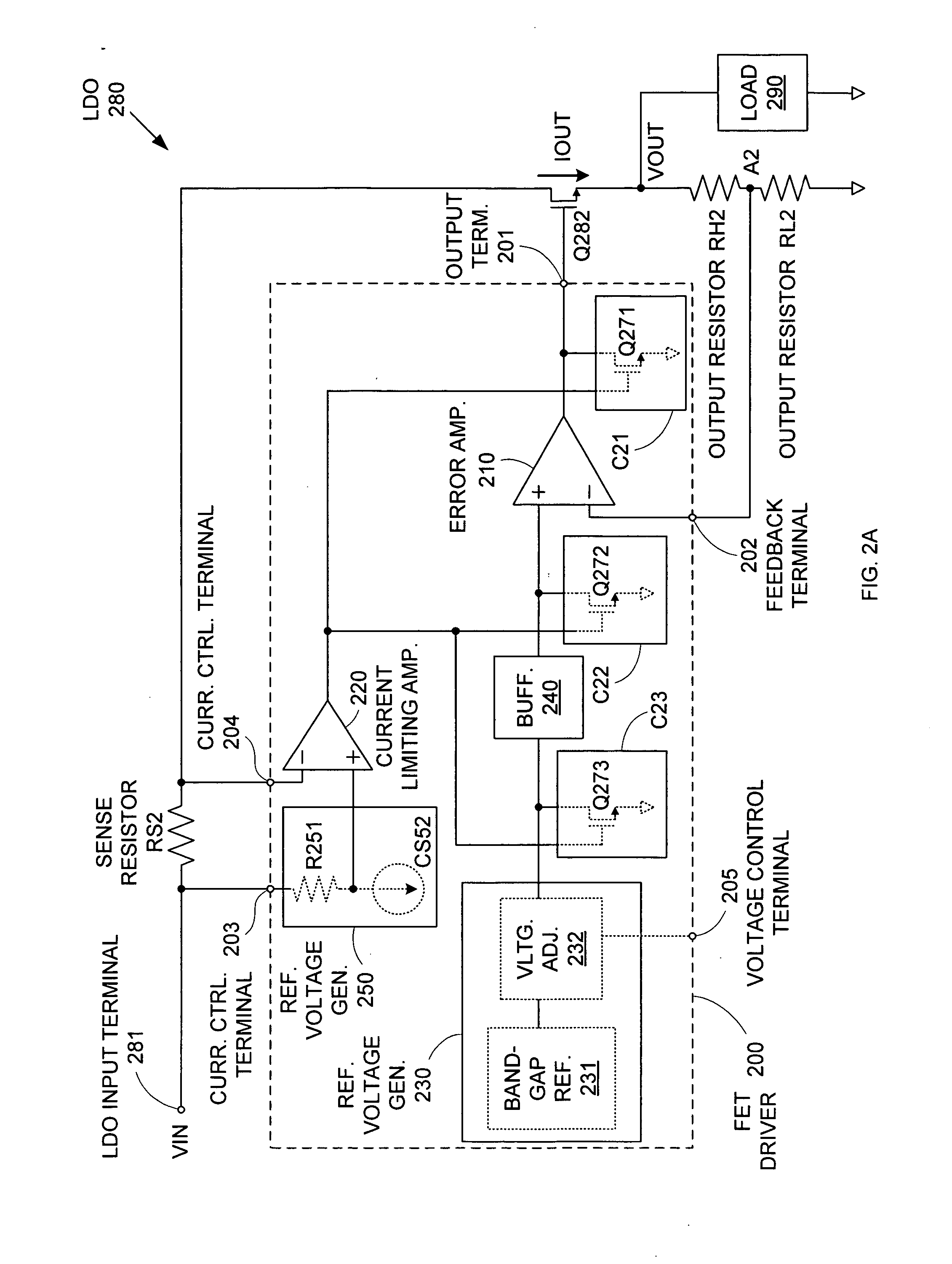
ActiveUS20050275394A1Preventing excessive current flow through the FETReduce voltagePower supply linesElectric variable regulationDriver circuitCurrent limiting
A field effect transistor (FET) driver circuit includes an error amplifier for providing a FET control signal and a current limiting amplifier for preventing excessive current flow through the FET. The current limiting amplifier generates an overcurrent signal when an excessive current is detected. In response to the overcurrent signal, a voltage control circuit adjusts the voltage at the output of the error amplifier to turn off the FET. Meanwhile, a pulldown circuit at an input of the error amplifier adjusts the voltage provided to that input to cause the error amplifier to provide an output voltage that also tends to turn off the FET. If a buffer is present at that input to the error amplifier, a second pulldown circuit is placed at the input to the buffer to maintain a stable unity gain across the buffer.
Owner:MICREL
Time-based current control in switching regulators
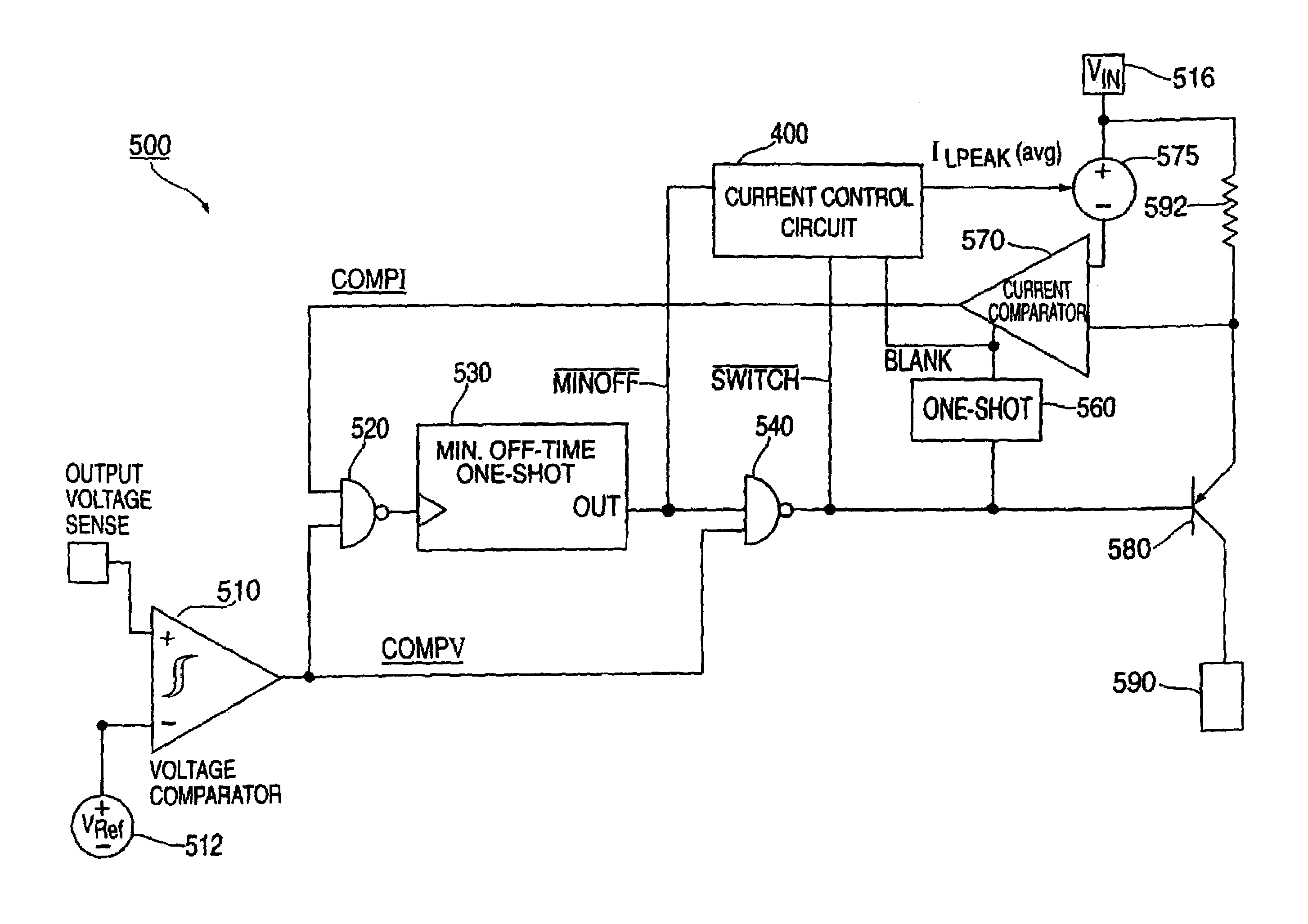
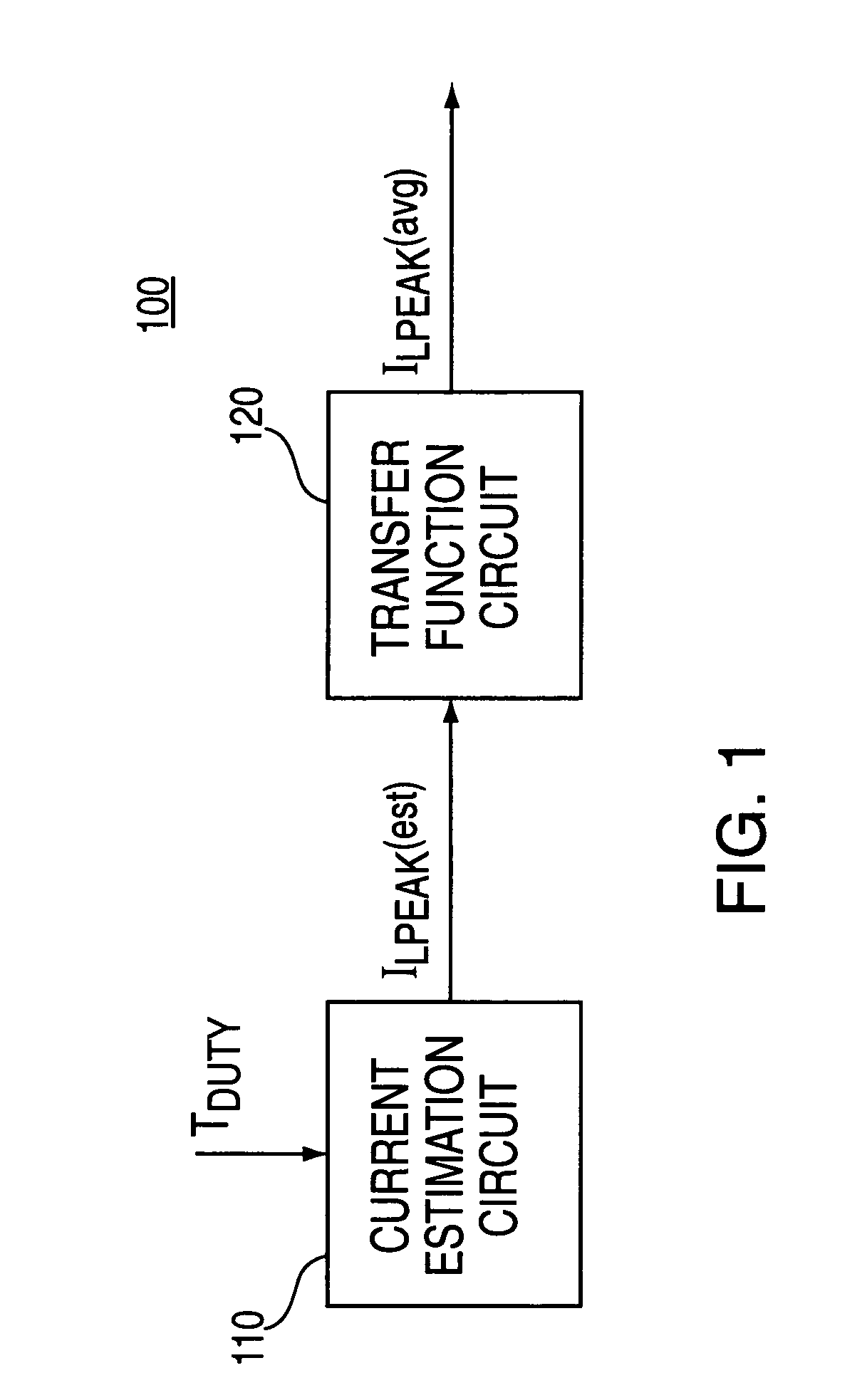
InactiveUS6987380B1Low rippleEfficient voltage regulationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent mode controlCurrent limiting
Control circuits that employ time-based current control methods for switching voltage regulators are provided. The control circuit includes a current estimation circuit and optionally, a transfer function circuit. The current estimation circuit generates estimates of regulator output current as function of switch period for use as a threshold indicative of peak current limit. This arrangement eliminates the need for error amplifiers to provide effective current mode control. The absence of error amplifiers allows fabrication of switching regulators on smaller die areas and provides switching regulators with reduced power consumption.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
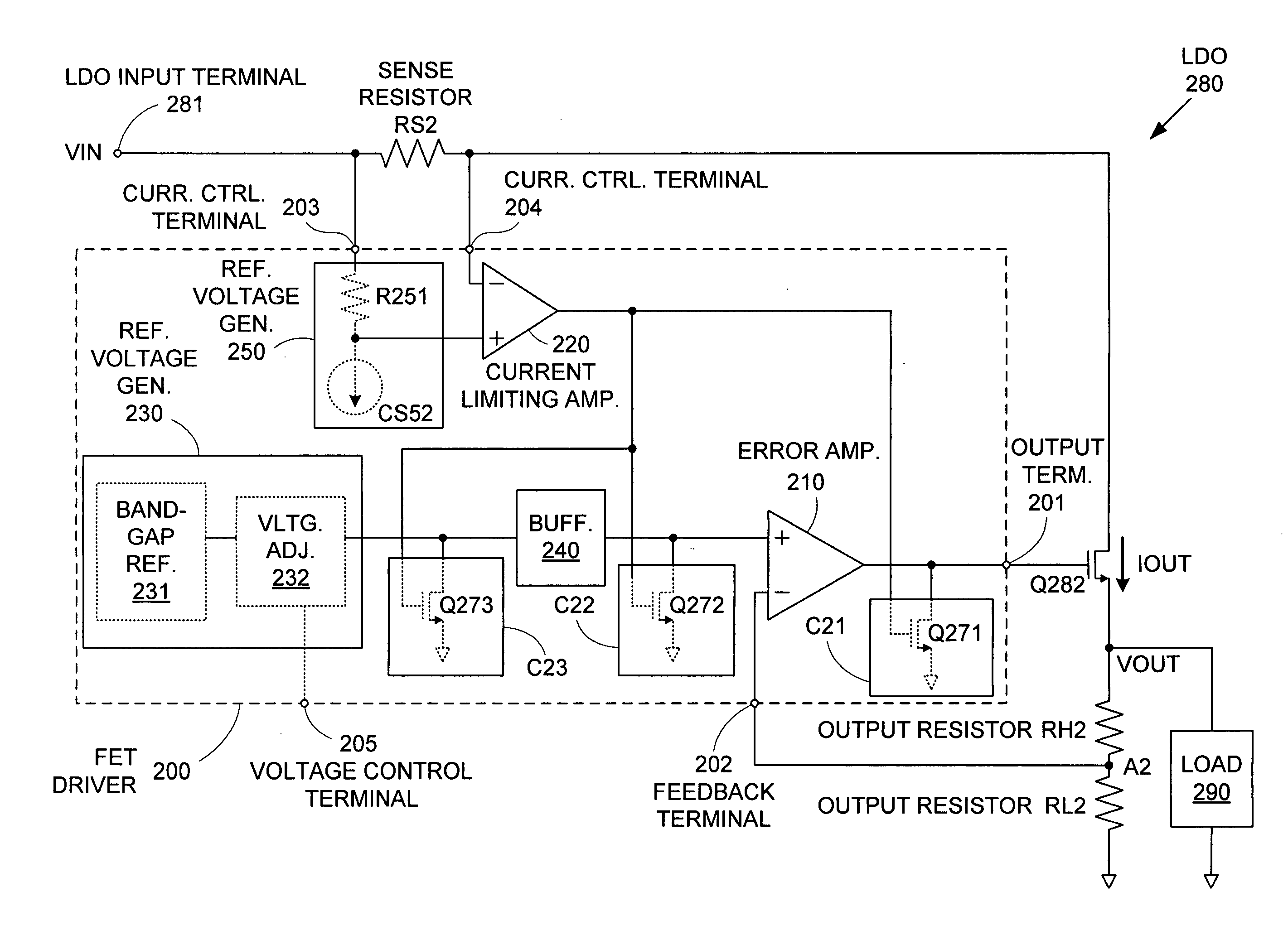
Low dropout voltage regulator providing adaptive compensation
InactiveUS20050242796A1Improve transient responseHigh bandwidthDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedEngineering
A method and apparatus to dynamically modify internal compensation of a low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator is provided. The LDO voltage regulator includes an output pass transistor, an error amplifier, a bias transistor and a compensation network. The compensation network is connected between a gate and a drain of the output pass transistor to compensate for the feedback loop. The compensation network and the bias transistor generate pole-zero pairs to perform a maximum 45 degrees phase shift before reaching the crossover frequency in the LDO voltage regulator. Therefore a minimum 45 degrees phase margin is provided for the feedback loop in various load conditions. Furthermore, the pole-zero pairs produced in the LDO voltage regulator are adaptively adjusted according to load conditions, so that the bandwidth is optimized and faster transient response is achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20090102444A1Simple configurationGood compensationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterFrequency characteristic
A DC-DC converter, which controls the output voltage supplied to a load at a desired magnitude by performing on / off control of the input voltage using a switch, includes: an error amplifier for outputting the difference voltage between the output voltage and a preset reference voltage; and a plurality of phase compensation circuits for compensating the phase of the output voltage fed back to the error amplifier with different characteristics, whereby the DC-DC converter is configured such that changes in either the input voltage or in the load current flowing into the load are detected, and switching between the plurality of phase compensation circuits is performed. The frequency characteristic of each of the phase compensation circuits is determined for each of a plurality of demarcated fluctuation ranges of the input voltage or the load current.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC SYST CO LTD
DC-DC converter
ActiveUS20050088159A1Quick responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterResponsivity
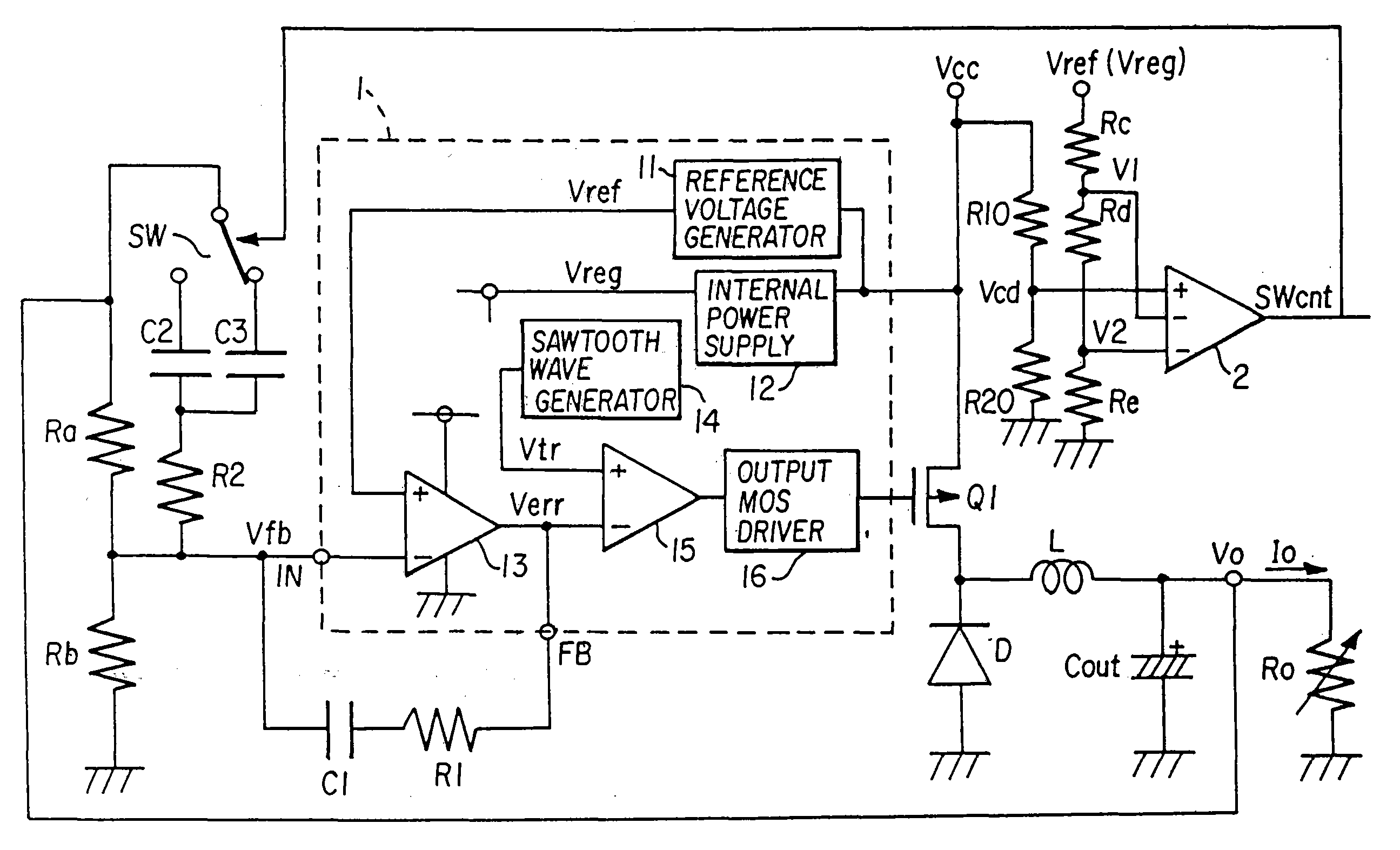
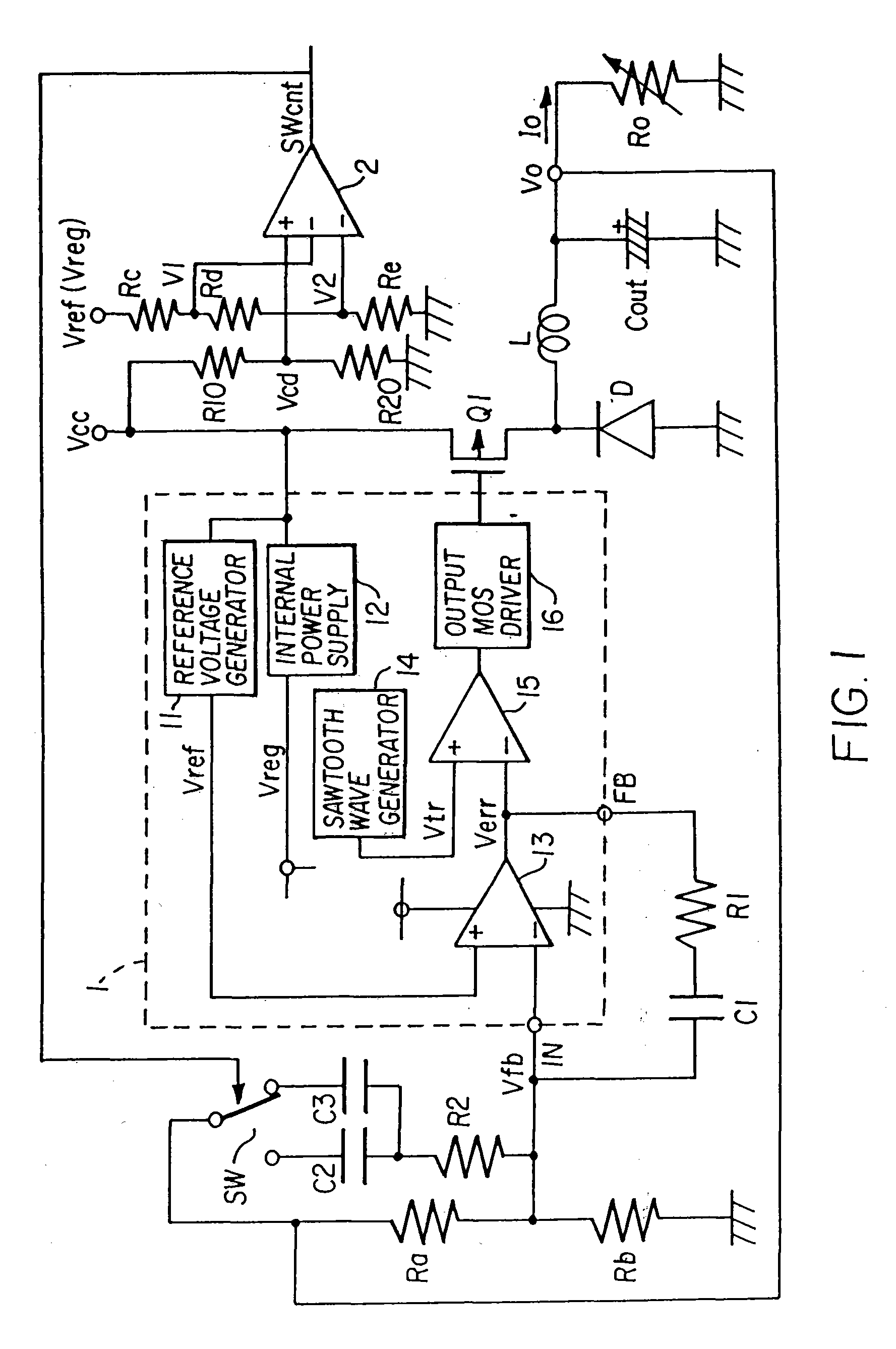
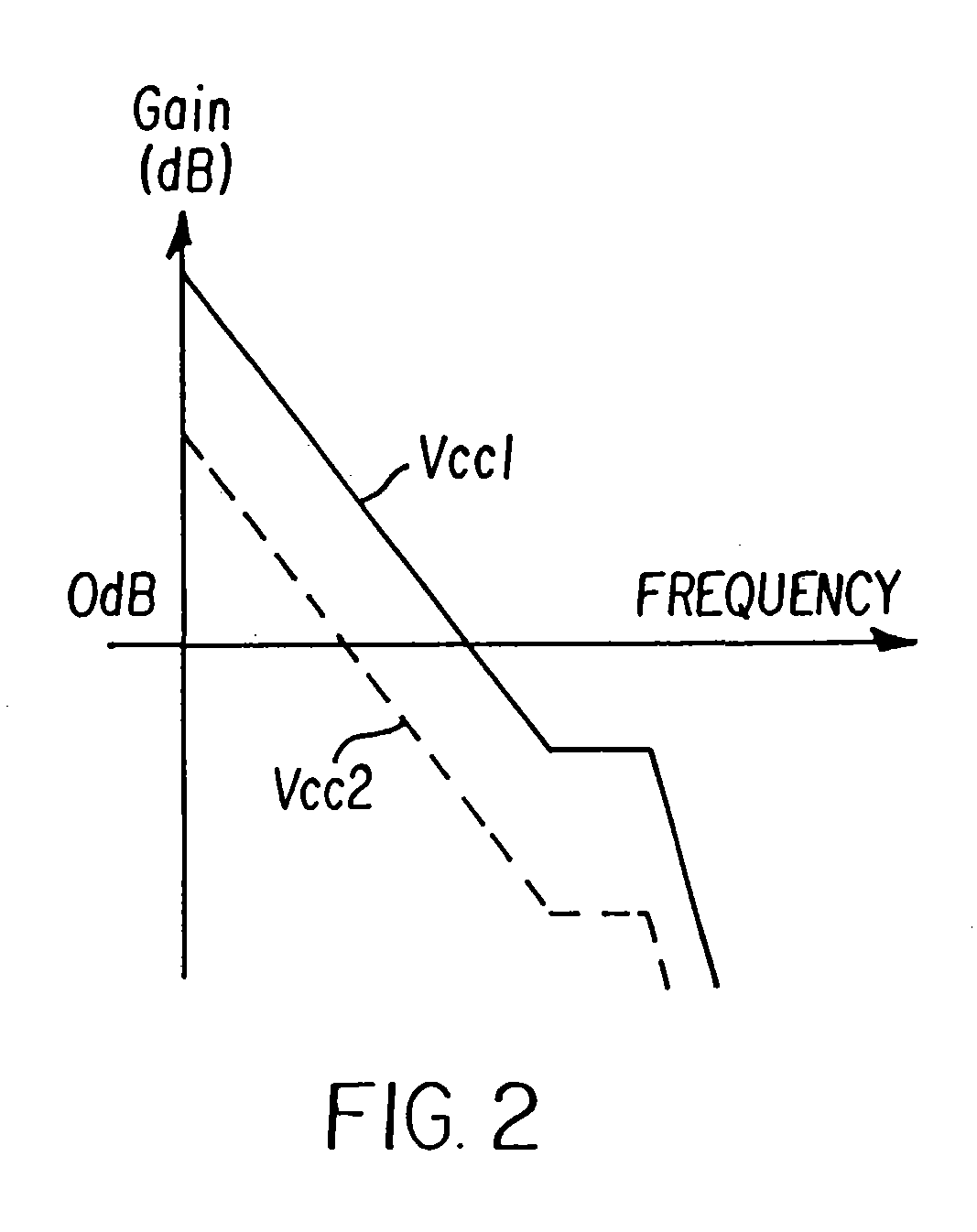
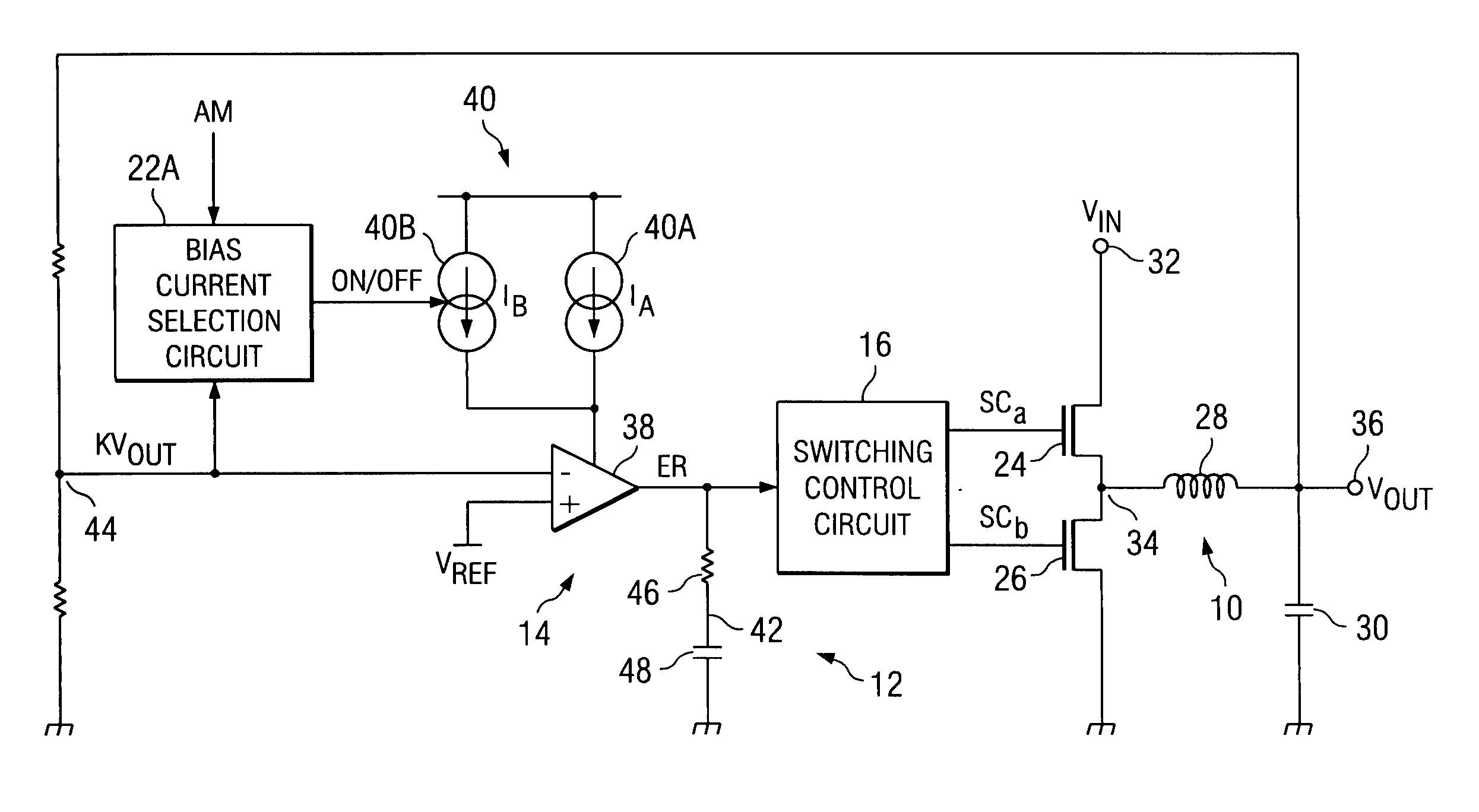
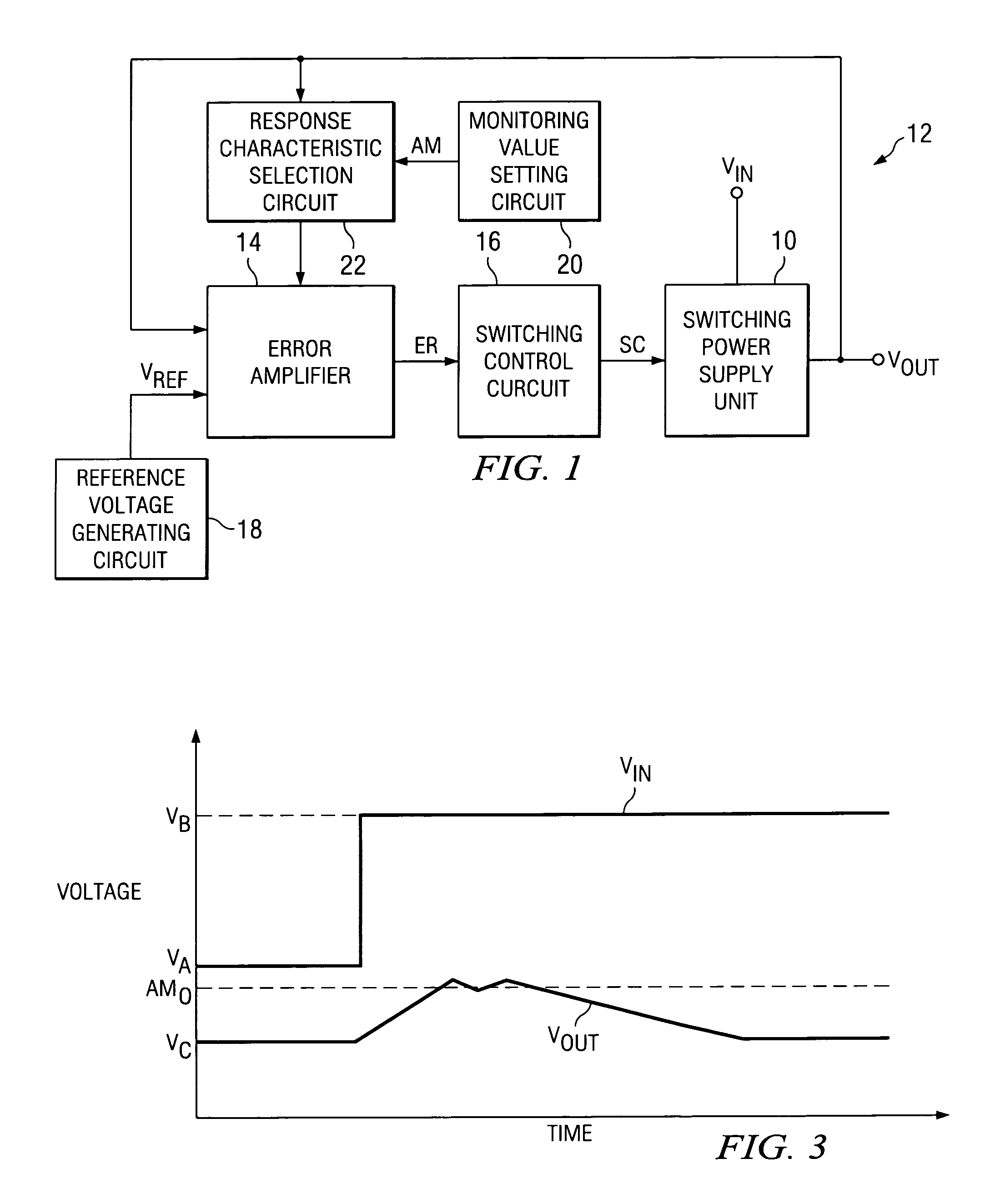
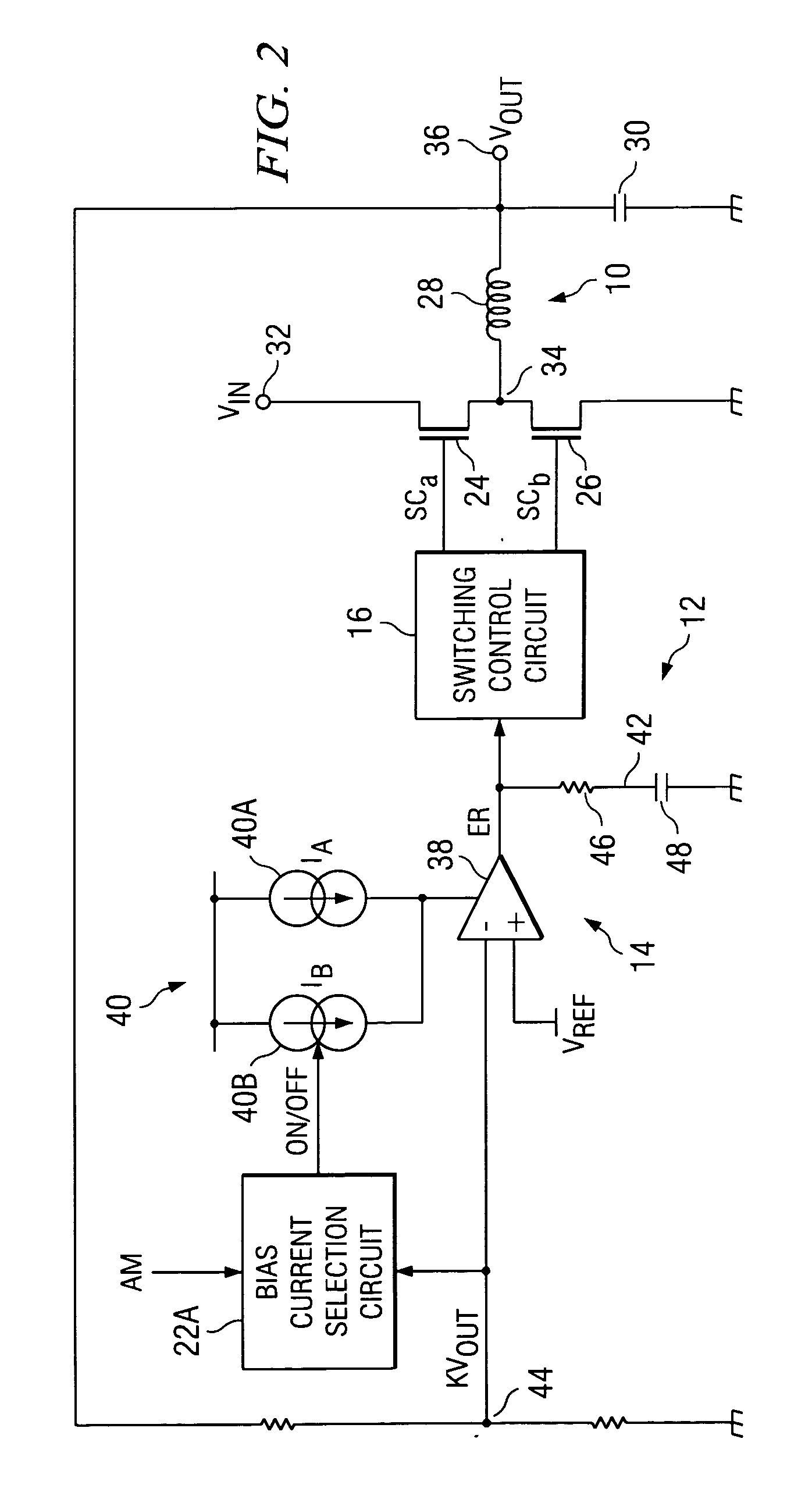
A DC-DC converter, which can respond quickly and suitably to changes in input voltage within the scope of normal operating conditions to return to the normal operating state. The DC-DC converter is comprised of switching power supply unit 10, which can turn on / off switching elements that can be turned on / off at high frequency to convert a DC input voltage Vin into a DC output voltage Vout, and a control unit 12, which is used to control the on / off operation of the switching elements of said switching power supply unit 10. In control unit 12, when DC output voltage Vout is out of the range of monitoring value AM, the response characteristic of the feedback loop (especially the response characteristic of error amplifier 14) is switched to a greater responsivity to continue the switching control operation of the control system without stopping it.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
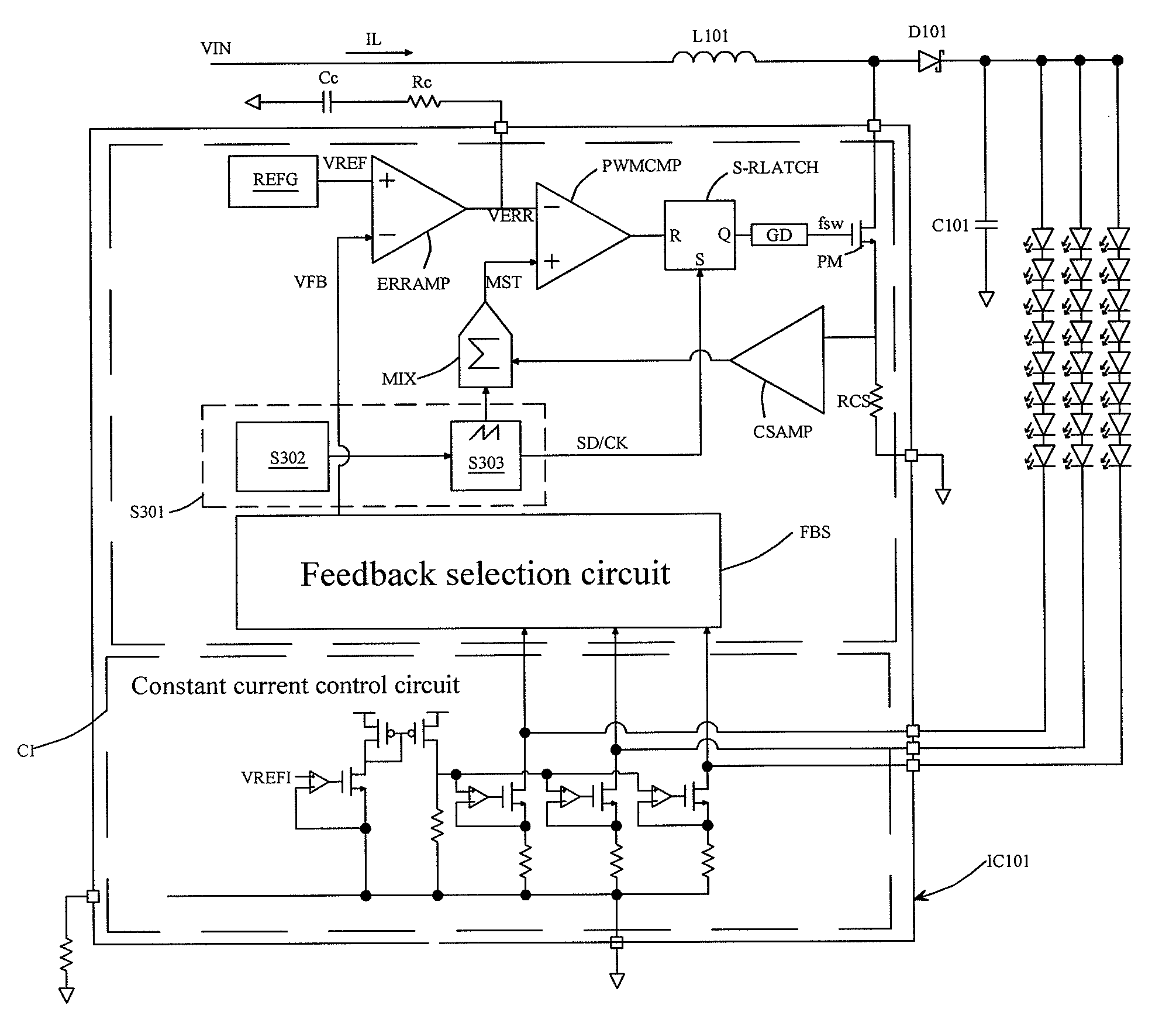
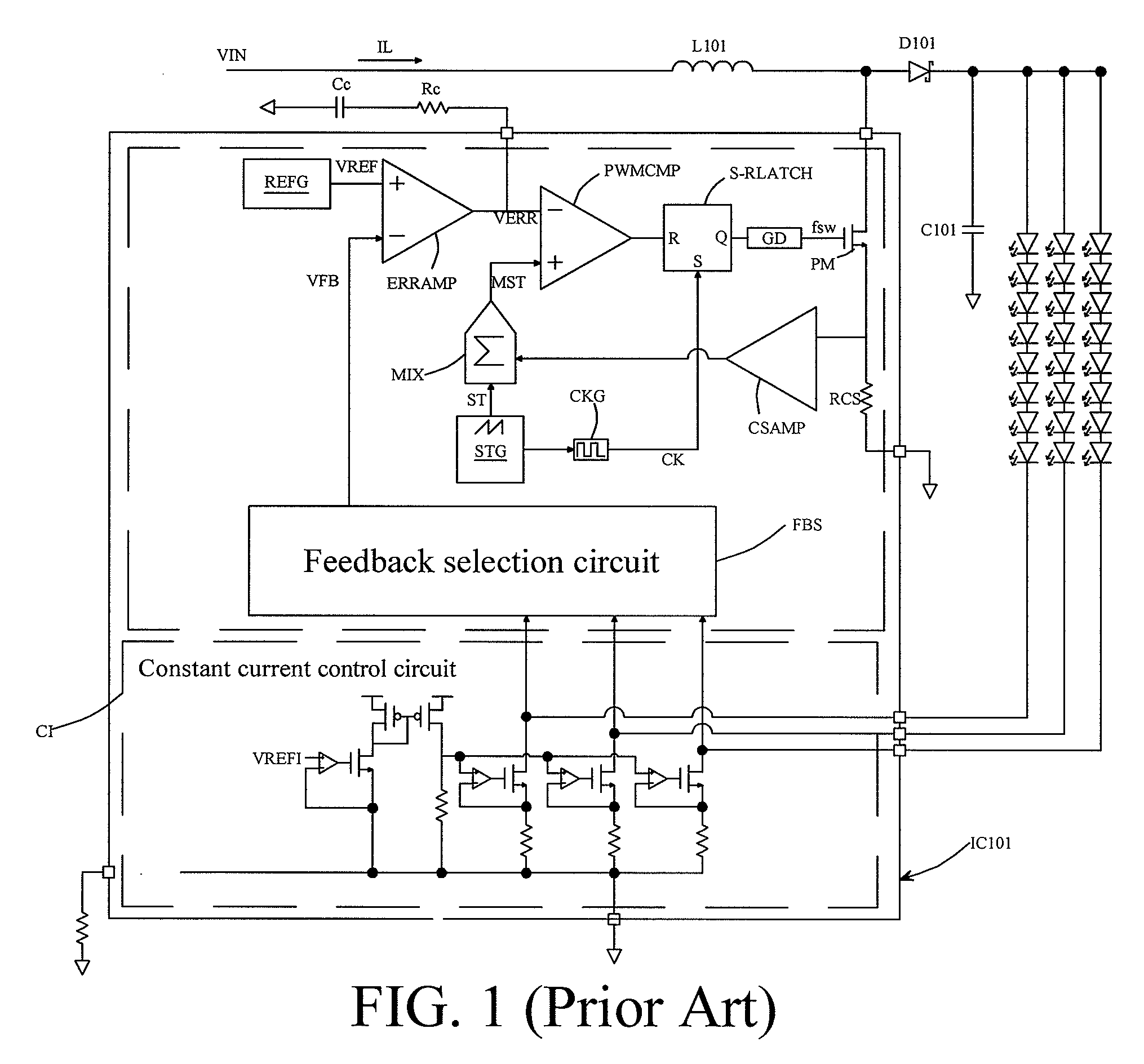
Control circuit and control method of primary side feedback constant current
ActiveCN103219884AGood constant current effectEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionIntegratorEngineering
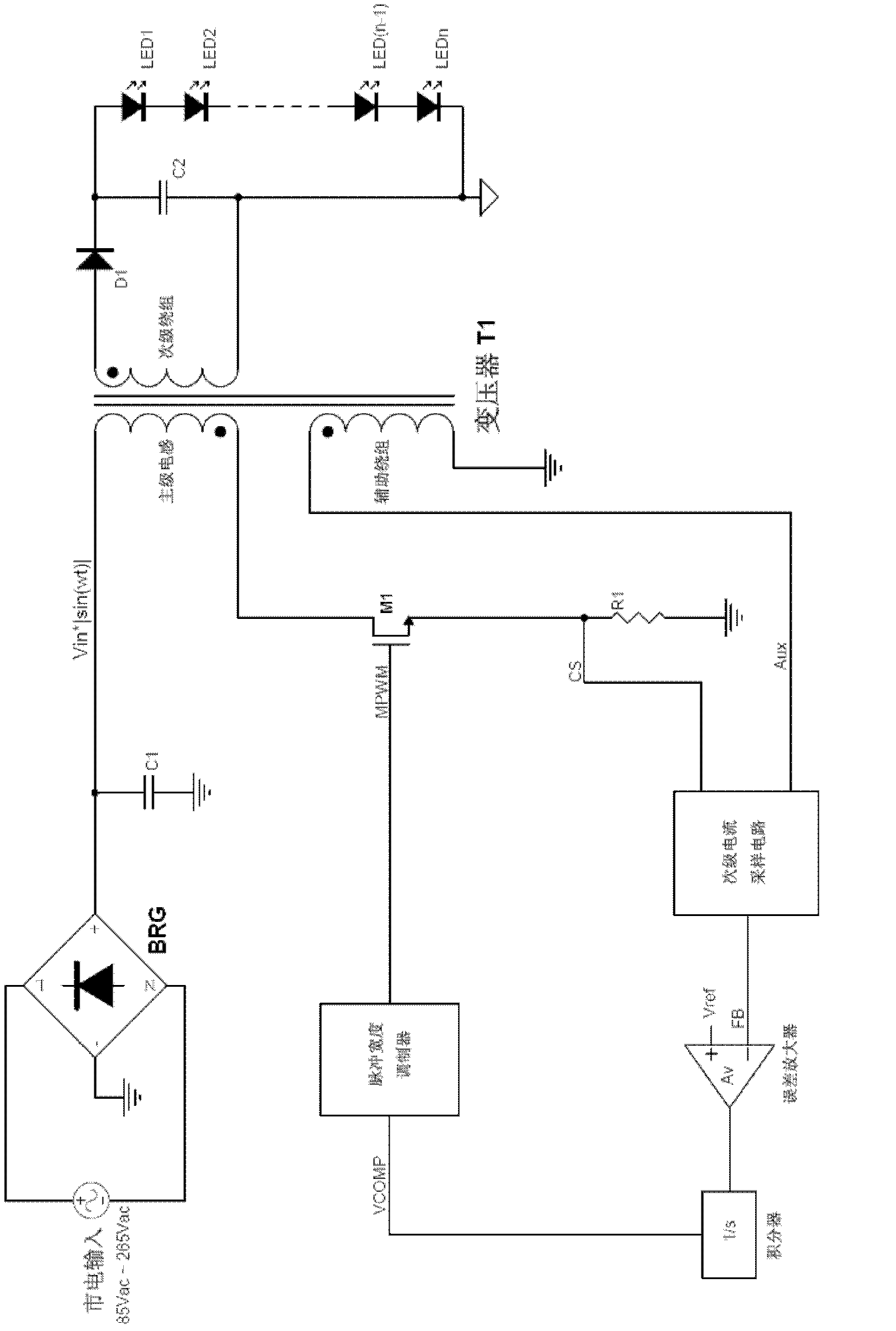
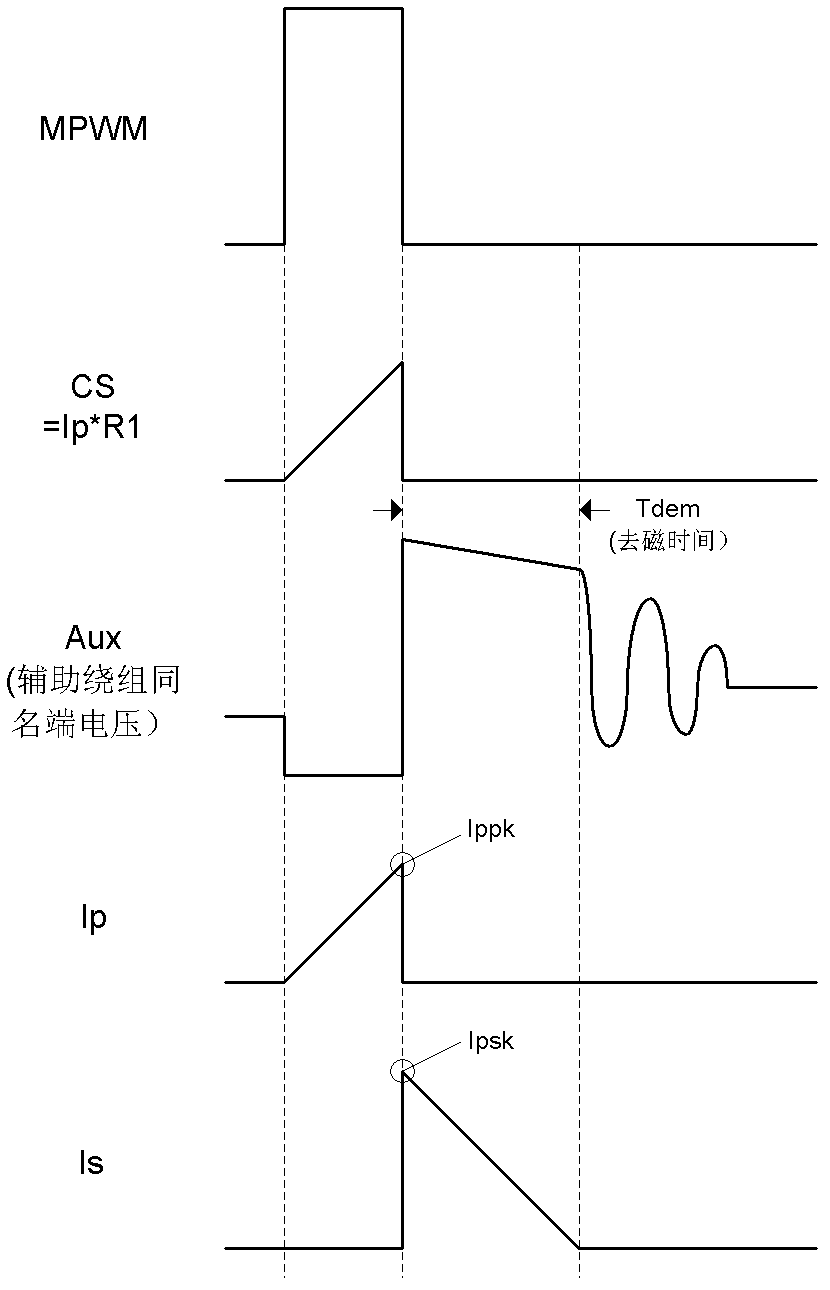
The invention discloses a control circuit and a control method of a primary side feedback constant current of a constant current actuator of an alternating current-direct current (AC-DC) light-emitting diode (LED). The control circuit comprises a power switch tube, a secondary current sampling circuit, an error amplifier, an integrator and a pulse width modulator, wherein the power switch tube controls the work of primary inductance in a discontinuous working mode, the secondary current sampling circuit takes samples of demagnetizing time of a secondary winding and the current peak value of the primary inductance through a primary side auxiliary winding and generates feedback signals corresponding to the average value of a secondary current in each switching period based on the demagnetizing time and the current peak value, the error amplifier amplifies the errors between reference voltage and the feedback signals of a sampling circuit of the secondary current, the integrator carries out integration on the value amplified by the error amplifier, and the pulse width modulator generates pulse width modulation signals to control the power switch tube to work based on the signals output by the integrator. The control circuit and the control method of the primary side feedback constant current improve a constant current effect of output currents, and achieves high-precision constant current control with high power factor control.
Owner:MAXIC TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
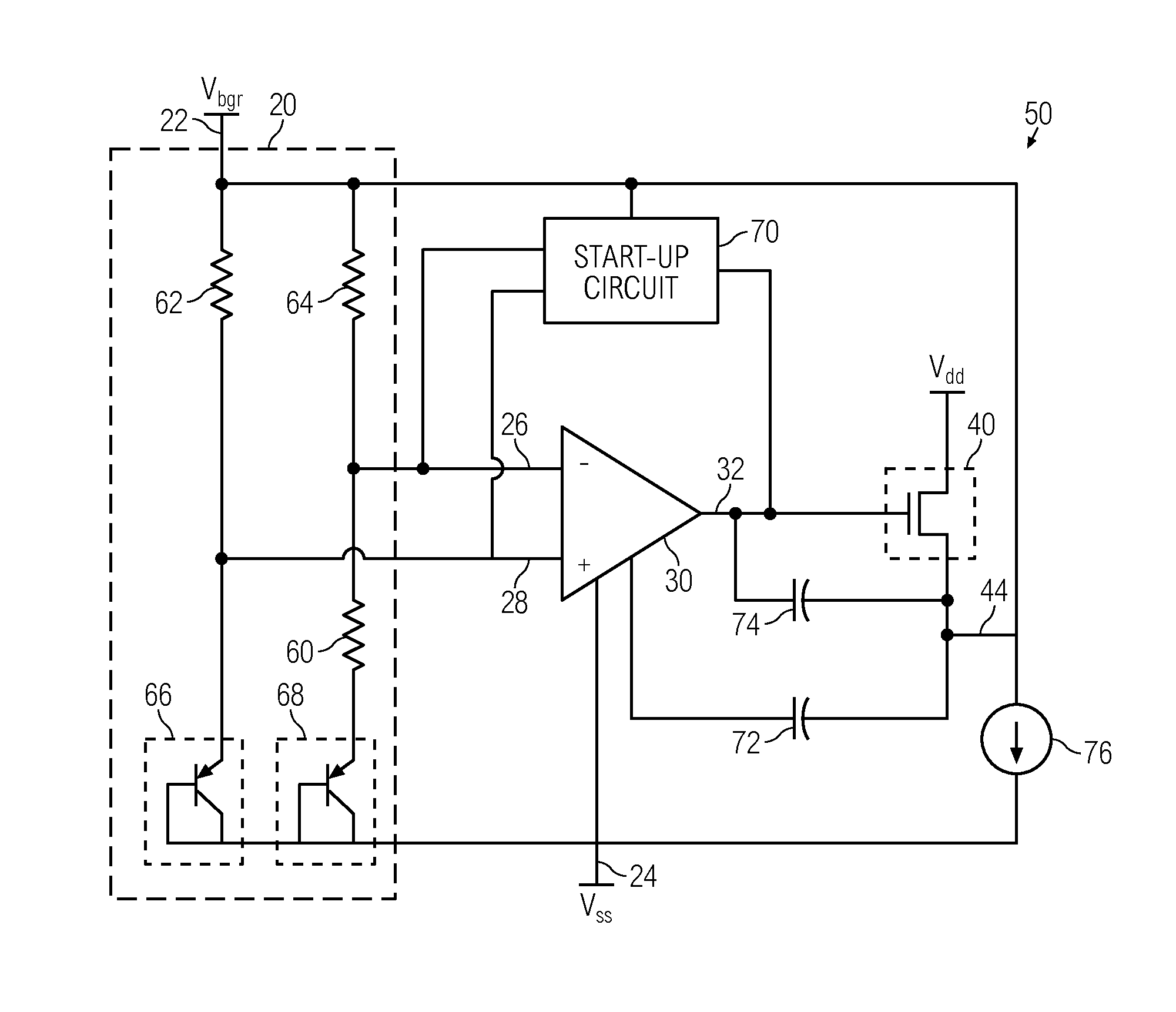
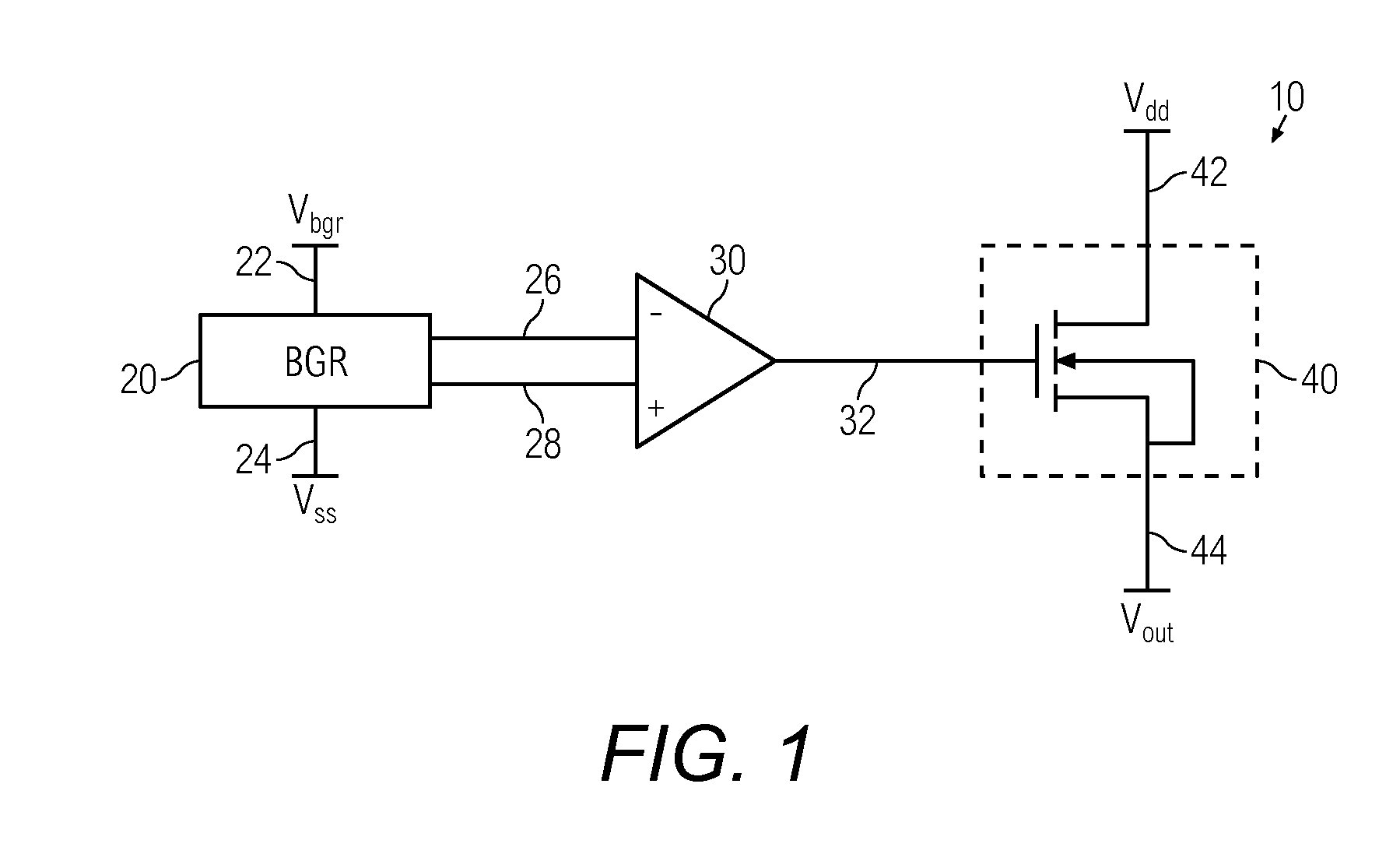
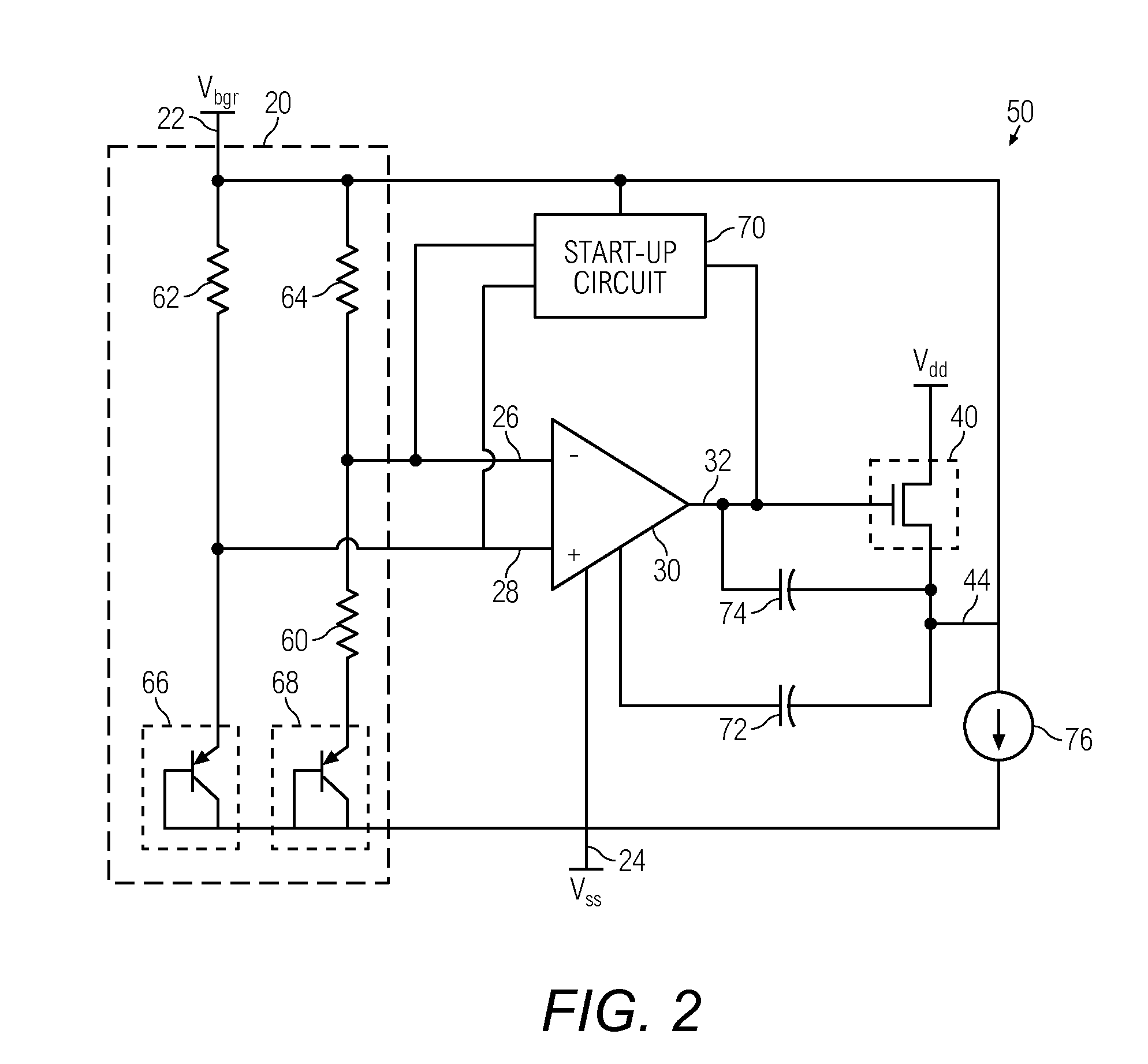
Bandgap reference circuit and regulator circuit with common amplifier
InactiveUS20140015509A1Power supply linesElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
A bandgap voltage reference and voltage regulator system includes a bandgap voltage reference circuit and a voltage regulator circuit that share a single, common amplifier. The amplifier acts as a gain stage for the reference circuit and as an error amplifier for a driver stage of the regulator circuit. The regulator circuit has an input reference generated by the reference circuit, and the reference circuit acts as a load to the driver stage, obviating the need for a bias resistance network. By sharing the amplifier and obviating the need for a resistance network, the area and overall quiescent current of the system are reduced. The system can be implemented in CMOS / BiCMOS technology and is suited for low power applications.
Owner:NXP USA INC
DC/DC converter
InactiveUS20050024033A1Semiconductor package can be decreasedDownsizing of the DC/DC converterDc-dc conversionPower supply linesEngineeringControl switch
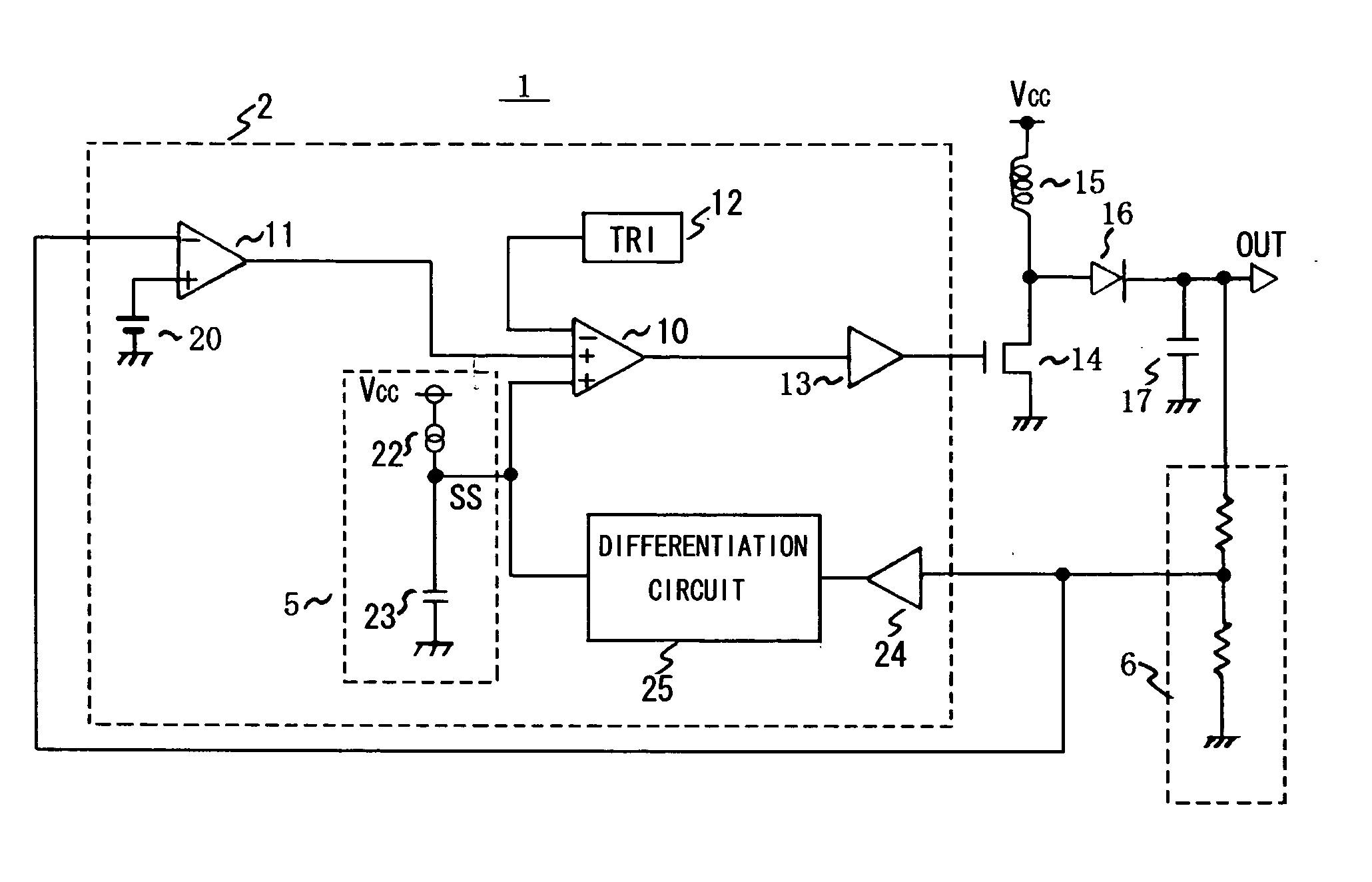
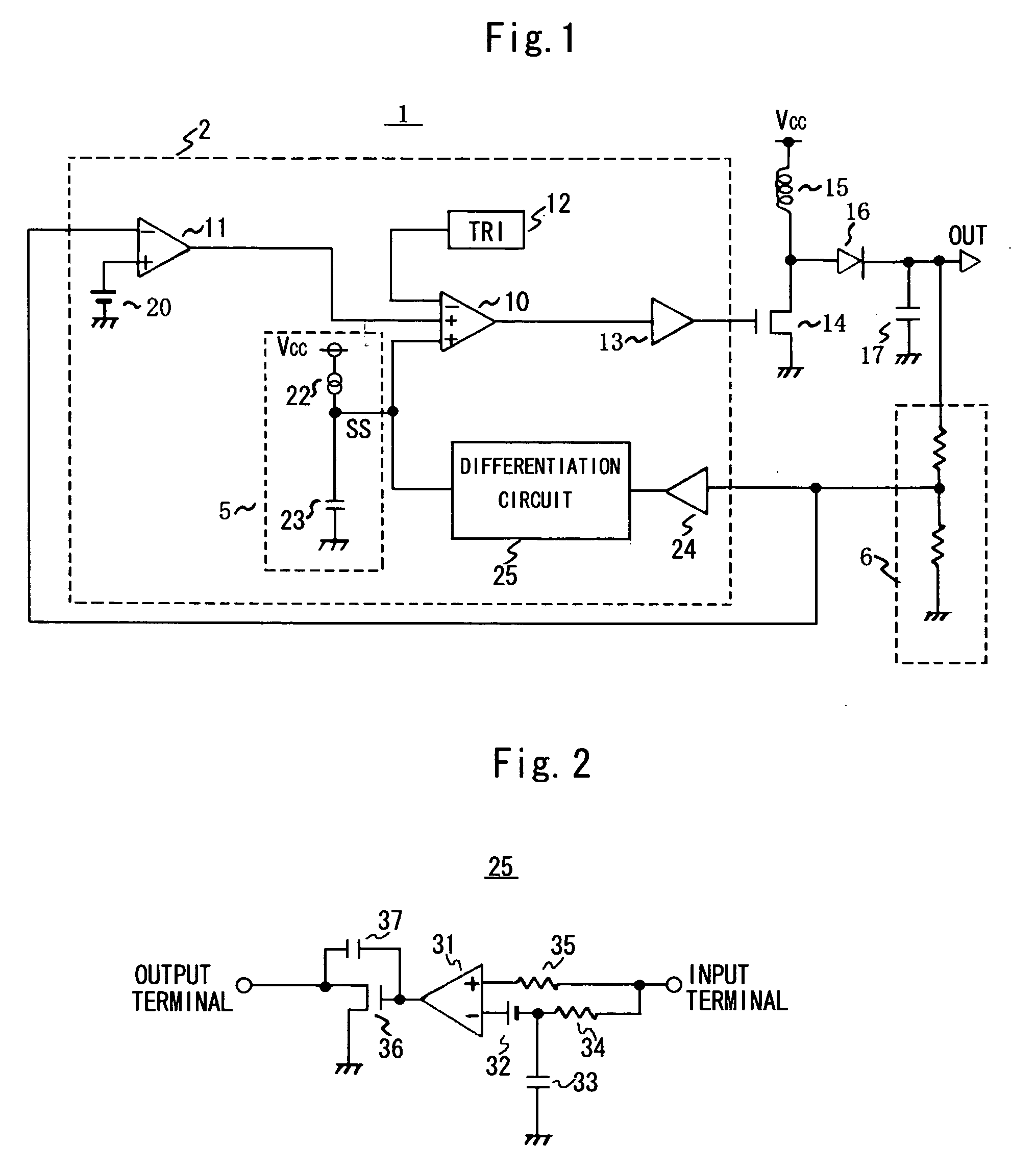
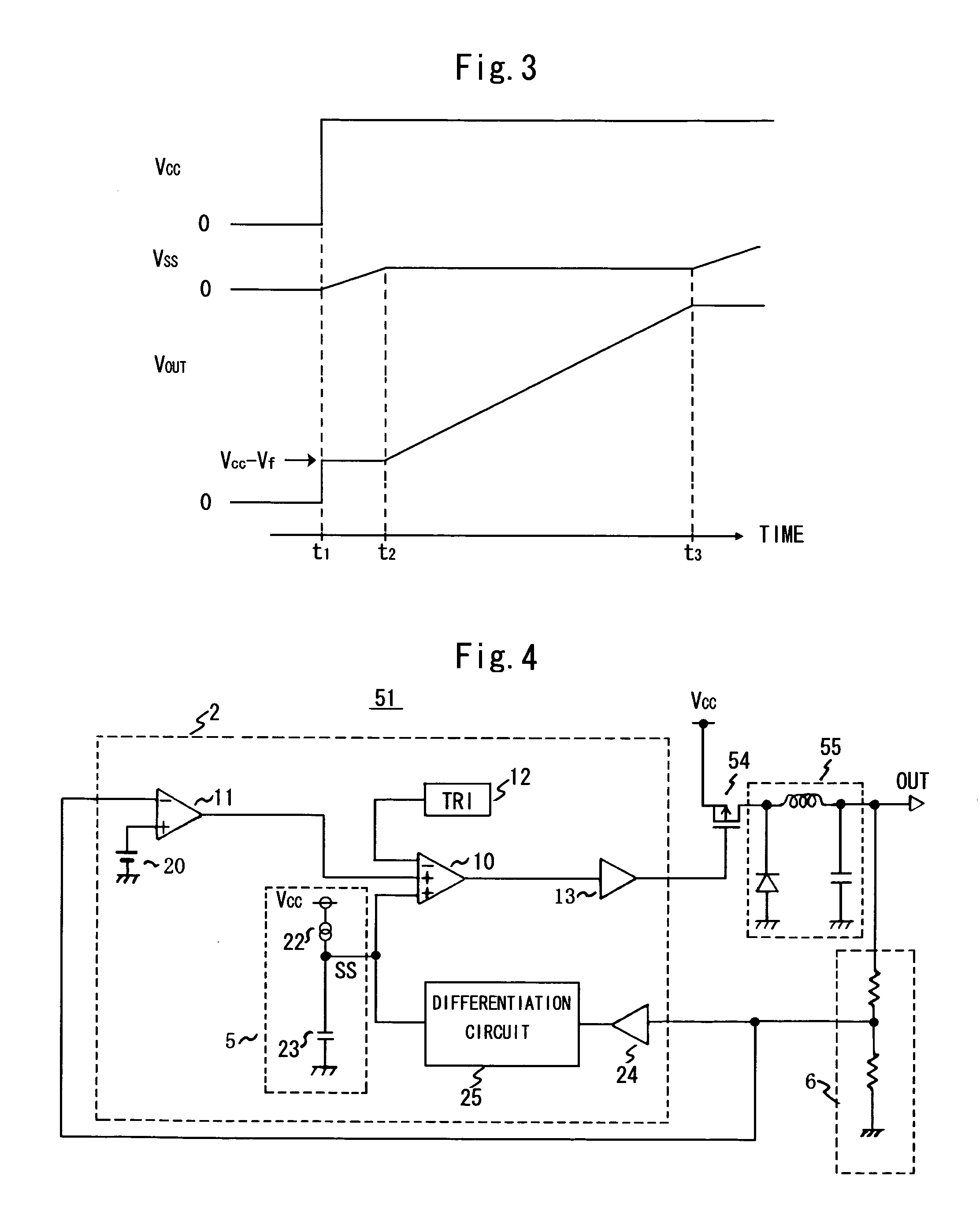
The present invention provides a DC / DC converter that can include a capacitor constituting a soft start circuit in a semiconductor integrated device. This DC / DC converter is comprised of a switching element for supplying power from a power supply (Vcc) to a load side output terminal (OUT) by switching, an error amplifier for amplifying the voltage from the load side output terminal (OUT), a differentiation circuit for differentiating the voltage from the load side output terminal (OUT) and adjusting the output current according to the value thereof, a soft start circuit comprising a constant current source and a capacitor, both of which are connected to the output terminal of the differentiation circuit, and a comparator for comparing the triangular wave voltage from a triangular wave generator (TRI) with the voltage from the soft start circuit or the output voltage of the error amplifier, and controlling the switching of the switching element according to the comparison output thereof.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Regulation circuit associated with synchronous rectifier providing cable compensation for the power converter and method thereof
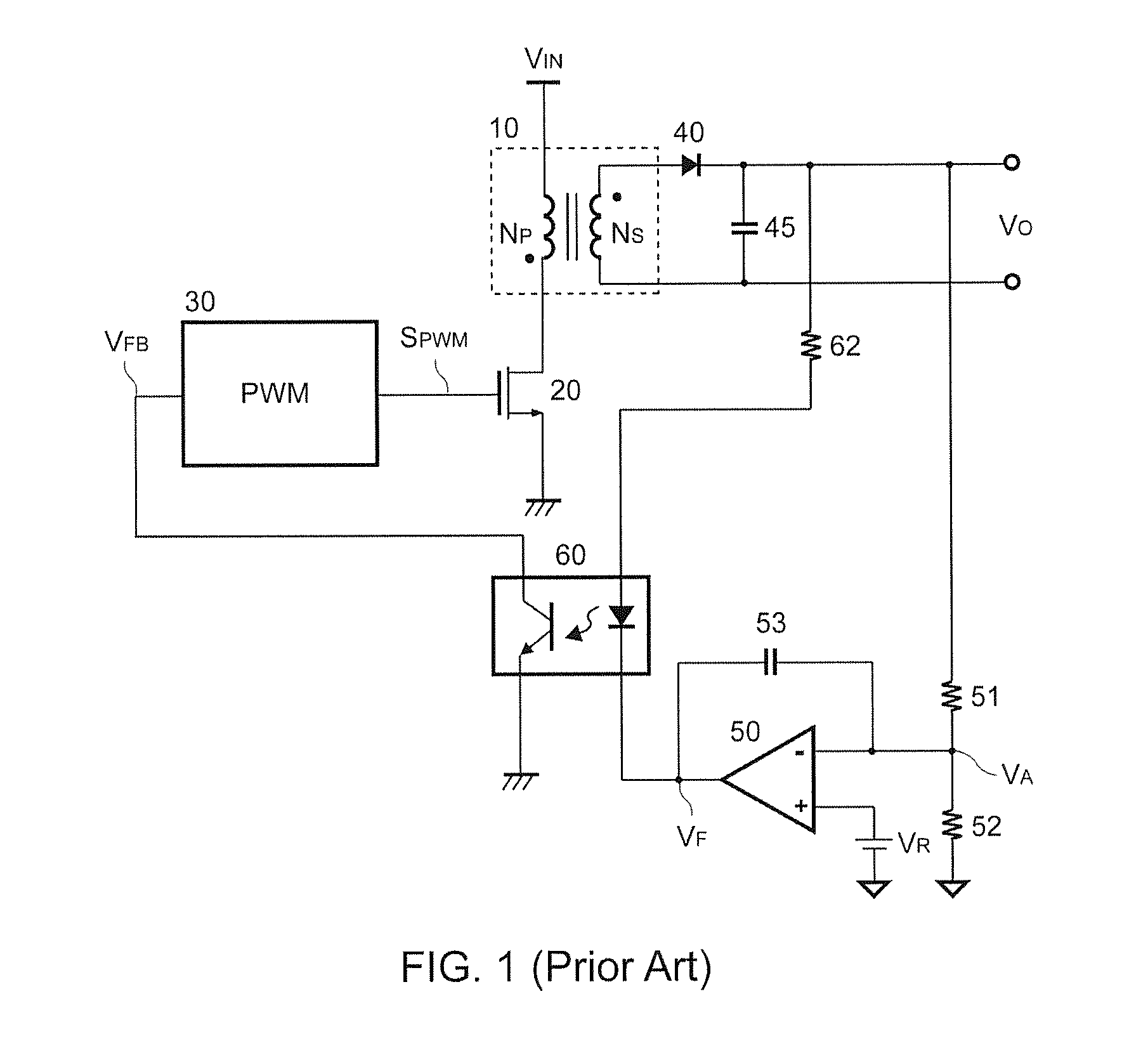
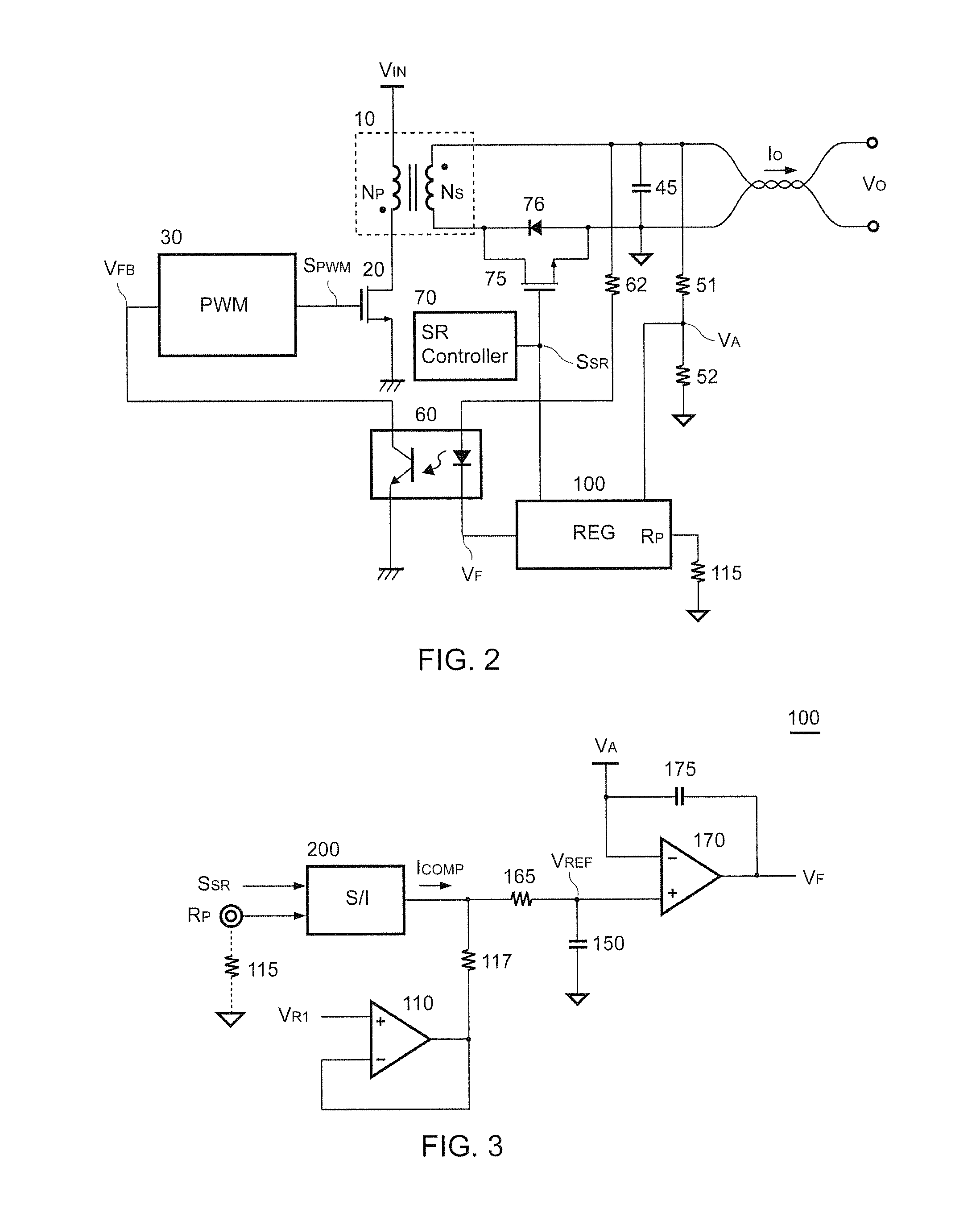
InactiveUS20150301542A1Reduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching signalEngineering
A regulation circuit of a power converter for cable compensation according to the present invention comprises a signal generator generating a compensation signal in accordance with a synchronous rectifying signal. An error amplifier has a reference signal for generating a feedback signal in accordance with an output voltage of the power converter. The compensation signal is coupled to program the reference signal. The feedback signal is coupled to generate a switching signal for regulating an output of the power converter. The regulation circuit of the present invention compensates the output voltage without a shunt resistor to sense the output current of the power converter for reducing power loss.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com