Patents
Literature
42148results about How to "Quick response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
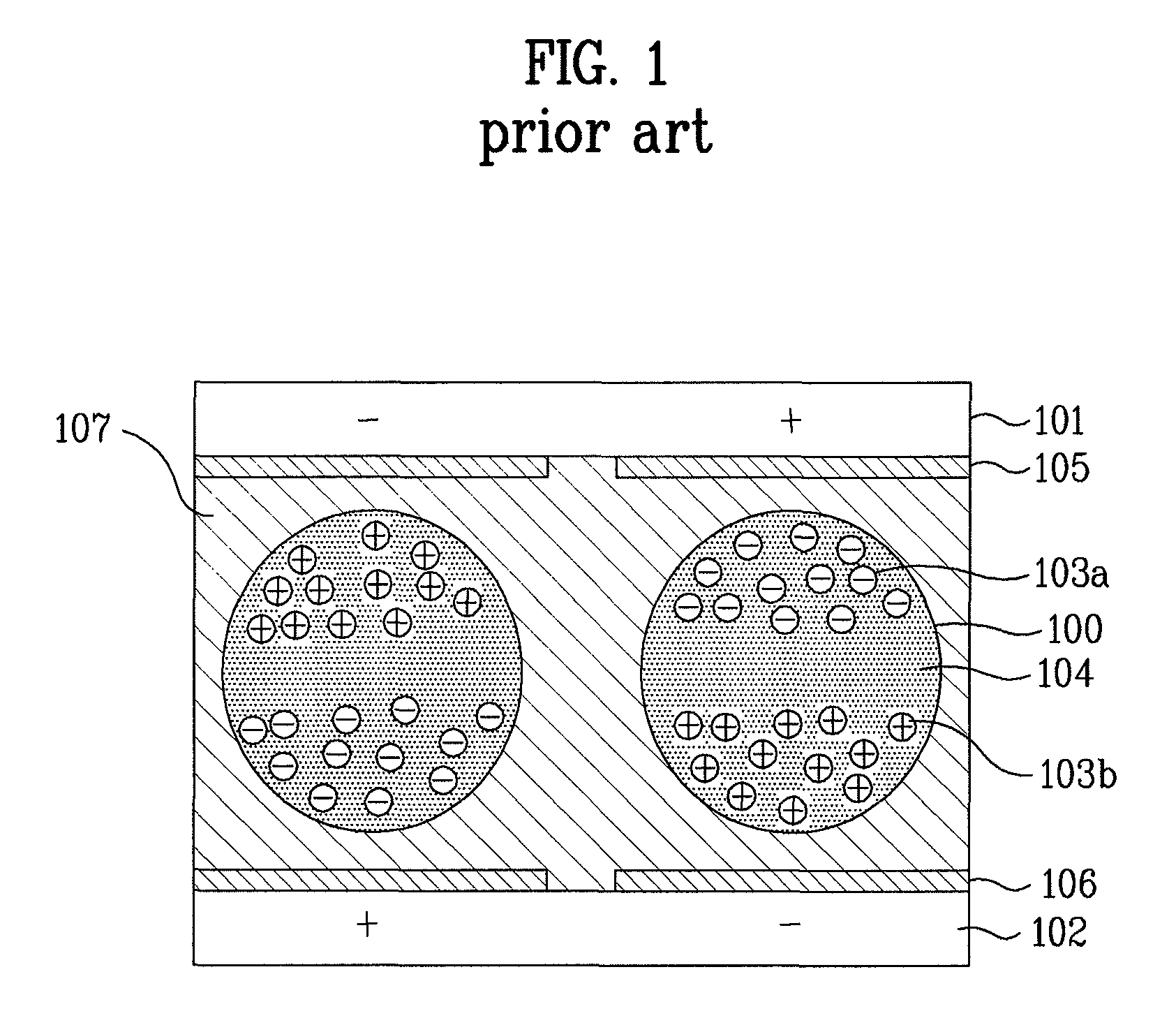
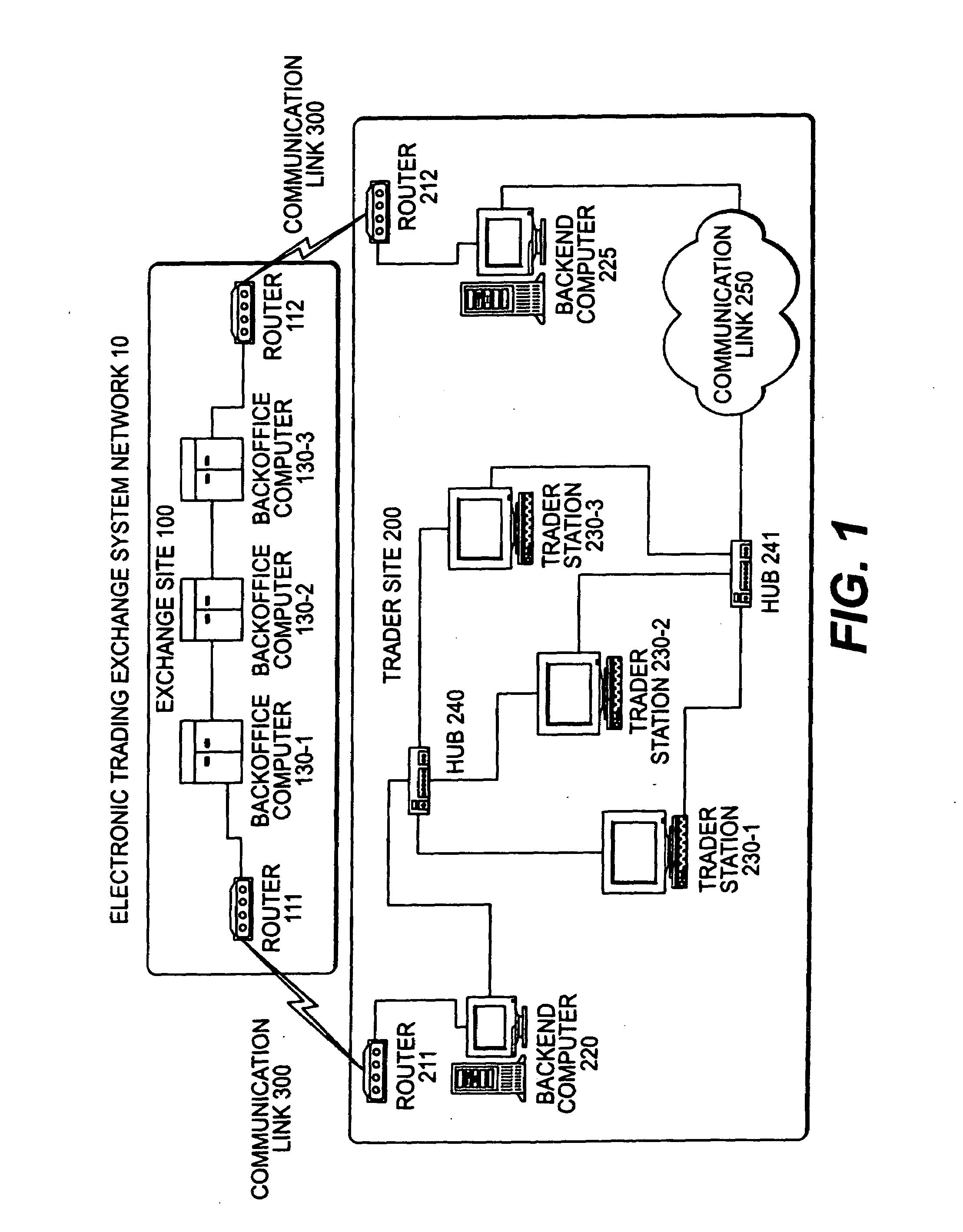
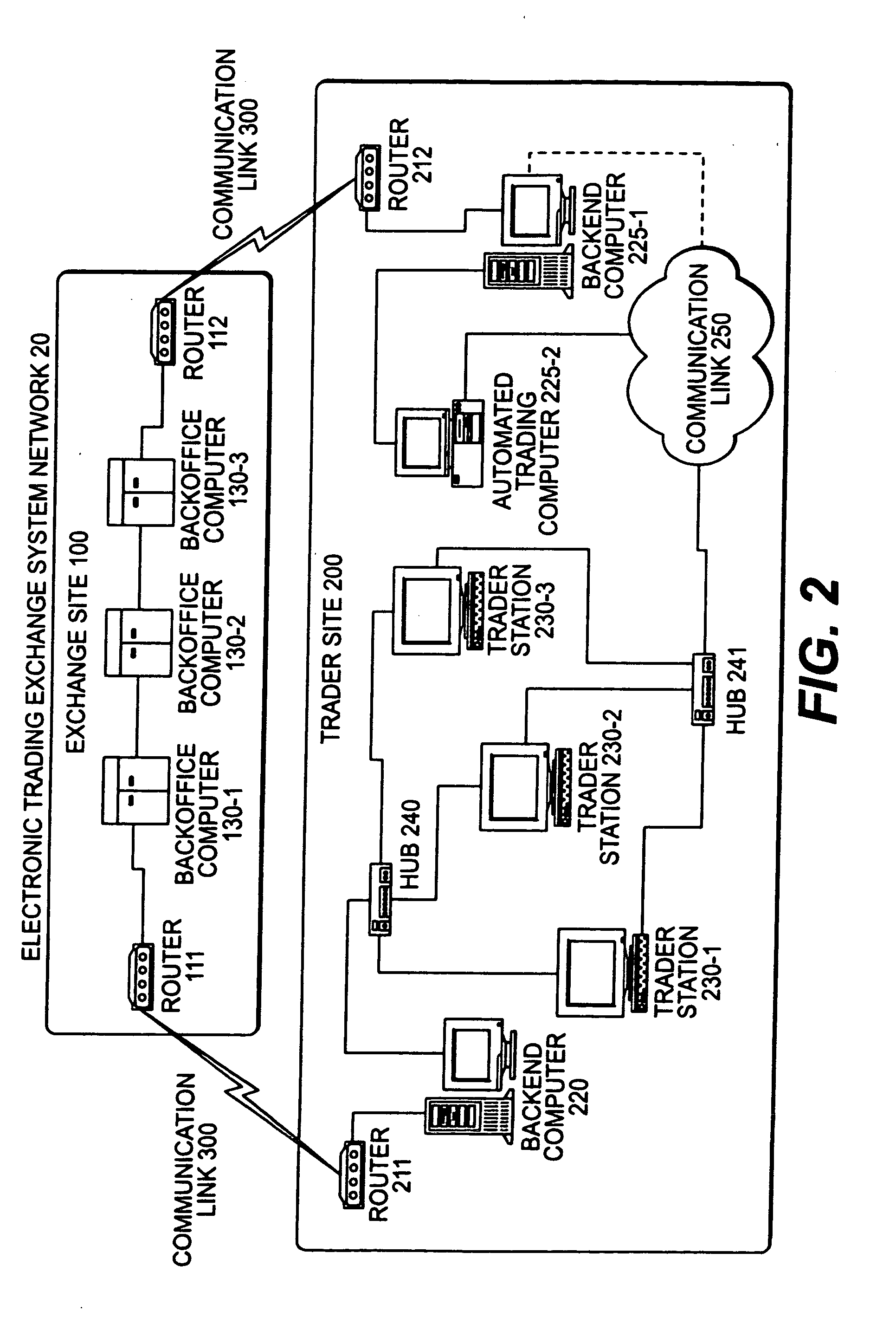
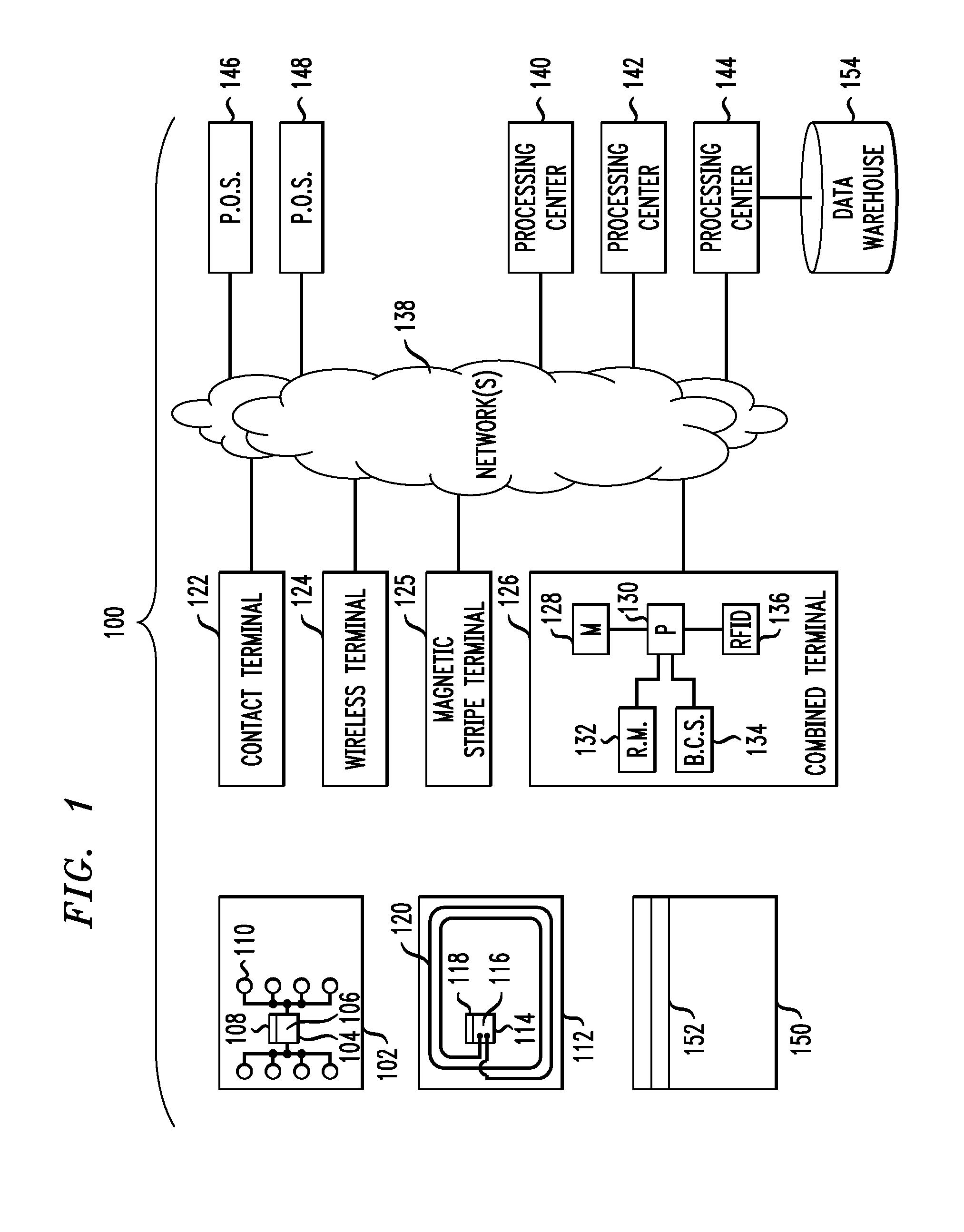
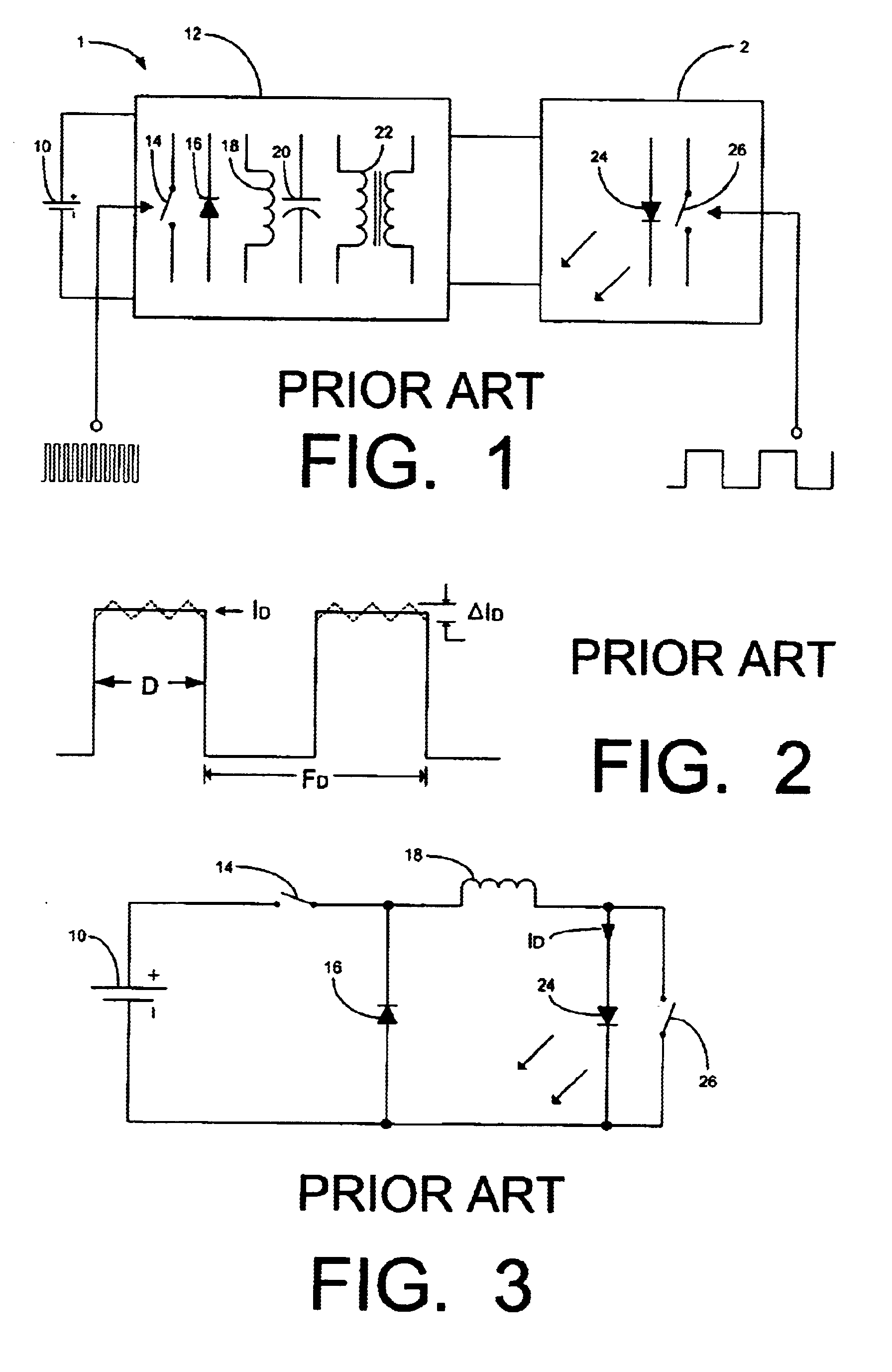
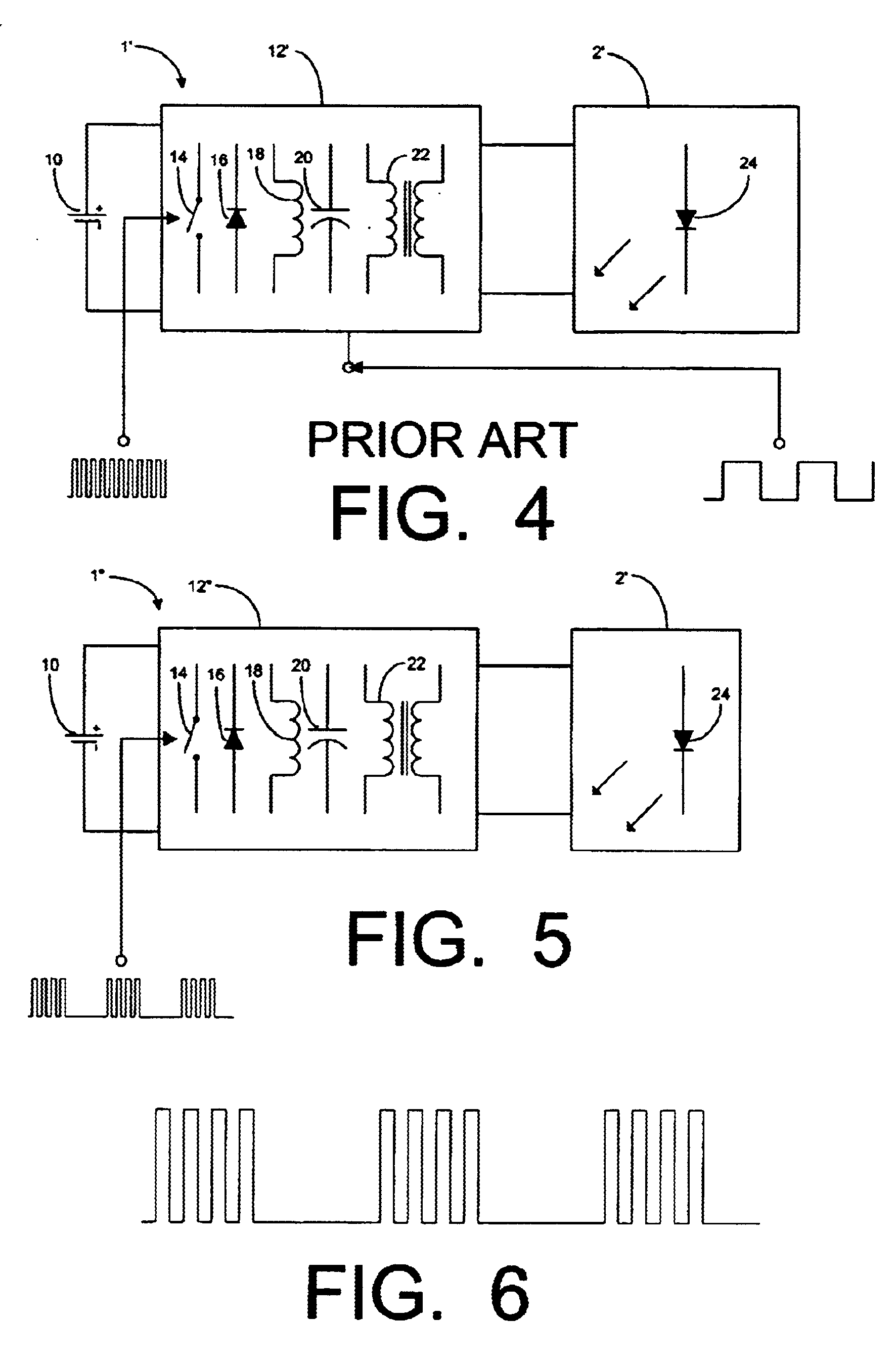
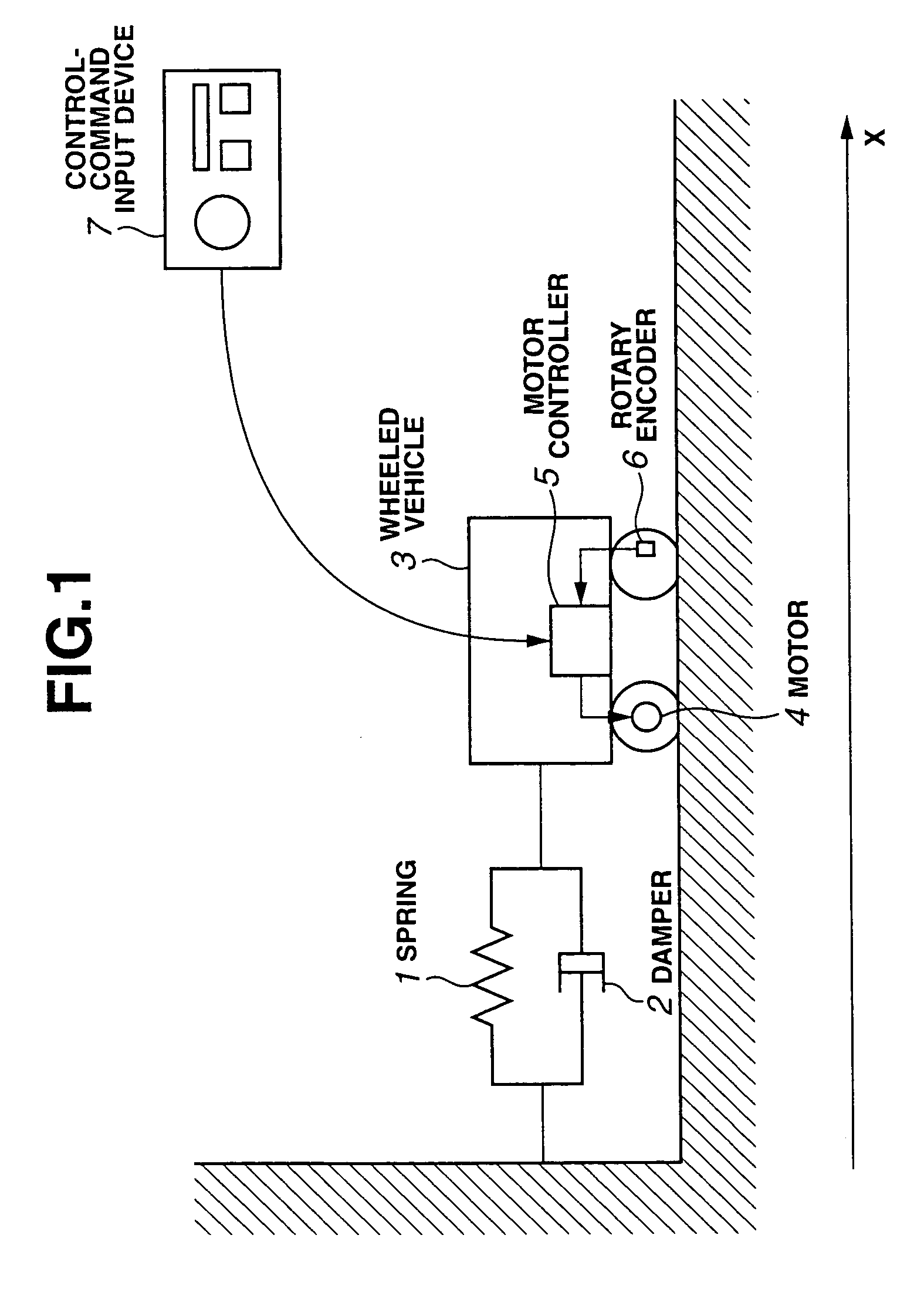
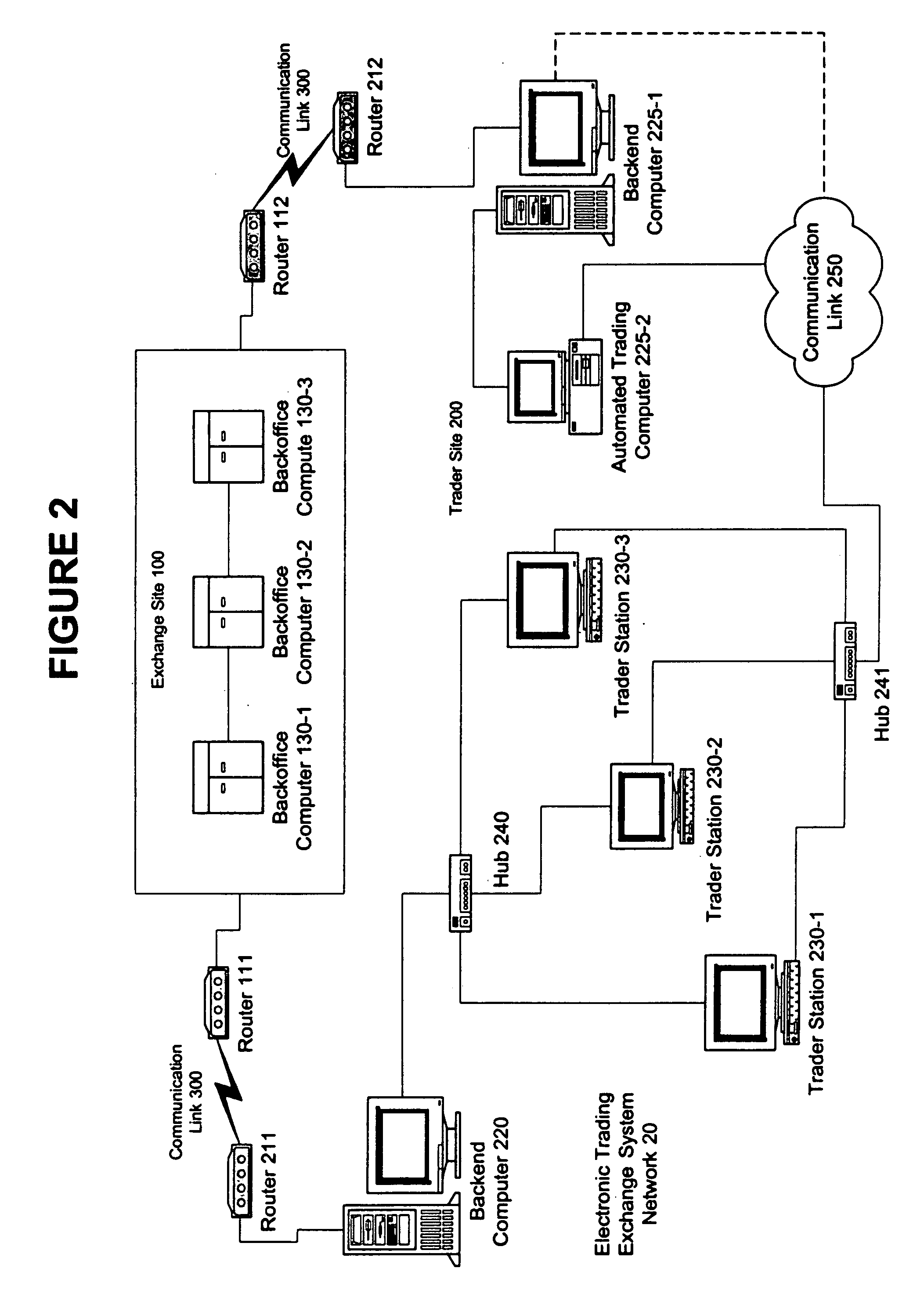
Automated trading system in an electronic trading exchange
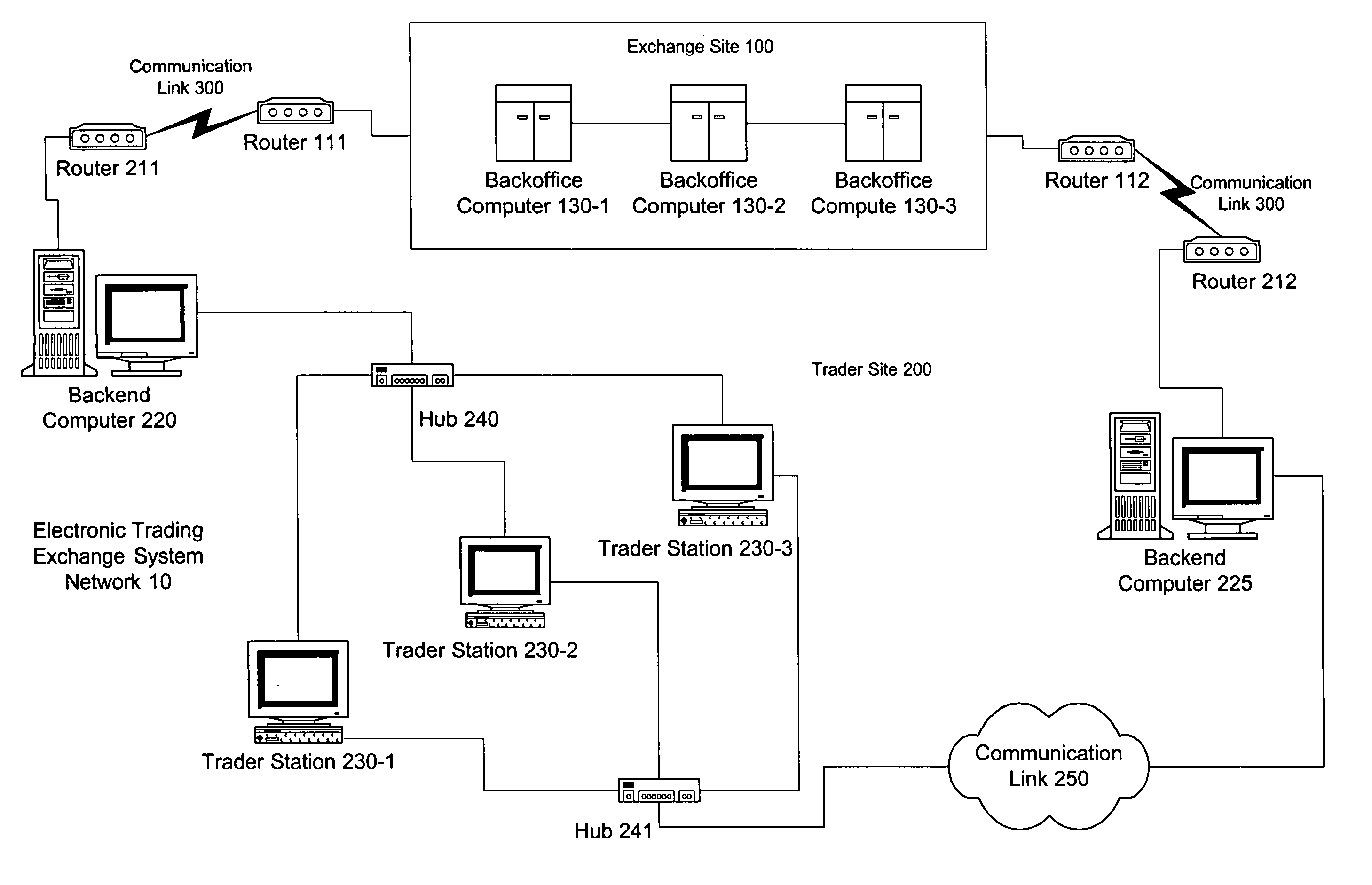
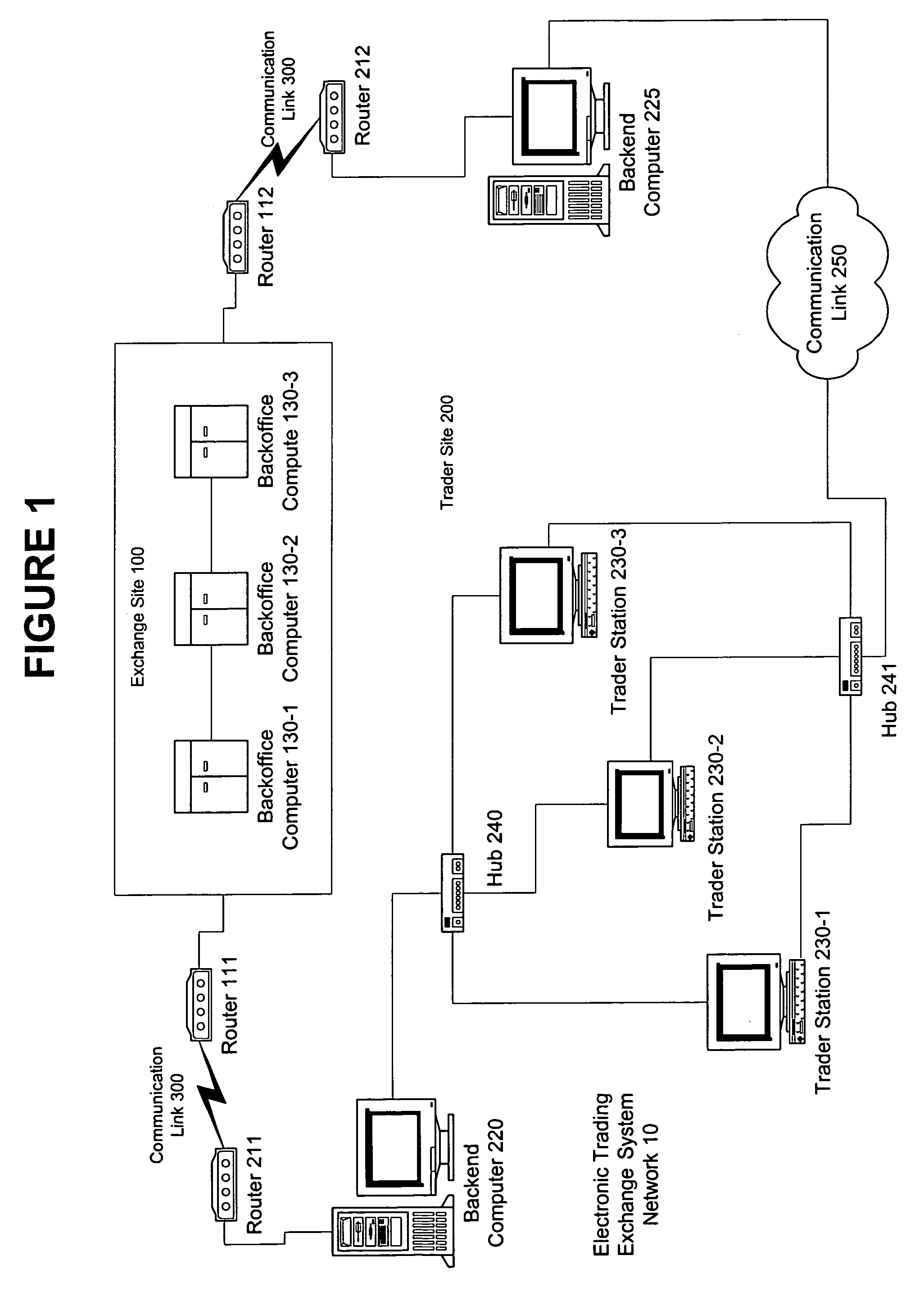
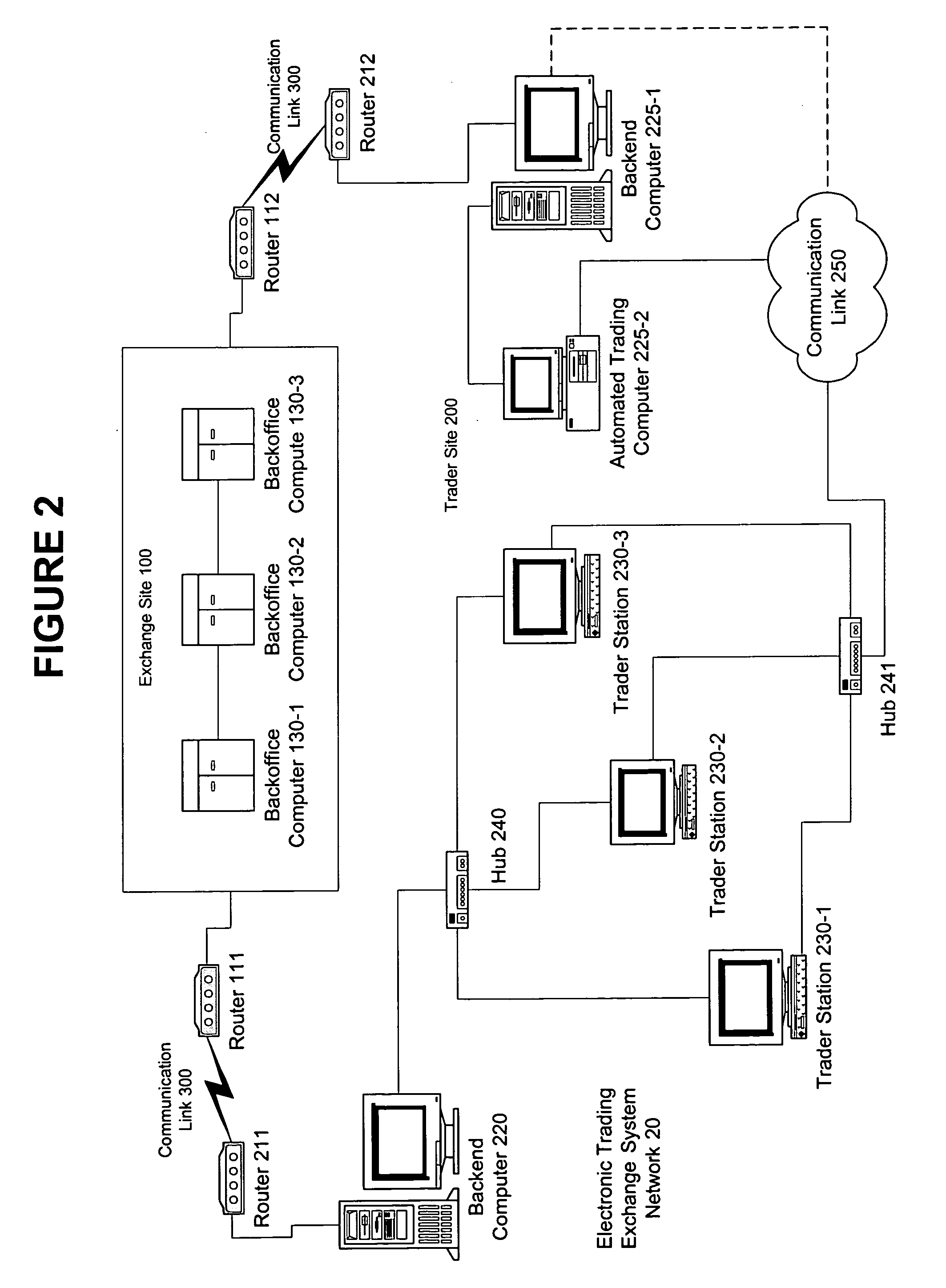
An electronic exchange system network includes a trader site having an automated trading system capable of submitting orders and / or quotes to an exchange site. The automated trading system determines whether an order or quote should be submitted based on, for example, the current market price of an option and theoretical buy and sell prices. The theoretical buy and sell prices are derived from, among other things, the current market price of the security underlying the option. The theoretical buy and sell prices are calculated when underlying factors that contribute to the theoretical prices change. Computation times of the theoretical prices may be reduced by using precalculated values and / or using interpolation and extrapolation. Other techniques may be used in addition or in the alternative to speed automatic decision-making. In addition, a system of checks may be conducted to ensure accurate and safe automated trading. The automated trading system may be capable of automatically submitting orders in connection with the underlying security in order to hedge part of the delta risk associated with the automated option trades.
Owner:DCFB
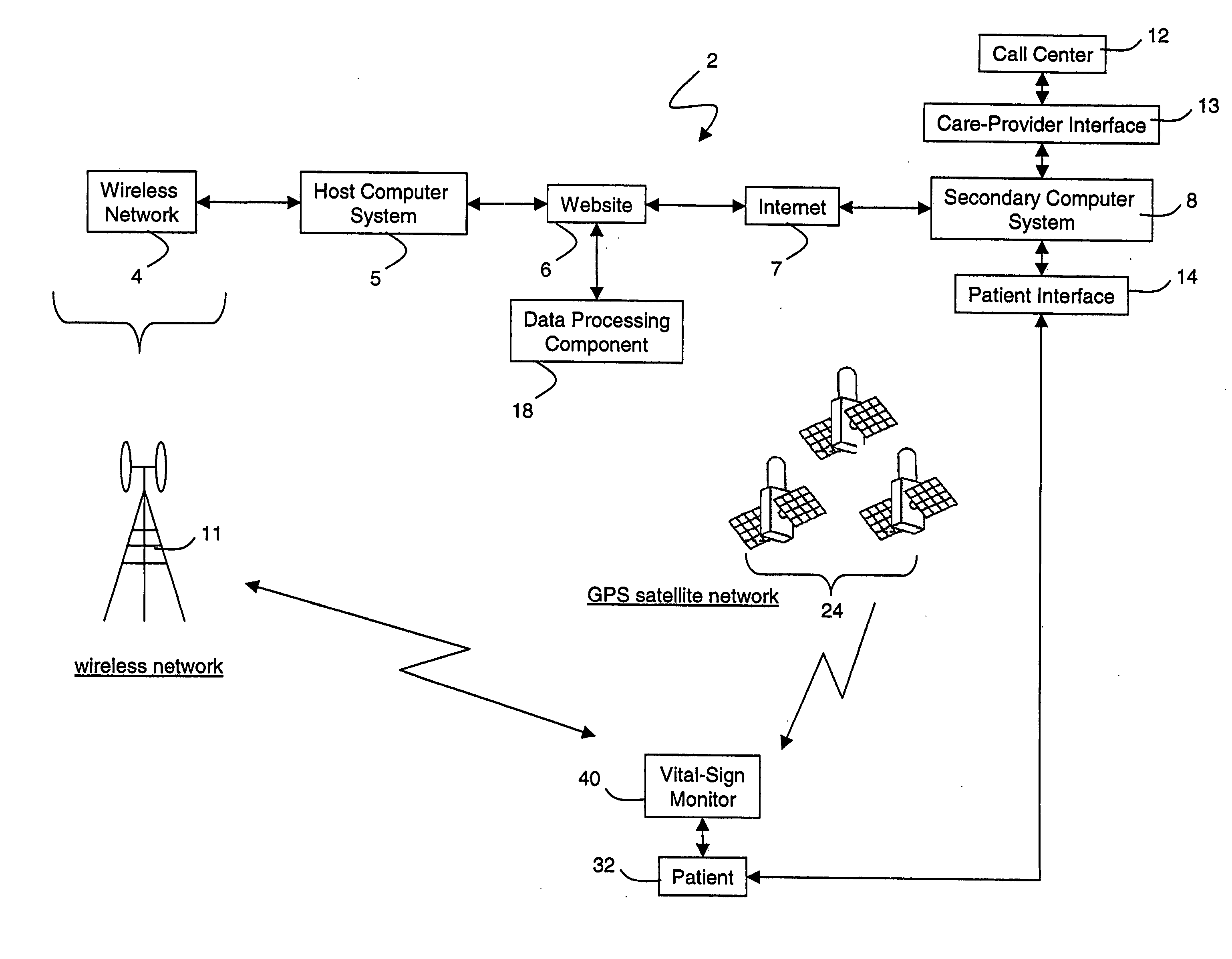
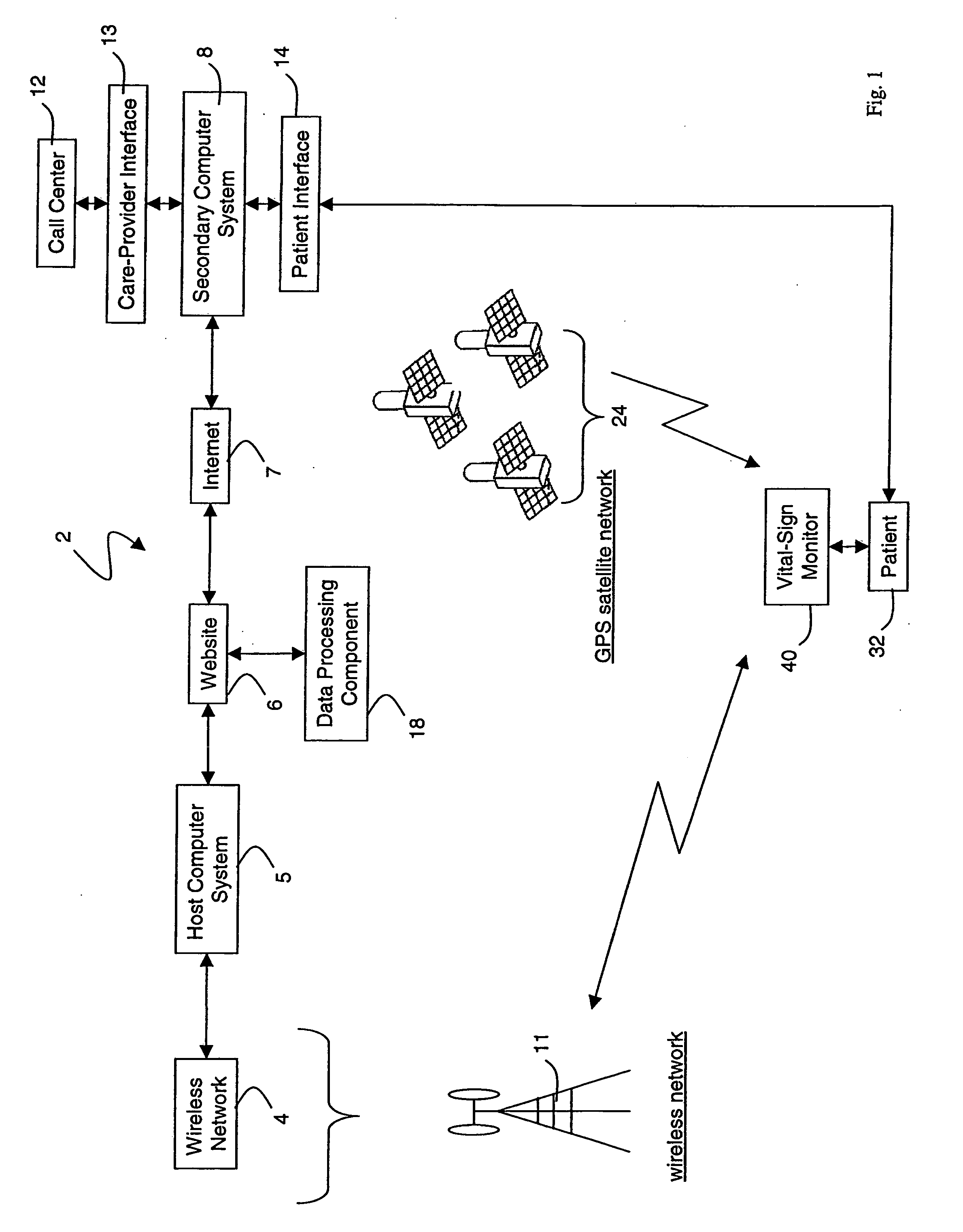
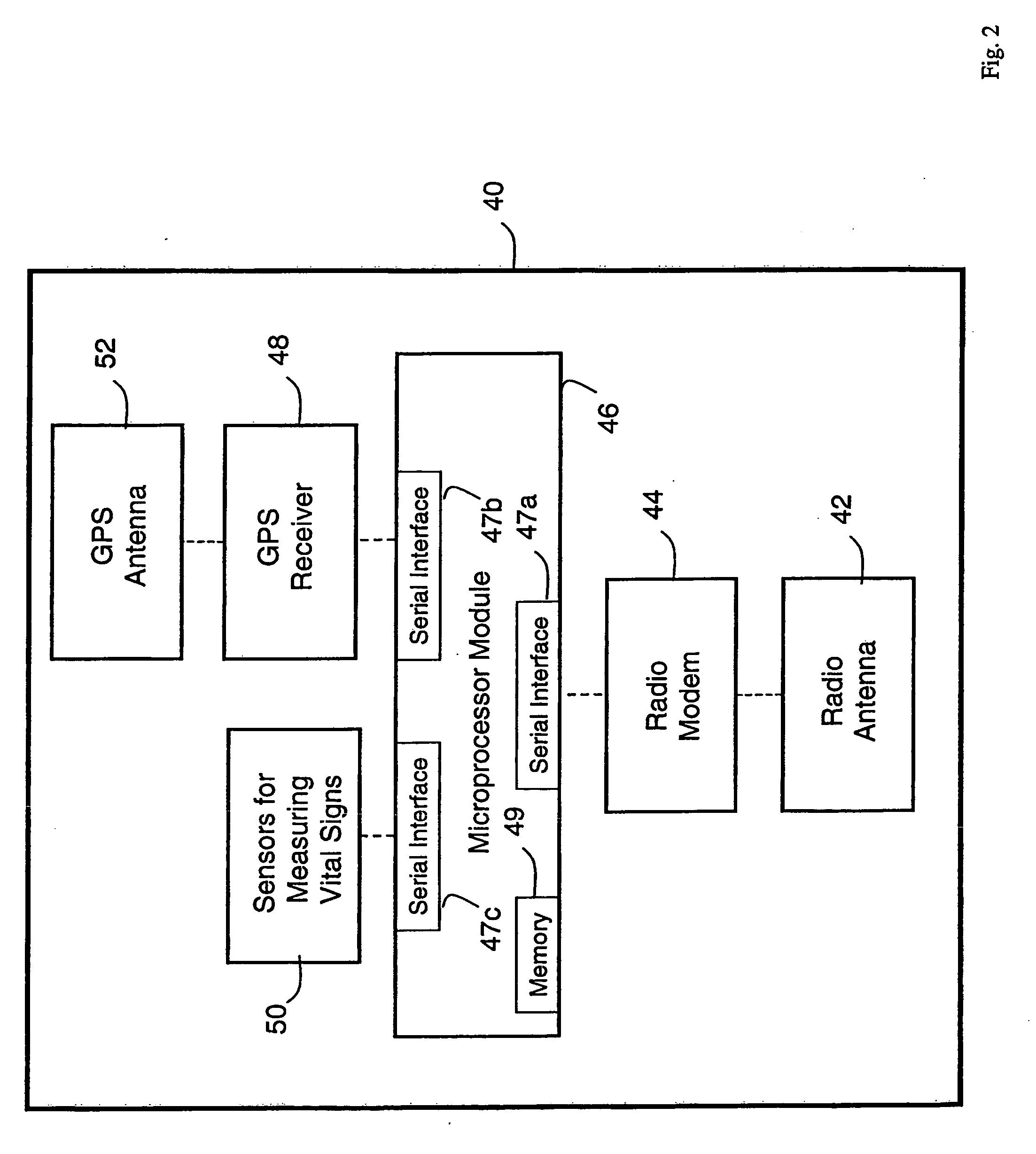
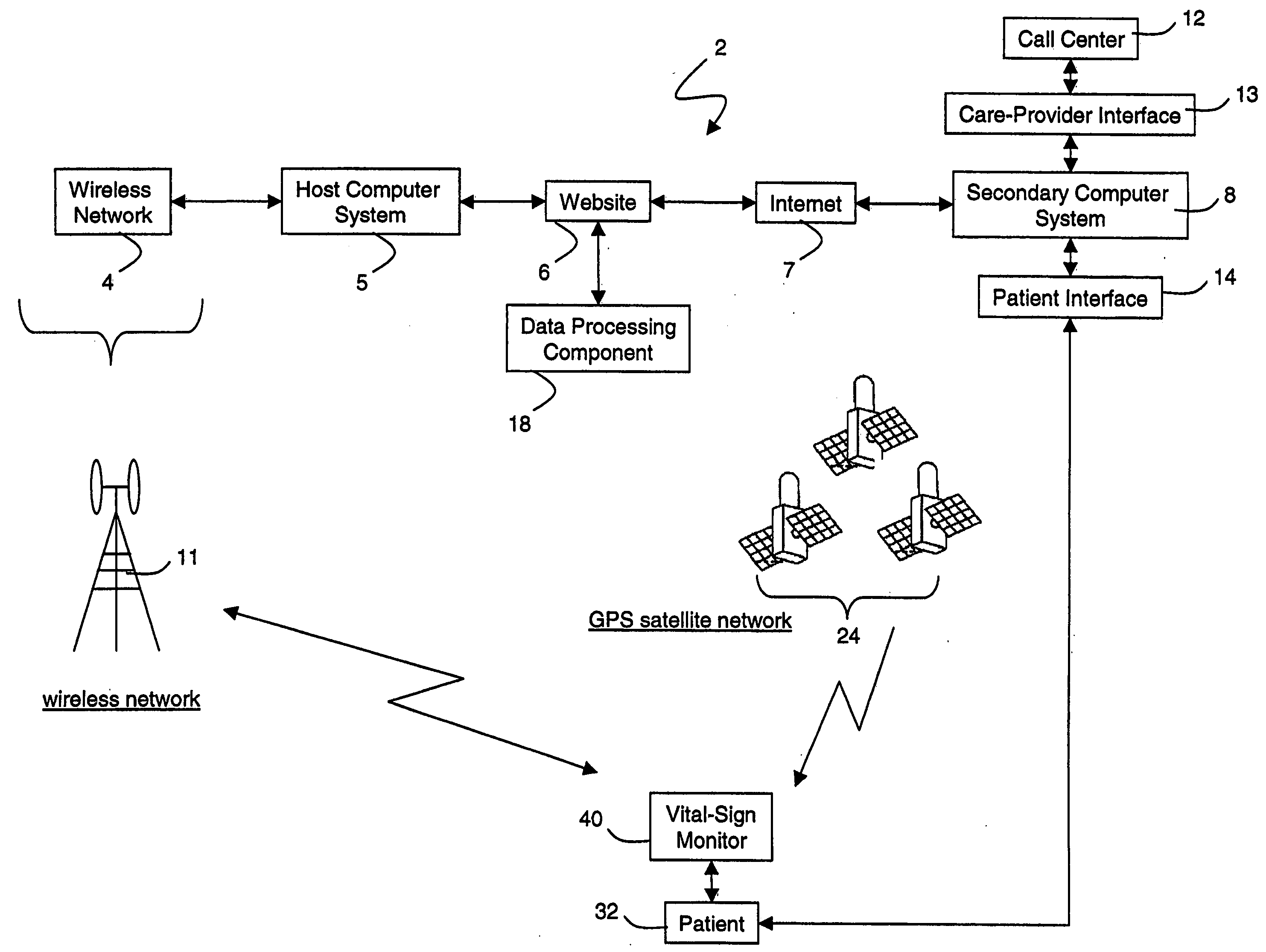
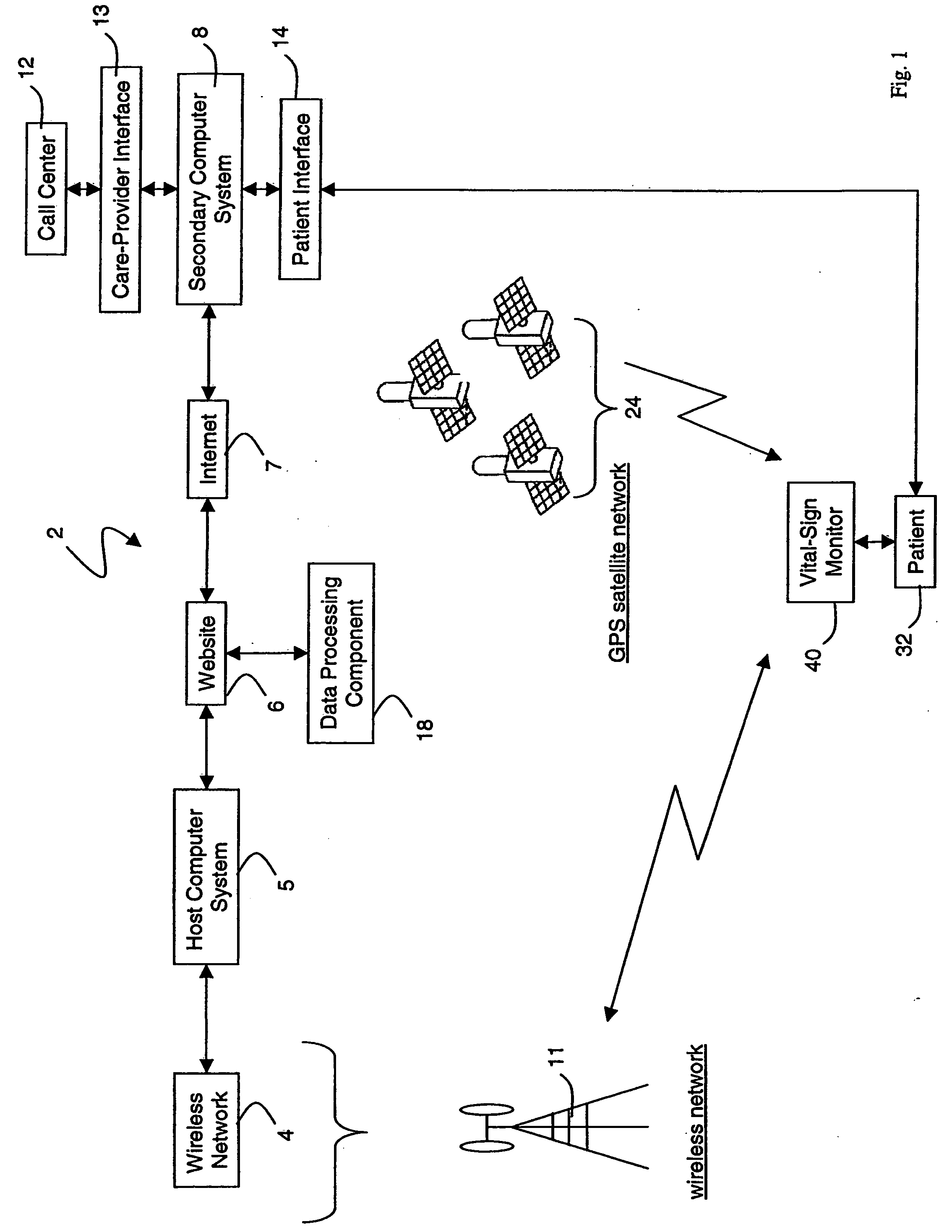
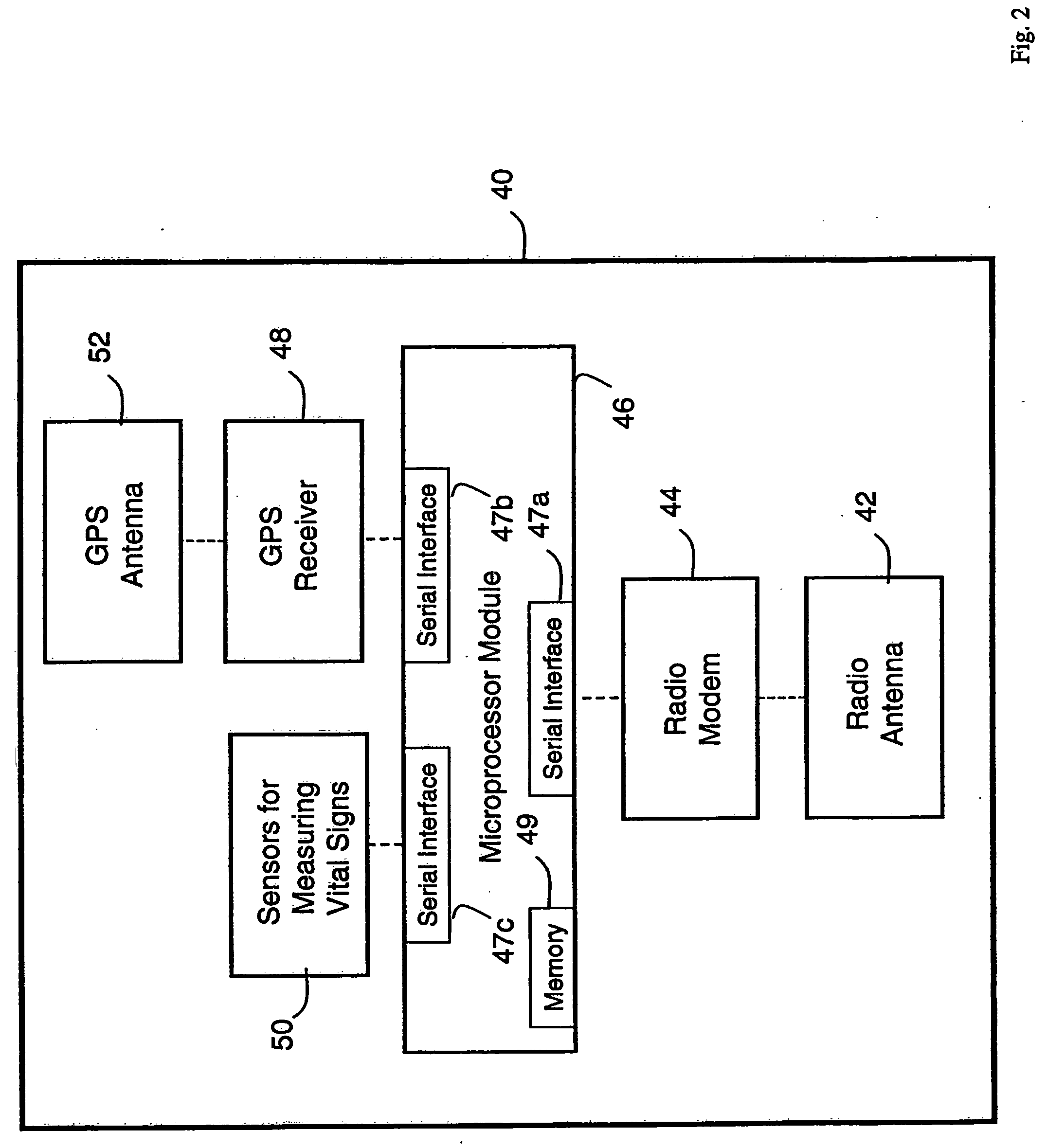
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS20050010087A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
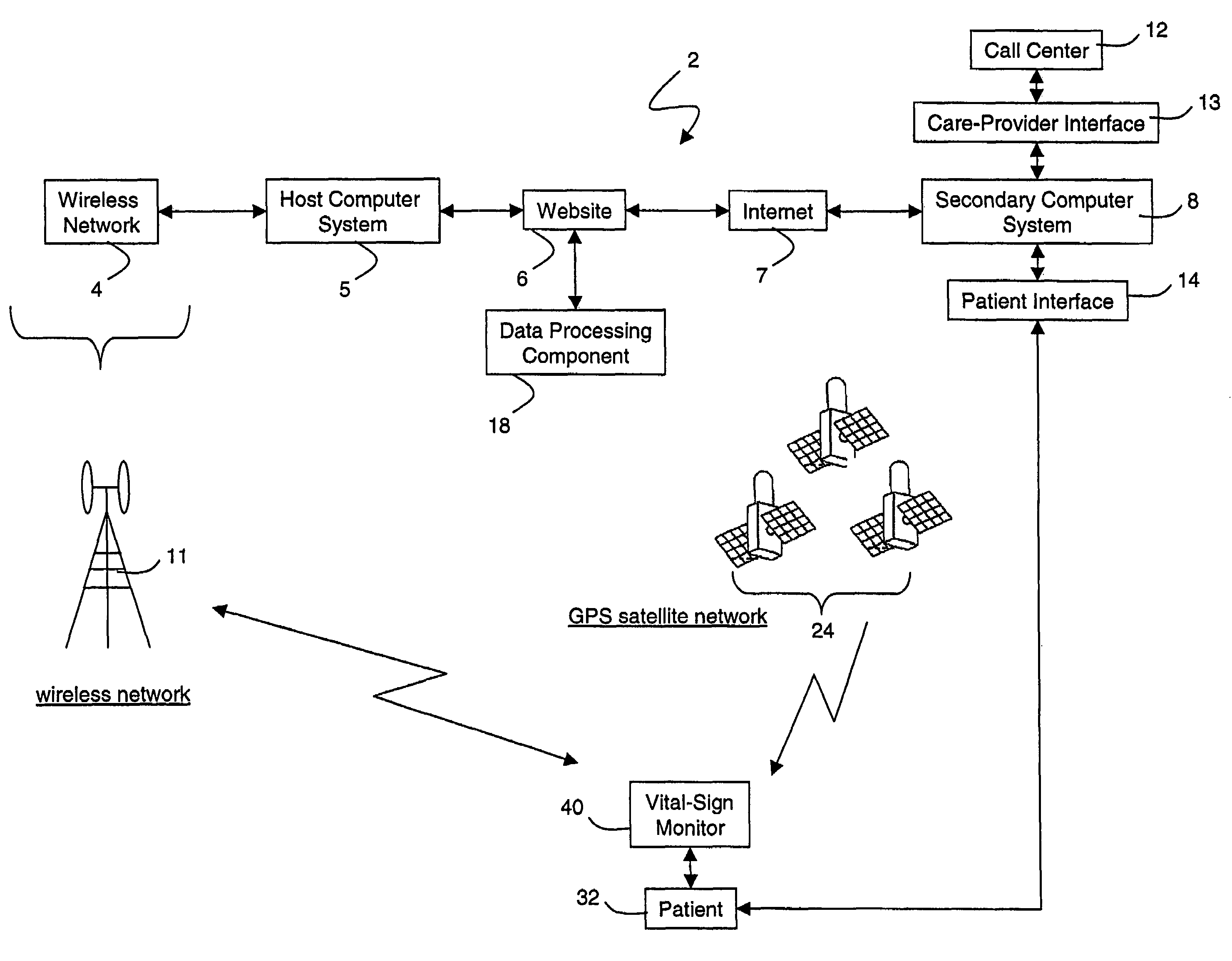
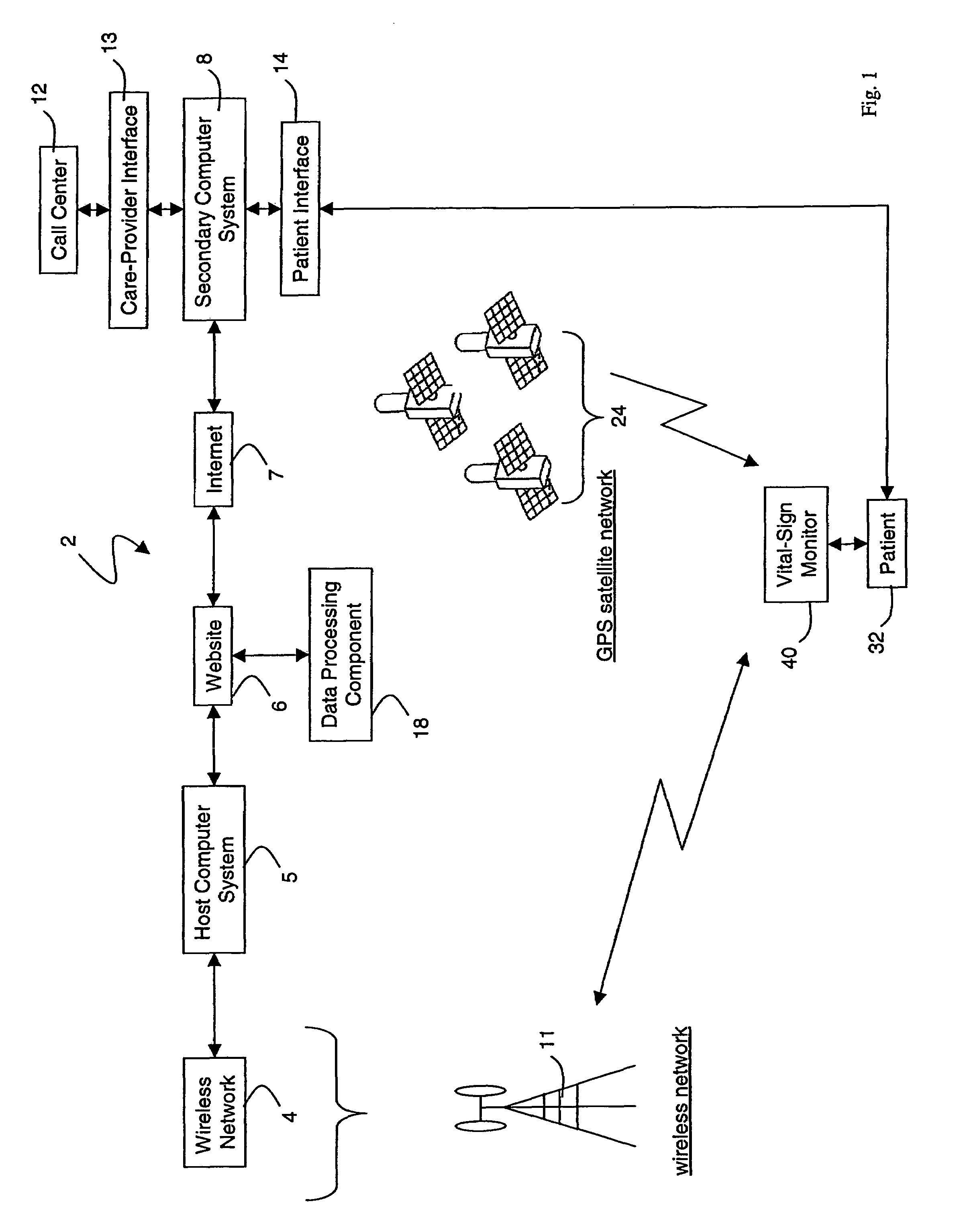
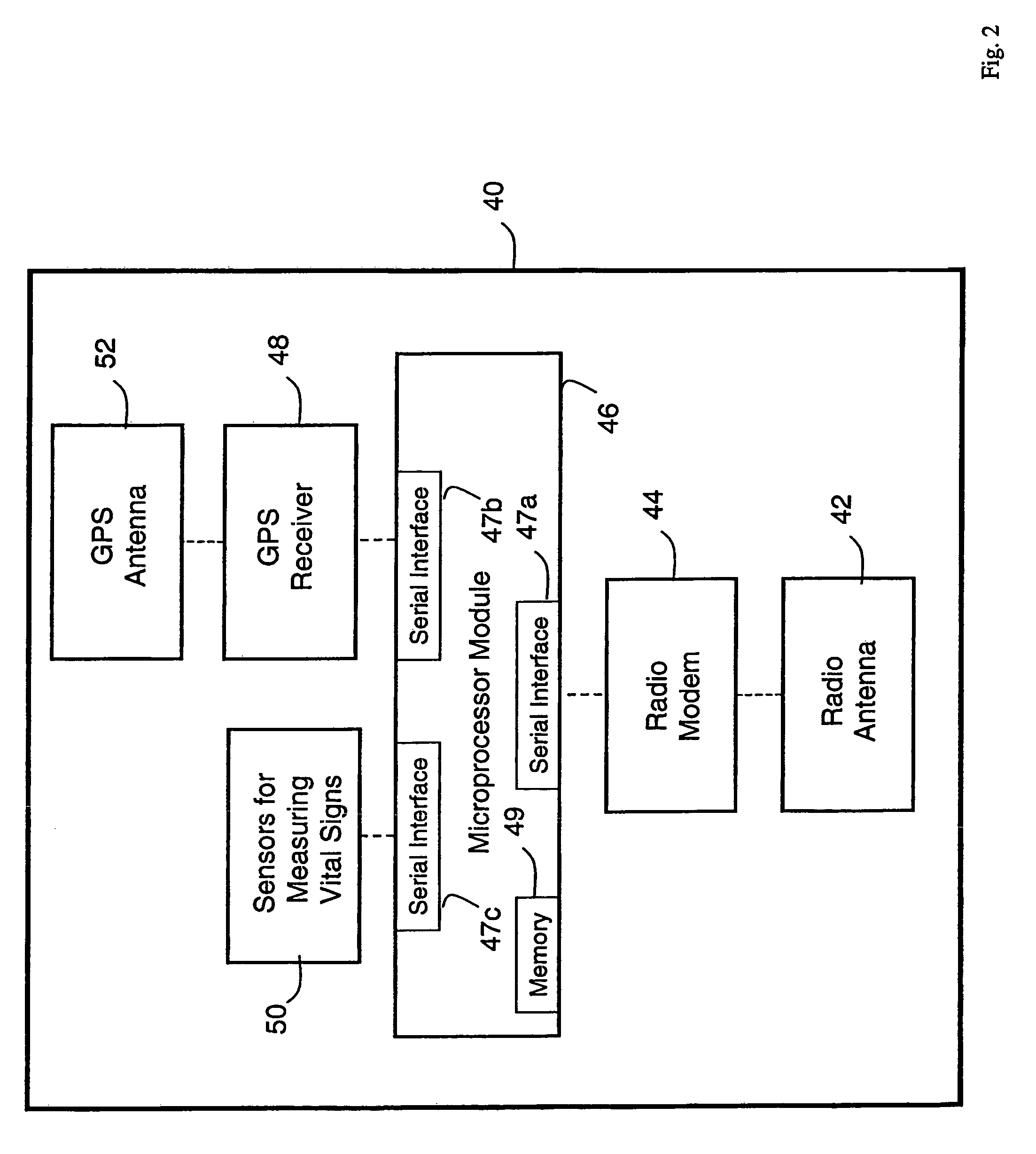
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
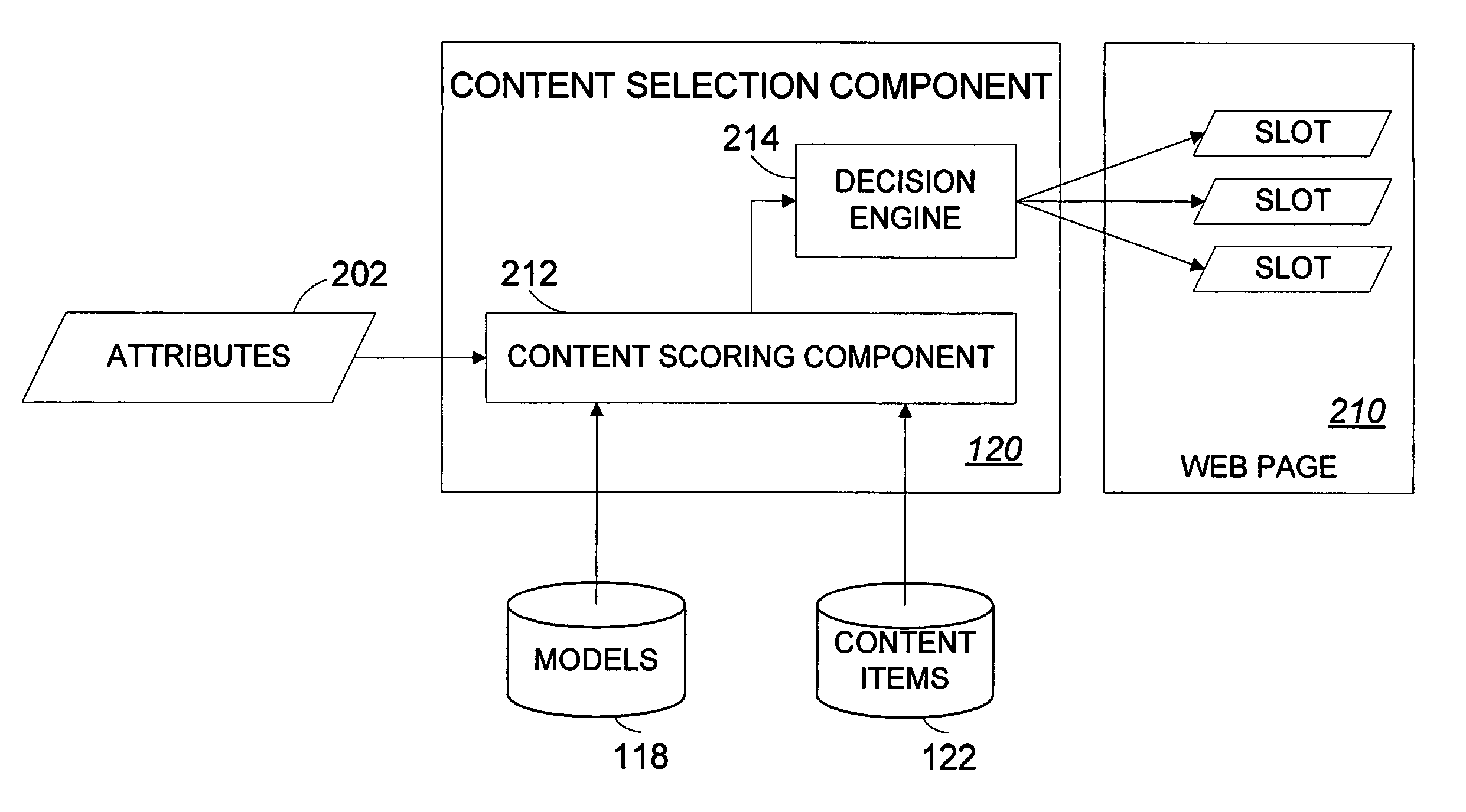
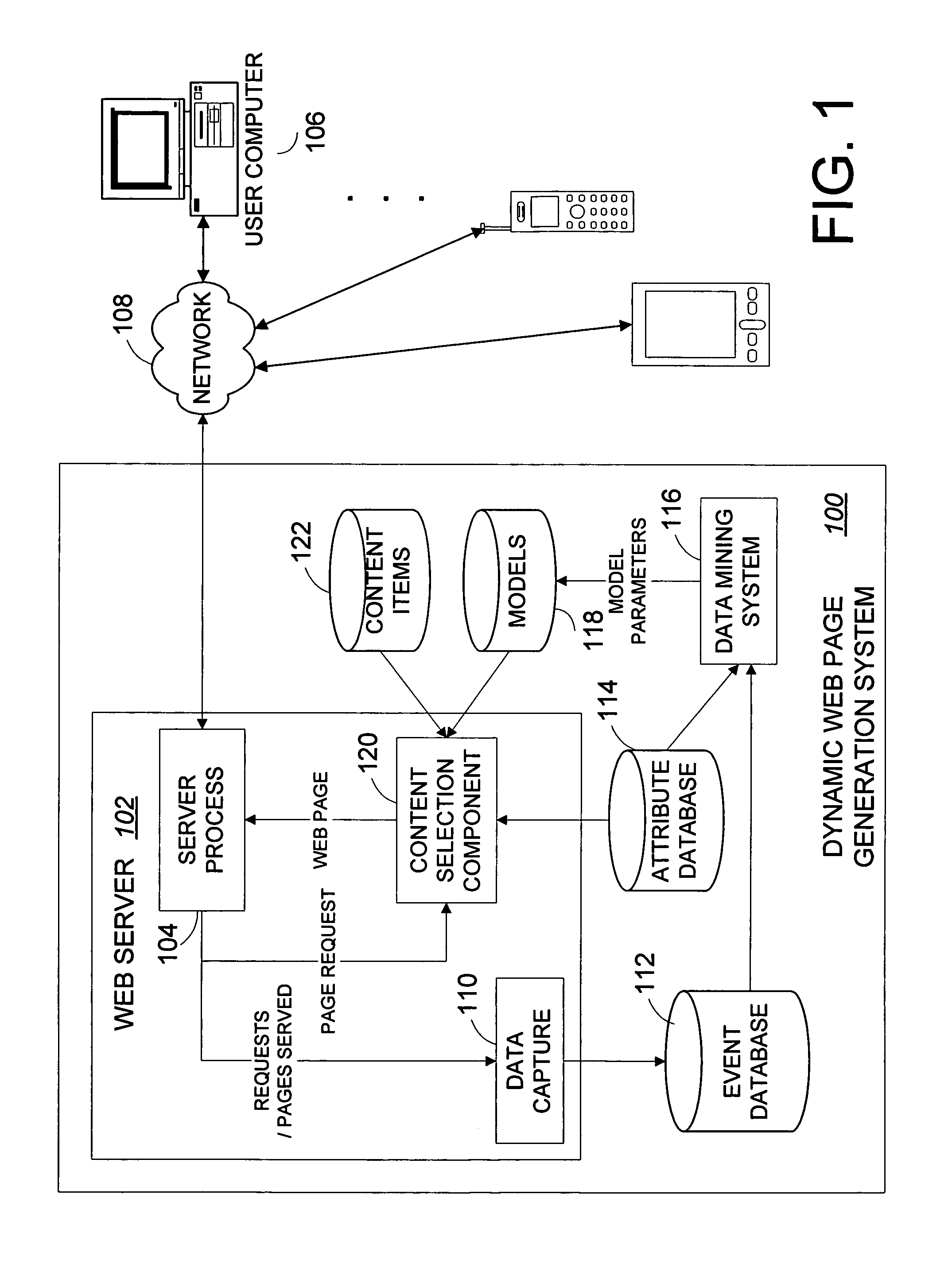
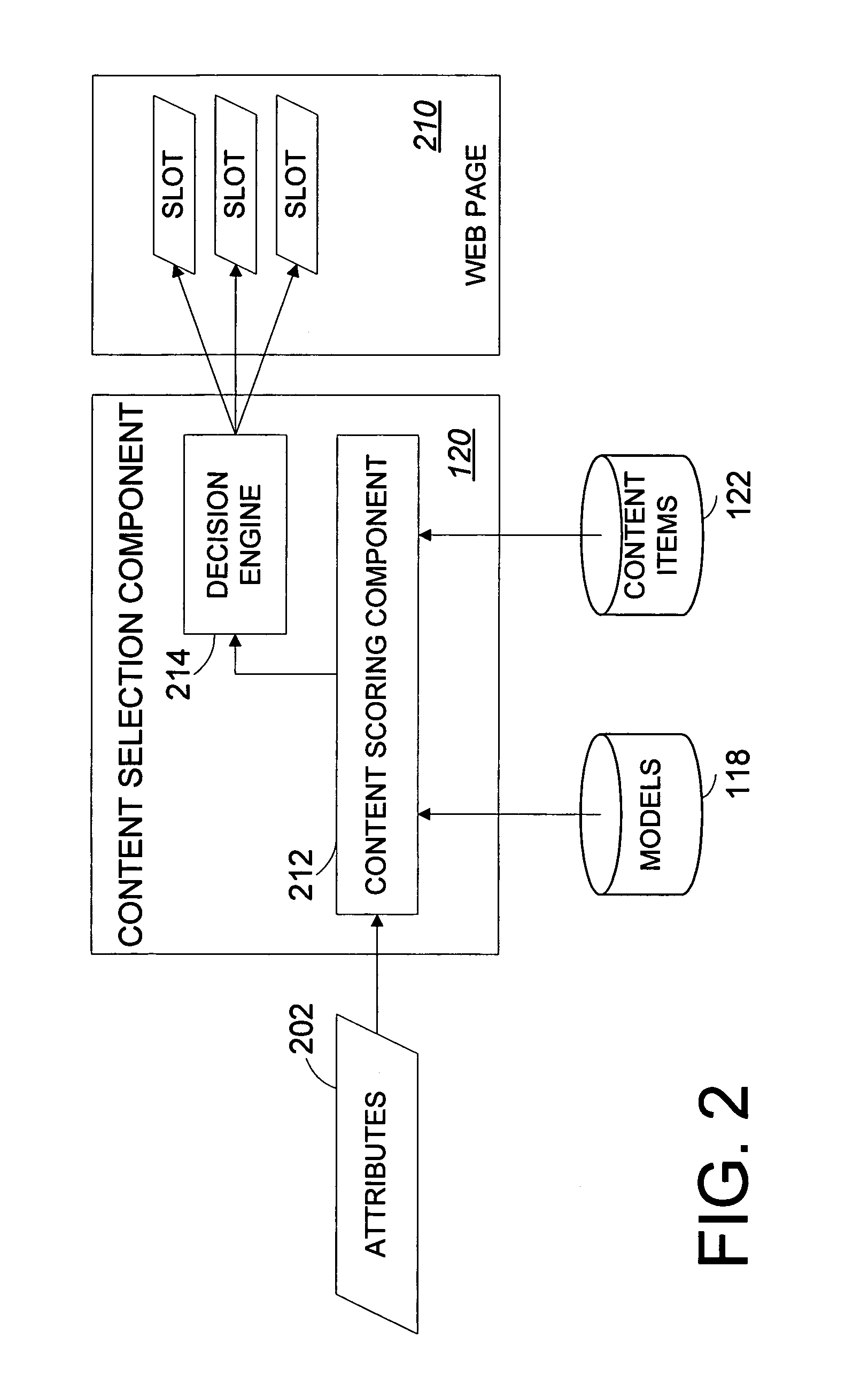
Systems and methods for statistically selecting content items to be used in a dynamically-generated display
InactiveUS7594189B1Quick responseLess time-consume and expensive manual laborDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteWeb page
An apparatus and methods advantageously select content items for dynamically-generated web pages in an intelligent and virtually autonomous manner. This permits the operator of the web site to rapidly identify and respond to trends, thereby advantageously updating the web site relatively quickly and efficiently without or with less time consuming and expensive manual labor. User interaction for a plurality of users with the web site is collected in a database. For various content items, the database is mined to extract relationships between probability and references of select attributes in probability models. When a new web page is requested, attributes, which can include attributes associated with a user, are used as references to the applicable probability models of selected content items, combined with value weighting to generate expected values, and selected for use in the web page at least partially based on the expected values.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Wireless, internet-based, medical diagnostic system
InactiveUS20060142648A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEmergency medicineGlobal Positioning System
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:TRIAGE DATA NETWORKS
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS7396330B2Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
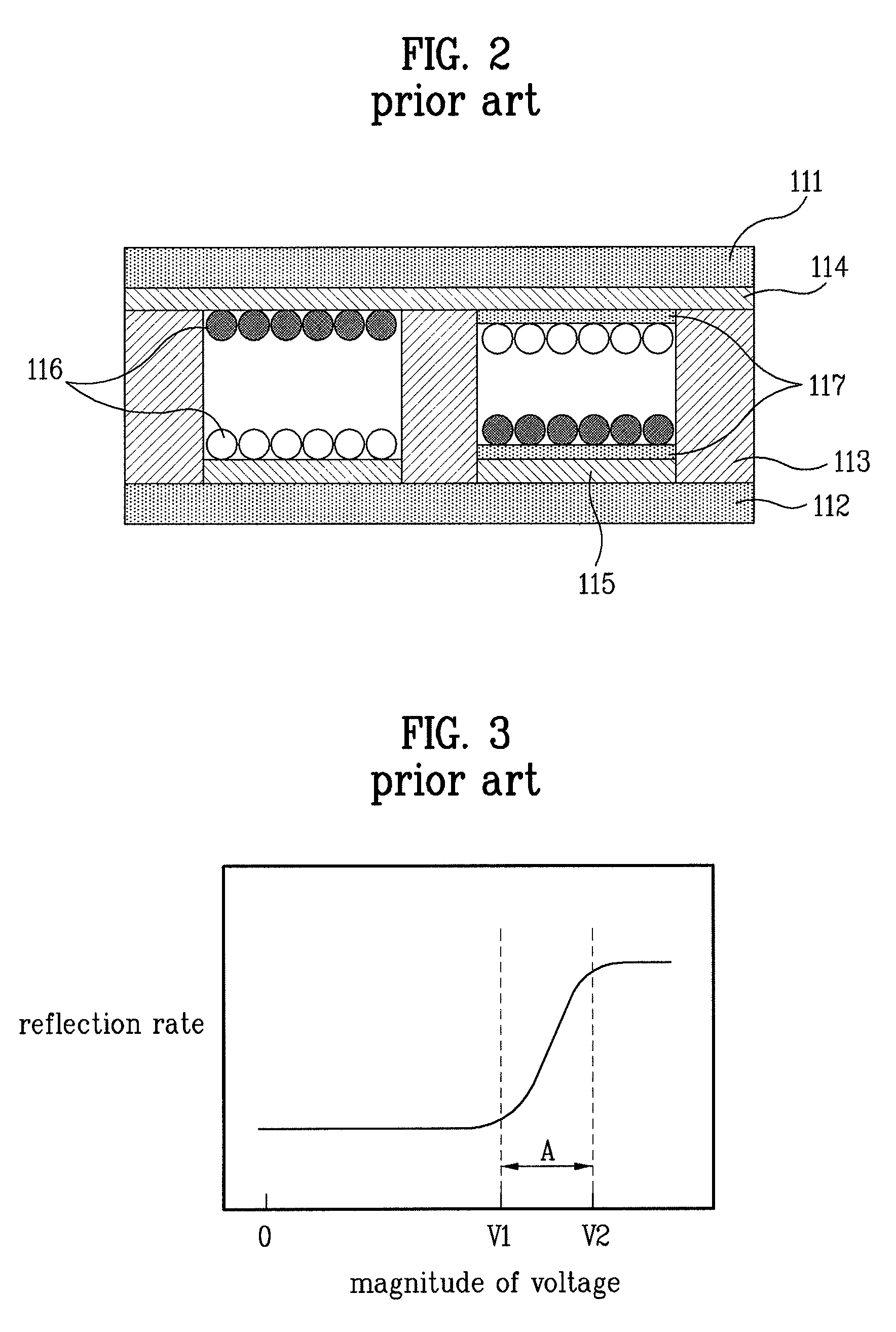
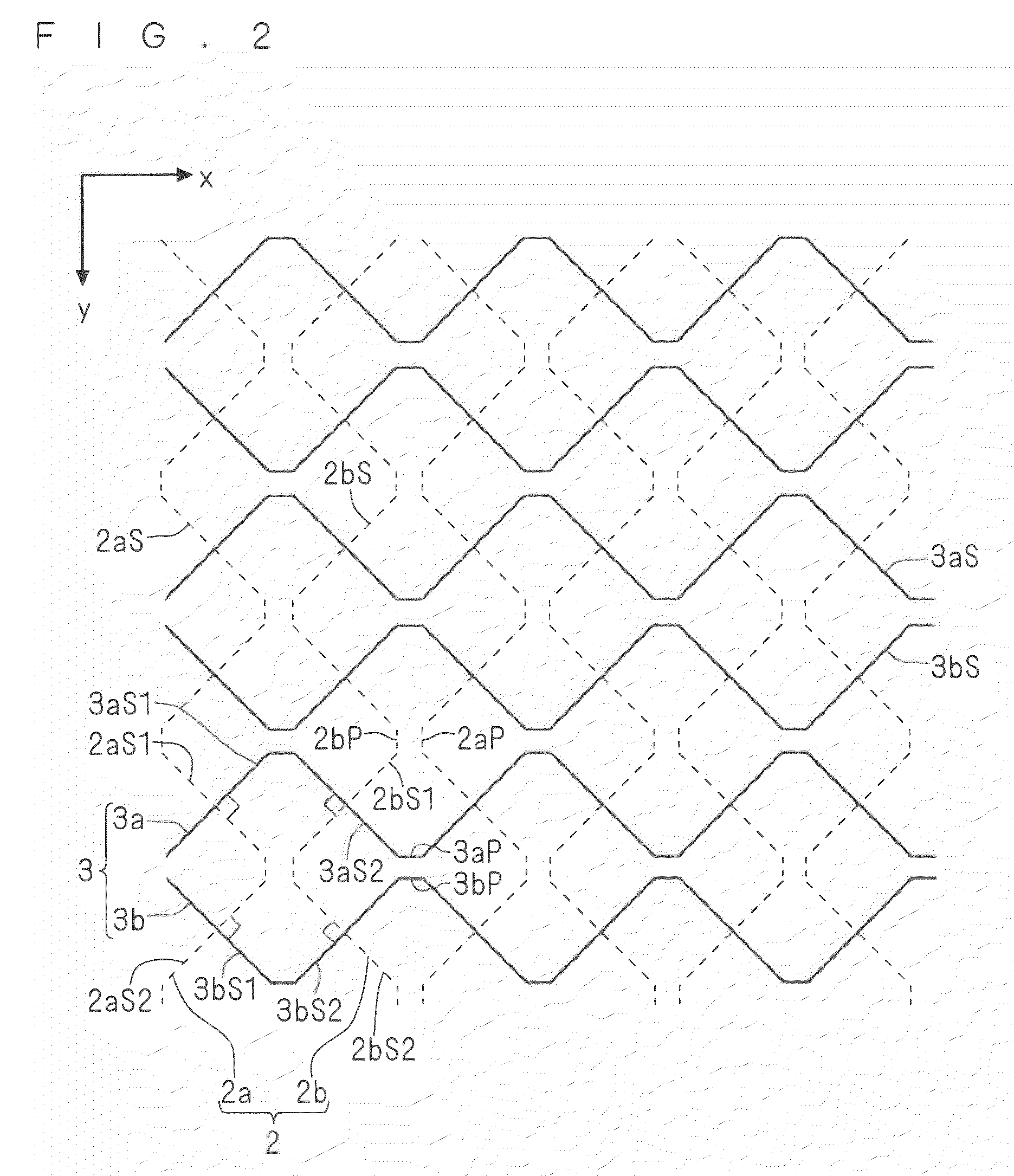
Electronic paper display device, manufacturing method and driving method thereof
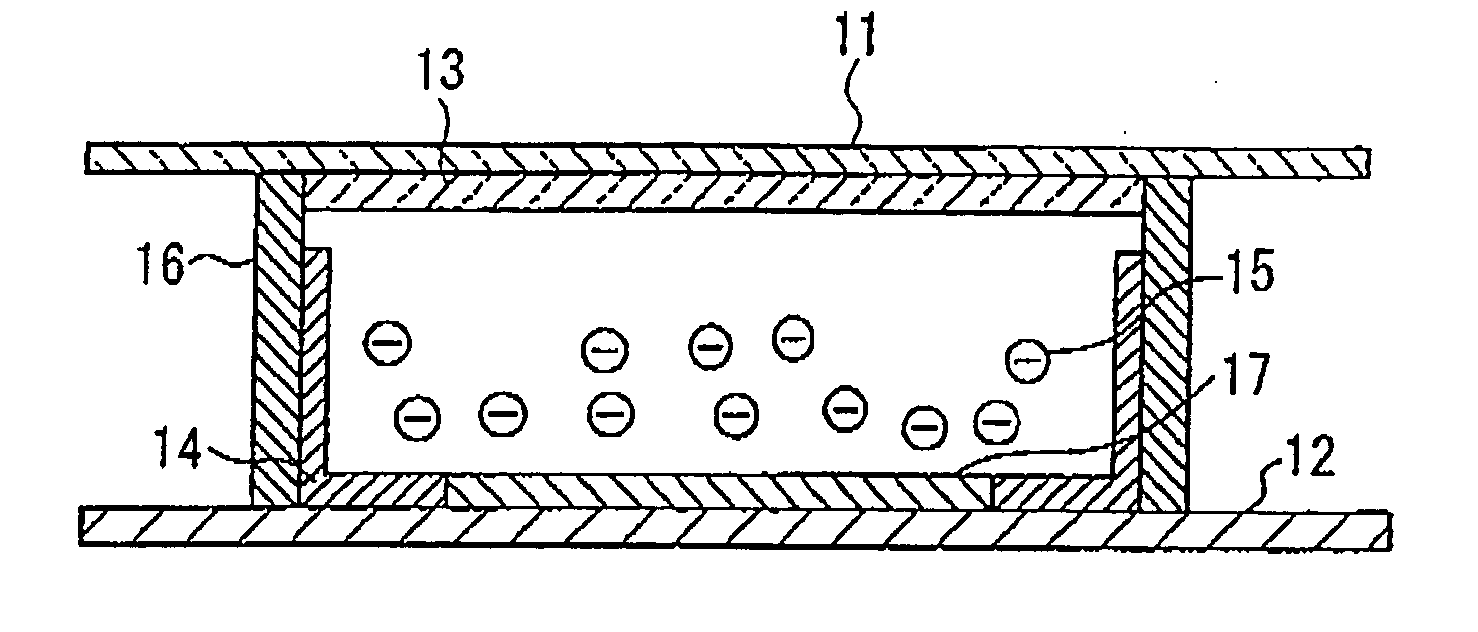
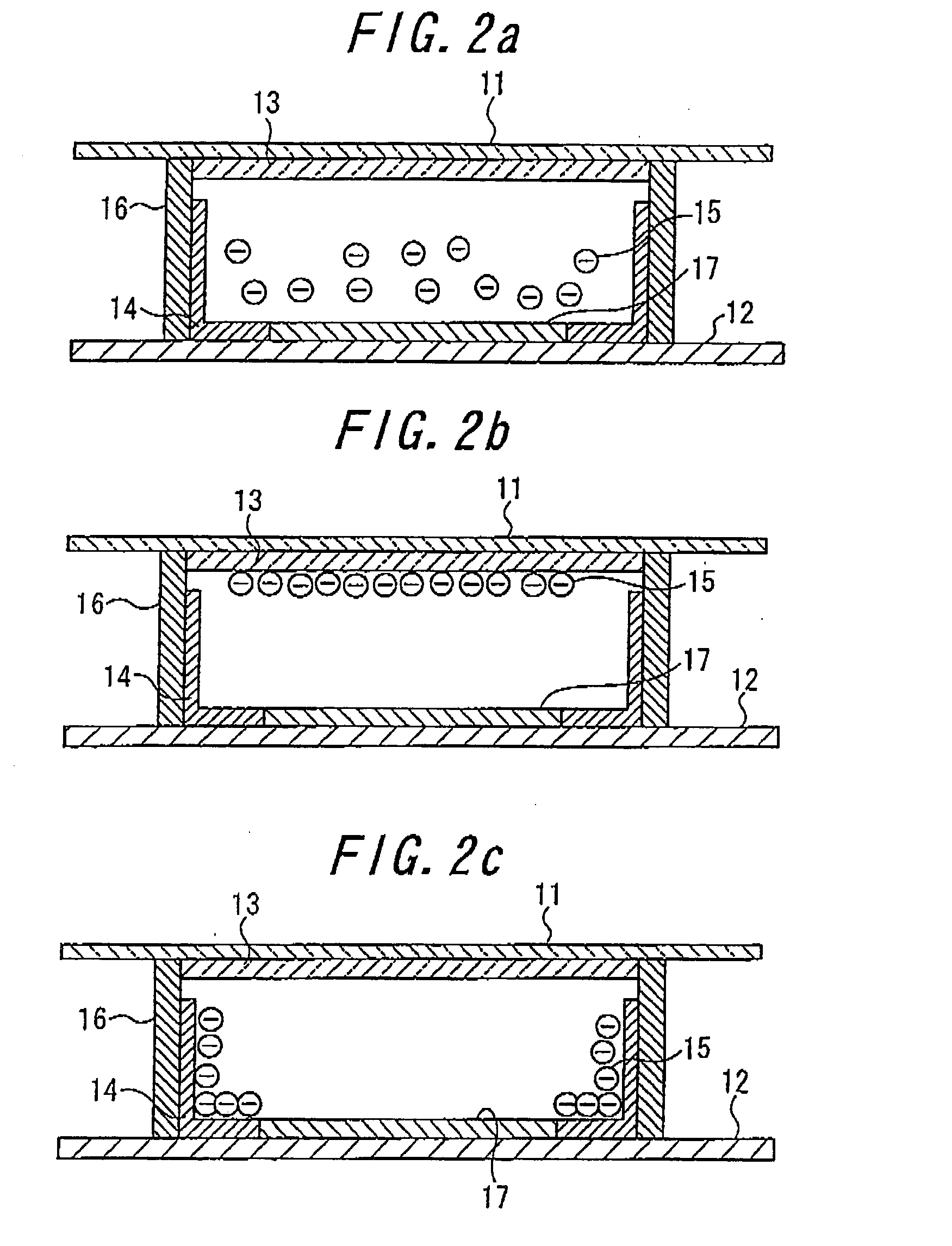
InactiveUS7751115B2Quick responseReduce voltageStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVoltage pulseElectrophoresis
An electronic paper display device, a manufacturing method and a driving method thereof are disclosed. Micro protrusion members are formed at electrodes or at insulating layers. Consequently, the electrophoretic particles are prevented from being securely attached to an upper or the lower structure, and therefore, the quality of pictures is improved, and the contrast ratio of the pictures is increased. The relative sizes and the injection amounts of two kinds of electrophoretic particles are changed such that the relative sizes and the injection amounts of the electrophoretic particles are different from each other. Consequently, the driving voltage is lowered by excessively electrifying the electrophoretic particles of one kind. Protrusions are formed at the corresponding electrode such that a relatively large electric field is distributed around the electrode at which electrophoretic particles are located in the initial stage of voltage application. Consequently, the electrophoretic particles are easily separated from the electrode and moved even at low driving voltage. As such, the voltage level of the driving voltage pulse is lowered. Consequently, it is possible to further increase the response speed of the driving devices and to lower the internal voltage of the devices, thereby reducing the costs related to the driving devices.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
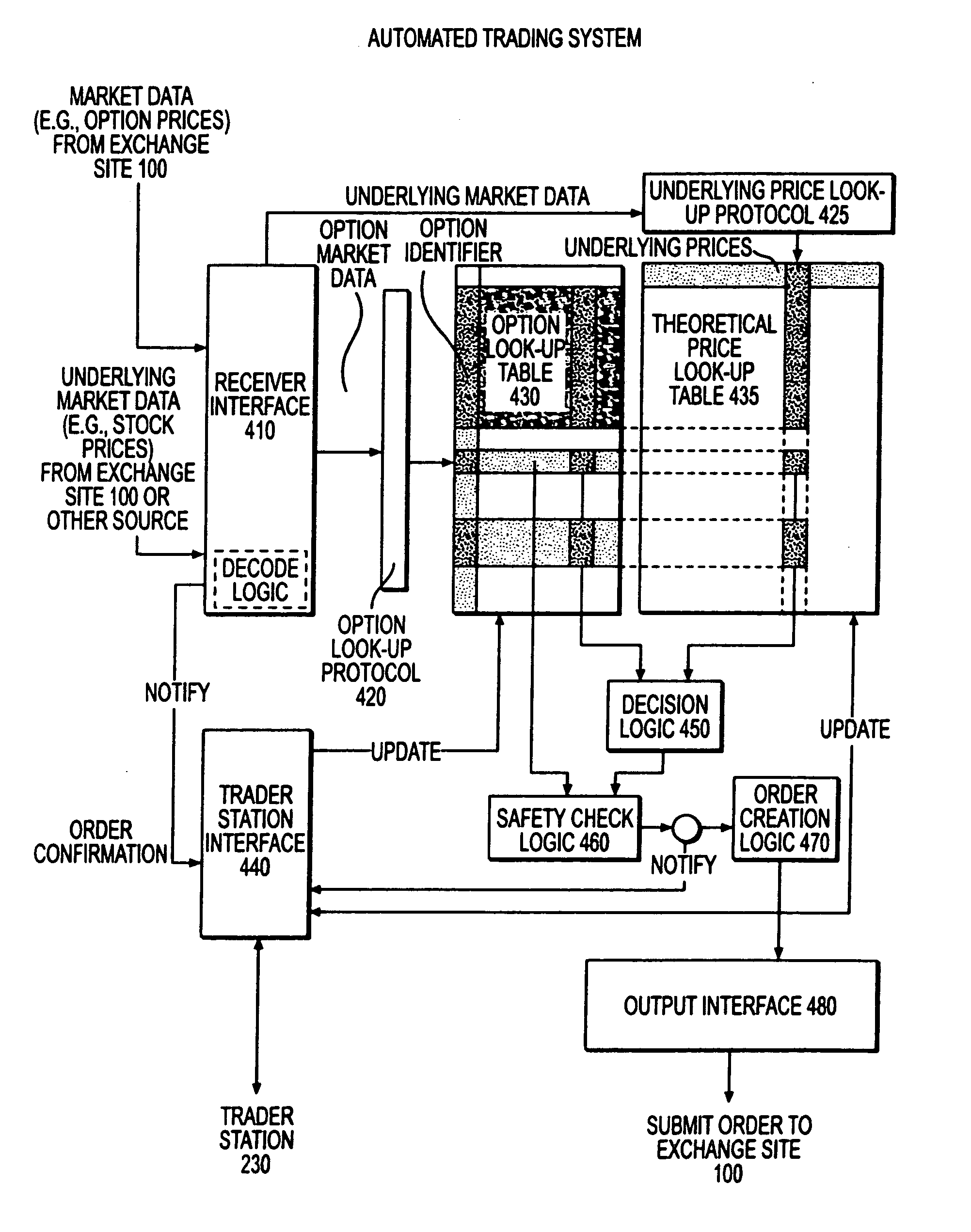
Automated trading system in an electronic trading exchange
InactiveUS7251629B1Quick responseGuaranteed accuracyComplete banking machinesFinanceData miningElectronic trading
An electronic exchange system network includes a trader site having an automated trading system capable of submitting orders to an exchange site. The automated trading system determines whether an order should be submitted based on, for example, the current market price of an option and theoretical buy and sell prices. The theoretical buy and sell prices are derived from, among other things, the current market price of the security underlying the option. A look-up table stores a range of theoretical buy and sell prices for a given range of current market price of the underlying security. Accordingly, as the price of the underlying security changes, a new theoretical price may be indexed in the look-up table, thereby avoiding calculations that would otherwise slow automated trading decisions. Other techniques may be used in addition or in the alternative to speed automatic decision-making. In addition, a system of checks may be conducted to ensure accurate and safe automated trading. The automated trading system may be capable of automatically submitting orders in connection with the underlying security in order to hedge part of the delta risk associated with the automated option trades.
Owner:DCFB
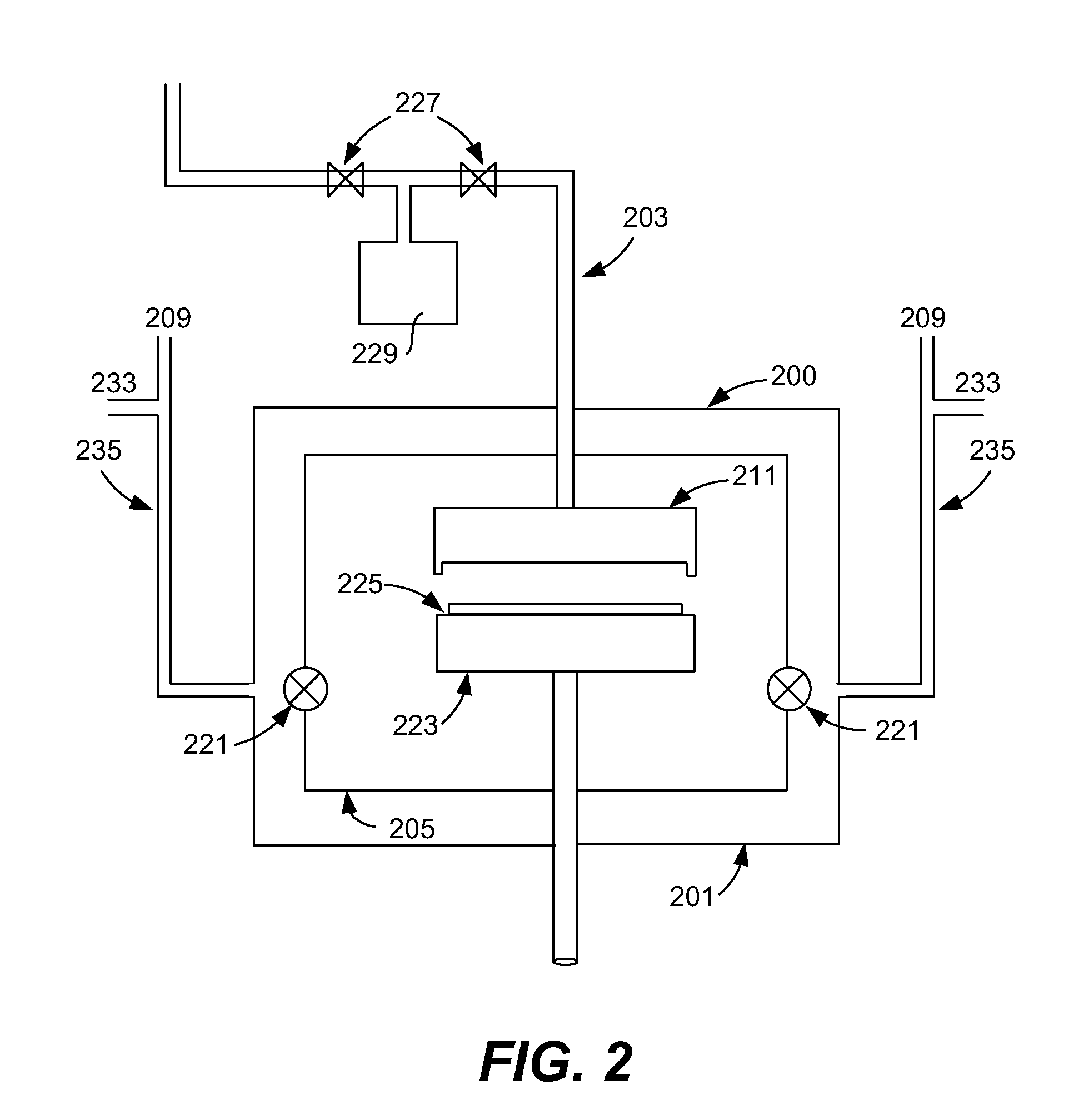
Deposition sub-chamber with variable flow
ActiveUS7993457B1Enhanced chamber performanceImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
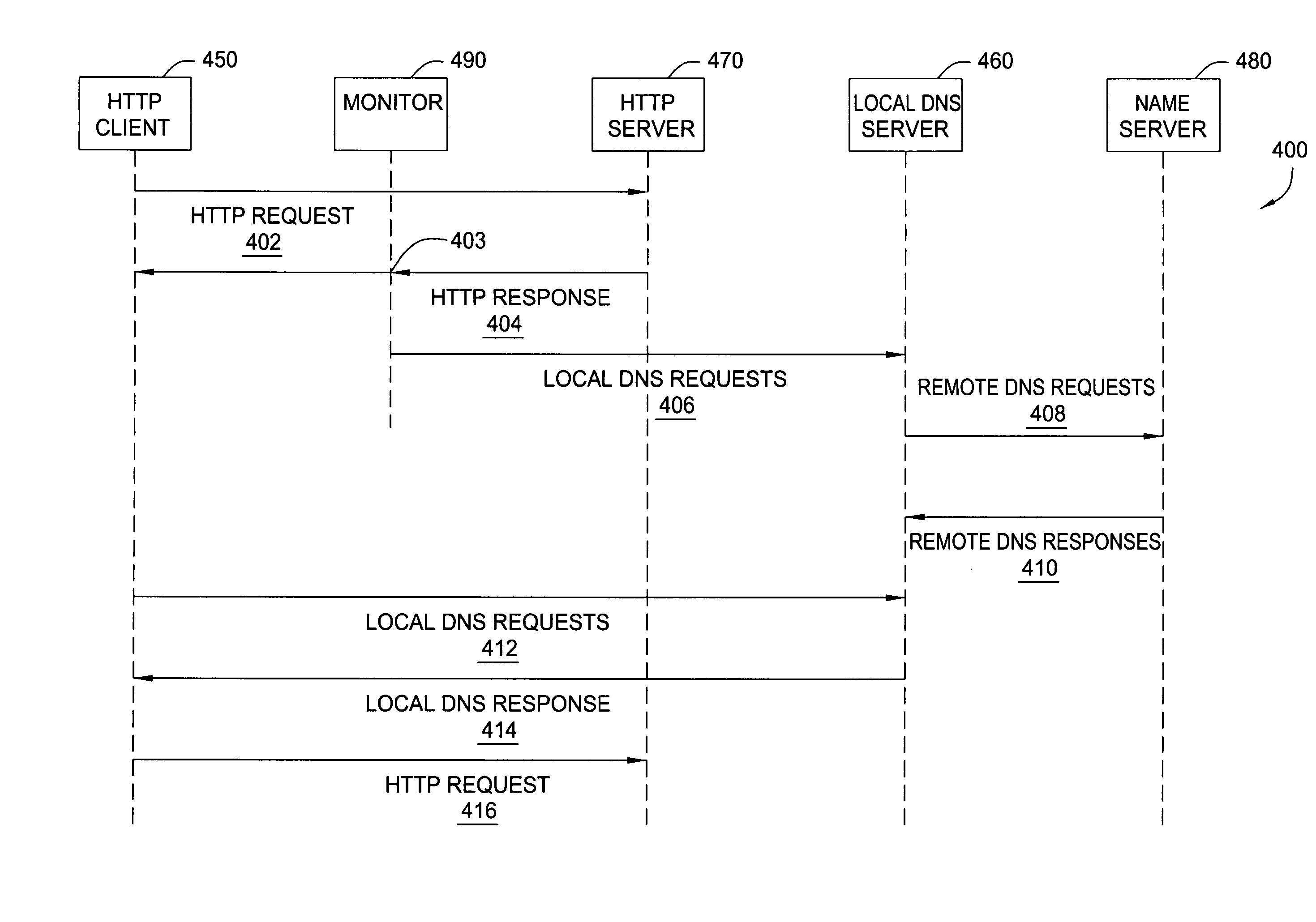
Method and apparatus for DNS pre-fetching for multiple clients
InactiveUS20050262248A1Quick responseQuick connectionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDomain nameData pack
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and apparatus for DNS pre-fetching for multiple clients. In one embodiment, all packets coming into or going out of a local network are scanned for application protocol, domain names, and / or other information. If pre-defined criteria indicate that the network is interested in a particular domain name, a DNS lookup is performed and the corresponding IP address is cached by the local DNS server. The local DNS server is thereby able to quickly respond to future requests for the cached domain name. Moreover, because the IP address is cached at the local DNS server, any client connected to the local DNS server on the local network can request the cached domain name from the local DNS server and be quickly connected to the indicated domain name.
Owner:IBM CORP
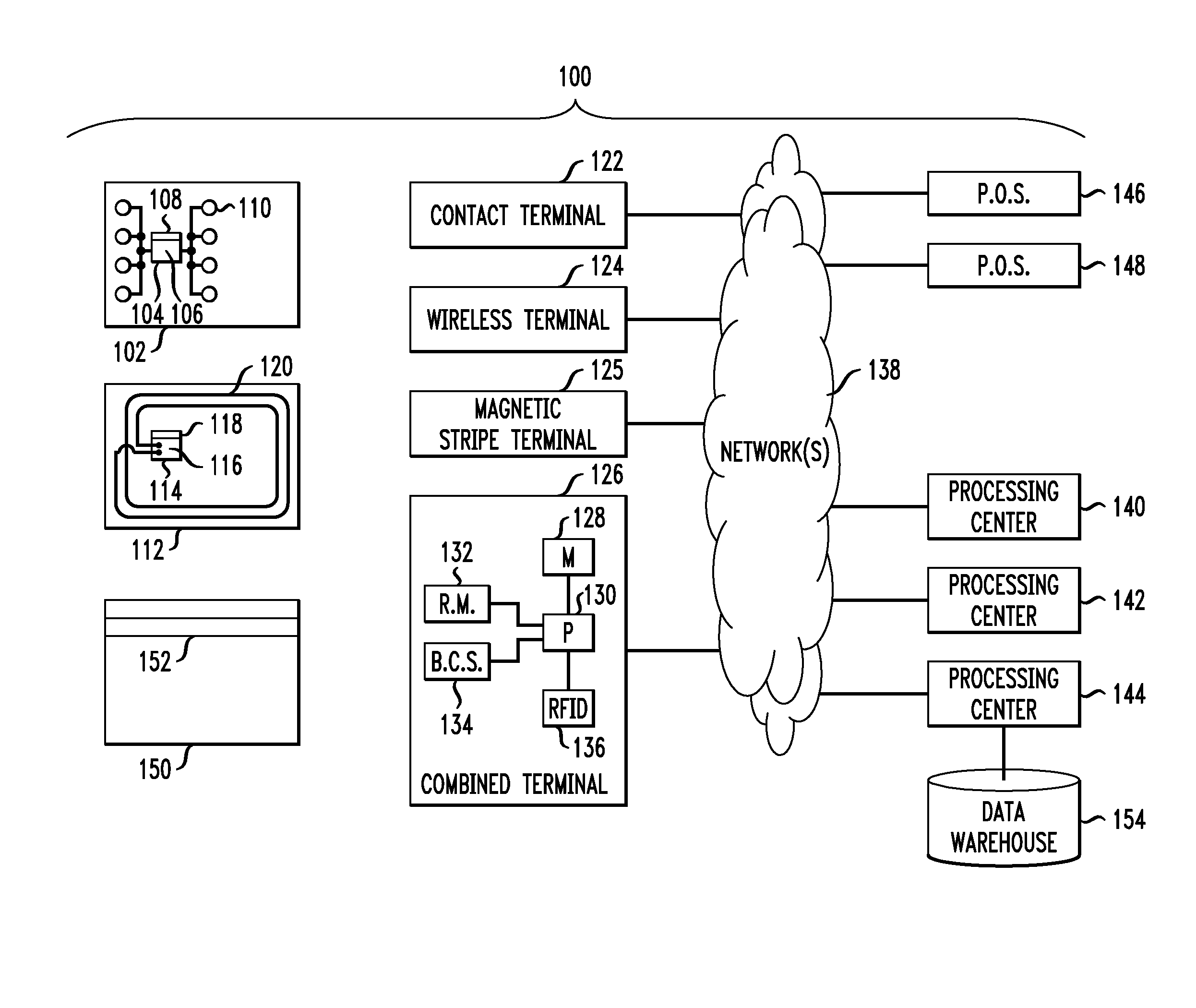
Techniques for authorization of usage of a payment device
ActiveUS20080033880A1High degreeRapid responseComplete banking machinesFinancePaymentInternet privacy
Techniques for authorization of usage of a payment device include facilitating an issuer of the device obtaining an authorization message for an account number associated with the device, based on desired spending limit parameters established by a merchant and / or an issuer of the device; facilitating obtaining an issuer authorization decision; and responsive to the issuer authorization decision, facilitating setting a spending limit for the account number based on at least an appropriate one of the parameters.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
Liquid Crystal Display Device and Driving Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080284719A1Increase contrastImprove image qualityStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
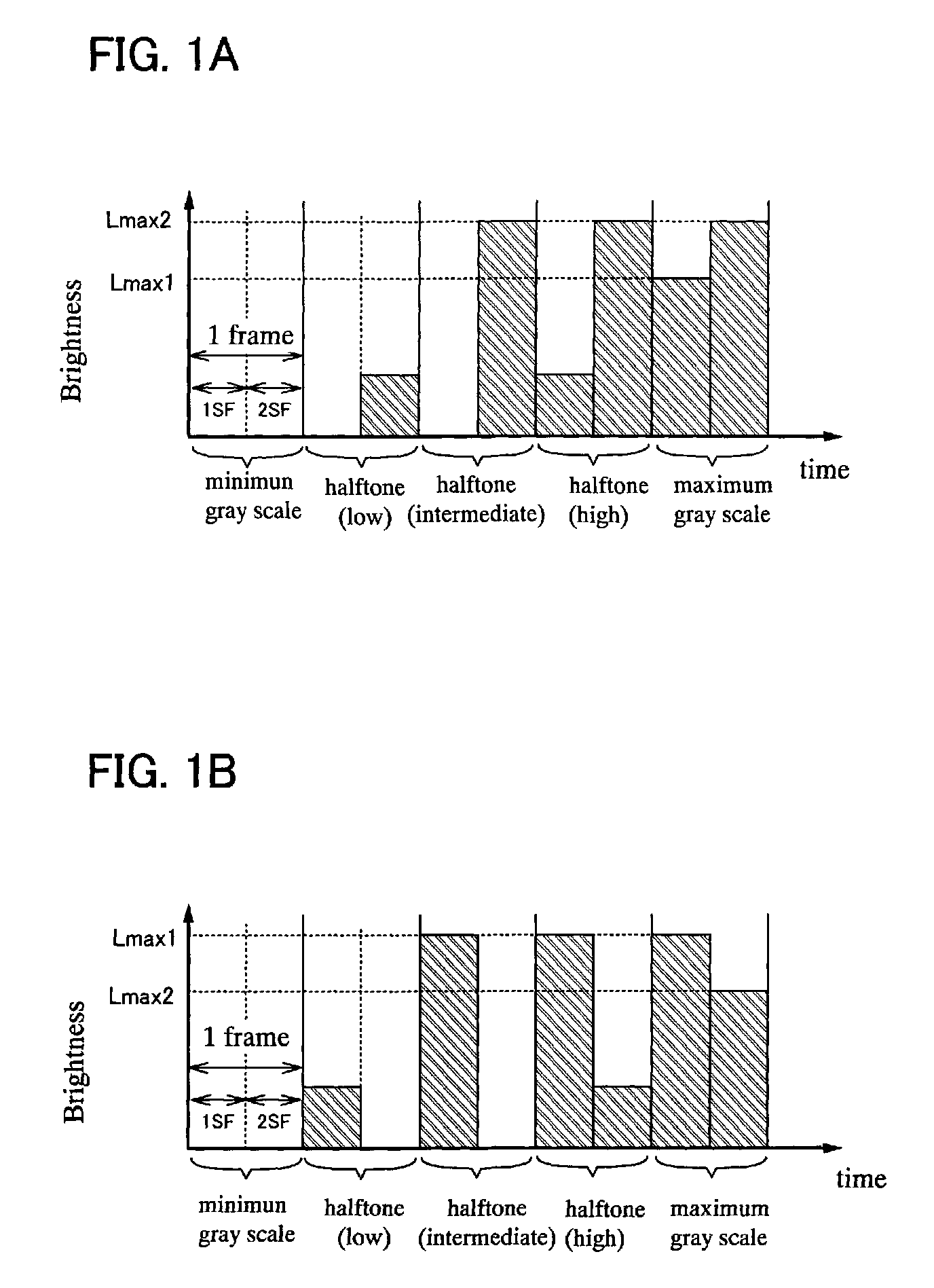
In a display device including a backlight and a display panel, the area of the backlight is divided into a plurality of unit regions; the display panel includes pixels which are larger in number than the unit regions; a frame rate of image data input to the device is converted to perform display while part of the unit regions in which black is displayed is in a non-light emission state; and the driving frequency of the backlight is converted in accordance with the display.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
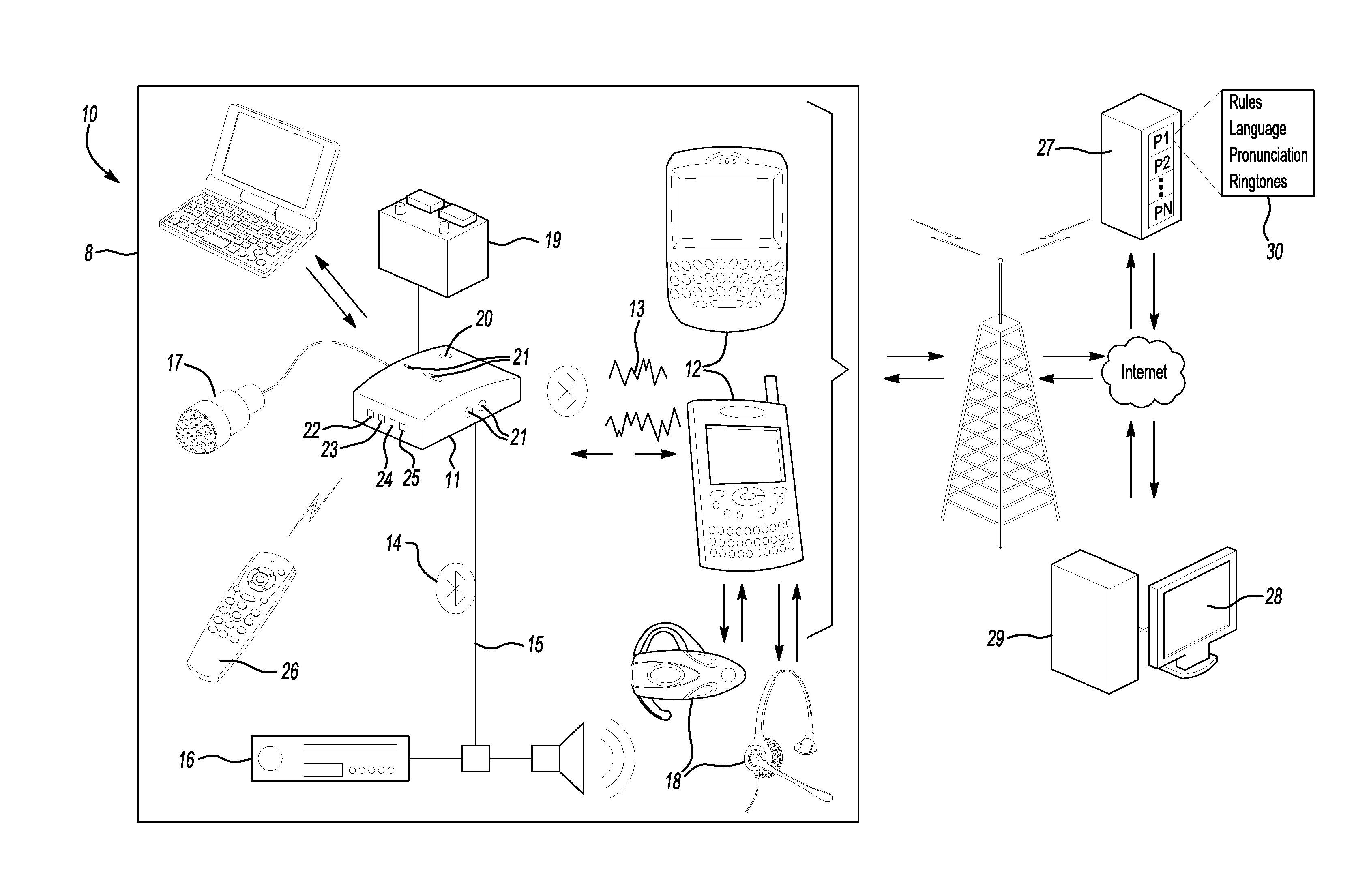
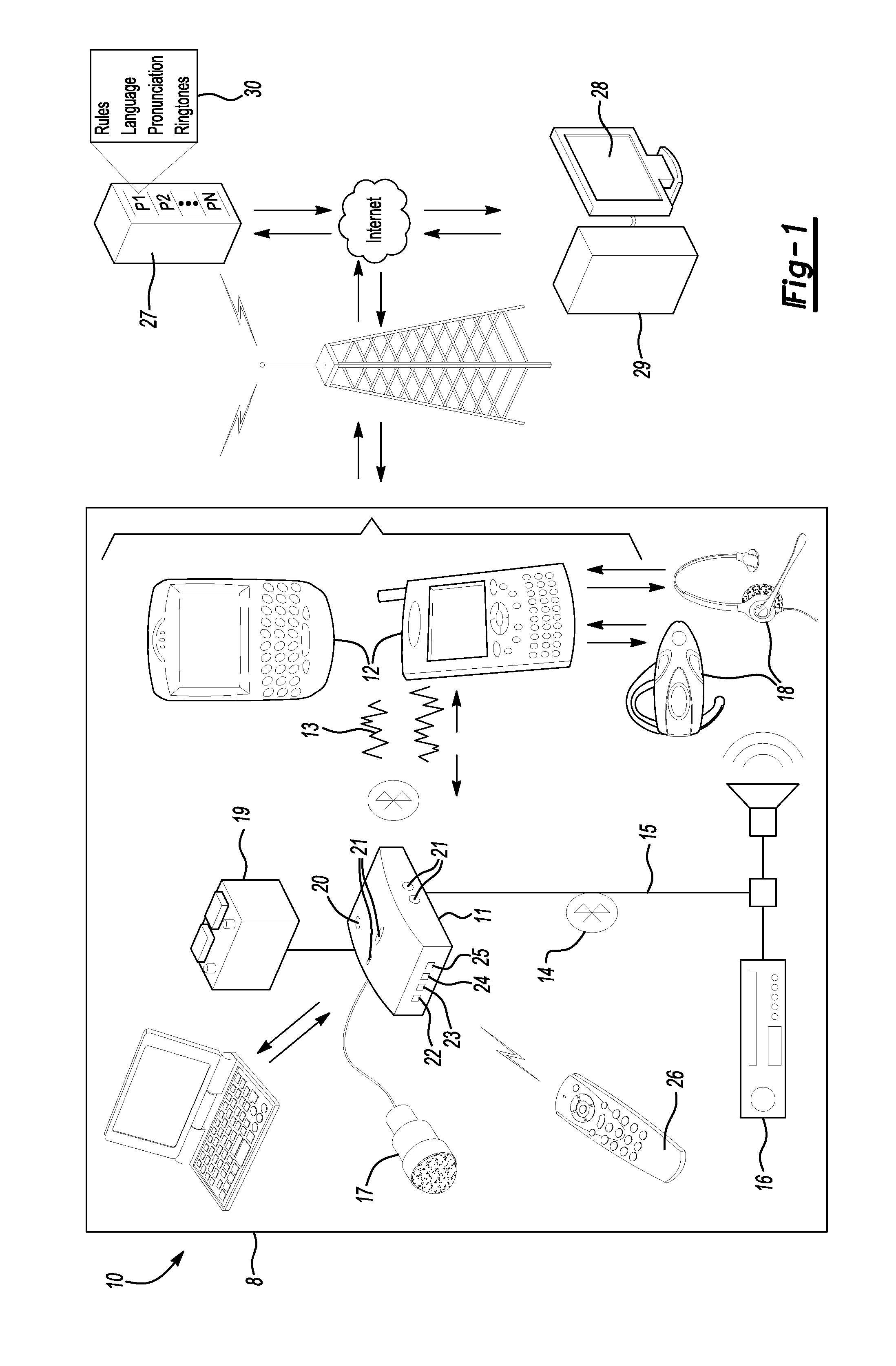
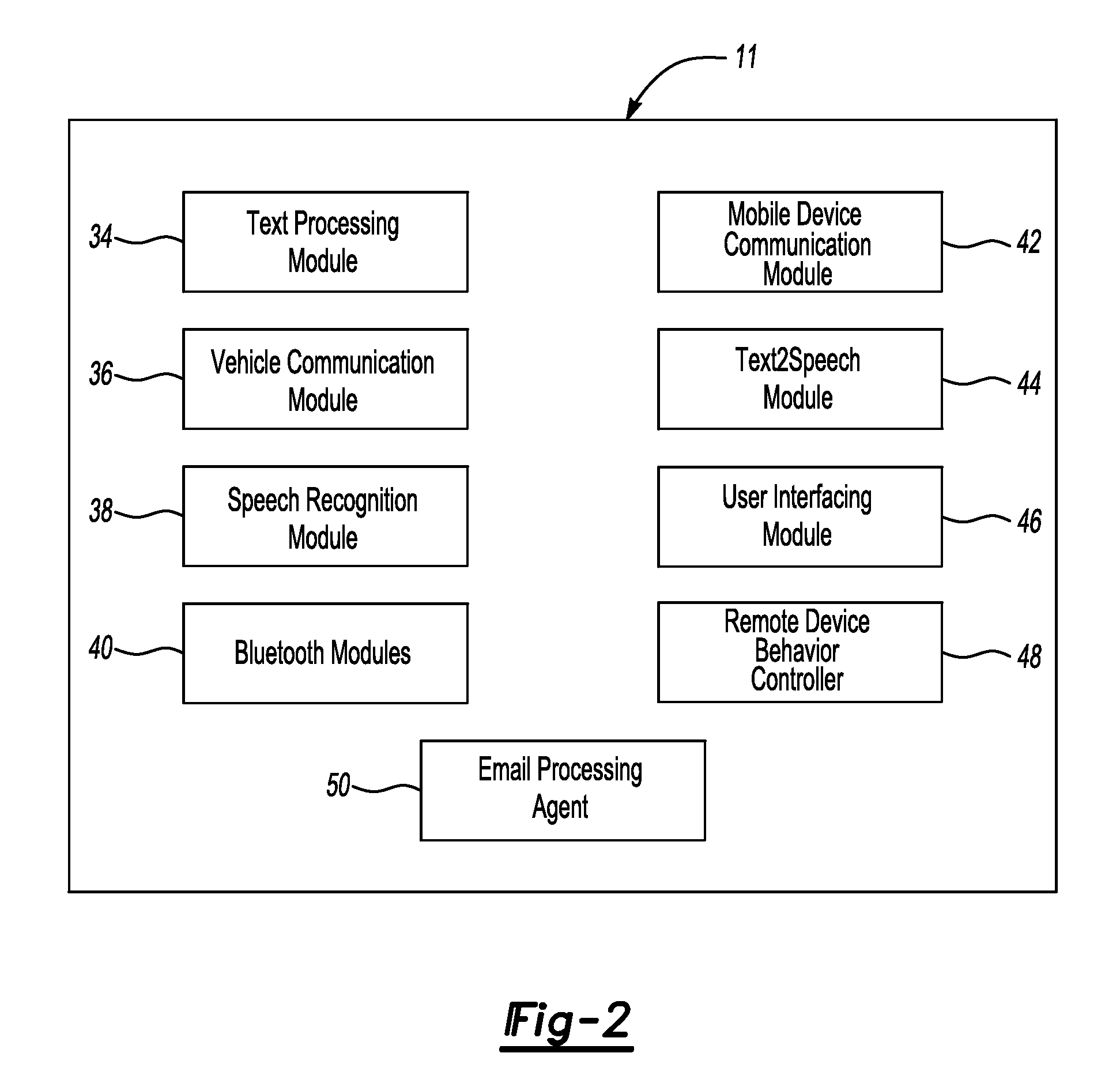
Vehicle immersive communication system
ActiveUS20070042812A1Convenient and safe hands-free interfaceImprove driving experienceDevices with voice recognitionDevices with bluetooth interfacesBluetoothNetwork service
A vehicle communication system facilitates hands-free interaction with a mobile device in a vehicle or elsewhere. Users interact with the system by speaking to it. The system processes text and processes commands. The system supports Bluetooth wireless technology for hands-free use. The system handles telephone calls, email, and SMS text messages. The user can customize the device via a user profile stored on an Internet web server.
Owner:VALUE8 CO LTD
Method and apparatus for path planning, selection, and visualization
InactiveUS20100241289A1Suffer from effectKeep movingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorGraphicsThree-dimensional space
New and Improved methods and apparatus for robotic path planning, selection, and visualization are described A path spline visually represents the current trajectory of the robot through a three dimensional space such as a room By altering a graphical representation of the trajectory—the path spline—an operator can visualize the path the robot will take, and is freed from real-time control of the robot Control of the robot is accomplished by periodically updating the path spline such that the newly updated spline represents the new desired path for the robot Also a sensor that may be located on the robot senses the presence of boundaries (obstacles) in the current environment and generates a path that circumnavigates the boundaries while still maintaining motion in the general direction selected by the operator The mathematical form of the path that circumnavigates the boundaries may be a spline
Owner:SANDBERG ROY
Supply assembly for a led lighting module
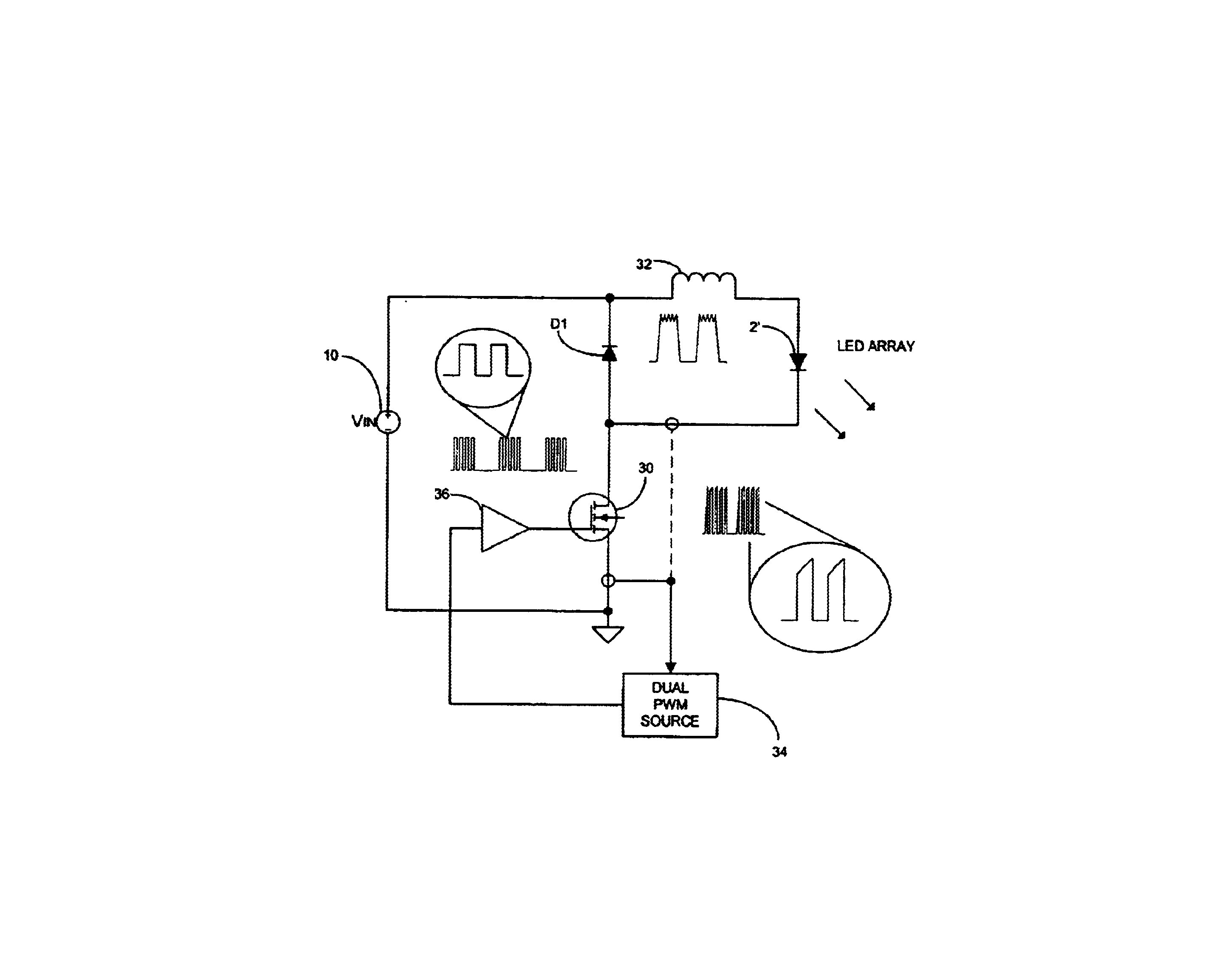
InactiveUS7071762B2Fast timeEliminate needElectroluminescent light sourcesPavement lightsControl switchHigh frequency
A supply assembly for an LED lighting module includes a control switch for supplying a constant current to the LED lighting module. A dual switching signal composed of low frequency bursts of high frequency pulses is applied to the control switch. By varying the low frequency component of the dual switching signal, the average current through the LED lighting module may be varied in order to vary the light intensity outputted by the LED lighting module.
Owner:SIGNIFY HOLDING B V
Touch screen, touch panel and display device
ActiveUS20100060602A1Reduce decreaseHigh sensitivityInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceEngineering
Each detection column wiring is constituted by a set of a first metal wiring having a zigzag pattern and a second metal wiring having a structure axisymmetric with the first metal wiring about a column direction as an axis, wherein the first metal wiring is constituted by first sloped portions which are obliquely sloped by an inclination angle of 45 degrees with respect to the column direction, and first parallel portions which are parallel with the column direction and are continuous with the first sloped portions, such that the first sloped portions and the first parallel portions are repeatedly placed in a zigzag shape along the column direction. Each detection row wiring also has the same structure. A sloped portion out of the first sloped portions of the first metal wiring is always orthogonally and spatially intersected, at its middle point, with a sloped portion out of the second sloped portions of the third metal wiring at its middle point. There is also the same orthogonal relationship among the other portions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
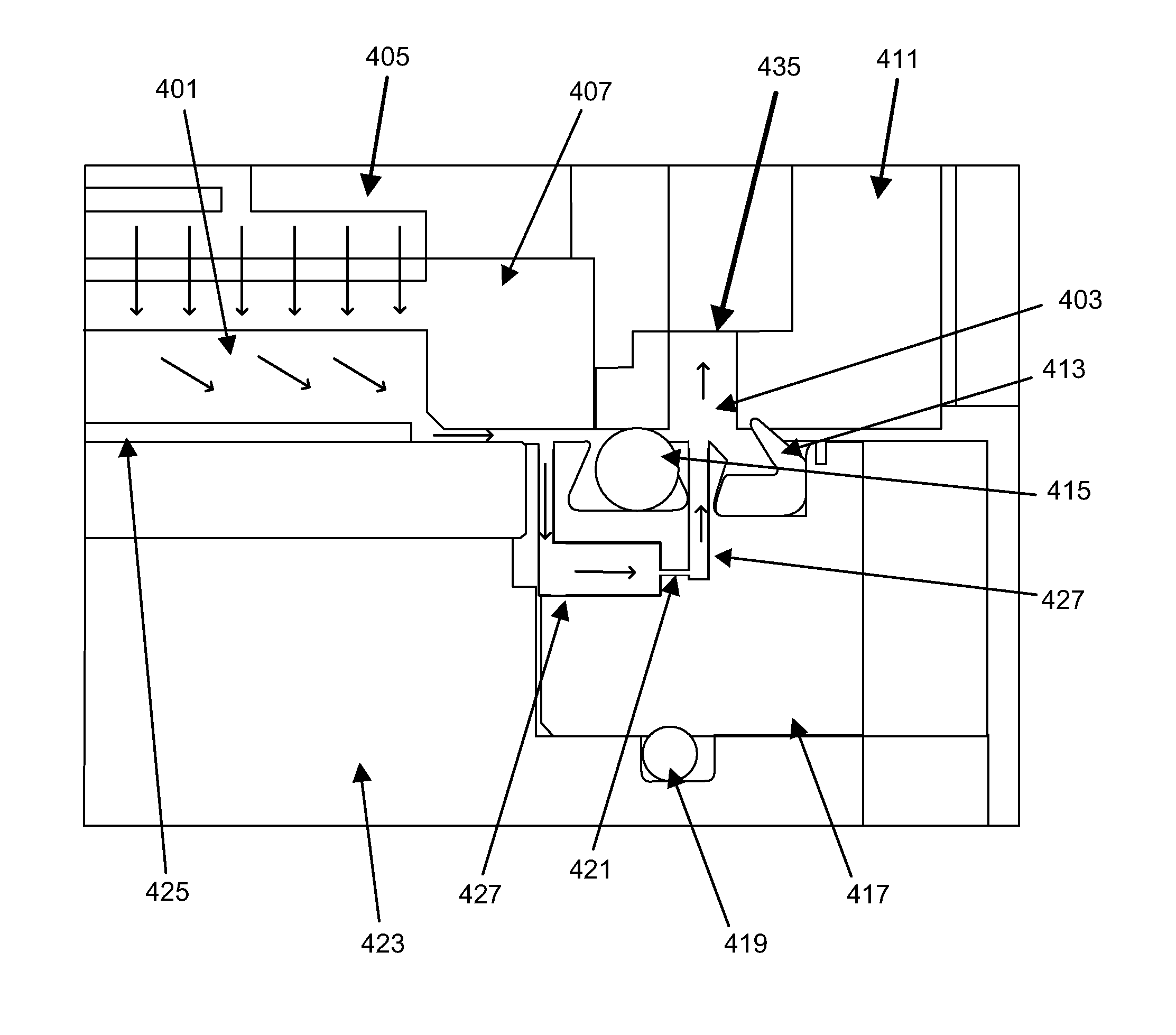
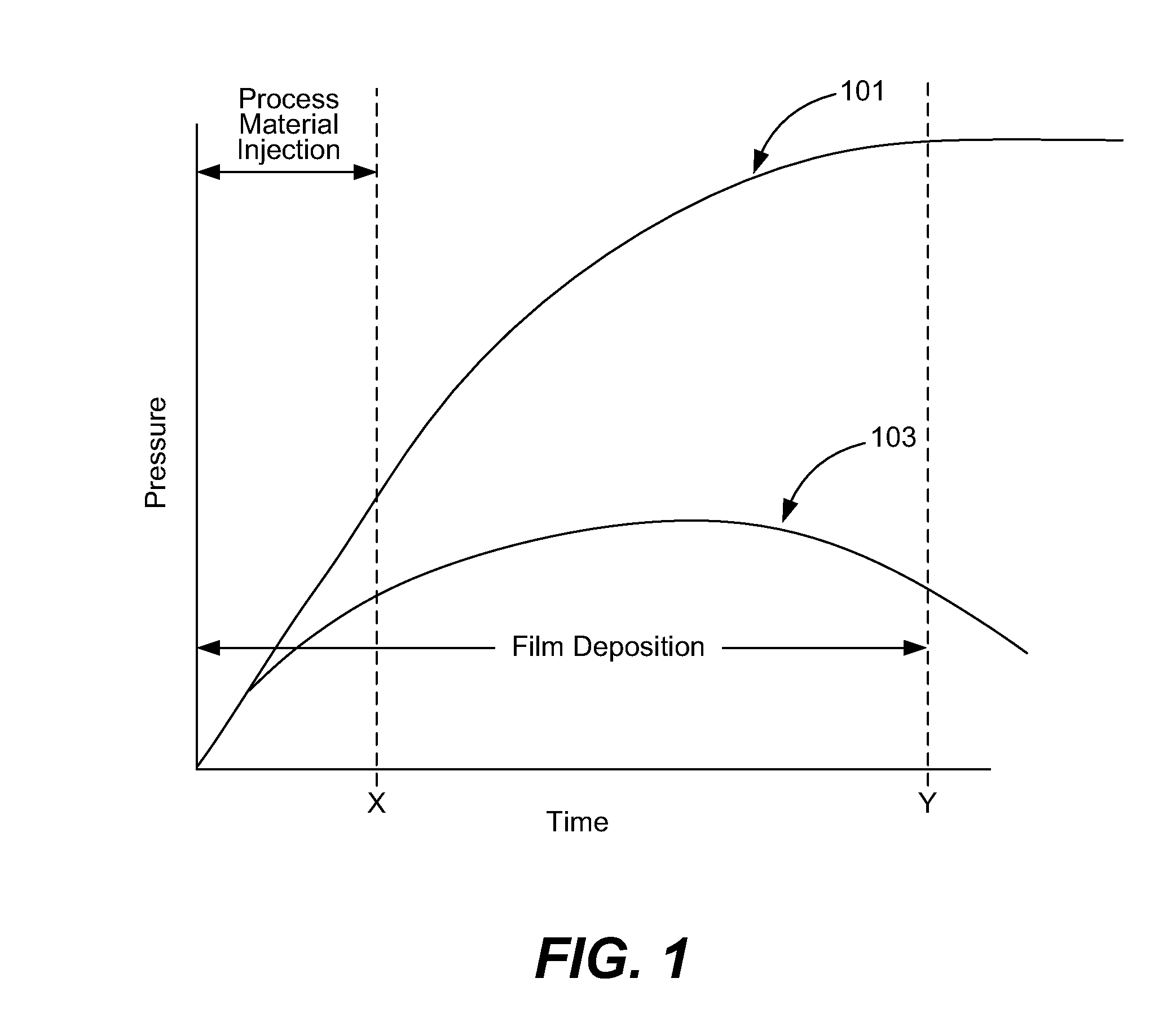
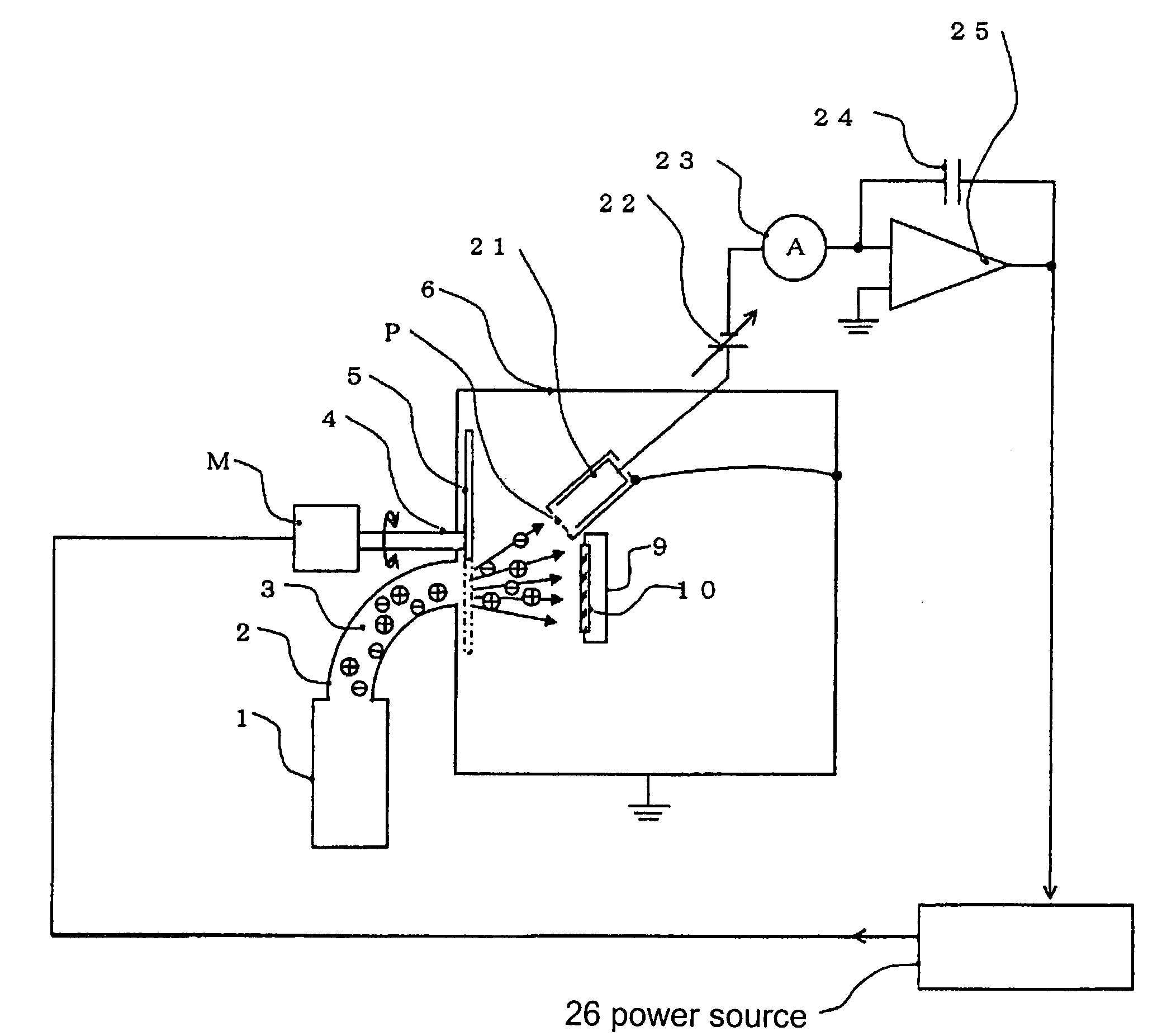
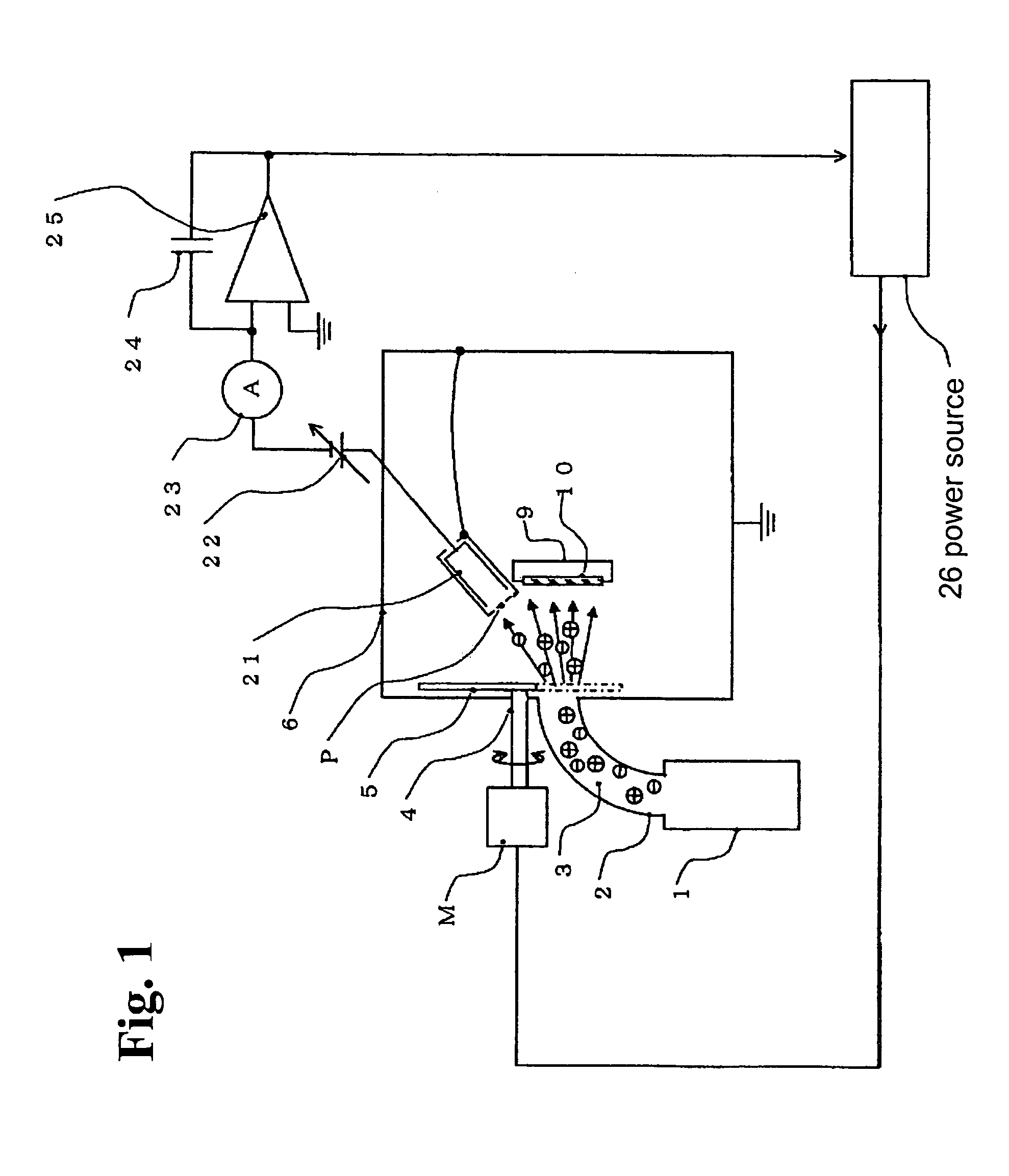
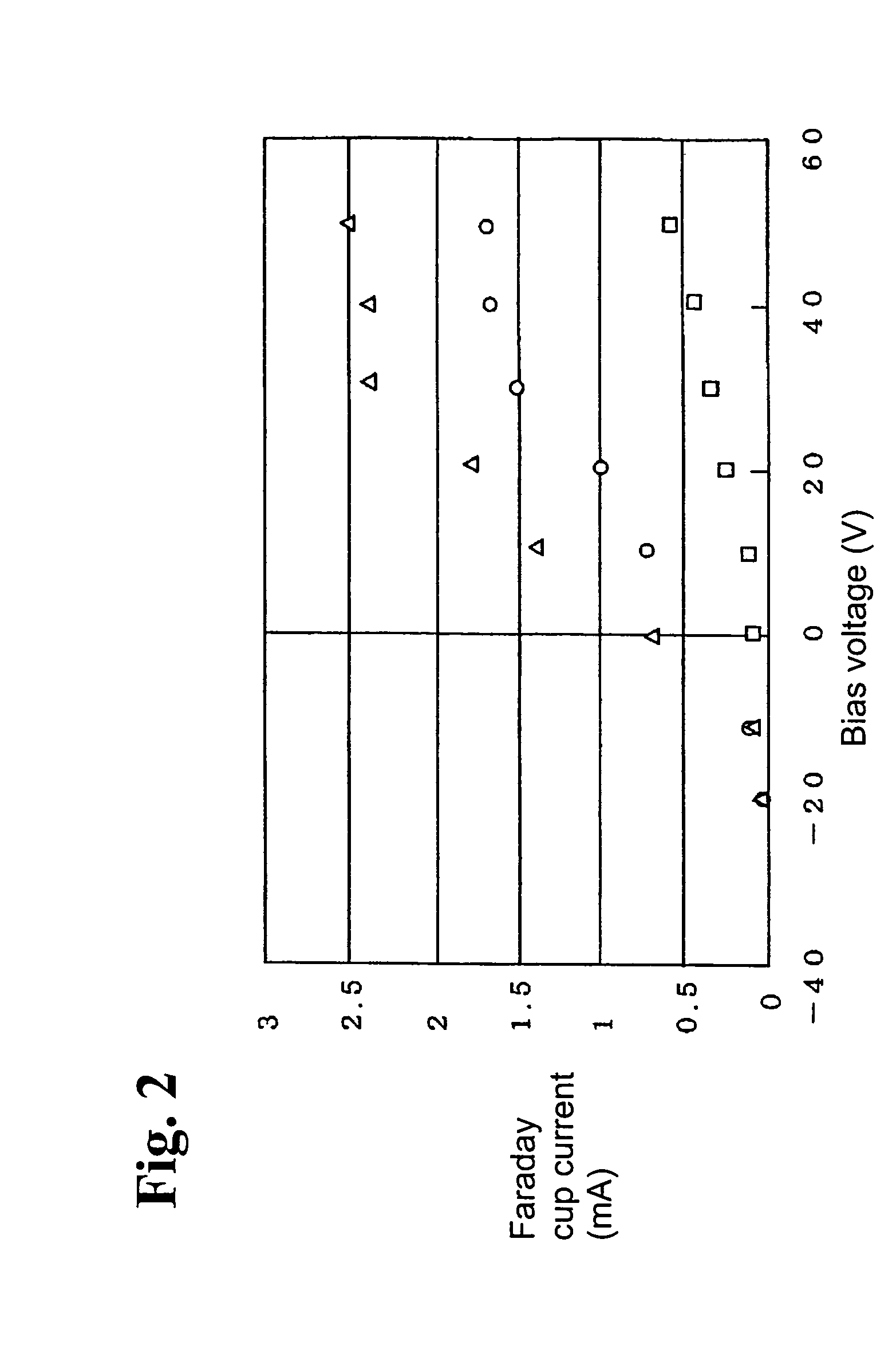
Film deposition device
InactiveUS7354482B2Accurate measurementEasy to controlCellsLiquid surface applicatorsPlasma depositionEngineering
A film deposition device for depositing a film includes a depositing chamber for depositing the film with plasma. A plasma quantity monitoring device is disposed in the depositing chamber for monitoring a plasma quantity entering the depositing chamber at real time. A calculating device is electrically connected to the plasma quantity monitoring device for calculating a thickness of the film from the plasma quantity so that the thickness is monitored at real time.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Image display
InactiveUS20060087489A1Excellent in image visibilityEasy constructionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsComputer scienceLight emission
An image display device constructed by: an image display means for displaying an image by moving chargeable particles arranged between electrodes by means of a voltage applied to the electrodes; and a light emission means for emitting a light to an image display surface of the image display means (first aspect of the invention). Moreover, an image display device which has an image display panel, in which two or more groups of particles or liquid powders having different colors and different charge characteristics are sealed between opposed two substrates, at least one of two substrates being transparent, and, in which the particles or the liquid powders, to which an electrostatic field produced by a pair of electrodes provided on one substrate or both substrates respectively is applied, are made to move so as to display an image, characterized in that a color filter is arranged to an outer surface or an inner surface of a transparent substrate of the image display panel so as to perform a color displaying (second aspect of the invention).
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
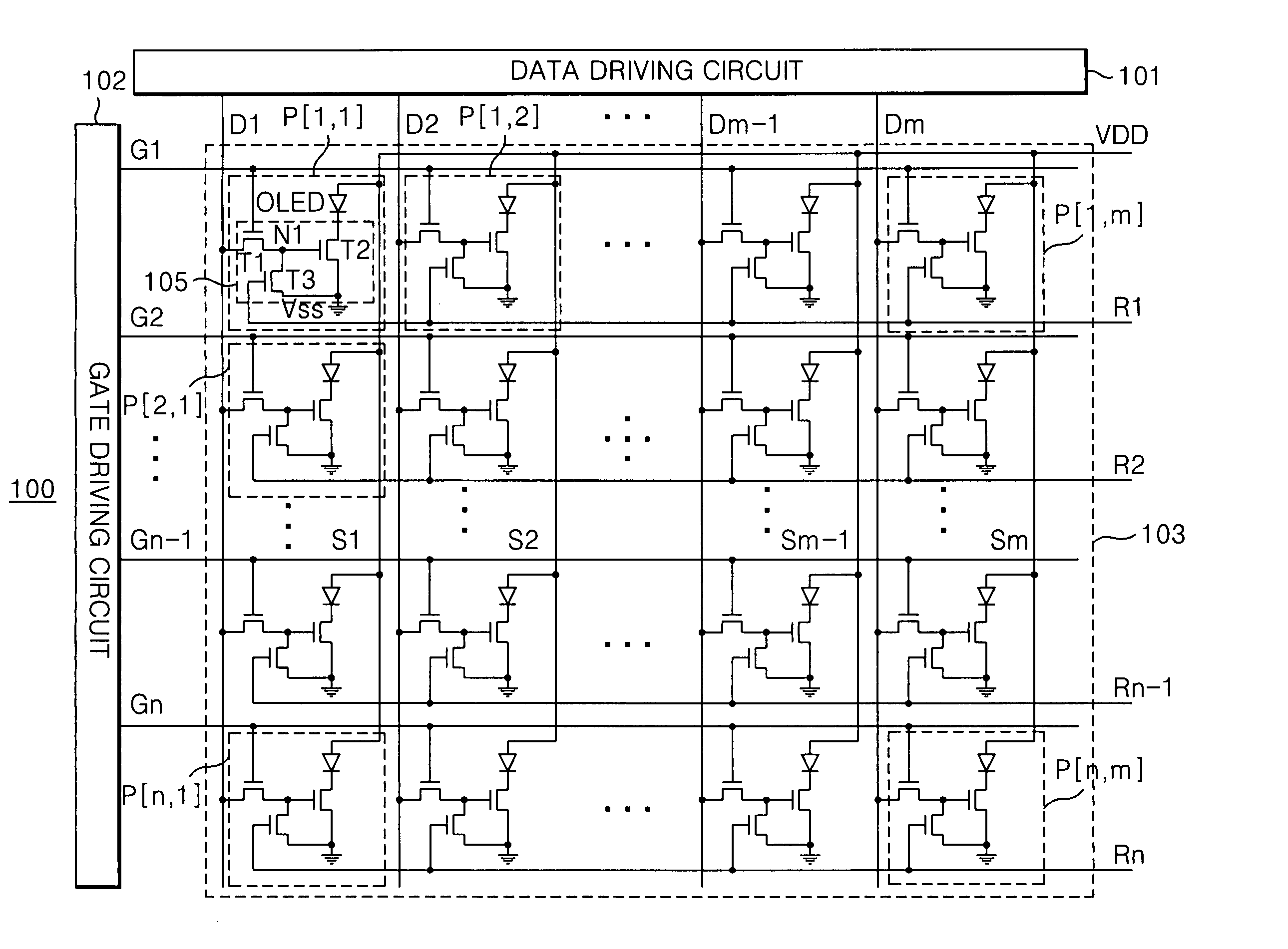
Driving circuit for organic light emitting diode, display device using the same and driving method of organic light emitting diode display device
ActiveUS20060284801A1Reduce generationReduce voltageElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
An organic light emitting diode drive circuit includes an organic light emitting diode which emits light with a current, a first transistor, a second transistor and a stress compensation circuit. The first transistor supplies a data voltage to a first node in response to a scan pulse. The second transistor controls a current flowing in the organic light emitting diode by the data voltage on the first node. The stress compensation circuit discharges the first node in response to a reset pulse. The organic light emitting diode driving circuit is adaptive to compensate characteristic changes of the organic light emitting diode drive circuit.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
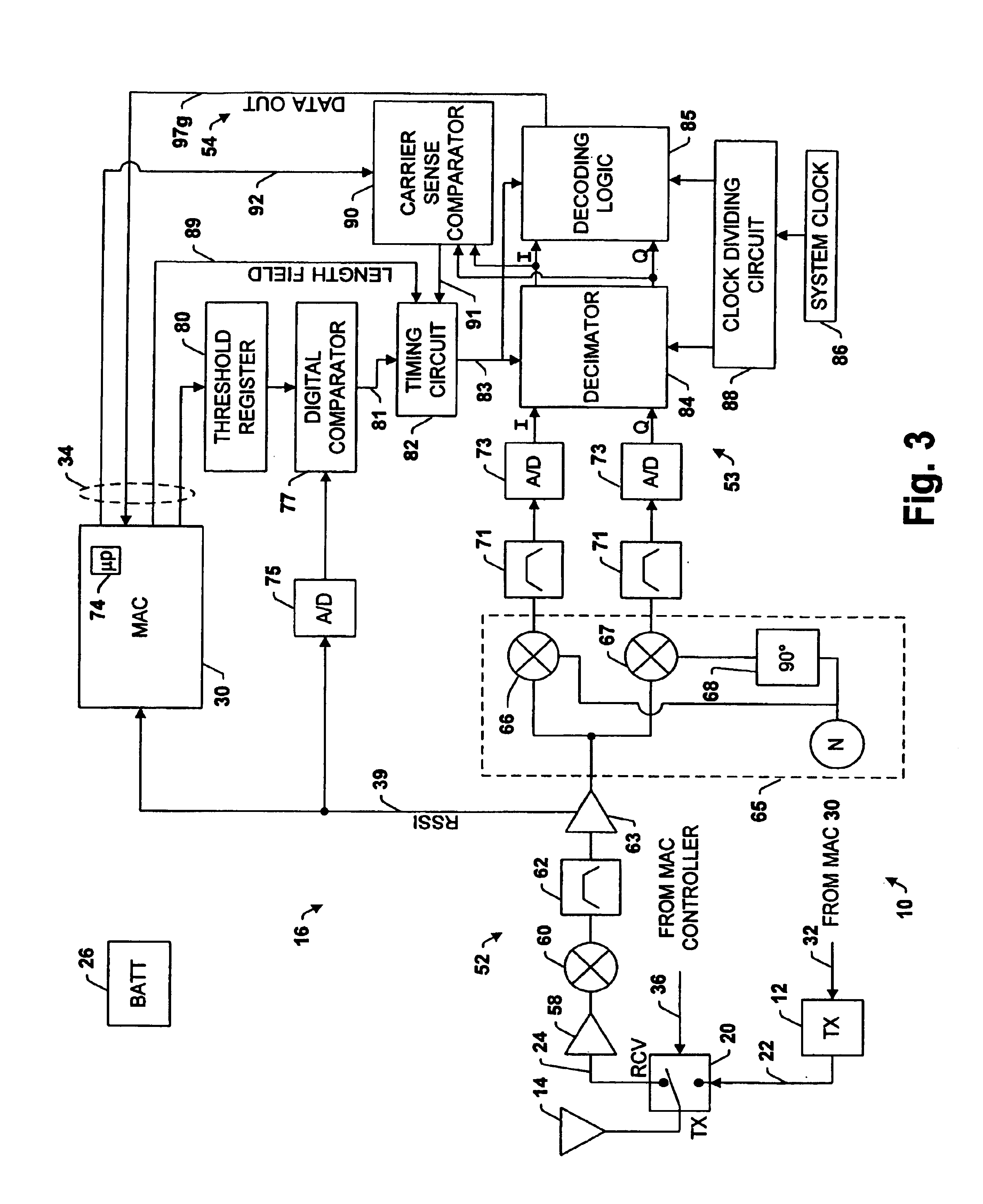
Transceiver control with sleep mode operation
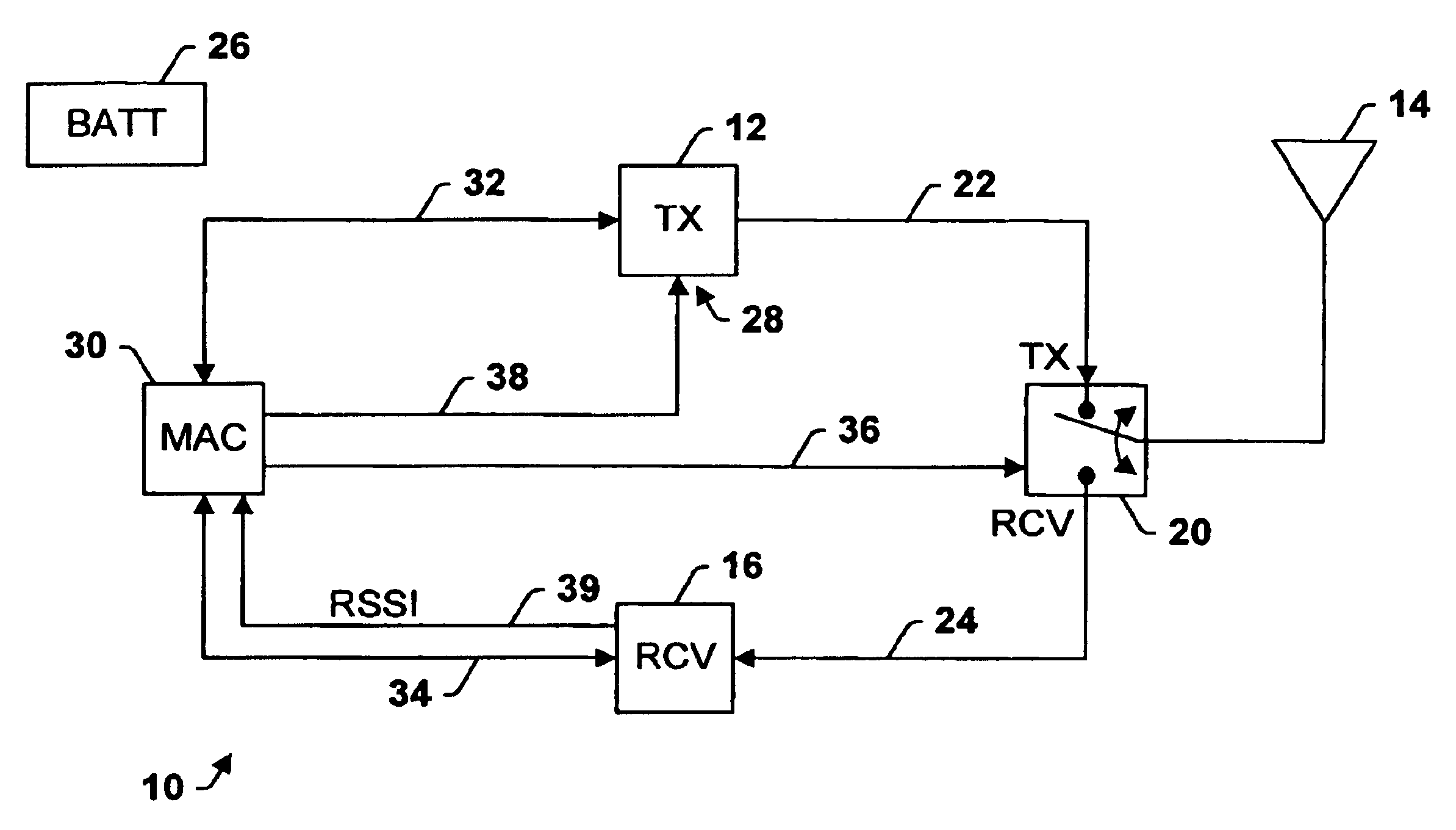
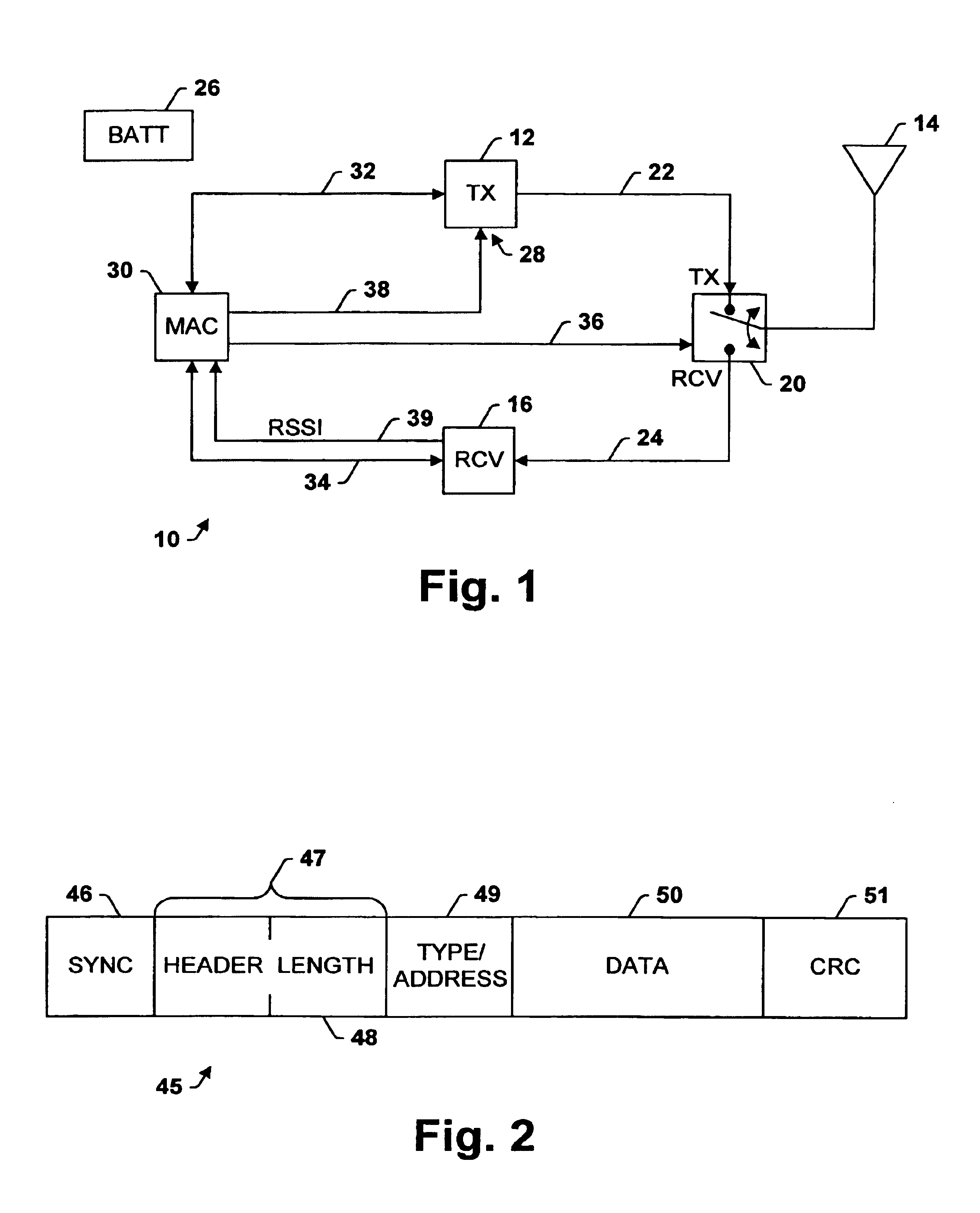
InactiveUS6978149B1No delay exchangeHigh strengthEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransceiverControl signal
A transceiver which keeps circuitry associated with a receiver in a powered down state during periods when a Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) indicates that a signal being received is below a pre-determined threshold level, and which begins to power up the transmitter as soon as it is determined that a packet being received requires a response. The RSSI signal represents the strength of any signal current being received, and if the RSSI signal falls below a given threshold level, digital circuitry associated with the back-end circuitry of the receiver system is disabled. If the RSSI signal rises above the threshold level, the digital circuitry of the receiver is enabled. A control circuit within the transceiver processes the packet as it is received to determine whether the packet requires a response. If it is determined that a response is necessary, the control circuit provides a control signal to the transmitter to power up the transmitter from a sleep mode even before the entire packet has been received and processed. The control circuit then continues to process the remainder of the packet as it is received while the transmitter powers up from the sleep mode. In this manner, the transmitter will become stabilized much earlier. Accordingly, the transceiver is able to respond more quickly than conventional devices and is thus able to increase response times and overall data exchange rates. Moreover, battery power of the transceiver is utilized more efficiently compared to devices which must continuously maintain the receiver and transmitter in fully powered modes.
Owner:TELXON INC
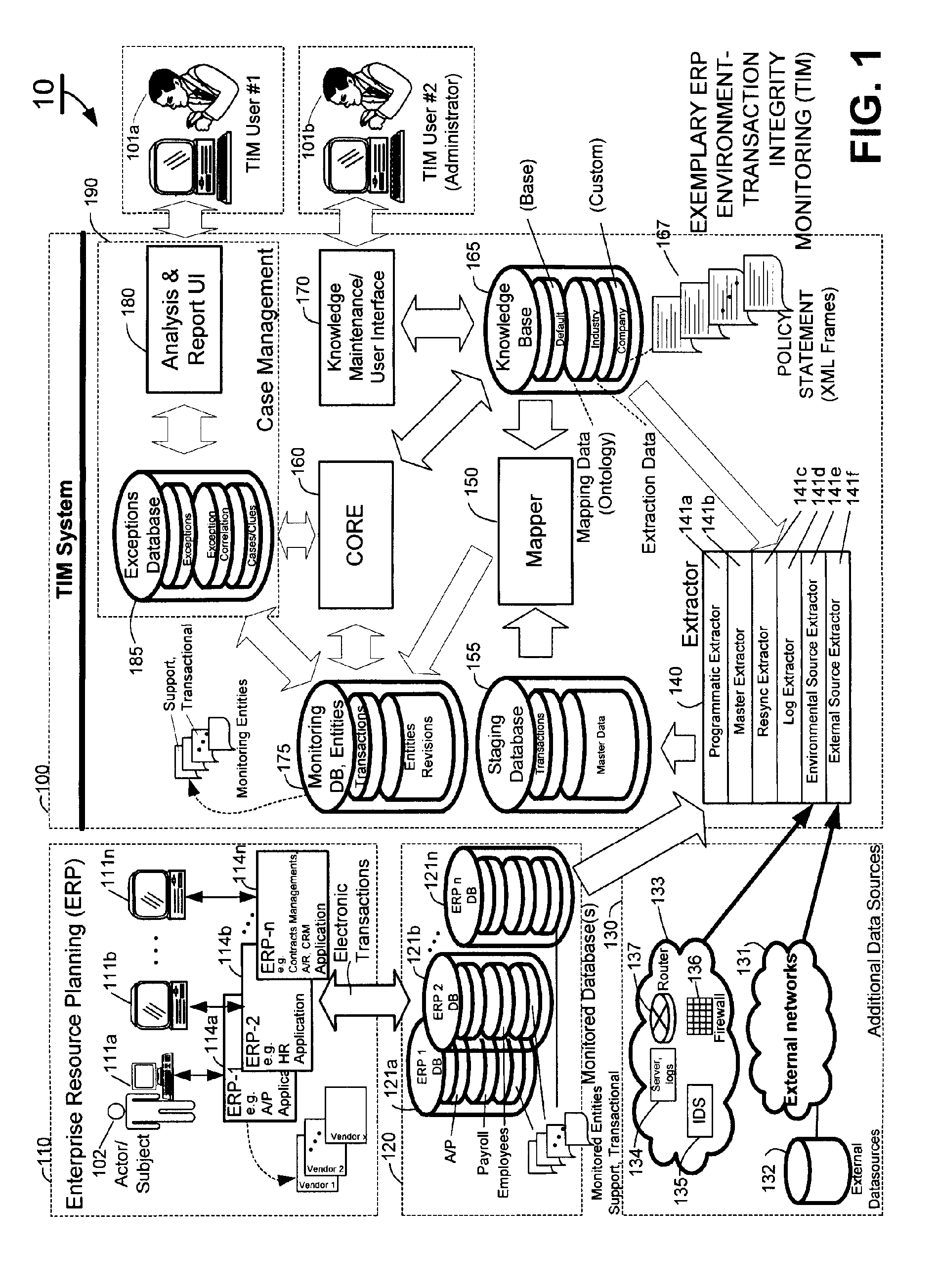
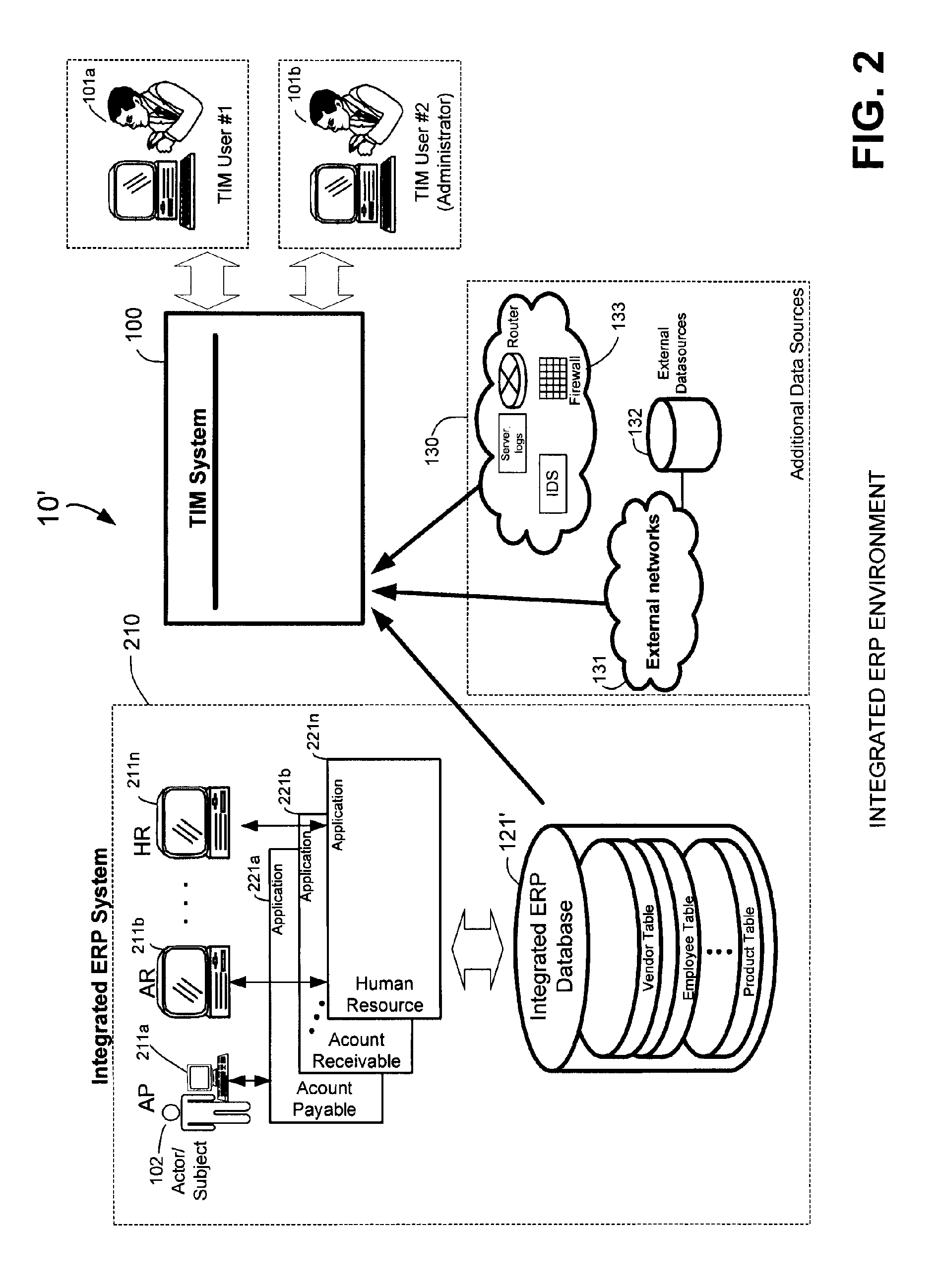
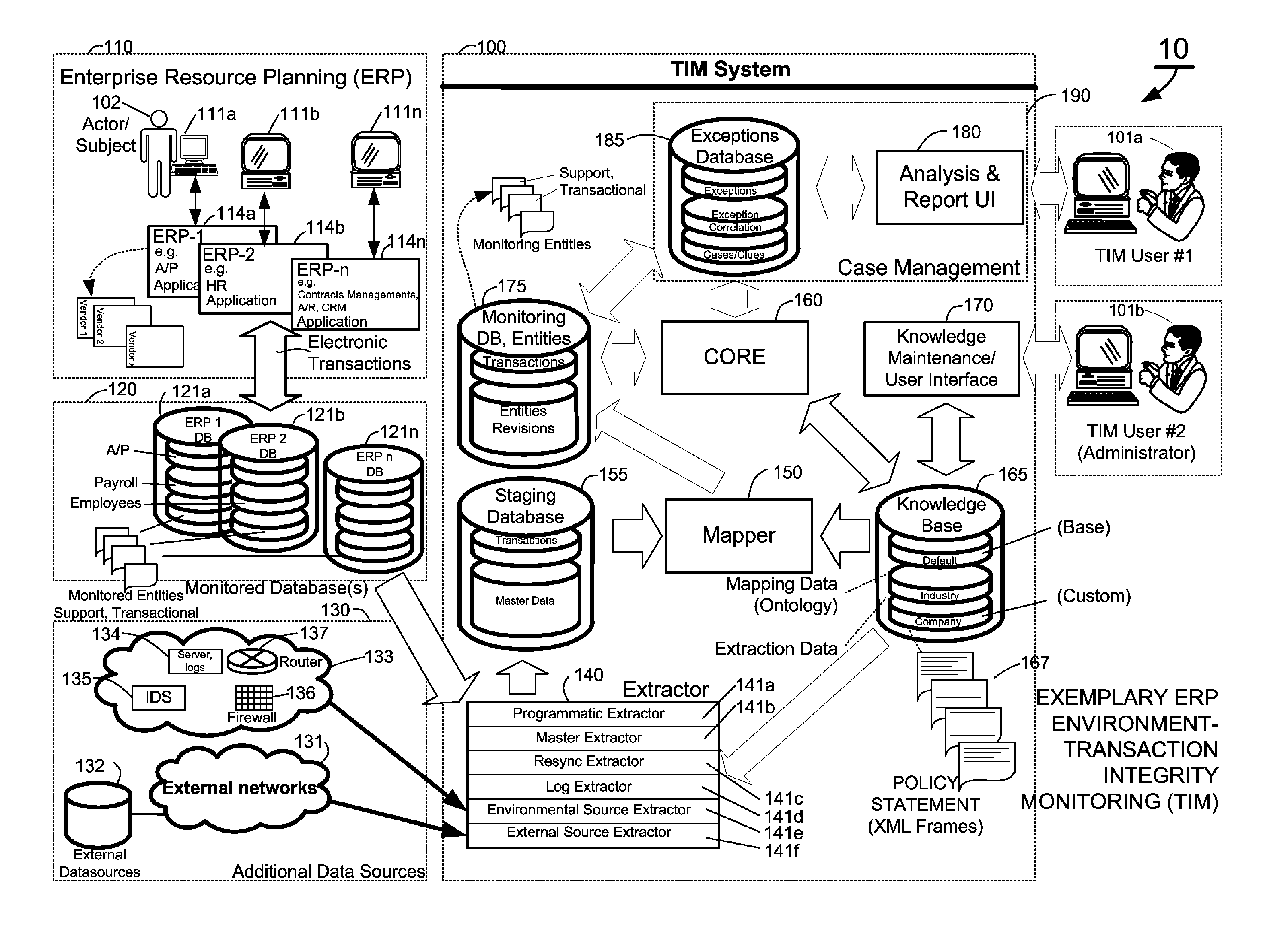
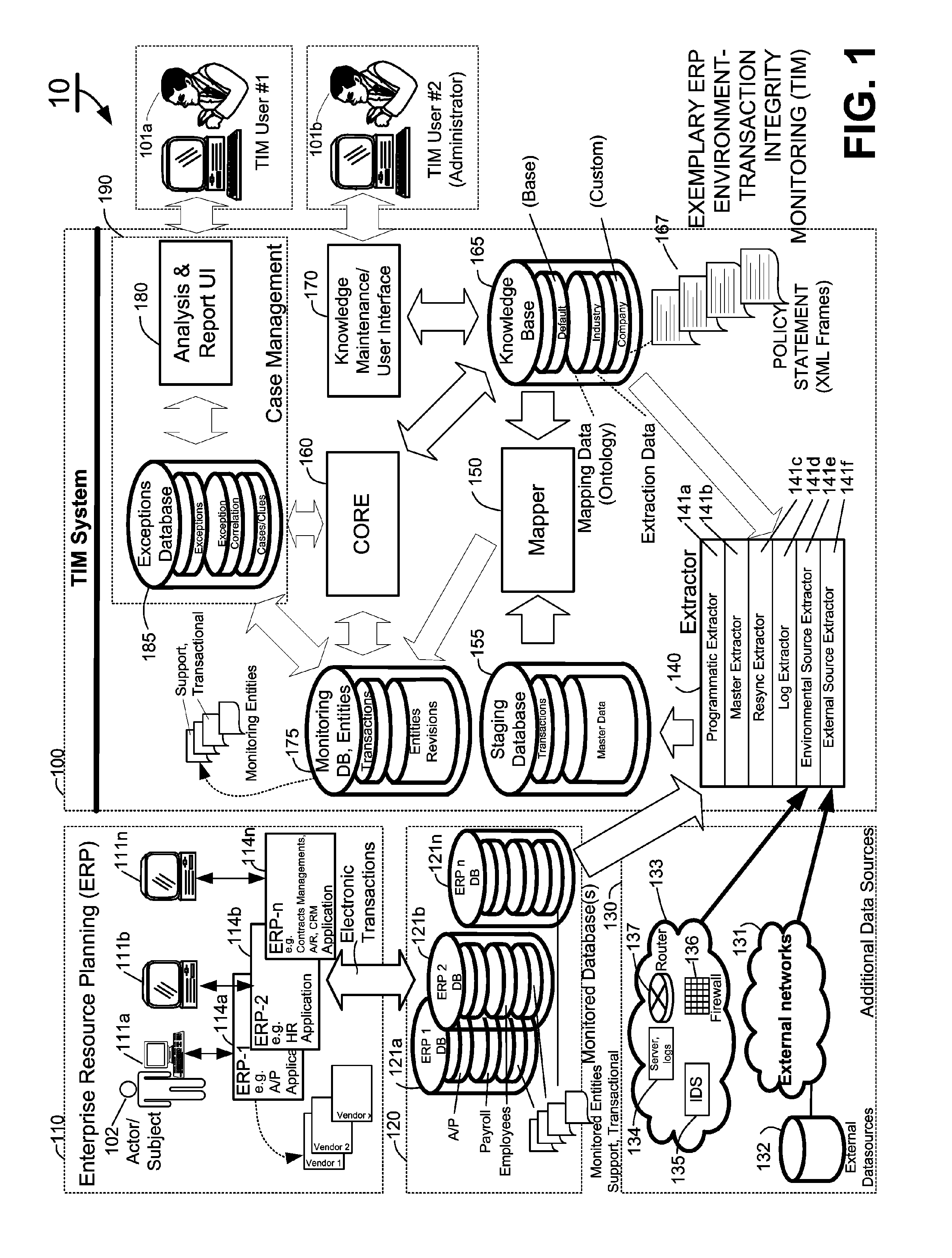
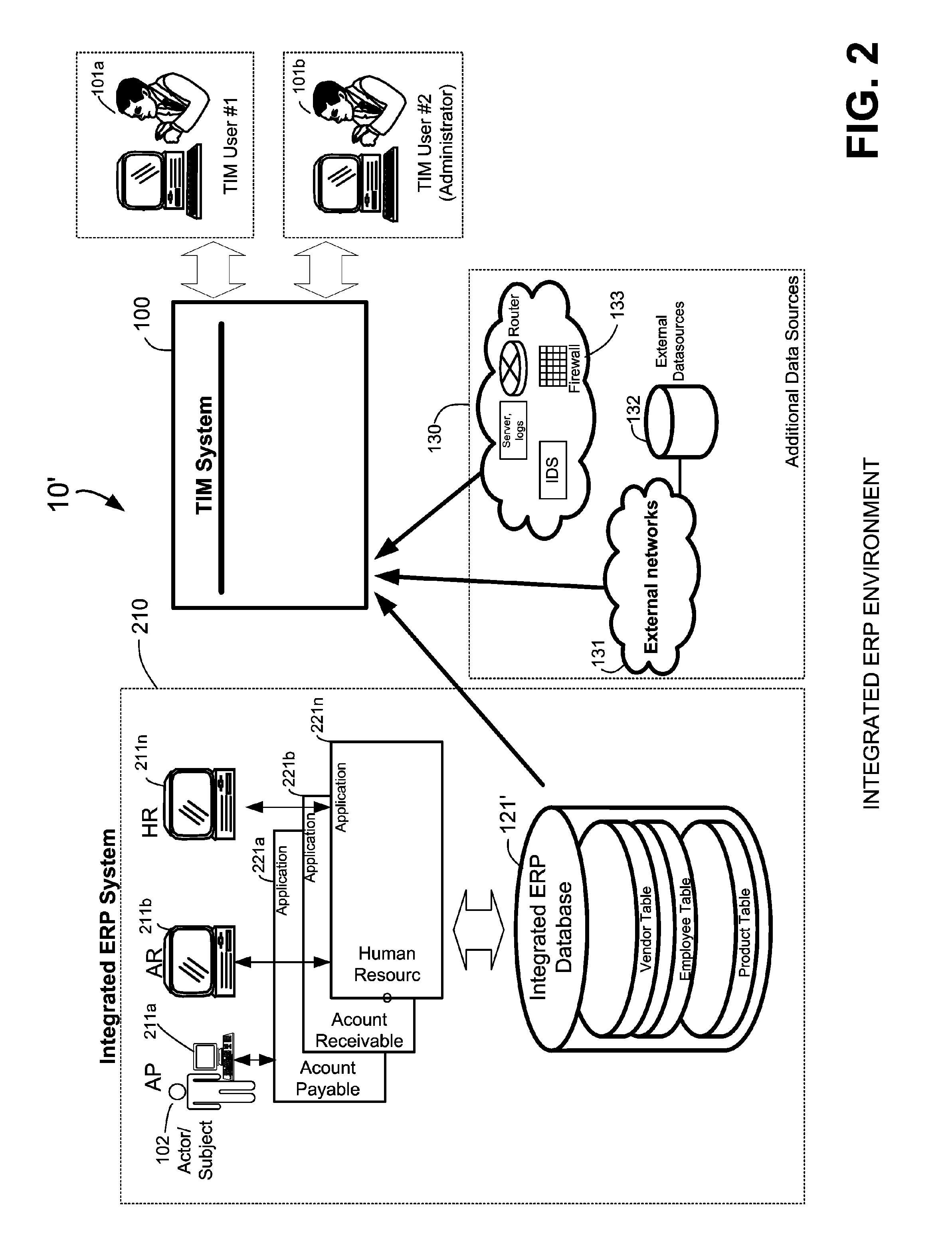
Methods and systems for compliance monitoring knowledge base
ActiveUS20060212486A1Reduced asset lossImprove operational efficiencyDigital data information retrievalFinanceCompliance MonitoringMonitoring system
A knowledge base and methods for use in connection with a policy compliance monitoring system operative to determine exceptions to policies expressed by computer-executable policy statements. The system allows establishment, codification, and maintenance of enterprise policies, monitors electronic transactions of the enterprise from various and possibly heterogeneous data sources, detects exceptions to established policies, reports exceptions to authorized users such as managers and auditors, and / or provides a case management system for tracking exceptions and their underlying transactions. The knowledge base comprises extractor files that are utilized for extracting information from data sources for utilization in policy compliance monitoring, a mapper for normalizing data from the data sources against a system ontology and storing normalized data in a monitoring database, and computer-executable compliance policy statements used by a transaction analysis engine. The policy statements represent predetermined policies of the enterprise that apply to data stored in the monitoring database.
Owner:OVERSIGHT SYST INC
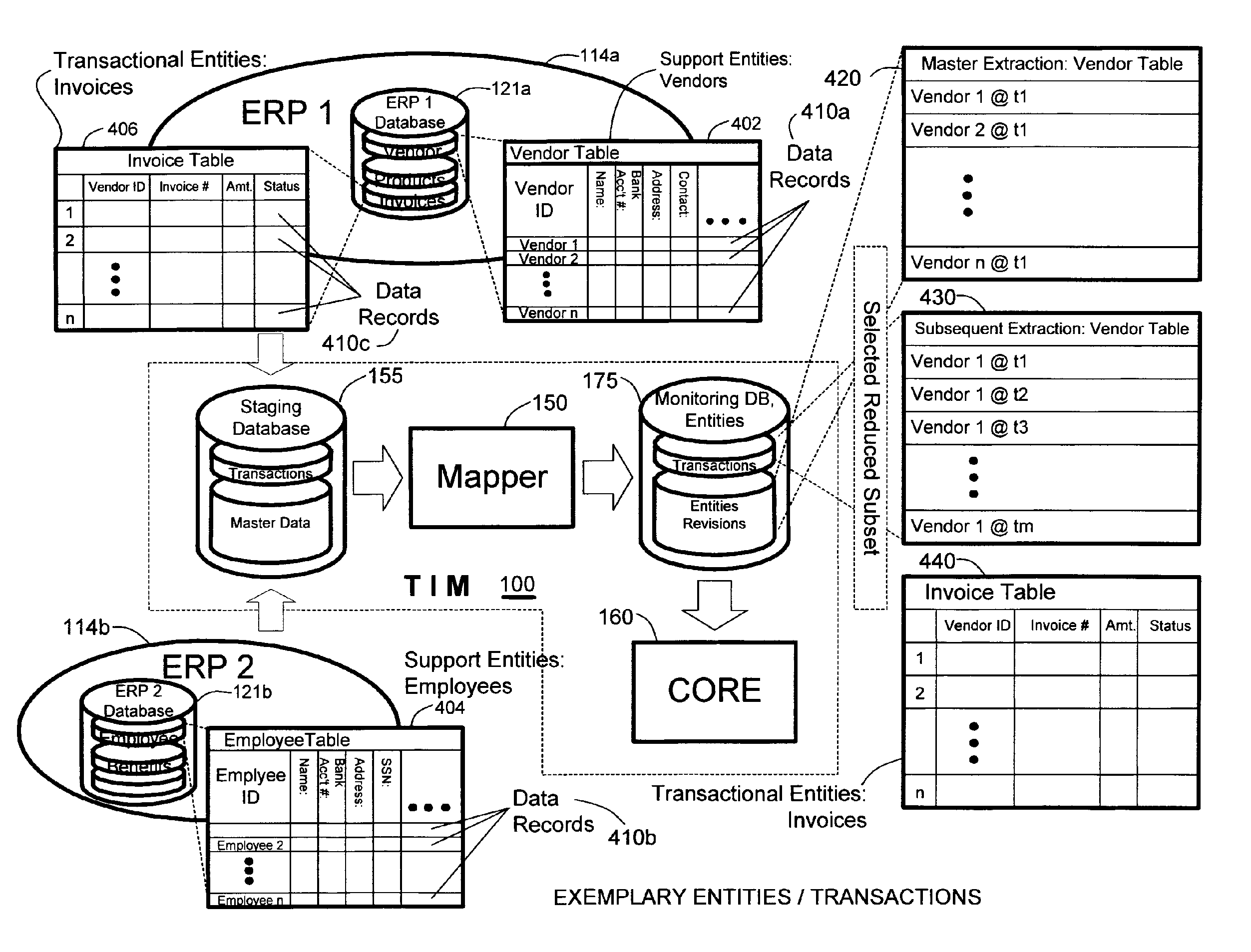
Methods and systems for mapping transaction data to common ontology for compliance monitoring
InactiveUS20080082374A1Improve performanceMinimizes financial lossDigital data information retrievalFinanceCompliance MonitoringData source
An automated transaction integrity monitoring system operative to monitor electronic transactions of an enterprise and detect exceptions indicating noncompliance with enterprise policies. The system allows establishment, codification, and maintenance of enterprise policies, monitors electronic transactions of the enterprise from various and possibly heterogeneous data sources, detects exceptions to established policies, reports such exceptions to authorized users such as managers and auditors, and / or provides a case management system for tracking such exceptions and their underlying transactions. The invention specifically relates to systems and methods for transforming or mapping information from a data source relating to a transactional entity associated with an enterprise into a form for processing by a transaction analysis engine operative upon data expressed in a predetermined ontology. The ontology expresses data items in a manner common across plural heterogeneous databases. The enterprise policies are expressed in terms of the ontology.
Owner:KENNIS PETER H +7
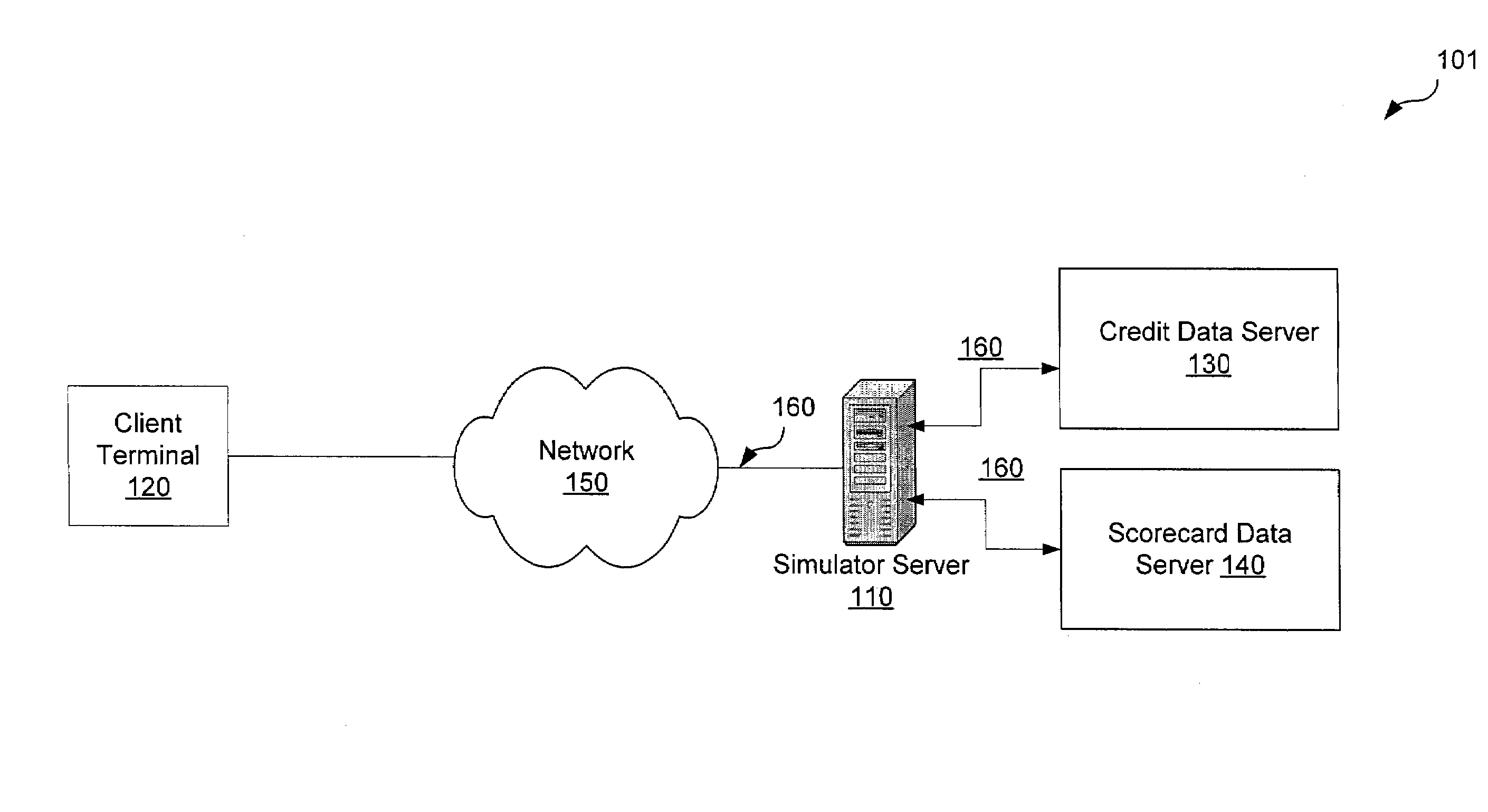
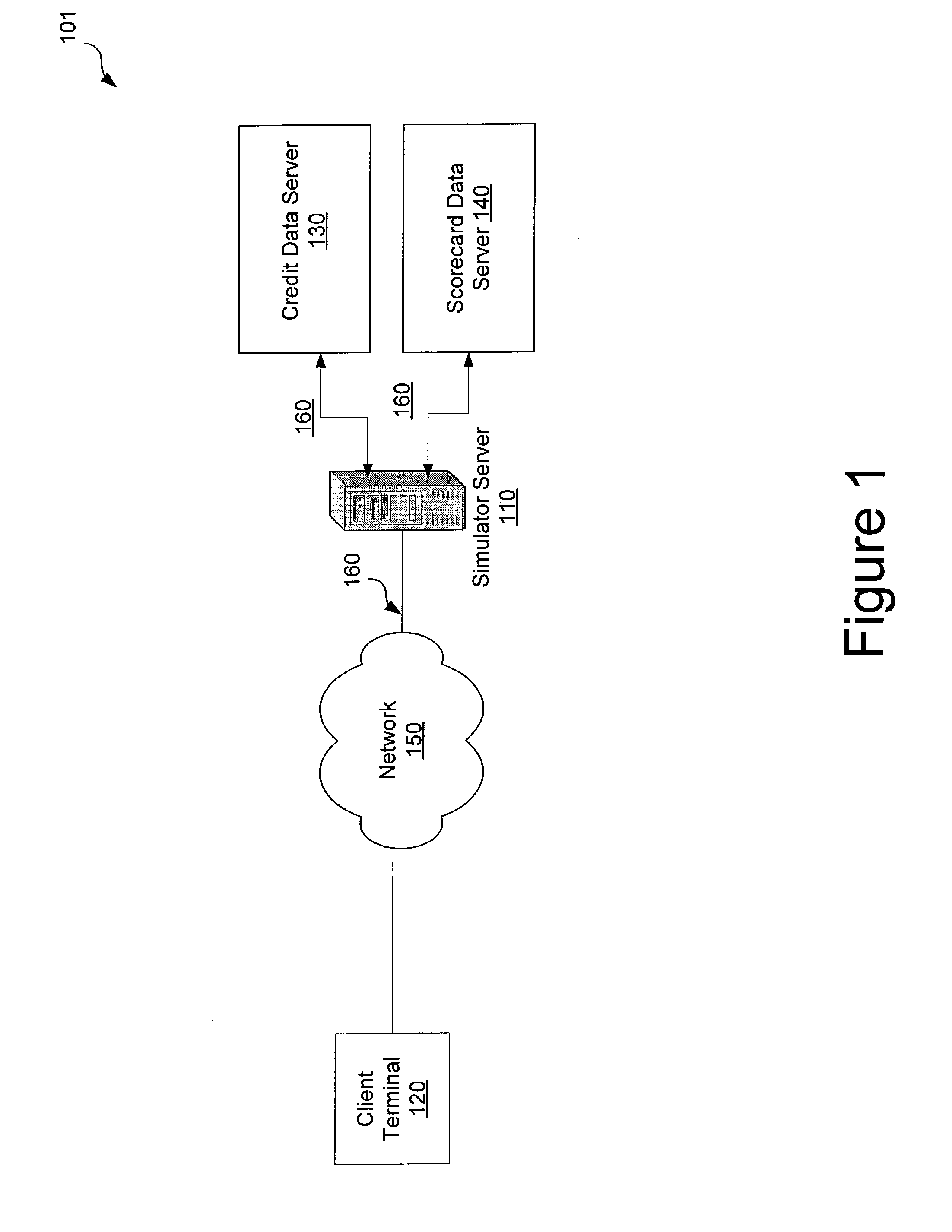
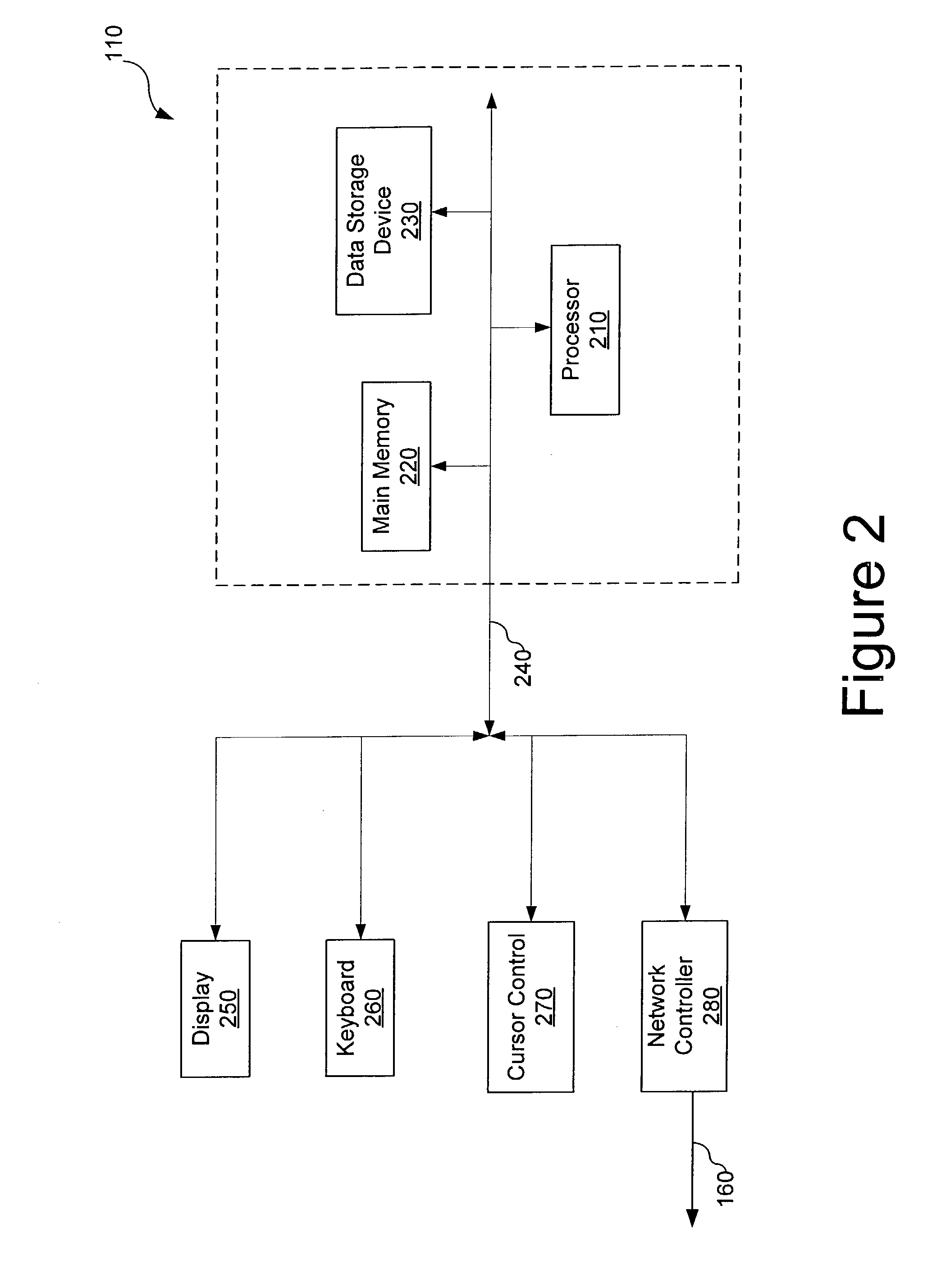
System and method for interactively simulating a credit-worthiness score
ActiveUS7610229B1Quick responseSimple interfaceFinancePayment architectureWeb serviceSimulation based
A system and method is provided to allow a consumer to interactively explore his credit score by submitting hypothetical values based on his actual credit data. The system uses the consumer's real credit data and the submitted hypothetical values to calculate a simulated credit score based on a simulator scorecard. The consumer may then observe the changes in the resultant scores. The system and the scorecard may utilize fewer data elements than a complete credit-worthiness scorecard and may instead focus on the key elements affecting a consumer's credit score. The system may be implemented in part on a web server or as a stand-alone application. The system may also update the score dynamically as the consumer adjusts the hypothetical values or may require the consumer to affirmatively submit the new hypothetical data.
Owner:CONSUMERINFO COM
Systems and methods for treating tissue with radiofrequency energy
ActiveUS10386990B2Reduce morbidityAccurate CalibrationPhysical therapies and activitiesDiagnosticsThermal treatmentRadio frequency
A system for controlling operation of a radiofrequency treatment device to apply radiofrequency energy to tissue to heat tissue to create lesions without ablating the tissue. The system includes a first treatment device having at least one electrode for applying radiofrequency energy to tissue, a controller including a connector to which a first treatment device is coupled for use, and a generator for applying radiofrequency energy to the electrodes. The controller controls application of energy so that the tissue is thermally treated to create lesions but preventing thermal treatment beyond a threshold which would ablate the tissue.
Owner:MEDERI RF LLC
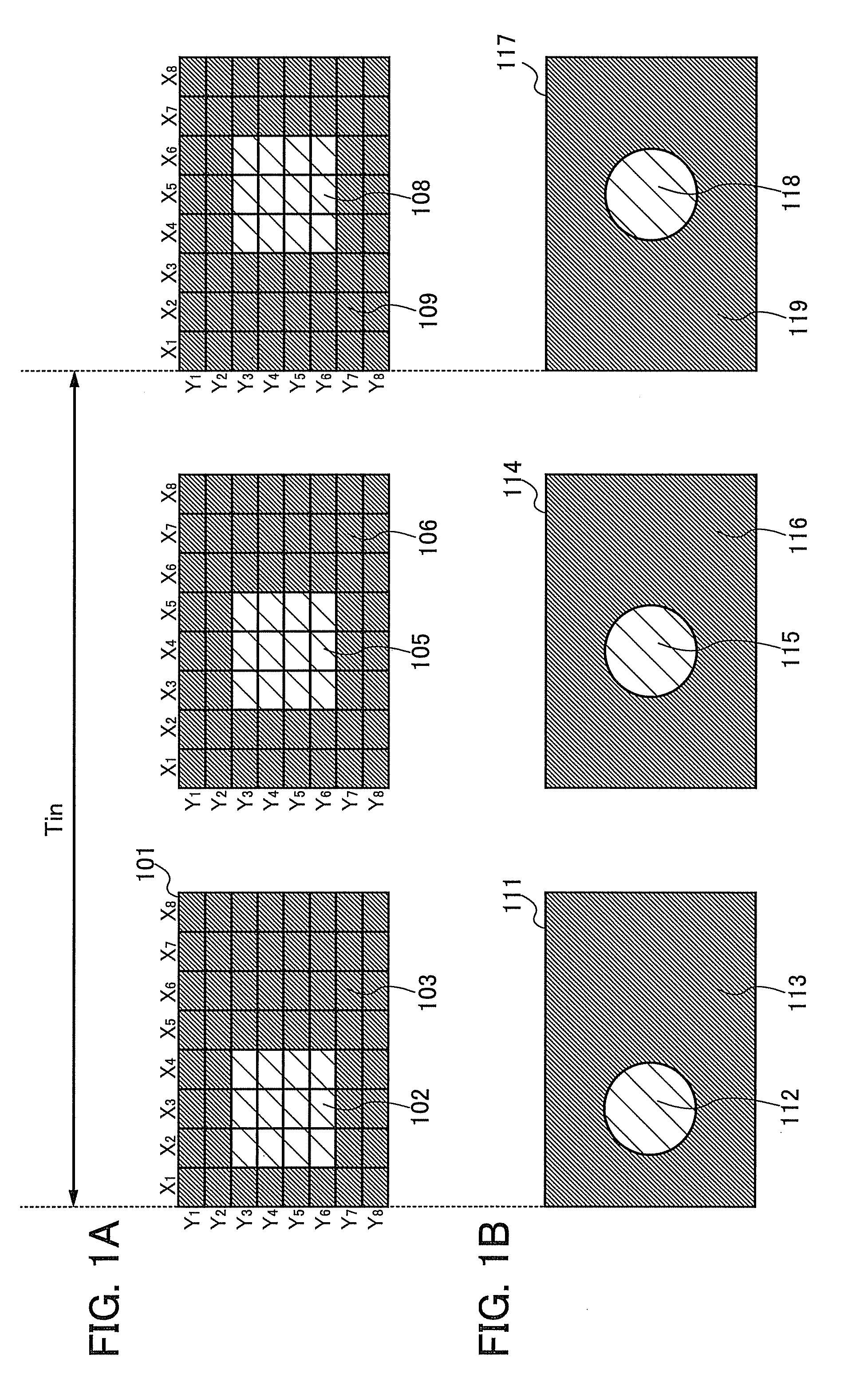
Method for driving liquid crystal display device
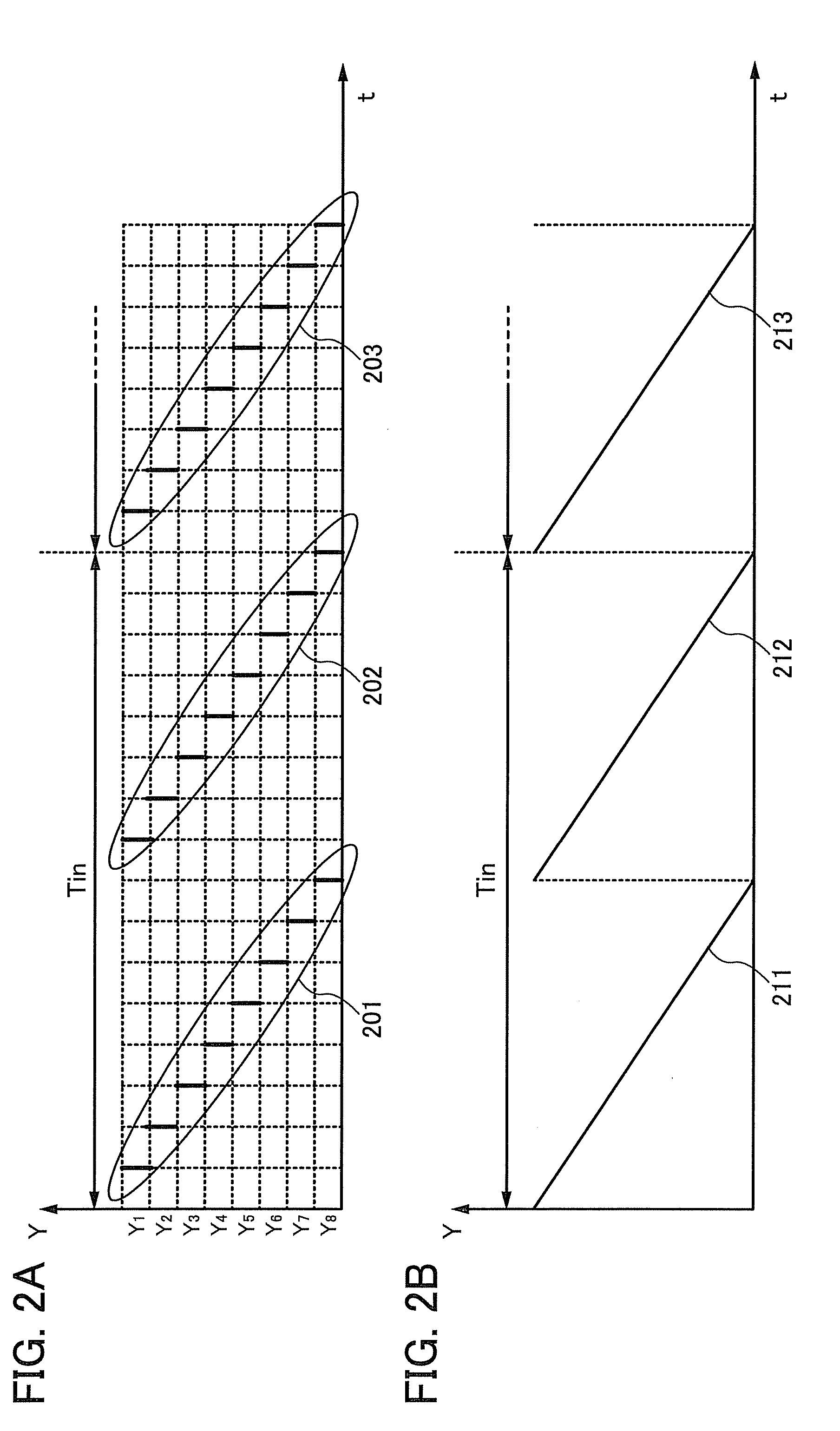
InactiveUS20080284768A1Flickers are increasedLuminance of image is decreasedSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionLiquid-crystal display
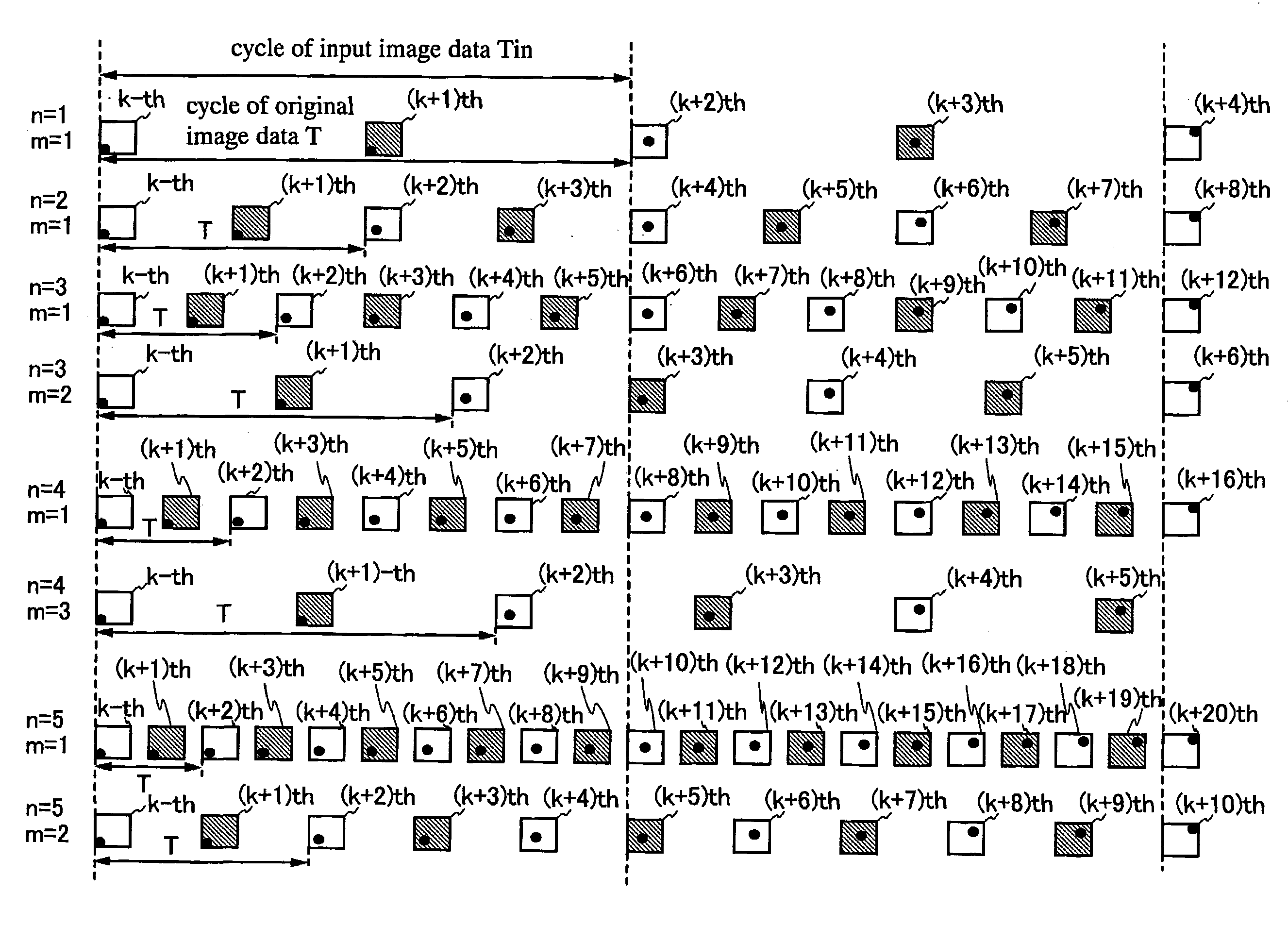
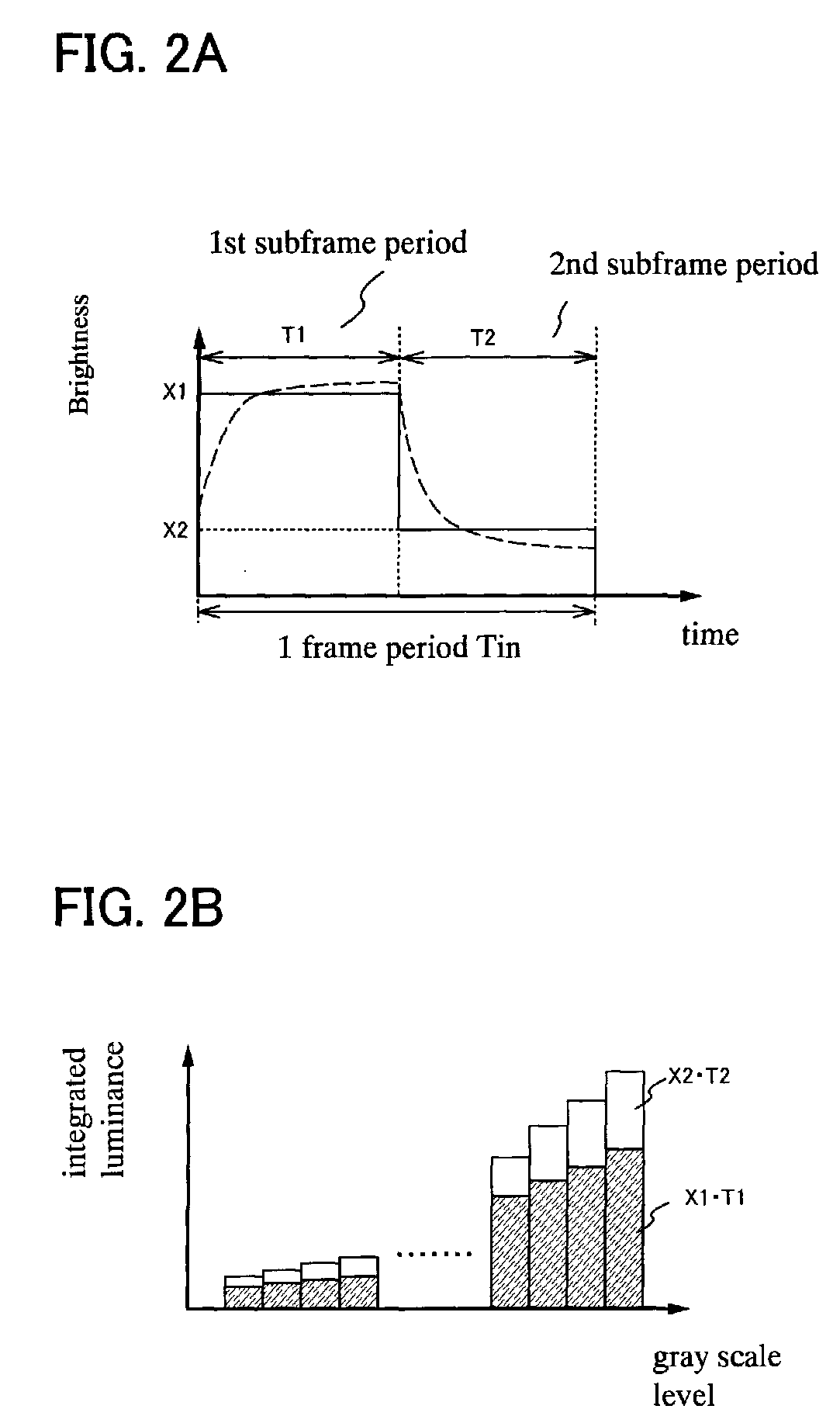
In a period Tin, p-th input image data (p is a positive integer) and (p+1)th input image data are input to a liquid crystal display device. In a period T, i-th original image data (i is a positive integer) and (i+1)th original image data are generated based on the input image data. J number of sub-images (J is an integer equal to or more than 3) are generated based on the i-th original image data. In the period T, the J number of sub-images are sequentially displayed. At least one of the i-th original image data and the (i+1)th original image data is in an intermediate state between the p-th input image data and the (p+1)th input image data. Each of the sub-images exhibits one of first brightness and second brightness. At least one sub-image among the J number of sub-images is different from the other sub-images.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device, image shifting device, and image display apparatus
ActiveUS6885412B2Quality improvementQuick responseLiquid crystal compositionsTelevision system detailsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
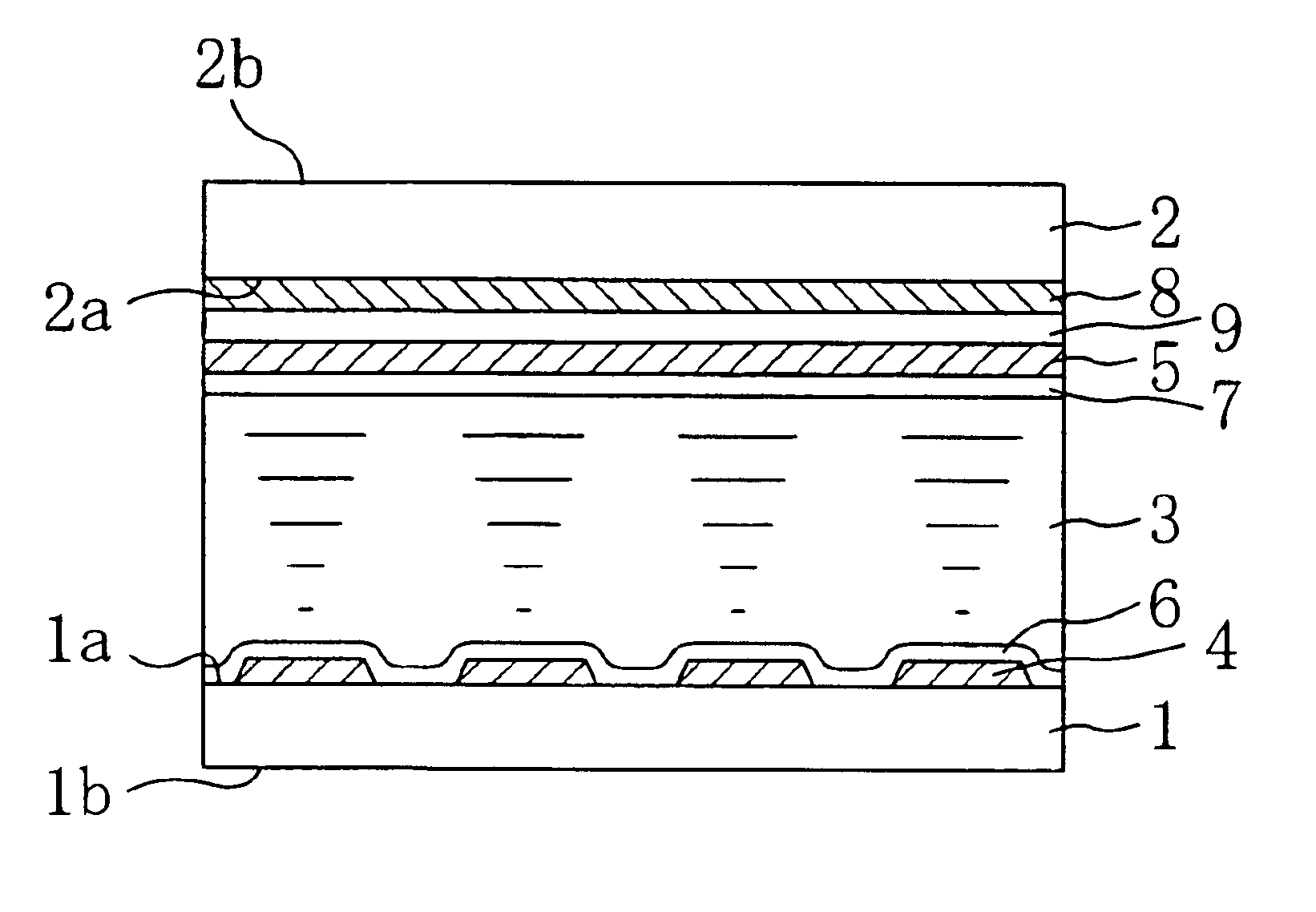
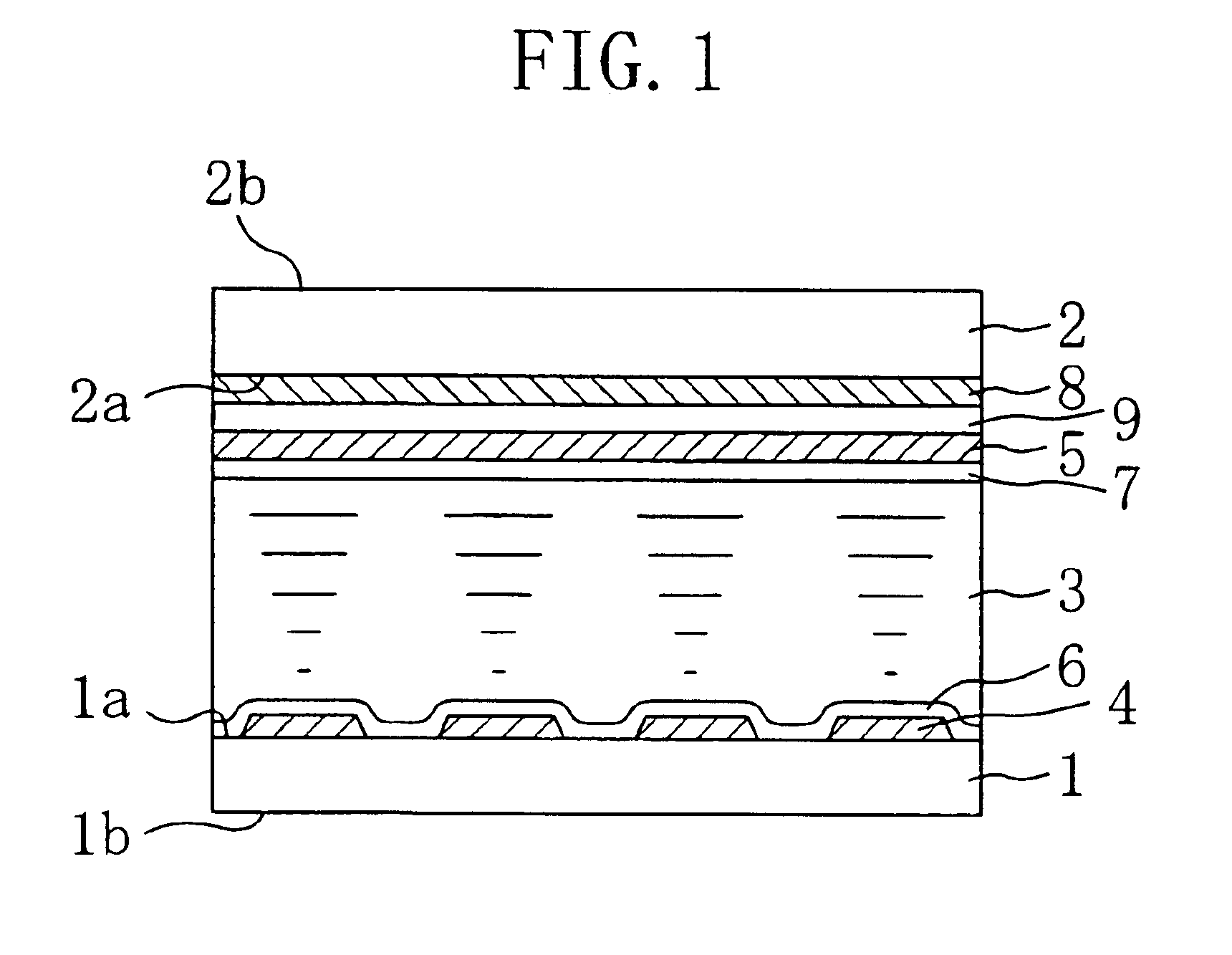
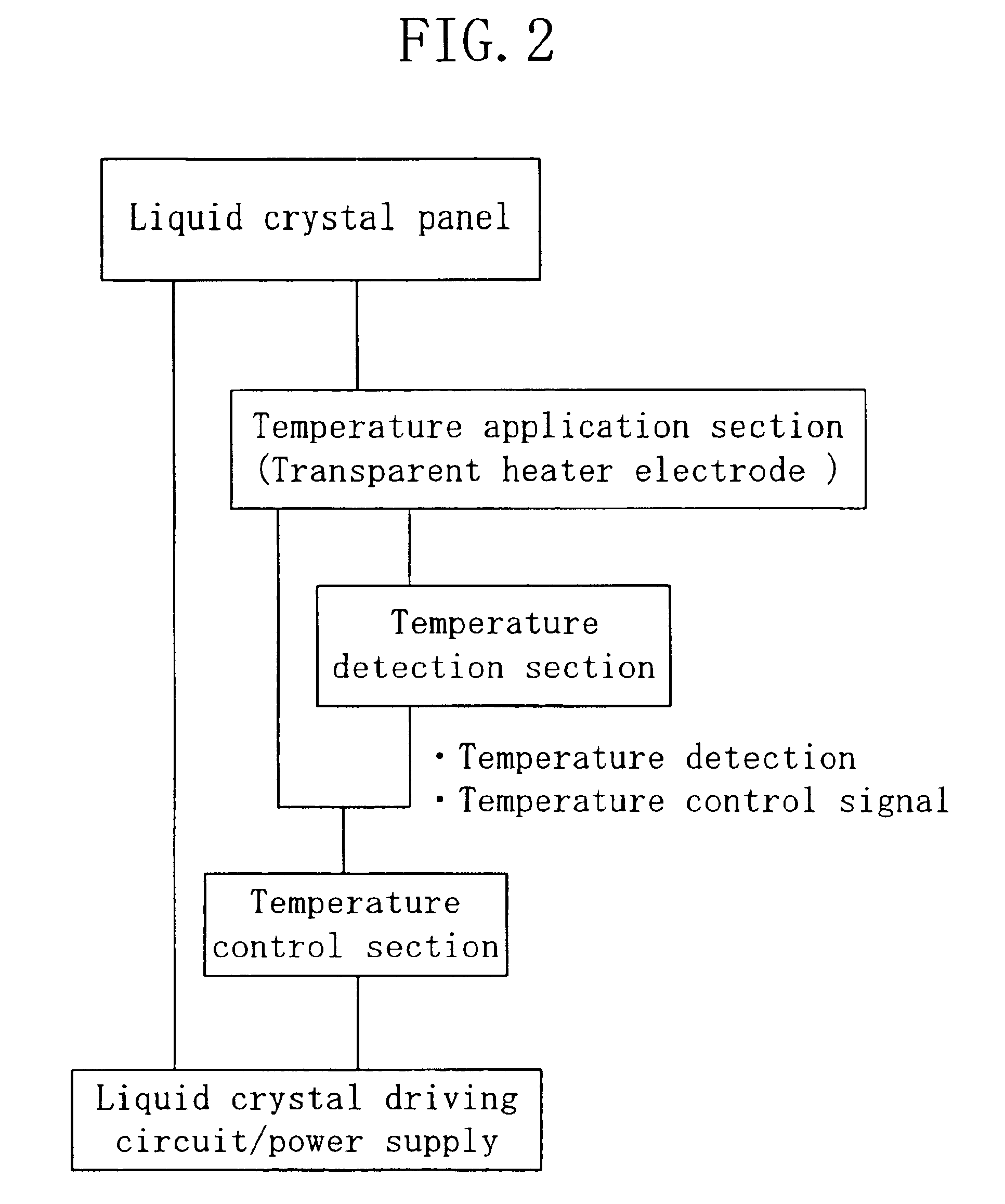
A liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate, a second substrate opposing the first substrate, a liquid crystal layer provided in a gap between the first substrate and the second substrate, and a temperature adjustment member formed on the first substrate and / or the second substrate. The panel temperature T (° C.) of the liquid crystal display device is controlled to be equal to or greater than TNI-65 and less than or equal to TNI-15, where TNI (° C.) is the nematic-isotropic phase transition temperature of the liquid crystal composition of the liquid crystal layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
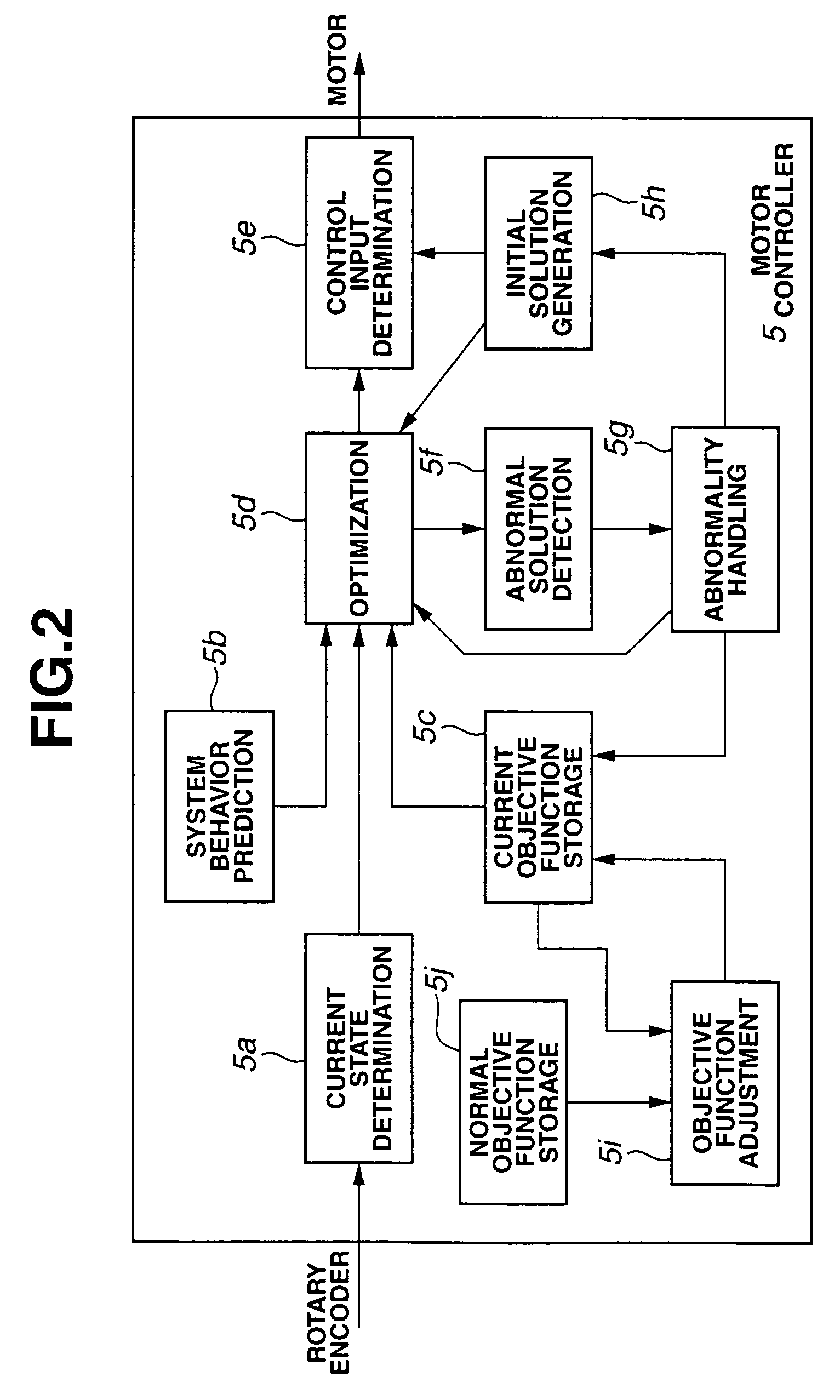
Model predictive control apparatus
InactiveUS7418372B2Quick responseAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle fittingsModel predictive controlEngineering
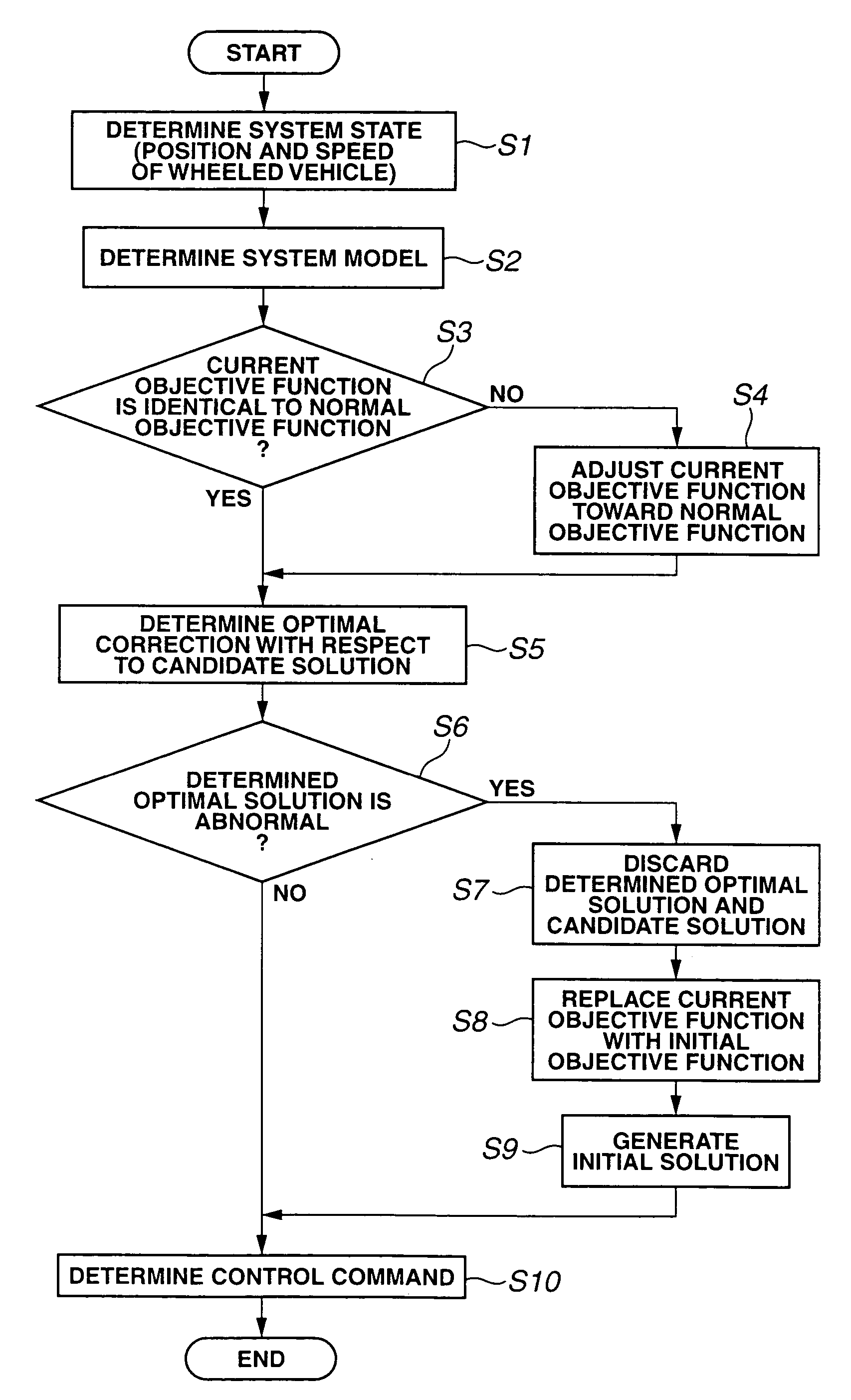
A model predictive control apparatus includes an initial solution generation section, an abnormality handling section, and an objective function adjustment section. The abnormality handling section performs initial solution generation when it is determined that performed optimization is abnormal. The initial solution generation section generates an initial optimal value of a future time series control input in accordance with an initial objective function, without reference to a candidate value of the time series control input. The objective function adjustment section adjusts the current objective function so that the current objective function varies stepwise with time toward the normal objective function when it is determined that the current objective function is different from the normal objective function.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Automated trading system in an electronic trading exchange
An electronic exchange system network includes a trader site having an automated trading system capable of submitting orders and / or quotes to an exchange site. The automated trading system determines whether an order or quote should be submitted based on, for example, the current market price of an option and theoretical buy and sell prices. The theoretical buy and sell prices are derived from, among other things, the current market price of the security underlying the option. The theoretical buy and sell prices are calculated when underlying factors that contribute to the theoretical prices change. Computation times of the theoretical prices may be reduced by using precalculated values and / or using interpolation and extrapolation. Other techniques may be used in addition or in the alternative to speed automatic decision-making. In addition, a system of checks may be conducted to ensure accurate and safe automated trading. The automated trading system may be capable of automatically submitting orders in connection with the underlying security in order to hedge part of the delta risk associated with the automated option trades.
Owner:DCFB
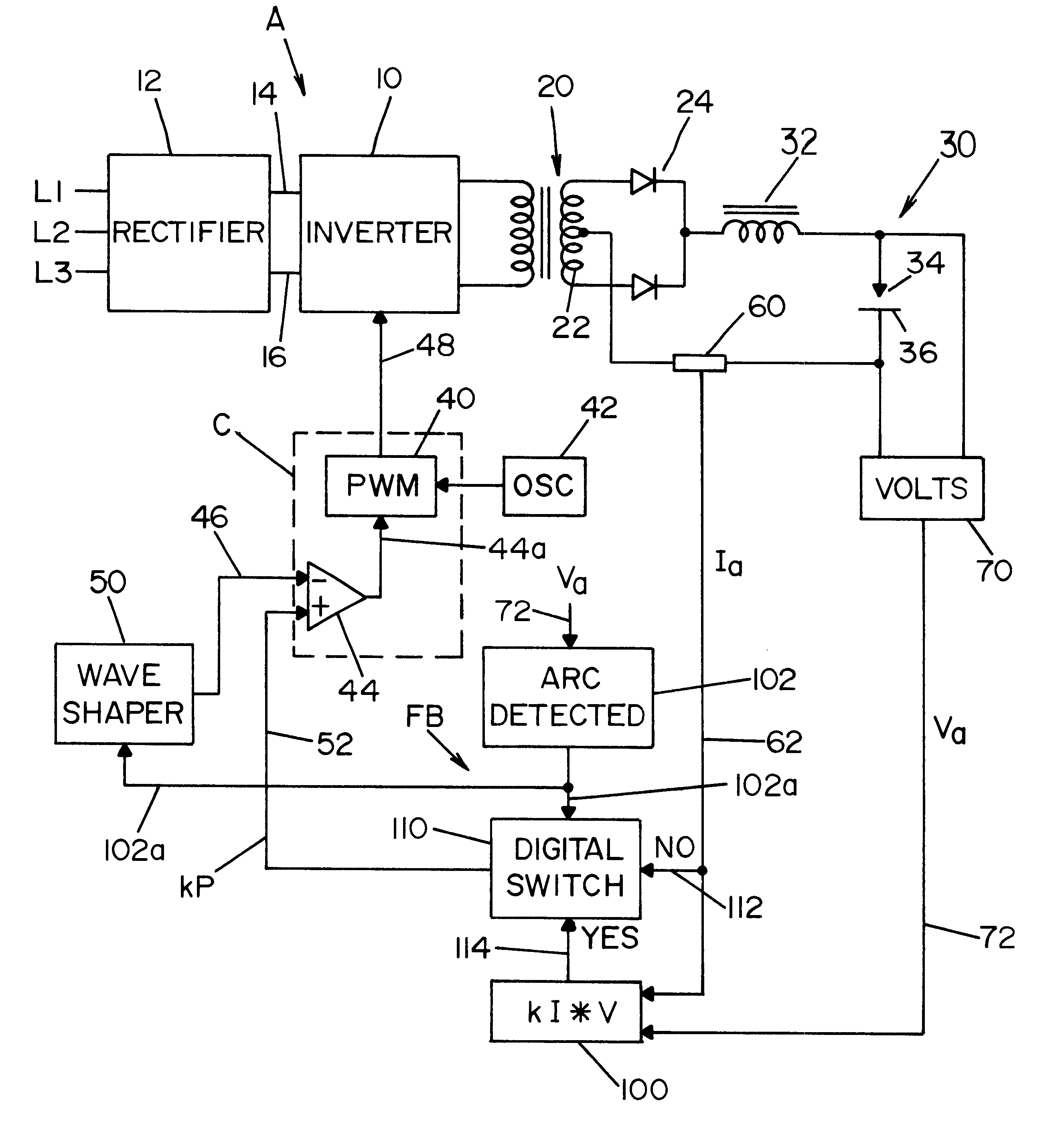
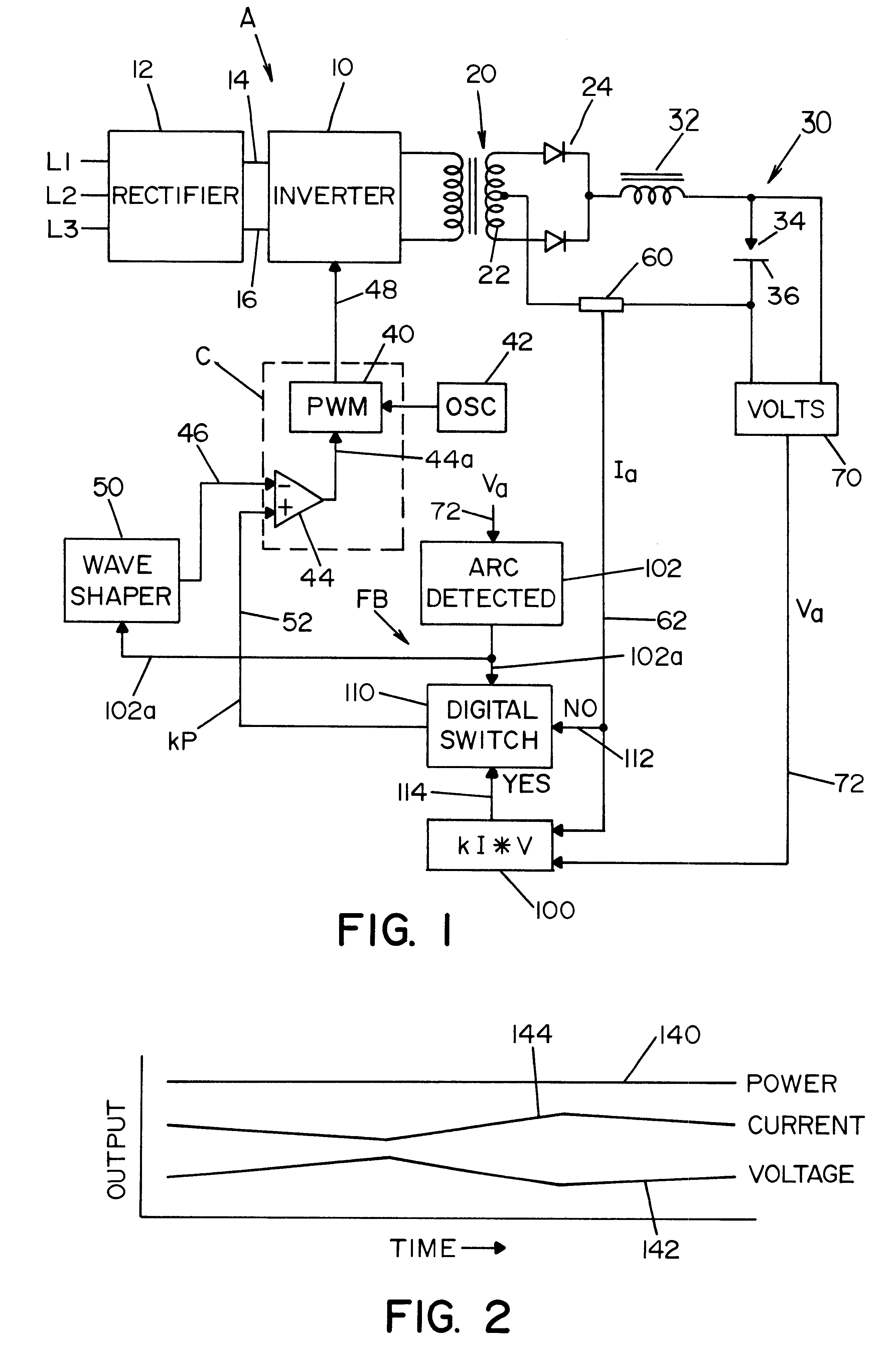
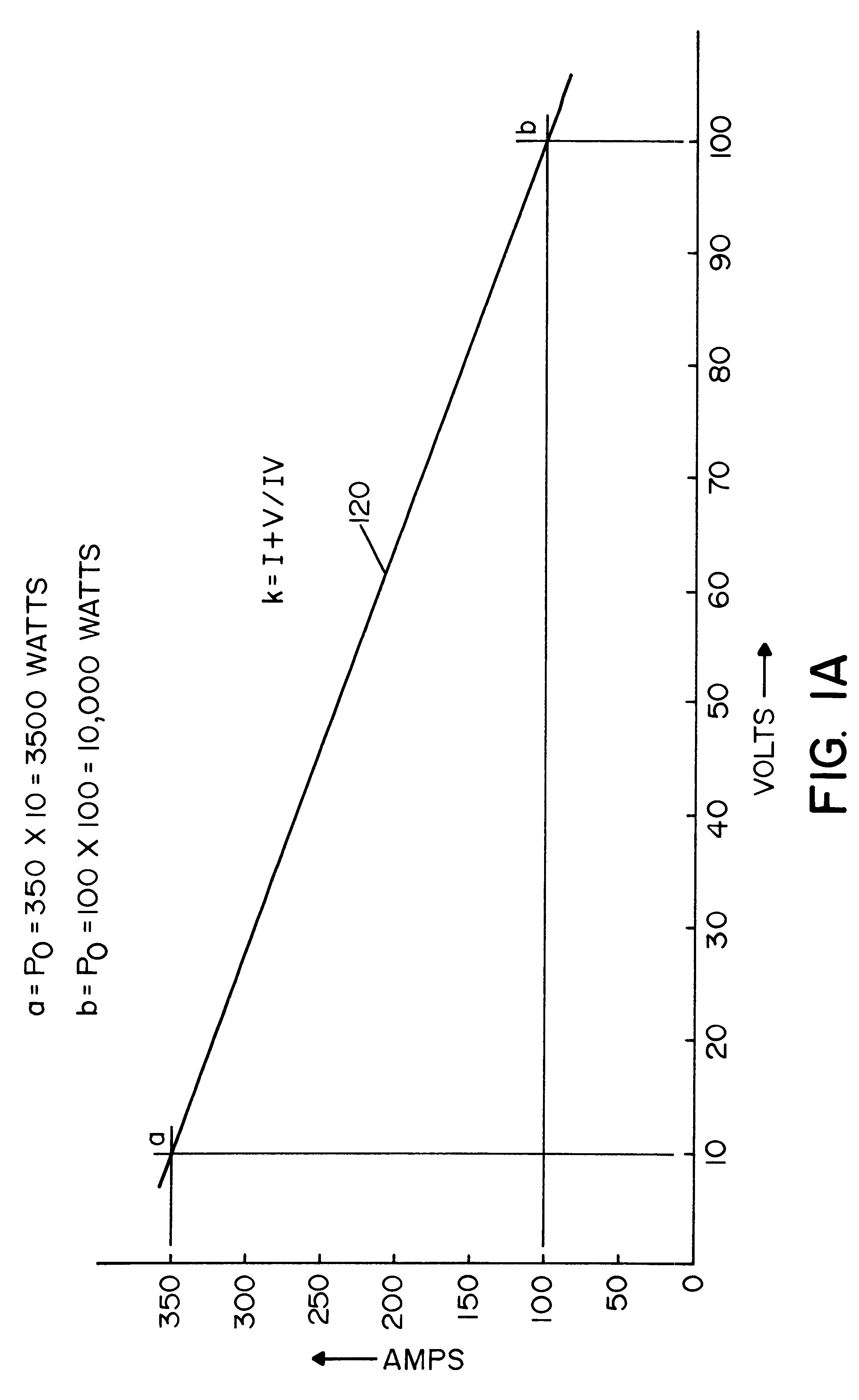
System and method for controlling an electric arc welder
InactiveUS6498321B1Inhibit currentRealize automatic adjustmentArc welding apparatusControl signalControl system
A control system for an electric arc welder performing a welding process between an electrode and a workpiece, which system comprises: a high speed switching type power supply with a controller operated at a switching frequency of at least about 10 kHz with an input current control signal to adjust the output current of the power supply; a first sensor sensing the actual arc voltage; a second sensor sensing the actual arc current; a first circuit for creating a power signal representing the desired real time power level at progressive times during the welding process; a second circuit for creating a function of the sensed actual voltage and the sensed actual current; and a third circuit for adjusting the current control signal in accordance with the difference between the power signal and the function of the actual voltage and current, preferably arc power.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Vehicle immersive communication system
ActiveUS20100137037A1Convenient and safe hands-free interfaceImprove driving experienceDevices with voice recognitionDevices with bluetooth interfacesCommunications systemWeb service
A vehicle communication system facilitates hands-free interaction with a mobile device in a vehicle or elsewhere. Users interact with the system by speaking to it. The system processes text and processes commands. The system supports Bluetooth wireless technology for hands-free use. The system handles telephone calls, email, and SMS text messages. The user can customize the device via a user profile stored on an Internet web server.
Owner:VALUE8 CO LTD
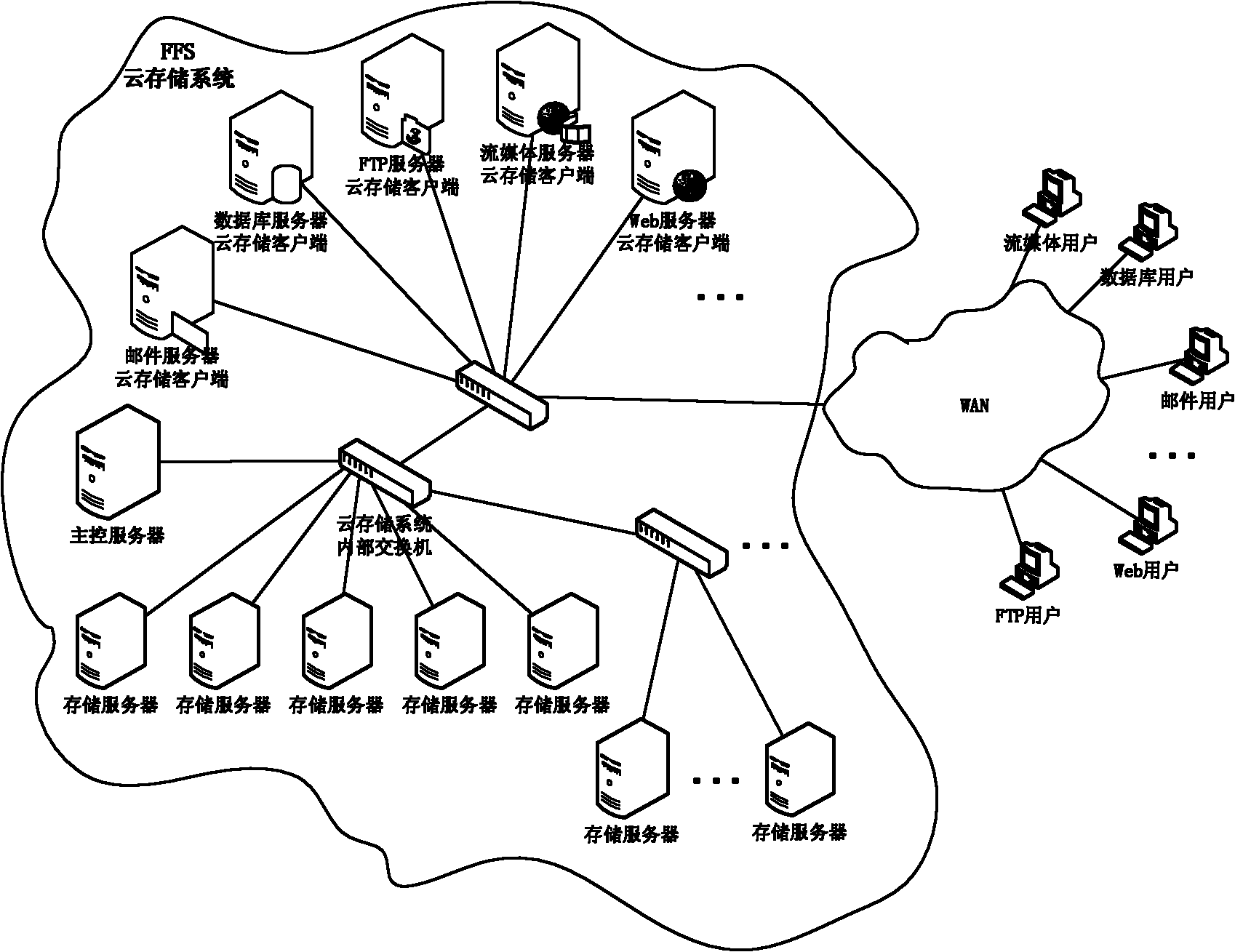
Network-based PB level cloud storage system and processing method thereof
InactiveCN102143215ASolve the problem of unbalanced load distributionSolve the problem of difficult expansionData switching networksGeneral purposeDynamic load balancing
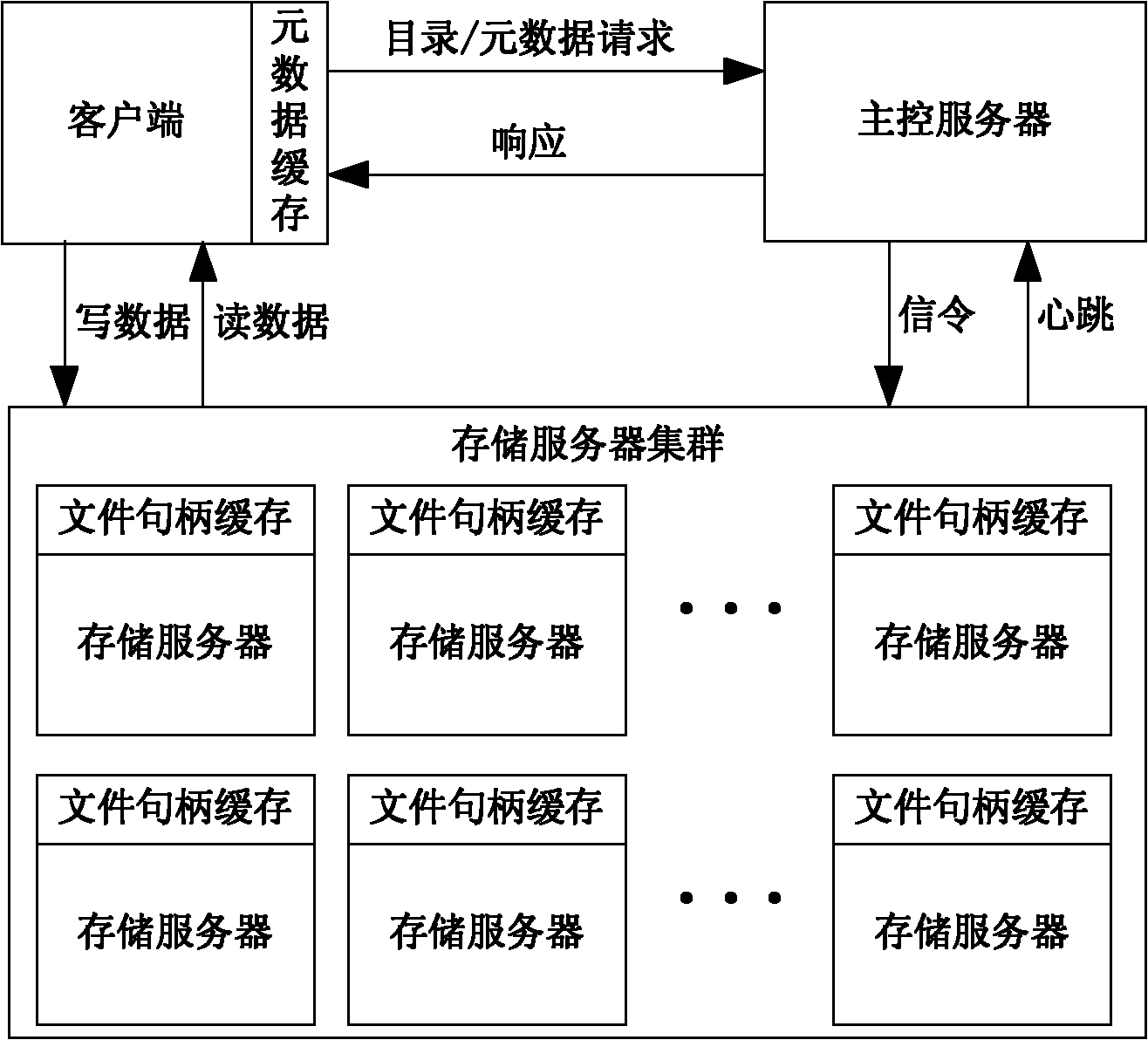
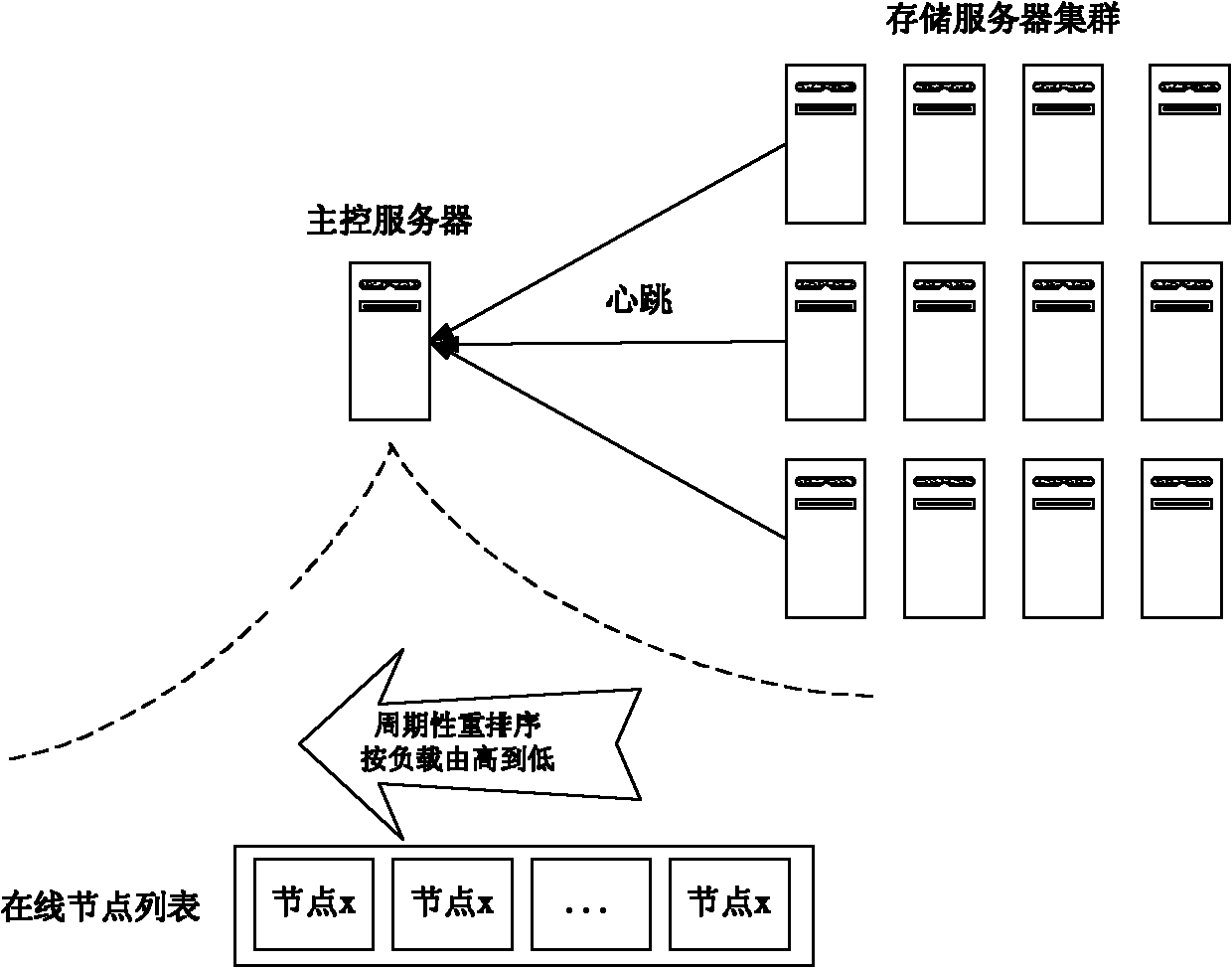
The invention relates to a network-based PB level cloud storage system and a processing method thereof. The network-based PB level cloud storage system comprises a main control server, a storage server cluster and a client side which are operated through an internal exchange, wherein the main control server is used for providing the directory information and the meta data information for a cloud storage client side and monitoring the storage server cluster; the storage server cluster comprises a plurality of storage servers used for data storage; the client side is used for providing the virtual disc service for a cloud storage client machine, submitting an operation request of the cloud storage client machine to a virtual disc to the main control server and reading / writing the file data from the storage server, and a client-side module is arranged on the cloud storage client machine. The invention is easy to expanded and is convenient to manage, solves the problem of storage island, can construct a cloud storage file system provided with the dynamic load balancing capability and the online backup and automatic recovery functions and capable of being expanded on demand on a general-purpose low-performance PC (personal computer) cluster.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com