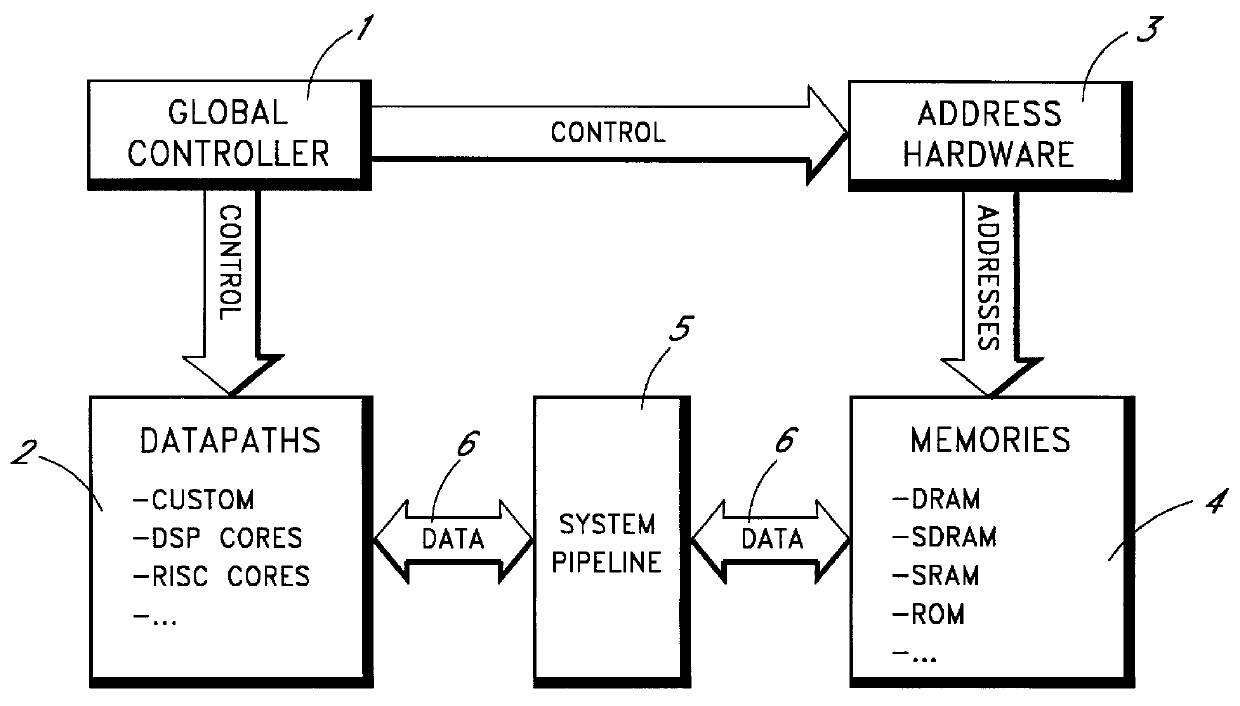
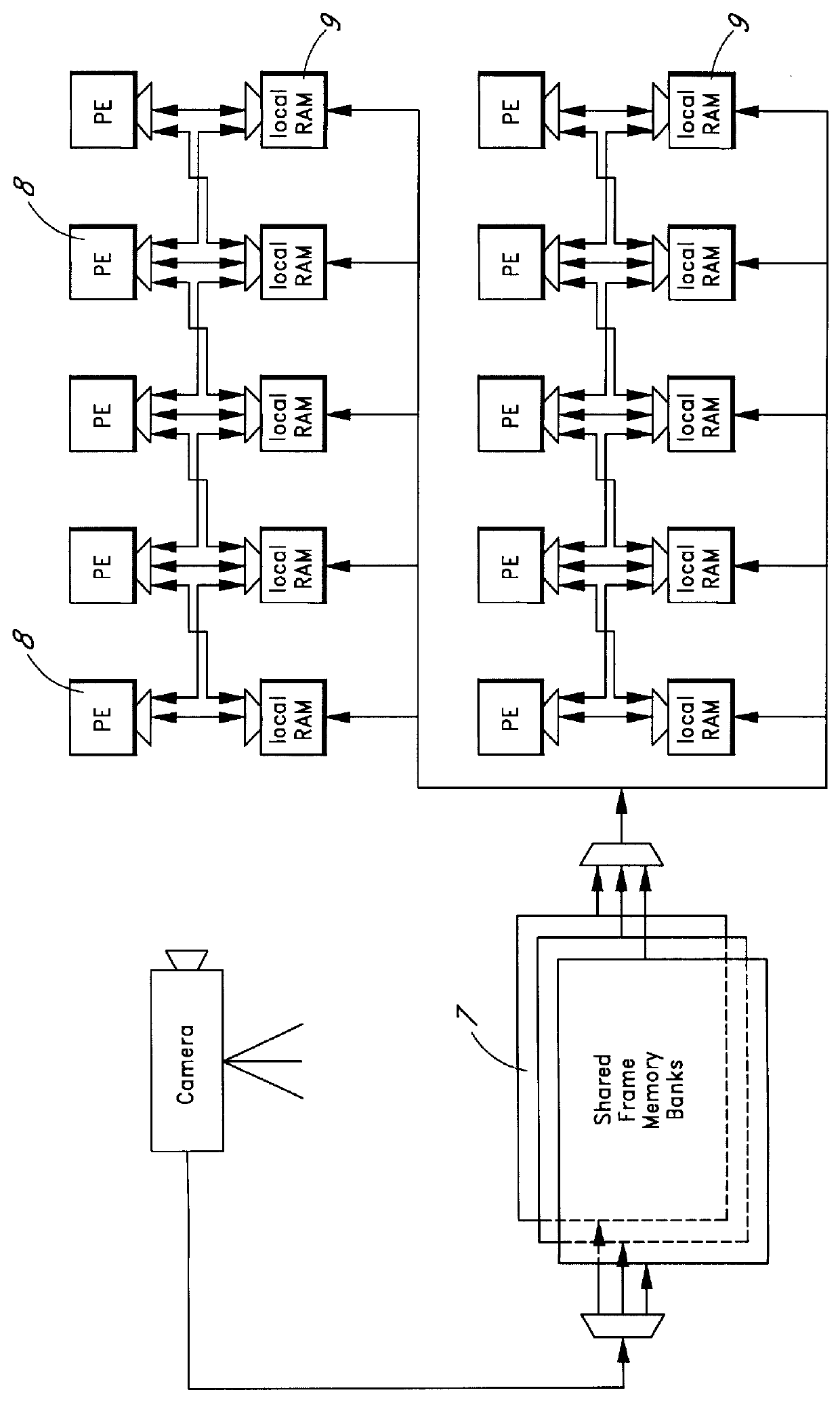
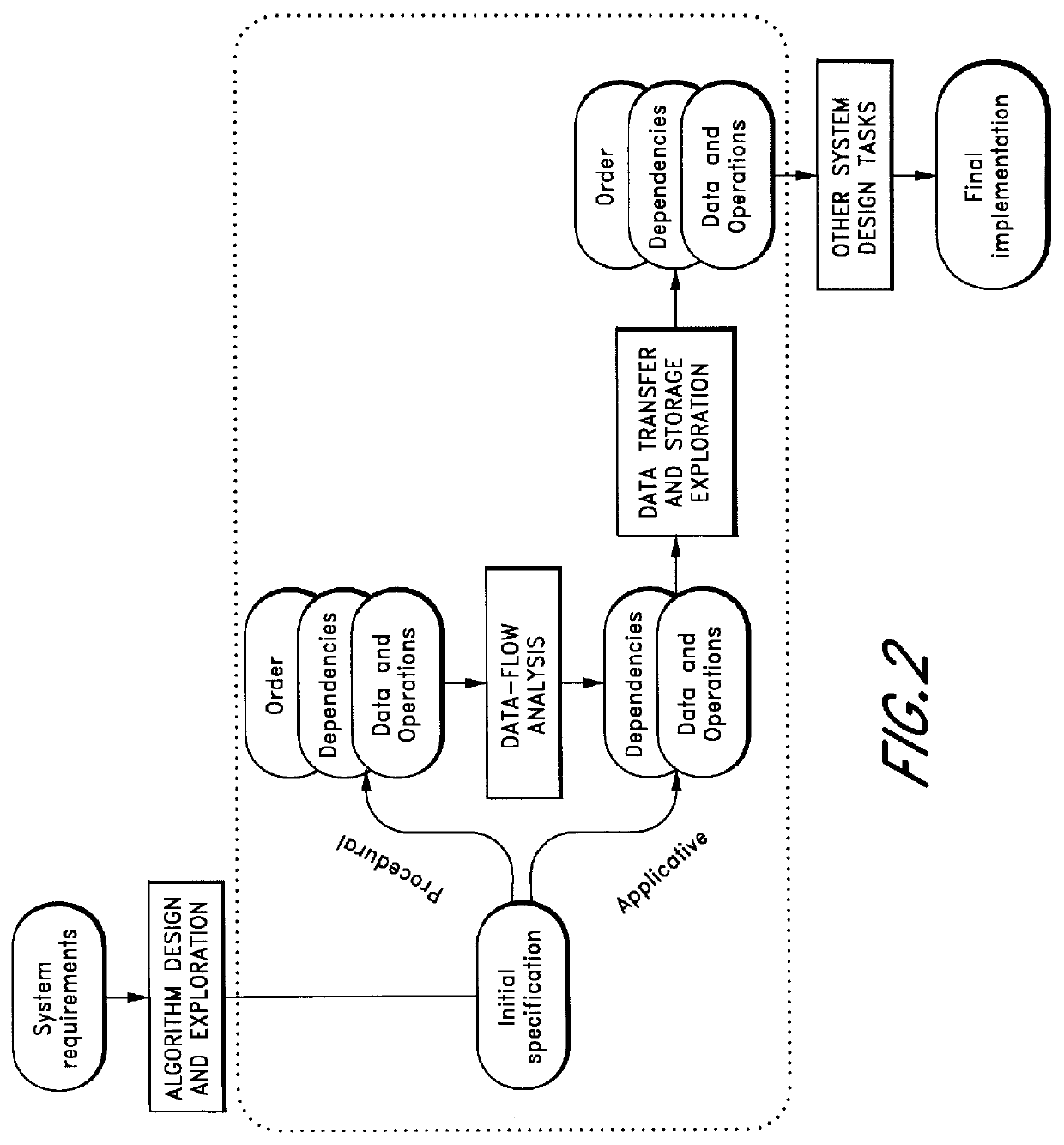
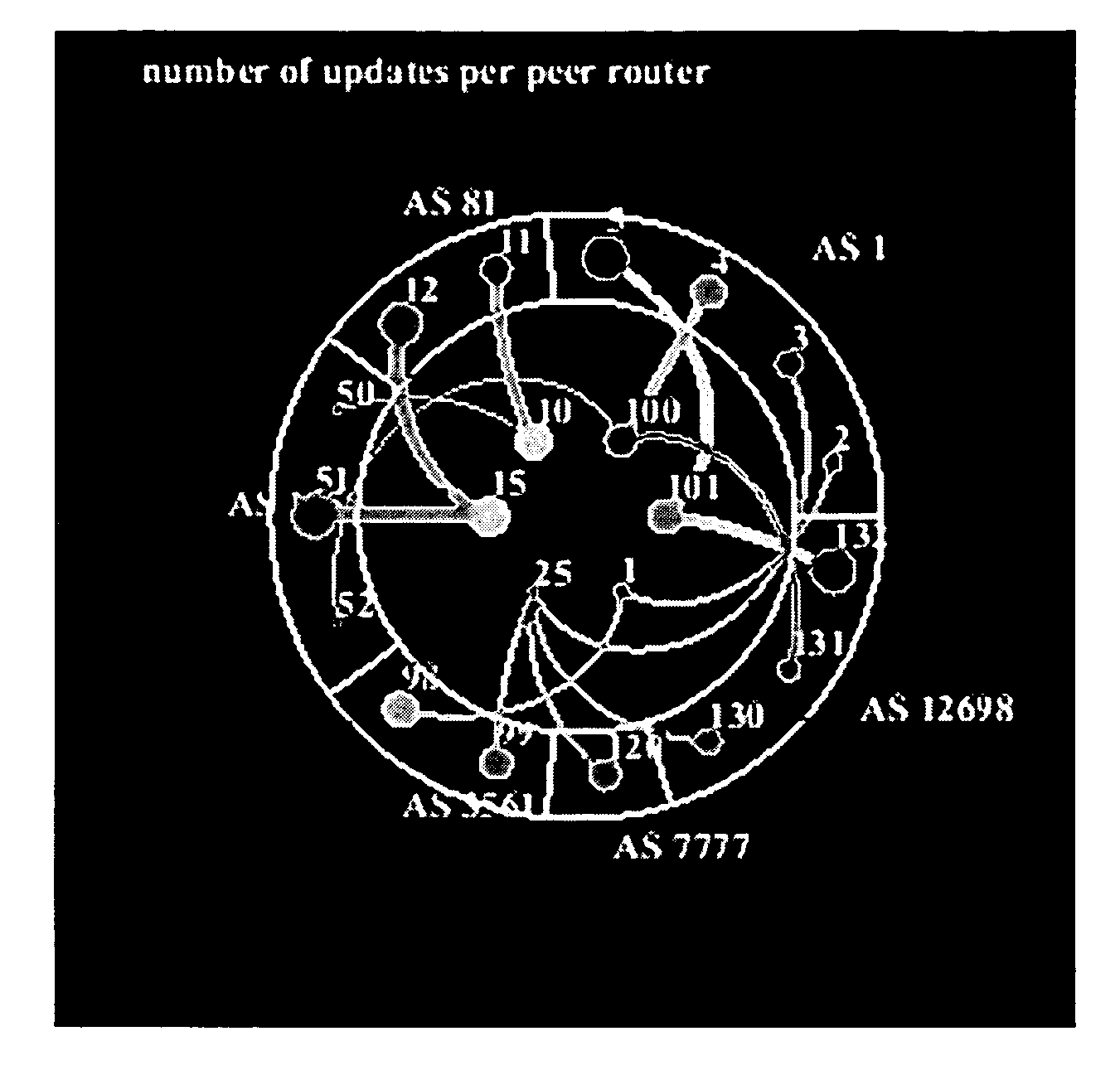
Patents
Literature
7324 results about "Time-Consuming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Requiring a great amount of time.
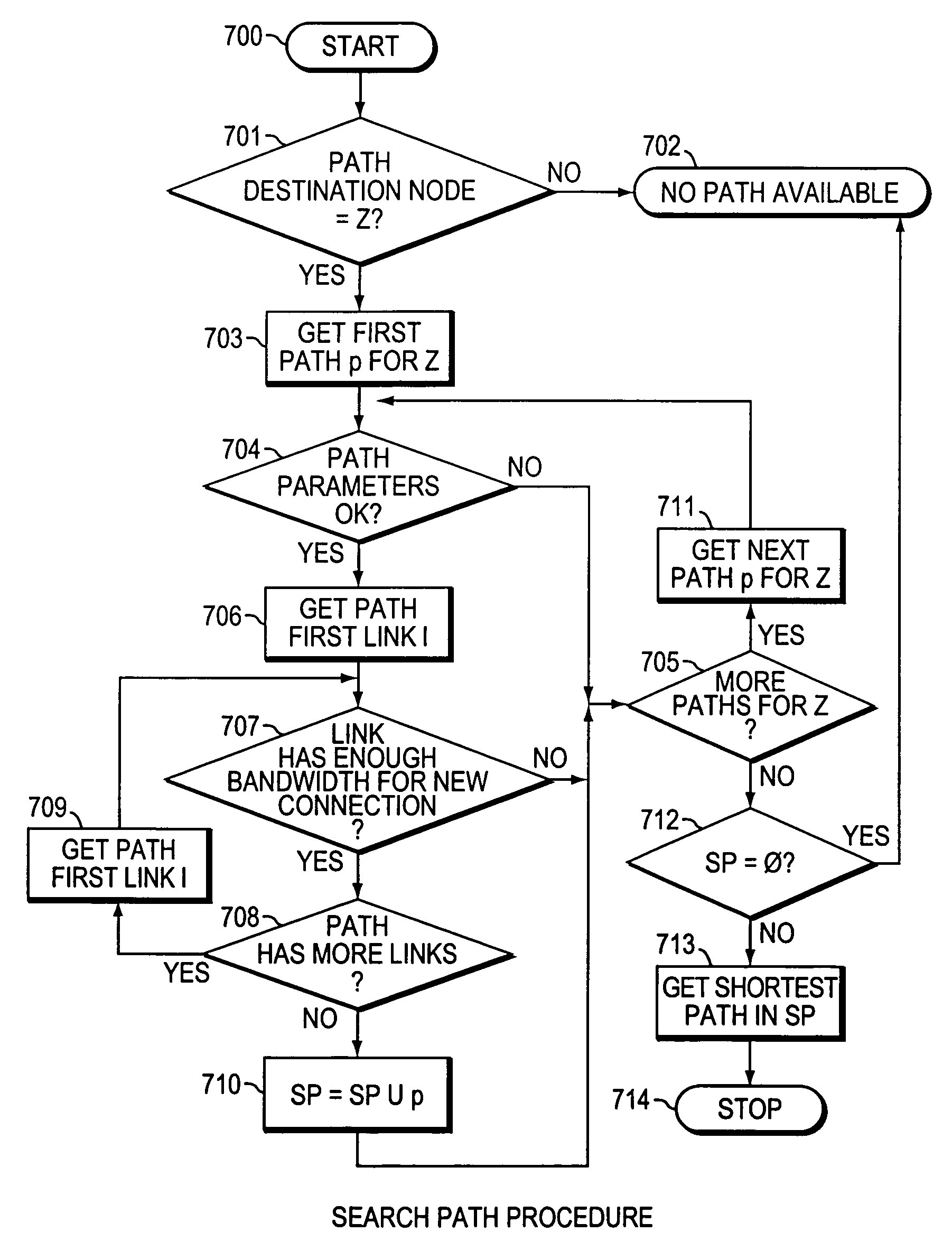
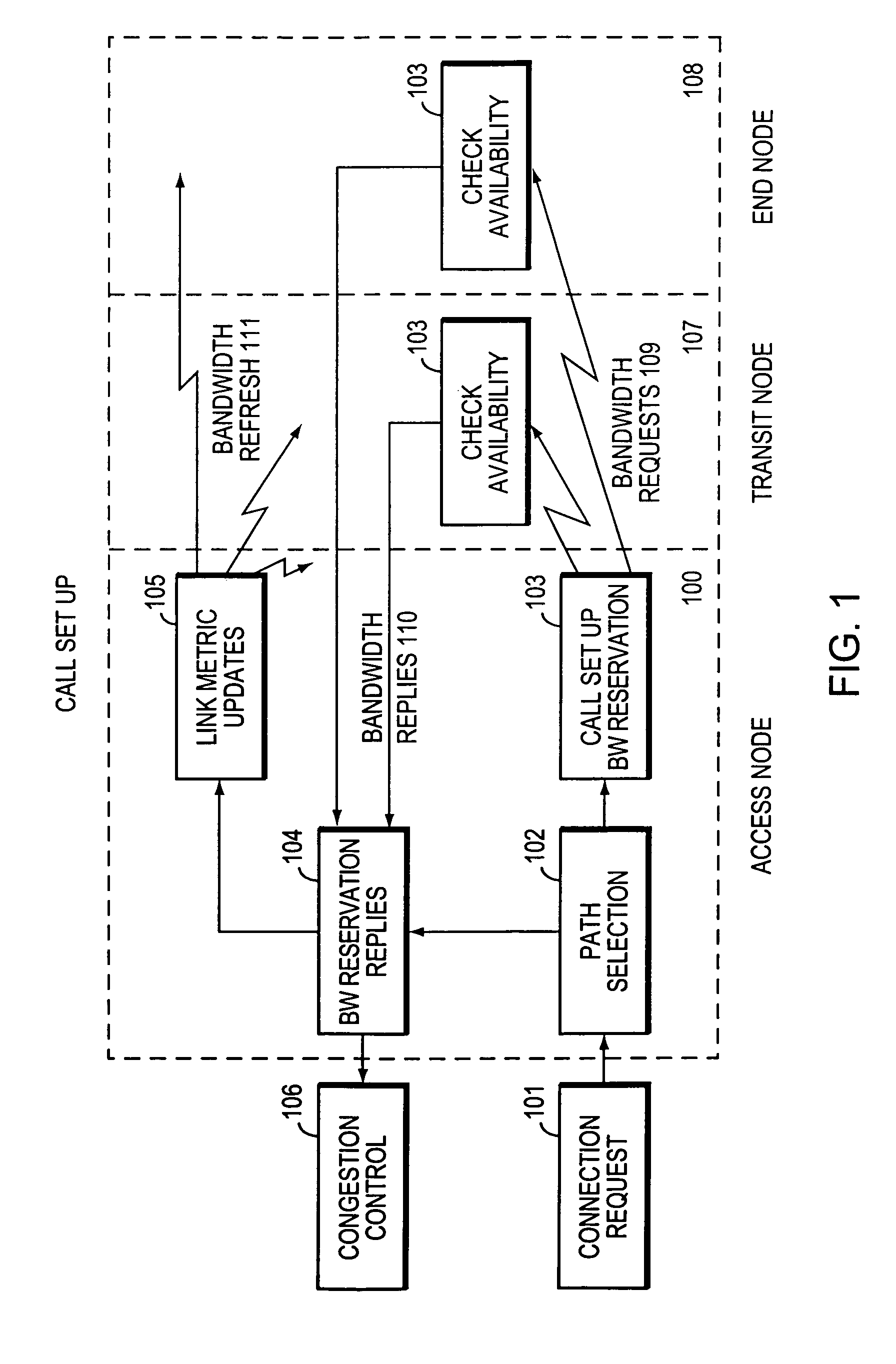
Method and system for minimizing the connection set up time in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS6934249B1Minimize delayMinimize in in to selectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket switched
The present invention is directed to a high speed packet switching network and, in particular to a method and system for minimizing the time to establish a connection between an origin and a destination node. Due to high dynamicity of the traffic on transmission links, it is important to select a routing path according to a fully up-to-date information on all network resources. The simpler approach is to calculate a new path for each new connection request. This solution may be very time consuming because there are as many path selection operations as connection set up operations. On another hand, the calculation of paths based on an exhaustive exploration of the network topology, is a complex operation which may also take an inordinate amount of resources in large networks. Many of connections originated from a network node flow to the same destination network node. It is therefore possible to take a serious benefit in reusing the same already calculated paths for several connections towards the same node. The path calculated at the time the connection is requested is recorded in a Routing Database and updated each time a modification occurs in the network. Furthermore, alternate paths for supporting non-disruptive path switch on failure or preemption, and new paths towards potential destination nodes can be calculated and stored when the connection set up process is idle. These last operations are executed in background with a low processing priority and in absence of connection request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
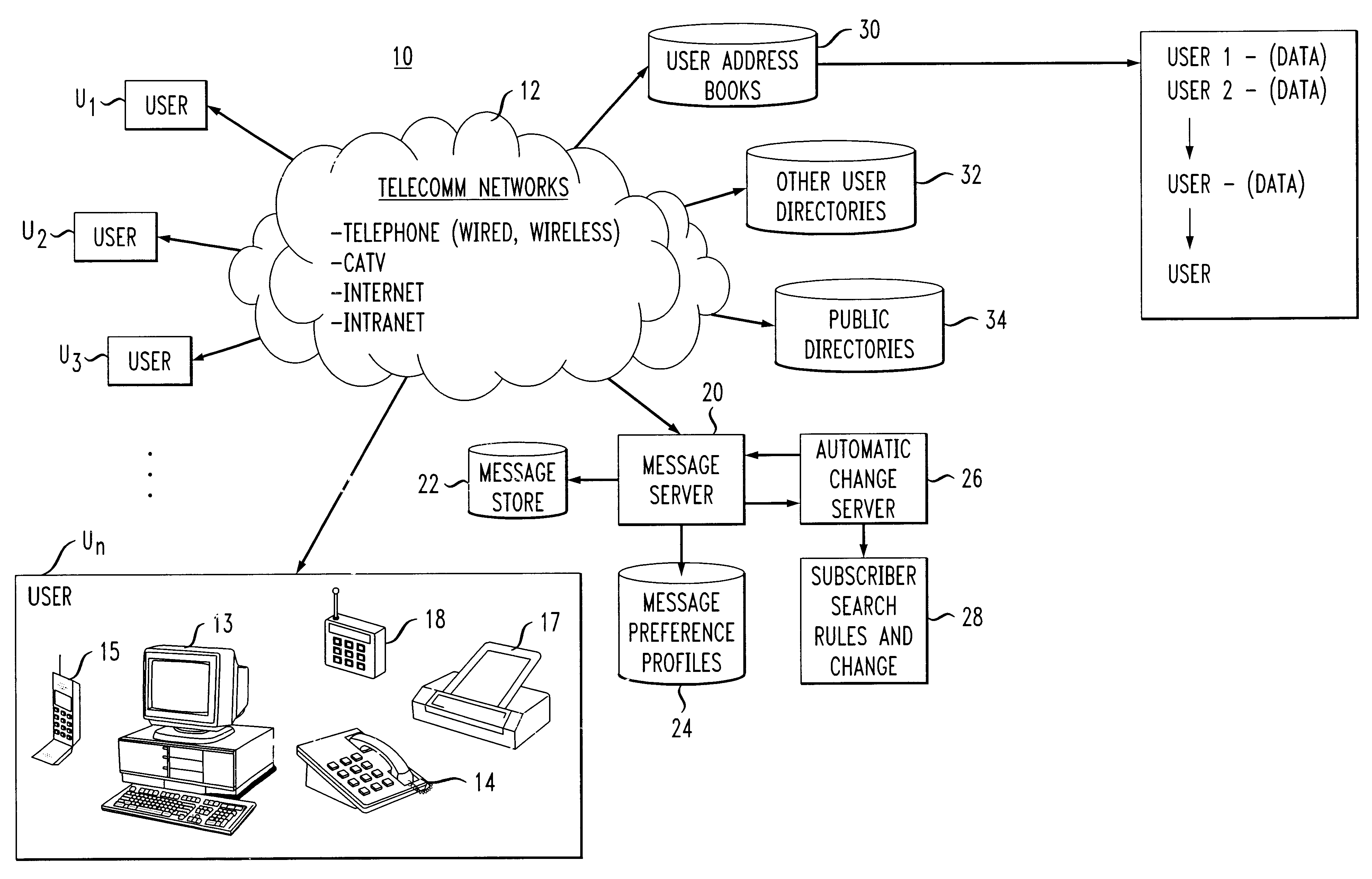
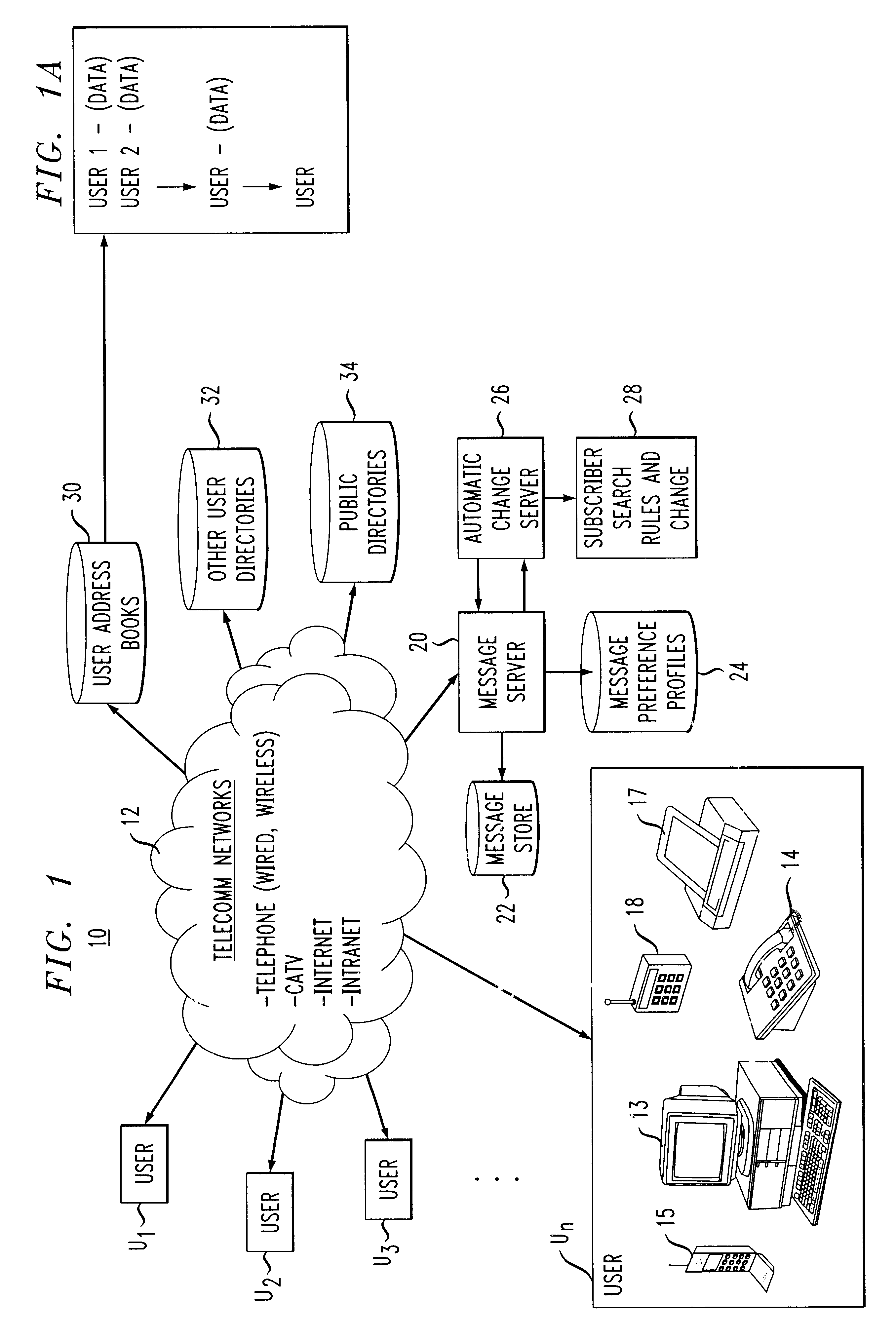
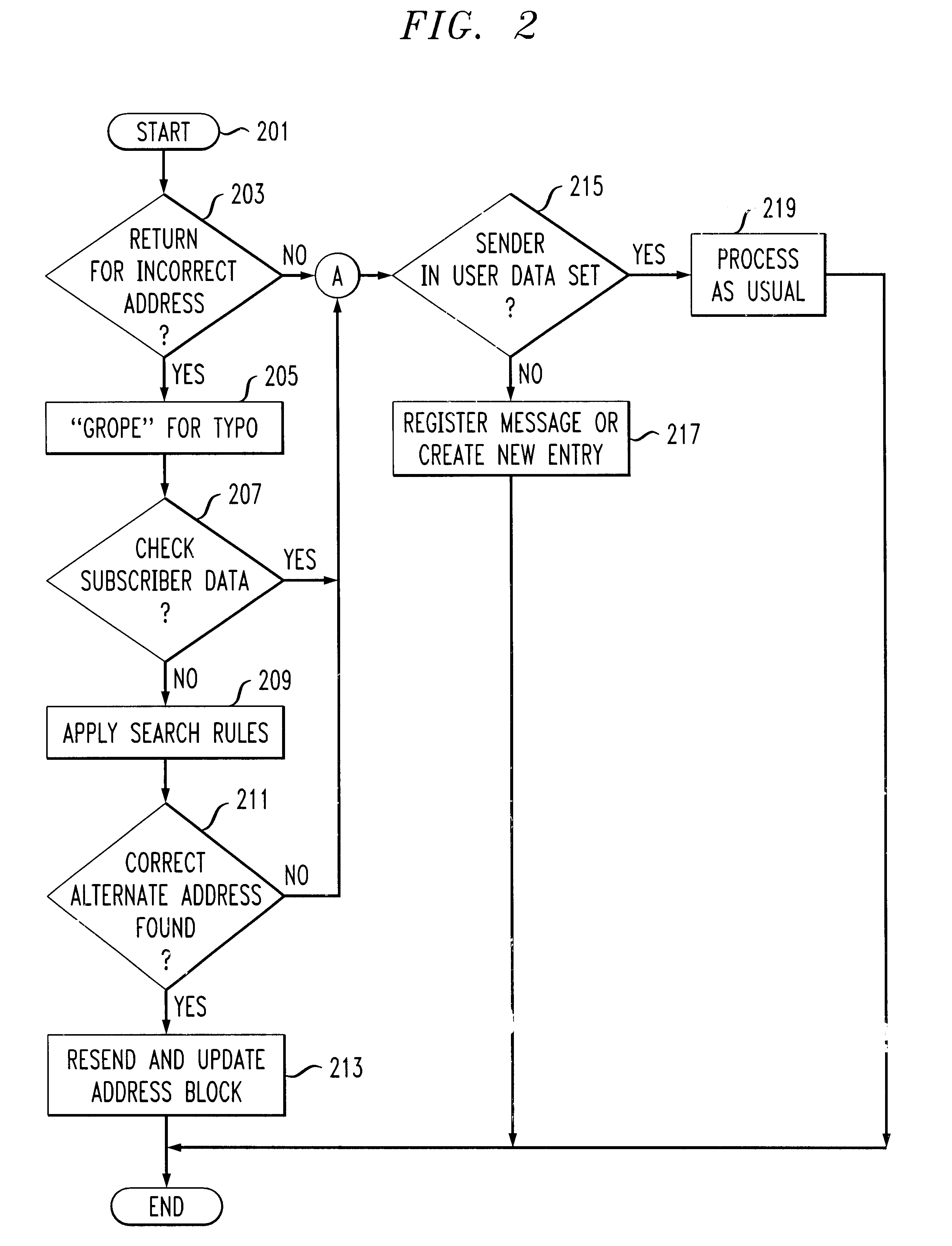
System, apparatus and method for automatic address updating of outgoing and incoming user messages in a communications network
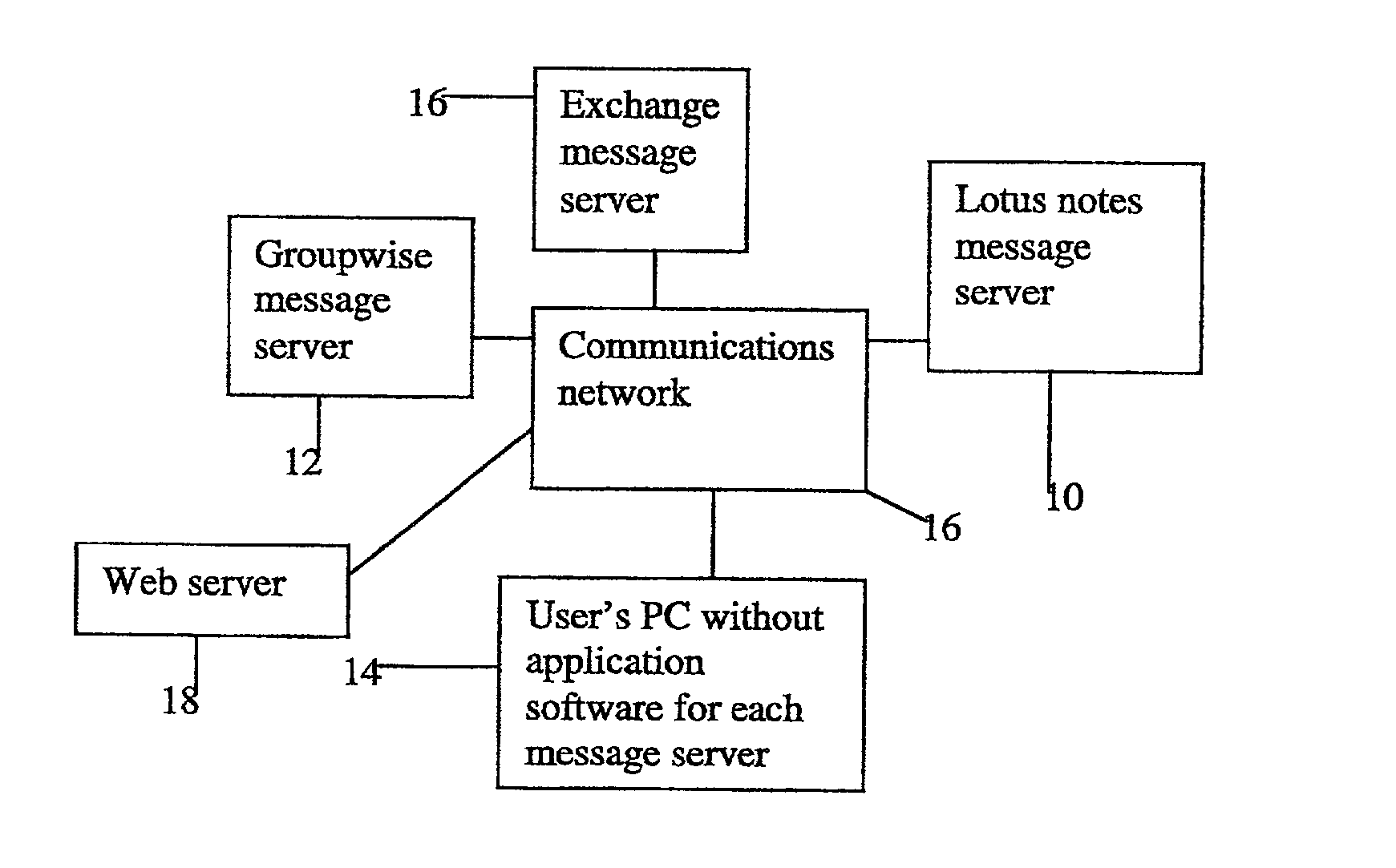
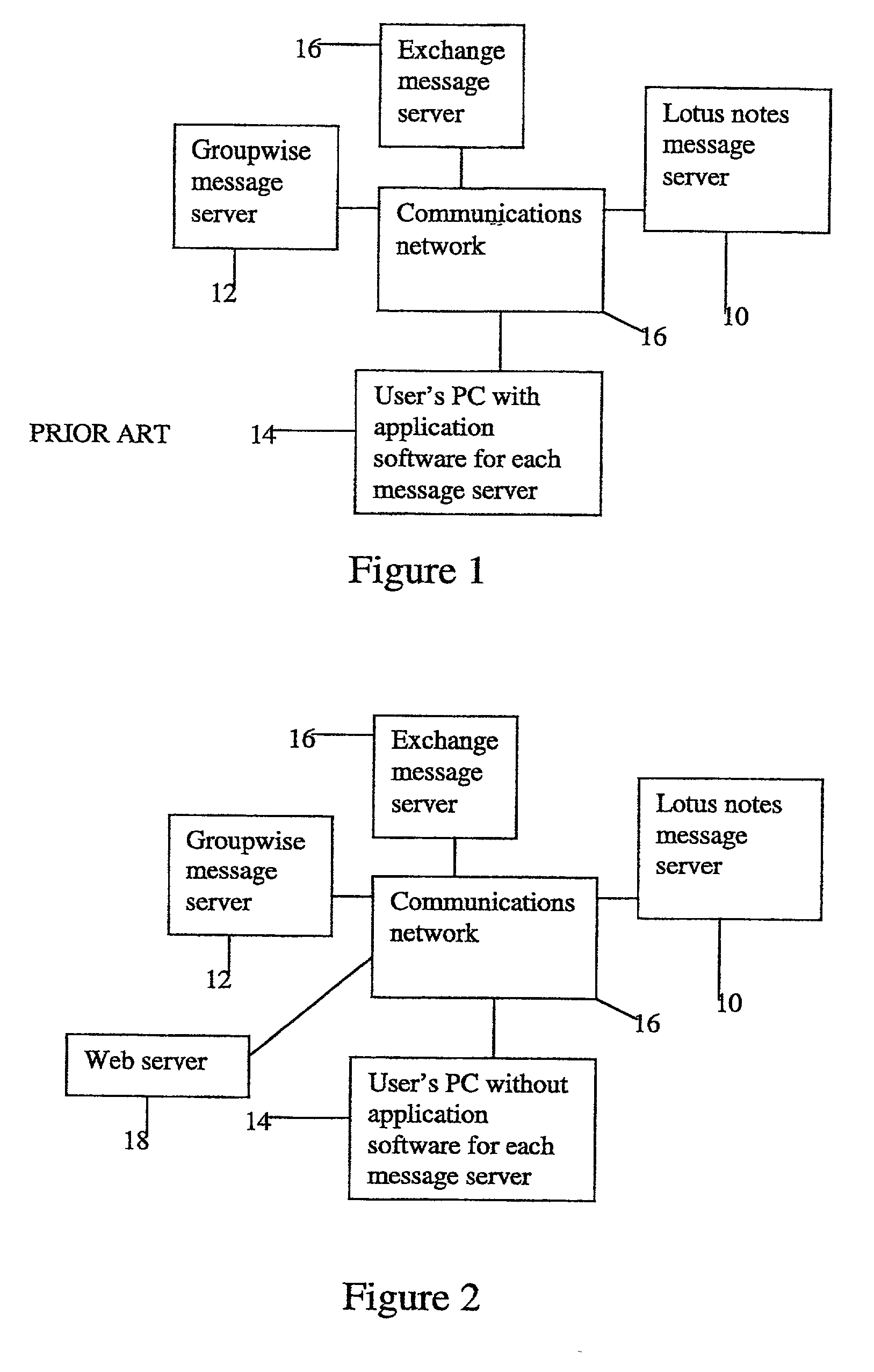
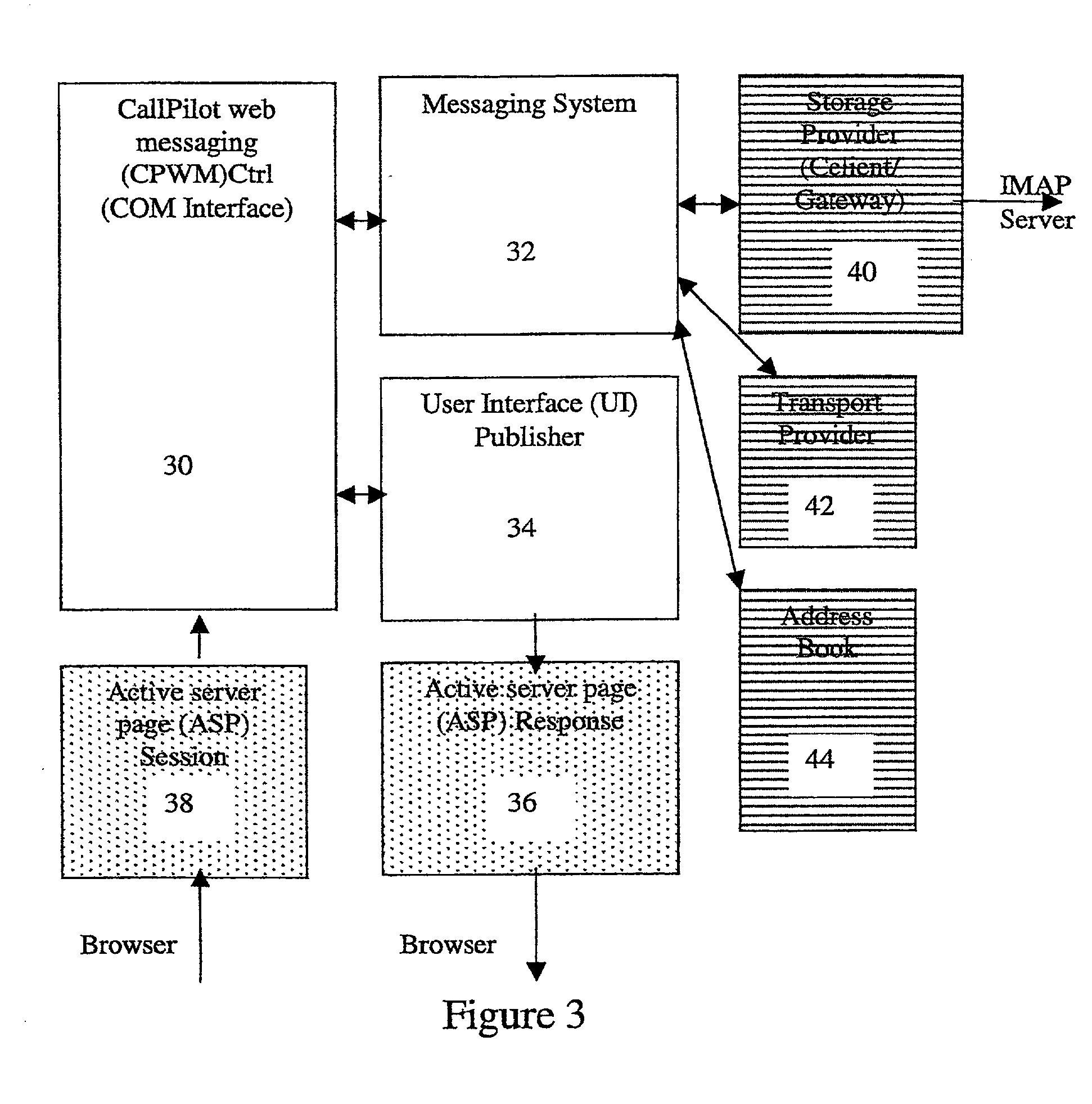
A system, apparatus and method automatically update address information of a user's outgoing and incoming messages to / from a communication network thereby relieving the user of the burden of manually entering address changes into a user address book. A plurality of users are coupled through terminals to a server in the communication network for exchanging telephone, CATV, Internet, intranet for messaging, facsimile, etc purposes. The server includes a message store; stored message profile; and is coupled to a change server linked to a network. The change server includes search rules and change options provided by the users in directing the change server in finding correct and alternative address information when erroneous or unknown information is detected in the outgoing and incoming messages. Each user address book includes a series of contacts for each user. Each contact is identified by an identification number, ID, including a name and address. The server detects message headers where a "Send To Address" is not in the address book. The change server is activated and accesses external databases for correct or alternative addresses in accordance with search rules provided by the user. The alternative or correct address books address information is installed in the users address book and the "Send To Message" process is executed. For returned messages incorporating erroneous information, the search server is again activated to access the databases for correct address information, after which the user's address book is updated thereby eliminating the time-consuming, irritating manual process of updating the user address book for outgoing and incoming messages.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
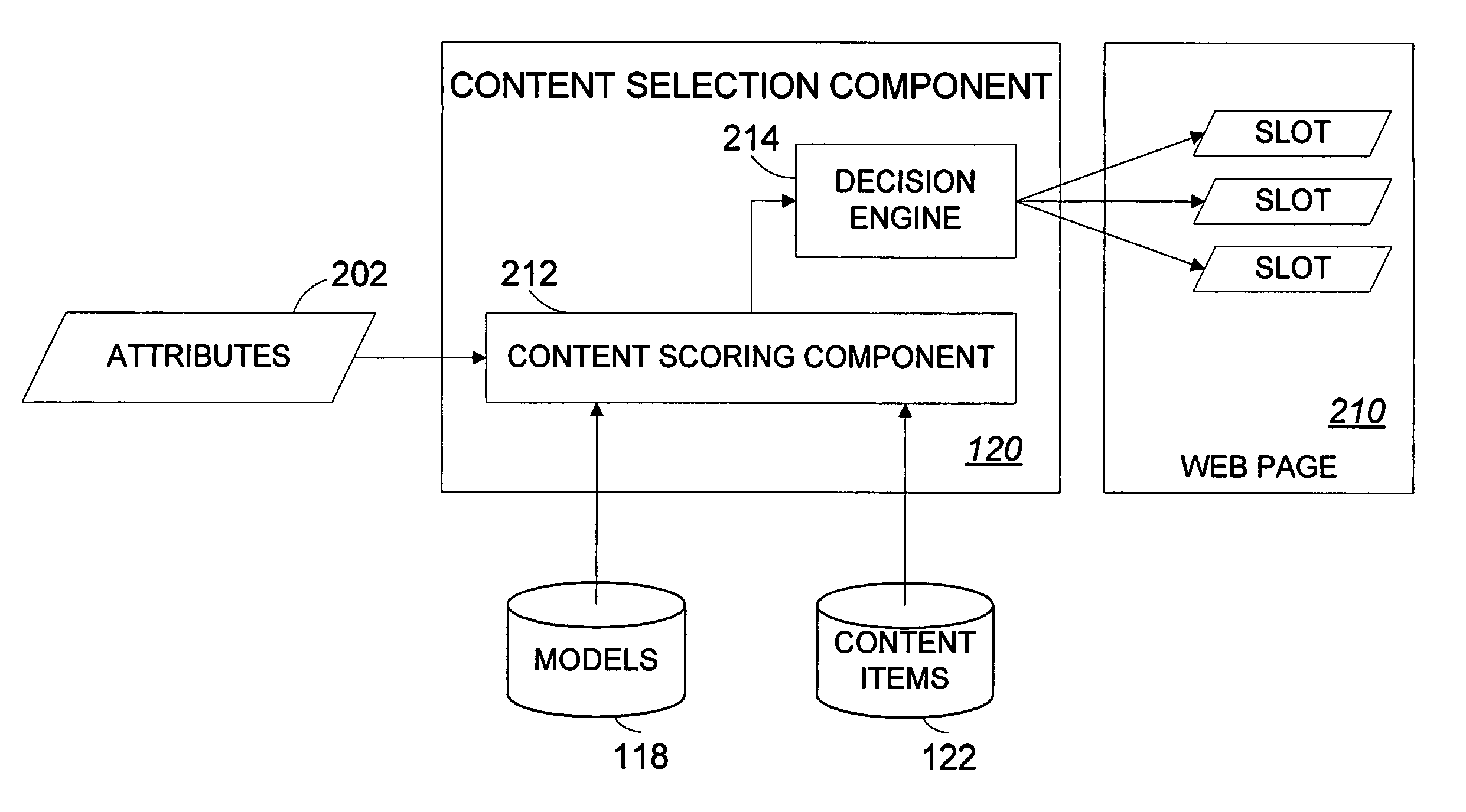
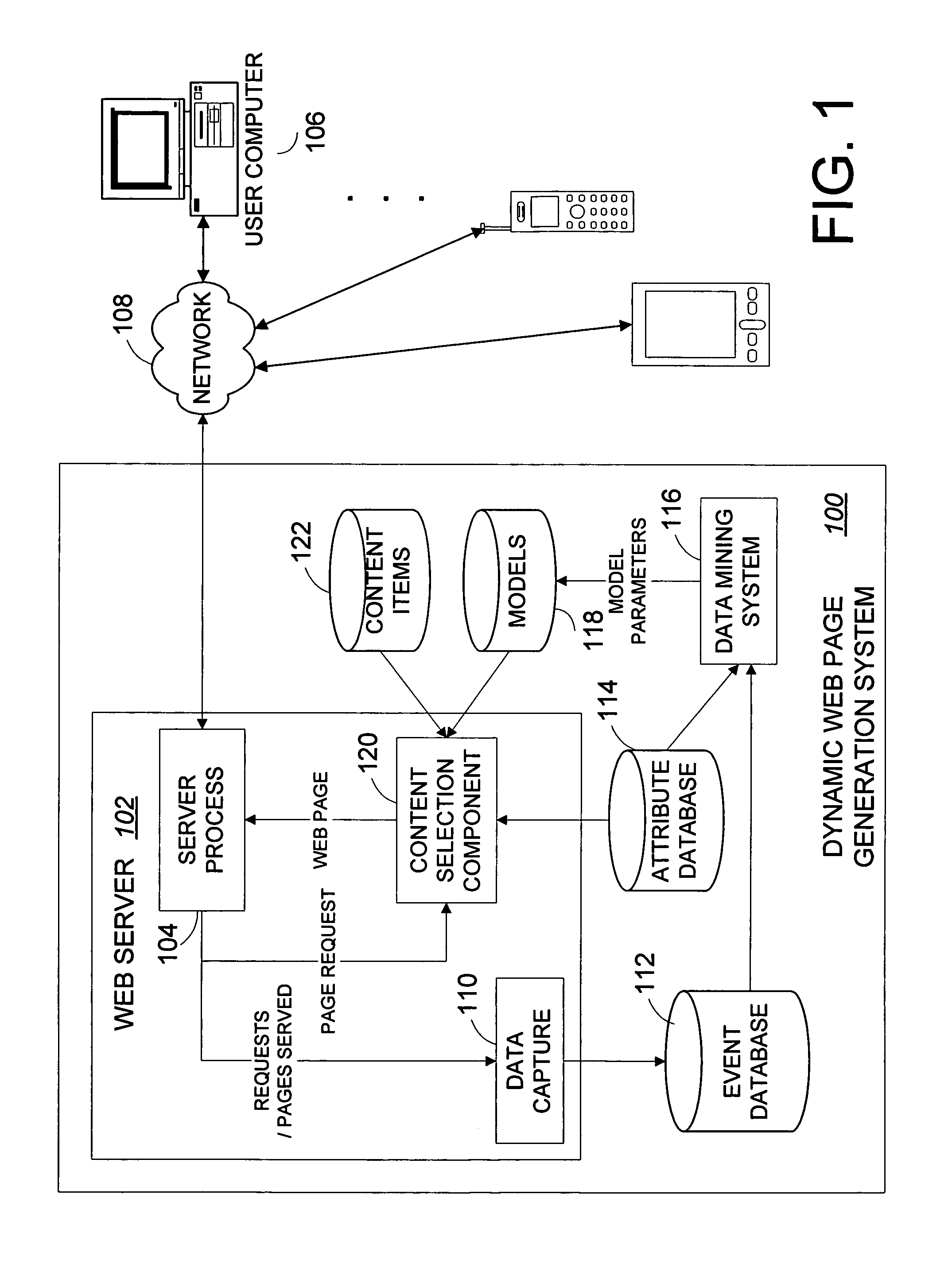
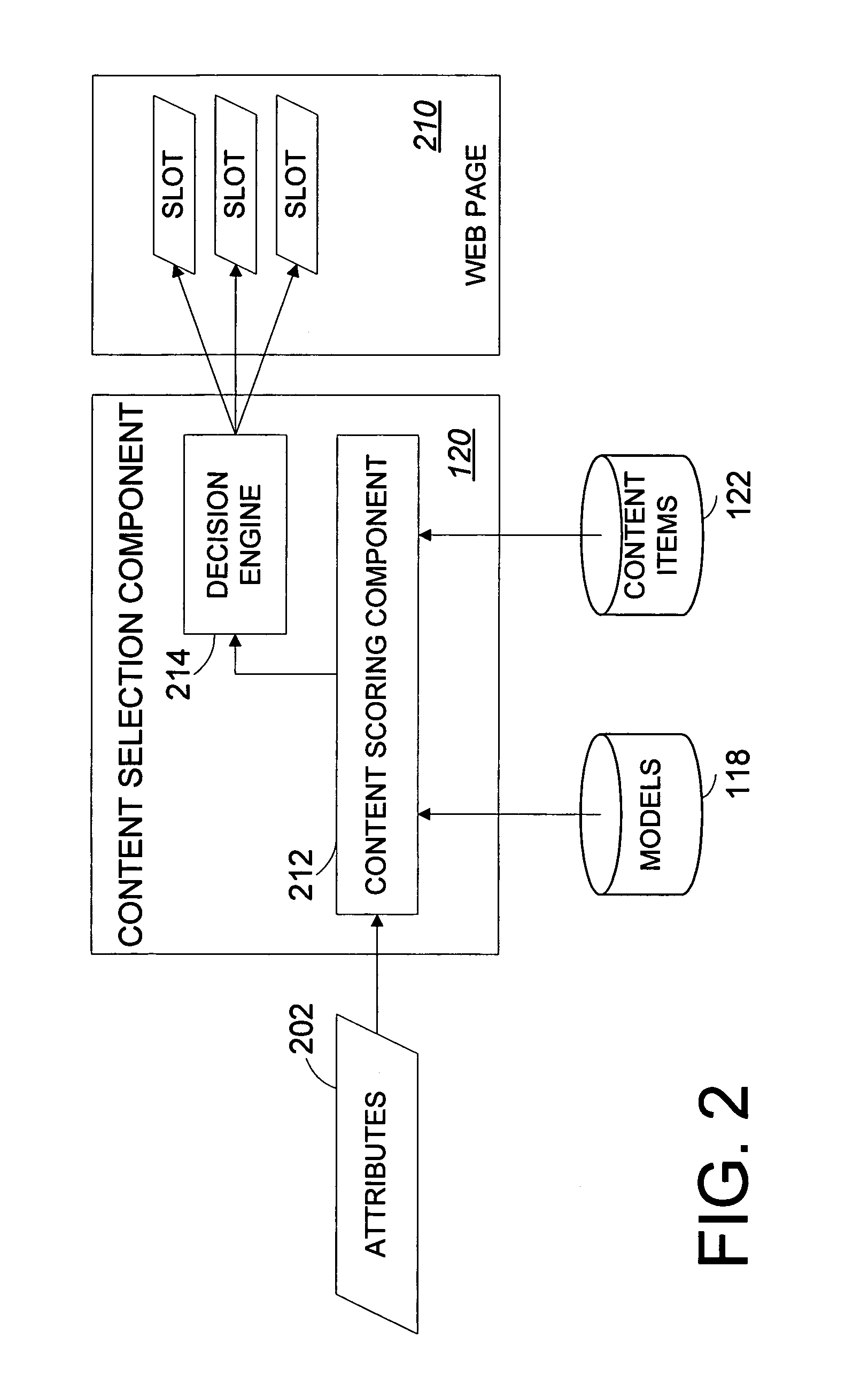
Systems and methods for statistically selecting content items to be used in a dynamically-generated display
InactiveUS7594189B1Quick responseLess time-consume and expensive manual laborDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteWeb page
An apparatus and methods advantageously select content items for dynamically-generated web pages in an intelligent and virtually autonomous manner. This permits the operator of the web site to rapidly identify and respond to trends, thereby advantageously updating the web site relatively quickly and efficiently without or with less time consuming and expensive manual labor. User interaction for a plurality of users with the web site is collected in a database. For various content items, the database is mined to extract relationships between probability and references of select attributes in probability models. When a new web page is requested, attributes, which can include attributes associated with a user, are used as references to the applicable probability models of selected content items, combined with value weighting to generate expected values, and selected for use in the web page at least partially based on the expected values.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Computer system and method for business data processing
ActiveUS20060167704A1Improve predictabilityImprove performanceOffice automationCommerceTime informationBusiness Personnel
The system enables business people to understand the impact of business transactions, changes and events in real-time using advanced rules and analytics to filter, categorize and interpret the significance of streams of real-time information. Most business performance analysis today is done manually and this process is a time consuming and skilled task leading to a time delay in producing the analysis. This time lag between the transaction or event happening and being able to take action on the analysis is measured in weeks or months at many companies. By blending real-time information with historical data and performance goals, this system enables business users to assess business events and collaborate within teams to drive optimal business performance. Using forecasting techniques enables business managers to predict the likelihood of achieving a particular goal without relying on manual analysis by a skilled analyst. The system automatically updates the forecast based on real-time changing data, enabling the business manager to have an up to the minute and statistically valid projection of future business performance.
Owner:SEEWHY ACQUISITION CORP +1
Providing access to a plurality of message accounts from a single web-based interface
InactiveUS20020174194A1SpeedReduce network bandwidth requirementsSpecial service for subscribersMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication softwareBandwidth requirement
Consider a user who has three different types of email account. Previously, in order to access those different email accounts the user has had a terminal with three desktop applications, one for accessing each type of email account. The user has been unable to access all of his or her email accounts simultaneously. Instead, the user has had to connect, for example, using a RAS connection, to one of the email accounts and then terminate that RAS connection before initiating a new RAS connection to the next type of email account. This is time consuming and problematic for users, particularly those who travel frequently. Another problem is that the user must maintain software applications on his or her terminal, one for each of the different types of message account. This takes up valuable memory and processing capacity on the user terminal. The present invention removes these problems by providing a single web based interface that gives the user access to a plurality of different message accounts on different message servers. In addition, logon times and network bandwidth requirements are reduced by storing retrieved message information in a cookie on the user's terminal.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method and apparatus for routing data to a load balanced server using MPLS packet labels
InactiveUS6856991B1Improve efficiencyDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsRouting decisionNetwork packet
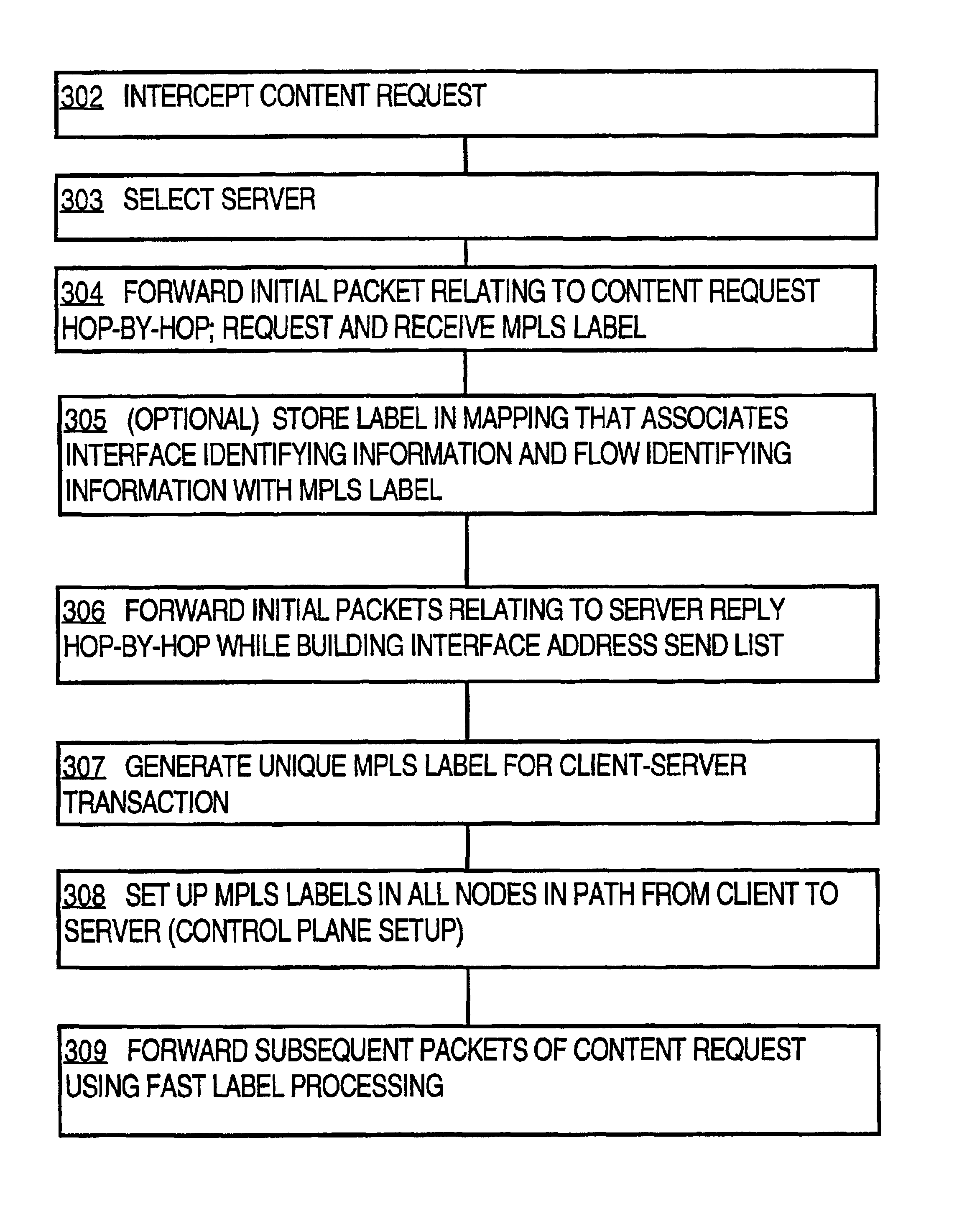
A method of routing data to a load-balanced server through a network having one or more load-balancing nodes is disclosed. The first packet of a client request is received at one of the load-balancing nodes, which stores information identifying a flow associated with the packet and an incoming interface identifier. The node then makes a server load-balancing decision and stores an outgoing interface identifier. When the packet reaches the last load-balancing node before the selected server, that last node also requests an MPLS label to uniquely identify the flow, connection and route. The label is stored in a mapping at the last node that associates the label with the flow and interface identifying information. The packet is routed to the selected server. The first server response packet is switched hop-by-hop and the MPLS label is stored at each node traversed by the response packets, in association with a flow identifier and incoming and outgoing interface identifiers. For all other packets in the request and response, nodes fast-switch the packets based on the label mappings. As a result, packet flows are rapidly routed from the same client to the same server without time-consuming hop-by-hop routing decisions or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
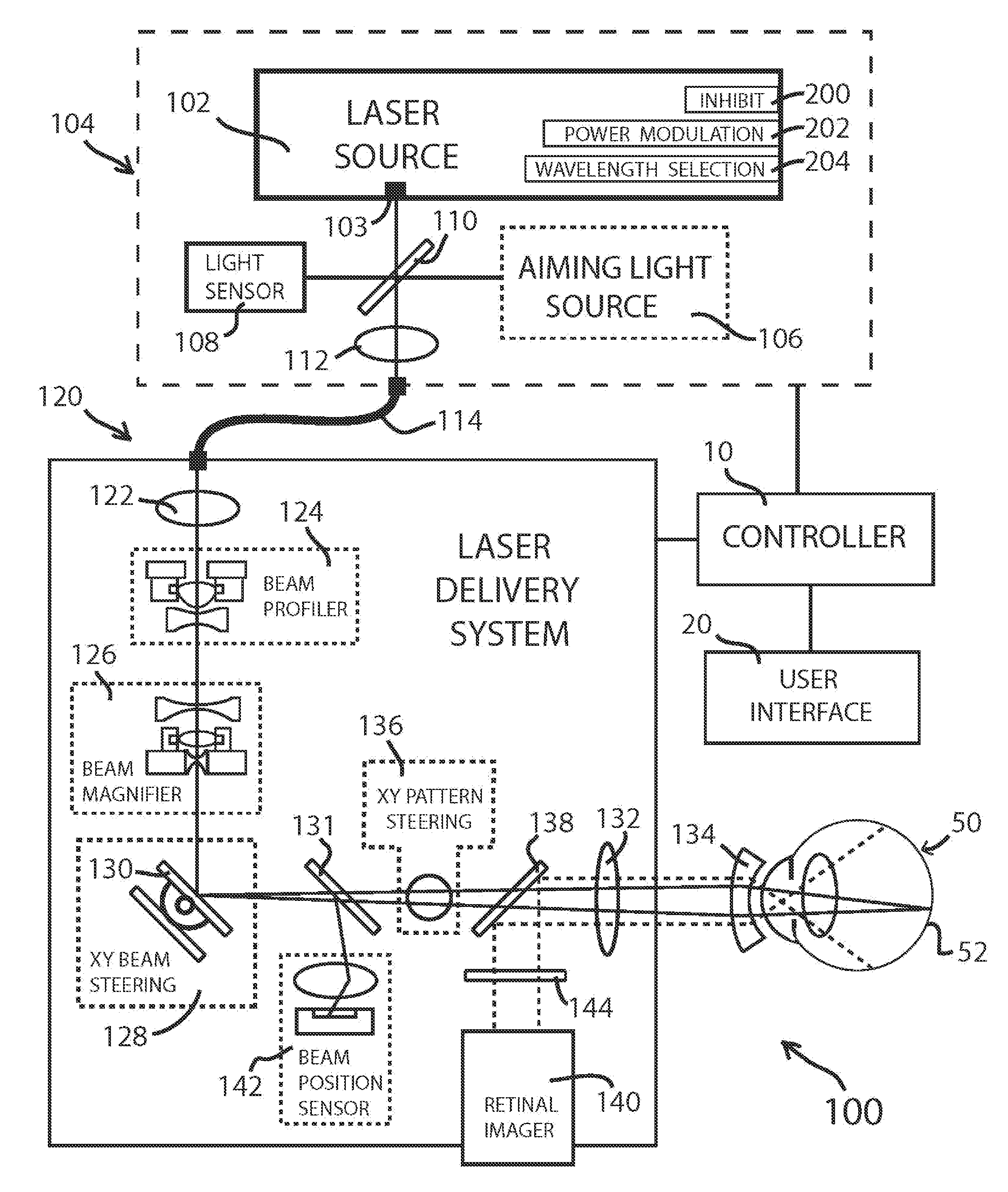
Steering laser treatment system and method of use
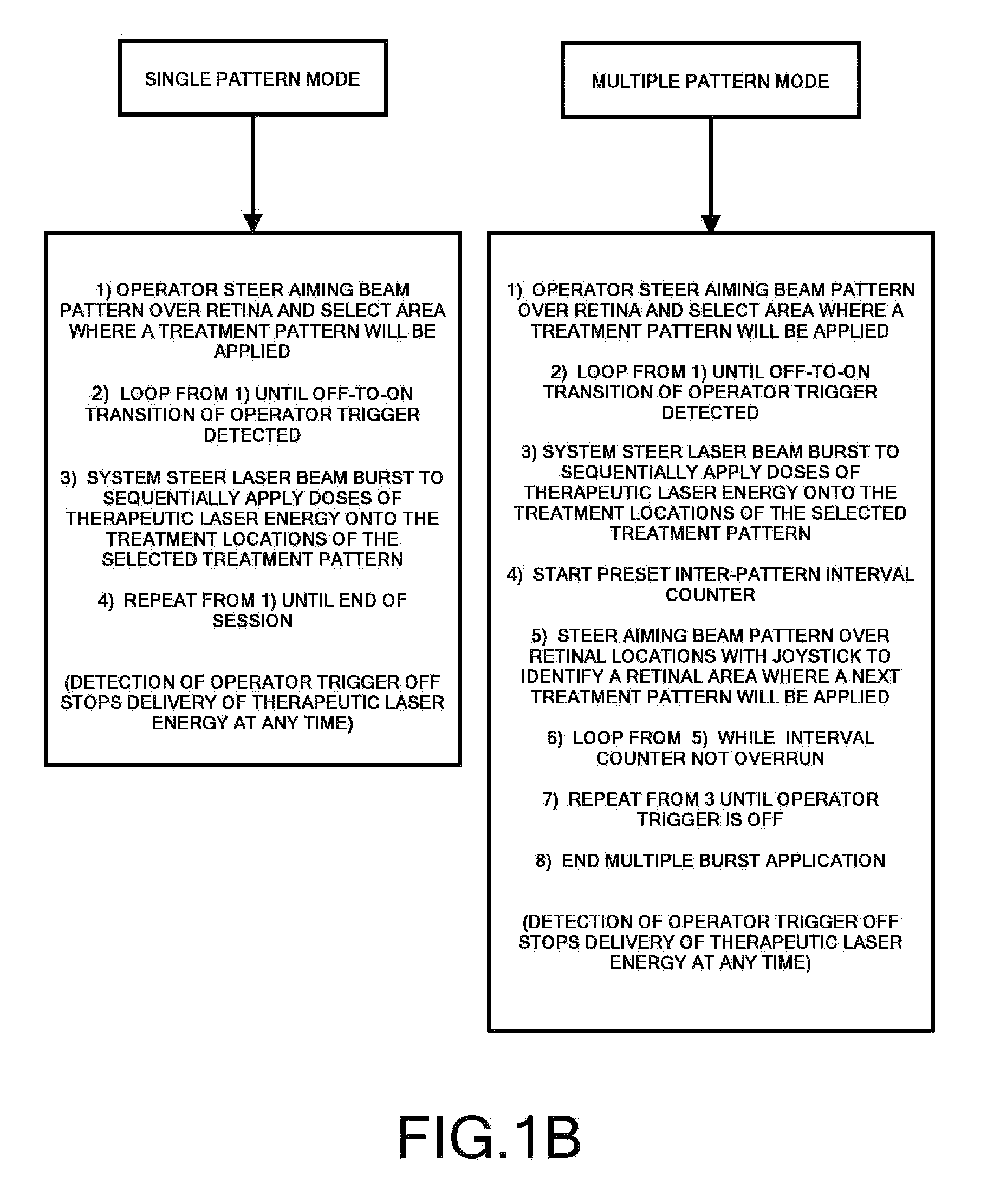
A system and method for delivering therapeutic laser energy onto selected treatment locations of the retina following a predetermined spatial distribution pattern using one single laser beam. A beam steering mechanism and control system delivers the laser energy sequentially to treatment locations forming a pre-selected treatment layout pattern. The invention allows time consuming therapeutic laser procedures such as pan-retinal photo-coagulation and segmental photocoagulation to be performed with increased accuracy and in a fraction of the time currently required for such procedures.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Module class objects in a process plant configuration system
ActiveUS7043311B2Configuration of process easyLess time-consumingProgram control using stored programsComputer controlComputer scienceTime-Consuming
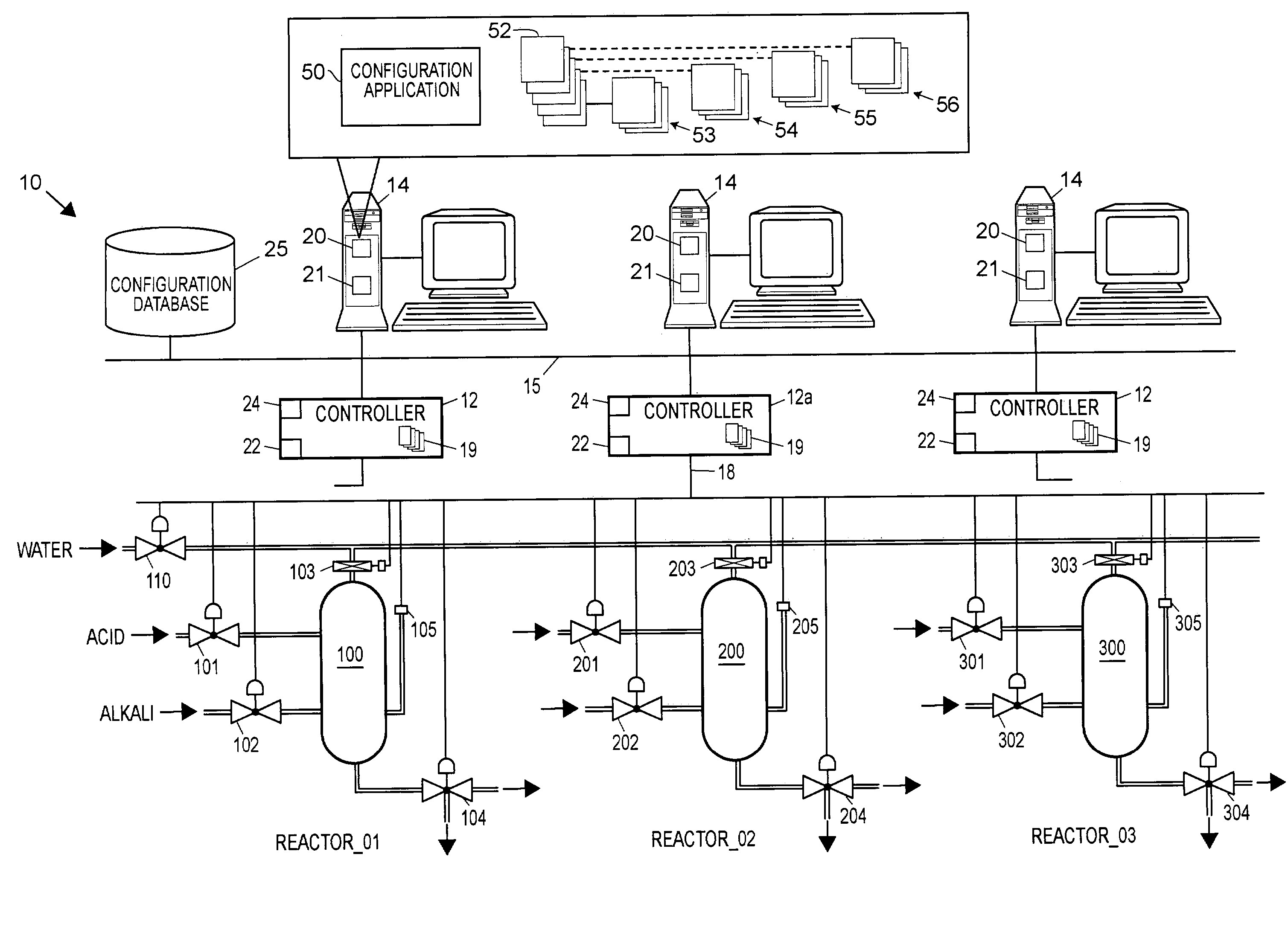
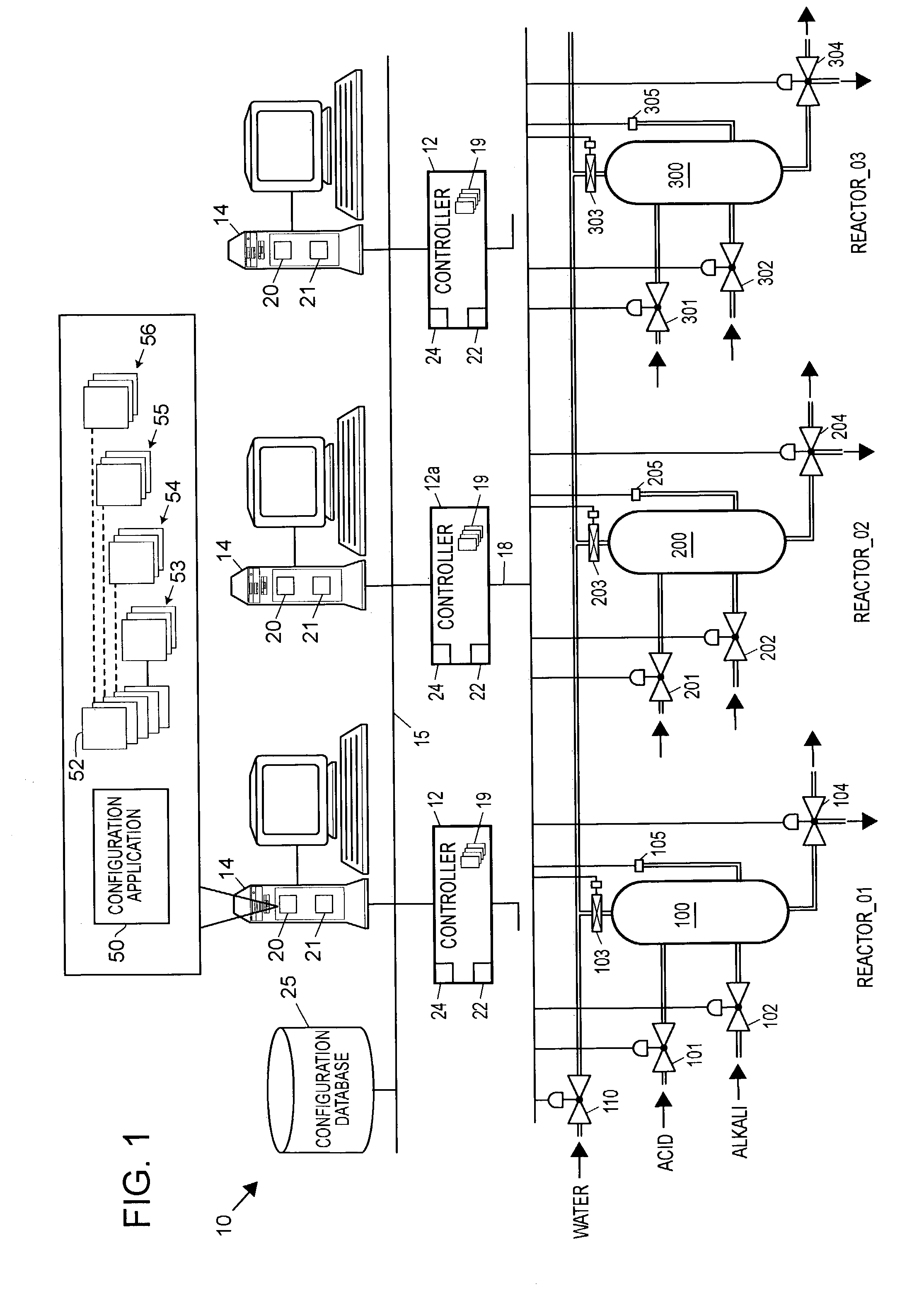
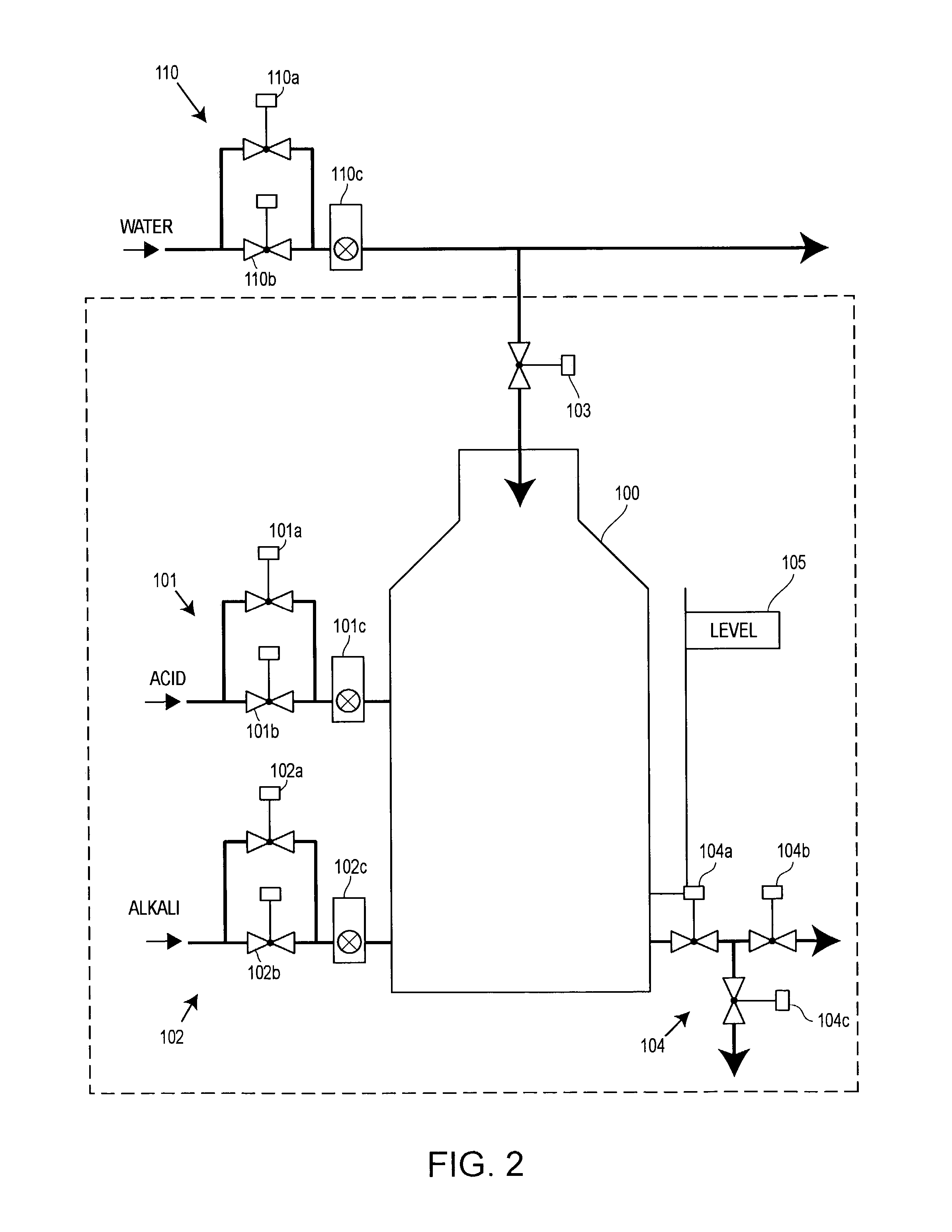
A configuration system for a process plant uses module class objects to assist in configuring, organizing and changing the control and display activities within the process plant. Each module class object generically models or represents a process entity, such as a unit, a piece of equipment, a control activity, etc., and may be used to create instances of the object, called module objects, which represent and are tied to specific equipment within the process plant. The module class objects may represent process entities of any desired scope, which means that a single module class object may be used to configure the control and display activities of process entities of any desired scope within the process plant, instead of just at a control module level. In particular, module class objects of a large scope may be used to configure large sections or portions of the process plant, which makes configuration of the process plant easier and less time consuming. A module class object may be a unit module class object reflecting a physical unit within the process plant, an equipment module class object reflecting a physical piece of equipment within the process plant, a control module class object reflecting a control module or scheme within the process plant, or a display module class object reflecting a display routine that provides information to a user within the process plant.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Transient Transfection with RNA
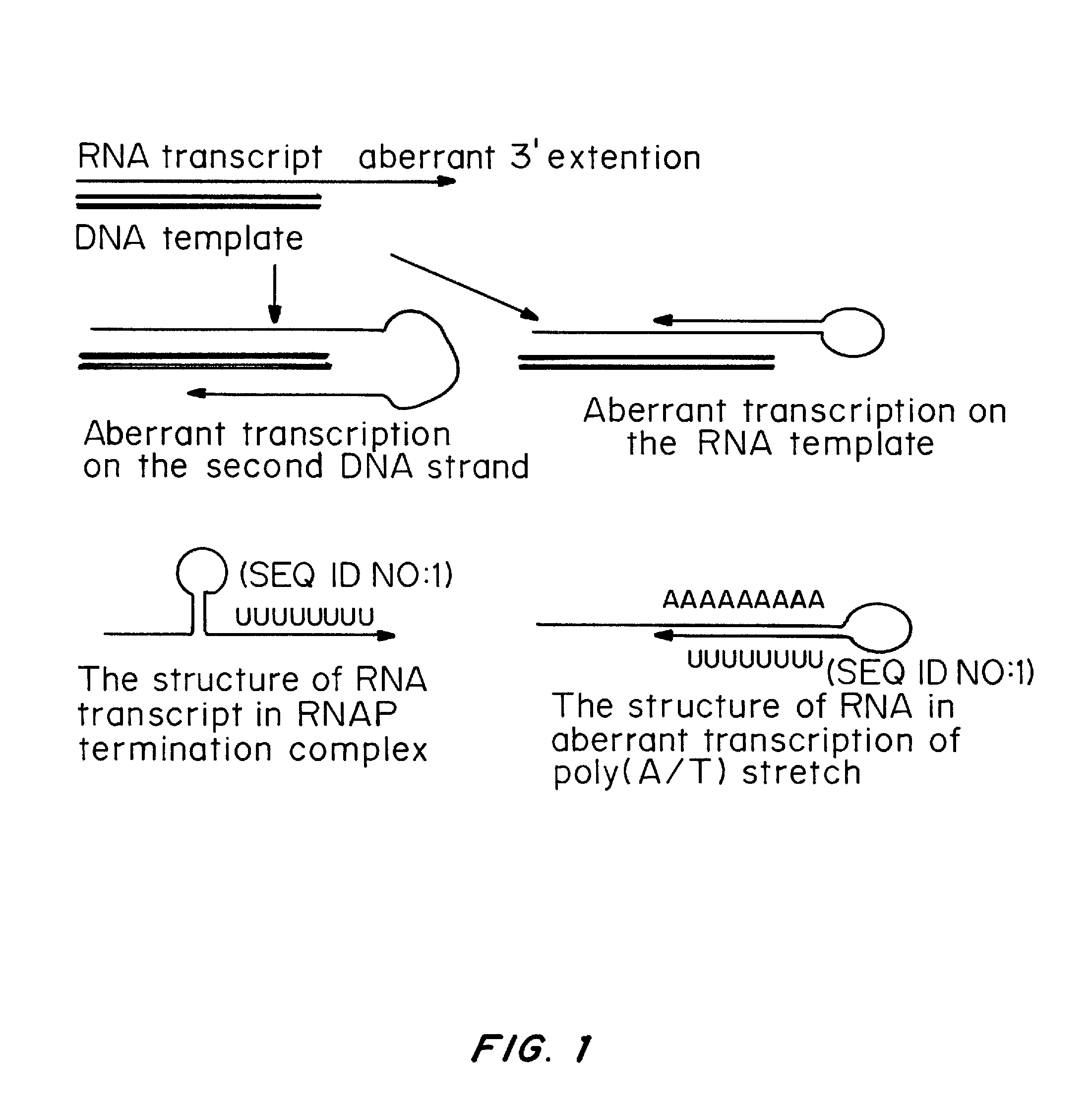
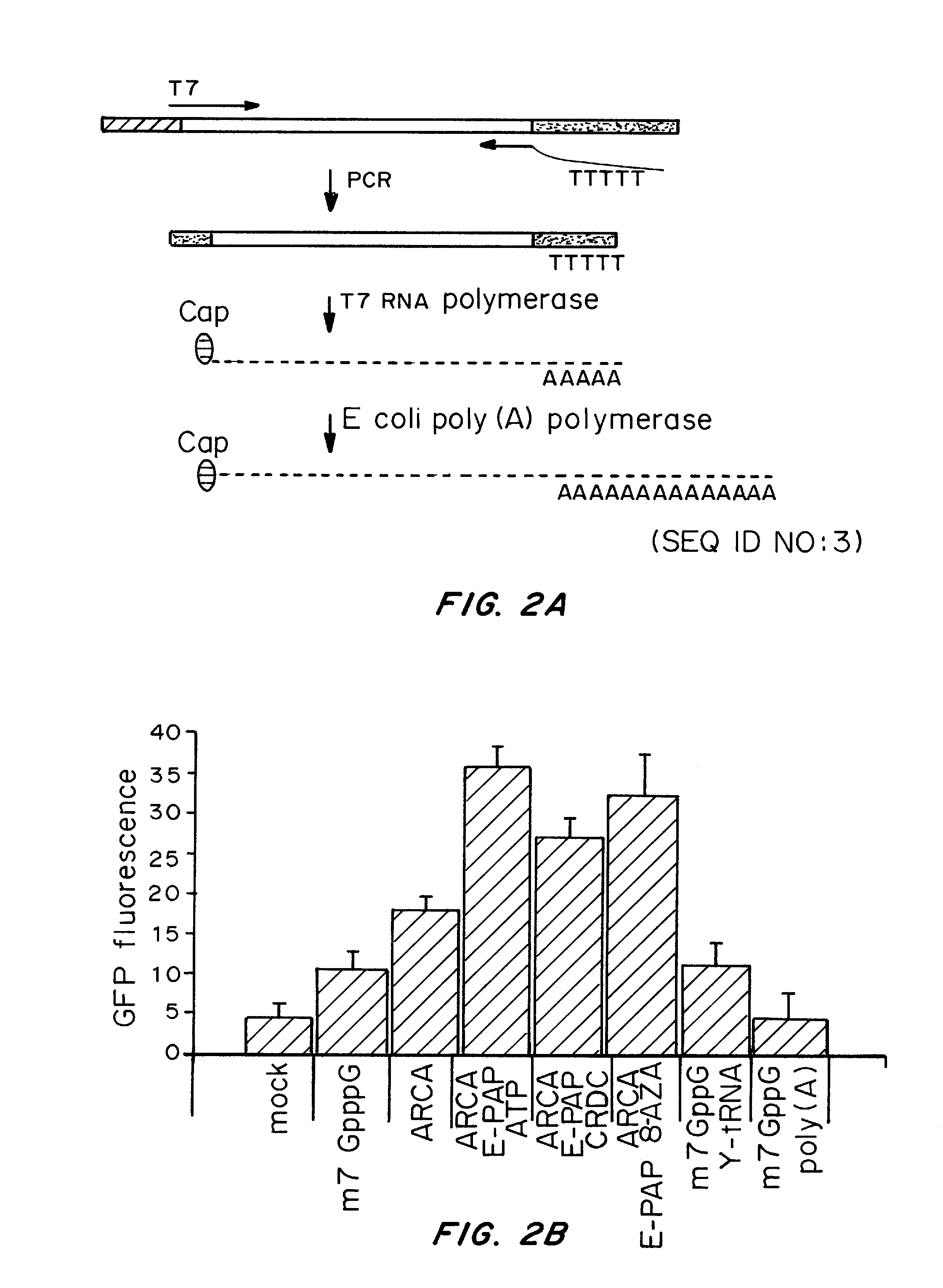
ActiveUS20080260706A1Lymphocyte transfectabilitySimilar efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDNA construct
A method of mRNA production for use in transfection is provided, that involves in vitro transcription of PCR generated templates with specially designed primers, followed by polyA addition, to produce a construct containing 3′ and 5′ untranslated sequence (“UTR”), a 5′ cap and / or Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES), the gene to be expressed, and a polyA tail, typically 50-2000 bases in length. This RNA can efficiently transfect different kinds of cells. This approach results in increased efficiency (fidelity and productivity) of mRNA synthesis and is less time consuming because it does not require cloning, and also consequently eliminates the unwanted errors and effects related to RNA made on DNA templates obtained with cloning techniques. The results of transfection of RNAs demonstrate that RNA transfection can be very effective in cells that are exceedingly difficult to transfect efficiently with DNA constructs. Further, the levels of gene expression following mRNA transfection are consistent from cell to cell in an experiment and these levels can be controlled over a wide range simply by changing the amount of mRNA that is transfected, and without obvious cytotoxic effects due to the levels of RNA per se. Due to high efficiency the cells can be simultaneously transfected with multiple genetic constructs. The method can be used to deliver genes into cells not- or only poorly transfectable for DNA, in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Pre-approval of computer files during a malware detection
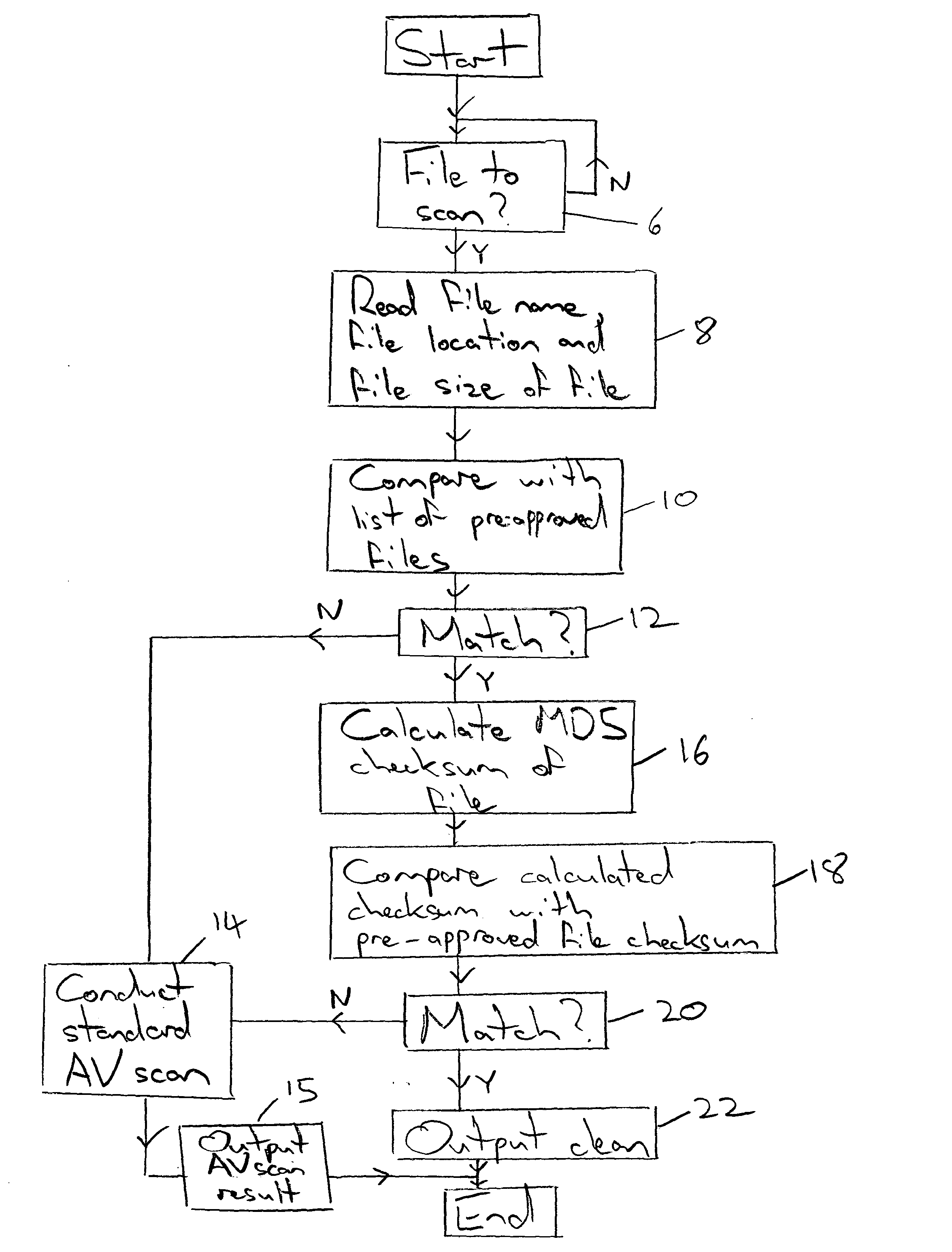
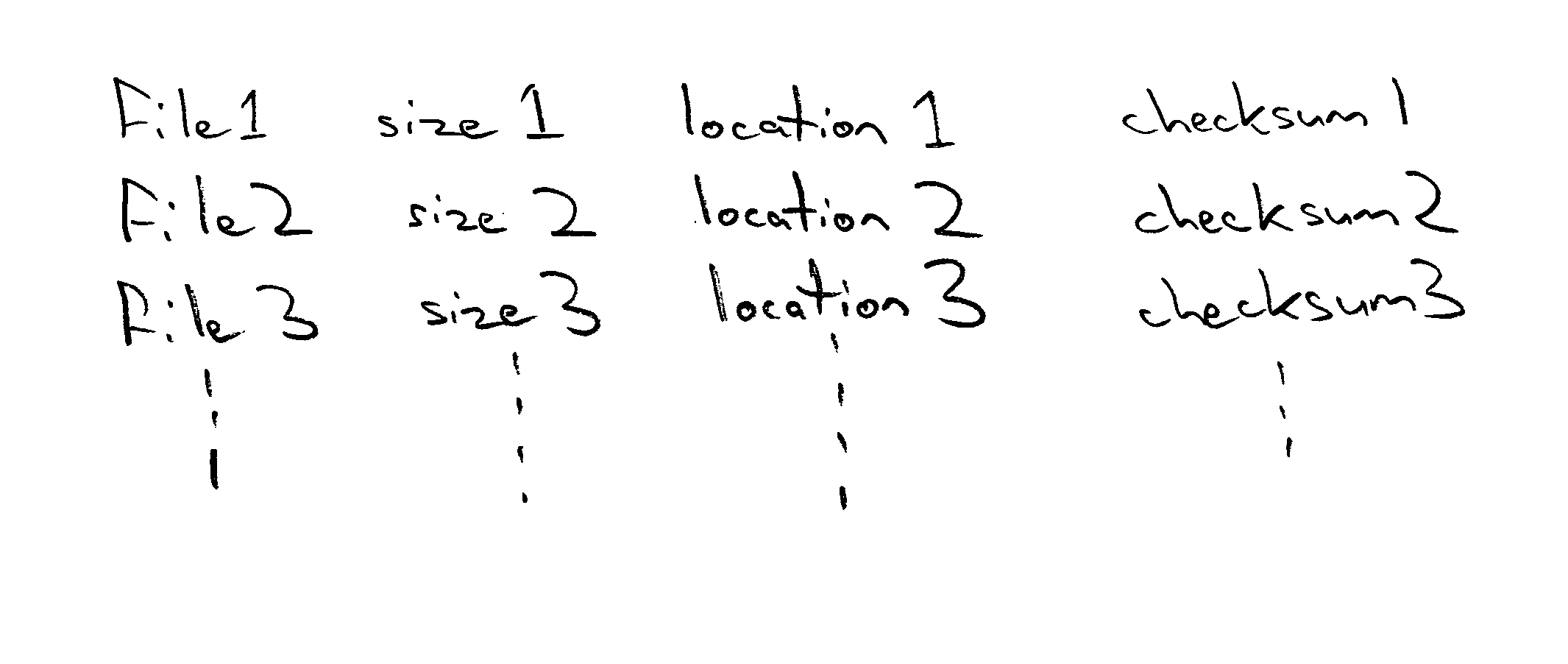
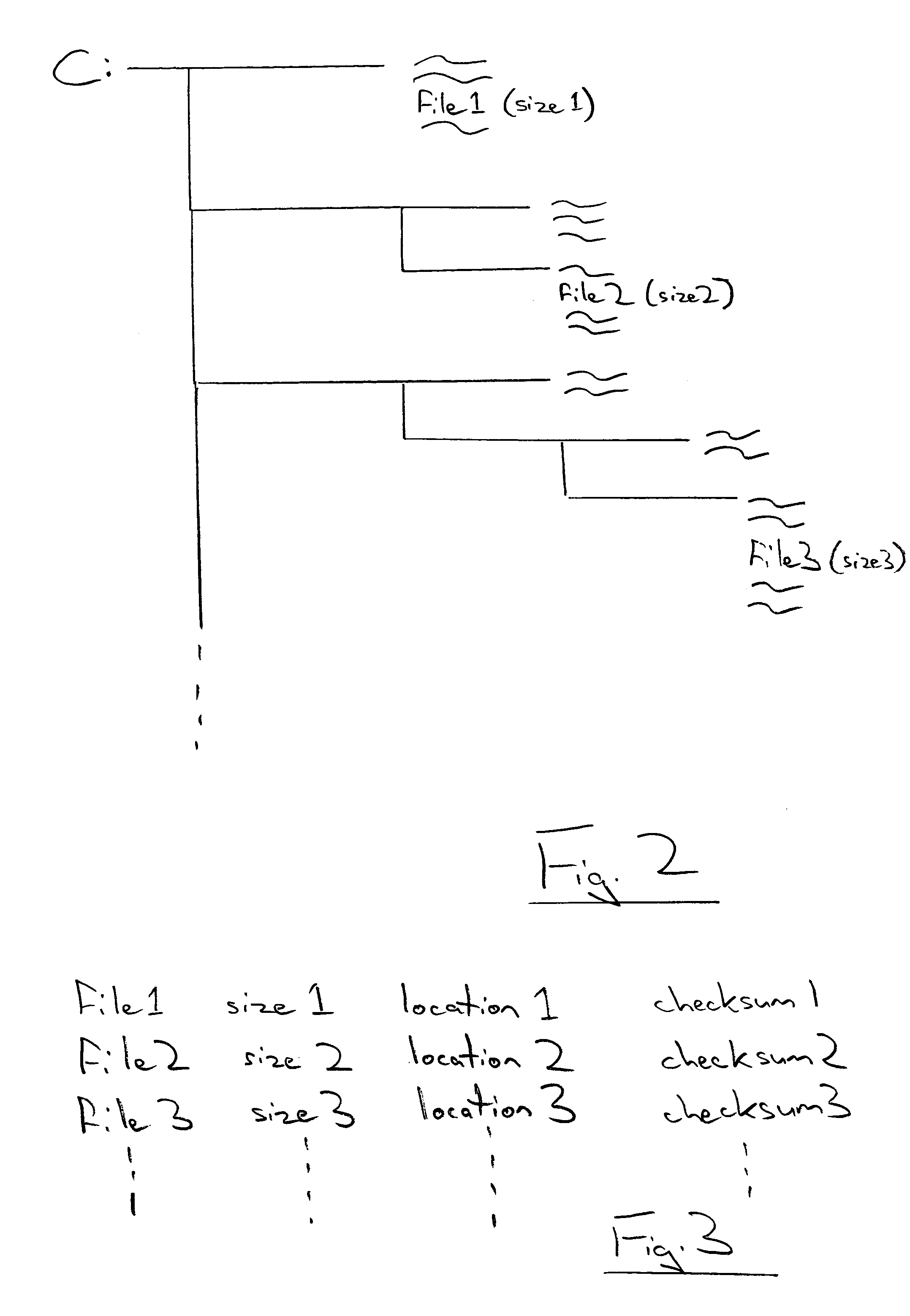
InactiveUS20050021994A1Addressing slow performanceEffectively ensureMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsChecksumFile size
A malware detection system seeking to identify computer viruses, worms, Trojans, banned files and the like acts to determine from the file name, file size and storage location of a computer file being tested, whether that computer file potentially matches a specific known malware free computer file stored within a list of such specific known malware free computer files. If a match occurs indicating that the candidate computer file is potentially the specific known malware free computer file, then this is confirmed by calculating a checksum of the candidate computer file and comparing this against a stored corresponding checksum of the specific known malware free computer file. If these checksums match, then the candidate computer file can be passed as clean without requiring further time consuming malware detection scanning.
Owner:MCAFEE INC
Server load balancing using IP option field approach to identify route to selected server
ActiveUS7088718B1Improve efficiencyData switching by path configurationRouting decisionNetwork packet
A method of routing data from a client through one or more load-balancing nodes to a selected load-balanced server among a plurality of servers in a network involves: receiving, at a last load balancing node associated with a selected server among the plurality of servers, a first packet of a server reply to a request from the client; setting a first flag value in the first packet of the server reply; storing one or more identifiers of ingress interfaces on which the packet arrives, in a send path list for server load balancing, as the first packet of the server reply is routed from the last load balancing node to the client using hop-by-hop decisions; receiving one or more subsequent packets of the client request; setting a second flag value in each of the subsequent packets; and forwarding the subsequent packets to the selected server only on a route that is defined by the send path list and without hop-by-hop routing decisions. As a result, packet flows are rapidly routed from the same client to the same server without time-consuming hop-by-hop routing decisions or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
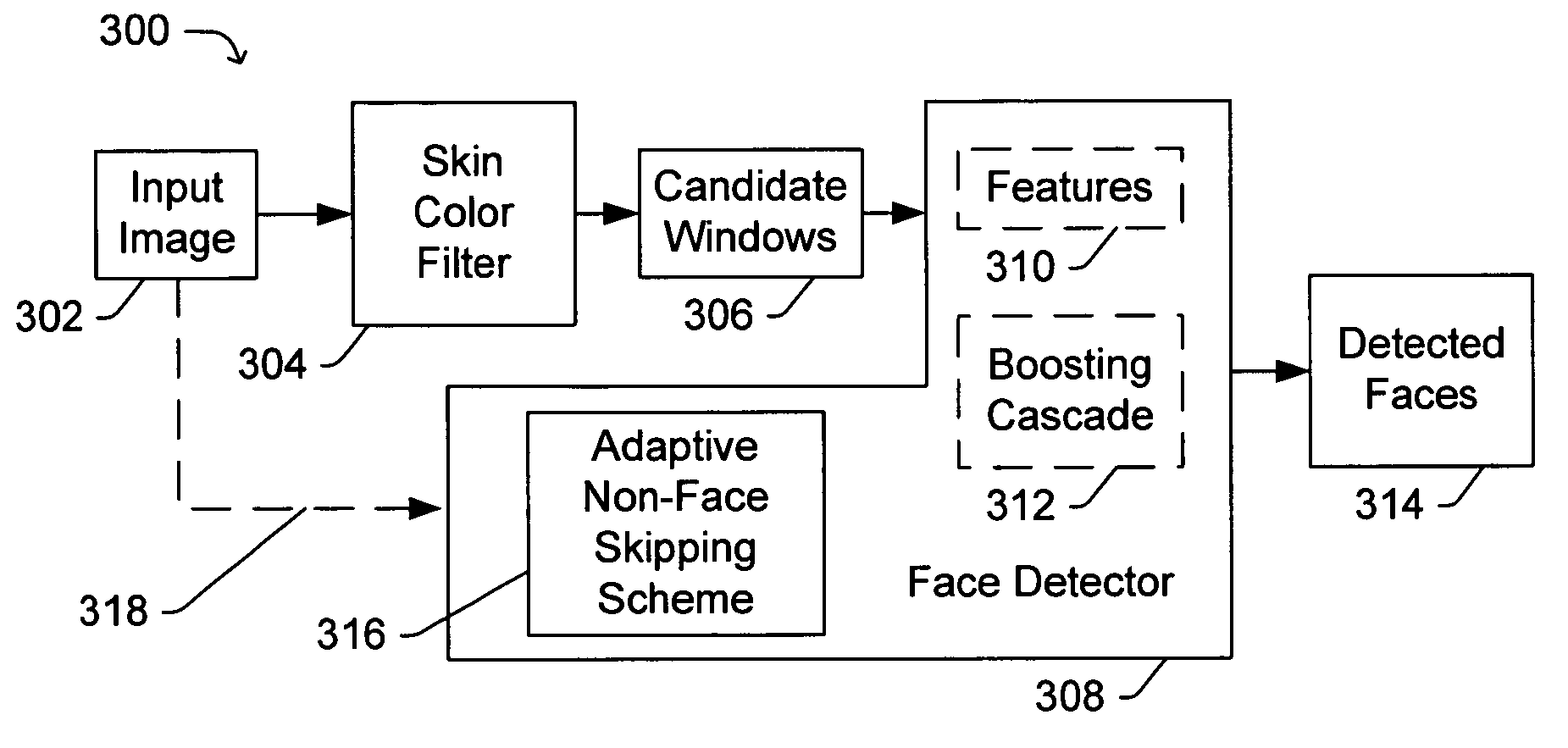
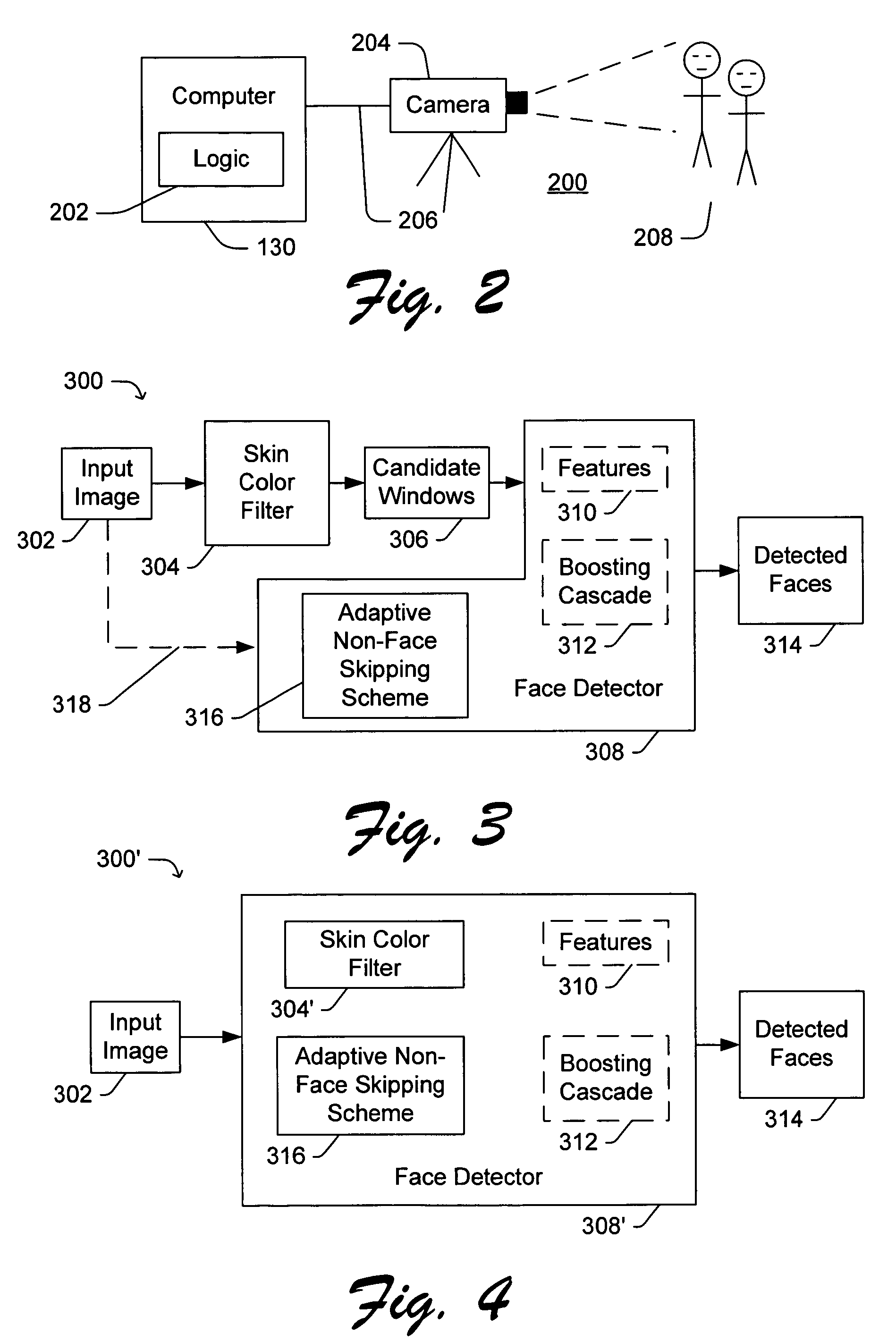
Speedup of face detection in digital images
ActiveUS7190829B2Increase face detection speedReduce in quantityCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionSkin color
Improved methods and apparatuses are provided for use in face detection. The methods and apparatuses significantly reduce the number of candidate windows within a digital image that need to be processed using more complex and / or time consuming face detection algorithms. The improved methods and apparatuses include a skin color filter and an adaptive non-face skipping scheme.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for user selection of advertising combinations
ActiveUS20120110620A1Easy to browseImprove user convenienceSelective content distributionElectrical cable transmission adaptationUser deviceTime-Consuming
A method, apparatus, article of manufacture, and a memory structure for providing advertisements with a media program transmitted to a user device are described. The method permits the user to control the presentation of advertisements to select prefacing advertisements in lieu of more time consuming or more numerous intervening advertisements presented during the media program.
Owner:HULU
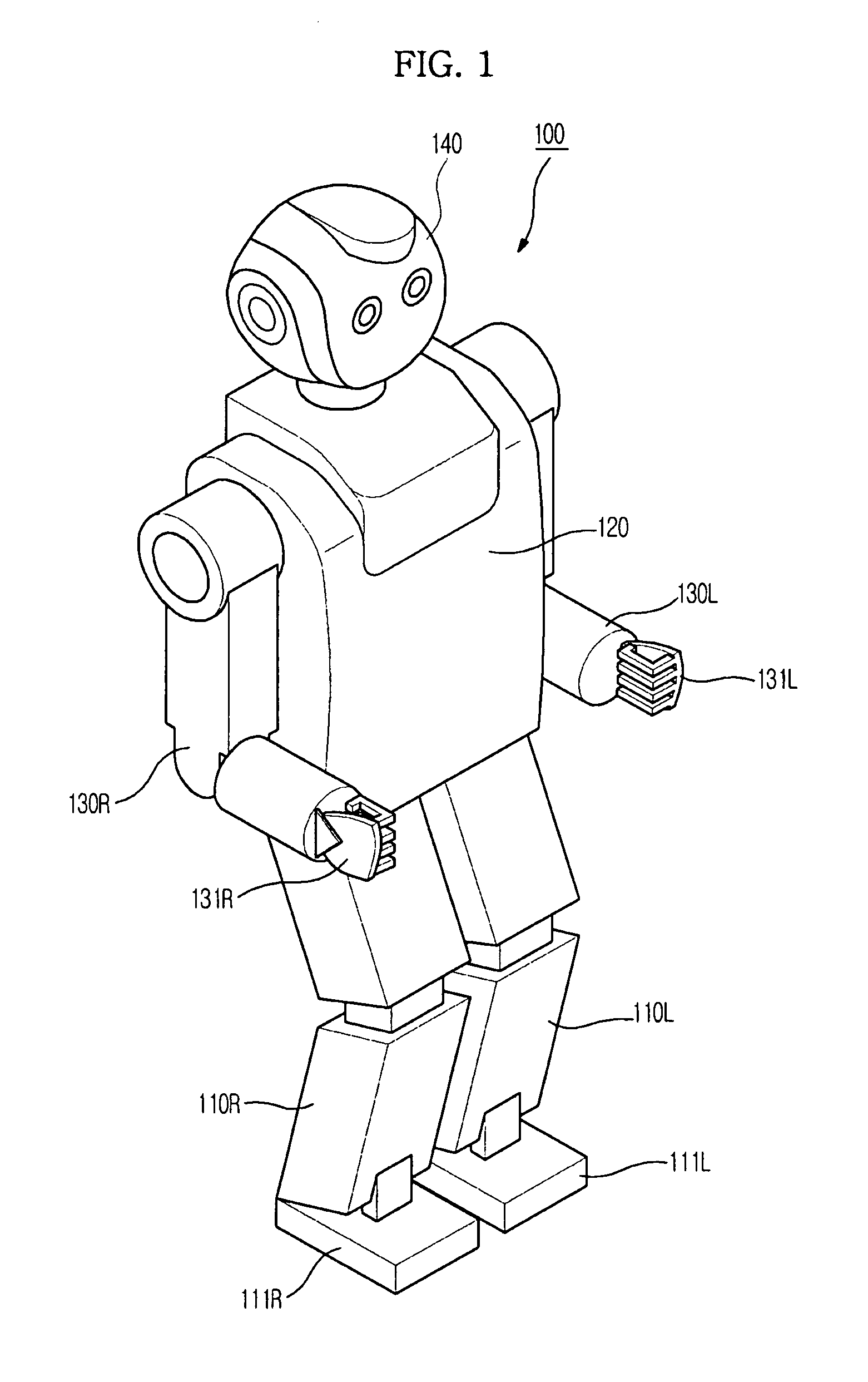
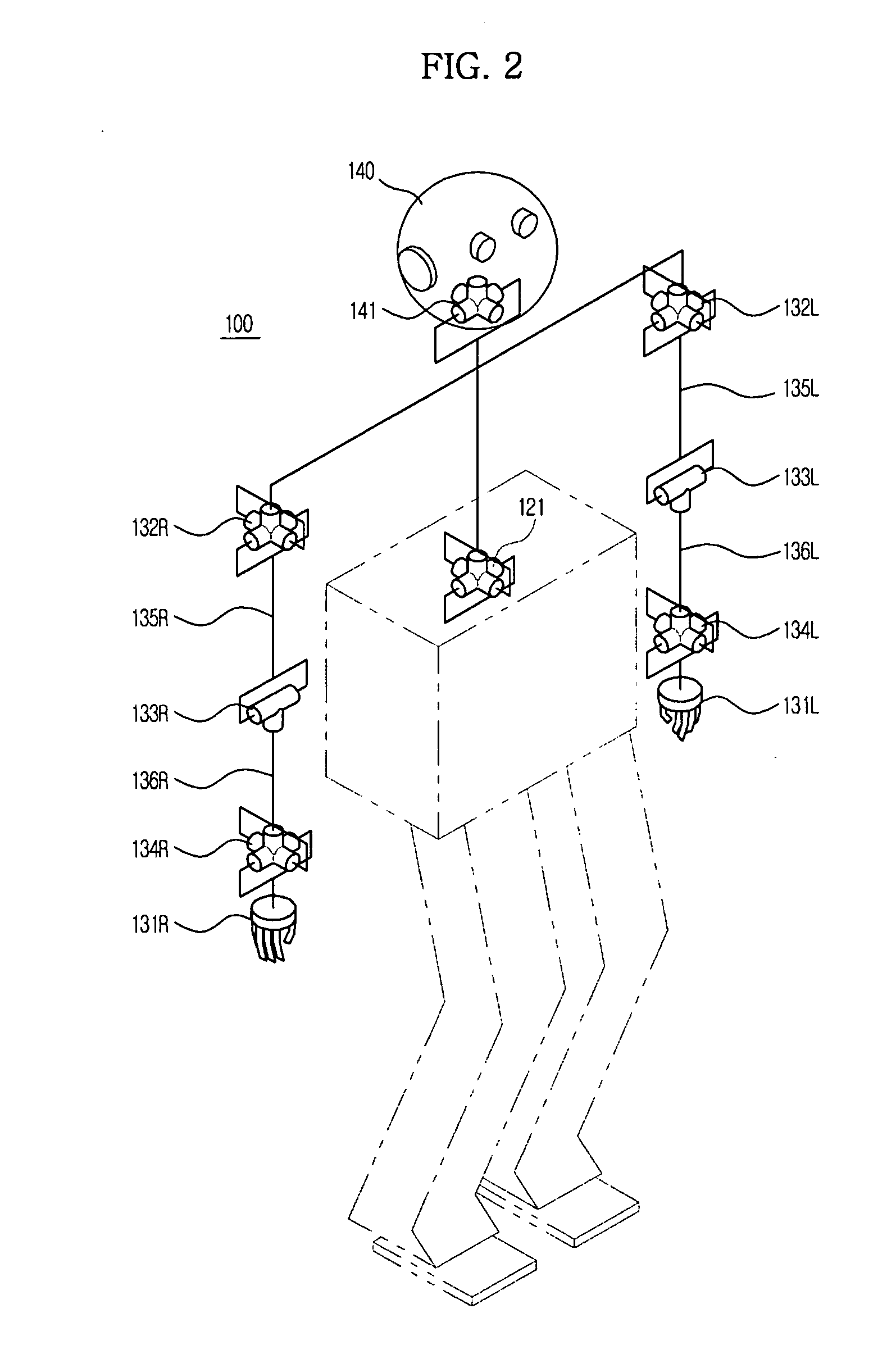
Method and apparatus to plan motion path of robot
ActiveUS20110035087A1Reduce probabilitySolution can be rapidly obtainedProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruments for road network navigationAlgorithmRandom tree
A suitable waypoint is selected using a goal score, a section from a start point to a goal point through the waypoint is divided into a plurality of sections based on the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, and trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections using a Best First Search & Rapidly Random Tree (BF-RRT) algorithm so as to generate a path. By this configuration, a probability of local minima occurring is decreased compared with the case where the waypoint is randomly selected. In addition, since the trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections each having the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, the solution may be rapidly obtained. A time consumed to search for an optimal motion path may be shortened and path plan performance may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for routing data to a load balanced server using MPLS packet labels
InactiveUS20050149531A1Improve efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLoad SheddingRouting decision
A method of routing data to a load-balanced server through a network having one or more load-balancing nodes is disclosed, comprising receiving a label value; storing the label value in a load balancing mapping at a load-balancing node in a network, wherein the load balancing mapping associates the label with a packet flow and with interface identifying information; and forwarding subsequent packets of the flow to a selected load-balancing server. The forwarding route is defined by the load-balancing mapping and without hop-by-hop routing decisions. The first server response packet is switched hop-by-hop and the label is stored at each node traversed by the response packets, with a flow identifier and interface identifiers. For other request and response packets, nodes fast-switch the packets based on the label mappings; thus, packet flows are rapidly routed from the client to the same server without time-consuming hop-by-hop routing or repeated load-balancing decisions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Data collection device and network having radio signal responsive mode switching
ActiveUS7712670B2Increase the display functionHybrid readersVisual presentationOperation modeComputer science
Owner:SAUERWEIN JR JAMES T +4
Method and apparatus for size optimization of storage units
InactiveUS6078745AOverall required size (number of locations) of the memories is minimalOptimize layoutSoftware engineeringMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTime domainArray data structure
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for reducing the storage size required for temporary data by storage order optimization. Advantageously, the execution order optimization and the storage order optimization may be treated independently. The storage size optimization is preferably performed by determining an optimum intra-array and / or inter-array storage order based on a geometrical model. The geometrical model provides a representation of the address space occupied by an array as a function of time and allows the calculation of the window size of the occupied address / time domain of the array. Where calculations would be time-consuming, these may be shortened by making simplifying assumptions, e.g. calculation of upper and lower bounds of the window size of the occupied address / time domain of an array rather than an exact calculation. Further, heuristical simplifications are described to reduce run-times for the optimization process.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
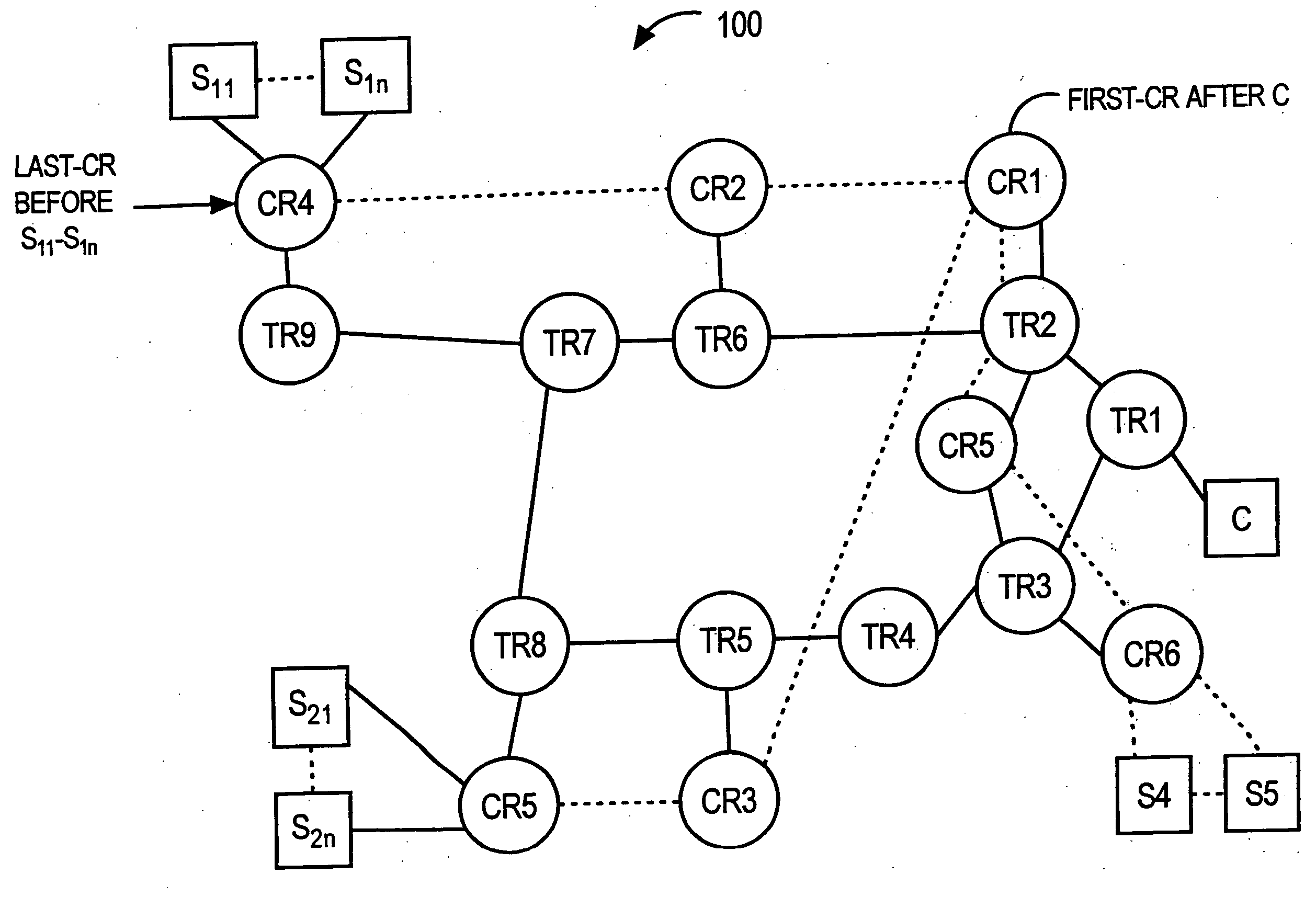
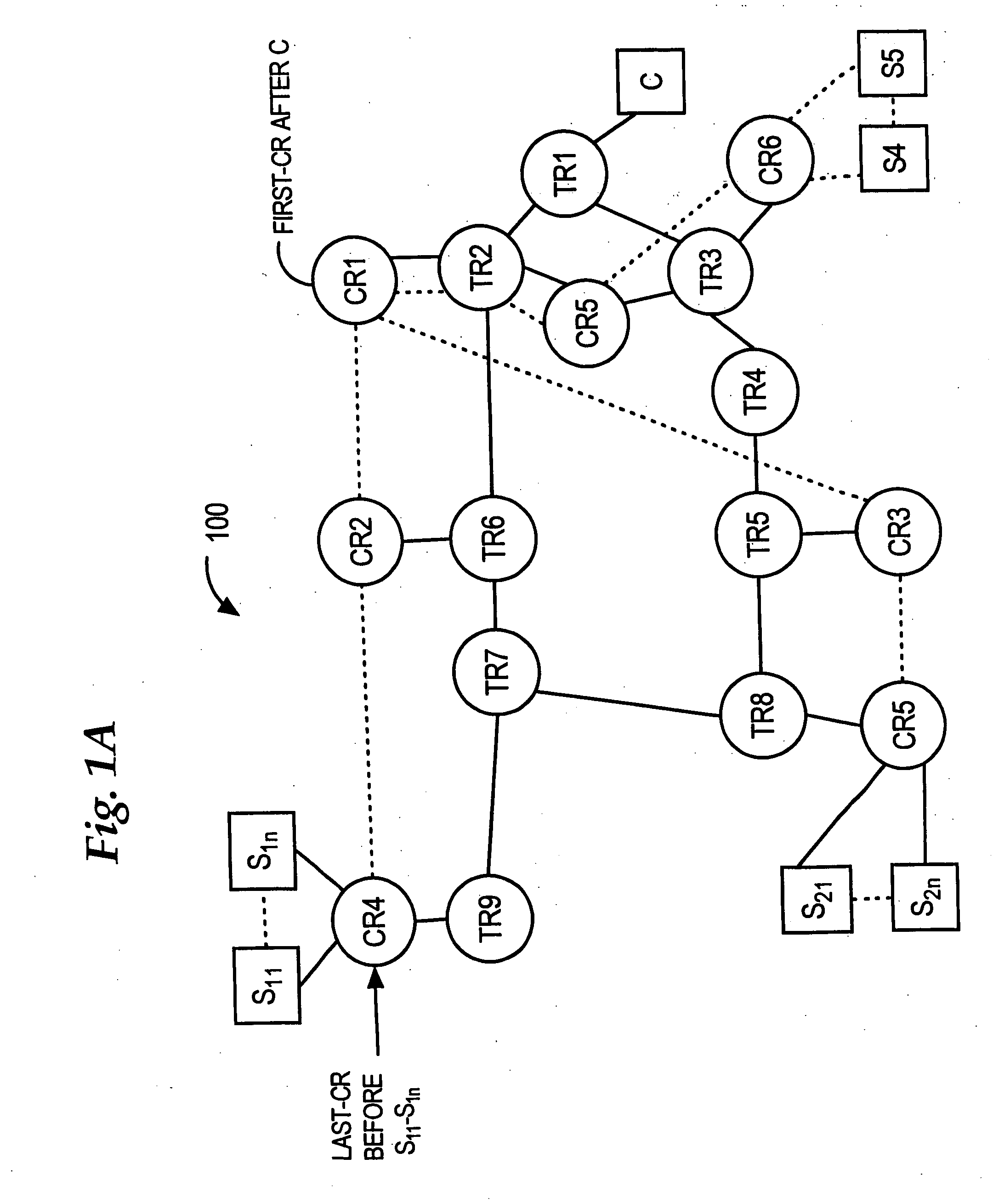
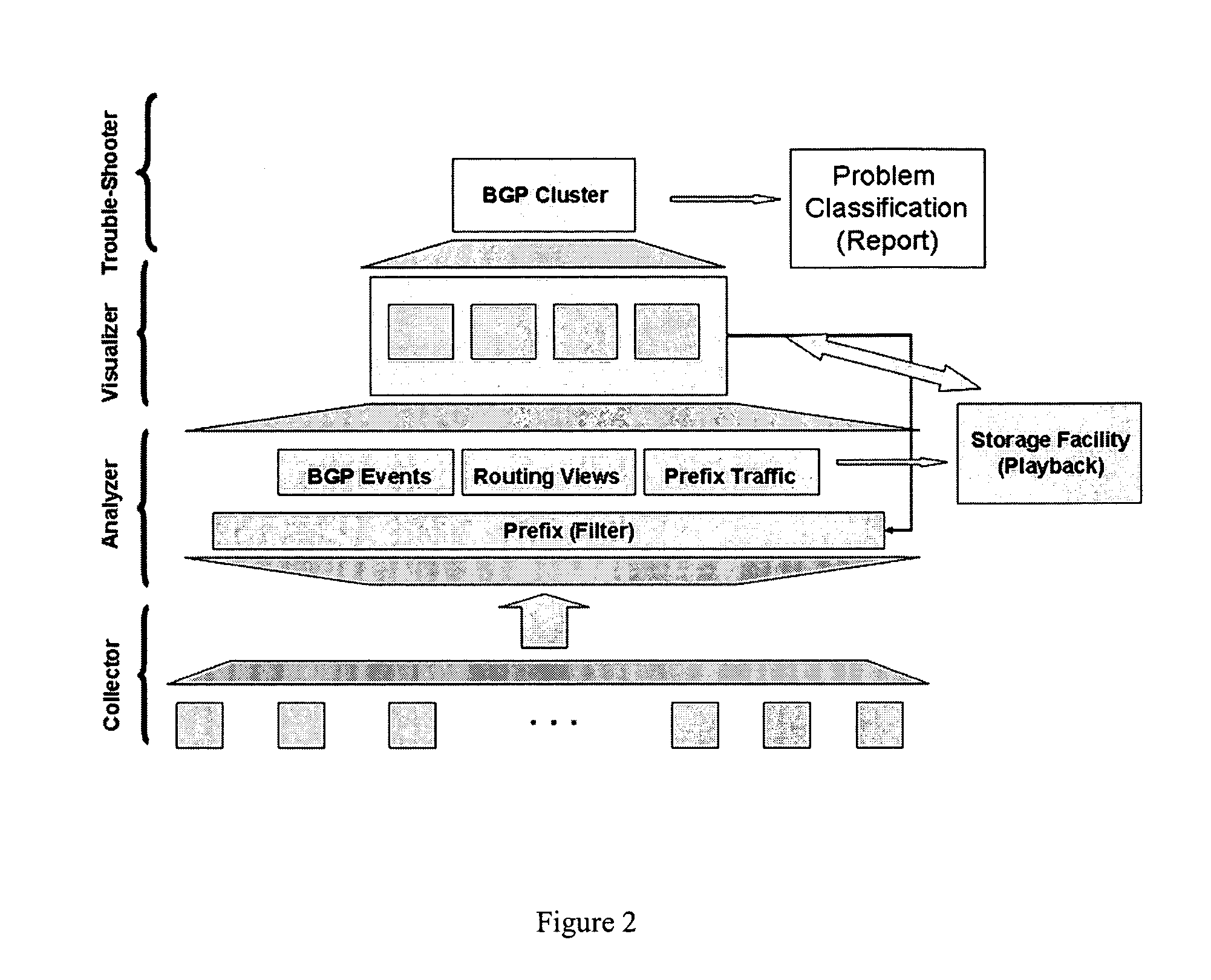
Method for real-time visualization of BGP analysis and trouble-shooting
InactiveUS7945658B1Efficient identificationEfficient reportingError preventionTransmission systemsThe InternetProblem identification
The present invention comprises a multi-tier system. Major goals of the system are to 1) clearly visualize BGP dynamics and alert / report important deviation of BGP dynamics to avoid overwhelming the operators with too much information and 2) analyze the root cause of the problems by using a multi-tier approach, with a light-computational analysis and high-level classification for a real-time problem identification followed by a more rigorous off-line analysis for a further and more detailed trouble shooting. An example embodiment is provided that comprises four modules. The first module comprises a distributed family of collectors in charge of collecting real-time network information. The second module filters out non-relevant prefixes and extracts and profiles key features of the network information. The third module monitors BGP activity from both an Internet-AS and single-AS perspectives by displaying the data in real time and highlighting major shifts or divergence from historical baselines with comprehensive layouts. The forth module is run off-line to focus on a few relevant events that are selected through the first three modules. This is usually a time-consuming phase of the process due to the different temporal and / or spatial correlation that must be run across several sets of data. During this phase, the system can spend more time to better identify the real cause of the problem.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Automatic ranking and scoring of meetings and its attendees within an organization
ActiveUS20170039527A1Reduce needDigital data information retrievalOffice automationSoftware agentComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for analyzing a history of meetings, the attendees, date of occurrence, and other content to determine the value of the meetings and the attendees. The importance of people and the meetings they attend can be derived based on patterns of attendees. In one embodiment, the meta-data of meetings and the attendees can be used to determine value without requiring time-consuming manual steps or manual evaluation of people and their titles. A graph of meetings and its attendees can be generated and used by one or more automated software agents to place value to the content of the meeting, its agenda, and other meeting collateral such as meeting briefs / attachments of meetings. Accordingly, embodiments dramatically reduce the need for human examination of meeting history.
Owner:CLARI INC
Pre-approval of computer files during a malware detection
InactiveUS7257842B2Abundant resourcesImpact speedMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsChecksumMalware
A malware detection system seeking to identify computer viruses, worms, Trojans, banned files and the like acts to determine from the file name, file size and storage location of a computer file being tested, whether that computer file potentially matches a specific known malware free computer file stored within a list of such specific known malware free computer files. If a match occurs indicating that the candidate computer file is potentially the specific known malware free computer file, then this is confirmed by calculating a checksum of the candidate computer file and comparing this against a stored corresponding checksum of the specific known malware free computer file. If these checksums match, then the candidate computer file can be passed as clean without requiring further time consuming malware detection scanning.
Owner:MCAFEE INC
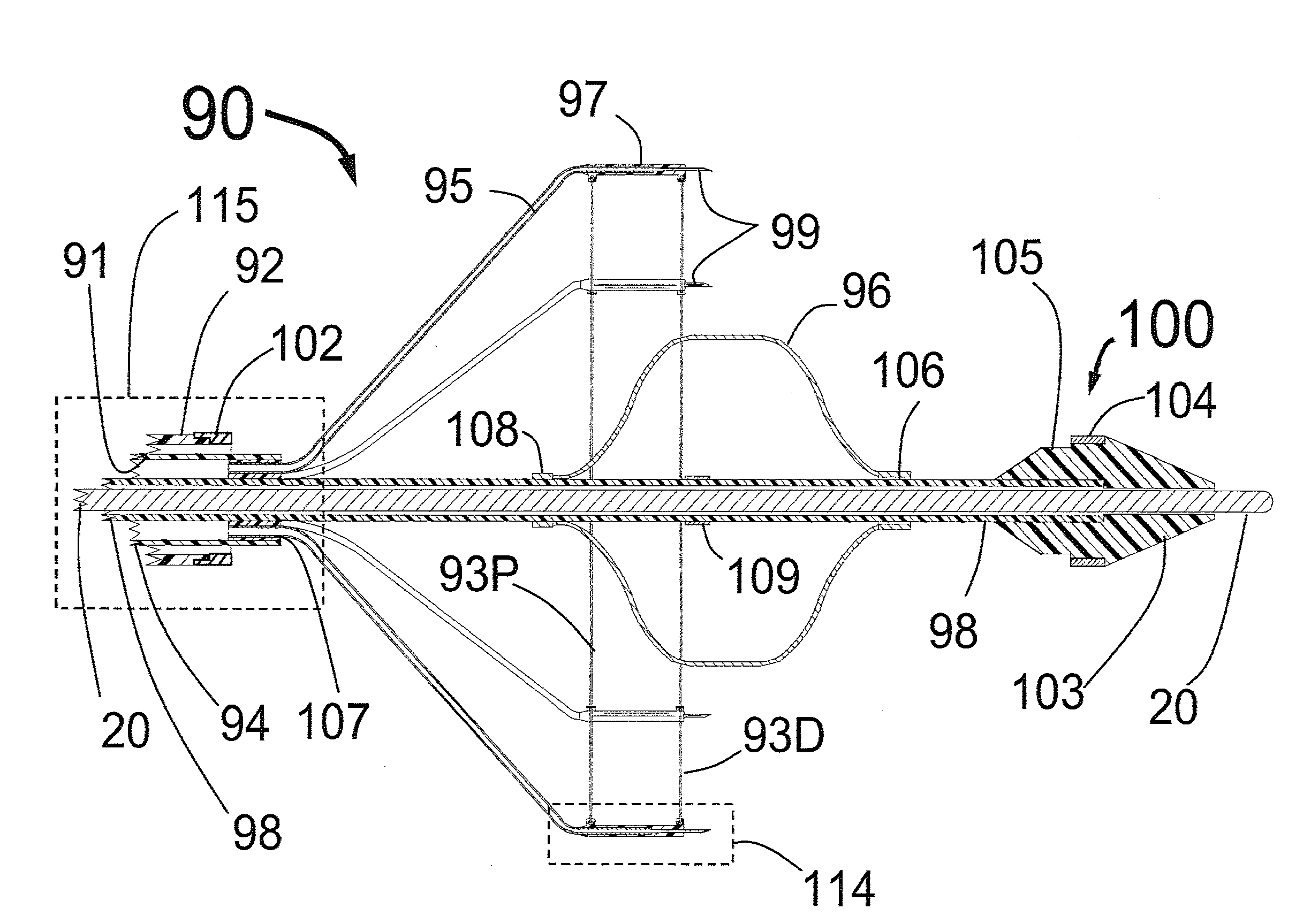
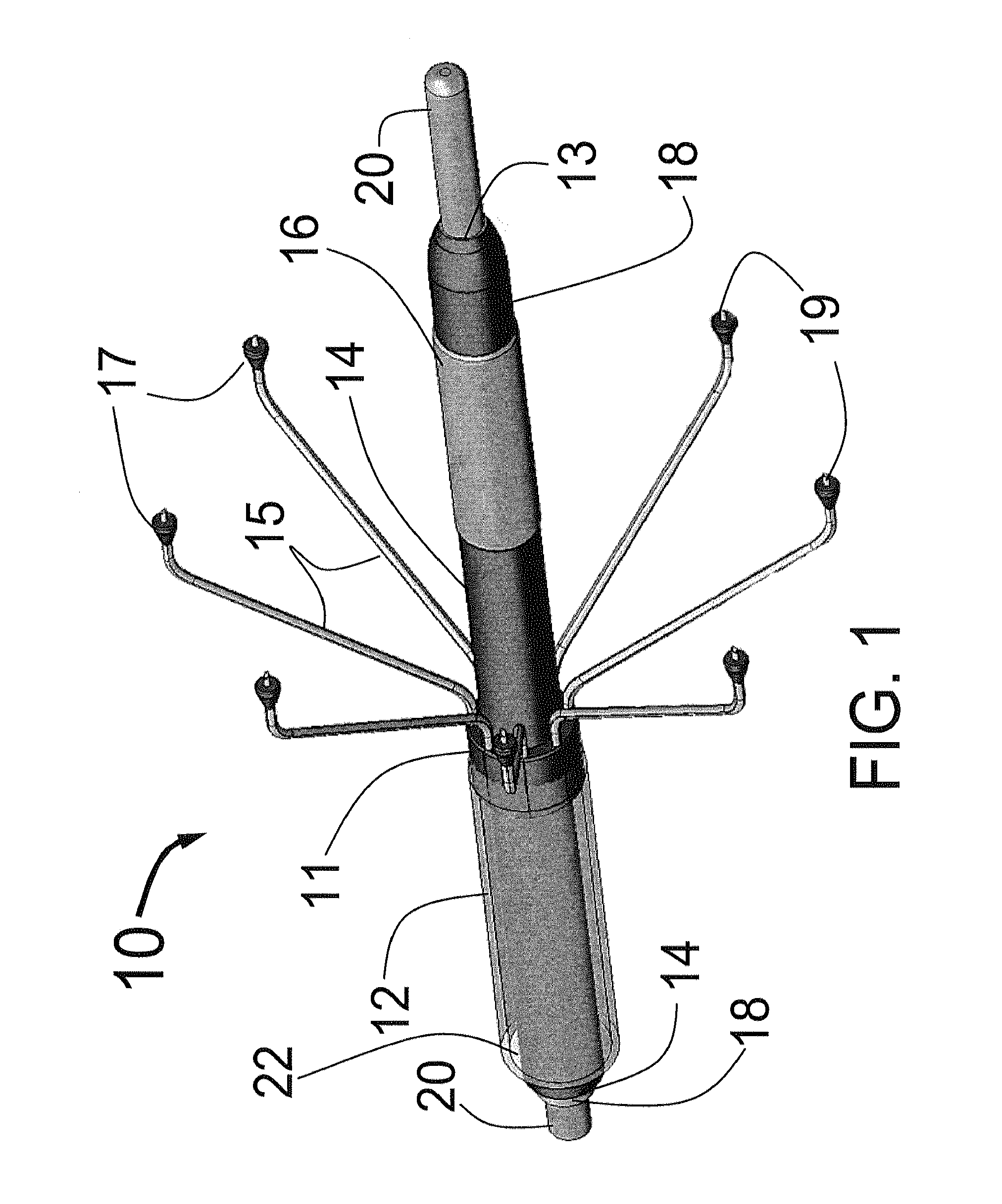
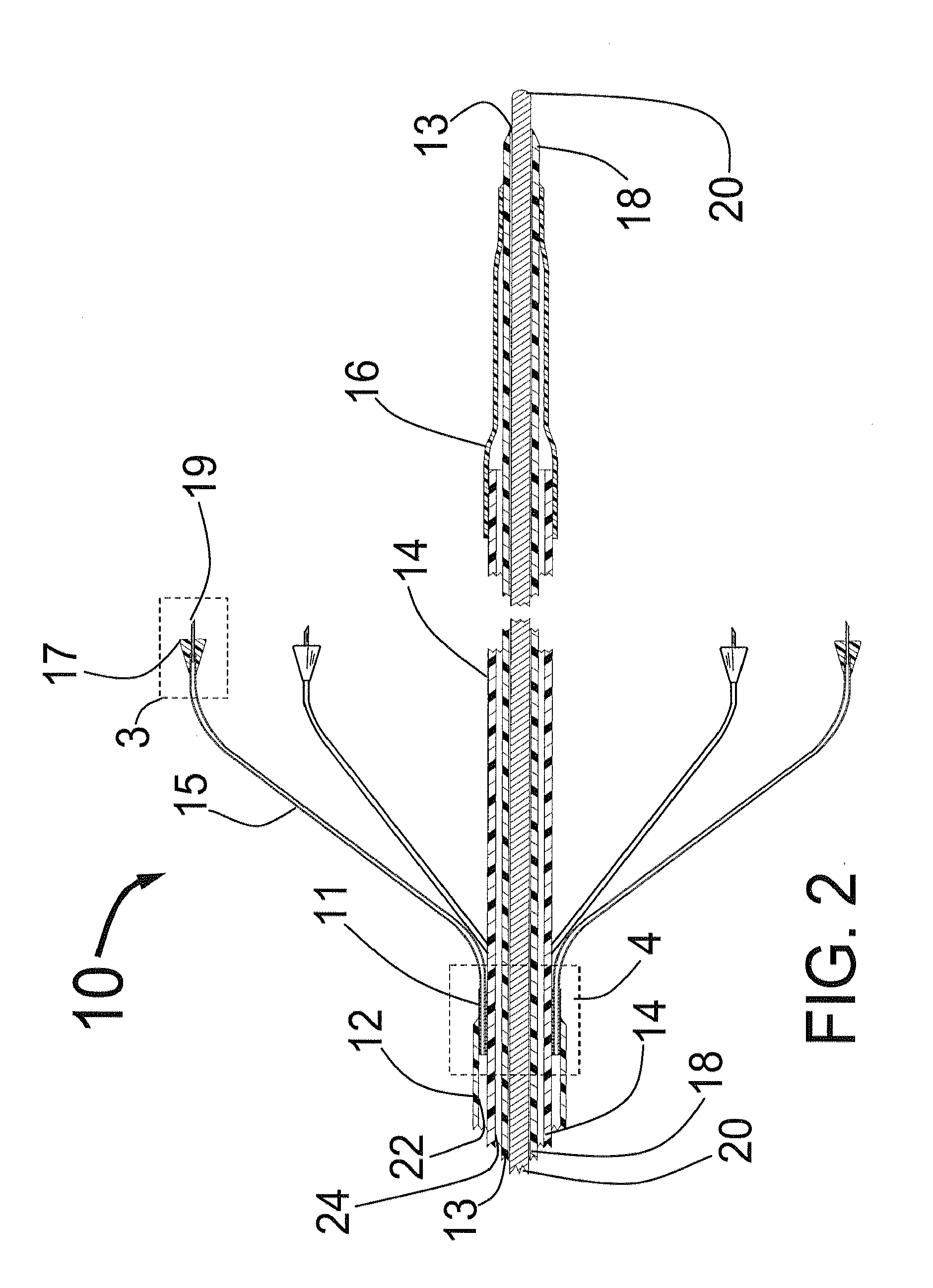
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20120271277A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
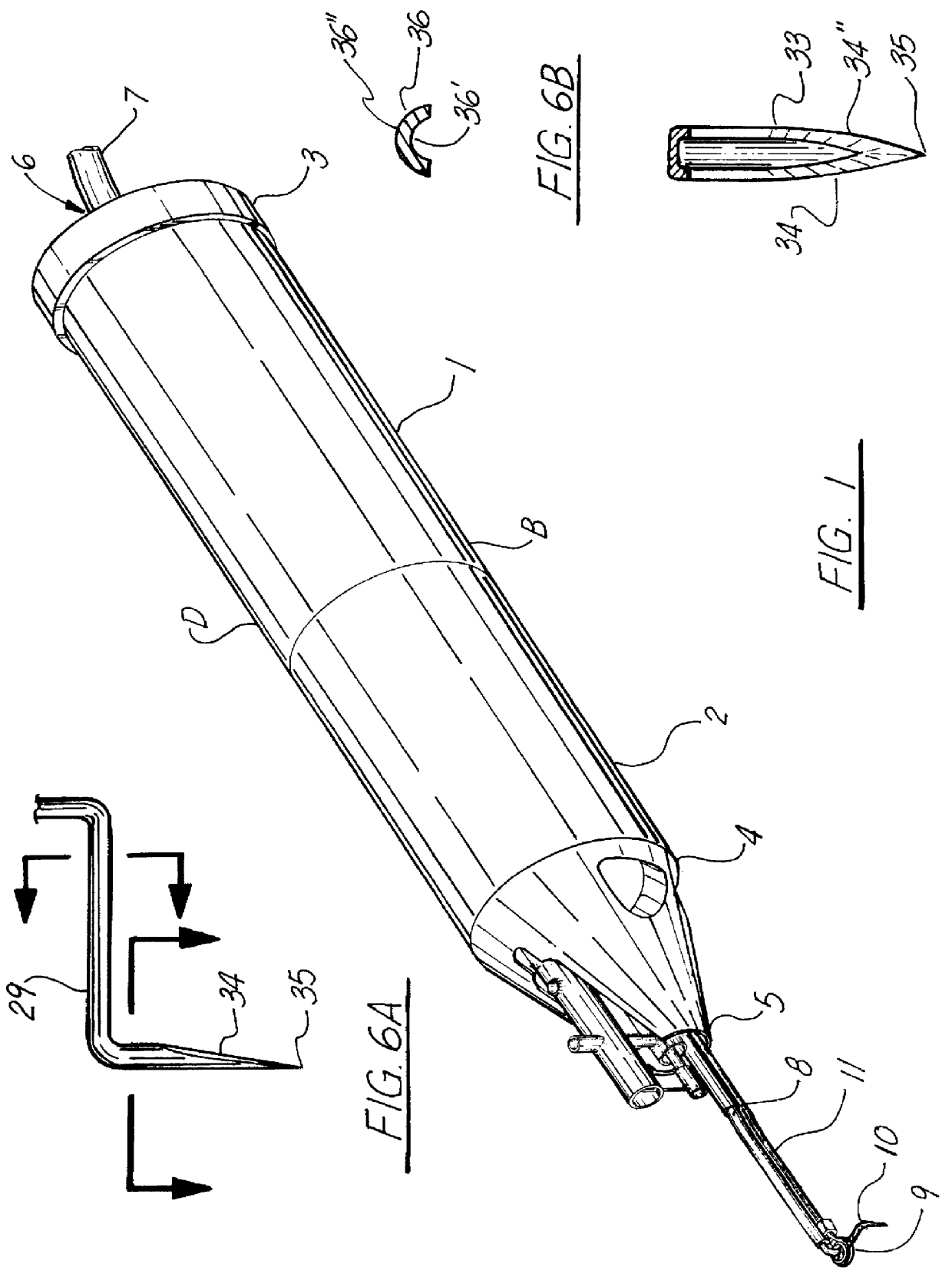
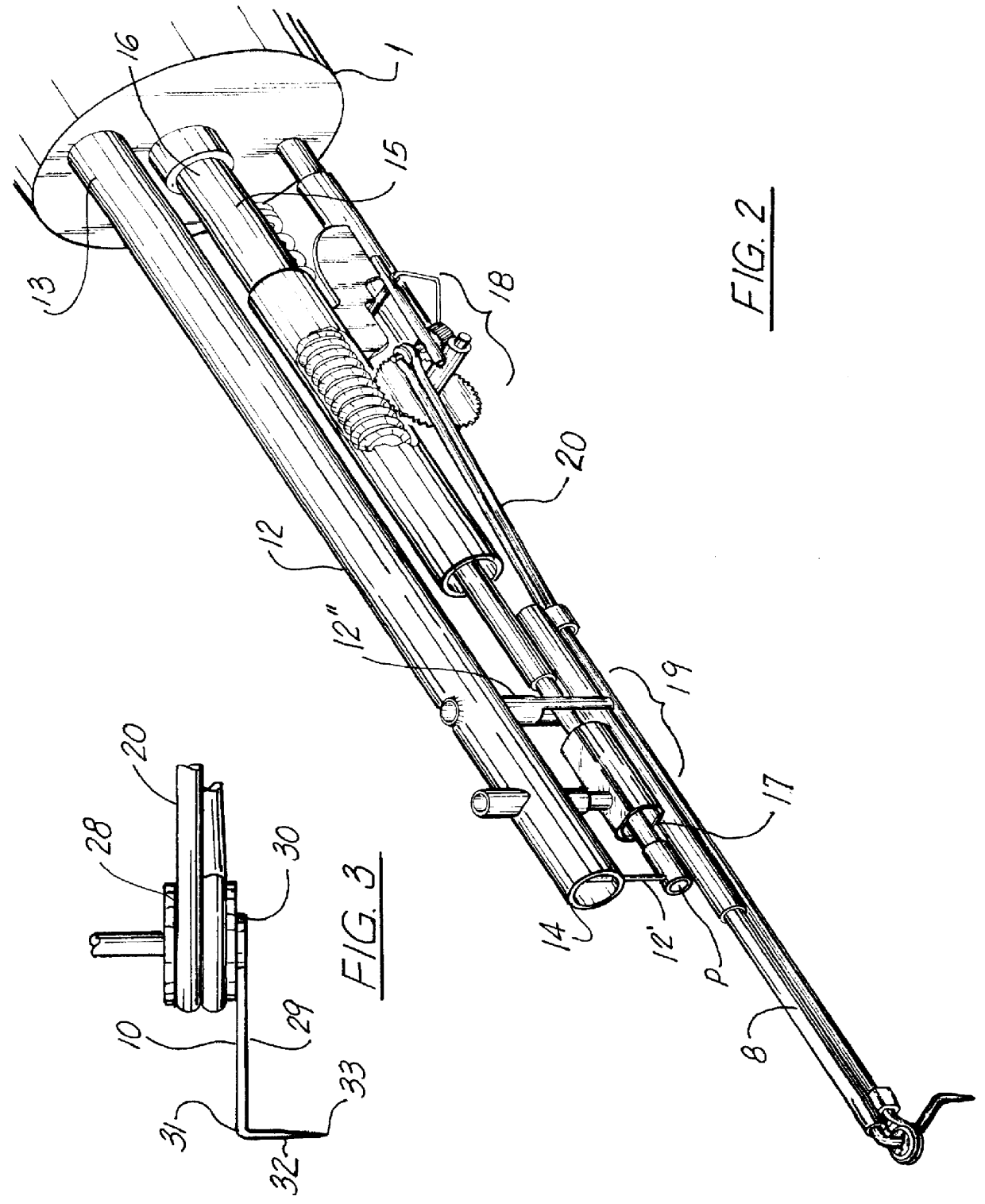
Capsulectomy device and method therefore
InactiveUS6165190AEasy to useCost-effective in manufacture and operation and maintenanceEye surgerySurgeryHand heldEngineering
A surgical instrument for ophthalmic surgery, allowing the user to form a uniform circular incision of the anterior lens capsule of an eyeball, as part of an anterior capsulotomy. The capsulectomy device of the preferred embodiment of the present invention has first and second ends, with a rotor emanating from one end, the rotor having a cutting blade or bin situated at the distal end of the rotor, the rotor rotating in pivotal fashion up to 360 degrees, while simultaneously reciprocating the cutting blade at a consistent stroke so as to provide optimal incision edge and depth of the anterior lens capsule of the eyeball. The device is hand held and relatively compact, having provided therein a motor and gear reduction / transmission system for driving the rotor and providing the reciprocating action to the cutting blade or pin. The device further includes a power supply, which is illustrated as a separate component fed to the device via wire, as well as controls for initiating power, as well as varying the speed of the motor. Unlike the prior art systems, which generally have relied upon the skill of the surgeon to perform the radial incision by hand, the present system provides a relatively easy and uniform system for performing the radial incision which is believed to be safer, more uniform, and less time consuming than prior techniques.
Owner:NGUYEN NHAN
Method and system for confident anomaly detection in computer network traffic
ActiveUS20150229661A1Quickly deployed into serviceReduce in quantityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAnomaly detectionNetwork service
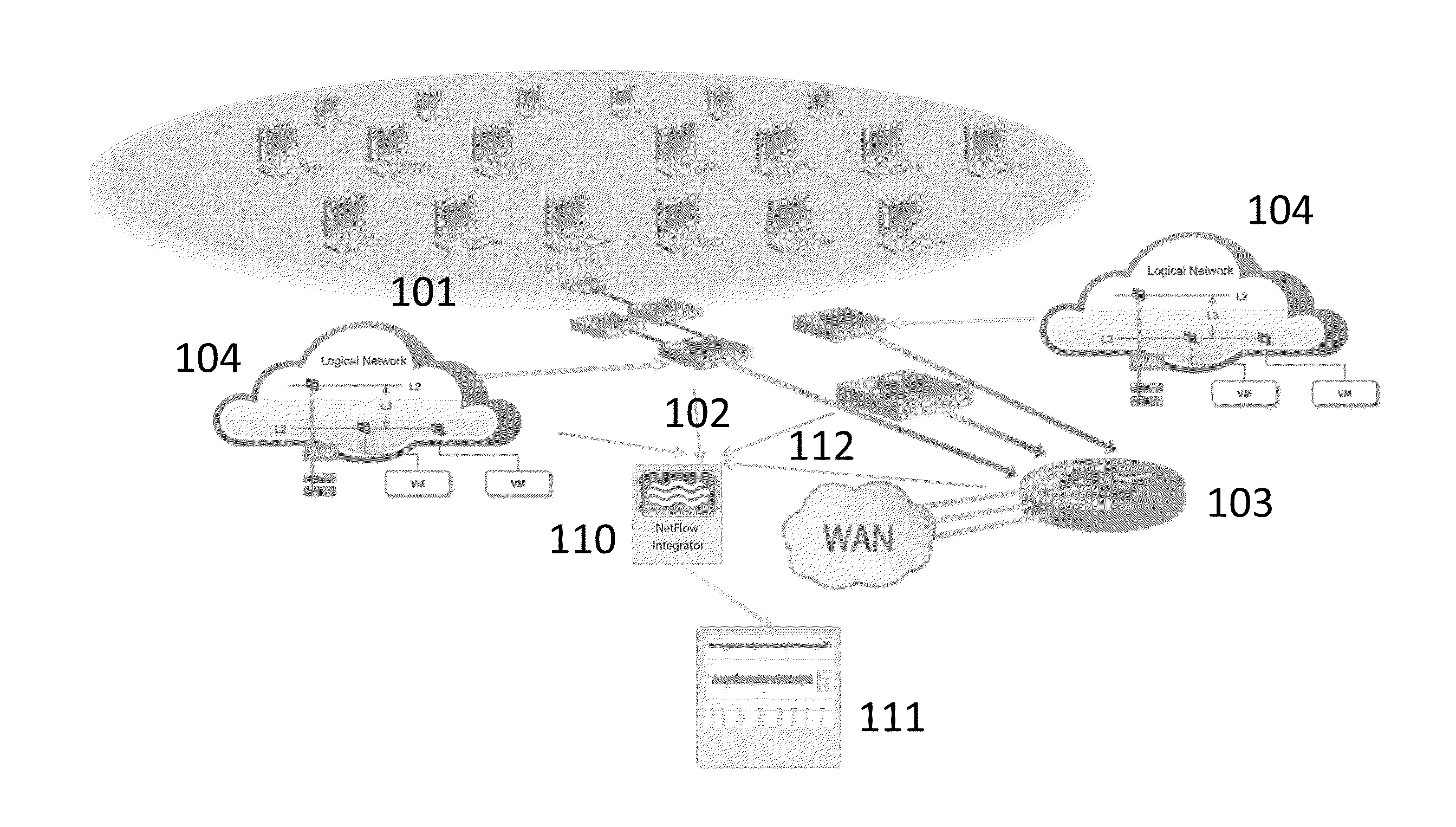
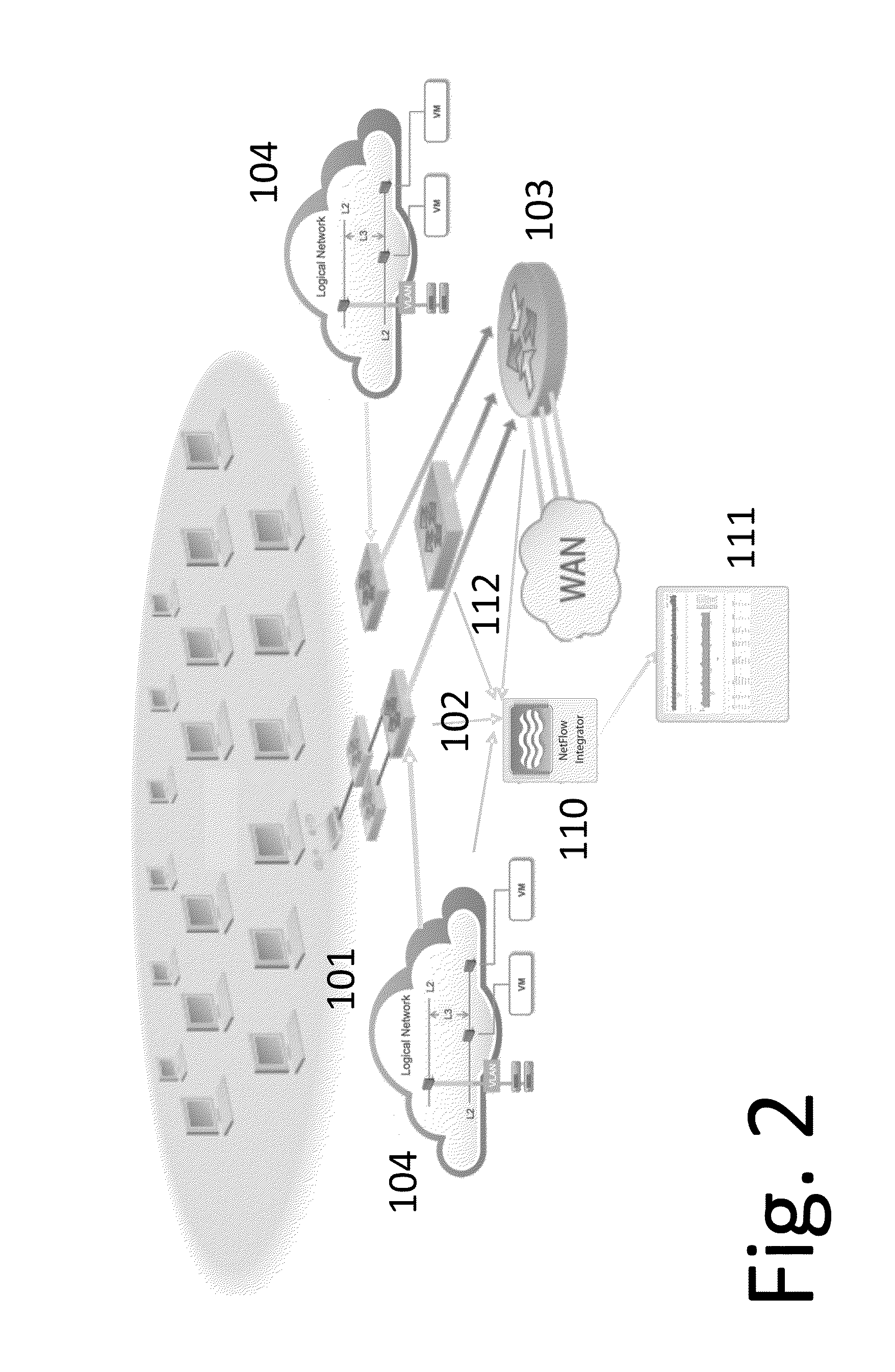
The present invention relates to systems and methods for detecting anomalies in computer network traffic with fewer false positives and without the need for time-consuming and unreliable historical baselines. Upon detection, traffic anomalies can be processed to determine valuable network insights, including health of interfaces, devices and network services, as well as to provide timely alerts in the event of attack.
Owner:NETFLOW LOGIC
Automated video interpretation system
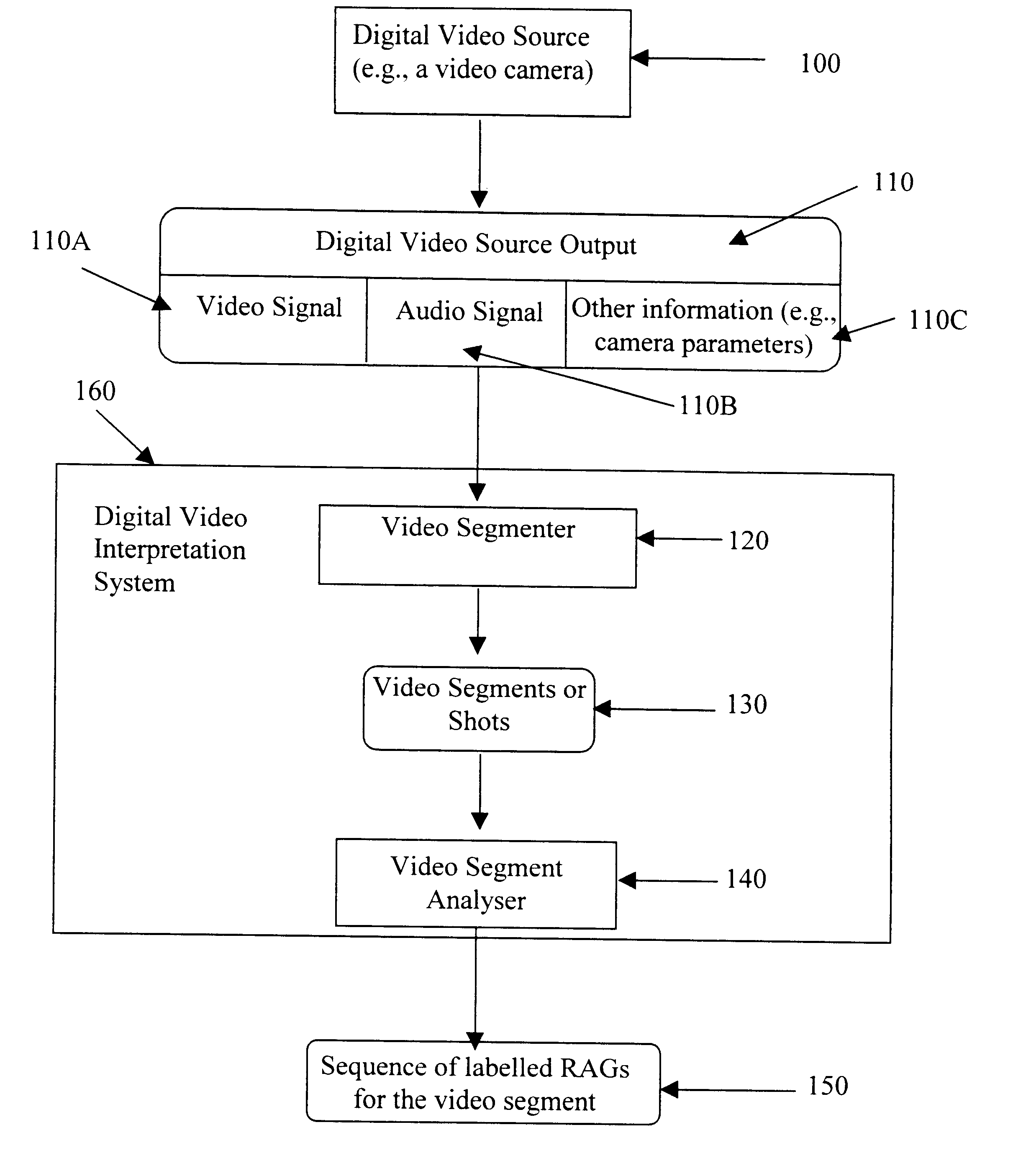
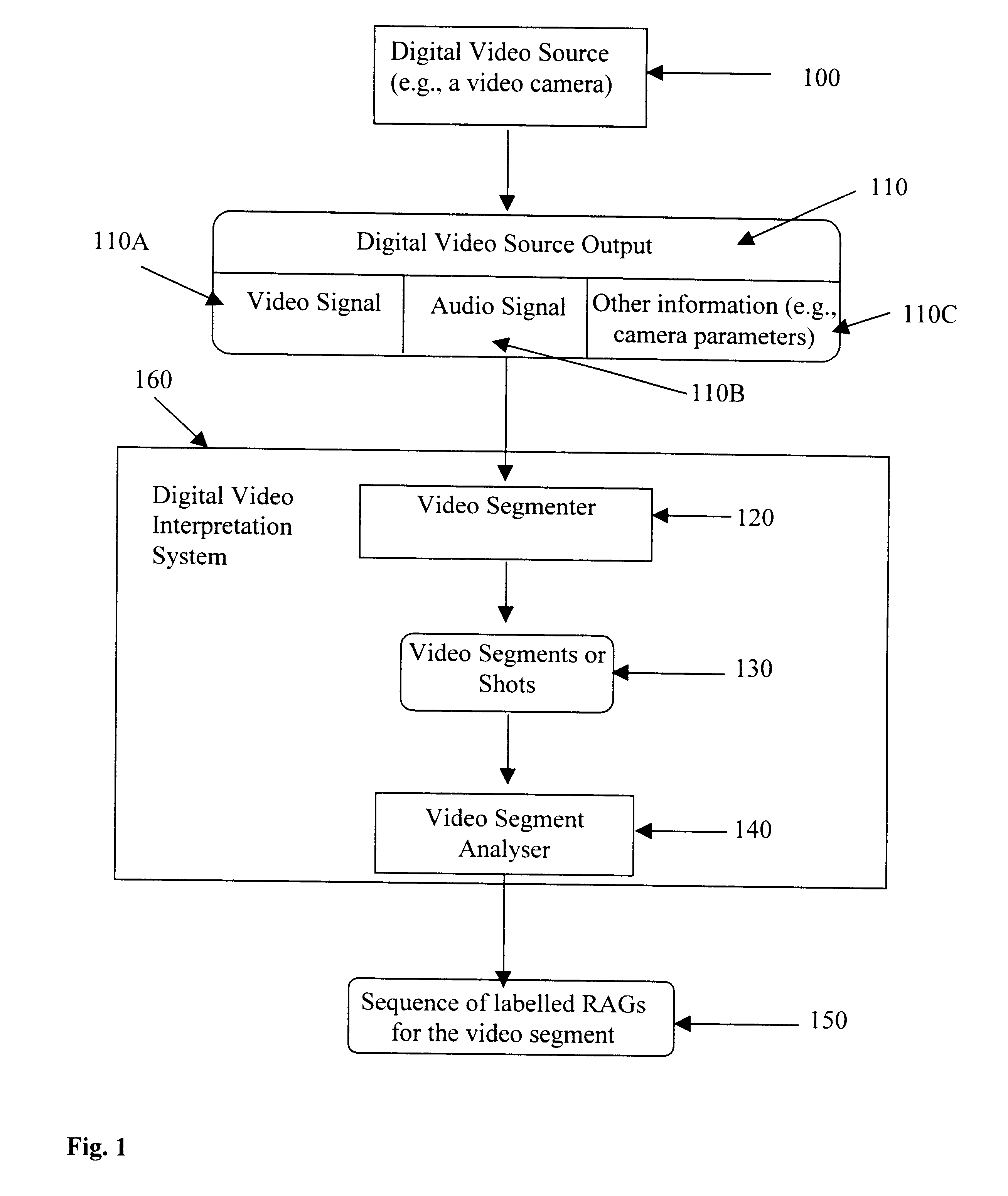
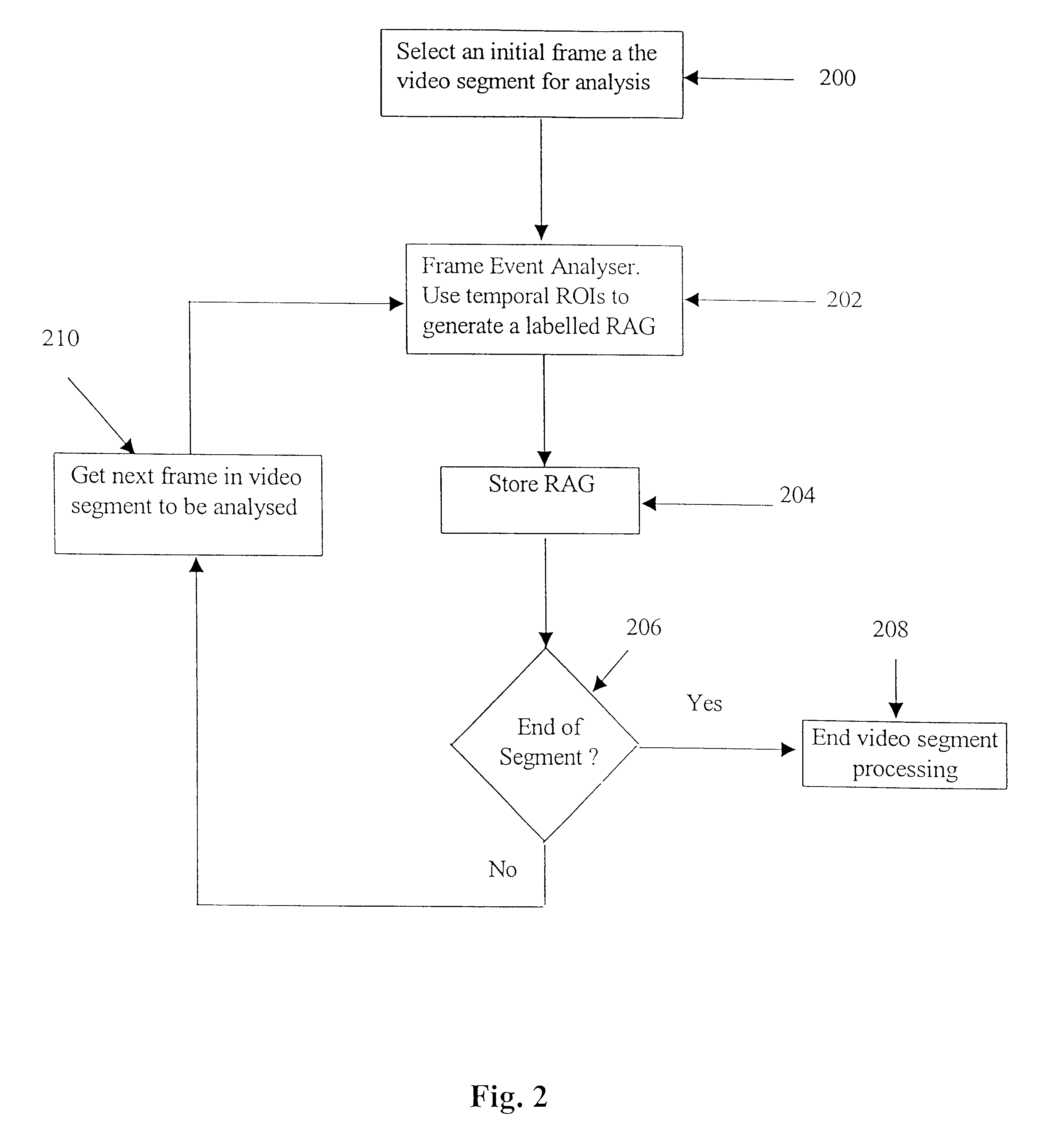
Digital image signal interpretation is the process of understanding the content of an image through the identification of significant objects or regions in the image and analysing their spatial arrangement. Traditionally the task of image interpretation required human analysis. This is expensive and time consuming, consequently considerable research has been directed towards constructing automated image interpretation systems. A method of interpreting a digital video signal is disclosed whereby the digital video signal has contextual data. The method comprising the steps of firstly, segmenting the digital video signal into one or more video segments, each segment having a corresponding portion of the contextual data. Secondly, analysing each video segment to provide a graph at one or more temporal instances in the respective video segment dependent upon the corresponding portion of the contextual data.
Owner:CANON KK
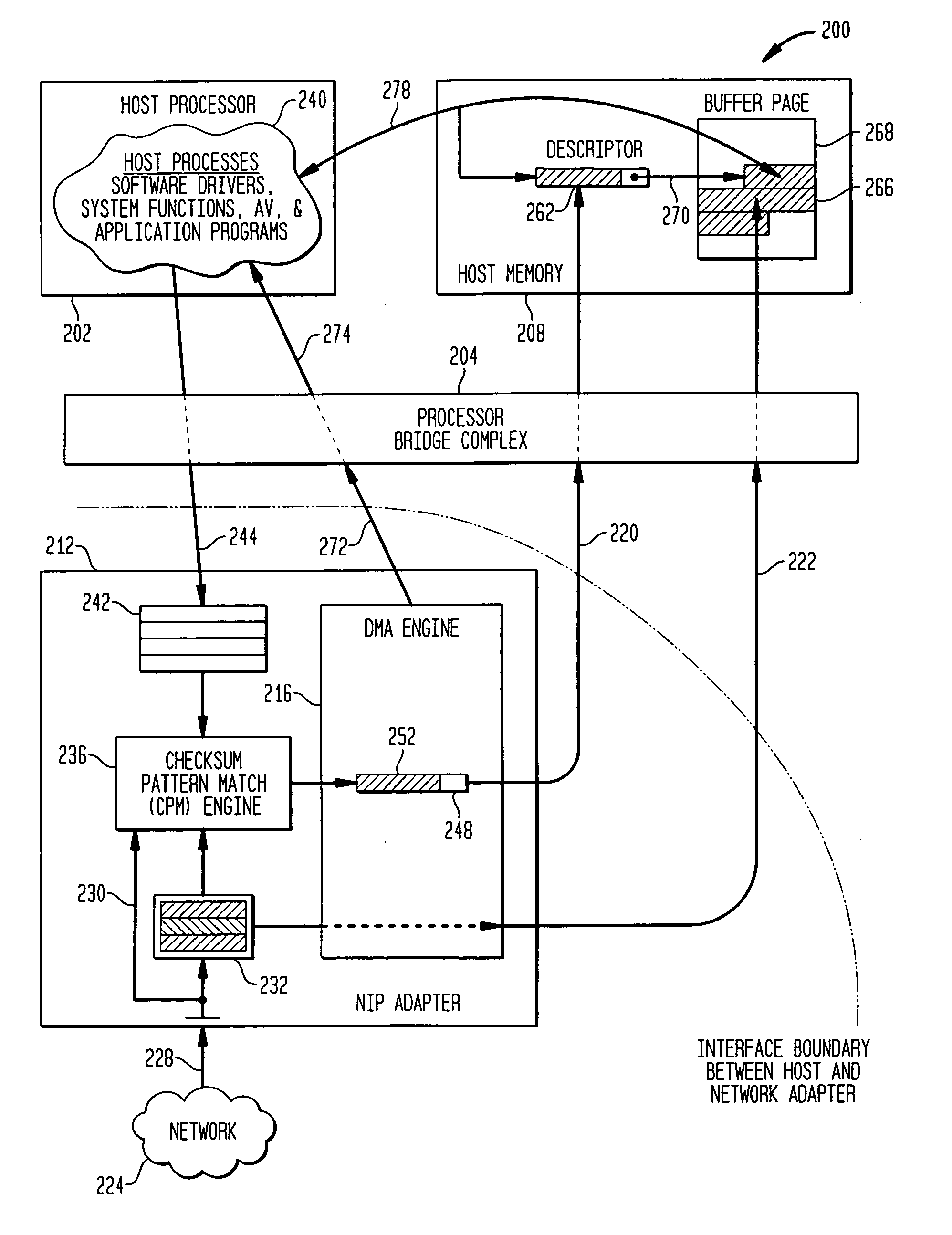
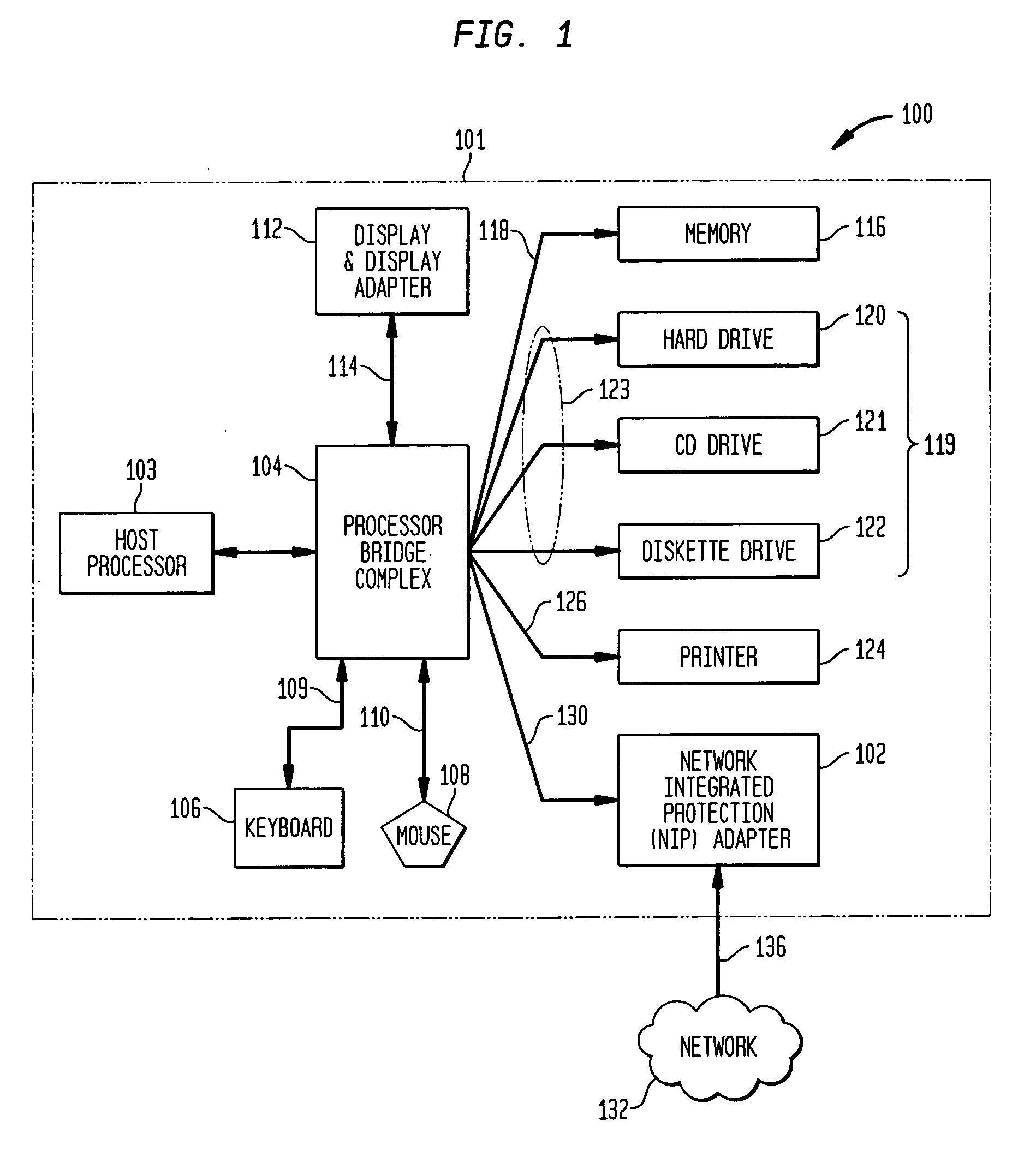
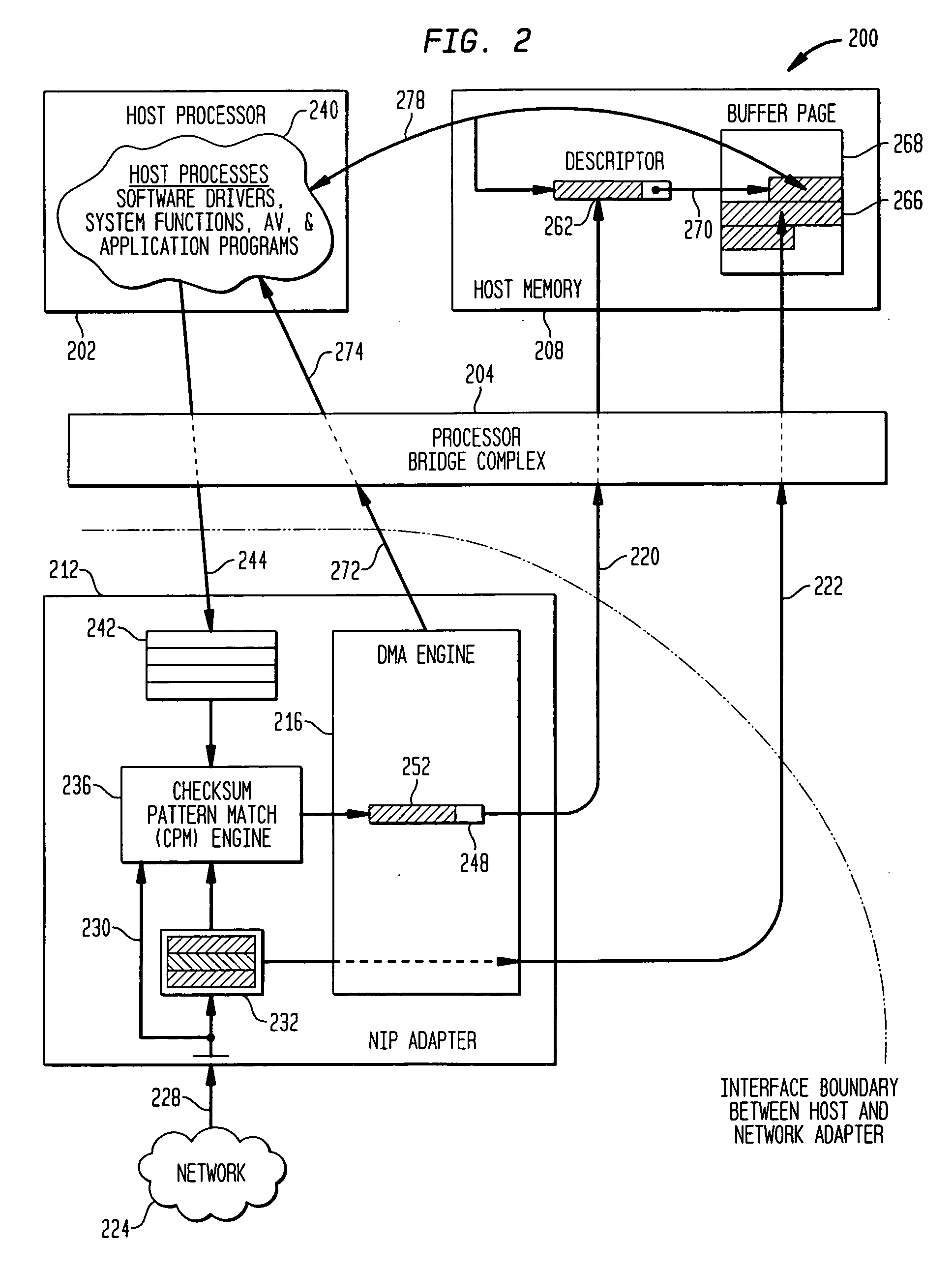
Methods and apparatus for interface adapter integrated virus protection
A virus detection mechanism is described in which virus detection is provided by a network integrated protection (NIP) adapter. The NIP adapter checks incoming media data prior to it being activated by a computing device. The NIP adapter operates independently of a host processor to receive information packets from a network. This attribute of independence allows NIP anti-virus (AV) techniques to be “always on” scanning incoming messages and data transfers. By being independent of but closely coupled to the host processor, complex detection techniques, such as using check summing or pattern matching, can be efficiently implemented on the NIP adapter without involving central processor resources and time consuming mass storage accesses. The NIP adapter may be further enhanced with a unique fading memory (FM) facility to allow for a flexible and economical implementation of polymorphic virus detection.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
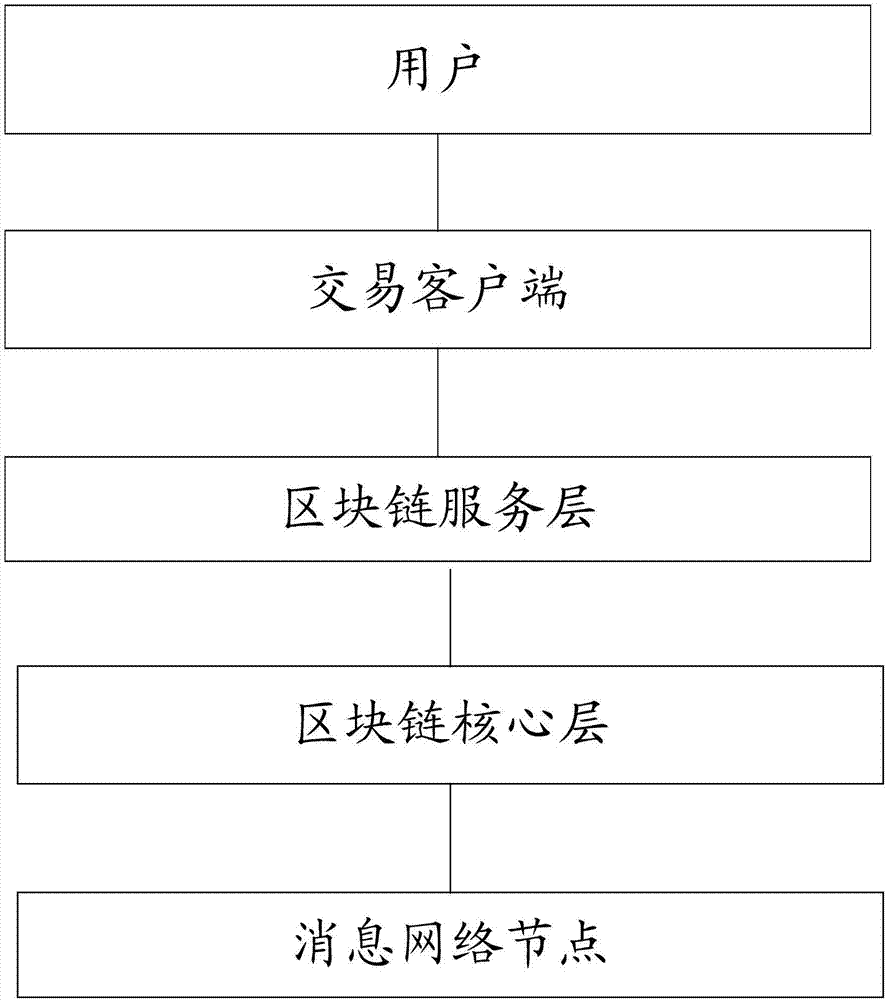
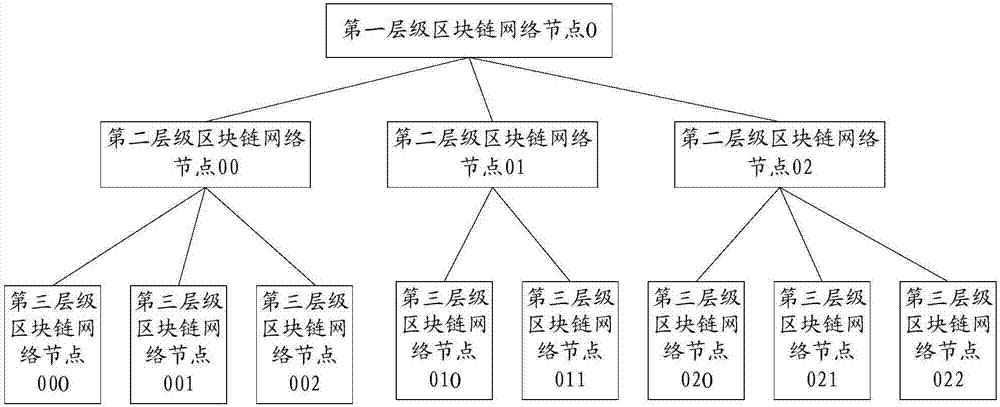
Network transaction method and apparatus based on block chain system
InactiveCN107239940AImprove transaction efficiencyEasy to operatePayment protocolsPayment circuitsFinancial transactionChain network
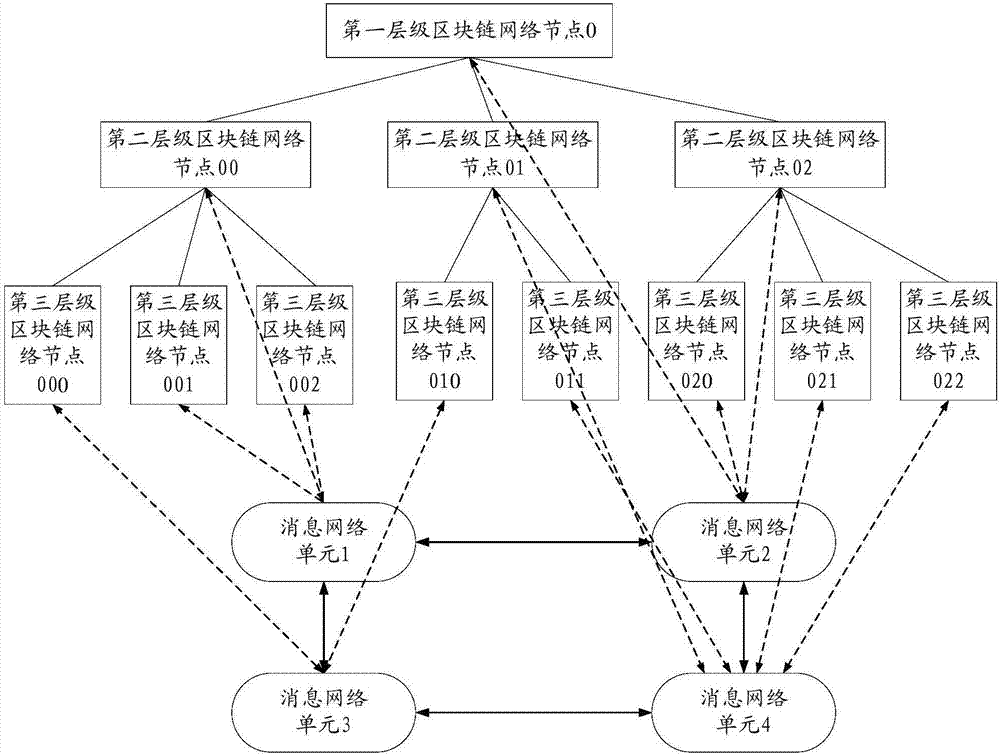
The invention discloses a network transaction method and apparatus based on a block chain system. The network transaction method and apparatus based on a block chain system are used for reducing time consuming of transaction and improving concurrency. The block chain system includes multiple levels of block chain network nodes; and the multiple levels of block chain network nodes at least include a first block chain network node of the first transaction party for network transaction, and a second block chain network node of the second transaction party for network transaction. The network transaction method based on a block chain system includes the steps: the first block chain network node generates transaction information corresponding to the network transaction; the transaction information is sent to the second block chain network node of the second transaction party for network transaction; the first block chain network node and the second block chain network node use a consensus algorithm to reach a consensus for the transaction information; and the first block chain network node and the second block chain network node synchronously keep accounts for the network transaction corresponding to the transaction information for which the first block chain network node and the second block chain network node reach a consensus.
Owner:北京博晨技术有限公司
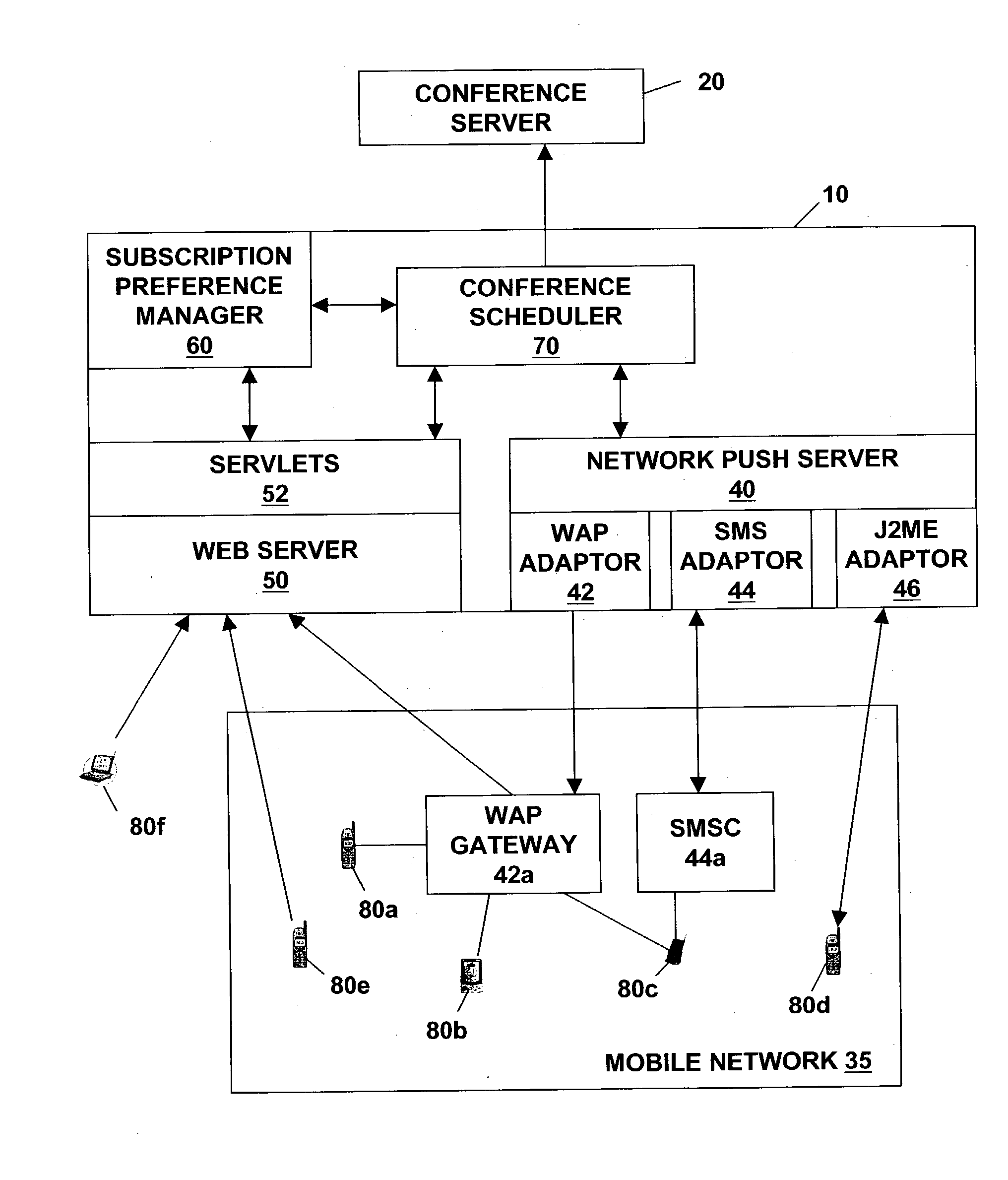
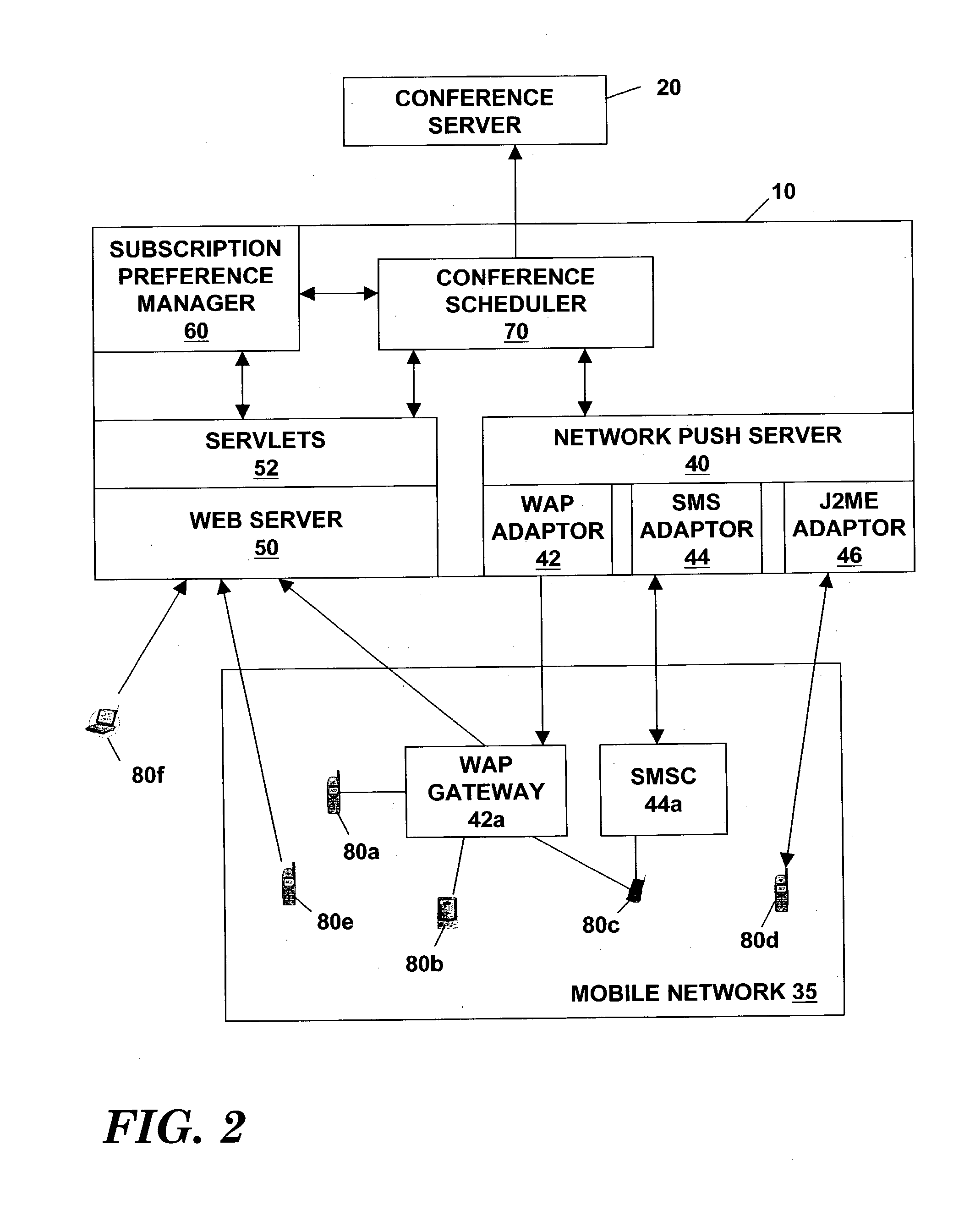
Method and system for supporting rendezvous based instant group conferencing among mobile users
ActiveUS20040001446A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTeleconferenceTime-Consuming
A method and a system for supporting rendezvous based instant group conferencing among mobile users allows a conference originator to initiate and setup instant group conferencing to a set of participants even when the participants may not be immediately available to commit to the conference call at the time of its initiation. All negotiations for obtaining commitments from the participants are performed by the system, thus relieving the originator of the time consuming task of negotiating with the participants. The system automatically decides as to when to actually dial out to the participants to setup the conference call after obtaining commitment from all (or a quorum of) required participants.
Owner:BHATIA RANDEEP +2
Methods and systems for file replication utilizing differences between versions of files
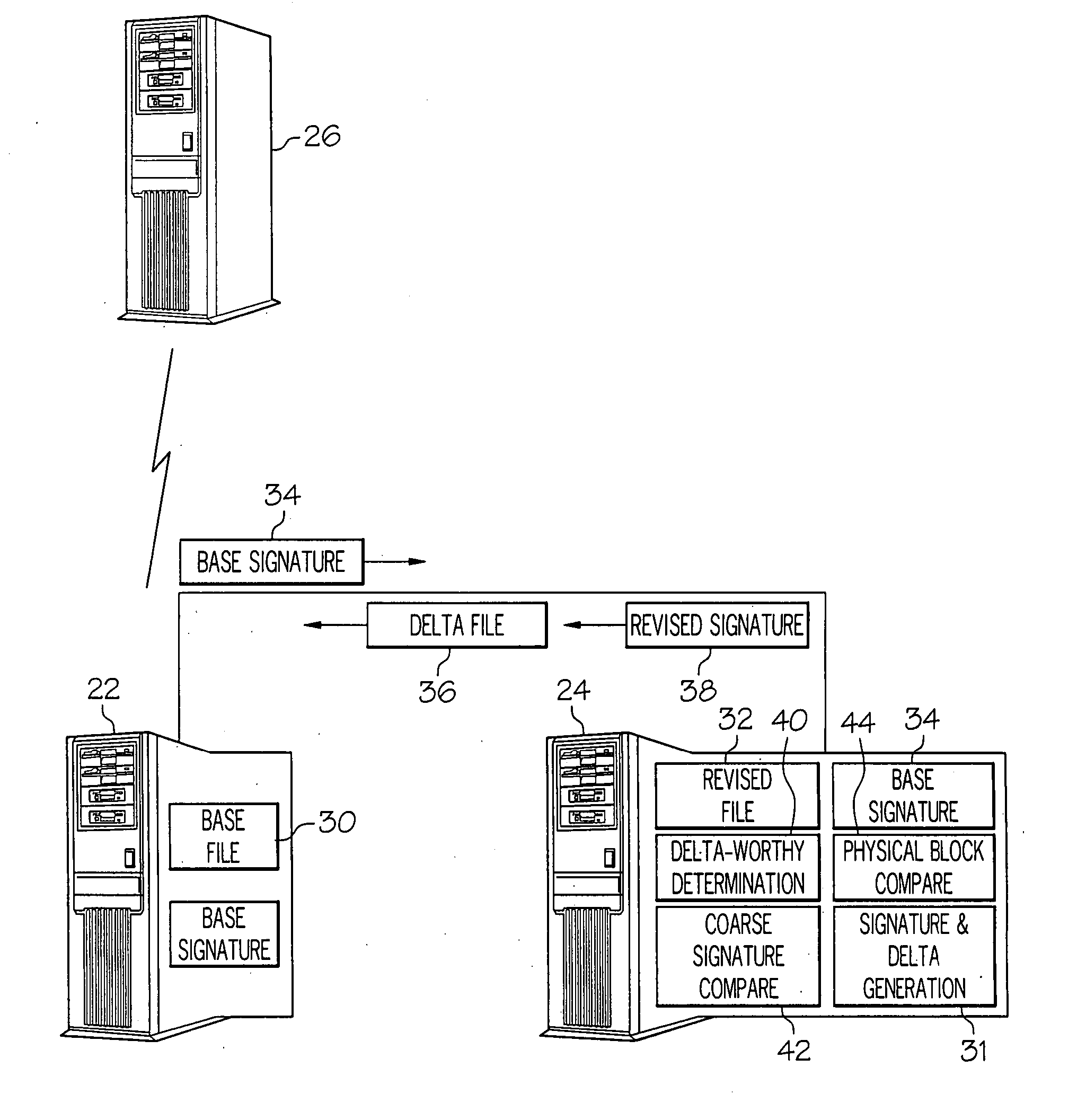
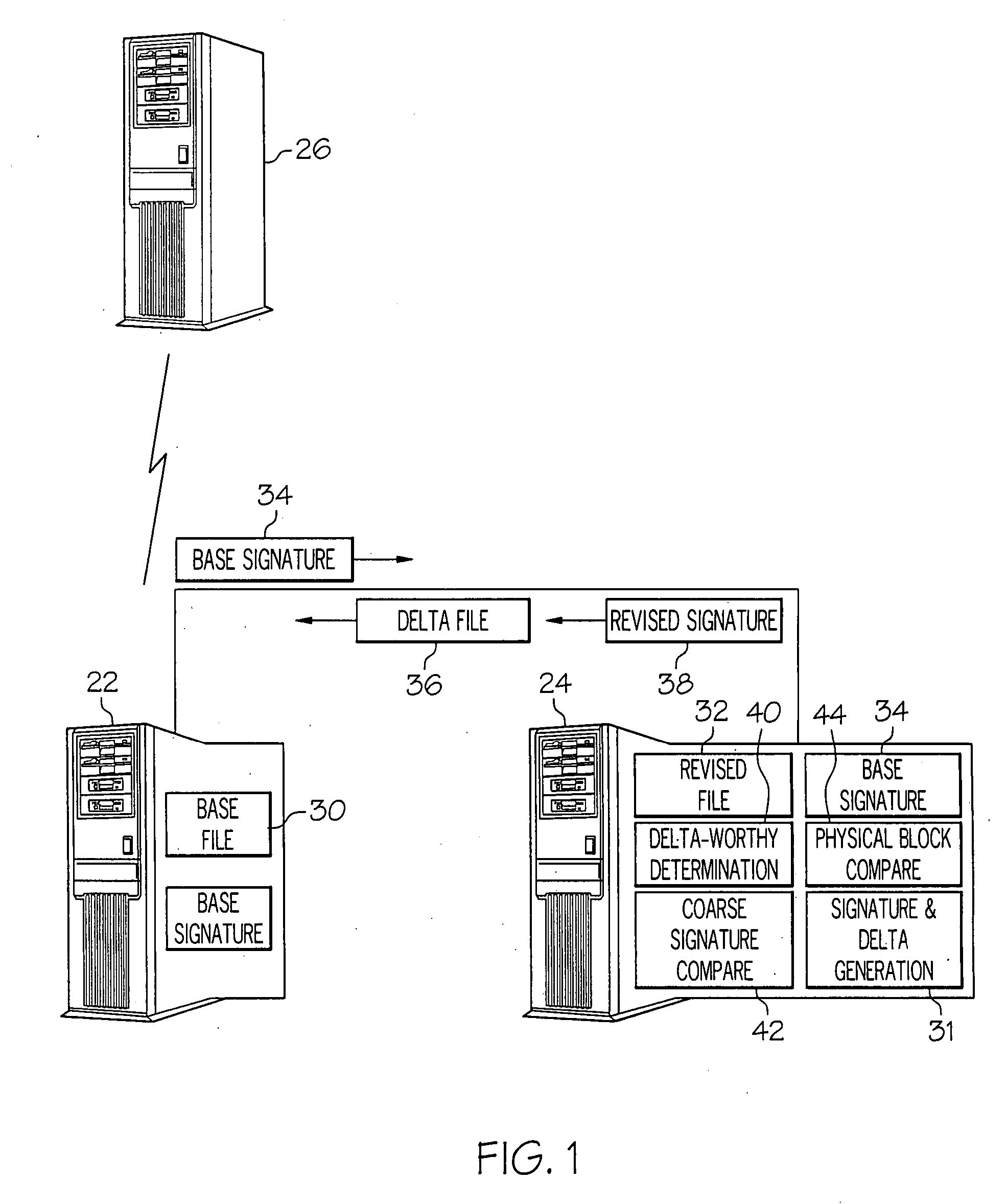
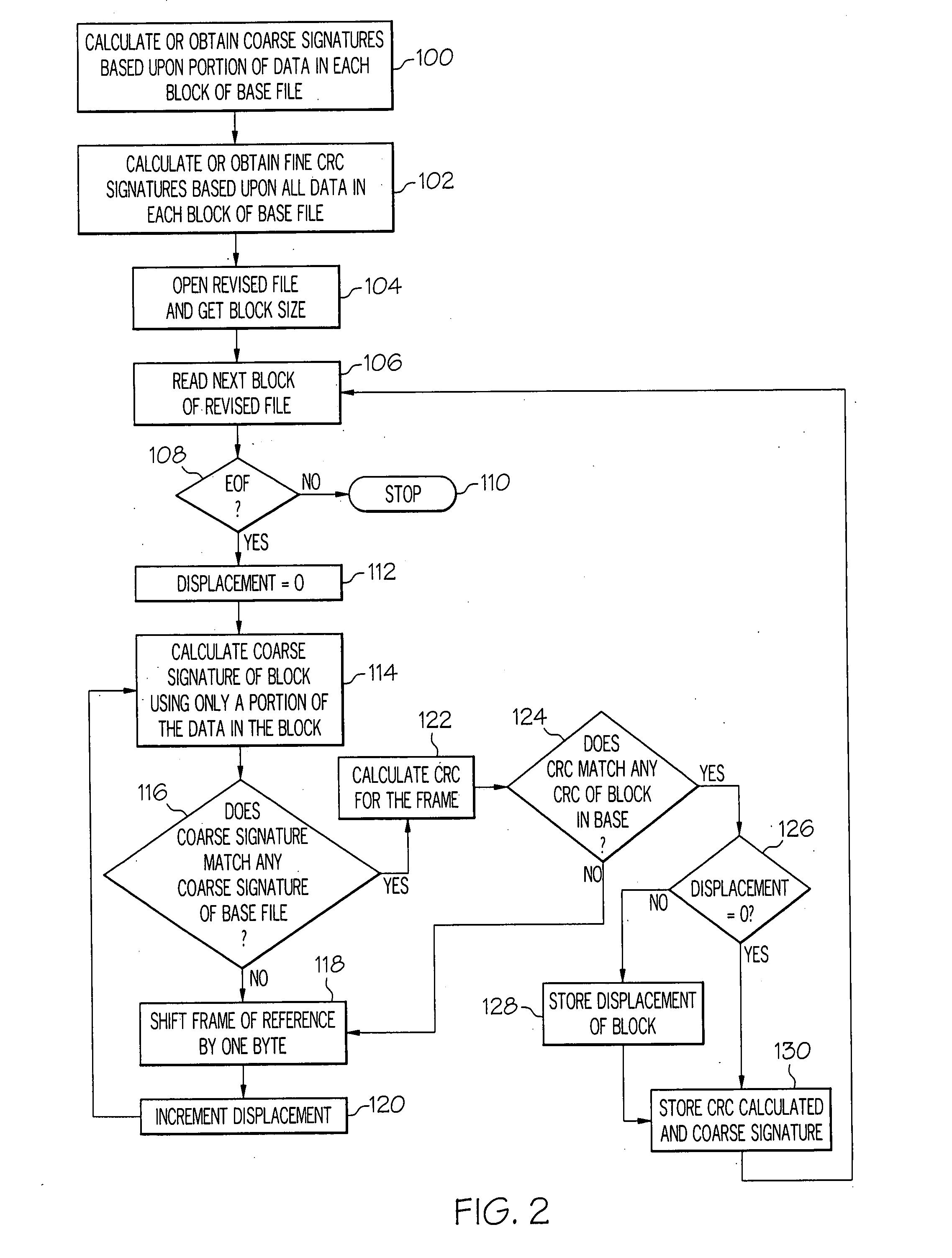
ActiveUS20070288533A1Block completeData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputer hardware
Methods and systems for efficient file replication are provided. In some embodiments, one or more coarse signatures for blocks in a base file are compared with those coarse signatures for blocks of a revised file, until a match is found. A fine signature is then generated for the matching block of the revised file and compared to a fine signature of the base file. Thus, fine signatures are not computed unless a coarse signature match has been found, thereby minimizing unneeded time-consuming fine signature calculations. Methods are also provided for determining whether to initiate a delta file generation algorithm, or whether to utilize a more efficient replication method, based upon system and / or file parameters. In accordance with additional embodiments, the lengths of valid data on physical blocks are obtained from physical block mappings for the files, and these lengths and mappings are utilized for delta file generation, to minimize unnecessary signature computations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
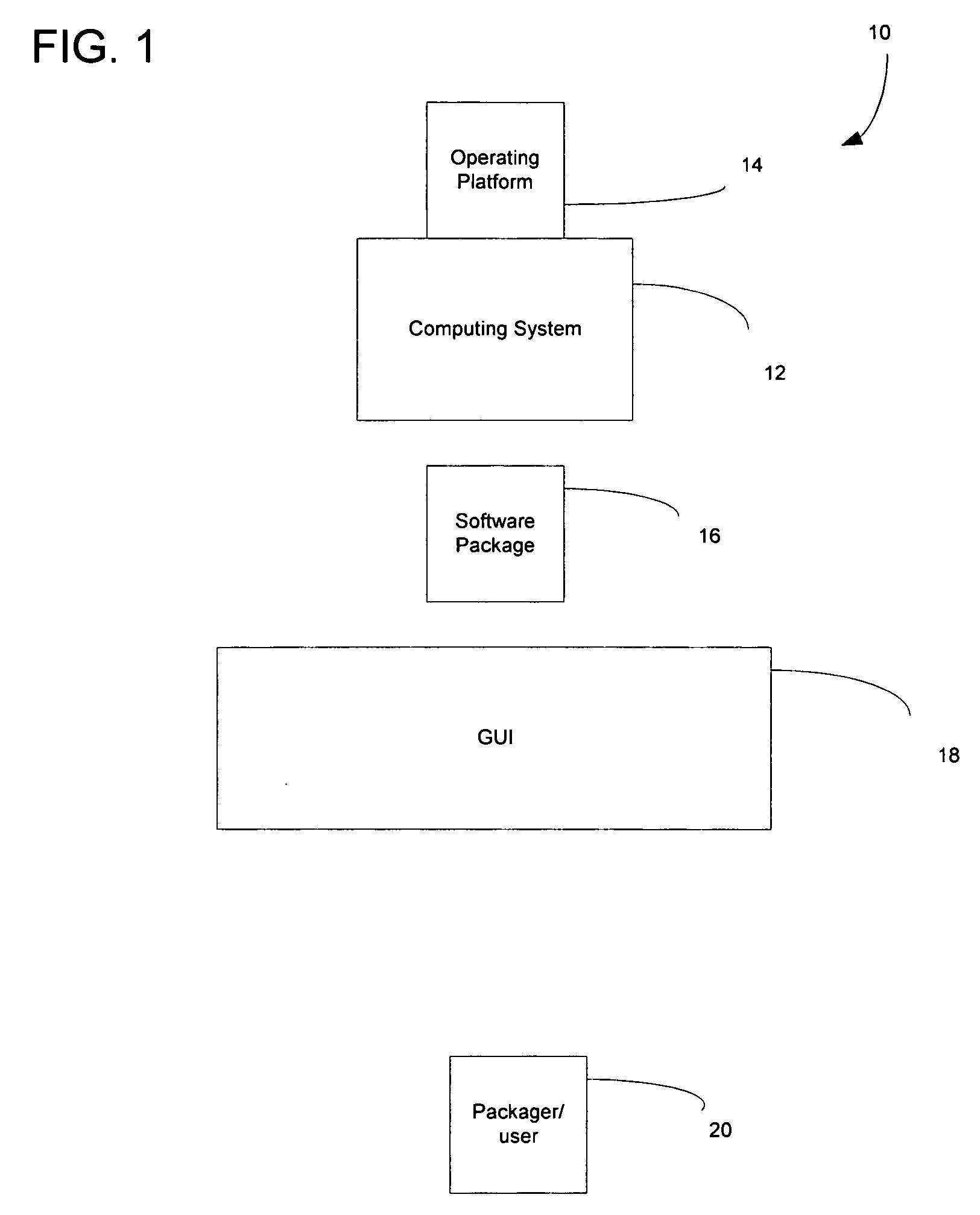
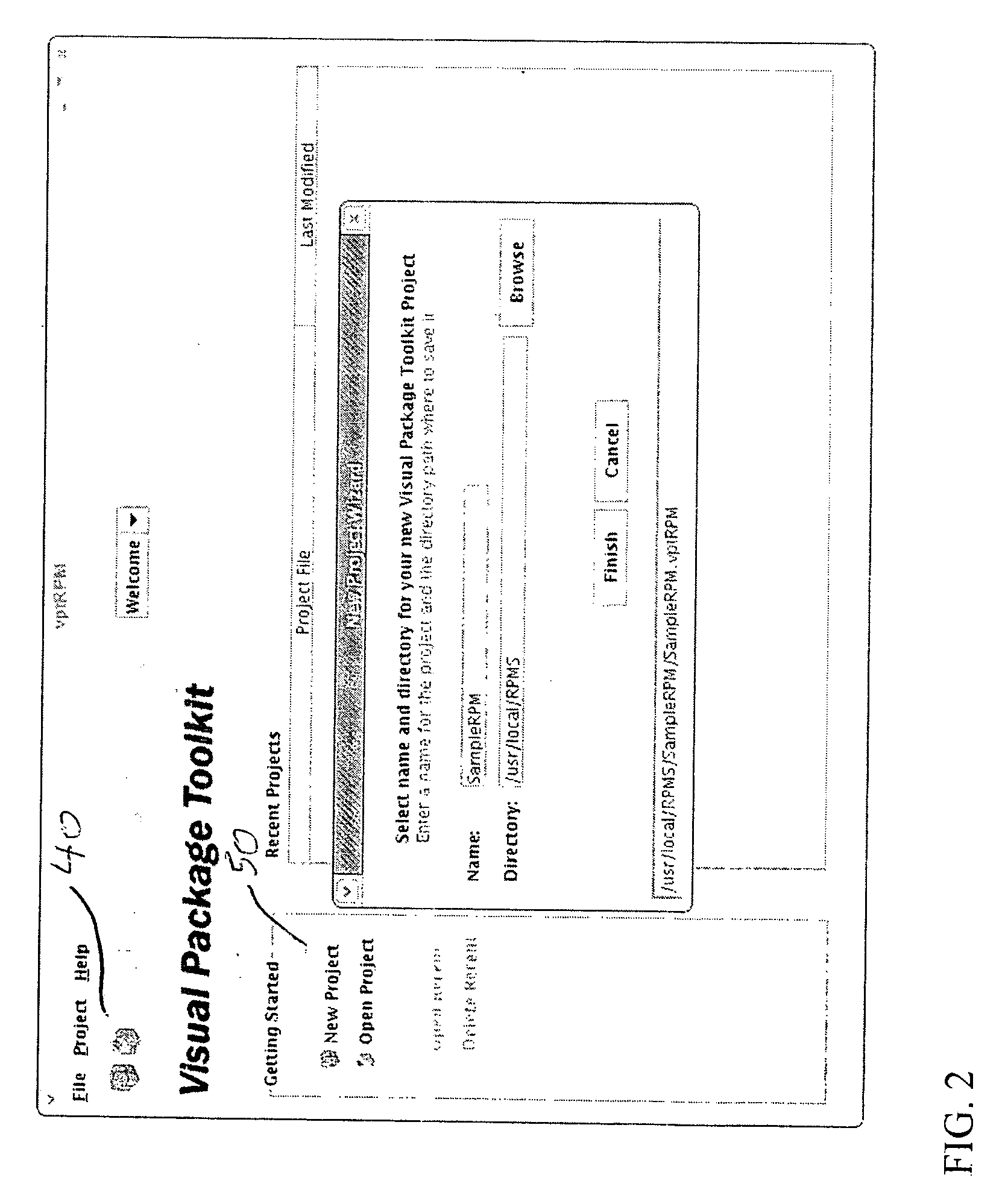
System and method for packaging software
A method and system for packaging software using a graphical user interface (GUI) to simplify the creation and modification of System V and Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) software packages. The software packaging system provides a fully interactive graphical interface portable across many platforms including Linux, Unix System V, Solaris, and AIX. RPM is a popular and powerful packaging system that installs and removes system software, enforces dependencies, and is freely available on a number of different platforms. The software packaging system of the present invention simplifies and speeds the creation of deployable RPM software packages, a complex and time consuming task if created using the RPM command line method. The GUI provides for the collection of information required for RPM software package creation, modification, and feature manipulation reducing the skill level and time that needed to perform these functions using the RPM command line.
Owner:NEXONE
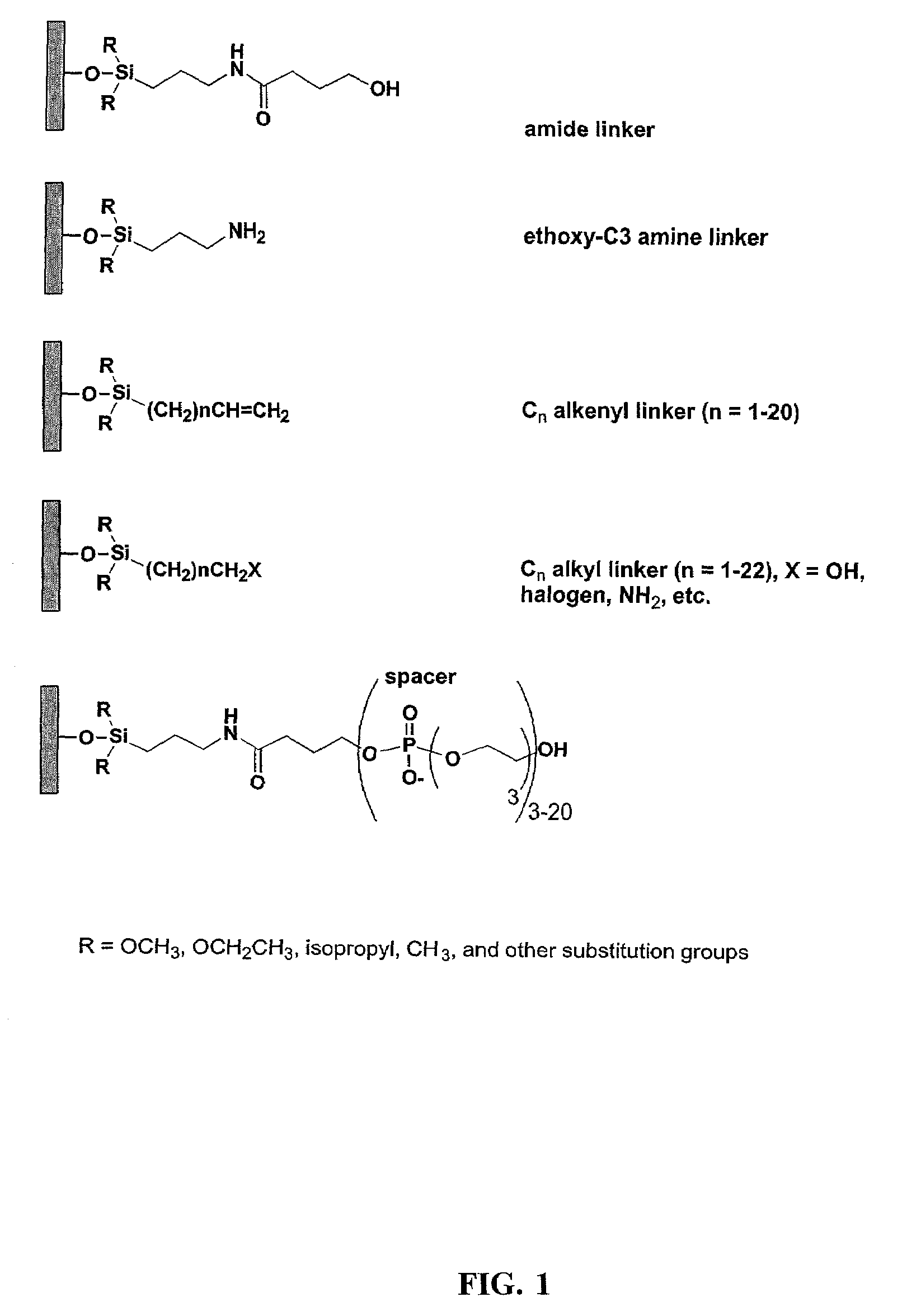
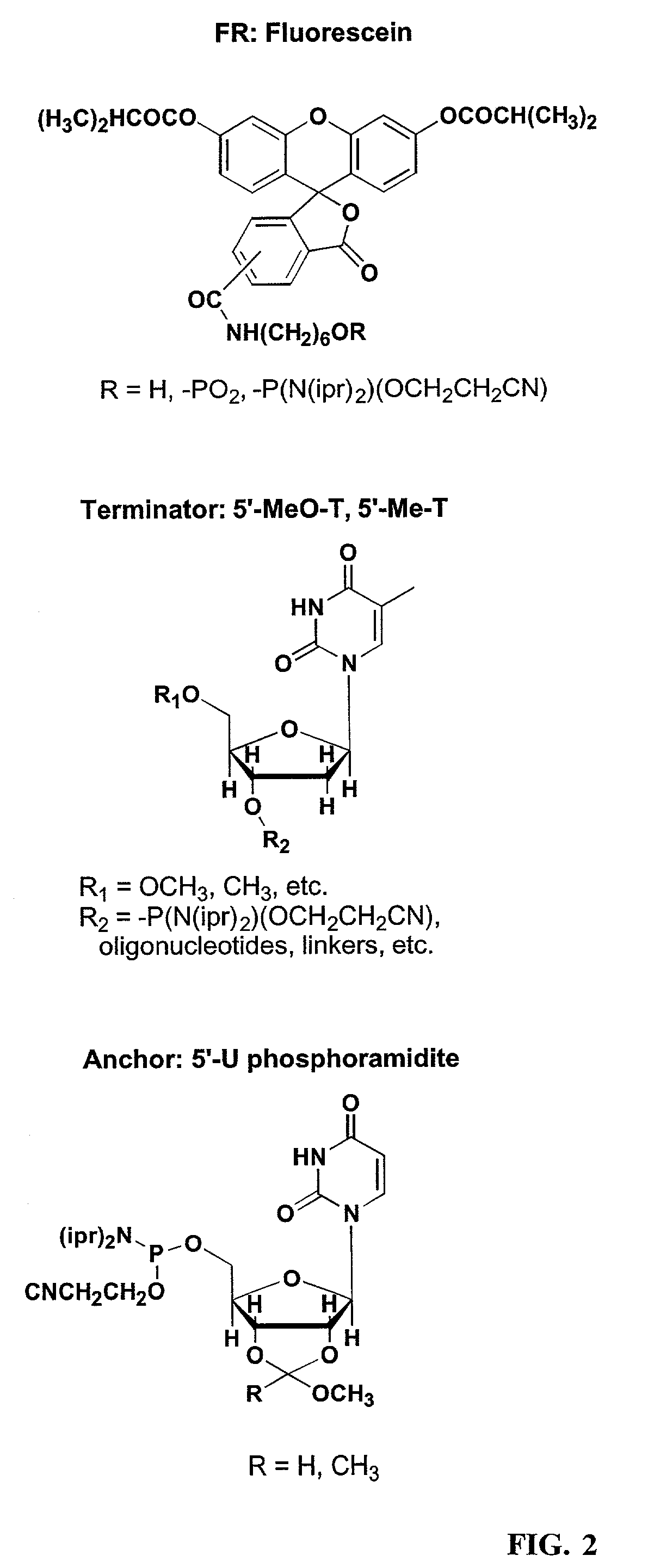
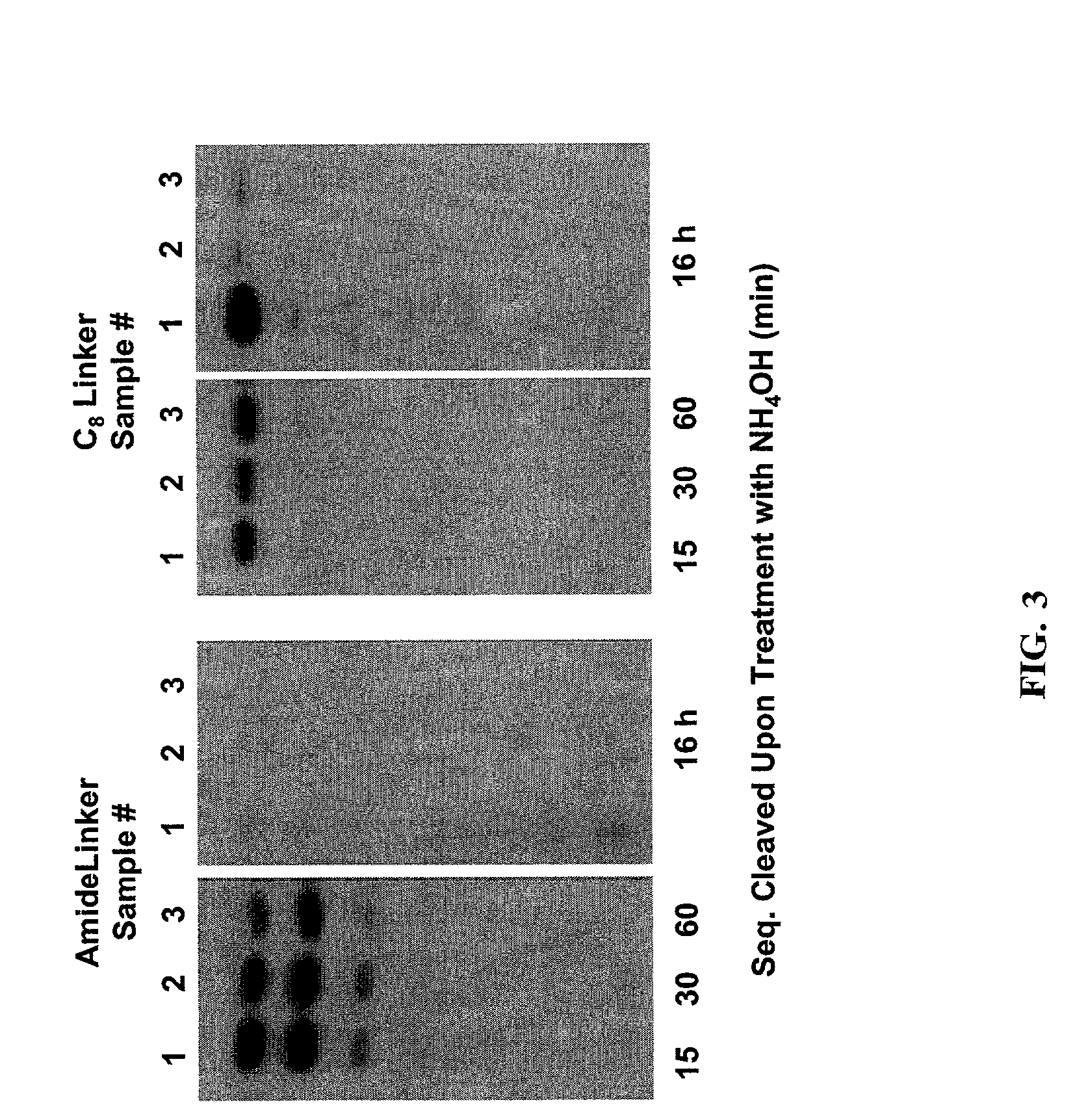
Linkers and co-coupling agents for optimization of oligonucleotide synthesis and purification on solid supports
InactiveUS7211654B2Promote hydrolysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSolid surfaceTime-Consuming
A method of modulation of synthesis capacity on and cleavage properties of synthetic oligomers from solid support is described. The method utilizes linker molecules attached to a solid surface and co-coupling agents that have similar reactivities to the coupling compounds with the surface functional groups. The preferred linker molecules provide an increased density of polymers and more resistance to cleavage from the support surface. The method is particularly useful for synthesis of oligonucleotides, oligonucleotides microarrays, peptides, and peptide microarrays. The stable linkers are also coupled to anchor molecules for synthesis of DNA oligonucleotides using on support purification, eliminating time-consuming chromatography and metal cation presence. Oligonucleotides thus obtained can be directly used for mass analysis, DNA amplification and ligation, hybridization, and many other applications.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com