Patents
Literature
2963 results about "Address space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
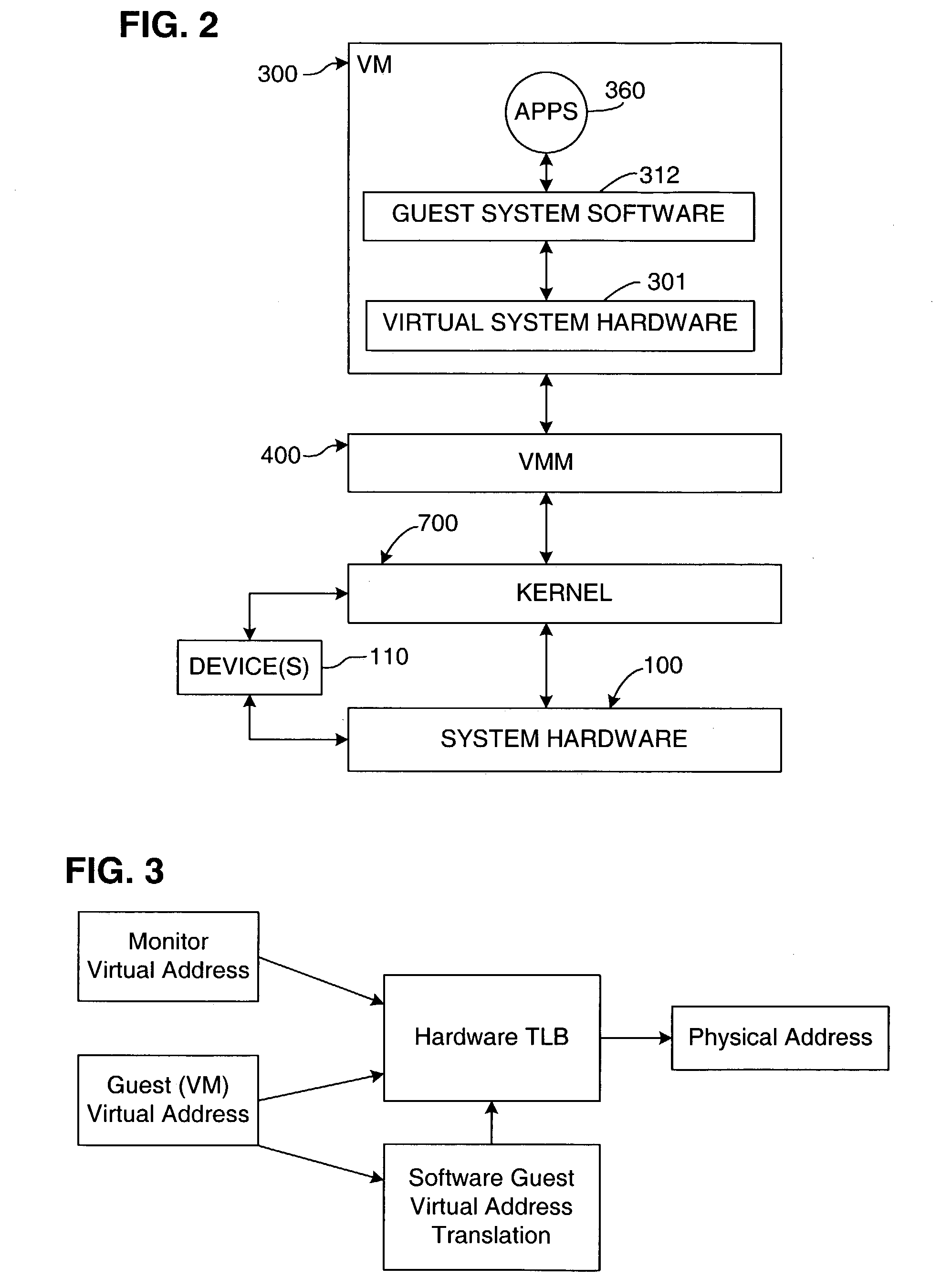
In computing, an address space defines a range of discrete addresses, each of which may correspond to a network host, peripheral device, disk sector, a memory cell or other logical or physical entity.
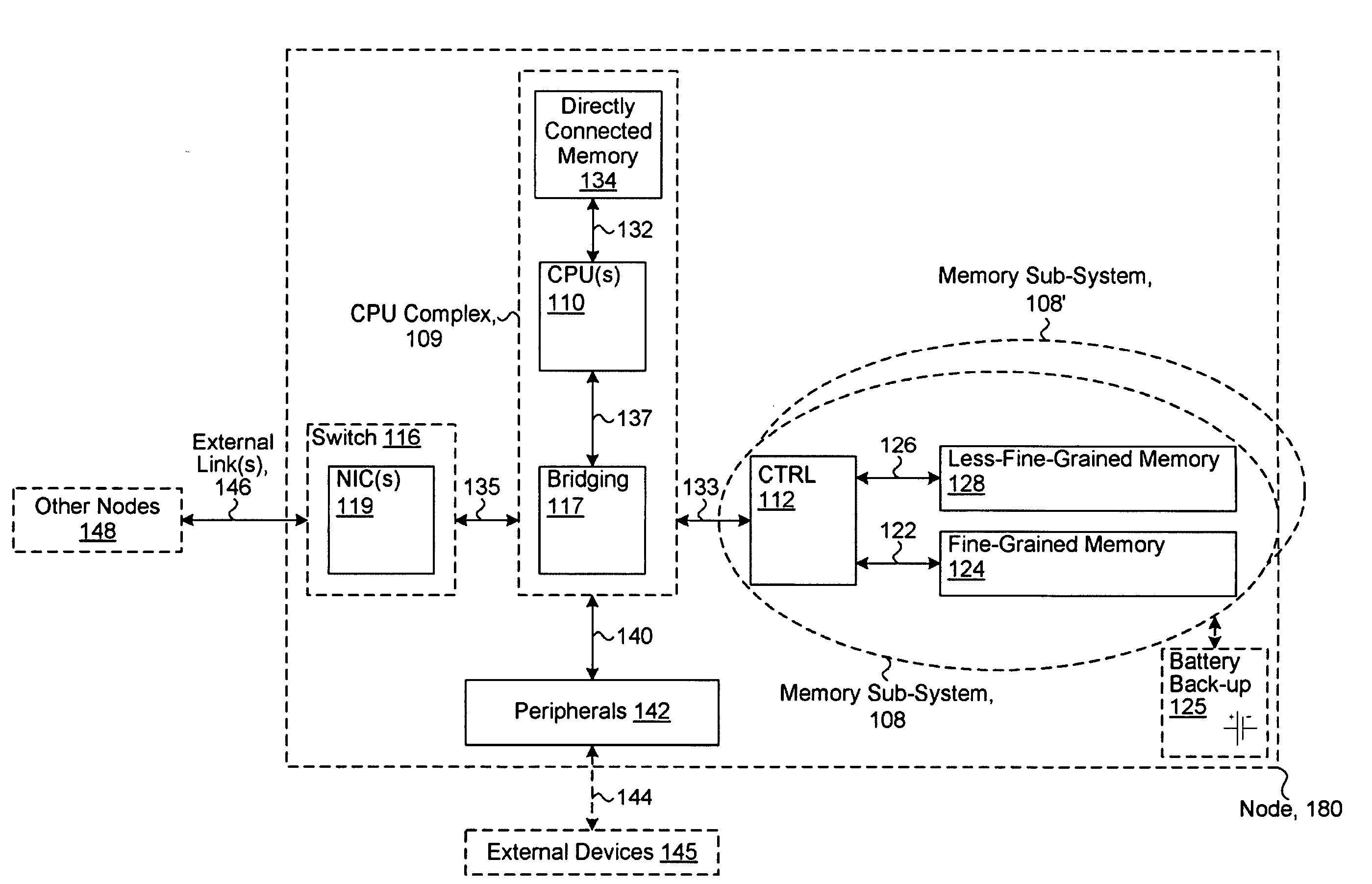
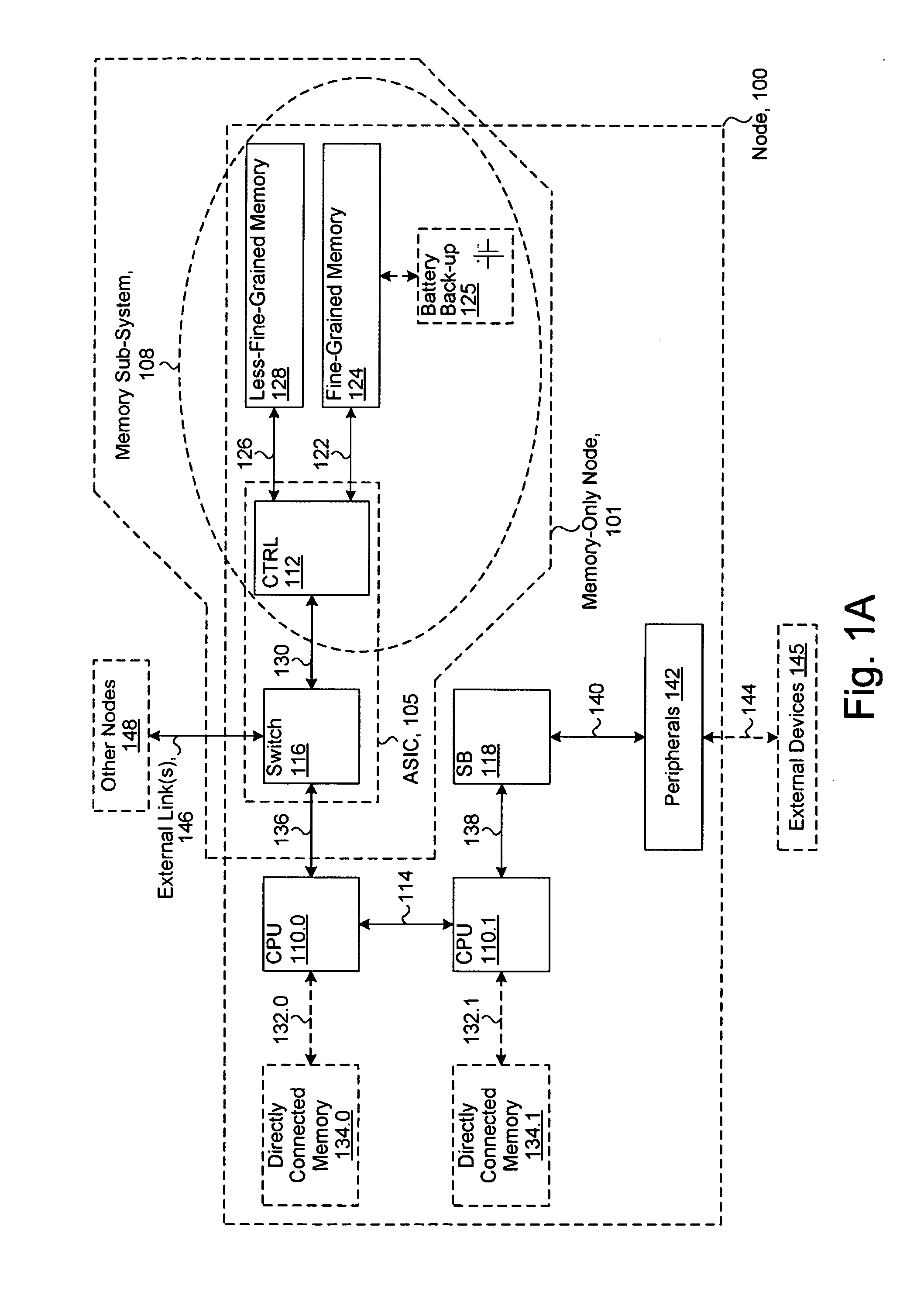
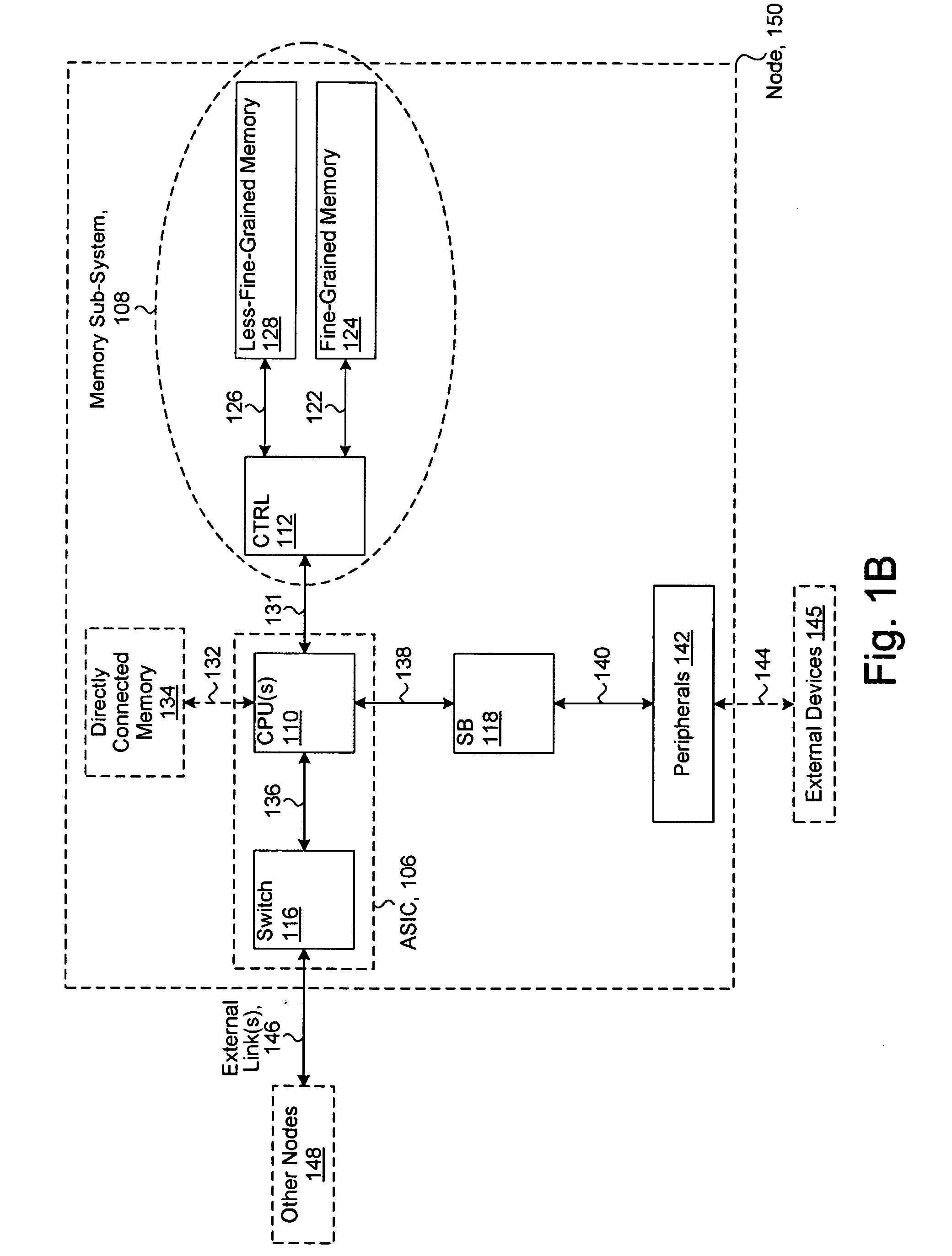
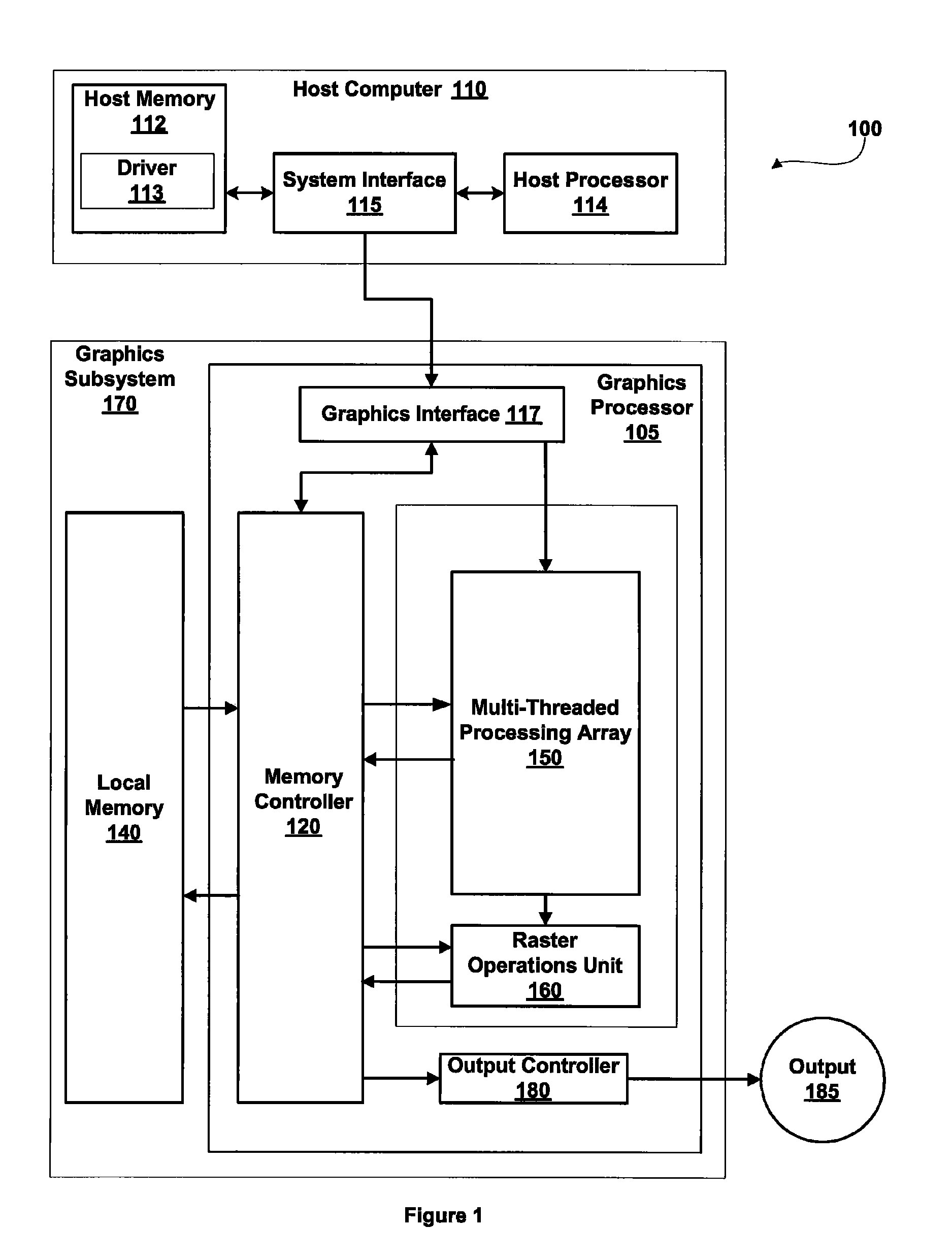
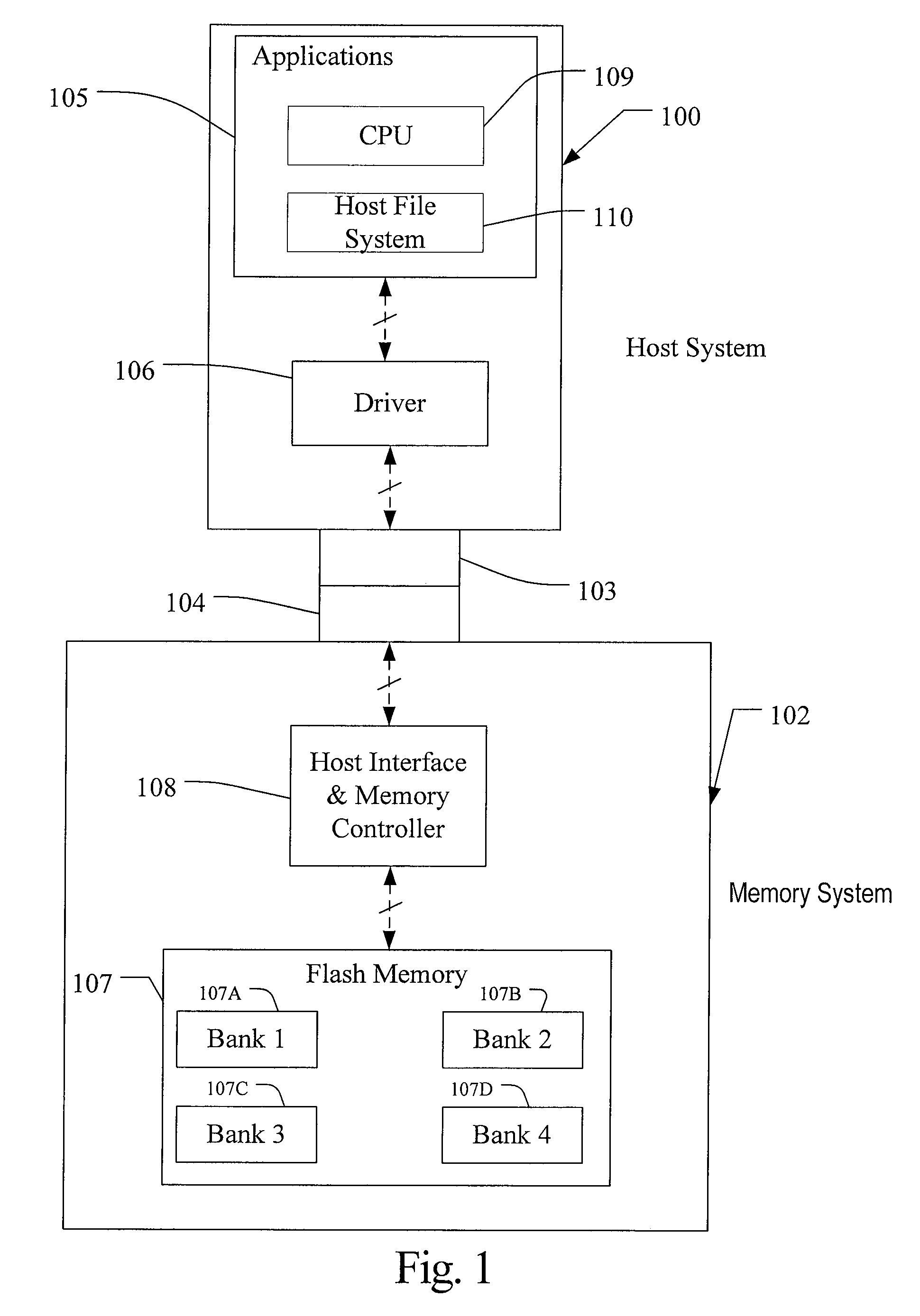
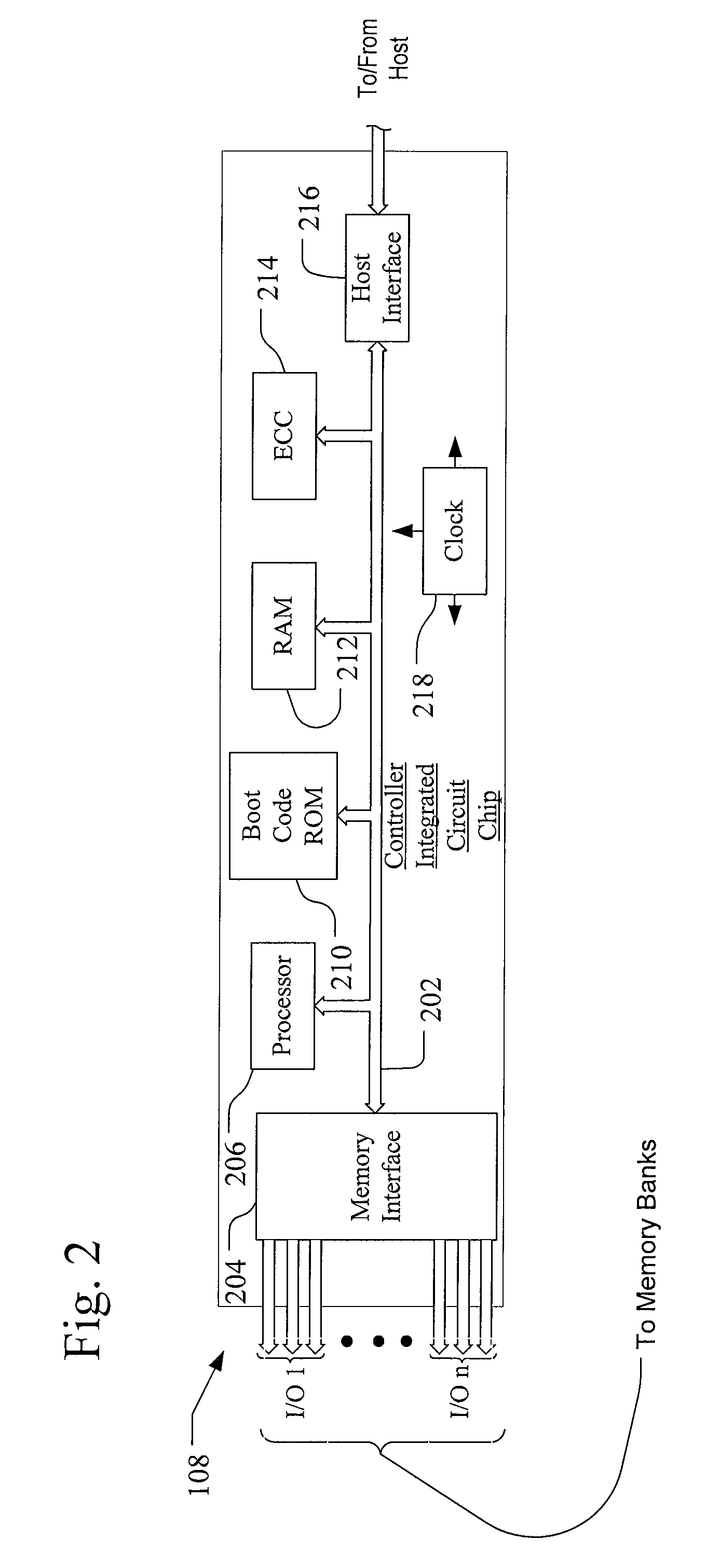
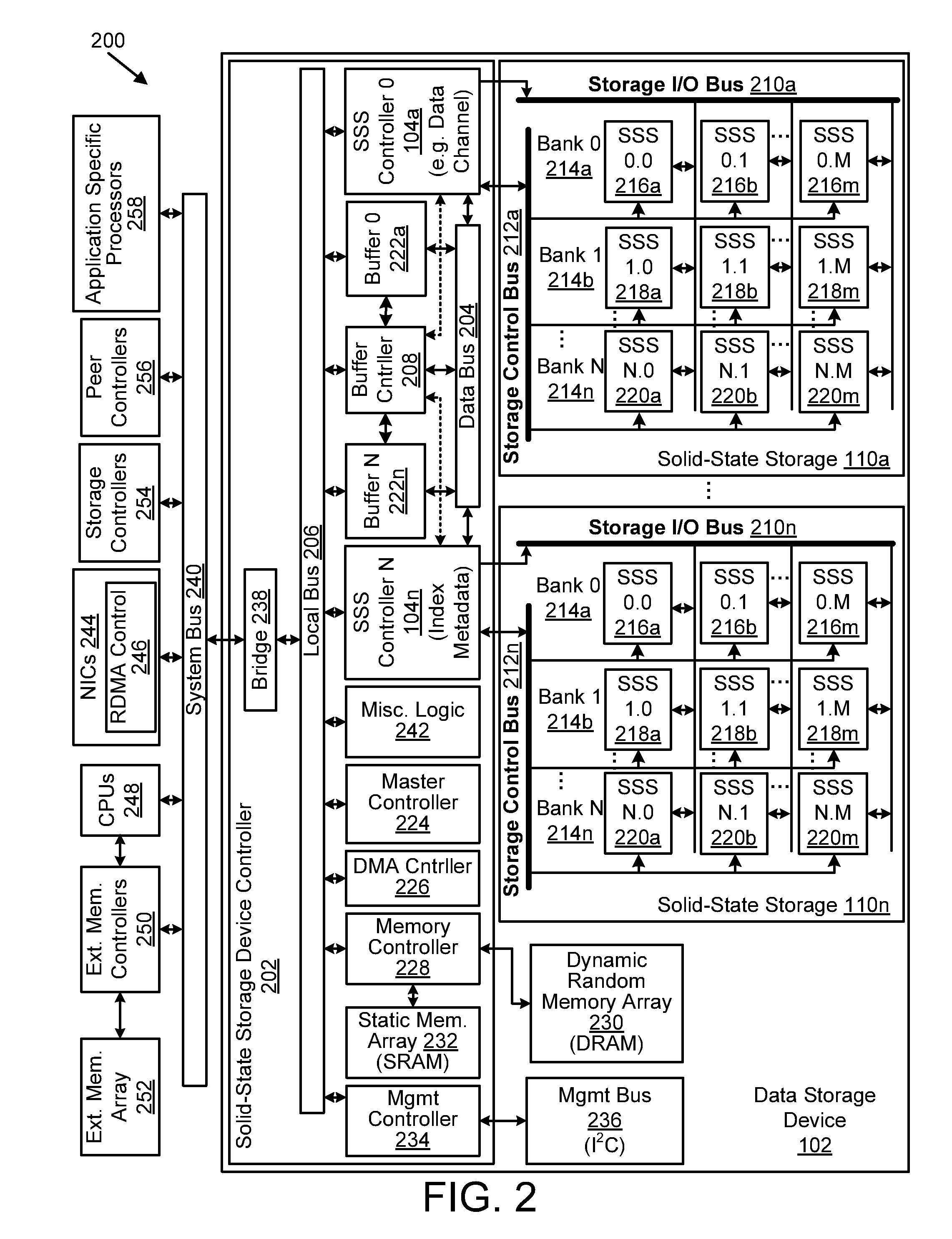
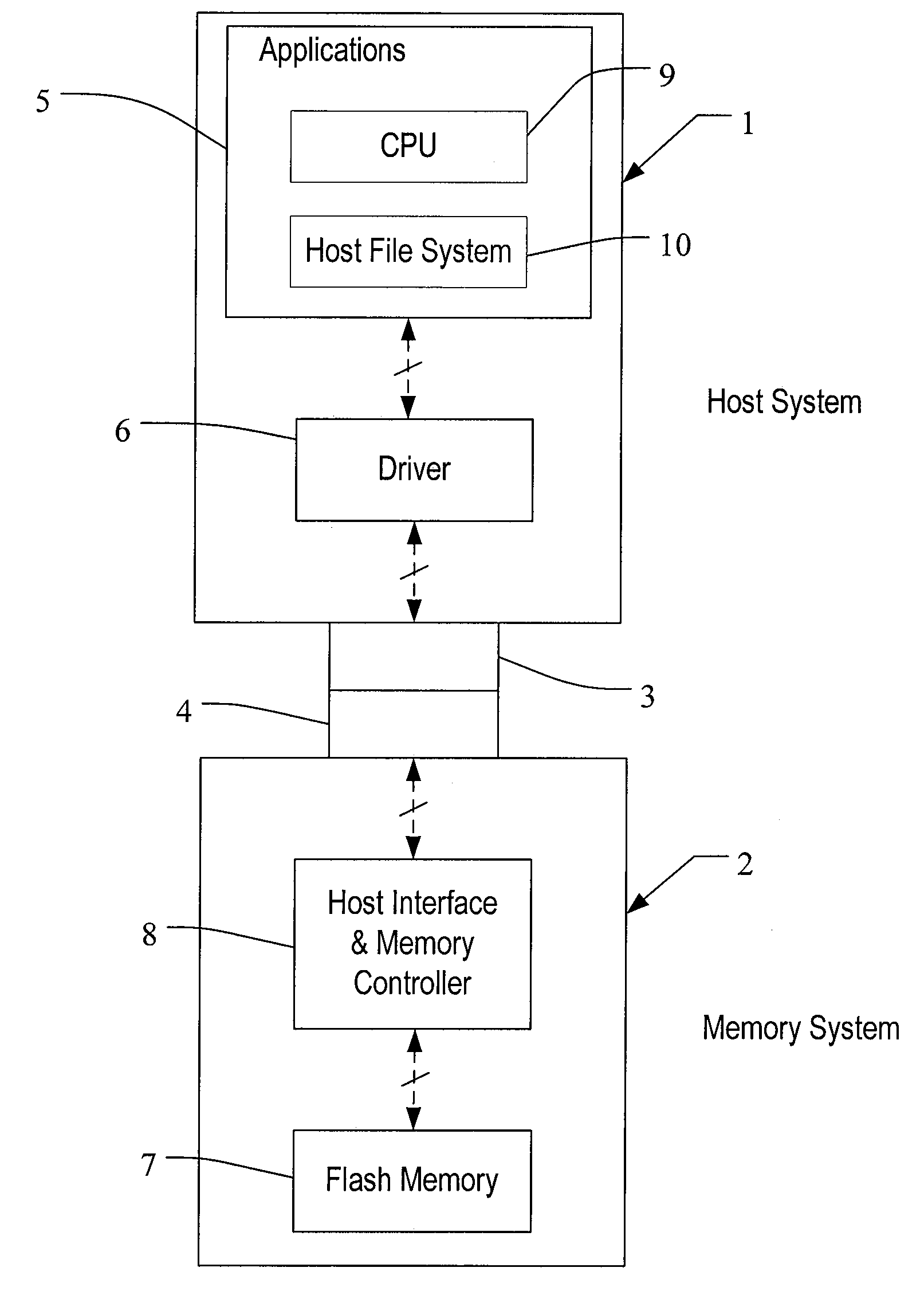
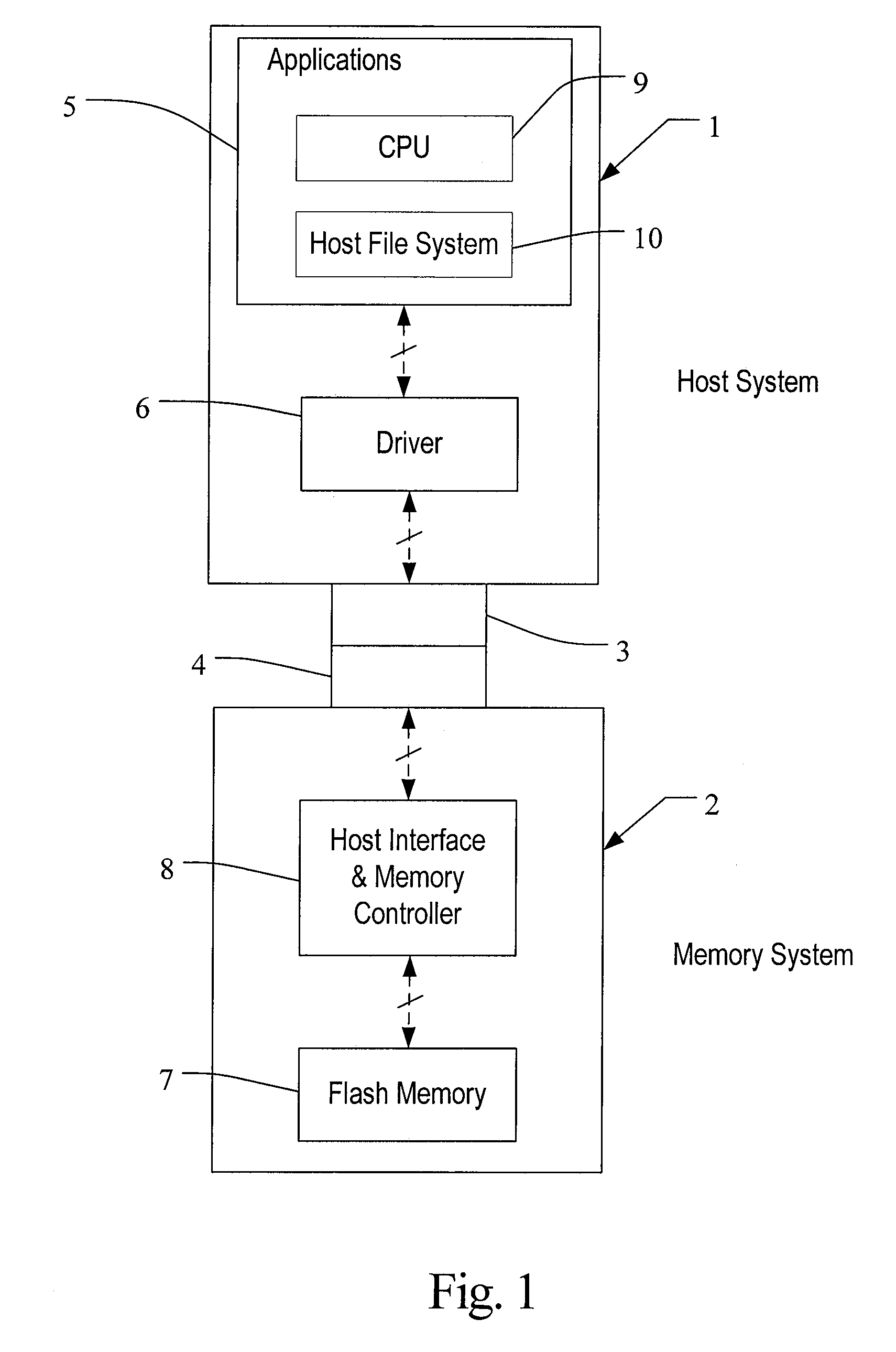
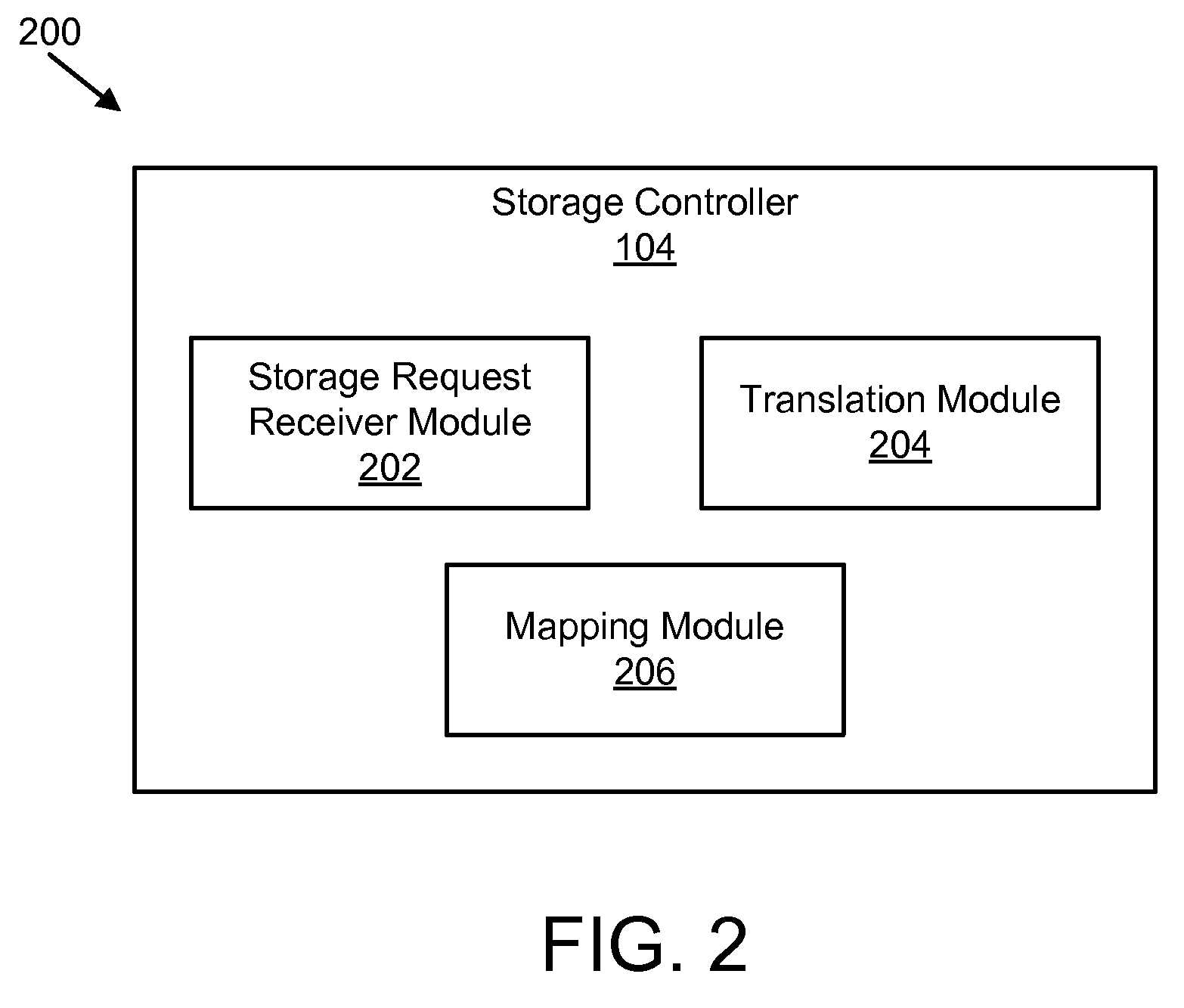
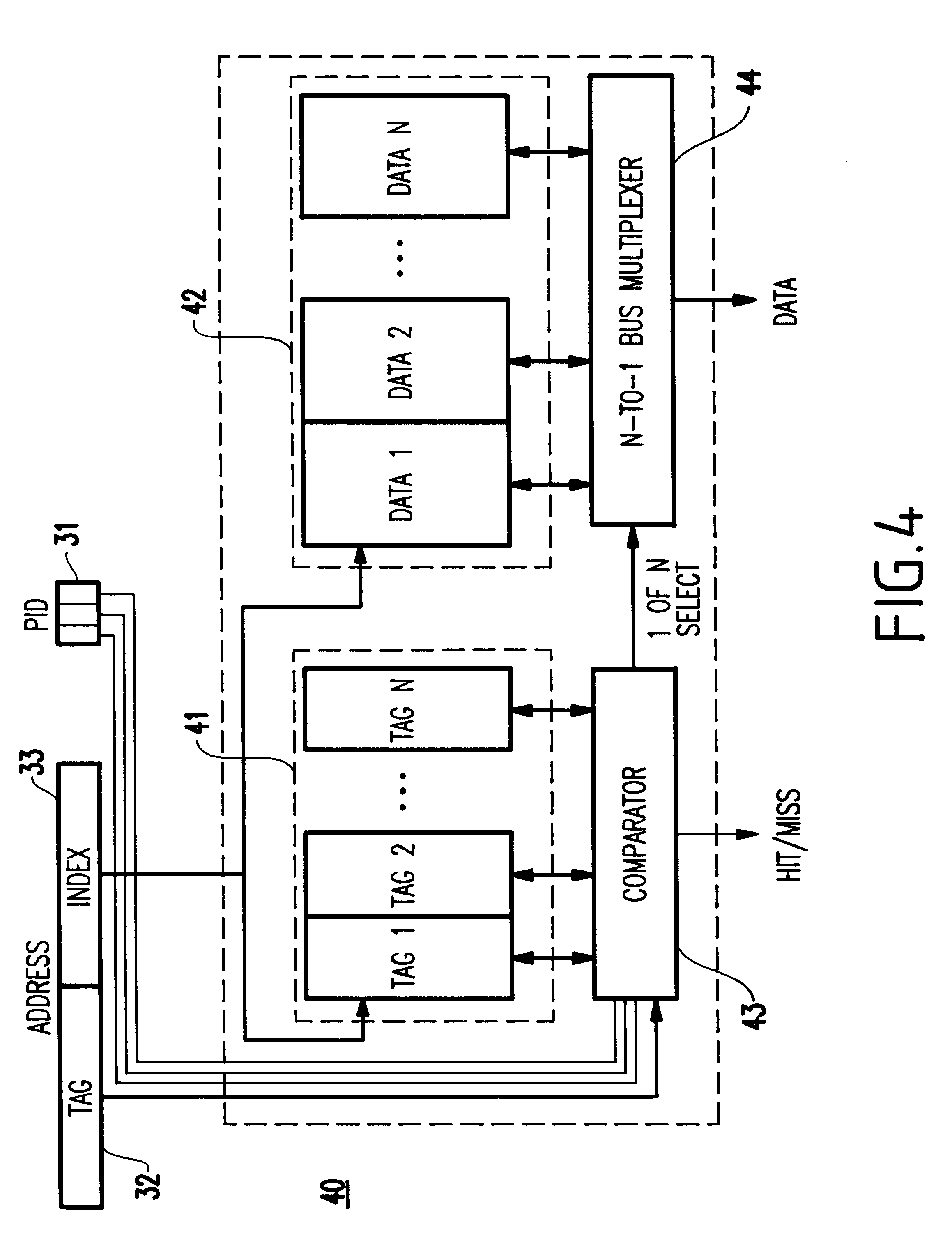
System including a fine-grained memory and a less-fine-grained memory
ActiveUS20080301256A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTData processing systemWrite buffer
A data processing system includes one or more nodes, each node including a memory sub-system. The sub-system includes a fine-grained, memory, and a less-fine-grained (e.g., page-based) memory. The fine-grained memory optionally serves as a cache and / or as a write buffer for the page-based memory. Software executing on the system uses n node address space which enables access to the page-based memories of all nodes. Each node optionally provides ACID memory properties for at least a portion of the space. In at least a portion of the space, memory elements are mapped to locations in the page-based memory. In various embodiments, some of the elements are compressed, the compressed elements are packed into pages, the pages are written into available locations in the page-based memory, and a map maintains an association between the some of the elements and the locations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
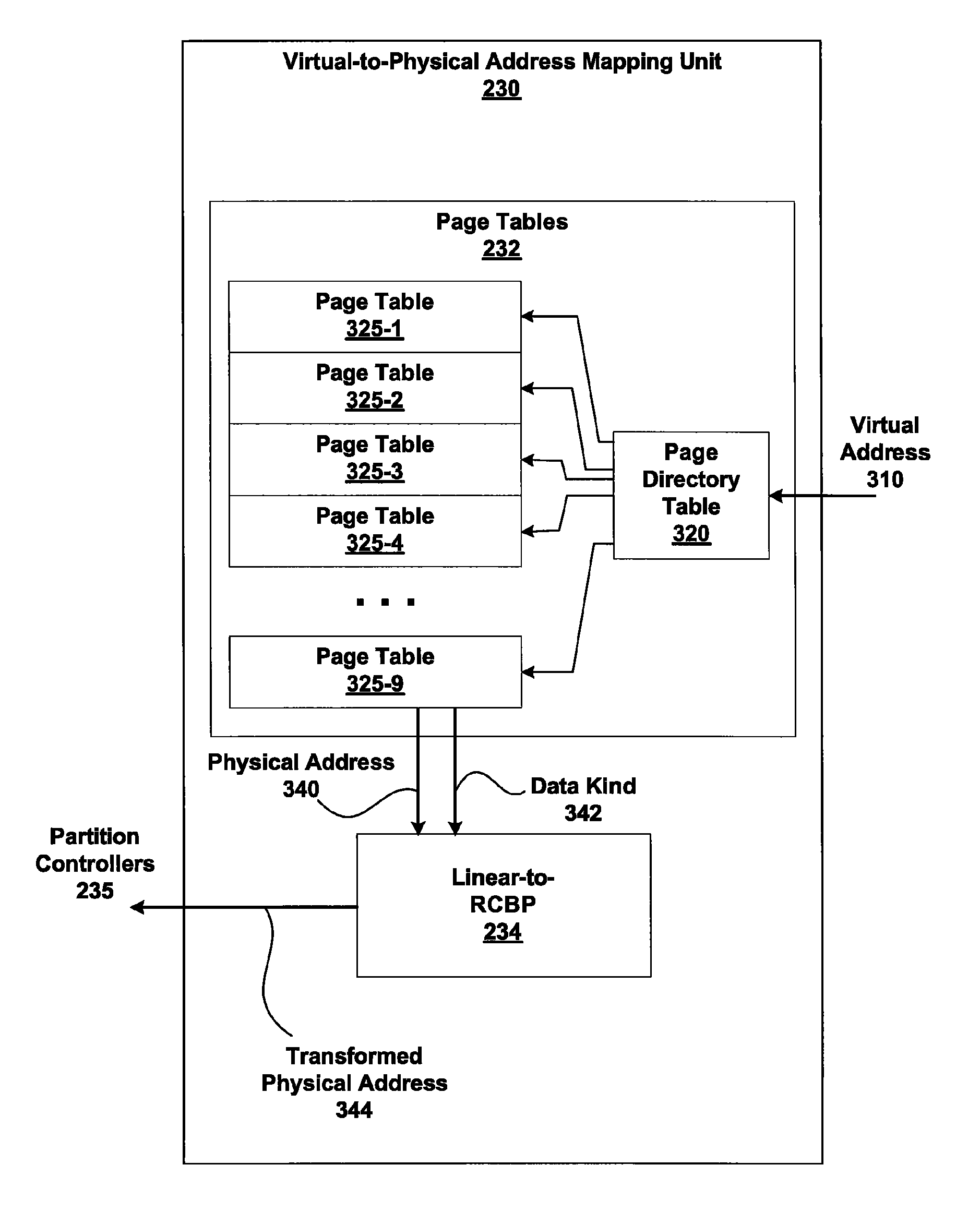
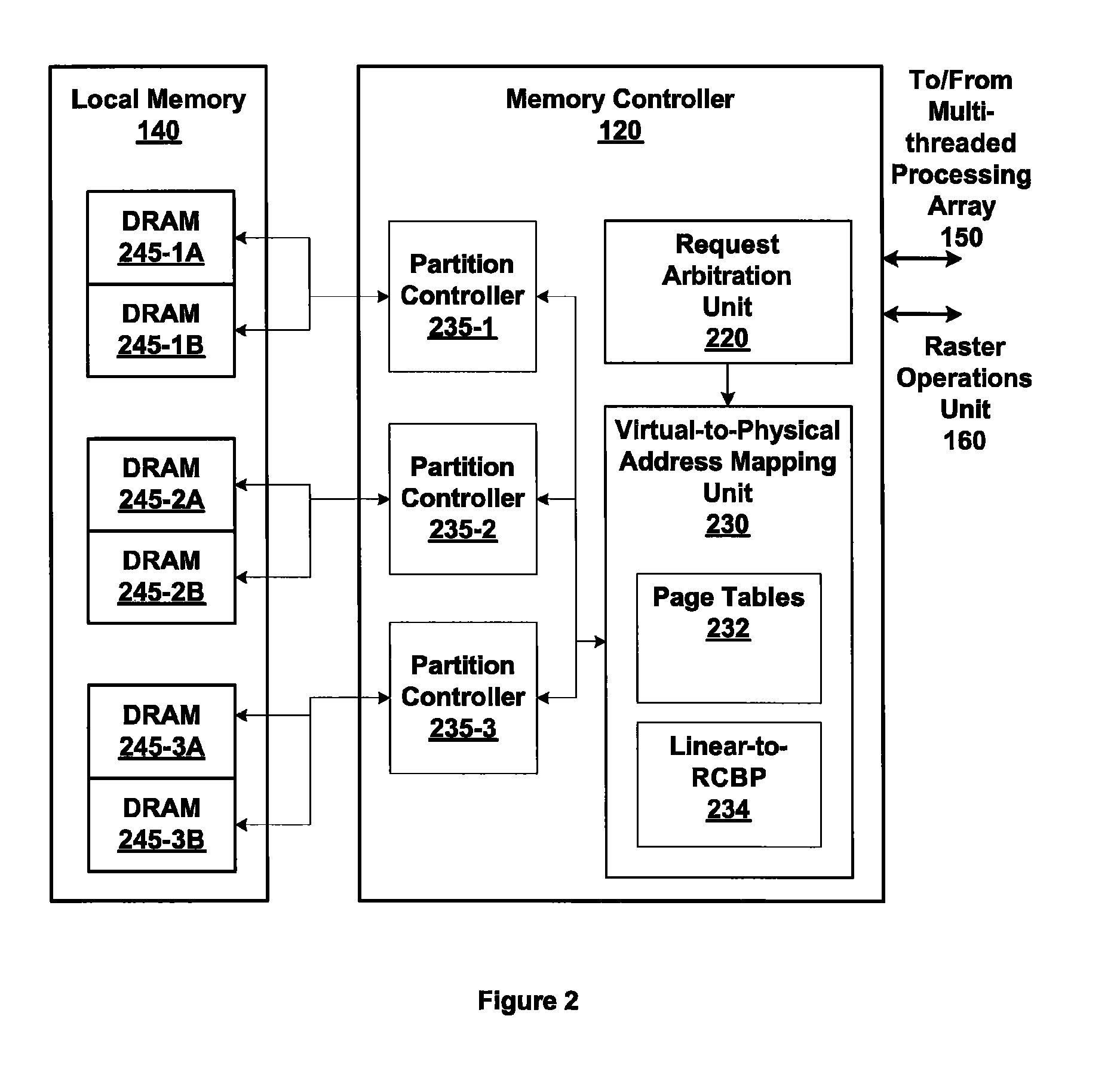
Memory addressing controlled by PTE fields
ActiveUS7805587B1Reduce accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsMemory addressDram memory
Embodiments of the present invention enable virtual-to-physical memory address translation using optimized bank and partition interleave patterns to improve memory bandwidth by distributing data accesses over multiple banks and multiple partitions. Each virtual page has a corresponding page table entry that specifies the physical address of the virtual page in linear physical address space. The page table entry also includes a data kind field that is used to guide and optimize the mapping process from the linear physical address space to the DRAM physical address space, which is used to directly access one or more DRAM. The DRAM physical address space includes a row, bank and column address. The data kind field is also used to optimize the starting partition number and partition interleave pattern that defines the organization of the selected physical page of memory within the DRAM memory system.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
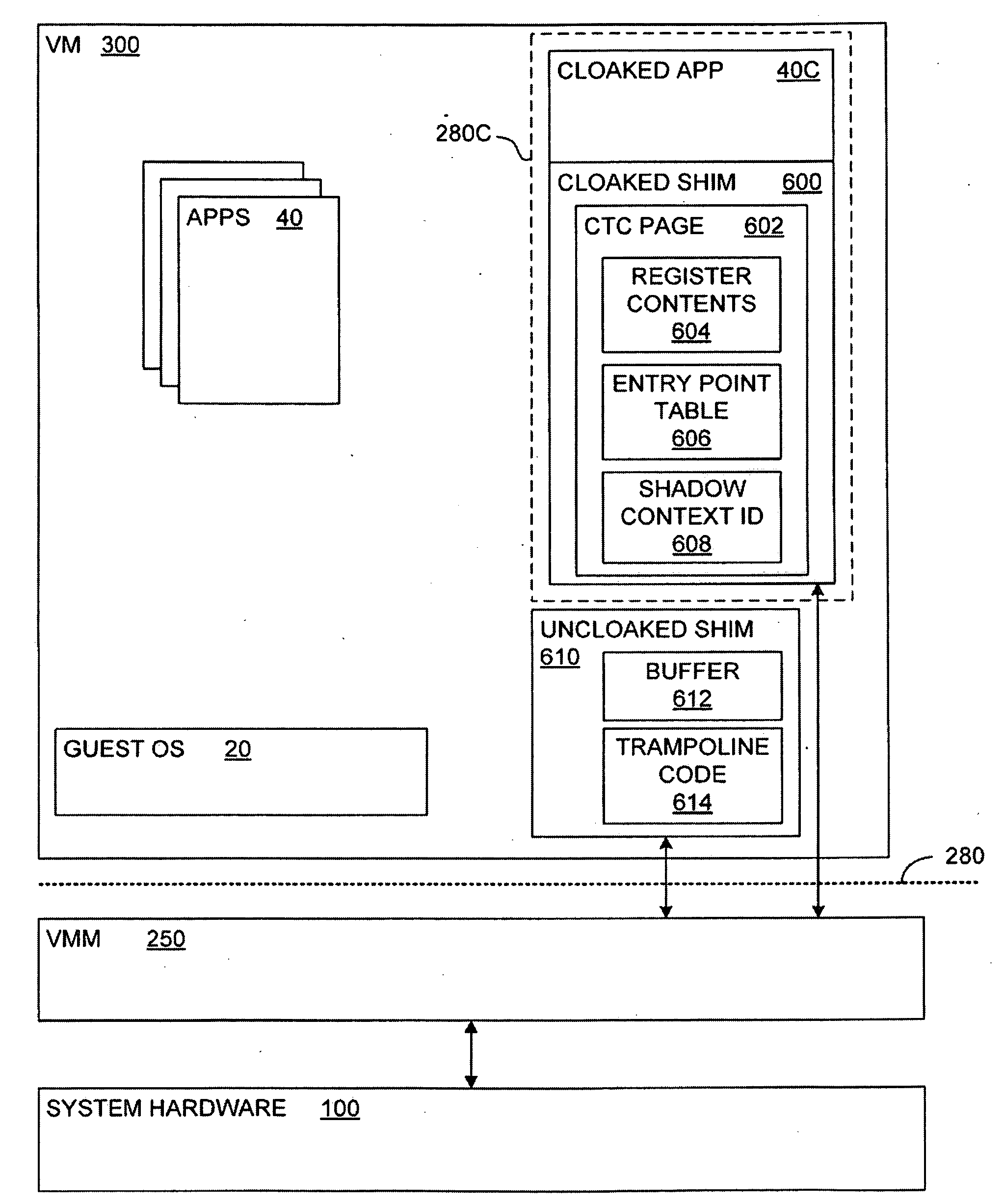
Transparent Memory-Mapped Emulation of I/O Calls
ActiveUS20090113425A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionSemanticsMemory map
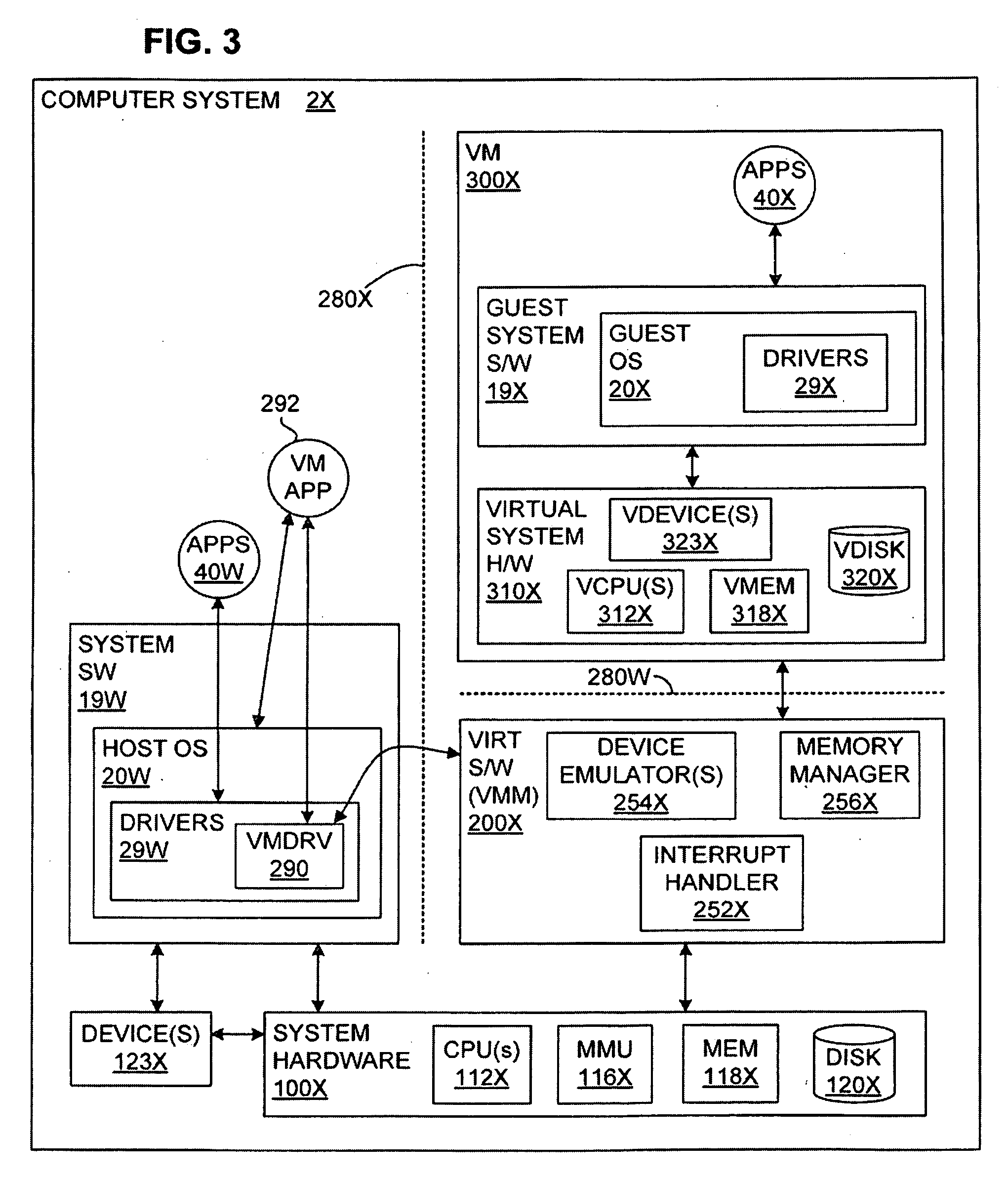
A virtual-machine-based system provides a mechanism to implement application file I / O operations of protected data by implementing the I / O operations semantics in a shim layer with memory-mapped regions. The semantics of these I / O operations are emulated in a shim layer with memory-mapped regions by using a mapping between a process' address space and a file or shared memory object. Data that is protected from viewing by a guest OS running in a virtual machine may nonetheless be accessed by the process.
Owner:VMWARE INC
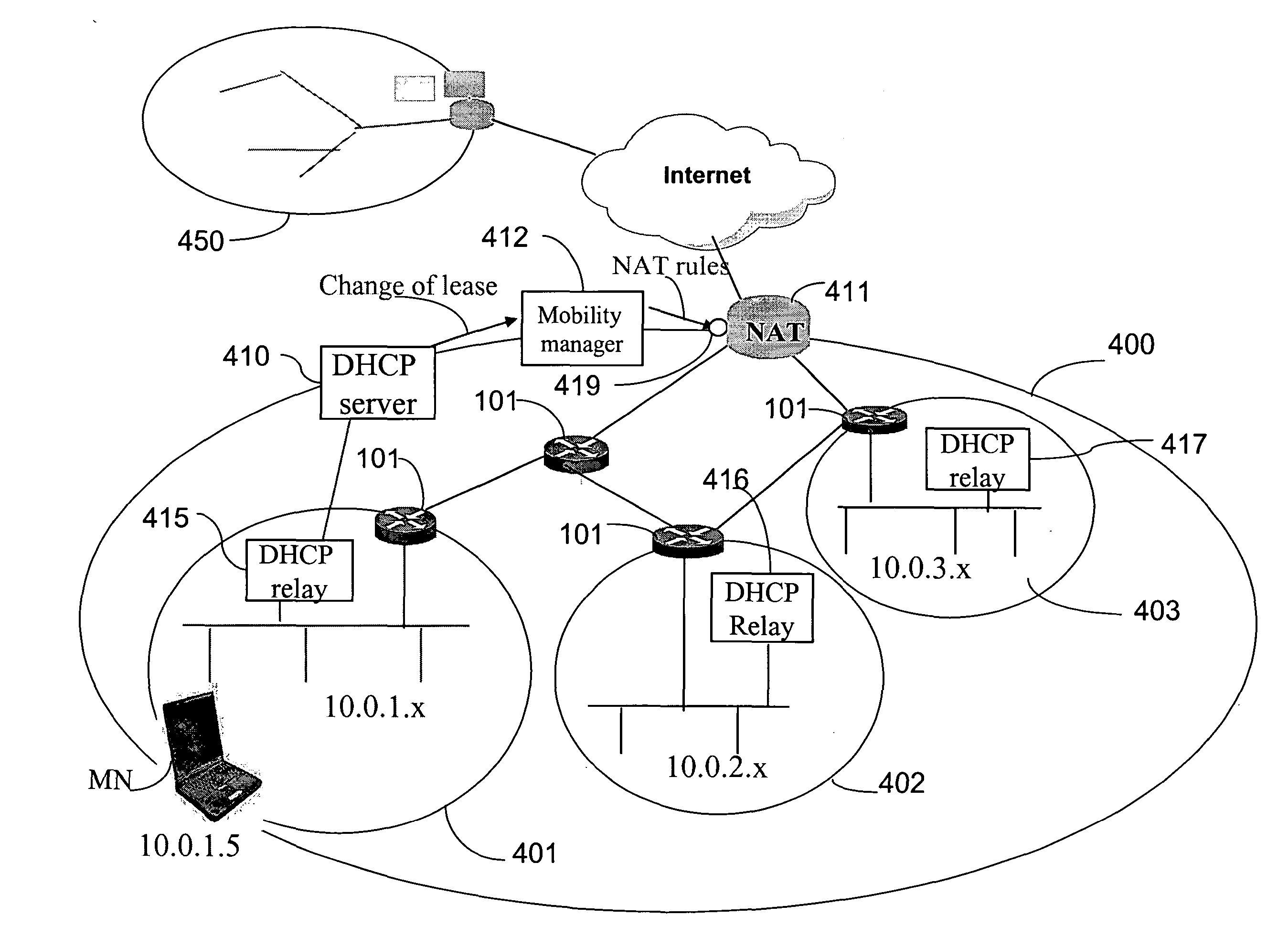
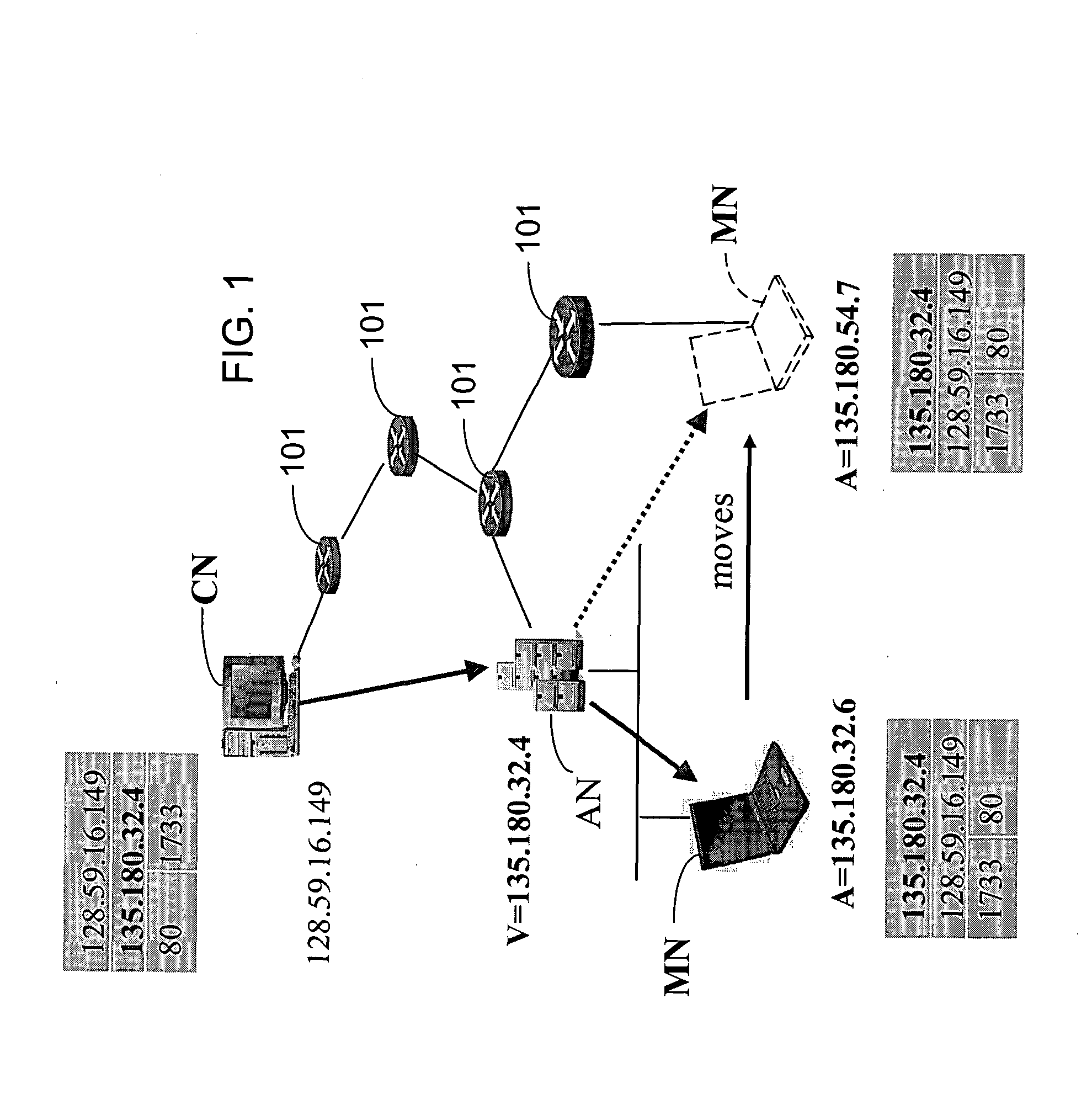
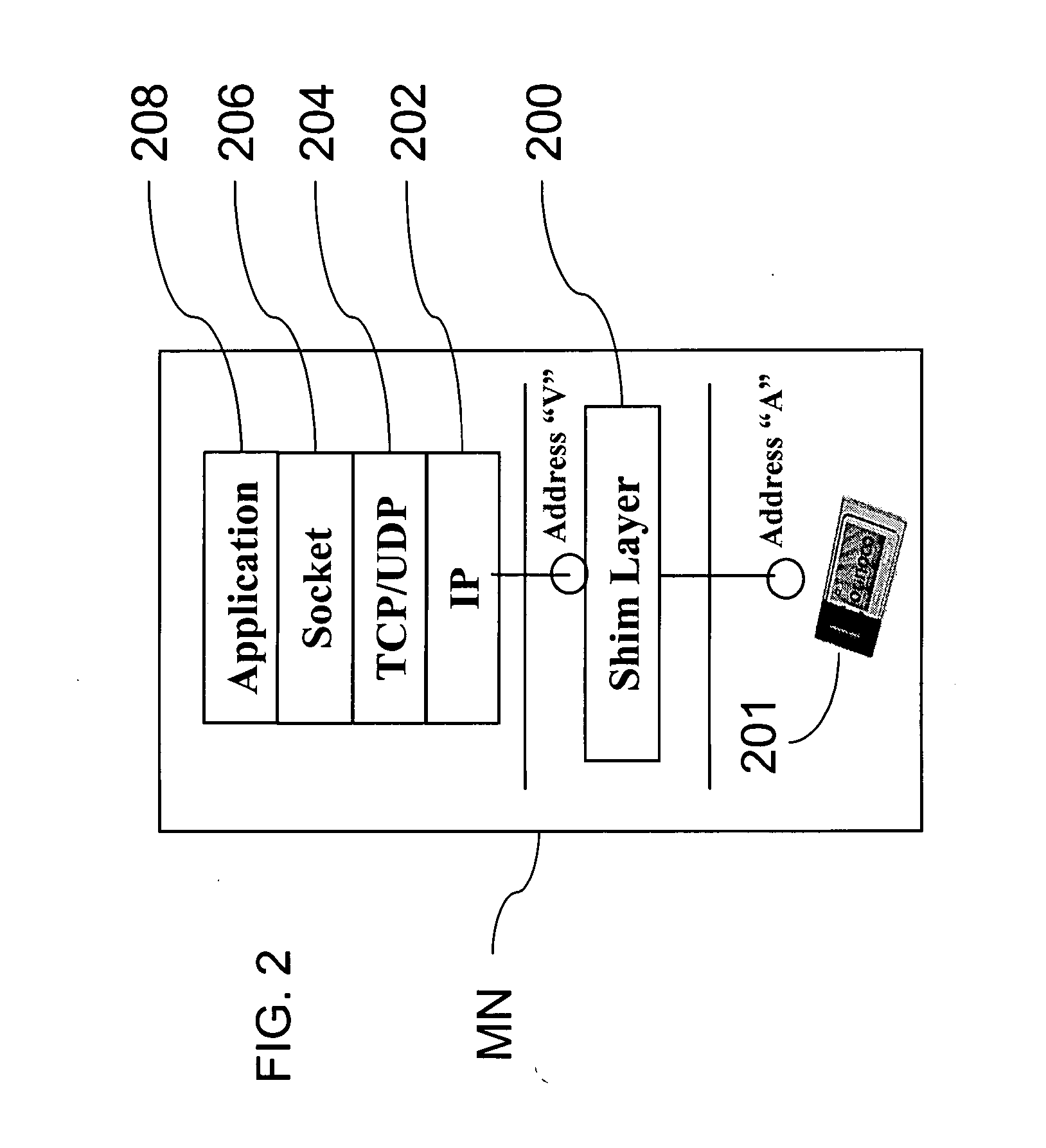
Method and system for mobility across heterogeneous address spaces
ActiveUS20050013280A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAddress spaceInternet Protocol
A mobile node includes a processor, a network interface, and a storage device having computer program code for execution by the processor. The computer program code includes a network layer for transmitting and receiving packets and an intermediate driver that transmits packets to the network layer and receives packets from the network layer using a virtual internet protocol (IP) address to identify the mobile node. The intermediate driver transmits packets to the network interface and receives packets from the network interface using a routable actual IP address to identify the mobile node. The intermediate driver permits the actual IP address to change when the mobile node moves from a first subnet to a second subnet without a corresponding change in the virtual IP address. A corresponding NAT associates the virtual IP address with a second actual IP address when the NAT is notified that the mobile node is in the second subnet.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
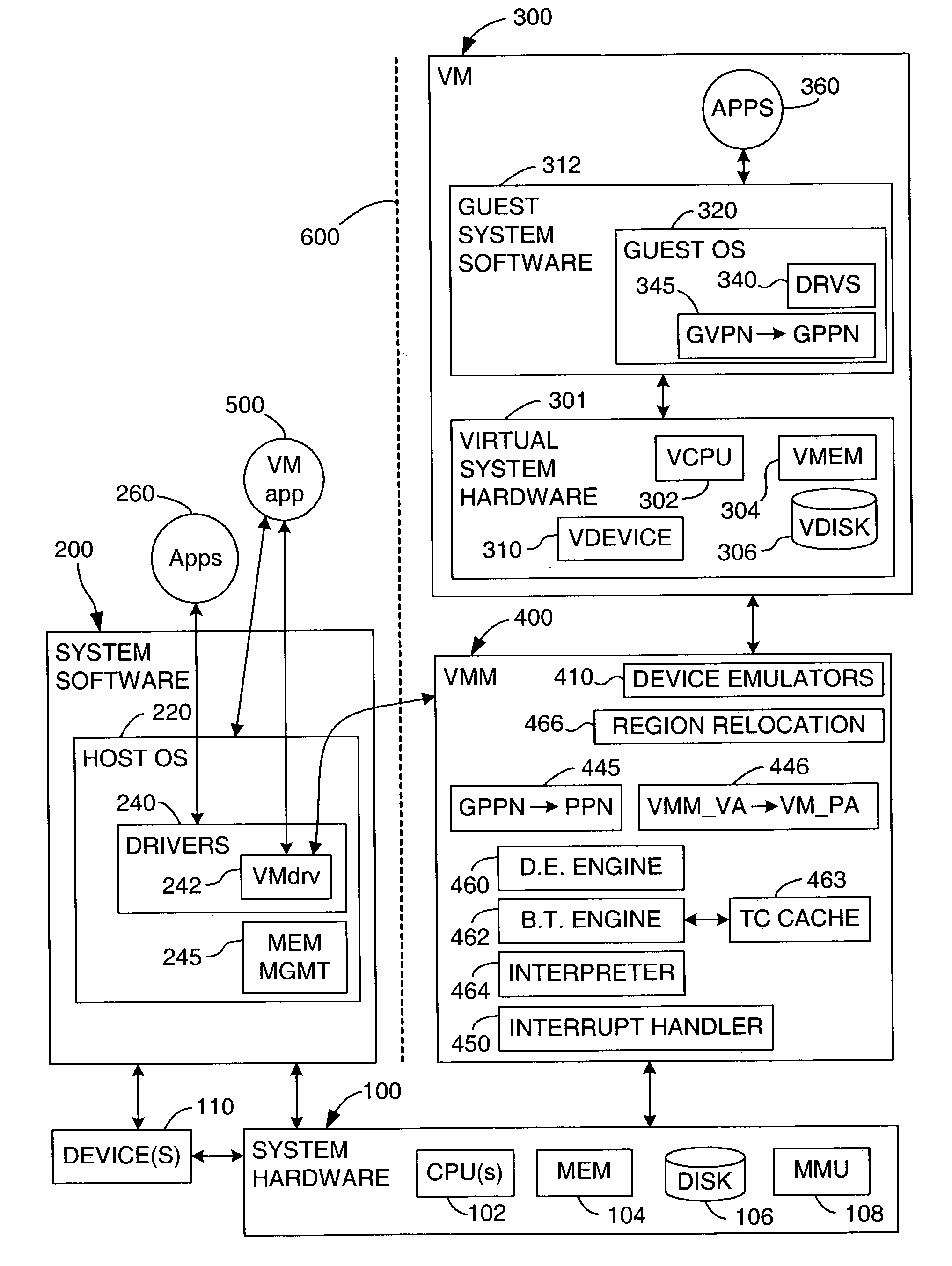
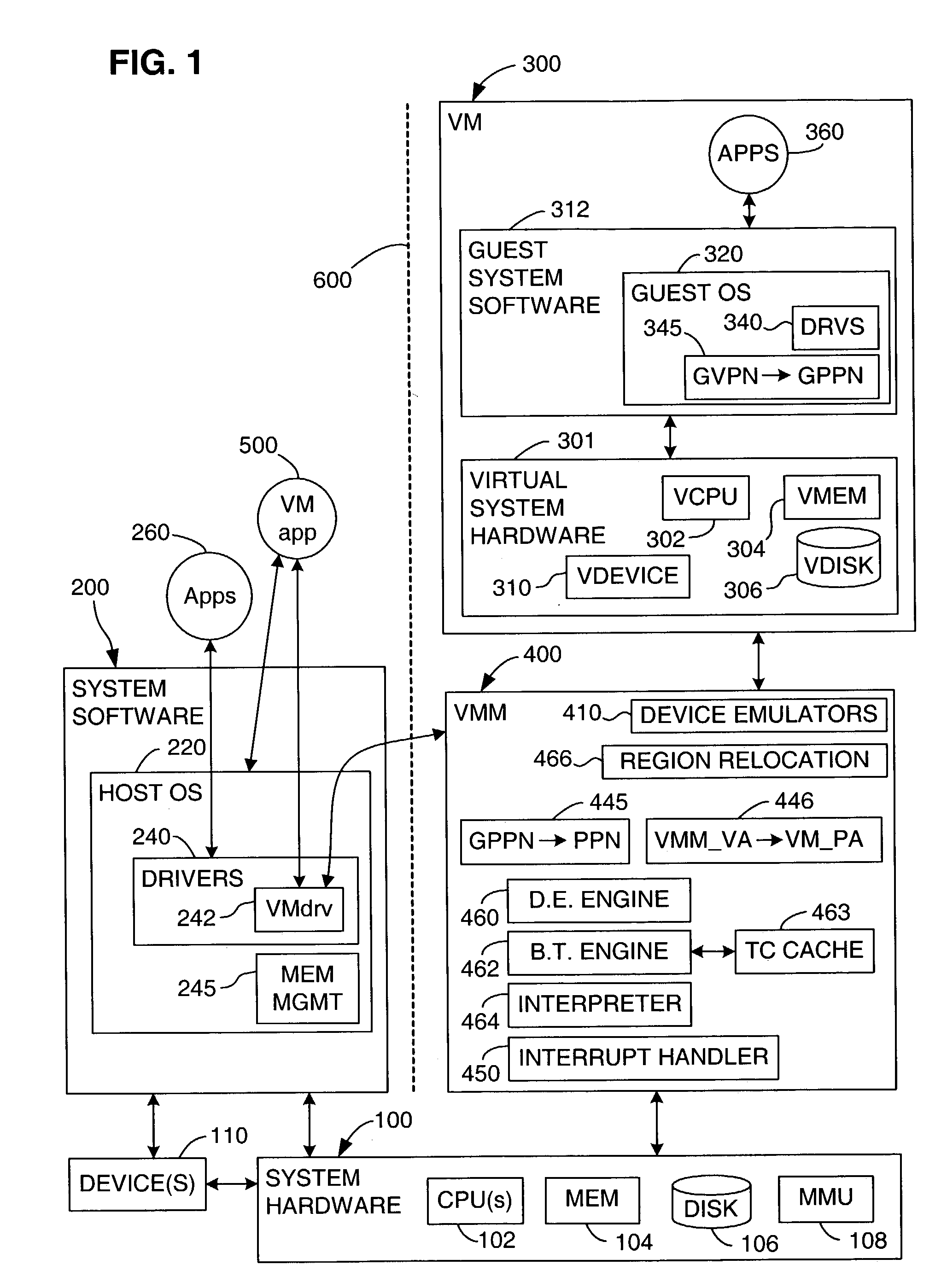
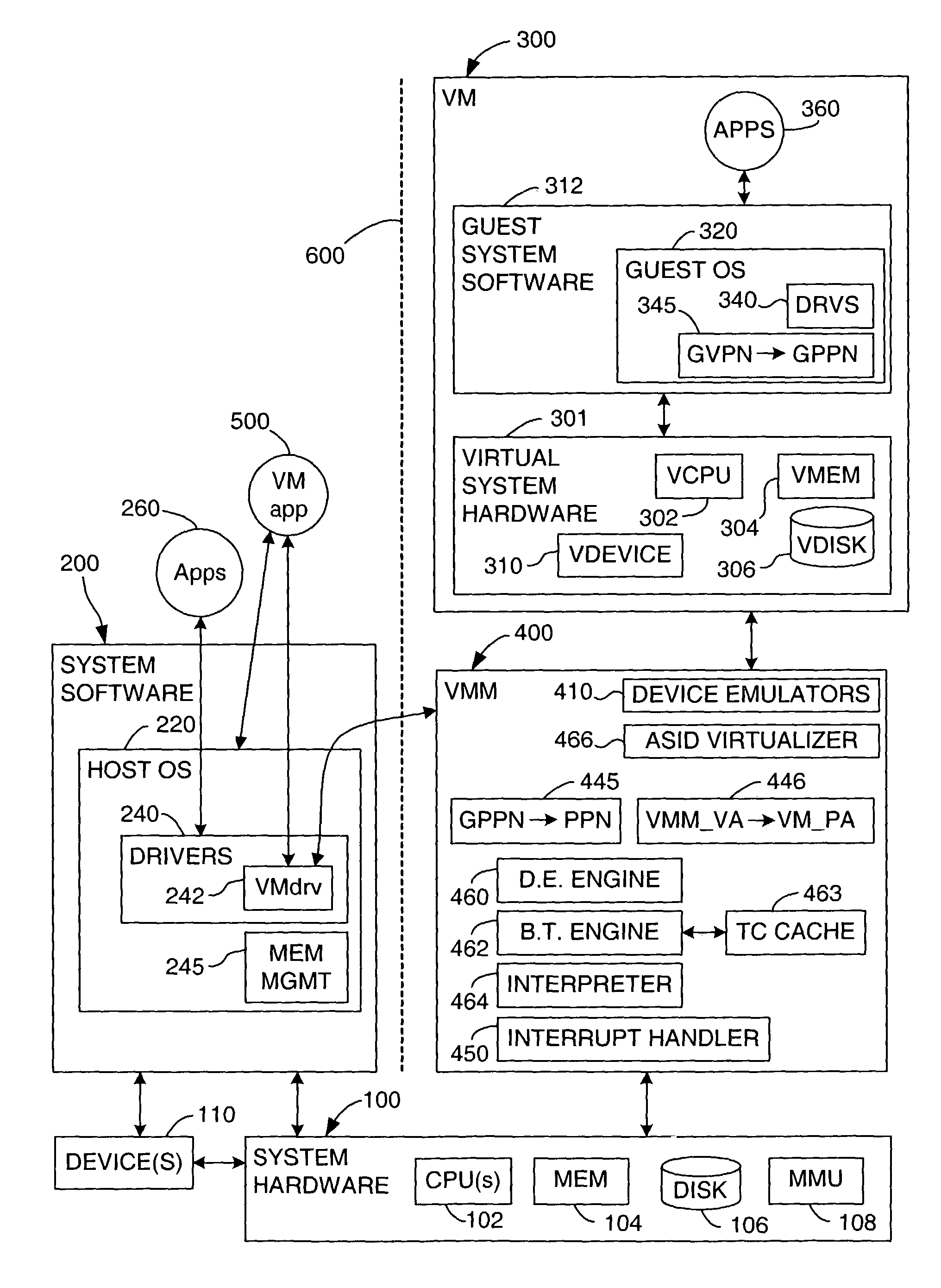
Processor-architecture for facilitating a virtual machine monitor
InactiveUS20050091652A1Easy to operateGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsVirtualizationVirtual address space
Virtual-machine-monitor operation and implementation is facilitated by number of easily implemented features and extensions added to the features of a processor architecture. These features, one or more of which are used in various embodiments of the present invention, include a vmsw instruction that provides a means for transitioning between virtualization mode and non-virtualization mode without an interruption, a virtualization fault that faults on an attempt by a priority-0 routine in virtualization mode attempting to execute a privileged instruction, and a flexible highest-implemented-address mechanism to partition virtual address space into a virtualization address space and a non-virtualization address space.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and system for storage address re-mapping for a multi-bank memory device
InactiveUS20090271562A1Improved memory managementMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAddress spaceLogical address
A method and system for storage address re-mapping in a multi-bank memory is disclosed. The method includes allocating logical addresses in blocks of clusters and re-mapping logical addresses into storage address space, where short runs of host data dispersed in logical address space are mapped in a contiguous manner into megablocks in storage address space. Independently in each bank, valid data is flushed within each respective bank from blocks having both valid and obsolete data to make new blocks available for receiving data in each bank of the multi-bank memory when an available number of new blocks falls below a desired threshold within a particular bank.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
TLB miss fault handler and method for accessing multiple page tables
ActiveUS7111145B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsVirtual memoryError processing
A virtual memory system implementing the invention provides concurrent access to translations for virtual addresses from multiple address spaces. One embodiment of the invention is implemented in a virtual computer system, in which a virtual machine monitor supports a virtual machine. In this embodiment, the invention provides concurrent access to translations for virtual addresses from the respective address spaces of both the virtual machine monitor and the virtual machine. Multiple page tables contain the translations for the multiple address spaces. Information about an operating state of the computer system, as well as an address space identifier, are used to determine whether, and under what circumstances, an attempted memory access is permissible. If the attempted memory access is permissible, the address space identifier is also used to determine which of the multiple page tables contains the translation for the attempted memory access.
Owner:VMWARE INC
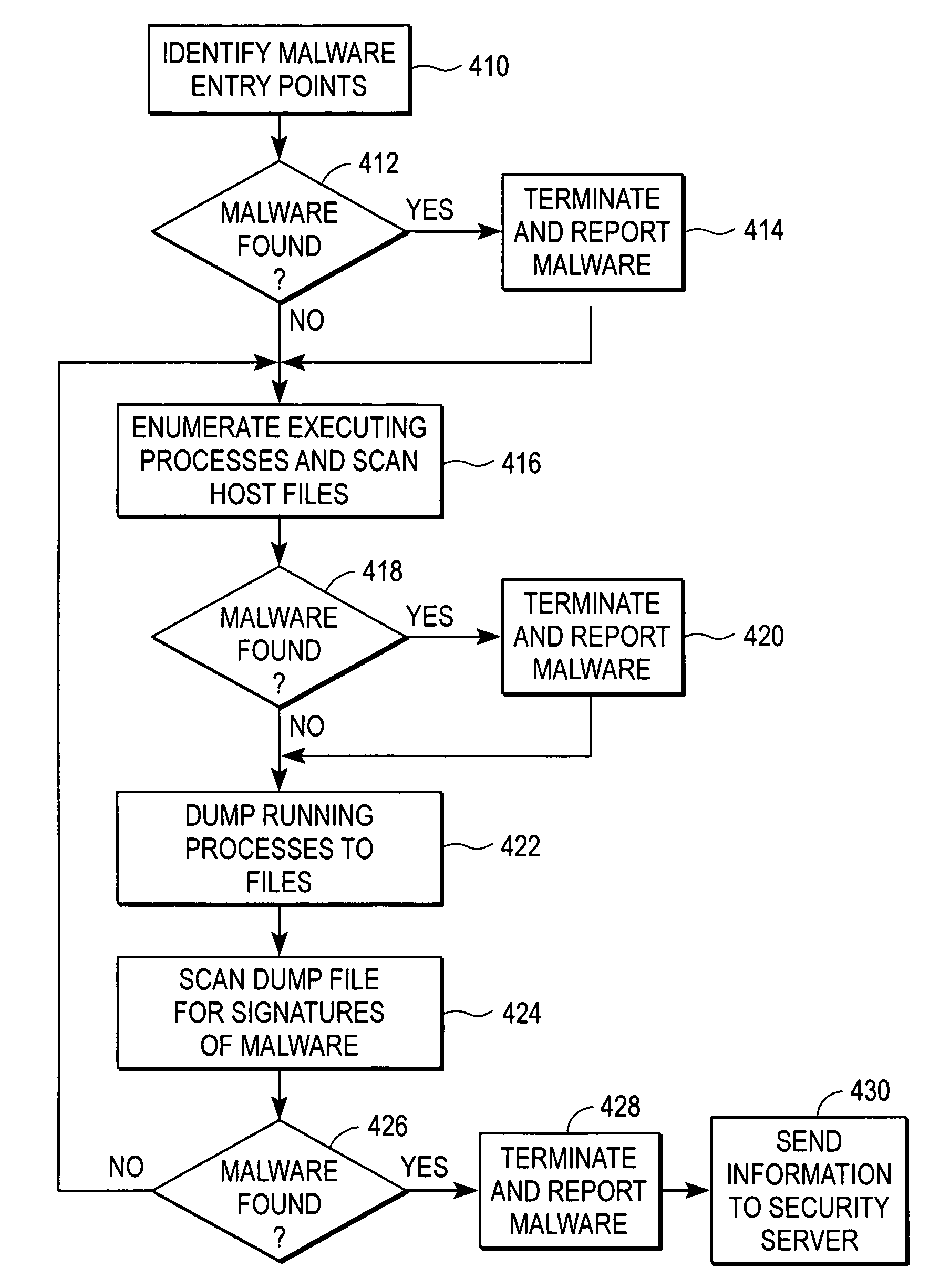
Detecting malicious software through process dump scanning
An executable file containing malicious software can be packed using a packer to make the software difficult to detect. The executable file is loaded into the computer's memory and executed as a process. A memory dump module analyzes the address space for the process and identifies an executable file image within it. The memory dump module creates a memory dump file on the computer's storage device containing the file image and modifies the file to make it resemble a normal executable file. A signature scanning module scans the memory dump file for signatures of malicious software. If a signature is found in the file, a reporting module sends the host file for the process and the memory dump file to a security server for analysis.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Method and system for caching address translations from multiple address spaces in virtual machines
InactiveUS20060259734A1Reduce memory overheadLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsVirtualizationPage table
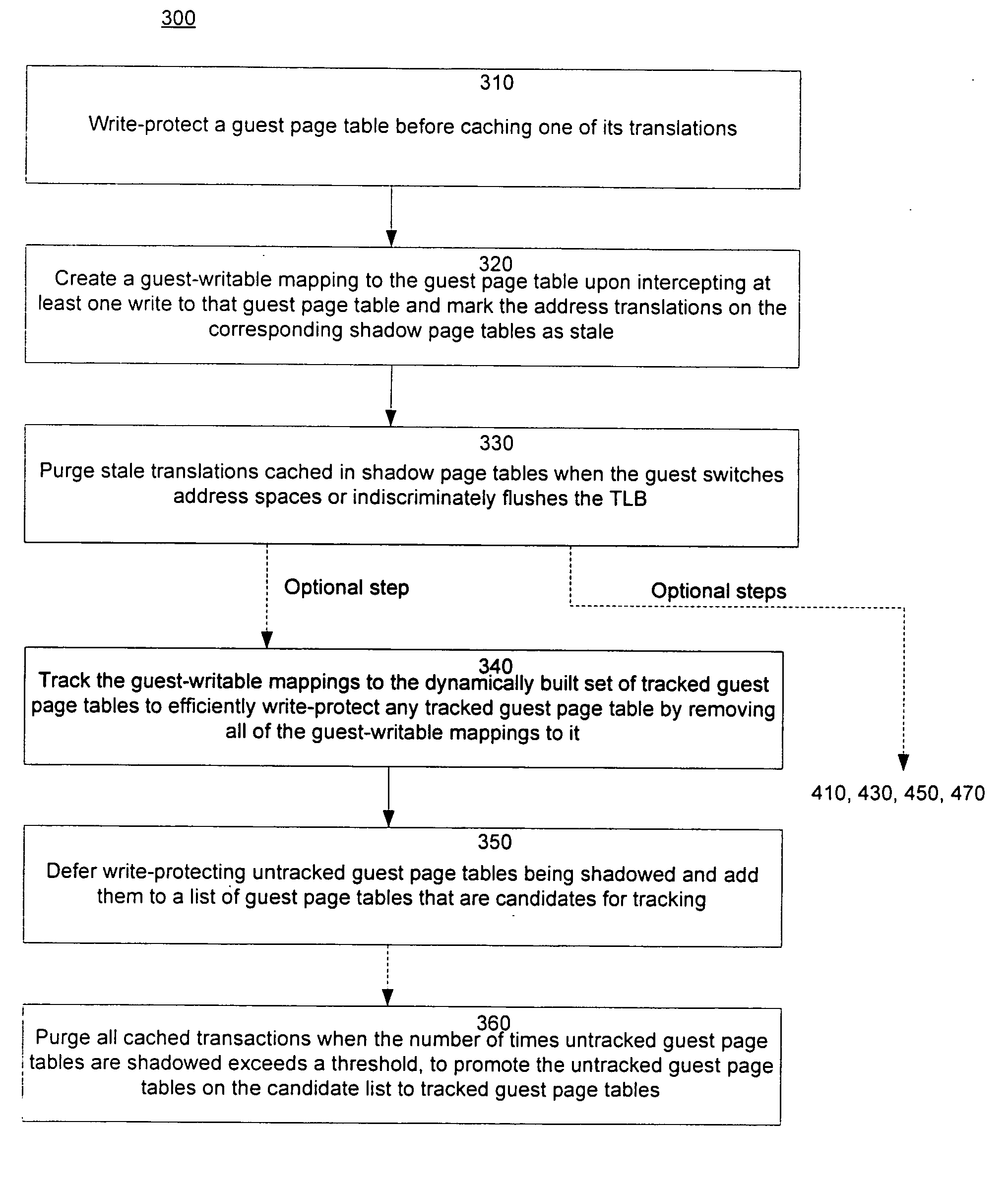
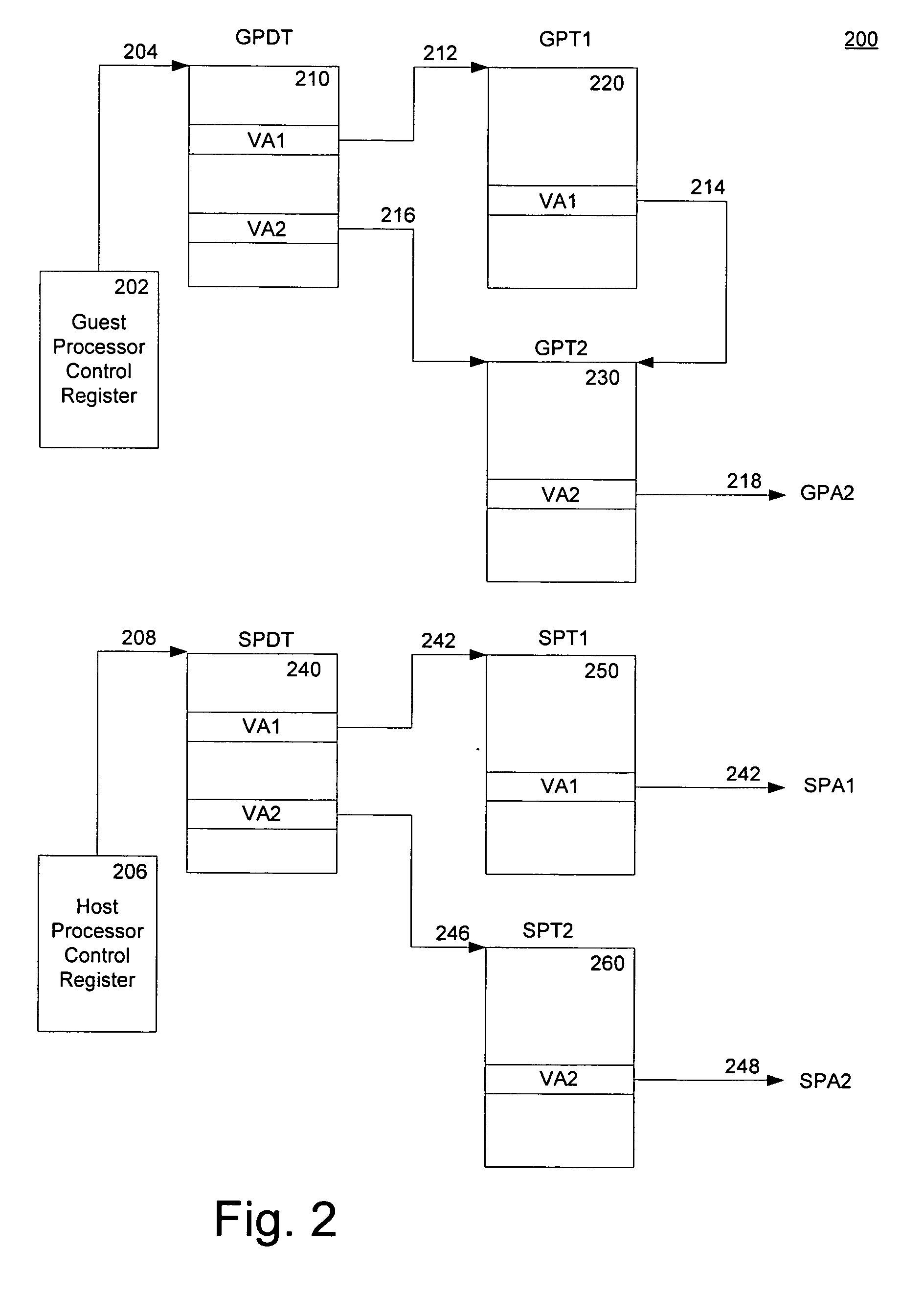
A method of virtualizing memory through shadow page tables that cache translations from multiple guest address spaces in a virtual machine includes a software version of a hardware tagged translation look-aside buffer. Edits to guest page tables are detected by intercepting the creation of guest-writable mappings to guest page tables with translations cached in shadow page tables. The affected cached translations are marked as stale and purged upon an address space switch or an indiscriminate flush of translations by the guest. Thereby, non-stale translations remain cached but stale translations are discarded. The method includes tracking the guest-writable mappings to guest page tables, deferring discovery of such mappings to a guest page table for the first time until a purge of all cached translations when the number of untracked guest page tables exceeds a threshold, and sharing shadow page tables between shadow address spaces and between virtual processors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Extension of logical networks across layer 3 virtual private networks
ActiveUS20130287026A1Increase heightGood serviceData switching by path configurationPrivate networkLogical network
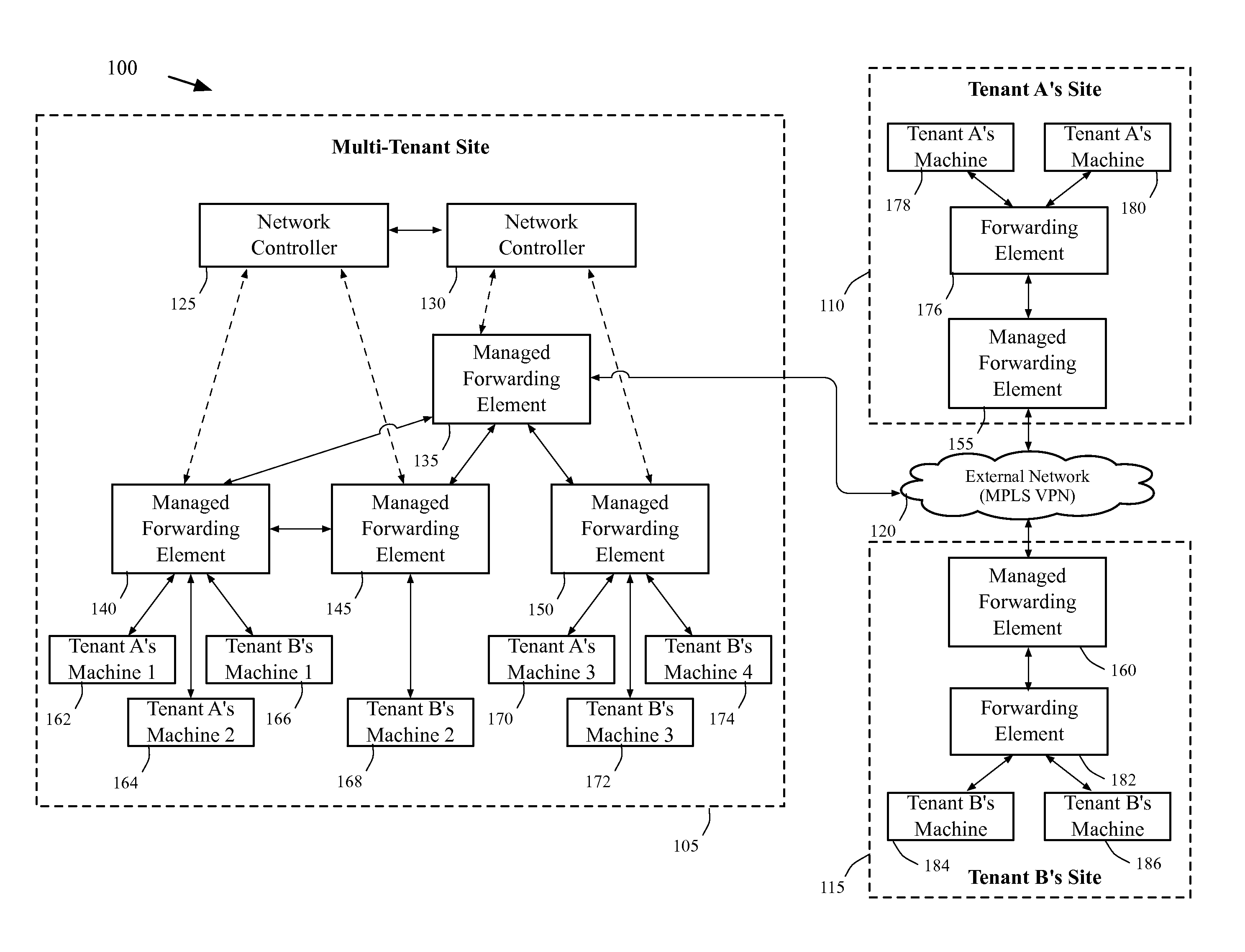
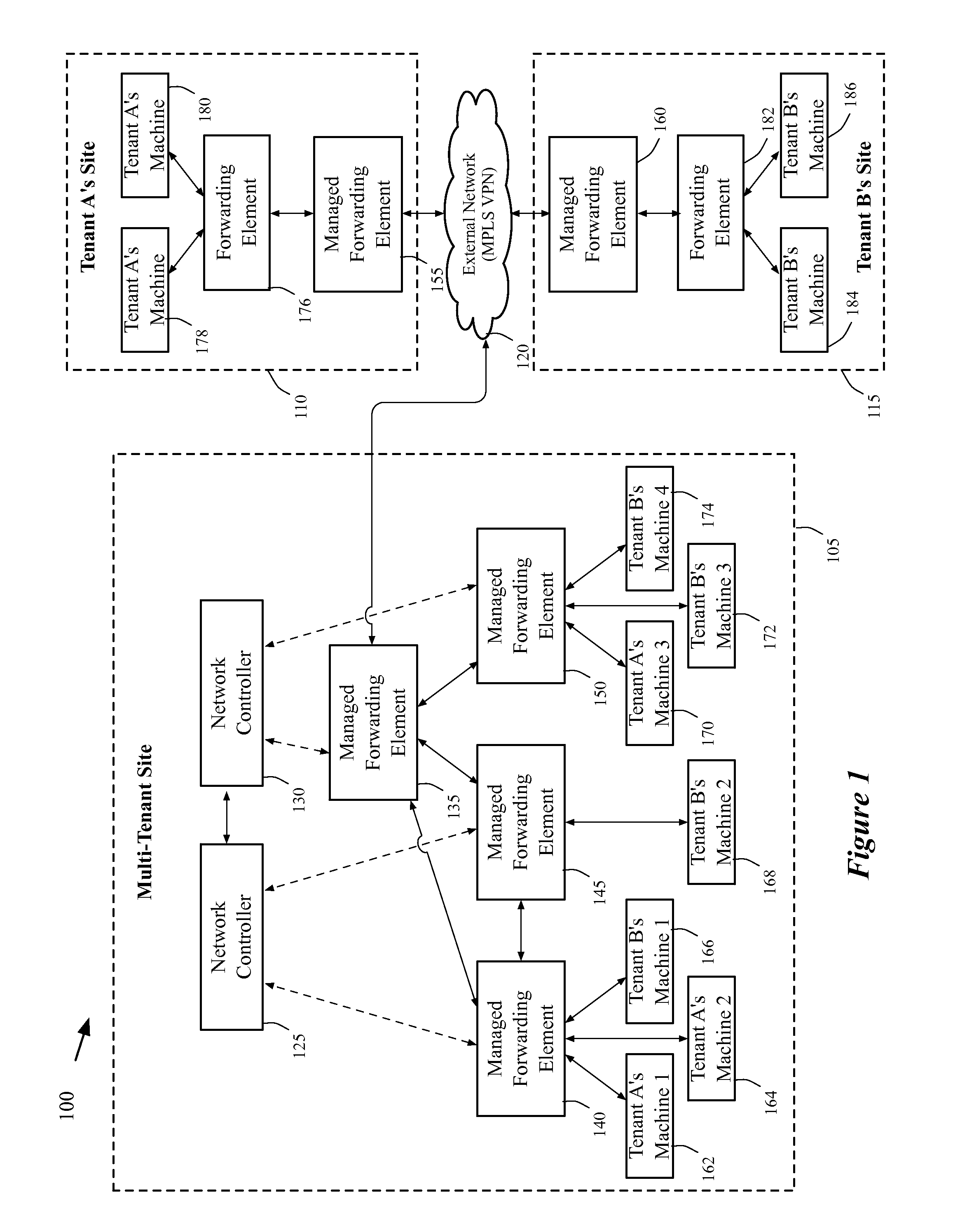
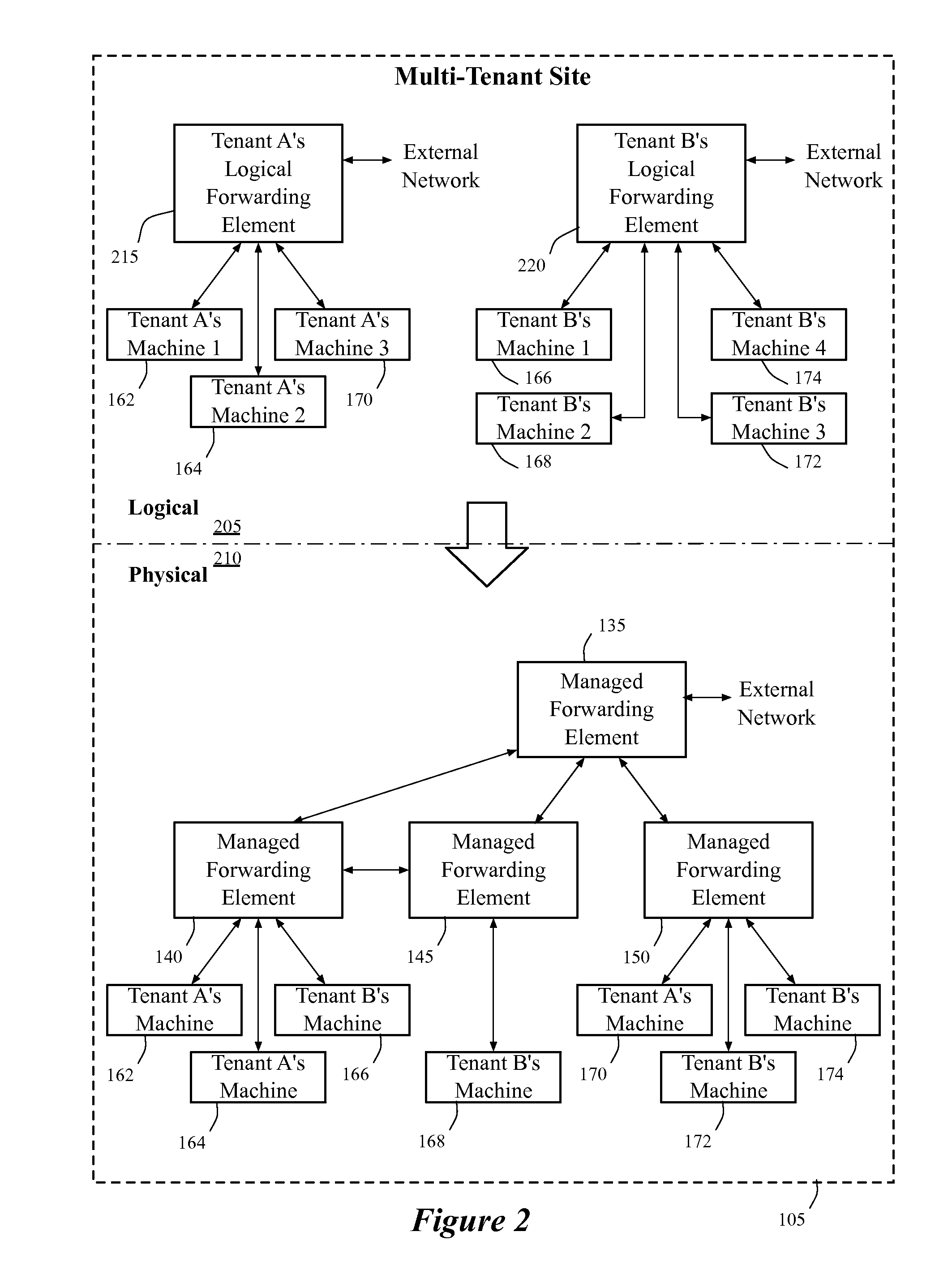
A method of manages a set of managed forwarding elements that forward data between machines. The method configures (1) a first managed forwarding element to operate in a first network that uses first and second address spaces that at least partially overlap with each other, (2) a second managed forwarding element to operate in a second network that uses the first address space, and (3) a third managed forwarding element to operate in a third network that uses the second address space. A machine in the second network and a machine in the third network have an identical address that belongs to both the first and second address spaces. The method directs the first managed forwarding element to connect to the second and third managed forwarding elements in a manner that enables the first managed forwarding element to forward data from a machine in the first network to the machine in the second network via the second managed forwarding element.
Owner:NICIRA
Apparatus, system, and method for application direct virtual memory management
ActiveUS20120210095A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationPosition dependentVirtual memory management
An apparatus, system, and method for application direct virtual memory management. The method includes detecting a system memory access to a virtual memory address within a monitored page of data not loaded in main memory of a computing system. The method includes determining a first swap address for a loaded page of data in the main memory. The first swap address is defined in a sparse virtual address space exposed by a persistent storage device. The first swap address is associated in an index with a first deterministic storage location. The index is managed by the persistent storage device. The method includes storing the loaded page on a persistent storage device at the first deterministic storage location. The method includes moving the monitored page from a second deterministic storage location to the main memory. The second deterministic storage location is associated with a second swap address in the index.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
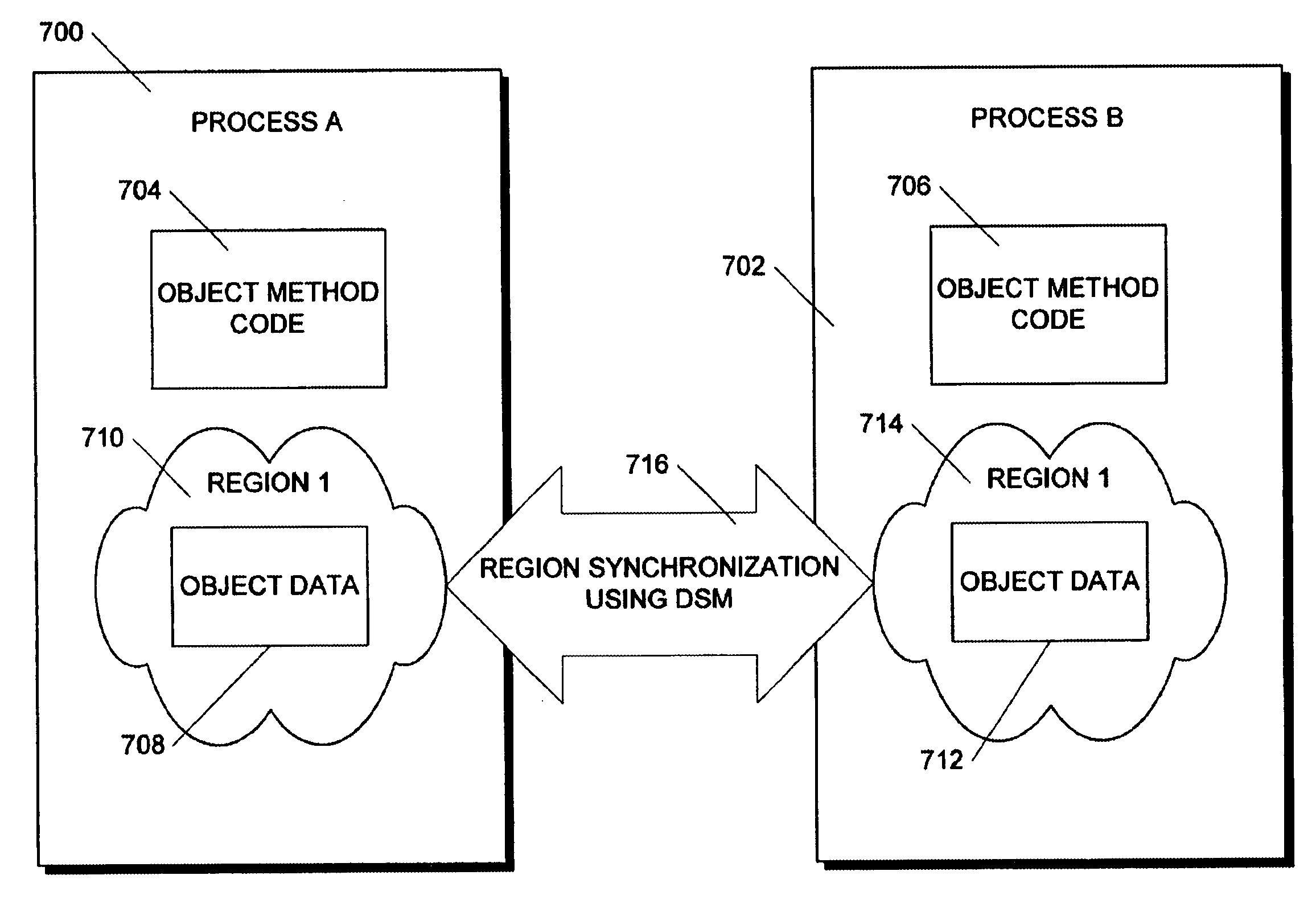
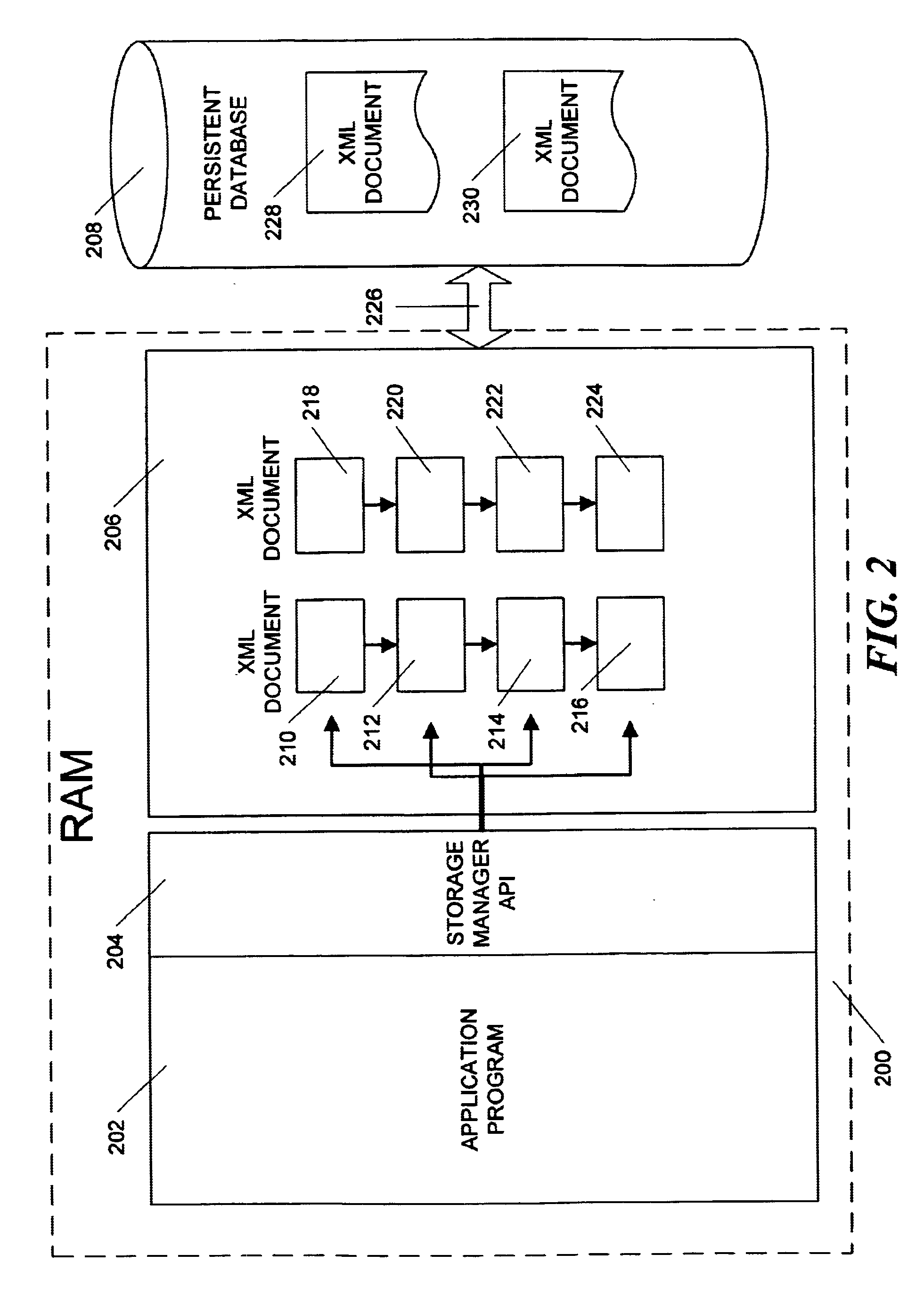
Method and apparatus for efficient management of XML documents
InactiveUS6941510B1Rapid positioningConsistent interfaceDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingLocking mechanismData Corruption
An in-memory storage manager represents XML-compliant documents as a collection of objects in memory. The storage manager allows real-time access to the objects by separate processes operating in different contexts. The data in the objects is stored in memory local to each process and the local memories are synchronized by means of a distributed memory system that stores the data in the same data region, but maps the data region to the address space of each process. Data corruption in the data region is prevented by a locking mechanism that prevents the processes from simultaneously modifying same data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
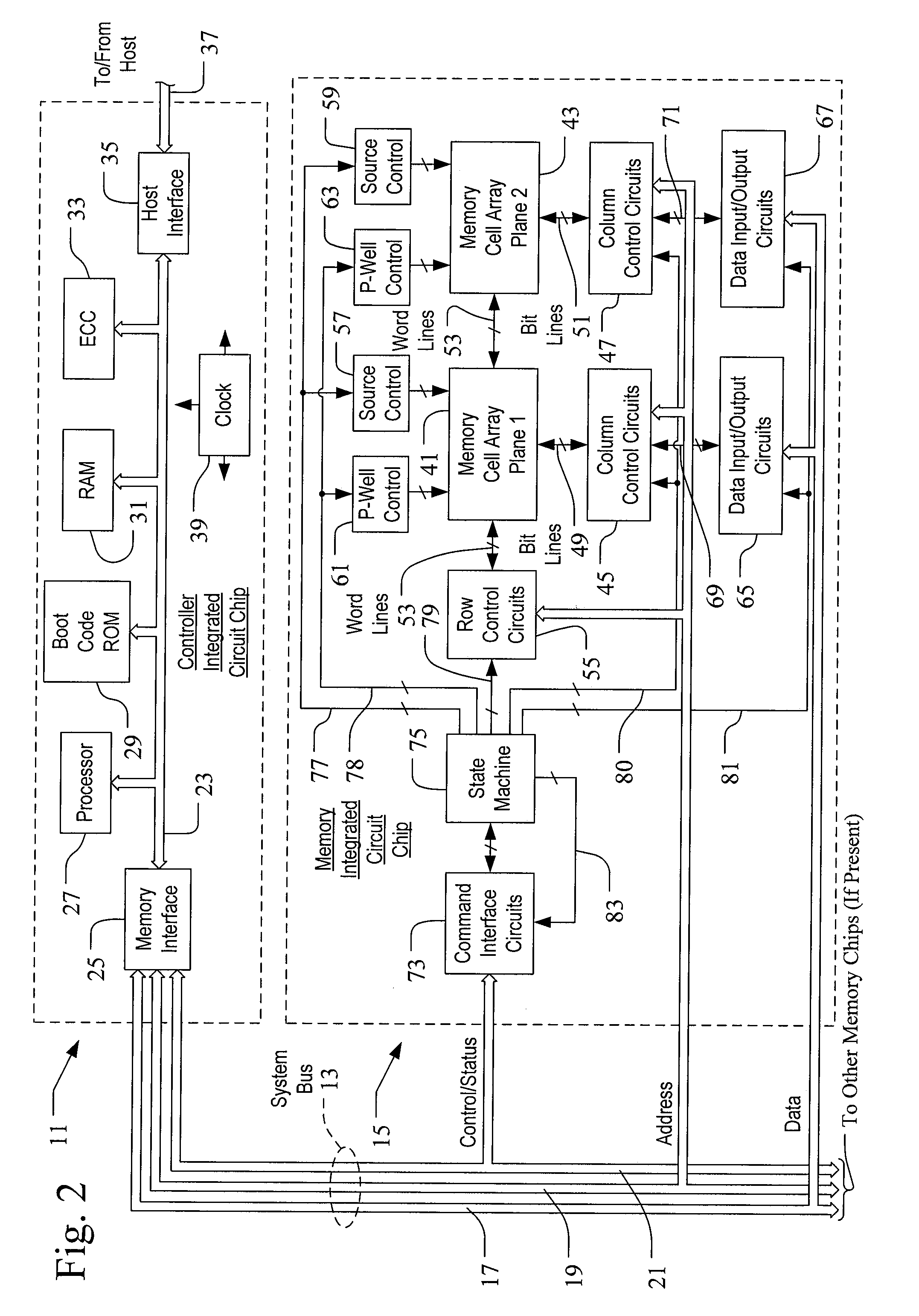
Method And System For Storage Address Re-Mapping For A Memory Device
ActiveUS20080307192A1Improve performanceImprove system performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsFile systemAddress space
A method and system for storage address re-mapping is disclosed. The method includes allocating logical addresses in blocks of clusters and re-mapping logical addresses into storage address space, where short runs of data dispersed in logical address space are mapped in a contiguous manner into blocks in storage address space. Valid data is flushed from blocks having both valid and obsolete data to make new blocks available for receiving data when an available number of new blocks falls below a desired threshold. The system includes a host file system, processor executable instructions residing on a host separately from the host file system or residing on a flash memory device such as an embedded solid state disk, or a backend memory manager of the flash memory device that is configured to map data from a logical address space to complete blocks in storage address space in a contiguous manner.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
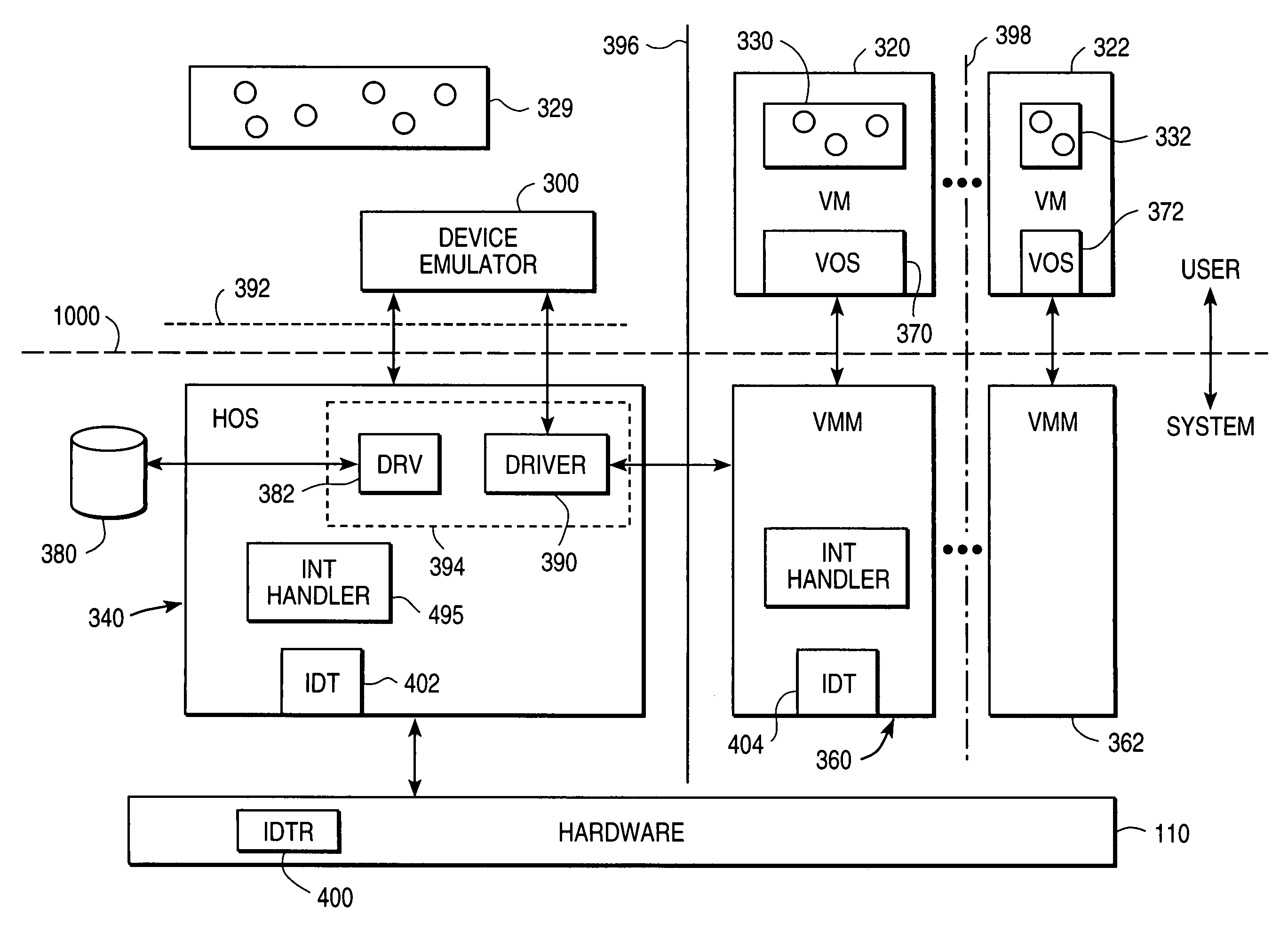
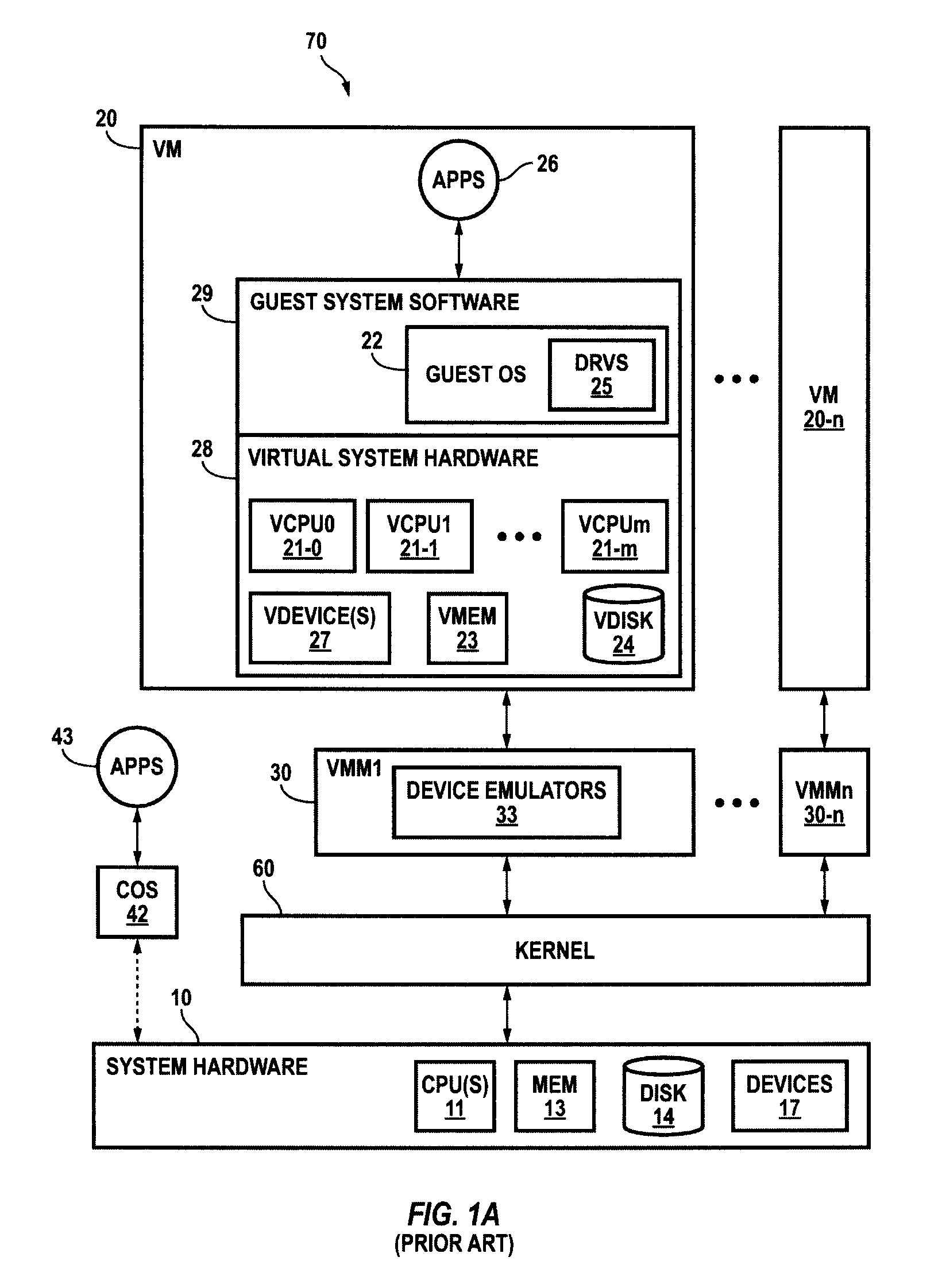
System and method for facilitating context-switching in a multi-context computer system
InactiveUS6944699B1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsOperational systemProcedure calls
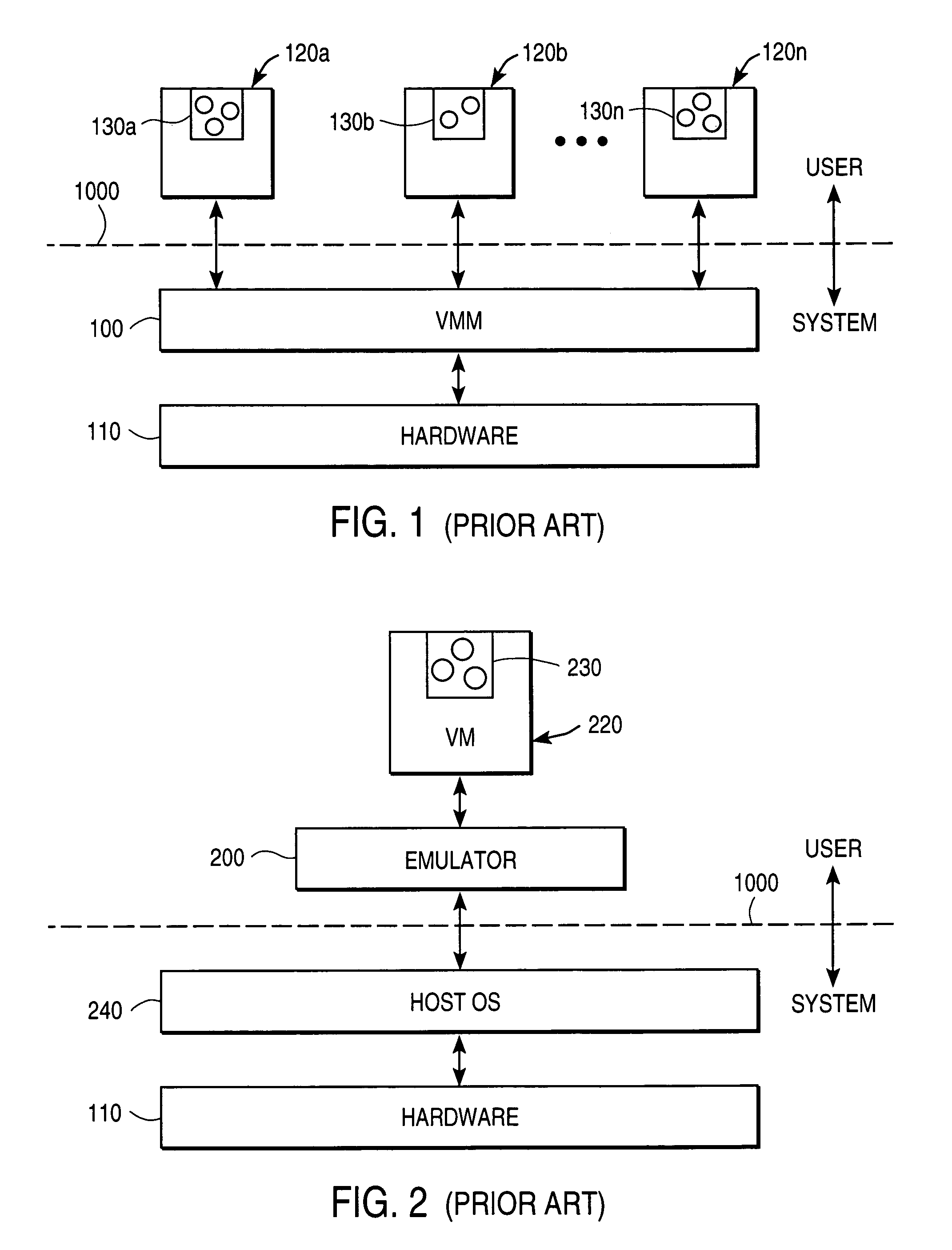
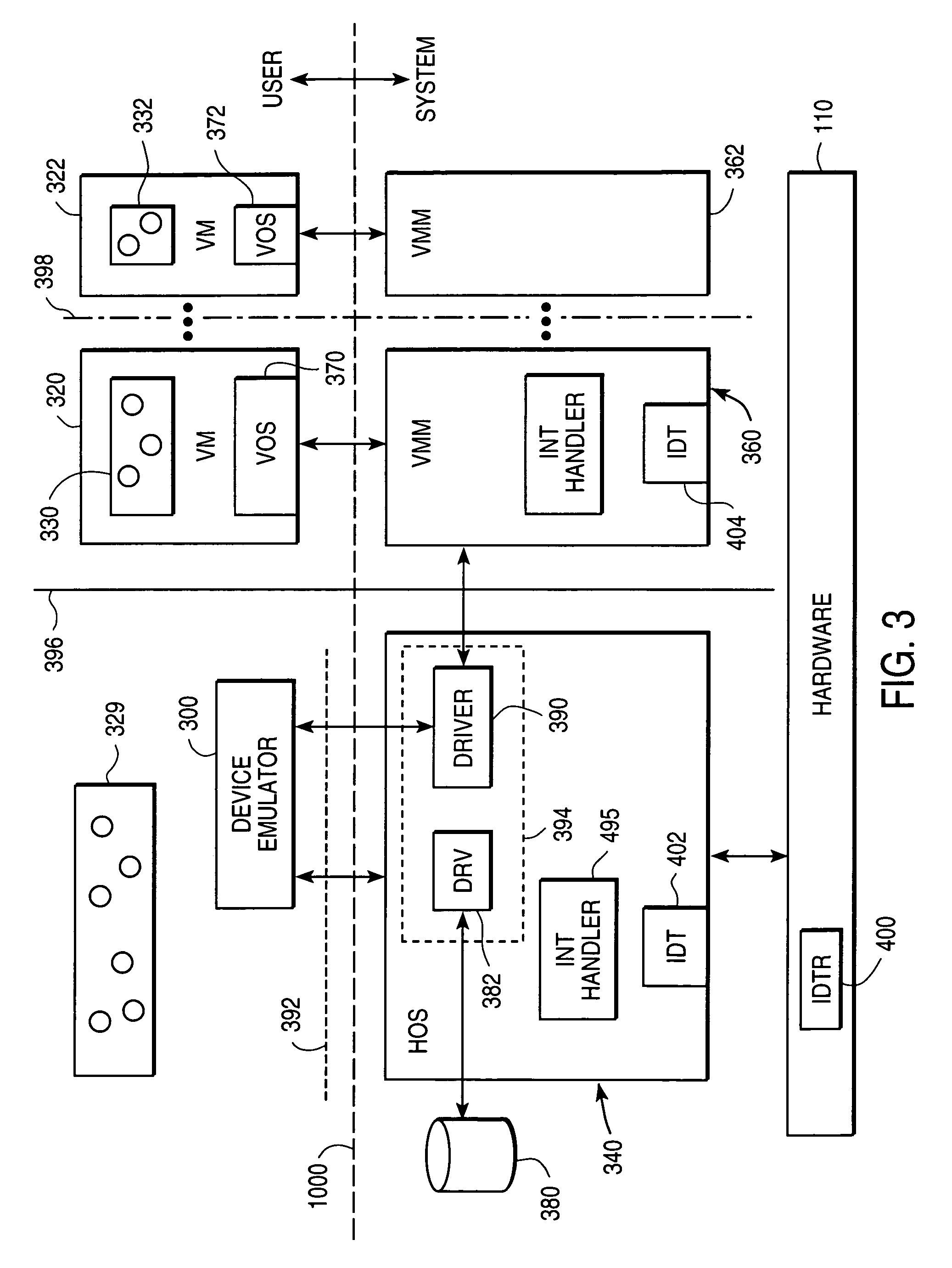
A virtual machine monitor (VMM) is included in a computer system that has a protected host operating system (HOS). A virtual machine running at least one application via a virtual operating system is connected to the VMM. Both the HOS and the VMM have separate operating contexts and disjoint address spaces, but are both co-resident at system level. A driver that is downloadable into the HOS at system level forms a total context switch between the VMM and HOS contexts. A user-level emulator accepts commands from the VMM via the system-level driver and processes these commands as remote procedure calls. The emulator is able to issue host operating system calls and thereby access the physical system devices via the host operating system. The host operating system itself thus handles execution of certain VMM instructions, such as accessing physical devices.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Apparatus, system, and method for efficient mapping of virtual and physical addresses
ActiveUS20090150641A1Efficient mappingEfficient identificationMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram synchronisationData segmentData store
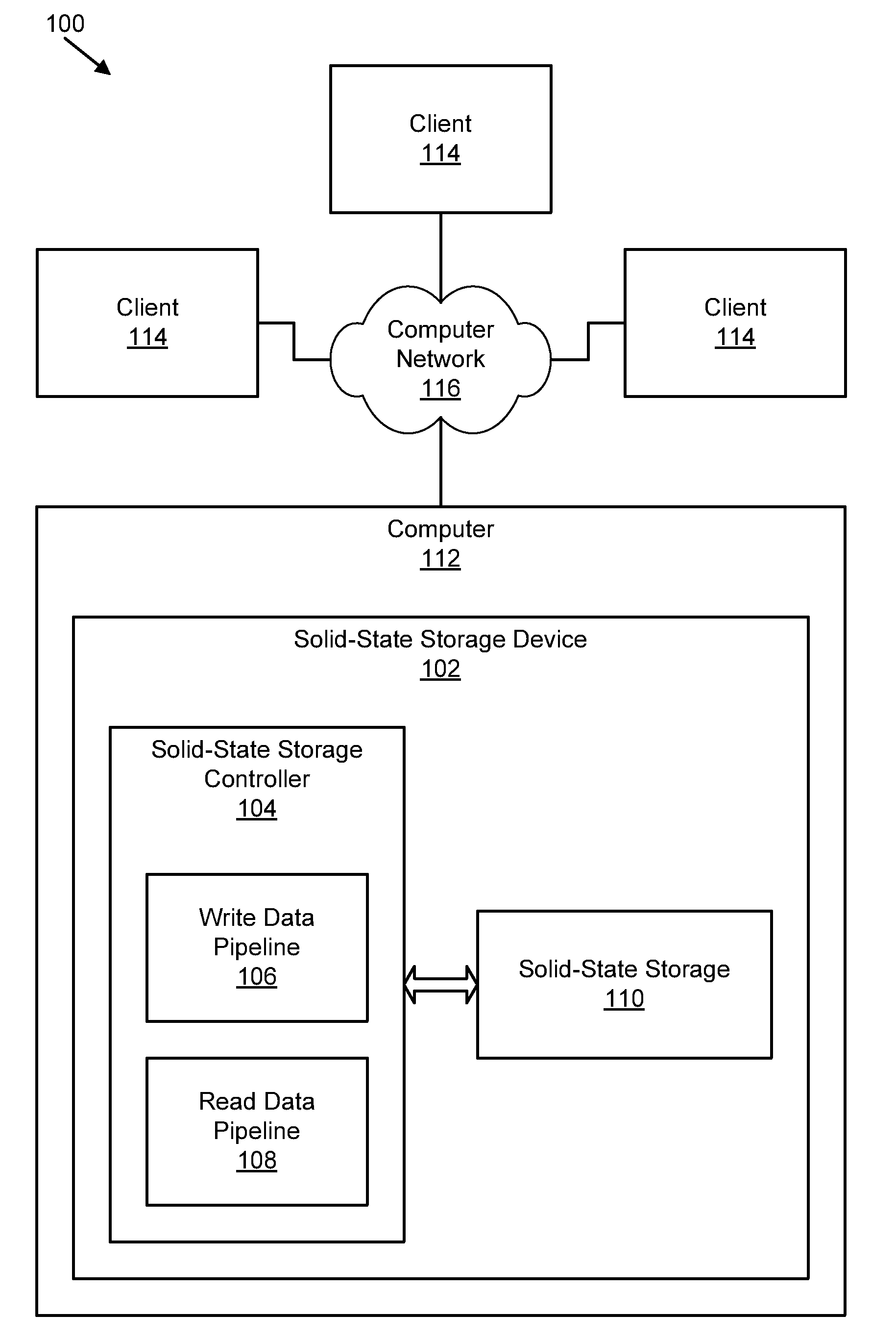
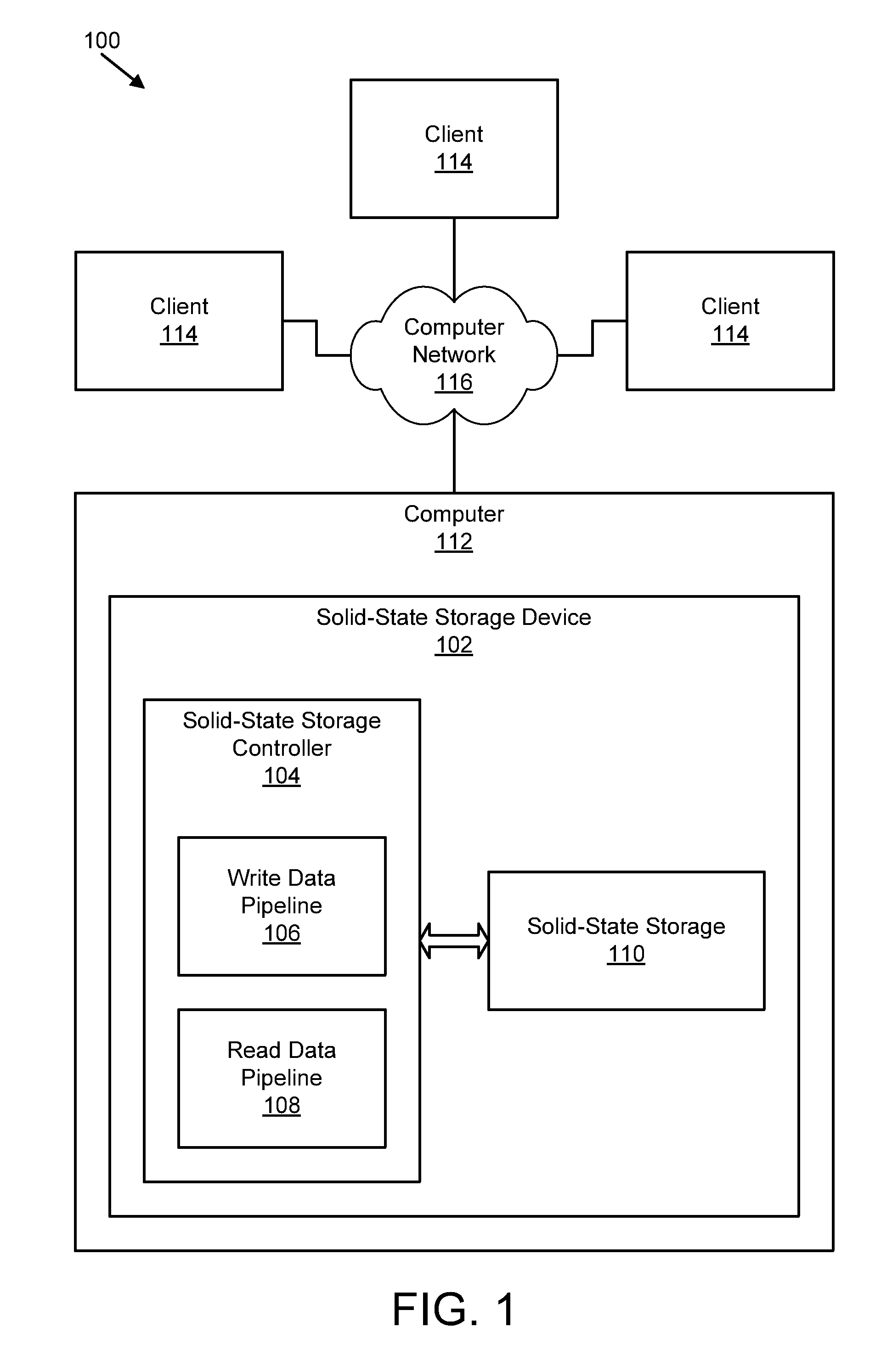
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for efficiently mapping virtual and physical addresses. A forward mapping module uses a forward map to identify physical addresses of data of a data segment from a virtual address. The data segment is identified in a storage request. The virtual addresses include discrete addresses within a virtual address space where the virtual addresses sparsely populate the virtual address space. A reverse mapping module uses a reverse map to determine a virtual address of a data segment from a physical address. The reverse map maps the data storage device into erase regions such that a portion of the reverse map spans an erase region of the data storage device erased together during a storage space recovery operation. A storage space recovery module uses the reverse map to identify valid data in an erase region prior to an operation to recover the erase region.
Owner:UNIFICATION TECH LLC
Method for extending a network map
ActiveUS7028083B2Reduce dimensionalityOvercome problemsMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksSystem usageIp address
An intelligent traffic redirection system performs global load balancing. The system uses a network map that is generated in part by extending a “sparse” IP address data map. In particular, a method of extending an IP address block map begins by defining a set of one or more upper bound block(s). These upper bound blocks are then used to partition a space of IP addresses into subsets or “territories”, wherein each territory represents a largest set of IP addresses to which a piece of mapping data may be extended. The “piece” of mapping data typically consists of a host (usually a “name server” identified by the core point discovery process) IP address and some data about that host, namely, a “nearest” data center or a flag indicating that either “no data” exists for that host or that the system is “indifferent” as to which of a set of mirrored data centers the host should be mapped. A unification algorithm partitions the territory of each upper bound block into the largest possible sub-blocks in which a given unanimity criterion is satisfied and extends the mapping data in each such sub-block to all of the territory of that sub-block.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Providing global translations with address space numbers
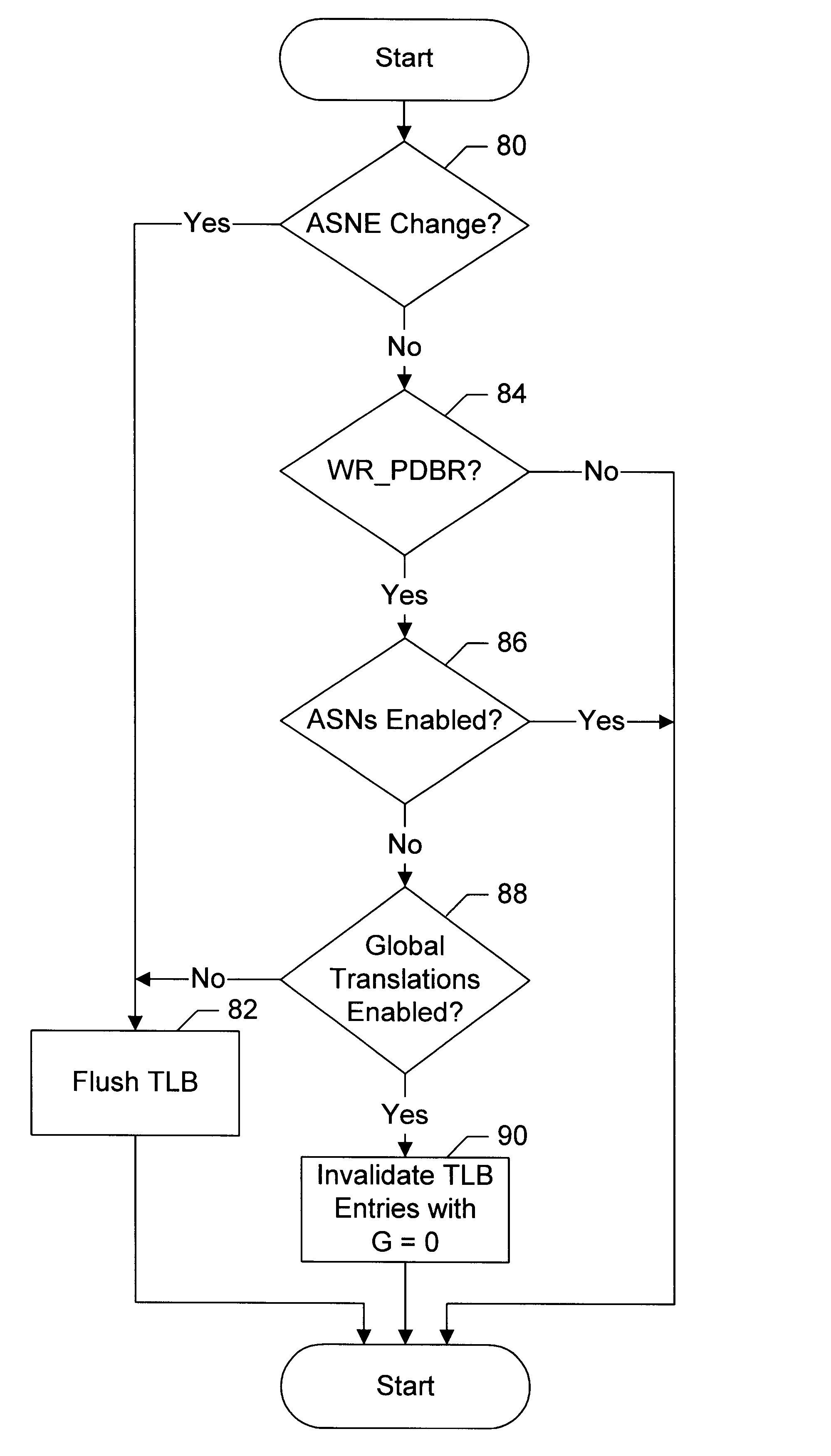
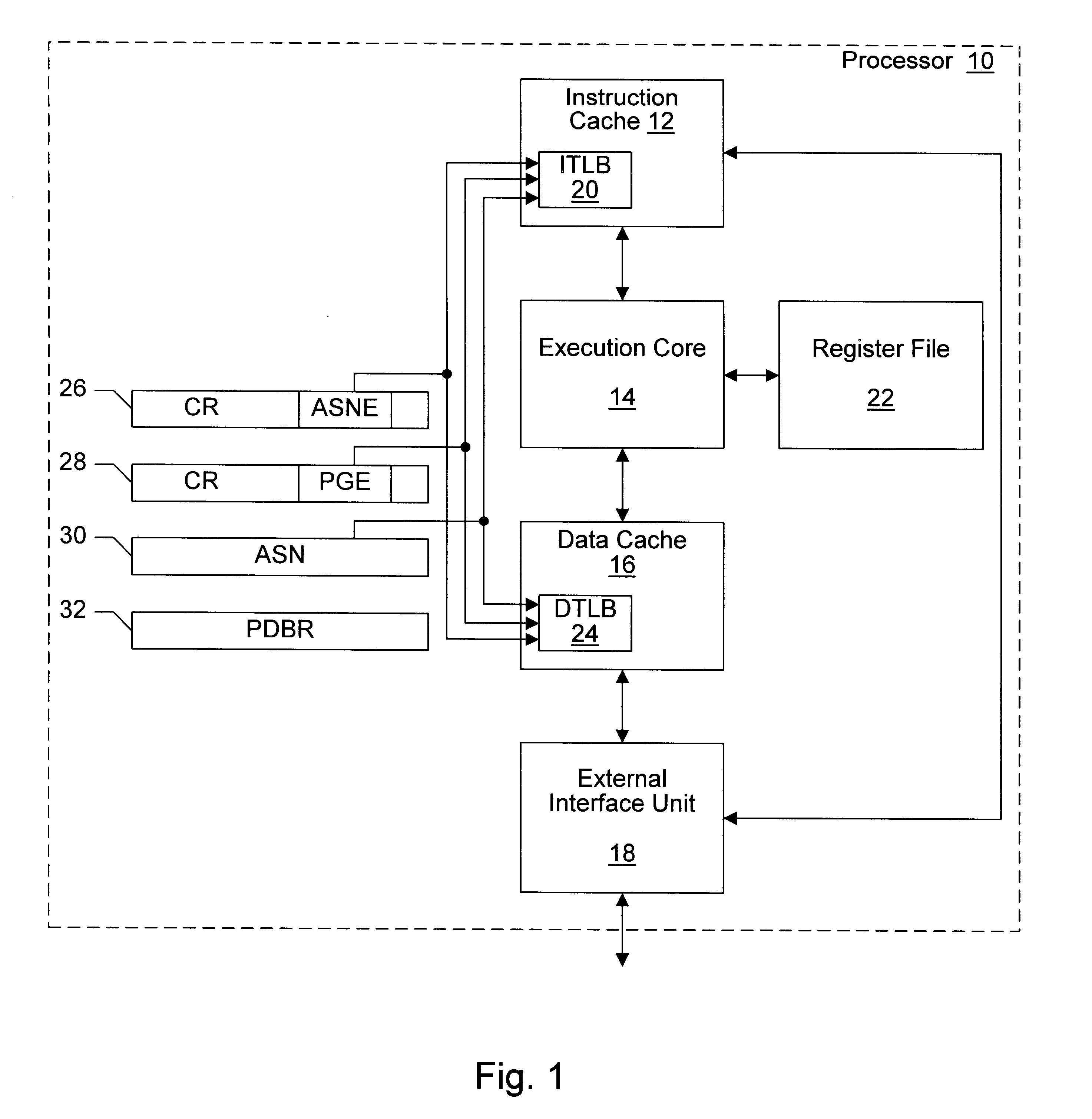
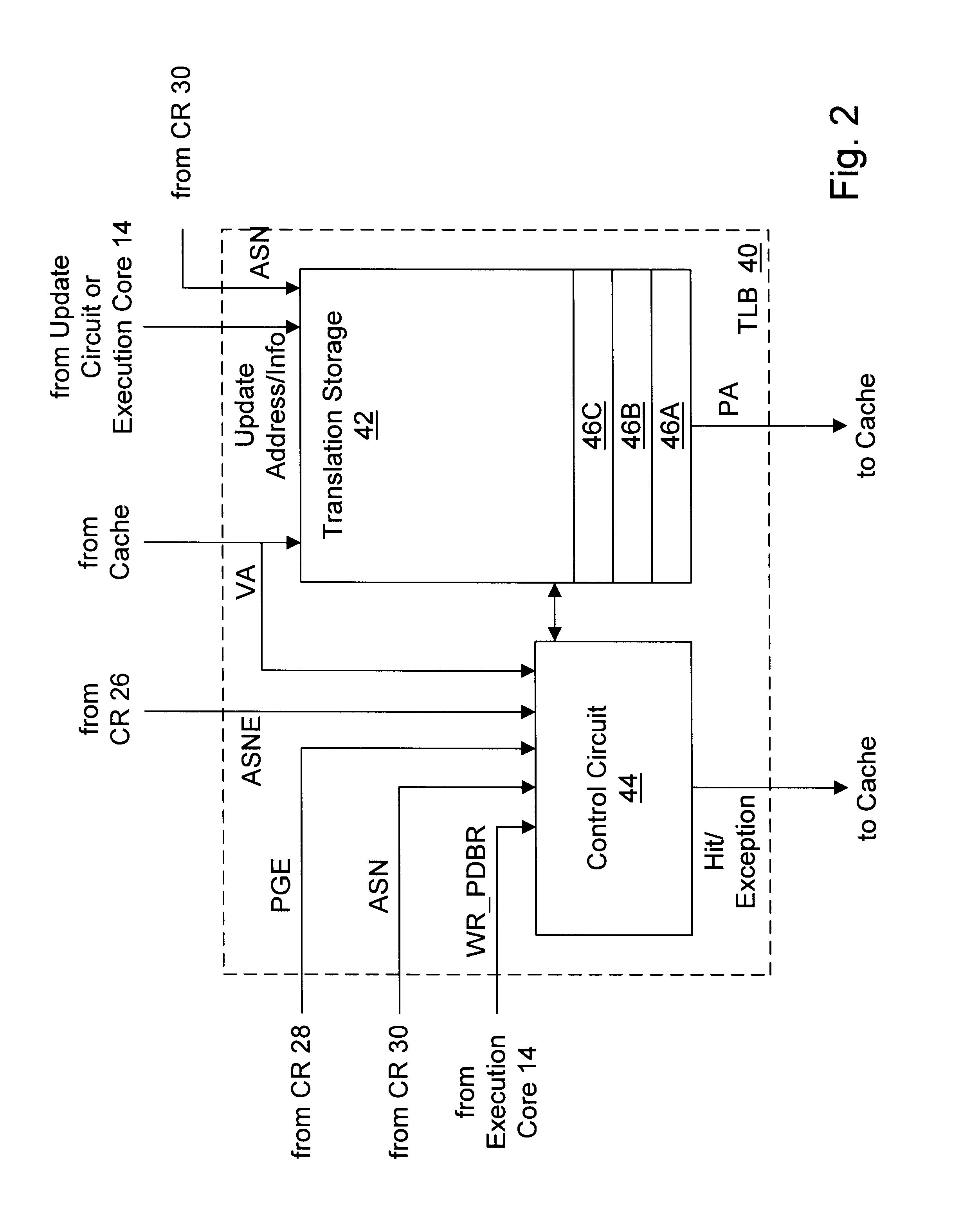
InactiveUS6604187B1Easy to useMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemProcessor register
A processor provides a register for storing an address space number (ASN). Operating system software may assign different ASNs to different processes. The processor may include a TLB to cache translations, and the TLB may record the ASN from the ASN register in a TLB entry being loaded. Thus, translations may be associated with processes through the ASNs. Generally, a TLB hit will be detected in an entry if the virtual address to be translated matches the virtual address tag and the ASN matches the ASN stored in the register. Additionally, the processor may use an indication from the translation table entries to indicate whether or not a translation is global. If a translation is global, then the ASN comparison is not included in detecting a hit in the TLB. Thus, translations which are used by more than one process may not occupy multiple TLB entries. Instead, a hit may be detected on the TLB entry storing the global translation even though the recorded ASN may not match the current ASN. In one embodiment, if ASNs are disabled, the TLB may be flushed on context switches. However, the indication from the translation table entries used to indicate that the translation is global may be used (when ASNs are disabled) by the TLB to selectively invalidate non-global translations on a context switch while not invalidating global translations.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
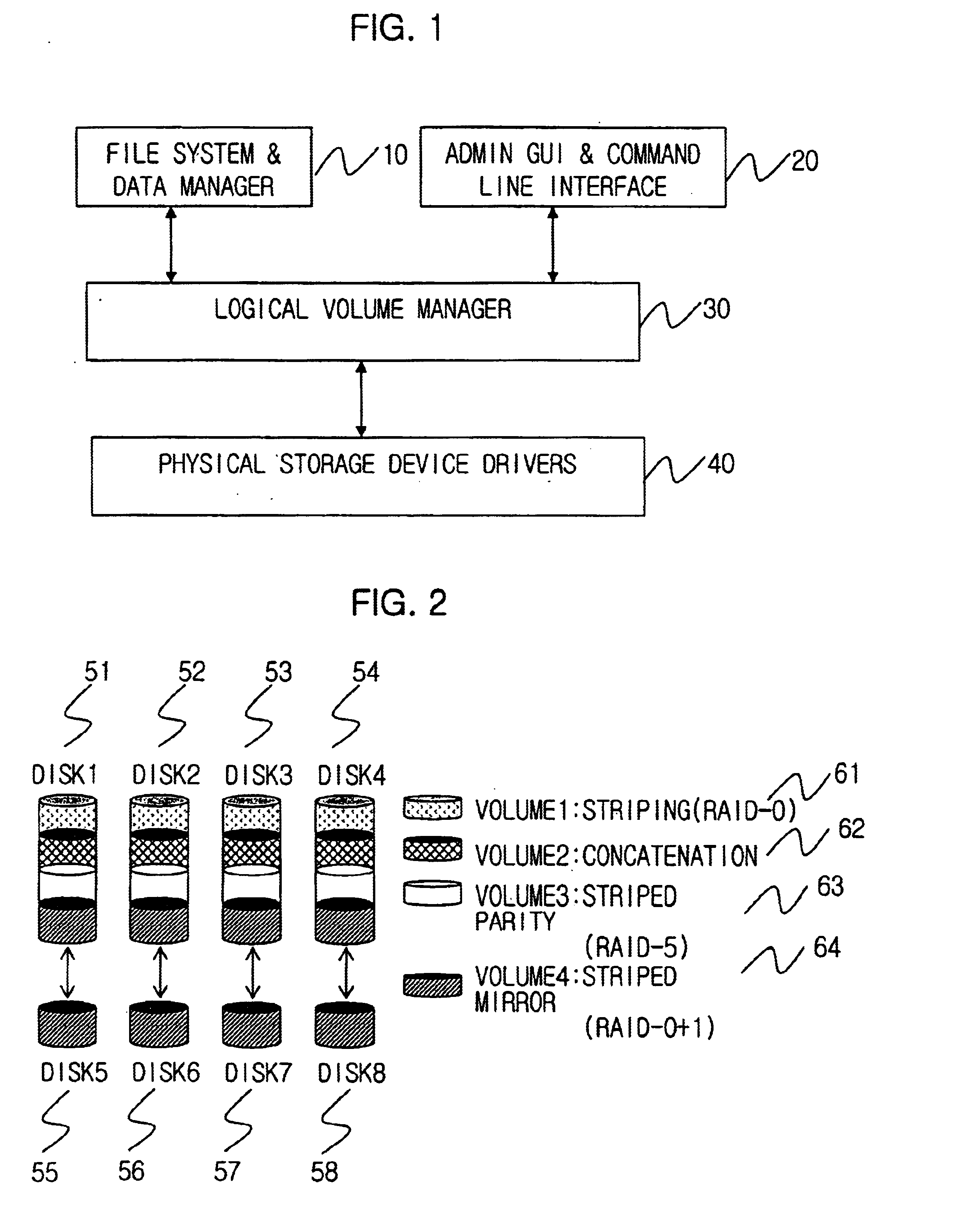
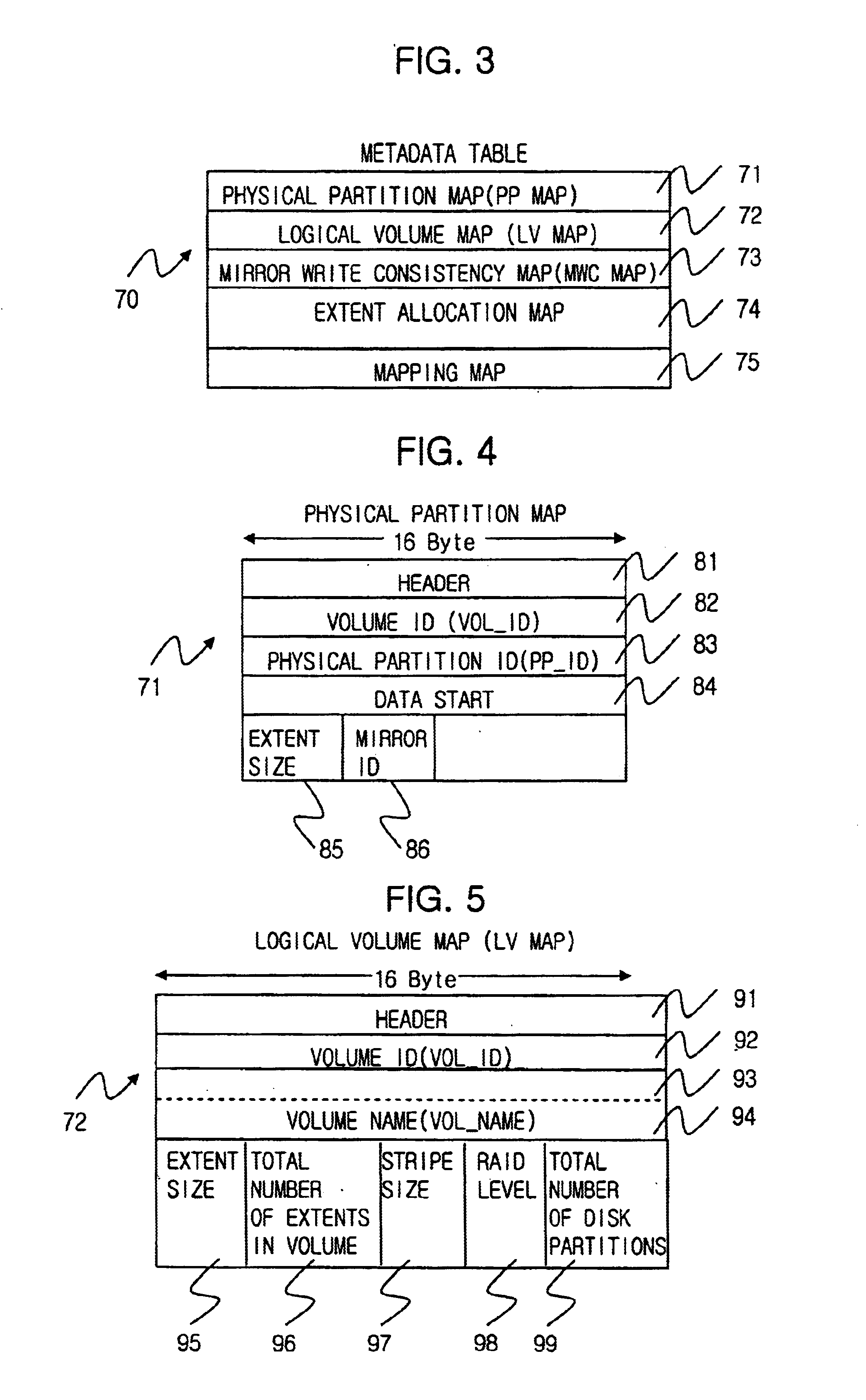
Method for managing logical volume in order to support dynamic online resizing and software raid and to minimize metadata and computer readable medium storing the same
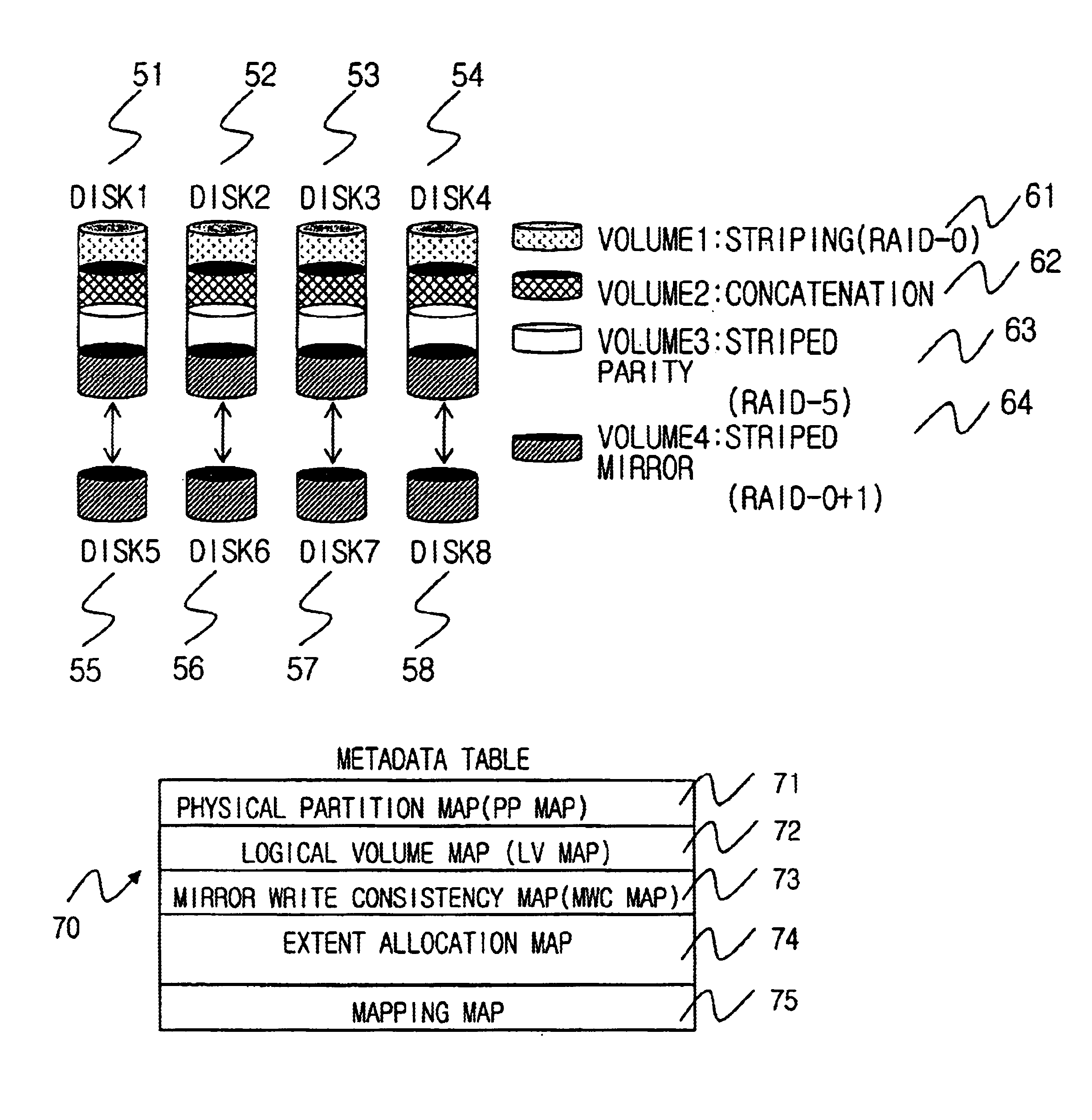
InactiveUS6718436B2Increase or decrease sizeIncrease spaceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDVolume table
A method for managing a logical volume for minimizing a size of metadata and supporting dynamic online resizing and software redundant array of independent disks (RAID), and a computer-readable recording medium storing instructions for embodying the method, are disclosed. The method includes the metadata having a disk partition table containing information of a disk partition in which the metadata is stored; a logical volume table for maintaining the information of the logical volume by storing duplicated information of the logical volume onto all disk partitions of the logical volume; an extent allocation table for indicating whether each extent in the disk partitions is used or not; and a mapping table for maintaining a mapping information for a physical address space corresponding to a logical address space which is a continuous address space equal in size of storage space of whole logical volume.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
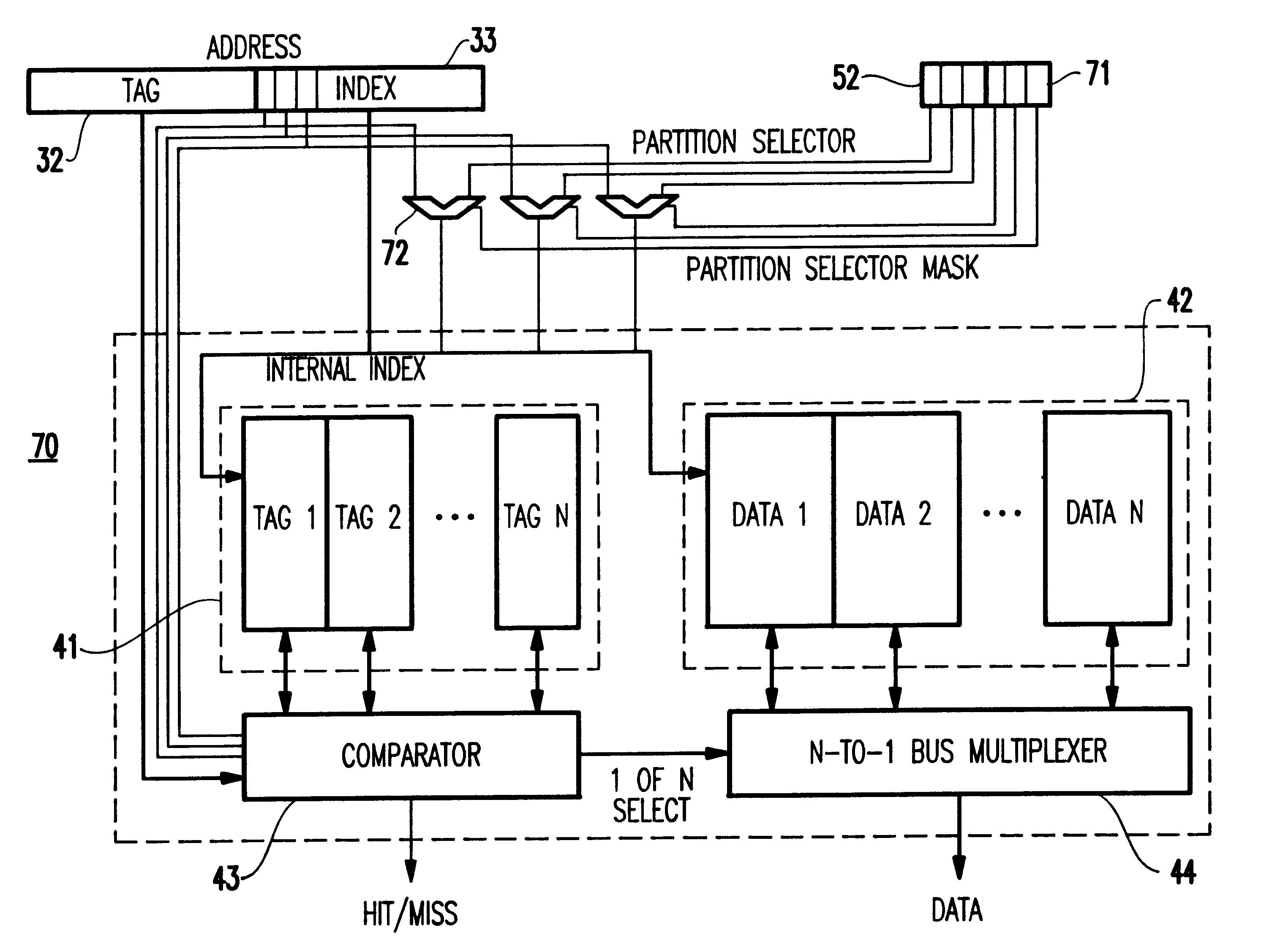
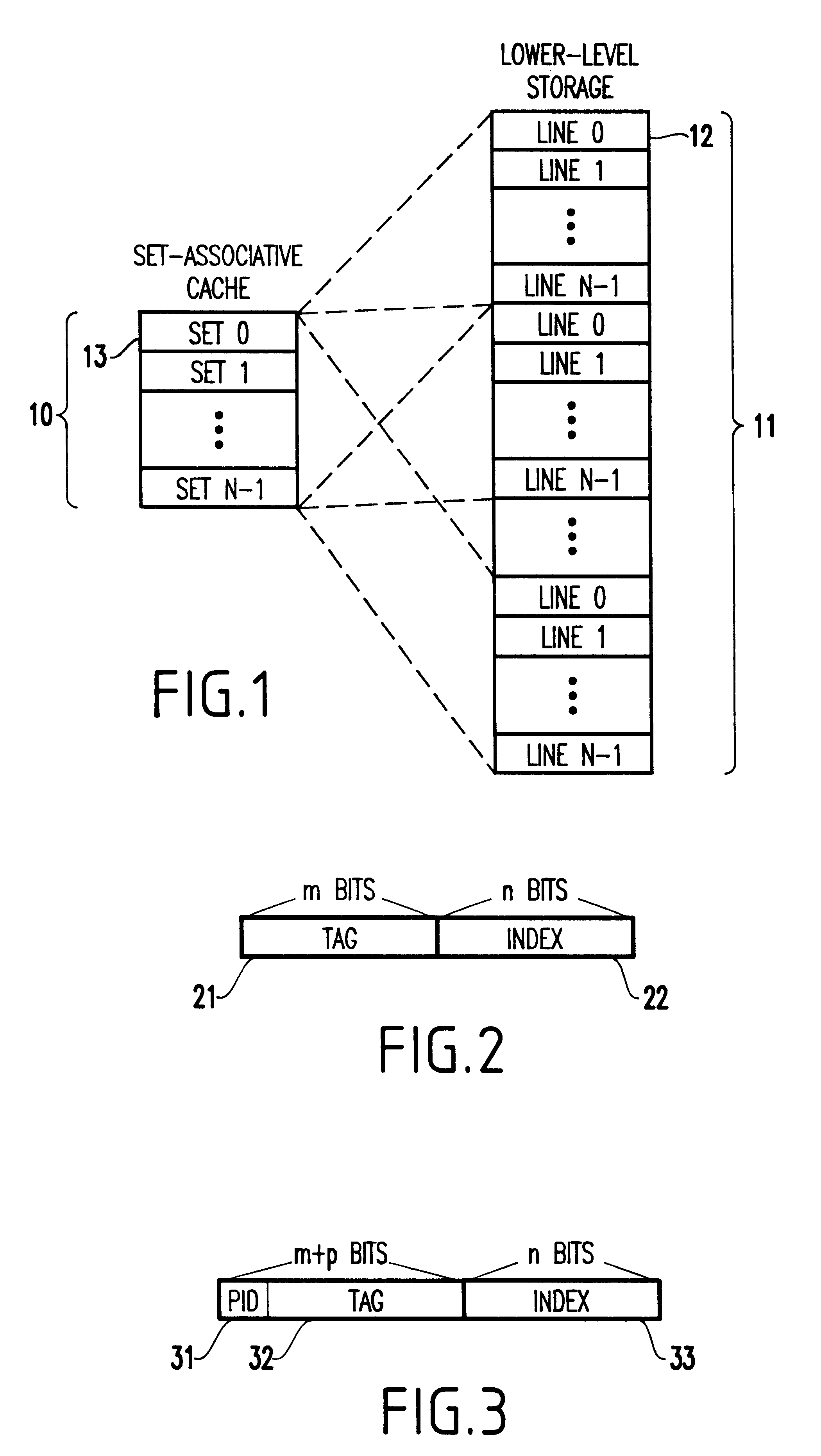
Method and system for dynamically partitioning a shared cache
InactiveUS6493800B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorParallel computing
A cache memory shared among a plurality of separate, disjoint entities each having a disjoint address space, includes a cache segregator for dynamically segregating a storage space allocated to each entity of the entities such that no interference occurs with respective ones of the entities. A multiprocessor system including the cache memory, a method and a signal bearing medium for storing a program embodying the method also are provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
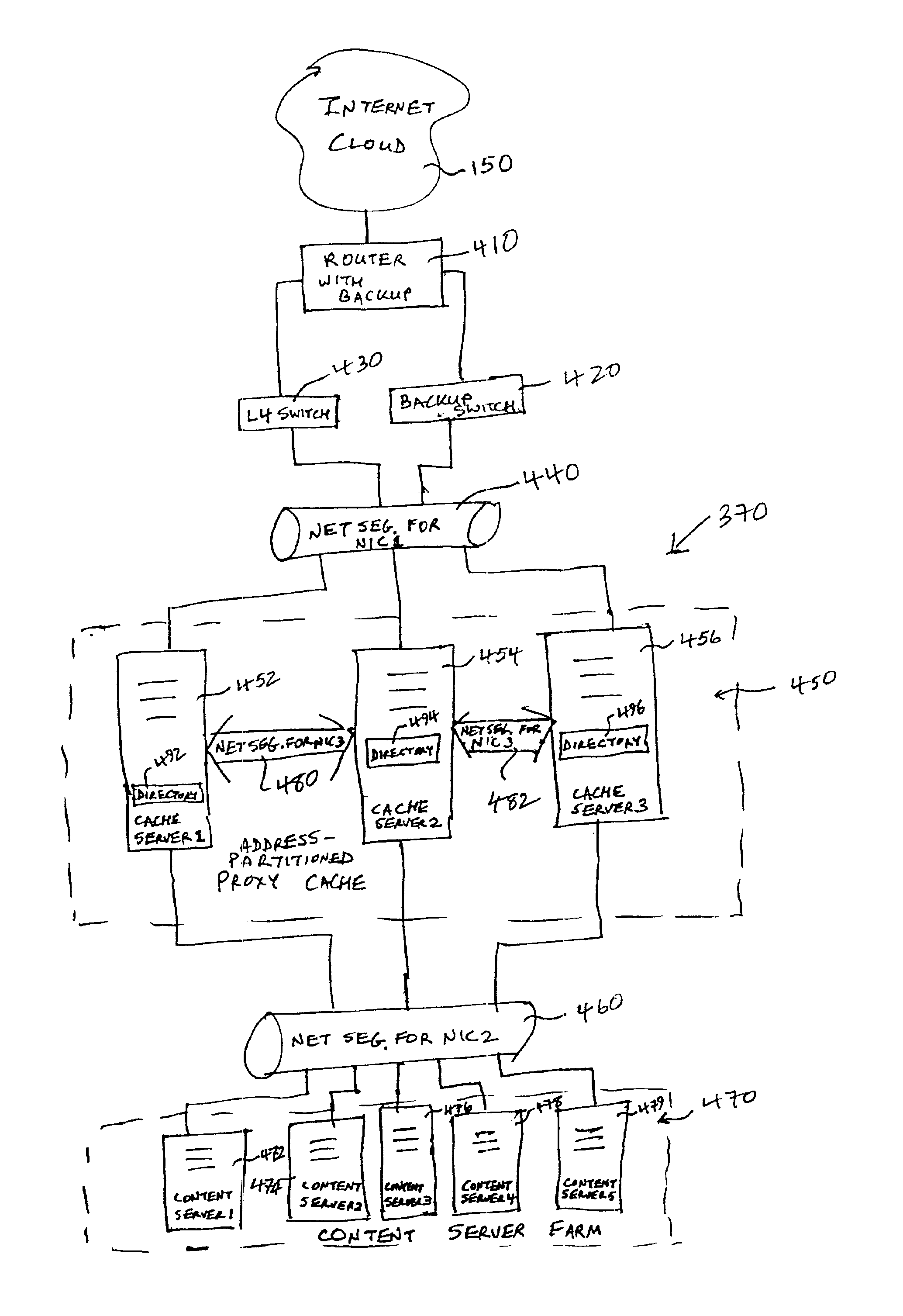
System and method for partitioning address space in a proxy cache server cluster
InactiveUS6862606B1Overcome disadvantagesReduce congestionMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationCache serverParallel computing
A proxy partition cache (PPC) architecture and a technique for address-partitioning a proxy cache consisting of a grouping of discrete, cooperating caches (servers) is provided. Client requests for objects (files) of a given size are redirected or reassigned to a single cache in the grouping, notwithstanding the cache to which the request is made by the load-balancing mechanism (such as a Layer 4 switch) based upon load-balancing considerations. The file is then returned to the switch via the switch-designated cache for vending to the requesting client. The redirection / reassignment occurs according to a function within the cache to which the request is directed so that the switch remains freed from additional tasks that can compromise speed.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Garbage collector for a virtual heap
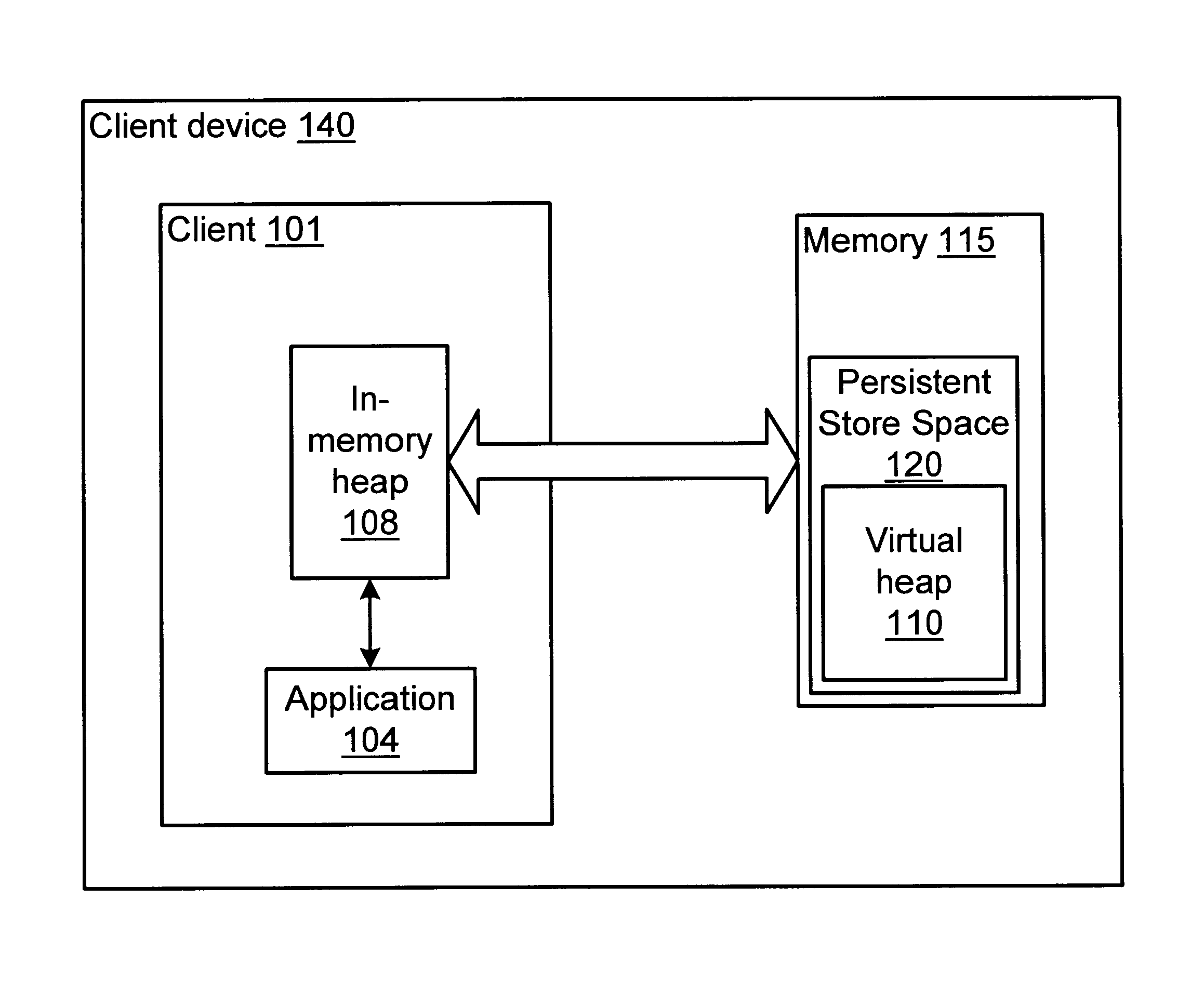
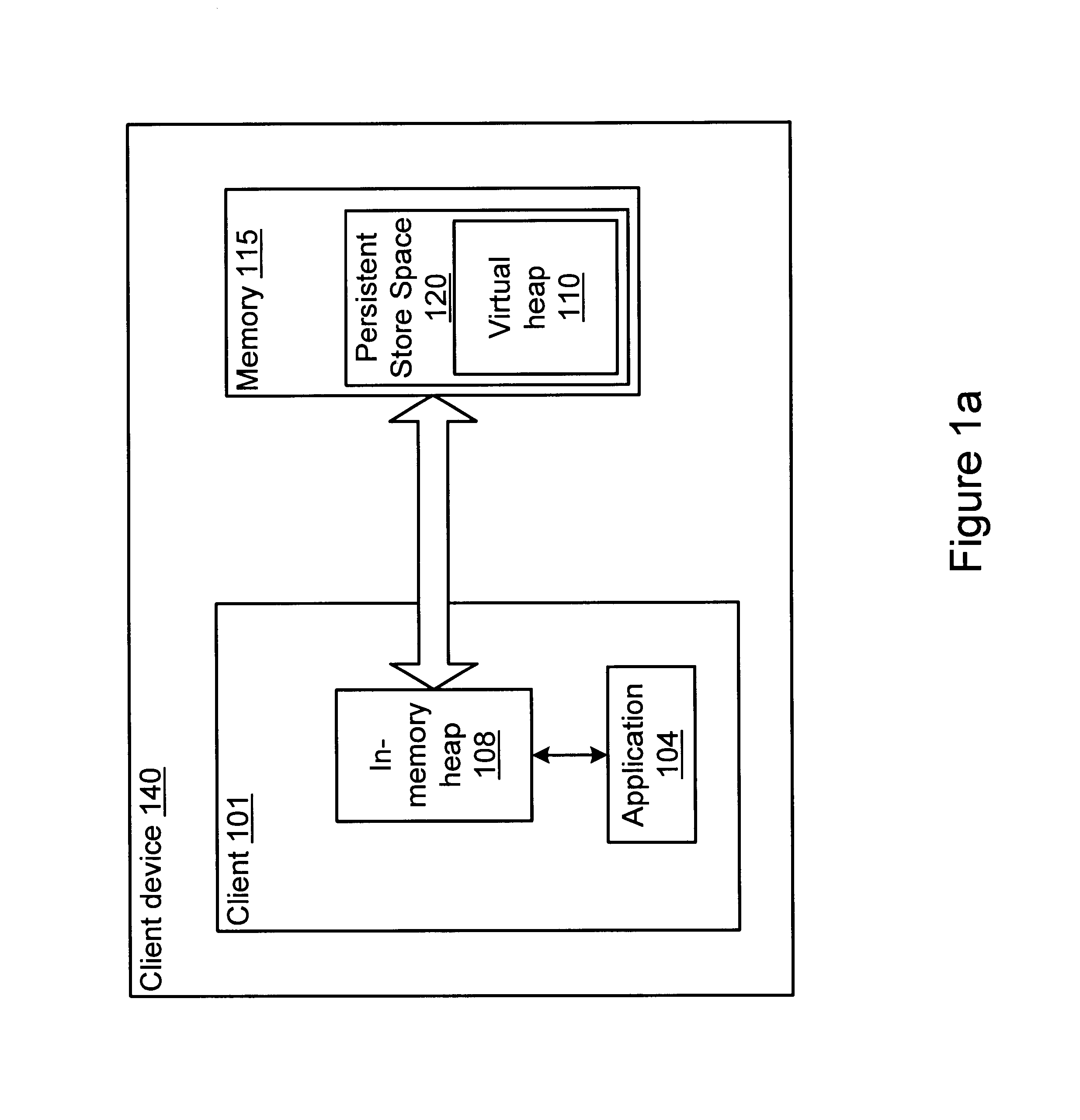
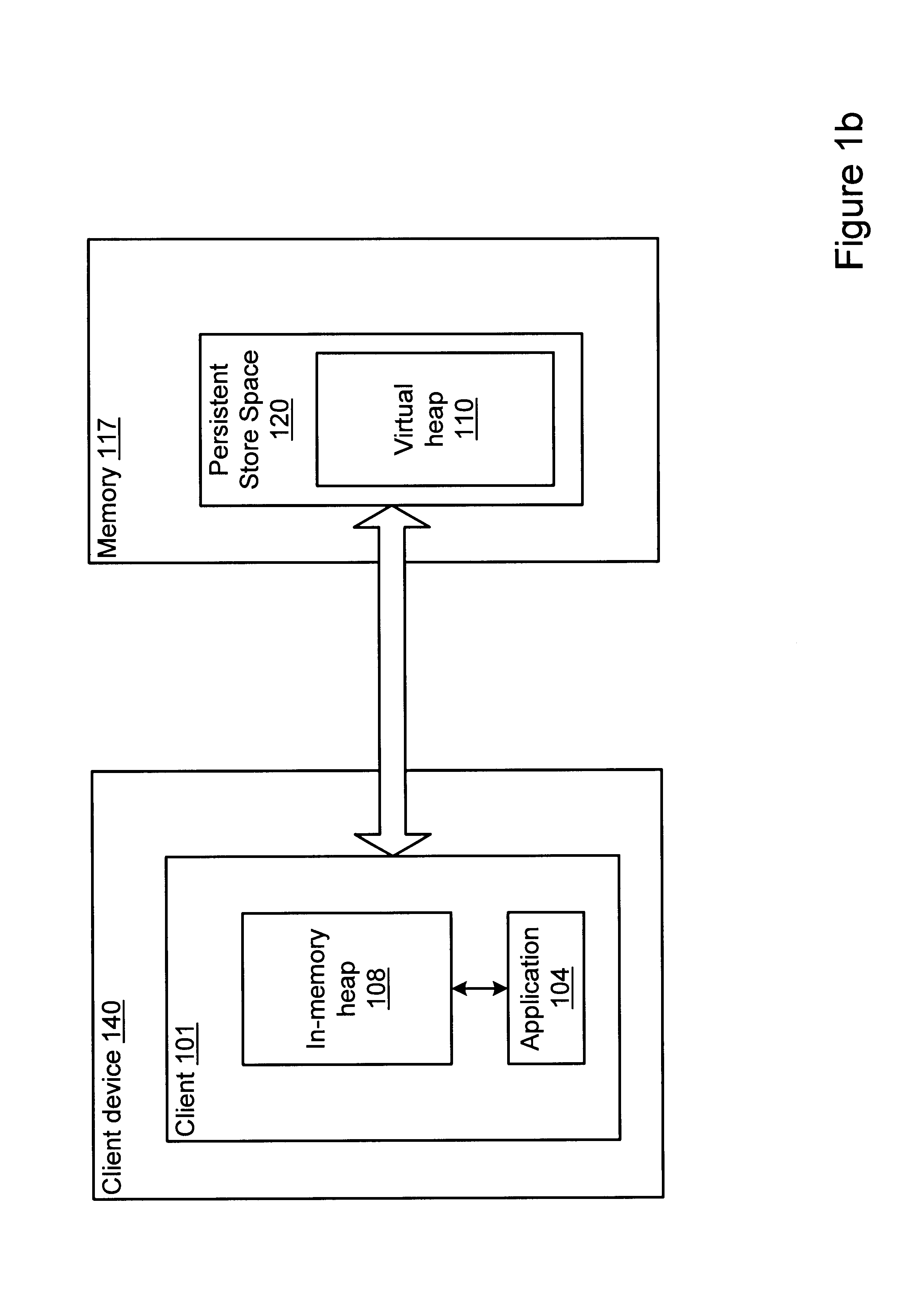
InactiveUS6865657B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsObject copyingRefuse collection
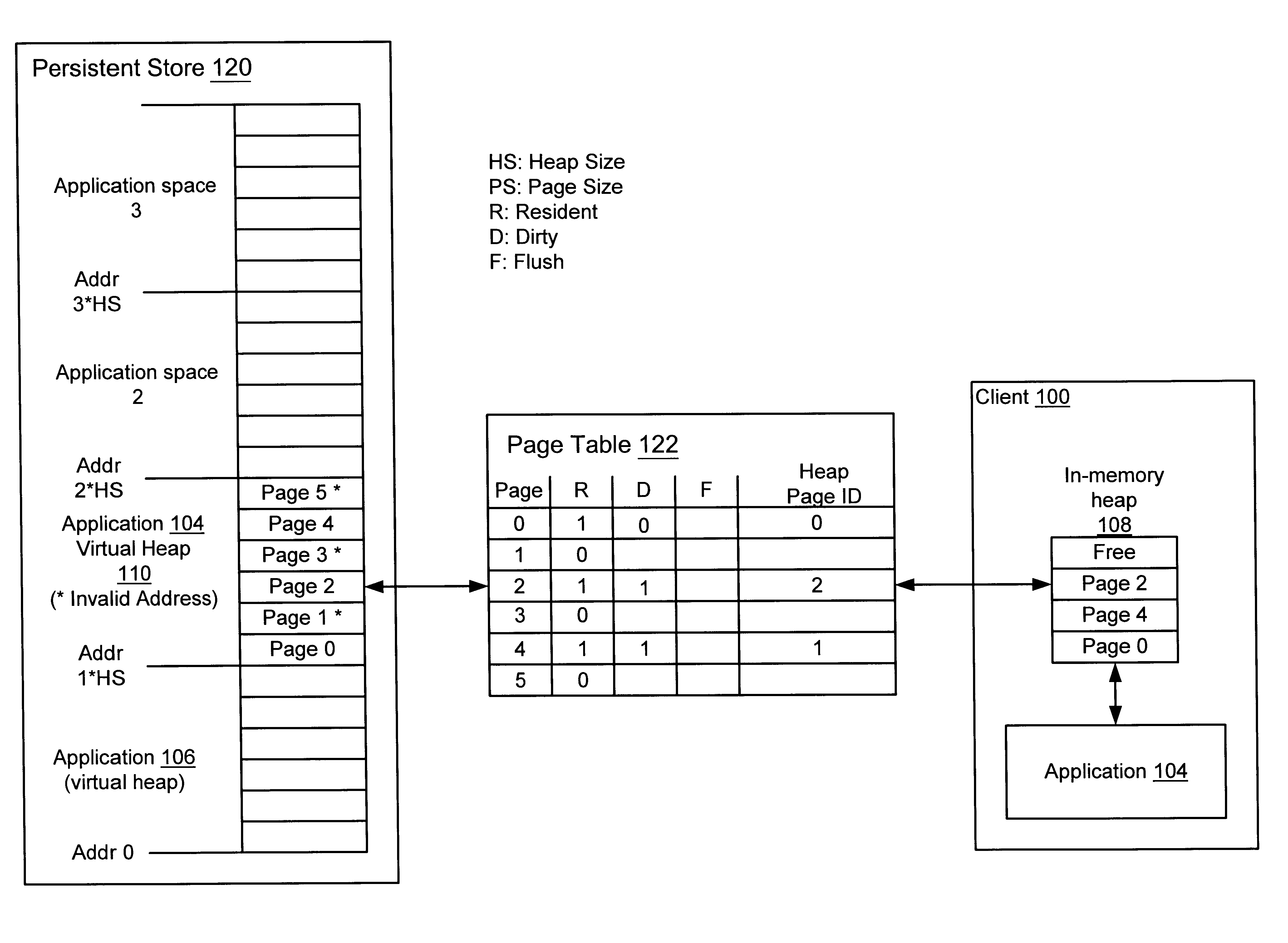
A method and system for performing generational garbage collection on a virtual heap in a virtual machine is provided. The garbage collection method is suited for use with small consumer and appliance devices that have a small amount of memory and may be using flash devices as persistent storage. The garbage collection method may provide good performance where only a portion of the virtual heap may be cached in the physical heap. The virtual heap may use a single address space for both objects in the store and the in-memory heap. In one embodiment, a single garbage collector is run on the virtual heap address space. The garbage collection method may remove non-referenced objects from the virtual heap. The garbage collection method may also include a compaction phase to reduce or eliminate fragmentation, and to improve locality of objects within the virtual heap. In one embodiment, the garbage collector for the virtual heap may be implemented as a generational garbage collector using working sets in the virtual heap, where each generation is confined to a working set of the heap. The generational garbage collector may allow the flushing of changes after each garbage collection cycle for each working set region. Heap regions with different flushing policies may be used. An object nursery region without flushing where objects are initially created may be used. When a garbage collection cycle is run, objects truly referenced in the object nursery may be copied back into heap regions to be flushed, while short-lived objects no longer referenced may be deleted without flushing.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP +1
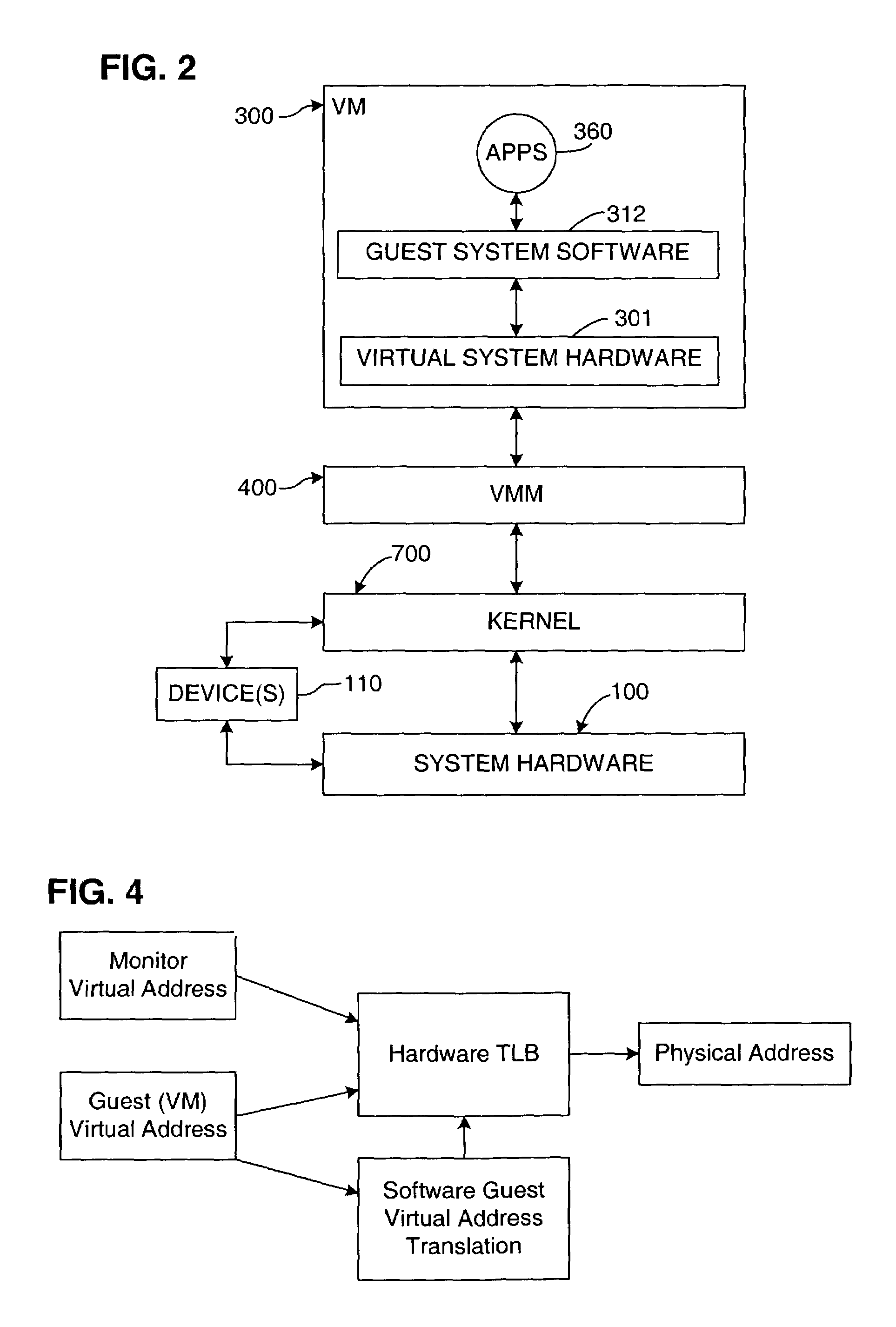
Virtualization system for computers that use address space indentifiers
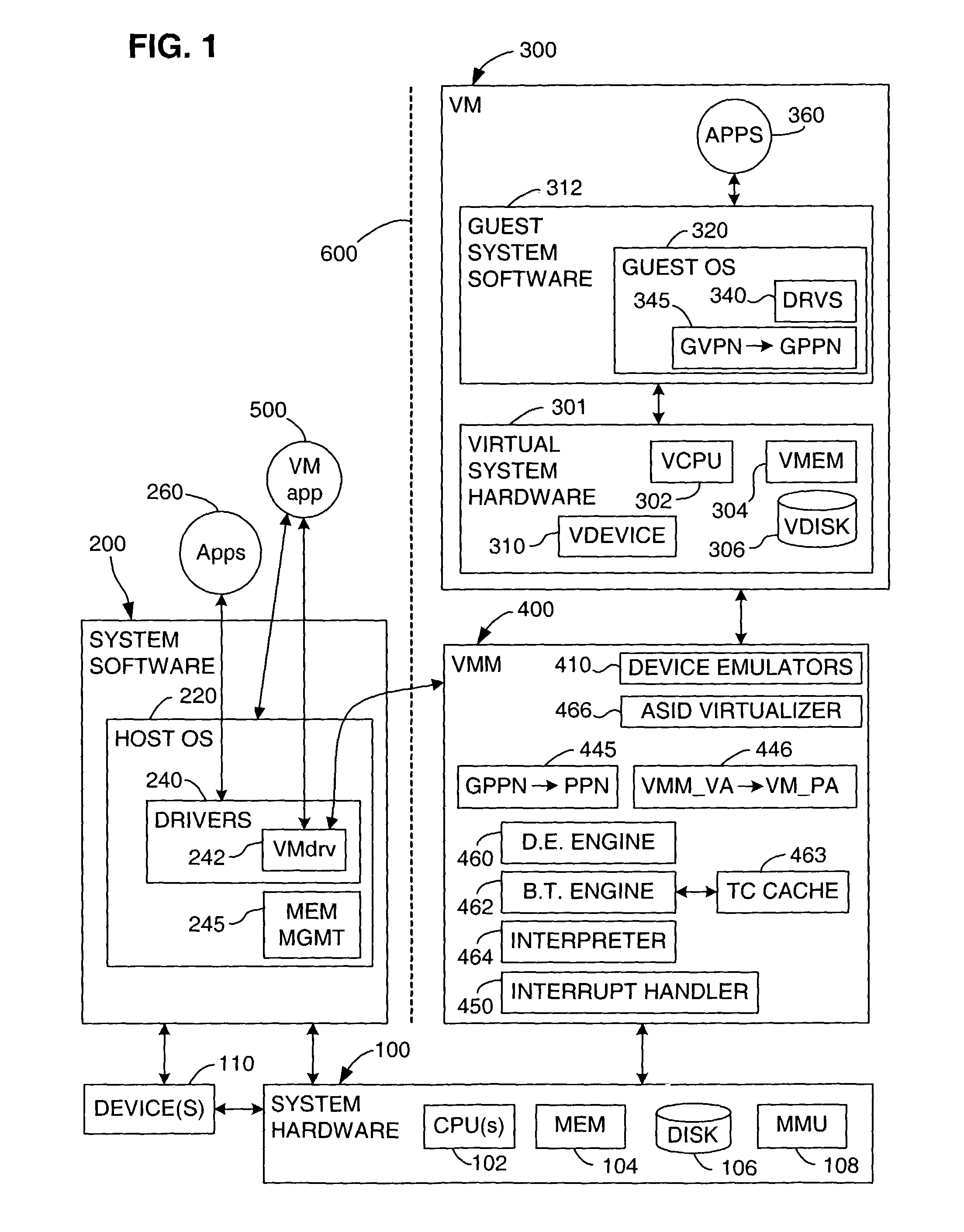
A virtual computer system including multiple virtual machines (VMs) is implemented in a physical computer system that uses address space identifiers (ASIDs). Each VM includes a virtual translation look-aside buffer (TLB), in which guest software, executing on the VM, may insert address translations, with each translation including an ASID. For each ASID used by guest software, a virtual machine monitor (VMM), or other software unit, assigns a unique shadow ASID for use in corresponding address translations in a hardware TLB. If a unique shadow ASID is not available for a newly used guest ASID, the VMM reassigns a shadow ASID from a prior guest ASID to the new guest ASID, purging any entries in the hardware TLB corresponding to the prior guest ASID. Assigning unique shadow ASIDs limits the need for TLB purges upon switching between the multiple VMs, reducing the number of TLB miss faults, and consequently improving overall processing efficiency.
Owner:VMWARE INC
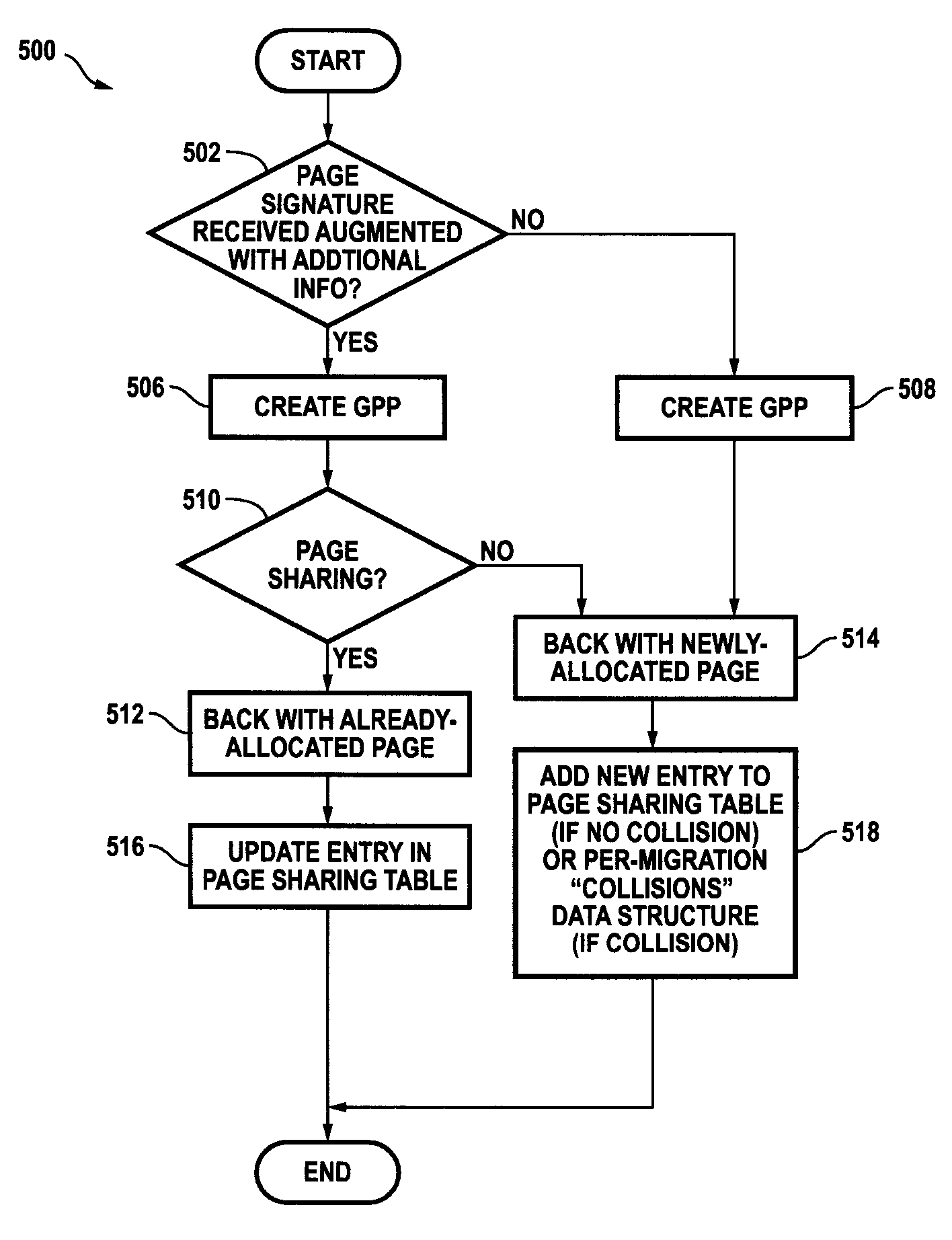
Page signature disambiguation for increasing the efficiency of virtual machine migration in shared-page virtualized computer systems
ActiveUS7925850B1Inhibitory contentAvoid collisionProgram controlMemory systemsVirtualizationAmbiguity
A system for increasing the efficiency of migrating, at least in part, a virtual machine from a source host to a destination host is described wherein the content of one or more portions of the address space of the virtual machine are each uniquely associated at the source host with a signature that may collide, absent disambiguation, with different content at the destination host. Code in both the source and destination hosts disambiguates the signature(s) so that each disambiguated signature may be uniquely associated with content at the destination host, and so that collisions with different content are avoided at the destination host. Logic is configured to determine whether the content uniquely associated with a disambiguated signature at the destination host is already present in the destination host memory, and, if so, to back one or more portions of the address space of the virtual machine having this content with one or more portions of the destination host memory already holding this content.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Garbage collection using nursery regions for new objects in a virtual heap
InactiveUS6763440B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsWorking setAddress space
A method and system for garbage collecting a virtual heap using nursery regions for newly created objects to reduce flushing of objects from an in-memory heap to a store heap is provided. The garbage collection method is suited for use with small consumer and appliance devices that have a small amount of memory and may be using flash devices as persistent storage. The garbage collection method may provide good performance where only a portion of the virtual heap may be cached in the physical heap. The virtual heap may use a single address space for both objects in the store and the in-memory heap. In one embodiment, a single garbage collector is run on the virtual heap address space. The garbage collection method may remove non-referenced objects from the virtual heap. The garbage collection method may also include a compaction phase to reduce or eliminate fragmentation, and to improve locality of objects within the virtual heap. In one embodiment, the garbage collector for the virtual heap may be implemented as a generational garbage collector using working sets in the virtual heap, where each generation is confined to a working set of the heap. The generational garbage collector may allow the flushing of changes after each garbage collection cycle for each working set region. Heap regions with different flushing policies may be used. An object nursery region without flushing where objects are initially created may be used. When a garbage collection cycle is run, objects truly referenced in the object nursery may be copied back into heap regions to be flushed, while short-lived objects no longer referenced may be deleted without flushing.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
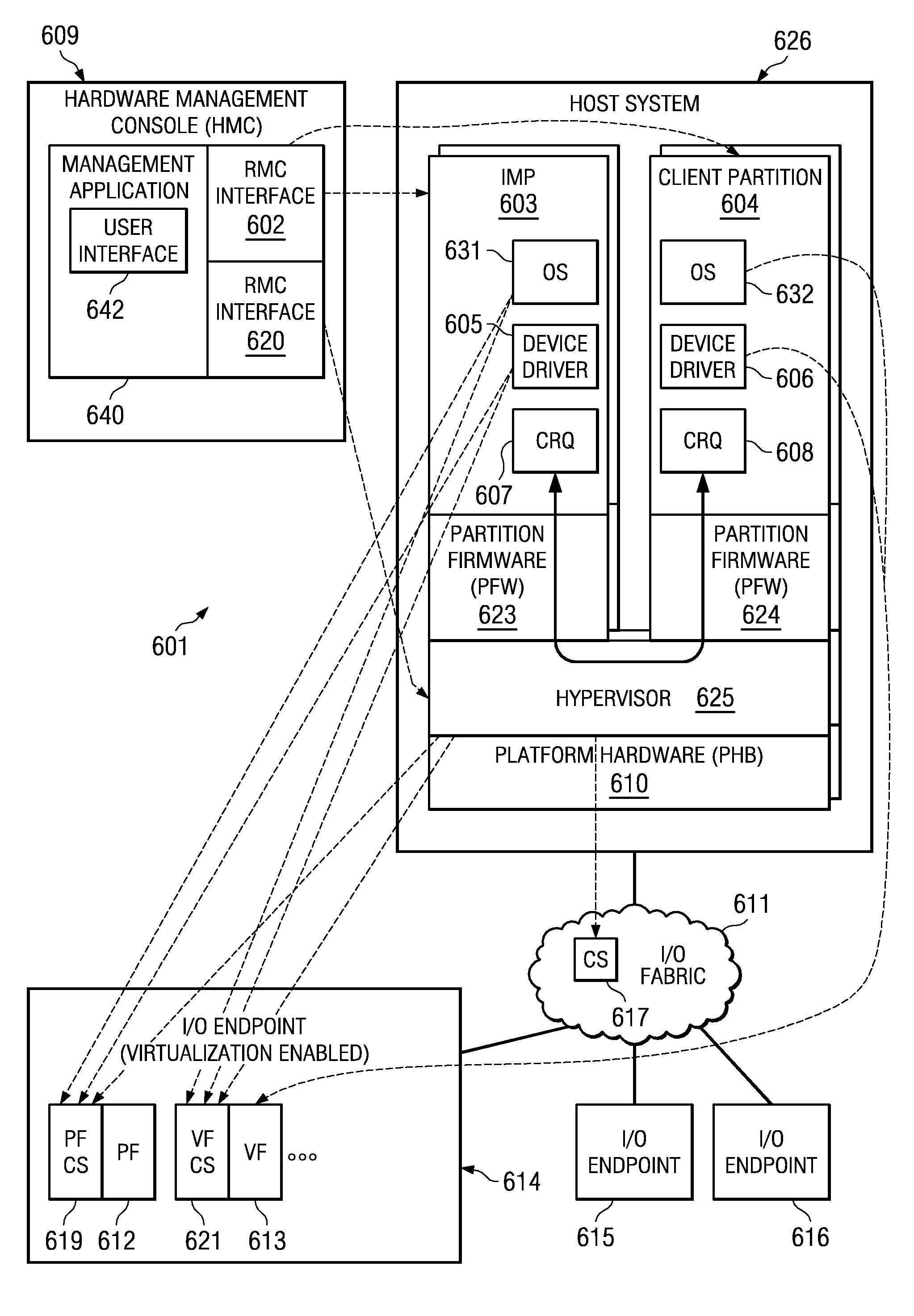
System and method for distribution of resources for an I/O virtualized (IOV) adapter and management of the adapter through an iov management partition
ActiveUS20090144731A1Multiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationClient-sideShared resource
The system and method address the situation where an input / output (I / O) fabric is shared by more than one logical partition (LPAR) and where each LPAR can share with the other LPARs an I / O adapter (IOA). In particular, each LPAR is assigned its own separate address space to access a virtual function (VF) assigned to it such that each LPAR's perception is that it has its own independent IOA. Each VF may be shared across multiple LPARs. Facilities are provided for management of the shared resources of the IOA via a Physical Function (PF) of the IOA by assignment of that PF to an I / O Virtualization Management Partition (IMP). The code running in the IMP acts as a virtual intermediary to the VFs for fully managing the VF error handling, VF reset, and configuration operations. The IMP also acts as an interface to the PF for accessing common VF functionality. Furthermore, the functions of resource assignment and management relative to the VFs and the client partitions that use those VFs, which might normally be done by an entity like a hypervisor, are implemented by this IMP.
Owner:IBM CORP
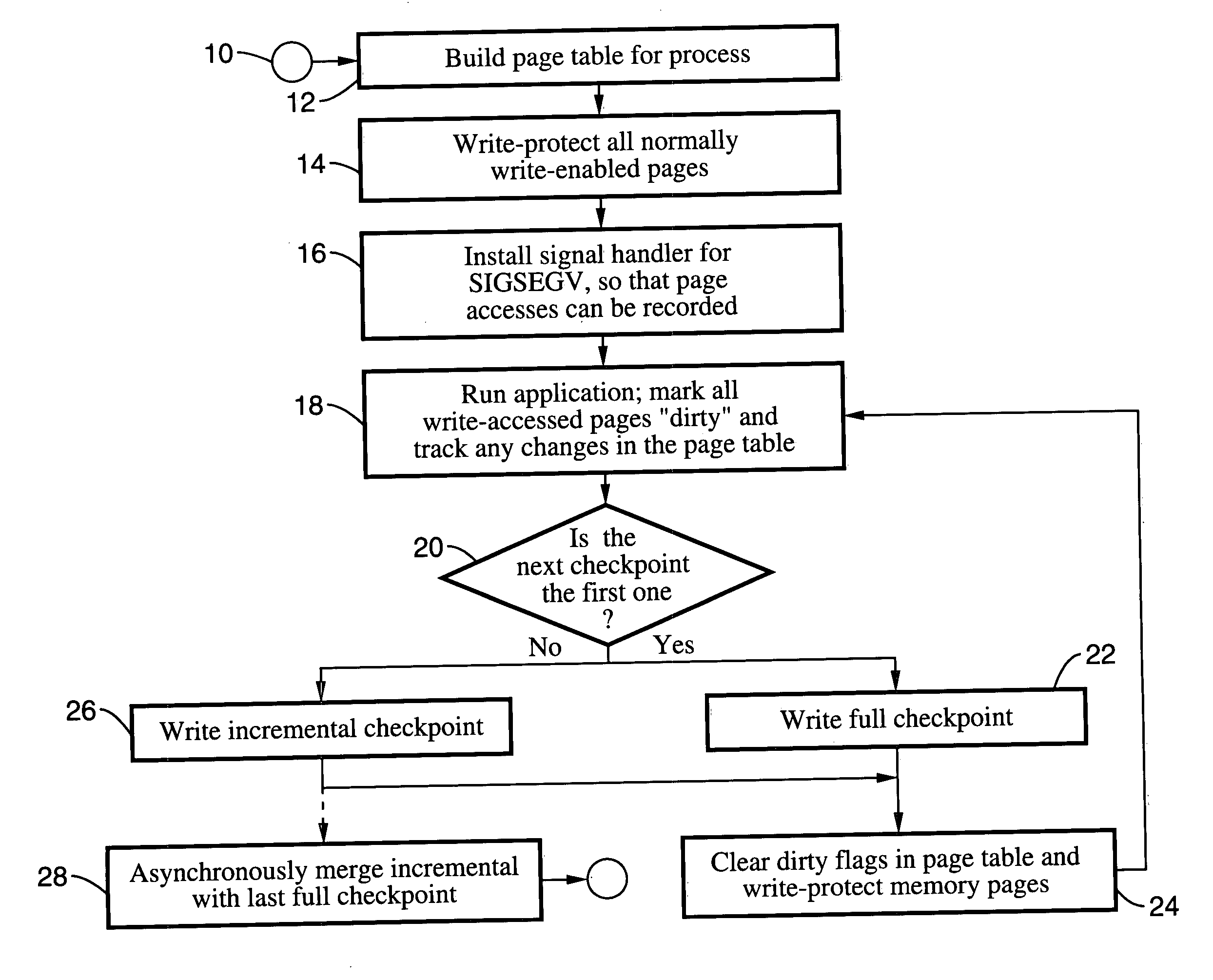
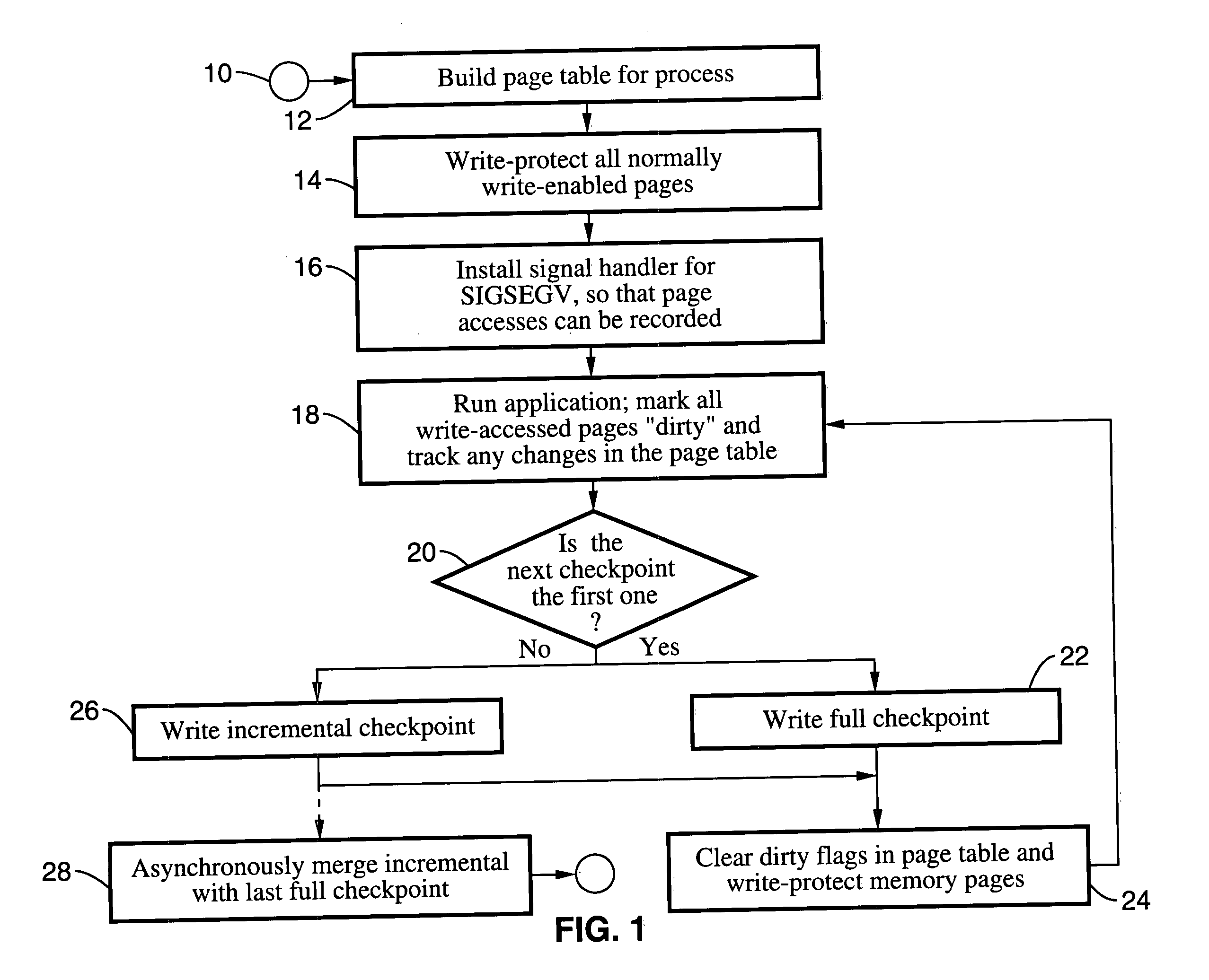
Method and system for providing transparent incremental and multiprocess checkpointing to computer applications
Incremental single and multiprocess checkpointing and restoration is described, which is transparent in that the application program need not be modified, re-compiled, or re-linked to gain the benefits of the invention. The processes subject to checkpointing can be either single or multi-threaded. The method includes incremental page-boundary checkpointing, as well as storage checkpointing of data files associated with applications to ensure correct restoration without the need to restore files for other application programs. Incremental and full checkpoints are asynchronously merged to ensure proper operation while reducing checkpointing delay. By way of example a user-level programming library is described for loading into the address space of the application in conjunction with a loadable kernel module (LKM) or device driver used to capture and restore process state on behalf of the application. These techniques are particularly well suited for use with high-availability (HA) protection programming.
Owner:RED HAT
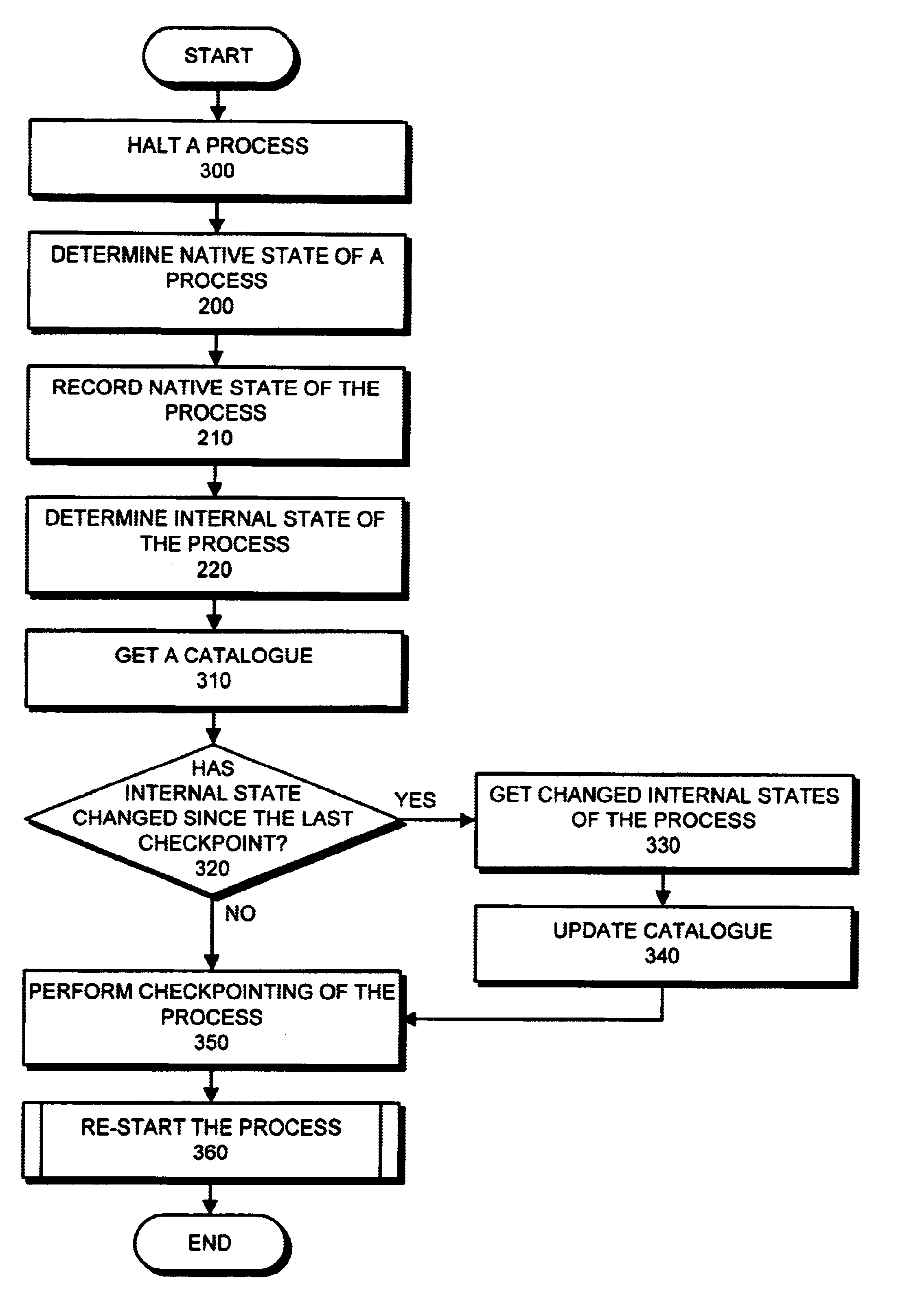
Method and apparatus for hybrid checkpointing
InactiveUS6718538B1Redundant operation error correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsPersistent objectNative state
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for hybrid checkpointing which captures the entire address space of a process: both language internal and language external (native) memory and program state. Initially, the invention halts a currently active process. Next, the invention gets and records the native state of a process, including threads. Next, the invention gets and records the internal state of a process and utilizes persistent object caching. Thereafter, the invention checkpoints the process. In one embodiment, the invention builds and utilizes a catalogue. The catalogue records the native and internal states from prior checkpoints. Upon the invocation of a new checkpoint, the invention accesses the catalogue and determines what native and internal states have changed since the last checkpoint. If some of the states have changed the invention updates the catalogue and only checkpoints those changed states, thereby operating more efficiently.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
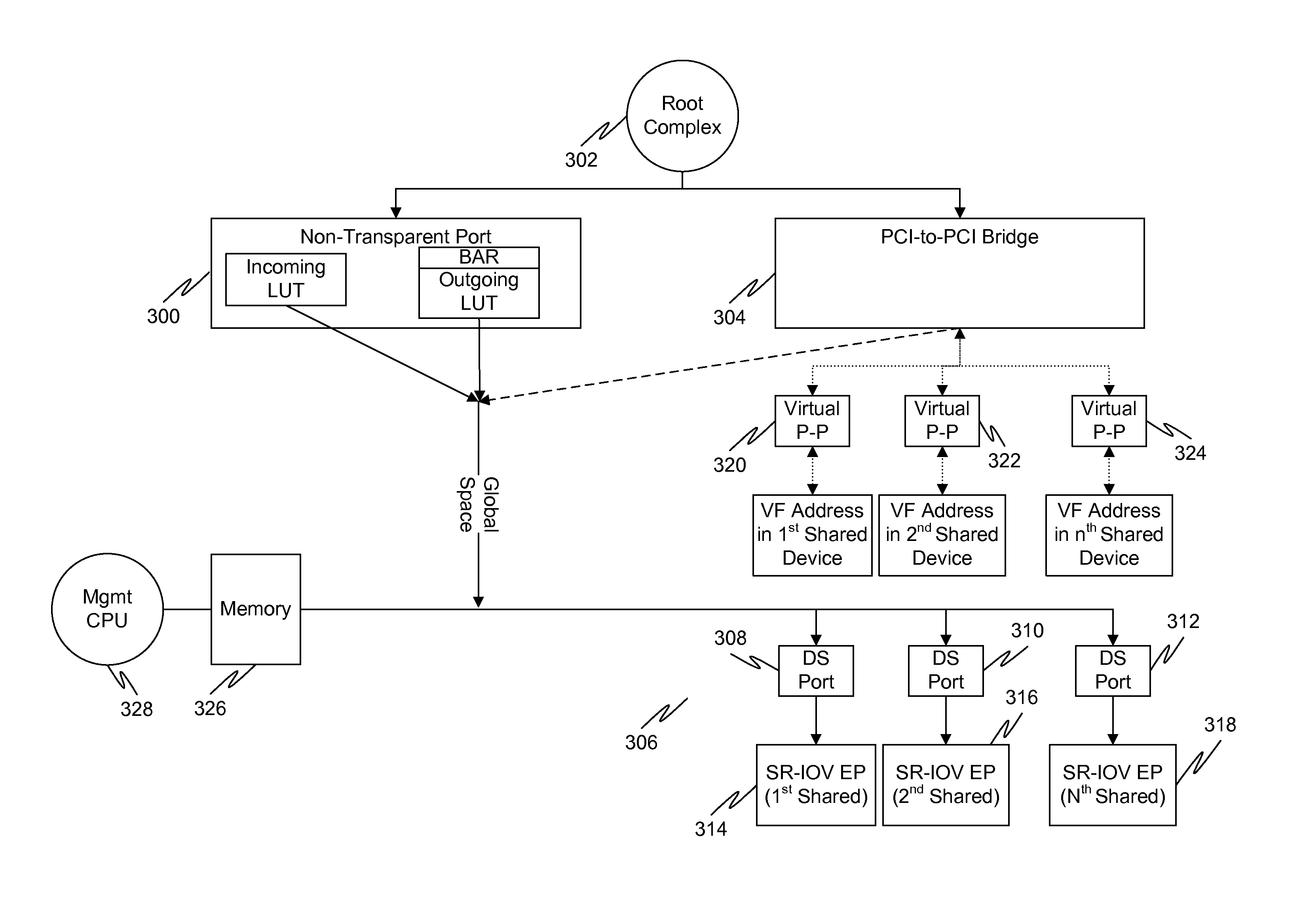
Multi-root sharing of single-root input/output virtualization
In a first embodiment of the present invention, a method for multi-root sharing of a plurality of single root input / output virtualization (SR-IOV) endpoints is provided, the method comprising: CSR redirection to a management processor which either acts as a proxy to execute the CSR request on behalf of the host or filters it and performs an alternate action, downstream routing of memory mapped I / O request packets through the switch in the host's address space and address translation with VF BAR granularity, upstream routing of requests originated by I / O devices by table lookup indexed by Requester ID, and requester ID translation using a fixed local-global RID offset.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for size optimization of storage units
InactiveUS6078745AOverall required size (number of locations) of the memories is minimalOptimize layoutSoftware engineeringMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTime domainArray data structure
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for reducing the storage size required for temporary data by storage order optimization. Advantageously, the execution order optimization and the storage order optimization may be treated independently. The storage size optimization is preferably performed by determining an optimum intra-array and / or inter-array storage order based on a geometrical model. The geometrical model provides a representation of the address space occupied by an array as a function of time and allows the calculation of the window size of the occupied address / time domain of the array. Where calculations would be time-consuming, these may be shortened by making simplifying assumptions, e.g. calculation of upper and lower bounds of the window size of the occupied address / time domain of an array rather than an exact calculation. Further, heuristical simplifications are described to reduce run-times for the optimization process.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Internet and related networks, a method of and system for substitute use of checksum field space in information processing datagram headers for obviating processing speed and addressing space limitations and providing other features
InactiveUS6330614B1Add featureIncrease internet speedElectric signal transmission systemsTime-division multiplexInformation processingPrivate network
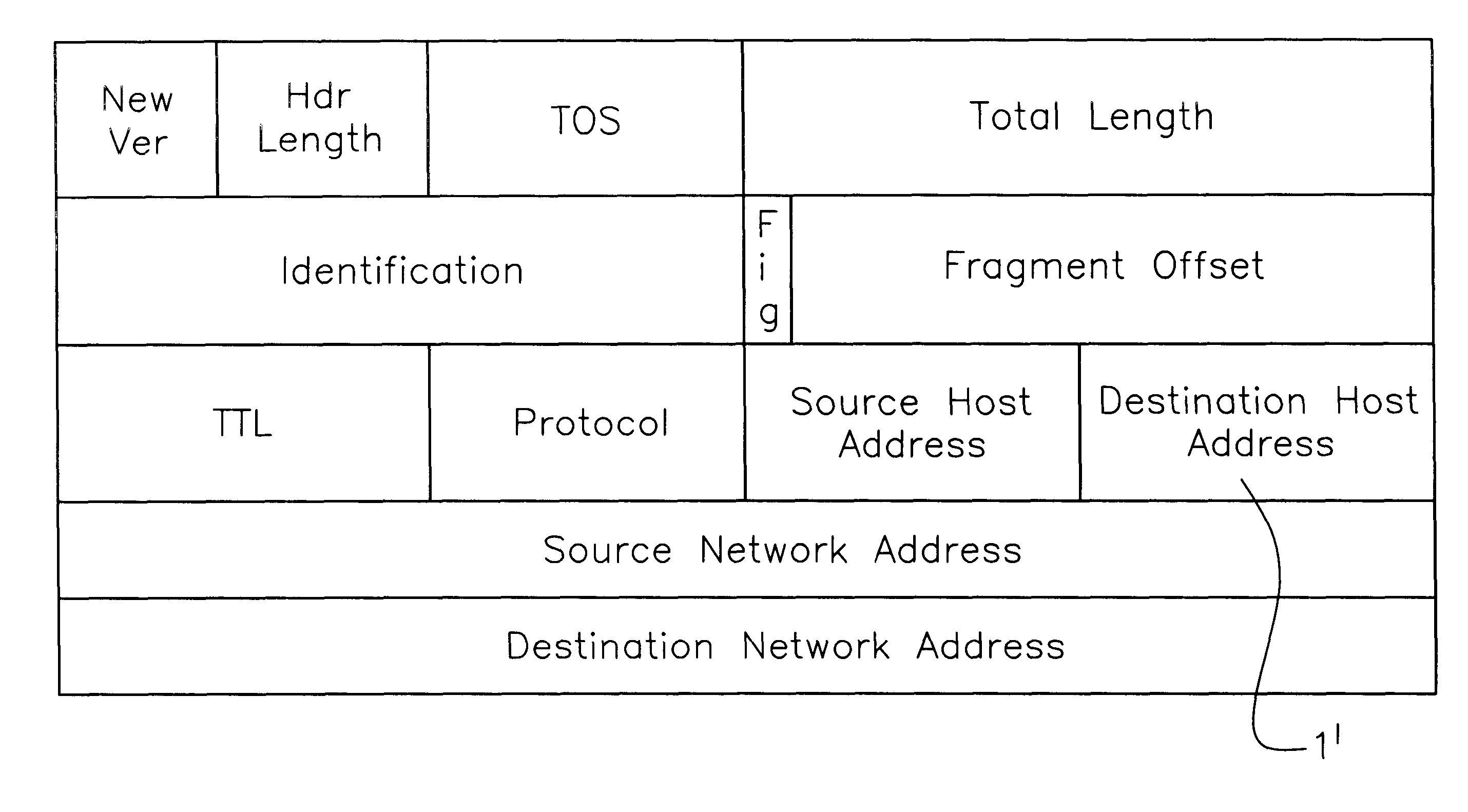
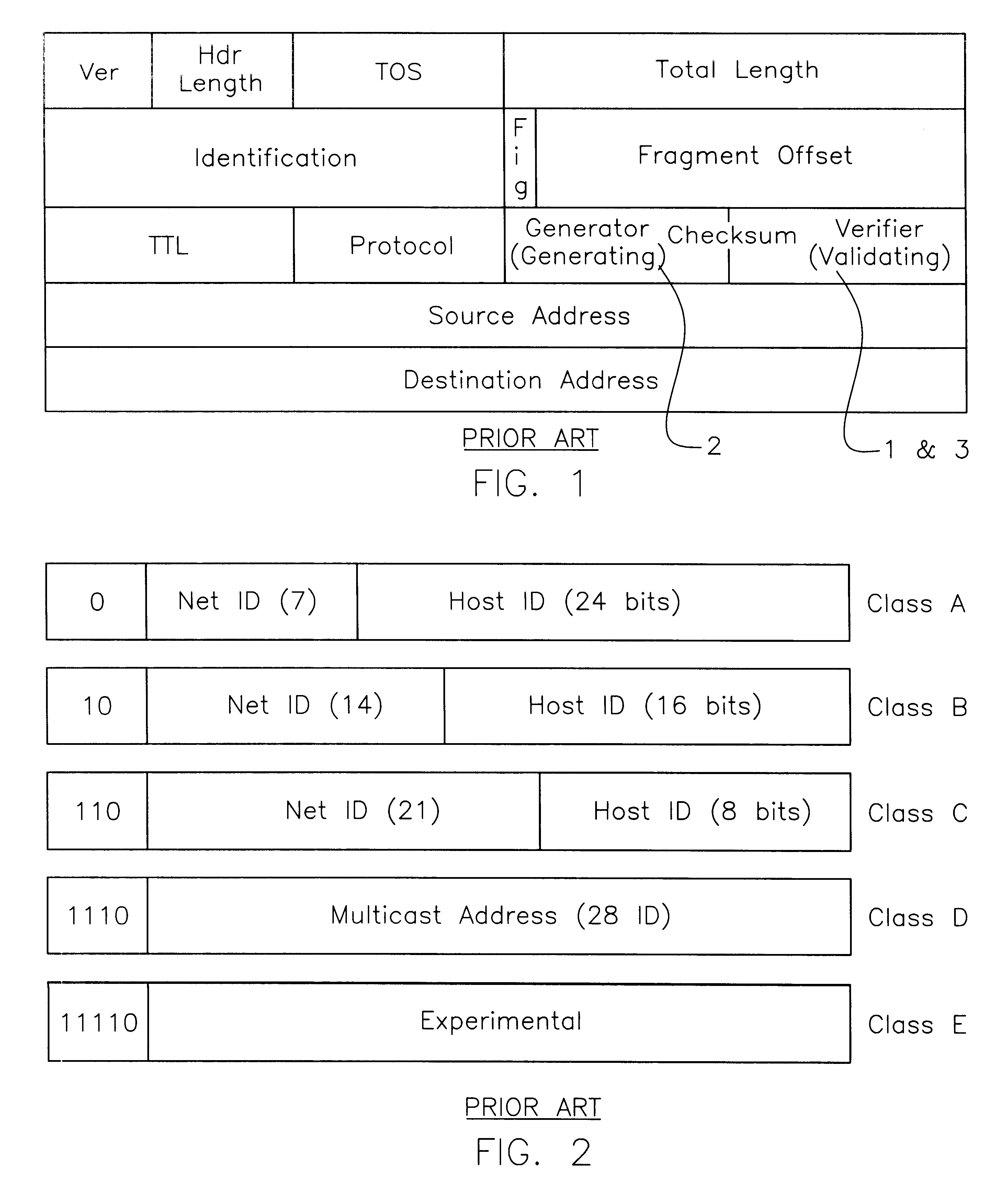
In Internet and related networks, a method of and system for substitute use of the normal checksum field space in information processing (IP) datagram headers for obviating current processing time and addressing space limitations, involving replacing the current checksum usage in the checksum field with its attendant processing time with further source host and destination host addresses of lesser processing time, thereby increasing the address space for the network and decreasing the require header processing time, and / or providing space for autonomous system numbers, a higher layer protocol-based routing information (including of the MPLS type) or for Virtual Private Networks Indentifiers in the header.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com