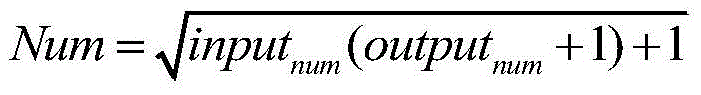Patents
Literature
584 results about "Distributed memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
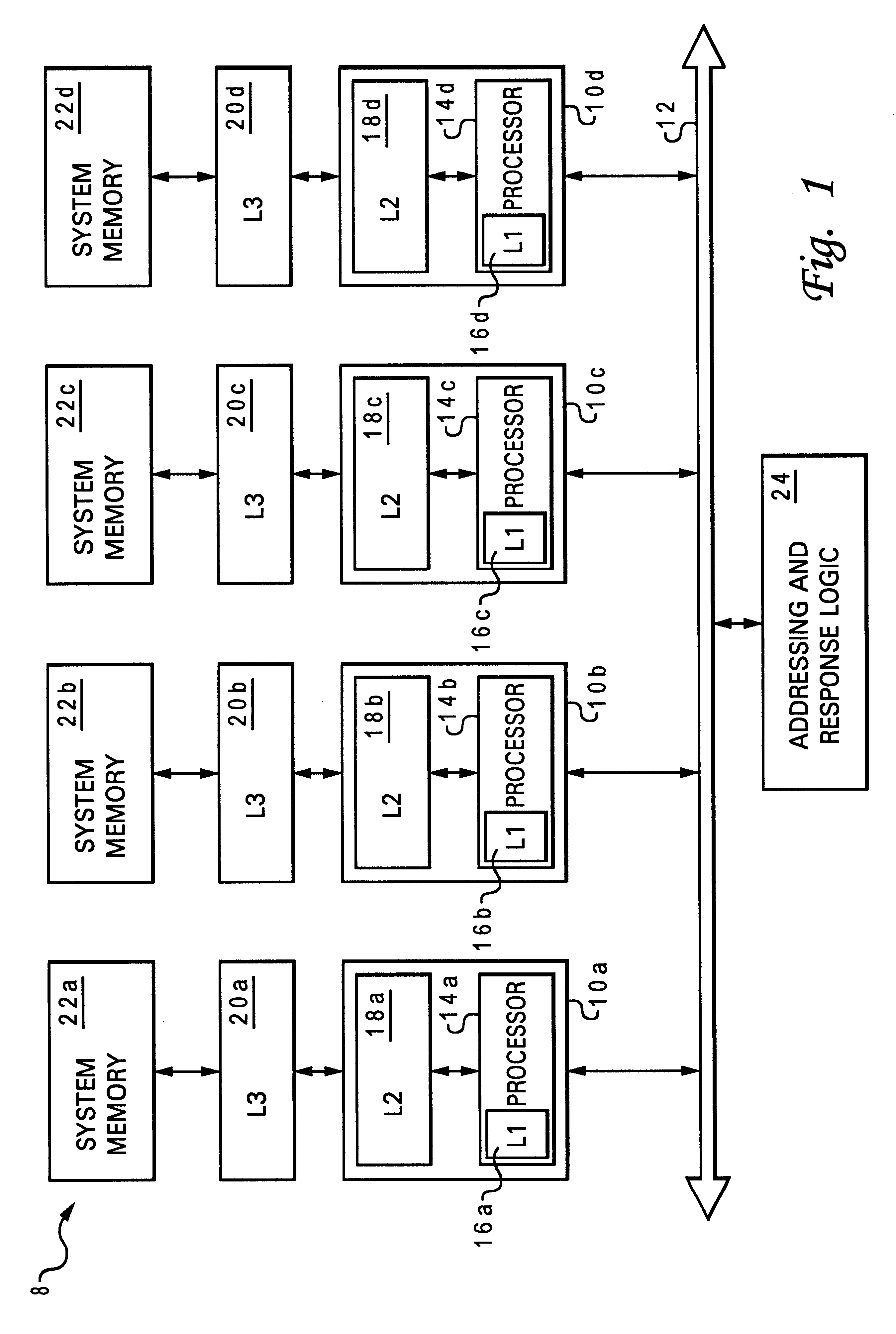
In computer science, distributed memory refers to a multiprocessor computer system in which each processor has its own private memory. Computational tasks can only operate on local data, and if remote data is required, the computational task must communicate with one or more remote processors. In contrast, a shared memory multiprocessor offers a single memory space used by all processors. Processors do not have to be aware where data resides, except that there may be performance penalties, and that race conditions are to be avoided.
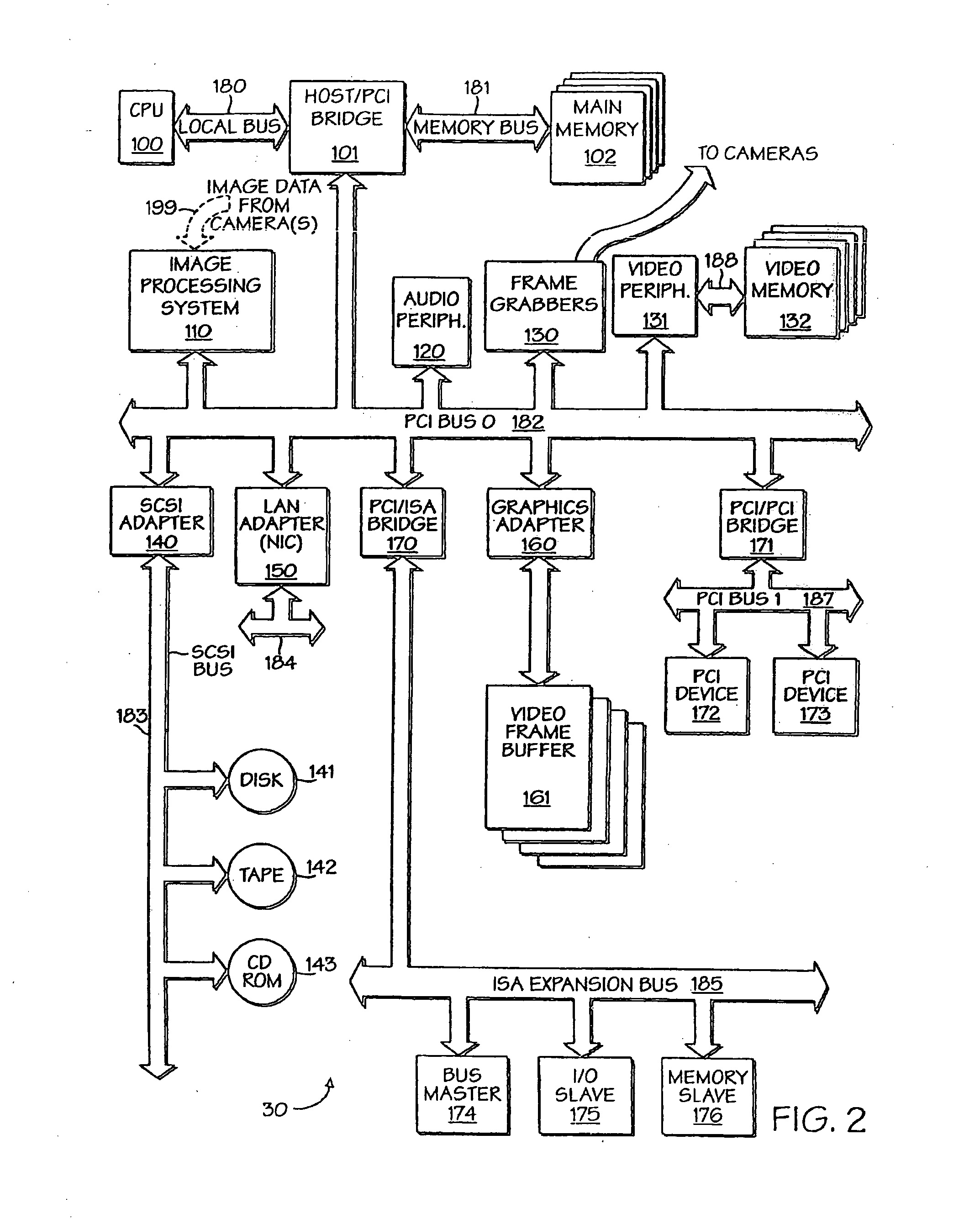
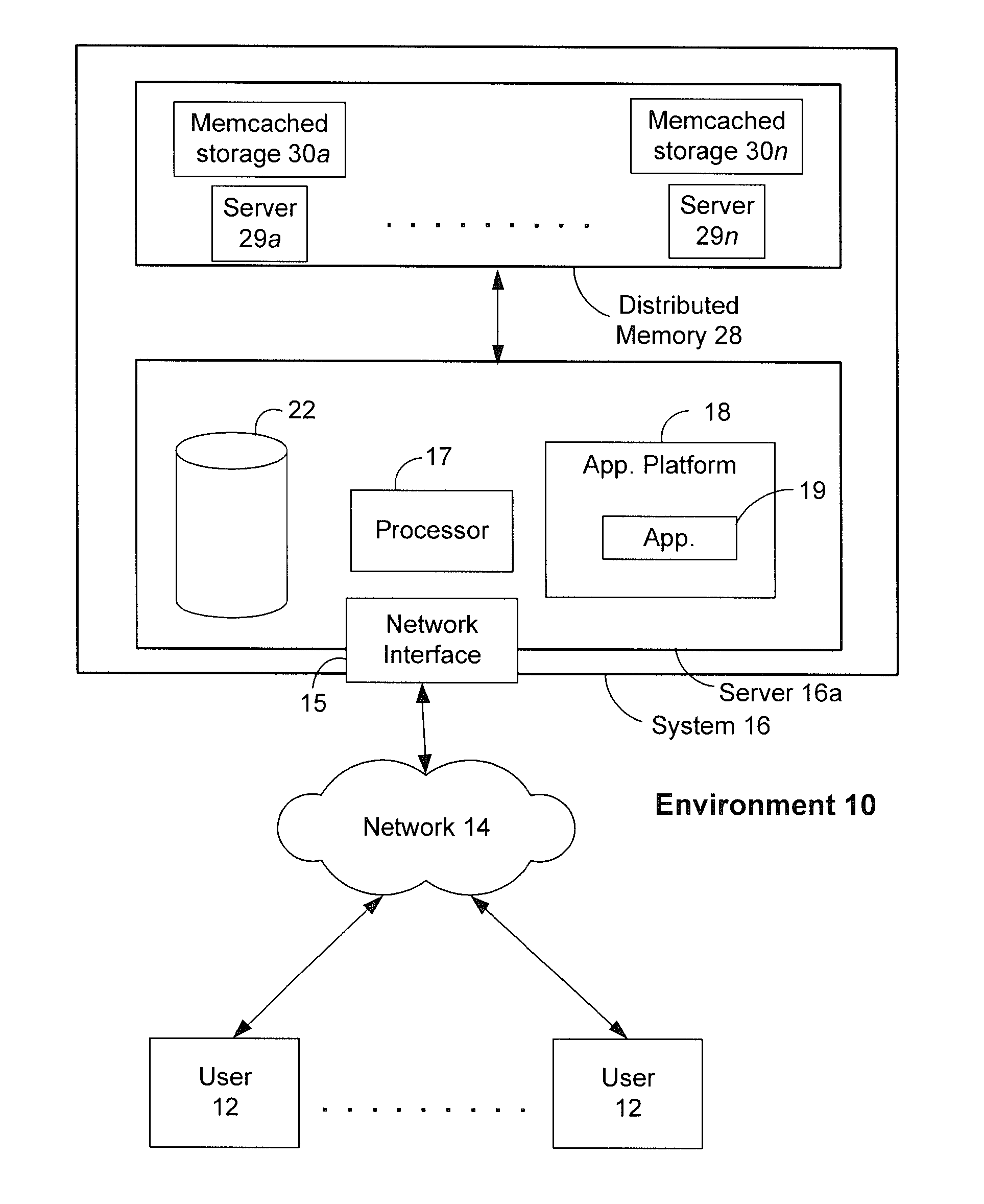
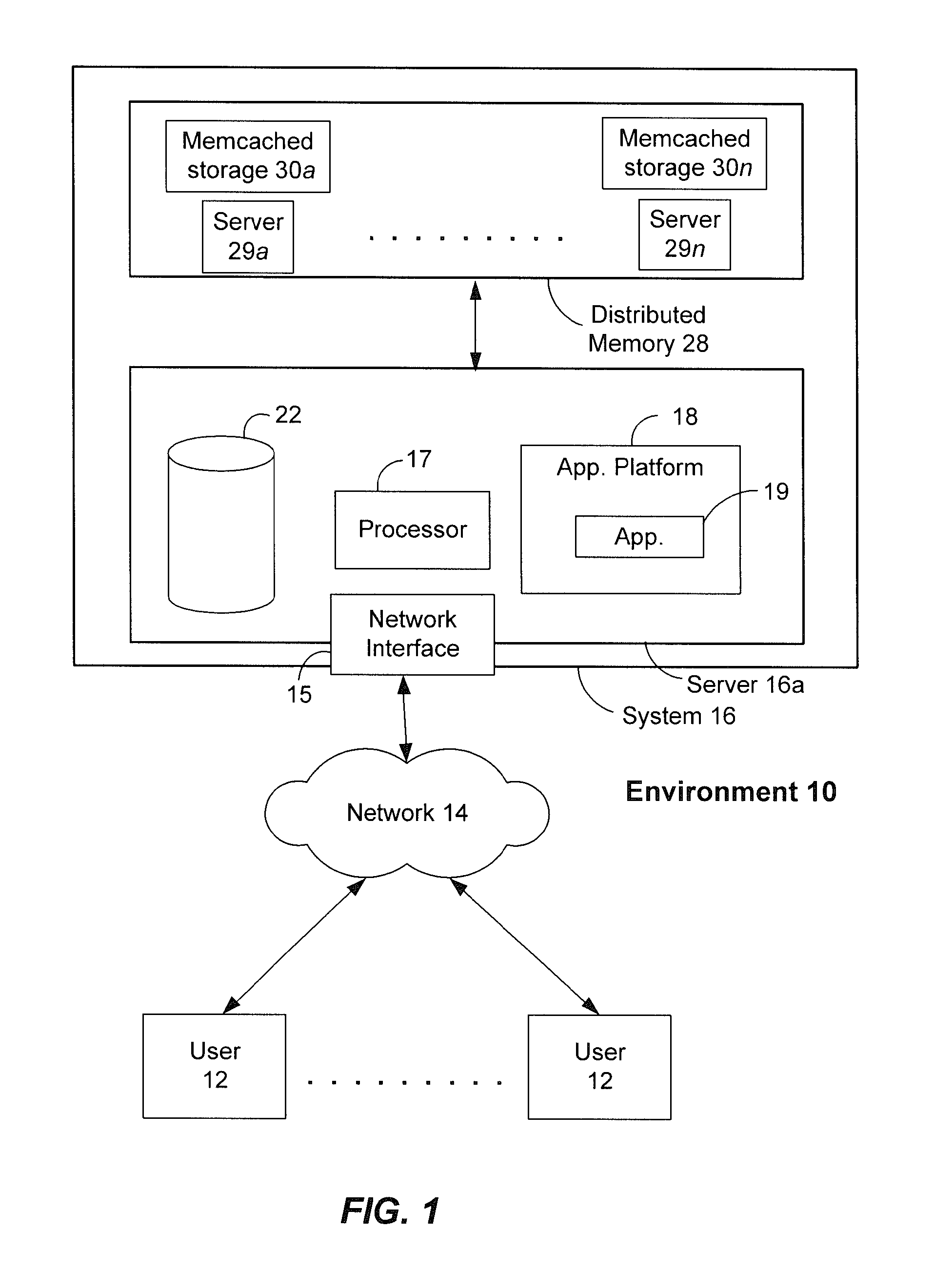
Data processing system and method
InactiveUS6215898B1Reduce overheadHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisStatic random-access memoryHigh memory
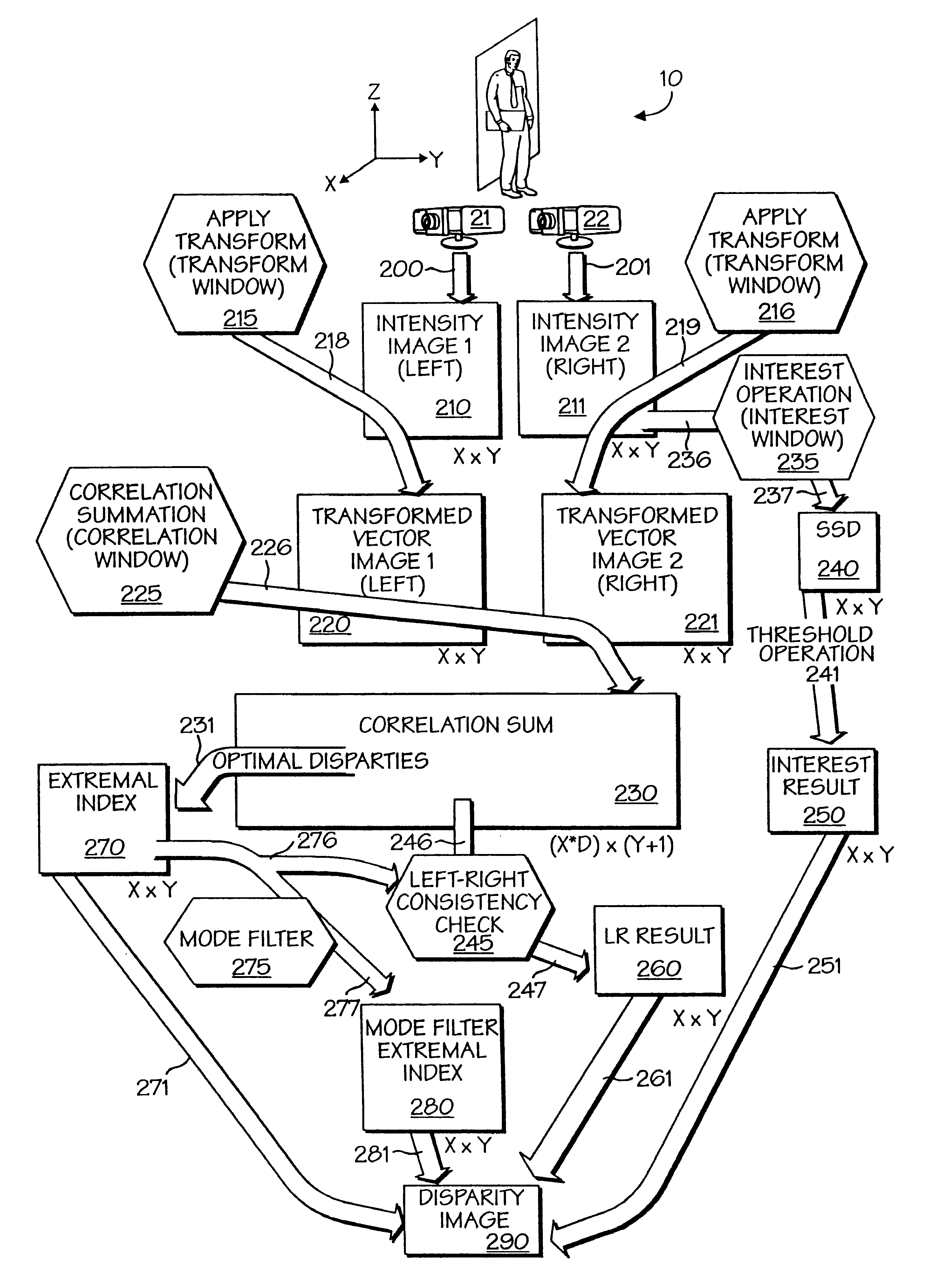
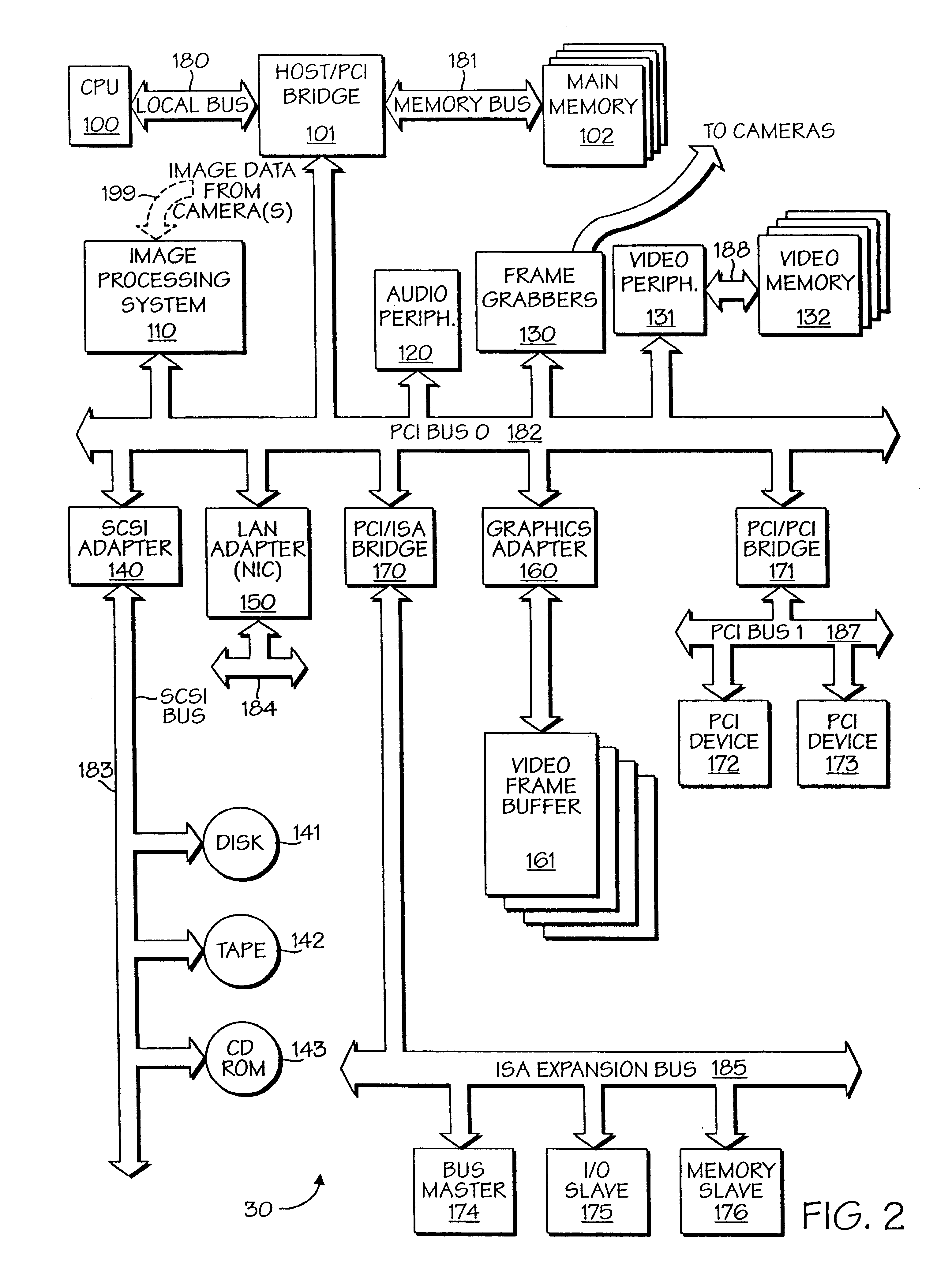
A powerful, scaleable, and reconfigurable image processing system and method of processing data therein is described. This general purpose, reconfigurable engine with toroidal topology, distributed memory, and wide bandwidth I / O are capable of solving real applications at real-time speeds. The reconfigurable image processing system can be optimized to efficiently perform specialized computations, such as real-time video and audio processing. This reconfigurable image processing system provides high performance via high computational density, high memory bandwidth, and high I / O bandwidth. Generally, the reconfigurable image processing system and its control structure include a homogeneous array of 16 field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and 16 static random access memories (SRAM) arranged in a partial torus configuration. The reconfigurable image processing system also includes a PCI bus interface chip, a clock control chip, and a datapath chip. It can be implemented in a single board. It receives data from its external environment, computes correspondence, and uses the results of the correspondence computations for various post-processing industrial applications. The reconfigurable image processing system determines correspondence by using non-parametric local transforms followed by correlation. These non-parametric local transforms include the census and rank transforms. Other embodiments involve a combination of correspondence, rectification, a left-right consistency check, and the application of an interest operator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Data collection and analysis system
ActiveUS20080228306A1Easy to useExcessive signalingTesting/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsDistributed memoryData harvesting
A sensor network collects time-series data from a process tool and supplies the data to an analysis system where pattern analysis techniques are used to identify structures and to monitor subsequent data based on analysis instructions or a composite model. Time-series data from multiple process runs are used to form a composite model of a data structure including variation. Comparison with the composite model gives an indication of tool health. A sensor network may have distributed memory for easy configuration.
Owner:KLA CORP
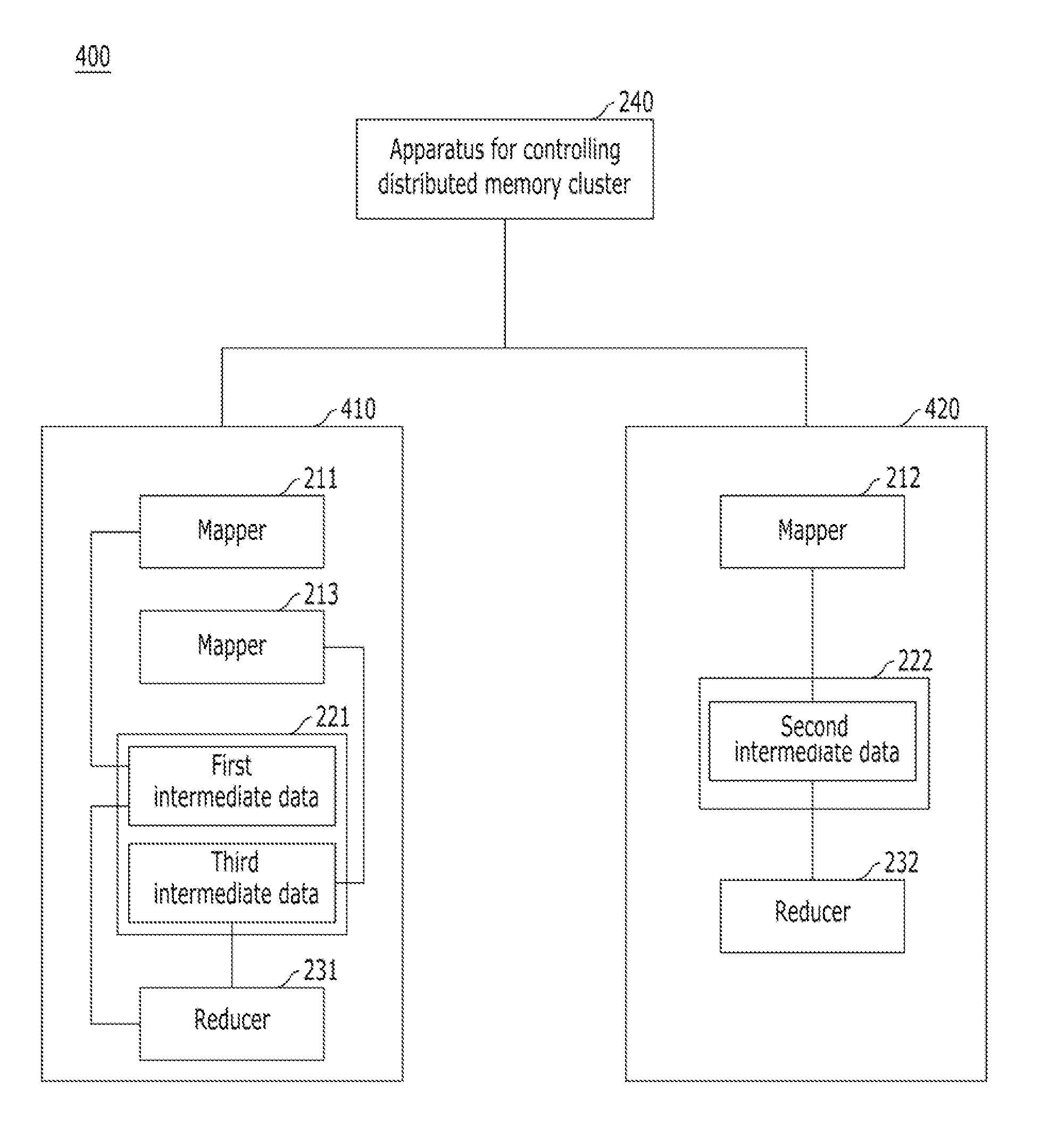
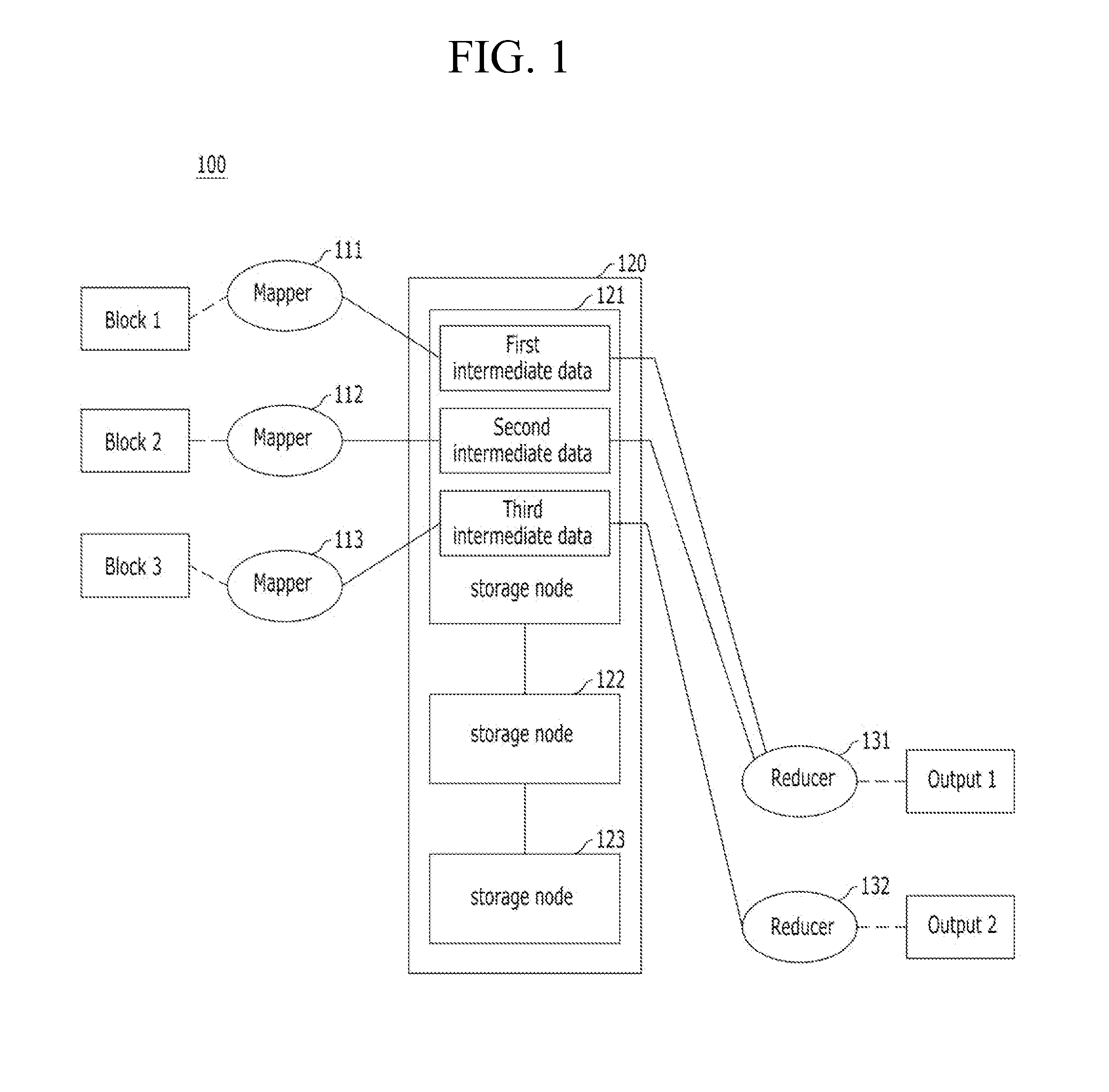
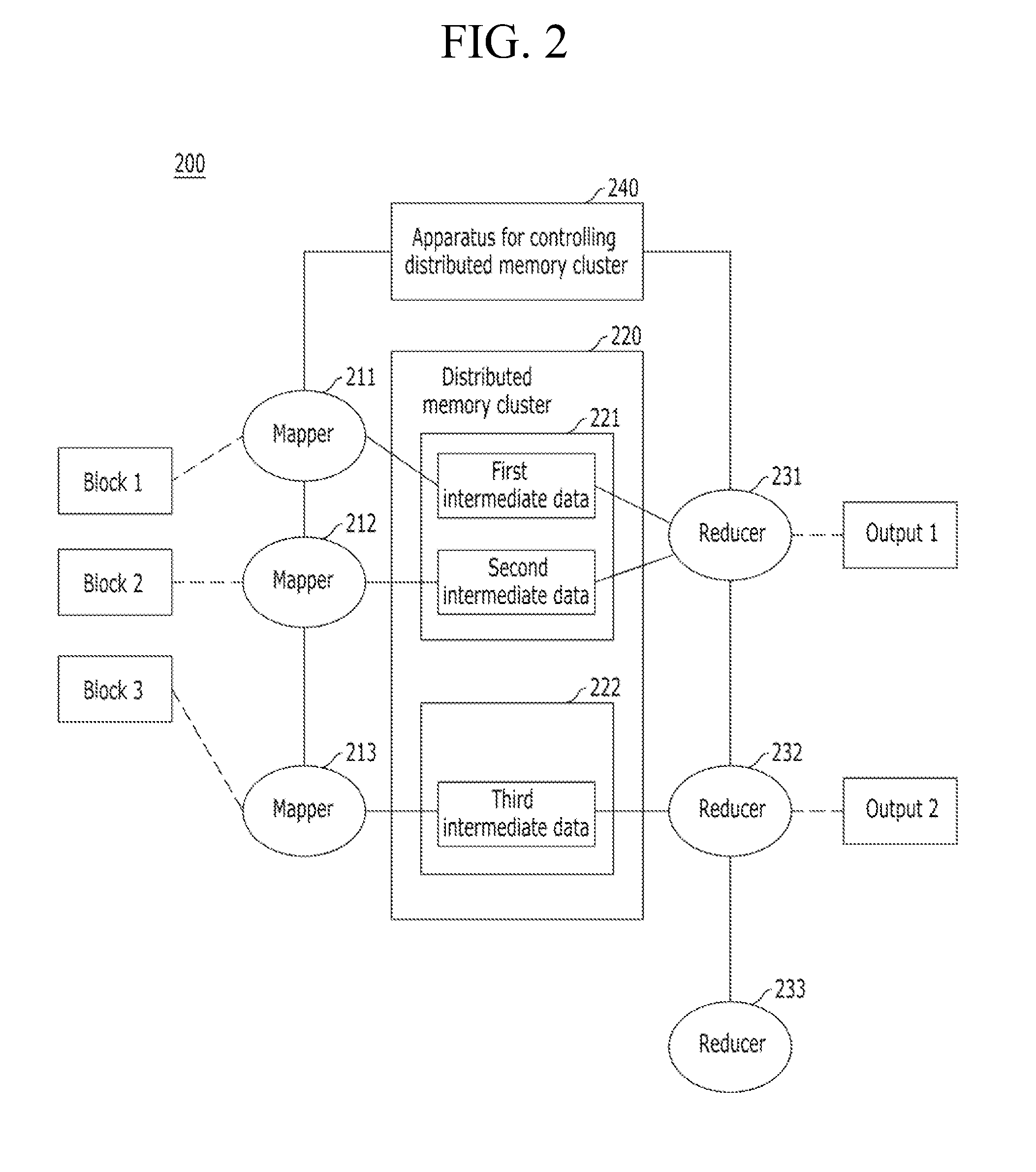
Apparatus and method for controlling distributed memory cluster
ActiveUS20120209943A1Valid choiceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsNode clusteringDistributed memory
Provided are an apparatus and method for controlling a distributed memory cluster. A distributed computing system may include a computing node cluster, a distributed memory cluster, and a controlling node. The computing node cluster may include a plurality of computing nodes including first computing nodes that each generates associated data. The distributed memory cluster may be configured to store the associated data of the first computing nodes. The controlling node may be configured to select memory blocks of the associated data for distribution on the distributed memory cluster based on a node selection rule and memory cluster structure information, and to select second computing nodes from the computing node cluster based on a location selection rule and the memory cluster structure information.
Owner:KT CORP
Data processing system and method
InactiveUS20060013473A1Eliminate informationImage enhancementImage analysisStatic random-access memoryHigh memory
A powerful, scaleable, and reconfigurable image processing system and method of processing data therein is described. This general purpose, reconfigurable engine with toroidal topology, distributed memory, and wide bandwidth I / O are capable of solving real applications at real-time speeds. The reconfigurable image processing system can be optimized to efficiently perform specialized computations, such as real-time video and audio processing. This reconfigurable image processing system provides high performance via high computational density, high memory bandwidth, and high I / O bandwidth. Generally, the reconfigurable image processing system and its control structure include a homogeneous array of 16 field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and 16 static random access memories (SRAM) arranged in a partial torus configuration. The reconfigurable image processing system also includes a PCI bus interface chip, a clock control chip, and a datapath chip. It can be implemented in a single board. It receives data from its external environment, computes correspondence, and uses the results of the correspondence computations for various post-processing industrial applications. The reconfigurable image processing system determines correspondence by using non-parametric local transforms followed by correlation. These non-parametric local transforms include the census and rank transforms. Other embodiments involve a combination of correspondence, rectification, a left-right consistency check, and the application of an interest operator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
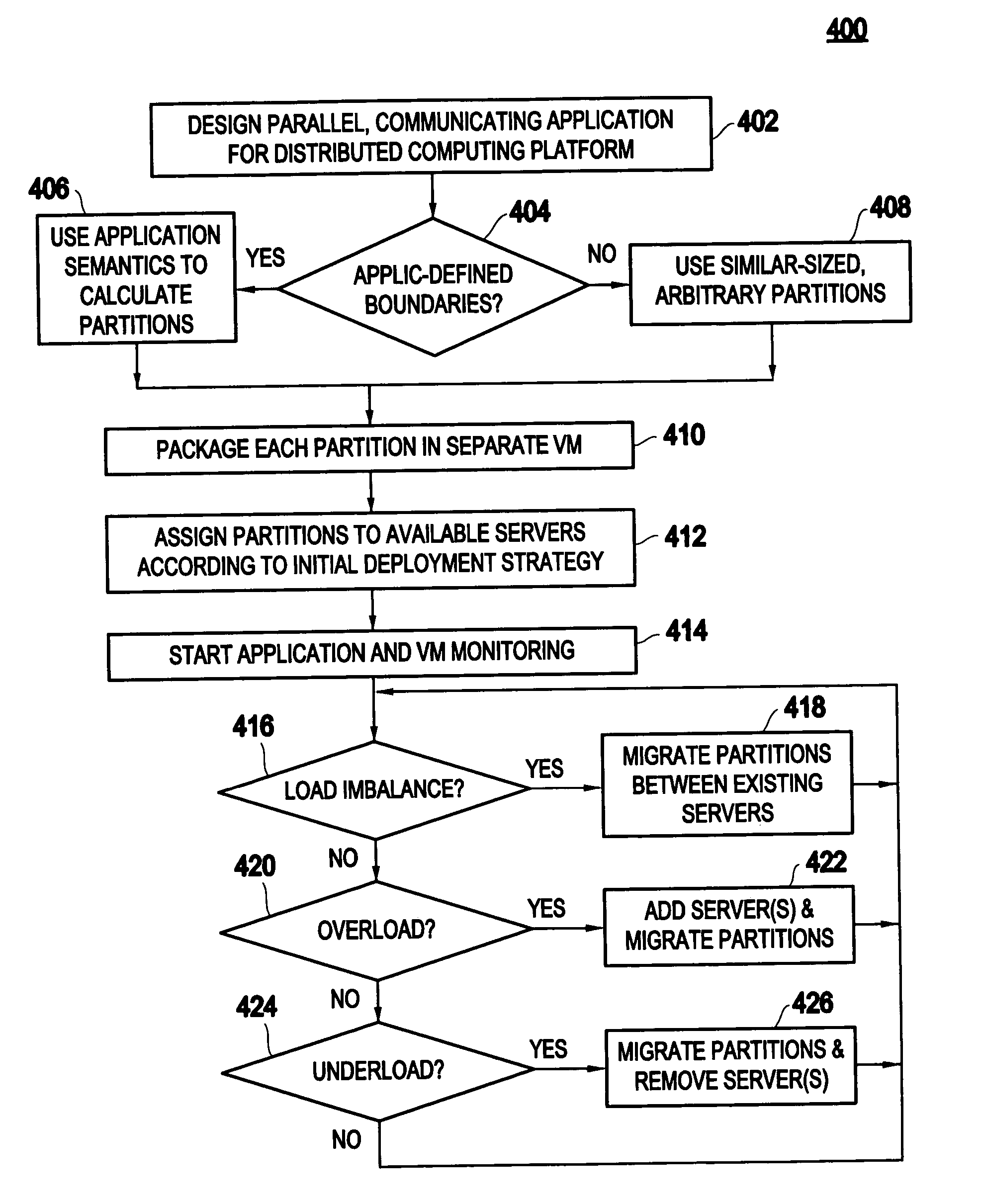
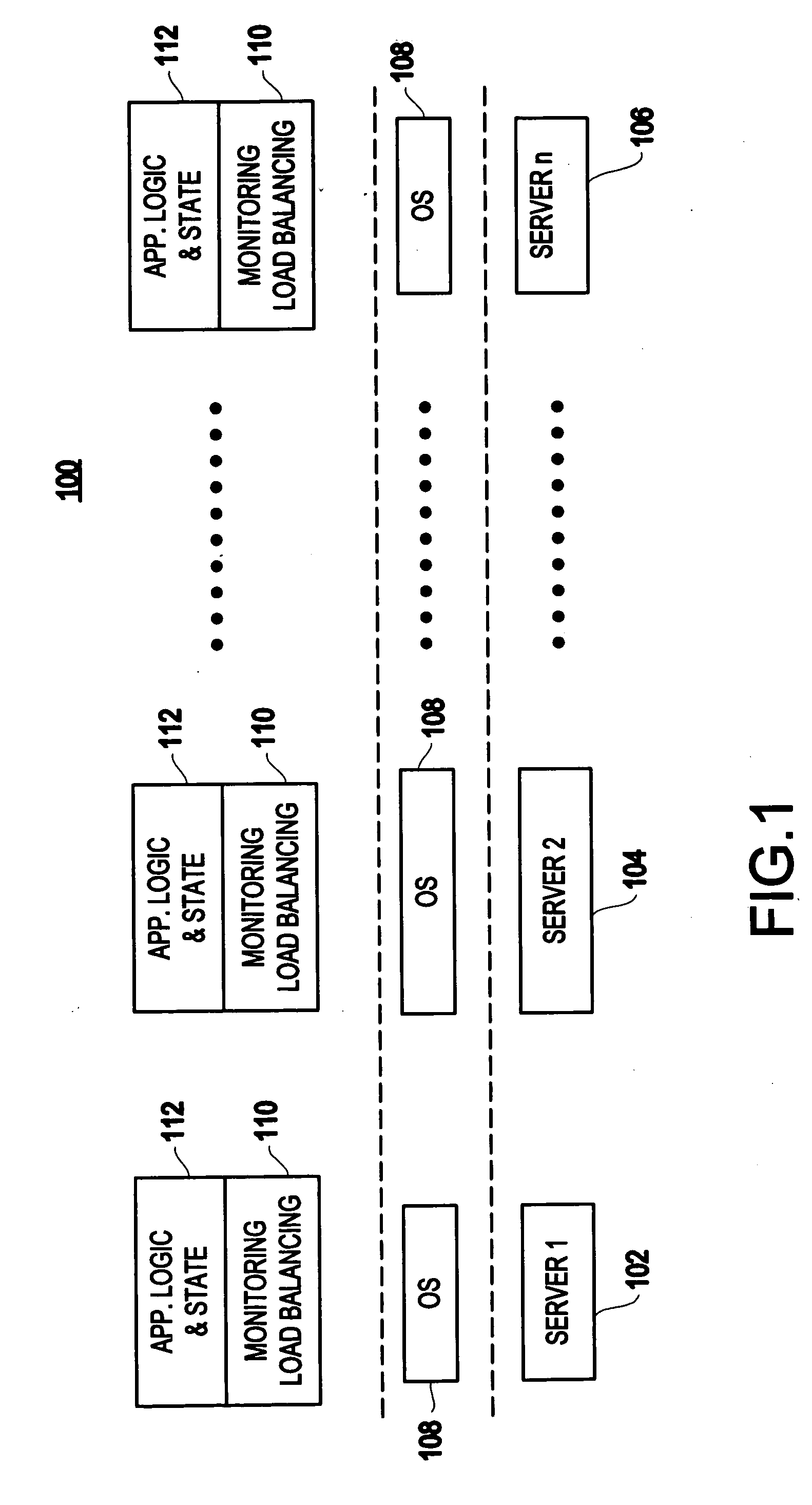
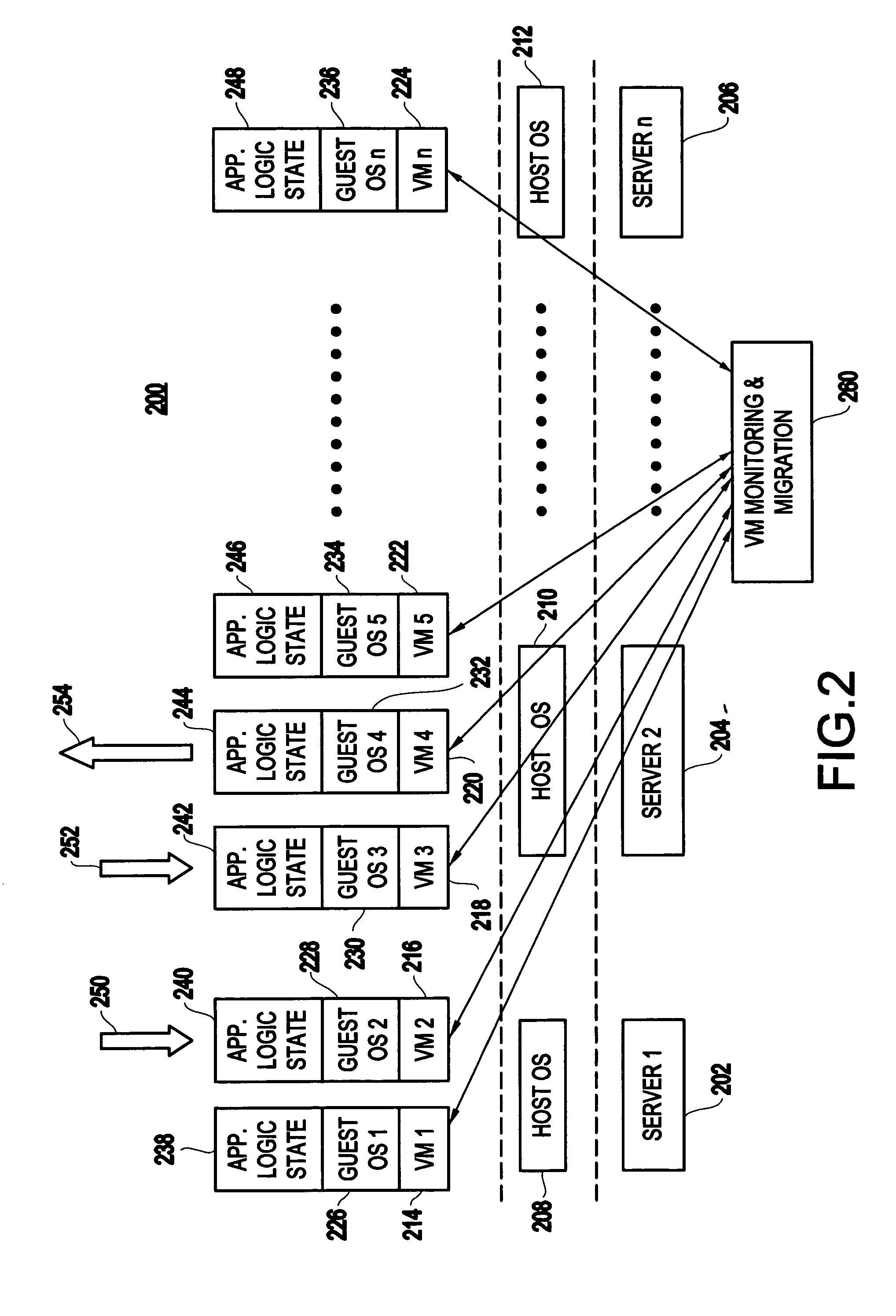
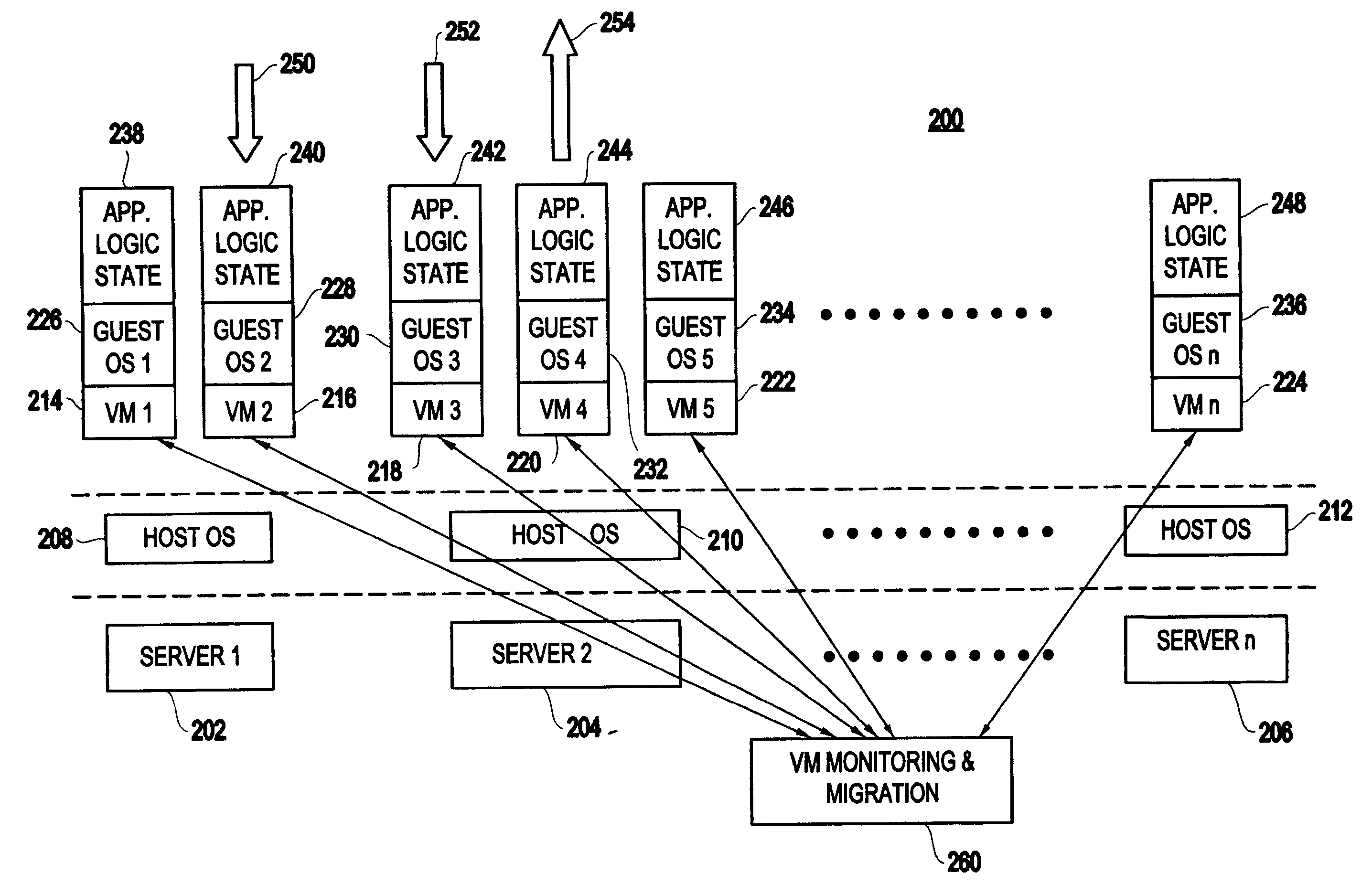
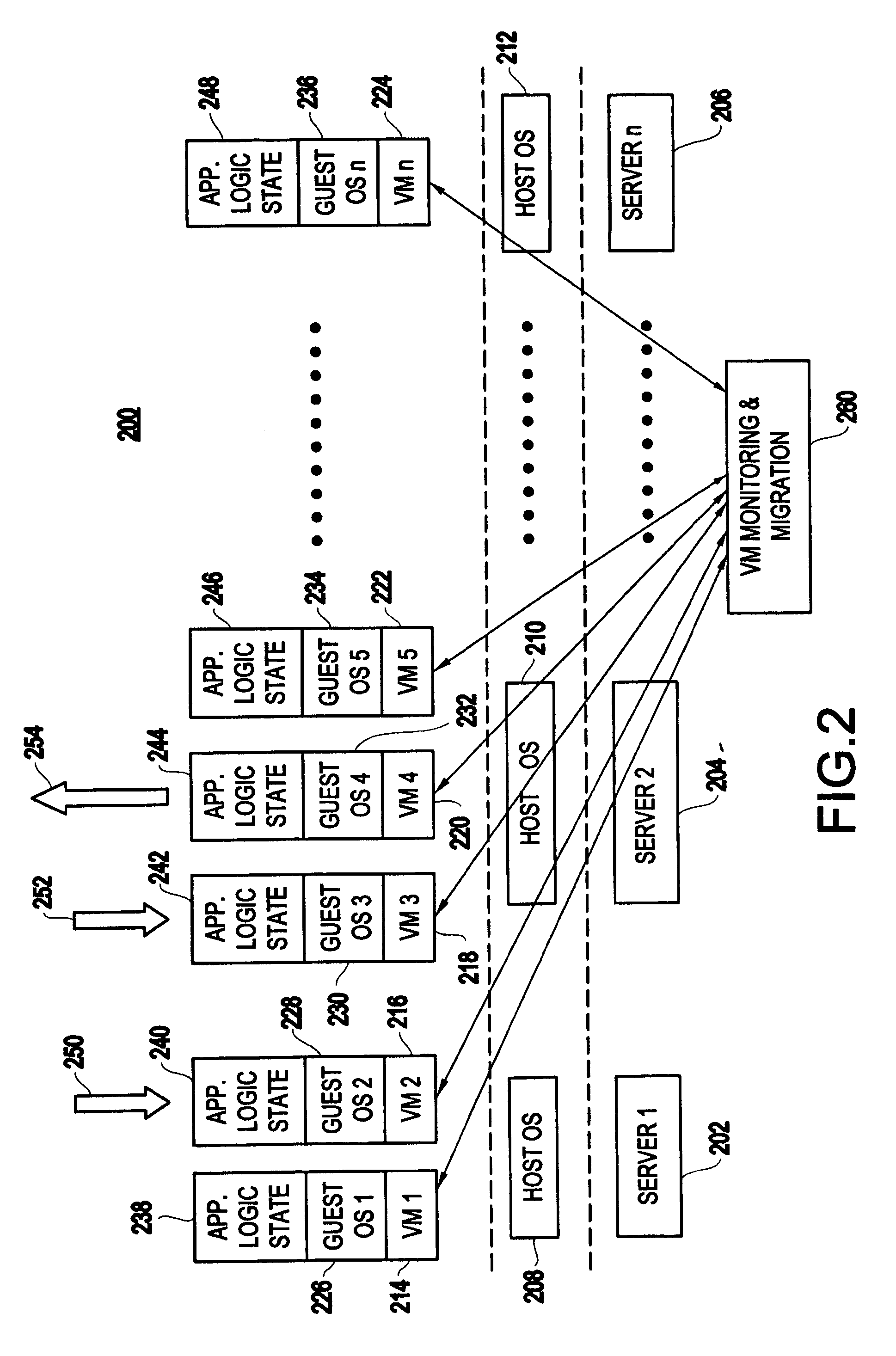
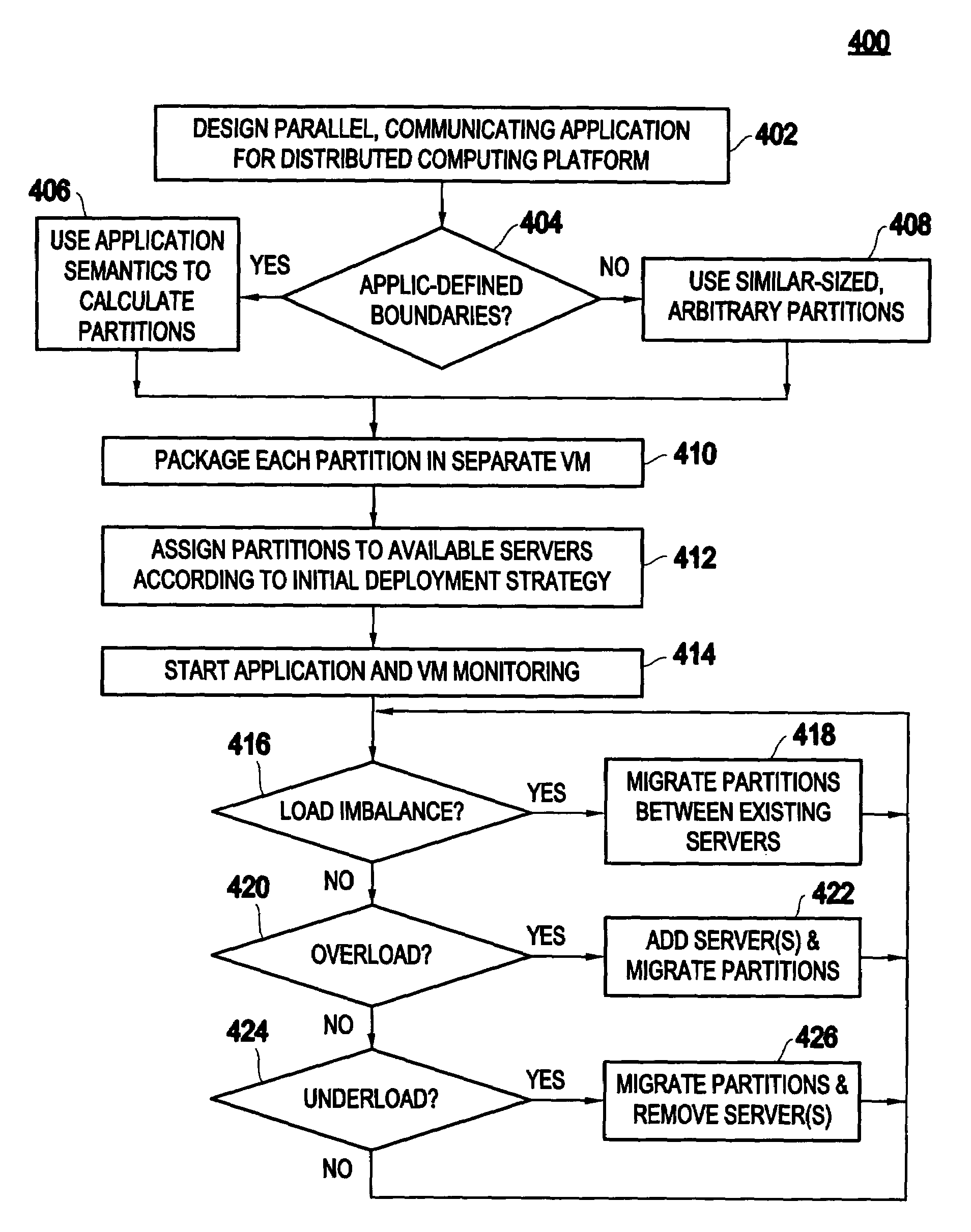
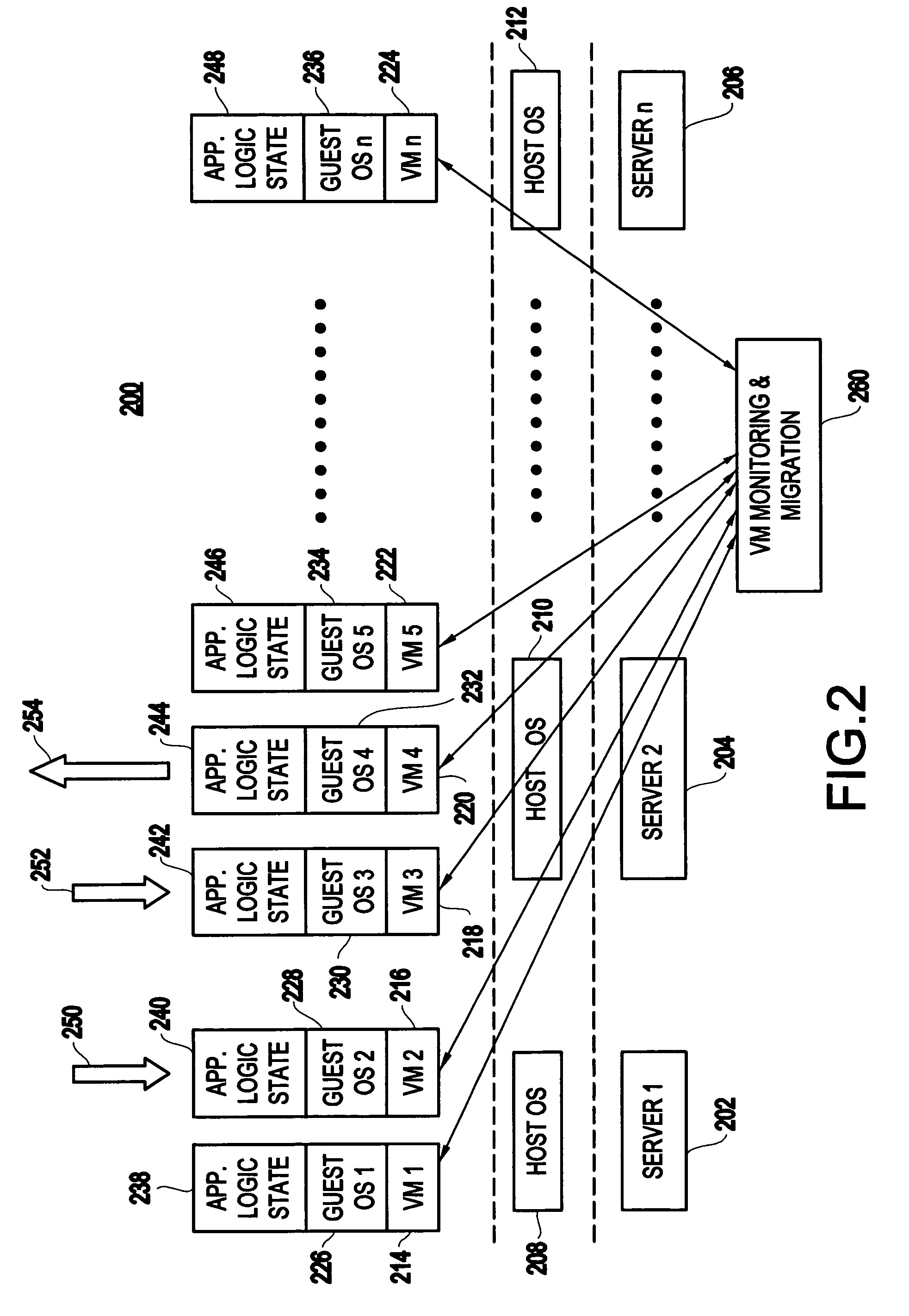
Method and apparatus for using virtual machine technology for managing parallel communicating applications
InactiveUS20060230407A1Designing can be facilitatedIncreasing complexityMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLoad SheddingDistributed memory
A method (and system) for managing a distributed-memory parallel application running on multiple servers, includes dynamically moving a plurality of executable program components, where each of the plurality of executable program components are running on one of a plurality of virtual machines, using migration of the virtual machines between physical servers. The load balancing is operated based on a workload of each of the virtual machines and servers, where a virtual machine, or a plurality of virtual machines, are transferred to balance the workload between each of the servers.
Owner:IBM CORP
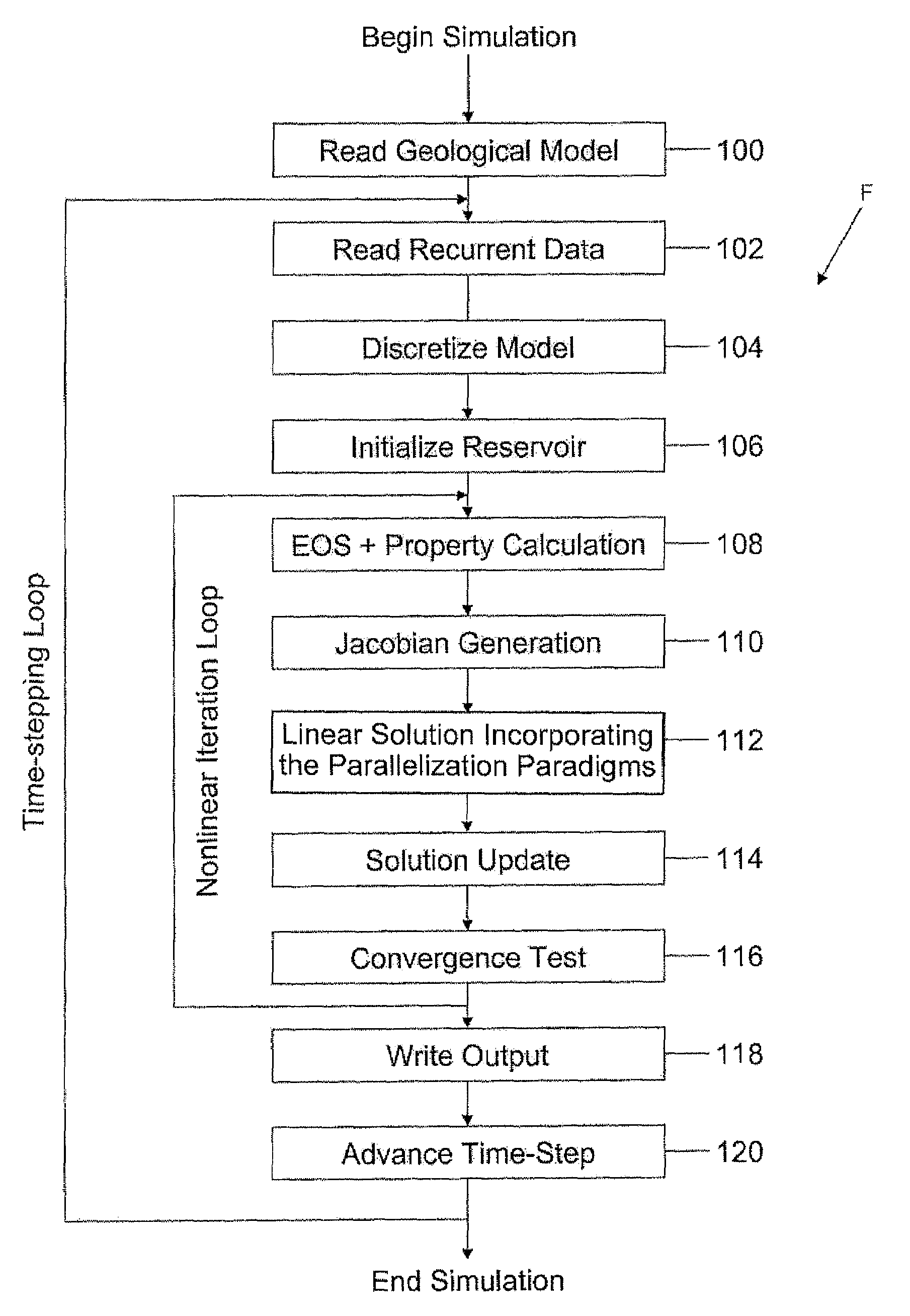
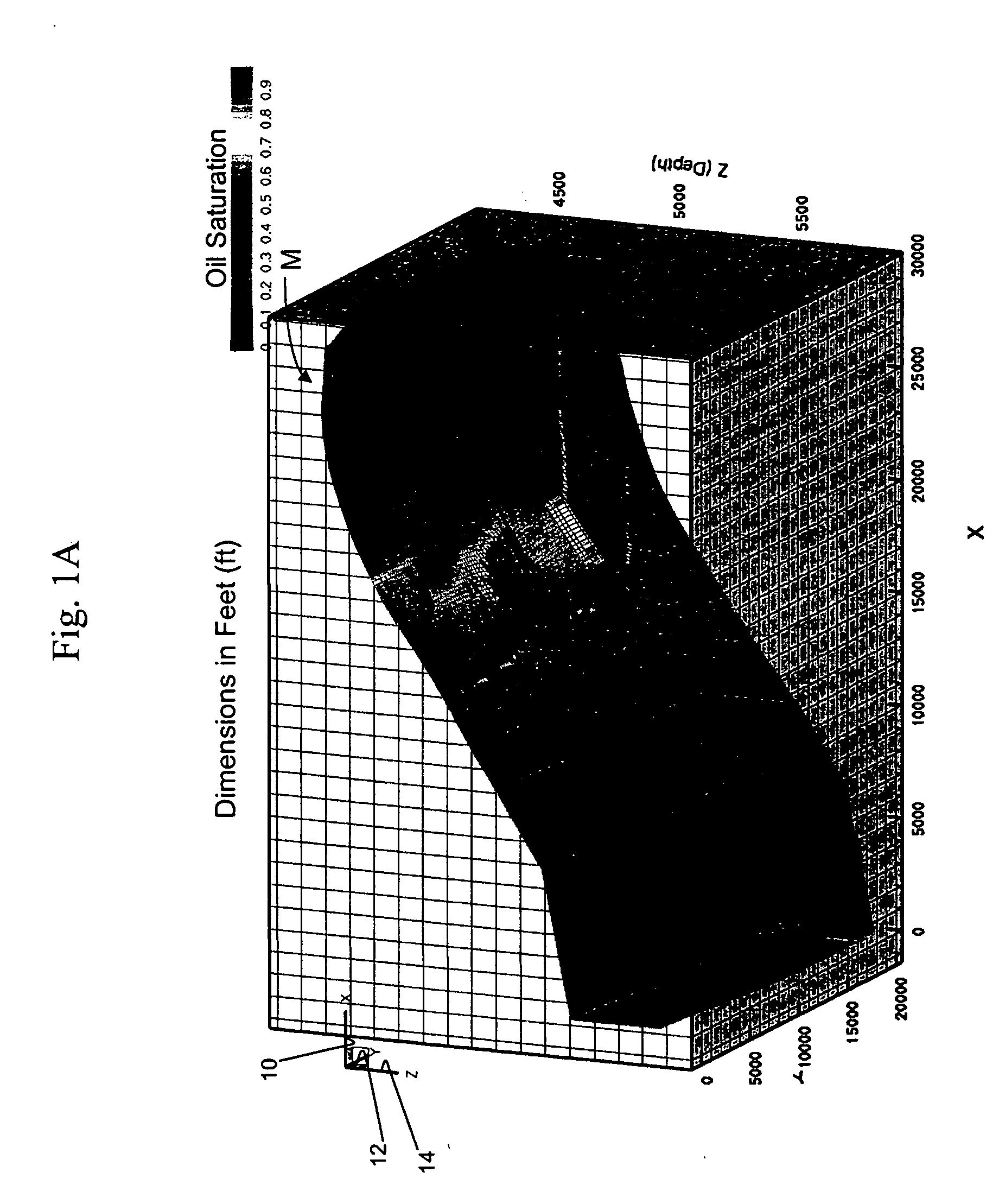
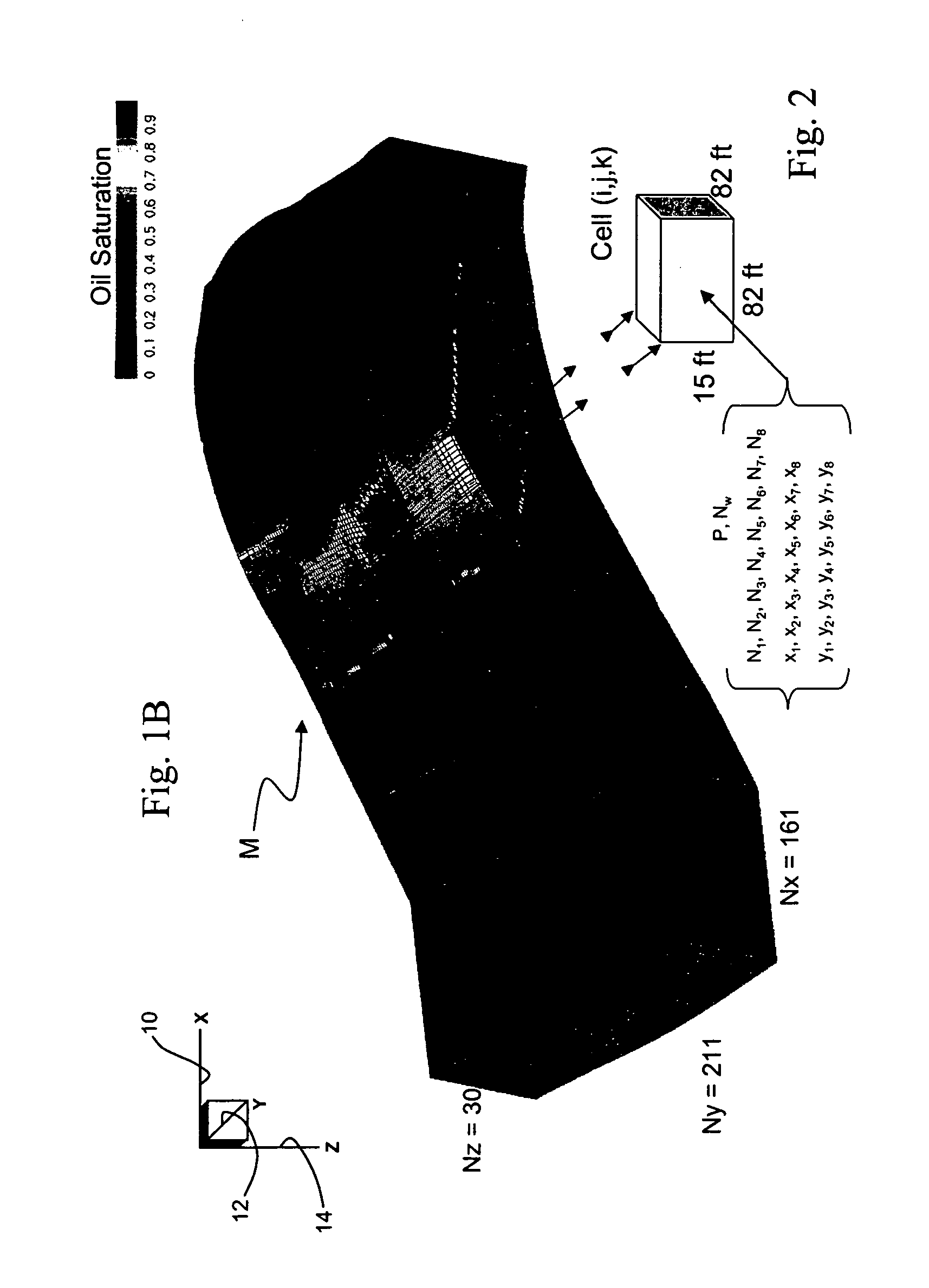
Highly-parallel, implicit compositional reservoir simulator for multi-million-cell models
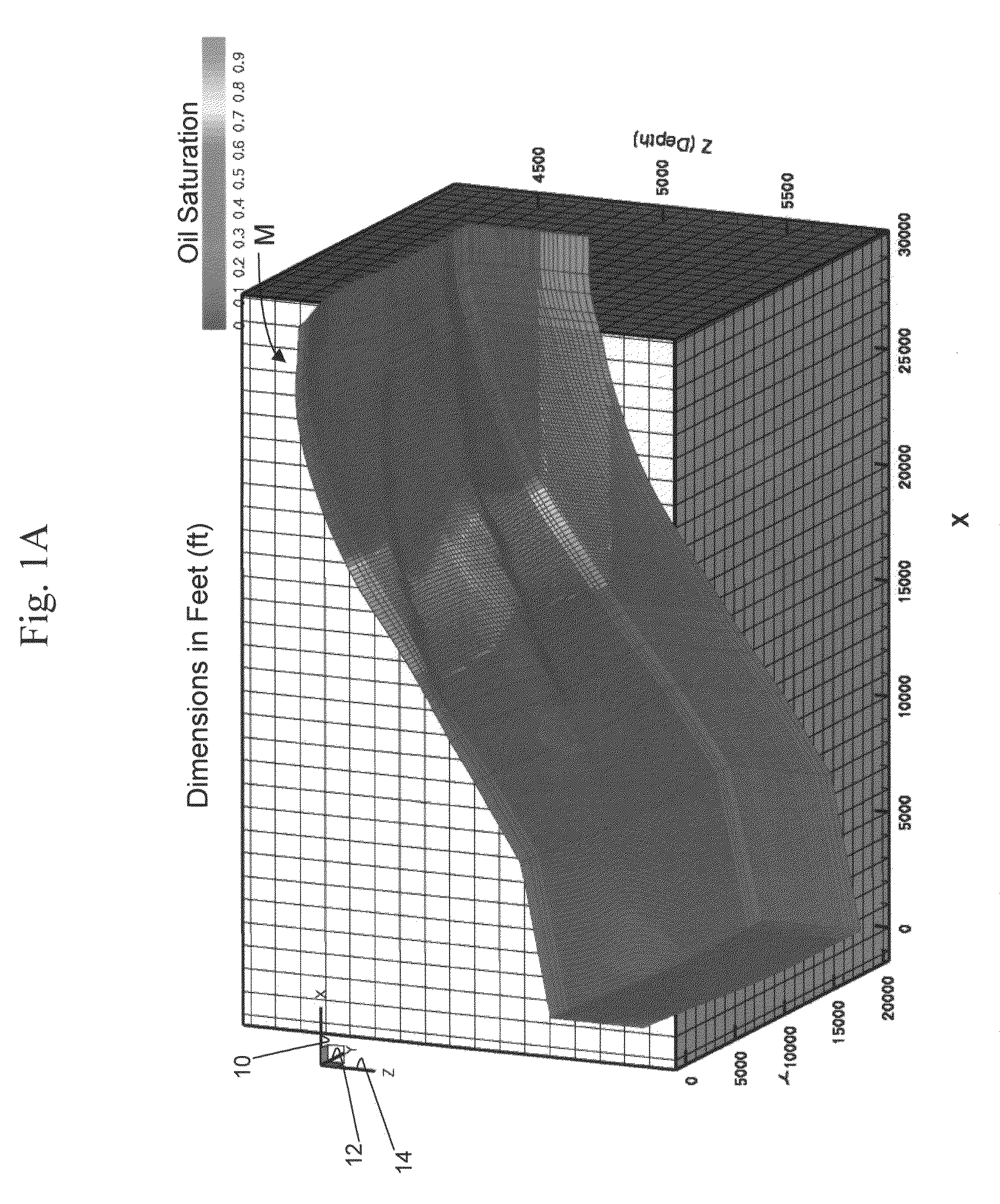
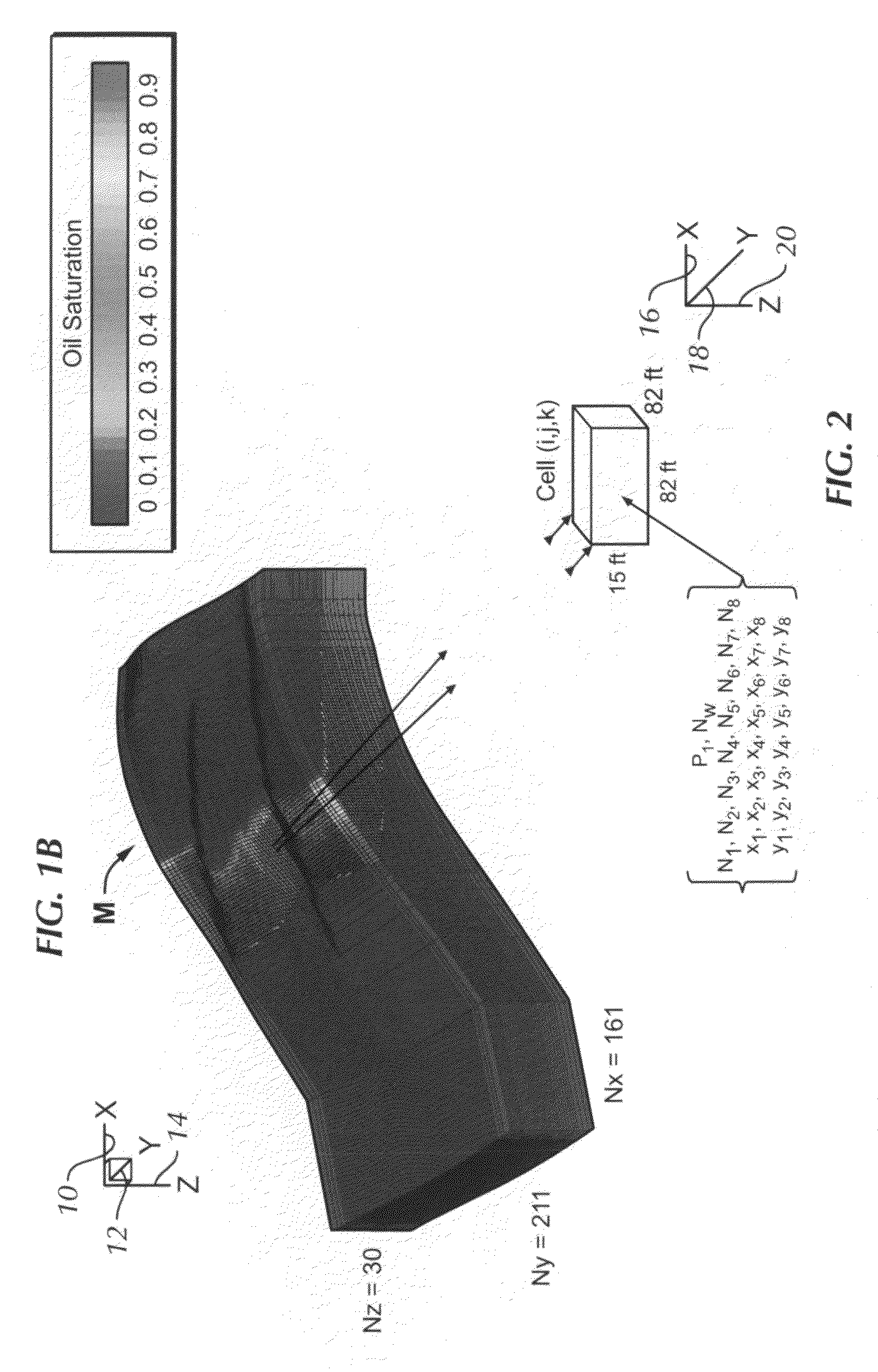
ActiveUS7526418B2Reduce processing timeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisSupercomputerDistributed memory
A fully-parallelized, highly-efficient compositional implicit hydrocarbon reservoir simulator is provided. The simulator is capable of solving giant reservoir models, of the type frequently encountered in the Middle East and elsewhere in the world, with fast turnaround time. The simulator may be implemented in a variety of computer platforms ranging from shared-memory and distributed-memory supercomputers to commercial and self-made clusters of personal computers. The performance capabilities enable analysis of reservoir models in full detail, using both fine geological characterization and detailed individual definition of the hydrocarbon components present in the reservoir fluids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Methods and apparatus for enabling bus connectivity over a data network
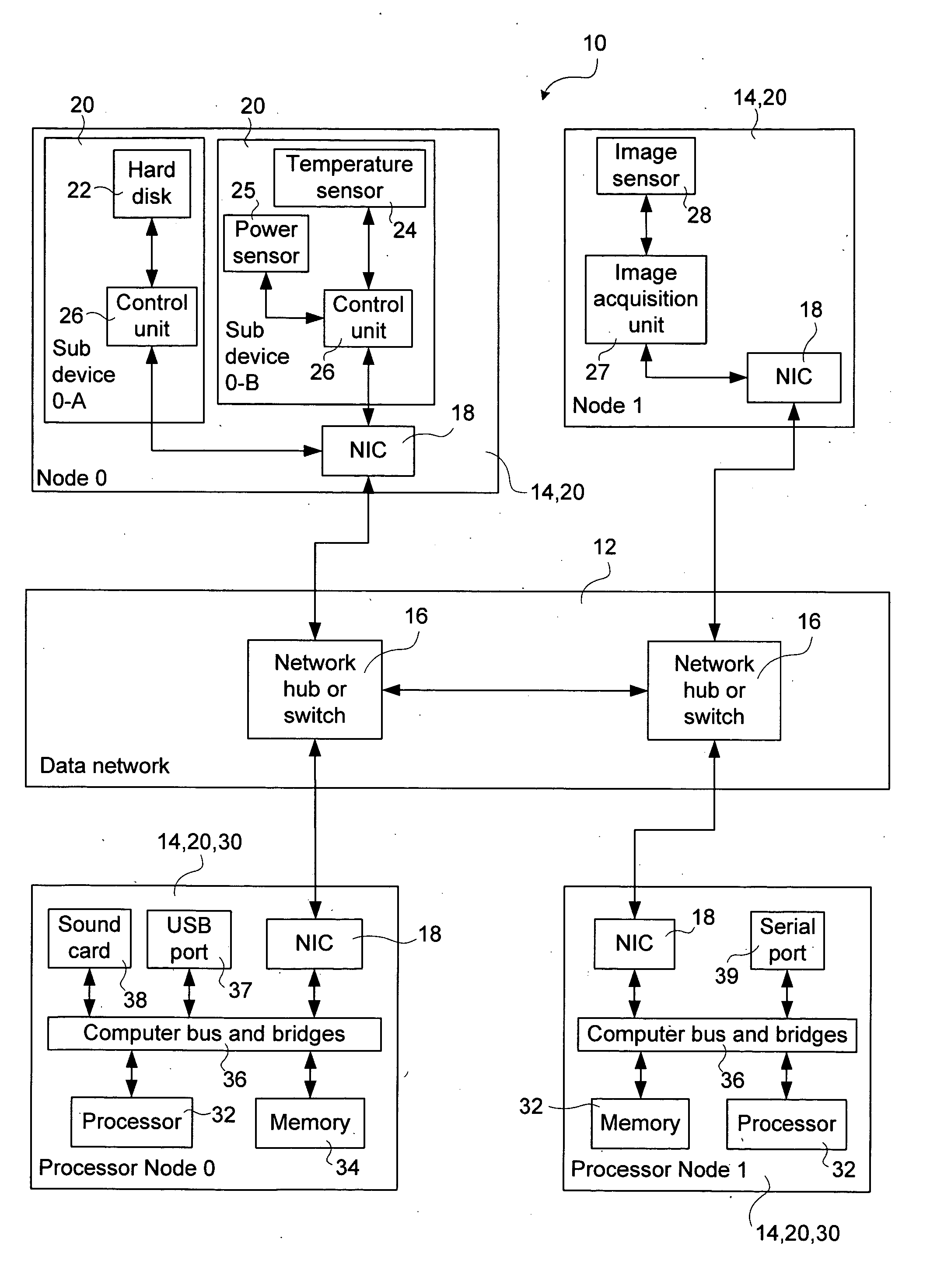
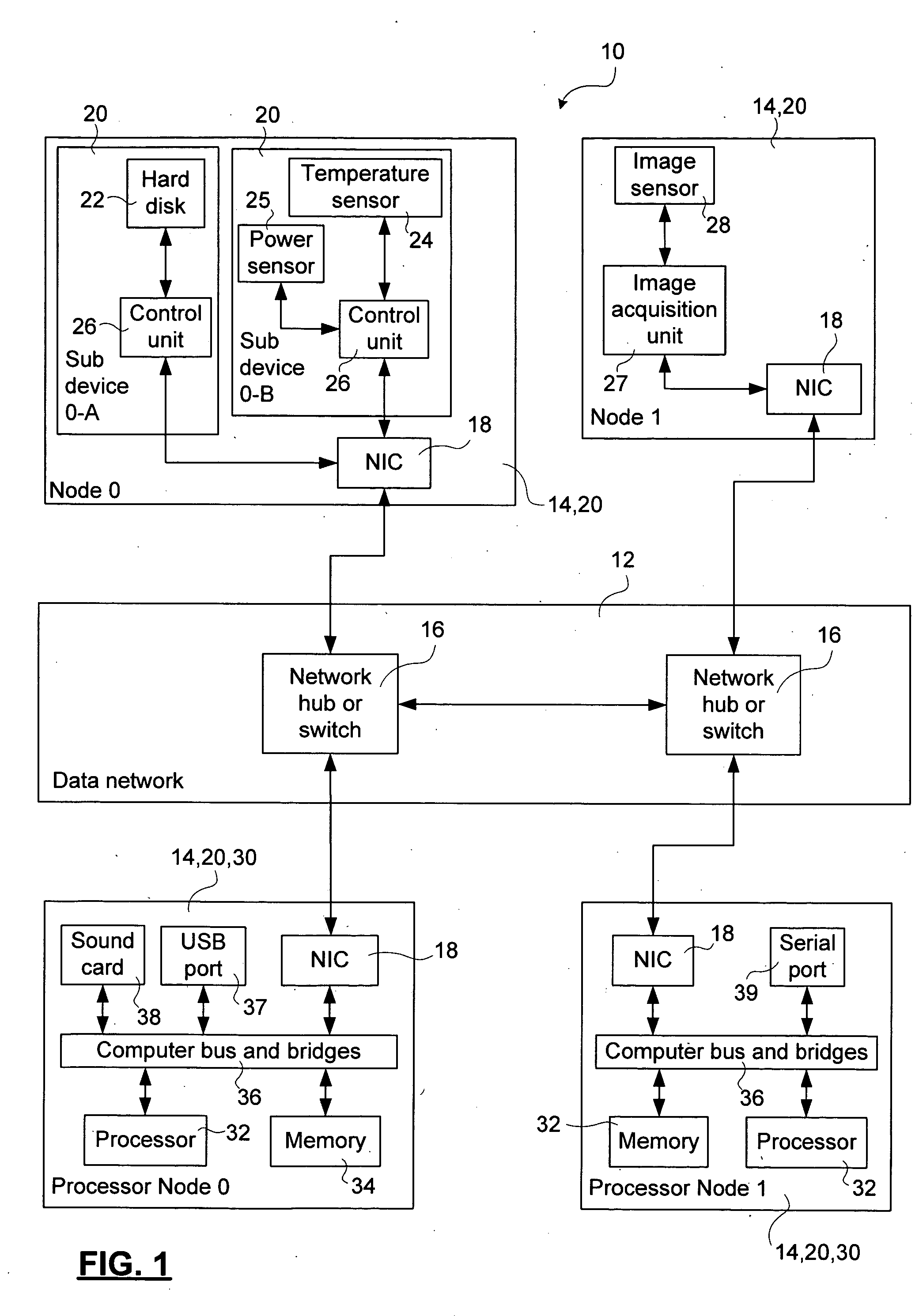
ActiveUS20060059287A1Facilitate communicationSelectively leverage operating system capabilitiesProgram synchronisationMemory addressAbstraction layer
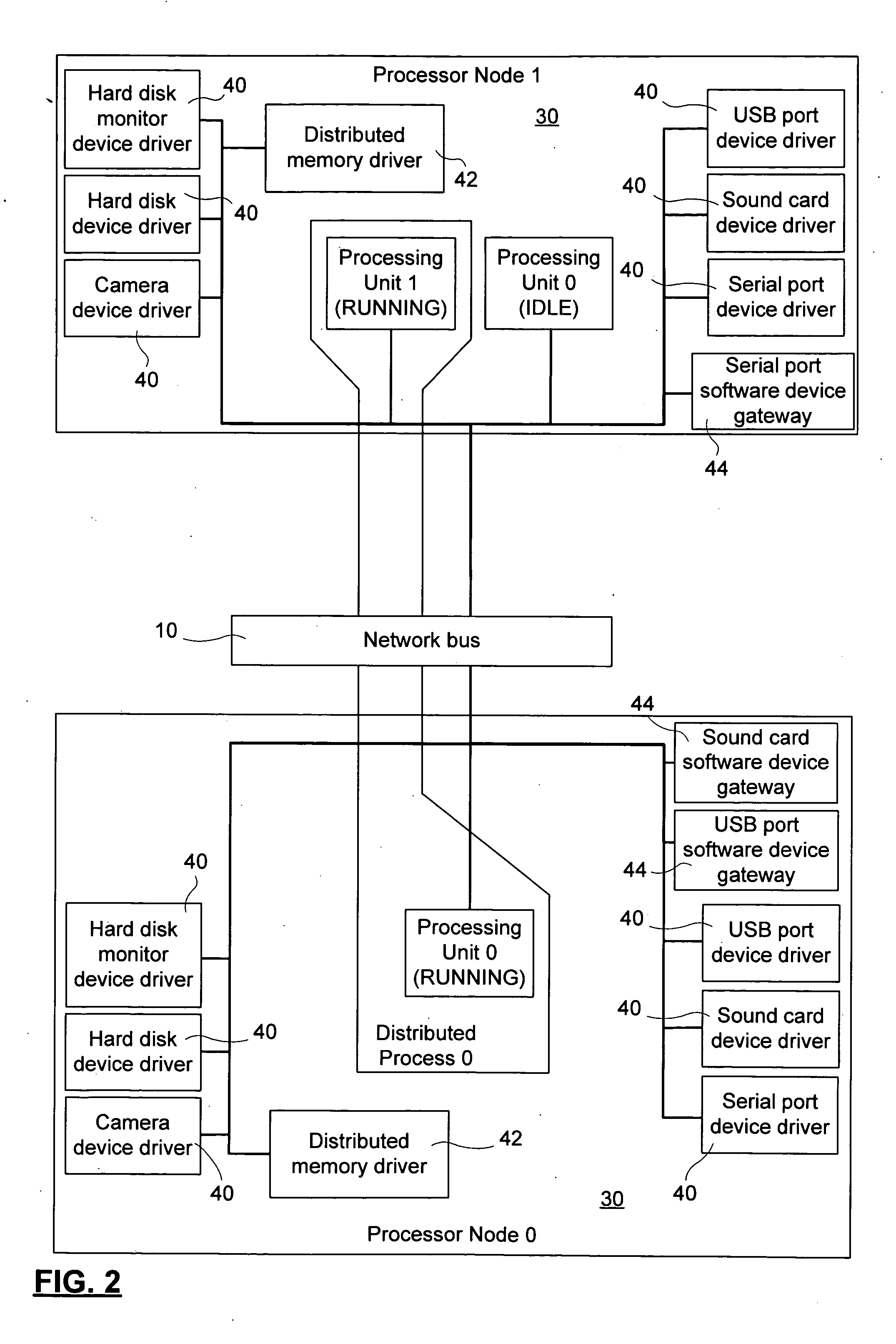
A method and system for interconnecting peripherals, processor nodes, and hardware devices to a data network to produce a network bus providing OS functionality for managing hardware devices connected to the network bus involves defining a network bus driver at each of the processor nodes that couples hardware device drivers to a network hardware abstraction layer of the processor node. The network bus can be constructed to account for the hot-swappable nature of the hardware devices using a device monitoring function, and plug and play functionality for adding and, removing device driver instances. The network bus can be used to provide a distributed processing system by defining a shared memory space at each processor node. Distributed memory pages are provided with bus-network-wide unique memory addresses, and a distributed memory manager is added to ensure consistency of the distributed memory pages, and to provide a library of functions for user mode applications.
Owner:PLEORA TECH
Data collection and analysis system
ActiveUS20060015294A1Easy to useExcessive signalingTesting/monitoring control systemsNuclear monitoringDistributed memoryData science
A sensor network collects time-series data from a process tool and supplies the data to an analysis system where pattern analysis techniques are used to identify structures and to monitor subsequent data based on analysis instructions or a composite model. Time-series data from multiple process runs are used to form a composite model of a data structure including variation. Comparison with the composite model gives an indication of tool health. A sensor network may have distributed memory for easy configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for using virtual machine technology for managing parallel communicating applications
InactiveUS20080184229A1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsLoad SheddingDistributed memory
A method (and system) for managing a distributed-memory parallel application running on multiple servers, includes dynamically moving a plurality of executable program components, where each of the plurality of executable program components are running on one of a plurality of virtual machines, using migration of the virtual machines between physical servers. The load balancing is operated based on a workload of each of the virtual machines and servers, where a virtual machine, or a plurality of virtual machines, are transferred to balance the workload between each of the servers.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Highly-parallel, implicit compositional reservoir simulator for multi-million-cell models
ActiveUS20060036418A1Reducing computer processing timeReduce processing timeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisSupercomputerDistributed memory
A fully-parallelized, highly-efficient compositional implicit hydrocarbon reservoir simulator is provided. The simulator is capable of solving giant reservoir models, of the type frequently encountered in the Middle East and elsewhere in the world, with fast turnaround time. The simulator may be implemented in a variety of computer platforms ranging from shared-memory and distributed-memory supercomputers to commercial and self-made clusters of personal computers. The performance capabilities enable analysis of reservoir models in full detail, using both fine geological characterization and detailed individual definition of the hydrocarbon components present in the reservoir fluids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method and apparatus for using virtual machine technology for managing parallel communicating applications
InactiveUS7607129B2Multiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDistributed memoryWorkload
A method (and system) for managing a distributed-memory parallel application running on multiple servers, includes dynamically moving a plurality of executable program components, where each of the plurality of executable program components are running on one of a plurality of virtual machines, using migration of the virtual machines between physical servers. The load balancing is operated based on a workload of each of the virtual machines and servers, where a virtual machine, or a plurality of virtual machines, are transferred to balance the workload between each of the servers.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
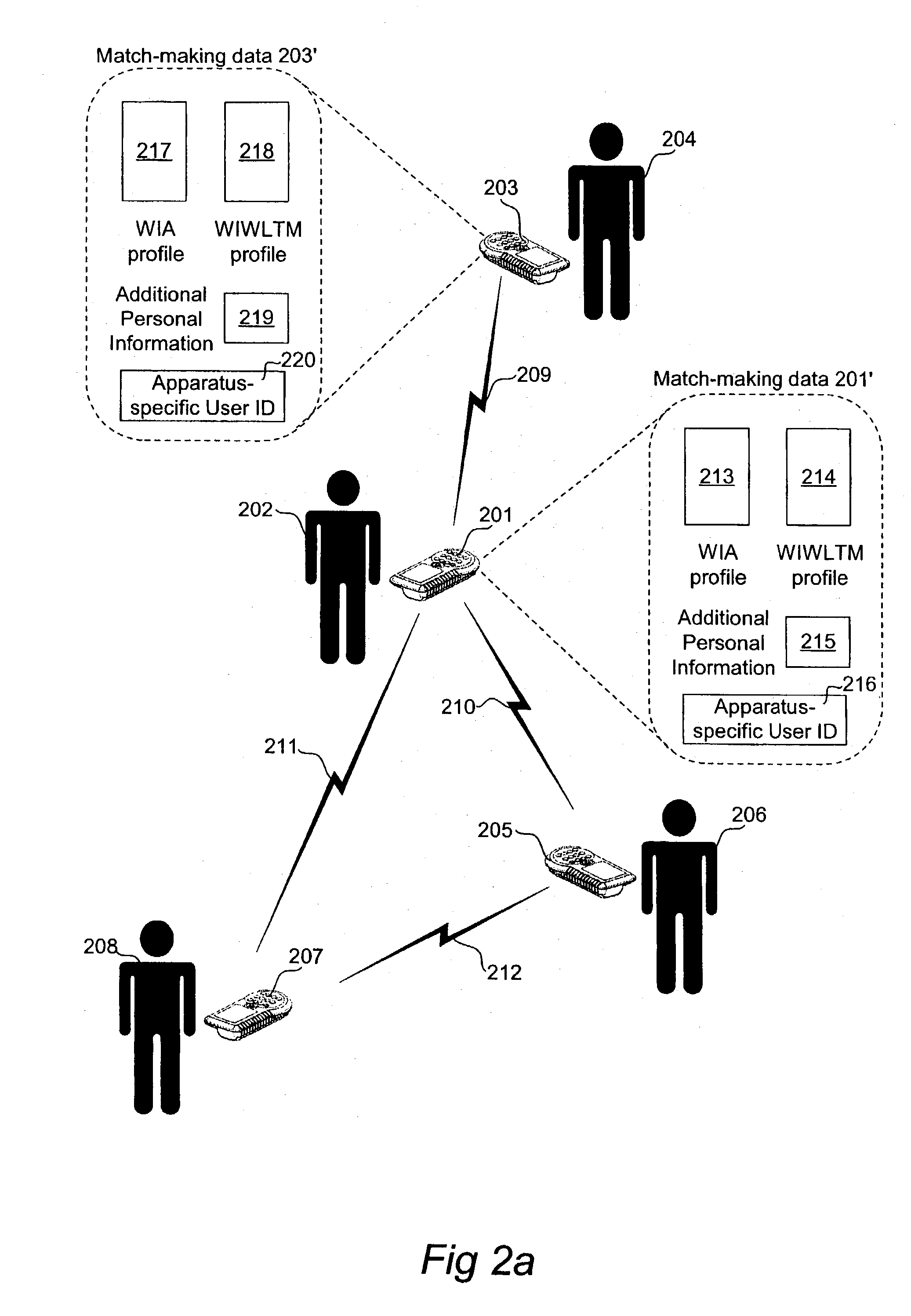
Portable communication apparatus and methods for match-making with distributed memory
A portable communication apparatus for match-making with a plurality of remote communication apparatuses has memory means adapted to store match-making data, including local match-making data associated with the portable communication apparatus. A transceiver is adapted for wireless communication with a first remote communication apparatus, so as to transmit the local match-making data to the first remote communication apparatus, as well as to receive first remote match-making data associated with the first remote communication apparatus. A processing device is adapted to perform a correlation analysis between the local match-making data and the first remote match-making data and-in case a result of the correlation analysis indicates a match between the portable communication apparatus and the first remote communication apparatus-provide an alert to a user of the portable communication apparatus. The memory means is adapted to store the first remote match-making data, and the transceiver is adapted to transmit the first remote match-making data, in addition to the local match-making data, to a second remote communication apparatus.
Owner:STEPHEN J CARLTON
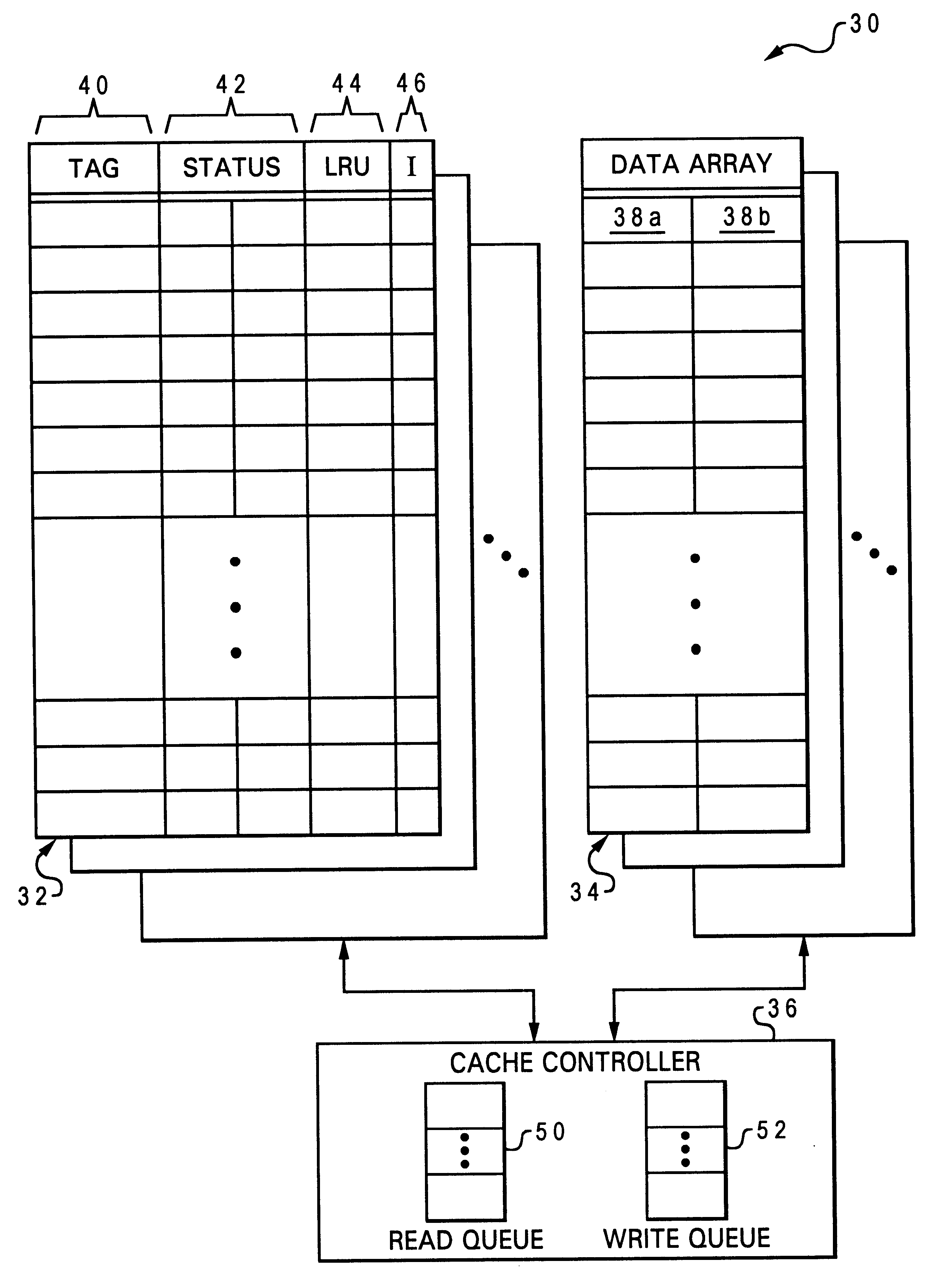
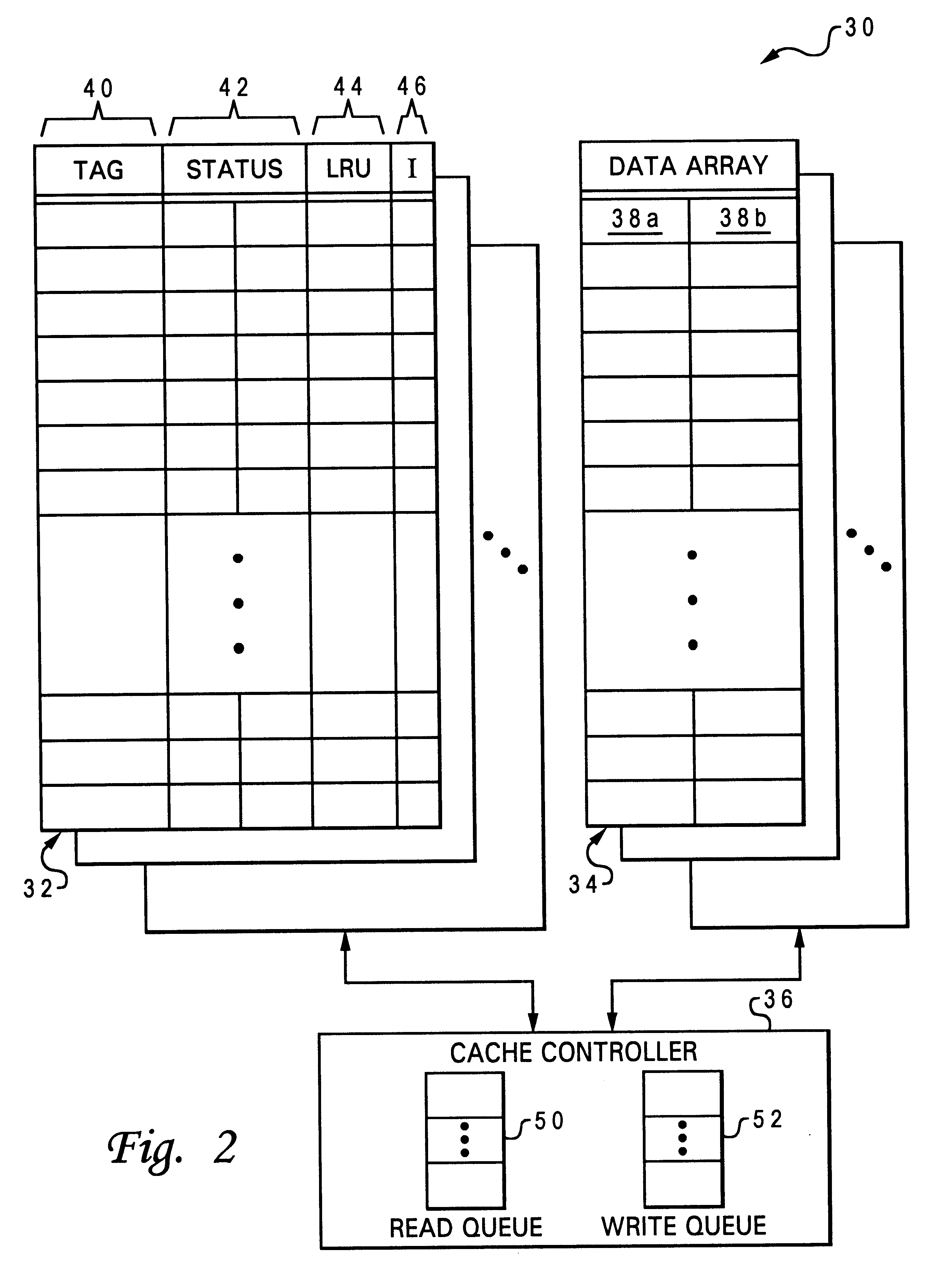
Data processing system, cache, and method that select a castout victim in response to the latencies of memory copies of cached data
A data processing system includes a processing unit, a distributed memory including a local memory and a remote memory having differing access latencies, and a cache coupled to the processing unit and to the distributed memory. The cache includes a congruence class containing a plurality of cache lines and a plurality of latency indicators that each indicate an access latency to the distributed memory for a respective one of the cache lines. The cache further includes a cache controller that selects a cache line in the congruence class as a castout victim in response to the access latencies indicated by the plurality of latency indicators. In one preferred embodiment, the cache controller preferentially selects as castout victims cache lines having relatively short access latencies.
Owner:IBM CORP
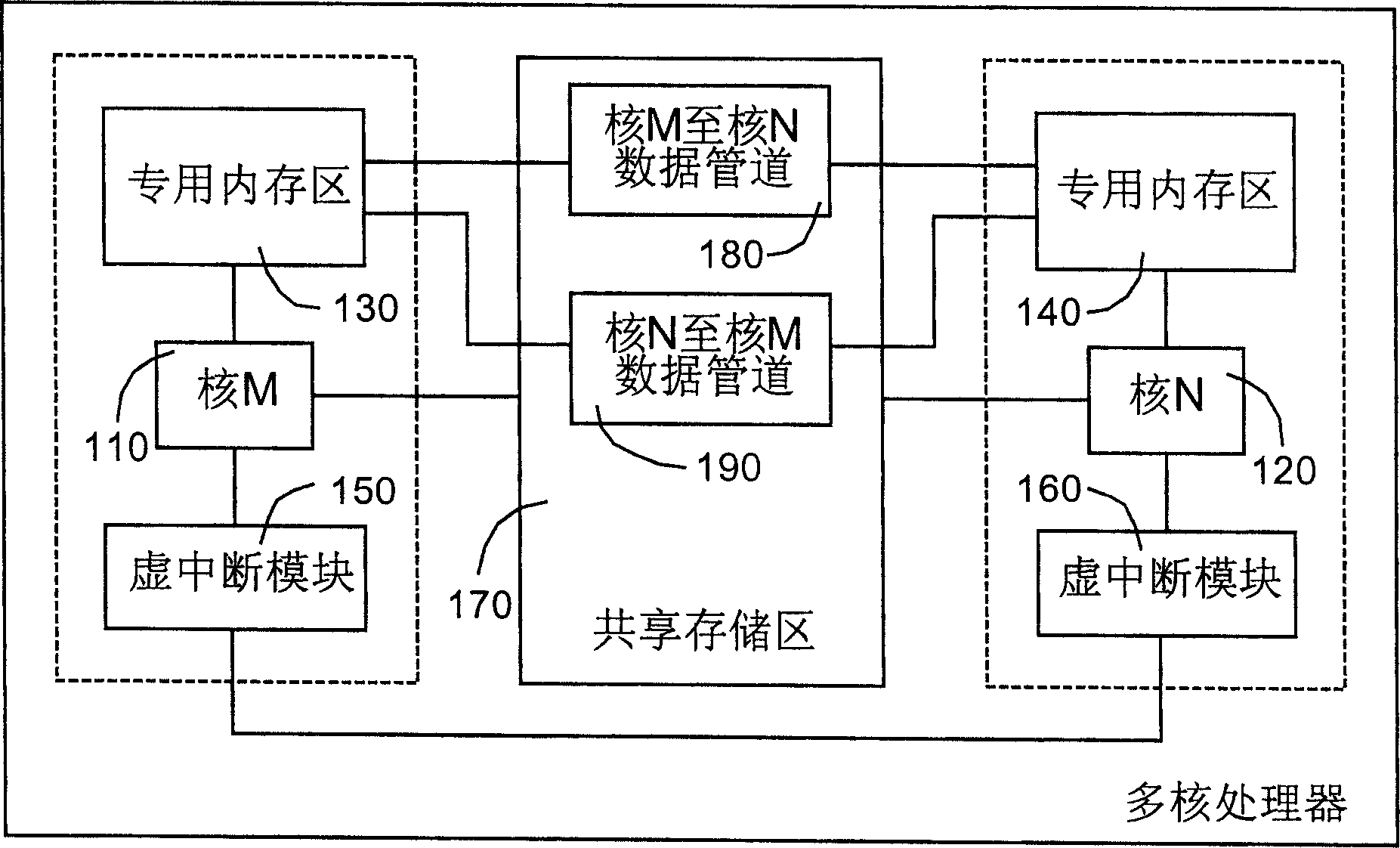
Inter core communication method and apparatus for multi-core processor in embedded real-time operating system
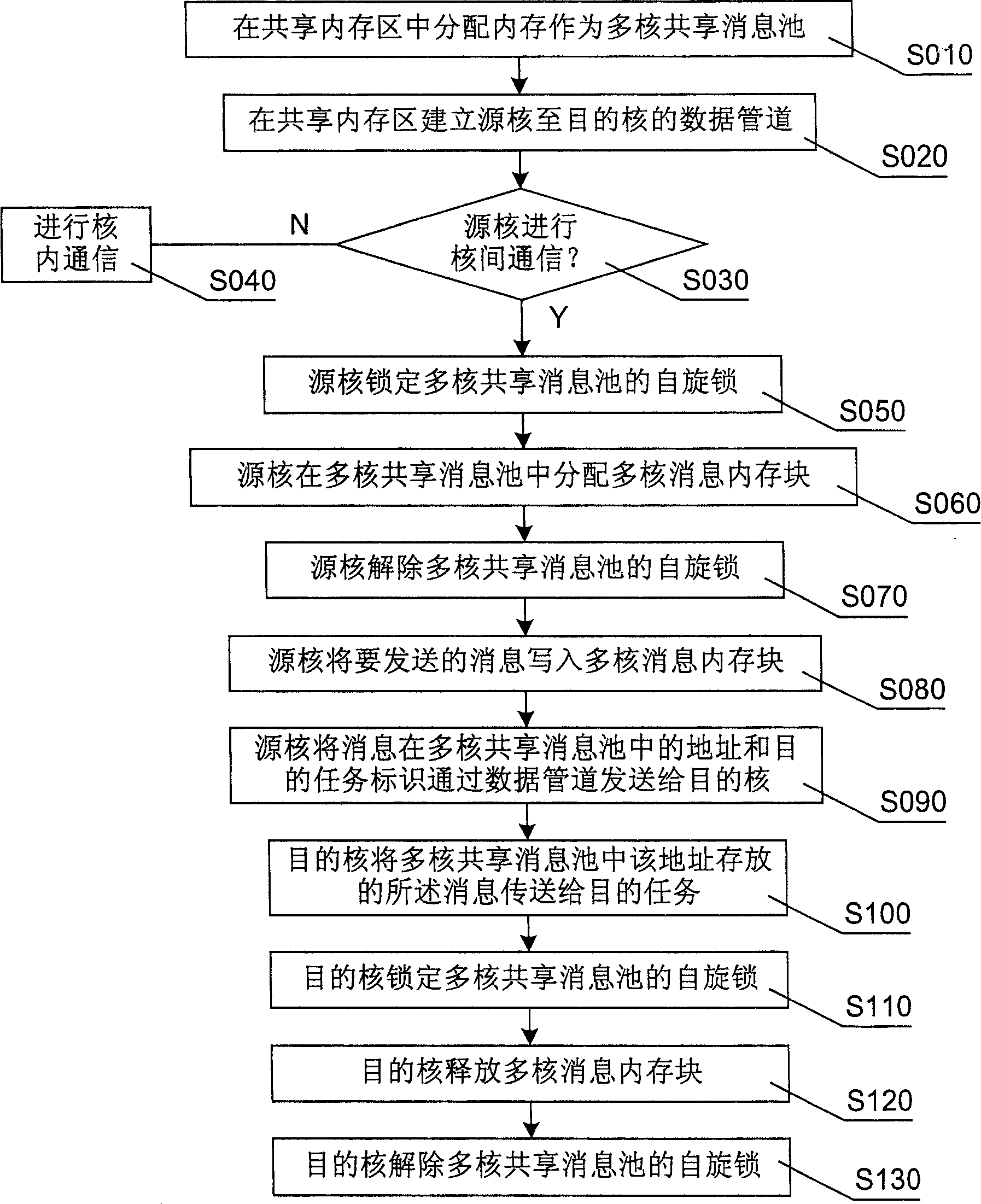
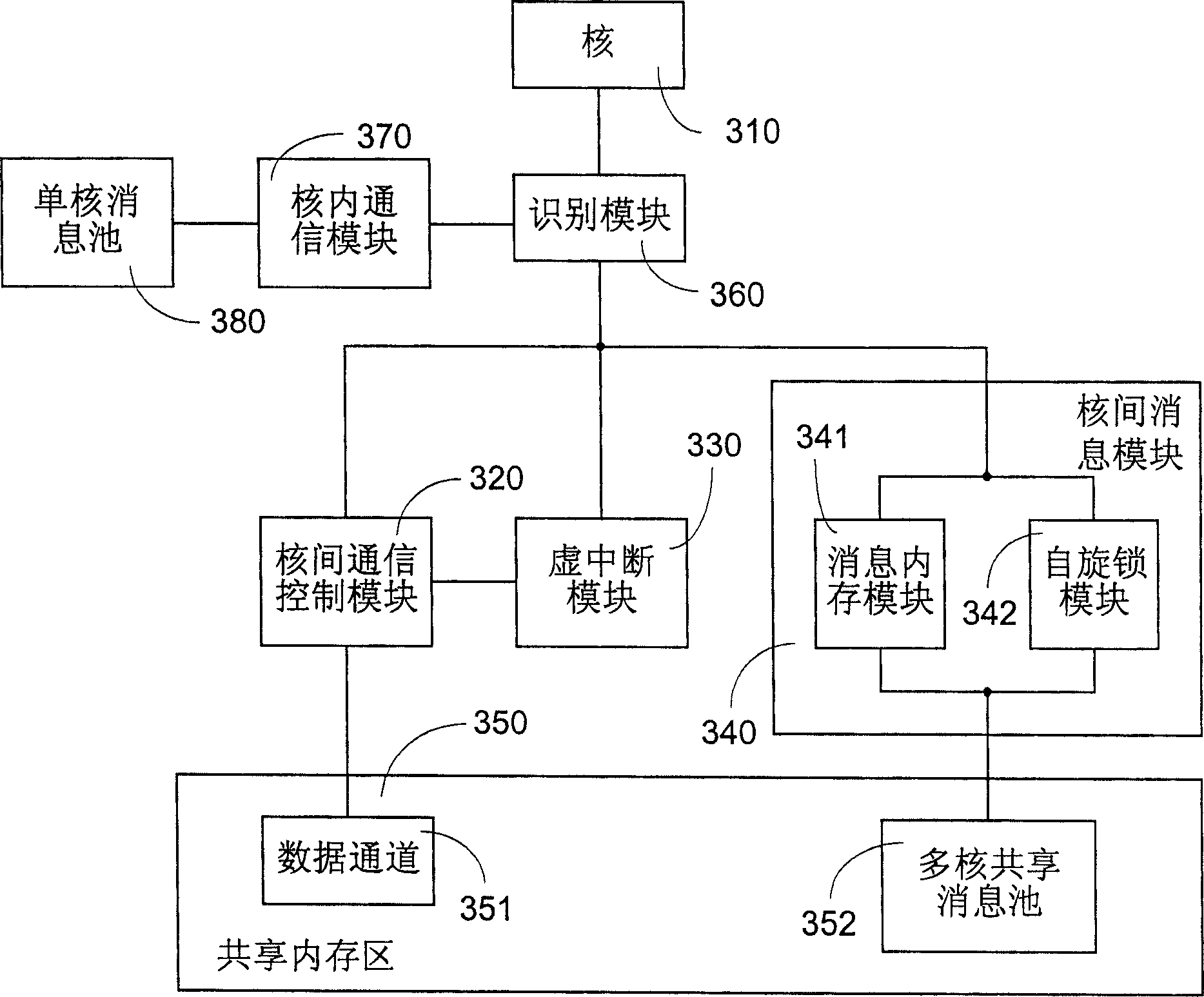
ActiveCN1904873APrevent copyingImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingMessage queueDistributed memory
The invention discloses an inter-core communicating method of multi-core processor in embedded real time operation system. It includes following steps: distributing memory as multi-core information sharing pool; writing information the source core would send into the pool; sending the information to target core; target core sending the information storing in pool to target mission. The invention also discloses an inter-core communicating device. It improves the inter-core communicating efficiency and realizes the unification of inner core communication and inter-core communication.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
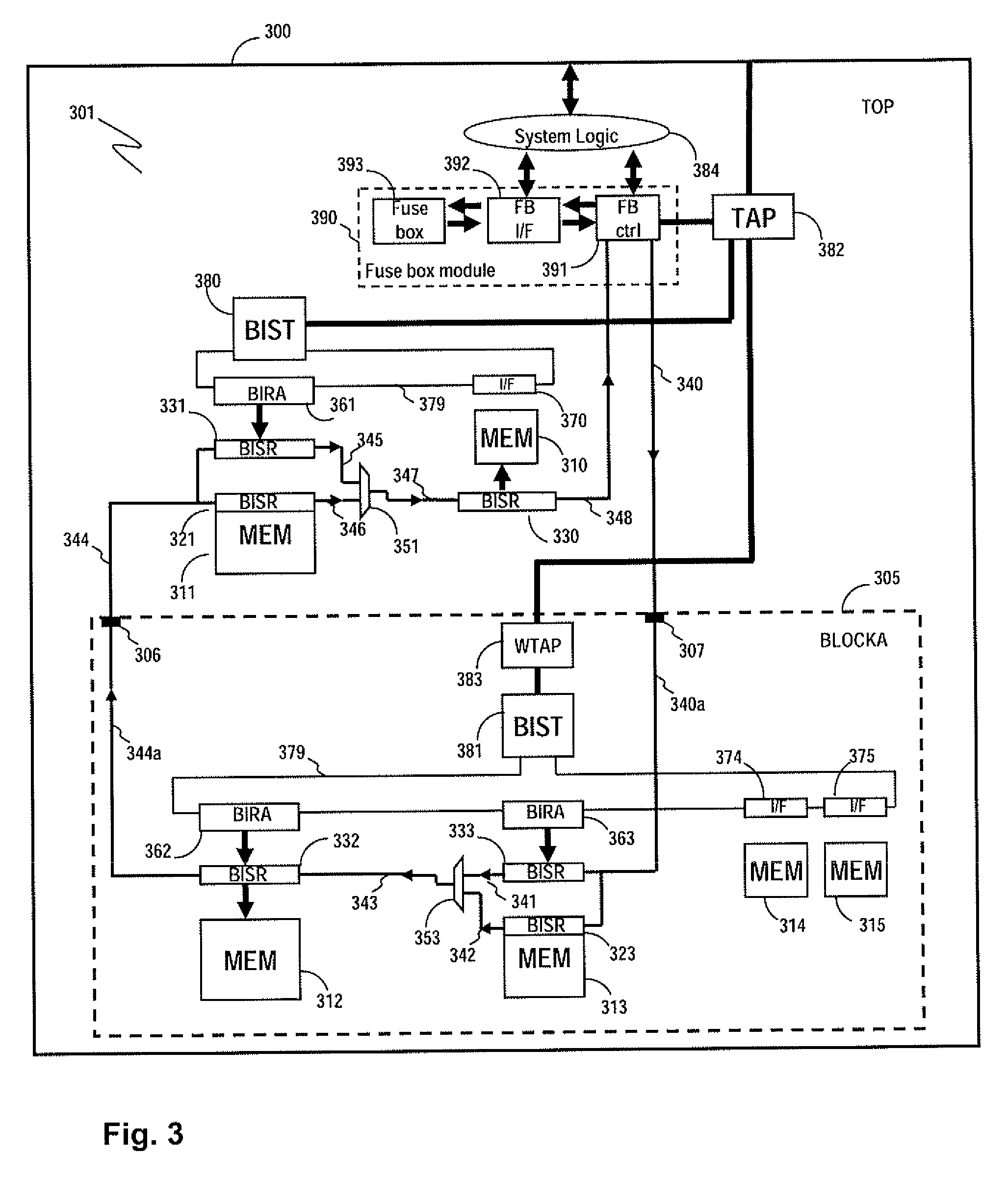
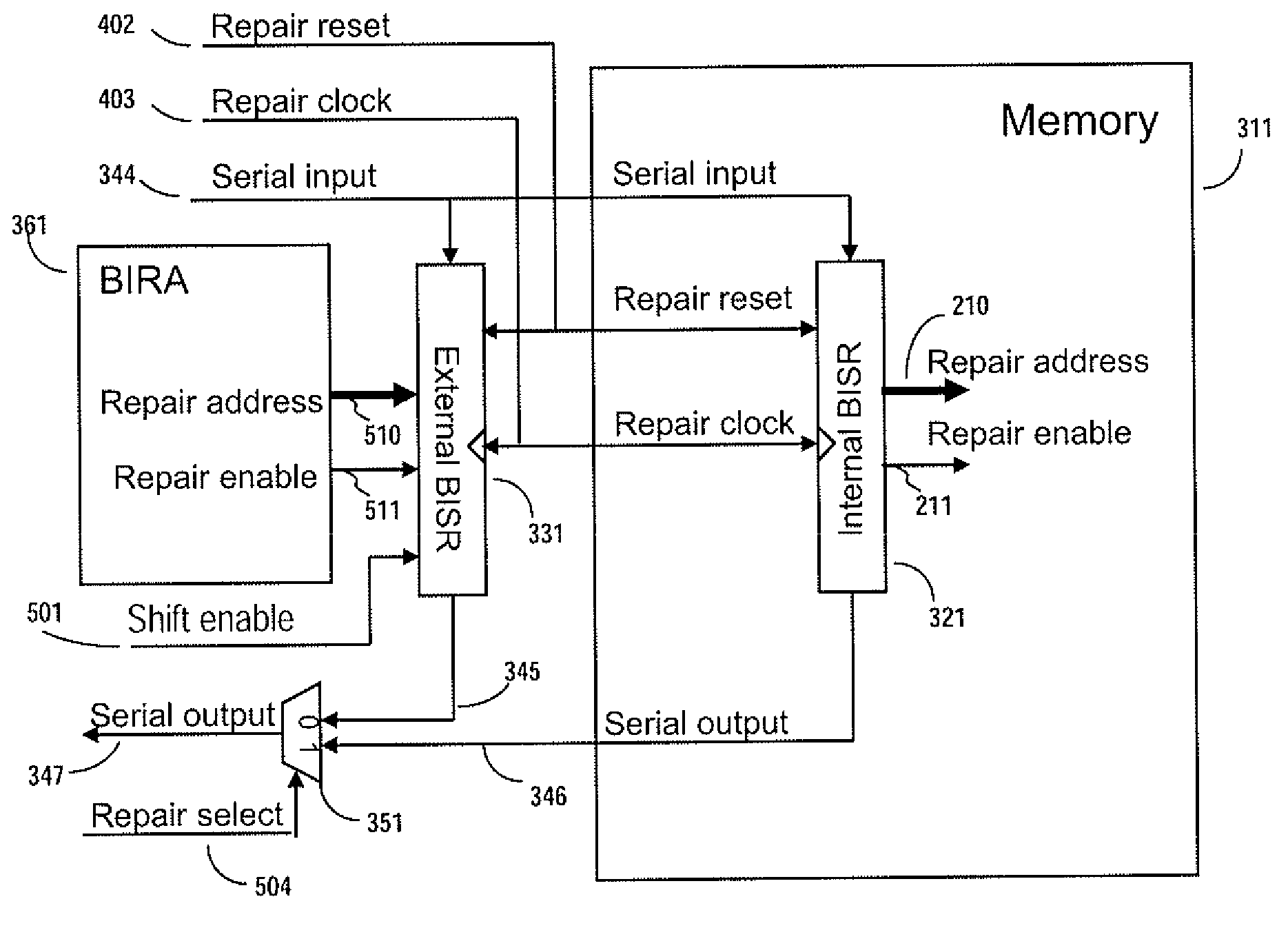
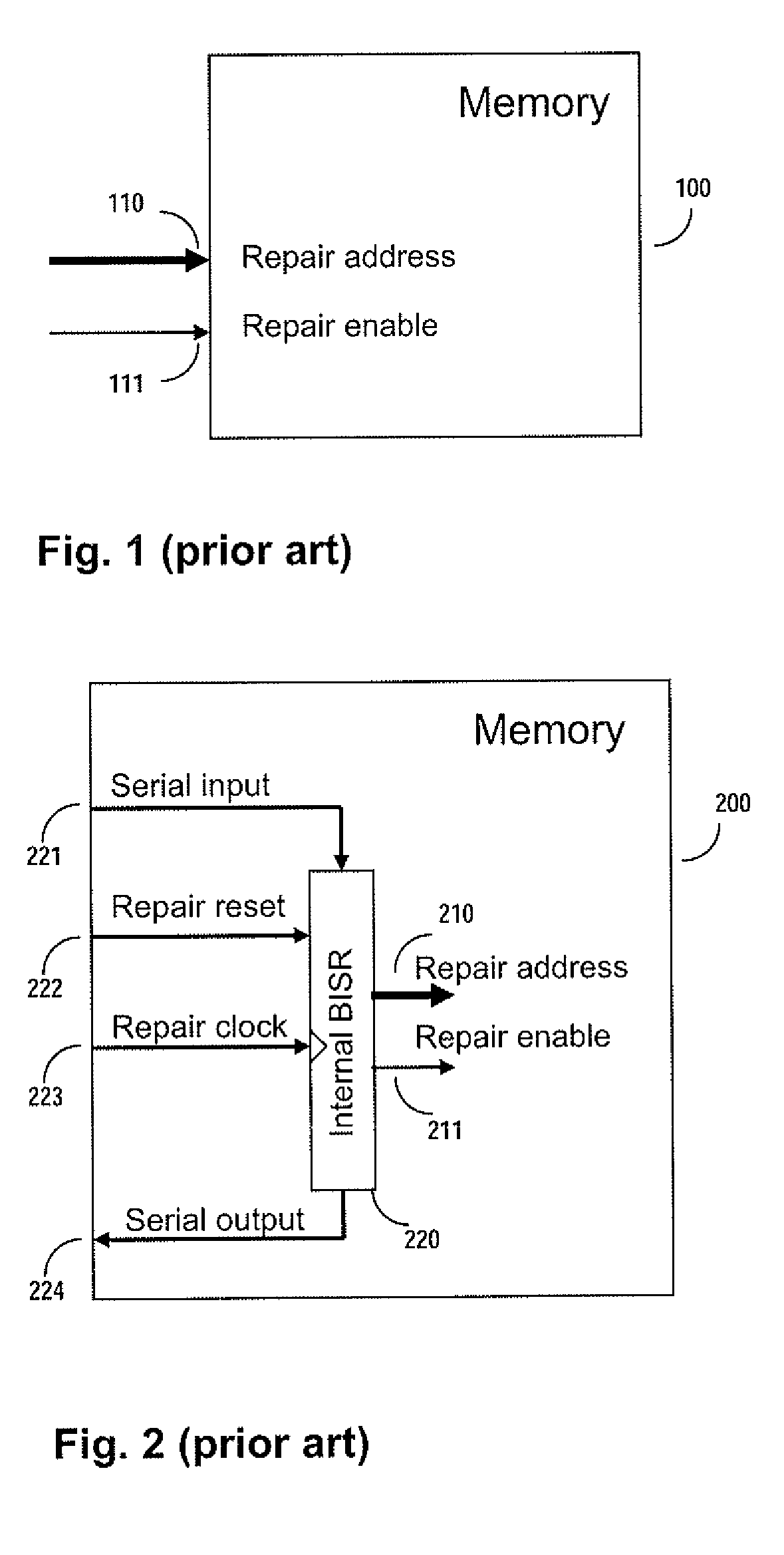
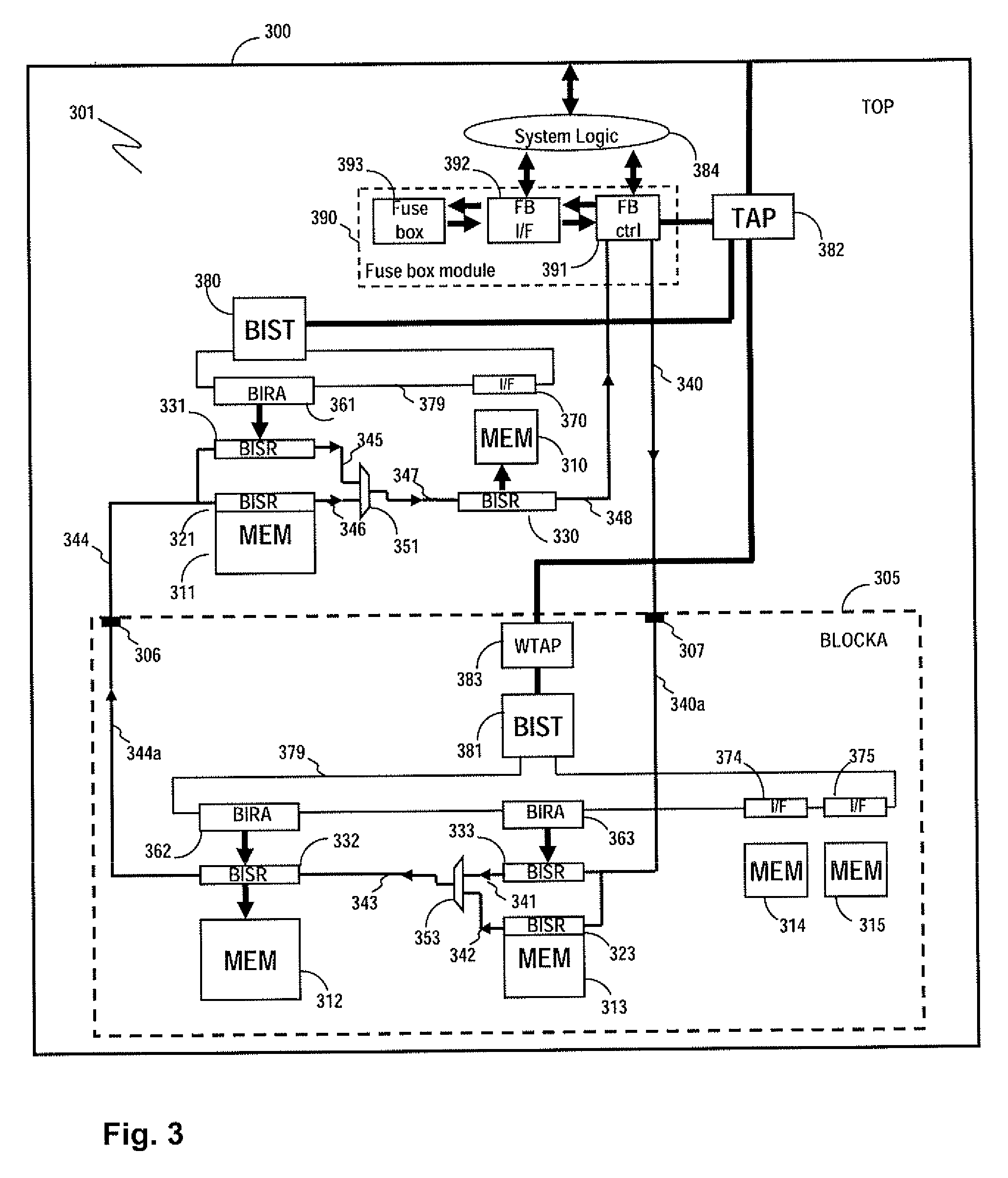
Method and apparatus for storing and distributing memory repair information
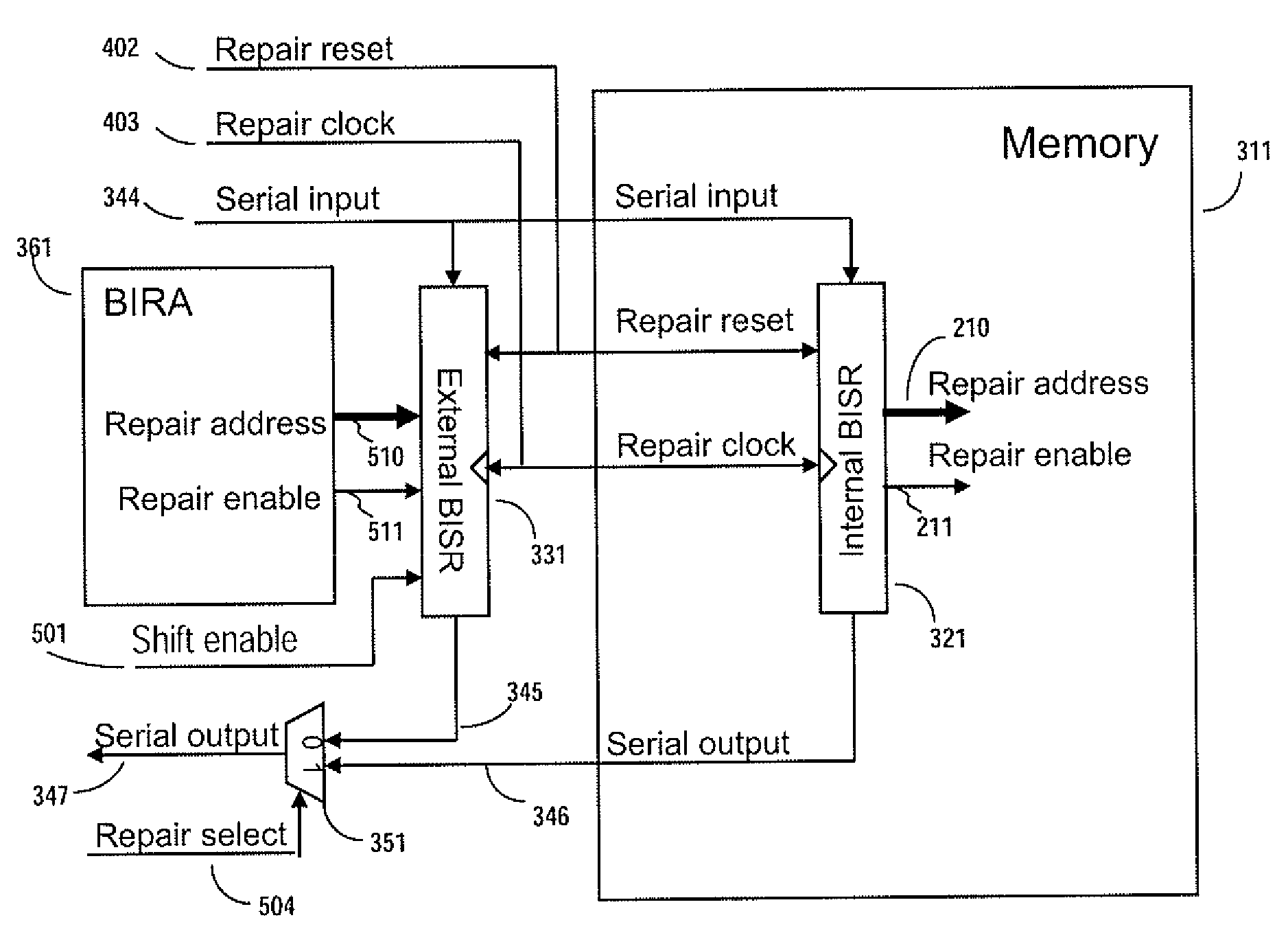
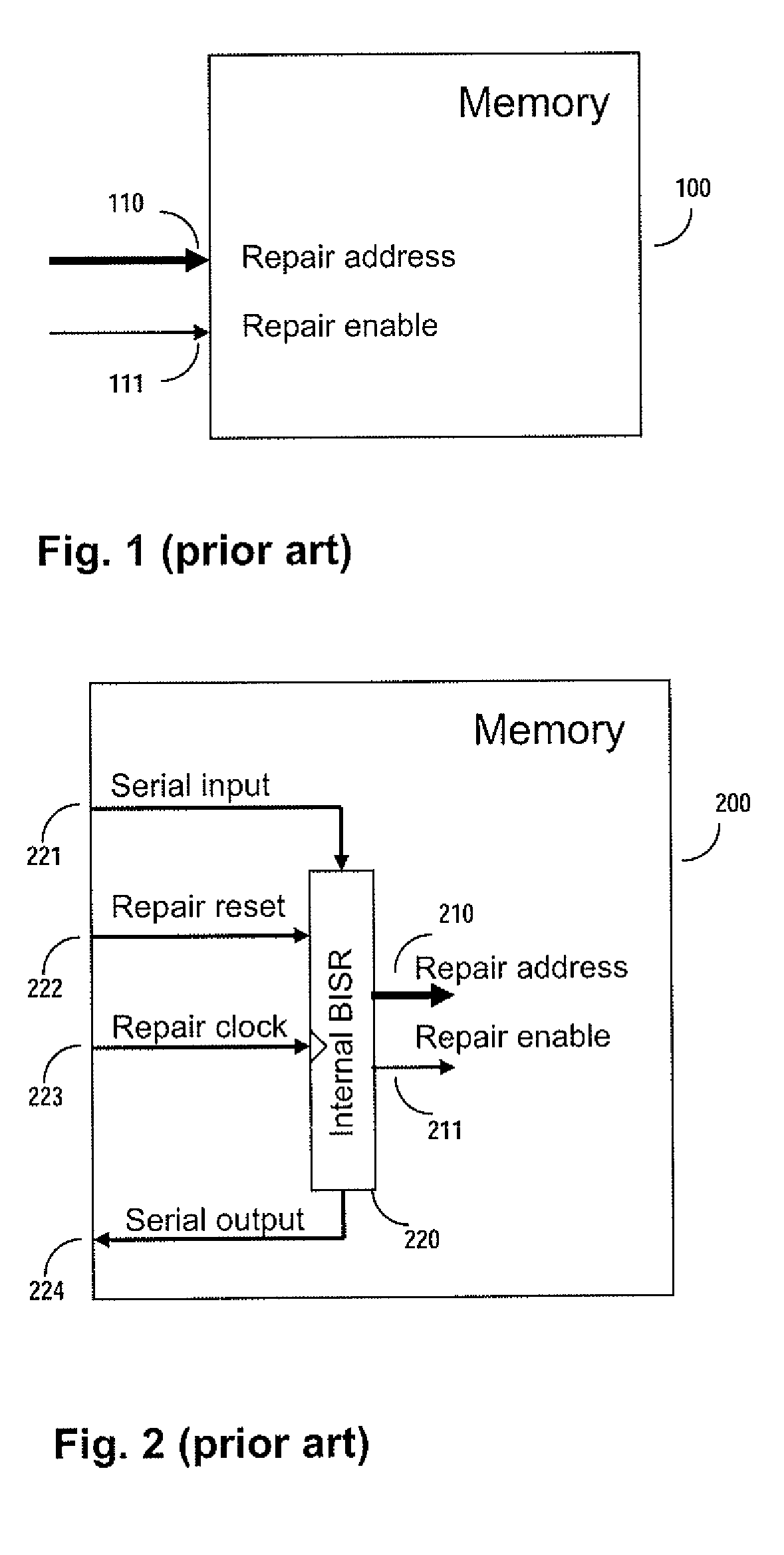
ActiveUS7757135B2Easy to integrateConvenient to accommodateElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionDistributed memoryProcessor register
A system for repairing embedded memories on an integrated circuit includes an external Built-In Self-repair Register (BISR) associated with every reparable memory. Each BISR is serially configured in a daisy chain with a fuse box controller. The controller determines the daisy chain length upon power up. The controller may perform a corresponding number of shift operations to move repair data between BISRs and a fuse box. Memories can have a parallel or serial repair interface. The BISRs may have a repair analysis facility into which fuse data may be dumped and uploaded to the fuse box or downloaded to repair the memory. Pre-designed circuit blocks provide daisy chain inputs and access ports to effect the system or to bypass the circuit block.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
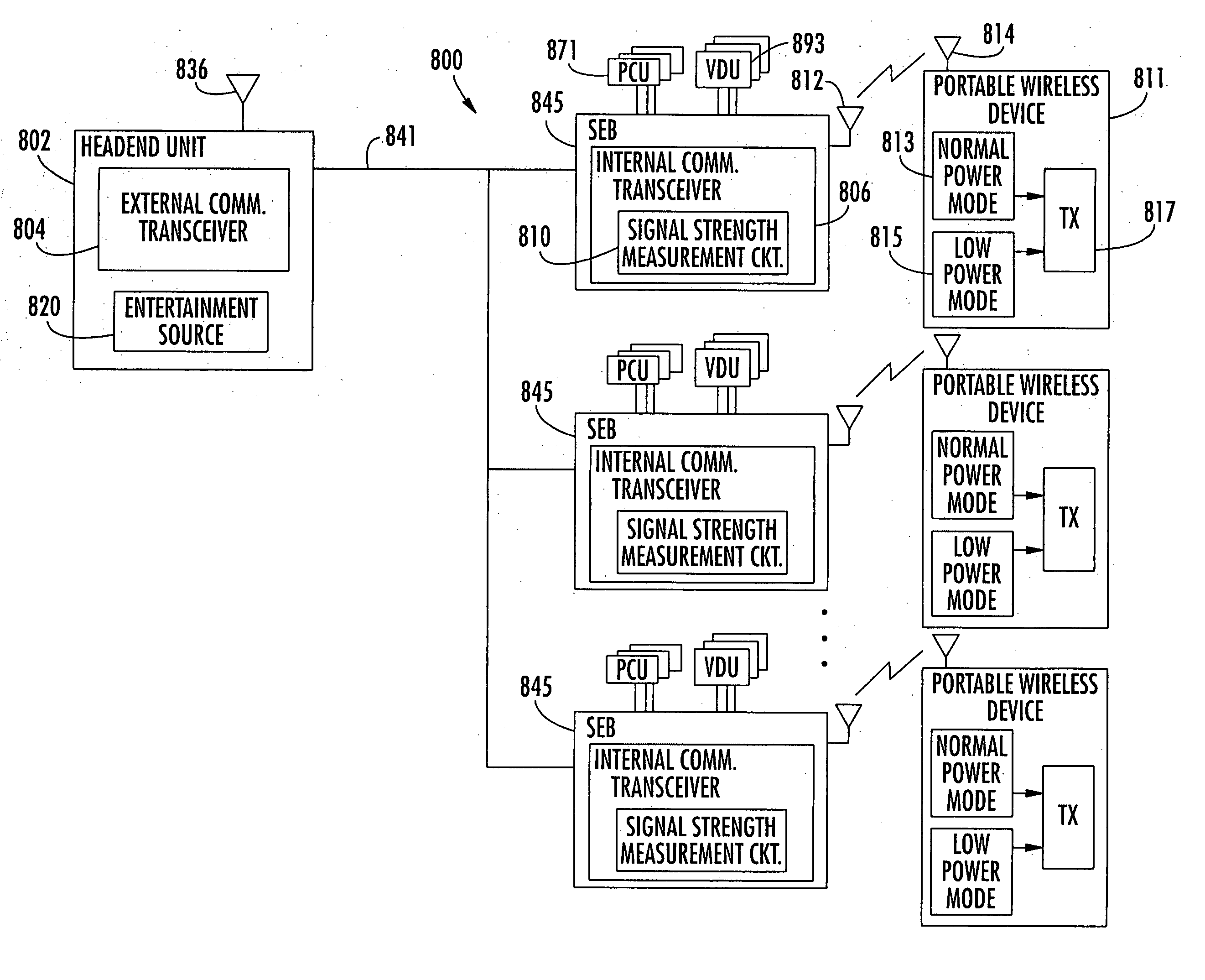
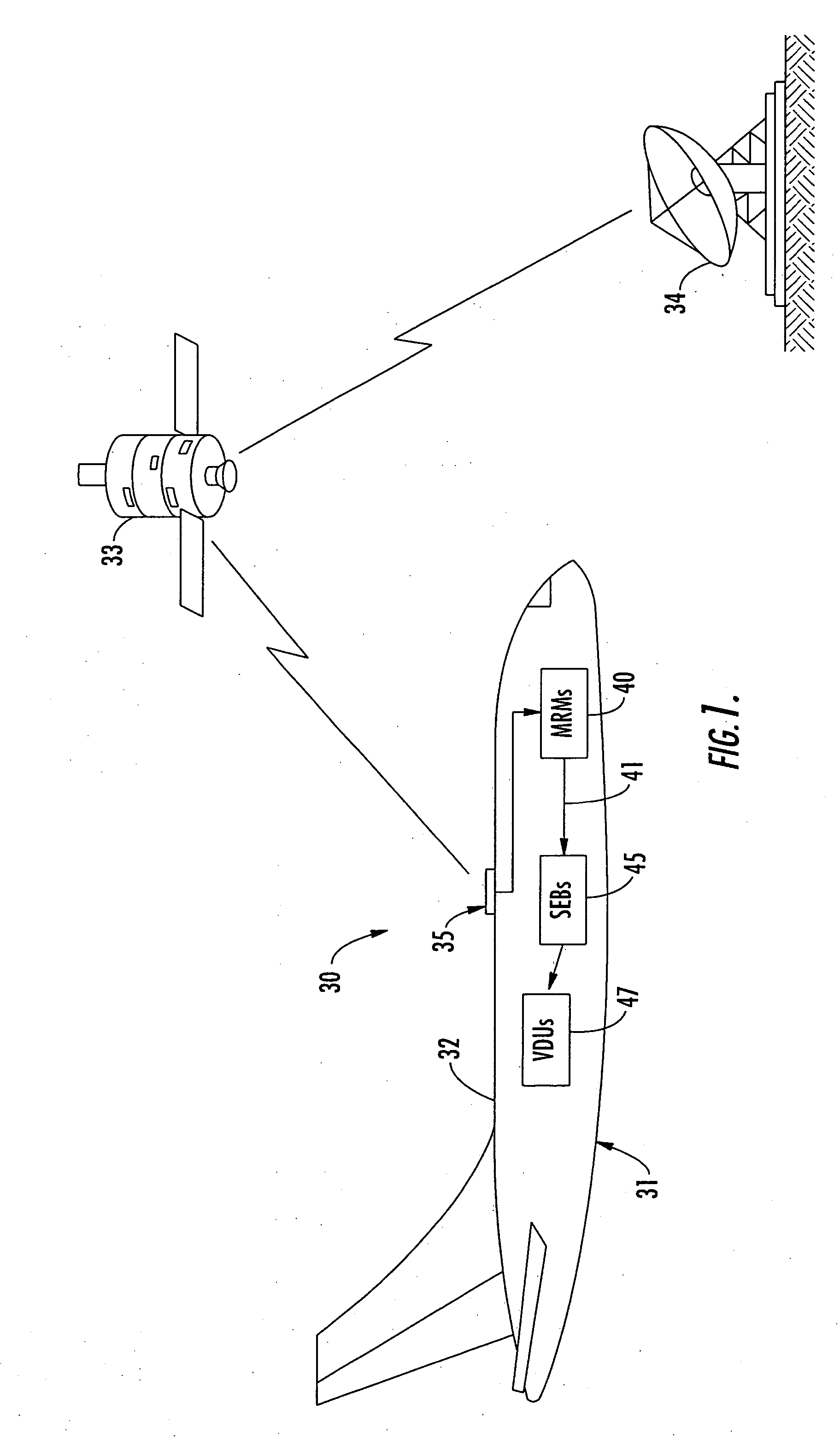
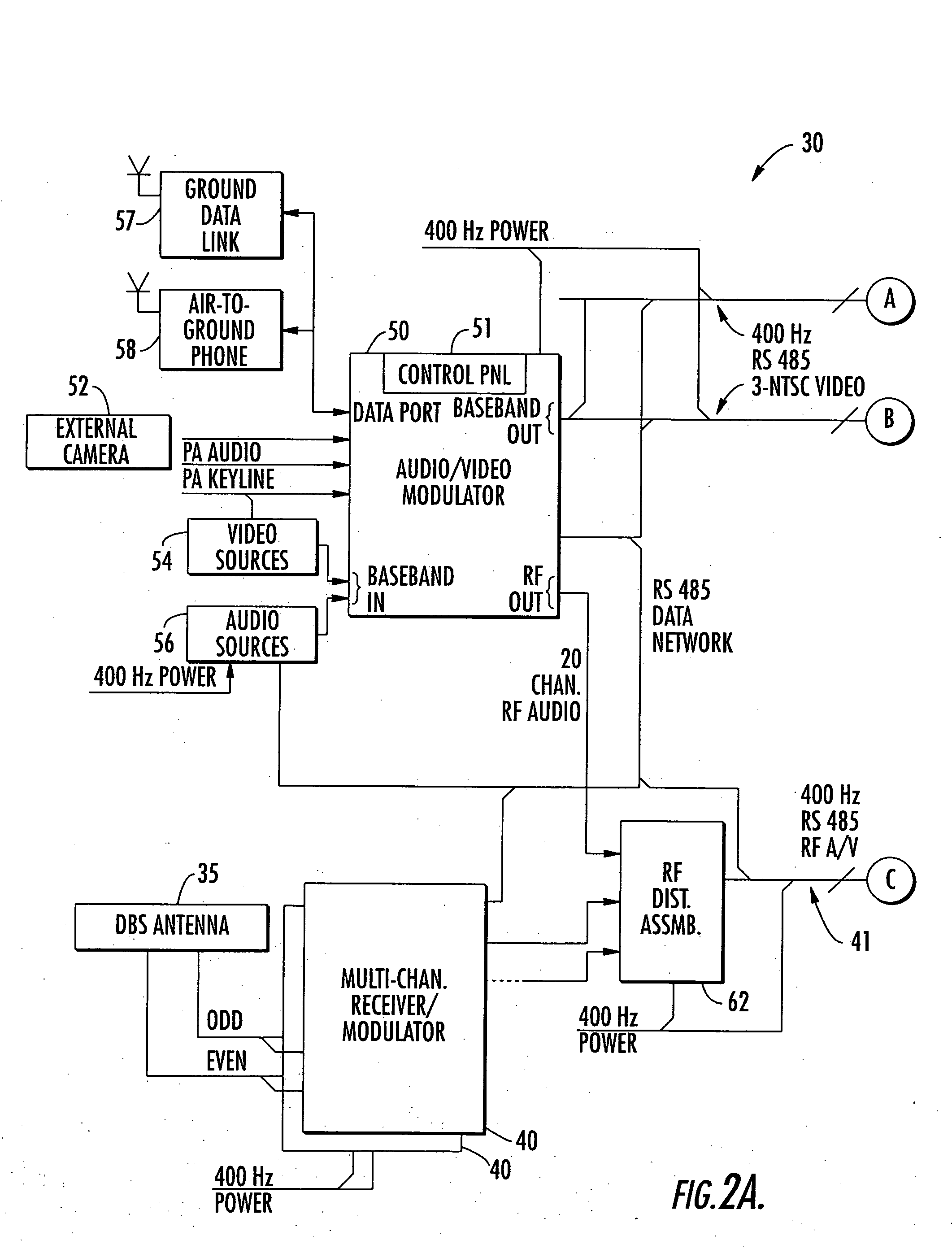
Aircraft in-flight entertainment system with a distributed memory and associated methods
ActiveUS20060143662A1Increasing weightWeight increaseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDistributed memoryReal-time computing
An aircraft in-flight entertainment (IFE) system includes a plurality of seat electronic boxes (SEBs) spaced throughout the aircraft. Each SEB comprises a memory including a shared memory portion for storing entertainment related data and an unshared memory portion. The SEBs cooperate with one another so that the entertainment related data in the shared memory portion of each SEB is available for at least one other SEB.
Owner:LIVETV
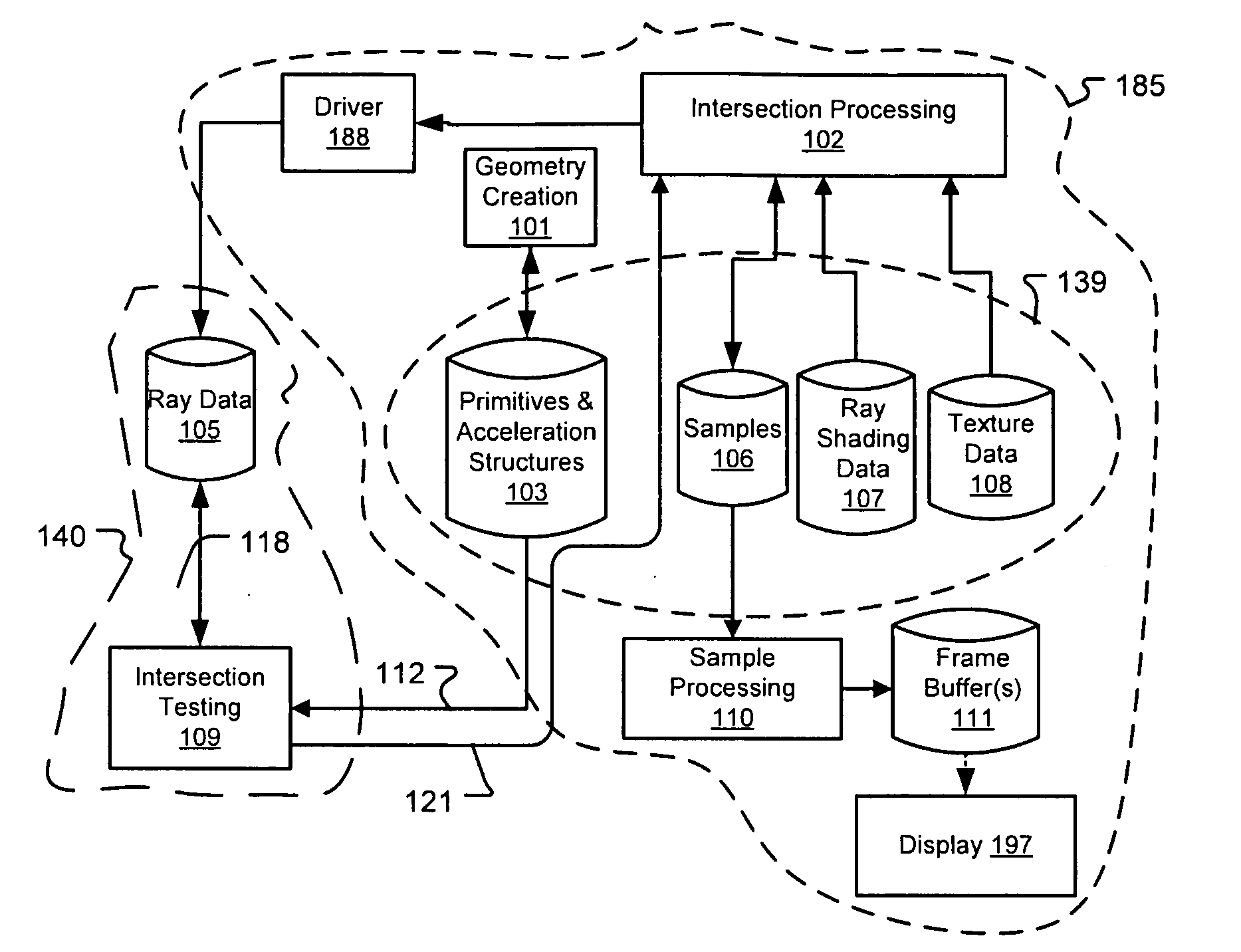
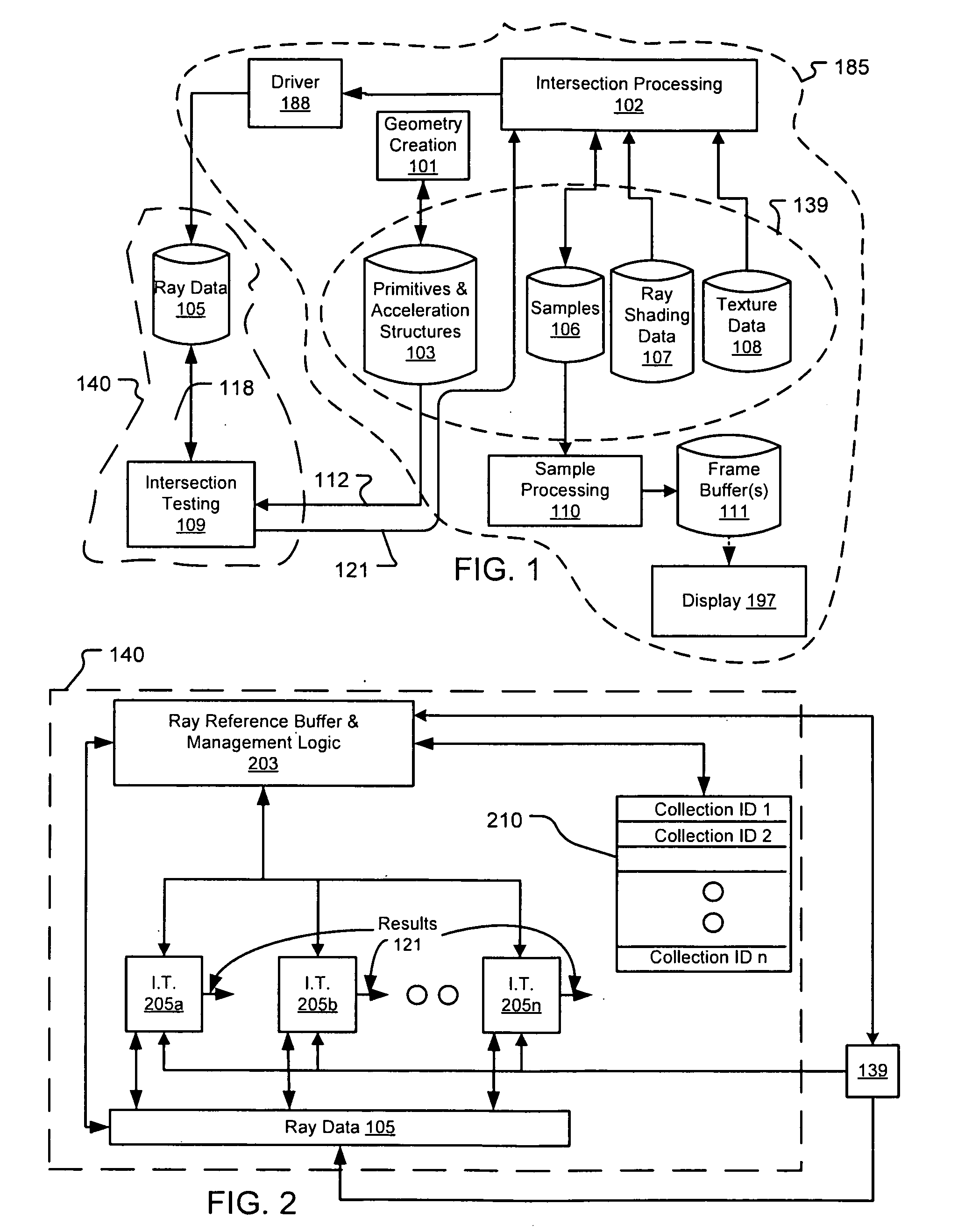
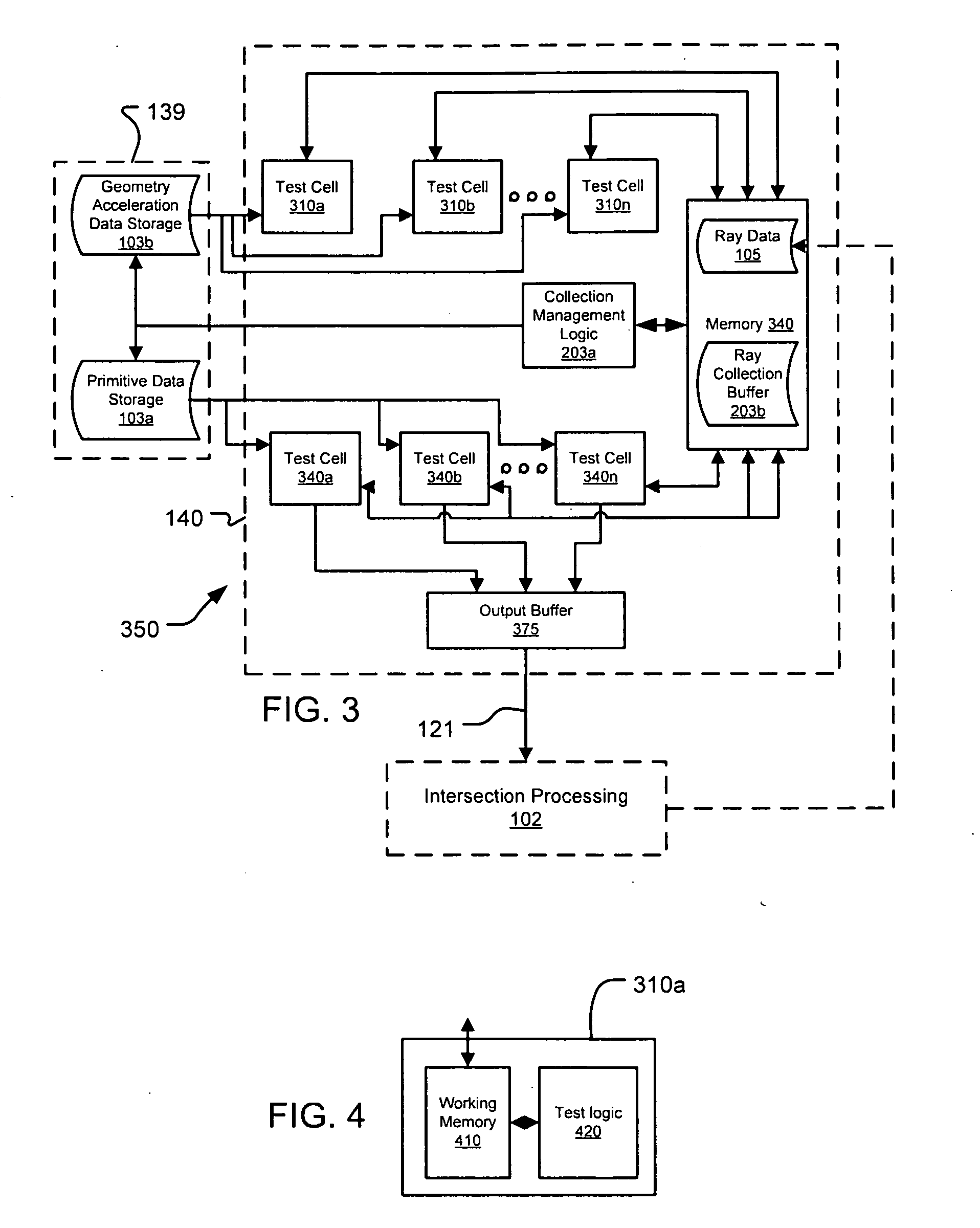
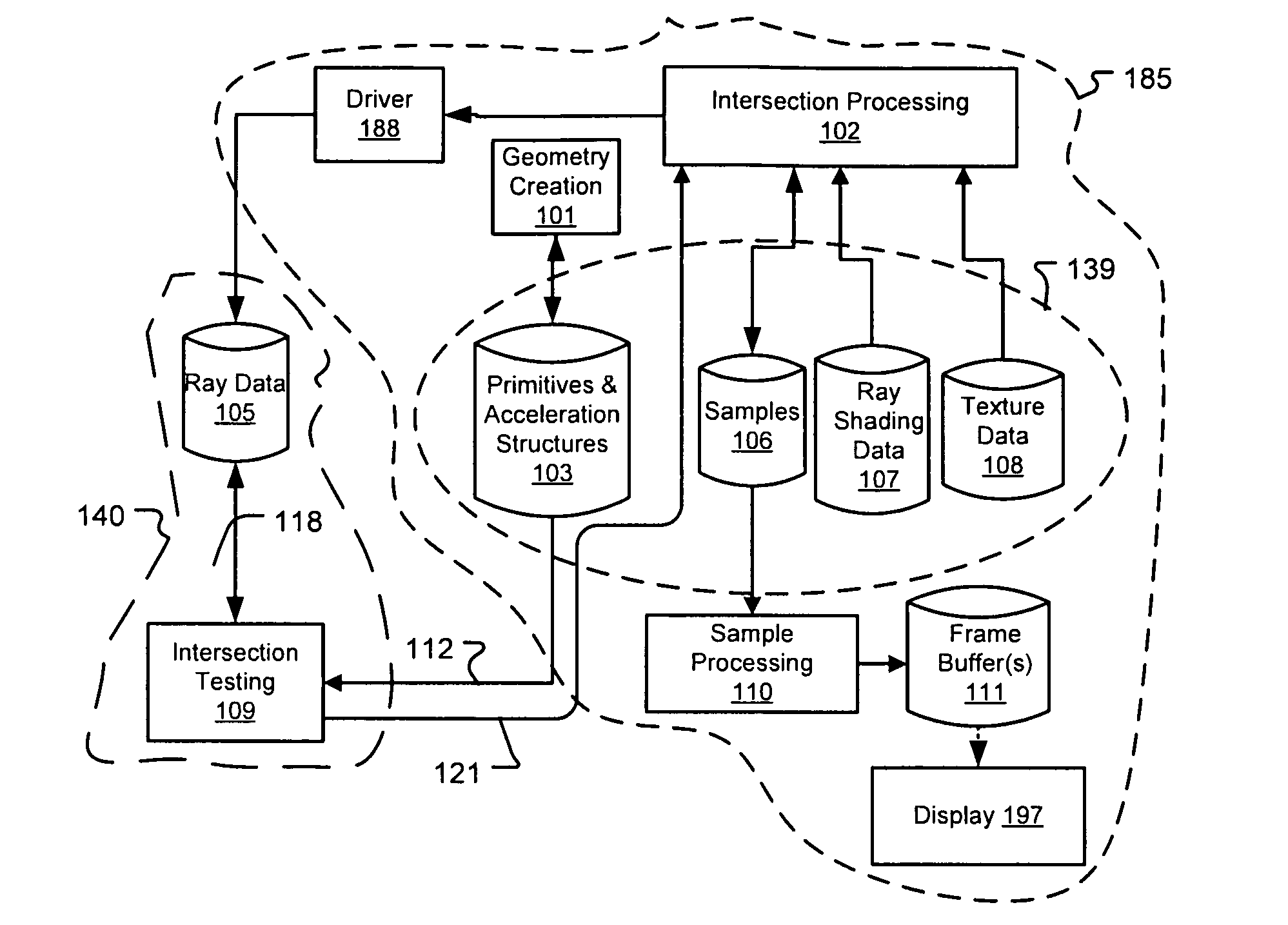
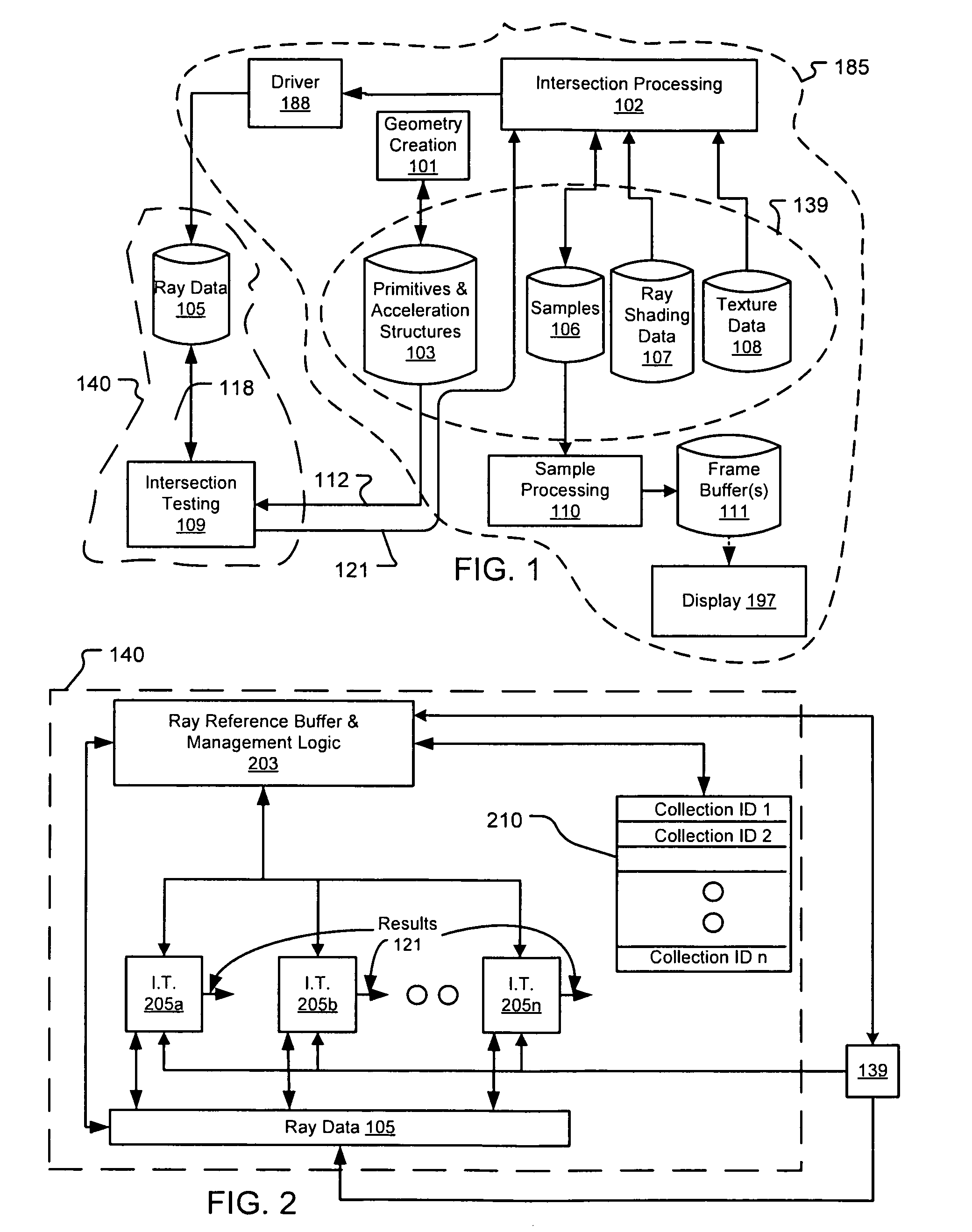
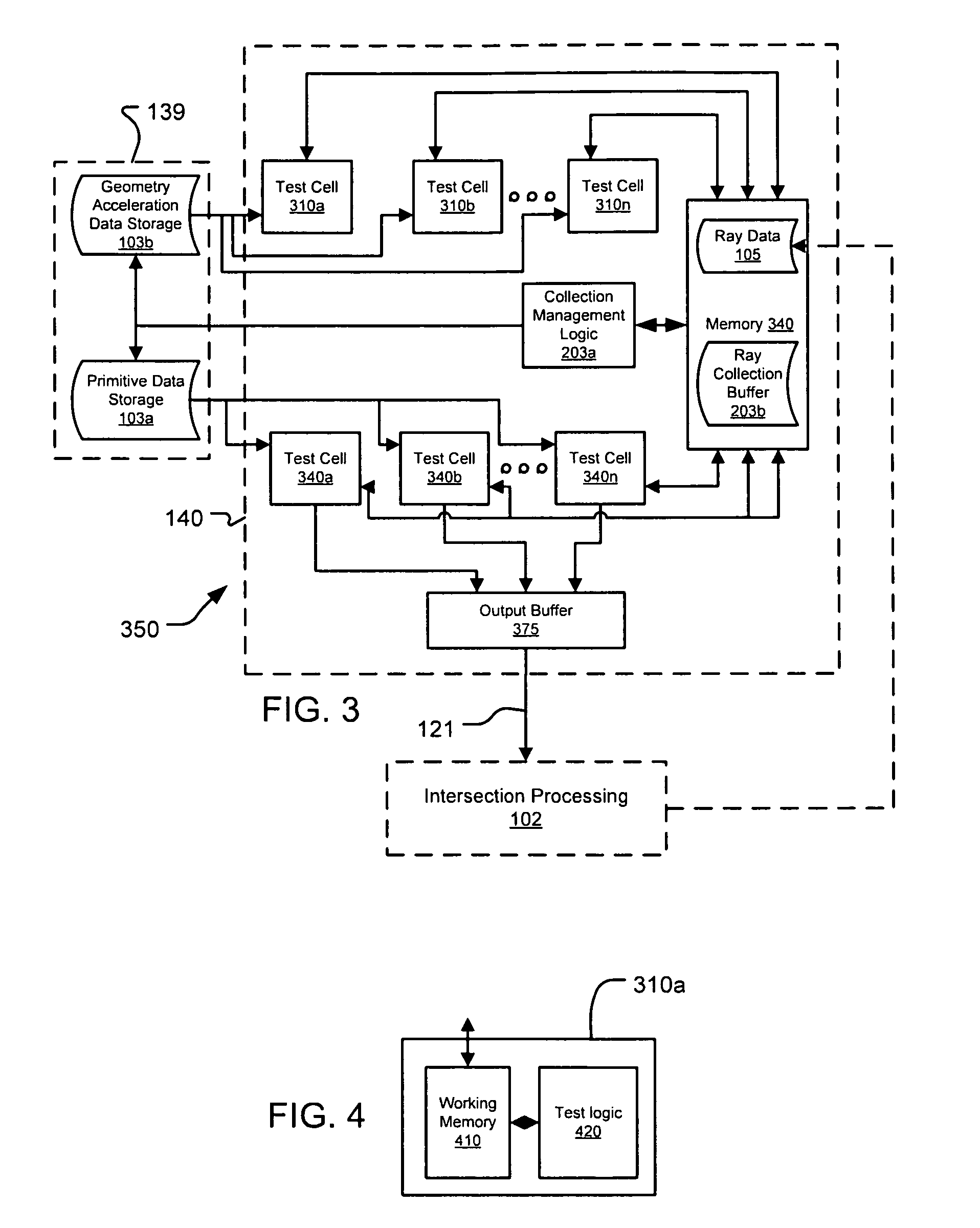
Architectures for parallelized intersection testing and shading for ray-tracing rendering
Ray tracing scenes is accomplished using a plurality of intersection testing resources coupled with a plurality of shading resources, communicative in the aggregate through links / queues. A queue from testing to shading comprises respective ray / primitive intersection indications, comprising a ray identifier. A queue from shading to testing comprises identifiers of new rays to be tested, wherein data defining the rays is separately stored in memories distributed among the intersection testing resources. Ray definition data can be retained in distributed memories until rays complete intersection testing, and be selected for testing multiple times based on ray identifier. A structure of acceleration shapes can be used. Packets of ray identifiers and shape data can be passed among the intersection testing resources, and each resource can test rays identified in the packet, and for which definition data is present in its memory. Test results for acceleration shapes are used to collect rays against acceleration shapes, and closest detection ray / primitive intersections are indicated by sending ray identifiers to shading resources.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
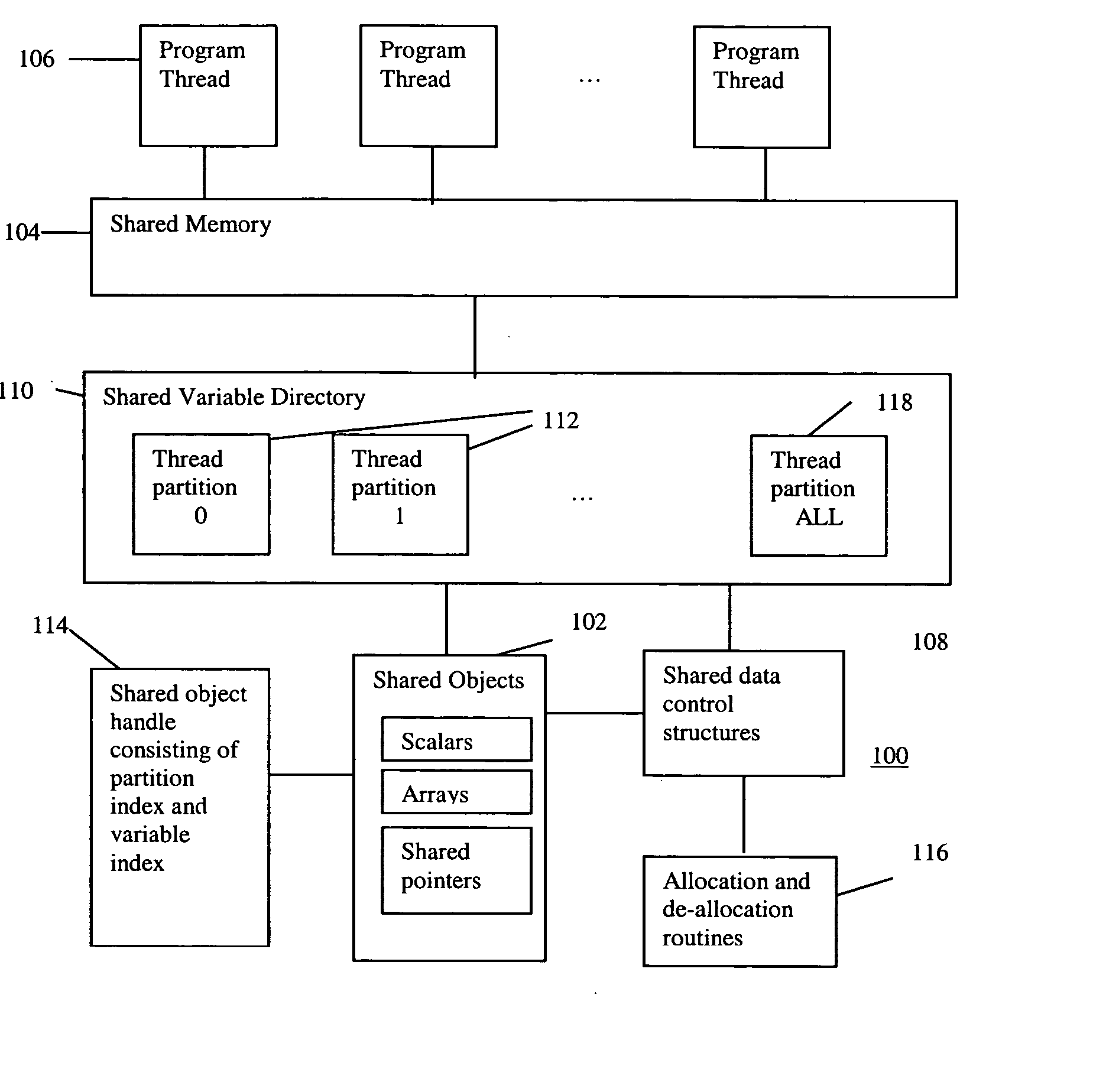
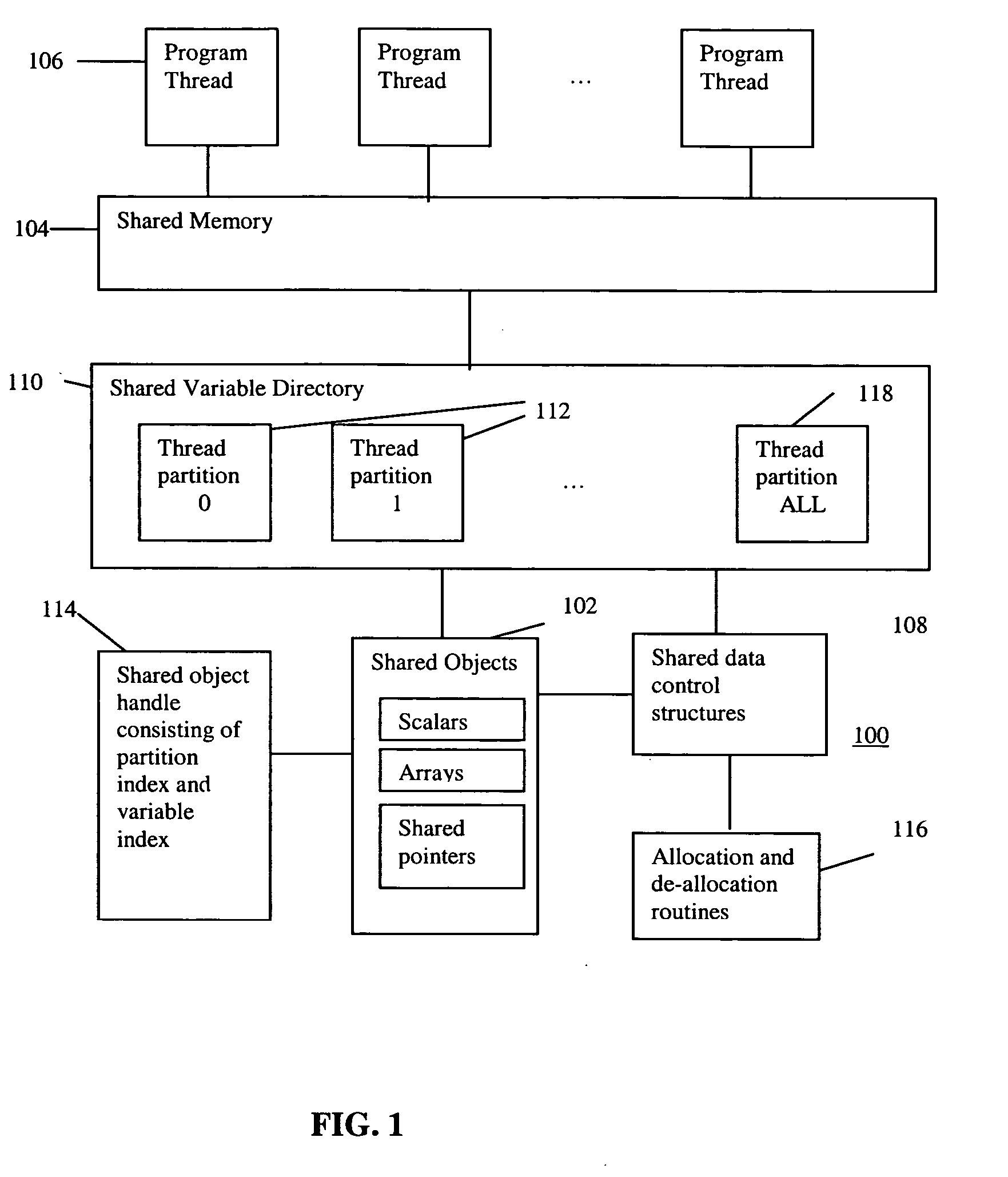
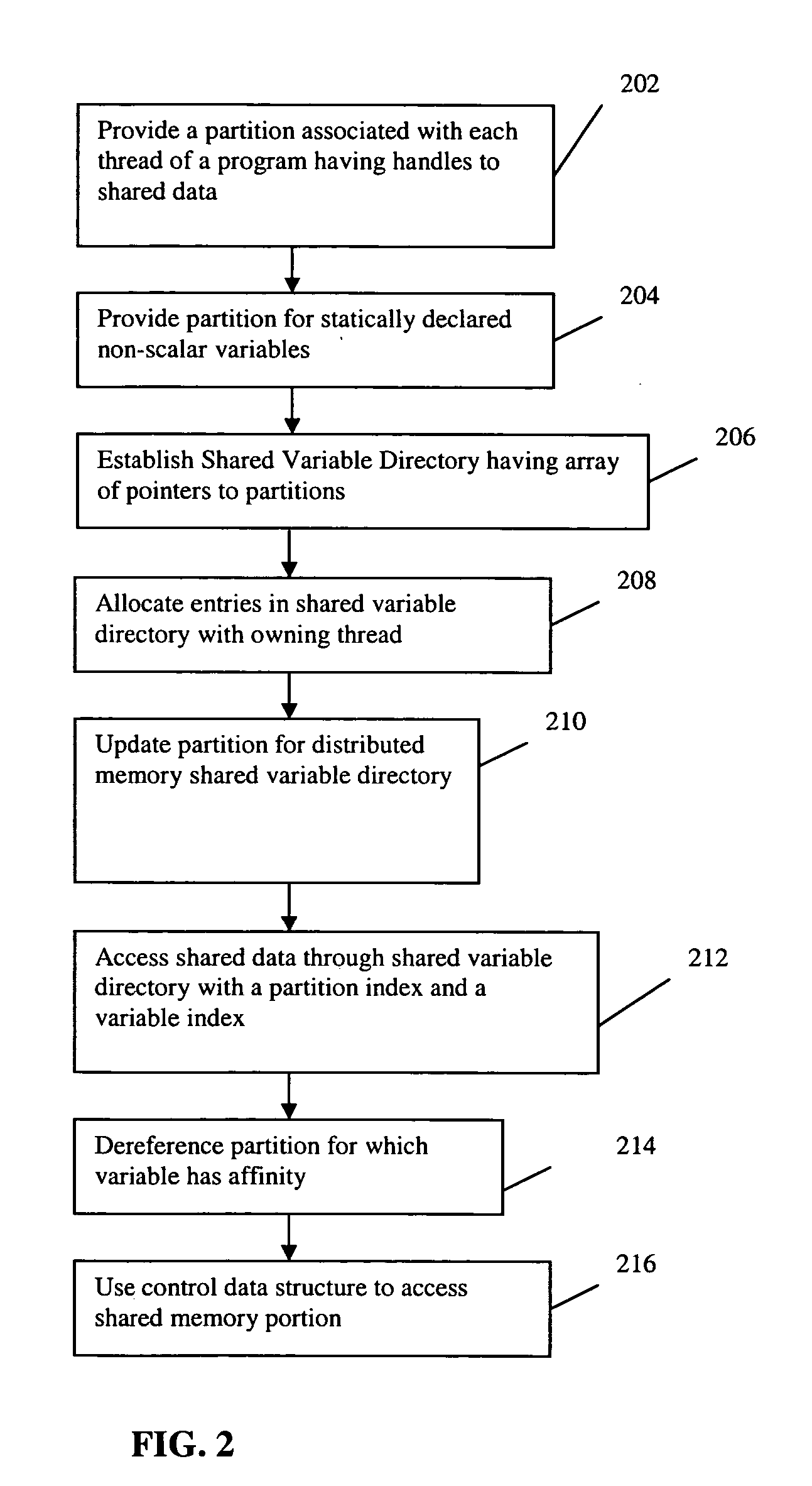
Scalable runtime system for global address space languages on shared and distributed memory machines
ActiveUS20050149903A1Improve scalabilityResource allocationSpecific program execution arrangementsExtensibilityGlobal address space
An improved scalability runtime system for a global address space language running on a distributed or shared memory machine uses a directory of shared variables having a data structure for tracking shared variable information that is shared by a plurality of program threads. Allocation and de-allocation routines are used to allocate and de-allocate shared variable entries in the directory of shared variables. Different routines can be used to access different types of shared data. A control structure is used to control access to the shared data such that all threads can access the data at any time. Since all threads see the same objects, synchronization issues are eliminated. In addition, the improved efficiency of the data sharing allows the number of program threads to be vastly increased.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Method and apparatus for storing and distributing memory repair information
ActiveUS20080065929A1Easy to integrateConvenient to accommodateElectronic circuit testingStatic storageDistributed memoryControl signal
A system for repairing embedded memories on an integrated circuit is disclosed. The system comprises an external Built-In Self-repair Register (BISR) associated with every reparable memory on the circuit. Each BISR is configured to accept a serial input from a daisy chain connection and to generate a serial output to a daisy chain connection, so that a plurality of BISRs are connected in a daisy chain with a fuse box controller. The fuse box controller has no information as to the number, configuration or size of the embedded memories, but determines, upon power up, the length of the daisy chain. With this information, the fuse box controller may perform a corresponding number of serial shift operations to move repair data to and from the BISRs and into and out of a fuse box associated with the controller. Memories having a parallel repair interface are supported by a parallel address bus and enable control signal on the BISR, while those having a serial repair interface are supported by a parallel daisy chain path that may be selectively cycled to shift the contents of the BISR to an internal serial register in the memory. Preferably, each of the BISRs has an associated repair analysis facility having a parallel address bus and enable control signal by which fuse data may be dumped in parallel into the BISR and from there, either uploaded to the fuse box through the controller or downloaded into the memory to effect repairs. Advantageously, pre-designed circuit blocks may provide daisy chain inputs and access ports to effect the inventive system therealong or to permit the circuit block to be bypassed for testing purposes.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Architectures for parallelized intersection testing and shading for ray-tracing rendering
Ray tracing scenes is accomplished using a plurality of intersection testing resources coupled with a plurality of shading resources, communicative in the aggregate through links / queues. A queue from testing to shading comprises respective ray / primitive intersection indications, comprising a ray identifier. A queue from shading to testing comprises identifiers of new rays to be tested, wherein data defining the rays is separately stored in memories distributed among the intersection testing resources. Ray definition data can be retained in distributed memories until rays complete intersection testing, and be selected for testing multiple times based on ray identifier. A structure of acceleration shapes can be used. Packets of ray identifiers and shape data can be passed among the intersection testing resources, and each resource can test rays identified in the packet, and for which definition data is present in its memory. Test results for acceleration shapes are used to collect rays against acceleration shapes, and closest detection ray / primitive intersections are indicated by sending ray identifiers to shading resources.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
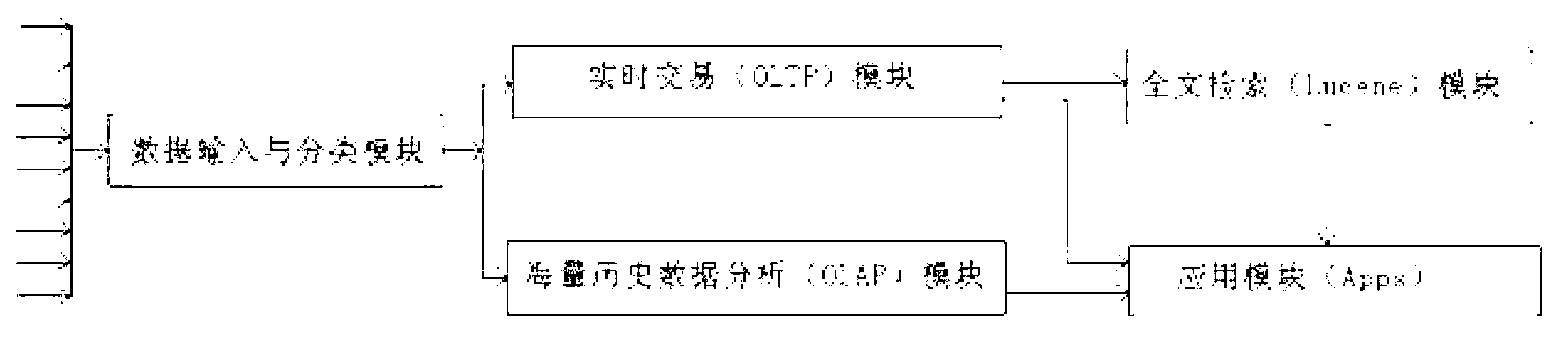
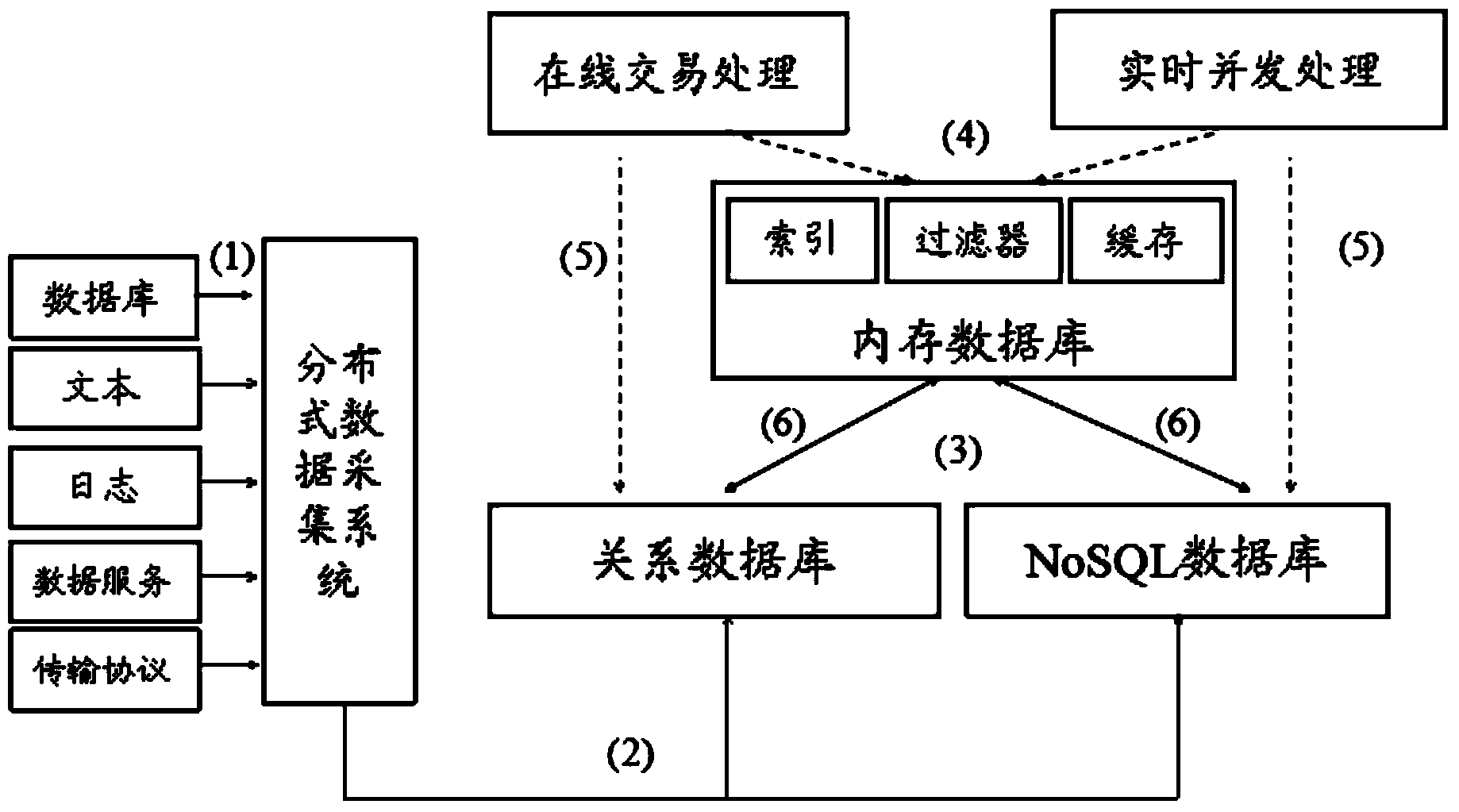
Fast data and big data combined data processing method and system
InactiveCN103268336AReduce the problem of slow reading and writingLow costSpecial data processing applicationsStatistical analysisEngineering
The invention discloses a fast data and big data combined data processing method which includes steps: (1) data input of different data sources is received and is classified and transmitted according to fast data and big data; (2) fast data enter a real-time trading module which performs real-time calculation and inquiring on fast data by aid of a distributed memory; (3) a full-text retrieval module performs full-text retrieval according to the fast data result; (4) big data enter a volume historical data analysis module, are stored and are subjected to complete inquiring and statistic analysis; and (5) an application module receives data processed in the step (2), the step (3) and the step (4), and terminal display is carried out as required. The invention further provides a fast data and big data combined data processing system. The fast data and big data combined data processing method and system are low in cost and convenient to maintain, resources are distributed according to needs, and the performance is linearly expanded.
Owner:刘峰
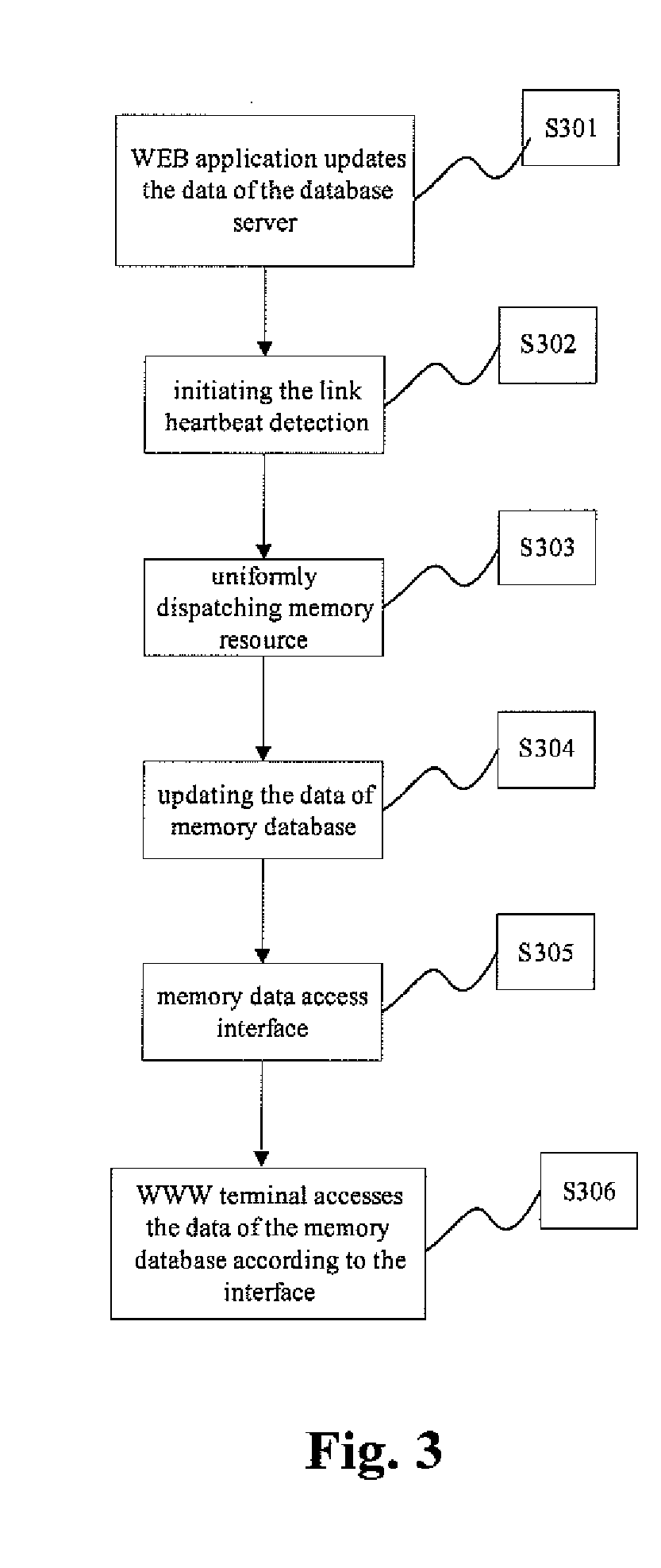
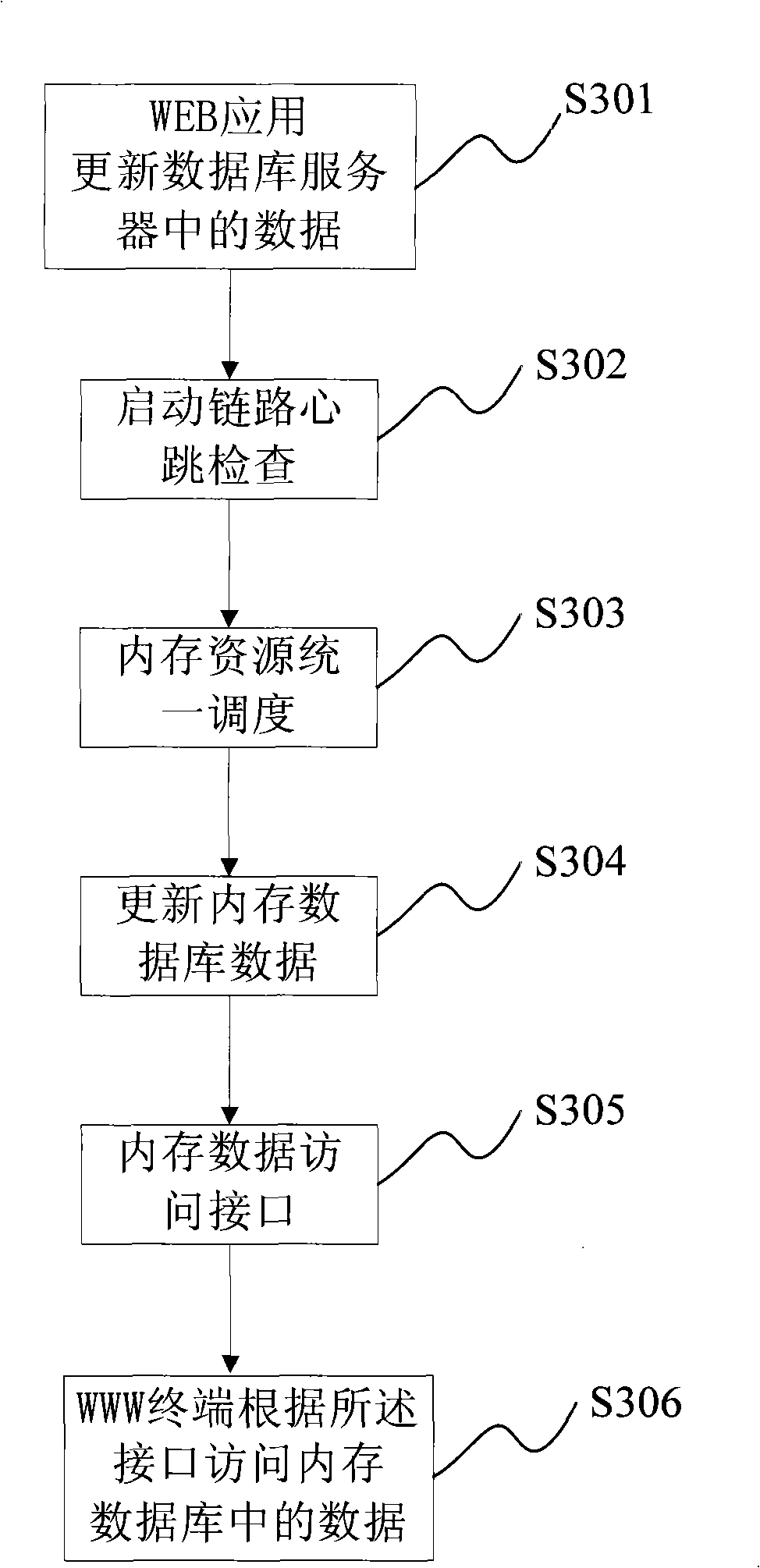
Database system based on web application and data management method thereof
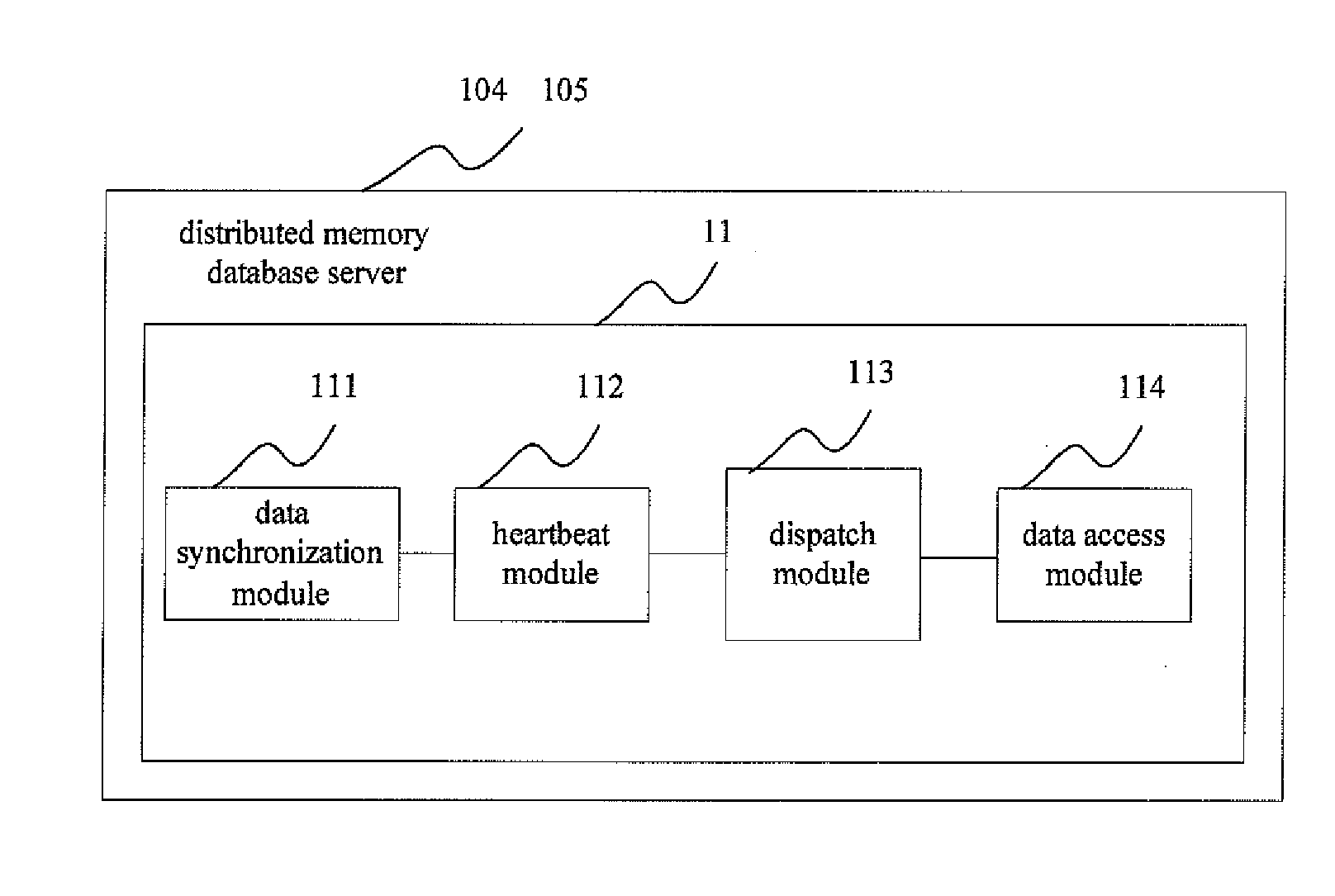
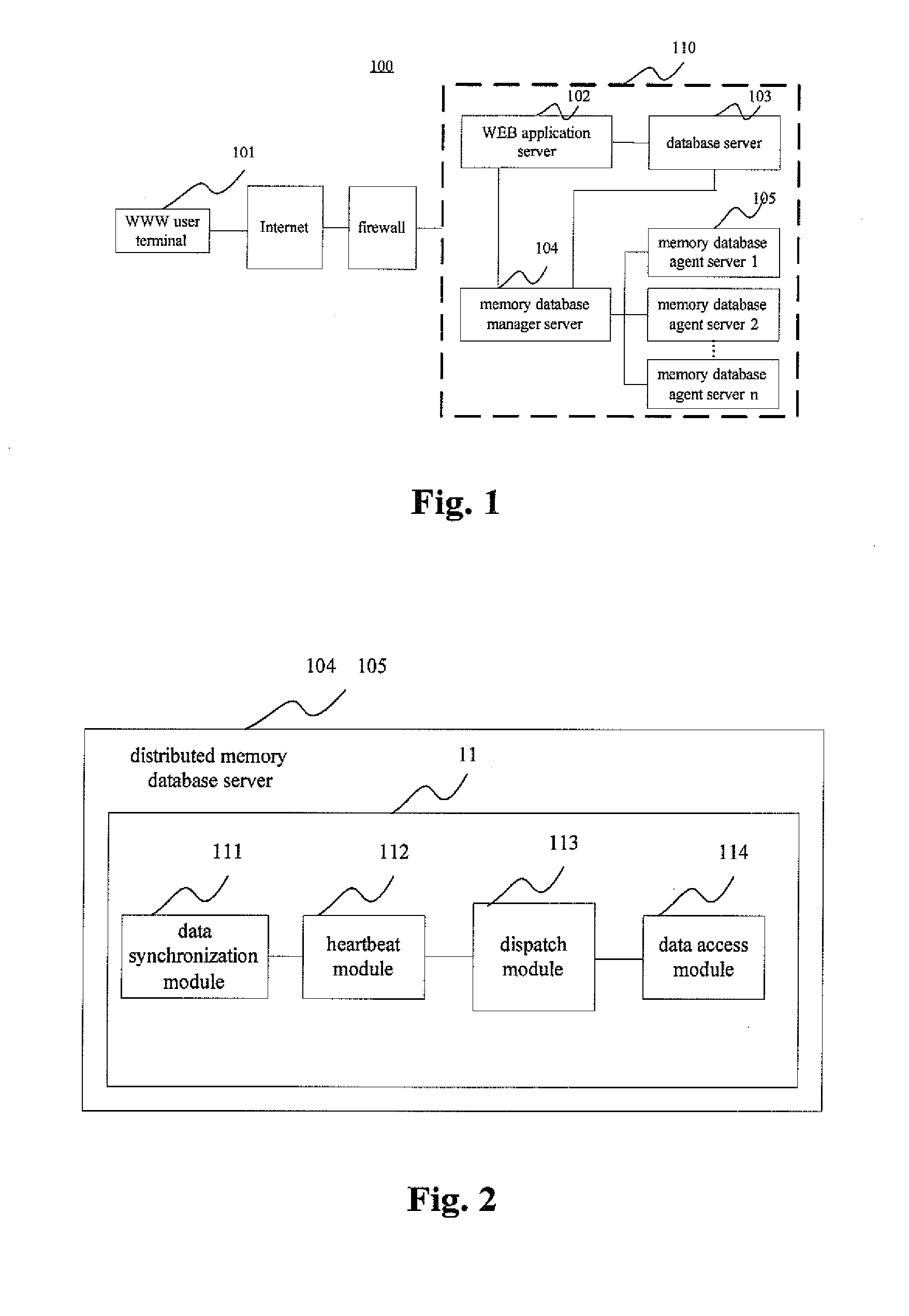
InactiveUS20110246420A1Lower capability requirementsLower performance requirementsDigital data processing detailsWebsite content managementData synchronizationIn-memory database
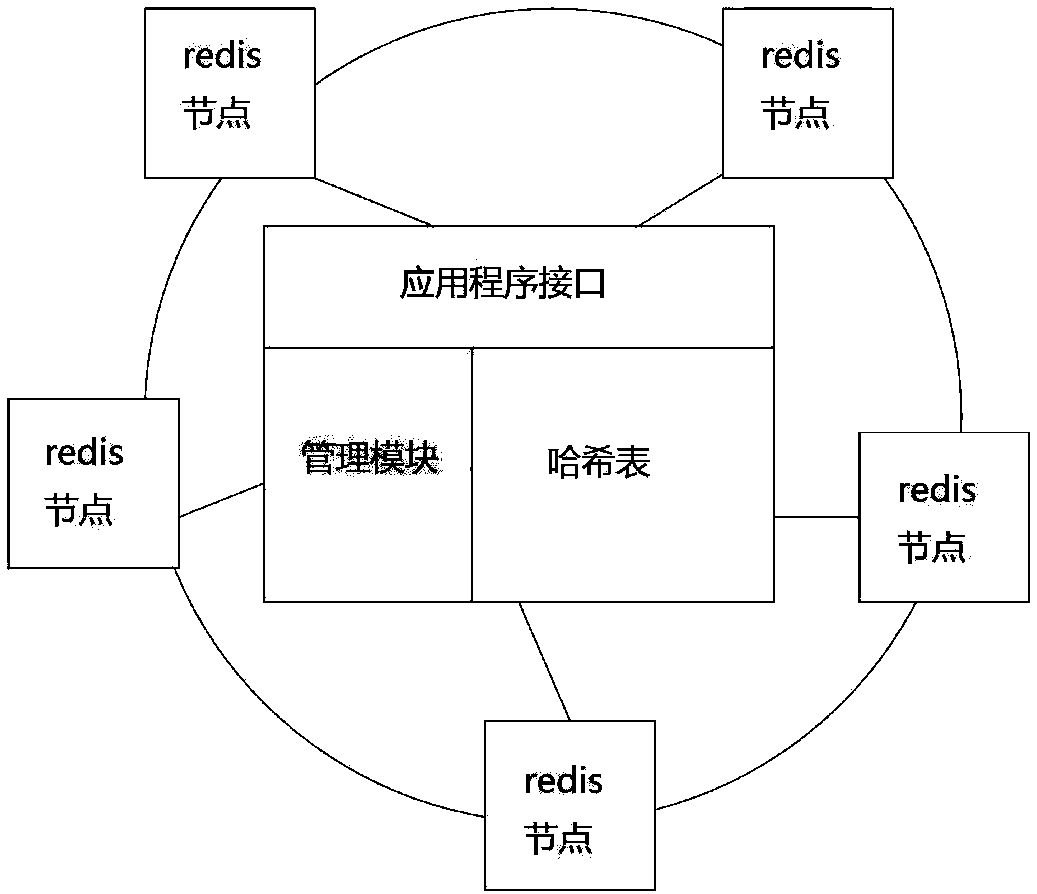
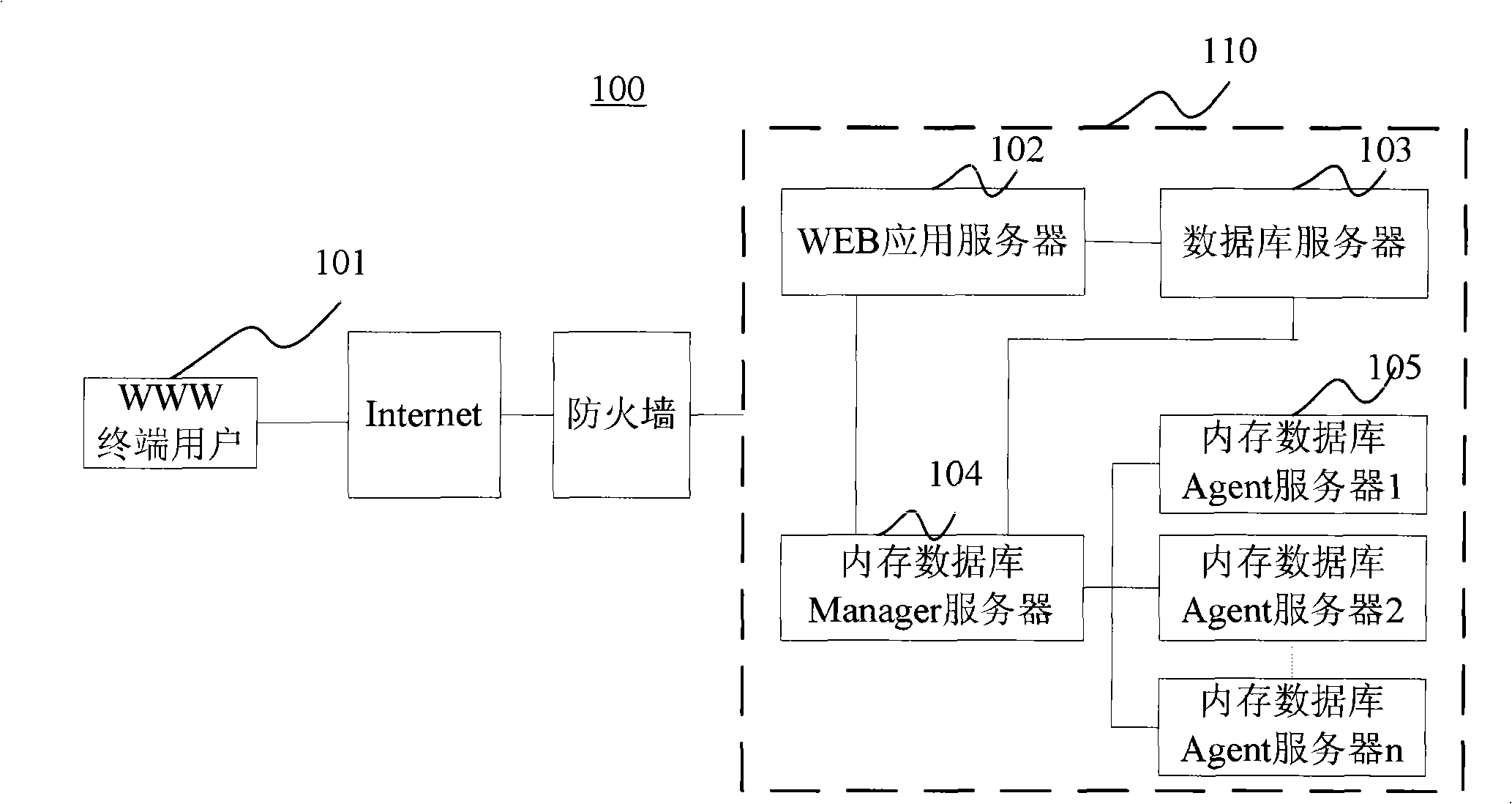
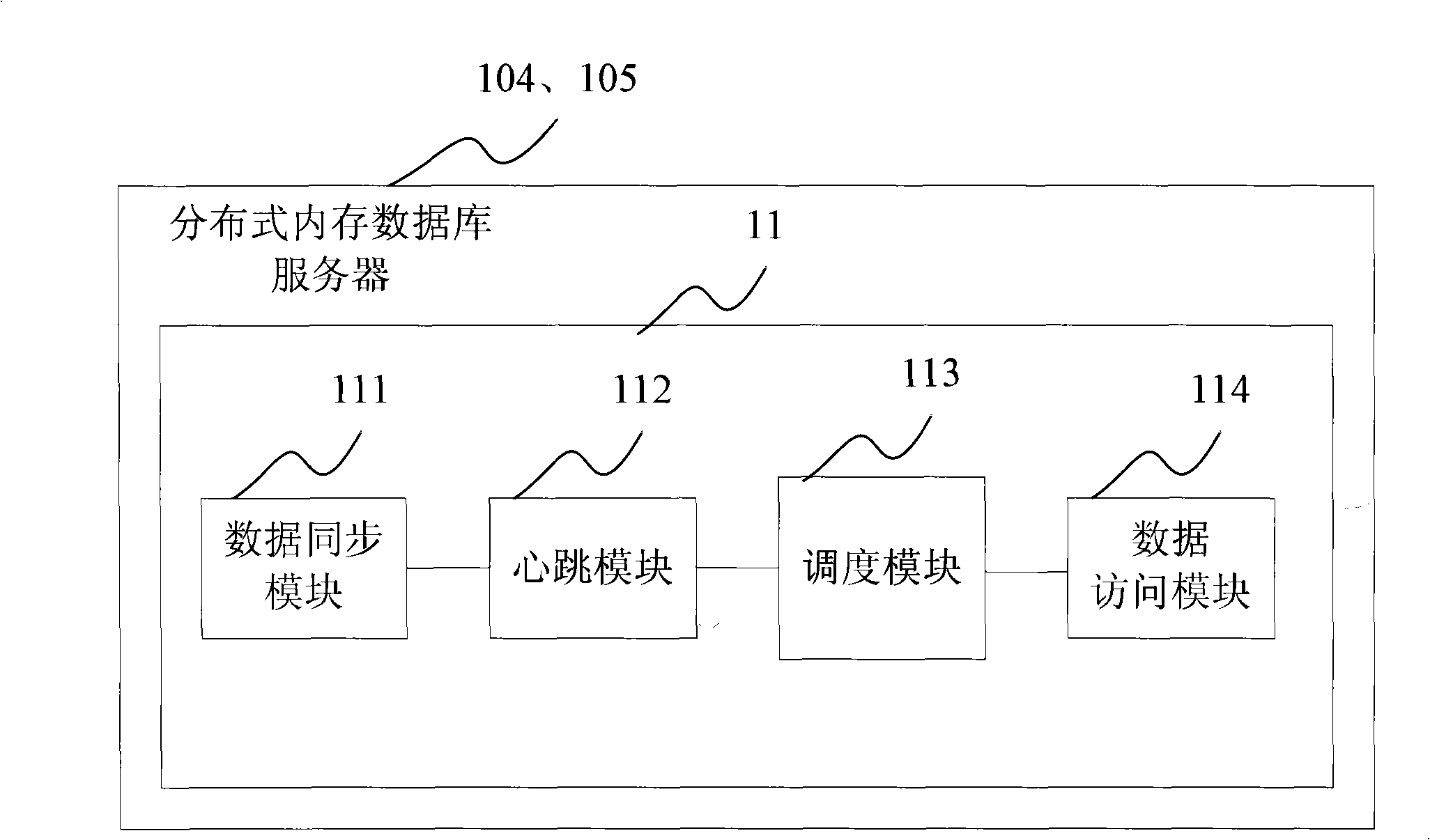
A database system based on a WEB application includes a database server (103) accessed by means of reading and writing a disk and a distributed memory database server (11), wherein the distributed memory database serve performs data synchronized with data read from the database server by a data synchronizing module (111); the distributed memory database server further includes a memory database Manager server (104) and more than one memory database Agent servers (105), wherein the memory database manager server performs uniform dispatch of memory resources, realizes the data synchronization between the database server and the distributed memory database, and provides the WEB application server (102) with a data access interface; and the memory database agent servers store specific data.
Owner:ZTE CORP
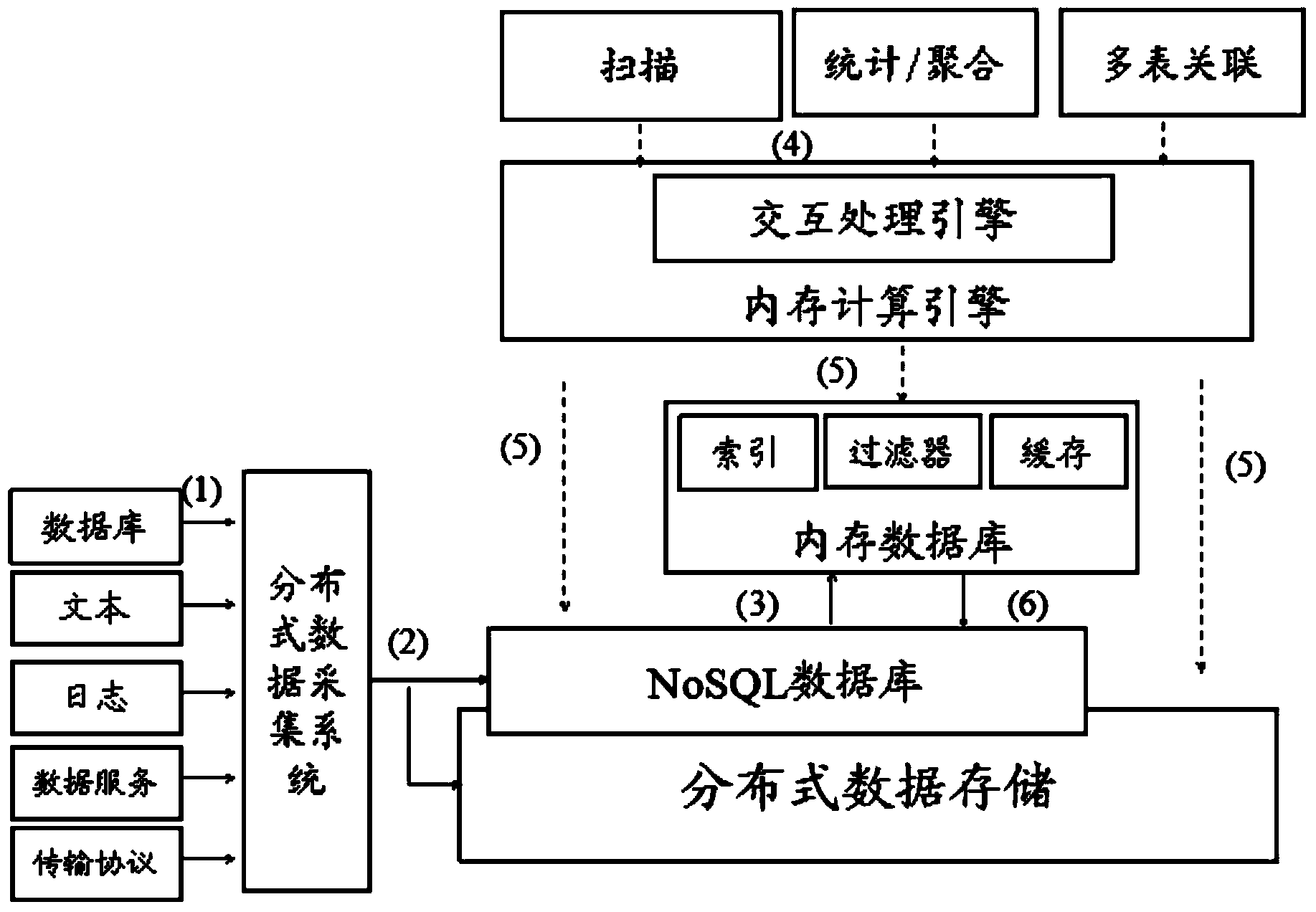
Mixed type processing system and method oriented to industry big data diversity application
InactiveCN104021194ASatisfy handlingMeet interaction analysisOther databases retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsHybrid typeData diversity
The invention discloses a mixed type processing system and method oriented to industry big data diversity application. The system comprises a distributed data collection subsystem used for collecting data from an external system, a storing and parallel calculating subsystem used for storing and calculating the collected data, and an integrated resource and system management platform used for managing the stored and calculated data. The storing and parallel calculating subsystem comprises a big data storing subsystem and a big data processing subsystem, wherein the big data processing subsystem comprises a memory calculating engine which is used for providing distributed memory abstract in a shared-nothing cluster and conducting parallel streamlined and thread lightweight processing on the collected data. The mixed type processing system and method can meet the requirements of industry big data diversity service application, the big data processing performance can be improved by ten or more times through acceleration of the memory calculating engine, and the usability, reliability and expandability of the system can be ensured through the integrated management platform.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
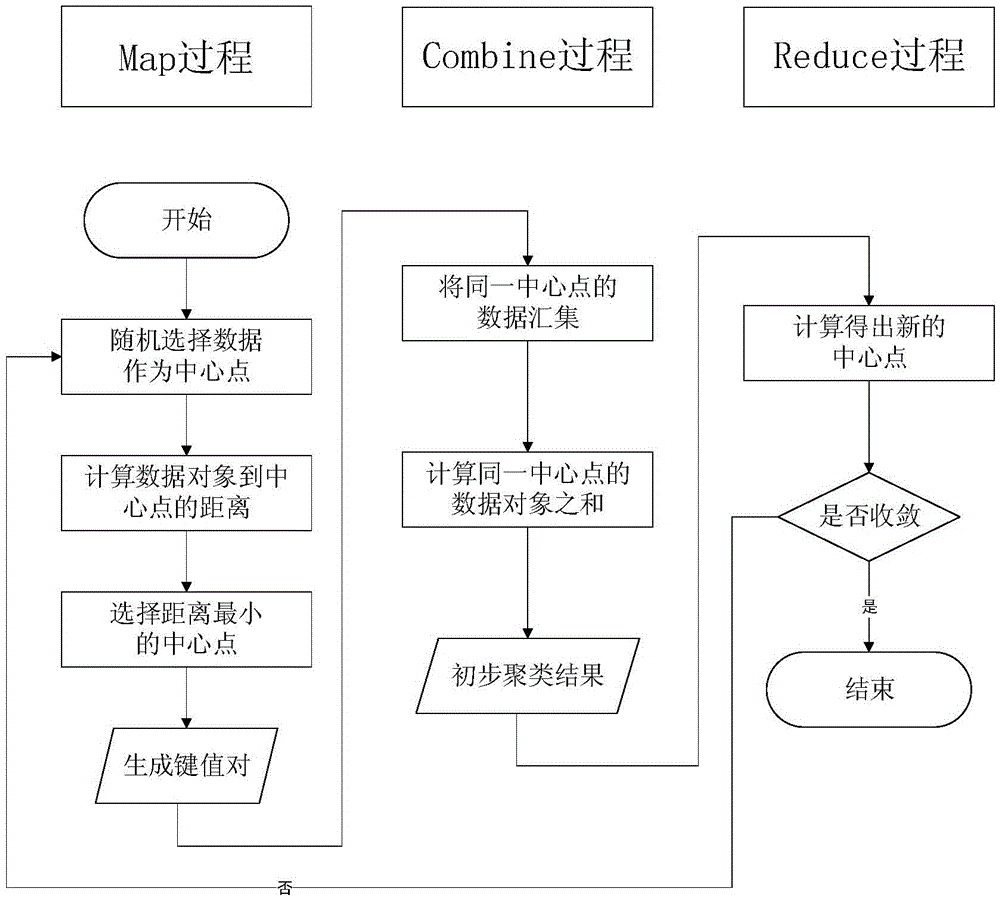
Short-term load forecasting method
InactiveCN105608512AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionLoad forecastingDistributed memory
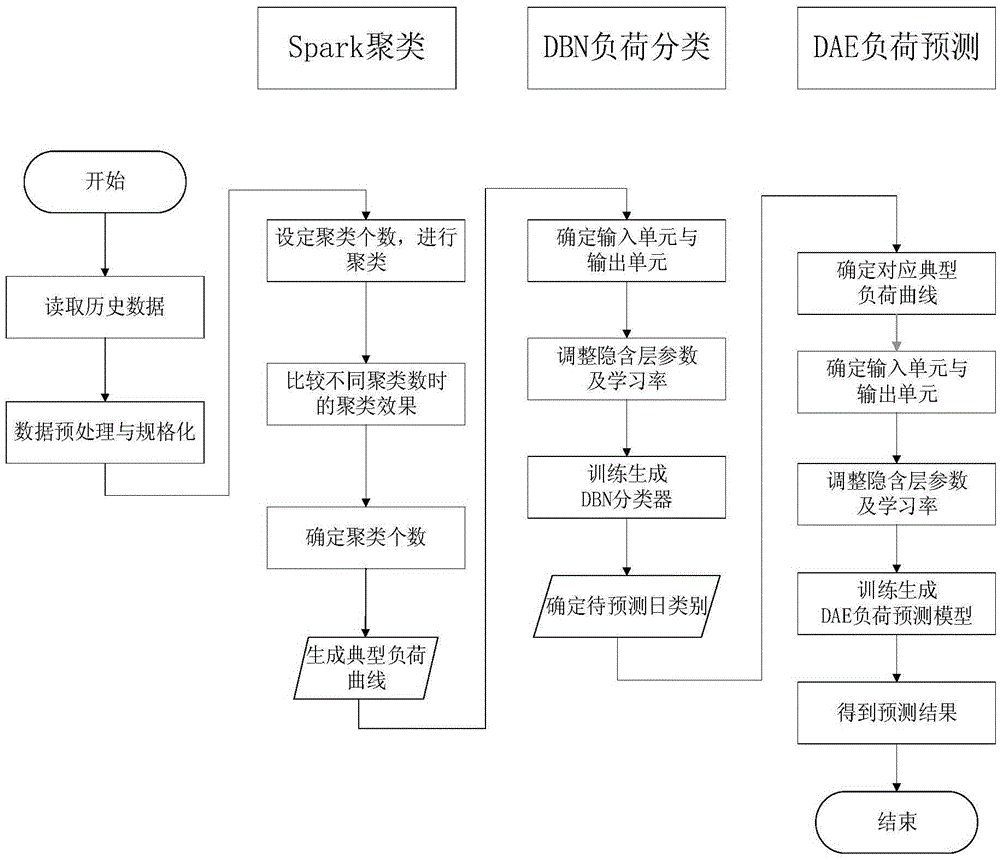
The invention discloses a short-term load forecasting method, and belongs to the technical field of power systems. Aiming at the problems that mass data have too much noise, are long in training time and are easily trapped in local minimum or over-fitting and the like in the prior art, the method comprises: performing cluster analysis on historical load data to generate a typical load curve, and digging the generality of mass historical load data to achieve the effect of screening and training data for later load forecasting, thus eliminating the noise influence of the mass data; performing strong fitting of a complex nonlinear function by deep learning to solve the problems of over-fitting and local minimum of a conventional neural network, thus realizing accurate and quick short-term load forecasting; and further constructing a forecasting model by using a distributed memory computation framework Spark, thus improving the efficiency and the instantaneity of the whole short-term load forecasting flow. Compared with the prior art, the method can realize accurate and quick short-term load forecasting.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
NUMA structure implementing method based on distributed internal memory virtualization
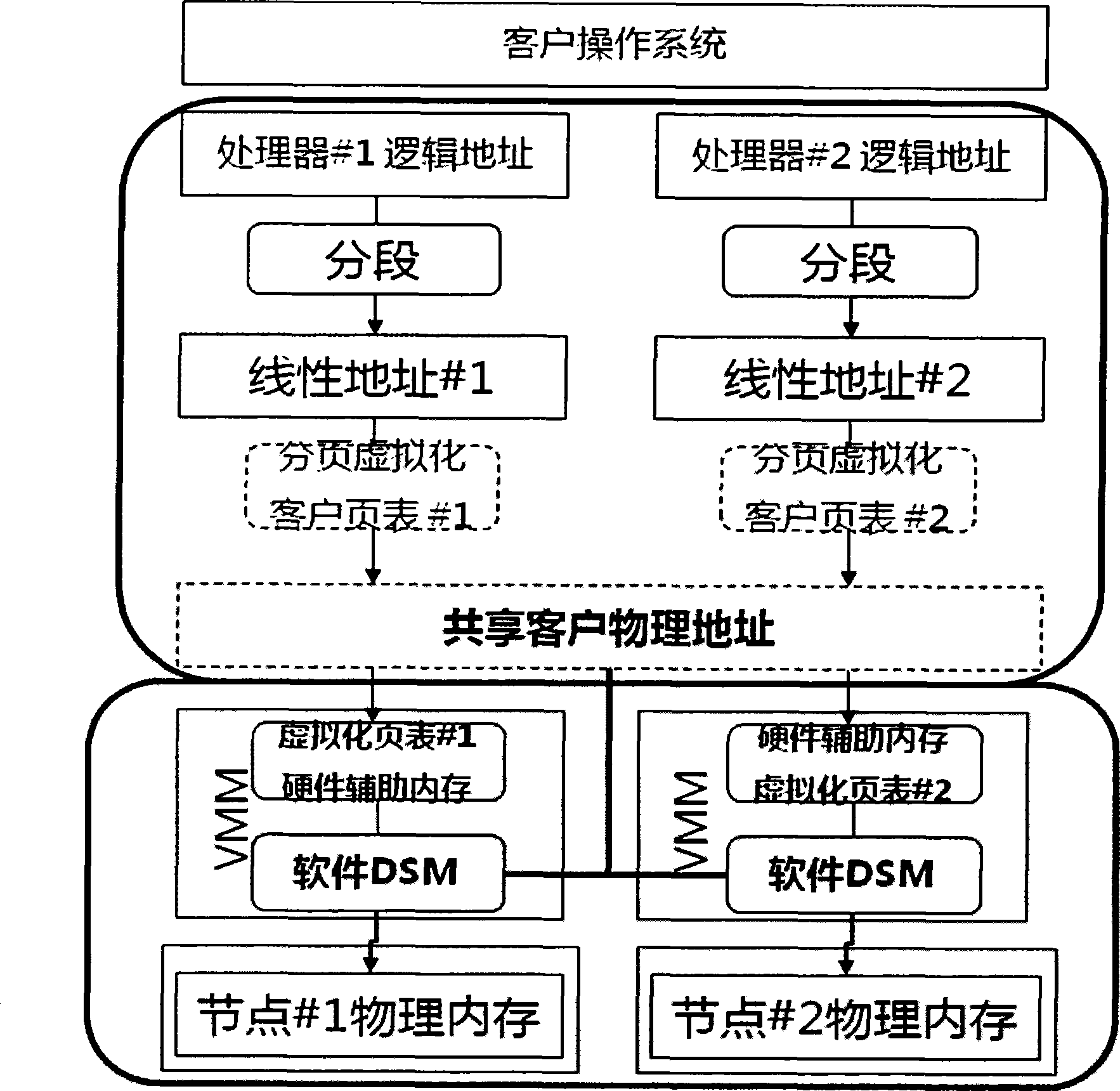
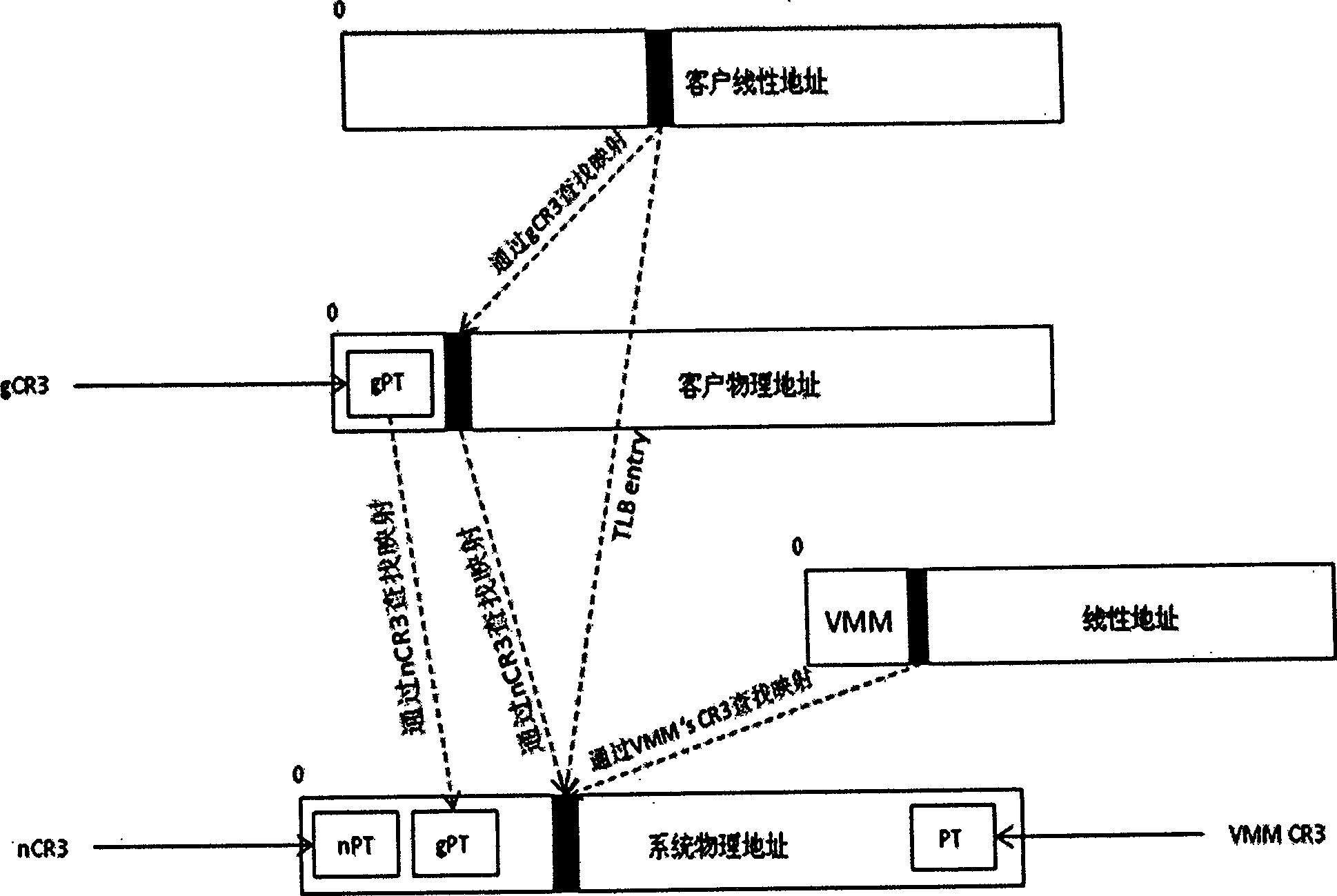
InactiveCN101477496AGuaranteed correctnessImprove manageabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionInternal memoryVirtualization
The invention discloses a realization method for NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access) structure based on distributed hardware-assisted memory virtualization. The method comprises the following four steps: step one, preparation stage; step two, normal work stage; step three, NUMA processing local request stage; and step four, NUMA processing remote request stage. The invention adopts the latest hardware-assisted memory virtualization technology and the distributed shared storage algorithm, provides a NUMA-structure shared single physical address space, and realizes the transparent and unified management to the multi-host memory resource by a guest operation system, so as to reduce the complexity of the application programming and increase the usability of system resource. Furthermore, the invention has the advantages of favorable use and development prospects.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Query engine system and query method of distributive memory column-oriented database
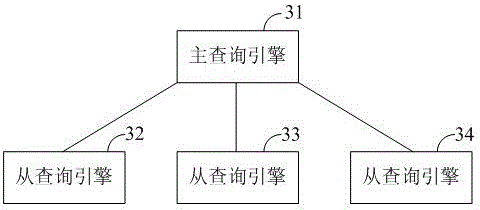
ActiveCN105824957AImprove query efficiencyImprove computing efficiencyResource allocationSpecial data processing applicationsTask completionQuery plan
The invention discloses a query engine system and a query method of a distributive memory column-oriented database. The query method comprises the following steps that a resource management module determines a conversation with a user in charge by a main query engine; the main query engine converts SQL (structured query language) sent by the user into a query plan; the resource management module allocates a sub query engine for the main query engine; the main query engine divides the query plan into at least two sub tasks and allocates sub query engine for each sub task; after the execution of the precursor sub tasks of the current sub task is completed, the current sub task is executed; middle data generated after the execution of the current sub task is completed is transmitted to the sub query engine in which the subsequent sub tasks are located; the current sub task completion state is sent to the main query engine; the main query engine notifies a customer to obtain final result data from the sub query engine. The query engine system and query method of the distributive memory column-oriented database provided by the invention have the advantage that good query efficiency can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods and systems for using distributed memory and set operations to process social networks
ActiveUS20120317121A1Not addressDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDistributed memorySocial web
Systems and methods for managing and evaluating a social network. The social network is represented as a graph structure and stored in distributed memory. A viable path from one node that is not directly connected to another node in the graph structure may be determined by traversing the graph in stages, moving outward from each node in stages until common midpoint nodes are found providing a connection between the nodes. When midpoint nodes are found, the paths connecting the one node to the other node may be reconstructed.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Graph data storage method and system based on distributed memory cloud
InactiveCN108600321AReduce overheadOptimize underlying storageTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed memoryServer allocation
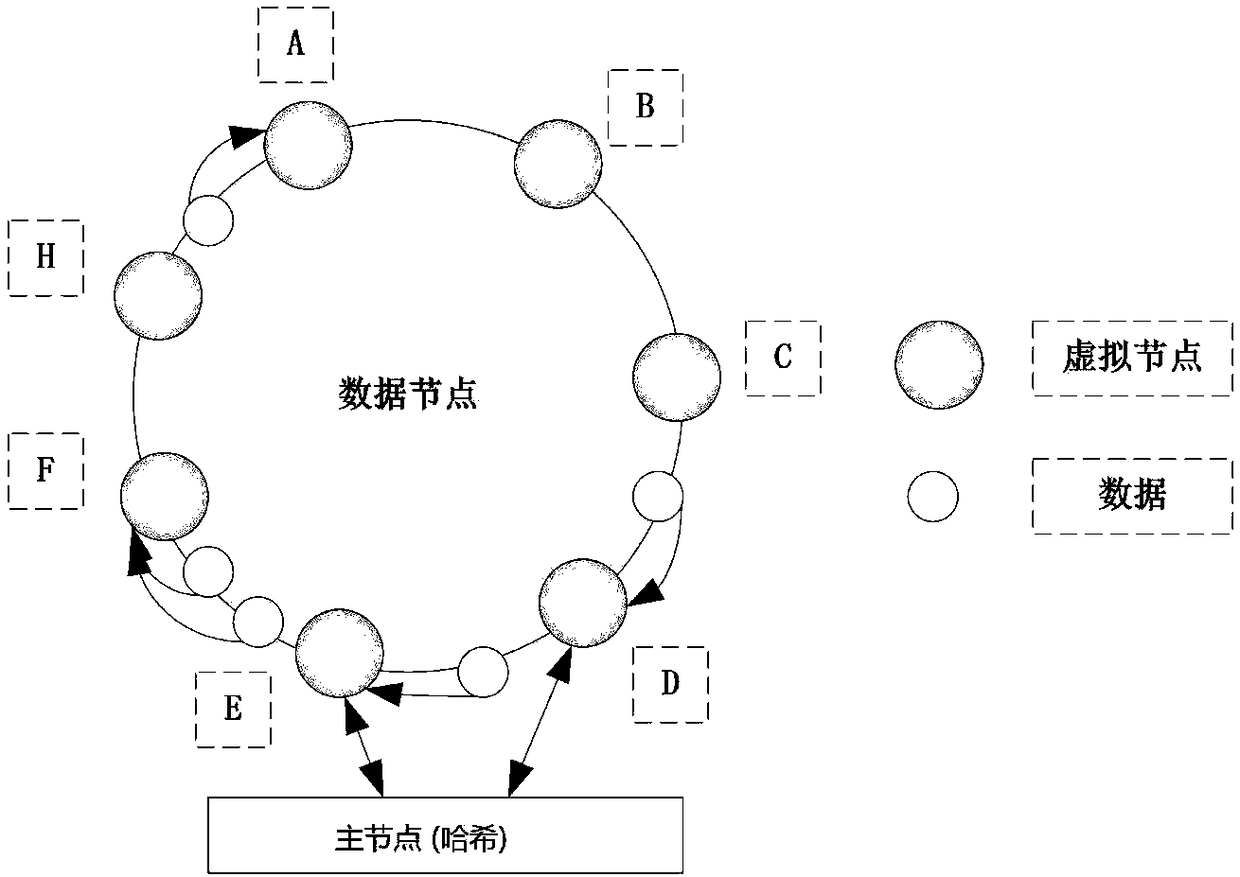
The invention relates to a graph data storage method and system based on distributed memory cloud. The system comprises a graph service layer which is used for allocating virtual nodes to each serverin the distributed memory cloud, mapping the virtual nodes to a Hash ring according to Hash values of the virtual nodes, storing a mapping relationship as a Hash mapping table, obtaining graph data stored by each server, searching the Hash values of the graph data on the Hash mapping table, storing the graph data to the corresponding virtual nodes, allocating new virtual nodes to new serves in thedistributed memory cloud when the new servers are increased, updating the Hash mapping table, adding the new virtual nodes to the Hash ring according to the Hash values of the new virtual nodes, andcarrying out data migration on each virtual node in the Hash ring according to the Hash values of the graph data stored by the virtual nodes and the updated Hash mapping table. Through utilization ofa consistent Hash algorithm, the method and the system support dynamic expansion, the nodes can be increased or deleted, and the loss can be reduced as much as possible when faults occur in the nodes.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Database system based on WEB application and data management method thereof
InactiveCN101493826ALoad balancingImprove timelinessWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationExtensibility
The invention relates to a WEB-based database system, which comprises a database server with disk mode read-write and a database server with distributed memory, wherein the database server with distributed memory carries out data synchronization by a data synchronization module and data read and written in the database server; the database server with distributed memory also comprises a Manager server of a memory database and more than one Agent server of the memory database, the Manager server of the memory database finishes united dispatching of memory resource, realizes data synchronization between the database sever and the database with distributed memory, and provides a data visit interface for the web application server, and the Agent server of the memory database stores specific data. The WEB-based database system adopts the database with distributed memory, shares memory resource of the server, realizes the load balancing of the memory database, and improves the timeliness ofdata response and the expansibility of an application program.
Owner:ZTE CORP
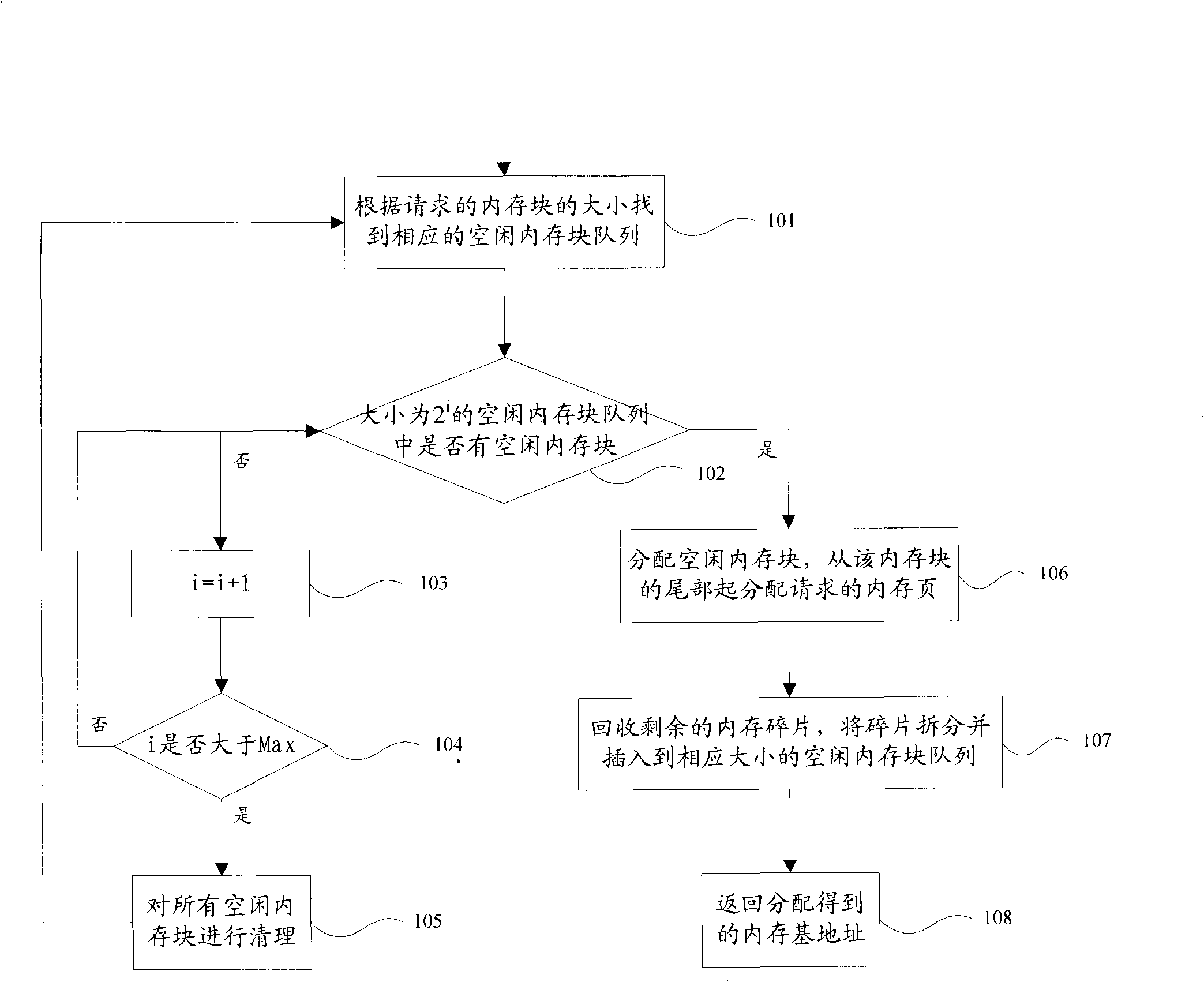
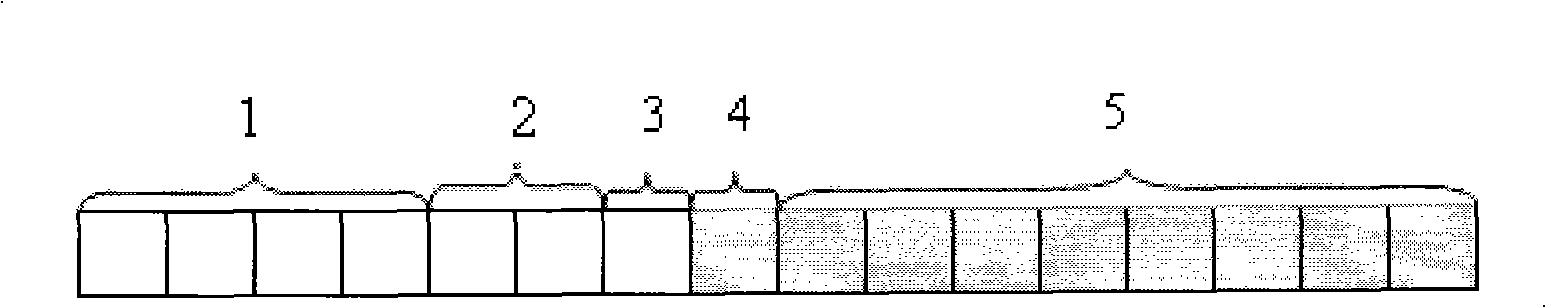
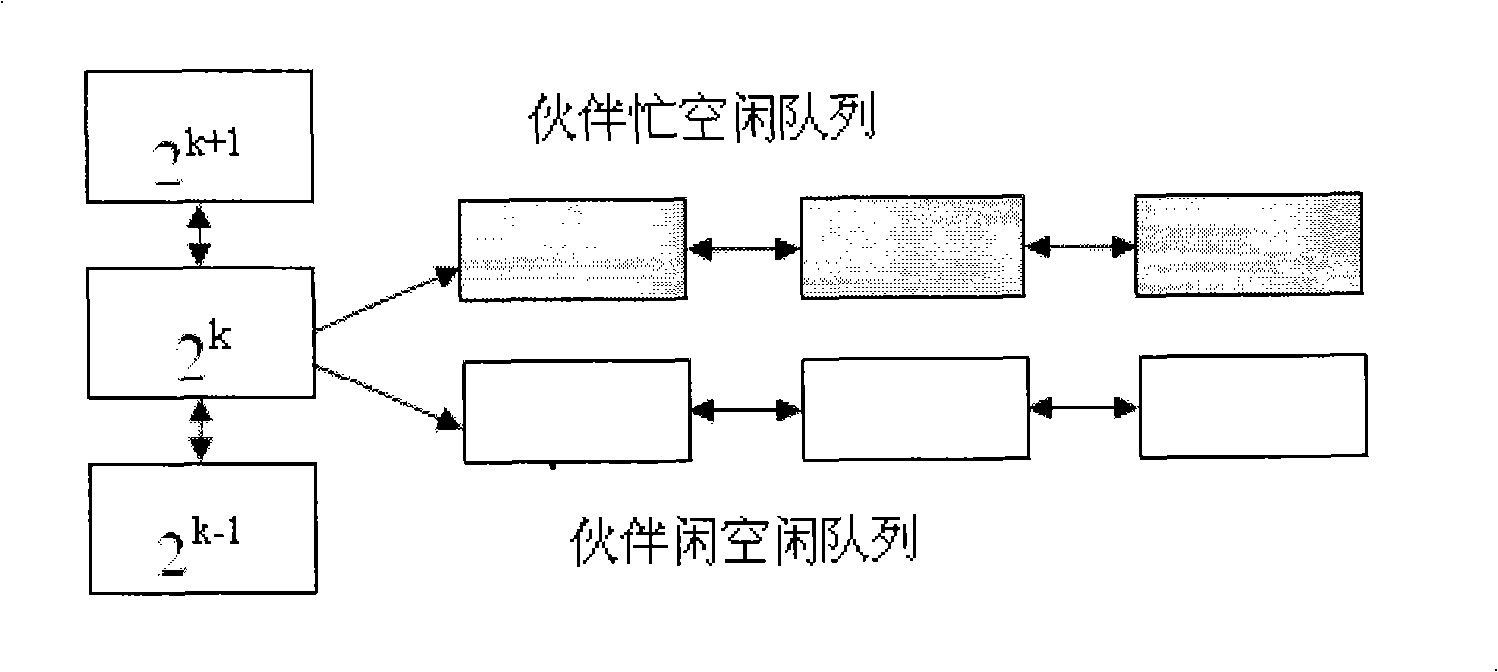
Internal memory distribution, cleaning and releasing method, and internal memory management apparatus
InactiveCN101320351AFlexible sizeReduce overheadMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternal memoryDistributed memory
The present invention discloses a memory distributing, clearing and releasing method and also discloses a memory management device which comprises a memory distributing module used for applying and distributing memory blocks for the memory from a vacant queue with most proper size, a fragment recovering module which is used for recovering internal chips which are produced when the memory is distributed and plugs the internal chips into different vacant queue and a memory combining module which is used for combining the memory blocks when a maximum vacant memory block can not satisfy the memory application. The present invention distributes the memory application according to need and can reduce the internal chips. The released memory blocks are processed for prolonging combination, and memory vibration caused by frequent cleavage and combination can be avoided, thereby reducing the cost for the frequent cleavage and combination of a system and improving the performance of the system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com