Patents
Literature
2070 results about "Clock control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Data processing system and method
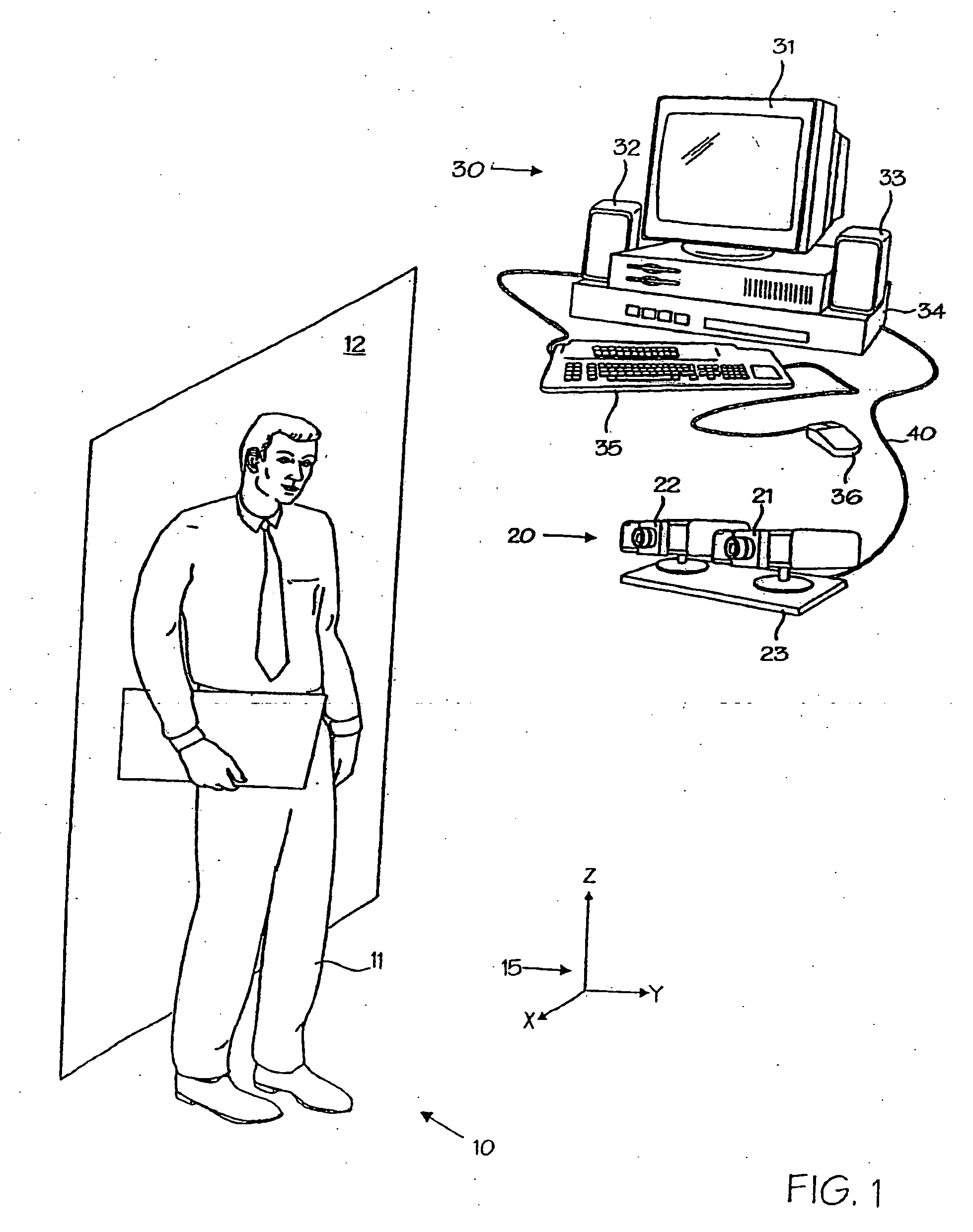
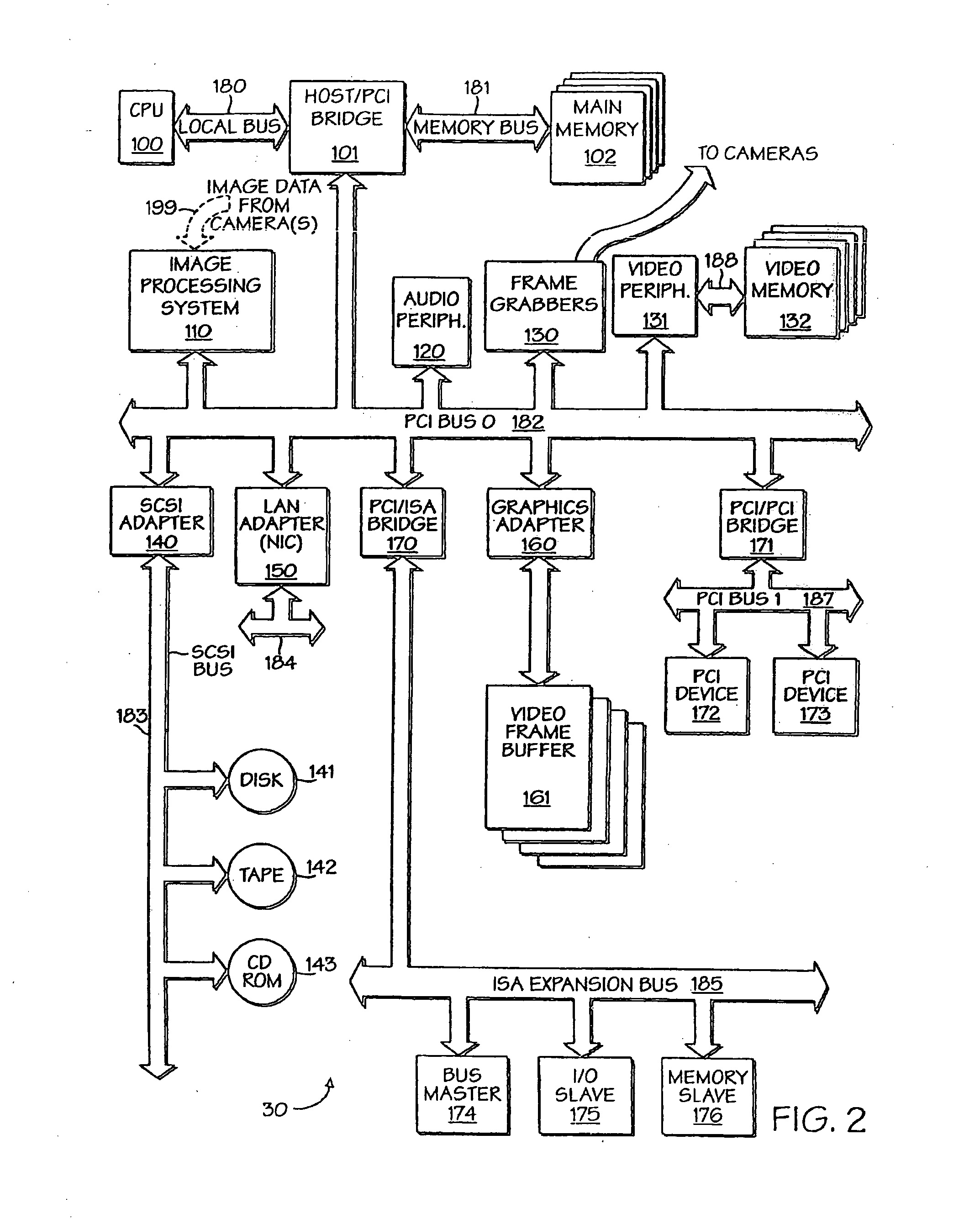
InactiveUS6215898B1Reduce overheadHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisStatic random-access memoryHigh memory
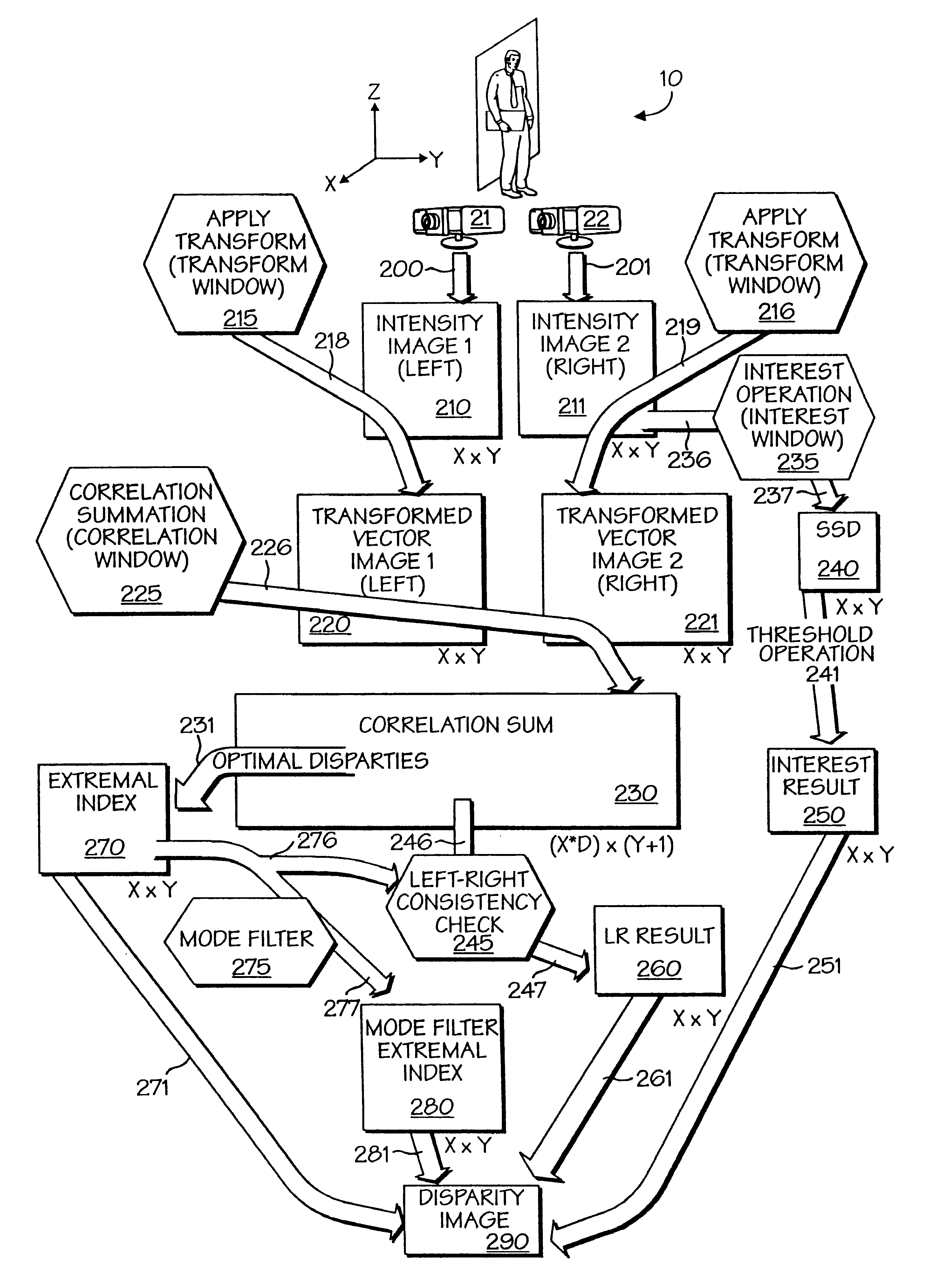
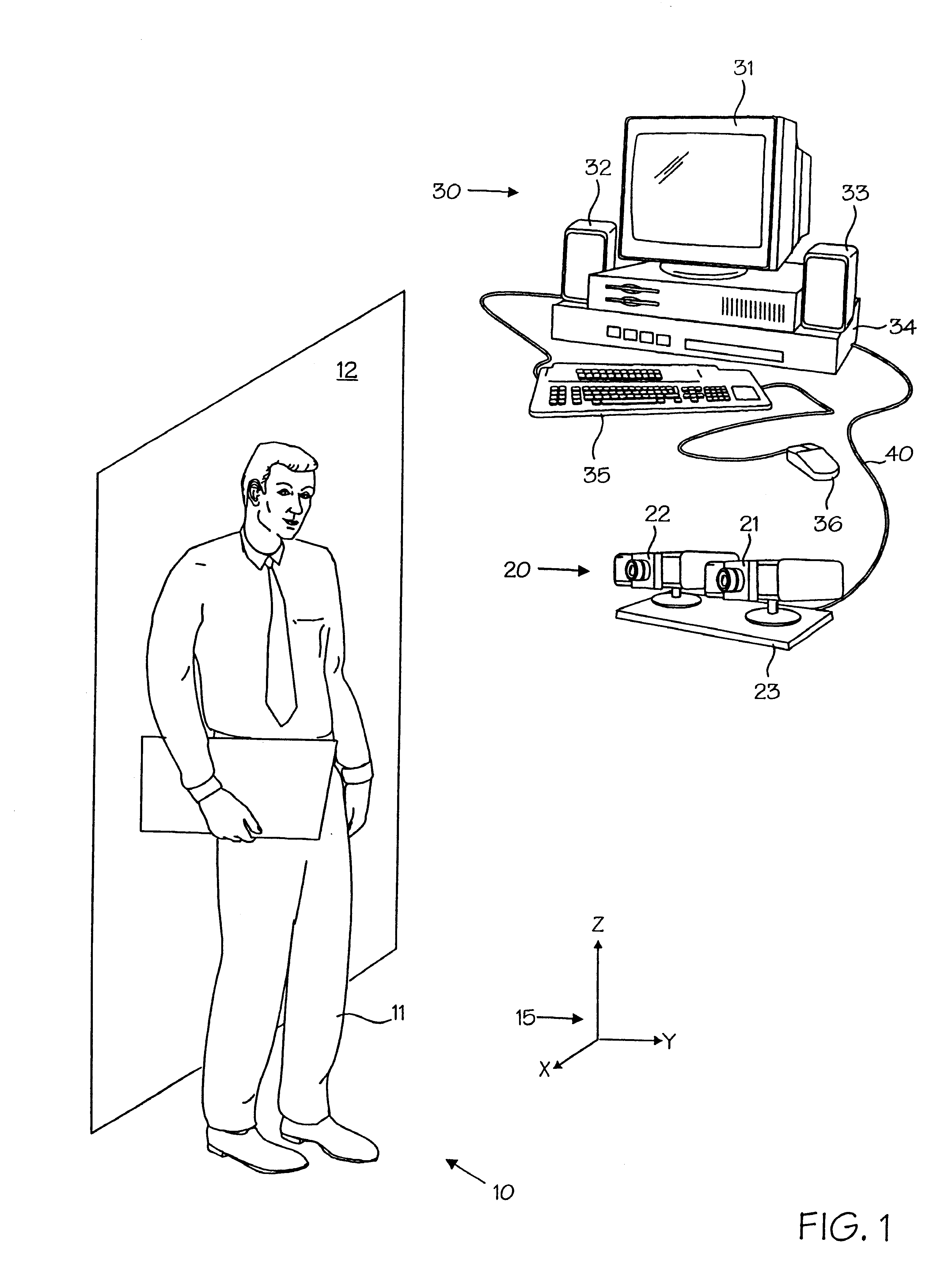
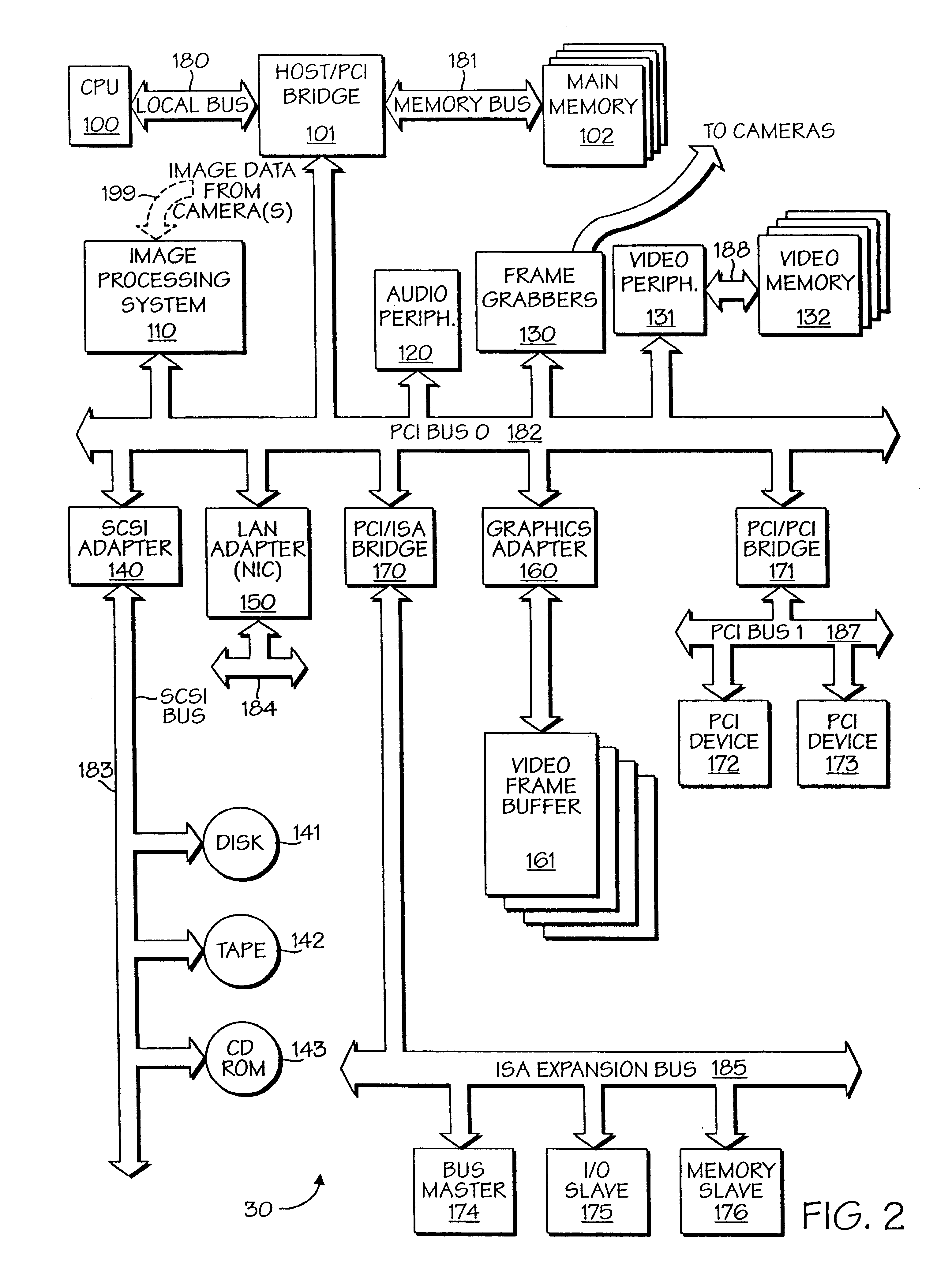
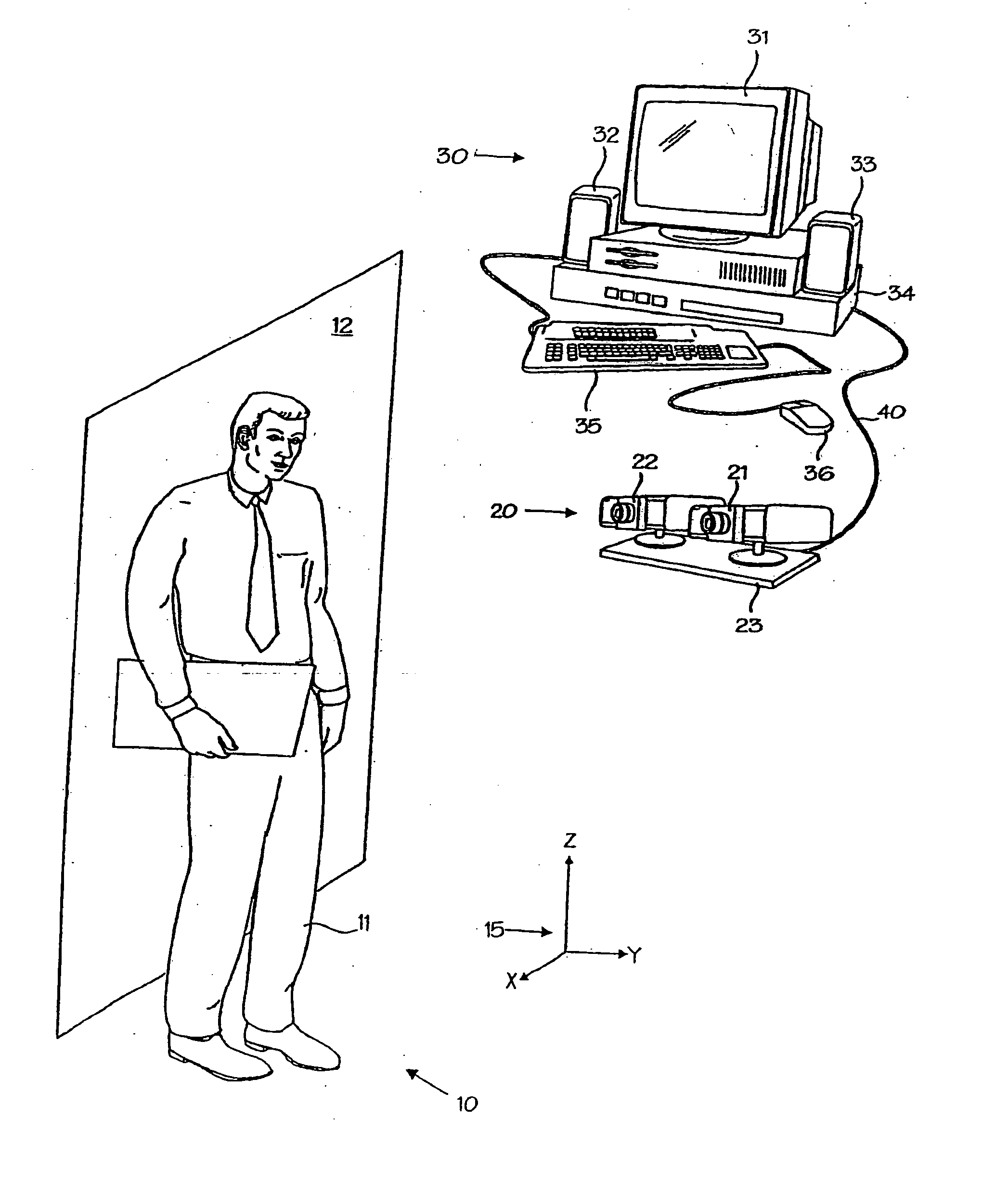
A powerful, scaleable, and reconfigurable image processing system and method of processing data therein is described. This general purpose, reconfigurable engine with toroidal topology, distributed memory, and wide bandwidth I / O are capable of solving real applications at real-time speeds. The reconfigurable image processing system can be optimized to efficiently perform specialized computations, such as real-time video and audio processing. This reconfigurable image processing system provides high performance via high computational density, high memory bandwidth, and high I / O bandwidth. Generally, the reconfigurable image processing system and its control structure include a homogeneous array of 16 field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and 16 static random access memories (SRAM) arranged in a partial torus configuration. The reconfigurable image processing system also includes a PCI bus interface chip, a clock control chip, and a datapath chip. It can be implemented in a single board. It receives data from its external environment, computes correspondence, and uses the results of the correspondence computations for various post-processing industrial applications. The reconfigurable image processing system determines correspondence by using non-parametric local transforms followed by correlation. These non-parametric local transforms include the census and rank transforms. Other embodiments involve a combination of correspondence, rectification, a left-right consistency check, and the application of an interest operator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Data processing system and method
InactiveUS20060013473A1Eliminate informationImage enhancementImage analysisStatic random-access memoryHigh memory
A powerful, scaleable, and reconfigurable image processing system and method of processing data therein is described. This general purpose, reconfigurable engine with toroidal topology, distributed memory, and wide bandwidth I / O are capable of solving real applications at real-time speeds. The reconfigurable image processing system can be optimized to efficiently perform specialized computations, such as real-time video and audio processing. This reconfigurable image processing system provides high performance via high computational density, high memory bandwidth, and high I / O bandwidth. Generally, the reconfigurable image processing system and its control structure include a homogeneous array of 16 field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and 16 static random access memories (SRAM) arranged in a partial torus configuration. The reconfigurable image processing system also includes a PCI bus interface chip, a clock control chip, and a datapath chip. It can be implemented in a single board. It receives data from its external environment, computes correspondence, and uses the results of the correspondence computations for various post-processing industrial applications. The reconfigurable image processing system determines correspondence by using non-parametric local transforms followed by correlation. These non-parametric local transforms include the census and rank transforms. Other embodiments involve a combination of correspondence, rectification, a left-right consistency check, and the application of an interest operator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
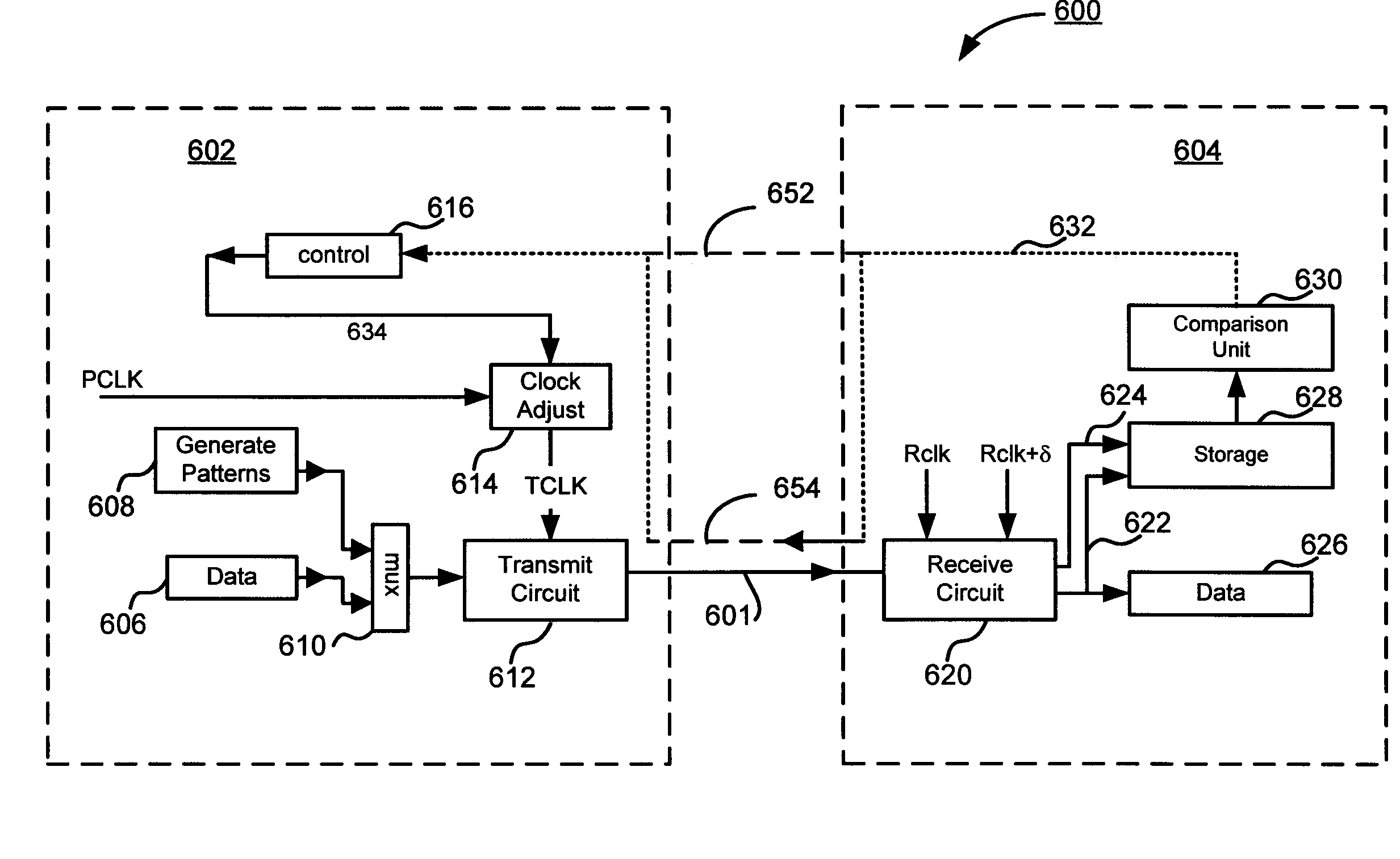
Techniques for improved timing control of memory devices
InactiveUS20100180143A1Digital storageGenerating/distributing signalsElectrical conductorTelecommunications link
Techniques for improved timing control of memory devices are disclosed. In one embodiment, the techniques may be realized as a memory controller to communicate with a memory device via a communications link. The memory controller may comprise a memory interface to exchange data with the memory device via a set of N conductors according to at least one clock, the data being encoded such that each M bits of data are represented by at least one symbol and each symbol is associated with a combination of signal levels on a group of n conductors, wherein M<N and n is equal to at least one and at most N. The memory may also comprise clock control logic to receive timing calibration information from the memory device and to output a signal to adjust a phase of the at least one clock based on the timing calibration information.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Method and apparatus for reducing power consumption in digital electronic circuits
InactiveUSRE36839E1Reduce power consumptionMinimize powerEnergy efficient ICTSolid-state devicesPower controllerData stream
An integrated circuit with power conservation includes a number of functional blocks, each of which includes a digital circuitry and at least one output control line, and a power controller coupled to the control lines. The output control lines develop clock control signals based upon a functional block's knowledge of the direction of data flow. The power controller the reduces power by deactivating functional blocks that are not needed as indicated by the clock control signals. More specifically, a system with power conservation includes a number of functional blocks capable of processing data, each of the functional blocks including a modulated clock input and N+1 clock control lines which reflect the direction of data flow, where N is a number of neighbors of a particular functional block, and a clock controller having an input clock, the clock controller being coupled to the modulated clock inputs and the clock control lines of the functional blocks. The clock controller is operative to modulate the input clock in accordance with the signals on the clock control lines to provide modulated clocks to each of the plurality of functional blocks. A method for reducing power consumption includes the steps of: a) receiving control signals from a number of functional blocks; b) selectively deactivating a particular functional block upon a request from that functional block or from another functional block; and c) activating the particular functional block upon a request from another functional block.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Apparatus and methods for testing a microprocessor chip using dedicated scan strings
InactiveUS6028983AReduce memory requirementsReduce scan timeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionTest inputJoint Test Action Group
A test apparatus and method for design verification of at least one microprocessor chip includes a compatible Joint Task Action Group (JTAG) terminal for access to a plurality of computer functional units contained in the chip. A test input terminal included in the JTAG terminal receives a scan string, the string being coupled to each computer functional unit through a first multiplexer. The scan input string is separated by the JTAG terminal under program control into a series of dedicated scan strings, each dedicated scan string being supplied to a selected functional unit through the first multiplexer. Each functional unit includes start and stop scan clocks for testing the functional under program control using the dedicated scan train for the functional unit. A test output terminal included in the JTAG terminal is coupled to each functional unit through a second multiplexer. The test results of the dedicated scan string under control of the scan clock are supplied to the output terminal through the second multiplexer. The compatible JTAG terminal includes further elements for controlling the scan clocks to select a targeted functional unit for testing purposes while the scan strings for non-targeted functional units remain in an inactive state.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
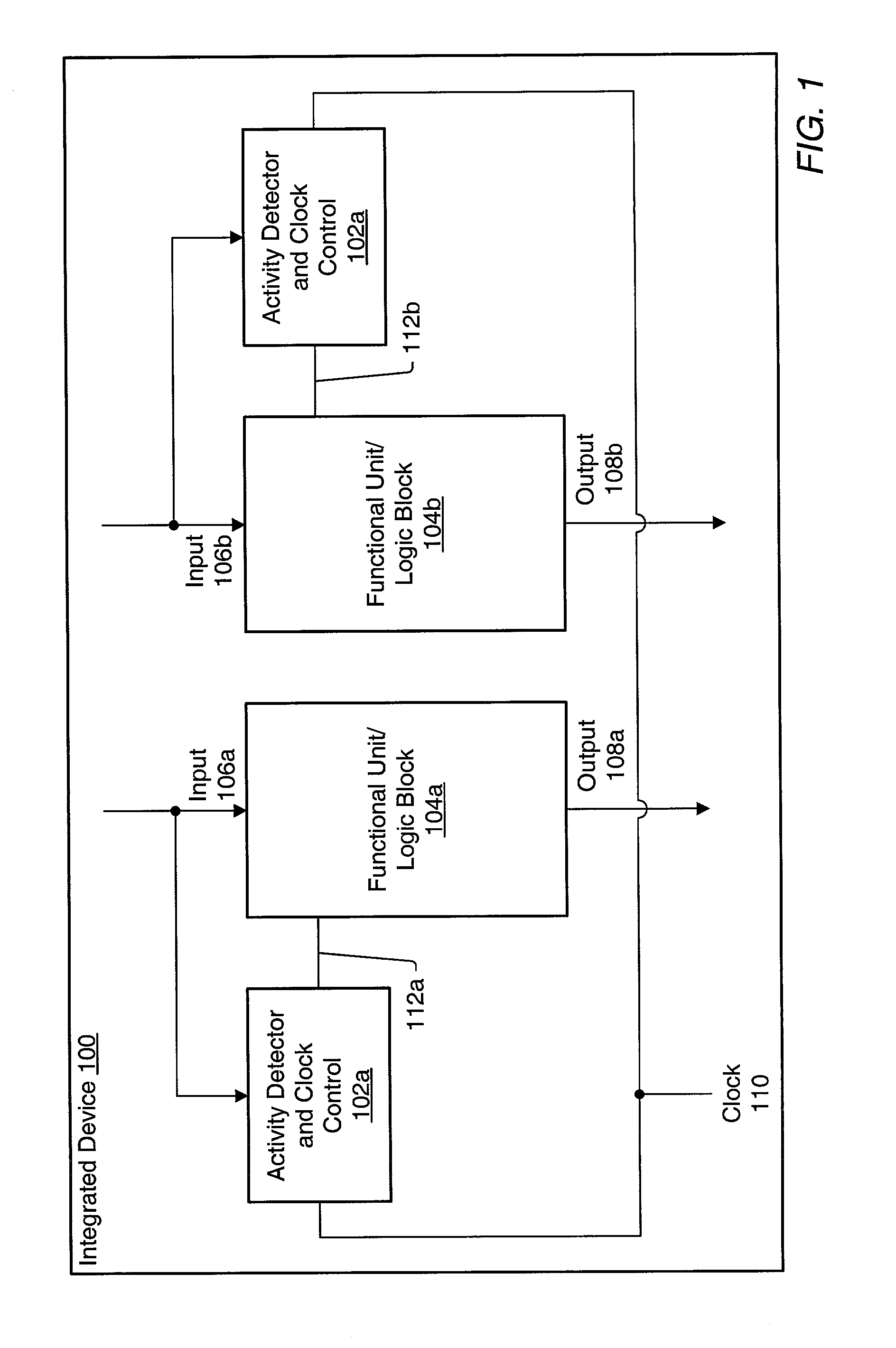
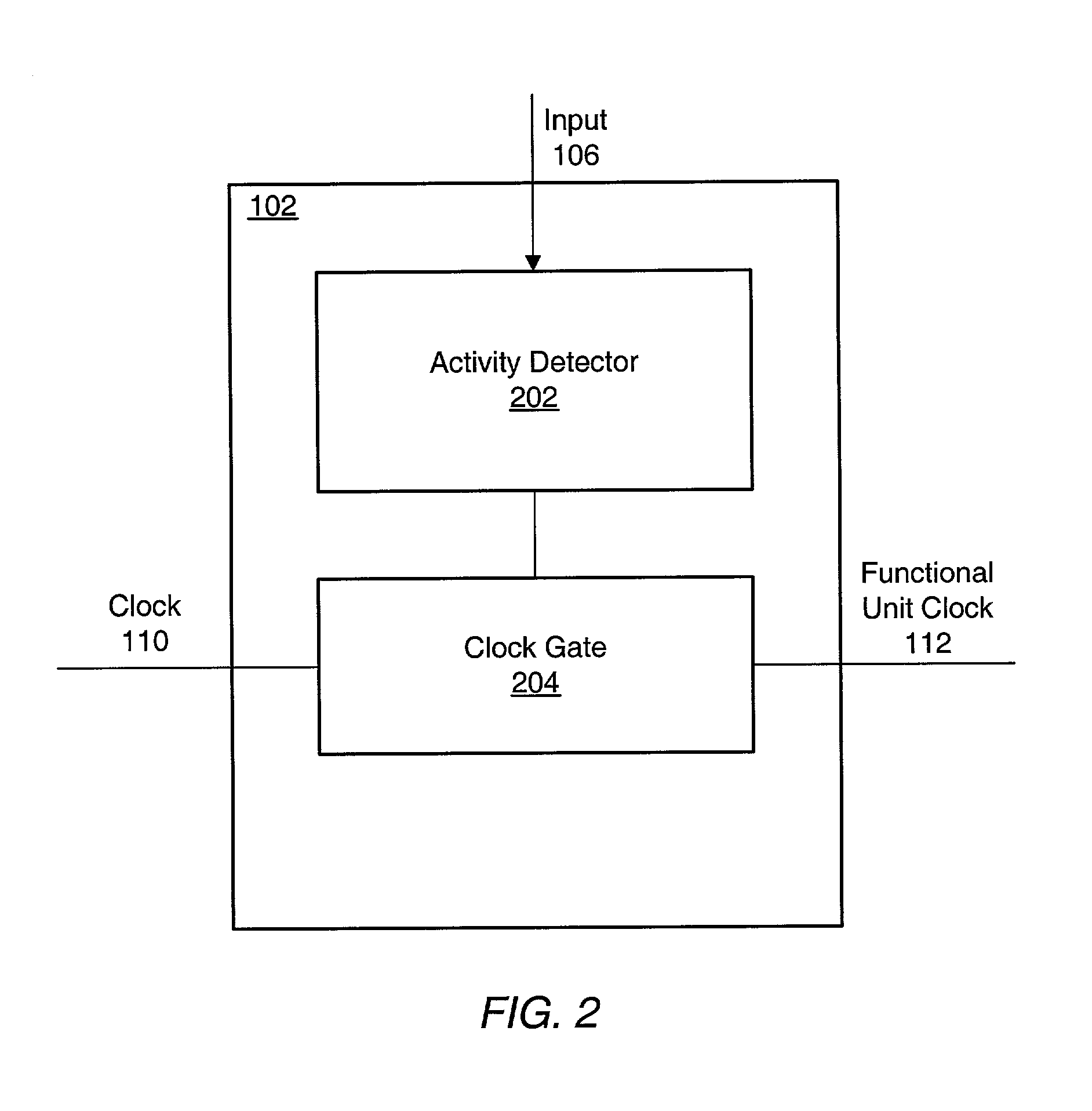
Clock control of functional units in an integrated circuit based on monitoring unit signals to predict inactivity
ActiveUS6983389B1Reduce overall static and dynamic power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingEngineeringEmbedded system
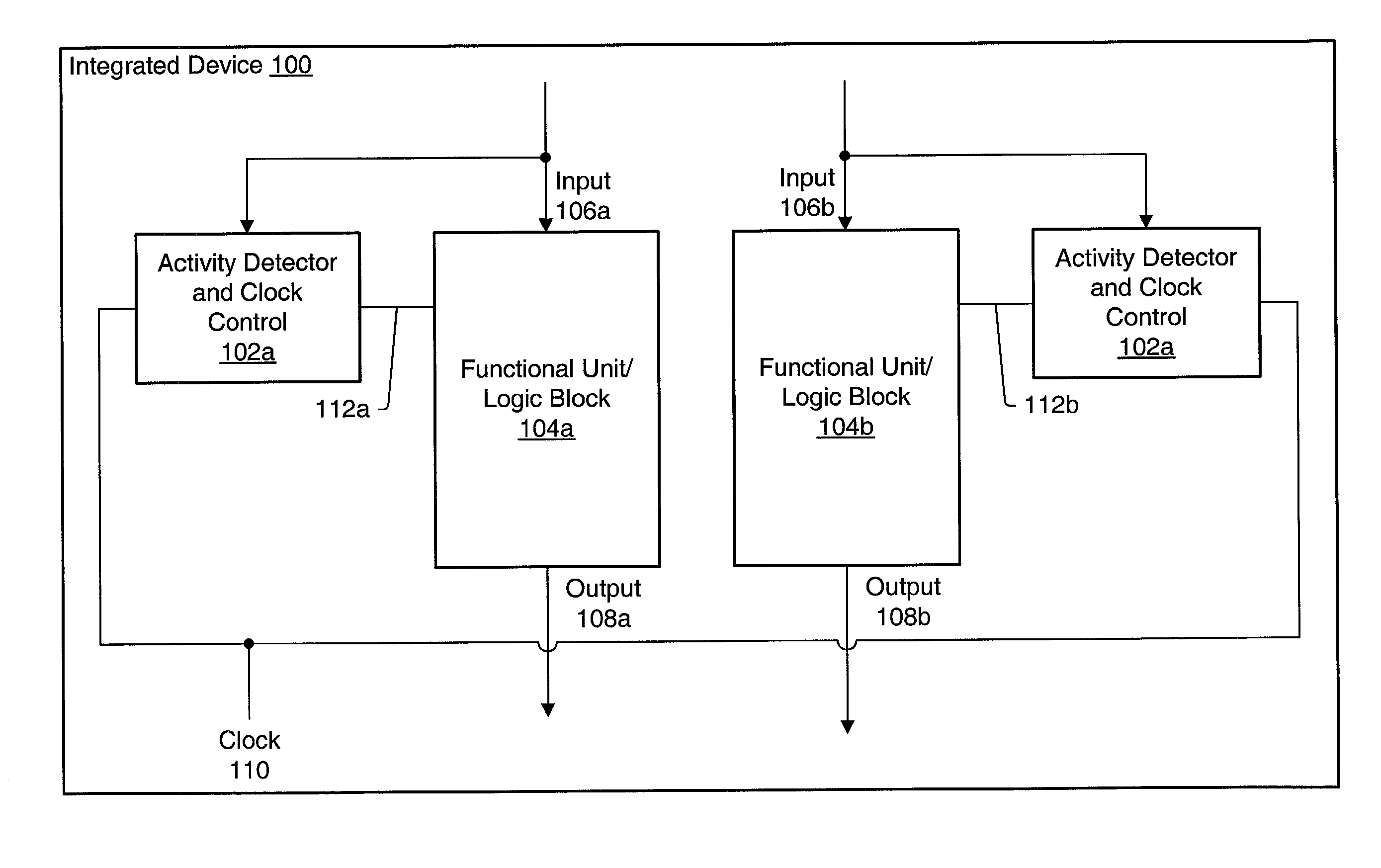
An integrated circuit may have separate clock control for a number of different functional units. Ancillary to some of the functional units may be an activity detector and clock control unit which monitors input to its functional unit to determine when the functional unit will be inactive. When an activity detector and clock control unit determines that a particular functional unit is or will be inactive, it may disable clocking to its functional unit while the functional unit is inactive. When activity detector and clock control unit determines that activity will resume for its functional unit, it enables clocking to its functional unit. Thus, the activity detector and clock control unit for each such functional unit functions to control clocking to its respective functional unit so that during periods of inactivity, inactive functional units are not clocked to reduce the overall static and / or dynamic power consumption for the integrated device.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
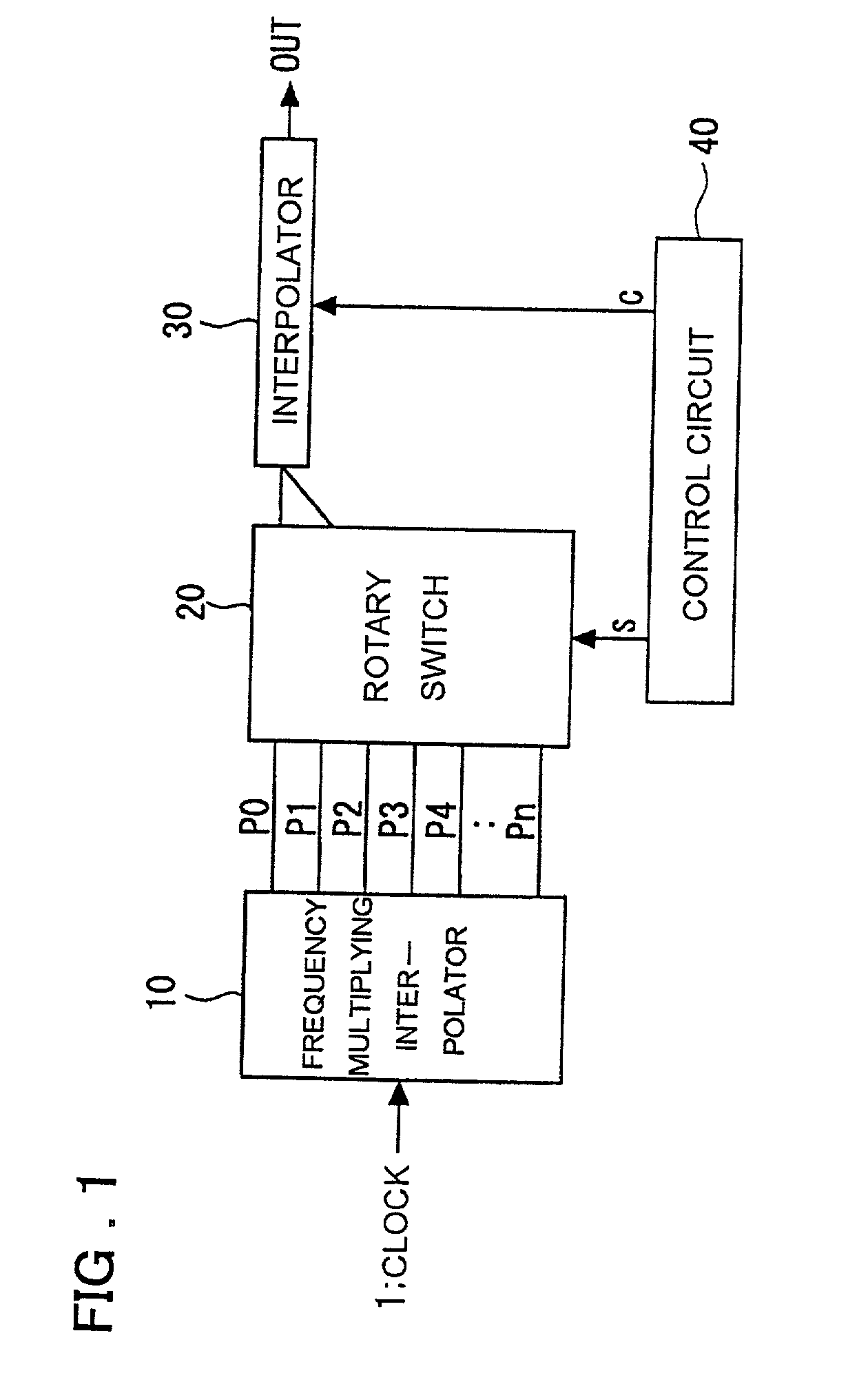
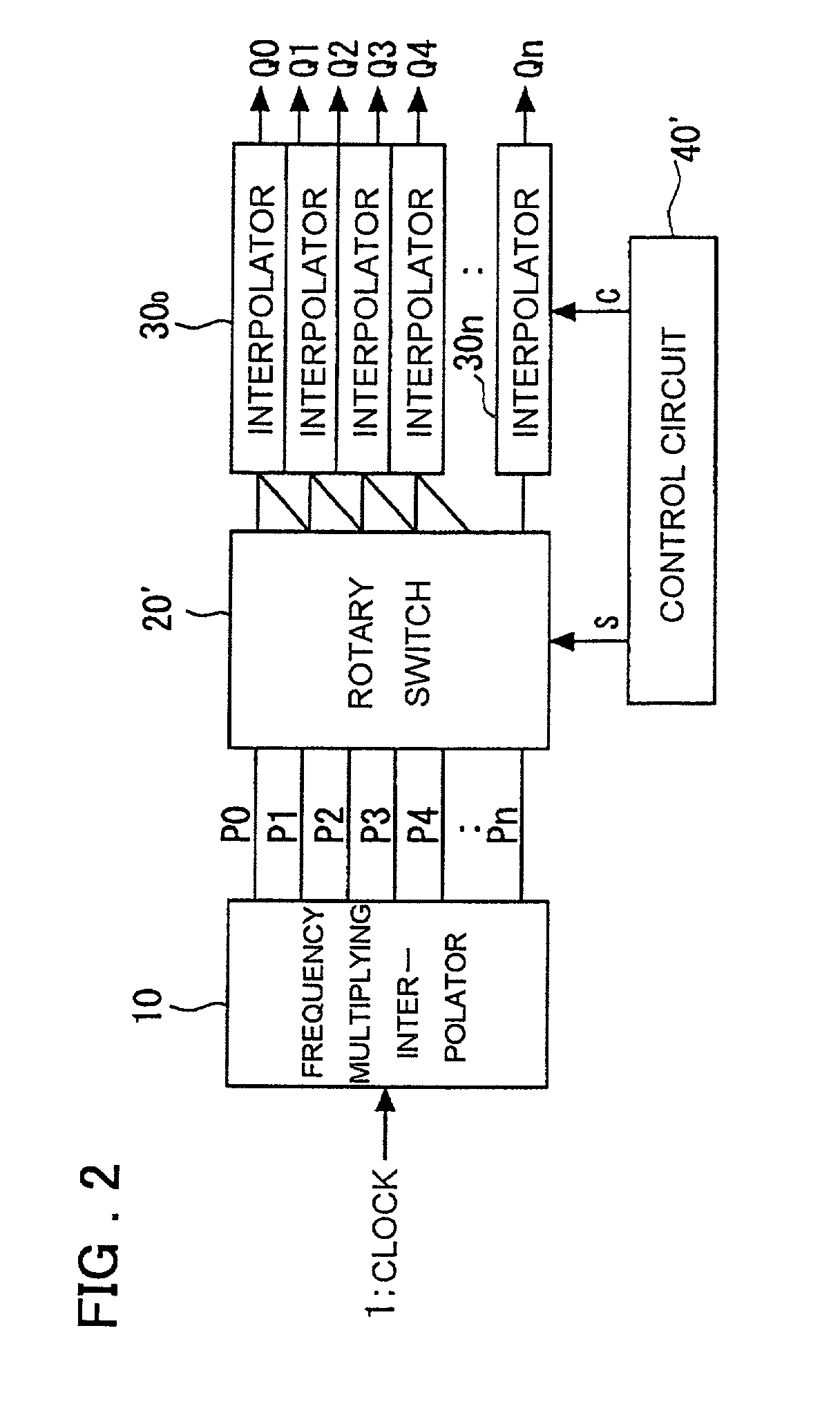
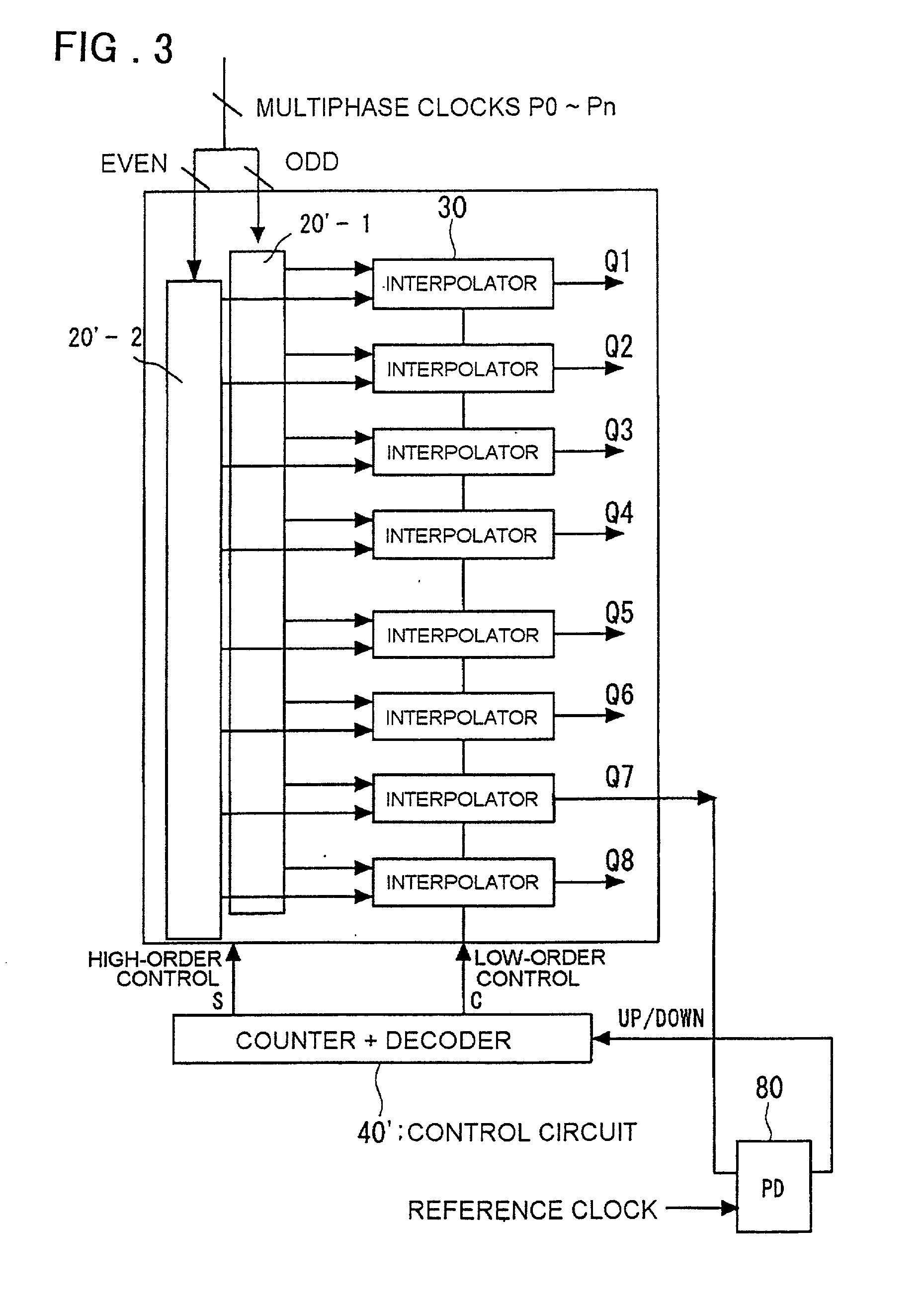
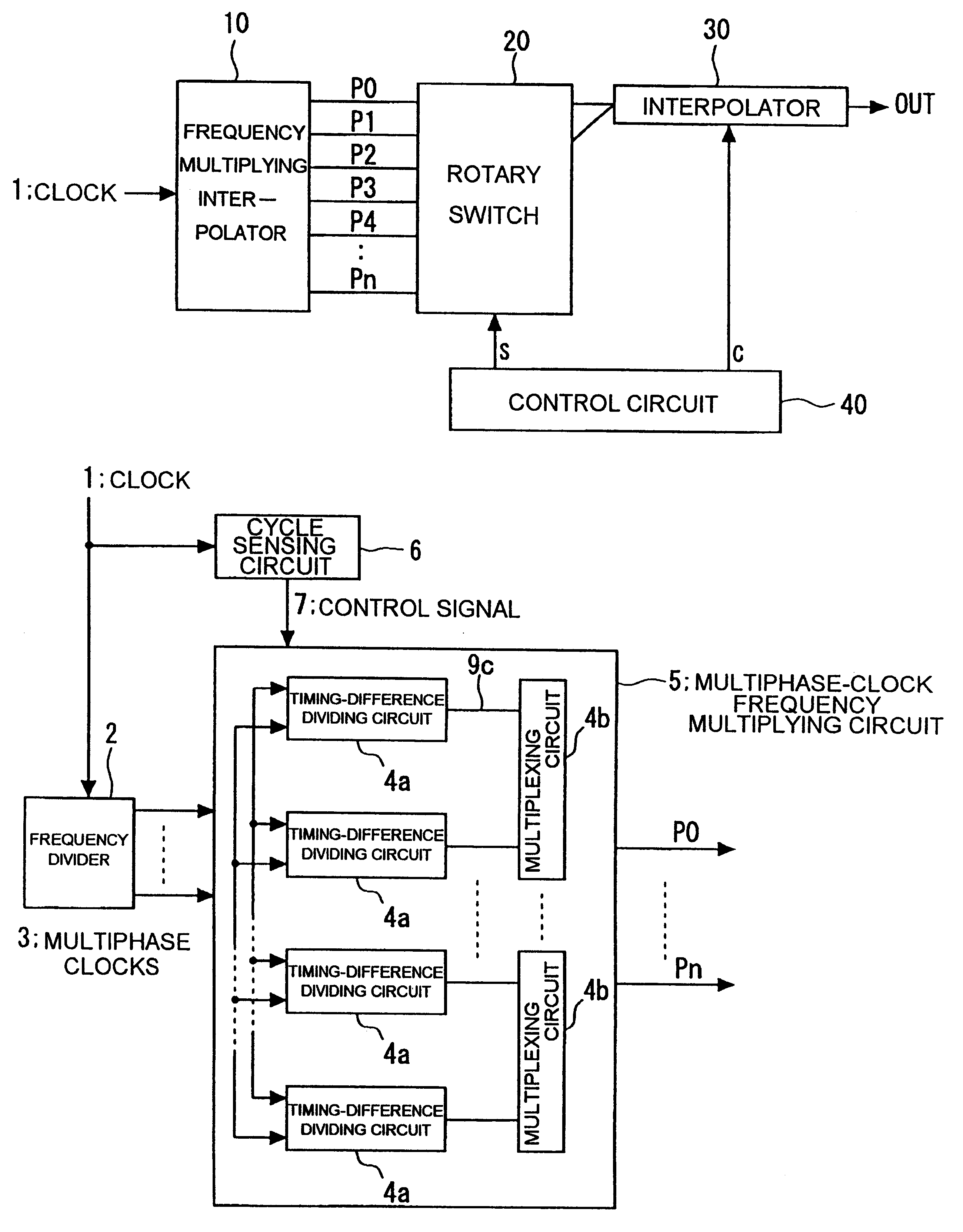
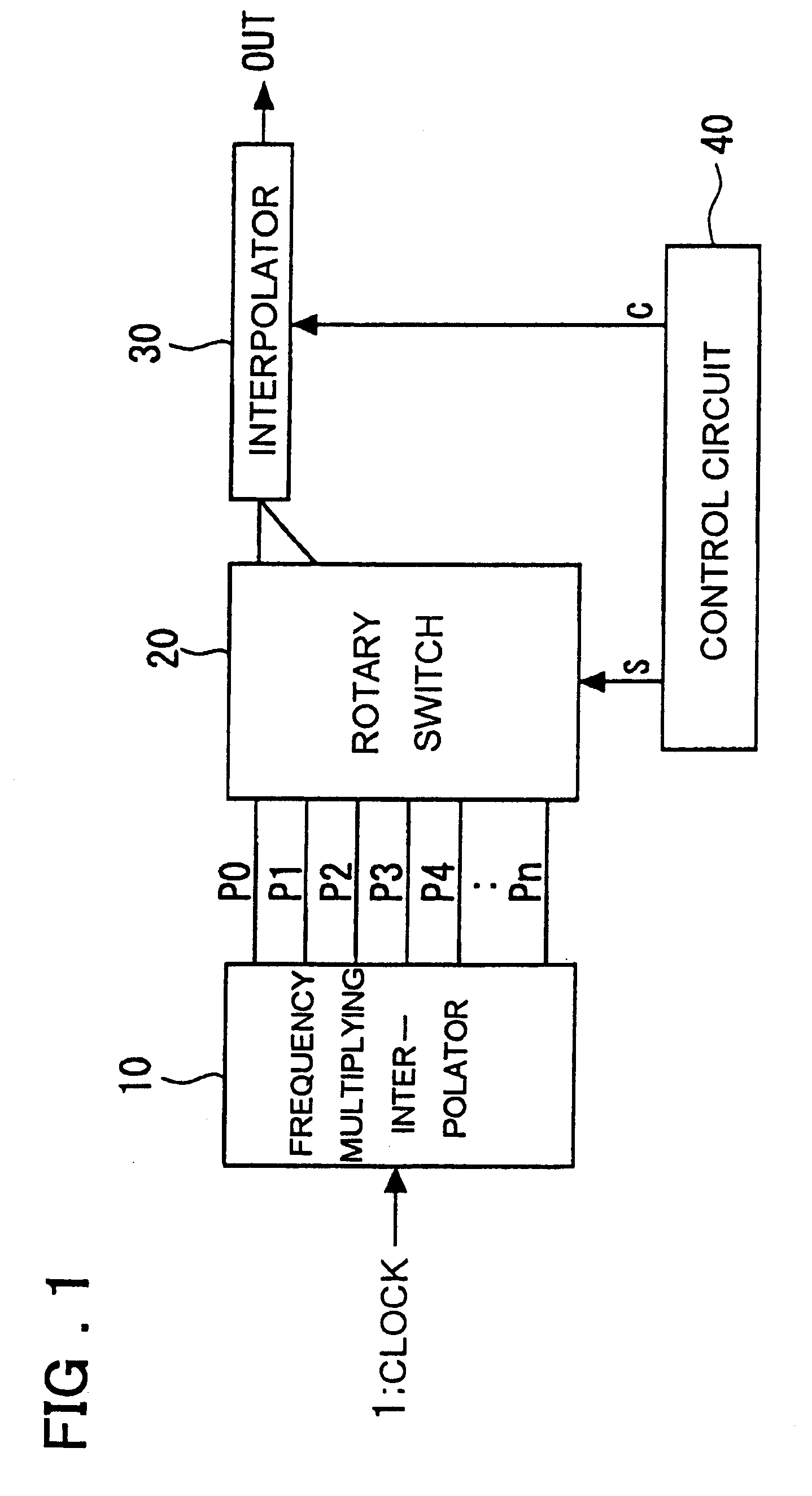
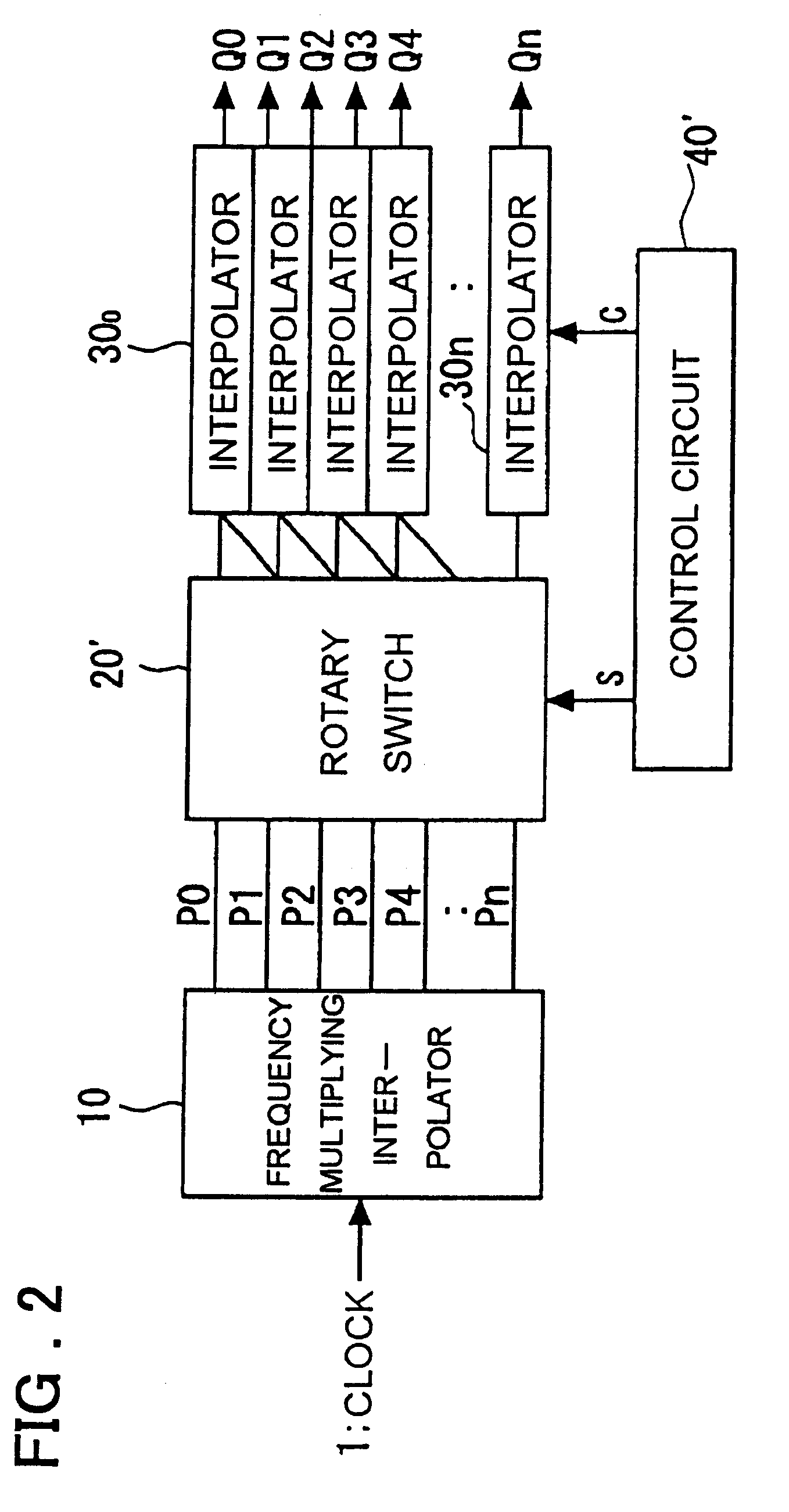
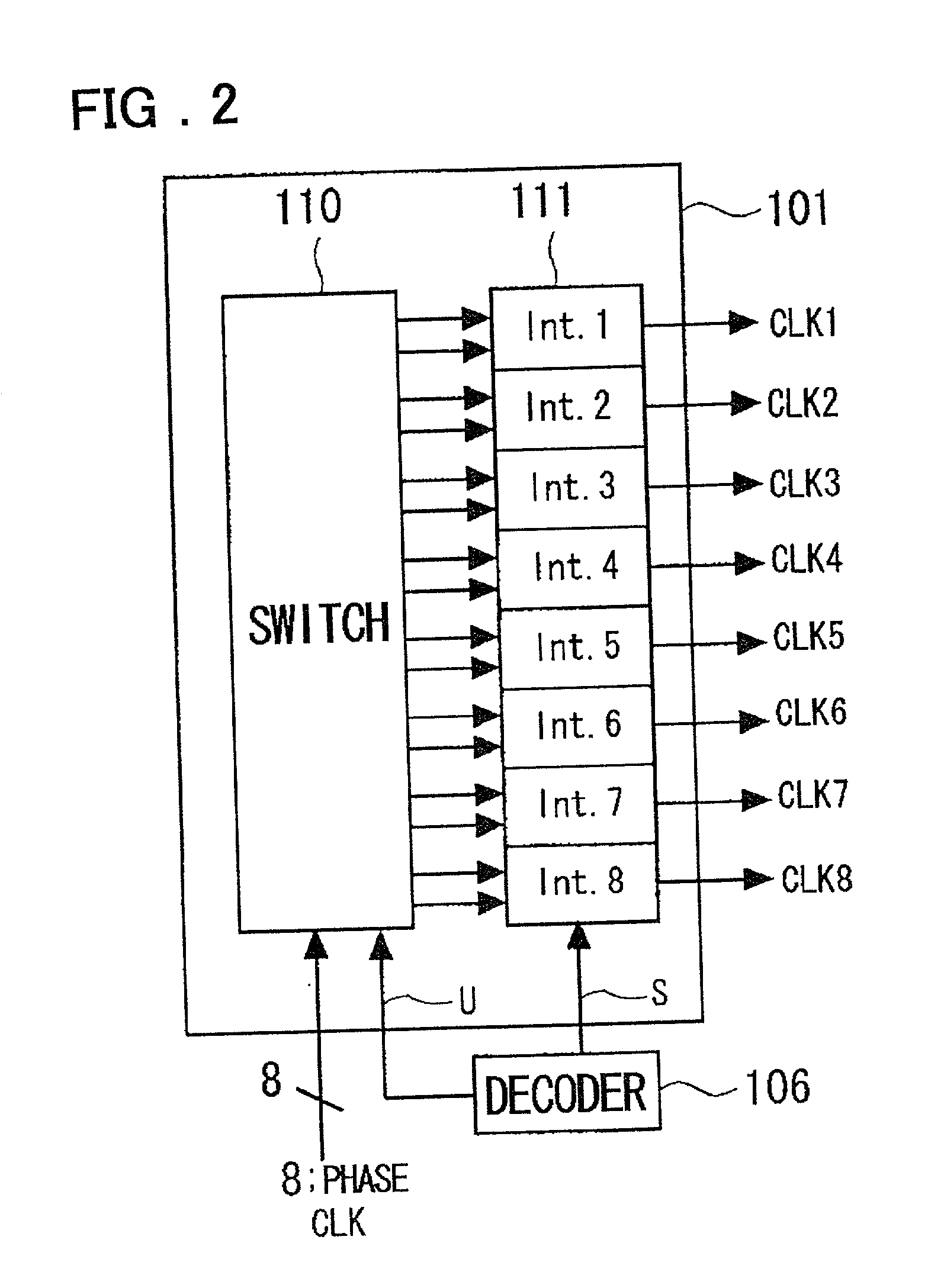
Clock control circuit and clock control method
InactiveUS20010026179A1Reduce errorsEliminate fluctuationsPulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationControl switchControl theory
A clock control circuit which includes a frequency multiplying interpolator for generating and outputting multiphase clocks by frequency multiplying an input clock; a switch for outputting two of the multiphase clocks input thereto from the frequency multiplying interpolator; a fine adjusting interpolator, to which the two outputs from the switch are applied, for outputting a signal obtained by internally dividing the phase difference between the two outputs; and a control circuit for controlling the switching of the switch and varying the internal-division ratio of the fine adjusting interpolator.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Clock control circuit and clock control method
InactiveUS6380774B2Inaccurate to some degreeReduce jitterPulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationPhase differenceEngineering
A clock control circuit which includes a frequency multiplying interpolator for generating and outputting multiphase clocks by frequency multiplying an input clock; a switch for outputting two of the multiphase clocks input thereto from the frequency multiplying interpolator; a fine adjusting interpolator, to which the two outputs from the switch are applied, for outputting a signal obtained by internally dividing the phase difference between the two outputs; and a control circuit for controlling the switching of the switch and varying the internal-division ratio of the fine adjusting interpolator.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Circuit, system and method for selectively turning off internal clock drivers
ActiveUS7089438B2Reduce operating currentExtend battery lifeEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageComputerized systemEngineering
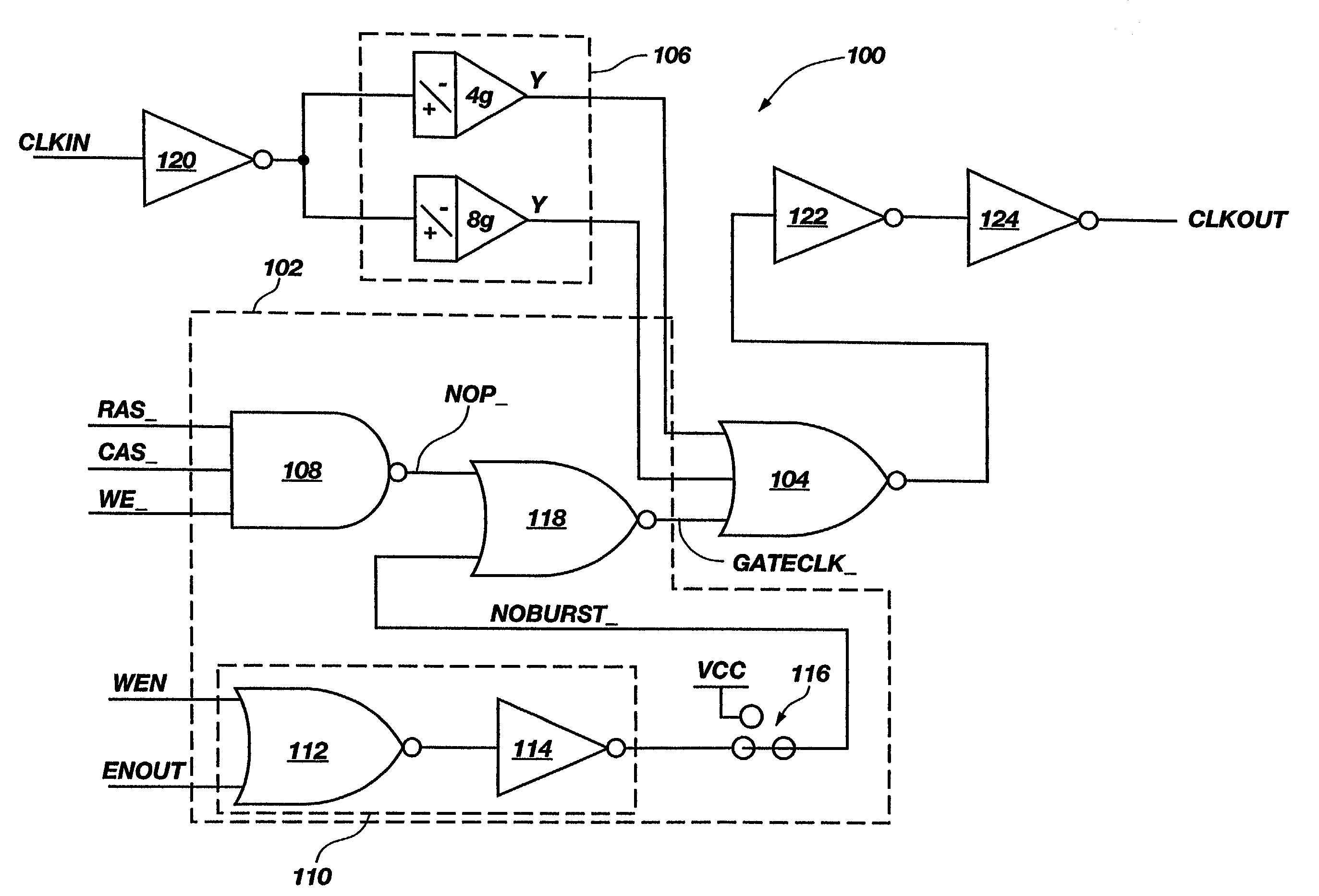
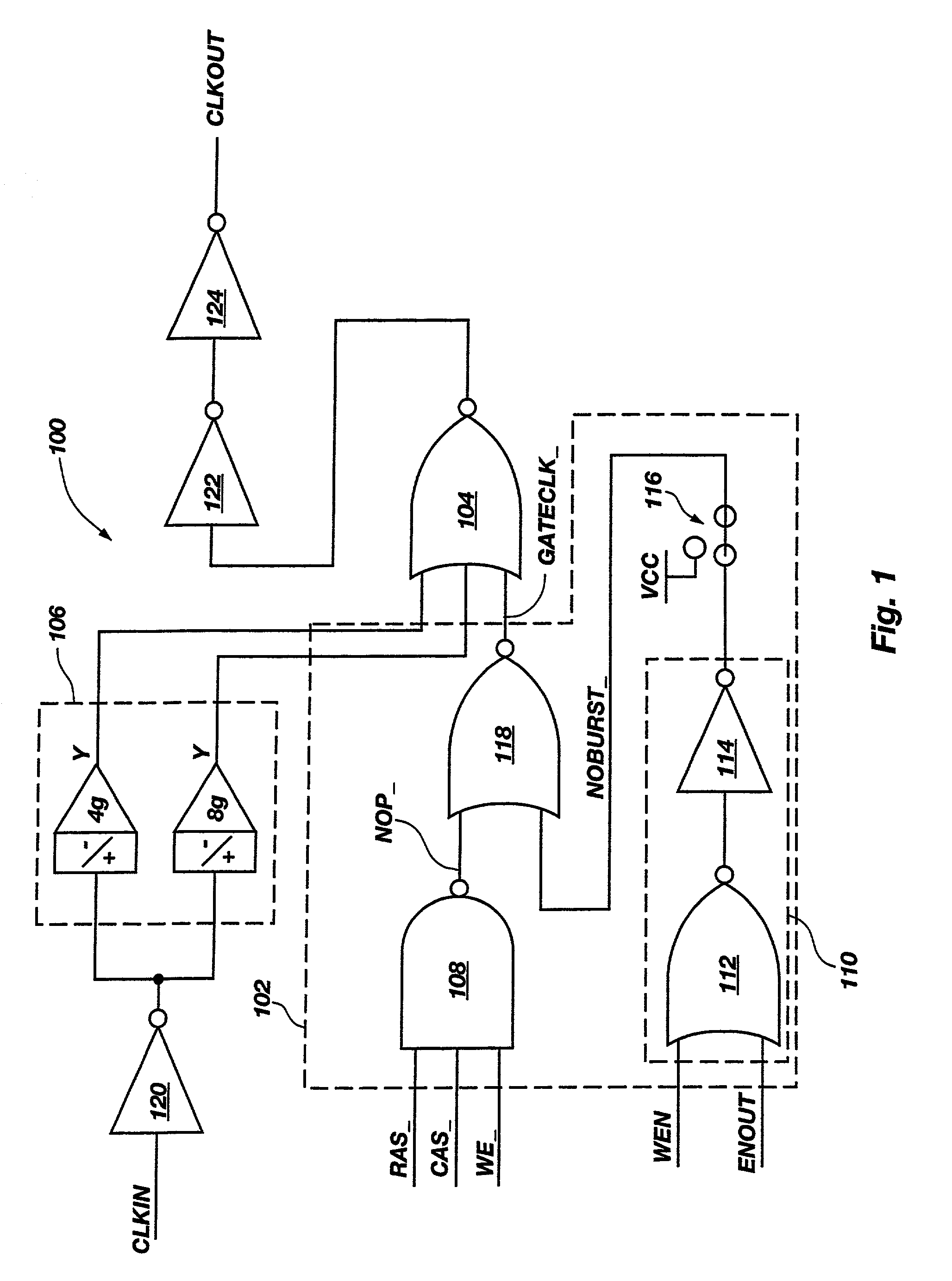
The present invention includes a circuit, system and method for selectively turning off internal clock drivers to reduce operating current. The present invention may be used to reduce power consumption by reducing operating current in a memory device. Operating current may be reduced by turning off internal clock drivers that deliver a clock signal during selected periods of time. According to an embodiment of clock control circuitry of the present invention, an internal clock is disabled if a no operation command is detected during periods of time when no read or write burst operation is taking place. Methods, memory devices and computer systems including the clock control circuitry and its functionality are also disclosed.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
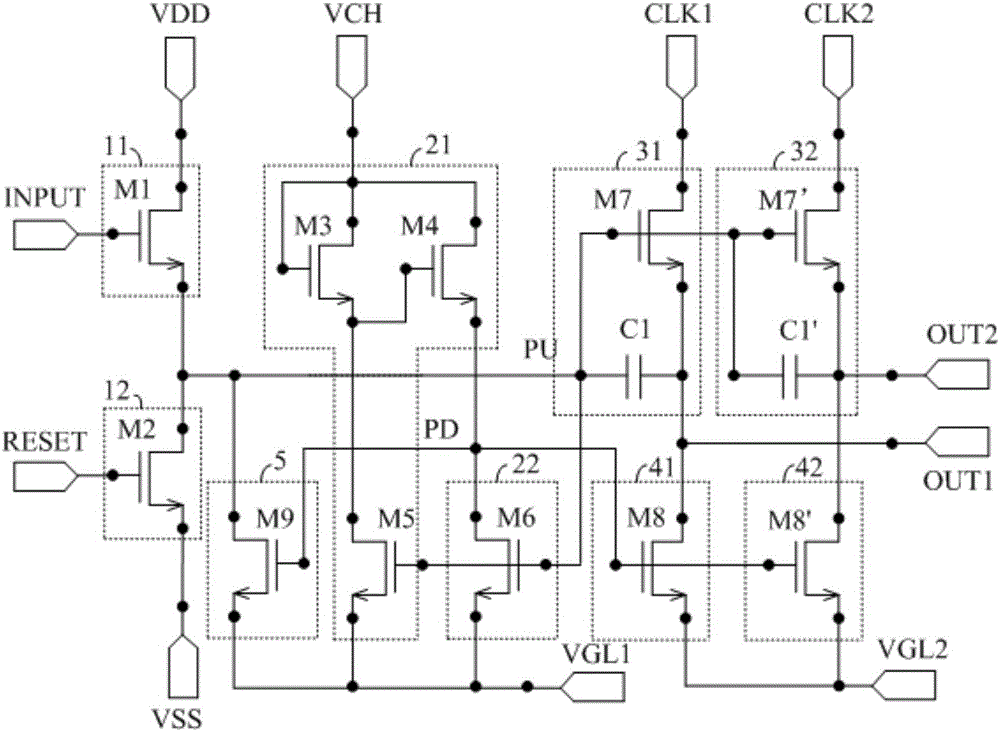
Shifting register and drive method thereof, grid drive circuit and display device
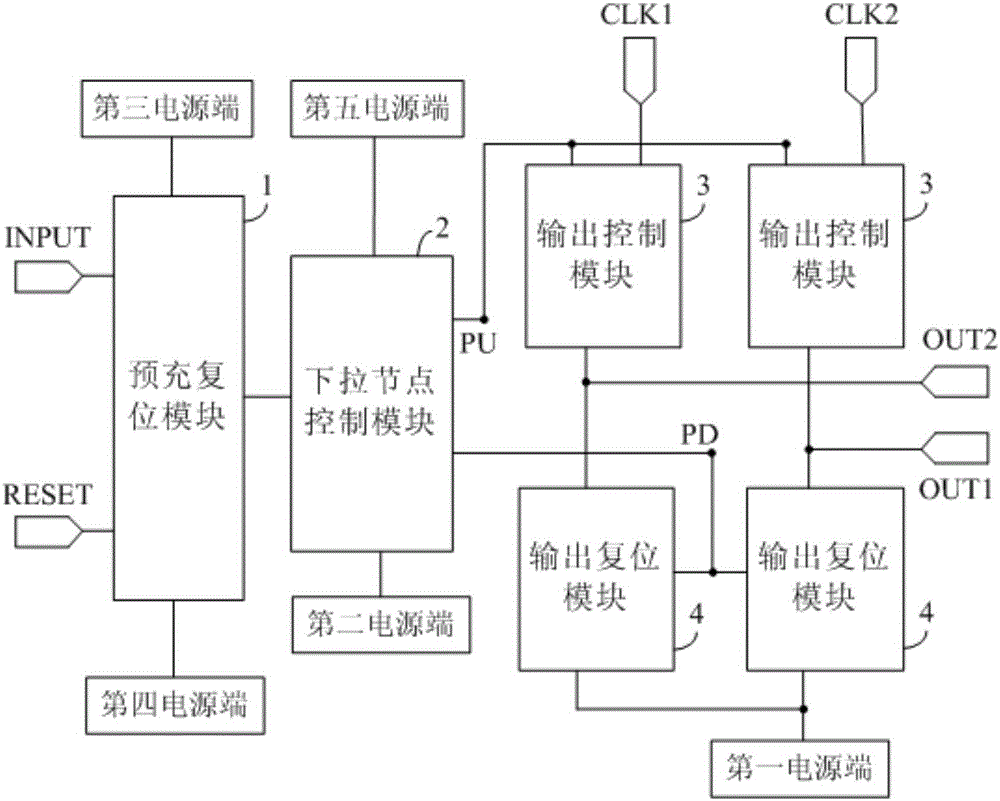
InactiveCN106023943ARealize ultra-narrow bezel designStatic indicating devicesDigital storageDriver circuitShift register
The invention discloses a shifting register and a drive method thereof, a grid drive circuit and a display device. The shifting register comprises a precharge reset module, a downward-pull node control module, a plurality of output control modules and a plurality of output reset modules. The output reset modules correspond to the output control modules one to one. The output control modules are used for transmitting clock control signals in corresponding clock control signal lines to corresponding signal output ends under control of potential of upward-pull nodes. The output reset modules are used for resetting the signal output ends connected with the corresponding output control modules under control of potential of downward-pull nodes. The shifting register is provided with the signal output ends, the output control modules for controlling the signal output ends to output the signals and the output reset modules, the shifting register can be used for driving a plurality of grid lines, and therefore the shifting register can achieve design of an ultra-narrow frame when applied to a display panel.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
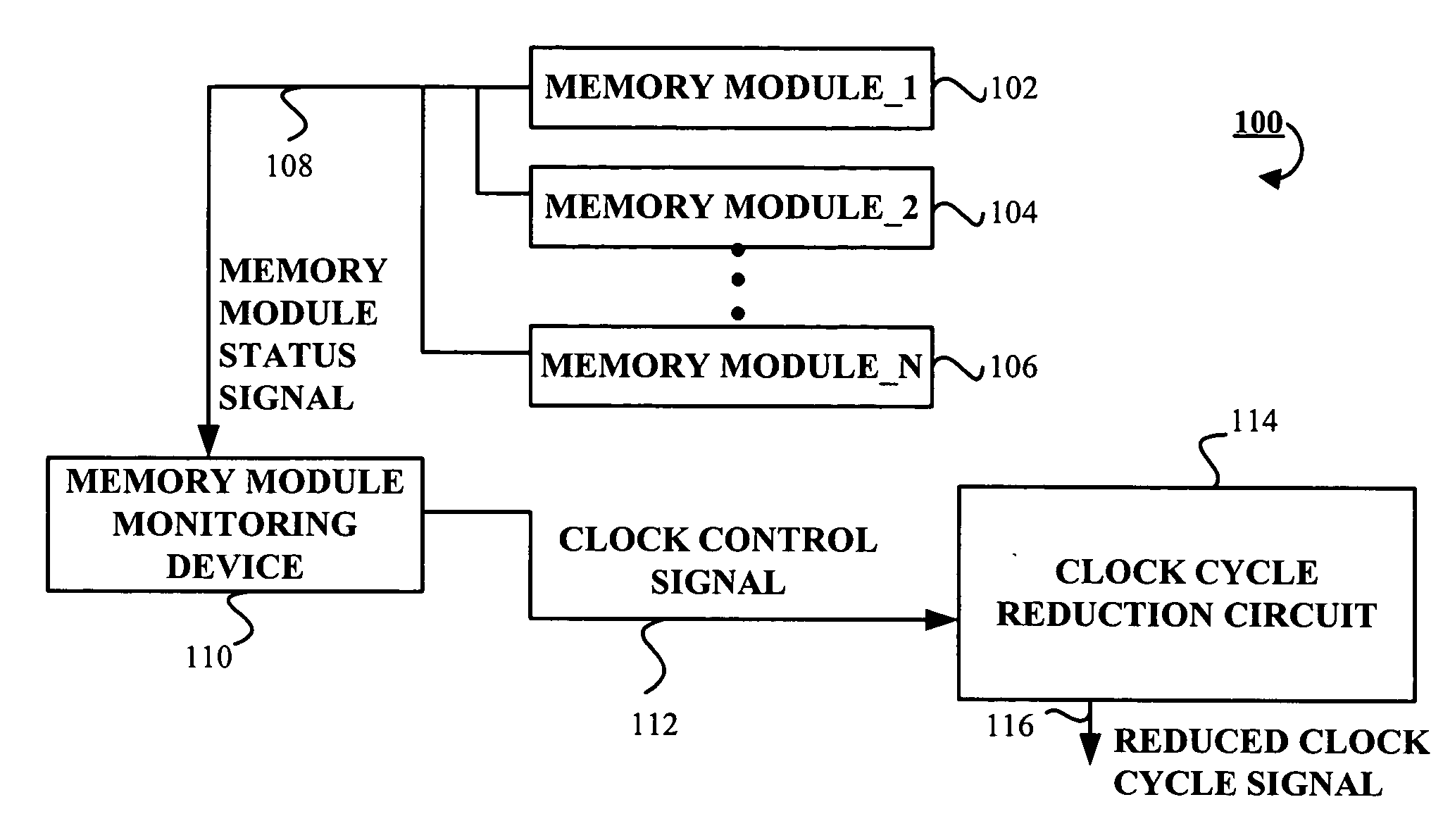
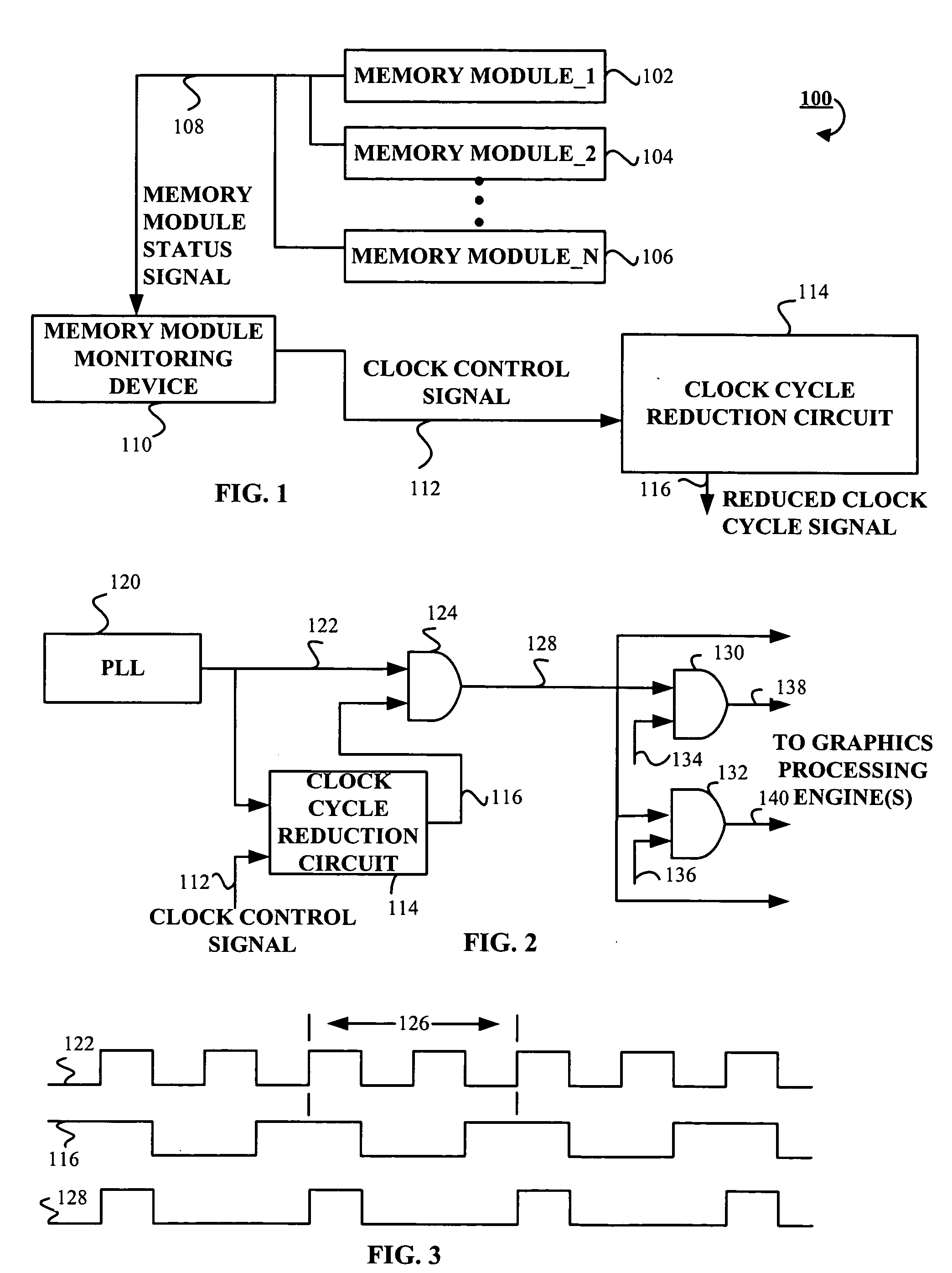
Apparatus and method for reducing power consumption in a graphics processing device
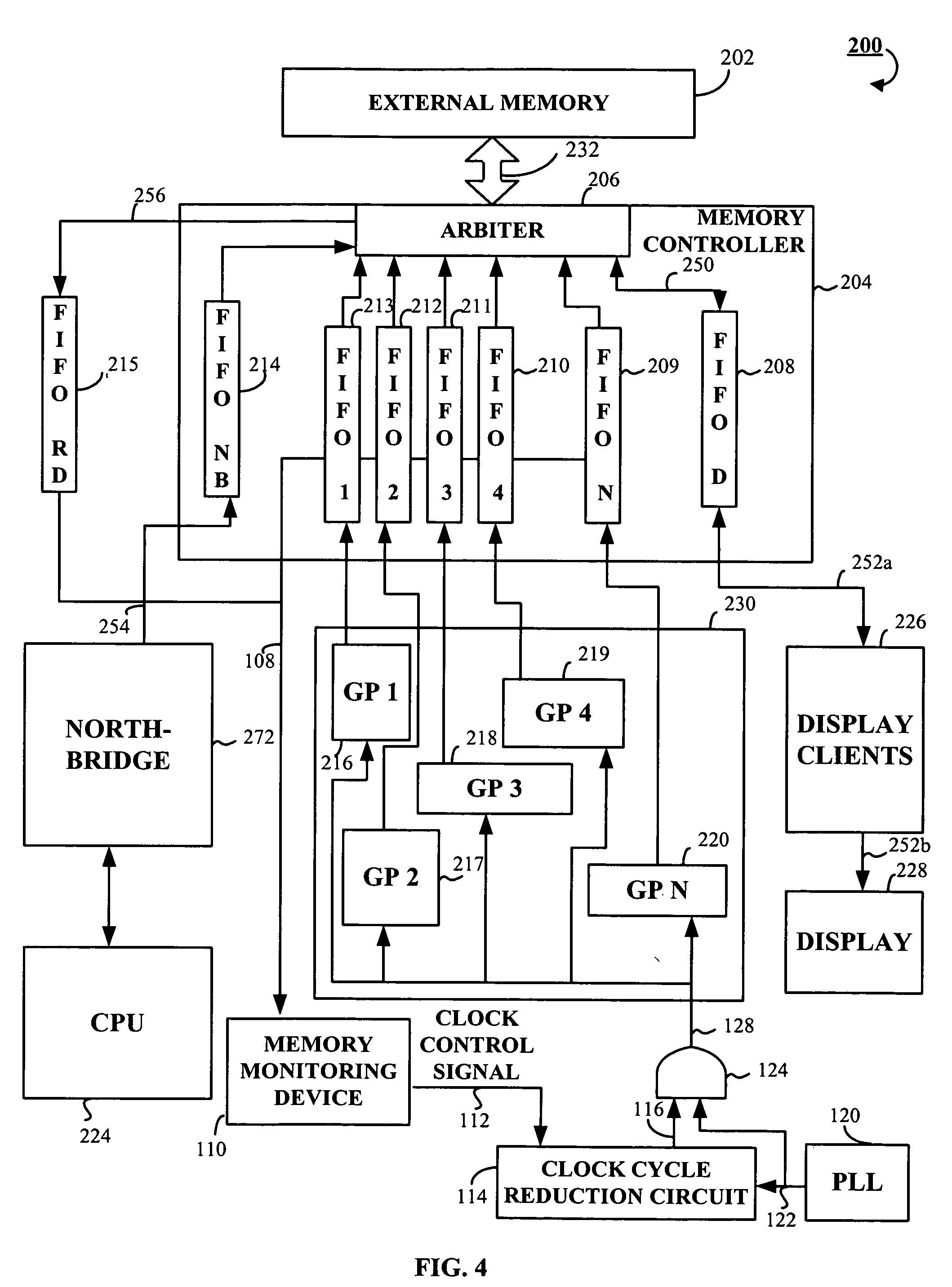
Briefly, the present invention includes a method and an apparatus for reducing power consumption in a graphics processing device. The apparatus and method include a memory module monitoring device operative to receive a memory module status signal from memory modules. The memory module monitoring device is operative to generate a clock control signal in response to the memory module status signal. The apparatus and method further include a clock cycle reduction circuit coupled to the monitoring module. The clock cycle reduction circuit receives the clock control signal. The clock cycle reduction circuit generates a reduced cycle clock signal in response to the clock control signal such that the reduced cycle clock signal reduces power consumption in the graphics processing device.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Bus clock controlling apparatus and method
InactiveUS7069463B2Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionCurrent loadData exchange
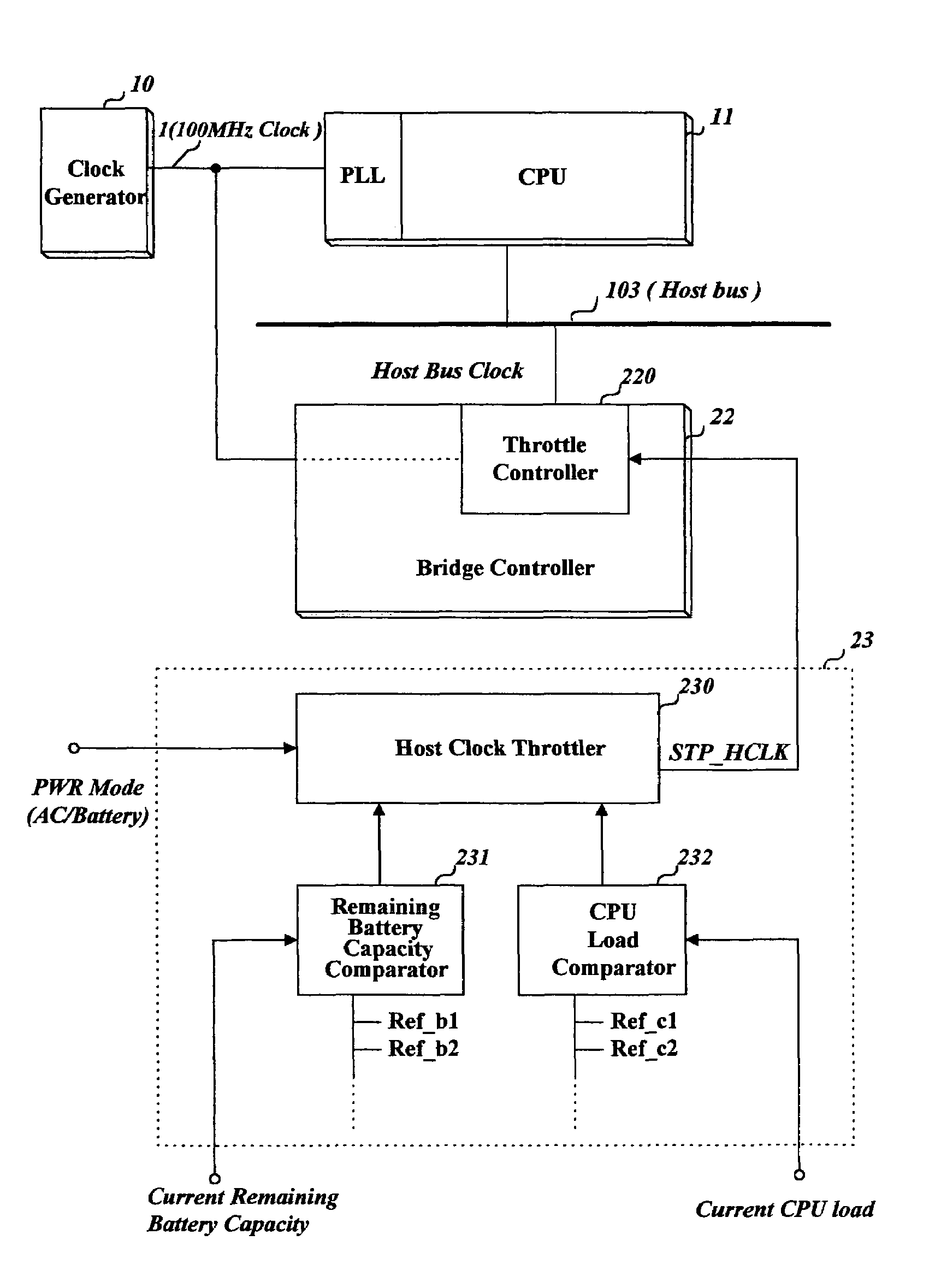
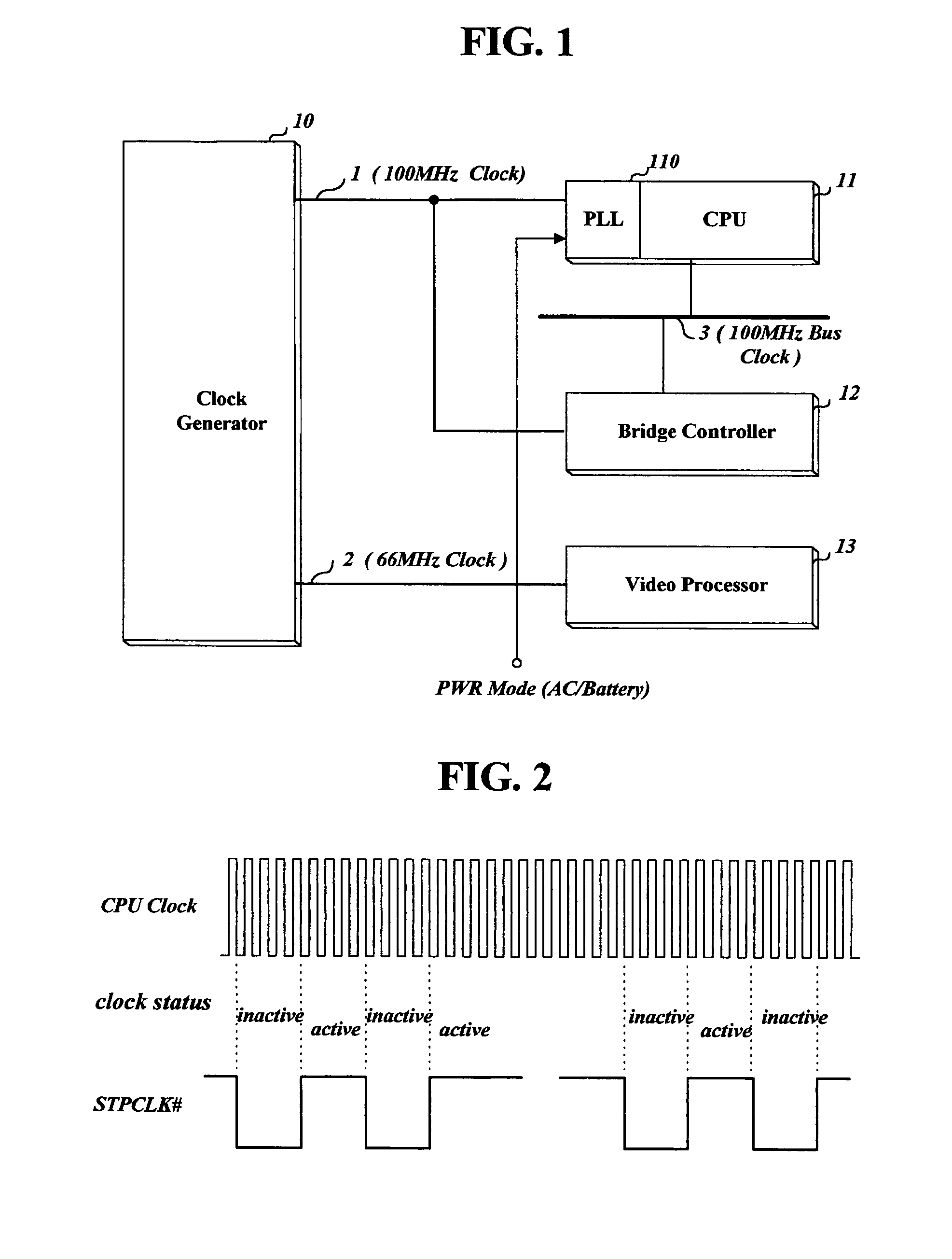
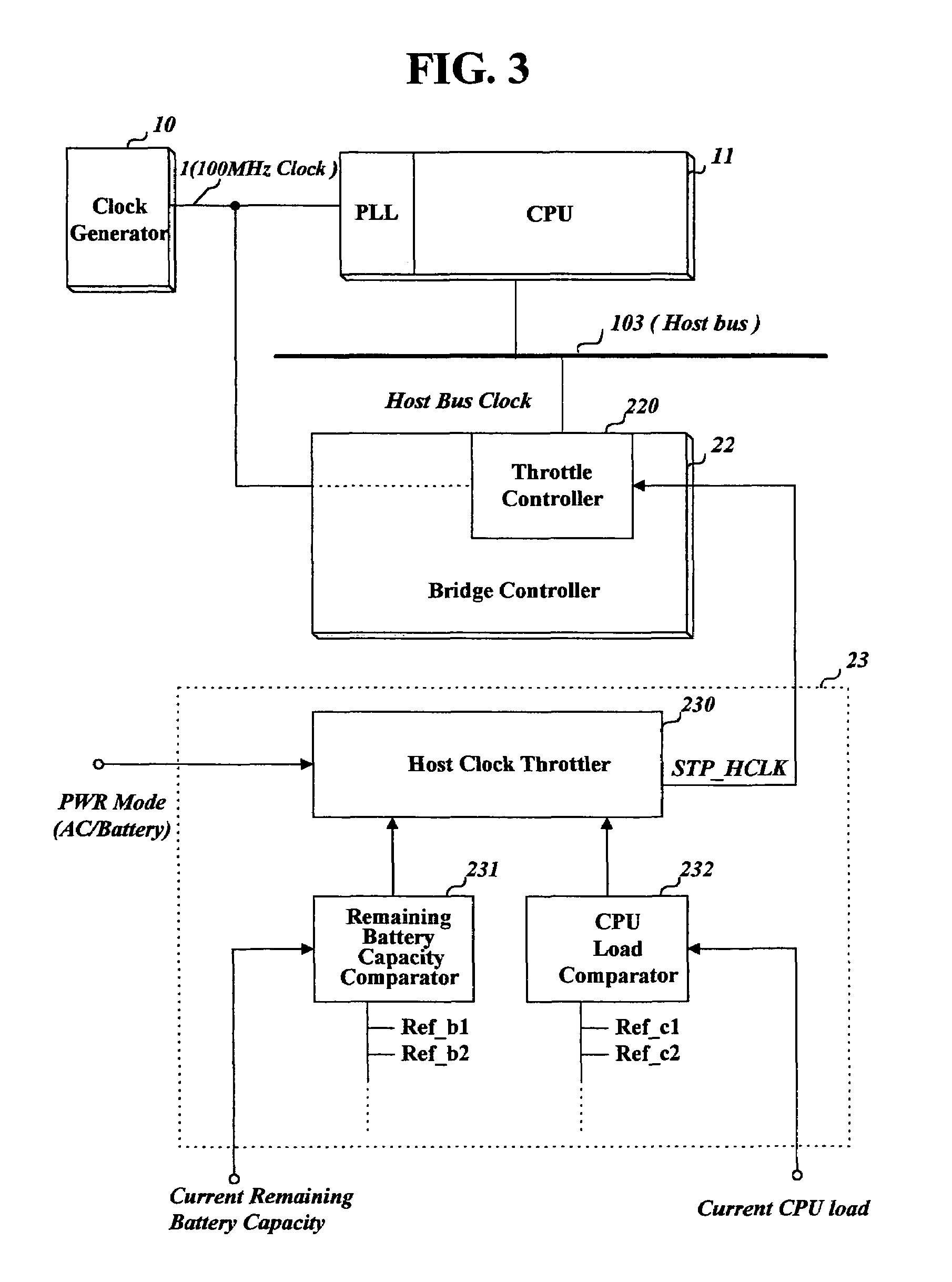
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for throttling a clock of a bus used for data exchange between devices in a computer such as a portable computer or notebook. Methods according to the invention can set a throttle rate of a clock to a predetermined initial value, detect a current remaining battery capacity or a current load to the CPU, and adjust the set throttle rate to a prescribed or calculated value according to the detected remaining battery capacity or the CPU load. Thus, power consumption is reduced, and, in the case of a battery-powered computer, battery life and operating time are extended.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Clock control apparatus and method, for a memory controller, that processes a block access into single continuous macro access while minimizing power consumption
InactiveUS7085941B2Efficient executionReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementControl signalMemory controller
A clock control apparatus for a memory controller comprises an interface unit which processes a block access to a plurality of banks of an SDRAM as a single continuous macro access in order to perform arbitration of the macro access, the block access externally supplied to the memory controller. A power-saving control unit controls both a clock signal of an internal circuit of the memory controller and a clock enable signal of the SDRAM in response to a control signal supplied from the interface unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
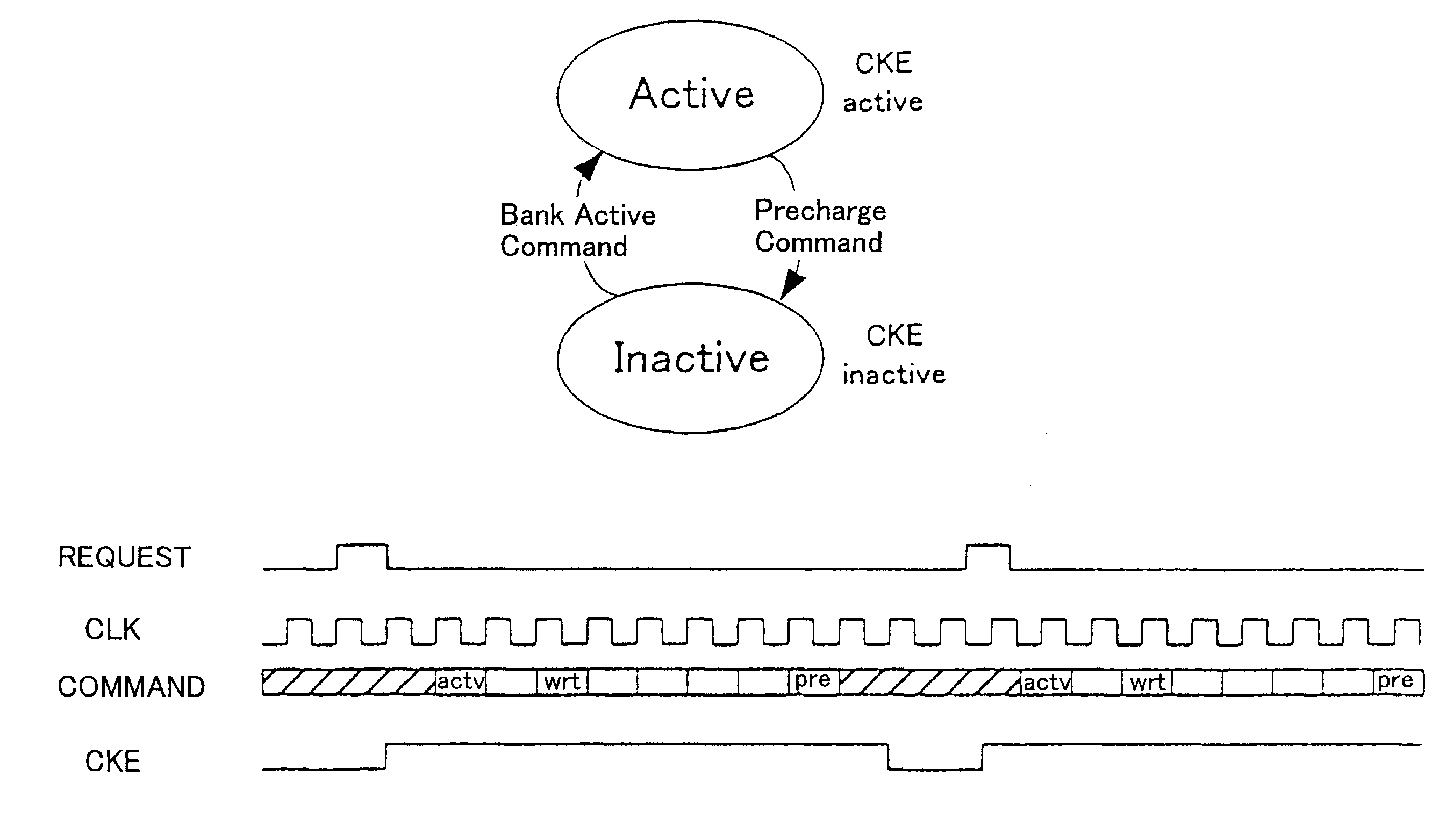
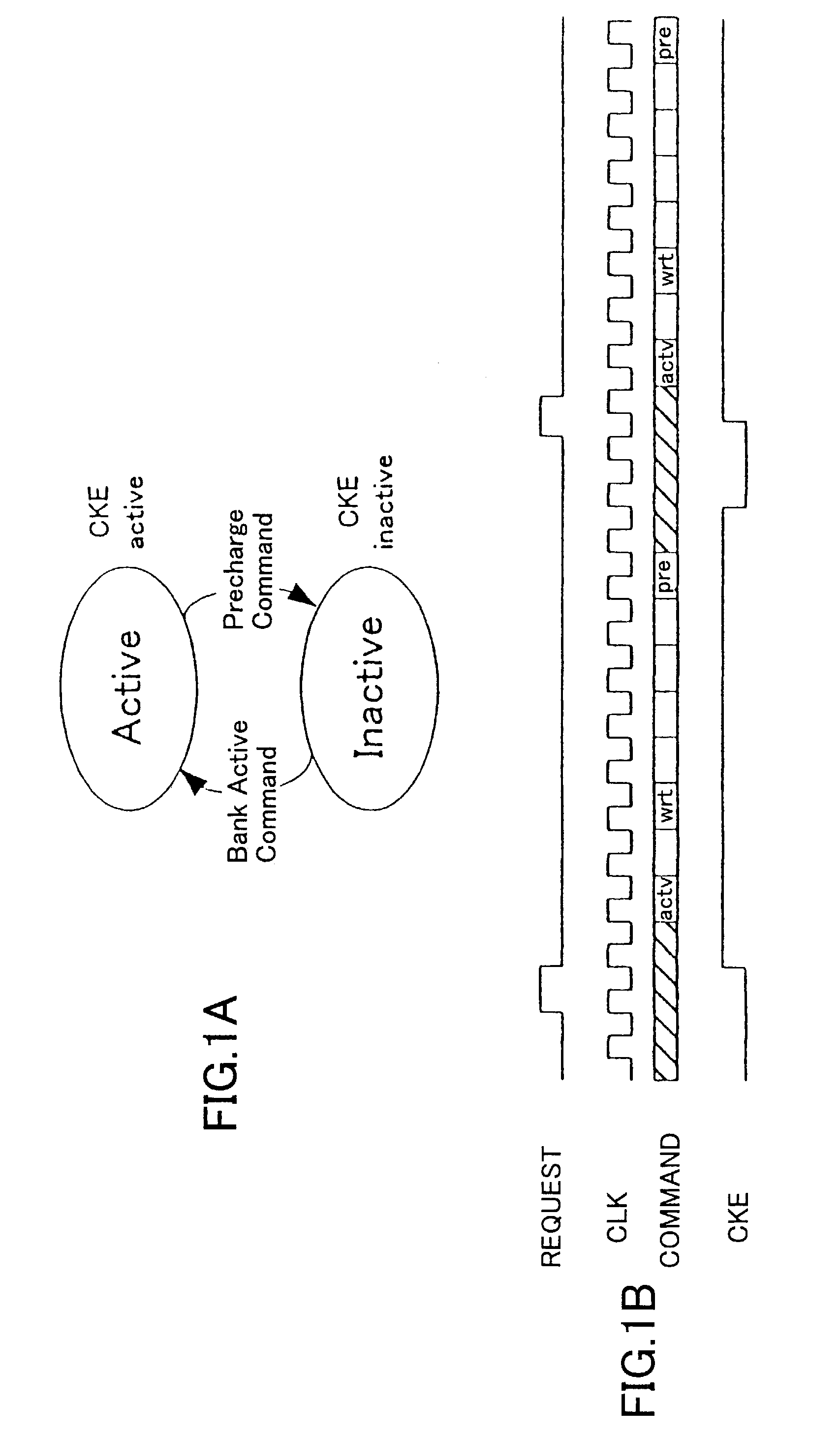
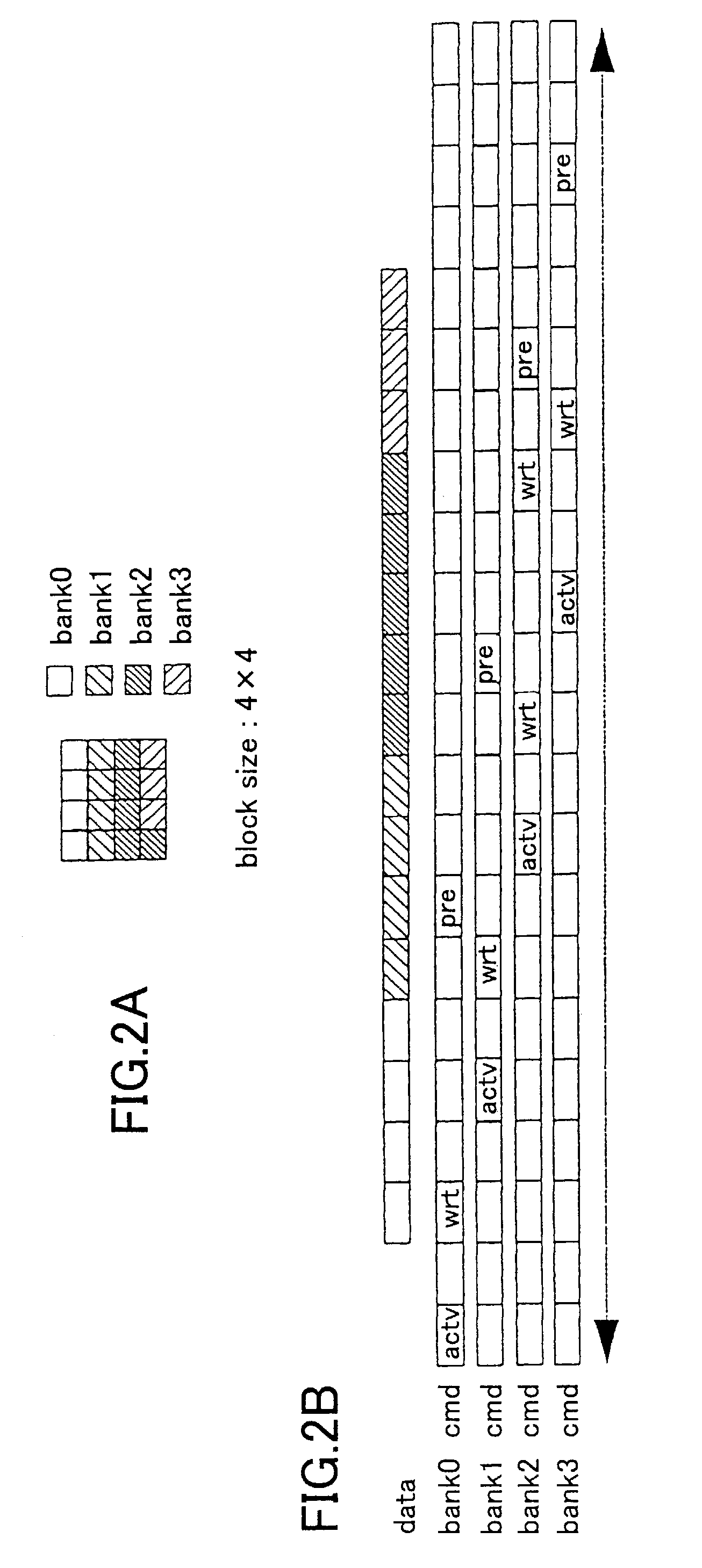
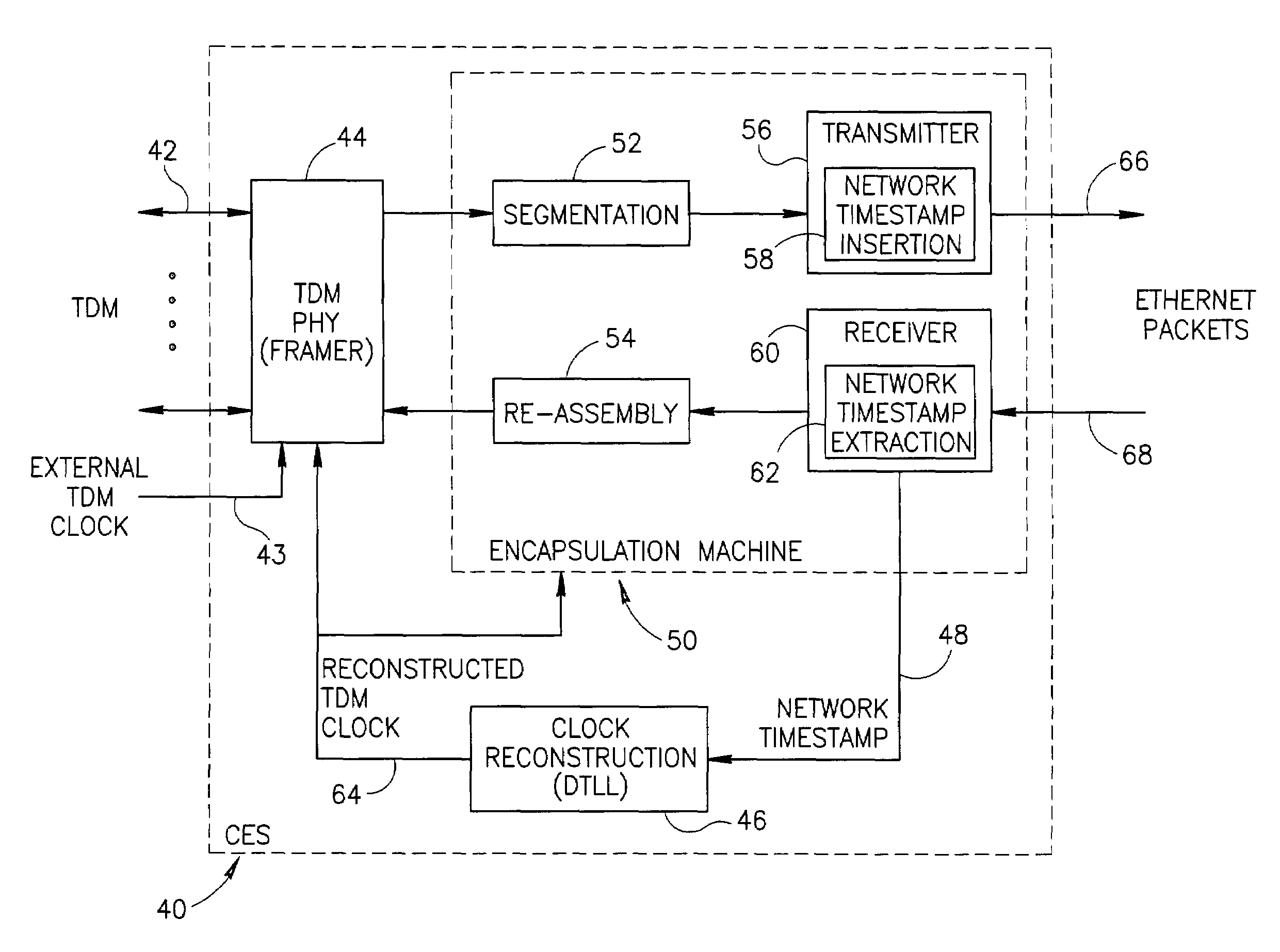
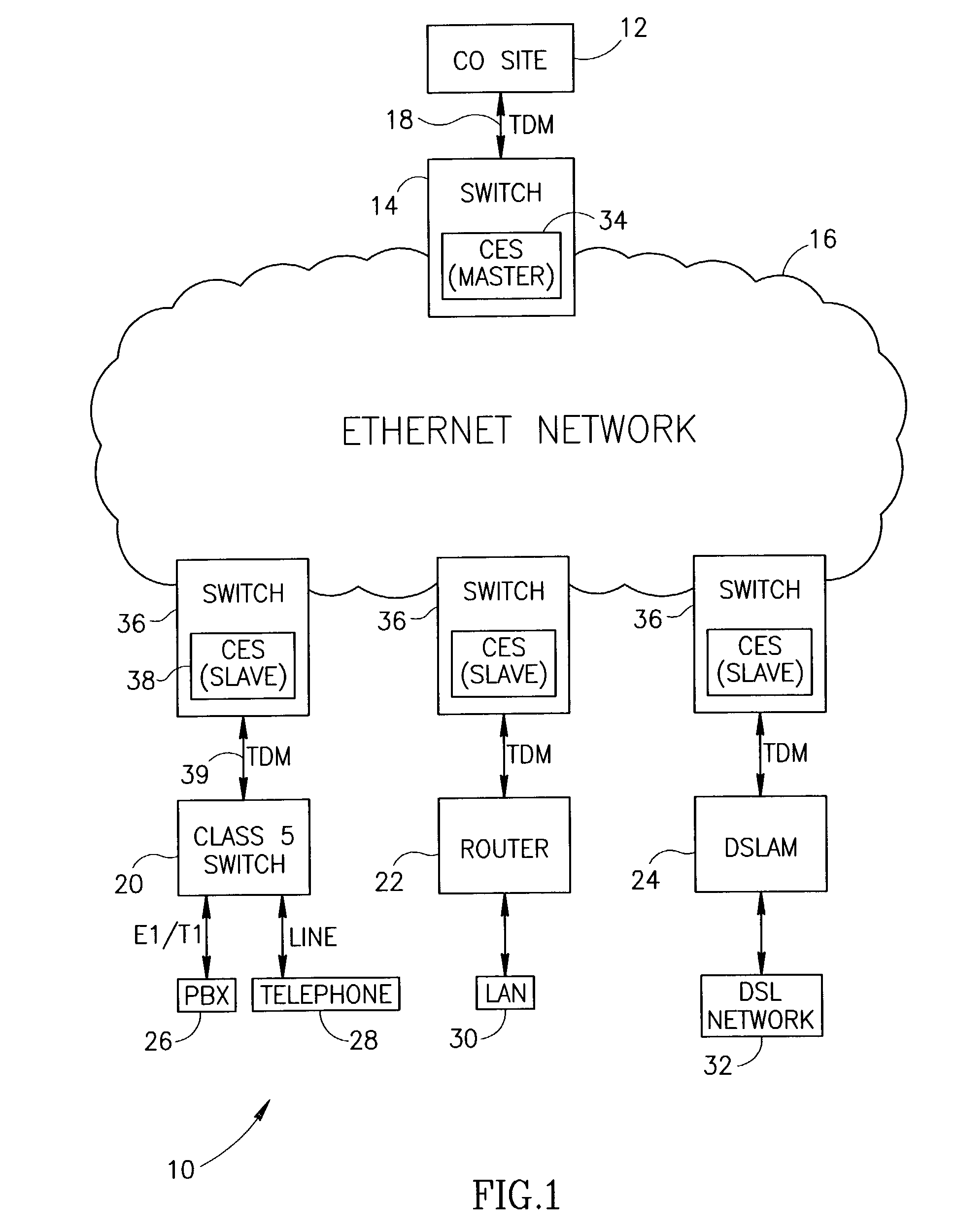
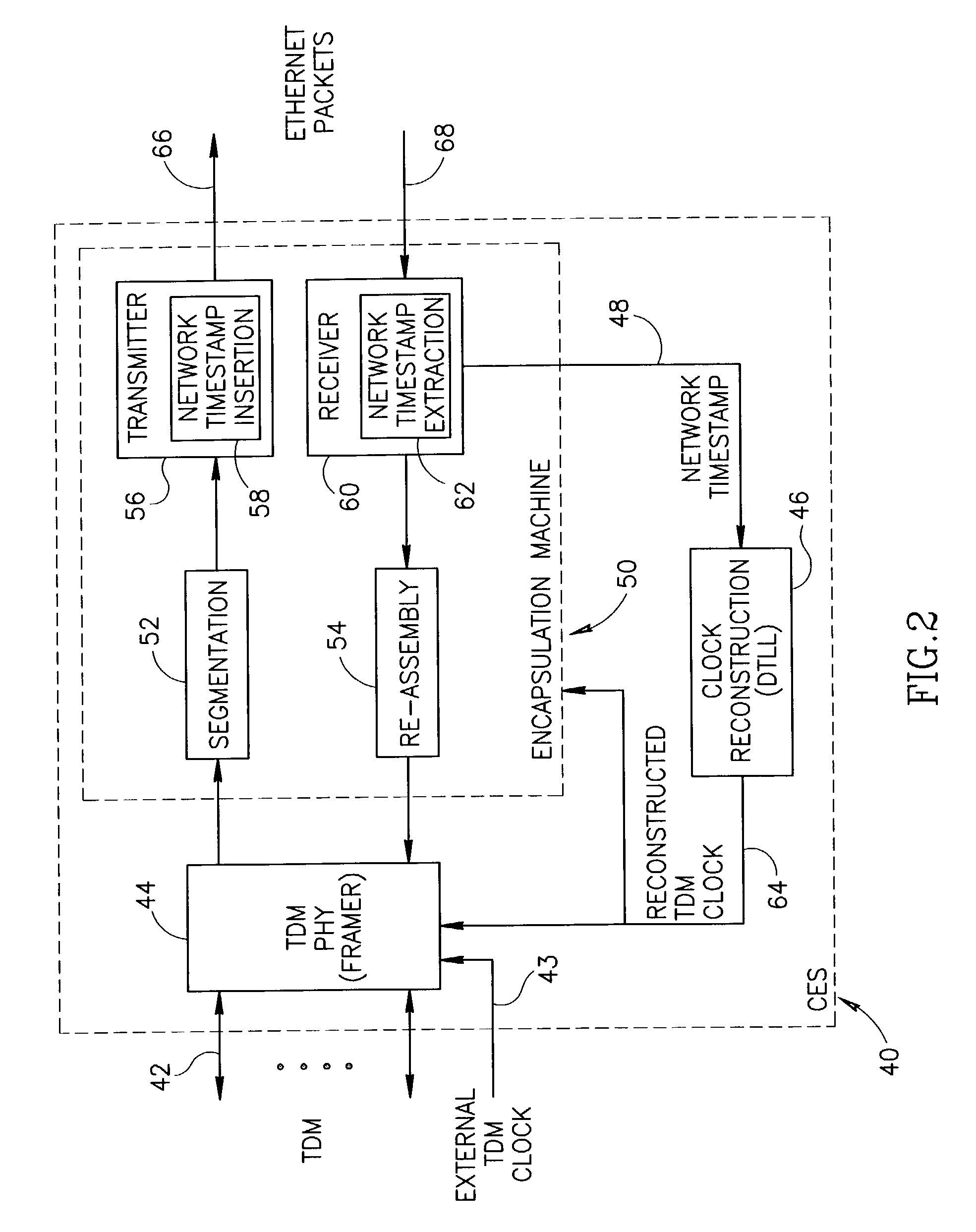
Clock reconstruction for time division multiplexed traffic transported over asynchronous ethernet networks
A clock reconstruction mechanism for synchronous TDM communications traffic transported over asynchronous networks such as Ethernet networks. The invention is applicable to edge switches in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) that transport legacy TDM traffic using a Circuit Emulation Services (CES) module whereby TDM traffic is encapsulated and transported across the Ethernet network where it is de-encapsulated and clocked out to the destination. The mechanism encapsulates the input TDM data stream into Ethernet packets and inserts a network timestamp within the packet. At the destination CES, a local timestamp is generated for each received packet as it is received. The network timestamp is extracted and input along with the local timestamp to a Digital Time Locked Loop (DTLL) which is operative to accurately reconstruct the original transmit TDM clock. The filter in the DTLL performs a Least Squares Regression (LSR) algorithm and Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter algorithm to generate a clock control signal for adjusting the clock generated.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III +1
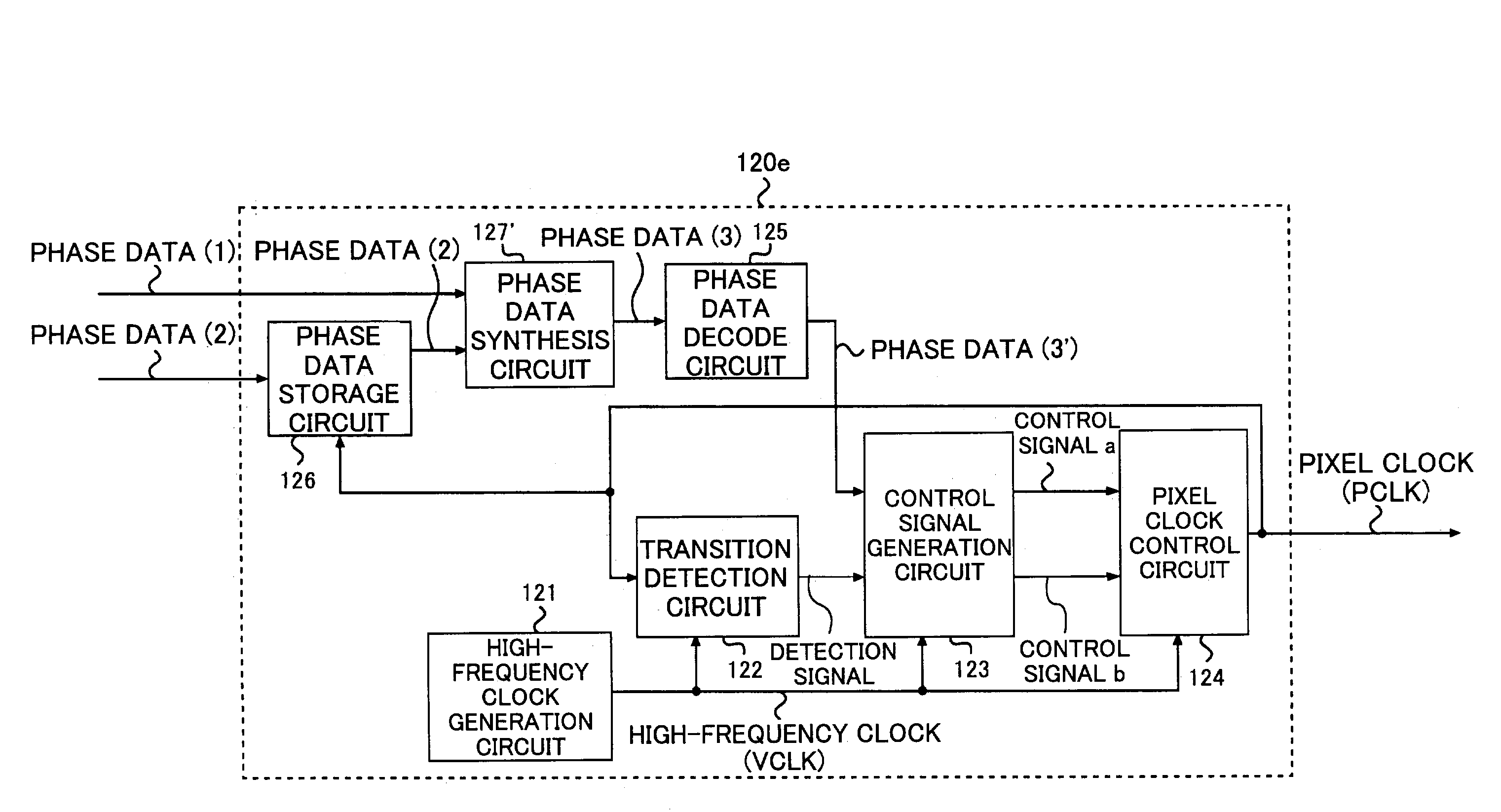
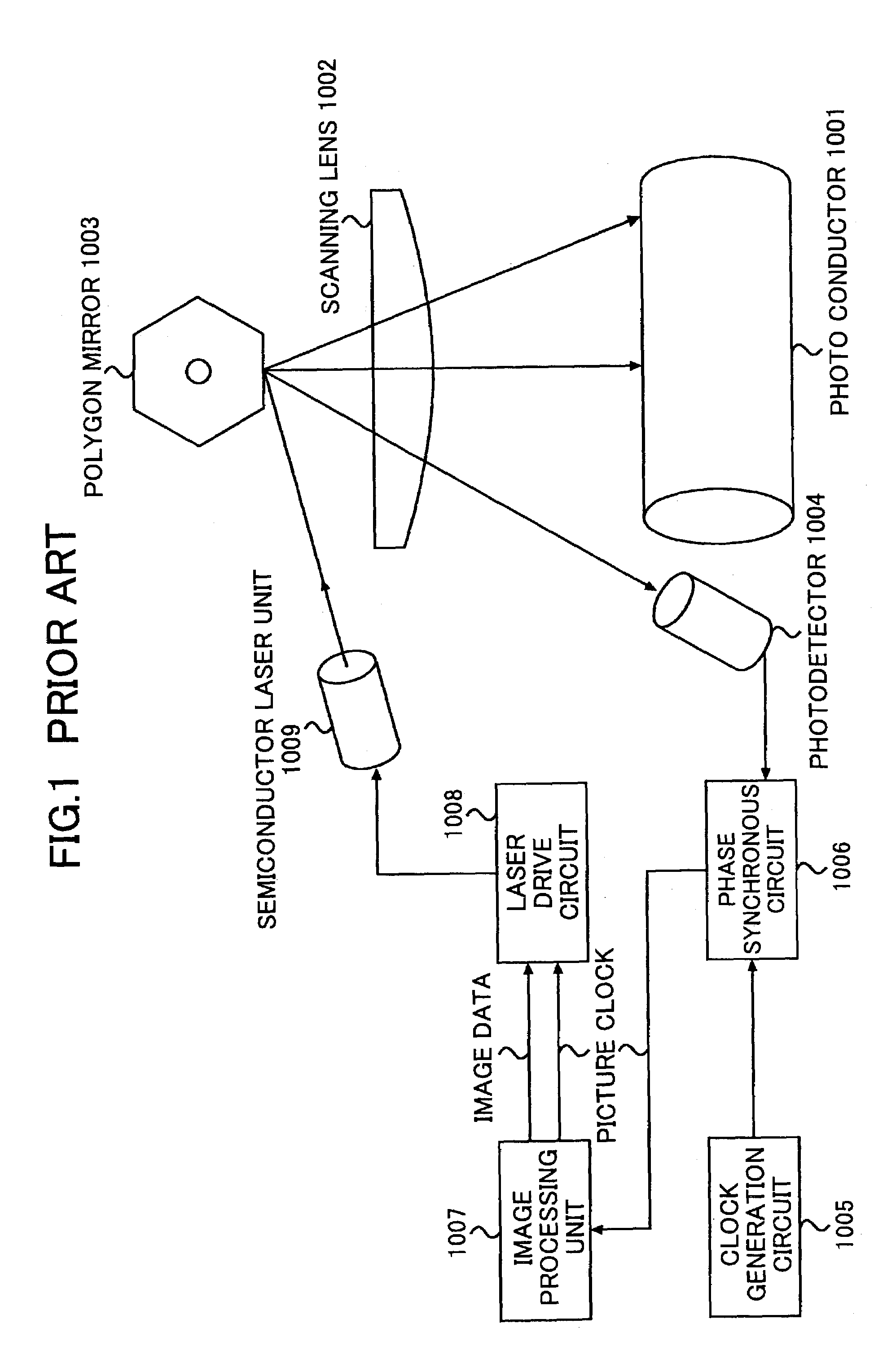
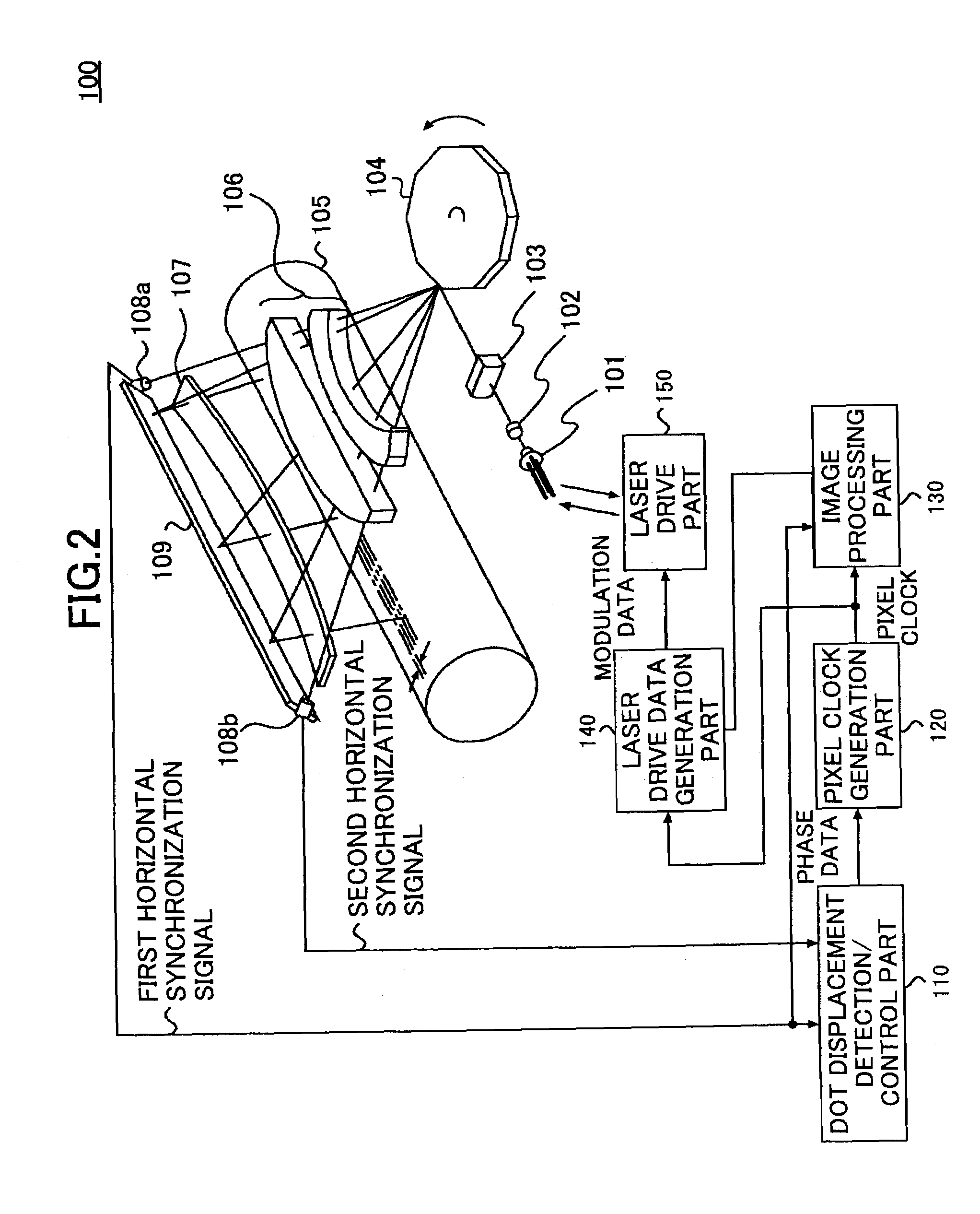
Pixel clock generation device causing state transition of pixel clock according to detected state transition and phase data indicating phase shift amount
InactiveUS7283151B2Simple structureEasy to controlVisual representatino by photographic printingPrintingPhase shiftedControl signal
A transition detection circuit detects a transition of a state of a pixel clock, and outputs a detection signal according to a timing of the detected state transition. A control signal generation circuit generates a control signal according to the detection signal and phase data indicating a transition timing of the pixel clock. A pixel clock control circuit causes the state of the pixel clock to transit according to the control signal.
Owner:RICOH KK
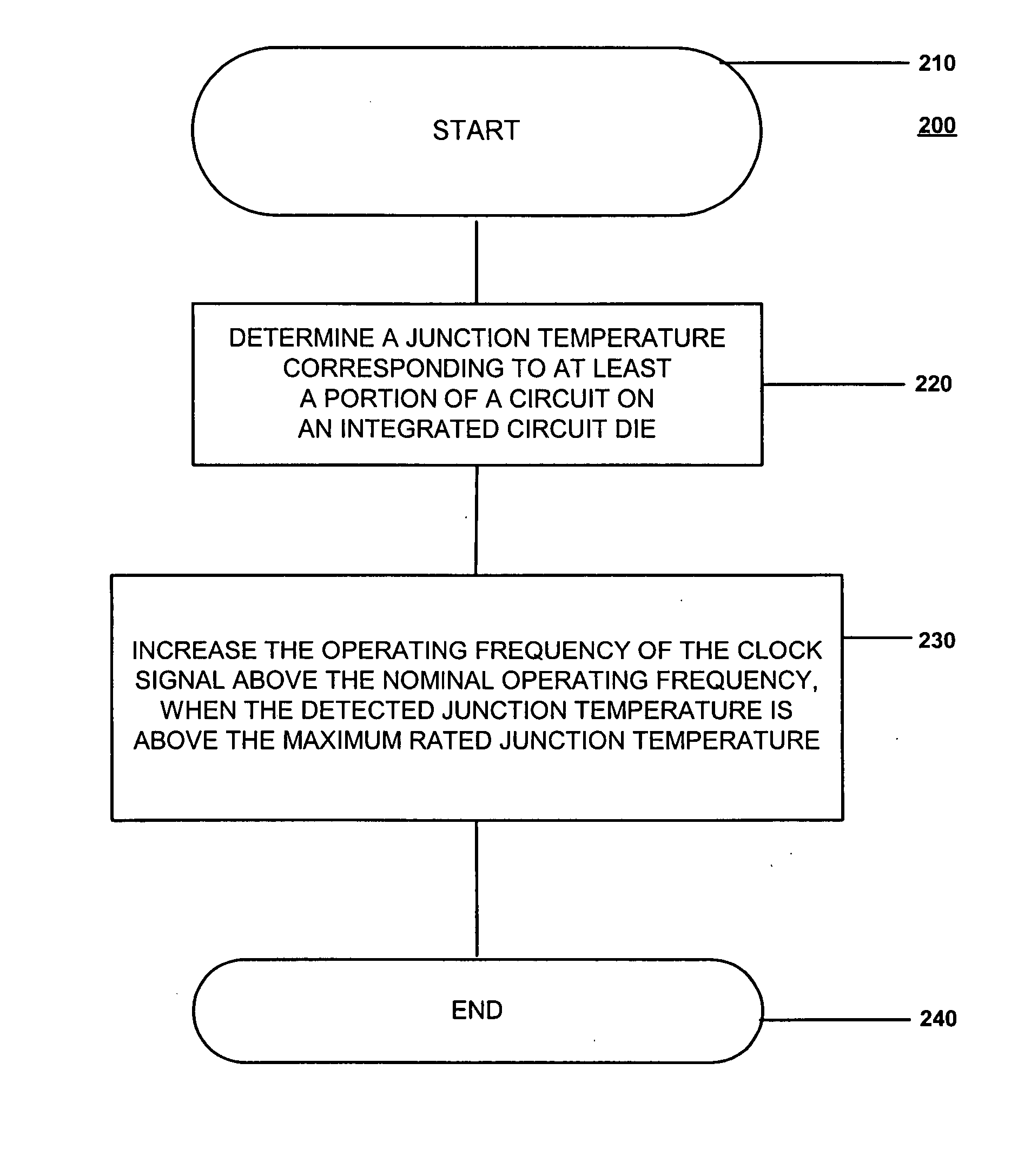
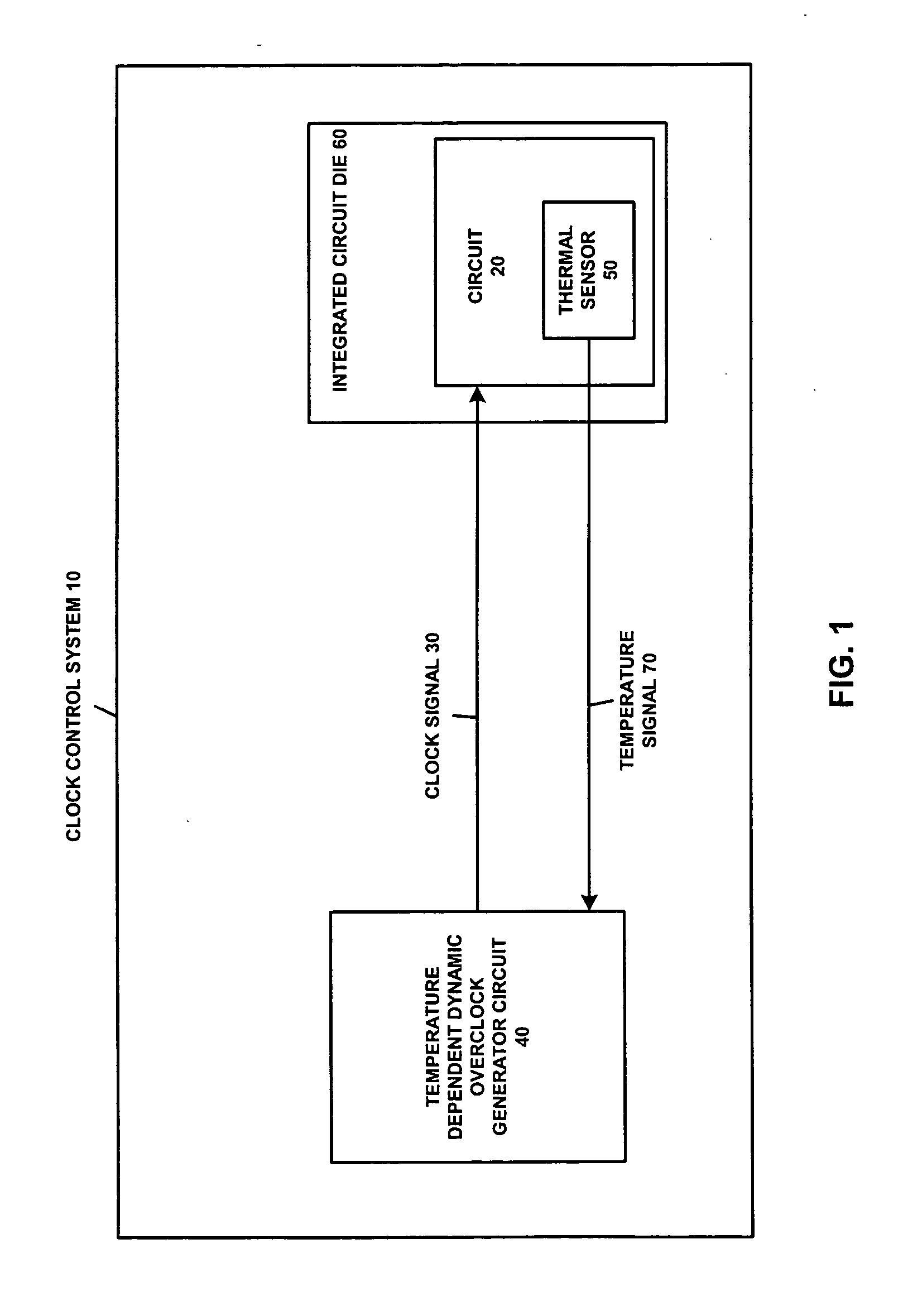
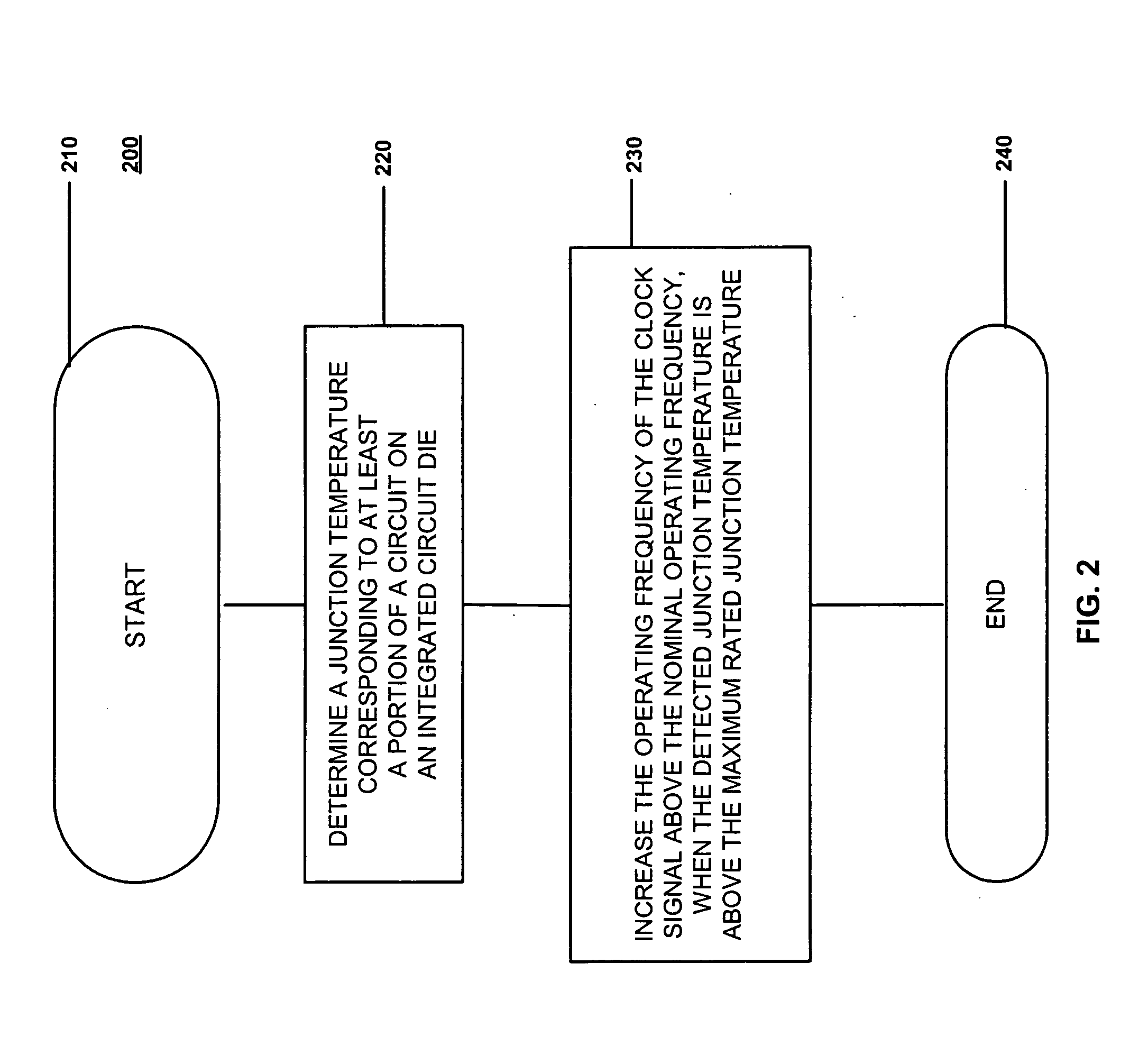
Adaptive temperature dependent feedback clock control system and method
An adaptive temperature dependent clock feedback control system and method for adaptively varying a frequency of a clock signal to a circuit such that the circuit may operate at a maximum safe operating clock frequency based on a circuit junction temperature. The clock control system includes a thermal sensor and a temperature dependent dynamic overclock generator circuit. The thermal sensor detects a junction temperature corresponding to at least a portion of the circuit on a semiconductor die. The temperature dependent dynamic overclock generator circuit varies the clock signal based on the semiconductor die junction temperature, such that the clock signal operates at the highest possible operating frequency associated with the detected junction temperature. The frequency of the clock signal is increased from a first frequency to at least a second frequency and a third frequency if the junction temperature is below a lower junction temperature threshold.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
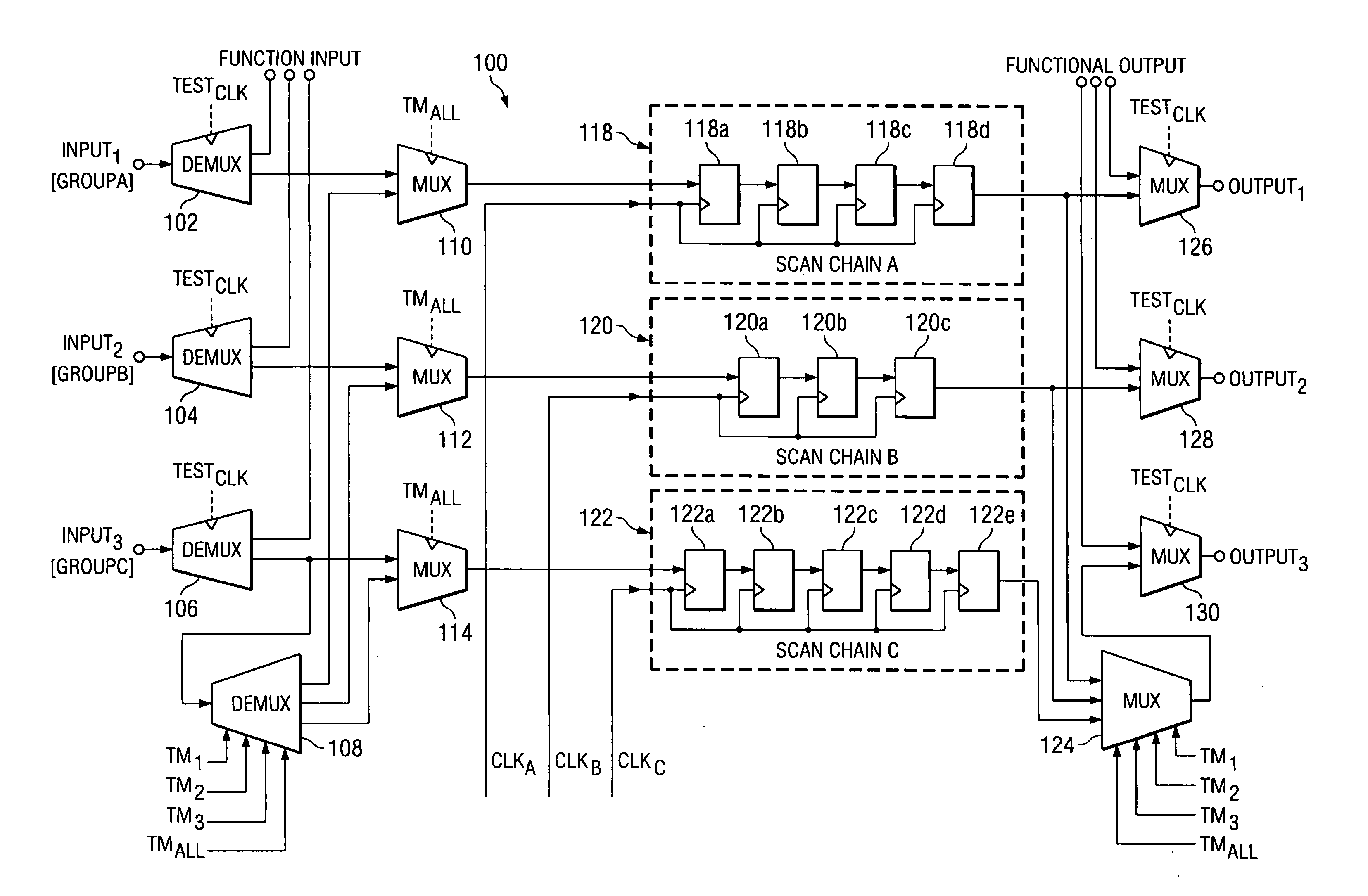
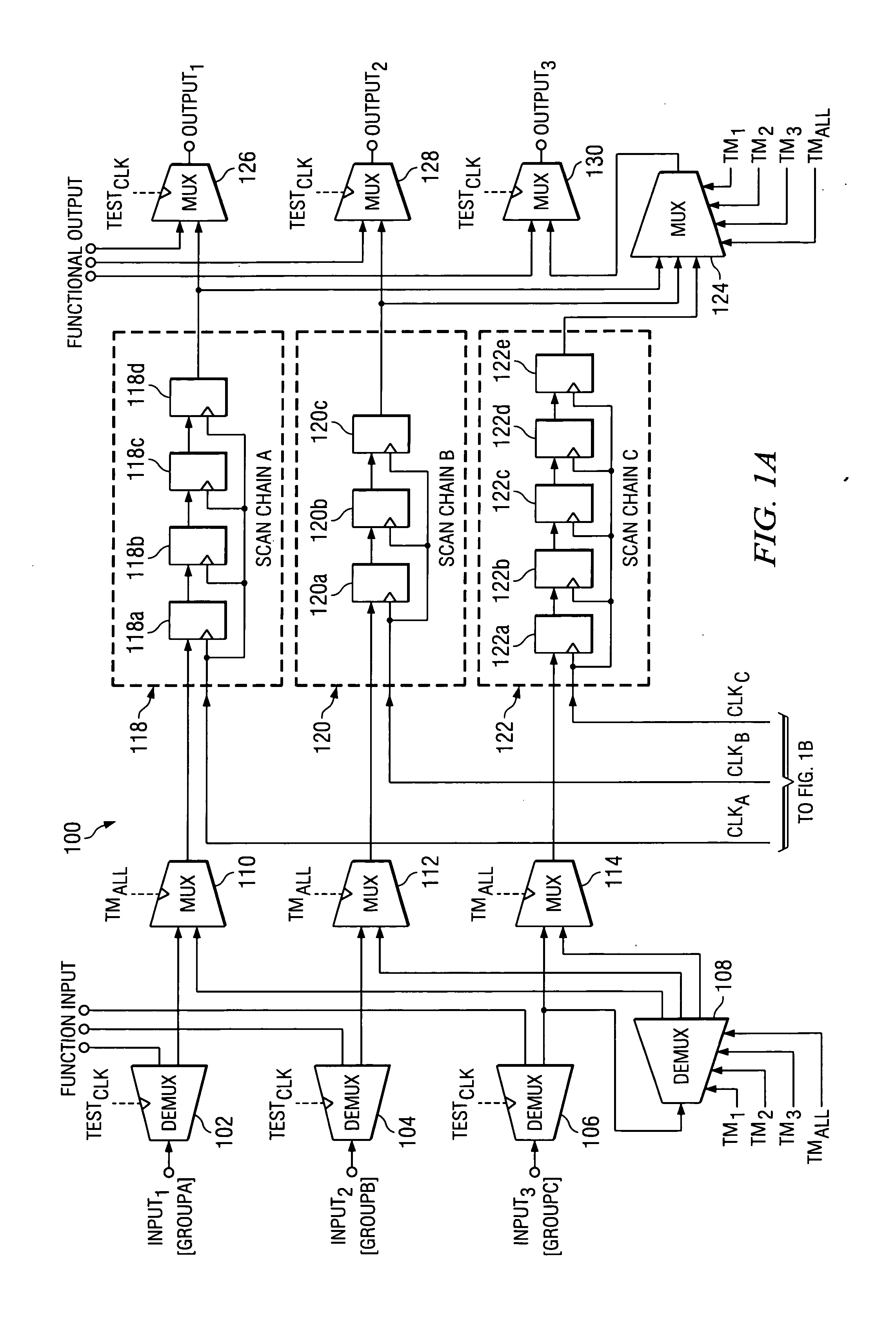
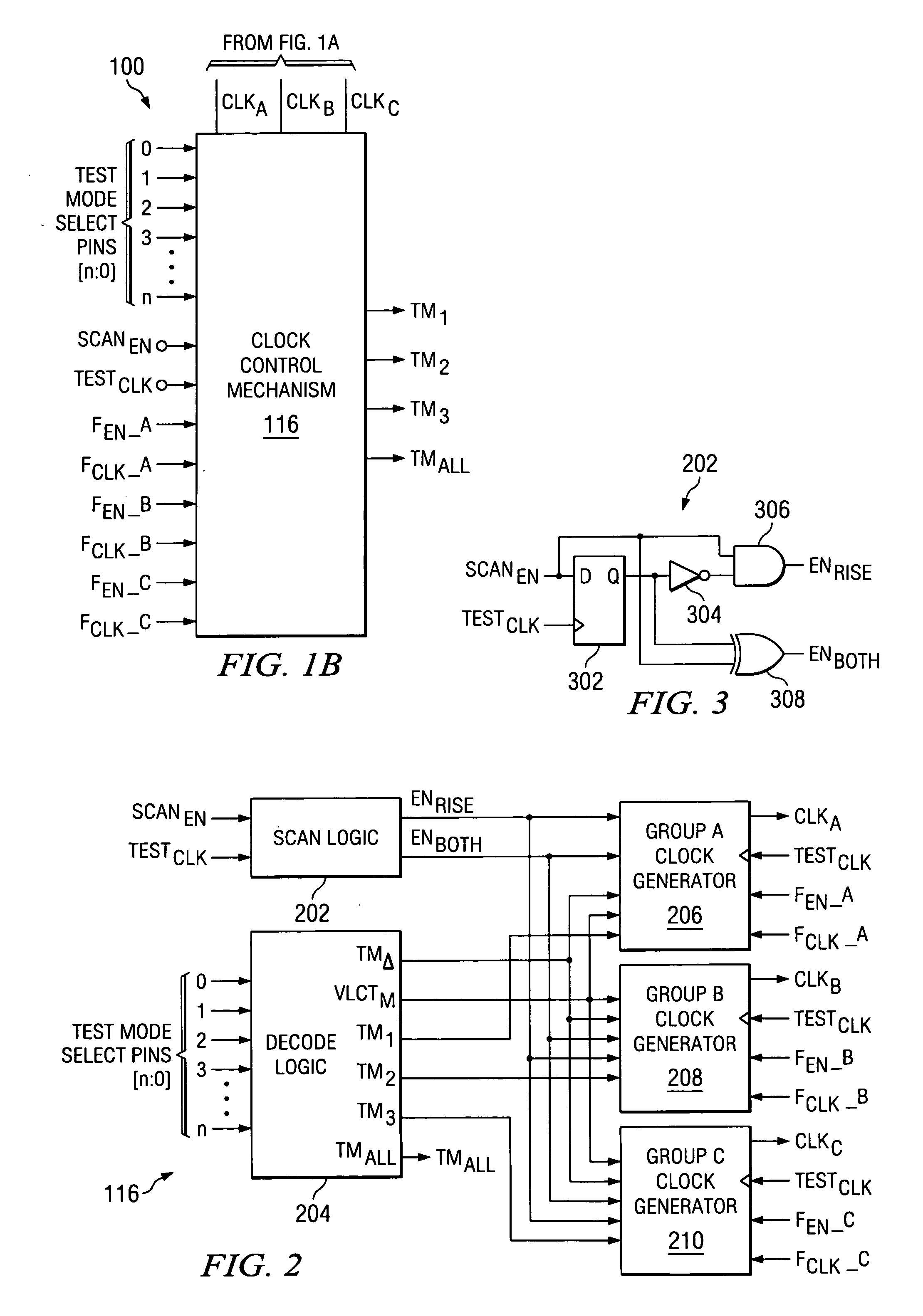
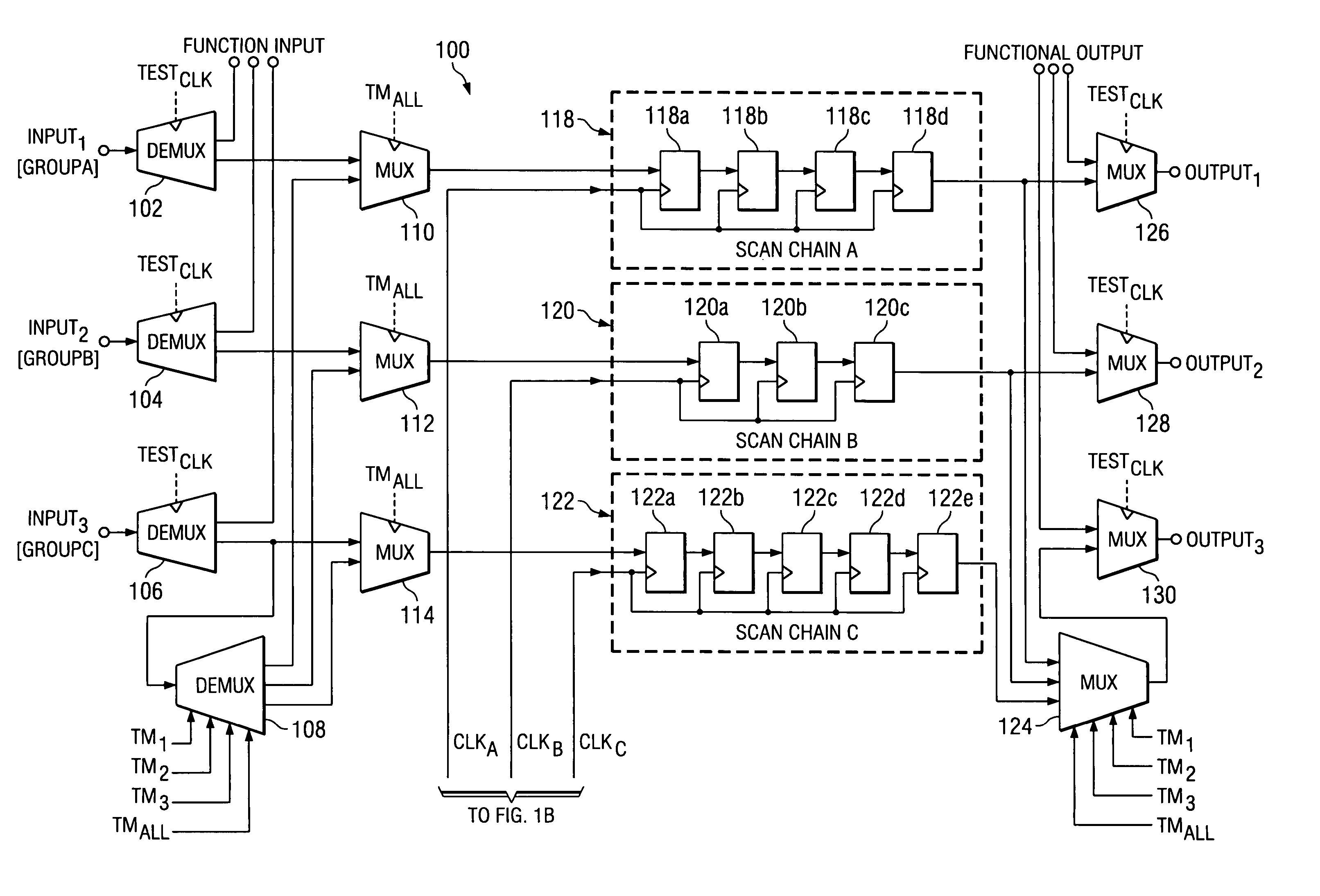
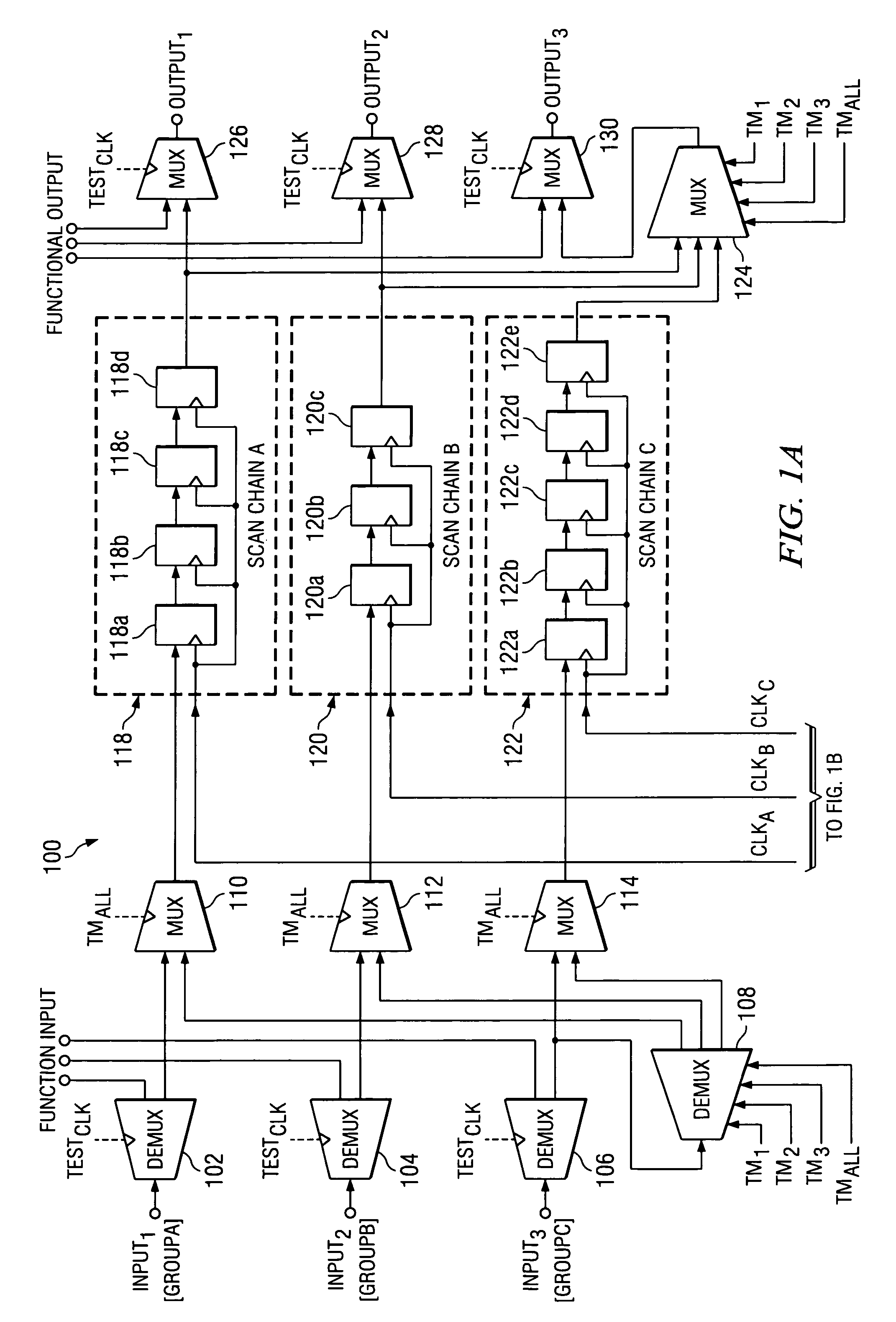
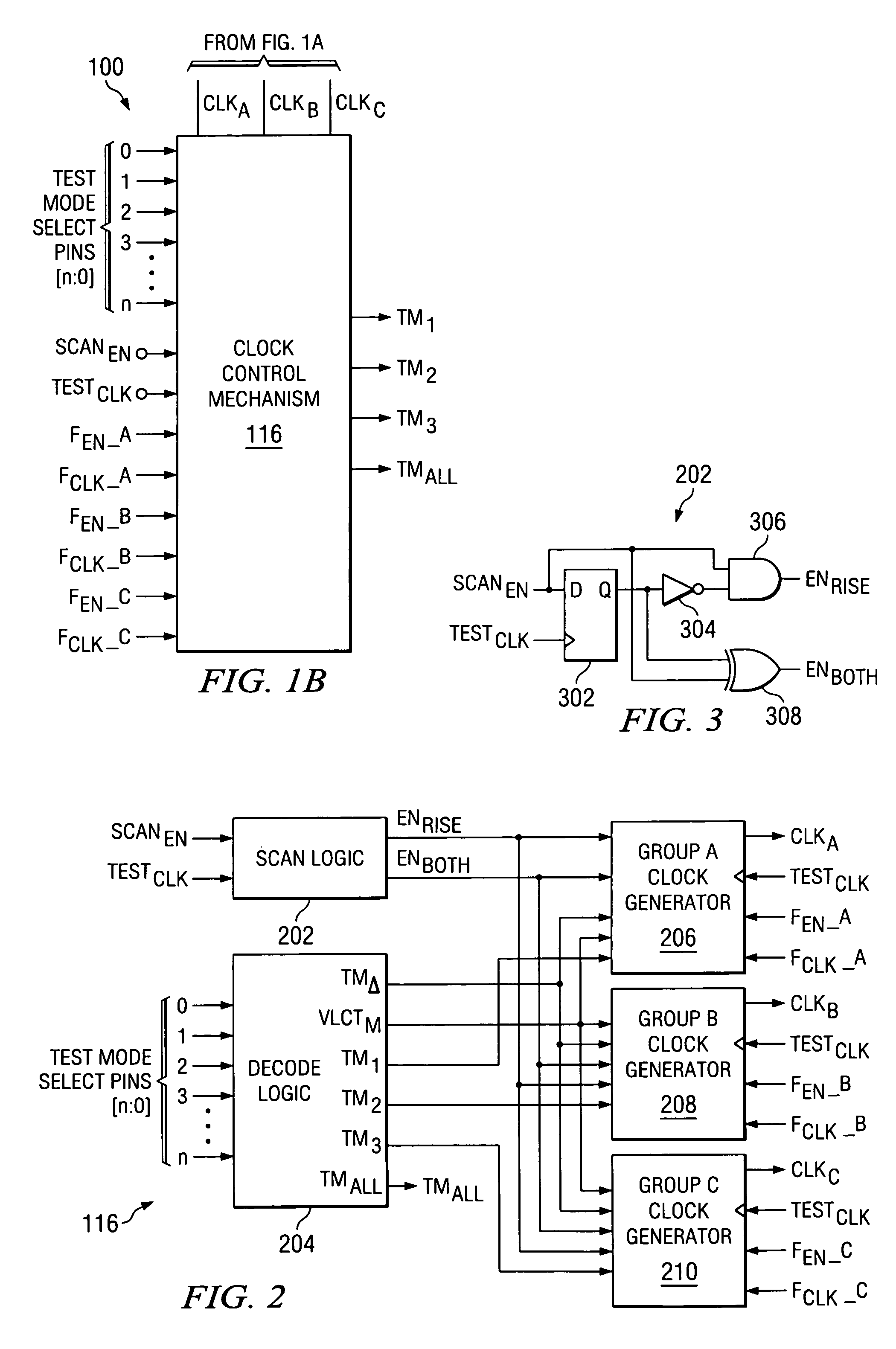
At-speed ATPG testing and apparatus for SoC designs having multiple clock domain using a VLCT test platform
ActiveUS20050055615A1Increase savingsThe testing process is simpleElectronic circuit testingControl signalClock rate
A scan test circuitry design imbedded on an SoC having the scan architecture of a VLCT platform is disclosed herein. This BIST circuitry design that is not limited in the number of scan test ports supported includes at least one scan chain group having a corresponding clock domain that couples to receive test stimulus data. Each scan chain group has a corresponding test mode signal to shift the test stimulus data at a shift clock rate derived from its corresponding clock domain. A controlling demultiplexer connects to each multiplexer unit within each scan chain group to provide control signals for shifting in the test stimulus. A clock control mechanism provides a control signal for each scan chain to shift test stimulus and capture resultant data. Furthermore, when a simultaneous test mode signal is enabled, the clock control mechanism couples to each scan chain to enable simultaneous capture of each scan chain group.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for measuring current as in sensing a memory cell
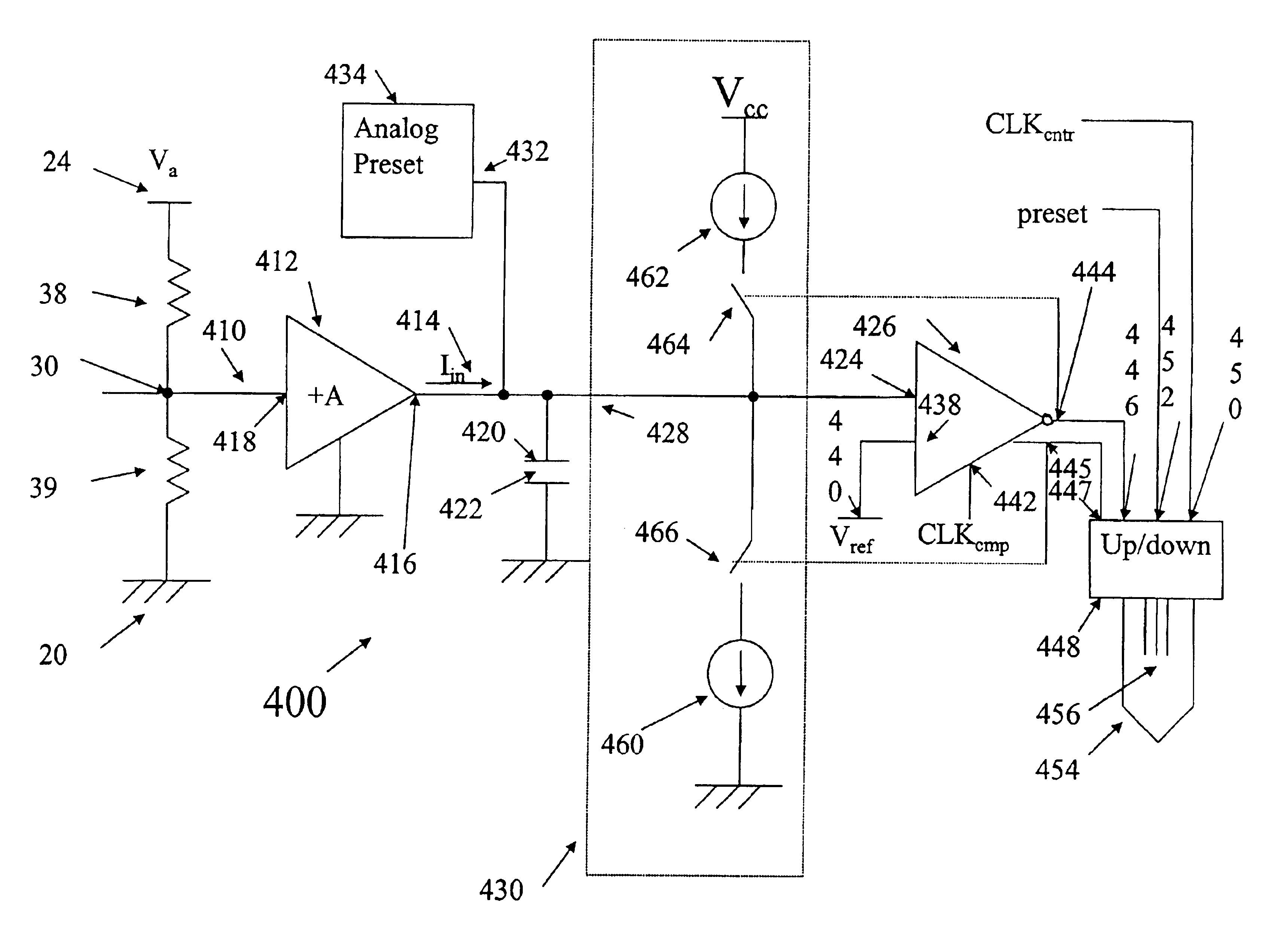
InactiveUS6930942B2Increase rangeShorten the counting processElectric analogue storesDigital storageAudio power amplifierCapacitor voltage
Apparatus and methods sense or measure an input current, such as a current indicating a logic state of a memory cell. A sensing circuit includes an amplifier, a capacitor, a current source circuit, a clocked comparator and a clocked counter. The current source circuit operates responsive to an output of the comparator to supply or withdraw current to and from the capacitor during respective charging and discharging intervals. The count in the clocked counter results from periodic comparisons of the capacitor voltage with a reference voltage and is, therefore, related to the logic state of the memory cell. The magnitude of current supplied during charging is less than the magnitude withdrawn during discharging, allowing use of a smaller counter.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Clock and data recovery circuit and clock control method
InactiveUS20020079938A1Easy to characterizeFacilitate change of frequencyPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase shiftedPhase difference
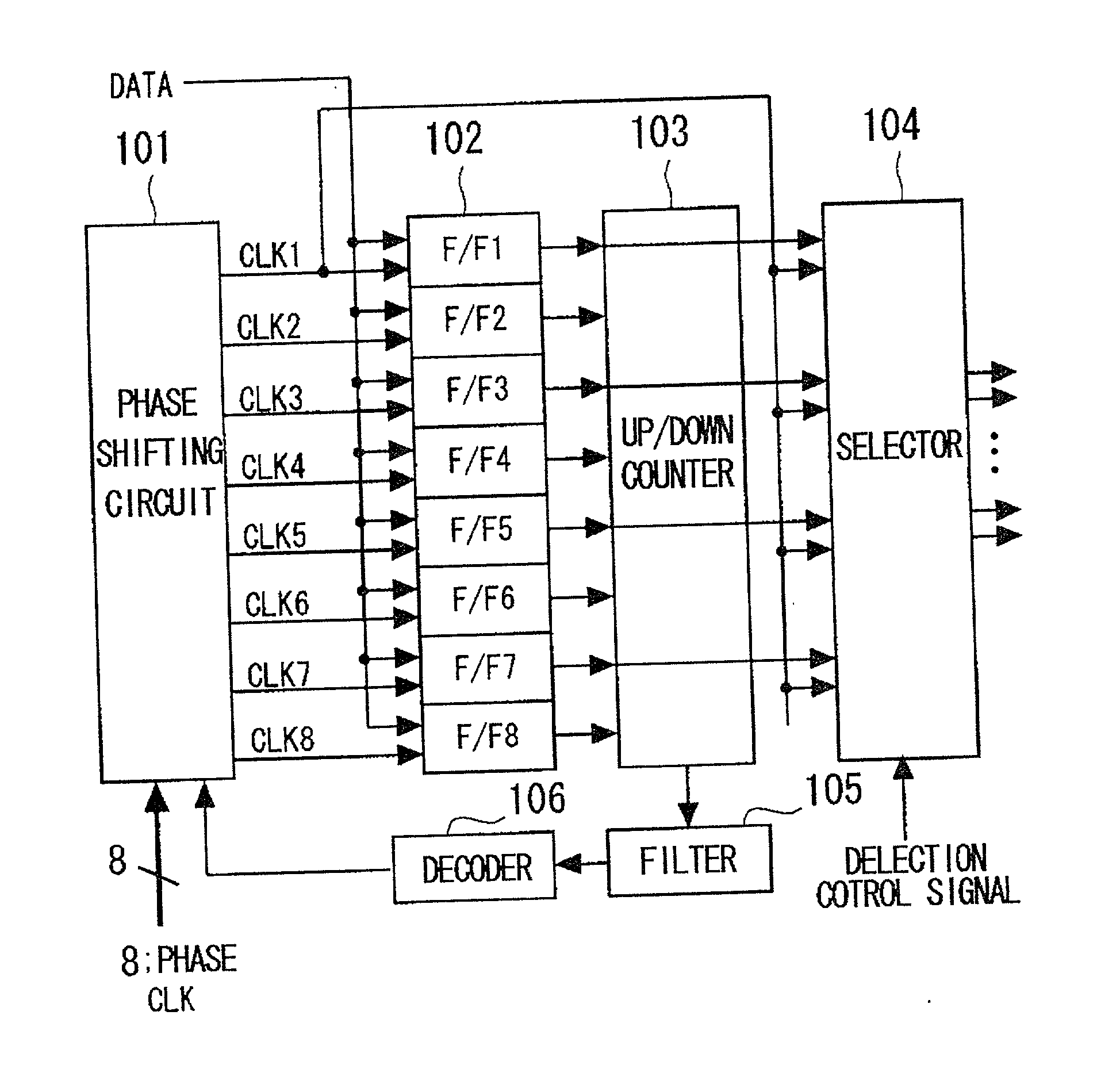
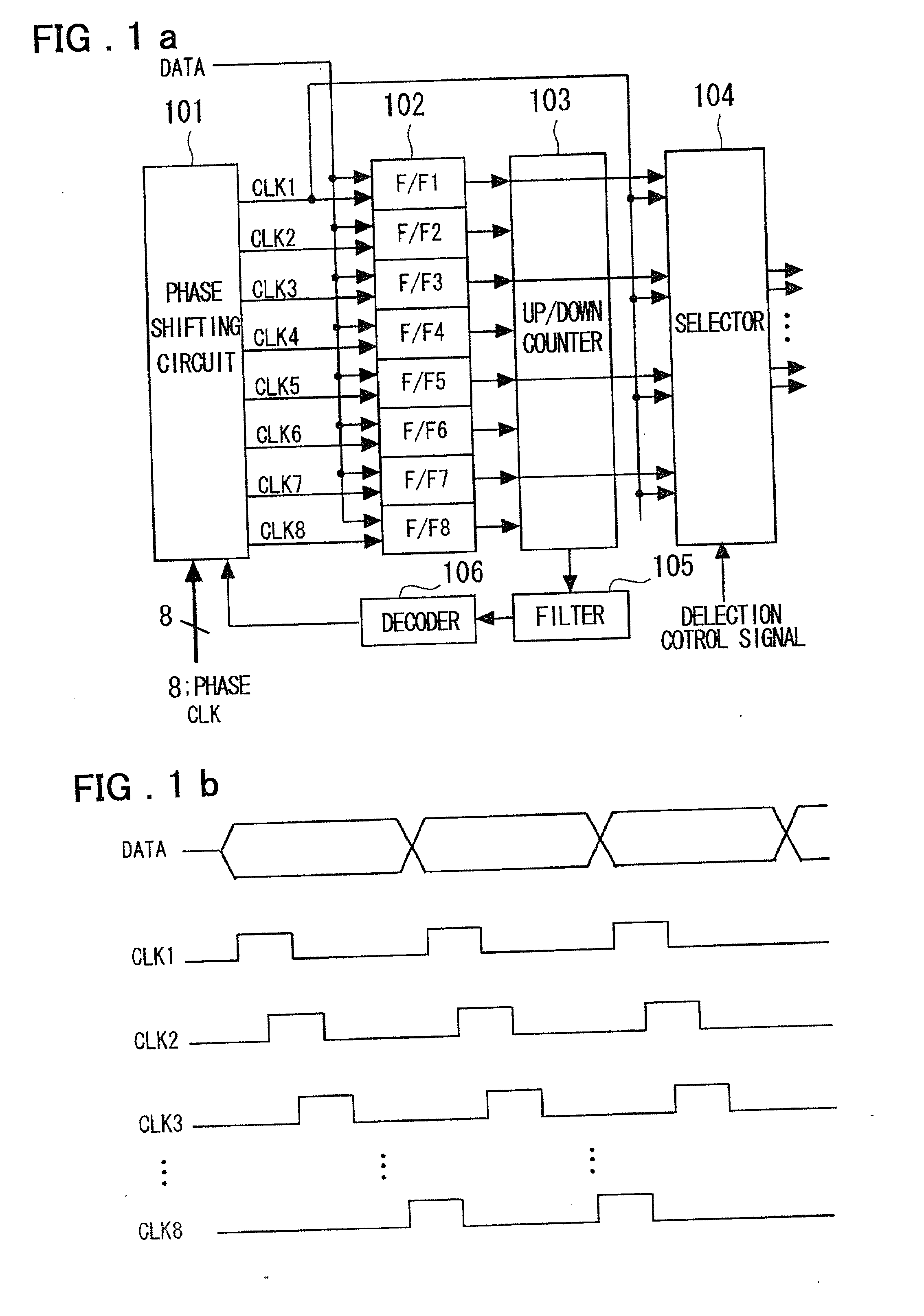
To provide a clock and data recovery circuit which facilitates alteration of the frequency range and adjustment of characteristics. The clock and data recovery circuit includes a phase shift circuit 101 having a switch receiving as inputs multi-phase clocks for selecting and outputting plural sets of the paired clocks from the input multi-phase clocks and a plural number of interpolators receiving the plural number of clock pairs output from the switch to output signals having the delay prescribed by the time corresponding to interior division of the phase difference of the clock pairs, a plural number of latch circuits 102 for latching the input data based on the signals output from the phase shift circuit 101, a counter 103 for counting the outputs of the plural latch circuits, a filter 105 for averaging the counter output over a preset time, a decoder 106 for decoding an output of the filter and a selection circuit 104 fed with a plural number of sets of data output by the plural latch circuits and clocks output from a preset one of the plural interpolators to select pairs of output data and clocks.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Optimally Clocked Trim Retarders
ActiveUS20070064163A1Liquid crystal compositionsColor television detailsContrast levelLiquid-crystal display
A trim retarder for a liquid crystal display based projection system including a light source, a polarizer / analyzer, a liquid crystal display panel, and a projection lens, is clocked to an optimal azimuthal angle that provides a system contrast level substantially unaffected by the orientation of the slow axis of the liquid crystal display panel.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
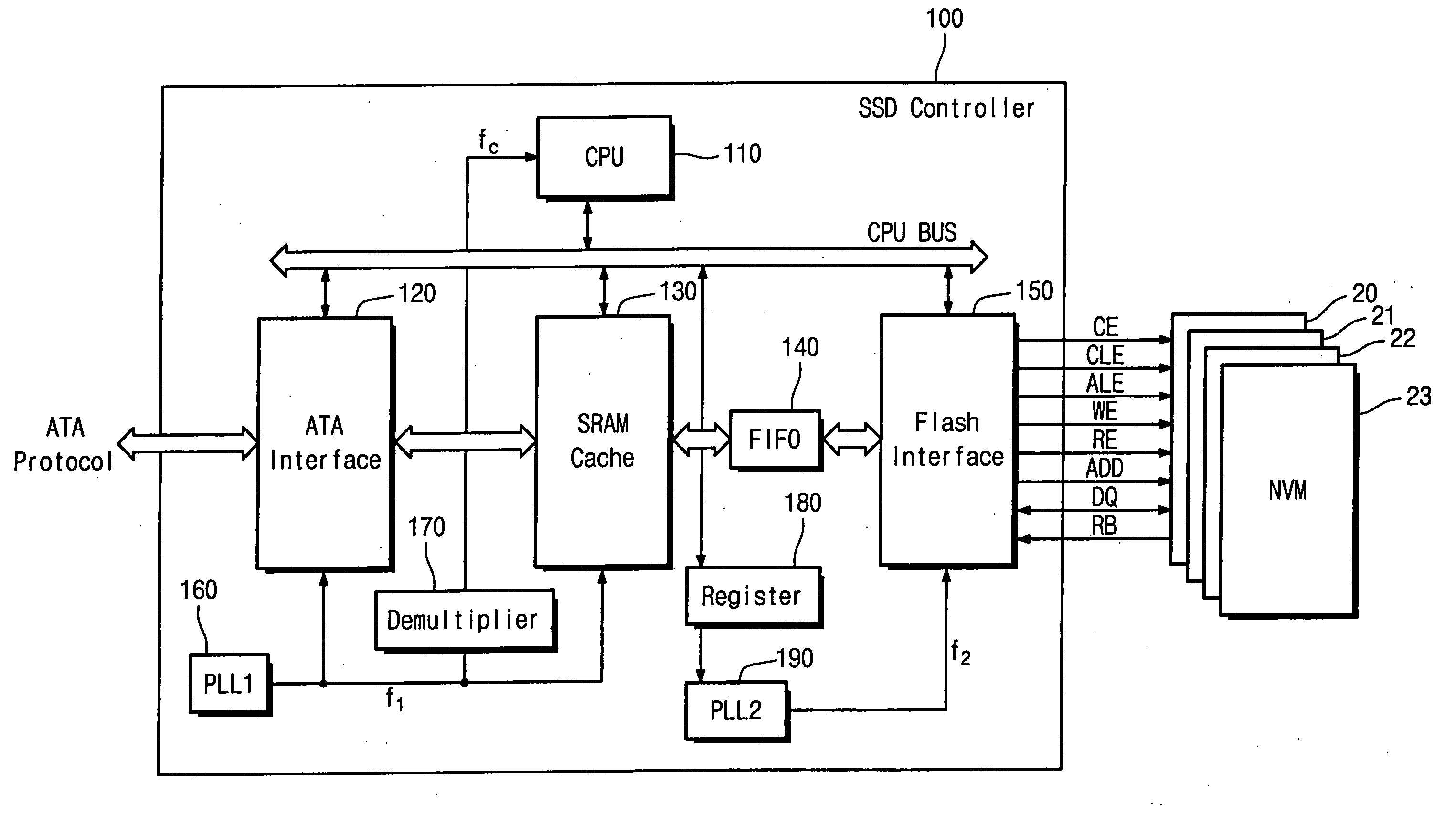
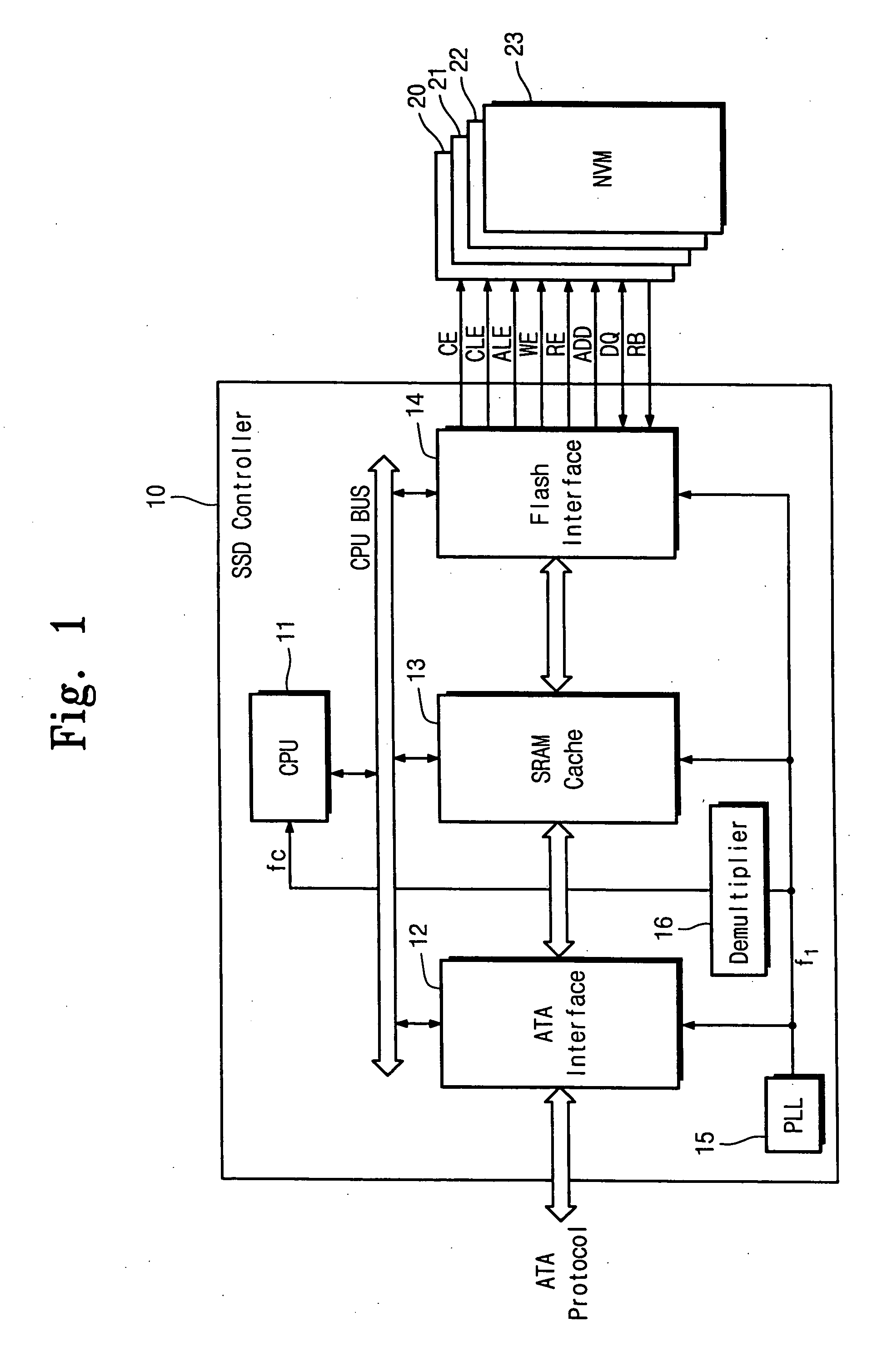
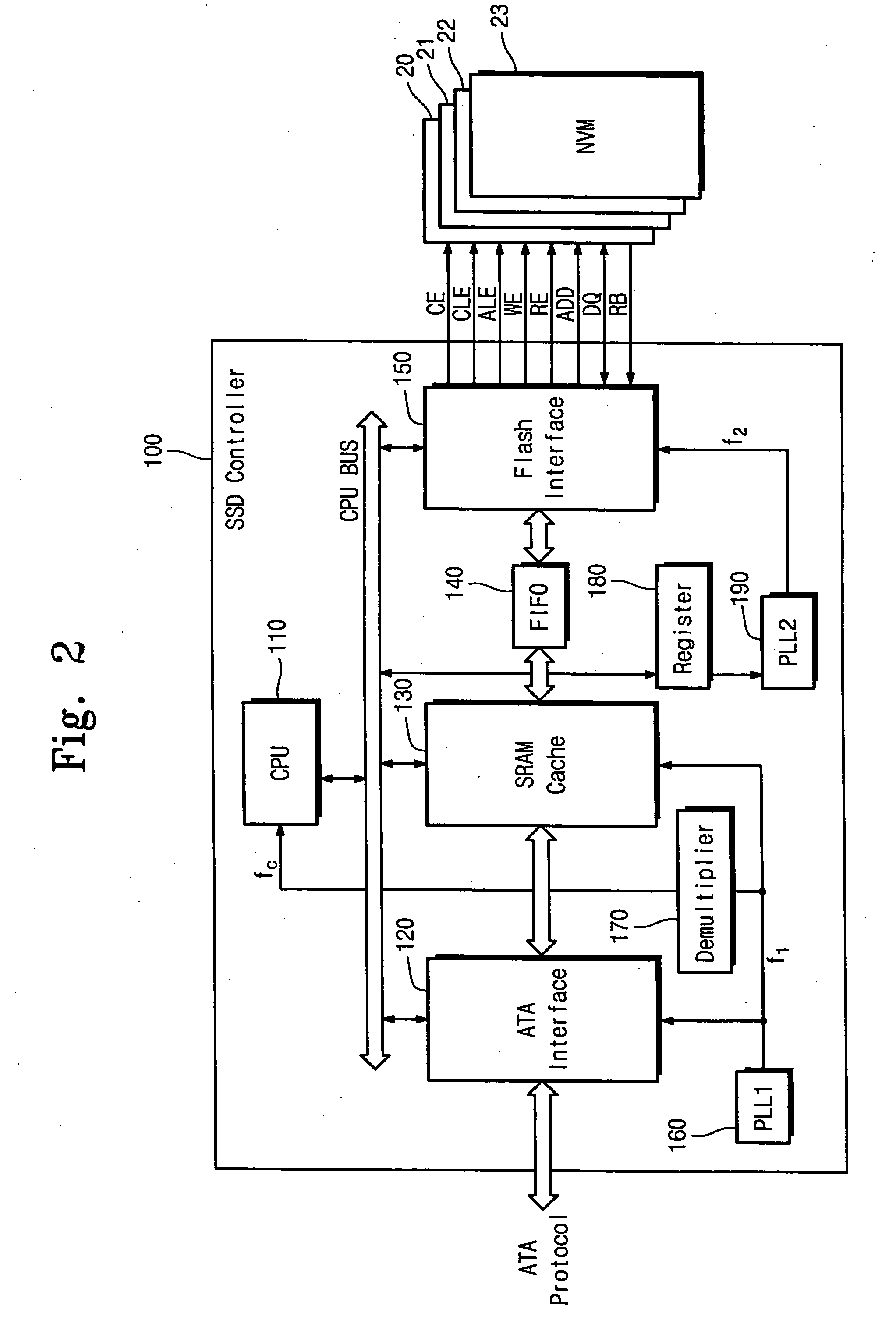
Semiconductor solid state disk controller
InactiveUS20070106836A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationGenerating/distributing signalsDisk controllerClock generator
A semiconductor solid state disk control device includes a flash interface configured to interface with the flash memory. The control device also includes a host interface configured to interface with the host. The control device also includes a first clock generator configured to generate a first driving clock to the host interface. The control device also includes a second clock generator configured to generate a second driving clock to the flash interface independent of the first clock generator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
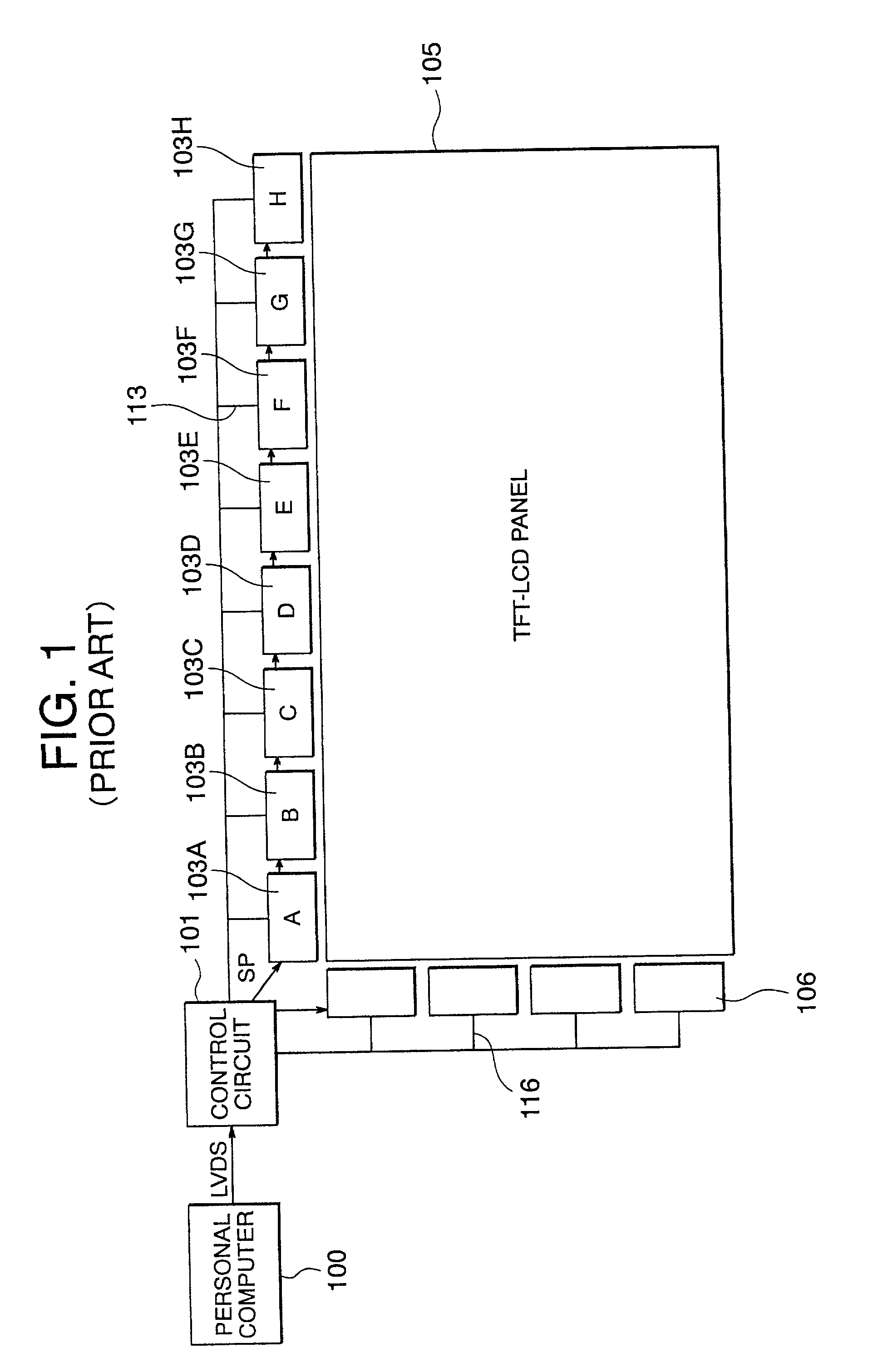
Device circuit of display unit
A drive circuit of a display unit has a control circuit and a plurality of source drivers that are cascade-connected to each other. A start pulse signal is inputted into the source driver at the first stage and digital image data signals and clock signals are inputted into the source drivers at the respective stages from the control circuit. Clock signals are generated by a clock control circuit of the control circuit. For the clock signals, a reading period and a transferring period appear alternately, and the frequency of the low frequency clock pulse signal in the transferring period is lower than that of the high frequency clock pulse signal in the reading period. A shift register of the source driver transfer the start pulse signal to said source driver at the next source driver within one transferring period, and the start pulse signal is thus transferred in order from the source driver at the first stage up to the source driver at the final stage. Then, the source driver inputted the start pulse signal reads the digital image data signals in the reading period.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
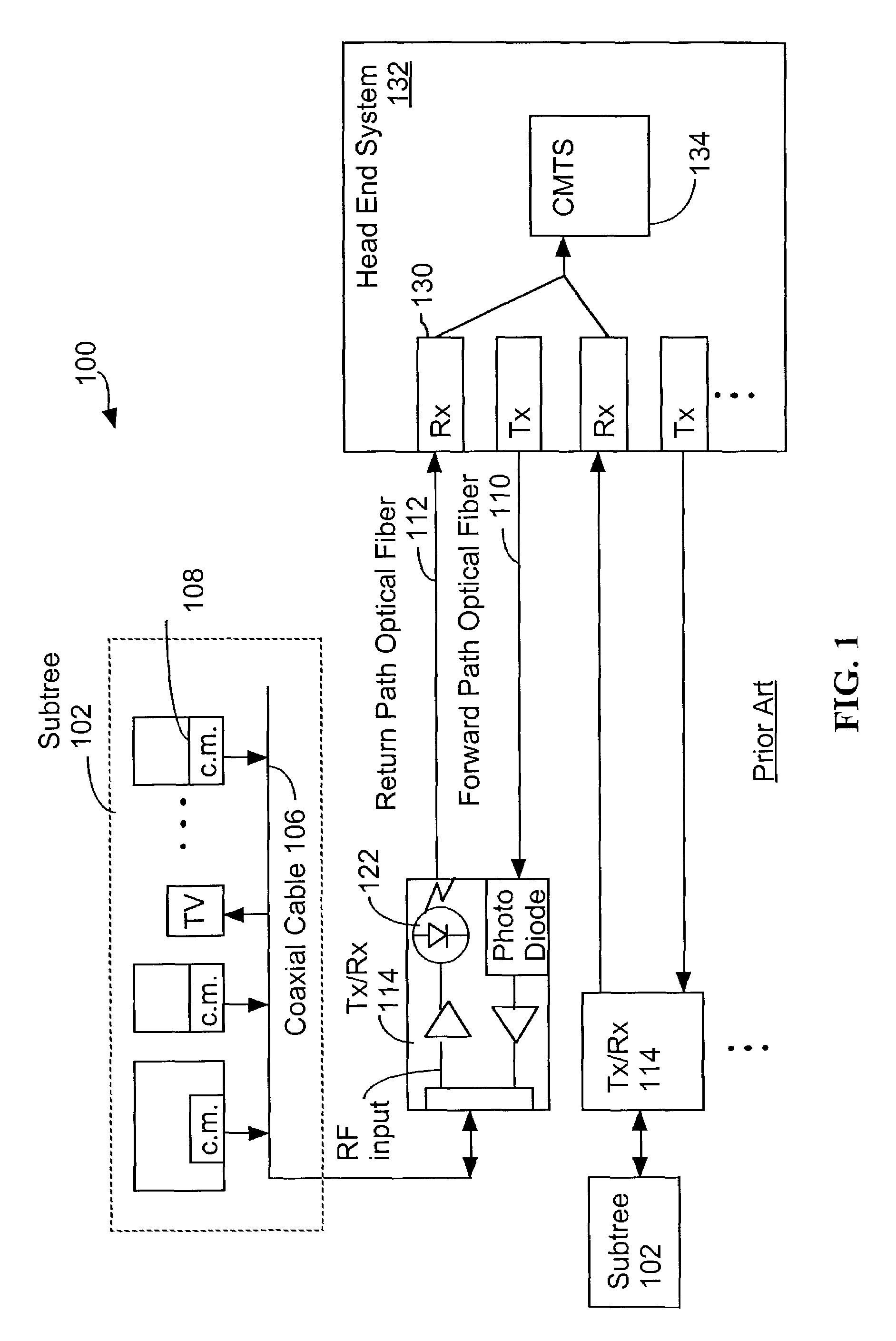
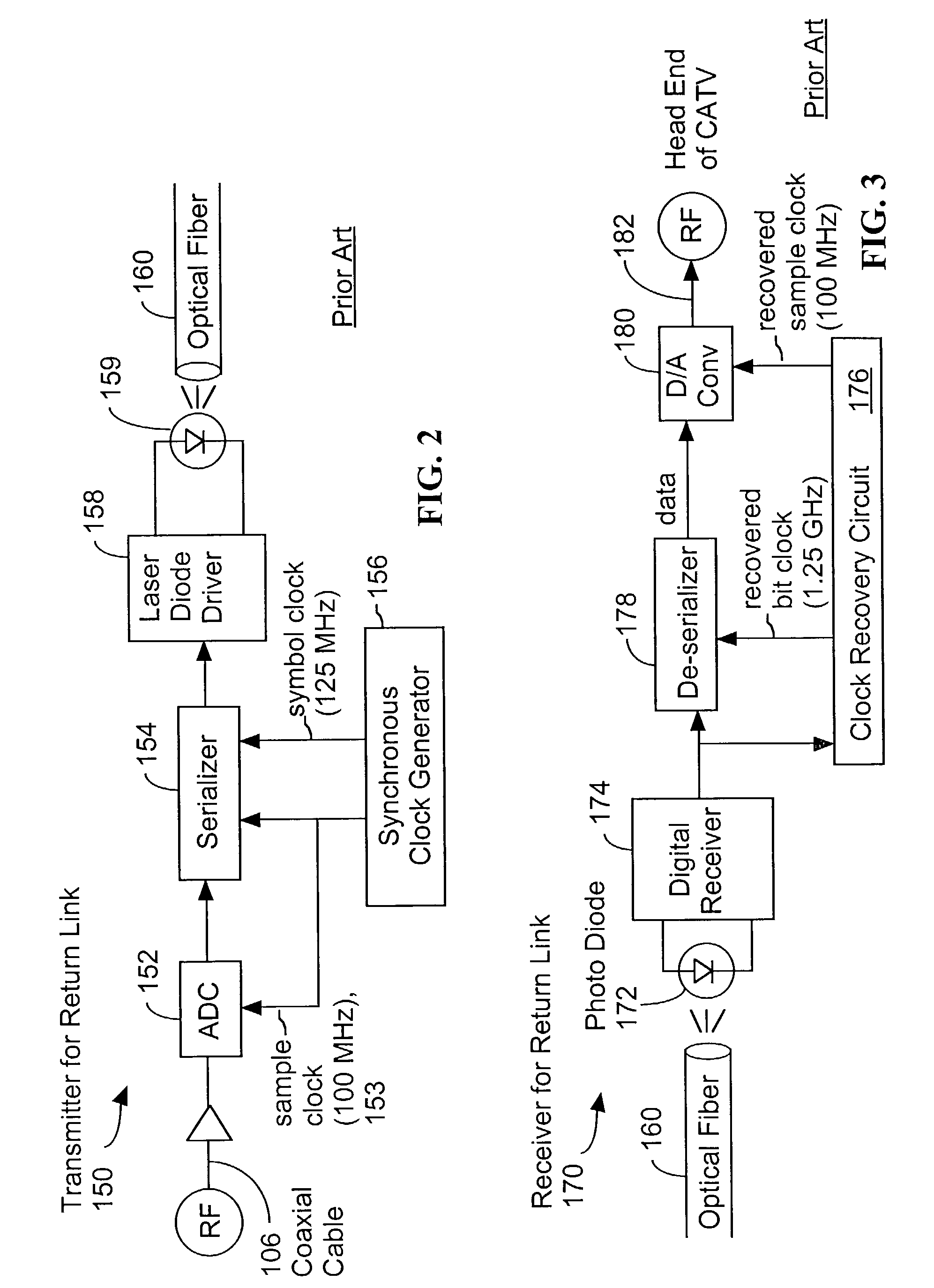
System and method for transmitting data on return path of a cable television system
InactiveUS7257328B2Easy to useOptical transmission adaptationsTwo-way working systemsDigital dataData stream
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
At-speed ATPG testing and apparatus for SoC designs having multiple clock domain using a VLCT test platform
ActiveUS7134061B2Increase savingsThe testing process is simpleElectronic circuit testingControl signalClock rate
A scan test circuitry design imbedded on an SoC having the scan architecture of a VLCT platform is disclosed herein. This BIST circuitry design that is not limited in the number of scan test ports supported includes at least one scan chain group having a corresponding clock domain that couples to receive test stimulus data. Each scan chain group has a corresponding test mode signal to shift the test stimulus data at a shift clock rate derived from its corresponding clock domain. A controlling demultiplexer connects to each multiplexer unit within each scan chain group to provide control signals for shifting in the test stimulus. A clock control mechanism provides a control signal for each scan chain to shift test stimulus and capture resultant data. Furthermore, when a simultaneous test mode signal is enabled, the clock control mechanism couples to each scan chain to enable simultaneous capture of each scan chain group.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Adaptive memory module
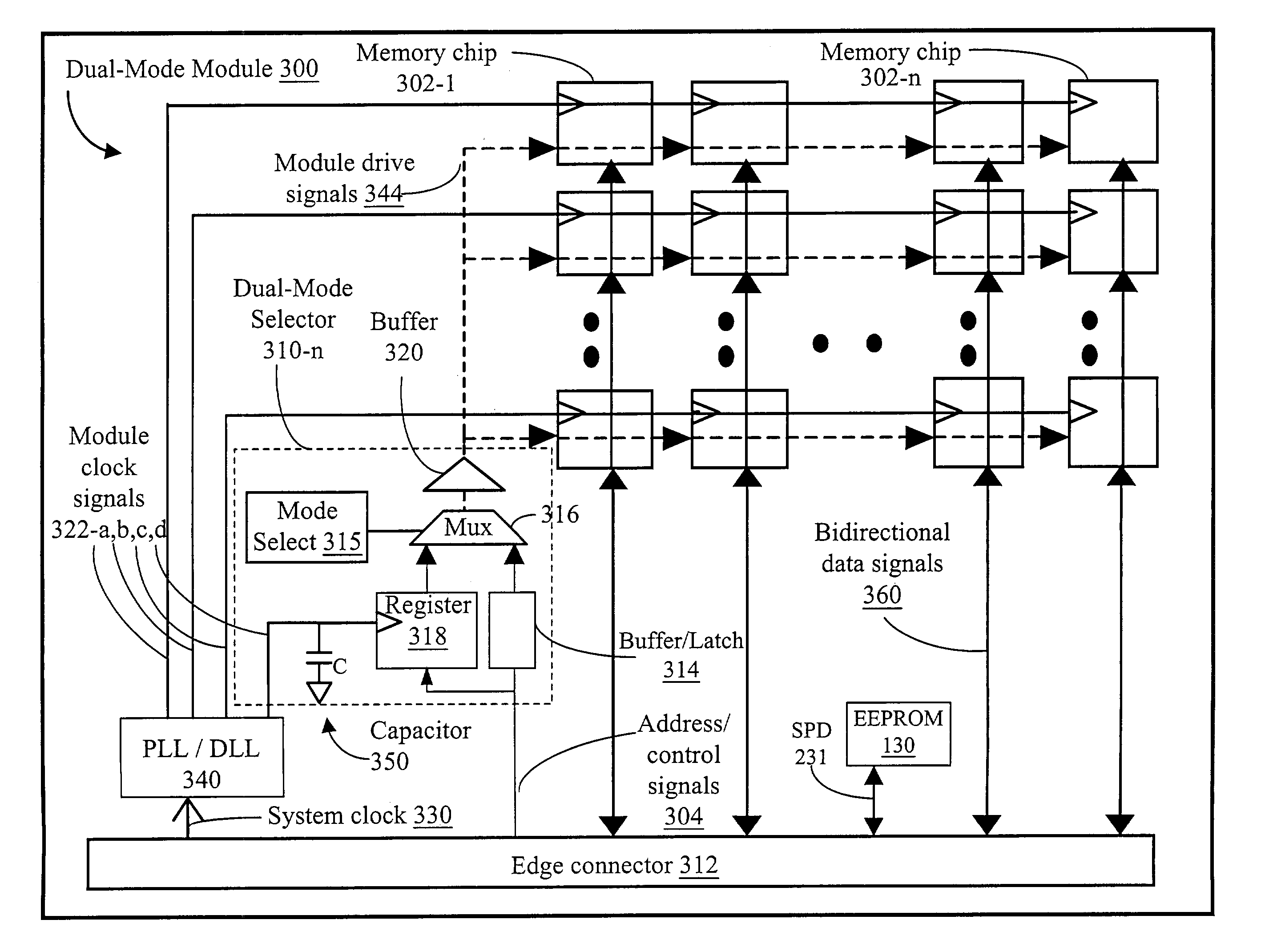
ActiveUS7089412B2Minimize skewLoad minimizationDigital computer detailsGenerating/distributing signalsControl signalMemory bus
A memory module contains a plurality of memory devices and receives control signals over a memory bus for accessing the memory devices. An adaptive buffering mechanism includes unregistered logic to electrically isolate the received control signals from one or more control drive signals. Register logic substantially synchronizes the control drive signals to a system clock to produce clocked control drive signals. A mode selection mechanism selectively outputs either the control drive signals or the clocked control drive signals to access the memory devices in accordance with a mode selection signal.
Owner:WINTEC IND INC
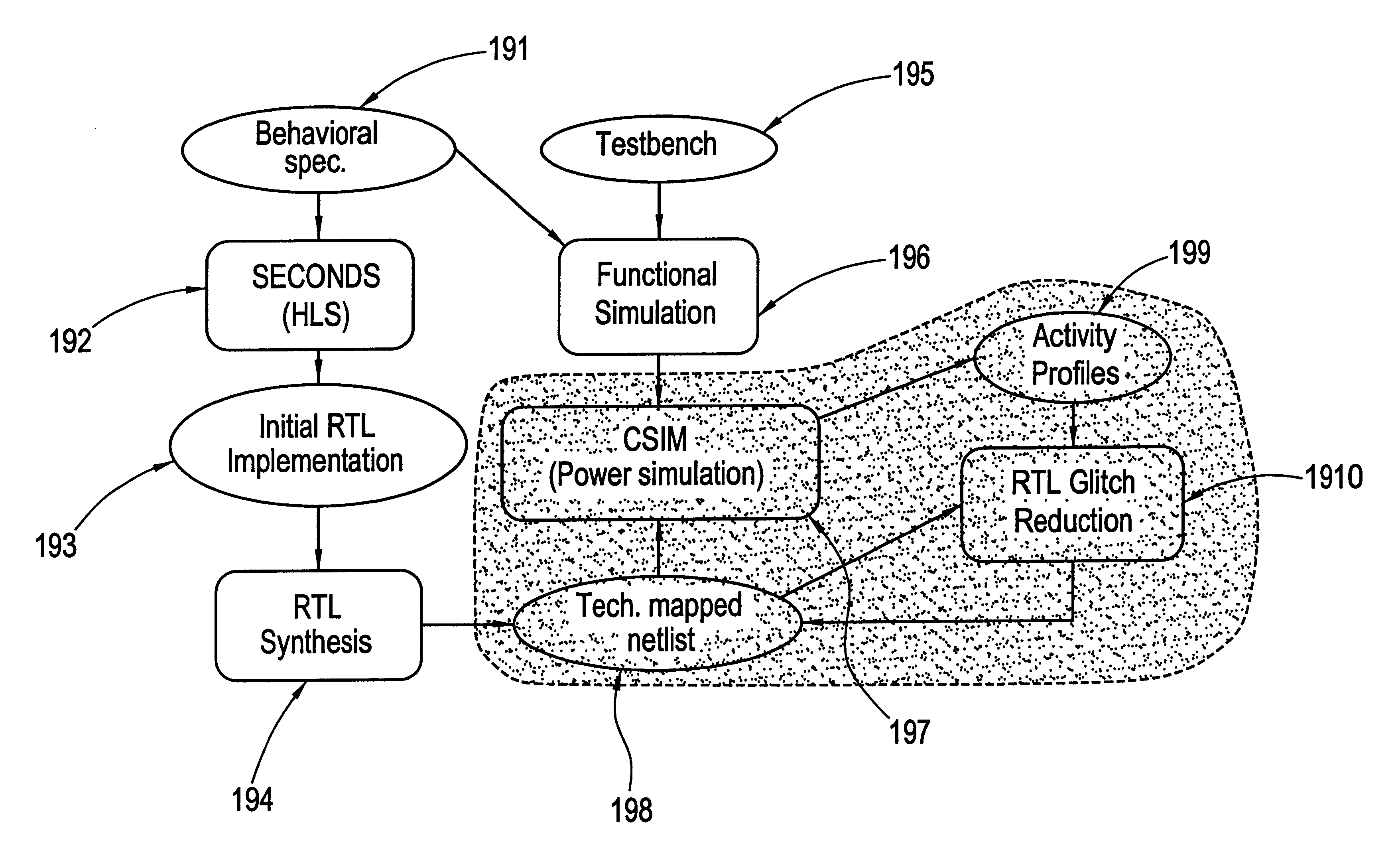
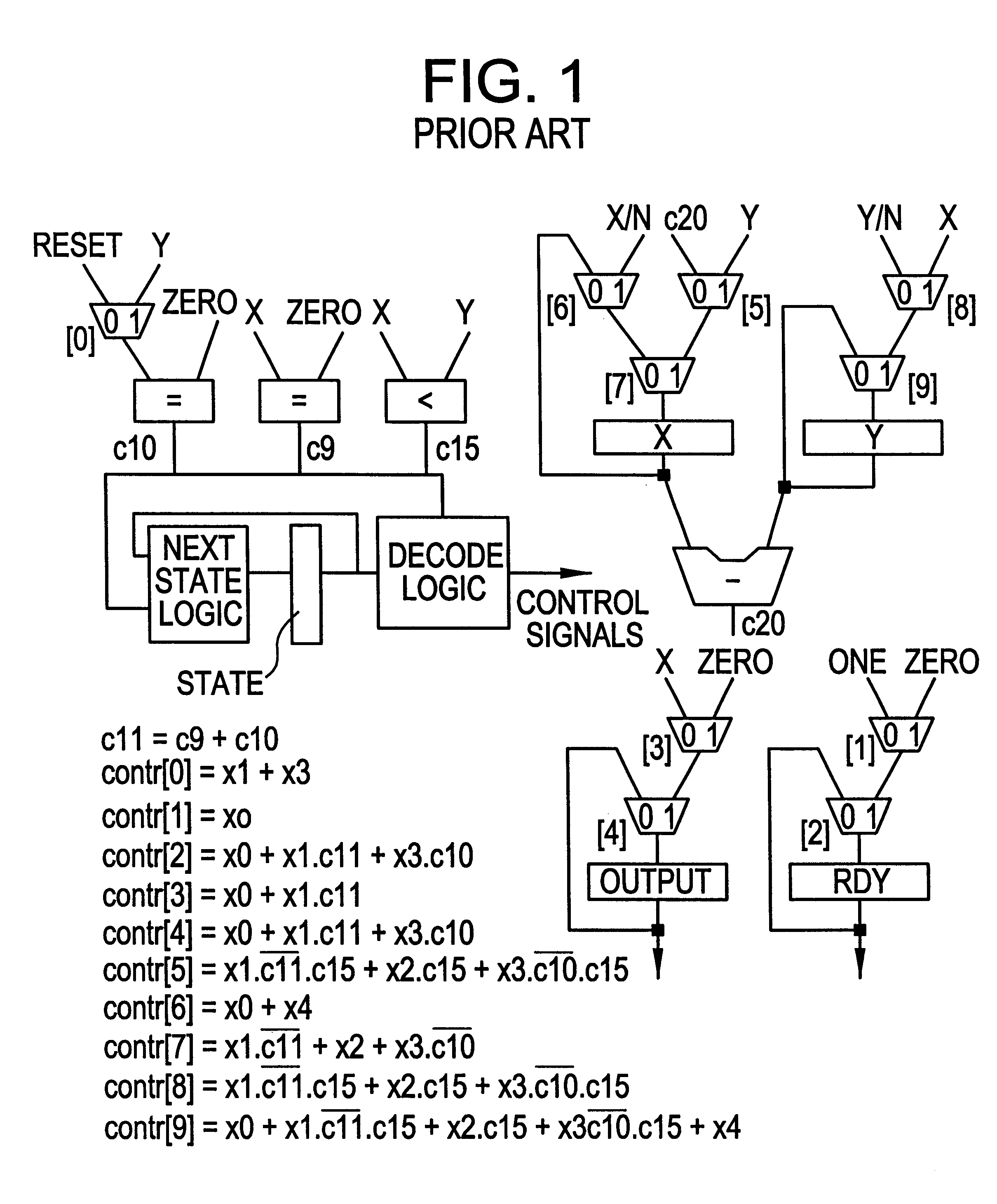
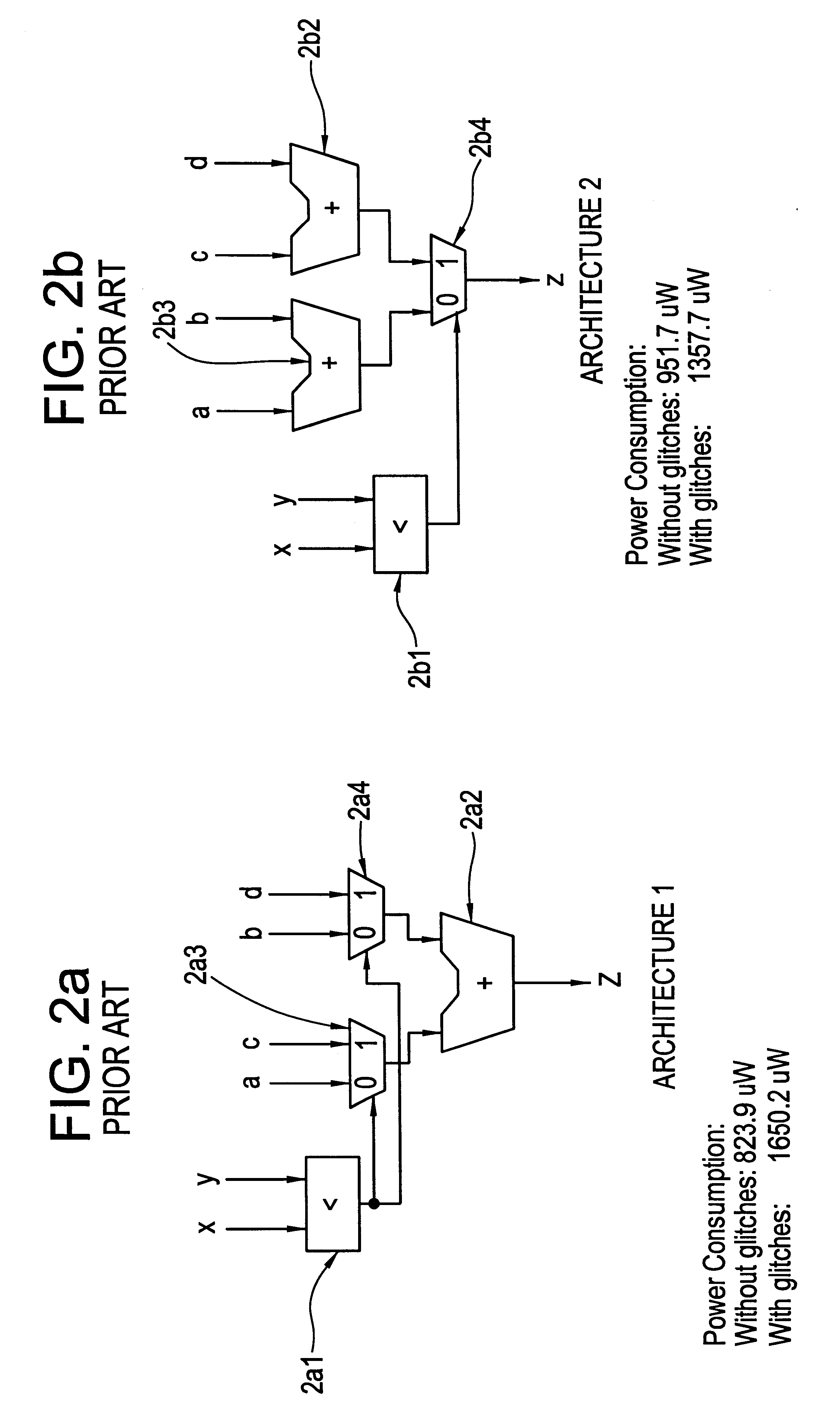
Register transfer level power optimization with emphasis on glitch analysis and reduction
InactiveUS6324679B1Reduce power consumptionLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital data processing detailsDatapath circuitsPathPing
A method and apparatus for design-for-low-power of register transfer level (RTL) controller / data path circuits that implement control-flow intensive specifications. The method of the invention focuses on multiplexer networks and registers which dominate the total circuit power consumption and reduces generation and propagation of glitches in both the control and data path parts of the circuit. Further the method reduces glitching power consumption by minimizing propagation of glitches in the RTL circuit through restructuring multiplexer networks (to enhance data correlations and eliminate glitchy control signals), clocking control signals, and inserting selective rising / falling delays, in order to kill the propagation of glitches from control as well as data signals. To reduce power consumption in registers, the clock inputs to registers are gated with conditions derived by an analysis of the RTL circuit, ensuring that glitches are not introduced on the clock signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
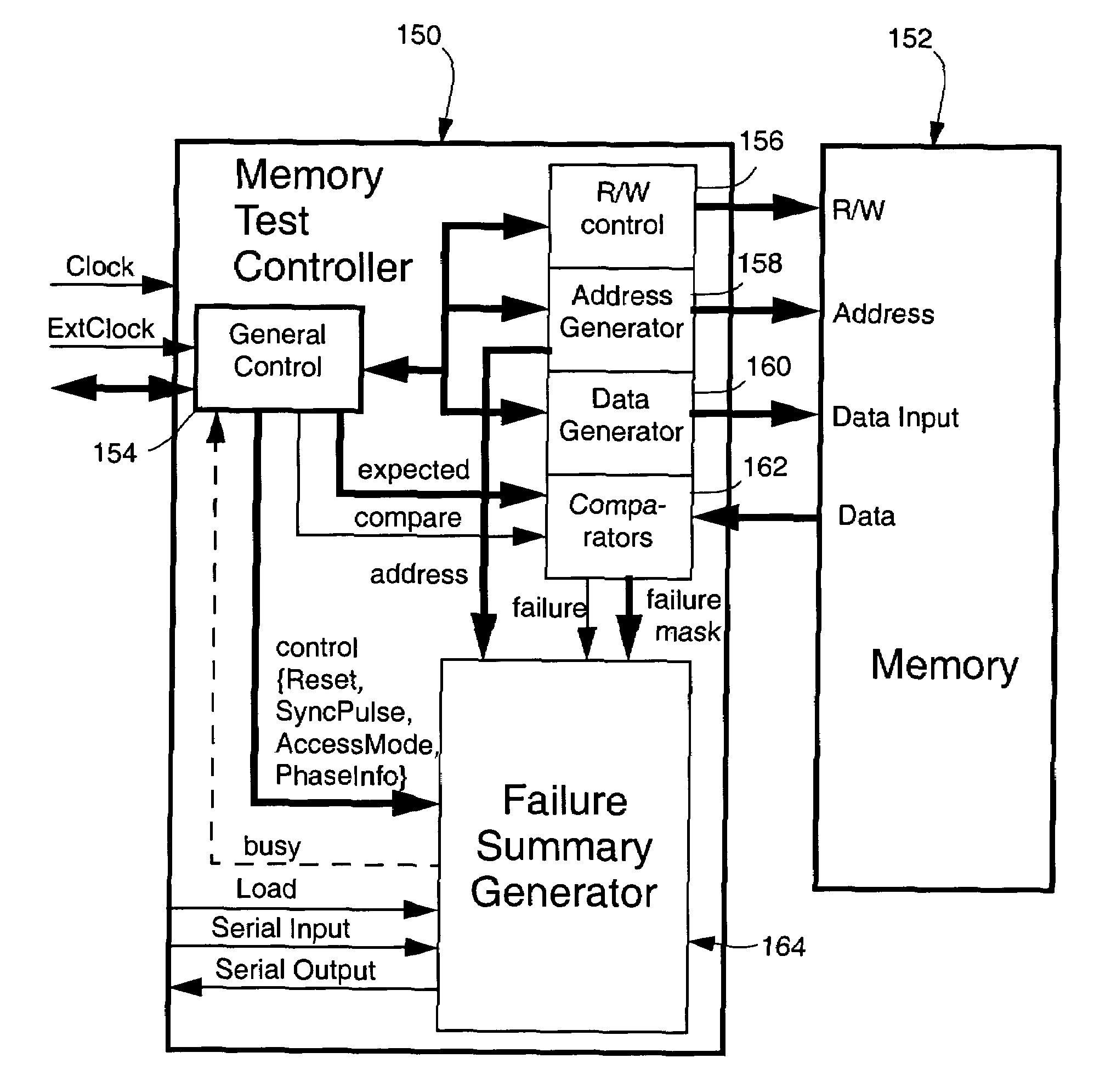
Method and circuit for collecting memory failure information
A method and circuit for collecting memory failure information on-chip and unloading the information in real time while performing a test of memory embedded in a circuit comprises, for each column or row of a memory under test, testing each memory location of the column or row according to a memory test algorithm under control of a first clock, selectively generating a failure summary on-circuit while testing each column or row of the memory; and transferring the failure summary from the circuit under control of a second clock within the time required to test the next column or row, if any, of the memory under test.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
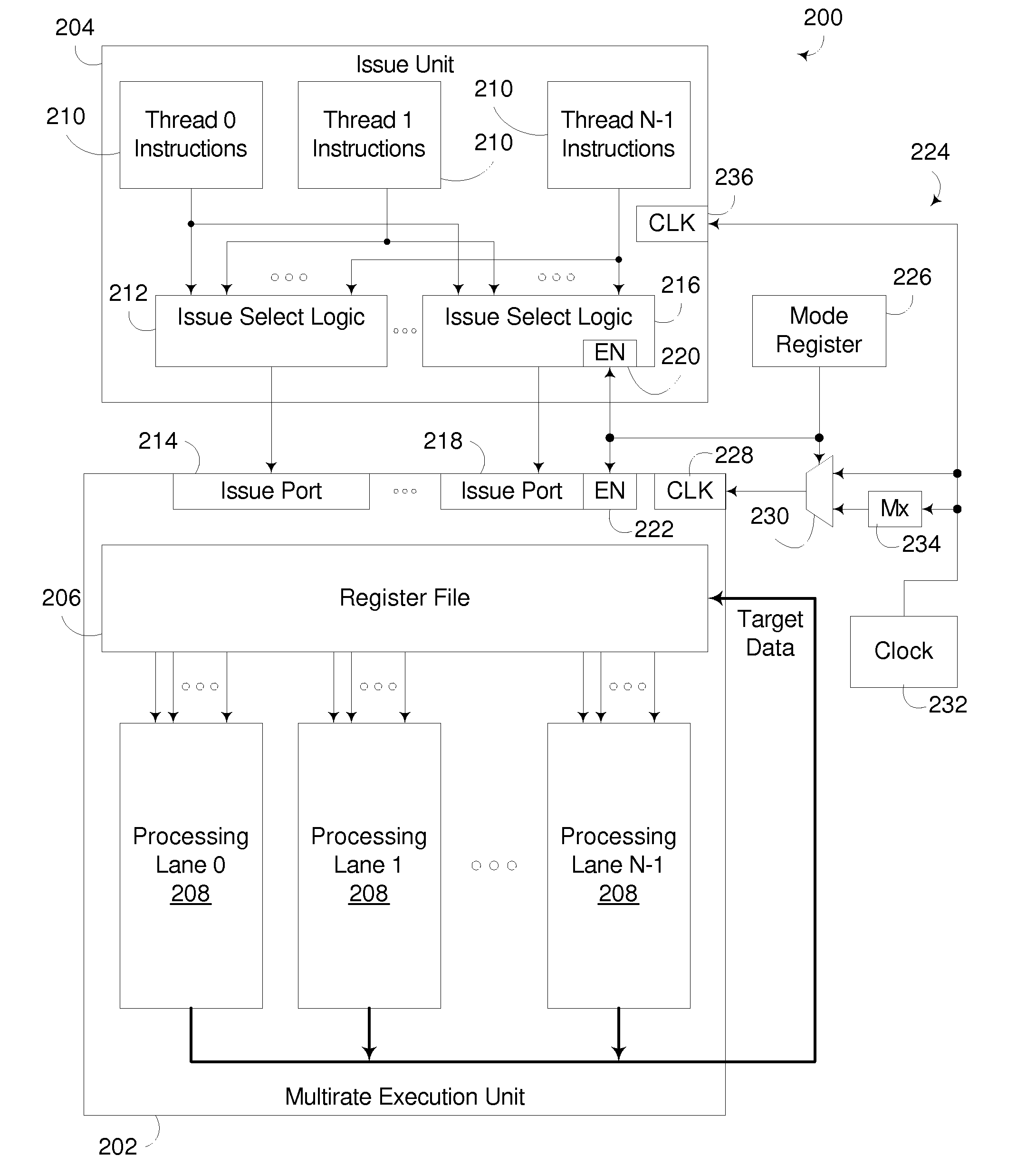
Processing Unit Incorporating Multirate Execution Unit
InactiveUS20090182987A1Reduce power consumptionReduce switchingEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsClock rateExecution unit
A multirate execution unit is capable of being operated in a plurality of modes, with the execution unit being capable of clocked at multiple different rates relative to a multithreaded issue unit such that, in applications where maximum performance is desired, the execution unit can be clocked at a rate that is faster than the clock rate for the multithreaded issue unit, and in applications where a lower power profile is desired, the execution unit can be throttled back to a slower rate to reduce the power consumption of the execution unit. When the execution unit is clocked at a faster rate than the multithreaded issue unit, the issue unit is permitted to issue more instructions per cycle than when the execution unit is throttled to the slower rate to increase overall instruction throughput.
Owner:IBM CORP
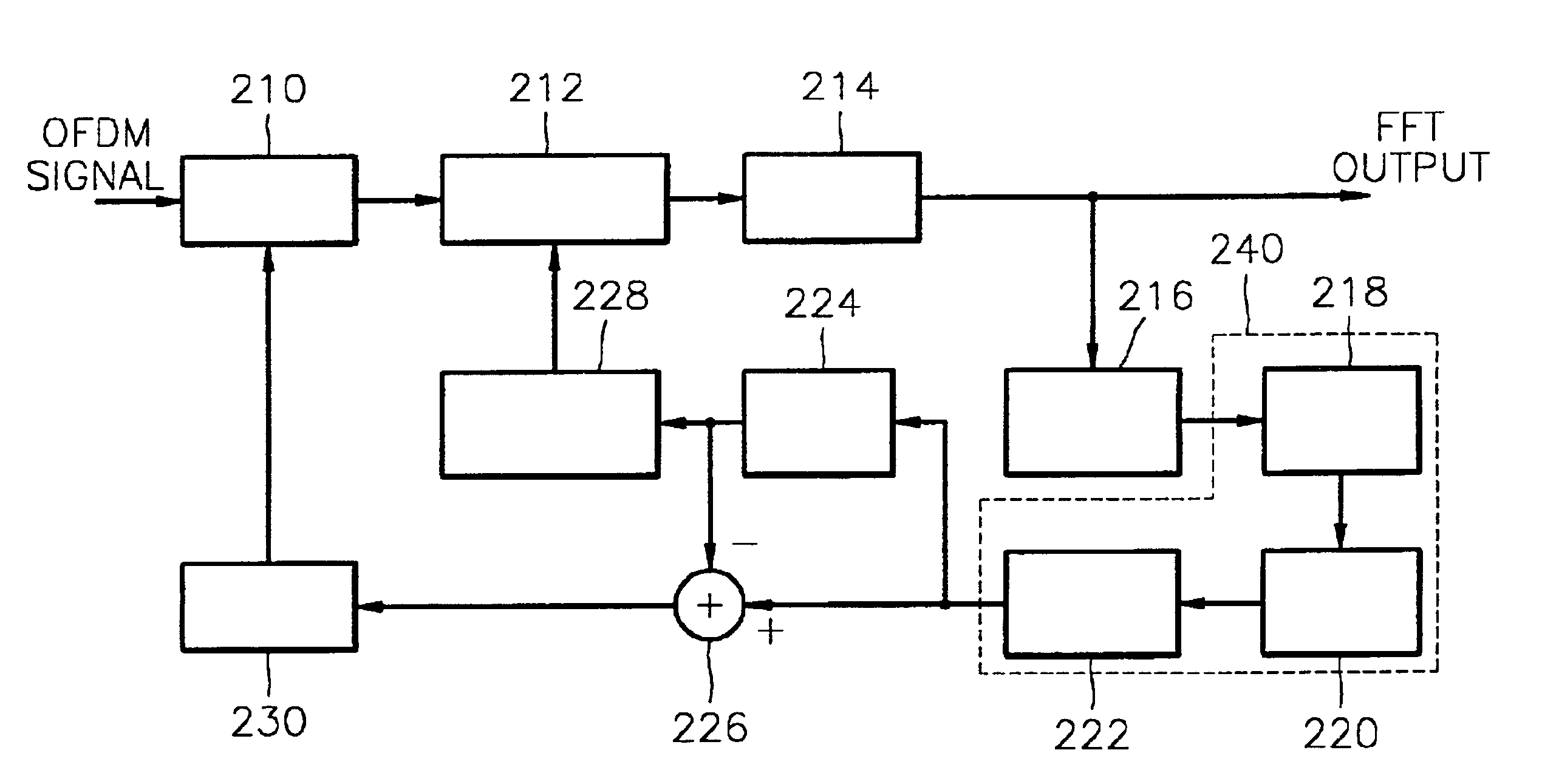
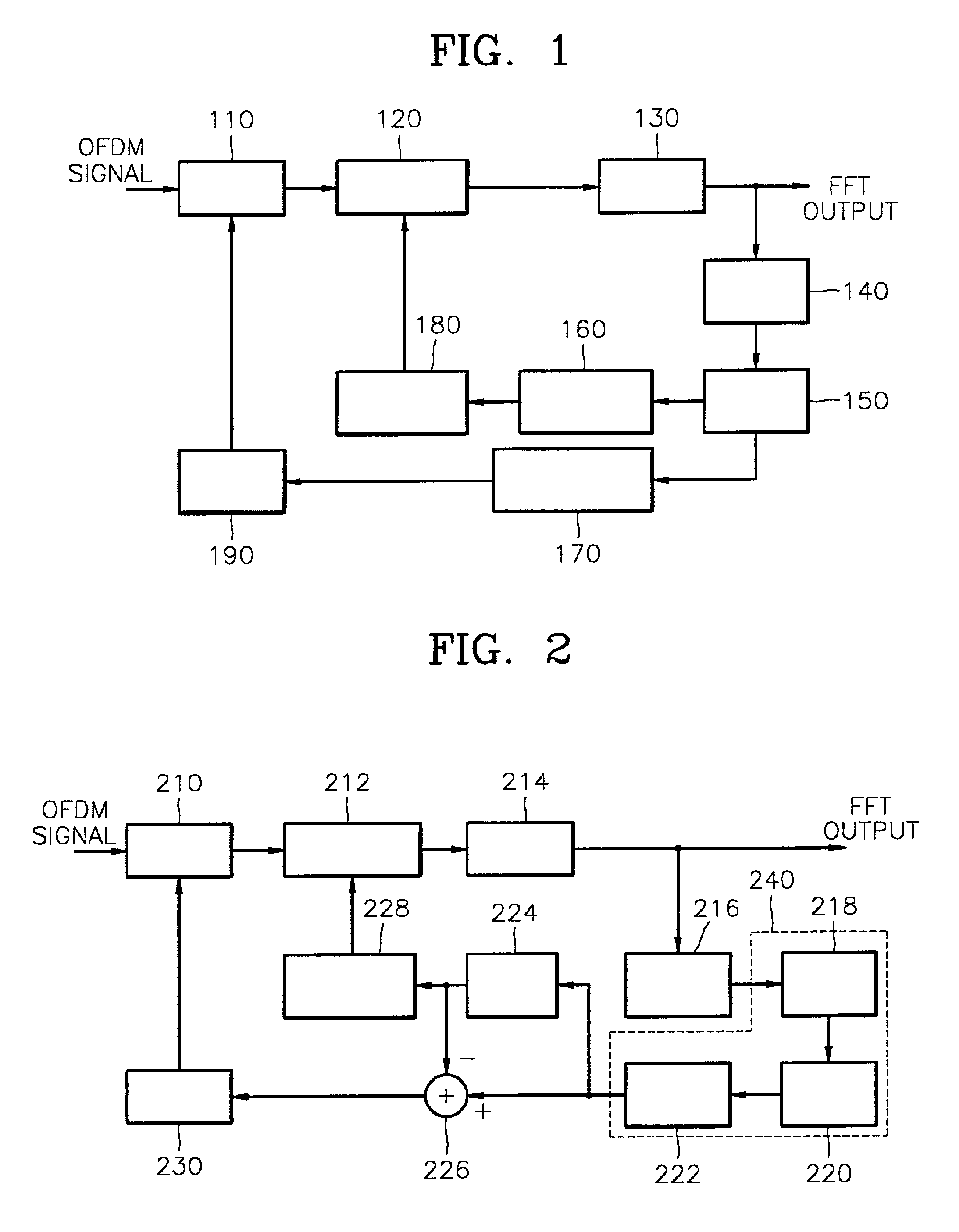
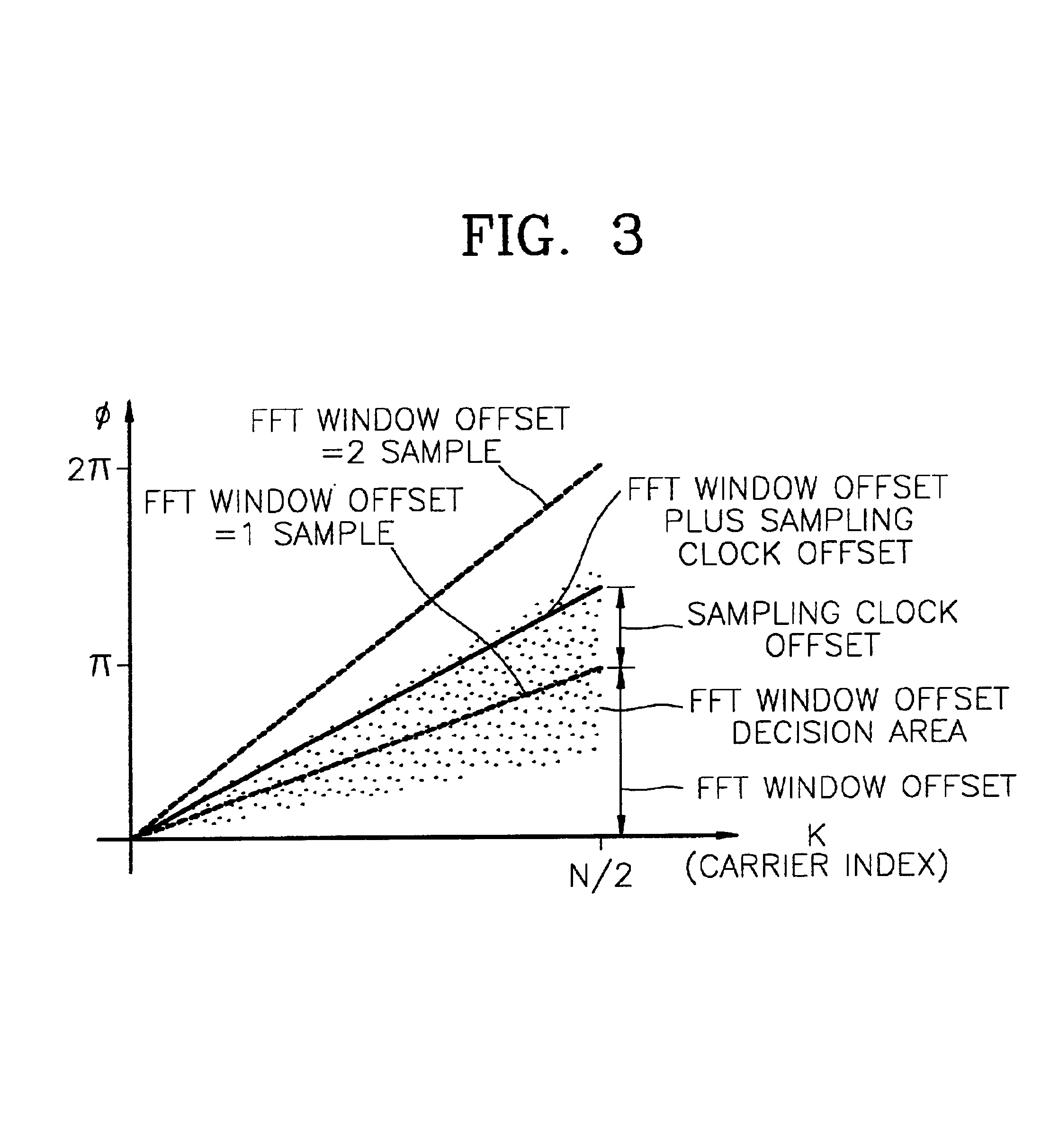
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiver where FFT Window position recovery interlocks with sampling clock adjustment and method thereof
InactiveUS6853616B1Transmission control/equlisationSecret communicationPhase differenceFourier transform on finite groups
An OFDM receiver for interlocking FFT window position recovery with sampling clock control, and a method thereof are provided. This method includes the steps of: extracting a pilot signal from fast-Fourier-transformed OFDM received signals, and detecting inter-pilot phase differences; averaging the detected phase differences for a symbol and normalizing the mean phase difference by dividing it into reference values corresponding to phase differences generated when FFT window errors of at least one sample exist; and simultaneously controlling the FFT window position offset using a value obtained by rounding off the normalized value, and the sampling clock offset using the difference between the round-off value and the normalized value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cross-chip communication mechanism in distributed node topology
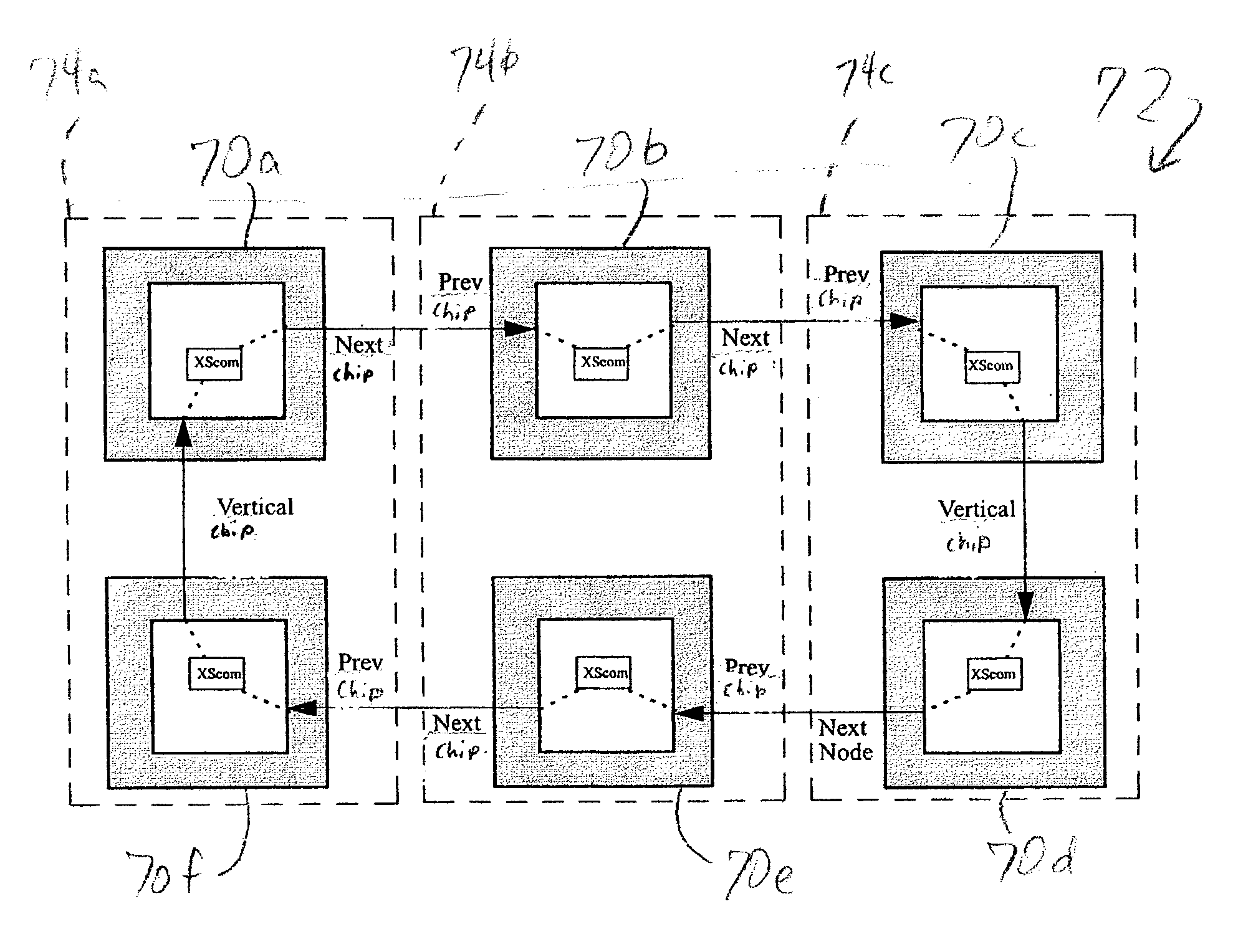
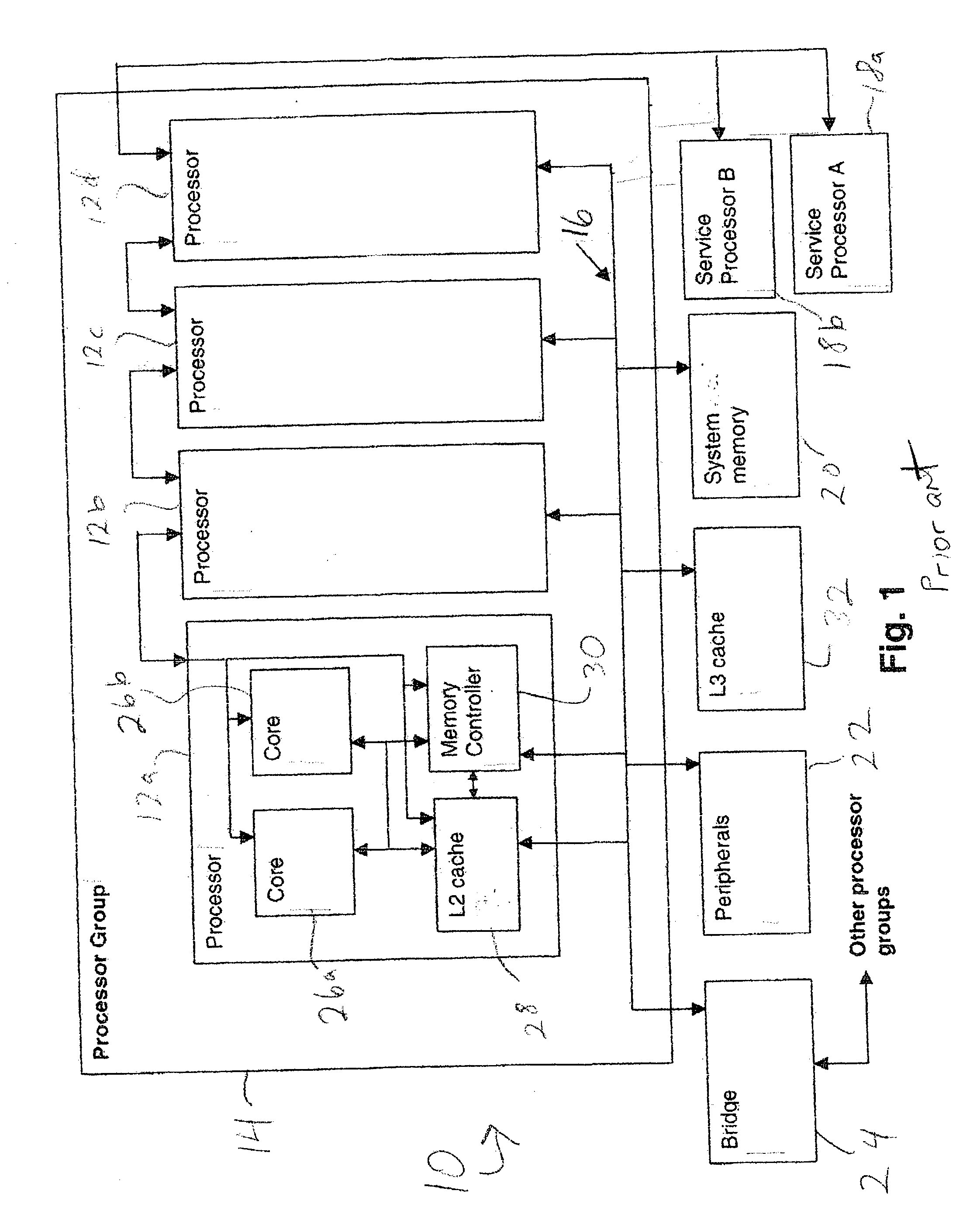
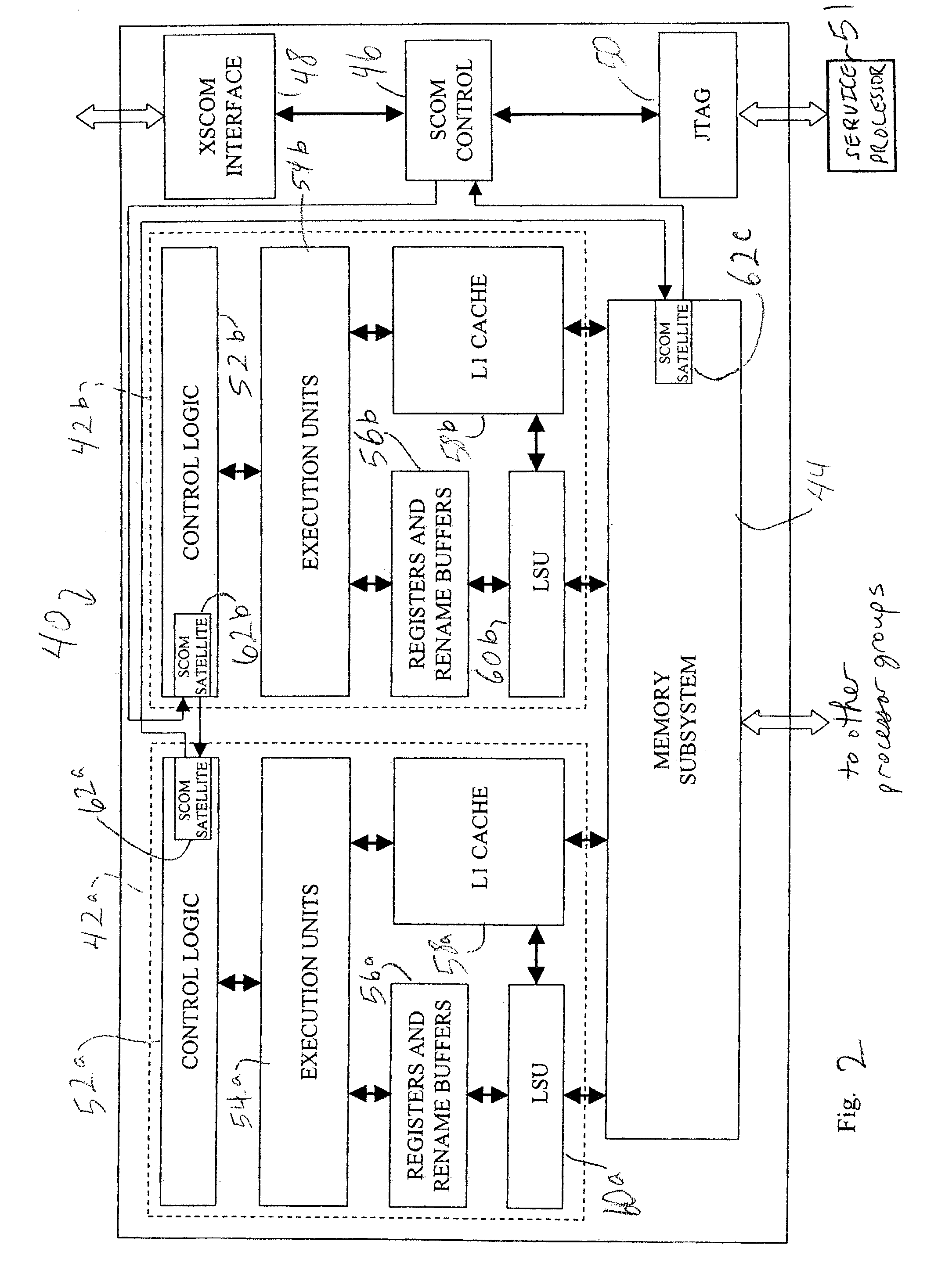
InactiveUS20040215929A1Promote disseminationSubstation/switching arrangement detailsElectric digital data processingTransmission protocolMain processing unit
A method of communicating between processing units on different integrated circuit chips in a multi-processor computer system by issuing a command from a source processing unit to a destination processing unit, receiving the command at the destination processing unit while the destination processing unit is processing program instructions, and accessing registers in clock-controlled components of the destination processing unit without interrupting processing of the program instructions by the destination processing unit. The access may be a read from status or mode registers of the destination processing unit, or write to control or mode registers. Many processing units can be interconnected in a ring topology, and the access command can be passed from the source processing unit through several other processing units before reaching the destination processing unit. Each of the processing units is assigned a respective, unique identification number (PID) in addition to one or more optional "special" tags which are not necessarily unique, and an external command (XSCOM) interface on a given chip recognizes only those commands that include the corresponding chip tag, unless the command is a broadcast. Commands may be directed to subgroups of processors by implementing masks against the PID, selected portion of the PID, or other "special" tag in a broadcast fashion. The XSCOM interface also has the ability to block any broadcast command (e.g., reset) to itself when that command was issued by its associated processing unit (a "Block Self" mode). The processing units are interconnected via a fabric bus, and the XSCOM interface preferably uses an additional communications line that follows the topology of the fabric bus or could alternately use command / data packets across the existing fabric transmission protocol. The service processor has access to this command interface through an external port (e.g. JTAG) and assembly code running on the processing unit has access to the command interface via special assembly code sequences.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com