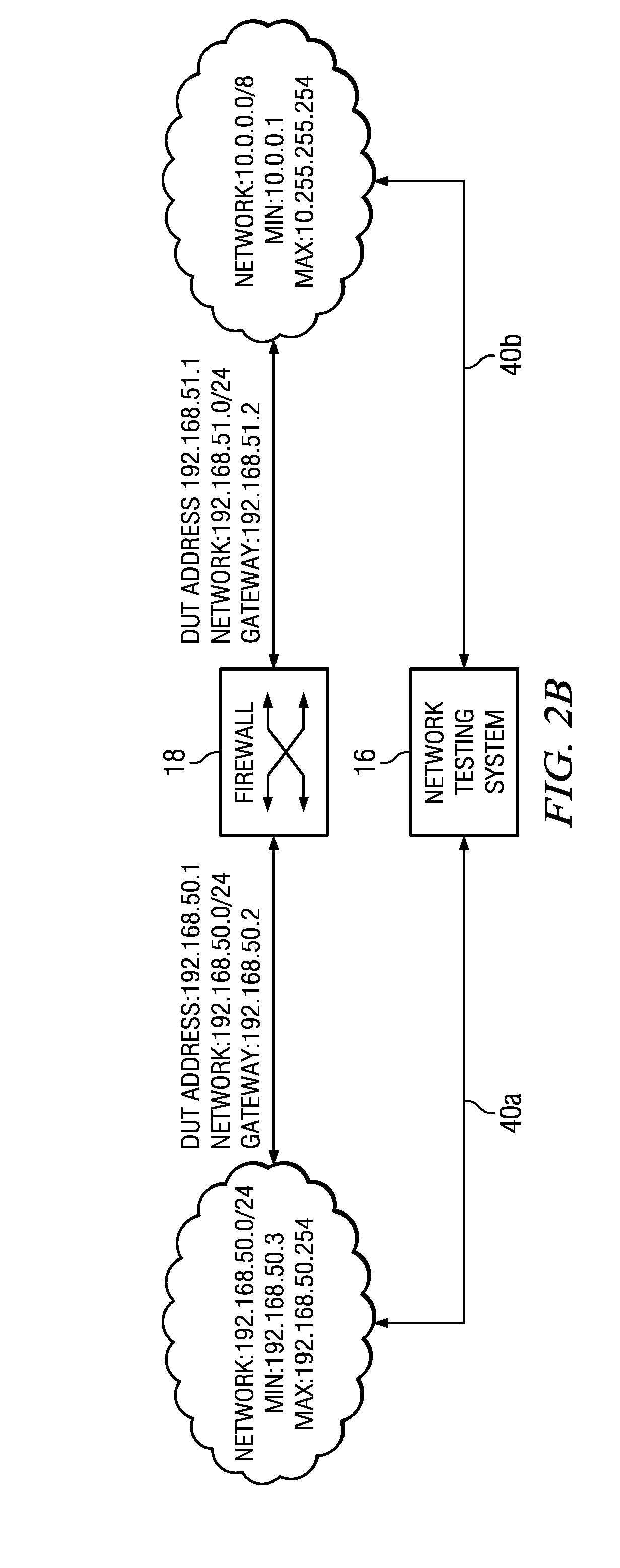
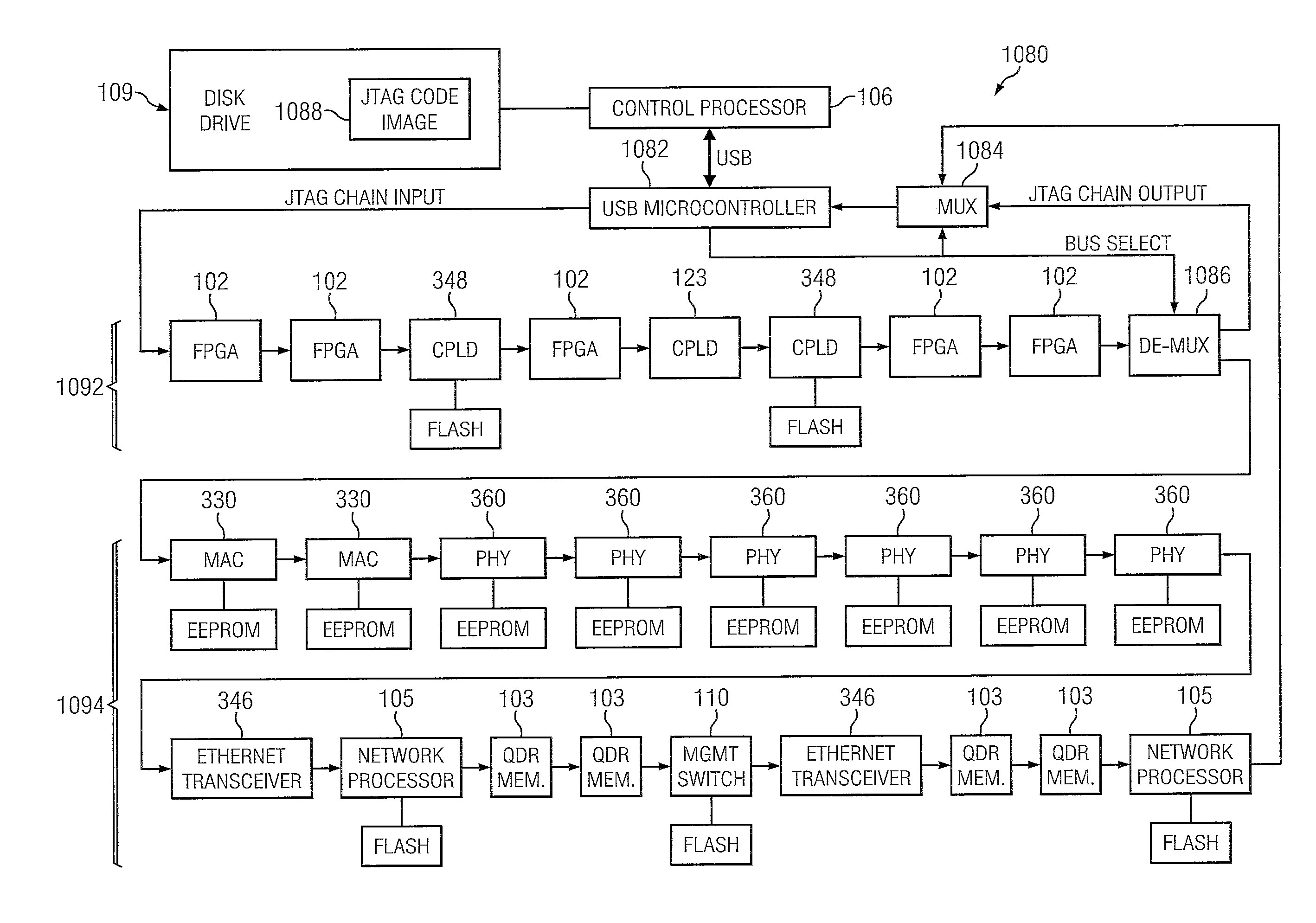
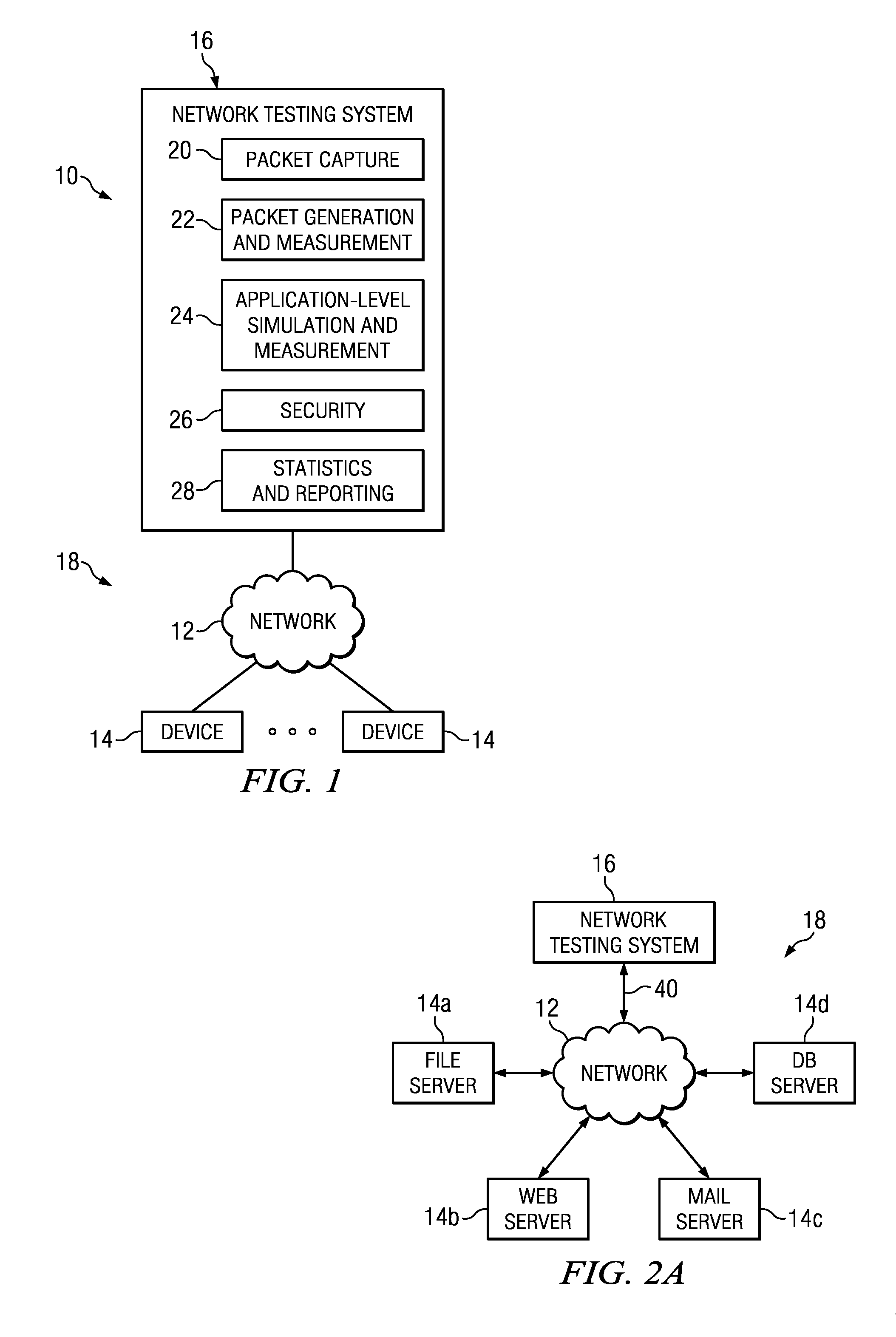
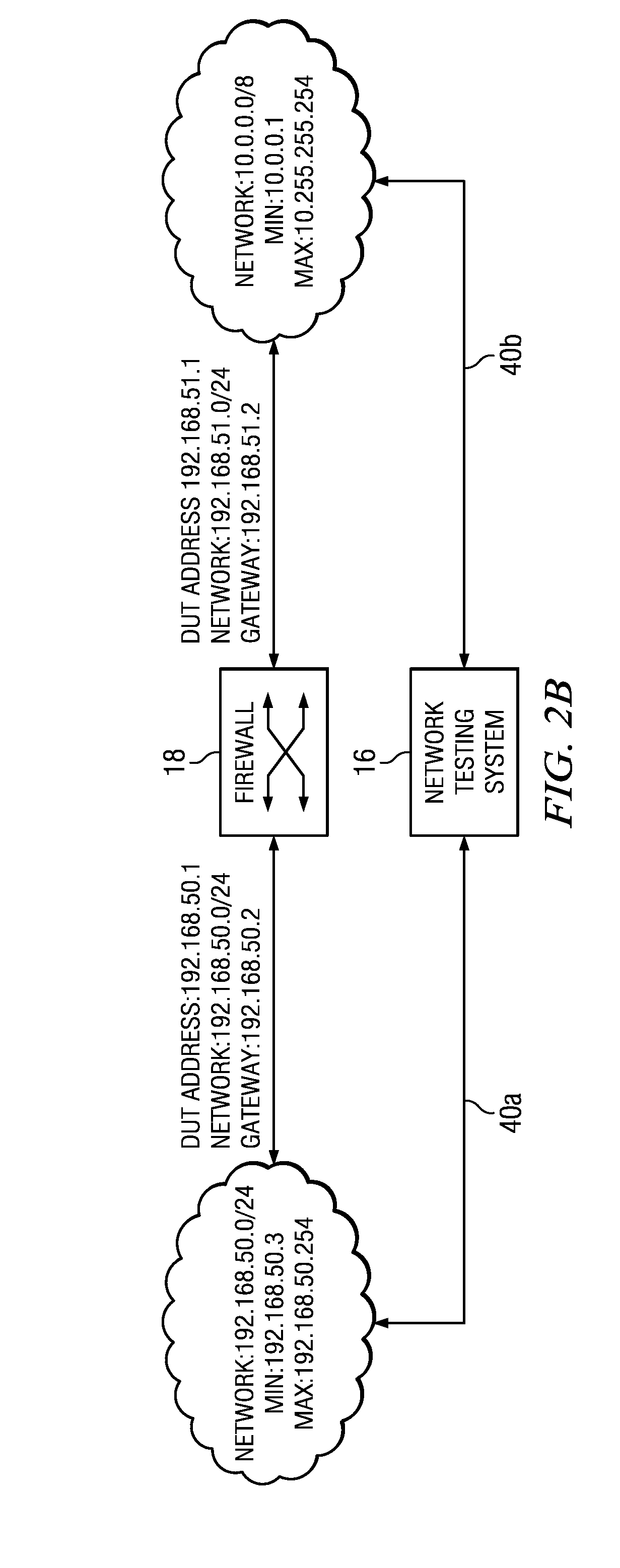
Patents
Literature
1179 results about "Joint Test Action Group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
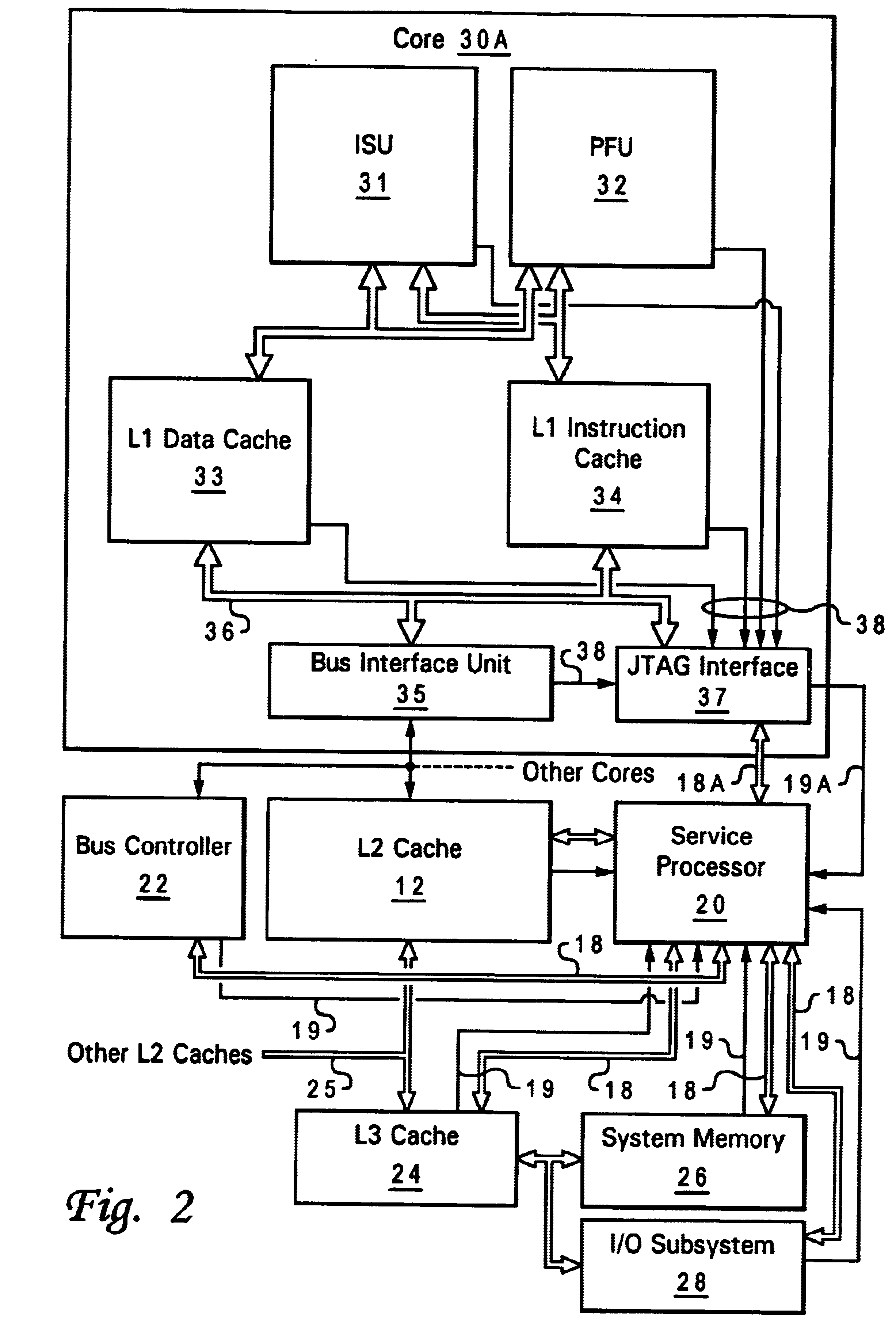
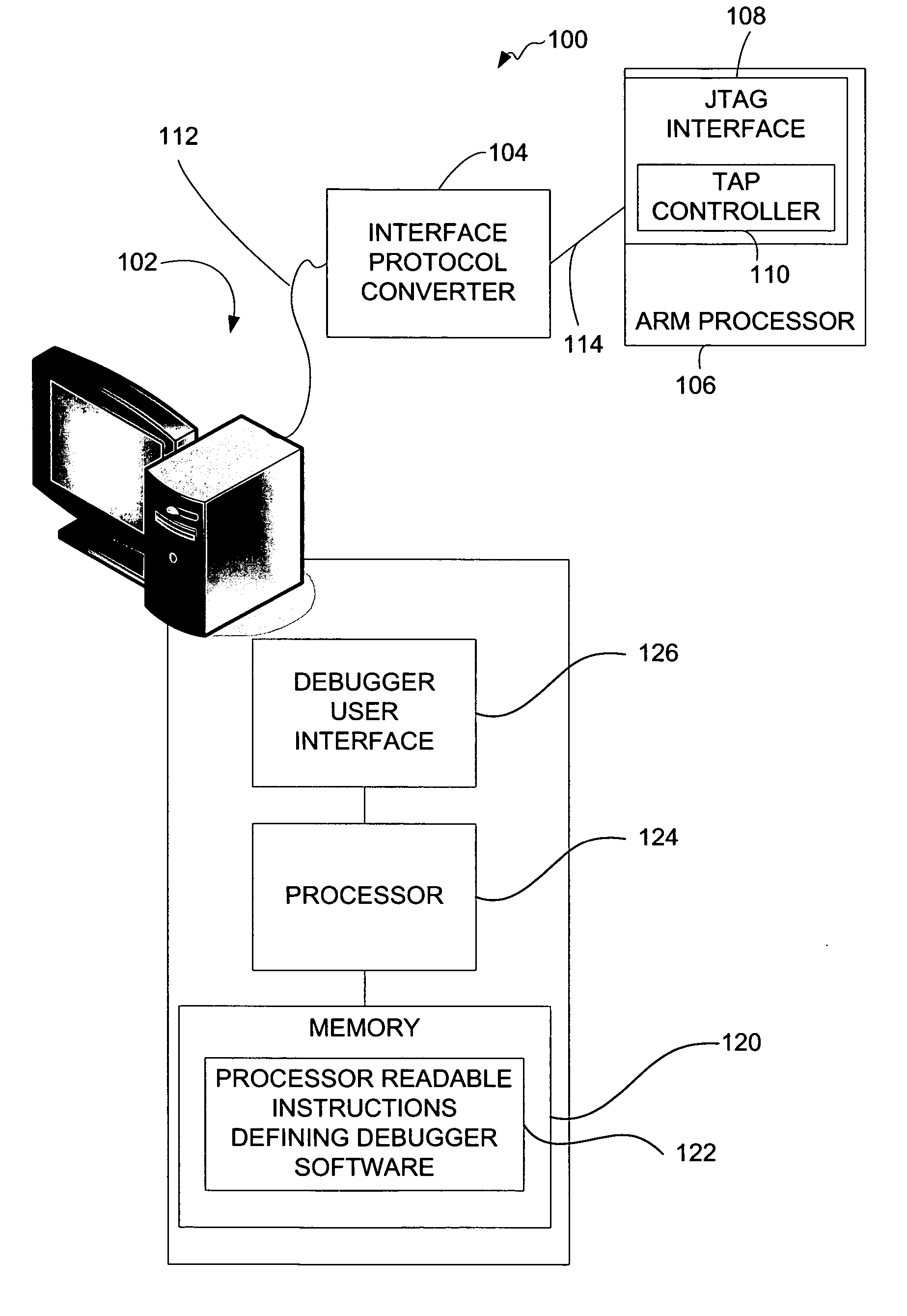
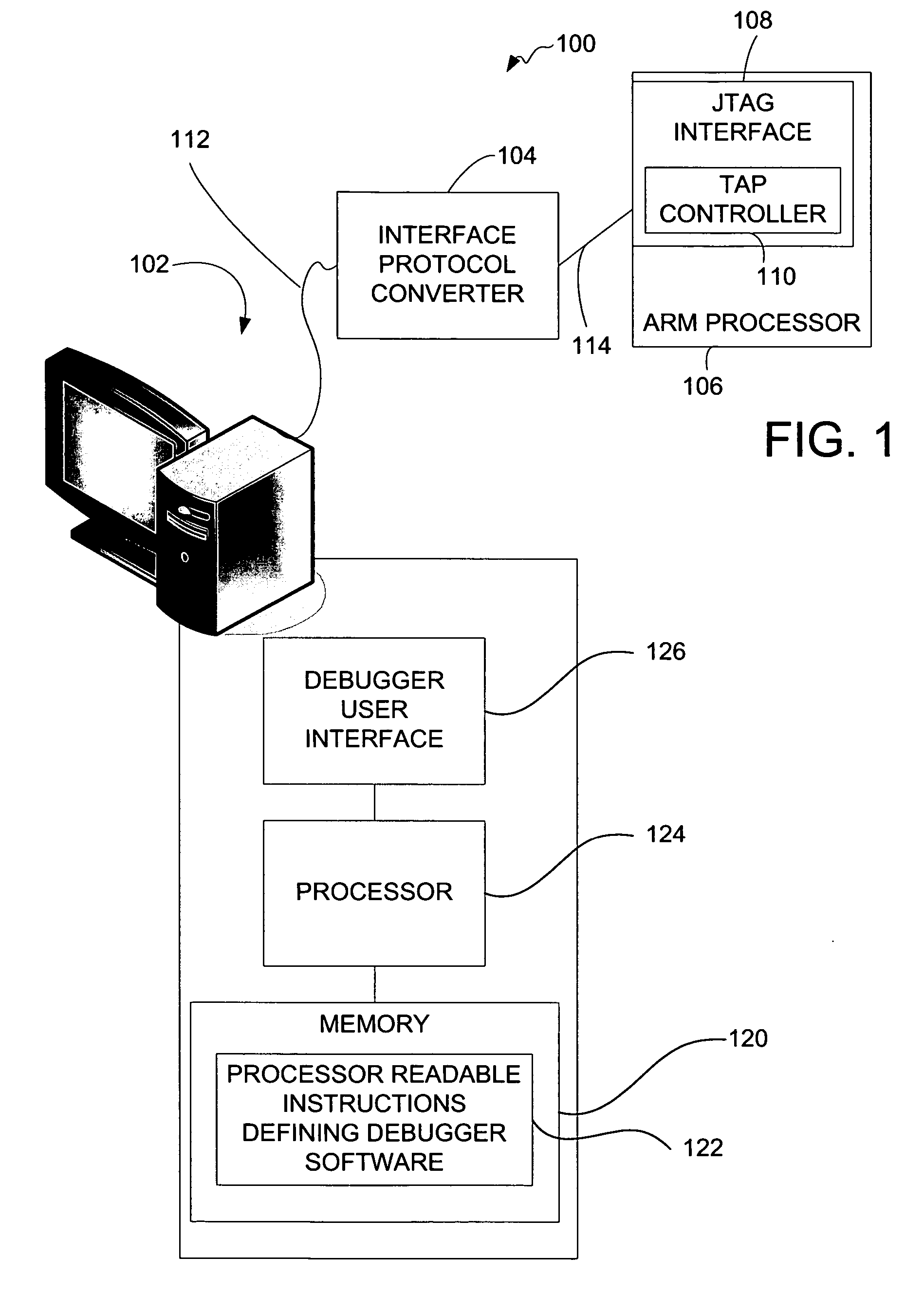
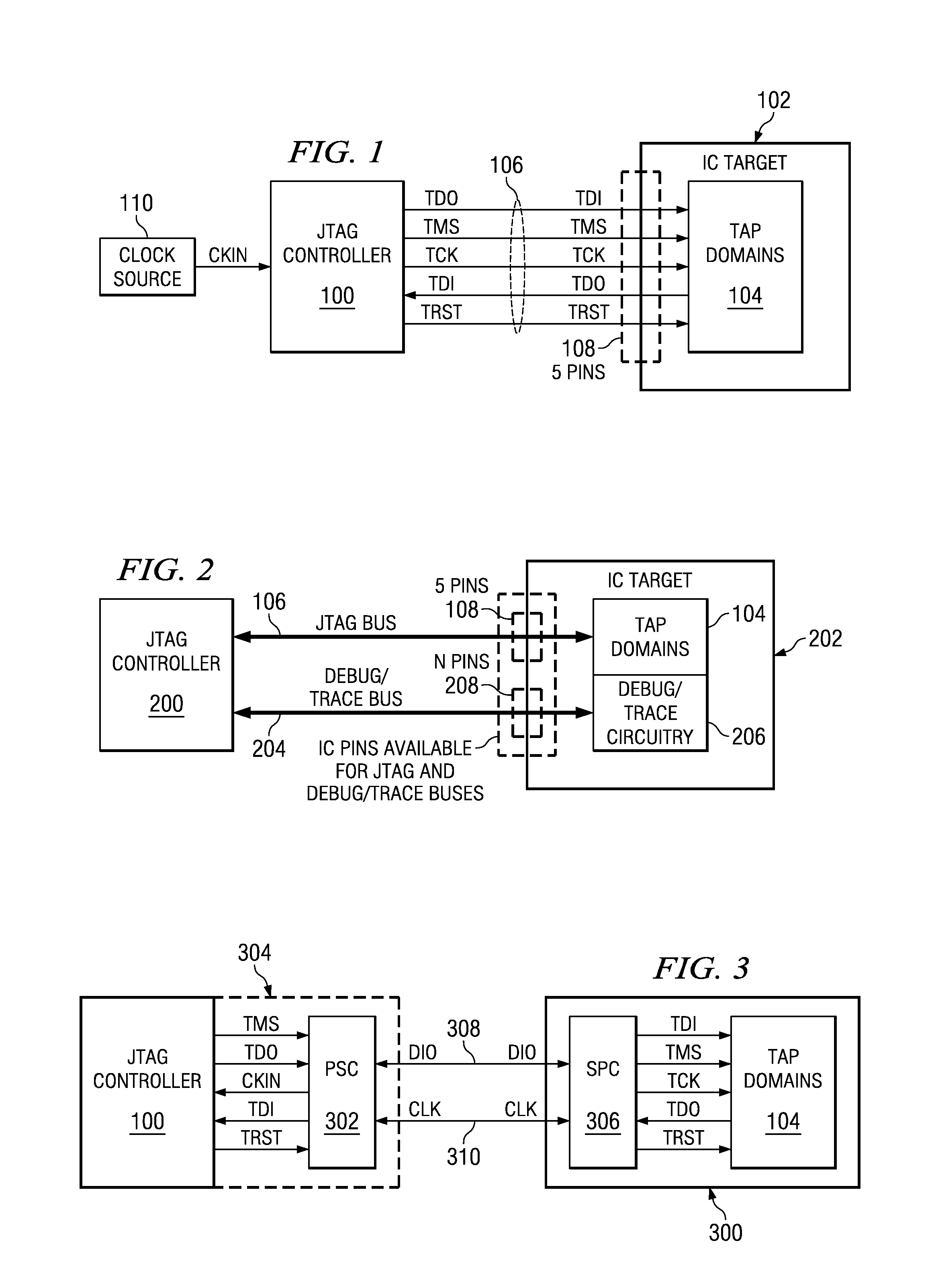
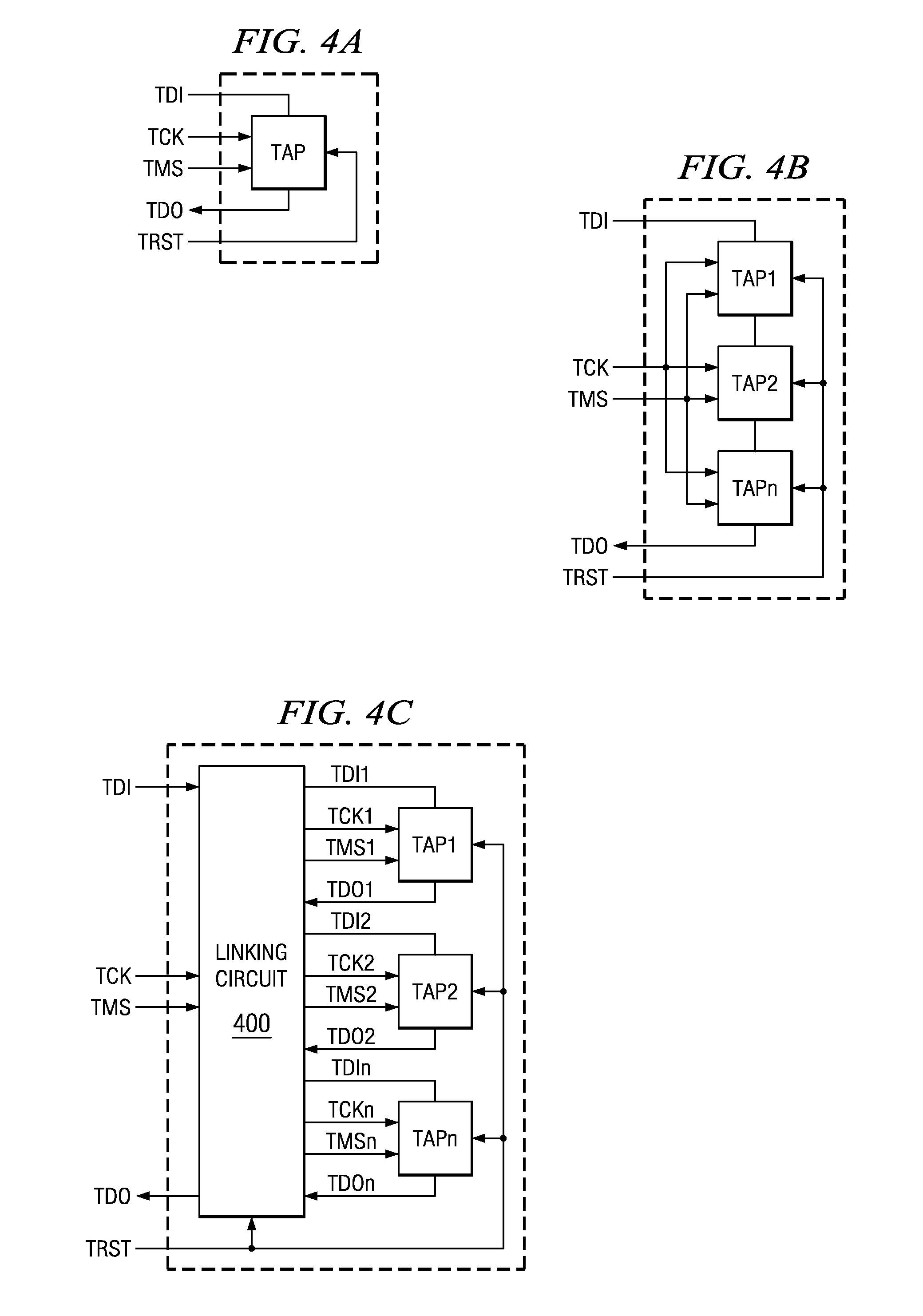
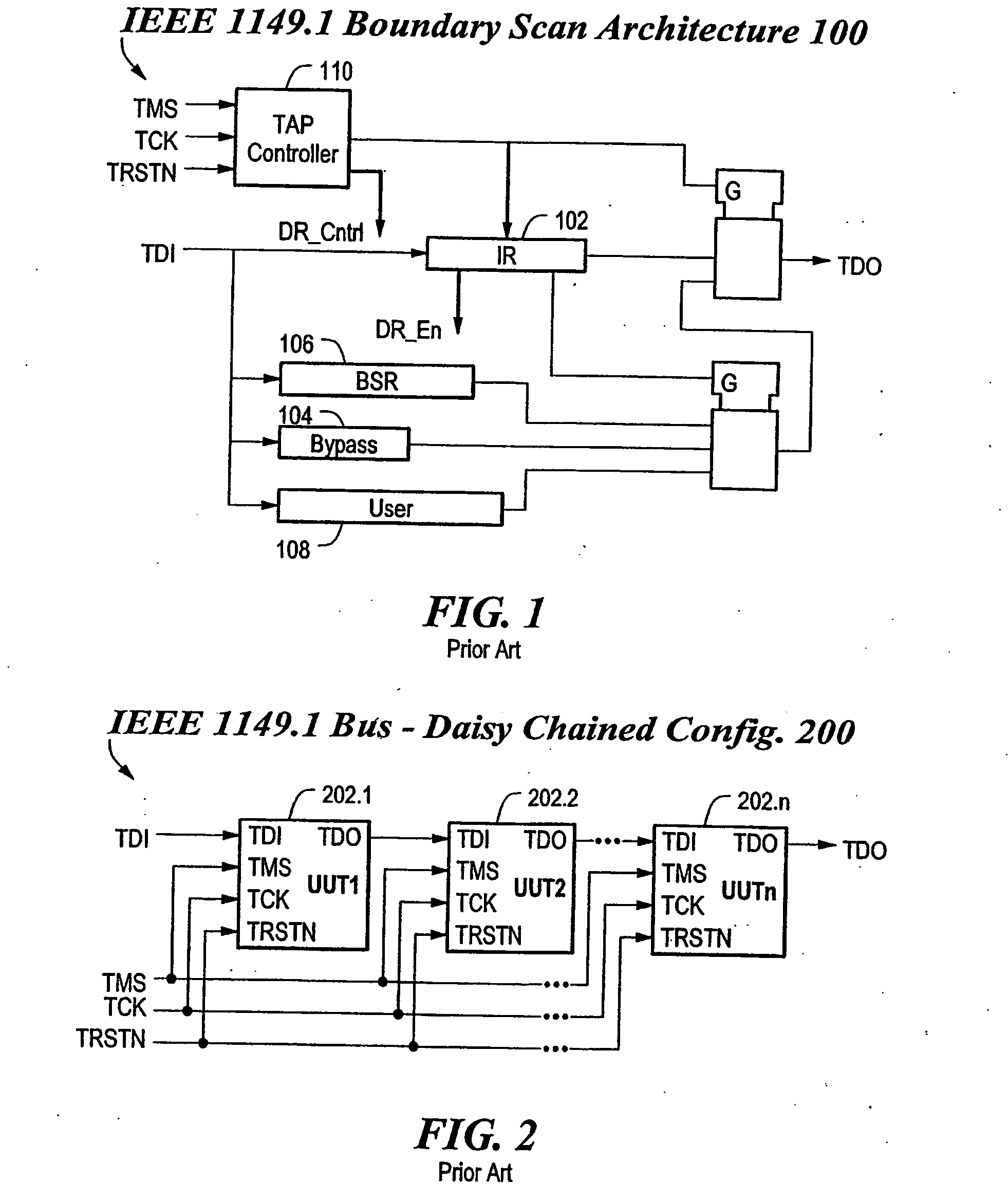
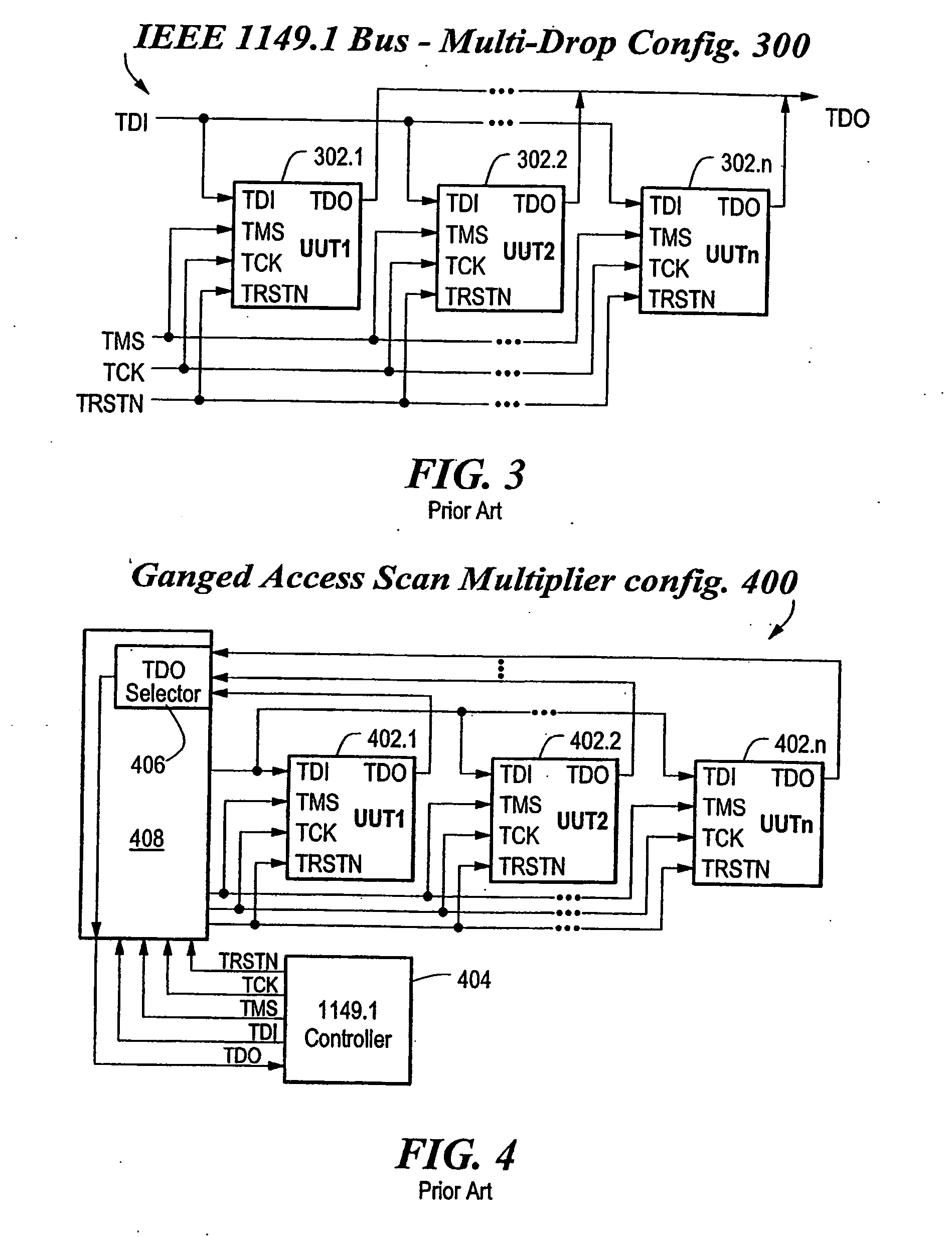
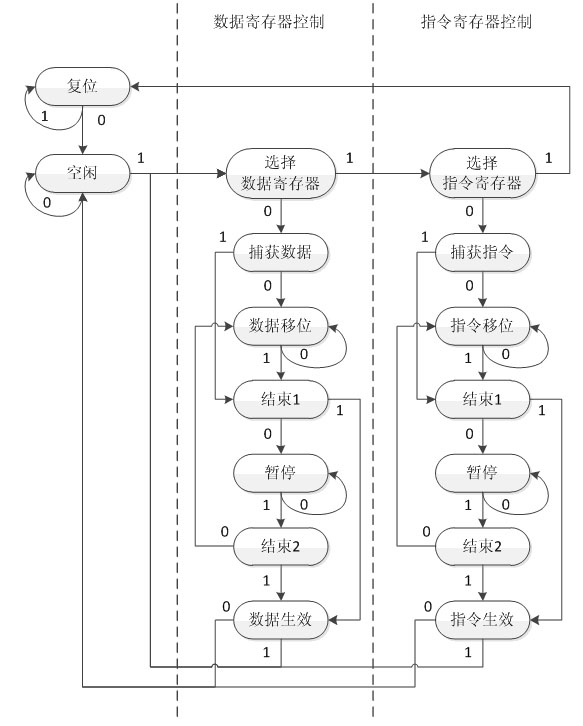
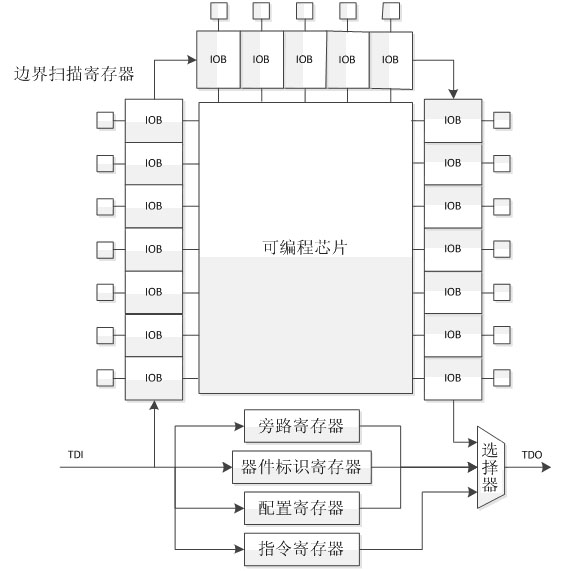
JTAG (named after the Joint Test Action Group which codified it) is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture. JTAG implements standards for on-chip instrumentation in electronic design automation (EDA) as a complementary tool to digital simulation. It specifies the use of a dedicated debug port implementing a serial communications interface for low-overhead access without requiring direct external access to the system address and data buses. The interface connects to an on-chip Test Access Port (TAP) that implements a stateful protocol to access a set of test registers that present chip logic levels and device capabilities of various parts.
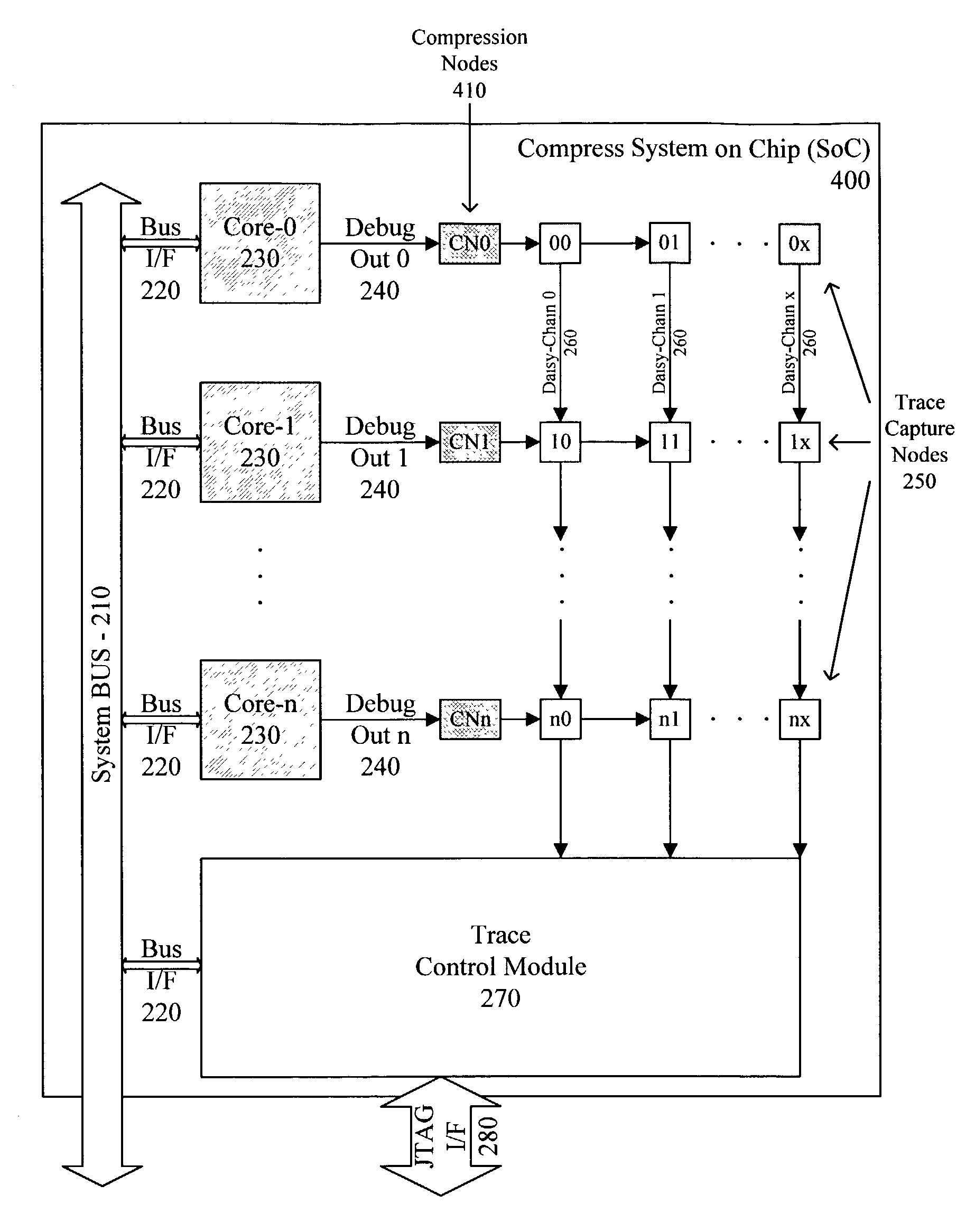
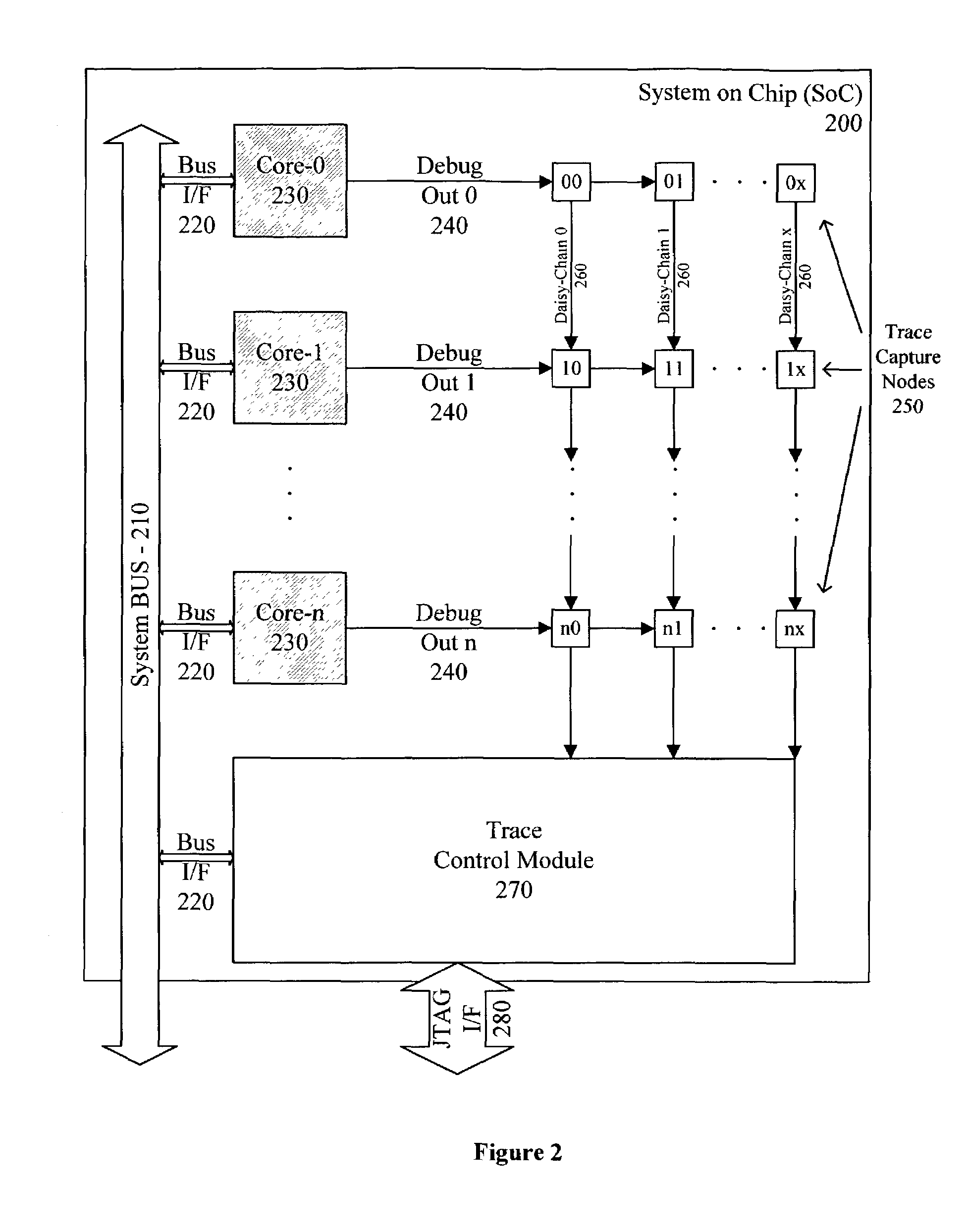
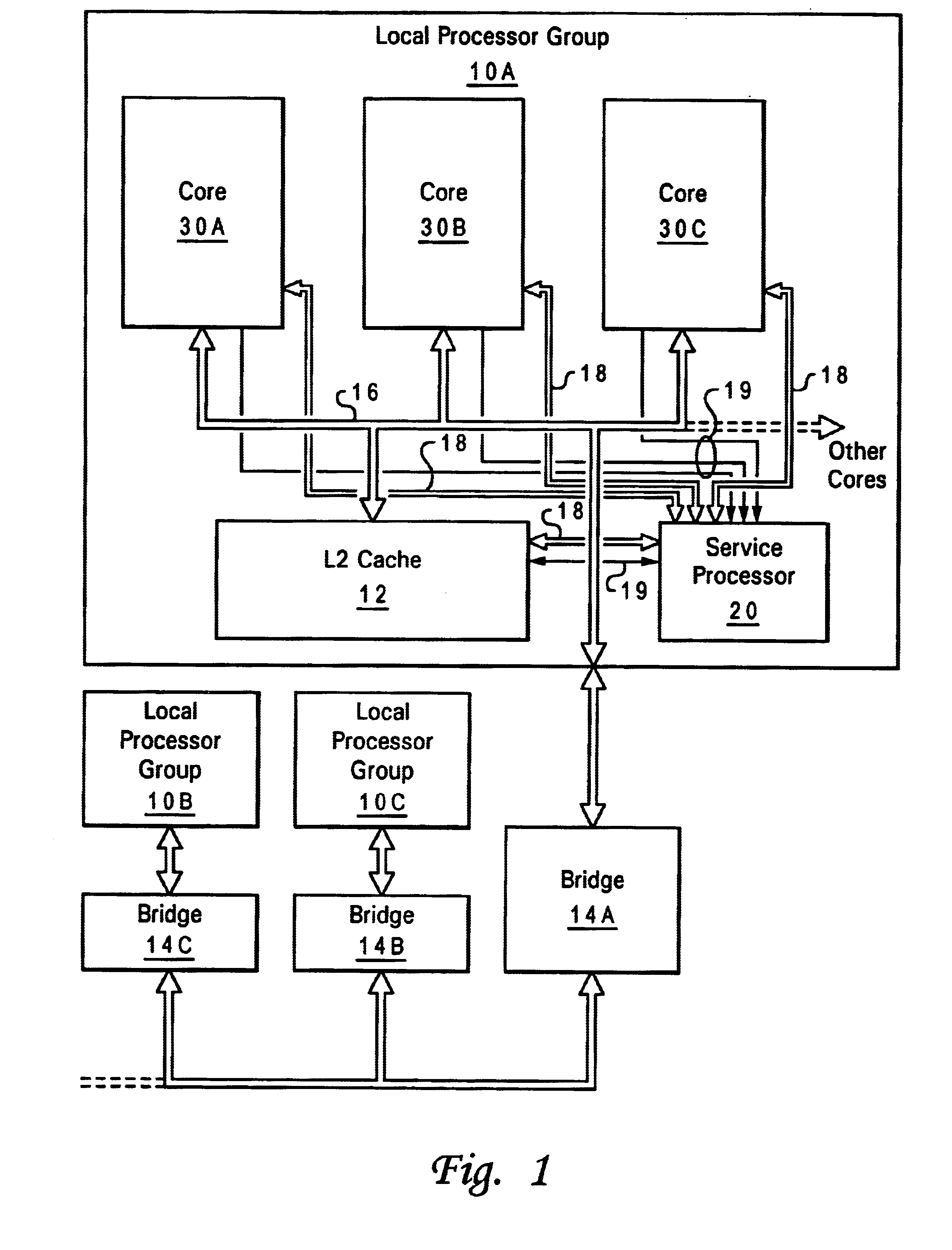
Simultaneous real-time trace and debug for multiple processing core systems on a chip
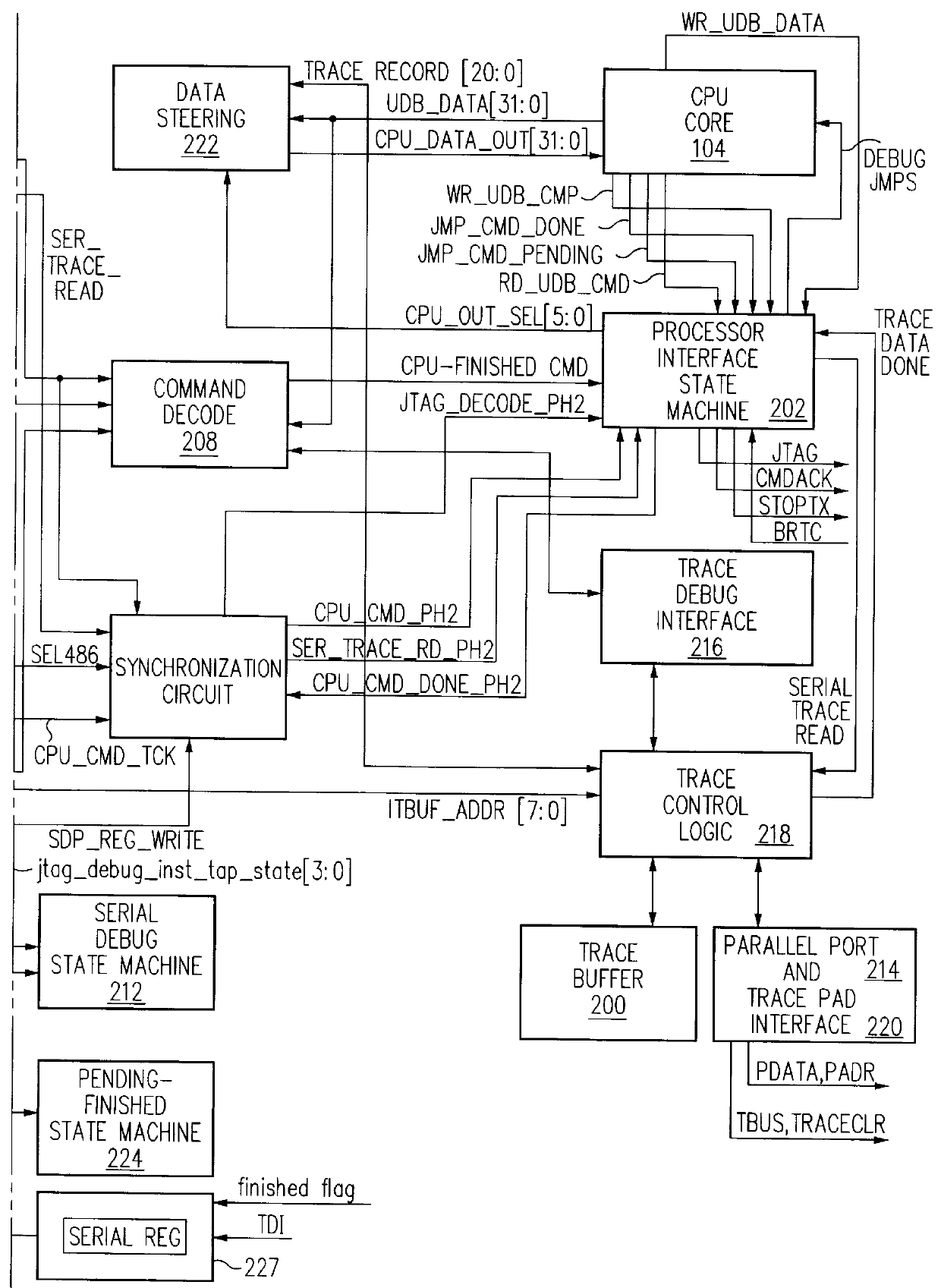
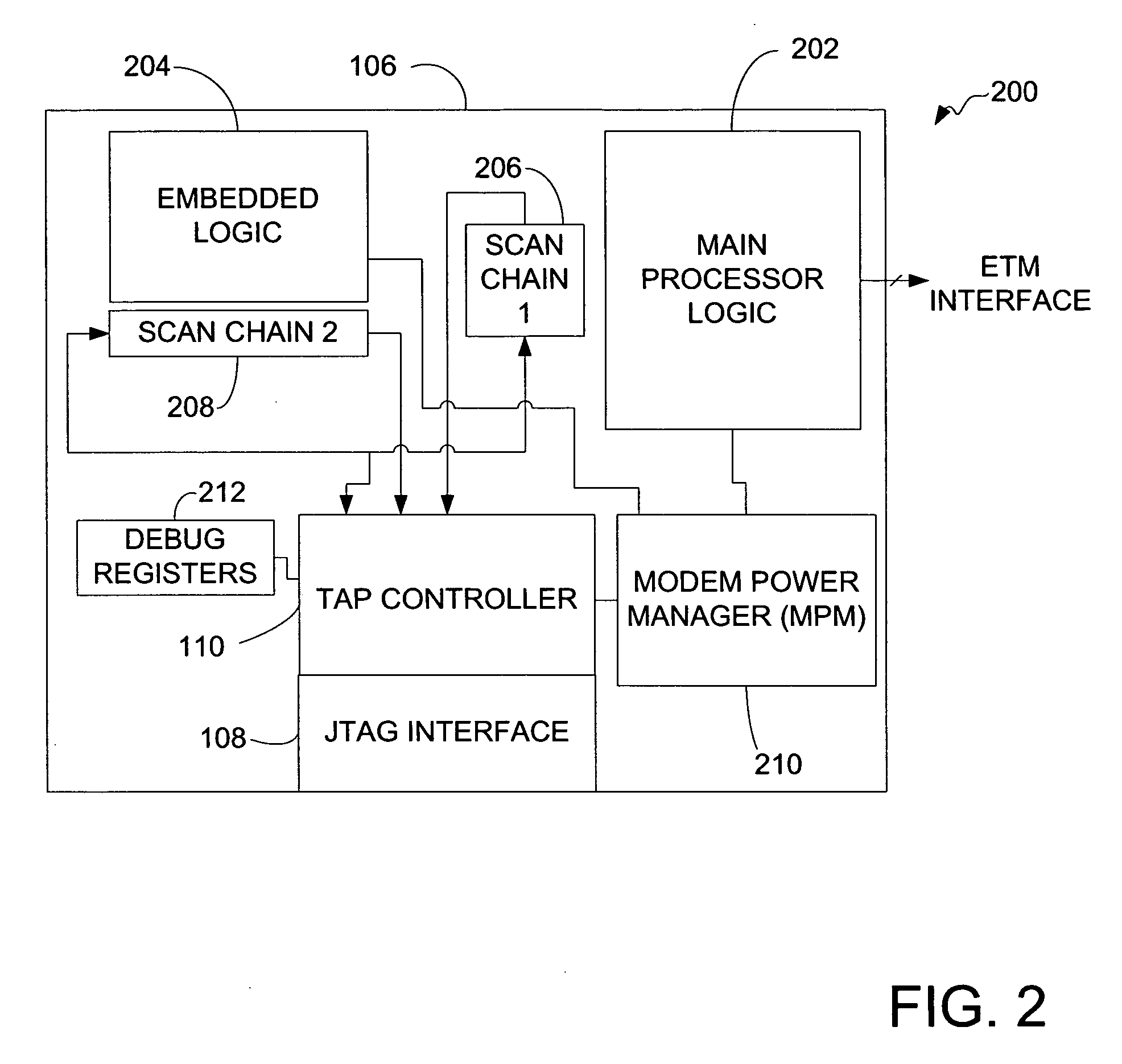
A system for providing simultaneous, real-time trace and debug of a multiple processing core system on a chip (SoC) is described. Coupled to each processing core is a debug output bus. Each debug output bus passes a processing core's operation to trace capture nodes connected together in daisy-chains. Trace capture node daisy-chains terminate at the trace control module. The trace control module receives and filters processing core trace data and decides whether to store processing core trace data into trace memory. The trace control module also contains a shadow register for capturing the internal state of a traced processing core just prior its tracing. Stored trace data, along with the corresponding shadow register contents, are transferred out of the trace control module and off the SoC into a host agent and system running debugger hardware and software via a JTAG interface.
Owner:TENSILICA
Apparatus and methods for testing a microprocessor chip using dedicated scan strings
InactiveUS6028983AReduce memory requirementsReduce scan timeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionTest inputJoint Test Action Group
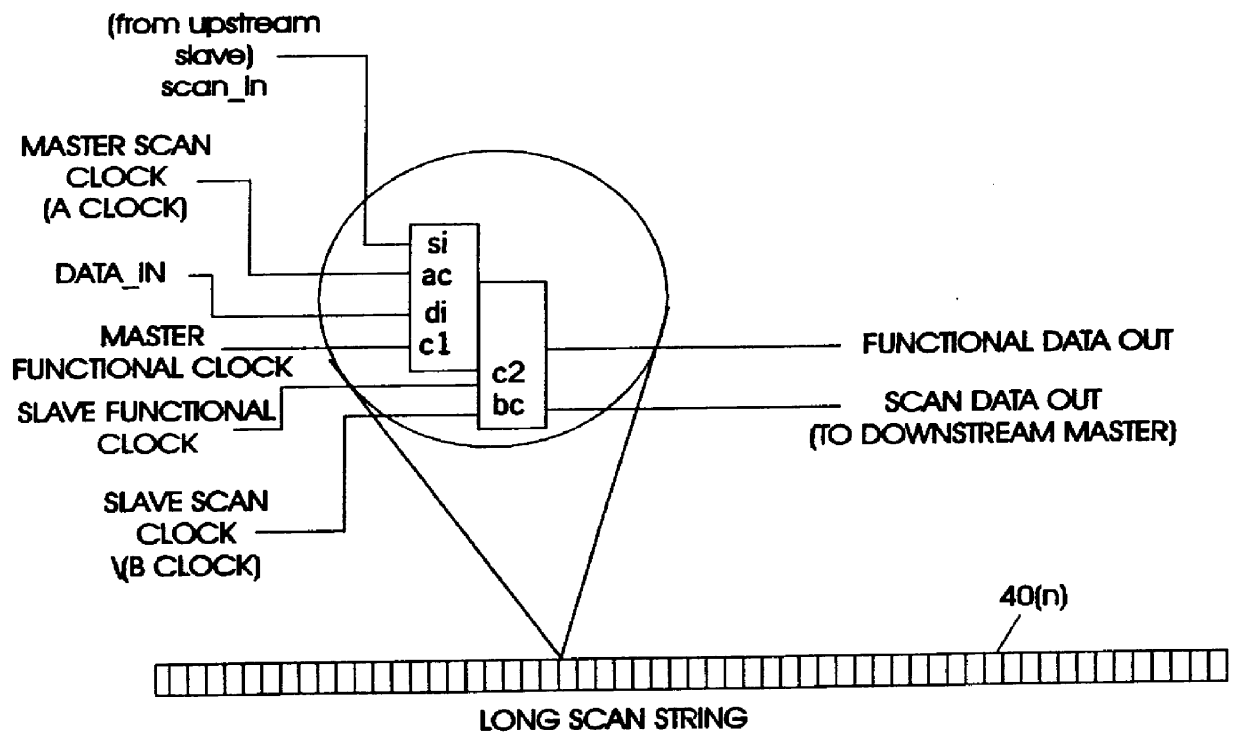
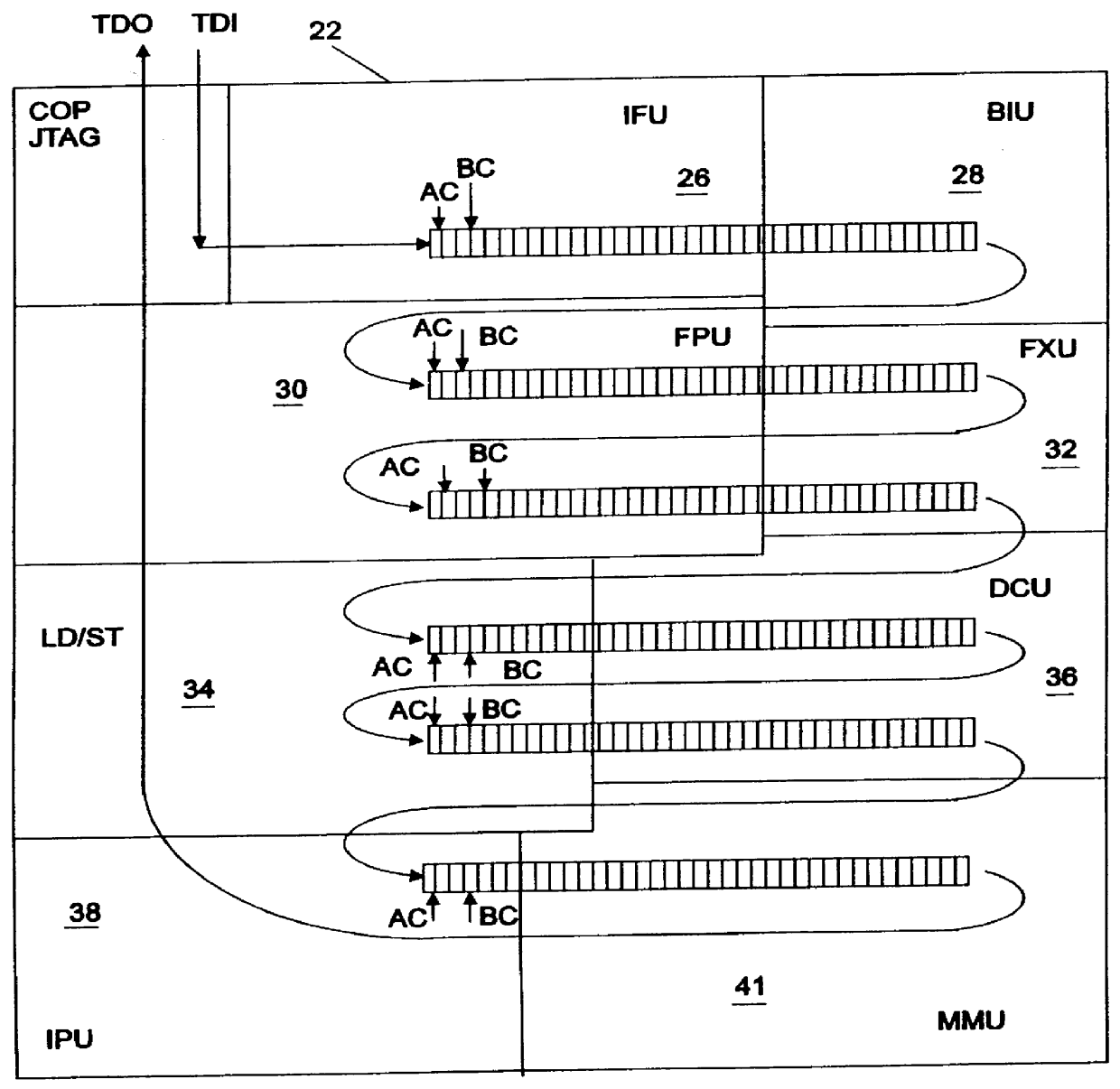
A test apparatus and method for design verification of at least one microprocessor chip includes a compatible Joint Task Action Group (JTAG) terminal for access to a plurality of computer functional units contained in the chip. A test input terminal included in the JTAG terminal receives a scan string, the string being coupled to each computer functional unit through a first multiplexer. The scan input string is separated by the JTAG terminal under program control into a series of dedicated scan strings, each dedicated scan string being supplied to a selected functional unit through the first multiplexer. Each functional unit includes start and stop scan clocks for testing the functional under program control using the dedicated scan train for the functional unit. A test output terminal included in the JTAG terminal is coupled to each functional unit through a second multiplexer. The test results of the dedicated scan string under control of the scan clock are supplied to the output terminal through the second multiplexer. The compatible JTAG terminal includes further elements for controlling the scan clocks to select a targeted functional unit for testing purposes while the scan strings for non-targeted functional units remain in an inactive state.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Scan based multiple ring oscillator structure for on-chip speed measurement
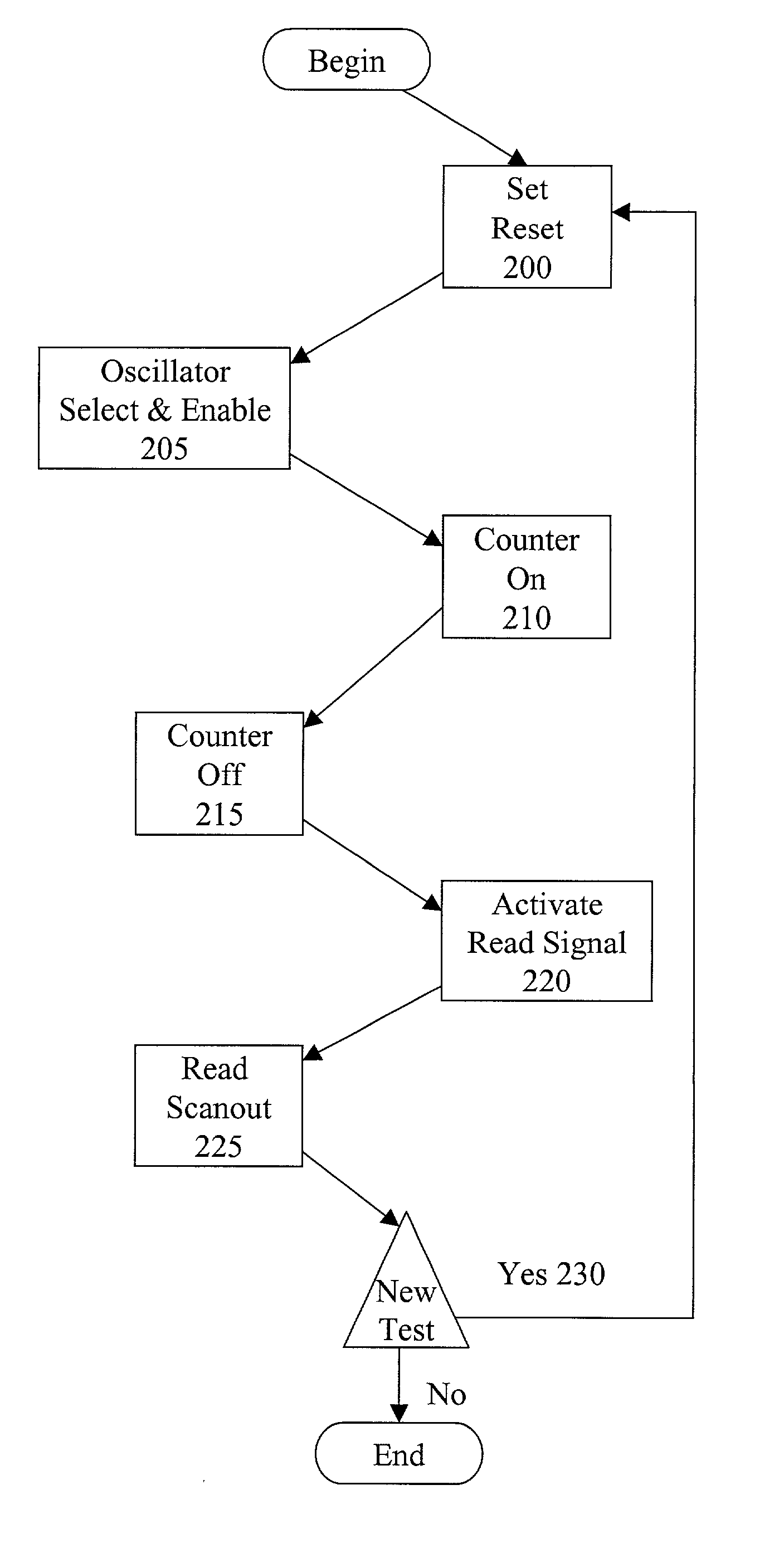
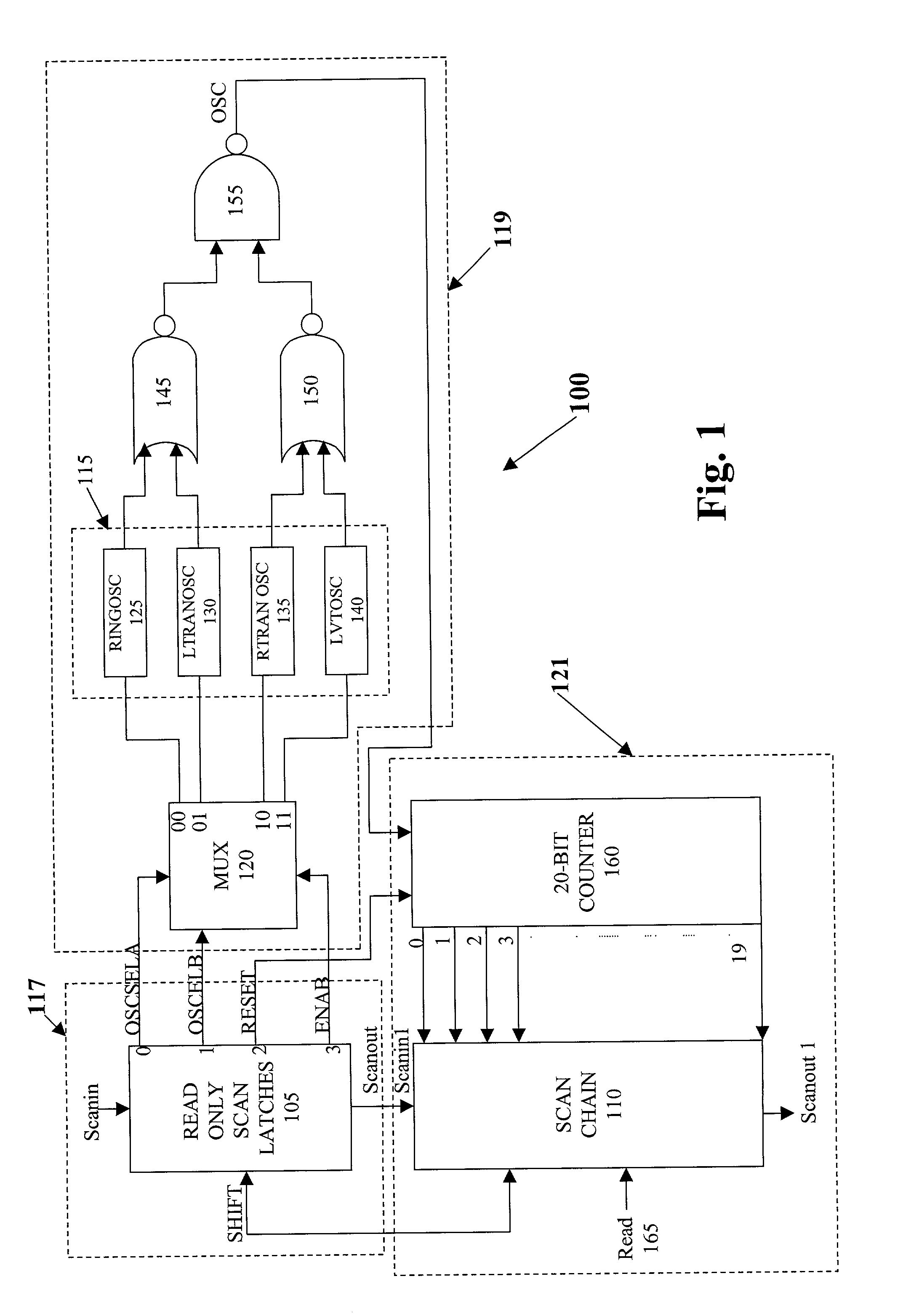
The present invention bundles four ring oscillators, a 20-bit ripple counter and the necessary control logic needed to implement a JTAG scan based interface. The present system can be located on every die, so that each location can be individually tested. It communicates with the outside world through a standard JTAG interface. It is accessible at wafer, package, and system test which allows for several methods of correlating the oscillator speed to the speed of a part in the actual system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
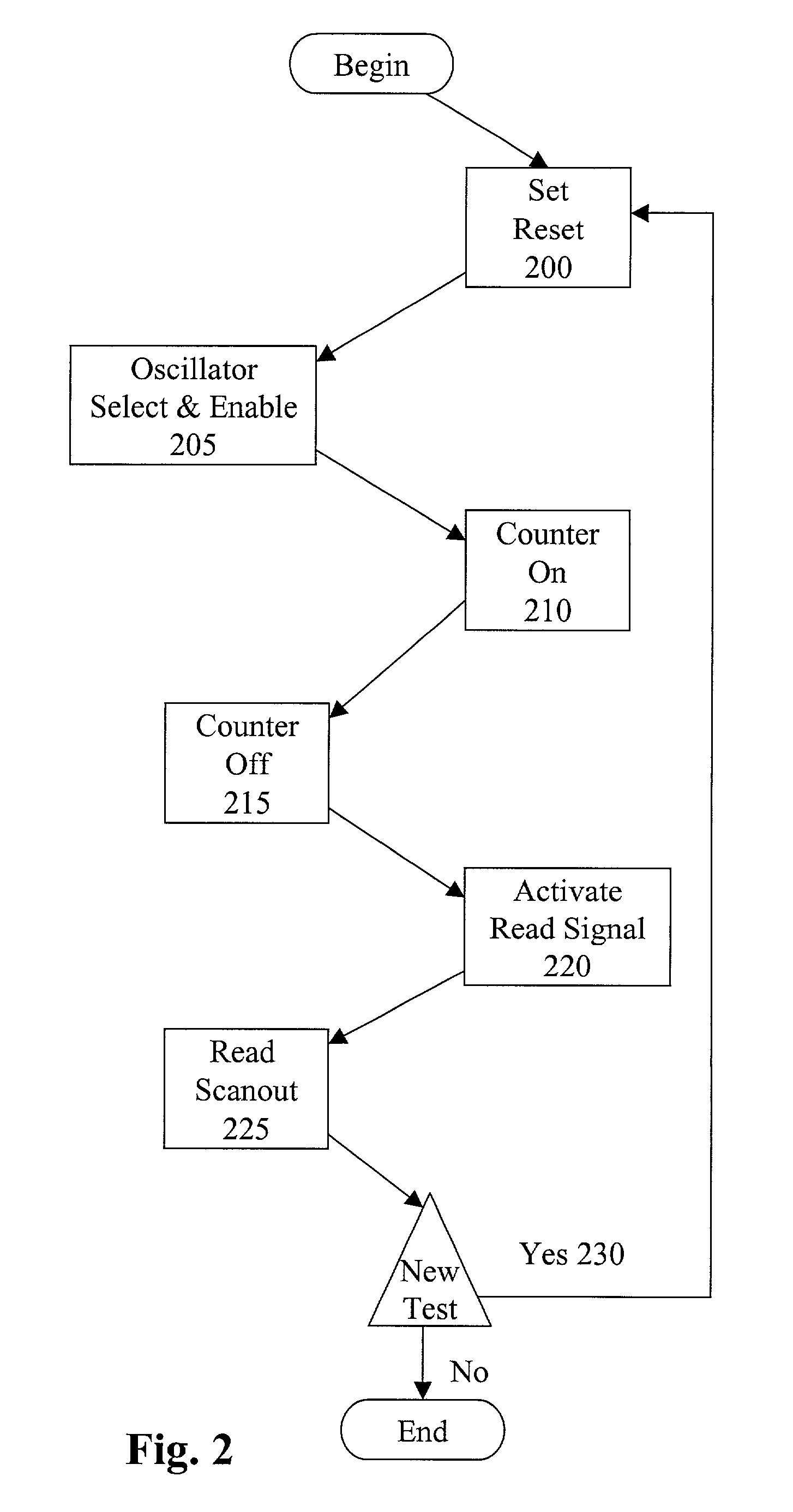
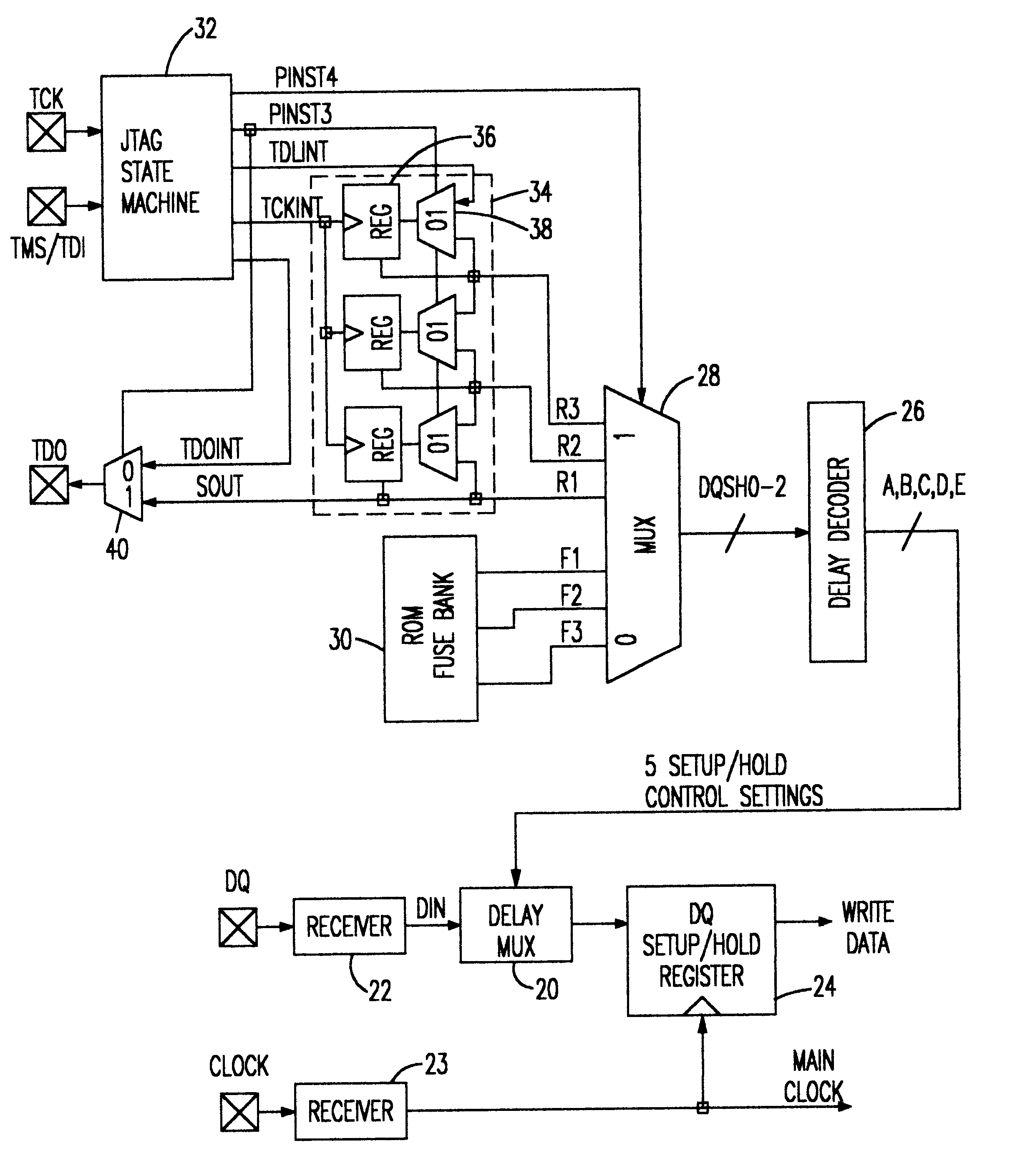
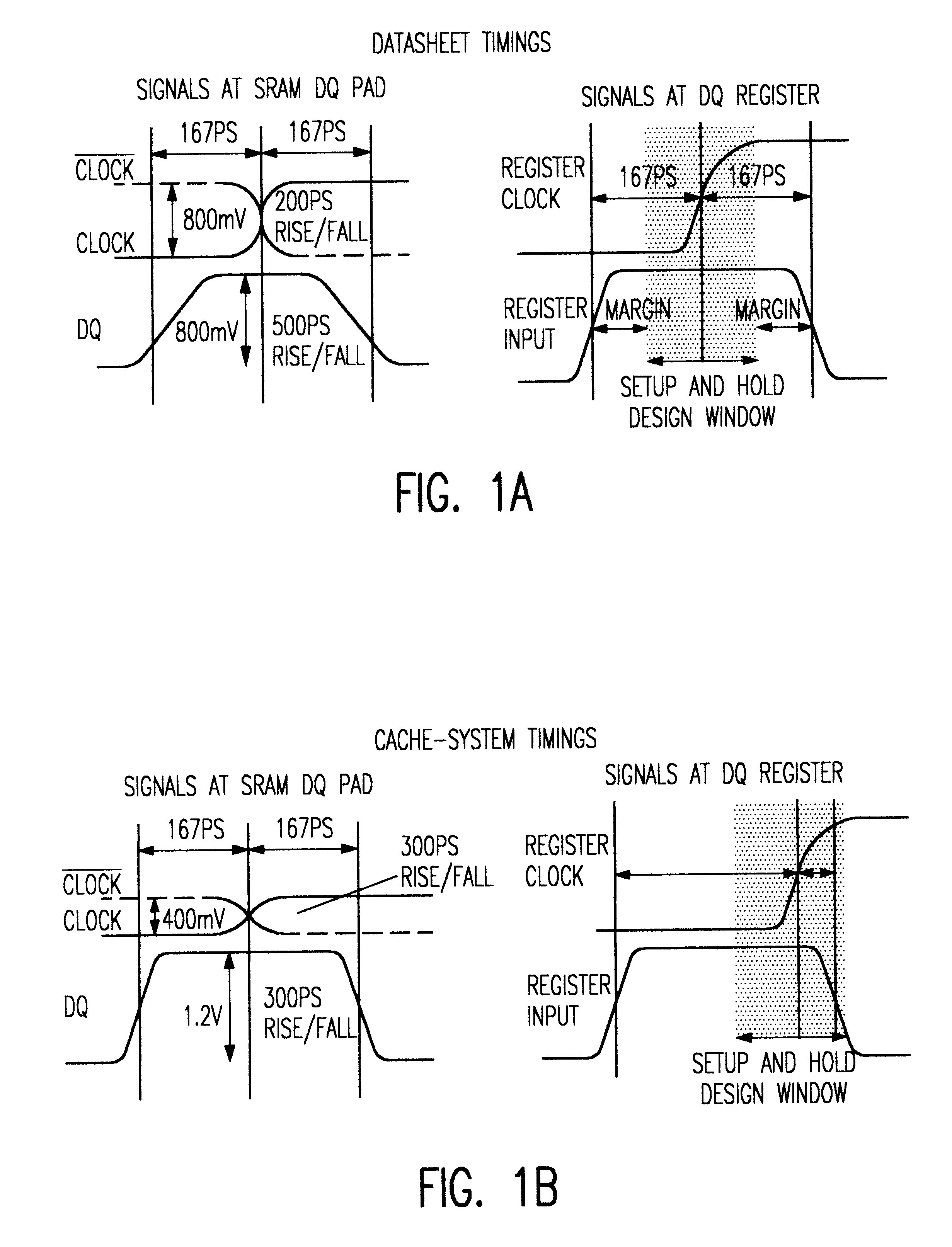
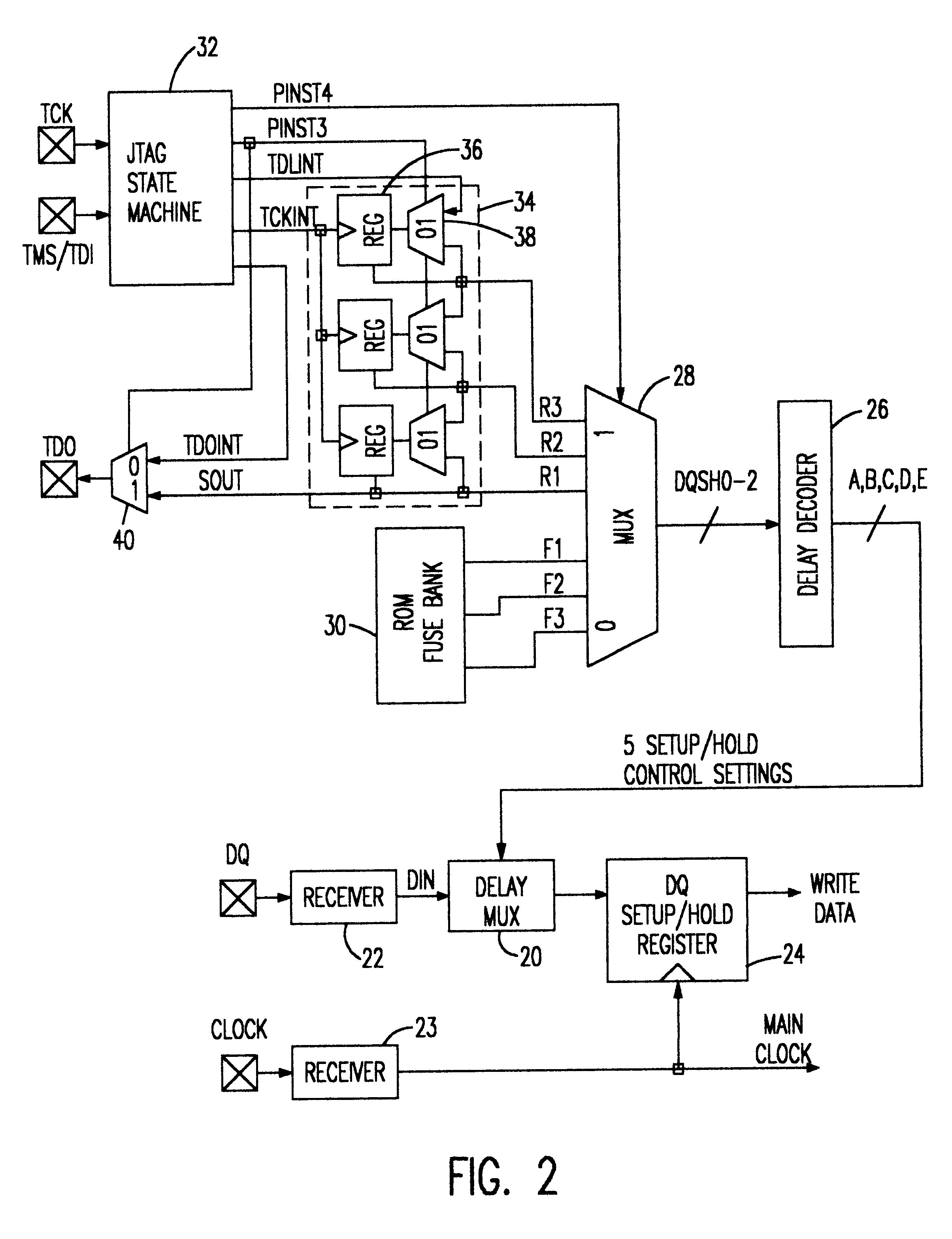
Memory having user programmable AC timings
A SRAM module provides programmability of AC timings such that an end user can adjust or "tweak" the AC timings to maximize system performance. A variable delay circuit is placed in the path between a signal (e.g., data signal or address signal)and the SRAM set-up and hold register which allows the user to shift the setup-and-hold window by selected increments. The delay circuit can either advance or retard the AC timings. A delay program controlling the delay circuit is selected in one of two ways; either by a default AC timing program stored in a ROM device and preset by the manufacturer, or by a private JTAG instruction and AC programming data input by the user through the JTAG state machine provided on the SRAM chip. Once the optimum delay (or advance) is selected to optimize the SRAM to the cache system this user program may be permanently burned into the default ROM such that the optimum timings are used thereafter as the default.
Owner:IBM CORP
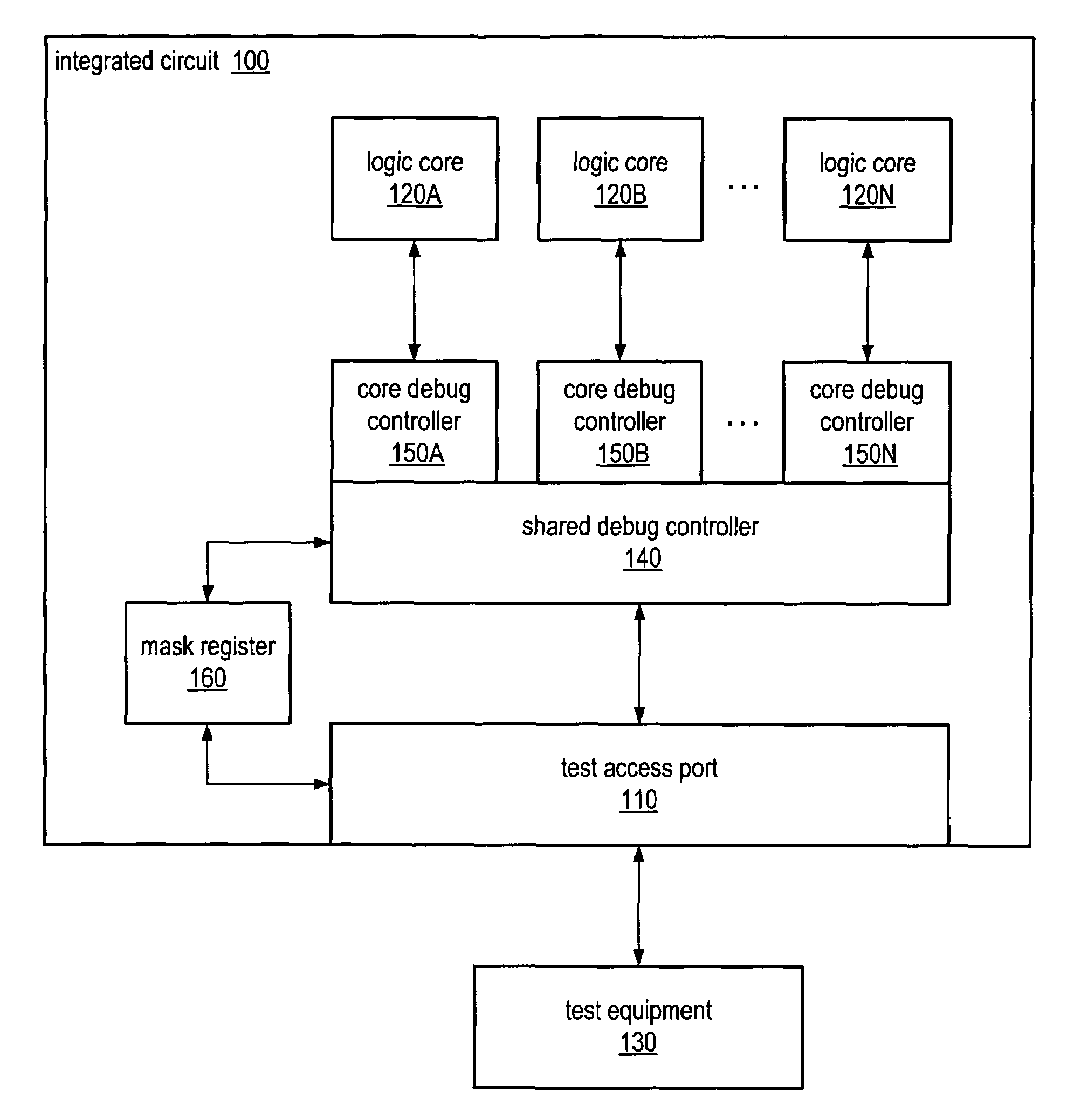
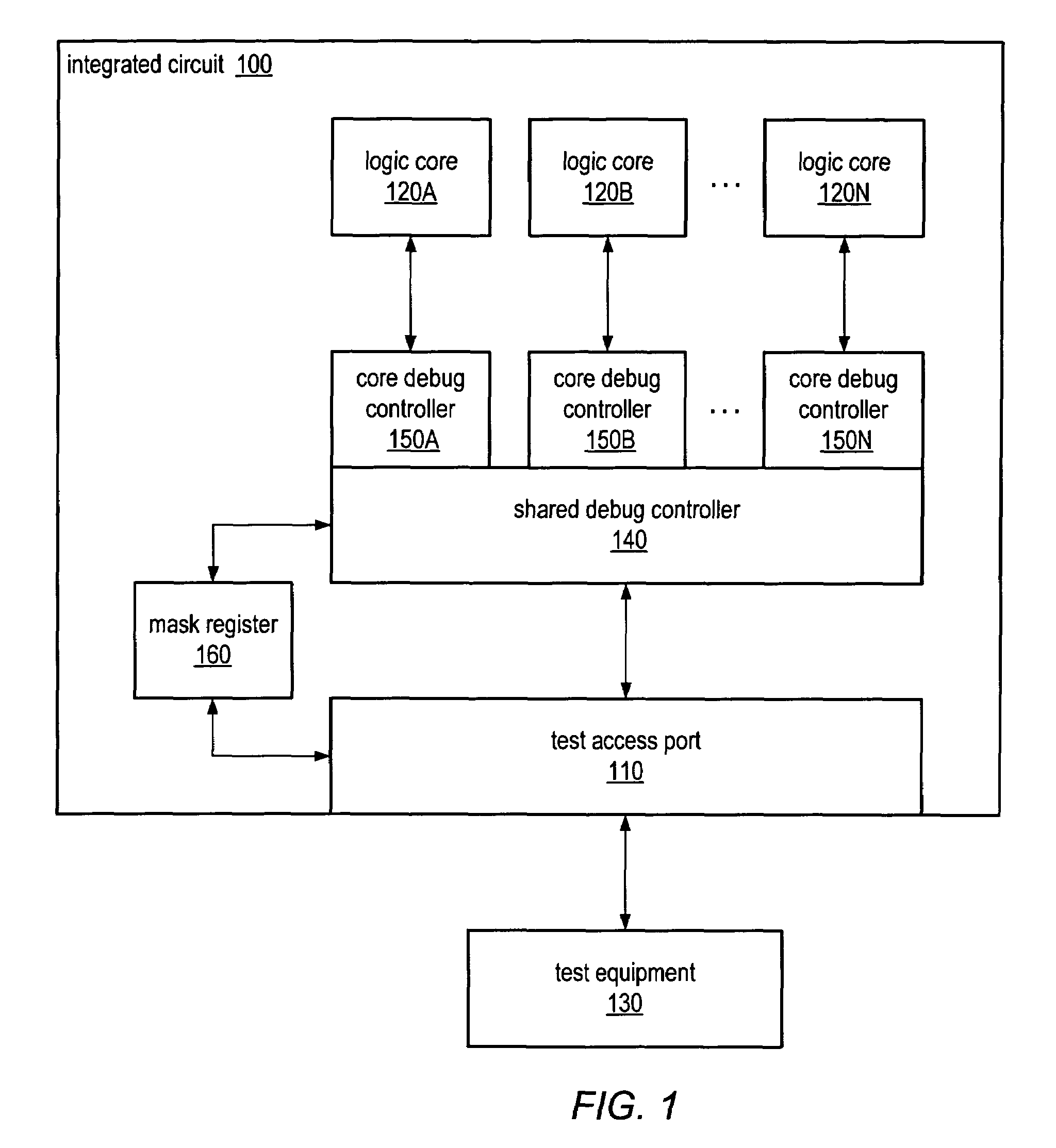
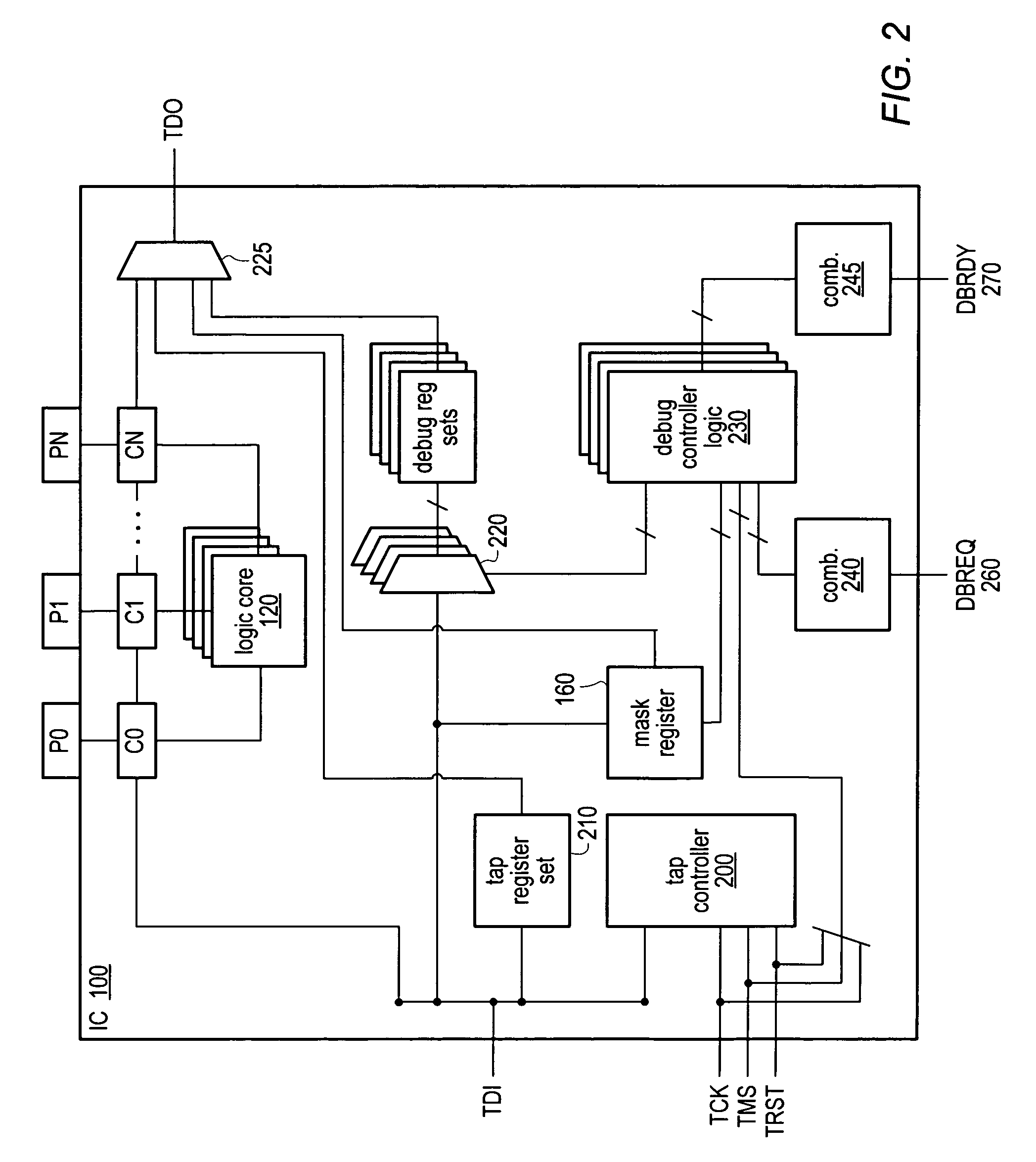
Multi-core integrated circuit with shared debug port
ActiveUS7665002B1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer architectureJoint Test Action Group
A single test access port, such as a JTAG-based debug port may be utilized to perform debug operations on logic cores of a multi-core integrated circuit, such as a multi-core processor. The shared debug port may respond to a particular command to enter a debugging mode and may be configured to forward all commands and data to a debugging controller of the integrated circuit during debugging. A mask register may be used to indicate which logic cores of the multi-core integrated circuit should be debugged. Additionally, custom debugging commands may include mask or core select fields to indicate which logic cores should be affected by the particular command. Debugging mode may be initialized for one or more logic cores either externally, such as be asserted a DBREQ signal, or internally, such as by configuring one or more breakpoints.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Distributed processor configuration for use in infusion pumps
The present invention provides an infusion pump control system comprises a plurality of computing components positioned on discrete hardware modules to complete an infusion task. Those discrete processors, which are internally redundant and communicate through a common medium that provides for redundancy of the communication ability to react to internal failures in a known manner, implement capabilities specific to infusion pump functions, to complete an infusion task. Also, this invention provides automatically switchable redundant power supplies and a new mechanism for firmware provisioning using multi-dropped JTAG for a plurality of computing components.
Owner:NUMIA MEDICAL TECH
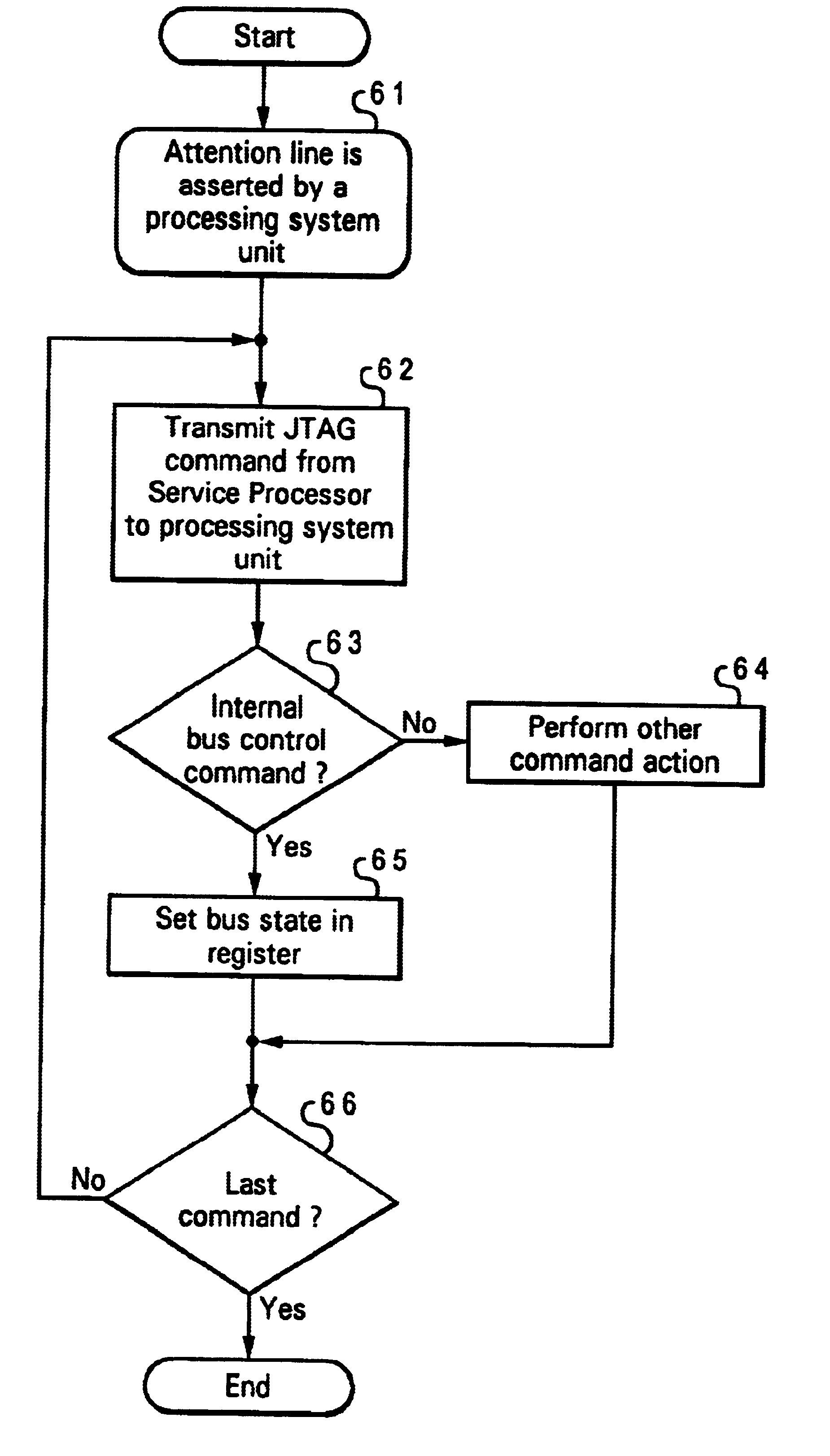
Method and apparatus for servicing a processing system through a test port
InactiveUS6629268B1Error detection/correctionMemory systemsProcessor registerJoint Test Action Group
A method and apparatus for servicing a processing system through a test port allow initialization and fault recovery capability including the ability to coherently access cache memory while the processing system is operating. A JTAG standard interface is used to access registers in a main processing component and has the additional capability to generate internal bus transactions to access registers, cache and memory both within the main processor, and externally by causing a bus interface in the main processor to generate external bus transactions. The service processor can coherently access cache by this mechanism, allowing fault tolerant recovery from operations in which the cache must be coherently flushed in order to maintain proper system operation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
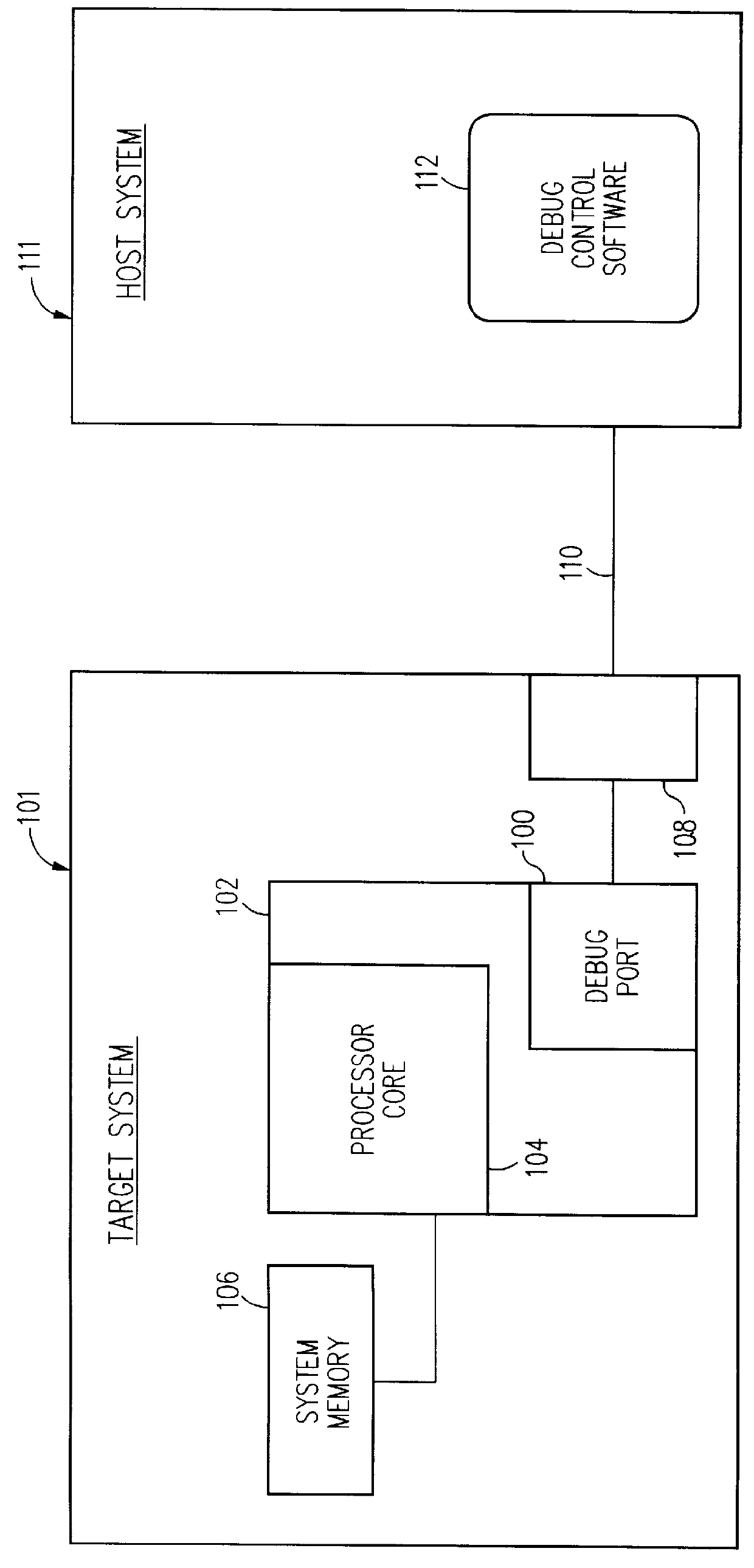
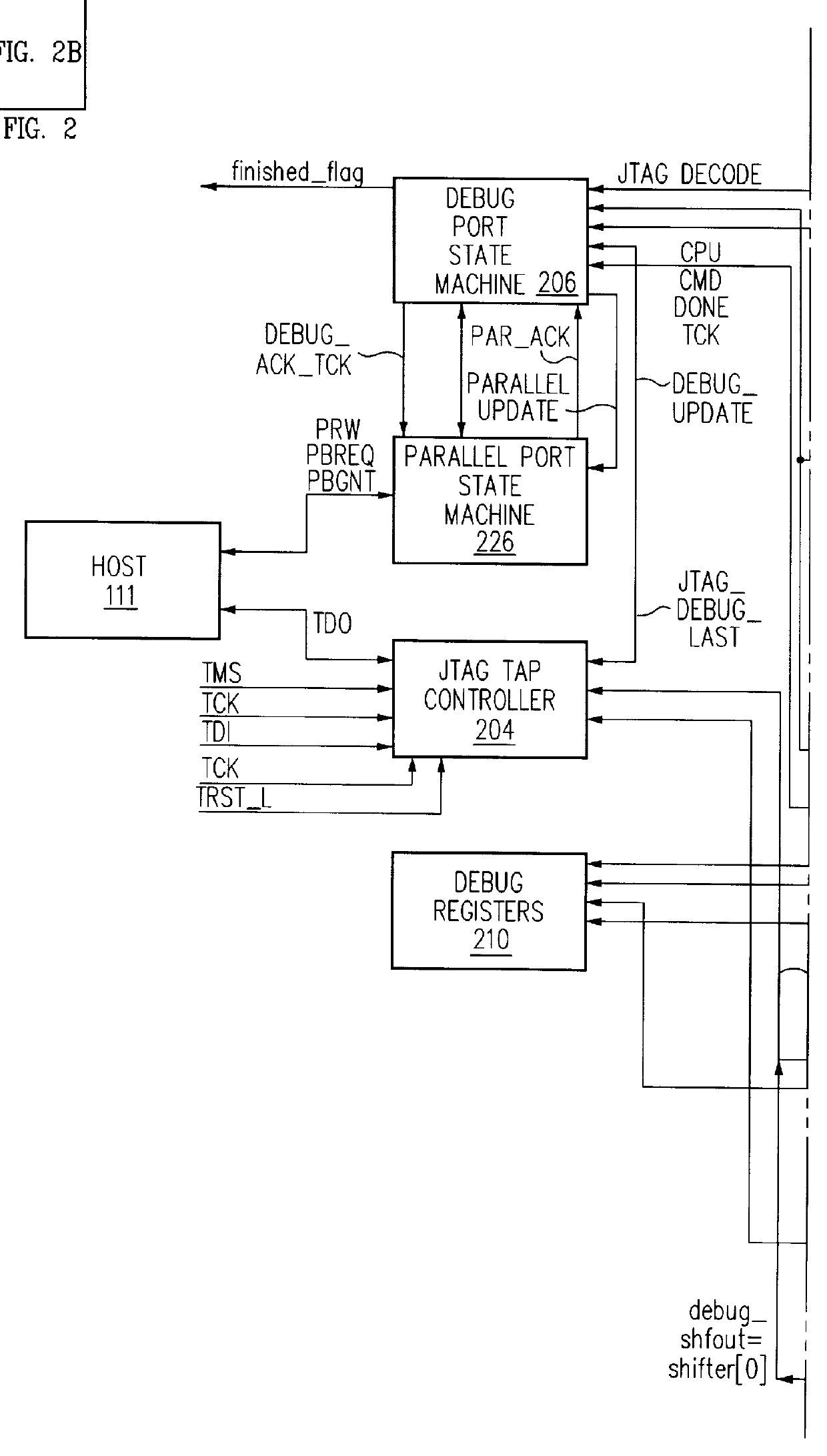
Debug interface including timing synchronization logic
A system for debugging a processor includes a logic circuit for communicating commands and data between an input / output port which operates at a first clock frequency, and trace control logic which operates at a second clock frequency that is different from the first clock frequency. In some embodiments, the input / output port is a JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) port operating at a maximum clock frequency of 25 MHz and the trace control logic operates at a clock frequency of 33 Mhz, 66 MHz, 99 MHz, or 133 mhz. A suitable JTAG clock frequency is a minimum of either half the CPU internal clock frequency or 2.25 Mhz for synchronizing the internal signals between different clock frequencies. When the input / output port, which is typically a serial / parallel input / output port, writes data to debug registers, including ITCR, DCSR, soft-address, and RX-DATA registers, timing strobe signals to the registers are synchronized to a processor clock to reduce the synchronization logic for register bits that are used by the processor and trace control logic. By synchronizing the debug register data write operations to the processor clock timing, the data bits of the registers are used by the processor and the trace logic without further synchronization. Advantageously, the amount of synchronization logic is reduced. Synchronizing the signals that cross the blocks with different clock timing facilitates communication between the processor, the trace control logic, and the serial and parallel input / output ports and reduces the amount of synchronization logic.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Adaptable scan chains for debugging and manufacturing test purposes
InactiveUS6018815AReducing scan time operationAvoid Design MistakesDigital circuit testingSolid-state devicesEngineeringJoint Test Action Group
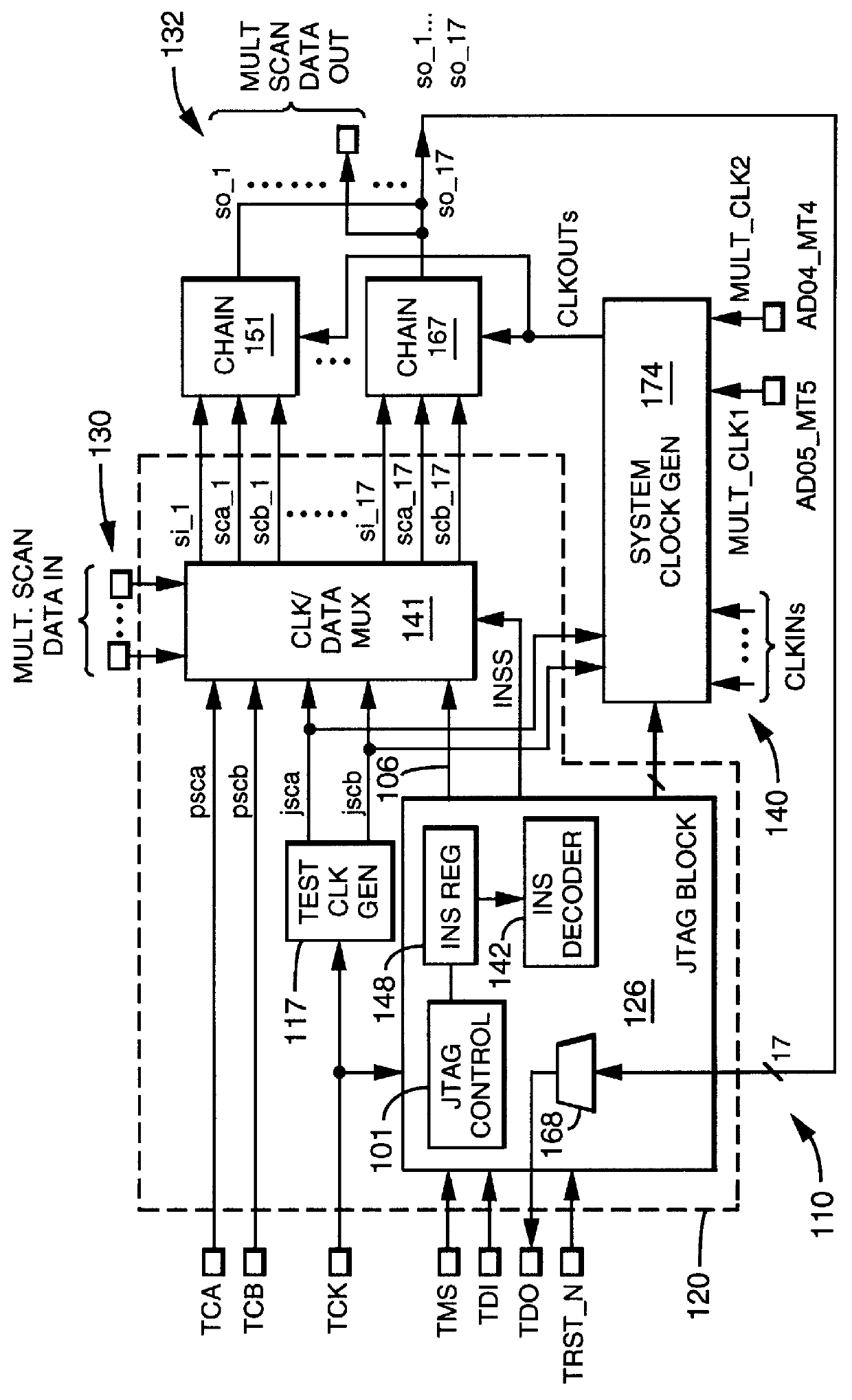
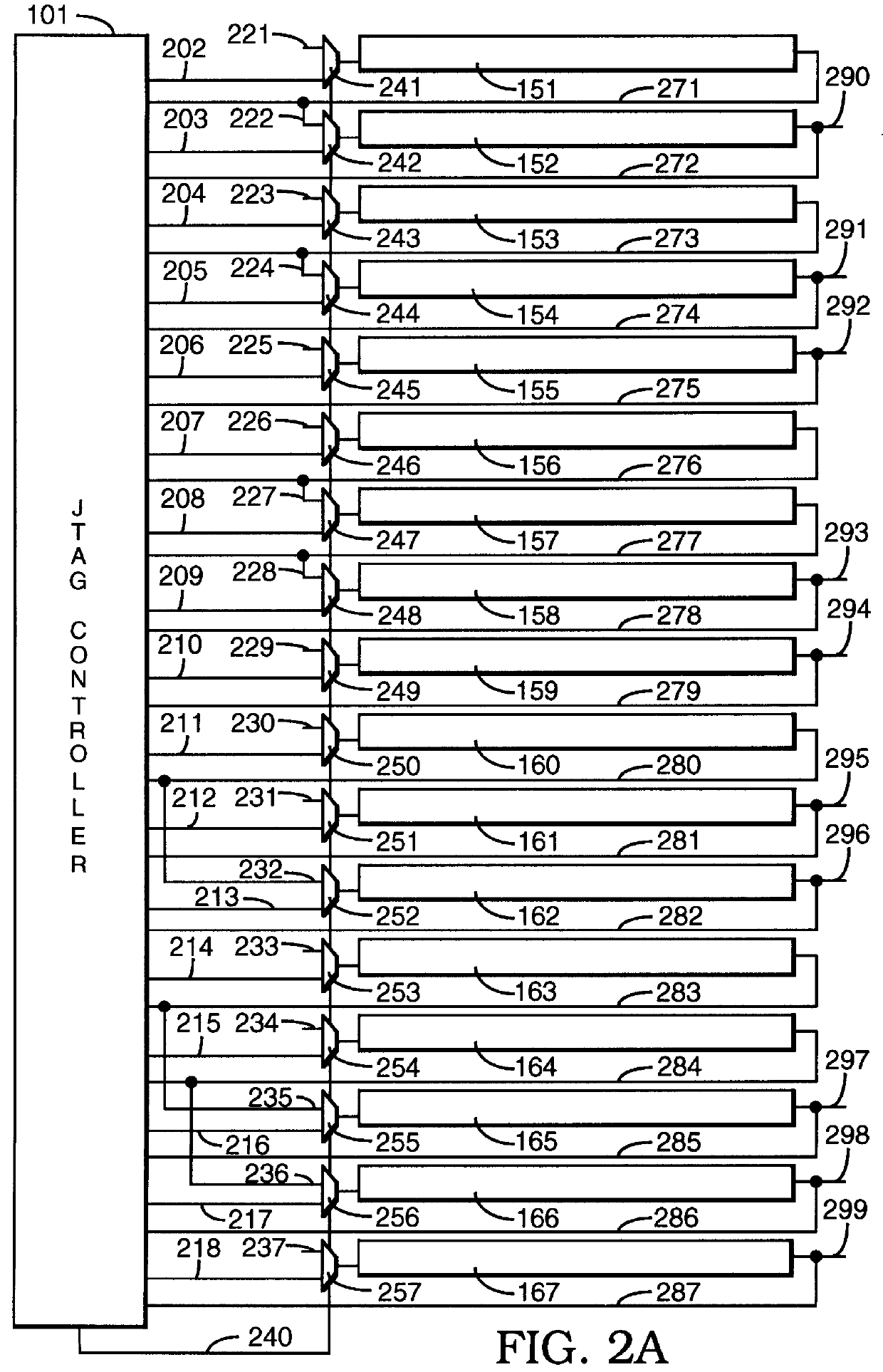
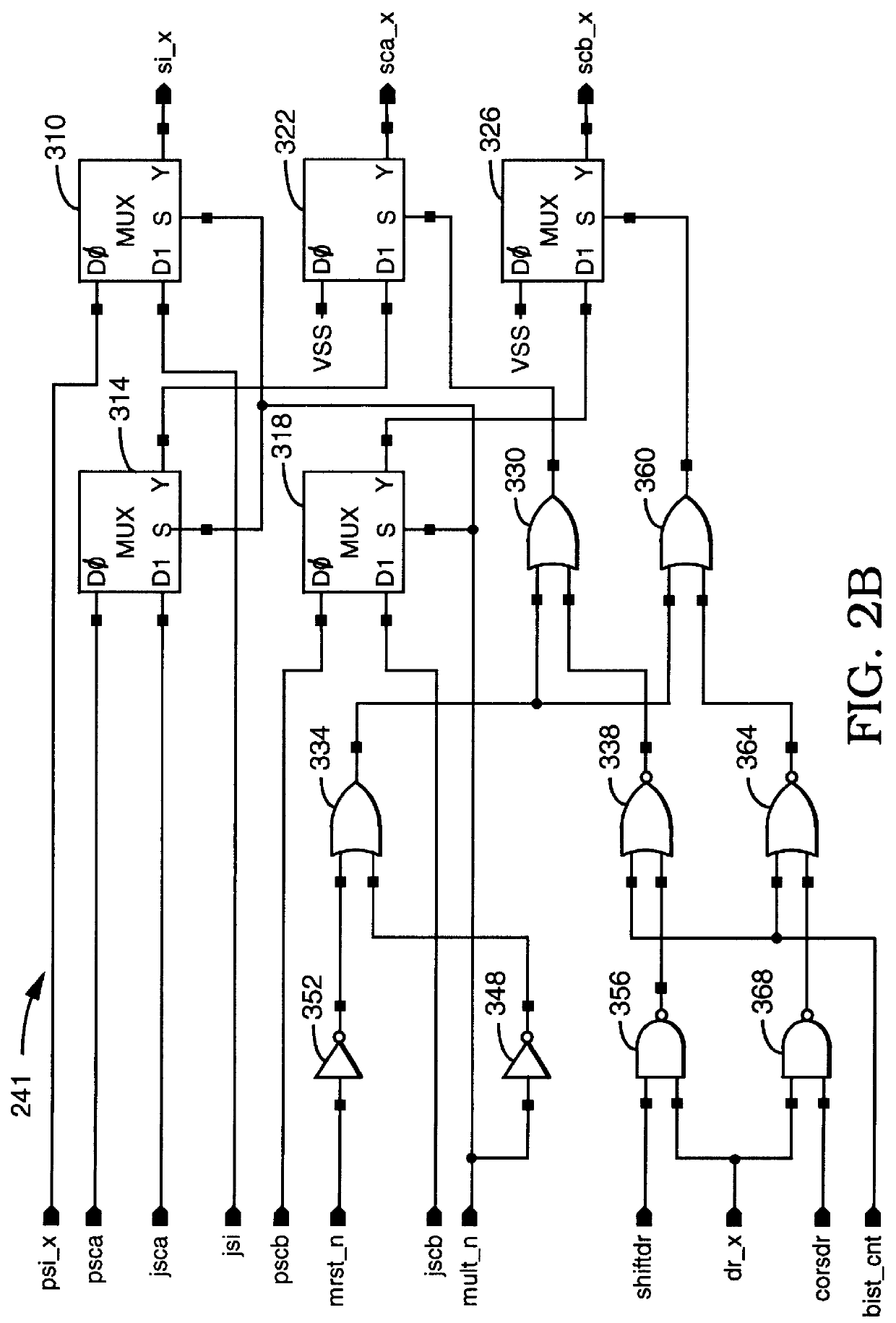
Scan chains to support debugging and manufacturing test modes for integrated circuit chips are made adaptable. Scan chains may be configured either in a multiple scan chain JTAG mode or in a multiple independent and parallel scan chain mode. The configuration transition between the scan modes is made by private instructions implemented in a JTAG controller, which supports the IEEE 1149.1 standard.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System debug and trace system and method, and applications thereof
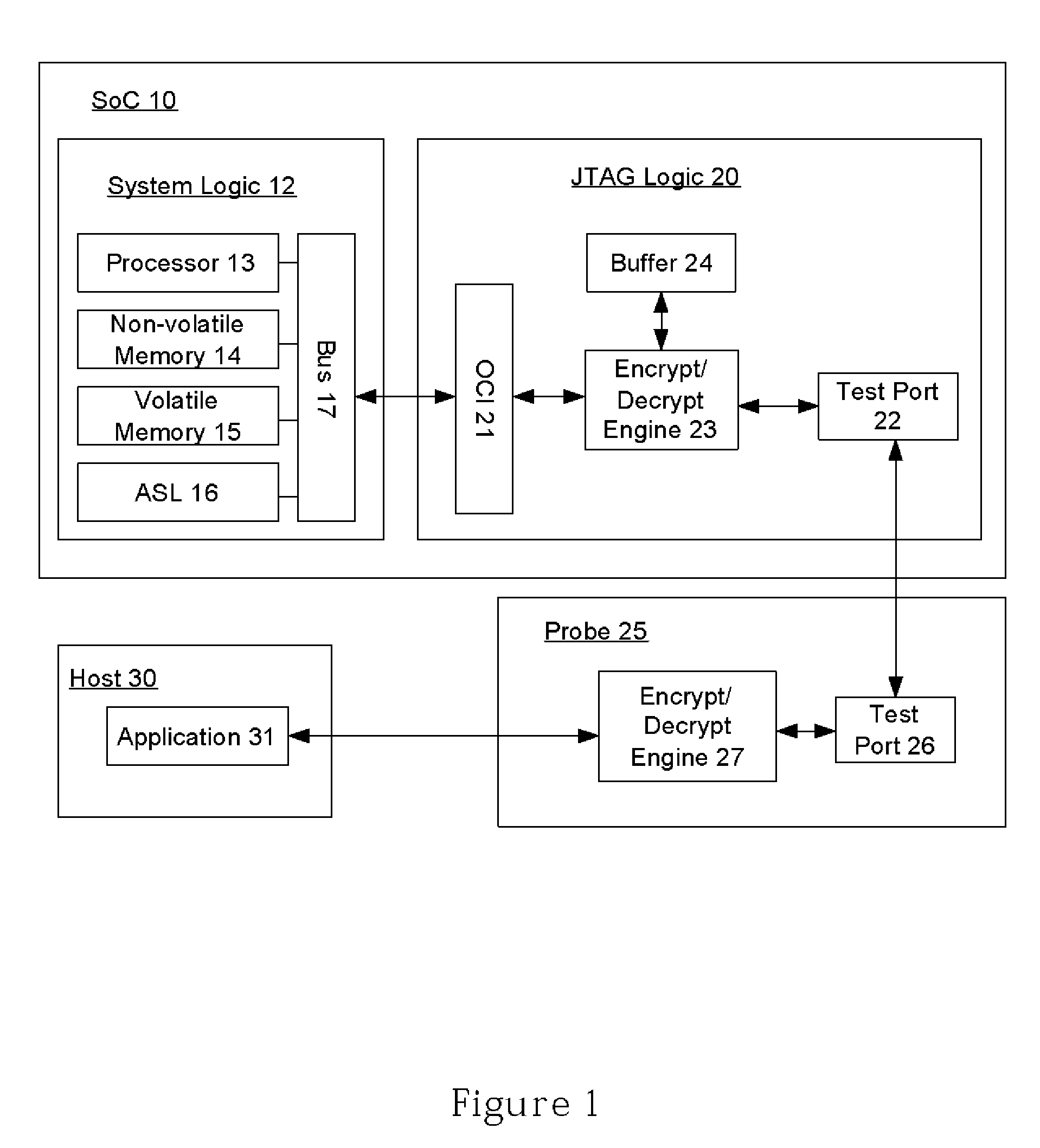
InactiveUS20080282087A1Risk minimizationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareJoint Test Action Group
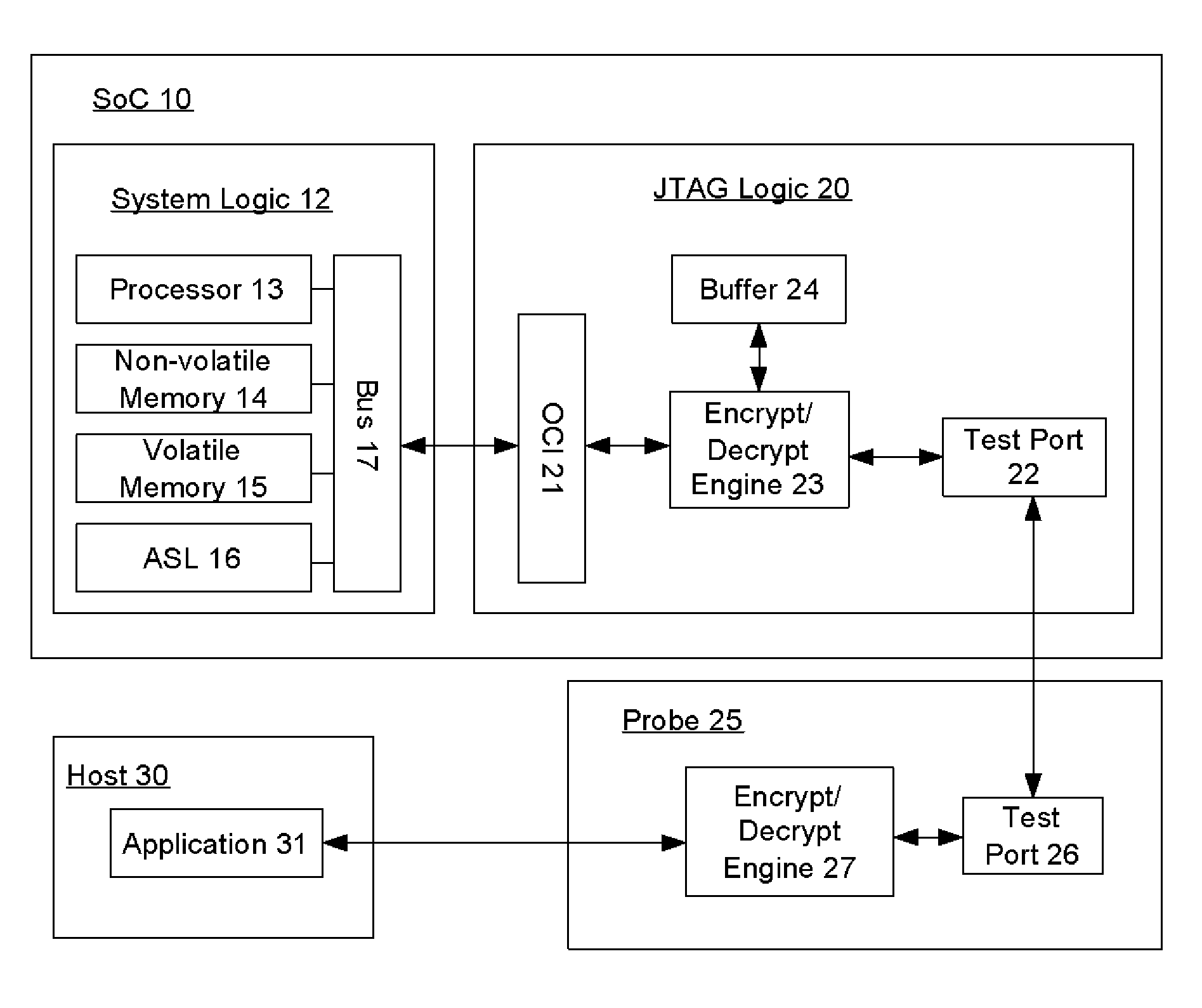
An embedded system or system on chip (SoC) includes a secure JTAG system and method to provide secure on-chip control, capture, and export of on chip information in an embedded environment to a probe. In one embodiment, the system comprises encryption logic associated with a JTAG subsystem and decryption logic in the probe for encrypted JTAG read traffic. Inverted encryption / decryption logic provides bi-directional encryption and decryption of JTAG traffic. Encrypted information includes both authentication of valid probe / target interface and encryption of debug data.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Jtag-based programming and debug
ActiveUS20130346814A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer hardwareJoint Test Action Group
A method of sending programming and debug commands, comprises loading control instructions on a processor from an attached tangible, non-transitory computer-readable medium, copying the contents of a program image file by the processor from the computer-readable medium across a bus to a programmable device on the same card as the processor, signaling the programmable device to send an instruction to a configurable logic device (CLD) on the same card as the processor via a debug channel.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
JTAG-based programming and debug
A method of sending programming and debug commands, comprises loading control instructions on a processor from an attached tangible, non-transitory computer-readable medium, copying the contents of a program image file by the processor from the computer-readable medium across a bus to a programmable device on the same card as the processor, signaling the programmable device to send an instruction to a configurable logic device (CLD) on the same card as the processor via a debug channel.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
JTAG power collapse debug
InactiveUS20070214389A1Enable performanceSoftware testing/debuggingComputer hardwareProcessor register
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Selectable JTAG or trace access with data store and output
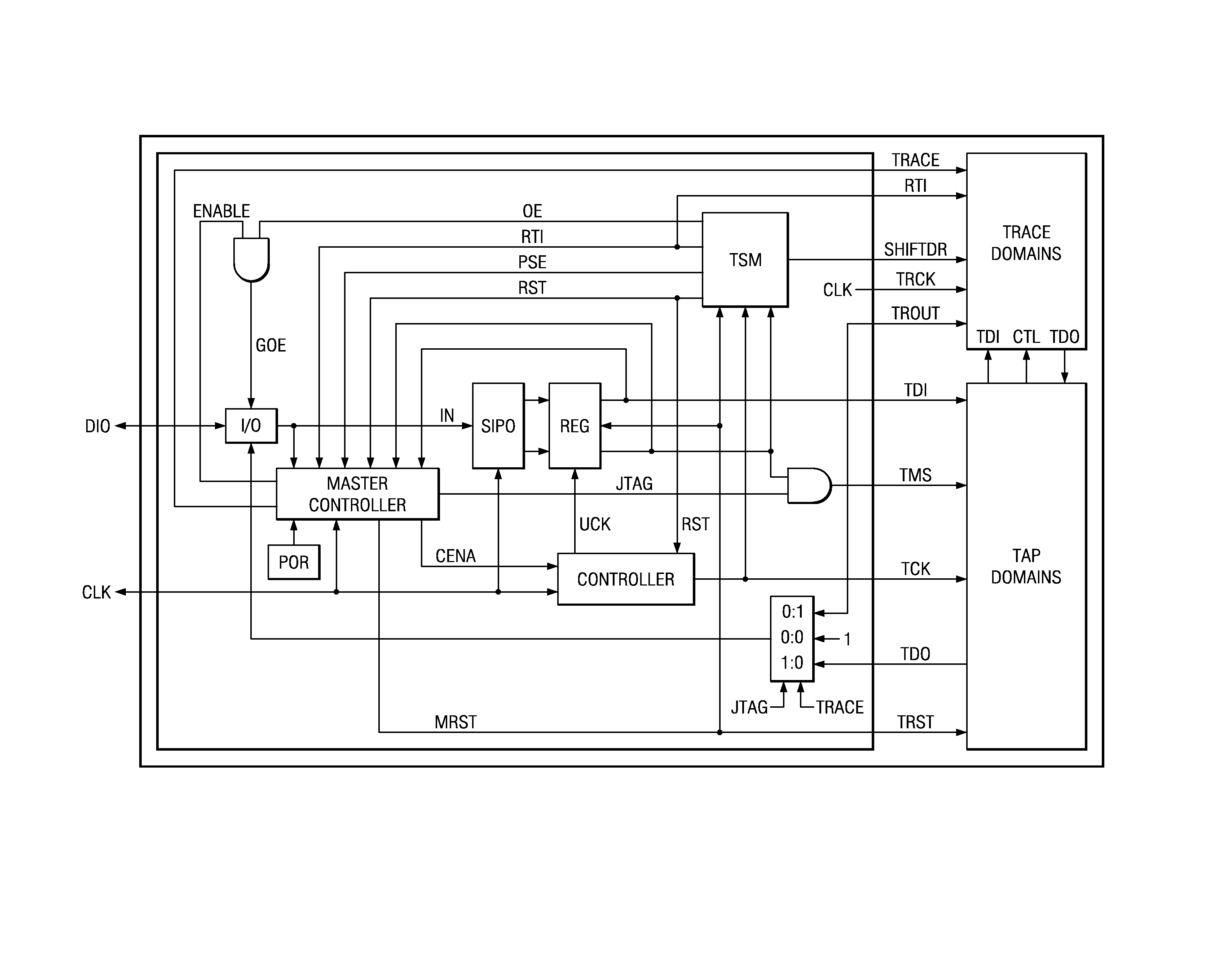
ActiveUS7571364B2Electronic circuit testingFunctional testingJoint Test Action GroupData transmission
An addressable interface selectively enables JTAG TAP domain operations or Trace domain operations within an IC. After being enabled, the TAP receives TMS and TDI input from a single data pin. After being enabled, the Trace domain acquires data from a functioning circuit within the IC in response to a first clock and outputs the acquired data from the IC in response to a second clock. An addressable two pin interface loads and updates instructions and data to a TAP domain within the IC. The instruction or data update operations in multiple ICs occur simultaneously. A process transmits data from an addressed target device to a controller using data frames, each data frame comprising a header bit and data bits. The logic level of the header bit is used to start, continue, and stop the data transmission to the controller. A data and clock signal interface between a controller and multiple target devices provides for each target device to be individually addressed and commanded to perform a JTAG or Trace operation. Trace circuitry within an IC can operate autonomously to store and output functional data occurring in the IC. The store and output operations of the trace circuitry are transparent to the functional operation of the IC. An auto-addressing RAM memory stores input data at an input address generated in response to an input clock, and outputs stored data from an output address generated in response to an output clock.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
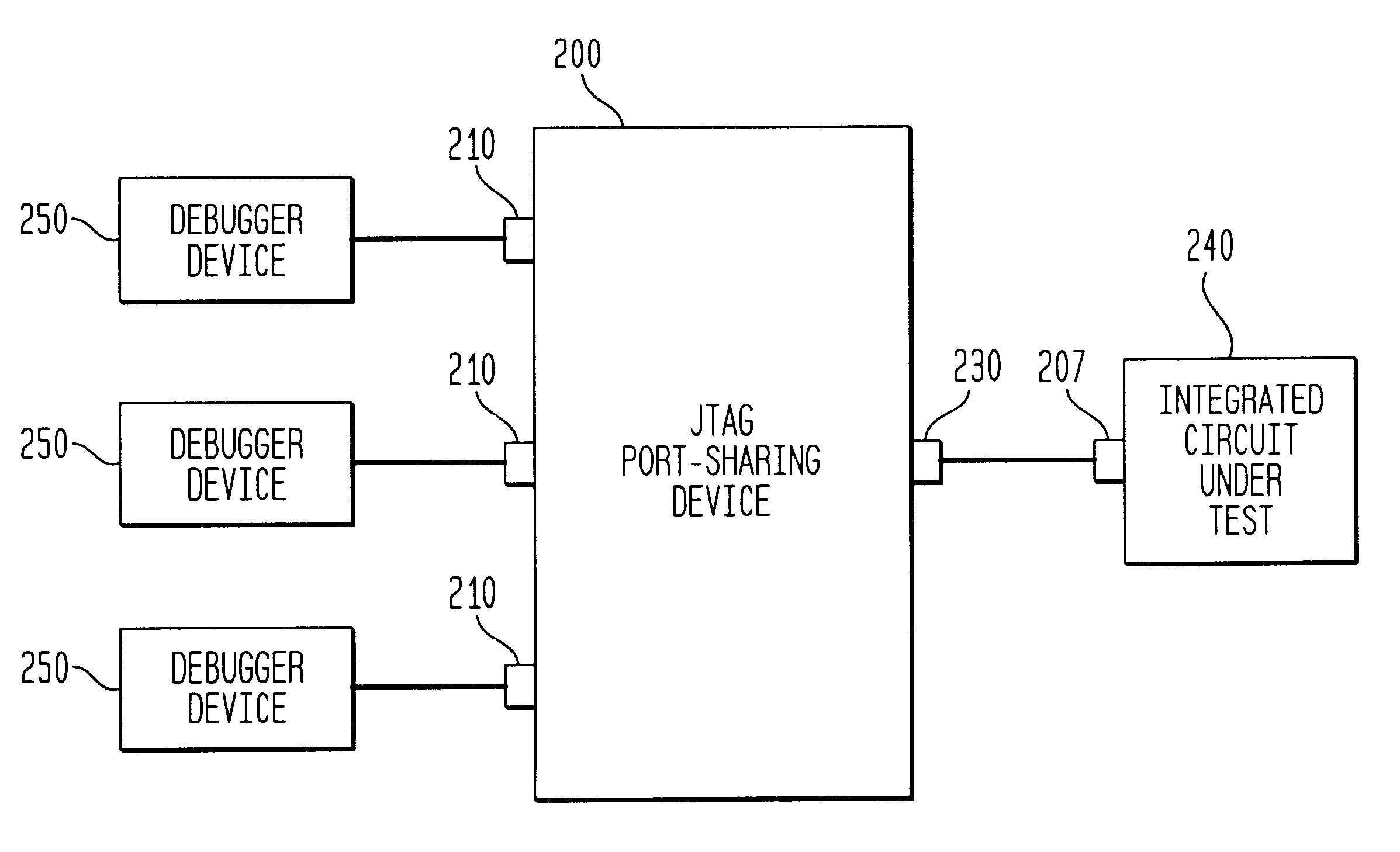
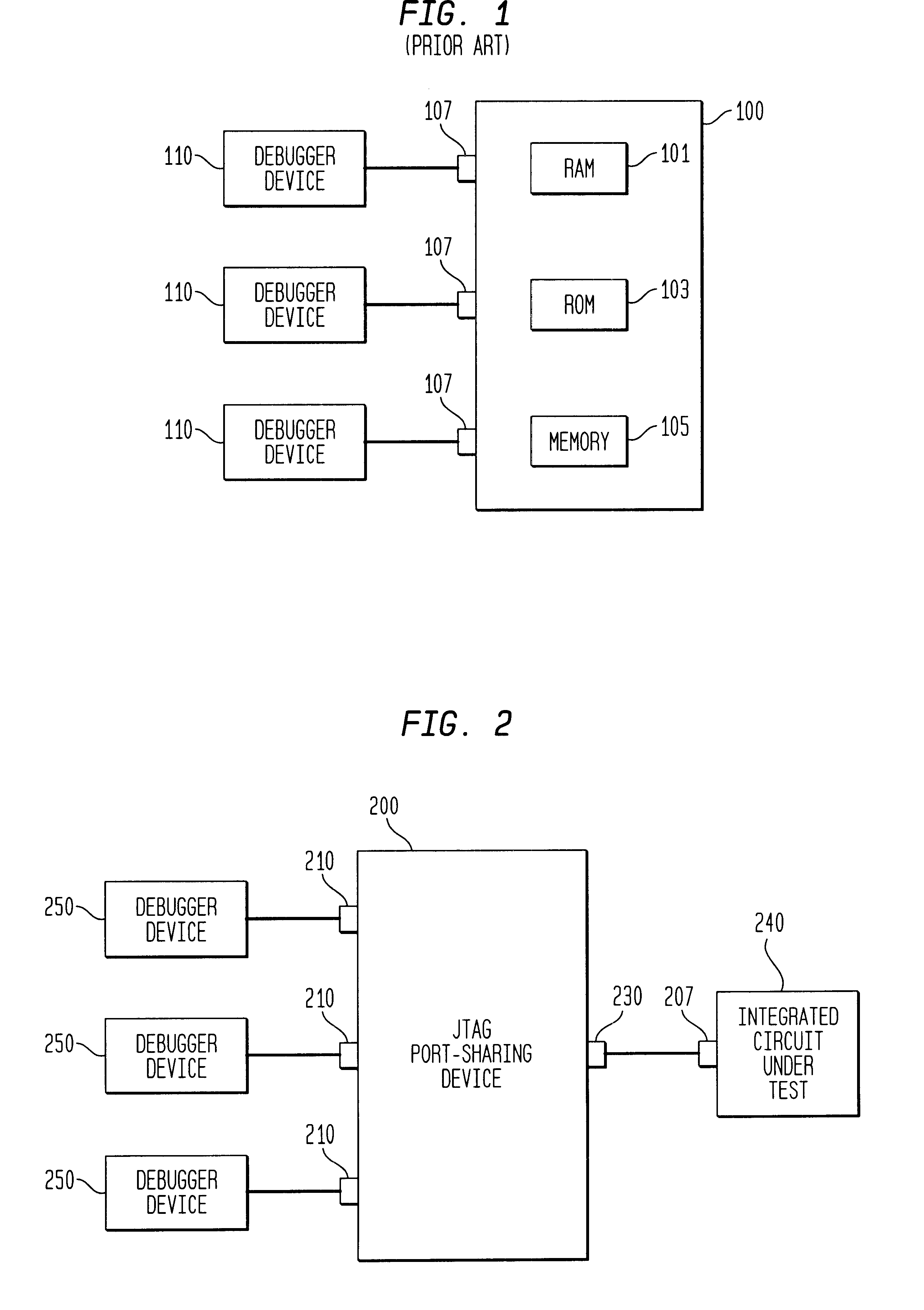
JTAG port-sharing device
InactiveUS6584590B1Electronic circuit testingTransmission monitoringOff the shelfJoint Test Action Group
A JTAG port-sharing device that reduces the required number of hardware pins on an integrated circuit without limiting the integrated circuit testing to a particular debugging platform is provided. The JTAG port-sharing device eliminates the need to have individual hardware pins for each functional block that requires JTAG test interface and allows one set of hardware pins to be shared by a plurality of functional blocks. The JTAG port-sharing device is not limited by a particular debugging platform and allows the use of pre-owned and / or off-the-shelf testing software and / or JTAG debugger devices thereby leading to shorter development cycles and lower development costs.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
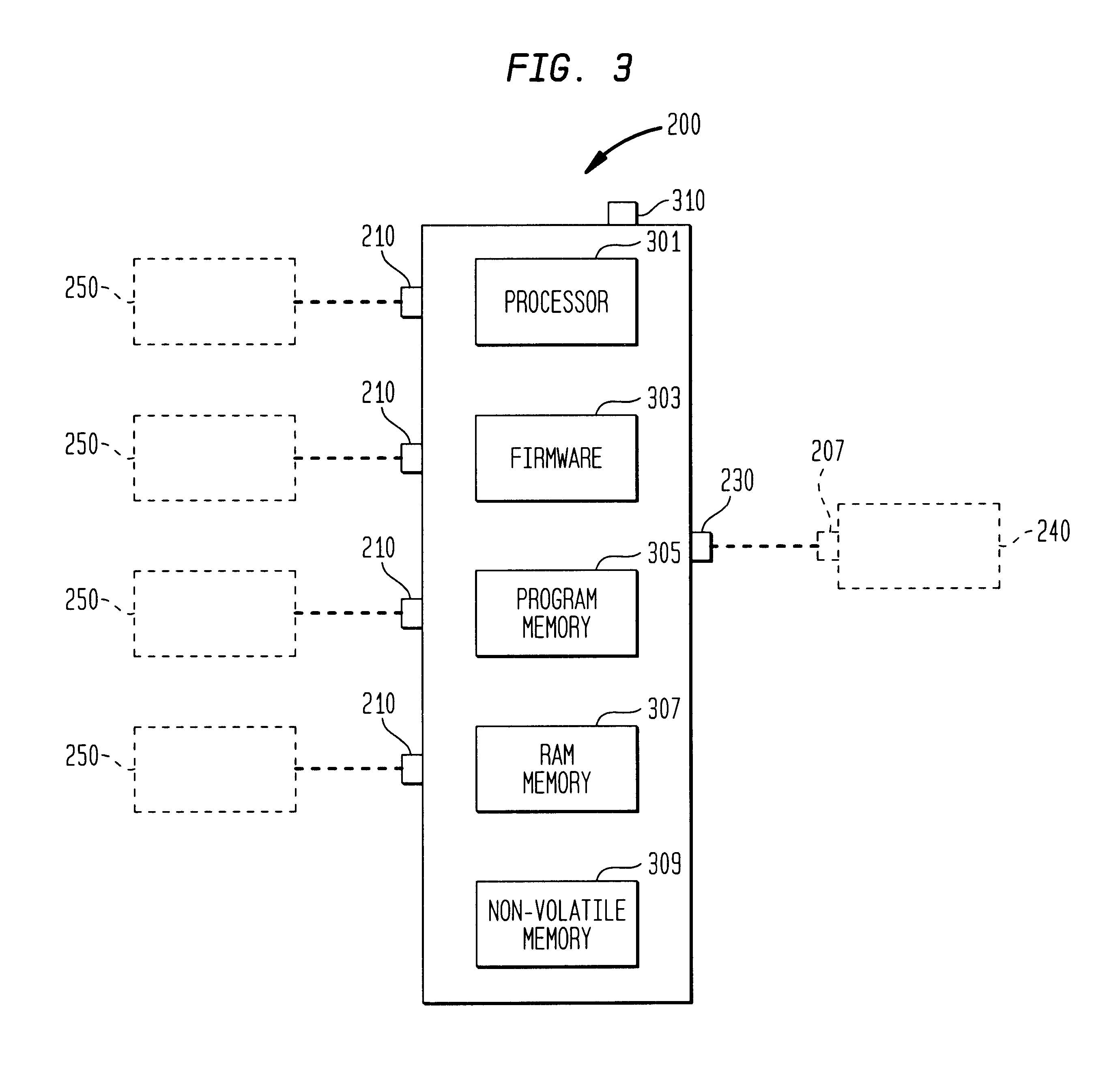
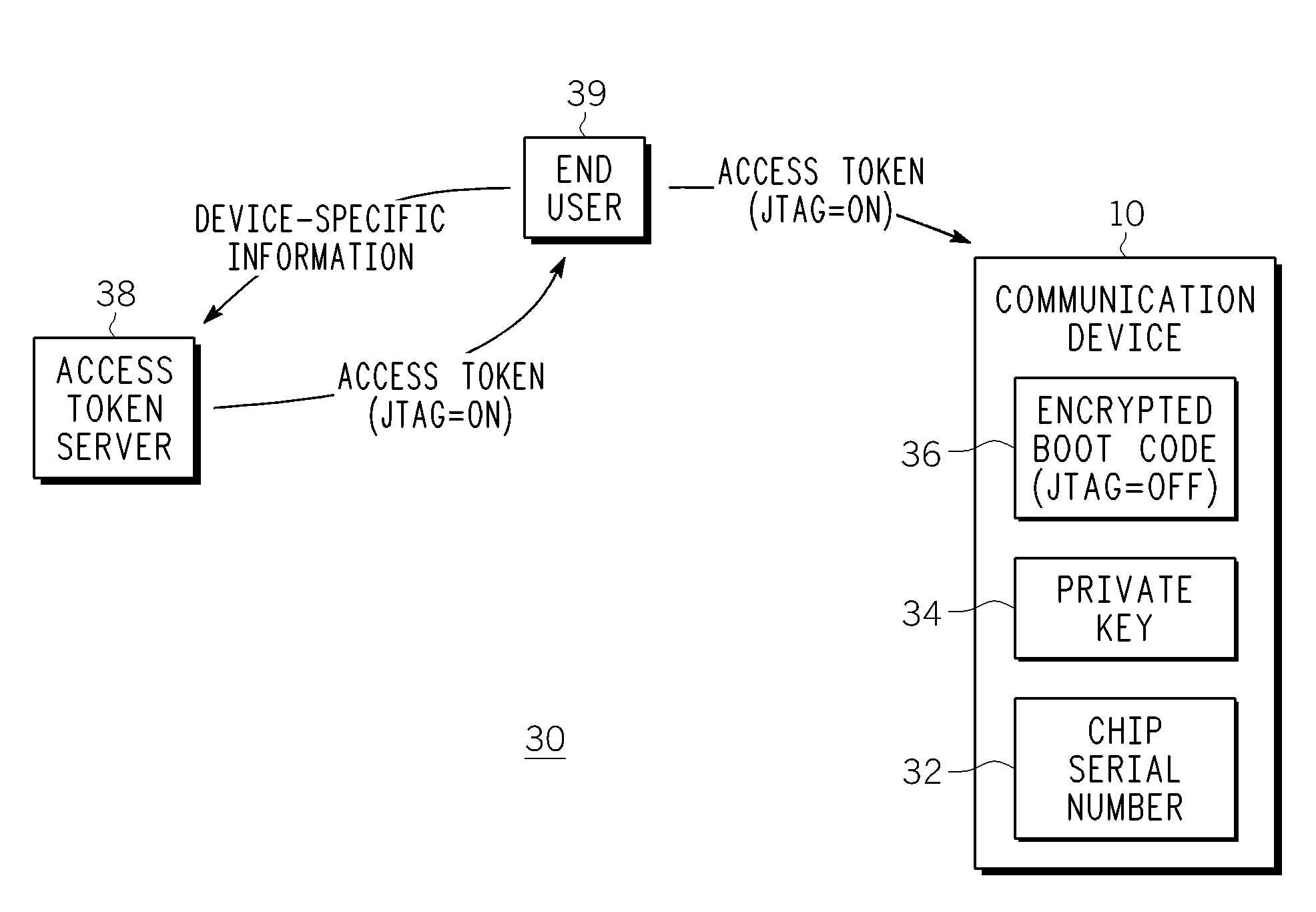
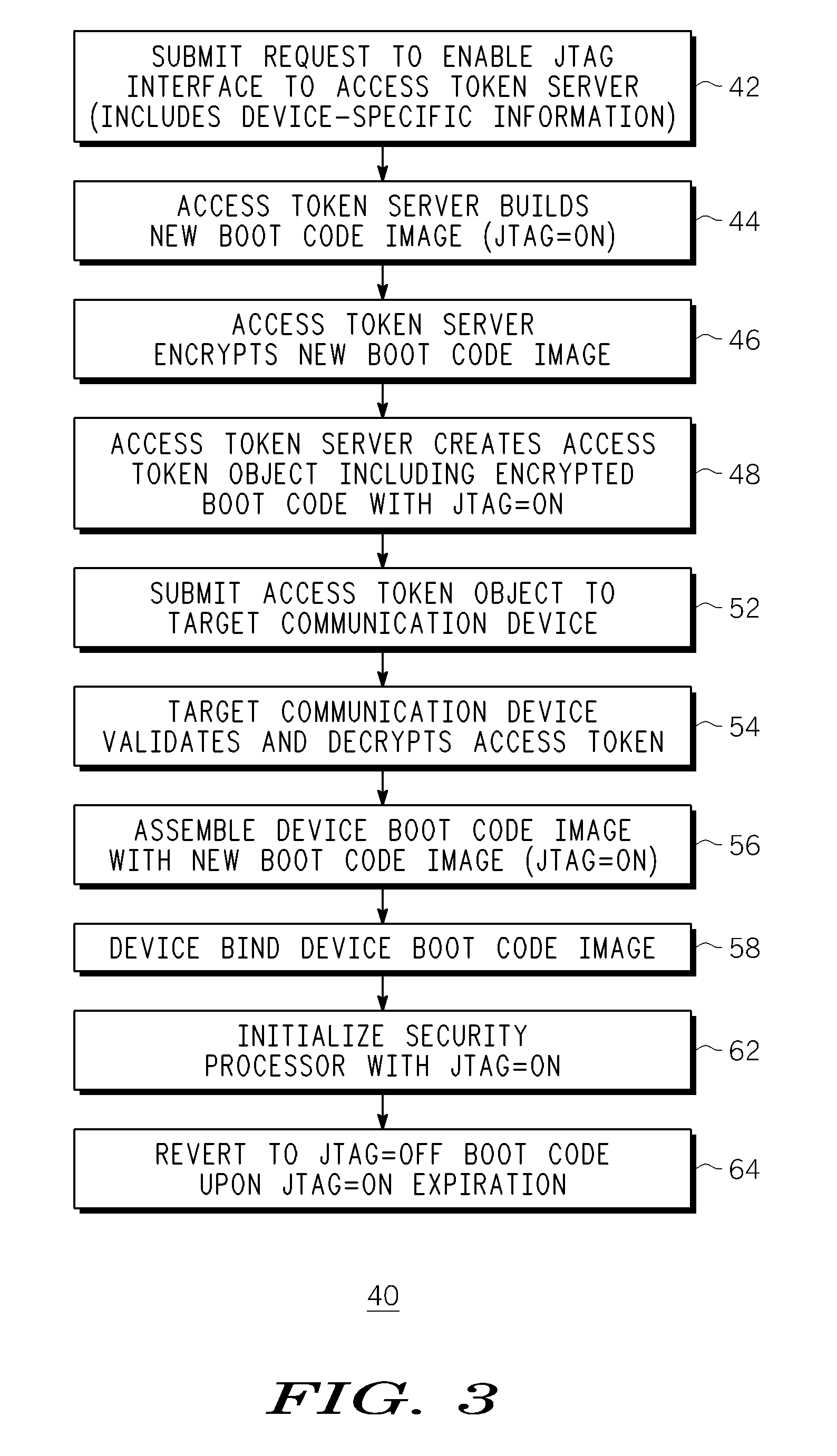
Method and apparatus for controlling enablement of jtag interface
ActiveUS20100217964A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsGeneral purposeControl communications
A method, device and system for controlling JTAG interface enablement within a communication device. The JTAG interface can be selectively enabled based on the receipt of an encrypted access token generated by an access token server. The access token server generates the access token in response to an end user providing appropriate device-specific information. The access token includes appropriate information that, upon appropriate authentication and decryption, can temporarily device bind the boot code image of the device in a manner that enables the JTAG interface. Alternatively, the access token includes appropriate information that instructs the general purpose processor to choose between JTAG interface enablement information and JTAG interface disablement information for use with the boot code image of the device. The access token can include expiration information that causes an enabled JTAG interface to revert back to its disabled status upon expiration of the access token.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
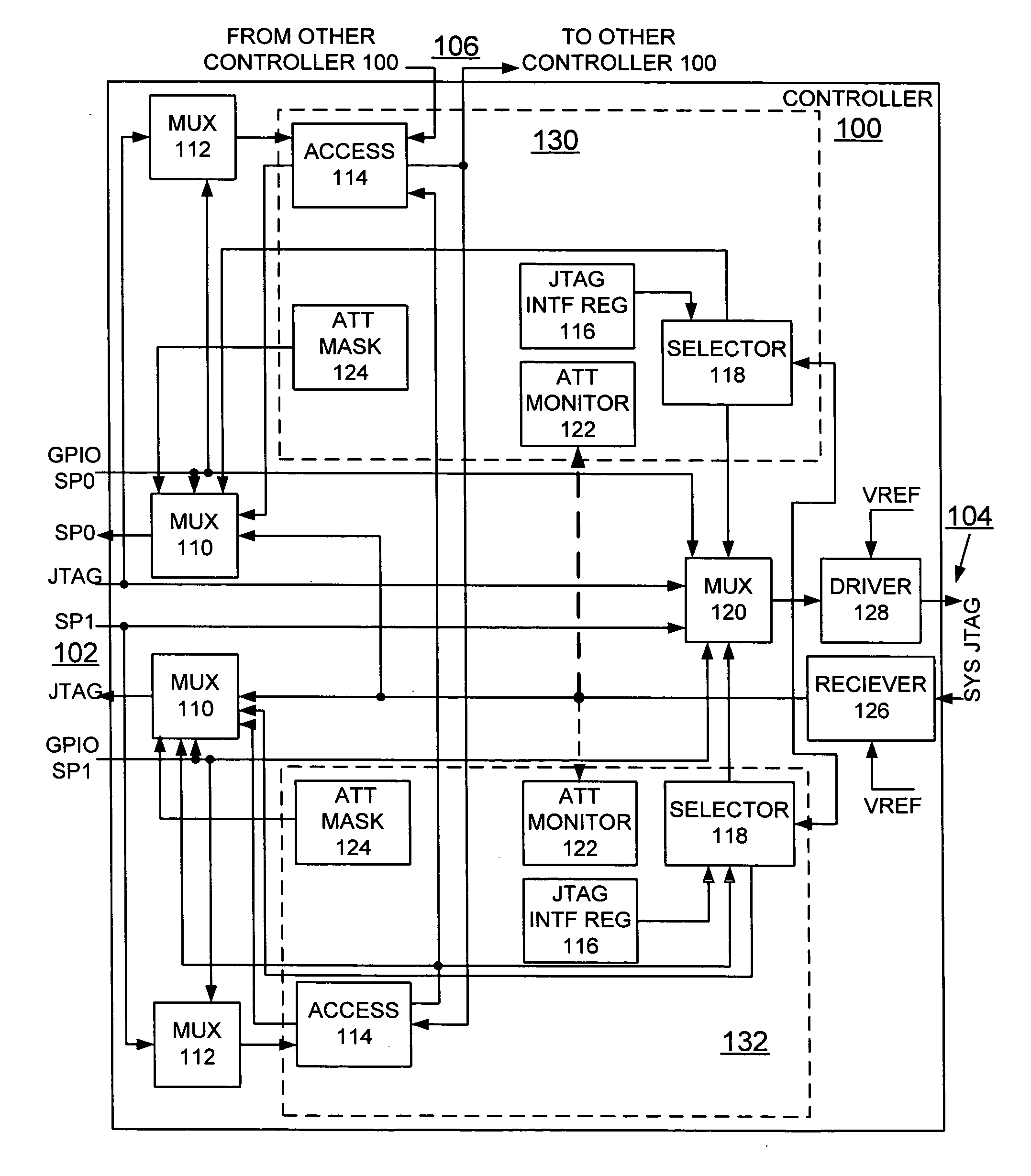
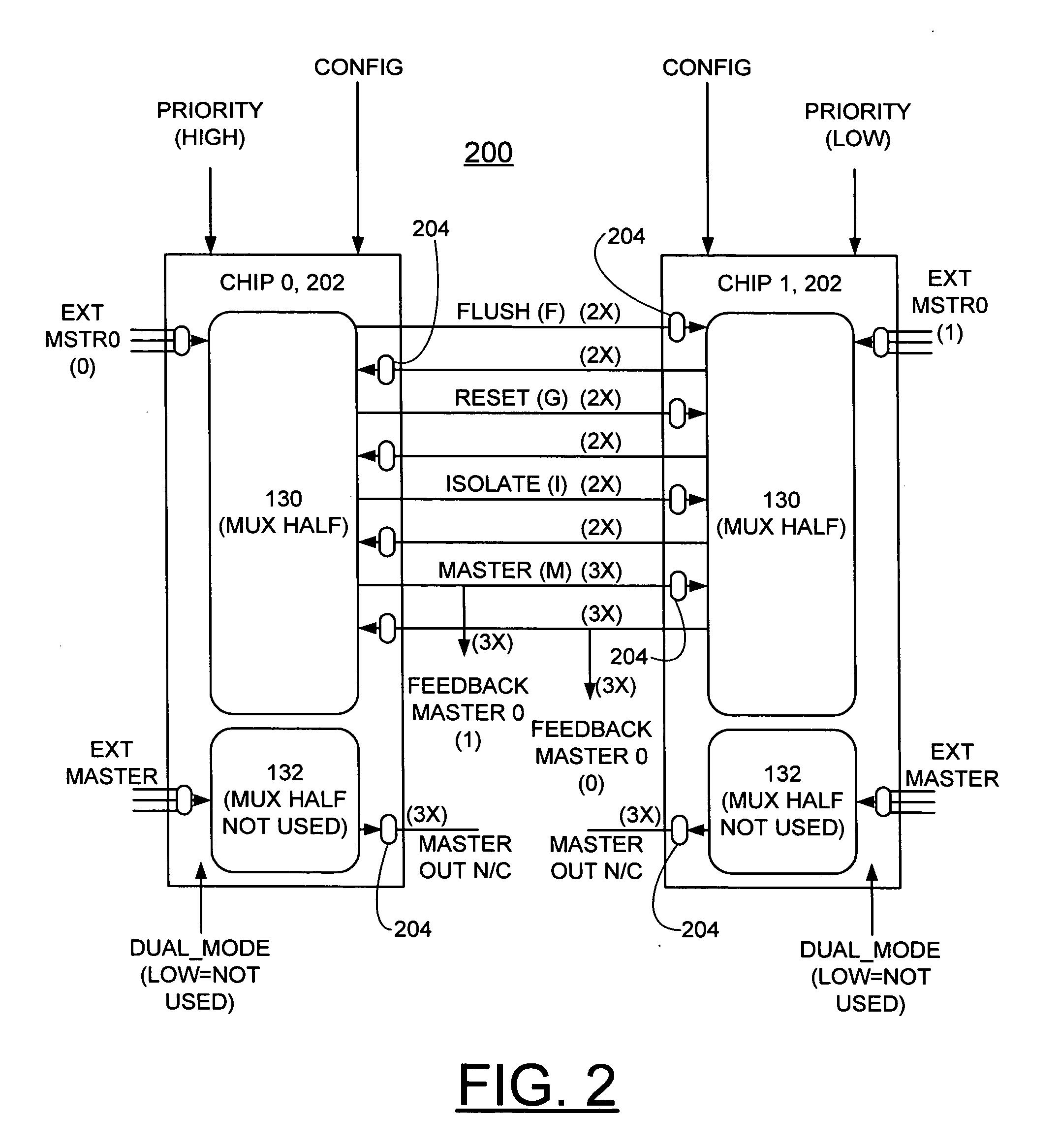
Method and apparatus for customizing and monitoring multiple interfaces and implementing enhanced fault tolerance and isolation features
InactiveUS20050204216A1Improve fault toleranceEnhanced isolation featureElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionFault toleranceMultiplexer
A method and apparatus are provided for customizing and monitoring multiple interfaces, such as, multiple IEEE 1149.1 standard joint test access group (JTAG) interfaces and implementing enhanced fault tolerance and isolation features. A first interface is connected to a pair of master sources. A second interface is connected to a plurality of target interfaces; and a third interface is provided for a plurality of predefined control signals. A pair of redundant selectors is provided for coupling a select signal to the first multiplexer for selecting one of the plurality of target interfaces. A pair of redundant ATTENTION monitor functions is provided for monitoring ATTENTION signals for each of the plurality of target interfaces
Owner:IBM CORP
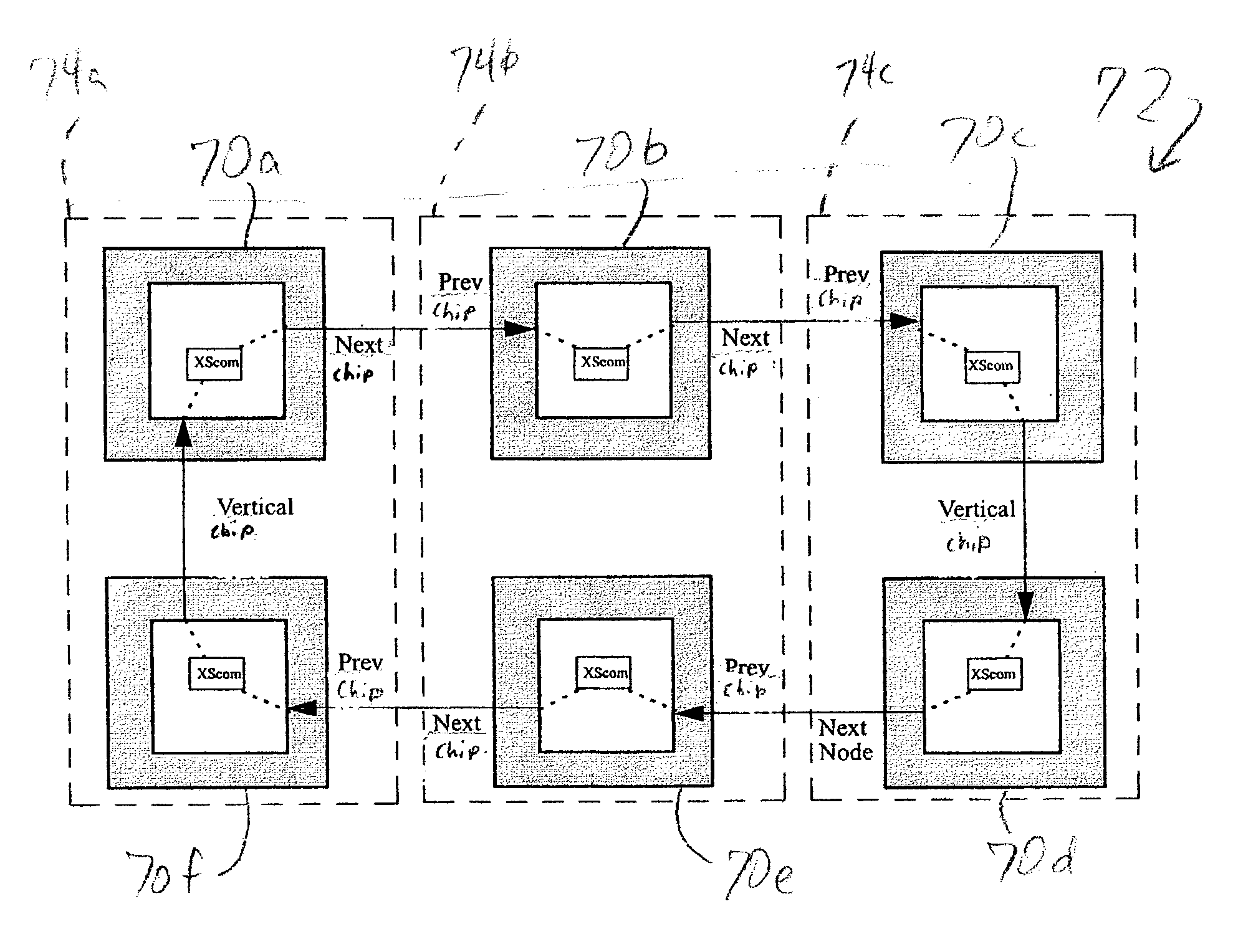
Cross-chip communication mechanism in distributed node topology
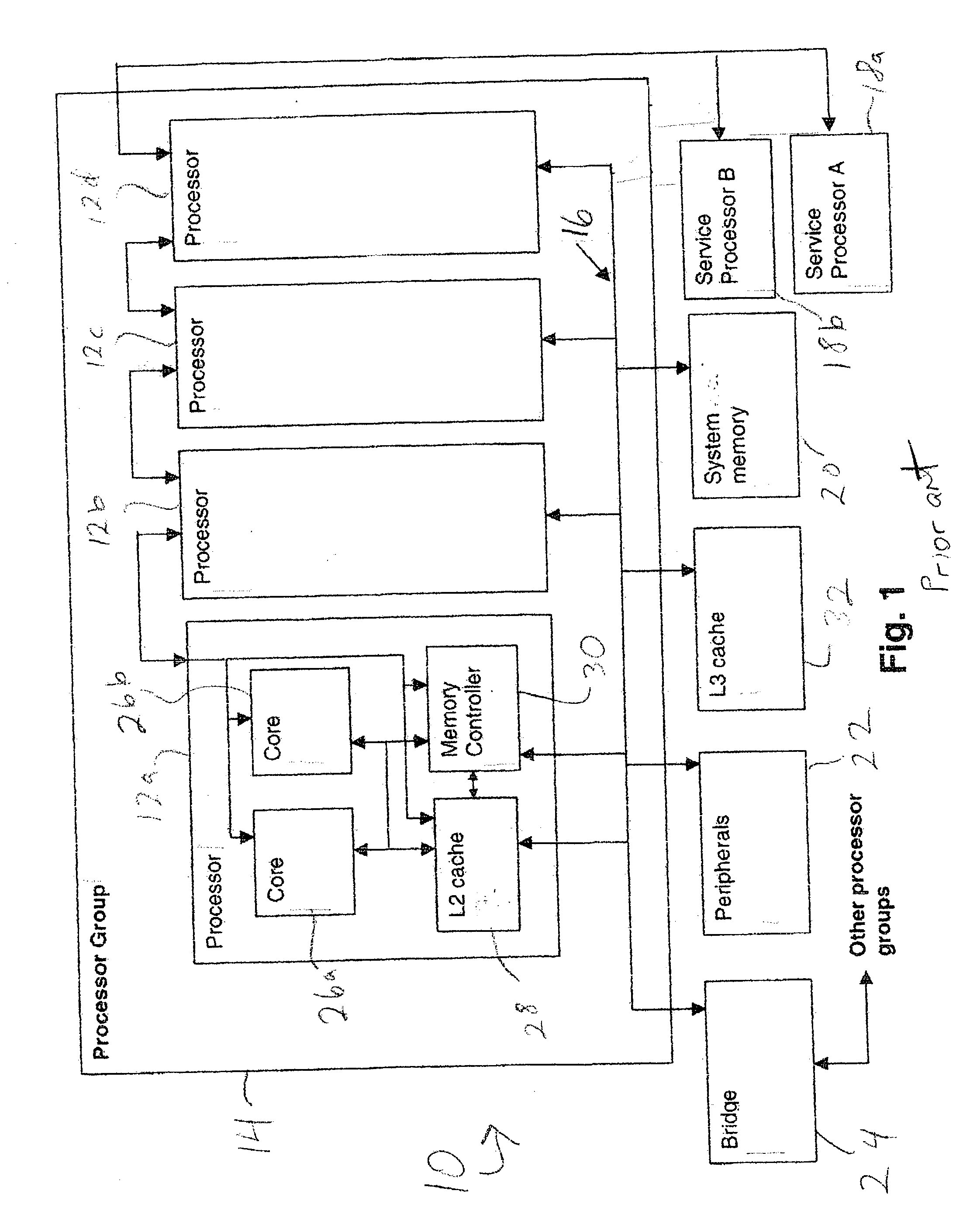
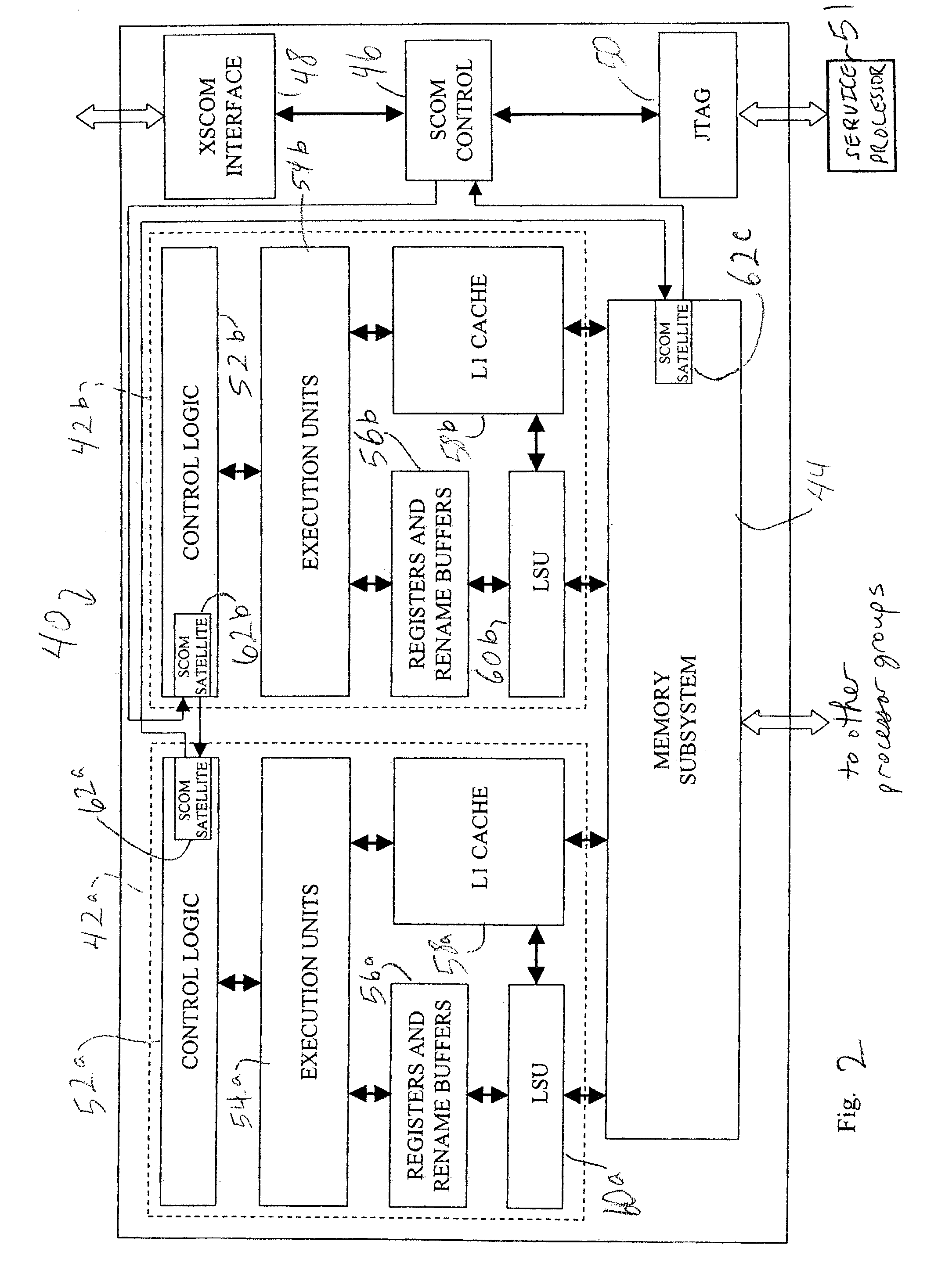
InactiveUS20040215929A1Promote disseminationSubstation/switching arrangement detailsElectric digital data processingTransmission protocolMain processing unit
A method of communicating between processing units on different integrated circuit chips in a multi-processor computer system by issuing a command from a source processing unit to a destination processing unit, receiving the command at the destination processing unit while the destination processing unit is processing program instructions, and accessing registers in clock-controlled components of the destination processing unit without interrupting processing of the program instructions by the destination processing unit. The access may be a read from status or mode registers of the destination processing unit, or write to control or mode registers. Many processing units can be interconnected in a ring topology, and the access command can be passed from the source processing unit through several other processing units before reaching the destination processing unit. Each of the processing units is assigned a respective, unique identification number (PID) in addition to one or more optional "special" tags which are not necessarily unique, and an external command (XSCOM) interface on a given chip recognizes only those commands that include the corresponding chip tag, unless the command is a broadcast. Commands may be directed to subgroups of processors by implementing masks against the PID, selected portion of the PID, or other "special" tag in a broadcast fashion. The XSCOM interface also has the ability to block any broadcast command (e.g., reset) to itself when that command was issued by its associated processing unit (a "Block Self" mode). The processing units are interconnected via a fabric bus, and the XSCOM interface preferably uses an additional communications line that follows the topology of the fabric bus or could alternately use command / data packets across the existing fabric transmission protocol. The service processor has access to this command interface through an external port (e.g. JTAG) and assembly code running on the processing unit has access to the command interface via special assembly code sequences.
Owner:IBM CORP
Simplified process to design integrated circuits
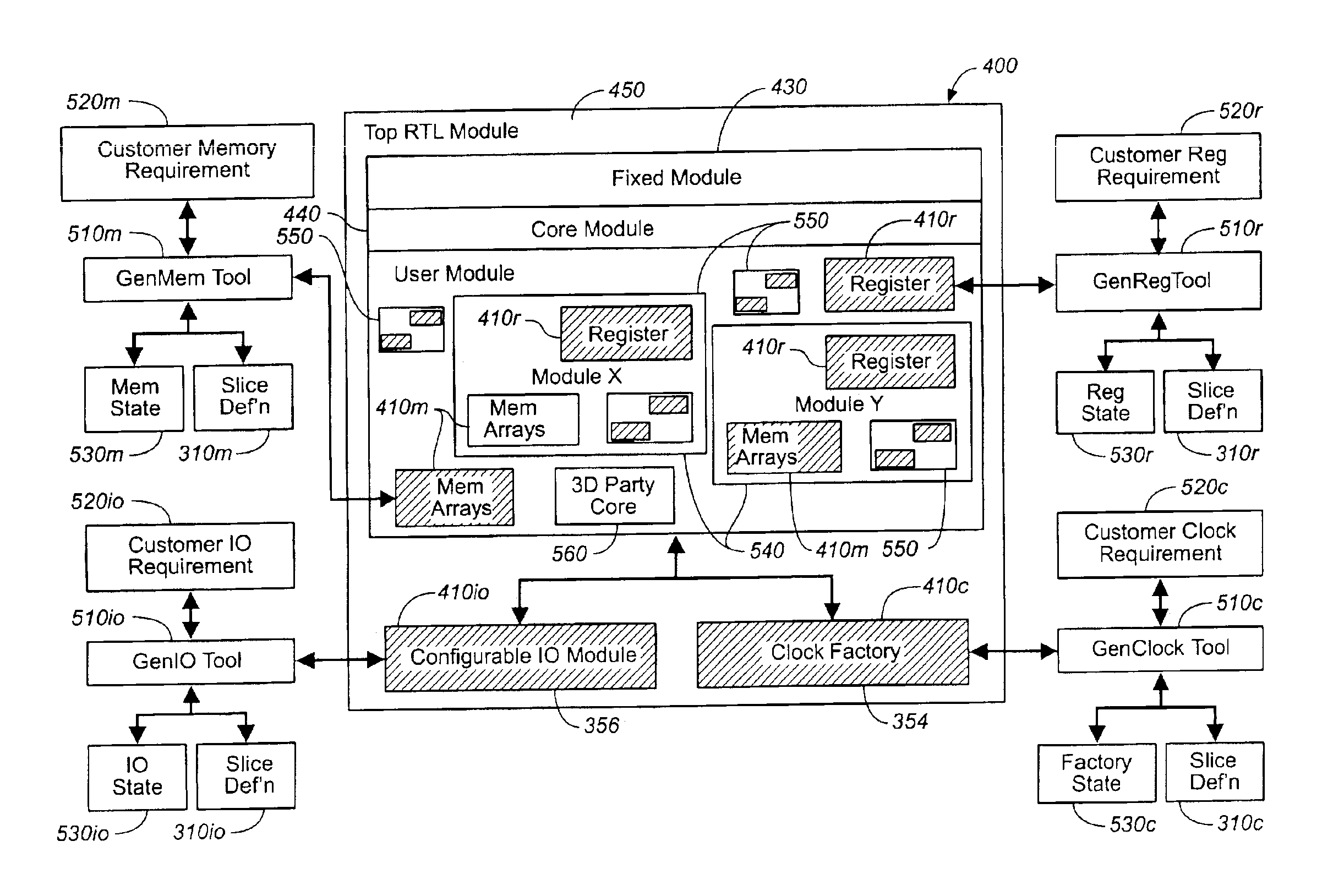
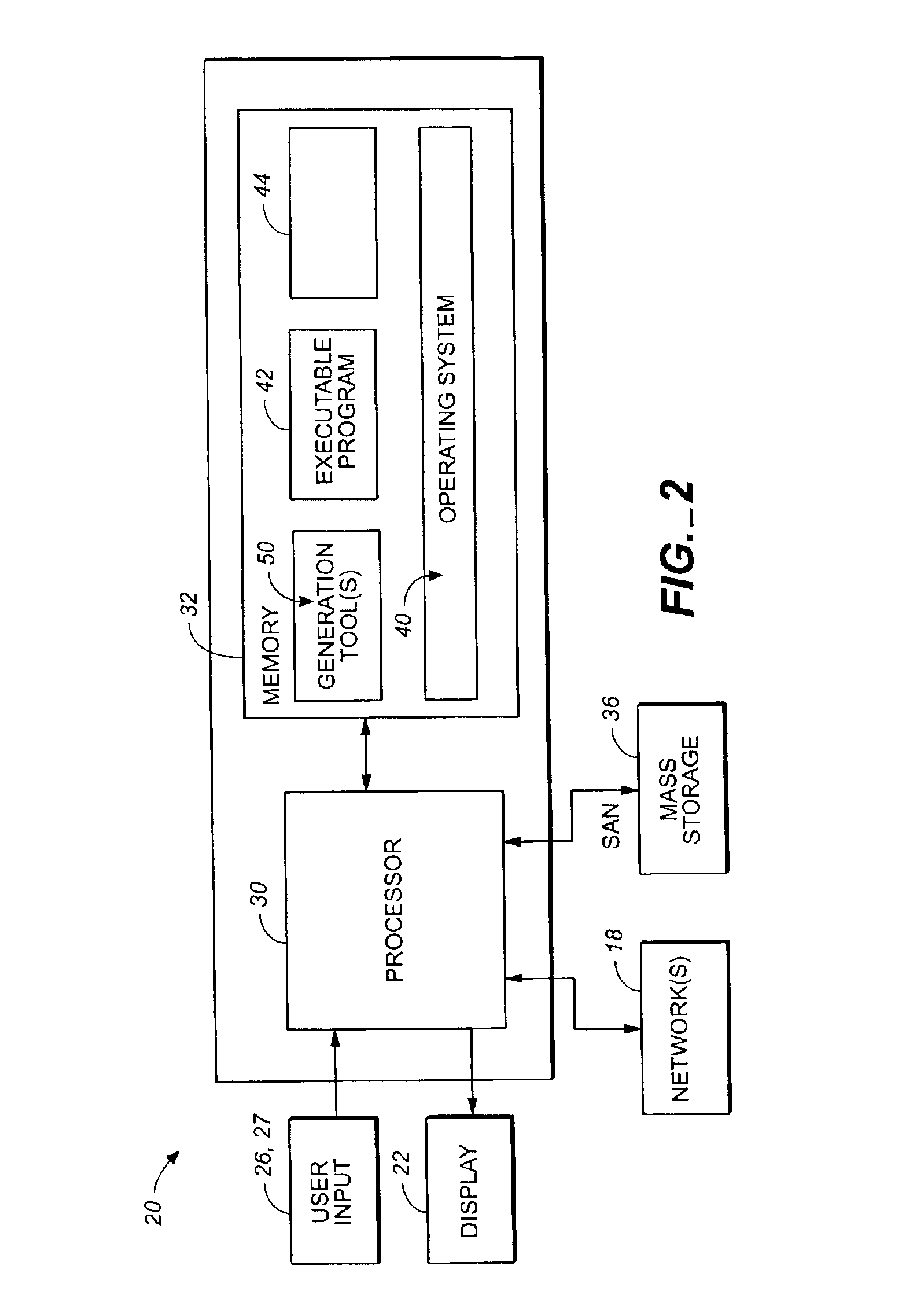
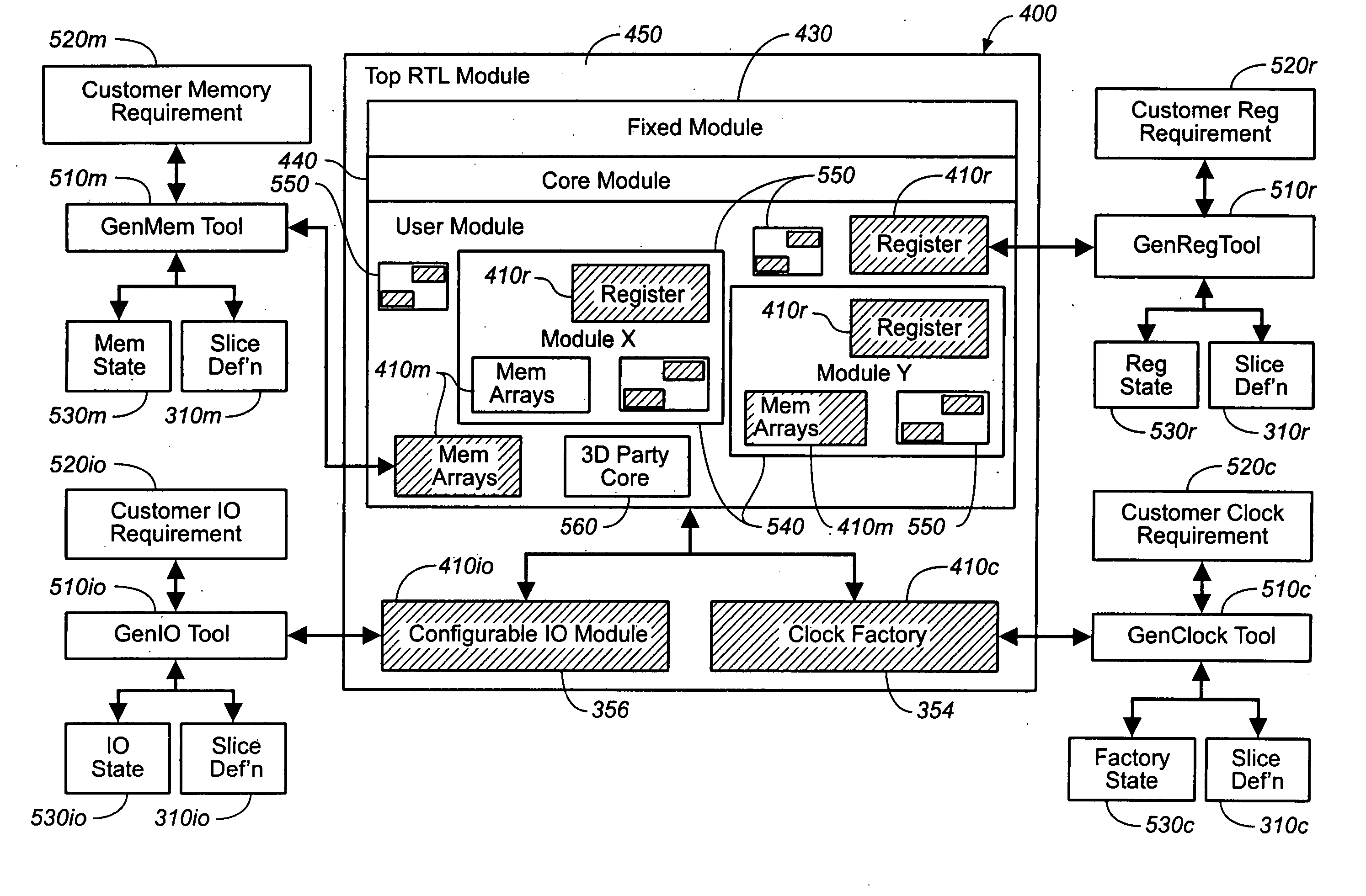
ActiveUS7055113B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCustomer requirementsFoundry
A set of tools is provided herein that produces useful, proven, and correct integrated semiconductor chips. Having as input either a customer's requirements for a chip, or a design specification for a partially manufactured semiconductor chip, the tools generate the RTL for control plane interconnect; memory composition, test, and manufacture; embedded logic analysis, trace interconnection, and utilization of spare resources on the chip; I / O qualification, JTAG, boundary scan, and SSO analysis; testable clock generation, control, and distribution; interconnection of all of the shared logic in a testable manner from a transistor fabric and / or configurable blocks in the slice. The input customer requirements are first conditioned by RTL analysis tools to quickly implement its logic. The slice definition and the RTL shell provides the correct logic for a set of logic interfaces for the design specification to connect. The tools share a common database so that logical interactions do not require multiple entries. The designs are qualified, tested, and verified by other tools. The tools further optimize the placement and timing of the blocks on the chip with respect to each other and with respect to placement on a board. The suite may be run as batch processes or can be driven interactively through a common graphical user interface. The tools also have an iterative mode and a global mode. In the iterative mode, one or more of the selected tools can generate the blocks or modify a design incrementally and then look at the consequences of the addition, or change. In the global mode, the semiconductor product is designed all at once in a batch process as above and then optimized altogether. This suite of generation tools generates design views including a qualified netlist for a foundry to manufacture.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
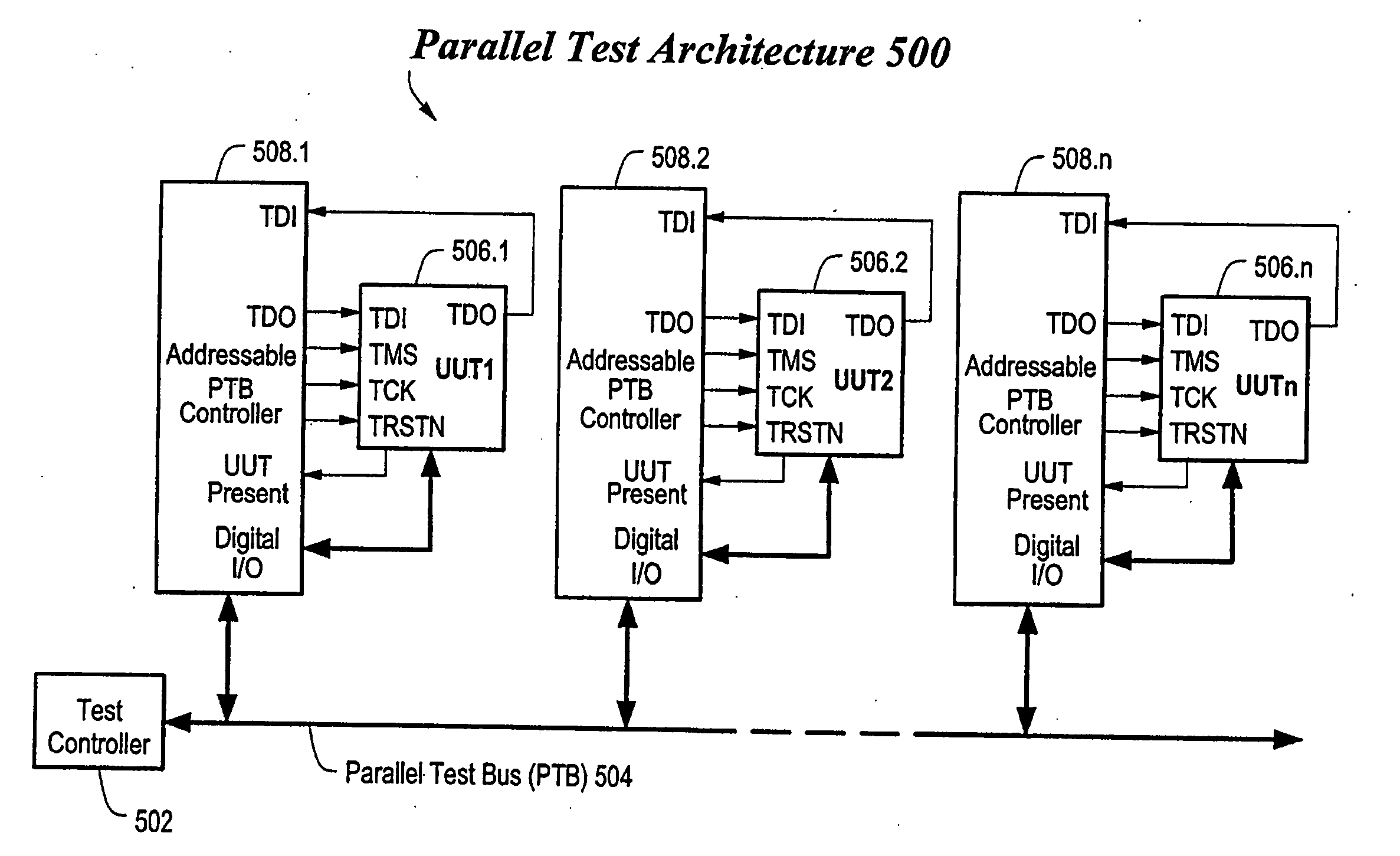
Method and apparatus for optimized parallel testing and access of electronic circuits
InactiveUS20060107160A1Easy accessIncreased “ parallel ” testingElectronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareMaster controllerJoint Test Action Group
Owner:INTELLITECH INC
Microcontroller controlled or direct mode controlled network-fabric on a structured ASIC
ActiveUS8677306B1Easy to switchElectronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareMicrocontrollerIntelligent Network
A network-fabric used for testing with an external or internal tester is shown for a Structured ASIC. In one embodiment, the Structured ASIC uses a microprocessor, network-aware IO routing fabric comprising network agents in a scalable novel configuration, with the network-aware IO having a plurality of blocks connected in series in a plurality of paths in the fabric leading to and from the microprocessor and memory and / or logic, the blocks acting as intelligent network agents under processor control to determine what state they can assume, whether to pass a data signal or not along these paths, comprising open loops and closed loops running to and from the microprocessor and memory and / or logic, primarily for testing and determining the state of the memory and logic. In another embodiment a JTAG controller may receive JTAG test commands from an external testing apparatus and set up to communicate along the fabric.
Owner:INTEL CORP
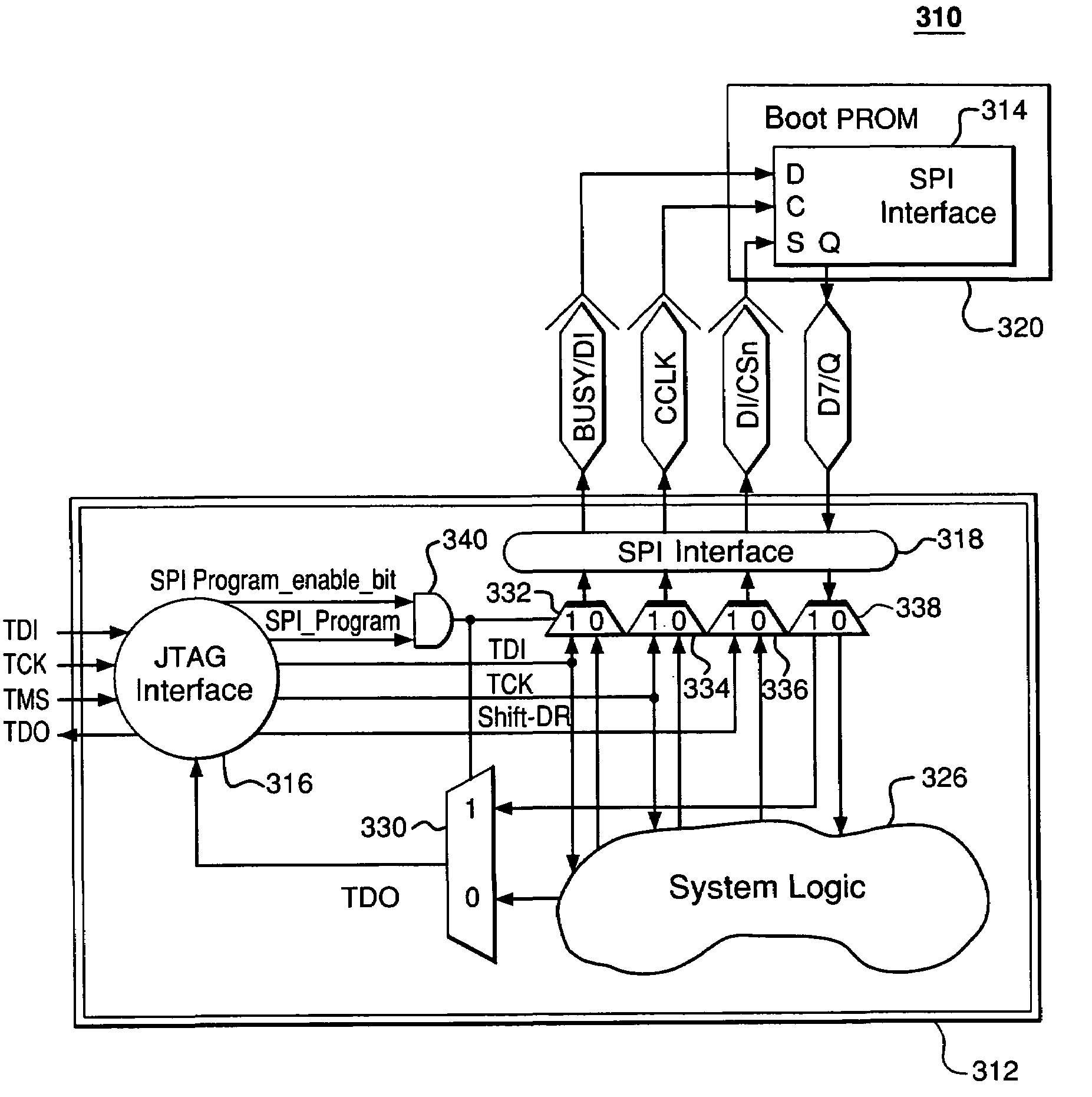
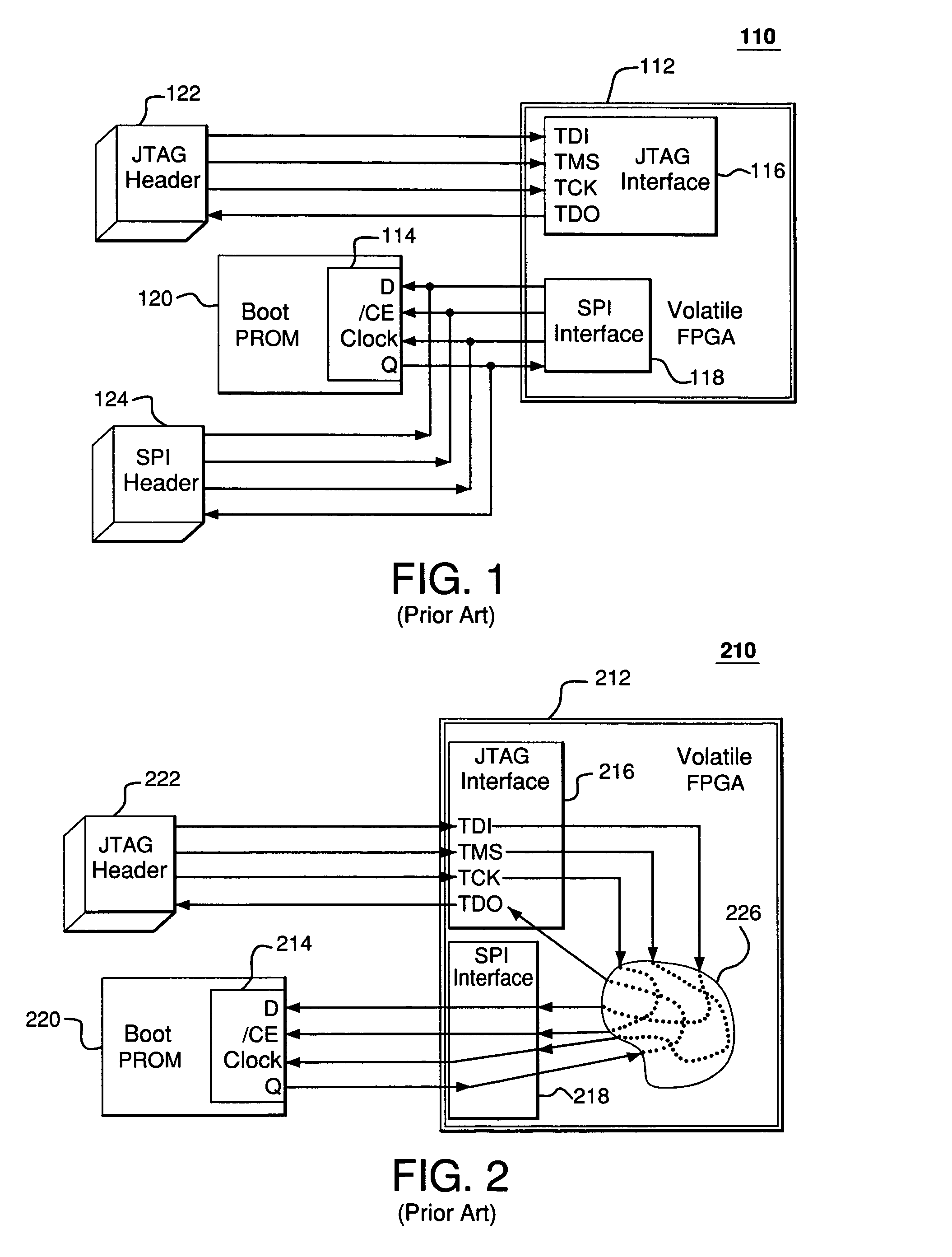
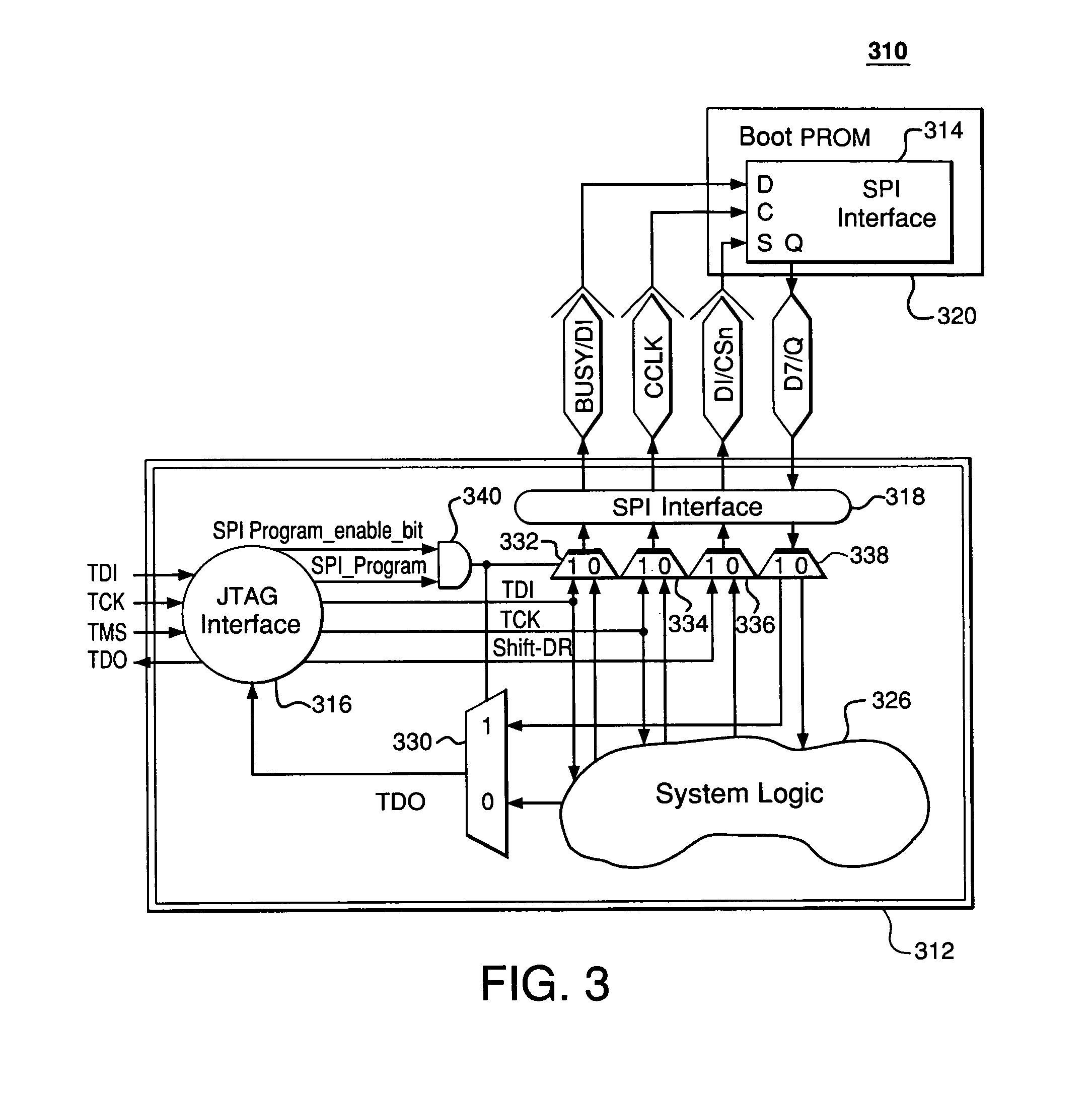
In-system programming of non-JTAG device using SPI and JTAG interfaces of FPGA device
ActiveUS7265578B1Electronic circuit testingLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsIn-system programmingJoint Test Action Group
A first programmable device comprises non-dedicated, programmable resources including programmable logic; dedicated circuitry; a Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) interface adapted to selectively interchange signals with the programmable logic via the dedicated circuitry; and a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) interface adapted to (1) selectively interchange signals with the programmable logic via the dedicated circuitry and (2) selectively interchange signals with the JTAG interface via the dedicated circuitry. The JTAG interface is adapted to be connected to a first external device. The SPI interface is adapted to be connected to a second external device. The first programmable device is adapted to transfer signals from the first external device to the second external device via the JTAG interface, the dedicated circuitry, and the SPI interface without relying on any of the programmable resources.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Automatic test system and method of programmable logic device on basis of boundary scan
The invention belongs to the field of electronic technology, in particular to an automatic test system and method of a programmable logic device on the basis of boundary scan. The test method comprises the following steps: generating a chip configuration file; downloading and configuring an FPGA (field programmable gate array) chip; generating and loading a test vector; comparing test results; building a corresponding test system; and completely realizing automation. In the invention, the test vector of an item to be tested is automatically generated by a user through software, and the on-line test of the hardware function of a user circuit is realized by combining JTAG (joint test action group) automatic downloading test software. Scripted test environment converts a series of complex manual test operation into full automatic software flow so as to greatly improve test speed and accuracy.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Programming flash memory via a boundary scan register
ActiveUS6937493B2Reduce effortElectronic circuit testingRead-only memoriesFunctional testingOn board
A method and parallel interface for on-board programming and / or In-System Configuration of a flash memory mounted on a printed circuit board by controlling its inputs with the aid of an ASIC mounted on the same circuit board via a Boundary Scan register of which the output signals are provided for activating or deactivating a write operation. The architecture description of the ASIC, flash memory, and the data format of the program and configuration data are stored in a Boundary-Scan Description Language file. The circuit board can be controlled via a JTAG interface suitable for performing function testing of the flash memory for input or output of standard bus signals and for input of the control signals of the ASIC. To reduce the programming effort, the data of the circuit diagram or of the network list derived from it is stored in the BSDL file.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
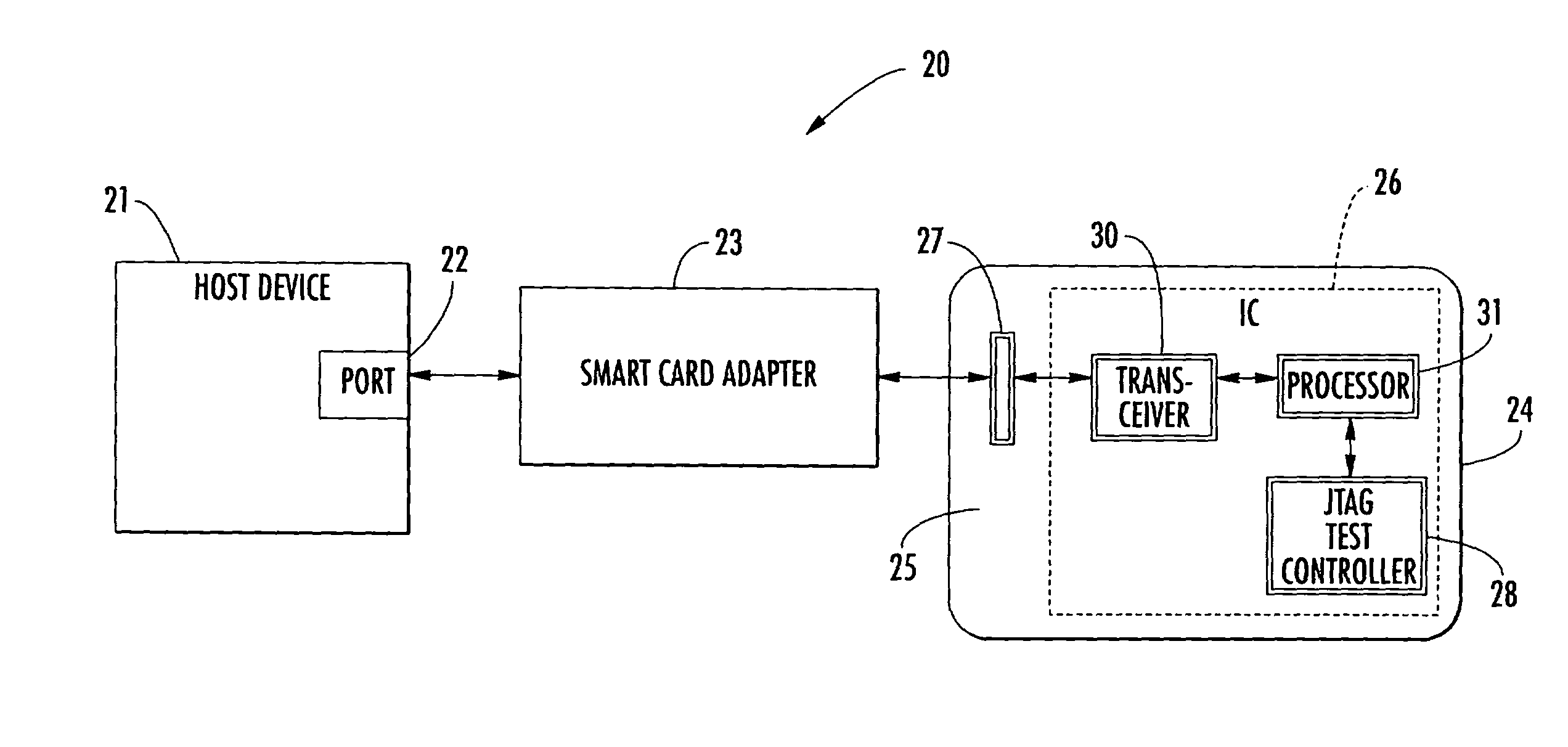
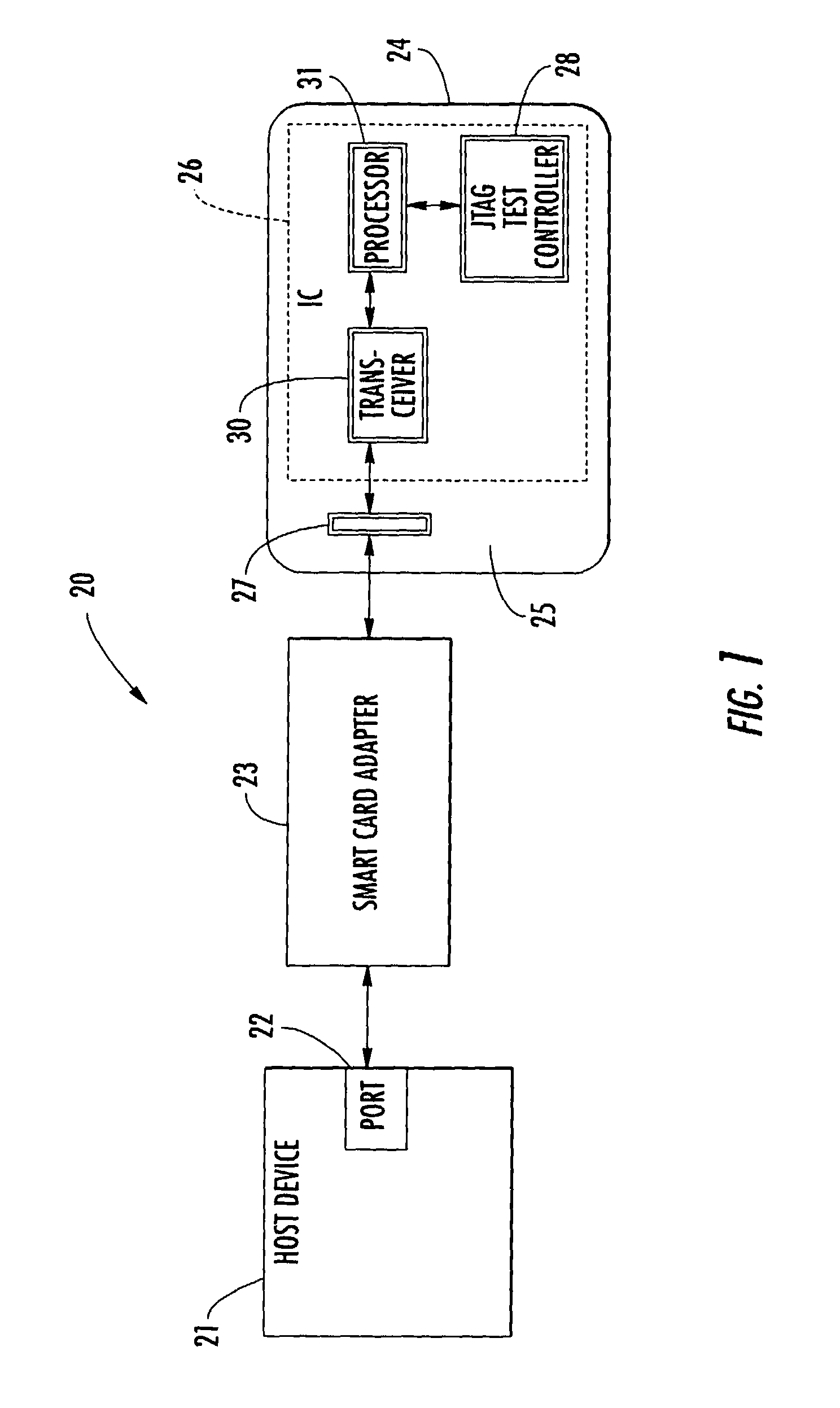
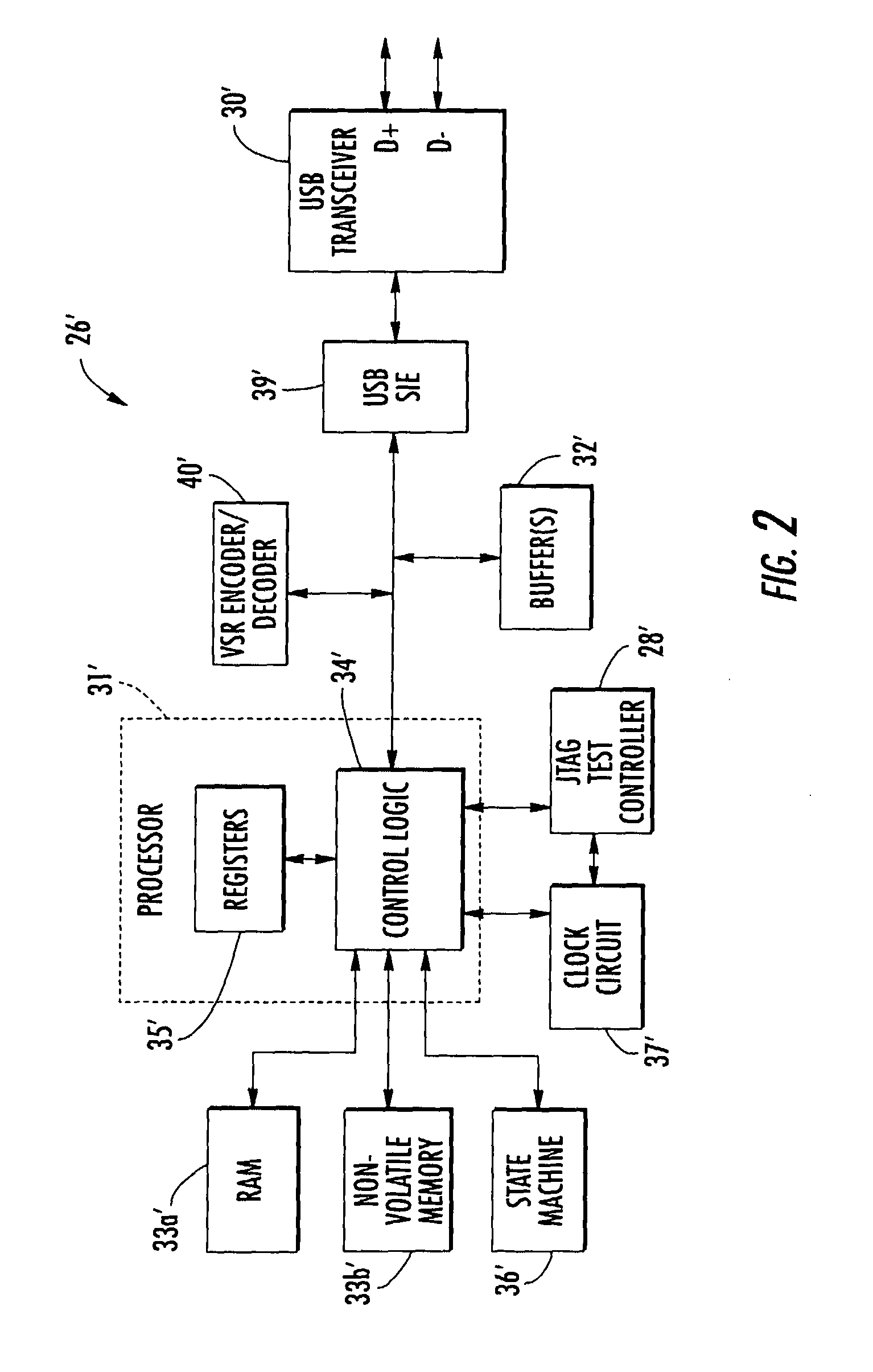
Smart card including a JTAG test controller and related methods
ActiveUS7080789B2Meet growth requirementsTesting sensing arrangementsError preventionTransceiverTest requirements
An integrated circuit for a smart card may include a transceiver for communicating with a host device and a Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) test controller for performing at least one test operation. Further, the integrated circuit may also include a processor for causing the JTAG test controller to initiate the at least one test operation based upon receiving at least one test request from the host device via the transceiver. More particularly, the processor may convert the at least one test request to JTAG data for the JTAG test controller. That is, the integrated circuit advantageously allows communications between the host device and the JTAG controller via a system bus, for example, without the need for a dedicated JTAG test access port (TAP) which is typically required for accessing JTAG controllers.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
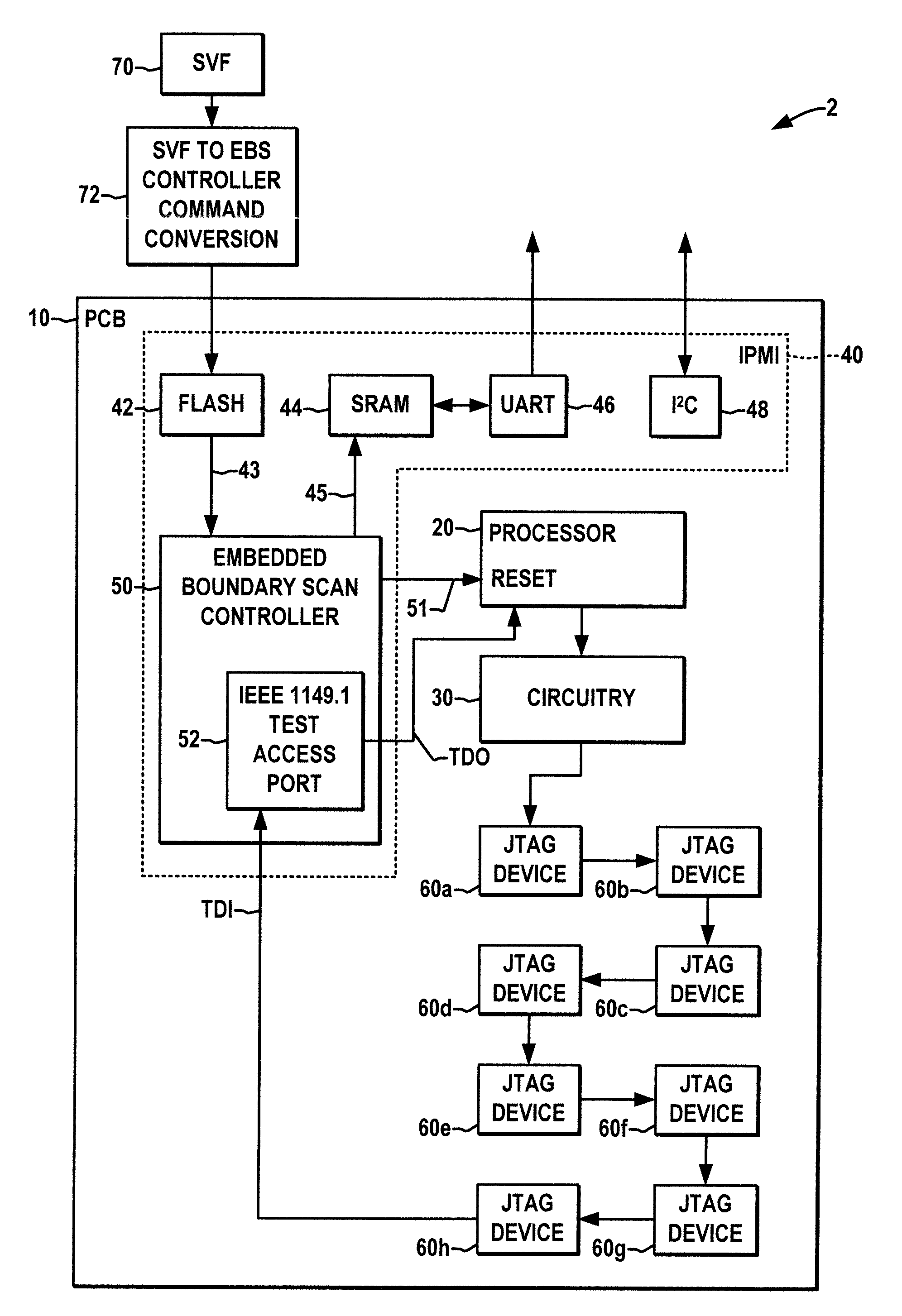
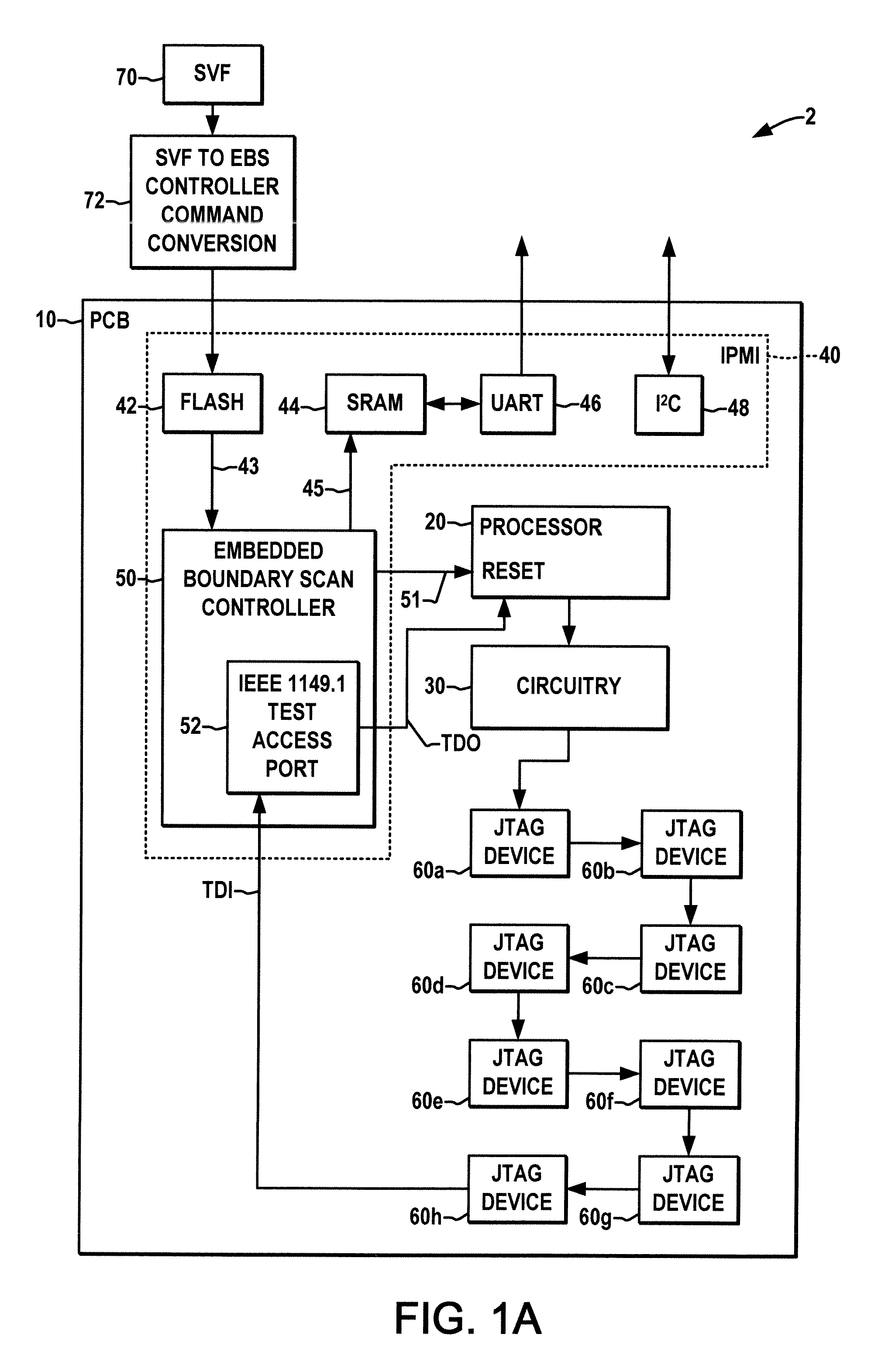
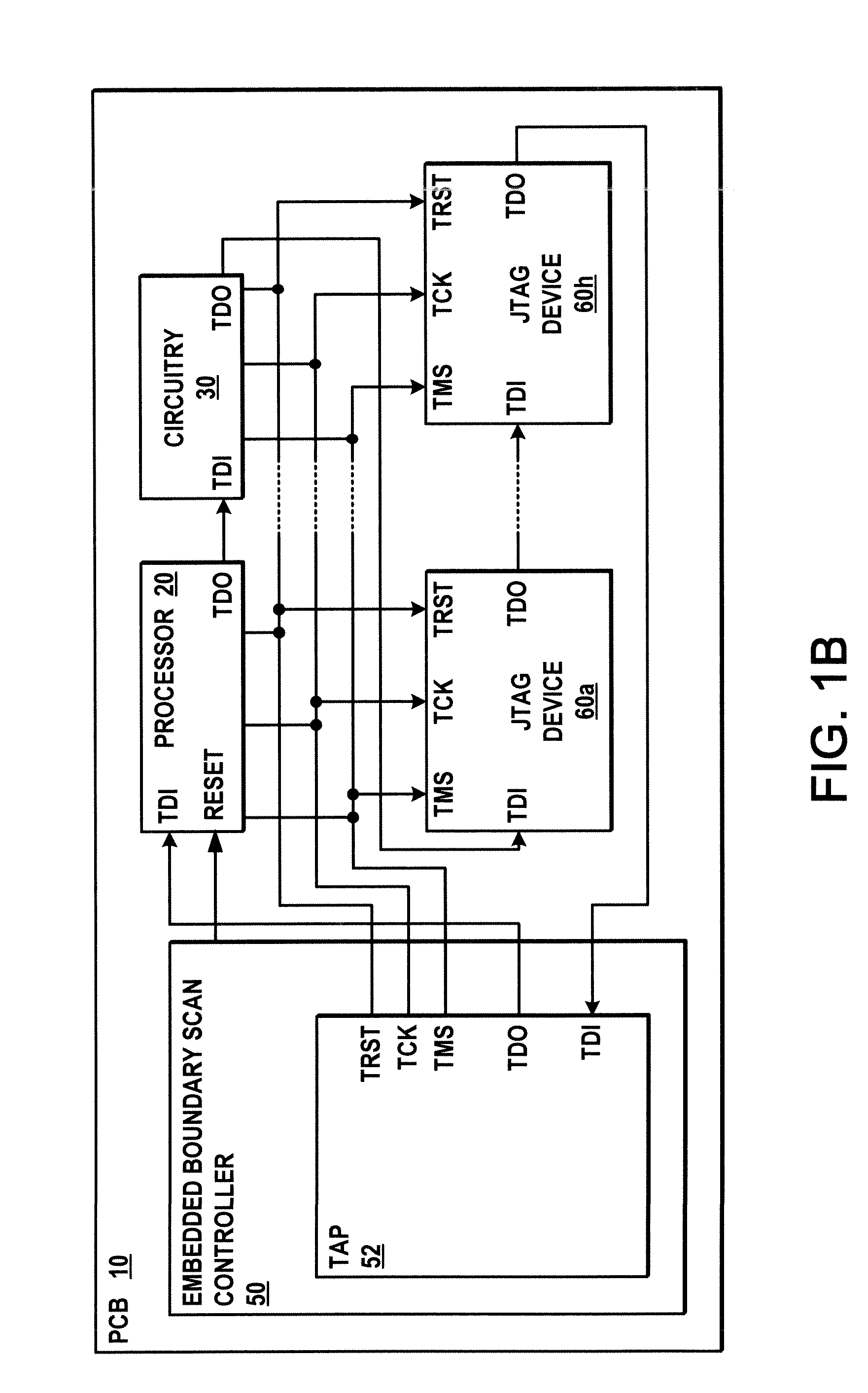
Apparatus and method for embedded boundary scan testing
ActiveUS20090006915A1Small sizeElectronic circuit testingLogical operation testingOn boardJoint Test Action Group
Embedded boundary scan testing apparatus and methodologies are disclosed for testing processor-based circuit boards without processor intervention. A boundary scan controller is embedded in a circuit board along with a boundary scan chain having JTAG devices connected with an electrical circuit of the board. Upon power up, the boundary scan controller holds an on-board processor system in reset, loads boundary scan test vectors and commands from an on-board non-volatile memory, and runs boundary scan testing while holding the processor system in the reset state. The boundary scan controller preferably includes a test access port controller that implements only a subset of the JTAG standard 16 machine states to optimize performance and minimize controller hardware. The test results may be stored in an externally accessible on-board memory for subsequent retrieval in order to facilitate board troubleshooting and / or repair, where the provision of on-board boundary scan testing allows testing of boards while installed in the field, and the embedded scan controller allows field testing of on-board processor systems and related circuitry to enhance the test coverage over processor-driven boundary scan testing.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
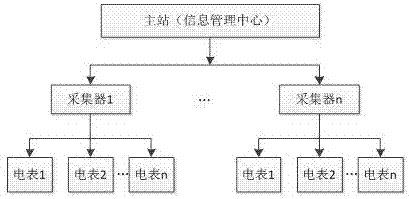
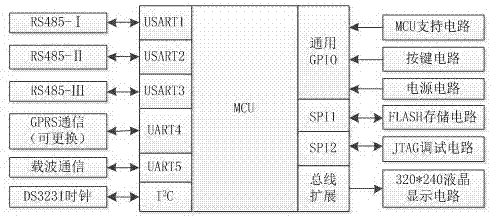
Online collecting and monitoring method of energy measuring data and its system
InactiveCN107967801ARich human-computer interaction interfaceLow costElectric signal transmission systemsActive radio relay systemsCarrier signalData acquisition
The invention discloses an online collecting and monitoring system of energy measuring data, which is composed of two parts, wherein the one part is a hardware platform centered by a MCU control module, and the other part is a management center platform centered by a master station; the management center platform can remotely manage the collector through a GPRS module, the hardware platform can perform data collection on an intelligent meter by 485 method and a wave carrier method and report to the management center; the online collecting and monitoring system is characterized in that the hardware platform comprises an embedded controller circuit, an RS-485 communication circuit, a GPRS communication circuit, an electricity carrier wave communication circuit, a clock circuit, a display circuit, a power circuit, a keyboard input circuit, a JTAG debugging circuit and a storage circuit; the collector adopts two communication methods totally, and two communication methods carry out the data communication by a serial port; the RS-485 communication circuit can modulate the signal to be symmetrical form so as to carry out signal transmission in the manner of balance sending; then the signal is received by a differential way; a half-duplex operation mode of master and slave structures is adopted.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Integrated circuit with embedded test functionality
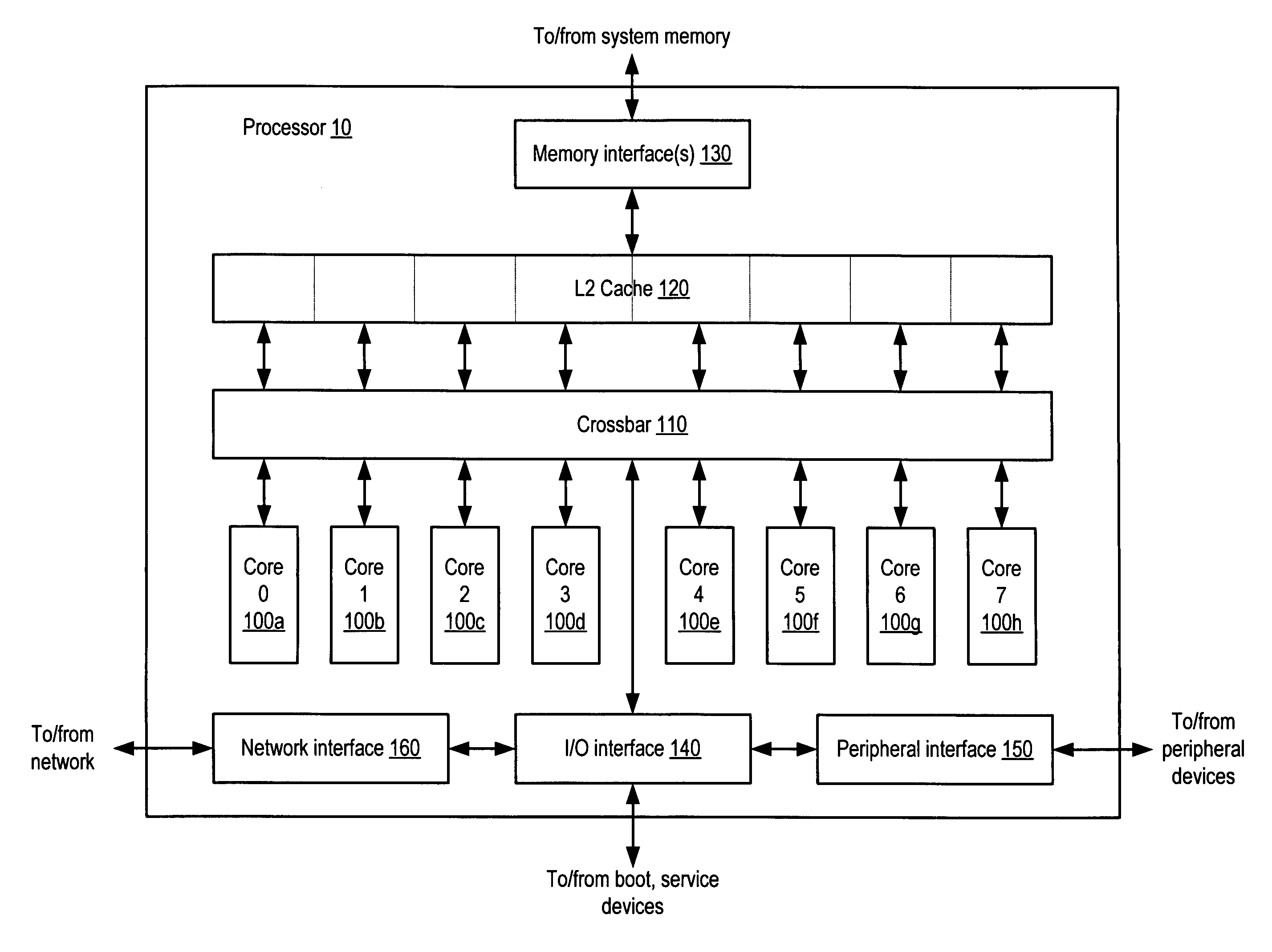
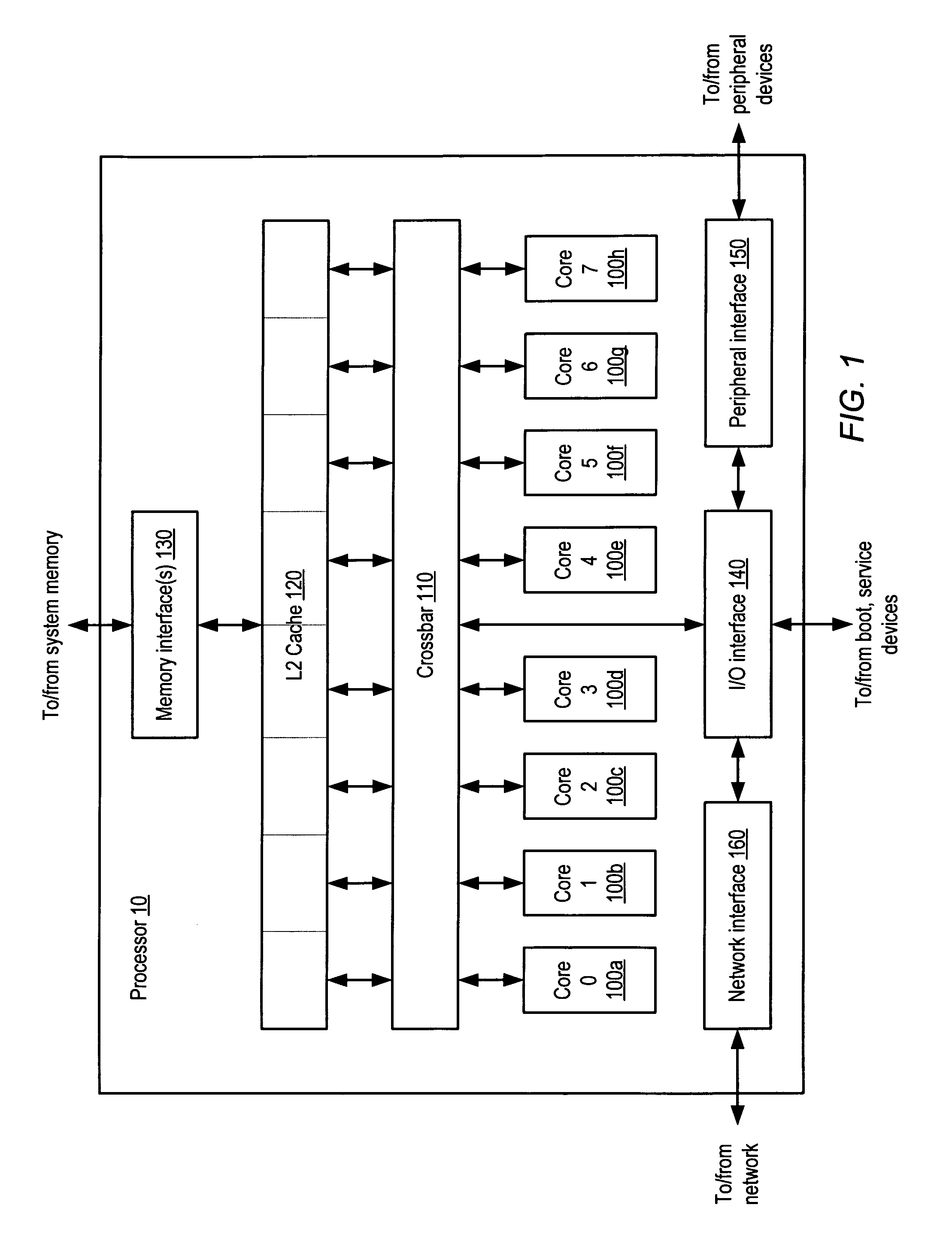
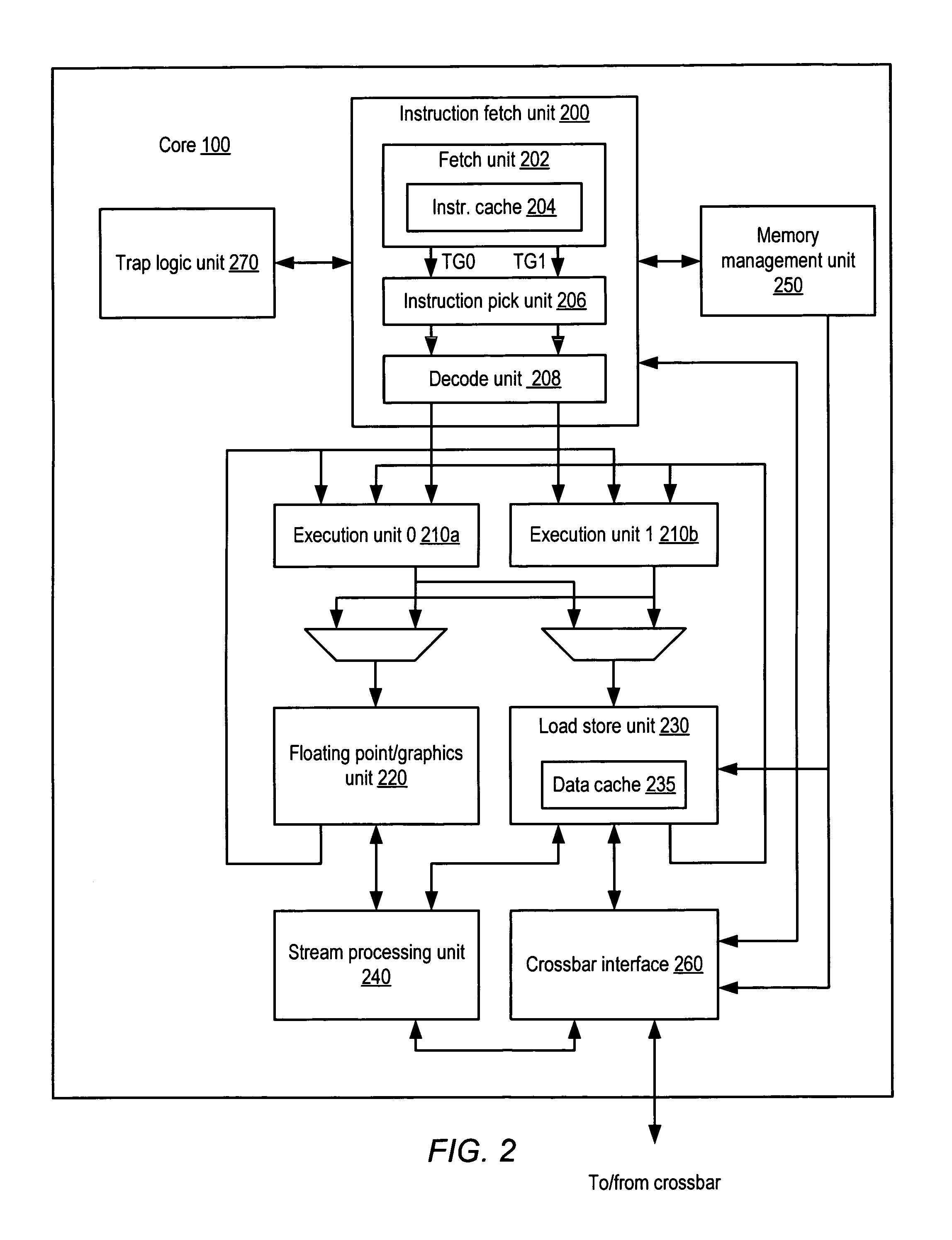
An integrated circuit including embedded test functionality. An integrated circuit may include a plurality of processor cores each configured to execute instructions, and a test access port configured to interface circuits included within the integrated circuit with a test environment external to the integrated circuit for testing of the circuits. The test access port may include virtualization logic configured to allow a first set of instructions executing on the given processor core to control activity of the test access port for testing of the circuits. In one embodiment, the circuits may be accessible for testing via a plurality of scan chains, wherein the scan chains and the test access port are compliant with a version of Joint Test Access Group (JTAG) standard IEEE 1149, and wherein the test access port includes a Test Data In (TDI) pin, a Test Data Out (TDO) pin, and a Test Clock (TCK) pin.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Suite of tools to design integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050240892A1Accelerate Design CycleI/O can be optimizedDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionFoundryCustomer requirements
A set of tools is provided herein that produces useful, proven, and correct integrated semiconductor chips. Having as input either a customer's requirements for a chip, or a design specification for a partially manufactured semiconductor chip, the tools generate the RTL for control plane interconnect; memory composition, test, and manufacture; embedded logic analysis, trace interconnection, and utilization of spare resources on the chip; I / O qualification, JTAG, boundary scan, and SSO analysis; testable clock generation, control, and distribution; interconnection of all of the shared logic in a testable manner from a transistor fabric and / or configurable blocks in the slice. The input customer requirements are first conditioned by RTL analysis tools to quickly implement its logic. The slice definition and the RTL shell provides the correct logic for a set of logic interfaces for the design specification to connect. The tools share a common database so that logical interactions do not require multiple entries. The designs are qualified, tested, and verified by other tools. The tools further optimize the placement and timing of the blocks on the chip with respect to each other and with respect to placement on a board. The suite may be run as batch processes or can be driven interactively through a common graphical user interface. The tools also have an iterative mode and a global mode. In the iterative mode, one or more of the selected tools can generate the blocks or modify a design incrementally and then look at the consequences of the addition, or change. In the global mode, the semiconductor product is designed all at once in a batch process as above and then optimized altogether. This suite of generation tools generates design views including a qualified netlist for a foundry to manufacture.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
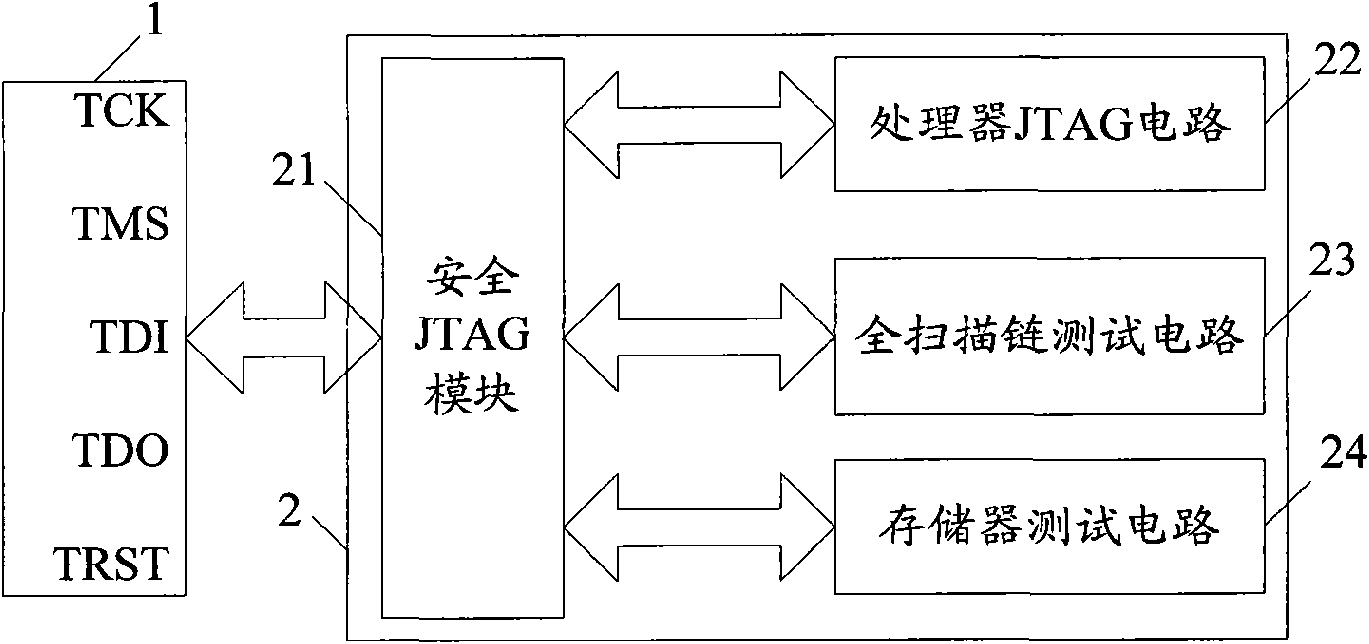
Safety JTAG module and method for protecting safety of information inside chip
InactiveCN101620656AReduce security risksImprove data security featuresInternal/peripheral component protectionProcessor registerPassword
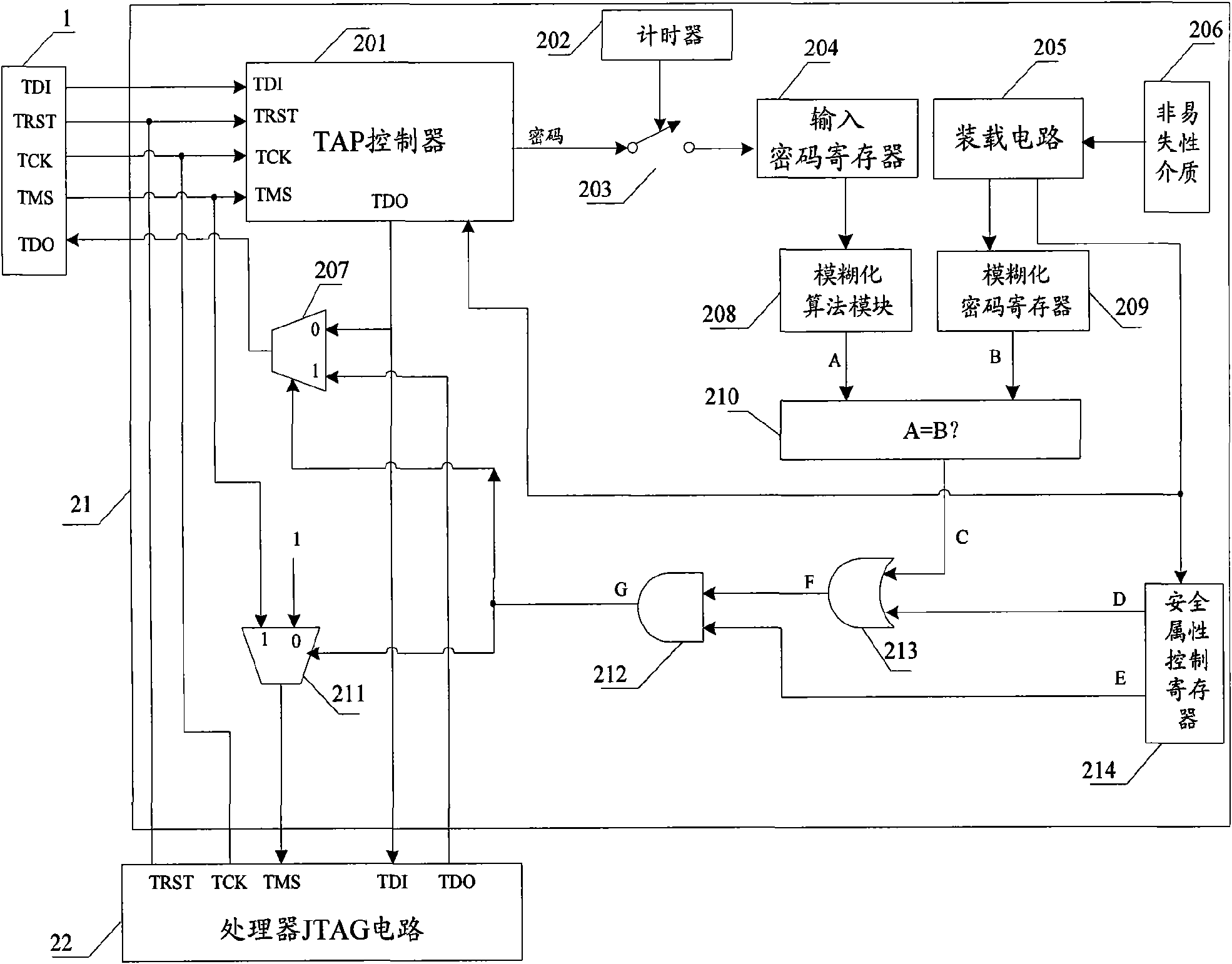
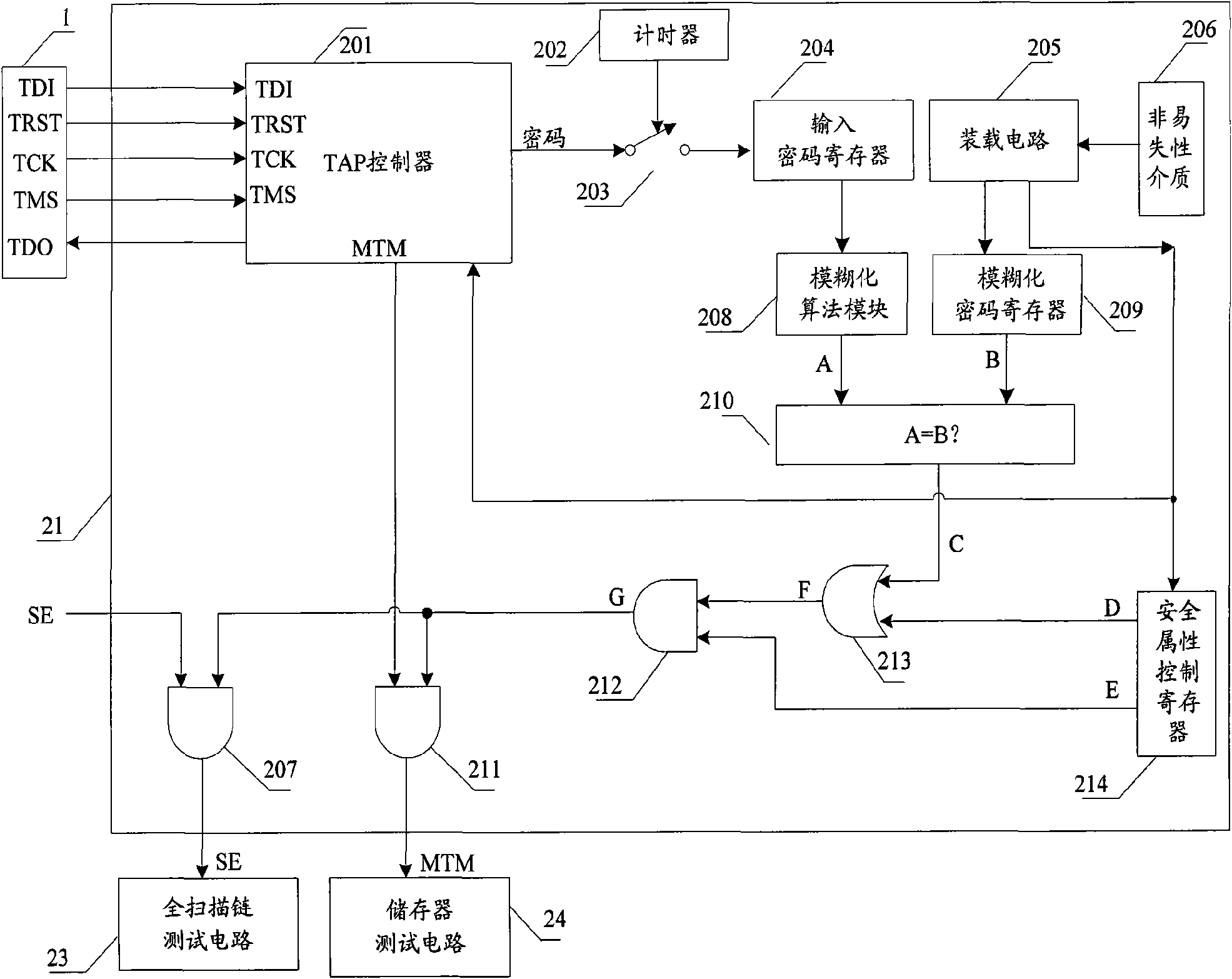
The invention relates to a safety JTAG module and a method for protecting security of information inside a chip, wherein the safety JTAG module comprises a nonvolatile medium (206), a loading circuit (205), a security attribute control register (214), a TAP controller (201), two selectors (207 and 211), a switch (203), a password authentication module and a logic processing module; the TAP controller (201) and the two selectors (207 and 211) are connected between a JTAG port (1) and a protected object inside the chip; the switch (203) is switched by the control of a timer (202); the password authentication module is used for authenticating whether a clear-text password input by a user is accordant with a fuzzification password or not; and the logic processing module is used for logically processing an authentication result output by the password authentication module and an indication signal output by the security attribute control register (214) and outputting an enable signal to the two selectors (207 and 211) so as to control whether the JTAG port (1) is allowed to be connected with the protected object inside the chip through the TAP controller (201) or not. The invention ensures the security and the convenience of an SOC chip in testing and debugging processes, thereby protecting the security of data inside the chip.
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICRO TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com