Patents
Literature
4592 results about "Clock rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency at which the clock circuit of a processor can generate pulses, which are used to synchronize the operations (such as adding two numbers or transferring a value from one register to another) of its components, and is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. It is measured in clock cycles per second or its equivalent, the SI unit hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers (PCs) to arrive throughout the 1970s and 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz), and in the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Video card and CPU manufacturers commonly select their highest performing units from a manufacturing batch and set their maximum clock rate higher, fetching a higher price.
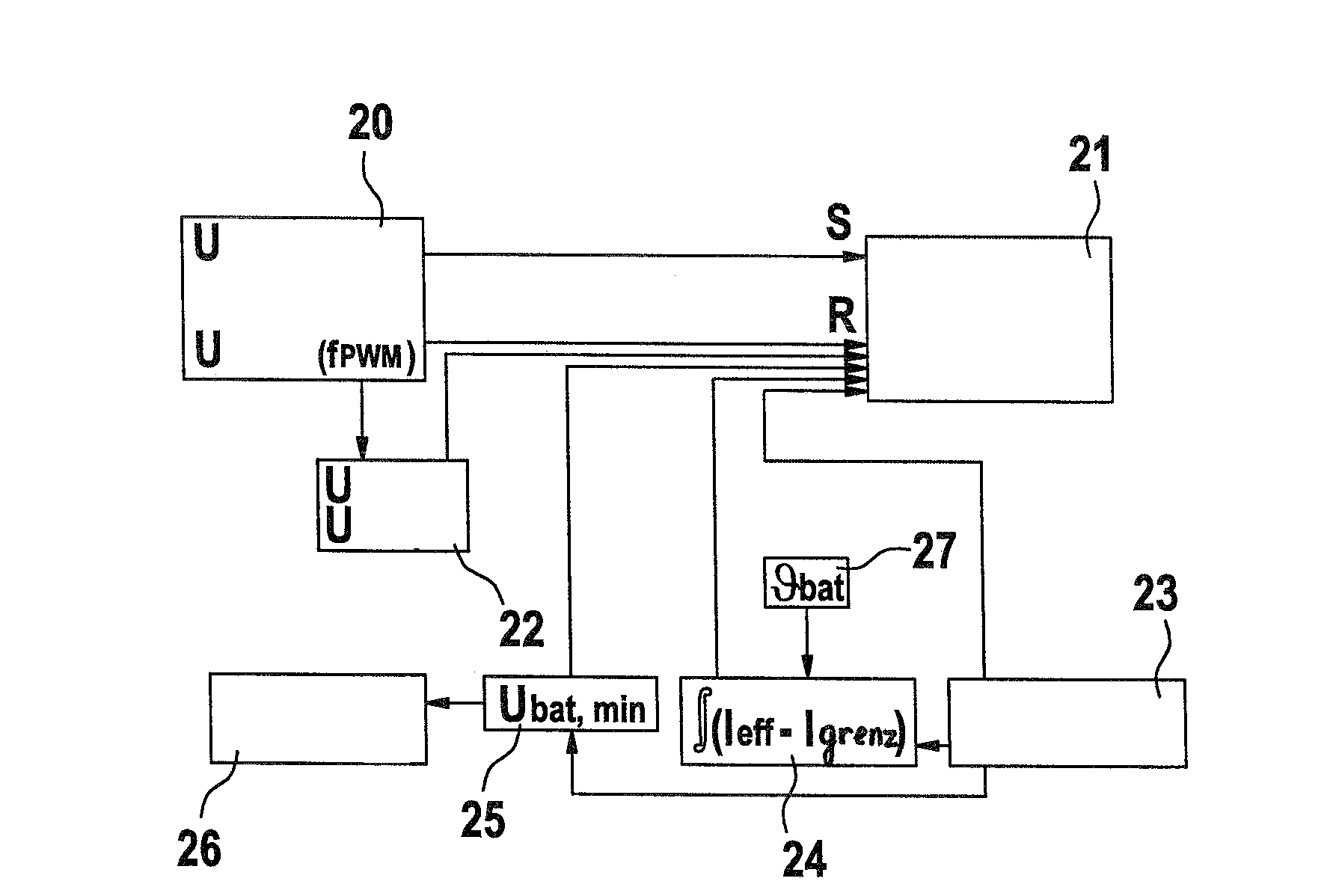
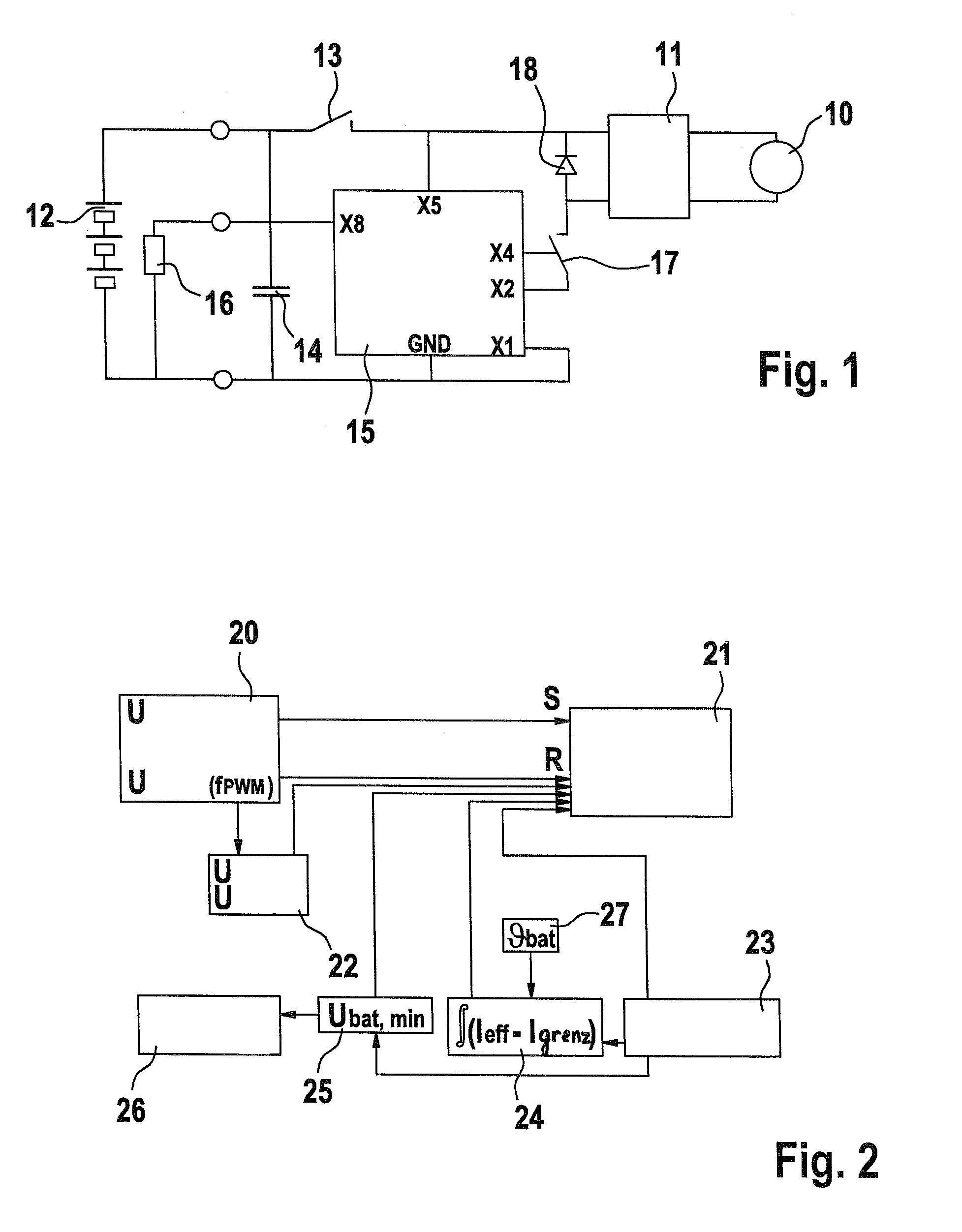
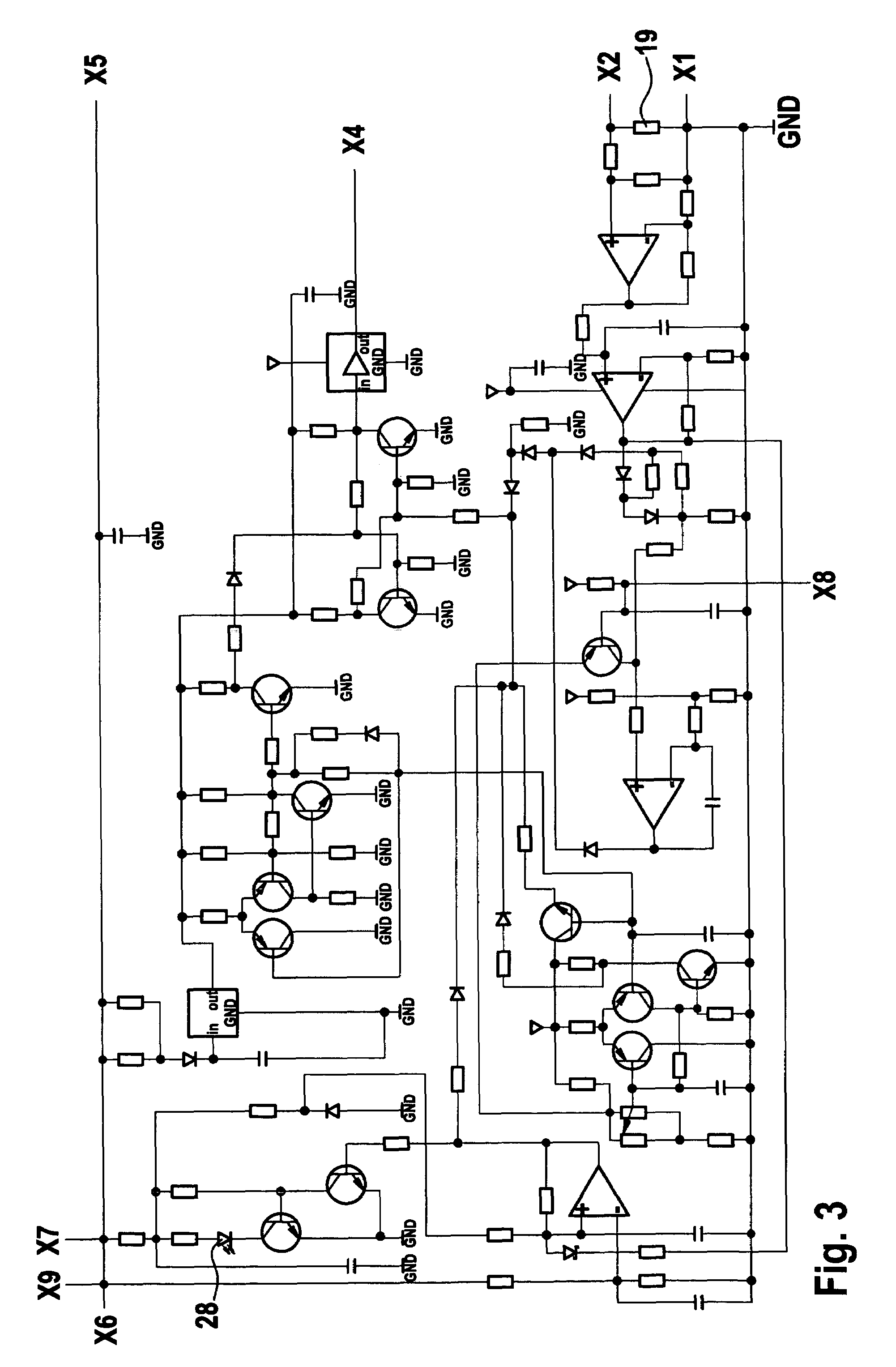
Method for operating a power tool
ActiveUS7336048B2Maintain good propertiesReduce widthTemperatue controlEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionMOSFETElectricity
In a method for operating a power tool with an energy accumulator, in particular a rechargeable energy accumulator, which supplies power to an electric drive motor, a clock frequency is generated by an electronic unit, with which a gate of a MOSFET—which supplies operating voltage to the drive motor—is switched on with each cycle, and a switching-off of the MOSFET is carried out within one cycle using different signals, as a function of operating parameters.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
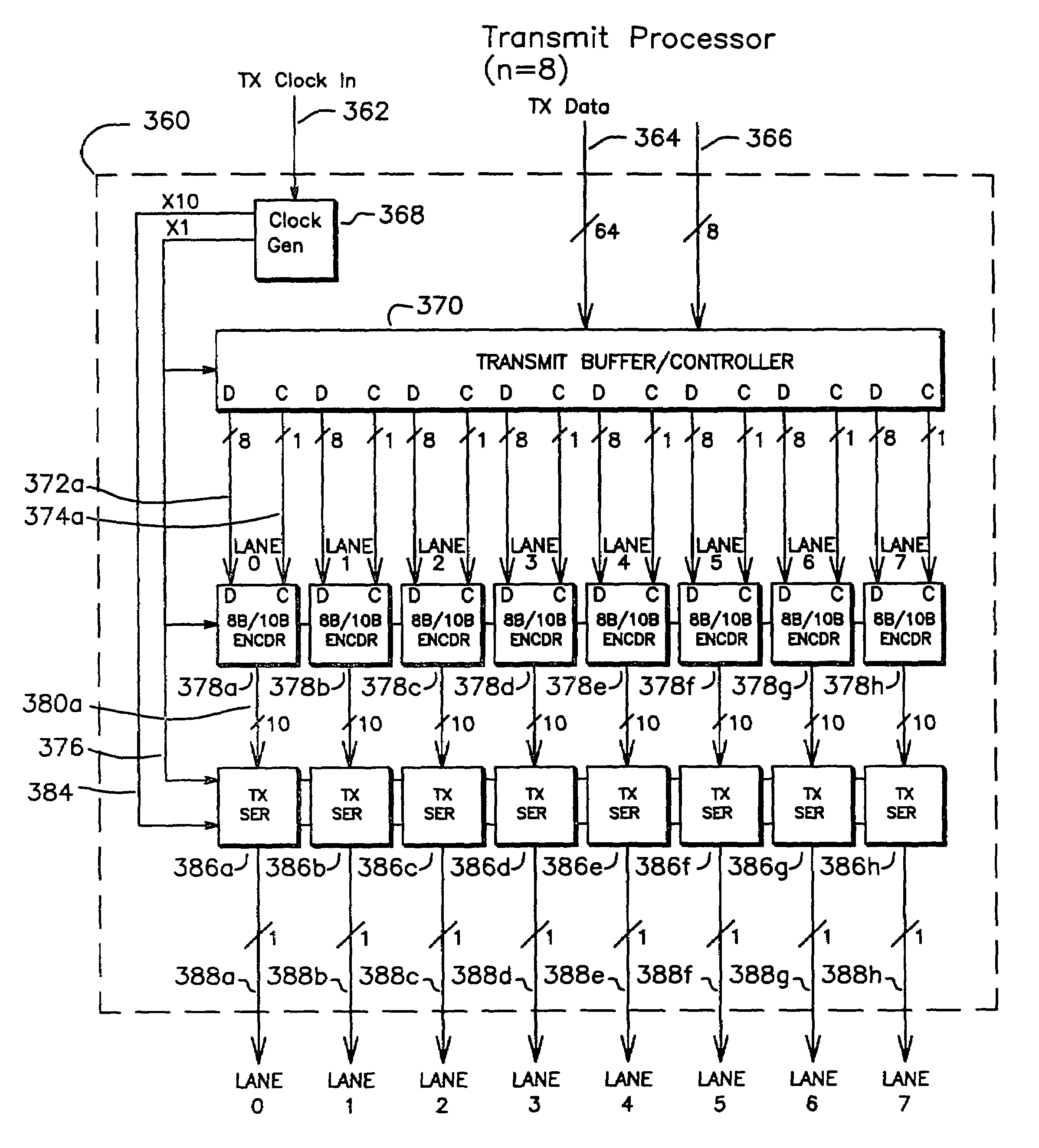
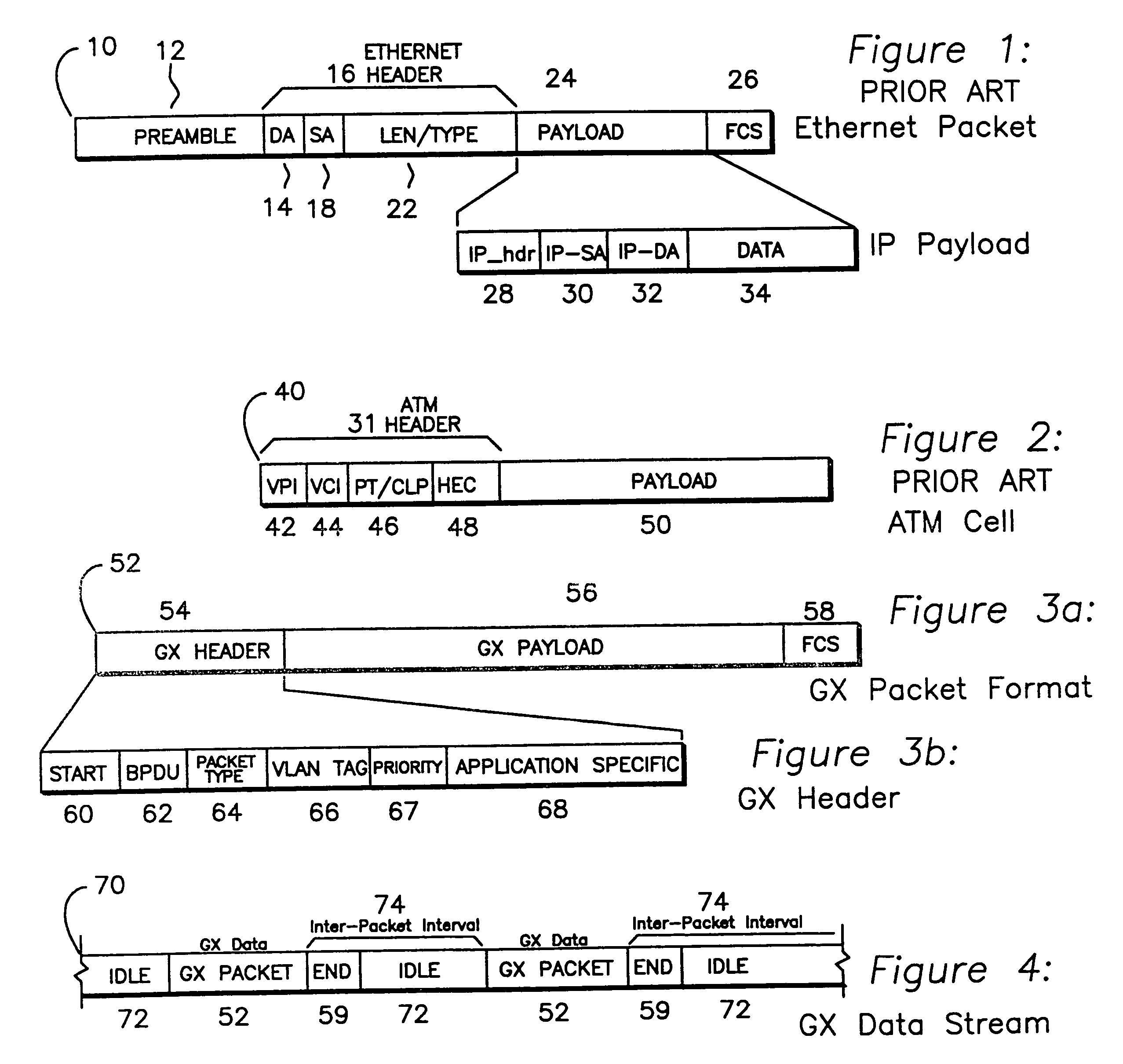
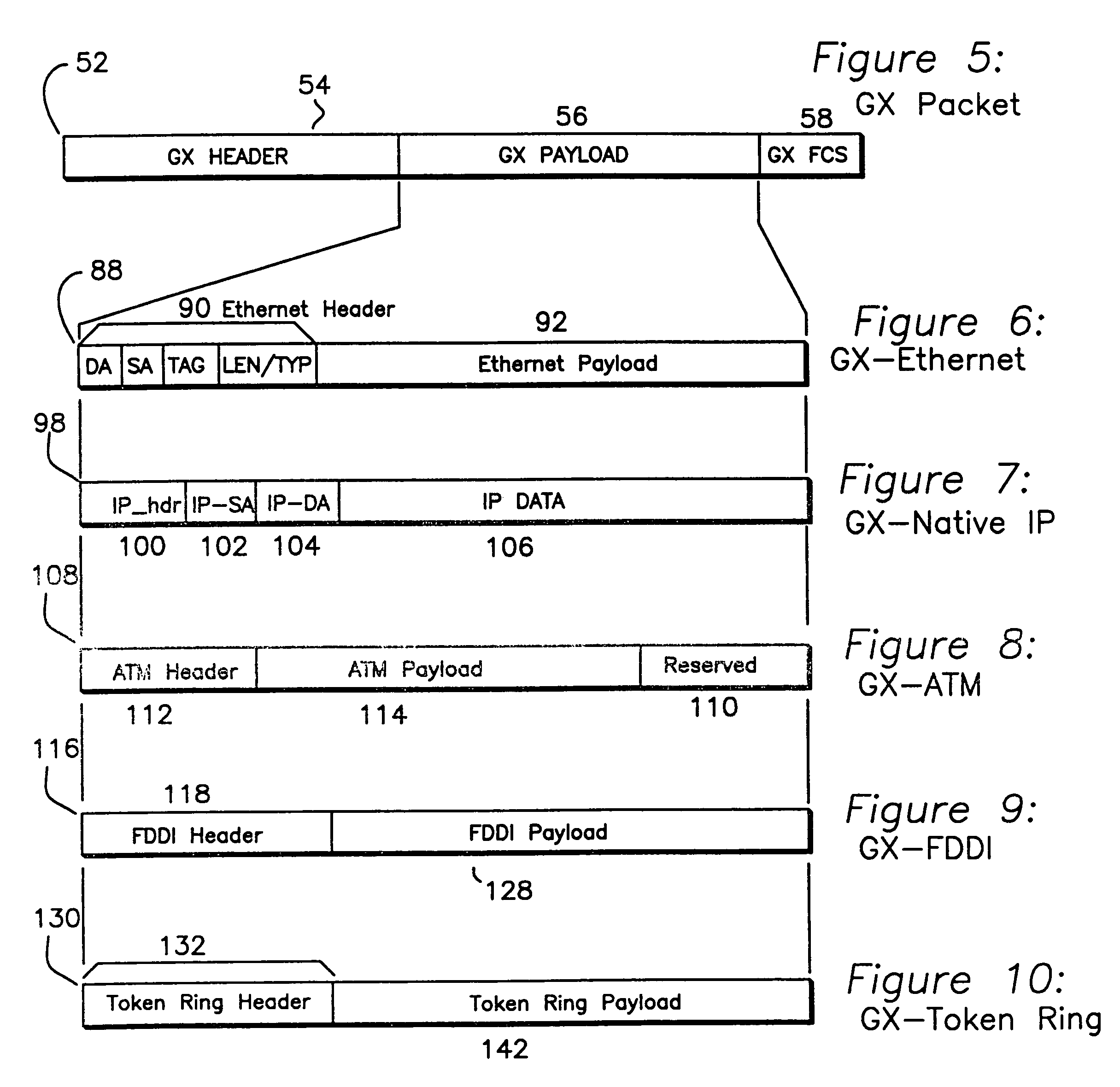
Multi-function high-speed network interface
InactiveUS7573916B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexCommunication interfaceClock rate
A high speed communications interface divides data into a plurality of lanes, each lane encoded with clocking information, serialized, and sent to an interface. During cycles when there is no available data to send, IDLE_EVEN and IDLE_ODD cells are sent on alternating cycles. Data is transmitted by sending a header which spans all lanes and includes a START symbol. The final data transaction includes a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) which operates over the entire header and data. The packet is terminated by an END symbol, which is sent after the final data, and the remainder of the lanes are padded with IDLE_EVEN, IDLE_ODD, IDLE_EVEN_BUSY, or IDLE_ODD_BUSY cycles. The interface has a variable clock rate.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and apparatuses for operating a data processing system
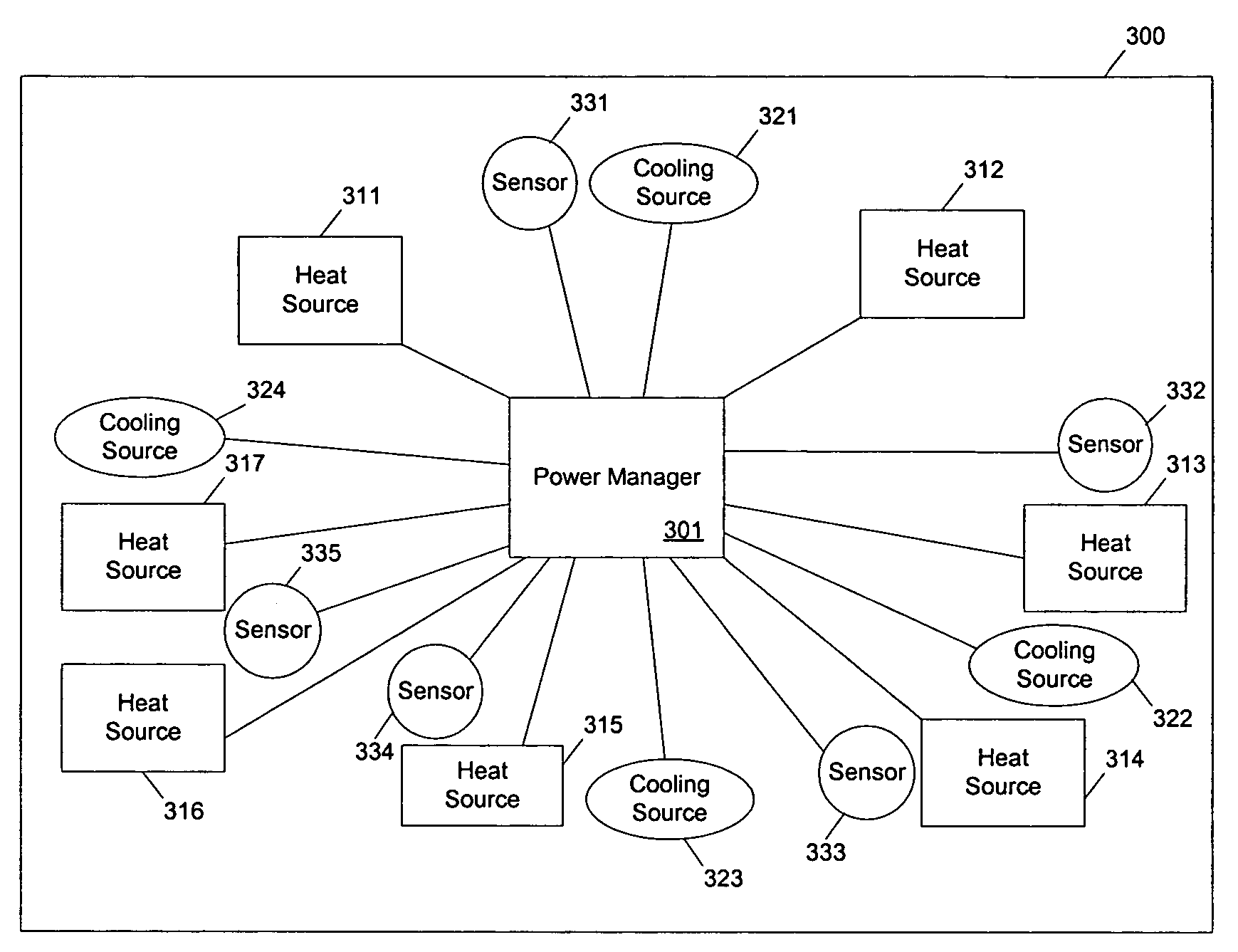
ActiveUS20050049729A1Balance performanceShorten speedMultiplex communicationVolume/mass flow measurementHeat sensitiveThermistor
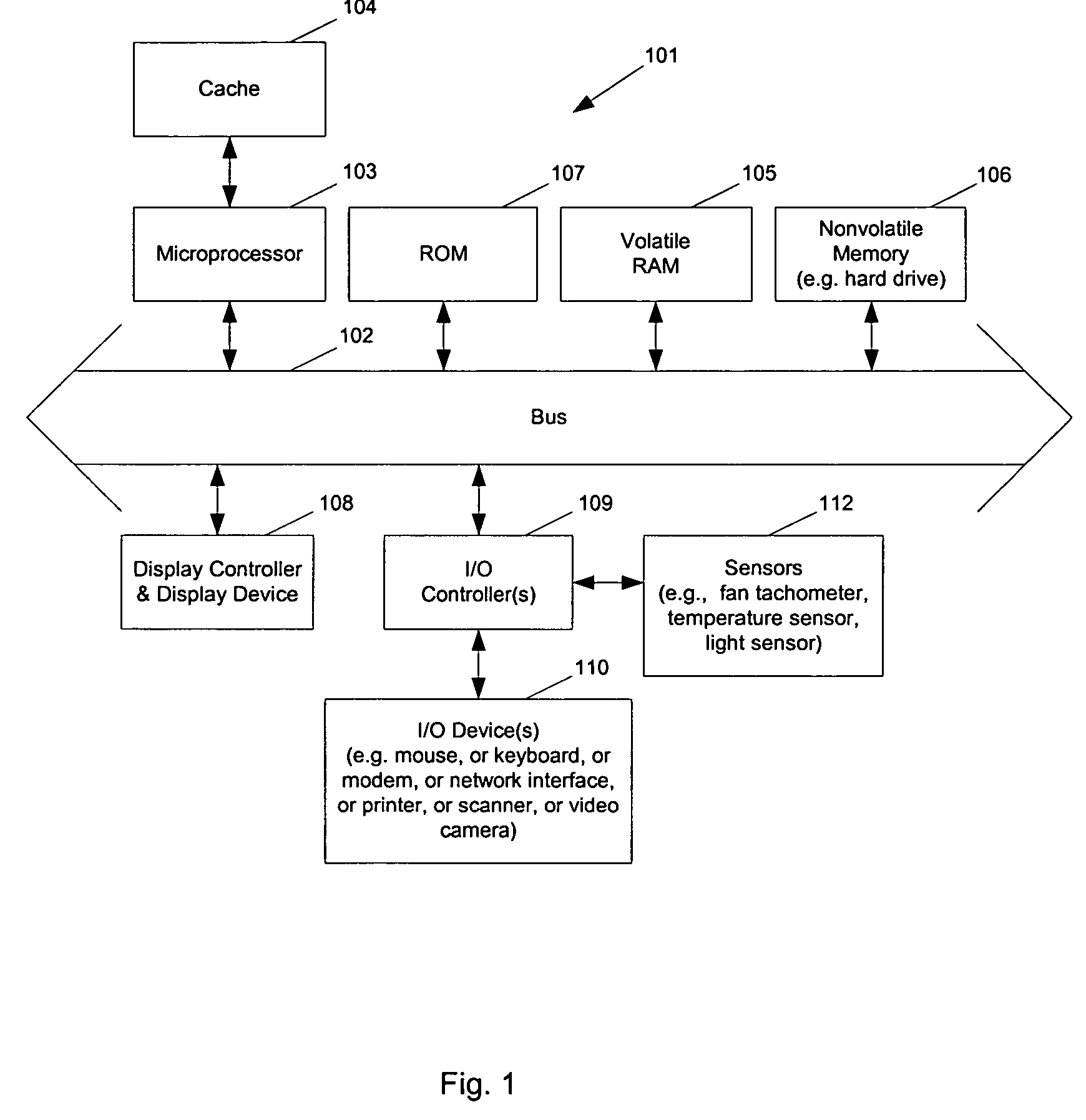
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
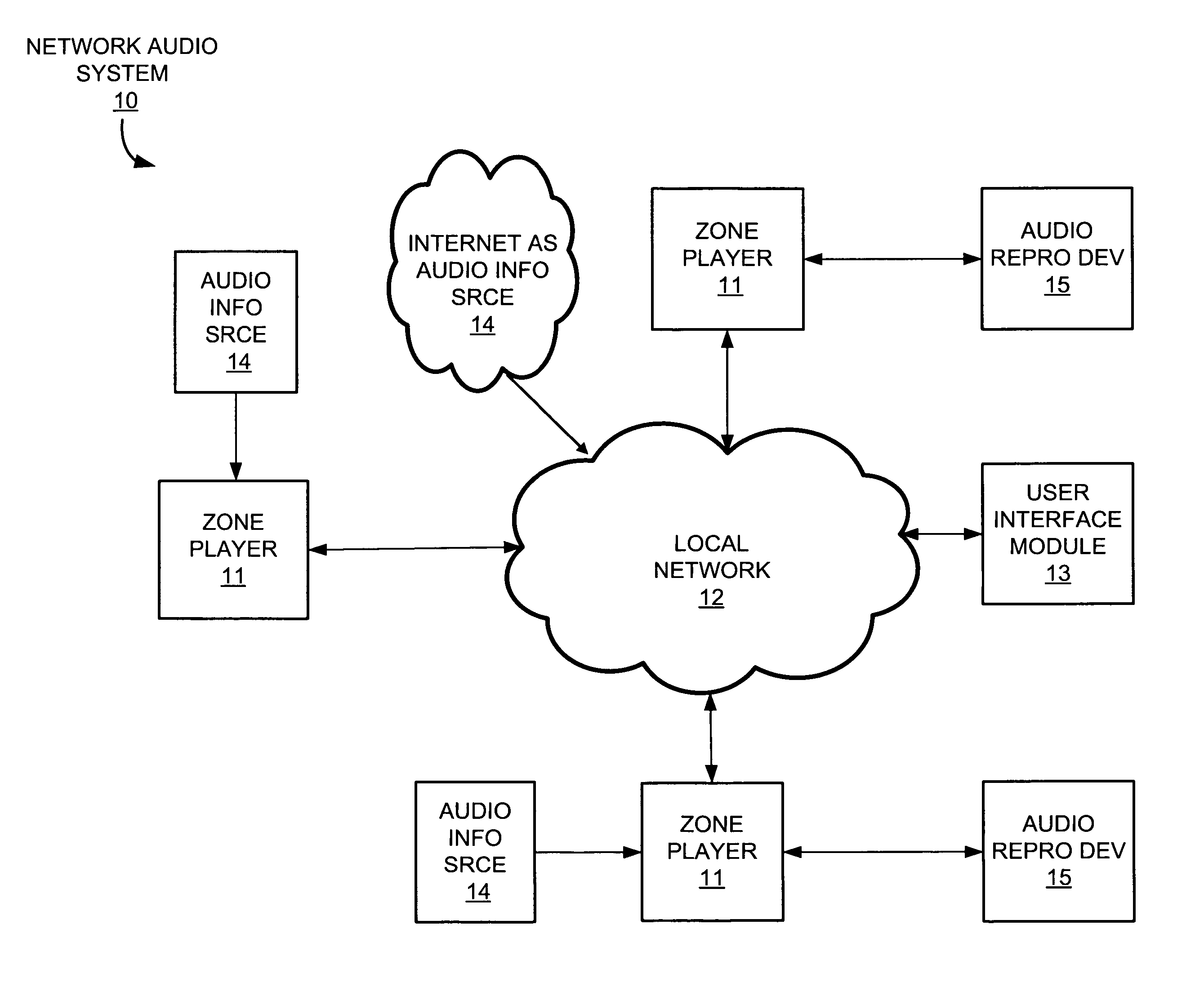
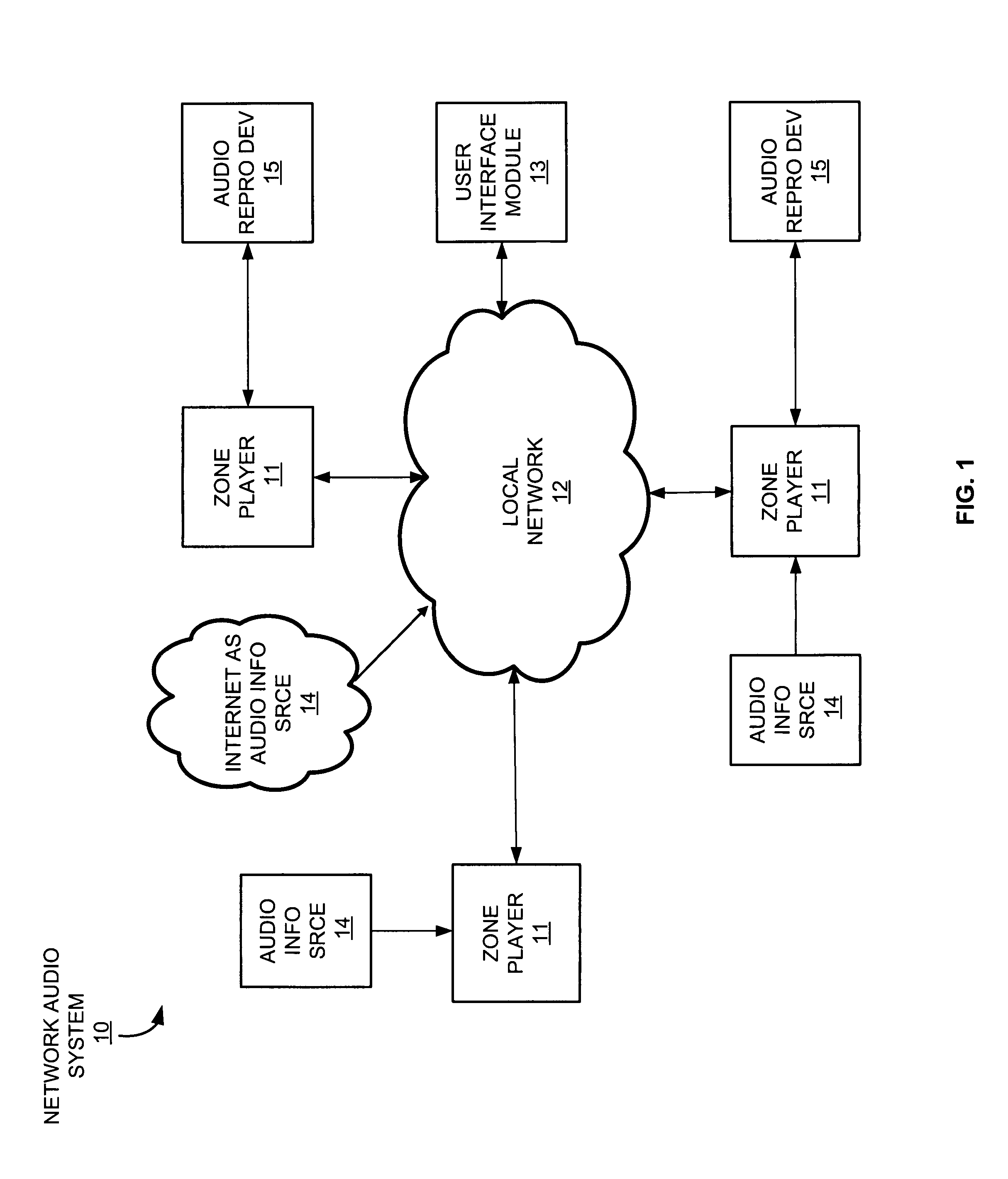
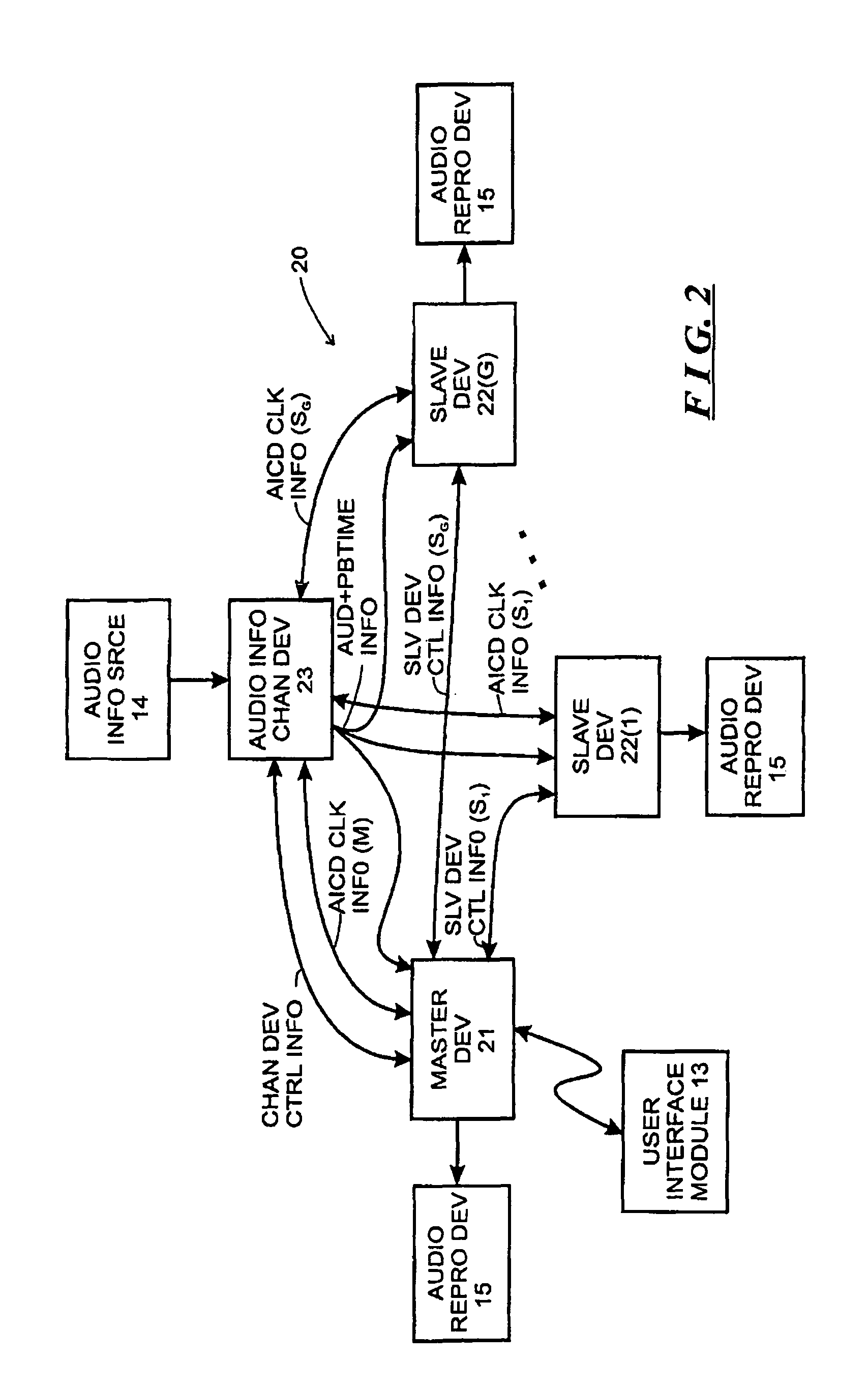
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices that independently source digital data
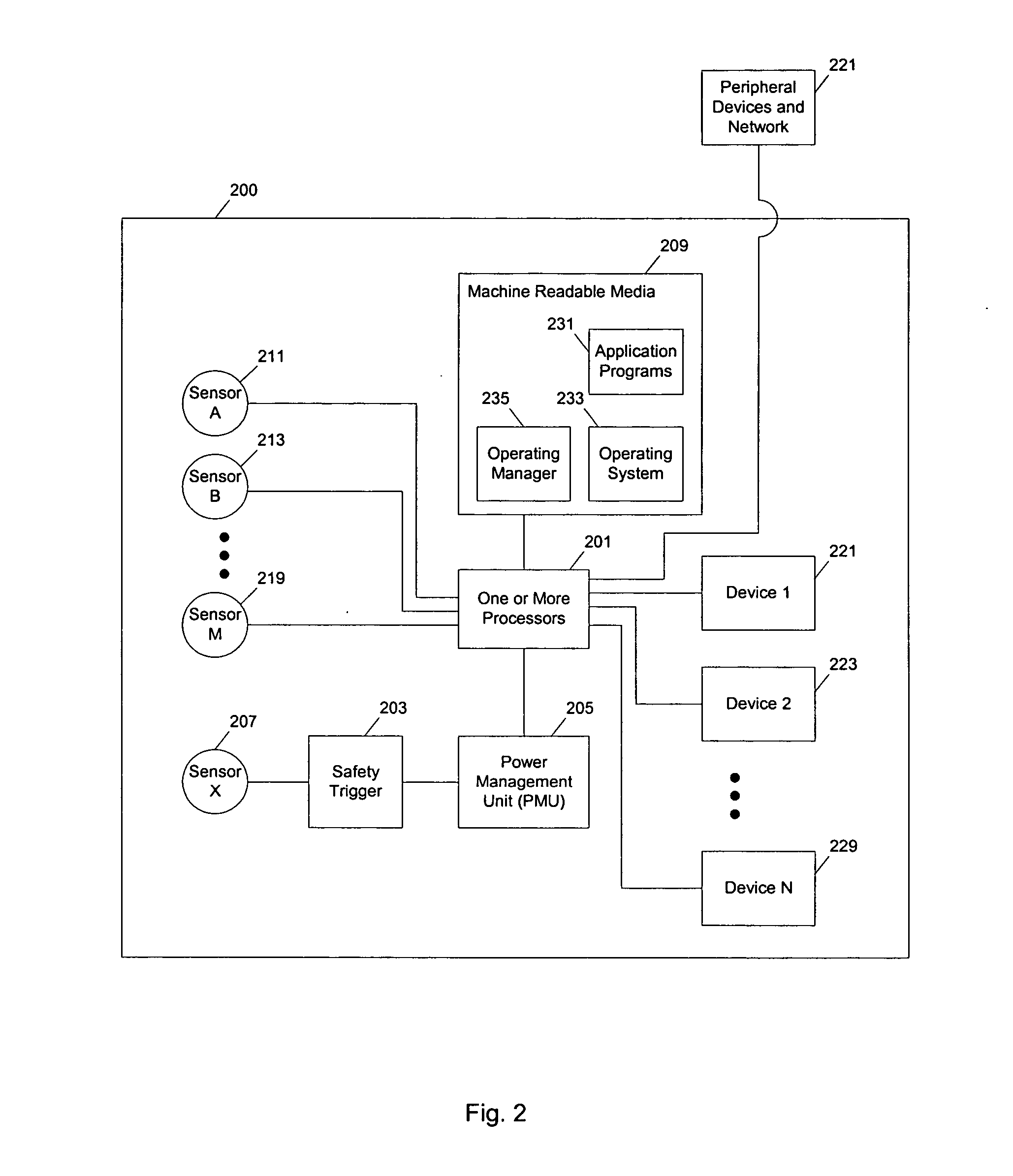
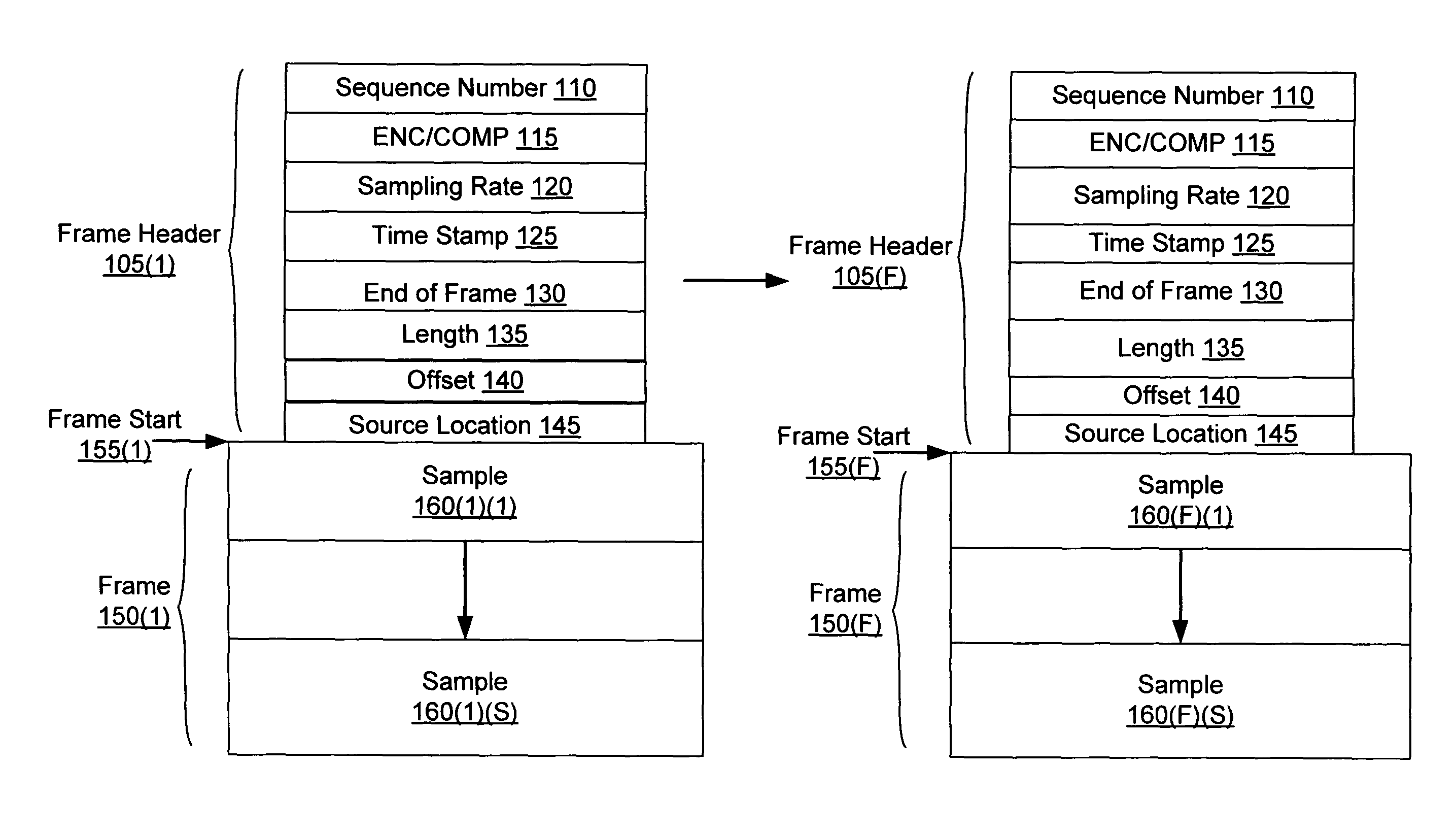
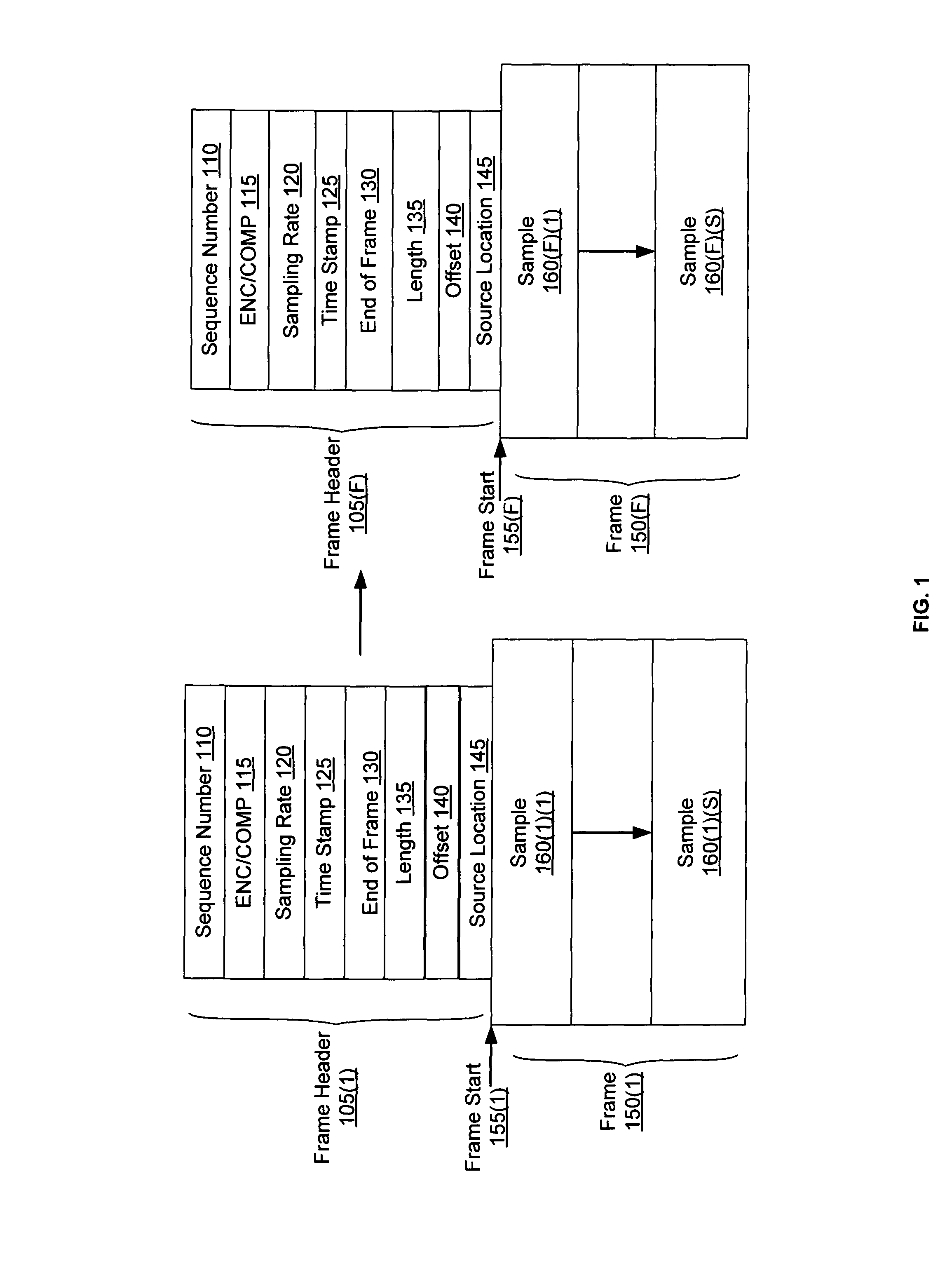
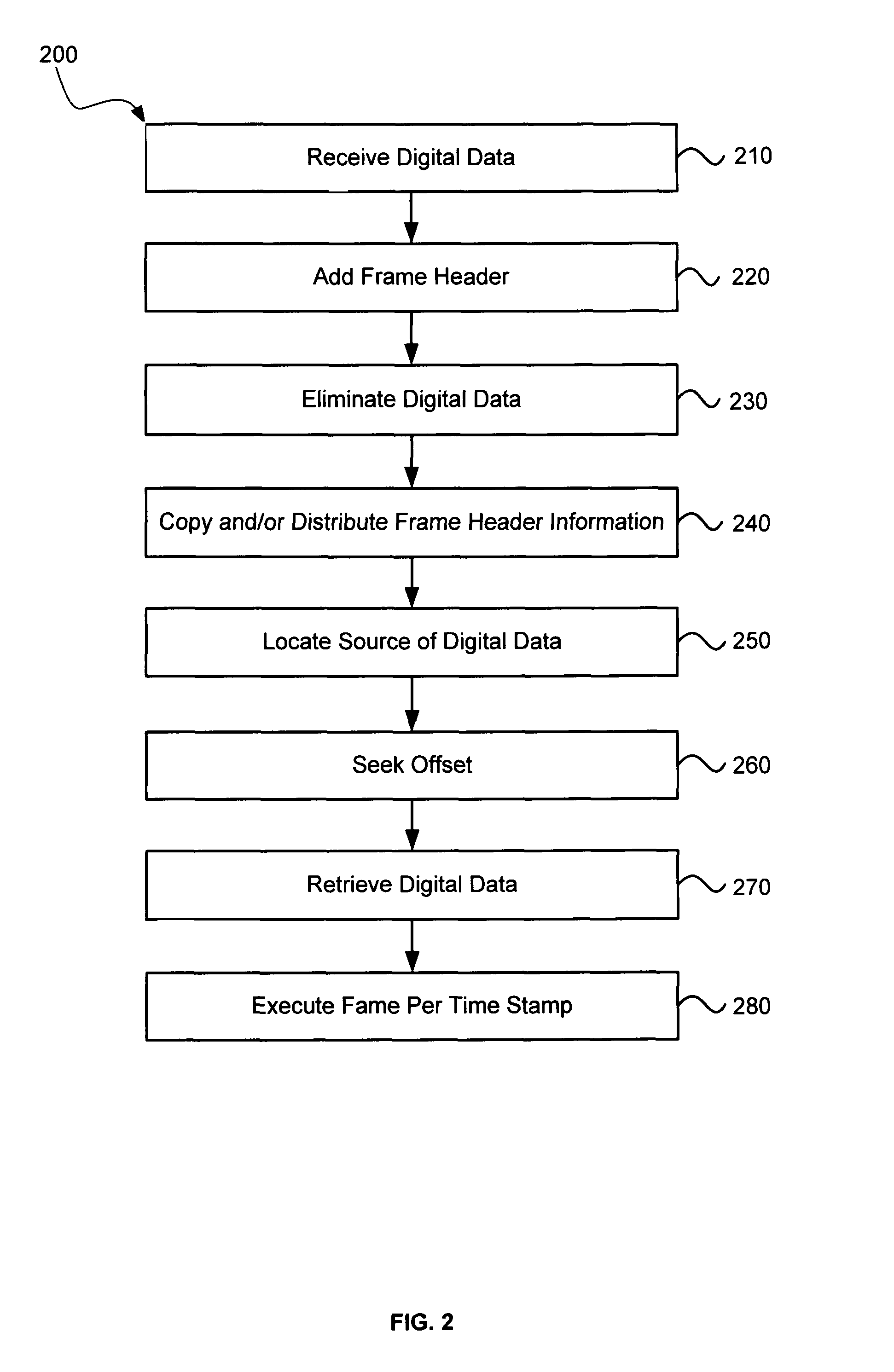
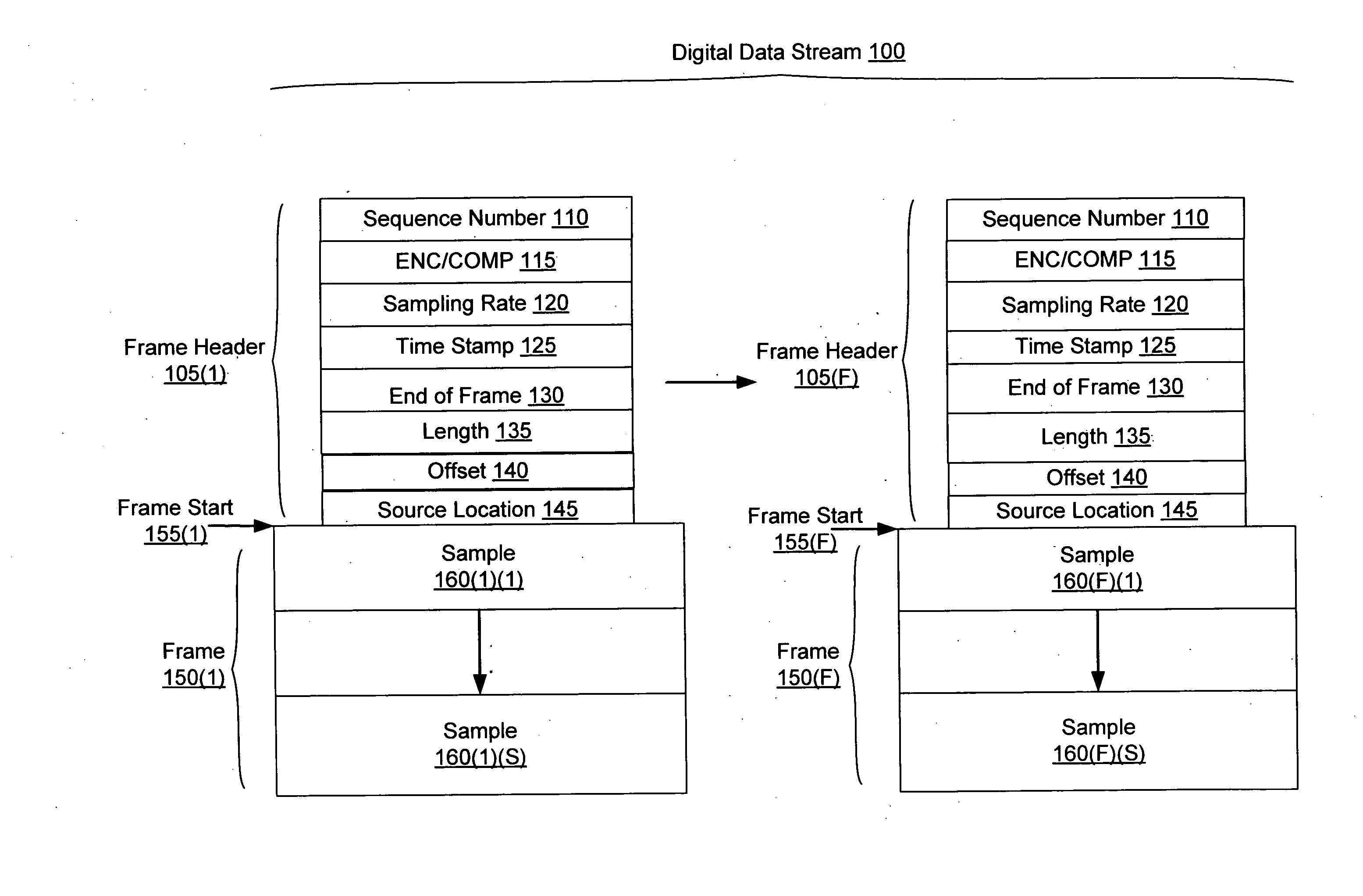
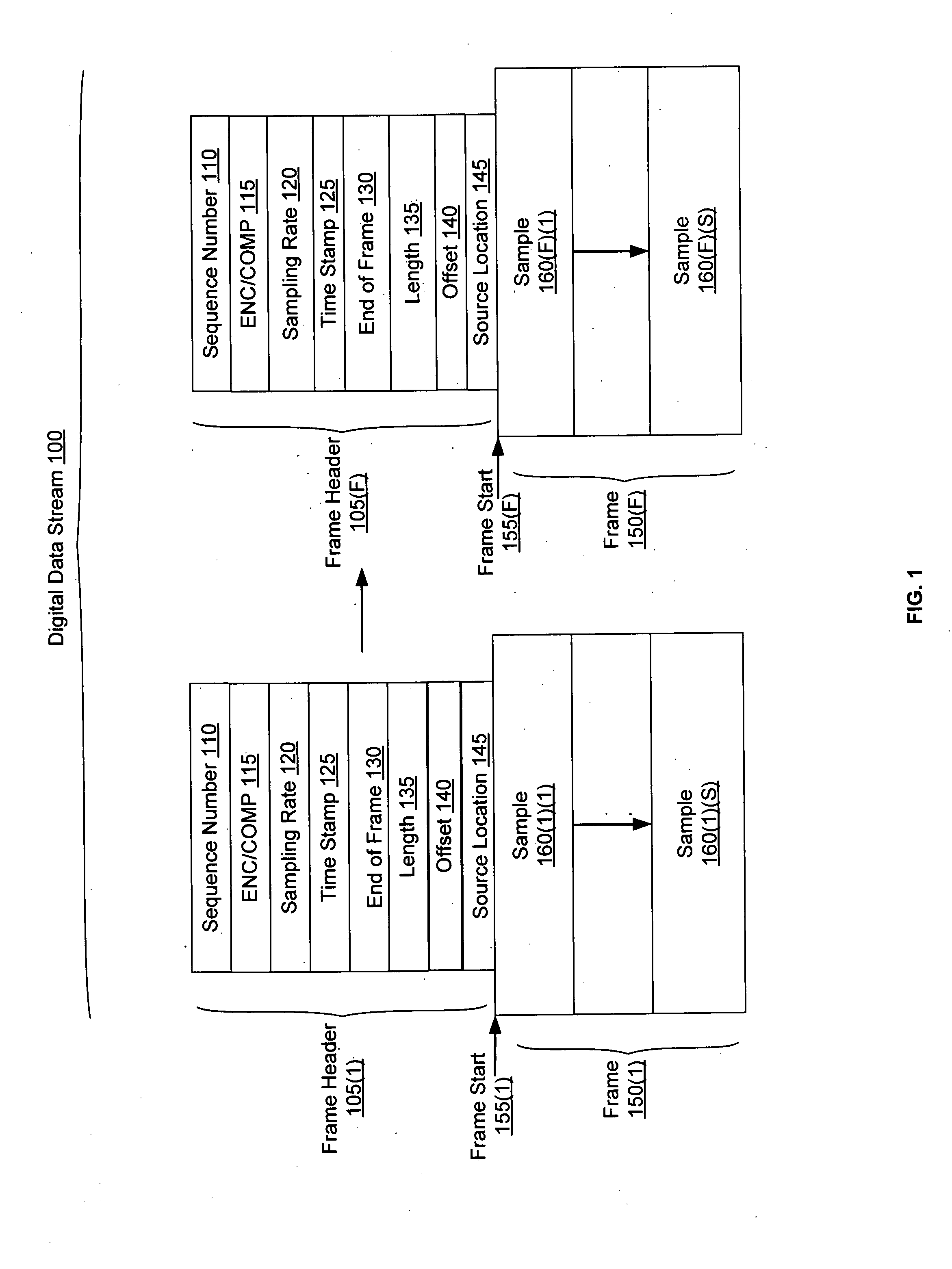
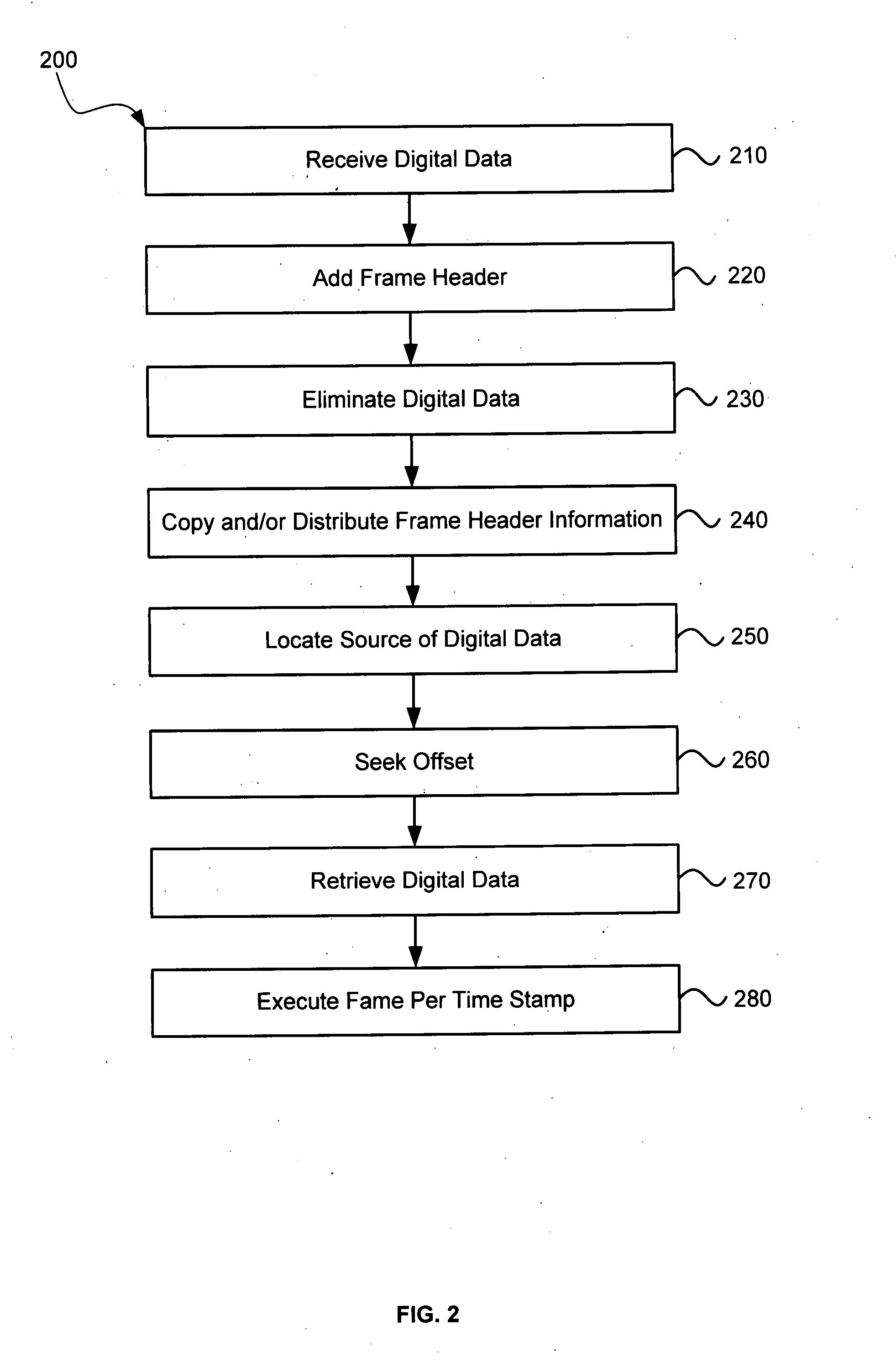
In a system for distributing data, distribution device is configured to distribute timestamp, offset and source location information for a digital data stream to an execution device, and the execution device is configured to seek digital data corresponding to the received information. The execution device is further configured to execute the digital data relative to a clock rate maintained by the distribution device. Related methods include receiving timestamp, offset and source location information for the digital data stream and seeking digital data corresponding to the received offset and source location information.
Owner:SONOS
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices that independently source digital data
ActiveUS20080120429A1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataData stream
In a system for distributing data, distribution device is configured to distribute timestamp, offset and source location information for a digital data stream to an execution device, and the execution device is configured to seek digital data corresponding to the received information. The execution device is further configured to execute the digital data relative to a clock rate maintained by the distribution device. Related methods include receiving timestamp, offset and source location information for the digital data stream and seeking digital data corresponding to the received offset and source location information.
Owner:SONOS
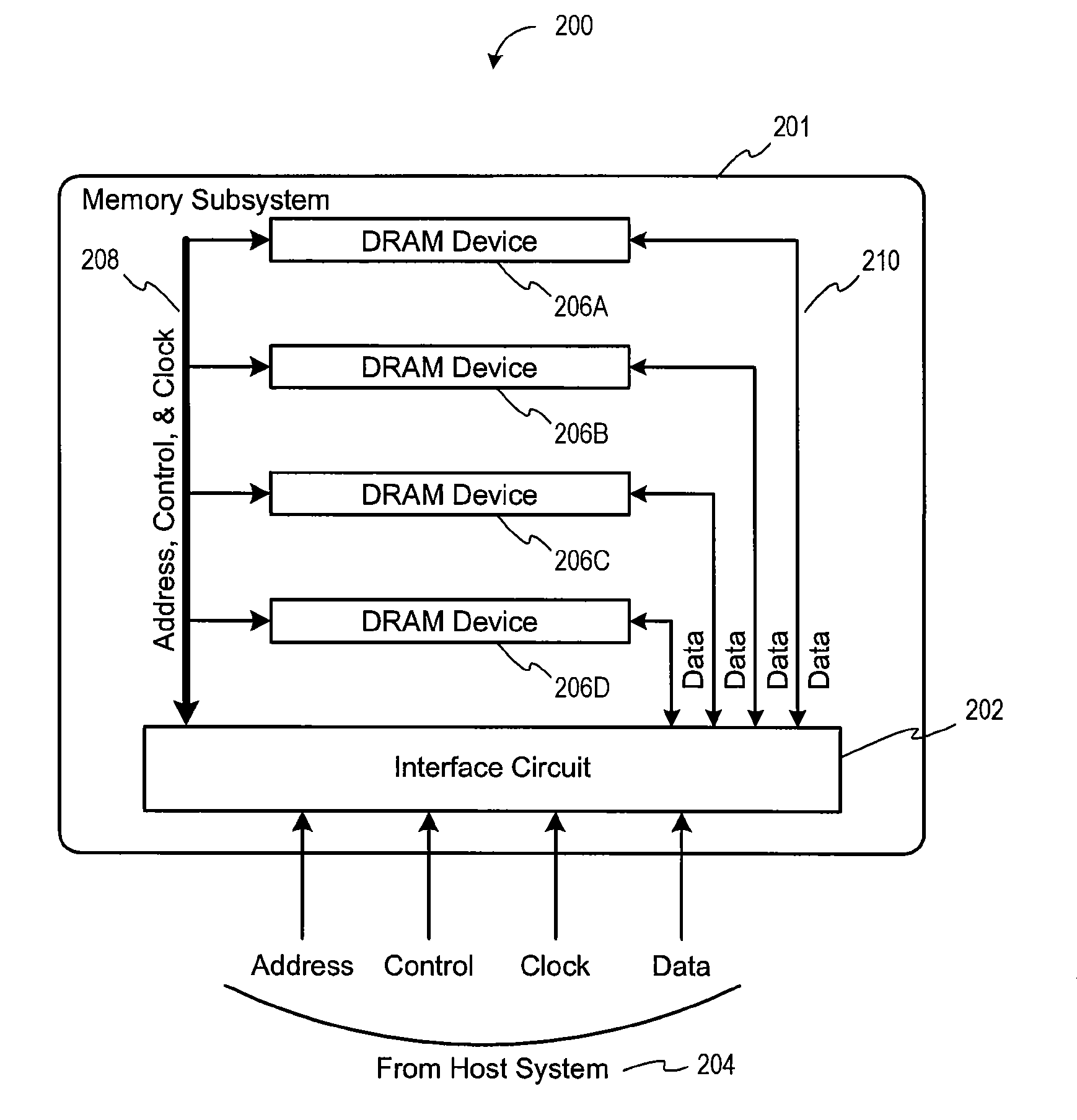
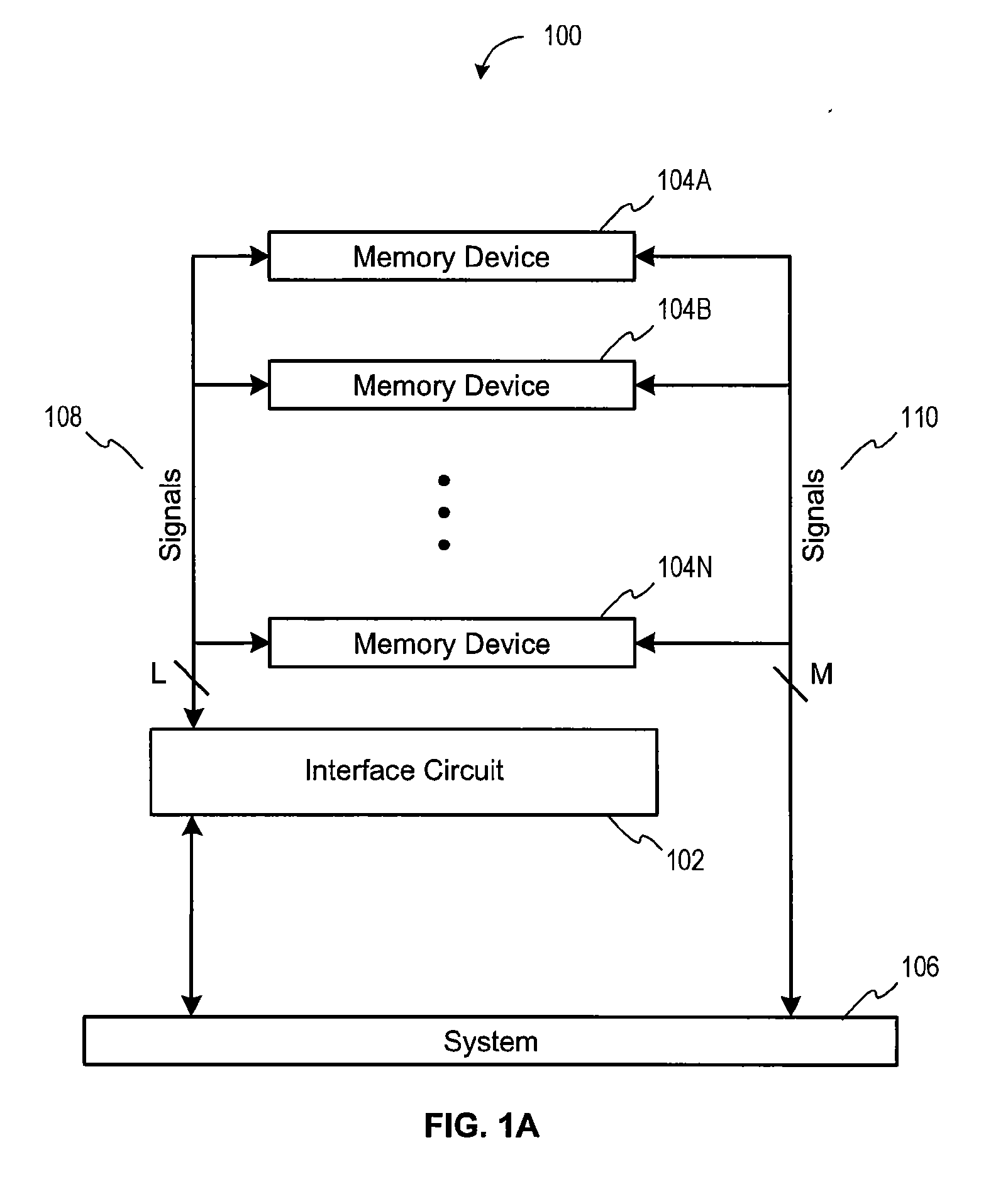
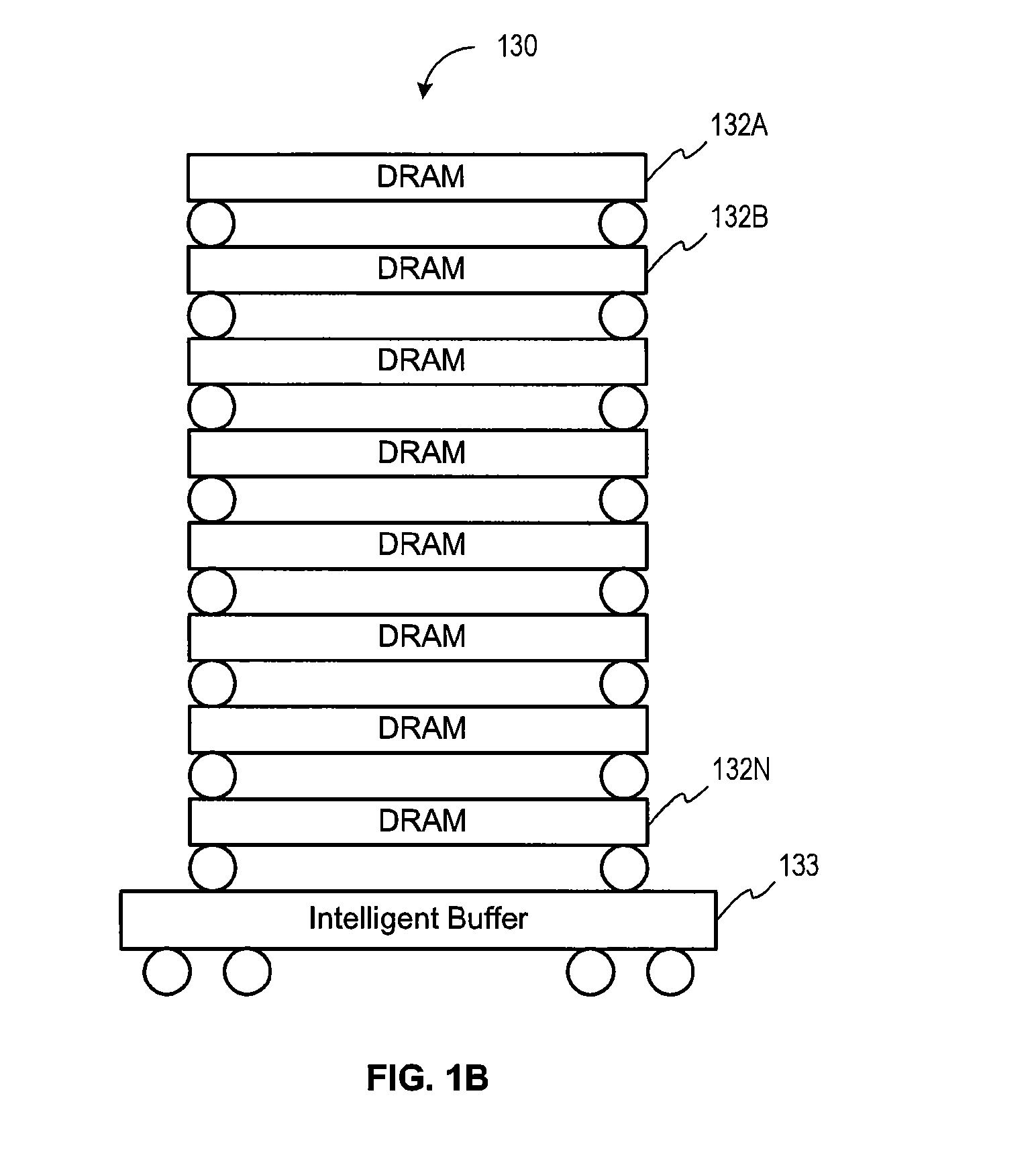
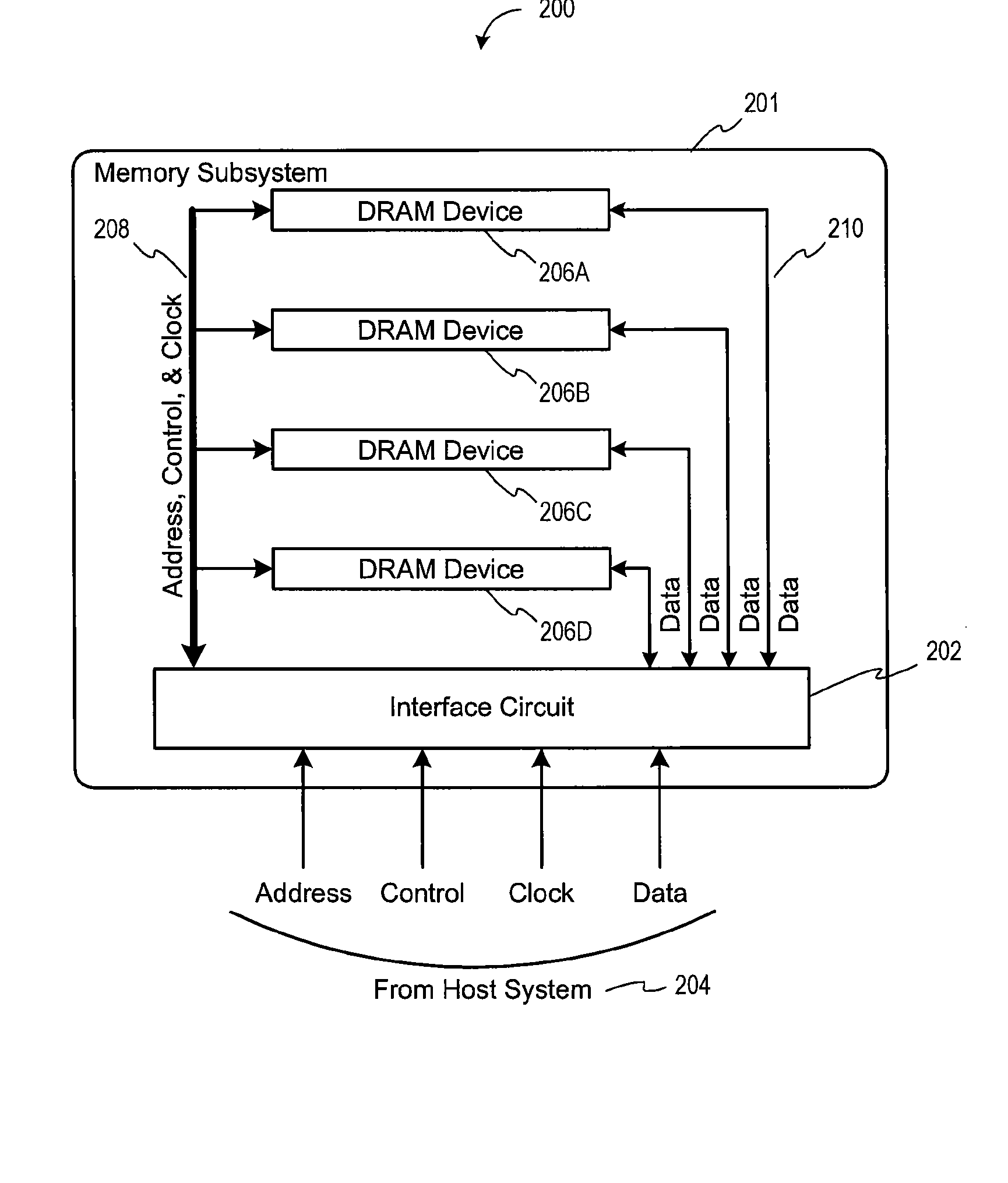
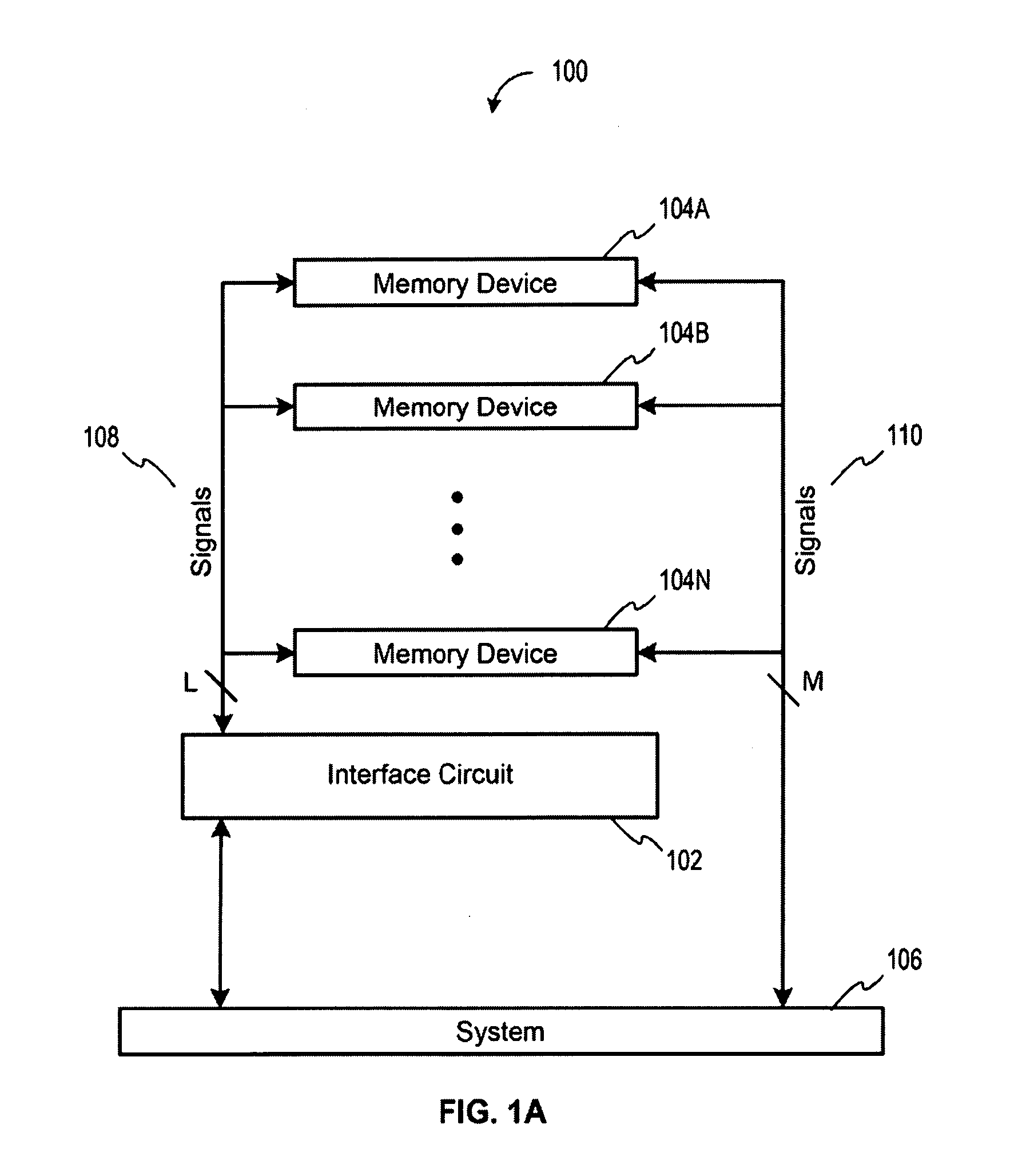
Method and Apparatus For Refresh Management of Memory Modules
One embodiment sets forth an interface circuit configured to manage refresh command sequences that includes a system interface adapted to receive a refresh command from a memory controller, clock frequency detection circuitry configured to determine the timing for issuing staggered refresh commands to two or more memory devices coupled to the interface circuit based on the refresh command received from the memory controller, and at least two refresh command sequence outputs configured to generate the staggered refresh commands for the two or more memory devices
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
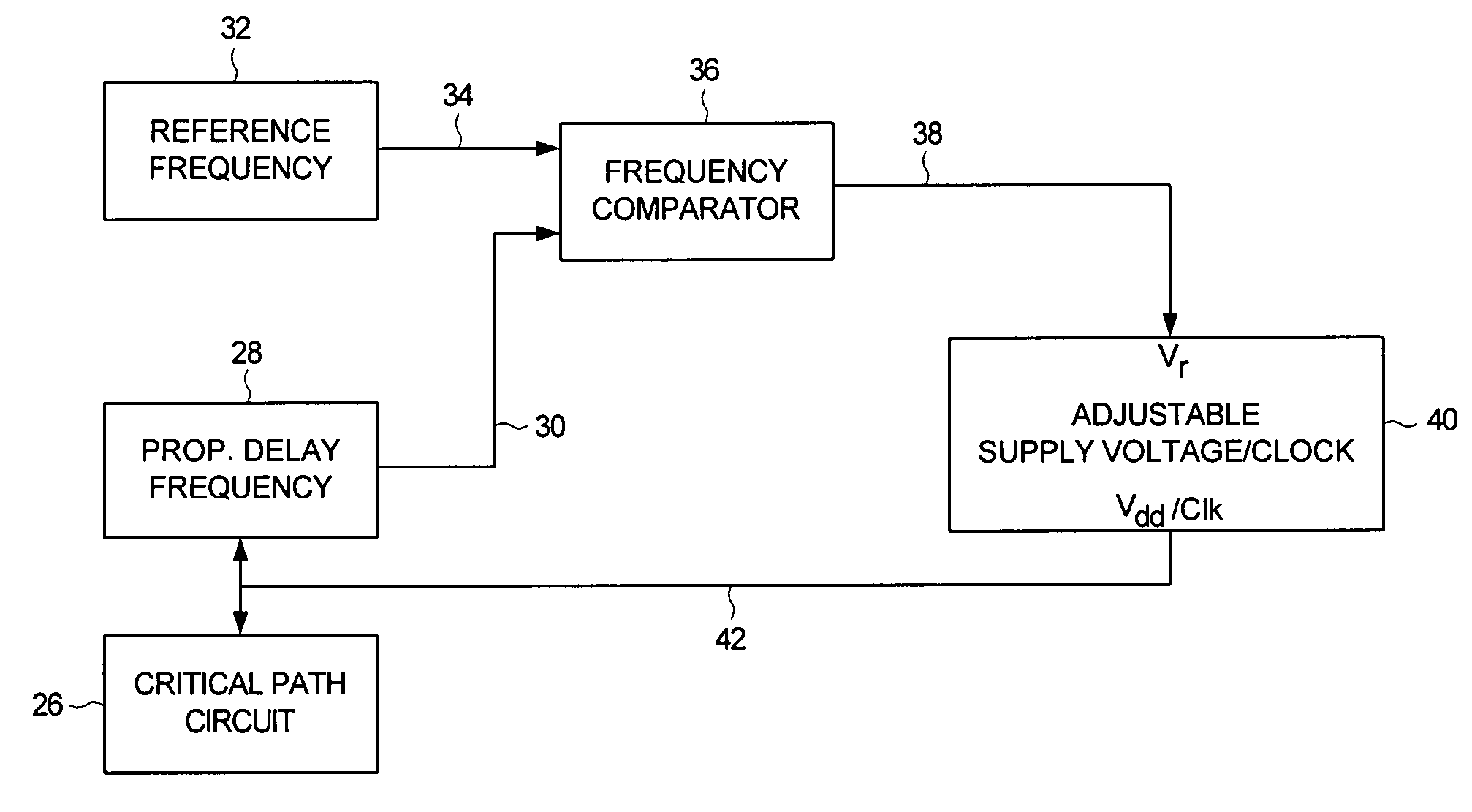
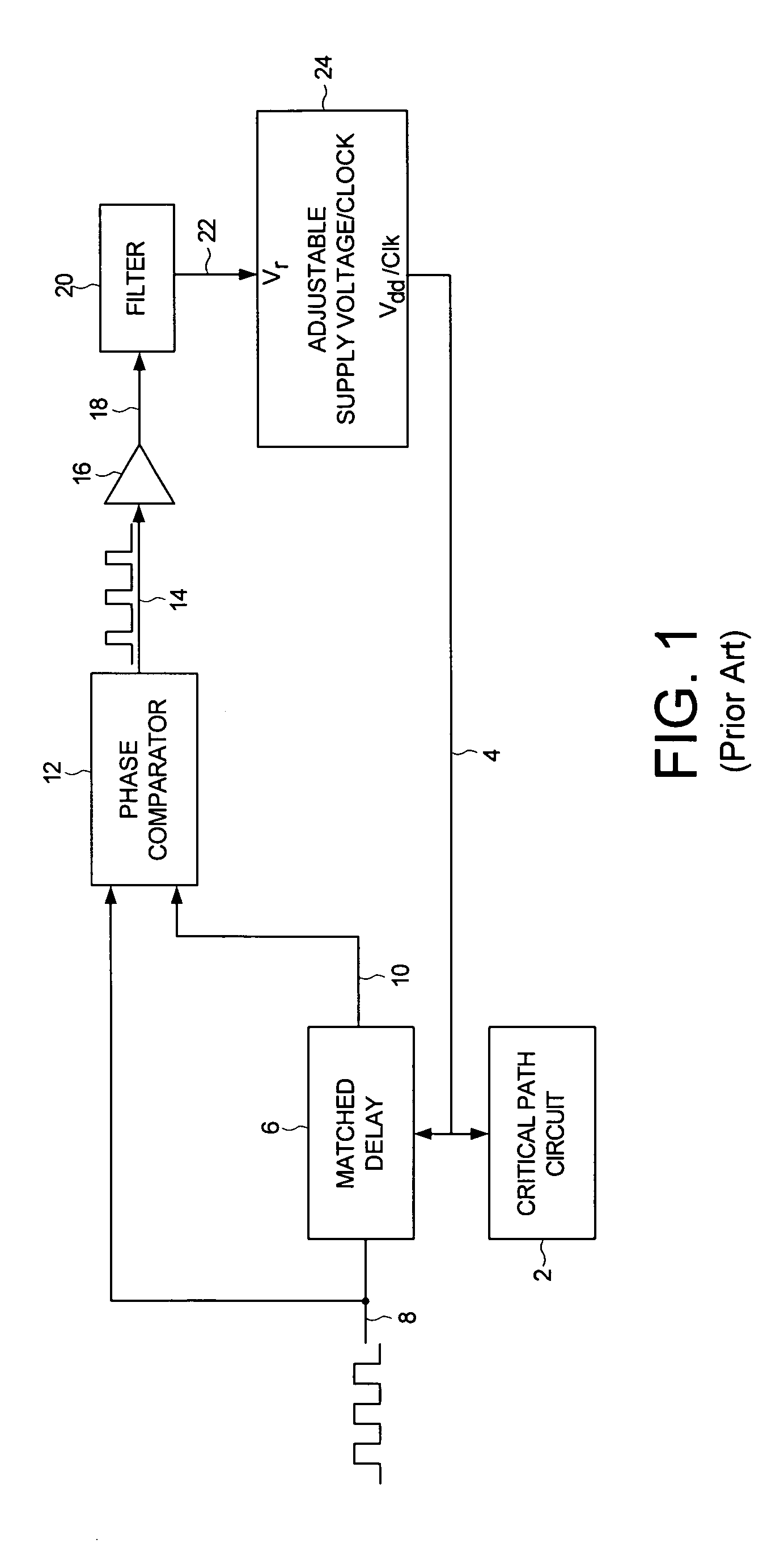
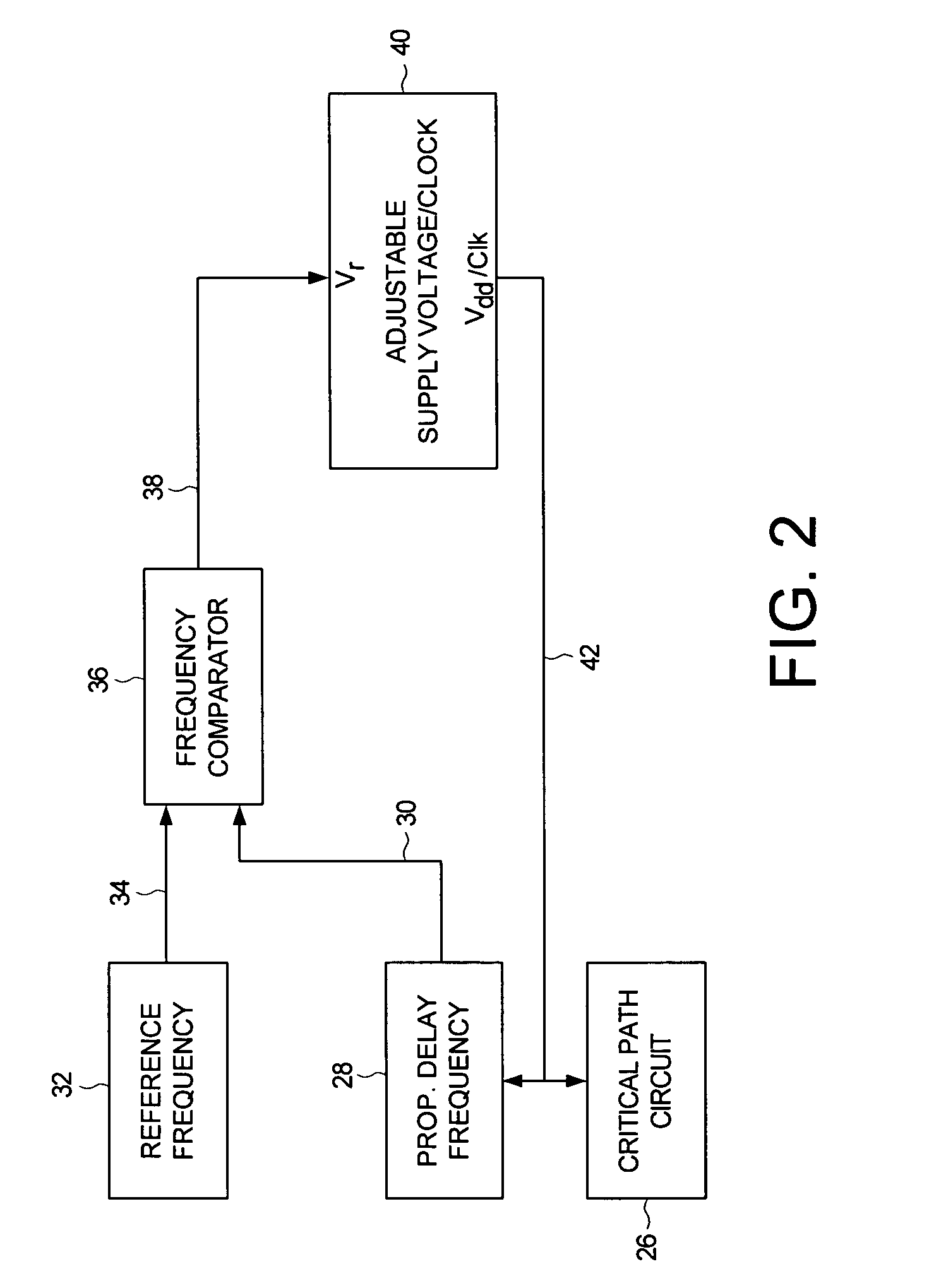
Adjusting power consumption of digital circuitry by generating frequency error representing error in propagation delay
A method and apparatus is disclosed for adjusting at least one of a supply voltage and a clocking frequency applied to digital circuitry of a computing device, wherein the digital circuitry comprises a critical path circuit. A propagation delay frequency representing a propagation delay of the critical path circuit is generated, and a frequency error signal is generated representing a difference between a reference frequency and the propagation delay frequency. At least one of the supply voltage and the clocking frequency is adjusted in response to the frequency error signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
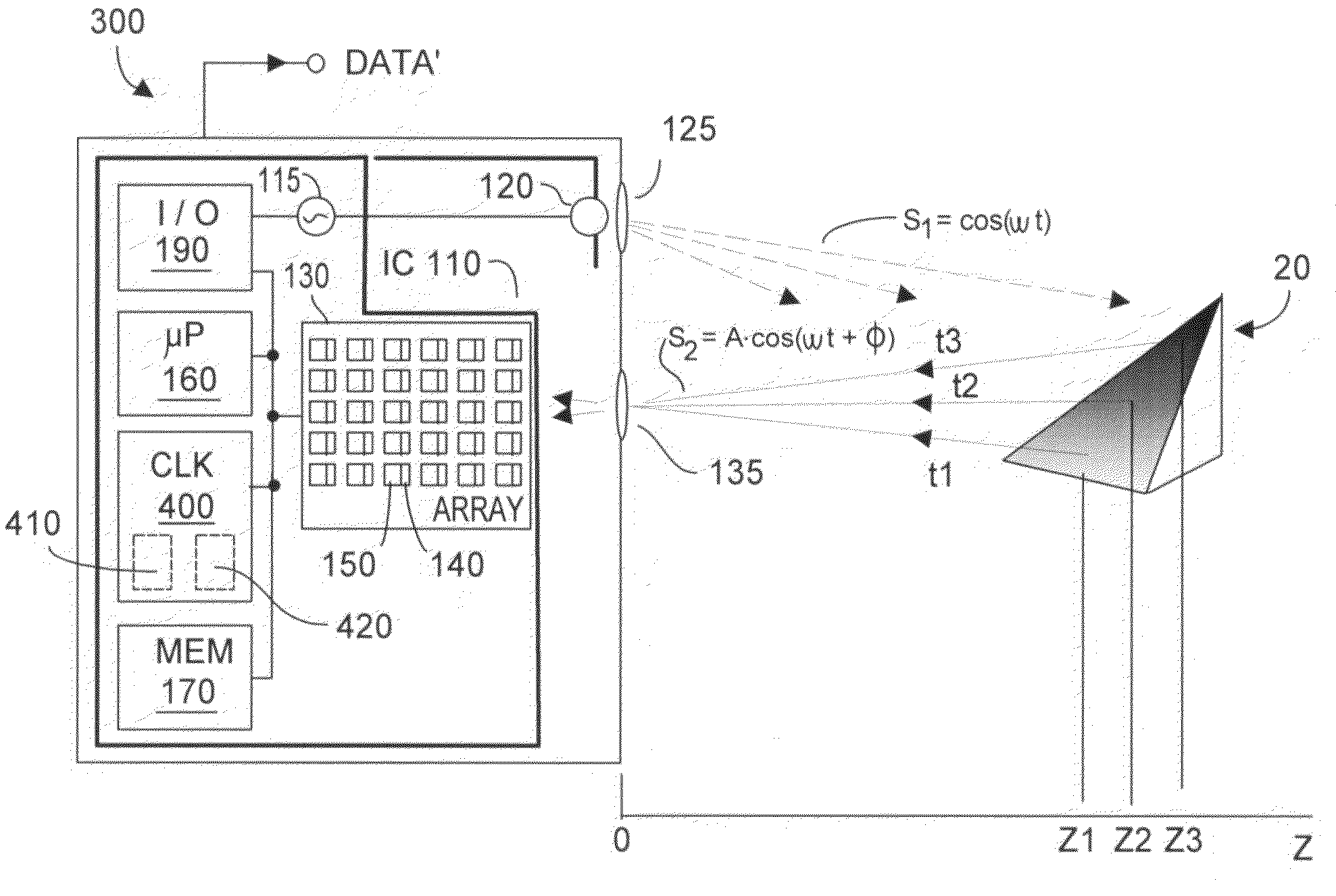
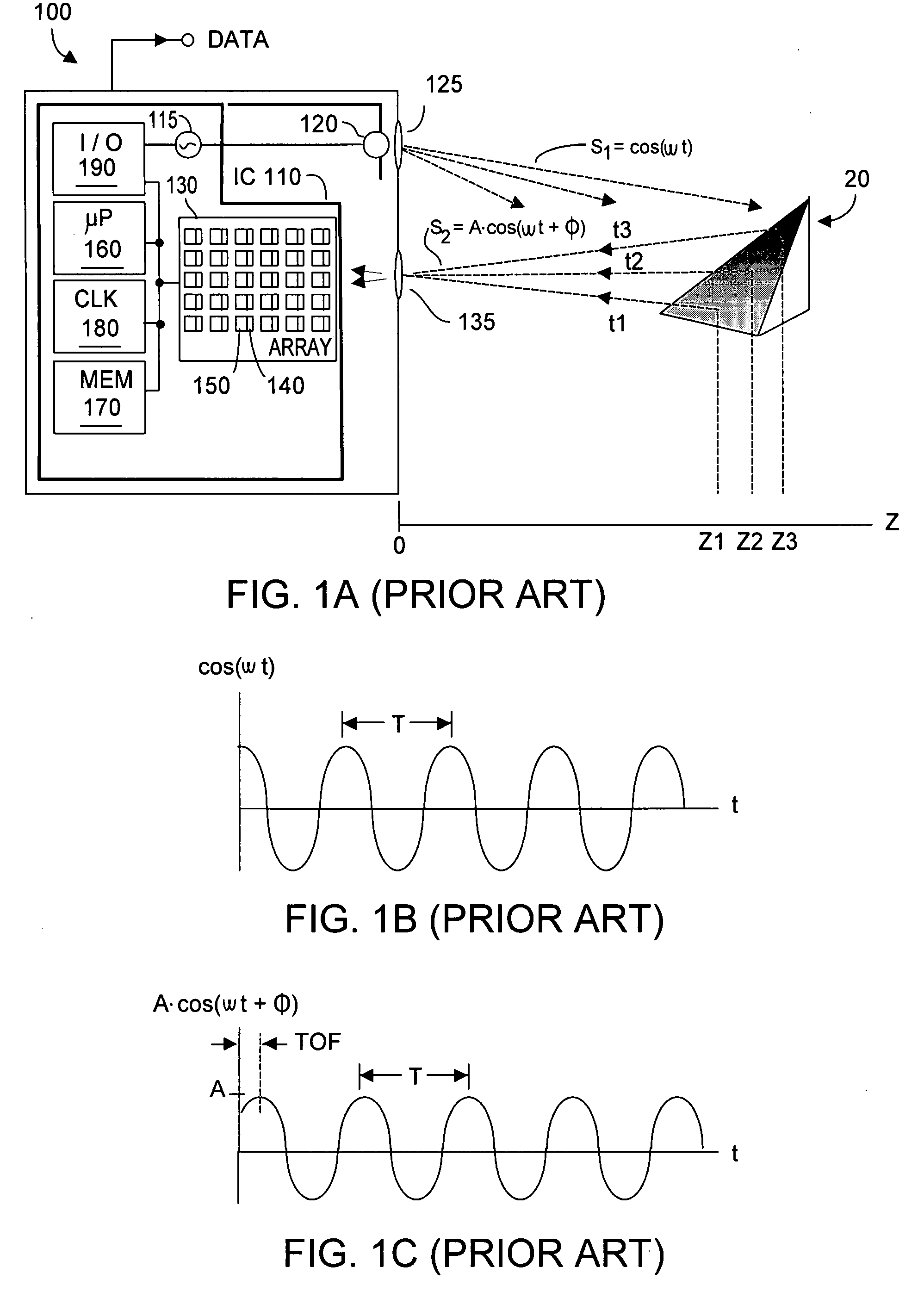
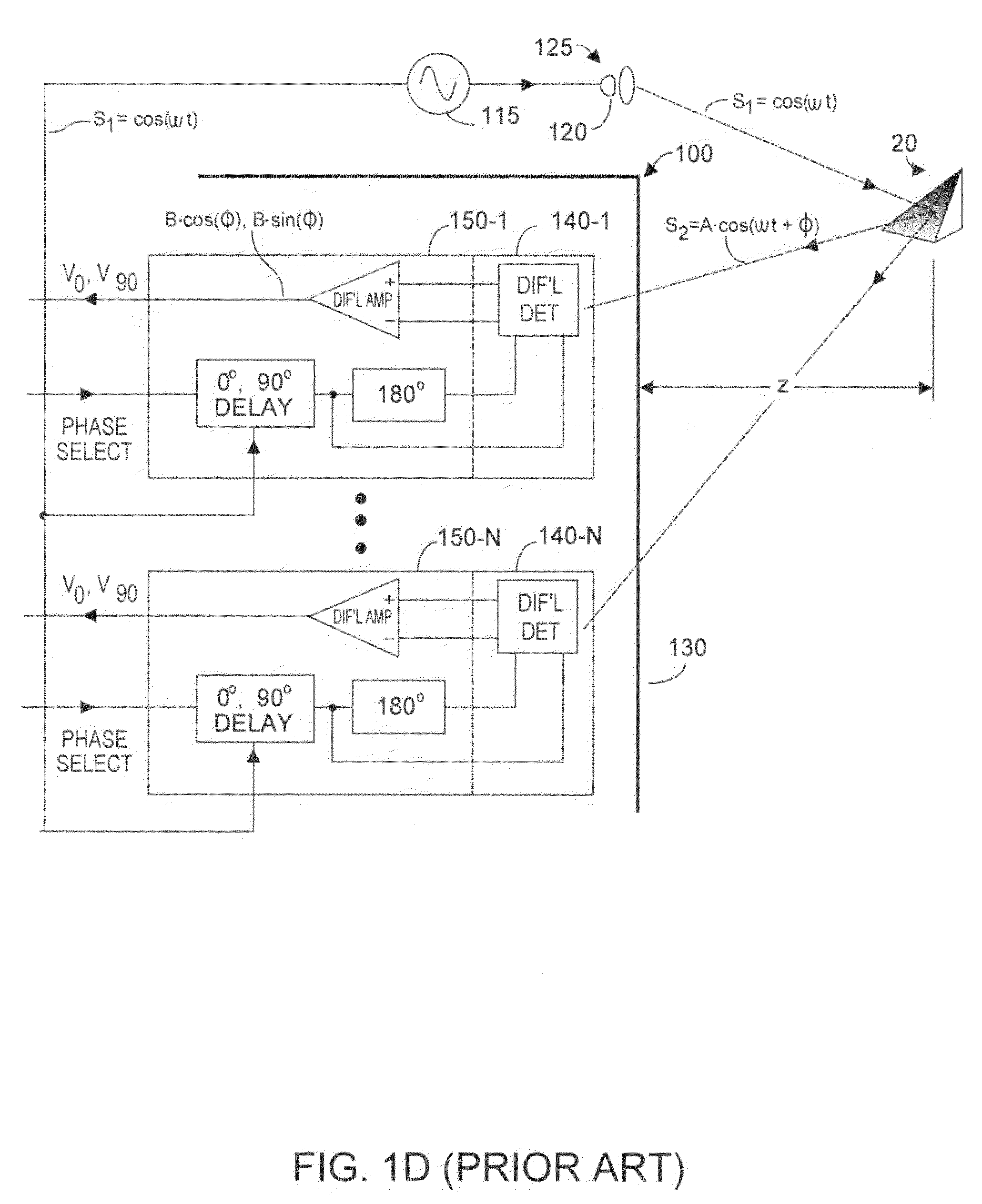
Method and system to avoid inter-system interference for phase-based time-of-flight systems
ActiveUS7405812B1Likelihood of interferenceReduce distractionsOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationClock rateOptical energy
Inter-system interference cross-produce P12 is reduced in a phase-based TOF system by randomizing instantaneous phase and / or frequency within a capture interval (or detection integration period). In one aspect, the TOF clock system frequency preserves long-term clock frequency stability but intentionally includes random or pseudo-random clock noise. The noise ensures the generated clock signals are temporally imperfect and lack substantial perfect periodicity. A second aspect causes the TOF clock system to hop frequency, preferably pseudo-randomly. TOF system homodyning favors detection of optical energy whose frequency correlates to the time-varying frequency of the emitted optical energy. Thus, the varying spectral spacing of the emitted optical energy reduces likelihood that an adjacent TOF system at any given time will emit optical energy of an interfering frequency. At least one aspect is employed, both aspects being mutually complementary to reduce the cross-correlation product P12 without substantially affecting TOF system performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for refresh management of memory modules
One embodiment sets forth an interface circuit configured to manage refresh command sequences that includes a system interface adapted to receive a refresh command from a memory controller, clock frequency detection circuitry configured to determine the timing for issuing staggered refresh commands to two or more memory devices coupled to the interface circuit based on the refresh command received from the memory controller, and at least two refresh command sequence outputs configured to generate the staggered refresh commands for the two or more memory devices
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Dynamic voltage control method and apparatus
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
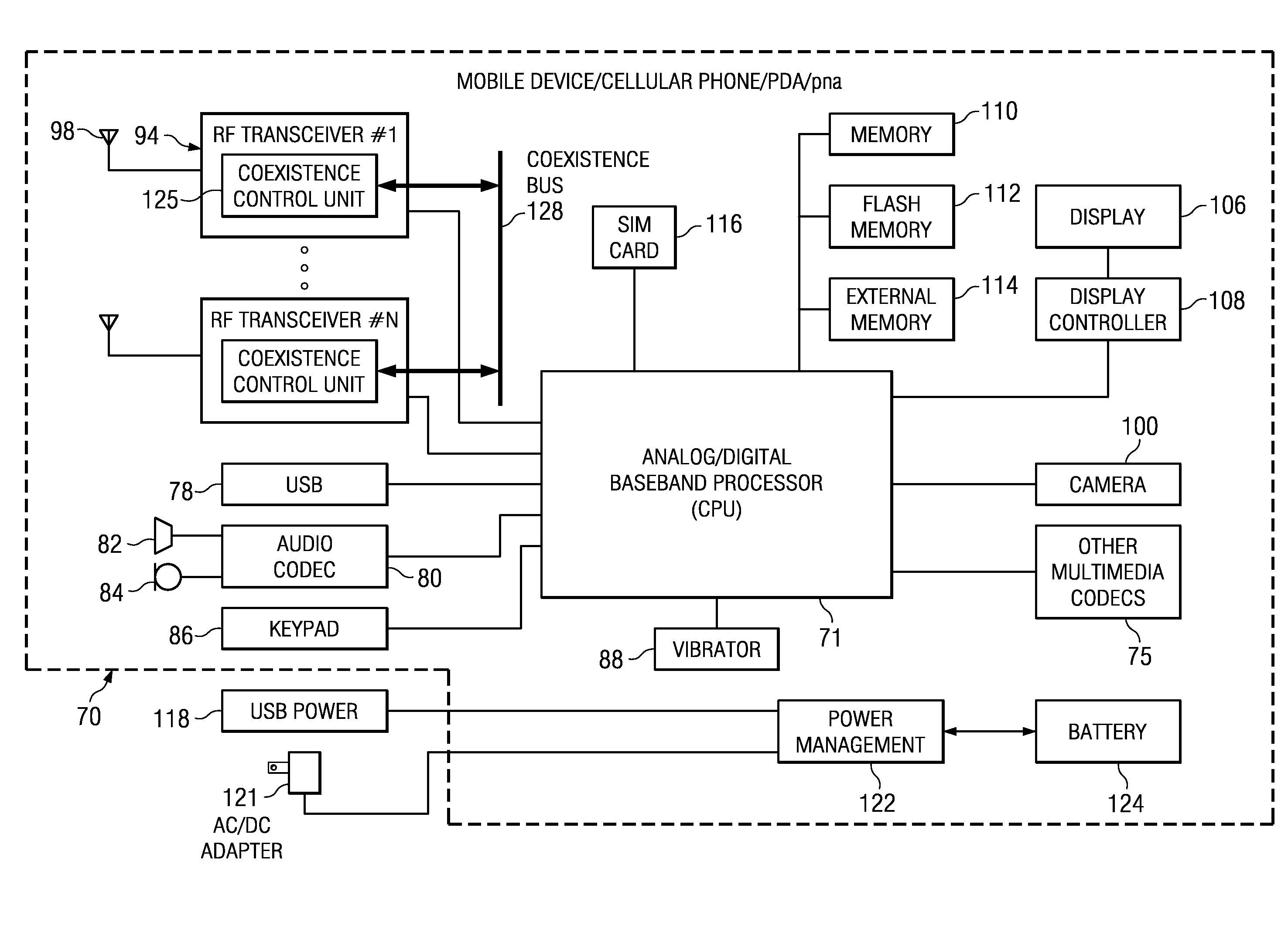
Distributed coexistence system for interference mitigation in a single chip radio or multi-radio communication device
ActiveUS20100137025A1Reduce distractionsAvoid interferenceCross-talk reductionSubstation equipmentTransceiverRadio reception
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of distributed coexistence for mitigating interference in a single chip radio and / or a multi-radio (i.e. multi-transceiver) communications device. The invention enables coexistence ‘friendly’ radio IPs having frequency agility in that they are capable of shifting their clock frequencies thereby avoiding frequency bands of potential victim radios. Frequency agility on the aggressor radio side (rather than by mitigating the effect of interference on the victim radio side) prevents harmonics from the aggressor's clock scheme from falling in the operating frequency band of the victim radio, and in turn causing degradation to its performance. Each aggressor radio, based on information received from other radios, configures the root clock frequency of its RX and / or TX chain clock generation circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Peripheral buses for integrated circuit
InactiveUS6064626AReduce power consumptionAverage power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageCapacitanceClock rate
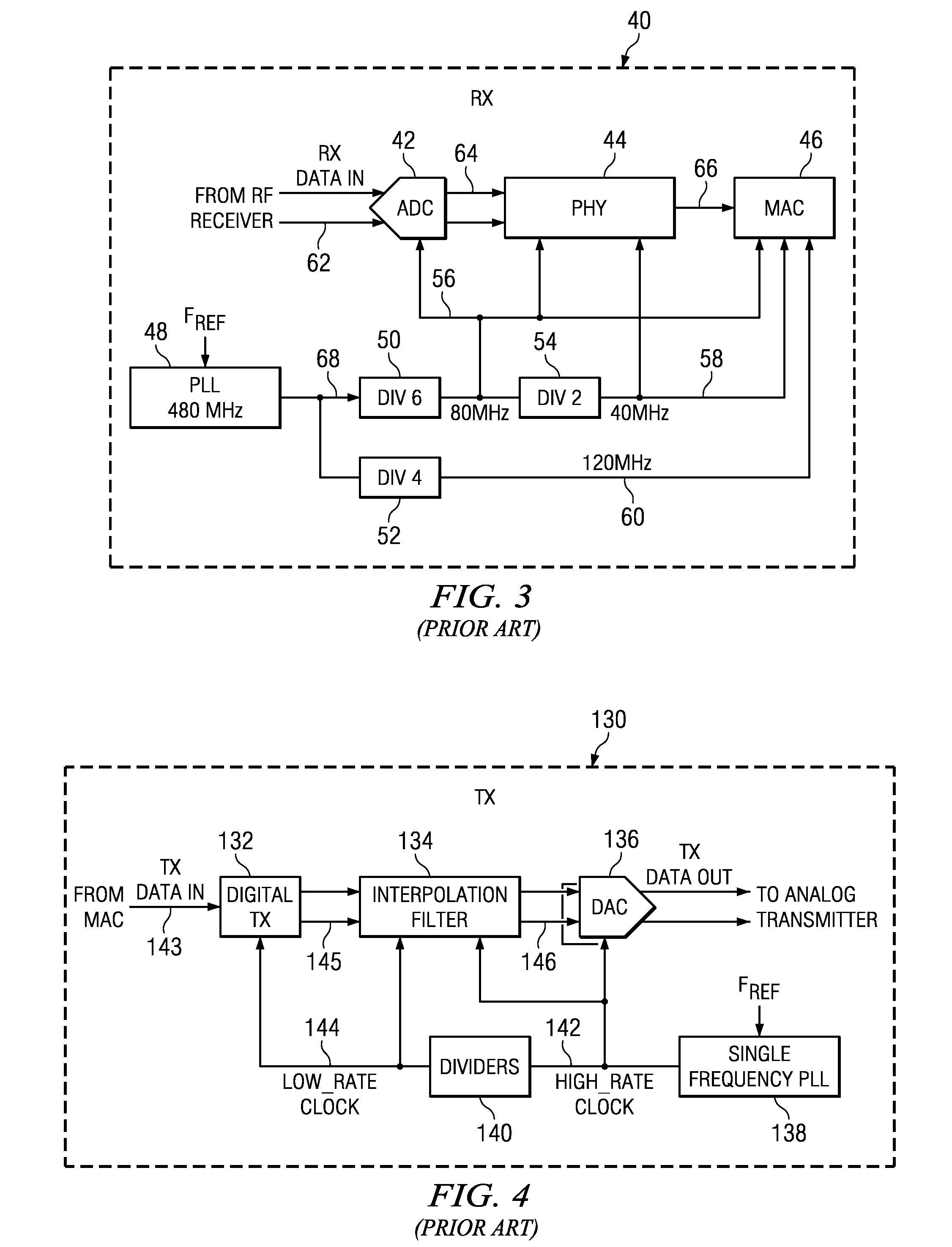
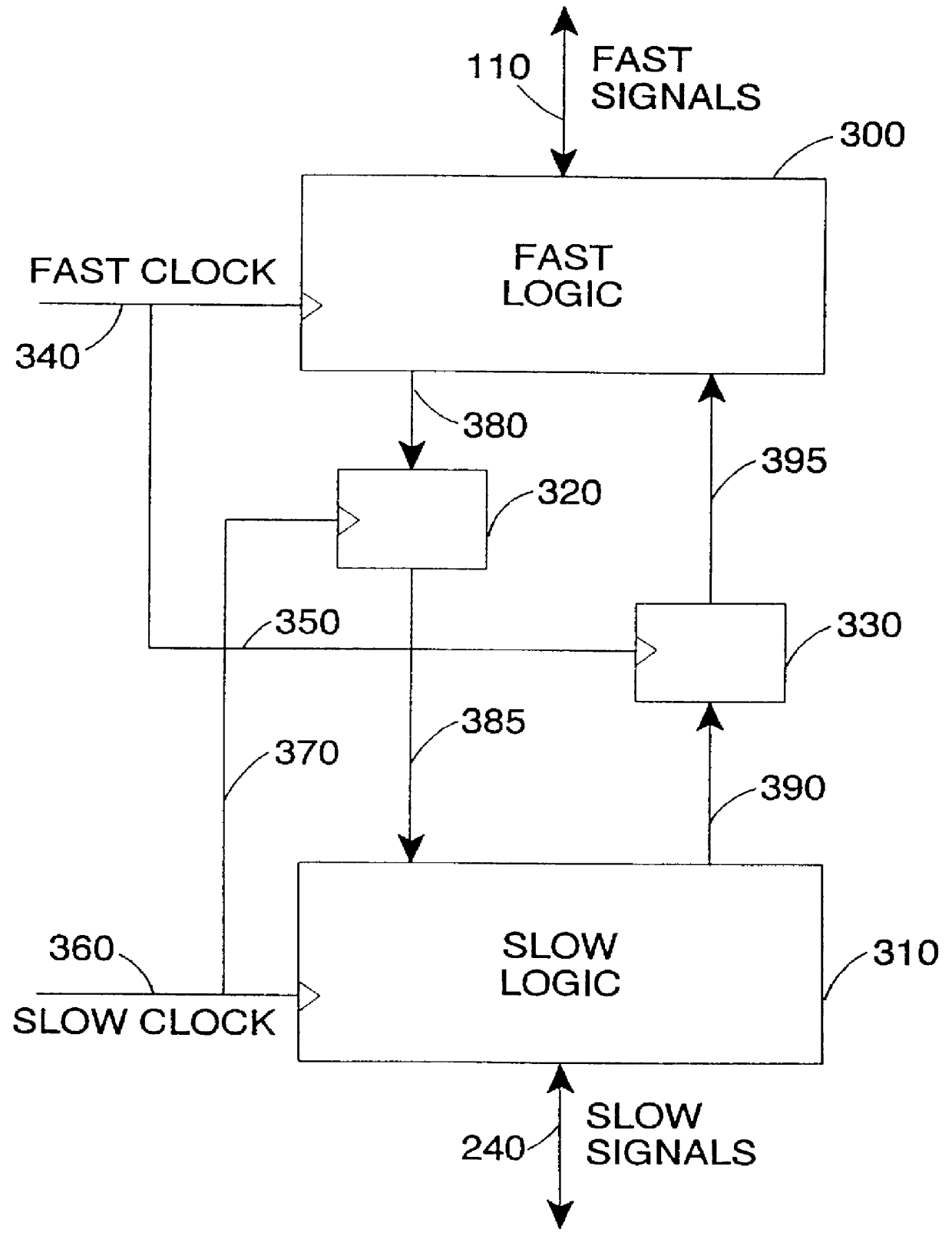
The present invention provides an integrated circuit comprising a system bus to which a processor is connectable, and first and second peripheral buses to which peripheral units used by said processor are connected, the first peripheral bus operating at a higher clock speed than the second peripheral bus. Further, the integrated circuit comprises bridge logic for providing an interface between the system bus and the peripheral buses to enable signals to be passed between the system bus and the peripheral buses, the bridge logic comprising clock resynchronisation logic for synchronising the system bus and the peripheral buses. Through the provision of first and second peripheral buses operating at different clock speeds, the integrated circuit of the present invention provides a great deal of flexibility for reducing the power consumption of the integrated circuit as compared with a similar integrated circuit having only one peripheral bus. Since the power consumption of each peripheral bus is proportional to the clock frequency and capacitance, significant power consumption savings can be realised by ensuring that each peripheral unit is connected to the slowest peripheral bus appropriate for that peripheral unit.
Owner:ARM LTD
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices without a voltage controlled crystal oscillator
Exemplary systems and methods include a distribution device that maintains a clock rate and distributes a series of tasks to a group of execution devices. Each task has a plurality of samples per frame associated with a time stamp indicating when the task is to be executed. The execution devices execute the series of tasks at the times indicated and adjust the number of samples per frame in relation to the clock rate maintained by the distribution device.
Owner:SONOS
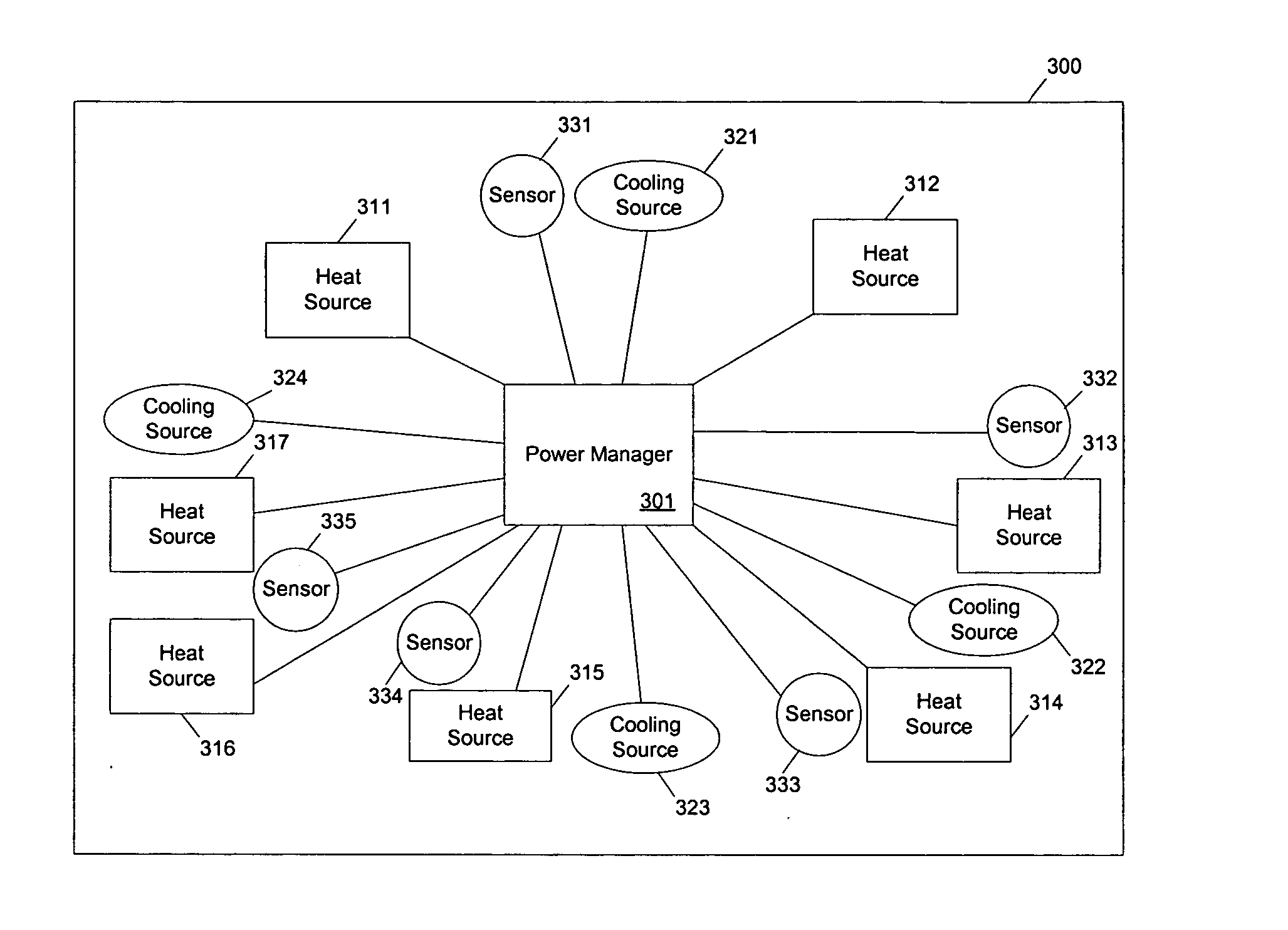
Methods and apparatuses for controlling the temperature of a data processing system
ActiveUS7451332B2Low heat generationImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementHard disc driveHeat sensitive
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
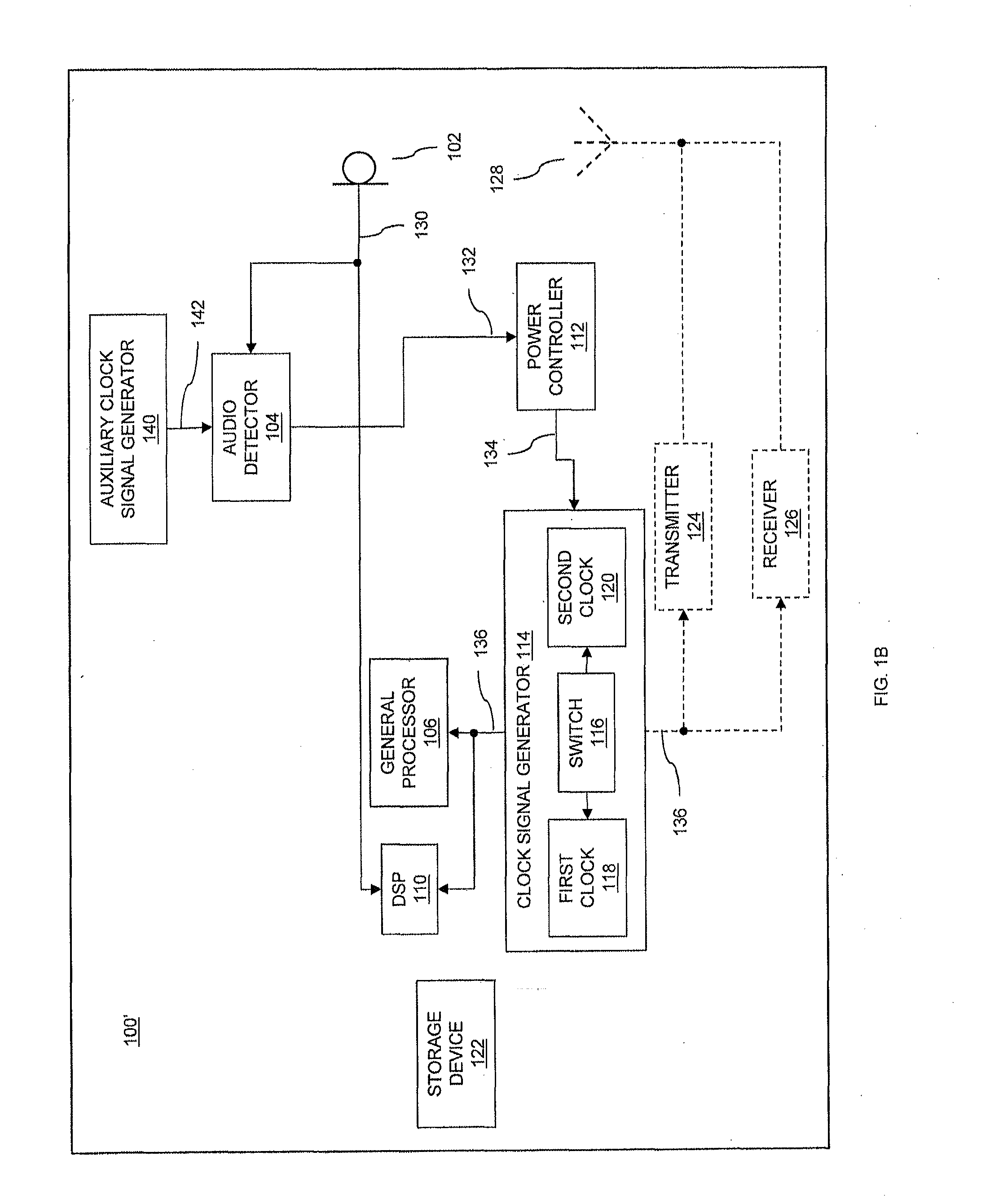
Low power audio detection
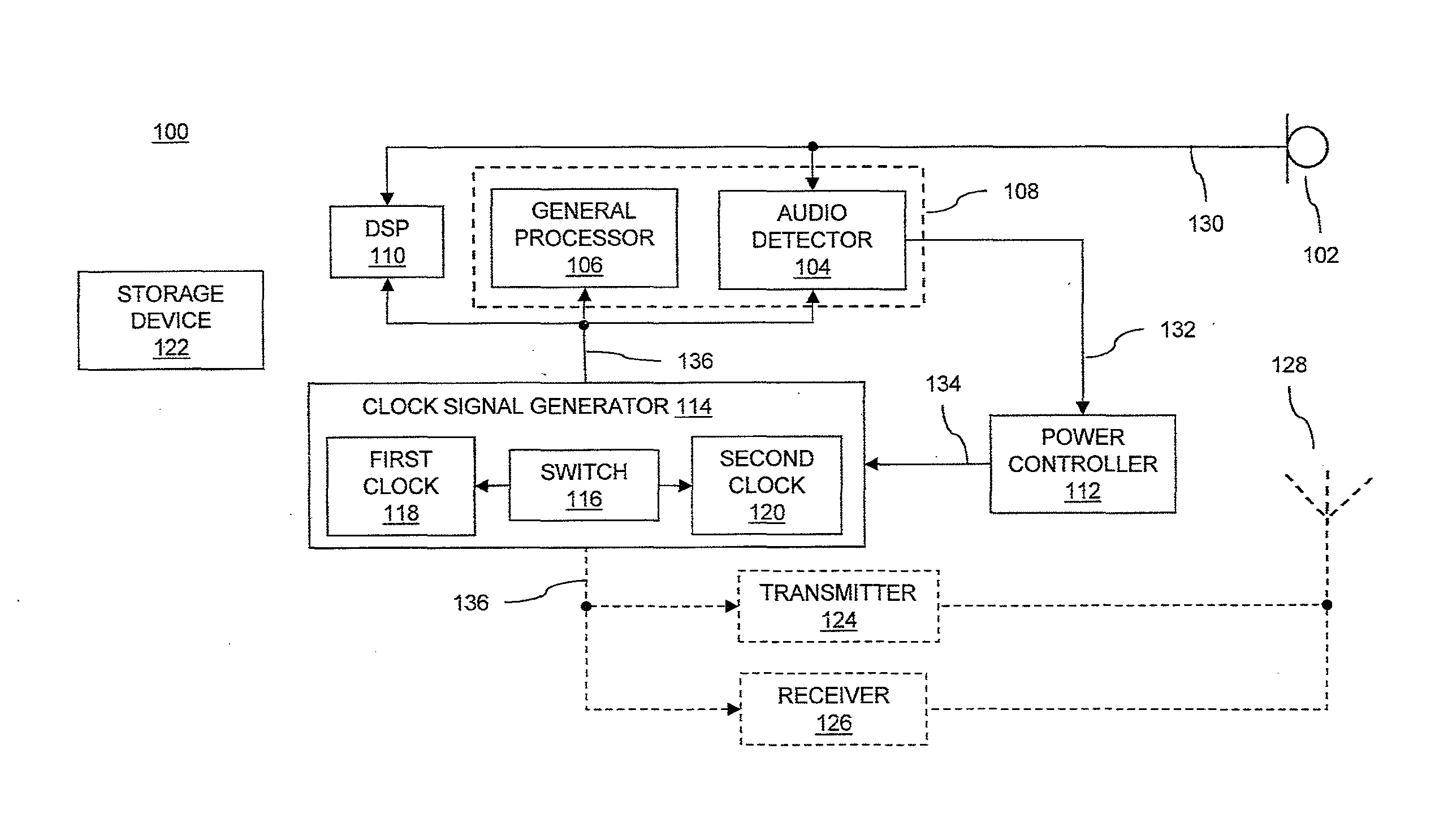
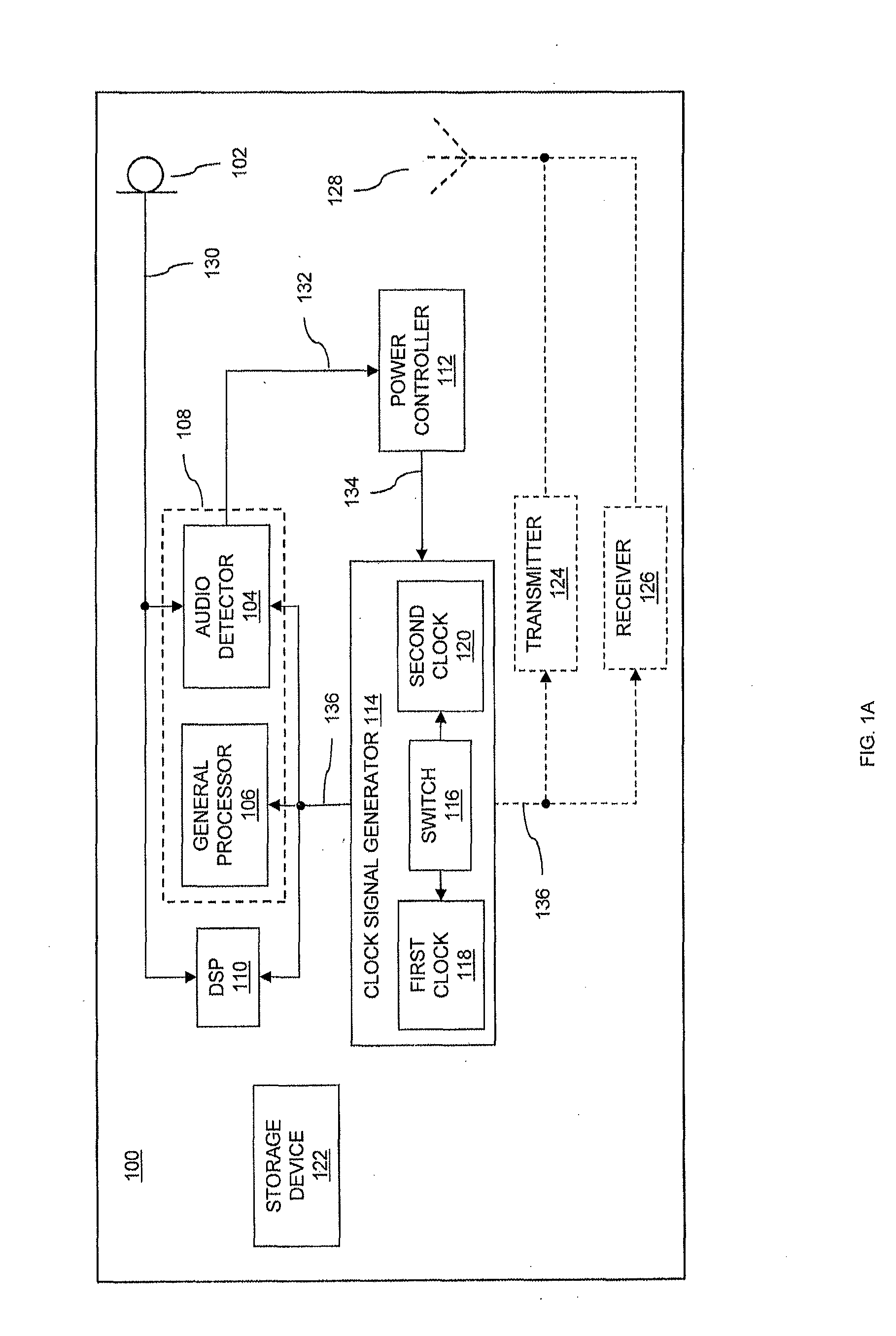
InactiveUS20130223635A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease power consumptionPower managementHearing device energy consumption reductionAudio signal flowLow power dissipation
Devices and methods of detecting a predetermined audio signal in audio signals are provided. A device includes a processor coupled to a clock signal generator, a power controller and an audio detector. The power controller controls a clock rate provided to the processor by the clock signal generator, to control the device to operate in a low power mode having a relatively low power consumption or in a normal power mode having a relatively high power consumption. The audio detector receives audio signals and detects, in the low power mode, probable presence of a predetermined audio signal in the audio signals. The power controller controls the device to switch from the low power mode to the normal power mode responsive to the detected presence of the predetermined audio signal by the audio detector.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
Method and apparatus for refresh management of memory modules
One embodiment sets forth an interface circuit configured to manage refresh command sequences that includes a system interface adapted to receive a refresh command from a memory controller, clock frequency detection circuitry configured to determine the timing for issuing staggered refresh commands to two or more memory devices coupled to the interface circuit based on the refresh command received from the memory controller, and at least two refresh command sequence outputs configured to generate the staggered refresh commands for the two or more memory devices
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
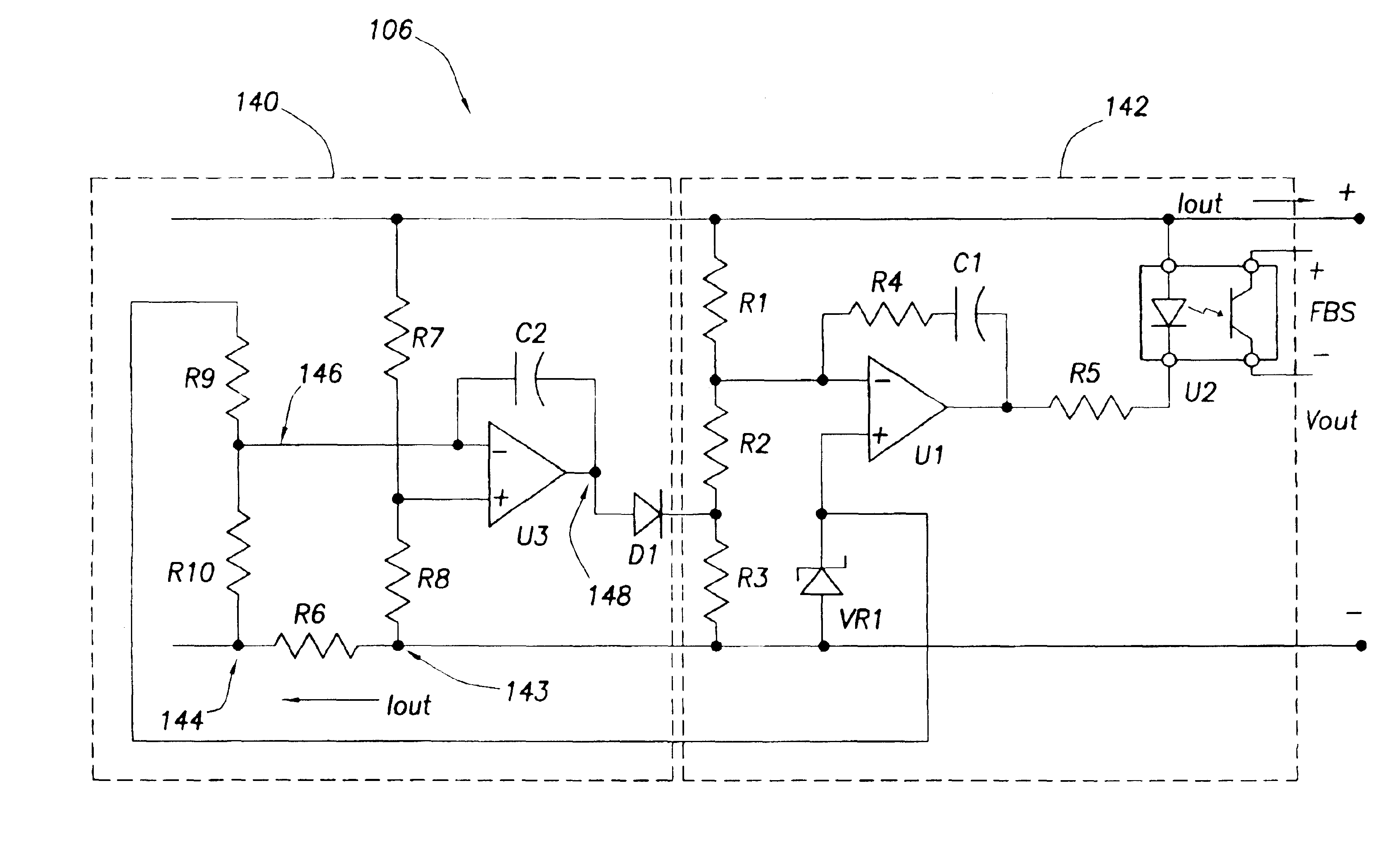
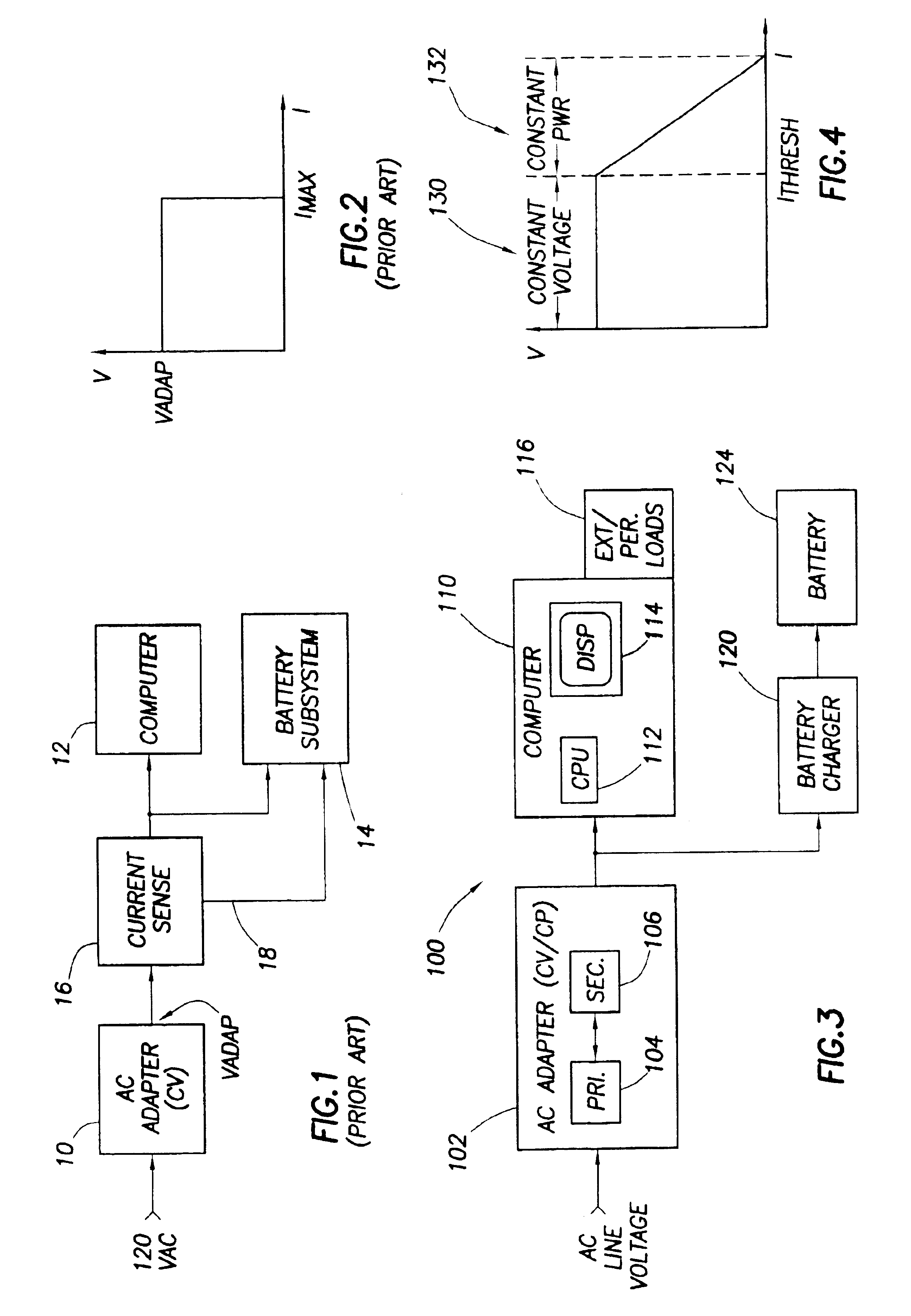
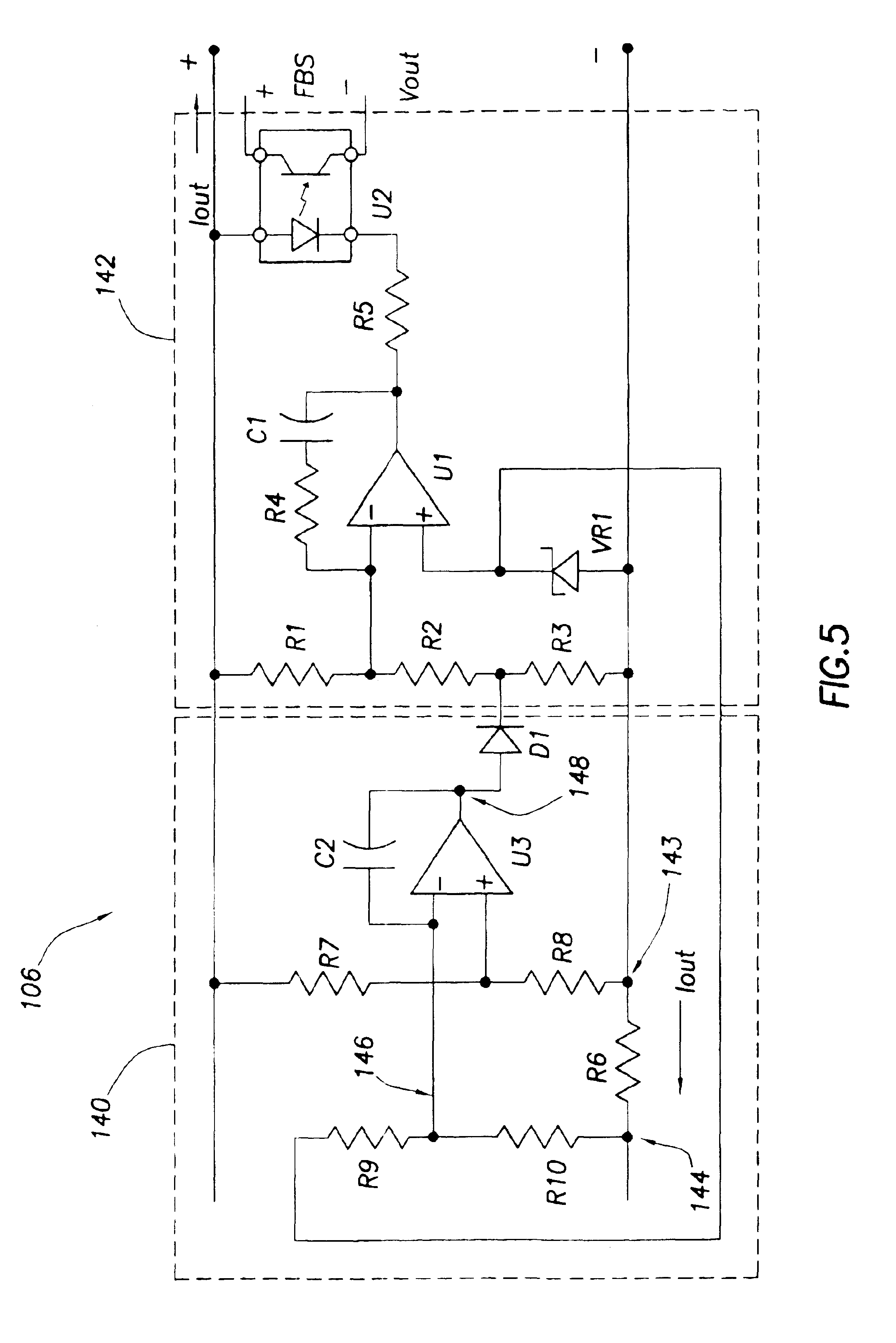
Technique for conveying overload conditions from an AC adapter to a load powered by the adapter
InactiveUS6950950B2Reduce power consumptionAlleviating excessive power draw conditionVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringElectric forceAC adapter
A constant voltage / constant power AC adapter converts AC voltage to DC voltage to provide power to a plurality of loads. The adapter's output characteristic is approximately a constant voltage as long as the output current draw by the loads is less than a threshold (e.g. a safety threshold for the adapter). If, however, the power draw on the adapter is such that the output current exceeds the threshold, the adapter then decreases its output voltage to maintain the power draw at a safe level. One or more loads that draw power from the adapter may be adapted to detect a drop in the AC adapter's output voltage. When such a voltage drop is detected, that information tells the load that too much current is being drawn from the adapter and that the load should throttle back (e.g., reducing battery charge current, CPU clock frequency, display brightness, etc.).
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
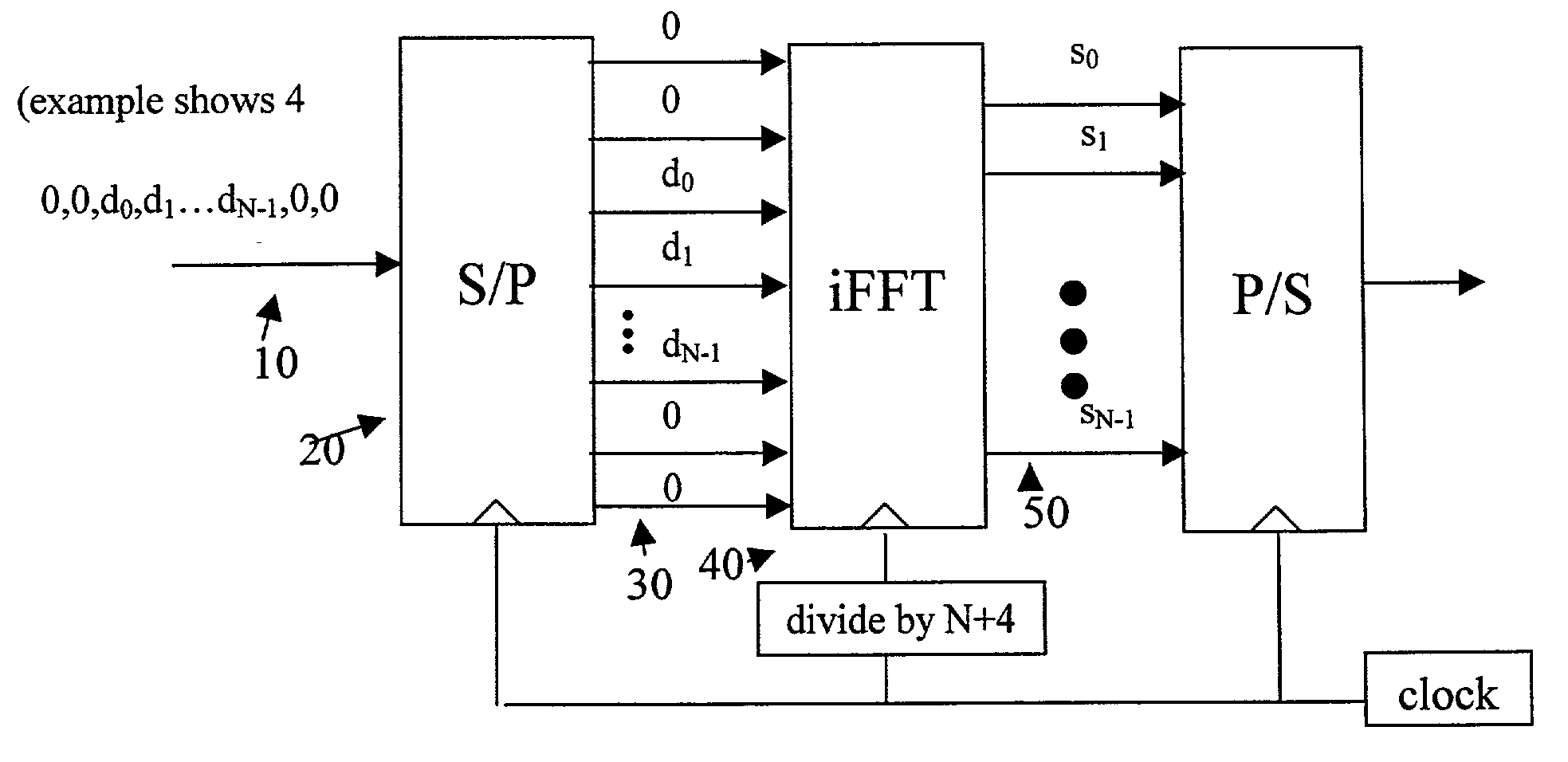
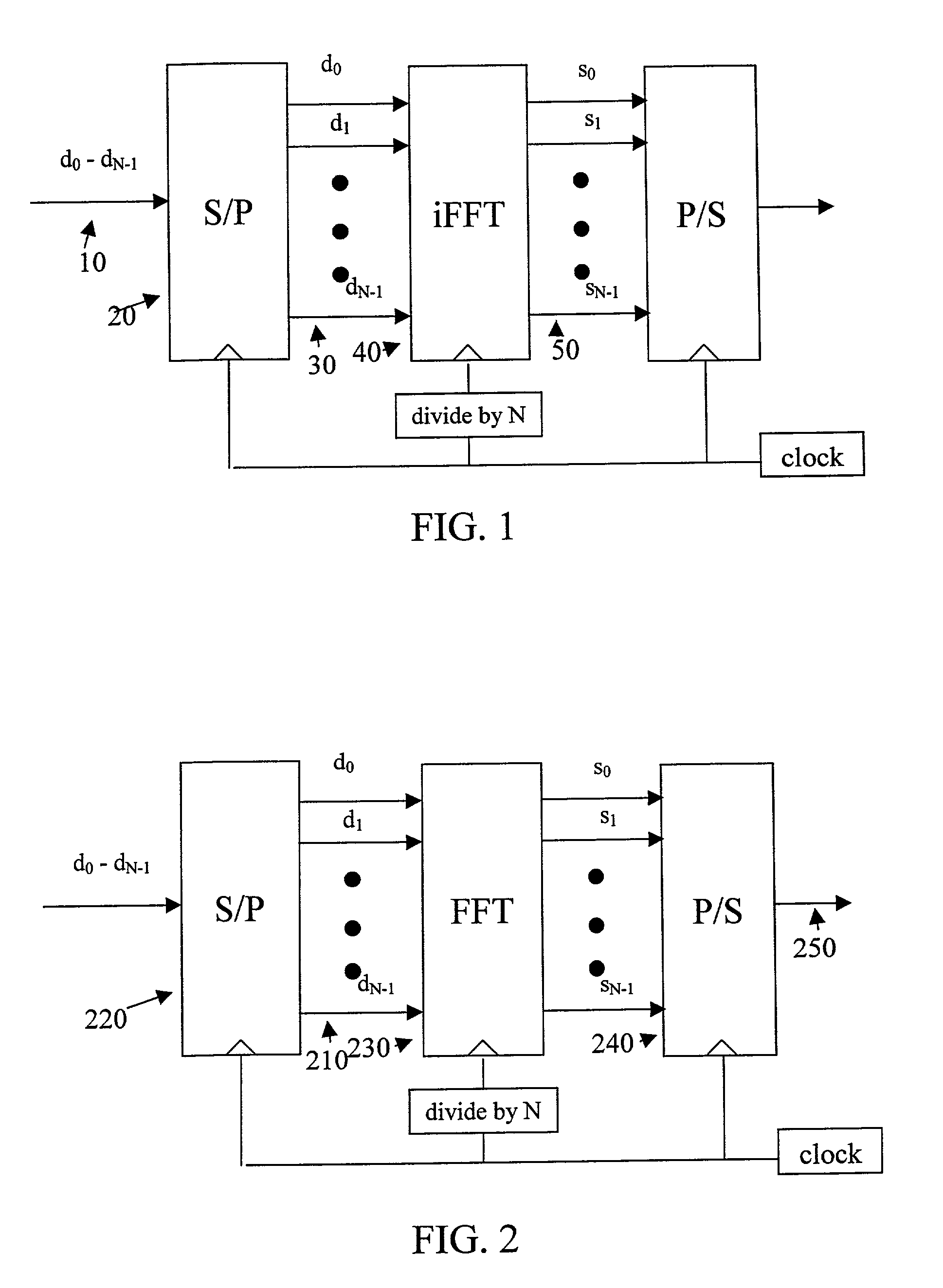
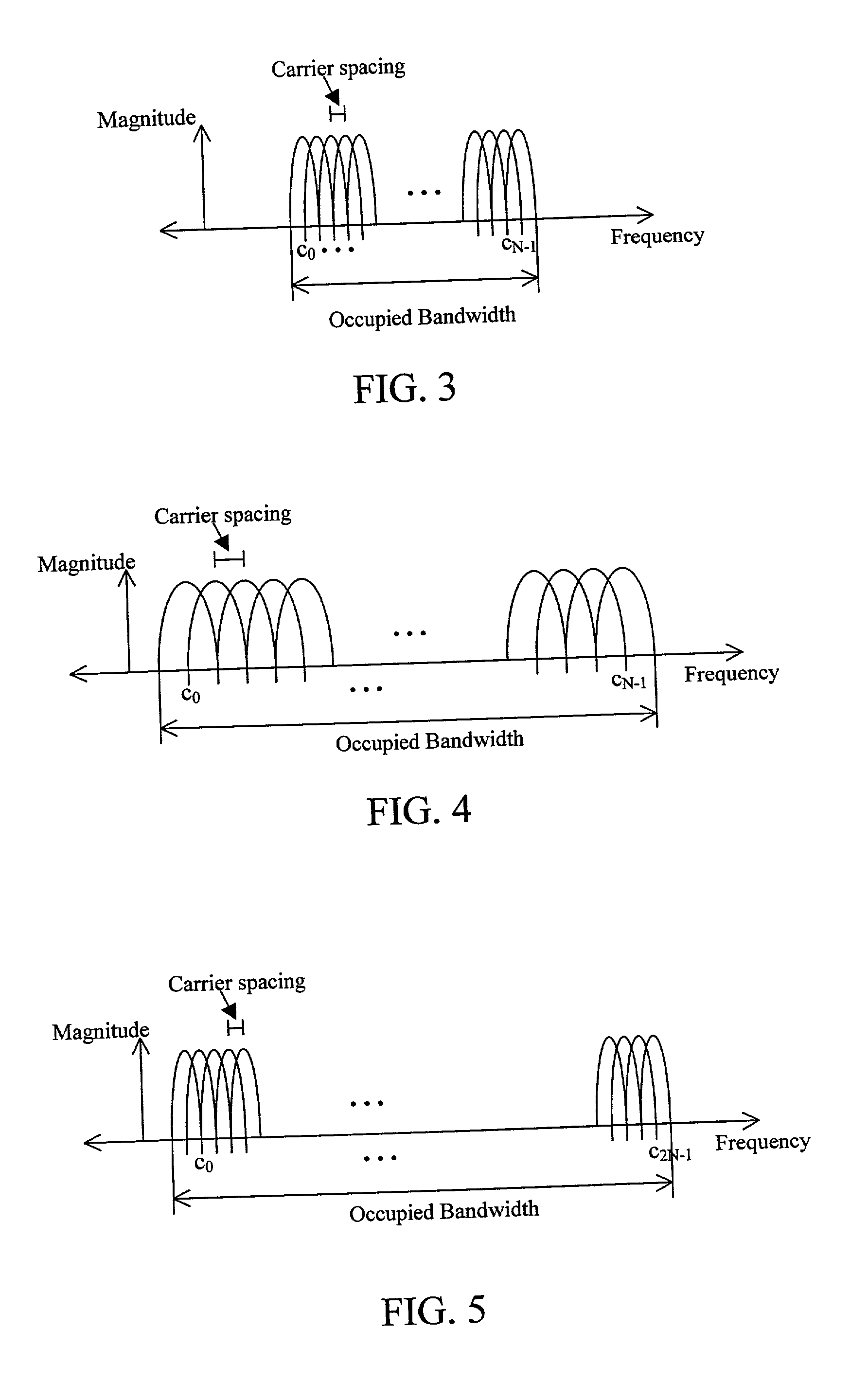
Multi-carrier communication systems employing variable symbol rates and number of carriers
ActiveUS20020006167A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission path divisionCommunications systemClock rate
A multi-carrier communication system such as an OFDM or DMT system has nodes which are allowed to dynamically change their receive and transmit symbol rates, and the number of carriers within their signals. Changing of the symbol rate is done by changing the clocking frequency of the nodes' iFFT and FFT processors, as well as their serializers and deserializers. The nodes have several ways of dynamically changing the number of carriers used. The selection of symbol rate and number of carriers can be optimized for a given channel based on explicit channel measurements, a priori knowledge of the channel, or past experience. Provision is made for accommodating legacy nodes that may have constraints in symbol rate or the number of carriers they can support. The receiver can determine the correct symbol rate and number of carriers through a priori knowledge, a first exchange of packets in a base mode that all nodes can understand, or an indication in the header of the data packet which is transmitted in a base mode of operation that all nodes can understand.
Owner:THE CONNECTIVITY PATENT TRUST
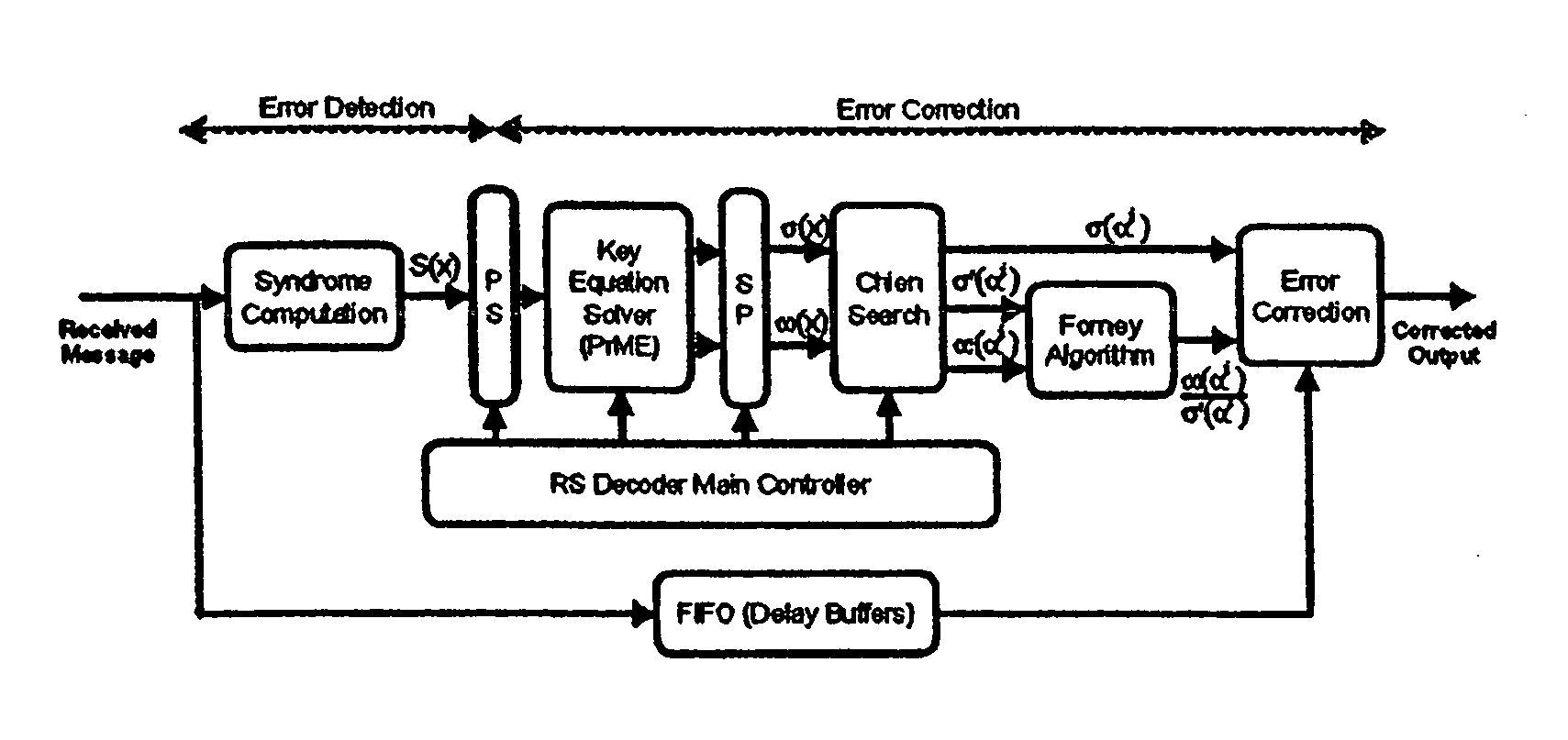
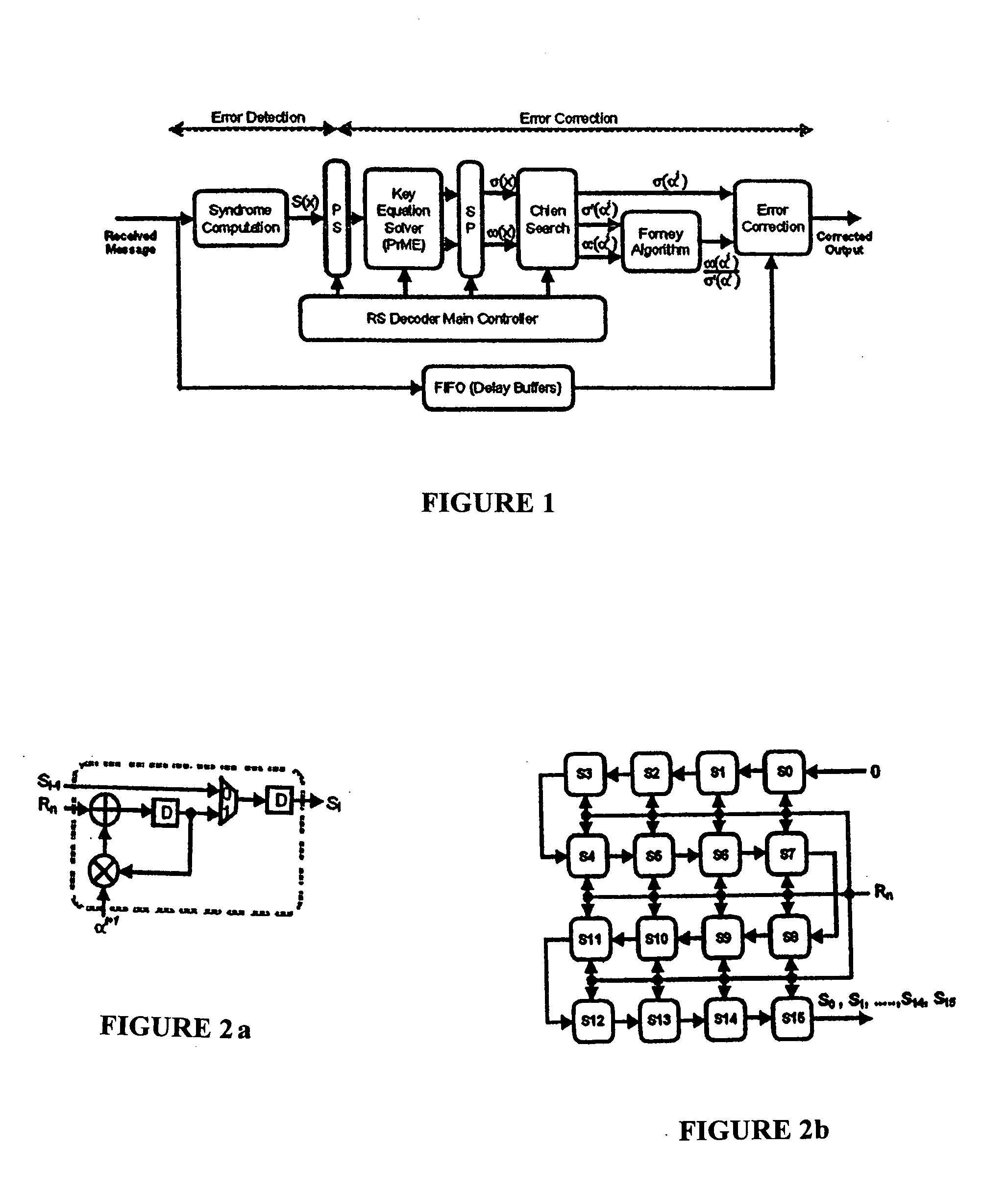
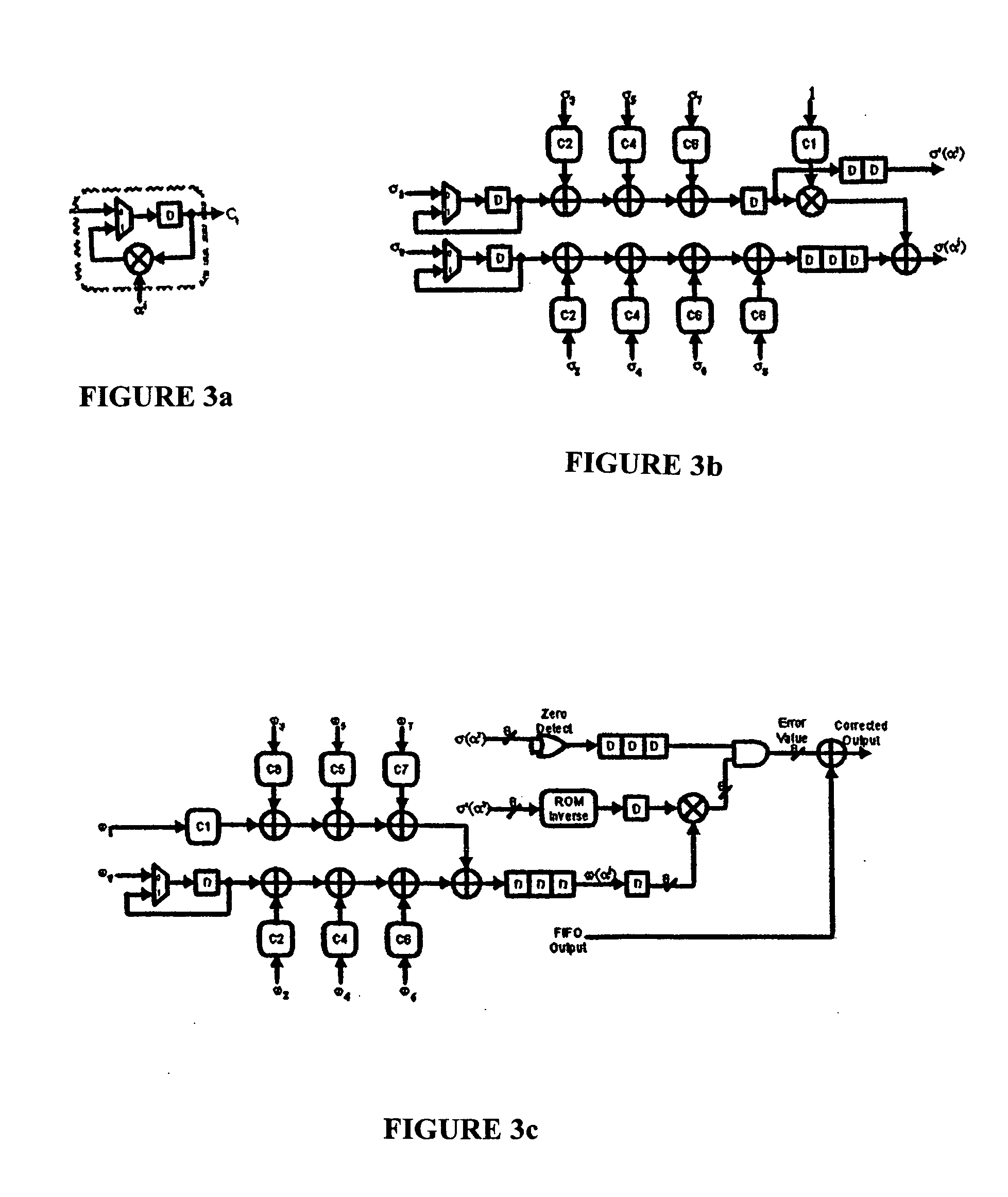
Reed-solomon decoder systems for high speed communication and data storage applications
InactiveUS20060059409A1Effective and reliable error correction functionalityReduce complexityCode conversionCoding detailsModem deviceHigh rate
A high-speed, low-complexity Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder architecture using a novel pipelined recursive Modified Euclidean (PrME) algorithm block for very high-speed optical communications is provided. The RS decoder features a low-complexity Key Equation Solver using a PrME algorithm block. The recursive structure enables the low-complexity PrME algorithm block to be implemented. Pipelining and parallelizing allow the inputs to be received at very high fiber optic rates, and outputs to be delivered at correspondingly high rates with minimum delay. An 80-Gb / s RS decoder architecture using 0.13-μm CMOS technology in a supply voltage of 1.2 V is disclosed that features a core gate count of 393 K and operates at a clock rate of 625 MHz. The RS decoder has a wide range of applications, including fiber optic telecommunication applications, hard drive or disk controller applications, computational storage system applications, CD or DVD controller applications, fiber optic systems, router systems, wireless communication systems, cellular telephone systems, microwave link systems, satellite communication systems, digital television systems, networking systems, high-speed modems and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
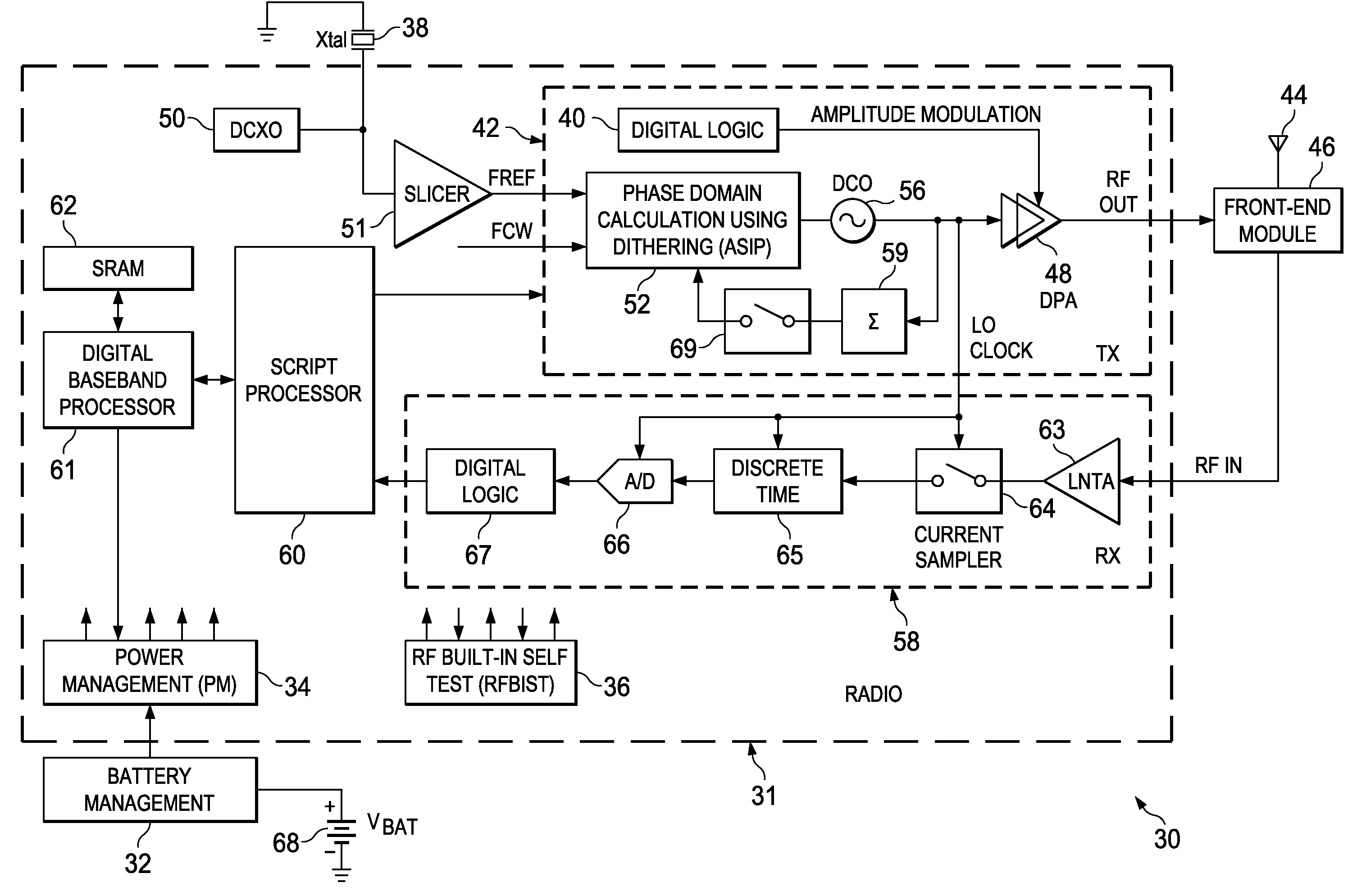
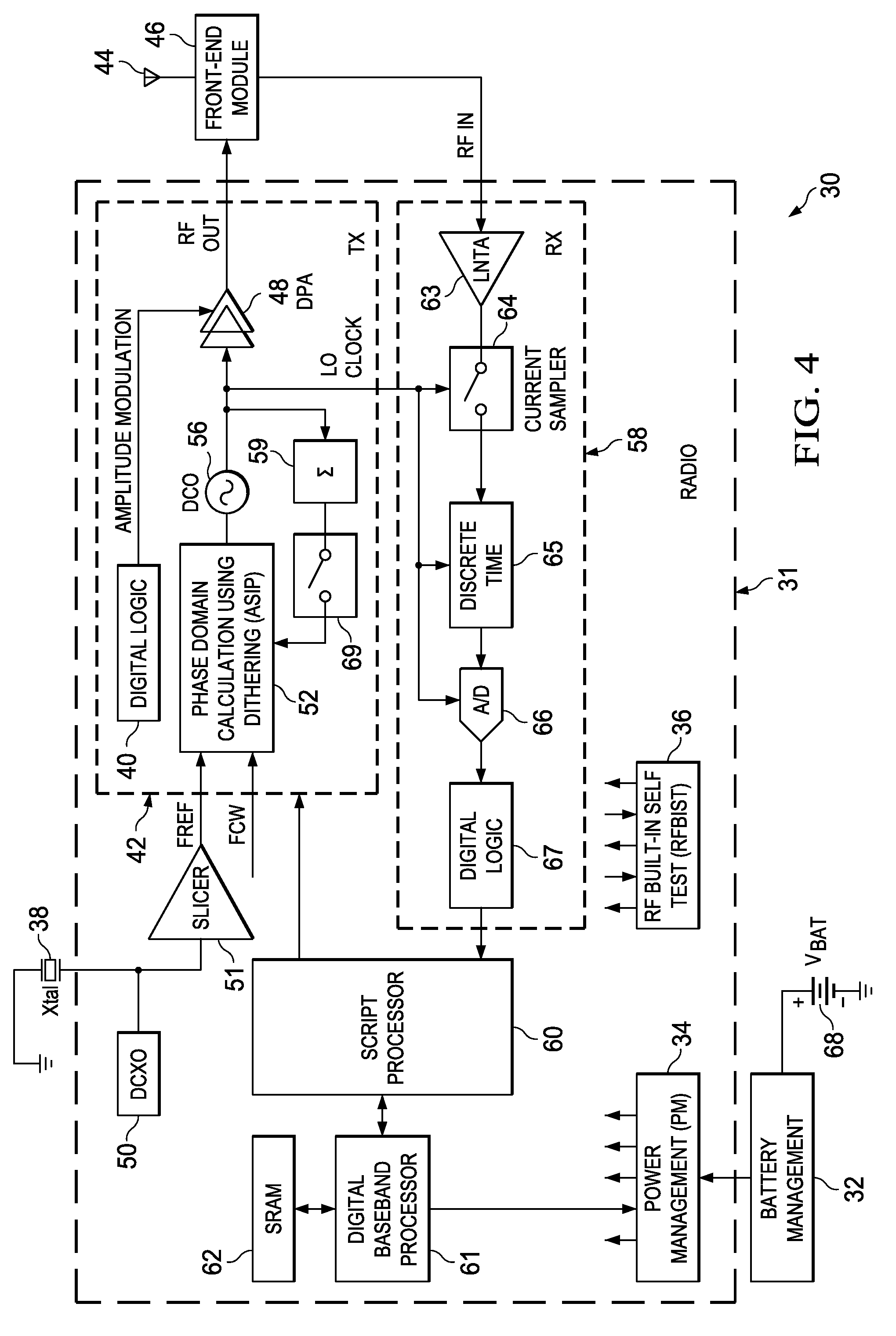
Computation spreading utilizing dithering for spur reduction in a digital phase lock loop
ActiveUS20090262877A1Easy to reconfigureReduce generationPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency spectrumClock rate
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of spur reduction using computation spreading with dithering in a digital phase locked loop (DPLL) architecture. A software based PLL incorporates a reconfigurable calculation unit (RCU) that is optimized and programmed to sequentially perform all the atomic operations of a PLL or any other desired task in a time sharing manner. An application specific instruction-set processor (ASIP) incorporating the RCU is adapted to spread the computation of the atomic operations out over a PLL reference clock period wherein each computation is performed at a much higher processor clock frequency than the PLL reference clock rate. This significantly reduces the per cycle current transient generated by the computations. The frequency content of the current transients is at the higher processor clock frequency which results in a significant reduction in spurs within sensitive portions of the output spectrum. Further reduction in spurs is achieved by dithering the duration of the software loop of atomic operations and / or by randomly shuffling one or more non-data dependent instructions within each iteration of the software loop.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
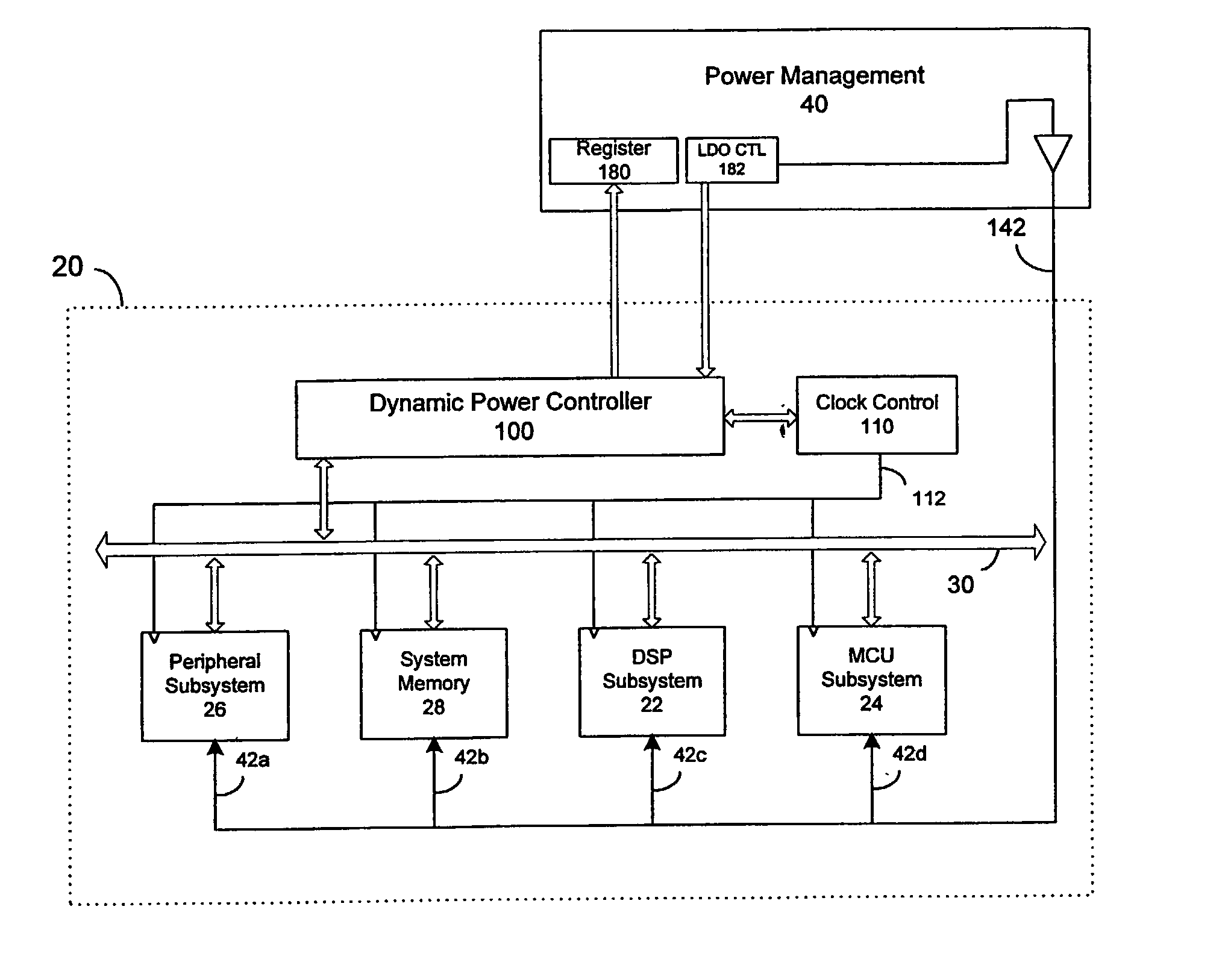
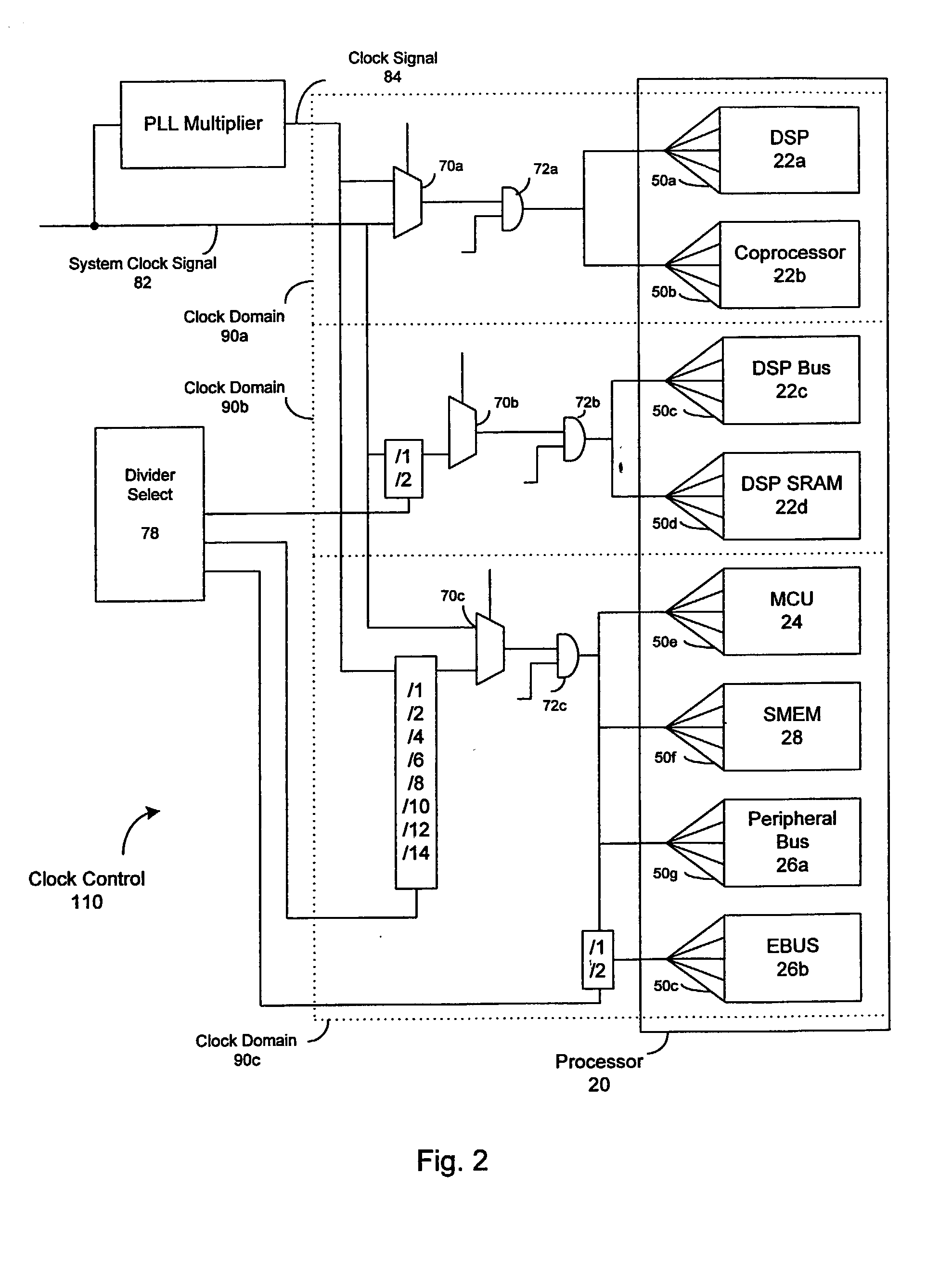
Dynamic voltage control method and apparatus
A dynamic power controller is provided that identifies a clock frequency requirement of a processor and determines a voltage requirement to support the clock frequency requirement. The dynamic power controller transitions the processor to a power state defined by the clock frequency requirement and the voltage requirement. In particular, a voltage level indicated by the voltage requirement is supplied to the processor and the frequency distribution indicated by the frequency requirement is provided to the clocks signals of the processor.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
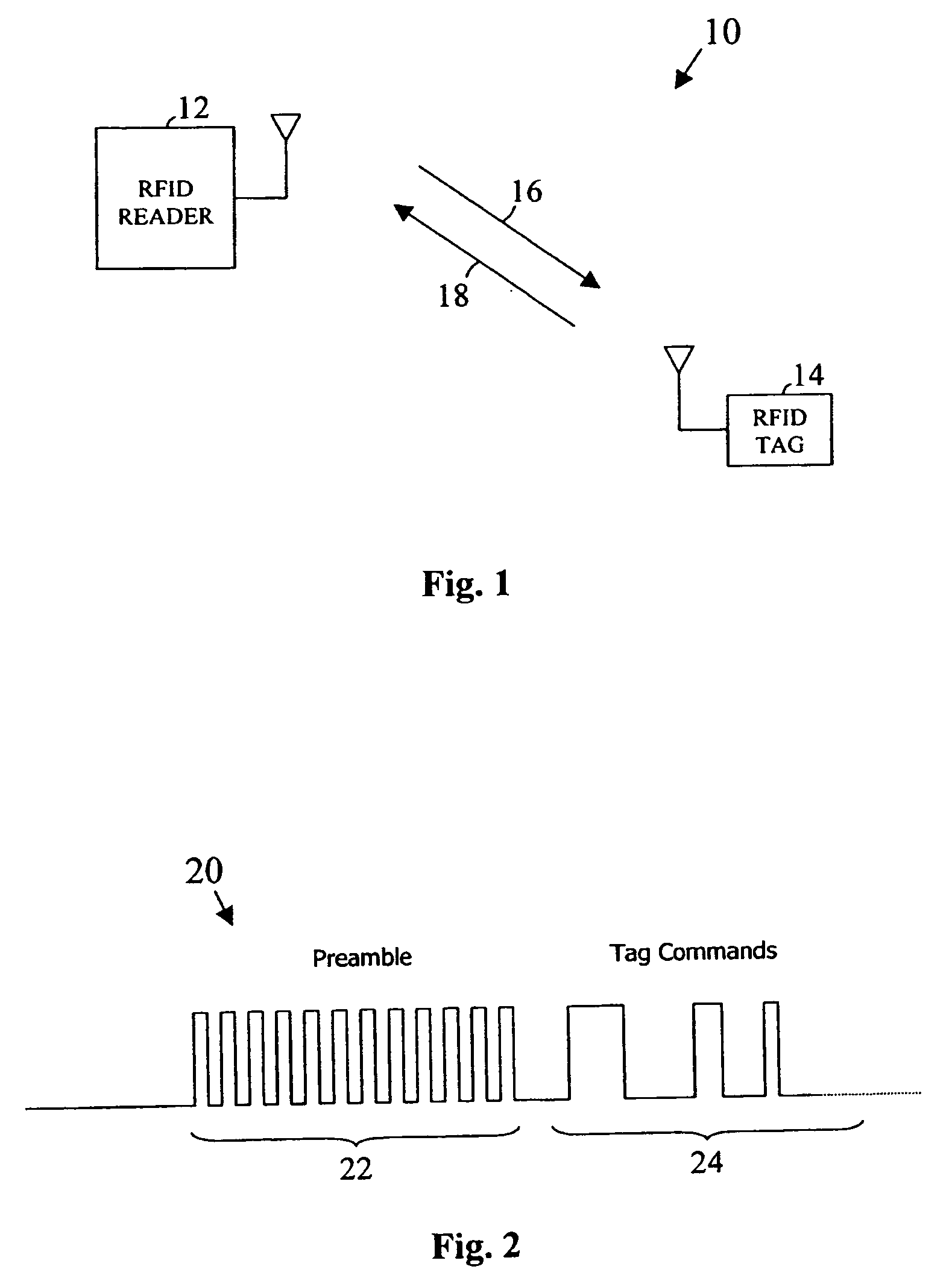
RFID tag with separate transmit and receive clocks and related method
InactiveUS20060273882A1Subscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesClock rateComputer science
Owner:INTEL CORP
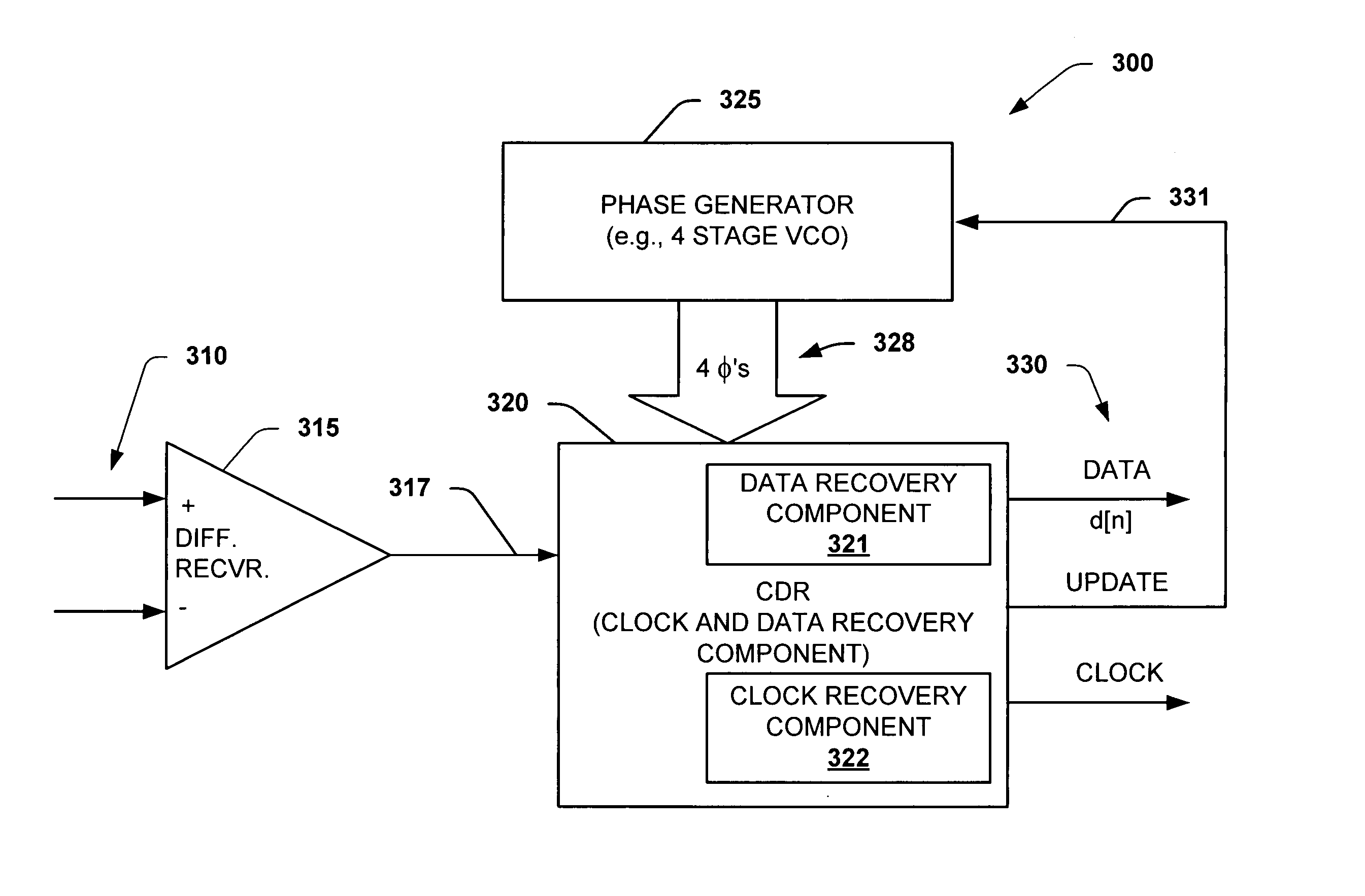
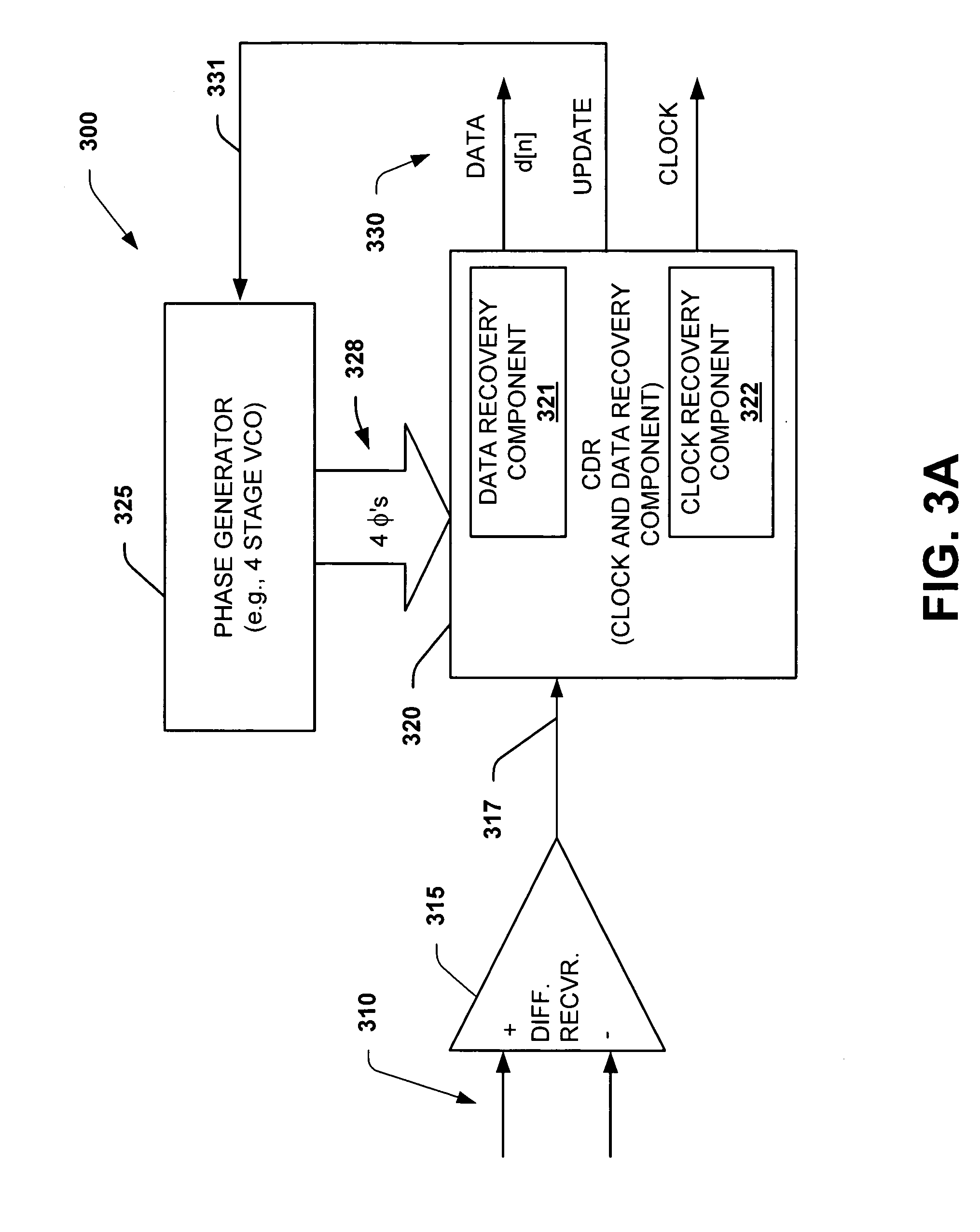
Interpolator based clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit with digitally programmable BW and tracking capability
ActiveUS20050180536A1High bandwidthLower latencyPulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementPhase correctionData stream
The present invention facilitates clock and data recovery (330,716 / 718) for serial data streams (317,715) by providing a mechanism that can be employed to maintain a fixed tracking capability of an interpolator based CDR circuit (300,700) at multiple data rates (e.g., 800). The present invention further provides a wide data rate range CDR circuit (300,700), yet uses an interpolator design optimized for a fixed frequency. The invention employs a rate programmable divider circuit (606,656,706) that operates over a wide range of clock and data rates (e.g., 800) to provide various phase correction step sizes (e.g., 800) at a fixed VCO clock frequency. The divider (606,656,706) and a finite state machine (FSM) (612,662,712) of the exemplary CDR circuit (600,650,700) are manually programmed based on the data rate (614,667). Alternately, the data rate may be detected from a recovered serial data stream (718) during CDR operations (on-the-fly) utilizing a frequency detection circuit (725) to automatically program the divider (706) and FSM (712) to provide CDR circuit operation at the nearest base clock rate (716).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
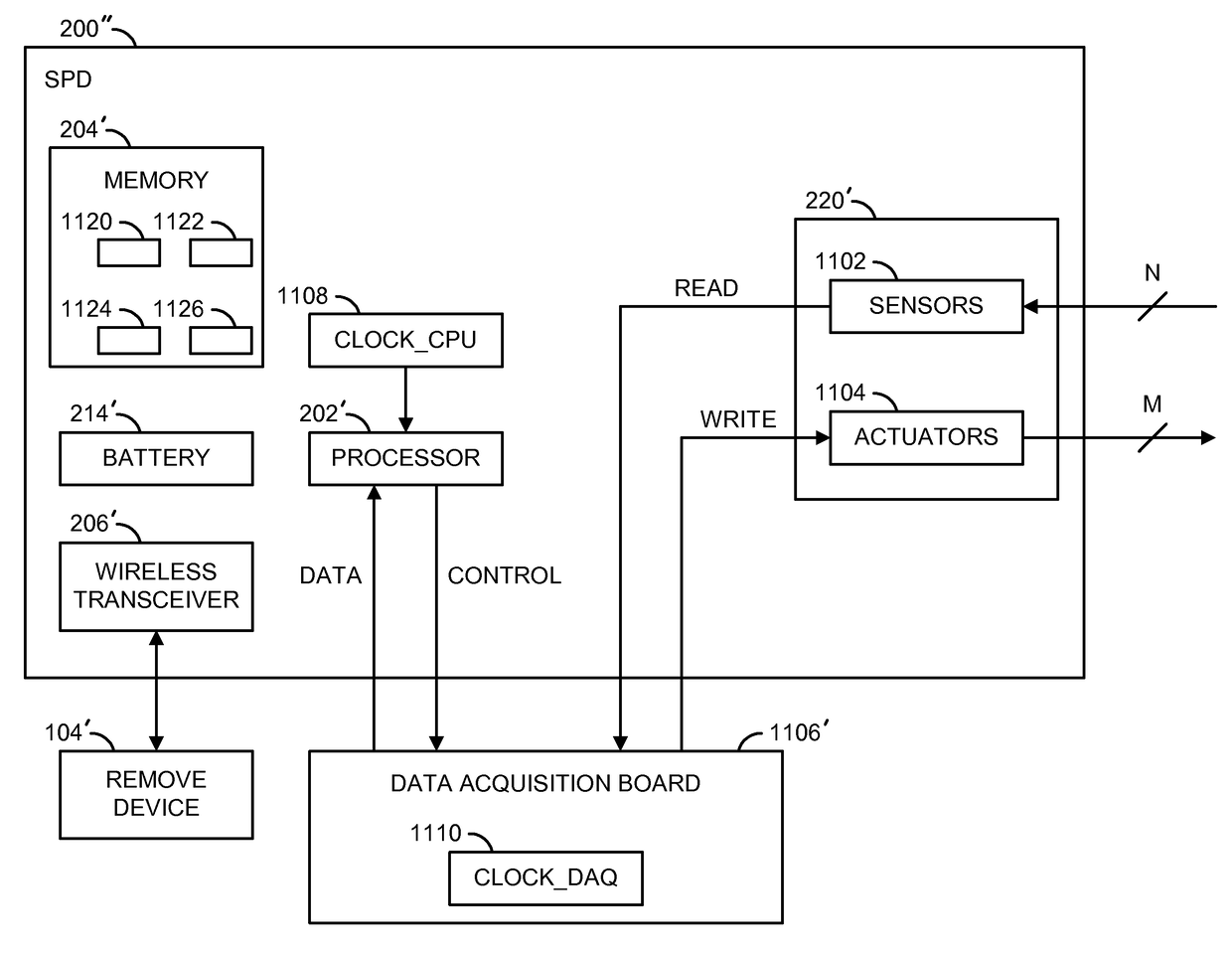
Power management for a self-powered device scheduling a dynamic process
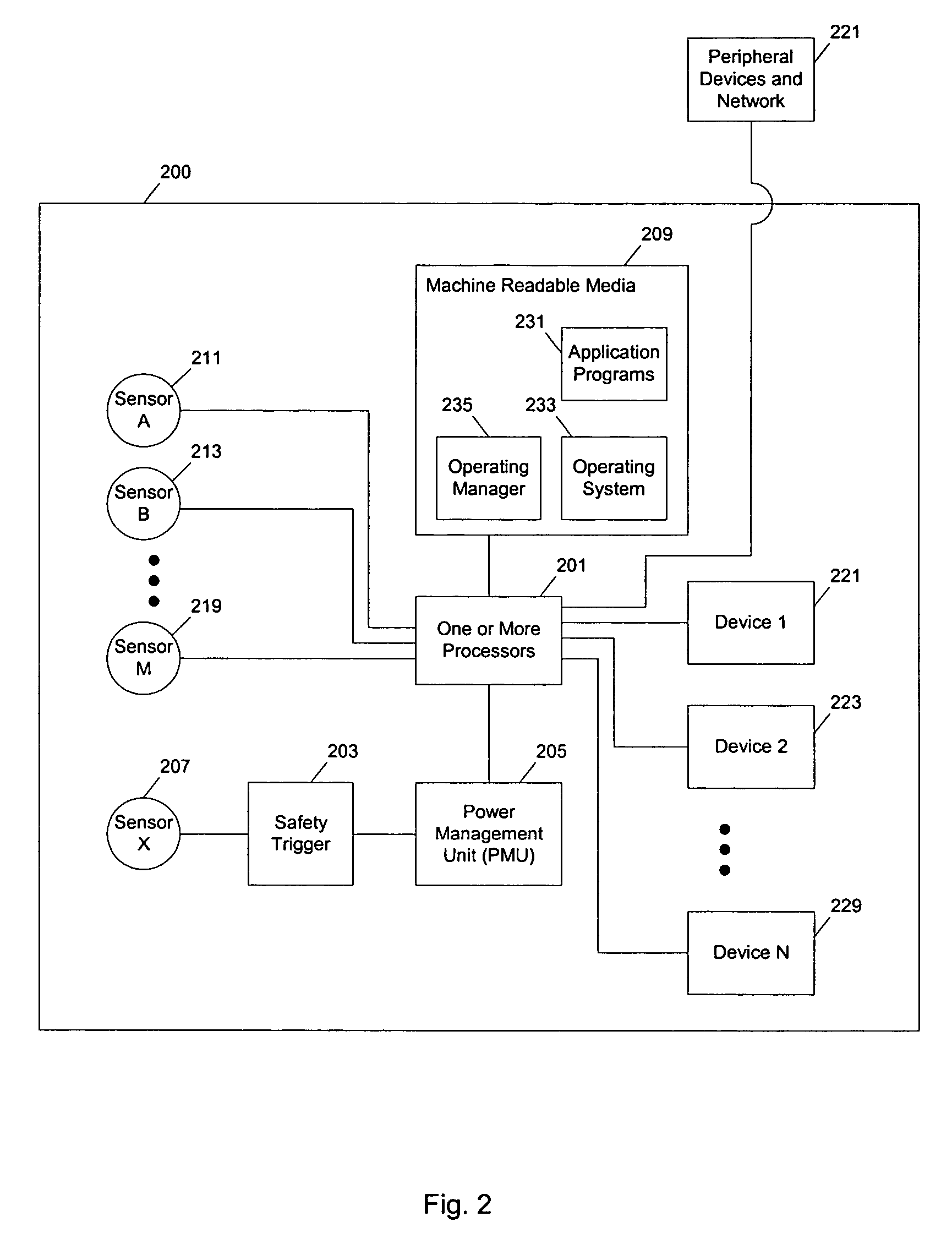
ActiveUS9874923B1Input/output to record carriersPower supply for data processingElectric forceClock rate
A device comprising a battery, a memory, a data acquisition circuit and a processor. The sensors may sample a current state of a dynamic process. The data acquisition circuit may have a first clock rate based on a sampling rate of the dynamic process. The data acquisition circuit may read sensor information from the sensors. The processor may have a second clock rate. The processor may process the sensor information and generate a monitoring signal based on at least one of the sensor information, a model of the dynamic process and a desired state of the dynamic process. The processor may schedule procedures for the device and determine computation times for the procedures based on context information. The second clock rate is faster than the first clock rate. The procedures are scheduled based on the sampling rate, the computation times for the procedures and opportunities to enter a standby mode to conserve power.
Owner:INVENT LY LLC
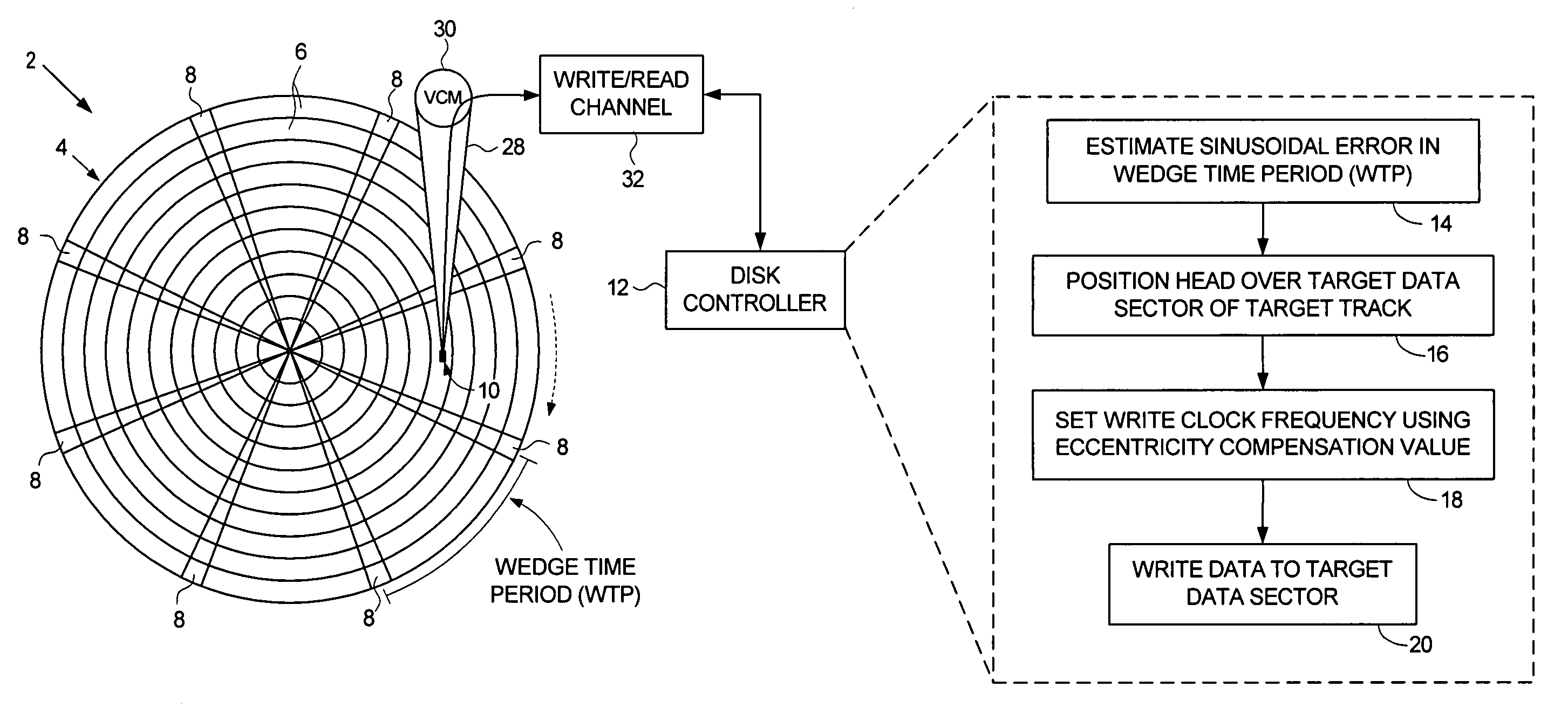
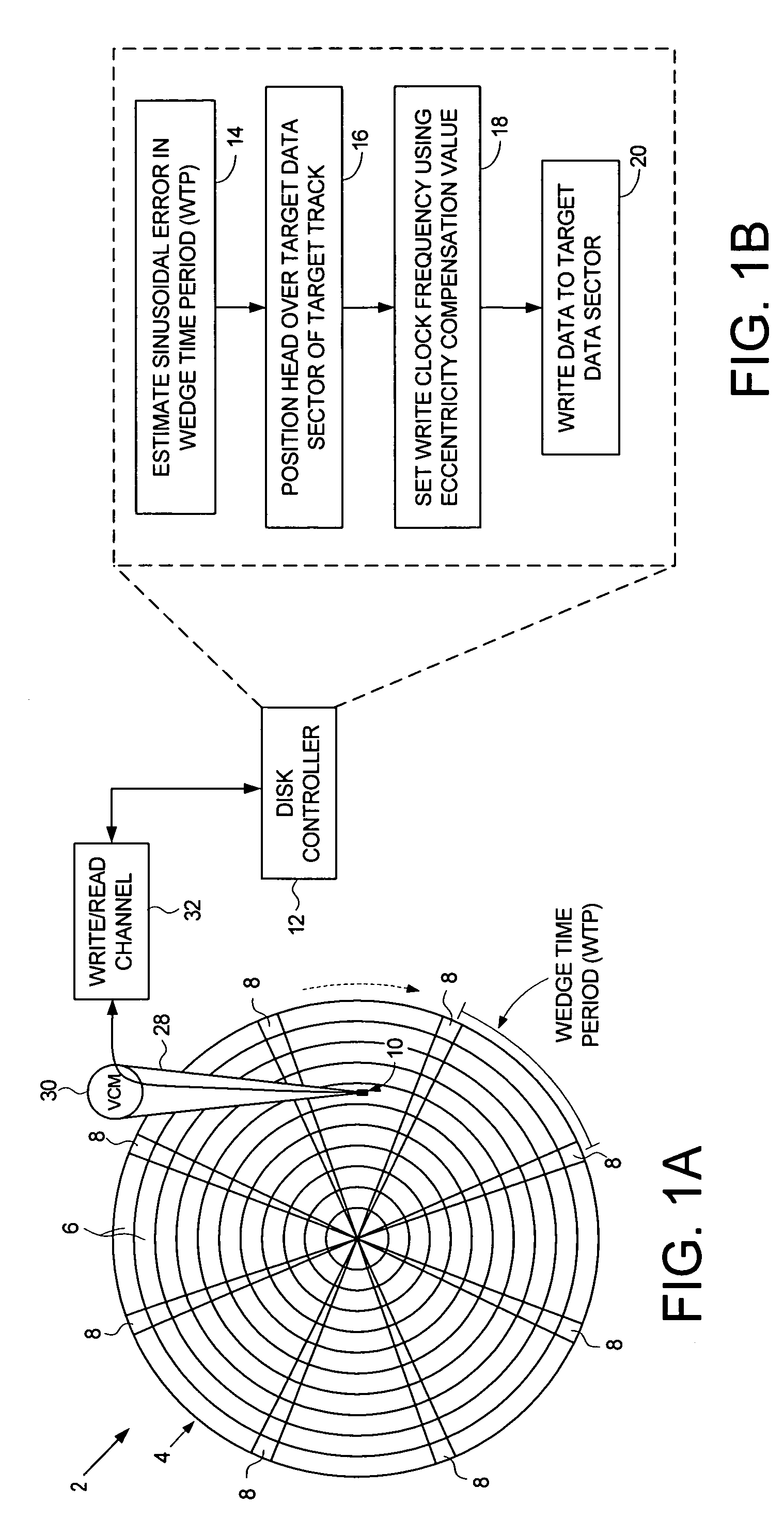
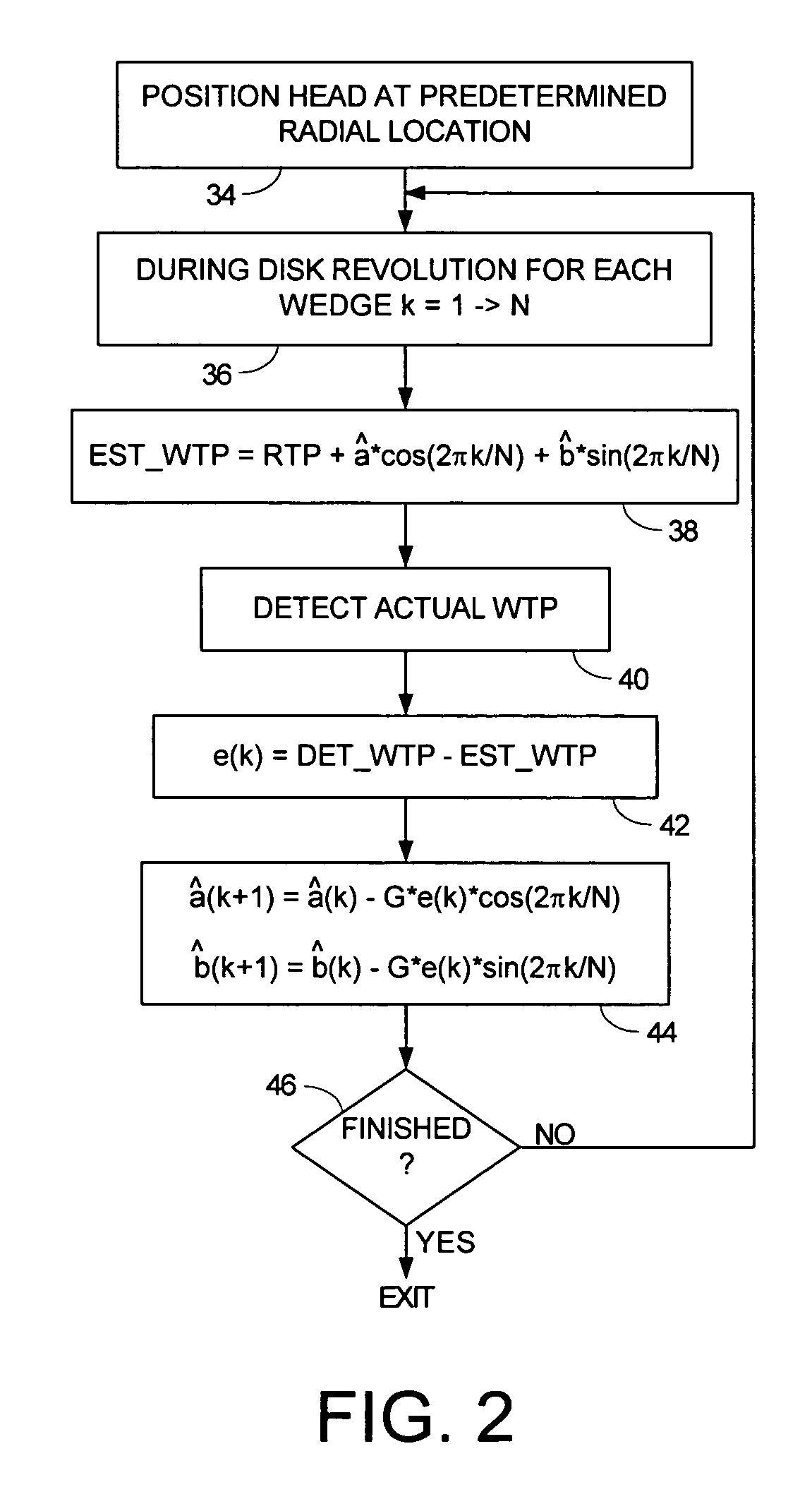
Disk drive adjusting write clock frequency to compensate for eccentricity in disk rotation
InactiveUS7251098B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksClock rateTime segment
A disk drive is disclosed that estimates a sinusoidal error in a wedge time period due to eccentricity in the disk rotating to generate eccentricity compensation values. During a write operation a head is positioned over a target data sector within a target track, a write clock frequency is set using an eccentricity compensation value corresponding to the target data sector, and data is written to the target data sector using the write clock frequency. In this manner, the eccentricity compensation value adjusts the write clock frequency to better optimize the linear bit density from the inner to outer diameter tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
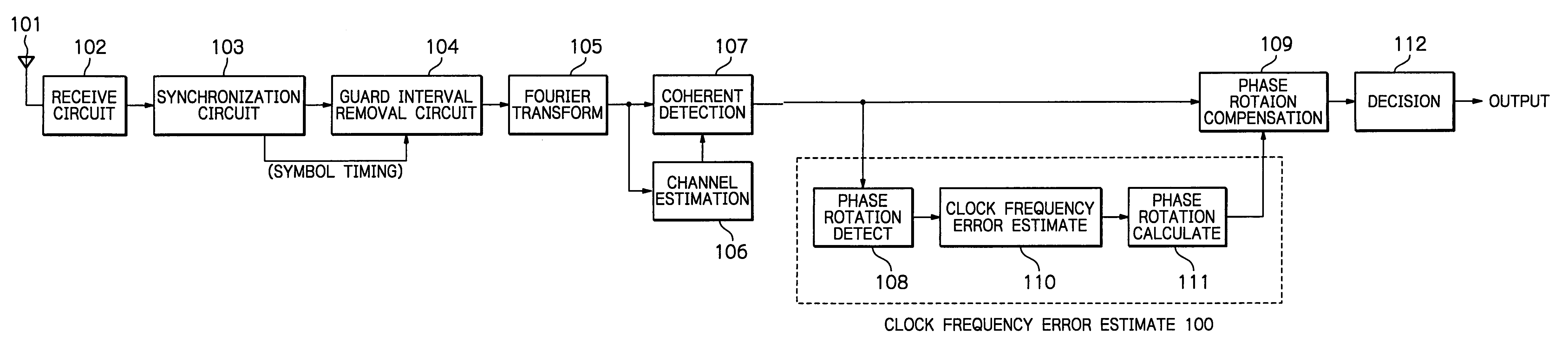
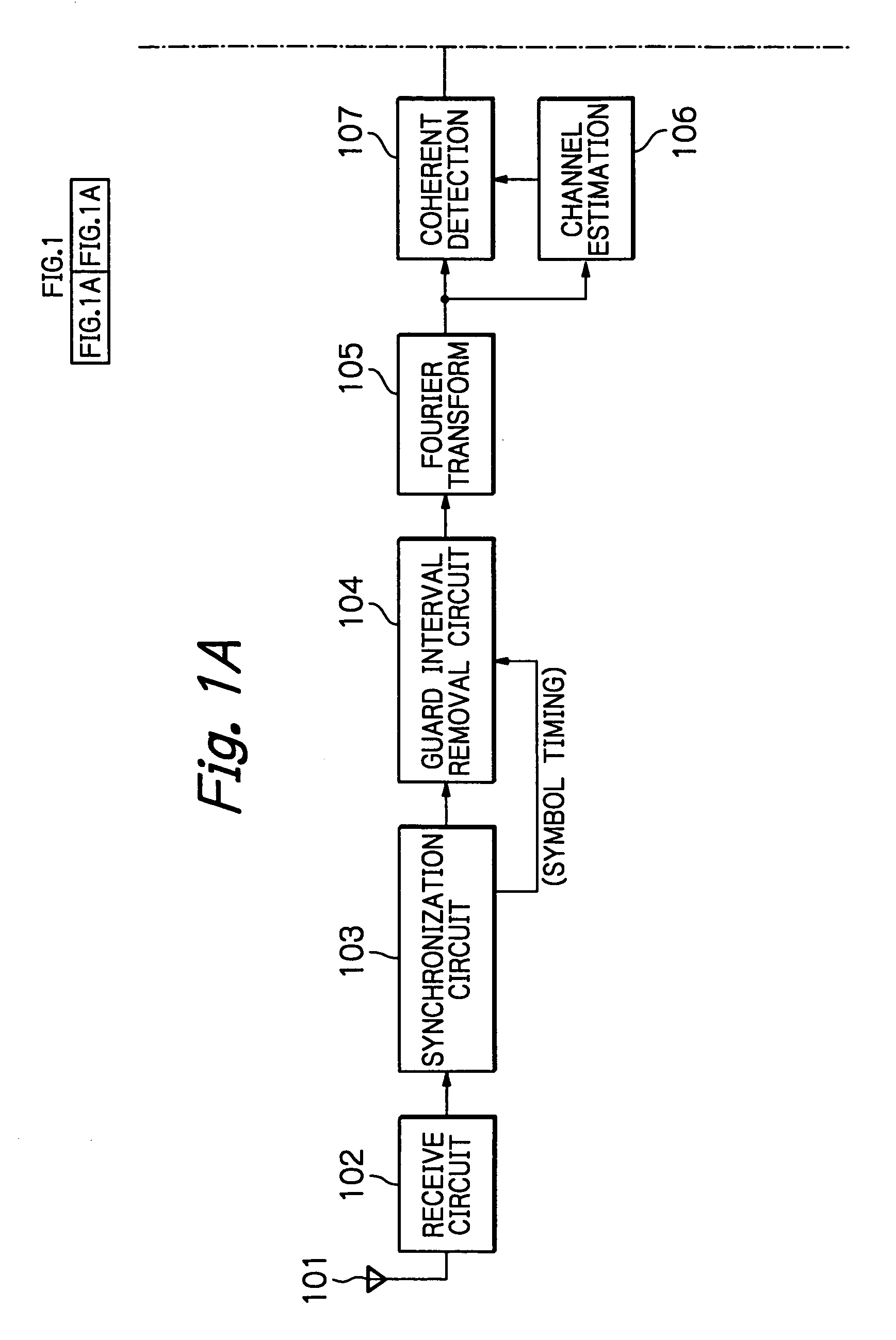
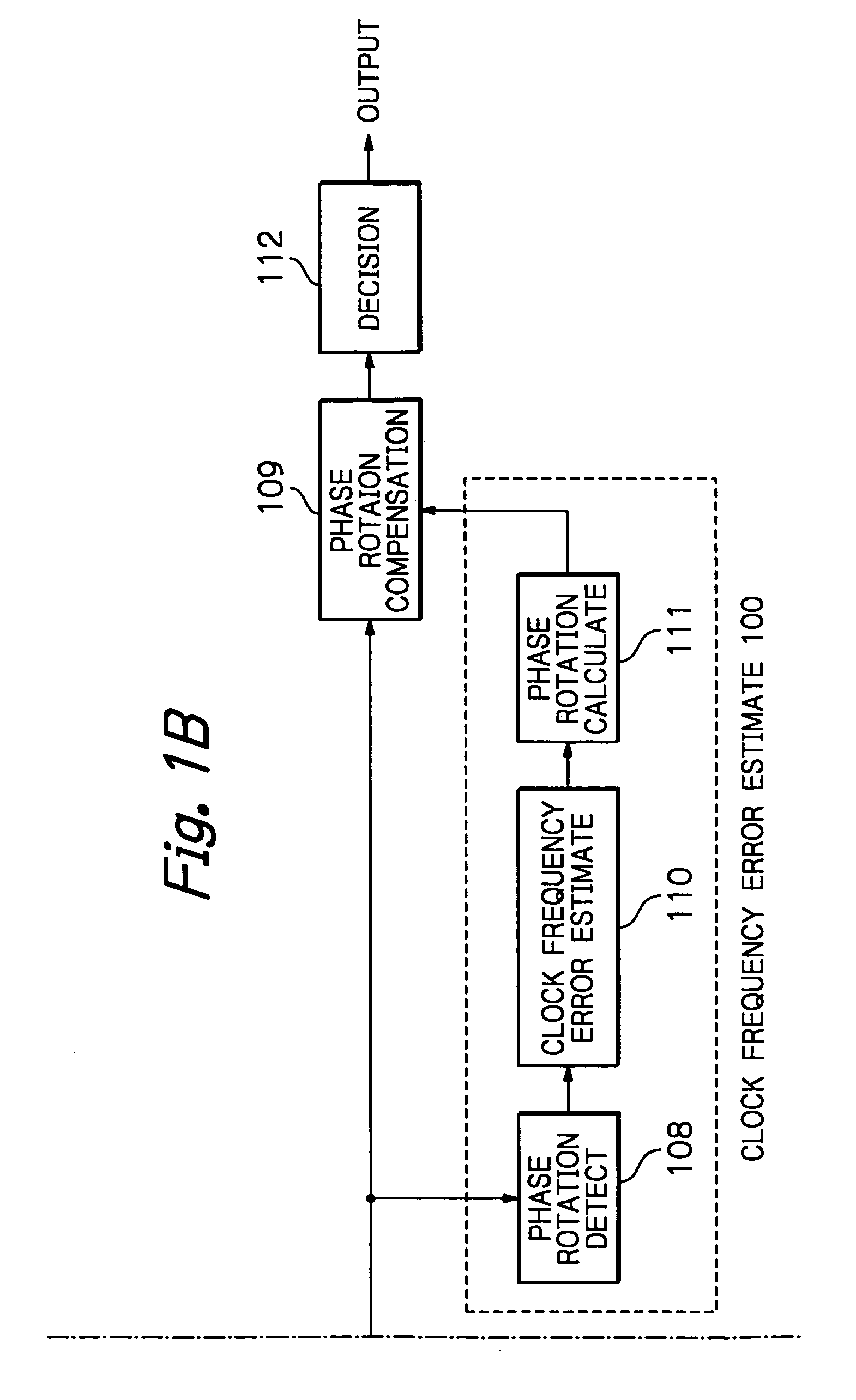
OFDM packet communication receiver
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
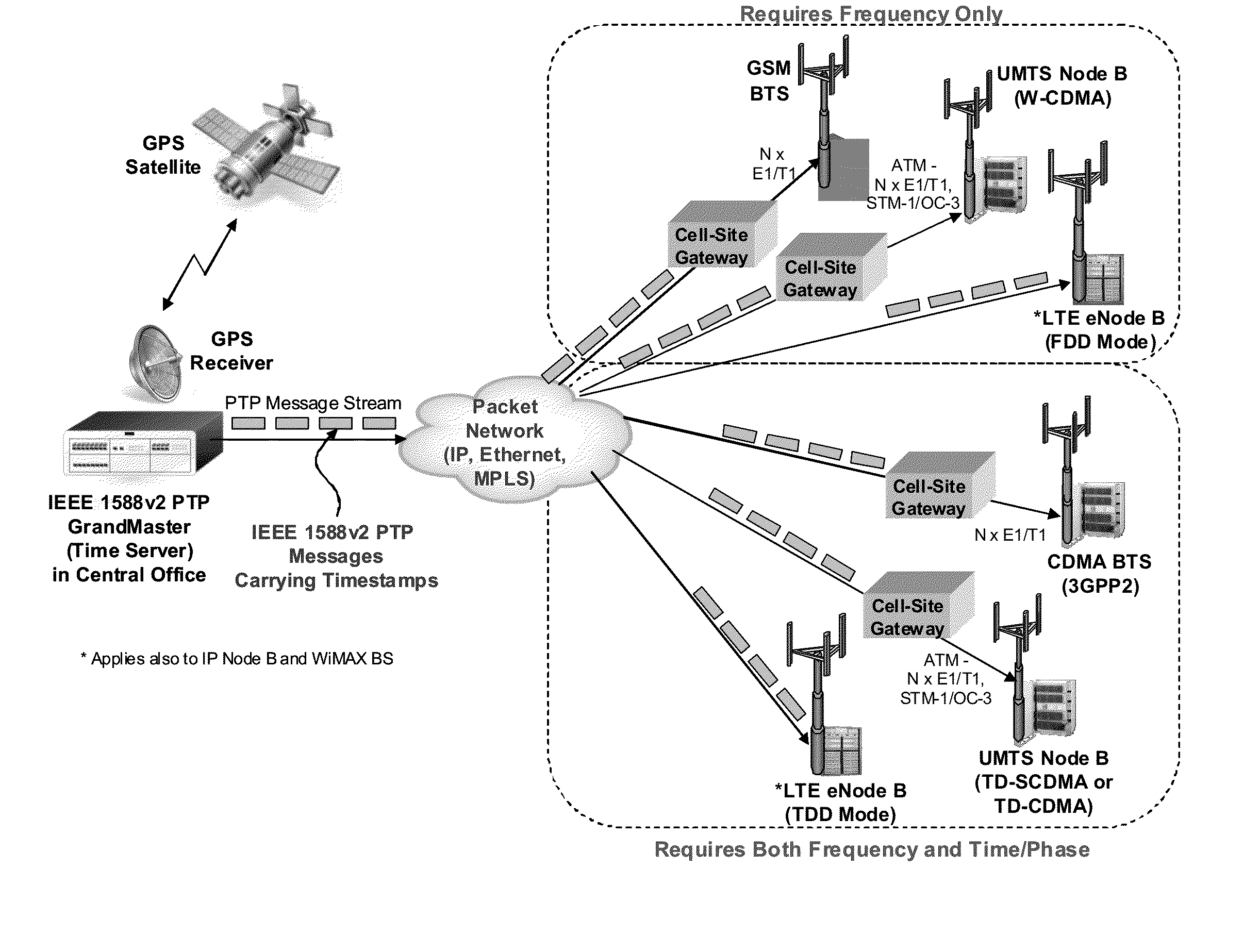
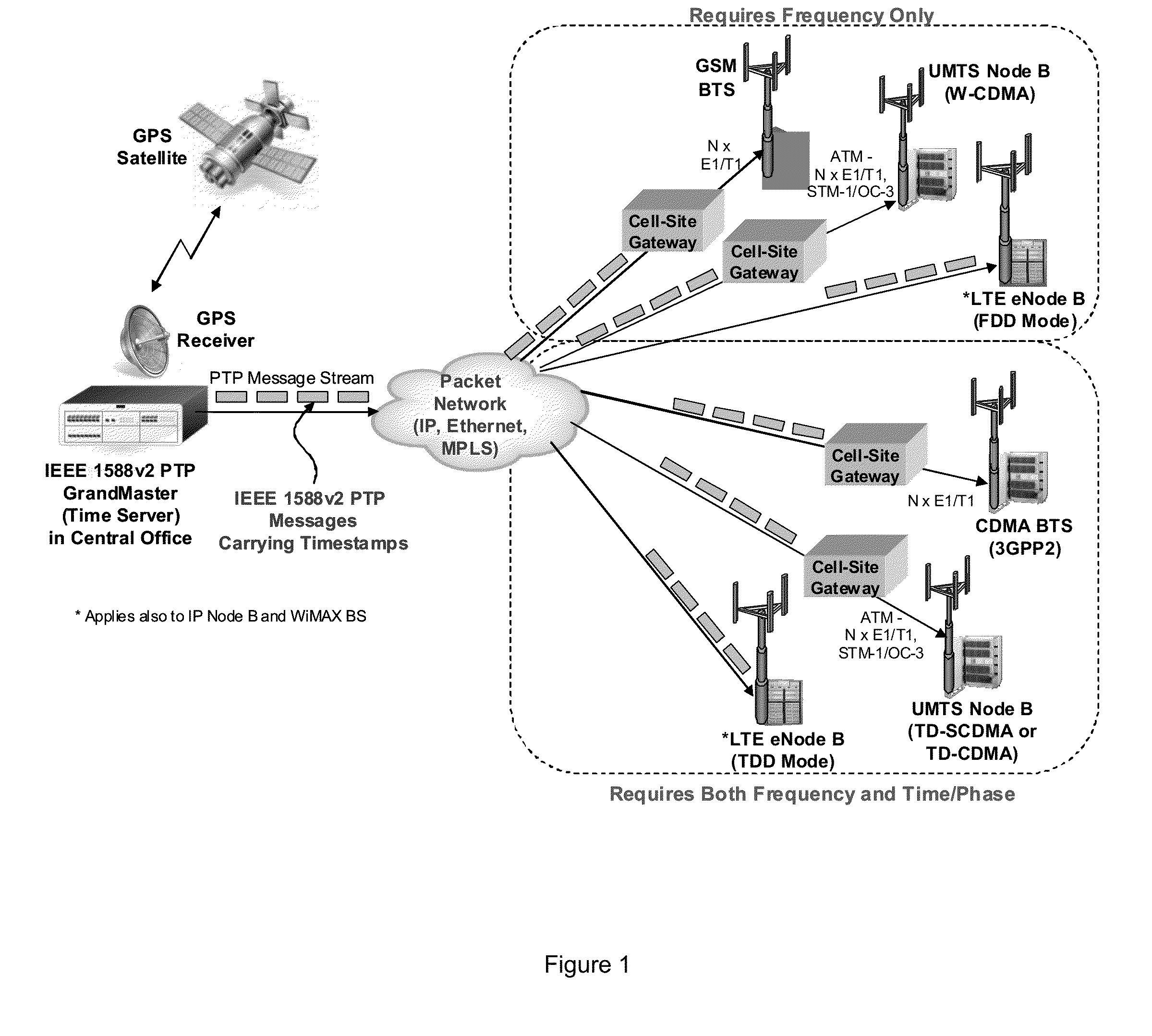
Method and system for frequency synchronization
The present invention provides a method of synchronising the frequency of a slave clock to that of a master, preferably using a packet network. An aspects of the invention provide a method of synchronizing the frequency of a slave clock in a slave device to a master clock in a master device, the method including the steps of: a) receiving in the slave device a first message from said master device having a first time-stamp which is a time-stamp of said master clock indicating the time of sending of said first message; b) extracting said time-stamp from said message and initializing a counter in the slave device which counts an output of said slave clock; c) receiving in the slave device a further message from said master device and reading the value of said counter at the time of receipt of said further message; d) extracting a further time-stamp which is the precise time of sending of the further message according to said master clock; e) determining an error signal which is representative of the difference between said value of the counter and the difference between said first and further time-stamps; and f) adjusting the frequency of said slave clock based on said error signal. An apparatus for synchronizing the frequency of a clock in a slave device which is communicatively coupled to a master device is also provided.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Cooling system for computing device
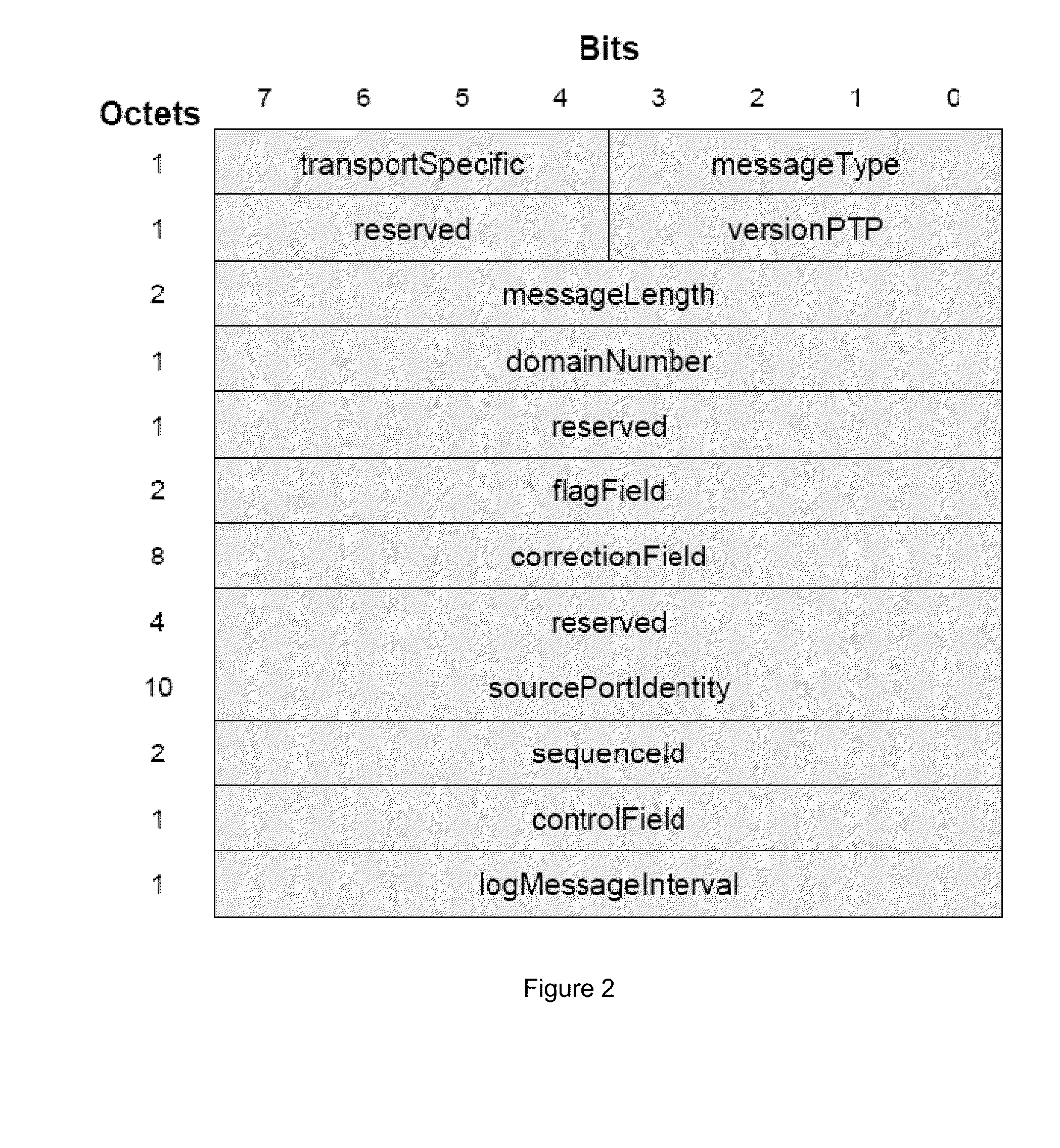
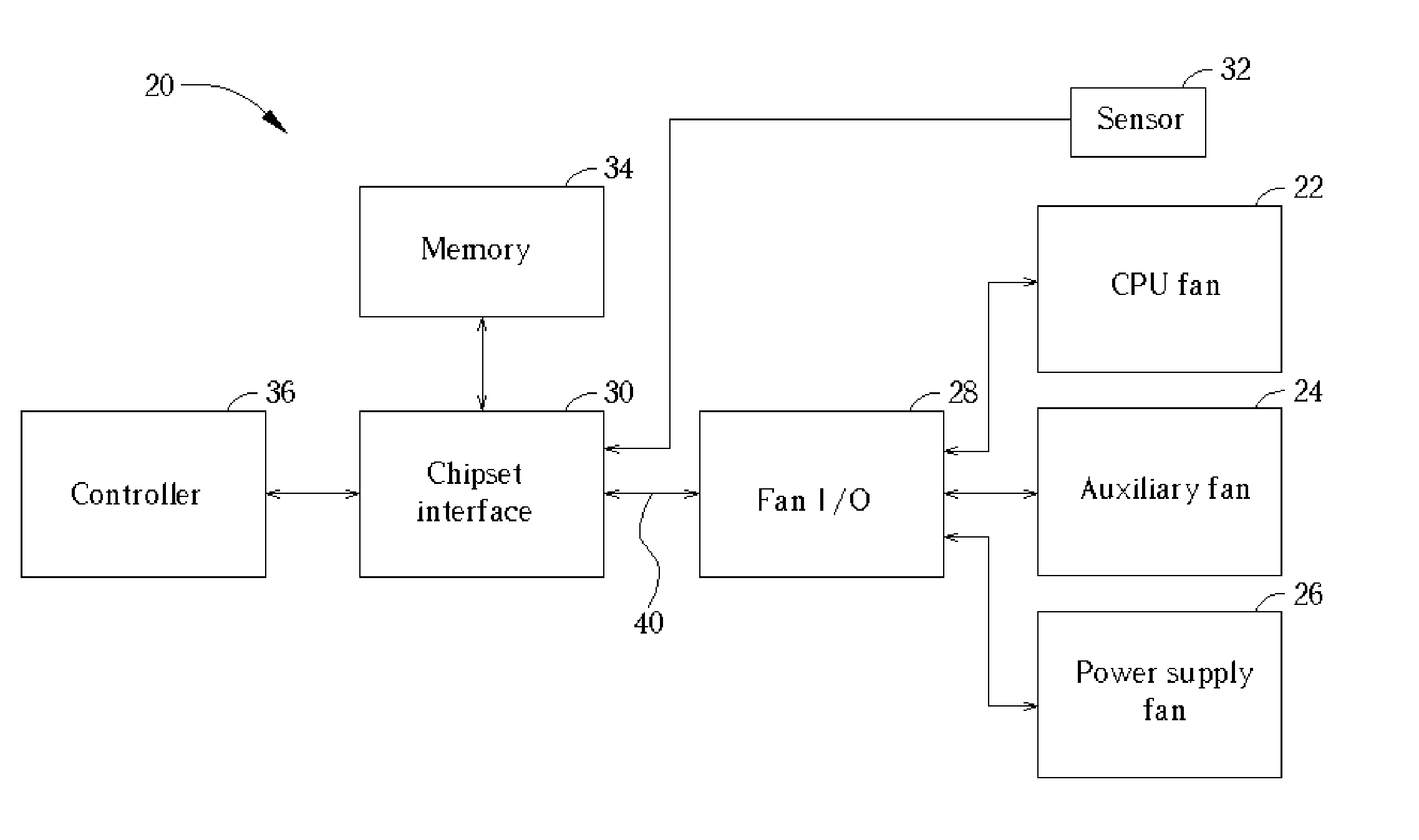
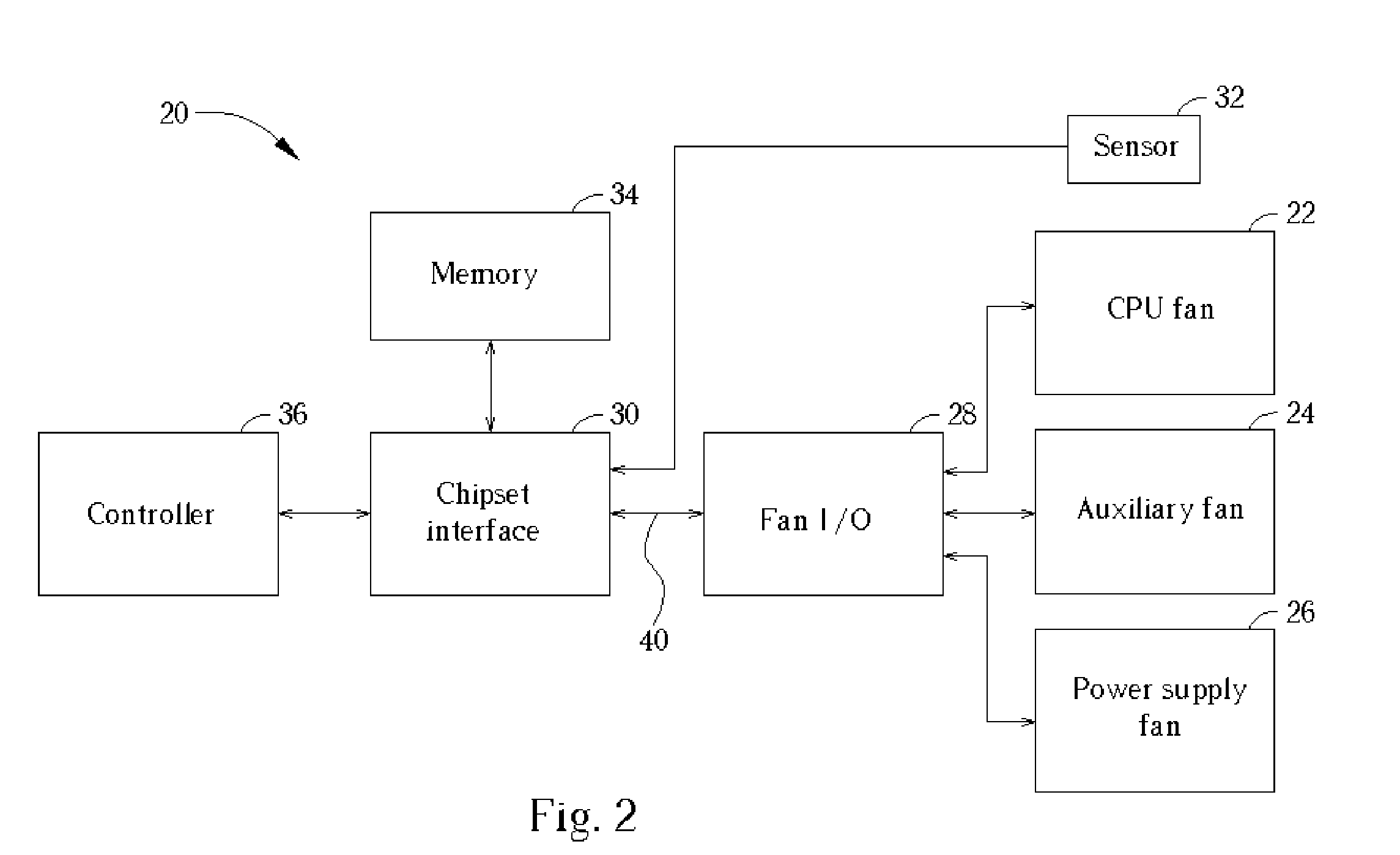
InactiveUS20050030171A1Minimize noise levelImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionClock rateControl signal
A cooling system includes a cooling fan, a fan input-output module for transmitting a control signal for controlling the rotational speed of the fan, a clock rate, and an operating voltage, and a chipset interface for generating the fan control signal based on a change in a vital temperature of the computer system. Further provided is a controller for receiving the vital temperature and forwarding the vital temperature to the chipset interface, and a temperature transducer for generating the vital temperature and outputting the vital temperature to the controller. The chipset interfacemonitors a rotational speed of the cooling fan, and monitors a vital temperature of the computer system. The chipset interface then sets the fan power based on a change in the vital temperature. When the vital temperature decreases, the fan power is reduced to slow the fan, and when the vital temperature increases, the fan power is increased to speed the fan.
Owner:AOPEN
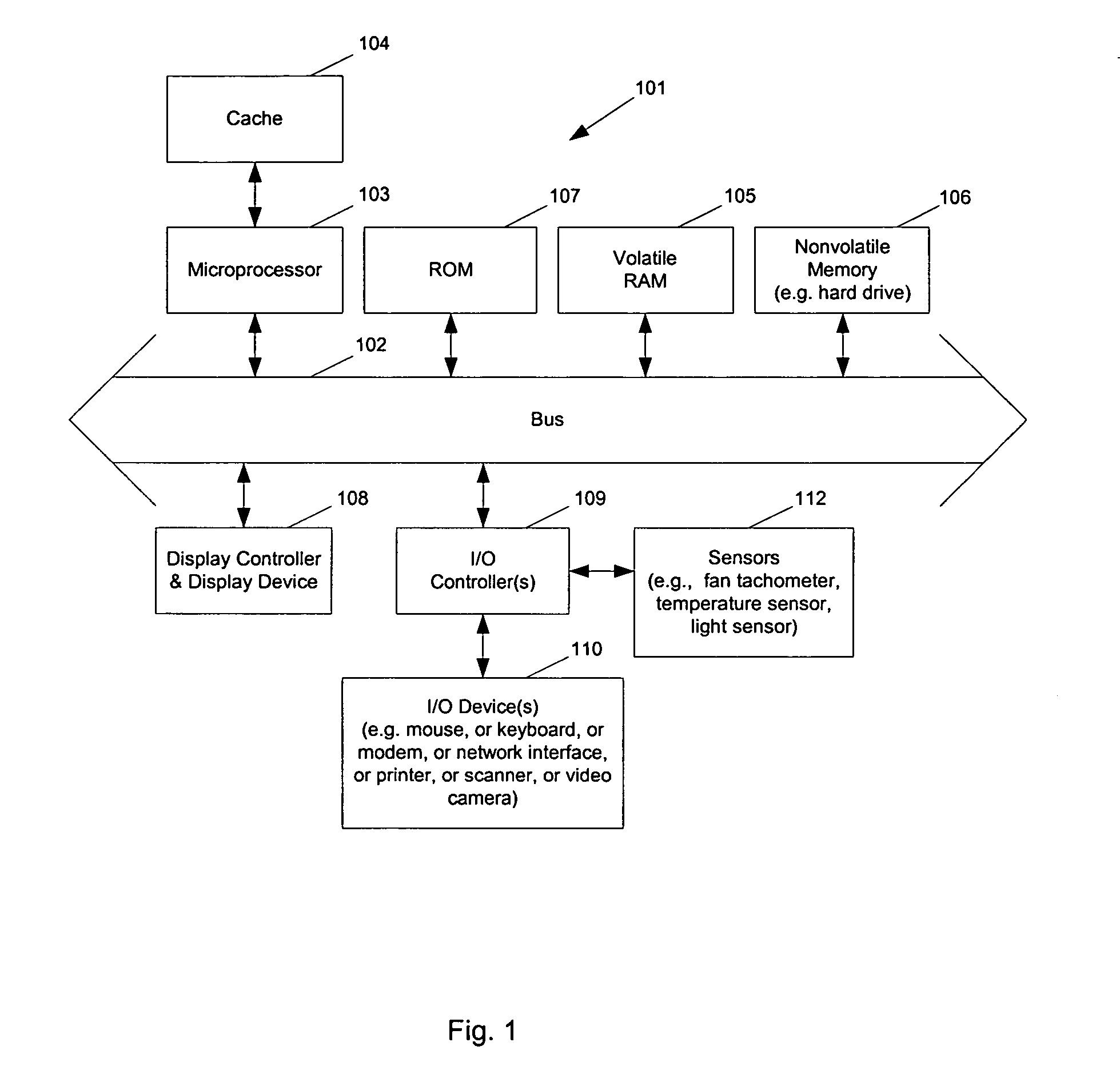
Battery powered device with dynamic power and performance management
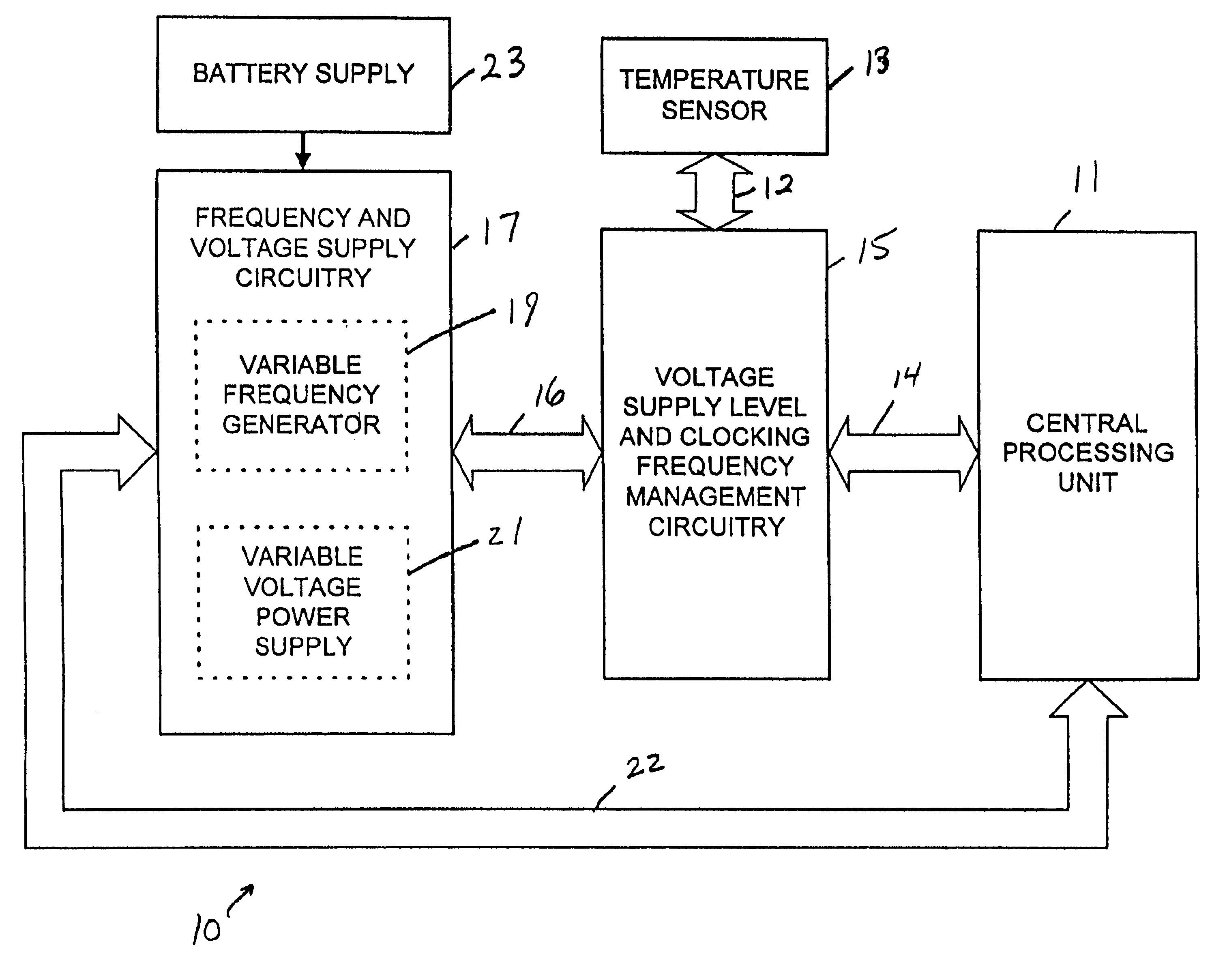
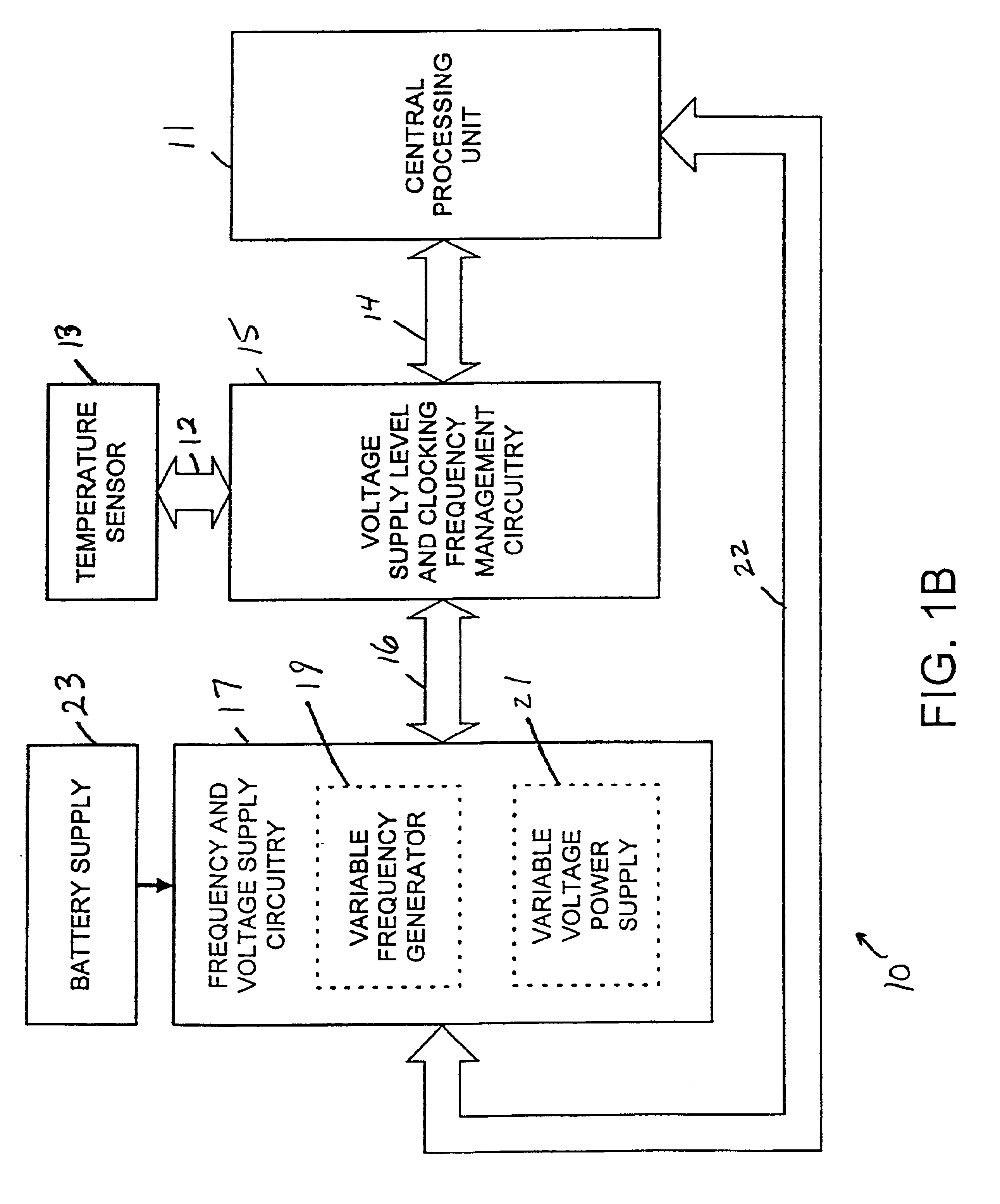
A computing device operates over a range of voltages and frequencies and over a range of processor usage levels. The computing device includes at least a variable frequency generator, a variable voltage power supply and voltage supply level and clocking frequency management circuitry. The variable frequency generator is coupled to the processor and delivers a clock signal to the processor. The variable voltage power supply is coupled to the processor and delivers voltage to the processor. The voltage supply level and clocking frequency management circuitry adjust both the voltage provided by the variable voltage power supply and the frequency of the signal provided by the variable frequency generator. The computing device includes a temperature sensor that provides signals indicative of the temperature of the processor and the voltage supply level and clocking frequency management circuitry adjusts the voltage and / or the clocking frequency provided by the variable voltage power supply. The computing device may also include a fan controlled by the voltage supply level and clocking frequency management circuitry, the fan adjusting the temperature of the processor when activated. In cold weather applications, the computing device may further include a heater controlled by the voltage supply level and clocking frequency management circuitry that raises the temperature of the processor when activated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
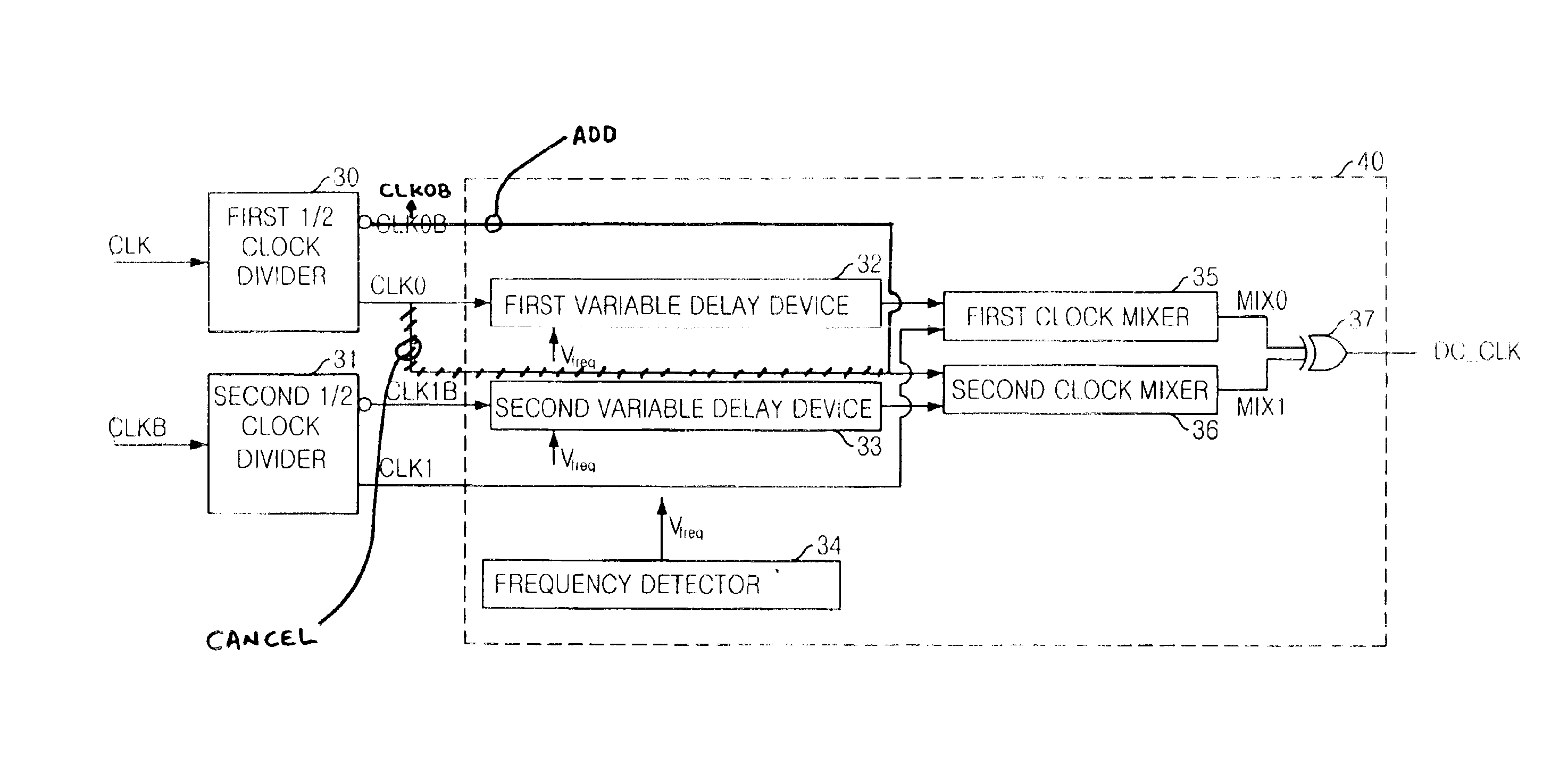
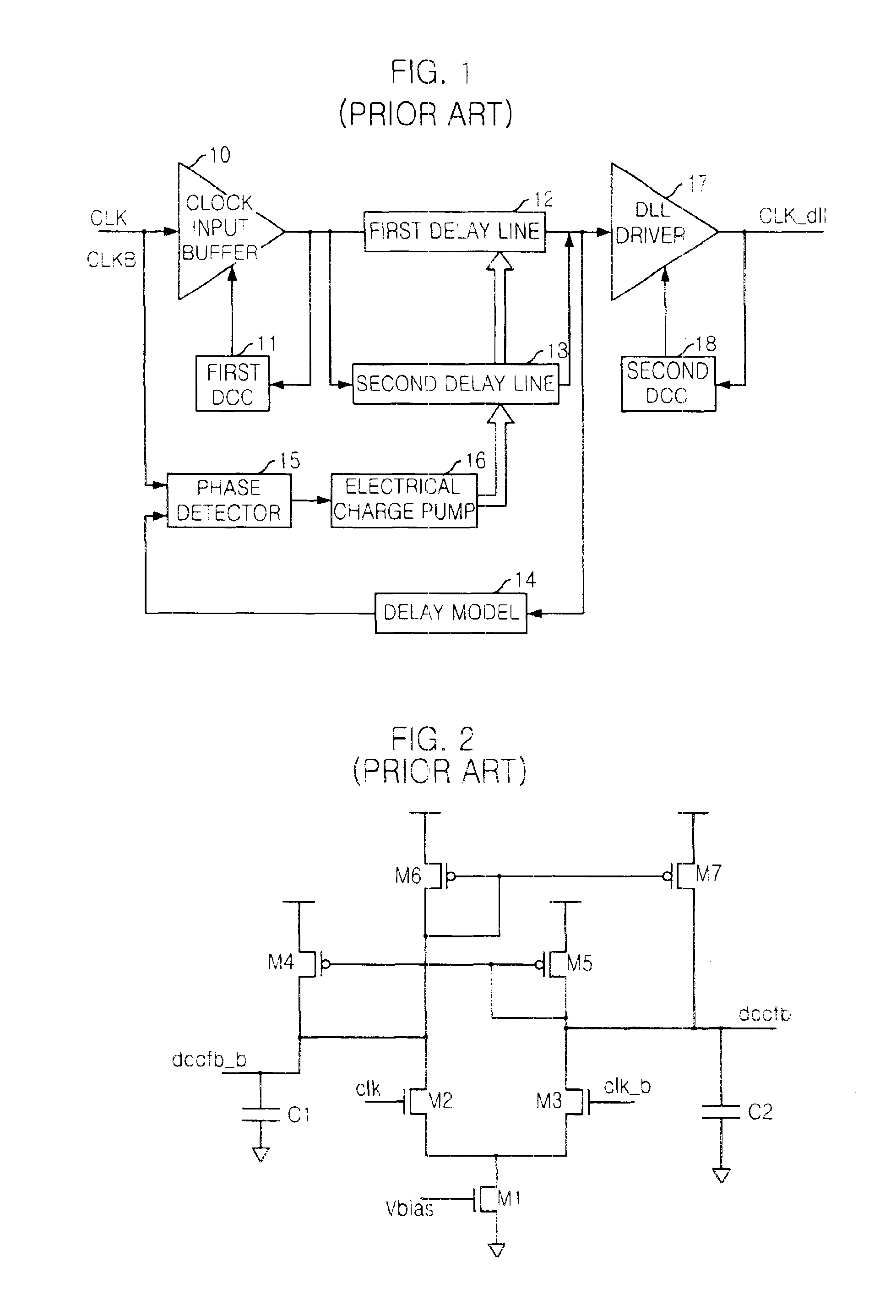
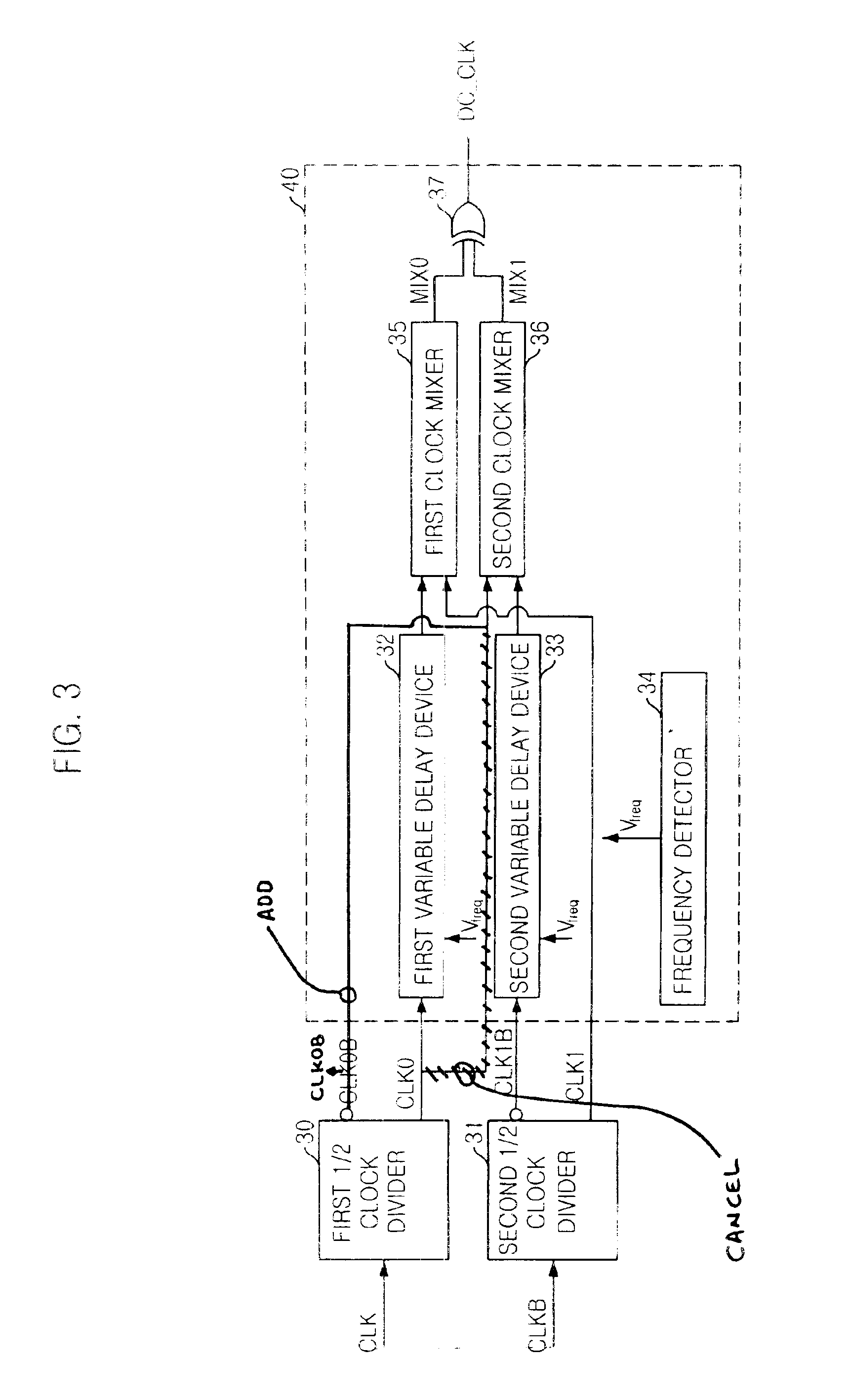
Duty cycle correction circuit and delay locked loop having the same
InactiveUS6859081B2Reduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationClock rateFrequency mixer
A duty cycle correction (DCC) circuit including first and second clock dividers for dividing ordinary and sub-input clocks. Optional first and second variable delay devices delay the divided clocks. First and second mixers mix an optionally delayed ordinary divided clock and sub-ordinary divided clock, or an ordinary divided clock and an optionally delayed sub-ordinary divided clock. A logic combination device is included to produce a clock at the same frequency as the ordinary and sub-input clocks, with a corrected duty cycle.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com