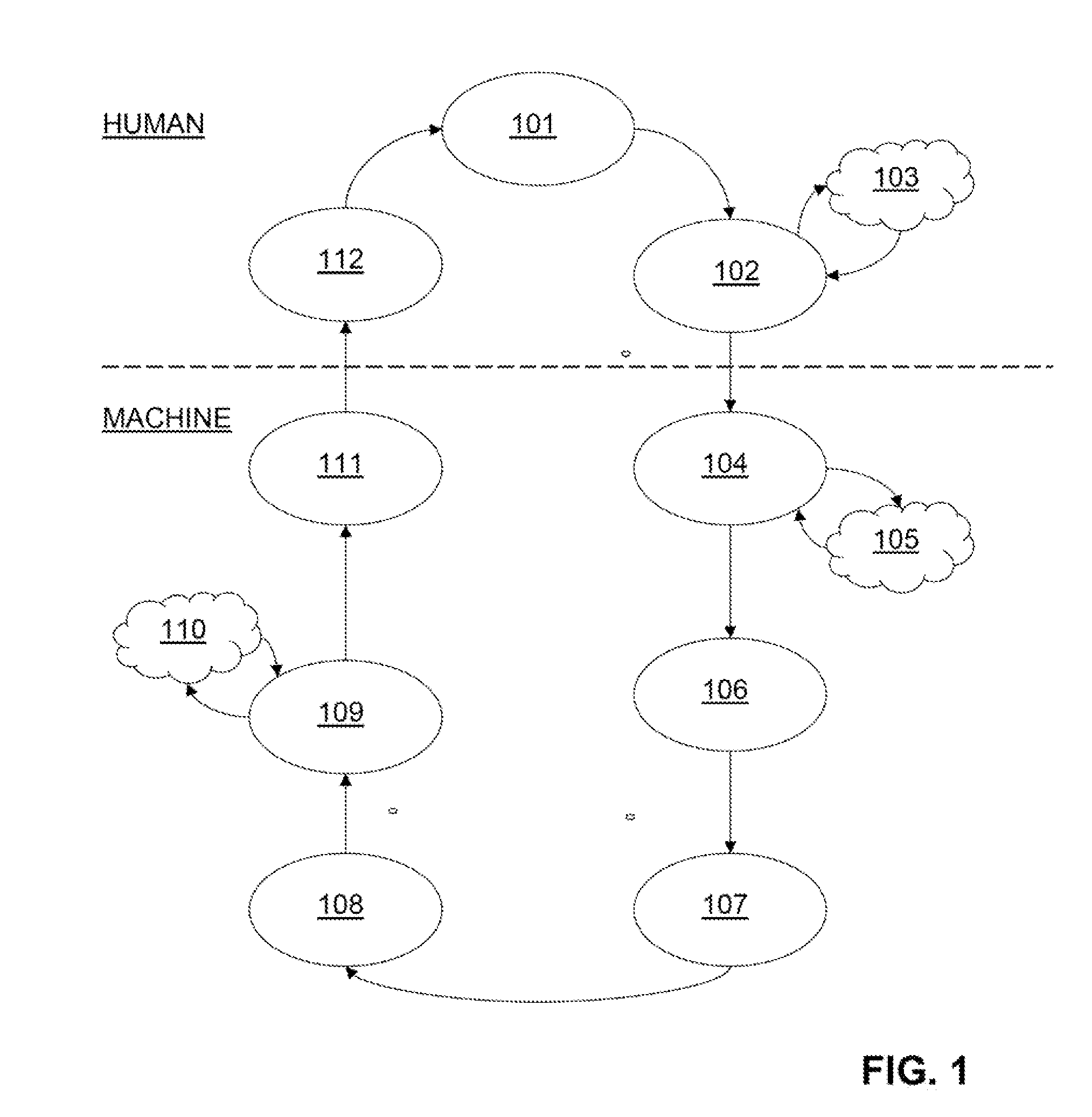
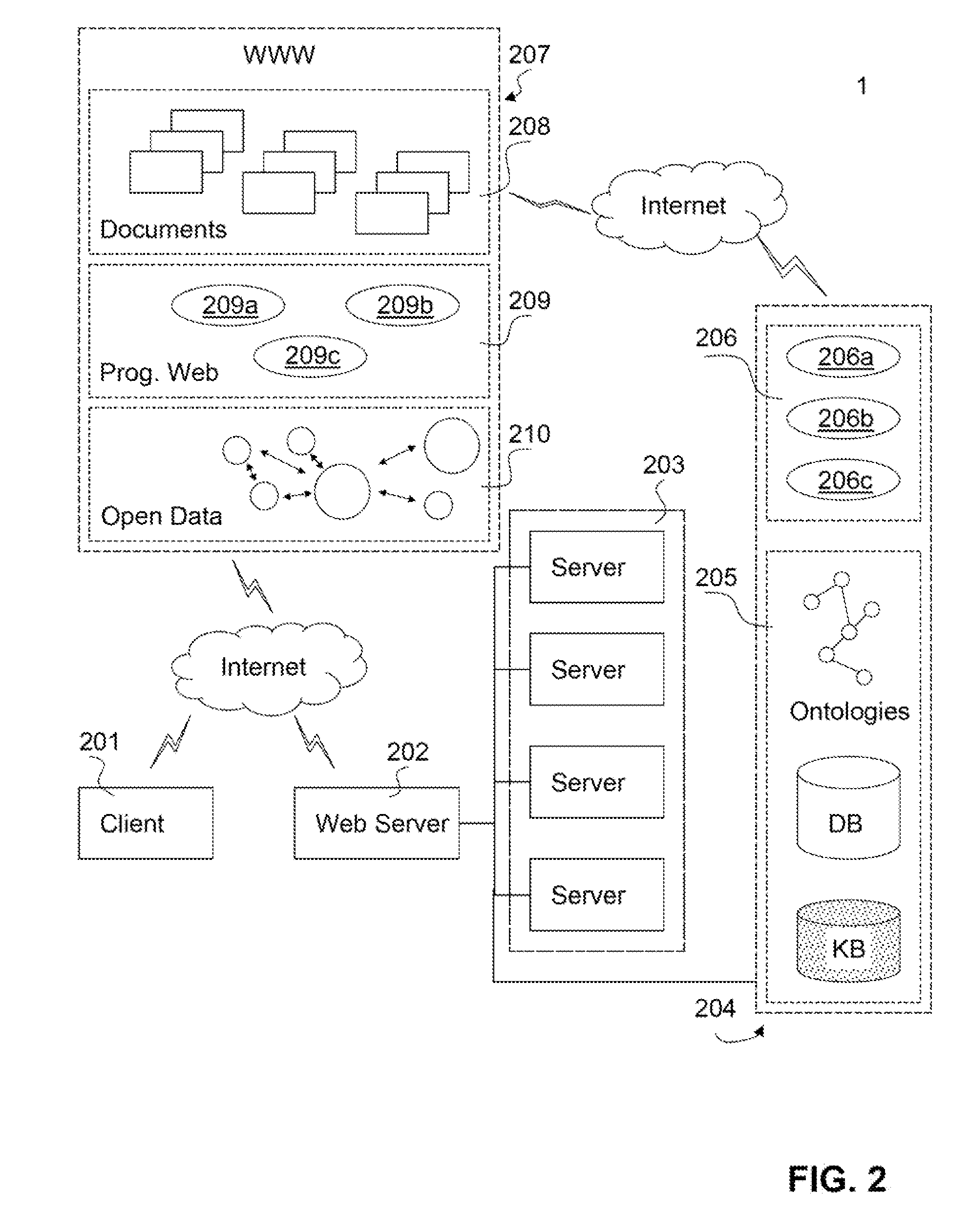
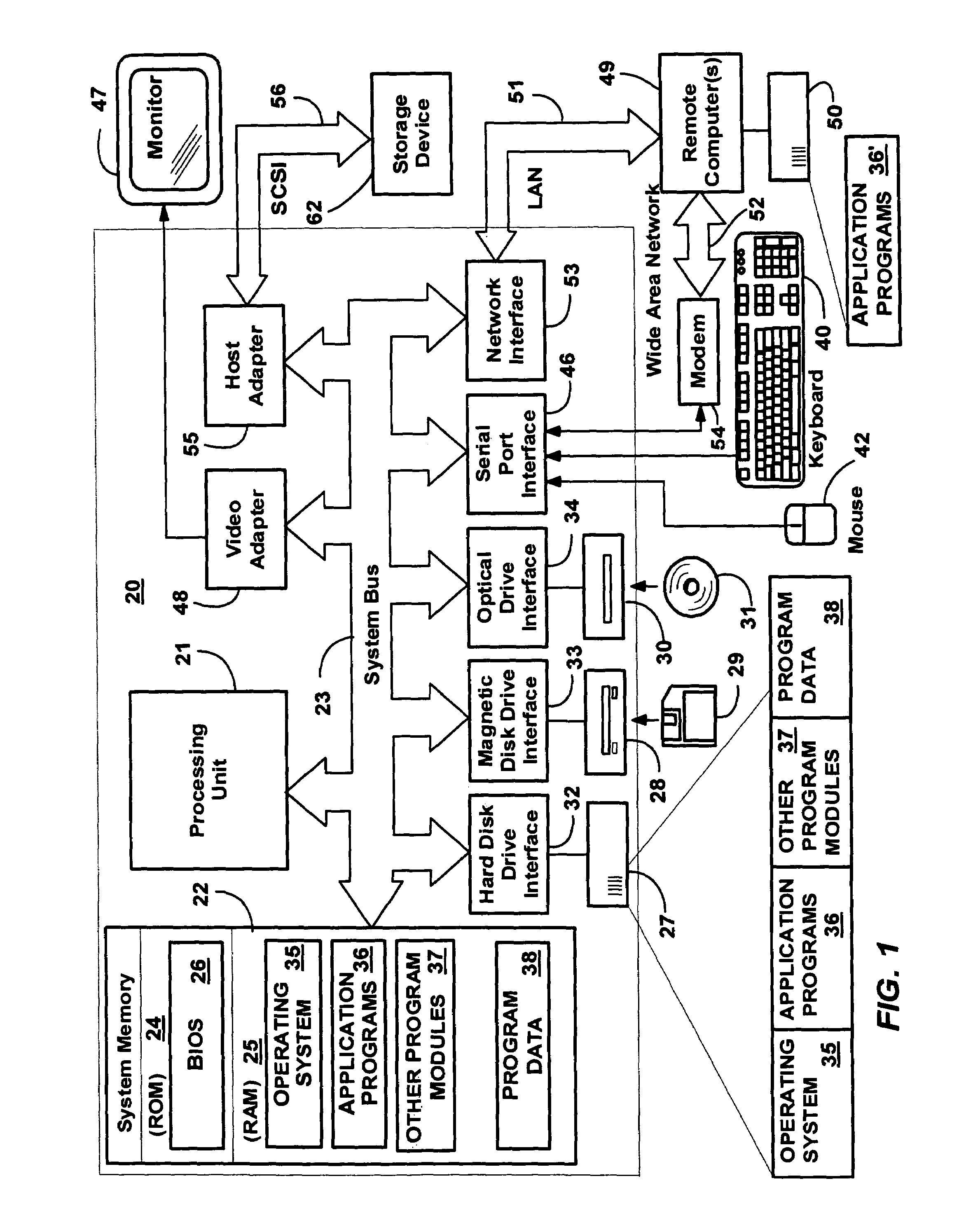
Patents
Literature
24155 results about "Term memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Memory is internal storage areas in the computer system. The term memory identifies data storage that comes in the form of chips, and the word storage is used for memory that exists on tapes or disks. Moreover, the term memory is usually used as a shorthand for physical memory, which refers to the actual chips capable of holding data.
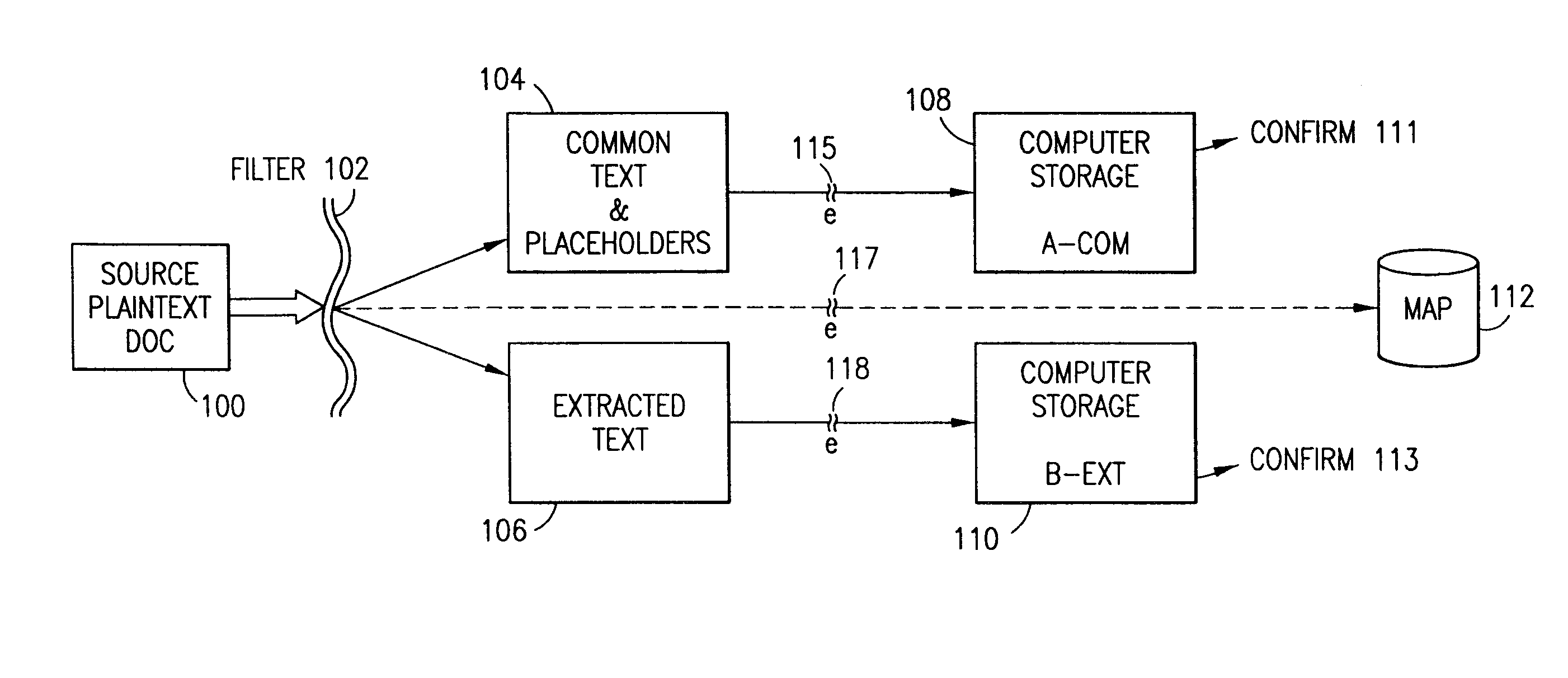
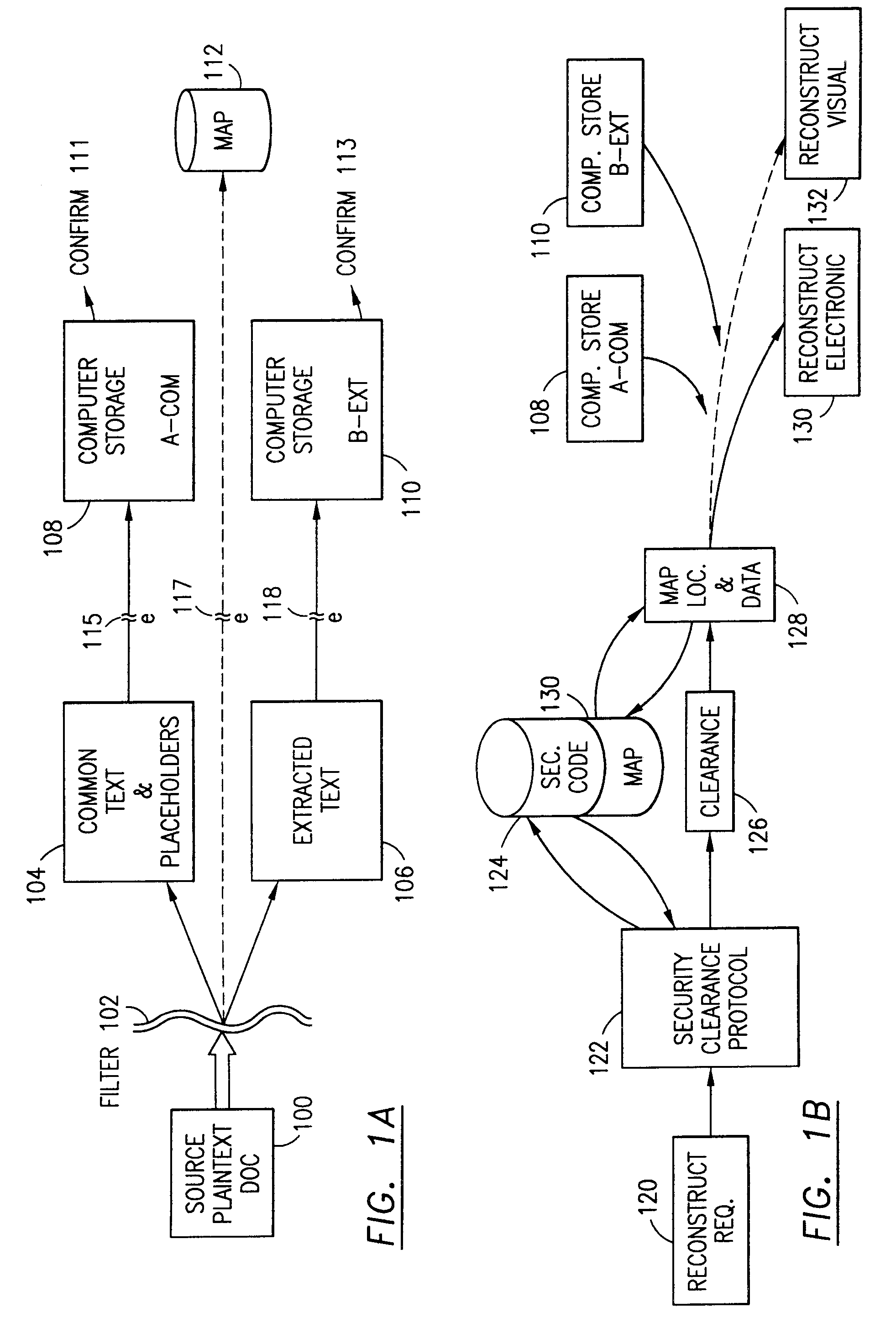
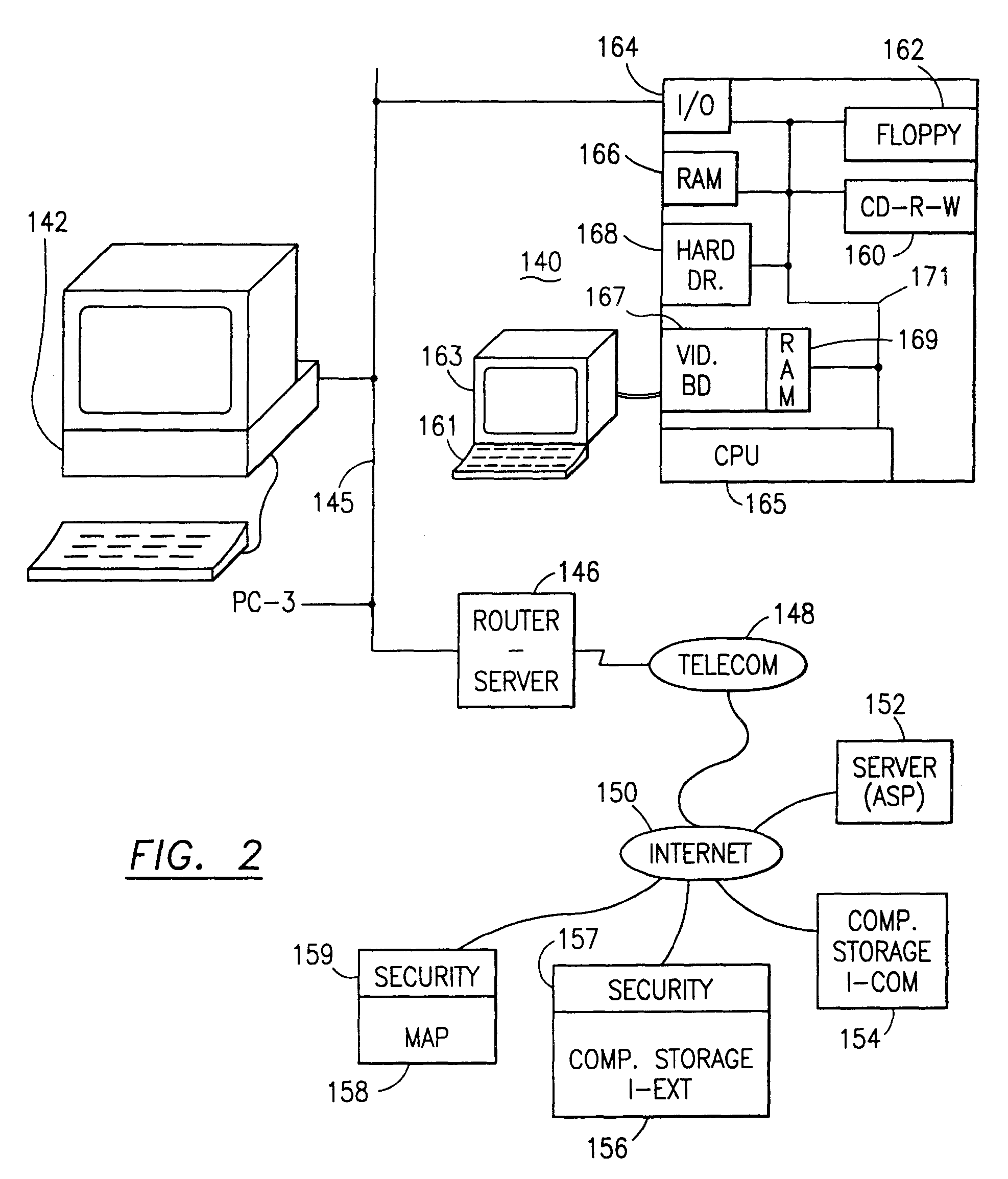
Data security system and method for separation of user communities
InactiveUS7140044B2Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsInformation processingPlaintext
Data is secured in a computer network to transparently establish and manage a separation of user-based communities of interest based upon crypto-graphically separated, need to know, security levels. Data from a source document, data object or data stream is filtered to form subsets of extracted data and remainder data based upon security levels for the communities. Extracts are stored in assigned memories. Full or partial plaintext reconstruction is permitted only in the presence of assigned security clearance for the community of the inquiring party. Encryption, corresponding to security levels, establishes separation of secured data. The information processing system uses a data filter to extract security sensitive words, data objects, etc., a distributed storage system and a compiler is used to reconstruct plaintext based on security clearance. Multiple level encryption in one document is also available.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
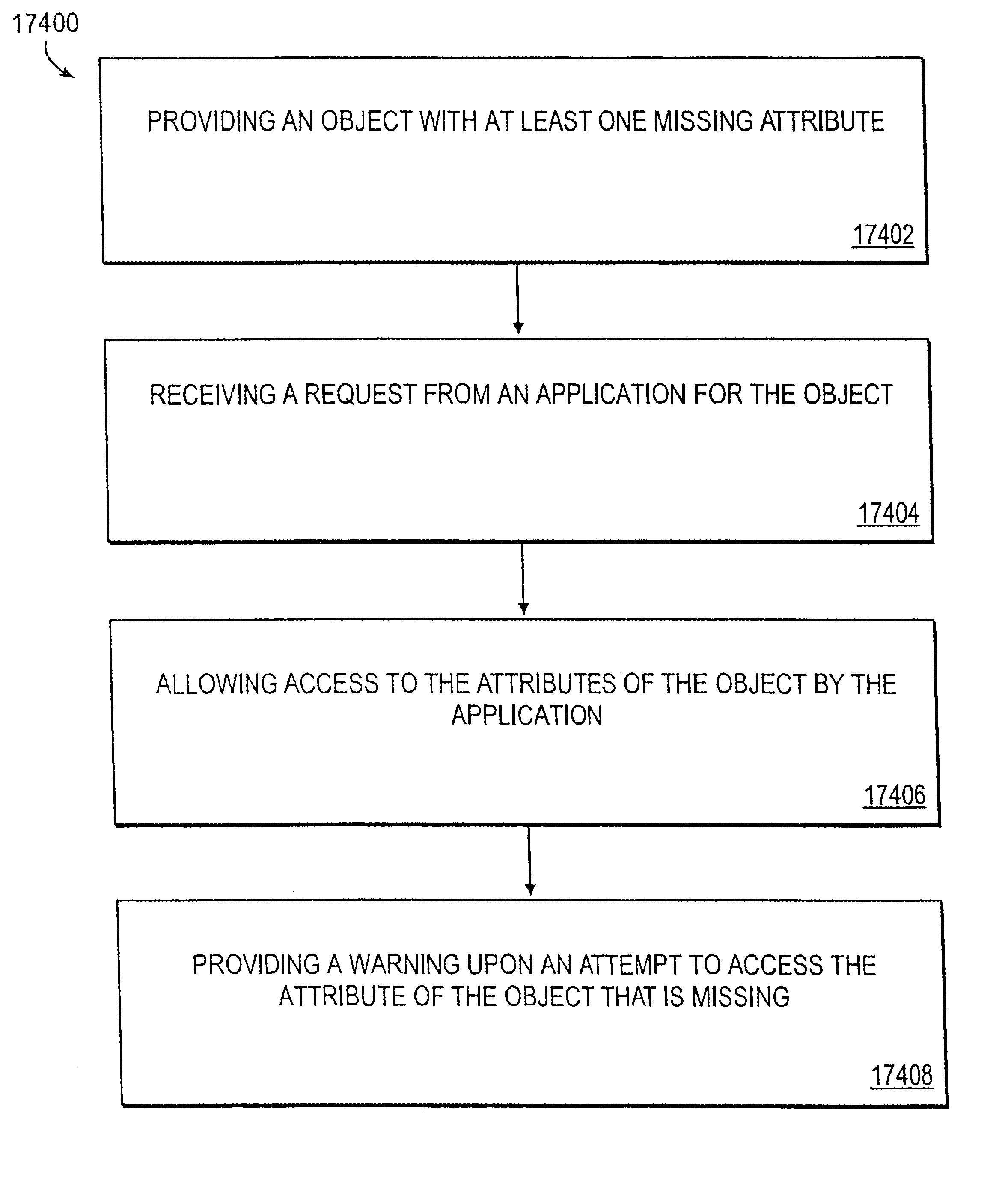
Multi-object fetch component
InactiveUS6529948B1Digital data processing detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsBusiness objectSoftware engineering
A system, method, and article of manufacture are provided for retrieving multiple business objects across a network in one access operation. A business object and a plurality of remaining objects are provided on a persistent store. Upon receiving a request for the business object, it is established which of the remaining objects are related to the business object. The related objects and the business object are retrieved from the persistent store in one operation and it is determined how the retrieved related objects relate to the business object and each other. A graph of relationships of the business and related objects is instantiated in memory.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Authentication and authorization methods for cloud computing security
ActiveUS8769622B2Retain controlKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsResource poolThird party
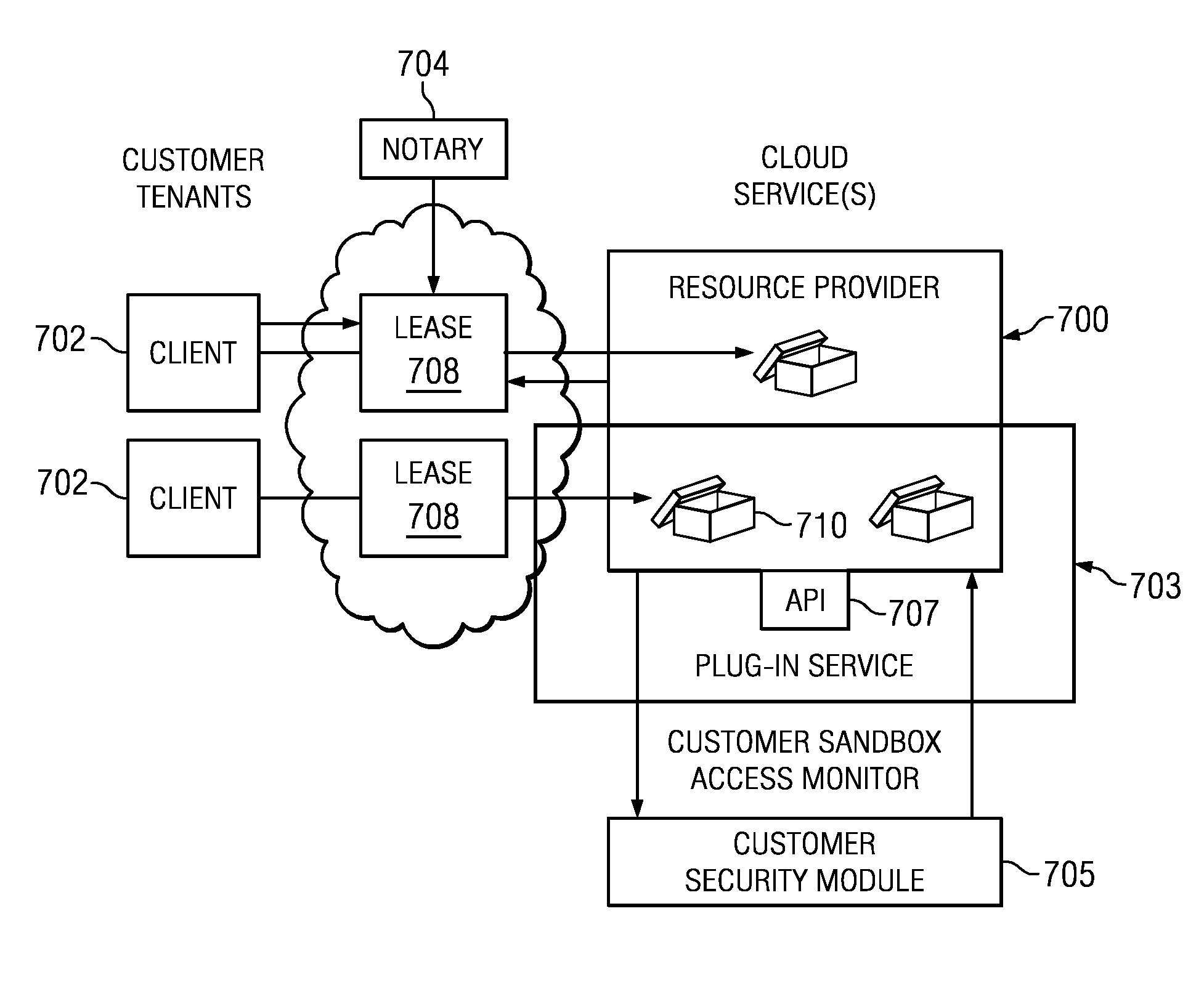
An authentication and authorization plug-in model for a cloud computing environment enables cloud customers to retain control over their enterprise information when their applications are deployed in the cloud. The cloud service provider provides a pluggable interface for customer security modules. When a customer deploys an application, the cloud environment administrator allocates a resource group (e.g., processors, storage, and memory) for the customer's application and data. The customer registers its own authentication and authorization security module with the cloud security service, and that security module is then used to control what persons or entities can access information associated with the deployed application. The cloud environment administrator, however, typically is not registered (as a permitted user) within the customer's security module; thus, the cloud environment administrator is not able to access (or release to others, or to the cloud's general resource pool) the resources assigned to the cloud customer (even though the administrator itself assigned those resources) or the associated business information. To further balance the rights of the various parties, a third party notary service protects the privacy and the access right of the customer when its application and information are deployed in the cloud.
Owner:IBM CORP
Source-clock-synchronized memory system and memory unit
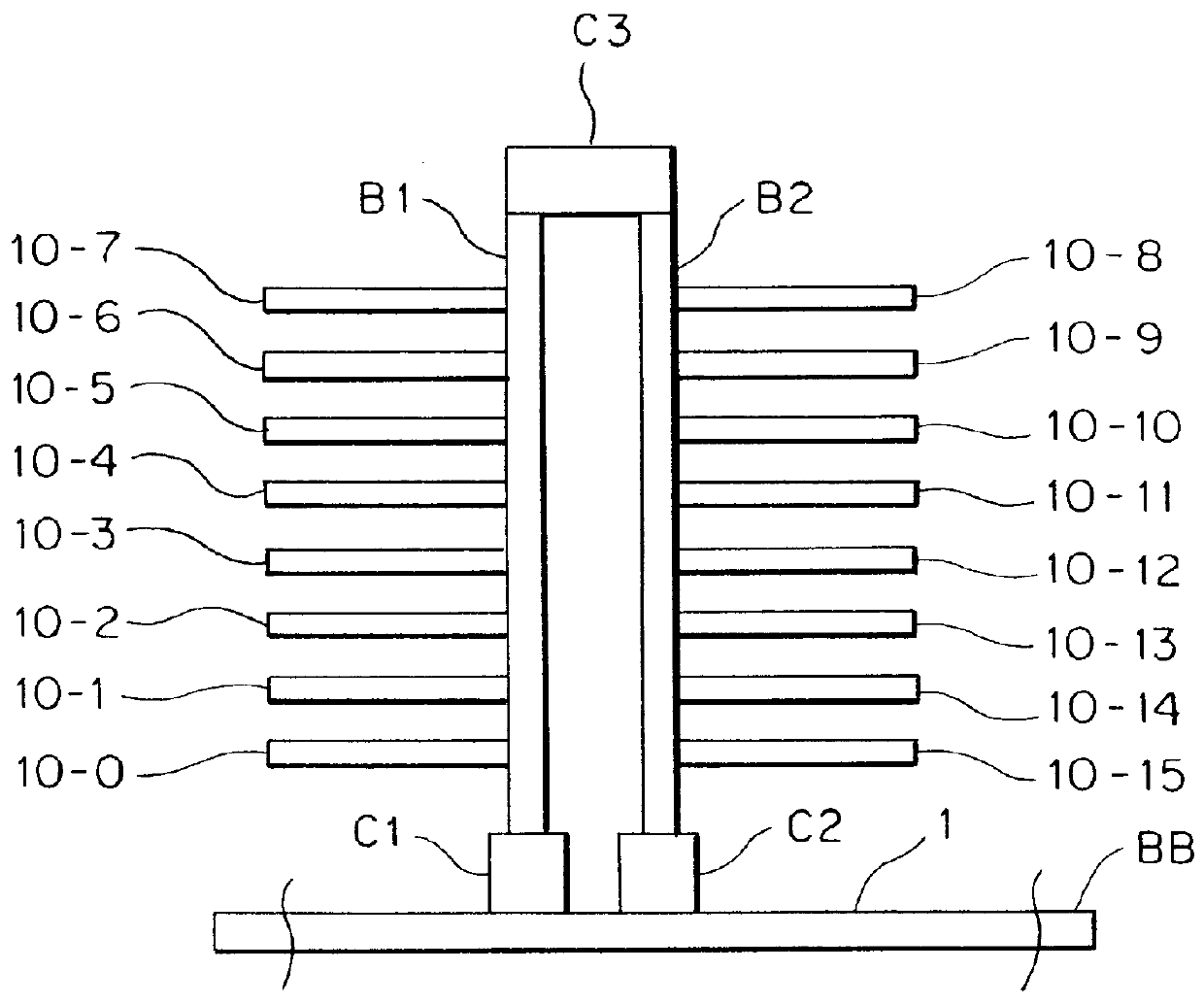
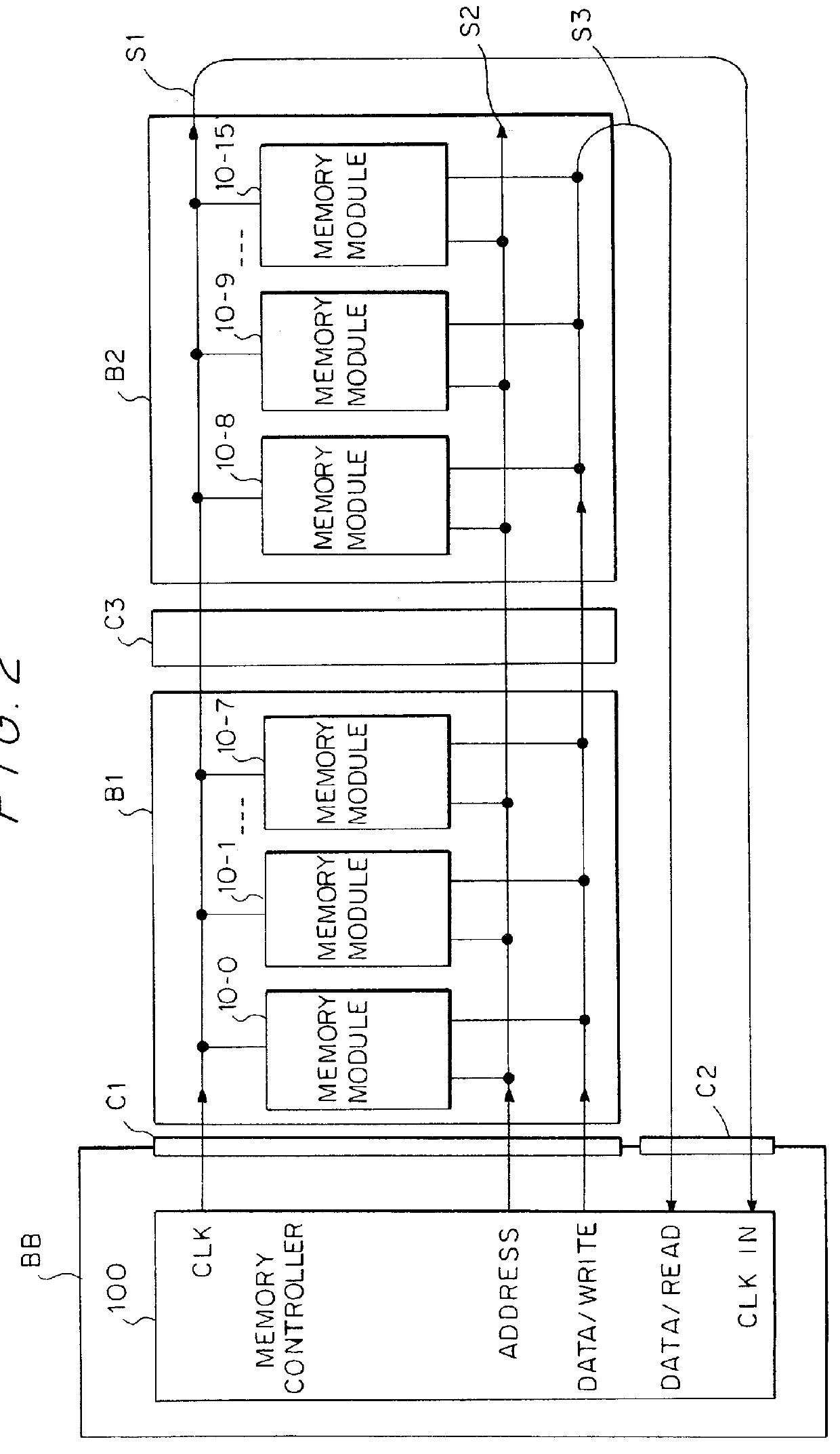
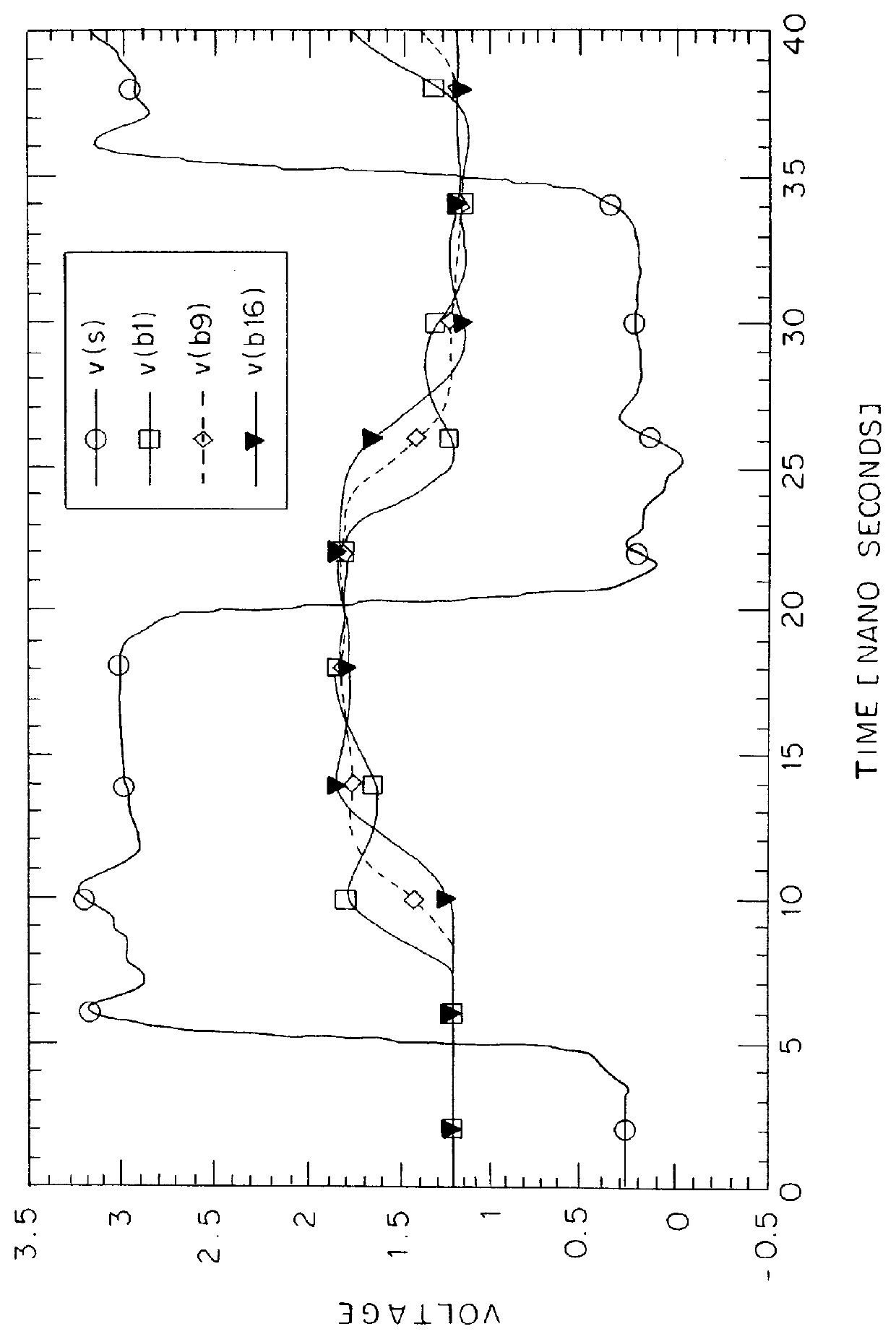
InactiveUS6034878ALarge data storage capacity per memoryImprove installation densityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory bankComputer module
A source-clock-synchronized memory system having a large data storage capacity per memory bank and a high mounting density. The invention includes a memory unit having a first memory riser board B1 mounted on a base board through a first connector C1 and a second memory riser board B2 mounted on the base board BB through a second connector C2. The first memory riser board has a plurality of first memory modules mounted on the front surface thereof and the second memory riser board has a plurality of second memory modules mounted on the front surface thereof. The first and second memory riser boards are arranged in such a way that the back surface of the first memory riser board faces the back surface of the second memory riser board. The invention further includes a board linking connector for connecting signal lines on the first memory riser board to corresponding signal lines on the second memory riser board.
Owner:DELTA KOGYO CO LTD +1
Performance/capacity management framework over many servers
InactiveUS6148335ADigital computer detailsData switching networksApplication programming interfaceColour coding
A method of monitoring a computer network by collecting resource data from a plurality of network nodes, analyzing the resource data to generate historical performance data, and reporting the historical performance data to another network node. The network nodes can be servers operating on different platforms, and resource data is gathered using separate programs having different application programming interfaces for the respective platforms. The analysis can generate daily, weekly, and monthly historical performance data, based on a variety of resources including CPU utilization, memory availability, I / O usage, and permanent storage capacity. The report may be constructed using a plurality of documents related by hypertext links. The hypertext links can be color-coded in response to at least one performance parameter in the historical performance data surpassing an associated threshold. An action list can also be created in response to such an event.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for generating a document representation
ActiveUS20100228693A1Without structureHighly to changeDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisPart of speechGrammatical relation
A method, system and computer program product for generating a document representation are disclosed. The system includes a server and a client computer, and the method involves: receiving into memory a resource containing at least one sentence of text; producing a tree comprising tree elements indicating parts-of-speech and grammatical relations between the tree elements; producing semantic structures each having three tree elements to represent a simple clause (subject-predicate-object); and storing a semantic network of semantic structures and connections therebetween. The semantic network may be created from a user provided root concept. Output representations include concept maps, facts listings, text summaries, tag clouds, indices; and an annotated text. The system interactively modifies semantic networks in response to user feedback, and produces personal semantic networks and document use histories.
Owner:IFWE
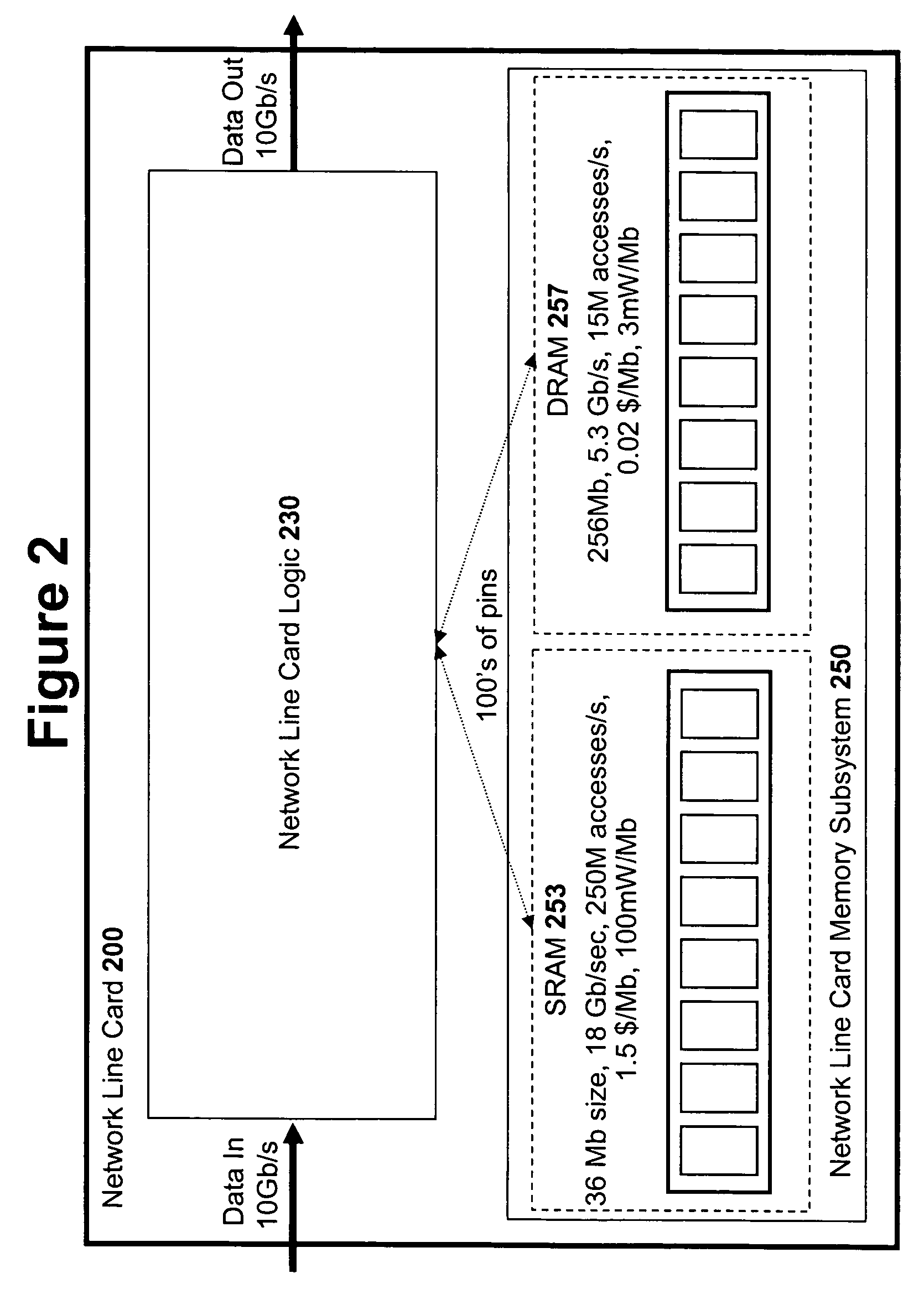
High speed memory control and I/O processor system
ActiveUS20050240745A1Easy to handleSimplify memory access taskMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh speed memoryTailored approach
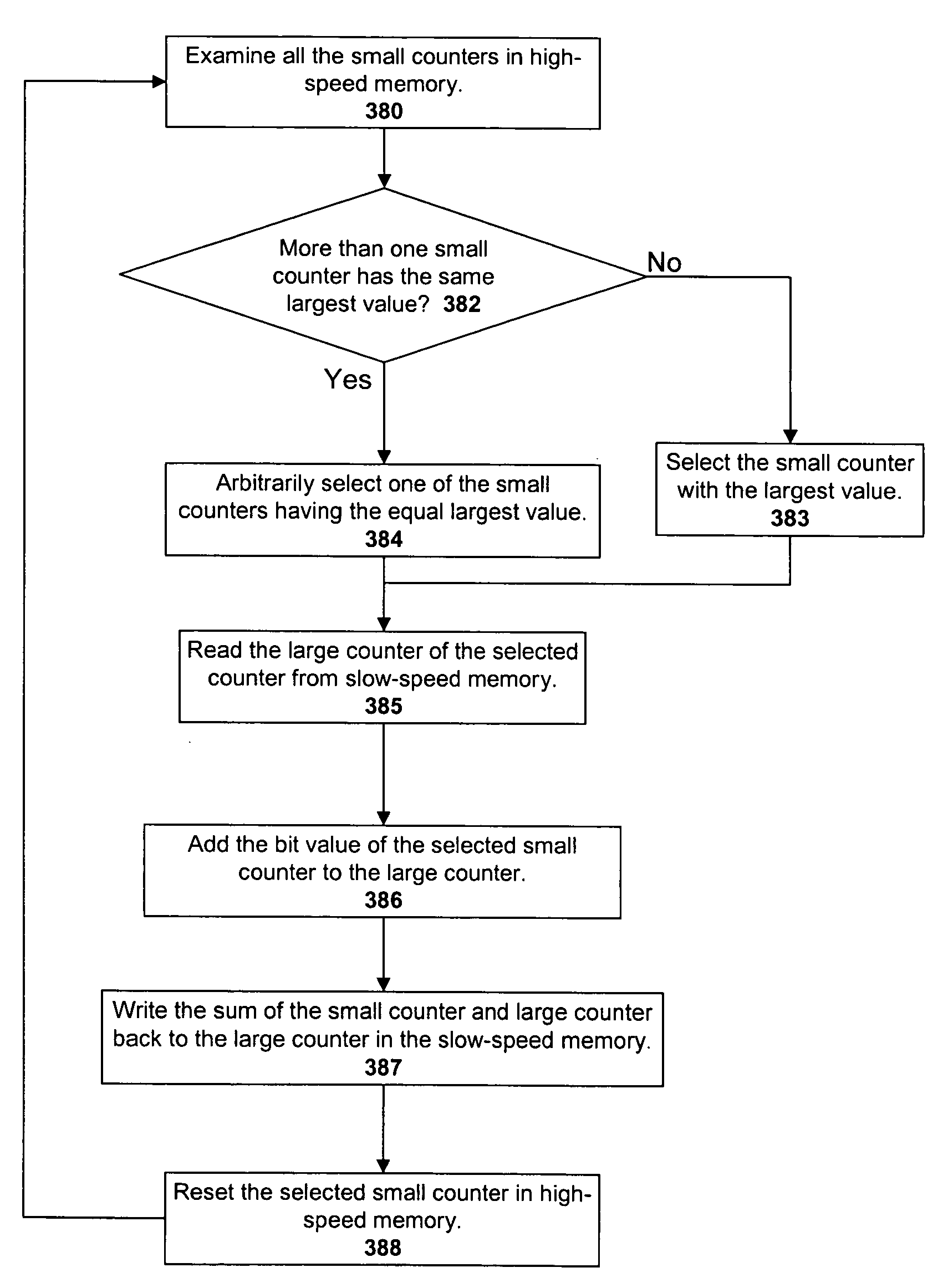
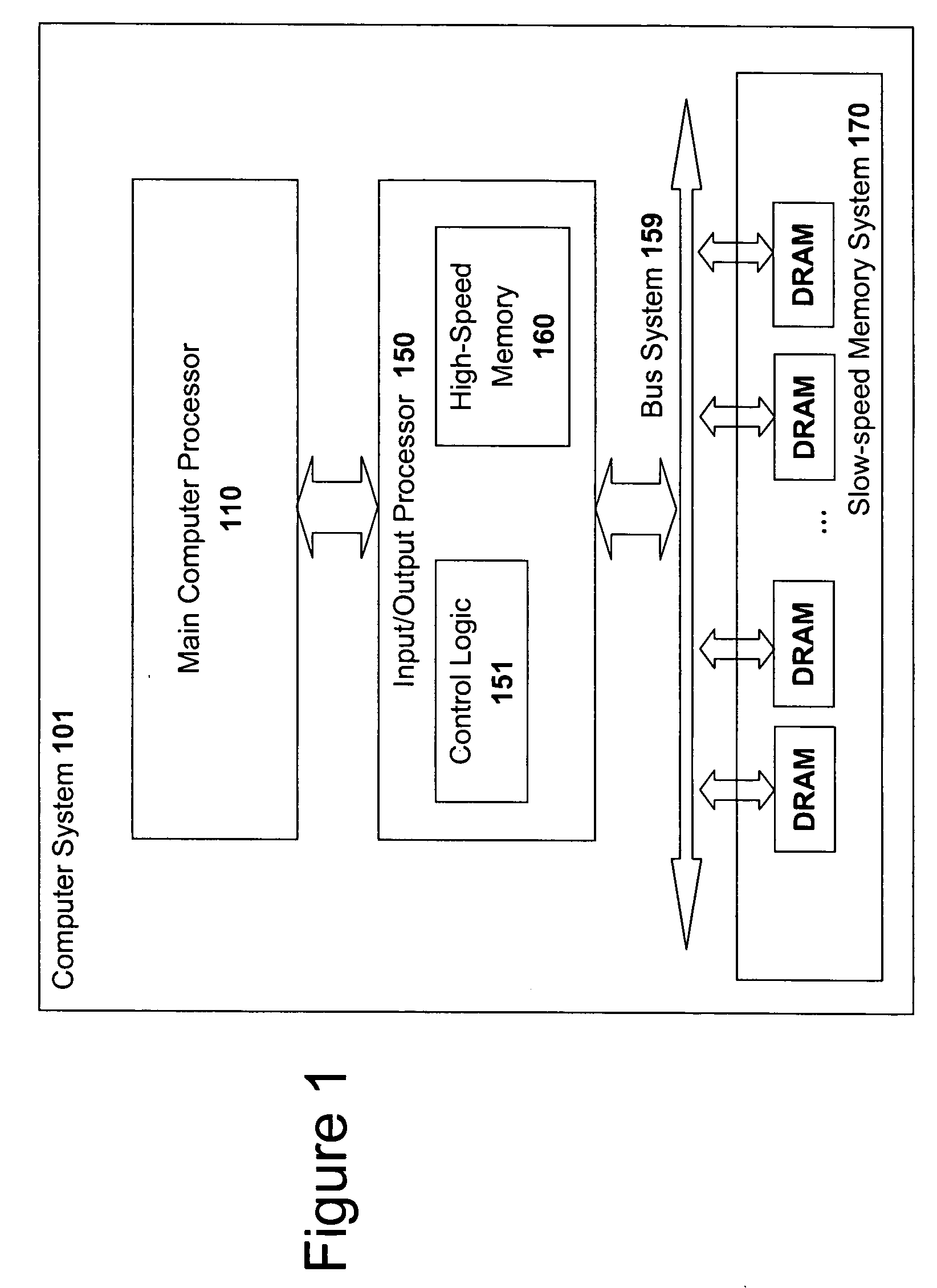
An input / output processor for speeding the input / output and memory access operations for a processor is presented. The key idea of an input / output processor is to functionally divide input / output and memory access operations tasks into a compute intensive part that is handled by the processor and an I / O or memory intensive part that is then handled by the input / output processor. An input / output processor is designed by analyzing common input / output and memory access patterns and implementing methods tailored to efficiently handle those commonly occurring patterns. One technique that an input / output processor may use is to divide memory tasks into high frequency or high-availability components and low frequency or low-availability components. After dividing a memory task in such a manner, the input / output processor then uses high-speed memory (such as SRAM) to store the high frequency and high-availability components and a slower-speed memory (such as commodity DRAM) to store the low frequency and low-availability components. Another technique used by the input / output processor is to allocate memory in such a manner that all memory bank conflicts are eliminated. By eliminating any possible memory bank conflicts, the maximum random access performance of DRAM memory technology can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
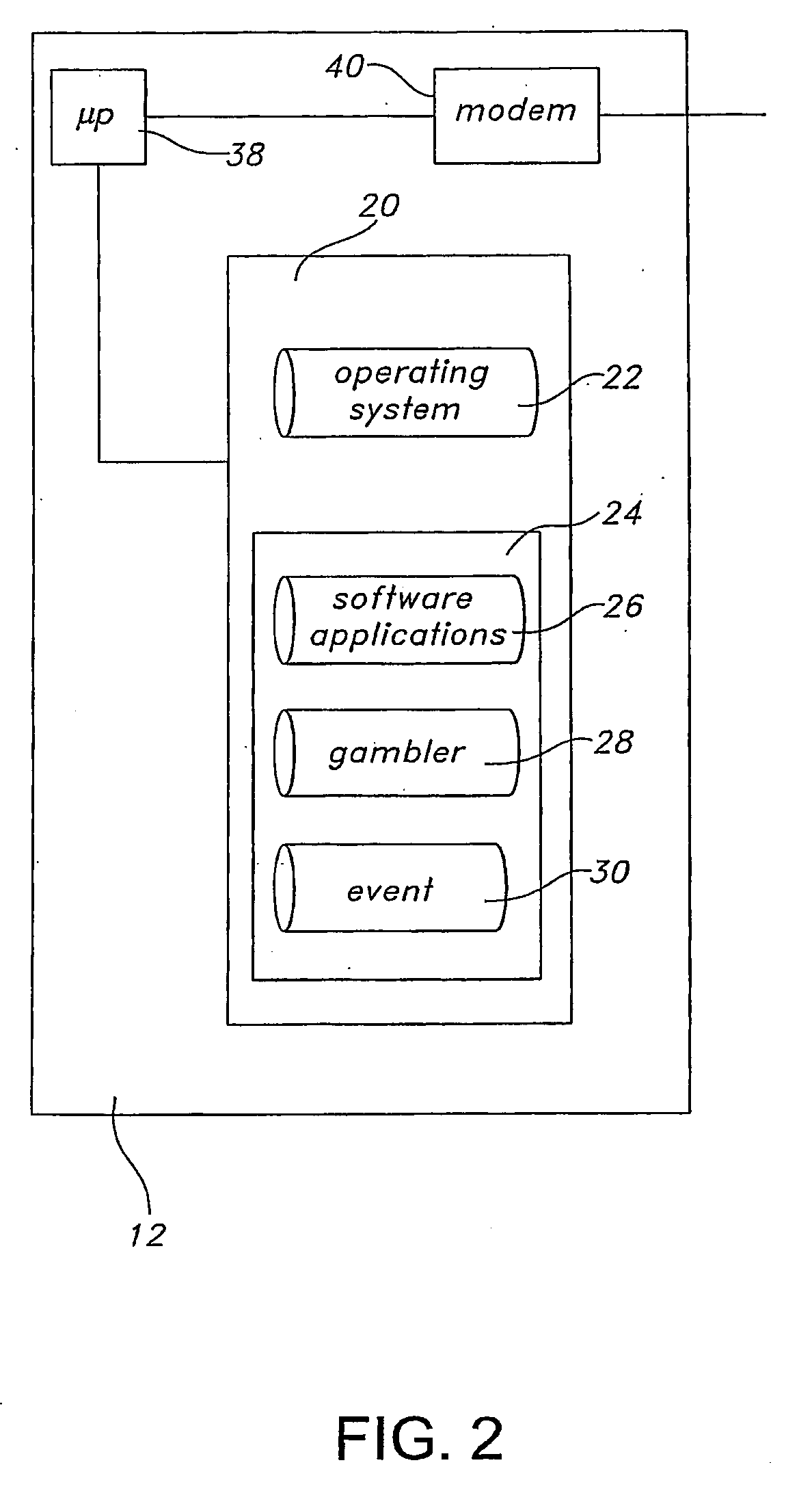
Methods and systems for betting with pari-mutuel payouts
InactiveUS20080113816A1Improved initial payoutQuick buildCard gamesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingOperational systemEvent data
A server for facilitating real-time betting, wherein the server communicates with clients via a distributed computing network. The server includes a memory storing an operating system, an instruction set, event data related to a sporting event, gambler data related to gamblers participating in a competition based upon the sporting event and site data related to electronic pages associated with the real-time para-mutuel betting. A processor runs the instruction set and communicates with the memory and the distributed computing network. The processor is operative to enroll the gamblers by presenting betting rules associated with the sporting event, collect wagering from the gamblers, accept predictions for discrete events within the sporting event from each gambler and determine a first winner of the competition based upon the predictions. Applications include lotteries with entries received from mobile devices.
Owner:HF SCI INC
Memory addressing controlled by PTE fields
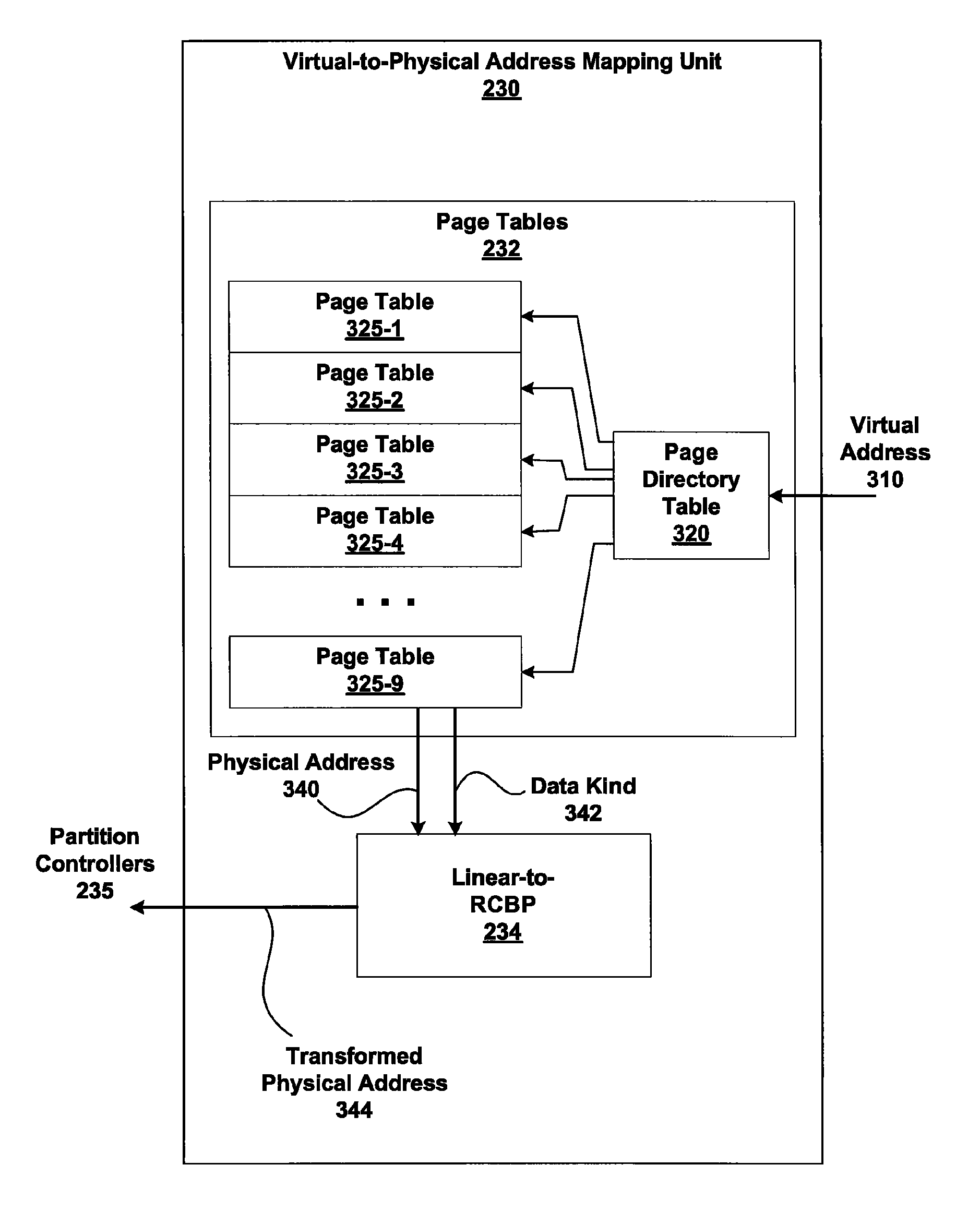
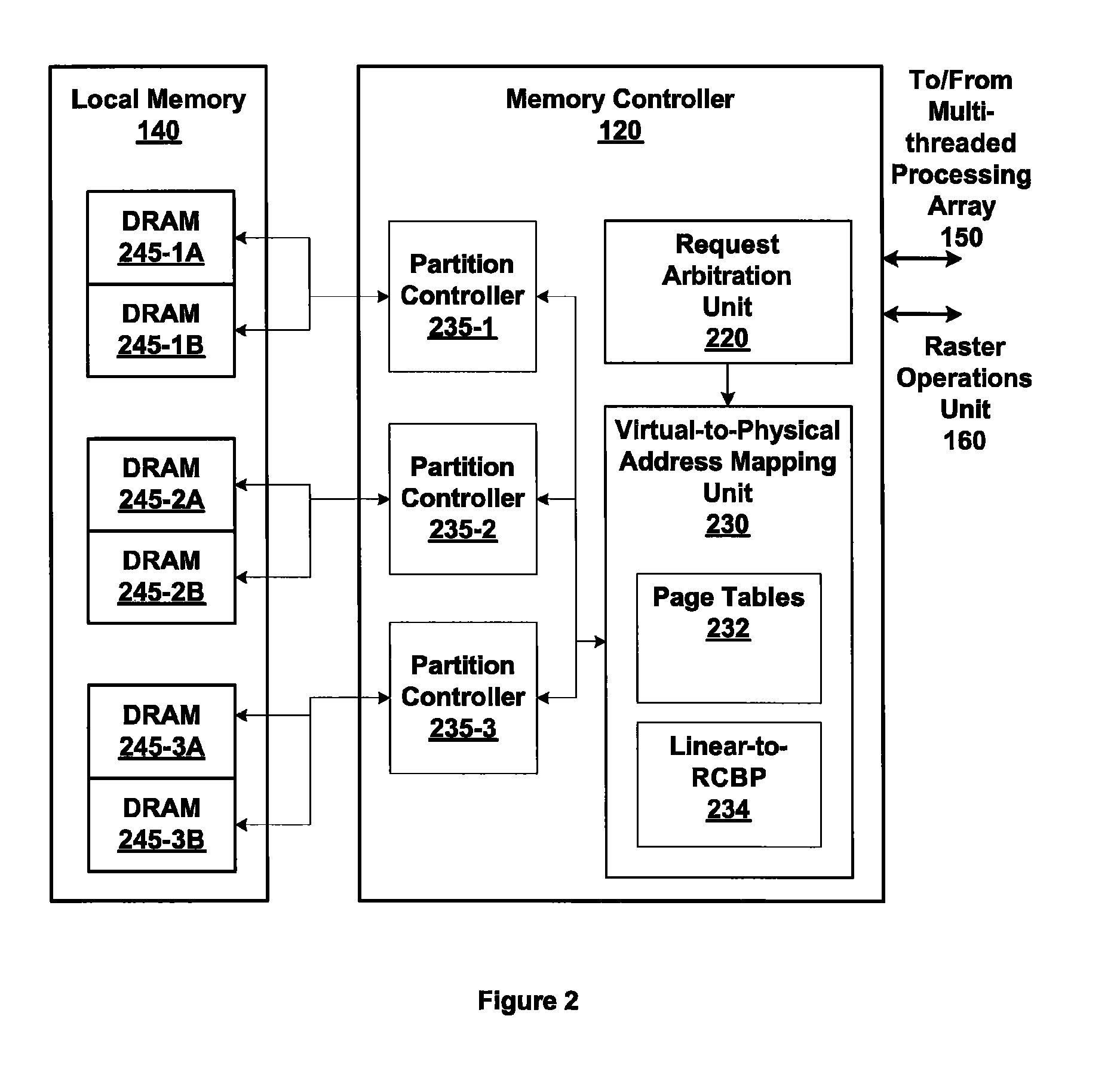
ActiveUS7805587B1Reduce accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsMemory addressDram memory
Embodiments of the present invention enable virtual-to-physical memory address translation using optimized bank and partition interleave patterns to improve memory bandwidth by distributing data accesses over multiple banks and multiple partitions. Each virtual page has a corresponding page table entry that specifies the physical address of the virtual page in linear physical address space. The page table entry also includes a data kind field that is used to guide and optimize the mapping process from the linear physical address space to the DRAM physical address space, which is used to directly access one or more DRAM. The DRAM physical address space includes a row, bank and column address. The data kind field is also used to optimize the starting partition number and partition interleave pattern that defines the organization of the selected physical page of memory within the DRAM memory system.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
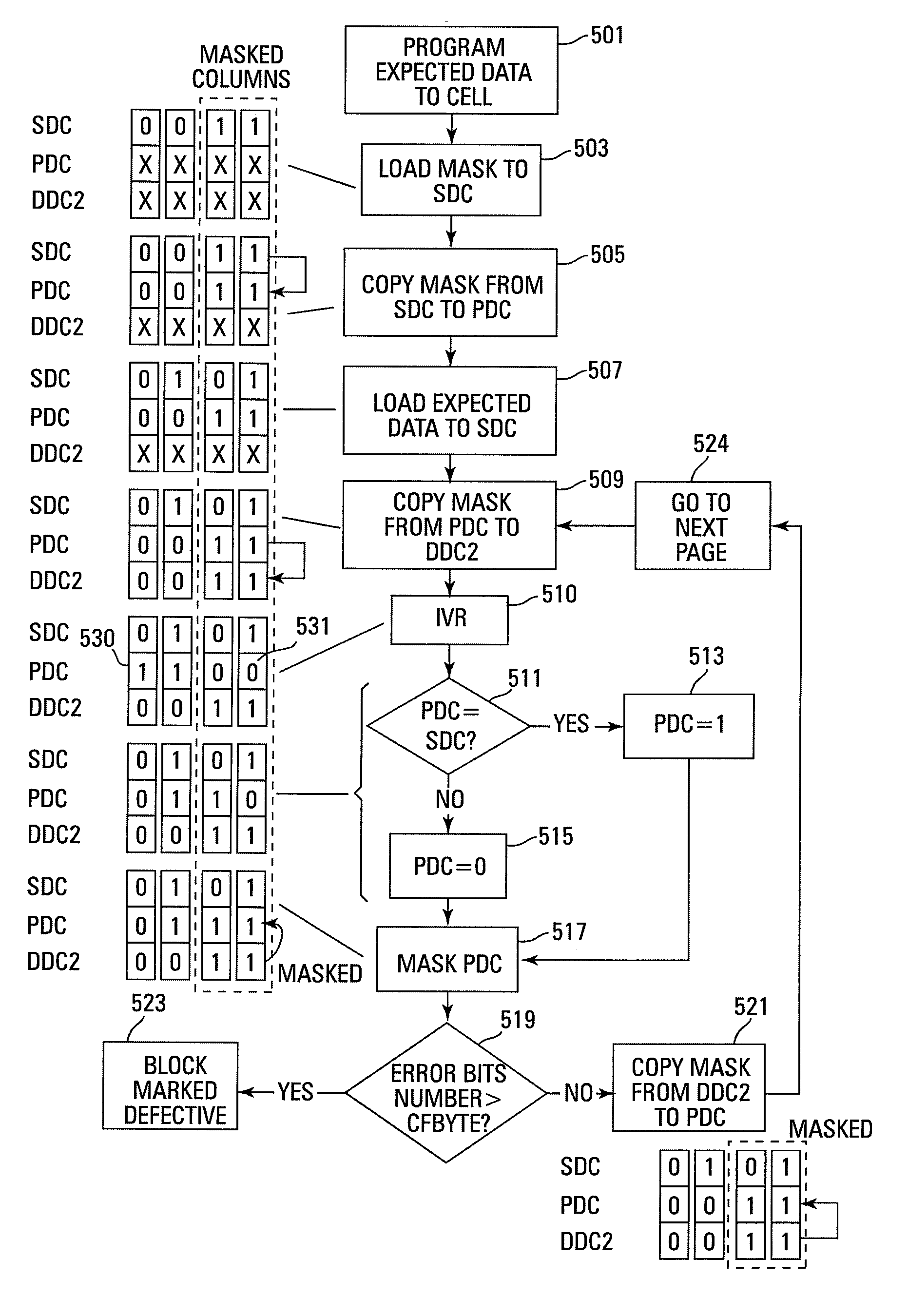
Small unit internal verify read in a memory device
Methods for small unit internal verify read operation and a memory device are disclosed. In one such method, expected data is programmed into a grouping of columns of memory cells (e.g., memory block). Mask data is loaded into a third dynamic data cache of three dynamic data caches. The expected data is loaded into a second data cache. After a read operation of programmed columns of memory cells, the read data is compared to the expected data and error bit indicators are stored in the second data cache in the error bit locations. The second data cache is masked with the mask data so that only those error bits that are unmasked are counted. If the number of unmasked error bit indicators is greater than a threshold, the memory block is marked as unusable.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
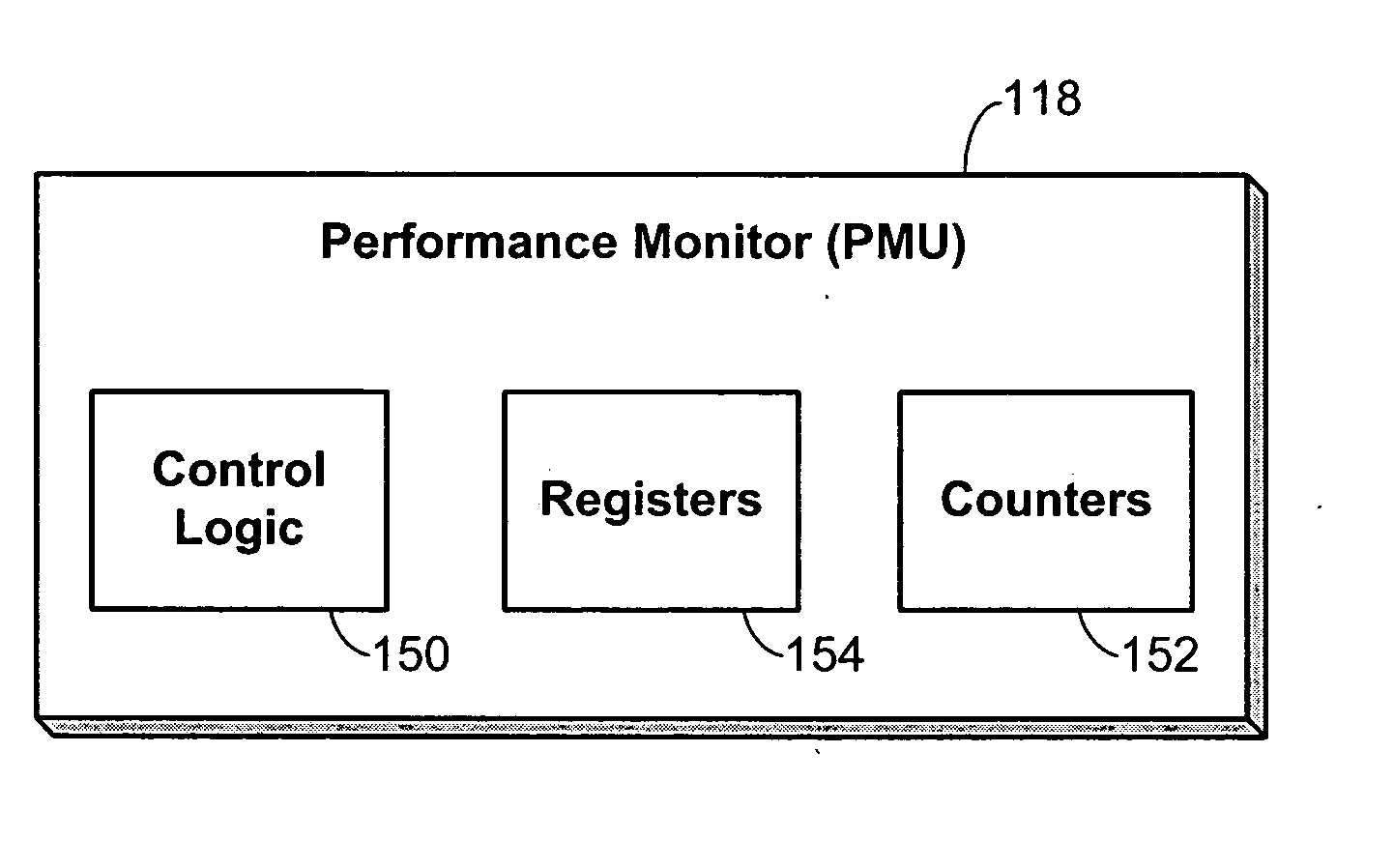
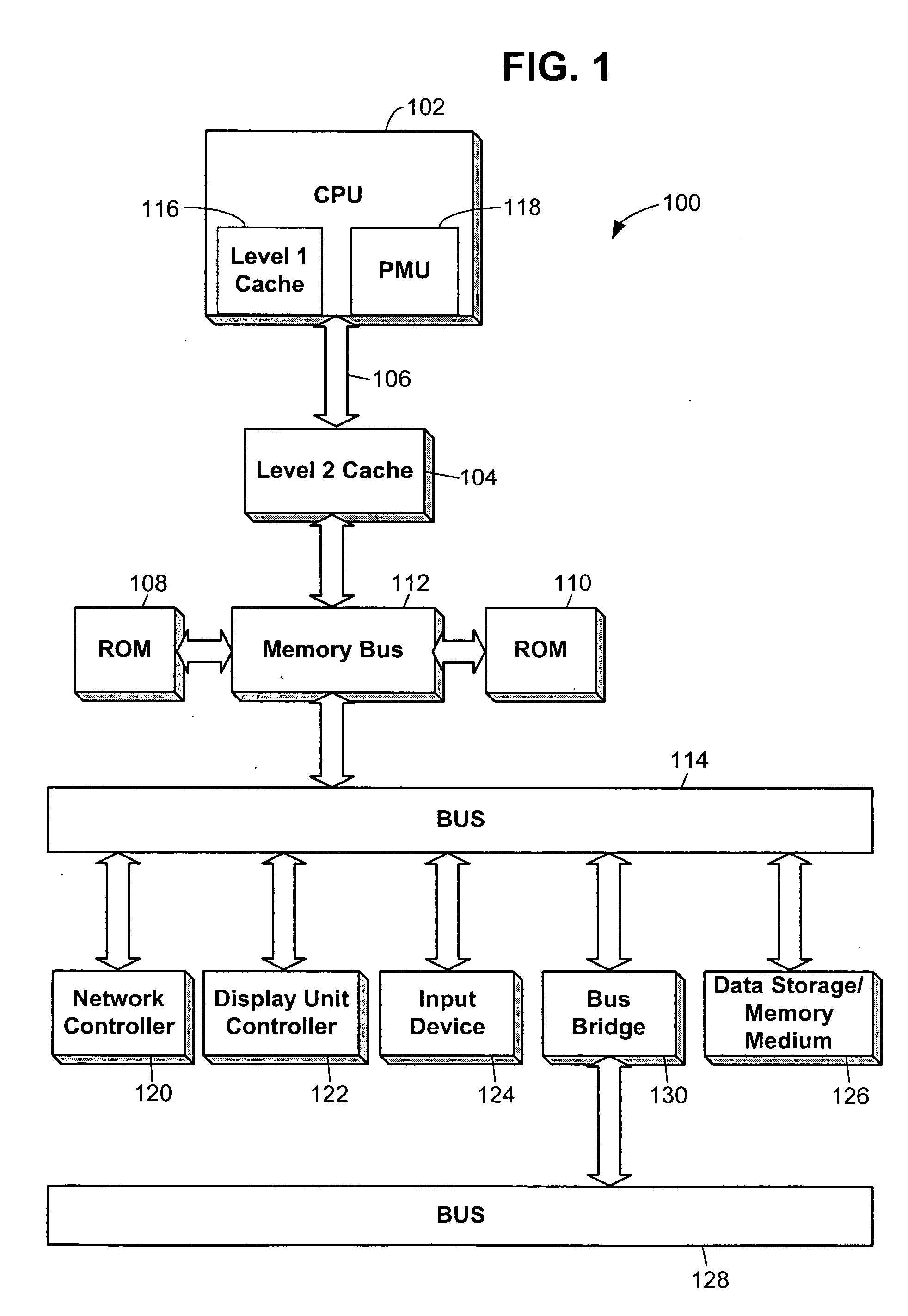
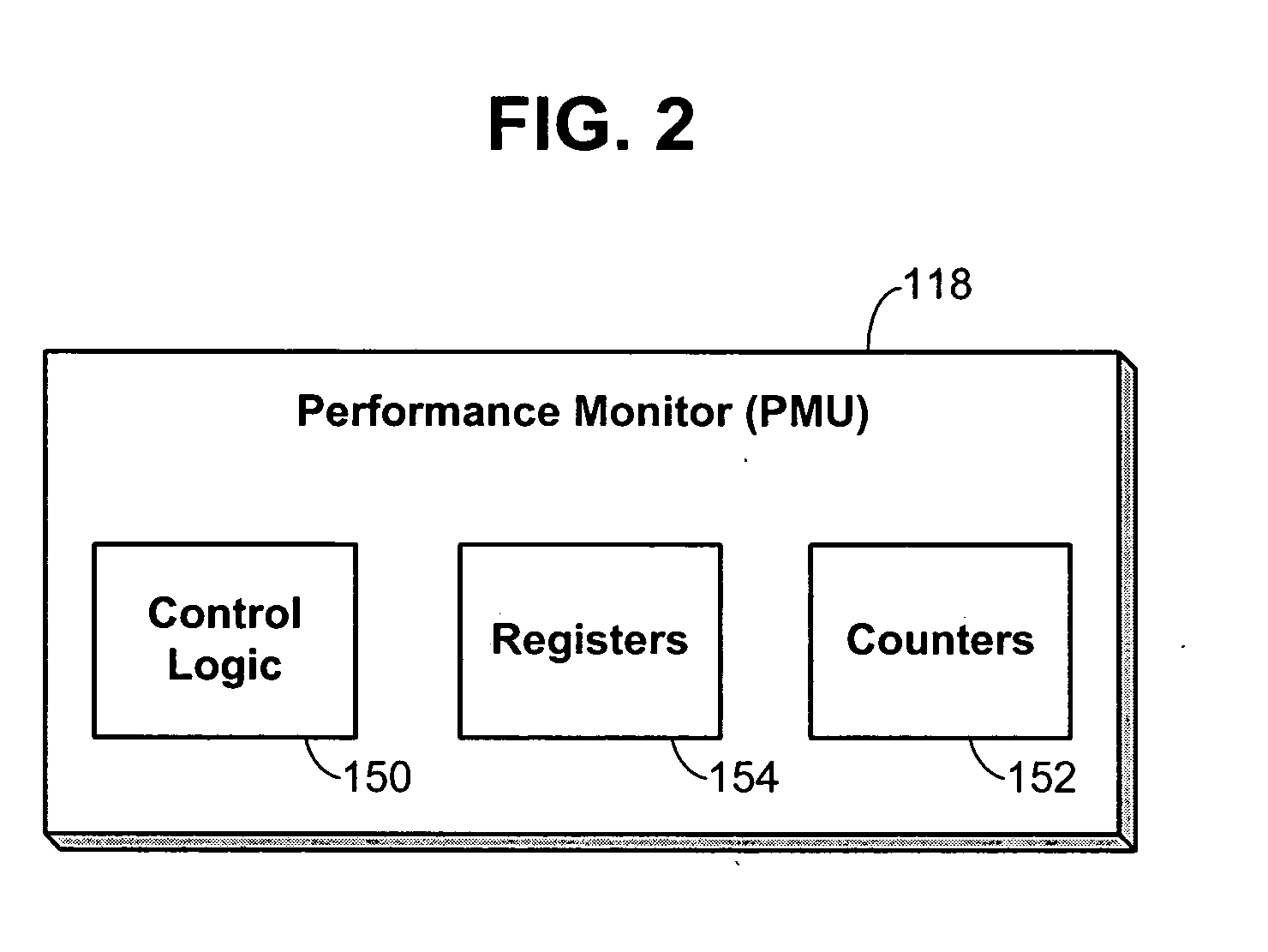
Performance monitoring based dynamic voltage and frequency scaling
Voltage and frequency scaling techniques that are based upon monitored data are provided. The techniques may be used to better manage the power and energy consumption of a processor in an embedded system, such as a cellular telephone, personal data assistant, smart device, or the like. The techniques may be used with processors that offer a performance monitoring capability. The performance monitor may monitor thread-level utilization at runtime. Instructions per cycle and memory references per cycle are example metrics that may be monitored by the performance monitor. The voltage and frequency scaling techniques may adjust the operating voltage and operating frequency of the processor based on the values of these two metrics. For example, the techniques may include accessing a voltage and frequency scheduler lookup table. The techniques may be employed with non-embedded systems, as well, embedded systems.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
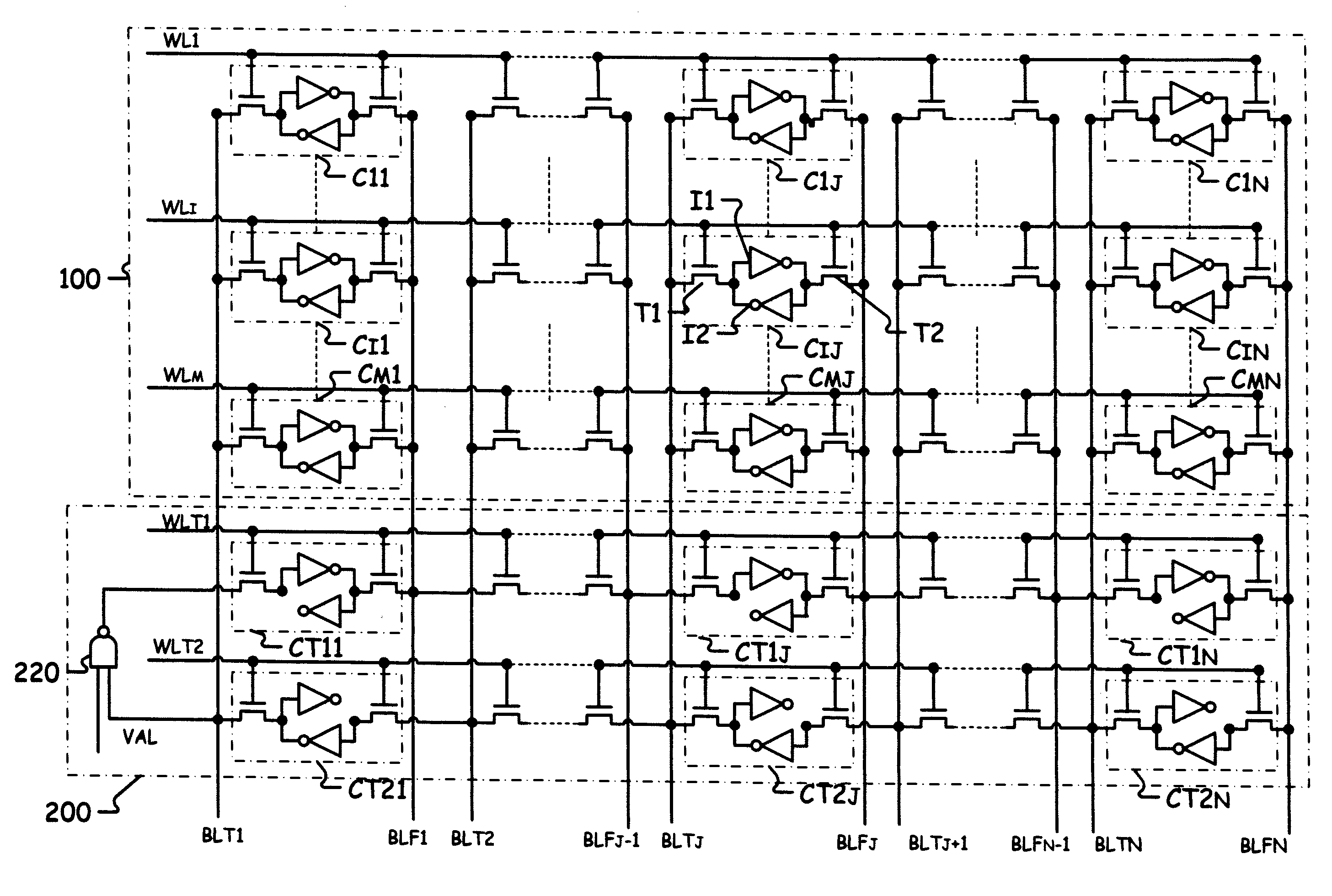
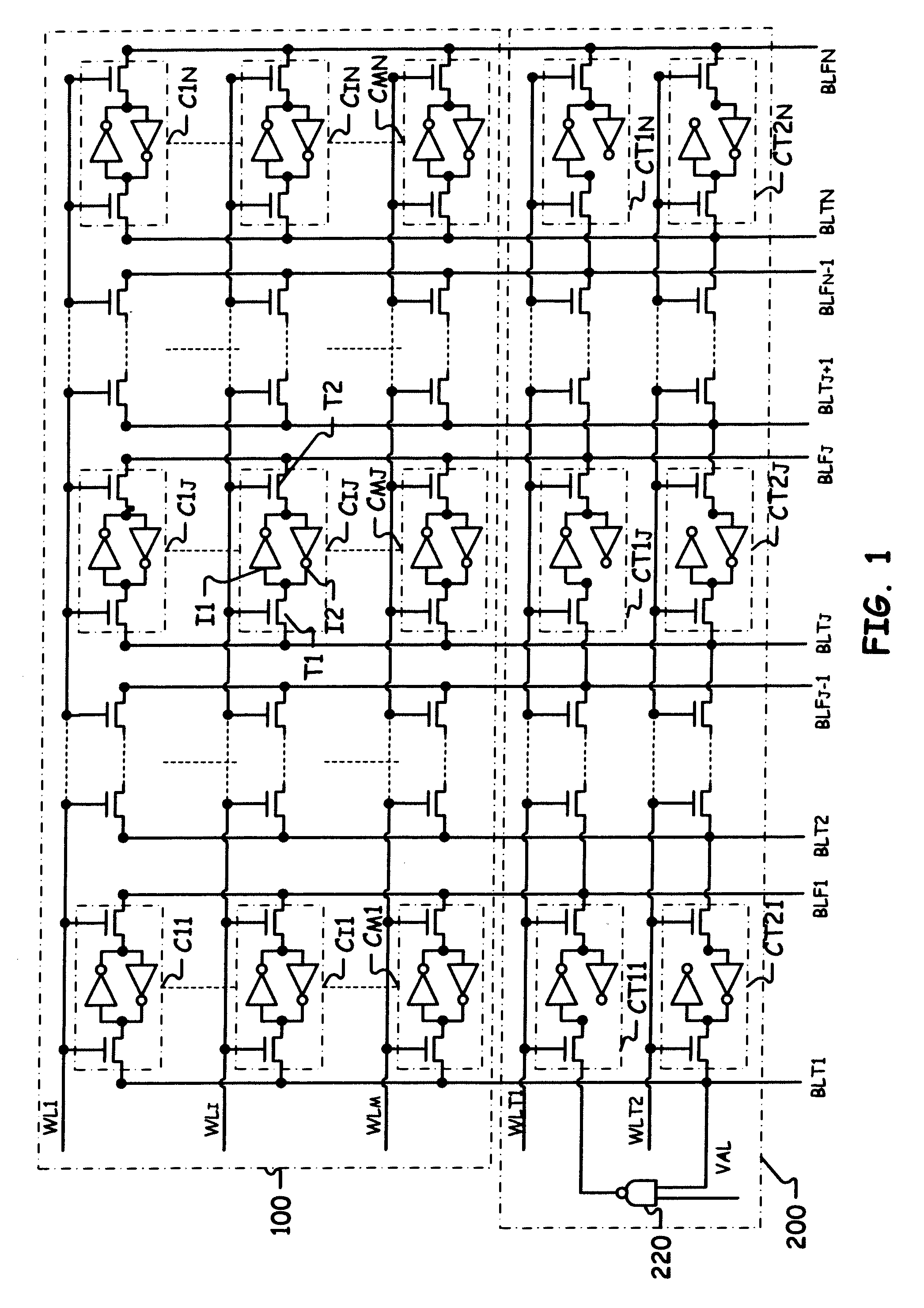
Memory including a performance test circuit
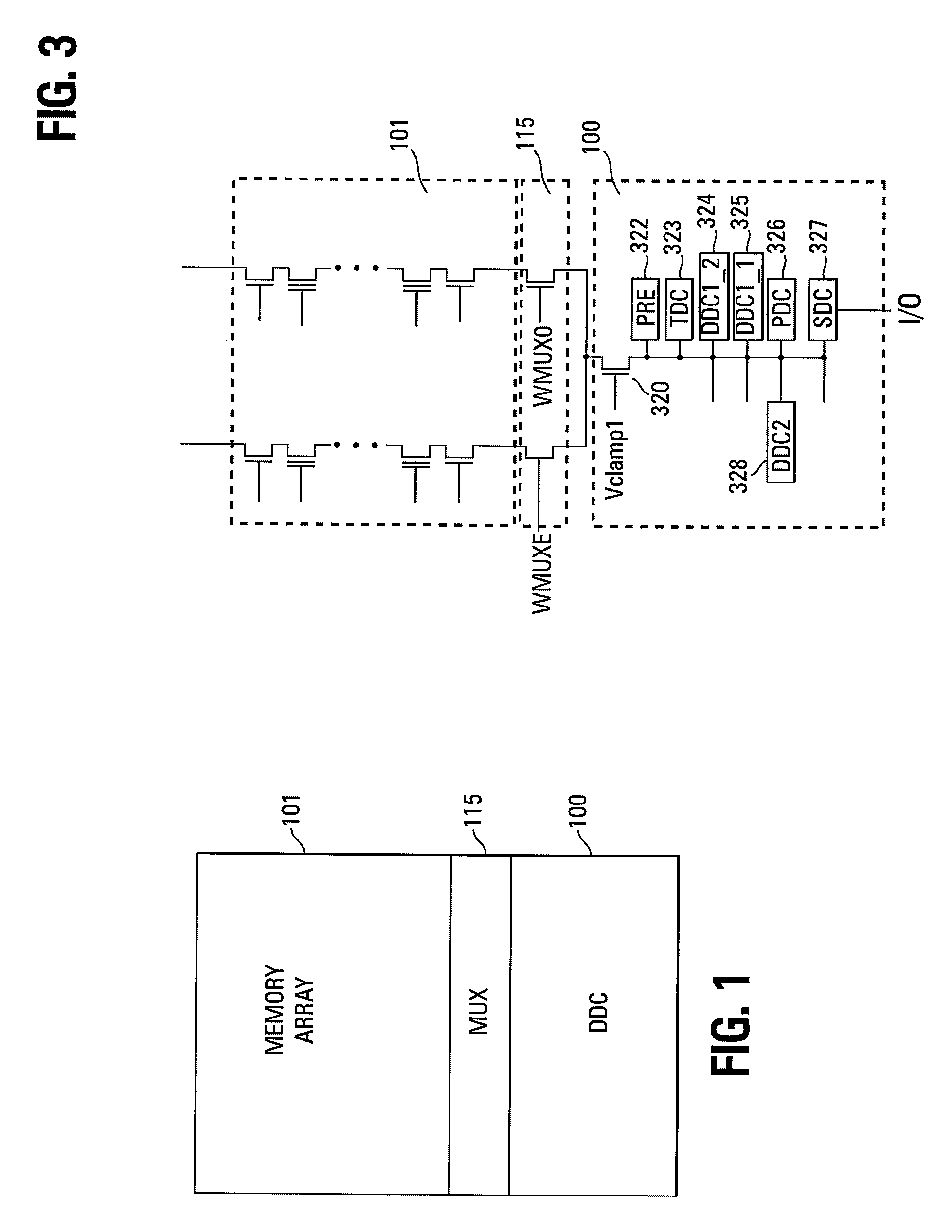
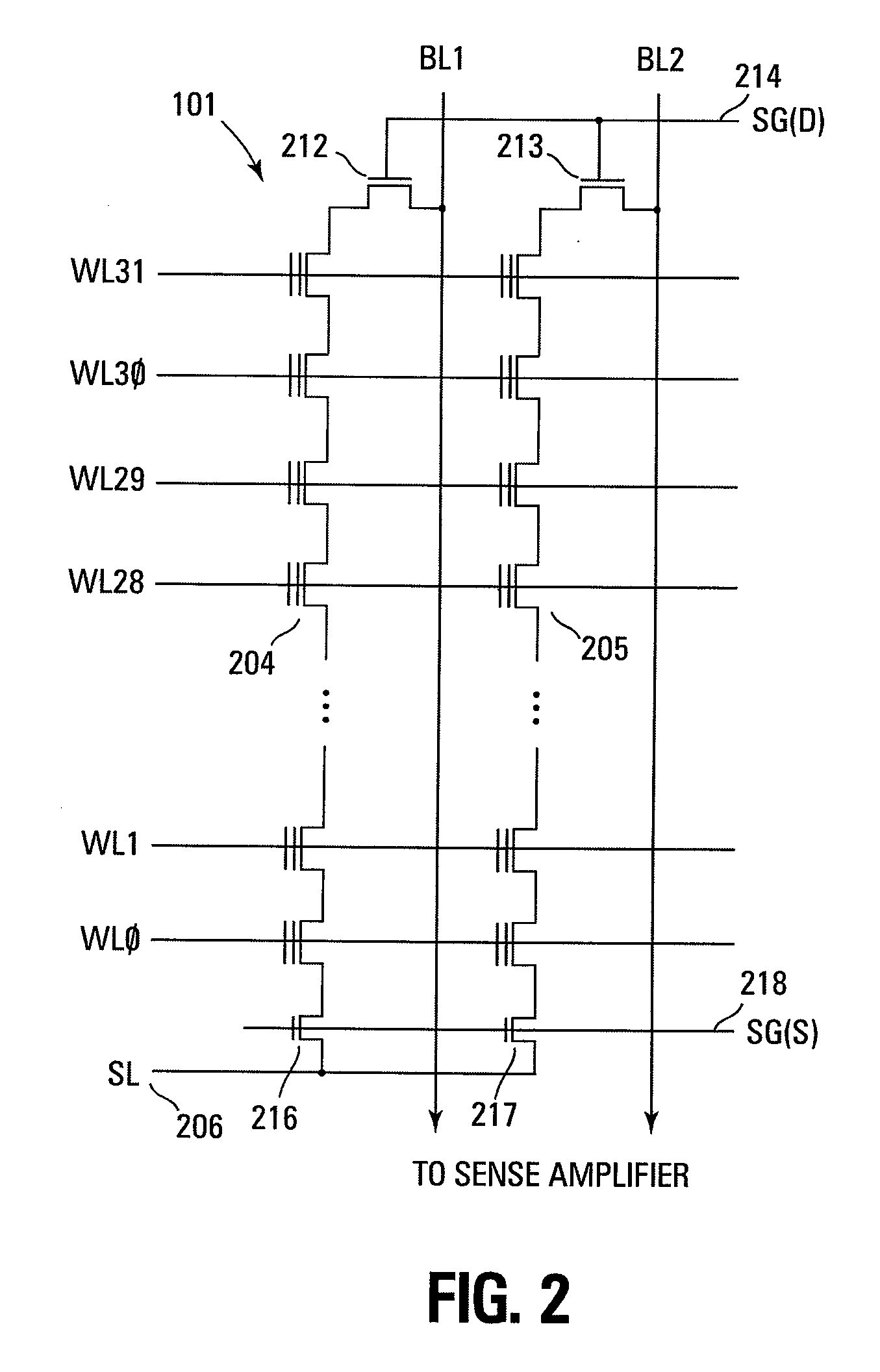
ActiveUS20090154273A1Easy to manufactureLimit memory consumptionElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionBit lineTerm memory
A memory includes a plurality of memory cells each including a true data input connected to a true bit line and complementary data input connected to a complementary bit line, and two inverters connected head-to-tail firstly to the true data input and secondly to the complementary data input. The memory also includes a test circuit includes a plurality of test cells, each test cell includes a true data input connected to a complementary data input of the preceding test cell and a complementary data input connected to the true data input of the following test cell, the complementary data input of the last test cell being connected to the true data input of the first test cell, each test cell comprising a first inverter connected between the true data input and the complementary data input. The looped chain thus formed propagates a signal whose period is a function of the performance of the storage cells.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
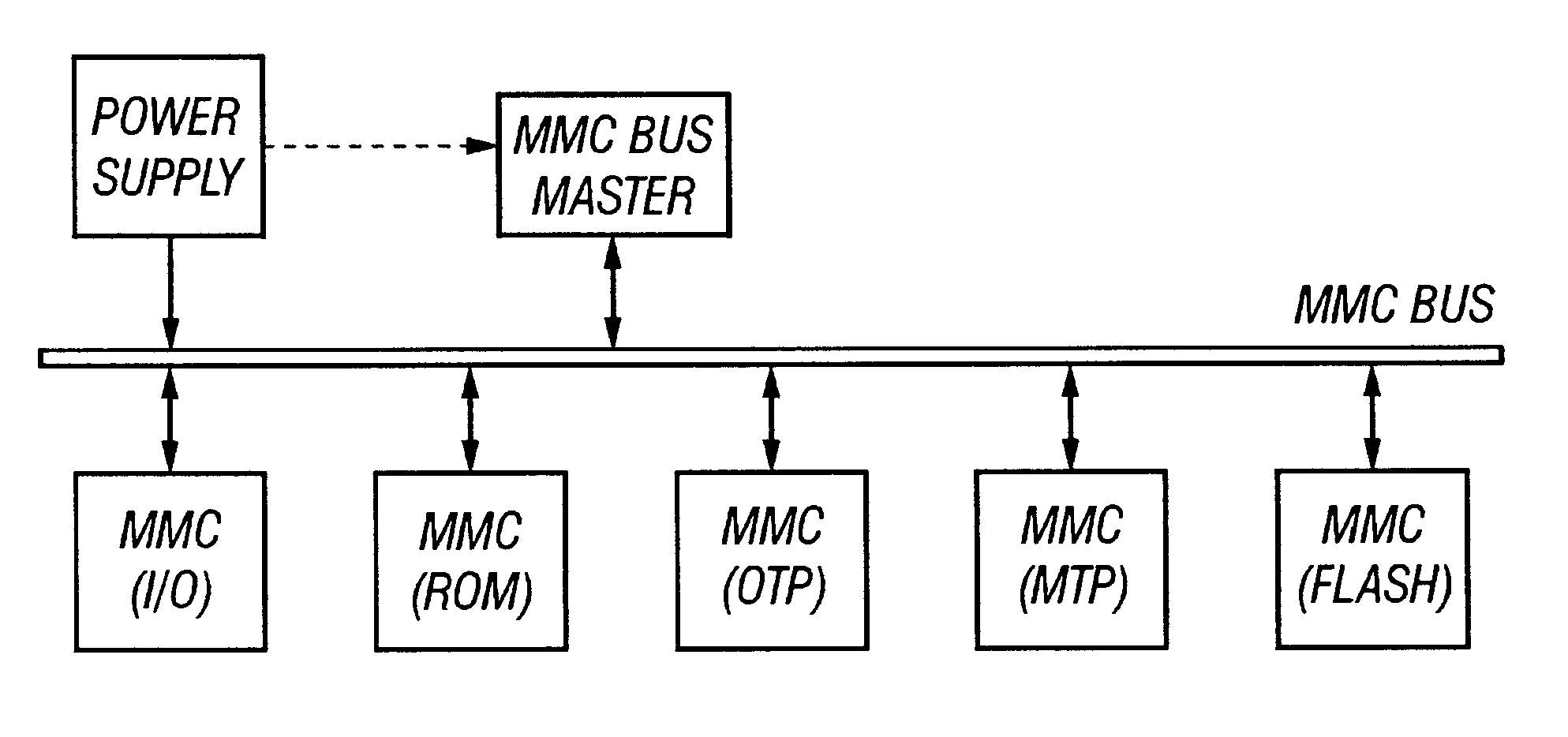
Voltage negotiation in a single host multiple cards system
InactiveUS6279114B1Avoid writingMemory architecture accessing/allocationVolume/mass flow measurementComputer hardwareCommunications system
A low cost data storage and communication system. The low cost data storage and communication system has a host and at least one card connected to the host. A voltage negotiator located in the system for determining a common operating voltage range that is a common demonminator of all independent operating voltage ranges of all of the cards connected to the system. In addition, there is a novel feature of partitioning the memory storages of the card. This feature provides the host the ability to simultaneously erase any combination of sectors in a single erase group, or any combination of the entire erase groups. Another feature feature provided by this novel method of partitioning the memory storages is the ability to write protect any combination of memory groups in the card.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
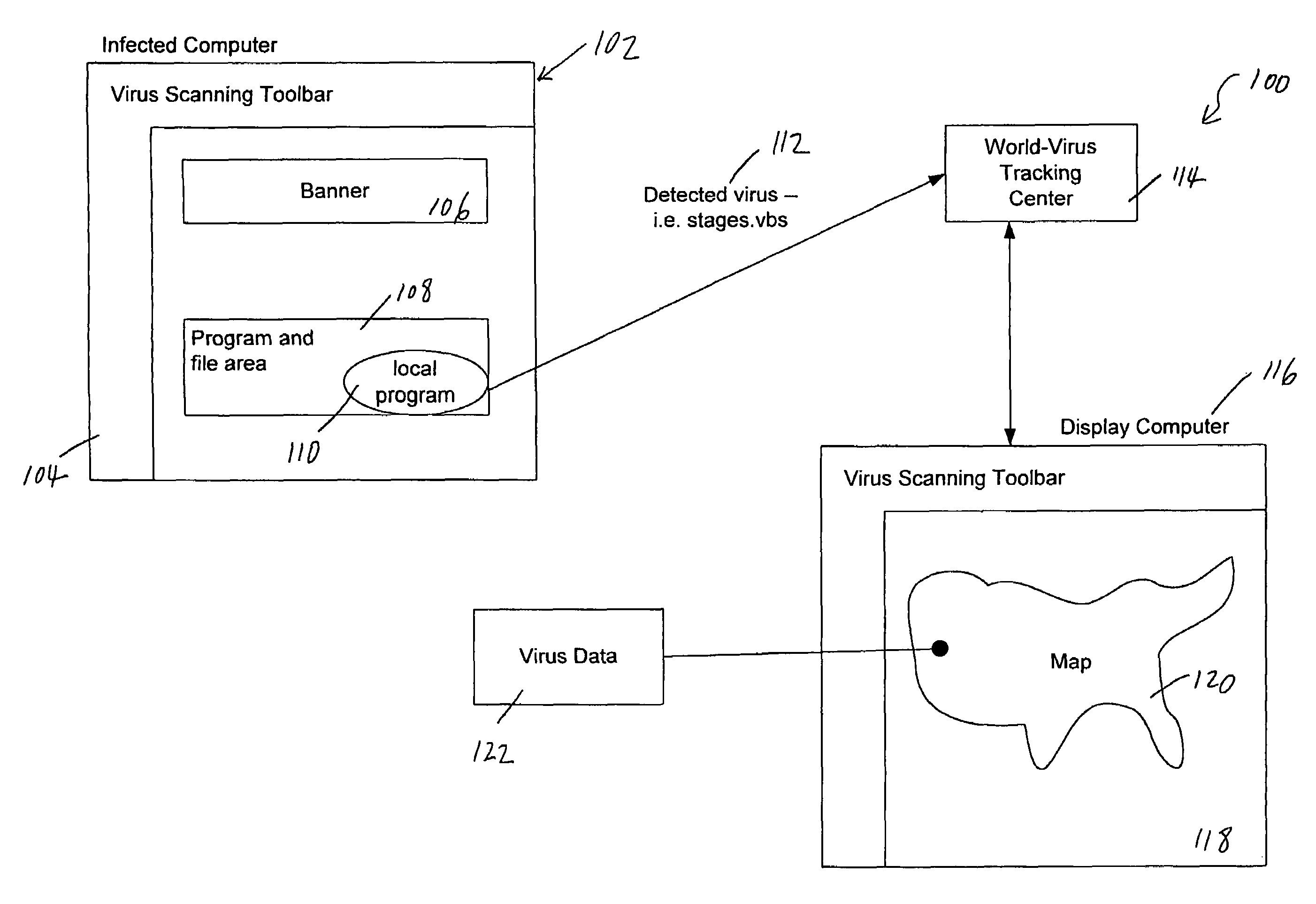
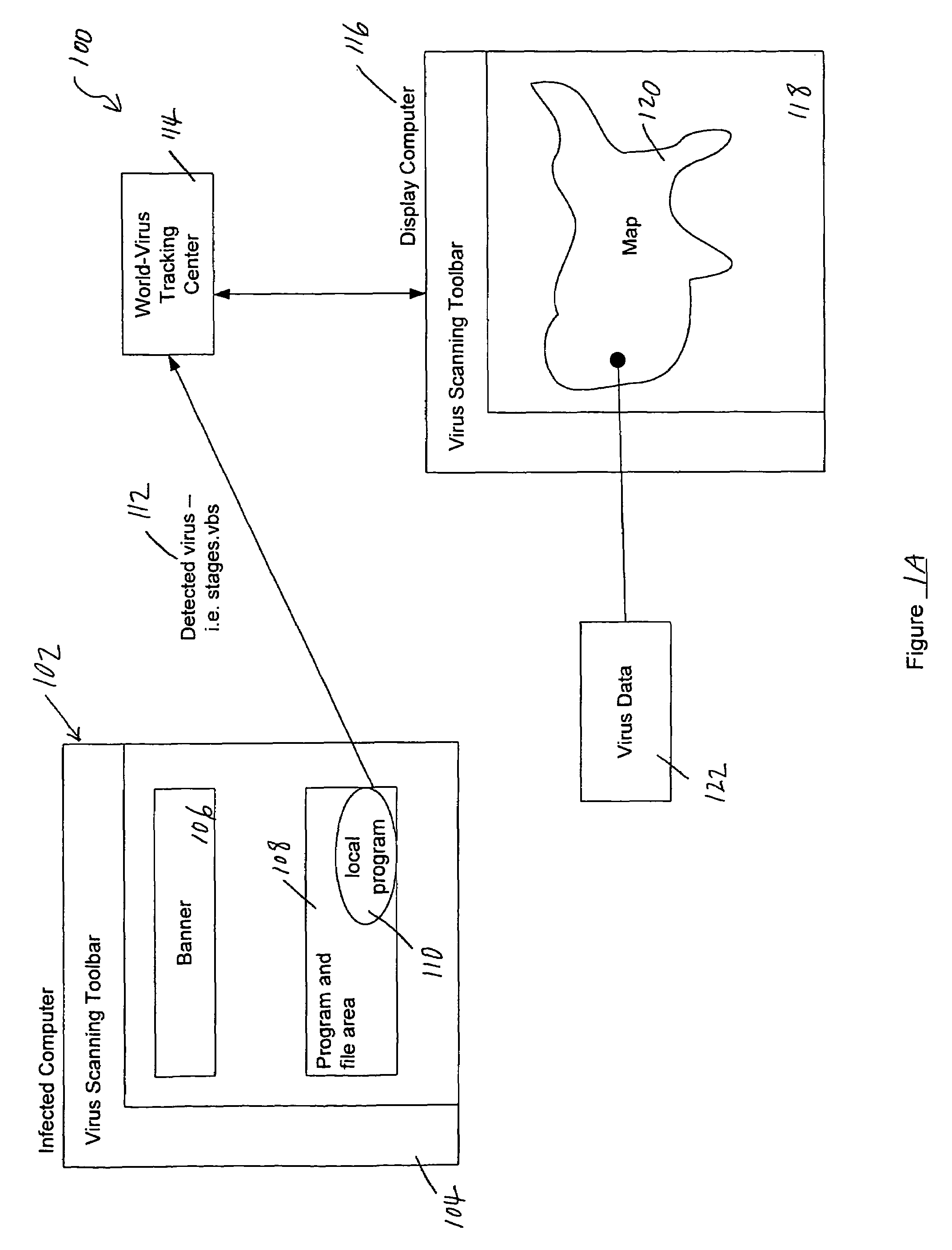
Tracking and reporting of computer virus information
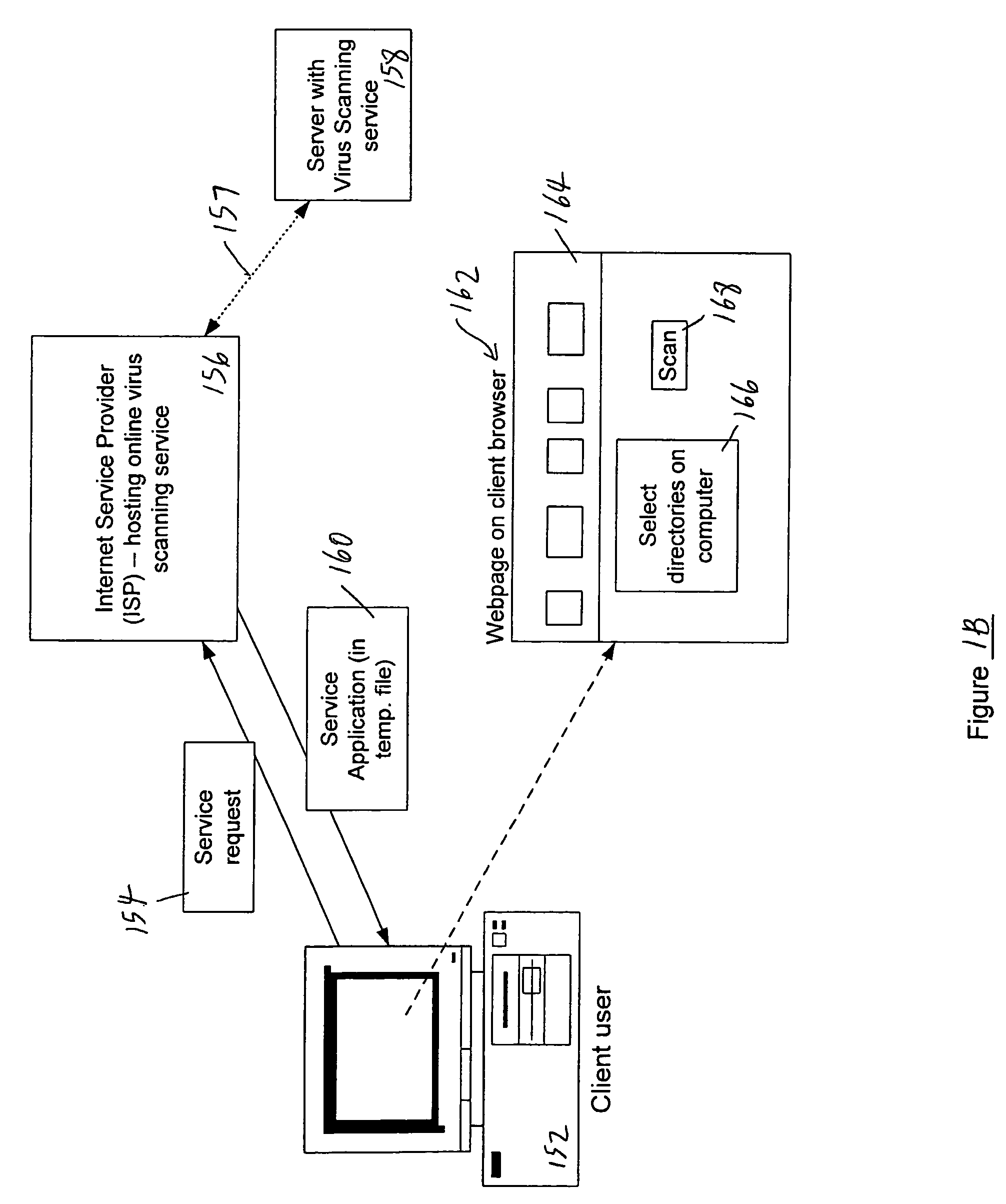
An apparatus and method for providing real-time tracking of virus information as reported from various computers on a distributed computer network. Each client computer on the distributed network contacts an anti-virus scanning site. The site provides a small program or applet that resides in temporary memory of the client computer. The client-user invokes the scan with supplied pattern updates for detecting recent viruses. When the scan has been completed, the user is prompted to supply a country of origin. The name of the virus, its frequency of occurrence, and the country are forwarded as a virus scan log to a virus tracking server, which receives the virus information and thereafter stores it in a database server, which is used to further calculate virus trace display information. A tracking user contacts the virus tracking server and receives map information, which traces the virus activity. The maps show, according to user preference, the names of the viruses encountered in each country, and their frequencies of occurrence.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
NAND flash memory management
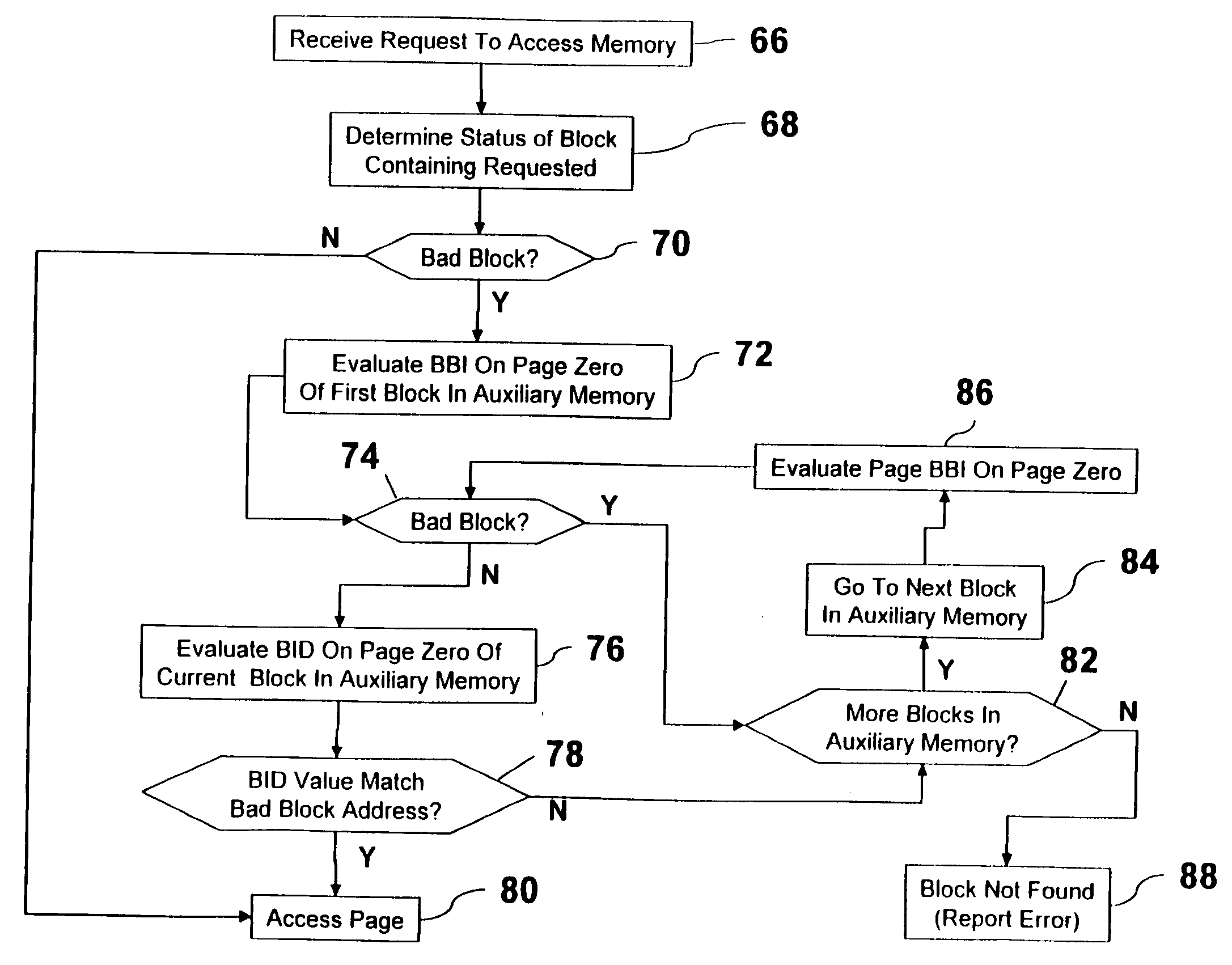
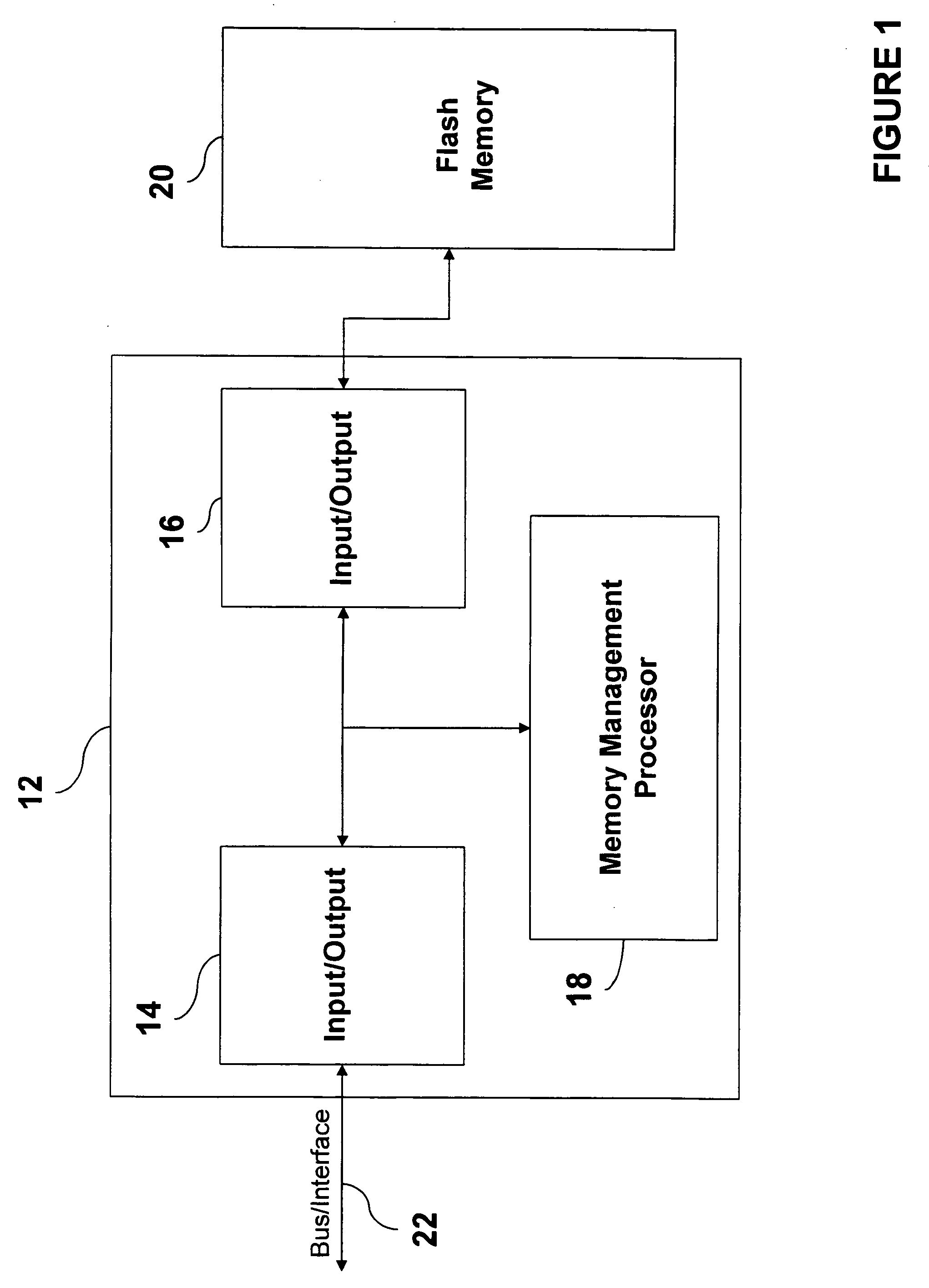
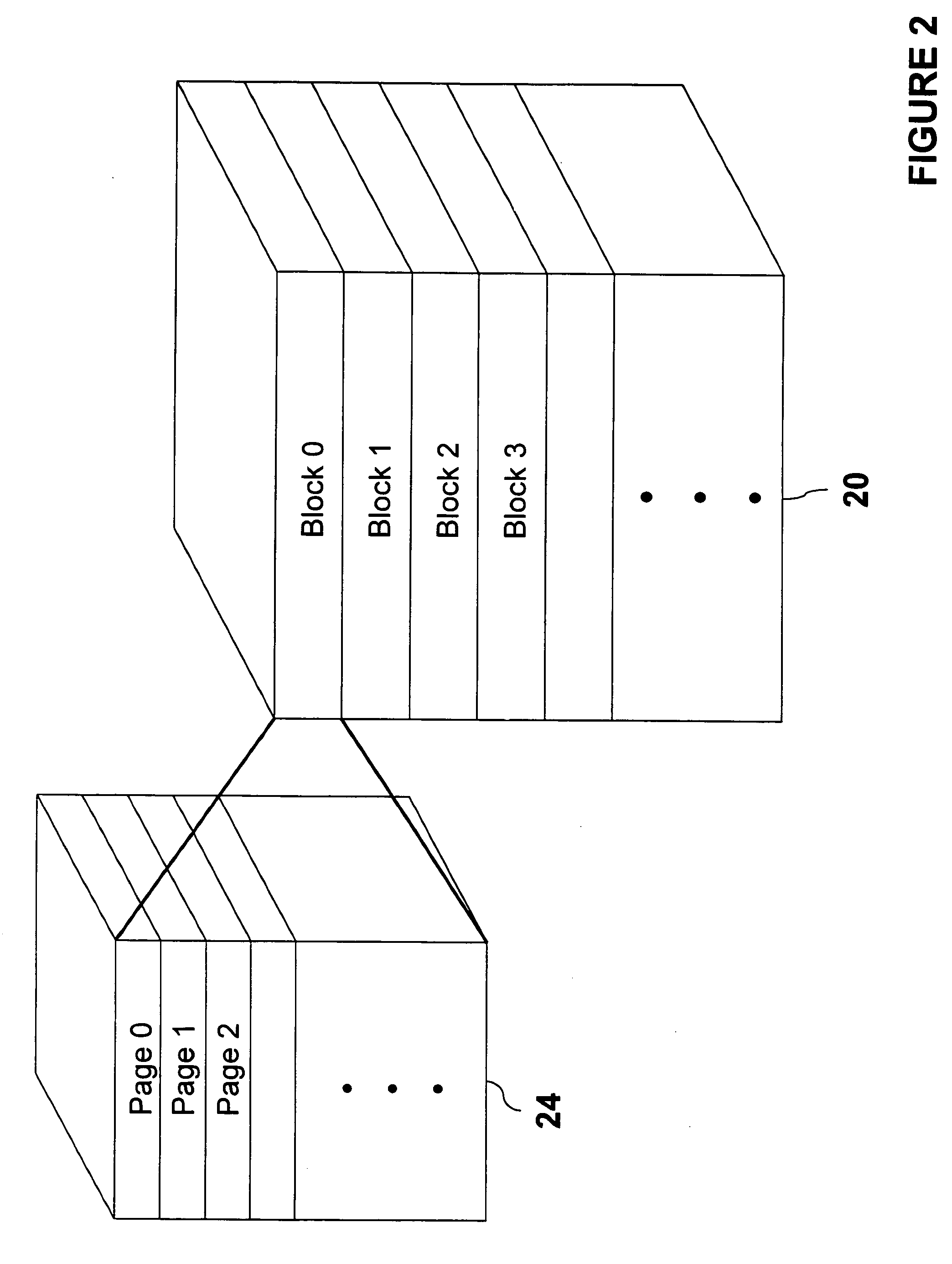
A memory controller is utilized to overcome NAND flash memory's propensity for comprising bad blocks of memory. The memory controller utilizes minimal hardware and is essentially transparent to a device requesting access to the NAND memory. A NAND flash memory device is configured to comprise a set of main blocks of memory and a set of auxiliary blocks of memory. Each block is divided into pages of memory and each page includes metadata. The metadata includes a block status indicator, indicating whether a block is good or bad. When receiving a request to access a page in the NAND flash memory, if the block in which the page resides is good, that block is accessed. If the block is bad, auxiliary memory is searched until a block containing the address of the bad block in its metadata is found. The found block is accessed in lieu of the bad block.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Management of non-volatile memory systems having large erase blocks
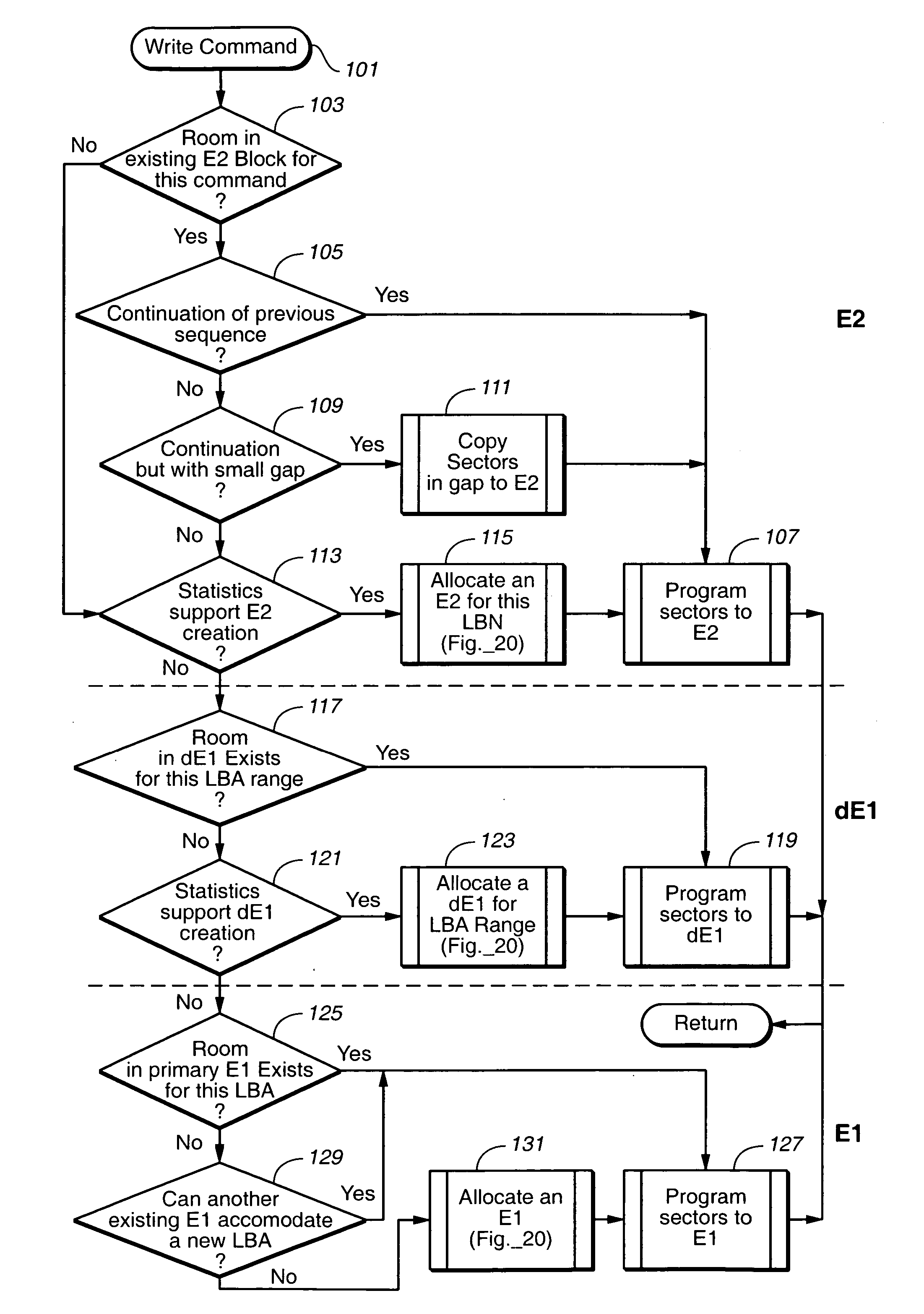
ActiveUS20050144358A1Reduce amountImprove system performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOriginal dataTerm memory
A non-volatile memory system of a type having blocks of memory cells erased together and which are programmable from an erased state in units of a large number of pages per block. If the data of only a few pages of a block are to be updated, the updated pages are written into another block provided for this purpose. Updated pages from multiple blocks are programmed into this other block in an order that does not necessarily correspond with their original address offsets. The valid original and updated data are then combined at a later time, when doing so does not impact on the performance of the memory. If the data of a large number of pages of a block are to be updated, however, the updated pages are written into an unused erased block and the unchanged pages are also written to the same unused block. By handling the updating of a few pages differently, memory performance is improved when small updates are being made. The memory controller can dynamically create and operate these other blocks in response to usage by the host of the memory system.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
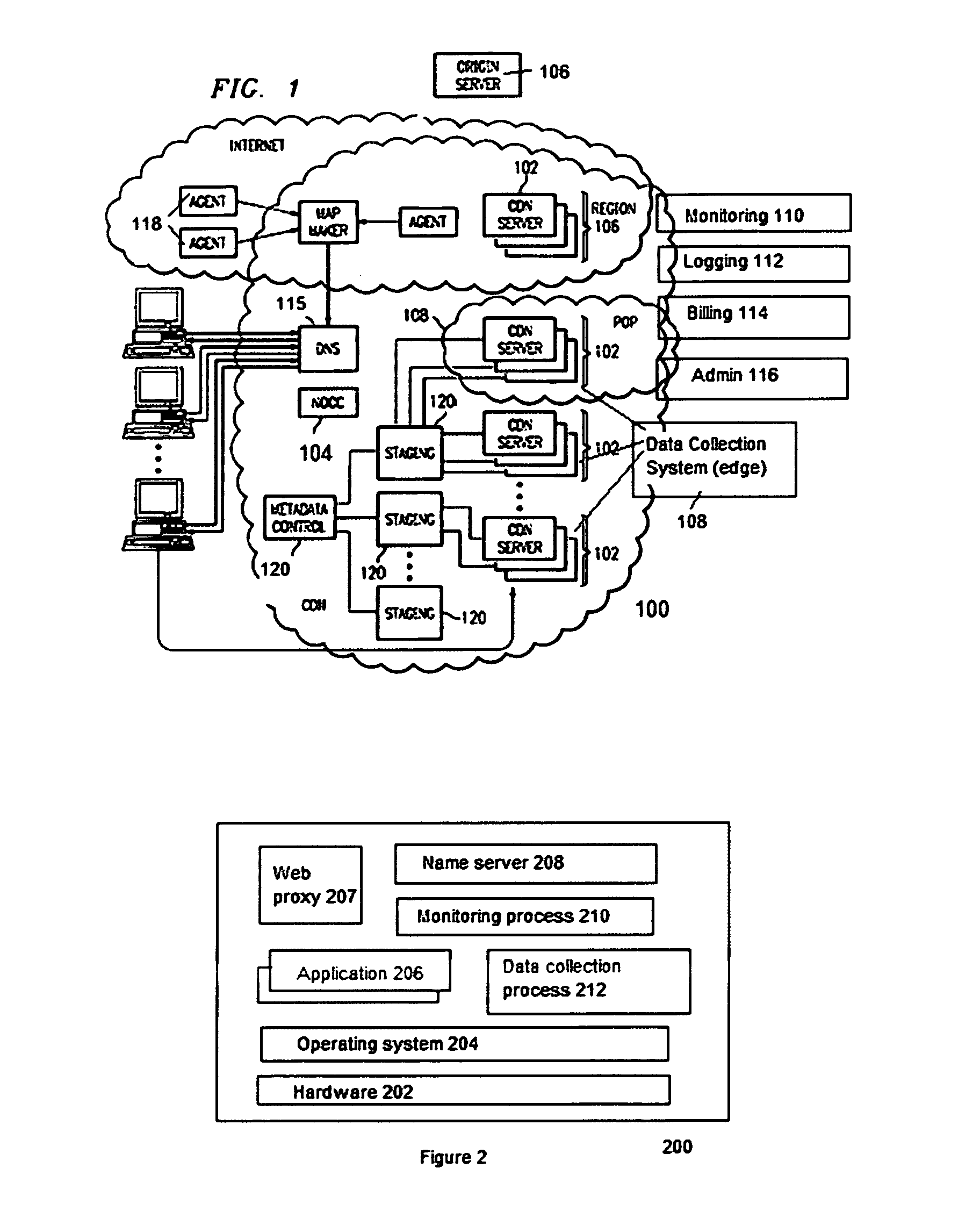
Site acceleration with content prefetching enabled through customer-specific configurations
ActiveUS20070156845A1More featureShorten the timeDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb siteEdge server
A CDN edge server is configured to provide one or more extended content delivery features on a domain-specific, customer-specific basis, preferably using configuration files that are distributed to the edge servers using a configuration system. A given configuration file includes a set of content handling rules and directives that facilitate one or more advanced content handling features, such as content prefetching. When prefetching is enabled, the edge server retrieves objects embedded in pages (normally HTML content) at the same time it serves the page to the browser rather than waiting for the browser's request for these objects. This can significantly decrease the overall rendering time of the page and improve the user experience of a Web site. Using a set of metadata tags, prefetching can be applied to either cacheable or uncacheable content. When prefetching is used for cacheable content, and the object to be prefetched is already in cache, the object is moved from disk into memory so that it is ready to be served. When prefetching is used for uncacheable content, preferably the retrieved objects are uniquely associated with the client browser request that triggered the prefetch so that these objects cannot be served to a different end user. By applying metadata in the configuration file, prefetching can be combined with tiered distribution and other edge server configuration options to further improve the speed of delivery and / or to protect the origin server from bursts of prefetching requests.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Multi-dimensional method and apparatus for automated language interpretation
A method and apparatus for natural language interpretation are described. The invention includes a schema and apparatus for storing, in digital, analog, or other machine-readable format, a network of propositions formed of a plurality of text and / or non-text objects, and the steps of retrieving a string of input text, and locating all associated propositions in the network for each word in the input string. Embodiments of the invention also include optimization steps for locating said propositions, and specialized structures for storing them in a ready access storage area simulating human short-term memory. The schema and steps may also include structures and processes for obtaining and adjusting the weights of said propositions to determine posterior probabilities representing the intended meaning. Embodiments of the invention also include an apparatus designed to apply an automated interpretation algorithm to automated voice response systems and portable knowledge appliance devices.
Owner:KNOWLEDGENETICA CORP
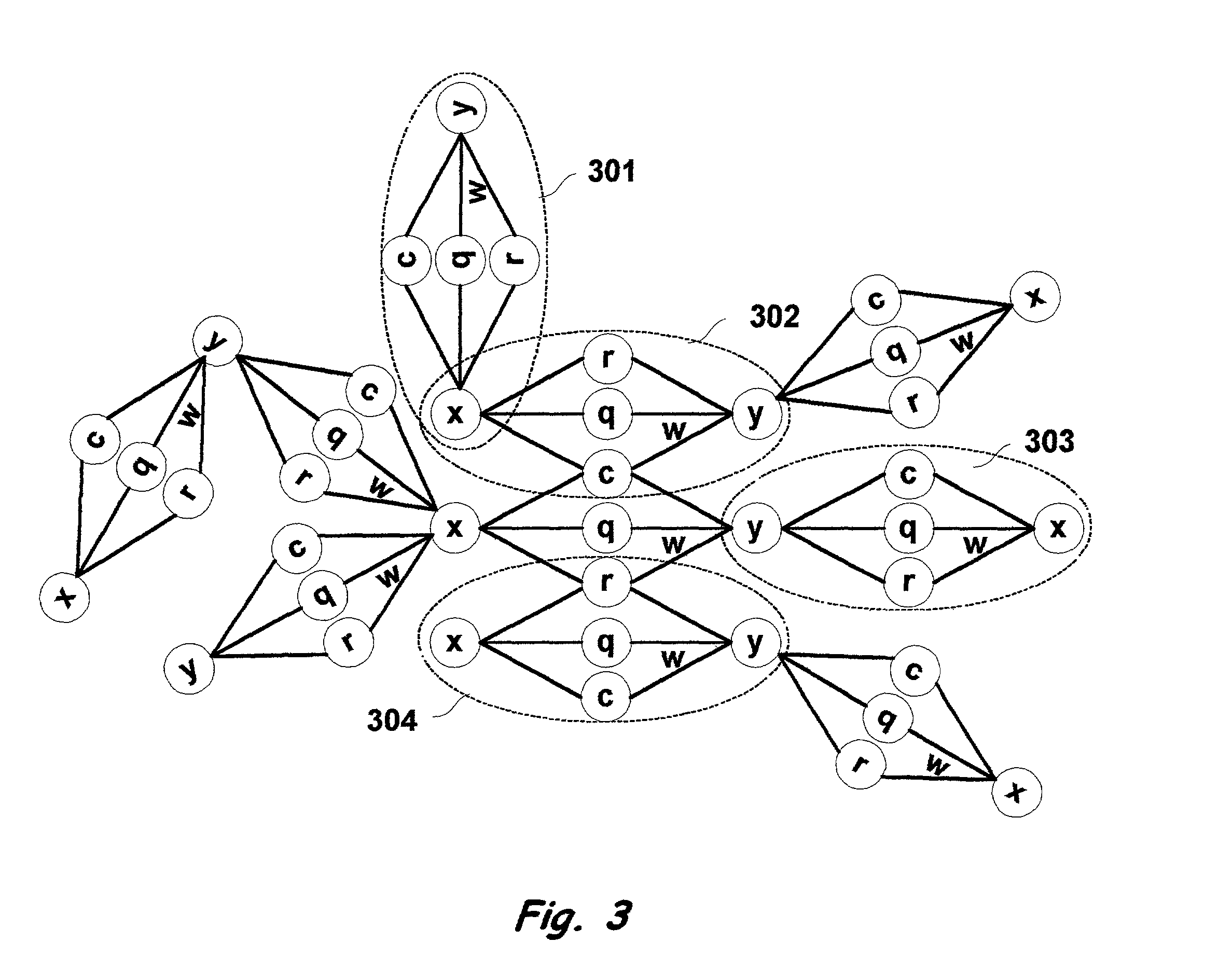
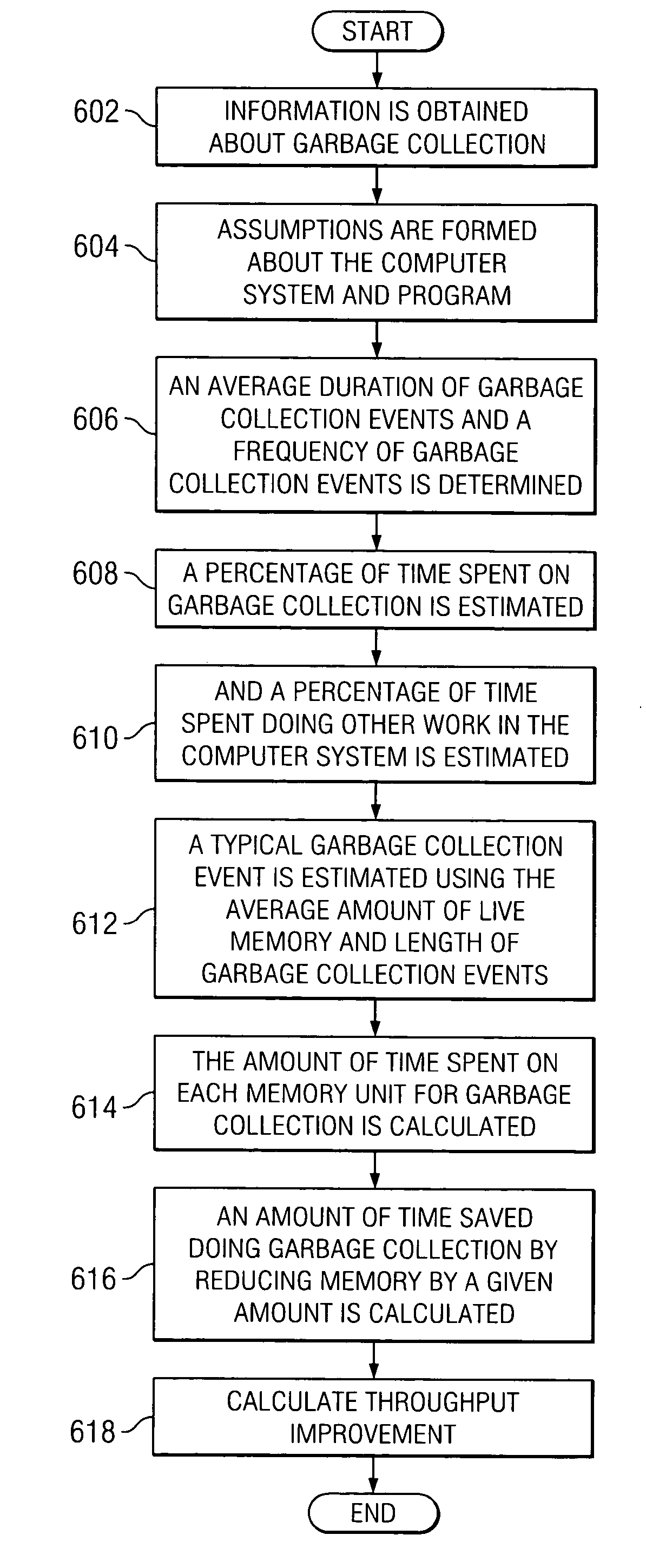
Method for determining a close approximate benefit of reducing memory footprint of a Java application
InactiveUS20050160416A1Improve performanceData processing applicationsSoftware engineeringMemory footprintParallel computing
Changes in performance in a Java program are deduced from information related to garbage collection events of the program. Assumptions are made about the system, the application and garbage collection, and changes in performance that will result from modifying the program are deduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
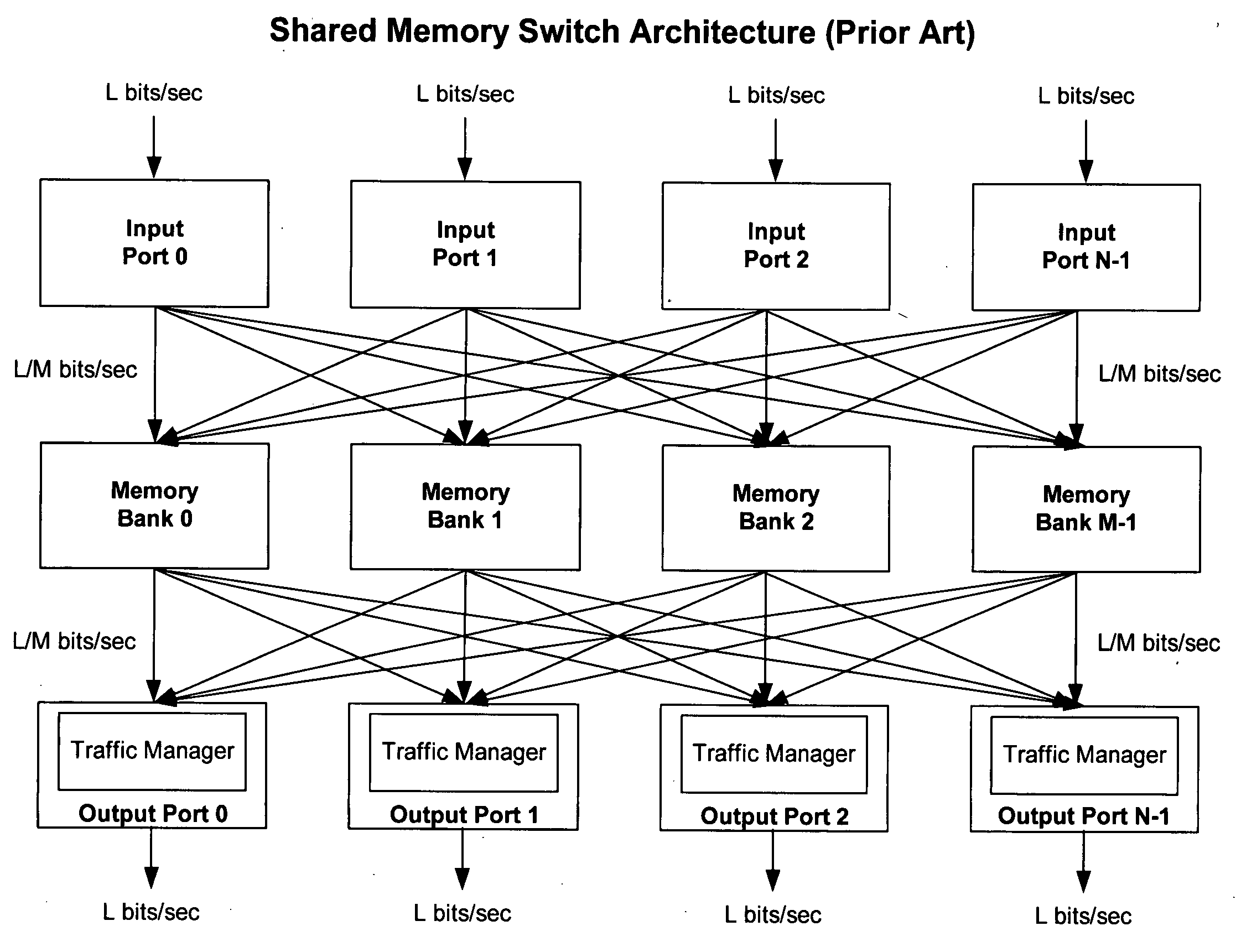
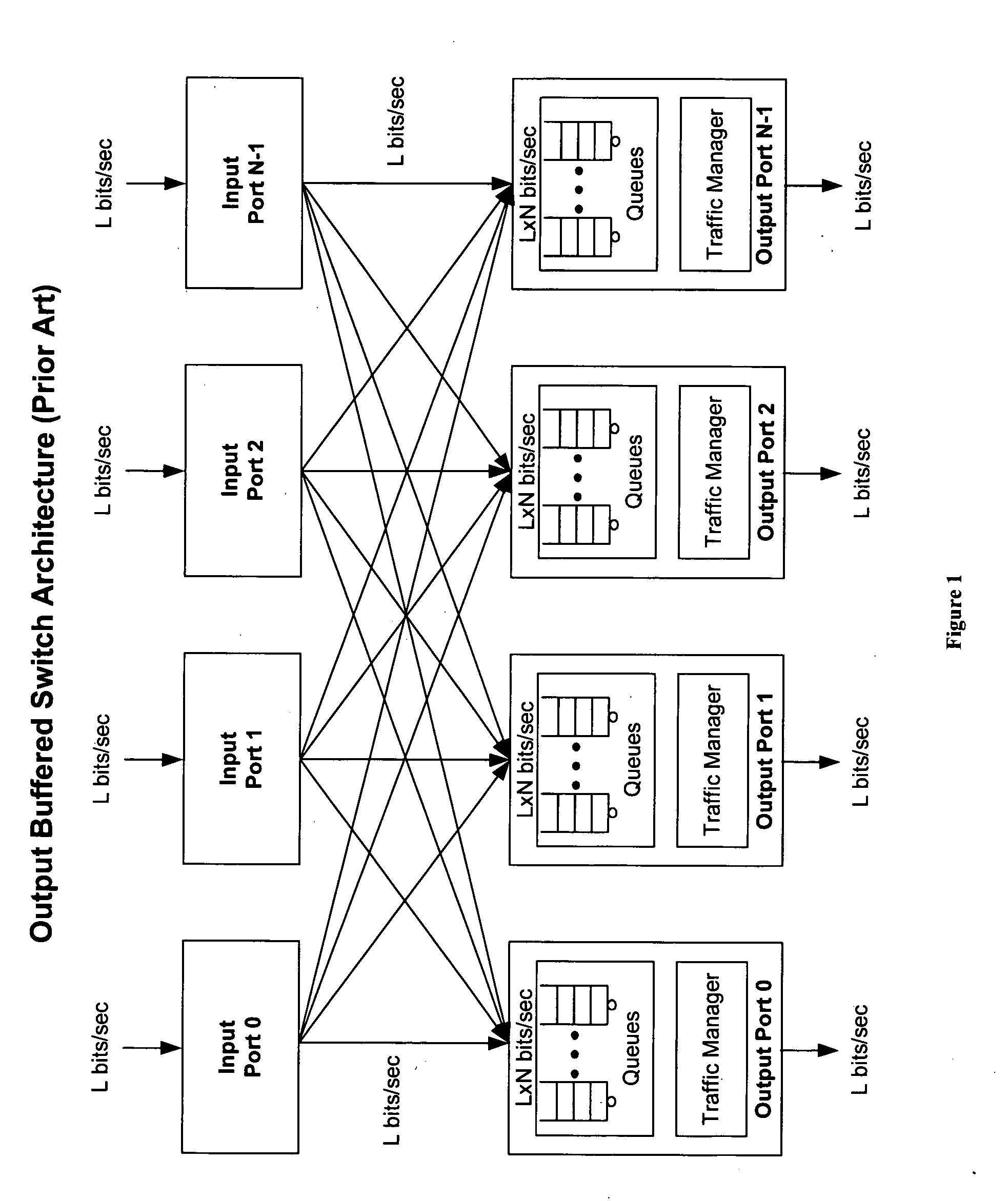
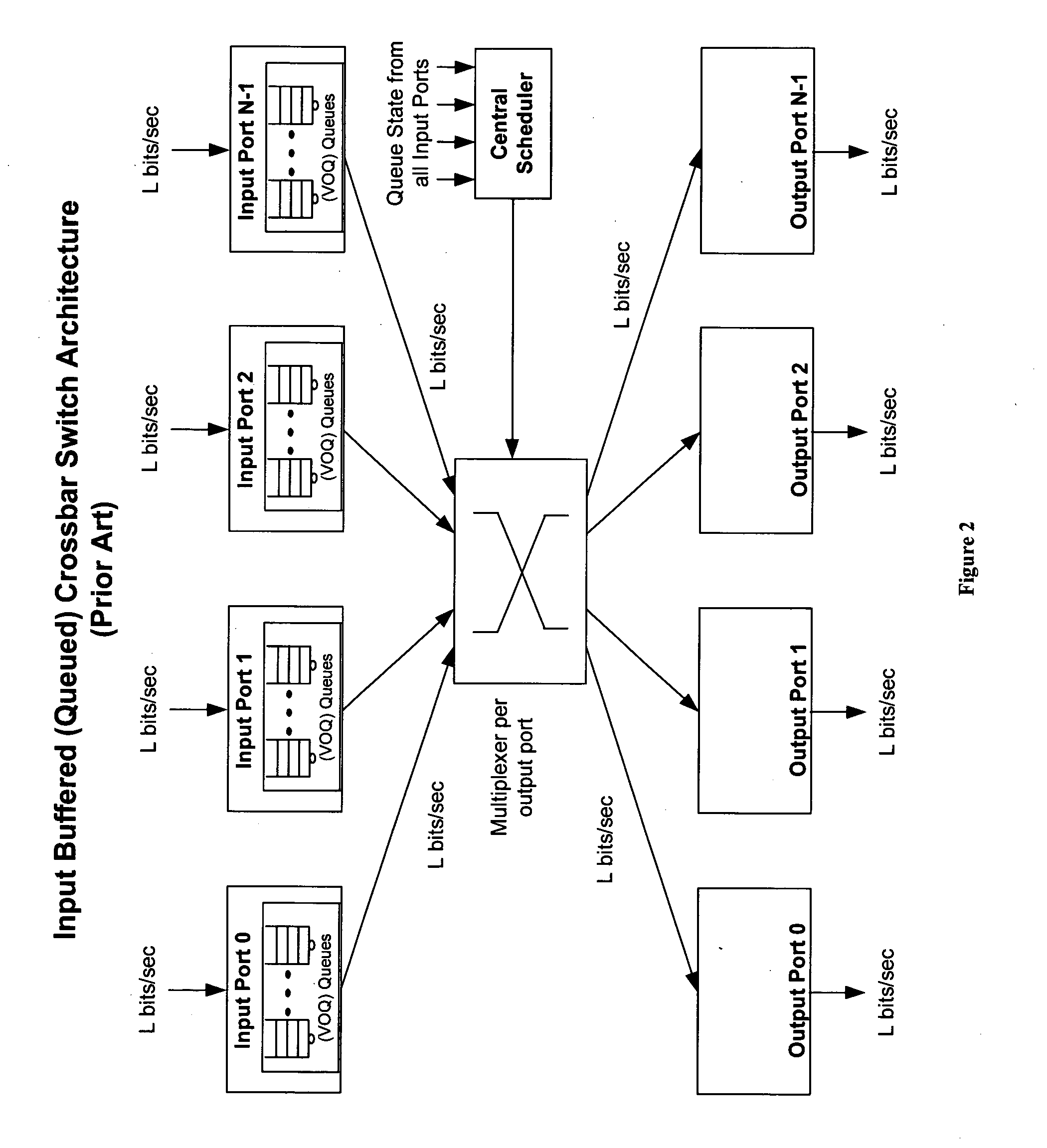
Method of and system for physically distributed, logically shared, and data slice-synchronized shared memory switching
An improved data networking technique and apparatus using a novel physically distributed but logically shared and data-sliced synchronized shared memory switching datapath architecture integrated with a novel distributed data control path architecture to provide ideal output-buffered switching of data in networking systems, such as routers and switches, to support the increasing port densities and line rates with maximized network utilization and with per flow bit-rate latency and jitter guarantees, all while maintaining optimal throughput and quality of services under all data traffic scenarios, and with features of scalability in terms of number of data queues, ports and line rates, particularly for requirements ranging from network edge routers to the core of the network, thereby to eliminate both the need for the complication of centralized control for gathering system-wide information and for processing the same for egress traffic management functions and the need for a centralized scheduler, and eliminating also the need for buffering other than in the actual shared memory itself,—all with complete non-blocking data switching between ingress and egress ports, under all circumstances and scenarios.
Owner:QOS LOGIX
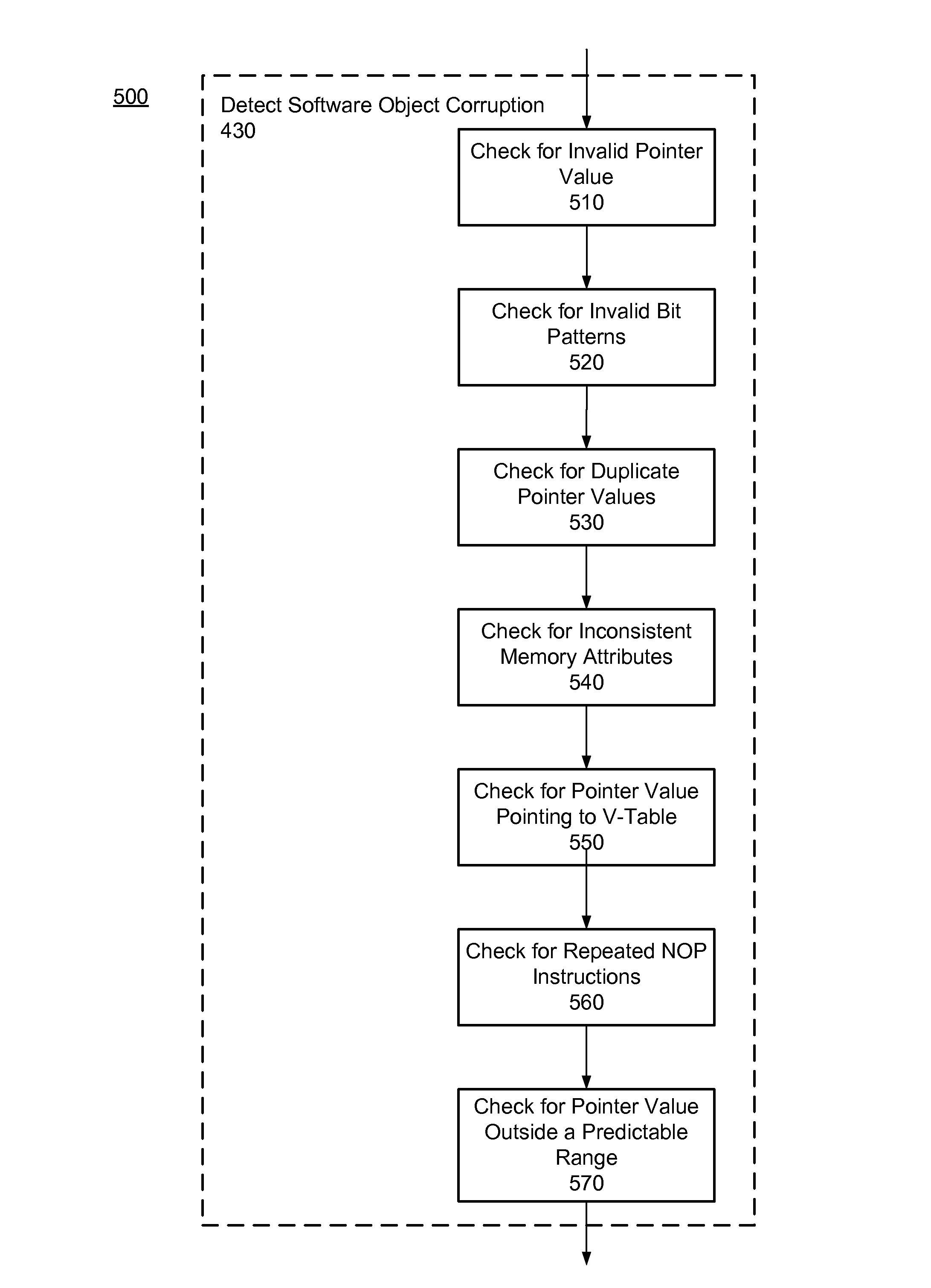
Software object corruption detection
ActiveUS8307435B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionSoftware engineeringApplication software
The execution of a software application is diverted to detect software object corruption in the software application. Software objects used by the software application are identified and their pointers are inspected. One or more tests are applied to pointers pointing to the virtual method tables of the software objects, addresses (or pointers) in the virtual method tables, and memory attributes or content of the memory buffer identified by the addresses for inconsistencies that indicate corruption. A determination of whether the software objects are corrupted is made based on the outcome of the tests. If software object corruption is detected, proper corrective actions are applied to prevent malicious exploitation of the corruption.
Owner:CA TECH INC
In-line non volatile memory disk read cache and write buffer
ActiveUS20060248387A1Read/write performance of hardReduce the number of timesData buffering arrangementsError detection/correctionHard disc driveWrite buffer
A method and apparatus to improve the read / write performance of a hard drive is presented. A device having solid state, non-volatile (NV) memory is added in-line to the conventional hard drive and acts as a read / write cache. Data specified by the operating system is stored in the NV memory. The operating system provides a list of data to be put in NV memory. The data includes data to be pinned in NV memory and data that is dynamic. Pinned data persists in NV memory until the operating system commands it to be flushed. Dynamic data can be flushed by the hard drive controller. Data sent by an application for storage is temporarily stored in NV memory in data blocks until the operating system commits it to the disk.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for operating the internet protocol over a high-speed serial bus
InactiveUS6219697B1Efficiently and correctly determineDigital computer detailsTransmissionInternet protocol suiteTransport layer
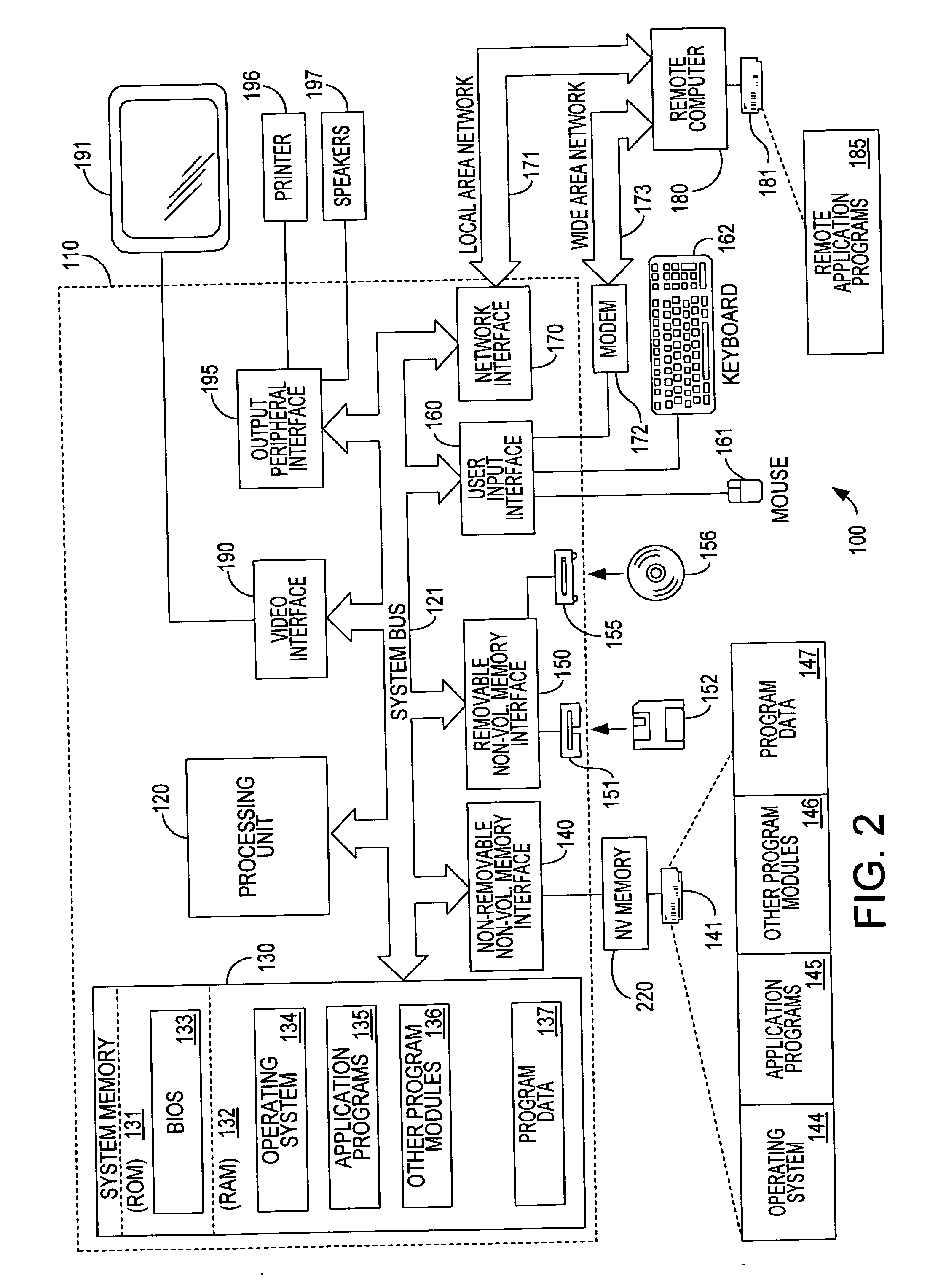
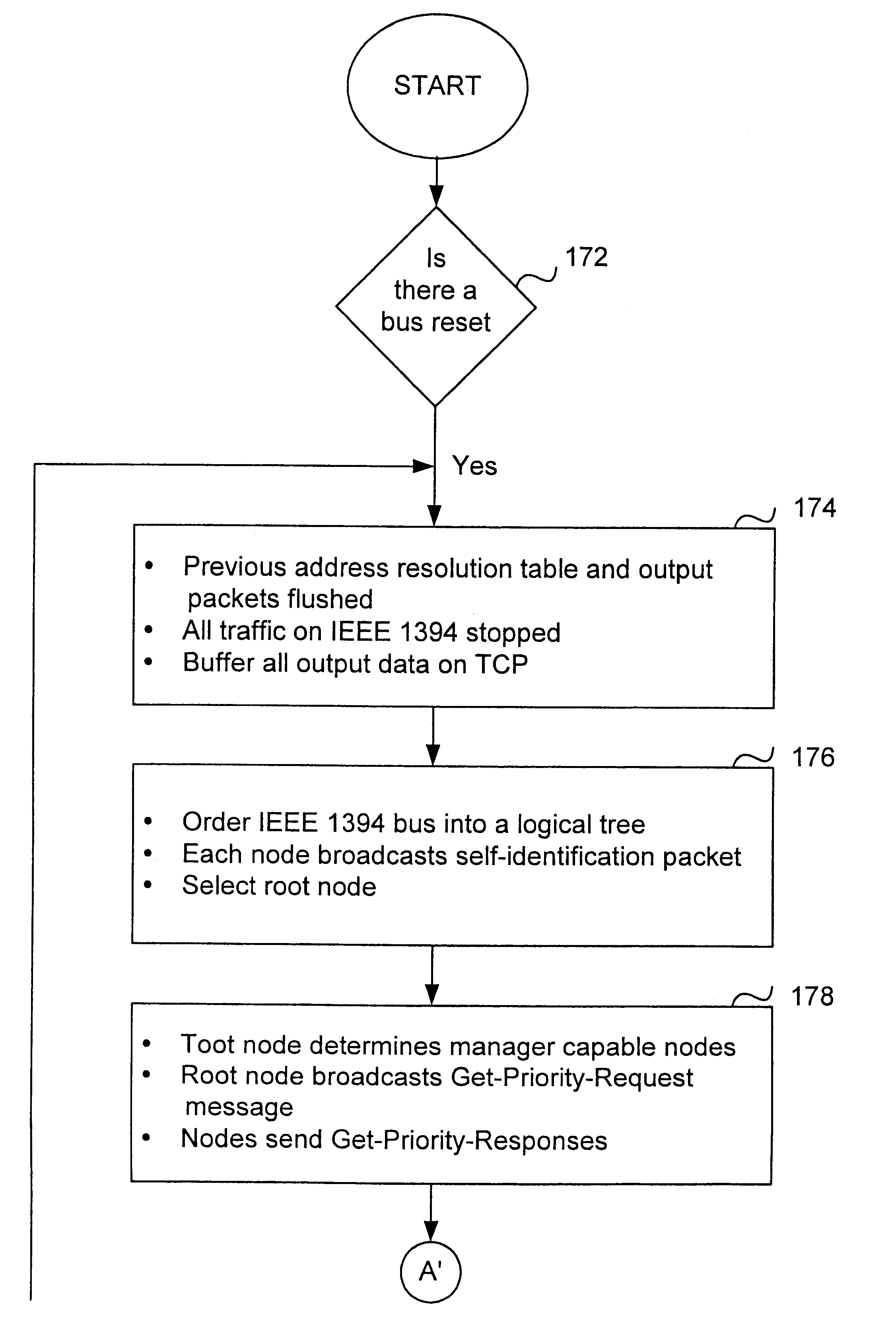
A method and apparatus of integrating the IEEE 1394 protocol with the IP protocol in which the IEEE 1394 high speed serial bus operates as the physical and link layer medium and the IP operates as the transport layer. There are differences in the protocols which require special consideration when integrating the two protocols. The IEEE 1394 configures packets with memory information and the IP operates under channel based I / O thereby necessitating a modification of the data transfer scheme to accomplish IP transfers over the IEEE 1394. Further, due to differences in packet headers, the IEEE 1394 packet header is modified to encapsulate IP packets. Moreover, in order to determine network packets quickly and efficiently, an identifier is inserted in each network packet header indicating that the packet should be processed by the network. Finally, in order to support the ability to insert or remove nodes on the network without a loss of data, the IP interface must not be disturbed. This is accomplished by maintaining constant IP addresses across bus resets which are caused by insertion or removal of nodes from the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
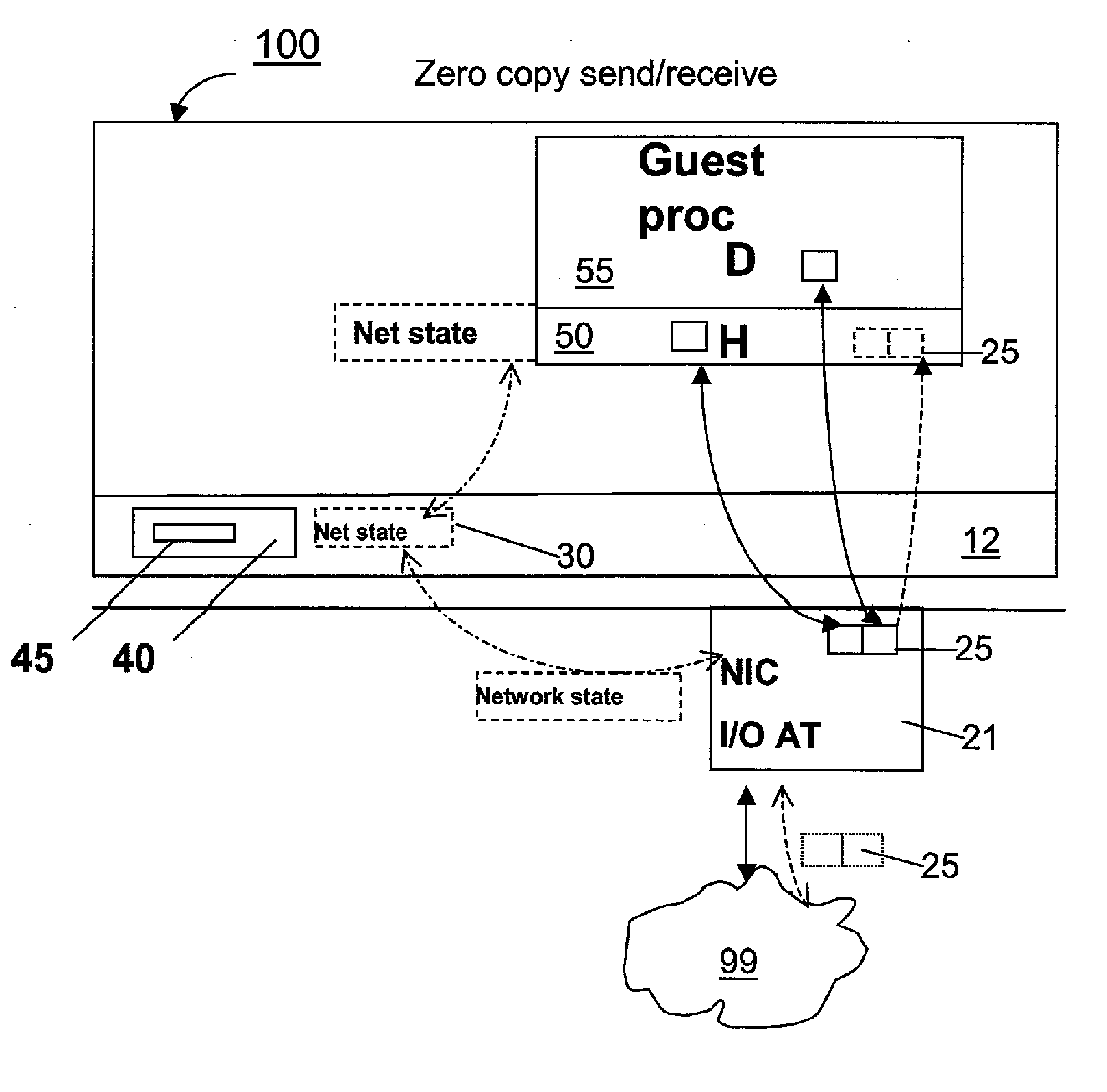
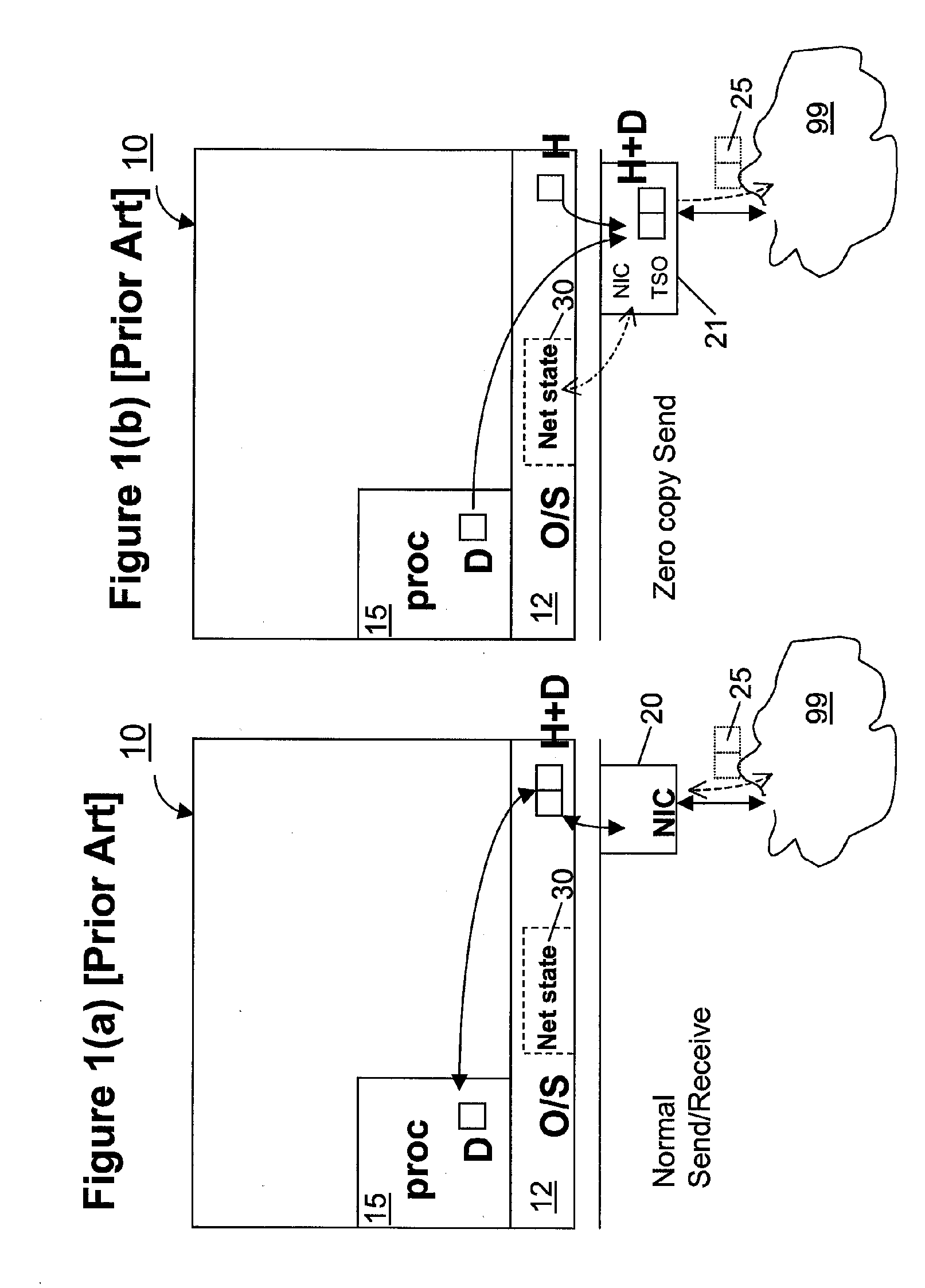
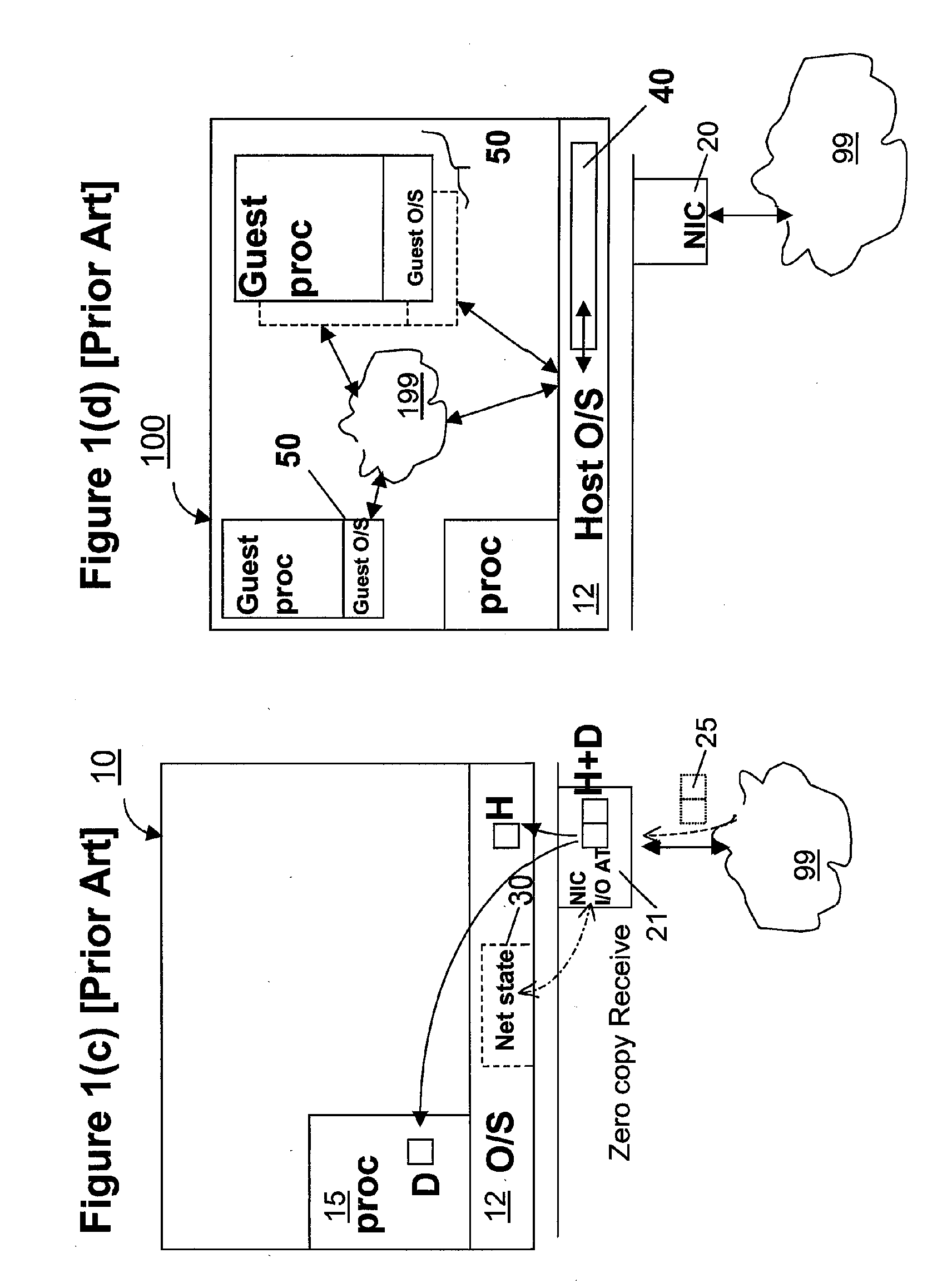
Zero-copy network I/O for virtual hosts
ActiveUS20070061492A1Eliminate the problemSolve excessive overheadDigital computer detailsTransmissionData packVirtualization
Techniques for virtualized computer system environments running one or more virtual machines that obviate the extra host operating system (O / S) copying steps required for sending and receiving packets of data over a network connection, thus eliminating major performance problems in virtualized environment. Such techniques include methods for emulating network I / O hardware device acceleration-assist technology providing zero-copy I / O sending and receiving optimizations. Implementation of these techniques require a host O / S to perform actions including, but not limited to: checking of the address translations (ensuring availability and data residency in physical memory), checking whether the destination of a network packet is local (to another virtual machine within the computing system), or across an external network; and, if local, checking whether either the sending destination VM, receiving VM process, or both, supports emulated hardware accelerated-assist on the same physical system. This optimization, in particular, provides a further optimization in that the packet data checksumming operations may be omitted when sending packets between virtual machines in the same physical system.
Owner:RED HAT
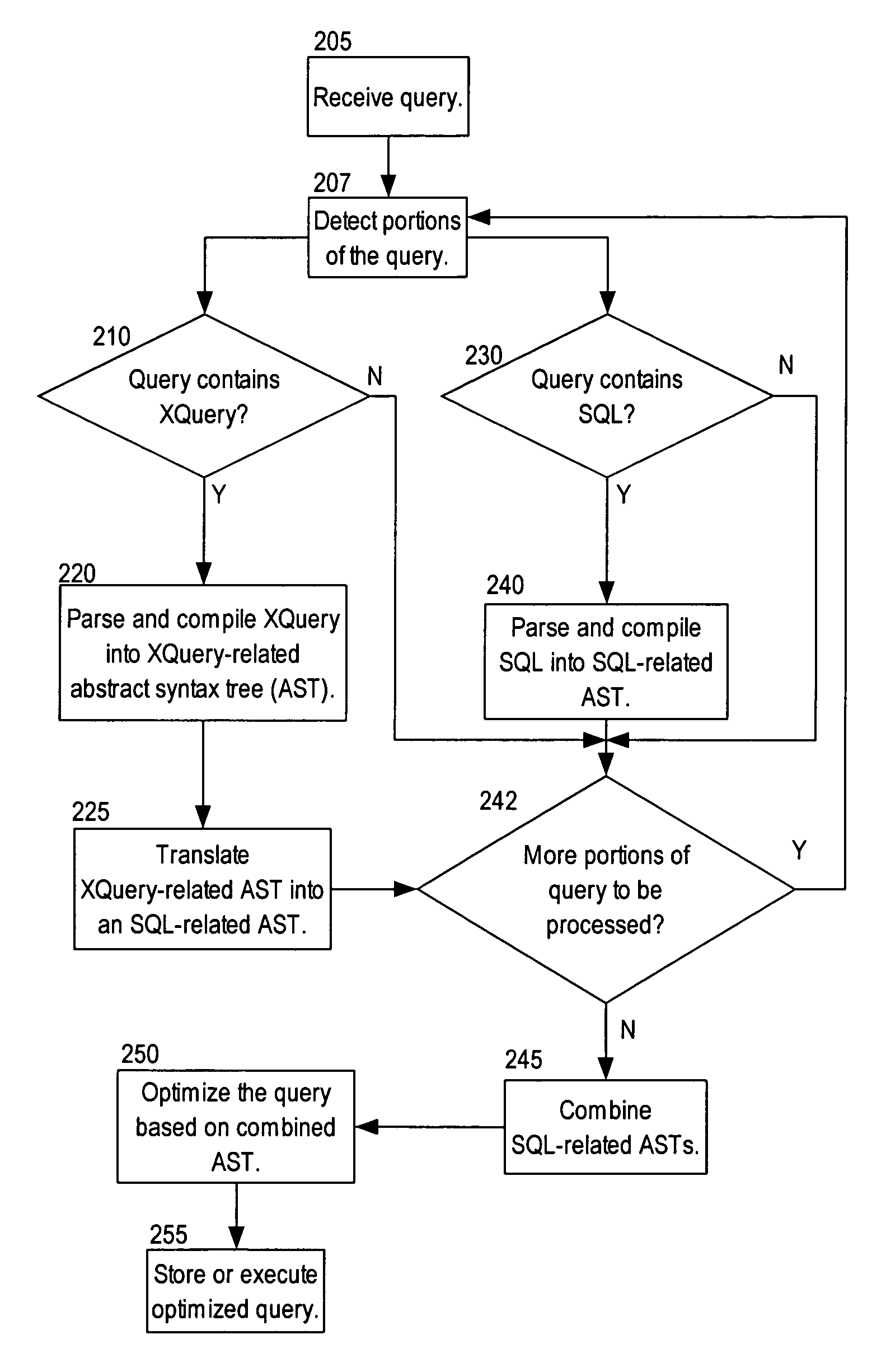
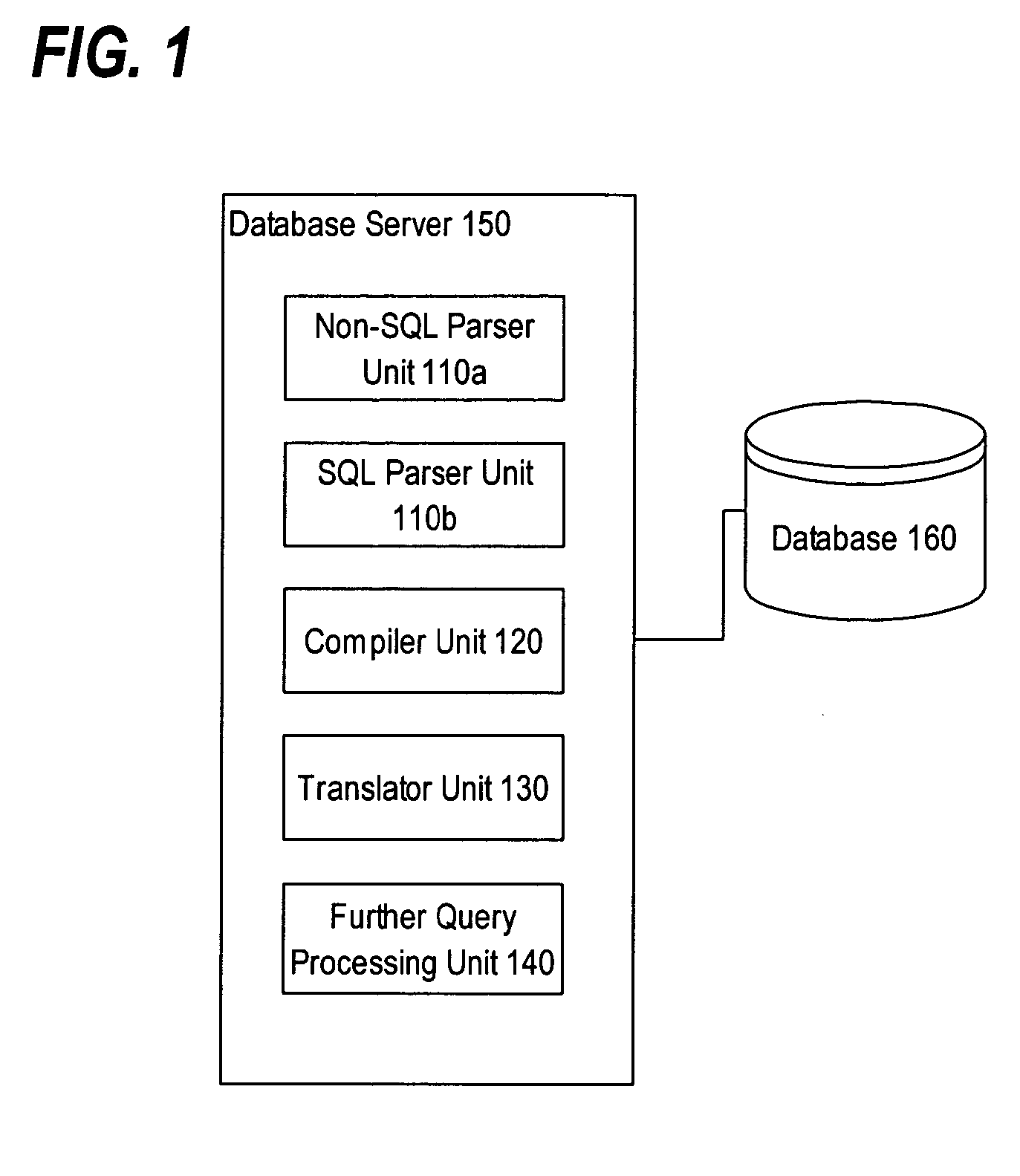
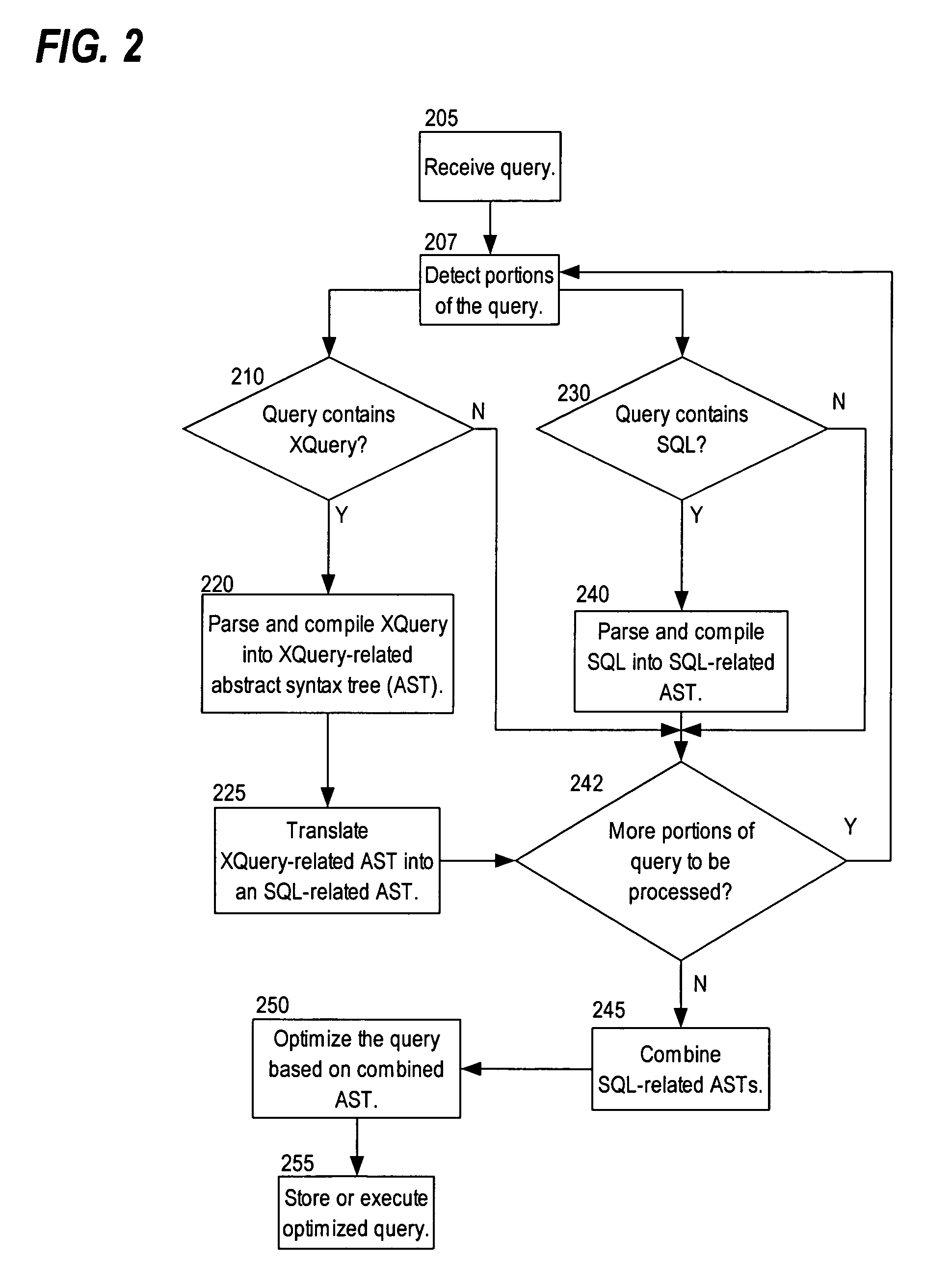
Efficient evaluation of queries using translation
ActiveUS20050289125A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTheoretical computer scienceTerm memory
Techniques are provided for processing a query including receiving the query, where the query specifies certain operations; determining that the query includes a first portion in a first query language and a second portion in a second query language; generating a first in-memory representation for the first portion; generating a second in-memory representation for the second portion; generating a third in-memory representation of the query based on the first in-memory representation and the second in-memory representation; and performing the certain operations based on the third in-memory representation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
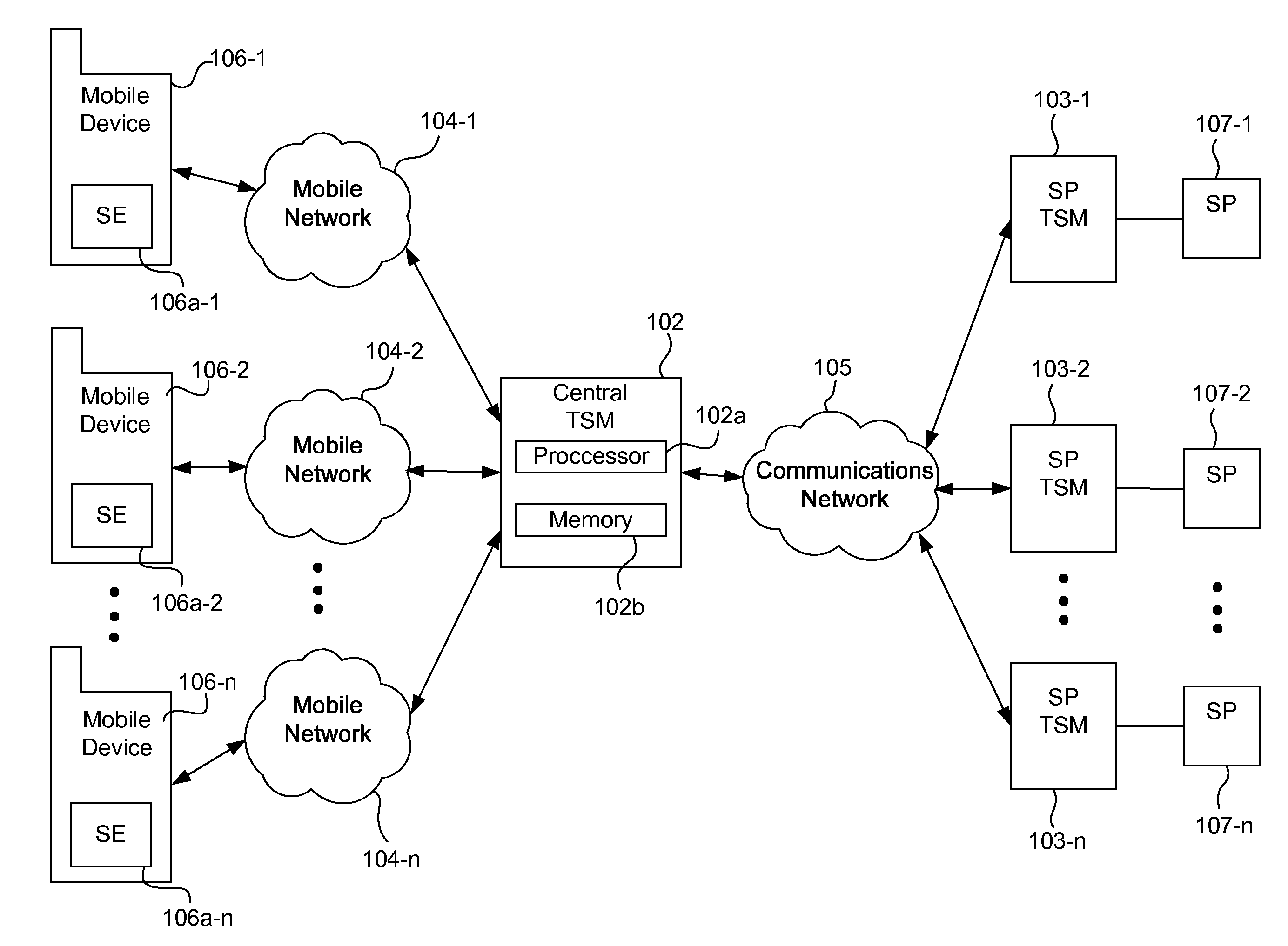
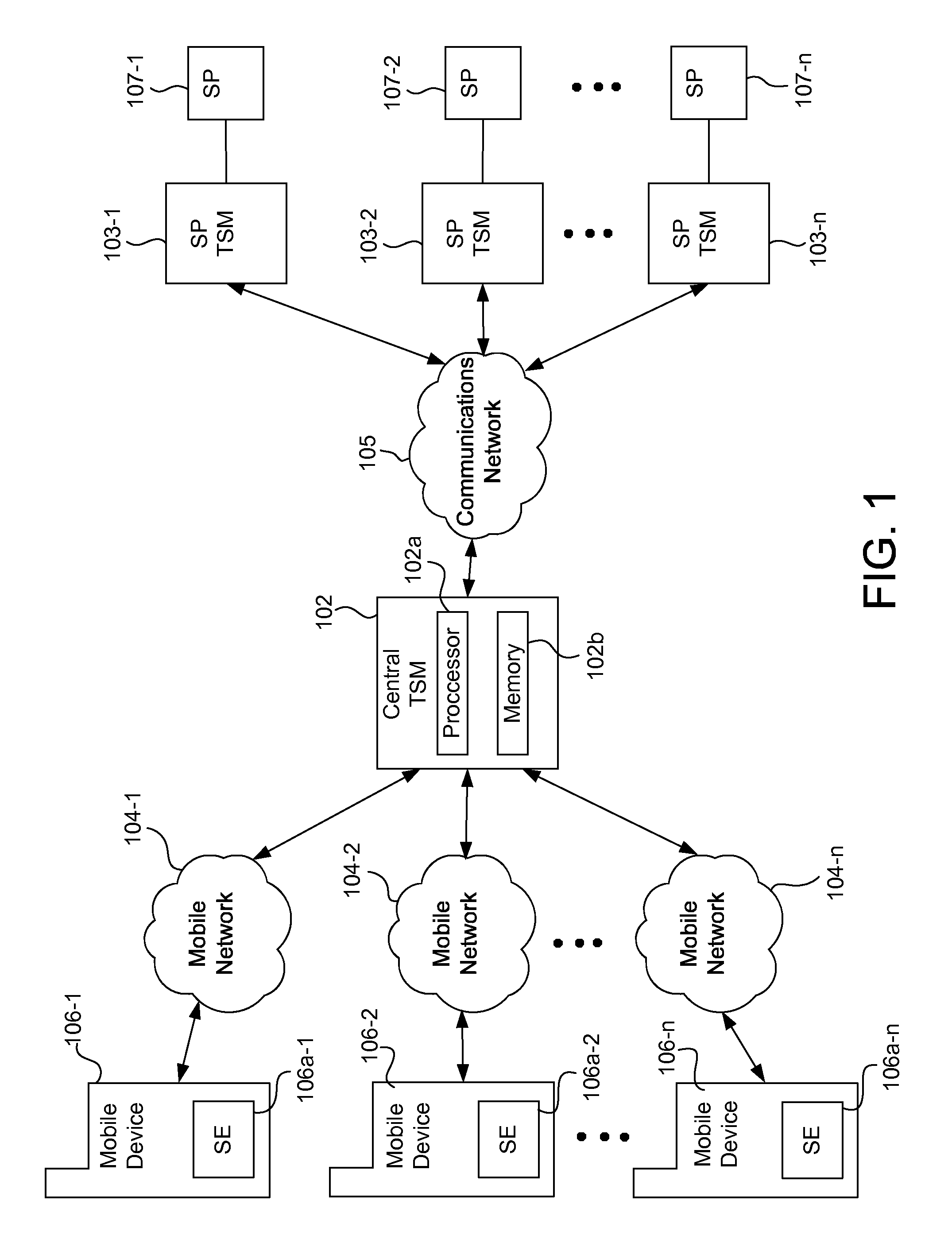
Systems, methods, and computer program products for interfacing multiple service provider trusted service managers and secure elements
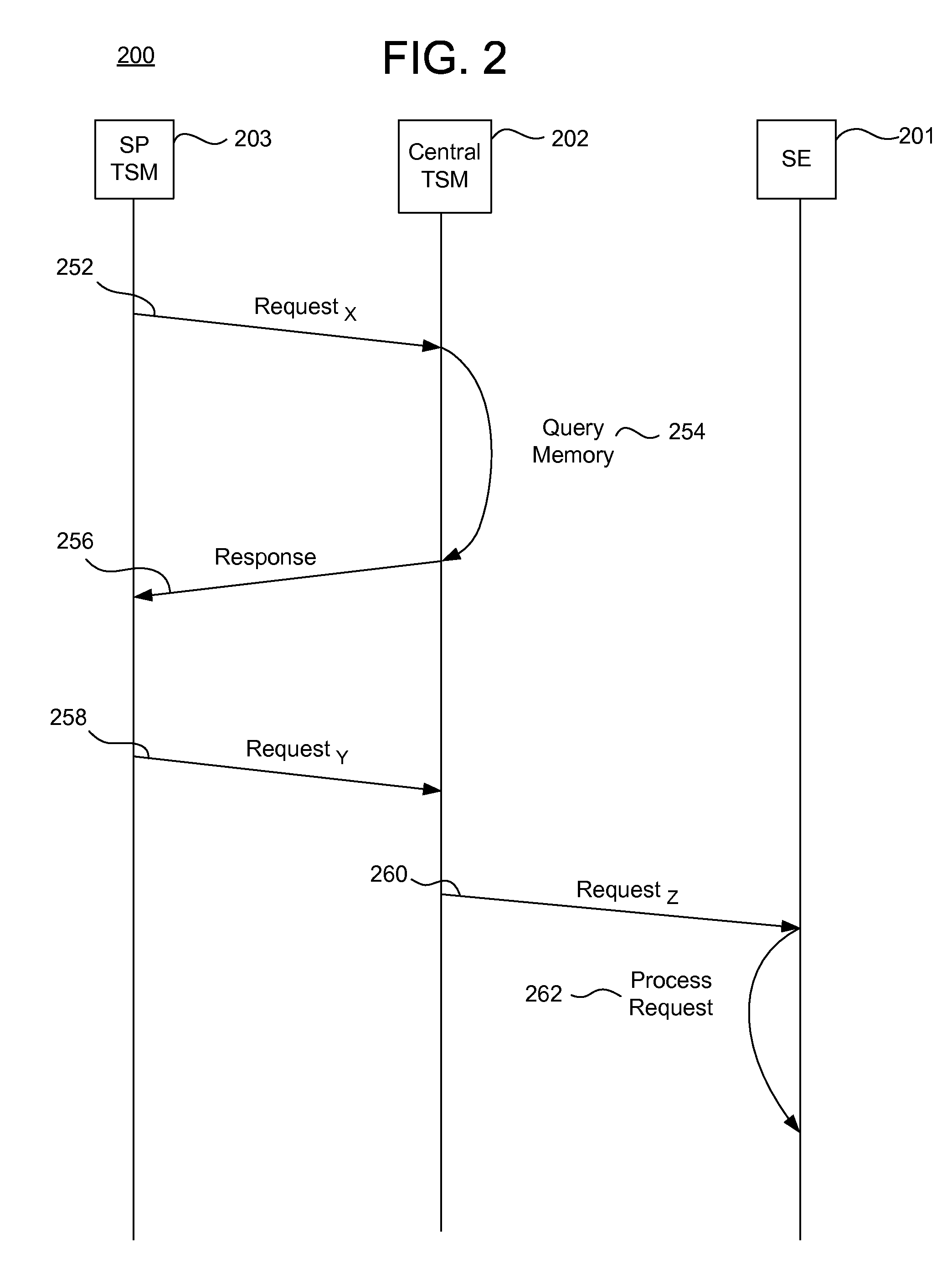
ActiveUS20130111599A1Easily and securely communicateKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer networkTerm memory
System, methods, and computer program products are provided for interfacing between one of a plurality of service provider (SP) trusted service managers (TSM) and one of a plurality of secure elements (SE). A first request including a mobile subscription identifier (MSI) is received from an SP TSM over a communications network. At least one memory is queried for SE data including an SE identifier corresponding to the MSI. The SE data is transmitted to the SP TSM over the communications network. A second request based on the SE data is received from the SP TSM over the communications network. A third request, based on the second request, is transmitted, over a mobile network, to an SE corresponding to the SE data. The mobile network is selected from multiple mobile networks, and is determined based on the SE data queried from the memory.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
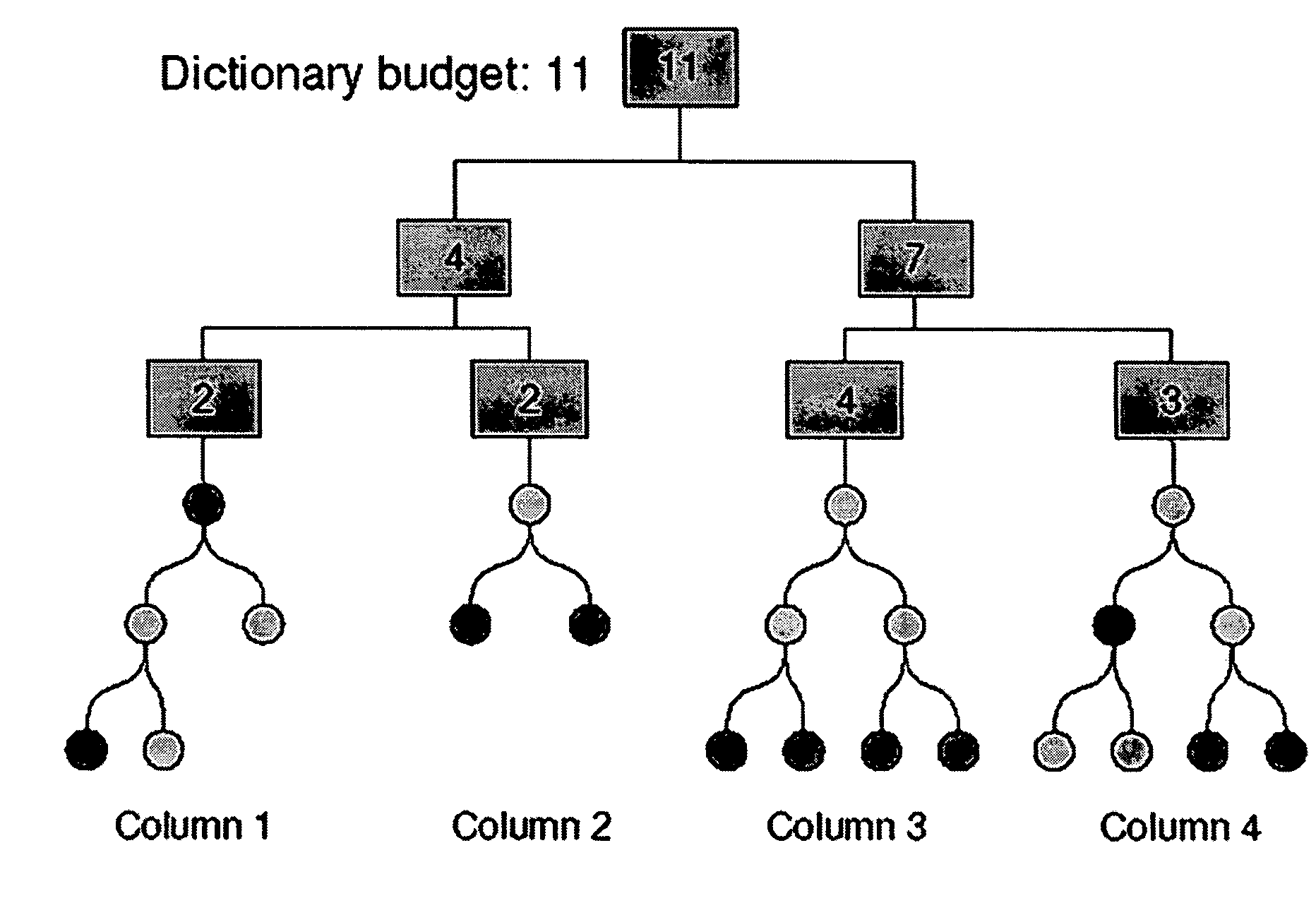
Method for compressed data with reduced dictionary sizes by coding value prefixes
The speed of dictionary based decompression is limited by the cost of accessing random values in the dictionary. If the size of the dictionary can be limited so it fits into cache, decompression is made to be CPU bound rather than memory bound. To achieve this, a value prefix coding scheme is presented, wherein value prefixes are stored in the dictionary to get good compression from small dictionaries. Also presented is an algorithm that determines the optimal entries for a value prefix dictionary. Once the dictionary fits in cache, decompression speed is often limited by the cost of mispredicted branches during Huffman code processing. A novel way is presented to quantize Huffman code lengths to allow code processing to be performed with few instructions, no branches, and very little extra memory. Also presented is an algorithm for code length quantization that produces the optimal assignment of Huffman codes and show that the adverse effect of quantization on the compression ratio is quite small.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
System and method for migrating processes on a network
InactiveUS6934755B1Prolong lifeMinimize the numberResource allocationDigital computer detailsApplication softwareNetwork service
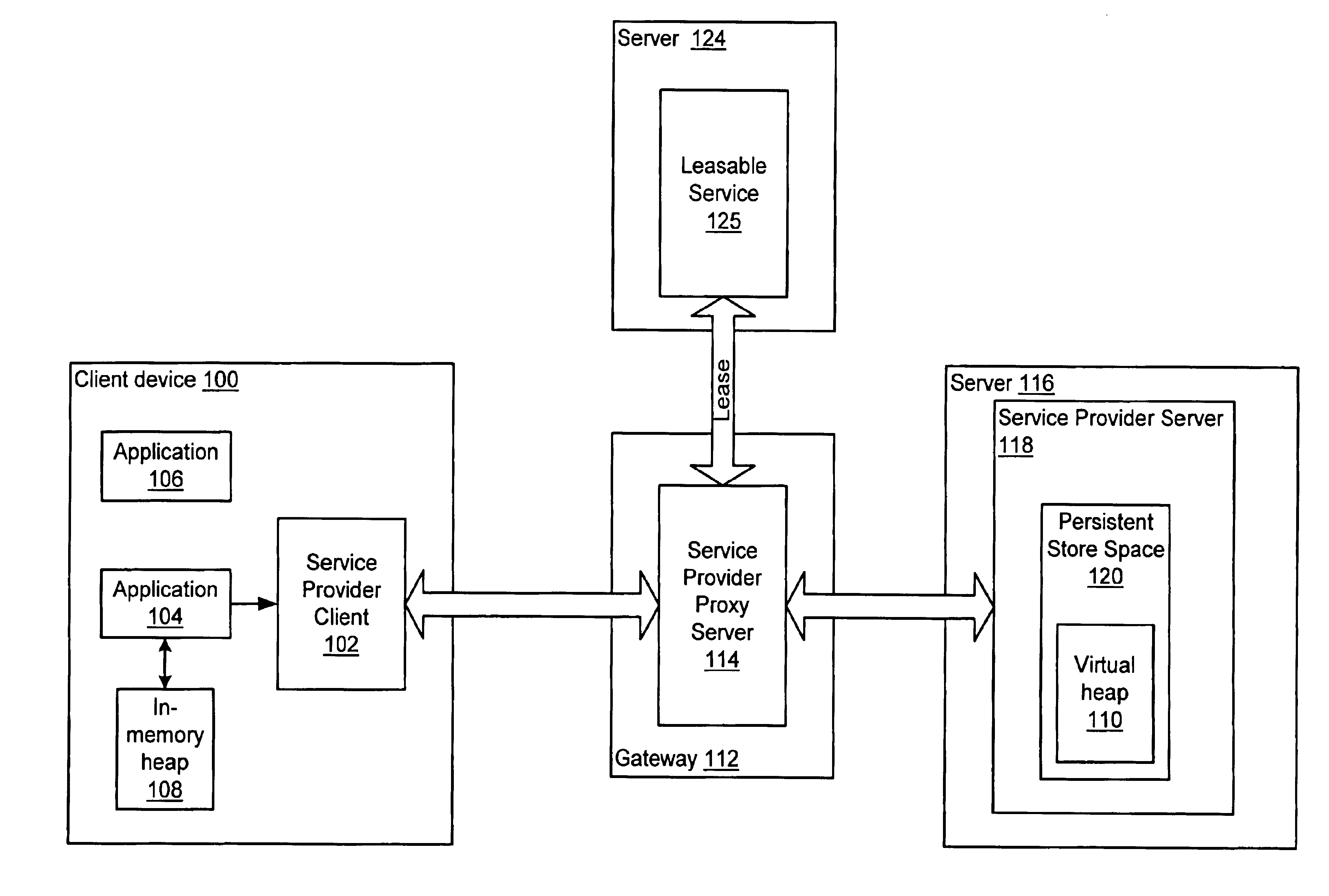
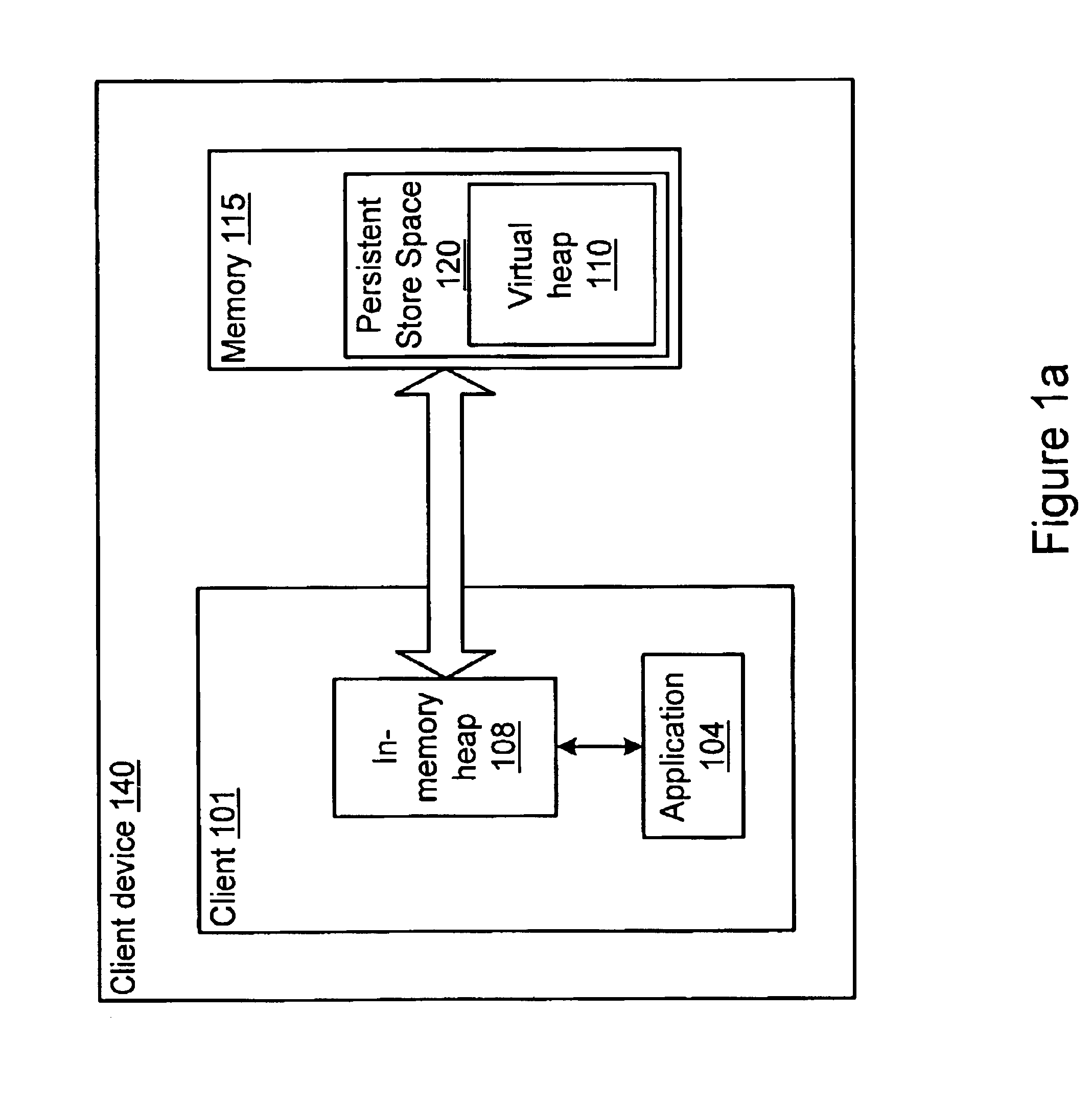
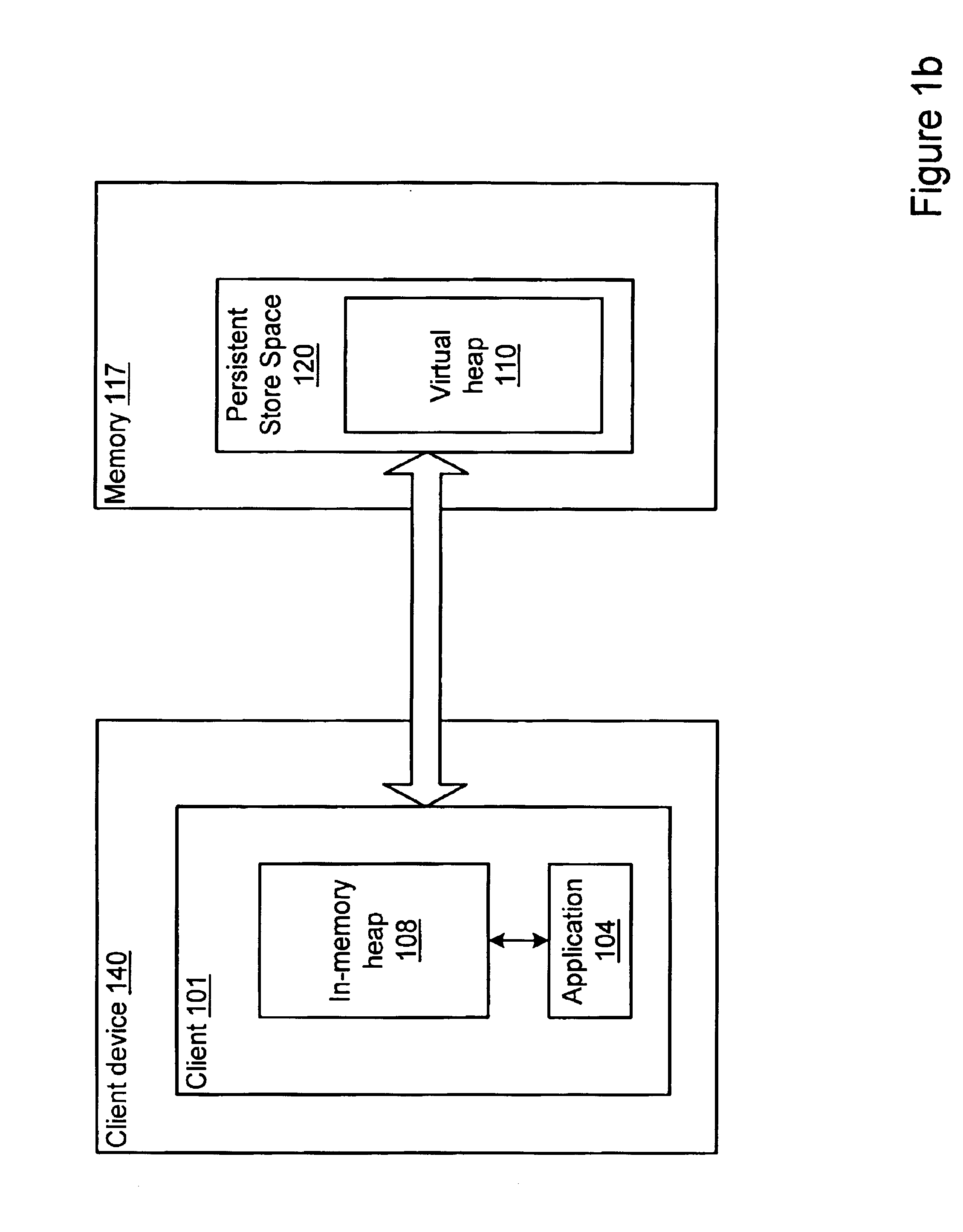
A method and system is provided for migrating processes from one virtual machine to another on a network. To migrate the external state of a process, the process may use a network service connection system or a compact network service connection system for accessing resources external to the virtual machine. A process may be migratable separately from other processes. A process may have an in-memory heap used for the execution of the process, a virtual heap that may include the entire heap of the process including at least a portion of the runtime environment, and a persistent heap where the virtual heap may be checkpointed. In one embodiment, the virtual heap may serve as the persistent heap. In another embodiment, the virtual heap may be checkpointed to a separate, distinct persistent heap. The combination of the in-memory heap, the virtual heap, and the persistent store may be referred to as a virtual persistent heap. One embodiment of a method for migrating an application may include checkpointing the application to a persistent heap. Current leases to local and / or remote resources may be expired. The persistent state of the process may be packaged in the persistent heap and sent to the node where the process is to migrate. A transaction mechanism may be used, where the process's persistent state is copied and committed as having migrated on both the sending and receiving nodes. The state of the process may then be reconstituted into a new virtual persistent heap on the node where the application migrated. Leases to local and / or remote resources for the process may be re-established. The process may then resume execution on the node where it migrated. In one embodiment, a versioning mechanism may be used whereby nodes where a process once lived may cache a previous state. In addition, a user interface (UI) may be provided to manage process checkpoints.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
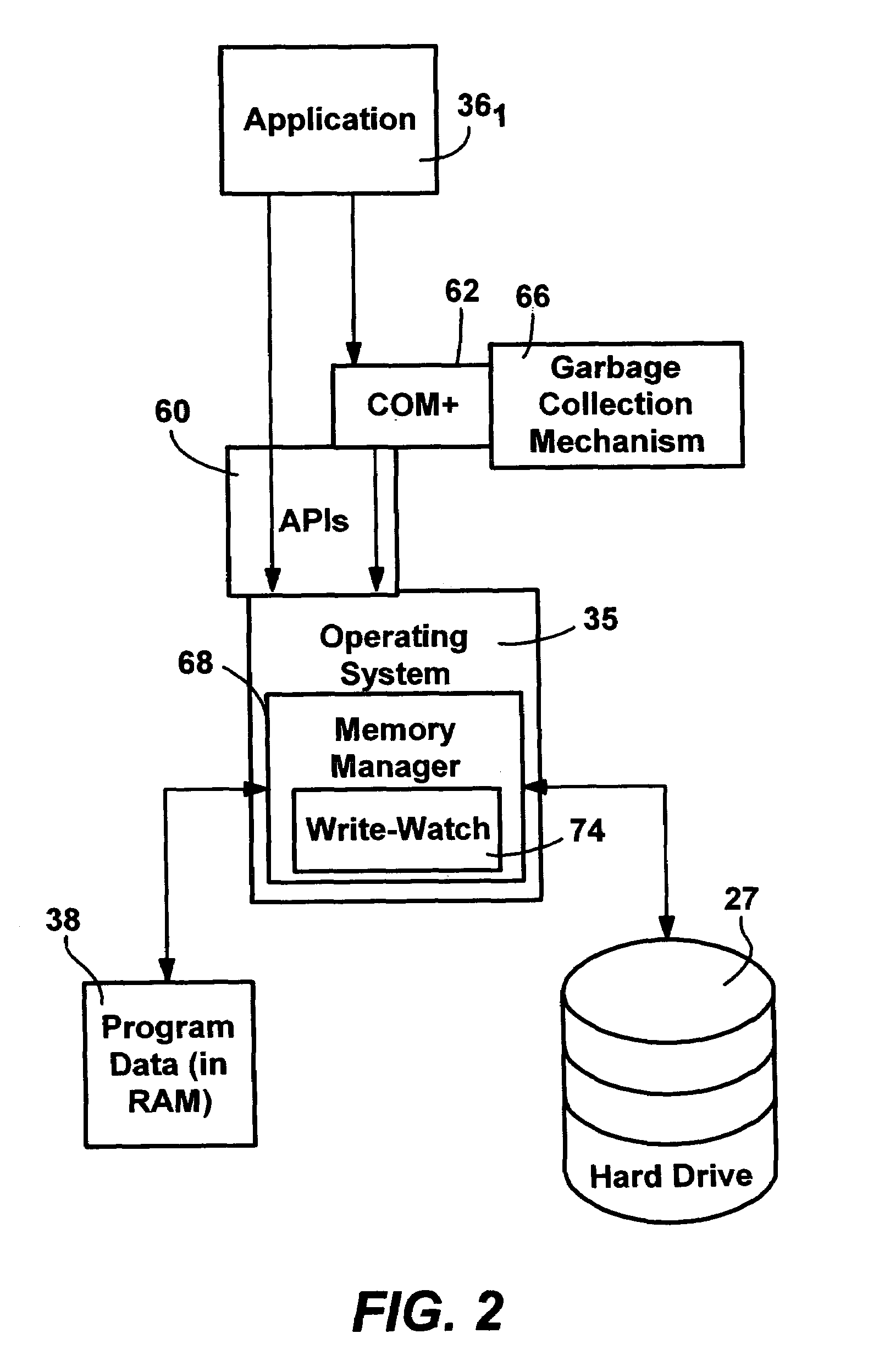
Efficient write-watch mechanism useful for garbage collection in a computer system
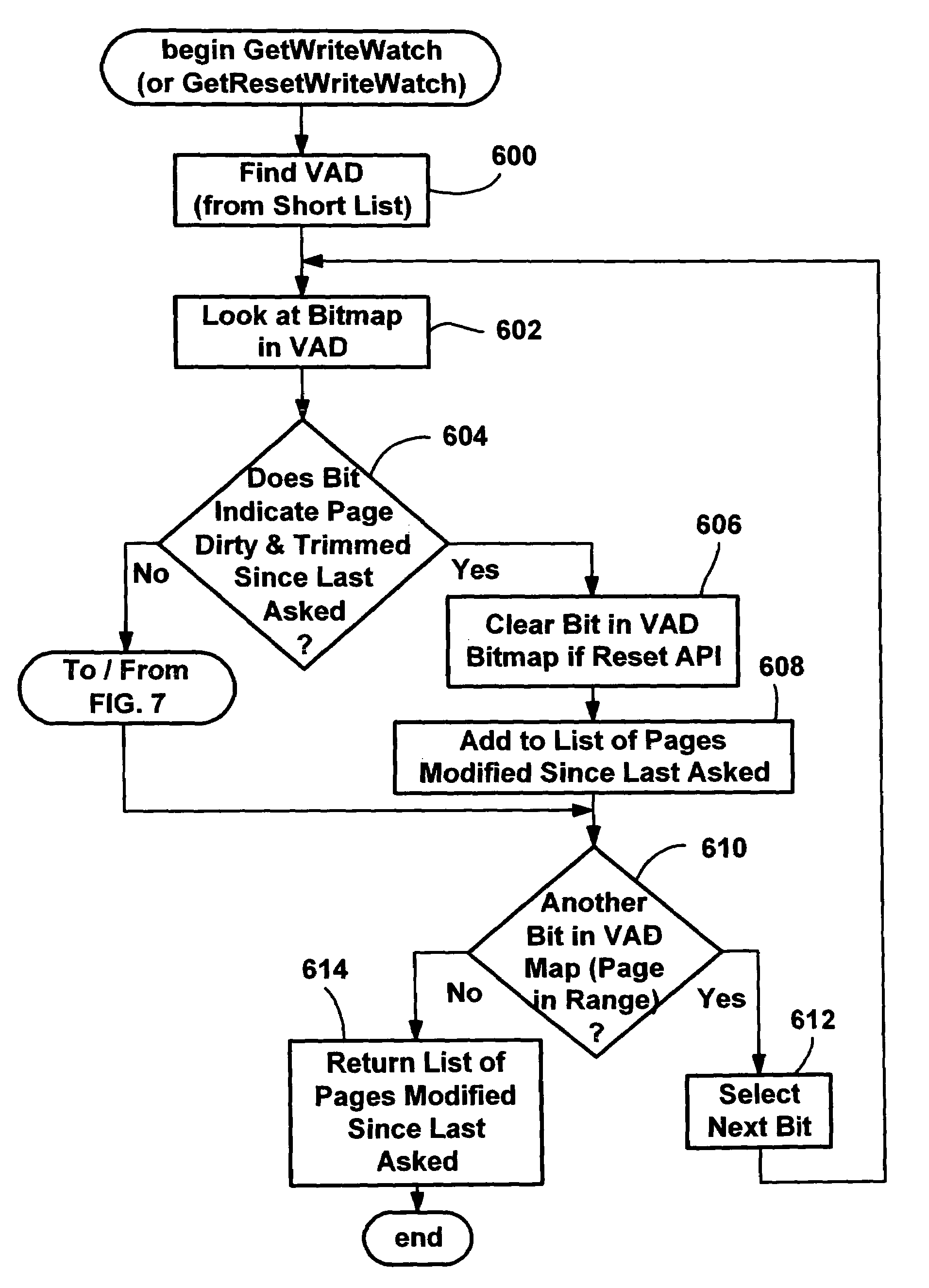
InactiveUS7065617B2Efficient write-watchReduce performanceData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputerized systemWaste collection
An efficient write-watch mechanism and process. A bitmap is associated with the virtual address descriptor (VAD) for a process, one bit for each virtual page address allocated to a process having write-watch enabled. As part of the write-watch mechanism, if a virtual address is trimmed to disk and that virtual address page is marked as modified, then the corresponding bit in the VAD is set for that virtual address page. In response to an API call (e.g., from a garbage collection mechanism) seeking to know which virtual addresses in a process have been modified since last checked, the memory manager walks the bitmap in the relevant VAD for the specified virtual address range for the requested process. If a bit is set, then the page corresponding to that bit is known to have been modified since last asked. If specified by the API, the bit is cleared in the VAD bitmap so that it will reflect the state since this time of asking. If the bit is not set, to determine if the page was modified, the page table entry (PTE) is checked for that page, and if the PTE indicates the page was modified, the page is known to be modified, otherwise that page is known to be unmodified since the last call. One enhancement uses page directory tables to locate a series of trimmed pages, sometimes avoiding the need to access the PTE.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
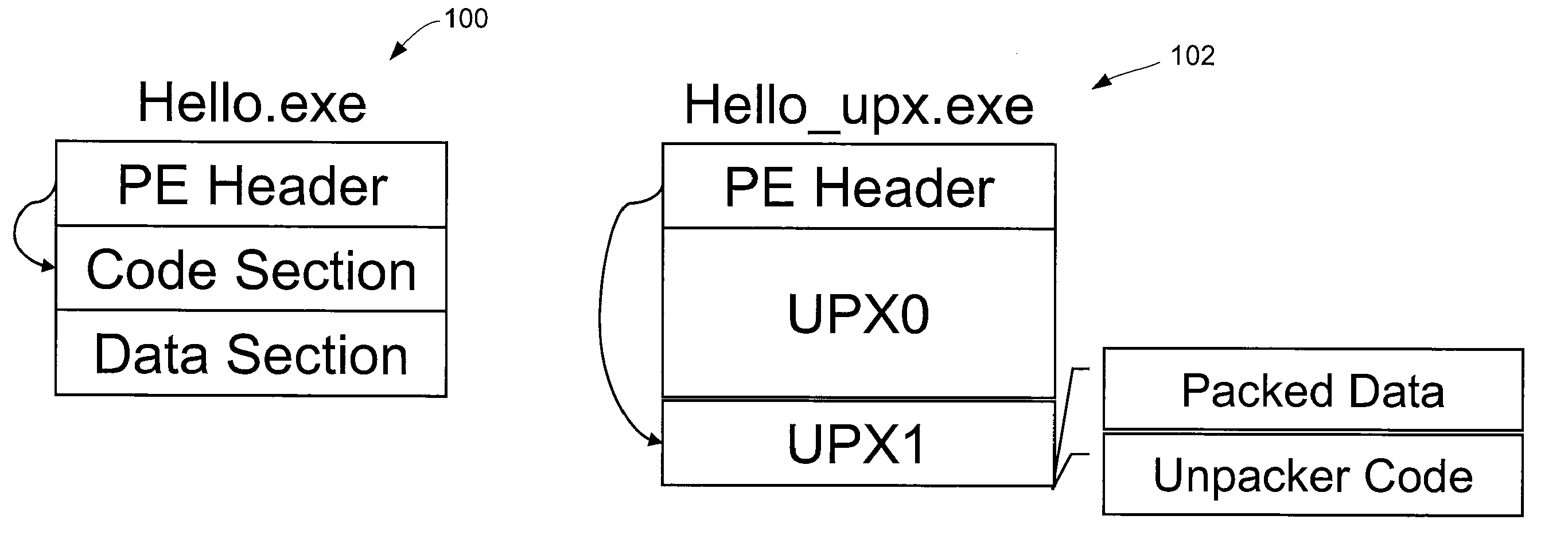
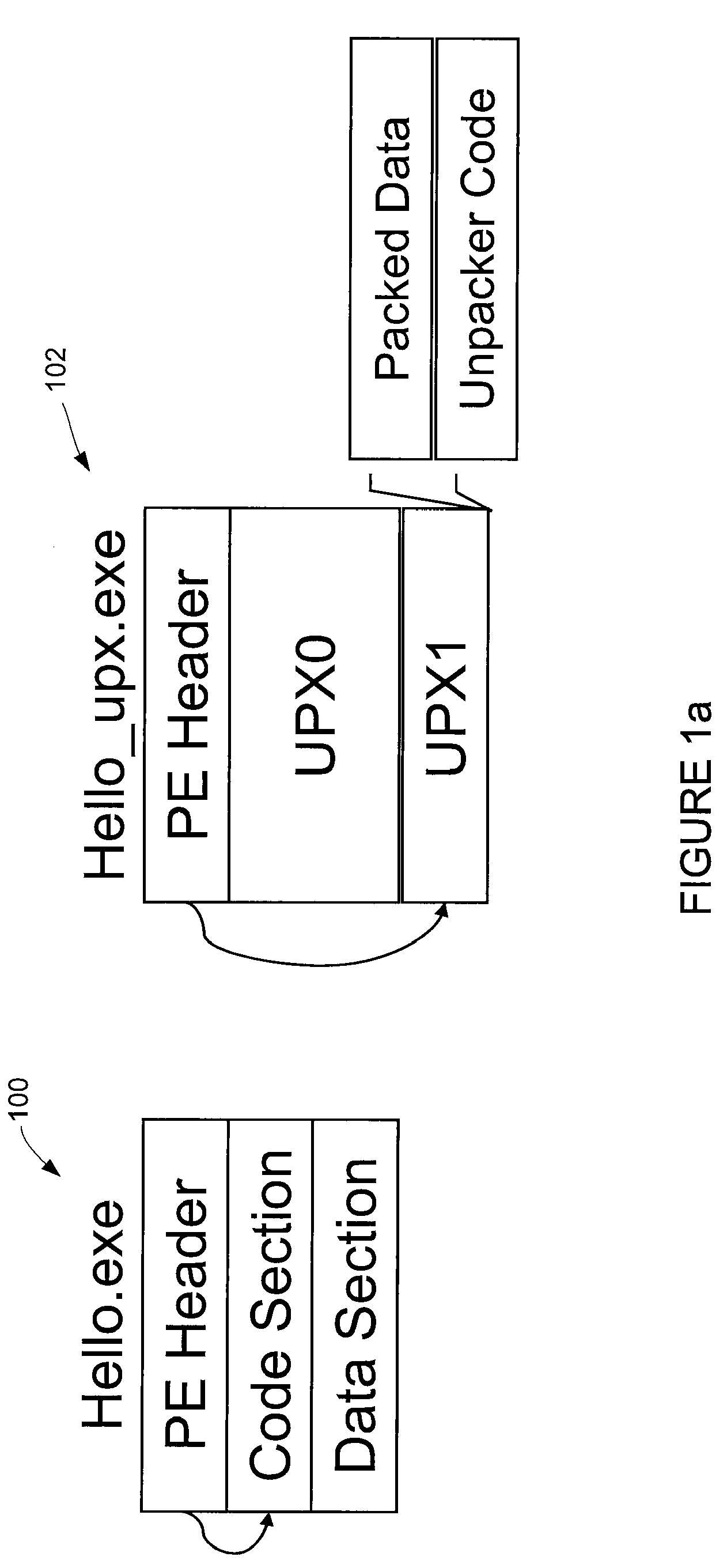
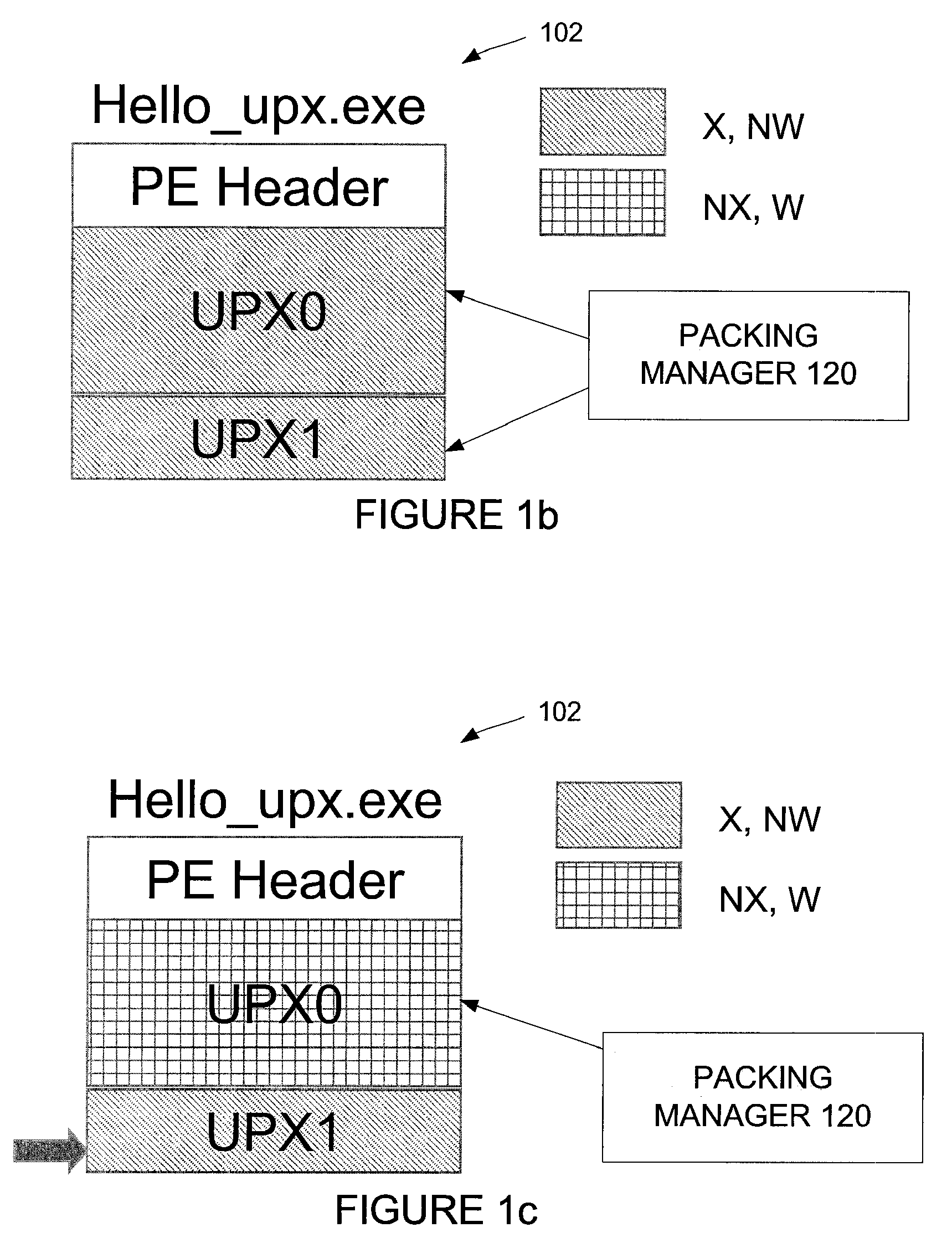
Automated unpacking of executables packed by multiple layers of arbitrary packers
The packing manager provides an automated method that allows existing AV scanning technology to be applied to detect known malware samples packed by one or more packers that are potentially proprietary. The packing manager tracks the memory areas to which an executable binary writes and executes, and so can unpack programs packed by multiple arbitrary packers without requiring reverse-engineering of the packers or any human intervention. By tracking page modification and execution of an executable binary at run time, the packing control module can detect the instant at which the program's control is first transferred to a page whose content is dynamically generated, so AV scanning can then be invoked. Thus, code cannot be executed under the packing control manager without being scanned by an AV scanner first.
Owner:NORTONLIFELOCK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com