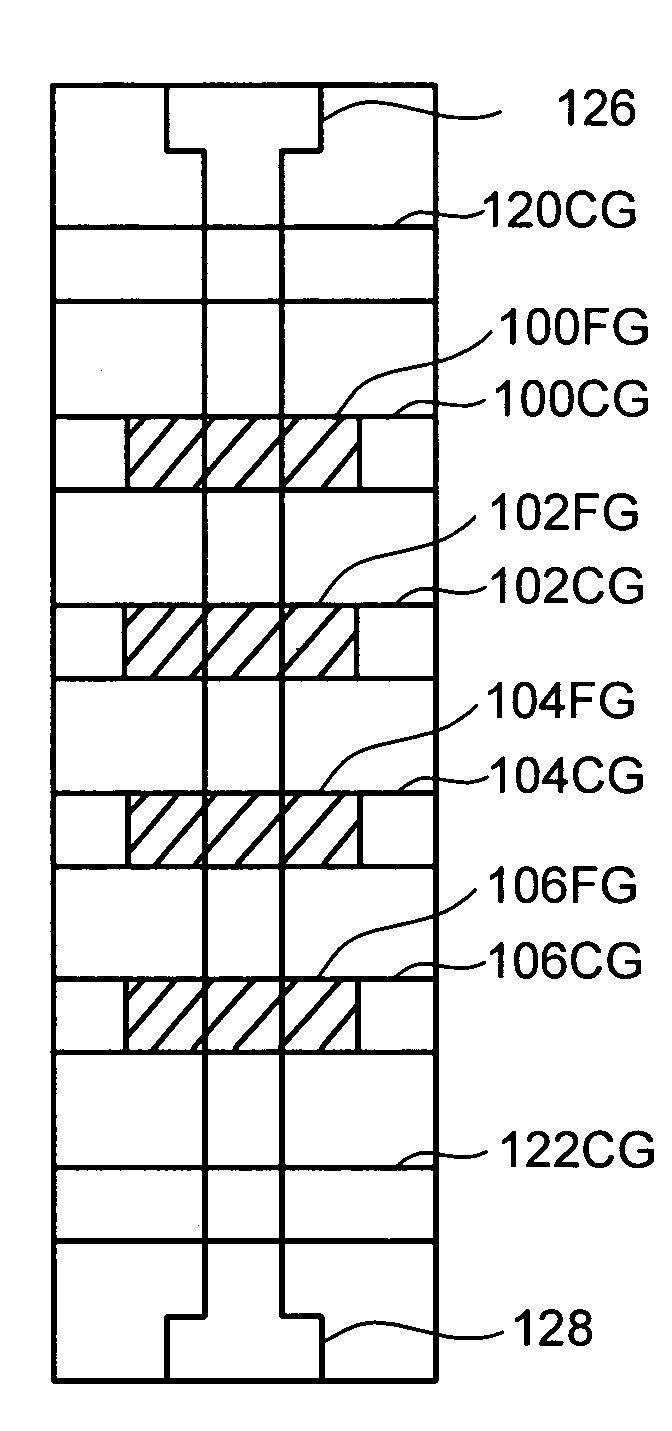
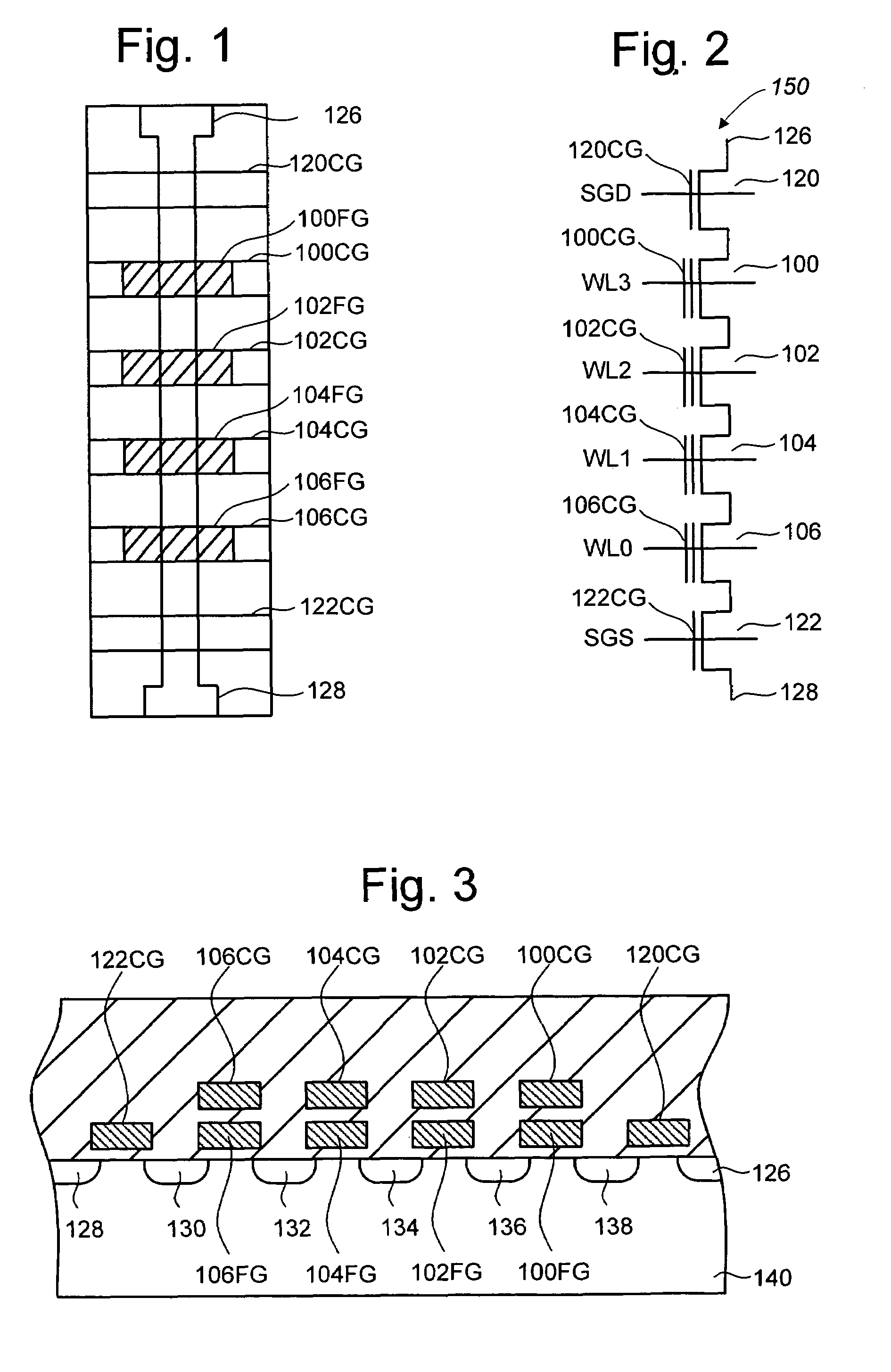
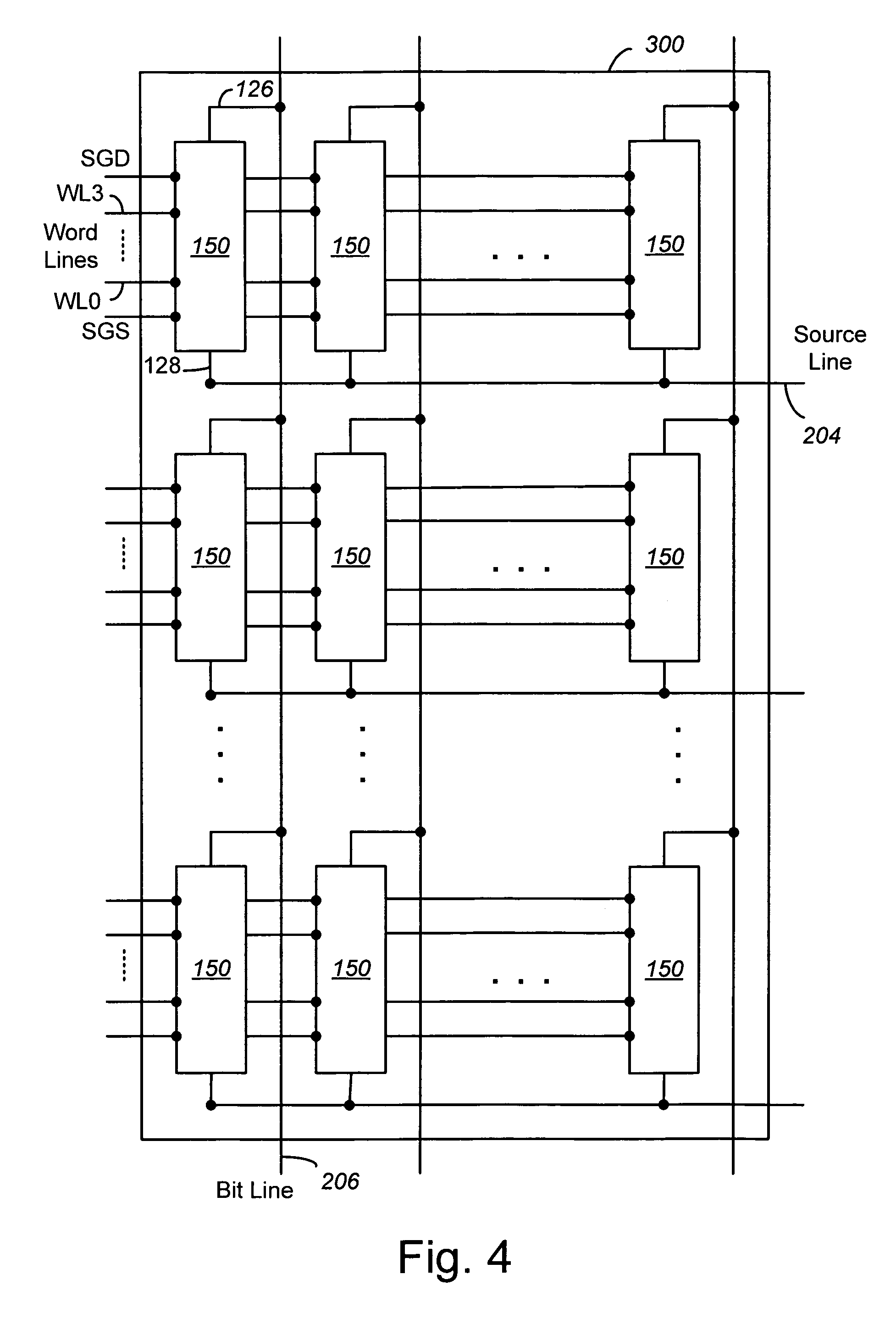
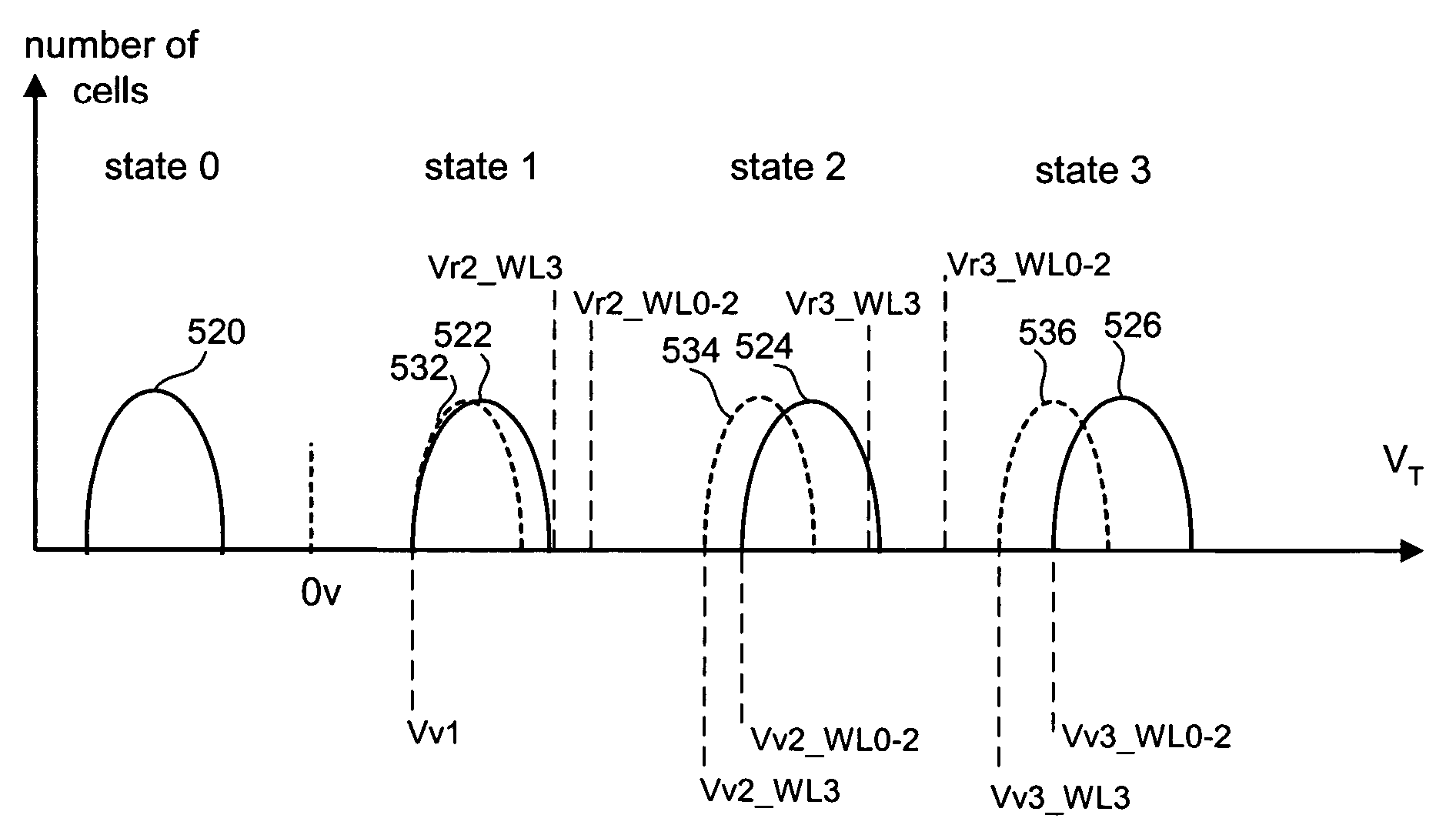
Patents
Literature
32547results about "Read-only memories" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
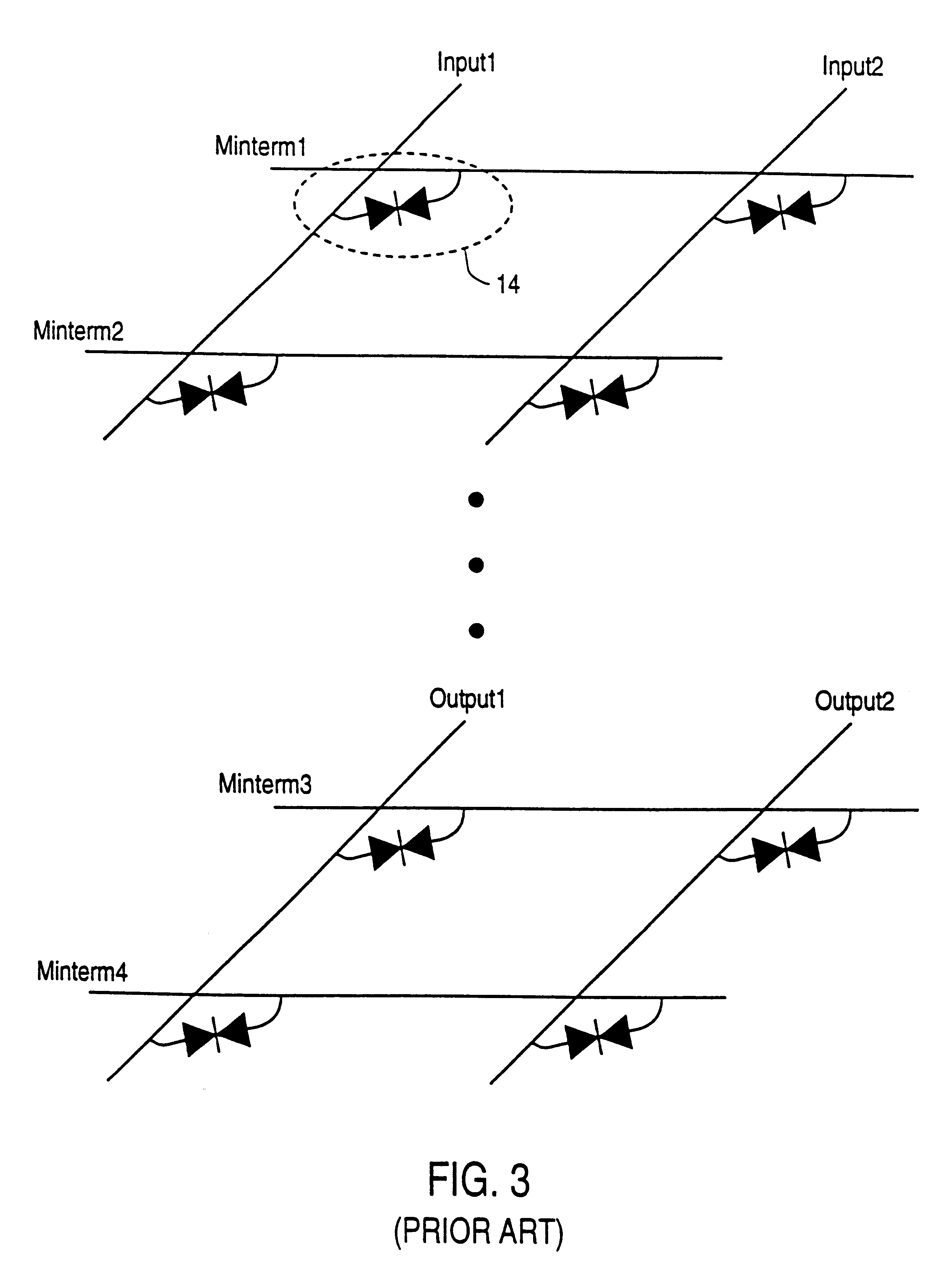
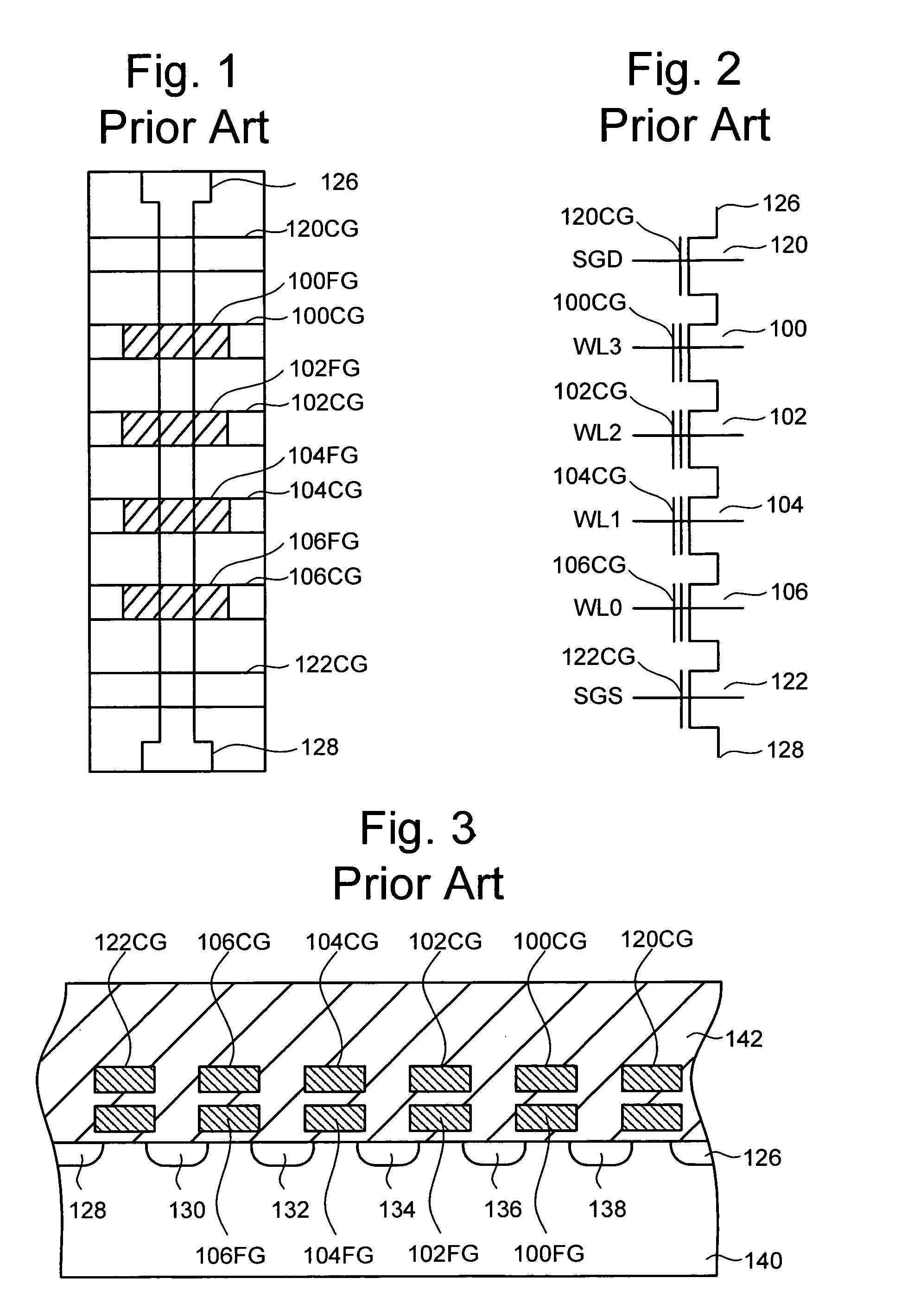
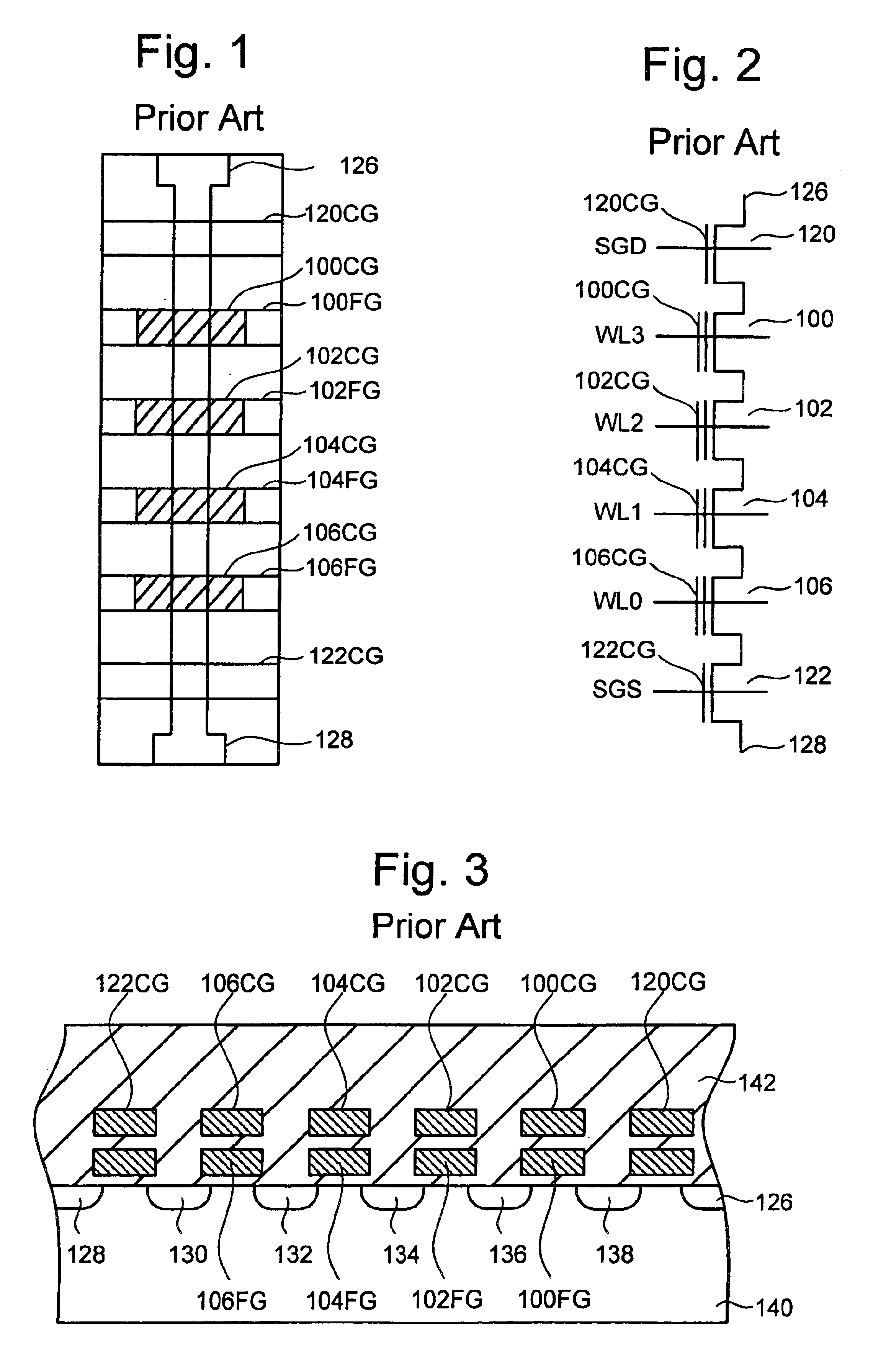
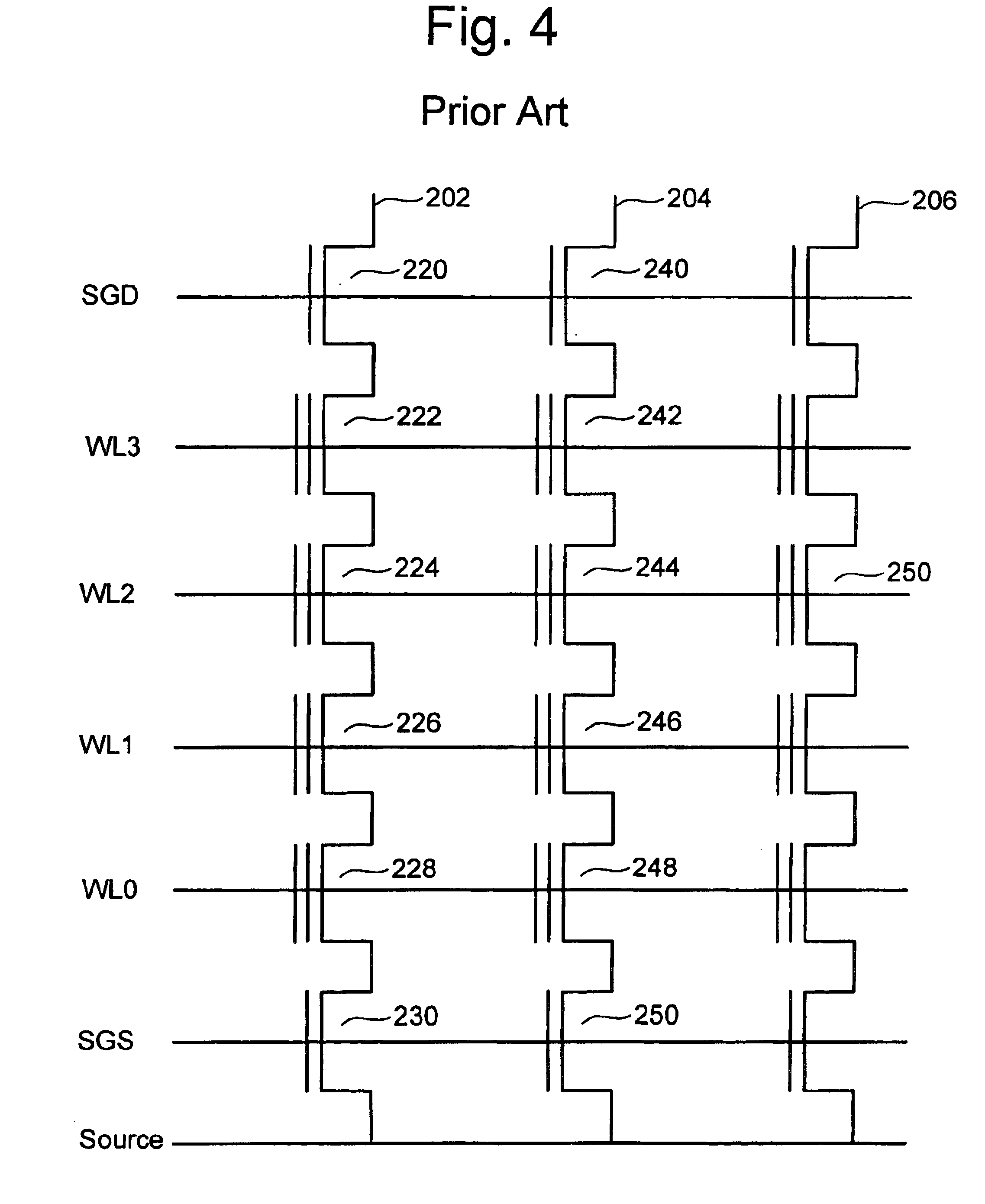
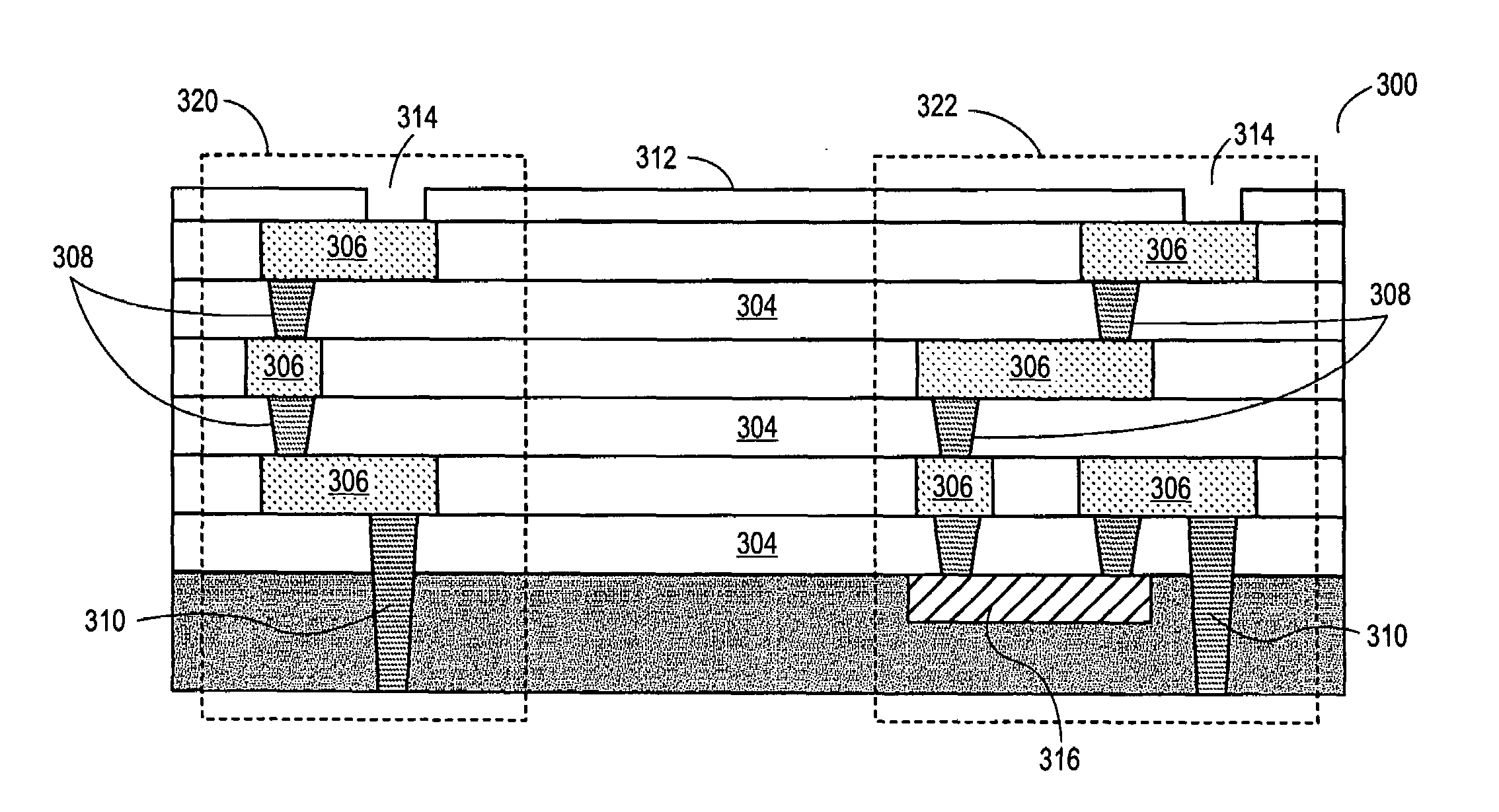
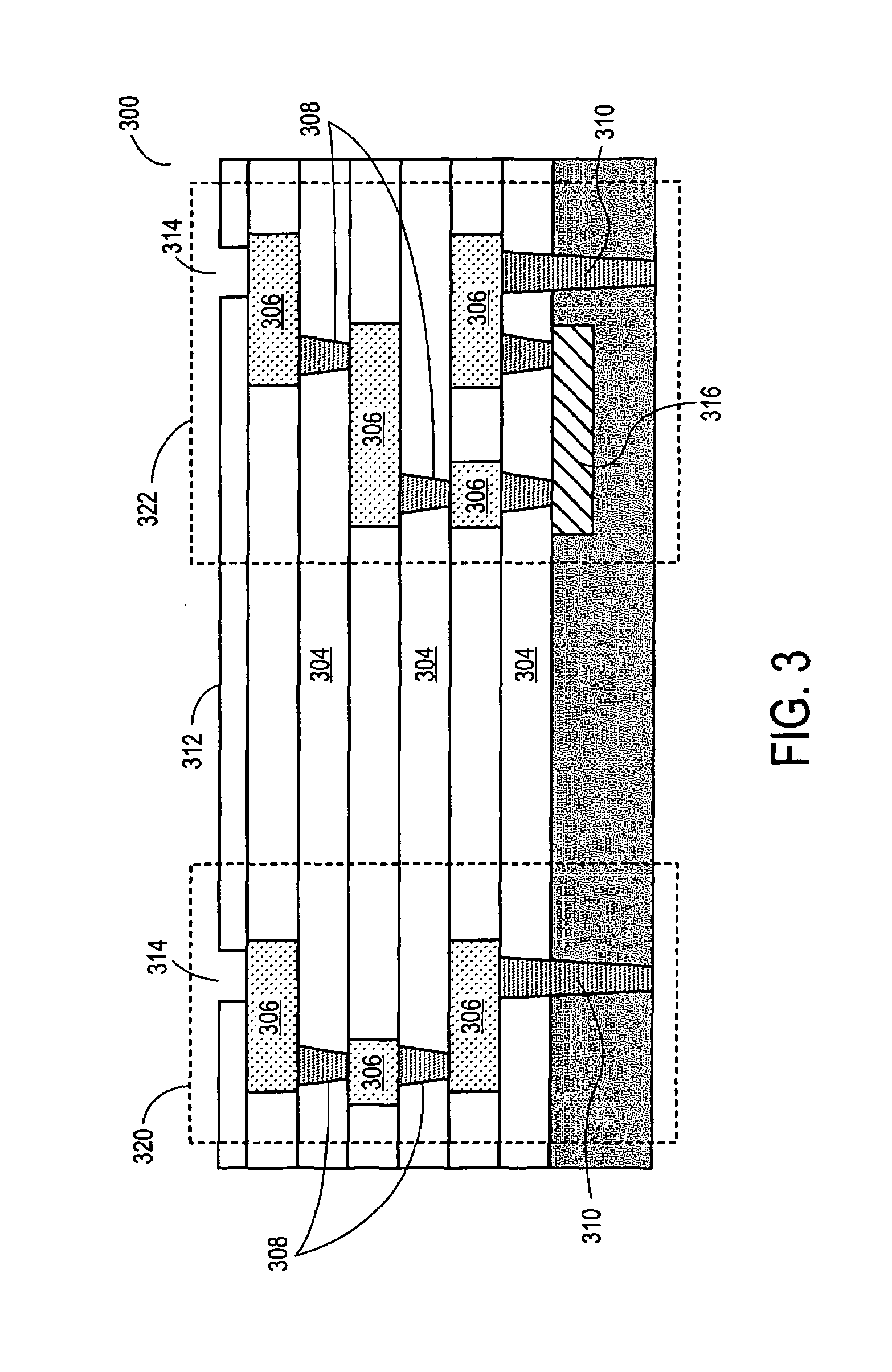
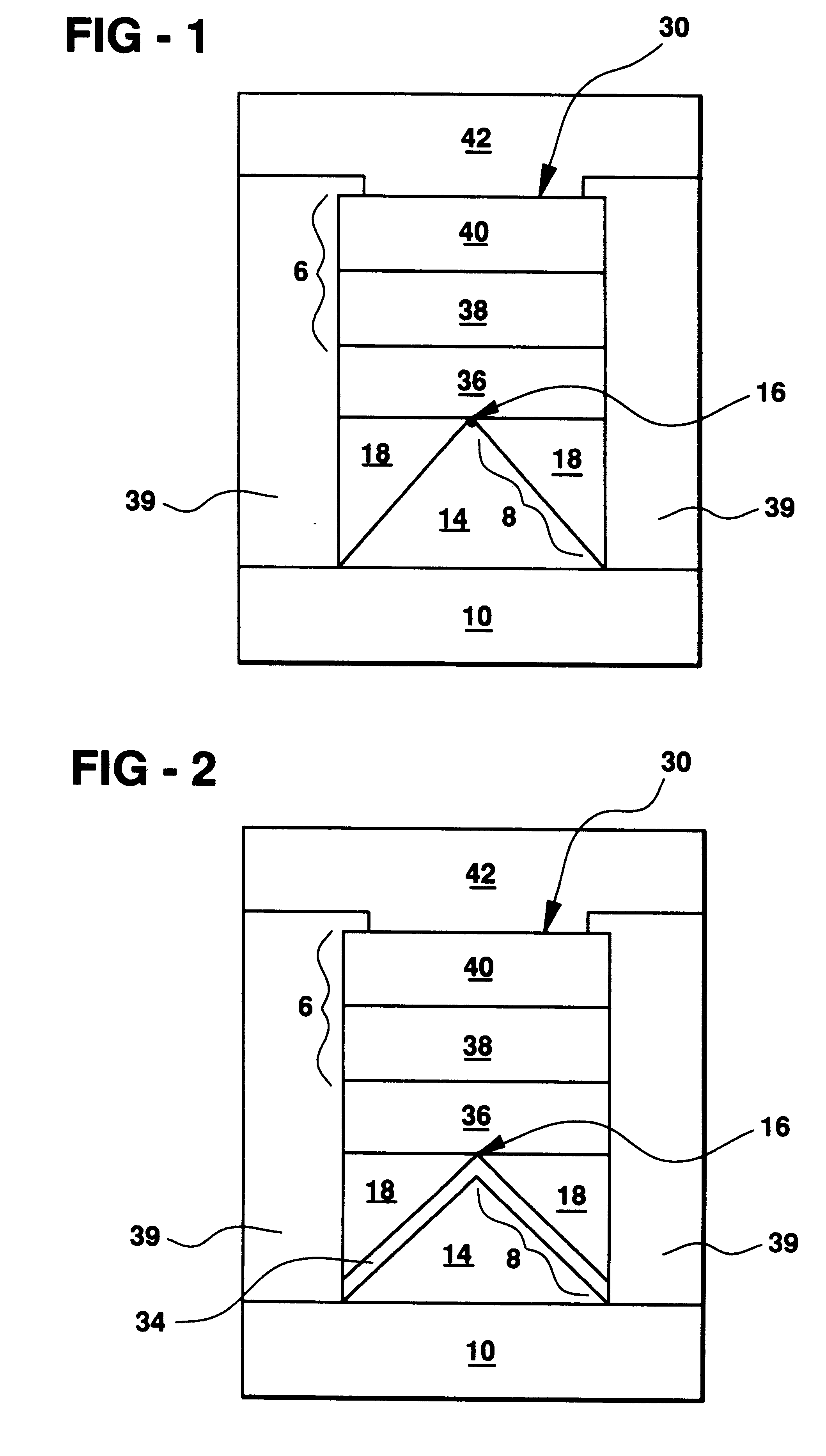
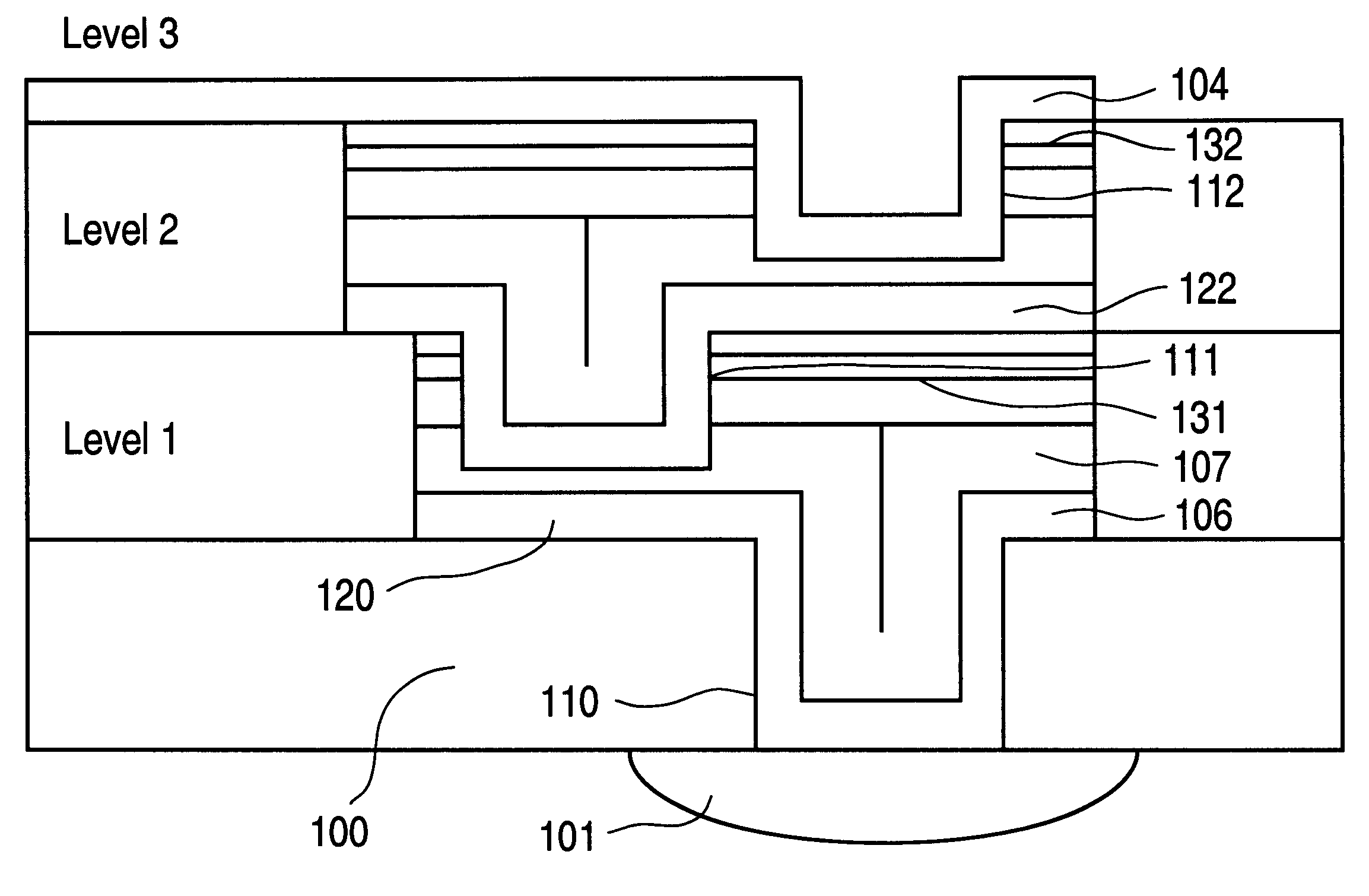
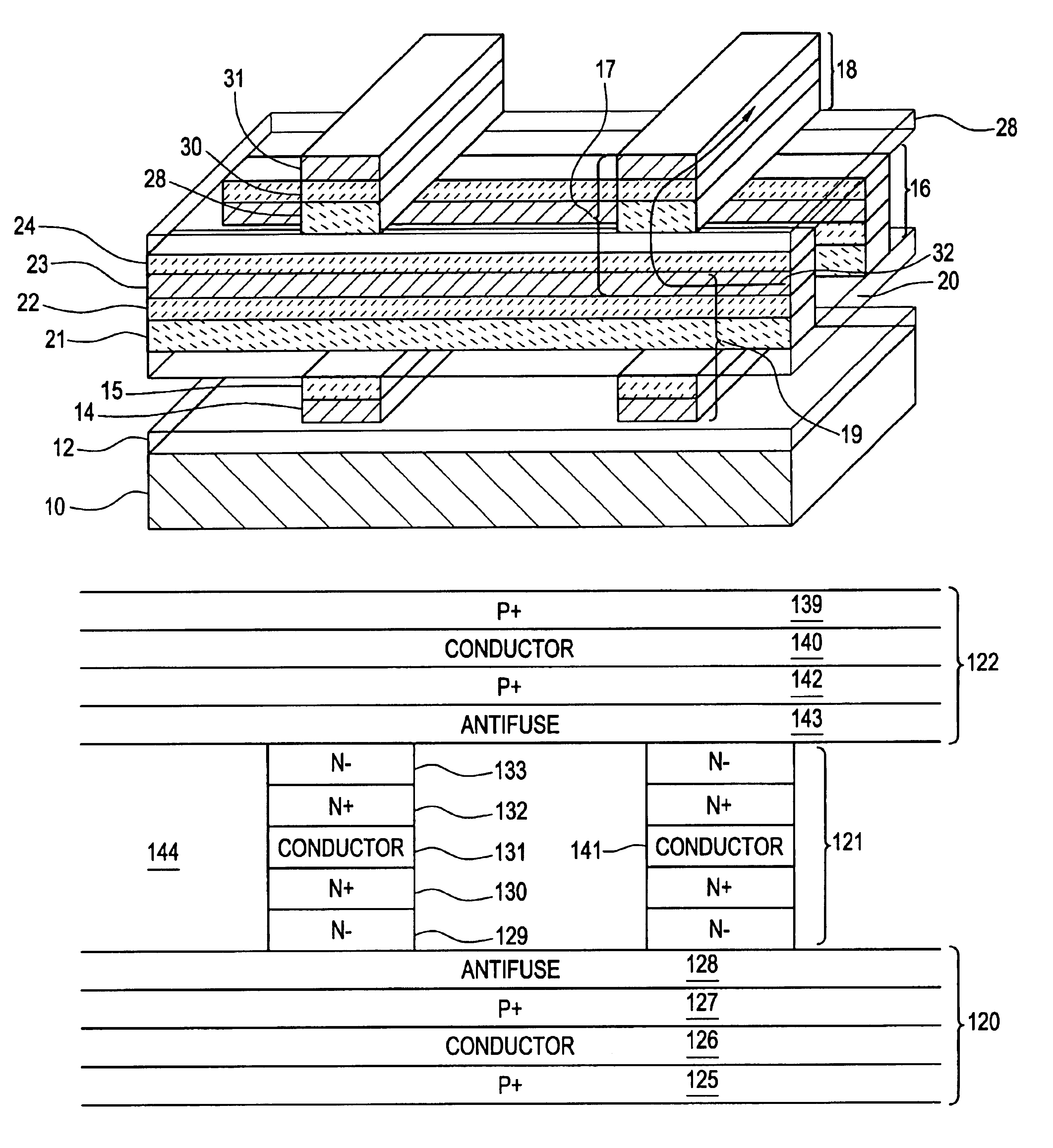
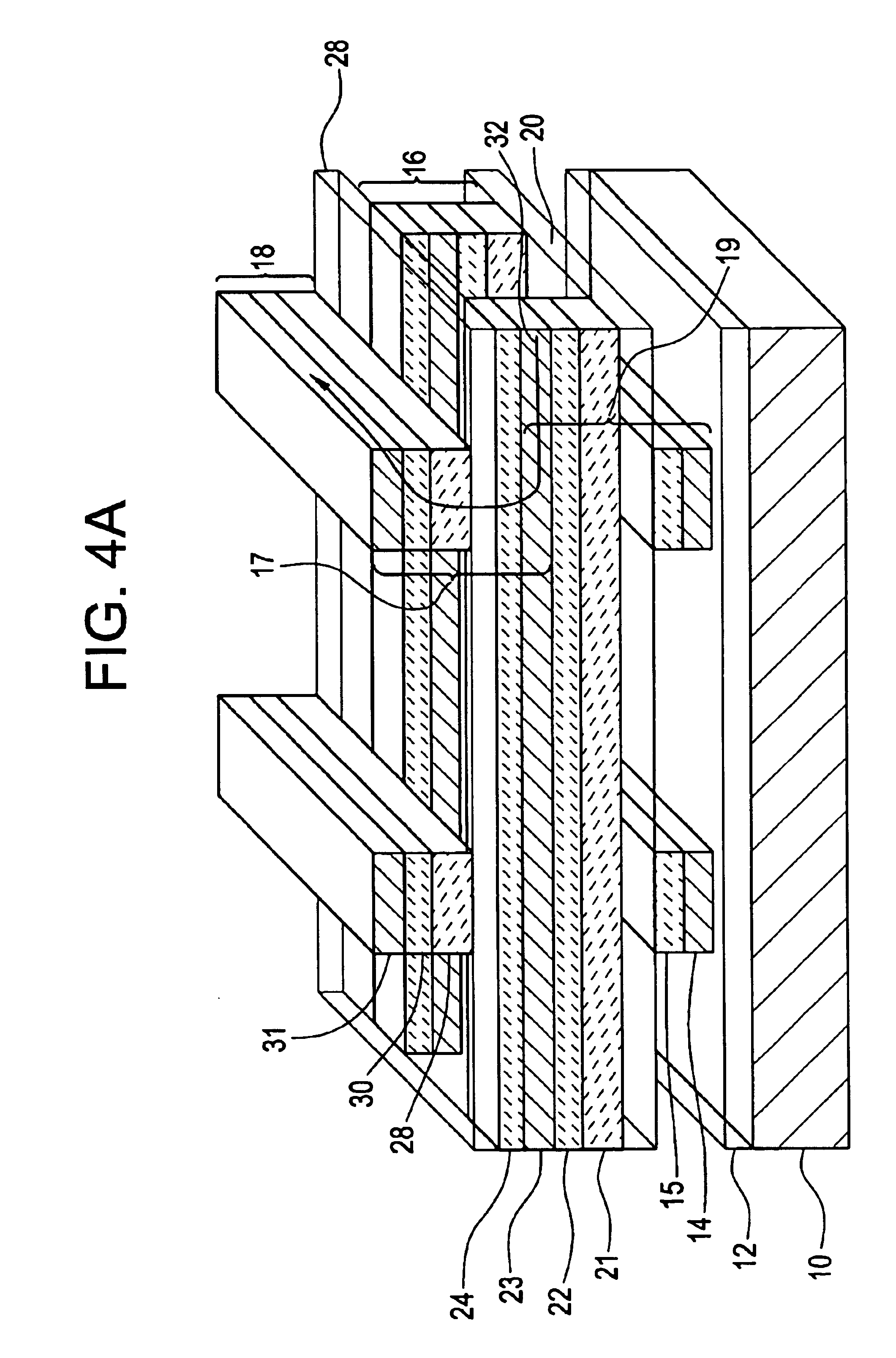
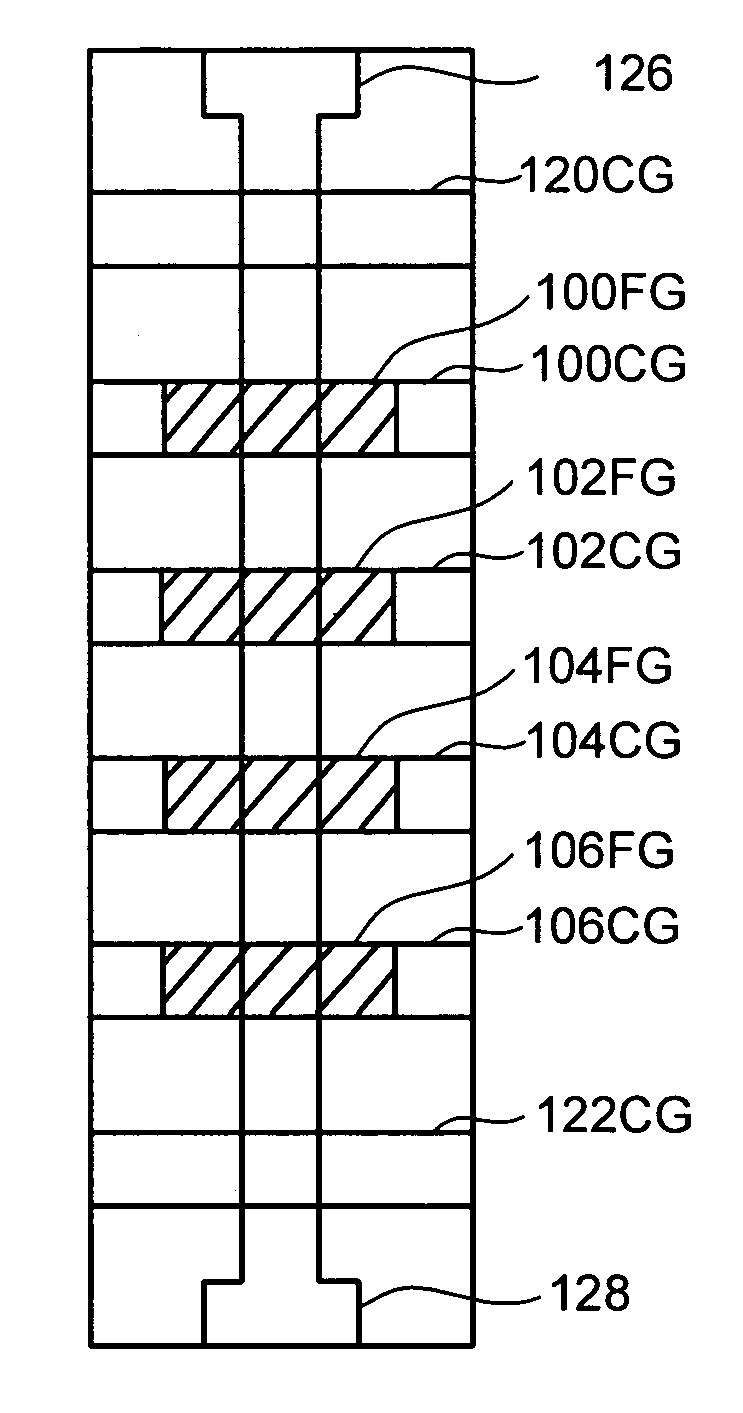
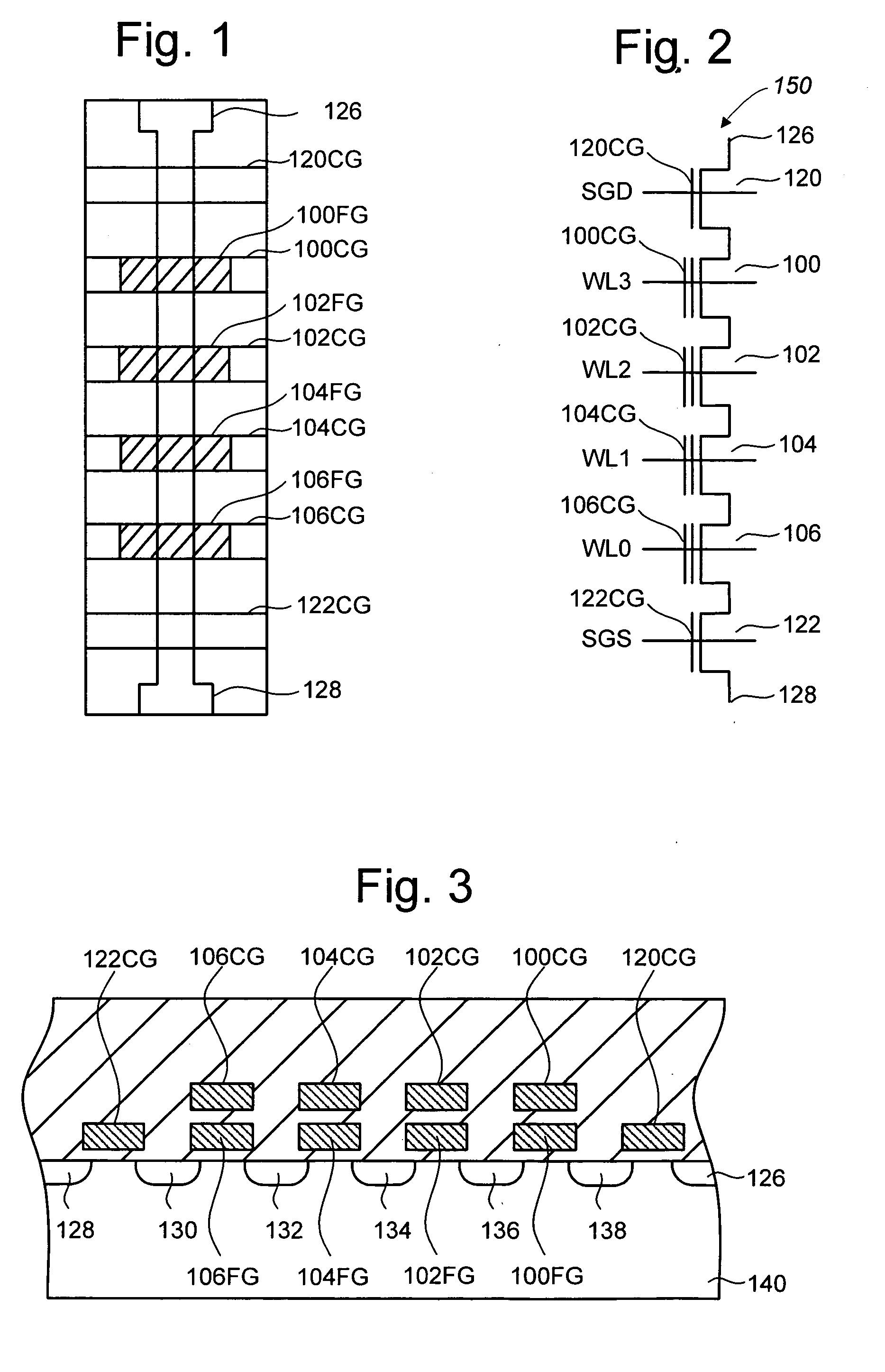
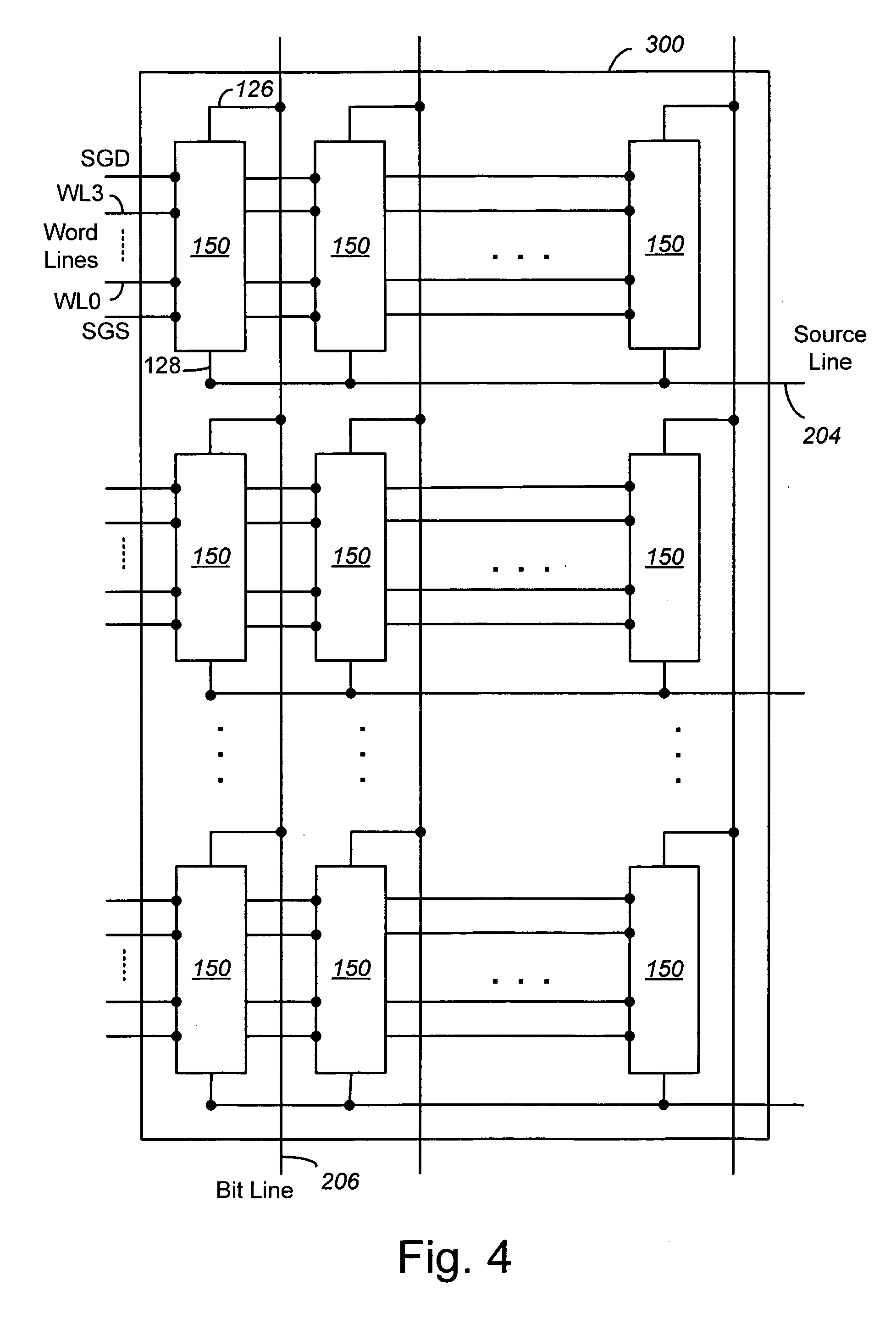
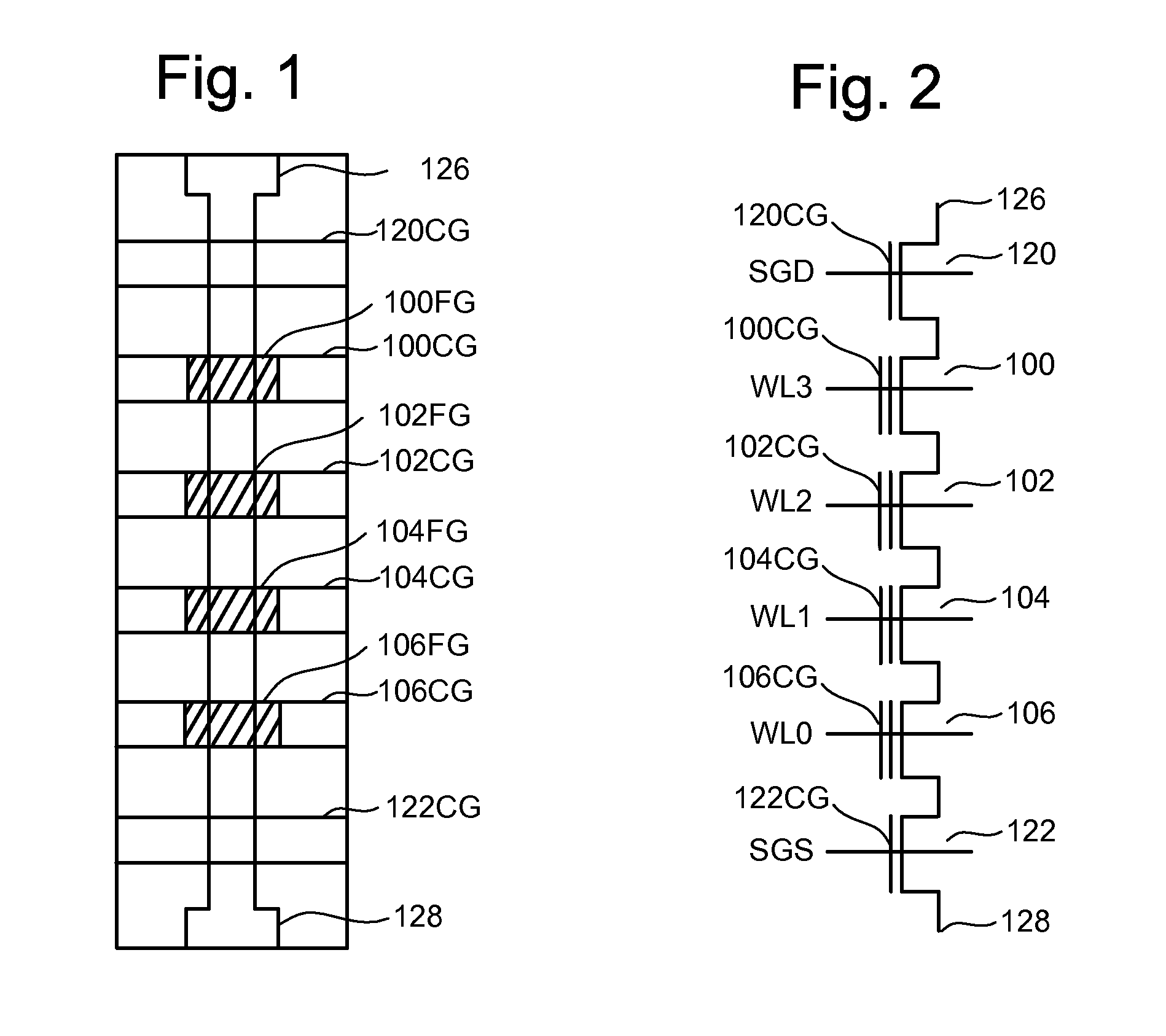
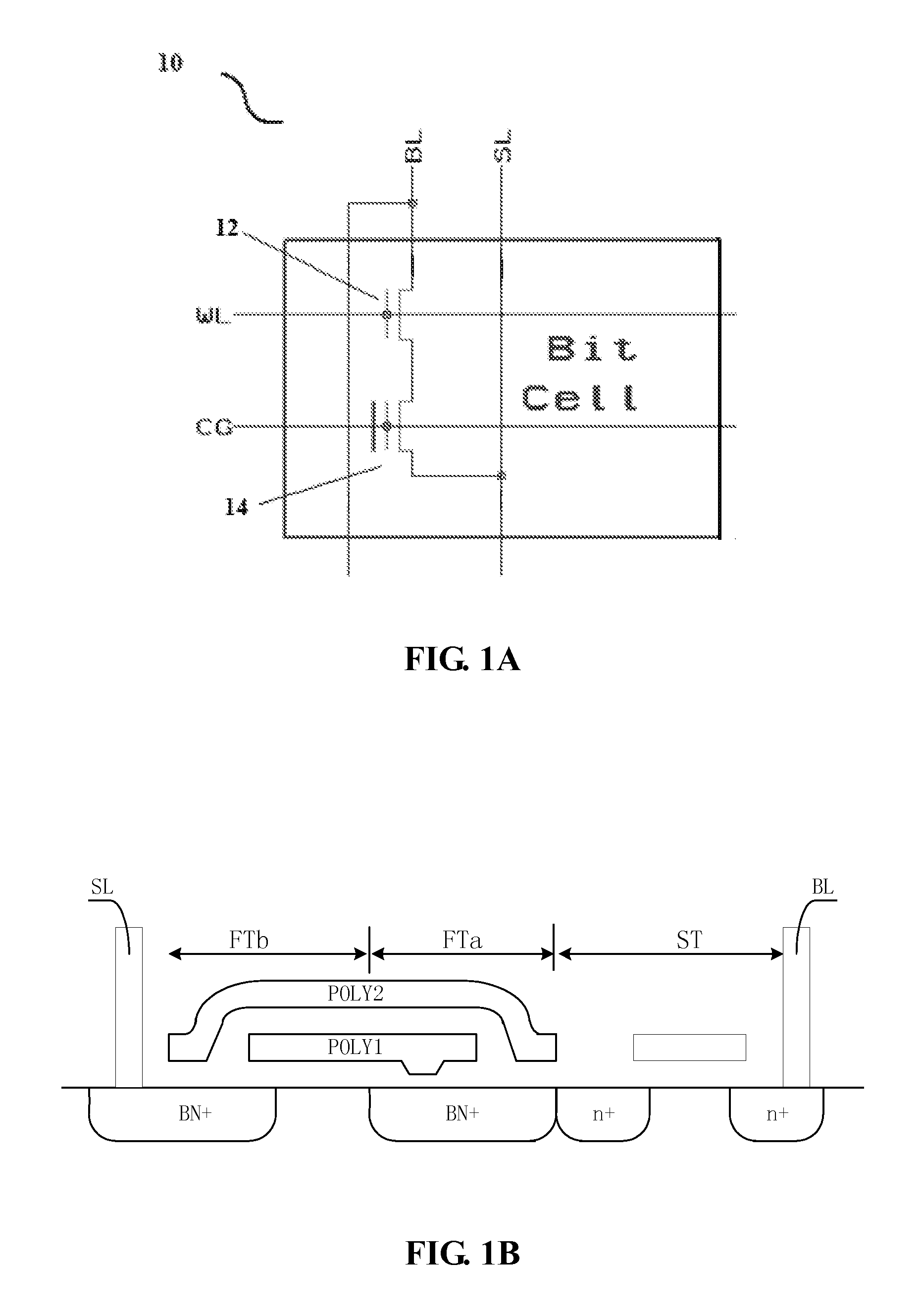
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:RHOMBUS
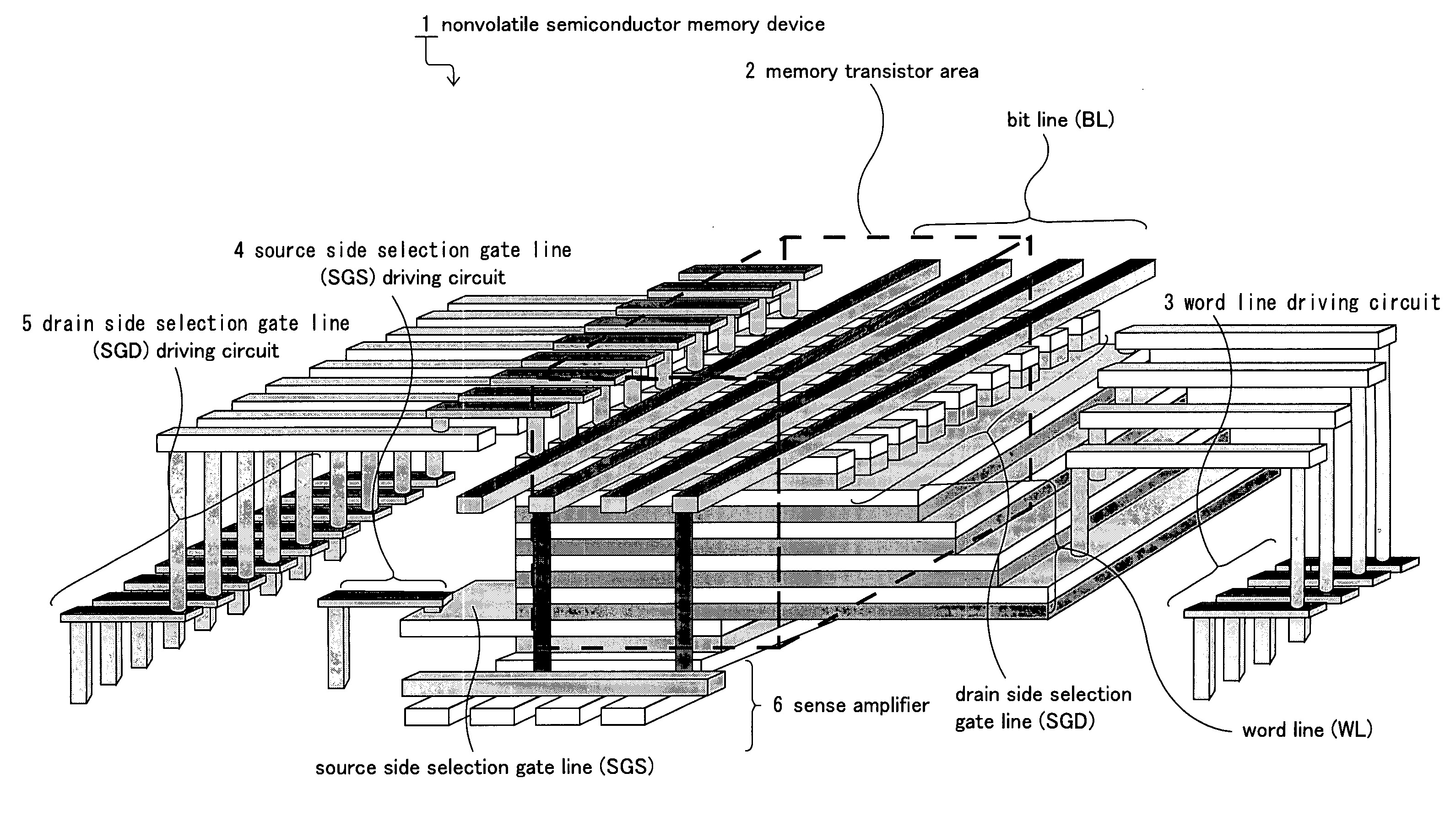
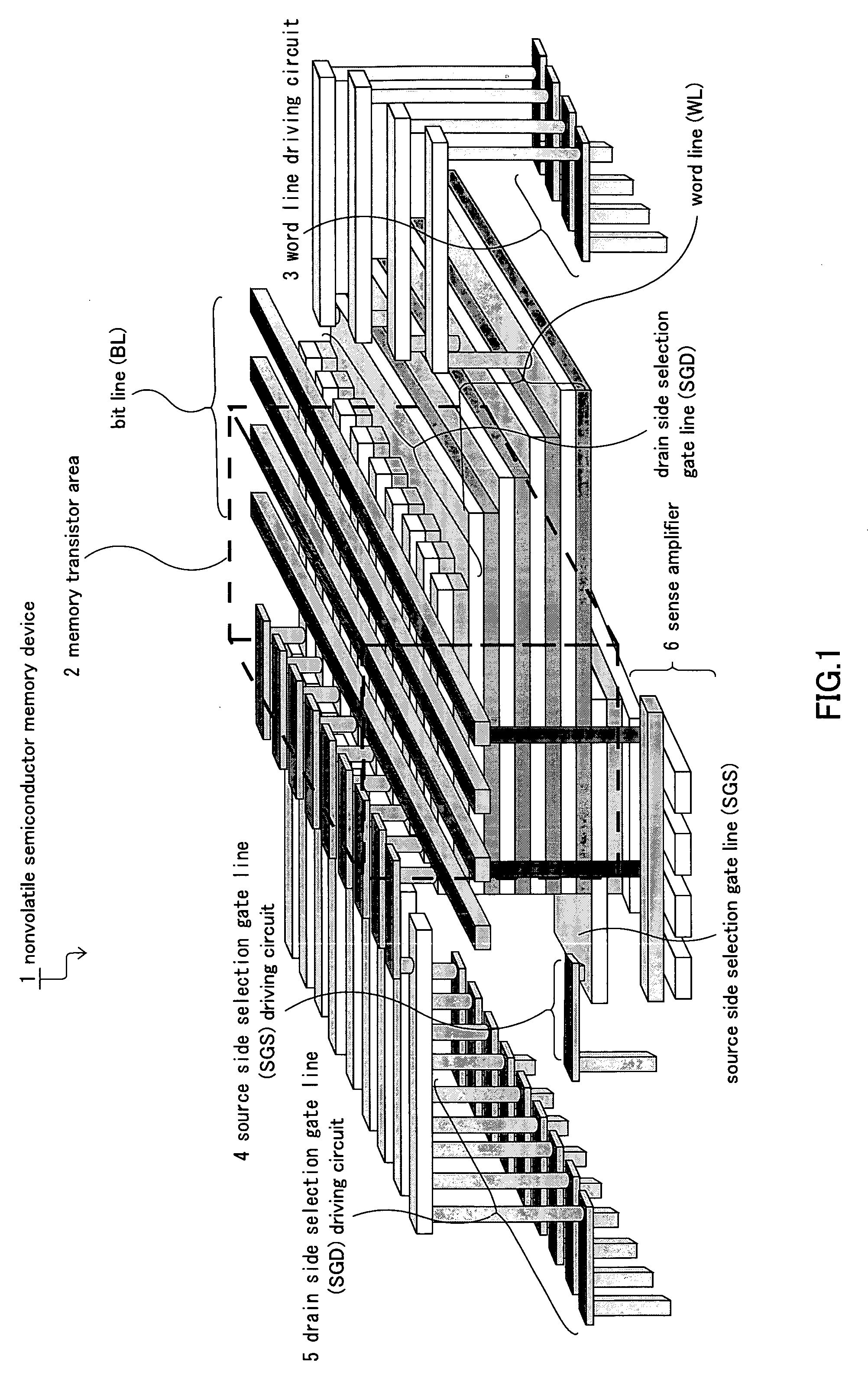
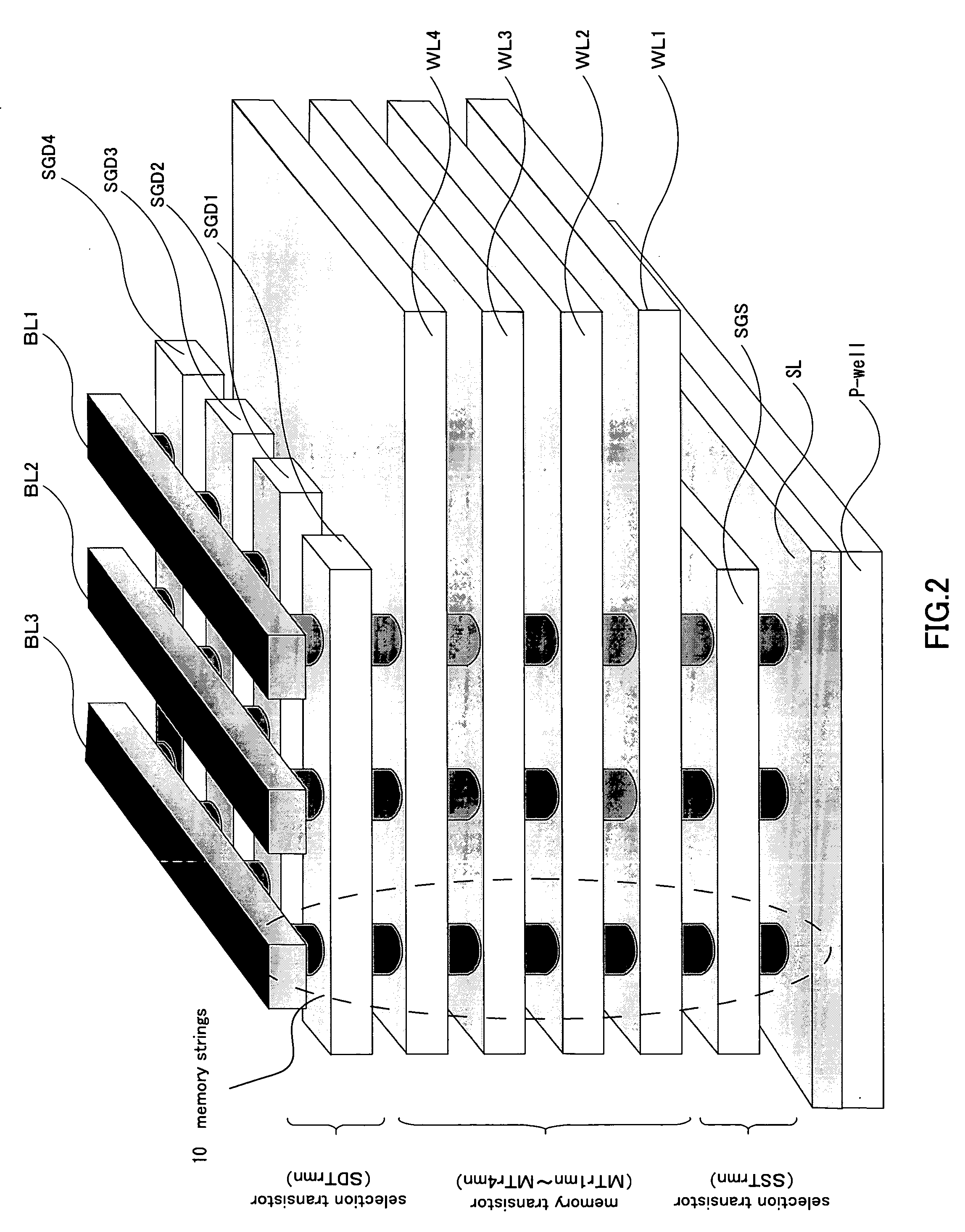
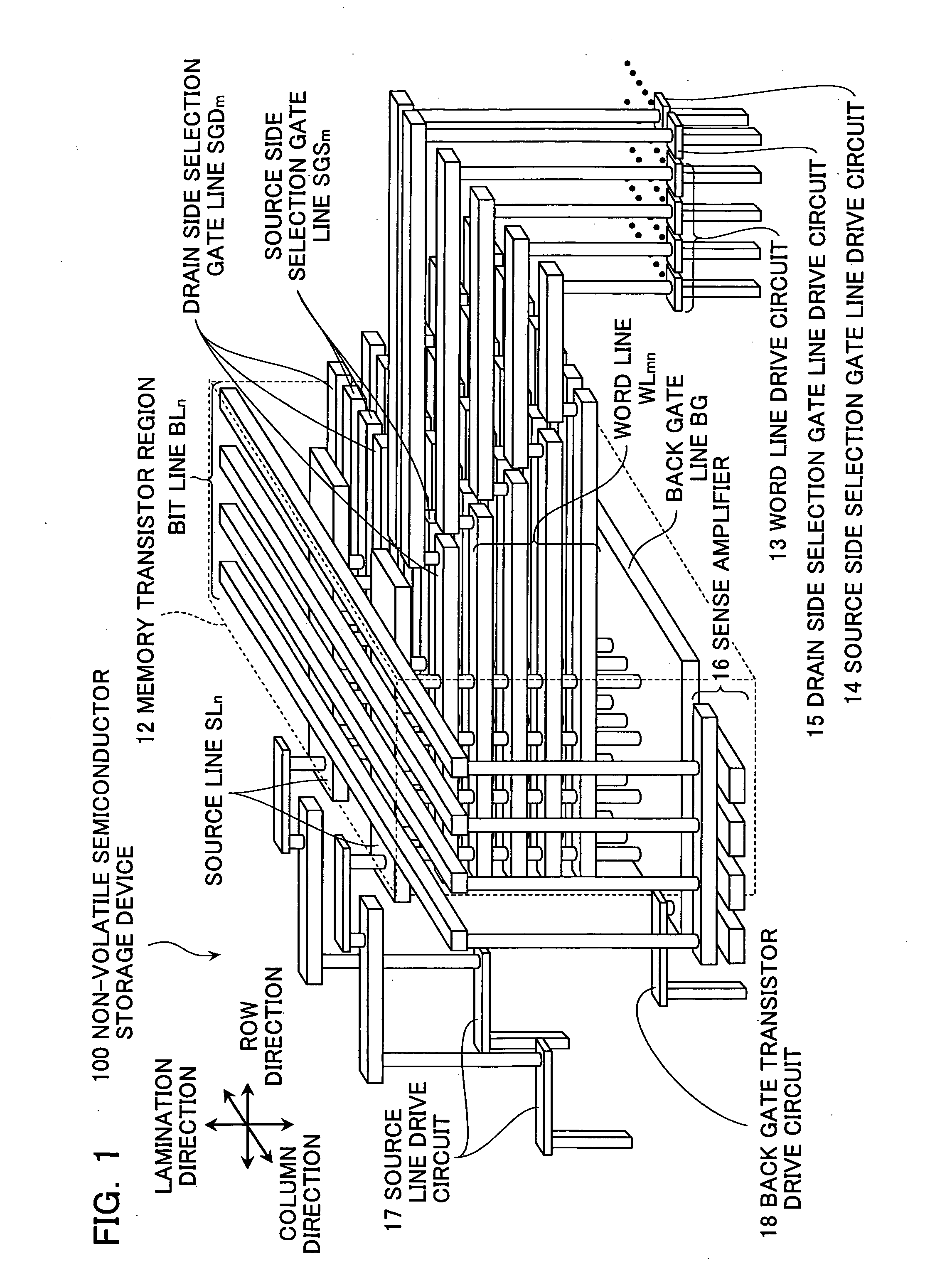
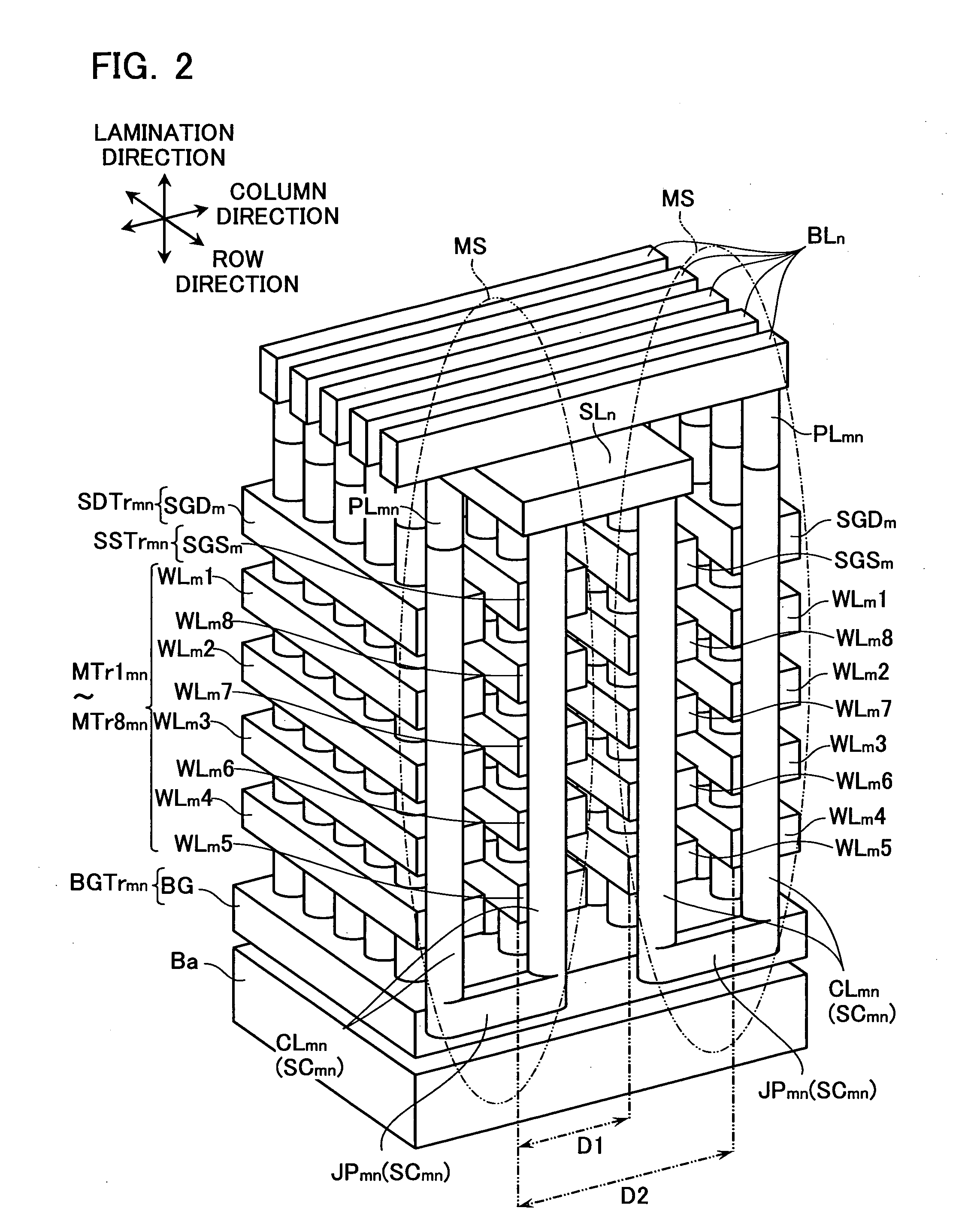
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device that have a new structure are provided, in which memory cells are laminated in a three dimensional state so that the chip area may be reduced. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of the present invention is a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device that has a plurality of the memory strings, in which a plurality of electrically programmable memory cells is connected in series. The memory strings comprise a pillar shaped semiconductor; a first insulation film formed around the pillar shaped semiconductor; a charge storage layer formed around the first insulation film; the second insulation film formed around the charge storage layer; and first or nth electrodes formed around the second insulation film (n is natural number more than 1). The first or nth electrodes of the memory strings and the other first or nth electrodes of the memory strings are respectively the first or nth conductor layers that are spread in a two dimensional state.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
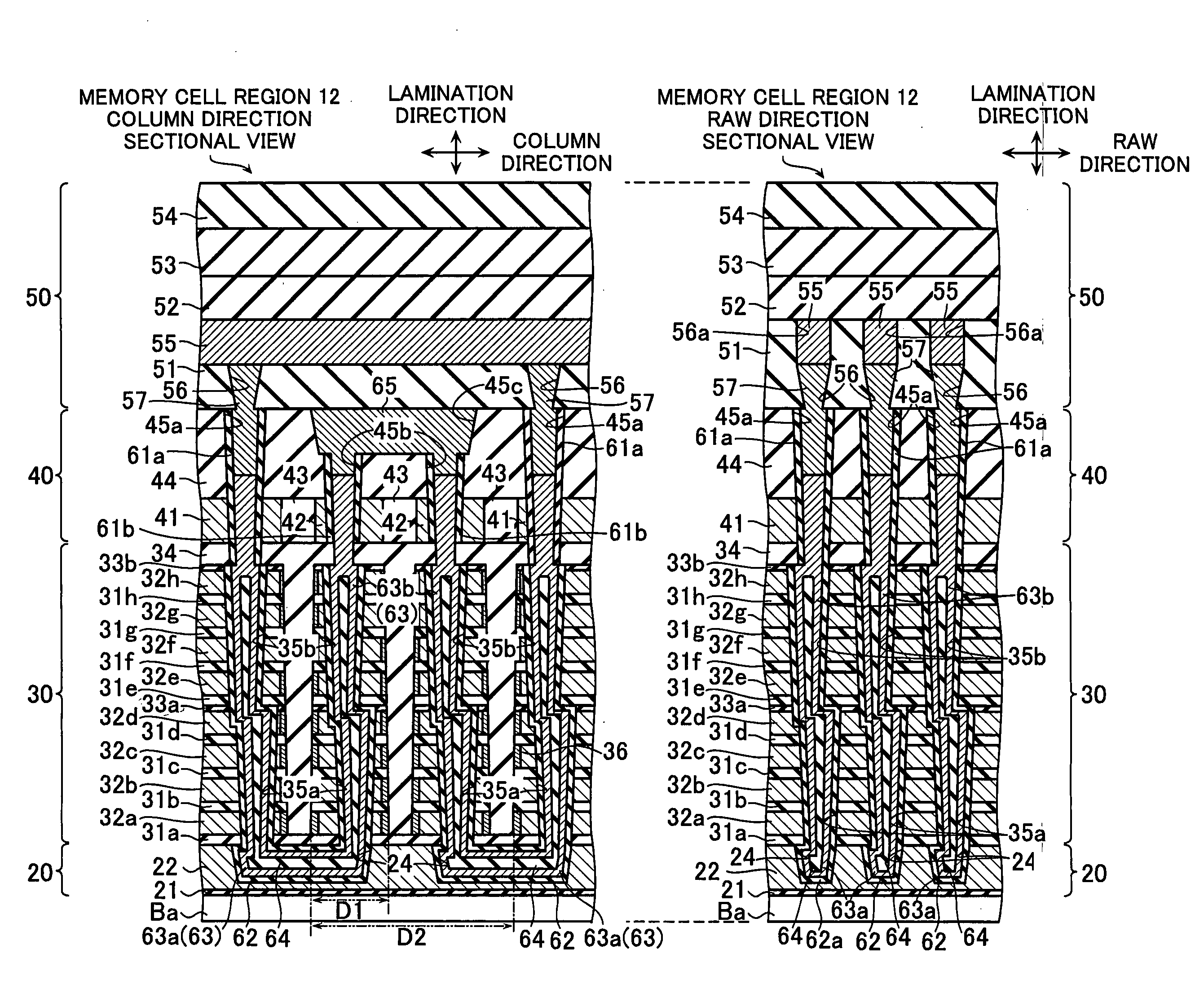
Non-volatile semiconductor storage device and method of manufacturing the same
A non-volatile semiconductor storage device has a plurality of memory strings to each of which a plurality of electrically rewritable memory cells are connected in series. Each of the memory strings includes first semiconductor layers each having a pair of columnar portions extending in a vertical direction with respect to a substrate and a coupling portion formed to couple the lower ends of the pair of columnar portions; a charge storage layer formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions; and first conductive layers formed to surround the side surfaces of the columnar portions and the charge storage layer. The first conductive layers functions as gate electrodes of the memory cells.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
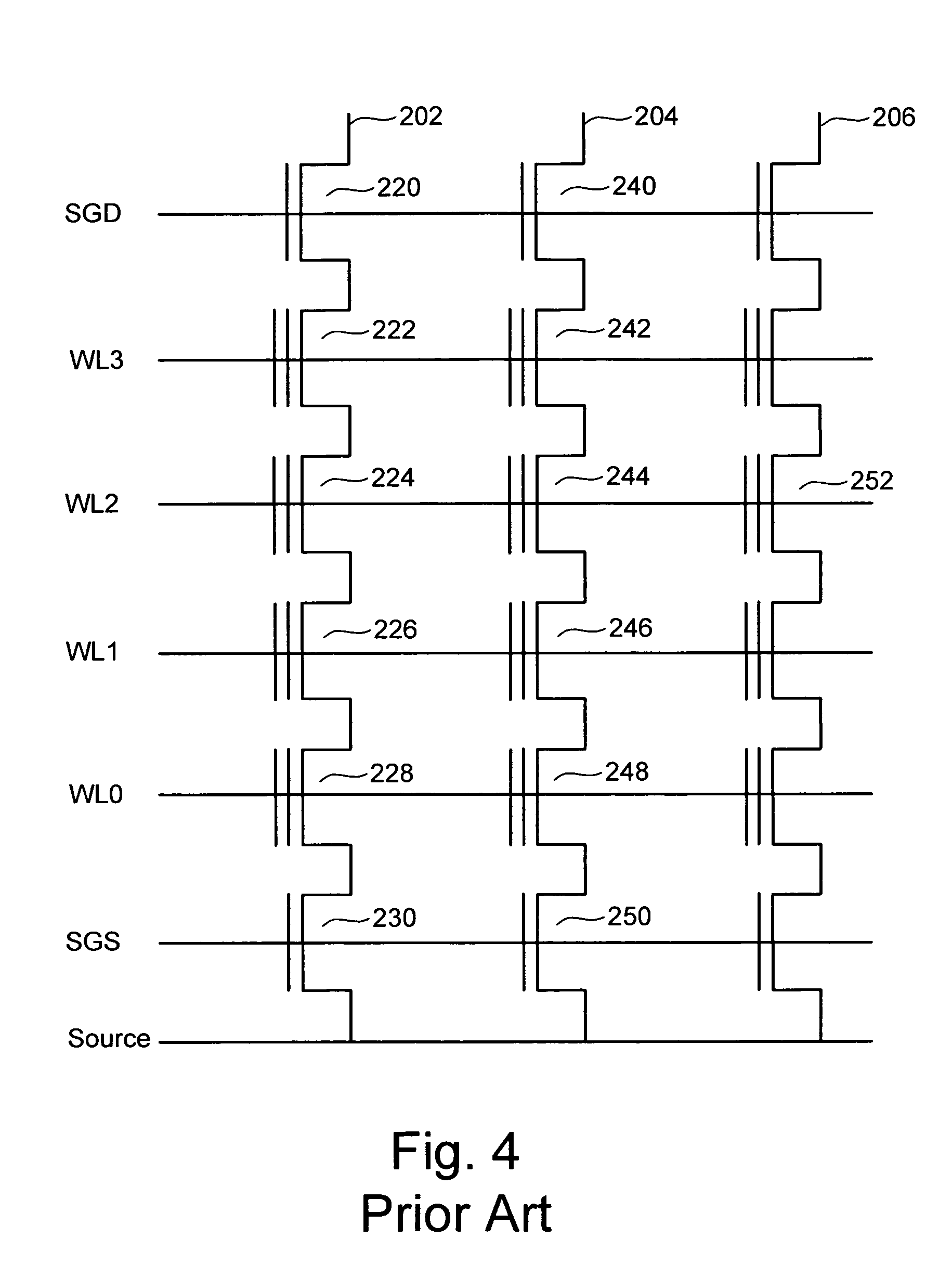
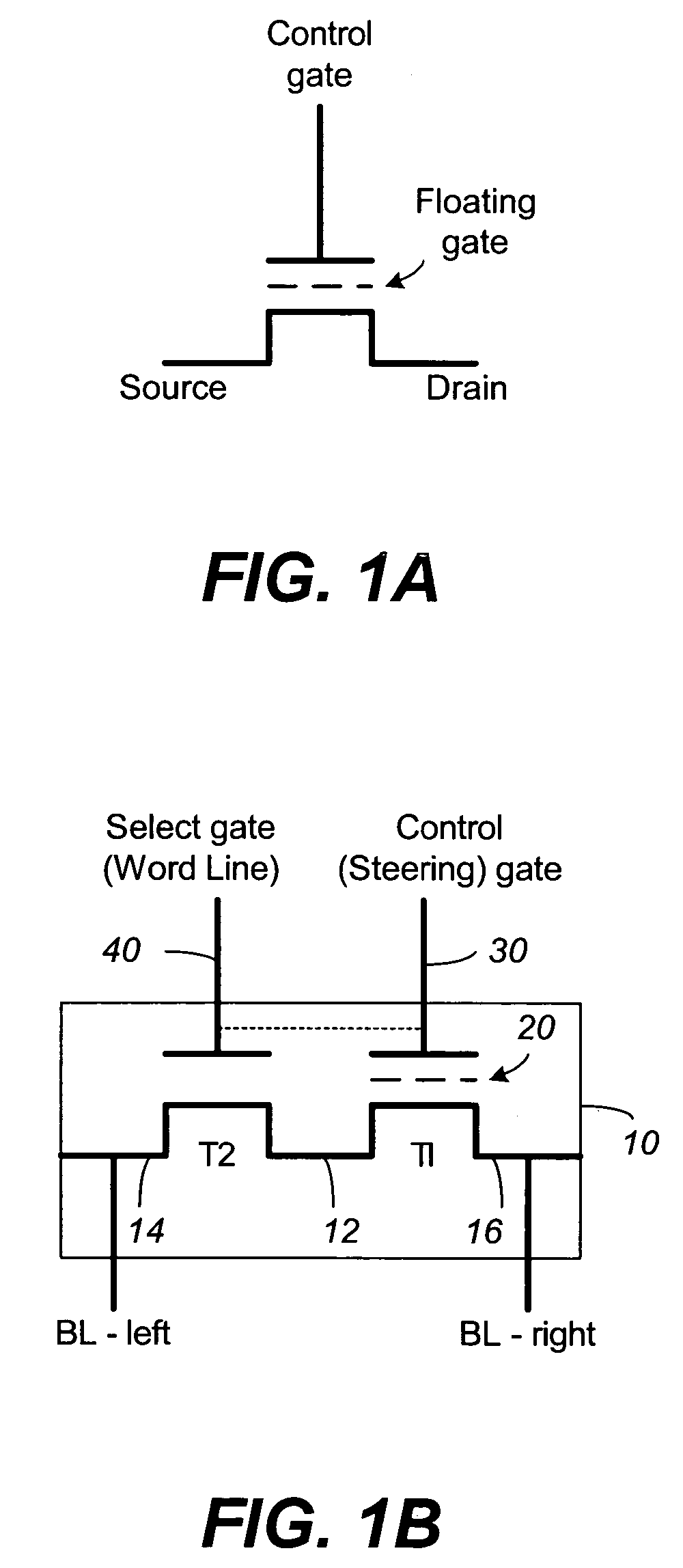
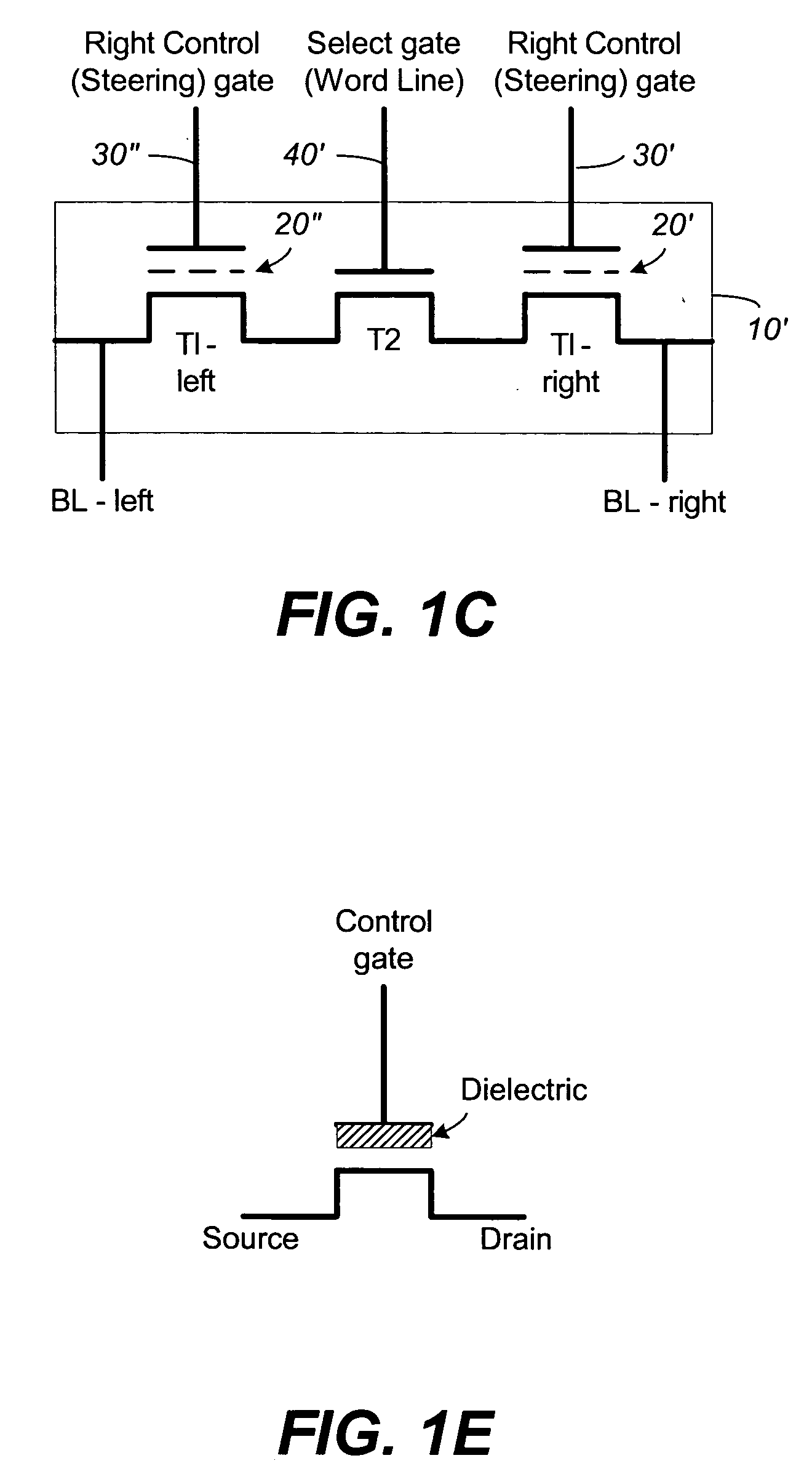
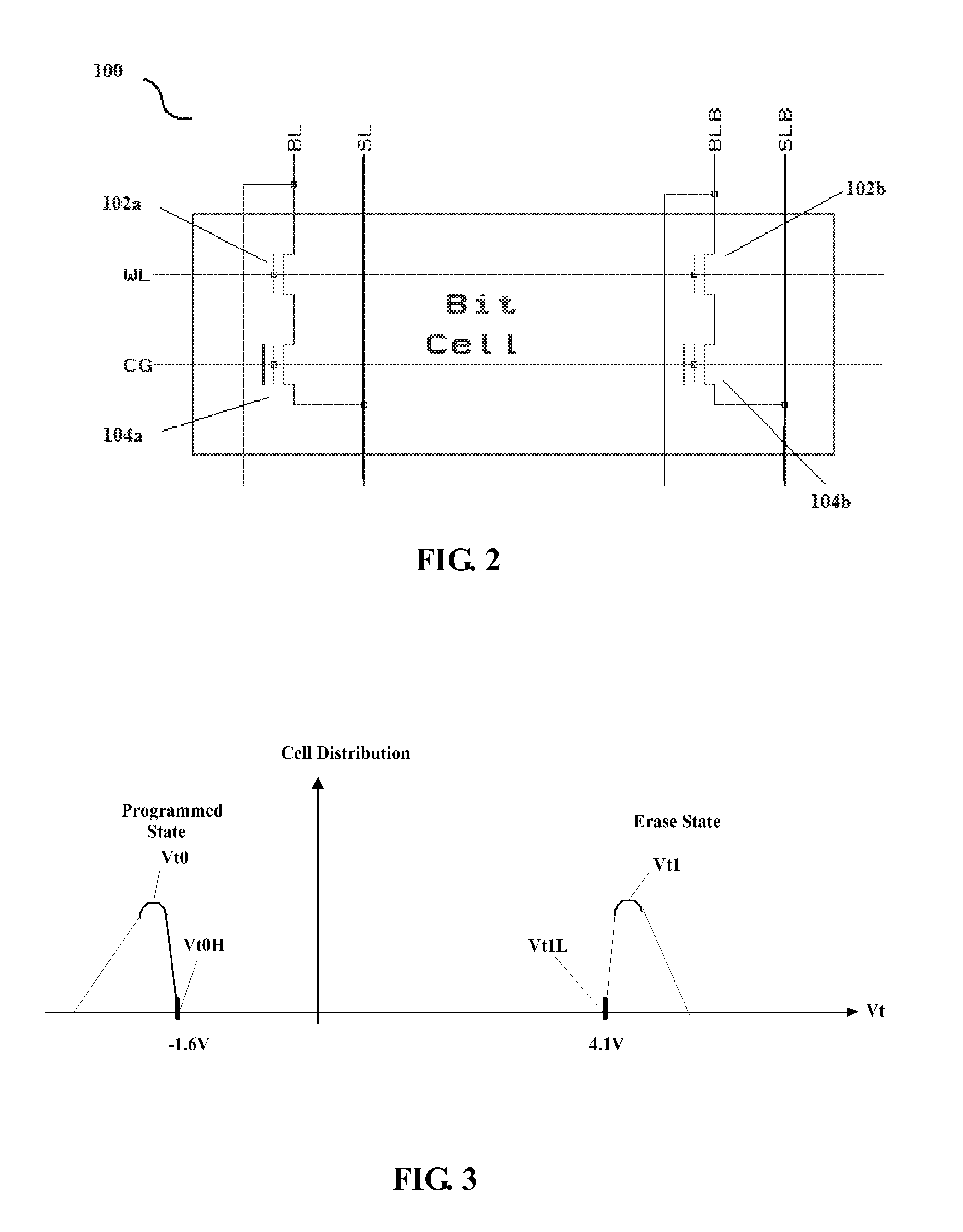
Compensating for coupling during read operations of non-volatile memory
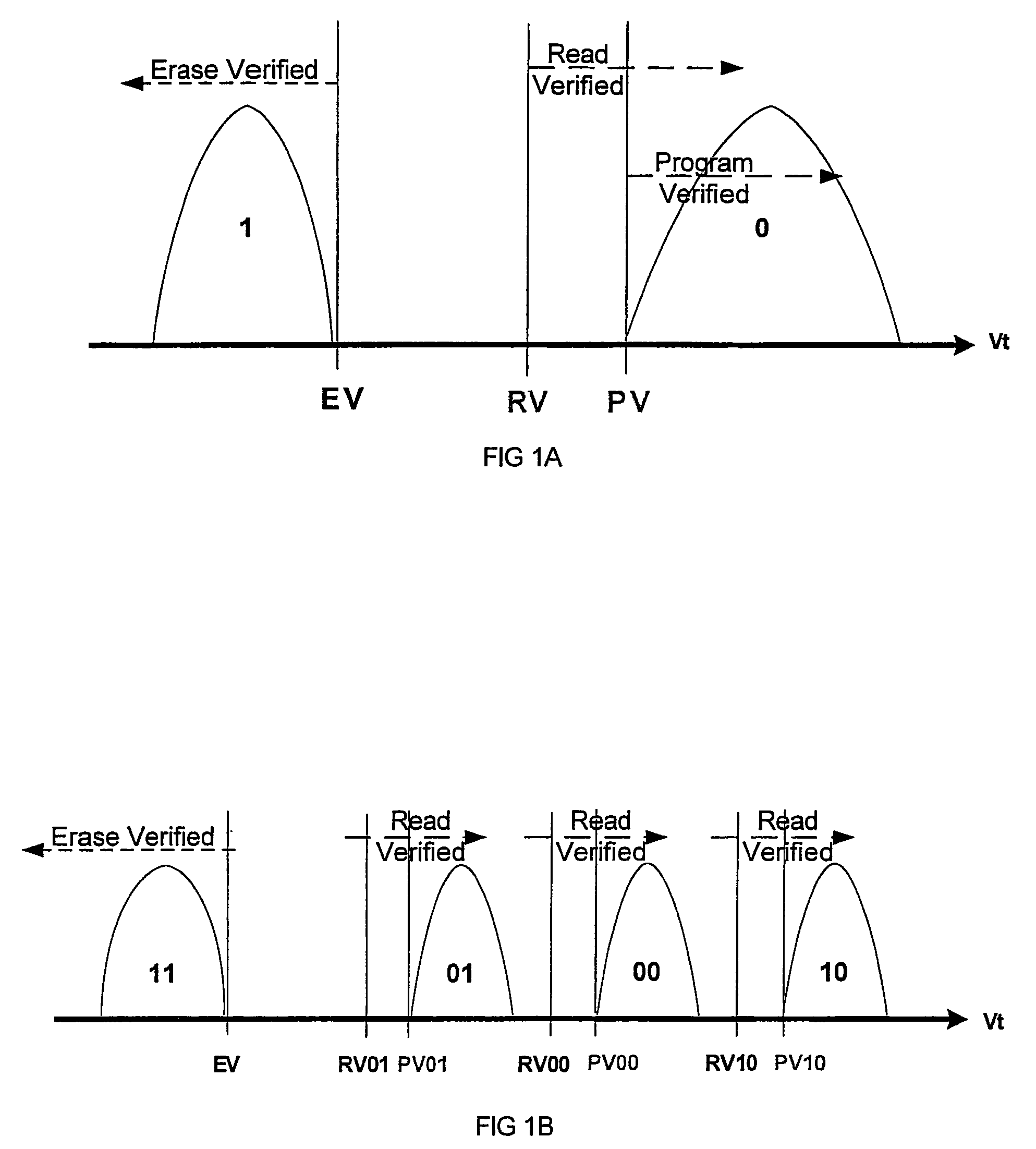
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
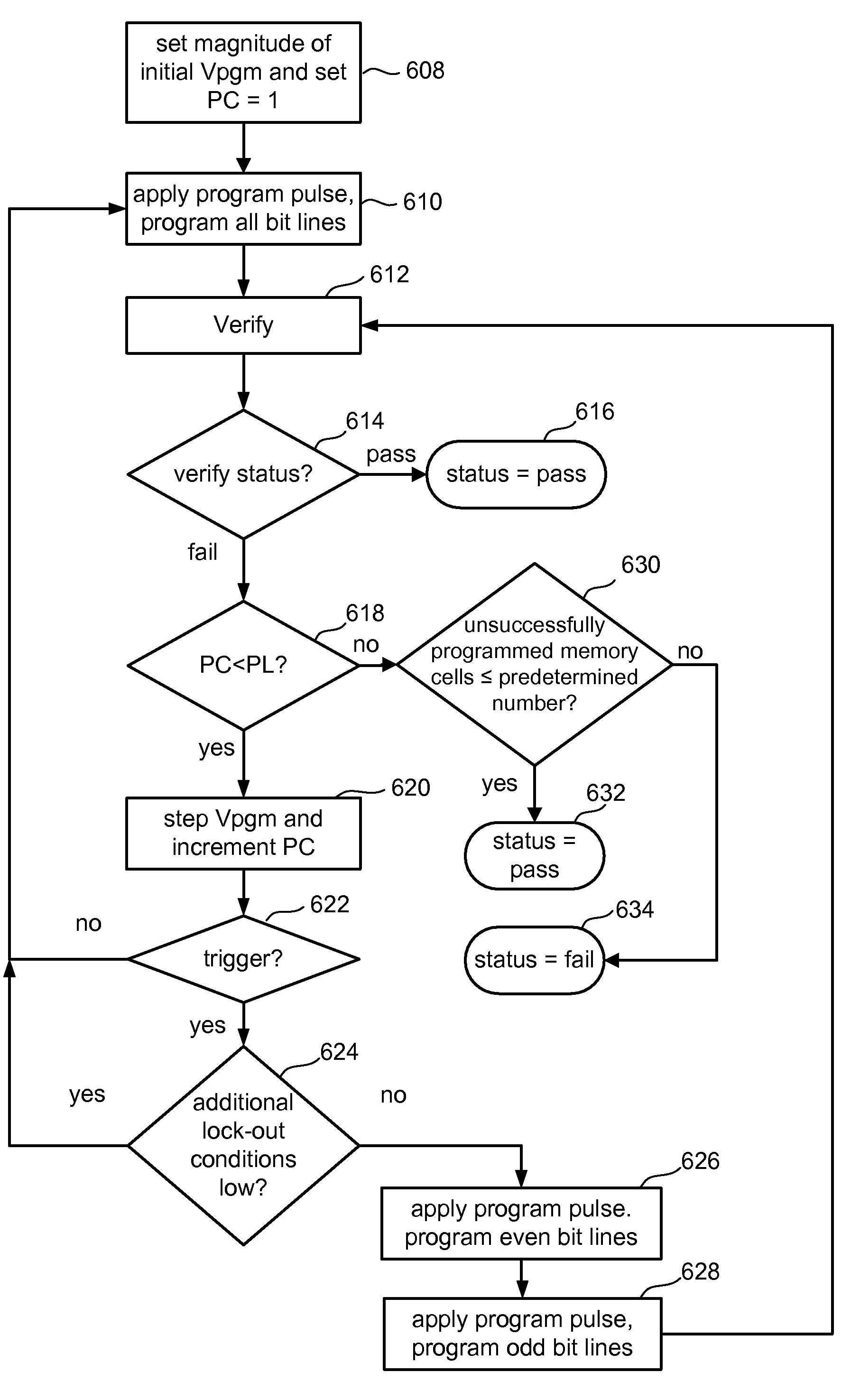
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Source side self boosting technique for non-volatile memory
InactiveUS6859397B2Improve performanceMinimize program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePre-chargeProgramming process
A non-volatile semiconductor memory system (or other type of memory system) is programmed in a manner that avoids program disturb. In one embodiment that includes a flash memory system using a NAND architecture, program disturb is avoided by increasing the channel potential of the source side of the NAND string during the programming process. One exemplar implementation includes applying a voltage (e.g. Vdd) to the source contact and turning on the source side select transistor for the NAND sting corresponding to the cell being inhibited. Another implementation includes applying a pre-charging voltage to the unselected word lines of the NAND string corresponding to the cell being inhibited prior to applying the program voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
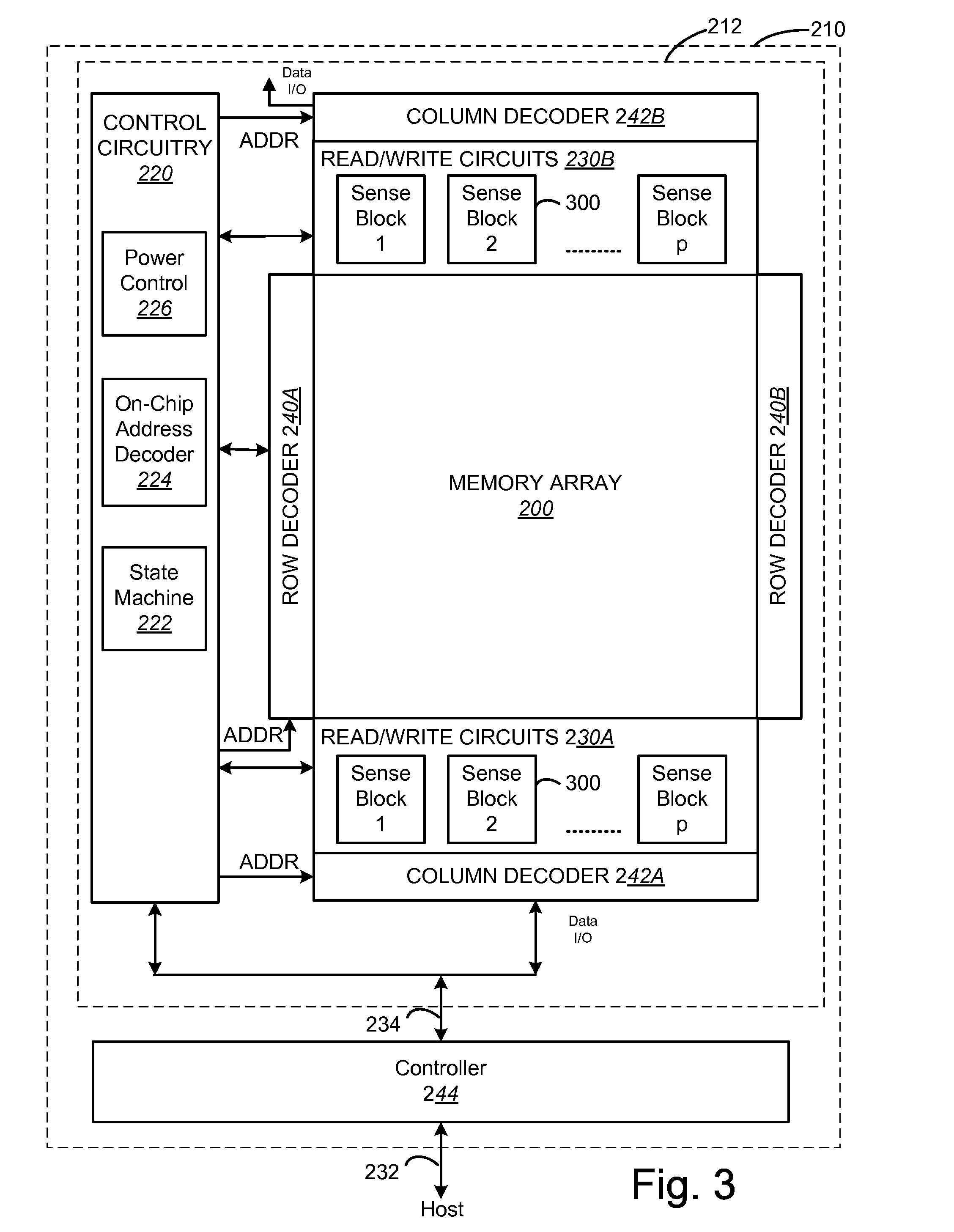
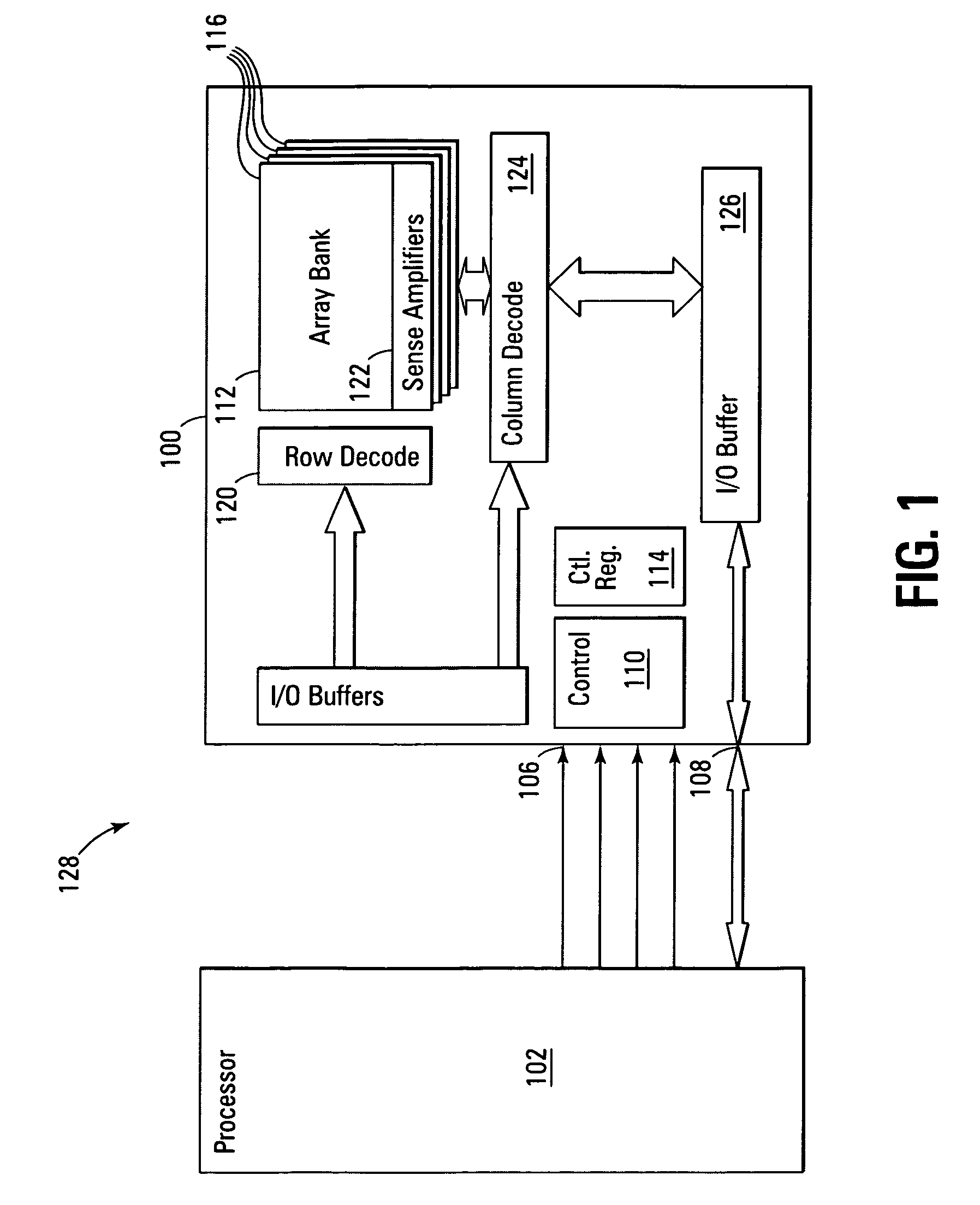
Non-volatile memory and method with shared processing for an aggregate of read/write circuits
InactiveUS20060140007A1Maximum versatilityMinimal componentRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierAssociative processor
A non-volatile memory device capable of reading and writing a large number of memory cells with multiple read / write circuits in parallel has an architecture that reduces redundancy in the multiple read / write circuits to a minimum. The multiple read / write circuits are organized into a bank of similar stacks of components. Redundant circuits such as a processor for processing data among stacks each associated with multiple memory cells are factored out. The processor is implemented with an input logic, a latch and an output logic. The input logic can transform the data received from either the sense amplifier or the data latches. The output logic further processes the transformed data to send to either the sense amplifier or the data latches or to a controller. This provides an infrastructure with maximum versatility and a minimum of components for sophisticated processing of the data sensed and the data to be input or output.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Multibit single cell memory element having tapered contact
InactiveUSRE37259E1Large electric resistance valueSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPeak valueEngineering
An electrically operated, directly overwritable, multibit, single-cell chalcogenide memory element with multibit storage capabilities and having at least one contact for supplying electrical input signals to set the memory element to a selected resistance value, the second contact tapering to a peak adjacent to the memory element. In this manner the tapered contact helps define the size and position of a conduction path through the memory element.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Flash memory data correction and scrub techniques
ActiveUS7012835B2Data disturbanceReduce storage dataMemory loss protectionRead-only memoriesData integrityData storing
In order to maintain the integrity of data stored in a flash memory that are susceptible to being disturbed by operations in adjacent regions of the memory, disturb events cause the data to be read, corrected and re-written before becoming so corrupted that valid data cannot be recovered. The sometimes conflicting needs to maintain data integrity and system performance are balanced by deferring execution of some of the corrective action when the memory system has other high priority operations to perform. In a memory system utilizing very large units of erase, the corrective process is executed in a manner that is consistent with efficiently rewriting an amount of data much less than the capacity of a unit of erase.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory and method with bit line compensation dependent on neighboring operating modes
ActiveUS6956770B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineHigh density
When programming a contiguous page of memory storage units, every time a memory storage unit has reached its targeted state and is program-inhibited or locked out from further programming, it creates a perturbation on an adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The present invention provides as part of a programming circuit and method in which an offset to the perturbation is added to the adjacent memory storage unit still under programming. The offset is added as voltage offset to a bit line of a storage unit under programming. The voltage offset is a predetermined function of whether none or one or both of its neighbors are in a mode that creates perturbation, such as in a program inhibit mode. In this way, an error inherent in programming in parallel high-density memory storage units is eliminated or minimized.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Read operation for non-volatile storage that includes compensation for coupling
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Tracking cells for a memory system
Tracking cells are used in a memory system to improve the read process. The tracking cells can provide an indication of the quality of the data and can be used as part of a data recovery operation if there is an error. The tracking cells provide a means to adjust the read parameters to optimum levels in order to reflect the current conditions of the memory system. Additionally, some memory systems that use multi-state memory cells will apply rotation data schemes to minimize wear. The rotation scheme can be encoded in the tracking cells based on the states of multiple tracking cells, which is decoded upon reading.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110101351A1Reduce power consumptionFrequency of refresh can be lowSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesSemiconductor materialsData storing
Disclosed is a semiconductor device capable of functioning as a memory device. The memory device comprises a plurality of memory cells, and each of the memory cells contains a first transistor and a second transistor. The first transistor is provided over a substrate containing a semiconductor material and has a channel formation region in the substrate. The second transistor has an oxide semiconductor layer. The gate electrode of the first transistor and one of the source and drain electrodes of the second transistor are electrically connected to each other. The extremely low off current of the second transistor allows the data stored in the memory cell to be retained for a significantly long time even in the absence of supply of electric power.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
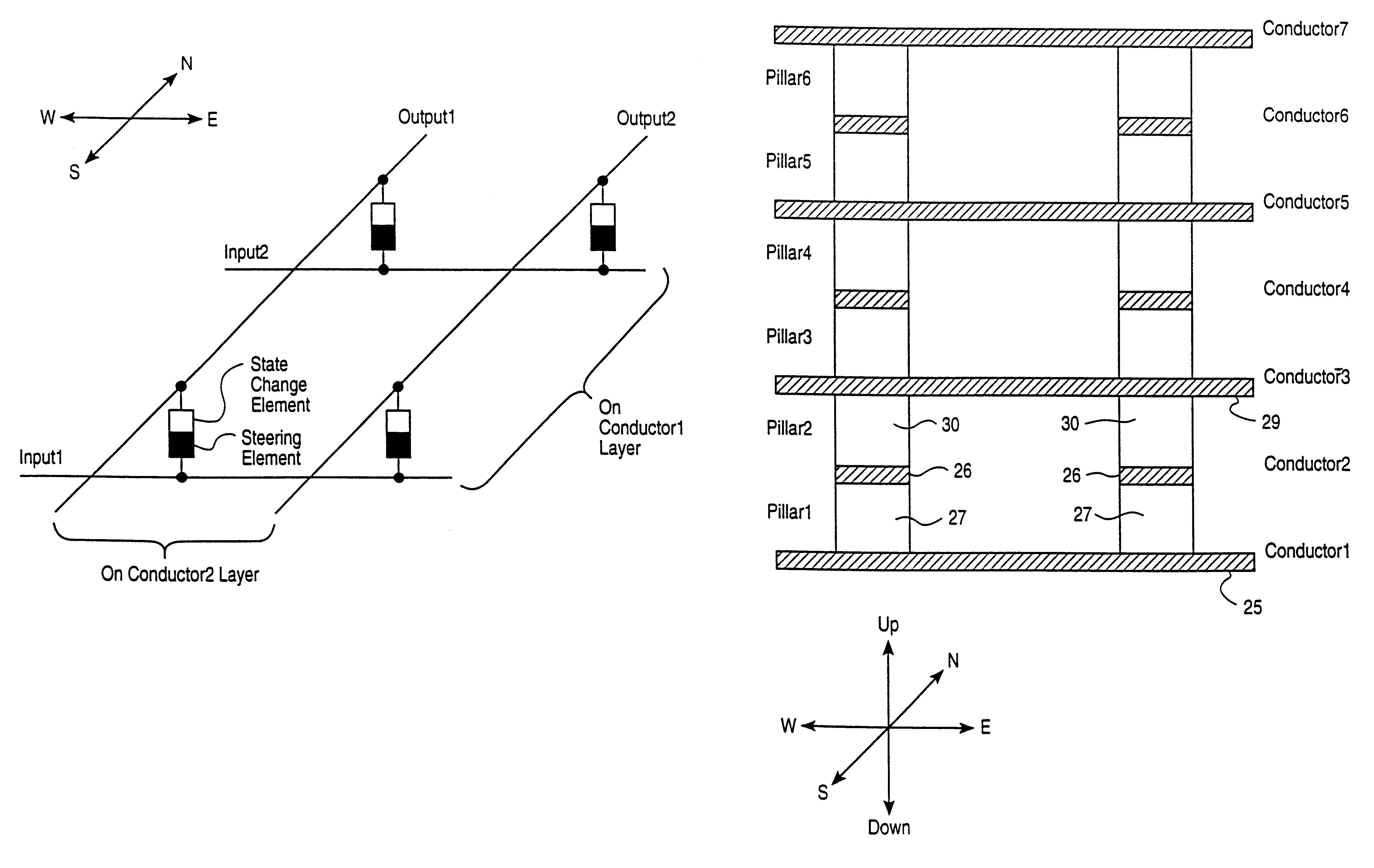
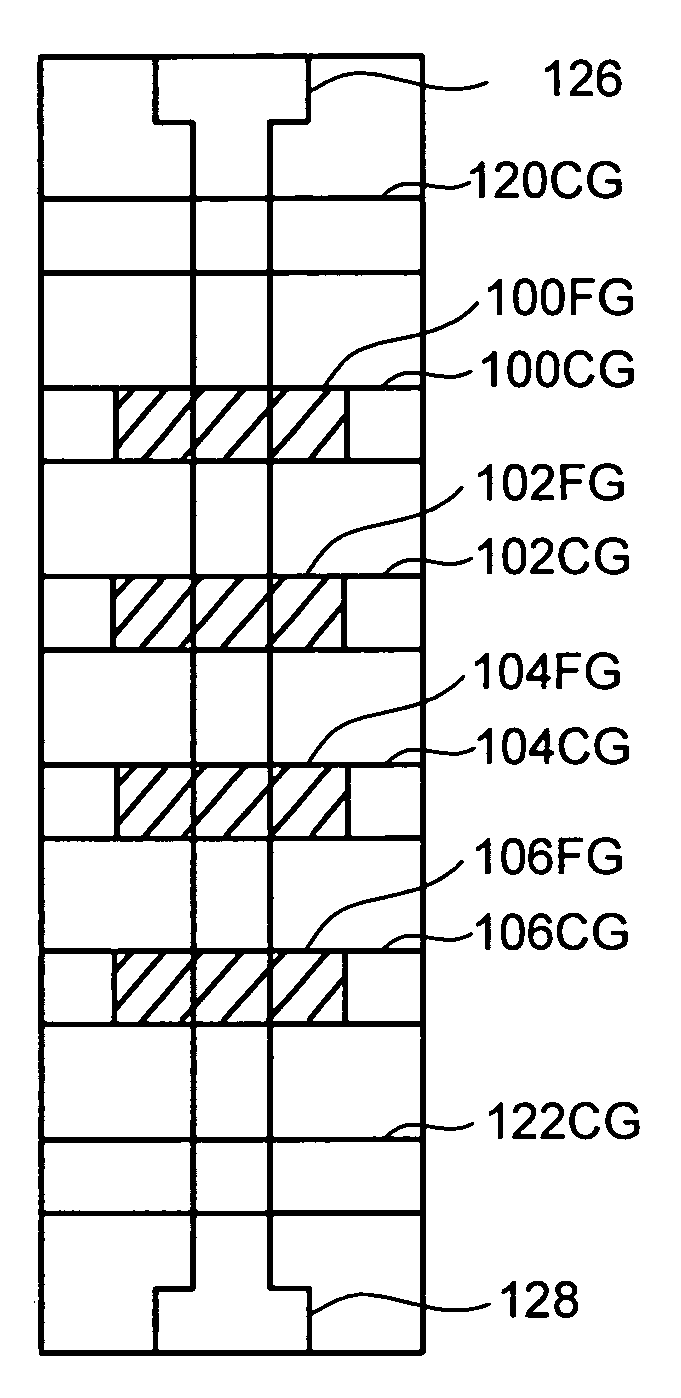
Monolithic three dimensional array of charge storage devices containing a planarized surface
There is provided a monolithic three dimensional array of charge storage devices which includes a plurality of device levels, wherein at least one surface between two successive device levels is planarized by chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
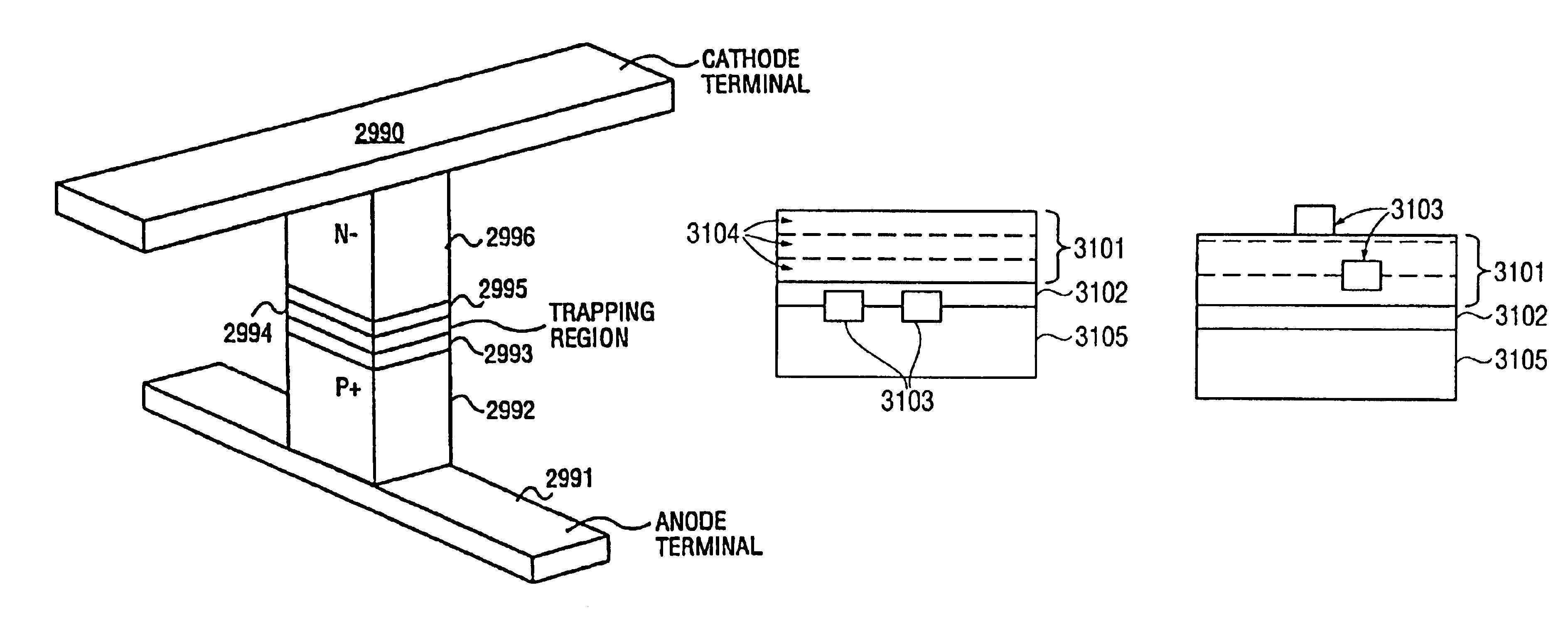
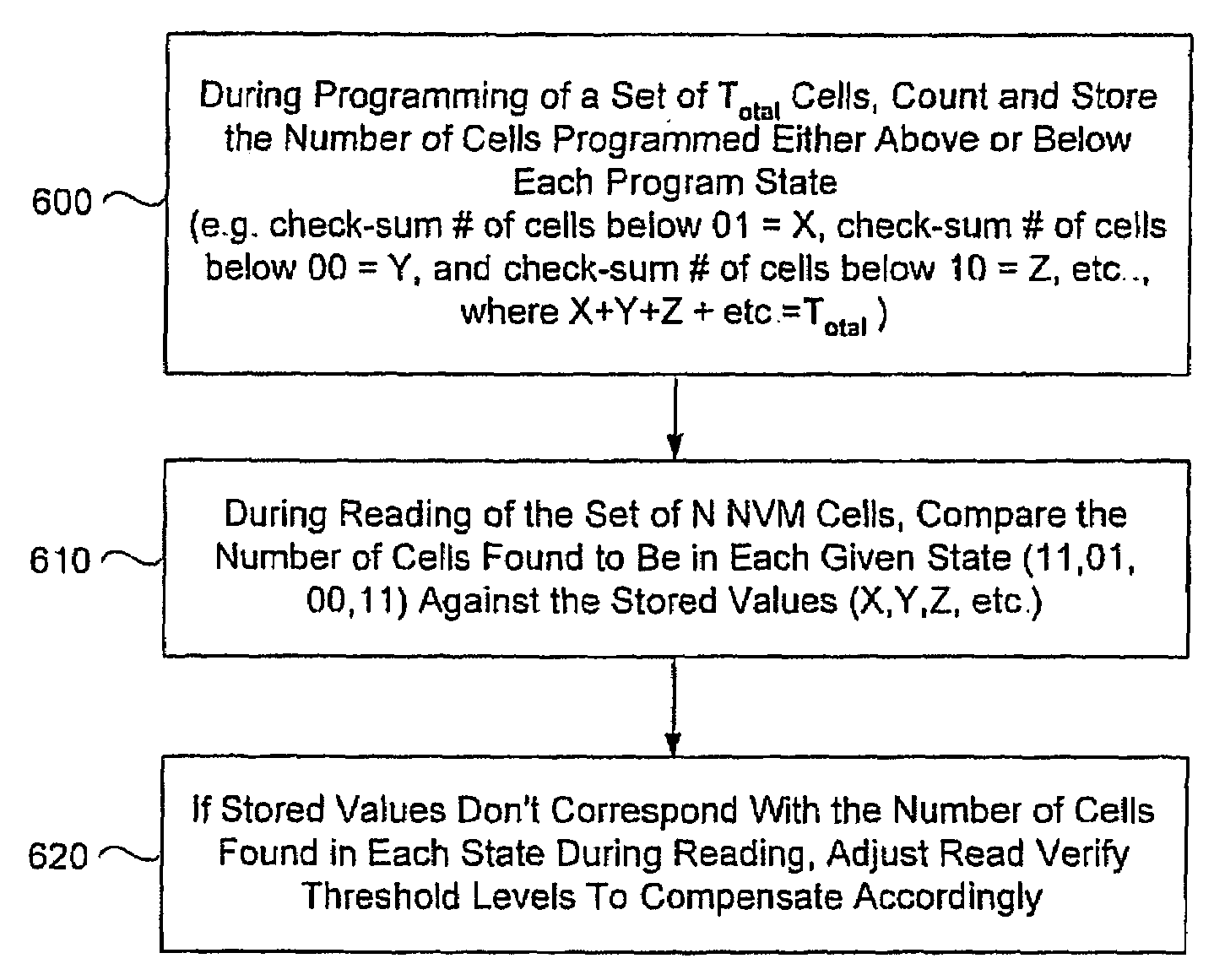
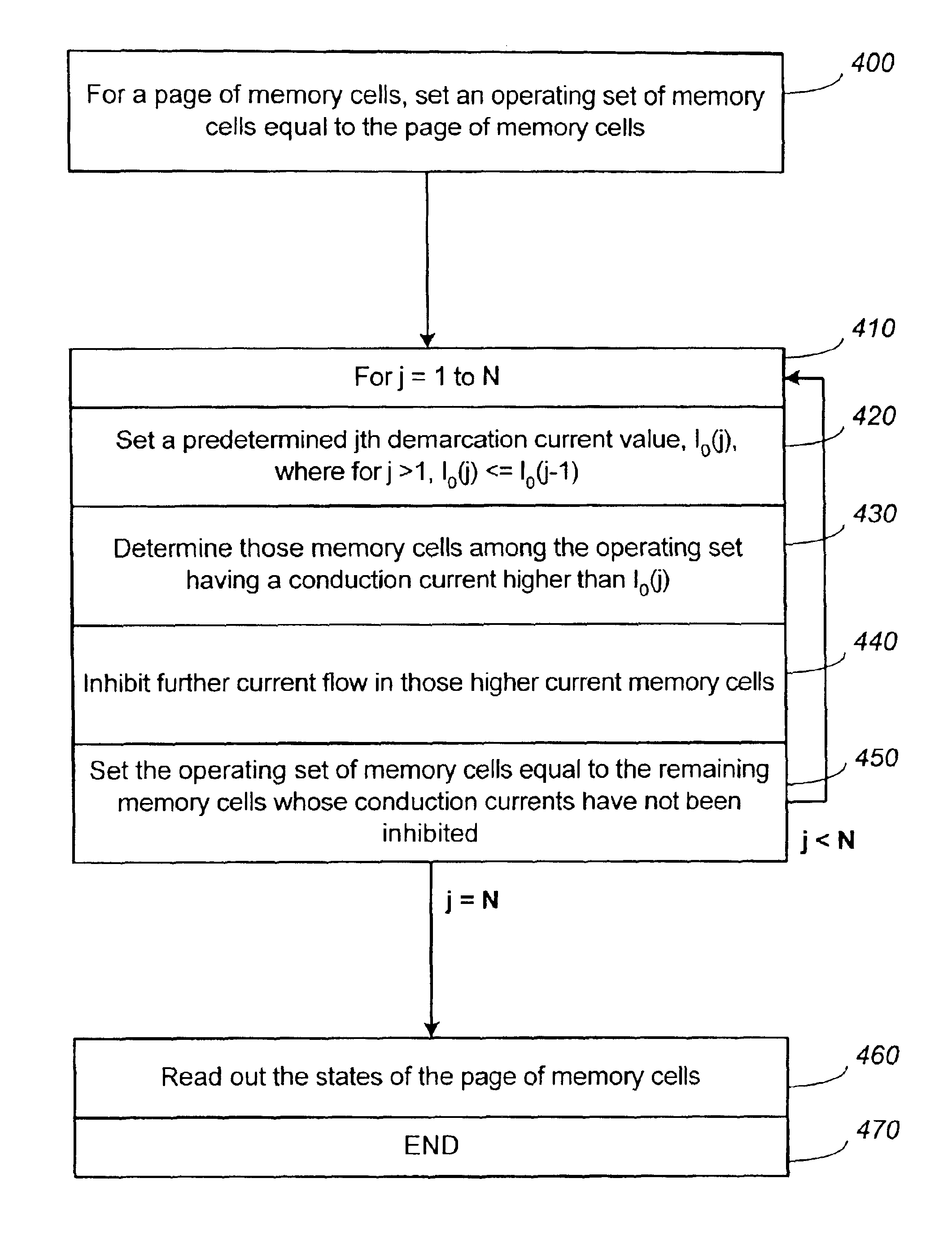
Method circuit and system for read error detection in a non-volatile memory array
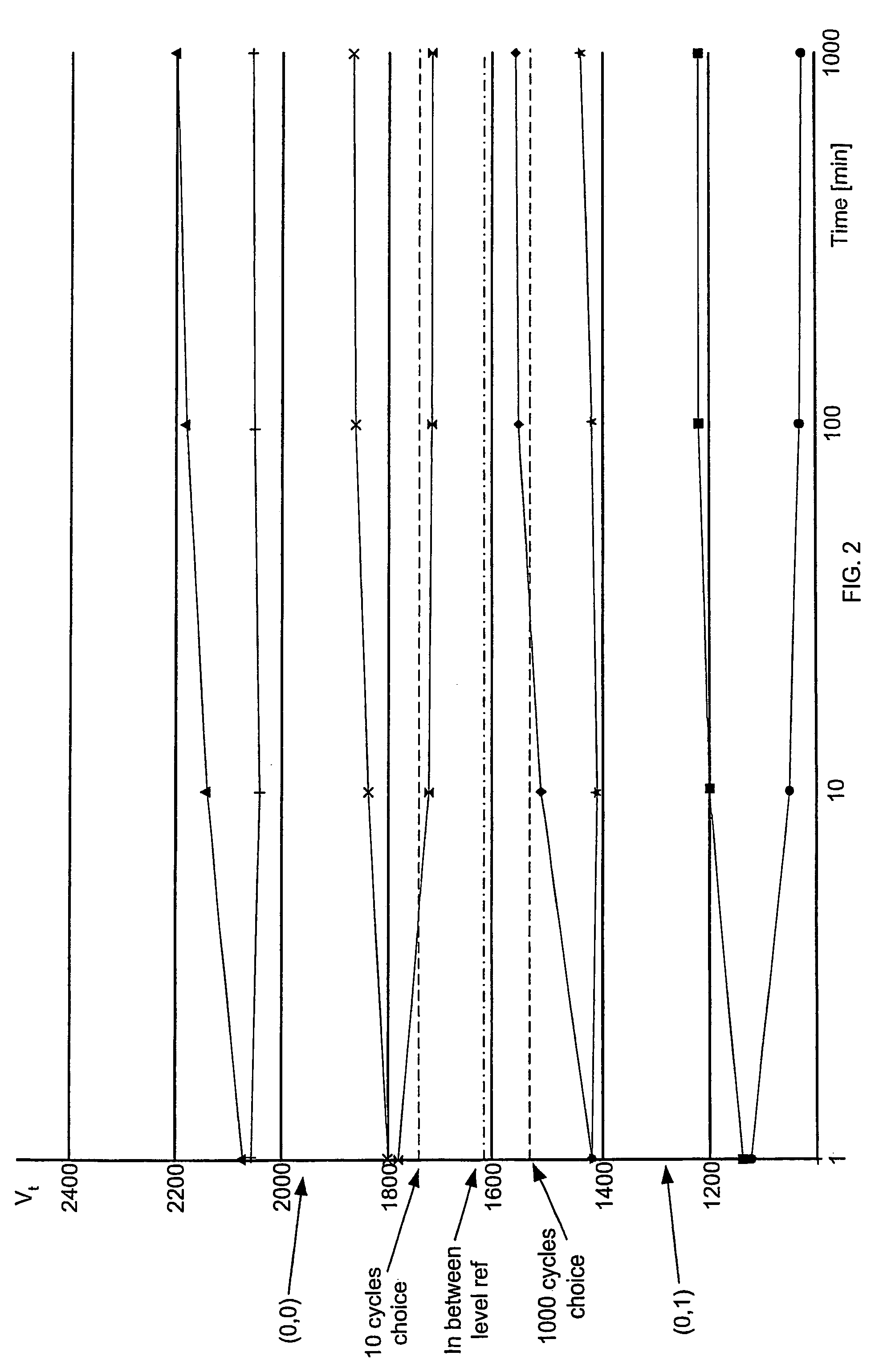
The present invention is a method, circuit and system for determining a reference voltage to be used in reading cells programmed to a given program state. Some embodiments of the present invention relate to a system, method and circuit for establishing a set of operating reference cells to be used in operating (e.g. reading) cells in a NVM block or array. As part of the present invention, at least a subset of cells of the NVM block or array may be read and the number of cells found at a given state associated with the array may be compared to one or more check sum values obtained during programming of the at least a subset of cells. A Read Verify threshold reference voltage associated with the given program state or associated with an adjacent state may be adjusted based on the result of the comparison.
Owner:SPANSION ISRAEL
Nonvolatile memory on SOI and compound semiconductor substrates and method of fabrication
A nonvolatile memory array is provided. The array includes an array of nonvolatile memory devices, at least one driver circuit, and a substrate. The at least one driver circuit is not located in a bulk monocrystalline silicon substrate. The at least one driver circuit may be located in a silicon on insulator substrate or in a compound semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory and method with reduced neighboring field errors
InactiveUS6987693B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageNon-volatile memoryParallel programing
A memory device and a method thereof allow programming and sensing a plurality of memory cells in parallel in order to minimize errors caused by coupling from fields of neighboring cells and to improve performance. The memory device and method have the plurality of memory cells linked by the same word line and a read / write circuit is coupled to each memory cells in a contiguous manner. Thus, a memory cell and its neighbors are programmed together and the field environment for each memory cell relative to its neighbors during programming and subsequent reading is less varying. This improves performance and reduces errors caused by coupling from fields of neighboring cells, as compared to conventional architectures and methods in which cells on even columns are programmed independently of cells in odd columns.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Compensating for coupling during read operations on non-volatile memory
Shifts in the apparent charge stored on a floating gate (or other charge storing element) of a non-volatile memory cell can occur because of the coupling of an electric field based on the charge stored in adjacent floating gates (or other adjacent charge storing elements). The problem occurs most pronouncedly between sets of adjacent memory cells that have been programmed at different times. To compensate for this coupling, the read process for a given memory cell will take into account the programmed state of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Reducing the impact of interference during programming
ActiveUS7869273B2Reduce the impact of interferenceRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingNon-volatile memory
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
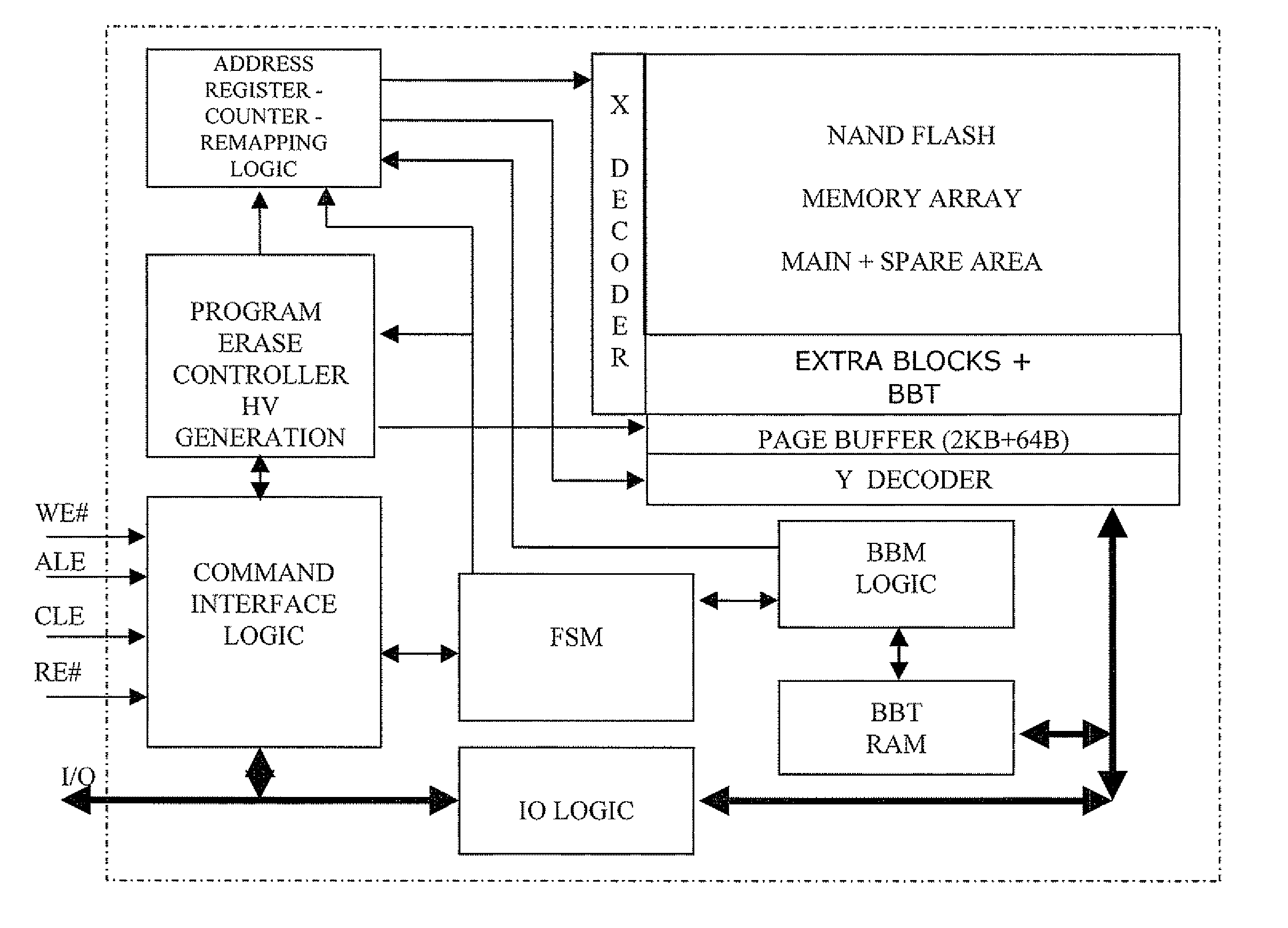
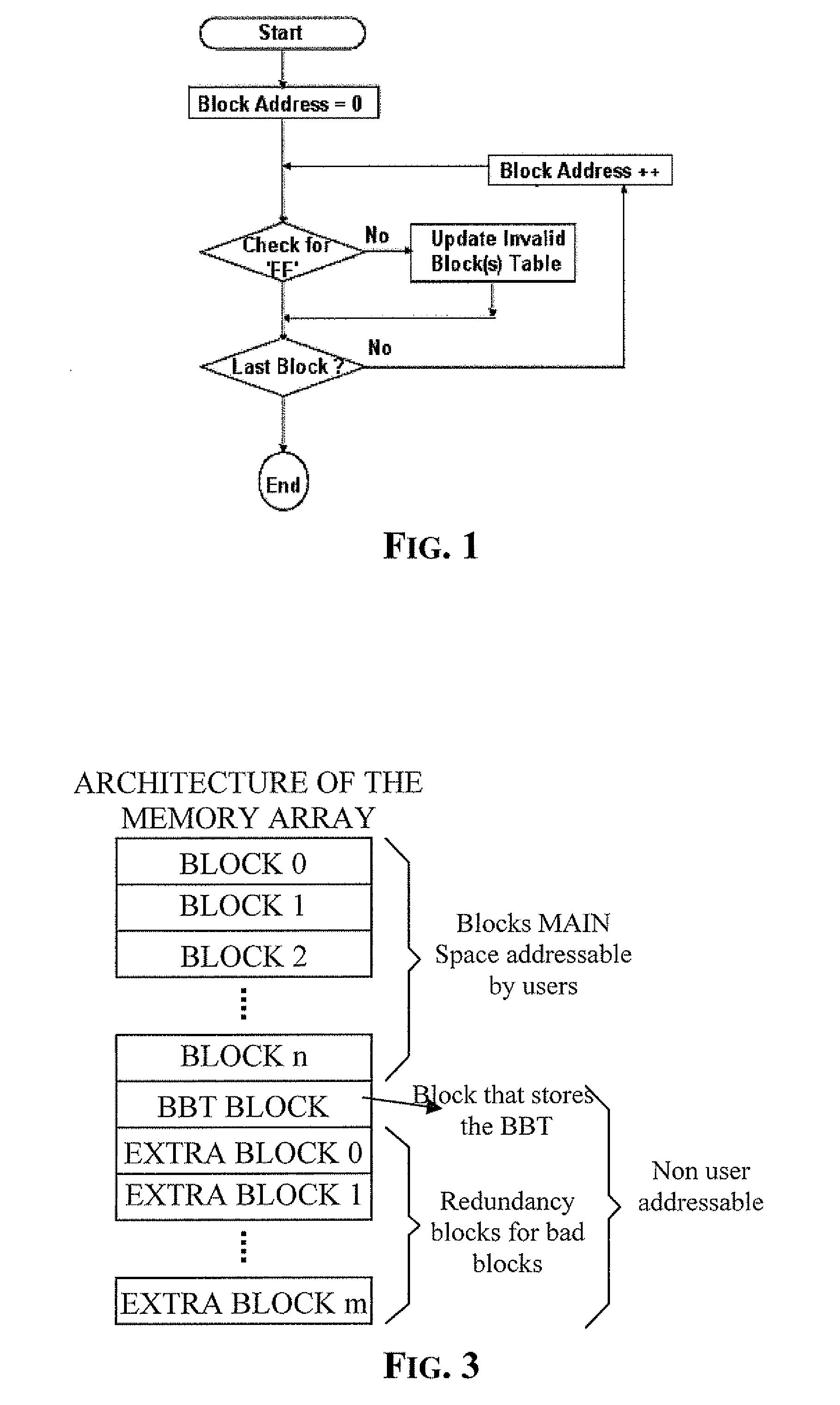
Method of managing fails in a non-volatile memory device and relative memory device
ActiveUS20070109856A1Easy to implementLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityWorking life
A method of managing fails in a non-volatile memory device including an array of cells grouped in blocks of data storage cells includes defining in the array a first subset of user addressable blocks of cells, and a second subset of redundancy blocks of cells. Each block including at least one failed cell in the first subset is located during a test on wafer of the non-volatile memory device. Each block is marked as bad, and a bad block address table of respective codes is stored in a non-volatile memory buffer. At power-on, the bad block address table is copied from the non-volatile memory buffer to the random access memory. A block of memory cells of the first subset is verified as bad by looking up the bad block address table, and if a block is bad, then remapping access to a corresponding block of redundancy cells. A third subset of non-user addressable blocks of cells is defined in the array for storing the bad block address table of respective codes in an addressable page of cells of a block of the third subset. Each page of the third subset is associated to a corresponding redundancy block. If during the working life of the memory device a block of cells previously judged good in a test phase becomes failed, each block is marked as bad and the stored table in the random access memory is updated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
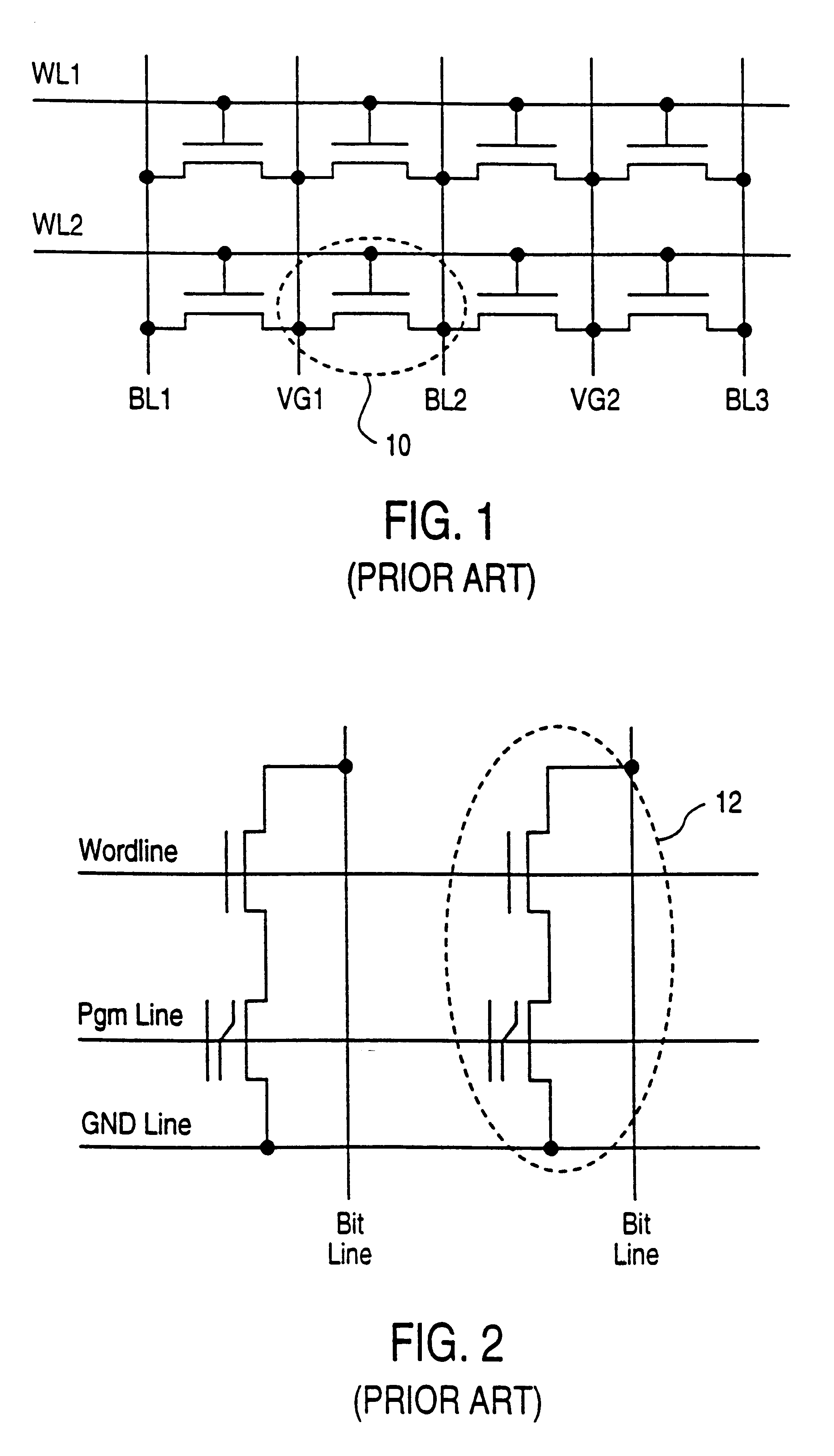
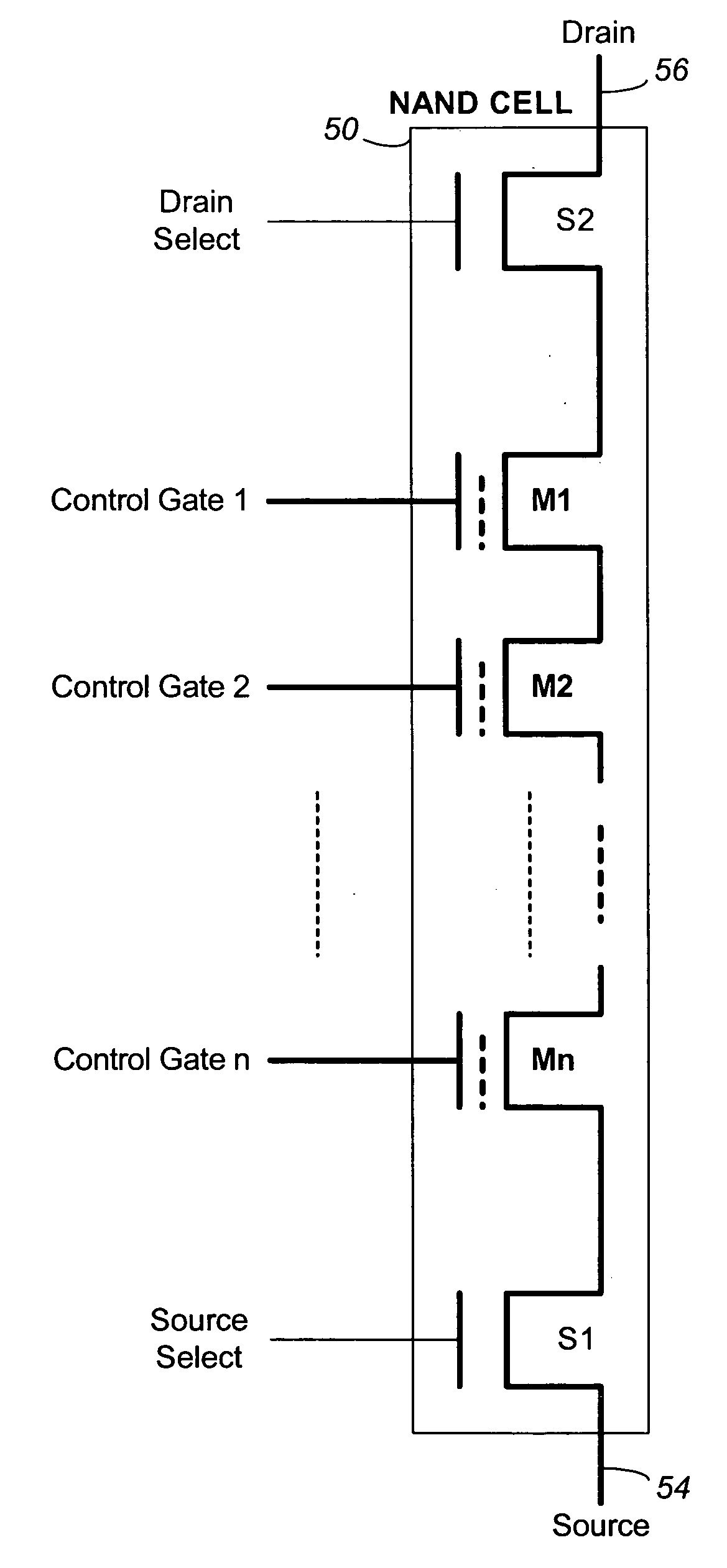
Method for fabricating programmable memory array structures incorporating series-connected transistor strings
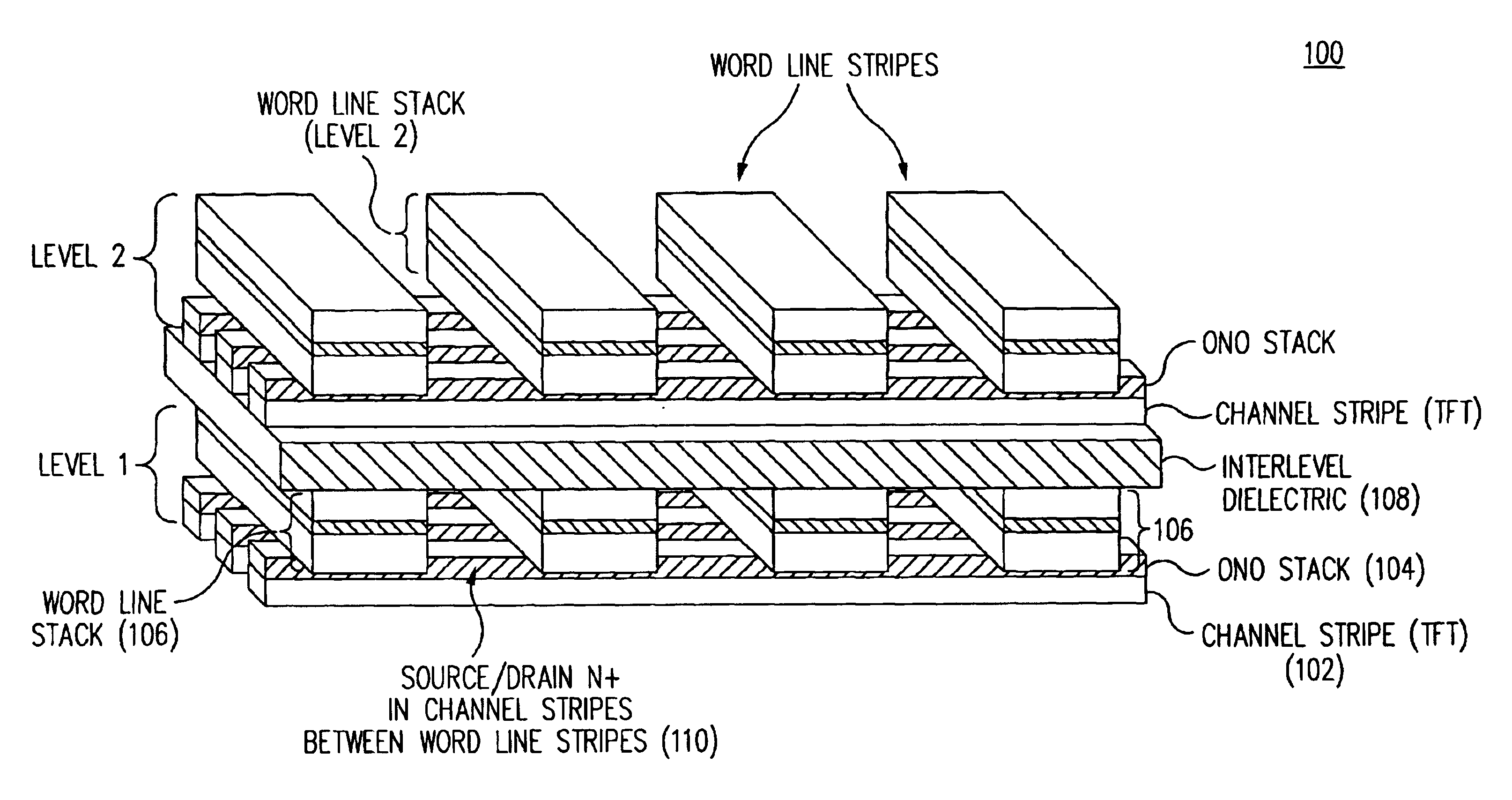
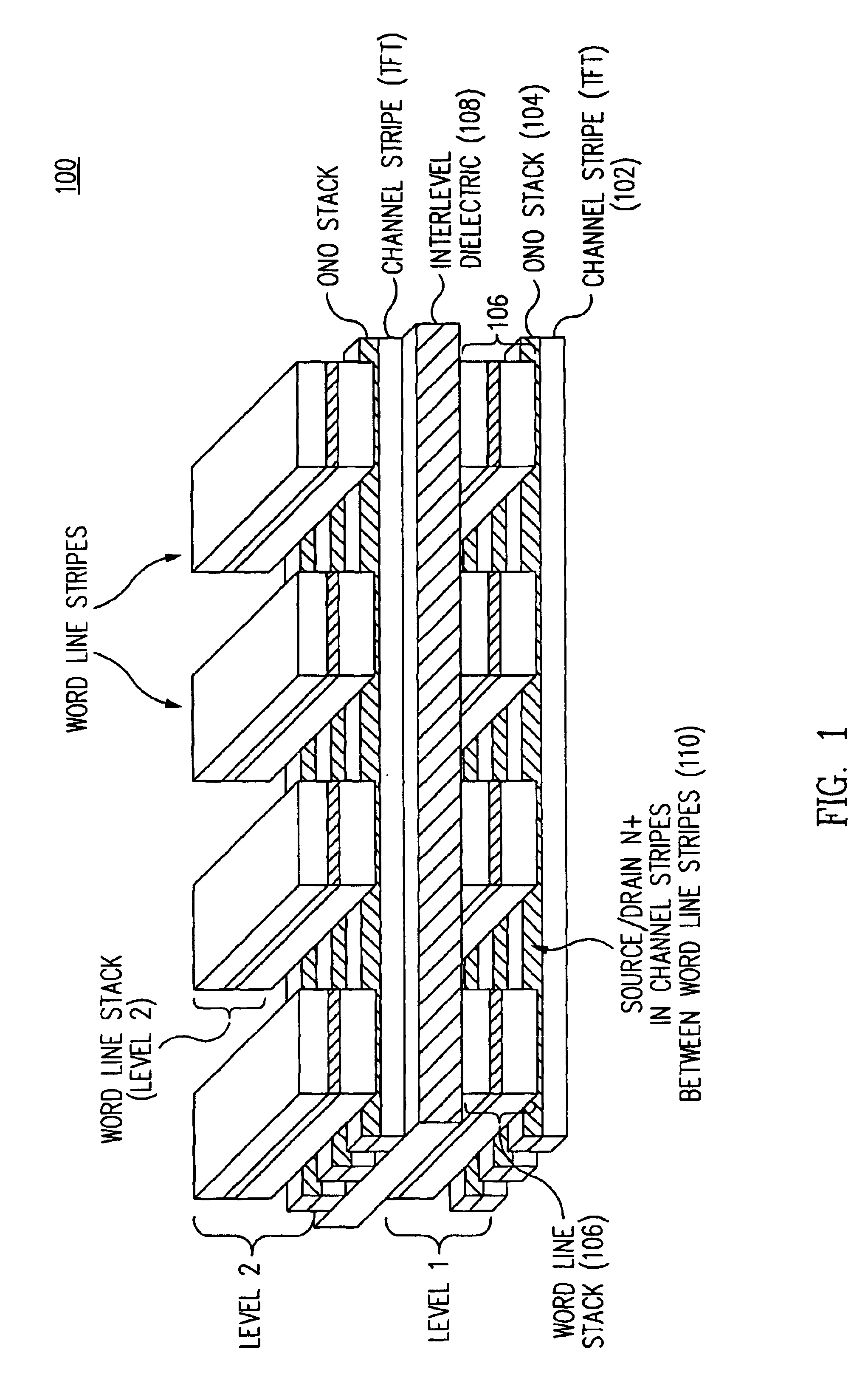
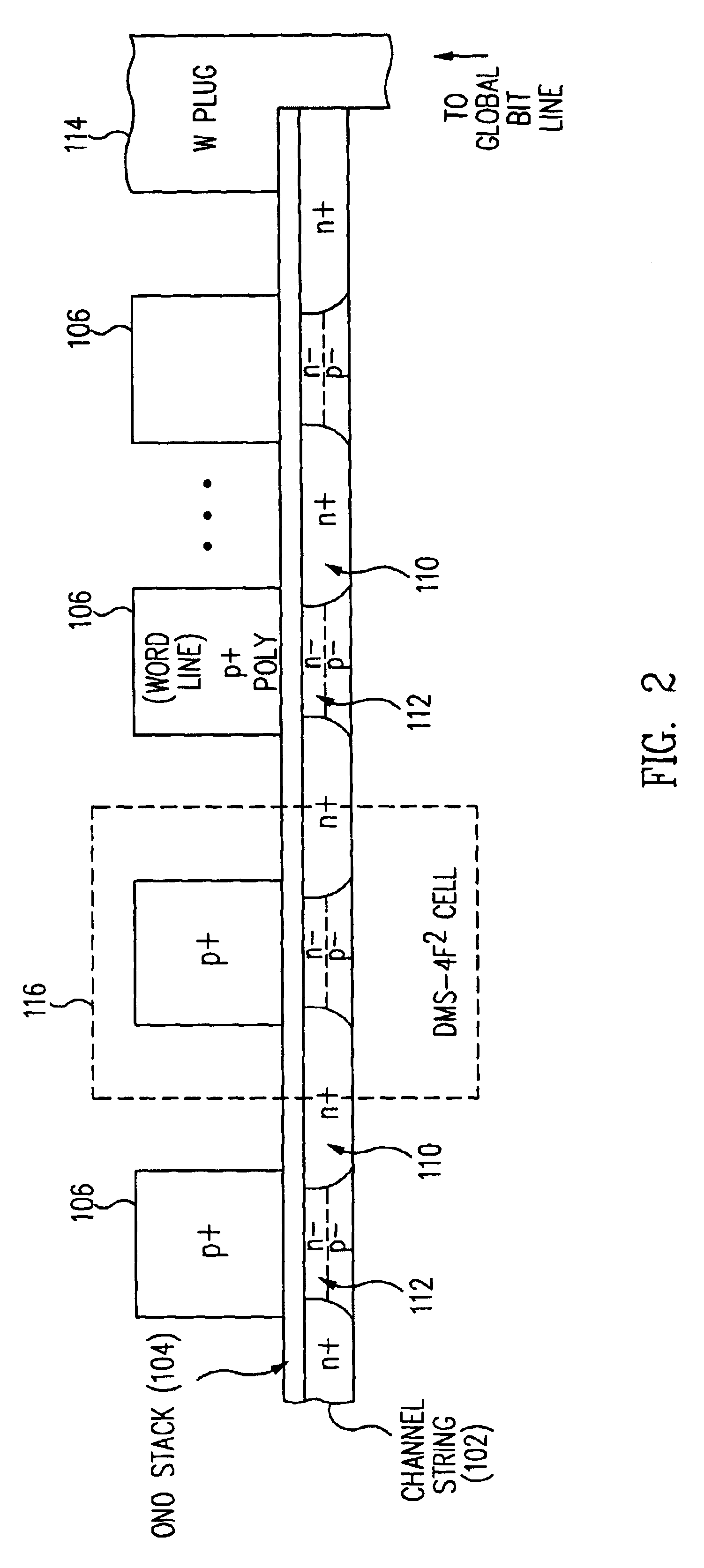
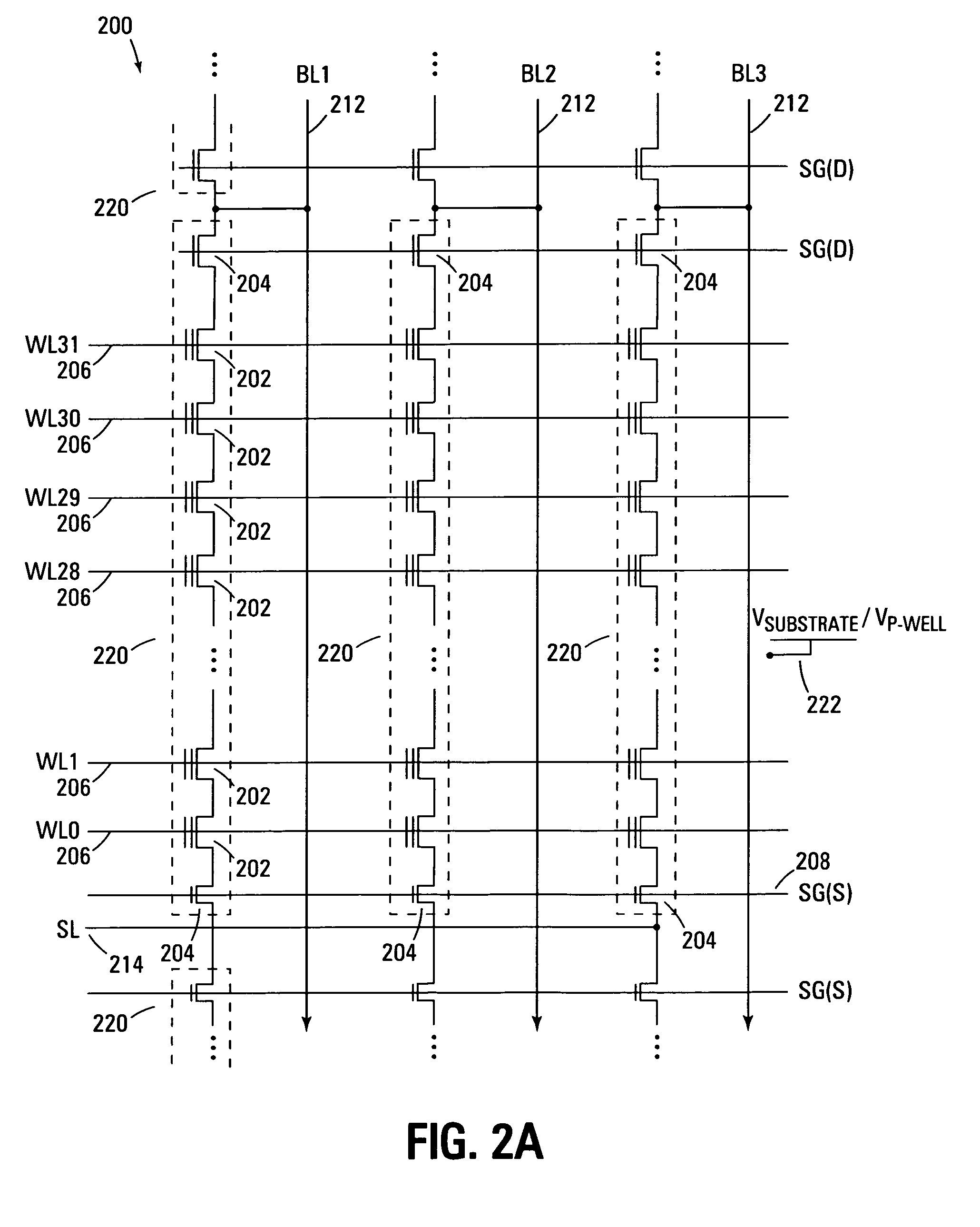
InactiveUS7005350B2Reduce in quantityDense memory arraySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineComputer architecture
A three-dimensional flash memory array incorporates thin film transistors having a charge storage dielectric arranged in series-connected NAND strings to achieve a 4F2 memory cell layout. The memory array may be programmed and erased using only tunneling currents, and no leakage paths are formed through non-selected memory cells. Each NAND string includes two block select devices for respectively coupling one end of the NAND string to a global bit line, and the other end to a shared bias node. Pairs of NAND strings within a block share the same global bit line. The memory cells are preferably depletion mode SONOS devices, as are the block select devices. The memory cells may be programmed to a near depletion threshold voltage, and the block select devices are maintained in a programmed state having a near depletion mode threshold voltage. NAND strings on more than one layer may be connected to global bit lines on a single layer. By interleaving the NAND strings on each memory level and using two shared bias nodes per block, very little additional overhead is required for the switch devices at each end of the NAND strings. The NAND strings on different memory levels are preferably connected together by way of vertical stacked vias, each preferably connecting to more than one memory level. Each memory level may be produced with less than three masks per level.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Maintaining erase counts in non-volatile storage systems
InactiveUS20040080985A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData structureVolatile memory
Methods and apparatus for storing erase counts in a non-volatile memory of a non-volatile memory system are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a data structure in a non-volatile memory includes a first indicator that provides an indication of a number of times a first block of a plurality of blocks in a non-volatile memory has been erased. The data structure also includes a header that is arranged to contain information relating to the blocks in the non-volatile memory.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Programming method to reduce gate coupling interference for non-volatile memory
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
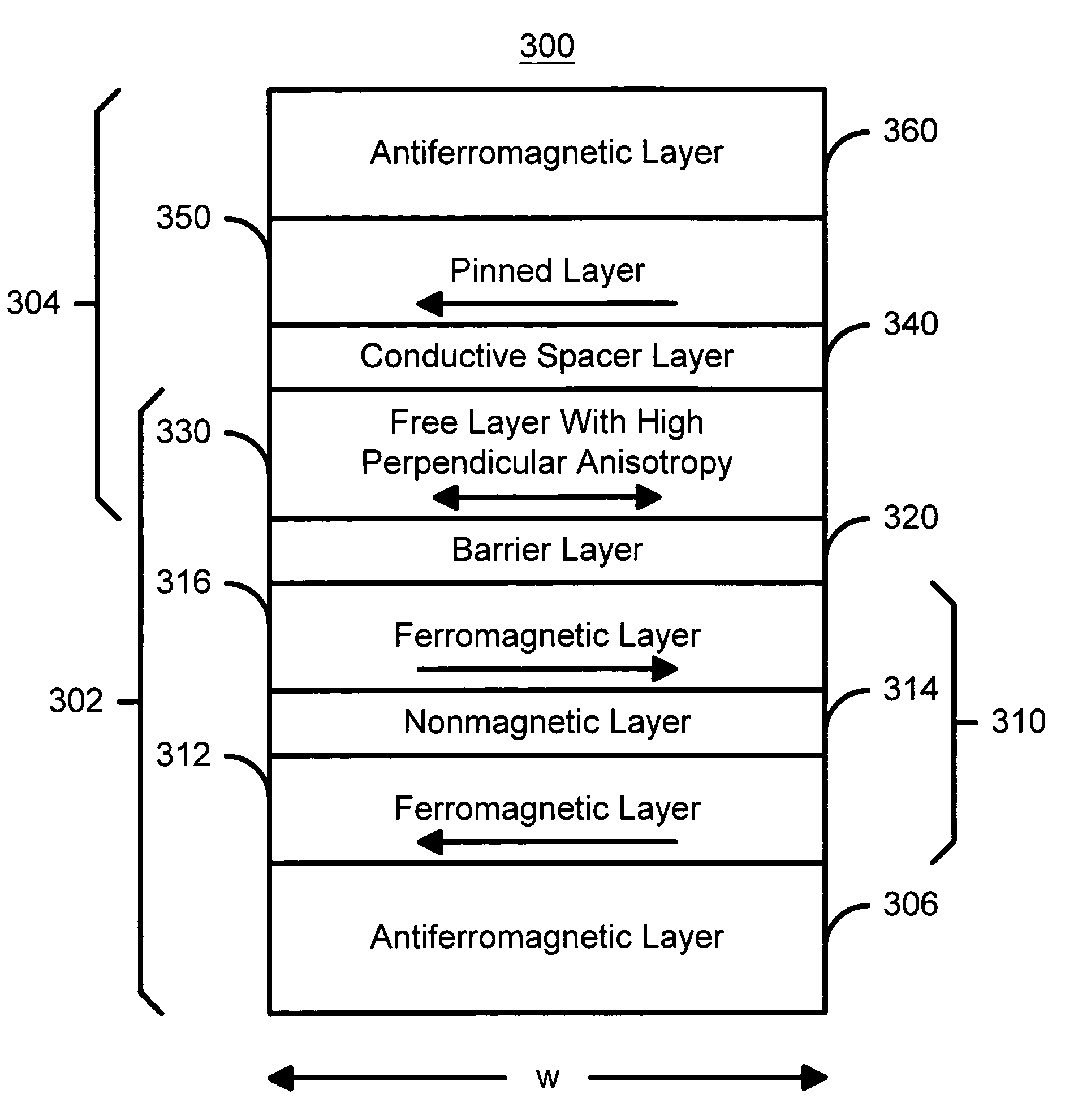
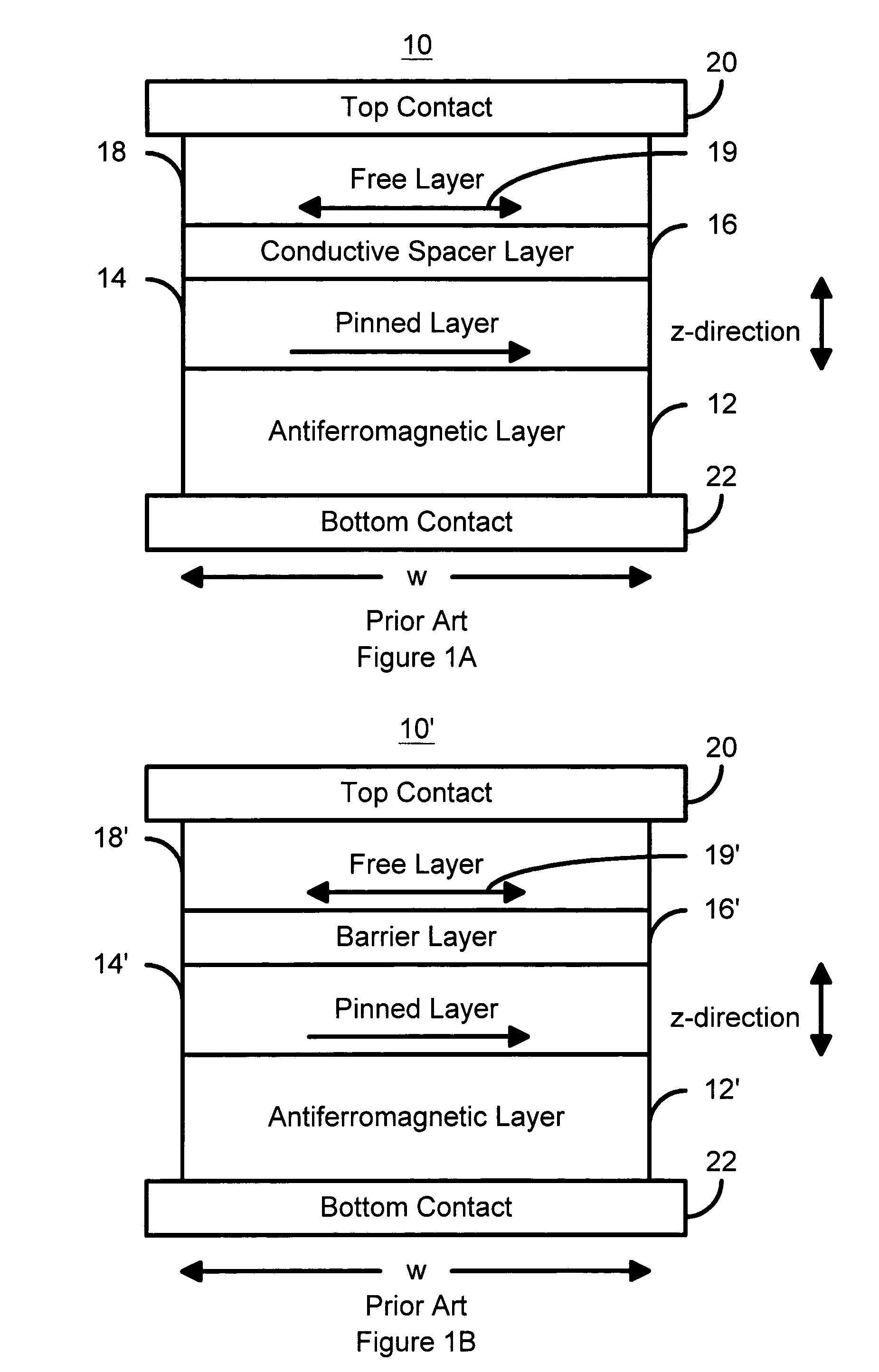
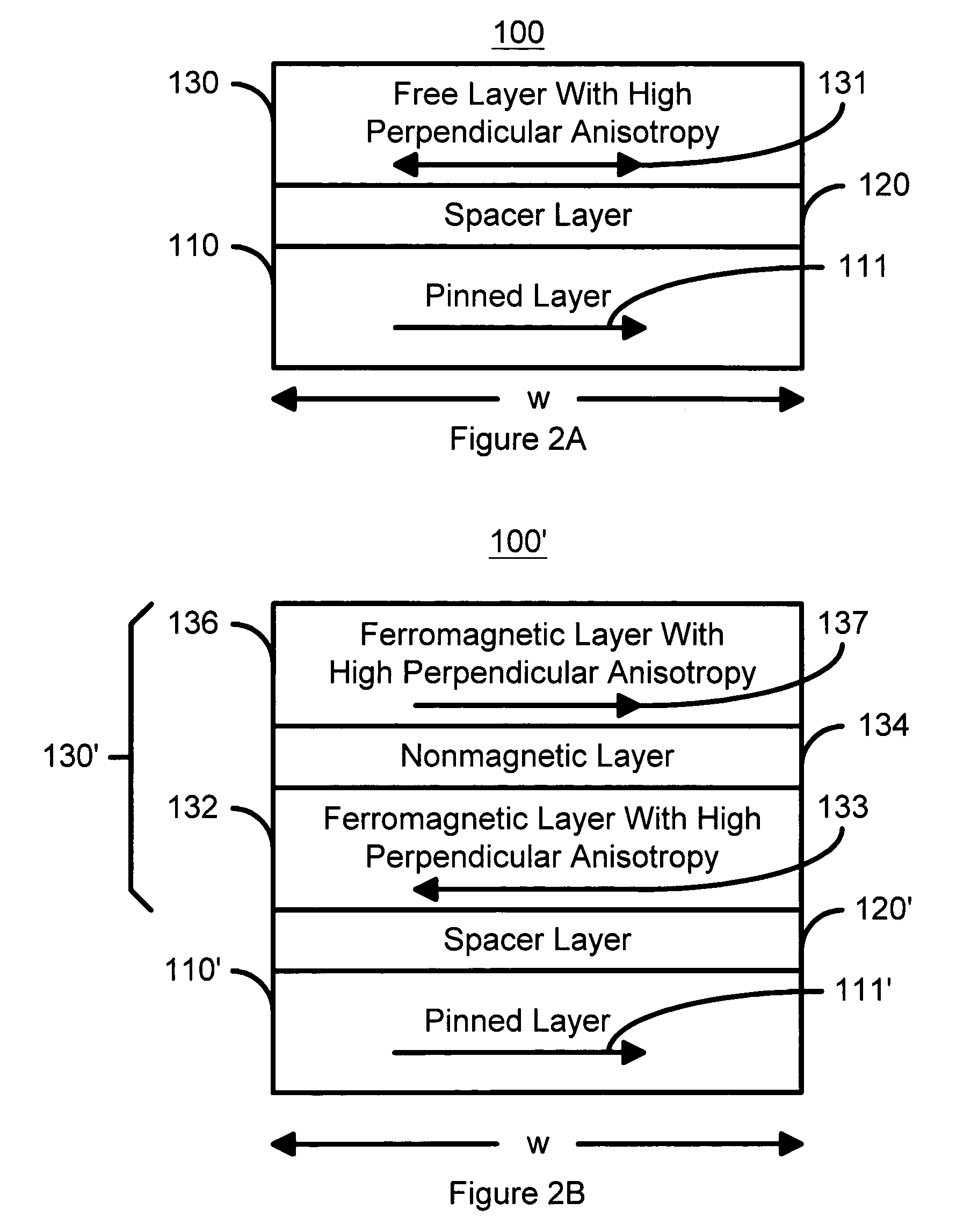
Spin transfer magnetic element with free layers having high perpendicular anisotropy and in-plane equilibrium magnetization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. At least one free layer has a high perpendicular anisotropy. The high perpendicular anisotropy has a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is at least twenty and less than one hundred percent of the out-of-plane demagnetization energy.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
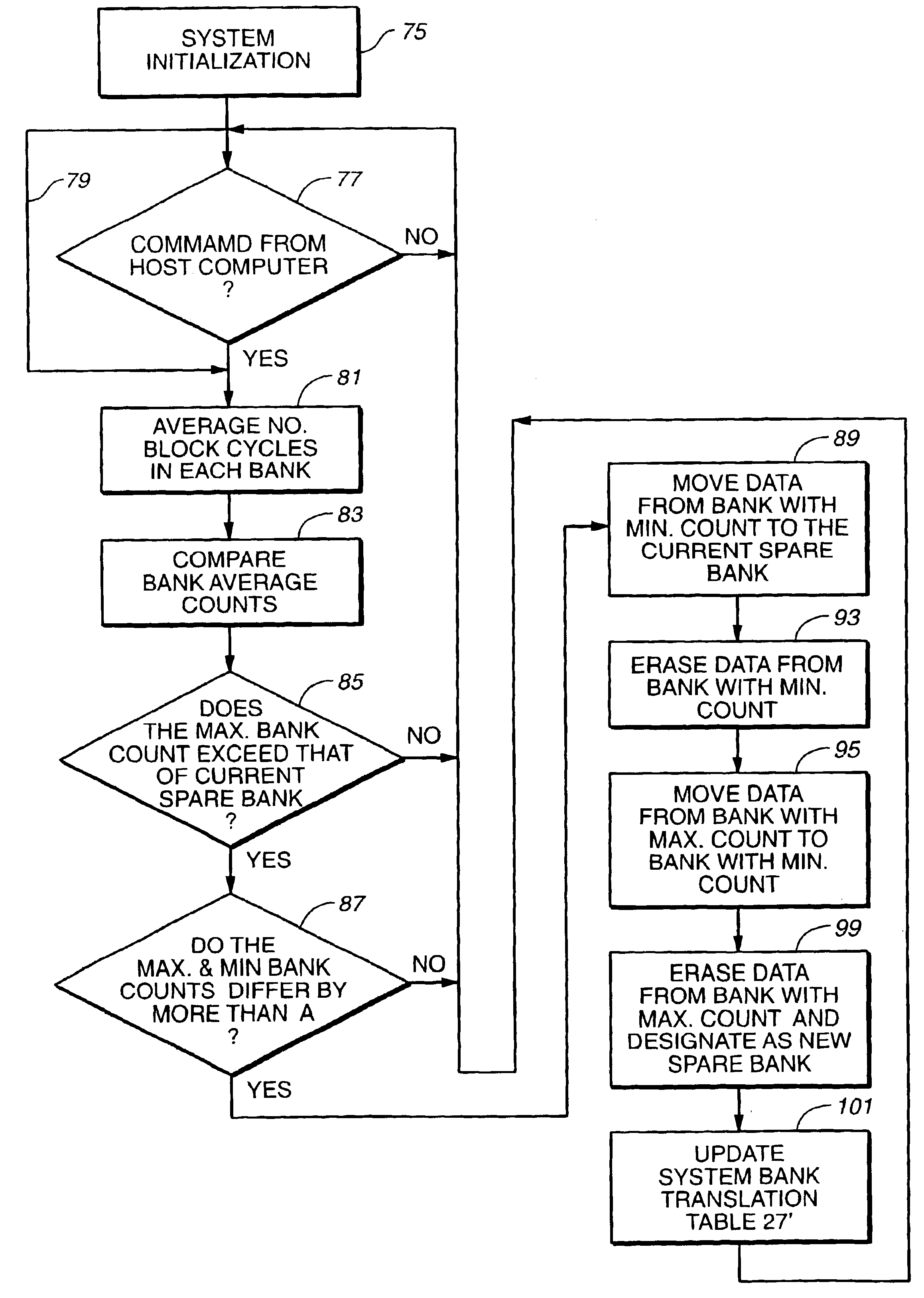
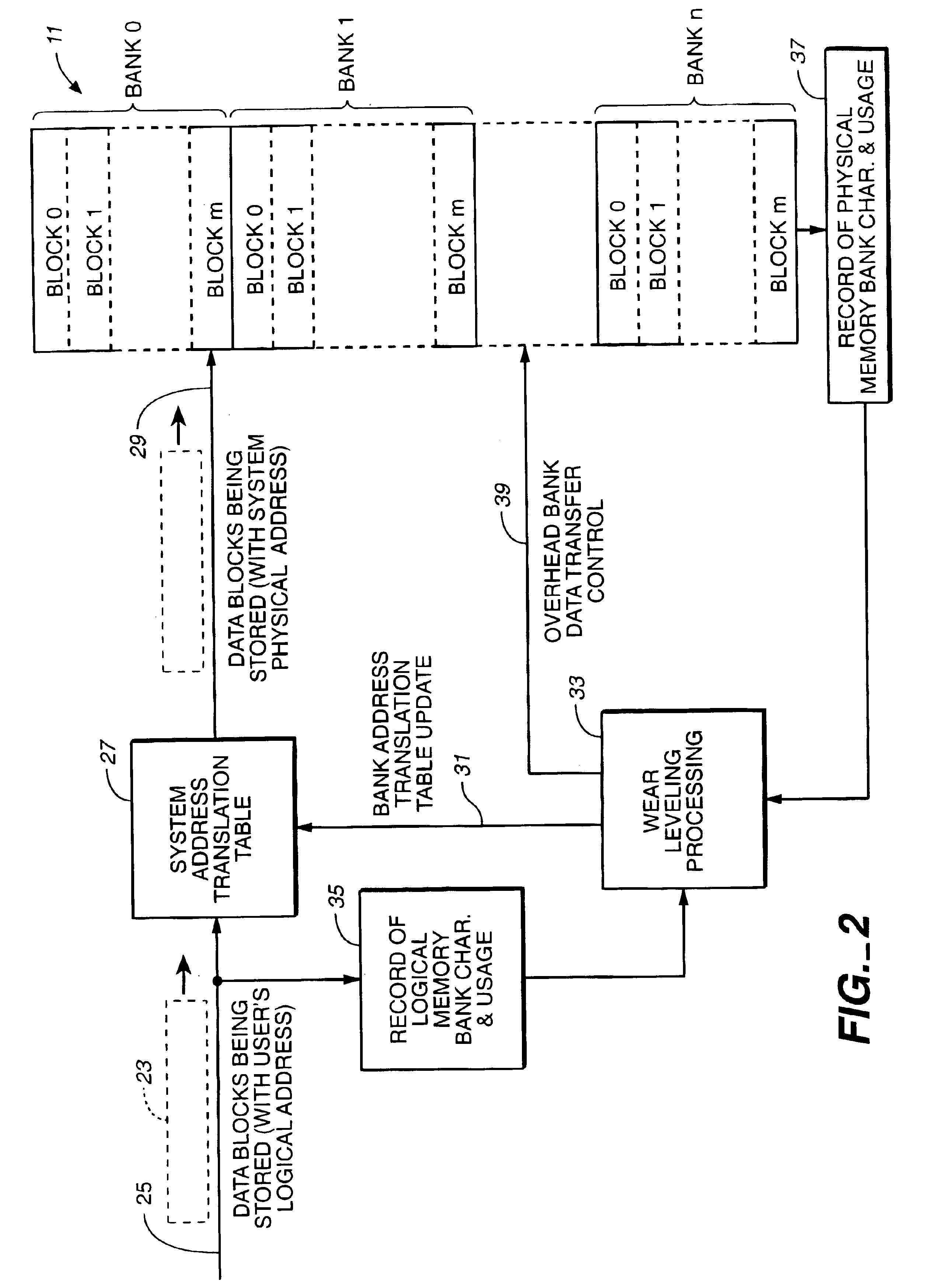
Wear leveling techniques for flash EEPROM systems
InactiveUS6850443B2Avoid uneven wearExtended service lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesElectricityProgrammable read-only memory
A mass storage system made of flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (“EEPROM”) cells organized into blocks, the blocks in turn being grouped into memory banks, is managed to even out the numbers of erase and rewrite cycles experienced by the memory banks in order to extend the service lifetime of the memory system. Since this type of memory cell becomes unusable after a finite number of erase and rewrite cycles, although in the tens of thousands of cycles, uneven use of the memory banks is avoided so that the entire memory does not become inoperative because one of its banks has reached its end of life while others of the banks are little used. Relative use of the memory banks is monitored and, in response to detection of uneven use, have their physical addresses periodically swapped for each other in order to even out their use over the lifetime of the memory.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Programmable sub-surface aggregating metallization structure and method of making same
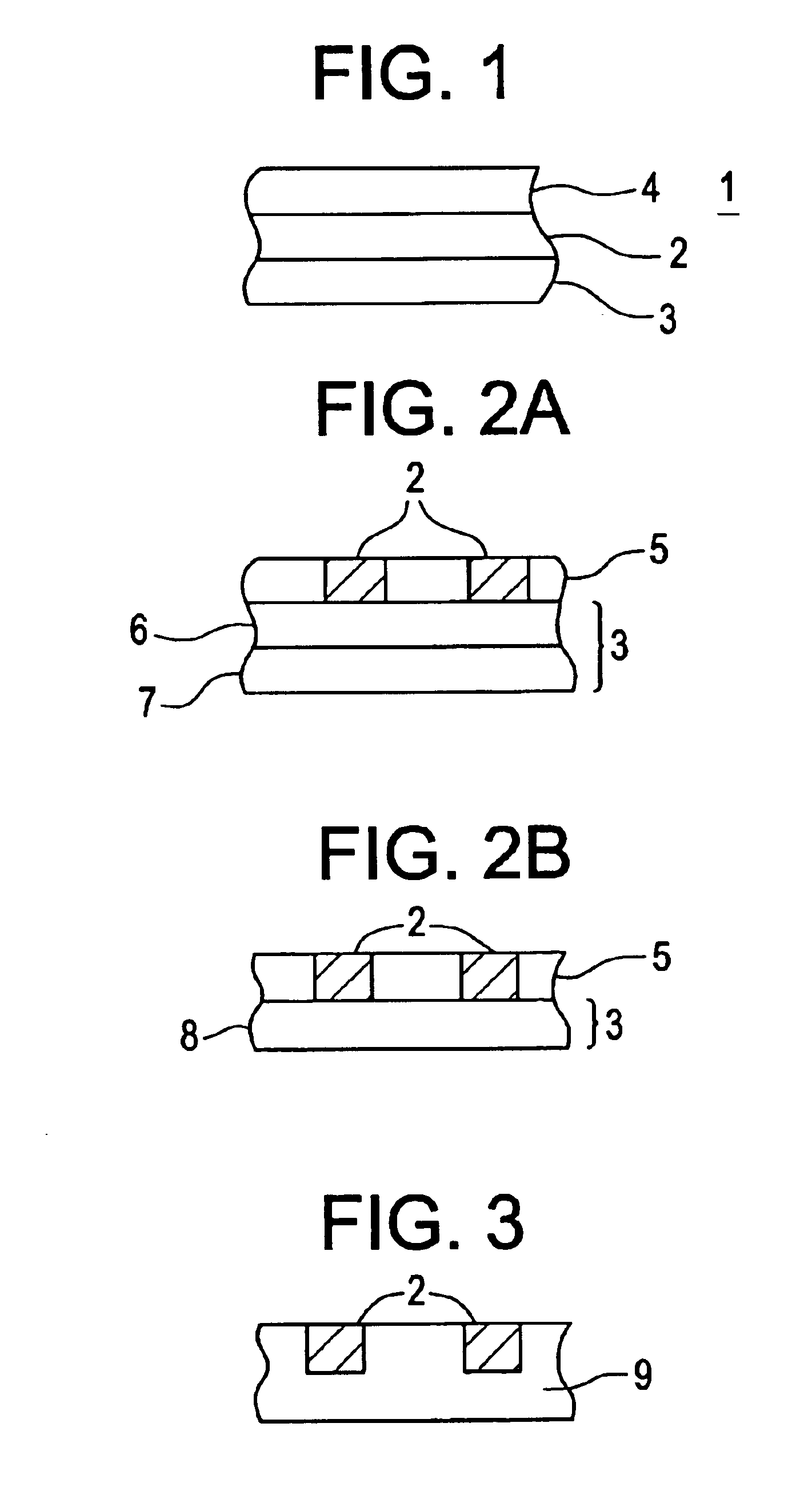
InactiveUS6418049B1Low costHighly manufacturableNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A programmable sub-surface aggregating metallization sructure ("PSAM") includes an ion conductor such as a chalcogenide-glass which includes metal ions and at least two electrodes disposed at opposing surfaces of the ion conductor. Preferably, the ion conductor includes a chalcogenide material with Group IB or Group IIB metals. One of the two electrodes is preferably configured as a cathode and the other as an anode. When a voltage is applied between the anode and cathode, a metal dendrite grows from the cathode through the ion conductor towards the anode. The growth rate of the dendrite may be stopped by removing the voltage or the dendrite may be retracted back towards the cathode by reversing the voltage polarity at the anode and cathode. When a voltage is applied for a sufficient length of time, a continuous metal dendrite grows through the ion conductor and connects the electrodes, thereby shorting the device. The continuous metal dendrite then can be broken by applying another voltage. The break in the metal dendrite can be reclosed by applying yet another voltage. Changes in the length of the dendrite or the presence of a break in the dendrite affect the resistance, capacitance, and impedance of the PSAM.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Dram-like nvm memory array and sense amplifier design for high temperature and high endurance operation
InactiveUS20110267883A1Improve threshold voltage sensing marginLarge silicon areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
A DRAM-like non-volatile memory array includes a cell array of non-volatile cell units with a DRAM-like cross-coupled latch-type sense amplifier. Each non-volatile cell unit has two non-volatile cell devices with respective bit lines and source lines running in parallel and laid out perpendicular to the word line associated with the non-volatile cell unit. The two non-volatile cell devices are programmed with erased and programmed threshold voltages as a pair for storing a single bit of binary data. The two bit lines of each non-volatile cell unit are coupled through a Y-decoder and a latch device to the two respective inputs of the latch-type sense amplifier which provides a large sensing margin for the cell array to operate properly even with a narrowed threshold voltage gap. Each non-volatile cell device may be a 2 T FLOTOX-based EEPROM cell, a 2 T flash cell, 11 T flash cell or a 1.5 T split-gate flash cell.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com