Patents
Literature
46 results about "Channel potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transient receptor potential channel, also called TRP channel, superfamily of ion channels occurring in cell membranes that are involved in various types of sensory reception, including thermoreception, chemoreception, mechanoreception, and photoreception.
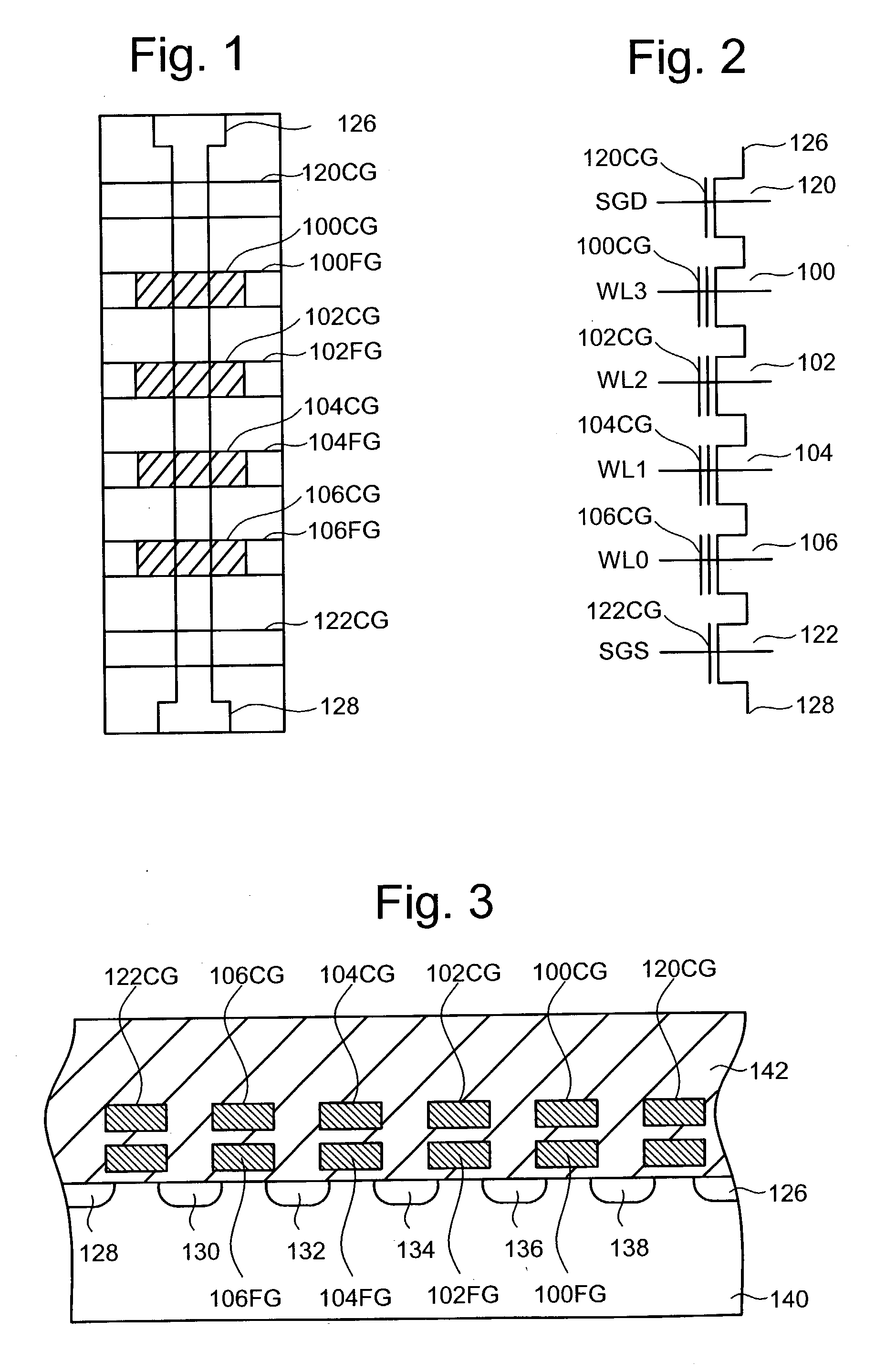
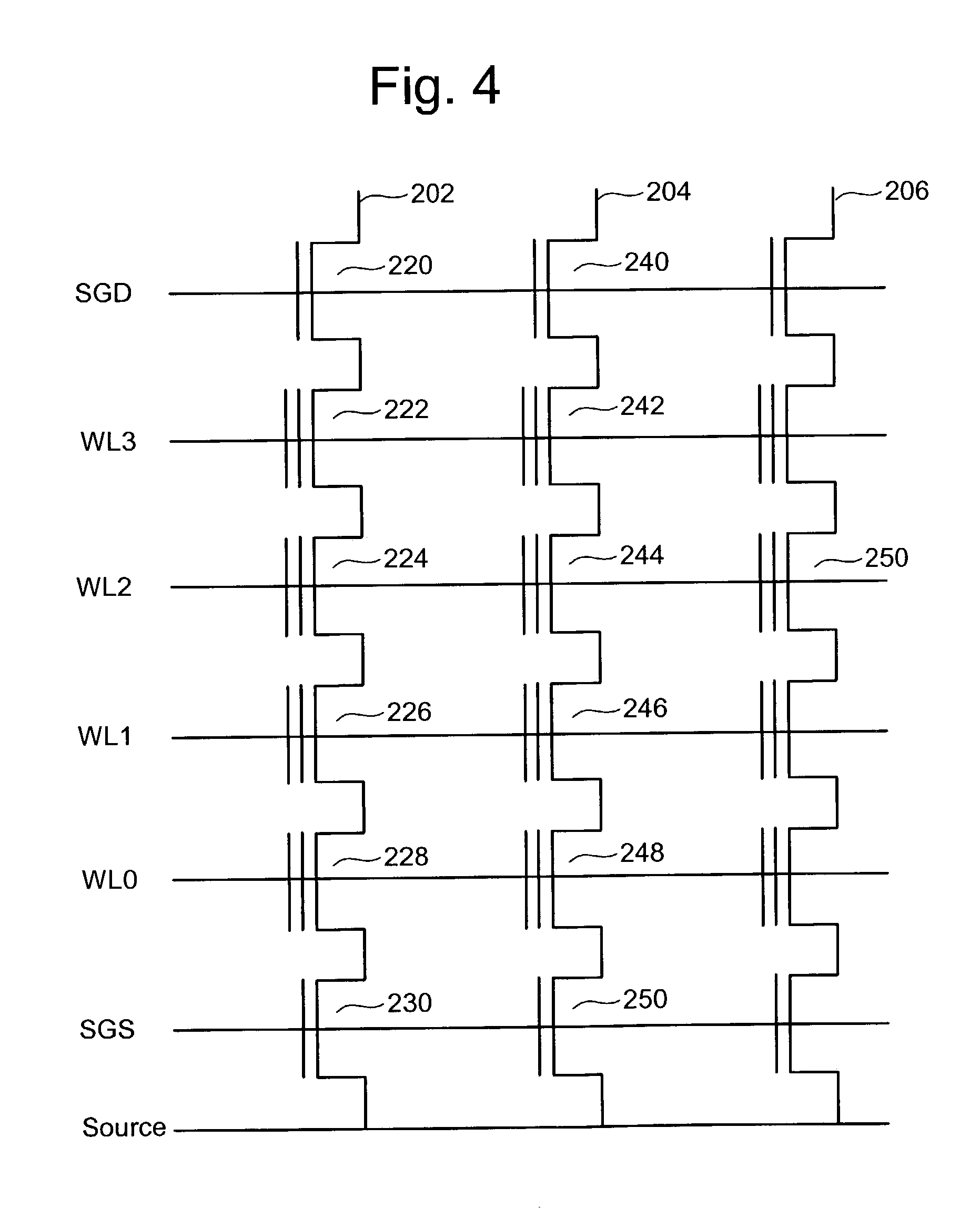
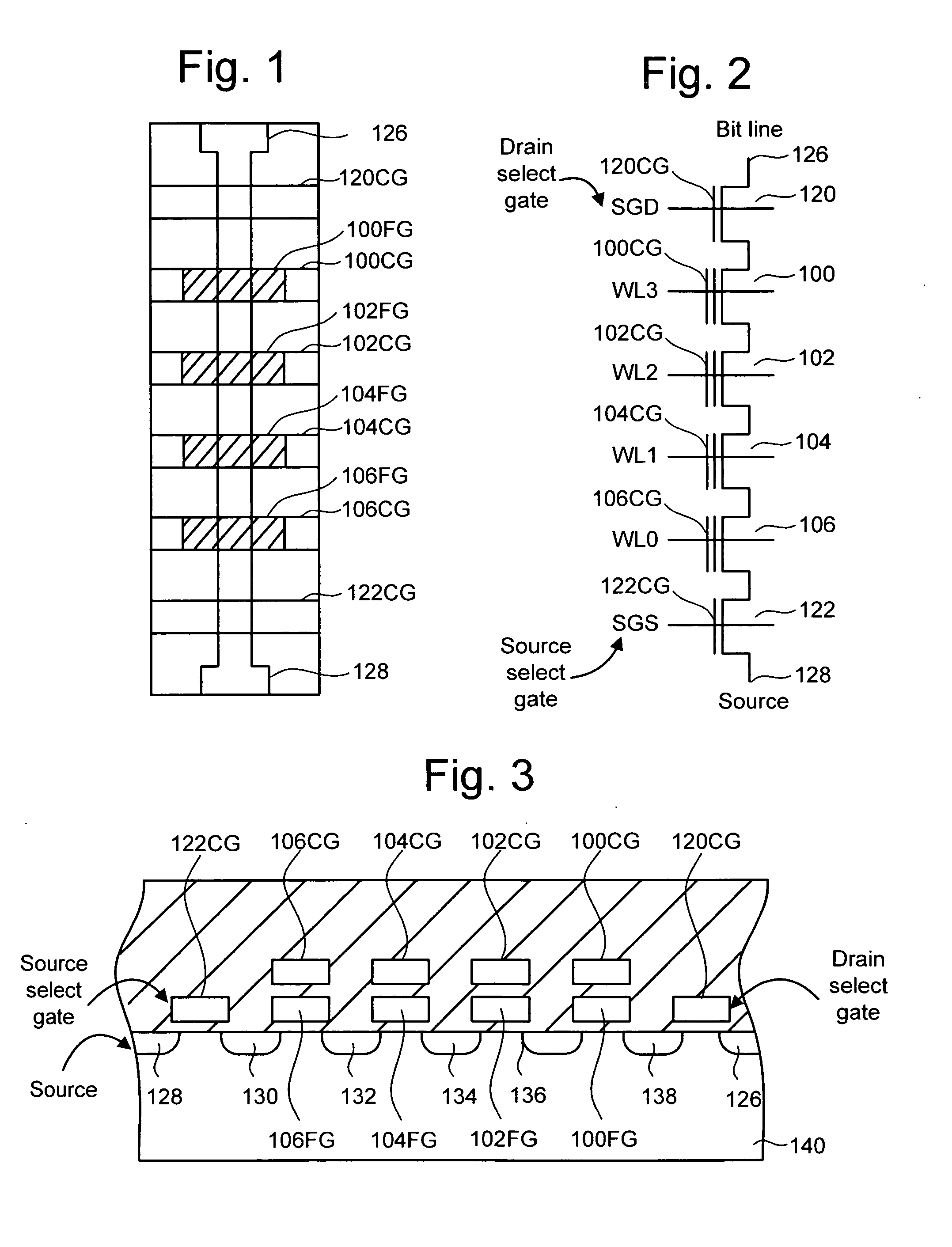
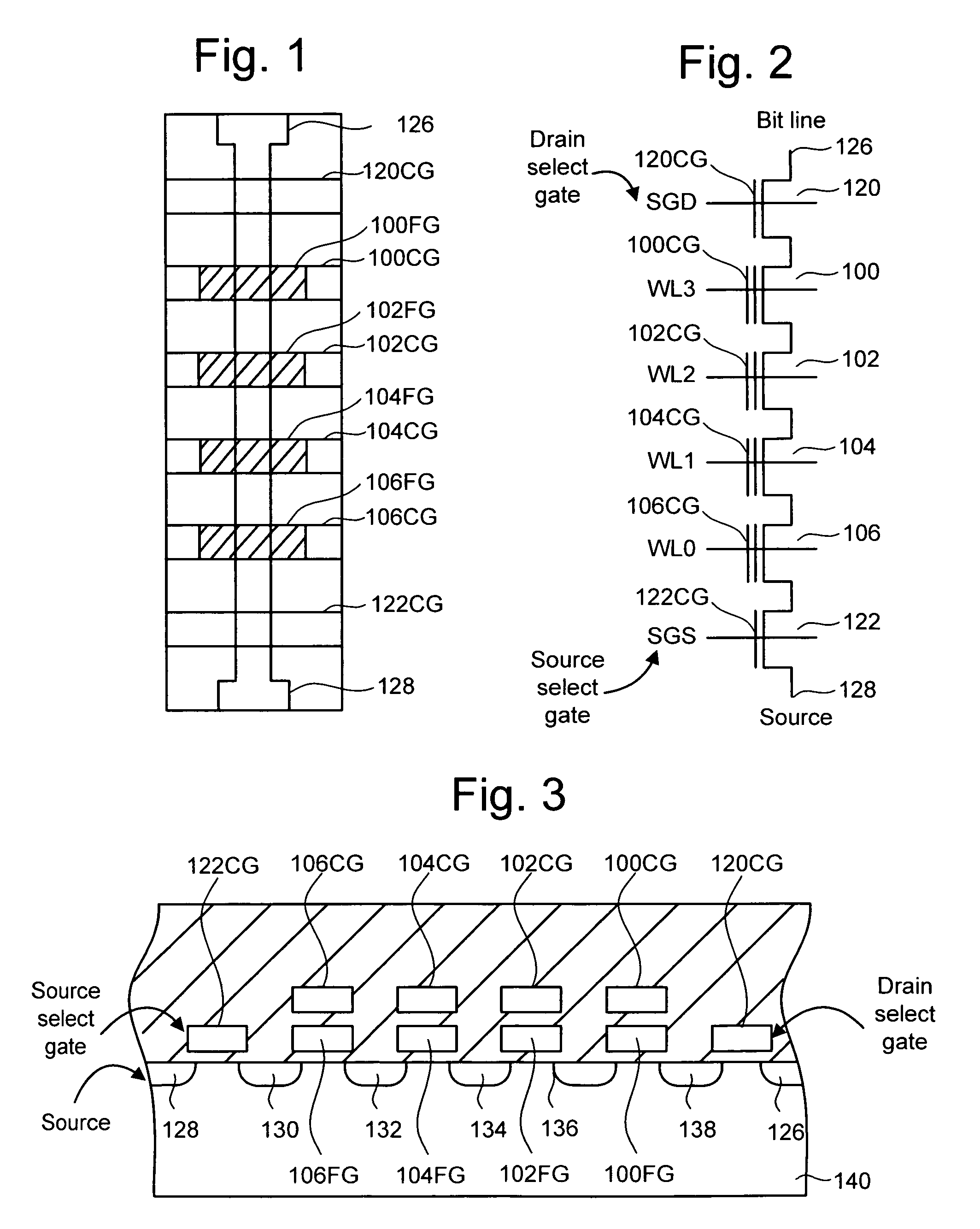
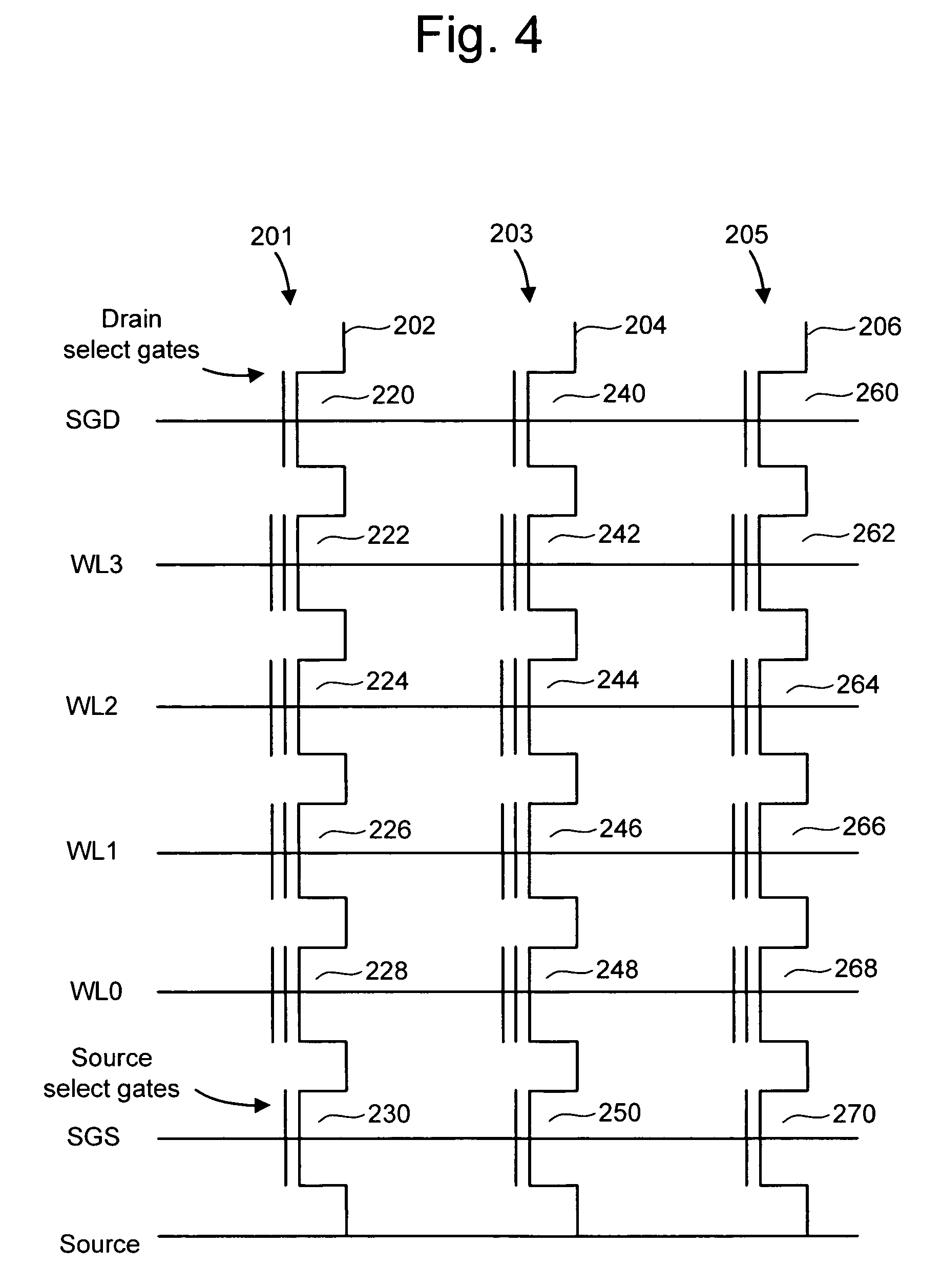
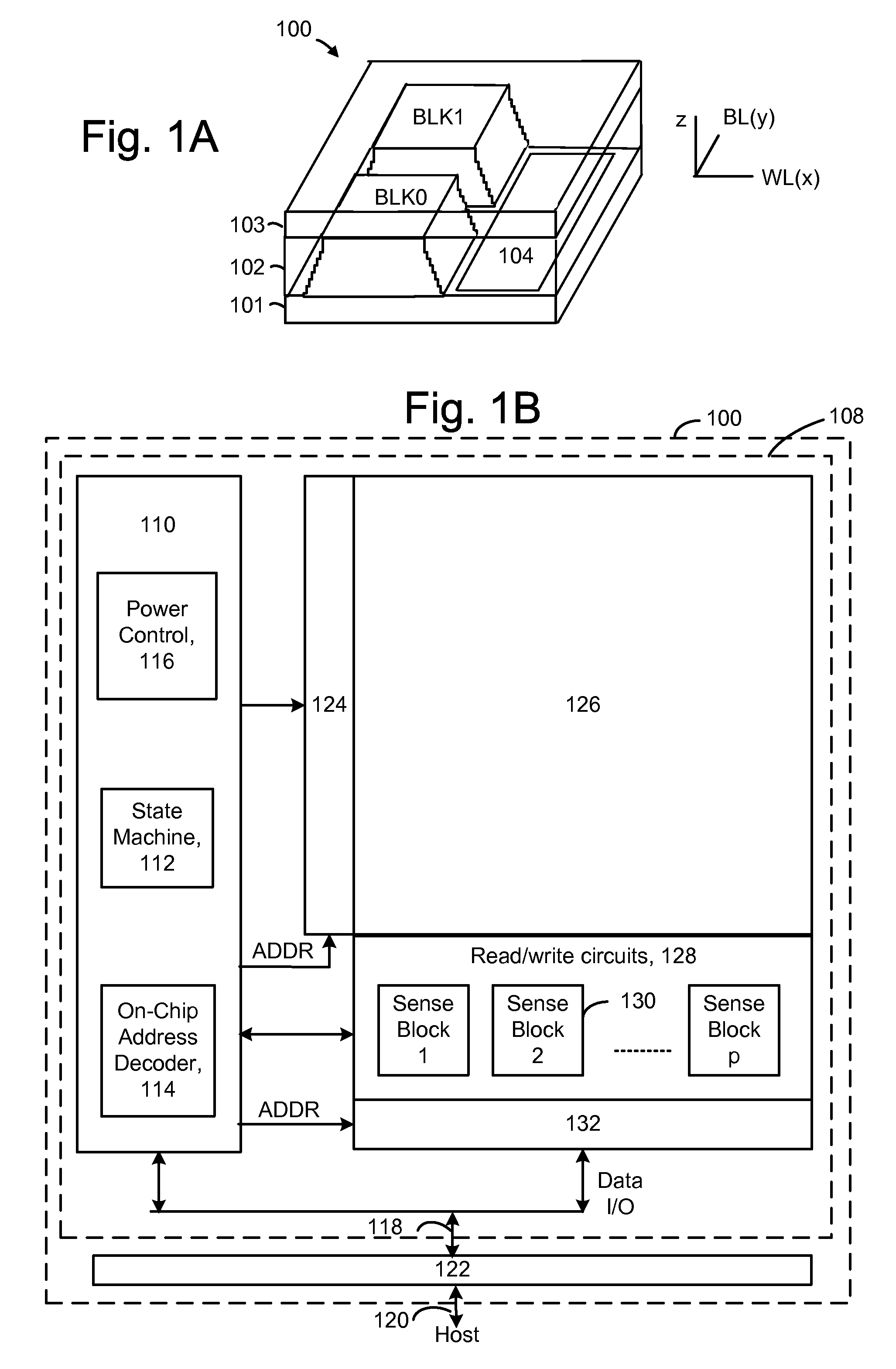
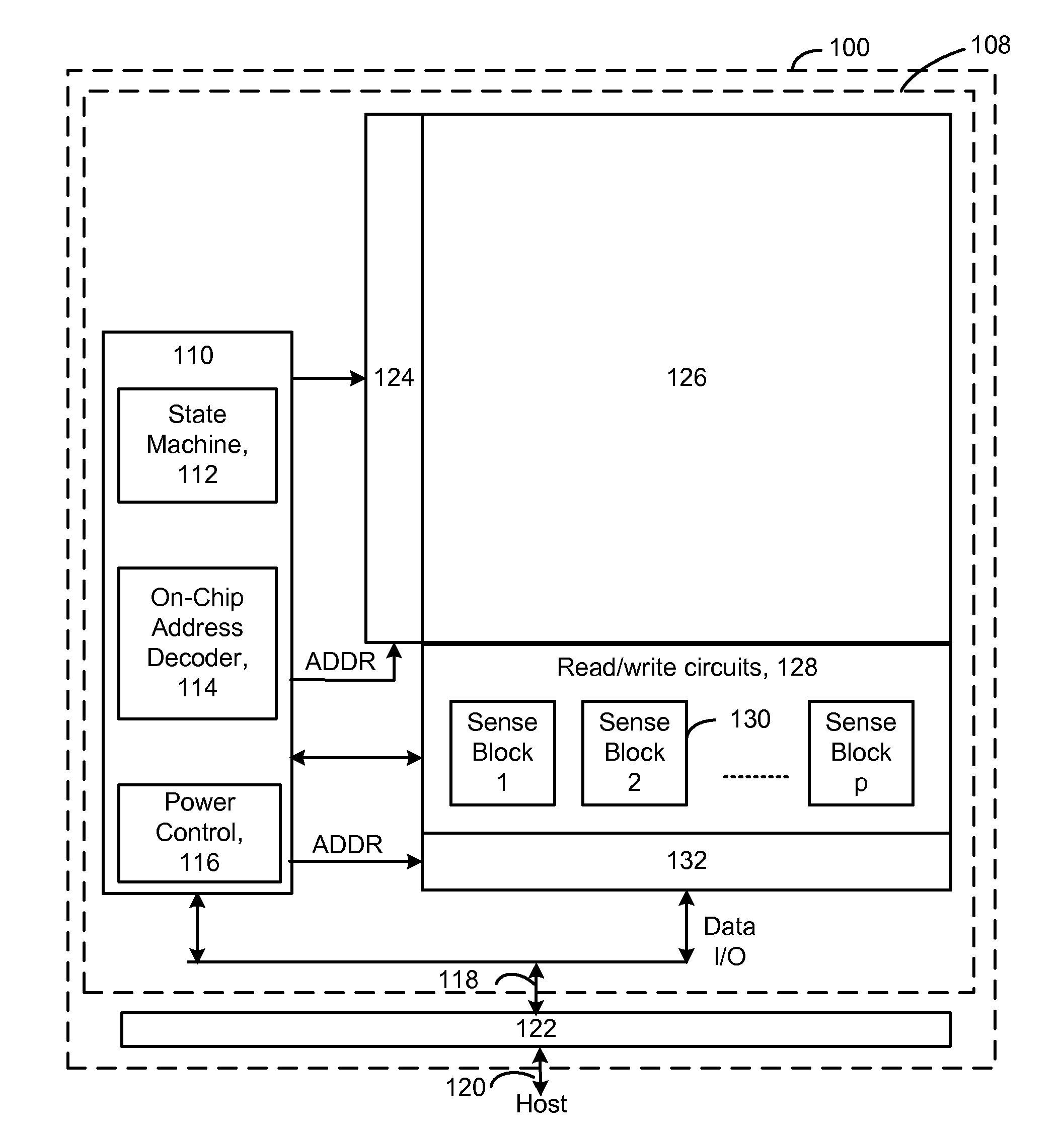
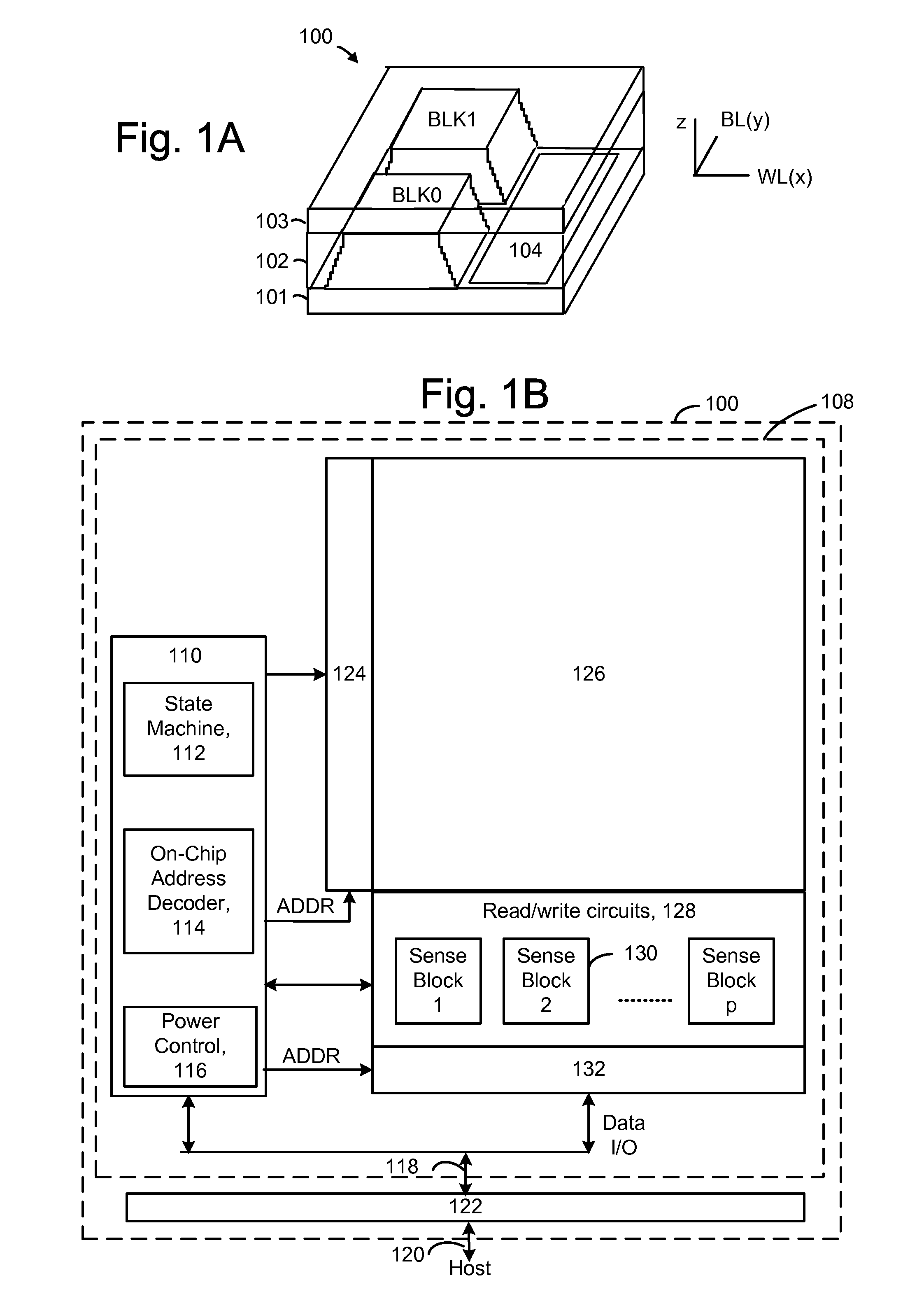
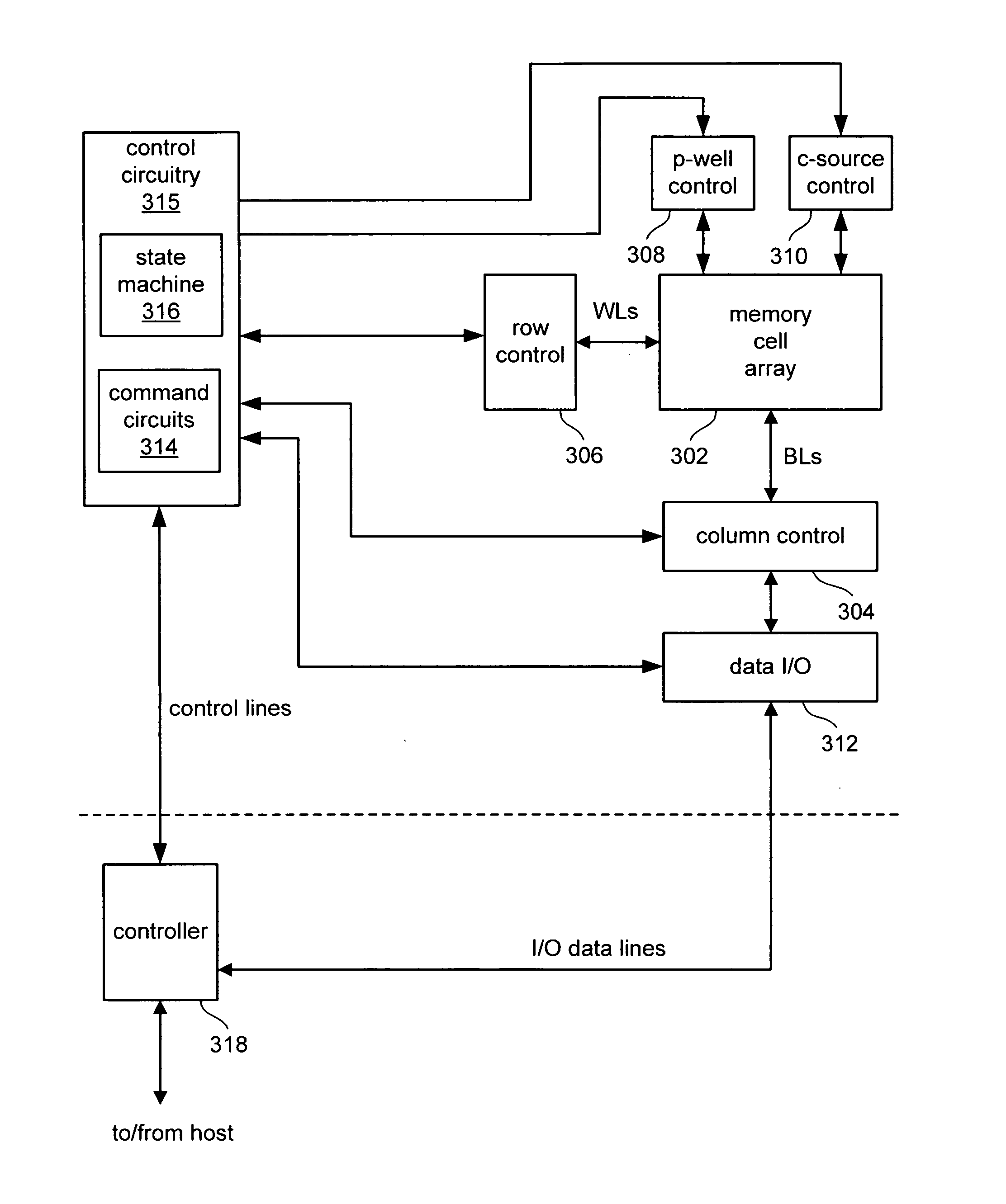
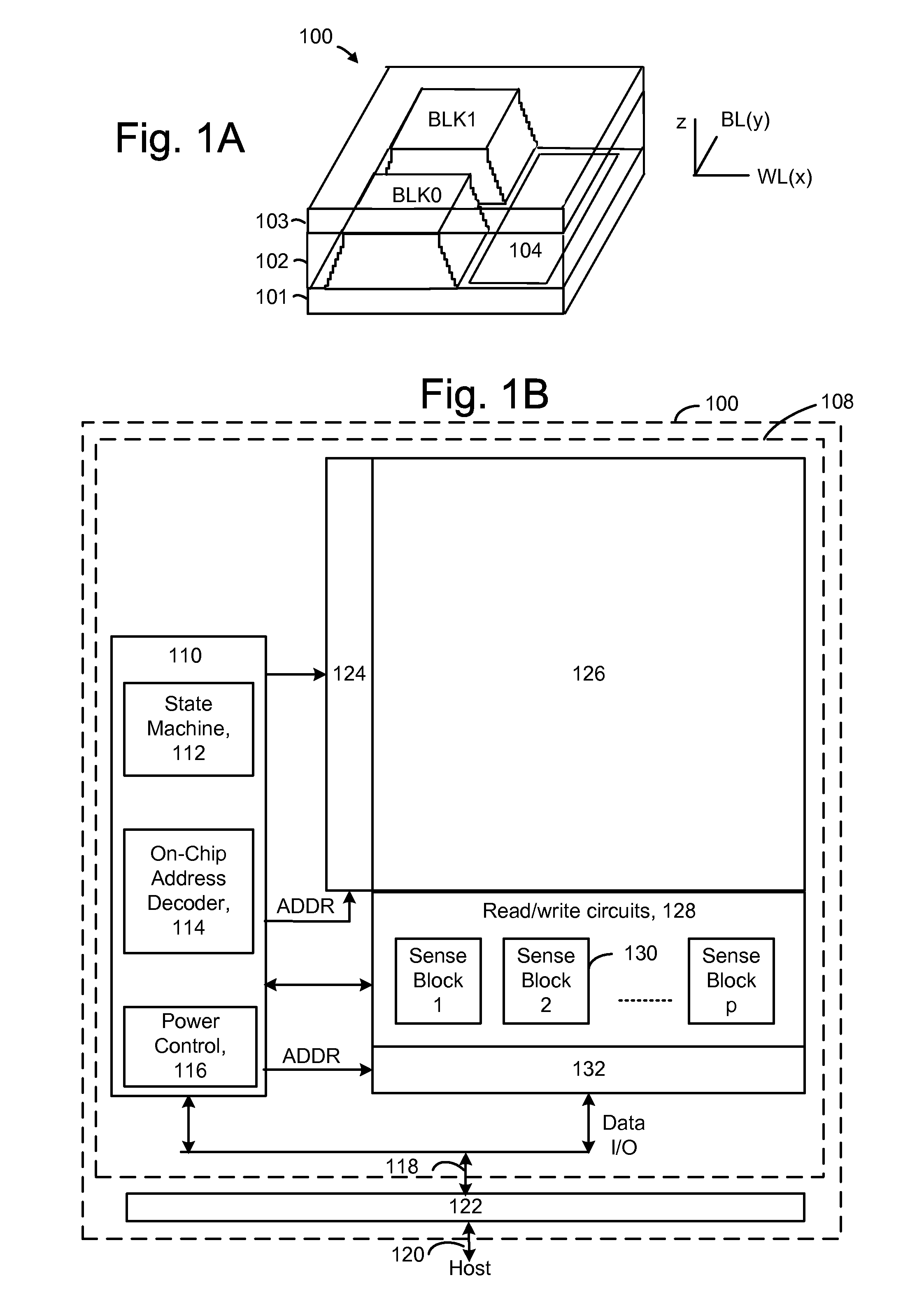
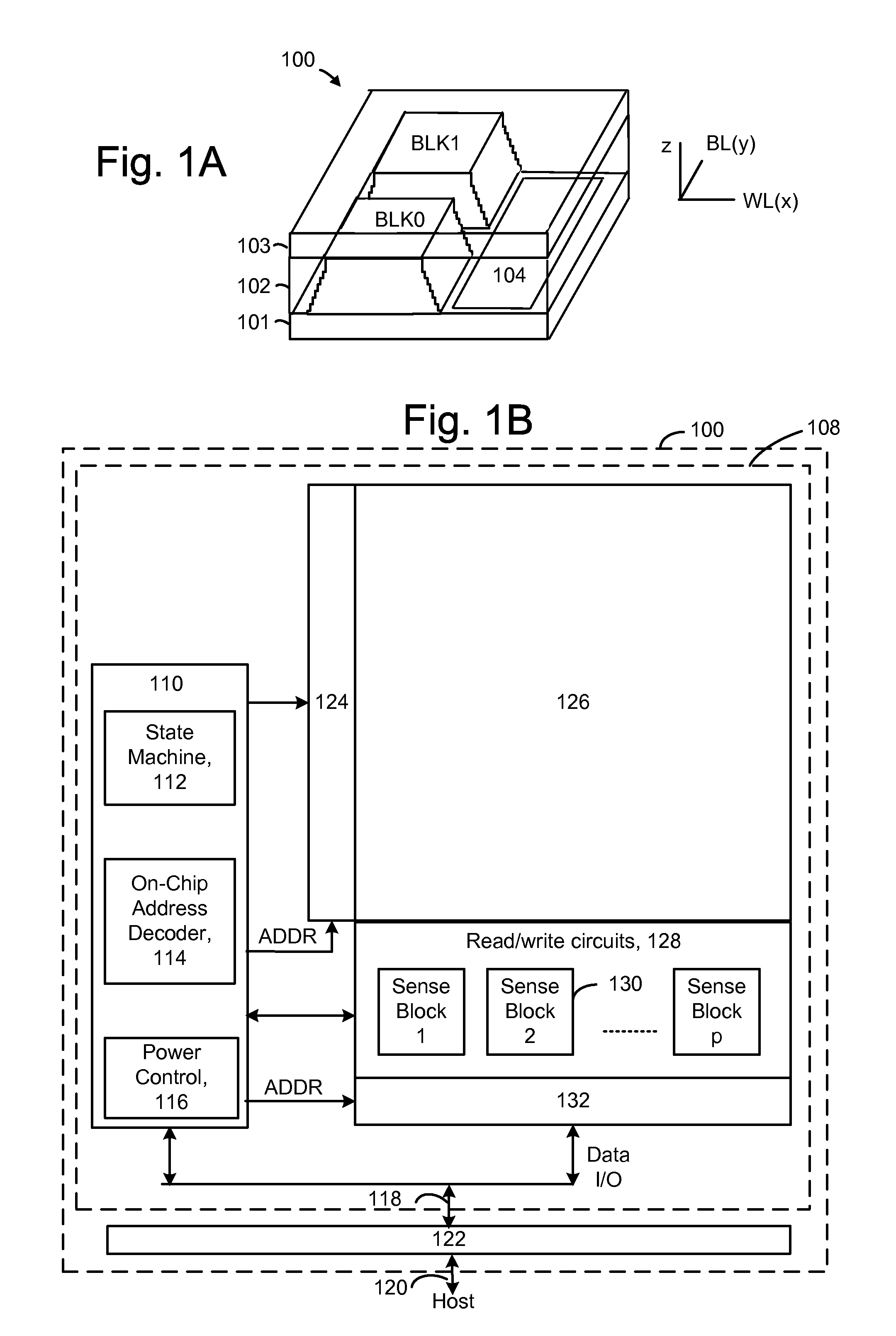
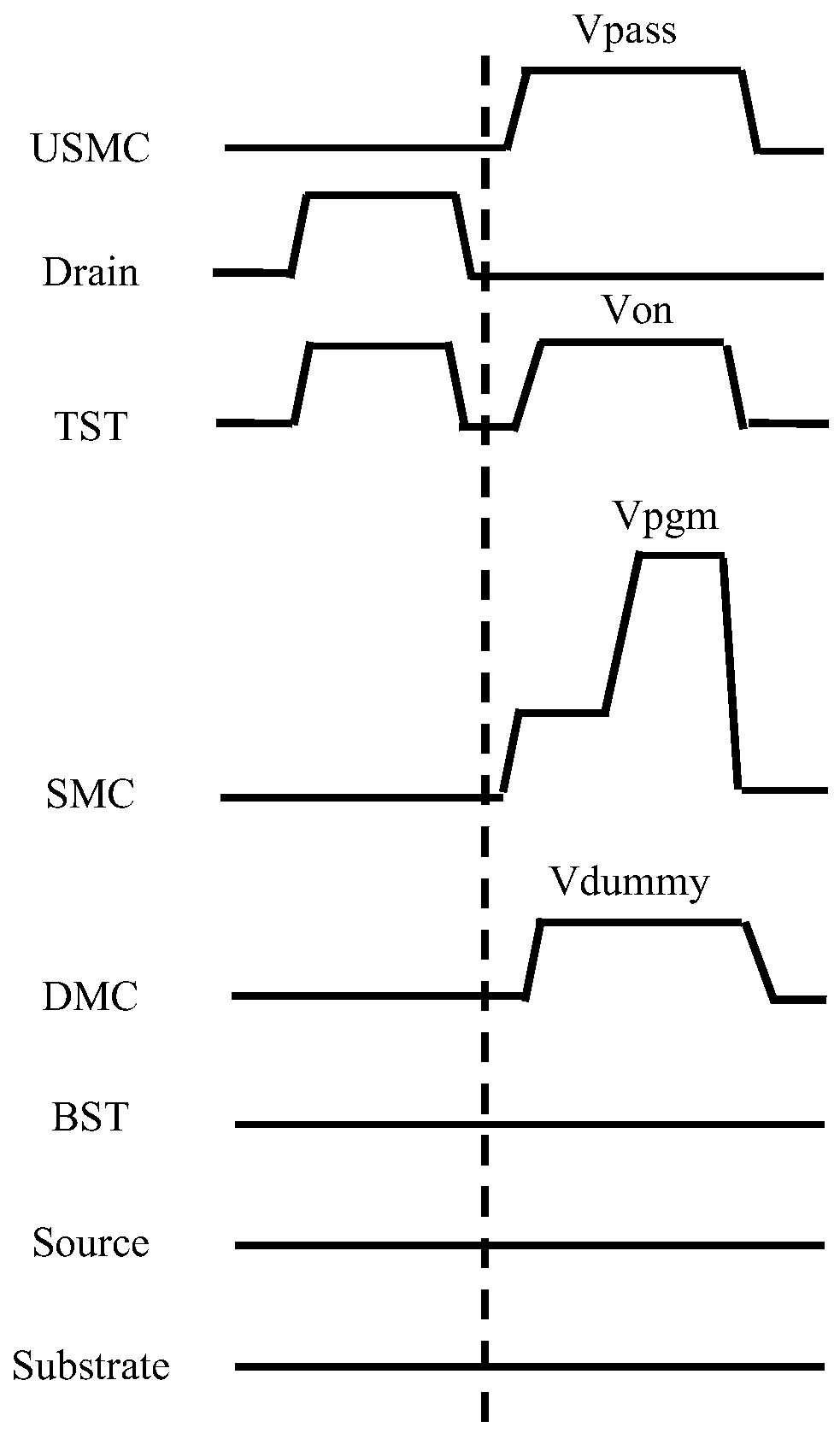
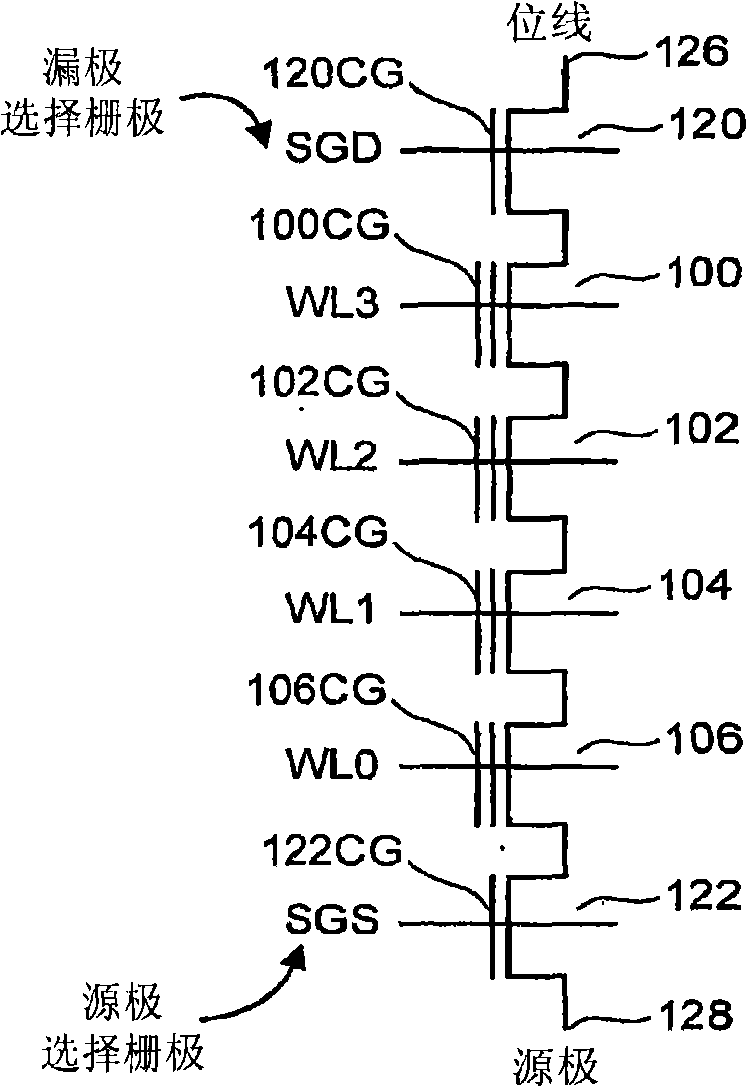
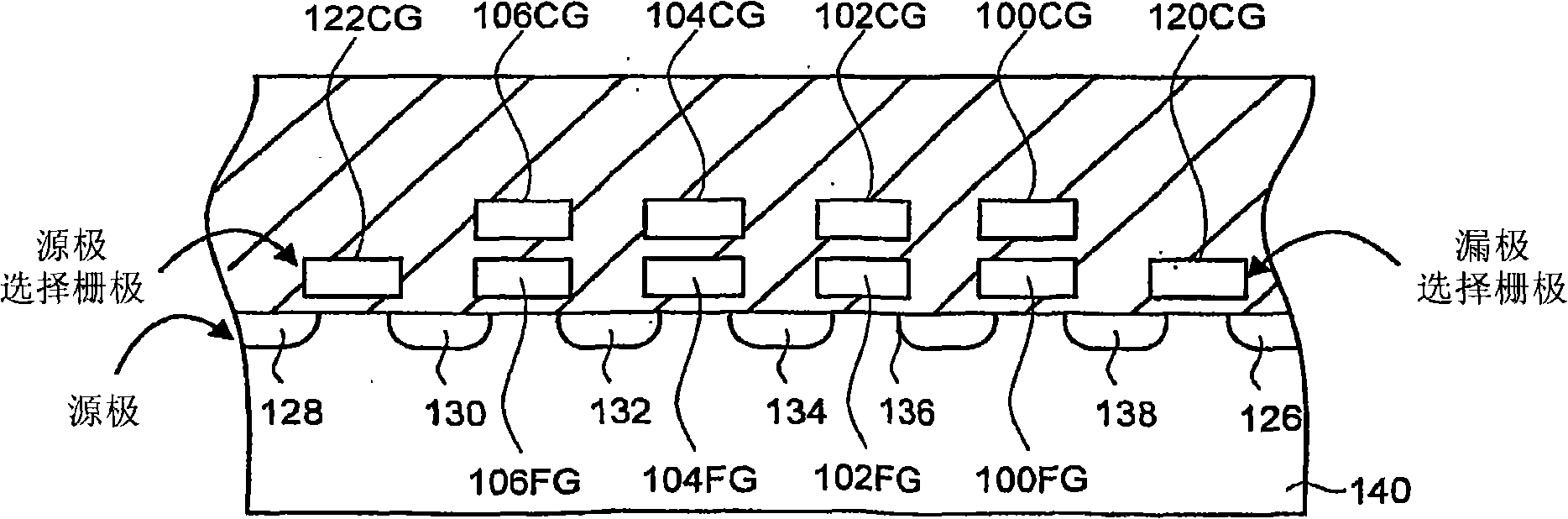
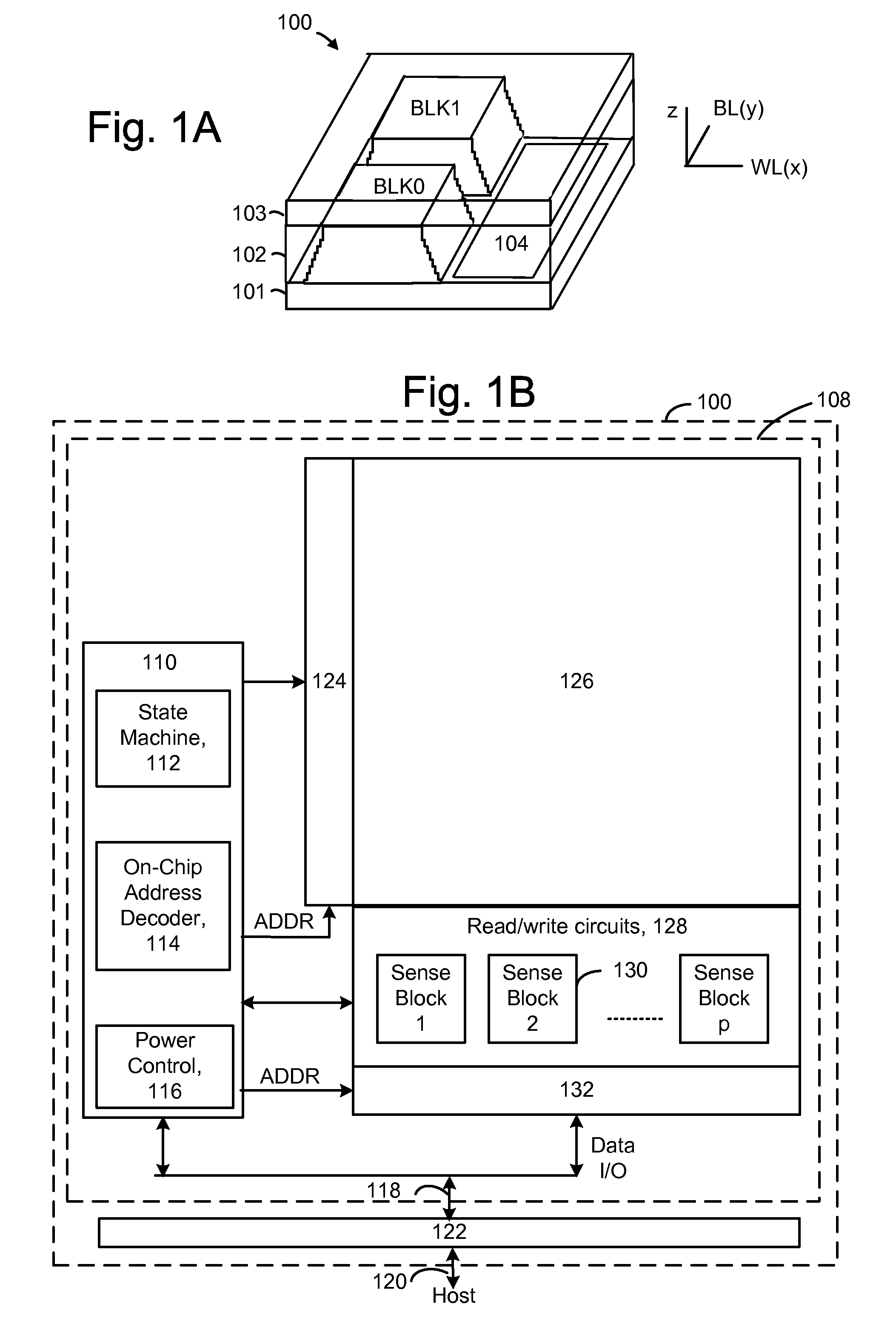
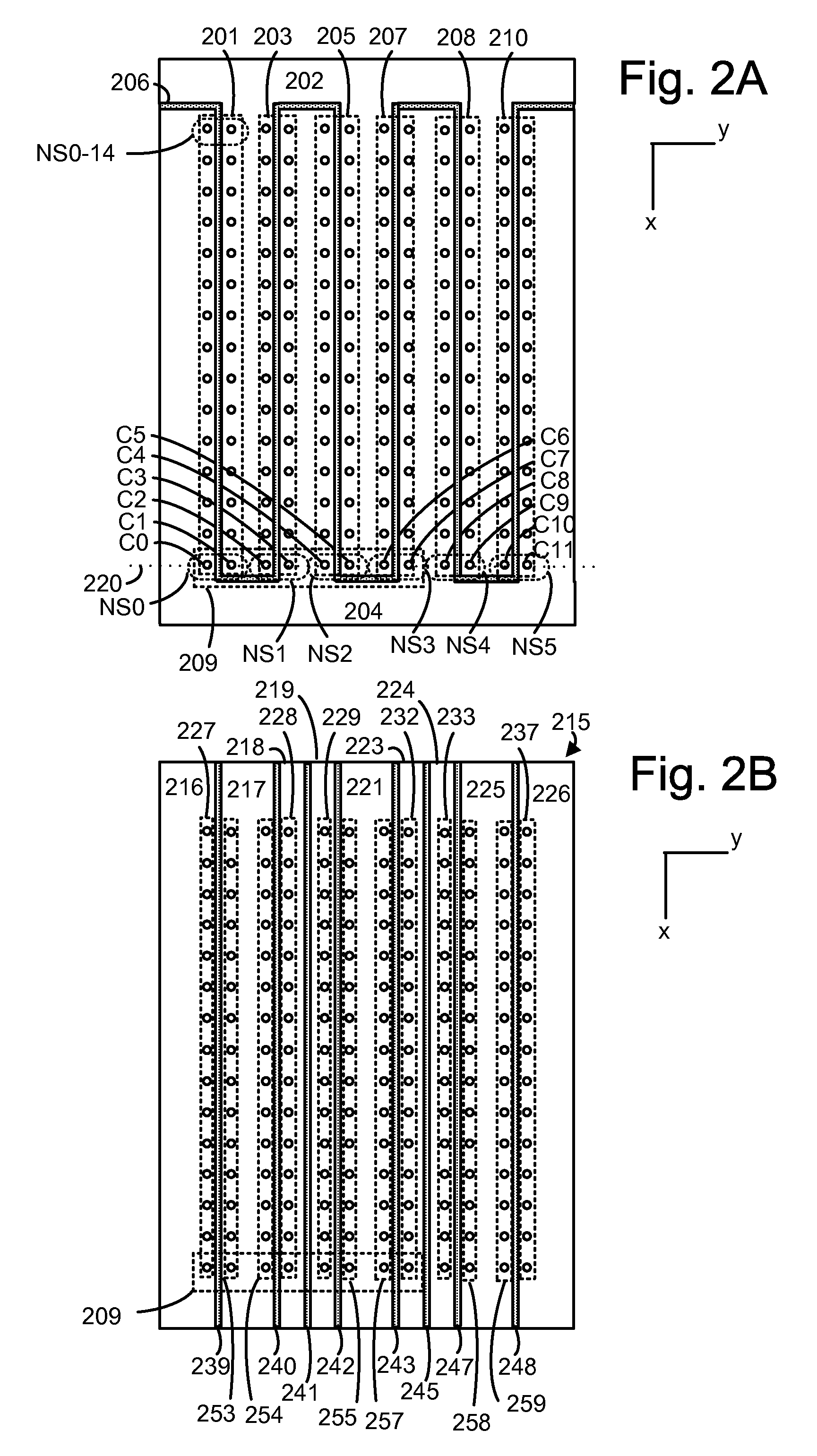
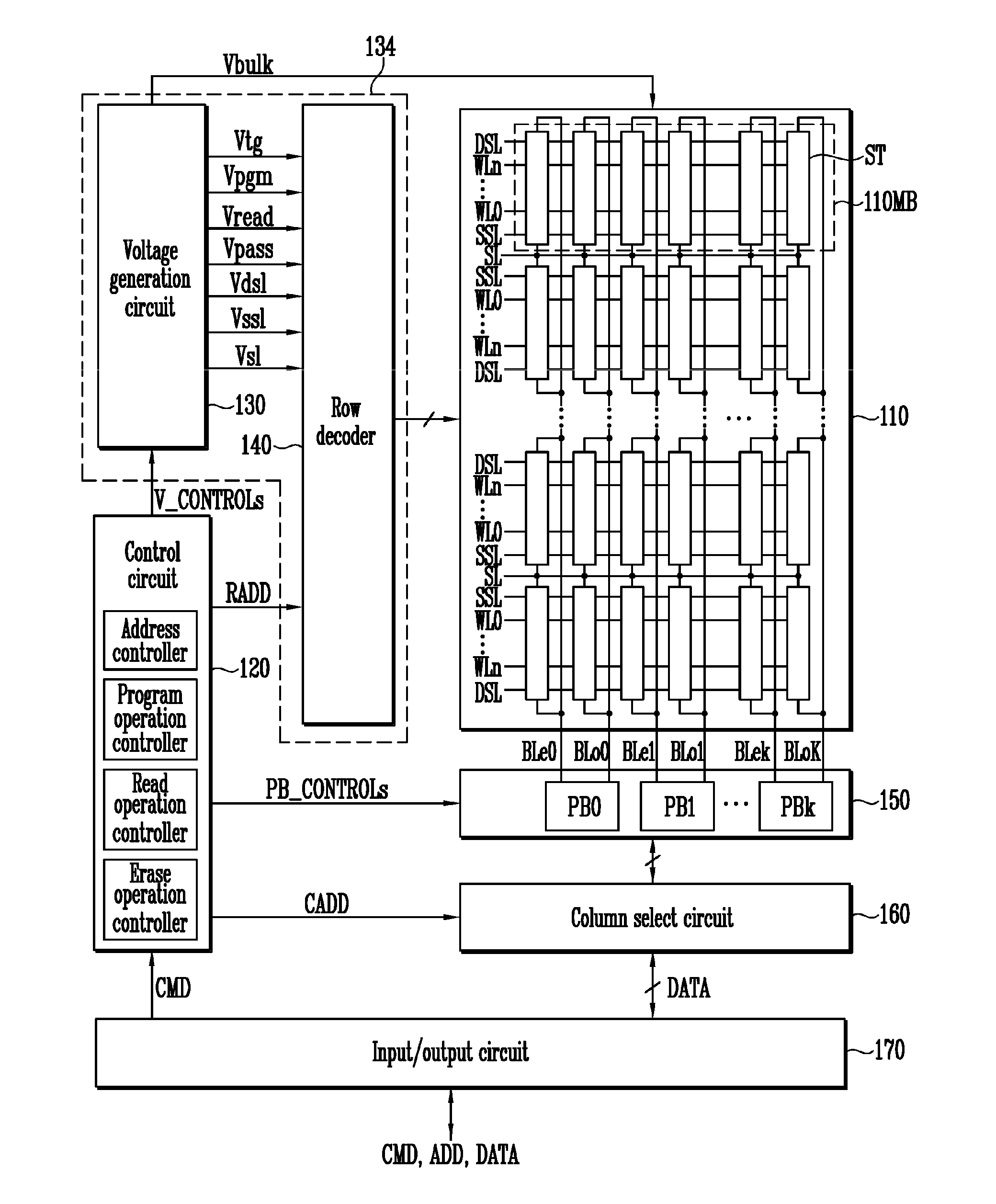
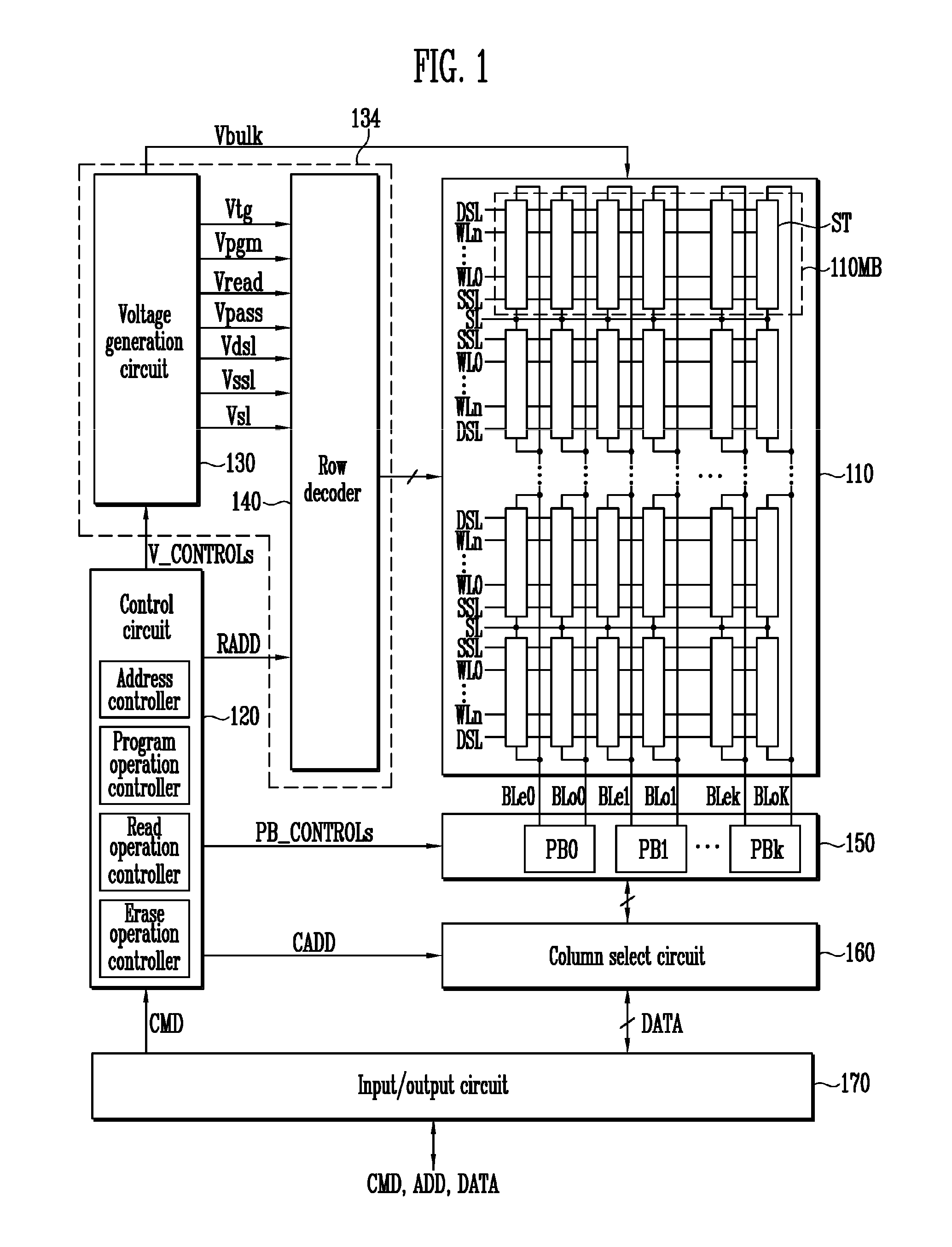
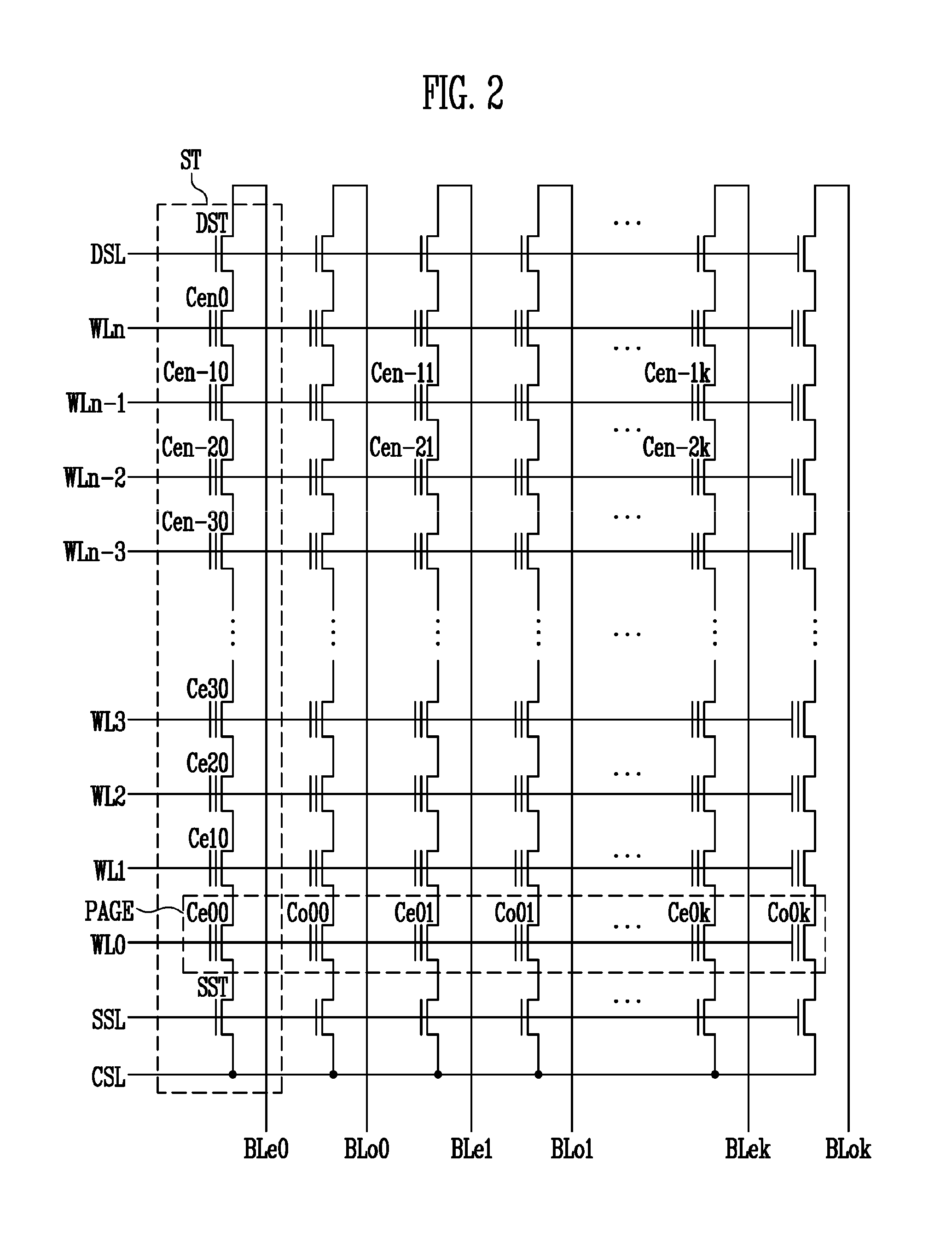
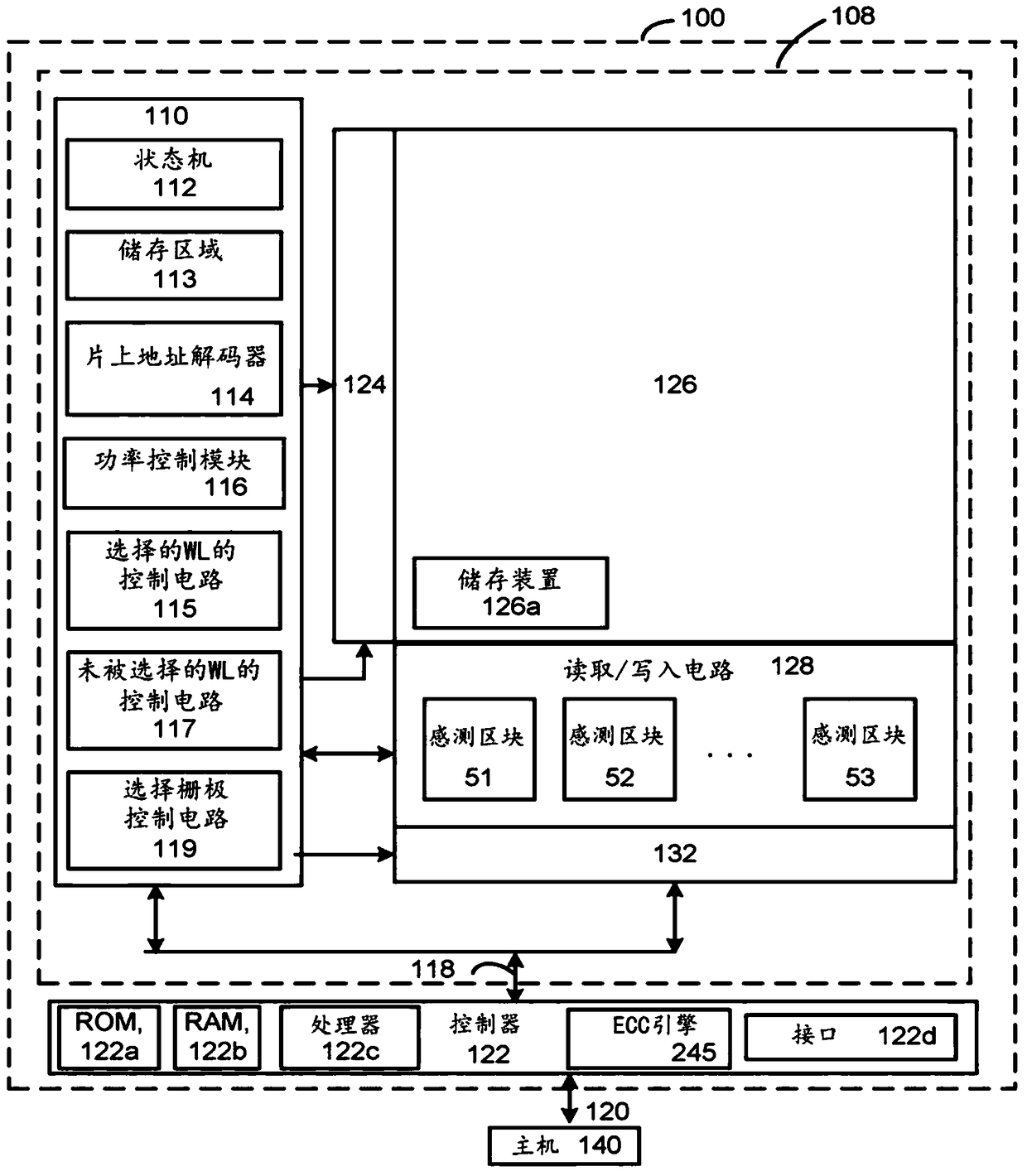
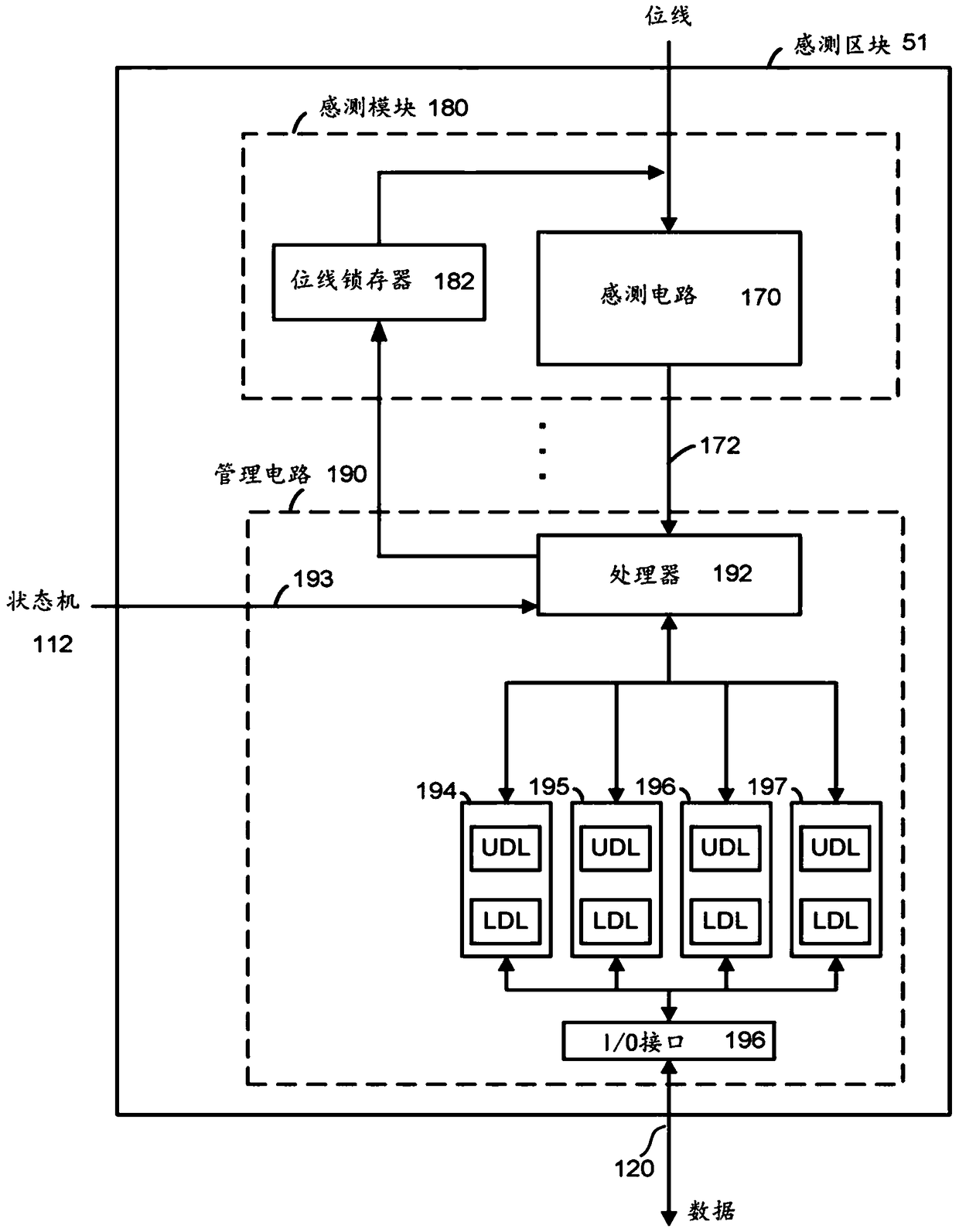
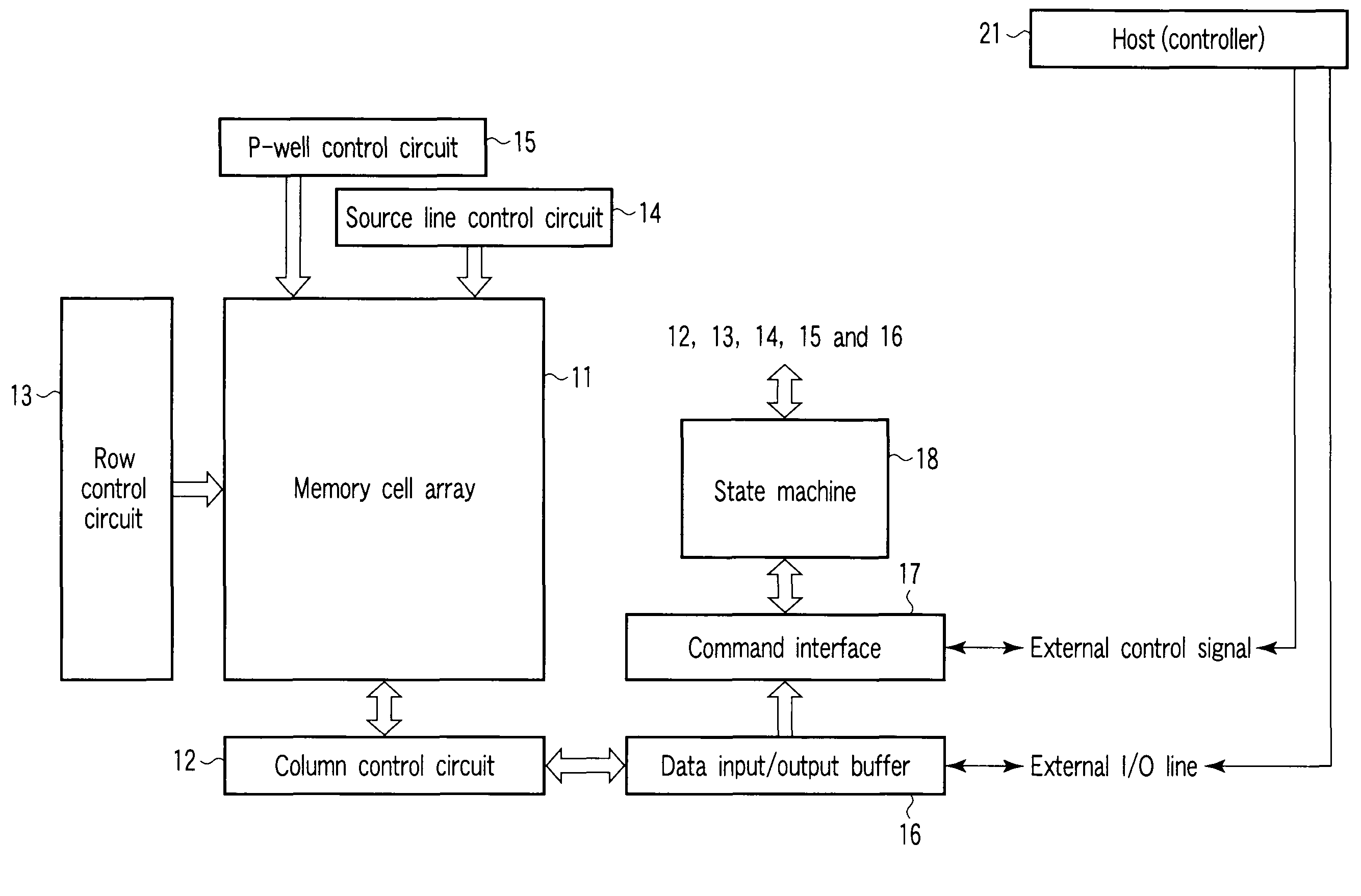
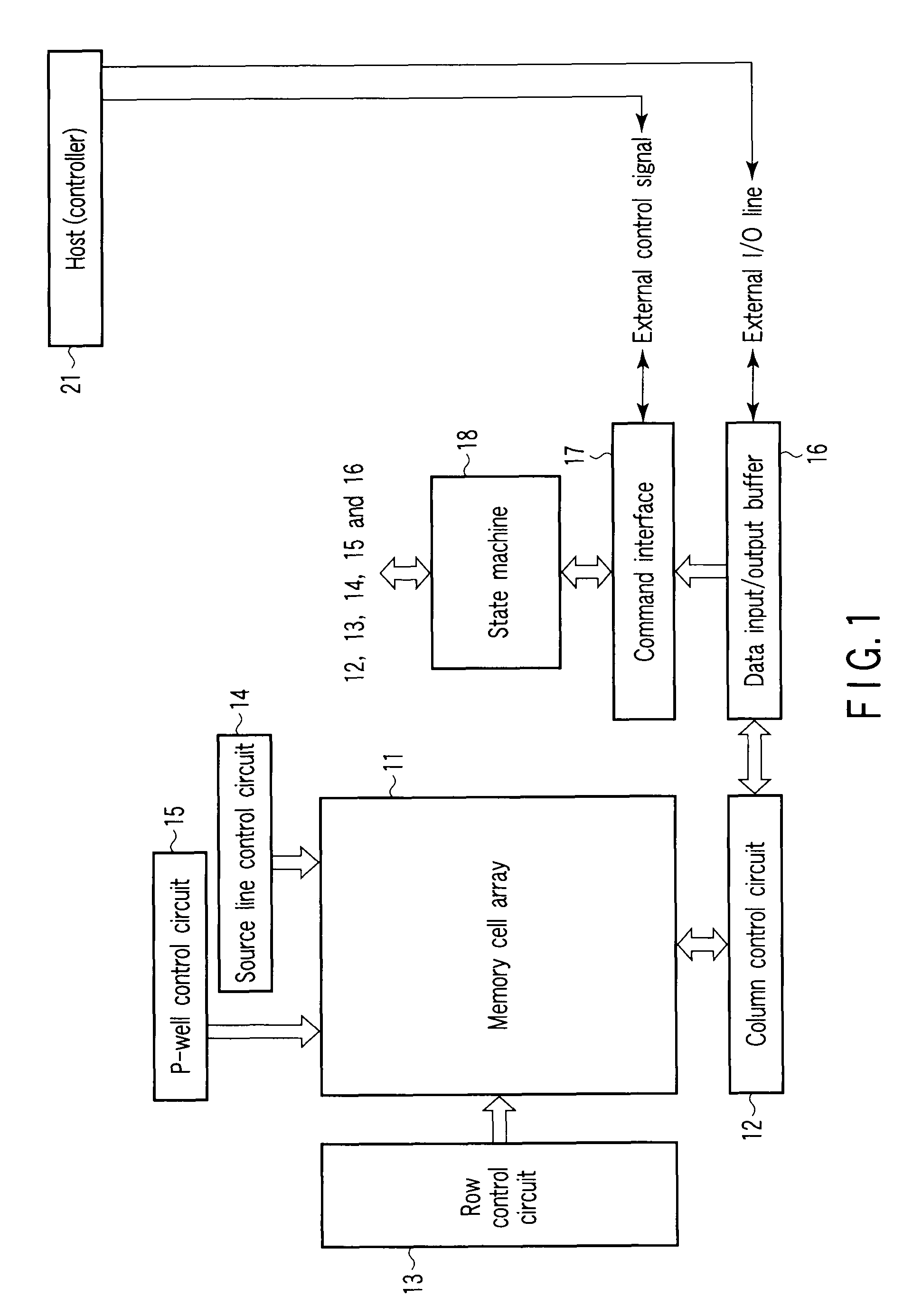
Source side self boosting technique for non-volatile memory
InactiveUS6859397B2Improve performanceMinimize program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePre-chargeProgramming process
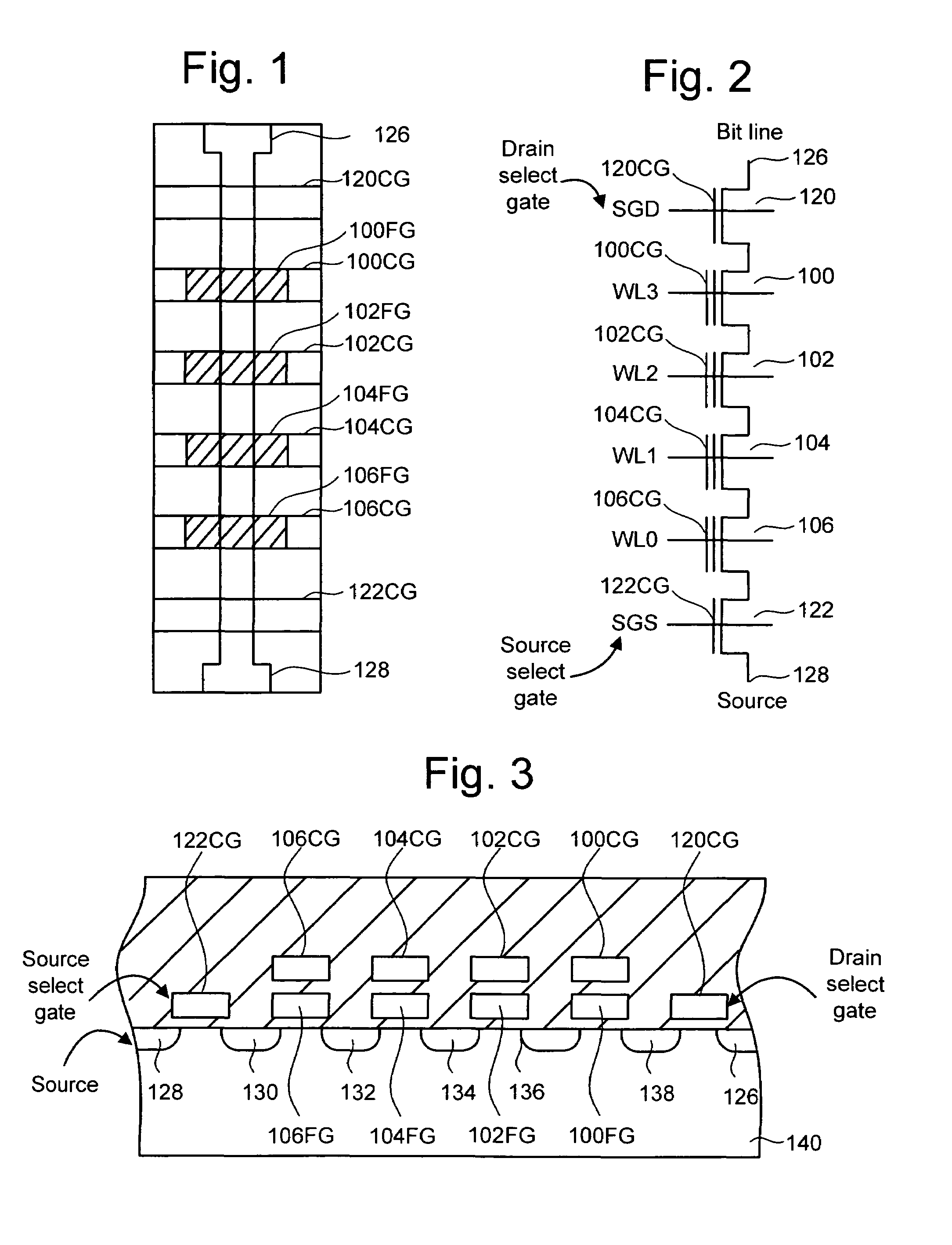
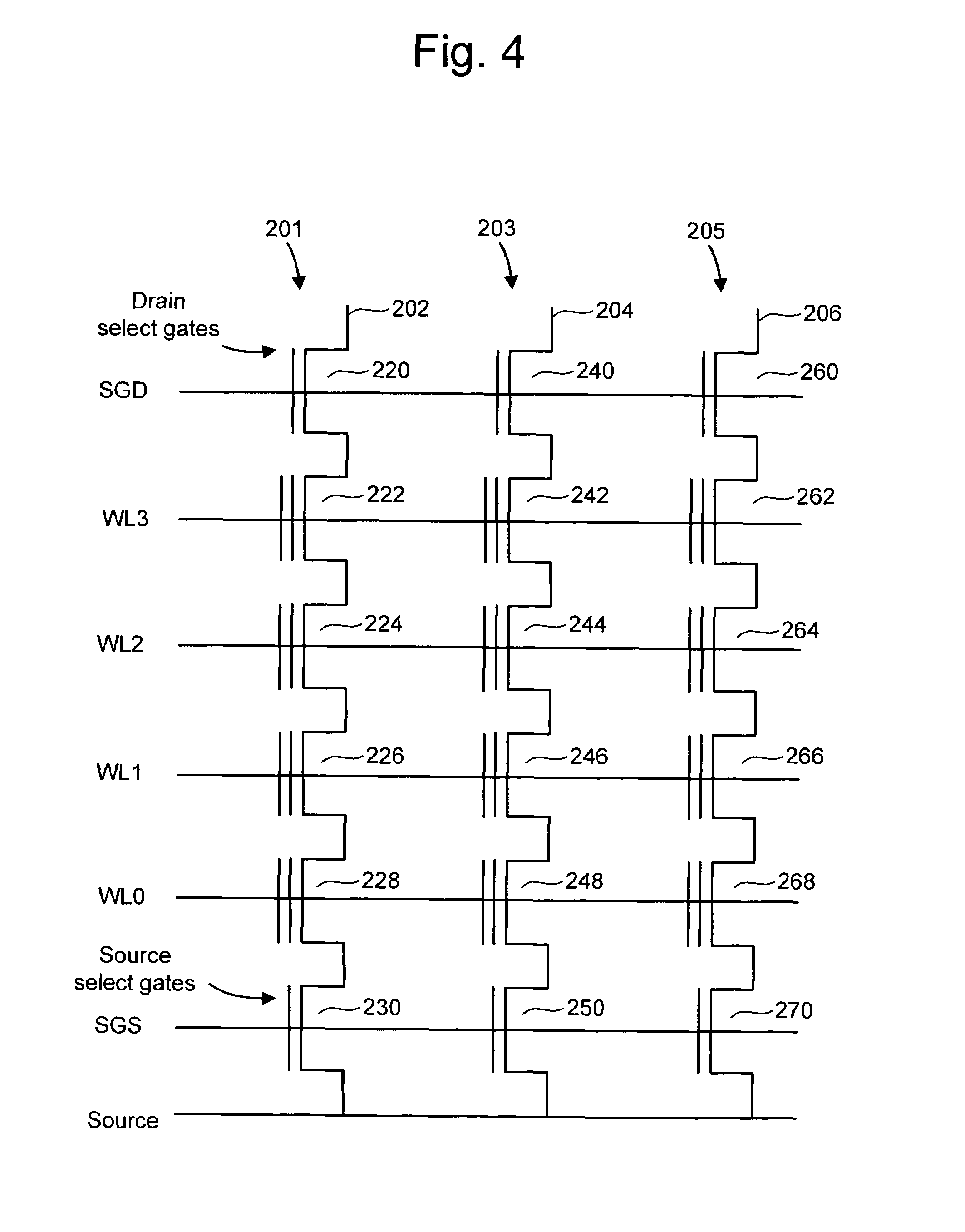
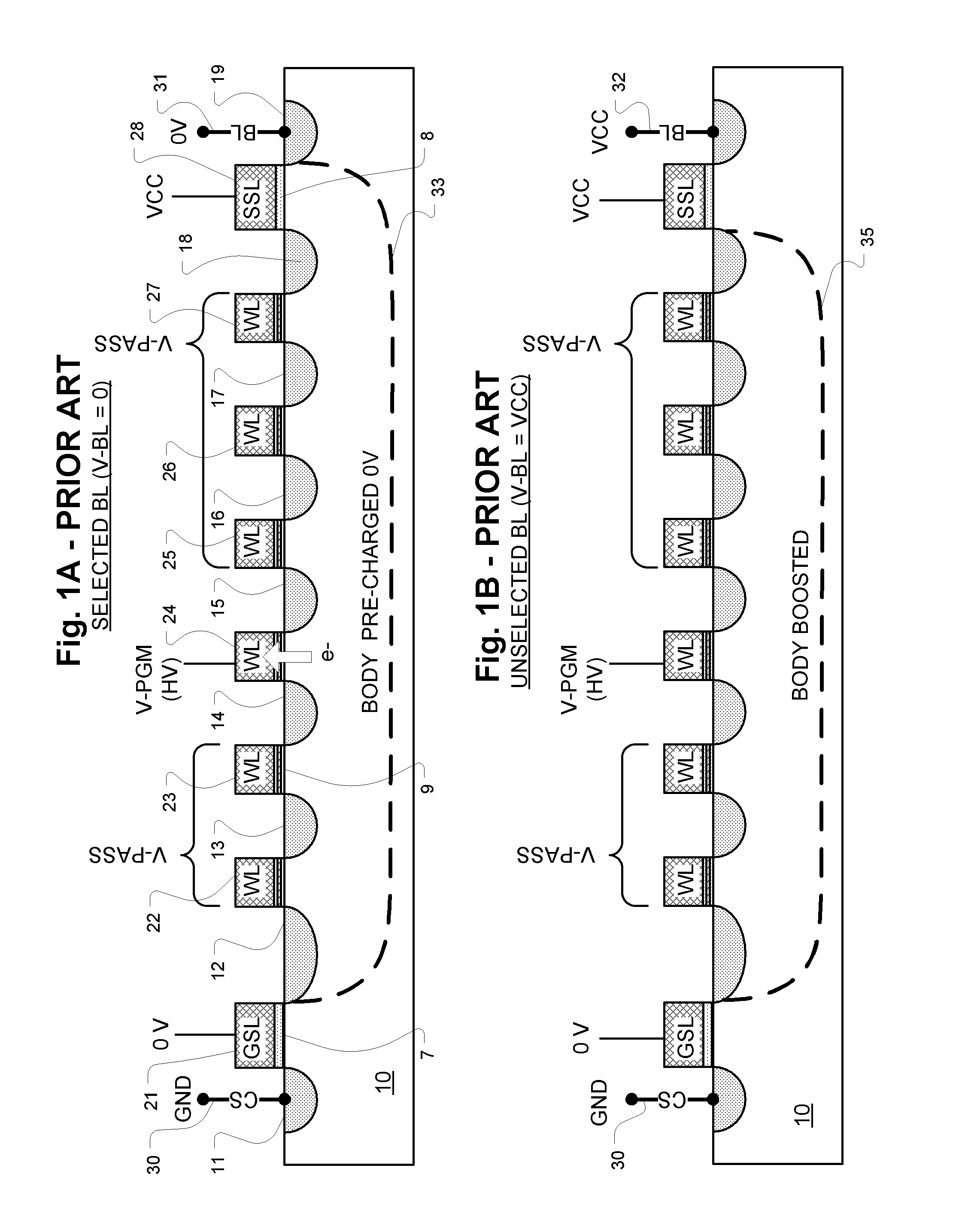
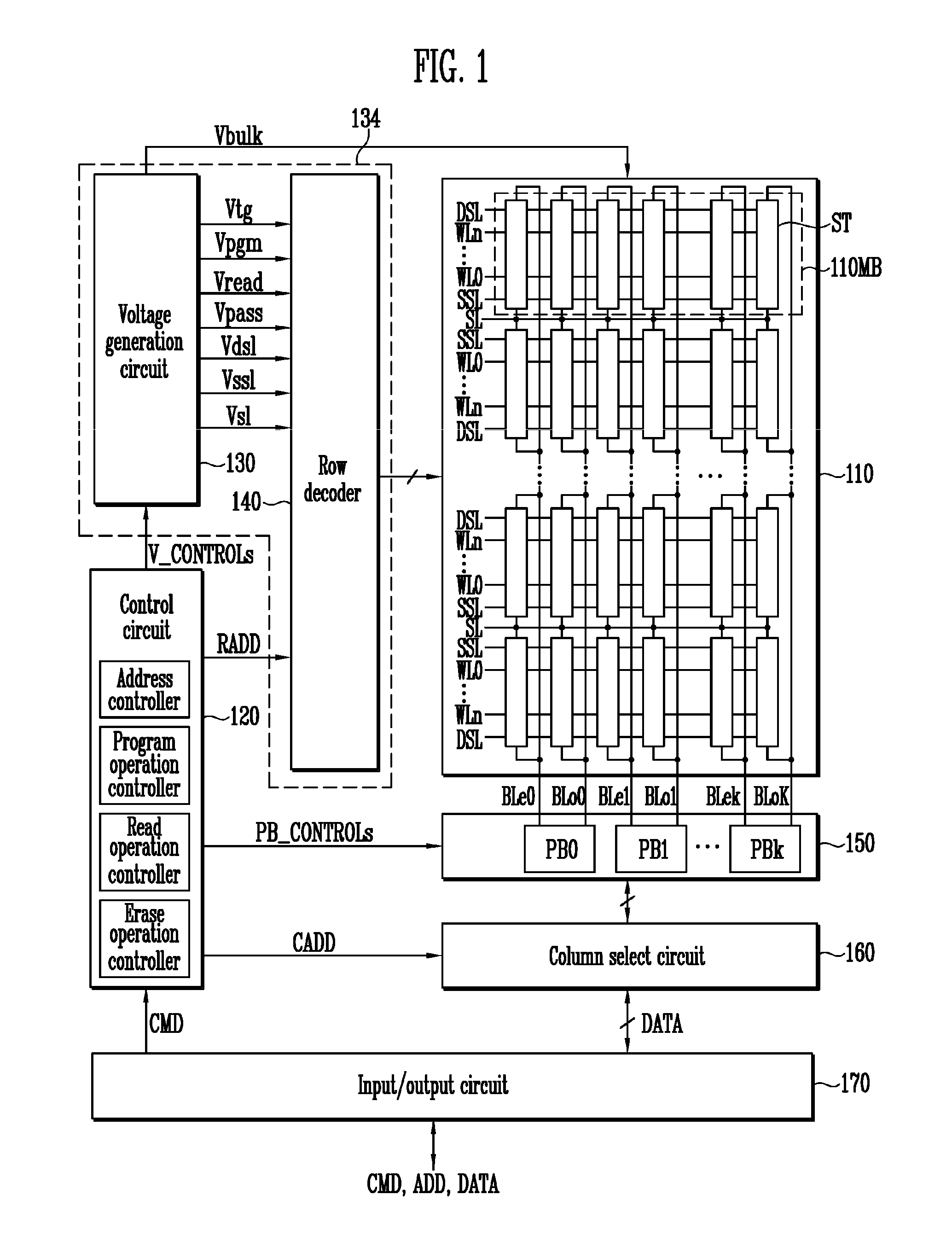
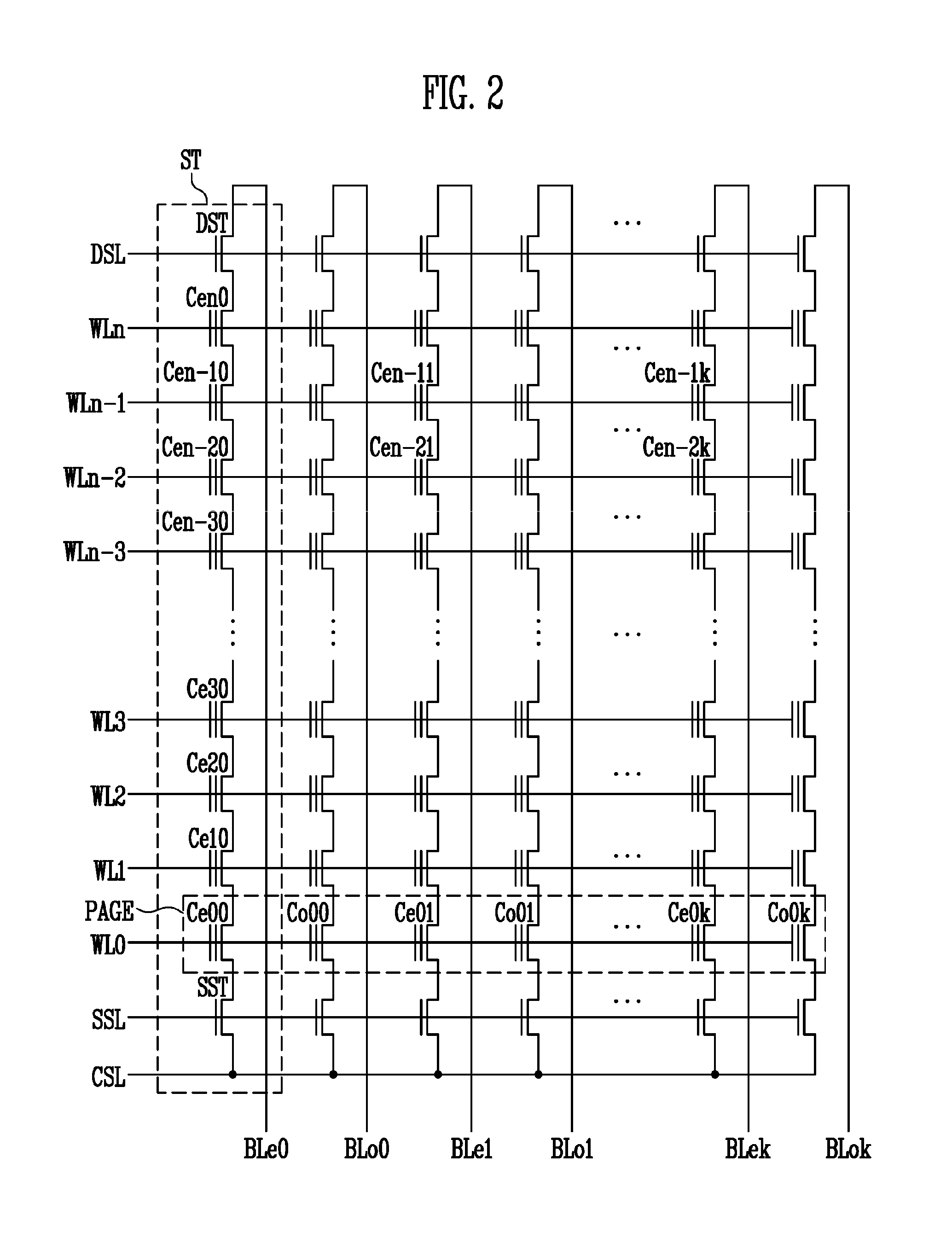
A non-volatile semiconductor memory system (or other type of memory system) is programmed in a manner that avoids program disturb. In one embodiment that includes a flash memory system using a NAND architecture, program disturb is avoided by increasing the channel potential of the source side of the NAND string during the programming process. One exemplar implementation includes applying a voltage (e.g. Vdd) to the source contact and turning on the source side select transistor for the NAND sting corresponding to the cell being inhibited. Another implementation includes applying a pre-charging voltage to the unselected word lines of the NAND string corresponding to the cell being inhibited prior to applying the program voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Self boosting technique
A non-volatile semiconductor memory system (or other type of memory system) is programmed in a manner that avoids program disturb. In one embodiment that includes a flash memory system using a NAND architecture, program disturb is avoided by increasing the channel potential of the source side of the NAND string during the programming process. One exemplar implementation includes applying a voltage (e.g. Vdd) to the source contact and turning on the source side select transistor for the NAND sting corresponding to the cell being inhibited. Another implementation includes applying a pre-charging voltage to the unselected word lines of the NAND string corresponding to the cell being inhibited prior to applying the program voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method for programming non-volatile memory with reduced program disturb using modified pass voltages
ActiveUS20070171719A1Raise the potentialReduce charge leakageRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceChannel potential
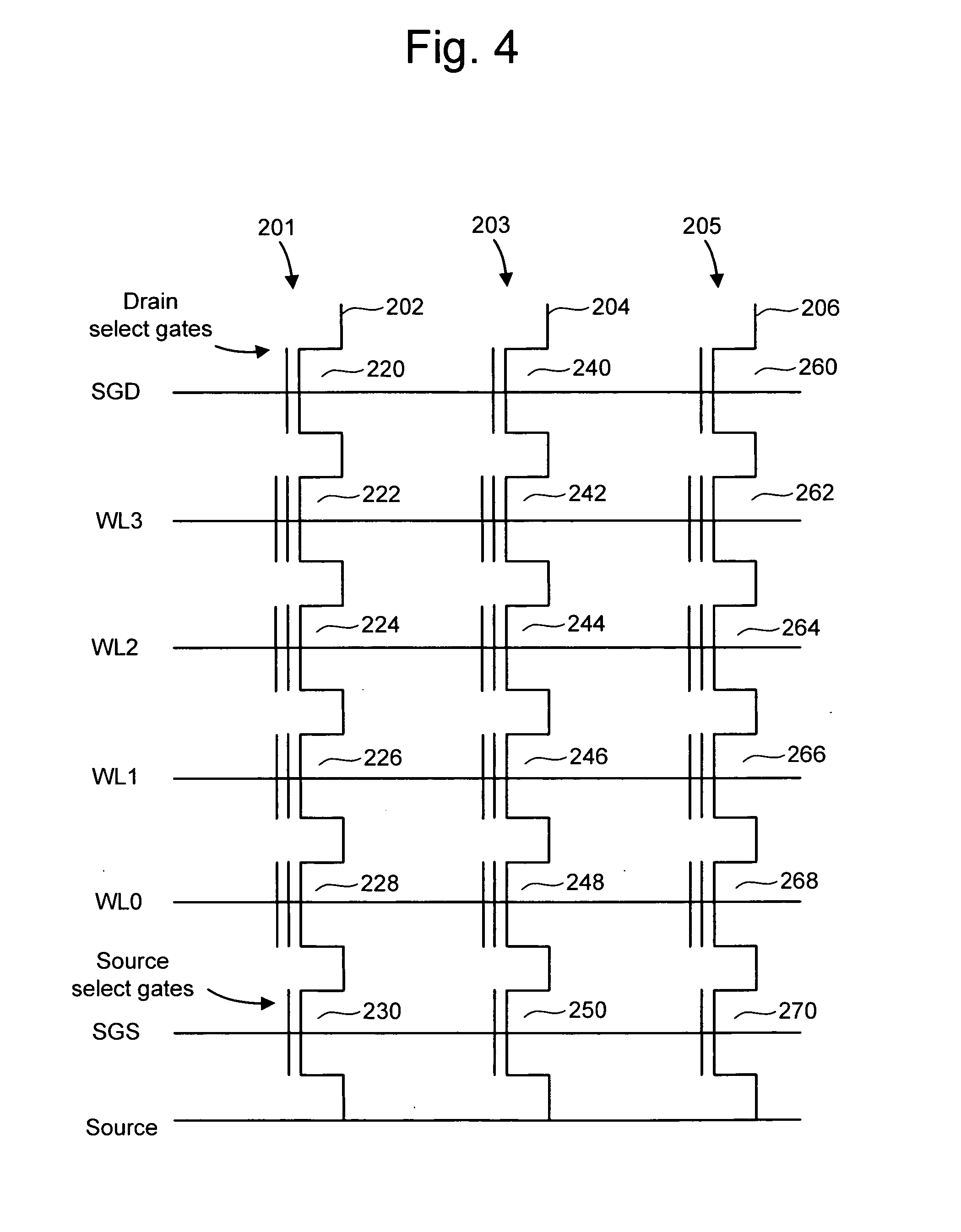
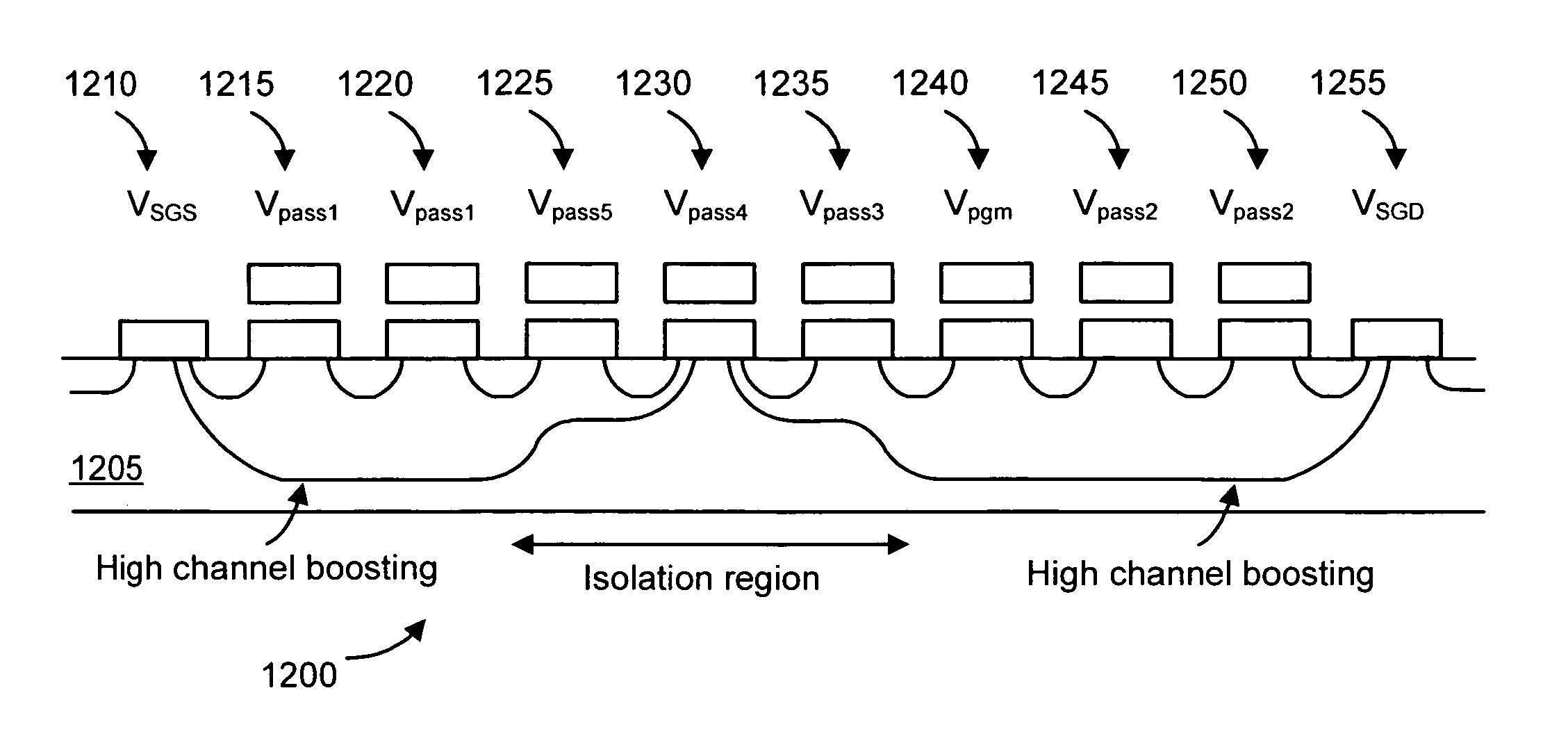
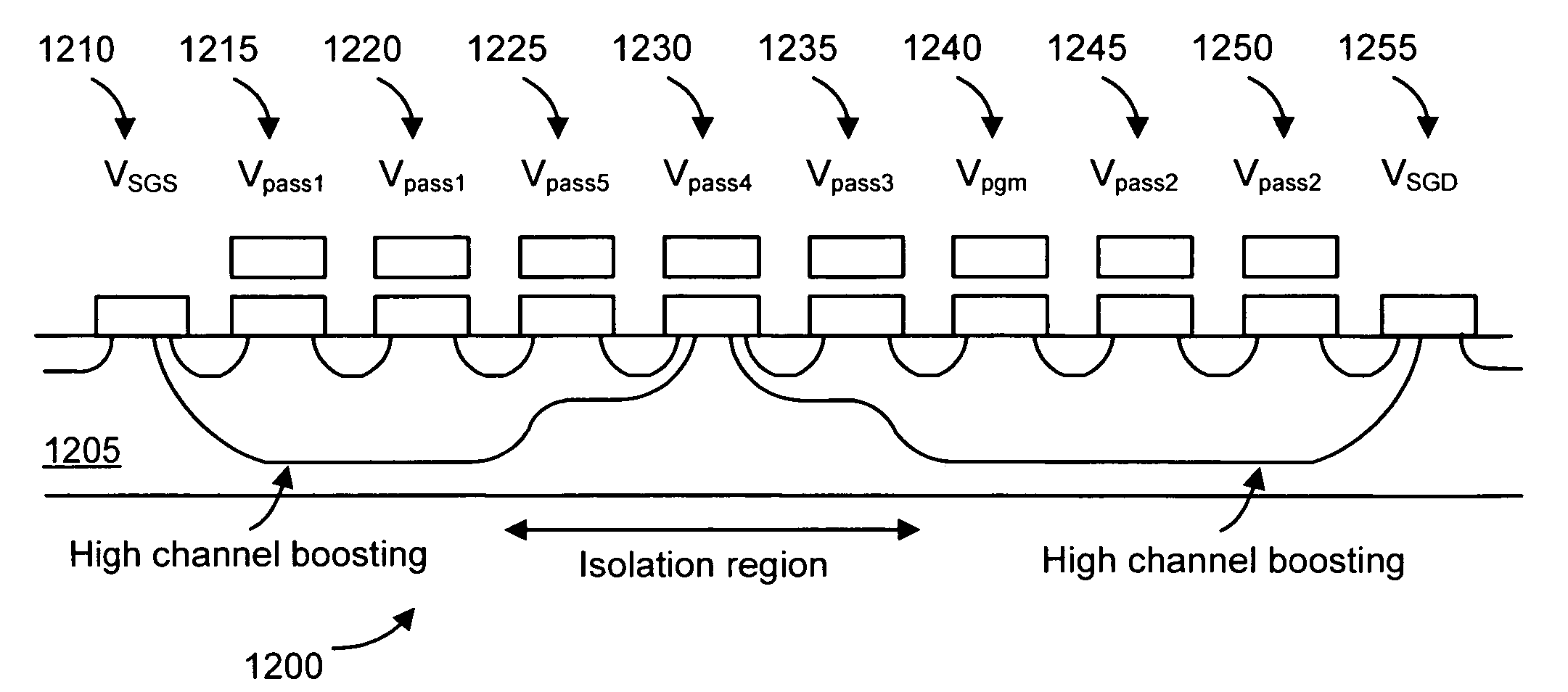
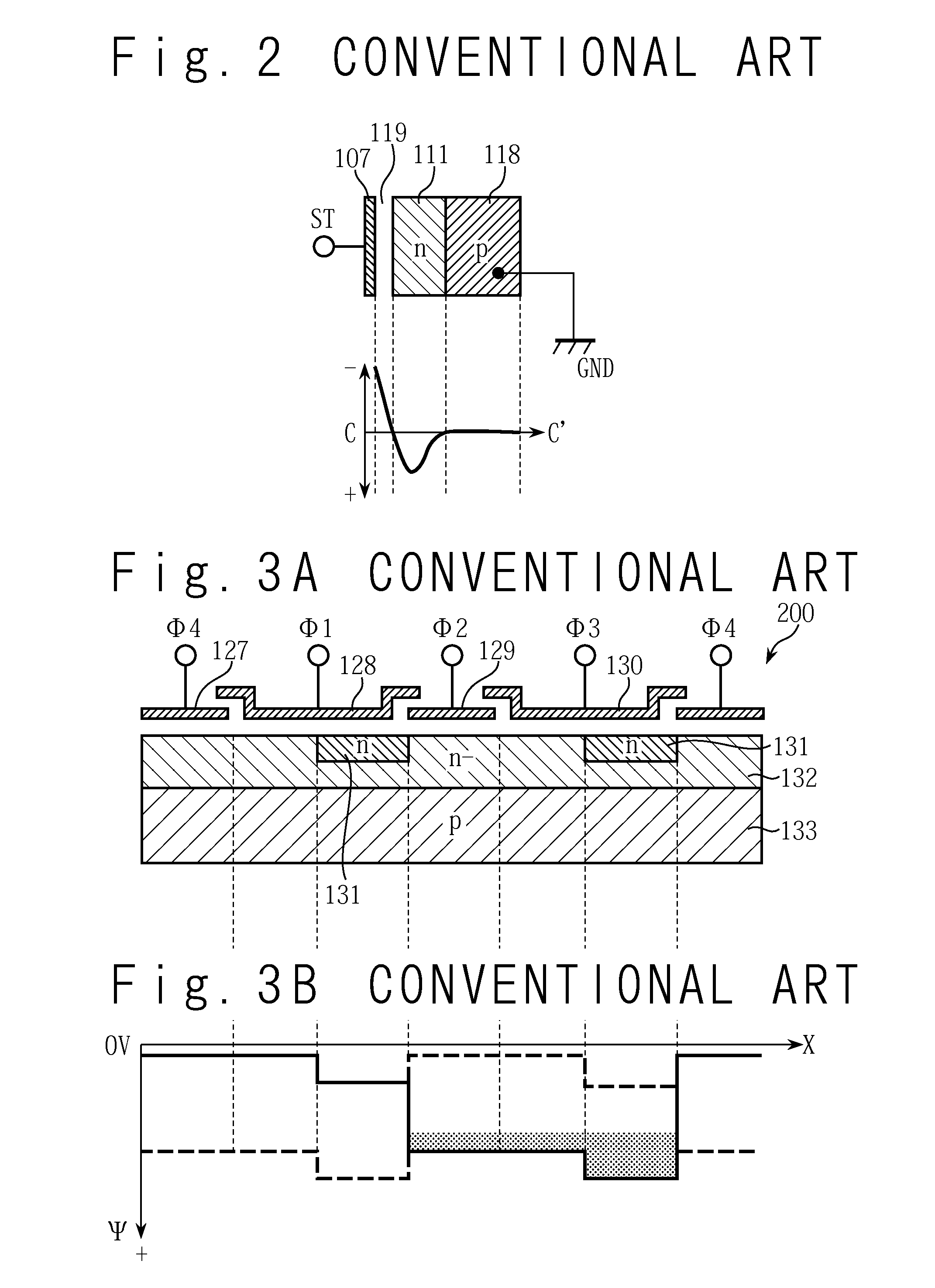
Non-volatile storage elements are programmed in a manner that reduces program disturb by using modified pass voltages. -In particular, during the programming of a selected storage element associated with a selected word line, a higher pass voltage is applied to word lines associated with previously programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set than to word lines associated with unprogrammed and / or partly programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set. The pass voltage is sufficiently high to balance the channel potentials on the source and drain sides of the selected word line and / or to reduce leakage of charge between the boosted channel regions. Optionally, an isolation region is formed between the boosted channel regions by applying a reduced voltage on one or more word lines between the selected word line and the word lines that receive the higher pass voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method for programming non-volatile memory with reduced program disturb using modified pass voltages
ActiveUS7355889B2Raise the potentialReduce charge leakageRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceChannel potential
Non-volatile storage elements are programmed in a manner that reduces program disturb by using modified pass voltages. In particular, during the programming of a selected storage element associated with a selected word line, a higher pass voltage is applied to word lines associated with previously programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set than to word lines associated with unprogrammed and / or partly programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set. The pass voltage is sufficiently high to balance the channel potentials on the source and drain sides of the selected word line and / or to reduce leakage of charge between the boosted channel regions. Optionally, an isolation region is formed between the boosted channel regions by applying a reduced voltage on one or more word lines between the selected word line and the word lines that receive the higher pass voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Apparatus for programming non-volatile memory with reduced program disturb using modified pass voltages
ActiveUS7355888B2Raise the potentialReduce charge leakageRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceChannel potential
Non-volatile storage elements are programmed in a manner that reduces program disturb by using modified pass voltages. In particular, during the programming of a selected storage element associated with a selected word line, a higher pass voltage is applied to word lines associated with previously programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set than to word lines associated with unprogrammed and / or partly programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set. The pass voltage is sufficiently high to balance the channel potentials on the source and drain sides of the selected word line and / or to reduce leakage of charge between the boosted channel regions. Optionally, an isolation region is formed between the boosted channel regions by applying a reduced voltage on one or more word lines between the selected word line and the word lines that receive the higher pass voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
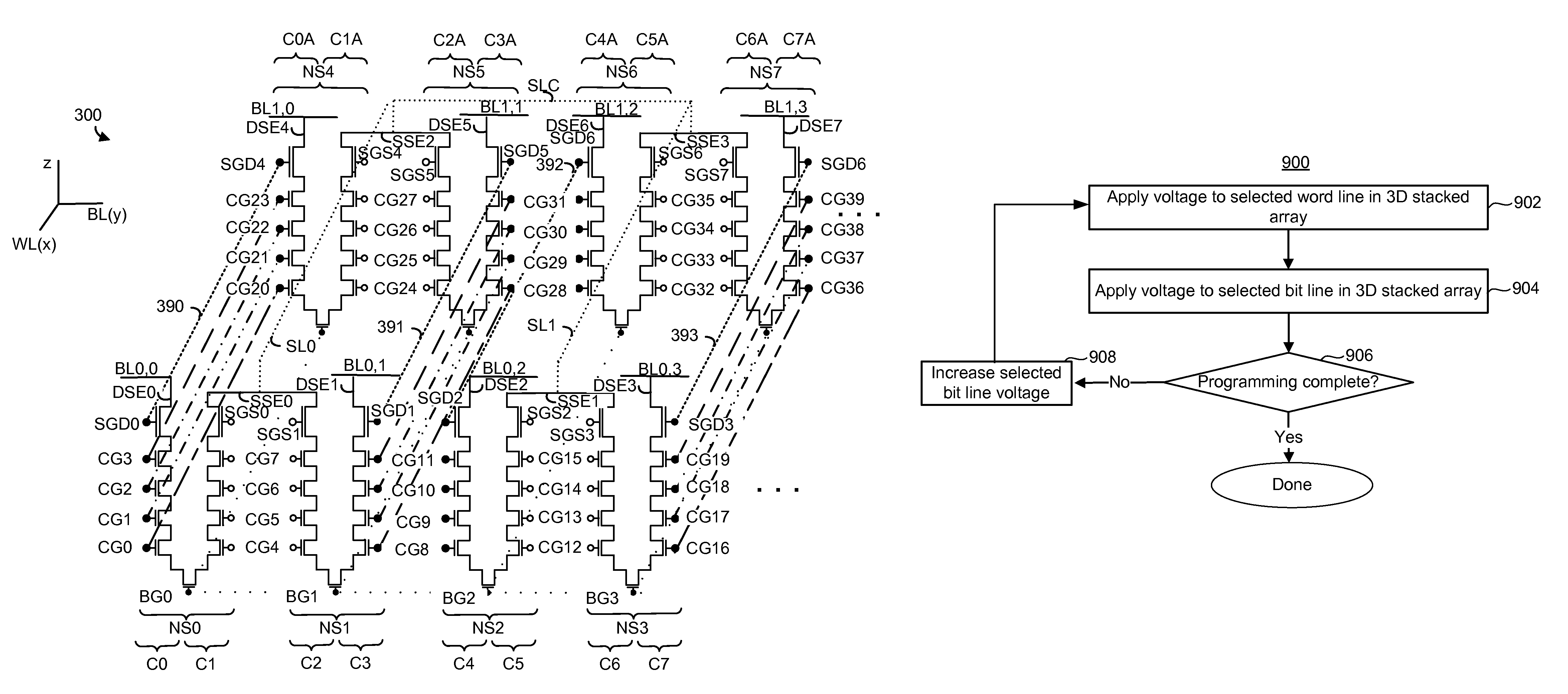
3D stacked non-volatile storage programming to conductive state
ActiveUS9099202B2Avoid programmingSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer scienceChannel potential
Programming NAND strings in a 3D stacked storage device to a conductive state. Storage elements may be erased by raising their Vt and programmed by lowering their Vt. Programming may include applying a series of increasing voltages to selected bit lines until the selected memory cell is programmed. Unselected bit lines may be held at about ground, or close to ground. The selected word line may be grounded, or be held close to ground. Unselected word lines between the selected word line and the bit line may receive about the selected bit line voltage. Unselected word lines between the source line and the selected word line may receive about half the selected bit line voltage. Programming may be achieved without boosting channels of unselected NAND strings to inhibit them from programming. Therefore, program disturb associated with leakage of boosted channel potential may be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
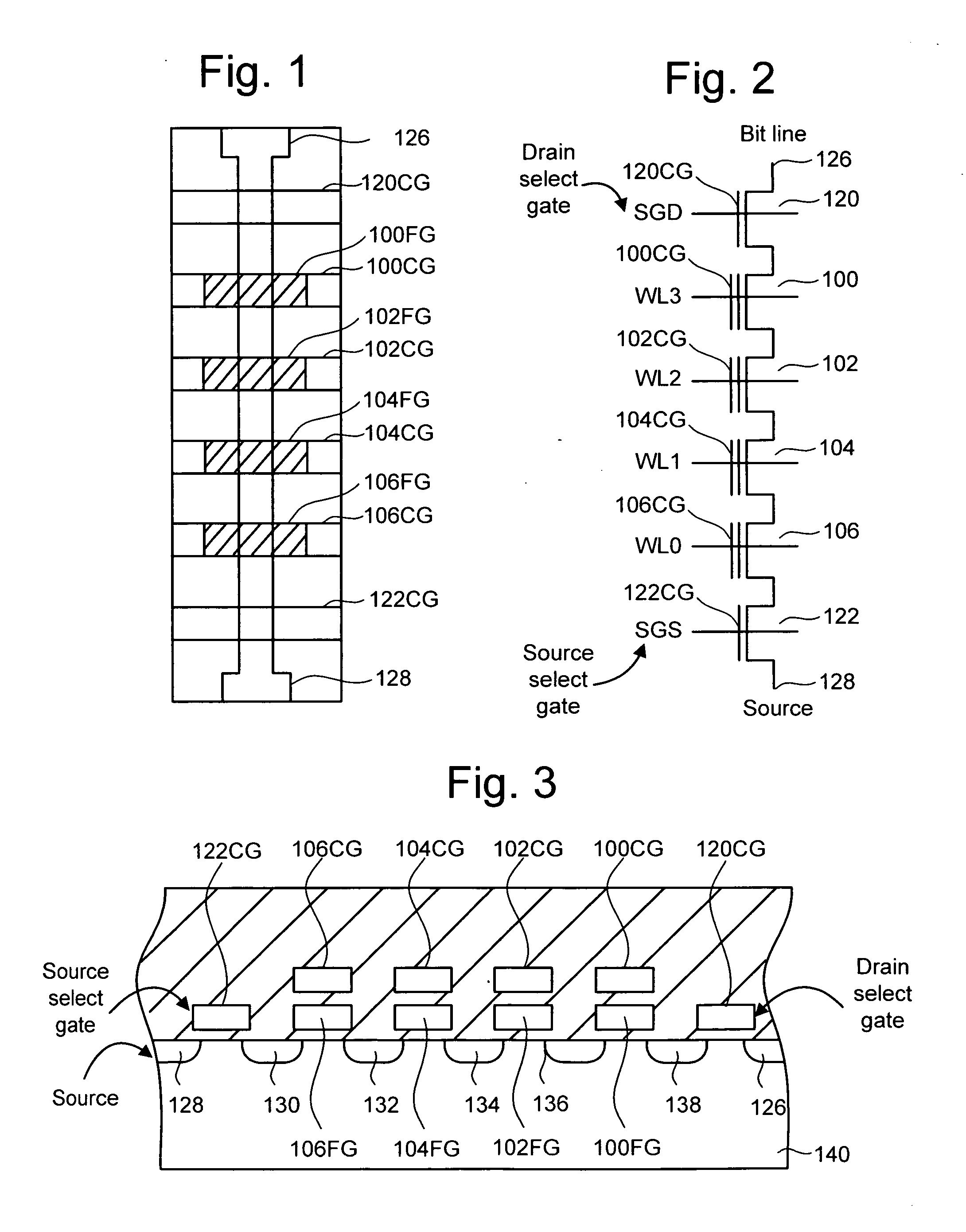
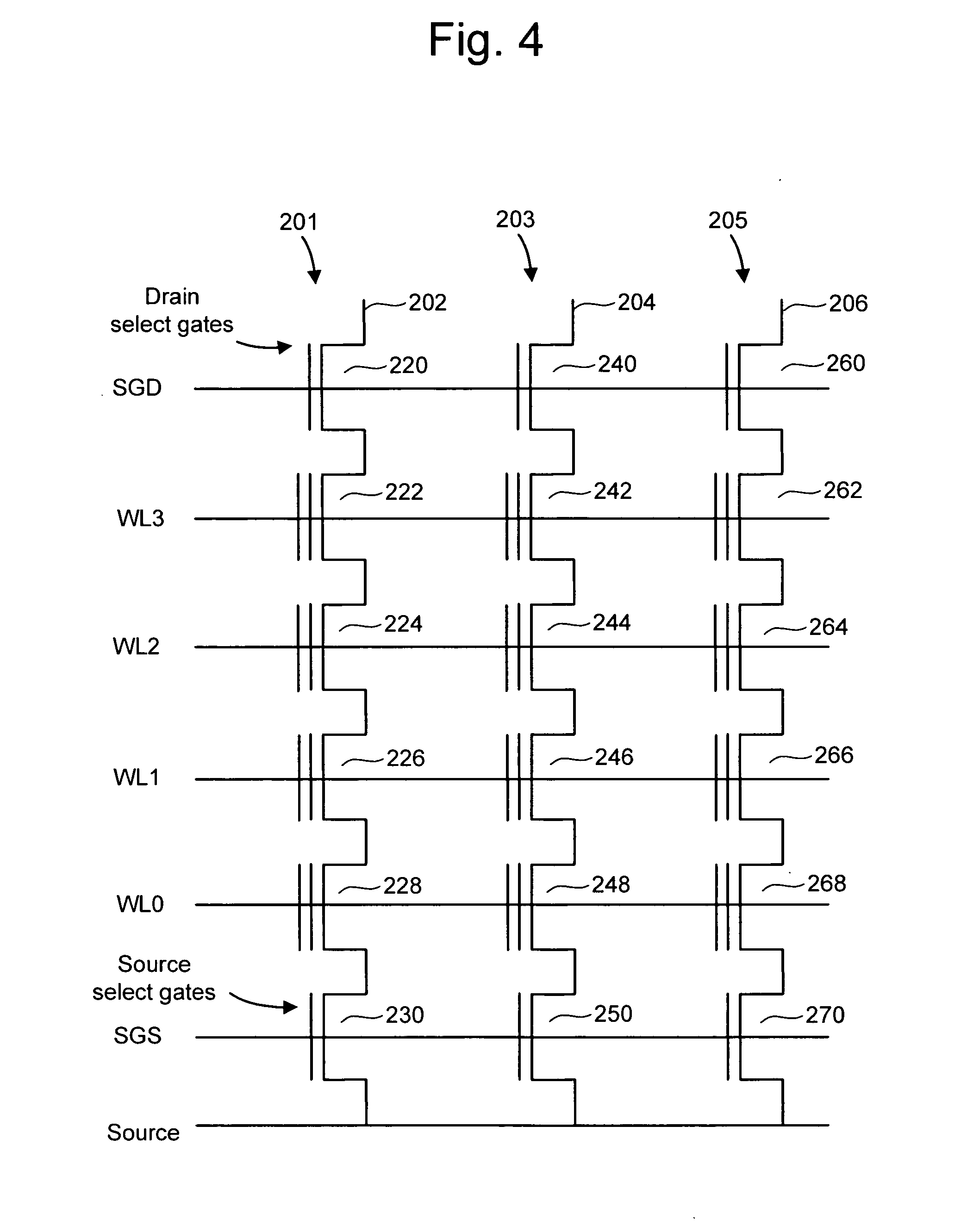
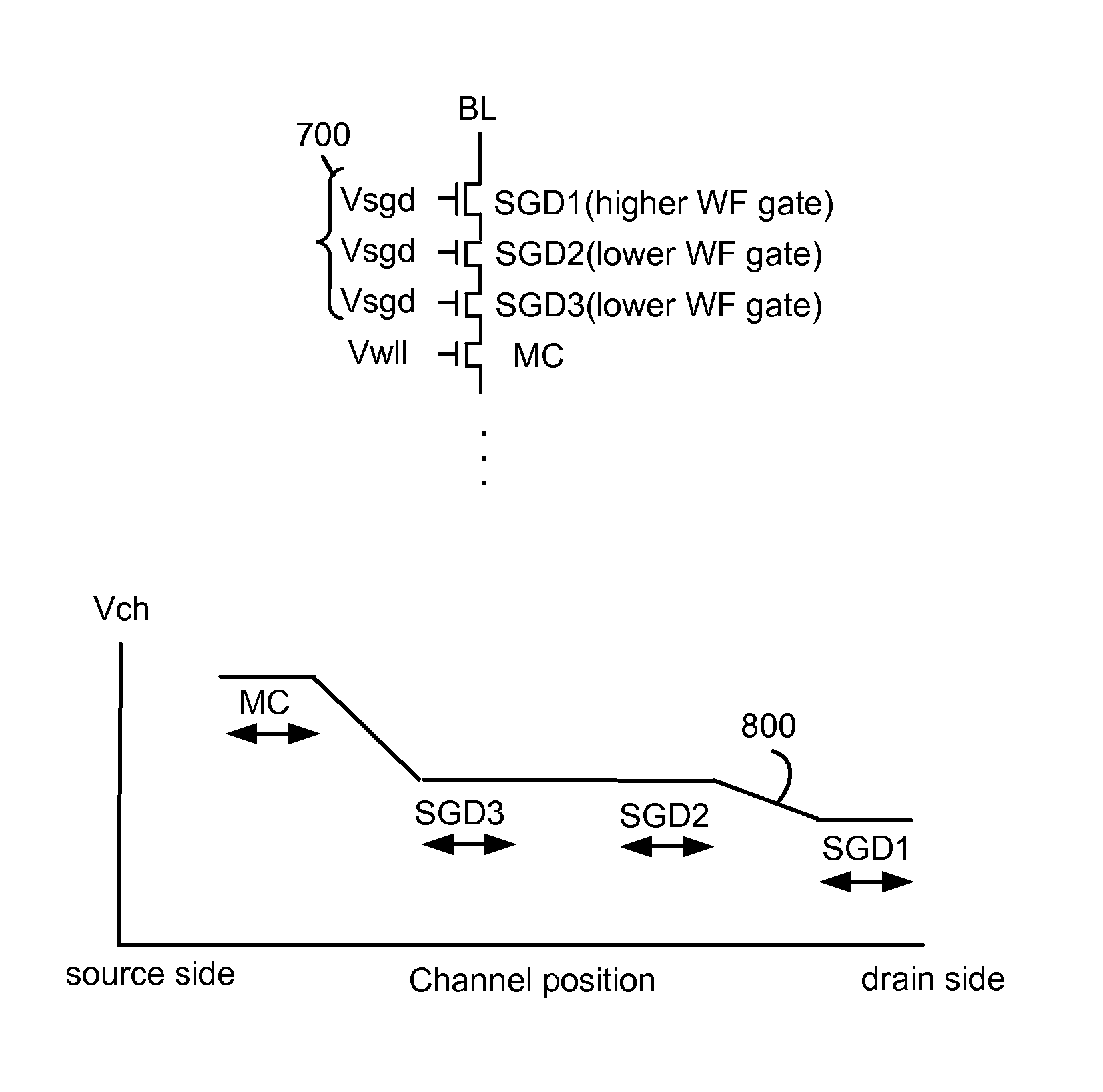
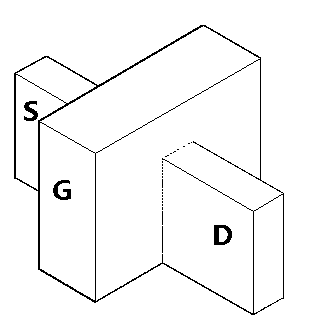
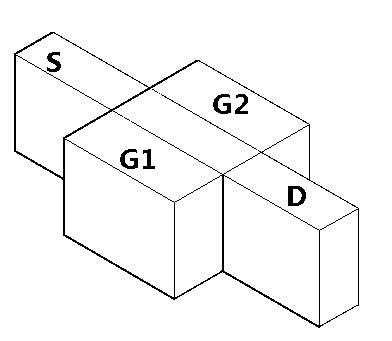
Select Gate Materials Having Different Work Functions In Non-Volatile Memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different work functions in their control gates so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a higher work function so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a lower work function so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different work functions can be provided by using different control gate materials for the SGD transistors. One option uses p+ polysilicon and n+ polysilicon to provide higher and lower work functions, respectively. Metal or metal silicide can also be used. A single SGD transistor with different control gate materials could also be used.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
3D stacked non-volatile storage programming to conductive state
Programming NAND strings in a 3D stacked storage device to a conductive state is disclosed. Storage elements may be erased by raising their Vt and programmed by lowering their Vt. Programming may include applying a series of increasing voltages to selected bit lines until the selected memory cell is programmed. Unselected bit lines may be held at about ground, or close to ground. The selected word line may be grounded, or be held close to ground. Unselected word lines between the selected word line and the bit line may receive about the selected bit line voltage. Unselected word lines between the source line and the selected word line may receive about half the selected bit line voltage. Programming may be achieved without boosting channels of unselected NAND strings to inhibit them from programming. Therefore, program disturb associated with leakage of boosted channel potential may be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Apparatus for programming non-volatile memory with reduced program disturb using modified pass voltages
ActiveUS20070171718A1Raise the potentialReduce charge leakageRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceChannel potential
Non-volatile storage elements are programmed in a manner that reduces program disturb by using modified pass voltages. In particular, during the programming of a selected storage element associated with a selected word line, a higher pass voltage is applied to word lines associated with previously programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set than to word lines associated with unprogrammed and / or partly programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set. The pass voltage is sufficiently high to balance the channel potentials on the source and drain sides of the selected word line and / or to reduce leakage of charge between the boosted channel regions. Optionally, an isolation region is formed between the boosted channel regions by applying a reduced voltage on one or more word lines between the selected word line and the word lines that receive the higher pass voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Select gate materials having different work functions in non-volatile memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different work functions in their control gates so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a higher work function so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a lower work function so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different work functions can be provided by using different control gate materials for the SGD transistors. One option uses p+ polysilicon and n+ polysilicon to provide higher and lower work functions, respectively. Metal or metal silicide can also be used. A single SGD transistor with different control gate materials could also be used.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Adjusting control gate overdrive of select gate transistors during programming of non-volatile memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different control gate overdrive voltages so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a lower control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a higher control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different control gate overdrive voltages can be provided by programming different threshold voltages, or by providing different control gates voltages, for the SGD transistors. Undesirable reductions in a Vsgd window due to drain-induced barrier lowering can be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Adjusting Control Gate Overdrive Of Select Gate Transistors During Programming Of Non-Volatile Memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different control gate overdrive voltages so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a lower control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a higher control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different control gate overdrive voltages can be provided by programming different threshold voltages, or by providing different control gates voltages, for the SGD transistors. Undesirable reductions in a Vsgd window due to drain-induced barrier lowering can be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Hot carrier programming in NAND flash
ActiveUS8531886B2Maximize capacitanceIncrease capacitanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory and operation method thereof
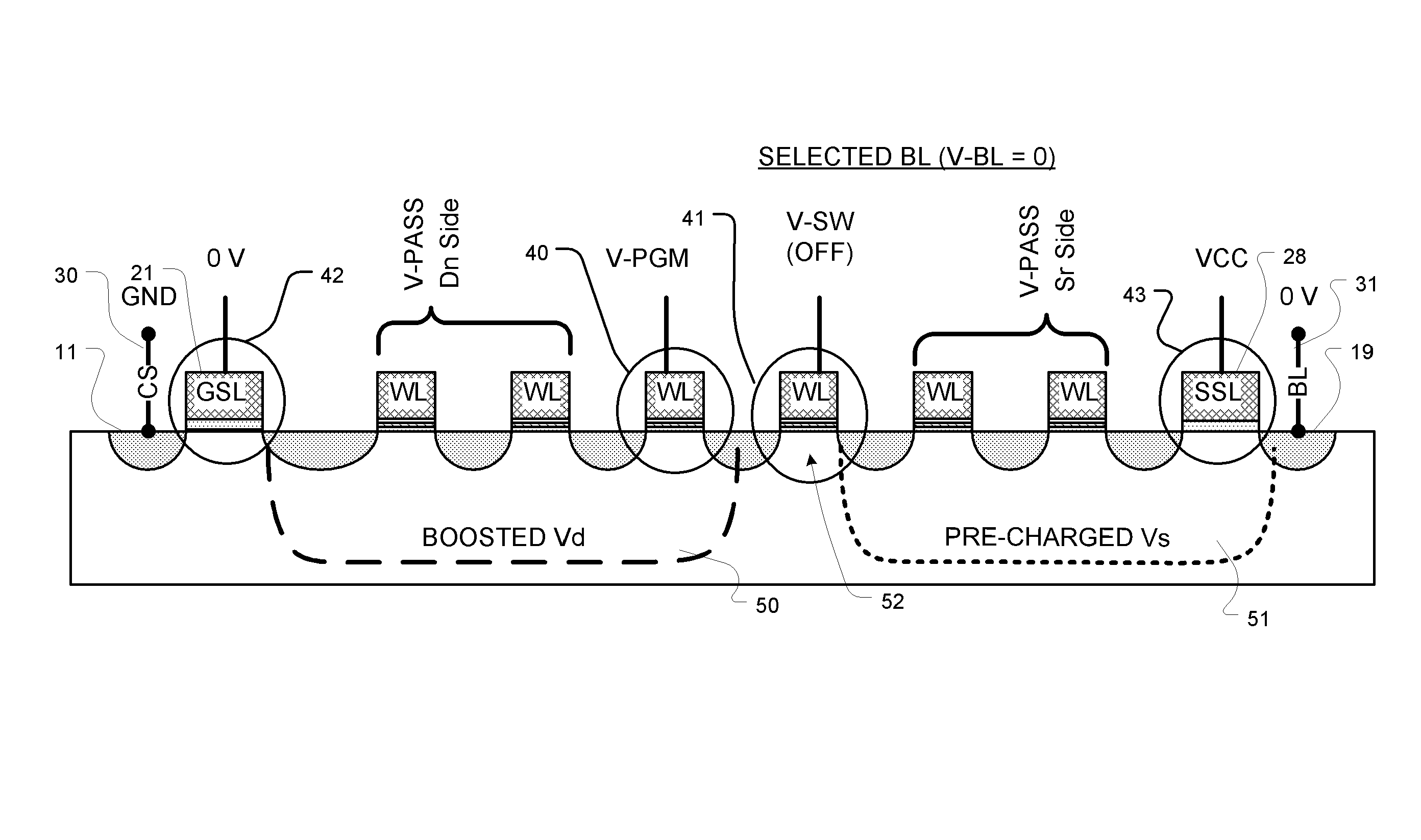
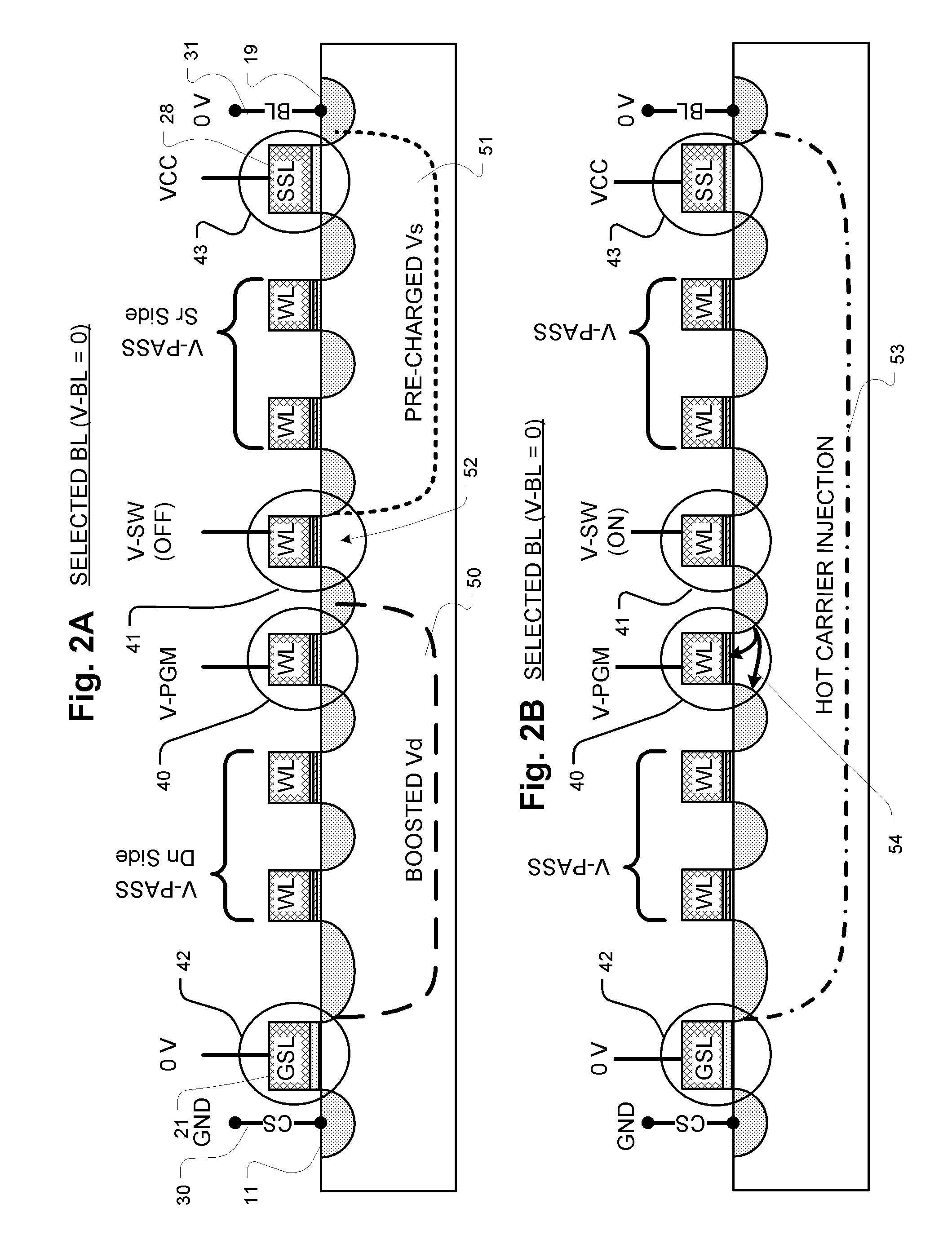
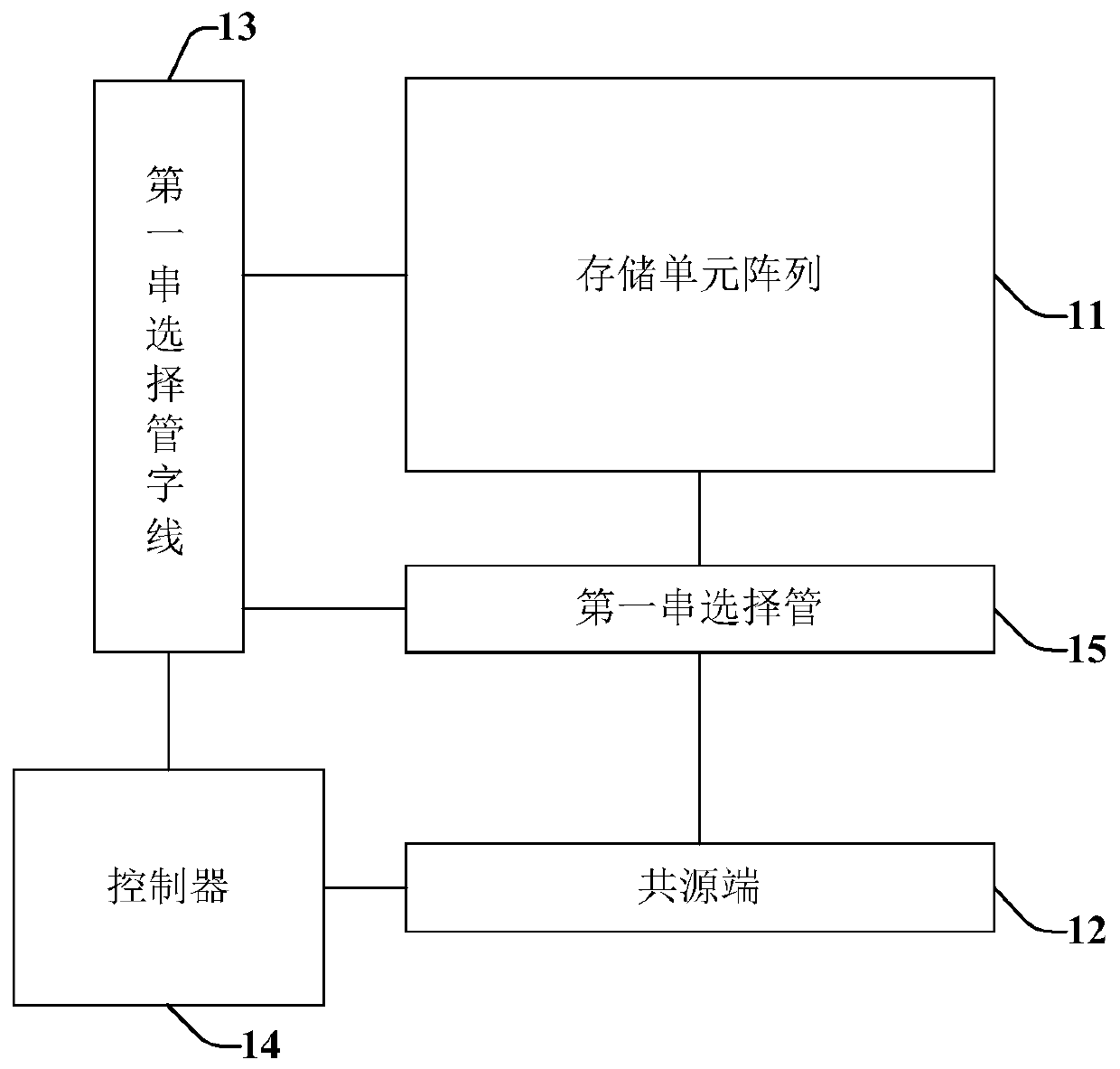
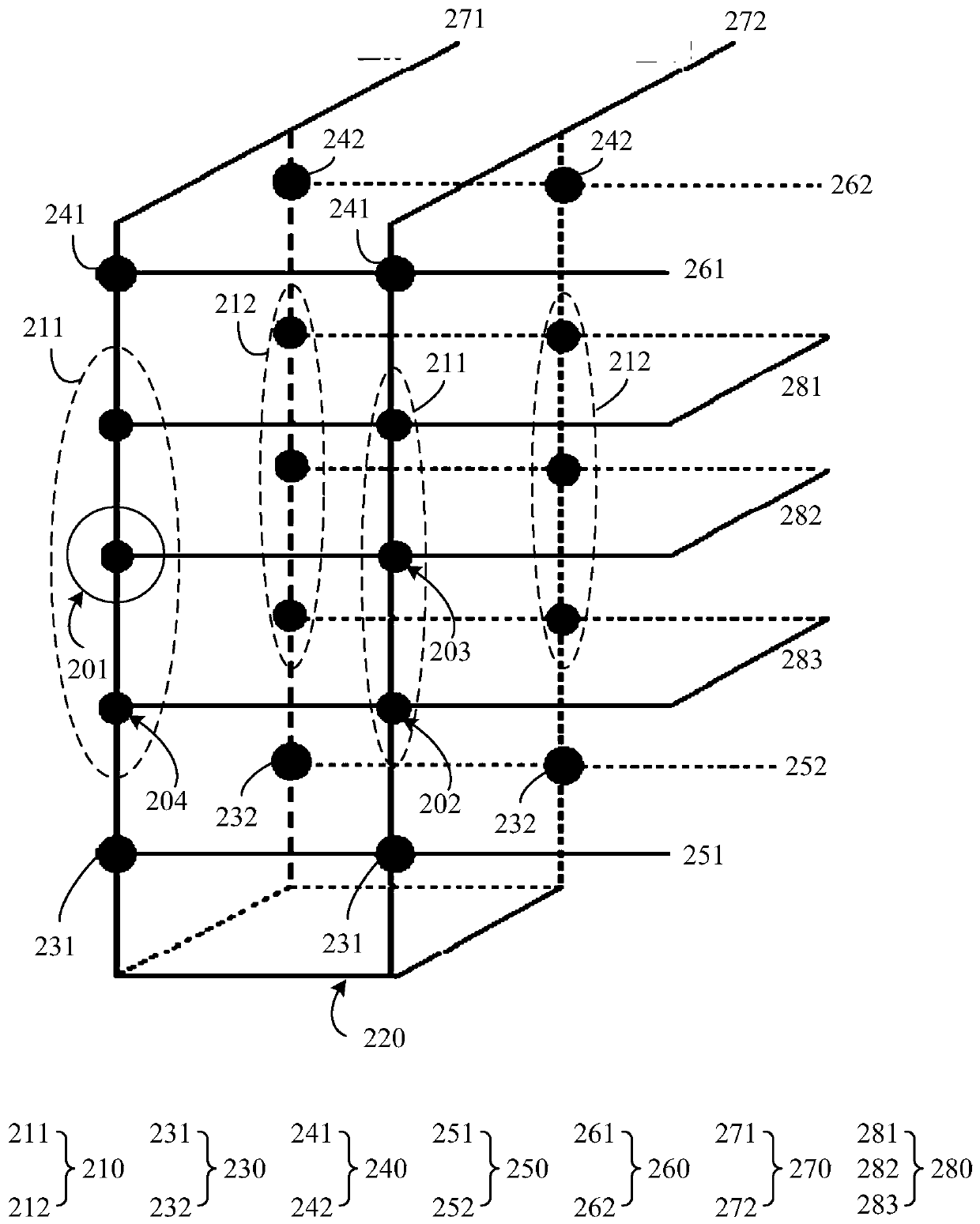
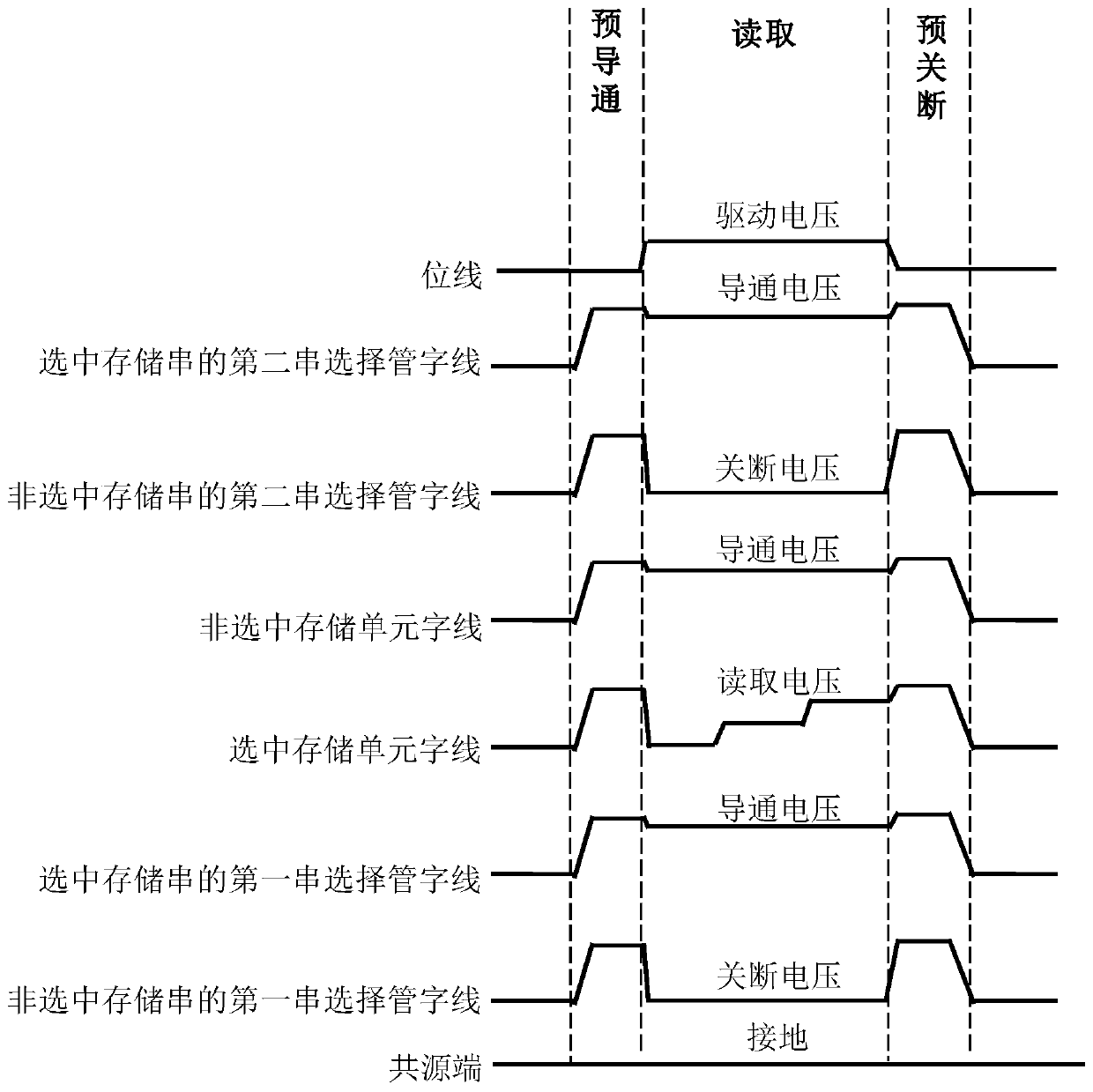
InactiveCN110289034AIncreased channel potentialReduce potential differenceRead-only memoriesString groupPre-charge
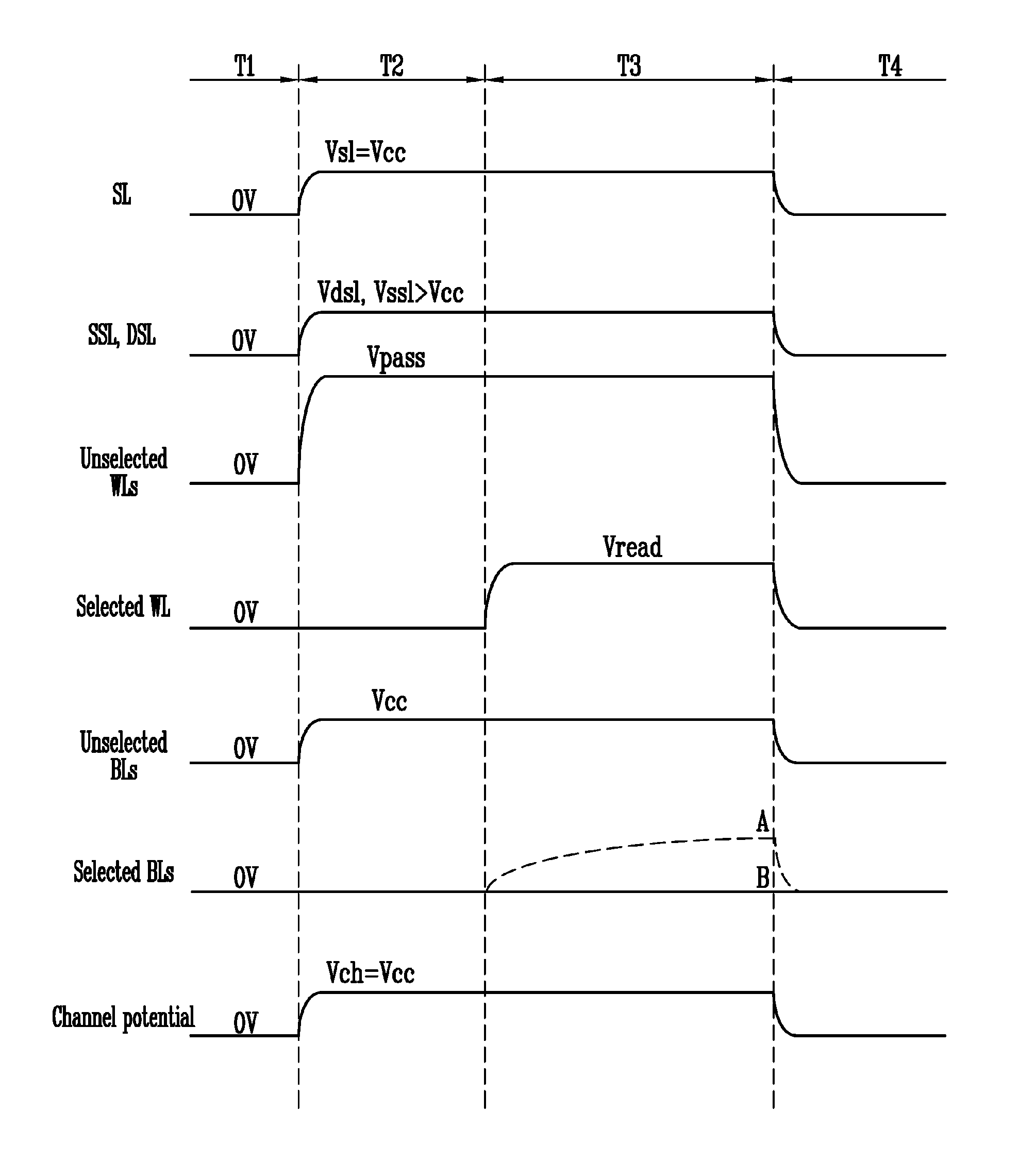
The present invention relates to a non-volatile memory and an operating method thereof, the non-volatile memory comprising: a memory cell array comprising a plurality of memory string groups, each memory string group comprising a plurality of memory strings; a common source end which is connected to the other end of each storage string through a first string selection tube; a plurality of first string selection tube word lines, wherein each first string selection tube word line is connected to the grid electrode of the first string selection tube of the corresponding storage string group; and a controller which is configured to conduct a first string selection tube of a selected memory string in the plurality of memory strings and a first string selection tube of a non-selected memory string in a pre-conduction stage before the reading stage, and apply a continuous first pre-charging voltage to the common source end. According to the nonvolatile memory and the operation method thereof, the read interference can be reduced by increasing the channel potential of the non-selected memory string.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
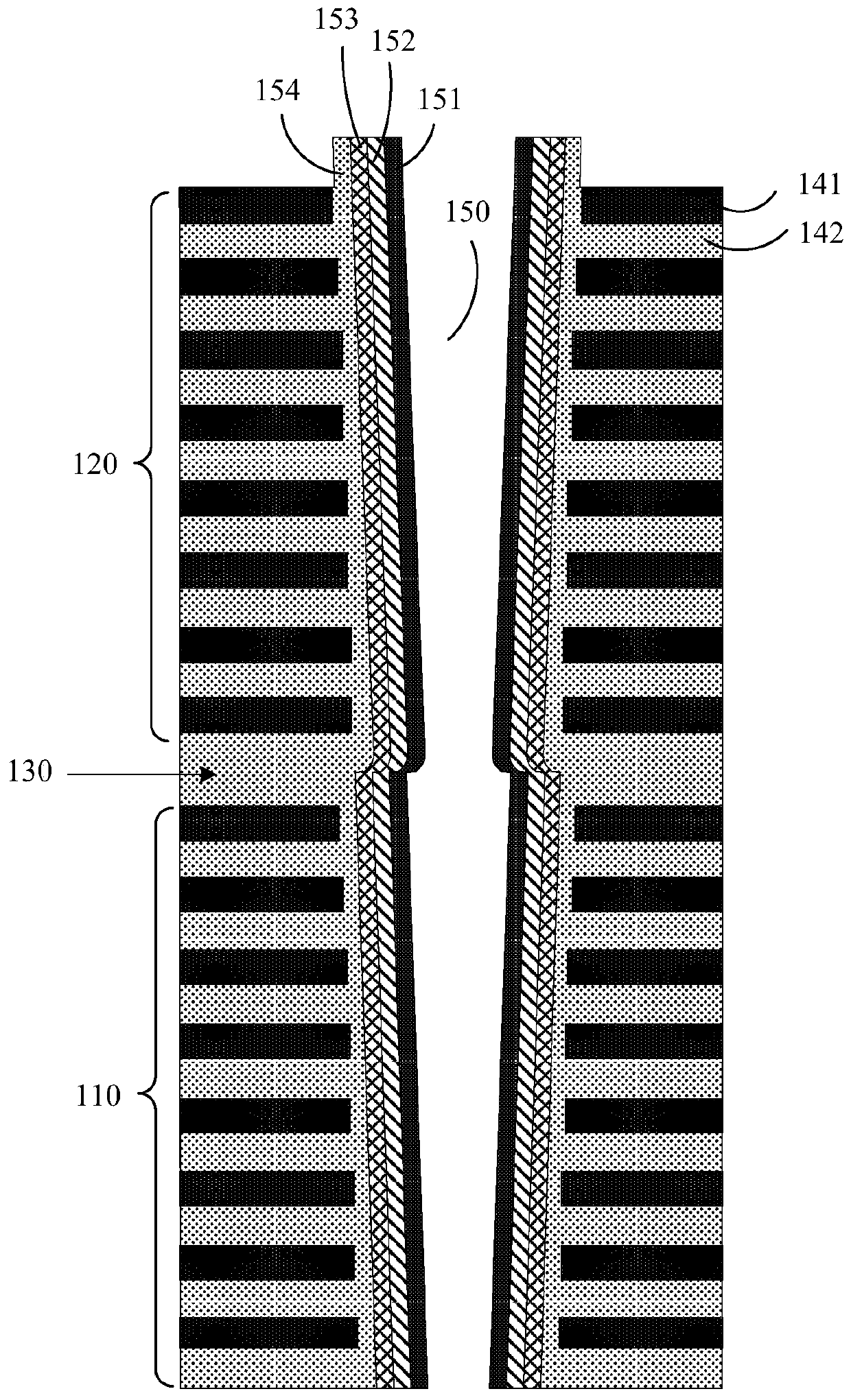
Nonvolatile memory and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN110428859ARaise the channel potentialImprove uniformitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer architectureChannel potential
The invention relates to a nonvolatile memory and a manufacturing method thereof. The non-volatile memory includes a memory cell array and an intermediate string selection tube without memory cells. The memory cell array comprises a plurality of memory strings, each memory string comprises a first sub-string and a second sub-string which are connected in series, and the first sub-string and the second sub-string respectively comprise a plurality of memory cells. And the intermediate string selection tube is connected between the first sub-string and the second sub-string. According to the nonvolatile memory, the intermediate string selection tube without the memory cell is connected between the memory strings, and during programming, the channel potential of the non-selected memory cell can be improved by applying a relatively high voltage to the intermediate string selection tube, so that the interference of programming operation on the non-selected memory cell is reduced.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Downlink self-adaptive transmission method in cellular relay network
InactiveCN101951645AImprove performanceCommunication service is goodNetwork traffic/resource managementActive radio relay systemsFrequency spectrumInformation quantity
The invention relates to a downlink self-adaptive transmission method in a cellular relay network, belonging to the technical field of mobile communication. The method comprises the following steps: a plurality of antennae are respectively arranged at a base station and a relay node of a cellular relay network; and the base station acquires the channel information of three down links, respectively estimates the message capacity of the cellular relay network in the three different signal transmission modes according to the channel information, provides two downlink cooperation transmission modes respectively based on the information quantity consolidation principle and the energy consolidation principle and compares them with the direct transmission mode, and finally, the base station selects an appropriate transmission mode after comprehensively considering the performance gain and resource expenses. The method improves the communication performance of cell-edge users, greatly explores the channel potential of the relay system three-node model and can obviously increase the spectrum efficiency of cell-edge users.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Semiconductor memory device including memory cells and a peripheral circuit and method of operating the same
ActiveUS8937833B2Improve operating characteristicsIncrease channel potentialRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsChannel potential
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory block including memory strings coupled to and disposed between bit lines and a common source line, and a peripheral circuit configured to perform a read operation of memory cells included in selected memory strings of the memory strings and increase channel potential of unselected memory strings in the read operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Method for programming non-volatile memory with reduced program disturb using modified pass voltages
Non-volatile storage elements (1110...1155) are programmed in a manner that reduces program disturb by using modified pass voltages (Vpassl, Vpass2). In particular, during the programming of a selected storage element associated with a selected word line, a higher pass voltage (Vpassl) is applied to word lines associated with previously programmed non-volatile storage elements in the set than to word lines associated with unprogrammed and / or partly programmed non- volatile storage elements in the set. (Vpass2) The pass voltage is sufficiently high to balance the channel potentials on the source and drain sides of the selected word line and / or to reduce leakage of charge between the boosted channel regions.; Optionally, an isolation region is formed between the boosted channel regions by applying a reduced voltage on one or more word lines between the selected word line and the word lines that receive the higher pass voltage.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
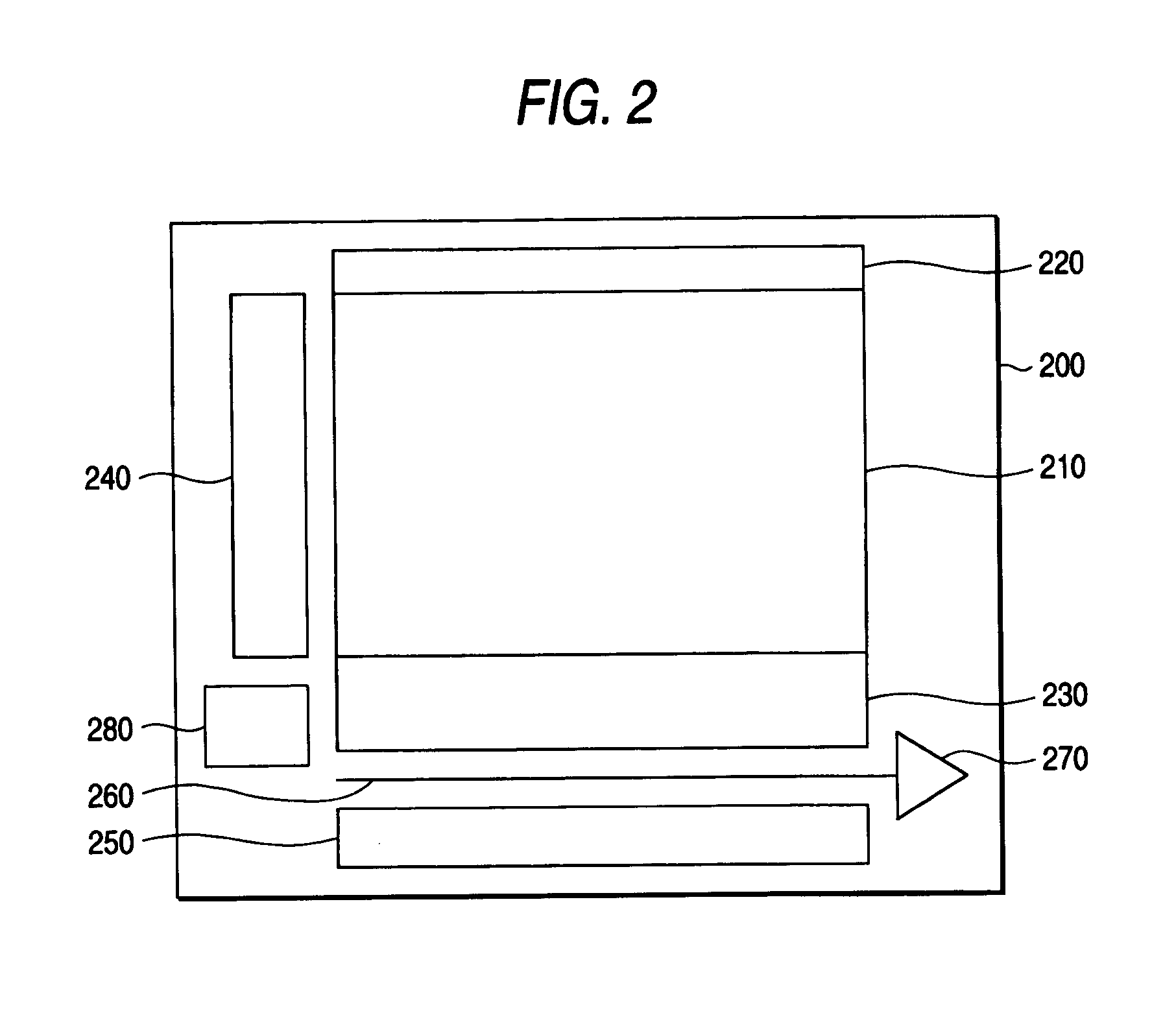
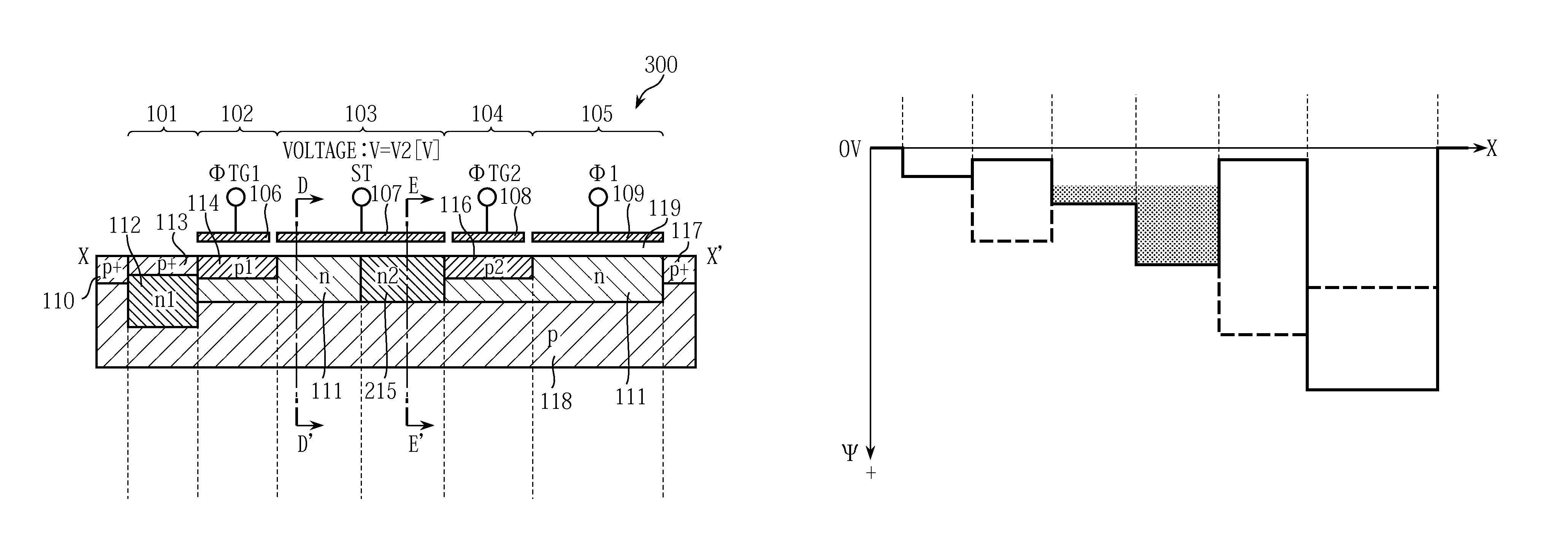
Solid-state imaging device and control method for same
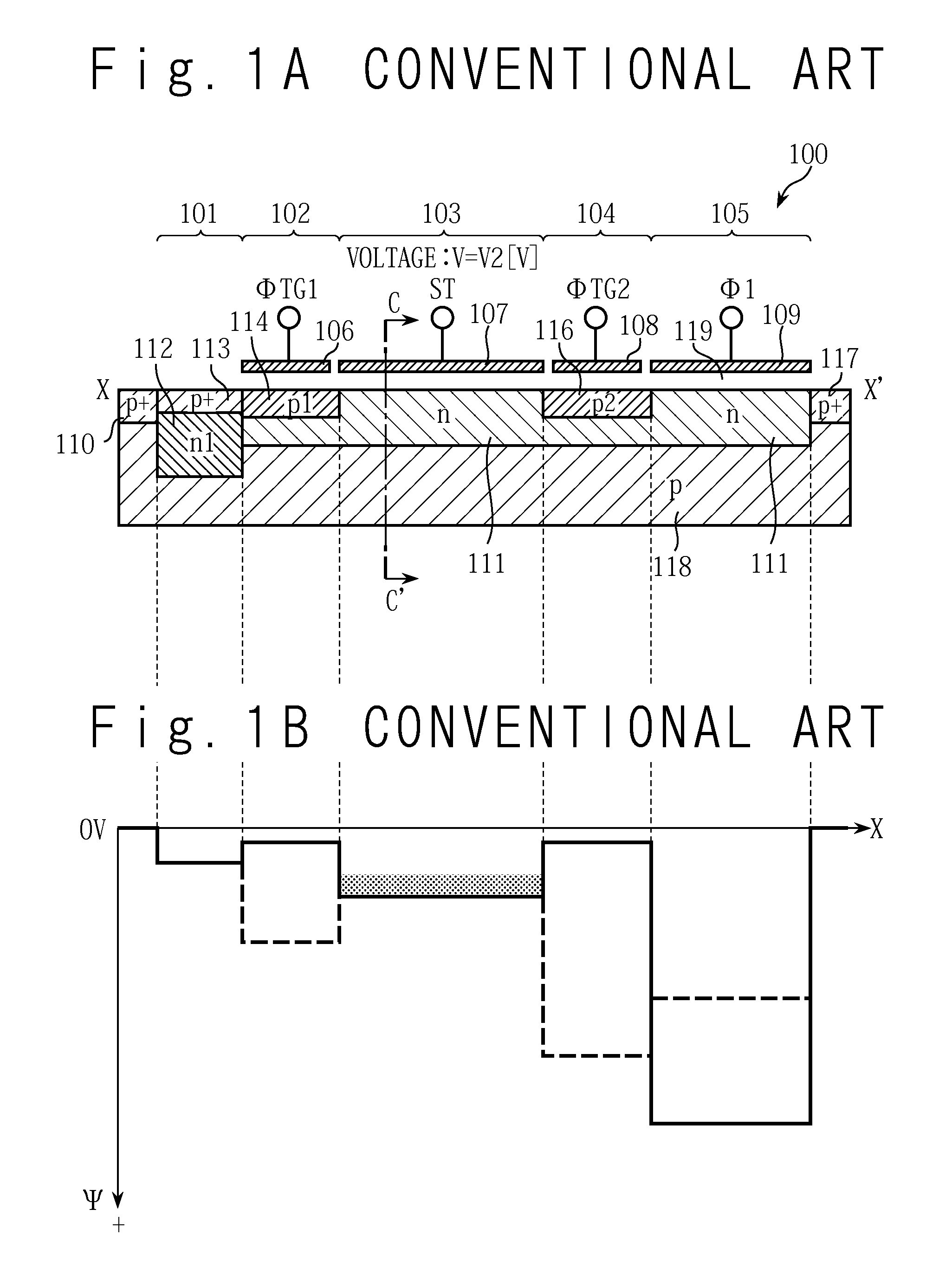
In realizing an entire-screen simultaneous shutter function using a solid-state imaging device having a device structure as a CMOS solid-state imaging device, the restriction undergone by exposure time is relieved to secure a sufficient exposure time with swift operation. Separately from a transfer Tr for transferring a signal charge of a buried-type PD to an FD, a drain Tr is provided to exclude a signal charge of the buried PD. Both a channel potential on the drain transistor when turned on and a channel potential on the transfer transistor when turned on are set higher than a depleting potential for the PD. This makes it possible to completely transfer the signal charge of the PD by both the transfer Tr and the drain Tr. In the operation to sequentially read out a signal charge from the FD on a pixel-row basis, PD exposure operation is started in a course of reading out the same.
Owner:SONY CORP
Solid-state imaging device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20110193137A1Improve charge transfer efficiencySuppress generationSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesControl signalPhotodiode
A solid-state imaging device includes: a photoelectric converting section comprising a photo-diode; a charge storage section; a charge transfer section; a first control gate section provided between the photoelectric converting section and the charge storage section to control transfer of a signal charge from the photoelectric converting section to the charge storage section; and a second control gate section provided between the charge storage section and the charge transfer section to control transfer of the signal charge from the charge storage section to the charge transfer section. The charge storage section includes: a first region formed on a side near to the first control gate section; and a second region formed on a side near to the second control gate section and configured to have a channel potential increased more than that of the first region. The second region is configured to hold the signal charge in a pinning condition.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
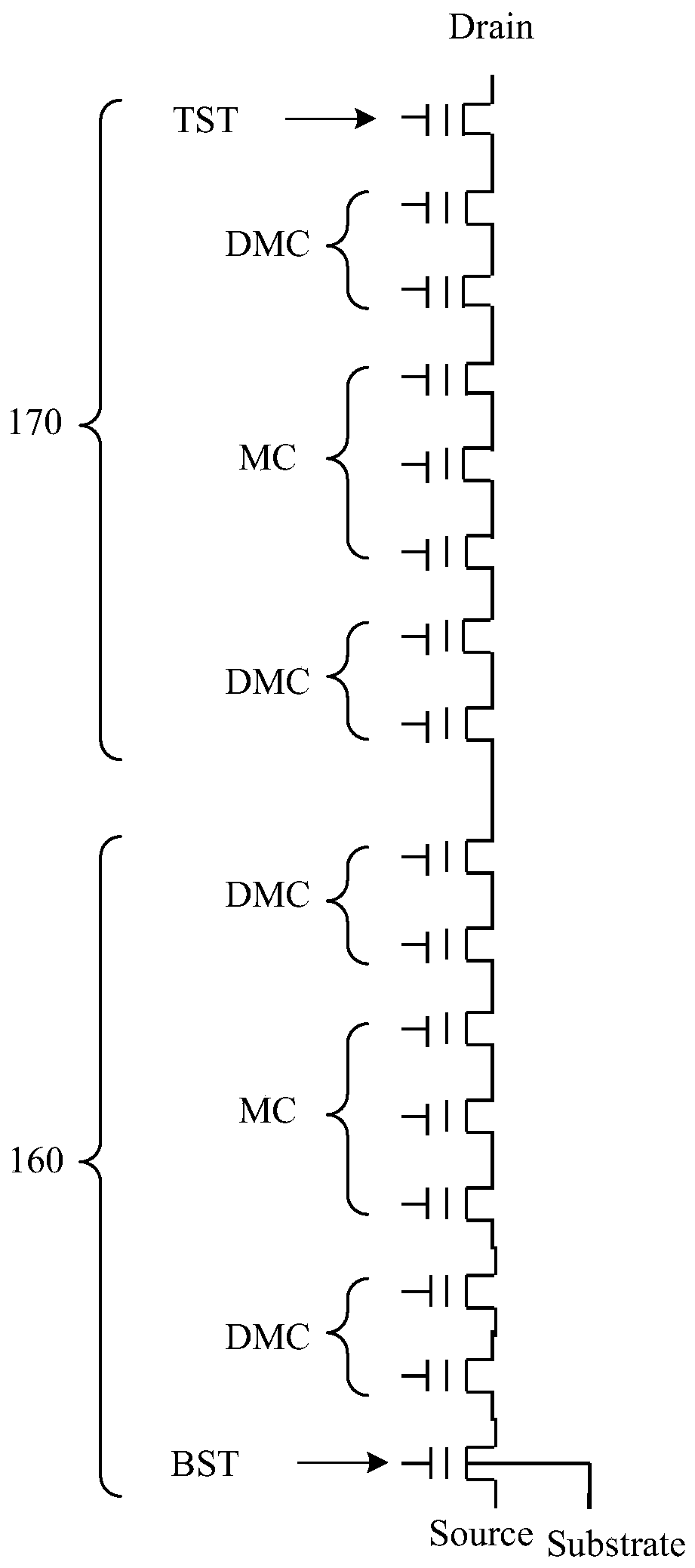
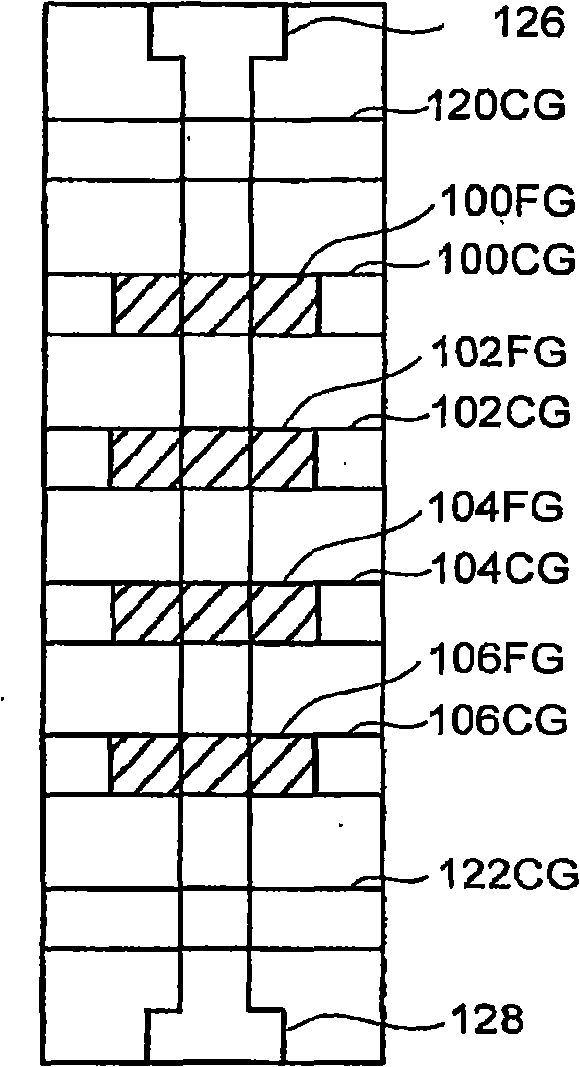
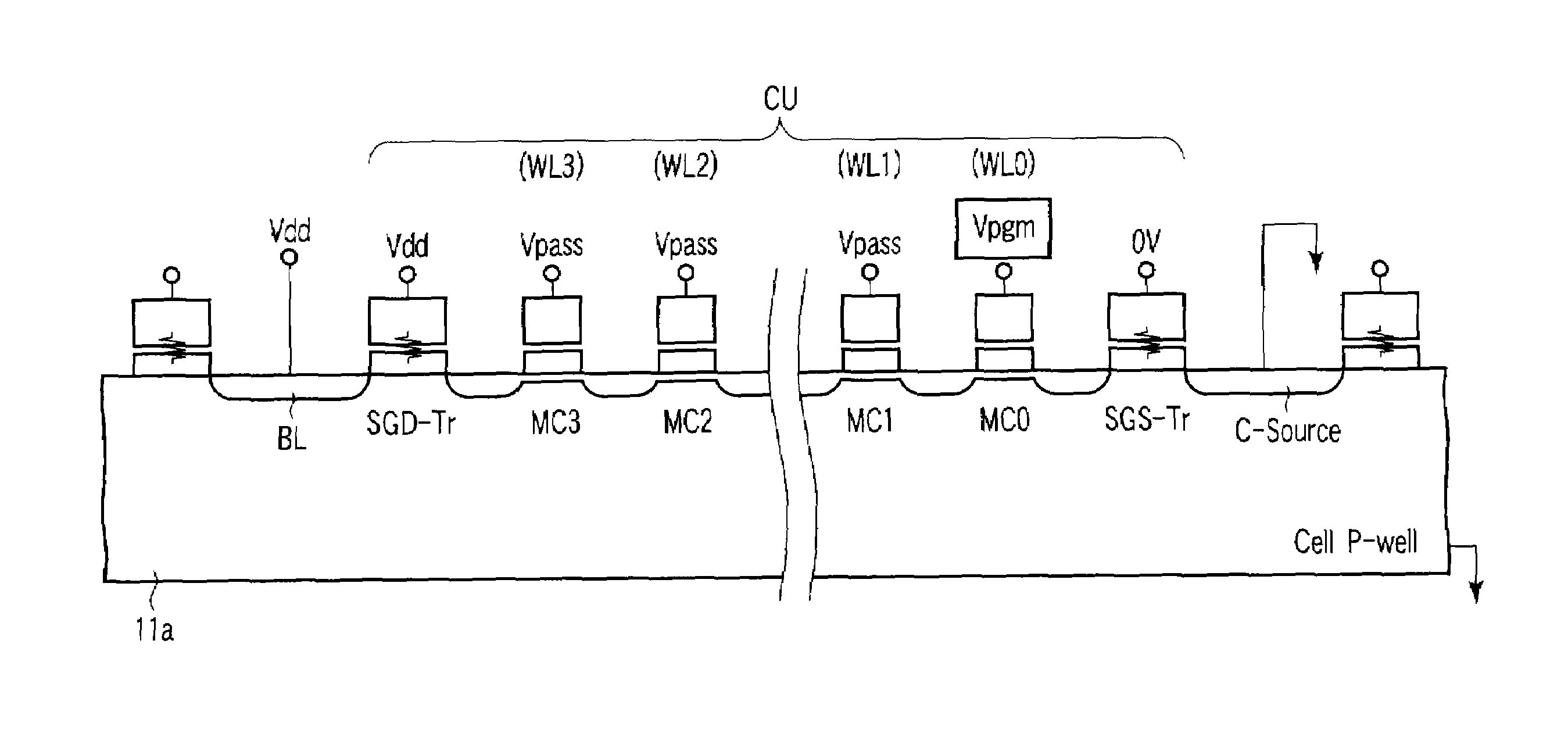
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device which realizes "1" write operation by boosting channel potential
InactiveUS20080304324A1Avoid it happening againRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsVoltage control
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array having a plurality of cell units each including a preset number of memory cells and select gate transistors on drain and source sides. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a voltage control circuit to prevent occurrence of an erroneous write operation due to excessively high boost voltage of a channel when “1” is written into the memory cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Select gate materials having different work functions in non-volatile memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different work functions in their control gates so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a higher work function so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a lower work function so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different work functions can be provided by using different control gate materials for the SGD transistors. One option uses p+ polysilicon and n+ polysilicon to provide higher and lower work functions, respectively. Metal or metal silicide can also be used. A single SGD transistor with different control gate materials could also be used.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
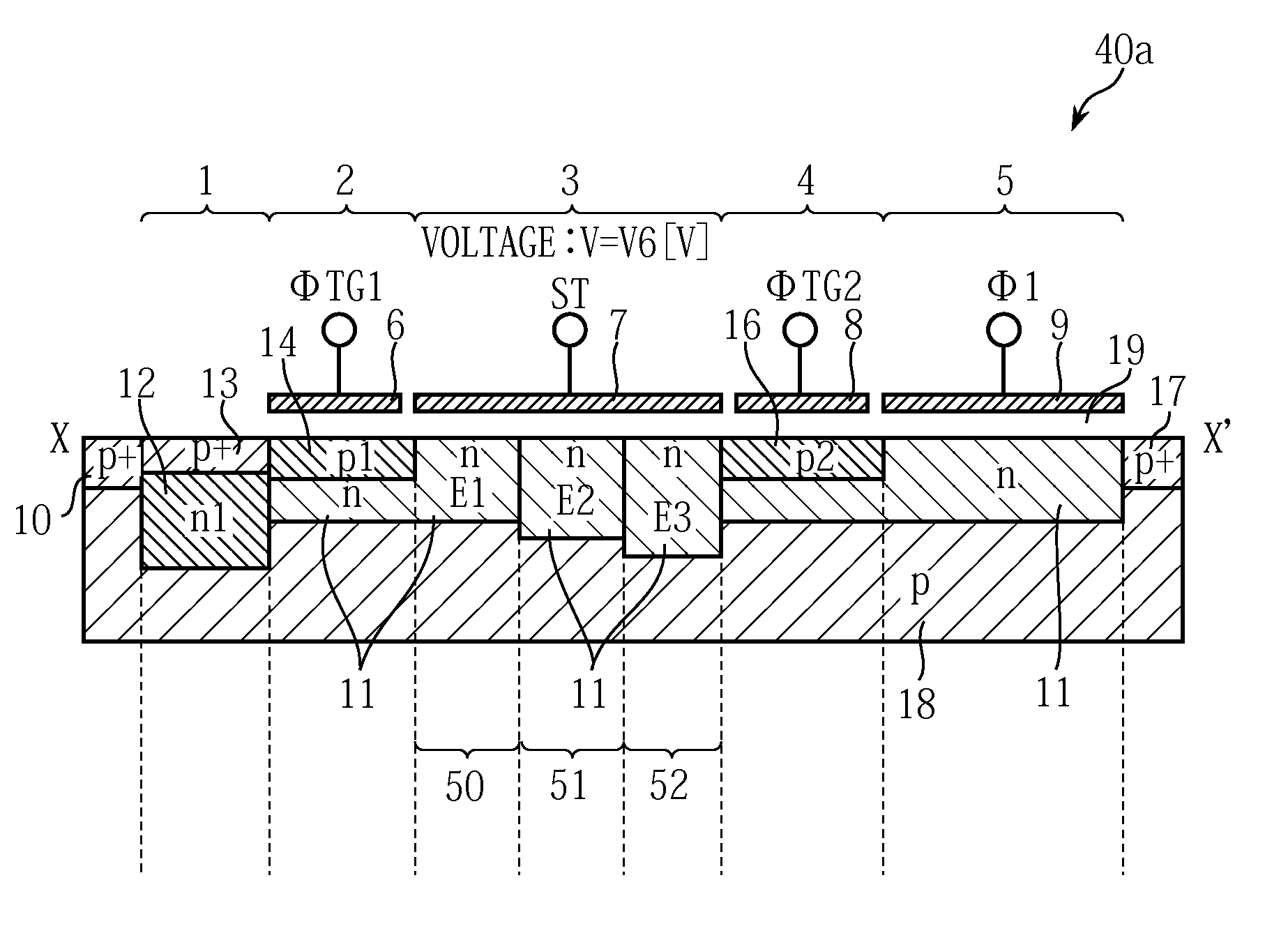
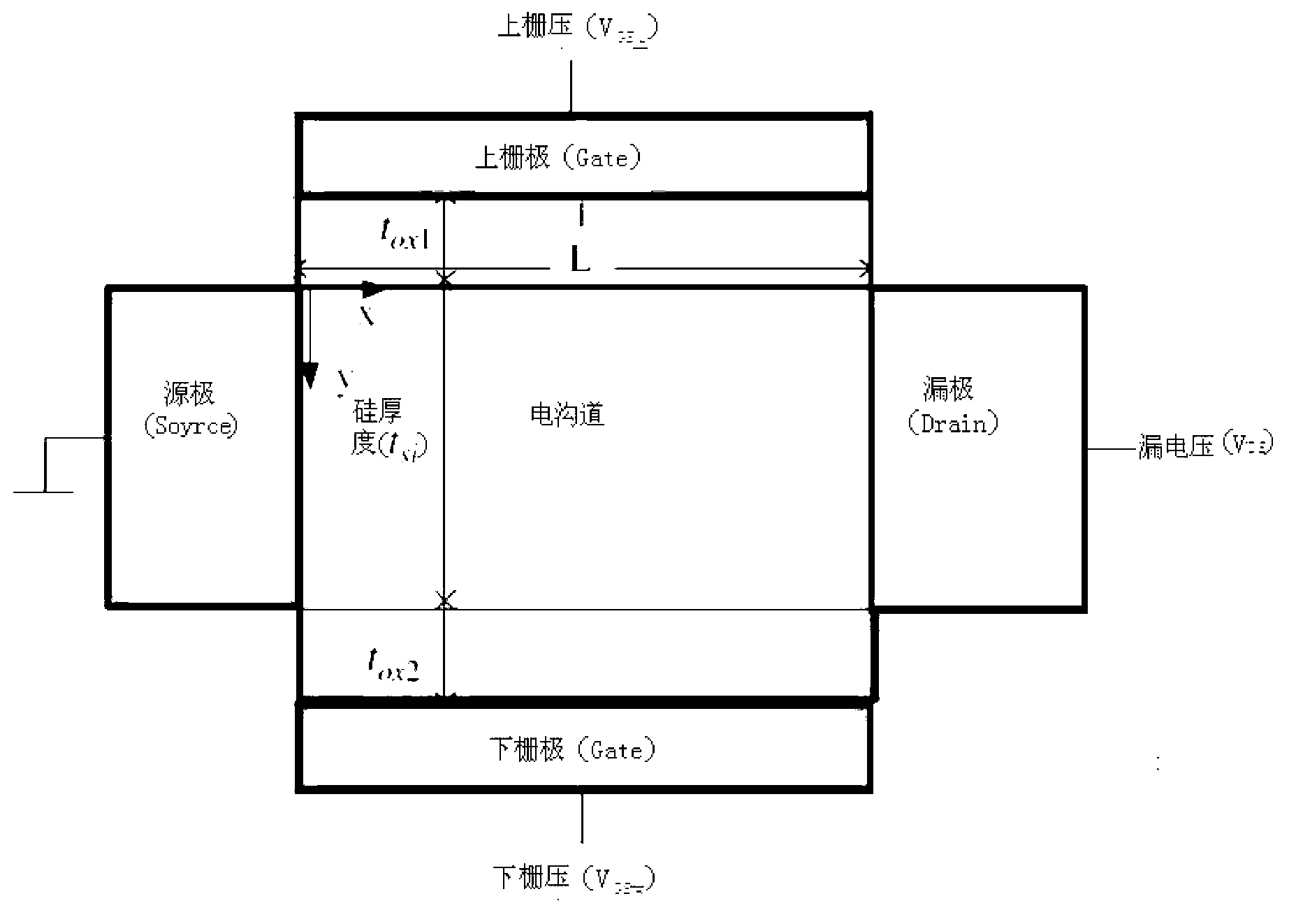
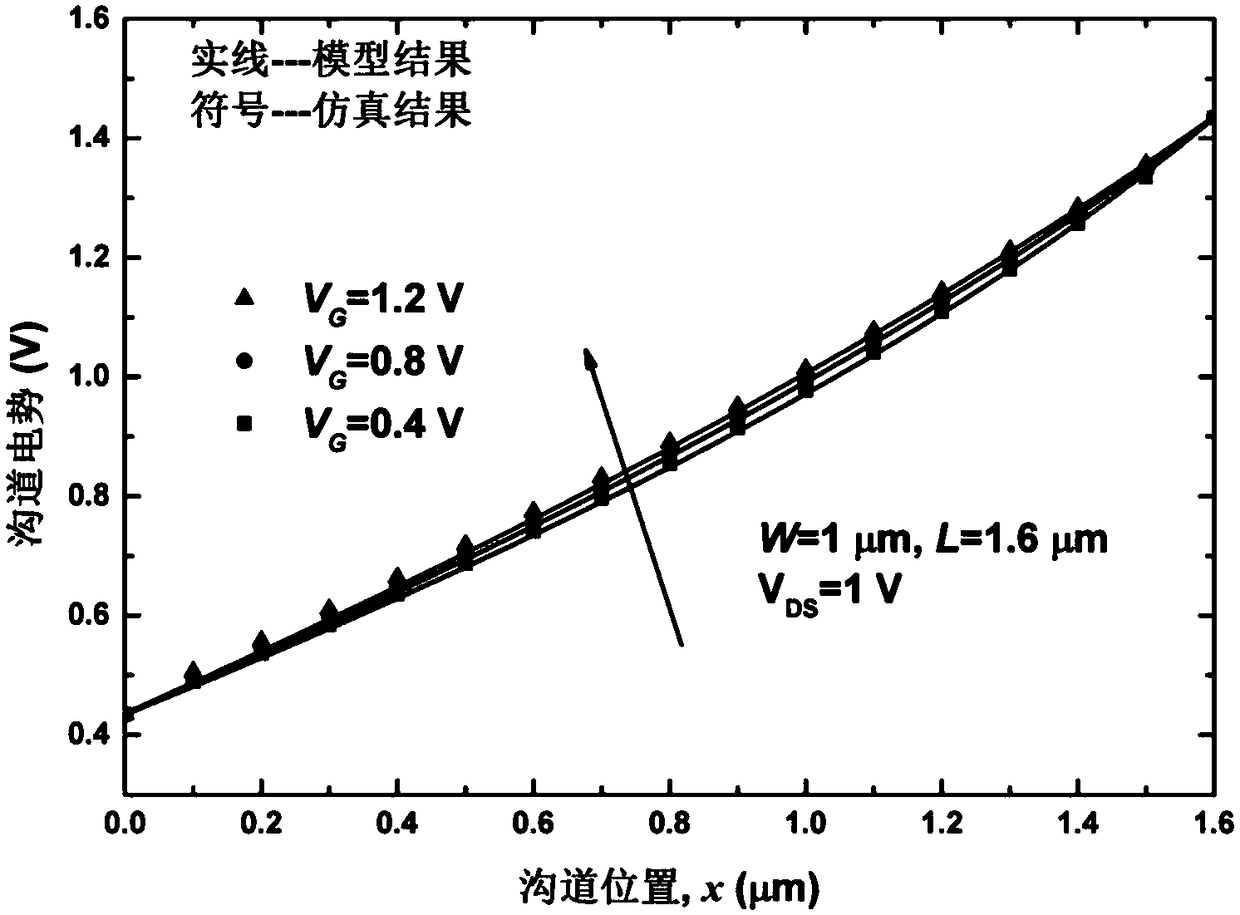
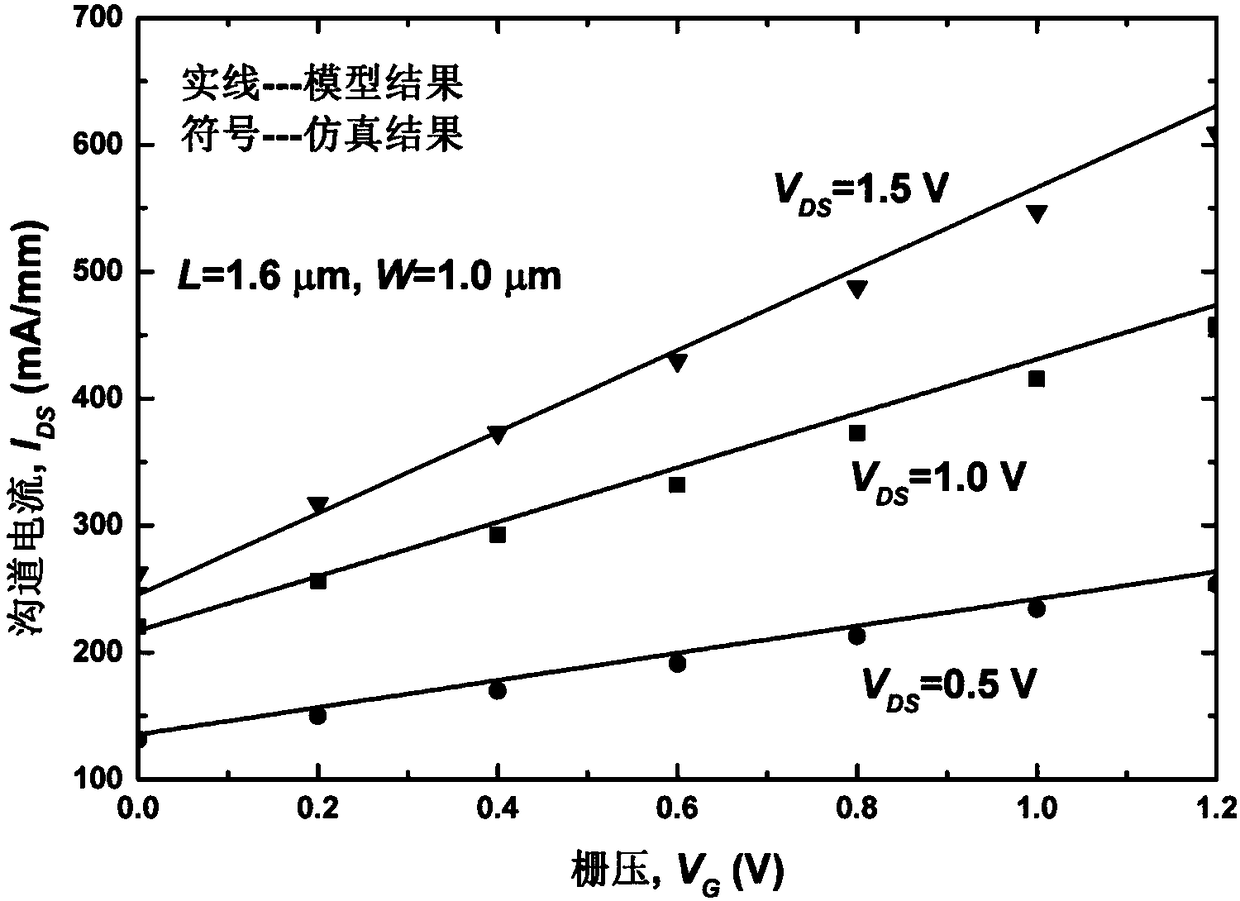
Independent double-grid FinFET channel potential distribution analysis model
InactiveCN103186691ALarge gate areaSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPoisson's equation
The invention provides an independent double-grid FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistor) channel potential distribution analysis model which comprises a source electrode, wherein the source electrode is arranged on one side of a powered channel; the side of the powered channel, which is deviated from the powered channel, is provided with a drain electrode; the top surface of the powered channel is provided with an upper grid electrode; and the bottom surface of the powered channel is provided with a lower grid electrode. The independent double-grid FinFET channel potential distribution analysis model is characterized in that the device structure adopts the following potential distribution model analysis formula. The independent double-grid FinFET channel potential distribution analysis model disclosed by the invention does not use more approximate conditions and solves a two-dimensional poisson equation by using a progression method so as to establish a channel potential analysis model; the analysis model adopts more reasonable boundary condition; complex geometrical structure parameters and experimental parameters are not introduced into the analysis model; and the analysis model is suitable for different conditions such as substrate reversed bias voltages, drain voltages and the like, well accords with a numerical simulation result and has the advantages of simple form, high computing accuracy and high computing speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20130194870A1Improve operating characteristicsIncrease channel potentialRead-only memoriesDigital storageChannel potentialSemiconductor
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory block including memory strings coupled to and disposed between bit lines and a common source line, and a peripheral circuit configured to perform a read operation of memory cells included in selected memory strings of the memory strings and increase channel potential of unselected memory strings in the read operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Reducing read disturb in memory device during signal switching transients
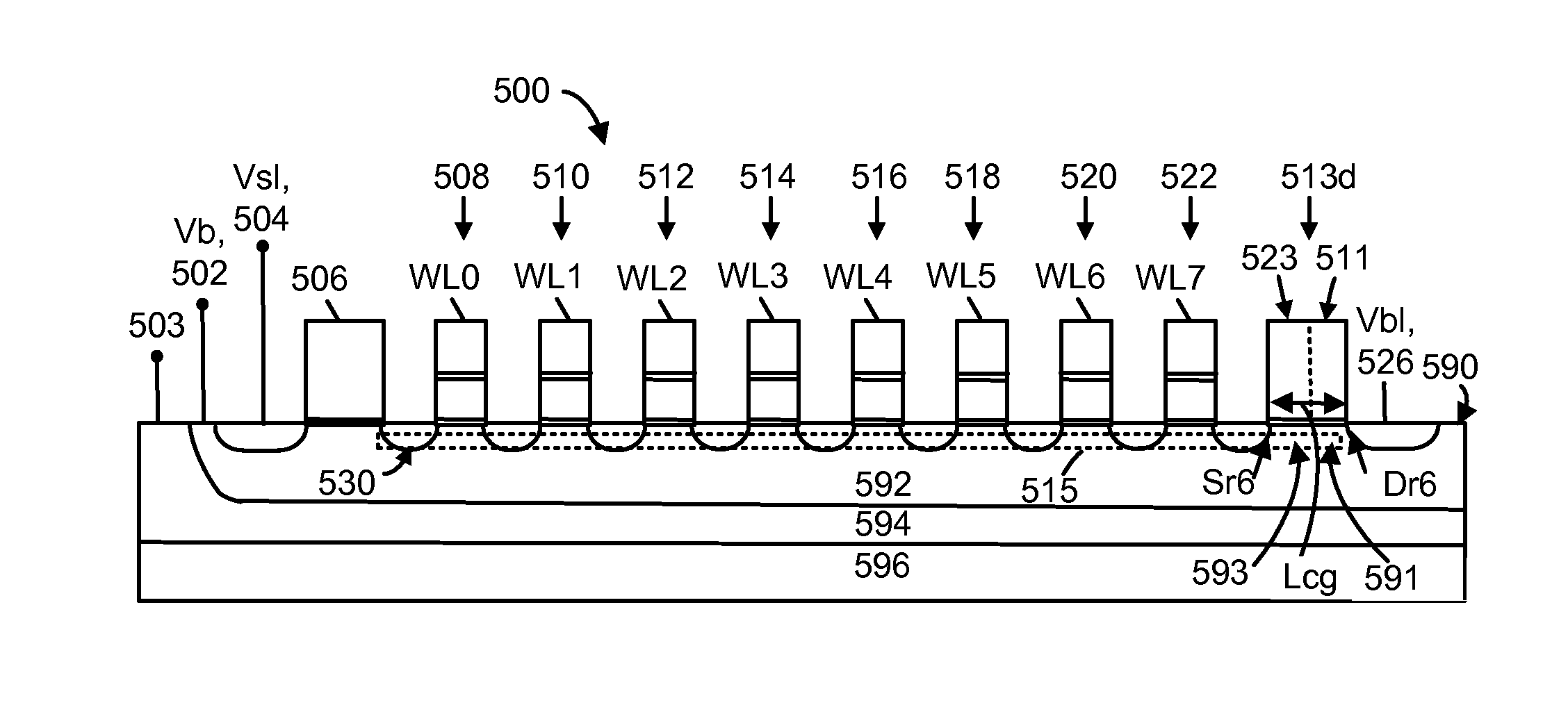
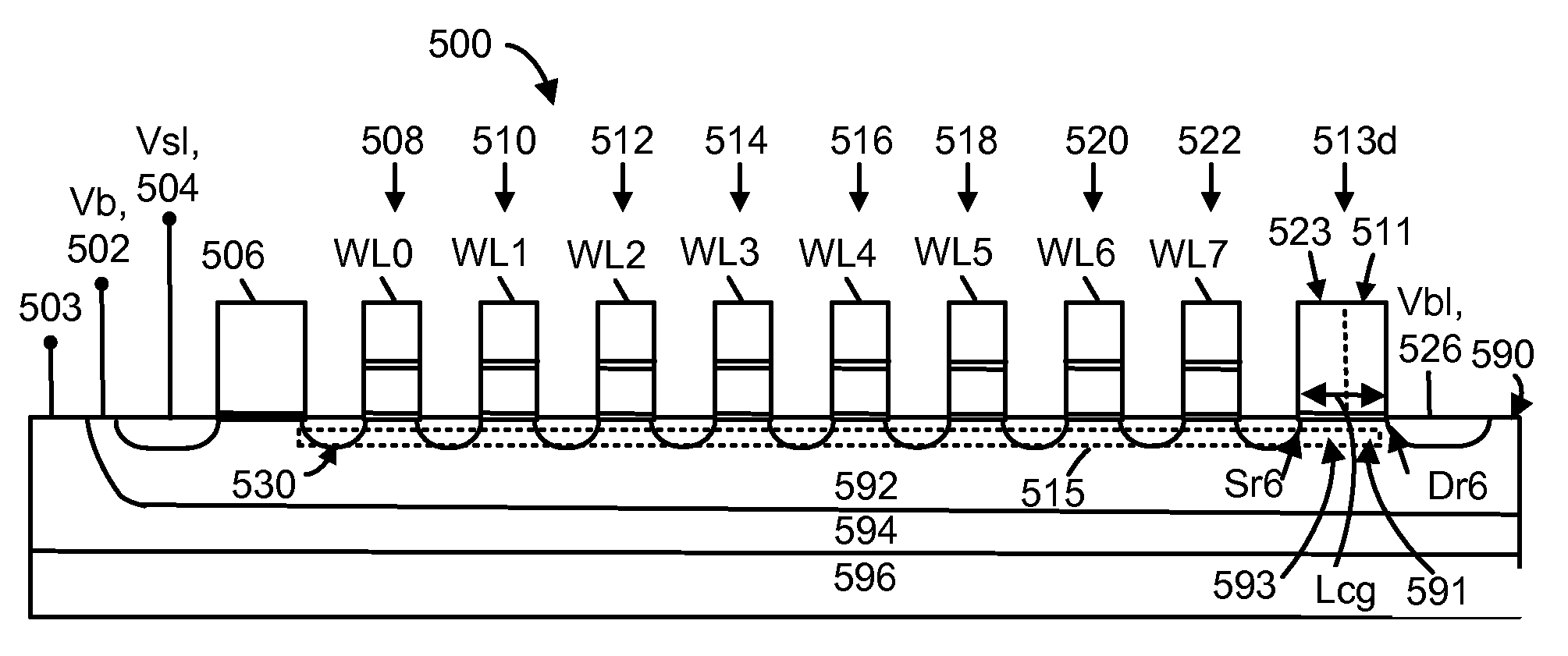
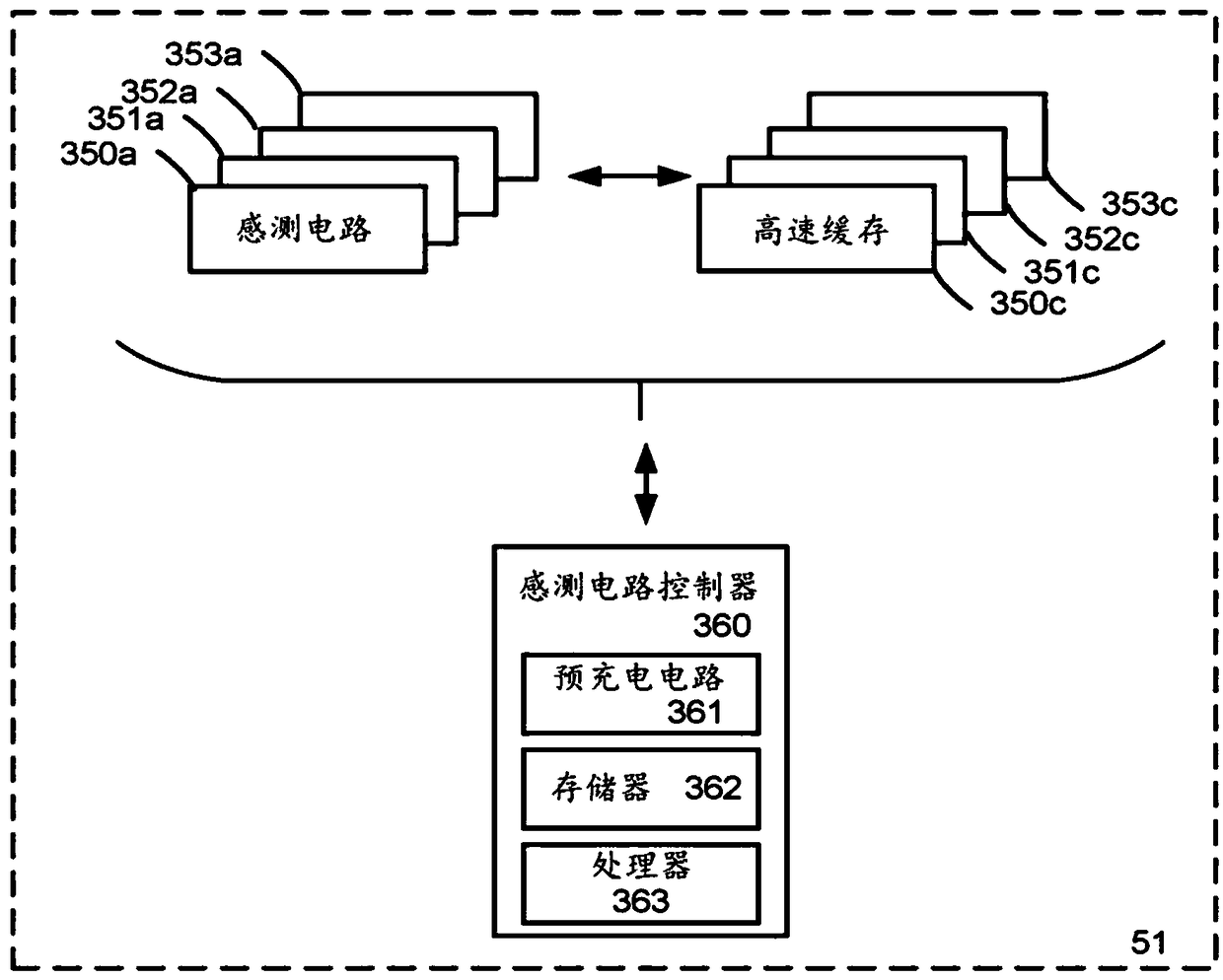
A memory device and associated techniques for reducing read disturb of memory cells during a sensing process. Select gate transistors are transitioned to a conductive state one or more time during a sensing process, at the drain and / or source ends of the memory strings in an unselected sub-block. The transitioning can occur periodically, multiple times during the sensing process. When the select gate transistors are in a conductive state, accumulated holes in the channel can be removed. This help provide a faster decrease of the channel potential when the unselected word line voltages are ramped down at the end of the sensing process. The duration of a disturb-inducing channel gradient which is created next to the edge data memory cell is reduced so that read disturb of this cell is also reduced.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
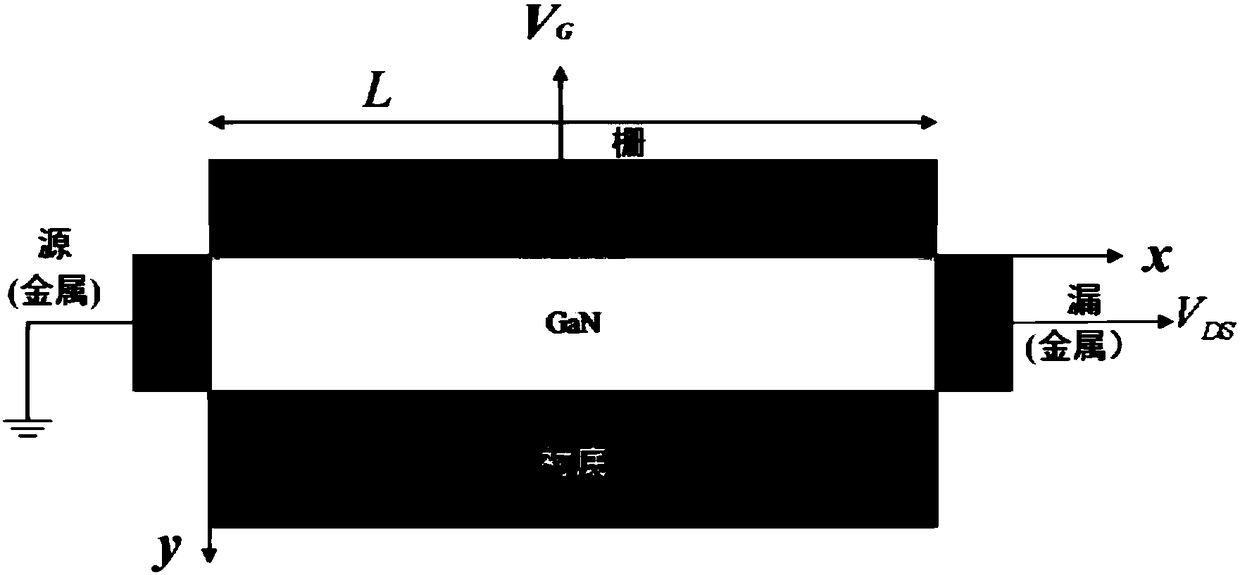
Model for calculating channel potential and current of gallium nitride-based high-power high electron mobility transistor with high power
ActiveCN108416115AWell formedPhysical concepts are clearCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsHeterojunctionGallium nitride
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit semiconductors, and specifically discloses a model for calculating channel potential and current of a gallium nitride-based high-power high electron mobility (HEMT) transistor with high power. The structure of the transistor is a heterojunction and the transistor is prepared through the following steps of: carrying out epitaxial growth on AlGaN on un-doped GaN through a molecular beam; carrying out n-type degenerate doping on the AlGaN; and arranging a layer of thin intrinsic AlGaN between the doped AlGaN and GaN so as to decrease scattering from donor atoms to electrons. The transistor can be used for high-power electrons. According to the model, channel potential and two-dimensional electron gas charge density of the transistor are solved, and drift and diffusion of electrons are considered, so that a relational expression between current at any channel and the potential is obtained; and compound and generated currentare neglected, and the current at different channel points is equal, so that an analytical expression between channel potential and source / drain current is obtained. The model has a concise form anda clear physical concept, and provides a rapid circuit simulation tool for circuit simulation software during the research of high-power HEMT devices.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device which realizes “1” write operation by boosting channel potential
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array having a plurality of cell units each including a preset number of memory cells and select gate transistors on drain and source sides. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a voltage control circuit to prevent occurrence of an erroneous write operation due to excessively high boost voltage of a channel when “1” is written into the memory cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
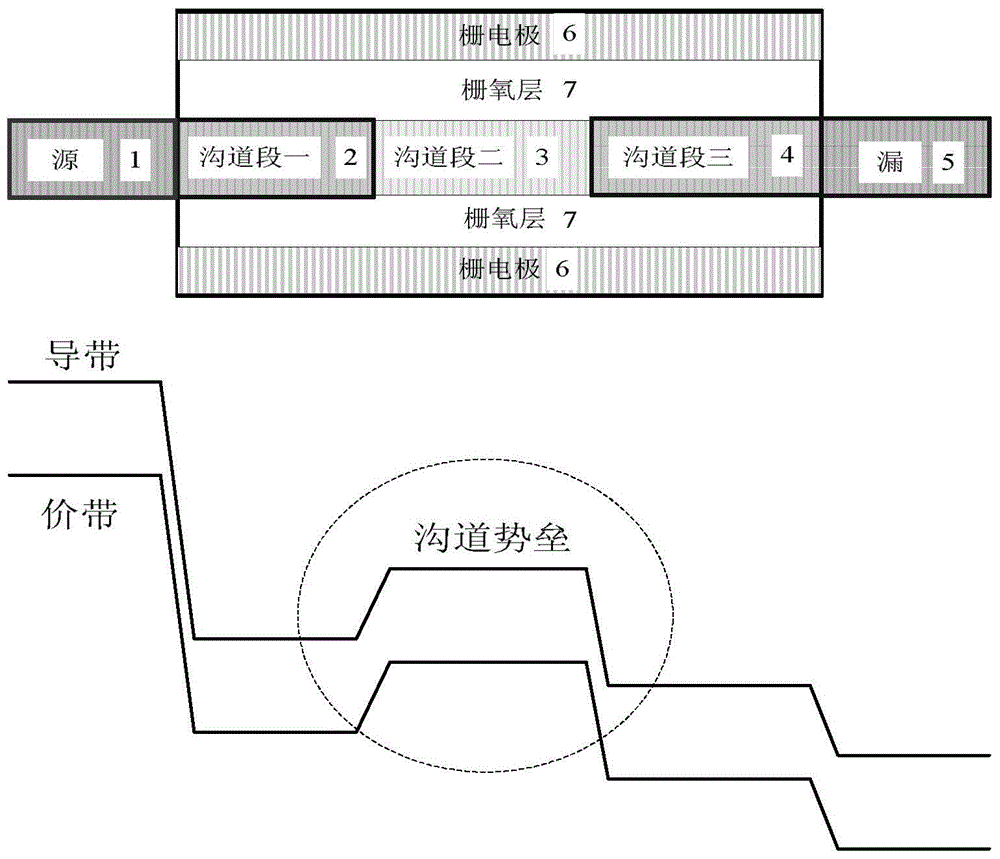
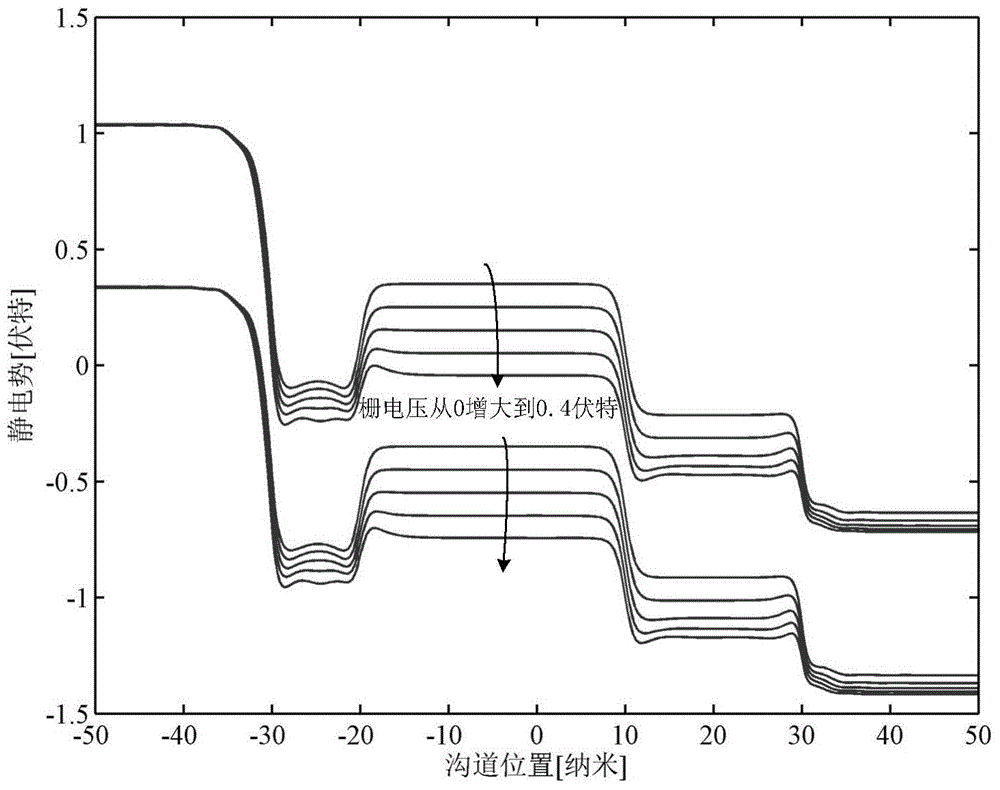
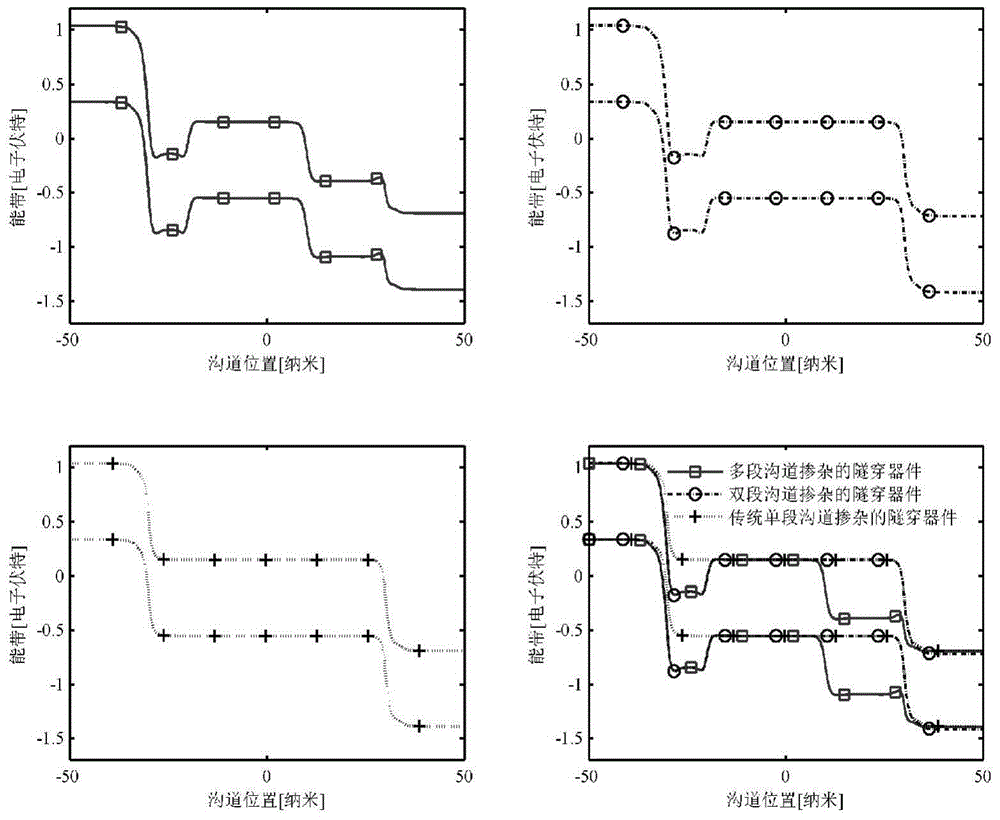
Tunneling field effect device for channel potential barrier height control
InactiveCN104882484AMaterial adjustableAdjustable thicknessSemiconductor devicesSub thresholdGate oxide
The invention belongs to the field of semiconductor integrated circuits, and specifically relates to a tunneling field effect device for channel potential barrier height control. The center of the device is provided with a channel, two ends of the channel are provided with a source terminal and a drain terminal of different conductive types, a tunneling junction is formed between the source terminal and the channel, the channel is formed by the adoption of three or more than three potential barrier areas, the energy band of the potential barrier area at the middle section is higher than the energy bands of the channel close to the drain terminal and the source terminal, the device also comprises a gate oxide layer fully covering the channel, and the gate oxide layer is fully covered by a gate electrode. The portion of the channel of the device employs materials of different doping concentrations or types, and three sections or more sections of the potential barrier structures are formed in the channel. According to the simulation research result of the tunneling device structure for channel potential barrier height control, the off-state leakage current of the device can be effectively reduced, the sub-threshold slope is reduced, the short-channel effect and the DIBL effect are suppressed, the transconductance characteristic is good, and comprehensive optimization of the performance of the device is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Solid-state imaging device driving method
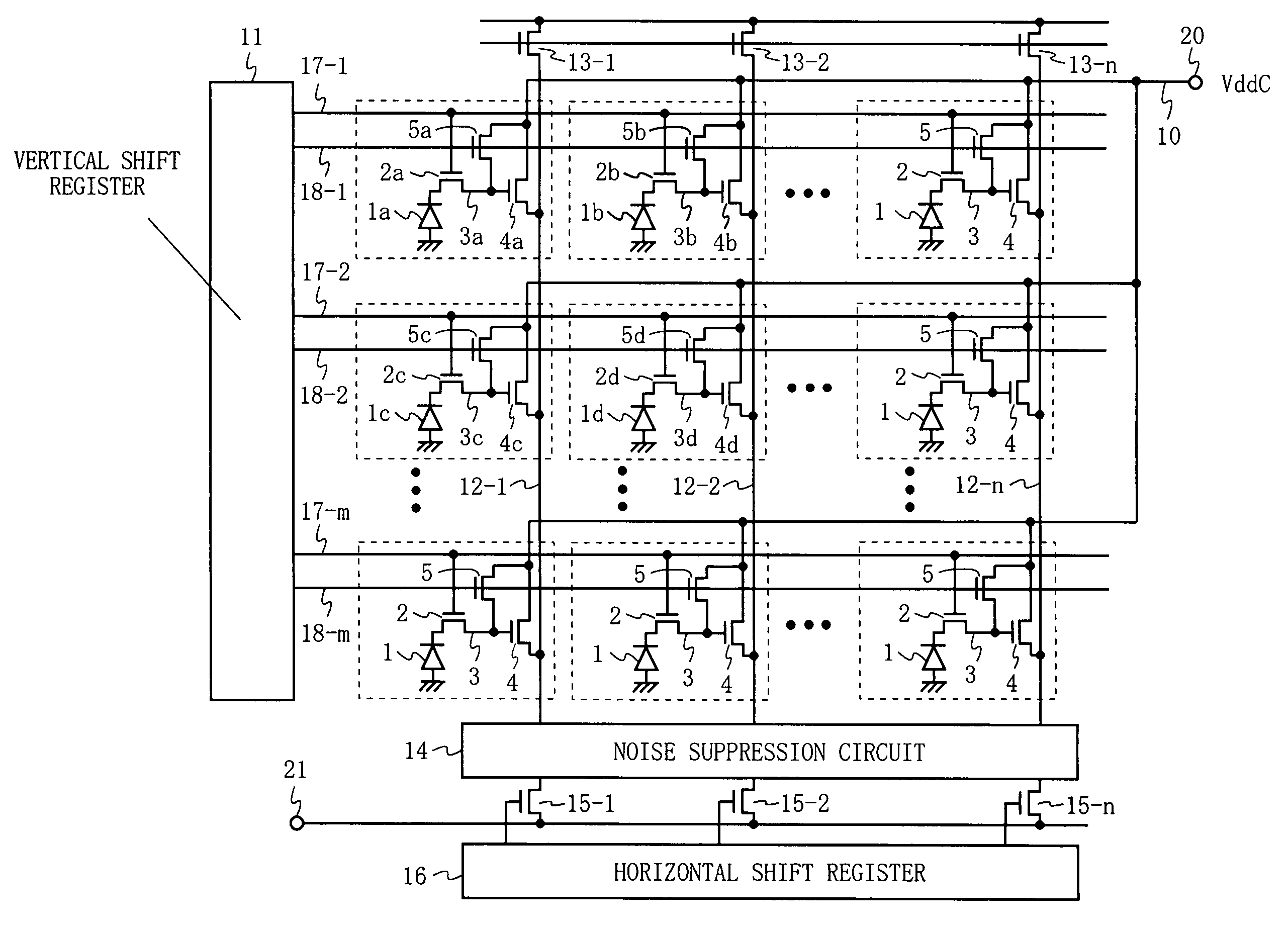
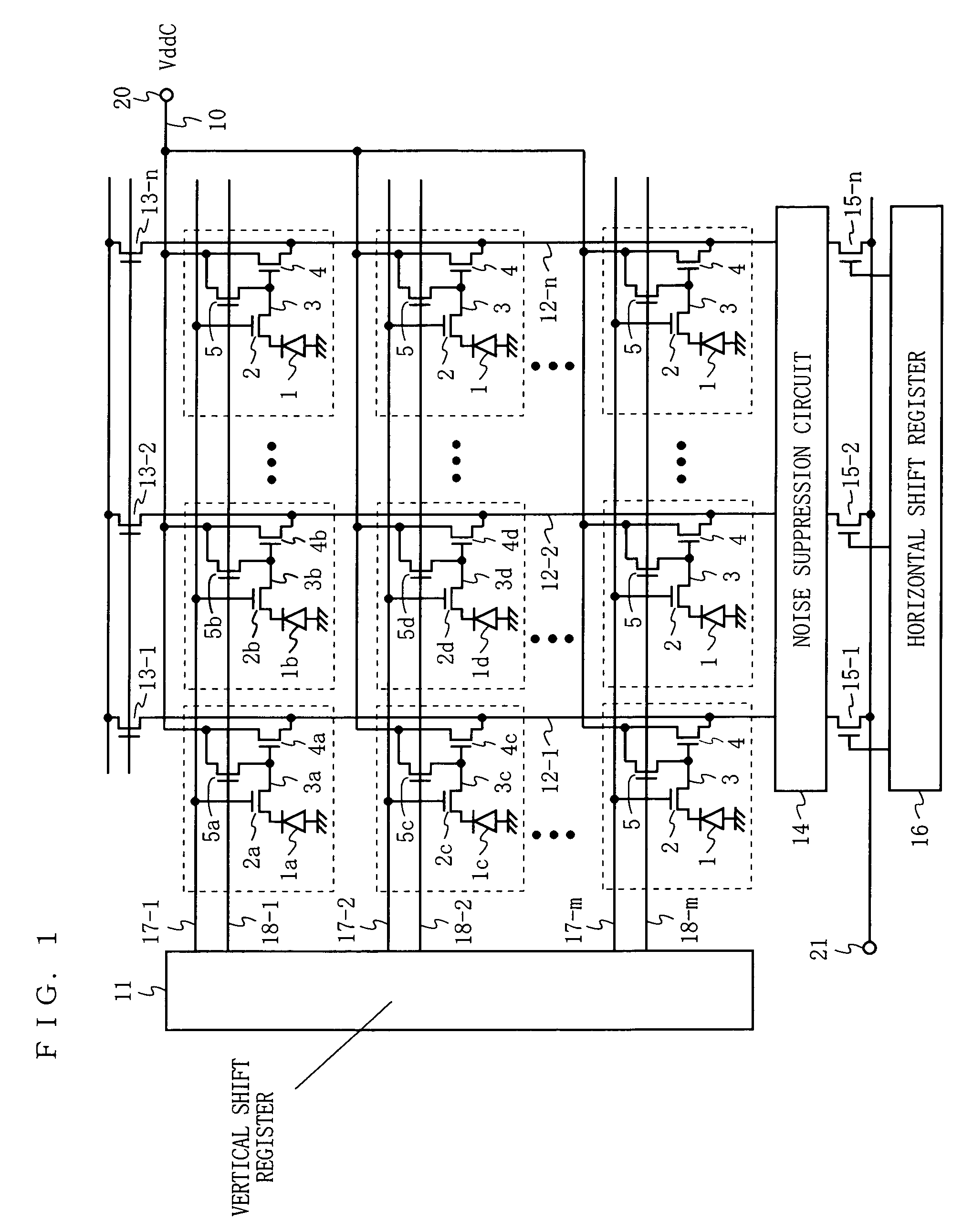
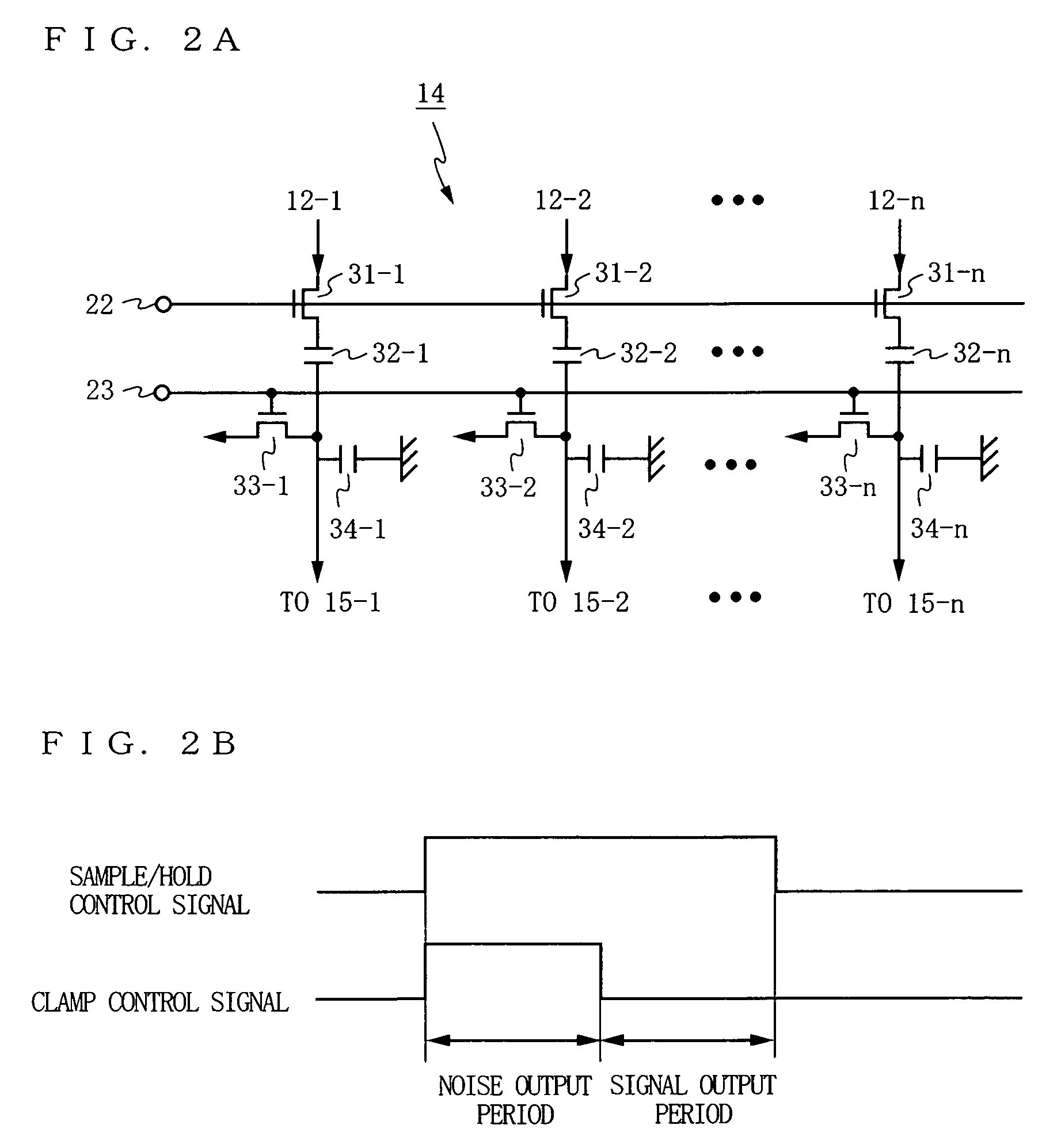
InactiveUS7352399B2Stabilize the potential of each pixelAvoid drivingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow noiseFloating diffusion
Photosensitive cells each includes a photodiode (1), a transfer gate (2), a floating diffusion layer portion (3), an amplifying transistor (4), and a reset transistor (5). Drains of the amplifying transistors (4) of the photosensitive cells are connected to a power supply line (10), and a pulsed power supply voltage (VddC) is applied to the power supply line (10). Here, a low-level potential (VddC_L) of the power supply voltage has a predetermined potential higher than zero potential. Specifically, by making the low-level potential (VddC_L) higher than channel potentials obtained when a low level is applied to the reset transistors (5), or channel potentials obtained when a low level is applied to the transfer gates (2), or channel potentials of the photodiodes (1), a reproduced image with low noise is read.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Solid-state imaging device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS8154057B2Suppress generationImprove charge transfer efficiencySolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesControl signalEngineering
A solid-state imaging device includes: a photoelectric converting section comprising a photo-diode; a charge storage section; a charge transfer section; a first control gate section provided between the photoelectric converting section and the charge storage section to control transfer of a signal charge from the photoelectric converting section to the charge storage section; and a second control gate section provided between the charge storage section and the charge transfer section to control transfer of the signal charge from the charge storage section to the charge transfer section. The charge storage section includes: a first region formed on a side near to the first control gate section; and a second region formed on a side near to the second control gate section and configured to have a channel potential increased more than that of the first region. The second region is configured to hold the signal charge in a pinning condition.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com