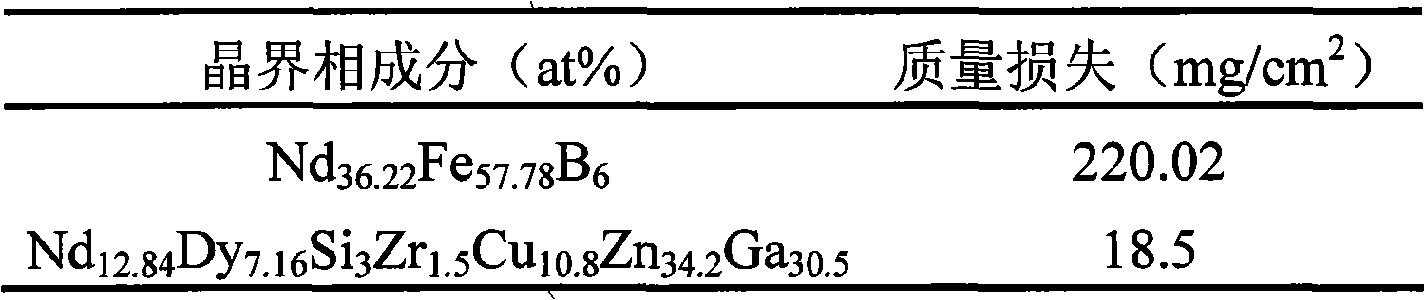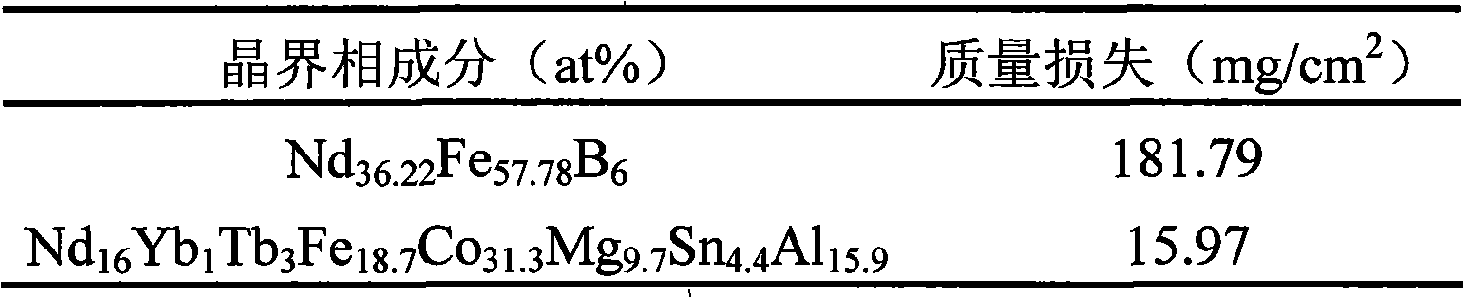Patents
Literature
415results about How to "Reduce potential difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grain boundary phase-reconstructed high-corrosion resistance Sintered NdFeB magnet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101320609ALow melting pointGuaranteed MagneticInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrode potentialPowder mixture
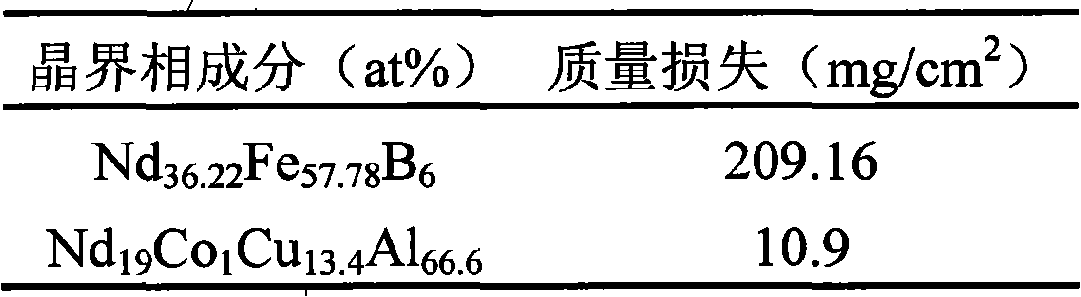
The invention discloses a sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with high corrosion resistance and the grain boundary reconstruction and a preparation method thereof. The composition of the invention is that: NdeFe100-e-f-gBfMg, wherein, e is greater than or equal to 6 and equal to or less than 24, f is greater than or equal to 5. 6 and equal to or less than 7, g is greater than or equal to 0.03 and equal to or less than 8, M is one or some of elements Dy, Tb, Pr, Sm, Yb, La, Co, Ni, Cr, Nb, Ta, Zr, Si, Ti, Mo, W, V, Ca, Mg, Cu, Al, Zn, Ga, Bi, Sn and In; The method is that: main phrase alloy and reconstructed grain boundary phase alloy are respectively pulverized and mixed uniformly; the powder mixture is pressed to a mould in the magnetic field, and fabricated into a sintering magnet in a high vacuum sintering furnace. By the reconstruction of the grain boundary phase composition, the invention can obtain the grain boundary phase alloy with low melting point and high electrode potential, decrease the potential difference between the main phase and the grain boundary phase on the basis of ensuring the magnetic properties, promote the intrinsic corrosion resistance of magnet, and has the advantages of simple process, low cost and being suitable for the batch production. Therefore, by combining the grain boundary reconstruction and double alloy method, the sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with high intrinsic corrosion resistance can be prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Surface-modification three-dimensional-network-carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material and preparing method
ActiveCN105818476AMitigating Galvanic CorrosionImprove resilienceLamination ancillary operationsLaminationCarbon nanotubeFiber-reinforced composite
The invention discloses a surface-modification three-dimensional-network-carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material and a preparing method.Three-dimensional carbon fiber frameworks with different bore diameters are prepared as required, and after surface pretreatment, diamond, carbon nanometer tubes and graphene are subjected to chemical vapor deposition; then the mixture and matrix materials are compounded, wherein the matrix materials are metal or polymers; the carbon-fiber-reinforced metal-based or polymer-based composite material with the three-dimensional net-shaped framework structure is obtained.A three-dimensional continuous heat conduction channel is formed in the composite material through the surface-modification three-dimensional net-shaped carbon fibers, and therefore the heat conduction performance of the composite material is greatly improved; meanwhile, according to space distribution of carbon fibers in the matrix material, the mechanical performance of the composite material can also be improved, and the density and the thermal expansion coefficient can be decreased; the thermal expansion coefficient, the mechanical performance and the thermal performance can be further regulated and controlled by adding zero-dimensional particle reinforcement.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
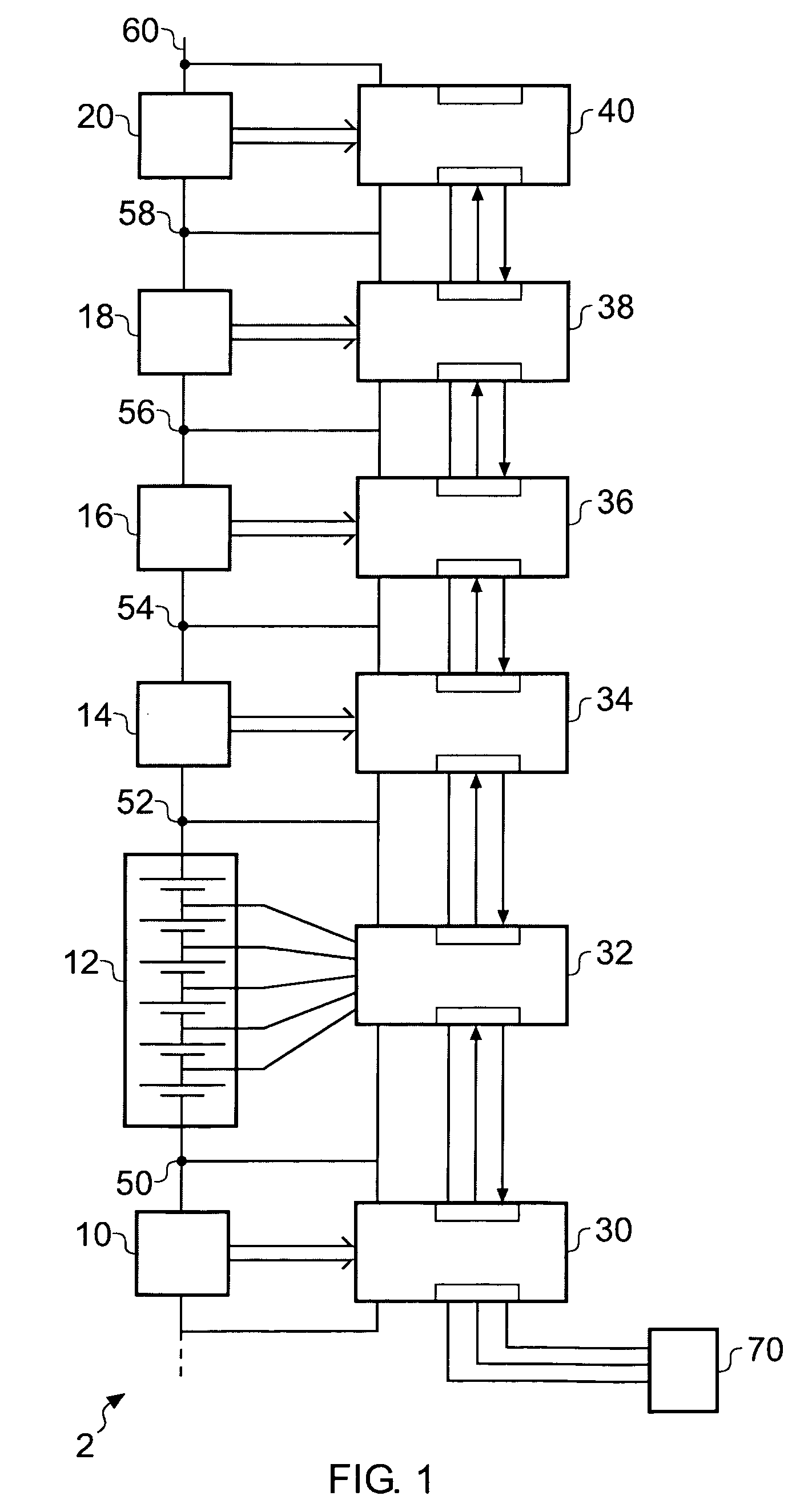
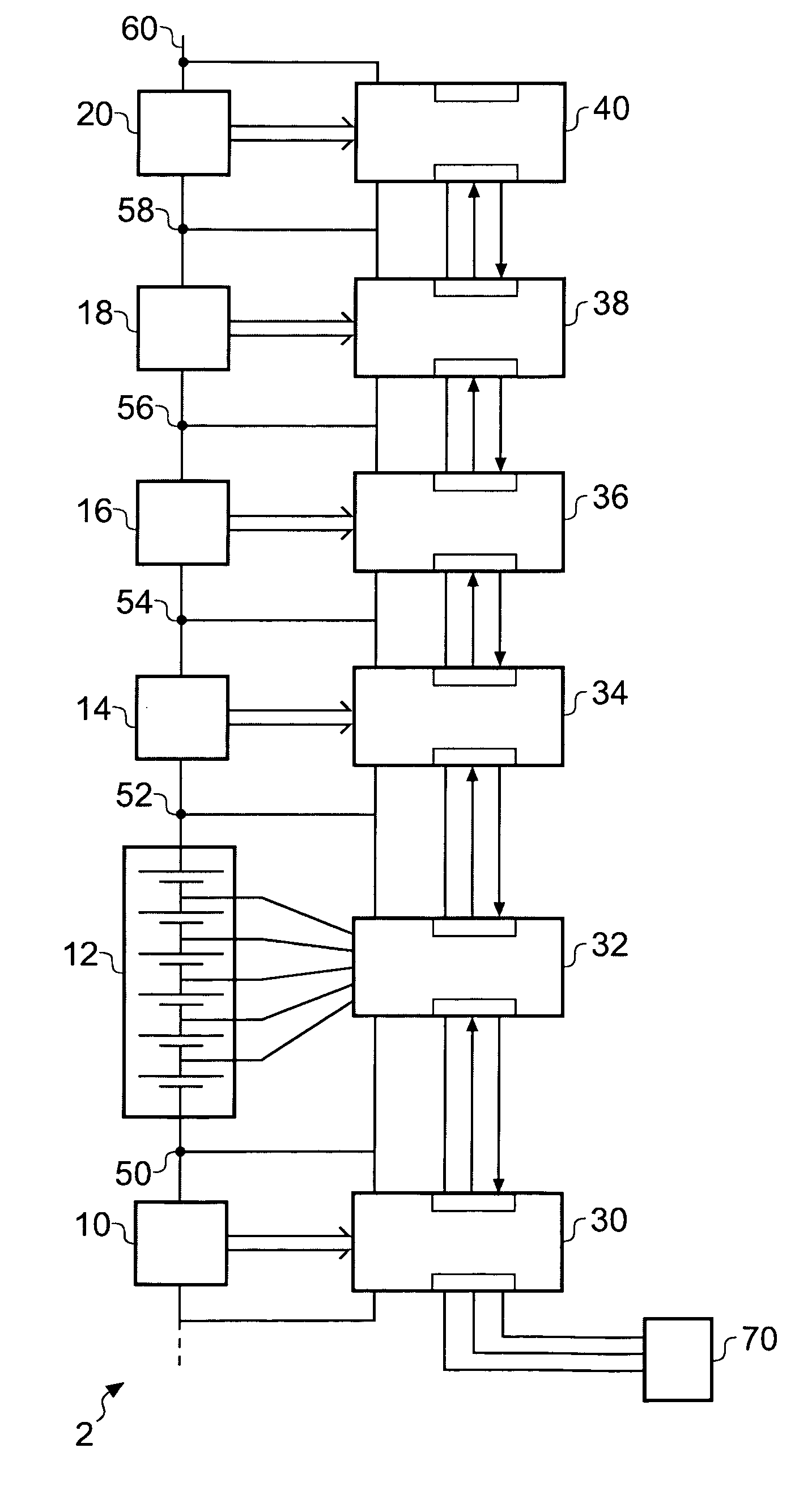
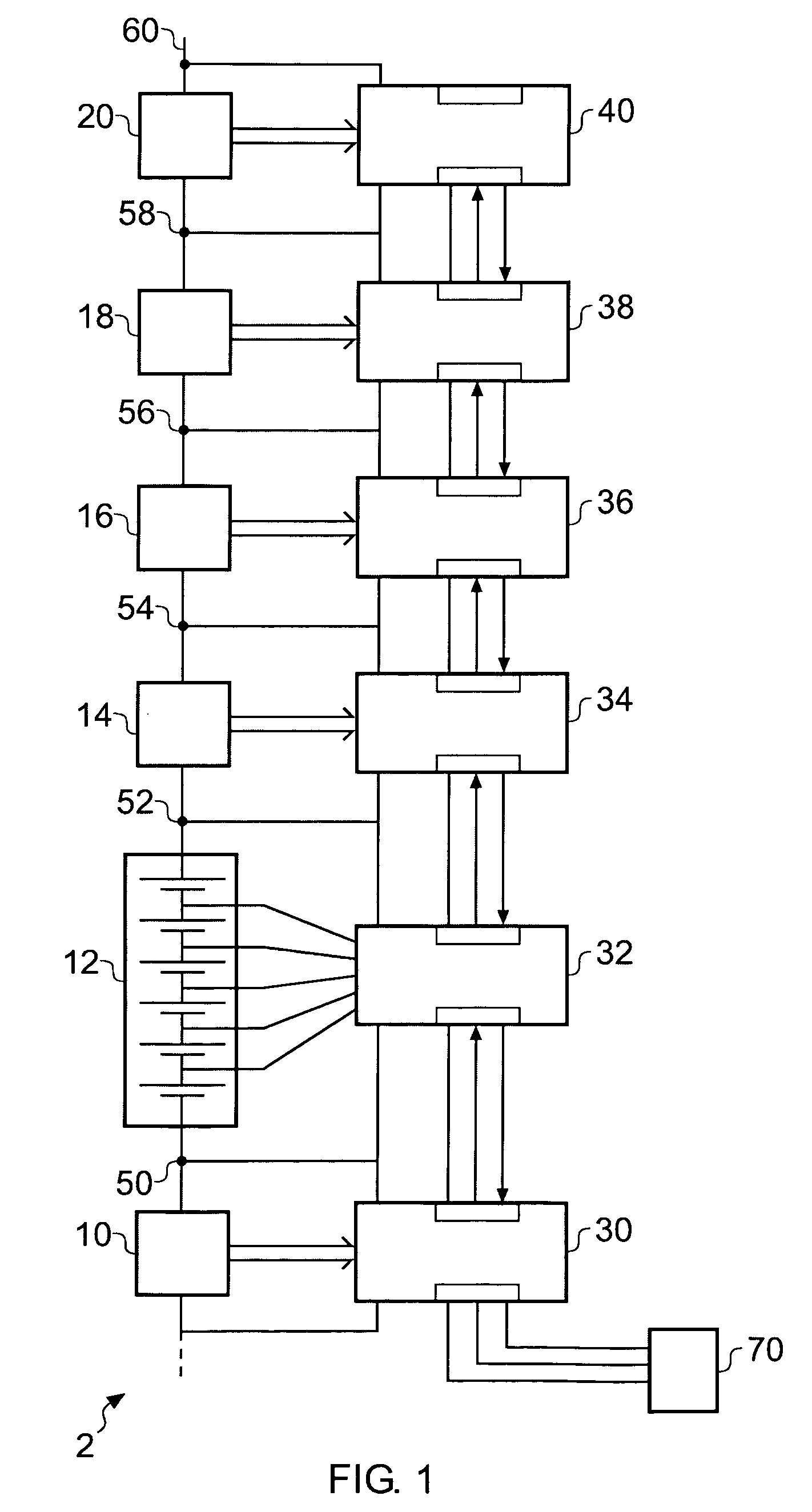
Battery montoring apparatus and daisy chain interface suitable for use in a battery monitoring apparatus
ActiveUS20080180106A1Reduce potential differenceCost reductionBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEmbedded systemElectrical battery
A battery monitor for monitoring the performance of at least one battery within an array of batteries, comprising: a data acquisition device for measuring at least one parameter of the at least one battery associated with the battery monitor, a first data interface operable to exchange data with a first device, and a second data interface operable to exchange data with a second device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
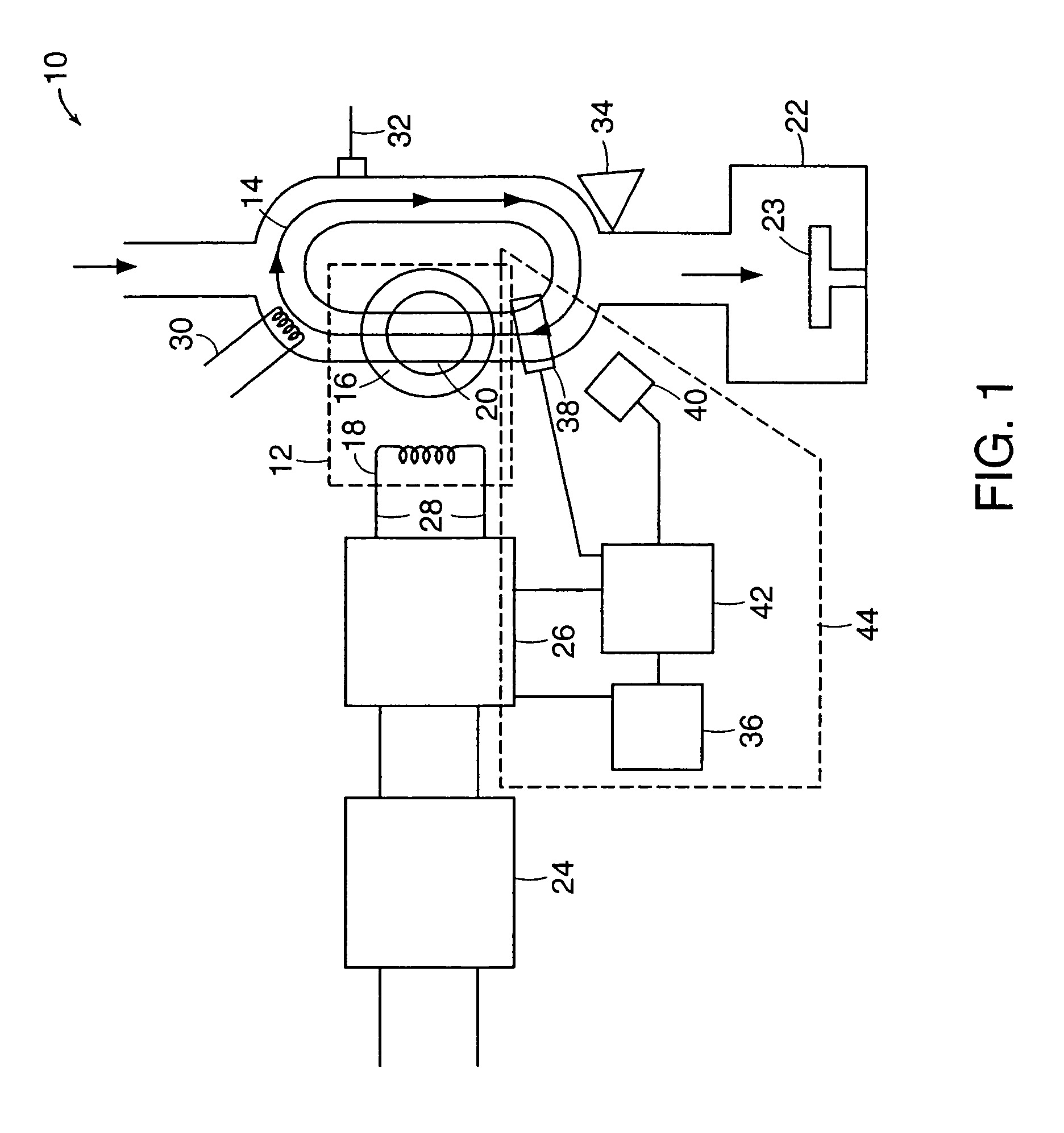
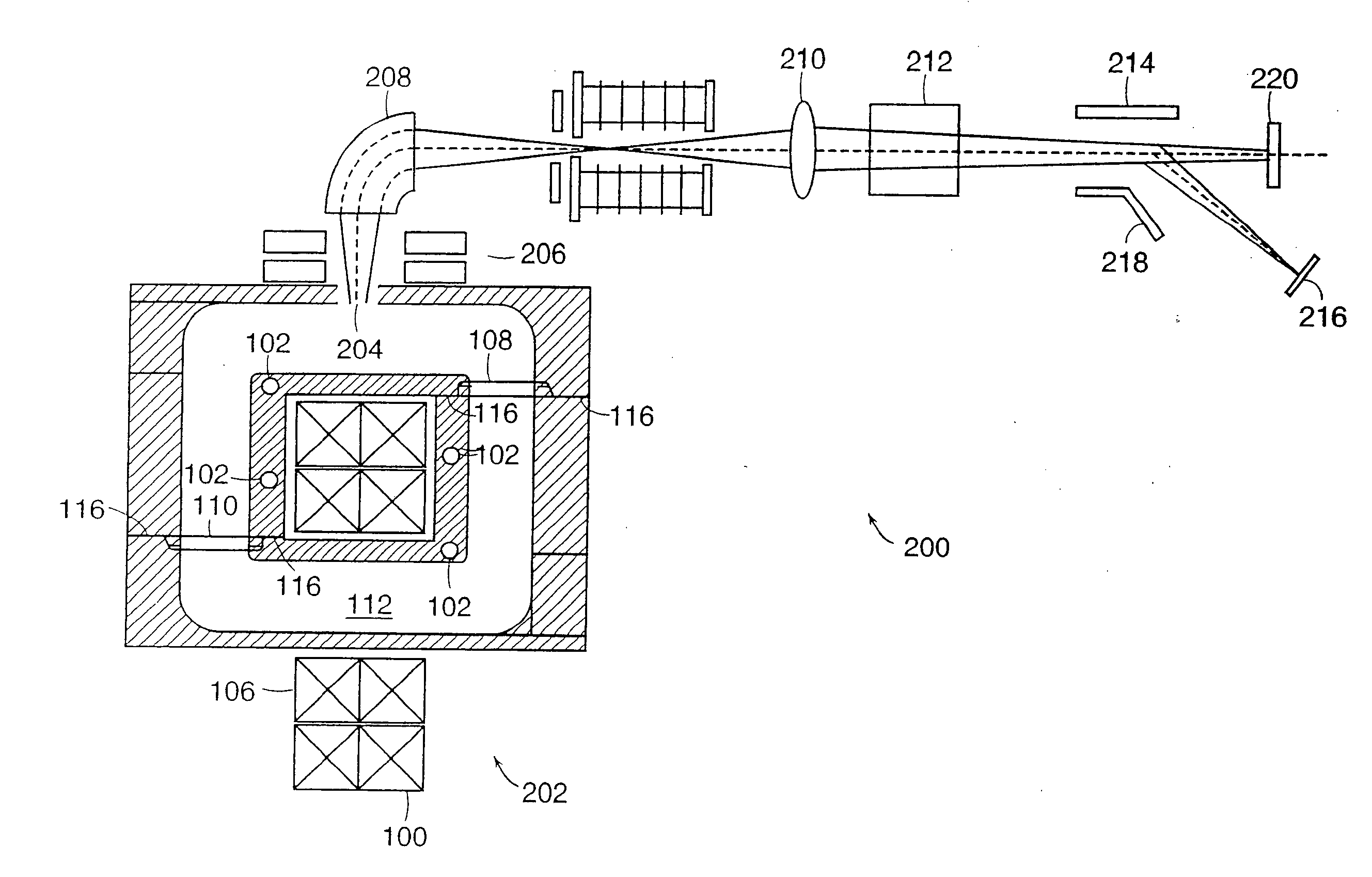
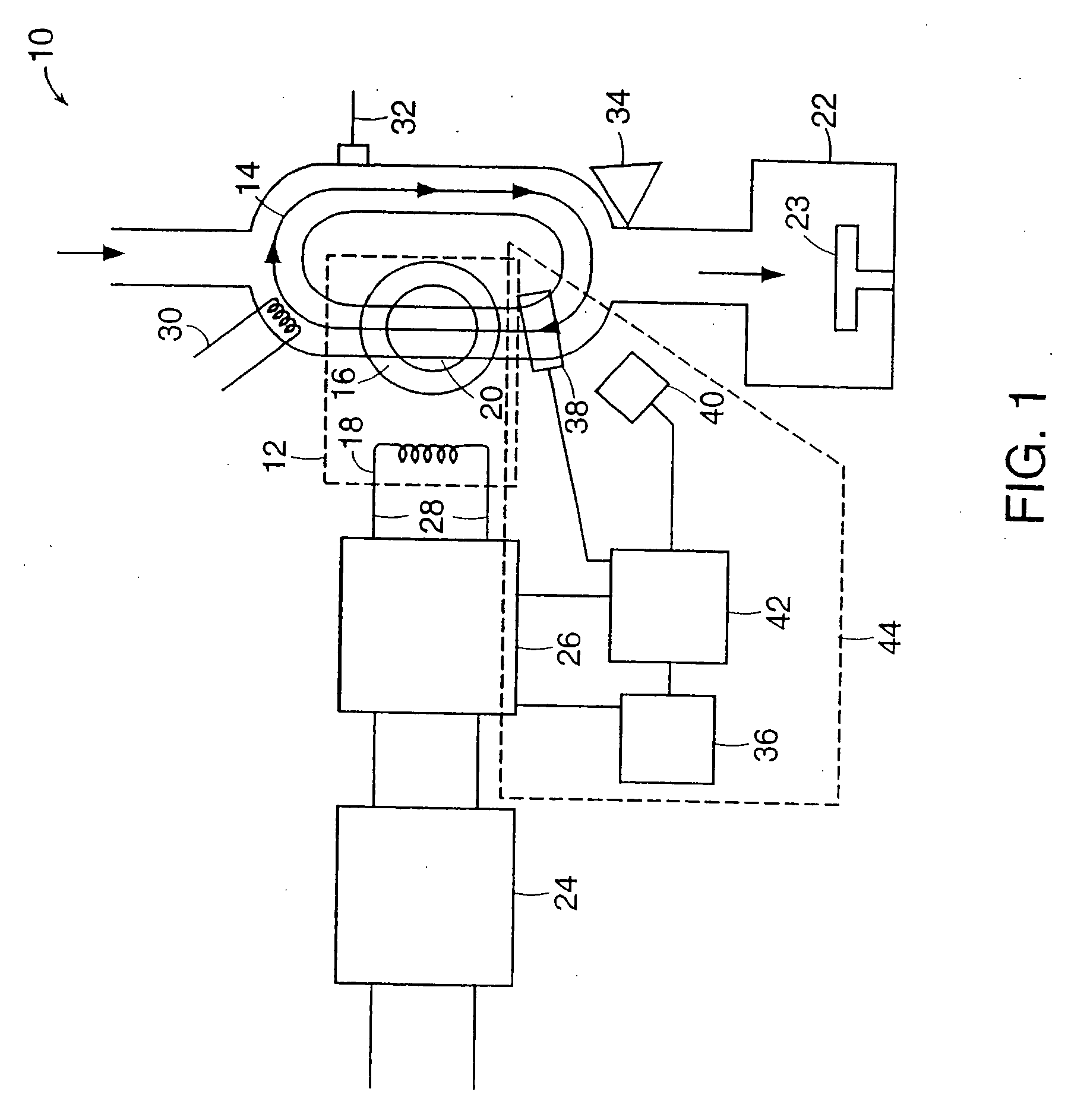
Inductively-coupled torodial plasma source
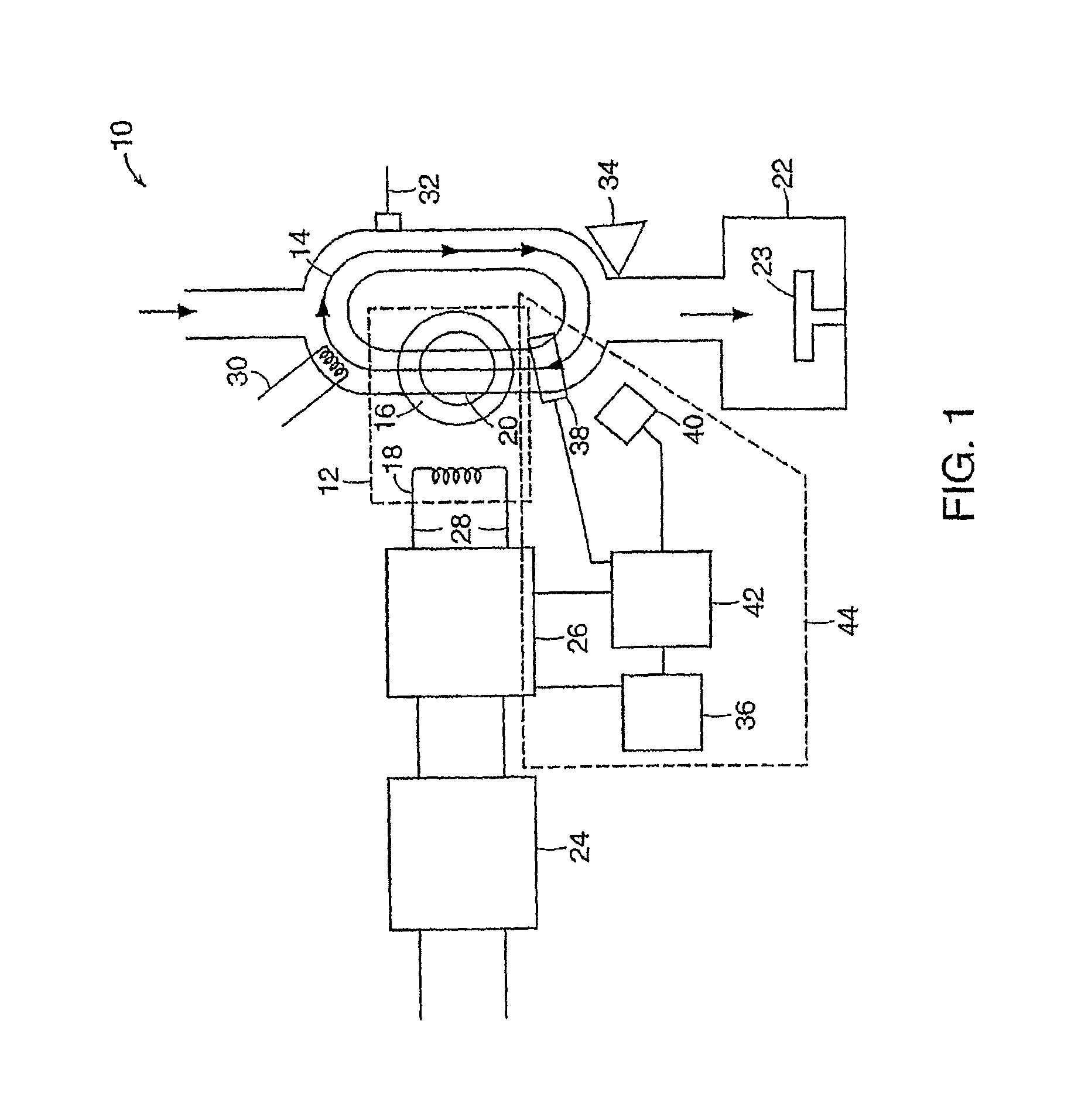
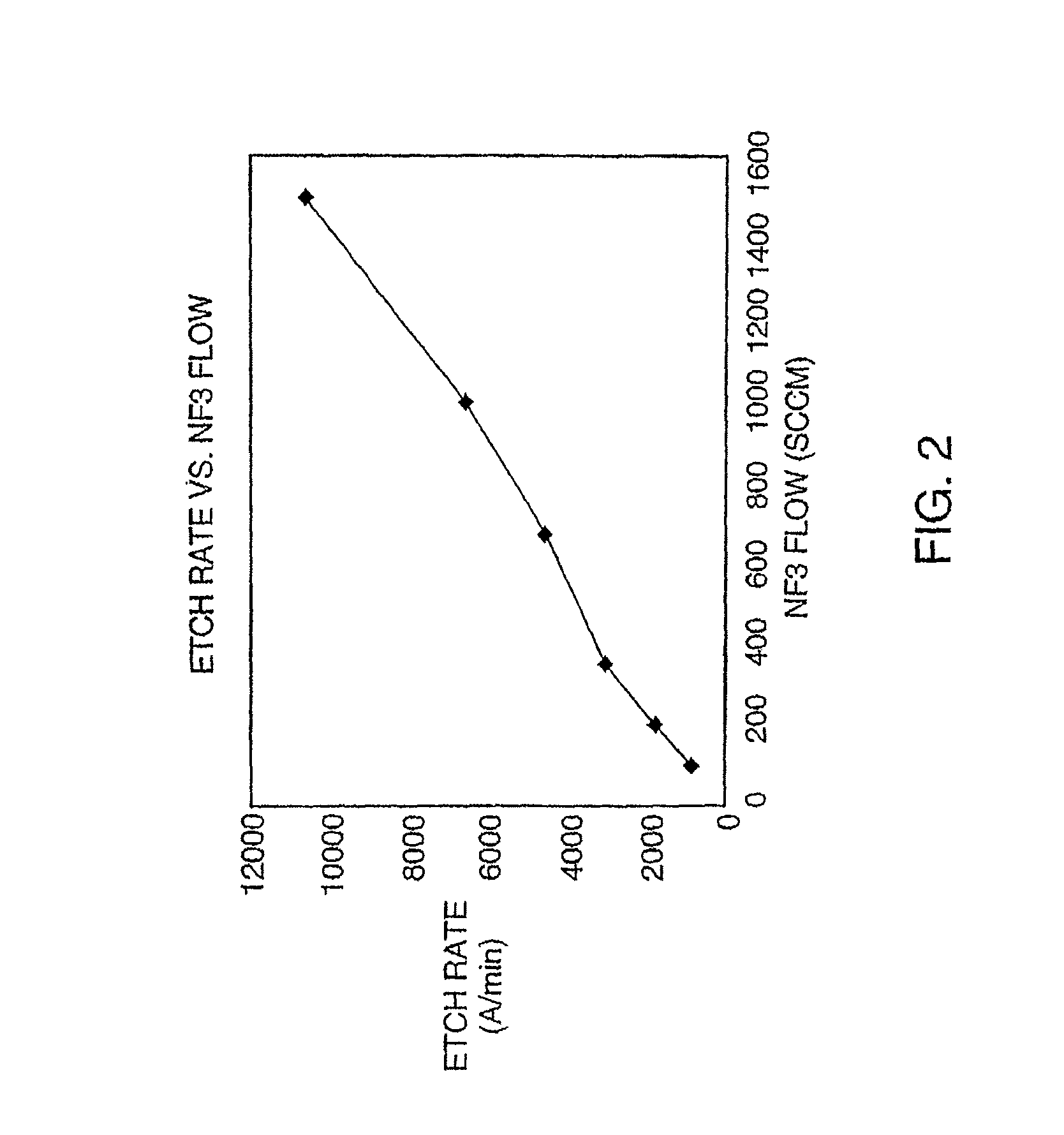
InactiveUS7166816B1Reduce potential differenceEasy to operateElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsEngineeringVoltage source
Apparatus for dissociating gases includes a plasma chamber comprising a gas. A first transformer having a first magnetic core surrounds a first portion of the plasma chamber and has a first primary winding. A second transformer having a second magnetic core surrounds a second portion of the plasma chamber and has a second primary winding. A first solid state AC switching power supply including one or more switching semiconductor devices is coupled to a first voltage supply and has a first output that is coupled to the first primary winding. A second solid state AC switching power supply including one or more switching semiconductor devices is coupled to a second voltage supply and has a second output that is coupled to the second primary winding. The first solid state AC switching power supply drives a first AC current in the first primary winding. The second solid state AC switching power supply drives a second AC current in the second primary winding. The first AC current and the second AC current induce a combined AC potential inside the plasma chamber that directly forms a toroidal plasma that completes a secondary circuit of the transformer and that dissociates the gas.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Reducing leakage current in guide wire assembly
InactiveUS7326088B2Reduce potential differenceReduce leakage currentElectrotherapyCoupling device detailsElectricityElectrical conductor
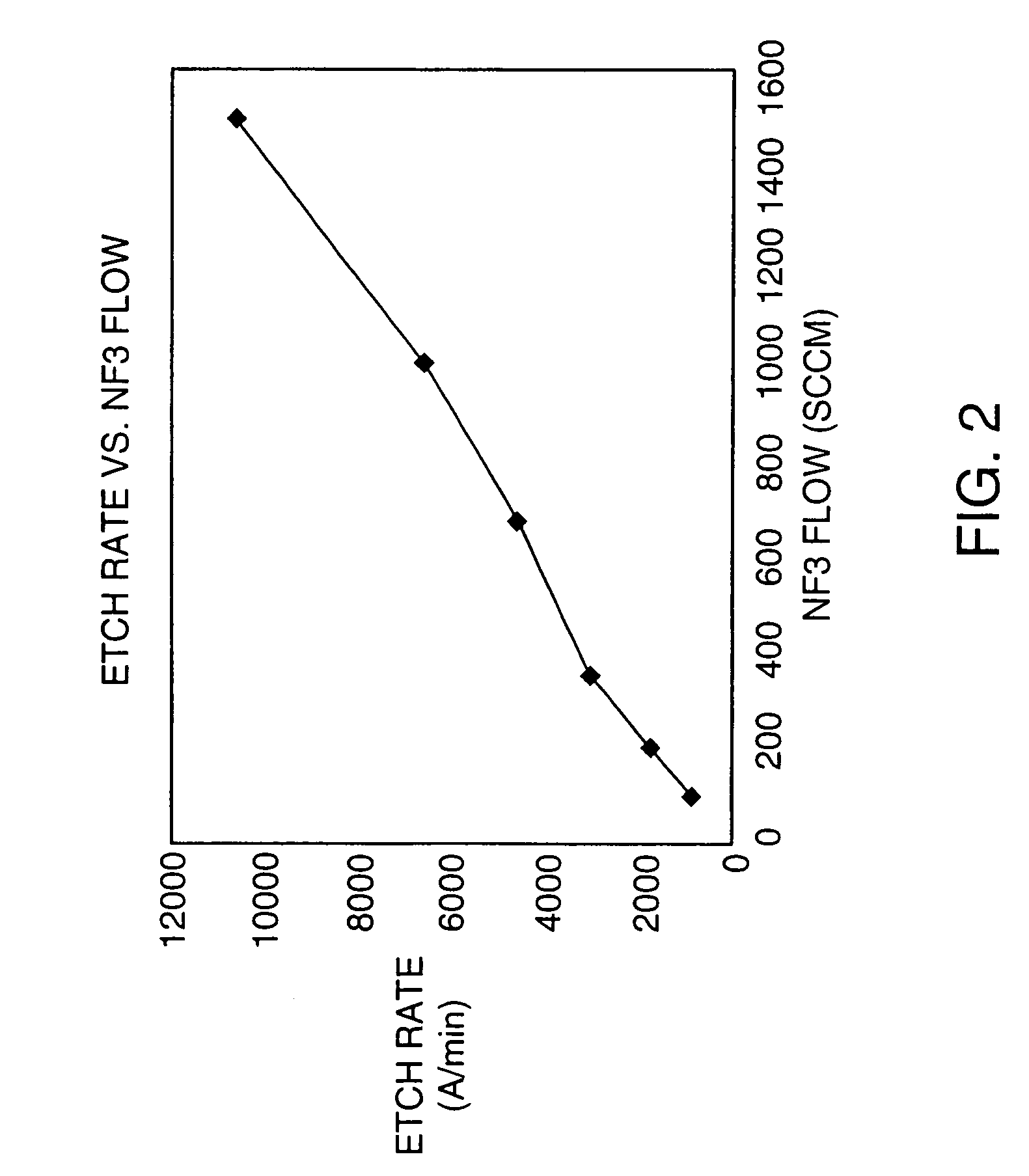
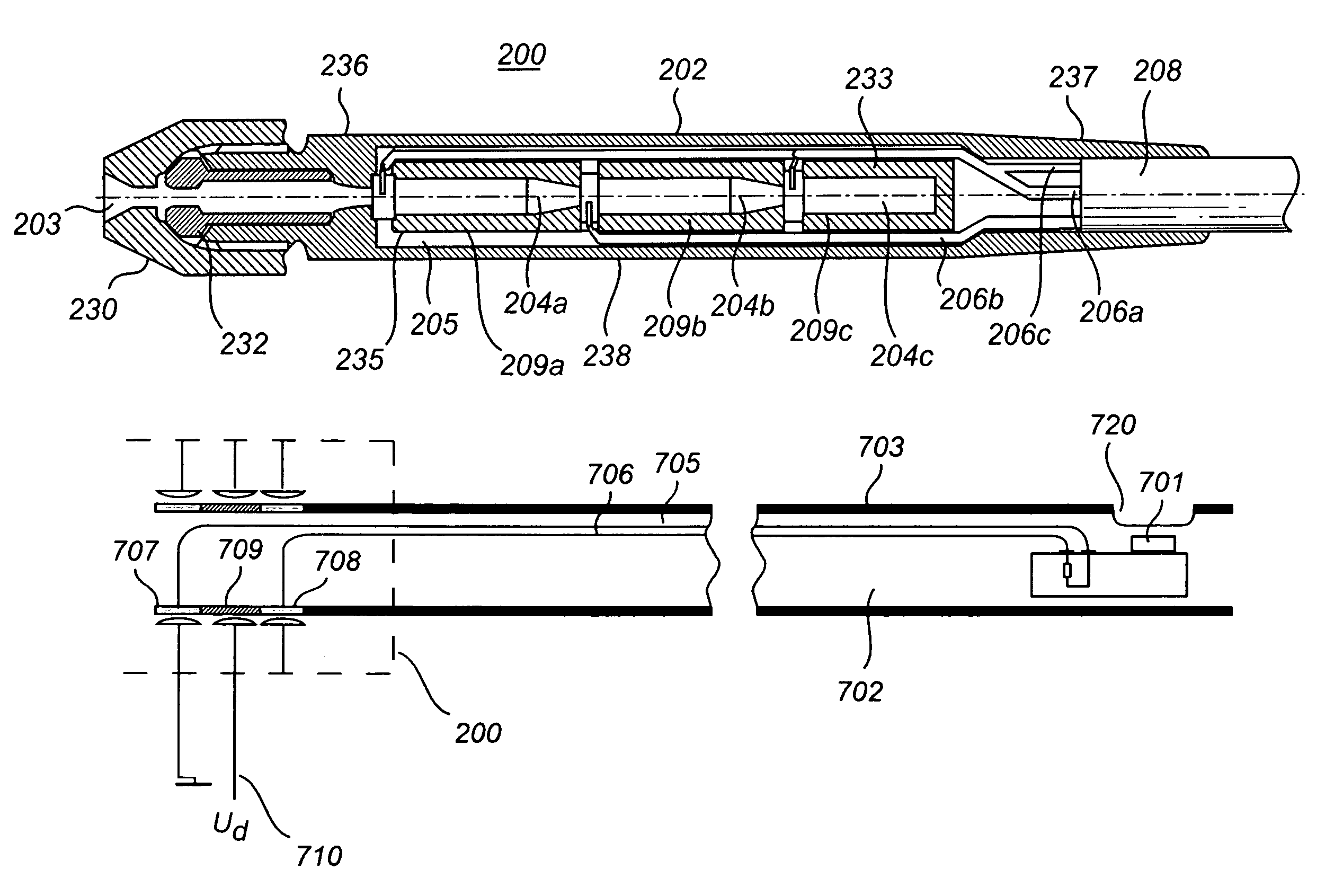
The present invention relates to a method and a device for reducing leakage current in a guide wire assembly having conductor members (707, 708) arranged at a connector end of the guide wire (702) to provide electrical contact with electrical leads (705, 706) of the guide wire and to provide signals transferred via the electrical leads to an external device, said conductor members being separated by at least one insulator (709). An idea of the present invention is to minimize leakage current via the at least one insulator. When a physician places the guide wire into an appropriate location in the body, a male connector (100) of the guide wire may be contaminated by, for example, dirt, fat, moisture, etc., which is attached to the physician's fingers and deposited onto the male connector. An electrode (710) mounted at the female connector is used to apply a guard potential (Ud) to the insulator (709) to reduce potential difference and thereby reduce current leakage between members (707, 708).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
Battery monitoring apparatus and daisy chain interface suitable for use in a battery monitoring apparatus
ActiveUS7859223B2Reduce potential differenceReduce the voltage rangeBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical batteryData acquisition
A battery monitor for monitoring the performance of at least one battery within an array of batteries, comprising: a data acquisition device for measuring at least one parameter of the at least one battery associated with the battery monitor, a first data interface operable to exchange data with a first device, and a second data interface operable to exchange data with a second device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
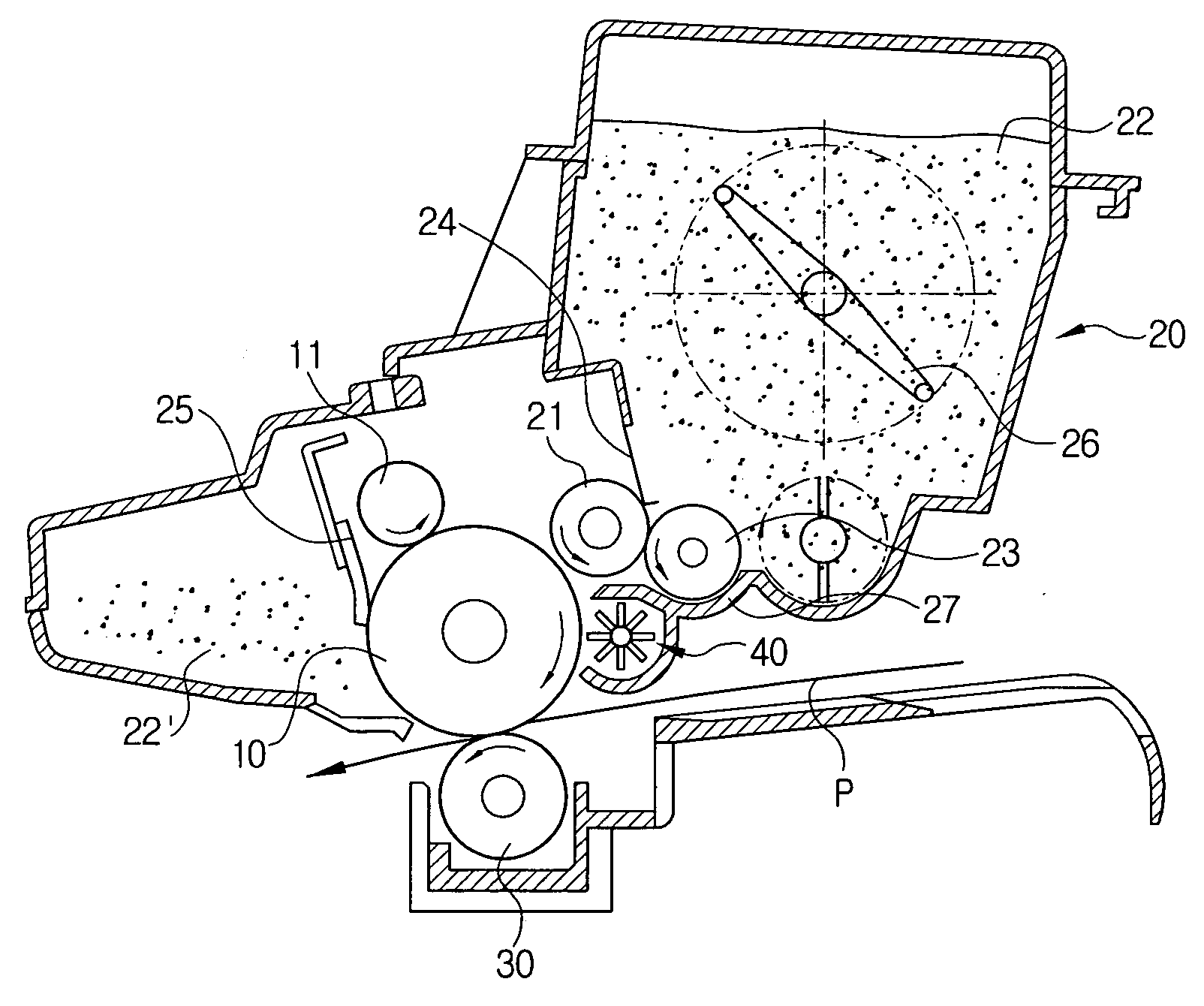
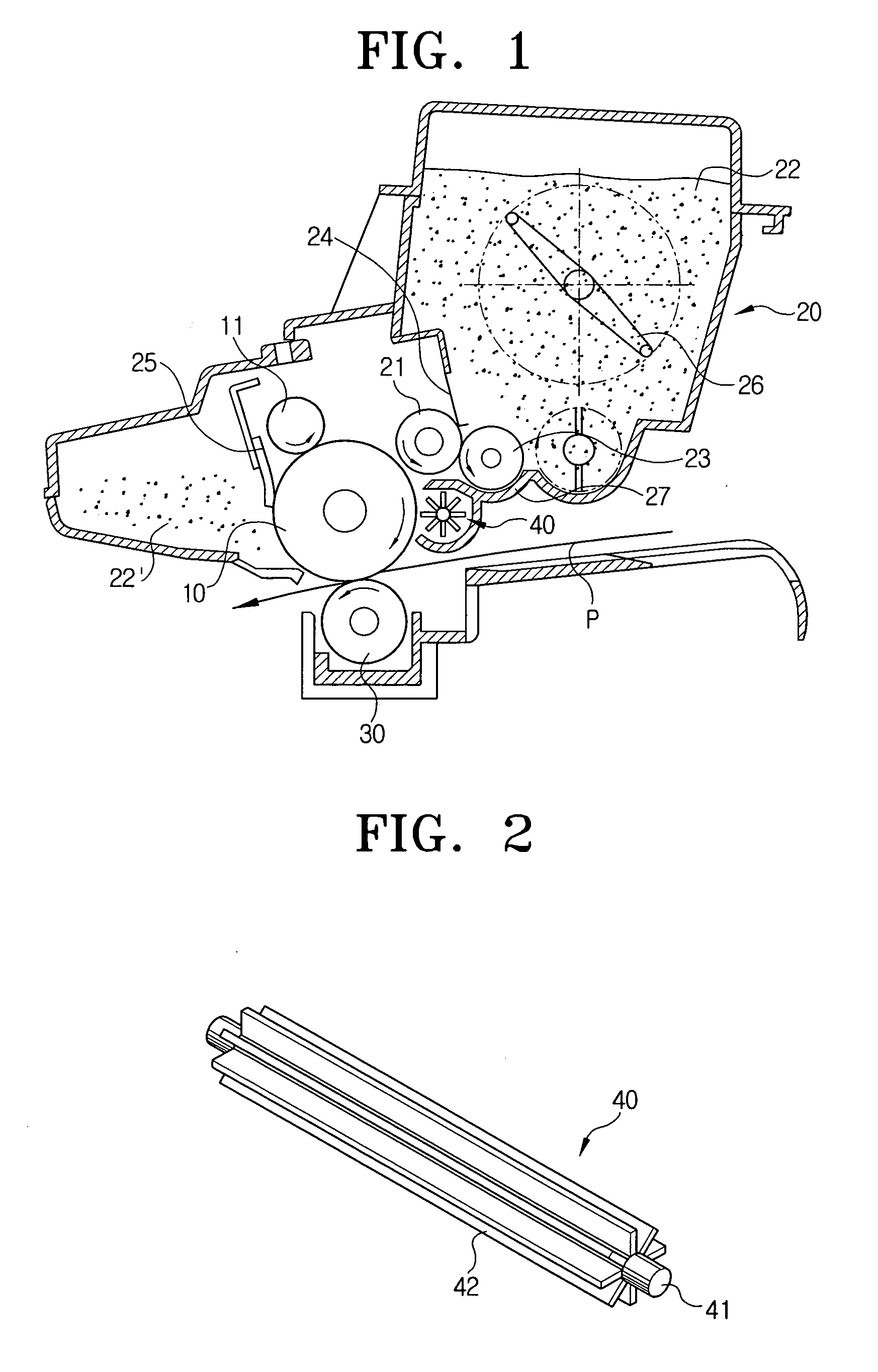
Developing apparatus and image forming equipment and method thereof
ActiveUS20050095028A1Avoid distractionReduce potential differenceElectrographic process apparatusLatent imageEngineering
A method and developing apparatus are provided. The method and apparatus comprise a developing carrier, spaced apart from an image carrier at a predetermined interval, for developing an electrostatic latent image formed on the image carrier during rotation; and a rotational member, rotatably installed adjacent to the image carrier, for generating an air stream reverse to that generated by rotation of both the image carrier and the developer carrier, thereby inhibiting a developer from being scattered.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
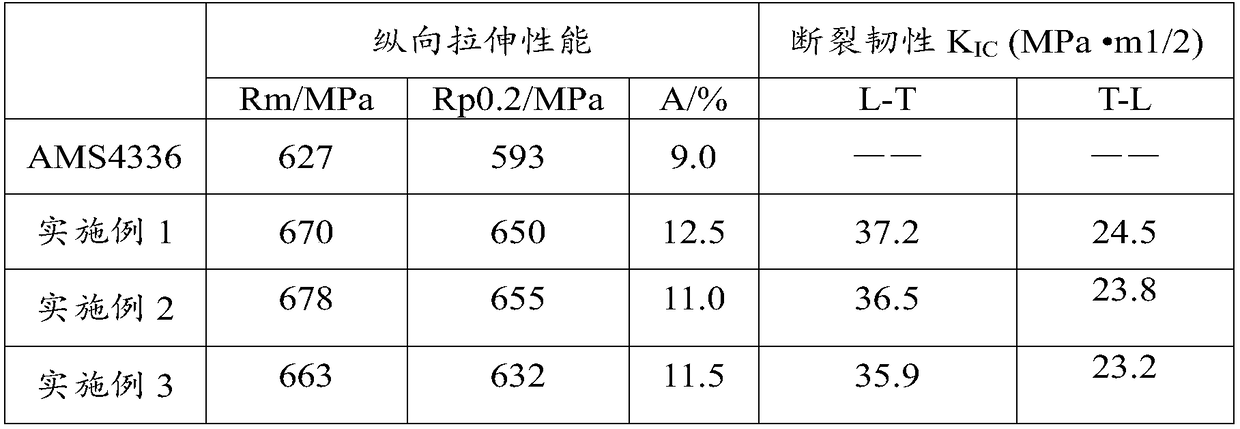
7-series aluminum alloy profile and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of aluminum alloys, and provides a 7-series aluminum alloy profile and a preparation method thereof. The 7-series aluminum alloy profile comprises the following components of, by mass, less than or equal to 0.06% of Si, less than or equal to 0.08% of Fe, 2.10%-2.40% of Cu, 1.90%-2.10% of Mg, less than or equal to 0.05% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.02% of Cr, 7.85%-8.25% of Zn, less than or equal to 0.06% of Ti, 0.10%-0.16% of Zr, 0.002%-0.005% of Be and the balance Al, wherein the content of other single element is less than or equal to 0.030%, and the total amount of other impurity elements is less than or equal to 0.100%. The preparation method comprises the following steps that aluminum raw materials and other alloy raw materials are smelted into melt, refining treatment is conducted on the melt, then casting into a rod is conducted, and then homogenization treatment, extrusion treatment, solid solution heat treatment, stretching and aging treatment are conducted to obtain the profile. The comprehensive performance of the profile is remarkably improved, and the fracture toughness value is high.
Owner:SHANDONG NANSHAN ALUMINUM +1
Inductively-coupled toroidal plasma source
InactiveUS20070145018A1Reduce potential differenceEasy to operateElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsEngineeringVoltage source
Apparatus for dissociating gases includes a plasma chamber comprising a gas. A first transformer having a first magnetic core surrounds a first portion of the plasma chamber and has a first primary winding. A second transformer having a second magnetic core surrounds a second portion of the plasma chamber and has a second primary winding. A first solid state AC switching power supply including one or more switching semiconductor devices is coupled to a first voltage supply and has a first output that is coupled to the first primary winding. A second solid state AC switching power supply including one or more switching semiconductor devices is coupled to a second voltage supply and has a second output that is coupled to the second primary winding. The first solid state AC switching power supply drives a first AC current in the first primary winding. The second solid state AC switching power supply drives a second AC current in the second primary winding. The first AC current and the second AC current induce a combined AC potential inside the plasma chamber that directly forms a toroidal plasma that completes a secondary circuit of the transformer and that dissociates the gas.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
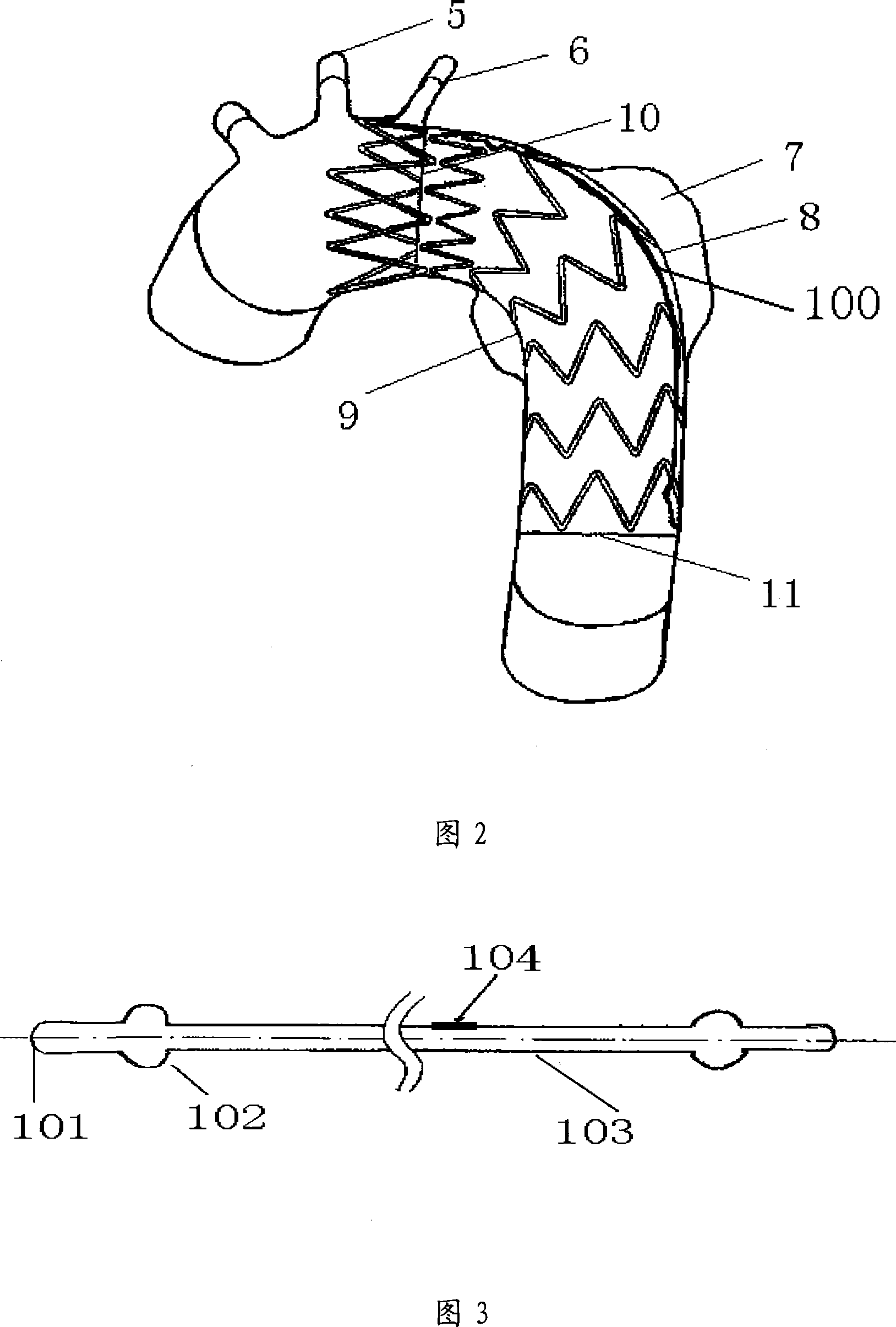
Tectorial bracket
ActiveCN101176686AReduced maximum outer profileEasy to installStentsSurgeryTectorial membraneLead blood
The invention discloses a coated stent, comprising a stent section, a coat and a reinforcement; wherein, two ends of a metal wire are connected to form the reinforcement which is fixed on the coat. The invention is characterized in that: since the coated stent adopts the independent reinforcement, the reinforcement is separated from the stent section, avoiding the risk that in prior art the integral connection of the reinforcement and the front and end stent sections can lead to fracture; furthermore, the hindrance produced in the course of releasing and assembling the whole stent is reduced,which is helpful for the releasing and assembling of the coated stent. The invention also discloses another coated stent comprising a stent section and a coat; wherein, two ends of a metal wire are connected by laser welding to form the stent section. Since two ends of the metal wire in each stent section are not fixedly connected, prior coated stent can lead blood damage; therefore, the risk is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT ENDOVASCULAR MEDTECH (GRP) CO LTD
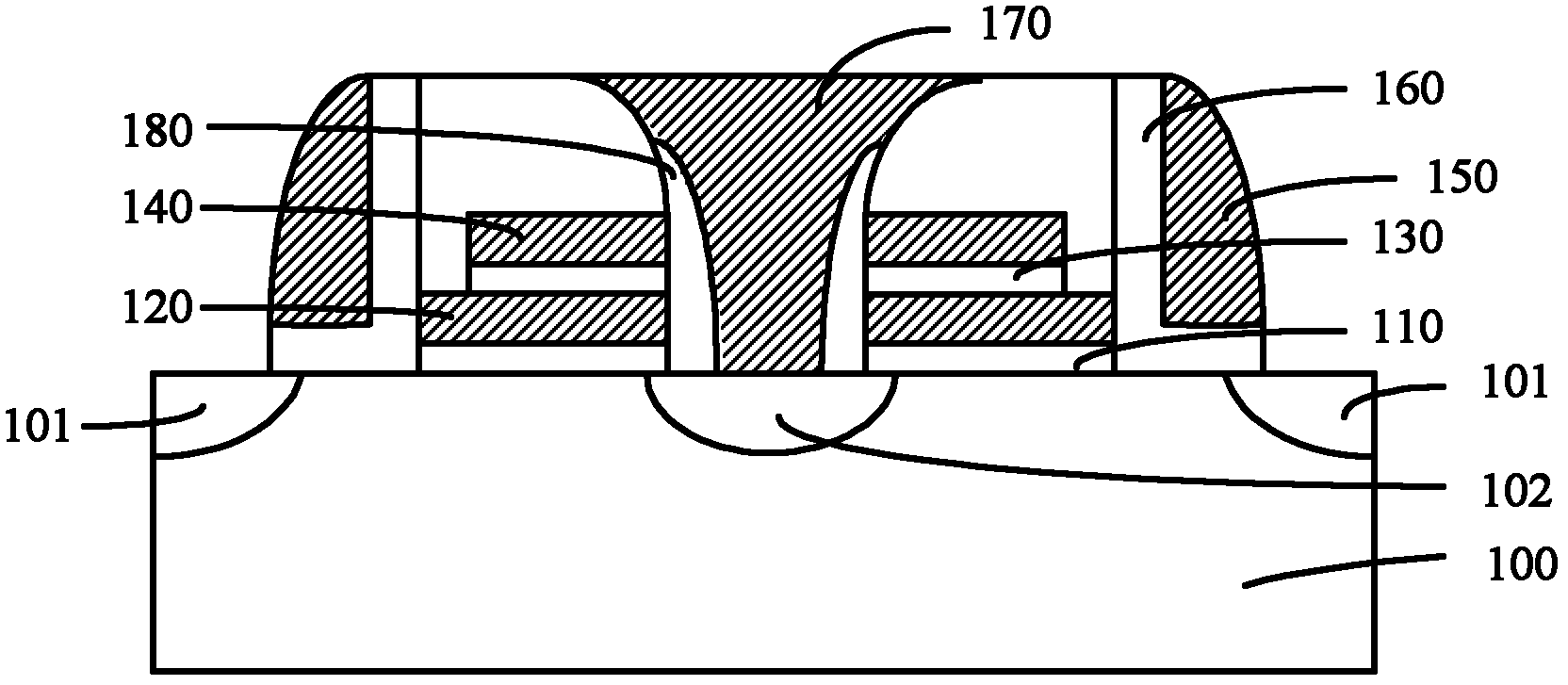
Flash memory unit for shared source line and forming method thereof
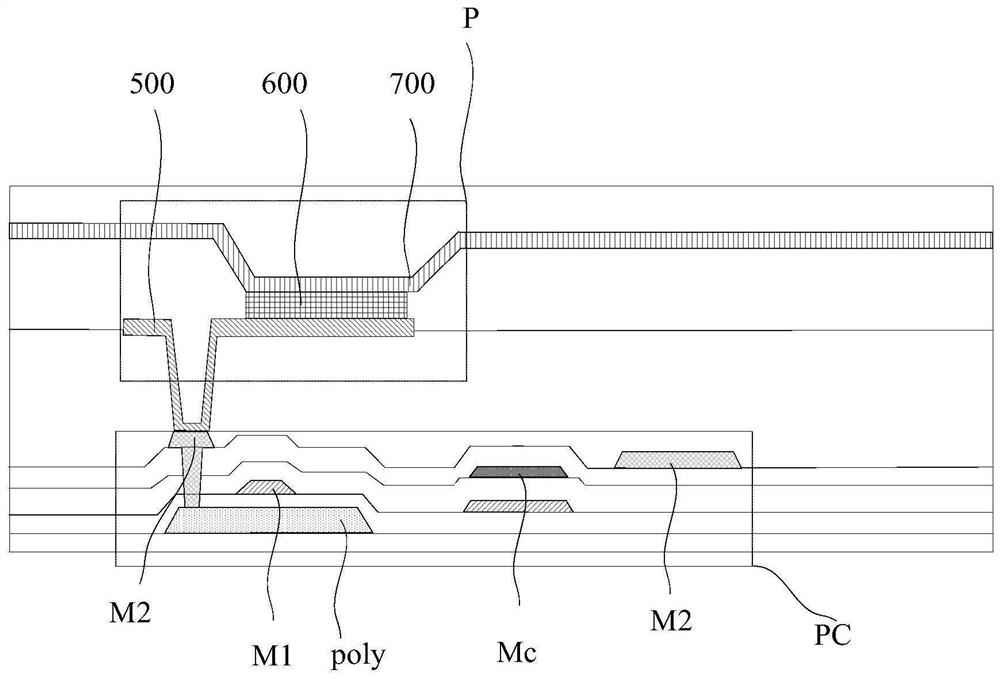
ActiveCN102315252AImprove coupling coefficientImproved Stress ReliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a flash memory unit for a shared source line and a forming method thereof. The provided flash memory unit for the shared source line comprises a semiconductor substrate, a source line, a floating gate dielectric layer, a floating gate, a control gate dielectric layer, a control gate, side wall dielectric layers, side walls, a tunneling oxide layer, a word line, a drain electrode and a source electrode, wherein the source line is positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; the floating gate dielectric layer, the floating gate, the control gate dielectric layer and the control gate are sequentially positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate on two sides of the source line; the side wall dielectric layers are positioned between the source line and the floating gate as well we between the source line and the control gate; the side walls are positioned on the floating gate and the control gate, which are far from the source line; the tunneling oxide layer is adjacent to the side wall and is positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; the word line is positioned on the surface of the tunneling oxide layer; the drain electrode is positioned in the semiconductor substrate at one side of the word line, which is far from the source line; the source electrode is positioned in the semiconductor substrate which is right opposite to the source line; and the floating gate is provided with a p-type doping end which is close to the source line, wherein the doping type of the floating gate is in a p type and the doping type of other parts is respectively in an n type.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
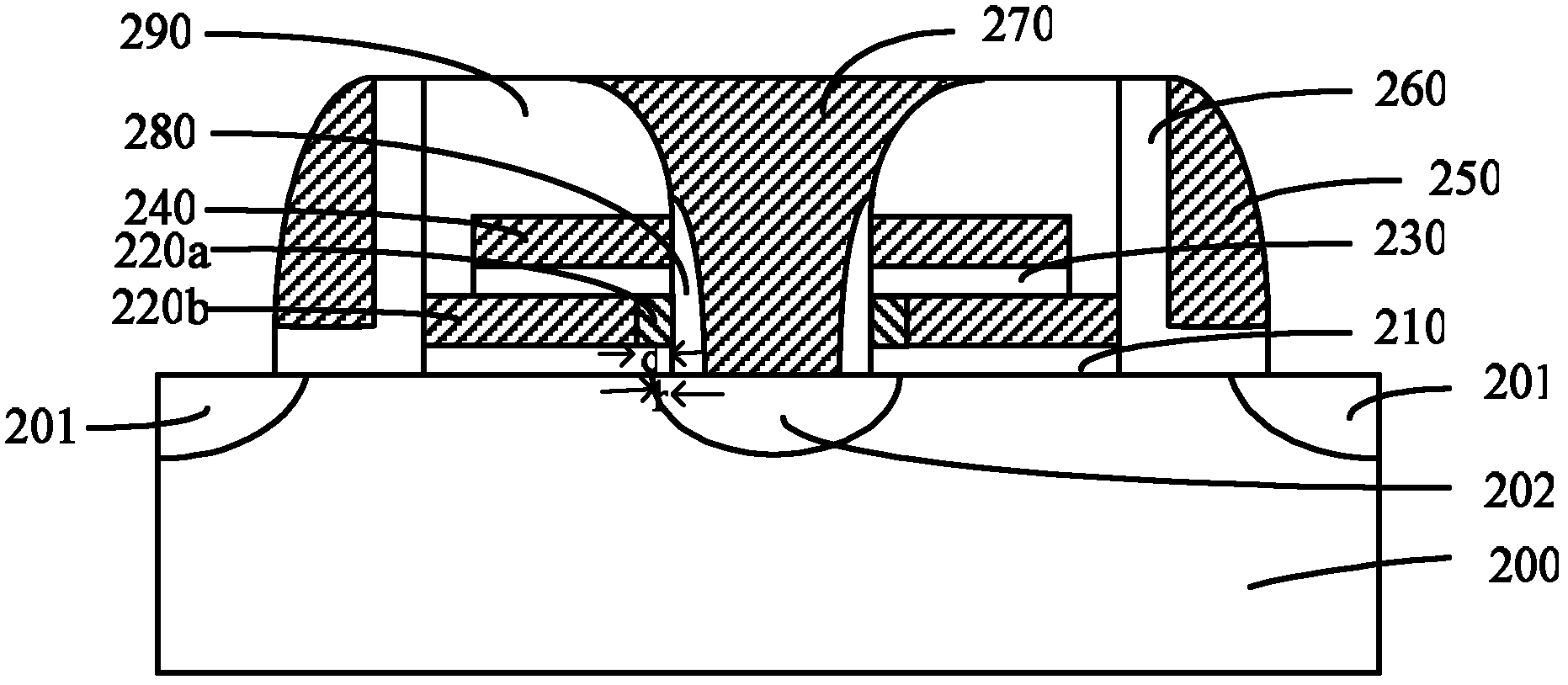
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN111816119AReduce leakage currentReduce potential differenceStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitPotential difference
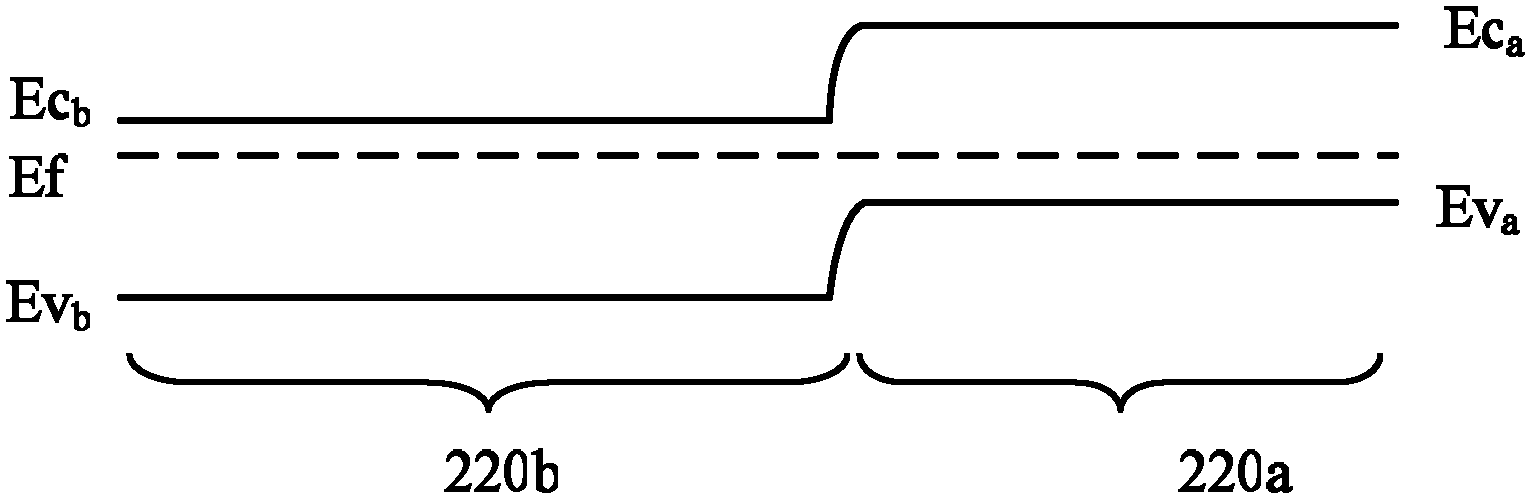
The embodiment of the invention provides a display panel and a display device. The display panel comprises: a pixel and a pixel driving circuit for driving the pixel, wherein the pixel driving circuitcomprises a driving transistor and a first double-gate transistor electrically connected with the control end of the driving transistor, the first double-gate transistor comprises a first transistor,a second transistor, a first node and an intermediate node which are connected in series, the first node is electrically connected with the control end of the driving transistor, and the intermediatenode is located between the first transistor and the second transistor which are connected in series; and a leakage current prevention module which is electrically connected to the intermediate nodeand is used for enabling the potential difference between the potential of the intermediate node and the potential of the first node to be smaller than a first threshold value. According to the embodiment of the invention, the leakage current of the control end of the driving transistor is reduced through the leakage current prevention module, thereby avoiding the splash screen problem.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
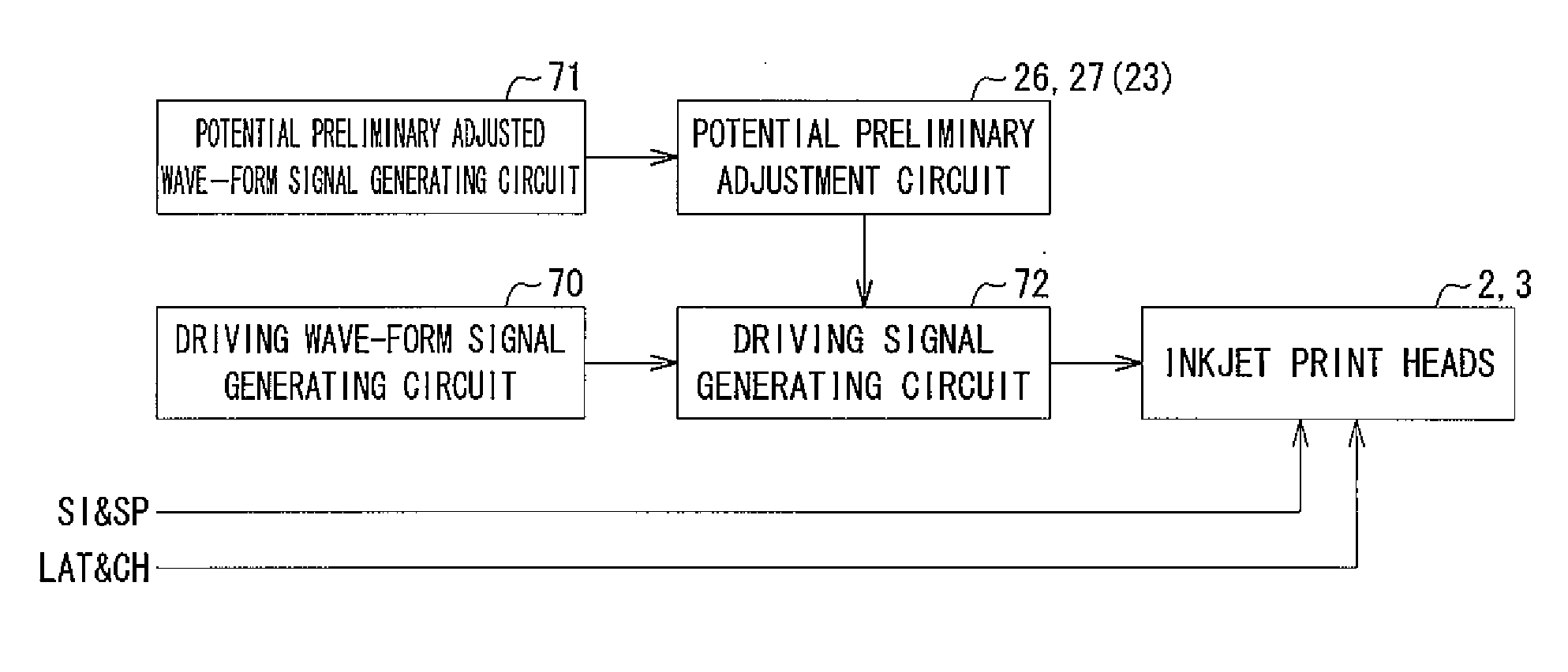
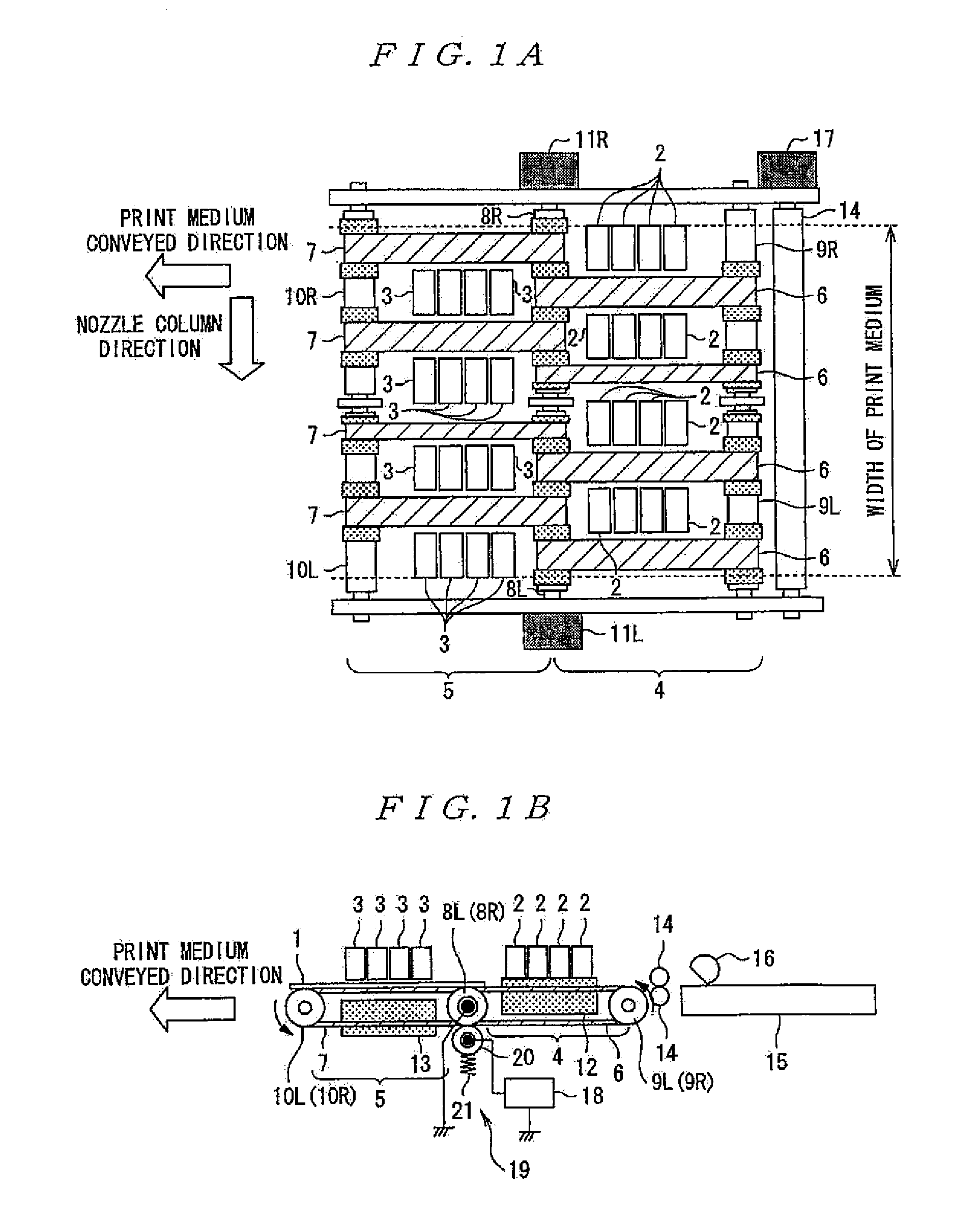
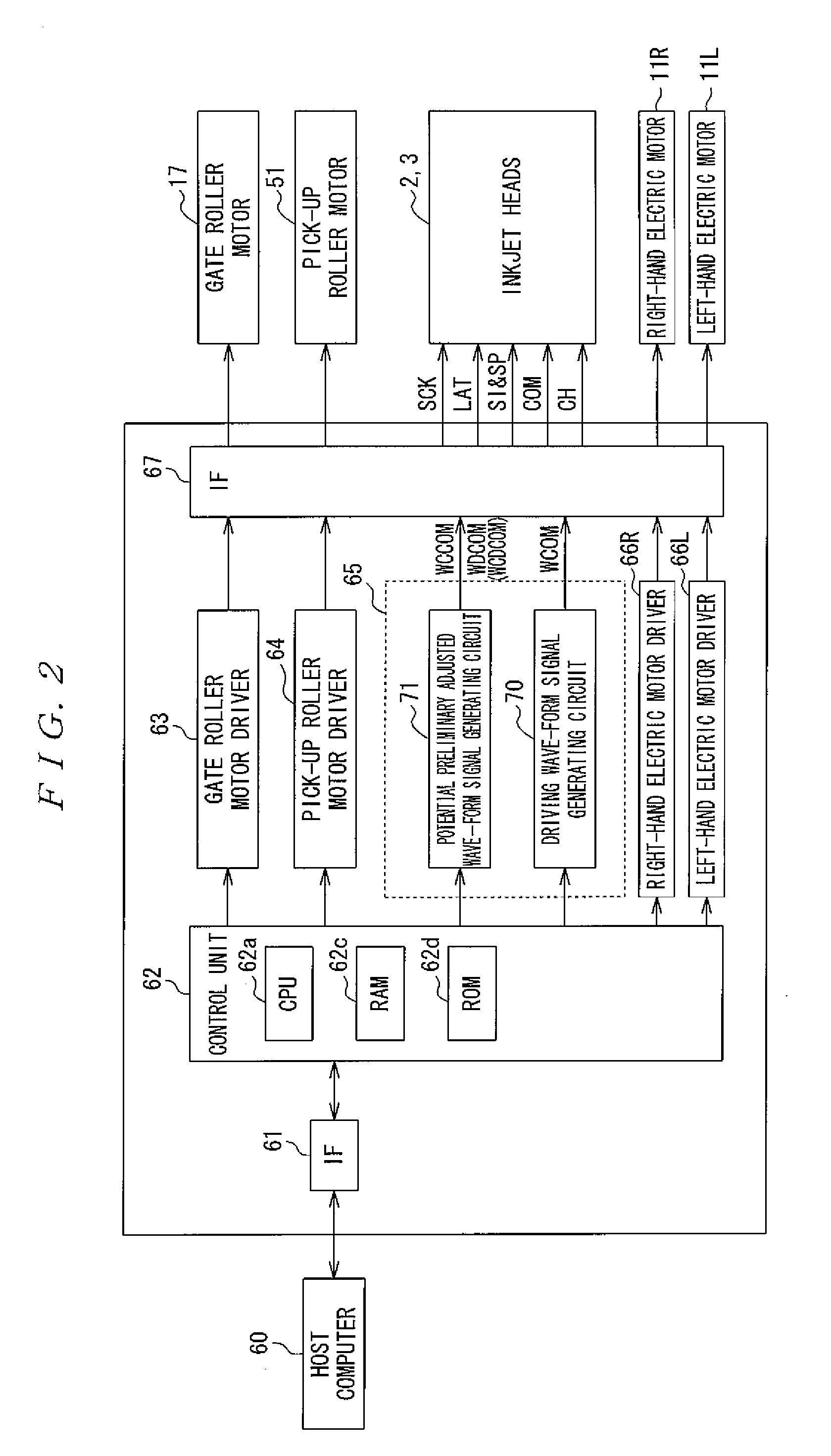
Liquid Jetting Device
InactiveUS20100097419A1Reduce potential differenceReduce power consumptionOther printing apparatusPush pullWave form
A liquid jetting device includes a plurality of nozzles. A driving signal generated by a driving signal generating section is applied to a charge-discharge actuator in correspondence with each nozzle to jet liquid from the nozzle. A charging source potential preliminary adjusted wave-form signal is pulse modulated and electrically amplified using a charging source potential transistor pair connected in a push-pull configuration, and output by a ripple filter to a collector of a charge-use transistor of the driving signal generating section to make a preliminary adjustment to the charging source potential for the driving signal generating section.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
High-Zn, high-Mg and low-Cu ultrahigh-strength corrosion-resisting aluminum alloy and heat treatment method
The invention discloses a high-Zn, high-Mg and low-Cu ultrahigh-strength corrosion-resisting aluminum alloy and a heat treatment method. The alloy comprises the following components by mass percentage: 6.5-8.3% of Zn, 2.3-3.0% of Mg, 0.8-1.2% of Cu, 0.1-0.2% of Zr, less than 0.15% of Fe, less than 0.1% of Si, and the balance of Al. A preparation method of the alloy comprises the steps of blending, smelting, semi-continuous casting, homogenizing, thermoplastic deformation, short time solid solution, and ageing heat treatment. For the high-Zn, high-Mg and low-Cu ultrahigh-strength corrosion-resisting aluminum alloy prepared with the method, the hardness (HV) is 185-209, the tensile strength sigma b is greater than or equal to 650Mpa, the percentage elongation delta is greater than or equal to 7%, the pitting resistance is high, the cast ingot yield is high, and the stress corrosion resistance is further improved while the mechanical property is kept after multiple regression reageing treatment. The alloy and the heat treatment method solve the problems that the cast ingot yield in the existing high-copper Al-Zn-Mg-Cu ultrahigh-strength aluminium alloy is low, and the strength, toughness and corrosion resistance cannot be compromised. The heat treatment method is simple to operate, and the industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Anti-explosion material and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to an anti-explosion material, which is made of a cut and extended aluminum alloy foil mesh and has mesh-like or beehive-like porous structure, and is characterized in that: an aluminum alloy foil comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.05 to 0.15 percent of silicon, 1.0 to 1.6 percent of copper, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of manganese, 1.0 to 3.0 percent of magnesium, 3.0 to 6.0 percent of zinc, 0.02 to 0.06 percent of titanium, 0.05 to 0.15 percent of zirconium, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of scandium and the balance of aluminum. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the anti-explosion material. The material obtained by the method has the advantages of high electric and heat conductivities and large specific area and has the characteristics of corrosion resistance and high strength. When used as an anti-explosion material, the material is free from scraps and deformation. The material is particularly suitable for safe protection of containers for flammable and combustible liquid containers with high corrosivity as well as skid-mounted gasoline and gas filling station containers.
Owner:北京福吉长安防爆材料有限责任公司 +1
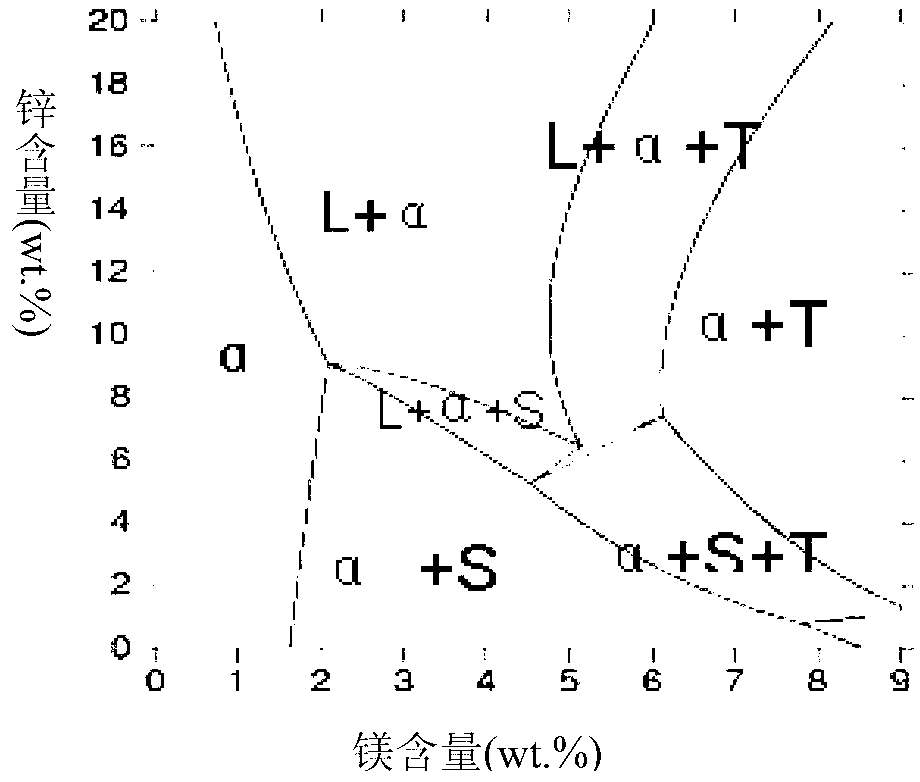
Degradable Mg-Zn-Y-Ca intravascular stent material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a degradable Mg-Zn-Y-Ca intravascular stent material and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the fields of design and manufacture of metal materials. The intravascular stent material is characterized by comprising the following chemical components in percentage by weight (wt%): Zn 1.00 to 4.00, Y 0.10 to 1.00, Ca 0.01 to 0.50 and the balance of Mg; the chemical components are subjected to sub-rapid solidification at (200+ / -10) K / S and heat treatment of heating at 320 to 420 DEG C and heat preservation for 20 to 30h; and the texture characteristic of the intravascular stent material is that: even and fine spherical quasicrystalline phases Mg3YZn6 are dispersed and distributed on an alpha-Mg matrix. The potential difference between the spherical quasicrystalline phases Mg3YZn6 and magnesium is lower so that the formation of a galvanic cell is restrained and galvanic corrosion is alleviated; the sphericity quasicrystal Mg3YZn6 has good corrosion resistance and can obviously enhance the corrosion resistant performance of magnesium alloy; and at the same time, the quasicrystal also has the characteristics of high hardness, low friction coefficient, low interface energy and the like and can greatly enhance the mechanical performance of the magnesium alloy.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
GOA (Gate Driver On Array) circuit of liquid crystal display panel and display device
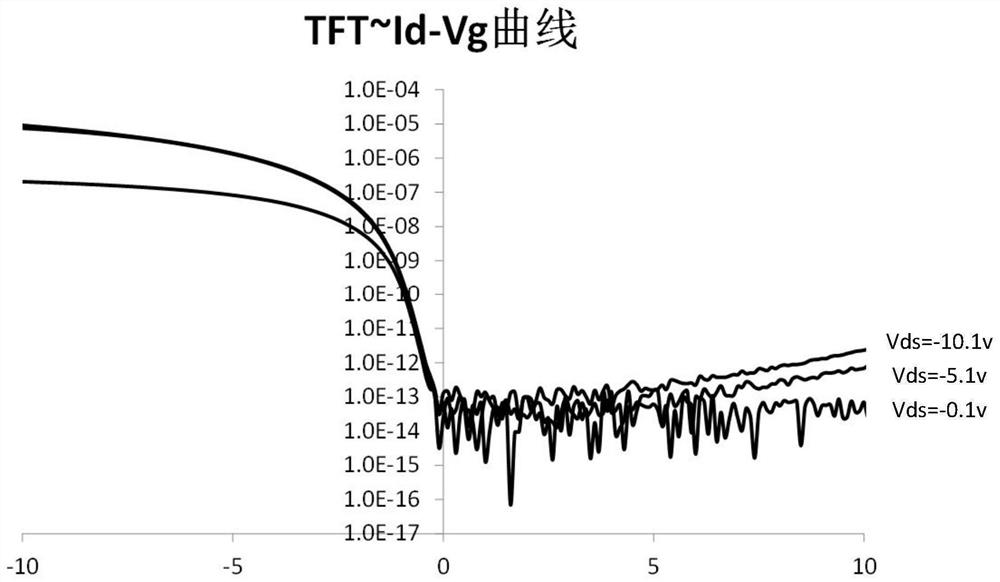
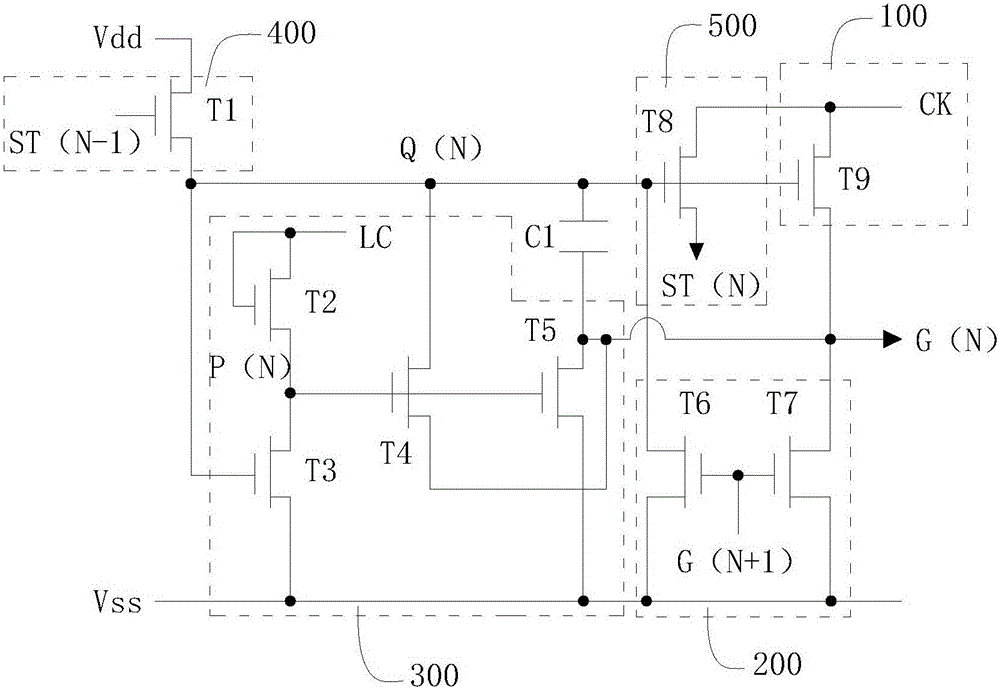
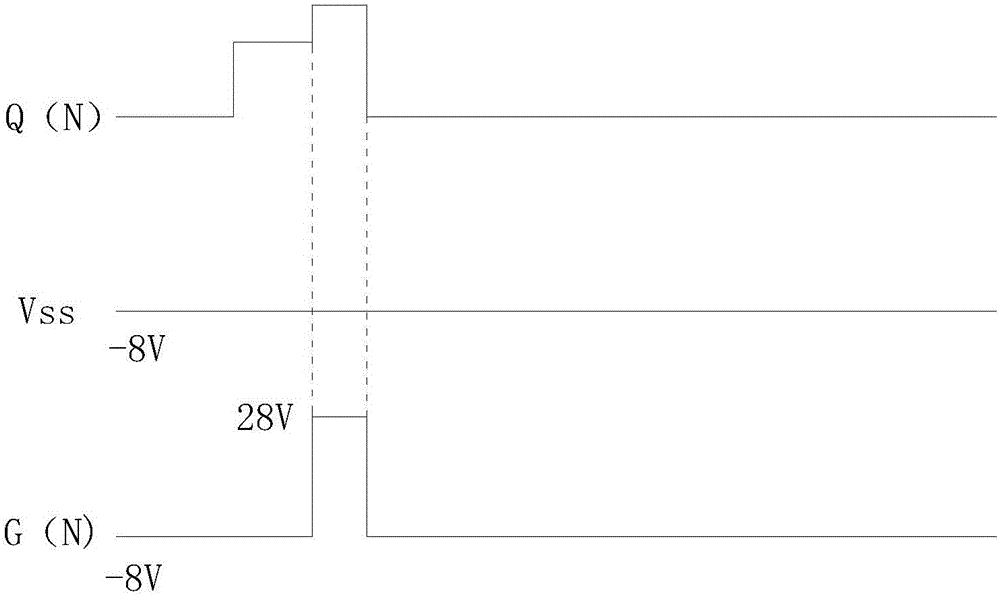
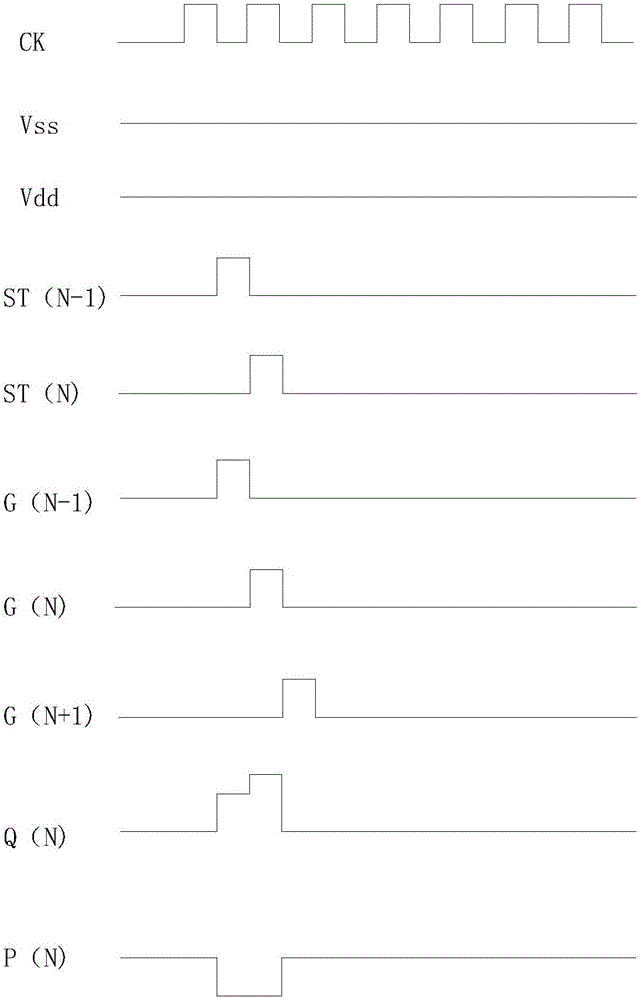
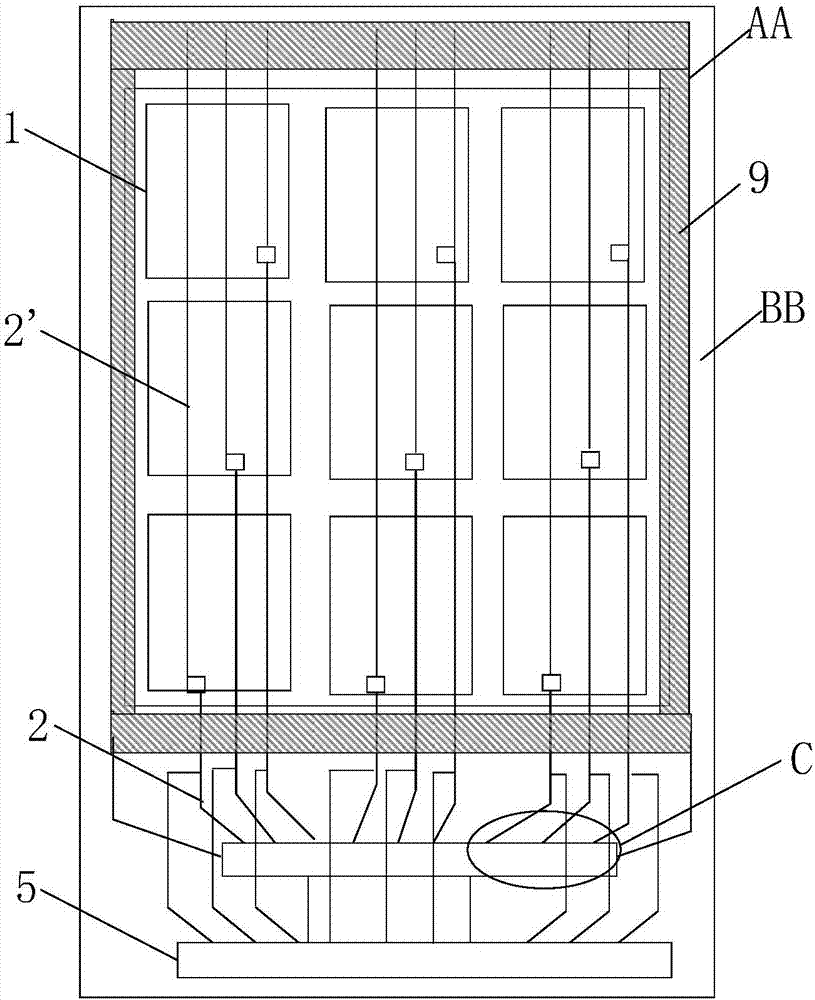
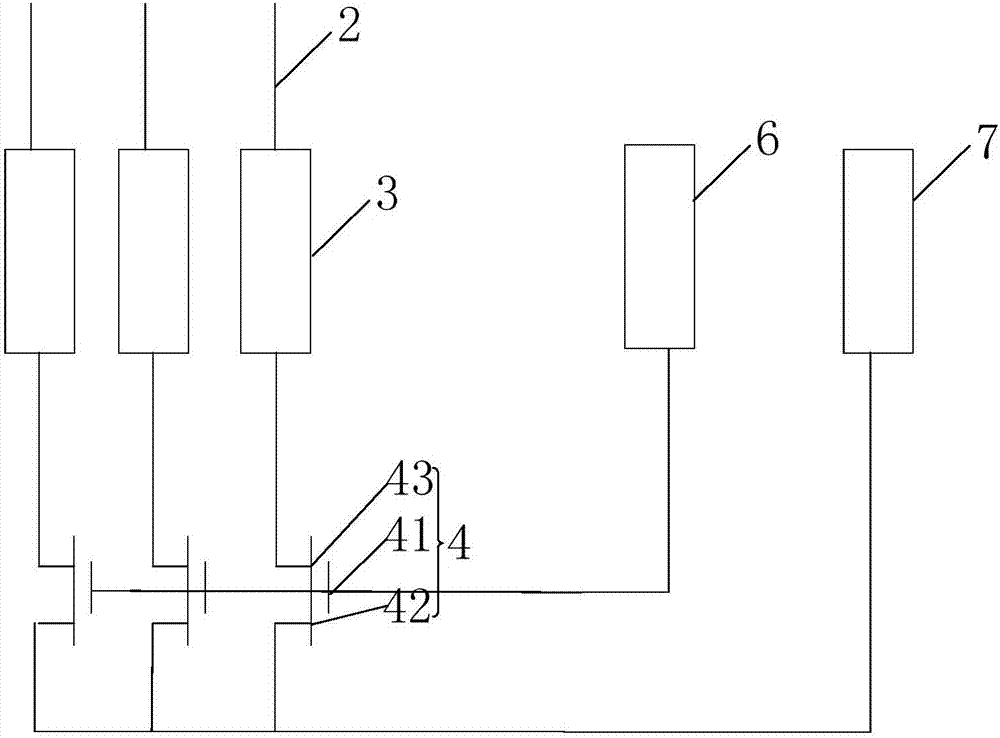
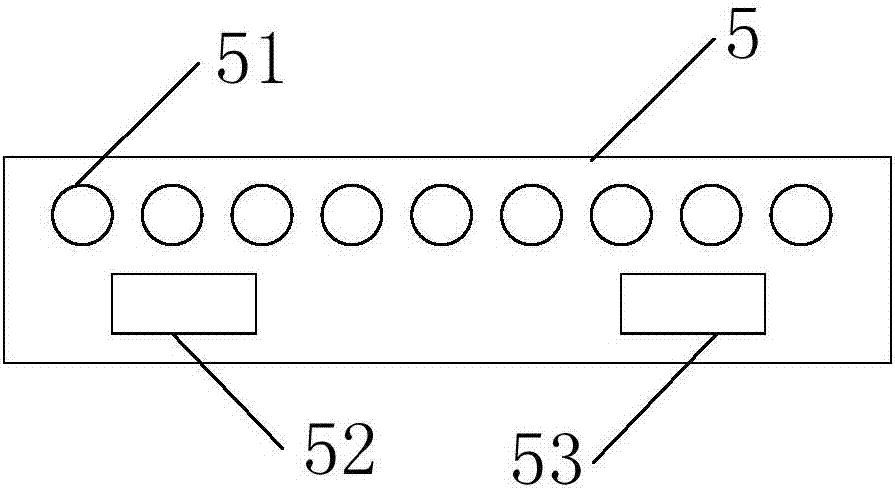
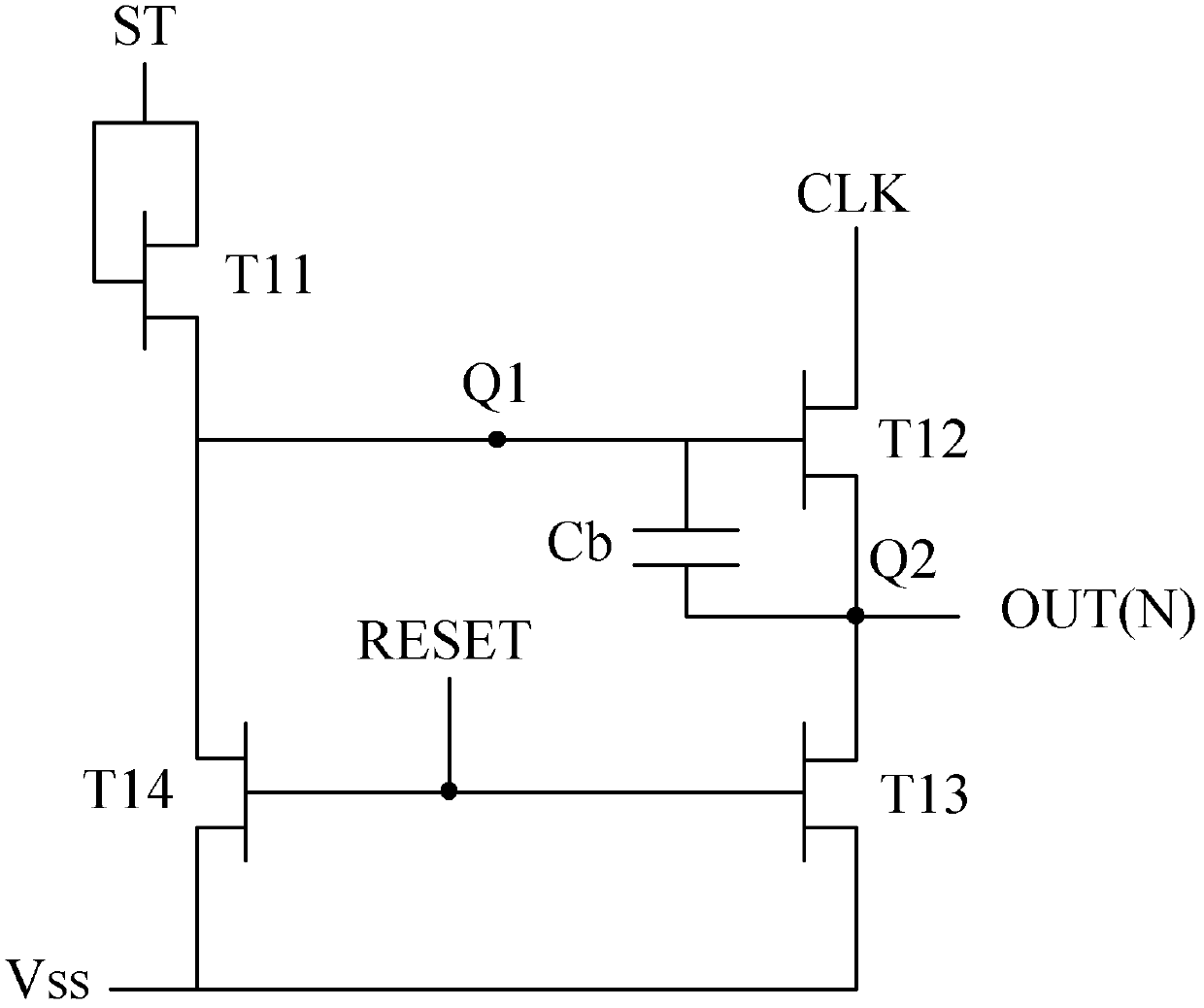
ActiveCN106448590AReduce potential differencePrevent leakageStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayPotential difference
The invention provides a GOA (Gate Driver On Array) circuit of a liquid crystal display panel and a display device. The GOA circuit comprises a plurality of cascaded GOA units, wherein the Nth-level GOA unit performs control on charging of an Nth-level scanning line. The Nth-level GOA unit comprises a pull-down holding circuit unit, a pull-down circuit unit, a pull-up circuit unit, a pull-up holding circuit unit, a transfer circuit unit, a bootstrap capacitor, a constant-voltage low level source and a constant-voltage high level source, wherein the gate of a thin film transistor of the pull-down holding circuit unit is connected to a first circuit point, the source and the drain of the thin film transistor are respectively connected to the constant-voltage low level source and the Nth-level scanning line. According to the invention, potential difference of the source and the drain of the thin film transistor at a second circuit point is relieved, so that the thin film transistor is enabled to be not prone to electric leakage. Meanwhile, a driving force of scanning signals is improved, and continuous transmission of the device is ensured.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
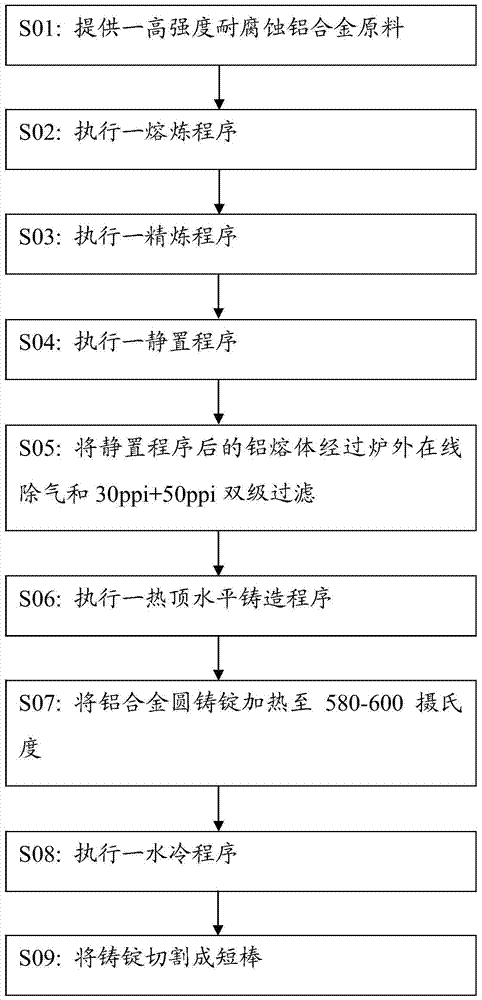
Preparation process of high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy and high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy
The application discloses a preparation process of a high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy and the high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy. High-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy is processed from high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy raw materials. The weight percent composition of the high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy raw material is: 0.45-0.60 weight percent silicon, 0-0.25 weight percent iron, 0.40-0.50 weight percent copper, 1.2-1.45 weight percent manganese, 0-0.04 weight percent magnesium, 0-0.04 weight percent chromium, 0-0.05 weight percent zinc, and the rest aluminum.
Owner:ASIA PACIFIC LIGHT ALLOY NANTONG TECH
Pixel circuit, display device, and driving method thereof
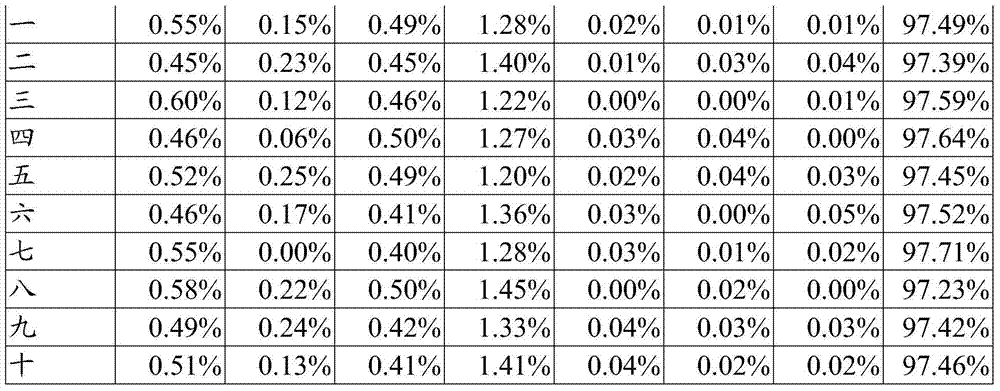
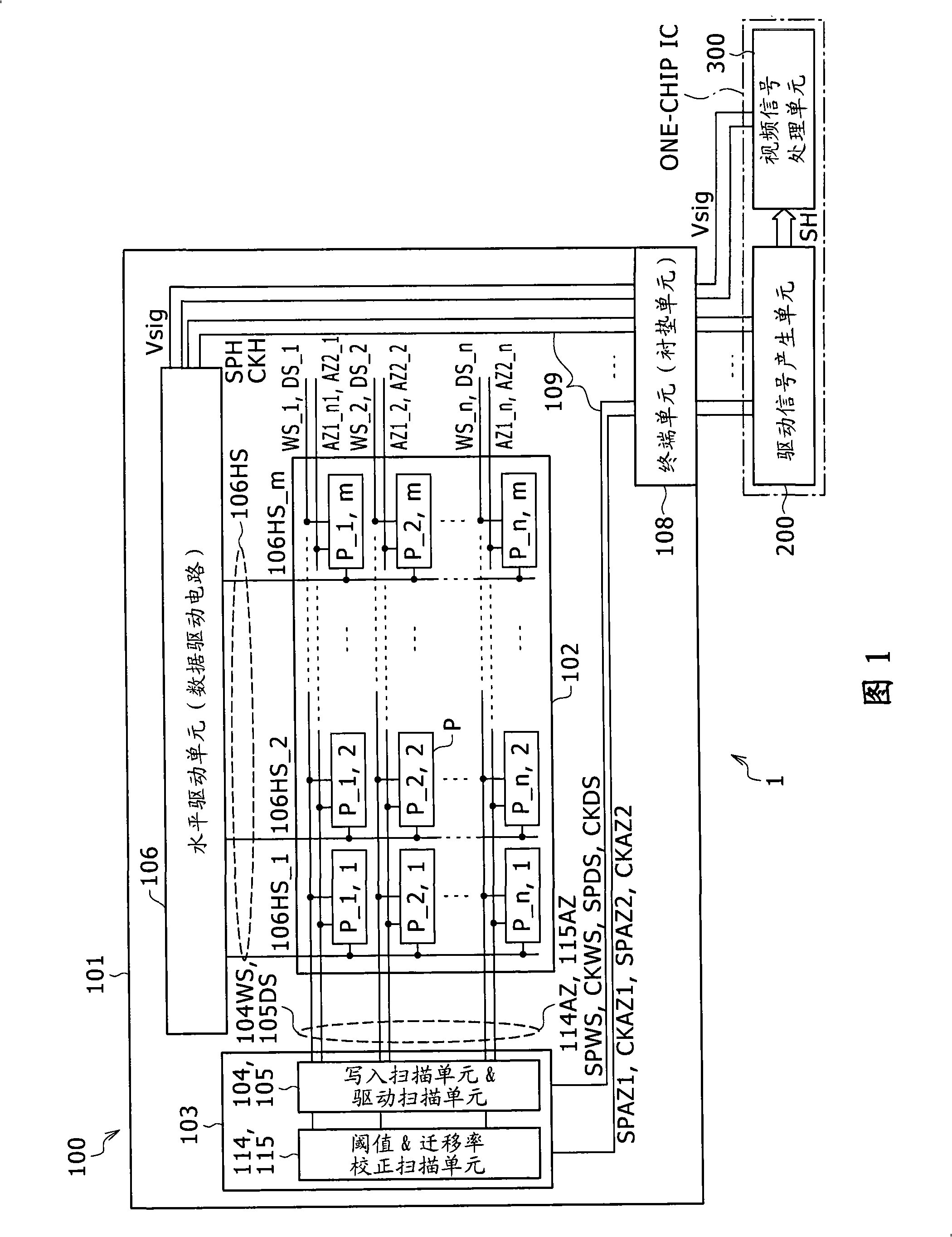
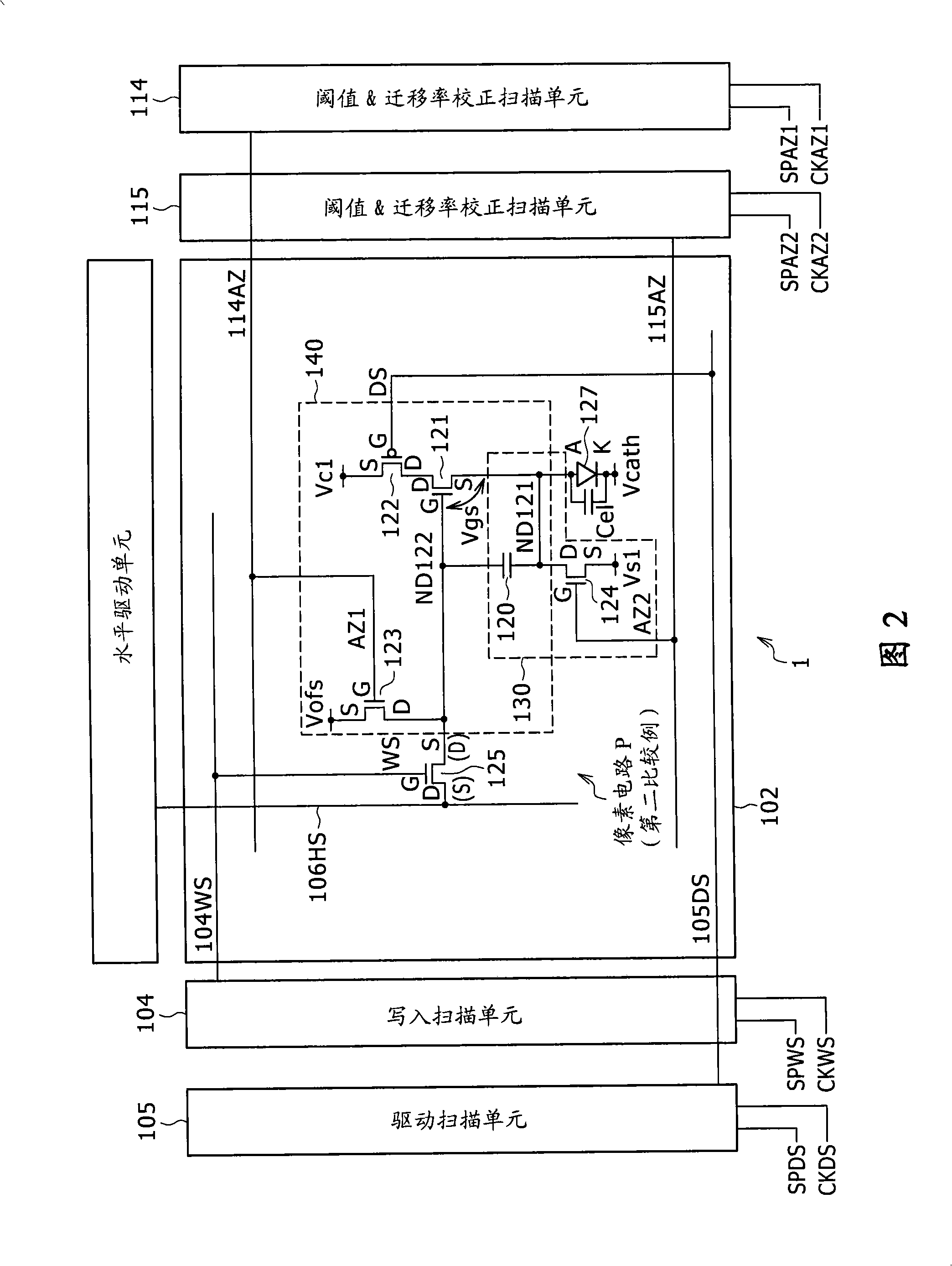
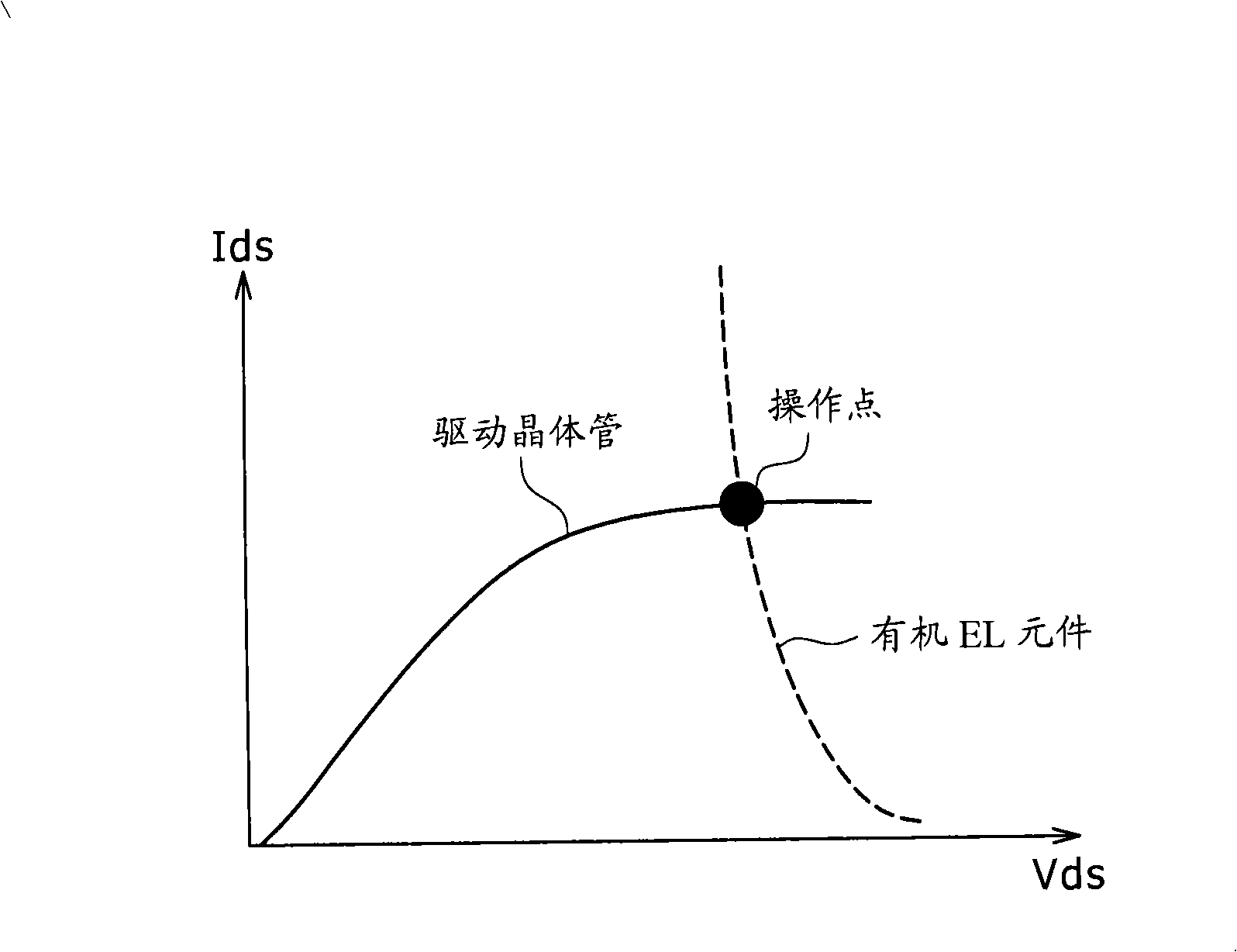
InactiveCN101266755AIncrease potential differenceReduce potential differenceStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceBrightness perception
The invention discloses a pixel circuit, a display device including the pixel circuit and a method for driving the pixel circuit. The display device includes a pixel array unit and a control unit. According with the invention, brightness decrease caused by mobility correction can be avoided, and video signal size needs not increased.
Owner:SONY CORP
Aluminum alloy brazing material, brazing member, brazed article and brazinh method therefor using said material, brazing heat exchanging tube, heat exchanger and manufacturing method thereof using sai
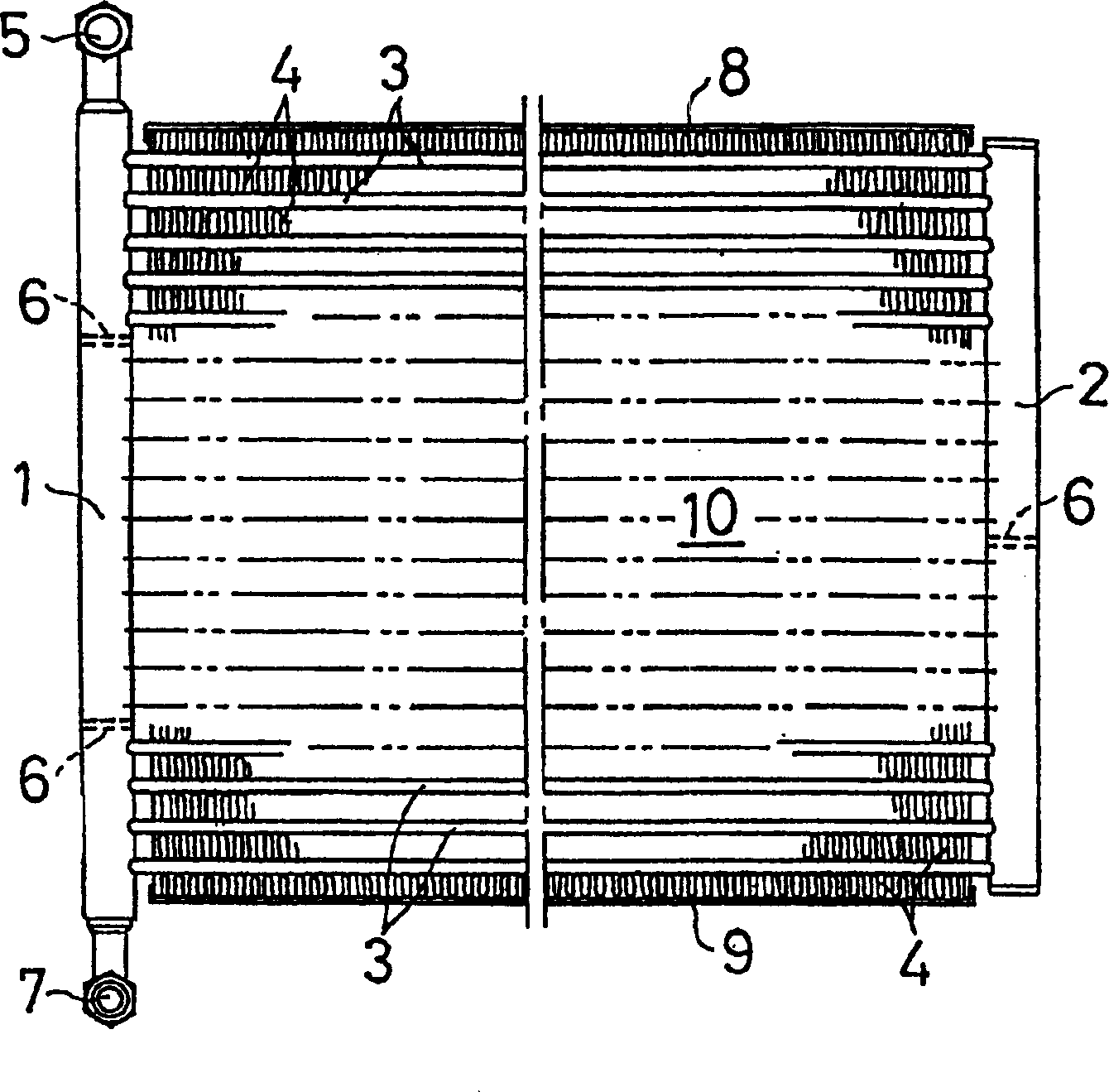
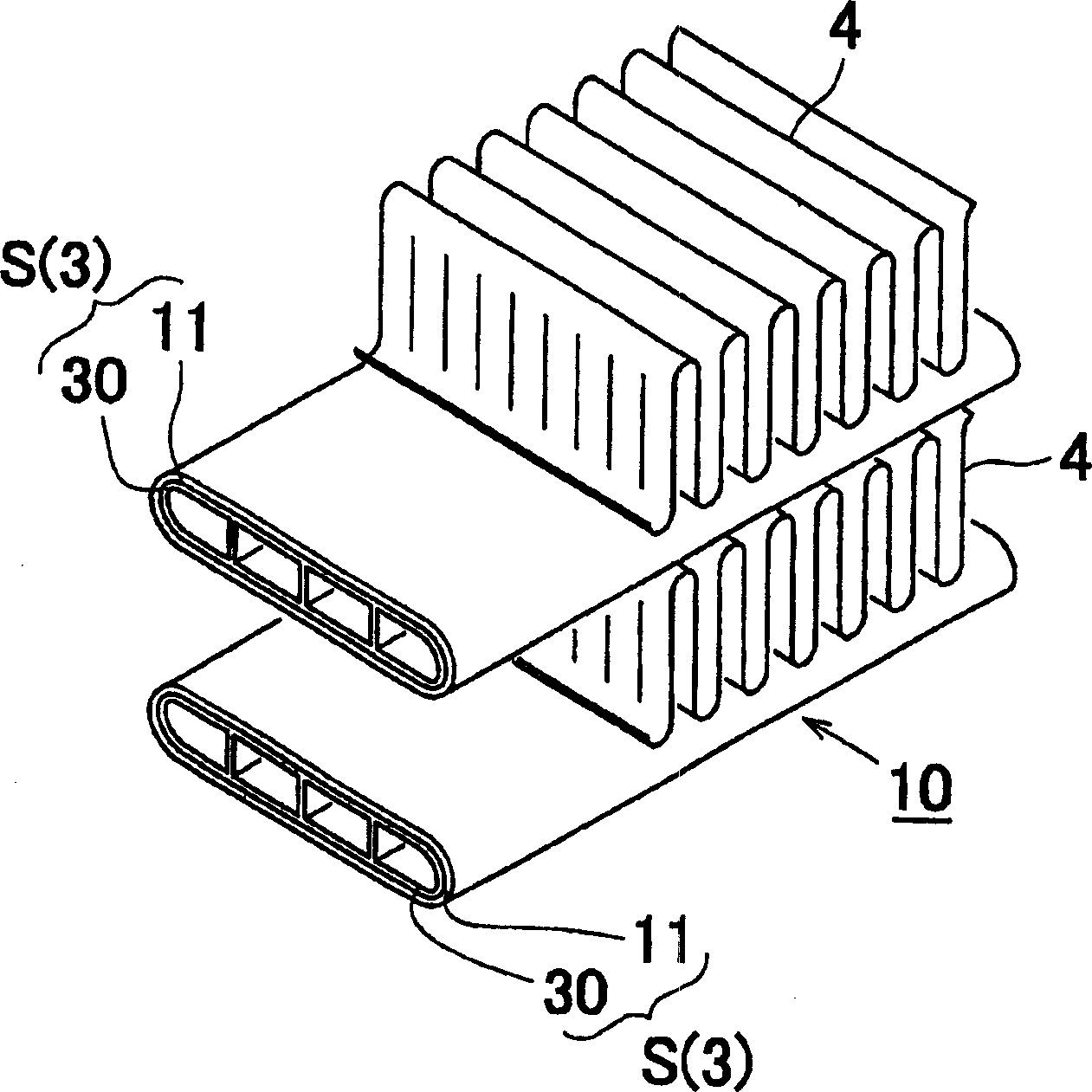
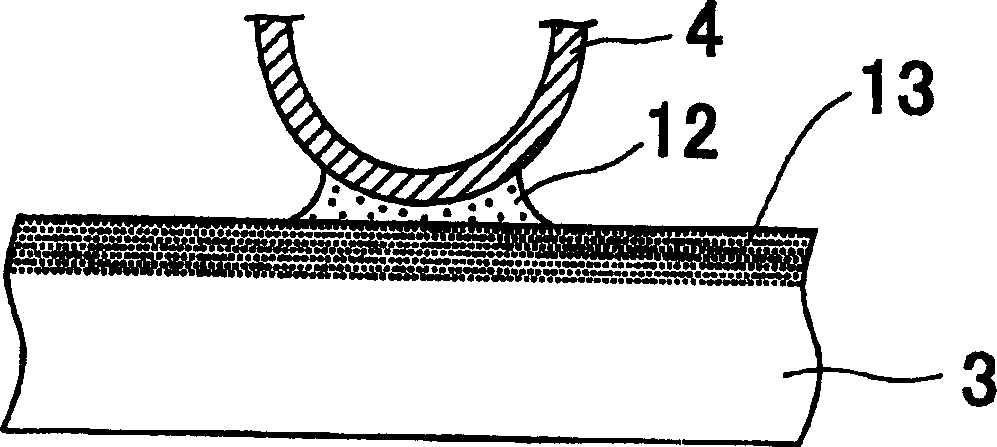
InactiveCN1726114AAvoid excessive corrosionReduce the predetermined thicknessWelding/cutting media/materialsHeat exchange apparatusPlate heat exchangerImpurity
A heat exchanger 10 includes a brazing heat exchanging tube S and a fin 4. The heat exchanging tube S and the fin 4 are brazed with each other via the brazing layer 11 of the heat exchanging tube S. The brazing layer 11 is formed by spraying of a brazing material consisting of Si: 6 to 15 mass%, Zn :1 to 20 mass%, at least one of Cu: 0.3 to 0.6 mass% and Mn: 0.3 to 1. 5 mass, and the balance being aluminum and inevitable impurities.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Touch Screen Panel and Display Device Including the Same
ActiveUS20190179445A1Reduce capacitanceReduction in charge quantityStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceTouchscreen
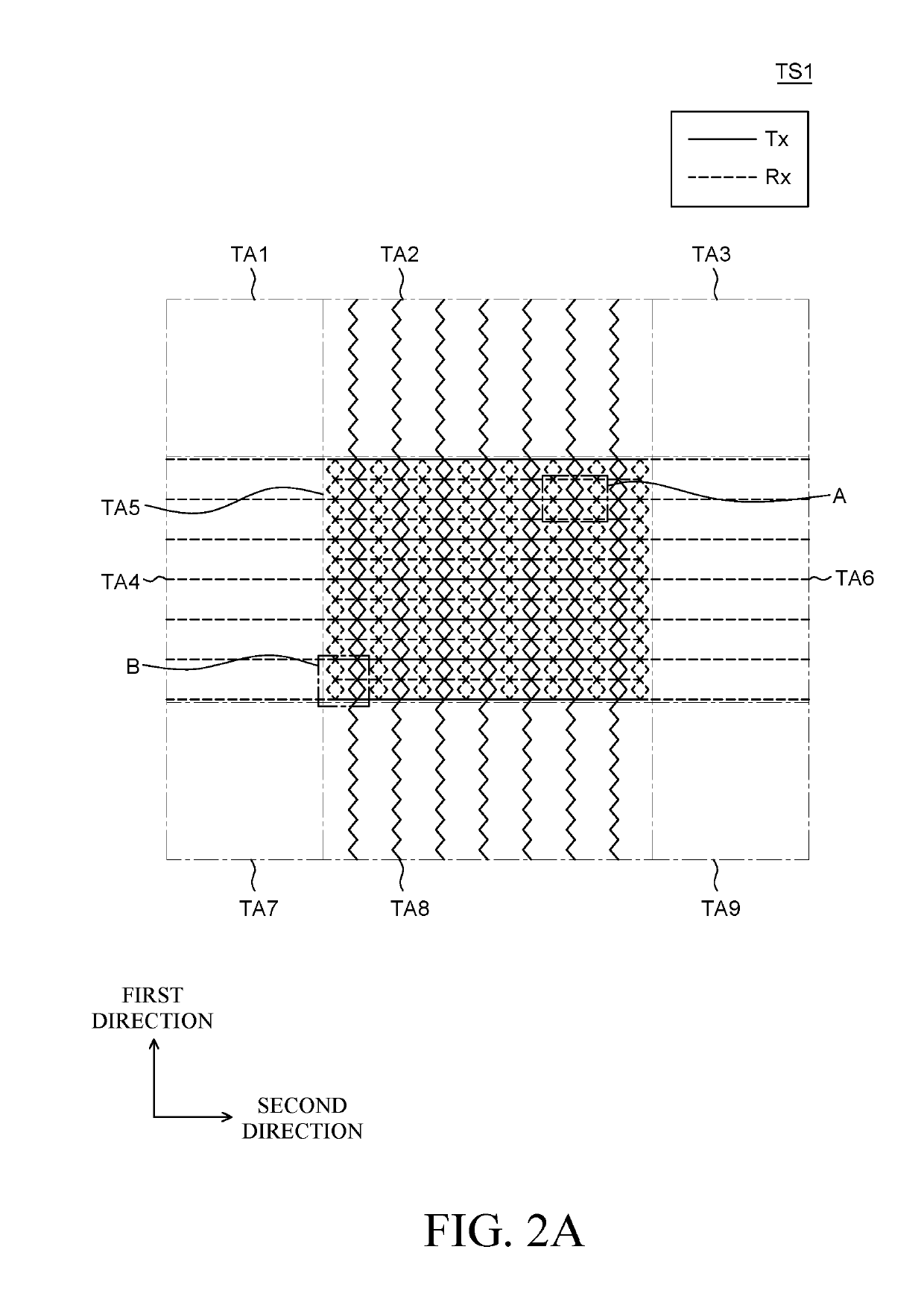
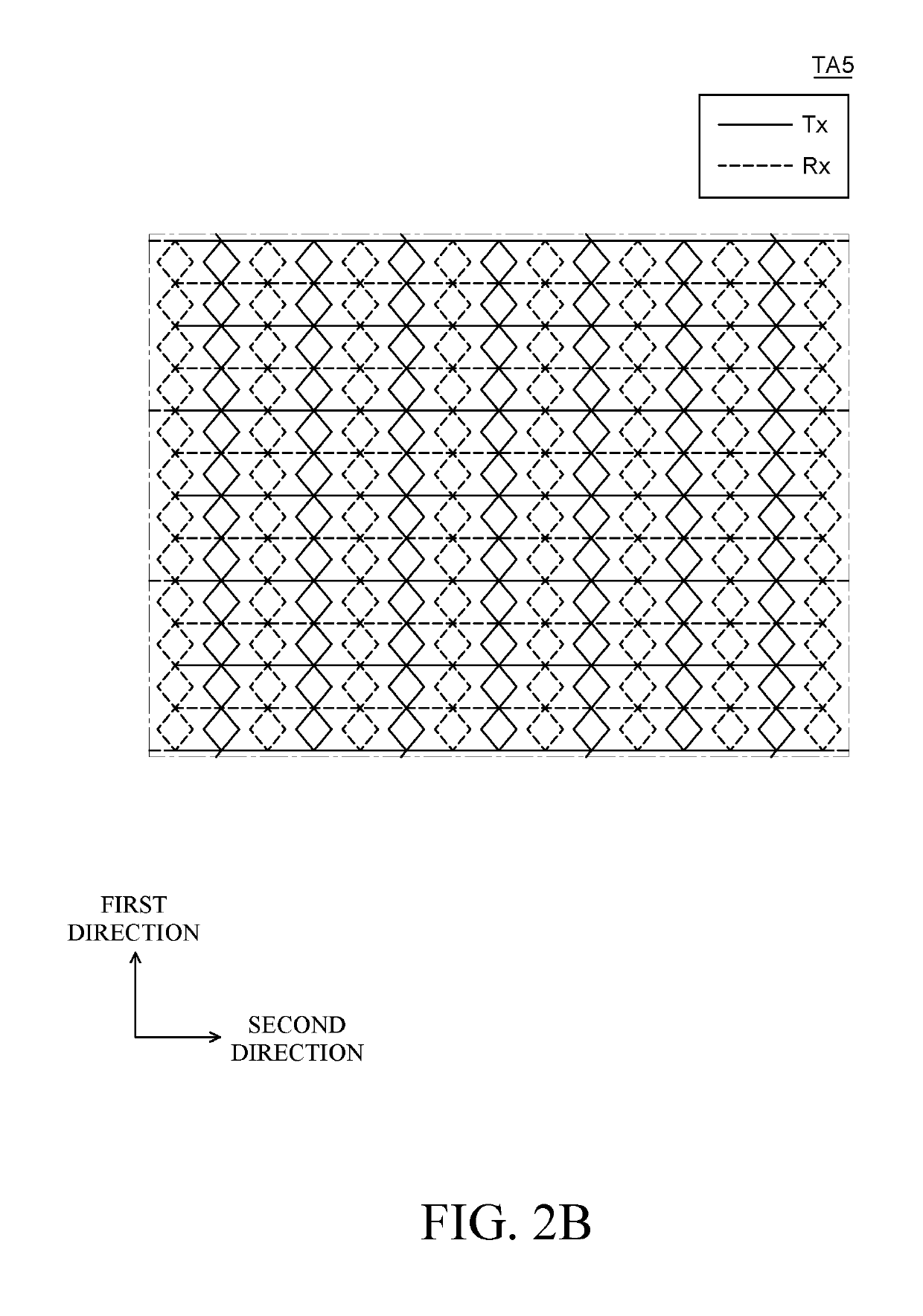
A touch screen panel includes a plurality of touch sensors. A touch sensor includes a first touch electrode unit that includes a plurality of first mesh pattern electrodes disposed to be spaced apart from each other in a sensing area where the first touch electrode unit and the second touch electrode unit intersect. The touch sensor also includes a second touch electrode unit that includes a plurality of second mesh pattern electrodes disposed between the plurality of first mesh pattern electrodes in the sensing area to be spaced apart from each other. The touch sensors also includes a at least one floating electrode disposed between the plurality of first mesh pattern electrodes and the plurality of second mesh pattern electrodes. The dielectric breakdown of the first touch electrode unit and the second touch electrode unit is suppressed to improve reliability of the touch screen panel.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
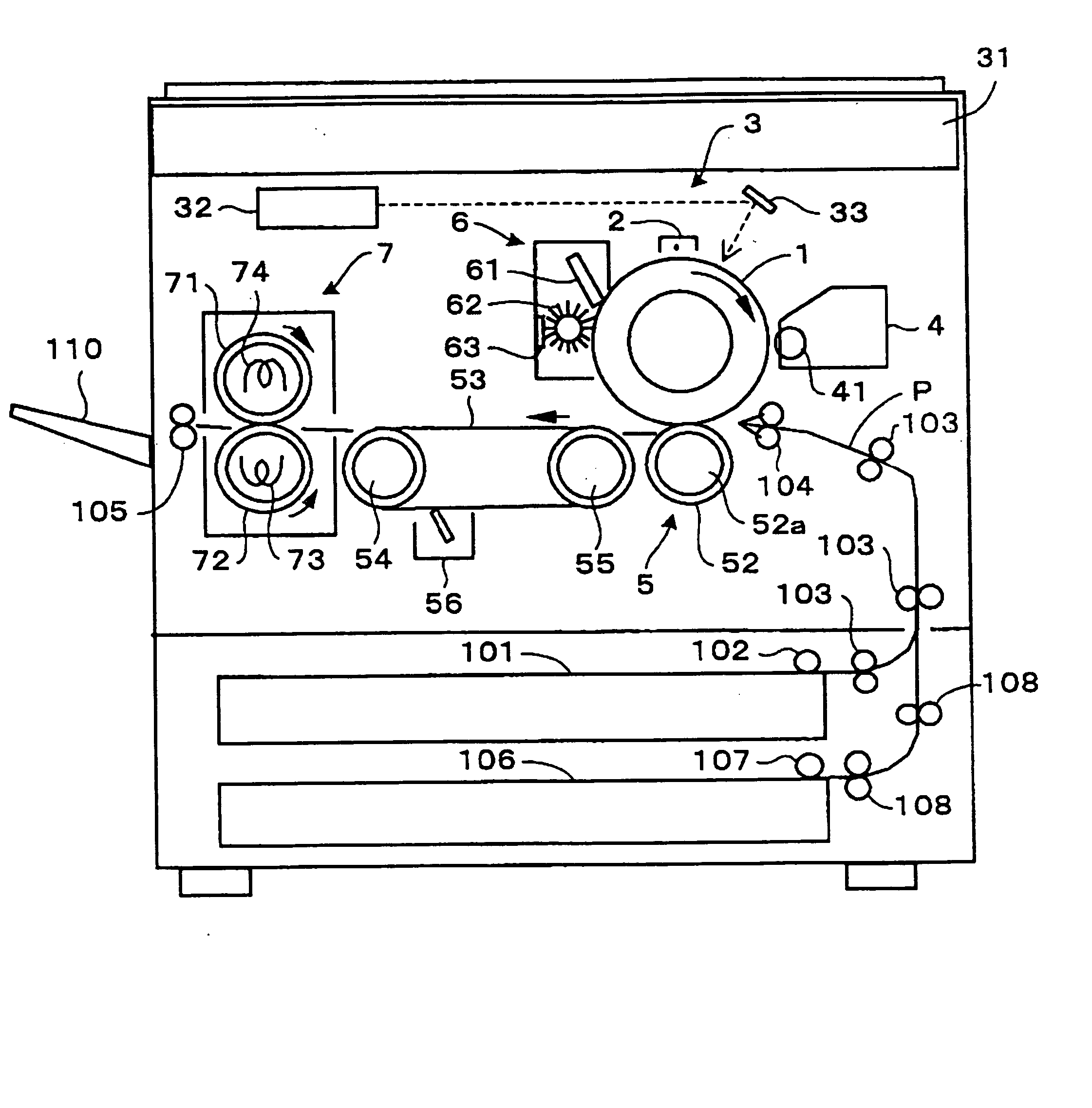
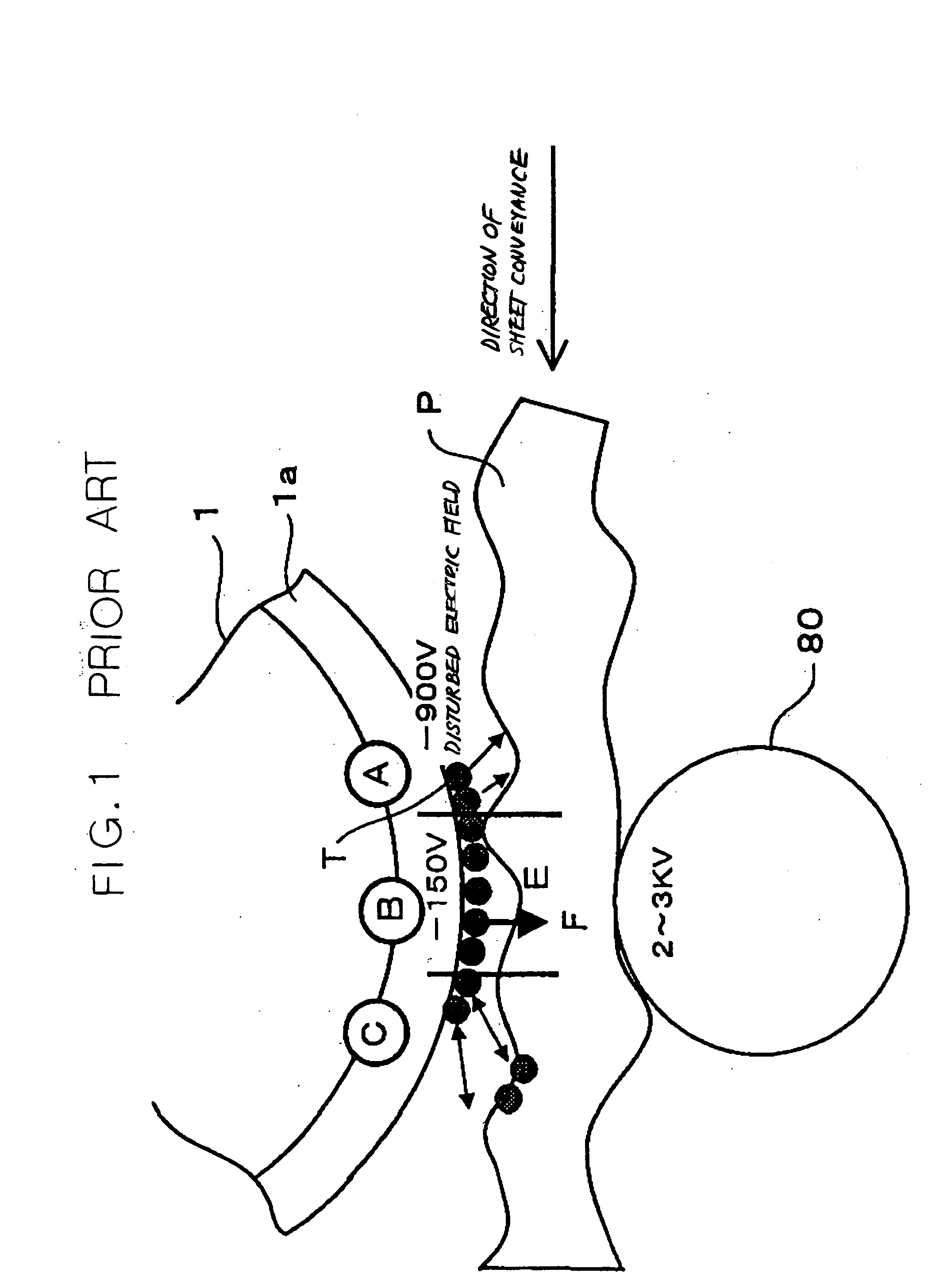
InactiveUS20050030595A1High hardnessReduce potential differenceElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersElectric fieldImage transfer
In an image forming apparatus configured to electrostatically transfer a toner image formed on an image carrier to a recording medium with image transferring means of the present invention, pressure is applied between the image carrier and the image transferring means. Toner is provided with relatively high hardness in accordance with the pressure beforehand. Image transfer is effected by reducing a potential difference between the image carrier and the recording medium while maintaining an electric field around the toner the same.
Owner:RICOH KK
Level shifter and electro-optical apparatus incorporating the same
InactiveUS6714046B2Reduce potential differenceReduce power consumptionSwitching accelaration modificationsStatic indicating devicesEngineeringVoltage reference
The invention simplifies the configuration of a level shifter and to allow fast operation. A level shifter includes a capacitor, to a first end of which a low-amplitude logic signal is input; first TFTs to apply an offset voltage to a second end of the capacitor; a capacitor, to a first end of which the low-amplitude logic signal is input; third TFTs to apply an offset voltage to a second end of the capacitor; and second TFTs connected in series between a supply line of a power supply voltage for a high-amplitude logic signal and a supply line of a reference voltage therefor, a node therebetween serving as an output terminal. A threshold voltage of one of the second TFTs is set to be not higher than the offset voltage applied by the first TFTs , and an offset voltage of the other of the second TFTs is set to be higher than or equal to the offset voltage applied by the third TFTs.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Electric motor and electrical machinery equipped therewith
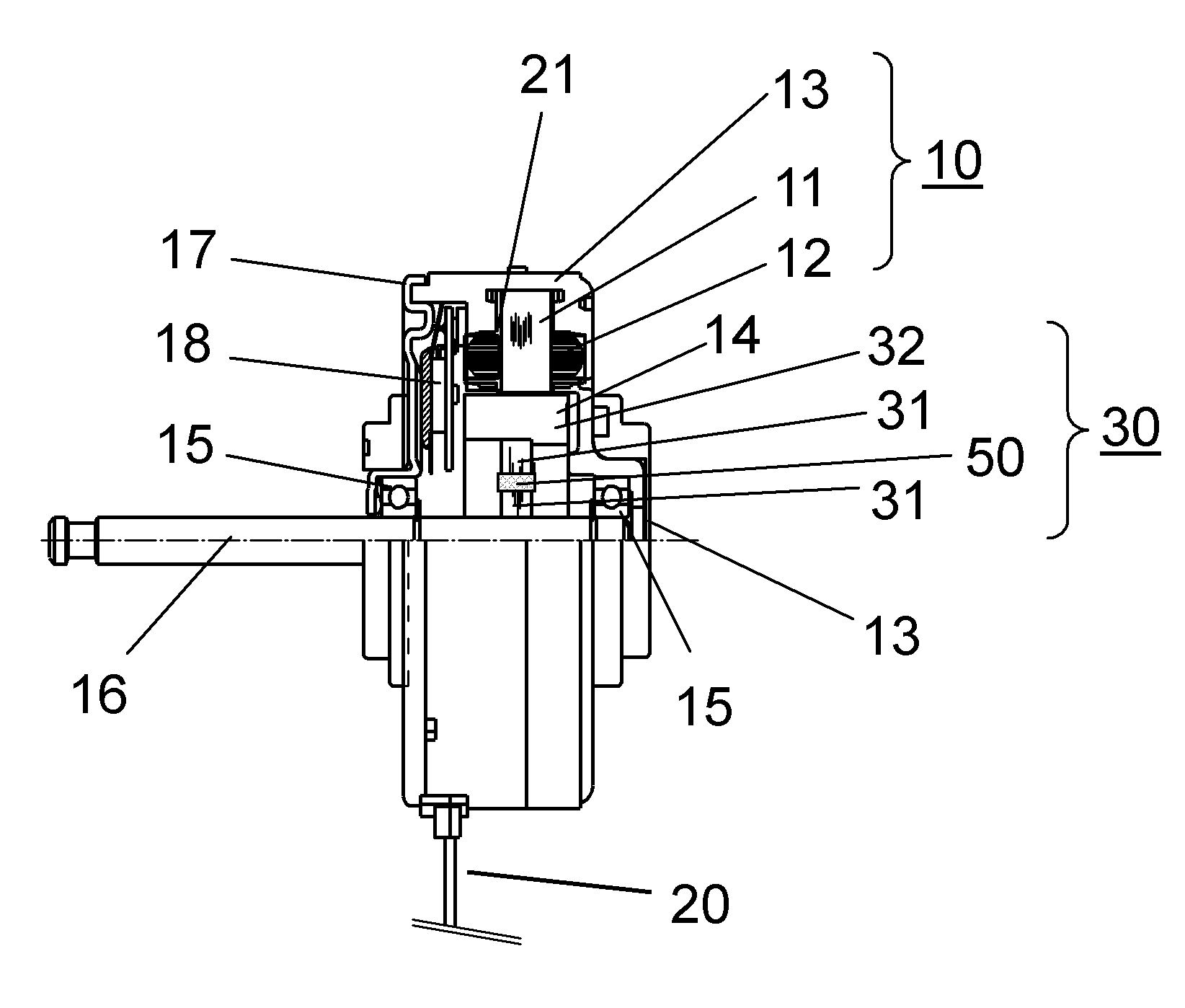
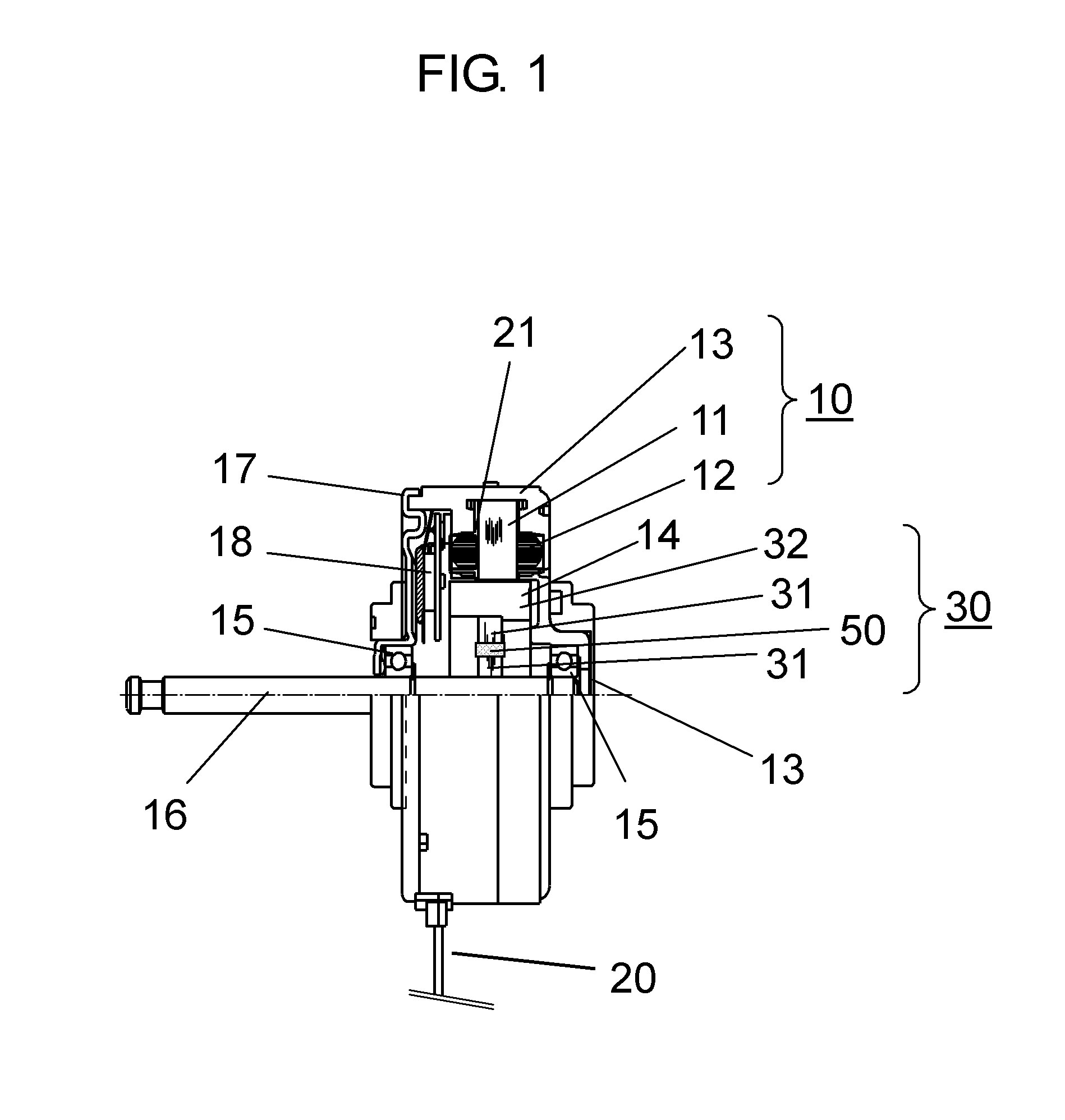
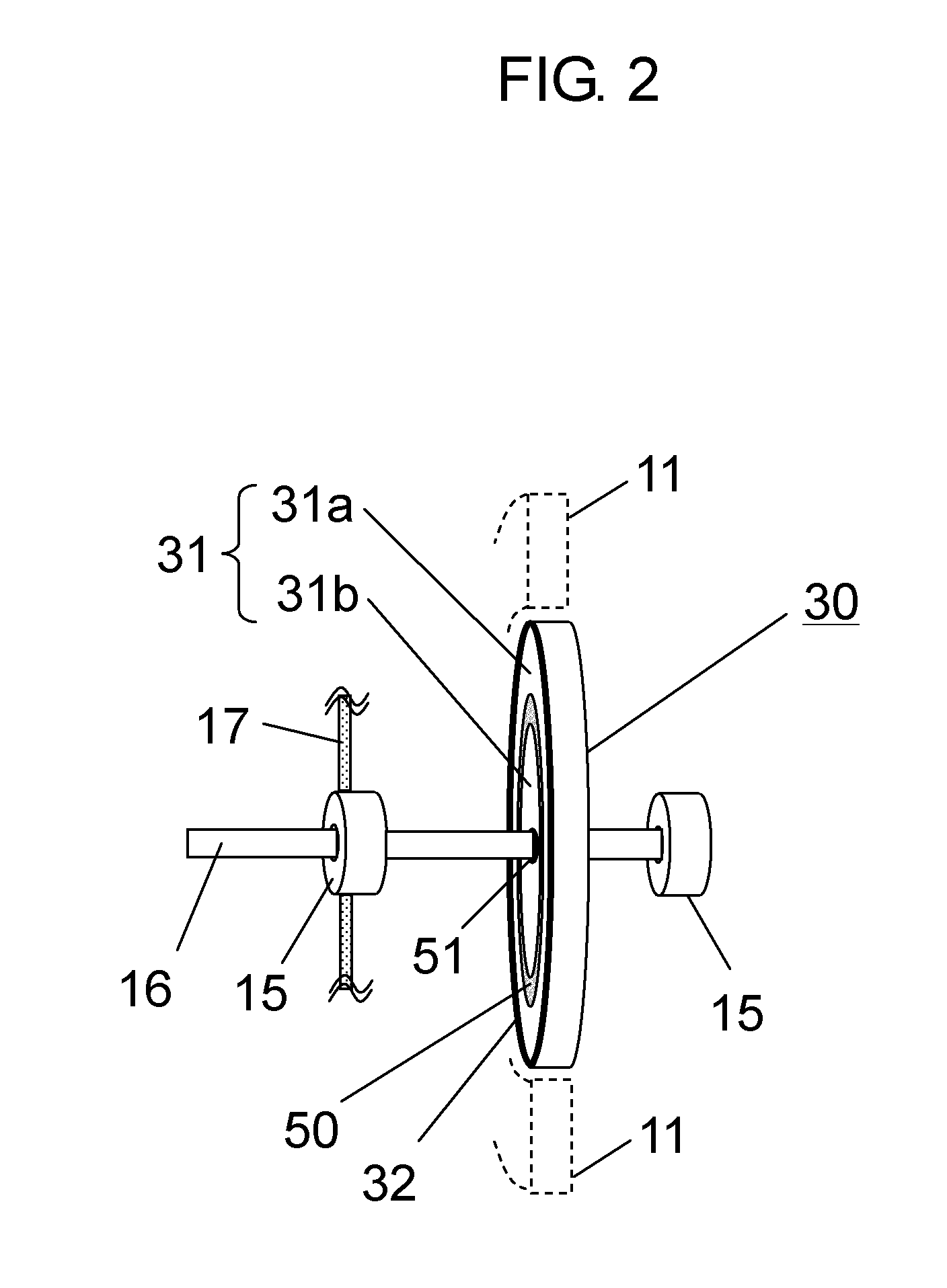
ActiveUS20110043071A1Preventing electrolytic corrosionImproving impedanceAssociation with grounding devicesMagnetic circuit rotating partsFixed bearingElectric machine
An electric motor includes a stator including stator steel core (11) around which a coil is wound; a rotor which includes rotating body (30) that holds a plurality of permanent magnets (32) in the circumferential direction to face the stator, and shaft (16) that fastens rotating body (30) so as to penetrate the center of rotating body (30); a bearing (15) for supporting shaft (16); and bracket (17) for fixing bearing (15), wherein dielectric layer (50) is provided between shaft (16) and the outer periphery of rotating body (30).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
NdFeB magnetic steel surface plating method
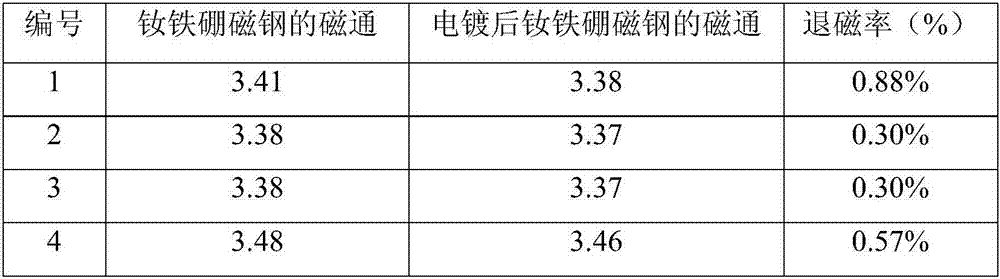
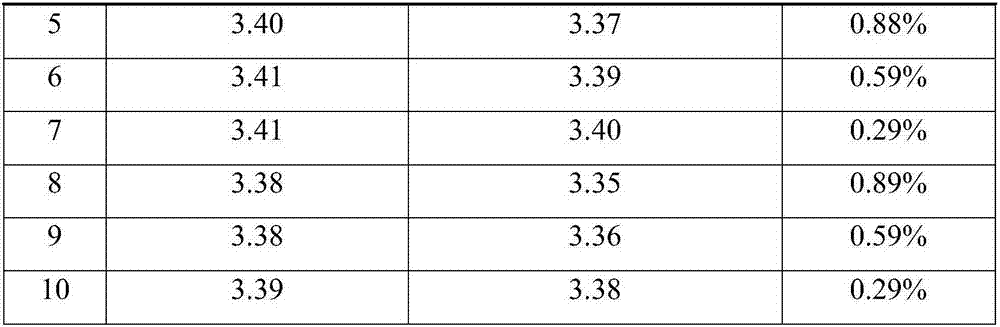
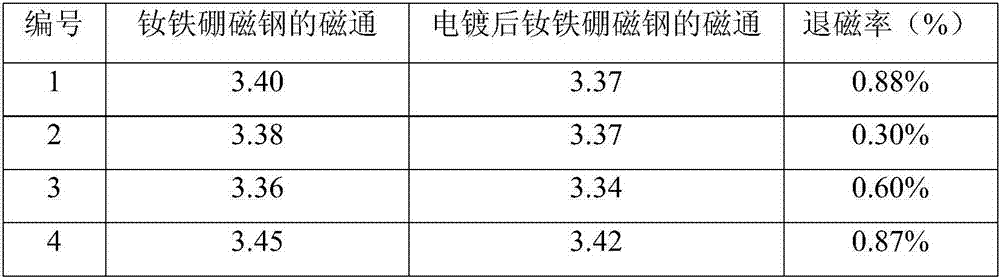
The invention discloses an NdFeB magnetic steel surface plating method. The method includes the steps that plating is conducted on an NdFeB magnetic steel surface, and a pre-galvanizing layer, a strong complexing copper or zinc alloy plating layer, a neutral nickel plating layer, a non-cyanide copper plating layer and a nickel plating layer are sequentially arranged from inside to outside; the galvanizing layer serves as a bottom layer, and then the strong complexing copper or zinc alloy plating layer is added, so that an NdFeB magnetic steel plating layer is high in bonding strength, high in preservative activity and small in magnetic loss. Through improvement, the binding force is increased by 10%-20% on average compared with a conventional process, and the average magnetic loss rate is lowered to 1%-5% from 5%-10% in the conventional process; and the quality of a magnetic steel surface electroplated layer is greatly improved, and the product percent of pass is increased.
Owner:陈治
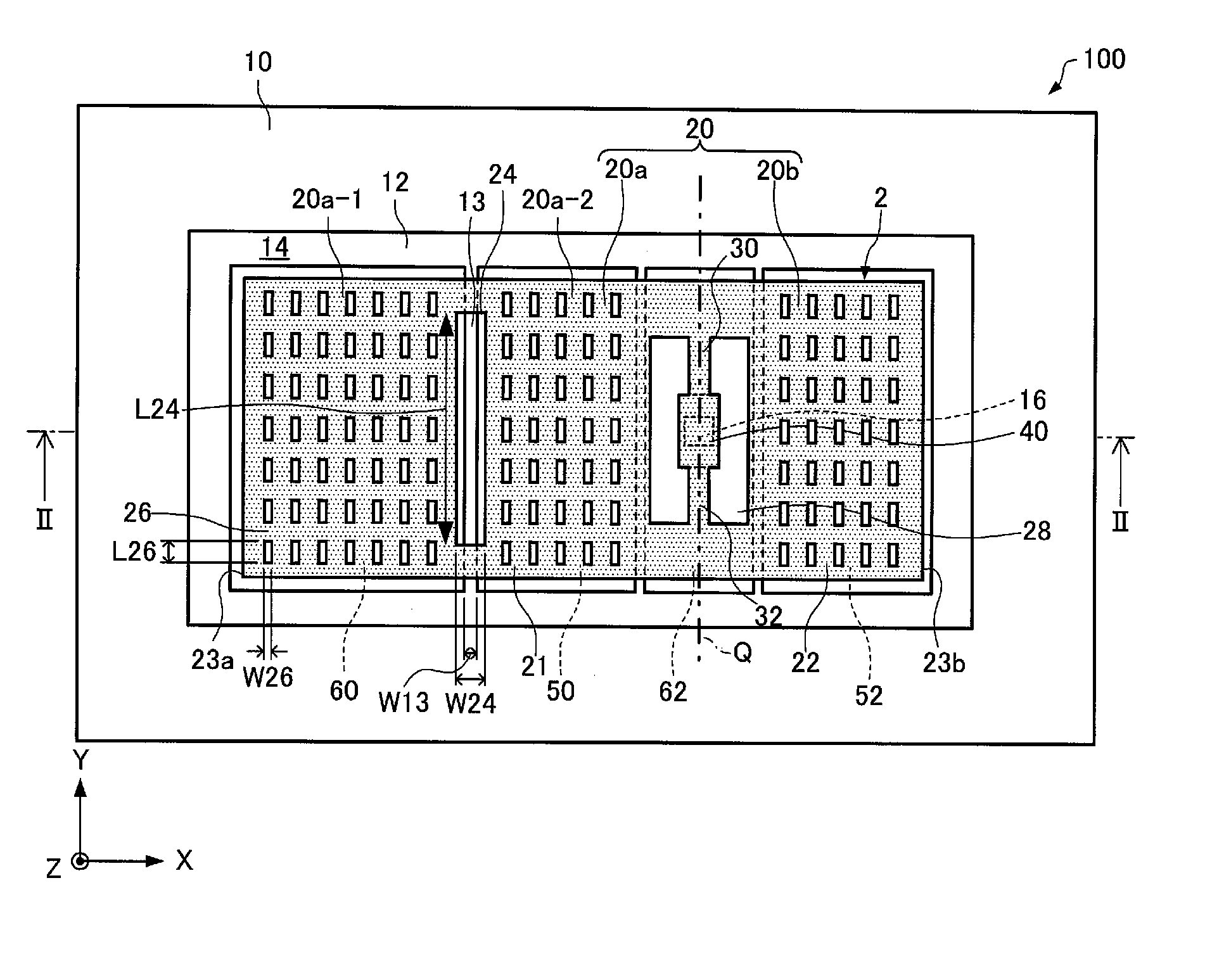
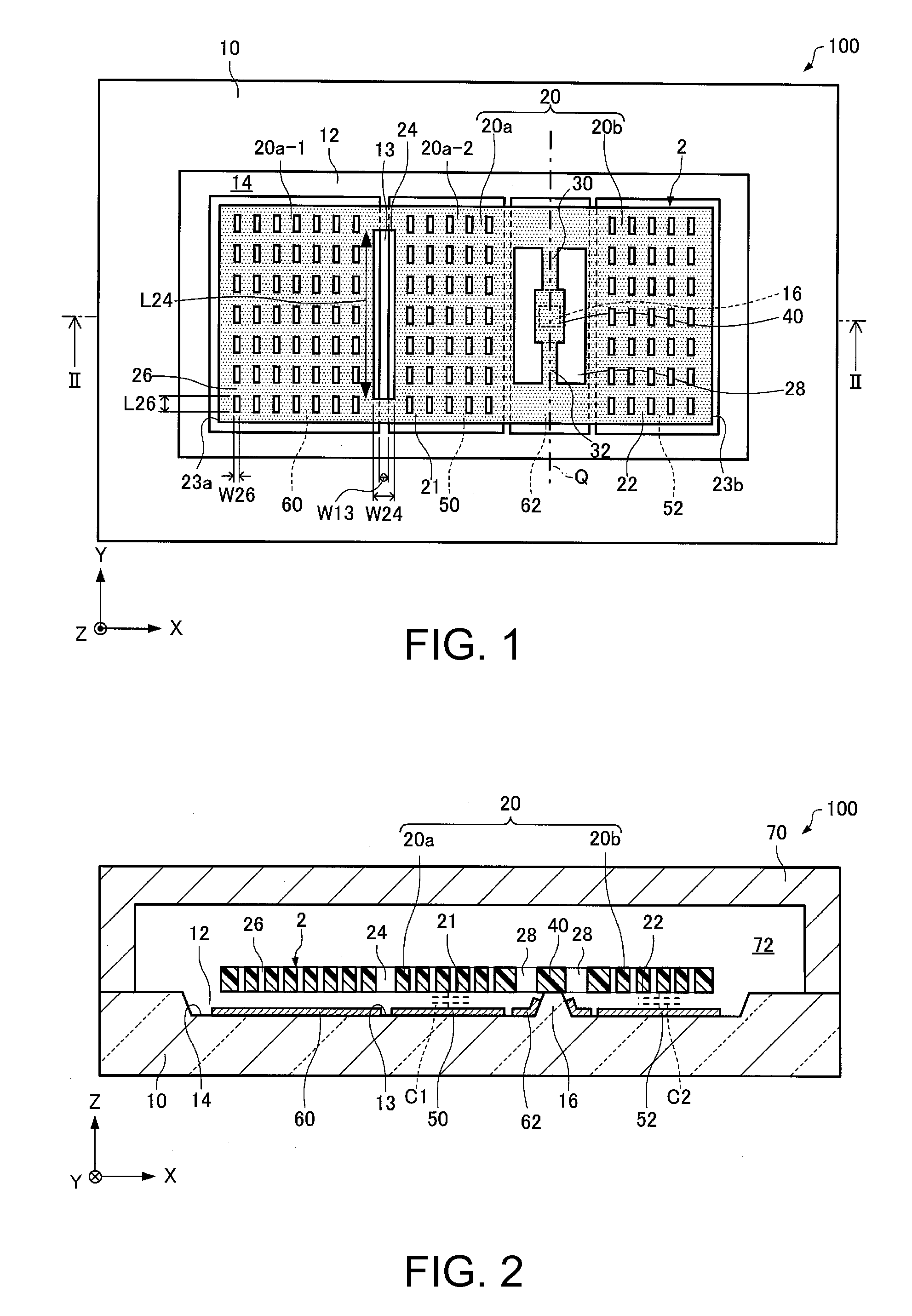
Functional element, electronic apparatus, and moving object
ActiveUS20150241466A1Improve reliabilityReduce adhesionAcceleration measurementPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesEngineeringElectrode
A functional element includes: a substrate; a movable body that includes a movable electrode portion; a support portion that supports the movable body; a first fixed electrode portion that is disposed on the substrate and a portion of which faces a first portion as one of portions of the movable body; a second fixed electrode portion that is disposed on the substrate and a portion of which faces a second portion as the other portion of the movable body; and a third fixed electrode portion that is disposed on the substrate and a portion of which faces the first portion. An opening that faces a region of the substrate between the first fixed electrode portion and the third fixed electrode portion is provided in the movable body, and the width of the opening is equal to or more than the width of the region.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for preparing babbitt alloy from residue containing silver of copper anode slime
InactiveCN102312097AEasy to separateLow costProcess efficiency improvementElectrolytic agentAntimony potassium tartrate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a babbitt alloy from residue containing silver of copper anode slime. The method comprises the following steps:1, adding sodium carbonate, powdered carbon and borax according to the mass of the residue containing silver, and uniformly mixing; 2, melting to obtain a crude alloy containing lead; 3, preparing an electrolyte from fluosilicic acid, lead fluorosilicate, stannous oxide and potassium antimonyl tartrate, and adding with gelatin and ethyl naphthol; 4, treating the crude alloy as an anode and a stainless steel plate as a cathode, and taking the cathode plate (the stainless steel plate) and peeling cathode products each 12h; and 5, adding lead, antimony and copper or tin, antimony and copper to the cathode products, and melting to obtain the lead-based or tin-based babbitt alloy. The method which has the advantages of short flow, low cost, and strong practicality and allows the lead-based or tin-based babbitt alloy to be prepared from the residue containing silver of the copper anode slime is especially suitable for anode slime processing in electrolyzing electronic wastes with regenerated copper, and has the characteristics of simple and feasible operation, and high recovery rate of valuable metals.
Owner:广东省资源综合利用研究所
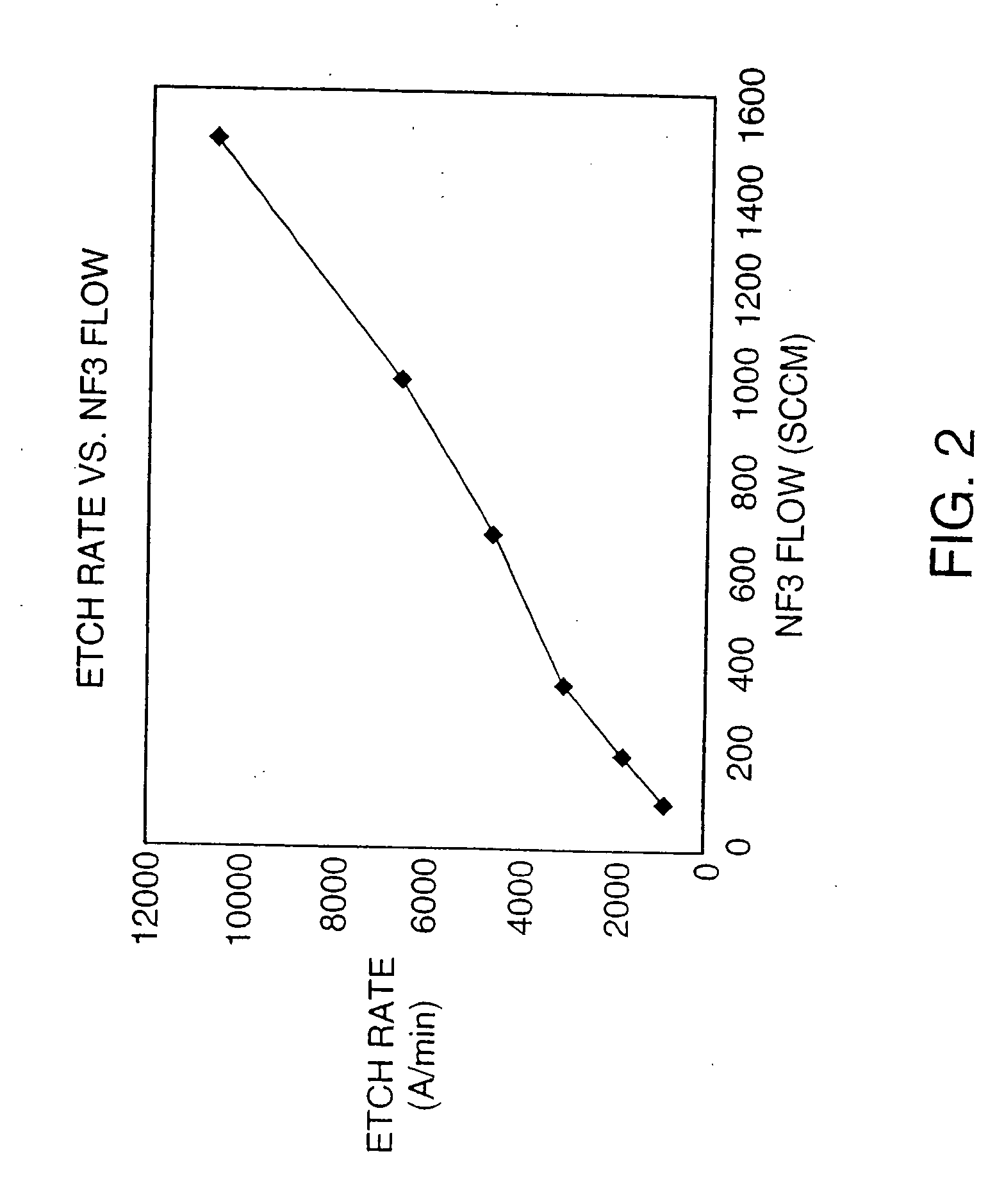
Method and apparatus for processing metal bearing gases
InactiveUS8779322B2Reduce potential differenceEasy to operateCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsMetallic materialsNitride
A method and apparatus for processing metal bearing gases involves generating a toroidal plasma in a plasma chamber. A metal bearing gas is introduced into the plasma chamber to react with the toroidal plasma. The interaction between the toroidal plasma and the metal bearing gas produces at least one of a metallic material, a metal oxide material or a metal nitride material.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Touch control display panel and touch control display device
ActiveCN106919287AReduce potential differenceImprove the display effectInput/output processes for data processingVoltage sourceDisplay device
Embodiments of the invention provide a touch control display panel and a touch control display device. A plurality of switches, each of which comprises a control terminal, an input terminal and an output terminal, are disposed between a common voltage source and common electrodes, wherein each control terminal is connected to a first control terminal, each input terminal is connected to a first input terminal, and each output terminal is connected to a corresponding touch control signal input pin; so that common voltage can be input into all common electrodes through a signal common voltage source in the display phase; and therefore potential difference among the common electrodes is reduced. In addition, according to the technical scheme, a plurality of touch control electrode test signals can be input into the plurality of common electrodes in the touch control test phase to complete the touch control test, and therefore an external equivalent test circuit is not required, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVIC OPTOELECTRONICS
Gate driving circuit of display
ActiveCN102610206AReduce potential differenceSolve the problem of driving voltage stabilityStatic indicating devicesDigital storagePotential differenceDisplay device
The invention discloses a gate driving circuit of a display, which is characterized in that at least one transistor is connected between a transistor providing a high potential node and a reference voltage signal input end in series, and a preset high potential is provided between the transistor that is connected to the node and an input end of the at least one transistor. For example, the drive voltage of a gate line corresponding to the gate is fed into the input end, and the preset high potential provided can reduce the potential difference between the source and the drain of the transistor, so that current leakage of the transistor can be reduced, and the stability of the drive voltage of the gate electrode driving circuit is further improved so as to improve the reliability of the gate electrode driving circuit.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com