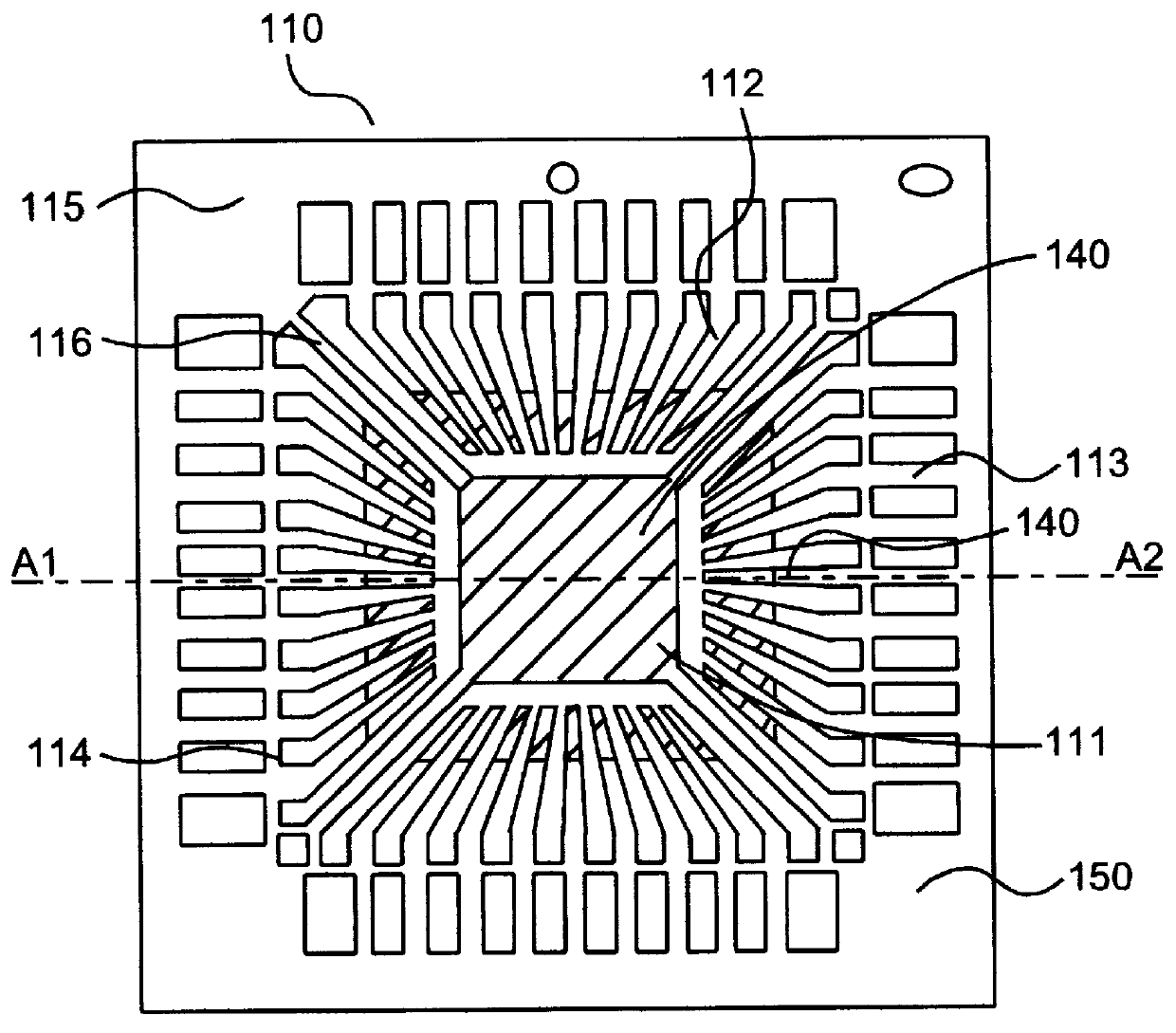
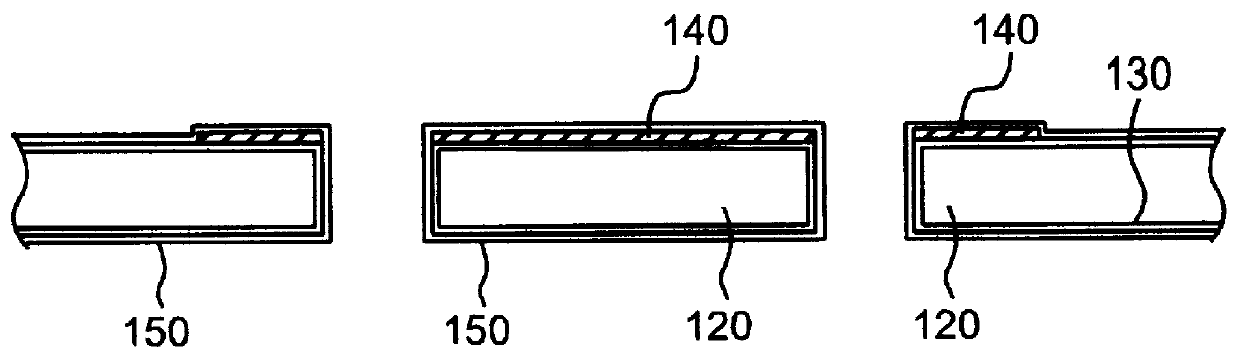
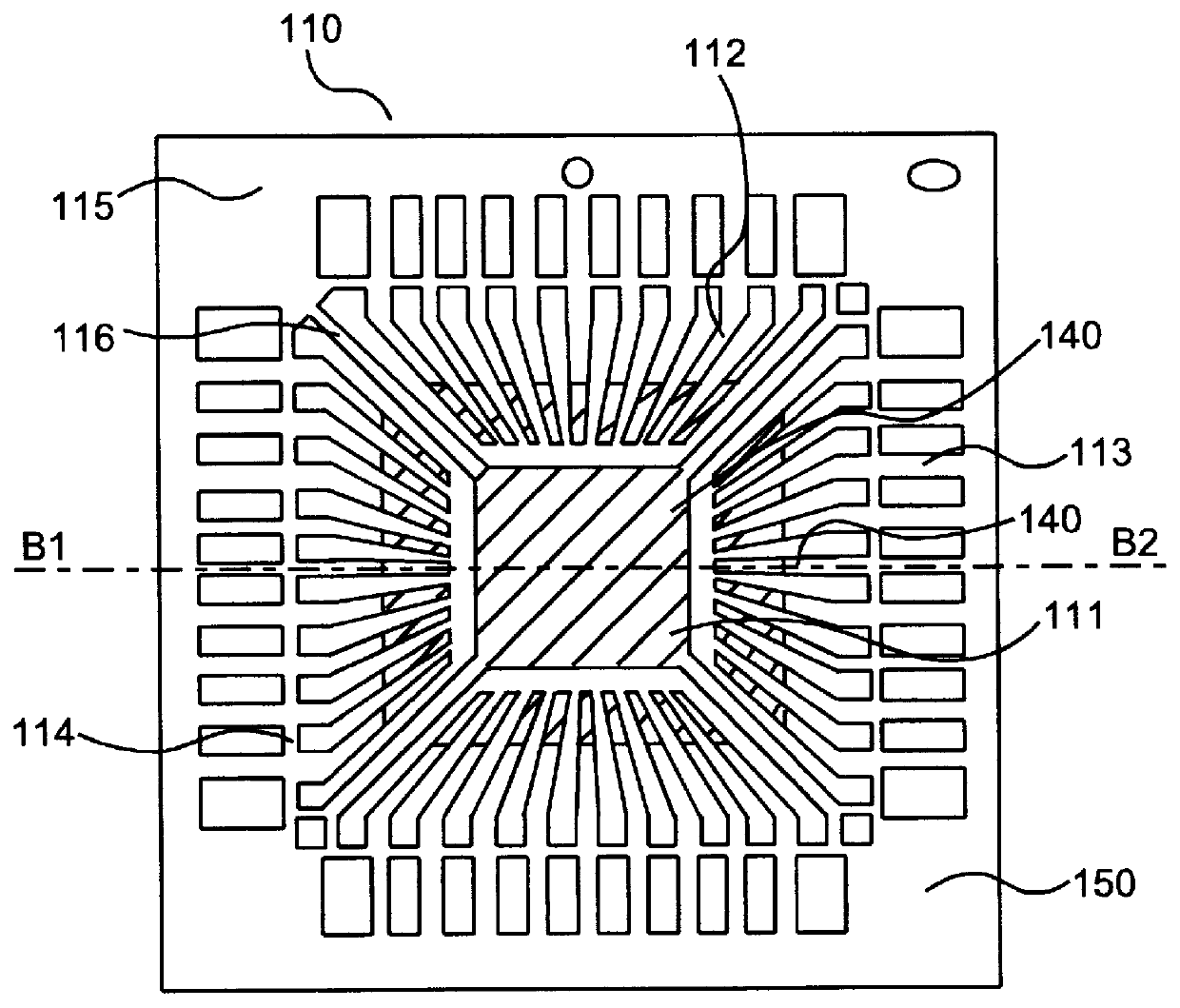
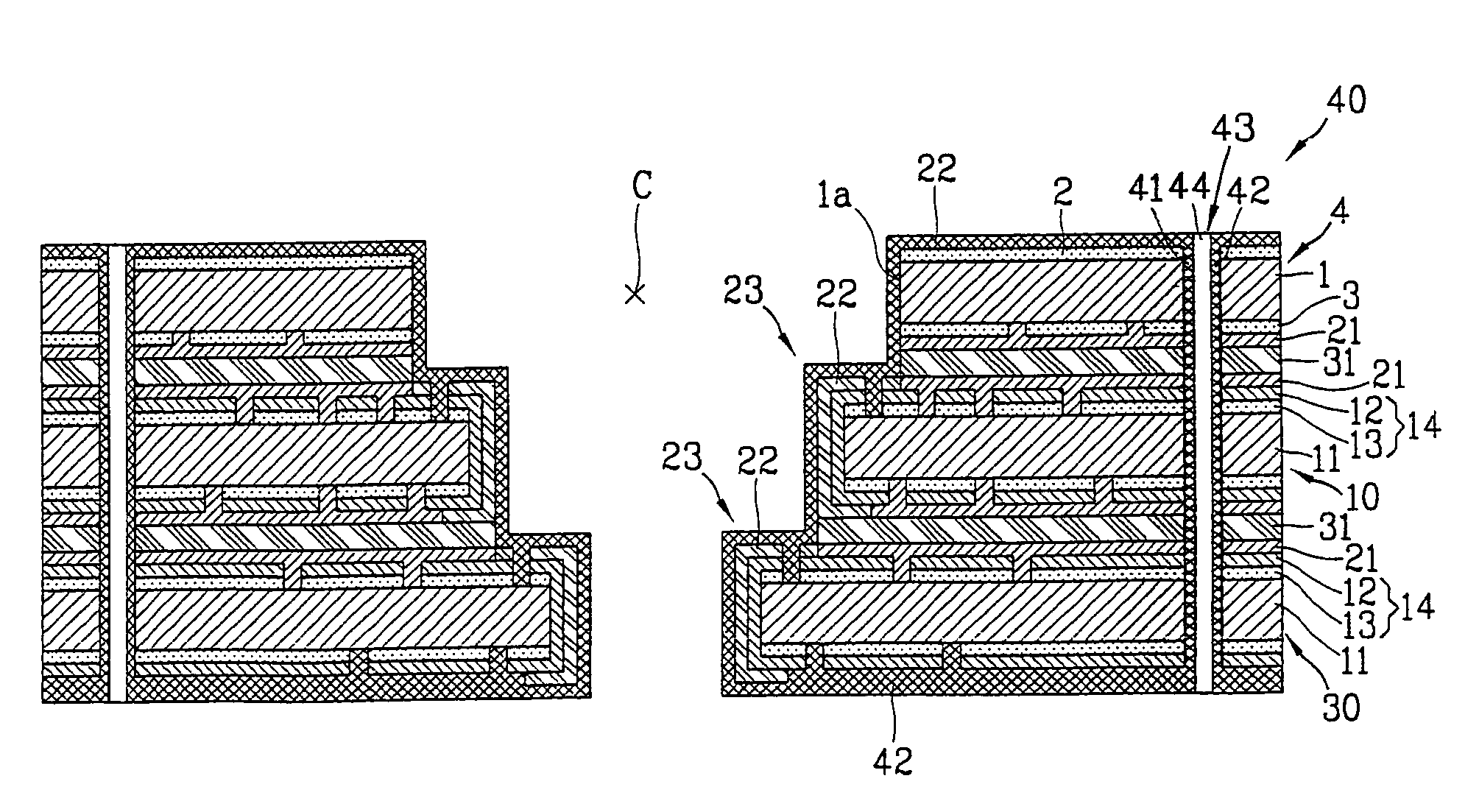
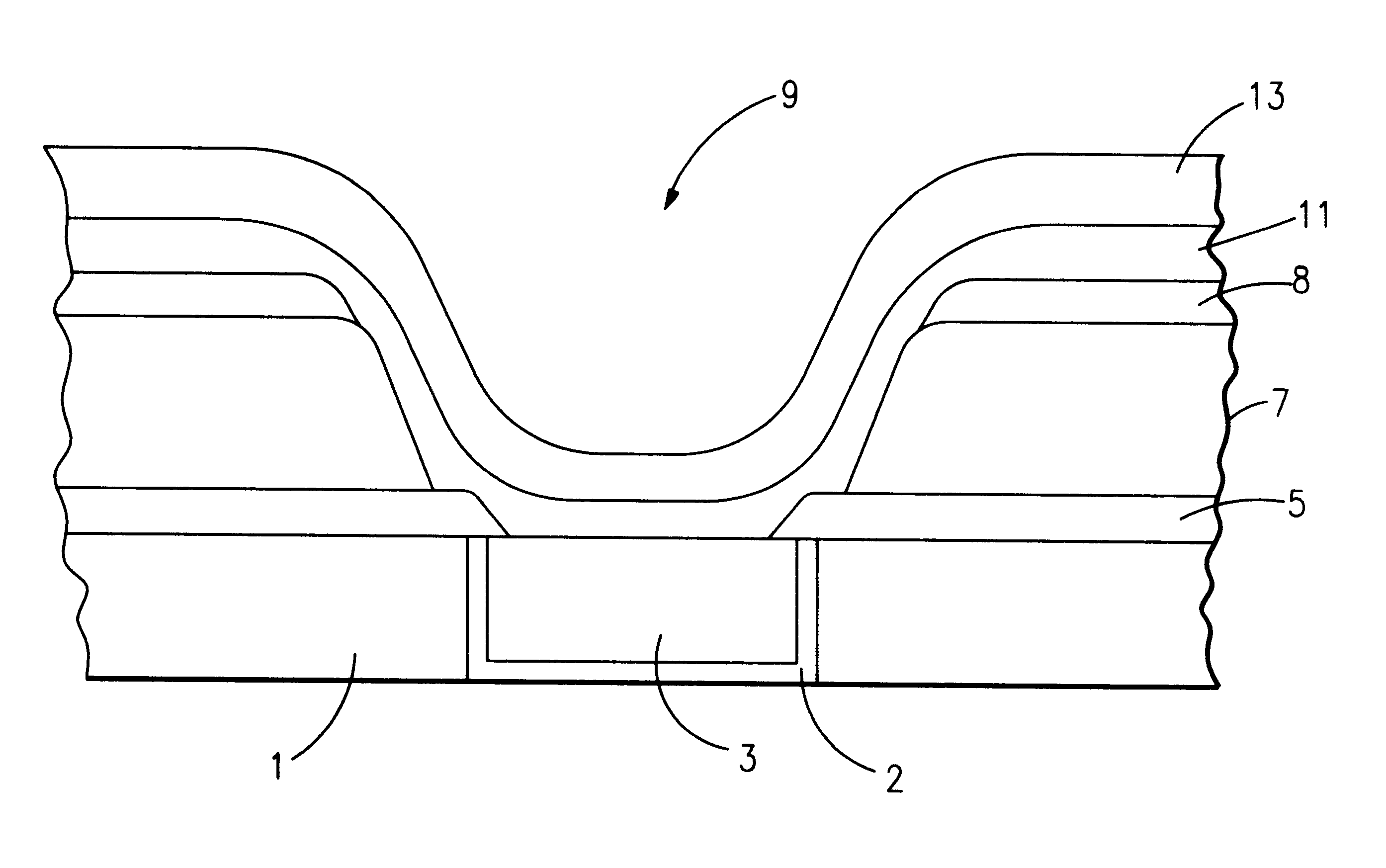
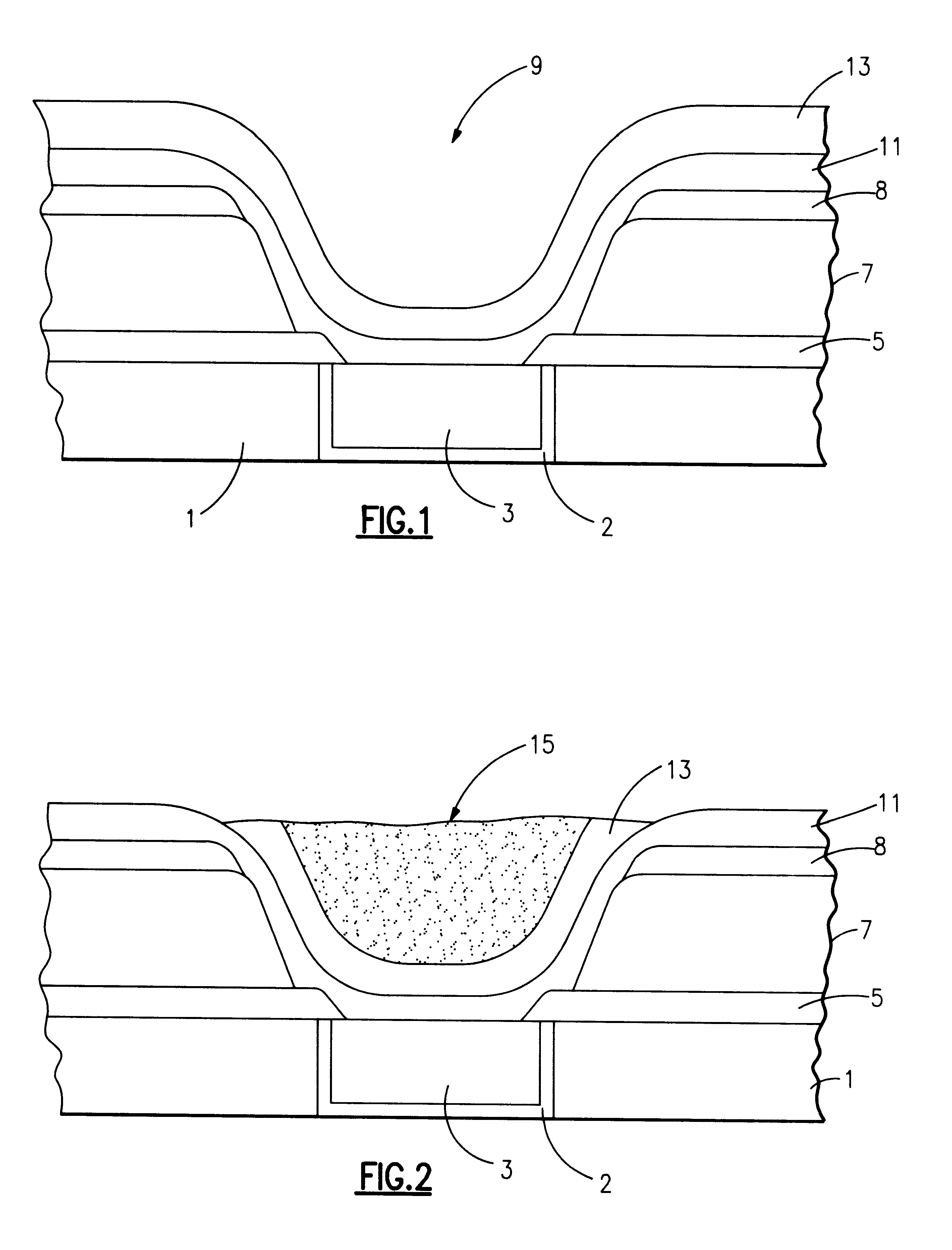
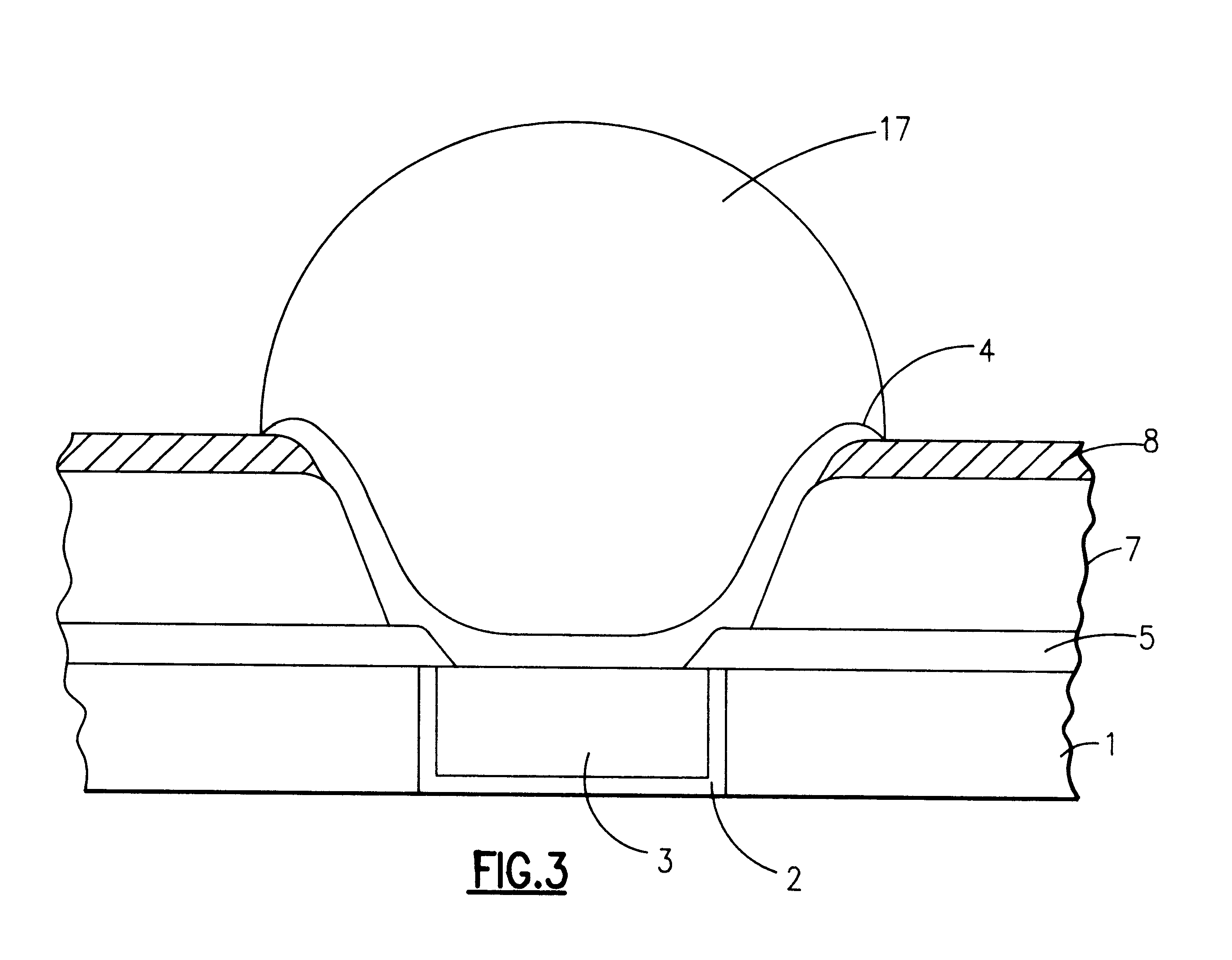
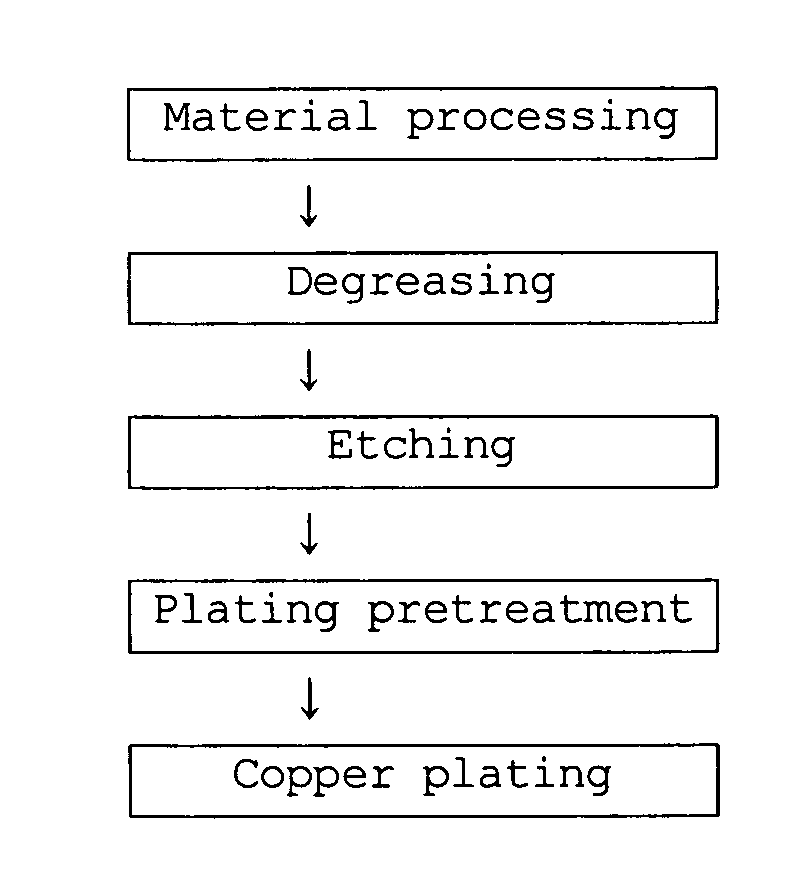
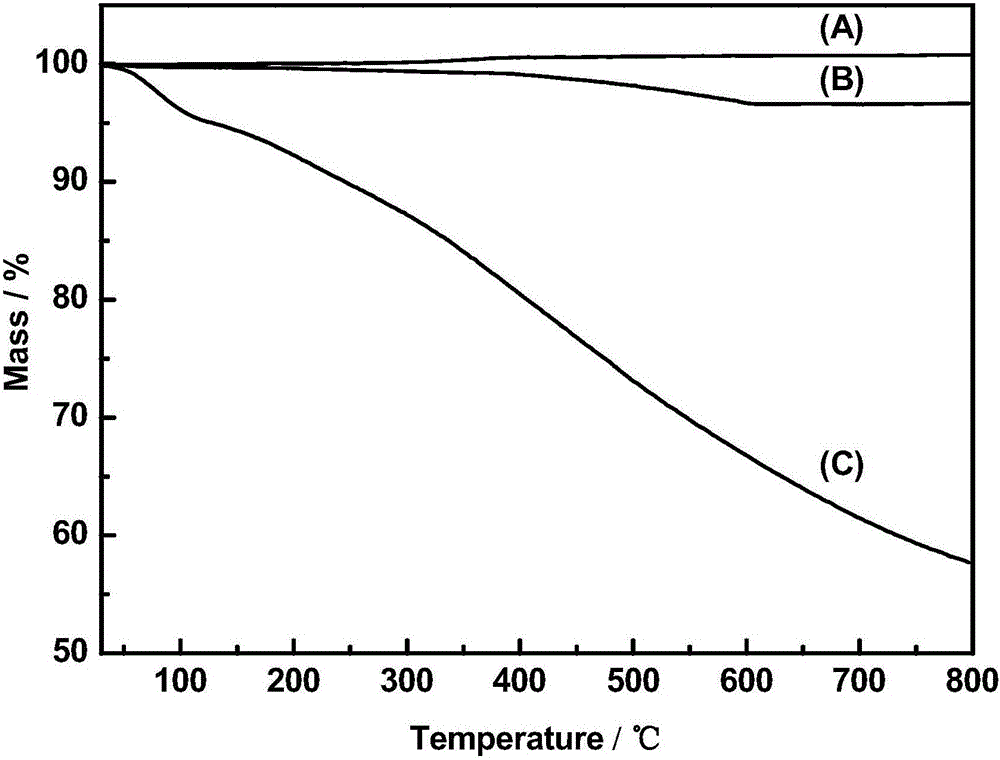
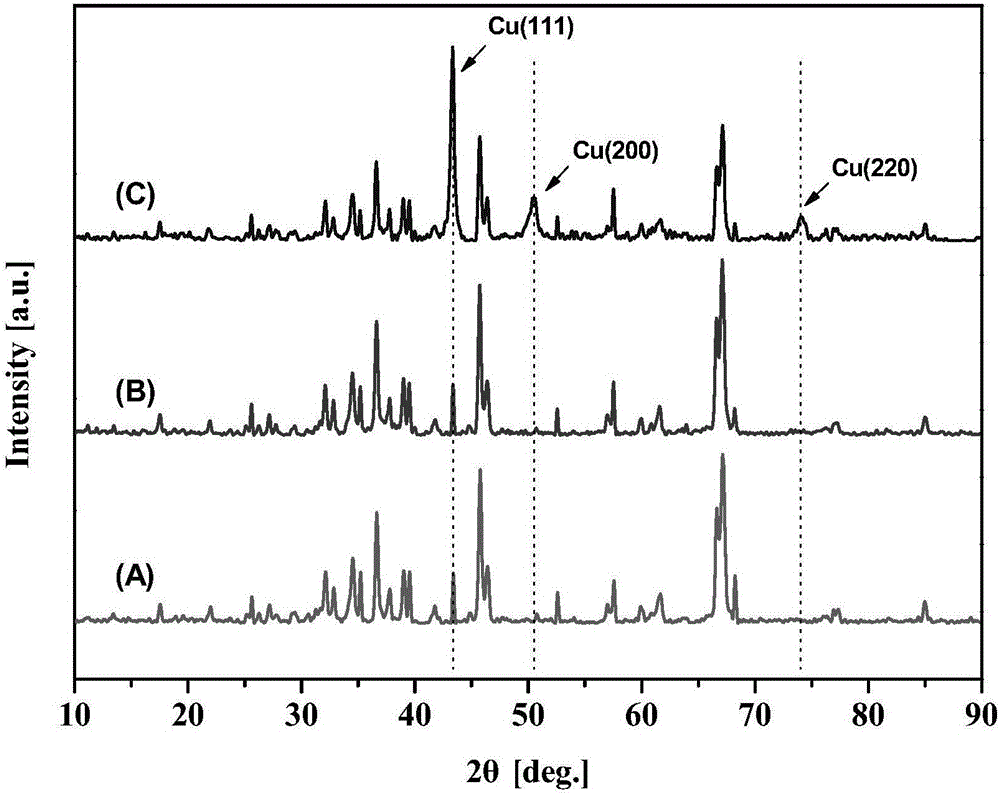
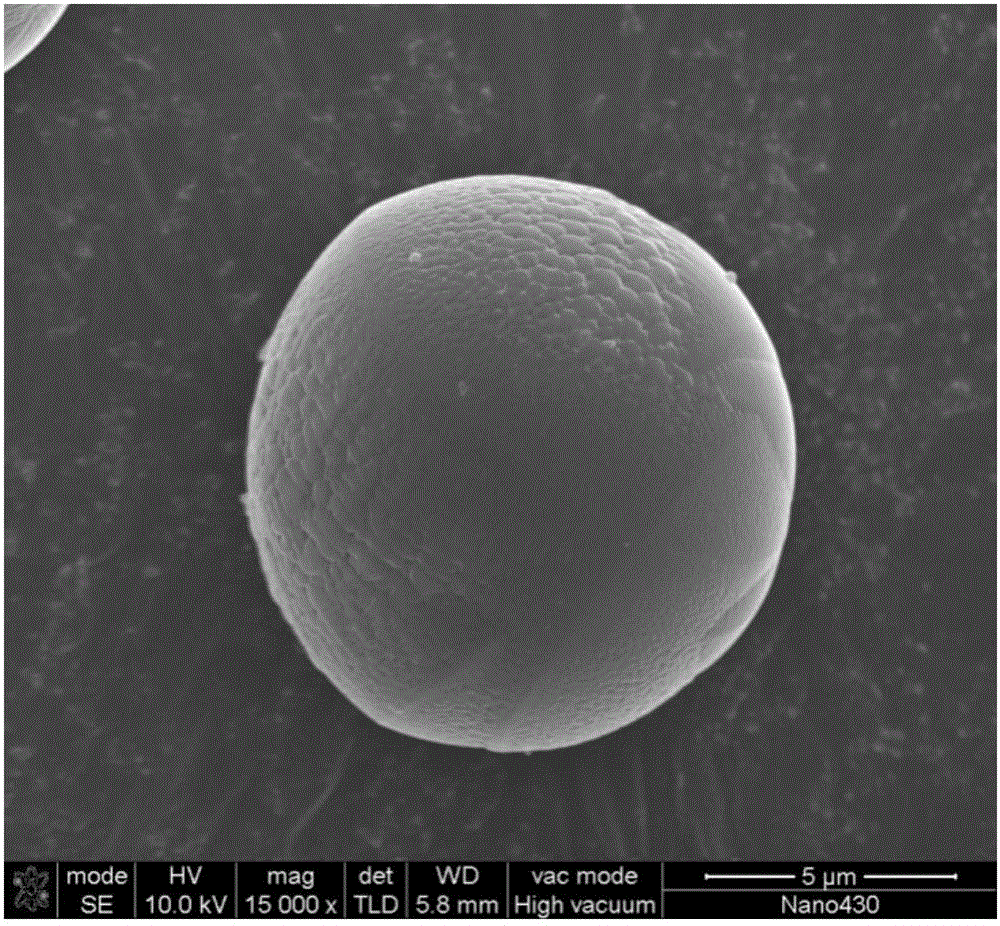
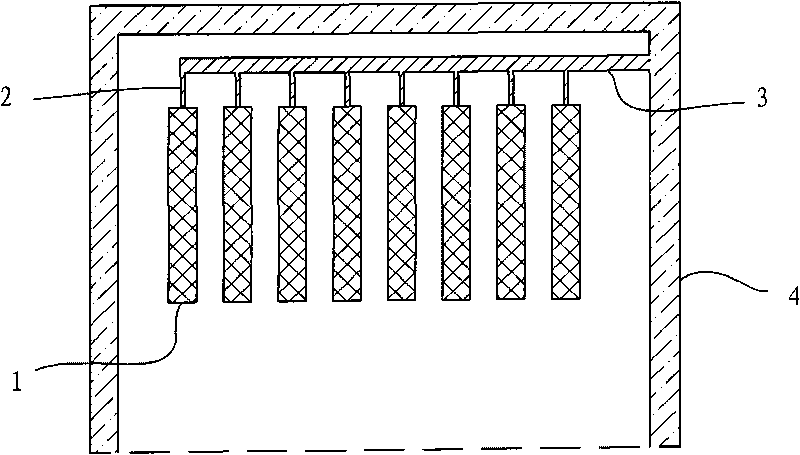
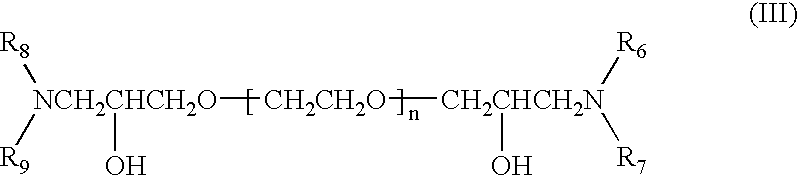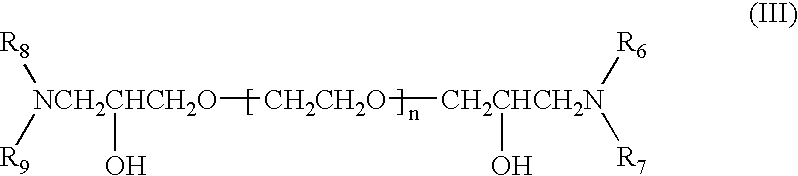Patents
Literature
4481 results about "Copper plating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
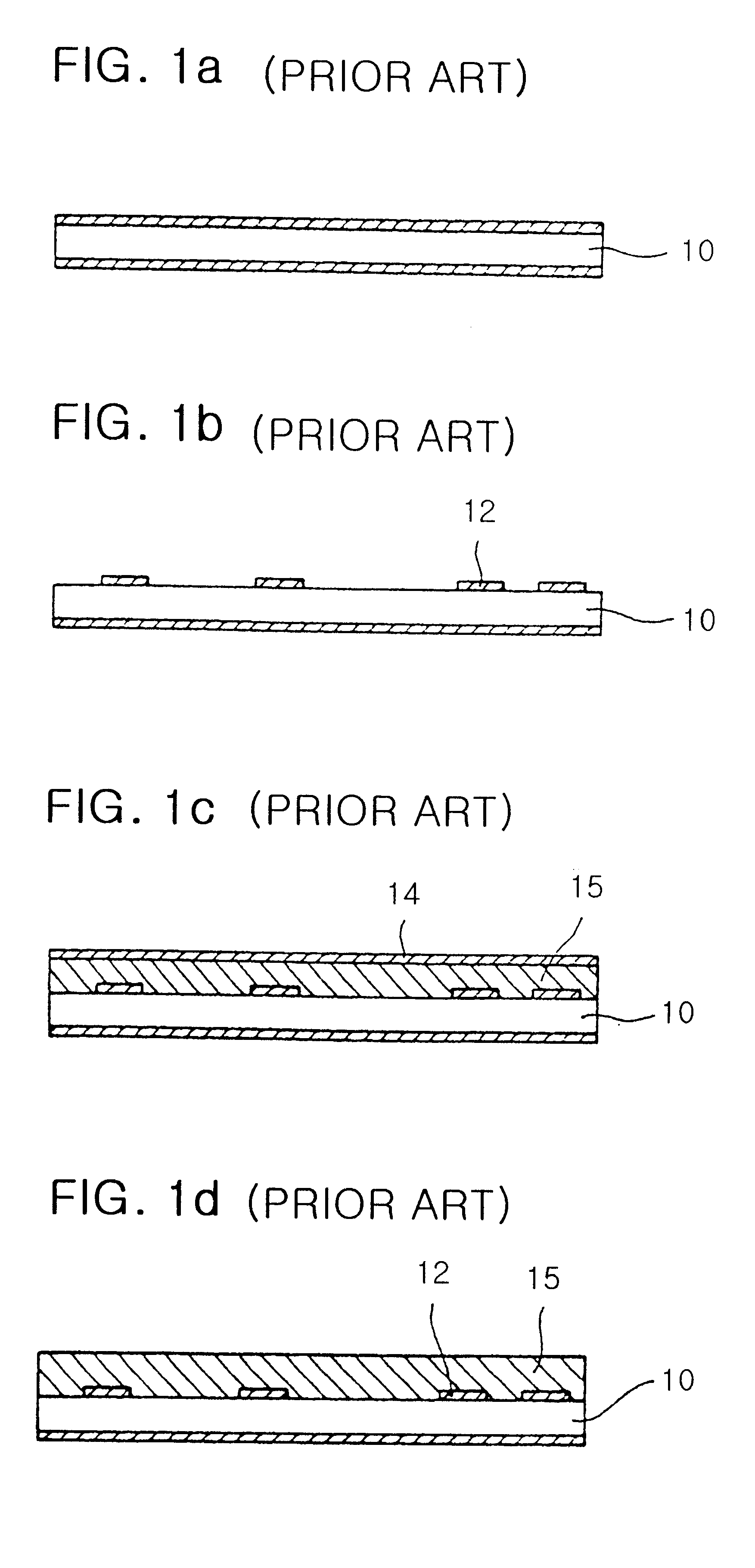
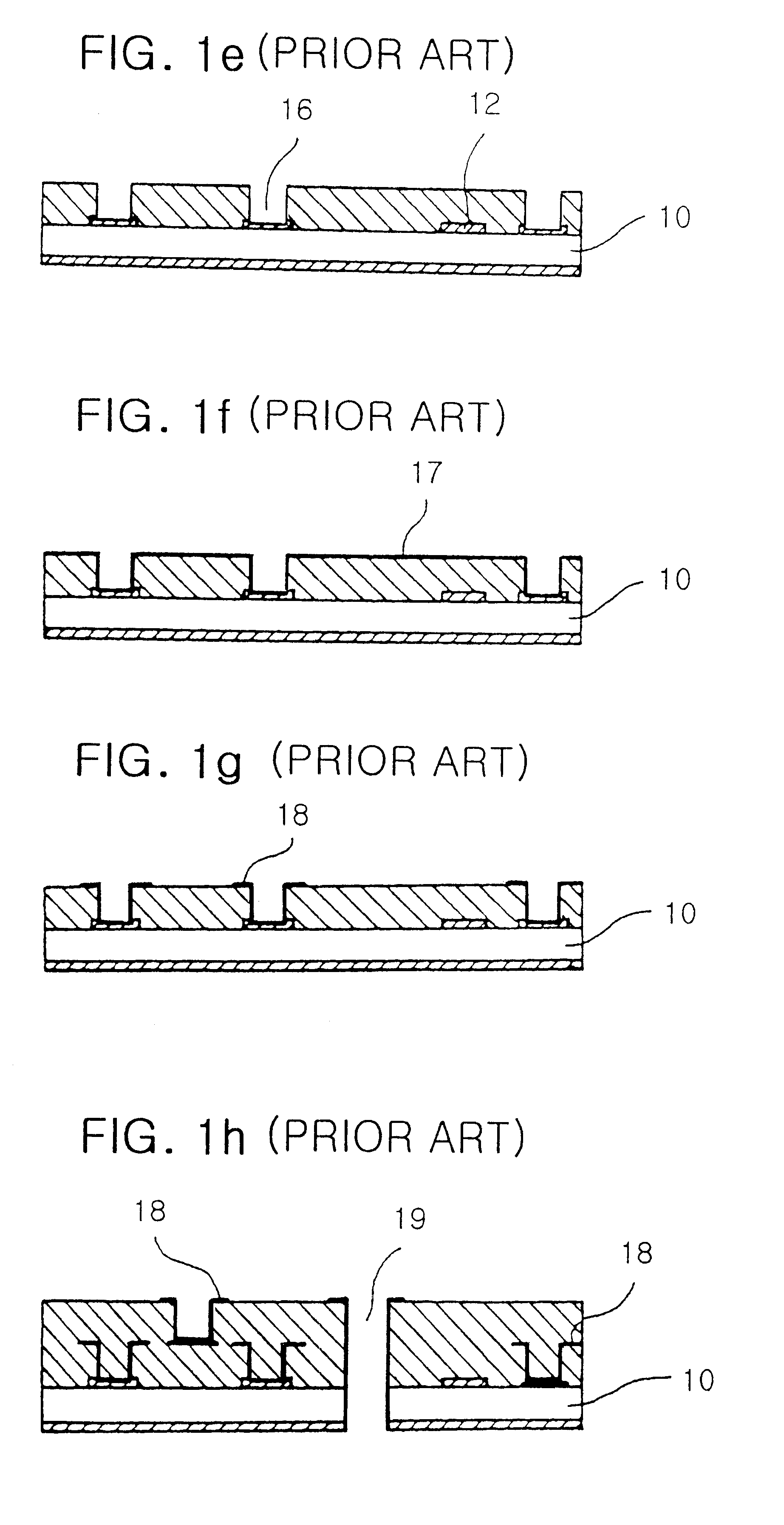
Copper plating is the process of plating a layer of copper electrolytically on the surface of an item. It takes place in an electrolytic cell where electrolysis which uses direct electric current to dissolve a copper rod and transport the copper ions to the item. Into a container of water are placed a copper rod, and the item. The water contains an ionic solution which allows a direct electric current to flow from the copper rod to the item. The copper rod is the anode and the item is the cathode. This current flow causes the copper to ionize, become oxidized which means each atom becomes positively charged by losing an electron. As the copper ions dissolve into the water, they form a coordination complex with salts already present. The copper then physically flows to the item, where it is reduced to the metallic state by gaining electrons. This forms a thin, solid, metallic copper film on the surface of the item.
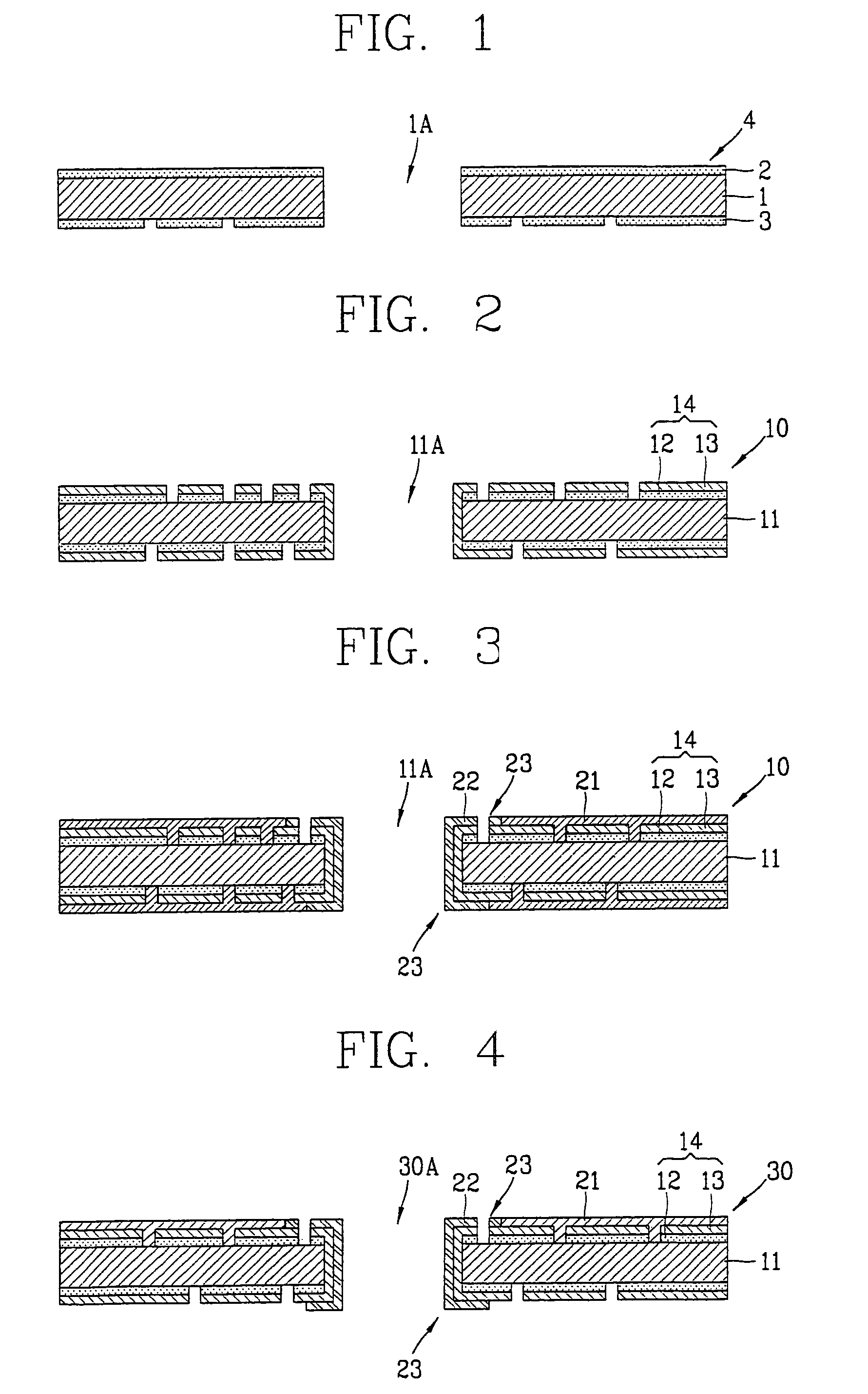
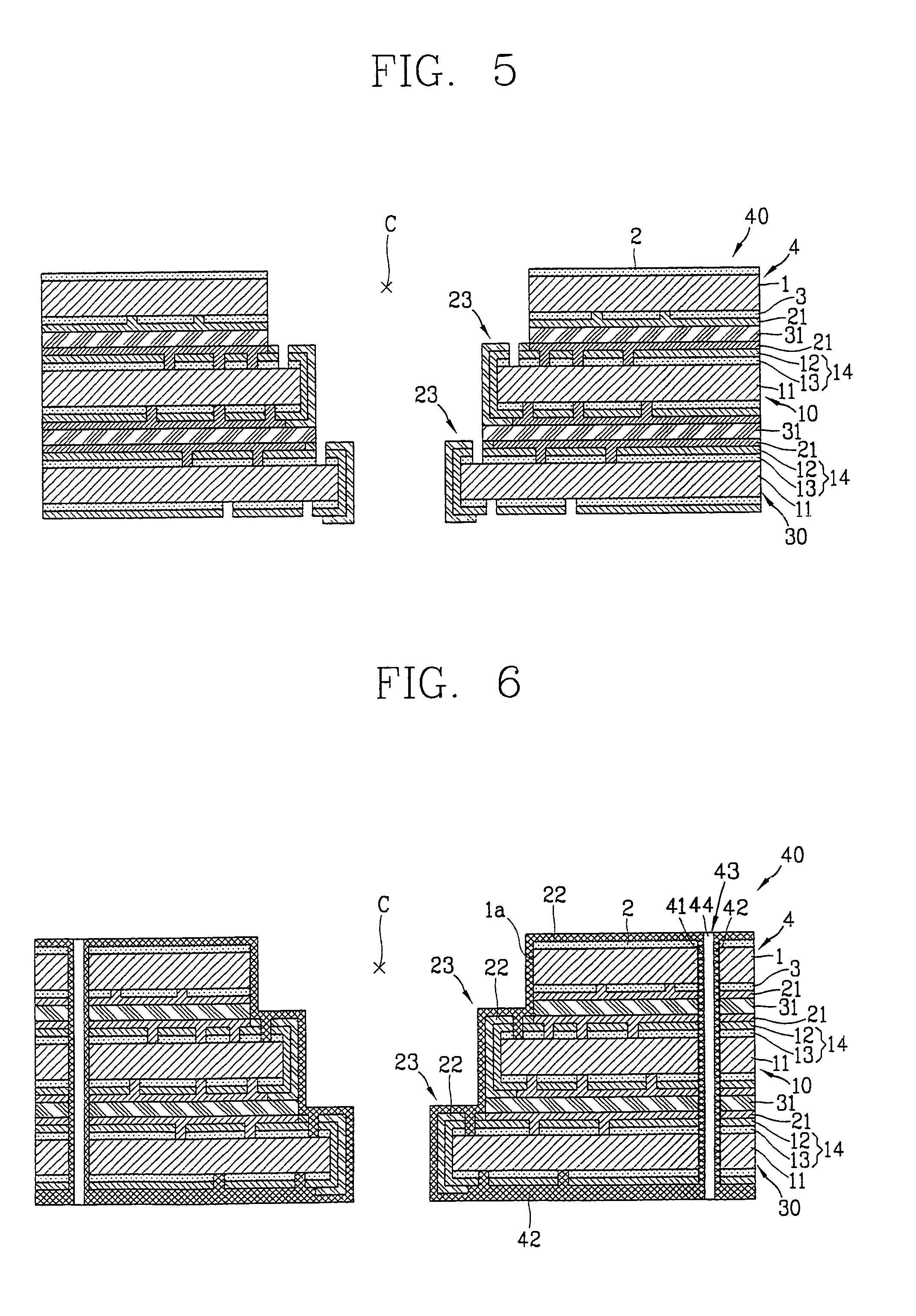
Method of electroless plating copper on nitride barrier
InactiveUS6436816B1Insulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSolid-state devicesCopper platingElectroless deposition
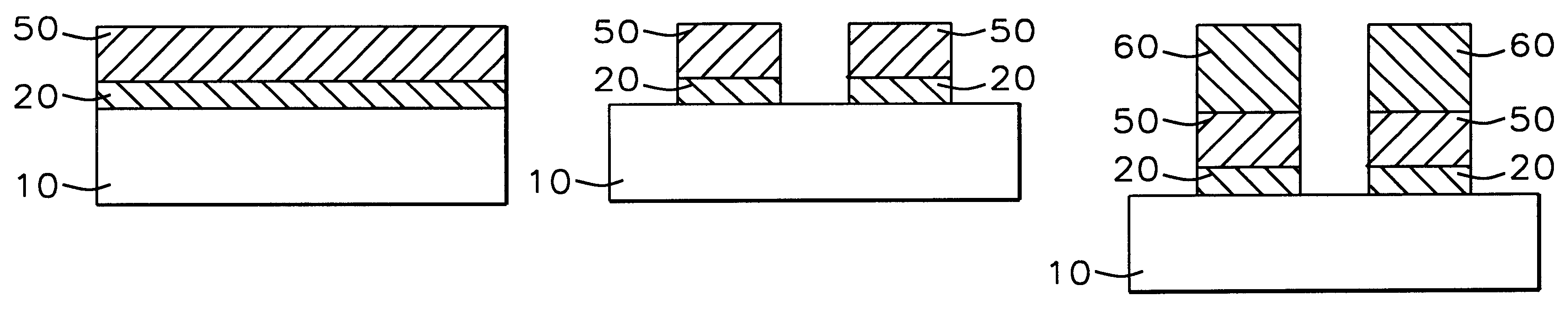
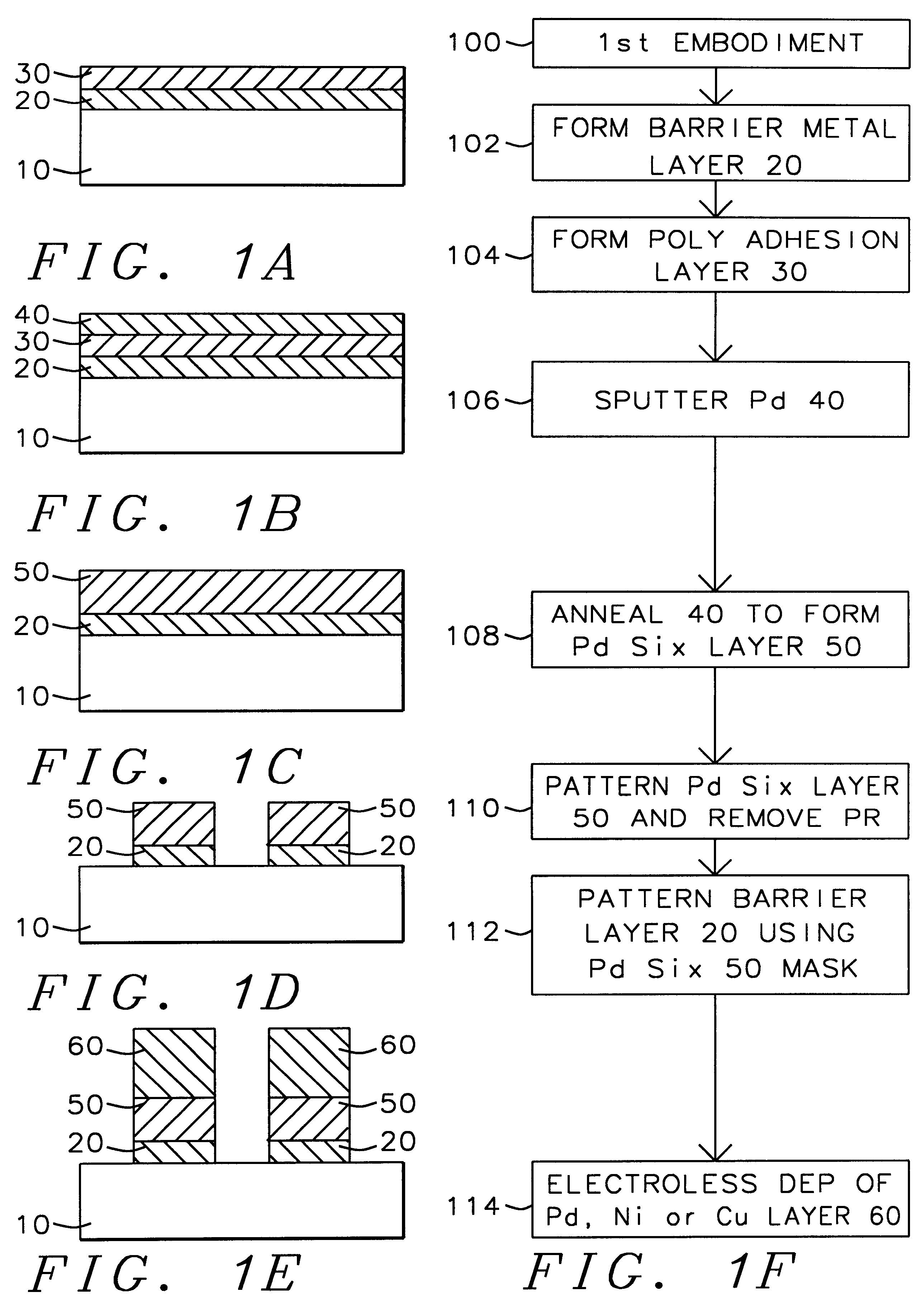
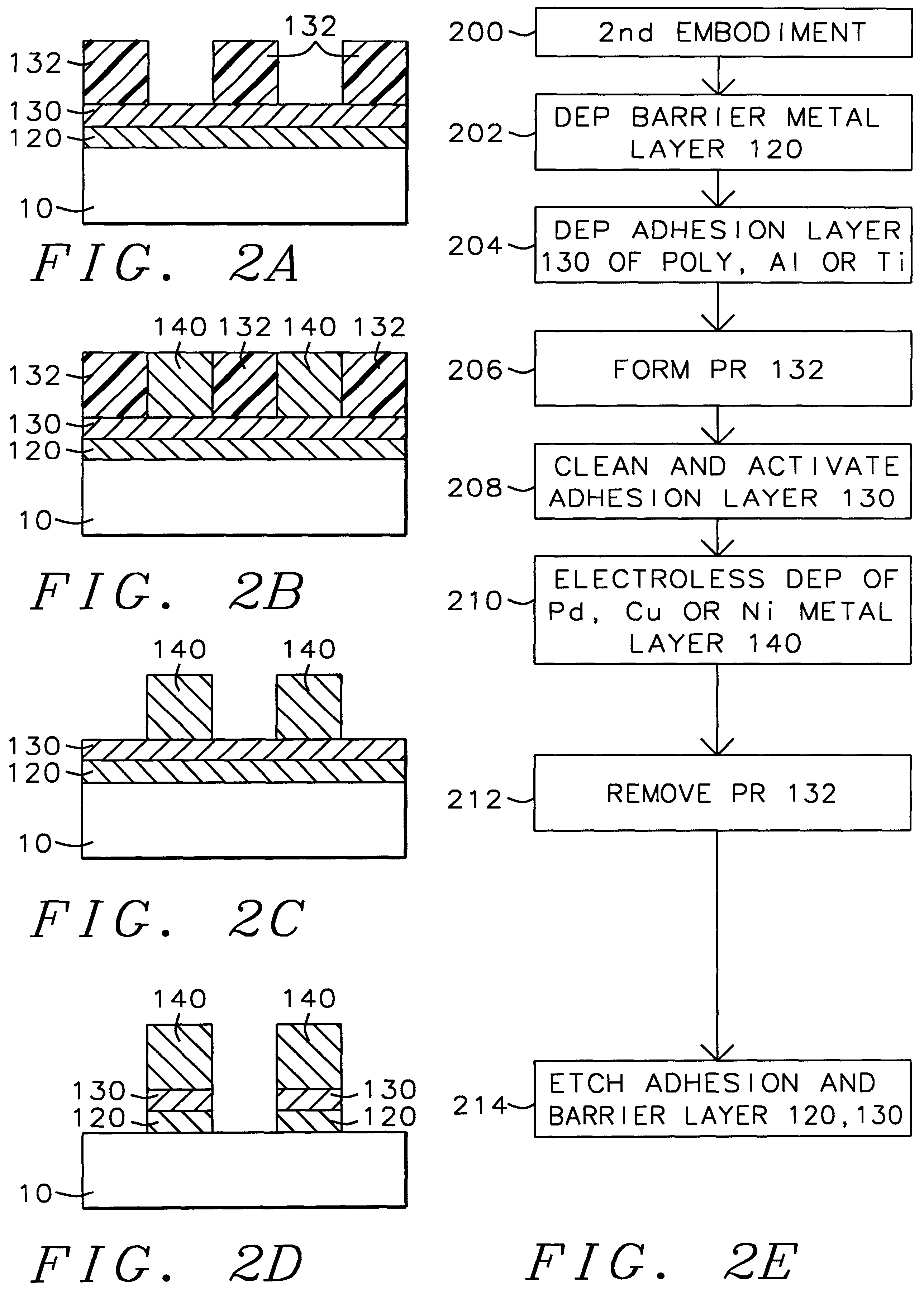
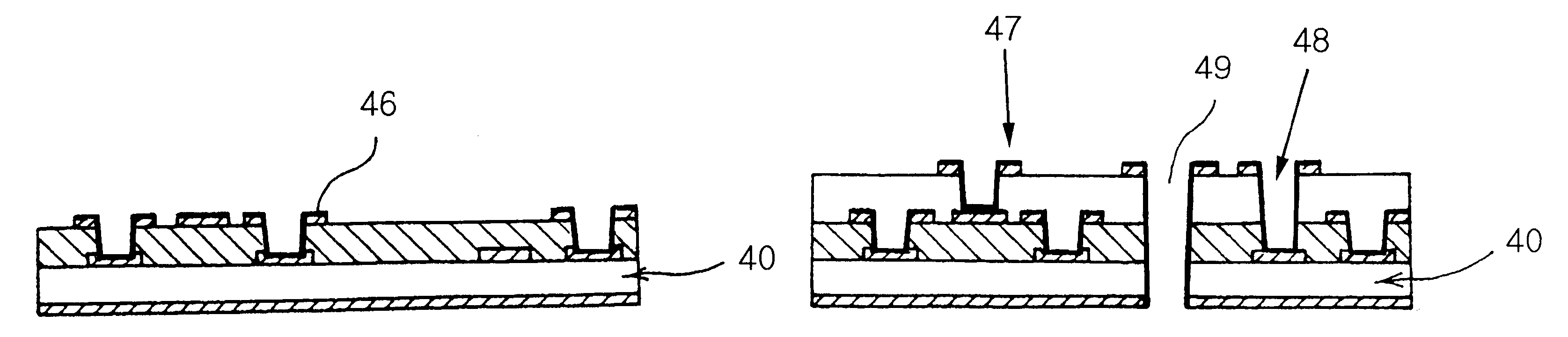
A method with three embodiments of manufacturing metal lines and solder bumps using electroless deposition techniques. The first embodiment uses a PdSix seed layer 50 for electroless deposition. The PdSix layer 50 does not require activation. A metal line is formed on a barrier layer 20 and an adhesion layer 30. A Palladium silicide seed layer 50 is then formed and patterned. Ni, Pd or Cu is electroless deposited over the Palladium silicide layer 50 to form a metal line. The second embodiment selectively electrolessly deposits metal 140 over an Adhesion layer 130 composed of Poly Si, Al, or Ti. A photoresist pattern 132 is formed over the adhesion layer. A metal layer 140 of Cu or Ni is electrolessly deposited over the adhesion layer. The photoresist layer 132 is removed and the exposed portion of the adhesion layer 130 and the underlying barrier metal layer 120 are etched thereby forming a metal line. The third embodiment electroless deposits metal over a metal barrier layer that is roughen by chemical mechanical polishing. A solder bump is formed using an electroless deposition of Cu or Ni by: depositing an Al layer 220 and a barrier metal layer 230 over a substrate 10. The barrier layer 230 is polished and activated. Next, the aluminum layer 220 and the barrier metal layer 230 are patterned. A metal layer 240 is electroless deposited. Next a solder bump 250 is formed over the electroless metal layer 240.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Leveler compounds
ActiveUS7128822B2No suppressed local platingOverplating is reduced or substantially eliminatedOrganic chemistrySpray nozzlesCopper platingMetal
Compounds that function to provide level or uniform metal deposits are provided. These compounds are particularly useful in providing level copper deposits. Copper plating baths and methods of copper plating using these compounds are also provided. These baths and methods are useful for providing a planarized layer of copper on a substrate having small apertures. The compositions and methods provide complete fill of small apertures with reduced void formation.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
Copper plating bath and plating method for substrate using the copper plating bath
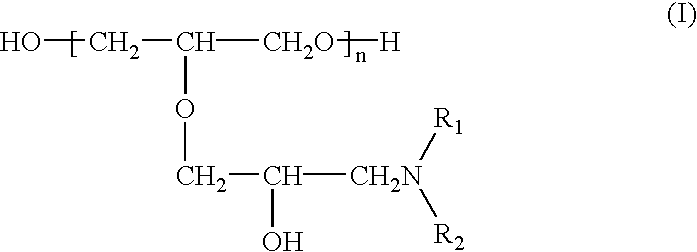
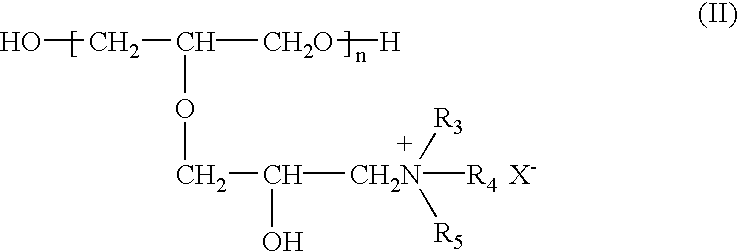
InactiveUS6800188B2Excellent characteristic and uniformityImprove reliabilityAnti-corrosive paintsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCopper platingGlycidyl ethers
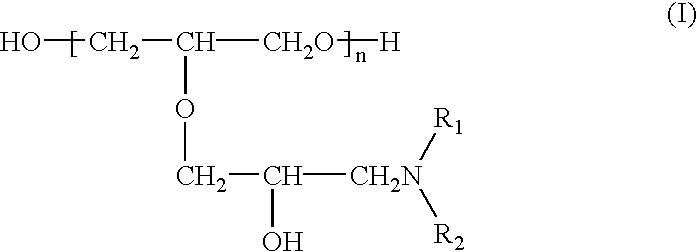
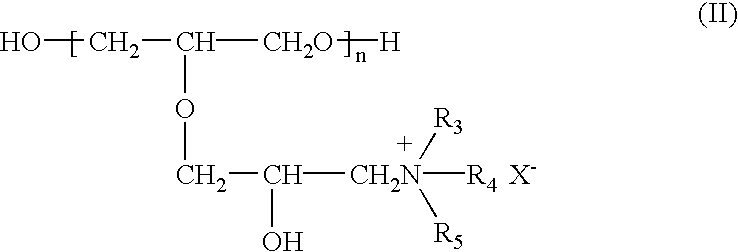
A copper plating bath comprising a reaction condensate of an amine compound and glycidyl ether and / or a quaternary ammonium derivative of this reaction condensate, and a plating method using this copper plating bath are disclosed. A copper plating bath capable of providing highly reliable copper plating on a substrate such as a silicone wafer semiconductor substrate or printed board having minute circuit patterns and small holes such as blind via-holes, through-holes, and the like, and a method of copper plating using the copper plating bath can be provided.
Owner:EBARA-UDYLITE CO LTD
Method for manufacturing build-up multi-layer printed circuit board by using yag laser
A method for manufacturing a build-up multi-layer printed circuit board is disclosed in which a YAG laser is used upon the formation of a via hole in the multi-layer printed circuit board, such that it can have the following advantages: the manufacturing process would become simple; the component packaging density and freedom for the design of the board would be improved; and a high speed of signal process would be ensured. The method for manufacturing a build-up multi-layer printed circuit board includes the steps of: forming a first printed circuit pattern on a copper clad laminate (CCL) by applying a general photo-etching process, the CCL having a copper foil on the one face thereof; stacking a resin-coated (on one face) copper foil (RCC) on the CCL with the first printed circuit pattern formed thereon, and heating and pressing this structure; irradiating a YAG laser to the board with said RCC stacked so as to form a via hole at a predetermined position by removing said RCC; carrying out an electroless and electro copper plating on the board with the via hole formed therein to form a plated layer; and forming a second printed circuit pattern on said plated layer to electrically connect the layers on which the first and second printed circuit patterns are formed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Process for electroless copper deposition
InactiveUS20070099422A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper platingRuthenium
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for depositing a copper material on a substrate by an electroless deposition process and also provide a composition of an electroless deposition solution. In one embodiment, the copper material is deposited from an electroless copper solution that contains an additive, such as an inhibitor, to promote a bottom-up fill process. In one aspect, the field of the substrate may be maintained free of copper material or substantially free of copper material during the electroless deposition process. Prior to the electroless deposition process for forming the copper material, a barrier layer may be deposited on the substrate, and thereafter, a ruthenium layer may be deposited thereon. In one example, the copper material is formed during a bottom-up, electroless deposition process directly on the ruthenium layer. Alternatively, a seed layer may be formed on the ruthenium layer prior to depositing the copper material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Lead frame, method for partial noble plating of said lead frame and semiconductor device having said lead frame
InactiveUS6034422ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper platingPalladium
A lead frame for a semiconductor device, made of a copper alloy, capable of preventing the creation of delamination between encapsuling resin and attributable to a lead frame without sacrificing the wire bondability and, a process for producing the lead frame and a semiconductor device using the lead frame. According to the present invention, (1) there is provided a lead frame for a plastic molded type semiconductor device, made of a copper alloy material partially plated with at least one noble metal, for wire bonding or die bonding purposes, selected from silver, gold, and palladium, wherein the whole area or a predetermined area of the surface of the copper at least on its side to be contacted with a encapsuling resin has a thin noble metal plating of at least one member selected from silver, gold, platinum, and palladium. (2) A copper strike plating is provided as a primer plating for the partial noble plating, a copper plating is provided on the thin noble metal plating, and the partial noble metal plating is provided on the copper plating in its predetermined area. (3) A die pad for mounting a semiconductor chip is provided, a partial silver plating is provided, and a zinc flash plating and a copper strike plating are provided in that order at least one on the surface of copper in the back surface of the die pad remote from the surface on which the semiconductor chip is mounted.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Method for fabricating semiconductor package and semiconductor package
InactiveUS7049178B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper platingSemiconductor chip
A method of fabricating a semiconductor package is disclosed in which a first Ni—Au plating is formed on a bonding pad for connection with a semiconductor chip, without a mechanical process or a masking operation. The method applies a copper plating on a through bore and the bonding pad, where the copper plated layer formed on the bonding pad is selectively removed, and then a second Ni—Au plating is formed on the bonding pad and a ball pad.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Multiple-step electrodeposition process for direct copper plating on barrier metals
InactiveUS20050006245A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCopper platingAdemetionine
Embodiments of the invention teach a method for depositing a copper seed layer to a substrate surface, generally to a barrier layer. The method includes placing the substrate surface into a copper solution, wherein the copper solution includes complexed copper ions. A current or bias is applied across the substrate surface and the complexed copper ions are reduced to deposit the copper seed layer onto the barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Copper plating solution and method for copper plating
InactiveCN1514889AImprove bindingReduce adverse effectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPermanent magnet manufactureAcetic acidEthylenediamine
A copper plating solution which comprises 0.03 mol / L to 0.5 mol / L of copper sulfate, 0.05 mol / L to 0.7 mol / L of ethylenetetraacetic acid and 0.02 mol / L to 0.3 mol / L of a sulfite salt, and has a pH adjusted to 5.0 to 8.5; and a method for copper plating which comprises using the copper plating solution. The method for copper plating allows a copper plating film being uniform and excellent in adhesion to be formed with stability on the surface of an article to be plated.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
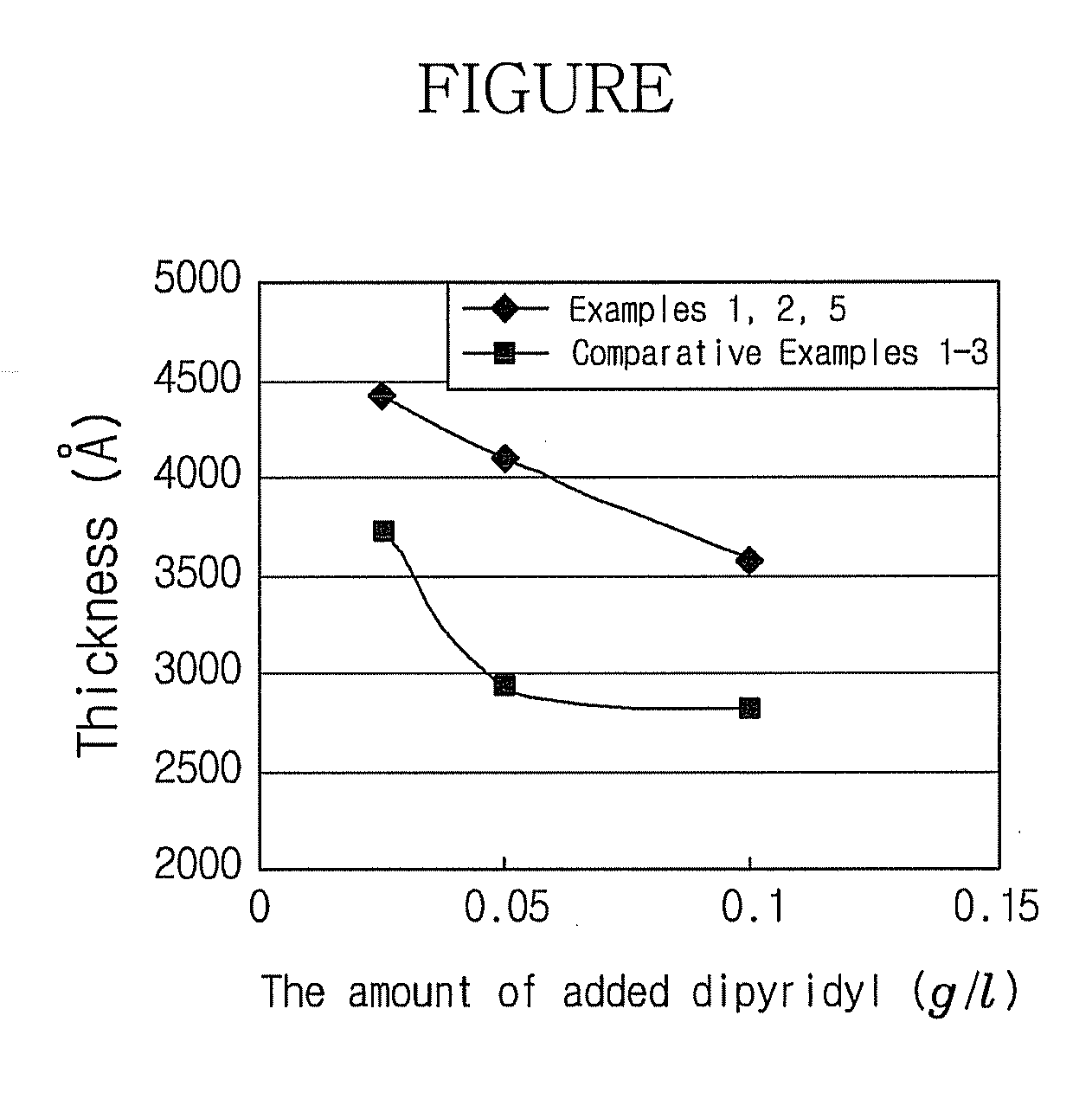
Electroless copper plating solution, method of producing the same and electroless copper plating method
ActiveUS20080223253A1Improve adhesionLower resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsAnti-corrosive paintsCopper platingHydrogen-Ion Concentrations
Disclosed herein is an electroless copper plating solution, including a copper salt, a completing agent, a reductant and a pH adjuster, in which the plating solution includes a 2,2-dipyridyl acid solution and the hydrogen ion concentration (pH) thereof is about 11.5 to about 13.0, a method of producing the same, and an electroless copper plating method. According to the plating solution of the present invention, an electroless copper plating film having stable and improved adhesivity and low electrical resistance can be obtained. Further, display devices including a metal pattern formed with the electroless copper plating solution can improve the reliability and price competitiveness of products prepared therefrom.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
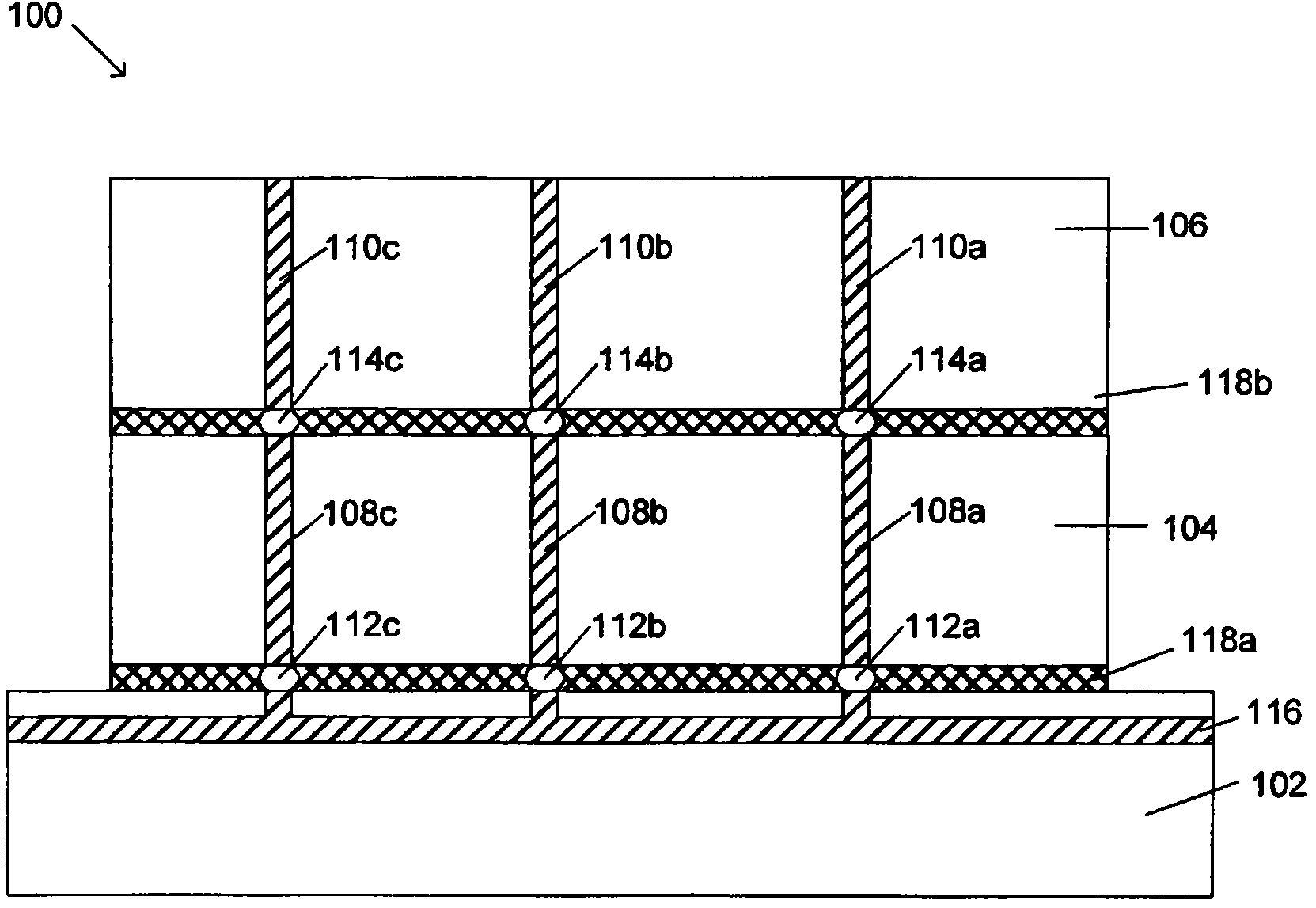
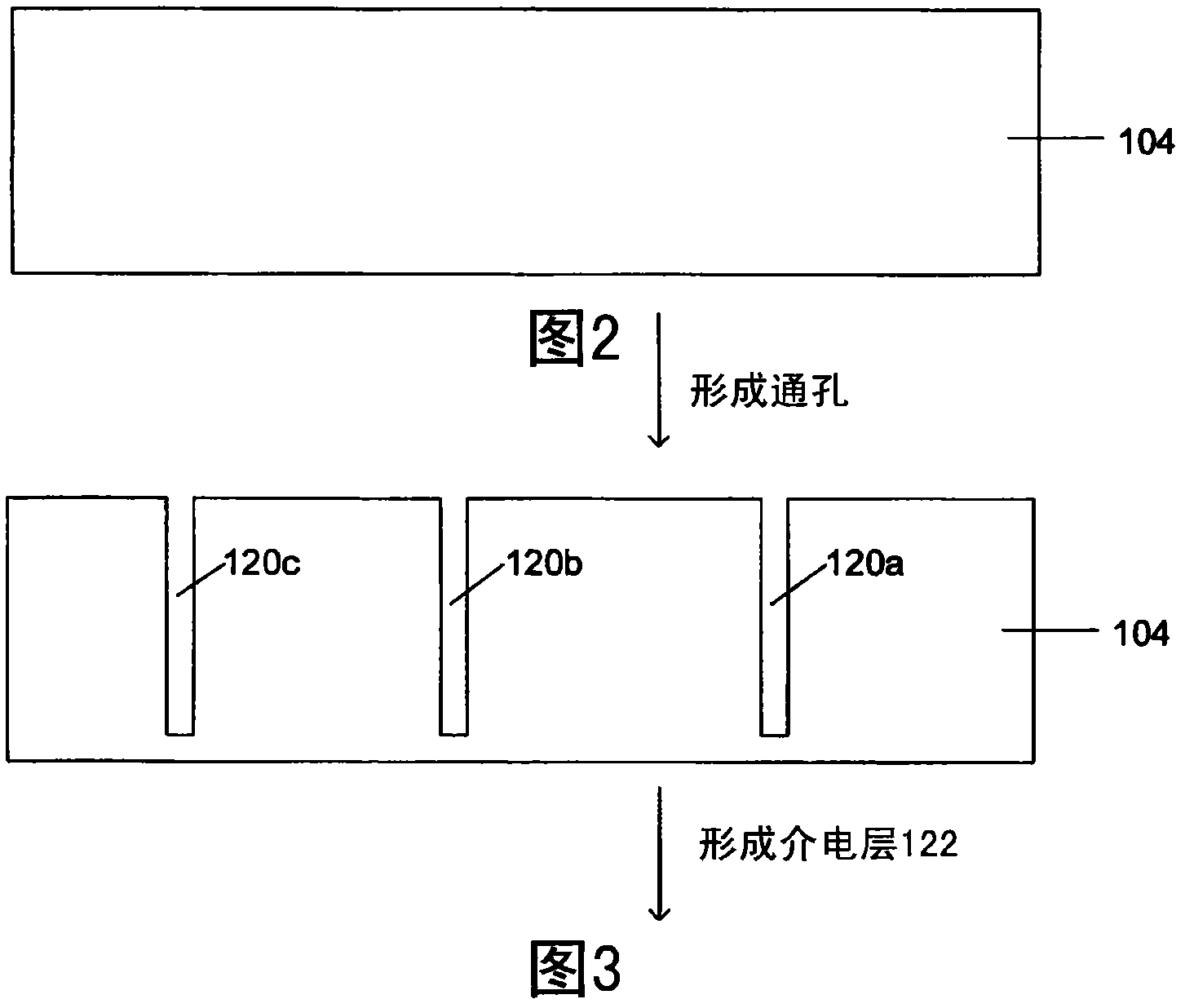
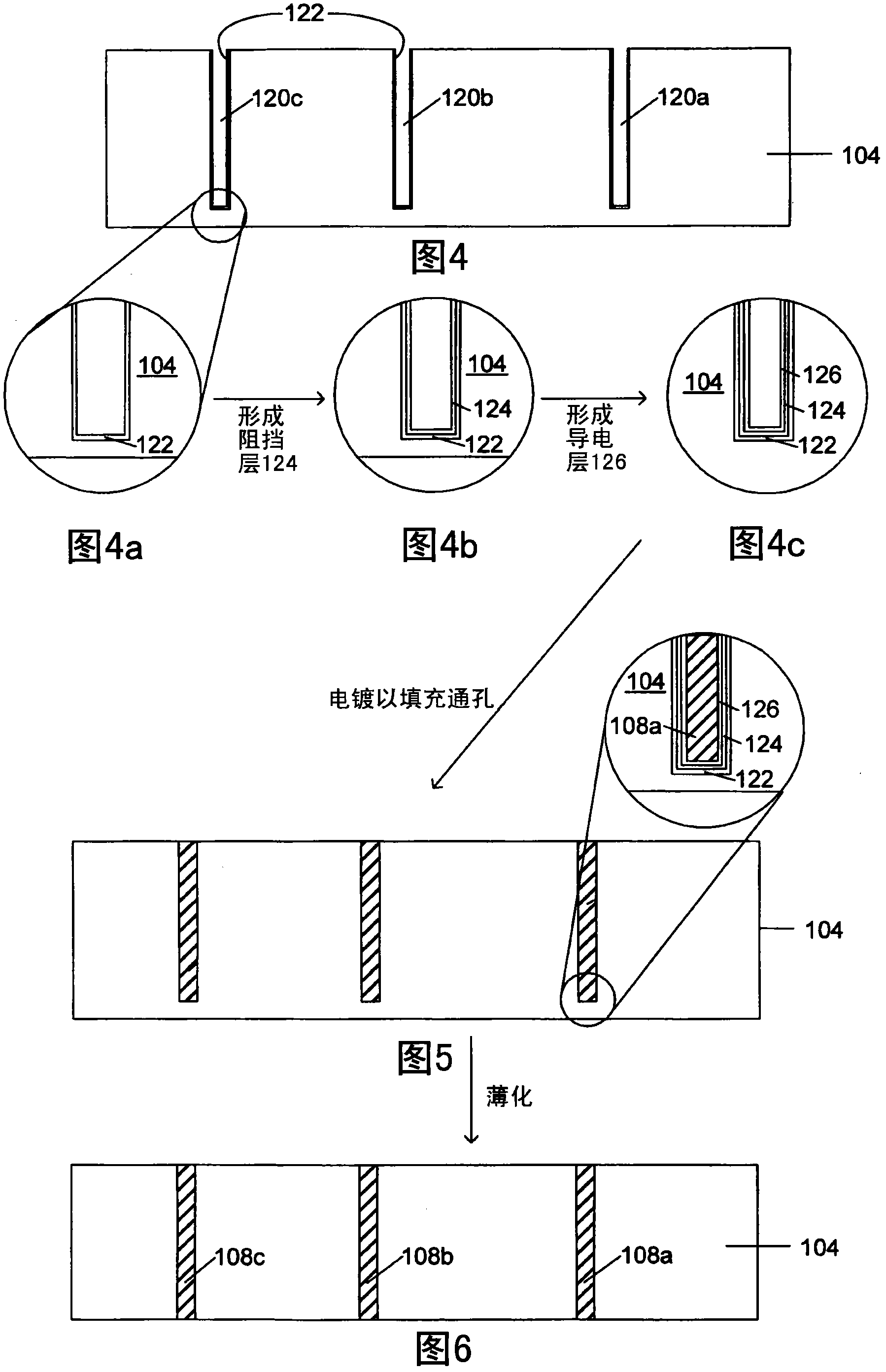
Deep filled vias
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Metal Plating Composition and Method for the Deposition of Copper-Zinc-Tin Suitable for Manufacturing Thin Film Solar Cell
InactiveUS20090205714A1Easy to manufactureClear processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic dyesCopper platingTin plating
To be able to form a copper-zinc-tin alloy which optionally comprises at least one chalcogenide and thus forms a semiconductor without the use of toxic substances a metal plating composition for the deposition of a copper-zinc-tin alloy is disclosed, wherein said metal plating composition comprises at least one copper plating species, at lease one zinc plating species, at least one tin plating species and at least one complexing agent and further, if the alloy contains at least one chalcogen, at least one chalcogen plating species.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Method to plate C4 to copper stud
InactiveUS6251528B1Removing platingImprove productivitySolid-state devicesExtrusion containersCopper platingPhotoresist
A method for plating a second metal directly to a first metal without utilizing a mask. A semiconductor substrate is provided including at least one metal feature and at least one insulating layer covering the metal feature and the substrate. At least one recess is formed in the at least one insulating layer thereby exposing at least a portion of the metal feature. At least one conductive barrier layer is formed over the insulating layer and the exposed portion of the metal feature. A plating seed layer of a first metal is formed over the at least one barrier layer. A photoresist layer is deposited over the plating seed layer. Portions of the photoresist layer and of the plating seed layer outside of the at least one recess are removed. Photoresist remaining in the at least one recess is removed. A second metal is electroplated to the plating seed layer in the recess.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Magnesium alloy non cyanogen plating copper chemical plating nickle and its plating process
InactiveCN1598059AImprove bindingUniform coating thicknessSuperimposed coating processCopper platingChemical plating
The invention discloses a method of plating Nickel with magnalium alloy without cyanogen and the plating technique. The direction for the plating solution is: 20 to 80g.dm-3 of copper charred phosphate; one or several of the 60 to 320g.dm-3 of sodium charred phosphate or Potassium charred phosphate or 60 to 250g.dm-3 of sodium citric acid, 5 to 20g.dm-3 of Potassium sodium tartaric acid, 60 to 250g.dm-3 of HEDP and 60 to 250g.dm-3 of amine ethylene; one or several of the 5 to 20g.dm-3 of hydrogen amine di-fluorin or 5 to20 g.dm-3 sodium fluoride or 5 to 20g.dm-3 of Potassium fluoride or 5 to 20g.dm-3 of lithium fluoride. The plating solution chooses the nickel sulfate or alkali type nickel carbonate or nickel acetic acid as the main salt and adds the reducing agent, combination agent and stabilization agent. The plating technique adopts the acid plating copper-plating three nickel-plating chromium. The invention has little pollution to the environment, high binding power and erosion-proof property.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH +1
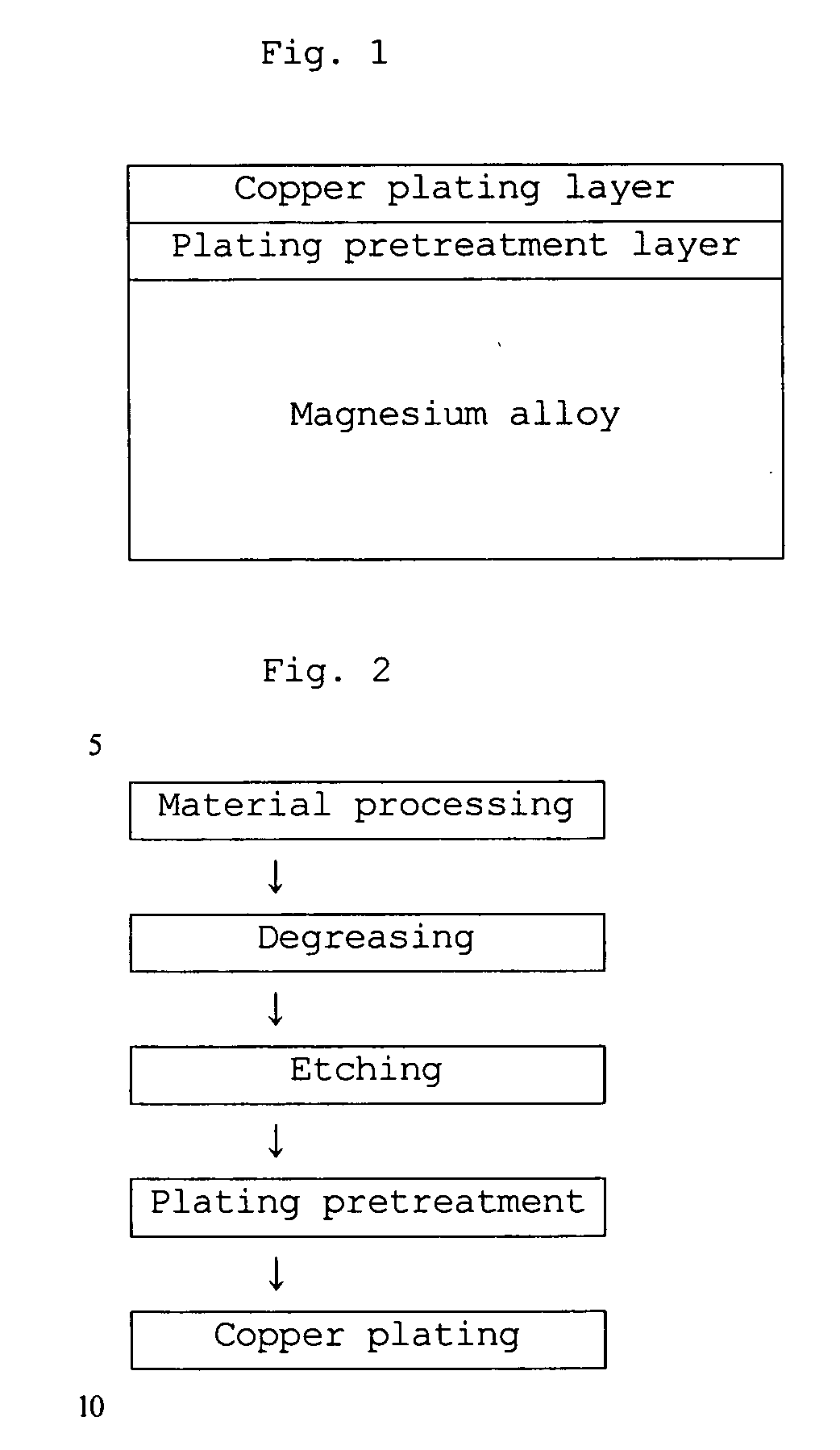
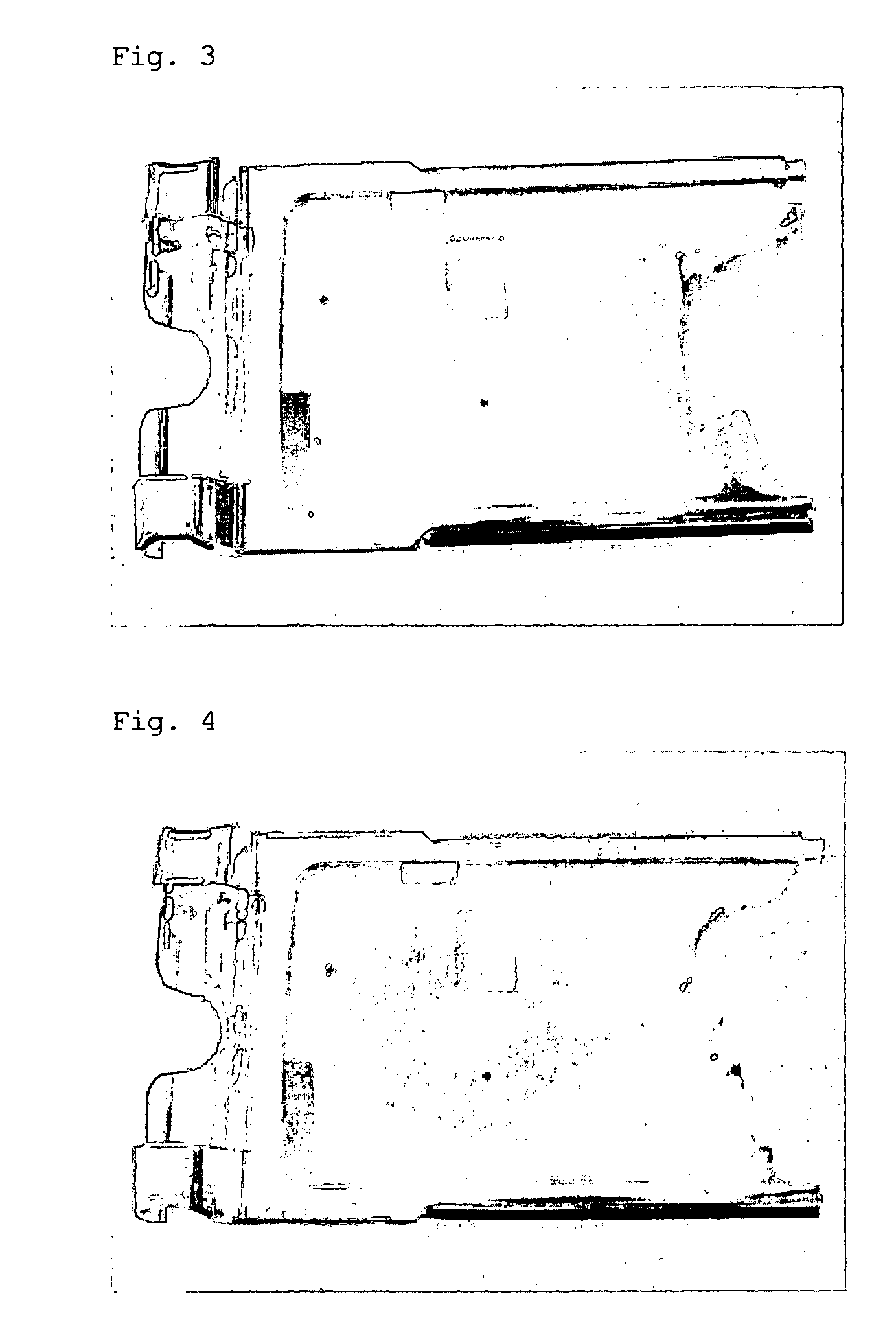
Method of preparing copper plating layer having high adhesion to magnesium alloy using electroplating
InactiveUS20070108060A1Improve adhesionImprove corrosion resistanceSuperimposed coating processCopper platingCurrent distribution
Disclosed is a method of preparing a copper electroplating layer having high adhesion to a magnesium alloy, which is advantageous because the usability of the magnesium alloy, having the highest specific strength among actually usable metals, can be increased through the development of a process of forming a uniform copper plating layer upon electroplating of the magnesium alloy. The method of preparing a copper electroplating layer having high adhesion to a magnesium alloy of this invention is characterized in that the magnesium alloy is pretreated with a plating pretreatment solution to form a film for electroplating, serving as a magnesium alloy pretreatment layer, exhibiting a uniform current distribution, which is then electroplated with copper to form the copper plating layer. According to this invention, through the pretreatment of the magnesium alloy, the adhesion of the copper plating layer to the film for electroplating formed on the magnesium alloy can be increased.
Owner:PANGRIM
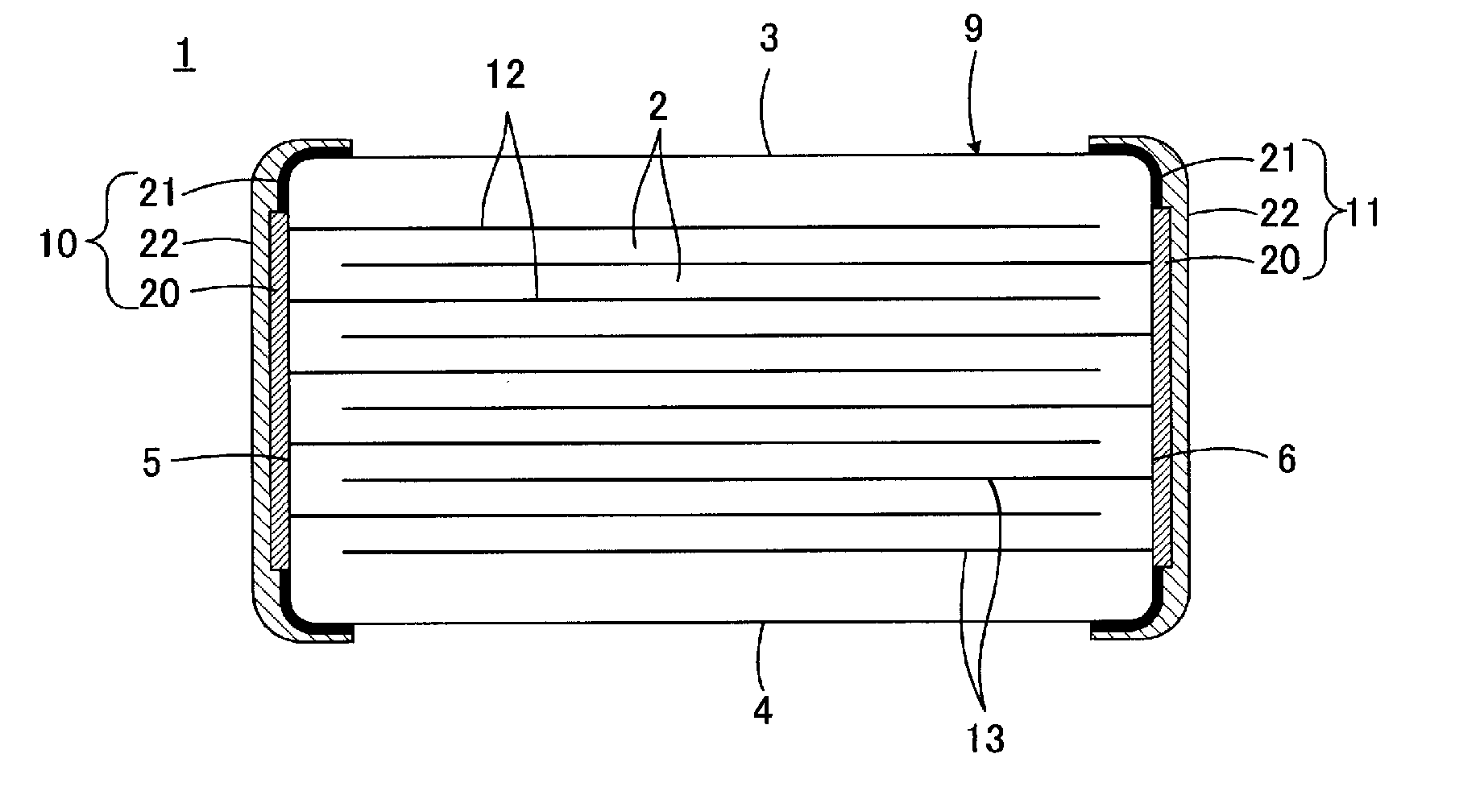
Alkaline non-cyanide plating solution for copper-plating used on iron and steel base and preparation method thereof
An alkaline non-cyanide plating solution for copper-plating used on iron and steel base and a preparation method thereof relate to a kind of plating solution. The invention provides the alkaline non-cyanide plating solution for copper-plating used on iron and steel base and the preparation method thereof. The plating solution comprises the following components: main salt, complexing agent, conductive salt, activator, cuprous ion complexing agent, pH stabilizer and brightening agent. The method comprises the following steps: adding complexing agent in water, stirring to dissolve complexing agent, obtaining a solution A; adding main salt in the solution A, stirring to dissolve main salt, obtaining a solution B; adding conductive salt in water, stirring to dissolve conductive salt, obtaininga solution C; mixing the solution B and solution C, adjusting the pH value to 2.0-4.5 with sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide, obtaining a solution D; adding additive in the solution D, adding water toperform constant volume process and obtaining the alkaline non-cyanide plating solution for copper-plating in the desired volume for use, wherein the additive is activator, cuprous ion complexing agent, pH stabilizer and brightening agent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Multilayer ceramic electronic component and method for making the same
ActiveUS20090323253A1Improve bindingFixed capacitor electrodesStacked capacitorsCopper platingElectrical conductor
A multilayer ceramic electronic component includes external terminal electrodes that are formed by depositing metal plating films on exposed portions of internal conductors embedded in a ceramic body, depositing a copper plating films that cover the metal plating films and make contact with the ceramic body around the metal plating films, and heat-treating the ceramic body to generate a copper liquid phase, an oxygen liquid phase, and a copper solid phase between the copper plating films and the ceramic body. The mixed phase including these phases forms a region at which a copper oxide is present in a discontinuous manner inside the copper plating film at least at the interfaces between the ceramic body and the copper plating films. The copper oxide securely attaches the copper plating films to the ceramic body and enhances the bonding force of the external terminal electrodes.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Composite lightweight copper plated aluminum wire
InactiveUS6178623B1Line/current collector detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCopper plating
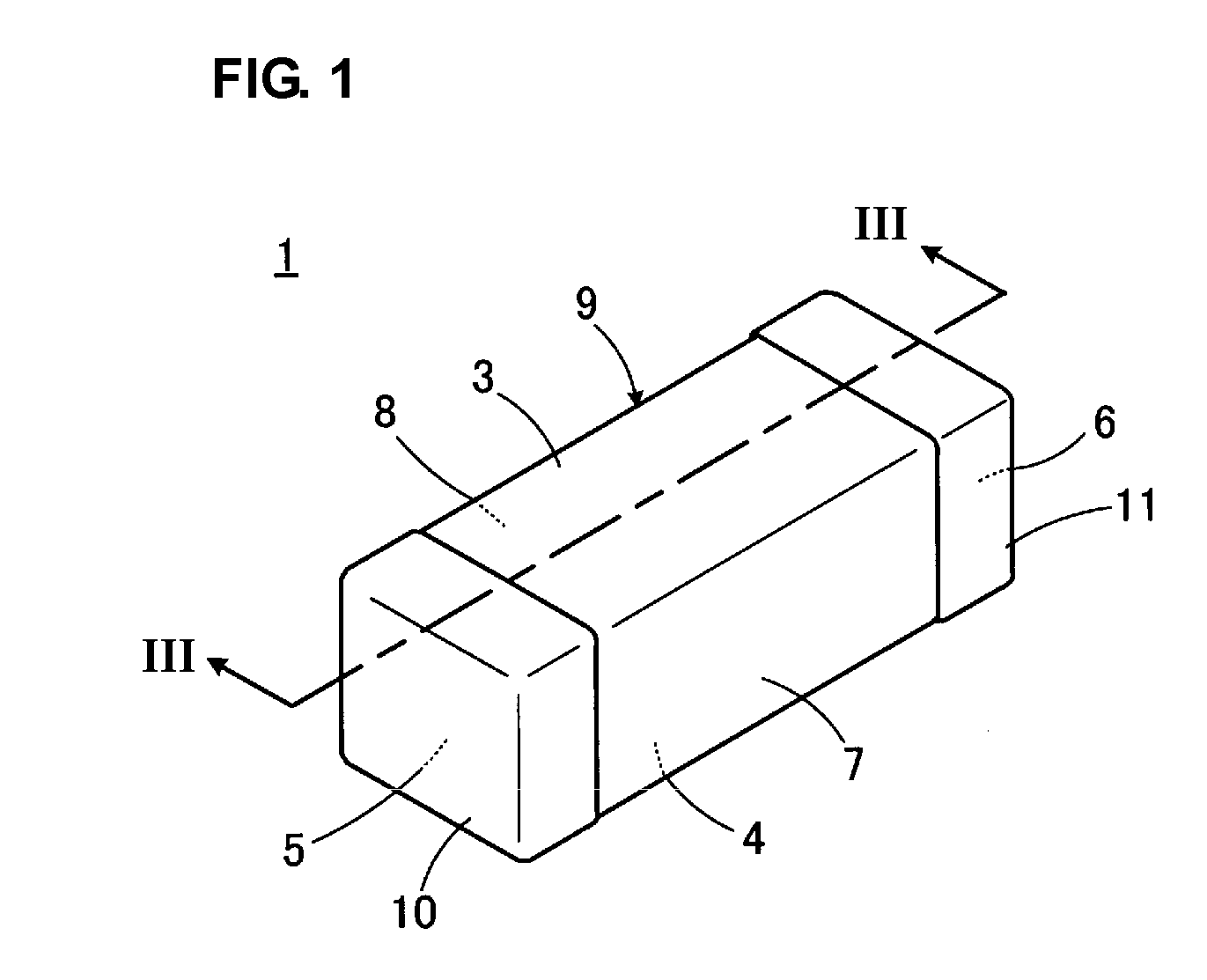
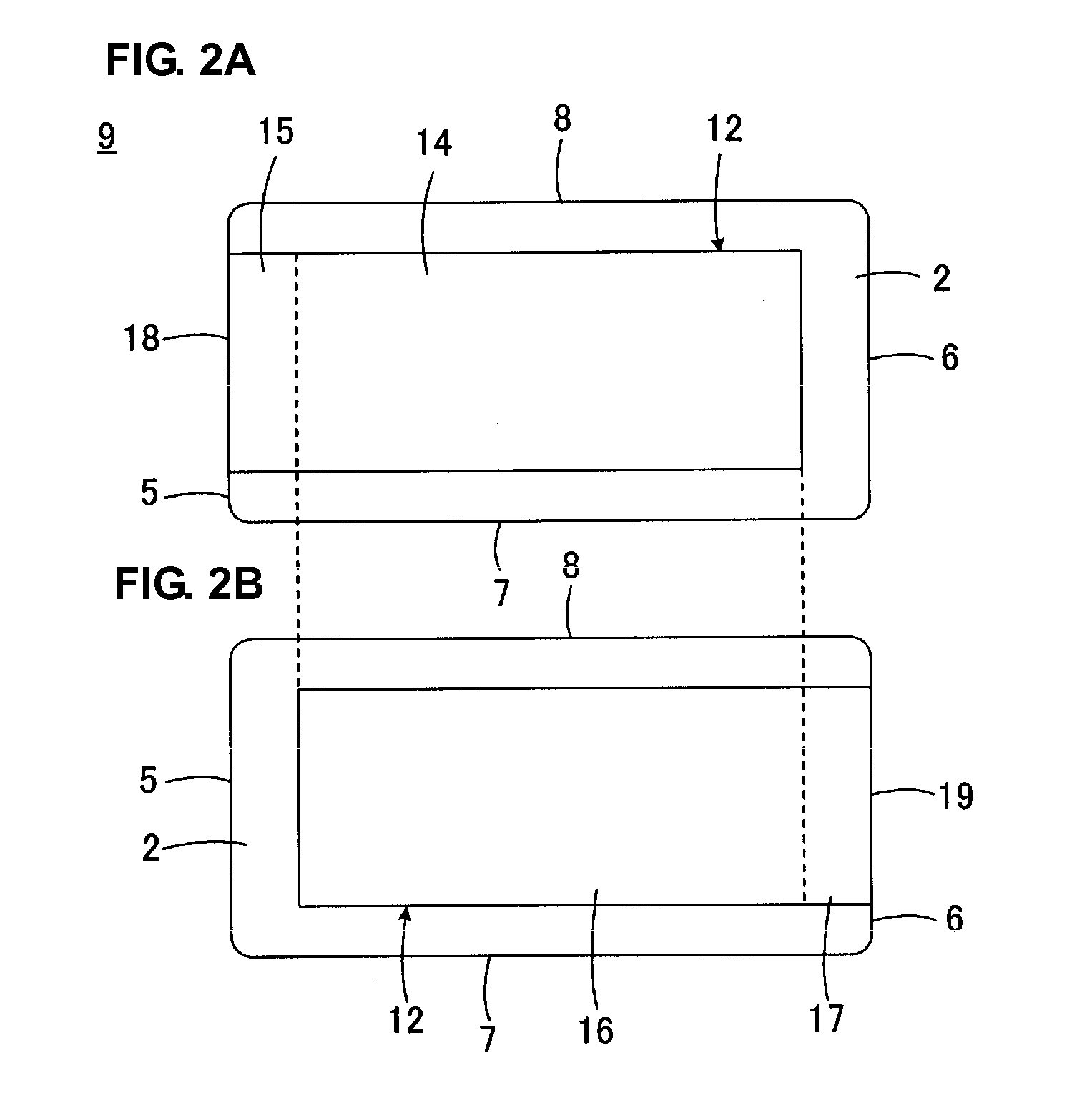
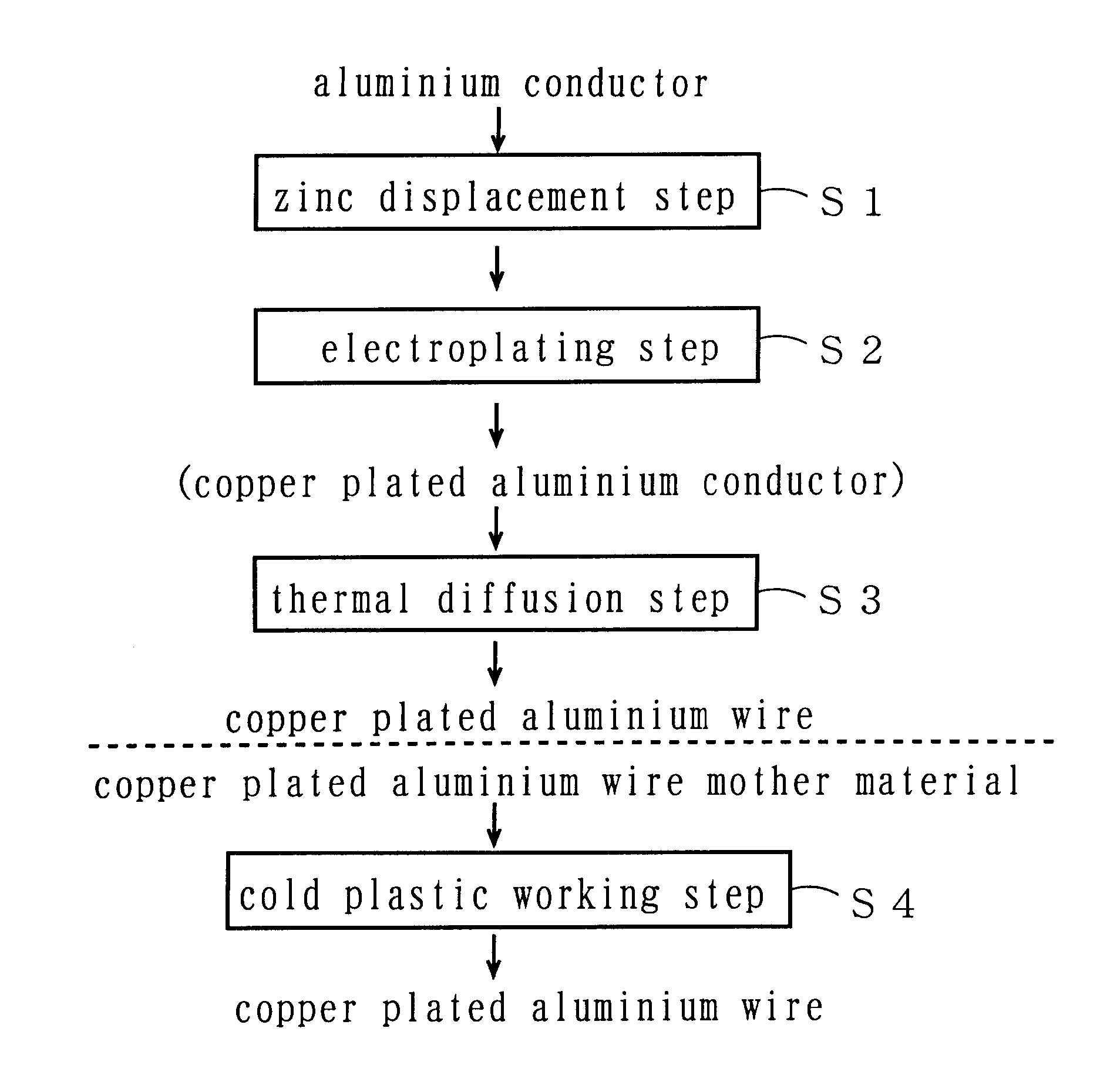
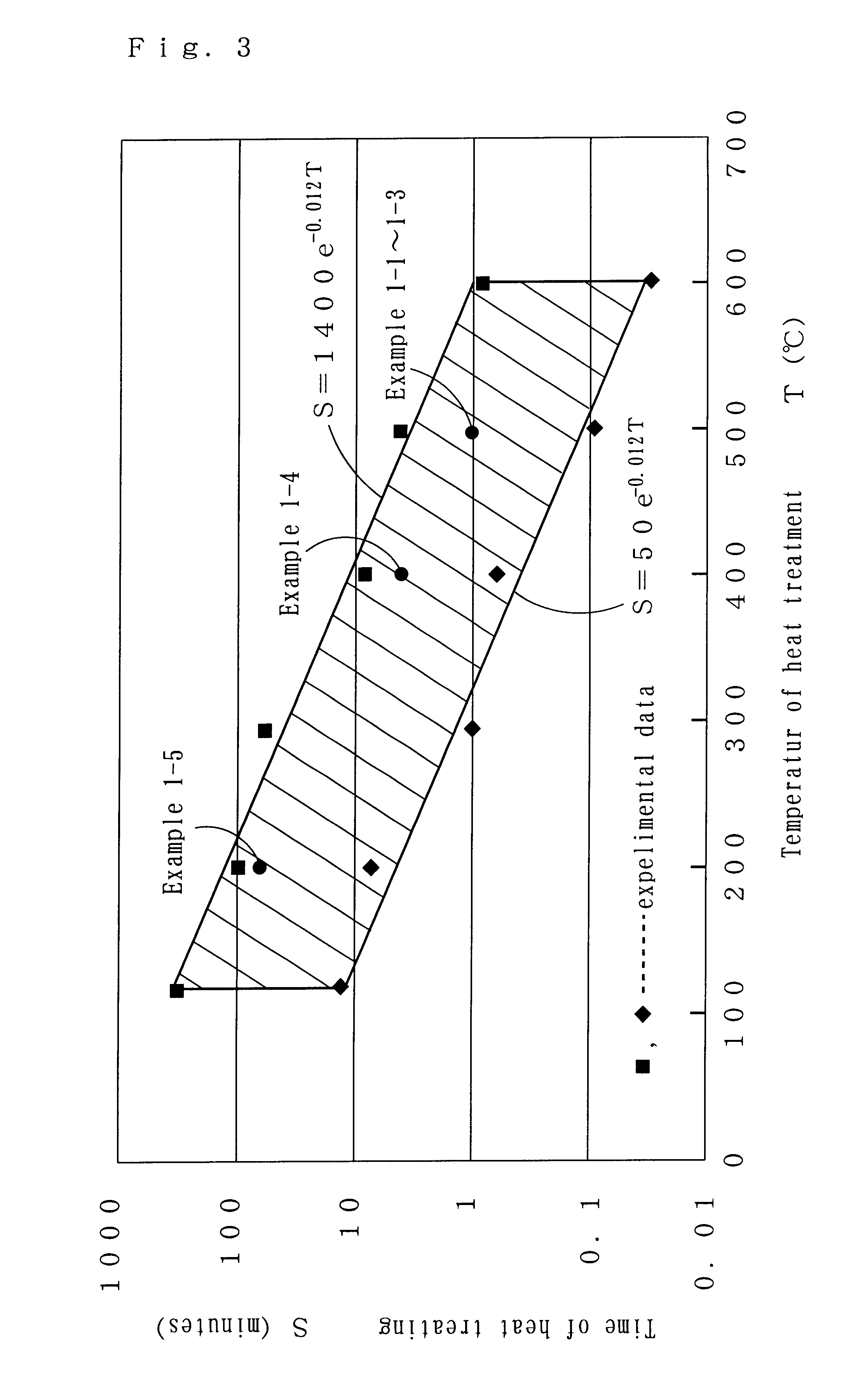
A copper plated aluminum wire with improvement in adhesive properties is fabricated by a method which includes a displacement step of forming a thin layer of a metal by displacement on a surface of an aluminum or aluminum alloy conductor, an electroplating step of coating a surface of the thin layer continuously with copper layers by electroplating to have a copper coated aluminum conductor, and a thermal diffusion step of heat treating the copper coated aluminum conductor at a temperature of 120° C. to 600° C. under an inert gas atmosphere for thermal diffusion. A plated aluminum wire is provided having an anchor metal layer formed by displacement plating, a low thermally conductive metal layer formed by electroplating, and a high electrically conductive metal layer formed by electroplating in which all of the layers are sequentially deposited on an outer surface of an aluminum or aluminum alloy conductor. A plated aluminum wire is provided having an anchor metal layer formed by displacement plating and a high electrically conductive metal layer formed by electroplating in which both of the layers are sequentially deposited on an outer surface of an aluminum or aluminum alloy conductor. A composite lightweight copper plated wire is provided having an electrically conductive metal layer that is deposited by electroplating on an outer surface of an anchor metal layer provided on an aluminum conductor.
Owner:TOTOKU ELECTRIC CO LTD
Copper plating bath and plating method for substrate using the copper plating bath
InactiveUS20030106802A1Excellent characteristic and uniformityImprove reliabilityAnti-corrosive paintsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCopper platingGlycidyl ethers
A copper plating bath comprising a reaction condensate of an amine compound and glycidyl ether and / or a quaternary ammonium derivative of this reaction, condensate, and a plating method using this copper plating bath are disclosed. A copper plating bath capable of providing highly reliable copper plating on a substrate such as a silicone wafer semiconductor substrate or printed board having minute circuit patterns and small holes such as blind via-holes, through-holes, and the like, and a method of copper plating using the copper plating bath can be provided.
Owner:EBARA-UDYLITE CO LTD
Cooper-plating solution, plating method and plating apparatus
InactiveUS20040022940A1High aspect ratioImprove performanceElectrolysis componentsPretreated surfacesCopper platingSulfur
There is provided a copper-plating solution which, when used in plating of a substrate having an seed layer and fine recesses of a high aspect ratio, can reinforce the thin portion of the seed layer and ensures complete filling with copper of the fine recesses, and which is so stable that its performance is not lowered after a long-term continuous use thereof. The plating solution contains monovalent or divalent copper ions, a complexing agent, and an organic sulfur compound as an additive, and optionally a surfactant.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Rigid-flexible printed circuit board and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080014768A1Low costEasy to implementCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsCopper platingElectrical connection
The present invention relates to a rigid-flexible printed circuit board and, more particularly, to a rigid-flexible printed circuit board including CL via holes which can facilitate electrical connection to an inner circuit pattern in a flexible region. Since the coverlays are layered on the entire surface of the double-sided FCCL without previous processing thereof, the via holes are formed in the coverlays while a drilling process is performed to form the via holes, and then the copper plating is performed over the entire surface thereof, it is possible to eliminate the cost of previously processing the coverlays, easily perform a process of provisionally layering the coverlays on the double-sided FCCL, and decrease the cost therefor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for conducting surface chemical copper plating on inorganic particles through dopamine
ActiveCN105112894AReduce pollutionShort processLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCopper platingElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a method for conducting surface chemical copper plating on inorganic particles through dopamine. The method comprises the steps that poly-dopamine layers are made to subside on the surfaces of the inorganic particles in an alkaline solution through the oxidative polymerization effect of the dopamine, then by utilizing functional groups of the poly-dopamine layers, and meanwhile under the effect of an additional auxiliary reducing agent of dimethylamine broane (DMAB), copper ions are reduced to pure copper on the surfaces of the inorganic particles, and a continuous and compact metal copper layer is formed. The method is simple to operate, low in equipment requirement and low in cost; the prepared copper-plated inorganic particles have the characteristics of being low in density, good in conductivity and the like; the method can be used for preparing electricity and thermal conductive coatings, electromagnetic shielding paint, wave-absorbing materials and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Manufacture method of golden finger printed board
ActiveCN101699940AGuaranteed to revealFlexible designConductive pattern reinforcementPrinted element electric connection formationCopper platingElectroplating
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a golden finger printed board, which comprises the steps of: producing a normal inner pattern, laminating, drilling, depositing copper, electroplating a board surface, and firstly transferring an outer layer pattern, wherein the copper surface of a pattern part of a circuit on an outer layer board is exposed, and a non-pattern part is covered by a first layer dry film; electroplating copper nickel golden on a circuit board, so that the pattern part which is not covered with the first layer dry film is plated with the copper by means of thickening, and a nickel layer and a normal golden layer is plated thereon; secondly transferring the outer layer pattern, arranging a light-resistant through window at the golden finger part of the film pattern, exposing the other part, and covering a second layer dry film on the board surface; exposing and developing, exposing a normal golden layer of the golden finger part in the window, and respectively covering the first layer dry film or the second layer dry film or the two layer dry films at the other part; and plating a hard golden layer, removing the film, and etching the outer layer. The manufacture method reduces a step for removing a golden finger lead wire, has a flexible designing way, saves cost, and improves production efficiency.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FASTPRINT CIRCUIT TECH
Wire saw for cutting hard and fragile materials and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101564828AReduce sheddingImprove bindingAbrasion apparatusGrinding machinesCopper platingUV curing
The invention relates to a wire saw for cutting hard and fragile materials and a manufacturing method thereof. The wire saw is fixed with an grinding material on a core wire through a bonding agent and is characterized in that the bonding agent consists of an inner layer UV resin bonding agent and an outer layer heat reactive resin bonding agent; and the grinding material is evenly and continuously distributed in a monolayer mode around the core wire, partial grinding material is embedded in the UV resin bonding agent, other partial grinding material is exposed outside the heat reactive resin bonding agent to form an exit lip, and the rest part is enwrapped by the outer layer heat reactive resin. The grinding material adopts a diamond or CBN adopting surface metal plating; and the core wire adopts a copperized music wire. The manufacturing method is performed continuously and quickly according to the following steps: under the traction of a driving device, setting out the core wire continuously through a wire plate, surface preparation, cleaning, drying, coating with the inner layer UV resin bonding agent, grinding material cementation, UV curing, coating with the outer layer heat reactive resin bonding agent, thermocuring and drawing in a cable to form a plate. The wire saw and the method solve the problem of driving aspects before cured resin is completely cured, and can effectively solve the problem that the grinding material in the prior art is easy to agglomerate.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor package, semiconductor device and electronic device
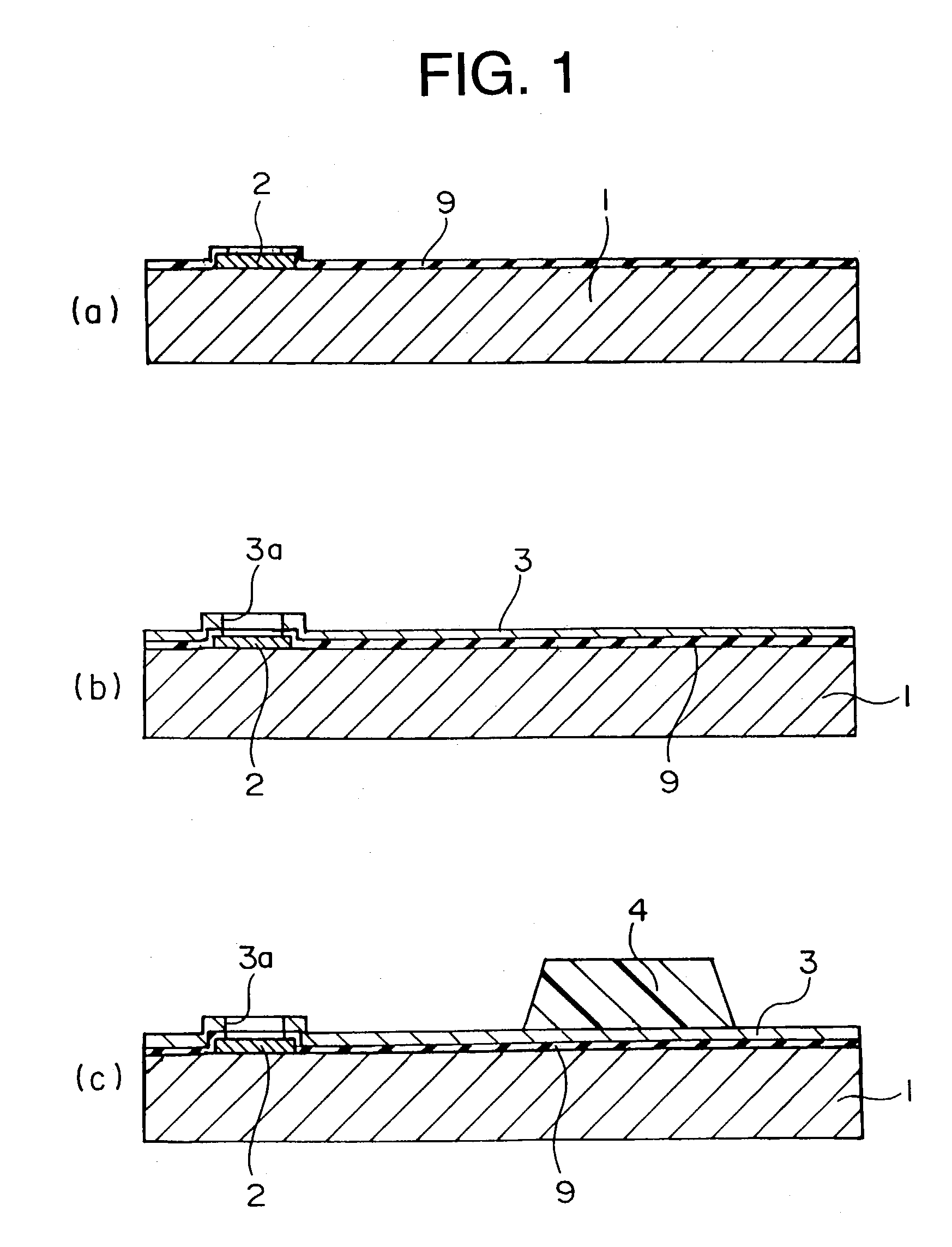
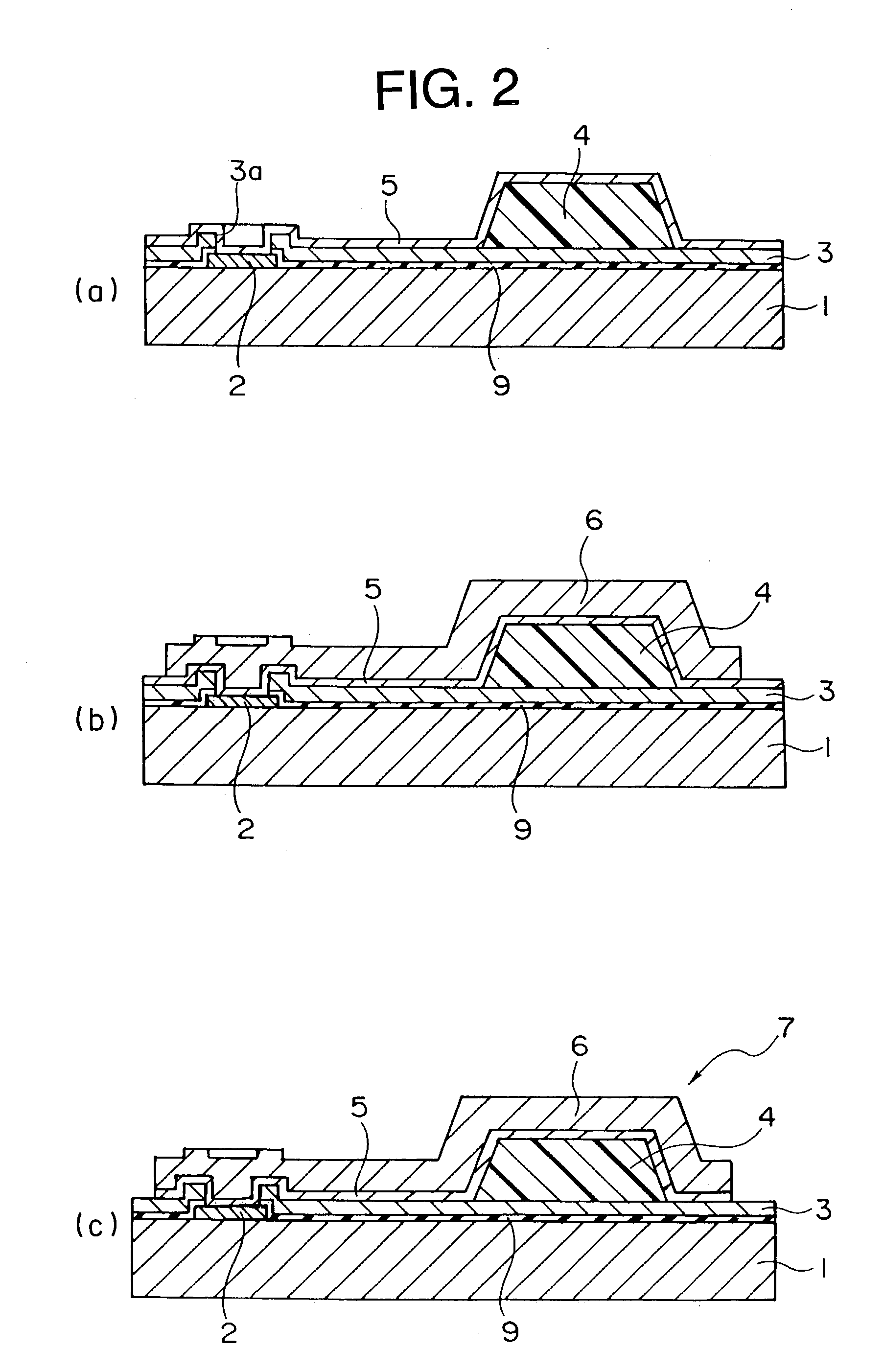
InactiveUS7023088B2Reduce processEasy to adjustSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistCopper plating
An insulating layer (3) having an opening portion (3a) at a position conformable to an electrode pad (2) is formed. Next, a resin projection portion (4) is formed on the insulating layer (3). Thereafter, a resist film is formed which has opening portions made in regions conformable to the opening portion (3a), the resin projection portion (4) and the region sandwiched therebetween. A Cu plating layer (6) is formed by electrolytic copper plating, using the resist film as a mask.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD +1
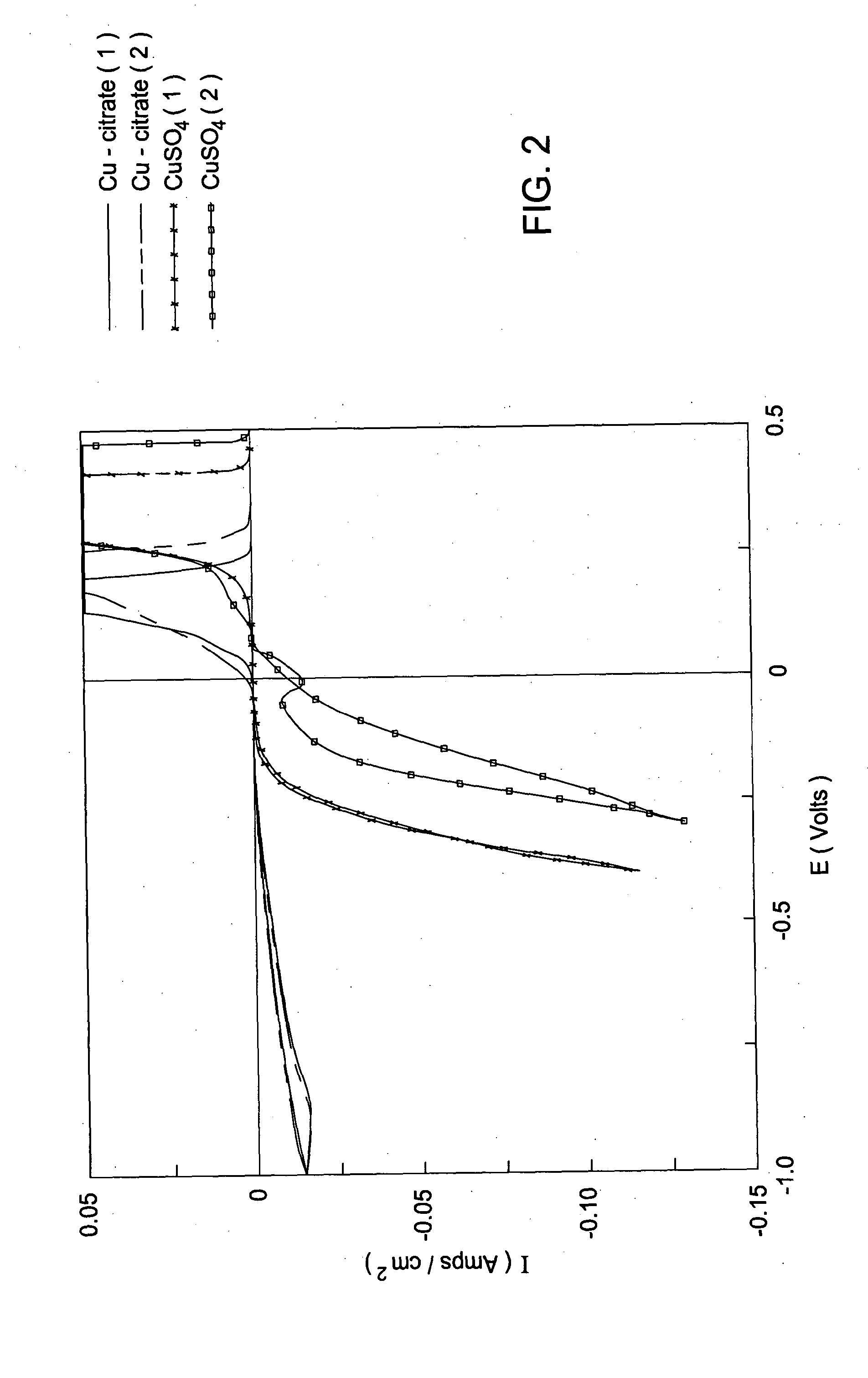
Method for analysis of three organic additives in an acid copper plating bath
InactiveUS6572753B2High sensitivityLittle interferenceCellsComponent separationElectricityCopper plating
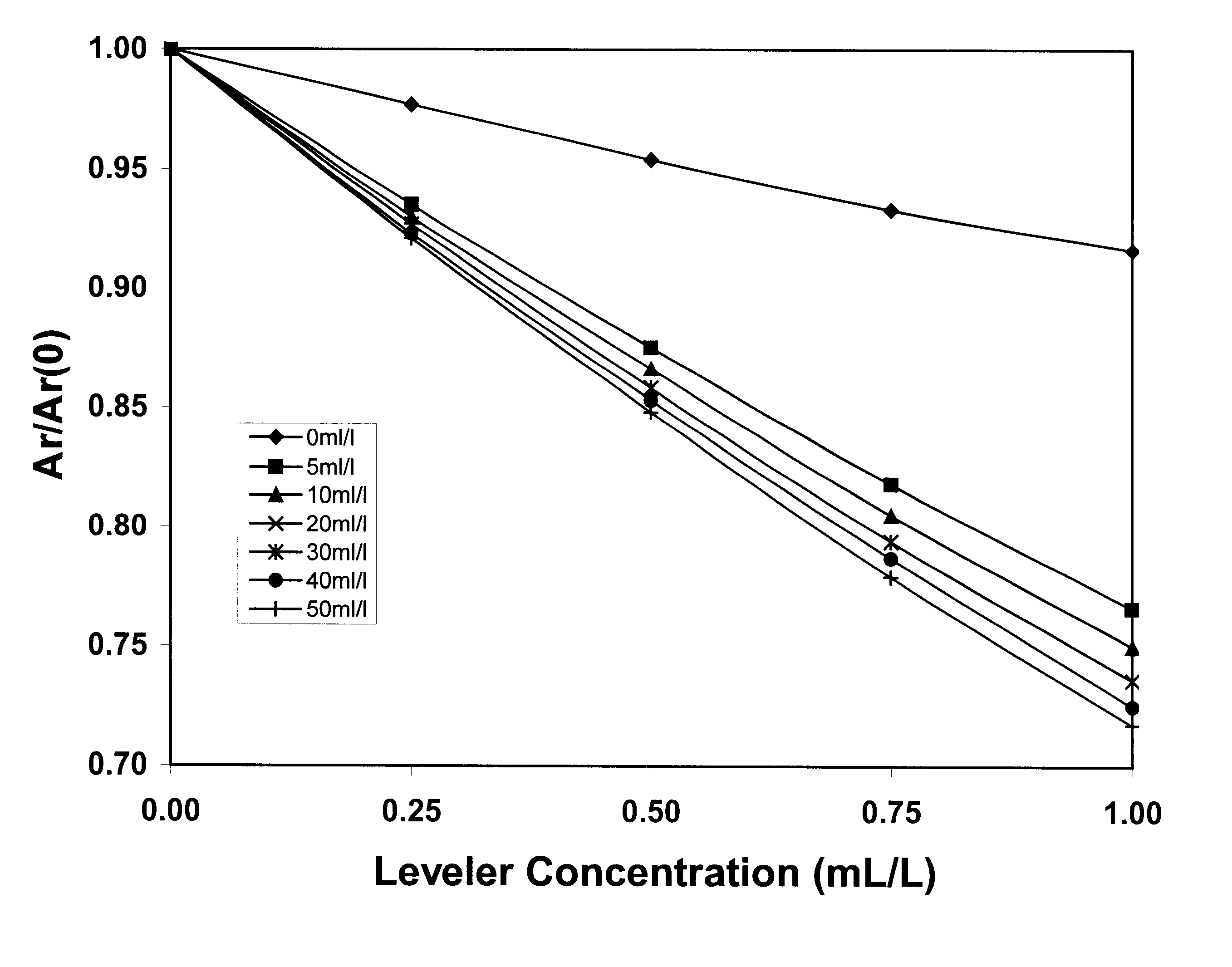
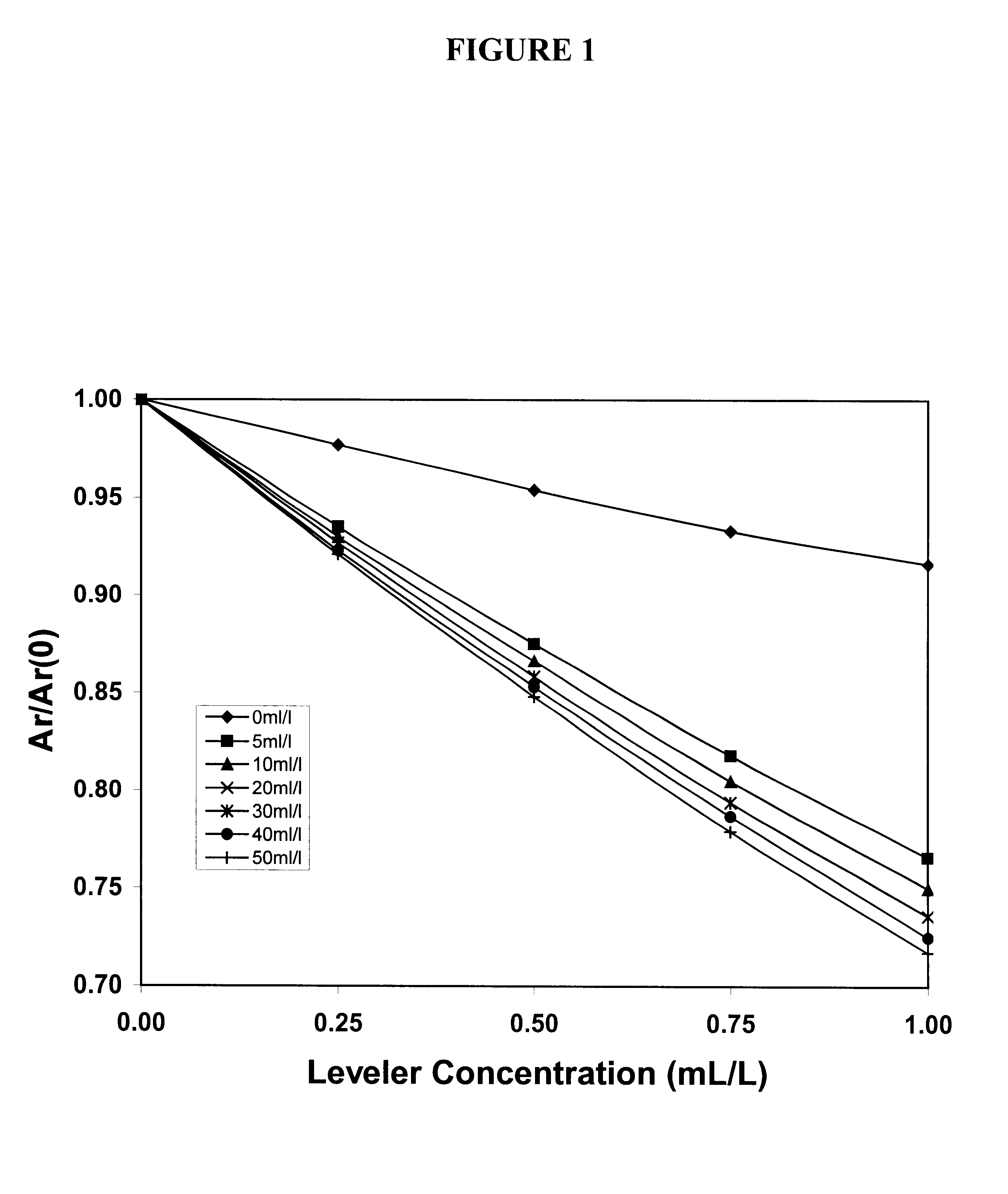
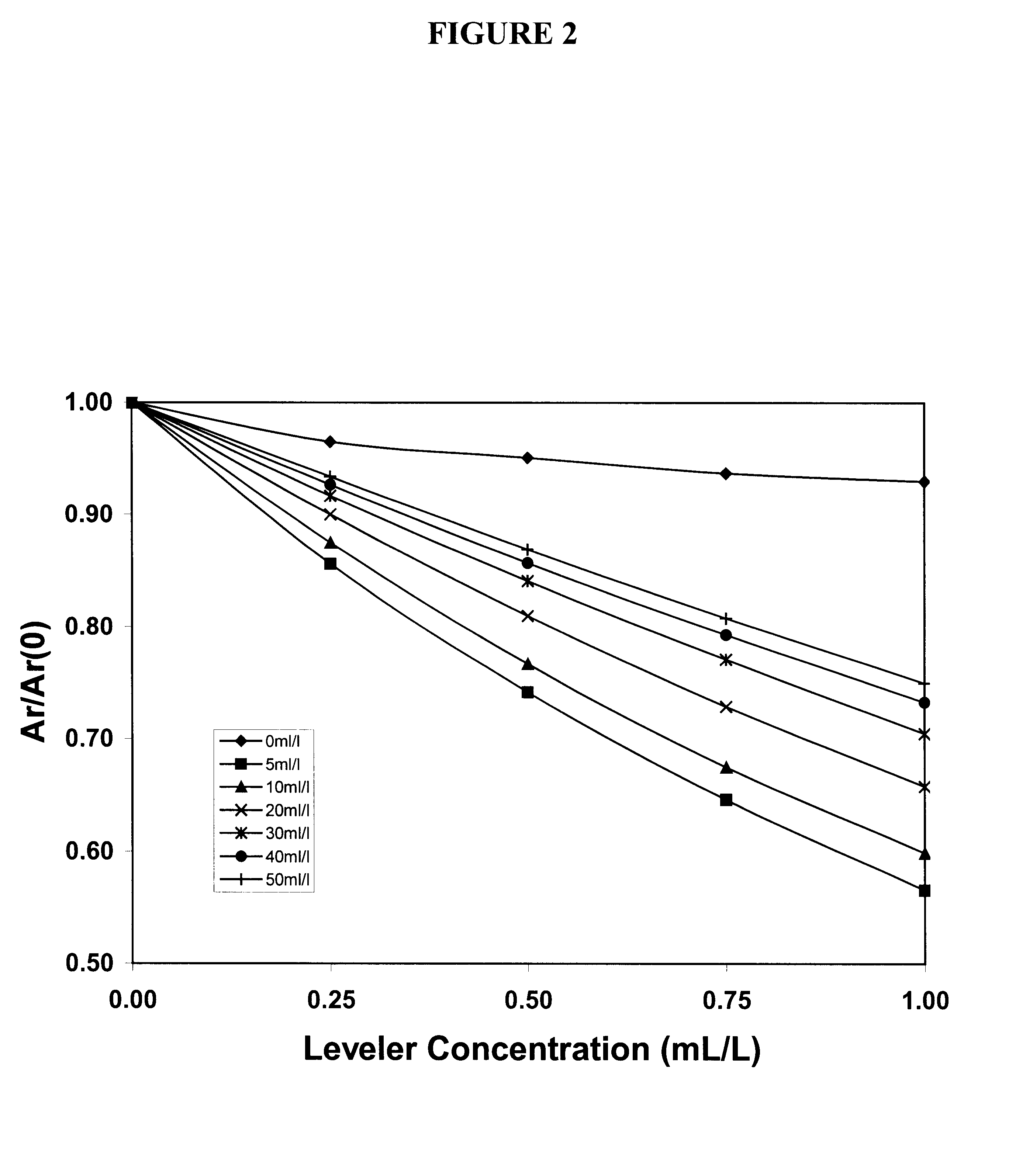
Acid copper electroplating baths used to form ultra-fine circuitry features on semiconductor chips contain suppressor, anti-suppressor and leveler additives that must be closely controlled in order to obtain acceptable copper deposits. Cyclic voltammetric stripping (CVS) methods are available to measure the concentrations of the suppressor and anti-suppressor based on the effects of these additives on the copper electrodeposition rate. The present invention is a method that also uses measurements of the copper electrodeposition rate to determine the concentration of the leveler additive. The other two additives are included in the measurement solution at concentrations determined to provide the optimum compromise between minimal interference, high sensitivity and good reproducibility for the leveler analysis. In this case, measurement precision is greatly improved compared to that provided by inclusion of the interfering additives in the measurement solution at their concentrations in the bath sample at the time of the analysis, which would be the standard analytical procedure.
Owner:KLA CORP
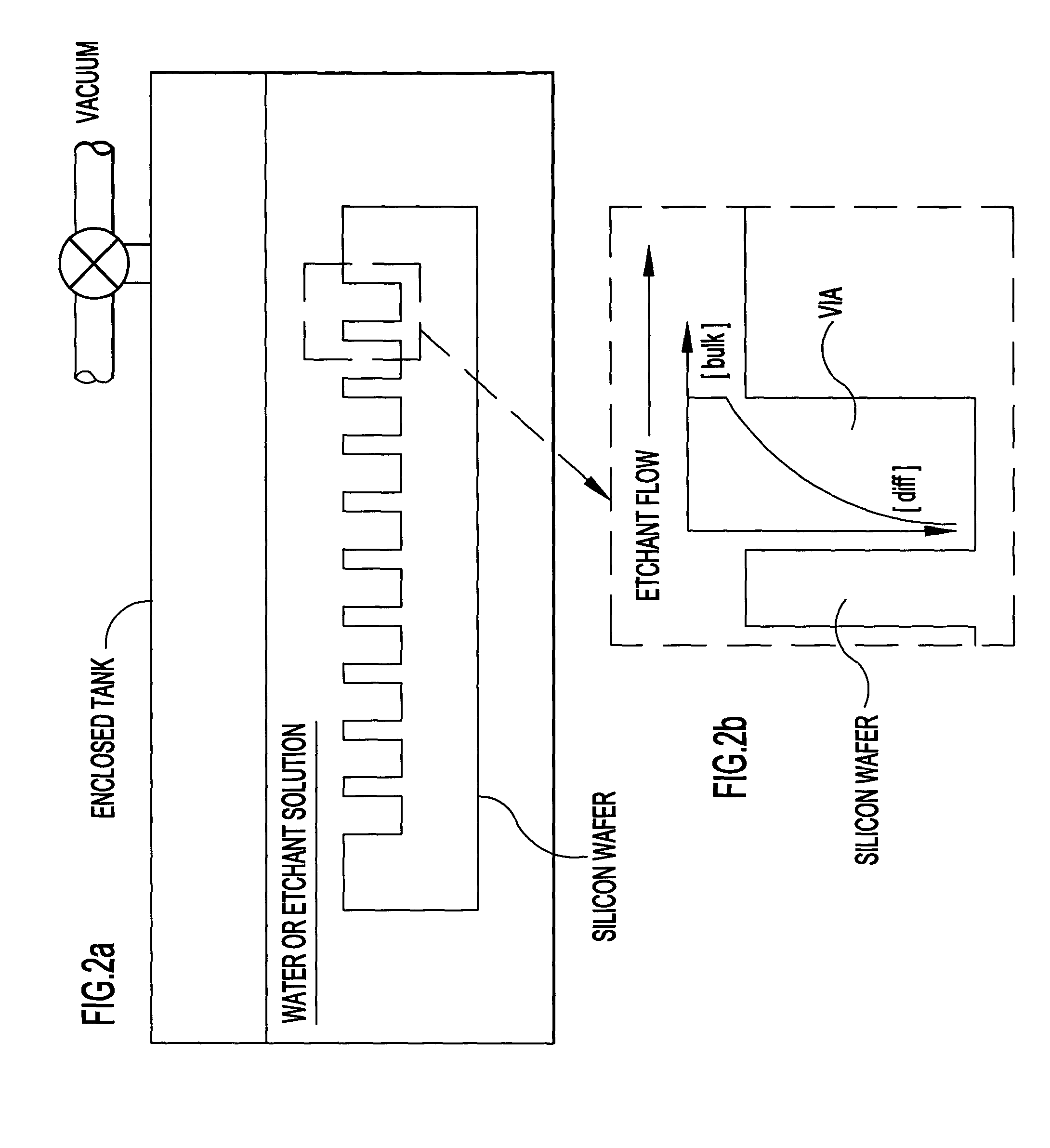
Process for electrodeposition of copper chip to chip, chip to wafer and wafer to wafer interconnects in through-silicon vias (TSV)
InactiveCN102318041AAvoids disadvantages of known processesAvoid disadvantagesCellsSolid-state devicesElectrolysisCopper plating
A process of electrodepositing high purity copper in a via in a silicon substrate to form a through-silicon-via (TSV), including immersing the silicon substrate into an electrolytic bath in an electrolytic copper plating system in which the electrolytic bath includes an acid, a source of copper ions, a source of ferrous and / or ferric ions, and at least one additive for controlling physical-mechanical properties of deposited copper; and applying an electrical voltage for a time sufficient to electrodeposit high purity copper to form a TSV, in which a Fe+2 / Fe+3 redox system is established in the bath to provide additional copper ions to be electrodeposited by dissolving copper ions from a source of copper metal.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Maintenance method for alkaline non-cyanide plating copper
The invention discloses a maintaining method for an alkalescent non-cyanide cuprodine. The method uses indissoluble anode, cathode in the alkalescent non-cyanide cuprodine liquor as the galvanized workpiece, adds cupric salt, complexing agents and additives and adjusts the pH value of the galvanizing liquor to control the current dense range between 0.1-7A / dm2; the galvanizing time is between 1min to 72h; then the galvanizing liquor is filtered; the galvanizing liquor is processed air bend or moves the workpiece while galvanizing. The invention uses the indissoluble anode comprising stainless steel, DSA coating, titanium, platinum, graphite which is simple to use, innoxious, harmless; the invention has a low production cost and even, smooth and shining fine galvanizing layer by using the indissoluble anode. The technique maintaining method of the invention has a simple operation, great stability of galvanizing liquor and convenient maintenance for the galvanizing liquor.
Owner:广州市二轻研究所股份有限公司
Copper plating solution for embedding fine wiring, and copper plating method using the same
InactiveUS20030085133A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCopper platingSulfur
The present invention provides a copper plating solution for embedding fine wiring, wherein it contains copper sulfate at 100 to 300 g / L as copper sulfate pentahydrate, sulfuric acid at 5 to 300 g / L, chlorine at 20 to 200 mg / L, a macromolecular surfactant at 0.05 to 20 g / L for controlling the electrodeposition reaction, sulfur-based saturated organic compound at 1 to 100 mg / L for accelerating the electrodeposition reaction, leveling agent composed of a macromolecular amine compound at 0.01 to 10 mg / L and reductant at 0.025 to 25 g / L for stabilizing the copper plating solution. The copper plating solution of the present invention for embedding fine wiring can plate the wafer surface provided with fine wiring patterns with sub-micron order gaps in-between and coated with copper serving as the metallic seed film, to fill the gaps neither leaving any defect therein nor dissolving the metallic seed film.
Owner:ELECTROPLATING ENGINEERS OF JAPAN LTD
Selective electroless-plated copper metallization
InactiveUS20050023699A1Reduce amountReduce environmental problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper platingOxygen plasma etching
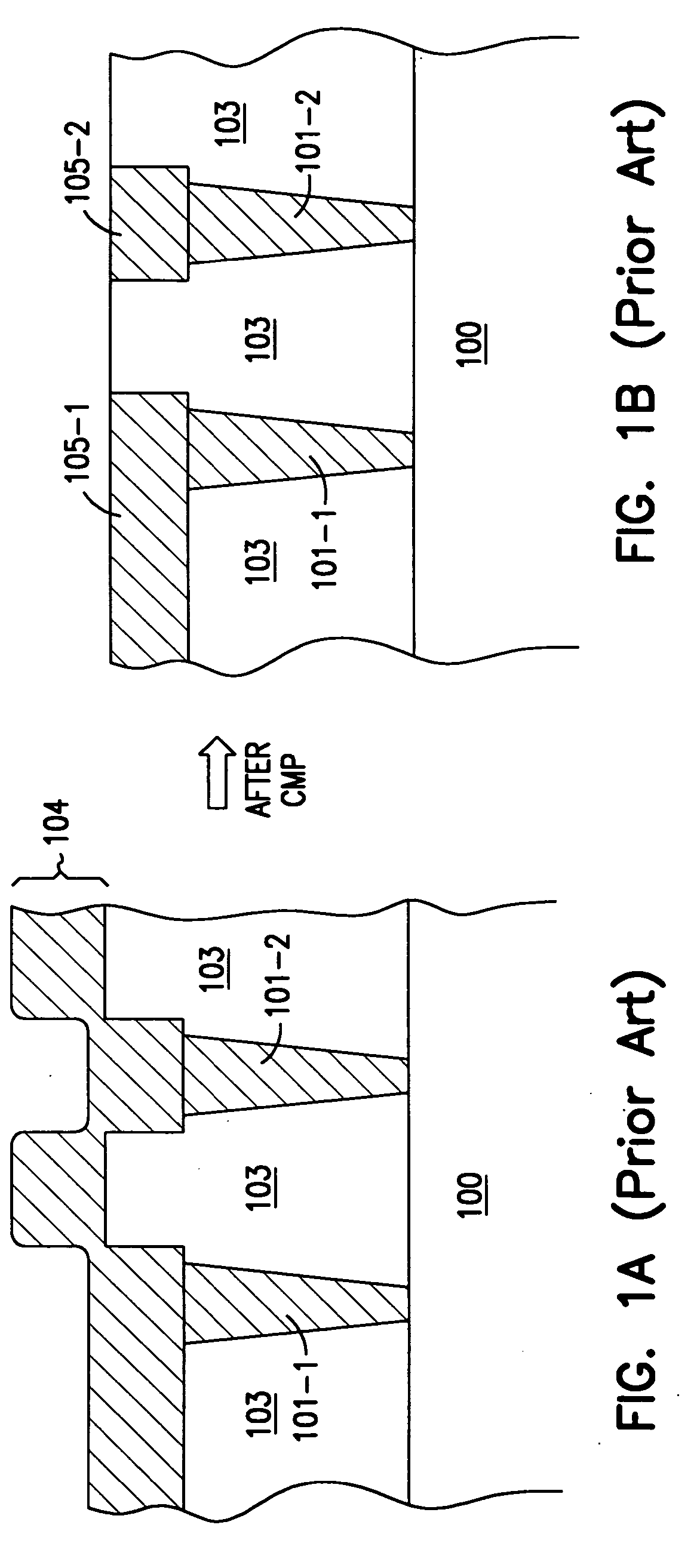
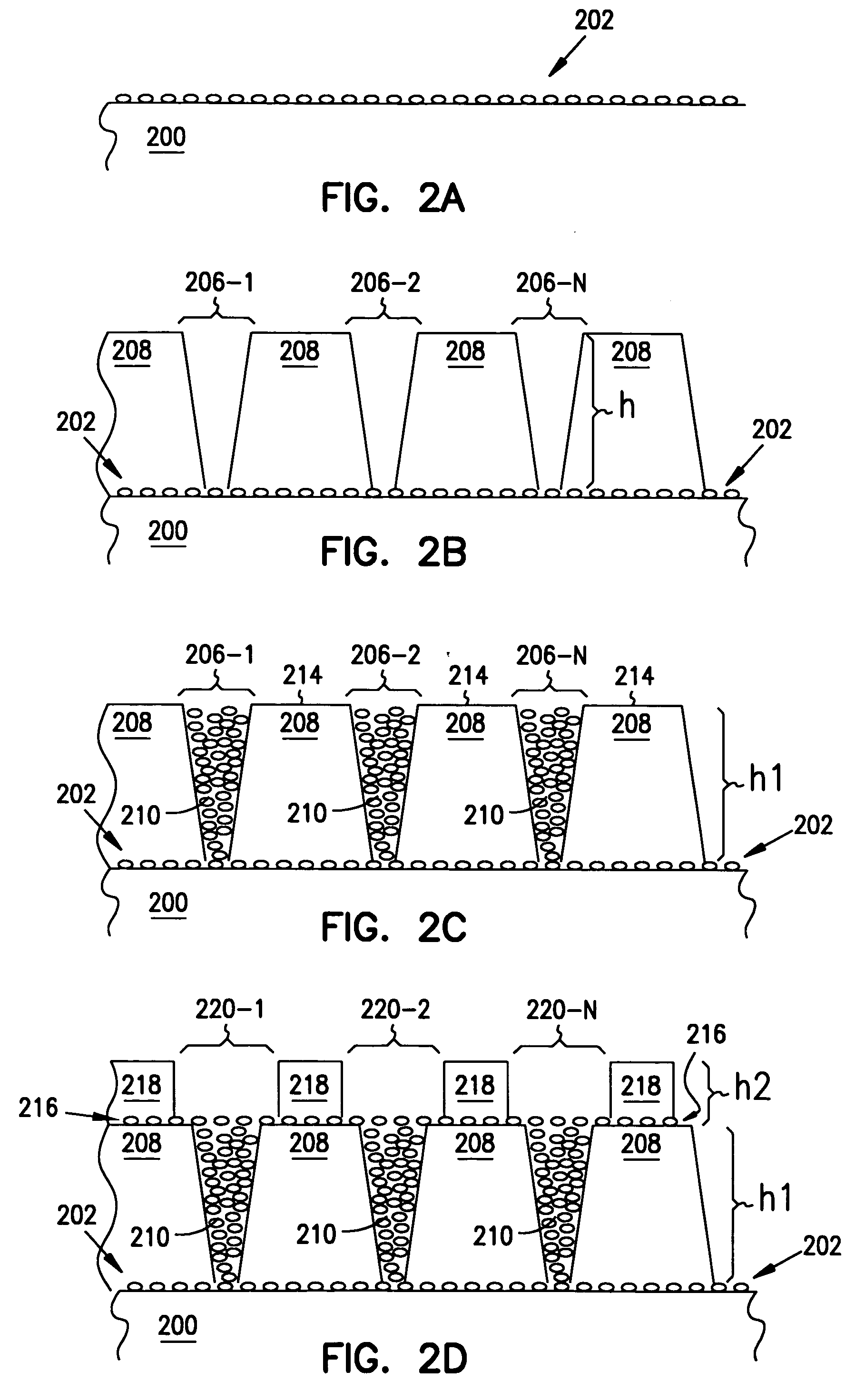
Structures and methods are provided which include a selective electroless copper metallization. The present invention includes a novel methodology for forming copper vias on a substrate, including depositing a thin film seed layer of Palladium (Pd) or Copper (Cu) on a substrate to a thickness of less than 15 nanometers (nm). A number of via holes is defined above the seed layer. A layer of copper is deposited over the seed layer using electroless plating to fill the via holes to a top surface of the patterned photoresist layer. The method can be repeated any number of times, forming second, third and fourth layers of copper. The photoresist layers along with the seed layers in other regions can then be removed, such as by oxygen plasma etching, such that a chemical mechanical planarization process is avoided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com