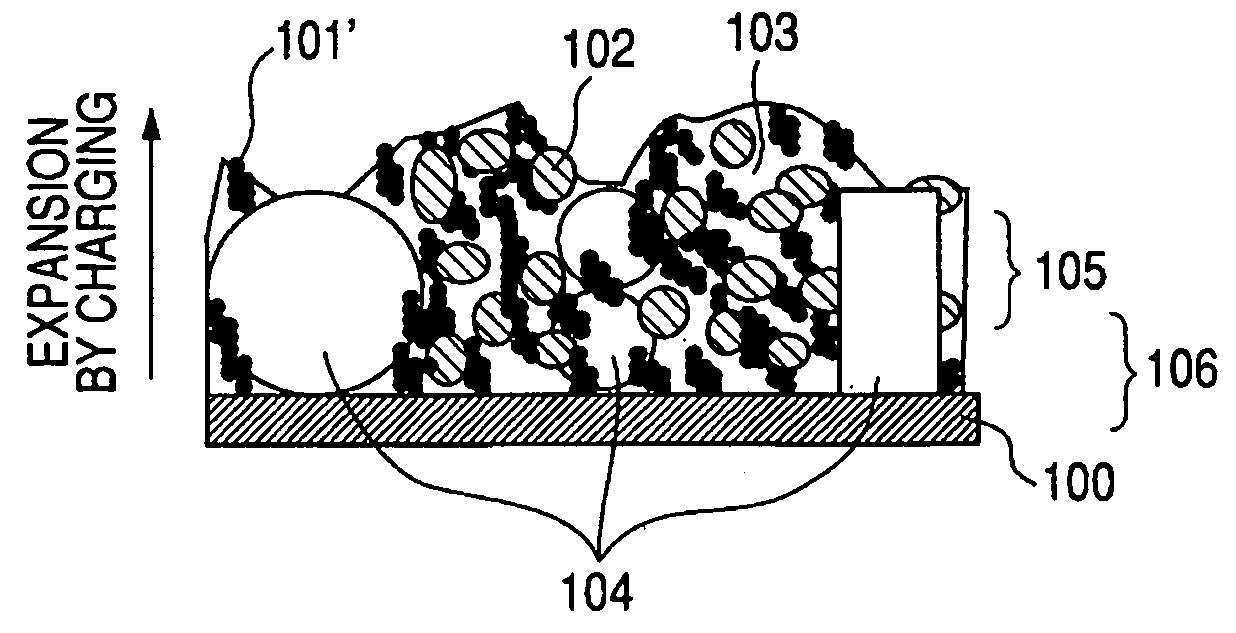
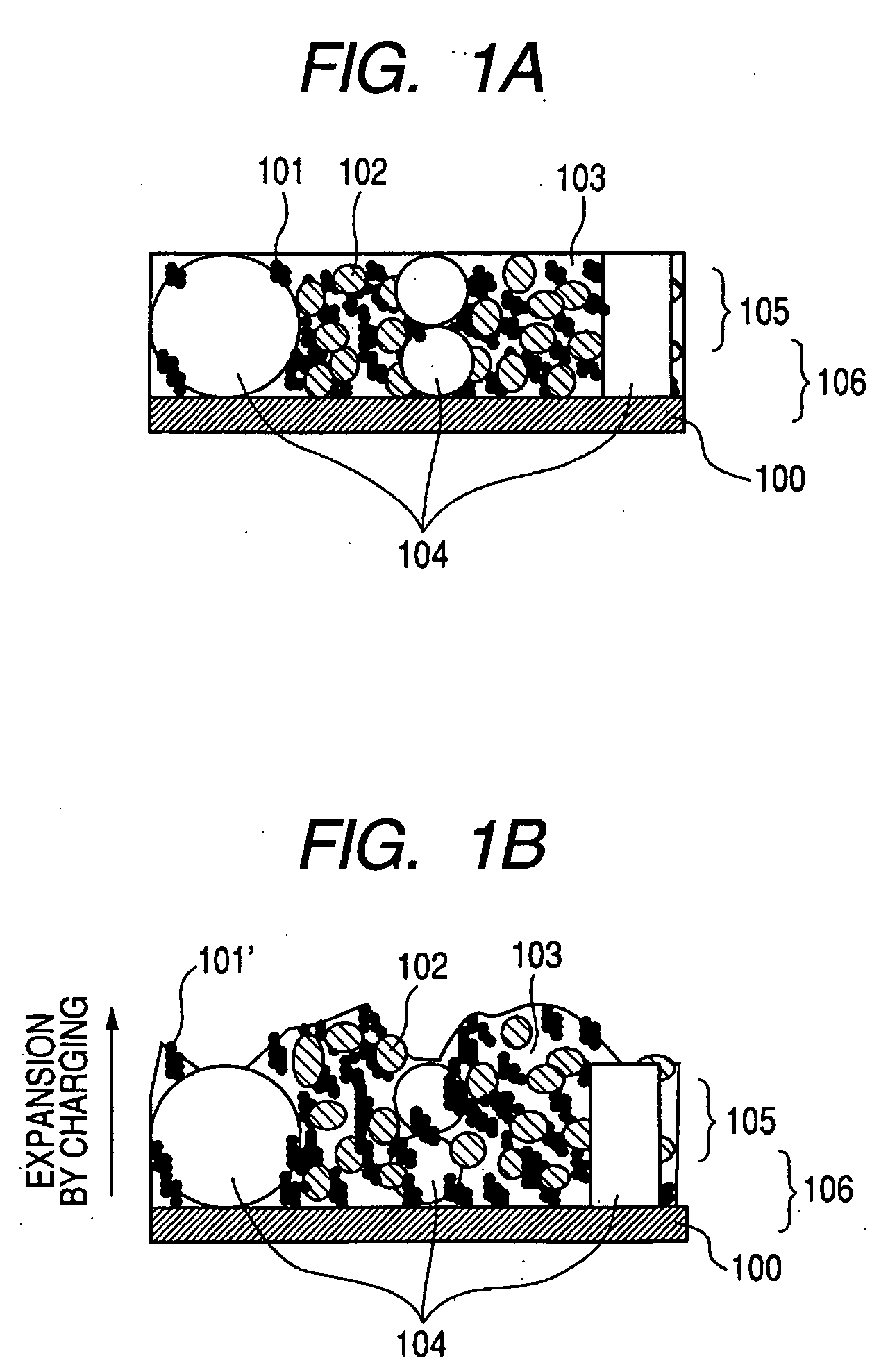
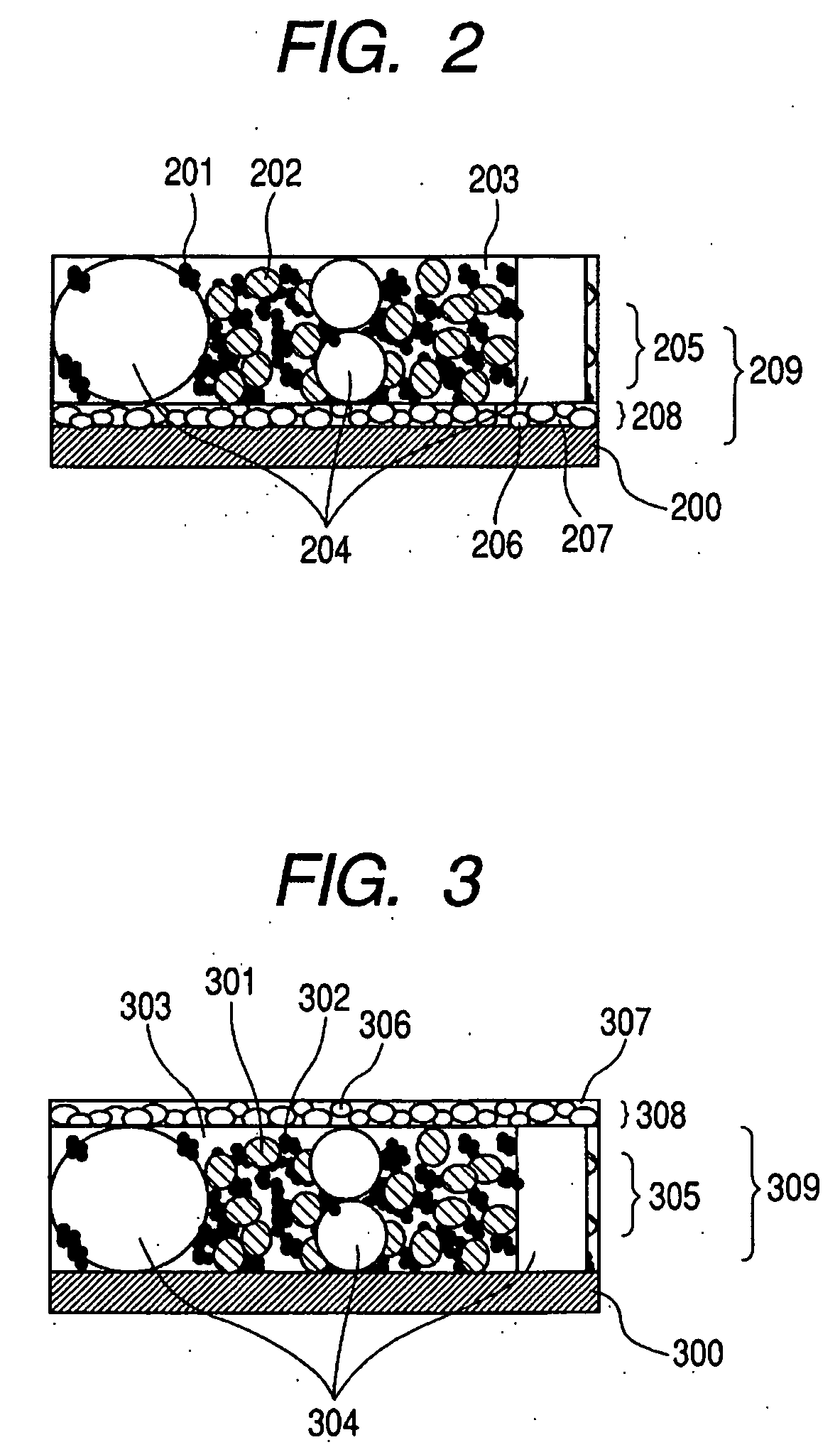
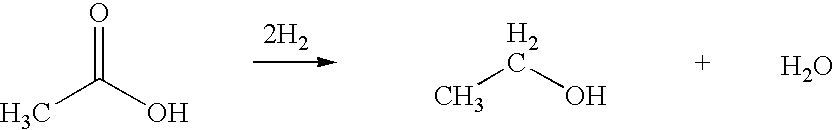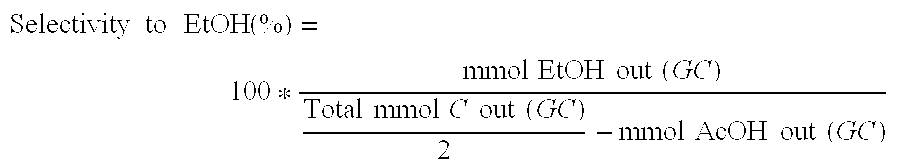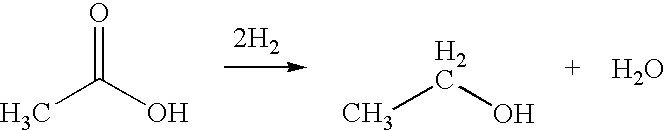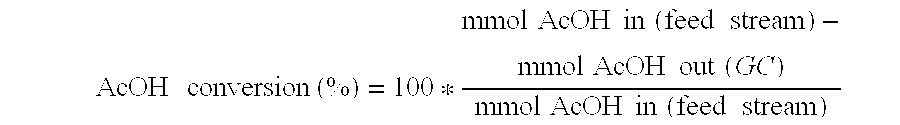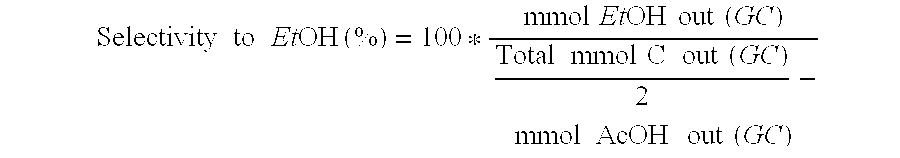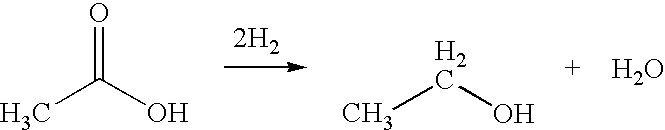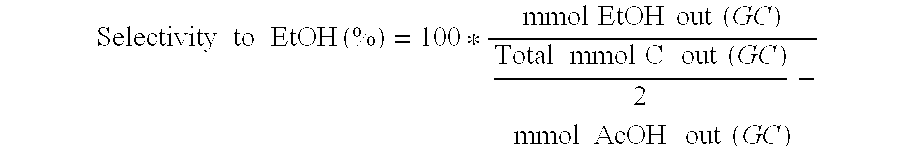Patents
Literature
65442 results about "Graphite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
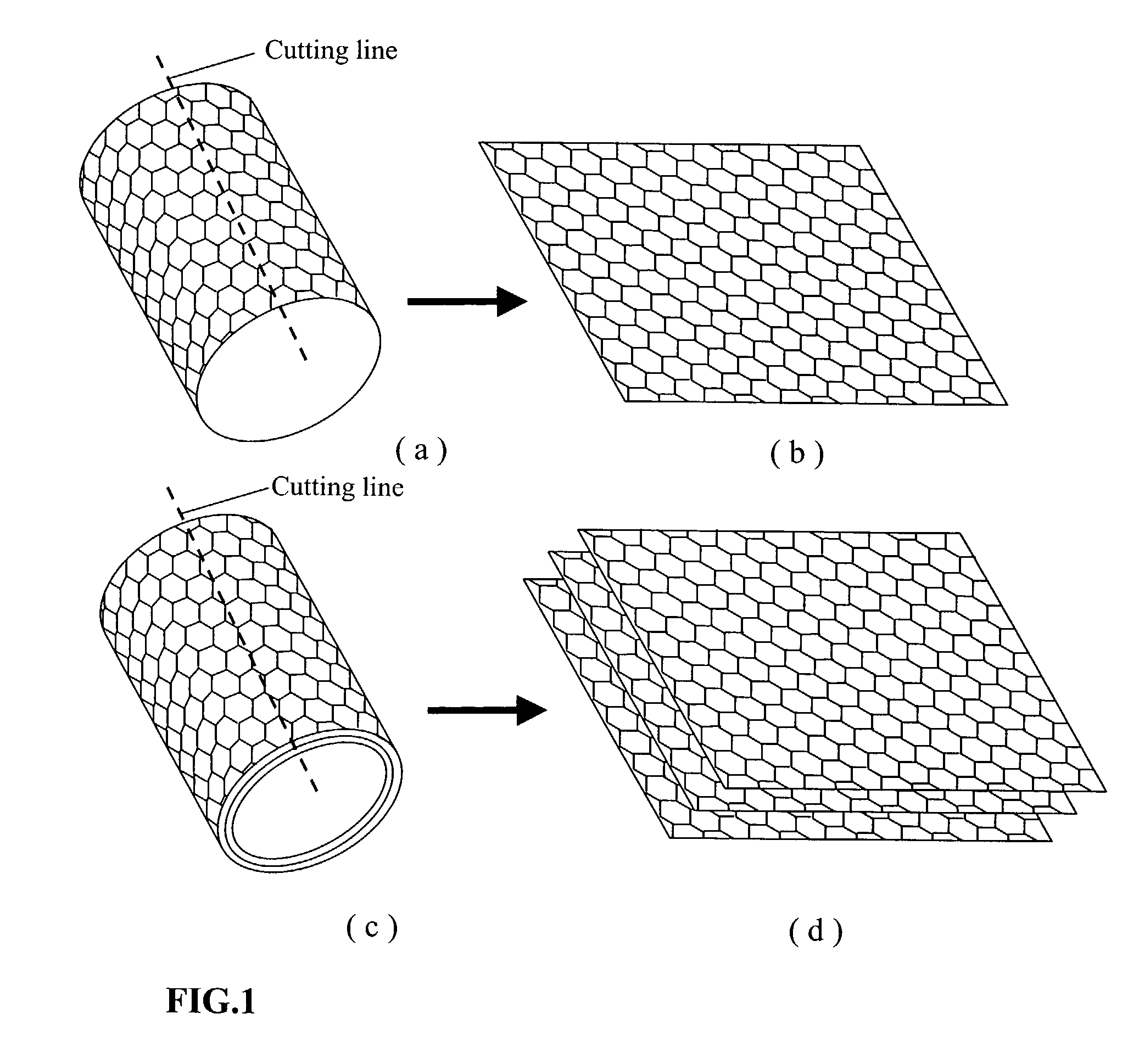
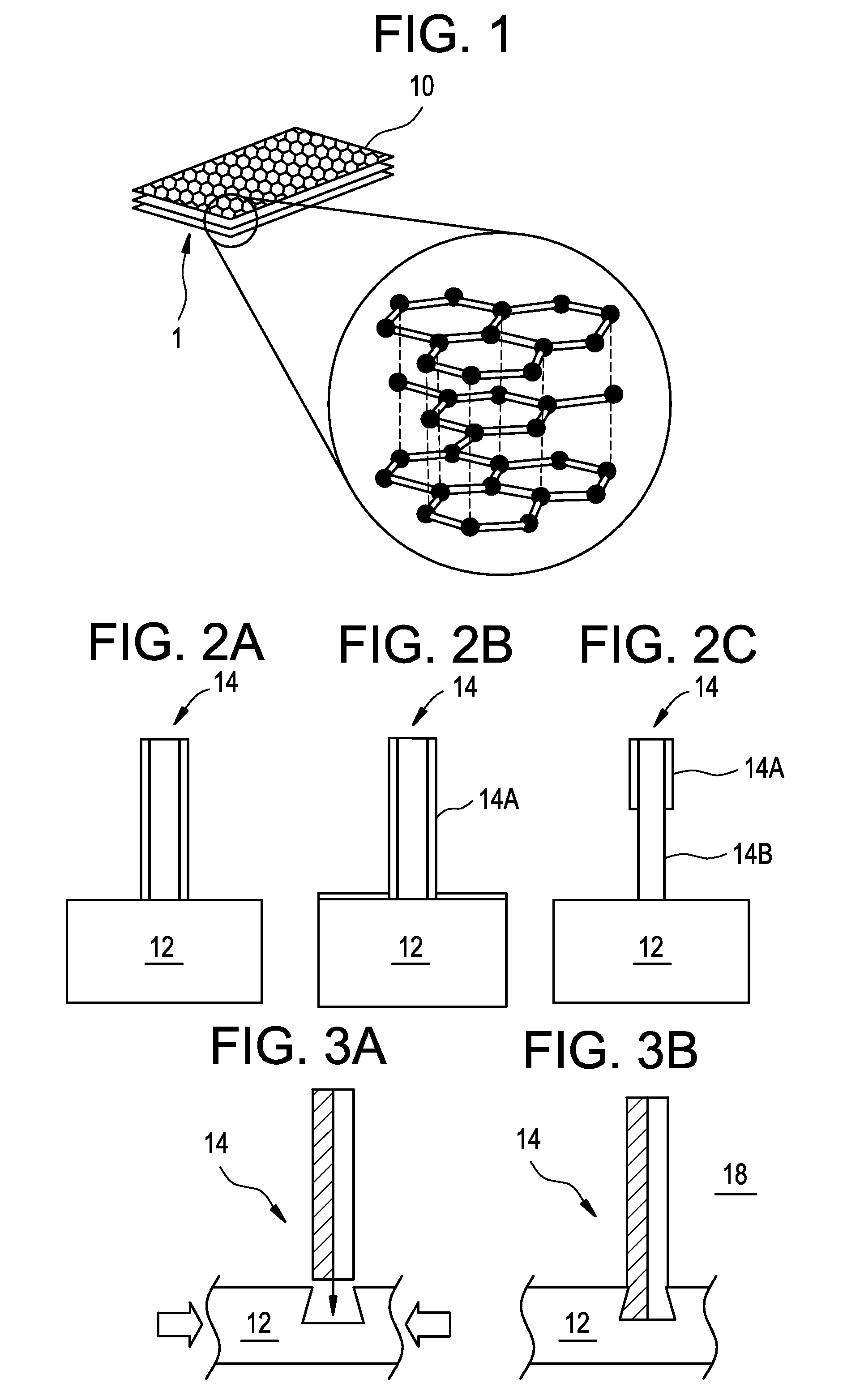
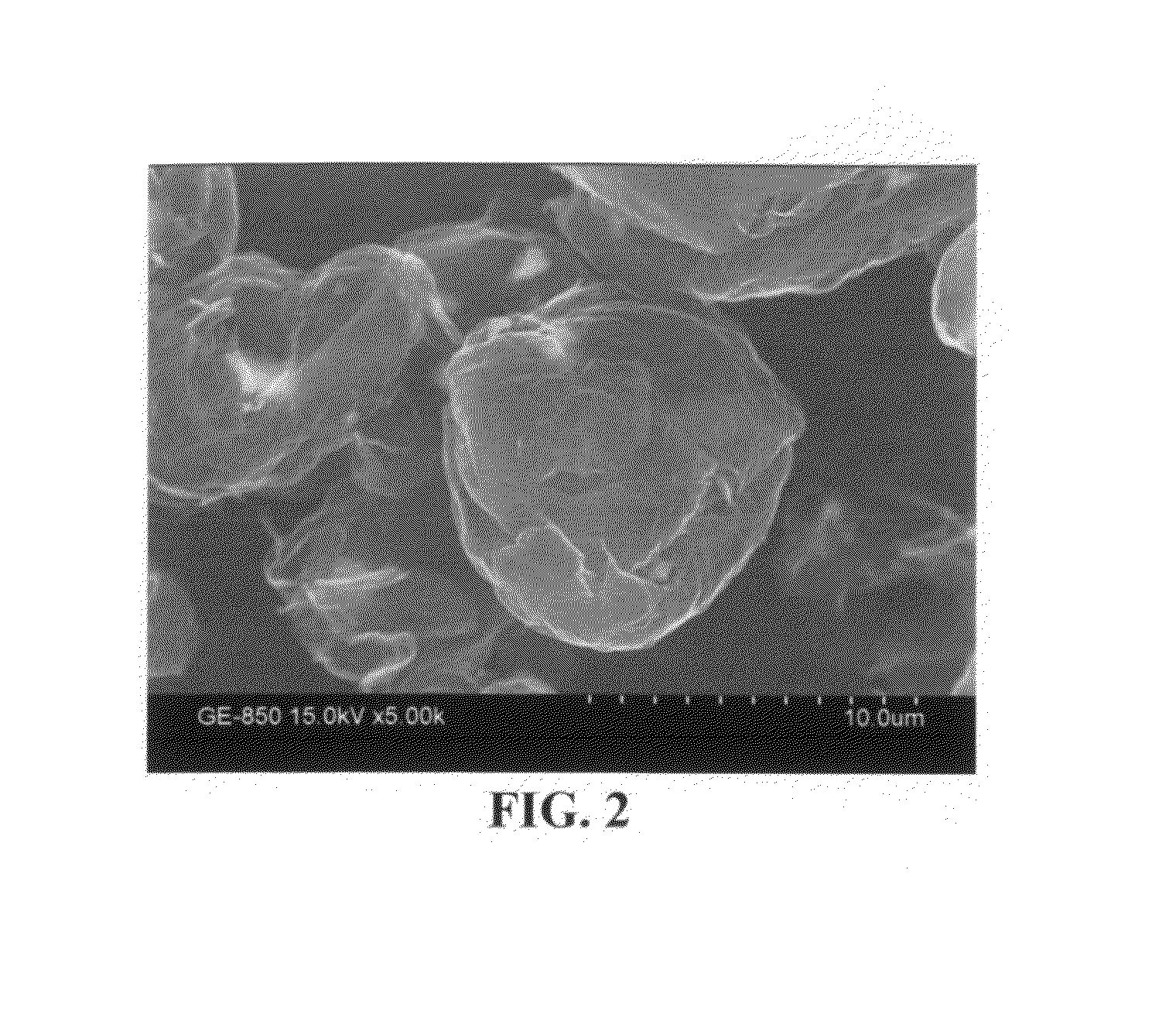
Graphite (/ˈɡræfaɪt/), archaically referred to as plumbago, is a crystalline form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a hexagonal structure. It occurs naturally in this form and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. Graphite is used in pencils and lubricants. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity. Its high conductivity makes it useful in electronic products such as electrodes, batteries, and solar panels.
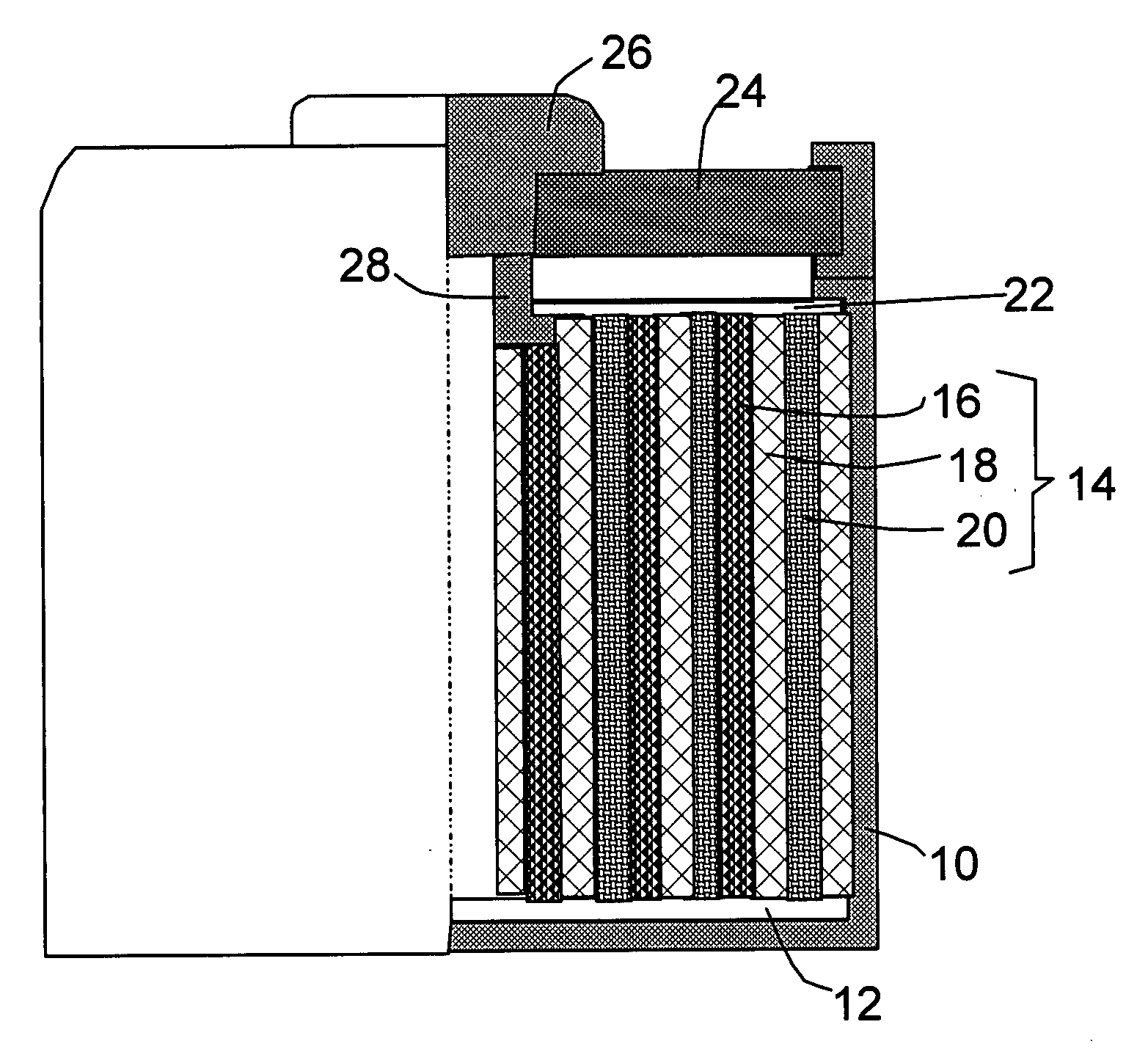
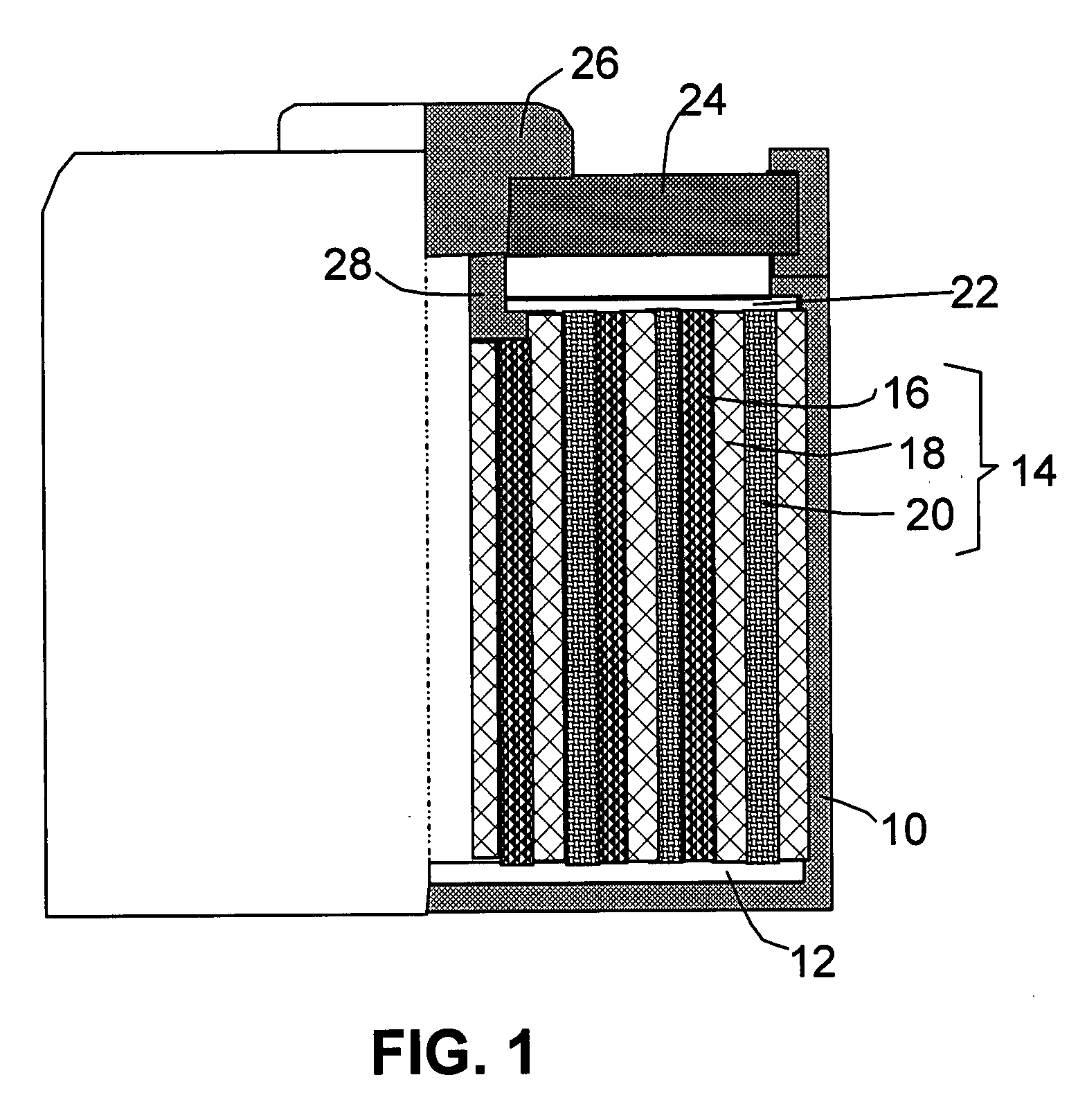
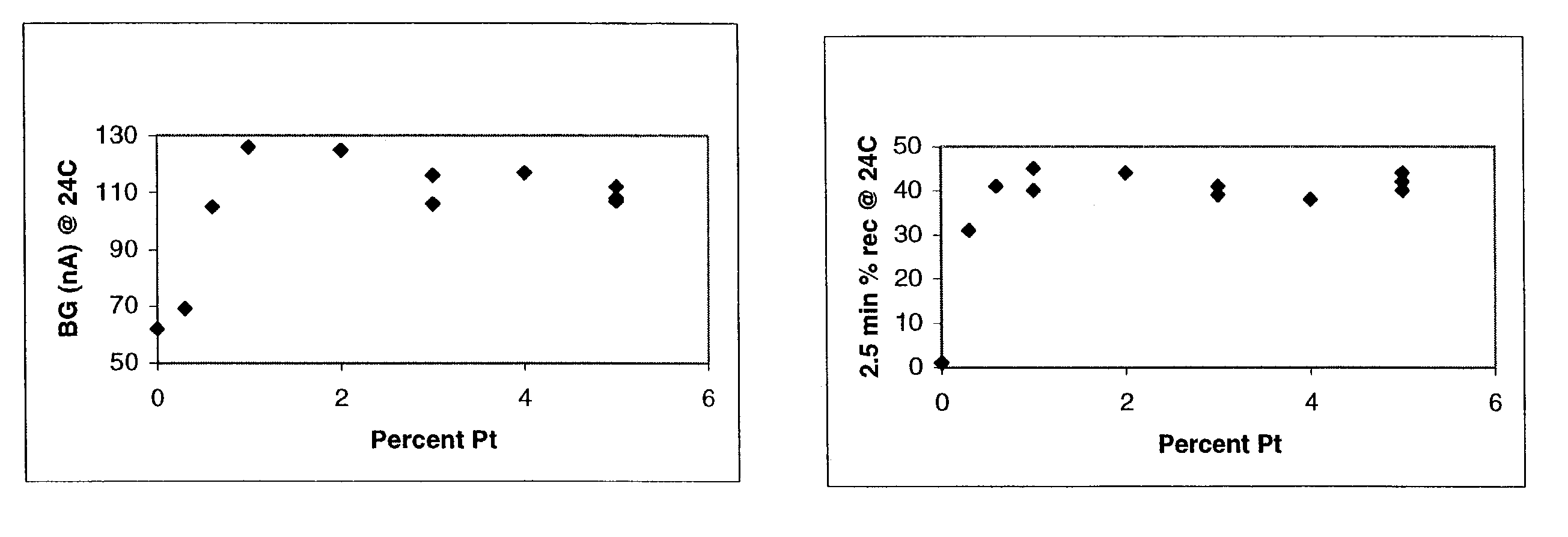
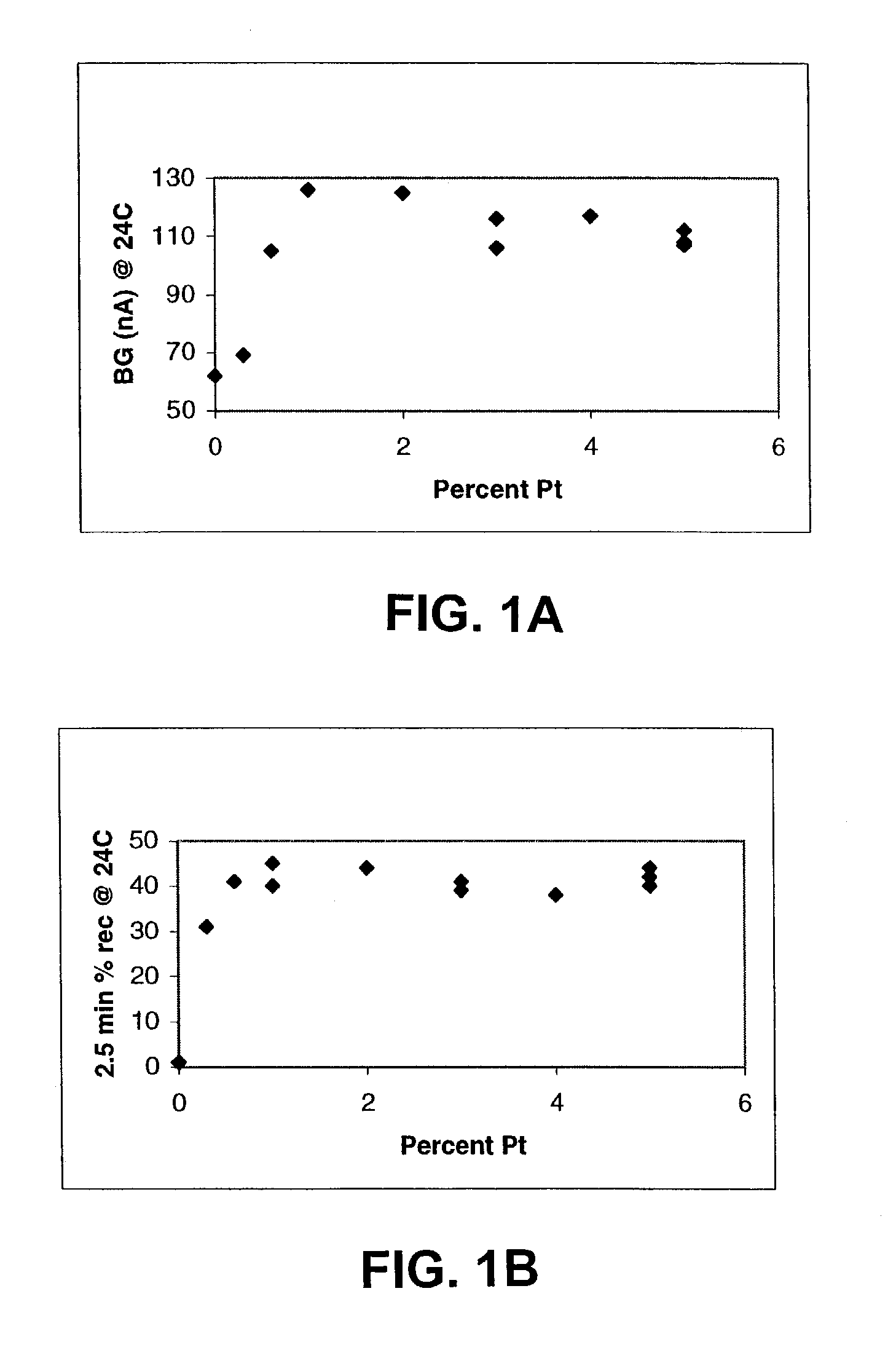
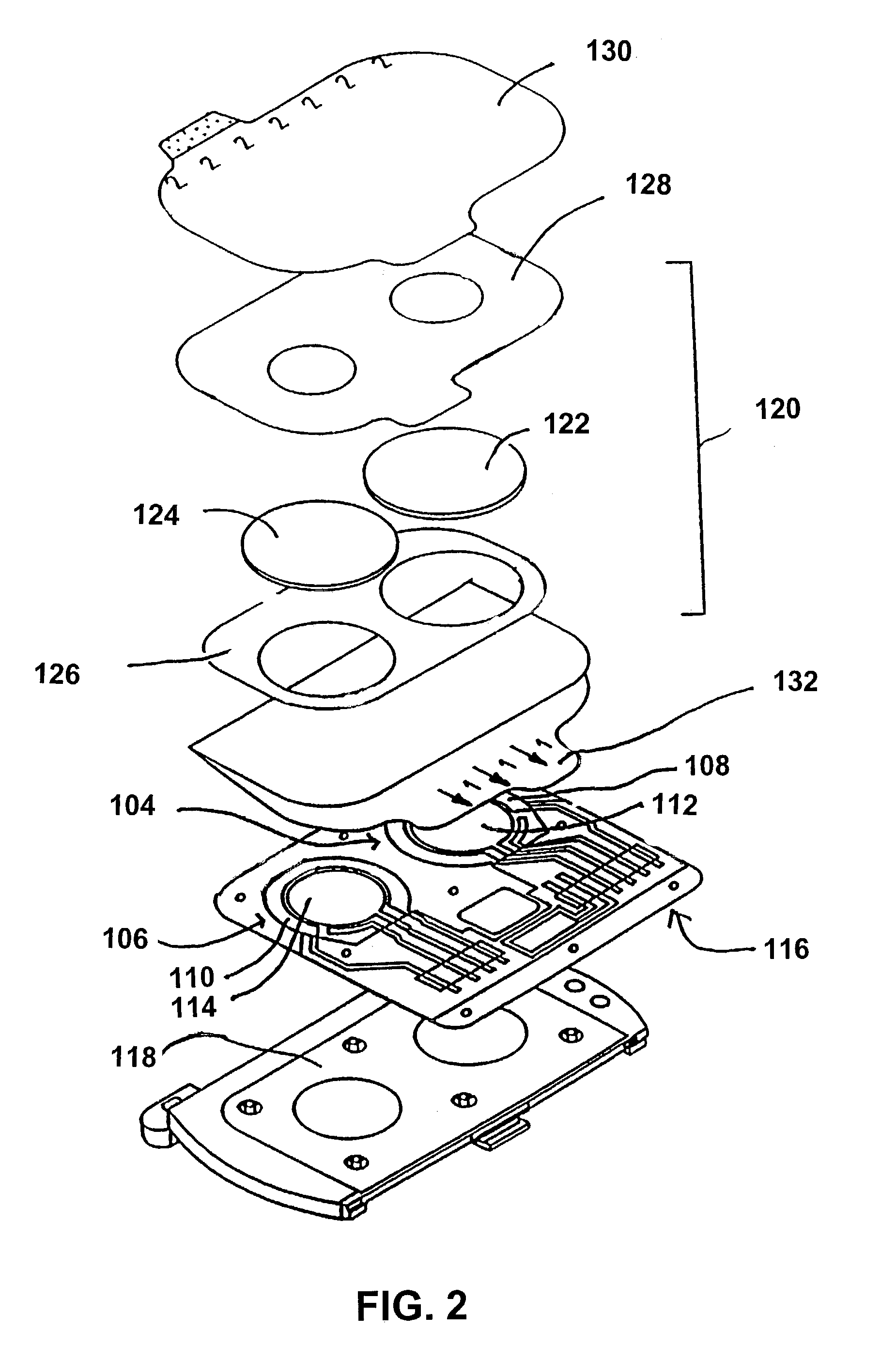
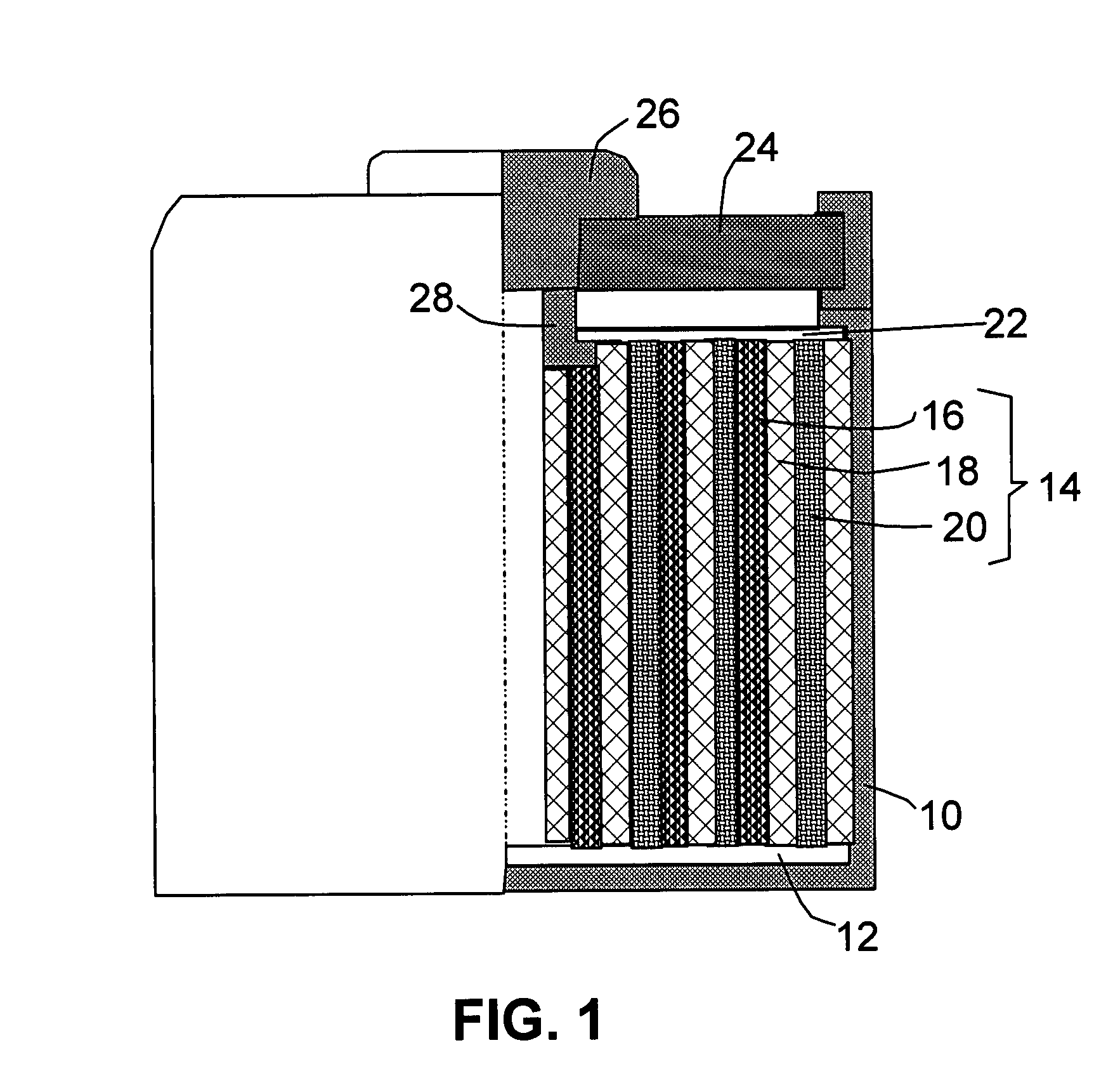
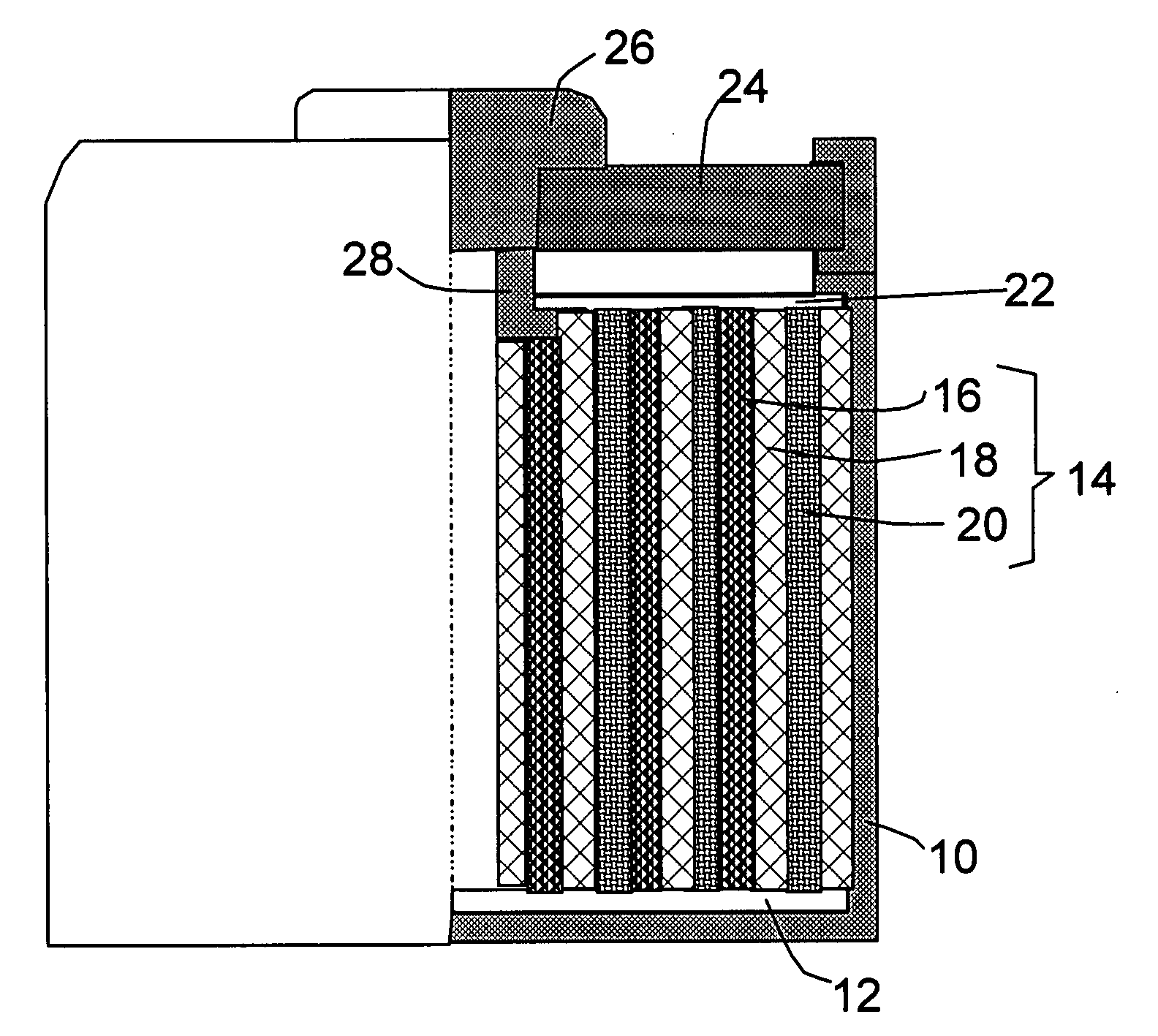
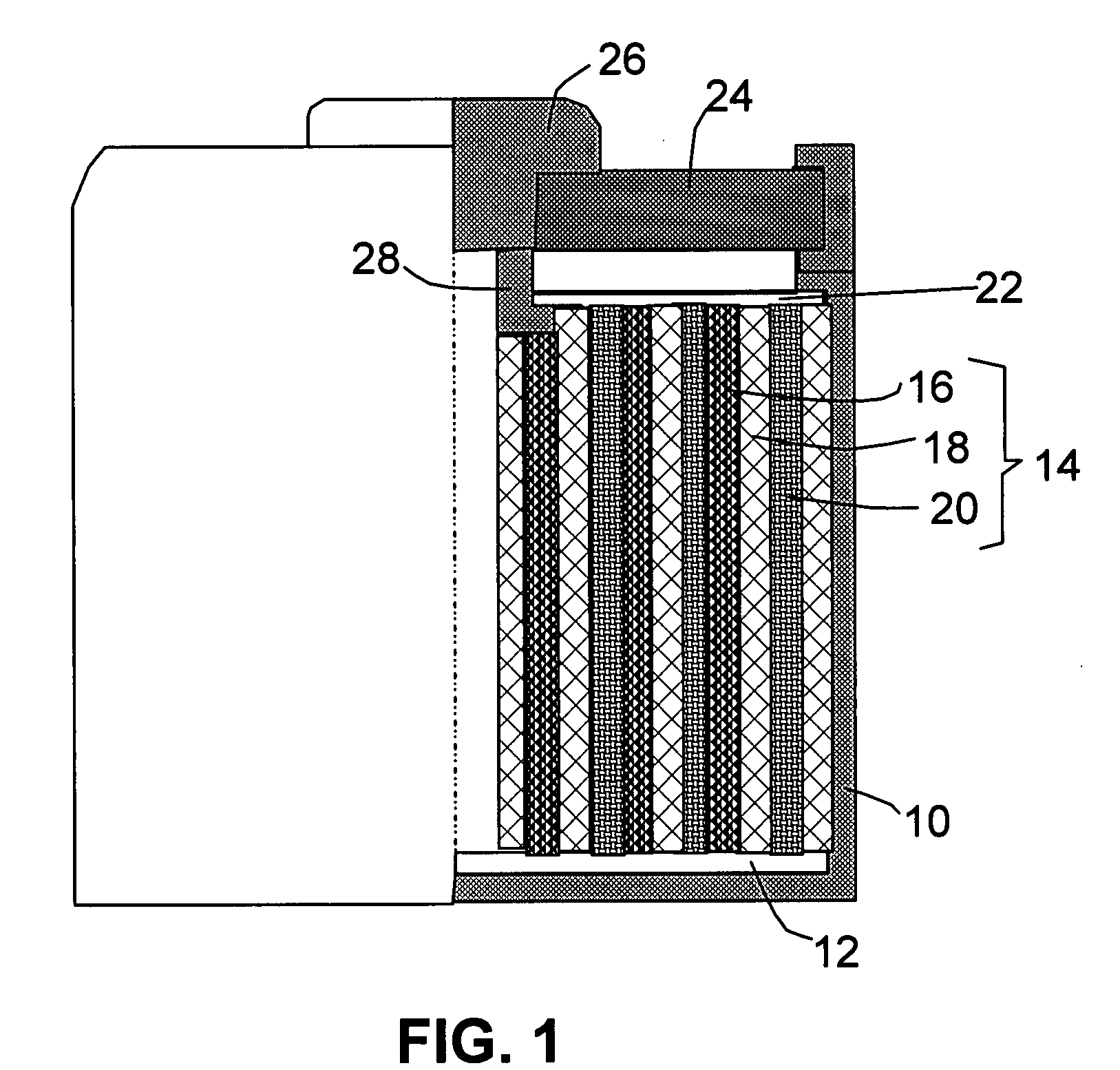
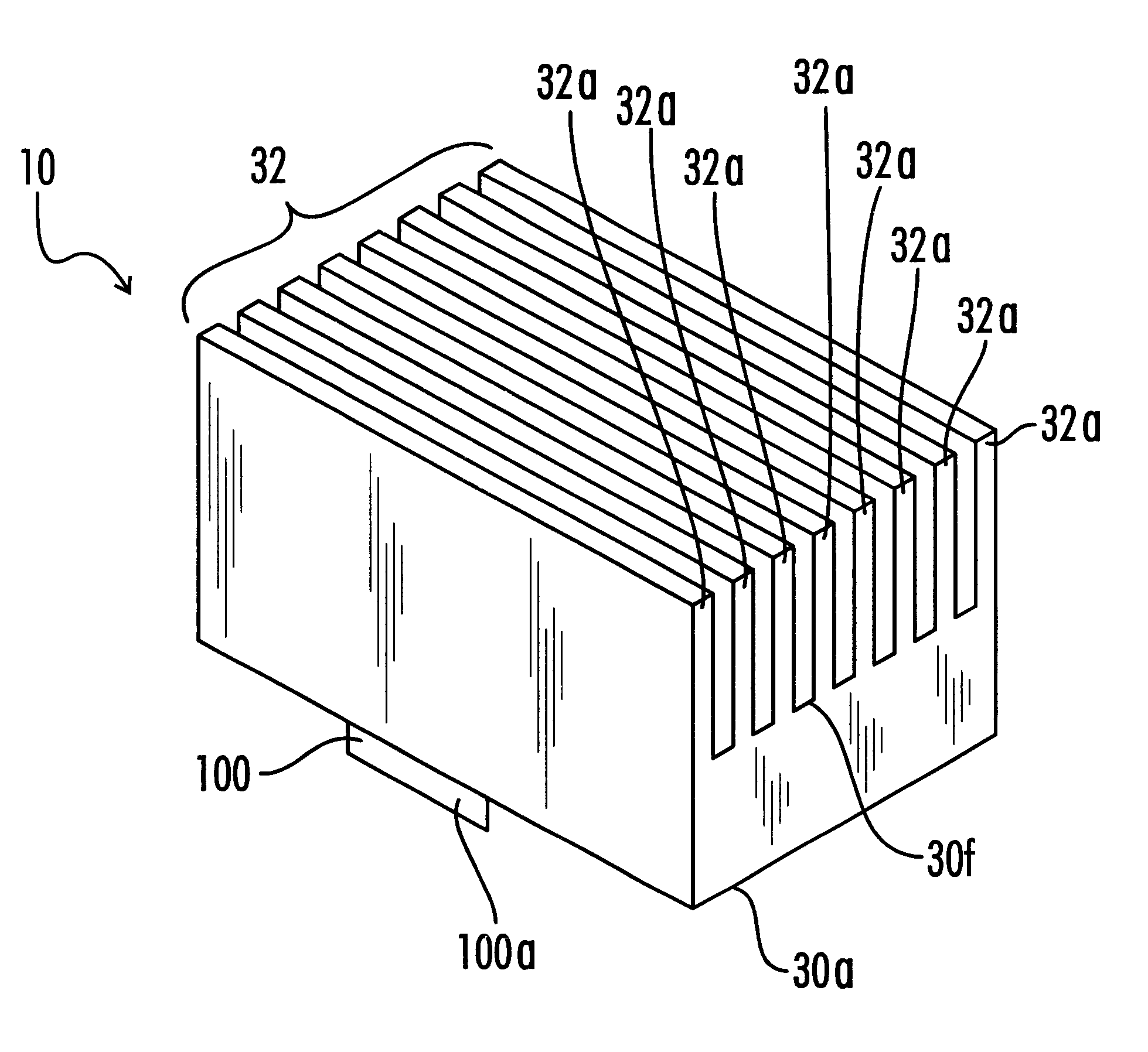
Surgical sealing surfaces and methods of use
ActiveUS7220951B2Fast transferHighly stable current-limitingDielectric heatingSurgical instruments for heatingOmni directionalSwitching time
Various embodiments provide compositions that exhibit positive temperature coefficient of resistance (PTCR) properties for use in thermal interactions with tissue—including thermal sensing and I2R current-limiting interactions. Embodiments also provide tissue-engaging surfaces having PTCR materials that provide very fast switching times between low resistance and high, current-limiting resistance. One embodiment provides a matrix for an electrosurgical energy delivery surface comprising a PTCR material and a heat exchange material disposed within an interior of the matrix. The PTCR material has a substantially conductive state and a substantially non-conductive state. The heat exchange material has a structure configured to have an omni-directional thermal diffusivity for exchanging heat with the PTCR material to cause rapid switching of the PTCR material between the conductive state and non-conductive state. Preferably, the structure comprises a graphite foam having an open cell configuration. The matrix can be carried by tissue contacting surfaces of various electrosurgical devices.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Nano-scaled graphene plates
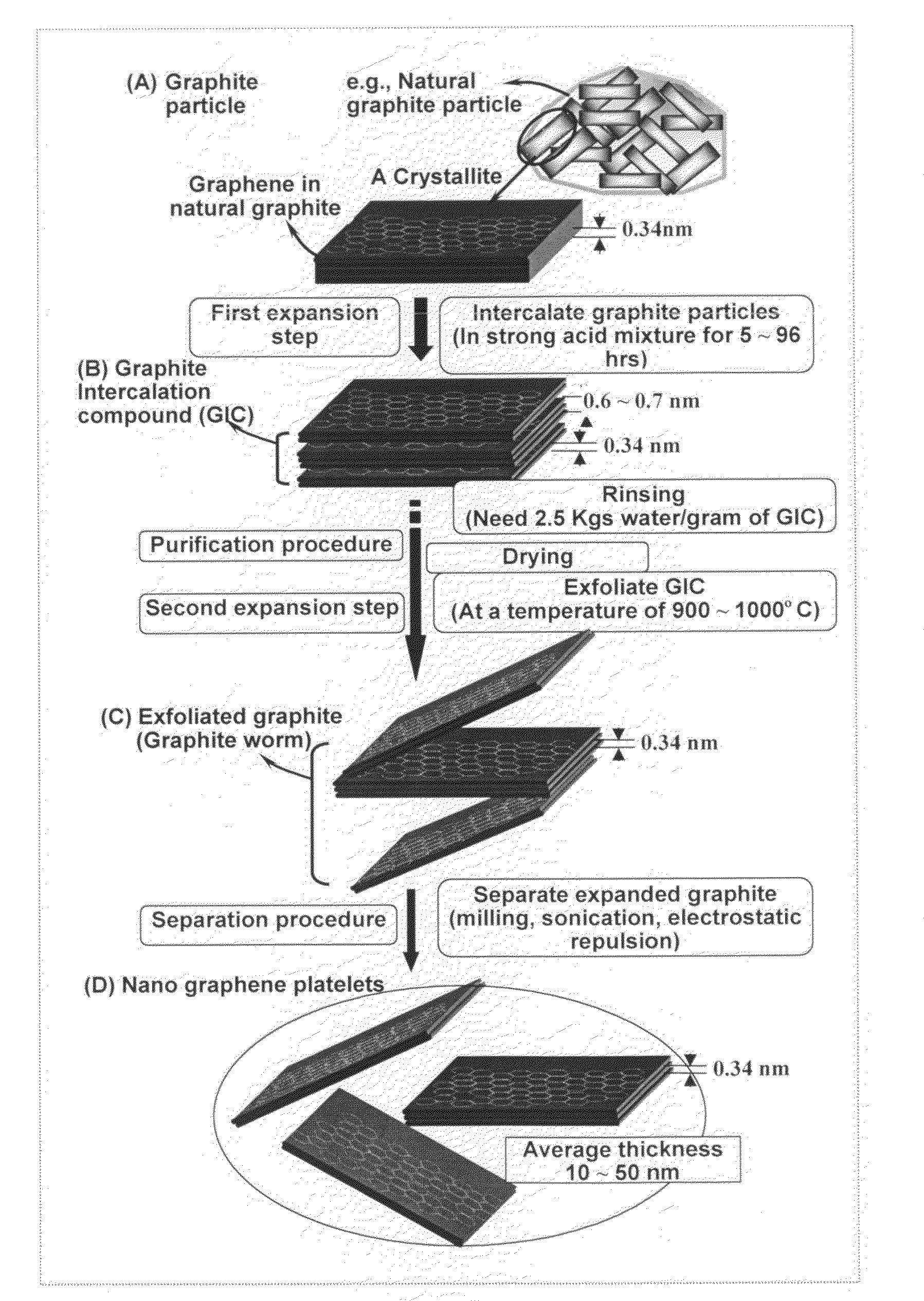
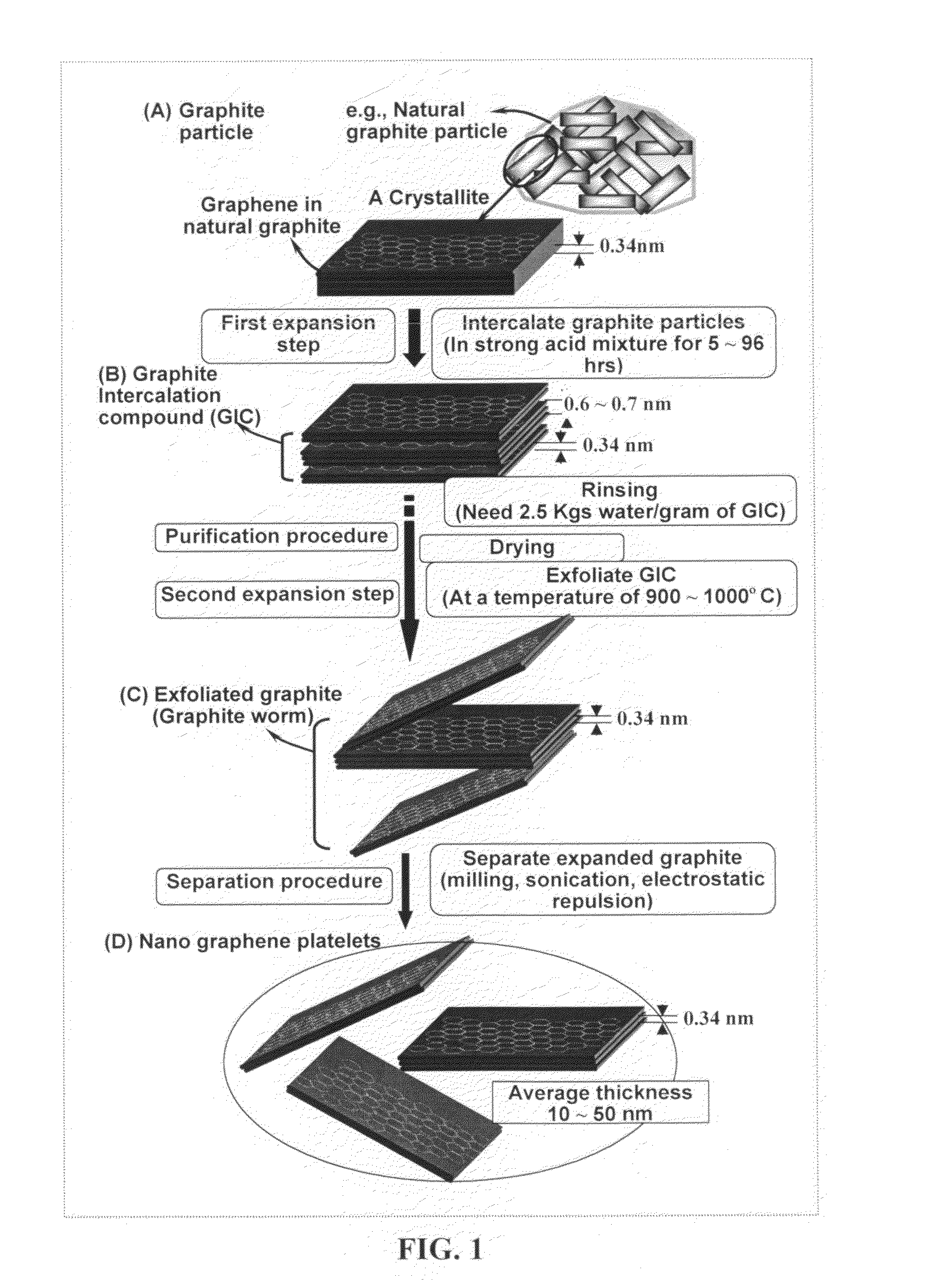
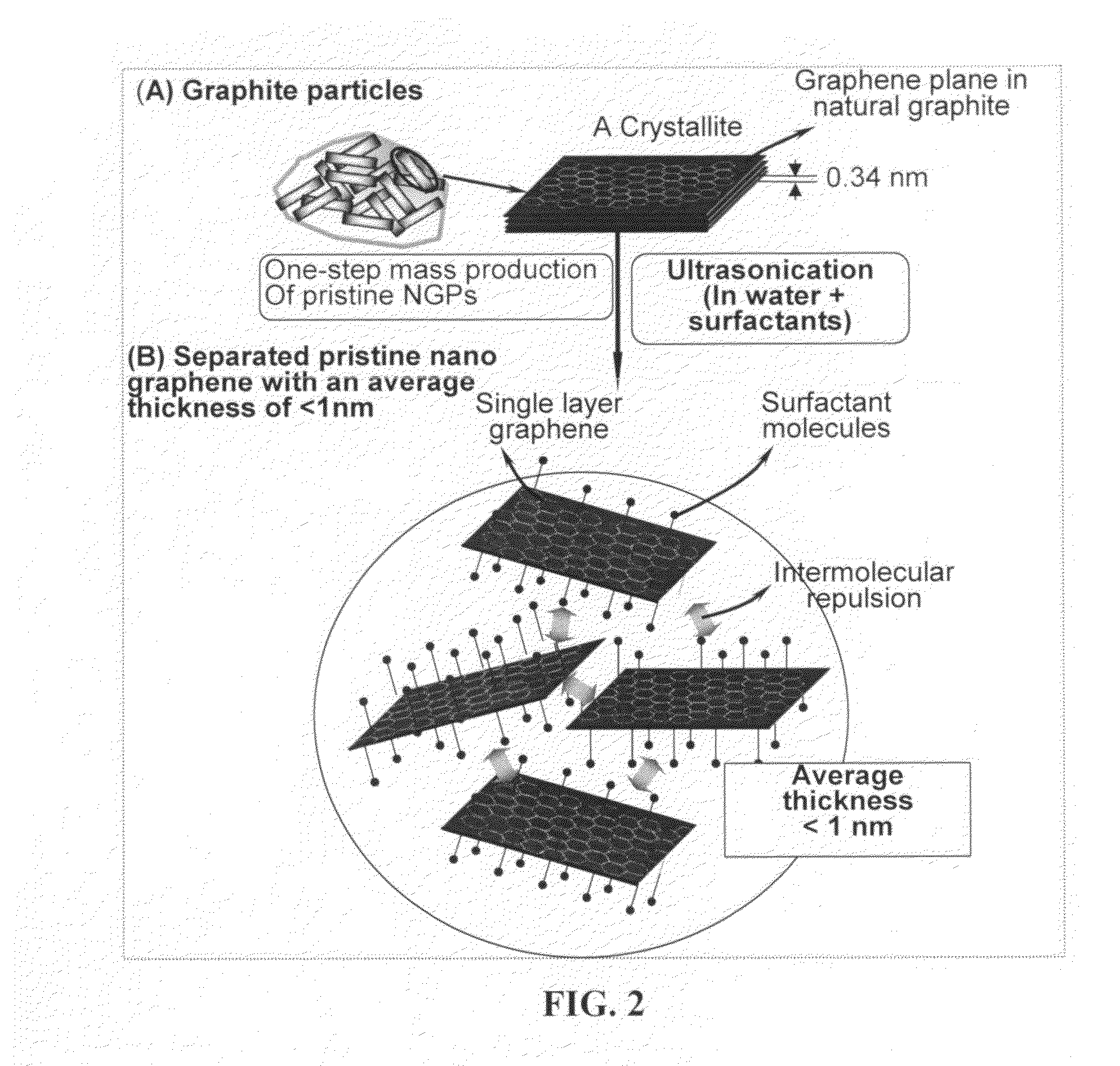
A nano-scaled graphene plate material and a process for producing this material. The material comprises a sheet of graphite plane or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane. The graphite plane is composed of a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms and the plate has a length and a width parallel to the graphite plane and a thickness orthogonal to the graphite plane with at least one of the length, width, and thickness values being 100 nanometers or smaller. The process for producing nano-scaled graphene plate material comprises the steps of: a). partially or fully carbonizing a precursor polymer or heat-treating petroleum or coal tar pitch to produce a polymeric carbon containing micron- and / or nanometer-scaled graphite crystallites with each crystallite comprising one sheet or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane; b). exfoliating the graphite crystallites in the polymeric carbon; and c). subjecting the polymeric carbon containing exfoliated graphite crystallites to a mechanical attrition treatment to produce the nano-scaled graphene plate material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Ethanol production from acetic acid utilizing a cobalt catalyst
InactiveUS7608744B1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidPlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either cobalt and palladium supported on graphite or cobalt and platinum supported on silica selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS7863489B2High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicateAcetic acid
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method of making functionalized nanotubes
InactiveUS6203814B1Good dispersionImprove adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsChemical MoietyFiber
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
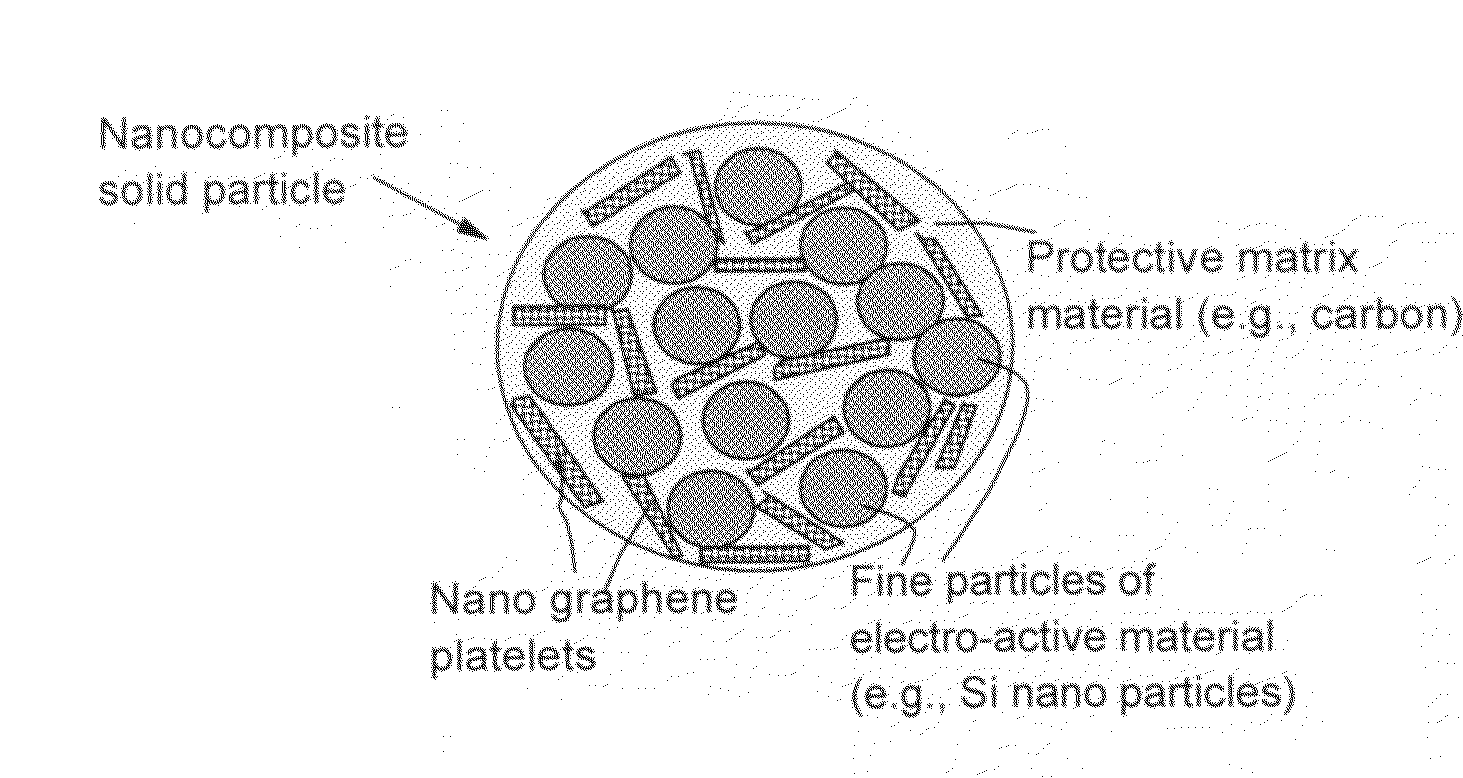
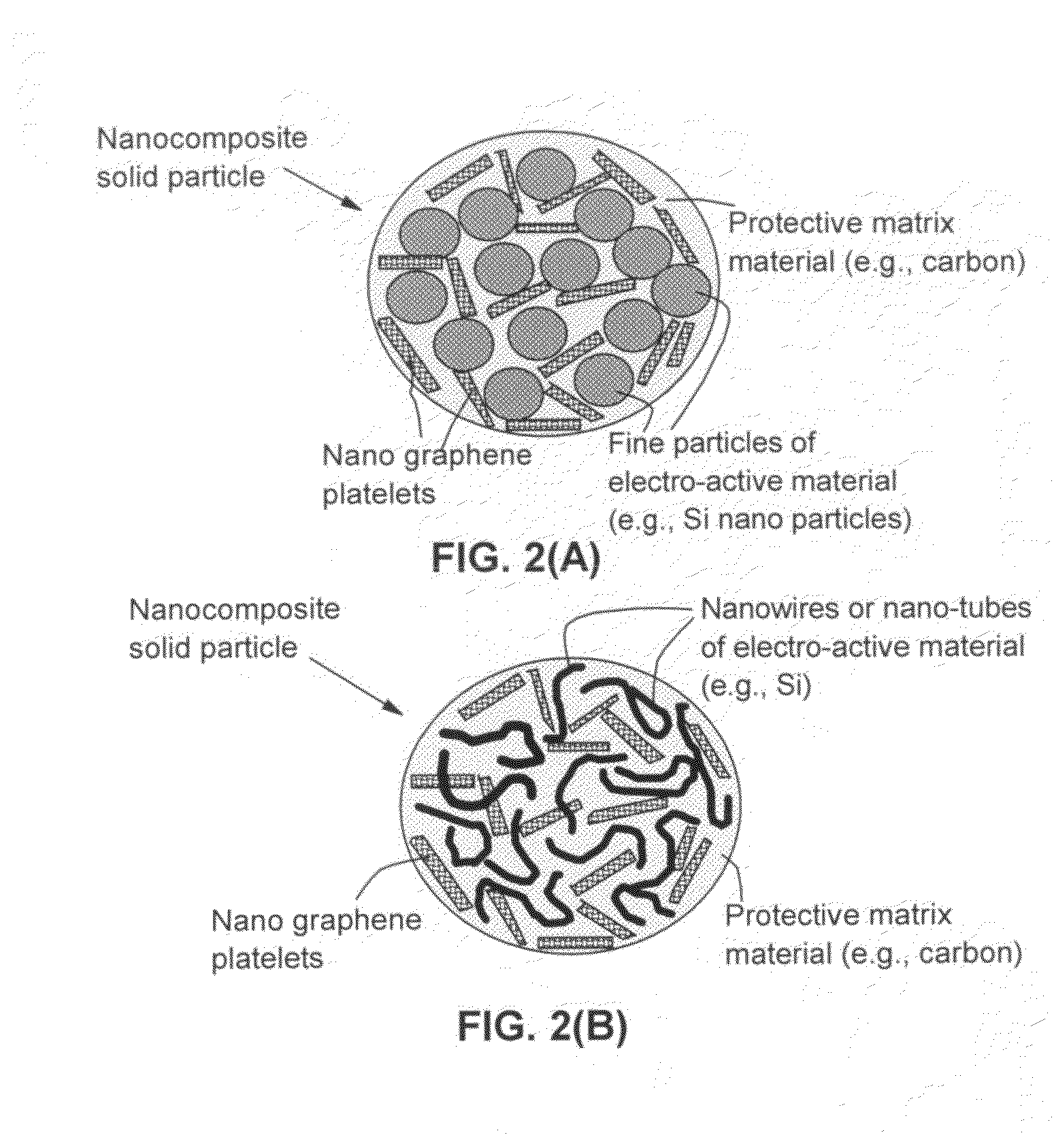
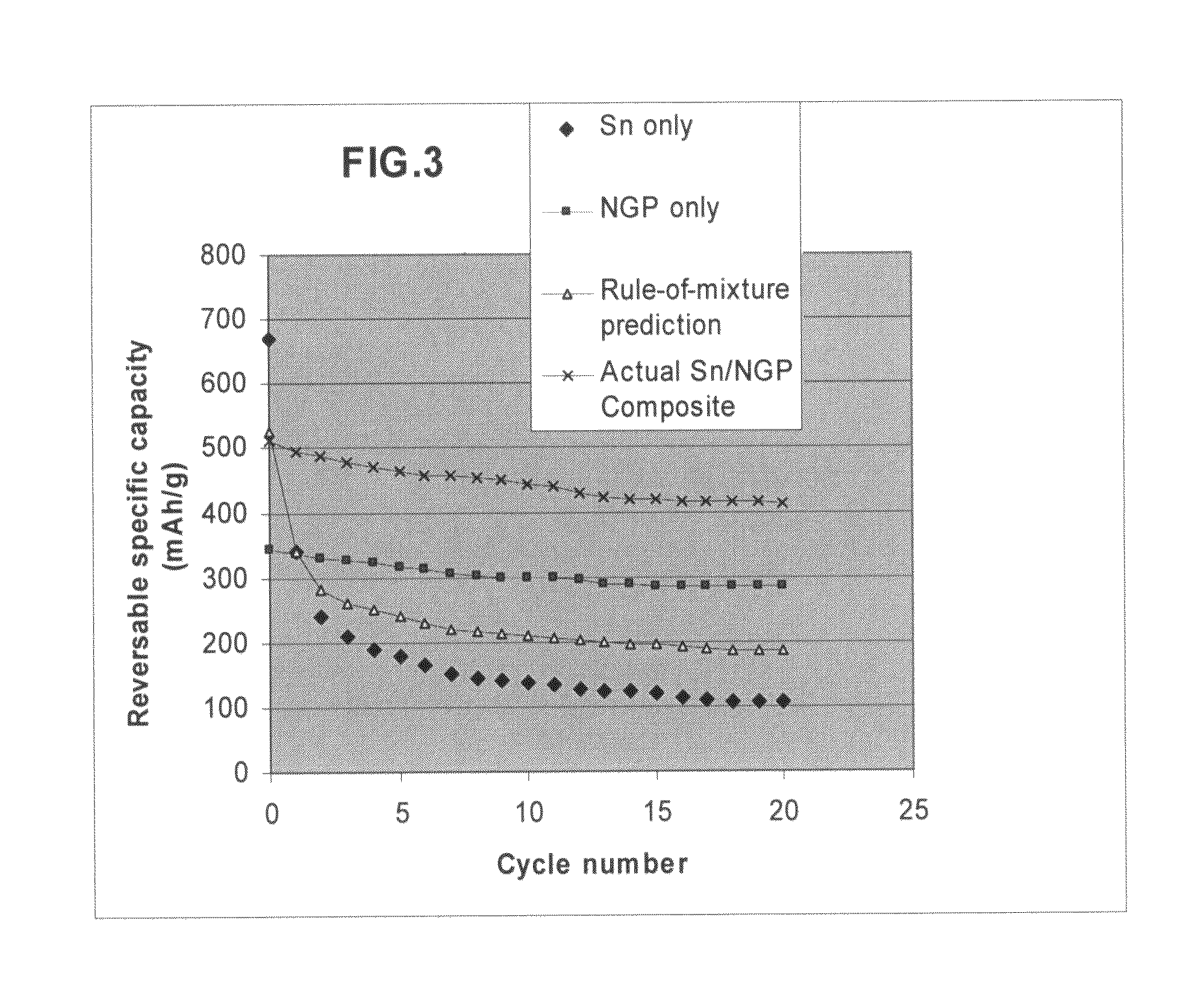
Nano graphene reinforced nanocomposite particles for lithium battery electrodes
ActiveUS20100143798A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthActive material electrodesSecondary cellsLithium metalNanocomposite
A solid nanocomposite particle composition for lithium metal or lithium ion battery electrode applications. The composition comprises: (A) an electrode active material in a form of fine particles, rods, wires, fibers, or tubes with a dimension smaller than 1 μm; (B) nano graphene platelets (NGPs); and (C) a protective matrix material reinforced by the NGPs; wherein the graphene platelets and the electrode active material are dispersed in the matrix material and the NGPs occupy a weight fraction wg of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, the electrode active material occupies a weight fraction wa of 1% to 90% of the total nanocomposite weight, and the matrix material occupies a weight fraction wm of at least 2% of the total nanocomposite weight with wg+wa+wm=1. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon, polymeric carbon, or meso-phase carbon. Such a solid nanocomposite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling stability. For a cathode application, the resulting lithium metal or lithium ion battery exhibits an exceptionally high cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nano graphene platelet-based composite anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20090117467A1Improve conductivityLower internal resistanceElectrolytic capacitorsSecondary cellsGraphene flakeGraphite
The present invention provides a nano-scaled graphene platelet-based composite material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing lithium ions; and (b) a plurality of nano-scaled graphene platelets (NGPs), wherein a platelet comprises a graphene sheet or a stack of graphene sheets having a platelet thickness less than 100 nm; wherein at least one of the particles or coating is physically attached or chemically bonded to at least one of the graphene platelets and the amount of platelets is in the range of 2% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating in the range of 98% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, an excellent reversible capacity, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
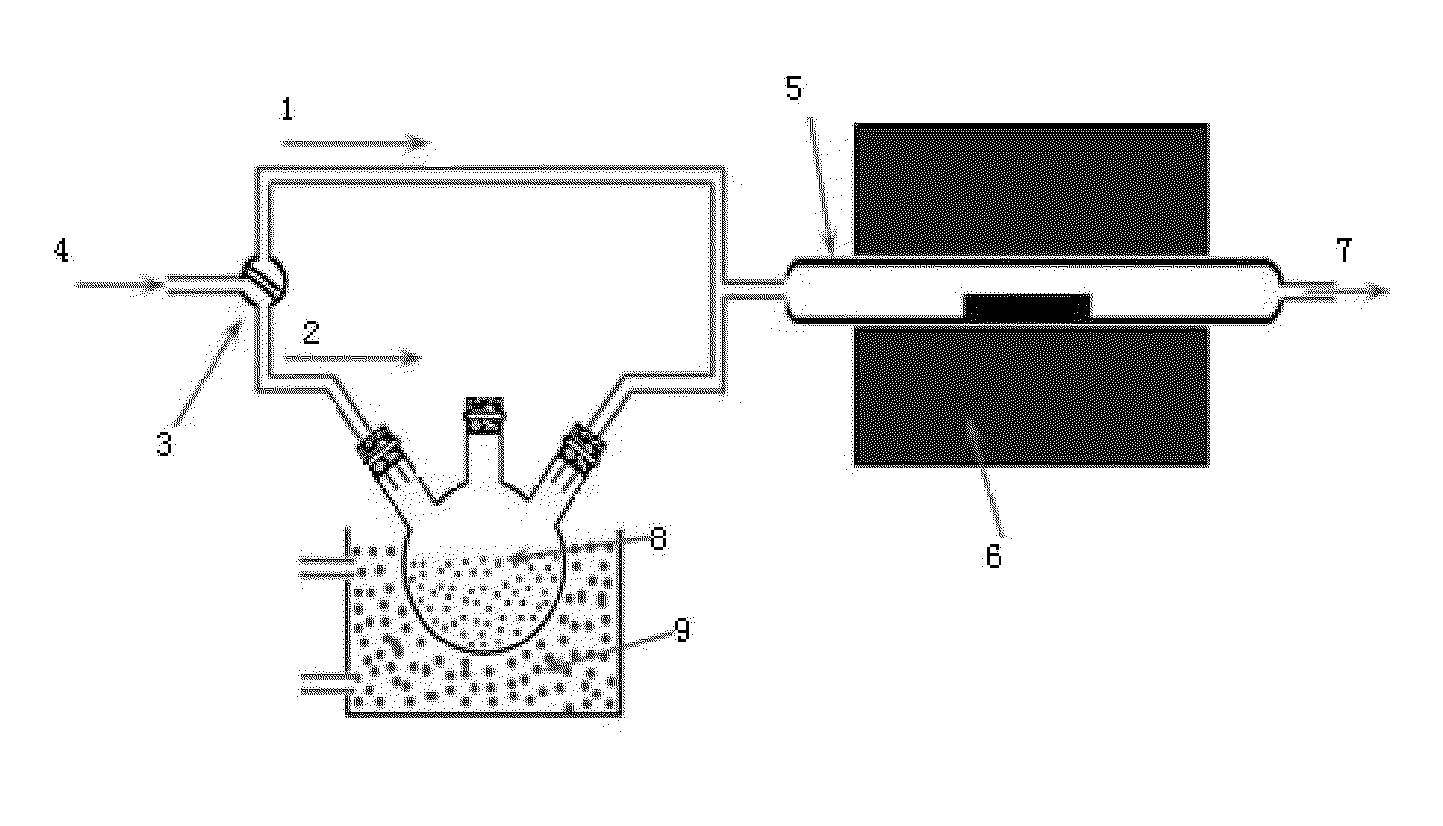
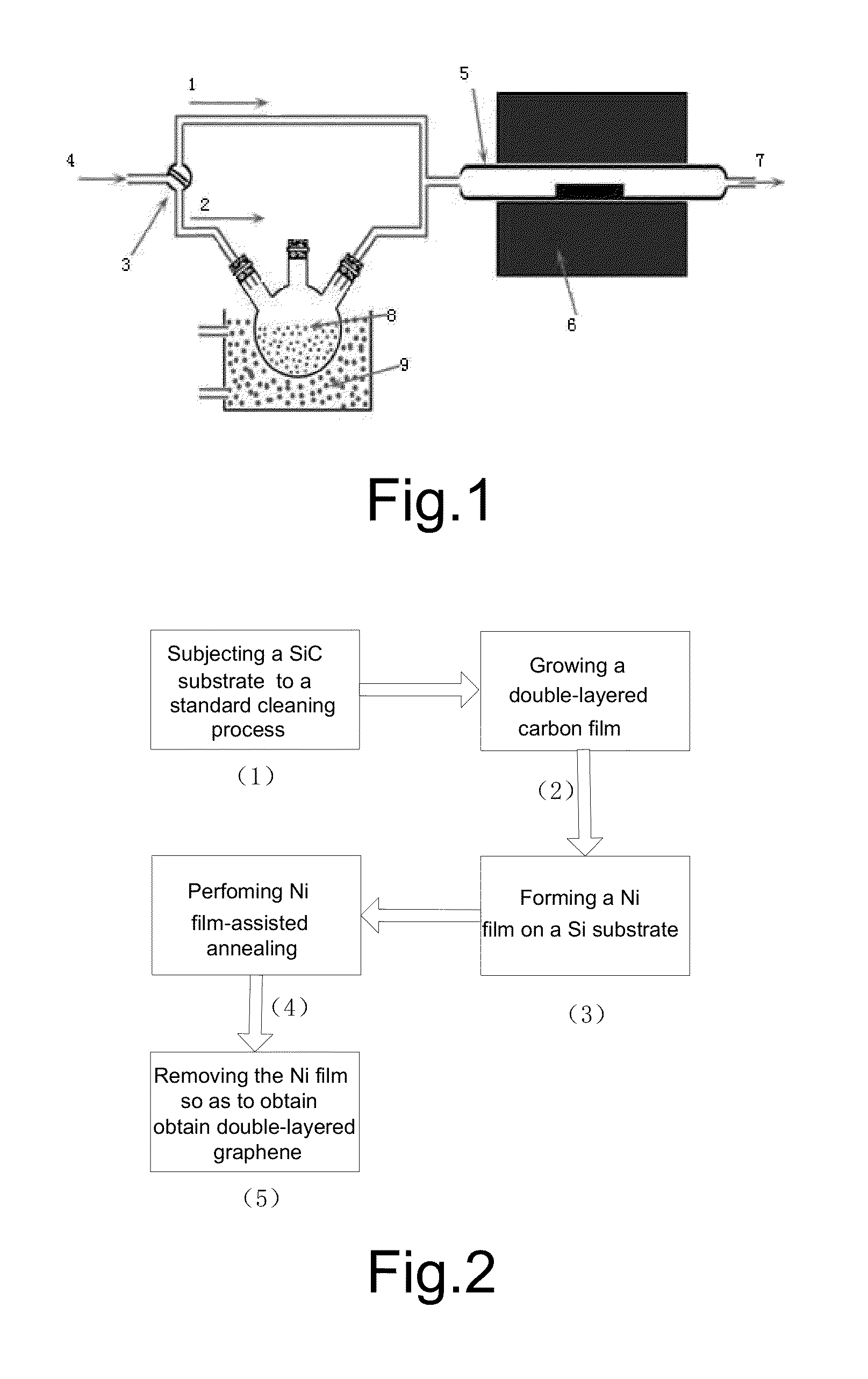
Process for Preparing Graphene on a SiC Substrate Based on Metal Film-Assisted Annealing
ActiveUS20140367642A1Simply and energy-efficientFlat surfaceMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon filmElectron beam deposition
Provided is a process for preparing graphene on a SiC substrate, based on metal film-assisted annealing, comprising the following steps: subjecting a SiC substrate to a standard cleaning process; placing the cleaned SiC substrate into a quartz tube and heating the quartz tube up to a temperature of 750 to 1150° C.; introducing CCl4vapor into the quartz tube to react with SiC for a period of 20 to 100 minutes so as to generate a double-layered carbon film, wherein the CCl4 vapor is carried by Ar gas; forming a metal film with a thickness of 350 to 600 nm on a Si substrate by electron beam deposition; placing the obtained double-layered carbon film sample onto the metal film; subsequently annealing them in an Ar atmosphere at a temperature of 900 to 1100° C. for 10-30 minutes so as to reconstitute the double-layered carbon film into double-layered graphene; and removing the metal film from the double-layered graphene, thereby obtaining double-layered graphene. Also provided is double-layered graphene prepared by said process.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
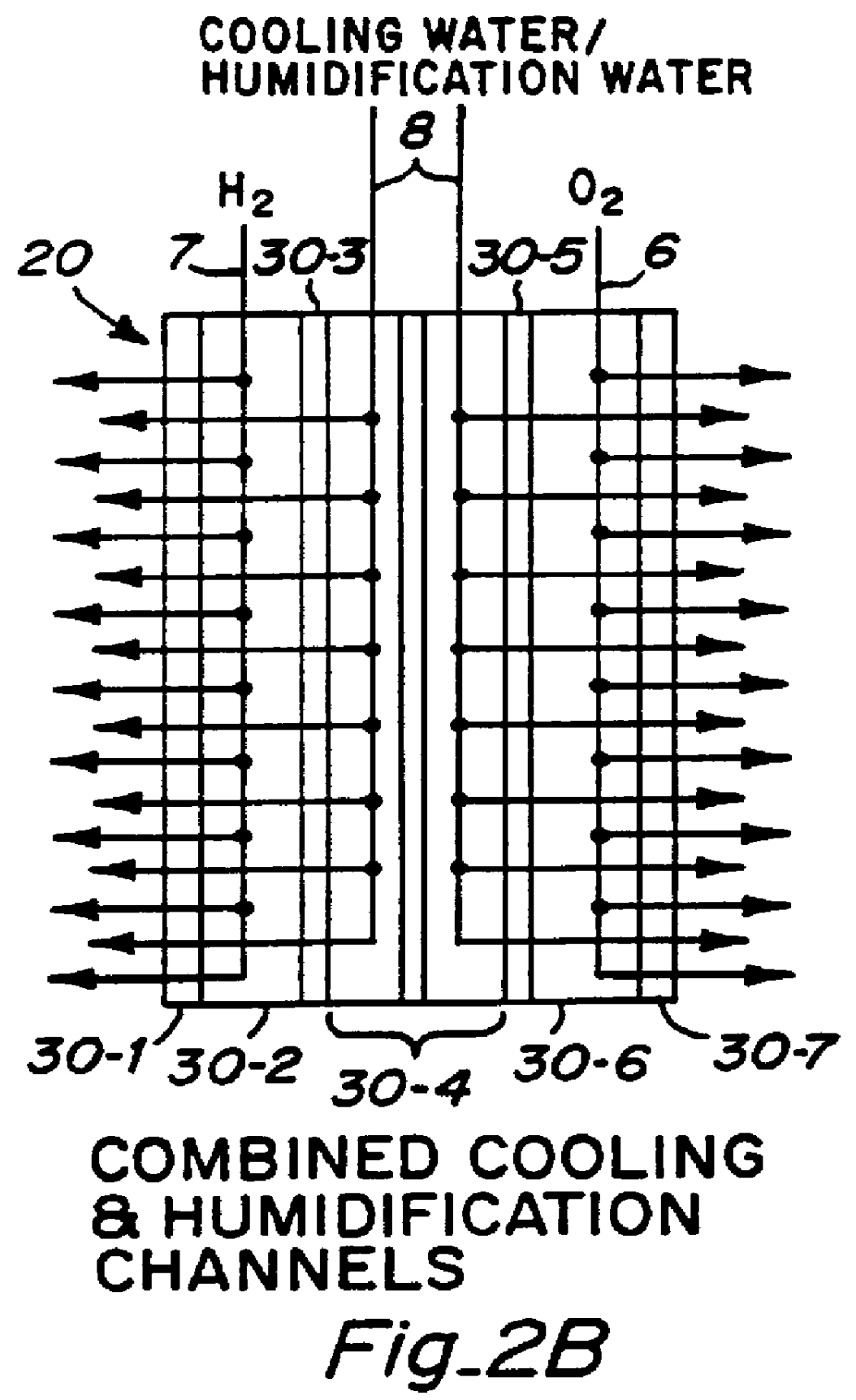
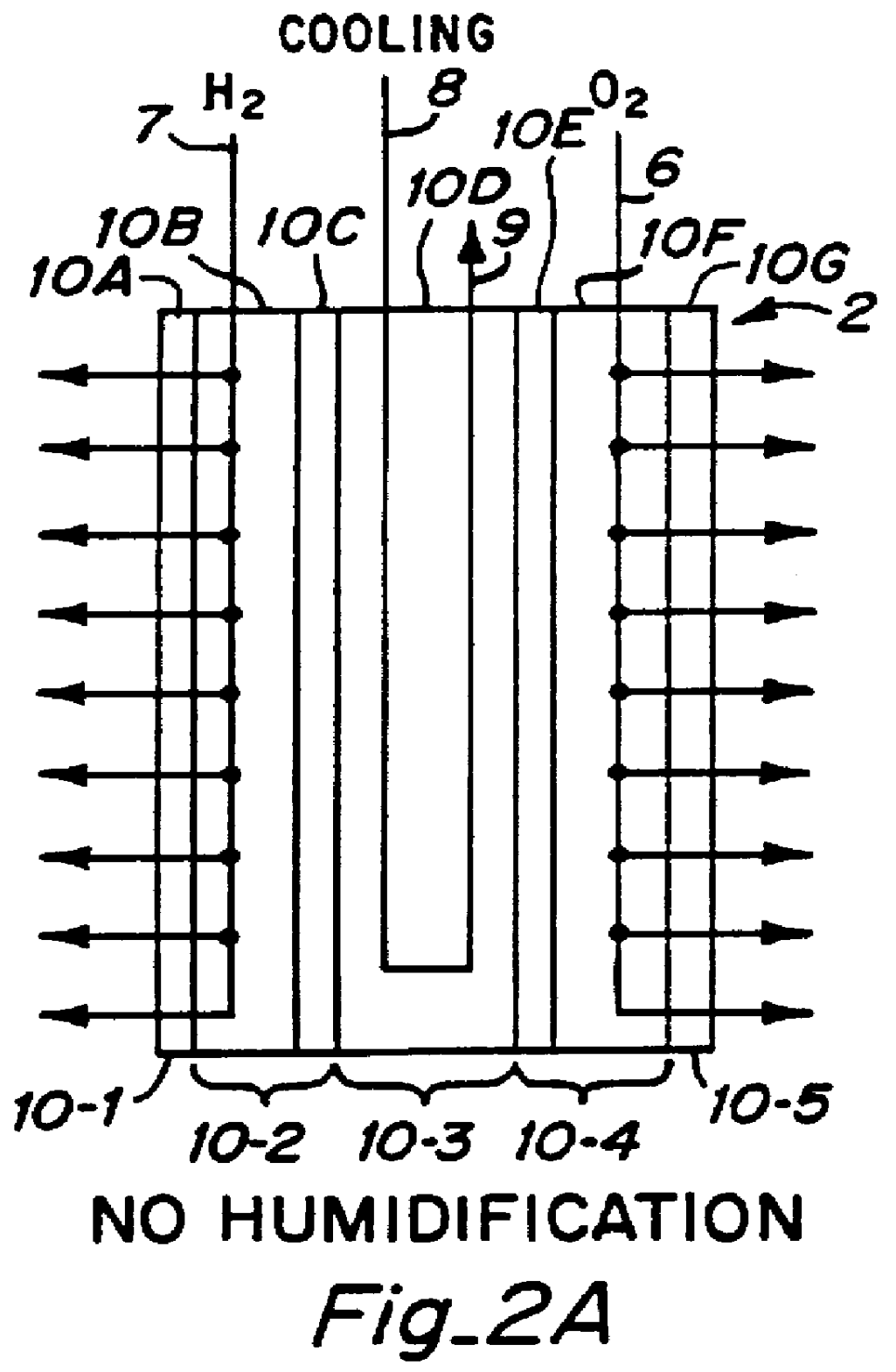
Thermal management system
InactiveUS6482520B1Improve cooling effectIncreased anisotropyLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringThermal management system
The present invention relates to a system for managing the heat from a heat source like an electronic component. More particularly, the present invention relates to a system effective for dissipating the heat generated by an electronic component using a thermal management system that includes a thermal interface formed from a flexible graphite sheet and / or a heat sink formed from a graphite article.
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
Temporary golf club shaft-component connection
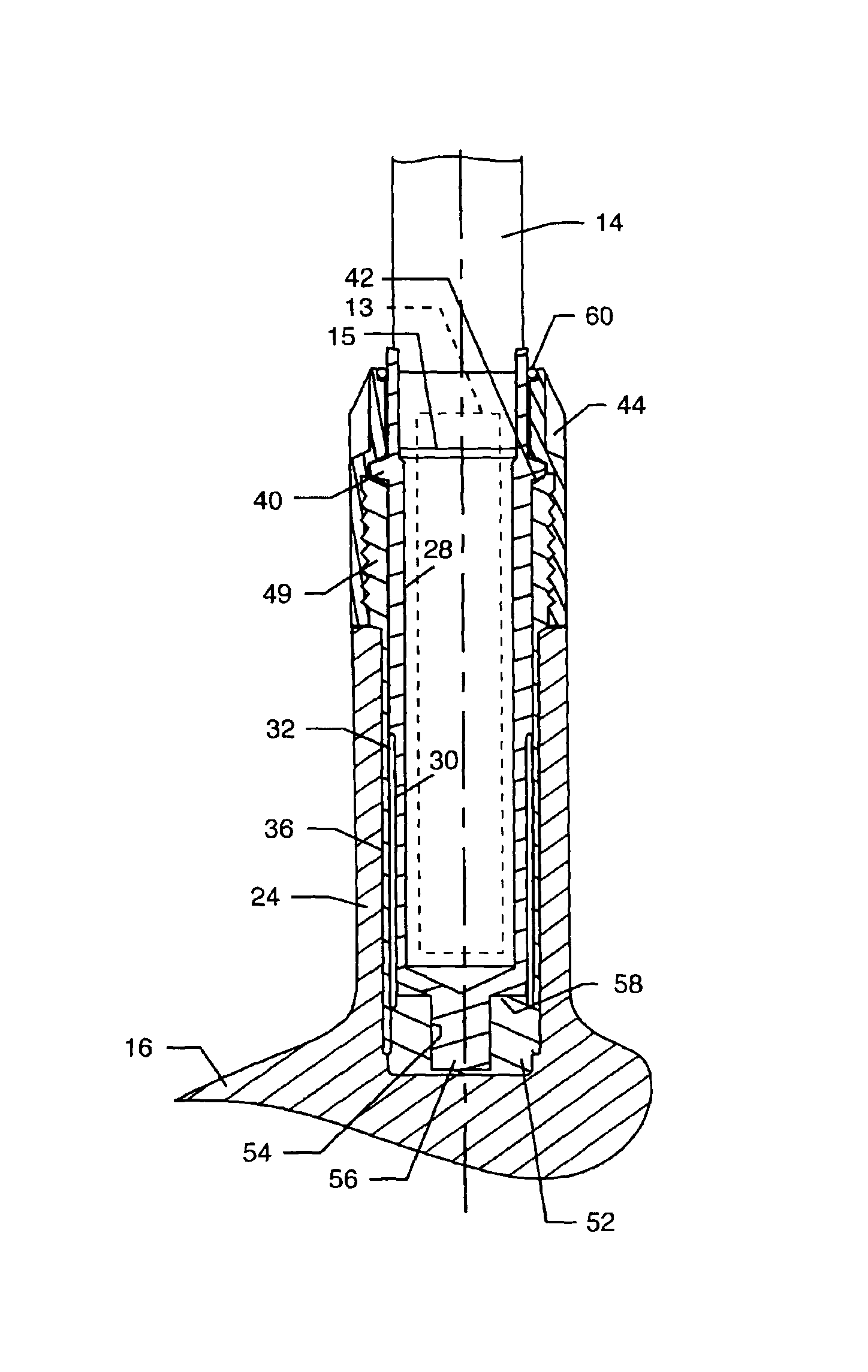
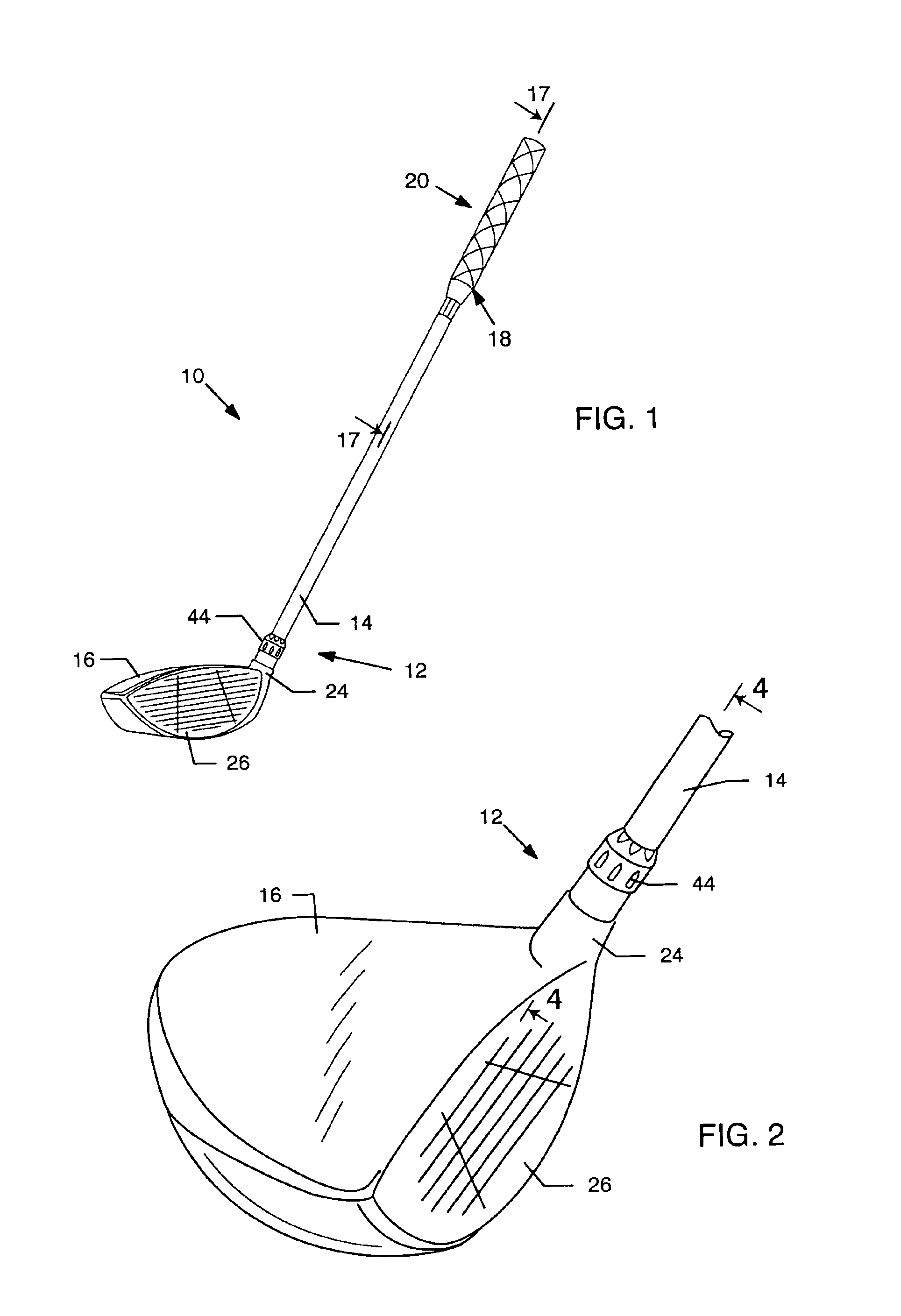
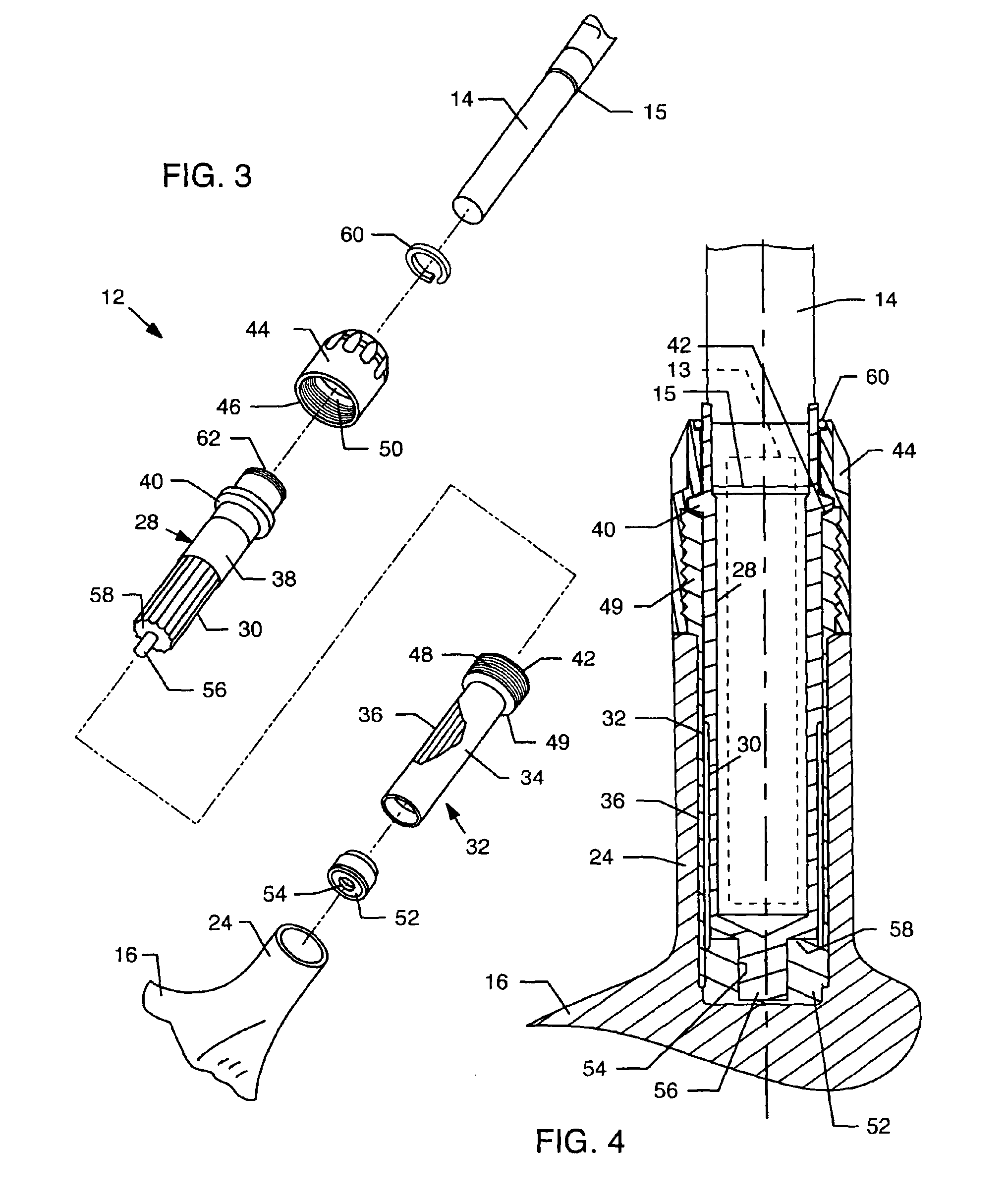
InactiveUS6890269B2Quickly and easily assemblingMinimize and limit rotationSpace saving gamesGolf clubsGraphiteEngineering
A temporary shaft-component connection for assembling a selected golf club shaft with a club head and / or hand grip segment, to facilitate custom club design and fitting to suit the needs and preferences of an individual golfer. The temporary shaft-component connection is particularly designed for use with nonmetallic club shafts formed from a graphite-based composite material or the like having a range of different lengths and stiffness (whip) characteristics. The temporary connection includes an adapter insert for slide-fit reception into an adapter socket, wherein the adapter insert and socket include interengaging flat surfaces such as splines to prevent relative rotation therebetween. The adapter insert is mechanically seated and secured relative to the adapter socket at a pair of axially spaced locations, with a resilient compressible anchor member disposed at one of these securement points for substantially eliminating undesired intercomponent movement.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP +1
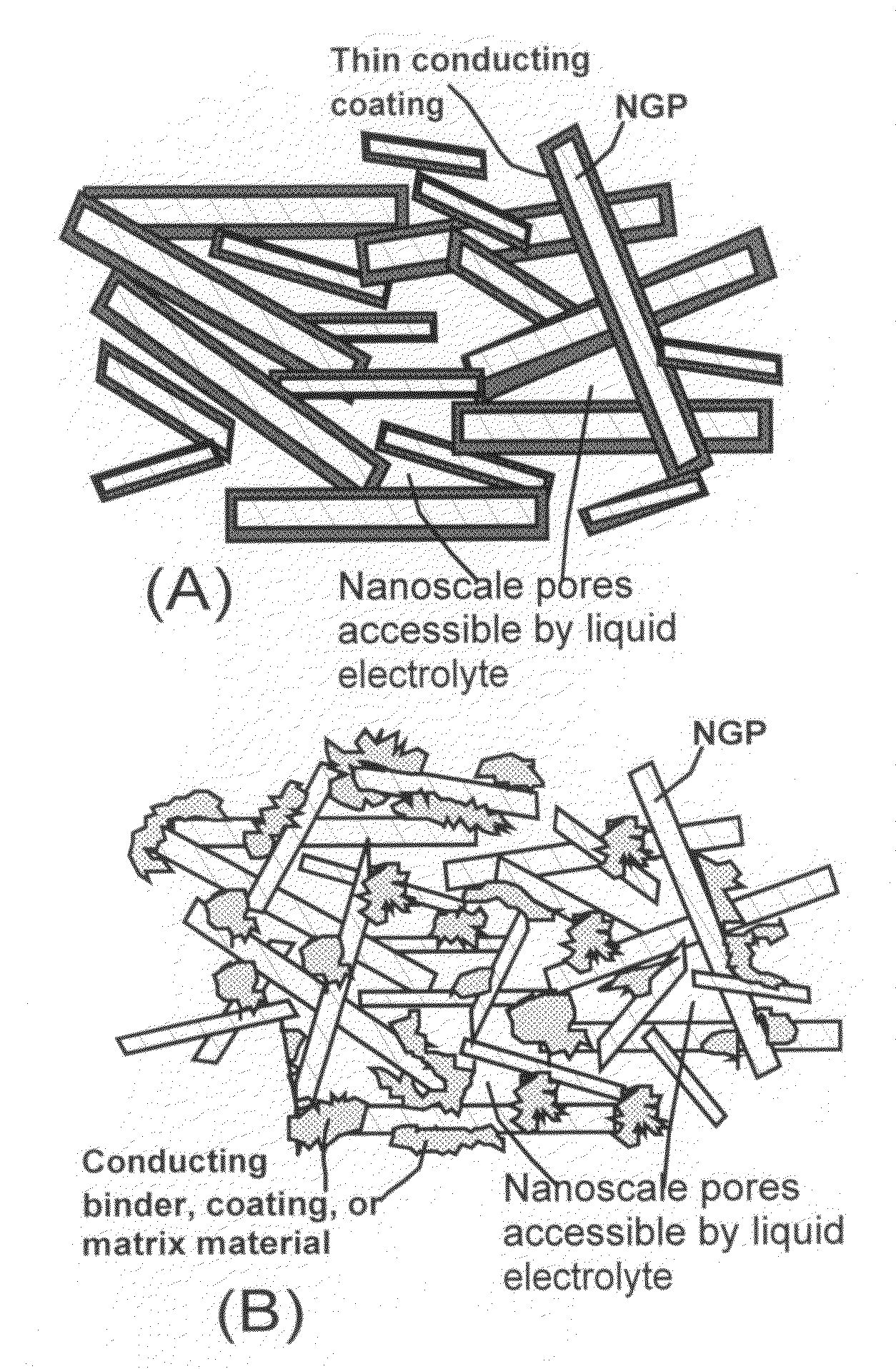
Nano-scaled graphene plate nanocomposites for supercapacitor electrodes
ActiveUS7623340B1Increase specific surface area and electrical conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitancePolymer science
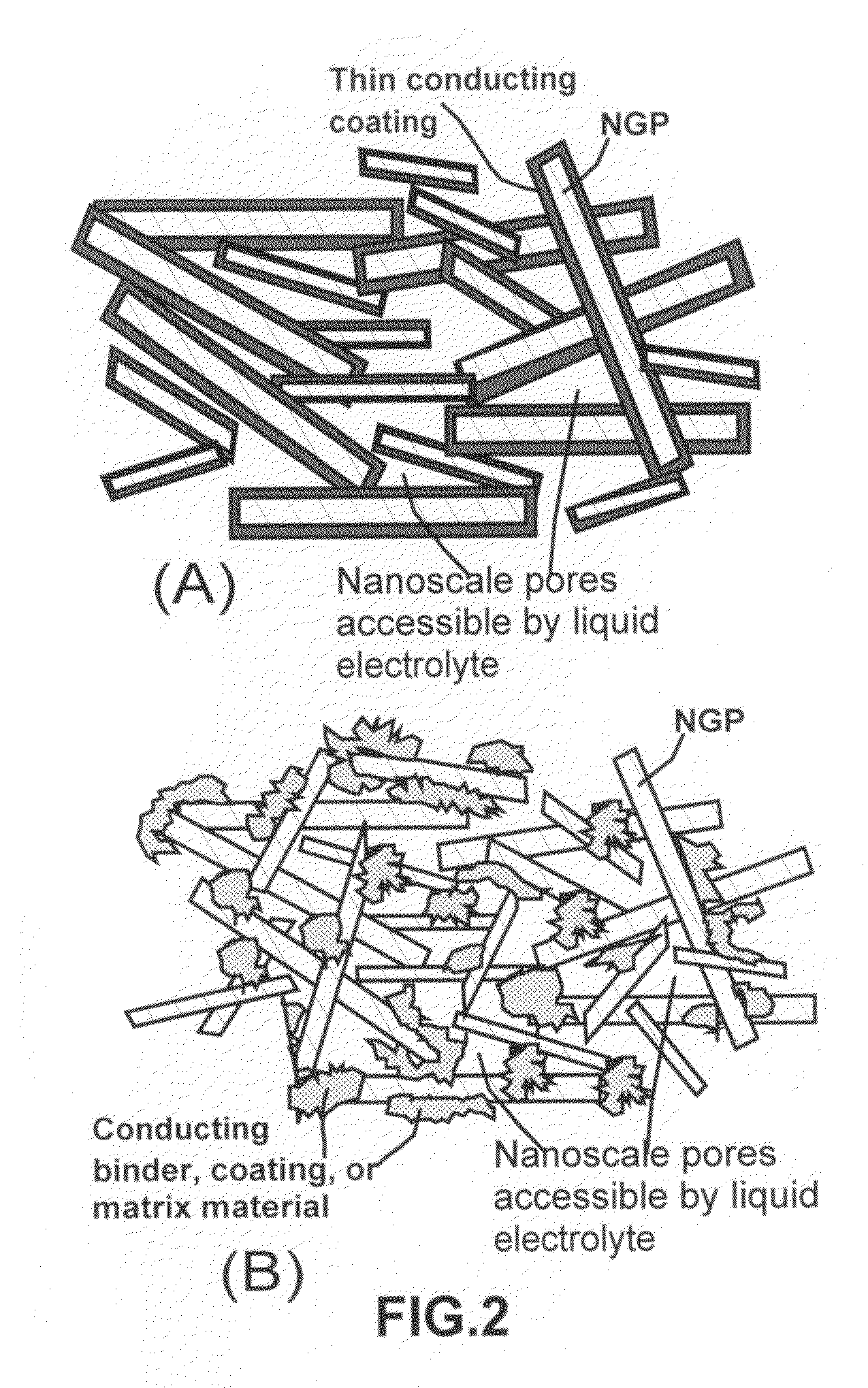
A preferred embodiment of the present invention is a meso-porous nanocomposite material comprising: (A) nano-scaled graphene platelets, wherein each of the platelets comprises a sheet of graphite plane or multiple sheets of graphite plane, and the platelets have a thickness no greater than 100 nm (preferably smaller than 10 nm) and an average length, width, or diameter no greater than 10 μm (preferably smaller than 500 nm); and (B) an electrically conducting binder or matrix material attached or bonded to the platelets to form the nanocomposite material having liquid accessible pores, which provide a surface area greater than about 100 m2 / gm, preferably greater than 500 m2 / gm, and most preferably greater than 1000 m2 / gm. Also disclosed is a capacitor that includes at least an electrode comprising such a meso-porous nanocomposite material. A supercapacitor featuring such a nanocomposite exhibits an exceptionally high capacitance value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS20100029995A1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicatePlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Highly catalytic screen-printing ink
ActiveUS7018568B2Easy to produceConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialConductive polymerPrinting ink
The invention is directed to conductive polymer compositions, catalytic ink compositions (e.g., for use in screen-printing), electrodes produced by deposition of an ink composition, methods of making, and methods of using thereof. An exemplary ink material comprises platinum black and / or platinum-on-carbon as the catalyst, graphite as a conducting material, a polymer binding material, and an organic solvent. The polymer binding material is typically a copolymer of hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers. The conductive polymer compositions of the present invention can be used, for example, to make electrochemical sensors. Such sensors can be used in a variety of analyte monitoring devices to monitor analyte amount or concentrations in subjects, for example, glucose monitoring devices to monitor glucose levels in subjects with diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Electrode material comprising graphene composite materials in a graphite network formed from reconstituted graphene sheets
ActiveUS20110111303A1Weight increaseIncrease storage capacityConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialGraphiteCvd graphene
A durable electrode material suitable for use in Li ion batteries is provided. The material is comprised of a continuous network of graphite regions integrated with, and in good electrical contact with a composite comprising graphene sheets and an electrically active material, such as silicon, wherein the electrically active material is dispersed between, and supported by, the graphene sheets.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Advanced heat sinks and thermal spreaders
InactiveUS20070053168A1Material nanotechnologyDigital data processing detailsGraphiteMaterials science
A heat sink assembly for an electronic device or a heat generating device(s) is constructed from an ultra-thin graphite layer. The ultra-thin graphite layer exhibits thermal conductivity which is anisotropic in nature and is greater than 500 W / m° C. in at least one plane and comprises at least a graphene layer. The ultra-thin graphite layer is structurally supported by a layer comprising at least one of a metal, a polymeric resin, a ceramic, and a mixture thereof, which is disposed on at least one surface of the graphite layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Graphitic nanotubes in luminescence assays
Graphitic nanotubes, which include tubular fullerenes (commonly called "buckytubes") and fibrils, which are functionalized by chemical substitution, are used as solid supports in electrogenerated chemiluminescence assays. The graphitic nanotubes are chemically modified with functional group biomolecules prior to use in an assay. Association of electrochemiluminescent ruthenium complexes with the functional group biomolecule-modified nanotubes permits detection of molecules including nucleic acids, antigens, enzymes, and enzyme substrates by multiple formats.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
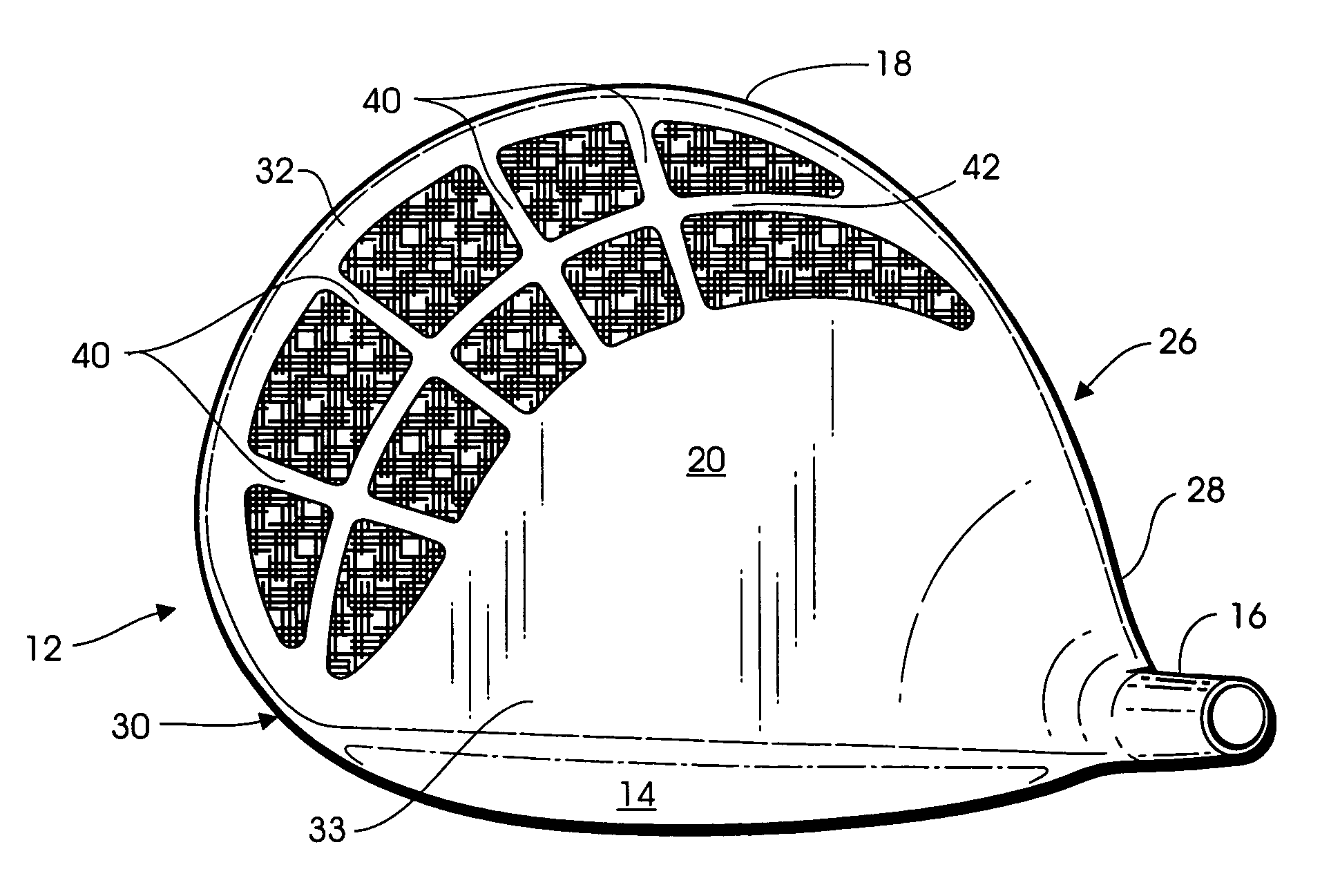
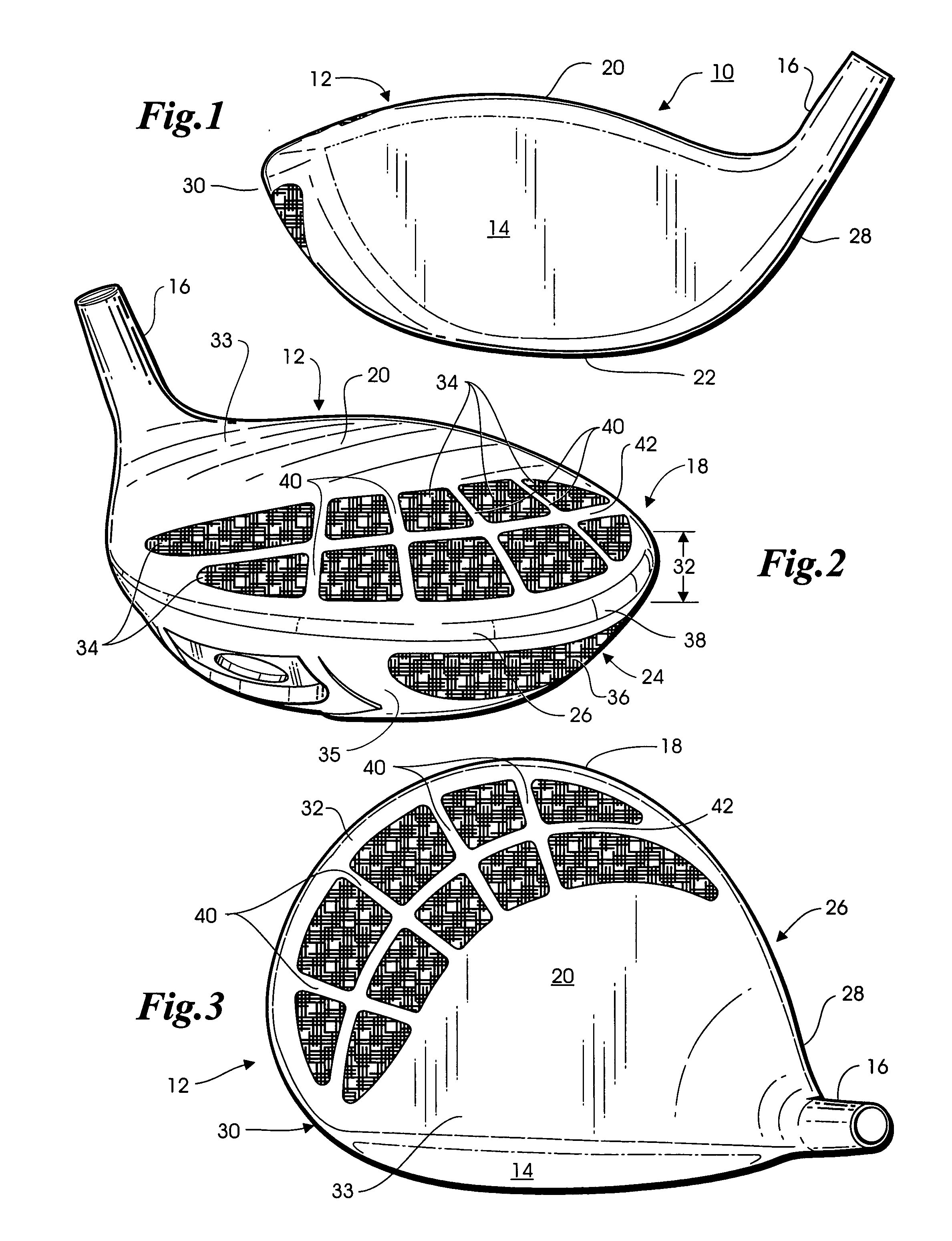
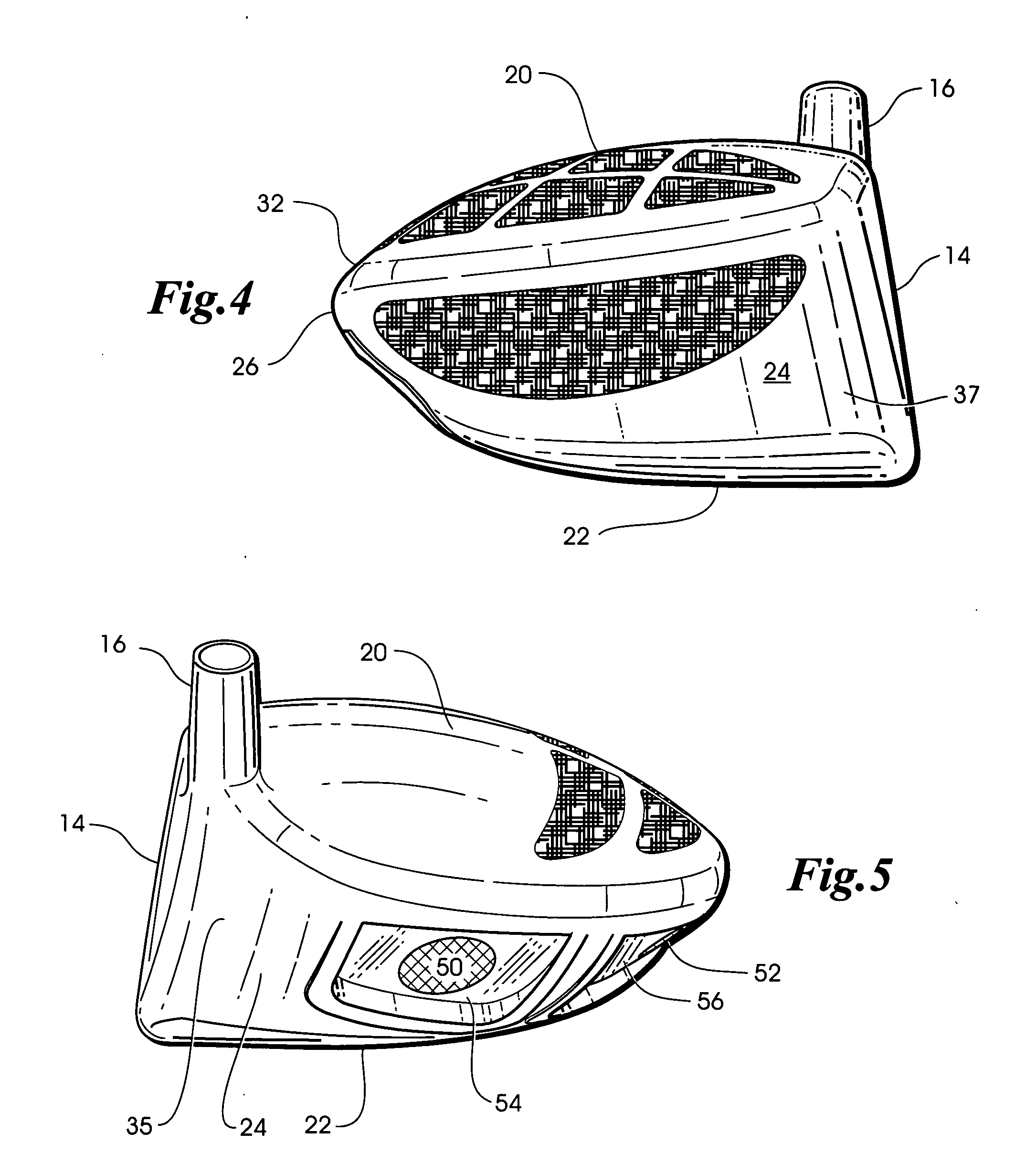
Metal-organic composite golf club head
A golf club head is formed of a hollow body, the rear body portion of which includes a metallic stringer that extends along the crown-skirt interface and a plurality of ribs intersecting the metallic stringer to form a lattice frame, the openings of which are filled with an organic composite material such as graphite epoxy. An additional aperture formed in the skirt is also filled with the same graphite epoxy material. Because the graphite epoxy is lighter than the surrounding metal frame, the rear body portion of the golf club head is lighter than a comparable all metal club head. Yet, the presence of the metallic stringer and frame renders the metal-organic composite rear body portion substantially stiffer than a comparable all-composite rear body portion.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP
Nano graphene platelet-base composite anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS7745047B2Improve conductivityLower internal resistanceAlkaline accumulatorsElectrolytic capacitorsGraphiteGraphene
The present invention provides a nano-scaled graphene platelet-based composite material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing lithium ions; and (b) a plurality of nano-scaled graphene platelets (NGPs), wherein a platelet comprises a graphene sheet or a stack of graphene sheets having a platelet thickness less than 100 nm; wherein at least one of the particles or coating is physically attached or chemically bonded to at least one of the graphene platelets and the amount of platelets is in the range of 2% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating in the range of 98% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, an excellent reversible capacity, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
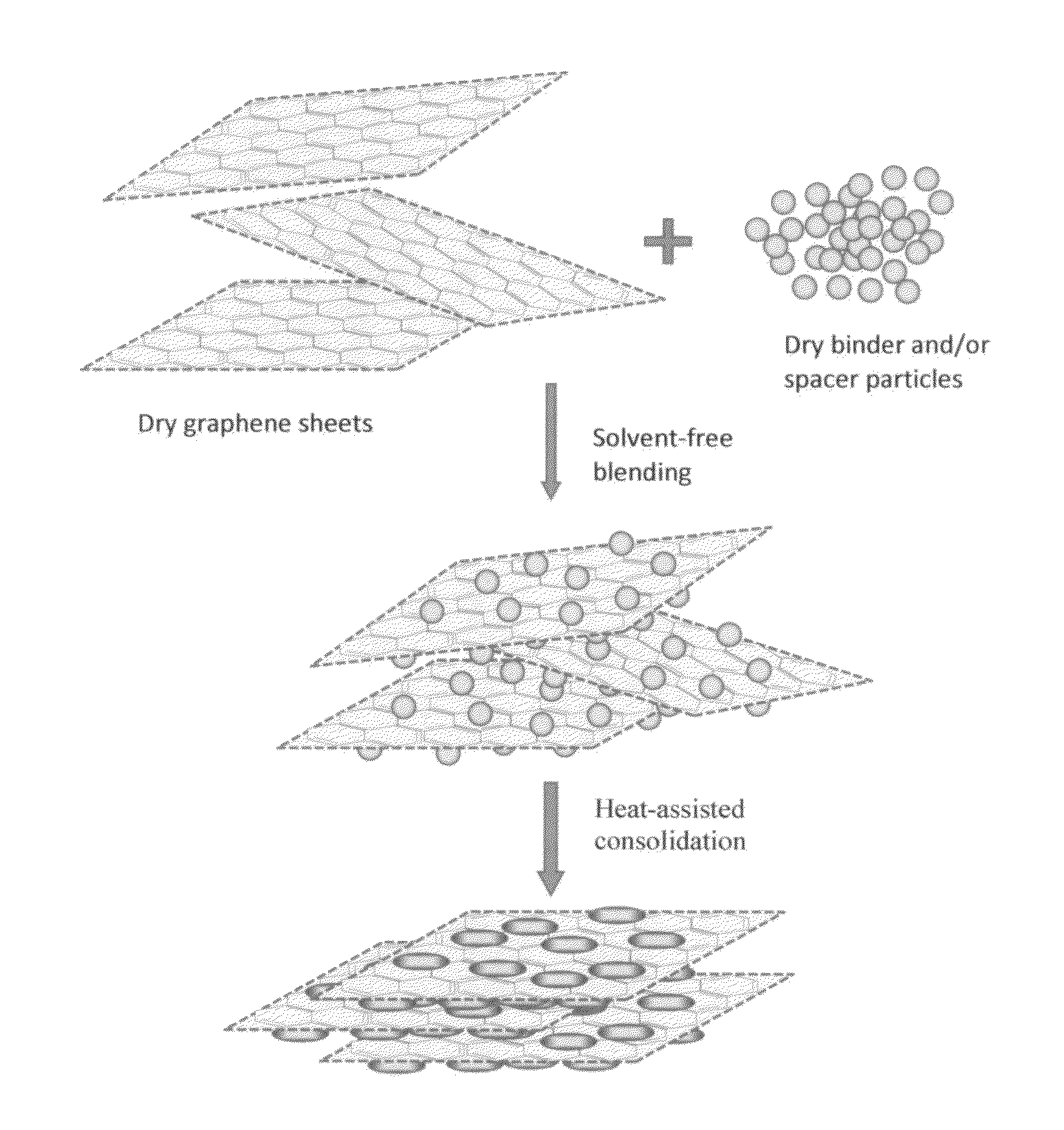
Solvent-free process based graphene electrode for energy storage devices
PendingUS20140030590A1Inexpensive and durable and highly reliableHigh capacitanceMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene flakeSolvent free
Disclosed is an electrode for an electrochemical energy storage device, the electrode comprising a self-supporting layer of a mixture of graphene sheets and spacer particles and / or binder particles, wherein the electrode is prepared without using water, solvent, or liquid chemical. The graphene electrode prepared by the solvent-free process exhibits many desirable features and advantages as compared to the corresponding electrode prepared by a known wet process. These advantages include a higher electrode specific surface area, higher energy storage capacity, improved or higher packing density or tap density, lower amount of binder required, lower internal electrode resistance, more consistent and uniform dispersion of graphene sheets and binder, reduction or elimination of undesirable effect of electrolyte oxidation or decomposition due to the presence of water, solvent, or chemical, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Hybrid anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20090117466A1Superior multiple-cycle behaviorSmall capacity fadeAlkaline accumulatorsConductive materialHybrid materialSodium-ion battery
The present invention provides an exfoliated graphite-based hybrid material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing alkali or alkaline metal ions (particularly, lithium ions); and (b) exfoliated graphite flakes that are substantially interconnected to form a porous, conductive graphite network comprising pores, wherein at least one of the particles or coating resides in a pore of the network or attached to a flake of the network and the exfoliated graphite amount is in the range of 5% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating is in the range of 95% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, excellent reversible capacity, and long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Graphite-based heat sink
InactiveUS6503626B1Improve cooling effectIncreased anisotropyLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear engineeringGraphite
The present invention relates to a system for managing the heat from a heat source like an electronic component. More particularly, the present invention relates to a system effective for dissipating the heat generated by an electronic component using a heat sink formed from a compressed, comminuted particles of resin-impregnated flexible graphite mat or sheet.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
Methods of high temperature infiltration of drill bits and infiltrating binder
A method of manufacturing a bit body, other drilling-related component, or other article of manufacture, including fabricating a particulate-based matrix and infiltrating the particulate-based matrix with a binder that includes cobalt or iron. The binder may be a cobalt alloy or an iron alloy. The particulate-based matrix may be disposed within a non-graphite mold. The particulate-based matrix and binder are placed within an induction coil and an alternating current is applied to the induction coil in order to directly heat the binder, permitting the binder to infiltrate or otherwise bind the particles of the matrix together. The molten binder may then be directionally cooled by forming a cooling zone around an end portion of the bit body and increasing the size of the cooling zone relative to the bit body. The invention also includes a bit body, other drilling-related component, or other article of manufacture which includes a particulate-based matrix that is bound together with a binder that includes iron or cobalt.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Nano graphene-modified lubricant
ActiveUS20110046027A1Modulate viscosityImprove the lubrication effectAdditivesBase-materialsCarbon nanotubeSingle layer graphene
A lubricant composition having improved lubricant properties, comprising:(a) a lubricating fluid; and (b) nano graphene platelets (NGPs) dispersed in the fluid, wherein nano graphene platelets have a proportion of 0.001% to 60% by weight based on the total weight of the fluid and the graphene platelets combined. Preferably, the composition comprises at least a single-layer graphene sheet. Preferably, the lubricating fluid contains a petroleum oil or synthetic oil and a dispersant or surfactant. With the addition of a thickener or a desired amount of NGPs, the lubricant becomes a grease composition. Compared with graphite nano particle- or carbon nanotube-modified lubricants, NGP-modified lubricants have much better thermal conductivity, friction-reducing capability, anti-wear performance, and viscosity stability.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
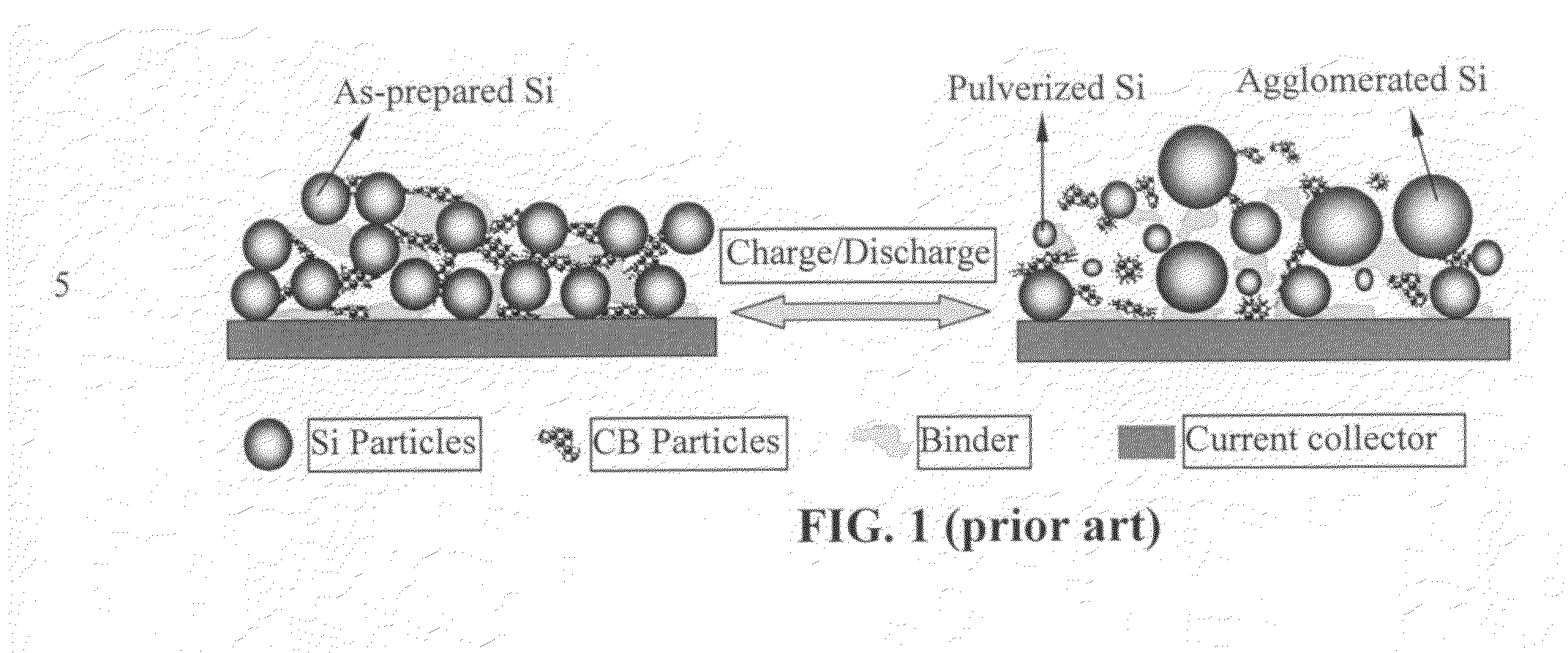
Electrode structure for lithium secondary battery and secondary battery having such electrode structure
InactiveUS20060127773A1Small capacity reductionLarge capacityElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureElectrochemical responseConductive polymer
In an electrode structure for a lithium secondary battery including: a main active material layer formed from a metal powder selected from silicon, tin and an alloy thereof that can store and discharge and capable of lithium by electrochemical reaction, and a binder of an organic polymer; and a current collector, wherein the main active material layer is formed at least by a powder of a support material for supporting the electron conduction of the main active material layer in addition to the metal powder and the powder of the support material are particles having a spherical, pseudo-spherical or pillar shape with an average particle size of 0.3 to 1.35 times the thickness of the main active material layer. The support material is one or more materials selected from a group consisting of graphite, oxides of transition metals and metals that do not electrochemically form alloy with lithium. Organic polymer compounded with a conductive polymer is used for the binder. There are provided an electrode structure for a lithium secondary battery having a high capacity and a long lifetime, and a lithium secondary battery using the electrode structure and having a high capacity, a high energy density and a long lifetime.
Owner:CANON KK
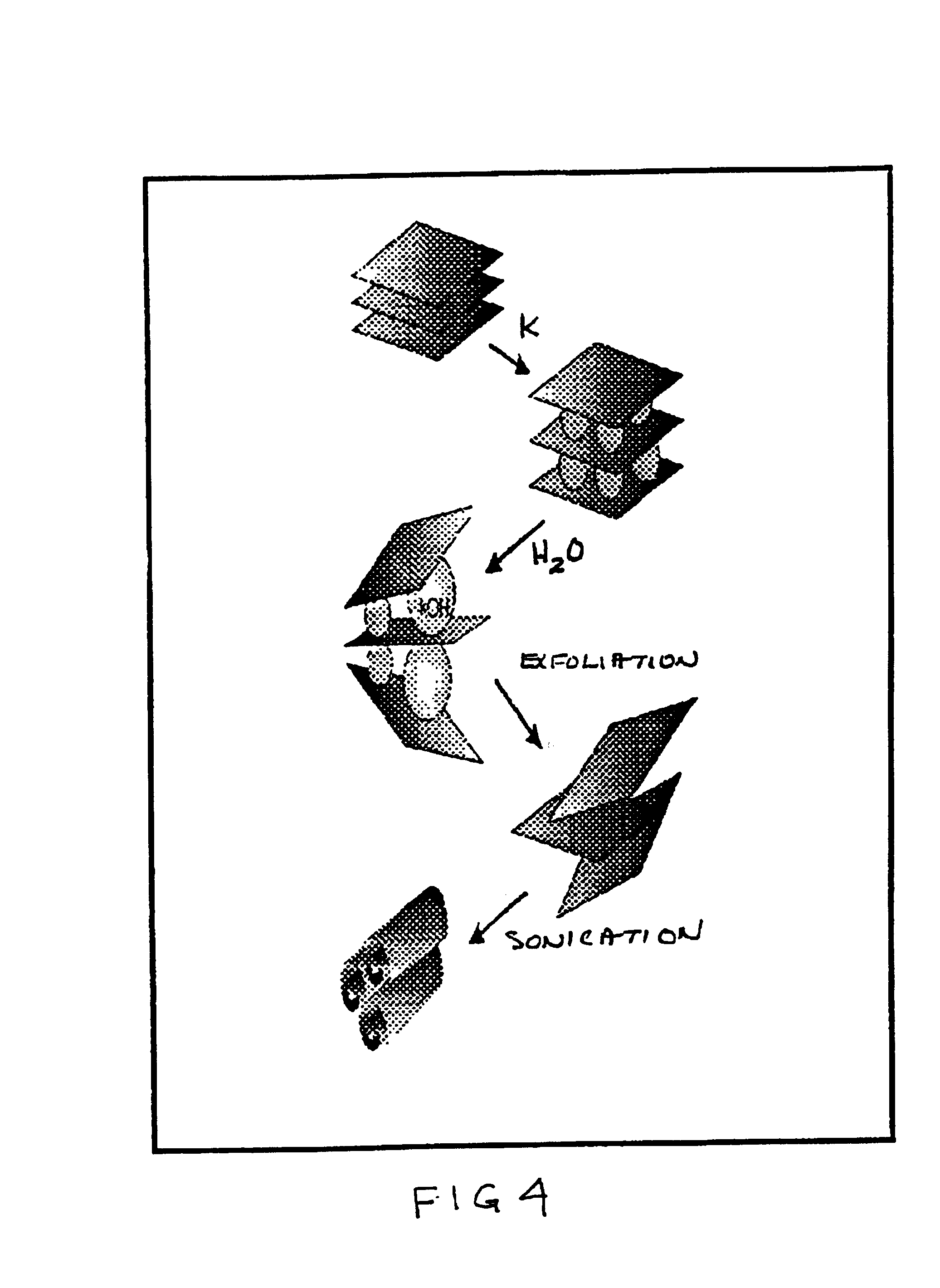
Chemical manufacture of nanostructured materials
InactiveUS6872330B2High strengthIncrease volumeMaterial nanotechnologyOxide/hydroxide preparationInorganic compoundTe element
A low temperature chemical route to efficiently produce nanomaterials is described. The nanomaterials are synthesized by intercalating ions into layered compounds, exfoliating to create individual layers and then sonicating to produce nanotubes, nanorods, nanoscrolls and / or nanosheets. It is applicable to various different layered inorganic compounds (for example, bismuth selenides / tellurides, graphite, and other metal complexes, particularly transition metal dichalcogenides compounds including oxygen, sulfur, tellurium or selenium).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
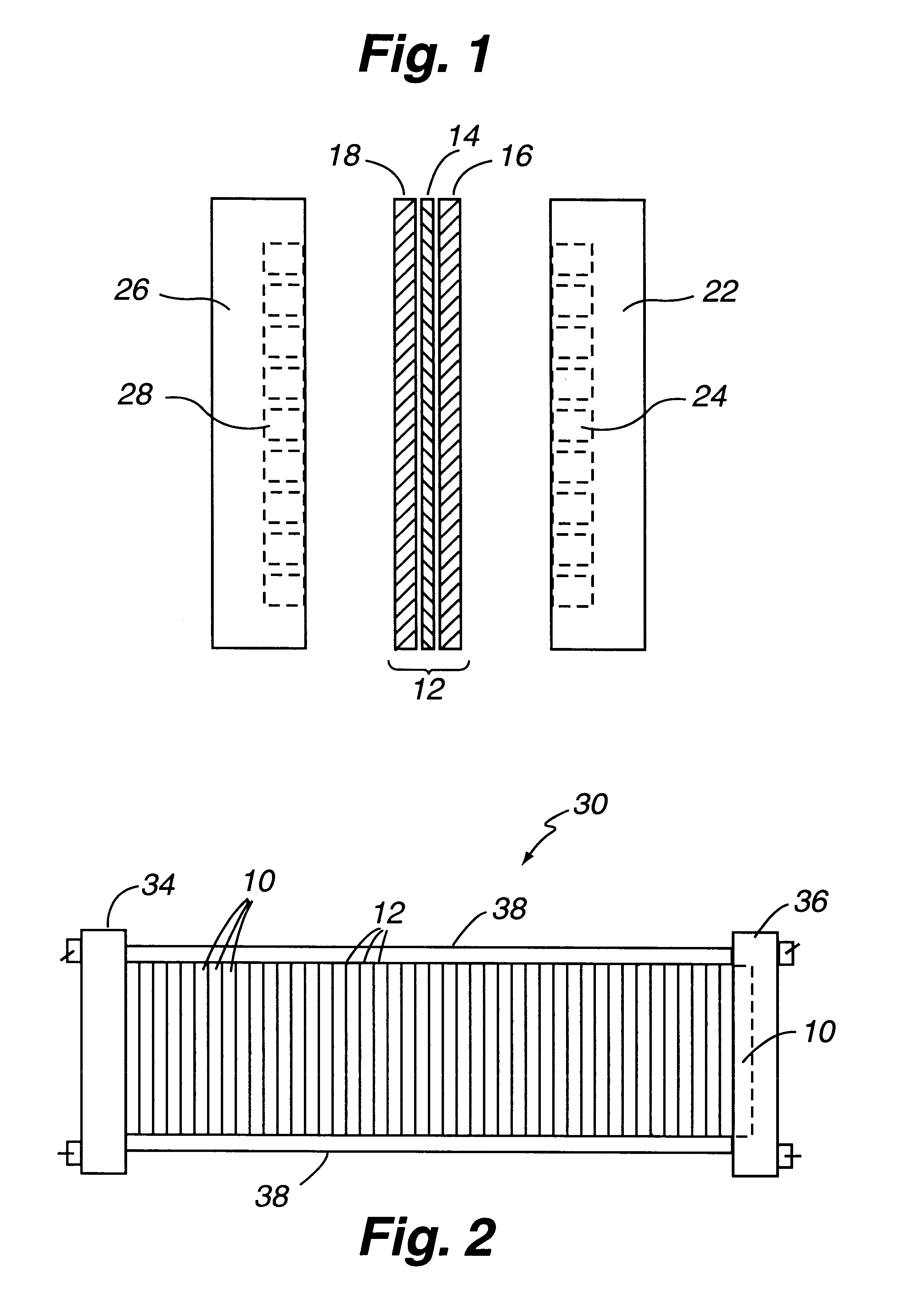
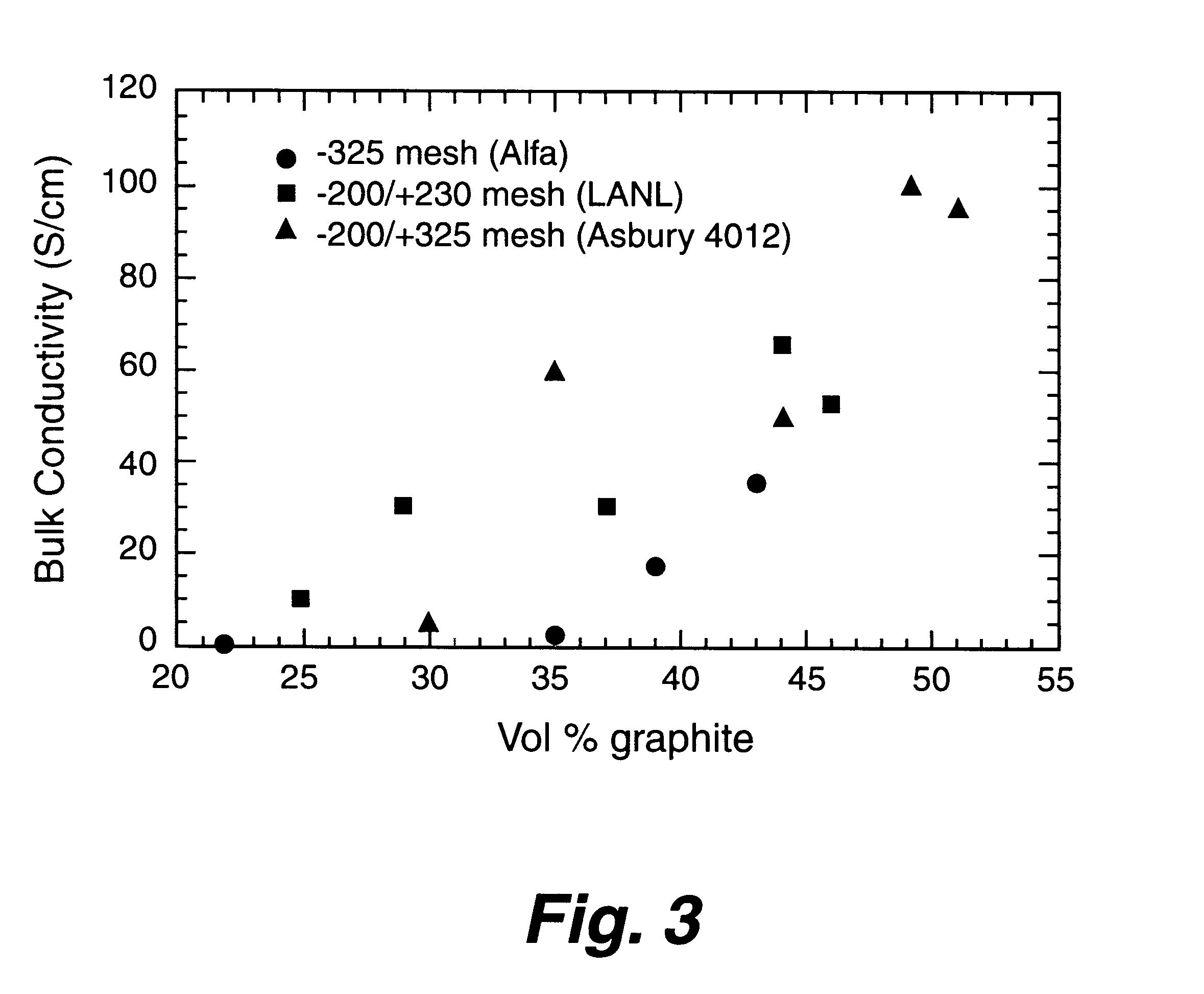
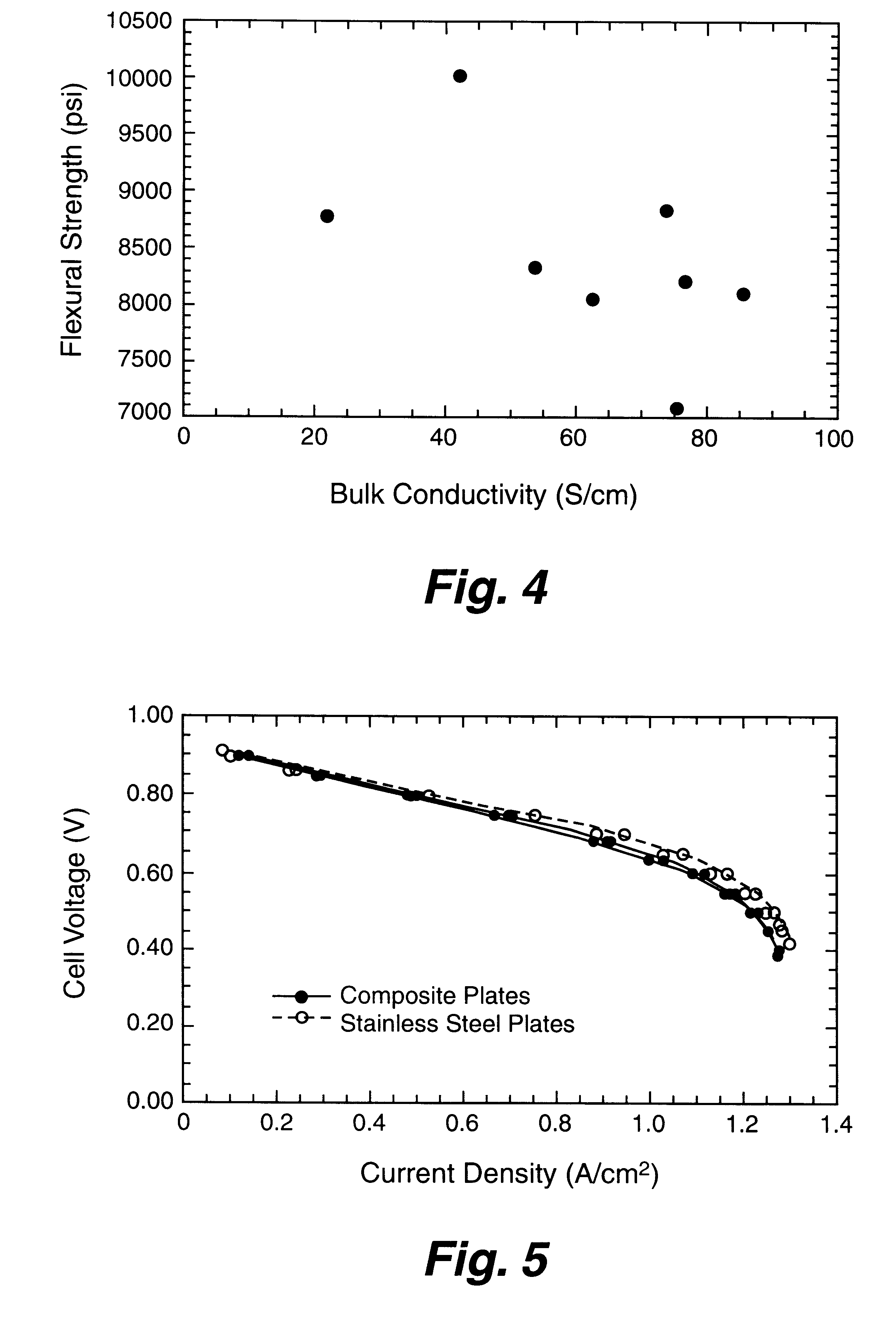
Composite bipolar plate for electrochemical cells
A bipolar separator plate for fuel cells consists of a molded mixture of a vinyl ester resin and graphite powder. The plate serves as a current collector and may contain fluid flow fields for the distribution of reactant gases. The material is inexpensive, electrically conductive, lightweight, strong, corrosion resistant, easily mass produced, and relatively impermeable to hydrogen gas. The addition of certain fiber reinforcements and other additives can improve the properties of the composite material without significantly increasing its overall cost.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
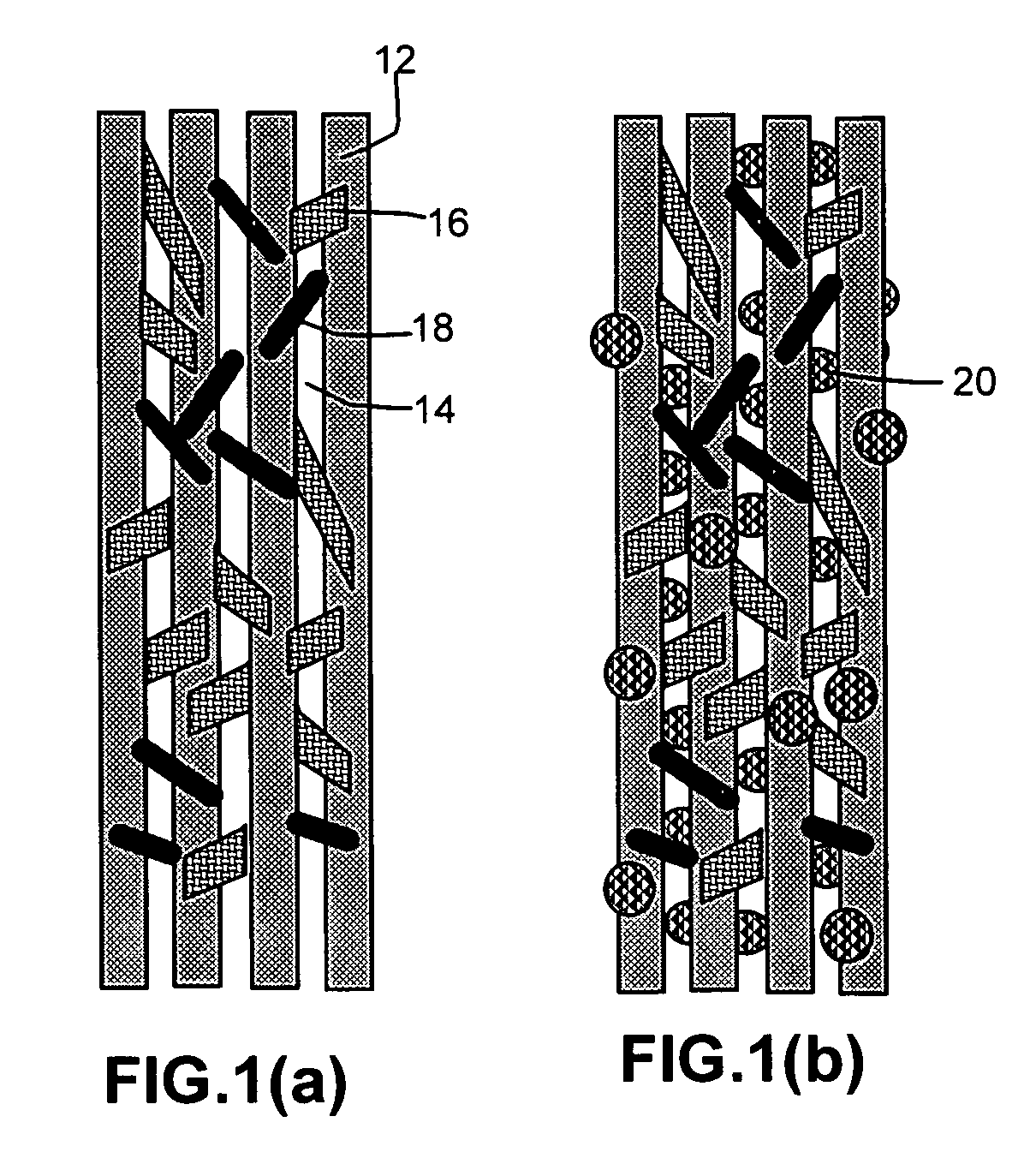
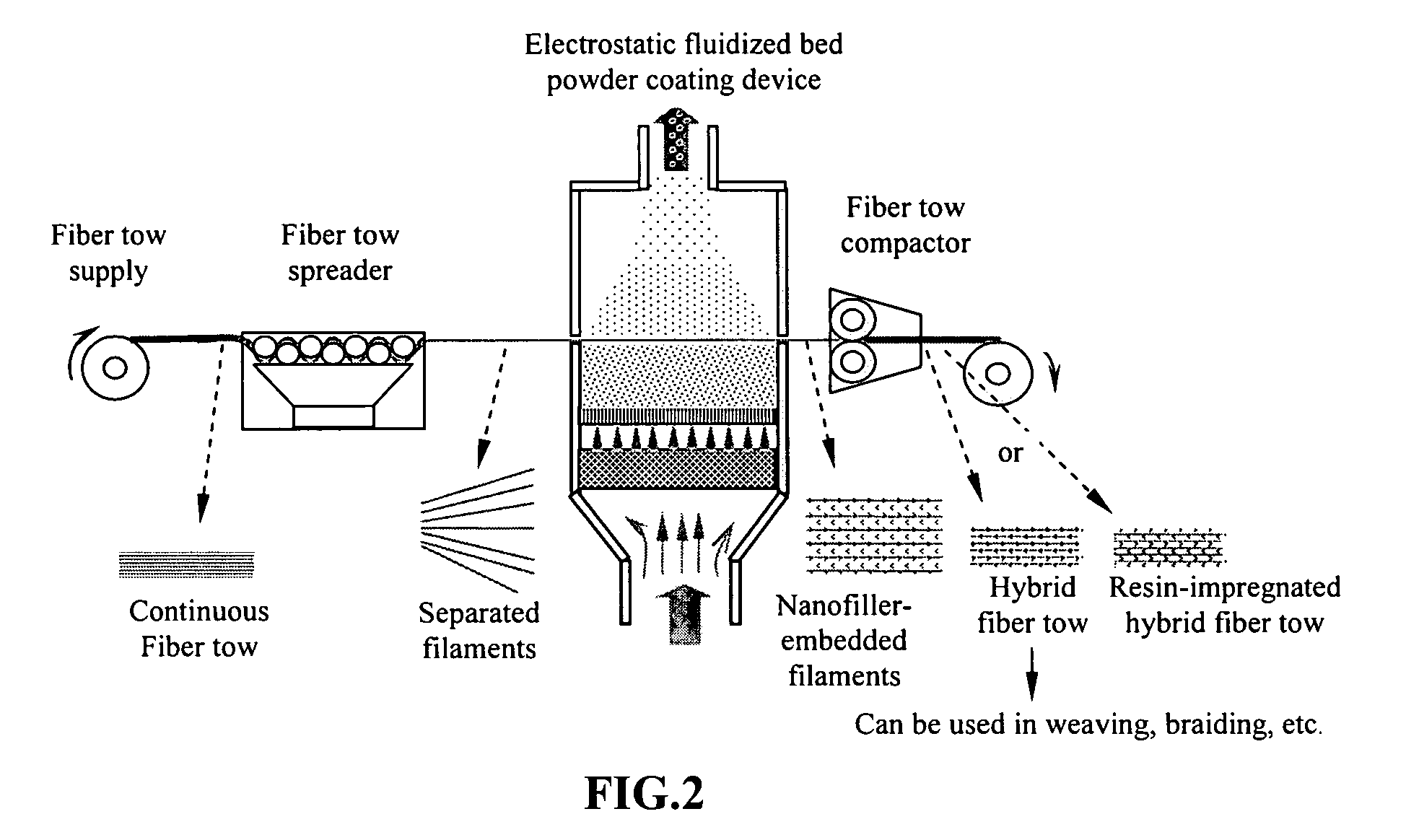
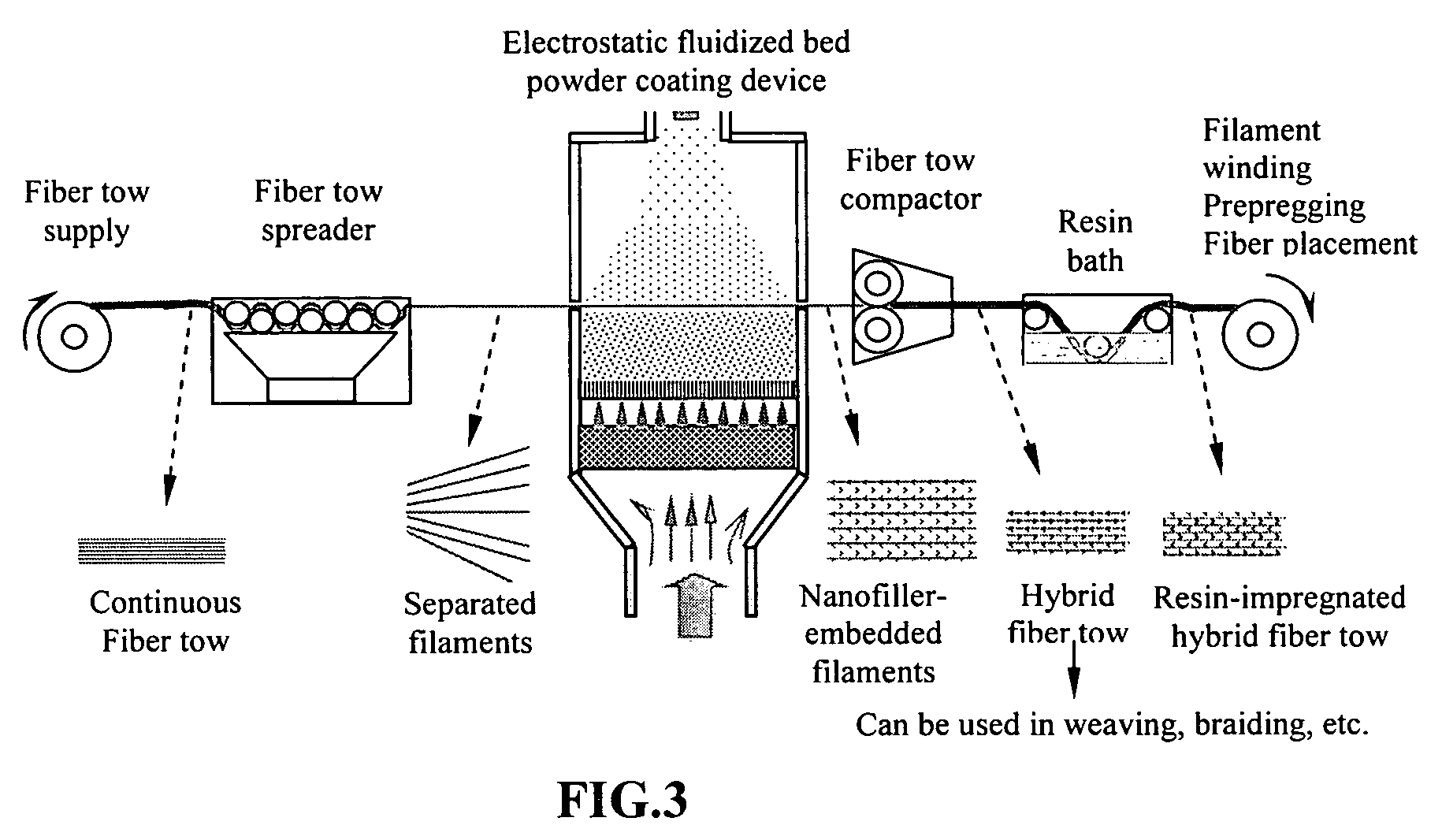
Hybrid fiber tows containning both nano-fillers and continuous fibers, hybrid composites, and their production processes
Disclosed is a hybrid fiber tow that comprises multiple continuous filaments and nanoscale fillers embedded in the interstitial spaces between continuous filaments. Nanoscale fillers may be selected from a nanoscale graphene plate, non-graphite platelet, carbon nano-tube, nano-rod, carbon nano-fiber, non-carbon nano-fiber, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed are a hybrid fiber tow impregnated with a matrix material and a composite structure fabricated from a hybrid fiber tow. The composite exhibits improved physical properties (e.g., thermal conductivity) in a direction transverse to the continuous fiber axis. A roll-to-roll process for producing a continuous fiber tow or matrix-impregnated fiber tow and an automated process for producing composite structures containing both continuous filaments and nanoscale fillers are also provided.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR
Fuel cell platelet separators having coordinate features
InactiveUS6051331ASimple designEvenly distributedSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingLaser etchingFuel cells
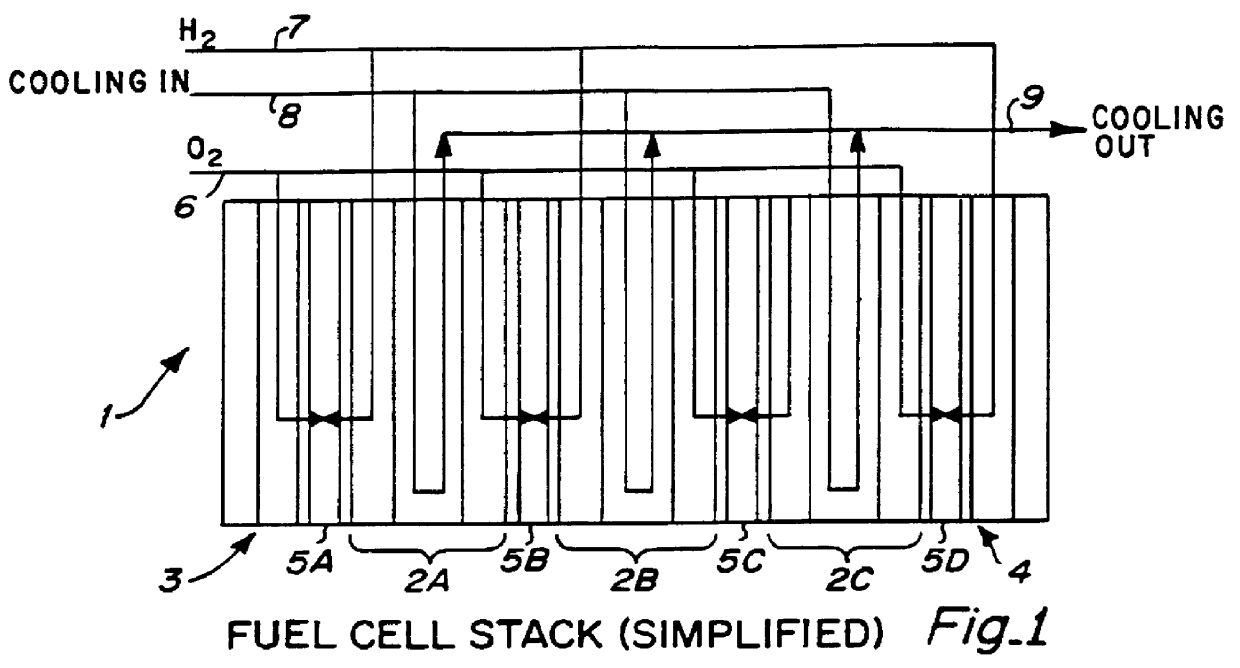
PCT No. PCT / US95 / 13325 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 28, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 28, 1997 PCT Filed Oct. 10, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 12316 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 25, 1996Fuel cell stacks comprising stacked separator / membrane electrode assembly fuel cells in which the separators comprise a series of thin sheet platelets, having individually configured serpentine micro-channel reactant gas humidification active areas and cooling fields therein. The individual platelets are stacked with coordinate features aligned in contact with adjacent platelets and bonded to form a monolithic separator. Post-bonding processing includes passivation, such as nitriding. Preferred platelet material is 4-25 mil Ti, in which the features, serpentine channels, tabs, lands, vias, manifolds and holes, are formed by chemical and laser etching, cutting, pressing or embossing, with combinations of depth and through etching preferred. The platelet manufacturing process is continuous and fast. By employing CAD based platelet design and photolithography, rapid change in feature design can accommodate a wide range of thermal management and humidification techniques. One hundred H2-O2 / PEM fuel cell stacks of this IFMT platelet design will exhibit outputs on the order of 0.75 kW / kg, some 3-6 times greater than the current graphite plate PEM stacks.
Owner:H POWER
Catheter with flexible cooled electrode
InactiveUS7264619B2Easy to manufactureEfficient preparationElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingElectrical resistance and conductanceHeat sensitive
Owner:FOGAZZI DI VENTURELLI ANDREA & C
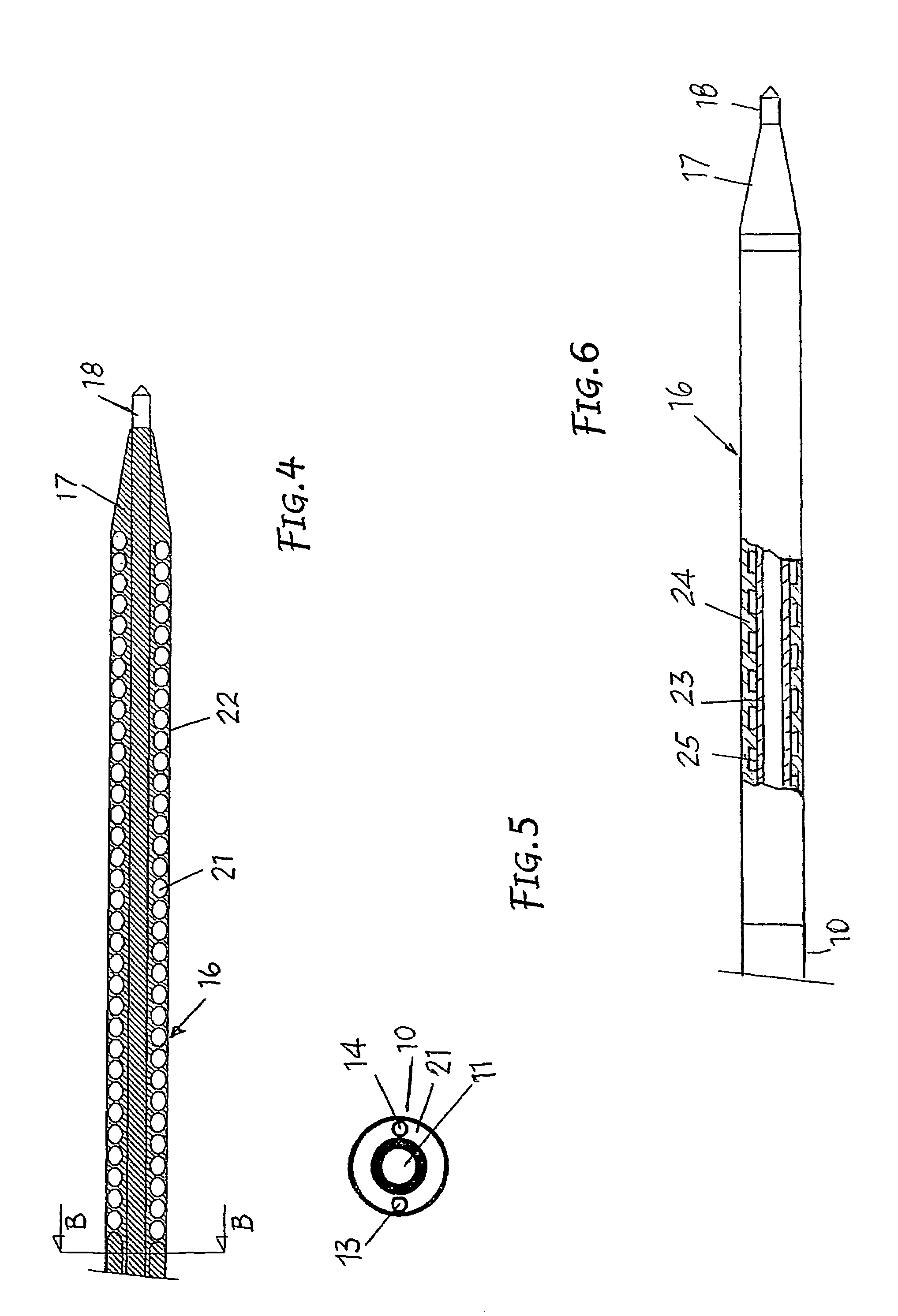
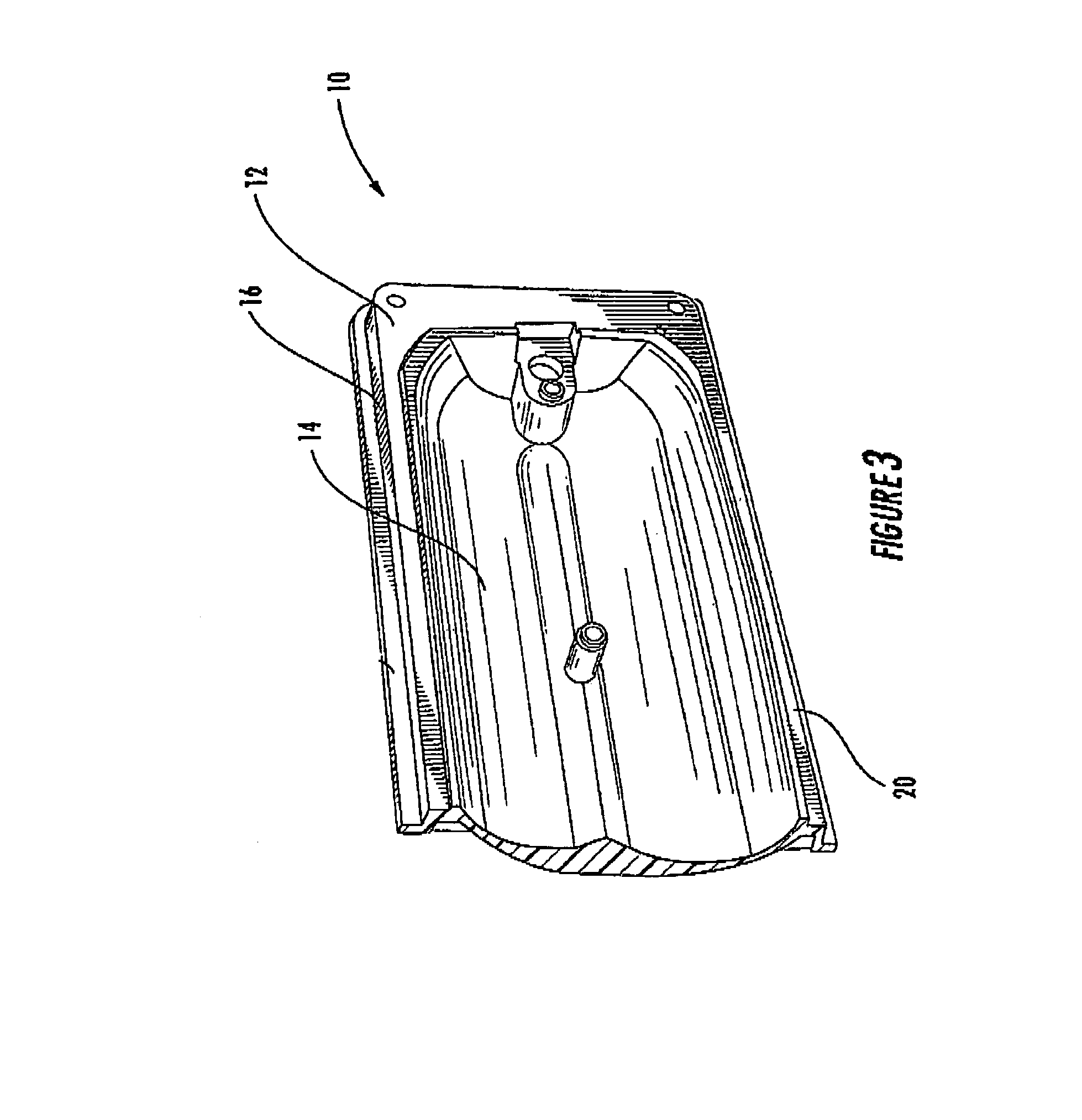
Thermally-conductive plastic articles having light reflecting surfaces
A thermally-conductive polymer composition suitable for making molded reflector articles having light-reflecting surfaces is provided. The composition comprises: a) about 20% to about 80% by weight of a base polymer matrix such as polycarbonate; and b) about 20% to about 80% by weight of a thermally-conductive carbon material such as graphite. The composition can be used to make reflector articles such as housings for automotive tail lamps, head lamps, and other lighting fixtures. A method for manufacturing reflector articles is also provided.
Owner:TICONA POLYMERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com